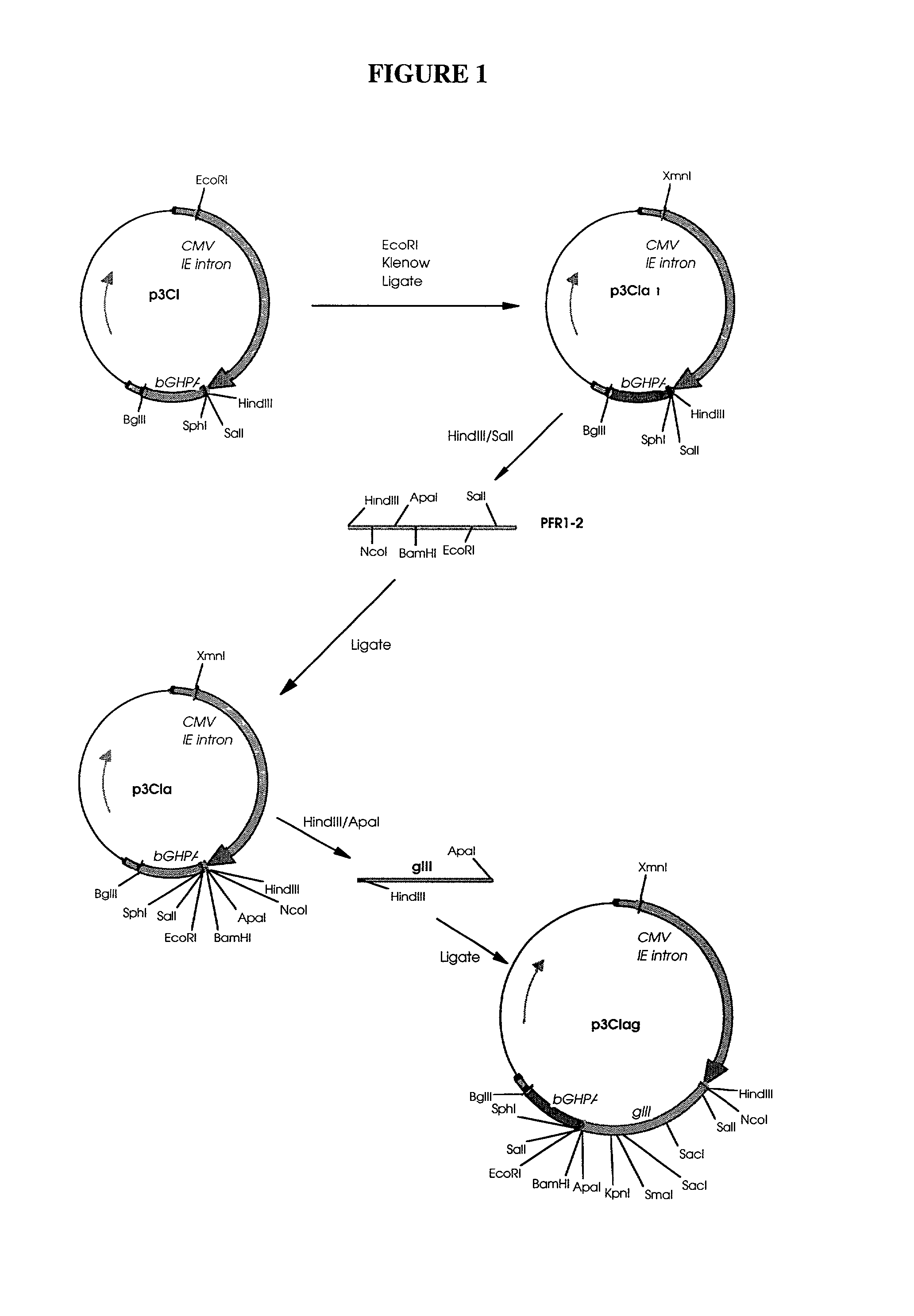
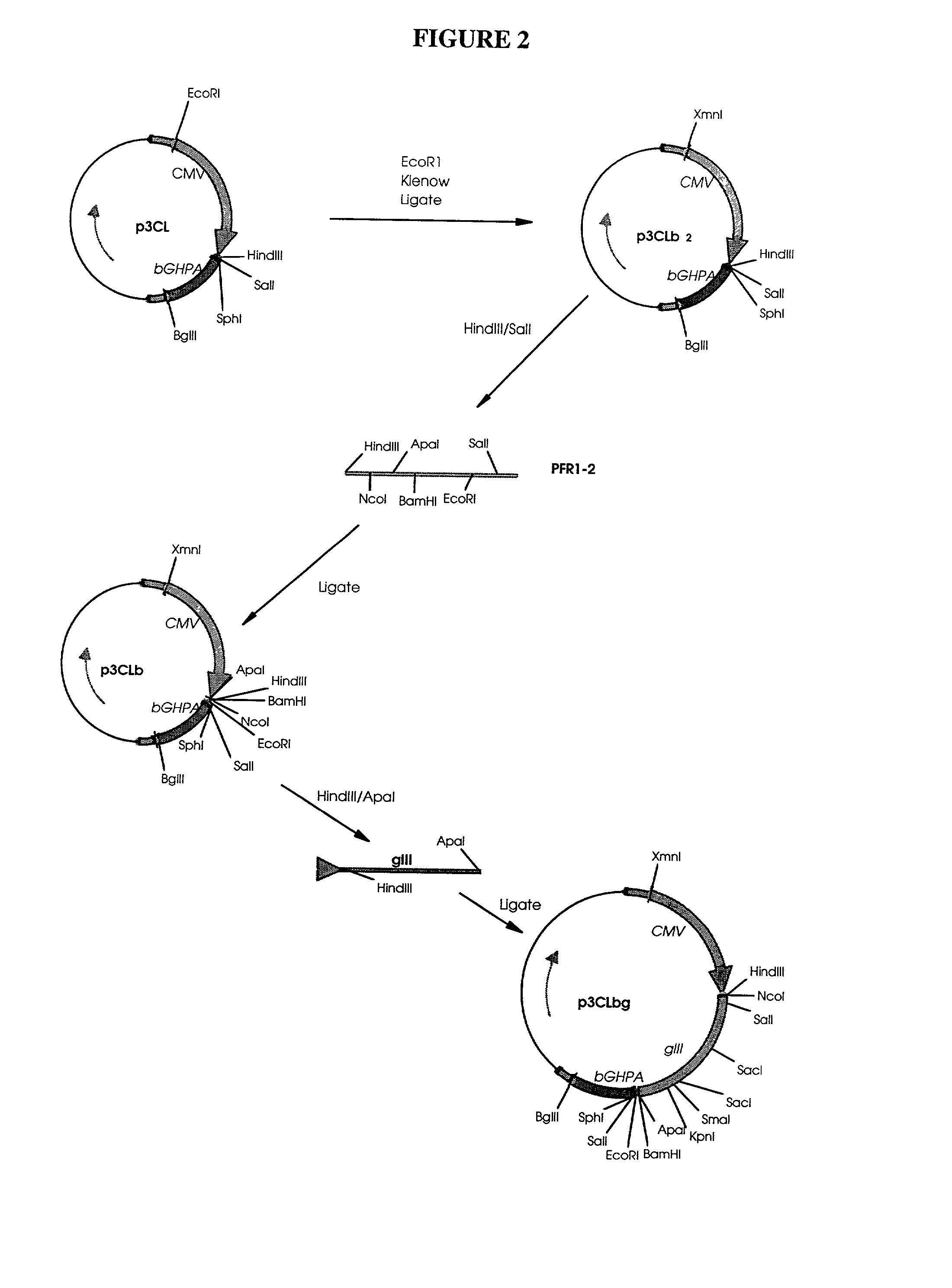
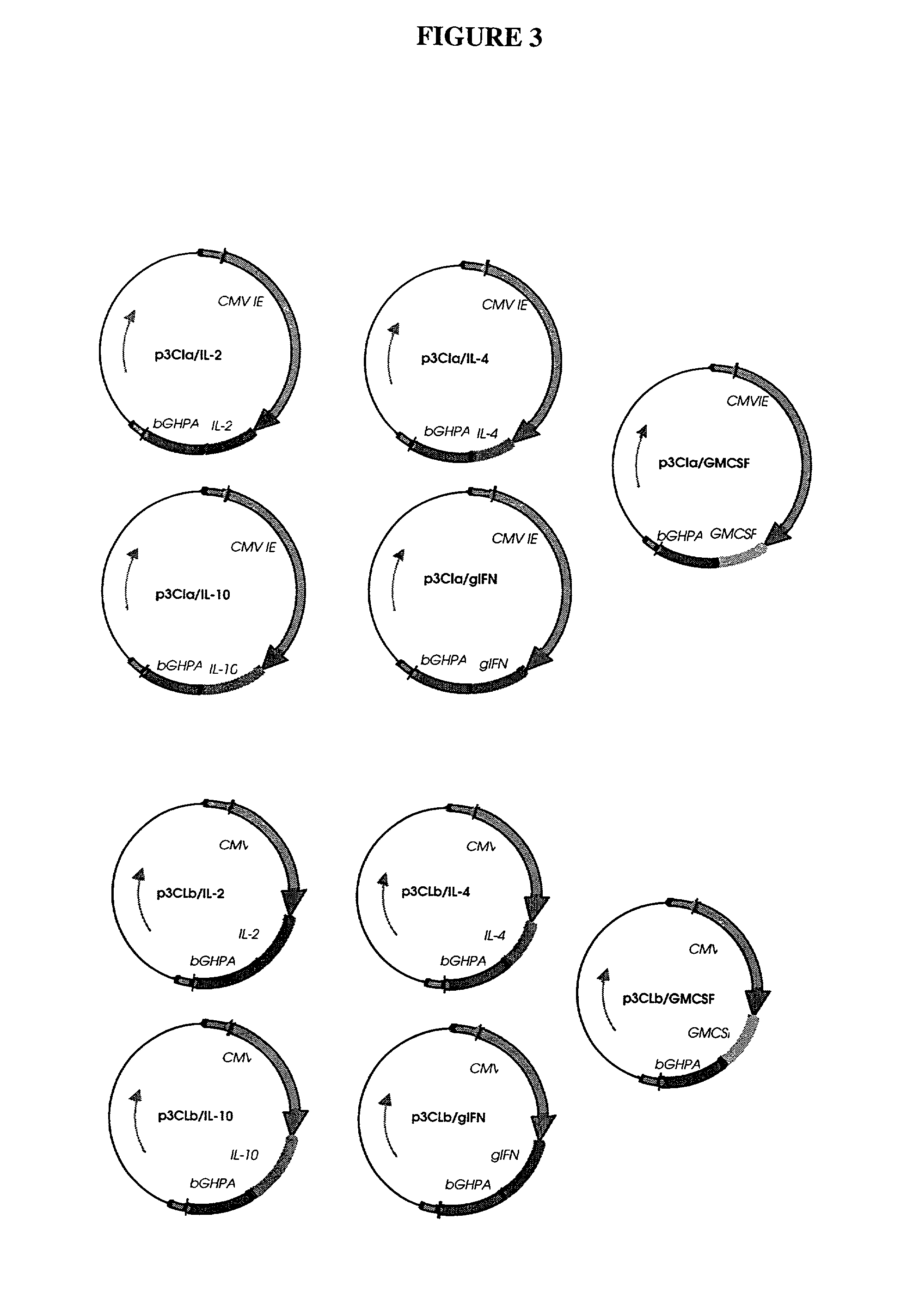
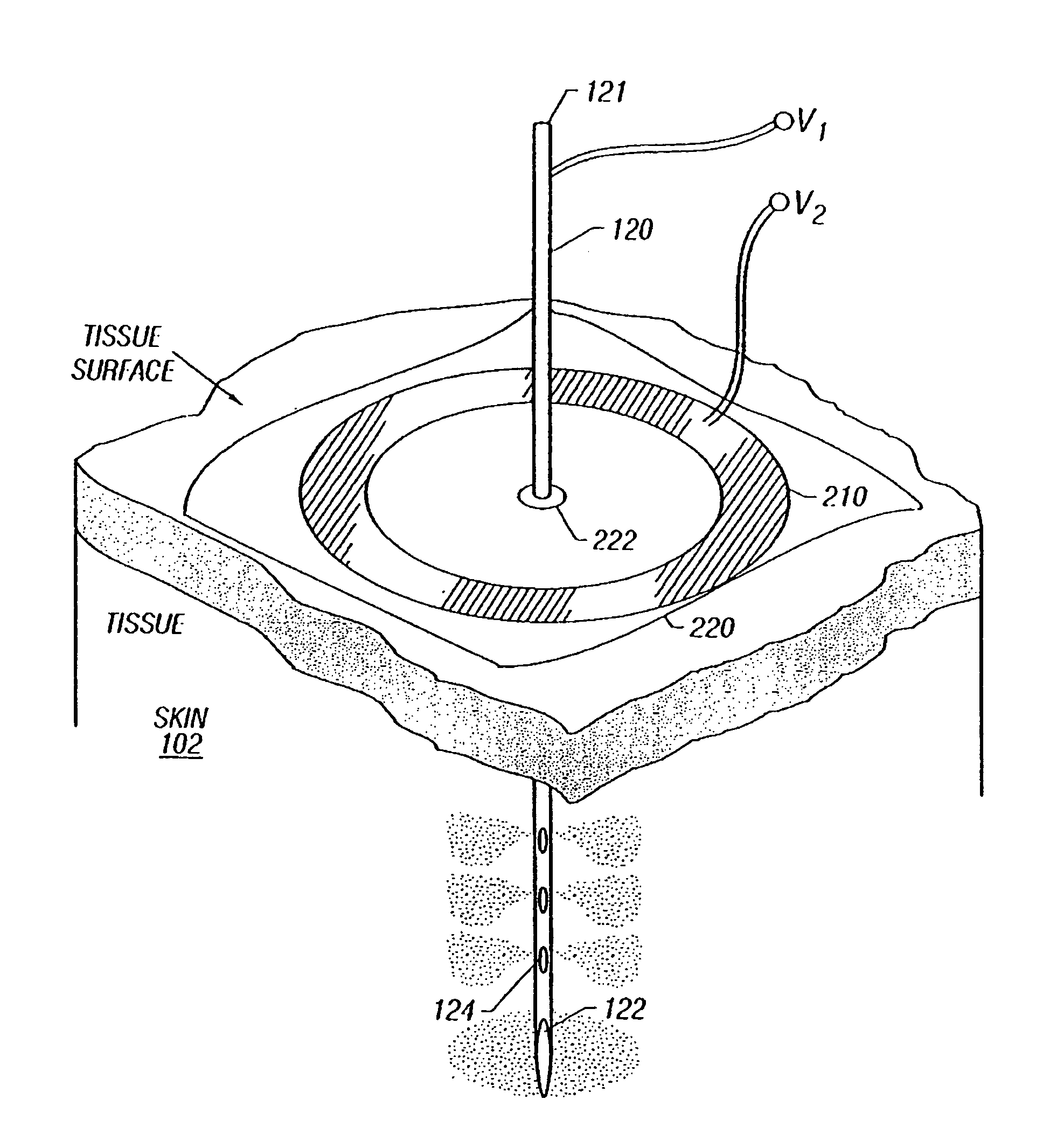
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Naked DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Naked DNA is histone-free DNA that is passed from cell to cell during a gene transfer process called transformation or transfection. In transformation, purified or naked DNA is taken up by the recipient cell which will give the recipient cell a new characteristic or phenotype. Transfection differs from transformation since the DNA is not generally incorporated into the cell's genome, it is only transiently expressed. In the field of DNA vaccines or genetic immunization, the term "naked DNA" was coined by Vical to mean DNA delivered free from agents which promote transfection. Research on the use of naked DNA for DNA vaccinations and gene therapy has shown some initial success, but have not yet resulted in any generally available therapy.
CE7-specific redirected immune cells
Genetically engineered, CE7-specific redirected immune cells expressing a cell surface protein having an extracellular domain comprising a receptor which is specific for CE7, an intracellular signaling domain, and a transmembrane domain, and methods of use for such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CE7+ neuroblastoma are disclosed. In one embodiment, the immune cell is a T cell and the cell surface protein is a single chain FvFc:ζ receptor where Fv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CE7 linked by peptide, Fc represents a hinge —CH2—CH3 region of a human IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. DNA constructs encoding a chimeric T-cell receptor and a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor are also disclosed.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor
InactiveUS7446179B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingTransmembrane domain
The present invention relates to a genetically engineered, CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor and to immune cells expressing the chimeric receptor The present invention also relates to the use of such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CD9+ malignancies and for abrogating any untoward B cell function. The chimeric receptor is a single chain scFvFc:ζ receptor where scFvFc designates the extracellular domain, scFv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CD19, Fc represents at least part of a constant region of an IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. The extracellular domain scFvFc and the intracellular domain ζ are linked by a transmembrane domain such as the transmembrane domain of CD4. In one aspect, the chimeric receptor comprises amino acids 23-634 of SEQ I DNO:2. The present invention further relates to a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
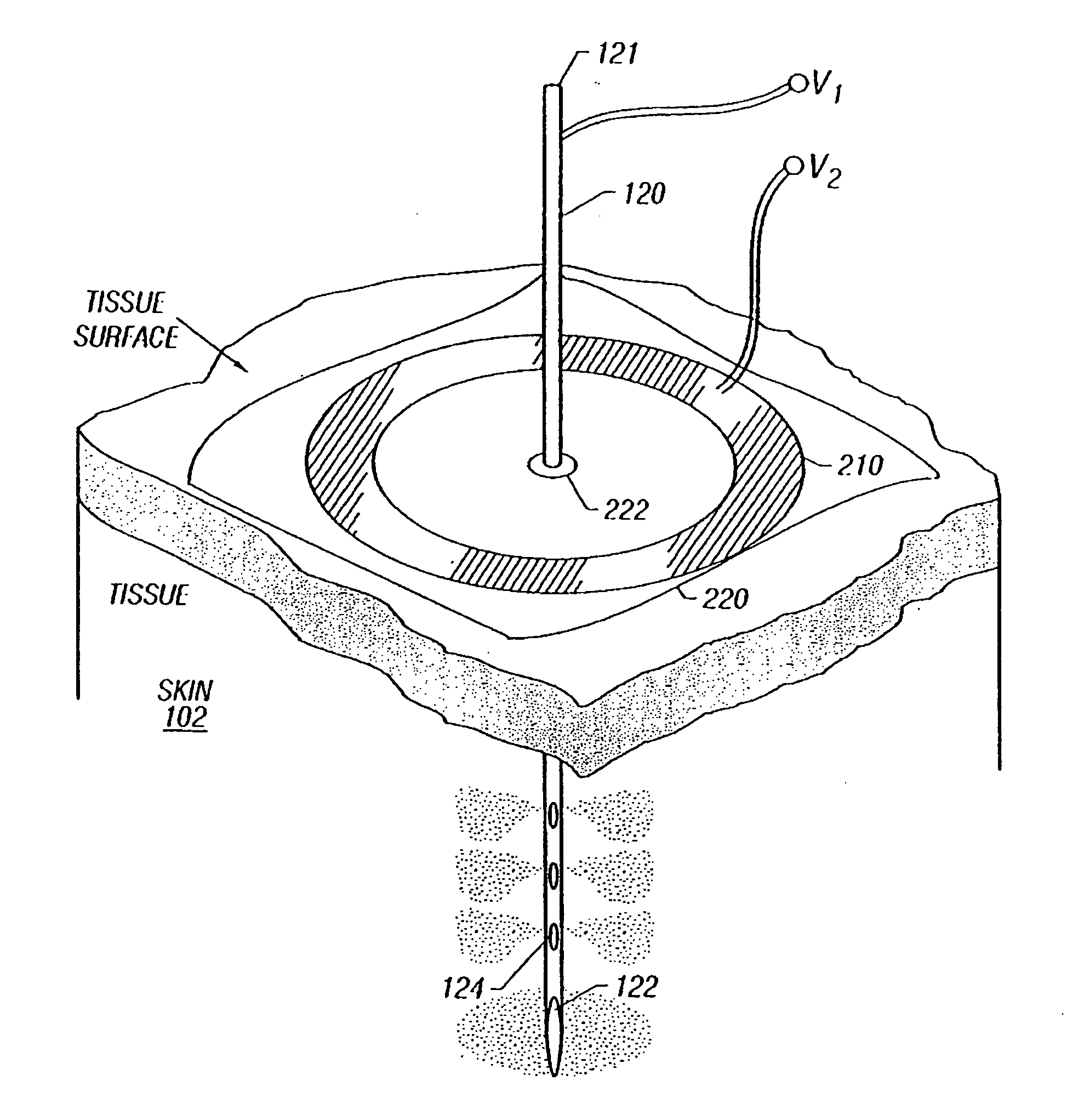
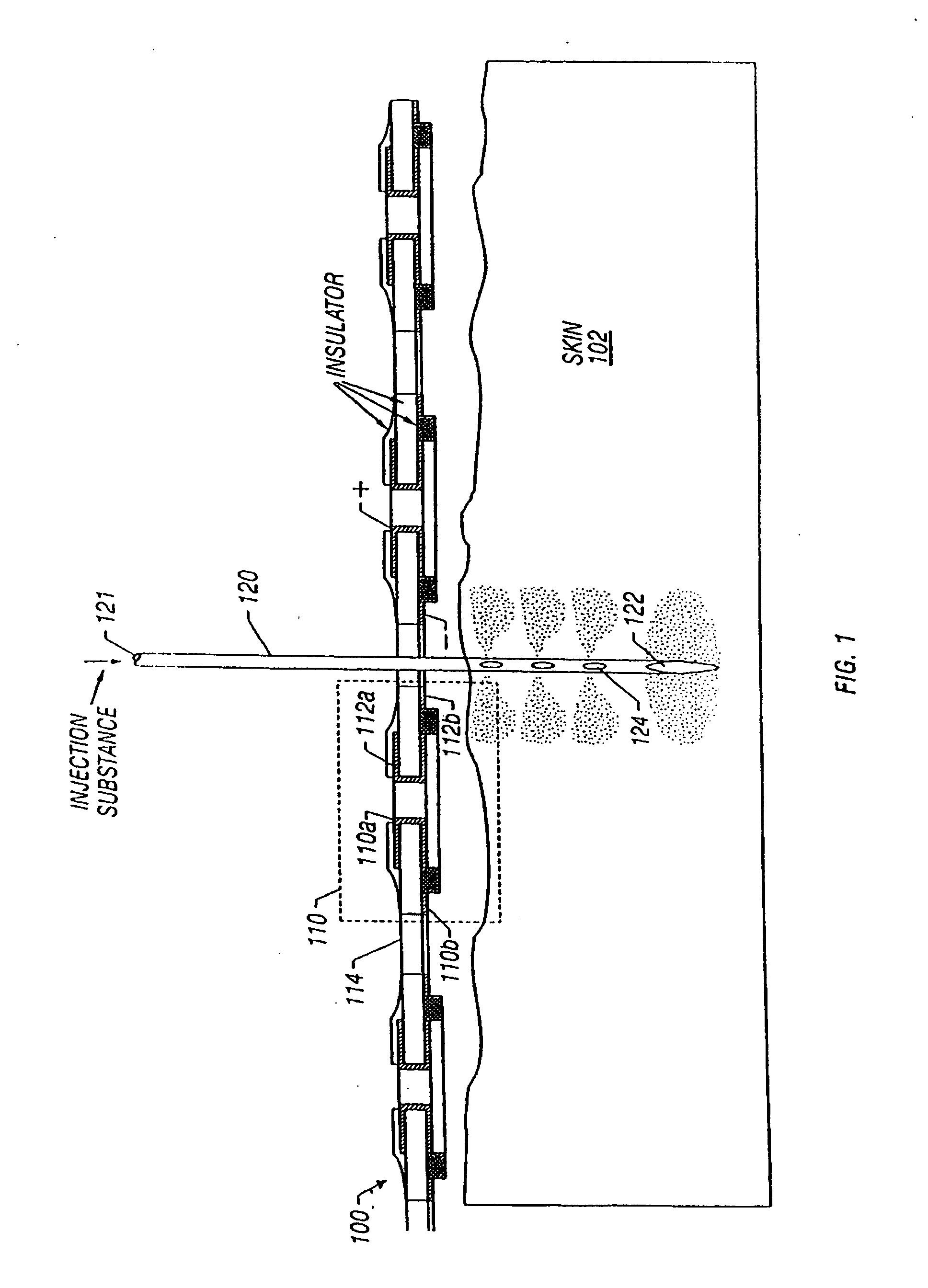
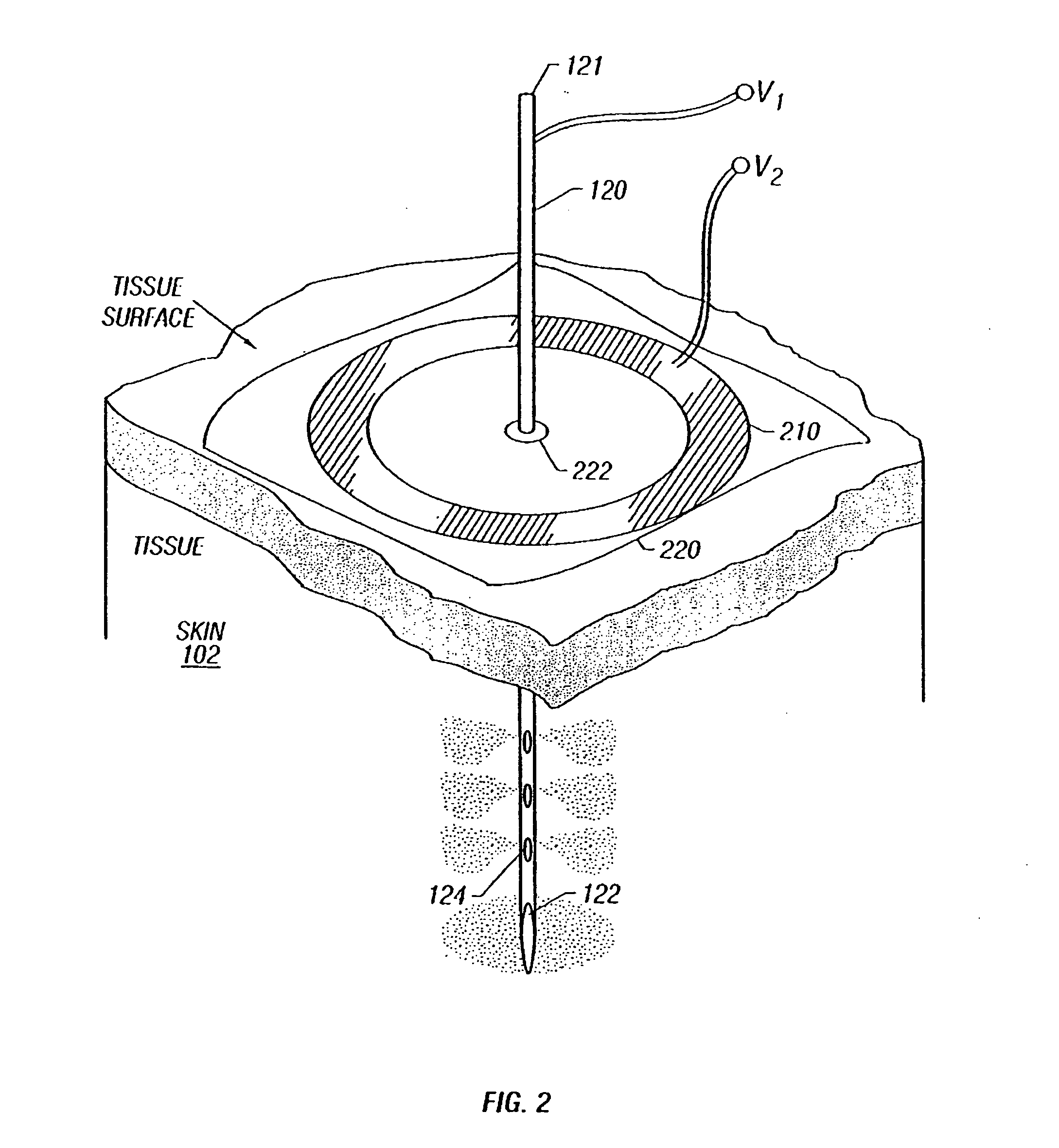
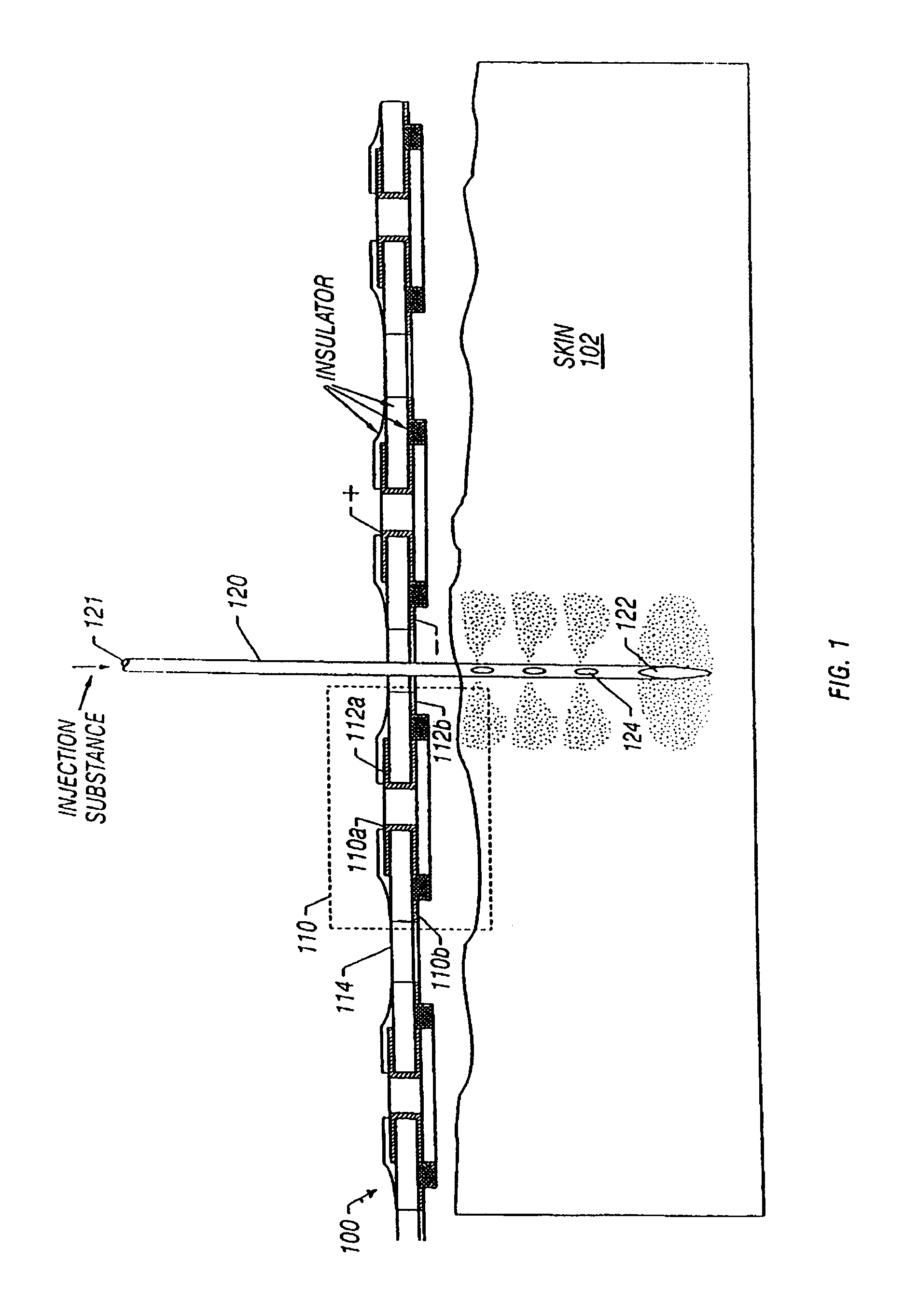
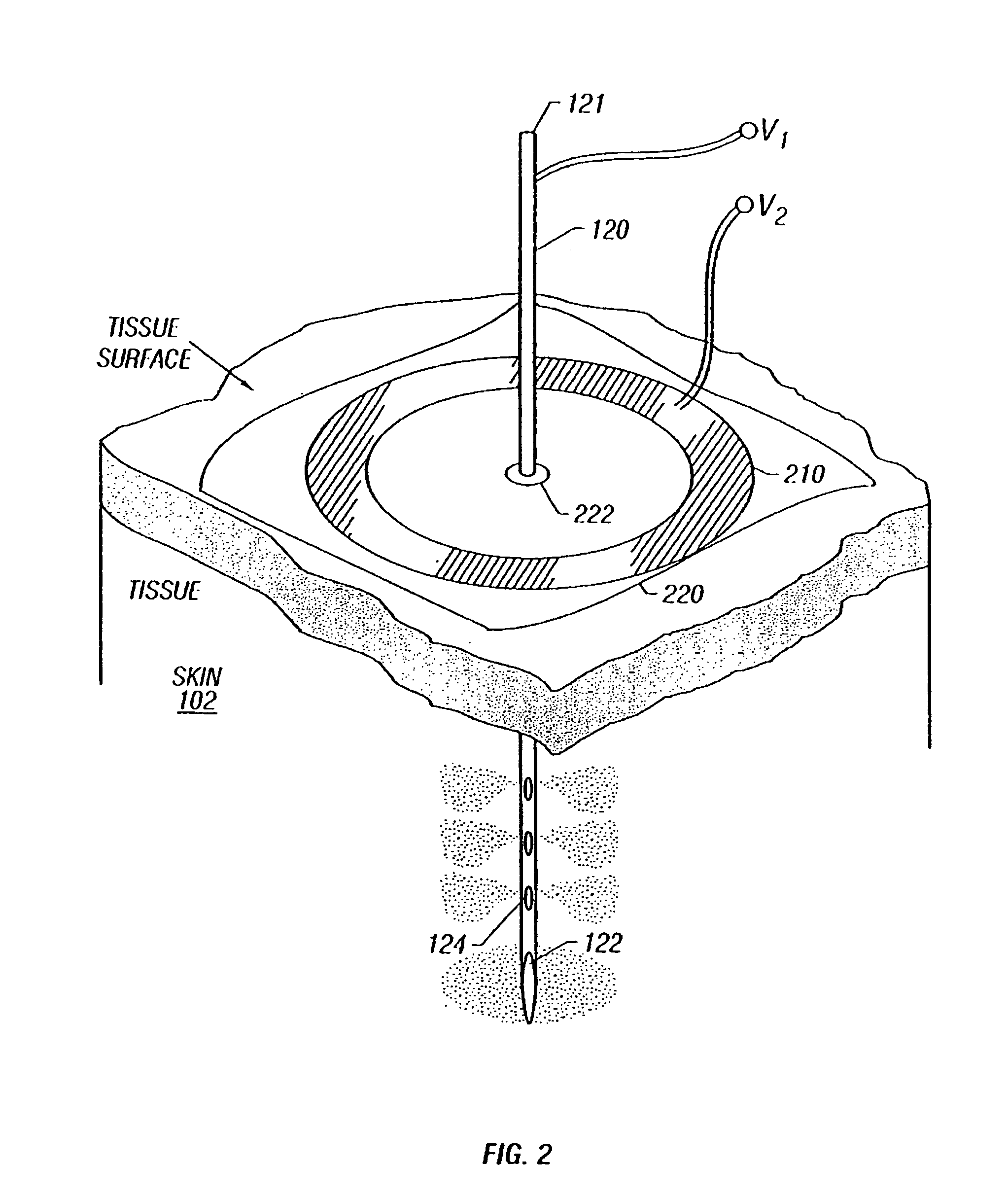
Enhanced delivery of naked DNA to skin by non-invasive in vivo electroporation
InactiveUS6972013B1Formidable physical barrier to gene transferHigh expressionElectrotherapyMedical devicesWhole bodyIn vivo
In vivo methods are provided for using an electric field to delivery therapeutic or immunizing treatment to a subject by applying non-invasive, user-friendly electrodes to the surface of the skin. Thus, therapeutic or immunizing agents can be delivered into cells of skin for local and systemic treatments or for immunization with optimal gene expression and minimal tissue damage. In particular, therapeutic agents include naked or formulated nucleic acid, polypeptides and chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:INOVIO PHARMA
Enhanced delivery of naked DNA to skin by non-invasive in vivo electroporation
In vivo methods are provided for using an electric field to delivery therapeutic or immunizing treatment to a subject by applying non-invasive, user-friendly electrodes to the surface of the skin. Thus, therapeutic or immunizing agents can be delivered into cells of skin for local and systemic treatments or for immunization with optimal gene expression and minimal tissue damage. In particular, therapeutic agents include naked or formulated nucleic acid, polypeptides and chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:INOVIO PHARMA
Influenza vaccines
InactiveUS20080299151A1Less protectionBroad and efficient protective immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsHemagglutininMammal
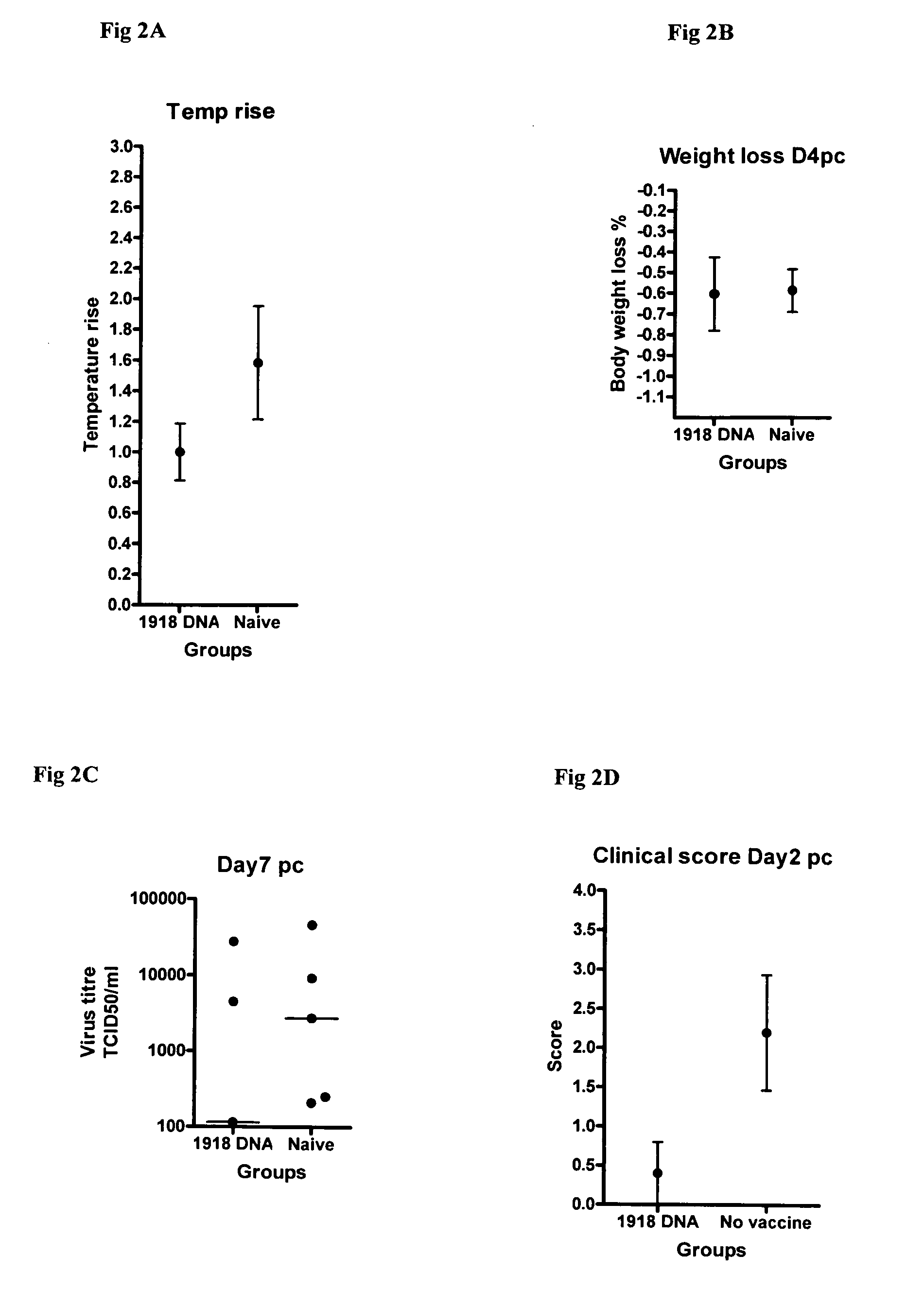
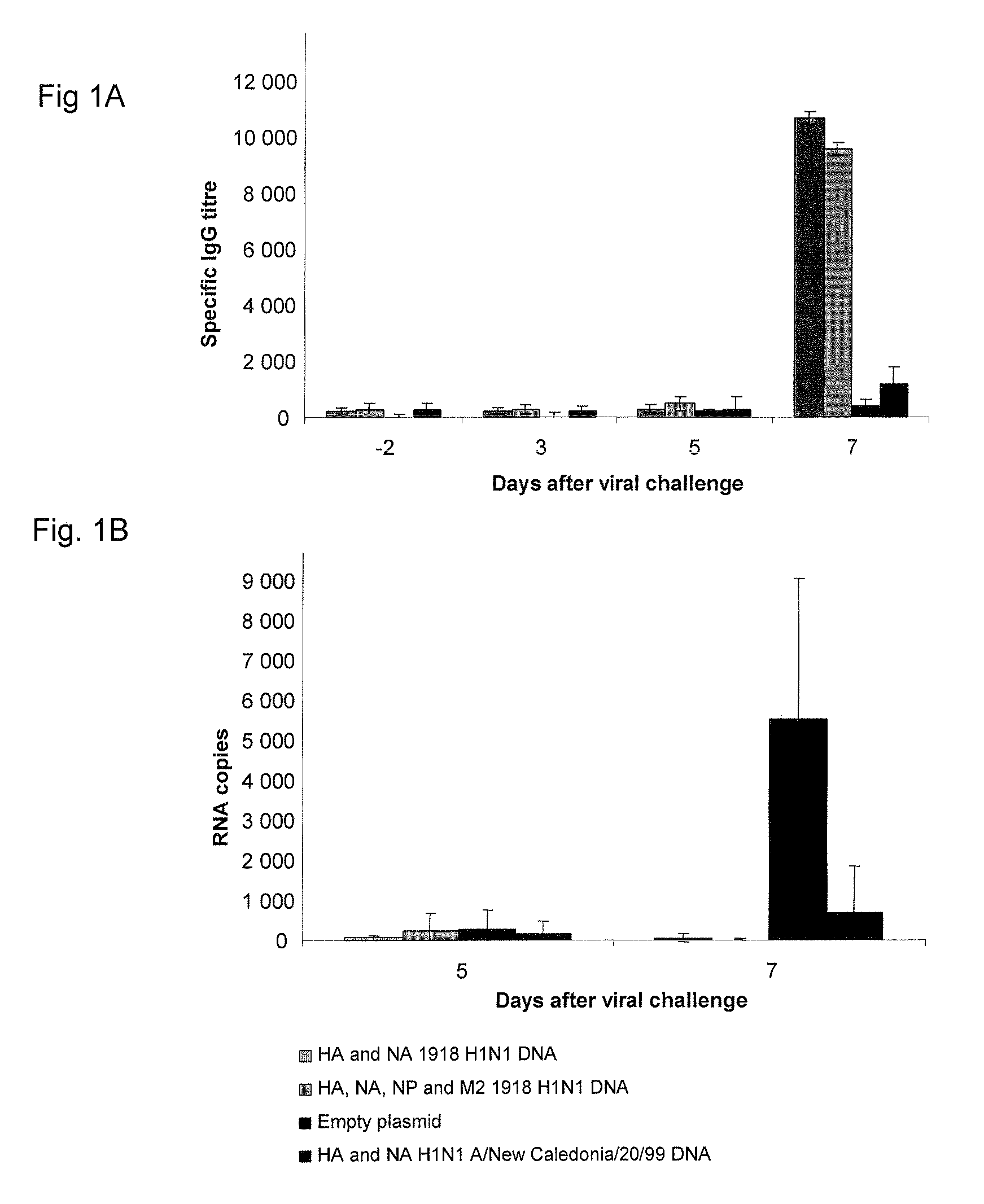
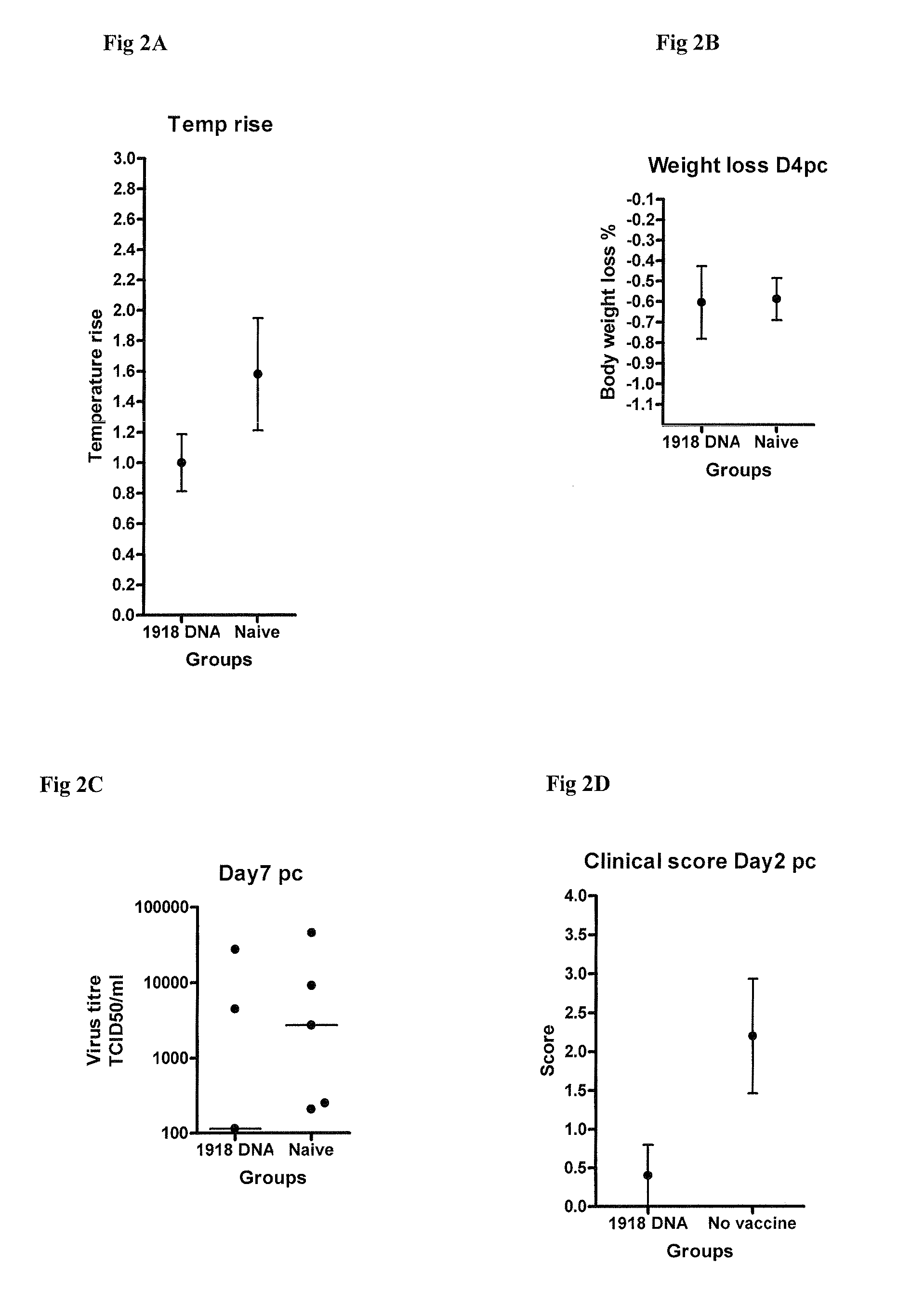
Described herein are vaccines and the use of naked DNA and / or RNA encoding hemagglutinin (HA) from pandemic influenza, e.g., the 1918 H1N1 and / or the 1957 H2N2 and / or the 1968 H3N2 influenza A virus, as a vaccine component against present day and coming H1, H2, H3, H5, N1, N2 containing influenza A infections in humans and swine optionally with the naked DNA and / or RNA encoding Neuraminidase (NA) and / or matrix protein (M) and / or the nucleoprotein (NP) from pandemic influenza virus included. If the vaccine components are used as DNA or RNA vaccines with or without the corresponding protein, the codons can optionally be “humanized” using preferred codons from highly expressed mammalian genes and the administration of this DNA vaccine can be by saline or buffered saline injection of naked DNA or RNA, or injection of DNA plasmid or linear gene expressing DNA fragments coupled to particles. Addition of the matrix protein (M) and / or the nucleoprotein (NP) from the 1918 influenza strain is also disclosed.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Superior molecular vaccine based on self-replicating RNA, suicidal DNA or naked DNA vector, that links antigen with polypeptide that promotes antigen presentation
InactiveUS7557200B2Efficiently presentedImprove effectivenessSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseMHC class I
Improved molecular vaccines comprise nucleic acid vectors that encode a fusion polypeptide that includes polypeptide or peptide physically linked to an antigen. The linked polypeptide is one that (a) promotes processing of the expressed fusion polypeptide via the MHC class I pathway and / or (b) promotes development or activity of antigen presenting cells, primarily dendritic cells. These vaccines employ one of several types of nucleic acid vectors, each with its own relative advantages: naked DNA plasmids, self-replicating RNA replicons and suicidal DNA-based on viral RNA replicons. Administration of such a vaccine results in enhance immune responses, primarily those mediated by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, directed against the immunizing antigen part of the fusion polypeptide. Such vaccines are useful against tumor antigens, viral antigens and antigens of other pathogenic microorganisms and can be used in the prevention or treatment of diseases that include cancer and infections.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Superior molecular vaccine based on self-replicating rna, suicidal dna or naked dna vector, that links antigen with polypeptide that promotes antigen presentation
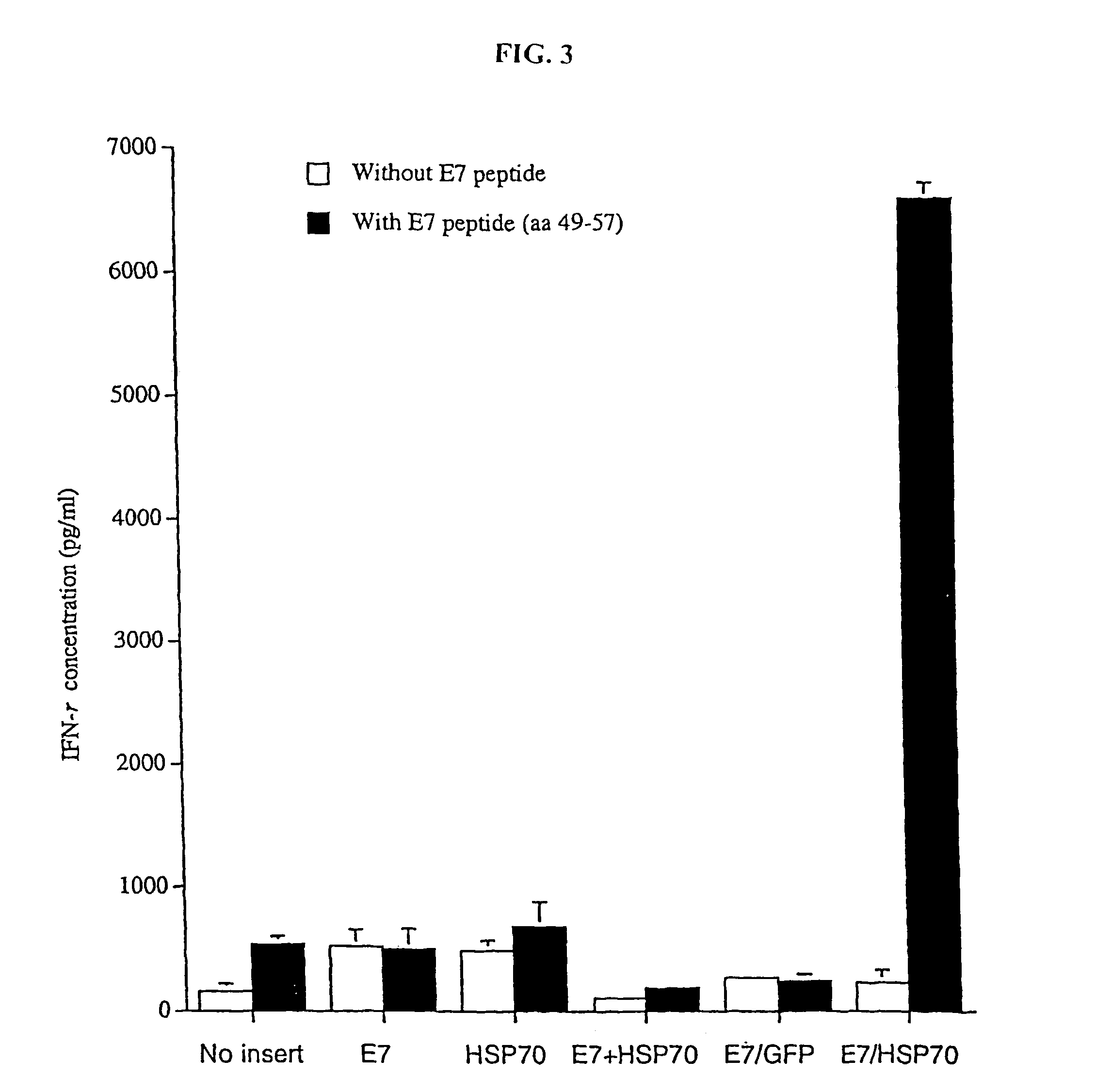
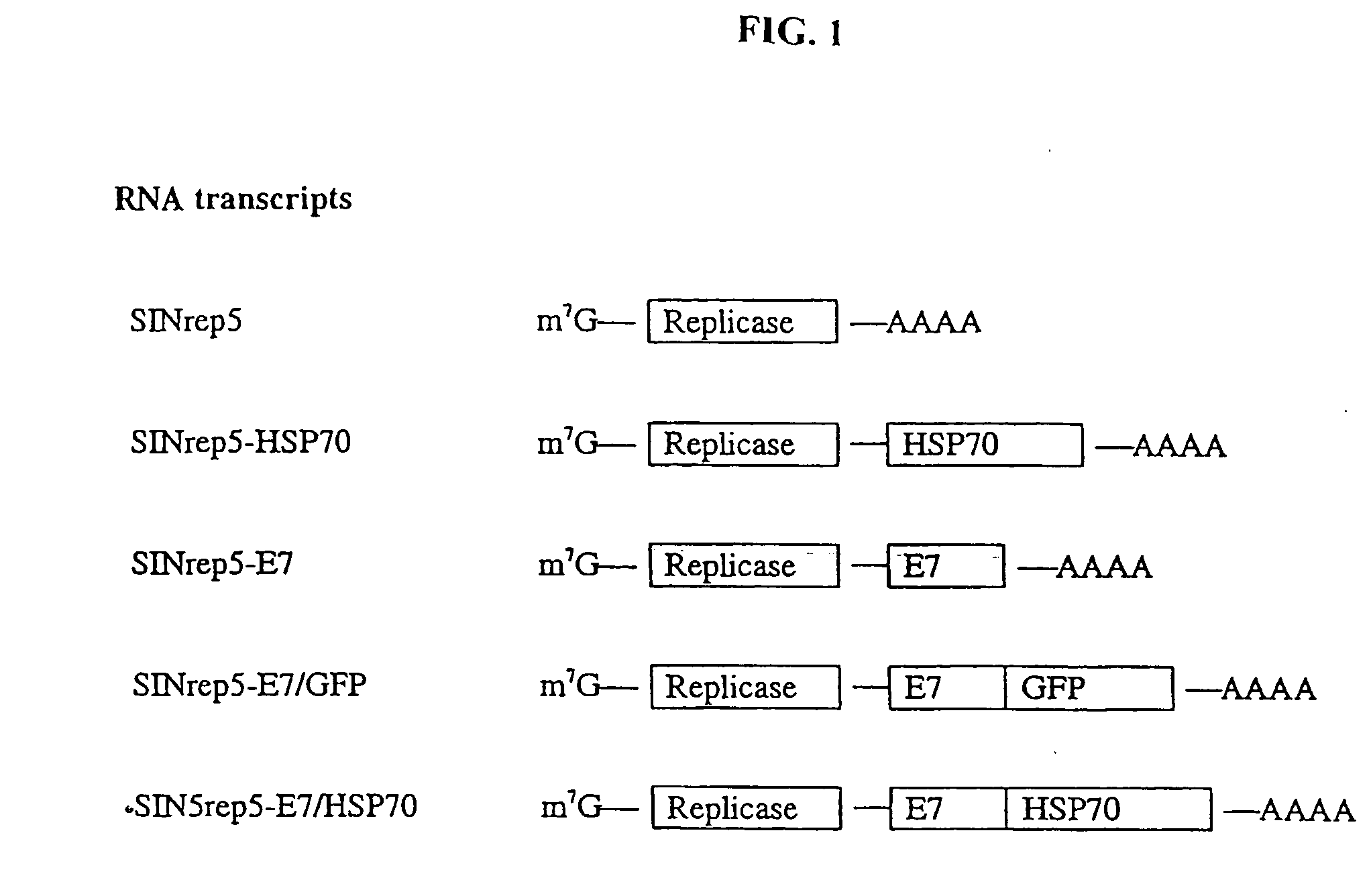
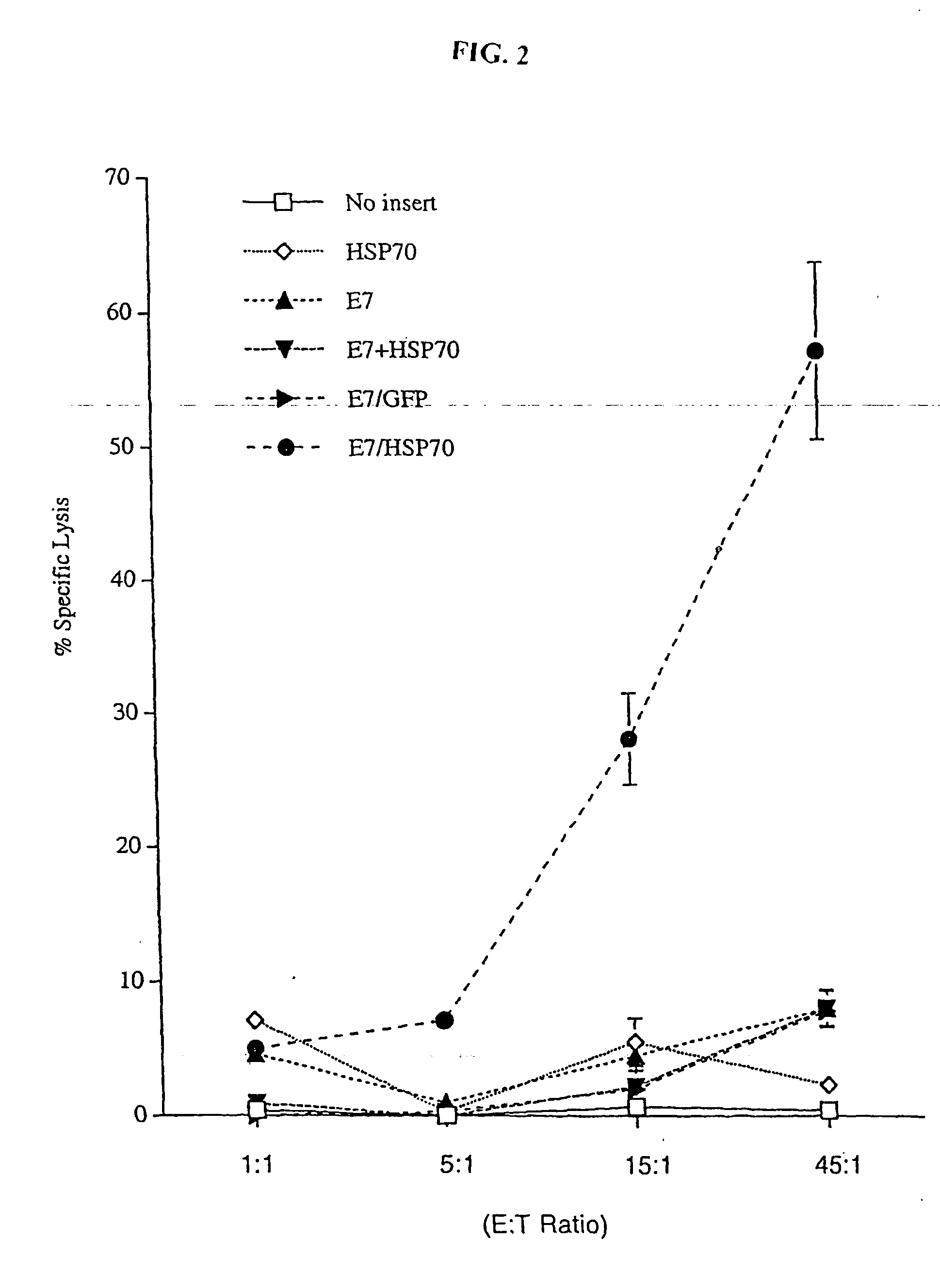
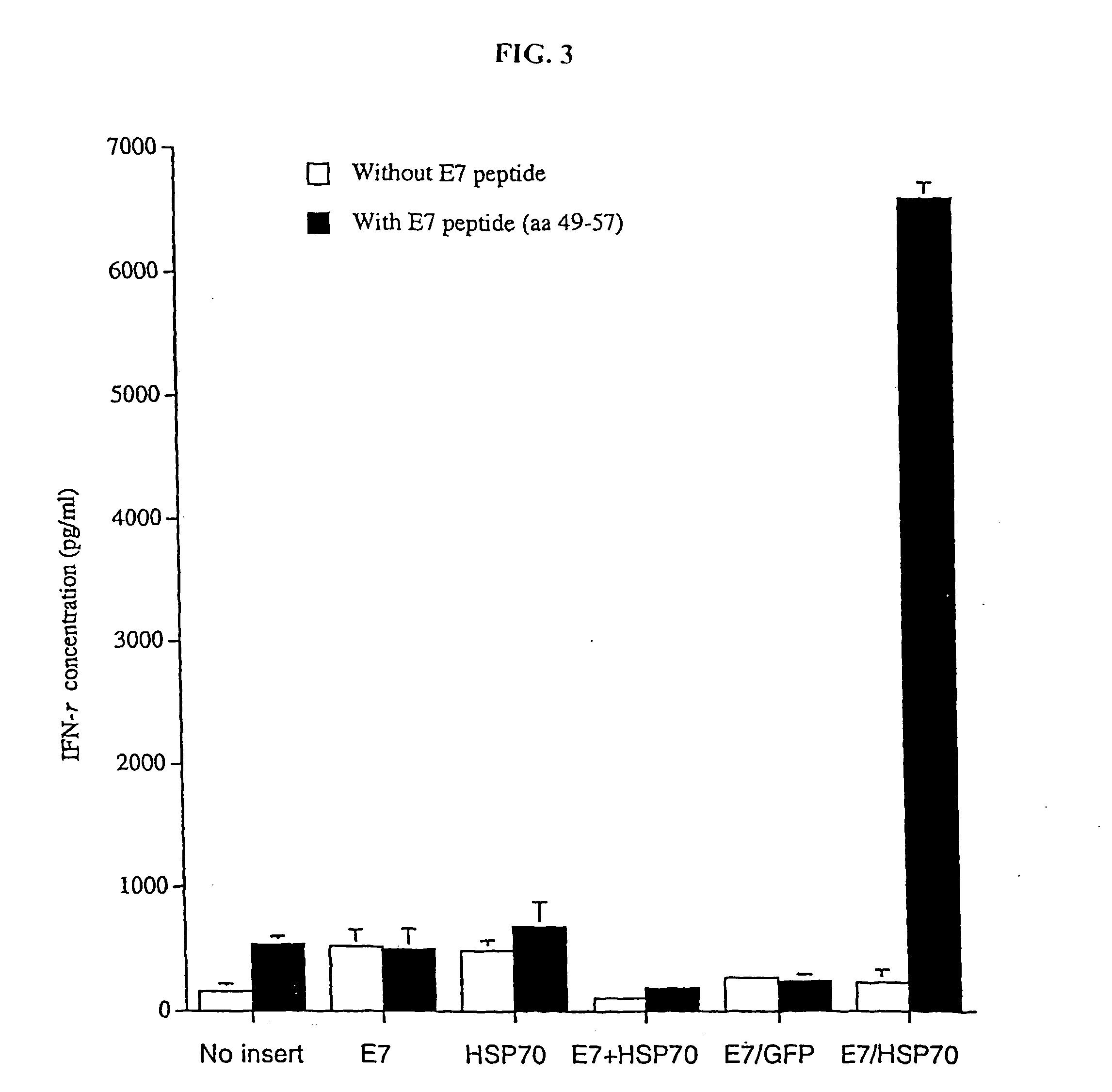
InactiveUS20050277605A1Great E7-specific T cell-mediated immunityEfficiently presentedSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IDisease
Improved molecular vaccines comprise nucleic acid vectors that encode a fusion polypeptide that includes polypeptide or peptide physically linked to an antigen. The linked polypeptide is one that (a) promotes processing of the expressed fusion polypeptide via the MHC class I pathway and / or (b) promotes development or activity of antigen presenting cells, primarily dendritic cells. These vaccines employ one of several types of nucleic acid vectors, each with its own relative advantages: naked DNA plasmids, self-replicating RNA replicons and suicidal DNA-based on viral RNA replicons. Administration of such a vaccine results in enhance immune responses, primarily those mediated by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, directed against the immunizing antigen part of the fusion polypeptide. Such vaccines are useful against tumor antigens, viral antigens and antigens of other pathogenic microorganisms and can be used in the prevention or treatment of diseases that include cancer and infections.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Introduction of naked DNA or RNA encoding non-human vertebrate peptide hormones or cytokines into a non-human vertebrate
The present invention relates to the introduction of naked DNA or RNA molecules encoding non-human vertebrate peptide hormones or cytokines into a non-human vertebrate to achieve delivery of the non-human vertebrate peptide hormone or cytokine. The invention thus provides an alternative to directly administering the polypeptide of interest.
Owner:MARTIN STEPHEN +1
Enhanced delivery of naked DNA to skin by non-invasive in vivo electroporation
In vivo methods are provided for using an electric field to delivery therapeutic or immunizing treatment to a subject by applying non-invasive, user-friendly electrodes to the surface of the skin. Thus, therapeutic or immunizing agents can be delivered into cells of skin for local and systemic treatments or for immunization with optimal gene expression and minimal tissue damage. In particular, therapeutic agents include naked or formulated nucleic acid, polypeptides and chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:INOVIO PHARMA
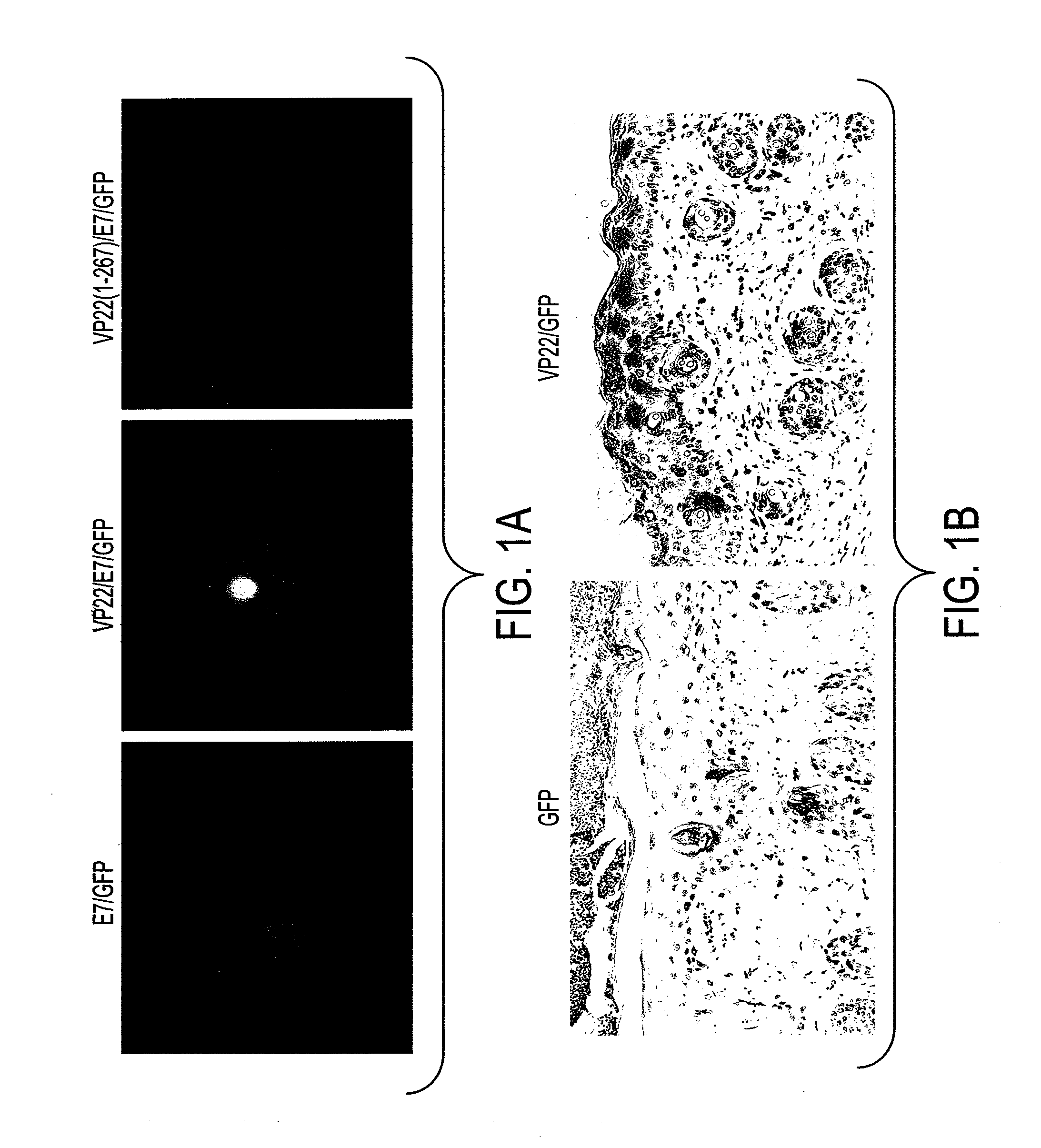
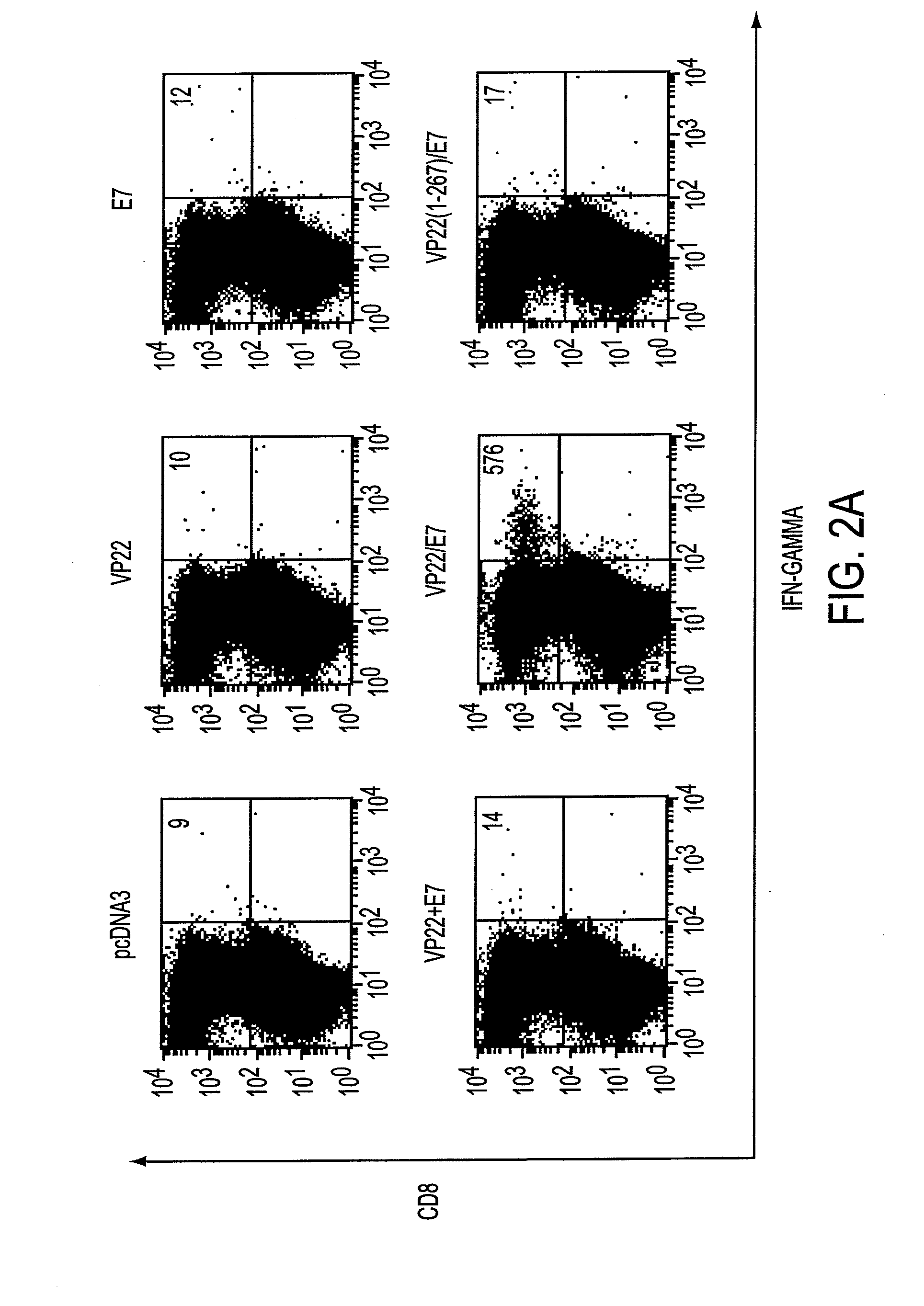
Molecular vaccine linking intercellular spreading protein to an antigen
InactiveUS7318928B2Enhancing vaccine potencyEasy to spreadAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsViral antigen ingredientsT lymphocyteOrganism
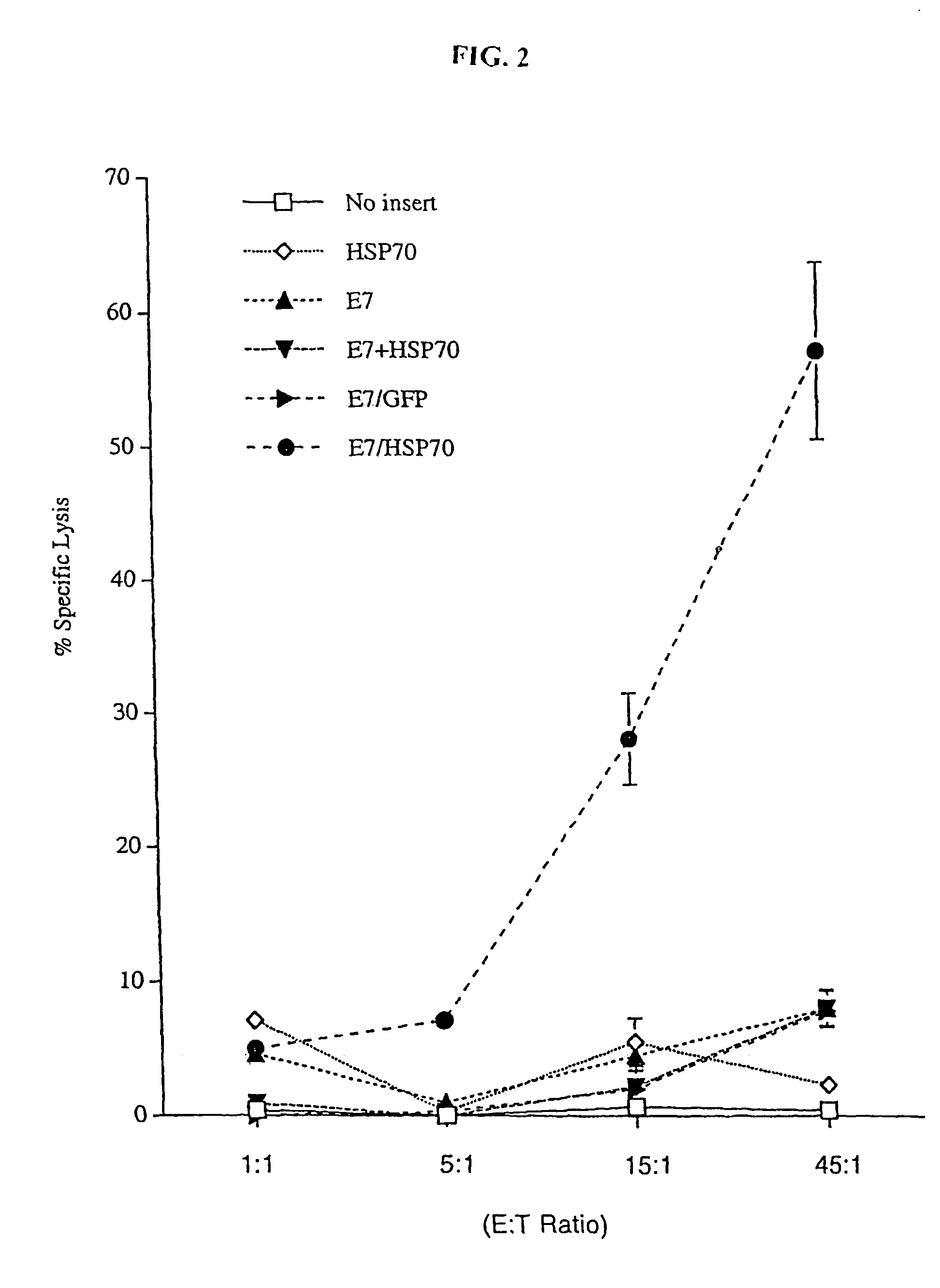
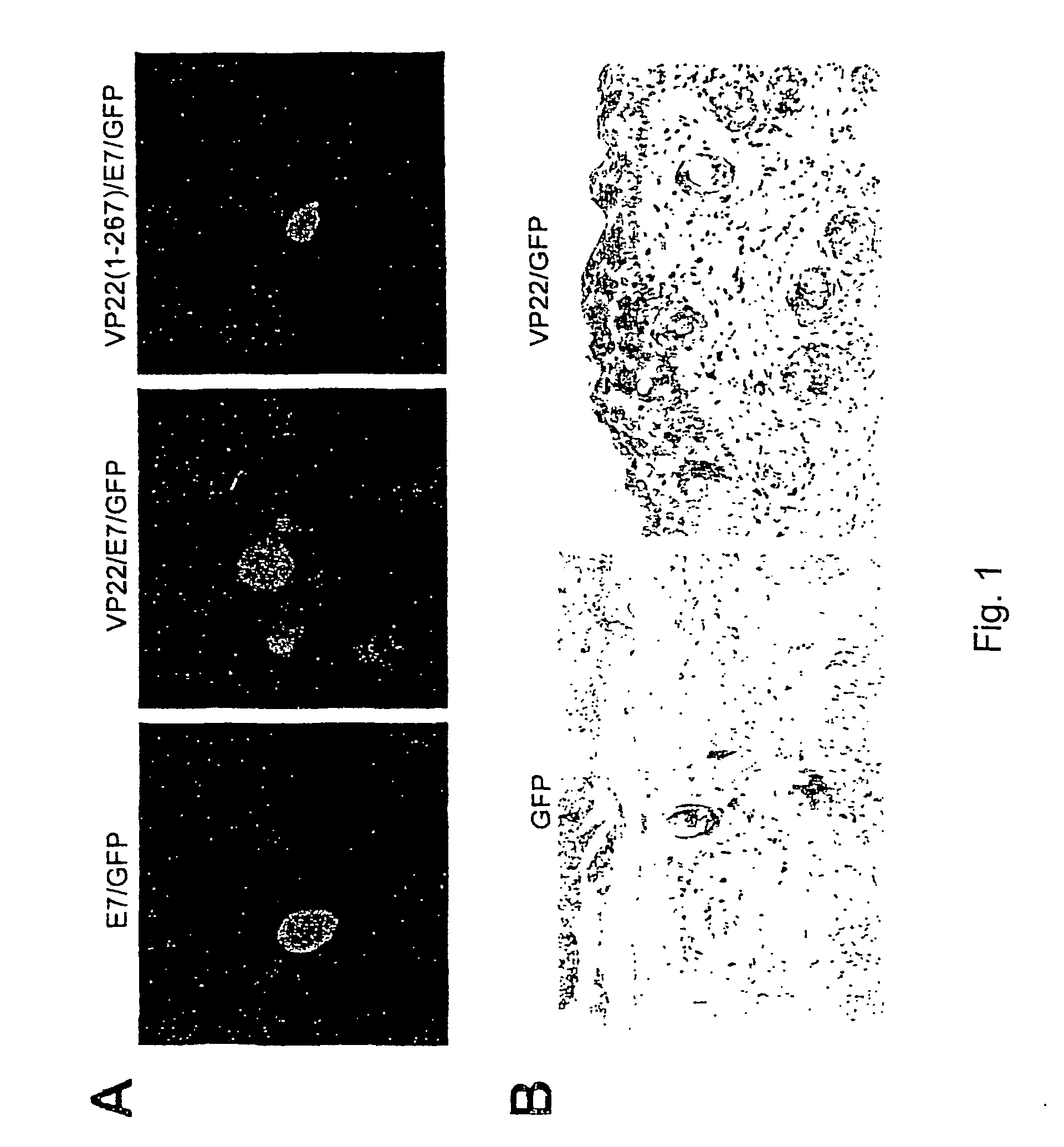
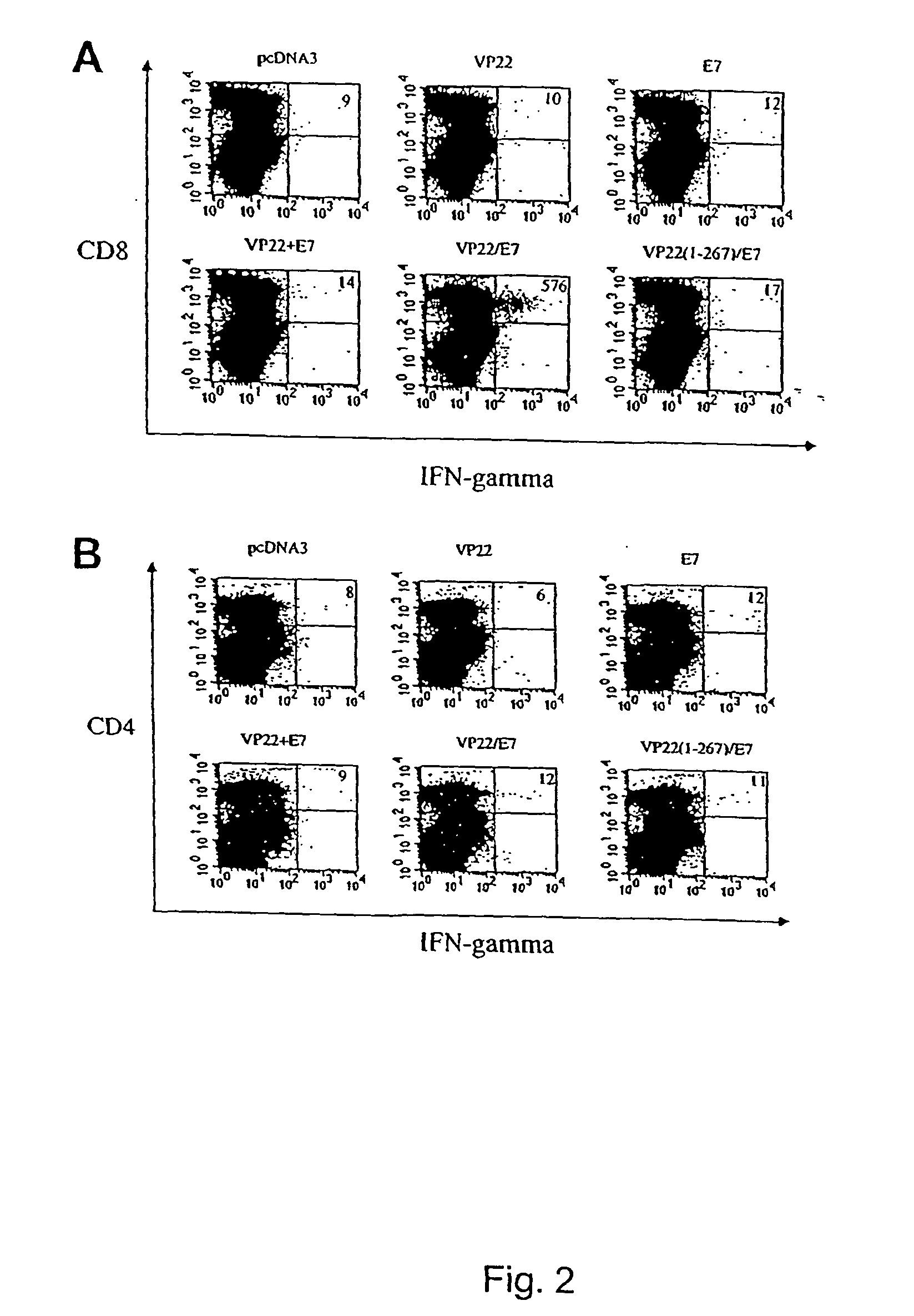
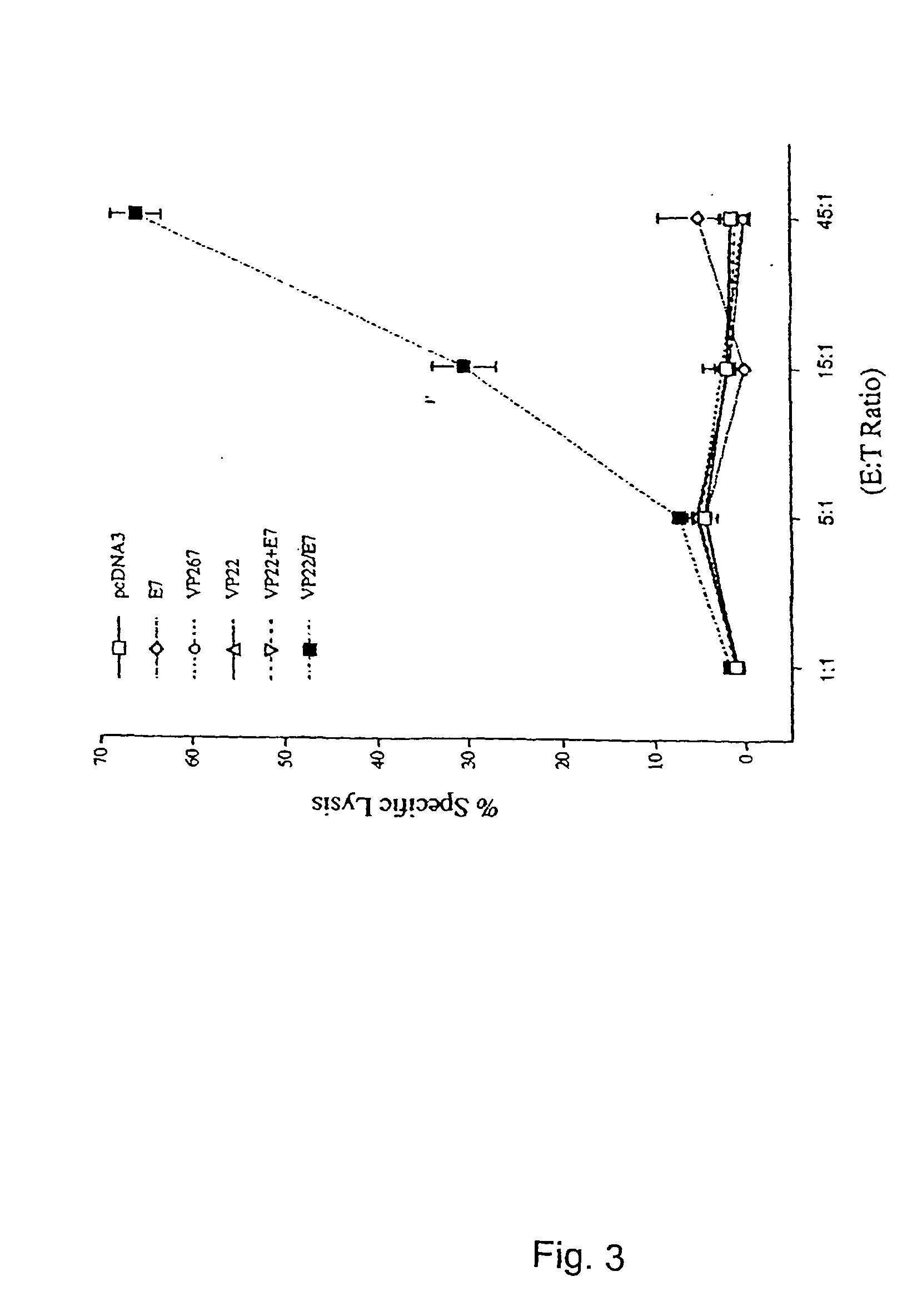
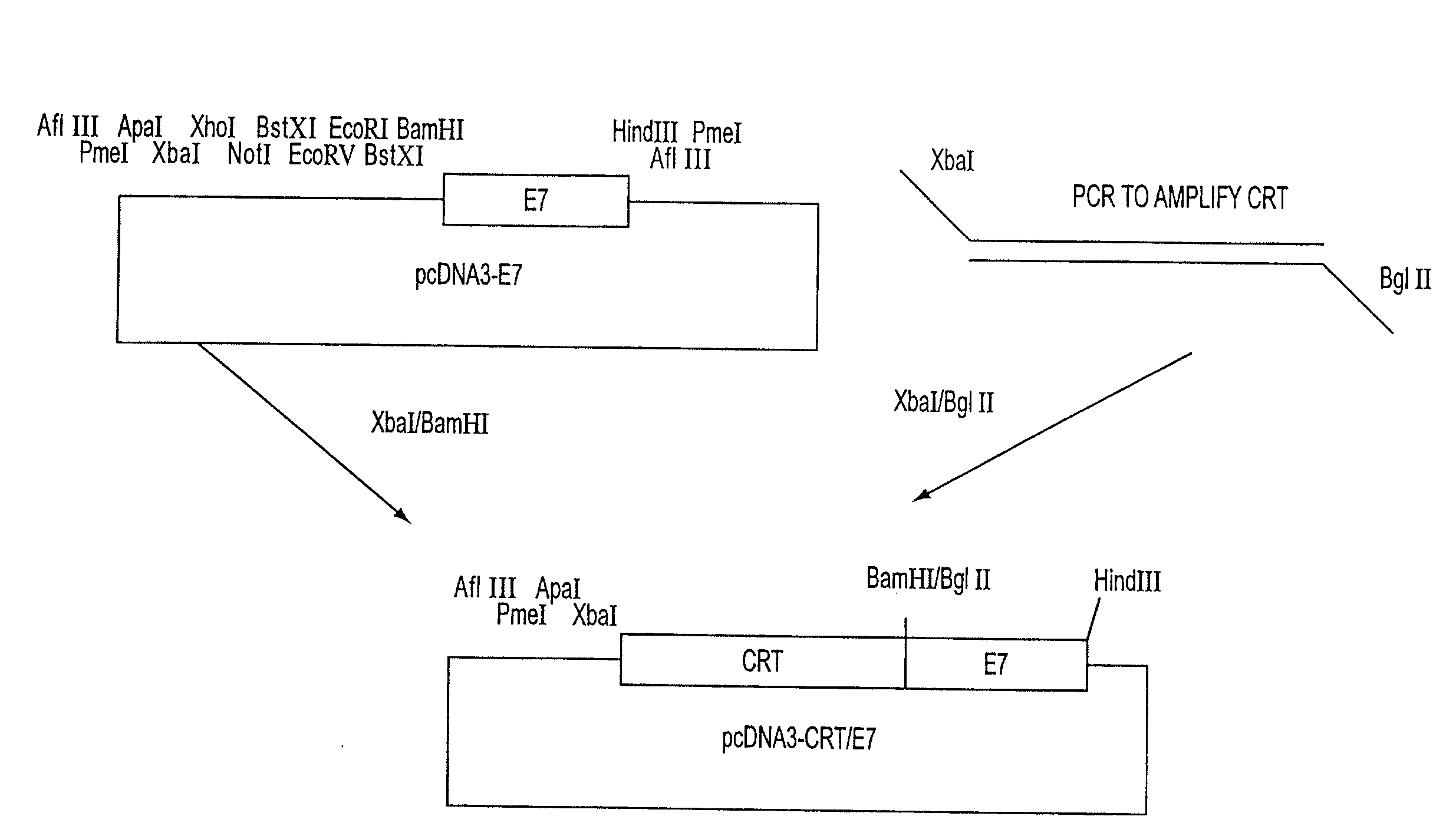
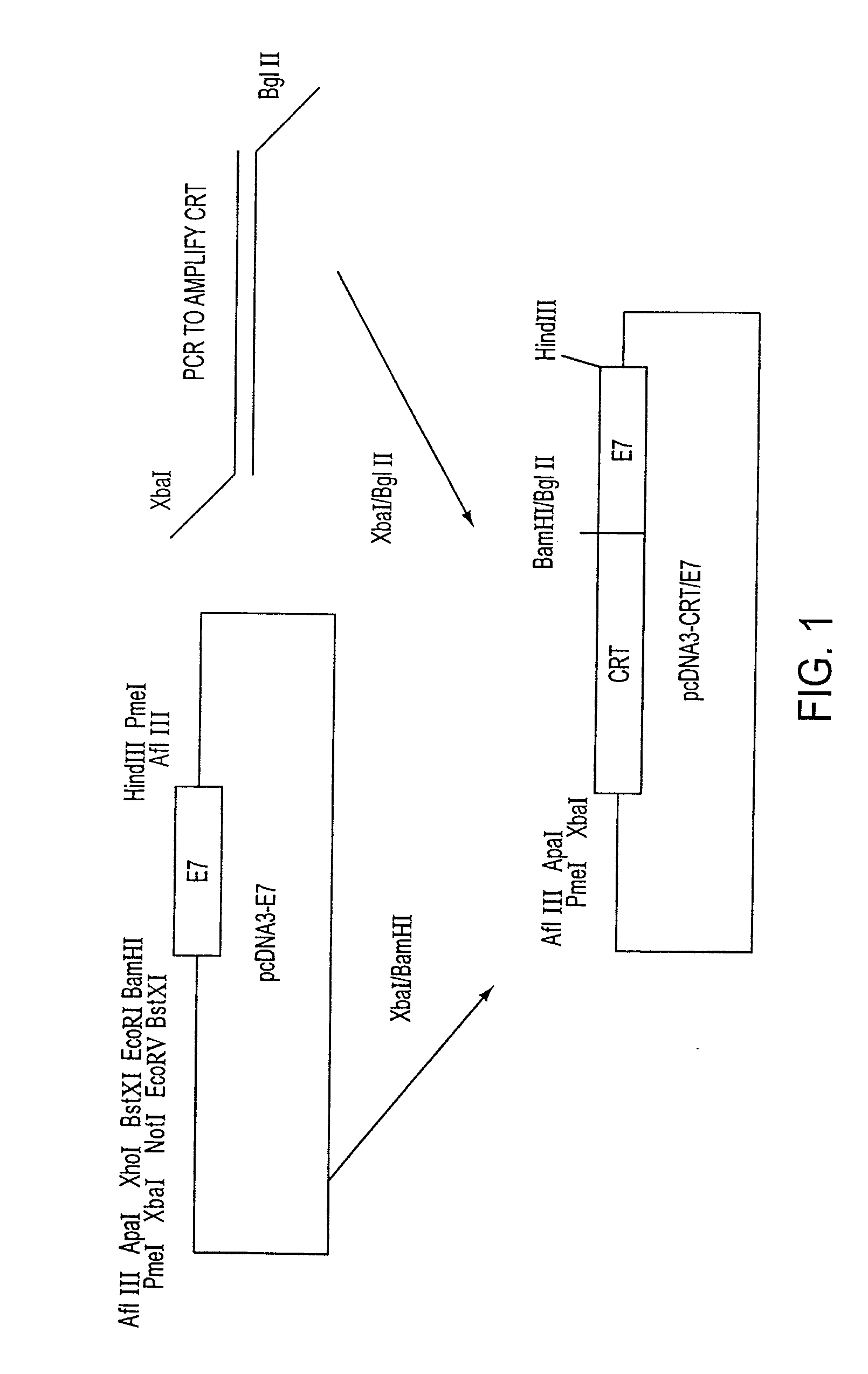
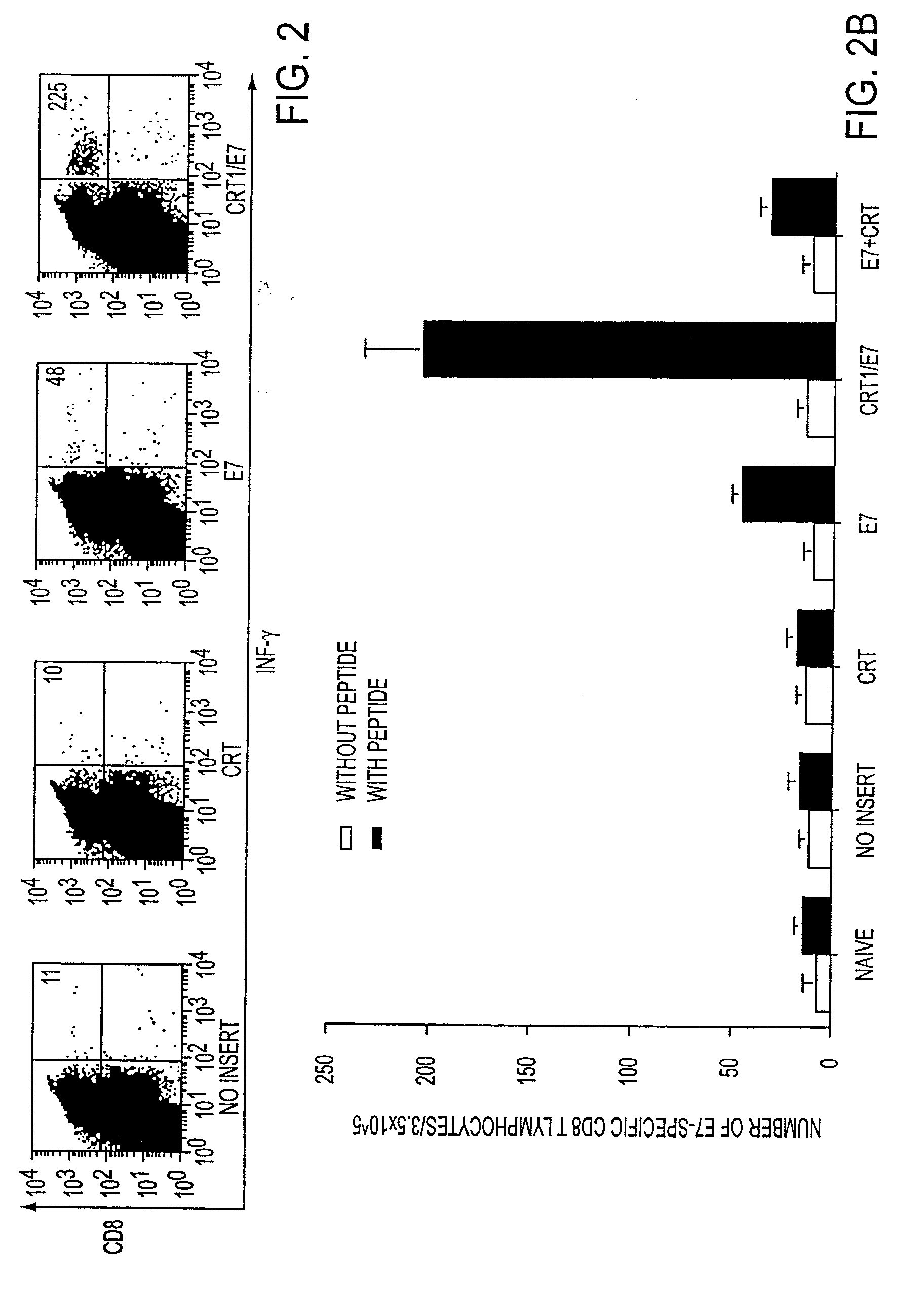
Superior molecular vaccines comprise nucleic acids, including naked DNA and replicon RNA, that encode a fusion polypeptide that includes an antigenic peptide or polypeptide against which an immune response is desired. Fused to the antigenic peptide is an intercellular spreading protein, in particular a herpes virus protein VP22 or a homologue or functional derivative thereof. Preferred spreading proteins are VP22 from HSV-1 and Marek's disease virus. The nucleic acid can encode any antigenic epitope of interest, preferably an epitope that is processed and presented by MHC class I proteins. Antigens of pathogenic organisms and cells such as tumor cells are preferred. Vaccines comprising HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein are exemplified. Also disclosed are methods of using the vaccines to induce heightened T cell mediated immunity, in particular by cytotoxic T lymphocytes, leading to protection from or treatment of a tumor.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
CE7-specific redirected immune cells
InactiveUS20060246548A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsDNA constructCell Surface Proteins
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Cationic lipid-mediated enhancement of nucleic acid immunization of cats
InactiveUS7314627B2Enhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationParenteral route
The present invention relates to a method to introduce a nucleic acid molecule into a felid by administration of a nucleic acid-cationic lipid complex composition. The method includes the step of administering to the felid, by a parenteral route, a nucleic acid-cationic lipid complex to elicit and / or enhance an immune response. In one embodiment, this method enhances the immune response in a felid compared to a method in which a naked DNA vaccine is administered to a felid. Also provided is a method to deliver a nucleic acid to a felid. This method comprises parenterally administering to the felid a composition that includes a nucleic acid molecule complexed with a cationic lipid.
Owner:HESKA
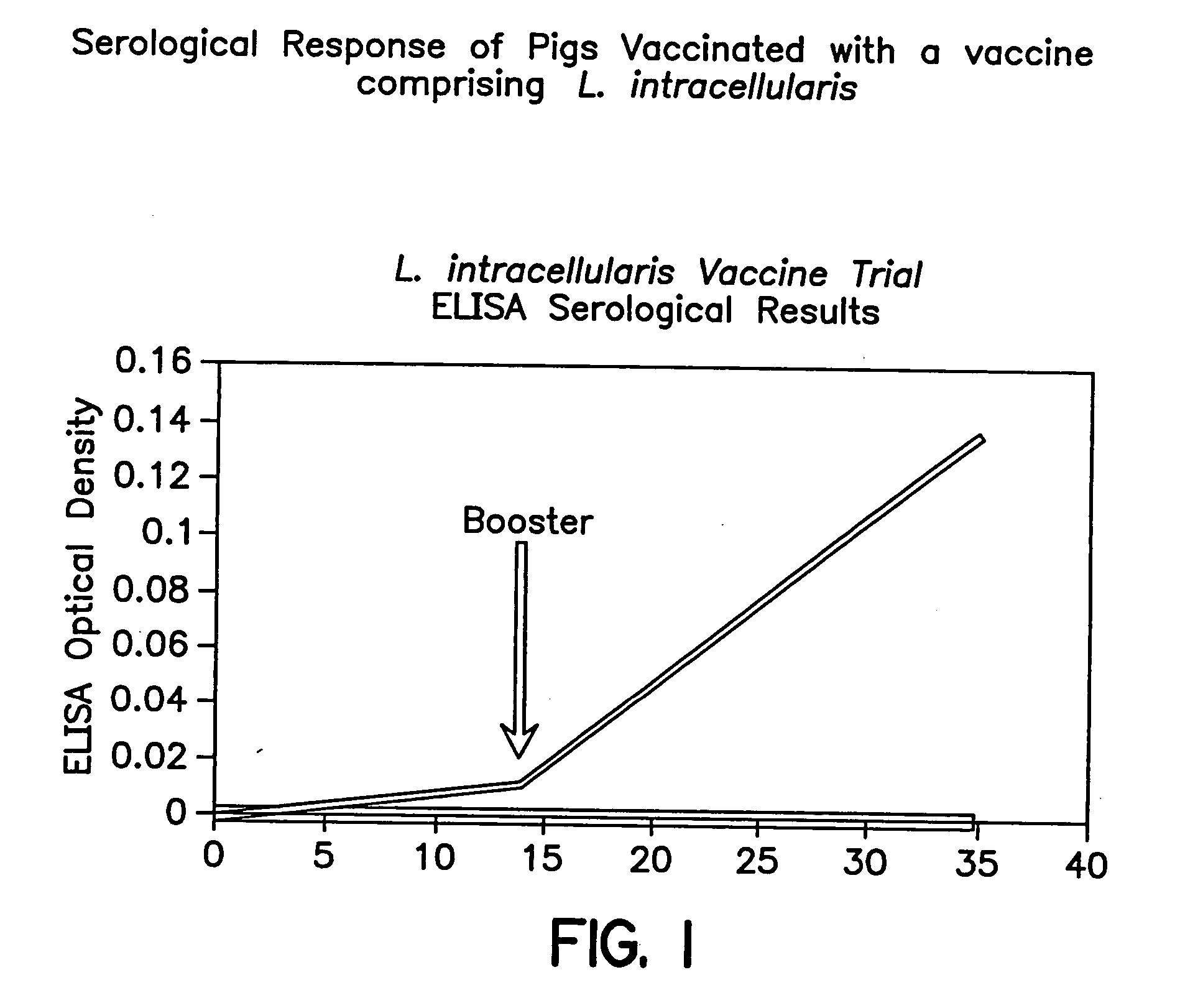
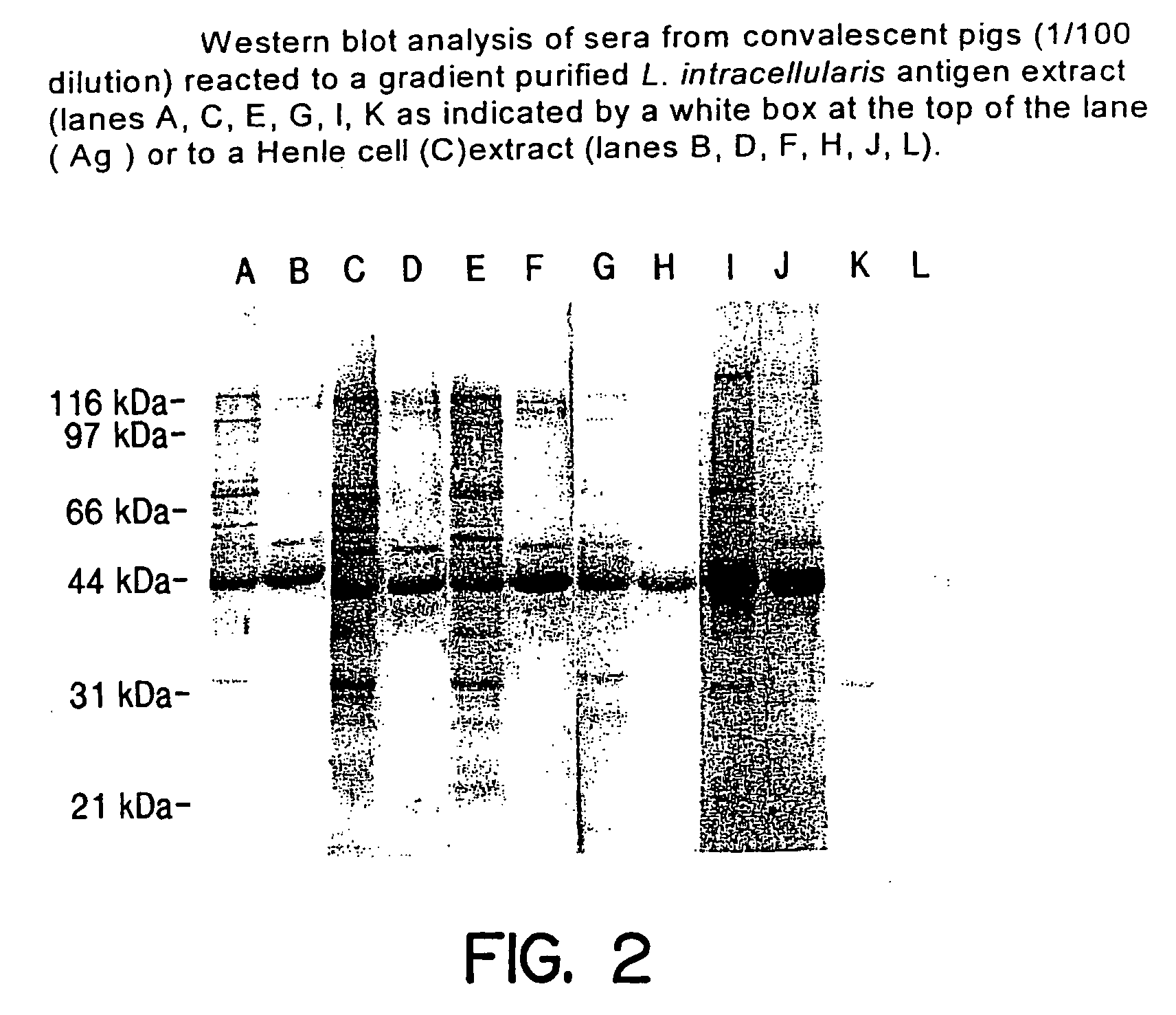
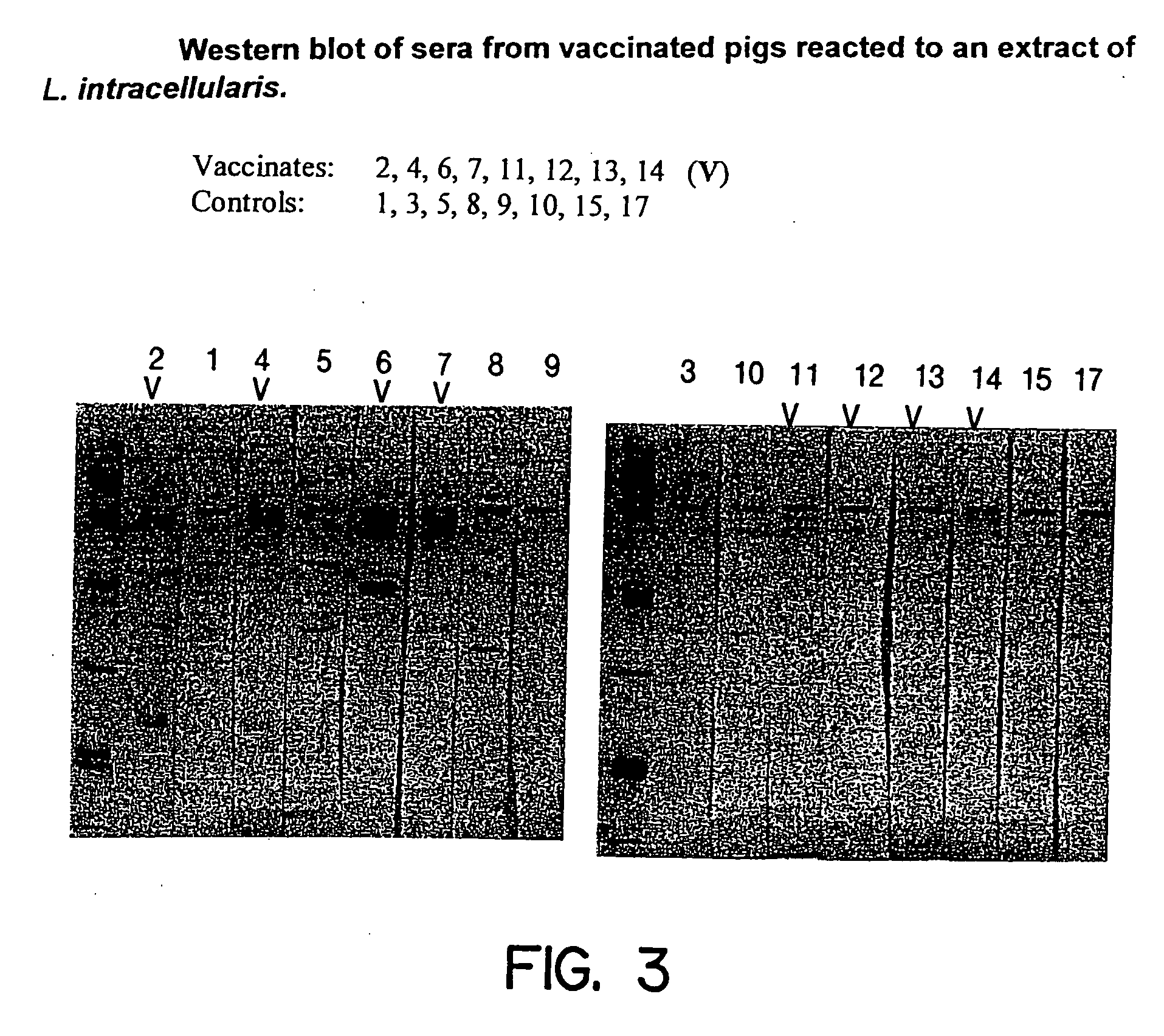
Vaccines for proliferative ileitis and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20060193874A1Avoid developmentAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantVaccine Production
A proliferative ileitis vaccine comprising tissue culture grown Lawsonia intracellularis and methods of making said vaccines. Proliferative ileitis vaccines described include those containing whole L. intracellularis, extracts of L. intracellularis, protective immunogenic subunits of L. intracellularis, recombinant immunogens of L. intracellularis and naked DNA of L. intracellularis. The vaccines of this invention may be inactivated or modified live and contain adjuvants and / or stabilizers. The vaccines of this invention may be in a liquid or lyophilized form. Also disclosed are monoclonal antibodies which neutralize the growth of L. intracellularis and which may be used for diagnosing proliferative ileitis as well as for quantitating antigen during vaccine production.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Influenza vaccines
ActiveUS20100160421A1Less protectionBroad and efficient immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsHemagglutininSaline injection
Described herein are vaccines and the use of naked DNA and / or RNA encoding hemagglutinin (HA) from pandemic influenza, e.g., the 1918 H1N1 and / or the 1957 H2N2 and / or the 1968 H3N2 influenza A virus, as a vaccine component against present day and coming H1, H2, H3, H5, N1, N2 containing influenza A infections in humans and swine optionally with the naked DNA and / or RNA encoding Neuraminidase (NA) and / or matrix protein (M) and / or the nucleoprotein (NP) from pandemic influenza virus included. If the vaccine components are used as DNA or RNA vaccines with or without the corresponding protein, the codons can optionally be “humanized” using preferred codons from highly expressed mammalian genes and the administration of this DNA vaccine can be by saline or buffered saline injection of naked DNA or RNA, or injection of DNA plasmid or linear gene expressing DNA fragments coupled to particles. Addition of the matrix protein (M) and / or the nucleoprotein (NP) from the 1918 influenza strain is also disclosed.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Prostatic cancer vaccine
InactiveUS20060024316A1Eliminate the problemAntibody ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsAntigenBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Vaccines capable of eliciting an immune antitumor response for prostate tumors are disclosed. The active ingredient in such vaccines is selected from the group consisting of at least one antigen over-represented in the prostate gland or an immunologically effective portion thereof; an expression system capable of generating in situ said antigen or portion; a naked DNA encoding such antigen and portion; and an anti-idiotypic antibody or fragment thereof which mimics said antigen or portion.
Owner:SPITLER LYNN E +1
Molecular Vaccine Linking an Endoplasmic Reticulum Chaperone Polypeptide to an Antigen
InactiveUS20090148471A1Increase the number ofOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsReticulum cellT lymphocyte
This invention provides compositions and methods for inducing and enhancing immune responses, such as antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses, using chimeric molecules comprising endoplasmic reticulum chaperone polypeptides and antigenic peptides. In particular, the invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing immune responses induced by polypeptides made in vivo by administered nucleic acid, such as naked DNA or expression vectors, encoding the chimeric molecules. The invention provides a method of inhibiting the growth of a tumor in an individual. The invention also provides novel self-replicating RNA virus constructs for enhancing immune responses induced by chimeric polypeptides made in vivo.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
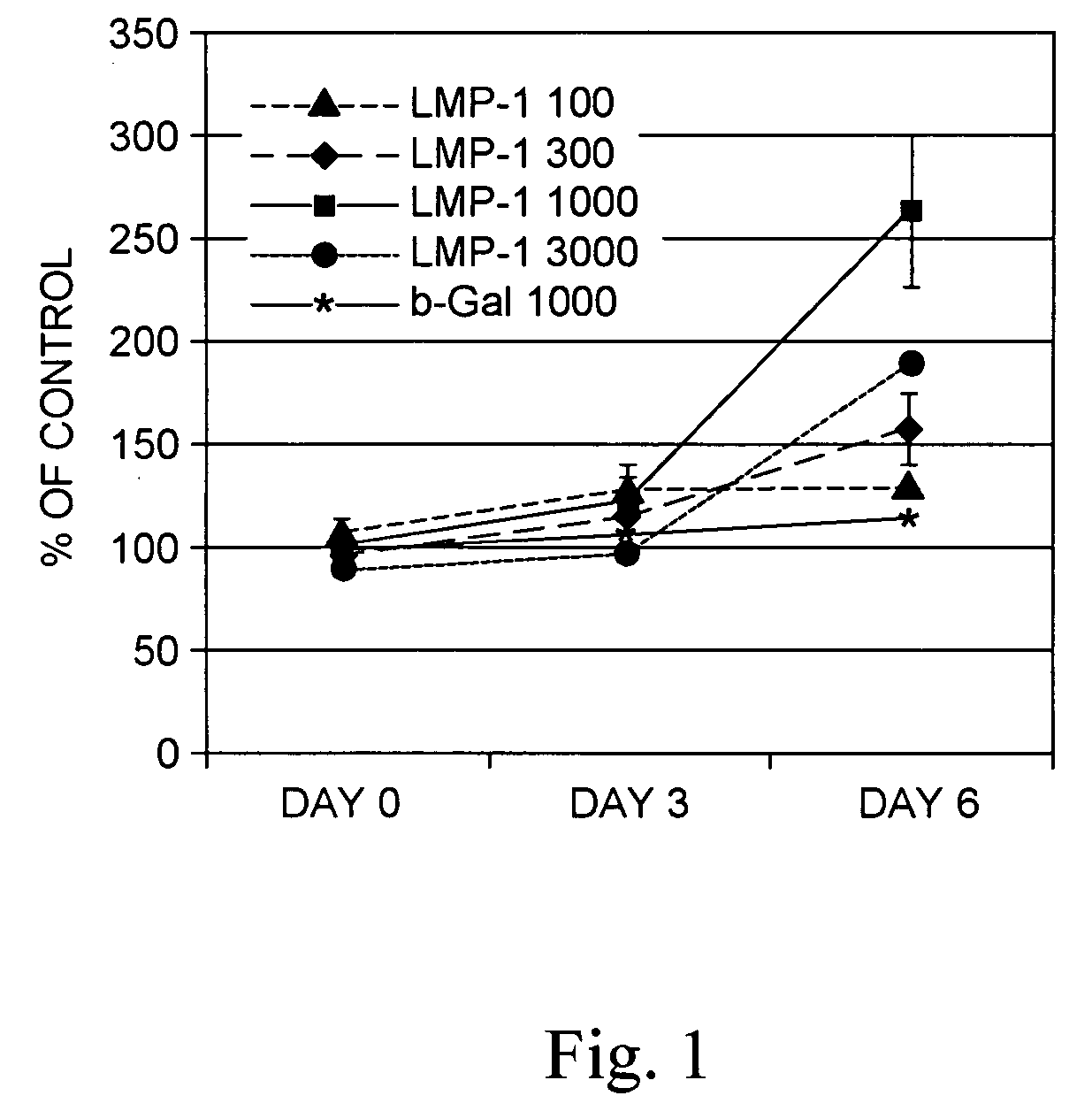
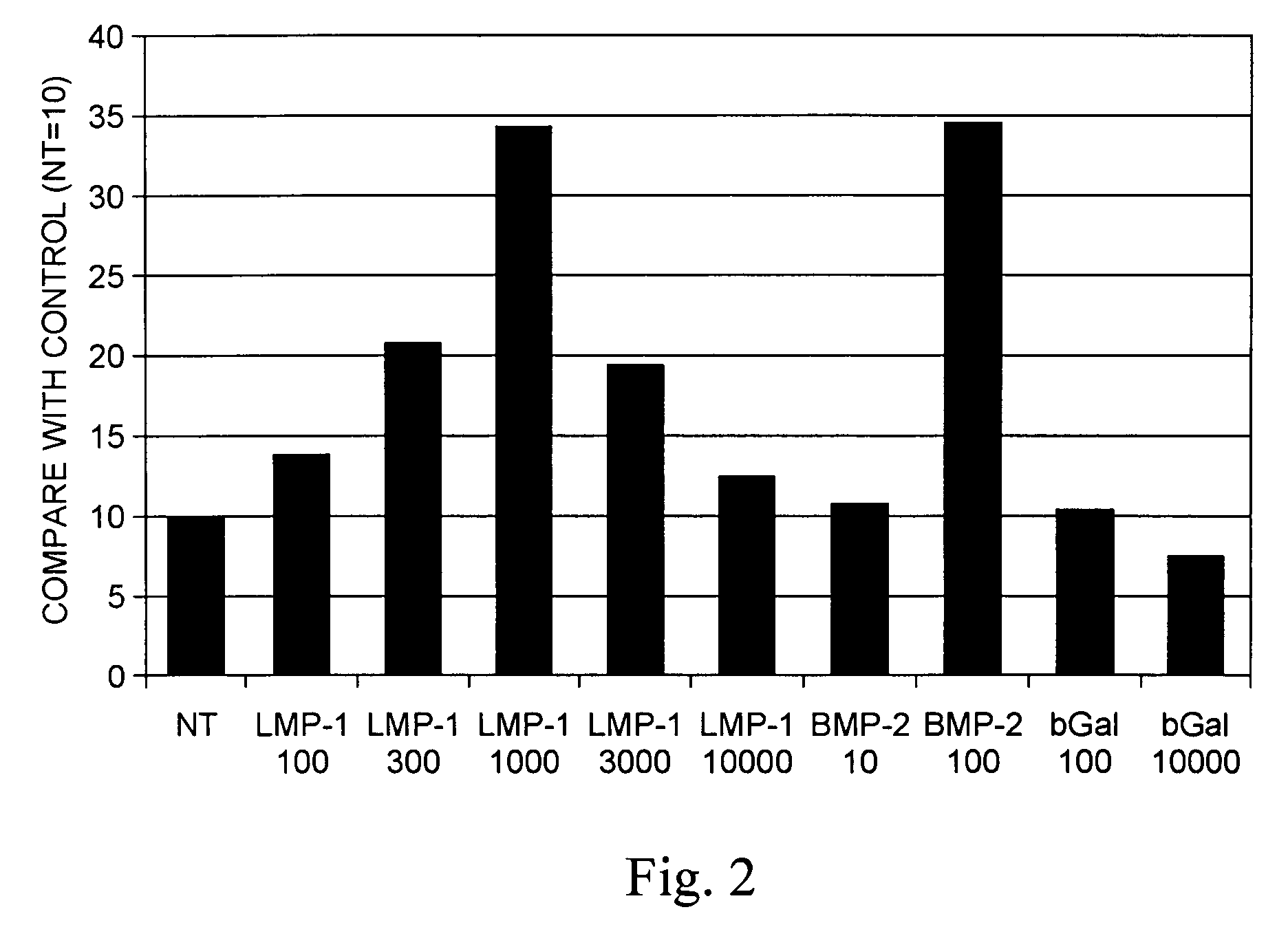
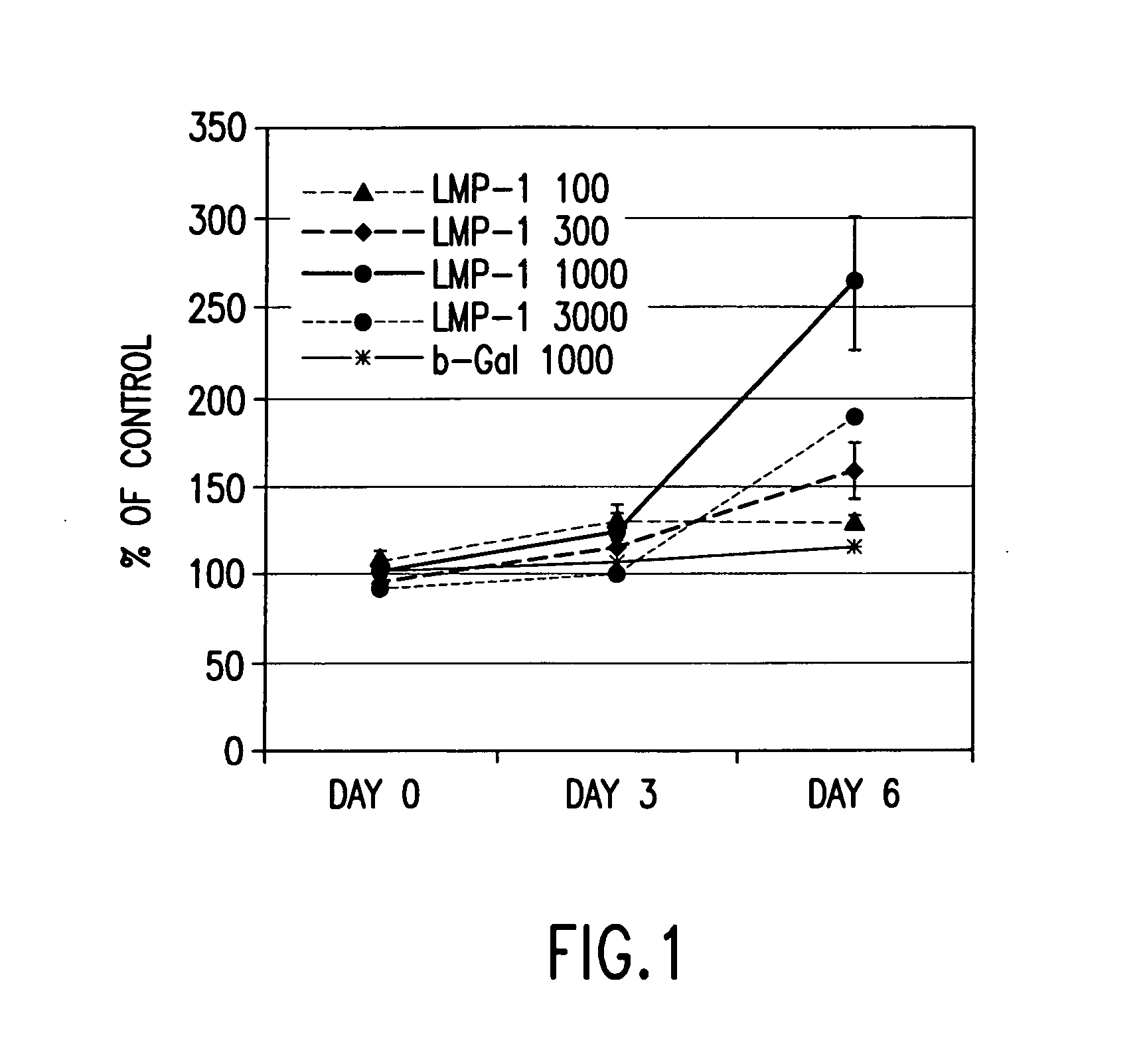
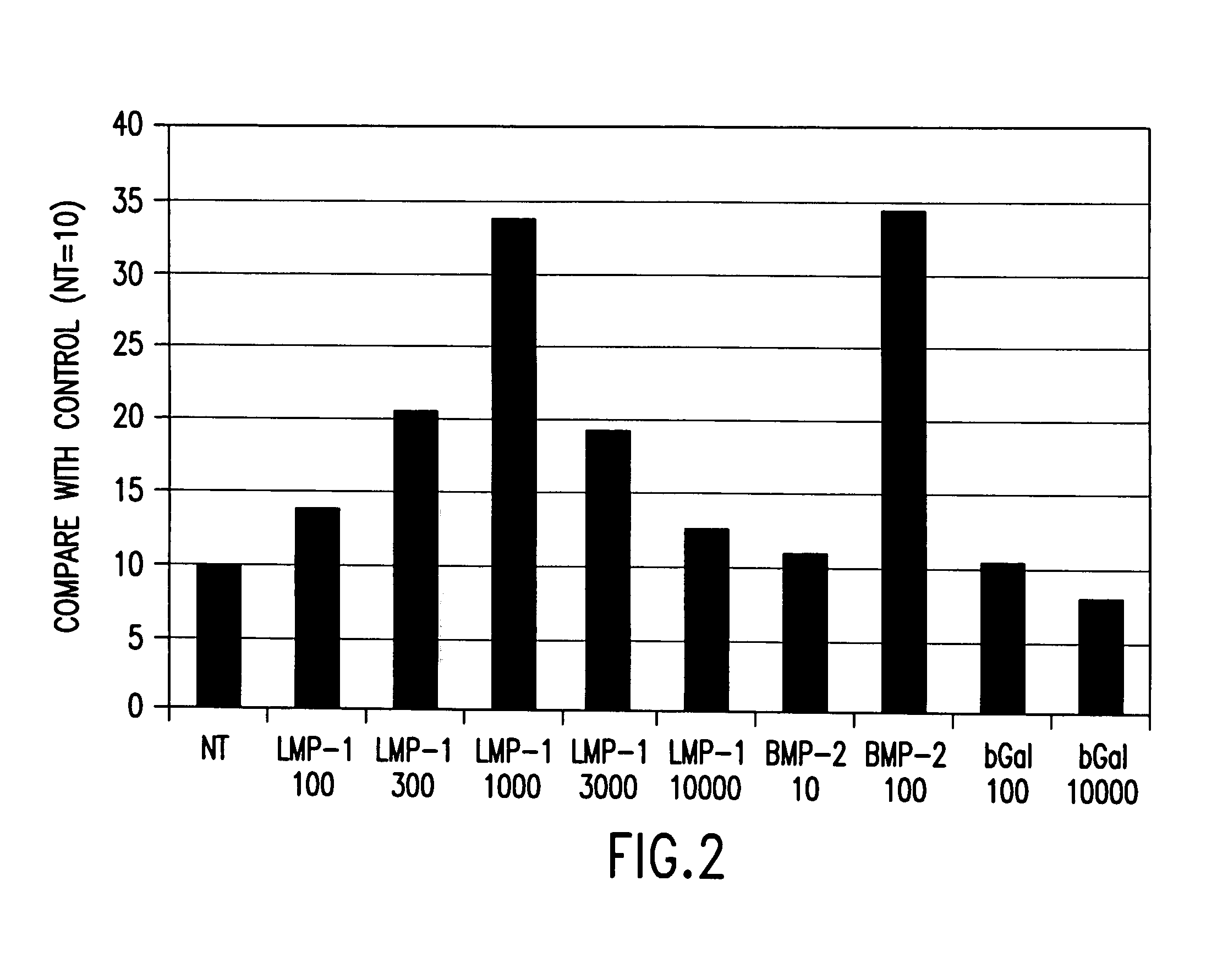
Methods of expressing LIM mineralization protein
ActiveUS20070099176A1Improve efficiencyVirusesGenetic material ingredientsEukaryotic plasmidsViral vector
Methods of expressing LIM mineralization protein in mammalian cells are described. Methods of expressing LIM mineralization protein and assessing glycosylation of the LIM mineralization protein in prokaryotic and non-mammalian eukaryotic cells are also described. The methods involve transfecting the cells with an isolated nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a LIM mineralization protein. Transfection may be accomplished in vitro, ex vivo or in vivo by direct injection of virus or naked DNA, or by a nonviral vector such as a plasmid.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Methods and compositions for the delivery of nucleic acids to seeds
InactiveUS20150040268A1Simple and efficientWiden meansOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationMicroorganismEukaryotic plasmids
The present invention relates to methods of seed treatment and introduction of nucleic acid particles into intact seeds. In particular, the methods are non-priming seed treatment protocols capable of delivering naked DNA plasmids into seeds, without the use of microorganism or any additional means, and which are not plant species limited.
Owner:MORFLORA ISRAEL
Nucleic acid therapy to enhance cartilage repair
InactiveUS20050197304A1Promote repairFacilitating regeneration of cartilagePowder deliveryCarbohydrate active ingredientsDNA constructActive agent
The present invention relates to the application of nucleic acid therapy for the repair and regeneration of cartilage. The invention encompasses the introduction of naked DNA encoding bioactive agent(s), whose expression stimulates and otherwise facilitates the repair and regeneration of cartilage. The present invention provides DNA constructs for introduction to the site of cartilage damage. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising nucleic acid encoding one or more bioactive factor, optionally with a matrix or polymer, are provided. Methods for expression of bioactive agent(s) are provided. Methods for enhancing cartilage repair and / or regeneration comprising introduction of bioactive factors as naked DNA are further provided. Methods for the treatment or prevention of cartilage damage in various orthopaedic and rheumatologic conditions are provided.
Owner:NEW YORK SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Recombinant plasmid capable of efficiently expressing human liver growth factor in eukaryotic cell
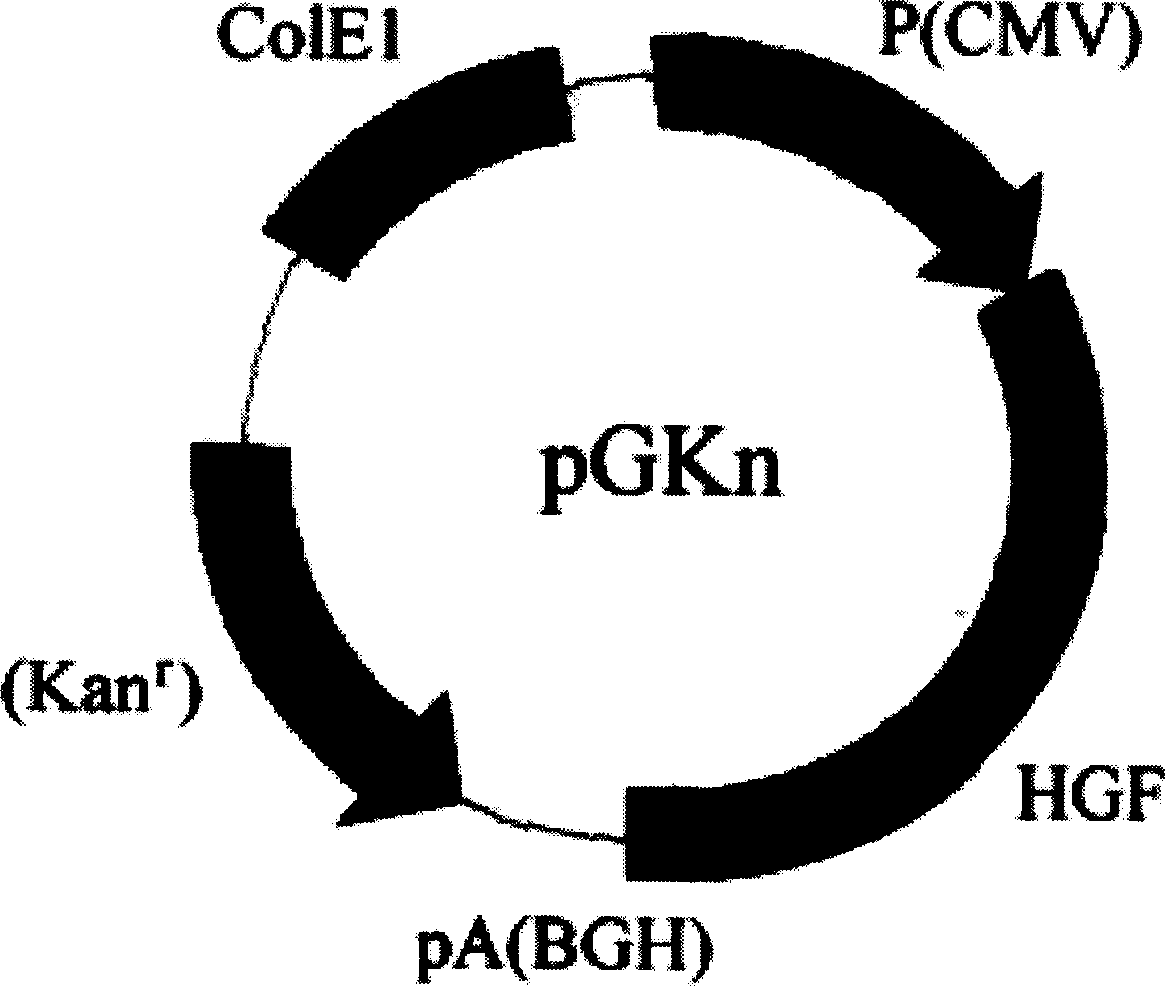
The invention relates to the naked DNA gene therapeutic category in biomedical domain. When the invention constructs the people,s hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) recombinant plasmid, it introduces partial included subsequence of HGF genomere DNA sequence, which makes the expression quantity of the said recombinant plasmid in eukaryotic cell largely increased (about 100 times) compared with the recombinant plasmid of cDNA sequence and accordingly overcomes the weak therapeutic efficacy problem caused by low therapeutic rate of present naked DNA gene.
Owner:BEIJING NORTHLAND BIOTECH
Nucleic Acid and Amino Acid Sequences, and Vaccine for the Control of Ectoparasite Infestations in Fish
ActiveUS20130280290A1Potential for inducing immune responseInduce immune responseFodderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenBiology
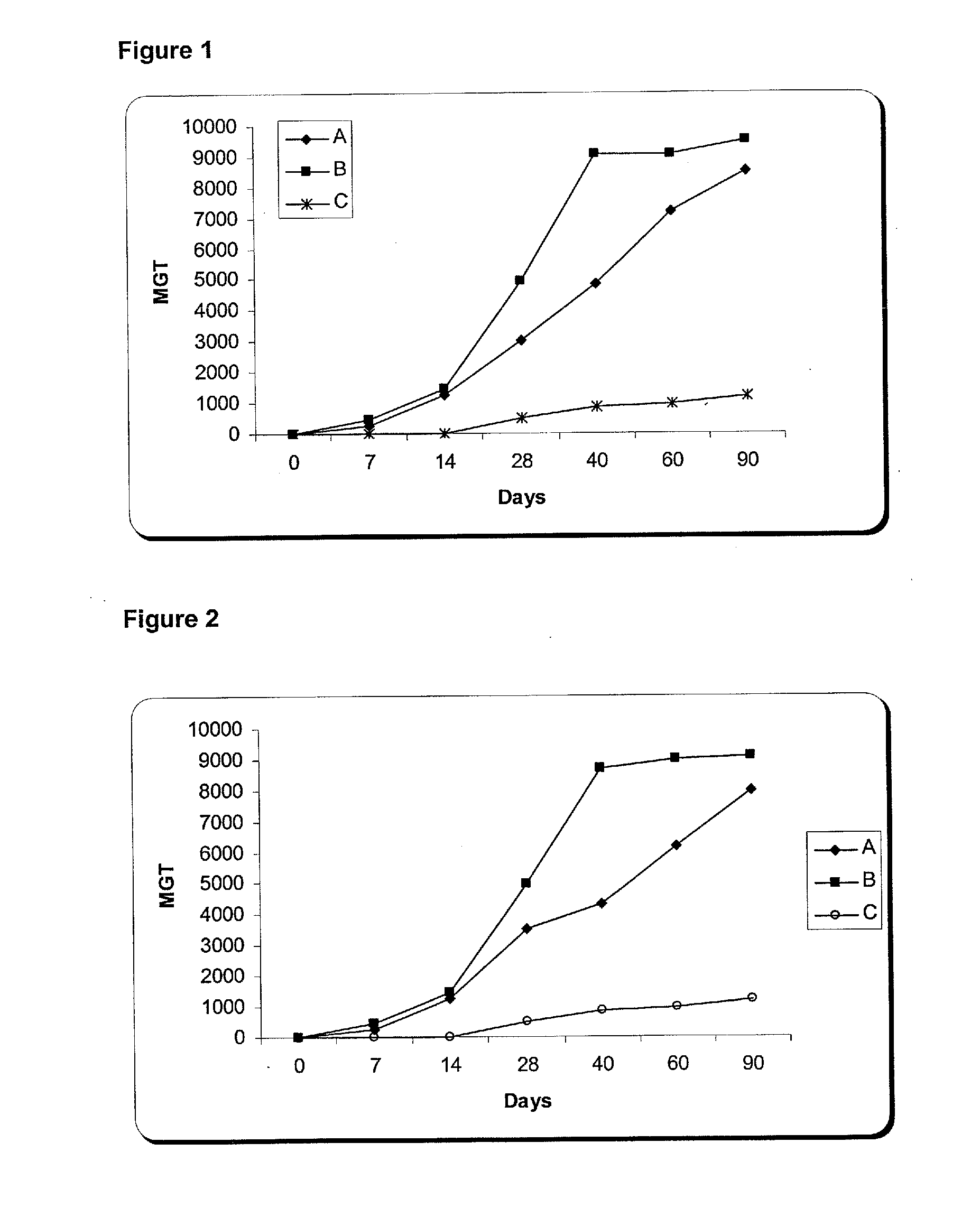
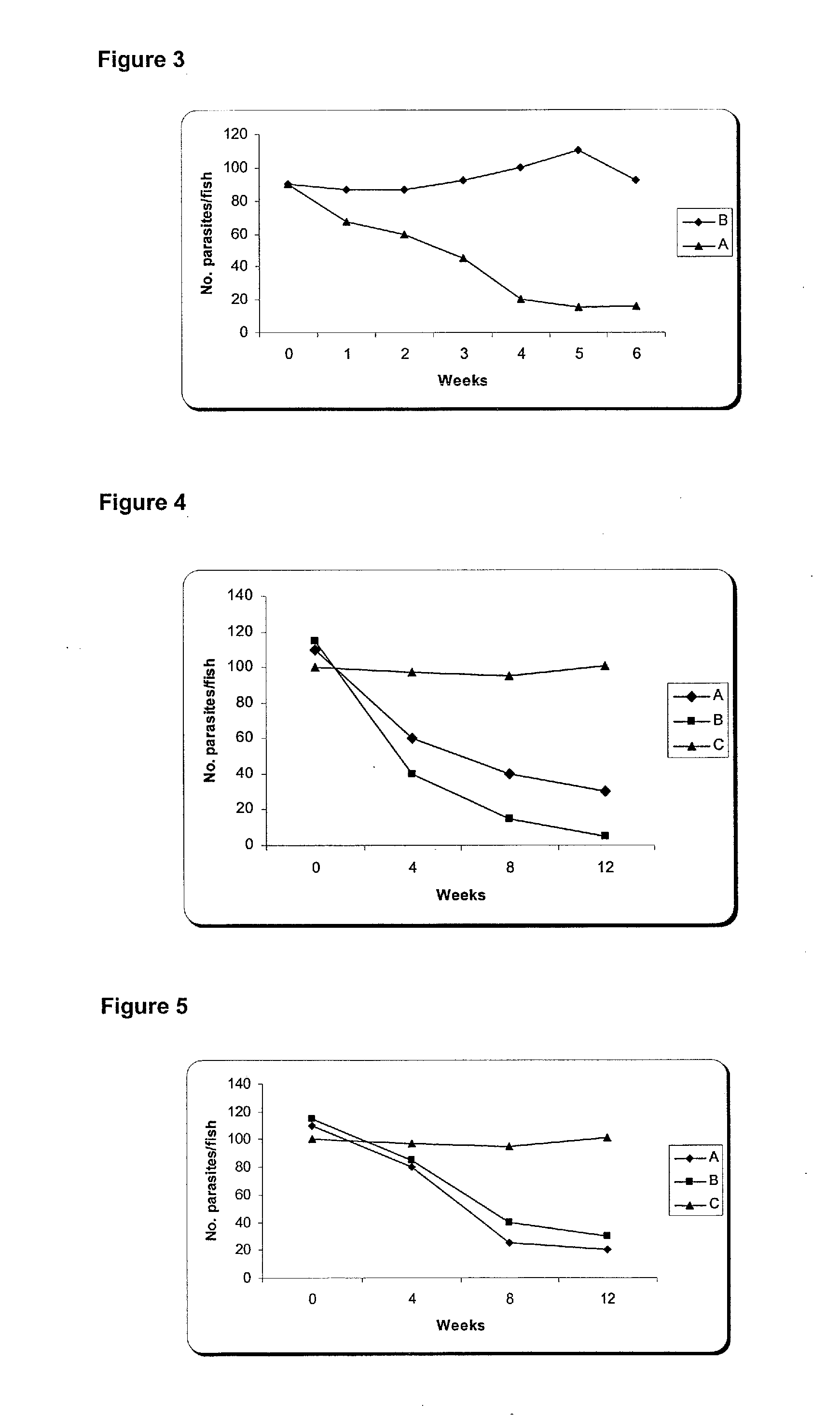
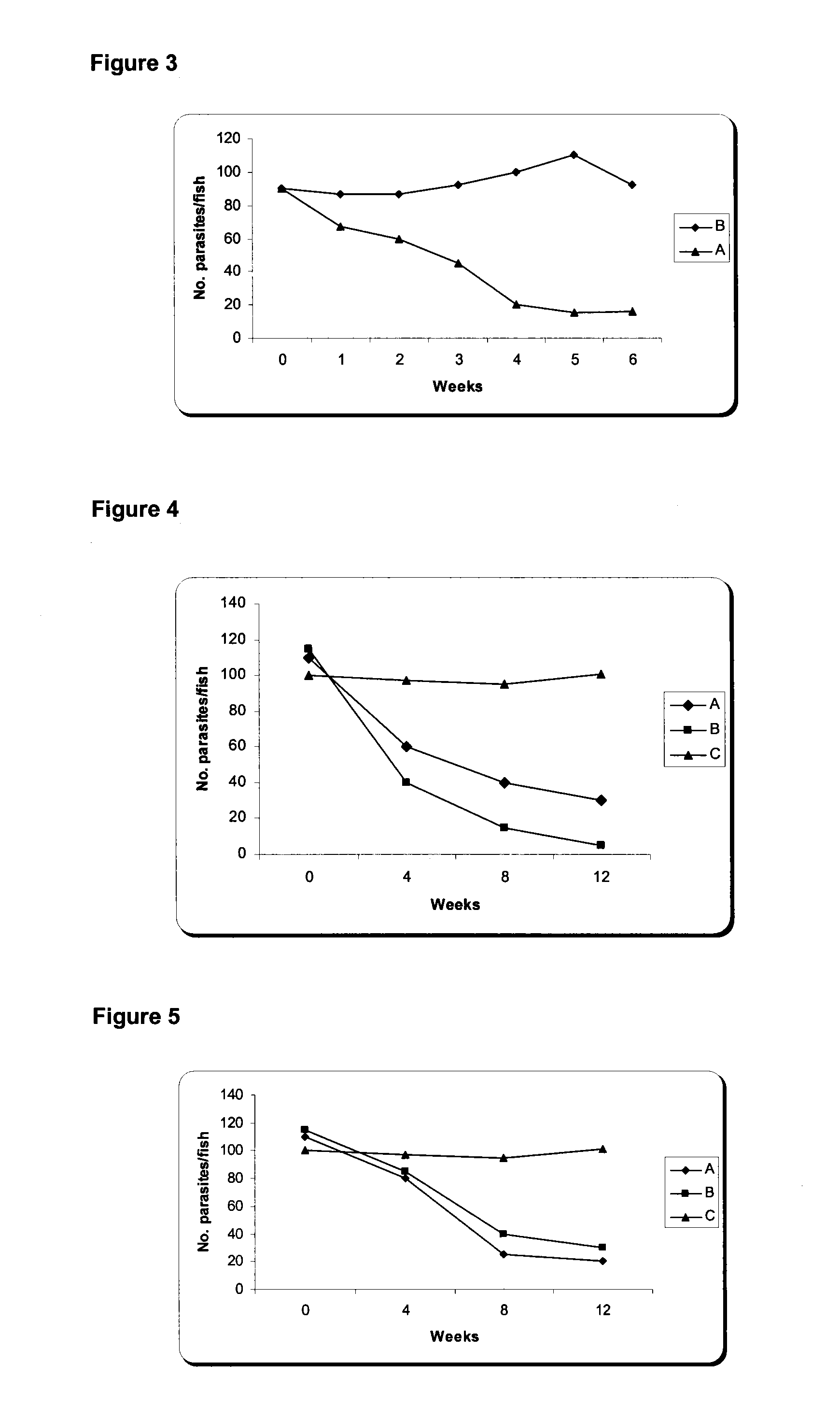
The present invention is related with the isolation and cloning of a new gene, the production of the protein encoded by this gene by using recombinant systems, and the use of this antigen in a vaccine formulation as a purified protein and / or naked DNA, to induce an immune response in aquatic organisms against different ectoparasite species, including the known as sea lice, and pathogens associated with these infestations. The vaccine preparations, administered by oral route, immersion bath or injection, demonstrated its efficacy by producing IgM humoral immune response and reducing the number of parasites per fish in the vaccinated fishes.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
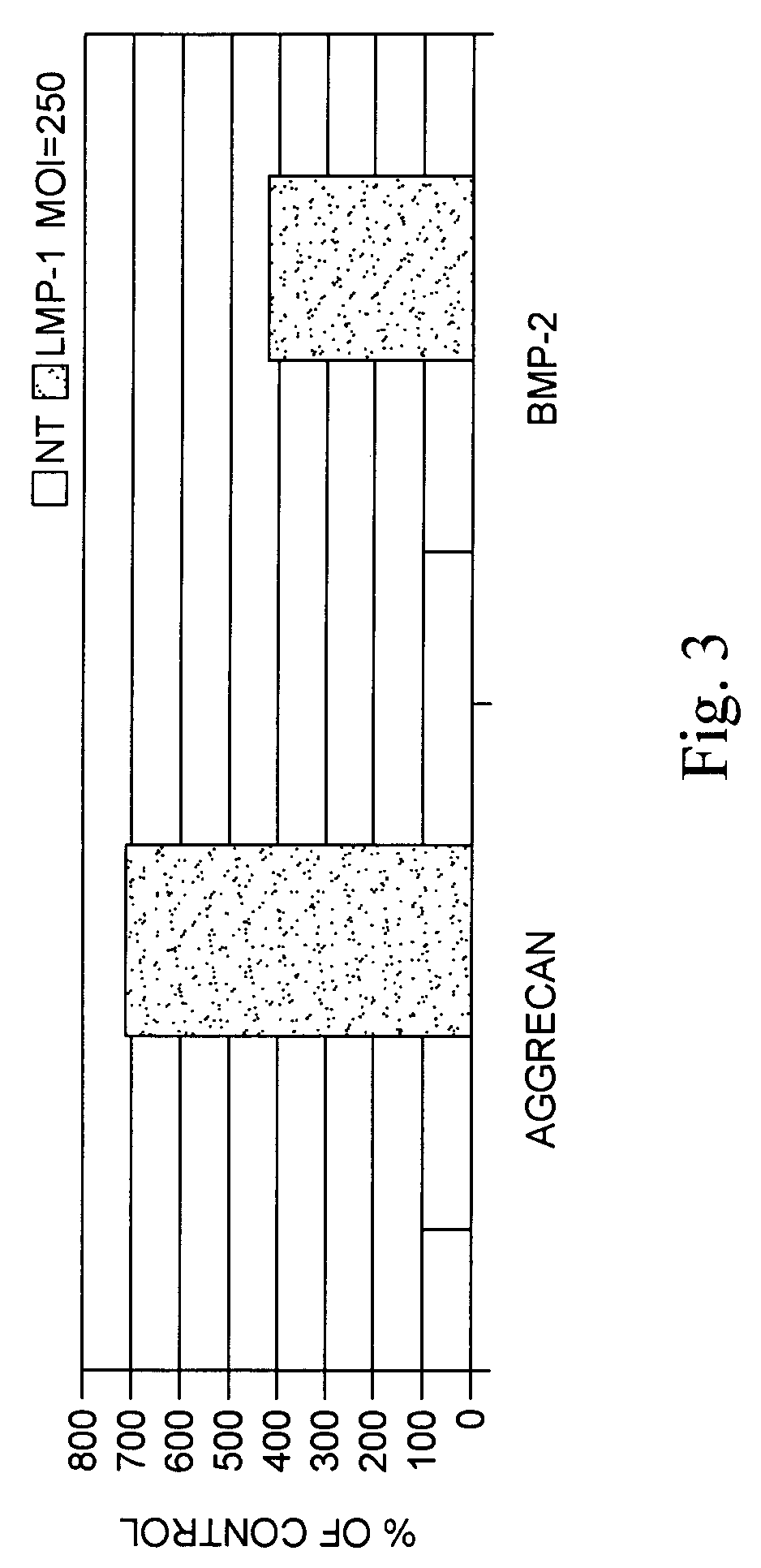
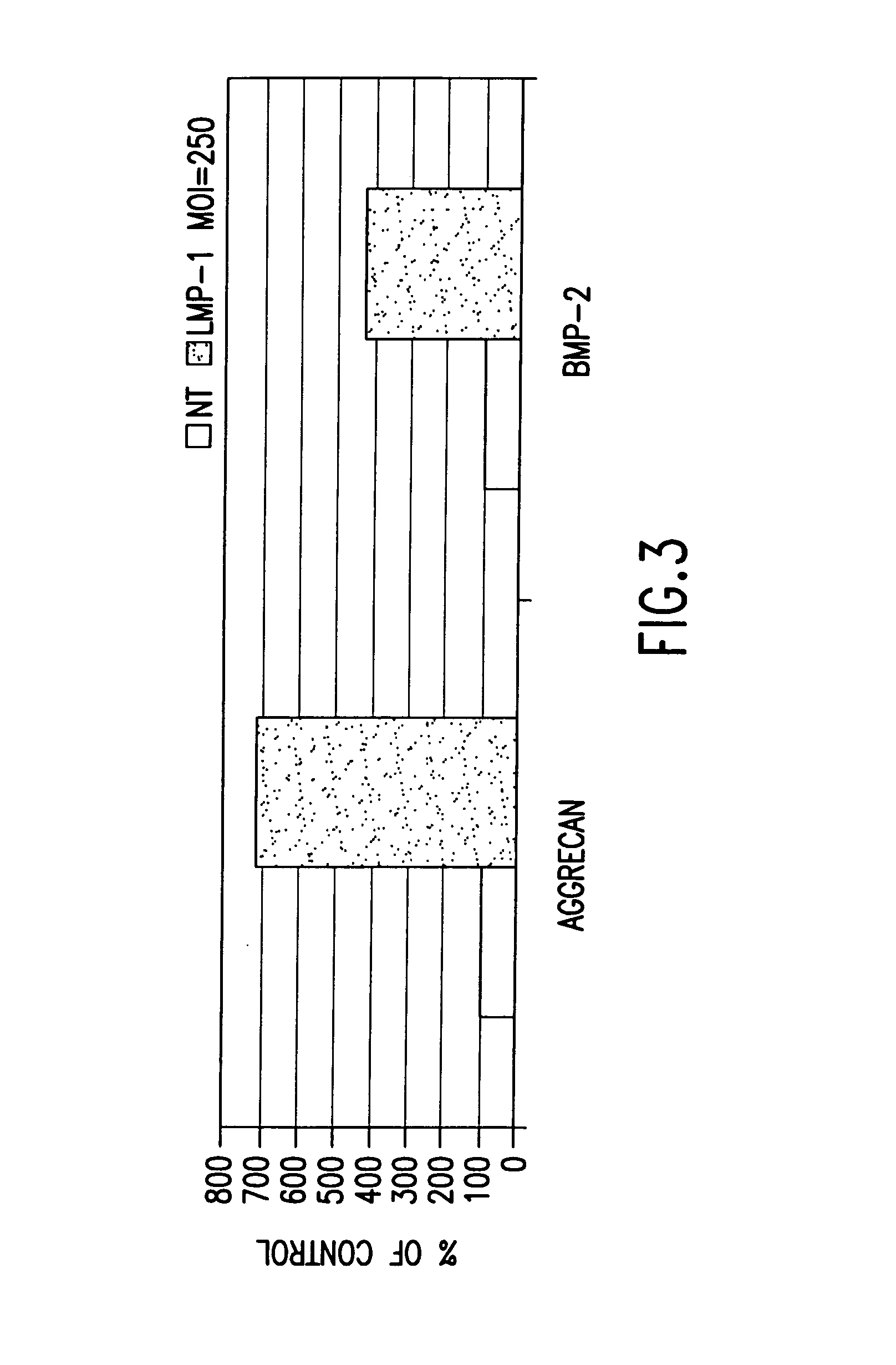
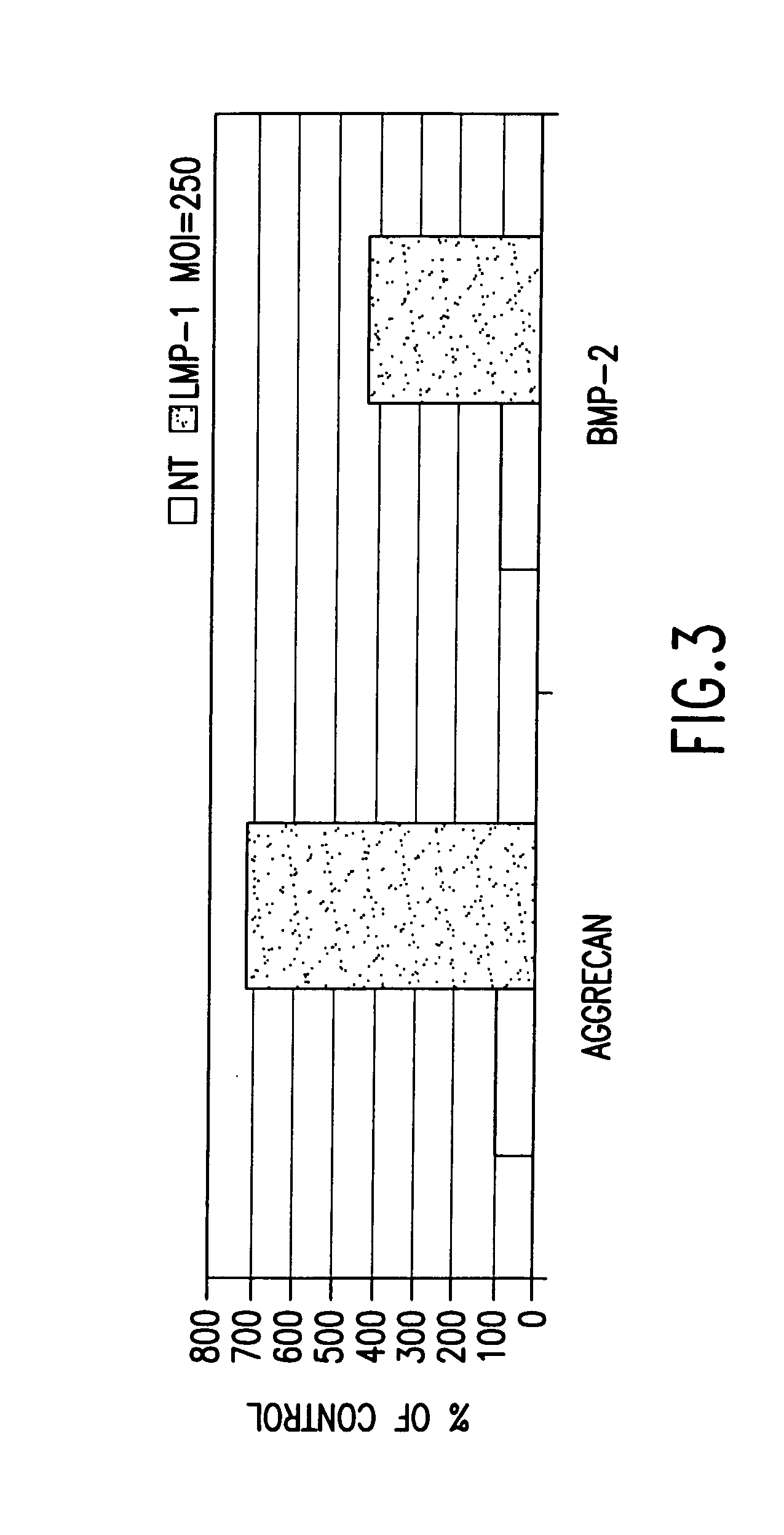
Methods of inducing or increasing the expression of proteoglycans such as aggrecan in cells
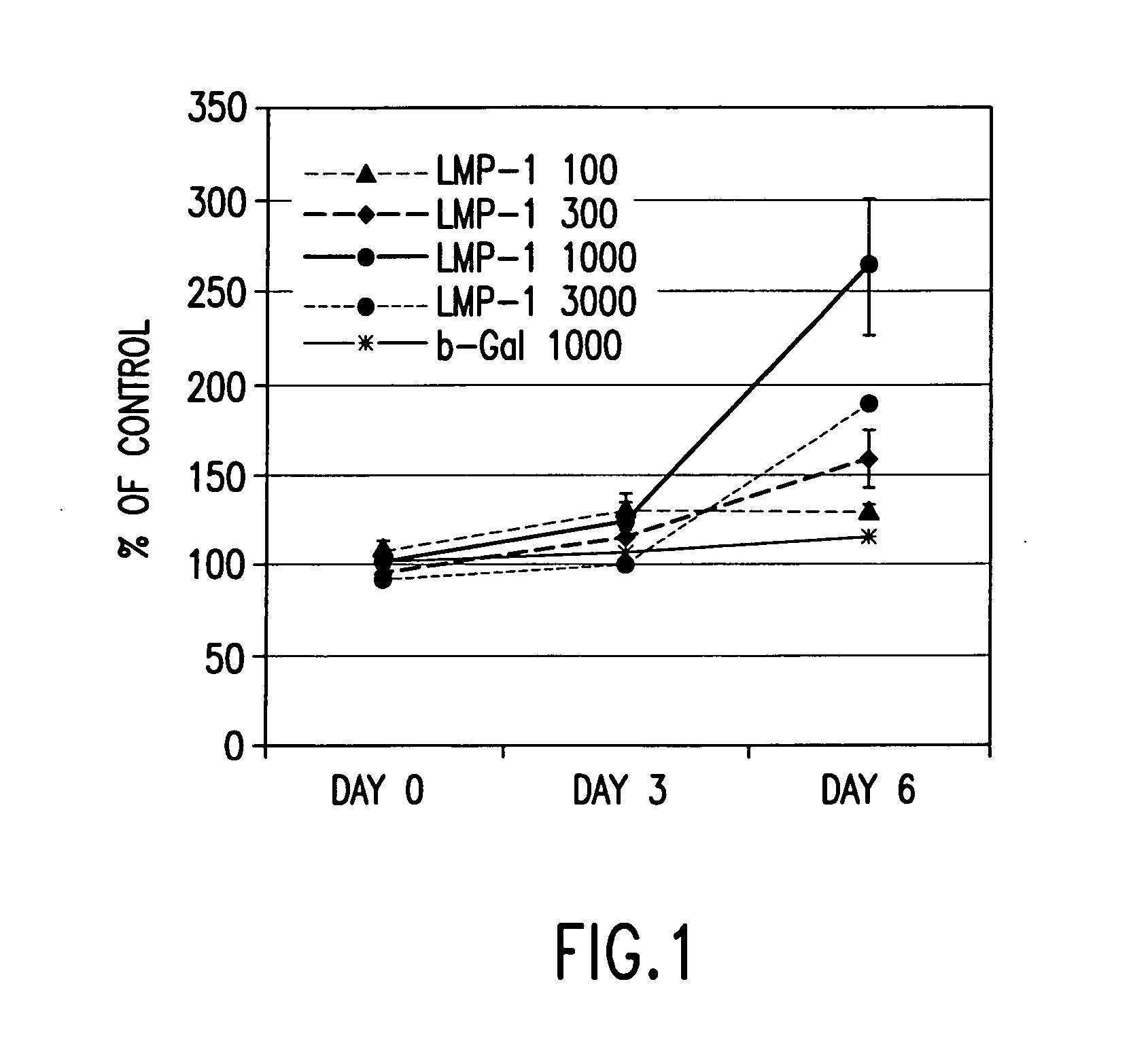
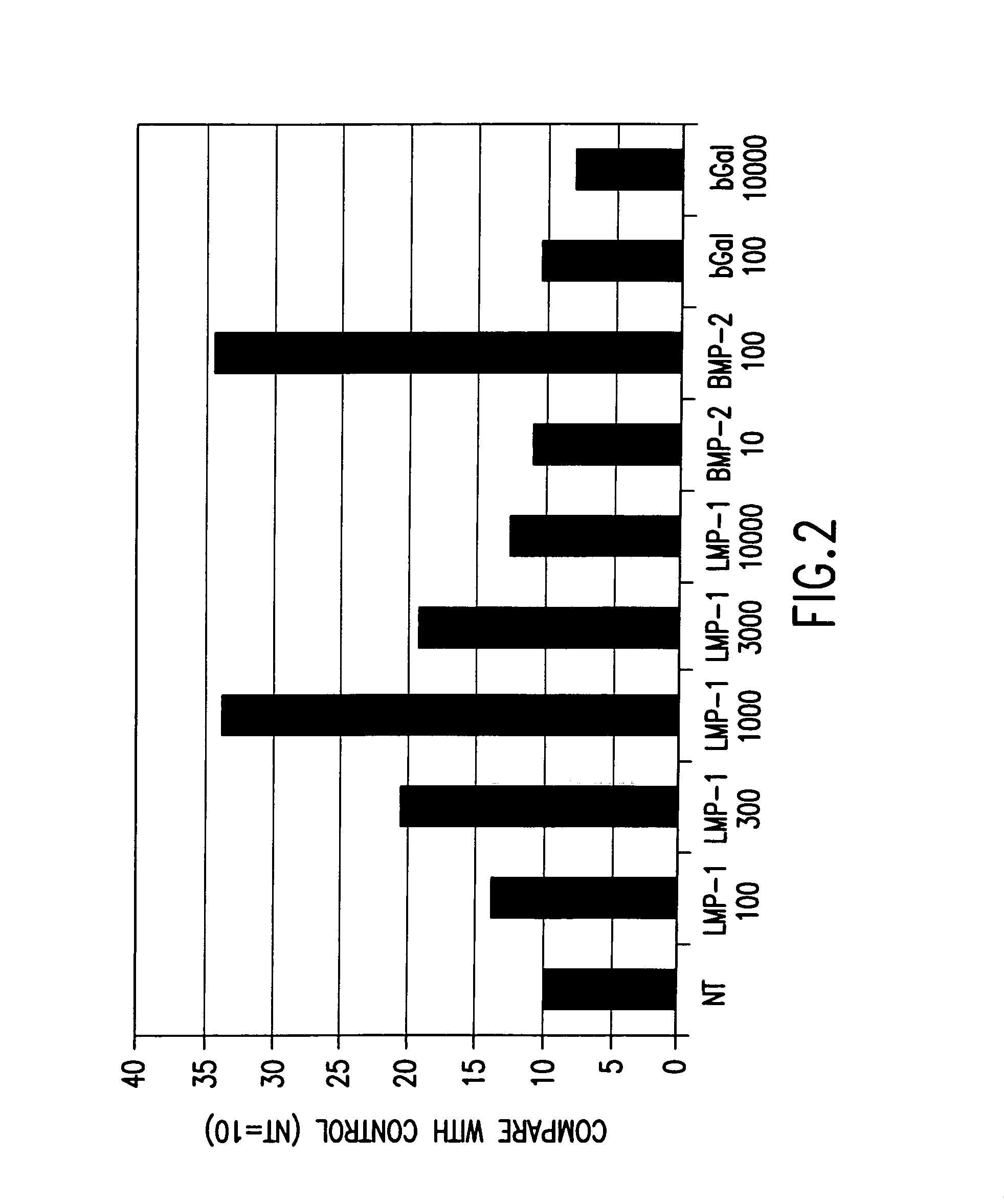
Methods of inducing the expression of a proteoglycan such as aggrecan in a cell are described. A method is described which includes transfecting a cell with an isolated nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a LIM mineralization protein operably linked to a promoter. The LIM mineralization protein can be rLMP, hLMP-1, hLMP-1s, or hLMP-3. Transfection maybe accomplished ex vivo or in vivo by direct injection of virus or naked DNA, or by a nonviral vector such as a plasmid. The method can be used to induce proteoglycan synthesis in osseous cells or to stimulate proteoglycan and / or collagen production in cells capable of producing proteoglycan and / or collagen (e.g., intervertebral disc cells including cells of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus).
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Nucleic Acid and Amino Acid Sequences, and Vaccine for the Control of Ectoparasite Infestations in Fish
ActiveUS20100221271A1Potential for inducing immune responseLose weightFodderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenOrganism
The present invention is related with the isolation and cloning of a new gene, the production of the protein encoded by this gene by using recombinant systems, and the use of this antigen in a vaccine formulation as a purified protein and / or naked DNA, to induce an immune response in aquatic organisms against different ectoparasite species, including the known as sea lice, and pathogens associated with these infestations. The vaccine preparations, administered by oral route, immersion bath or injection, demonstrated its efficacy by producing IgM humoral immune response and reducing the number of parasites per fish in the vaccinated fishes.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
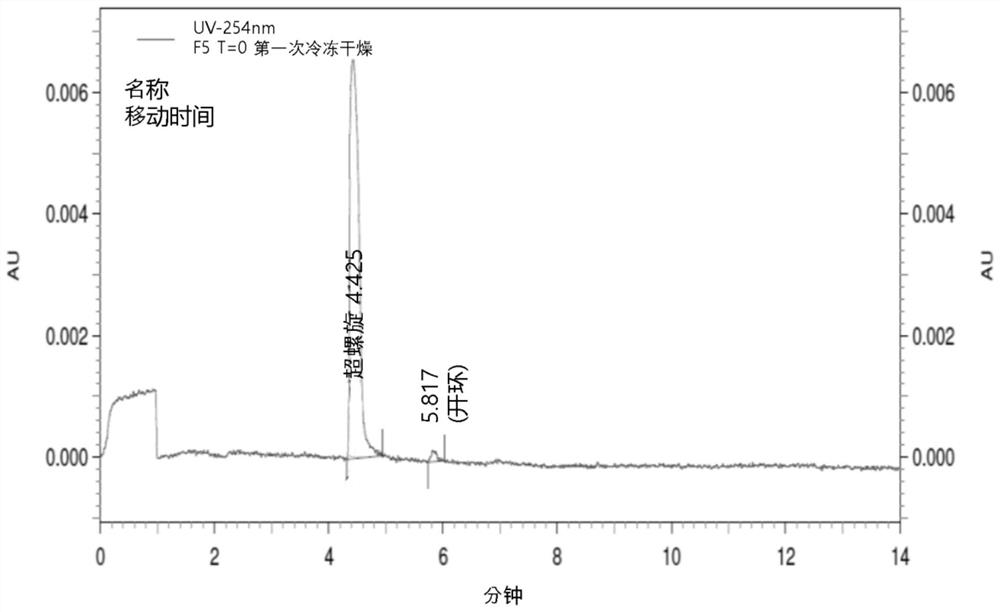
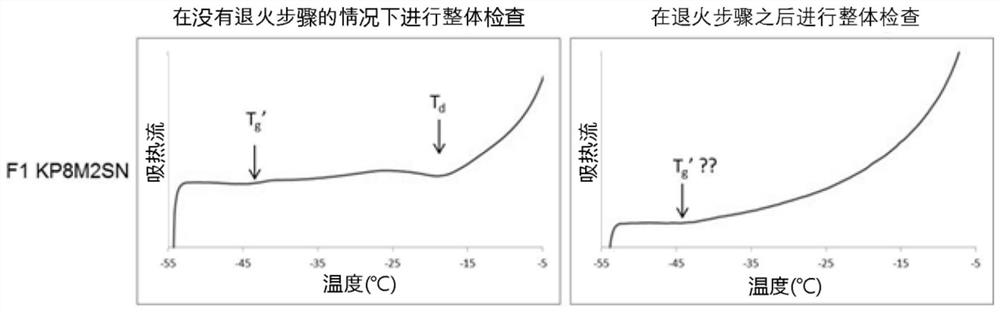
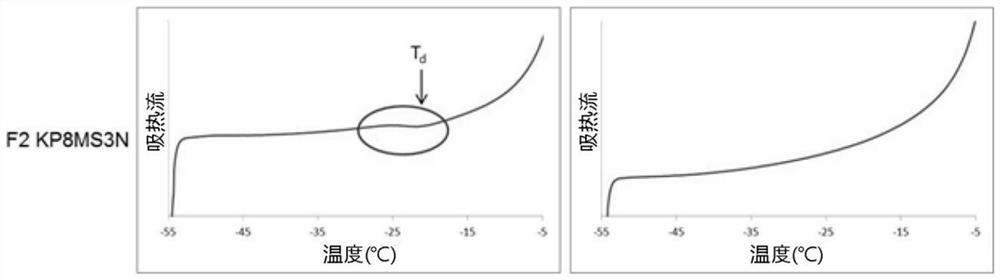
Lyophilized pharmaceutical compositions for naked DNA gene therapy
The present invention provides a novel lyophilized pharmaceutical composition that maintains the stability of a DNA plasmid while forming a uniform and elegant cake during lyophilization. The novel lyophilization formulation further allows uniform reconstitution of the DNA plasmid in a pharmaceutically acceptable solution, enabling complete recover of the active ingredients, minimizing partial loss of potency and allowing administration of the active ingredients in an accurate and consistent manner. Additionally provided herein include methods of making the lyophilized pharmaceutical composition and methods of administering the composition for treatment of various diseases.
Owner:HELIXMITH CO LTD
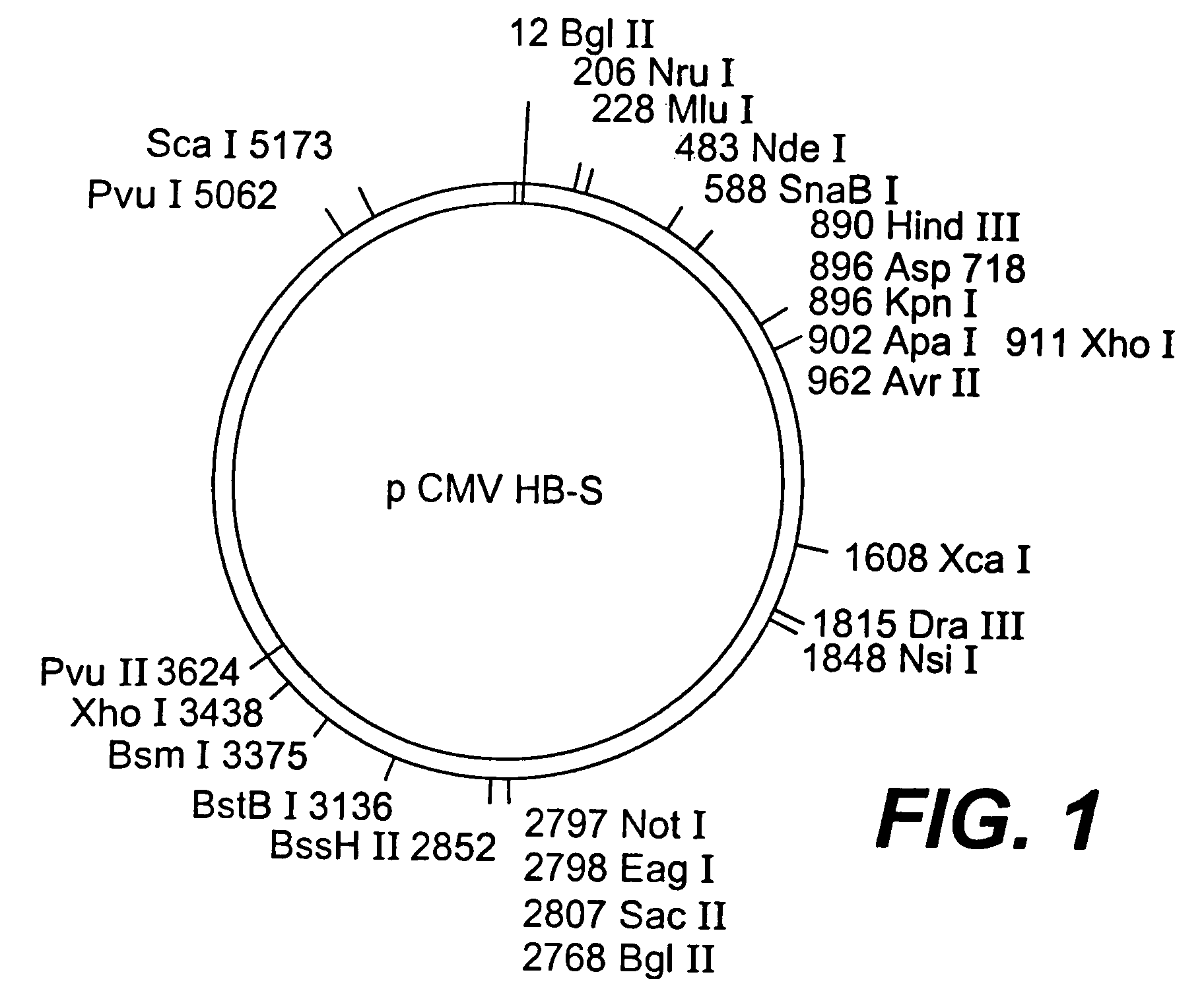
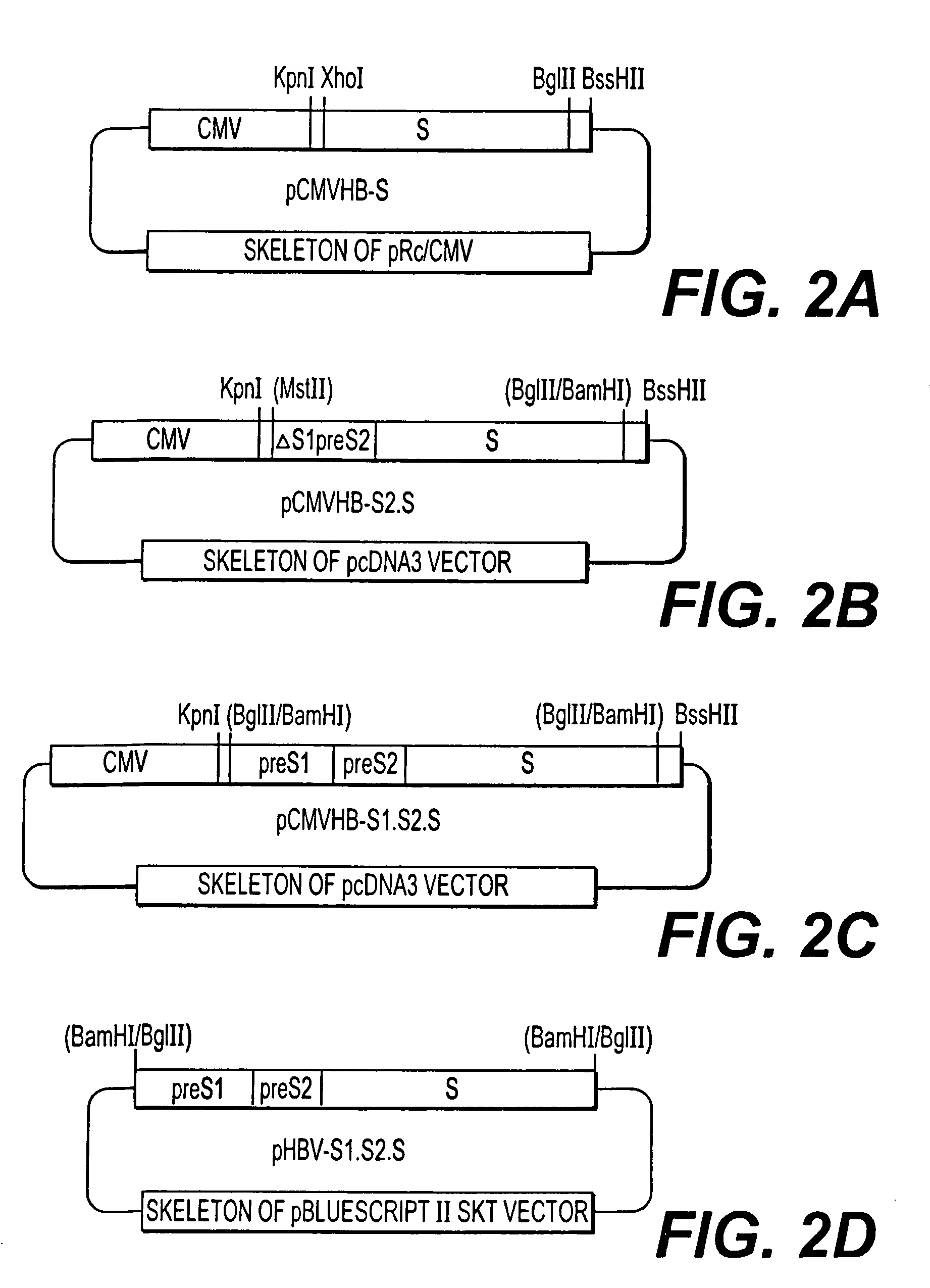
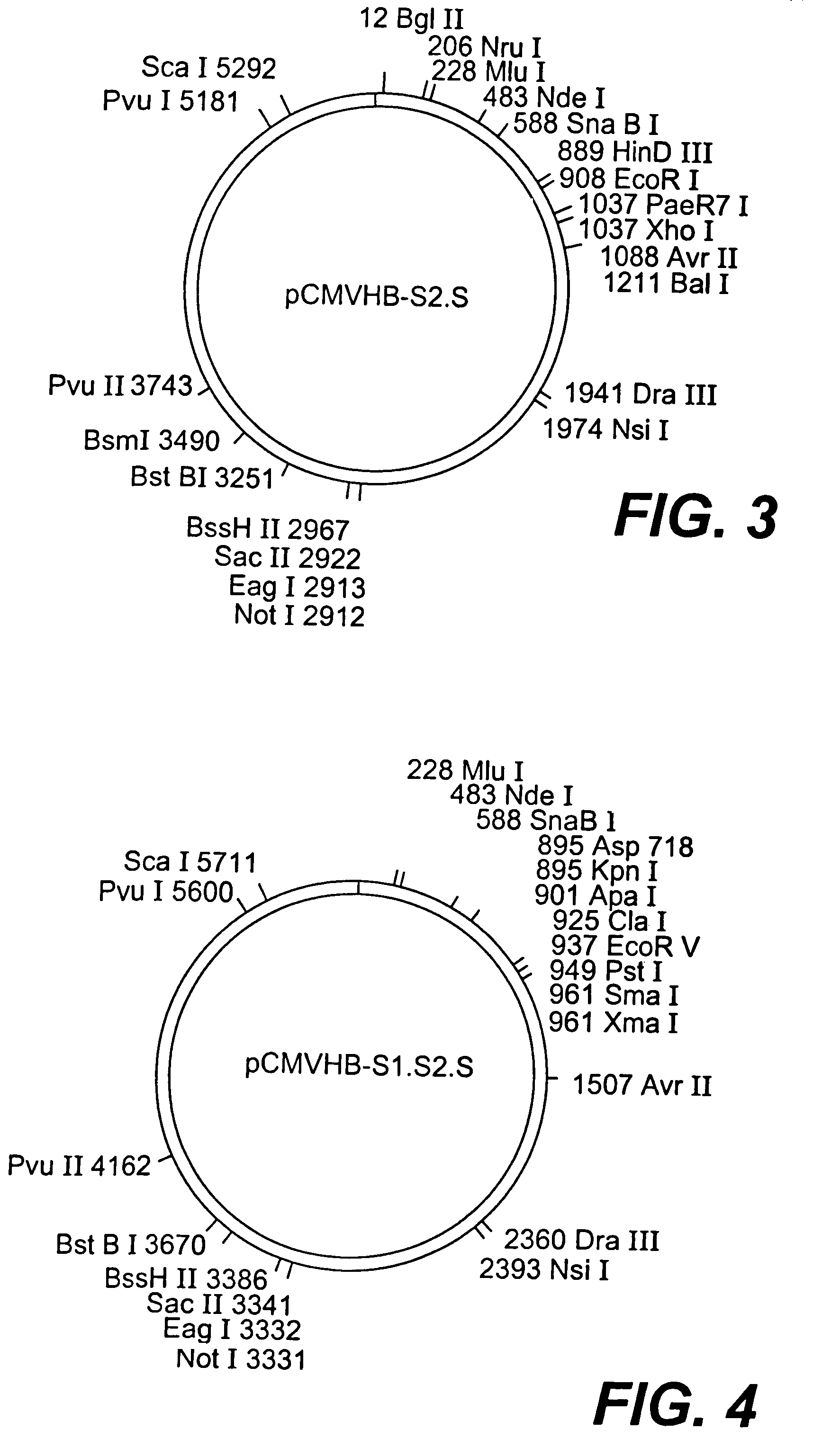
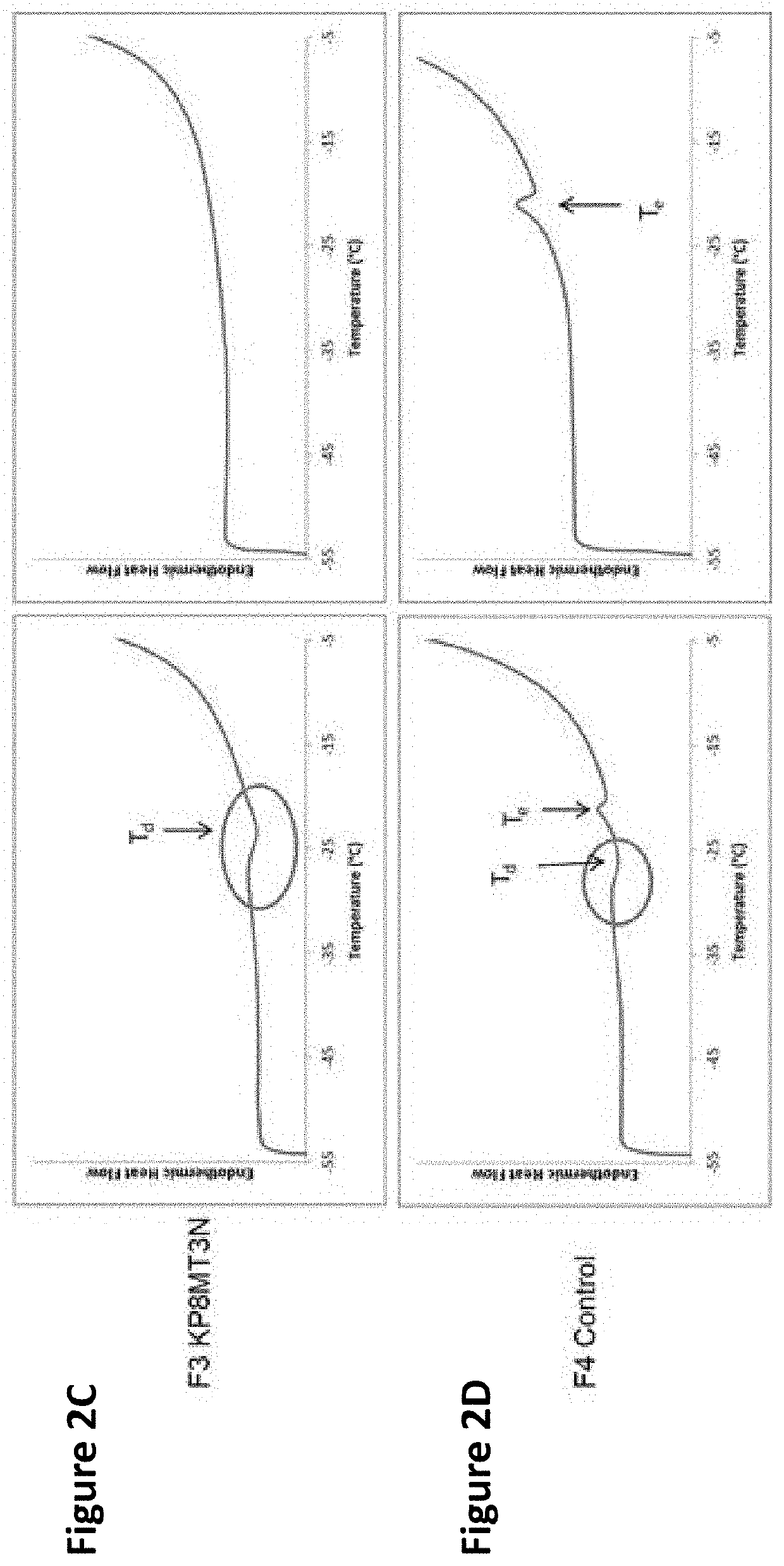
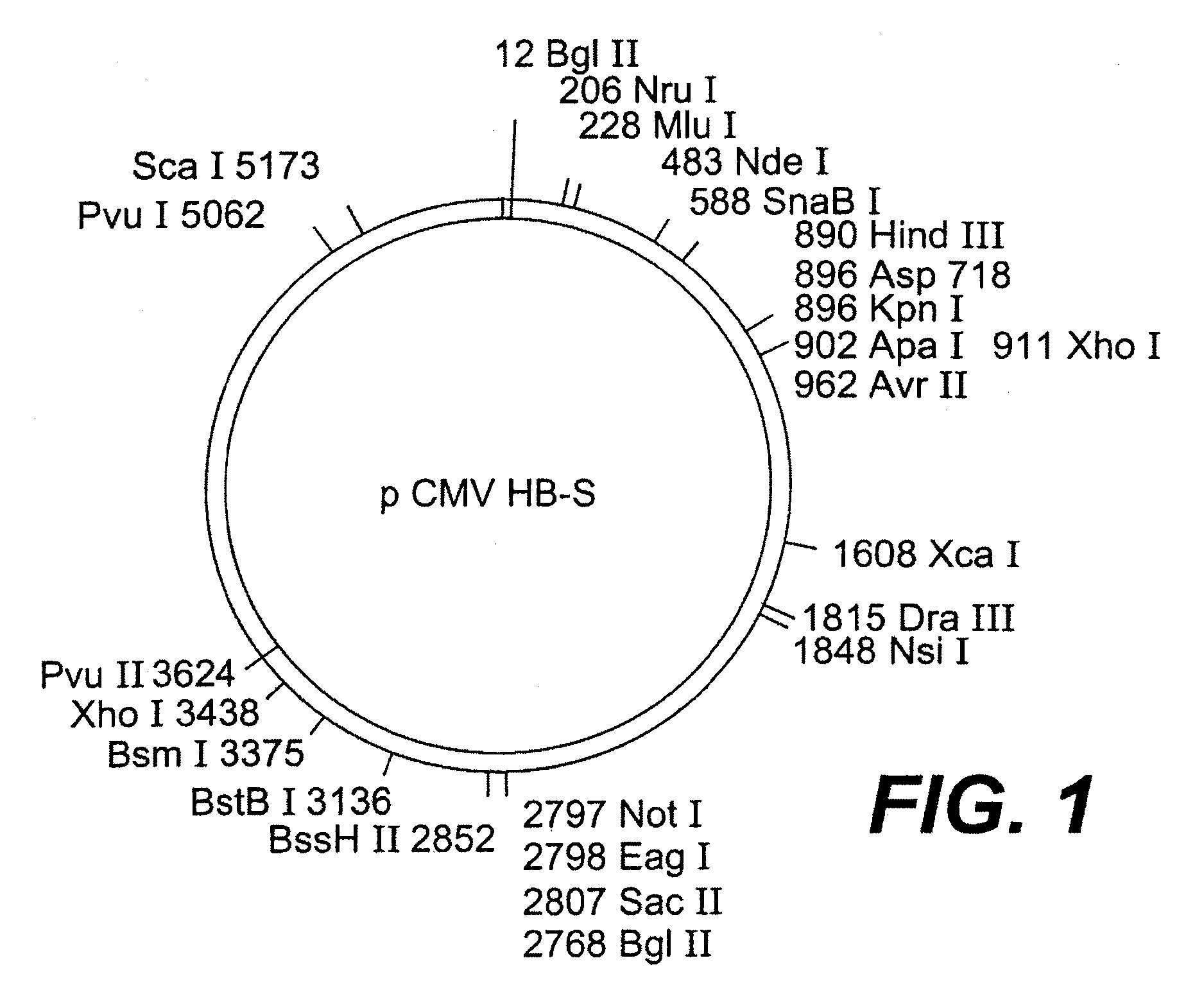
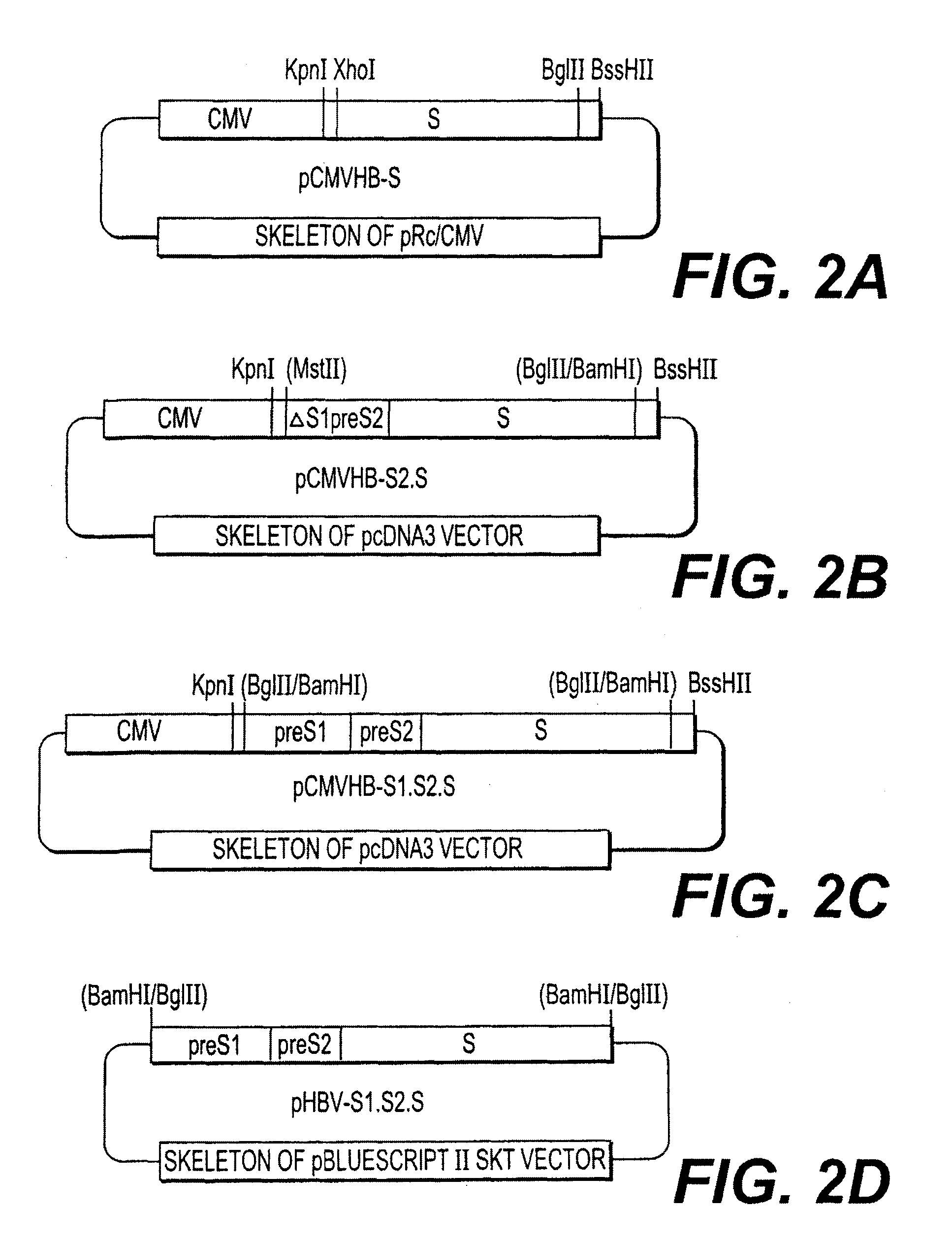
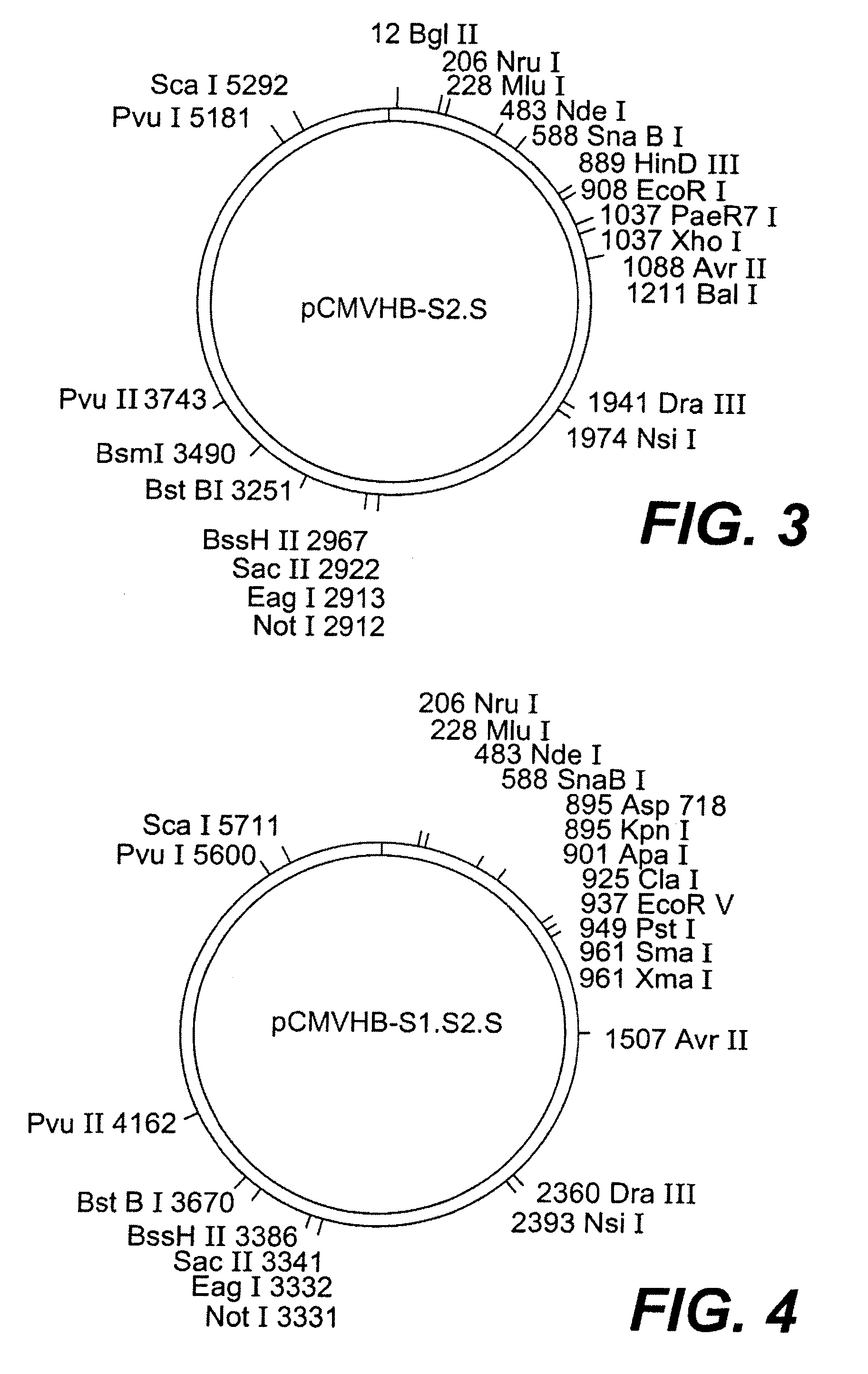
Nucleotide vector, composition containing such vector, and vaccine for immunization against hepatitis
Nucleotide composition containing a vector and vaccine for immunization against hepatitis. Nucleotide vector comprising at least one gene or one complementary DNA coding for at least a portion of a virus, and a promoter providing for the expression of the gene in muscle cells. The gene may be the S gene of the hepatitis B virus. A nucleotide vector composition when administered to even chronic HBV carriers is capable of breaking T cell tolerance to the surface antigens of hepatitis B virus. A vaccine preparation containing bare DNA is injected into the host previously treated with a substance capable of inducing a coagulating necrosis of the muscle fibers.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Methods of inducing or increasing the expression of proteoglycans such as aggrecan in cells
InactiveUS20070134218A1Prevent mineralizationDecrease osteocalcin productionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideEukaryotic plasmids
Methods of inducing the expression of a proteoglycan such as aggrecan in a cell are described. A method is described which includes transfecting a cell with an isolated nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a LIM mineralization protein operably linked to a promoter. The LIM mineralization protein can be rLMP, hLMP-1, hLMP-1s, or hLMP-3. Transfection maybe accomplished ex vivo or in vivo by direct injection of virus or naked DNA, or by a nonviral vector such as a plasmid. The method can be used to induce proteoglycan synthesis in osseous cells or to stimulate proteoglycan and / or collagen production in cells capable of producing proteoglycan and / or collagen (e.g., intervertebral disc cells including cells of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus).
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Molecular vaccine linking intercellular spreading protein to an antigen
InactiveUS20080286292A1Enhanced spreading and MHC class I presentation of antigenEnhance vaccine potencyVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsT lymphocyteWilms' tumor
Superior molecular vaccines comprise nucleic acids, including naked DNA and replicon RNA, that encode a fusion polypeptide that includes an antigenic peptide or polypeptide against which an immune response is desired. Fused to the antigenic peptide is an intercellular spreading protein, in particular a herpes virus protein VP22 or a homologue or functional derivative thereof. Preferred spreading proteins are VP22 from HSV-1 and Marek's disease virus. The nucleic acid can encode any antigenic epitope of interest, preferably an epitope that is processed and presented by MHC class I proteins. Antigens of pathogenic organisms and cells such as tumor cells are preferred. Vaccines comprising HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein are exemplified. Also disclosed are methods of using the vaccines to induce heightened T cell mediated immunity, in particular by cytotoxic T lymphocytes, leading to protection from or treatment of a tumor.
Owner:WU TZYY CHOOU +1
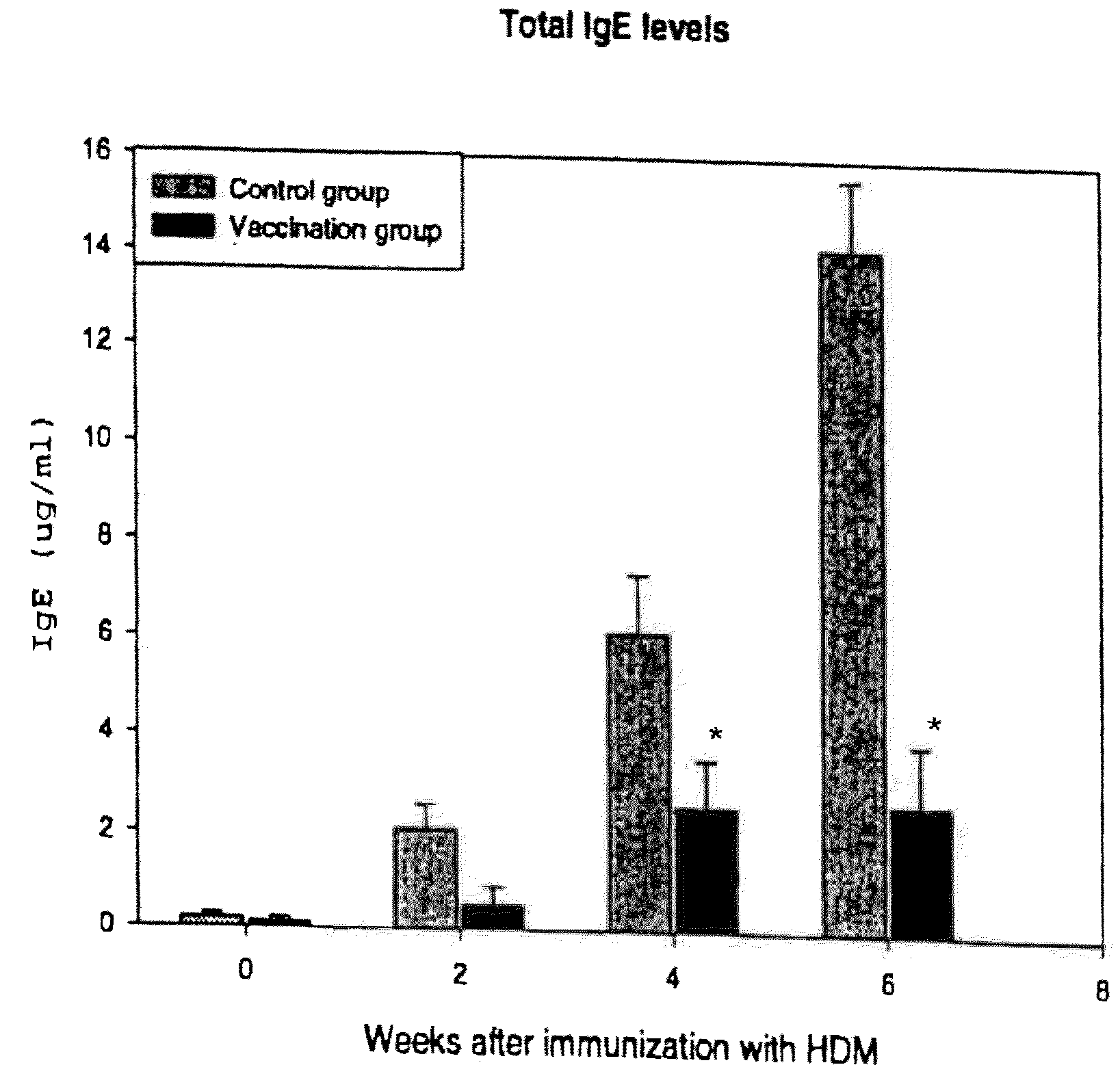
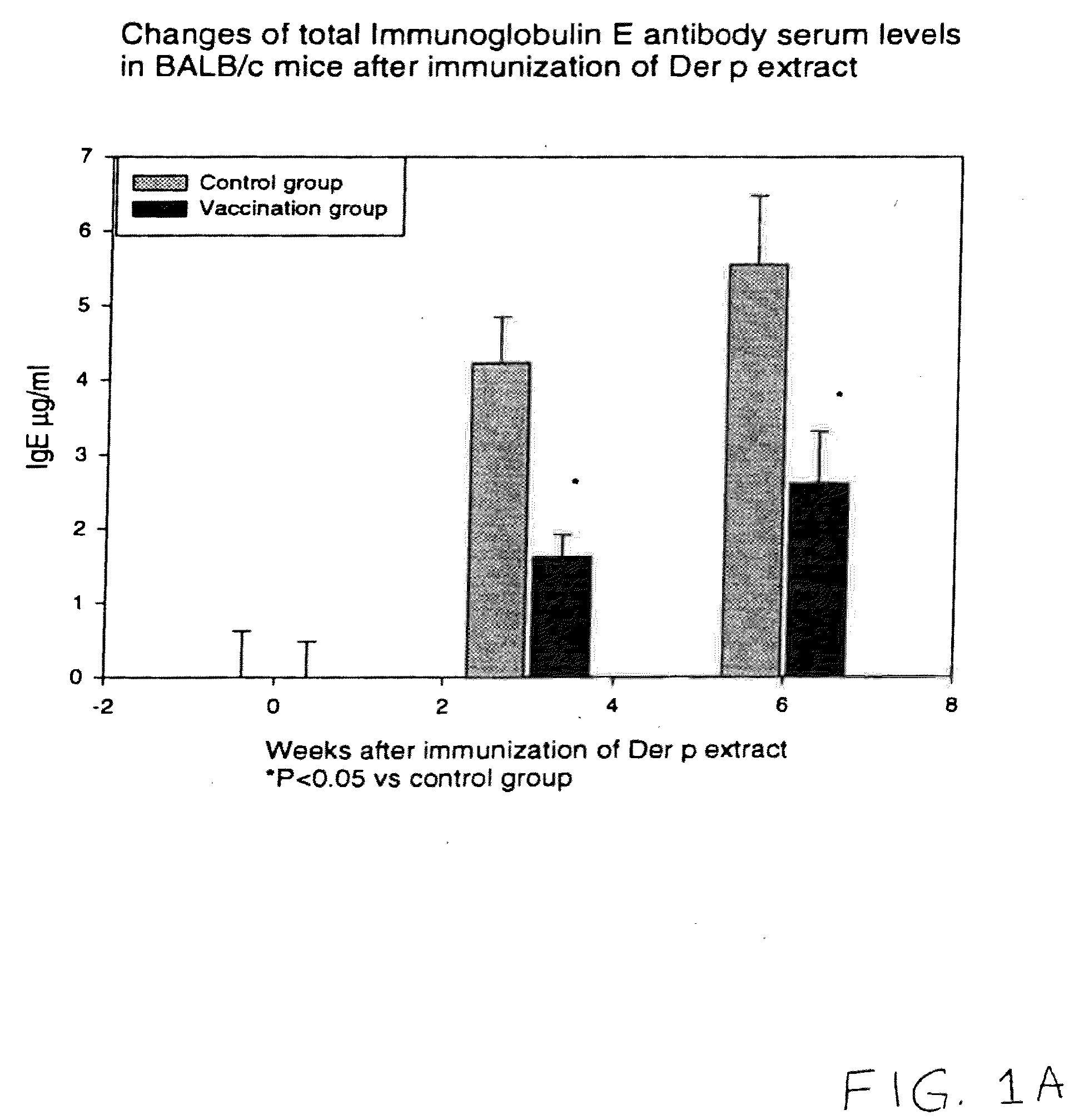
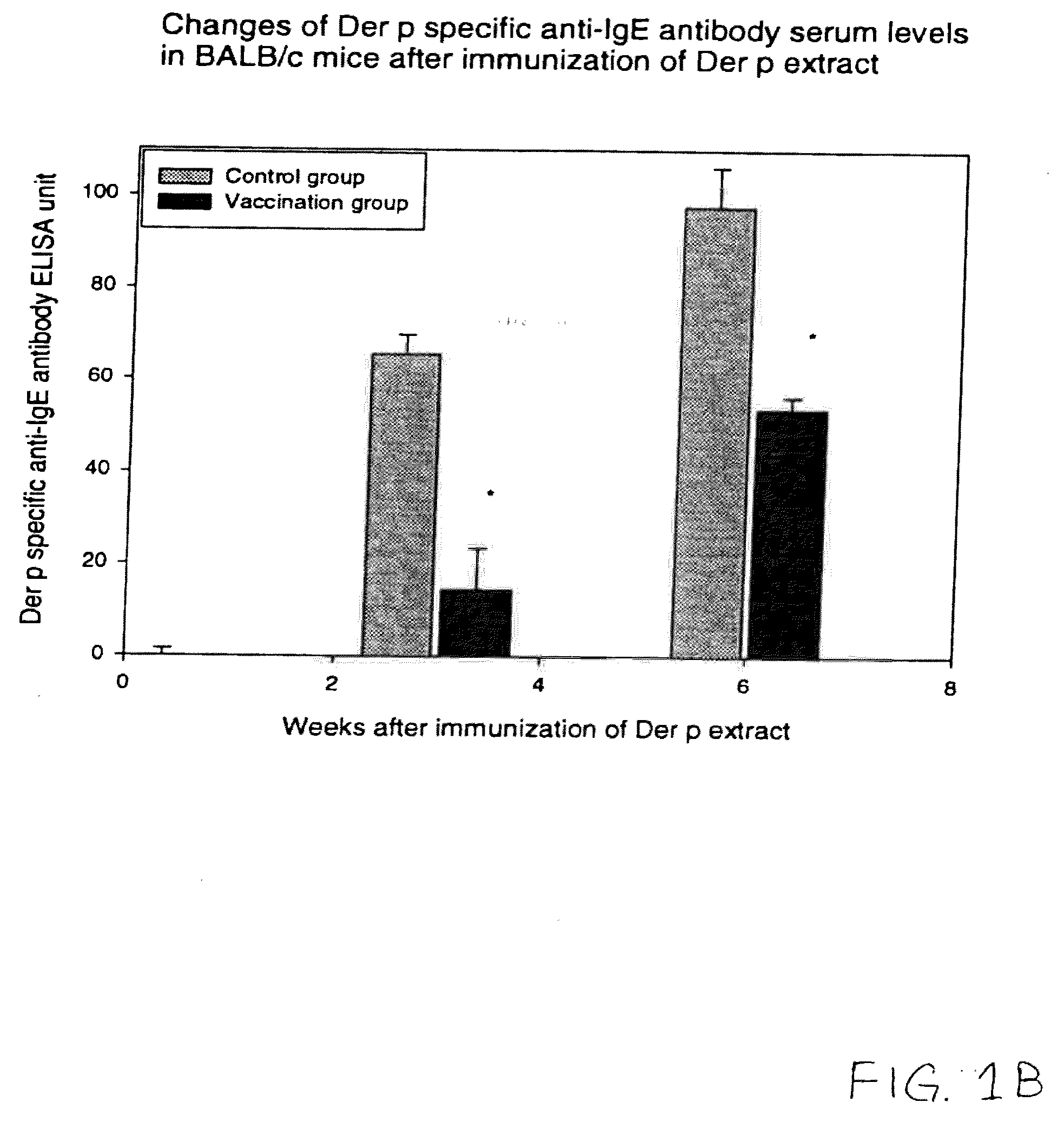
Vaccine for House Dust Mite Allergen Using Naked DNA
Vaccination with the DNA encoding T-cell epitopes to the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssimus (Der p) and Dermatophagoides farinae (Der f were effective in the inhibition of the allergen induced IgE synthesis. Gene therapy using T-cell epitope encoding DNA is useful in combating allergic disease.
Owner:YOO TAI JUNE
Lyophilized pharmaceutical compositions for naked DNA gene therapy
ActiveUS20200023075A1Reduce changesMinimizing partial lossOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPharmaceutical drugPharmaceutical medicine
The present invention provides a novel lyophilized pharmaceutical composition that maintains the stability of a DNA plasmid while forming a uniform and elegant cake during lyophilization. The novel lyophilization formulation further allows uniform reconstitution of the DNA plasmid in a pharmaceutically acceptable solution, enabling complete recover of the active ingredients, minimizing partial loss of potency and allowing administration of the active ingredients in an accurate and consistent manner. Additionally provided herein include methods of making the lyophilized pharmaceutical composition and methods of administering the composition for treatment of various diseases.
Owner:HELIXMITH CO LTD
Nucleotide vector, composition containing such vector, and vaccine for immunization against hepatitis
Nucleotide vector composition containing such vector and vaccine for immunization against hepatitis. Nucleotide vector comprising at least one gene or one complementary DNA coding for at least a portion of a virus, and a promoter providing for the expression of such gene in muscle cells. The gene may be the S gene of the hepatitis B virus. A nucleotide vector composition when administered to even chronic HBV carriers is capable of breaking T cell tolerance to the surface antigens of hepatitis B virus. A vaccine preparation containing said bare DNA is injected into the host previously treated with a substance capable of inducing a coagulating necrosis of the muscle fibers.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com