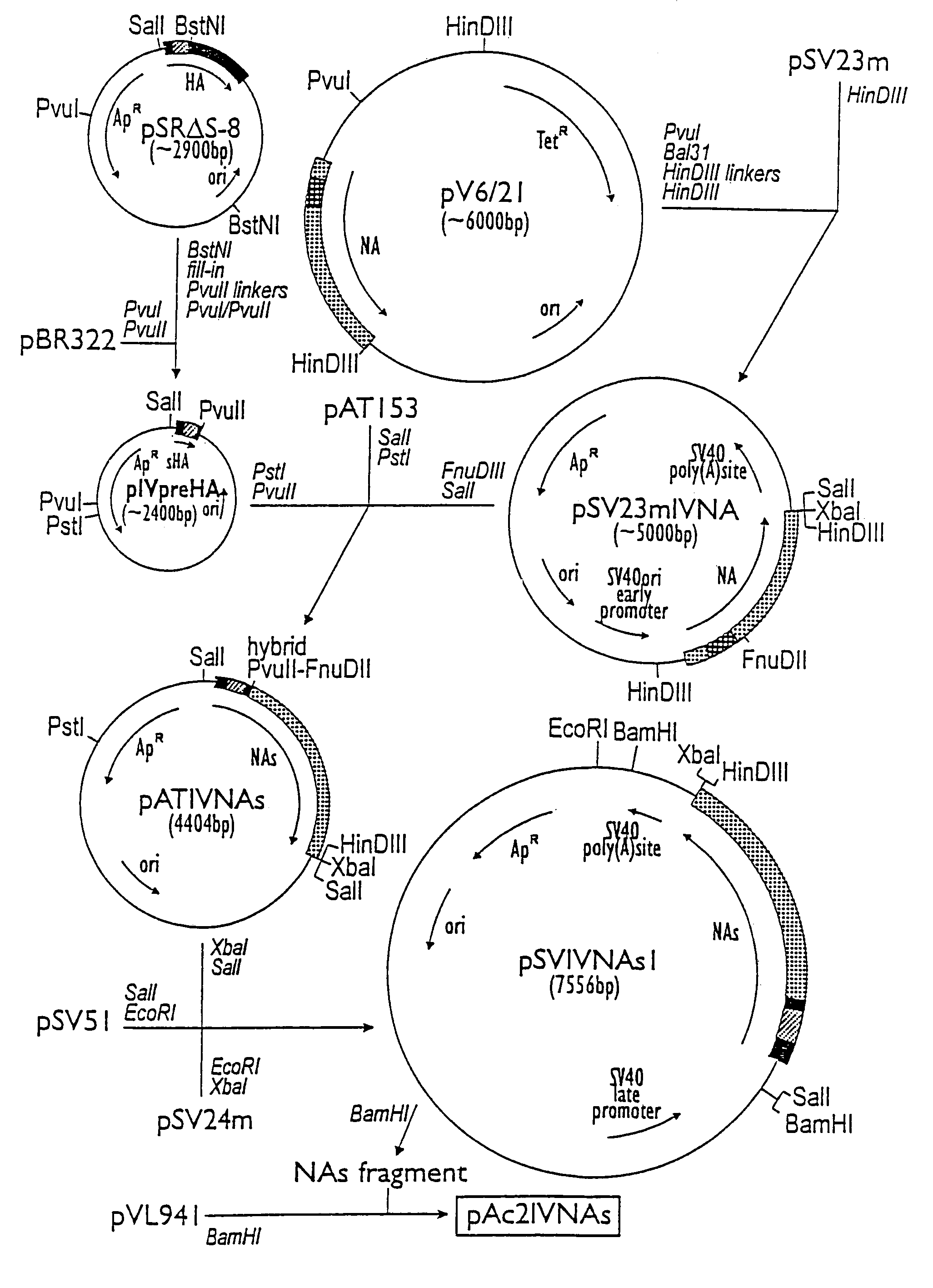
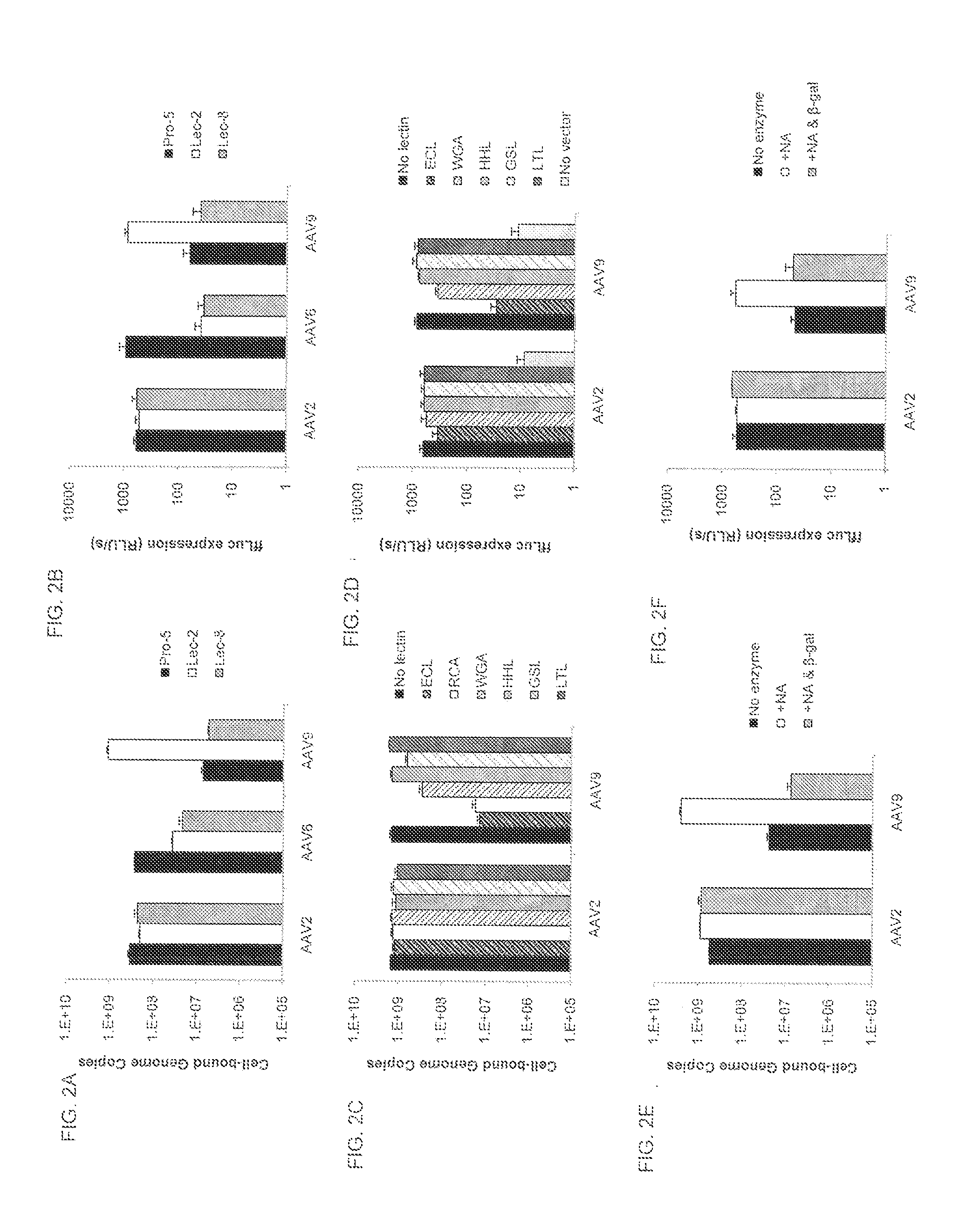Patents
Literature
343 results about "Neuraminidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neuraminidase enzymes are glycoside hydrolase enzymes that cleave (cut) the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids. Neuraminidase enzymes are a large family, found in a range of organisms. The best-known neuraminidase is the viral neuraminidase, a drug target for the prevention of the spread of influenza infection. The viral neuraminidases are frequently used as antigenic determinants found on the surface of the influenza virus. Some variants of the influenza neuraminidase confer more virulence to the virus than others. Other homologues are found in mammalian cells, which have a range of functions. At least four mammalian sialidase homologues have been described in the human genome (see NEU1, NEU2, NEU3, NEU4).
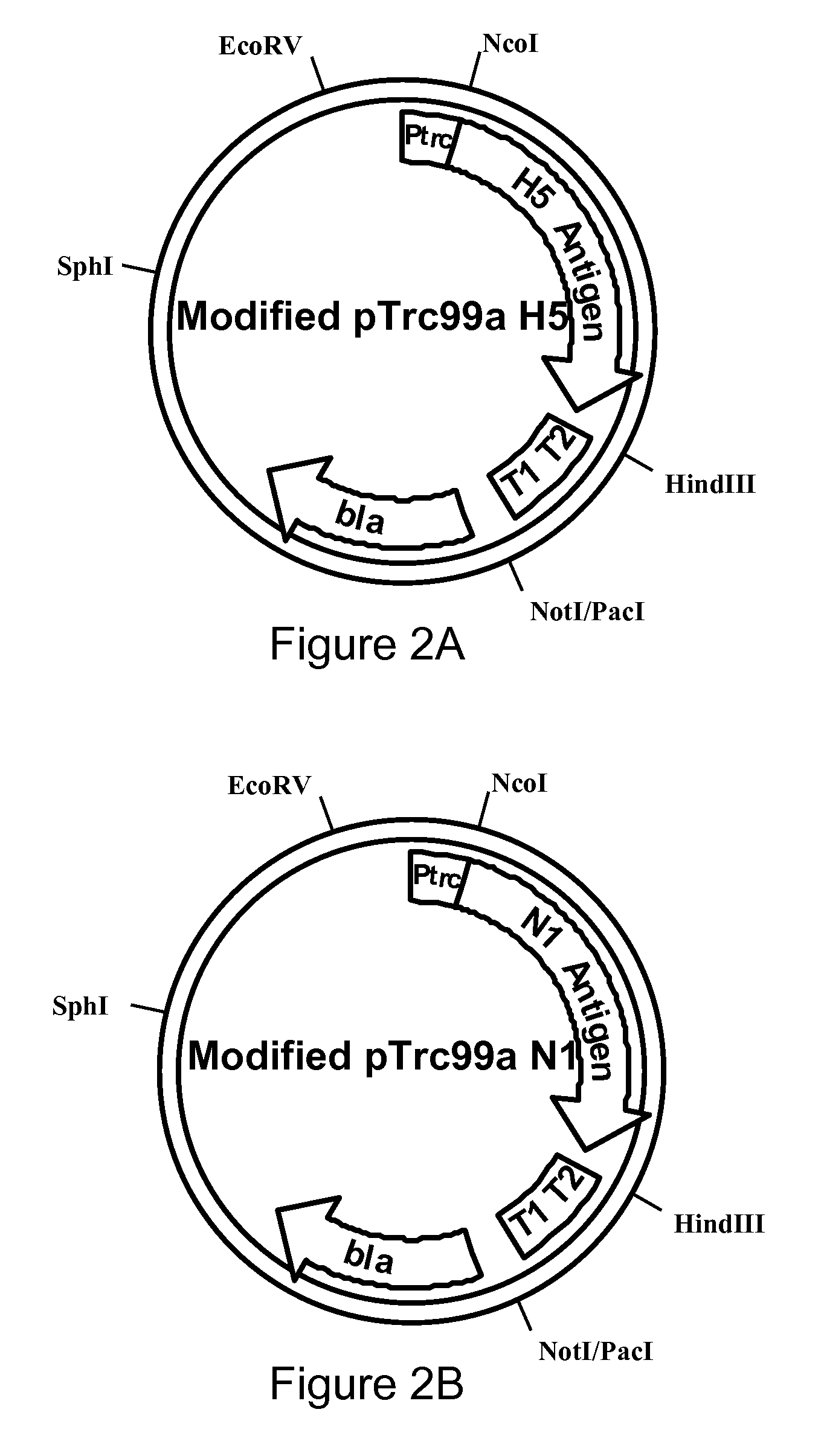
Influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants
InactiveUS20050042229A1Efficient productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseHydrolasesHemagglutininNeuraminidase
Polypeptides, polynucleotides, methods, compositions, and vaccines comprising influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants are provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
DNA transfection system for the generation of infectious influenza virus
The present invention is based on the development of a dual promoter system (preferably a RNA pol I-pol II system) for the efficient intracellular synthesis of viral RNA. The resultant minimal plasmid-based system may be used to synthesize any RNA virus, preferably viruses with a negative single stranded RNA genome. The viral product of the system is produced when the plasmids of the system are introduced into a suitable host cell. One application of the system is production of attenuated, reassortant influenza viruses for use as antigens in vaccines. The reassortant viruses generated by cotransfection of plasmids may comprise genes encoding the surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin and neuramimidase from an influenza virus currently infecting the population and the internal genes from an attenuated influenza virus. An advantageous property of the present invention is its versatility; the system may be quickly and easily adapted to synthesize an attenuated version of any RNA virus. Attenuated or inactivated RNA viruses produced by the present invention may be administered to a patient in need of vaccination by any of several routes including intranasally or intramuscularly.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Compositions and Methods for Altering Tissue Specificity and Improving AAV9-Mediated Gene Transfer
ActiveUS20130323226A1Improve efficiencyImprove usabilityOrganic active ingredientsVectorsViral vectorFhit gene
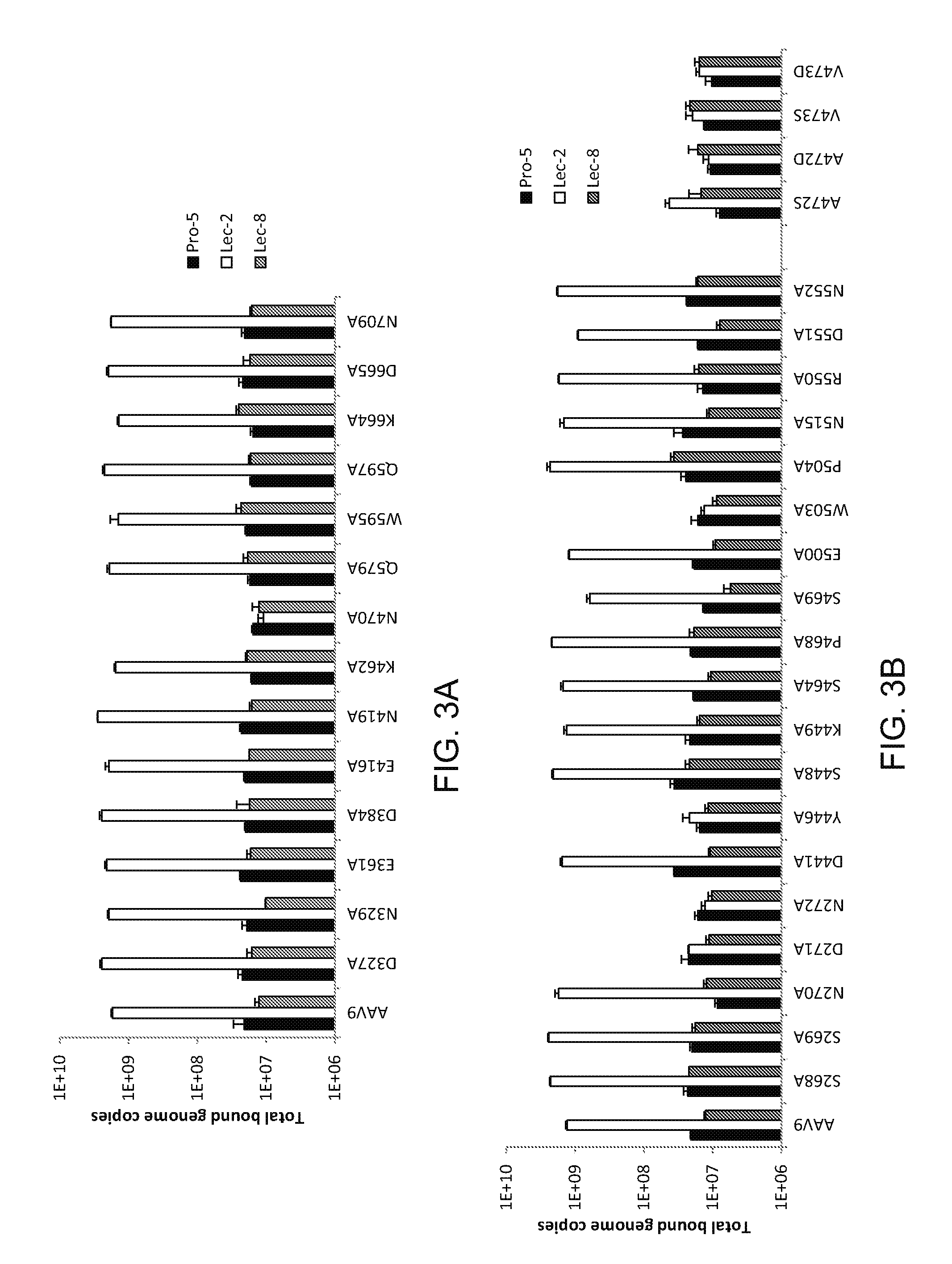
A method of altering the targeting and / or cellular uptake efficiency of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) viral vector having a capsid containing an AAV9 cell surface binding domain is described. The method involves modifying a clade F cell surface receptor which comprises a glycan having a terminal sialic acid residue and a penultimate β-galactose residue. The modification may involve retargeting the vector by temporarily functionally ablate AAV9 binding in a subset of cells, thereby redirecting the vector to another subset of cells. Alternatively, the modification may involve increasing cellular update efficiency by treating the cells with a neuraminidase to expose cell surface β-galactose. Also provided are compositions containing the AAV9 vector and a neuraminidase. Also provided is a method for purifying AAV9 using β-galactose linked to solid support. Also provided are mutant vectors which have been modified to alter their targeting specificity, including mutant AAV9 in which the galactose binding domain is mutated and AAV in which an AAV9 galactose binding domain is engineered.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Neuraminidase-supplemented compositions
InactiveUS6485729B1Less importancePrevents and lessens HA immunodominanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNasal cavityAdjuvant
An anti-influenza vaccine composition wherein the improvement is that the vaccine includes, as an additive, neuraminidase (NA). The base anti-influenza vaccine can be any commercially available anti-influenza vaccine. The composition can include and be administered with an adjuvant. The vaccine composition provides protection in a host, animal or human, against influenza infection, including viral replication and systemic infection. Oral, nasal or other mucosal or per needle administration, including intracutaneous, intradermal, intramuscular, intravascular, and intravenous, are included.
Owner:PROTEIN SCI
Influenza Hemagglutinin And Neuraminidase Variants
InactiveUS20080069821A1Extended half-lifeReducing/increasing polypeptide antigenicityFungiVirusesHemagglutininNeuraminidase
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC +1
DNA transfection system for the generation of infectious influenza virus
InactiveUS20050186563A1Improve effectivenessElicit protective immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiDual promoterSingle-Stranded RNA
The present invention is based on the development of a dual promoter system (preferably a RNA pol I-pol II system) for the efficient intracellular synthesis of viral RNA. The resultant minimal plasmid-based system may be used to synthesize any RNA virus, preferably viruses with a negative single stranded RNA genome. The viral product of the system is produced when the plasmids of the system are introduced into a suitable host cell. One application of the system is production of attenuated, reassortant influenza viruses for use as antigens in vaccines. The reassortant viruses generated by cotransfection of plasmids may comprise genes encoding the surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase from an influenza virus currently infecting the population and the internal genes from an attenuated influenza virus. An advantageous property of the present invention is its versatility; the system may be quickly and easily adapted to synthesize an attenuated version of any RNA virus. Attenuated or inactivated RNA viruses produced by the present invention may be administered to a patient in need of vaccination by any of several routes including intranasally or intramuscularly.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants
Polypeptides, polynucleotides, methods, compositions, and vaccines comprising influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants are provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants
InactiveUS20060008473A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininNeuraminidase
Polypeptides, polynucleotides, methods, compositions, and vaccines comprising (avian pandemic) influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants are provided.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH SERVICES NAT INSTITTUTE OF HEALTH
Influenza vaccines
InactiveUS20080299151A1Less protectionBroad and efficient protective immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsHemagglutininMammal
Described herein are vaccines and the use of naked DNA and / or RNA encoding hemagglutinin (HA) from pandemic influenza, e.g., the 1918 H1N1 and / or the 1957 H2N2 and / or the 1968 H3N2 influenza A virus, as a vaccine component against present day and coming H1, H2, H3, H5, N1, N2 containing influenza A infections in humans and swine optionally with the naked DNA and / or RNA encoding Neuraminidase (NA) and / or matrix protein (M) and / or the nucleoprotein (NP) from pandemic influenza virus included. If the vaccine components are used as DNA or RNA vaccines with or without the corresponding protein, the codons can optionally be “humanized” using preferred codons from highly expressed mammalian genes and the administration of this DNA vaccine can be by saline or buffered saline injection of naked DNA or RNA, or injection of DNA plasmid or linear gene expressing DNA fragments coupled to particles. Addition of the matrix protein (M) and / or the nucleoprotein (NP) from the 1918 influenza strain is also disclosed.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Live bacterial vaccines for viral infection prophylaxis or treatment
InactiveUS20080124355A1Enhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsHemagglutininBacteroides
The present invention provides a vaccine, method of use, and kit employing genetically isolated and stabilized, live attenuated bacterial strains including Salmonella that express one or more avian influenza antigens for use in live vaccine compositions that can be orally administered to an individual to protect against avian influenza. Genetic stabilization may be achieved through deletion of IS200 elements and bacteria phage and prophage elements. The bacterial strains may be genetically isolated from external phage infection by constitutive expression of a P22 phage repressor. Nucleic acid sequences encoding antigenic hemagglutinin and neuraminidase avian influenza proteins, having at least one modified codon for optimum expression when transferred into a prokaryotic microorganism for improved immunogenicity
Owner:AVIEX TECH
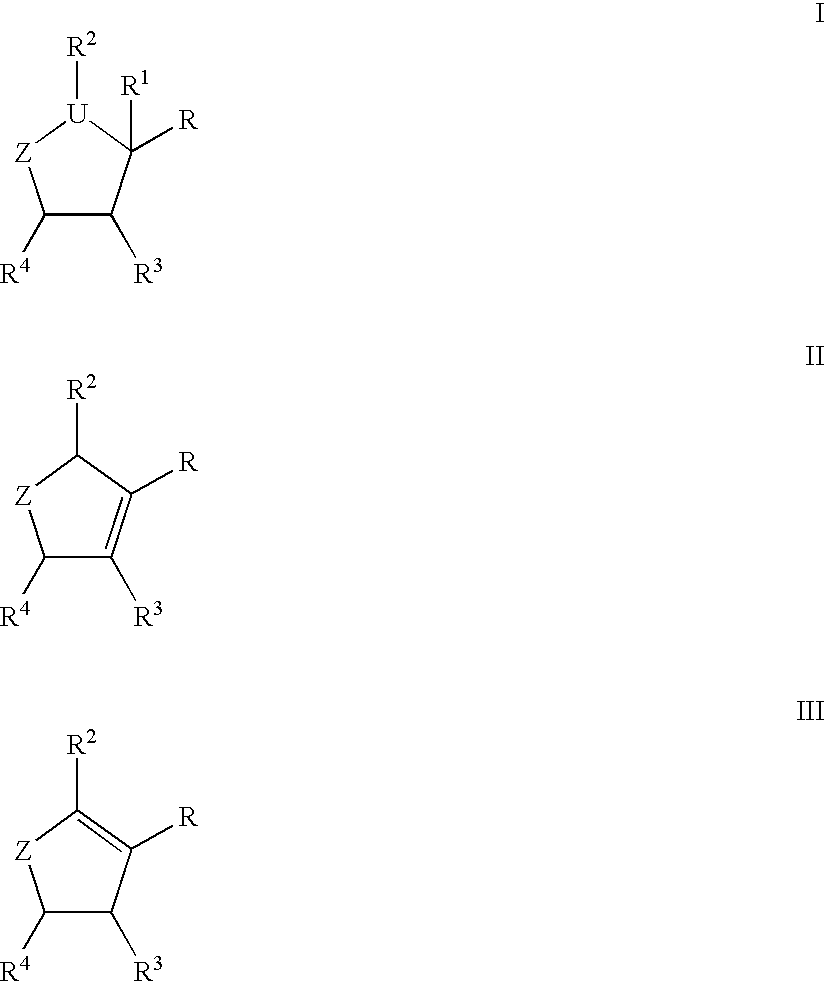
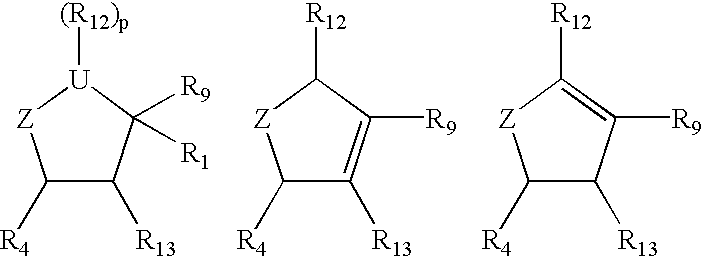
Substituted cyslopentane and cyclopentene compounds useful as neuraminidase inhibitors
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Substituted cyclopentane and cyclopentene compounds useful as neuraminidase inhibitors
Compounds I-III wherein U is CH, O, or S; Z is mono- or di-substituted carbon; R is (CH2)nCO2H, (CH2)nSO3H, (CH2)nPO3H2, (CH2)nNO2, CH(SCH3)3, esters; R1 is H, hydroxyalkyl, aminoalkyl, alkoxyalkyl; RR1 is O; n is 0-4; R2, R3 is H, hydroxyalkyl, aminoalkyl, alkoxyalkyl, haloalkyl; R4 is (CH2)nOH, (CH2)nNH2, substituted alkyl were prepd. as neuraminidase inhibitors. Thus, (1R,3R,4R,1'S)-(-)-(1'-acetylamino-2 '-ethyl)butyl-4-(aminoimino)methylaminocyclopentan-1-carboxylic acid was prepd. and tested in vitro as neuraminidase inhibitor (IC50<1.mu.M).
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Prophylactic and therapeutic influenza vaccines, antigens, compositions and methods
The present invention relates to the intersection of the fields of immunology and protein engineering, and particularly to antigens and vaccines useful in prevention of infection by influenza virus. Provided are recombinant protein antigens, compositions, and methods for the production and use of such antigens and subunit vaccine compositions. In some embodiments, influenza antigens include hemagglutinin polypeptides neuraminidase polypeptides, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
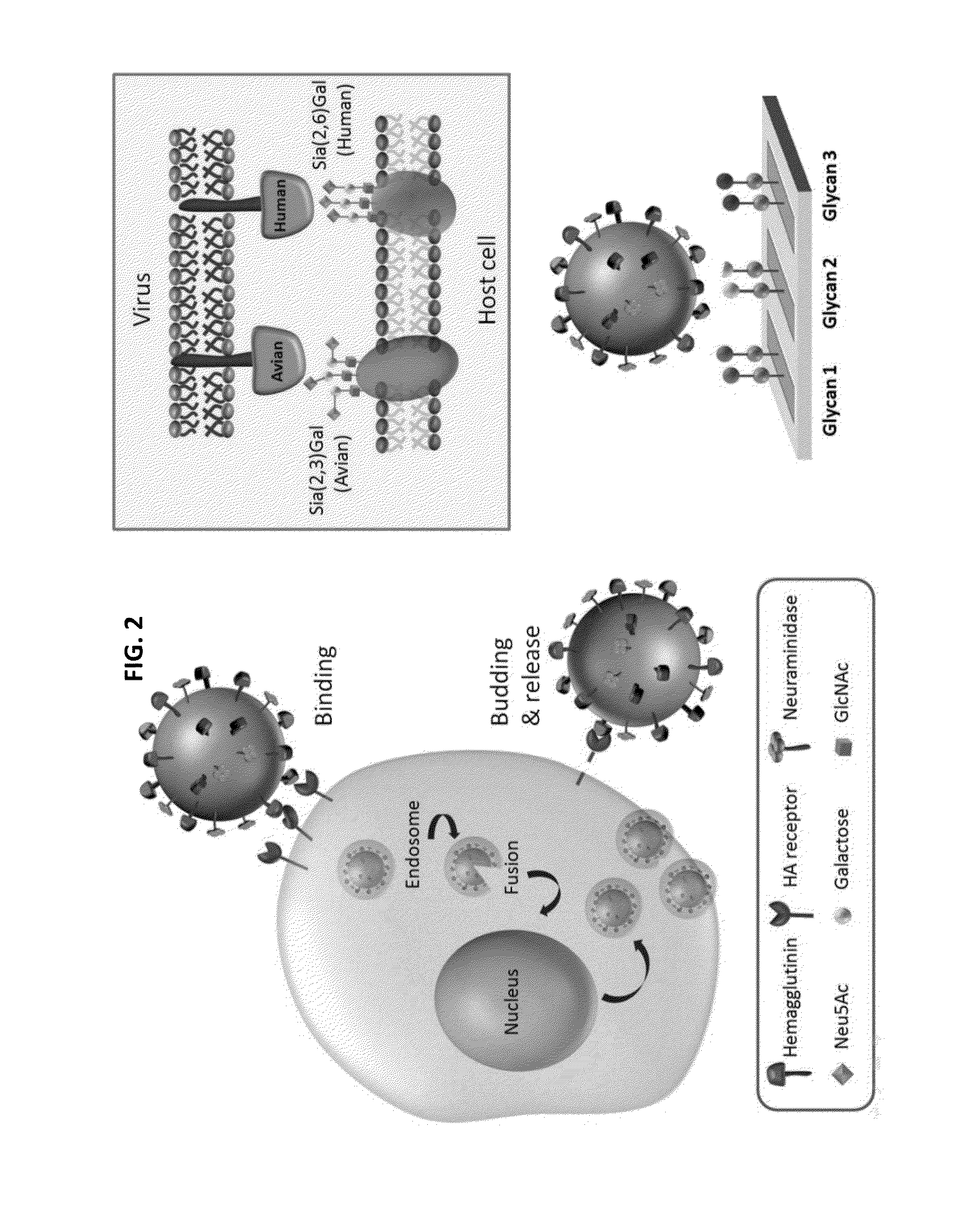
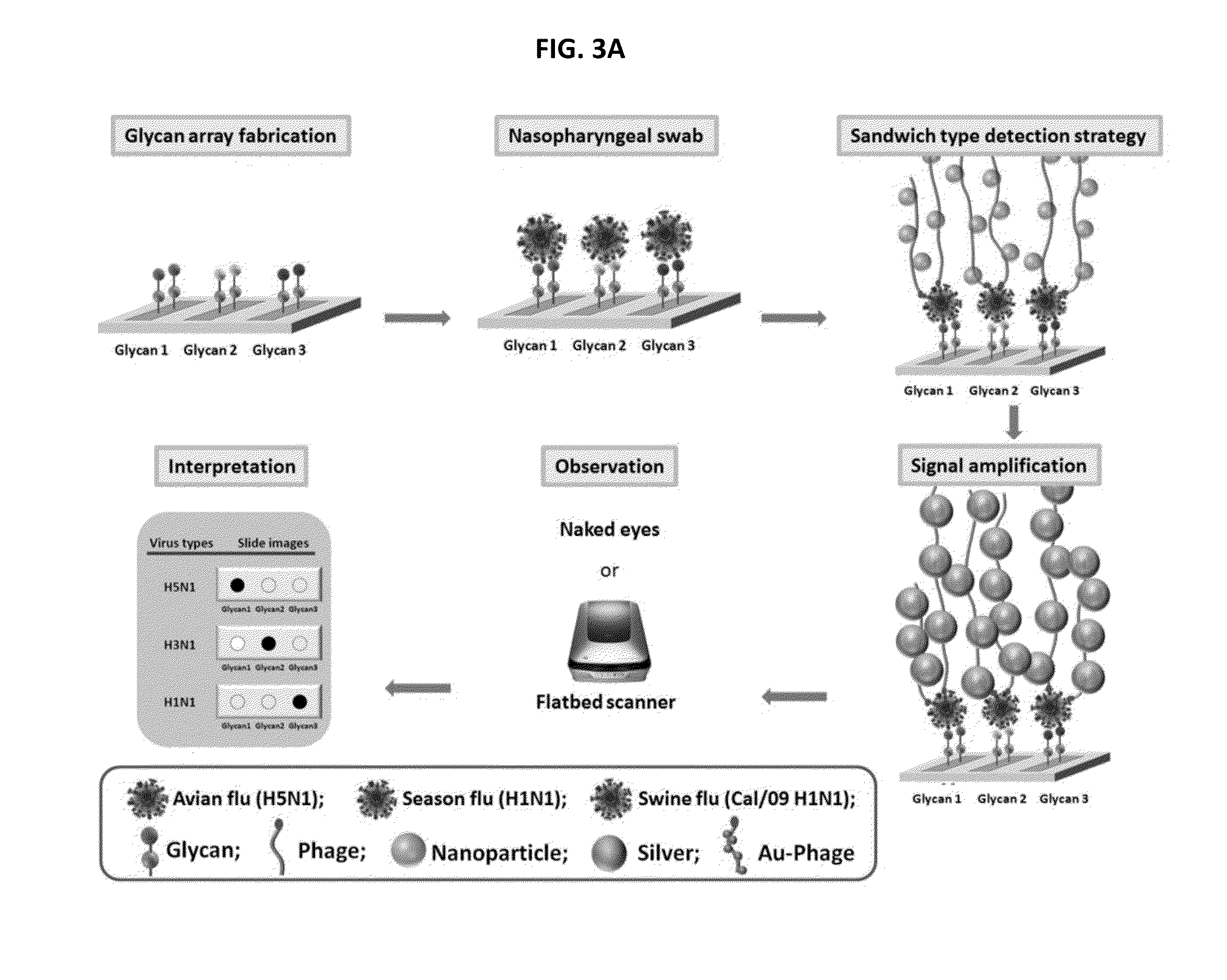
Glycan arrays for high throughput screening of viruses
ActiveUS20150160217A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioThe process is simple and fastSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHemagglutininHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Glycan arrays that can detect and distinguish between various sub-types and strains of influenza virus are provided. Methods for using the glycan arrays with assays using nanoparticle amplification technique are disclosed. Sandwich assays using gold nanoparticles conjugated to phage particles comprising influenza virus-specific antibodies for detecting multiple serotypes using a single reaction are provided. Plurality of glycans directed to specific target HA of influenza virus comprises the array. Detector molecules comprising noble metals conjugated to (a) phage display particles expressing antibodies against hemagglutinin and (b) neuraminidase binding agents are disclosed.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
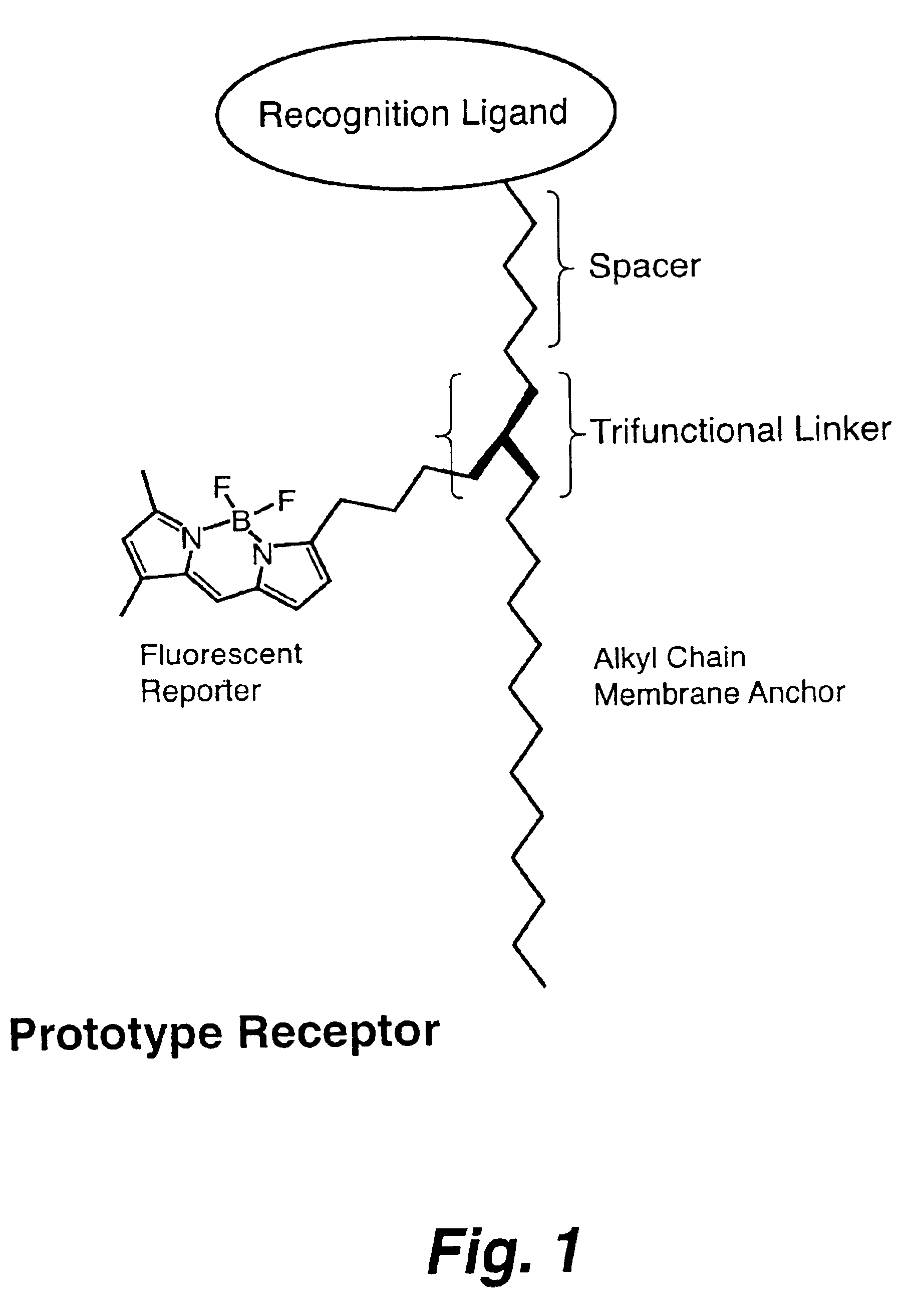
Influenza sensor
InactiveUS6893814B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNeuraminidaseFluorescence
A sensor for the detection of tetrameric multivalent neuraminidase within a sample is disclosed, where a positive detection indicates the presence of a target virus within the sample. Also disclosed is a trifunctional composition of matter including a trifunctional linker moiety with groups bonded thereto including (a) an alkyl chain adapted for attachment to a substrate, (b) a fluorescent moiety capable of generating a fluorescent signal, and (c) a recognition moiety having a spacer group of a defined length thereon, the recognition moiety capable of binding with tetrameric multivalent neuraminidase.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Reagents and kits for detection of influenza virus and the like
ActiveUS20080286758A1Simple and rapid and specific and sensitive detectionHigh detection sensitivityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementNeuraminidaseFluorescein
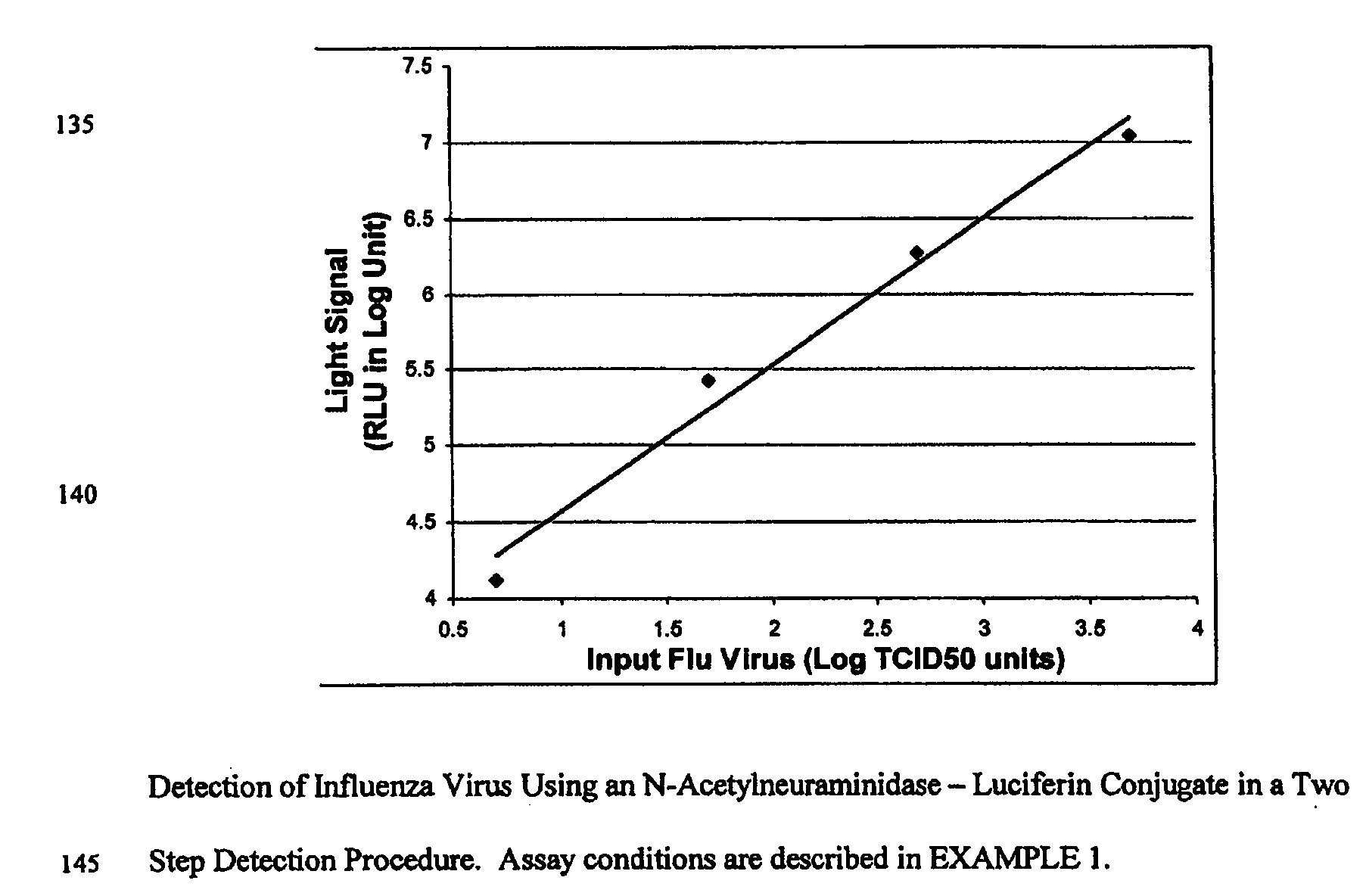
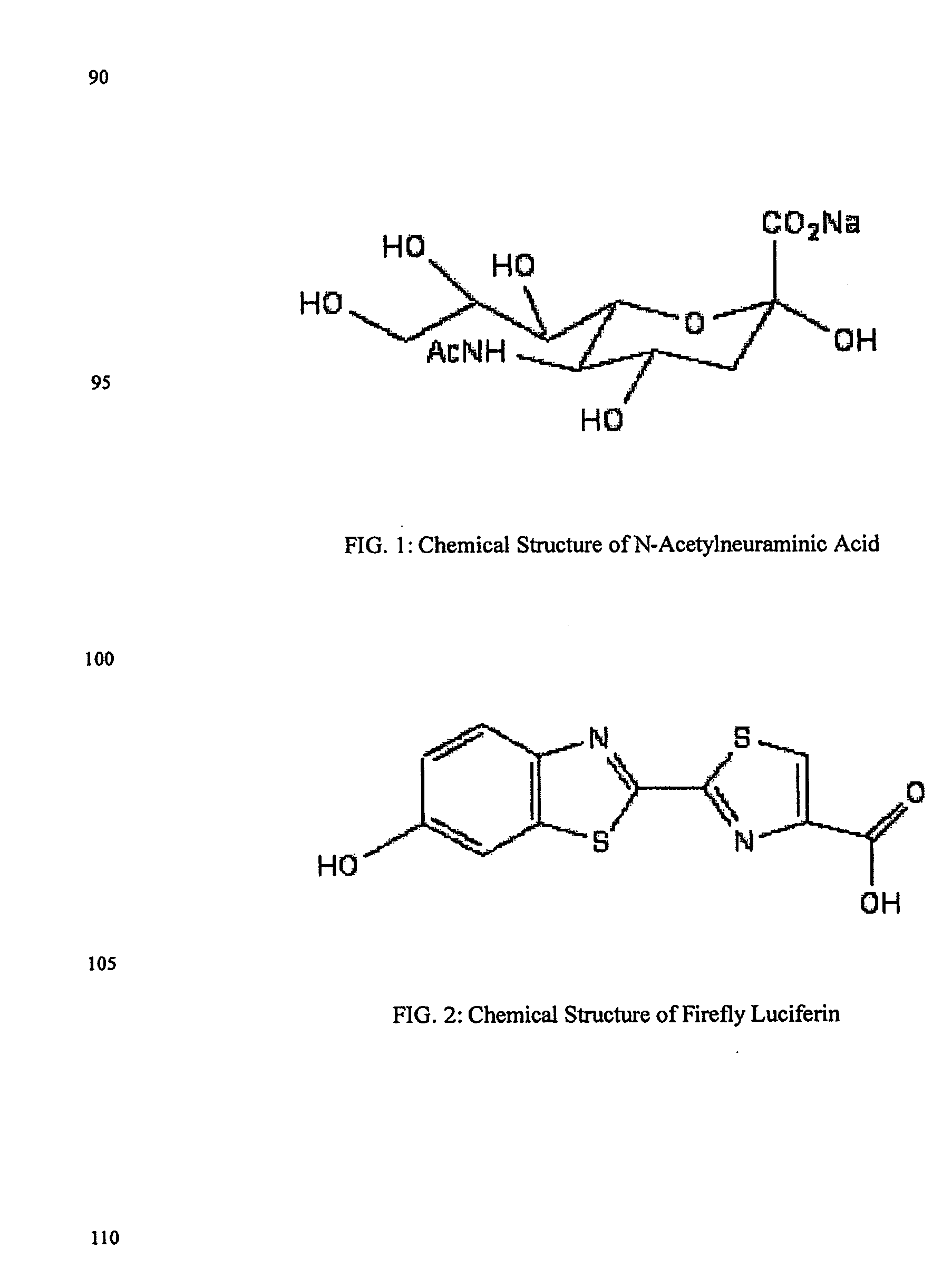
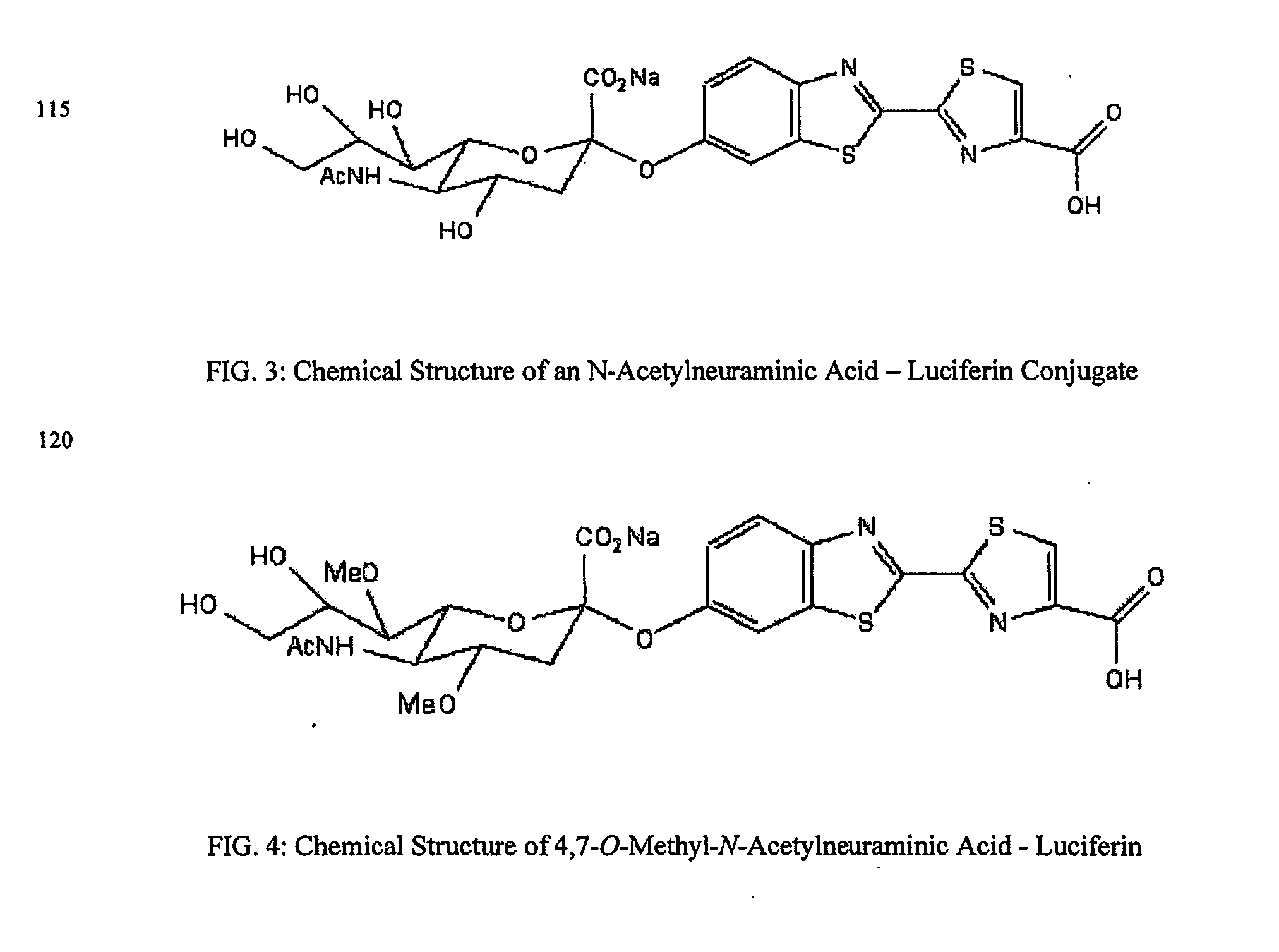
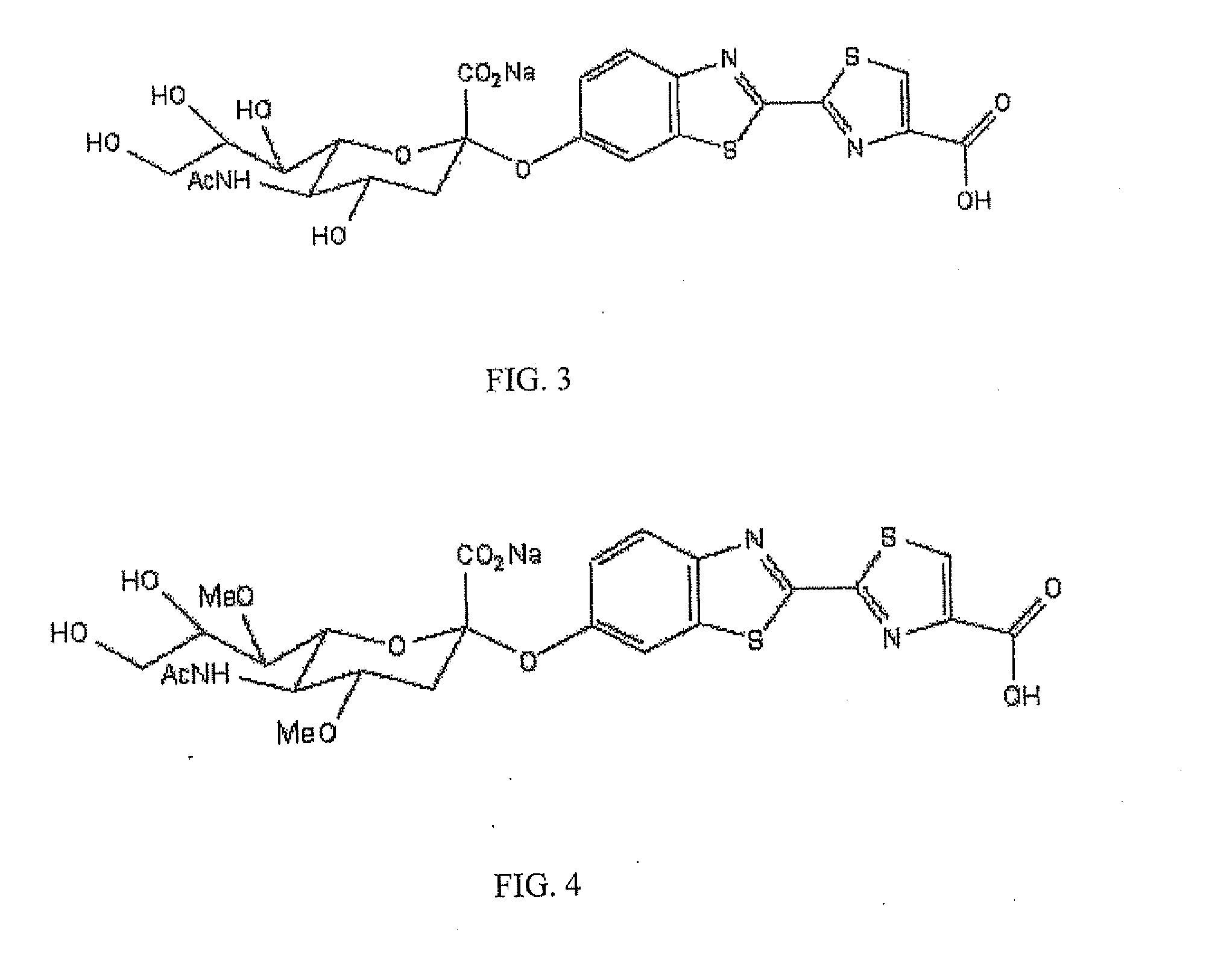
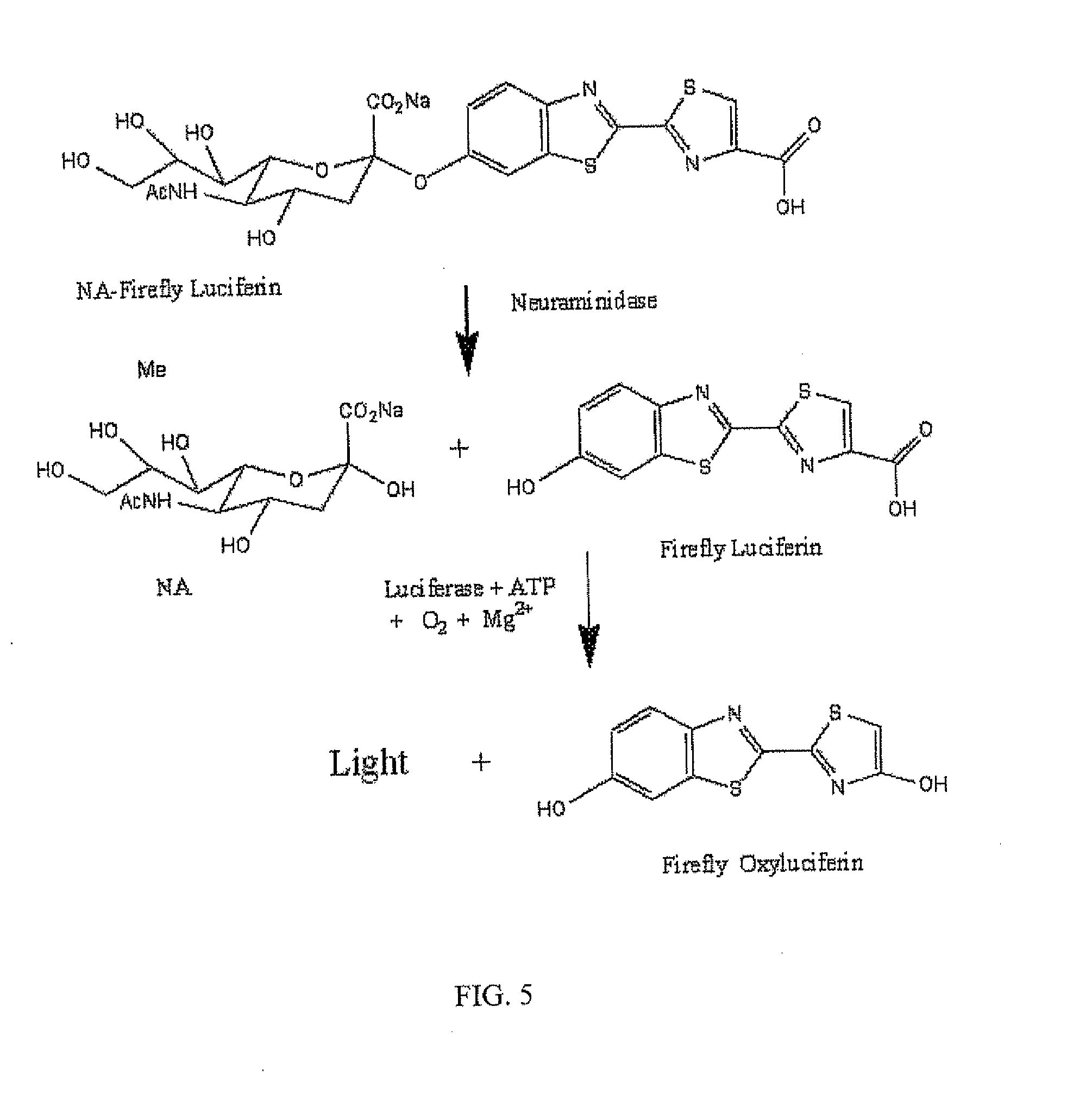
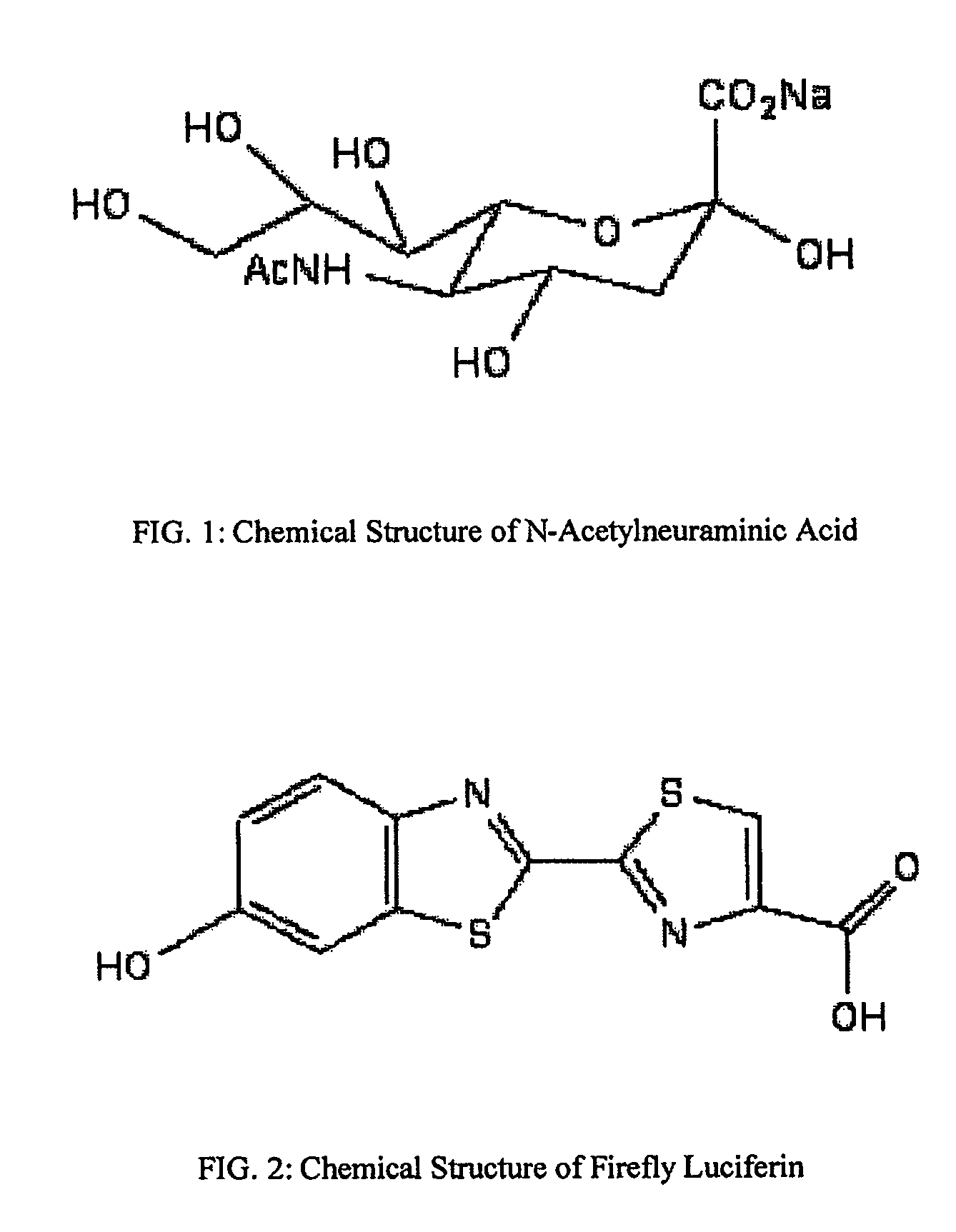
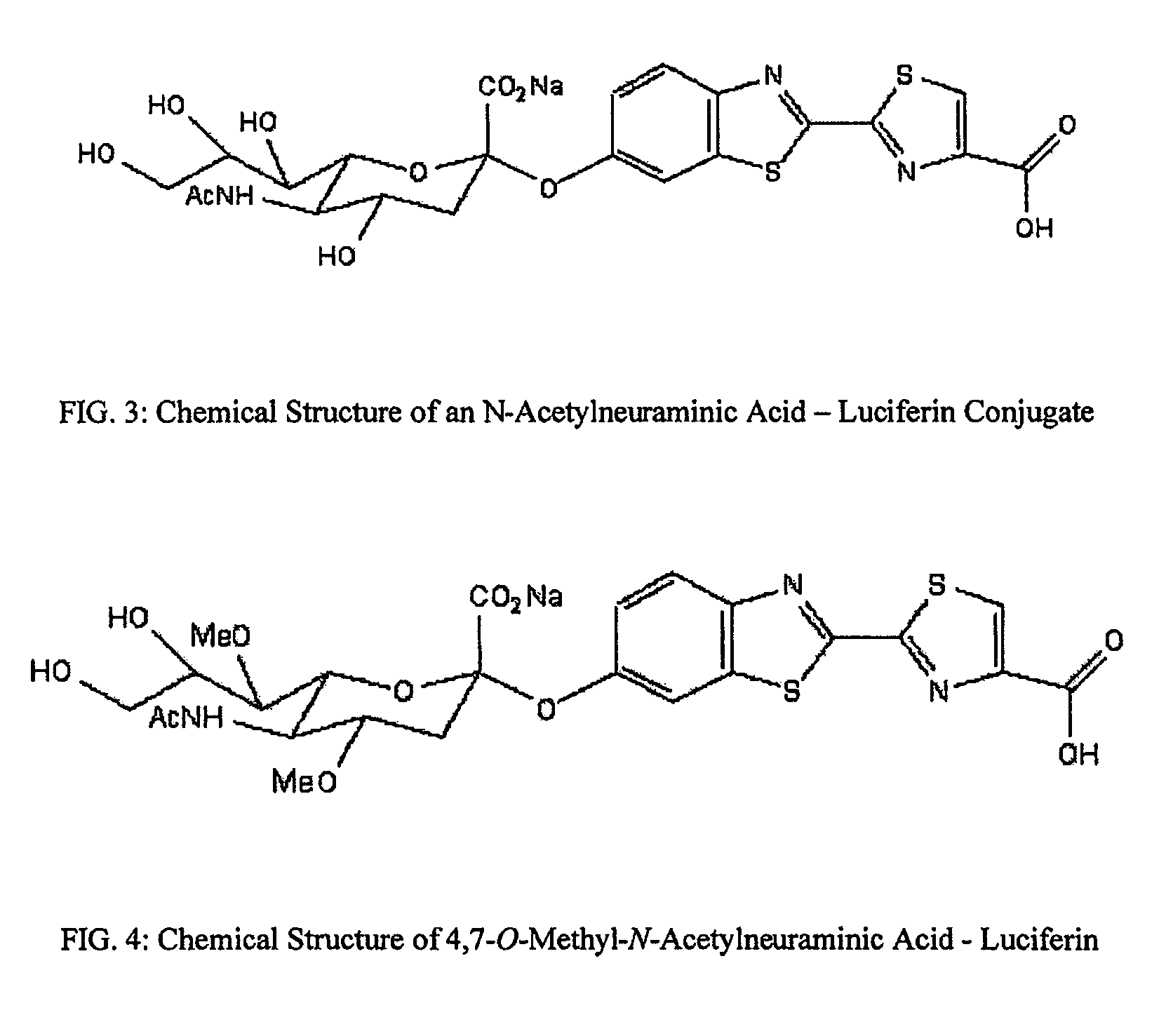
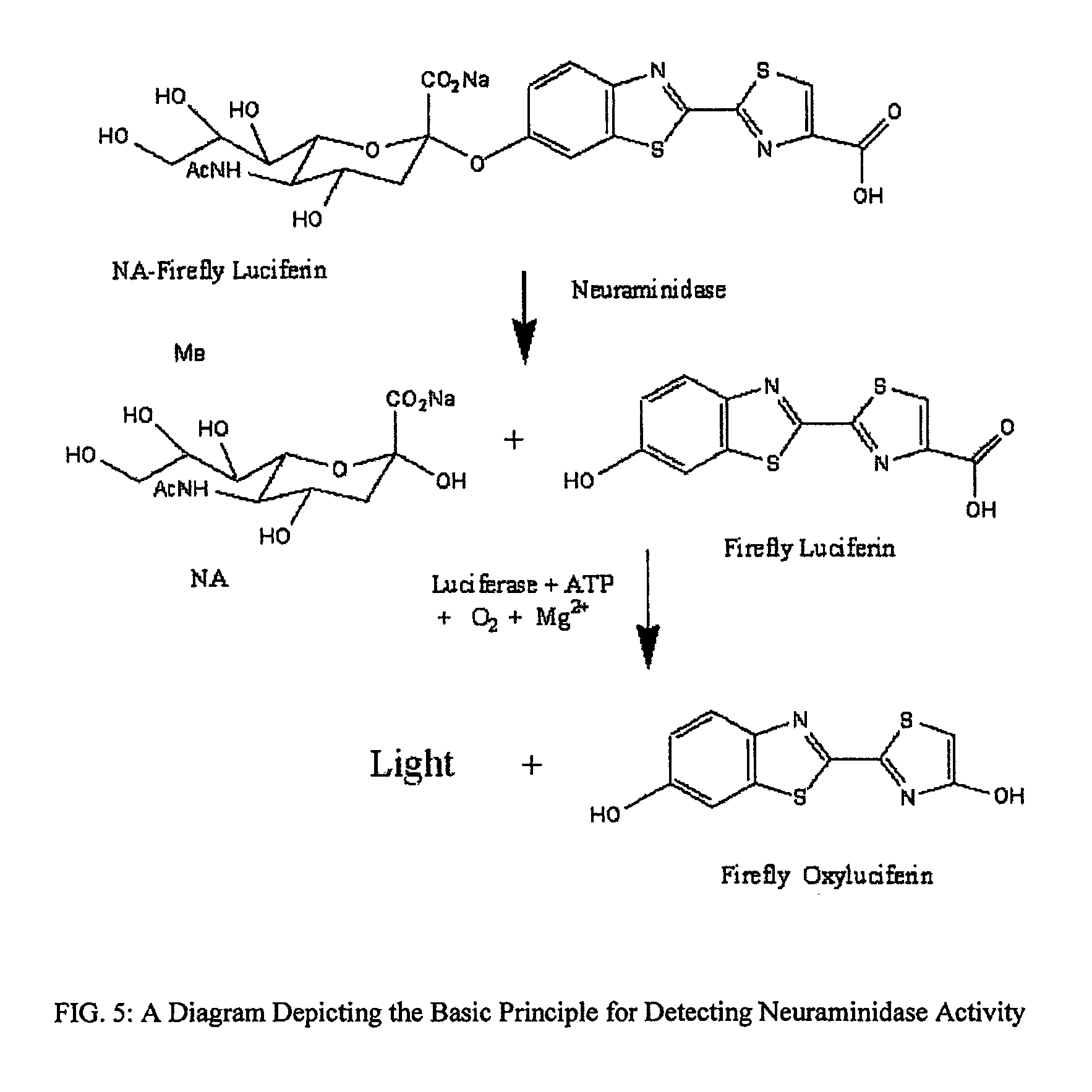
The present invention relates to reagents and methods for influenza virus detection. These reagents and methods disclosed in the present invention enable simple, rapid, specific and sensitive detection of influenza virus types A and B. These reagents are N-acetylneuraminic acid-firefly luciferin conjugates which can be cleaved by influenza virus neuraminidase.
Owner:CELLEX BIOLOGICAL TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
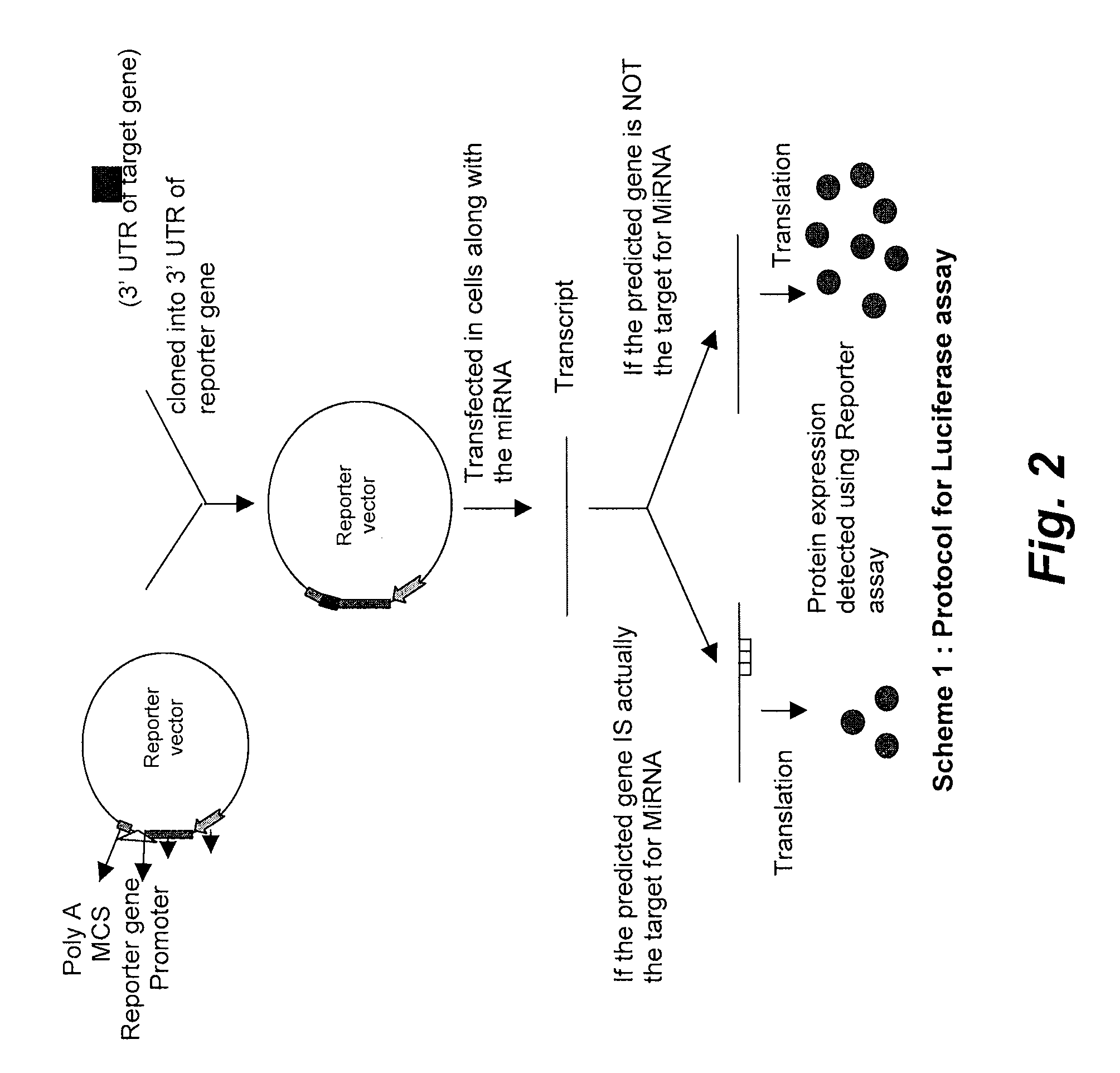
Targets for human micro rnas in avian influenza virus (H5N1) genome
The present invention relates to targets for Human microRNAs in Avian Influenza Virus (H5N1) Genome and provides specific miRNA targets against H5N1 virus. Existing therapies for Avian flu are of limited use primarily due to genetic re-assortment of the viral genome, generating novel proteins, and thus escaping immune response. In animal models, baculovirus-derived recombinant H5 vaccines were immunogenic and protective, but results in humans were disappointing even when using high doses. Currently, two classes of drugs are available with antiviral activity against influenza viruses: inhibitors of the M2 ion channel, amantadine and rimantadine, and inhibitors of neuraminidase, oseltamivir, and zanamivir. There is paucity of information regarding effectiveness of these drugs in H5N1 infection. These drugs are also well known to have side effects like neurotoxicity. Thus there exists a need to develop alternate therapy for targeting the Avian flu virus (H5N1). The present invention addresses this need in the field.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants
Polypeptides, polynucleotides, methods, compositions, and vaccines comprising influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants are provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Influenza Hemagglutinin And Neuraminidase Variants
InactiveUS20090175898A1Efficient productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininNeuraminidase
Polypeptides, polynucleotides, methods, compositions, and vaccines comprising influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants are provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Influenza vaccine
InactiveUS7468259B2High protection levelSsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiNeuraminidaseMembrane anchor
A method for manufacturing recombinant neuraminidase by culturing in a suitable culture medium host cells which are transformed with a neuraminidase expression vector or infected with a virus which is transformed with a neuraminidase expression vector, wherein the expression vector comprises at least a part of the coding region of a neuraminidase gene of an influenza virus minus the region which codes for the membrane anchor, or a modified version thereof, preceded in phase by a signal sequence; and isolating the expression product neuraminidase from the culture medium. The invention further relates to vectors expressing the neuraminidase.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW
Novel vaccines against multiple subtypes of influenza virus
ActiveUS20090169505A1Elicit immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHemagglutininMammal
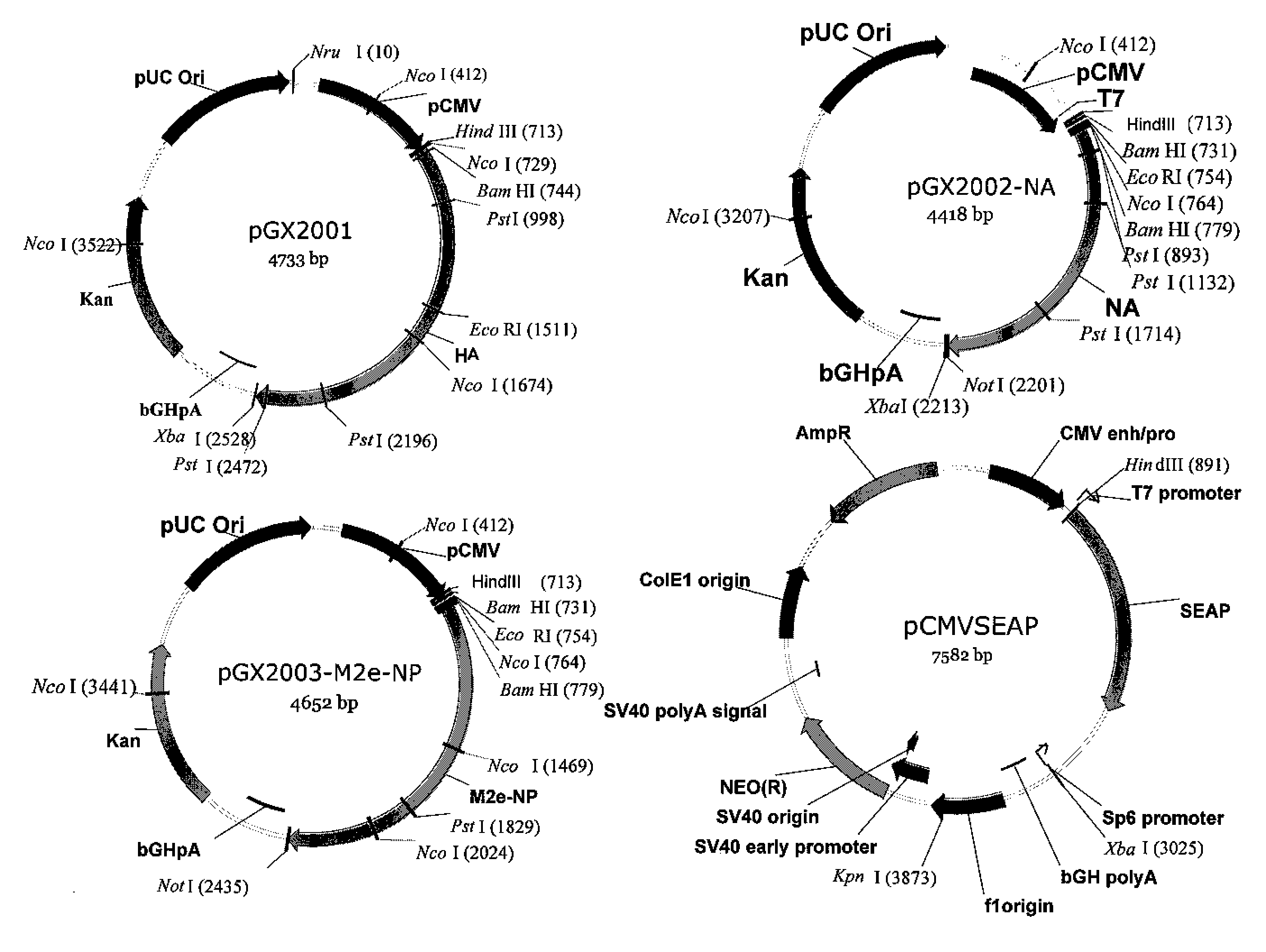
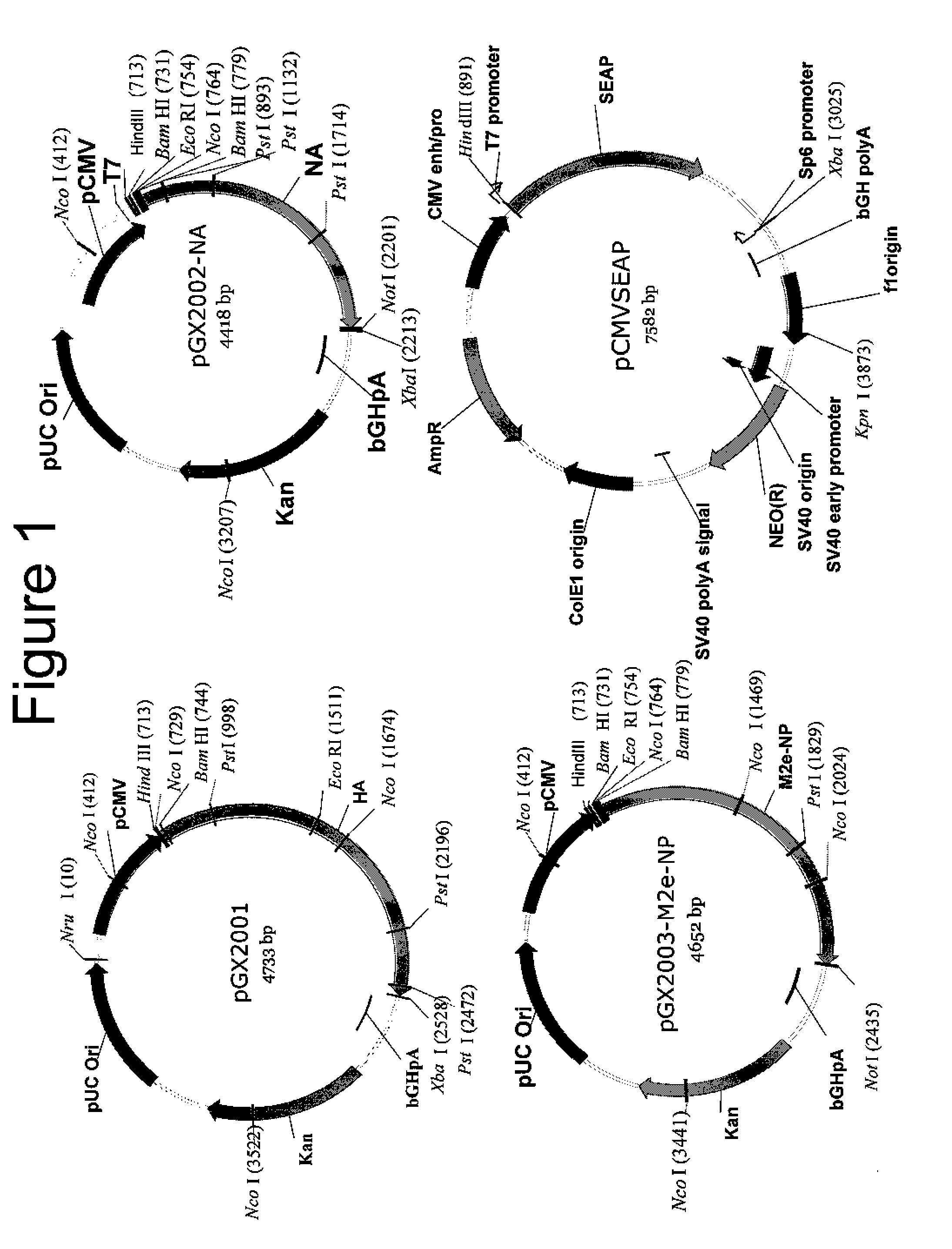
An aspect of the present invention is directed towards DNA plasmid vaccines capable of generating in a mammal an immune response against a plurality of influenza virus subtypes, comprising a DNA plasmid and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The DNA plasmid is capable of expressing a consensus influenza antigen in a cell of the mammal in a quantity effective to elicit an immune response in the mammal, wherein the consensus influenza antigen comprises consensus hemagglutinin (HA), neuraminidase (NA), matrix protein, nucleoprotein, M2 ectodomain-nucleo-protein (M2e-NP), or a combination thereof. Preferably the consensus influenza antigen comprises HA, NA, M2e-NP, or a combination thereof. The DNA plasmid comprises a promoter operably linked to a coding sequence that encodes the consensus influenza antigen. Additionally, an aspect of the present invention includes methods of eliciting an immune response against a plurality of influenza virus subtypes in a mammal using the DNA plasmid vaccines provided.
Owner:VGX PHARMA +1
Influenza Hemagglutinin And Neuraminidase Variants
InactiveUS20080057081A1Efficient productionExtended half-lifeSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininNeuraminidase
Polypeptides, polynucleotides, methods, compositions, and vaccines comprising (avian pandemic) influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants are provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Influenza virus reassortment
ActiveUS20130216573A1Reduce transcriptionReduce translationSsRNA viruses negative-senseAnimal cellsHemagglutininNeuraminidase
Methods for producing reassortant viruses are provided wherein the transcription and / or translation of the hemagglutinin and / or neuraminidase genes are suppressed.
Owner:SEQIRUS UK LTD
Influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants
InactiveUS20050287172A1Efficient productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininNeuraminidase
Polypeptides, polynucleotides, methods, compositions, and vaccines comprising (avian pandemic) influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase variants are provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Reagents and kits for detection of influenza virus and the like
ActiveUS20110189655A1Simple and rapid and specific and sensitive detectionHigh detection sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNeuraminidaseFirefly luciferin
The present invention relates to reagents and methods for influenza virus detection. These reagents and methods disclosed in the present invention enable simple, rapid, specific and sensitive detection of influenza virus types A and B. These reagents are N-acetylneuraminic acid-firefly luciferin conjugates which can be cleaved by influenza virus neuraminidase.
Owner:CELLEX INC
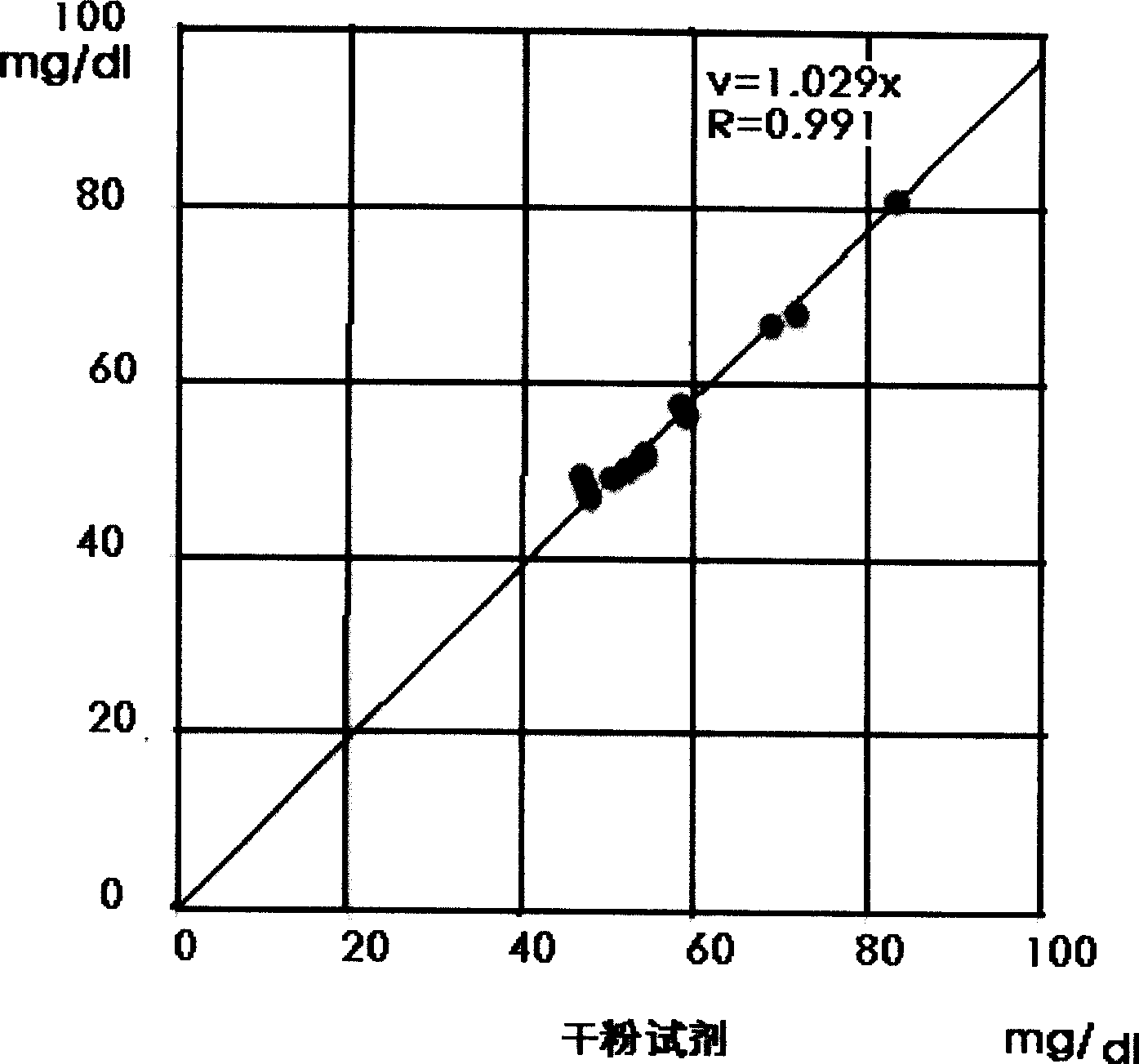
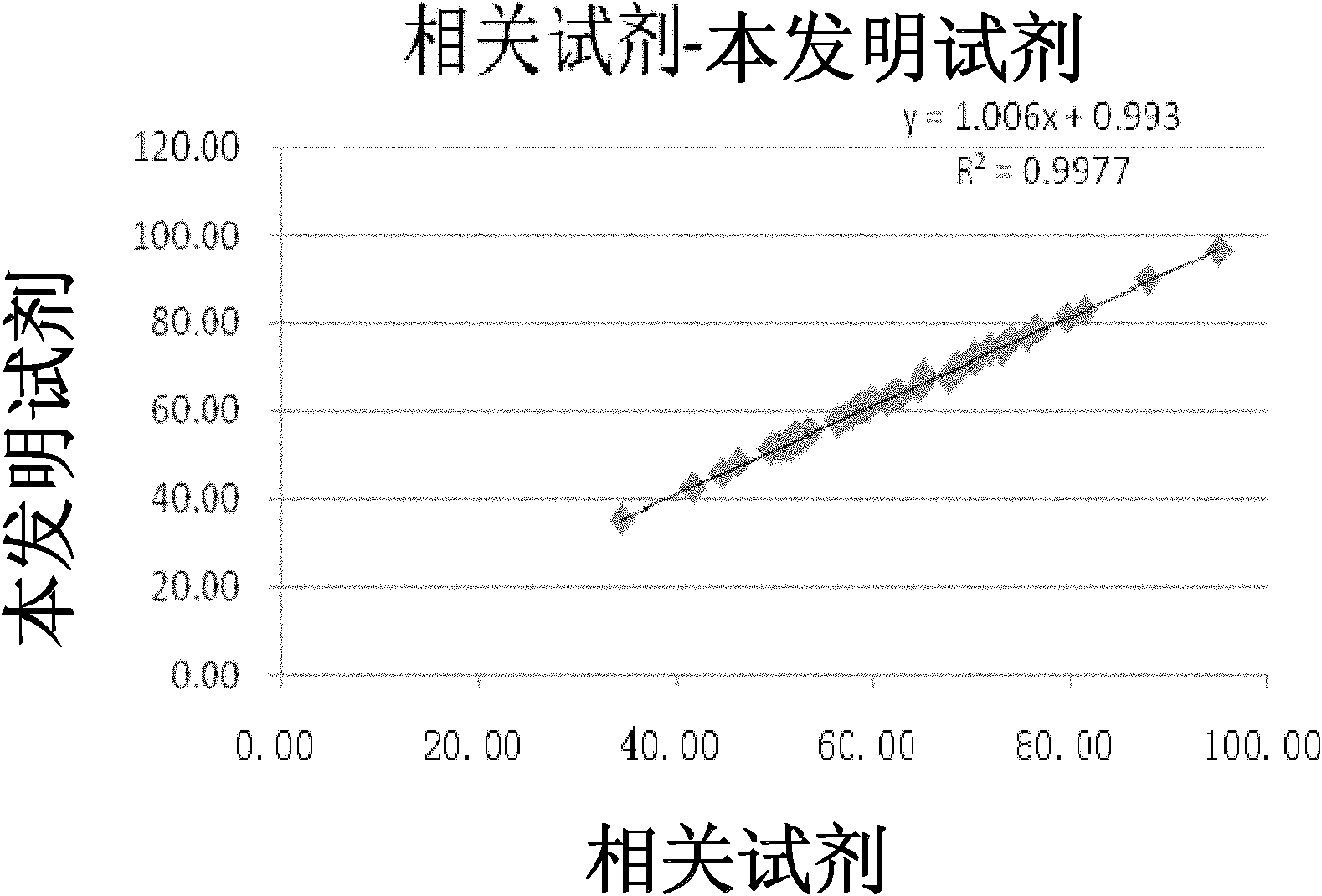
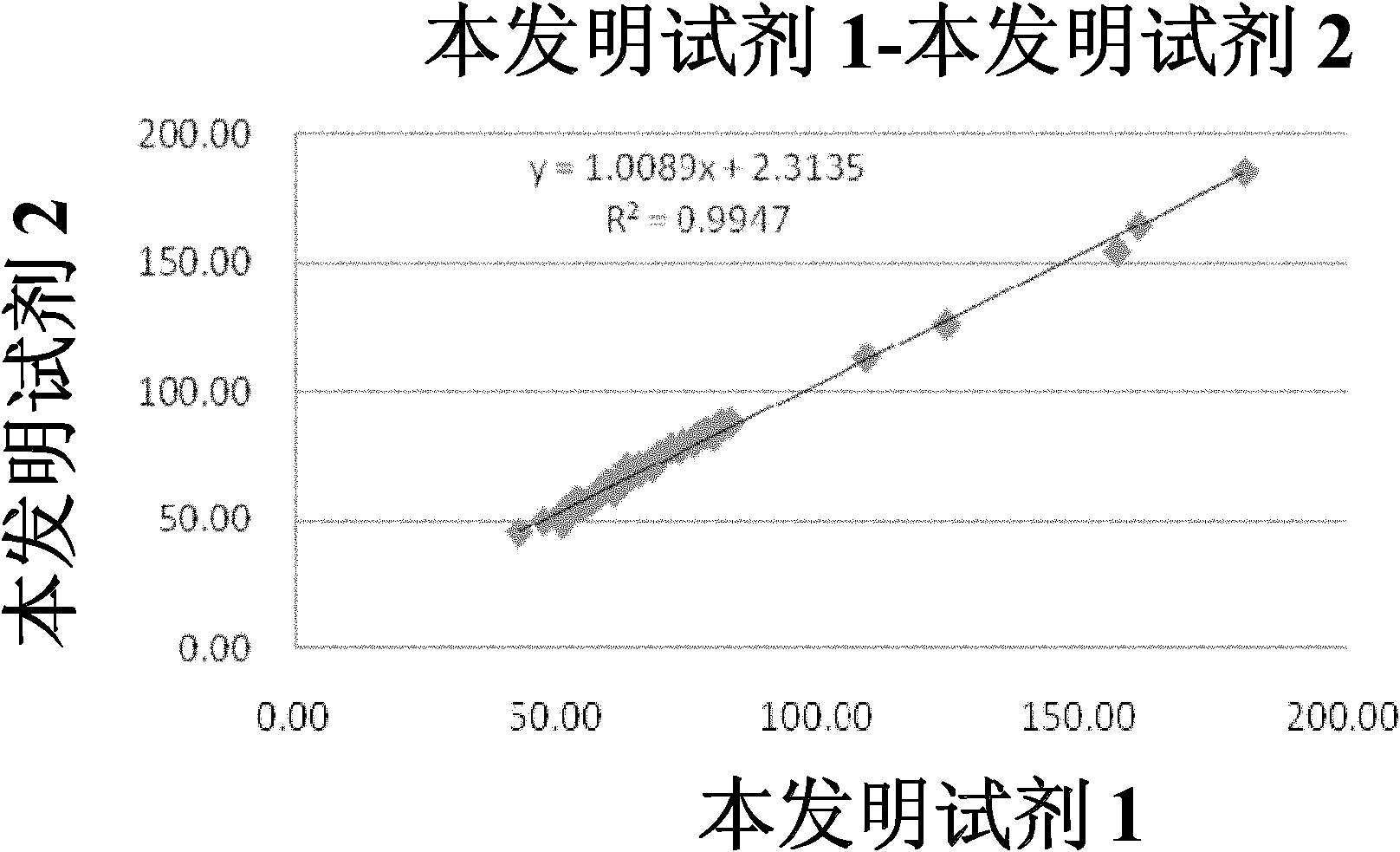
Double reagent for detecting sialic acid liquid by stable enzyme method and use thereof
ActiveCN101469344AEasy to useLittle difference between bottlesMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseNeuraminidase
The invention relates to a double reagent, in particular to a liquid double reagent for determining sialic acid by an enzyme method and application thereof. The technical proposal of the liquid double reagent comprises: the steady liquid double reagent for determining the sialic acid by the enzyme method consists of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises 0.01 to 50KU / L of neuraminidase, 0.1 to 50KU / L of lactate dehydrogenase, and 25 to 100mmol / L of buffer liquid; and the reagent 2 comprises 0.1 to 50KU / L of N-acetyleuraminic acid aldolase, 0.05 to 5mmol / L of reducing coenzyme NADH, 0.1 to 10000U / L of glucose dehydrogenase, 0.1 to 500mmol / L of glucose, and 5 to 100mmol / L of the buffer liquid. The liquid double reagent has the advantages that the liquid double reagent has convenient use, does not need a dissolving solution to redissolve, has small difference among bottles, ensures that the packaging of the liquid double reagent can adapt to various automatic biochemical analyzers, can avoid secondary pollution, and simplify a production technology method.
Owner:上海微鸿企业管理有限公司
Method and kit for stably detecting sialic acid by enzyme method
The invention relates to a method and a kit for stably detecting sialic acid by an enzyme method. The method comprises the following steps of: generating N-acetylneuraminic acid from bound sialic acid under the catalysis of neuraminic acid aldolase; transforming the N-acetylneuraminic acid into N-acetylmannosamine under the catalysis of neuraminidase; reacting the product with mannosamine dehydrogenase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to generate reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH); and measuring the sialic acid content by detecting the amount of the generated NADH. The invention also relates to the kit prepared according to the method. The method and the kit are conveniently and quickly used, the sialic acid is not required to be redissolved by dissolving liquid, is stable for a long time and has small inter-bottle variation, the method and the kit are suitable for various biochemical analyzers, secondary pollution is avoided, and a production process method is simplified.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
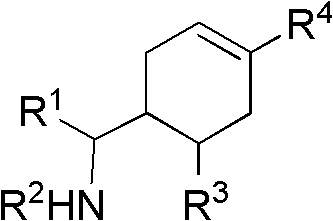
Cyclohexene compound having influenza virus neuraminidase inhibition activity, preparation method and application
InactiveCN102964267AHas neuraminidase inhibitory activityOvercoming drug resistanceCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationCyclohexeneEnantiomer
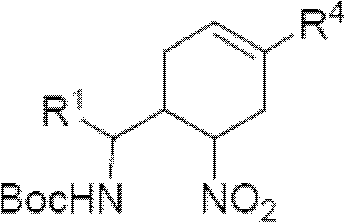
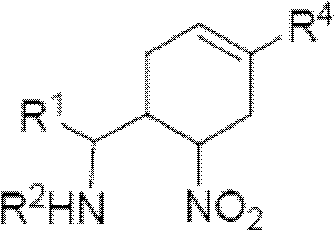
The invention provides a compound expressed by a general formula I, or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, and an analyzed enantiomer and a purified diastereomer, wherein R<1>is H or C1-12 alkyl groups; R<2> is H, -C(O)R<1a>, -C(O)OR<1a> or -S(O)2R<1b>, wherein R<1a> is H or C1-6 alkyl groups, R<1b> is selected from H or C1-6 alkyl groups halogenated hydrocarbon, phenyl or aryl group; R<3> is selected from C1-4 alkyl groups substituted amino, halogen, hydroxyl, sulfydryl, guanidyl, nitryl or cyano group; and R<4> is -(CH2)nCO2H, -(CH2)nP(O)(OH)2, -(CH2)nCO2R<1a> and -(CH2)nP(O)(OR<1a>)2, wherein R<1a> is H or C1-6 alkyl groups, n is an integer between 0 and 4, or a salt of the above groups. The invention also provides a preparation method of the cyclohexene compound expressed by the general formula I, and an application of the cyclohexene compound taken as an influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitor for preparing the medicines to prevent or treat the influenza diseases.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
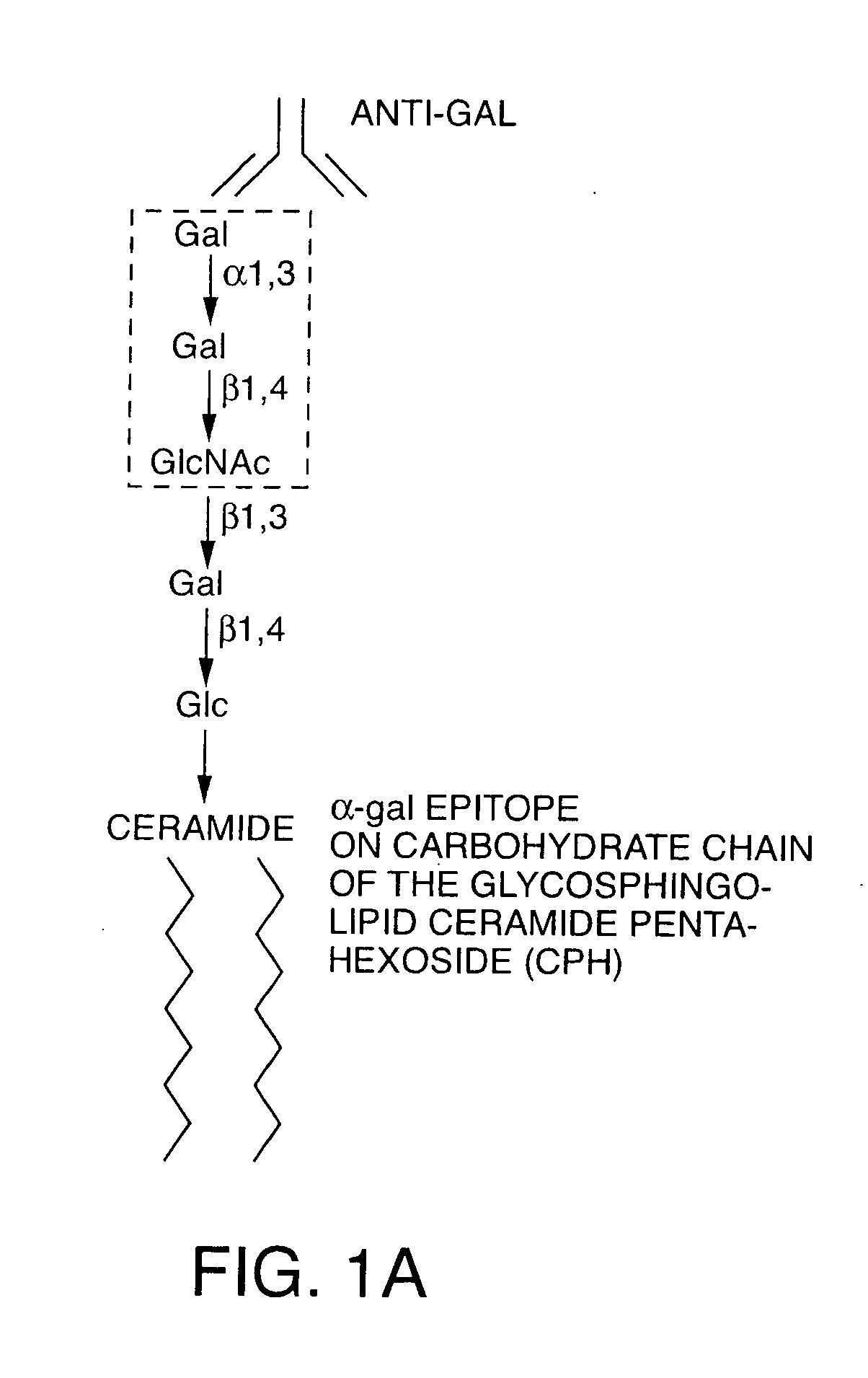
Tumor lesion regression and conversion in situ into autologous tumor vaccines by compositions that result in anti-Gal Antibody Binding
InactiveUS20060251661A1Reduce the overall heightBiocideSugar derivativesAntigenAbnormal tissue growth
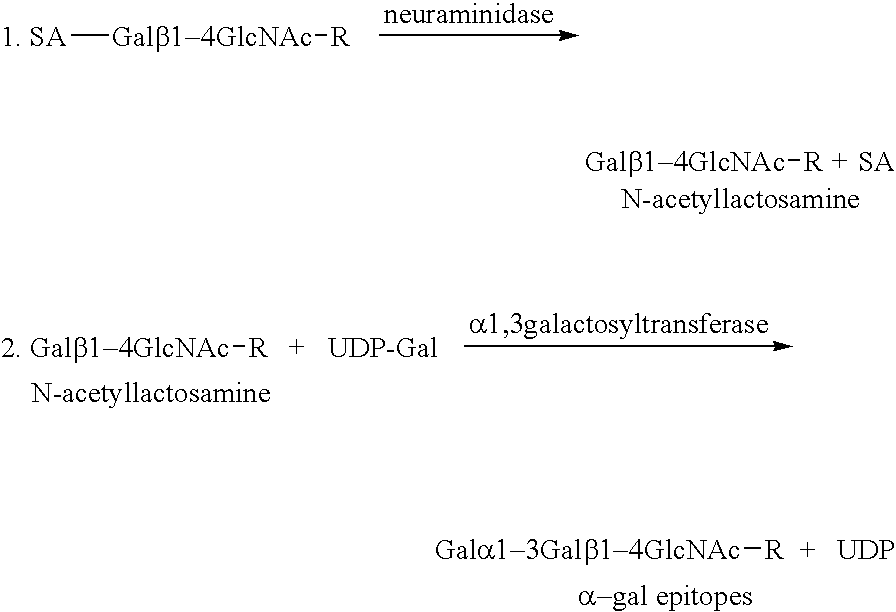
The present invention discloses that an intratumoral injection of: i) glycolipids with α-gal epitope; ii) gene vectors comprising an α1,3galactosyltransferase gene; or iii) a mixture of α1,3galactosyltransferase, neuraminidase, and uridine diphosphate galactose results in tumor regression and / or destruction. Binding of the natural anti-Gal antibody to de novo expressed tumoral α-gal epitopes induces inflammation resulting in an anti-Gal antibody mediated opsonization of tumor cells and their uptake by antigen presenting cells. These antigen presenting cells migrate to draining lymph nodes and activate tumor specific T cells thereby converting the treated tumor lesions into in situ autologous tumor vaccines. This therapy can be applied to patients with multiple lesions and in neo-adjuvant therapy to patients before tumor resection. In addition to the regression and / or destruction of the treated tumor, such a vaccine will help in the immune mediated destruction of micrometastases that are not detectable during the removal of the treated tumor.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL SCHOOL
Reagents and kits for detection of influenza virus and the like
ActiveUS7893272B2Simple and rapid and specific and sensitive detectionHigh detection sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideNeuraminidaseFluorescein
The present invention relates to reagents and methods for influenza virus detection. These reagents and methods disclosed in the present invention enable simple, rapid, specific and sensitive detection of influenza virus types A and B. These reagents are N-acetylneuraminic acid-firefly luciferin conjugates which can be cleaved by influenza virus neuraminidase.
Owner:CELLEX BIOLOGICAL TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com