Patents
Literature
53 results about "Clade" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
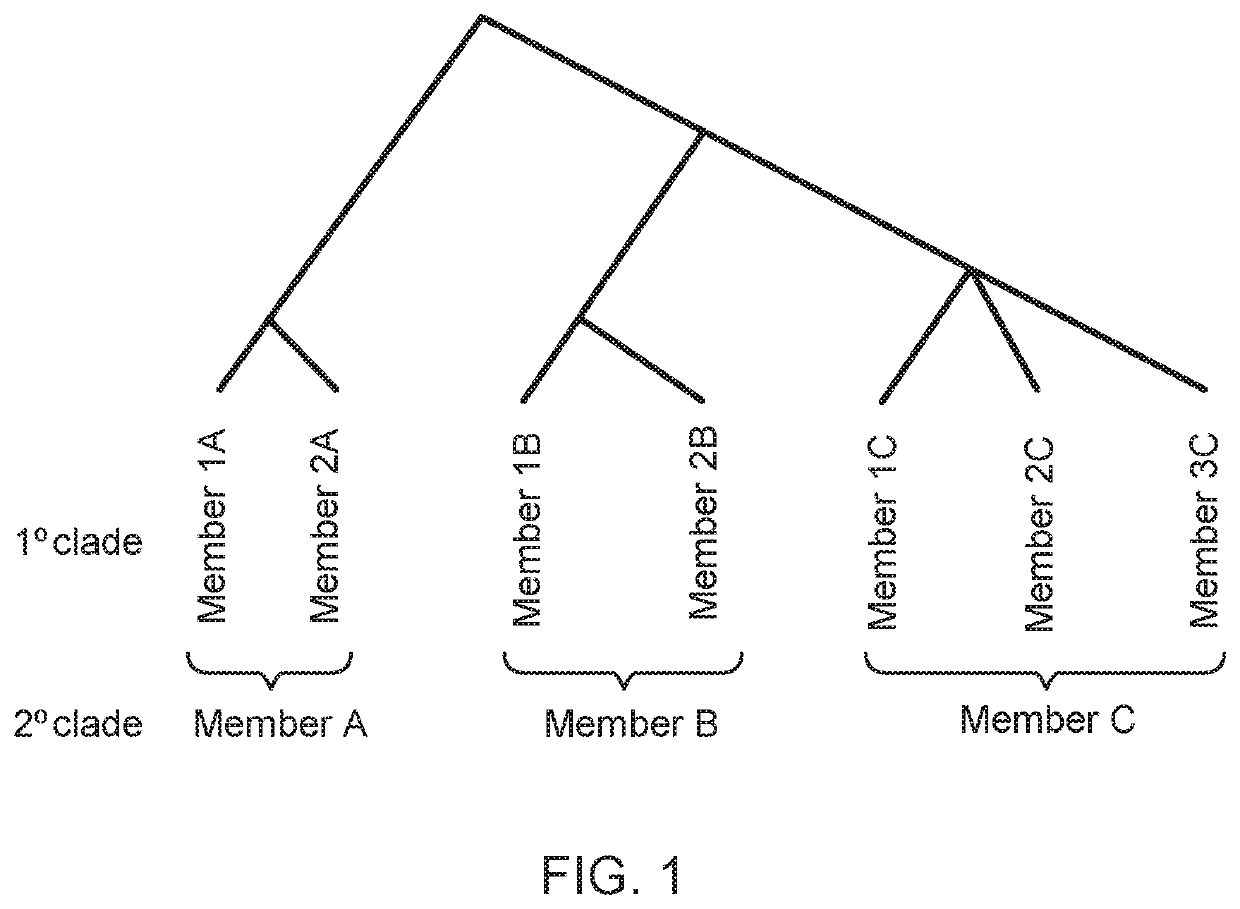
A clade (from Ancient Greek: κλάδος, klados, "branch"), also known as monophyletic group, is a group of organisms that consists of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants, and represents a single "branch" on the "tree of life". Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term cladus (plural cladi) is often used in taxonomical literature.
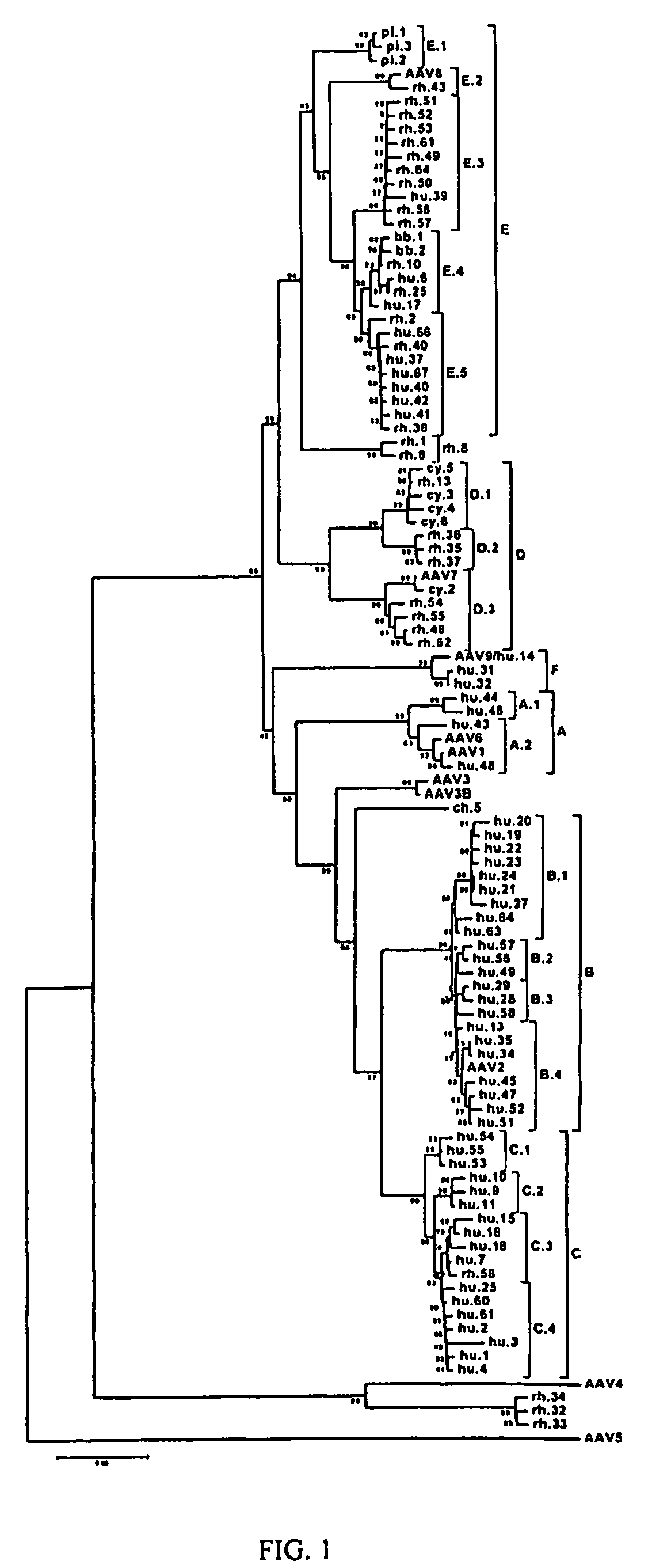
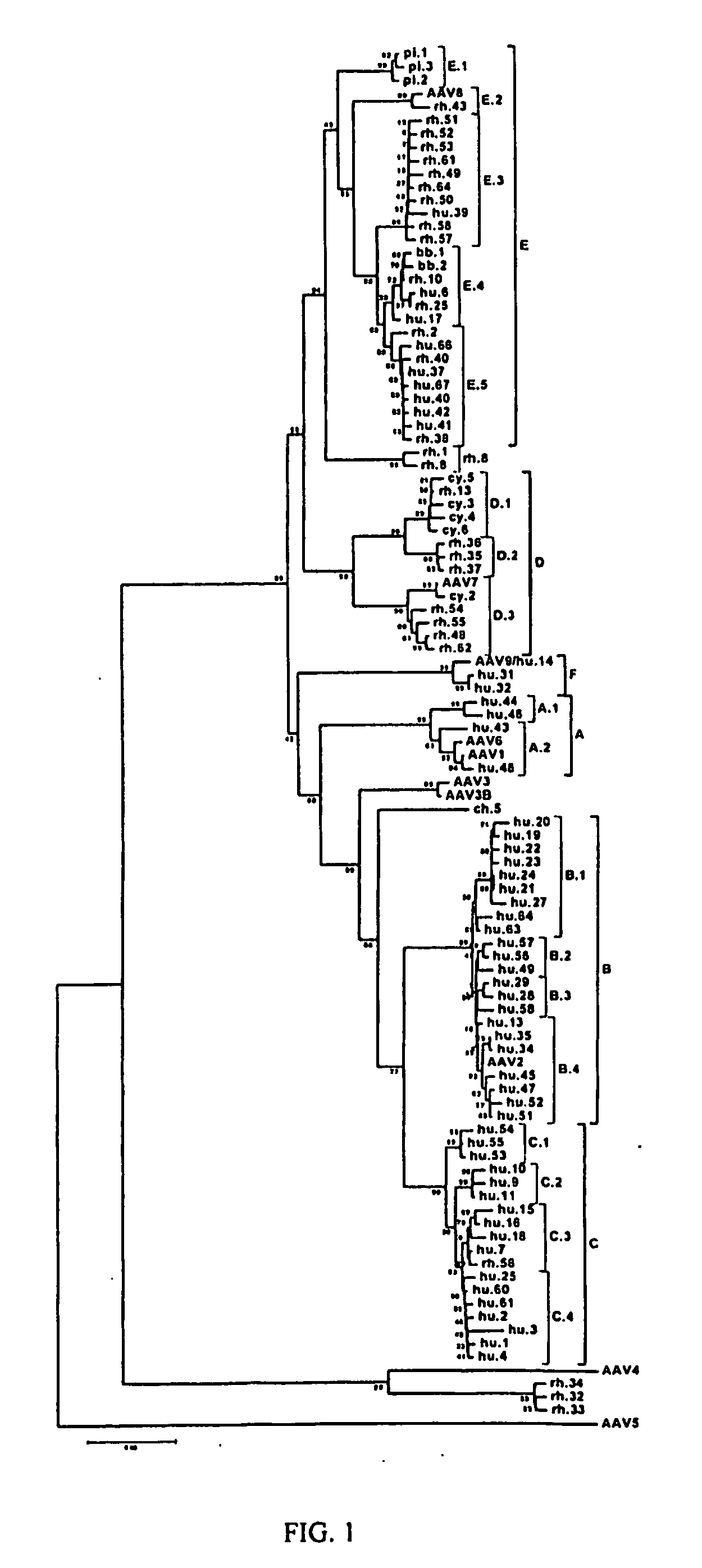
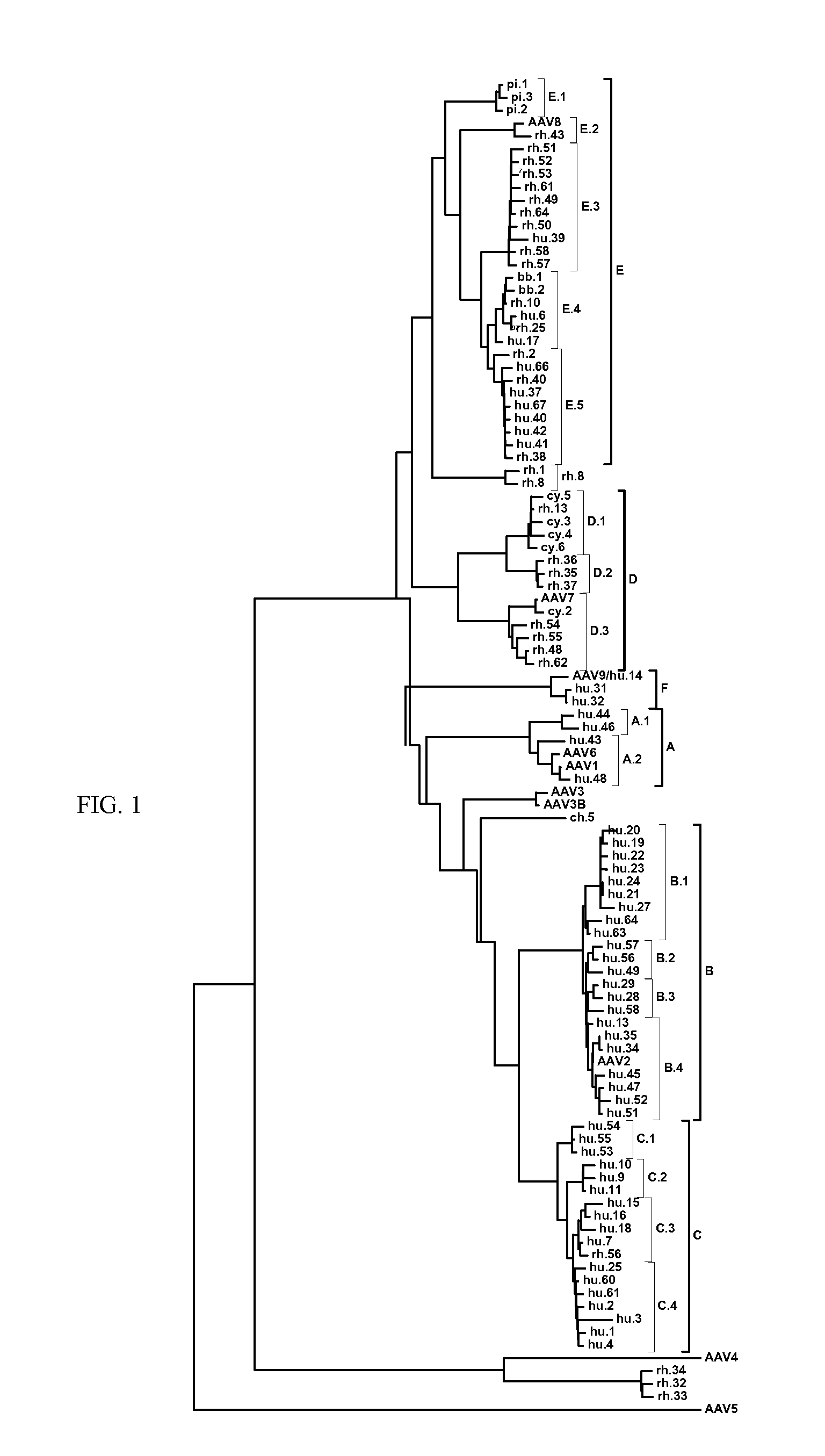
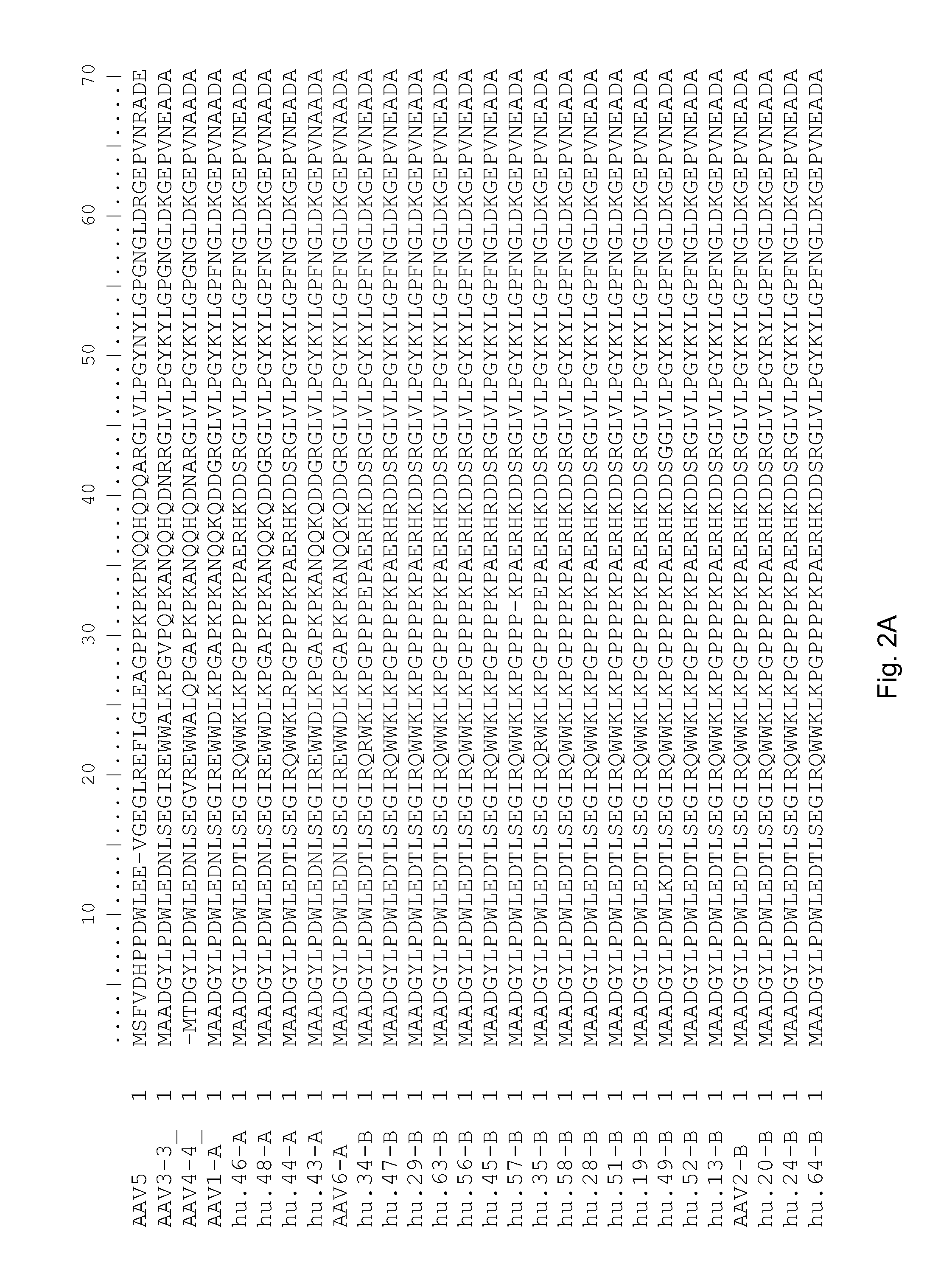
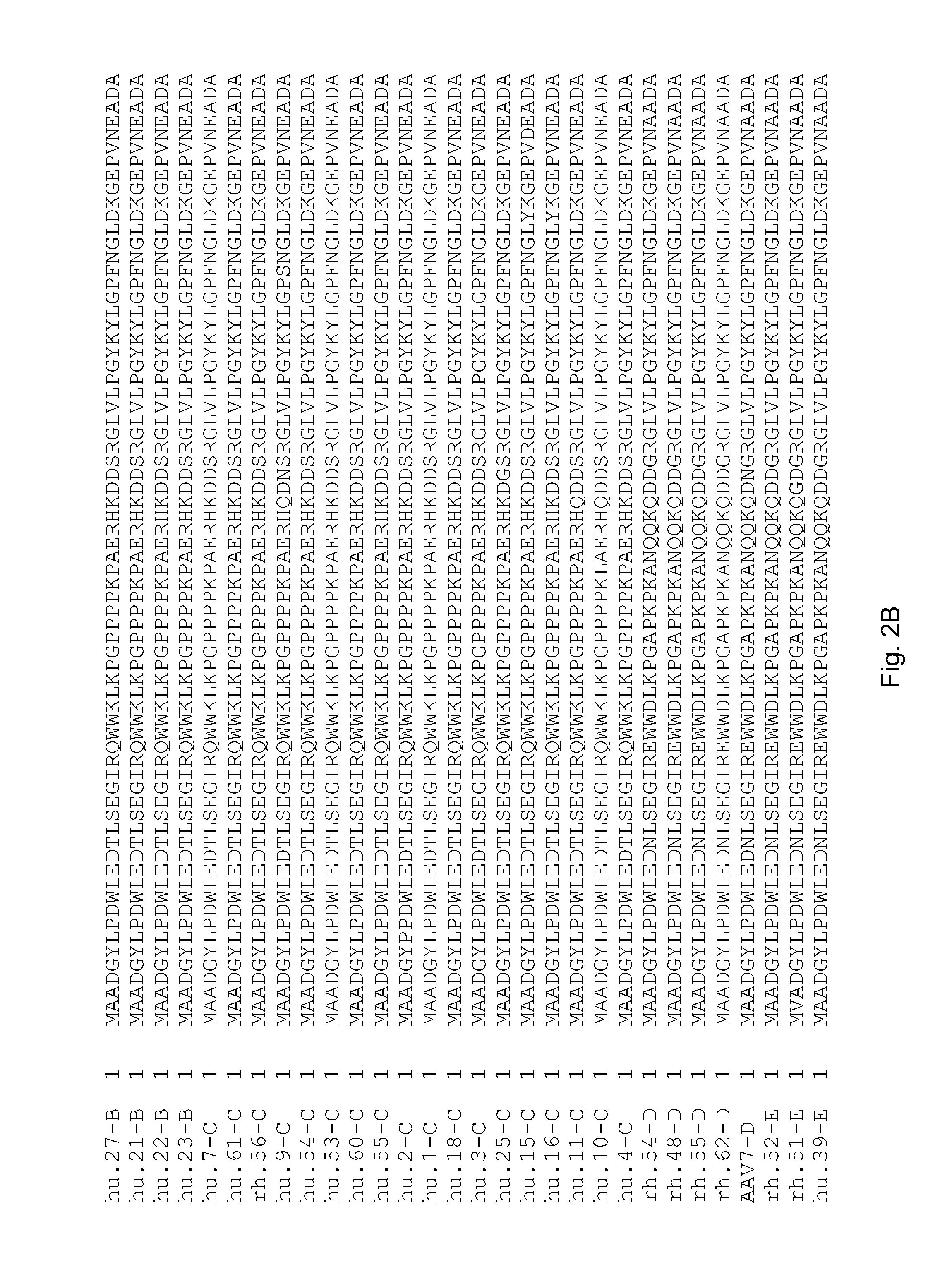
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Adeno-associated virus (aav) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
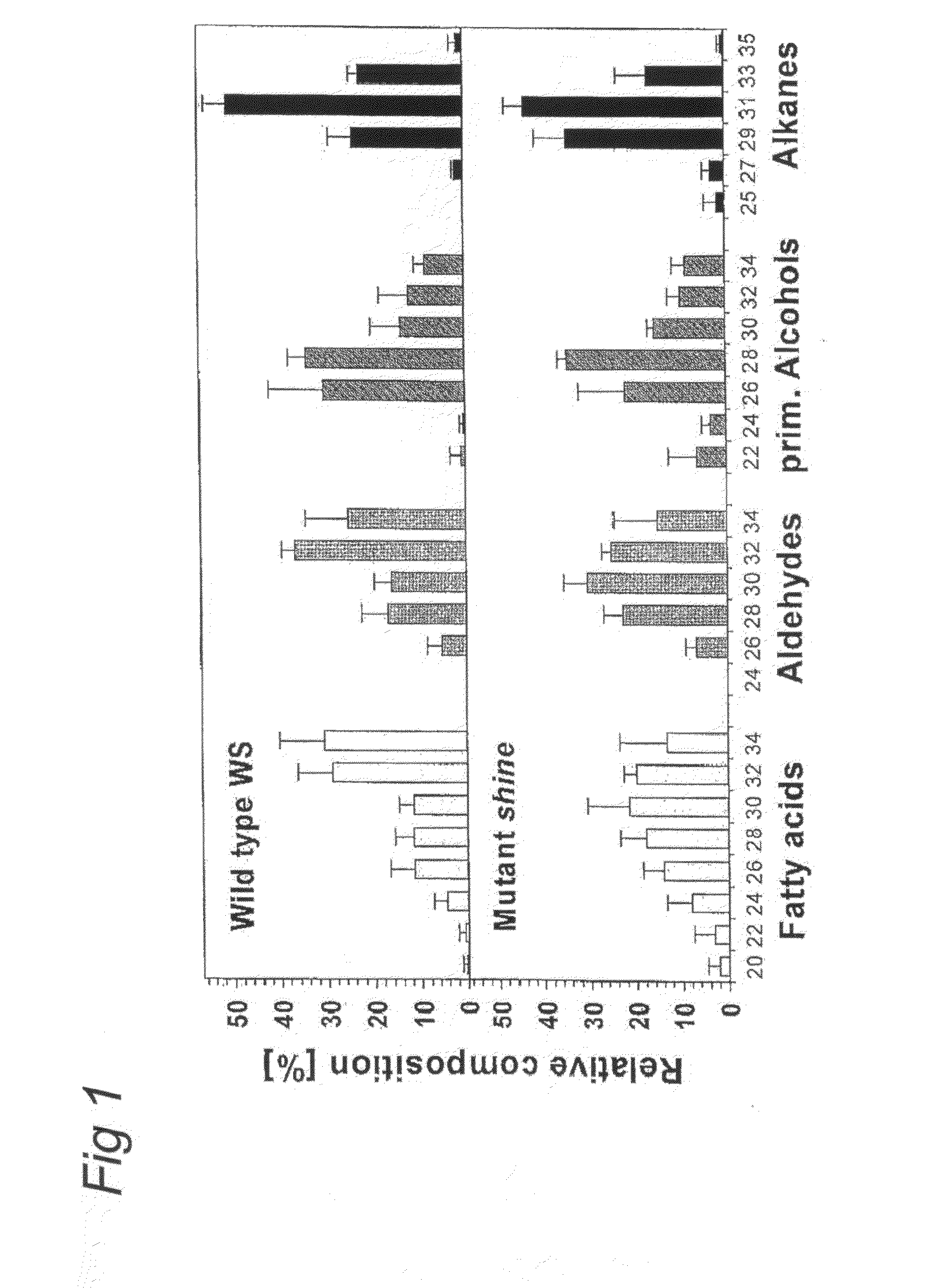
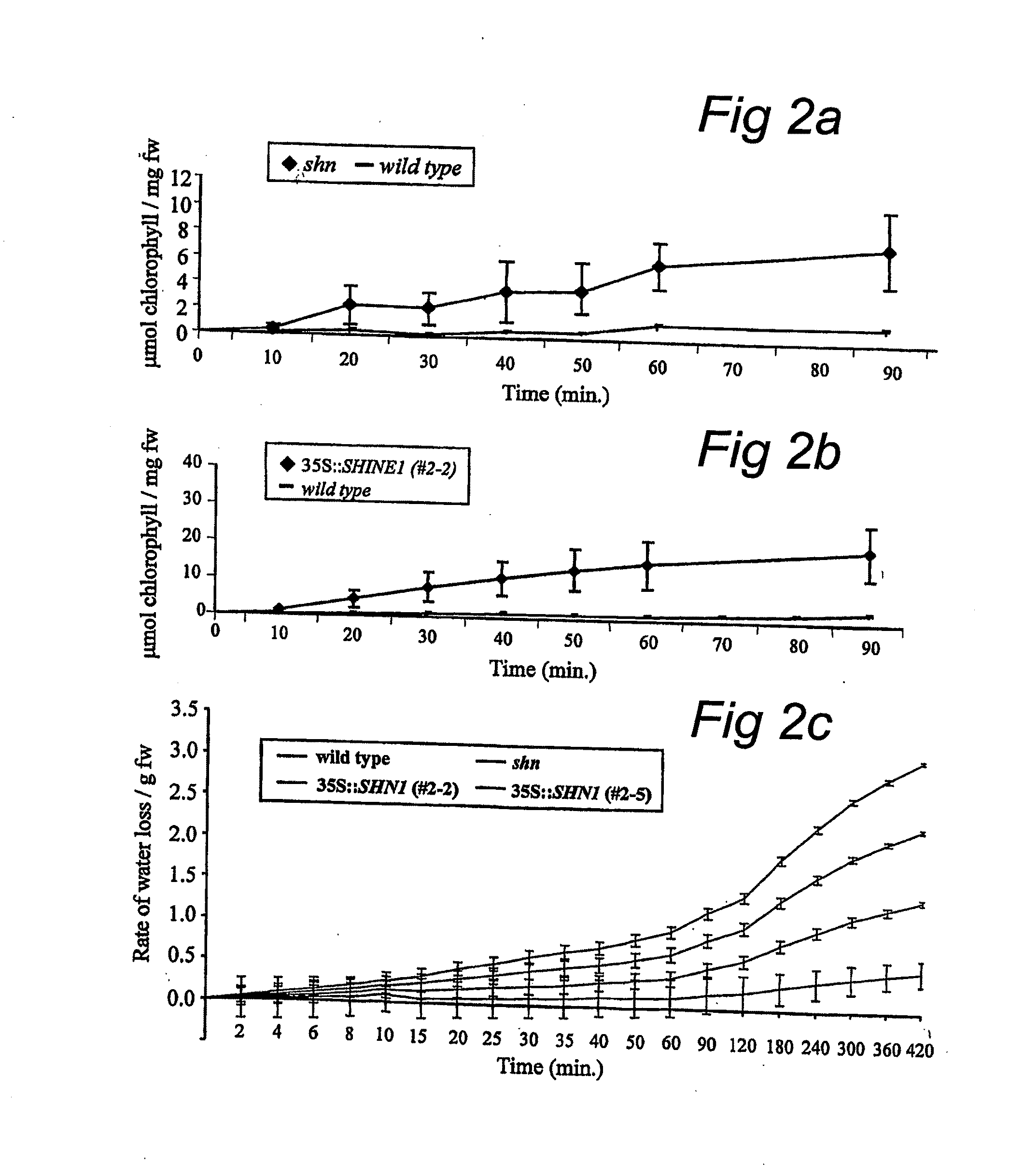
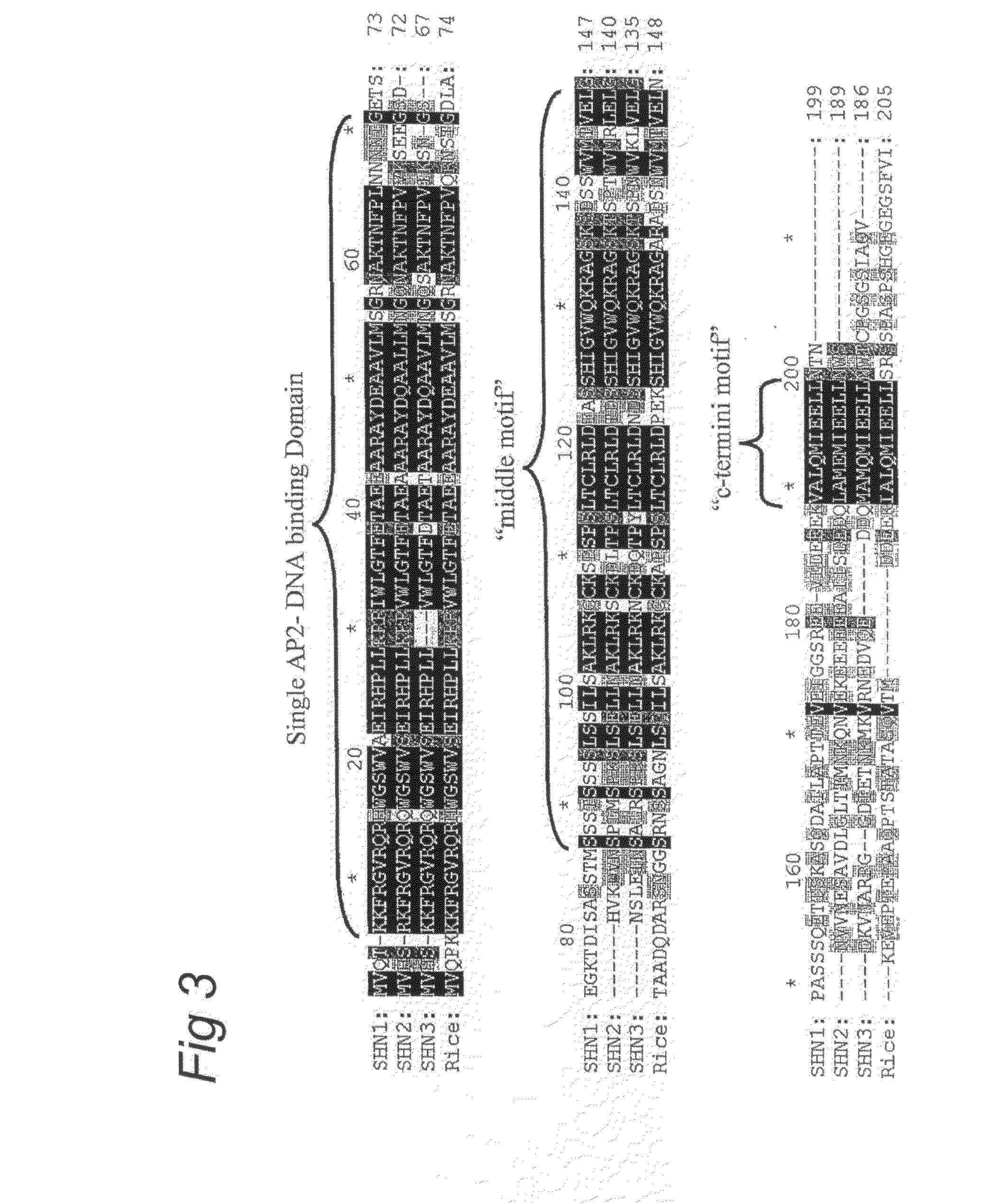
Shine clade of transcription factors and their use
InactiveUS20090300790A1Increase in cuticular water lossPromote recoverySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleic acid sequencingGMO Plants
The present invention relates to the field of transgenic plants with given phenotypes, especially plants with enhanced drought tolerance. Provided are SHINE proteins and nucleic acid sequences encoding these, which are useful in conferring these phenotypes to plants.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20110044994A1Sugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against virusesVaccinationImmunodeficiency virus
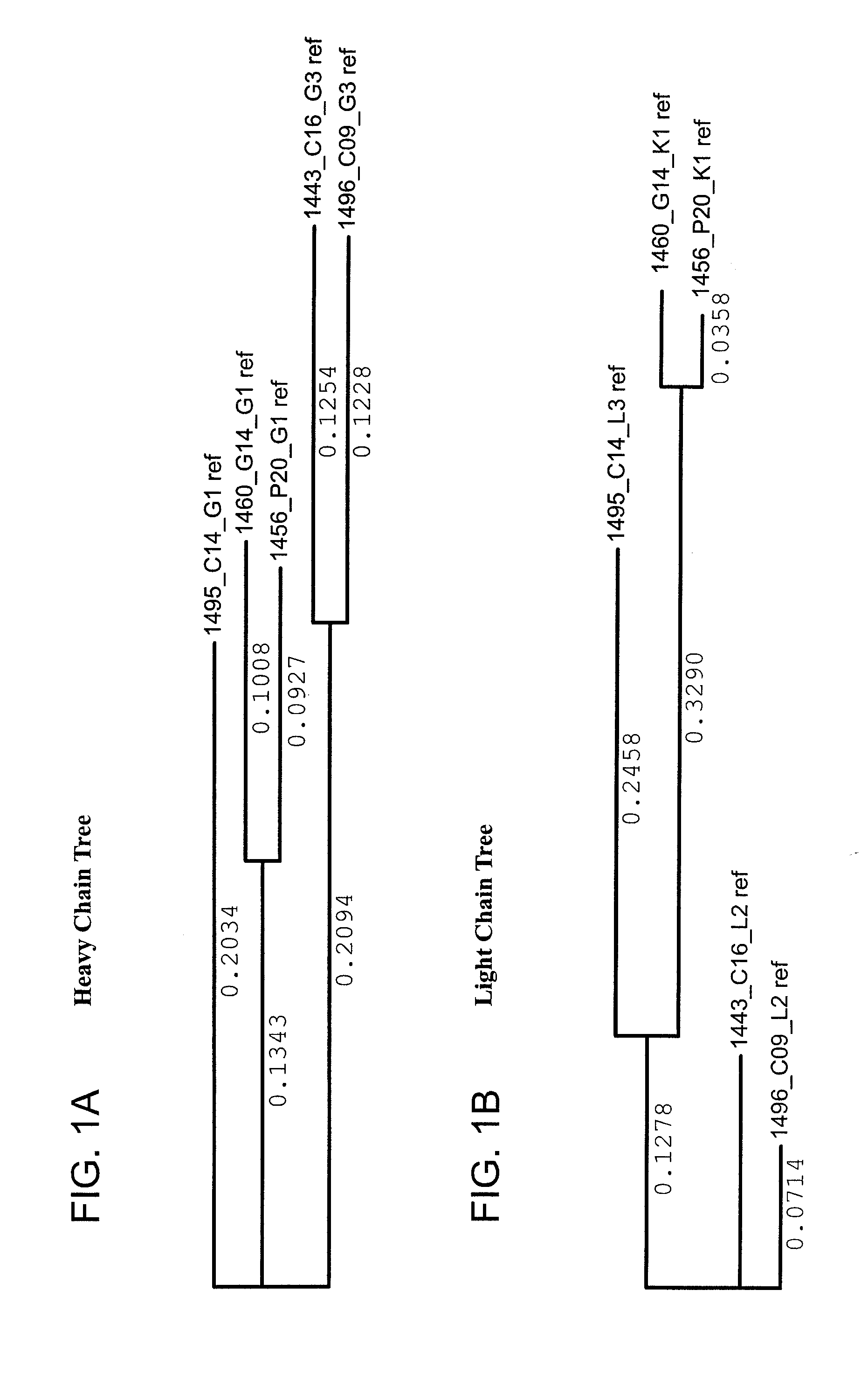
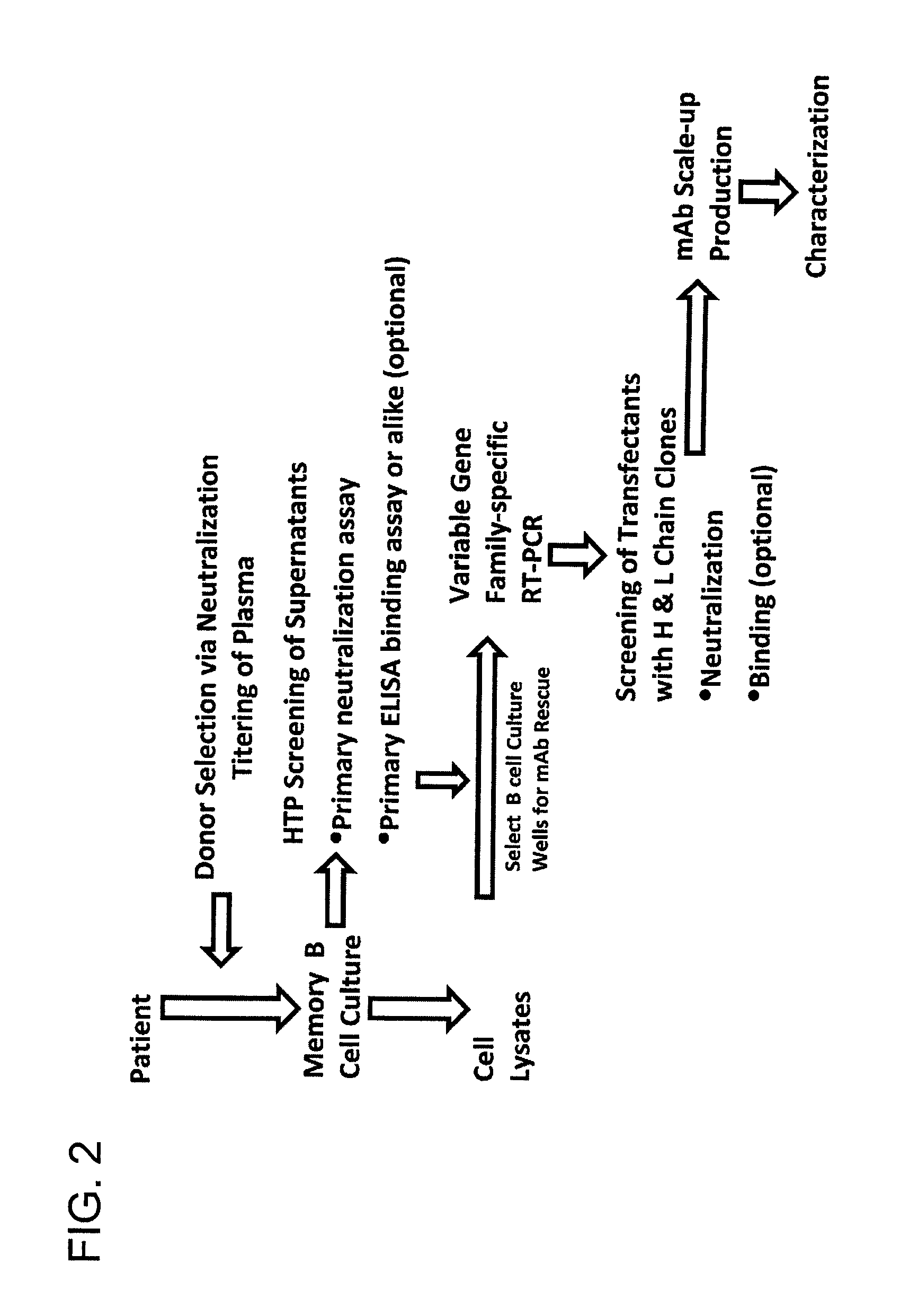
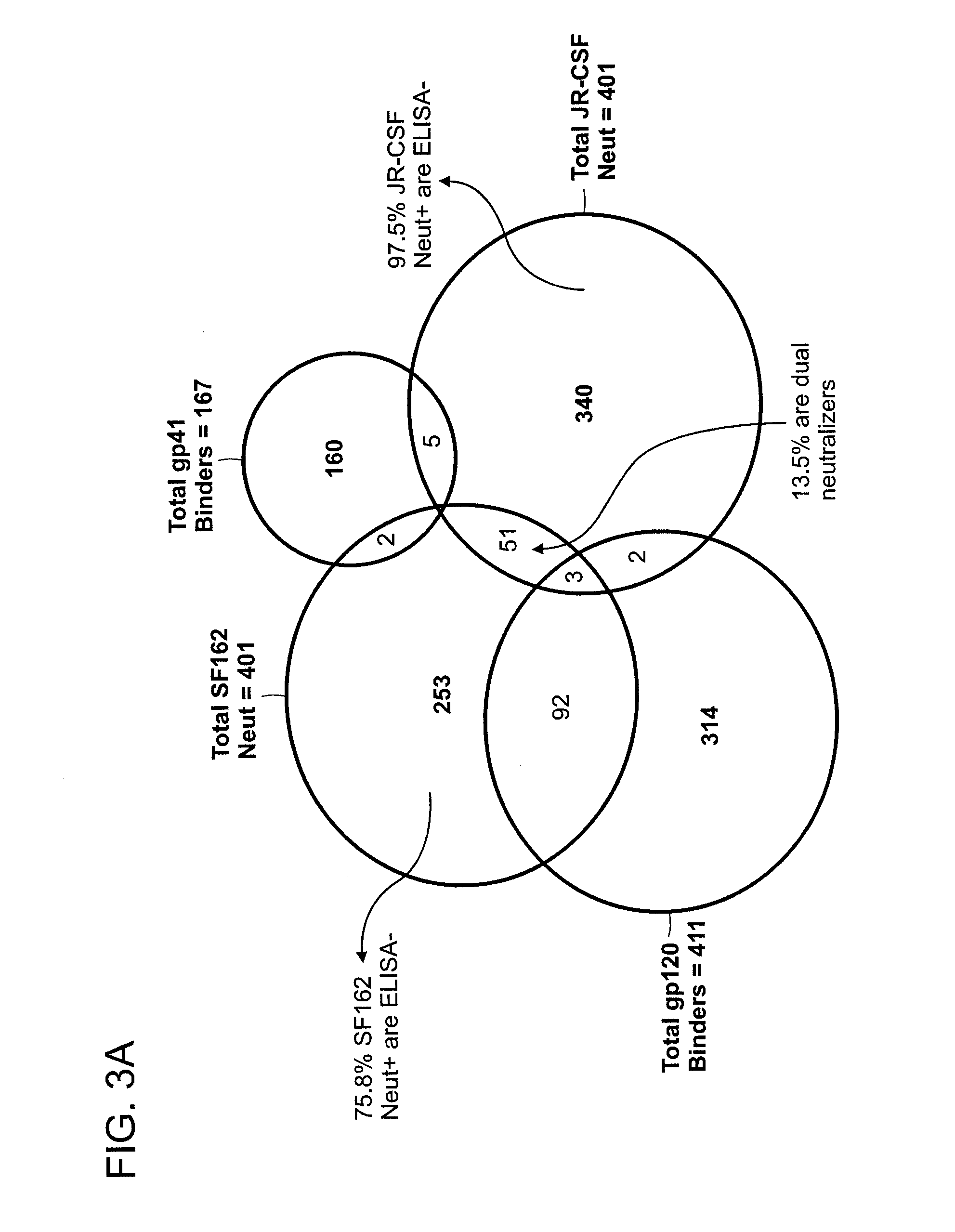
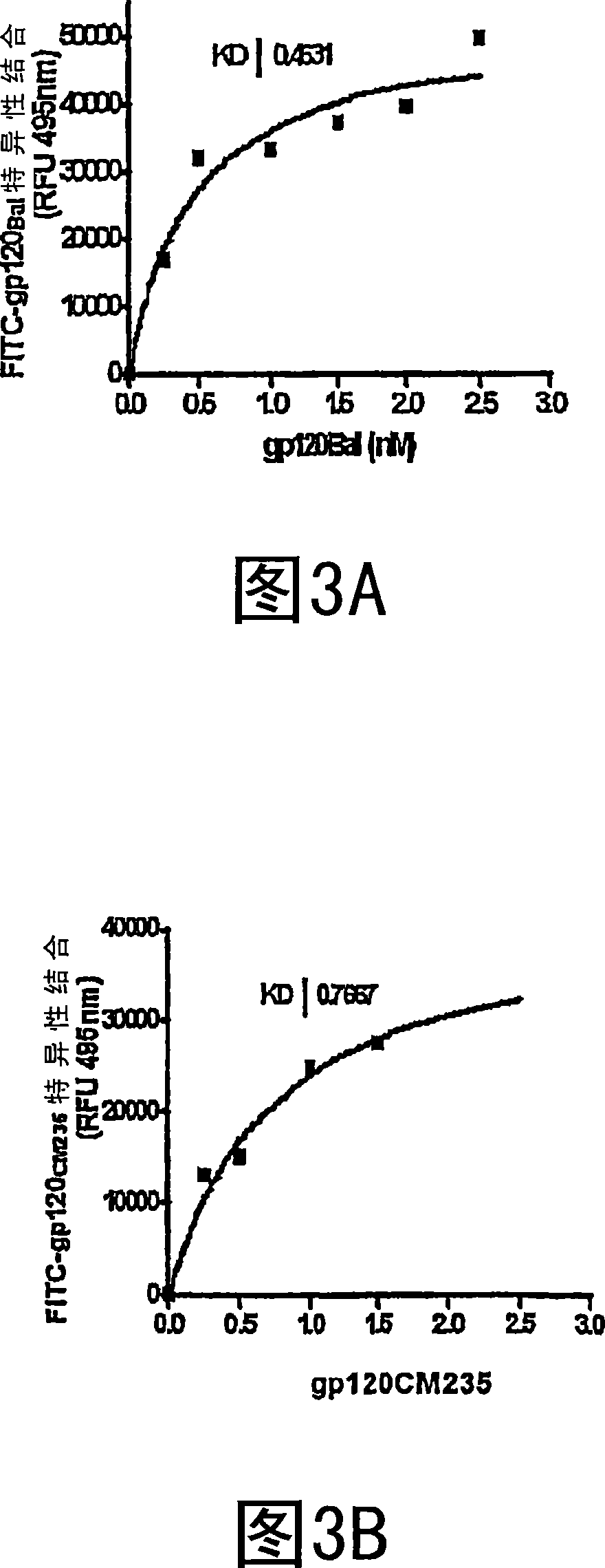
The invention provides a method for obtaining a broadly neutralizing antibody (bNab), including screening memory B cell cultures from a donor PBMC sample for neutralization activity against a plurality of HIV-1 species, cloning a memory B cell that exhibits broad neutralization activity; and rescuing a monoclonal antibody from that memory B cell culture. The resultant monoclonal antibodies are characterized by their ability to selectively bind epitopes from the Env proteins in native or monomeric form, as well as to inhibit infection of HIV-1 species from a plurality of clades. Compositions containing human monoclonal anti-HIV antibodies used for prophylaxis, diagnosis and treatment of HIV infection are provided. Methods for generating such antibodies by immunization using epitopes from conserved regions within the variable loops of gp120 are provided. Immunogens for generating anti-HIV1 bNAbs are also provided. Furthermore, methods for vaccination using suitable epitopes are provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +2
Modified HIV-1 clade C envelope glycoprotein immunogens comprising deletions in the gp120/gp41 cleavage site and gp41 fusion domain
The present invention relates, in general, to an immunogen and, in particular, to an immunogen for inducing antibodies that neutralize a wide spectrum of HIV primary isolates and / or to an immunogen that induces a T cell immune response. The invention also relates to a method of inducing anti-HIV antibodies, and / or to a method of inducing a T cell immune response, using such an immunogen. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding the present immunogens.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Detection of human immunodeficiency virus using cells transduced with a complex viral vector
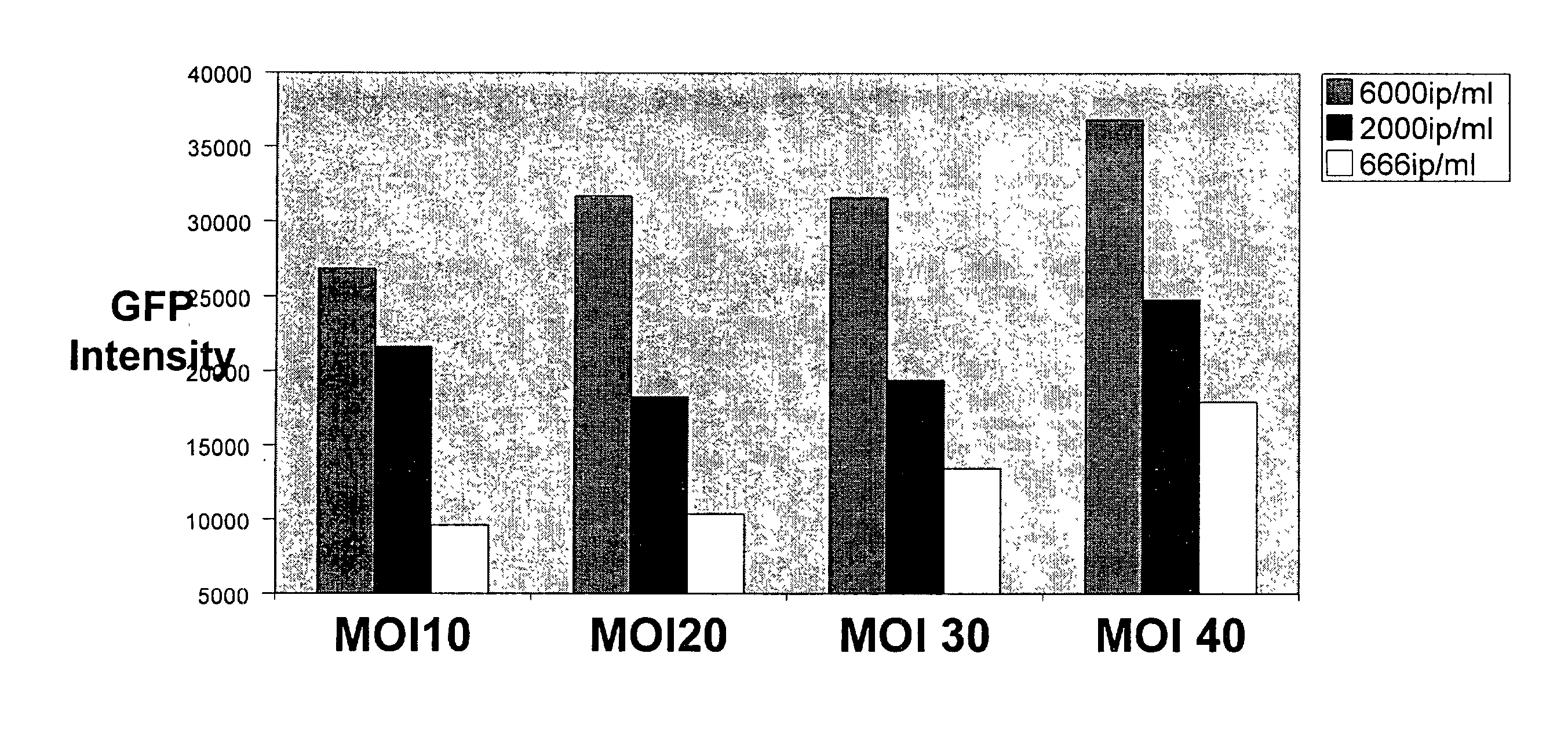
InactiveUS20030064054A1Convenient and cost-effective and ultra sensitiveImprove throughputBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousInfected cell
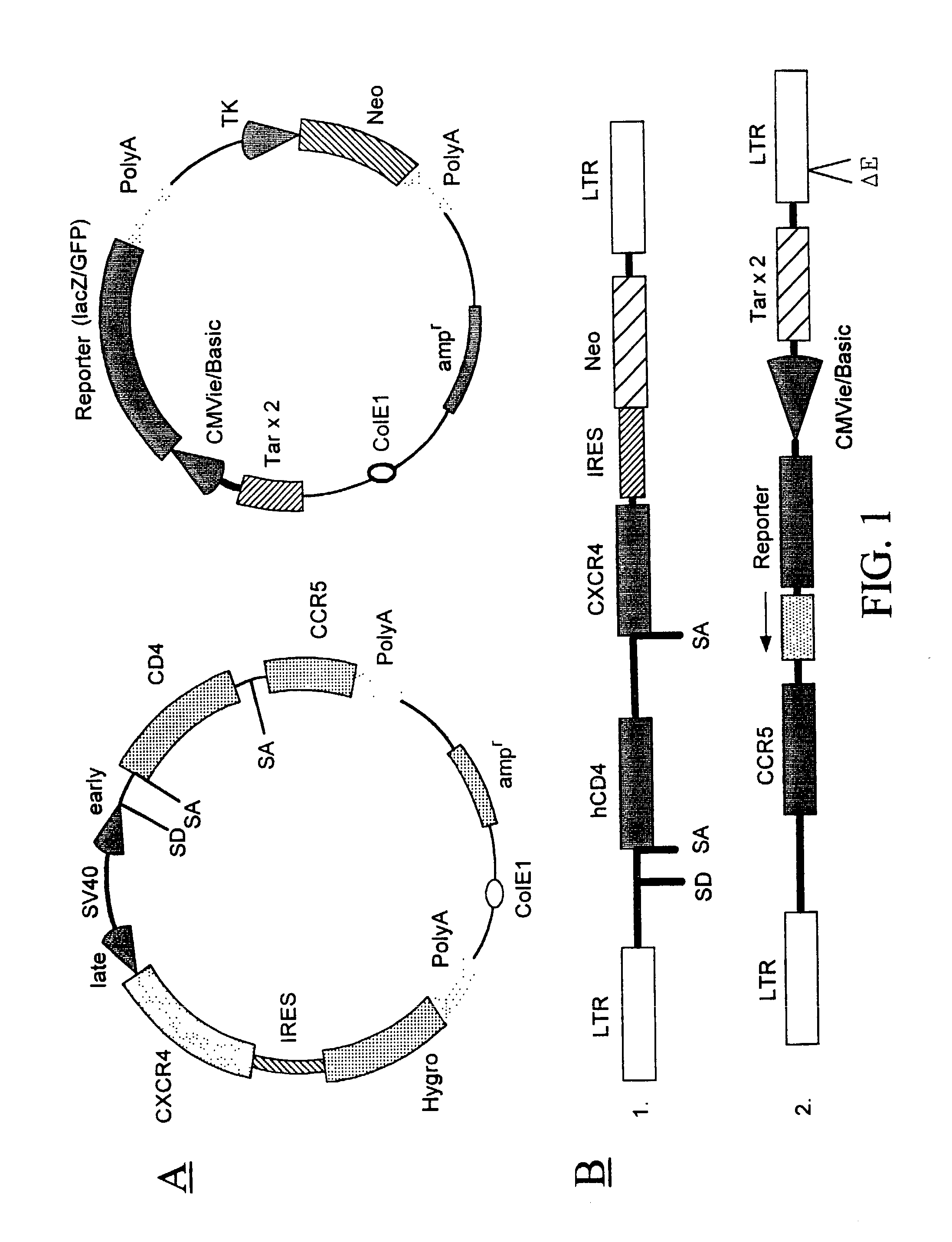
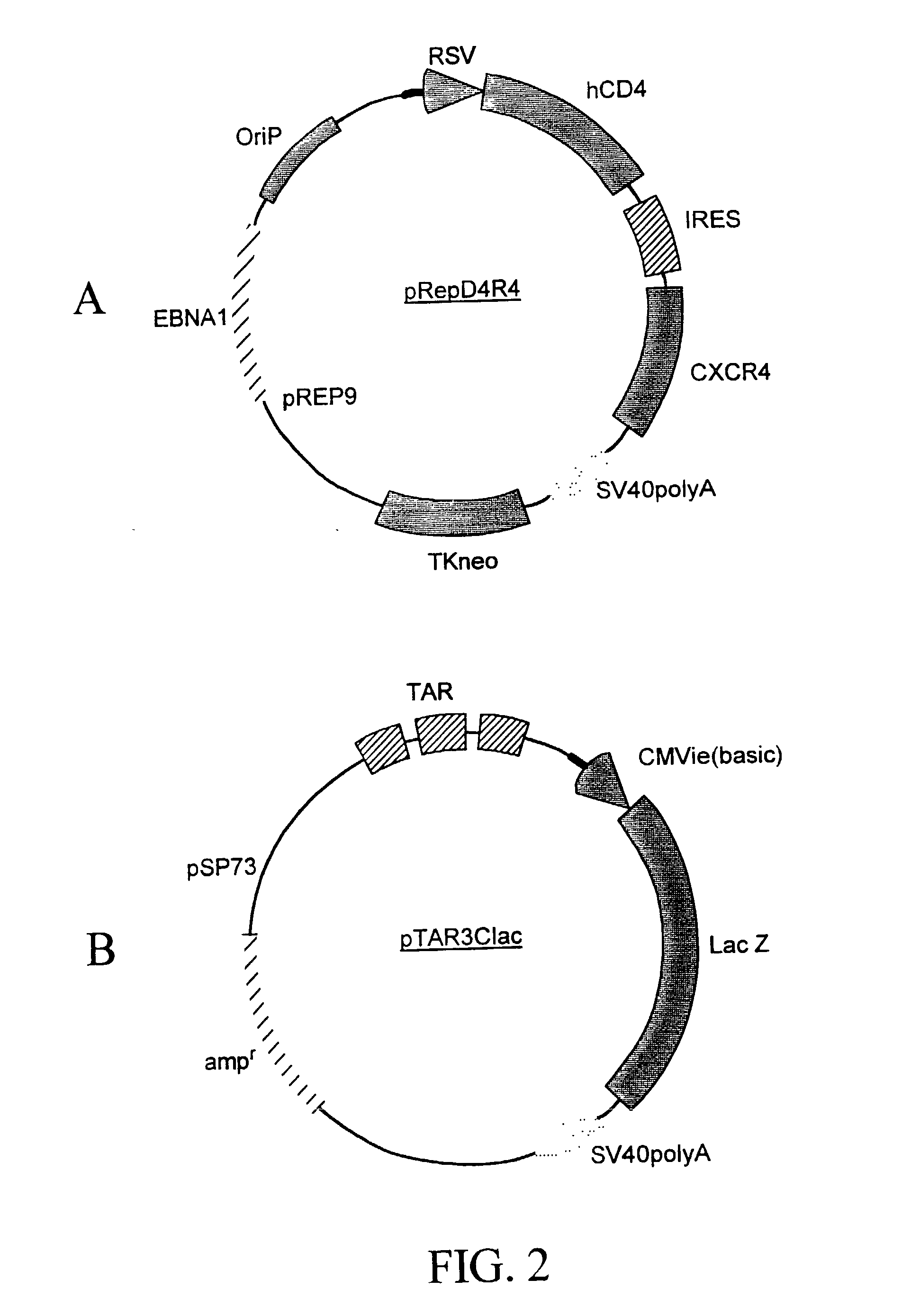
Methods are provided for screening natural and synthetic anti-HIV agents using recombinant cells that are rendered susceptible to productive infection of various strains, subtypes or clades of HIV from both laboratory and clinical isolates. The method comprises: taking a culture of recombinant cells in which at least one of the recombinant cells comprises a reporter sequence comprising a reporter gene whose expression is regulated by a protein specific to HIV, and a heterologous sequence which encodes CD4 and one or more additional cell surface receptors, wherein the heterologous sequence expresses CD4 and the one or more additional cell surface receptors at elevated levels as compared to the cell in the absence of expression by the heterologous sequence such that productive infection of the recombinant cell by HIV is achieved, which is defined by HIV viral replication and the infection of non-infected cells in the culture of the recombinant cells; contacting the cell culture with a sample containing HIV; adding a tester agent to the cell culture; and detecting a change in a level of expression of the reporter gene in the cells in the culture.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
HIV vaccine composition
An anti-HIV vaccine composition is disclosed. The vaccine comprises an combination of immunogenic peptide mixtures, which mixtures may be prepared in a single synthesis. The composition collectively represents the in vivo variability seen in immunogenic epitopes from highly variable regions of HIV. Immunization with the vaccine elicits broadly reactive immunity (CTL and T helper cell responses) against the divergent strains of HIV upon which it is based. The vaccine may be formulated to target regionally distinct variability based on an HIV clade predominant in a geographical region.
Owner:VARIATION BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
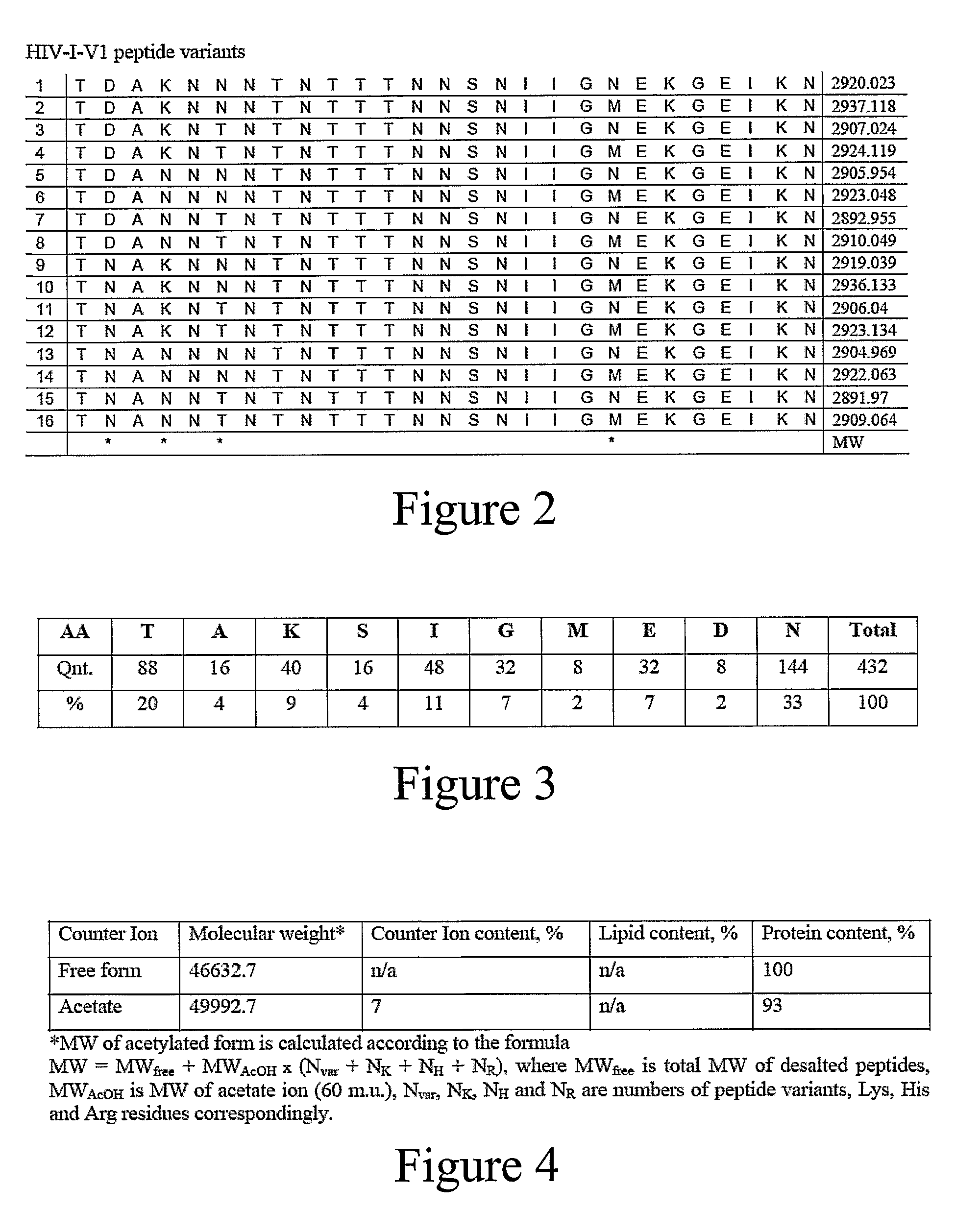
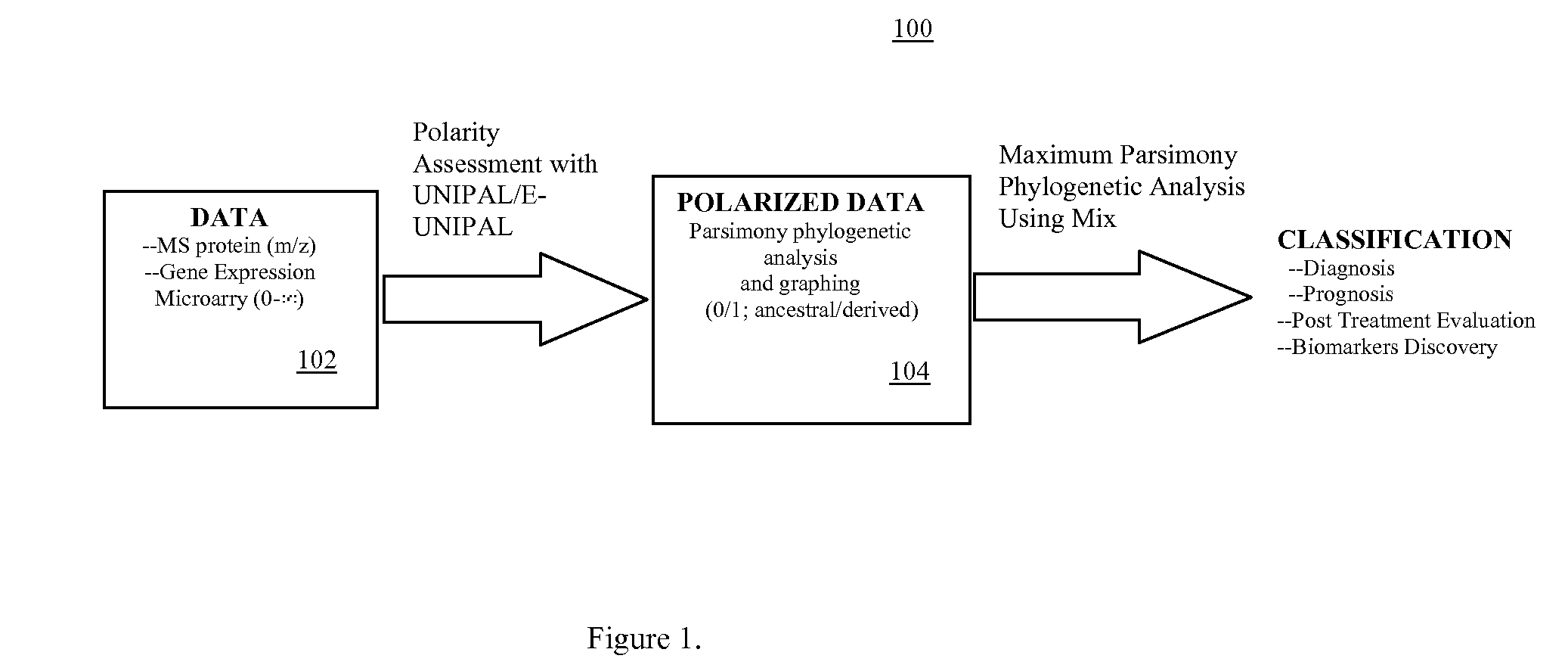
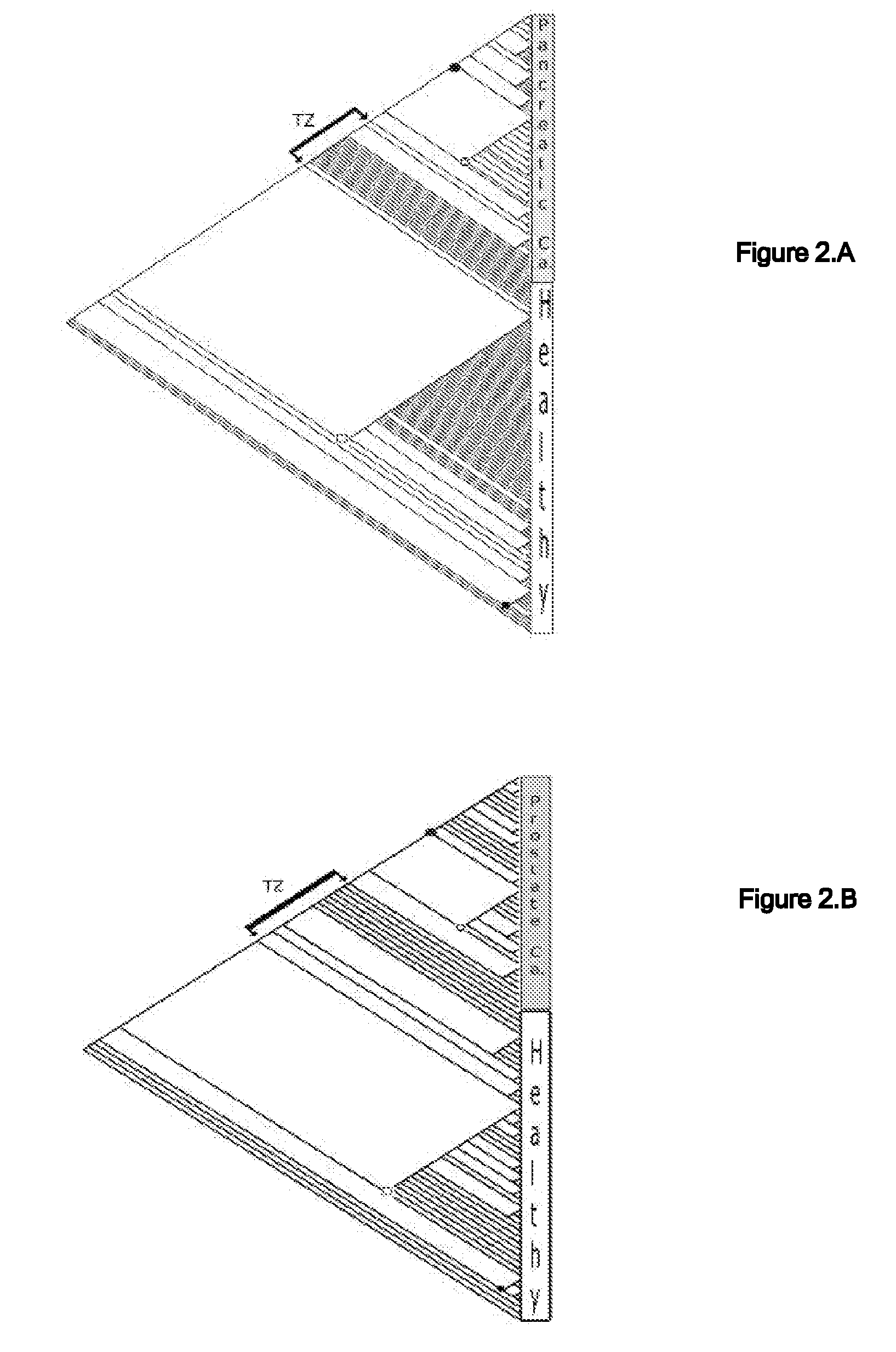
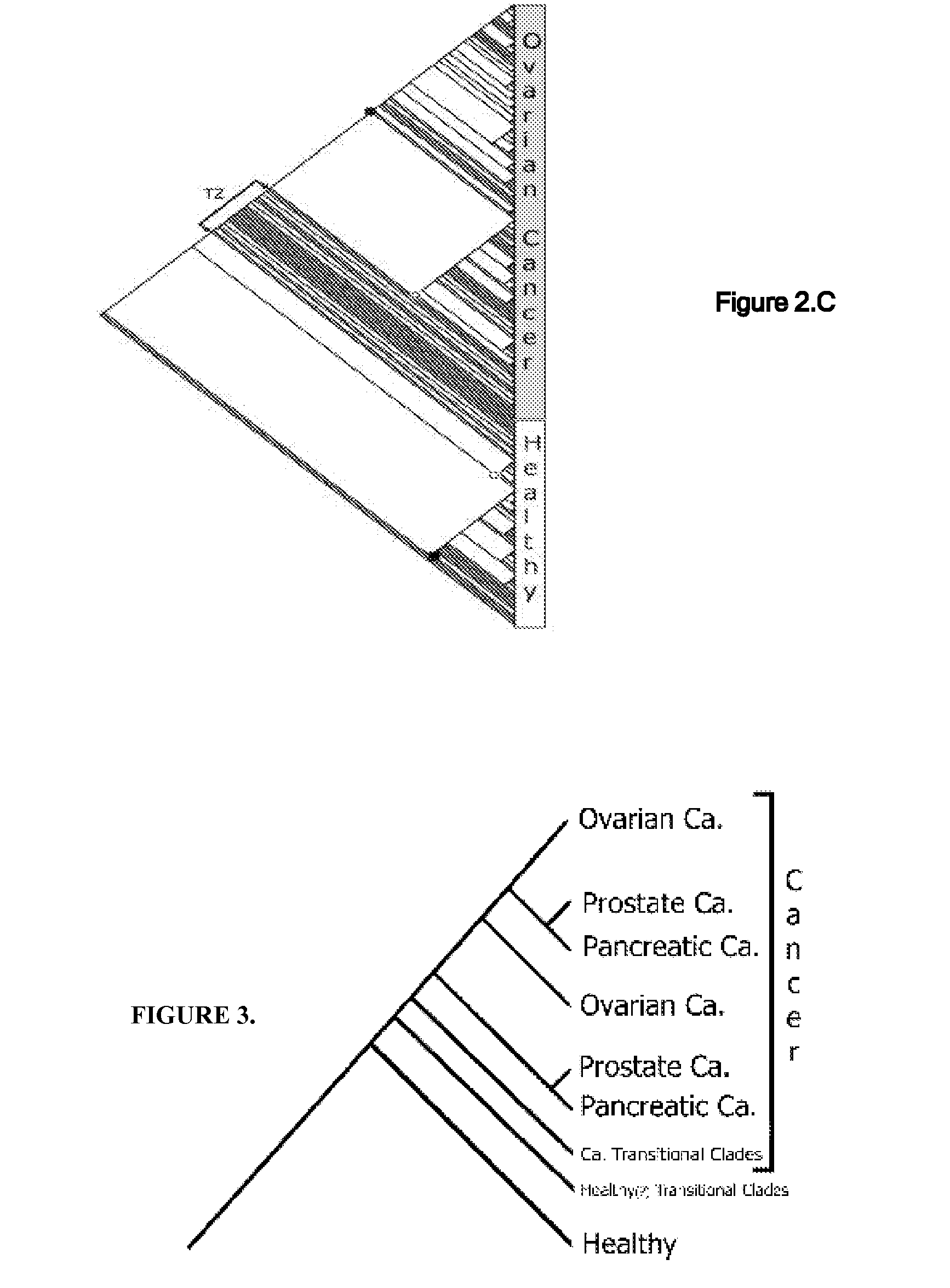
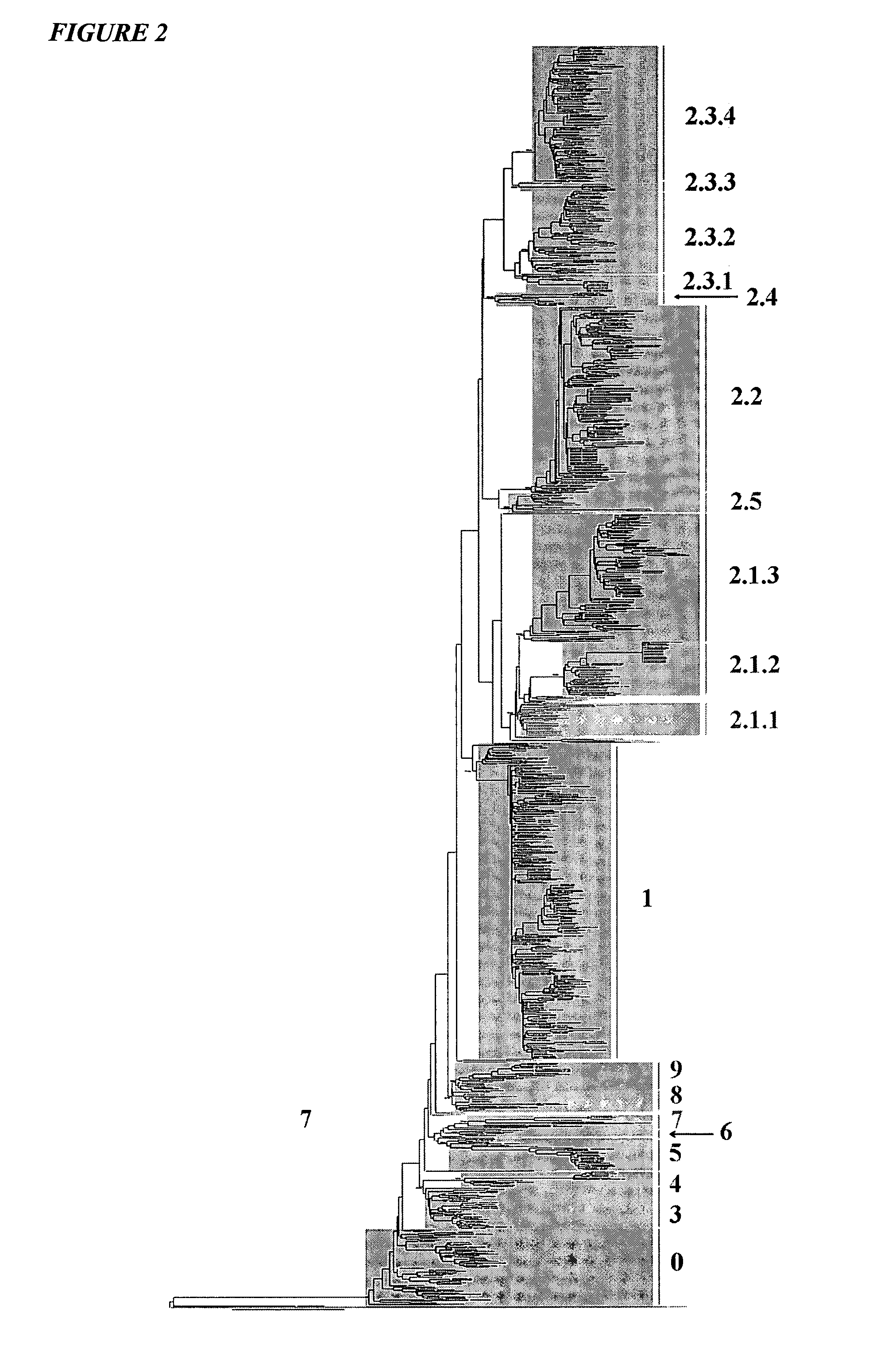
Phylogenetic Analysis of Mass Spectrometry or Gene Array Data for the Diagnosis of Physiological Conditions
ActiveUS20070259363A1Facilitates interplatform comparabilityMedical simulationMedical data miningDiseasePotential biomarkers
A universal data-mining platform capable of analyzing mass spectrometry (MS) serum proteomic profiles and / or gene array data to produce biologically meaningful classification; i.e., group together biologically related specimens into clades. This platform utilizes the principles of phylogenetics, such as parsimony, to reveal susceptibility to cancer development (or other physiological or pathophysiological conditions), diagnosis and typing of cancer, identifying stages of cancer, as well as post-treatment evaluation. To place specimens into their corresponding clade(s), the invention utilizes two algorithms: a new data-mining parsing algorithm, and a publicly available phylogenetic algorithm (MIX). By outgroup comparison (i.e., using a normal set as the standard reference), the parsing algorithm identifies under and / or overexpressed gene values or in the case of sera, (i) novel or (ii) vanished MS peaks, and peaks signifying (iii) up or (iv) down regulated proteins, and scores the variations as either derived (do not exit in the outgroup set) or ancestral (exist in the outgroup set); the derived is given a score of “1”, and the ancestral a score of “0”—these are called the polarized values. Furthermore, the shared derived characters that it identifies are potential biomarkers for cancers and other conditions and their subclasses.
Owner:AMRI HAKIMA +2
Methods of screening for onychomycotic fungi
ActiveUS20170029906A1Microbiological testing/measurementInvestigating phase/state changePresent methodScreening method
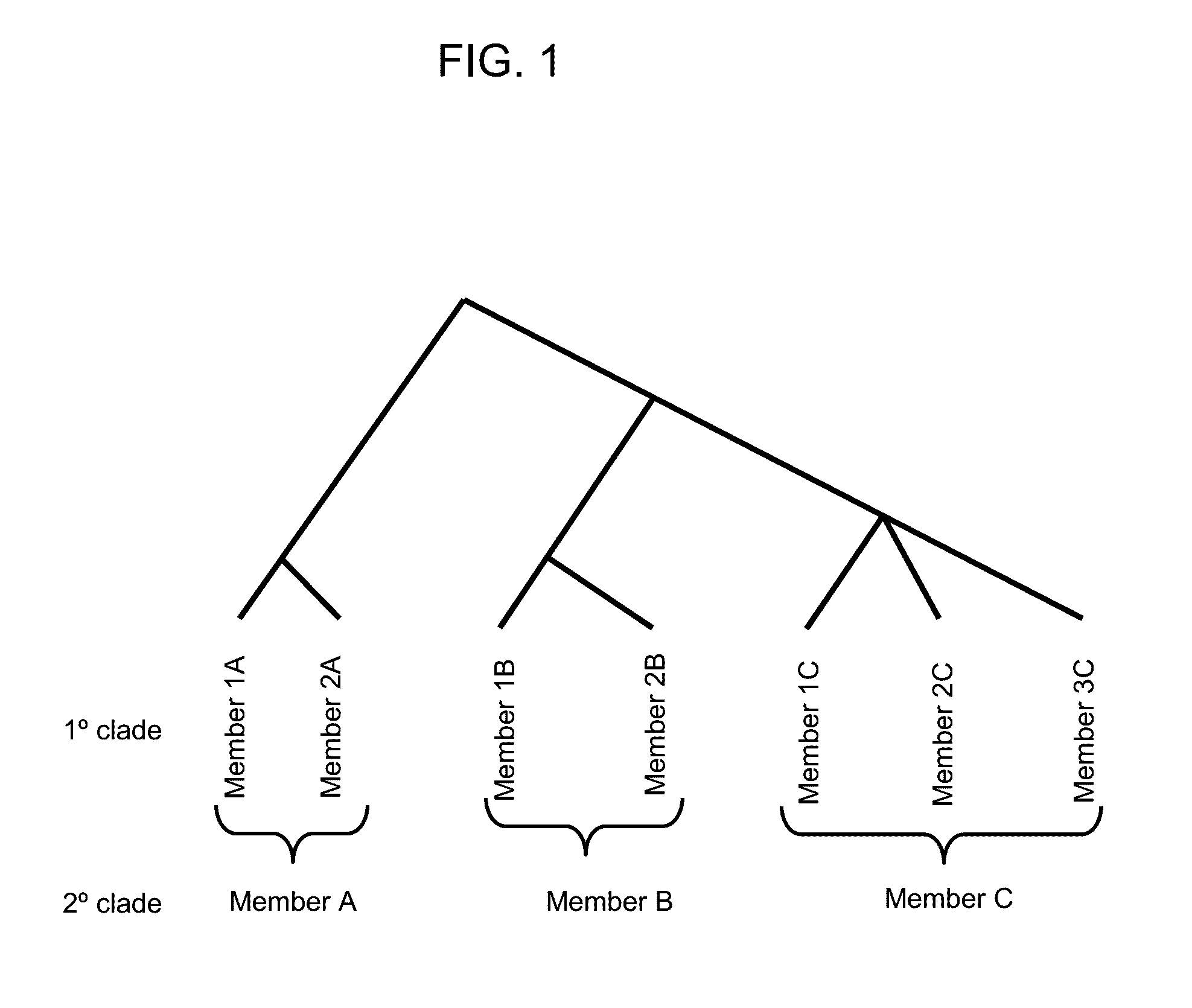
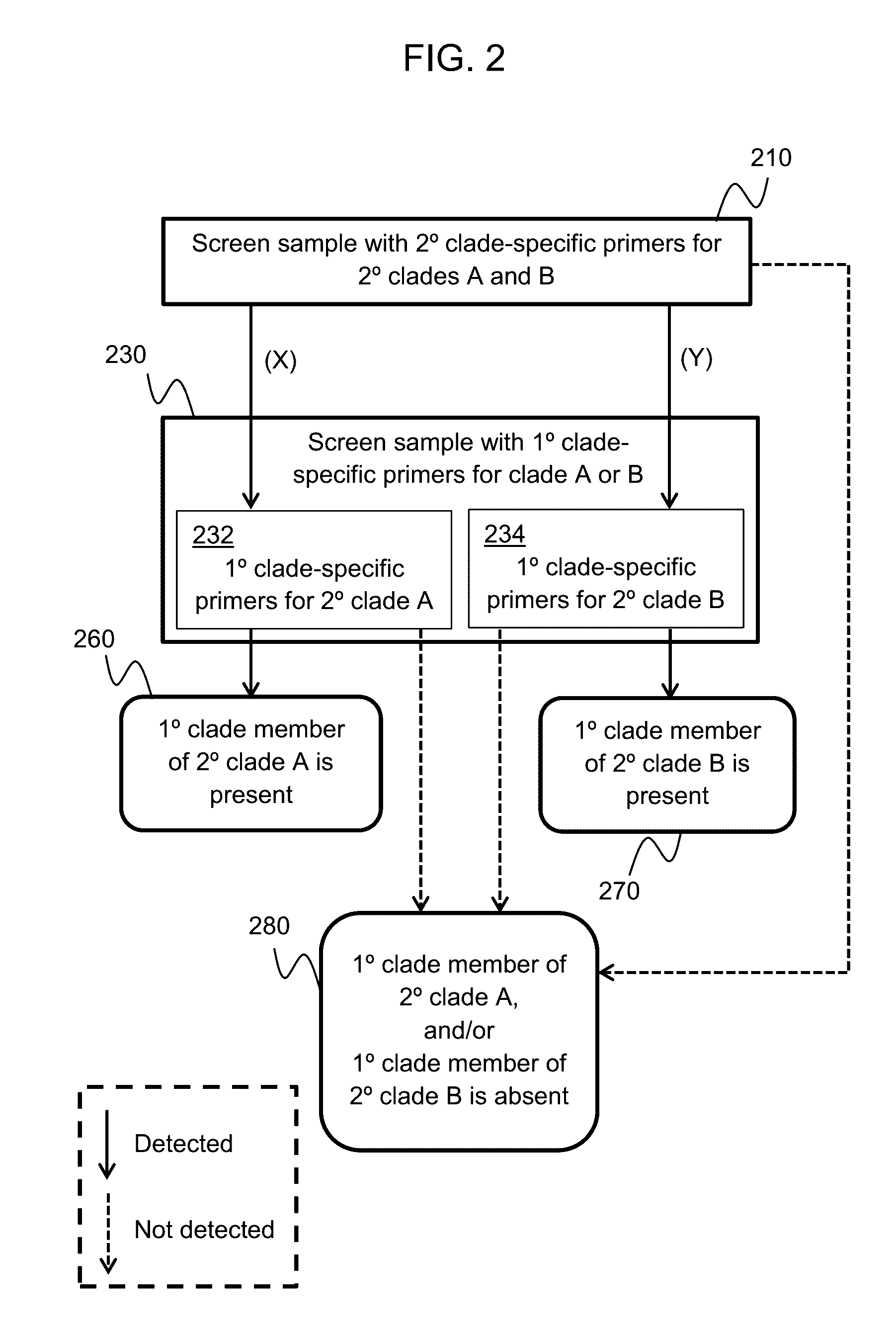
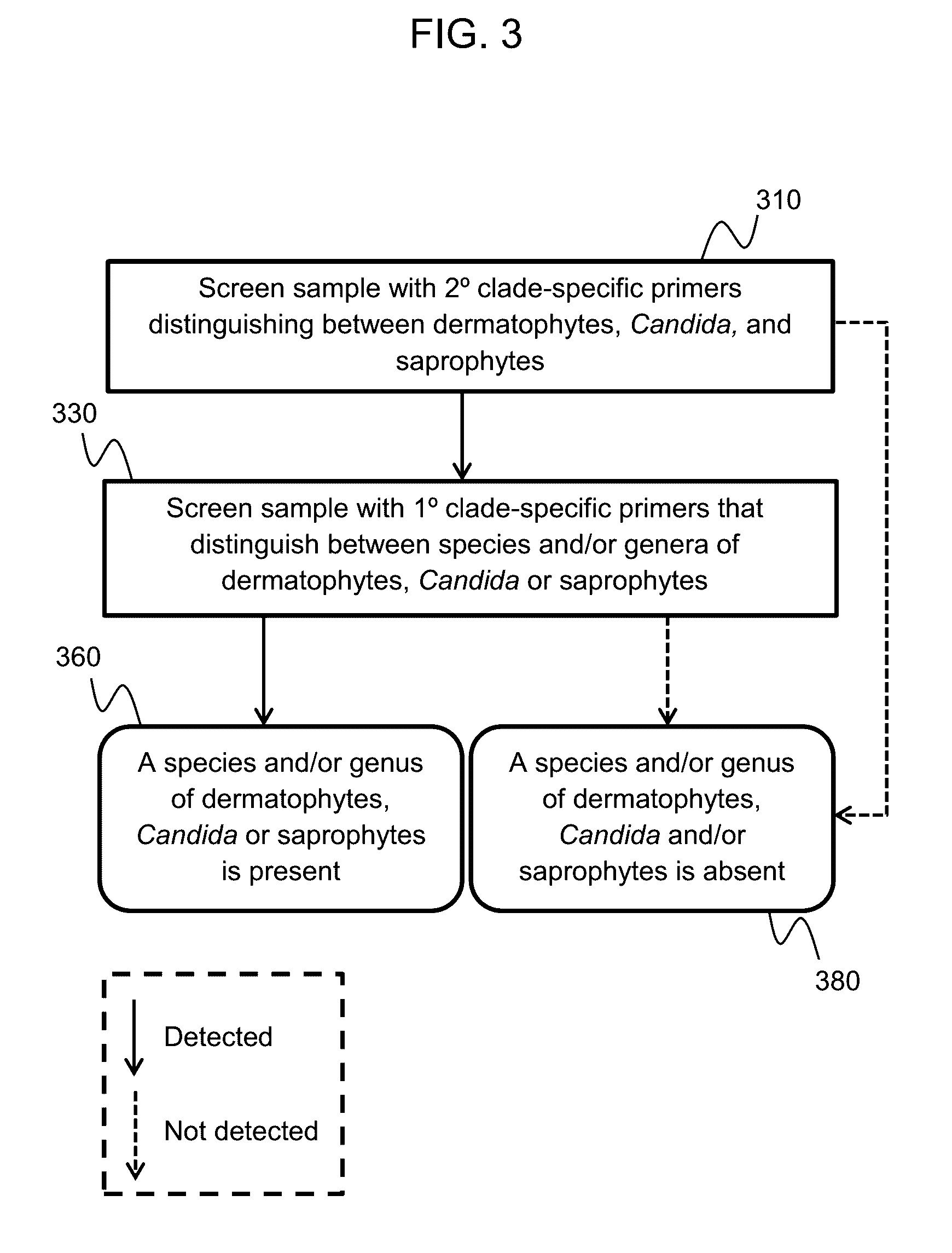
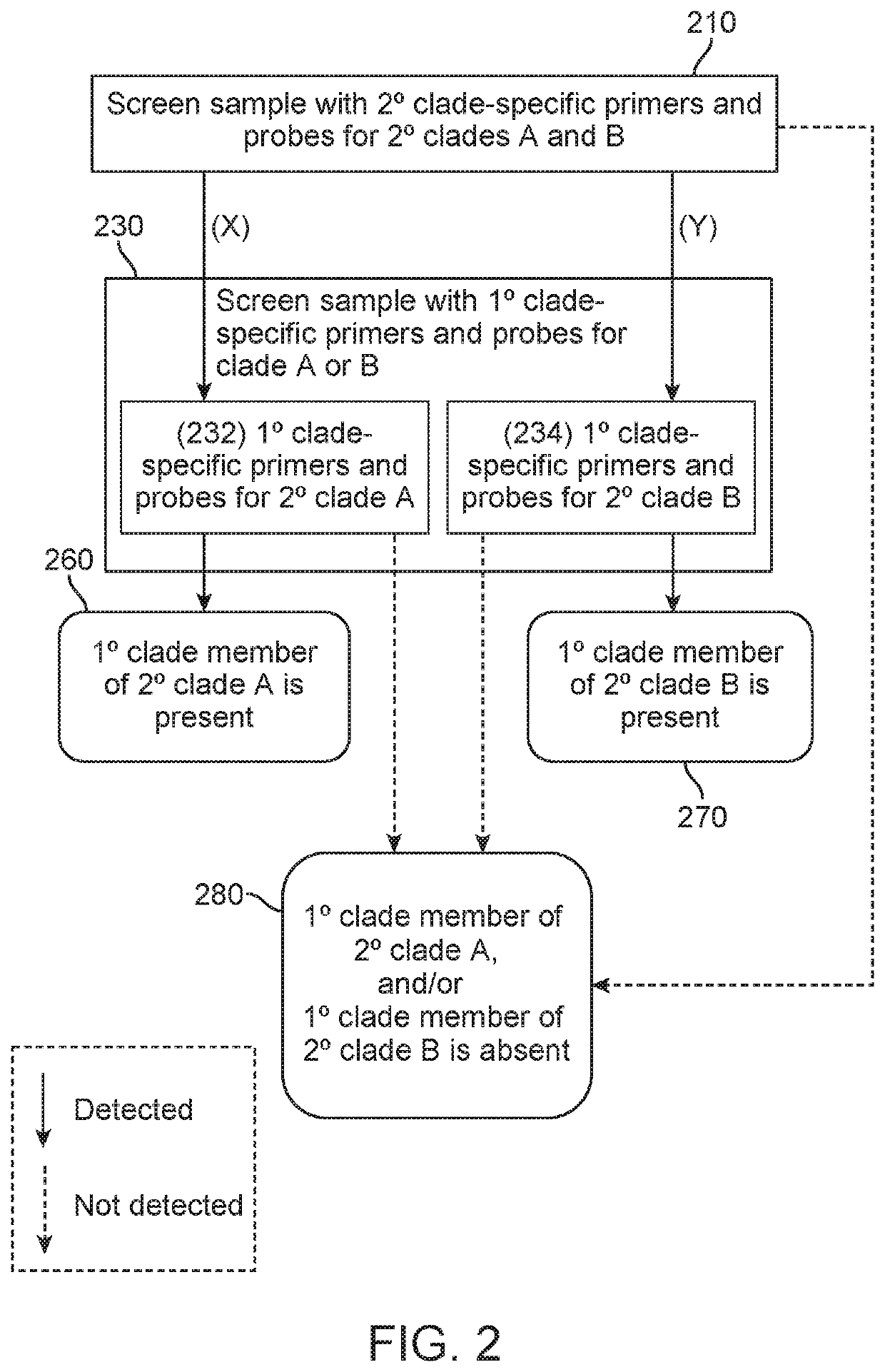
Provided herein is a method of detecting an onychomycotic fungus in a sample, wherein the onychomycotic fungus belongs to a secondary clade member including one or more primary clade members. The method may include the steps of i) screening a sample using a first and second sets of secondary clade-specific primers to determine whether a secondary clade member among a plurality of secondary clade members is present or absent in the sample, where the plurality of secondary clade members includes (a) a dermatophyte, (b) a candida, and (c) a saprophyte, and ii) after determining the presence of the secondary clade member, screening the sample to determine whether an onychomycotic fungus is present or absent in the sample using primary clade-specific primers that are specific to a primary clade member that belongs to the secondary clade member. Also provided is a kit that finds use in implementing the present method.
Owner:BAKOTIC PATHOLOGY ASSOC LLC
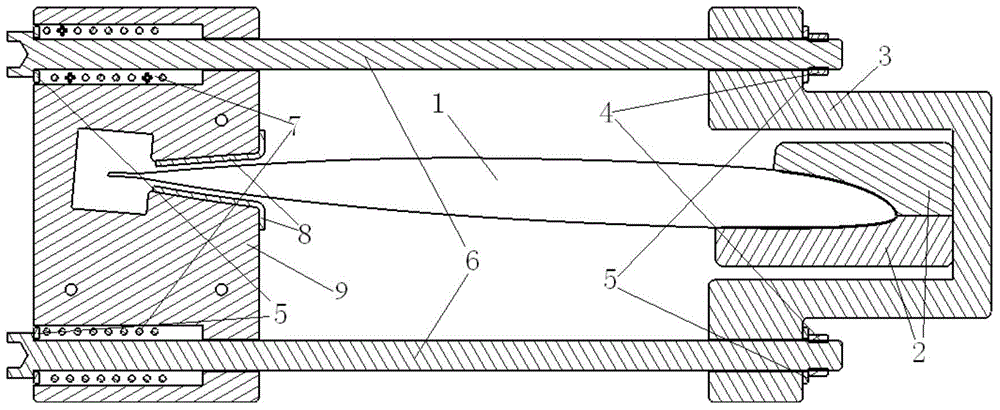
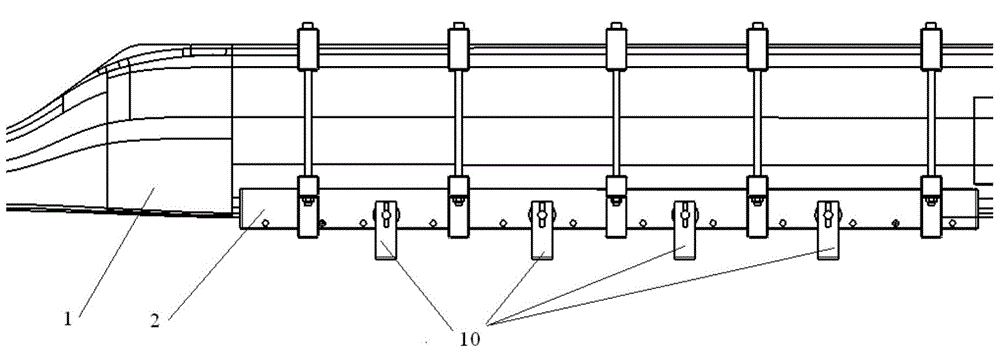
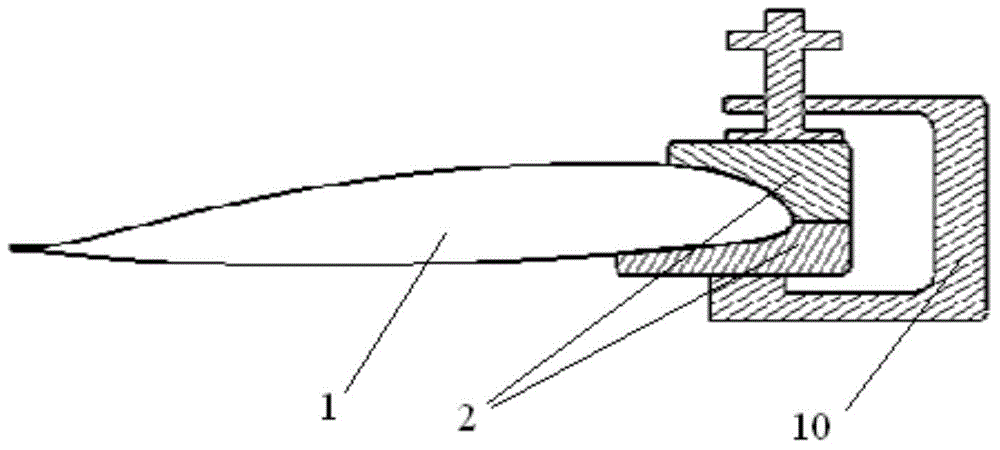
Process method for replacement and repair of iron clad of main blade made of composite material
InactiveCN104691779AImprove repair efficiencyIncrease success rateAircraft maintainanceAdhesion strengthPolyresin
The invention belongs to the technique of repair of aircrafts, and relates to a process method for replacement and repair of an iron clad of a main blade made of a composite material. The surface of the blade is marked in a spanwise position where the iron clade needs to be replaced, and the iron clad is separated from the main blade; an original resin system is selected and used, dry glass cloth is dipped in glue with 45% glue content, the glass cloth after glue dipping is cut according to the size of the glass cloth, and the layers of the laid glass cloth are one more than those of the stripped glass cloth; a tooling is fixed by adhesive tape and vacuumized, and a upper wing surface and a lower wing surface of the iron clad are pressurized; finally, the method that the blade is fully packaged with a vacuum bag is adopted, so that the iron clad of the blade can be replaced and repaired. The repair quality of the iron clad of the main blade is improved after ungluing, the theoretical appearance and the adhesion strength of the blade are guaranteed, the blade scrap rate caused by faults of the iron clade is effectively reduced, the repair efficiency and the repair success rate of the blade are increased, and the repair quality and the product stability are guaranteed.
Owner:HARBIN
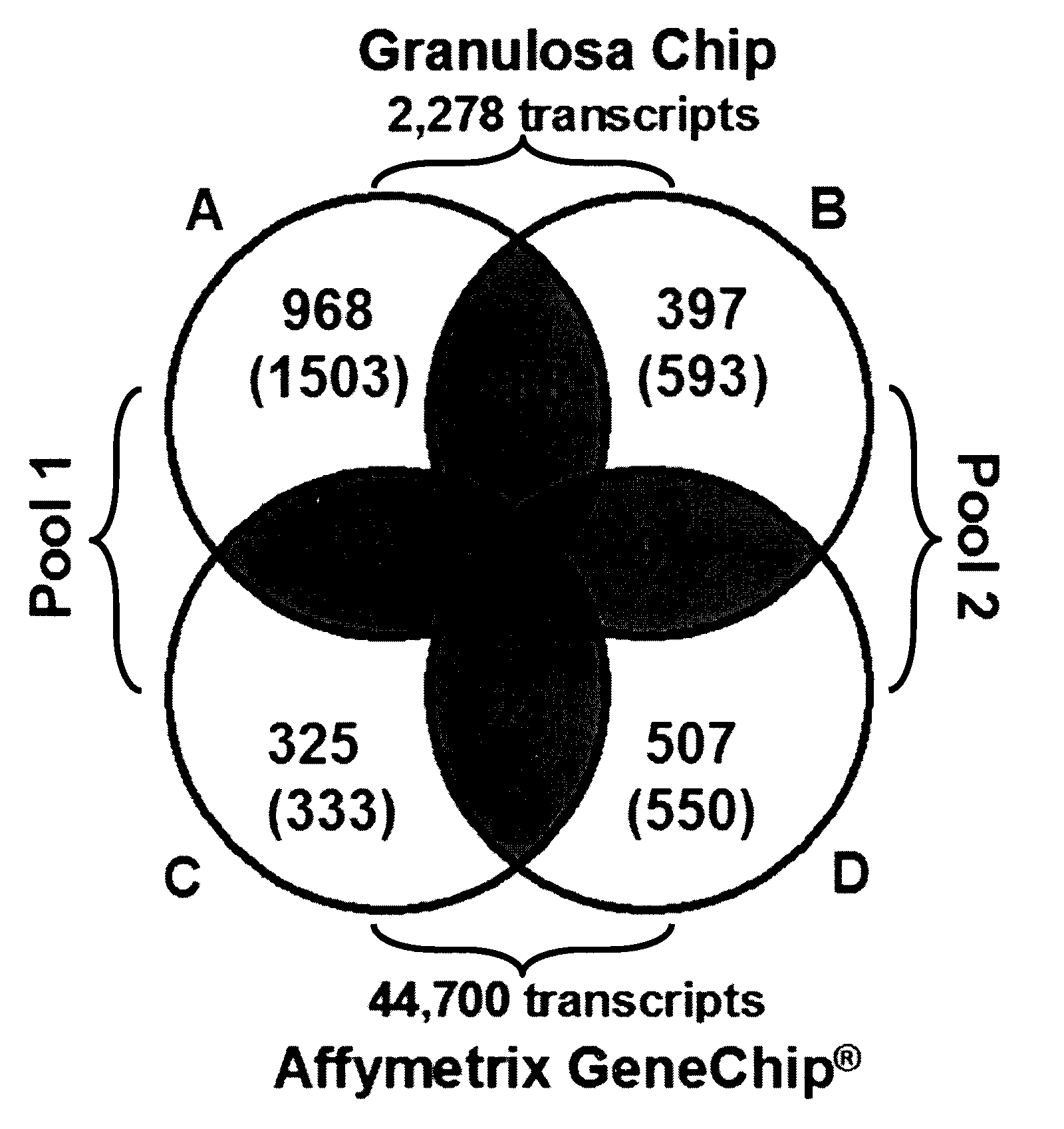
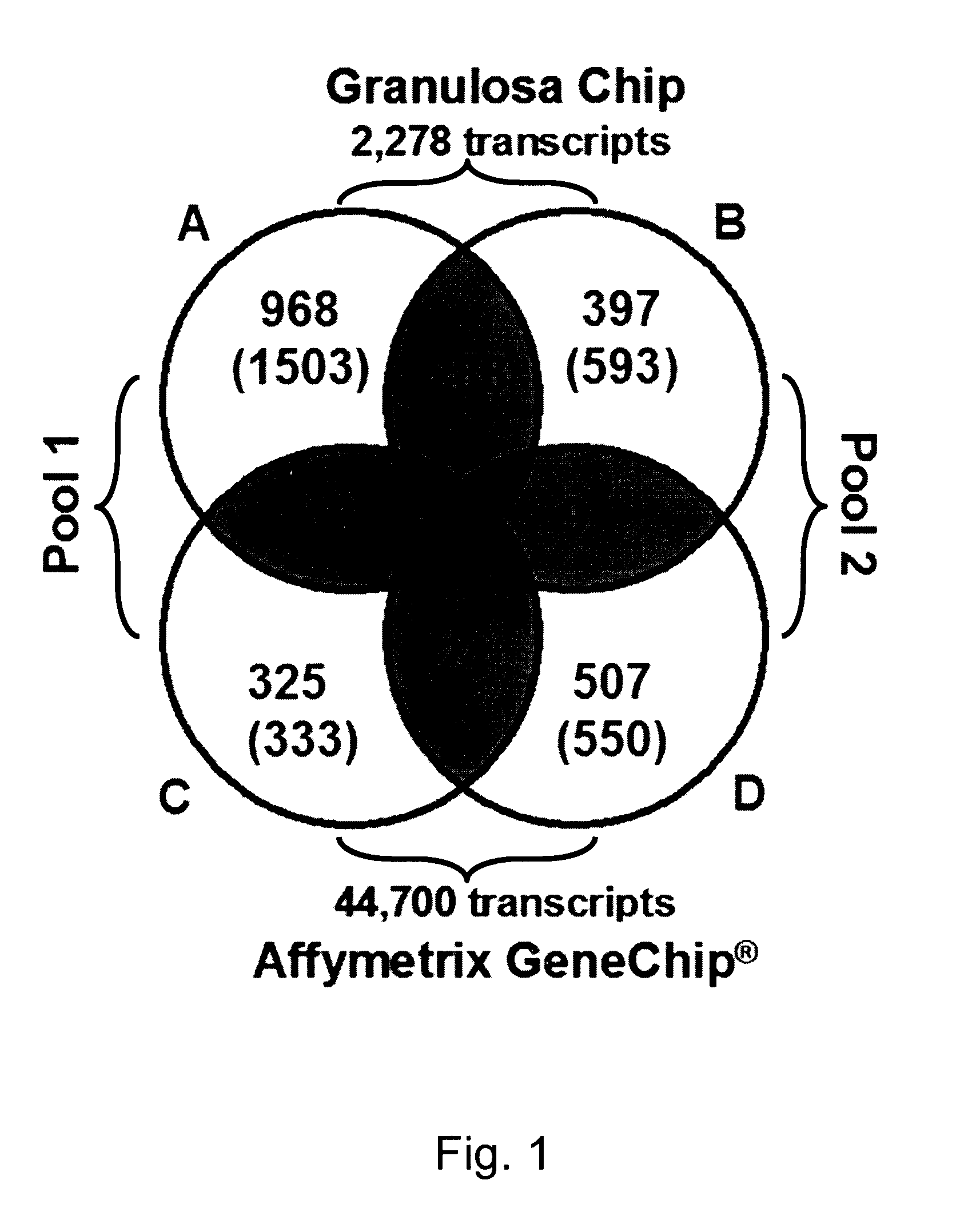
Mammalian oocyte development competency granulosa markers and uses thereof
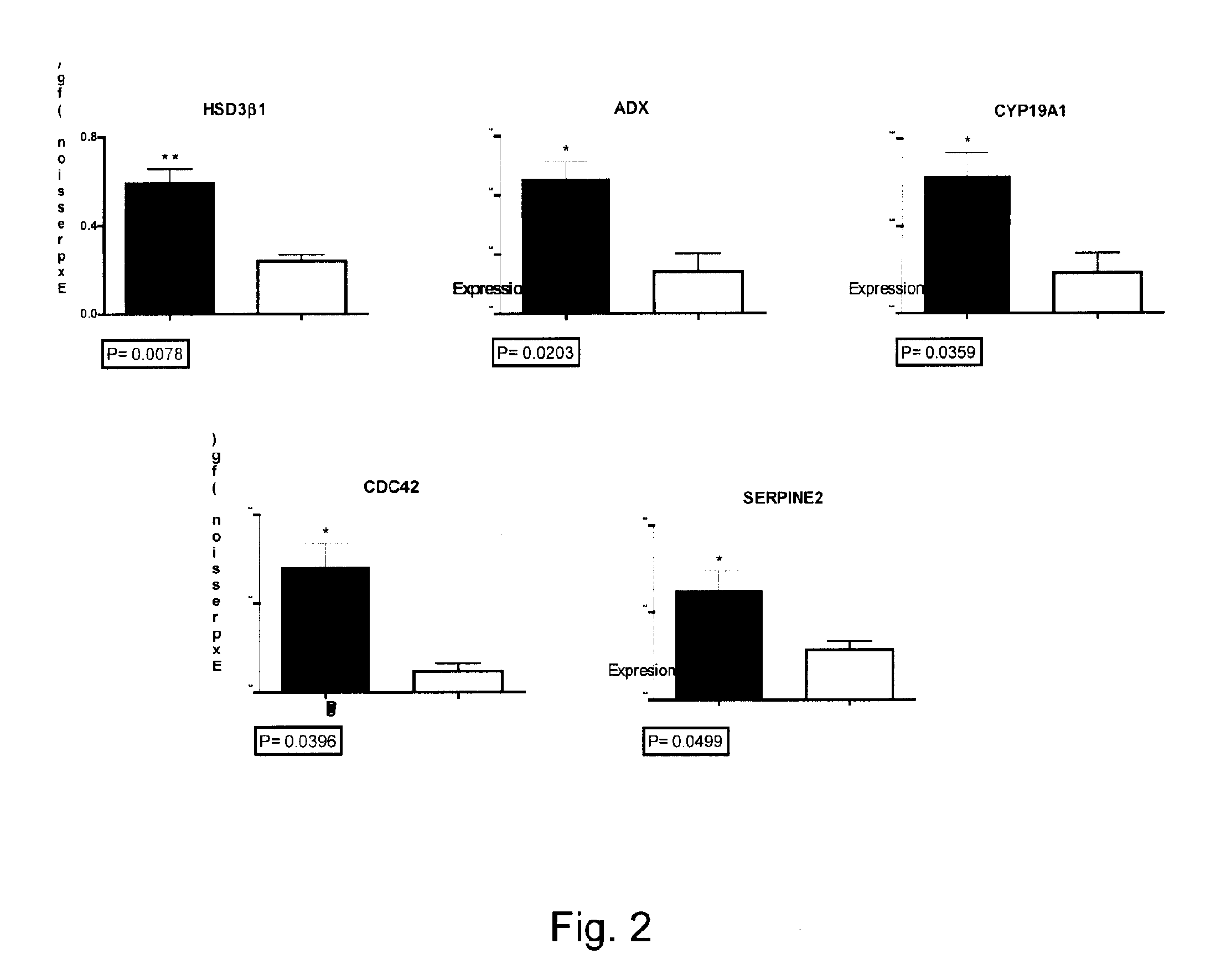
The present invention relates to the competence of oocytes for uterine implantation and development into living individuals. The invention more particularly relates to markers that are detected and measured in granulosa cells collected along with the oocytes during oocyte aspiration as it is done in assisted reproduction techniques. Markers include cytochrome P450 aromatase (CYP19A1), cell division cycle 42 (CDC42), 3-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 (3βHSD1), serpm peptidase inhibitor clade E member 2 (SERPINE 2), and adrenodoxm (ADX) that are detected and measured, using RT-PCR.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Therapeutic peptides and vaccines
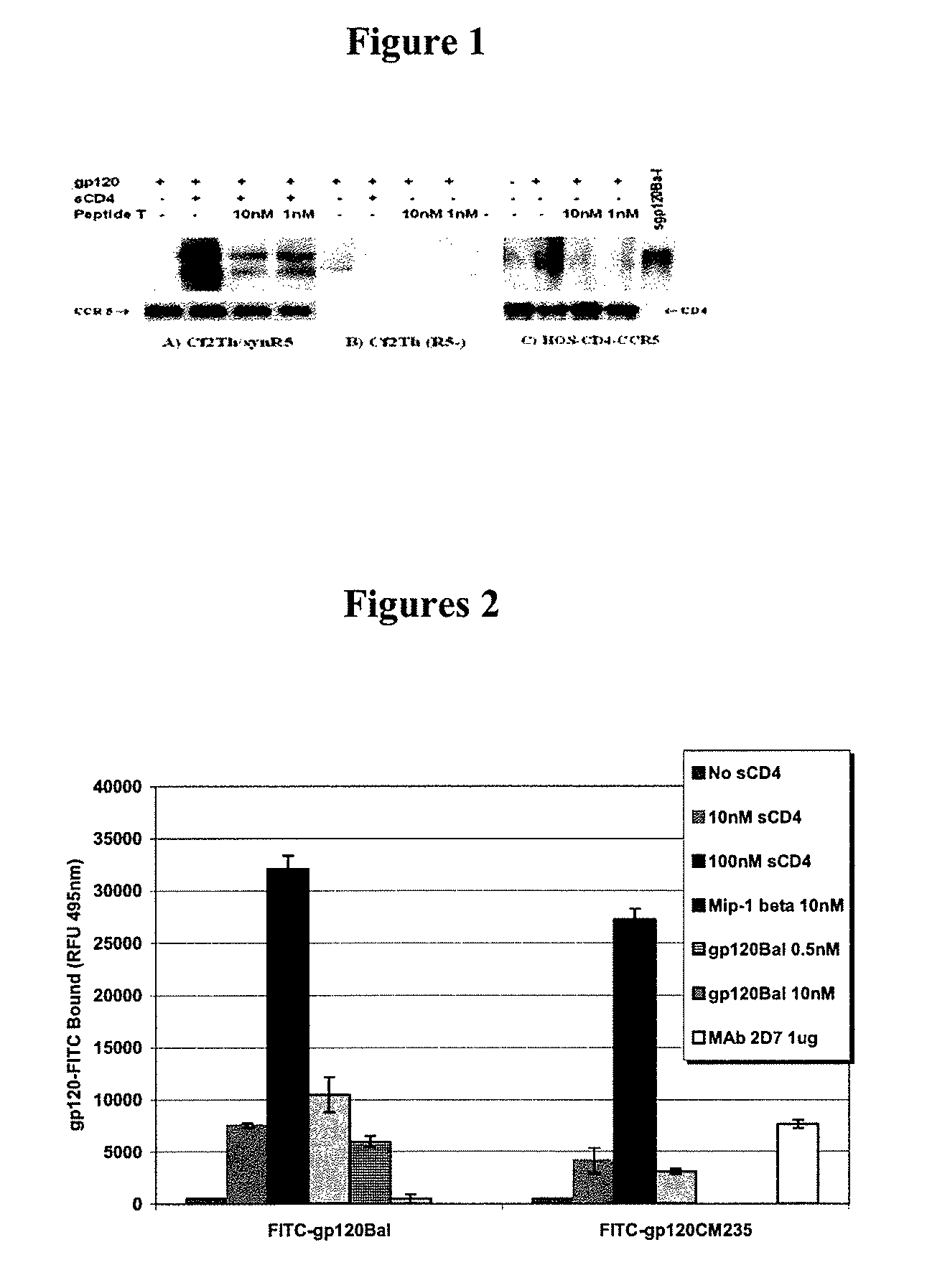
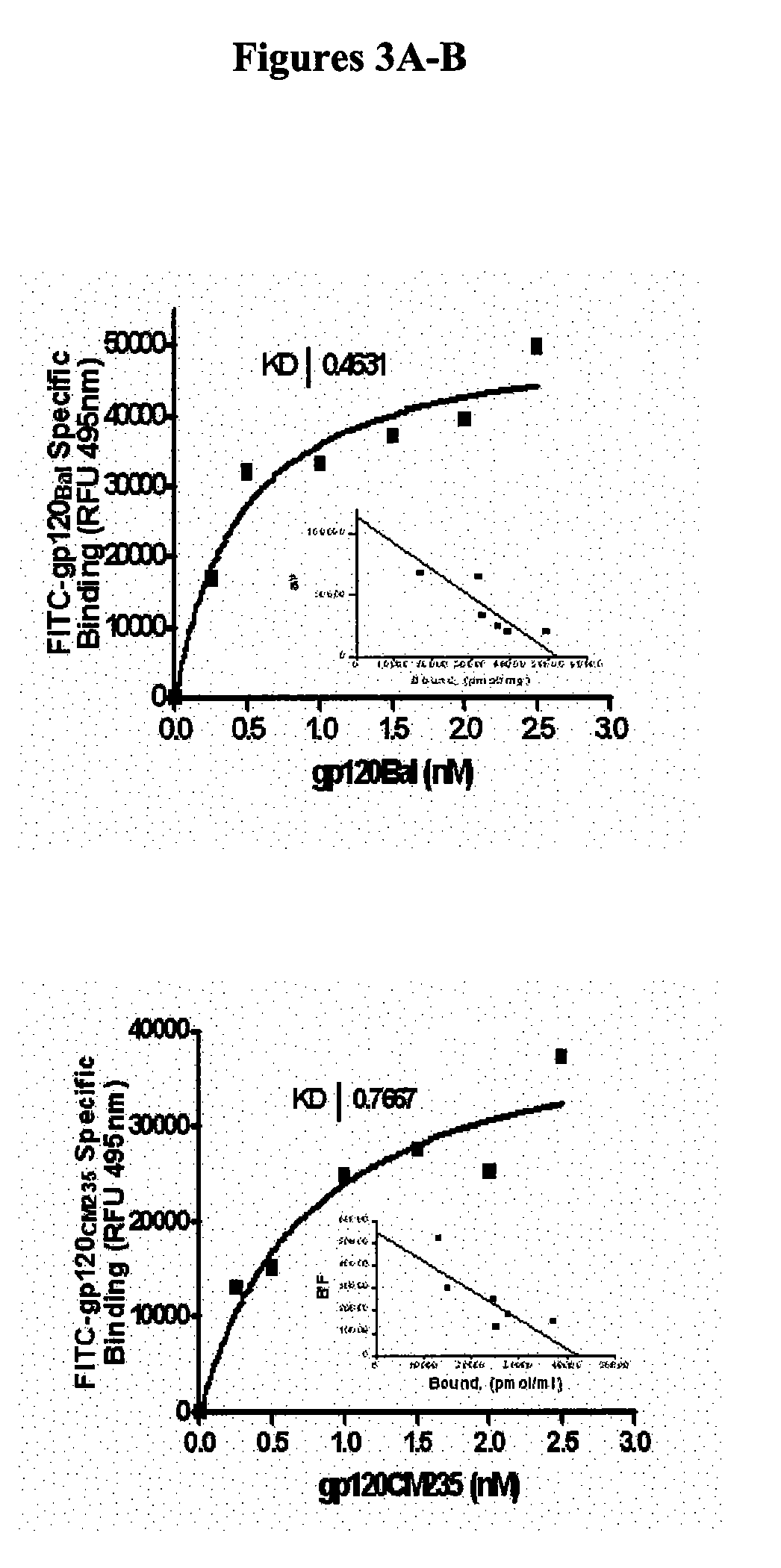
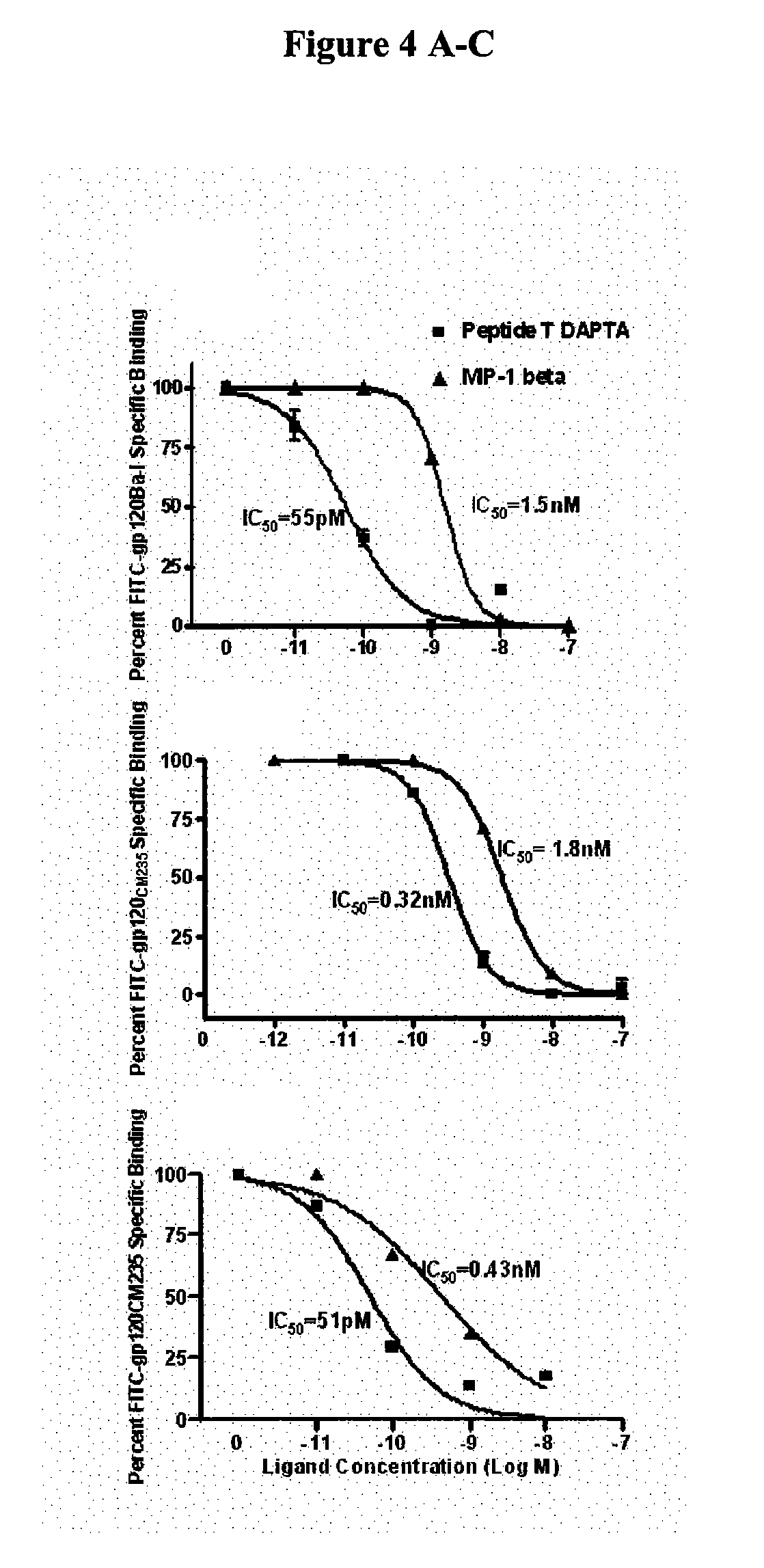
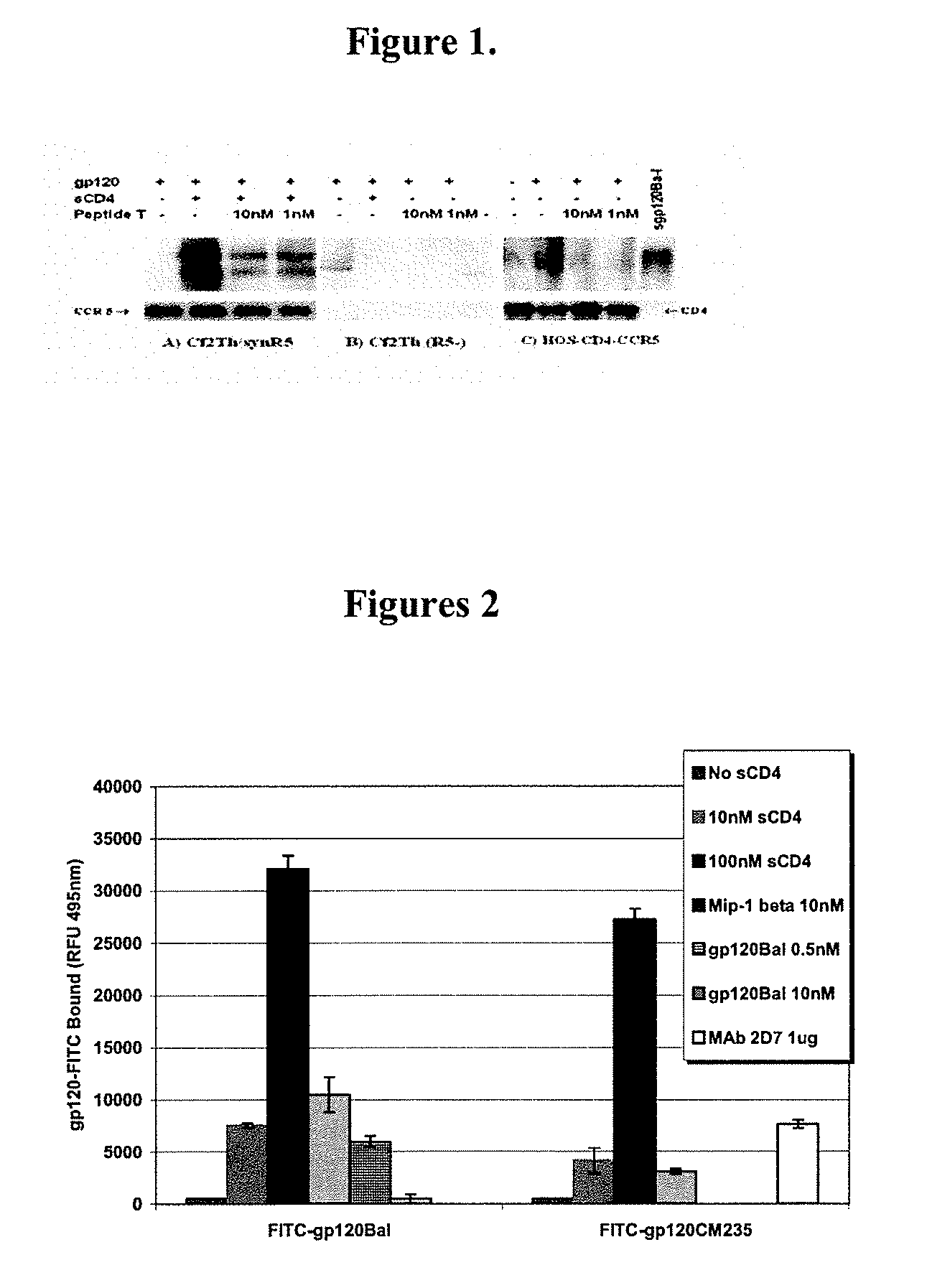
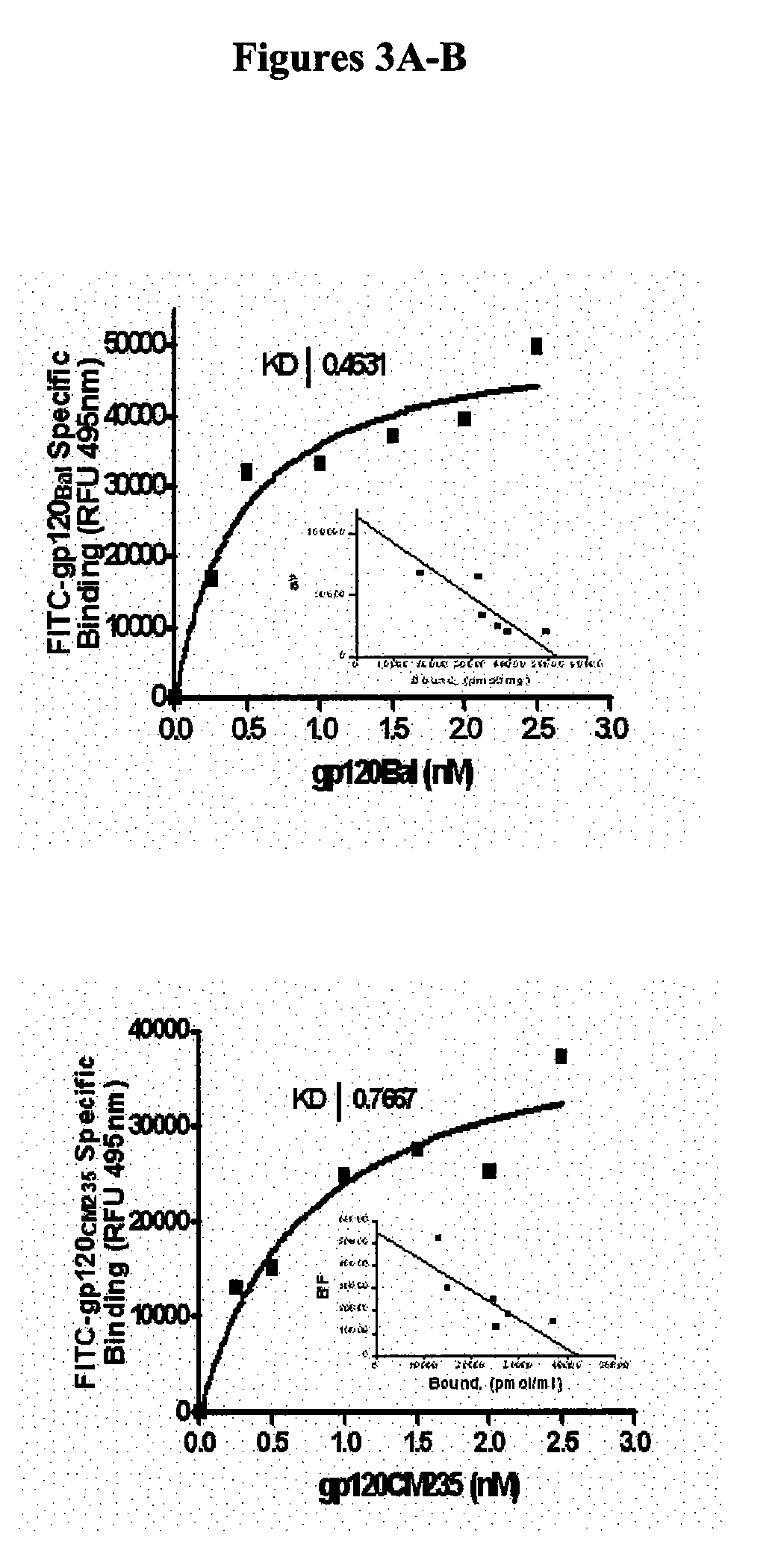
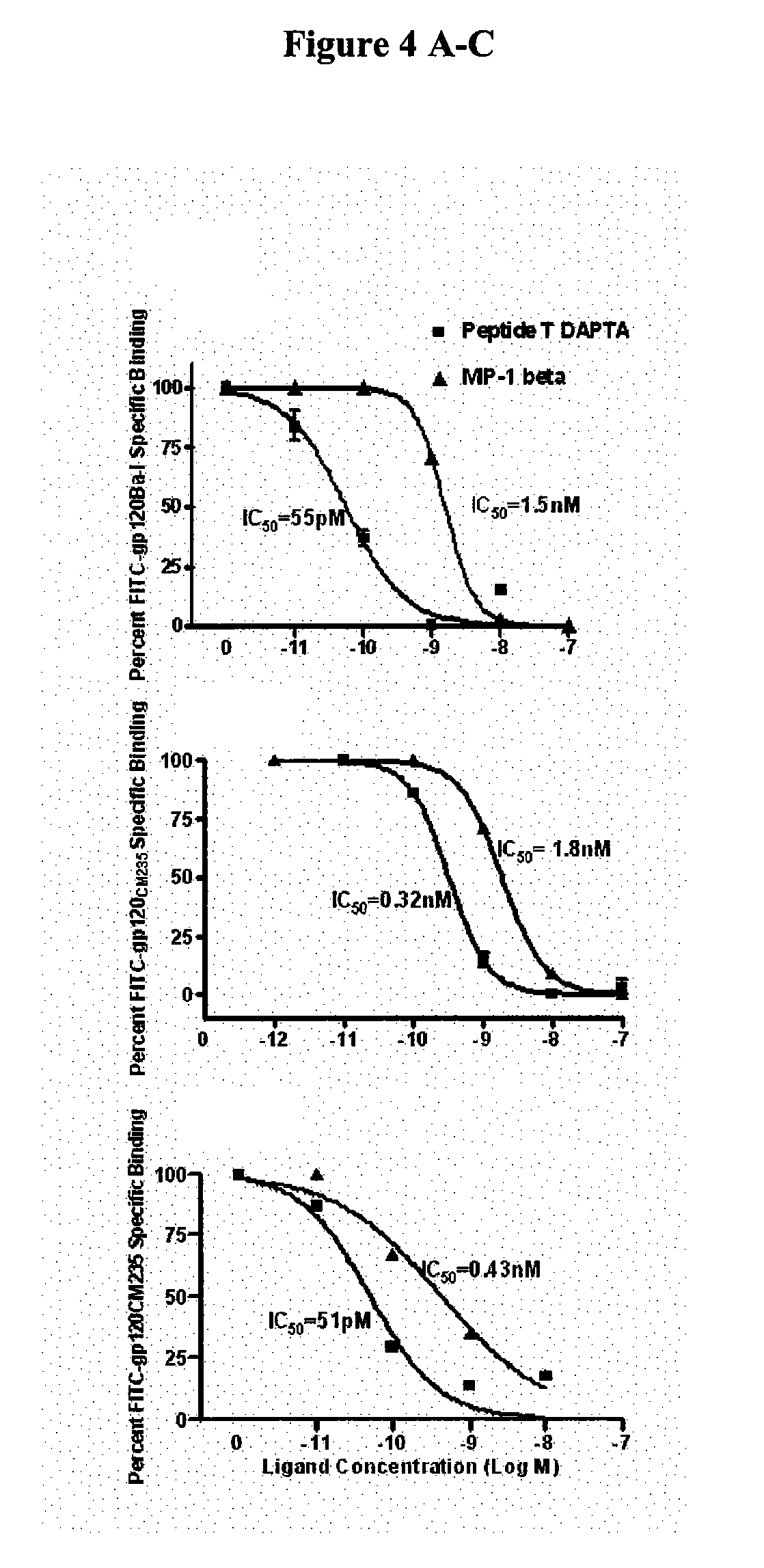
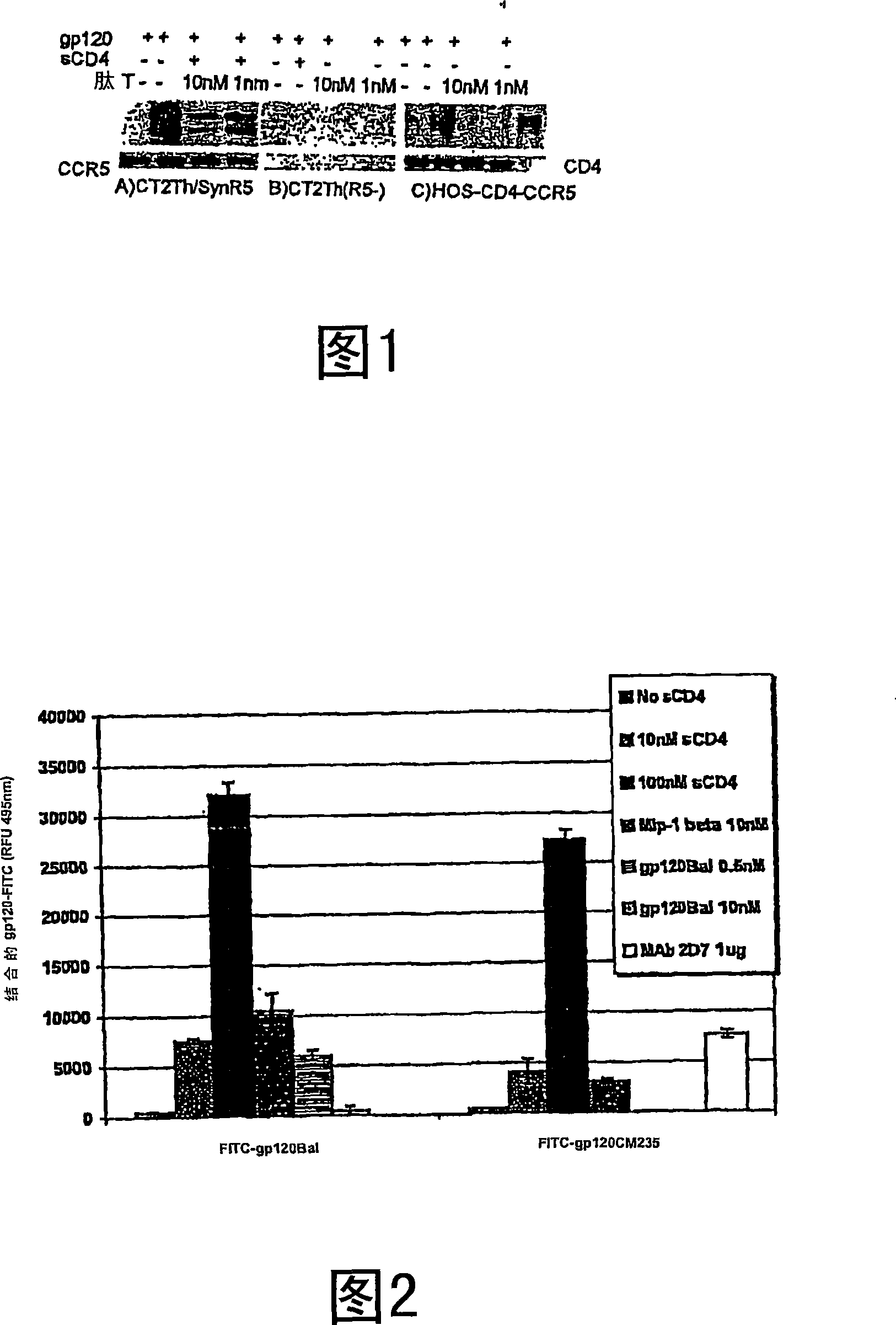
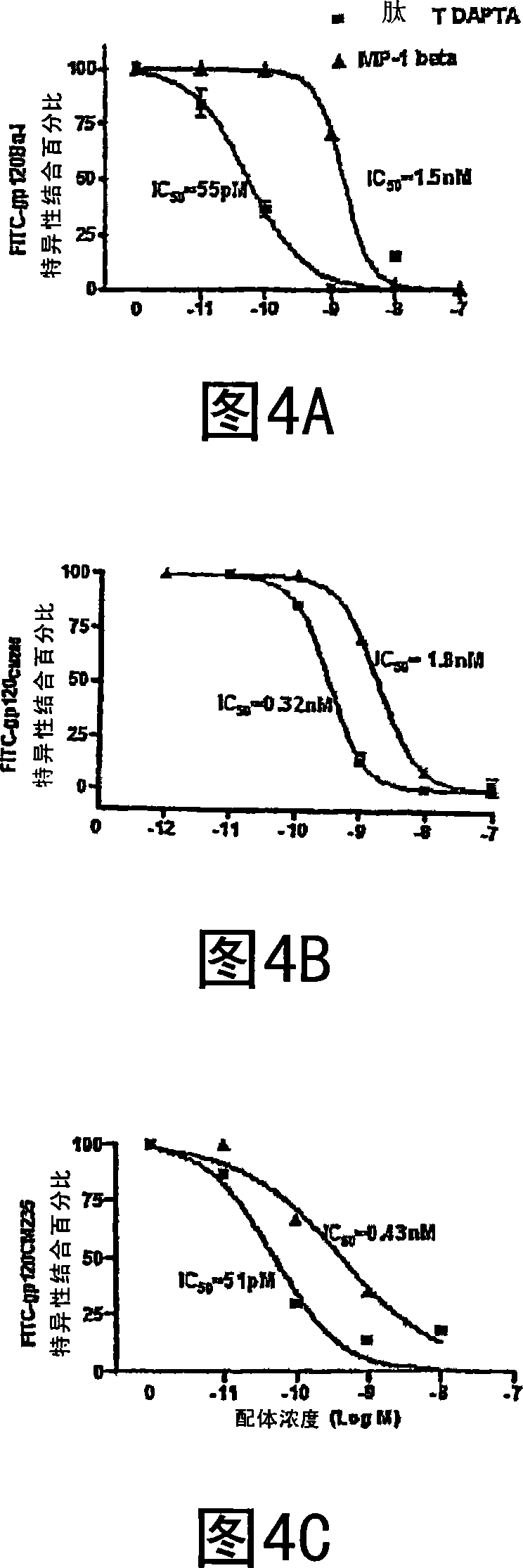
Compositions are disclosed that induce broadly HIV therapeutic and vaccine inducing antibodies against diverse HIV clades and relate to the ability to identify HIV gp120-derived short peptide sequence immunogens and various therapeutic compositions made from the identified peptides which compose CCR5 binding sites. Also disclosed are methods of selecting peptide sequences that are likely candidates for drugs which will offer effective treatment in such areas as Alzheimer's disease, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis and other diseases associated with the human inflammatory cascade as well as related retroviruses such as HTLV-1, the cause of tropical spastic paraparesis.
Owner:PEPTIDE ACCOUNT LLC
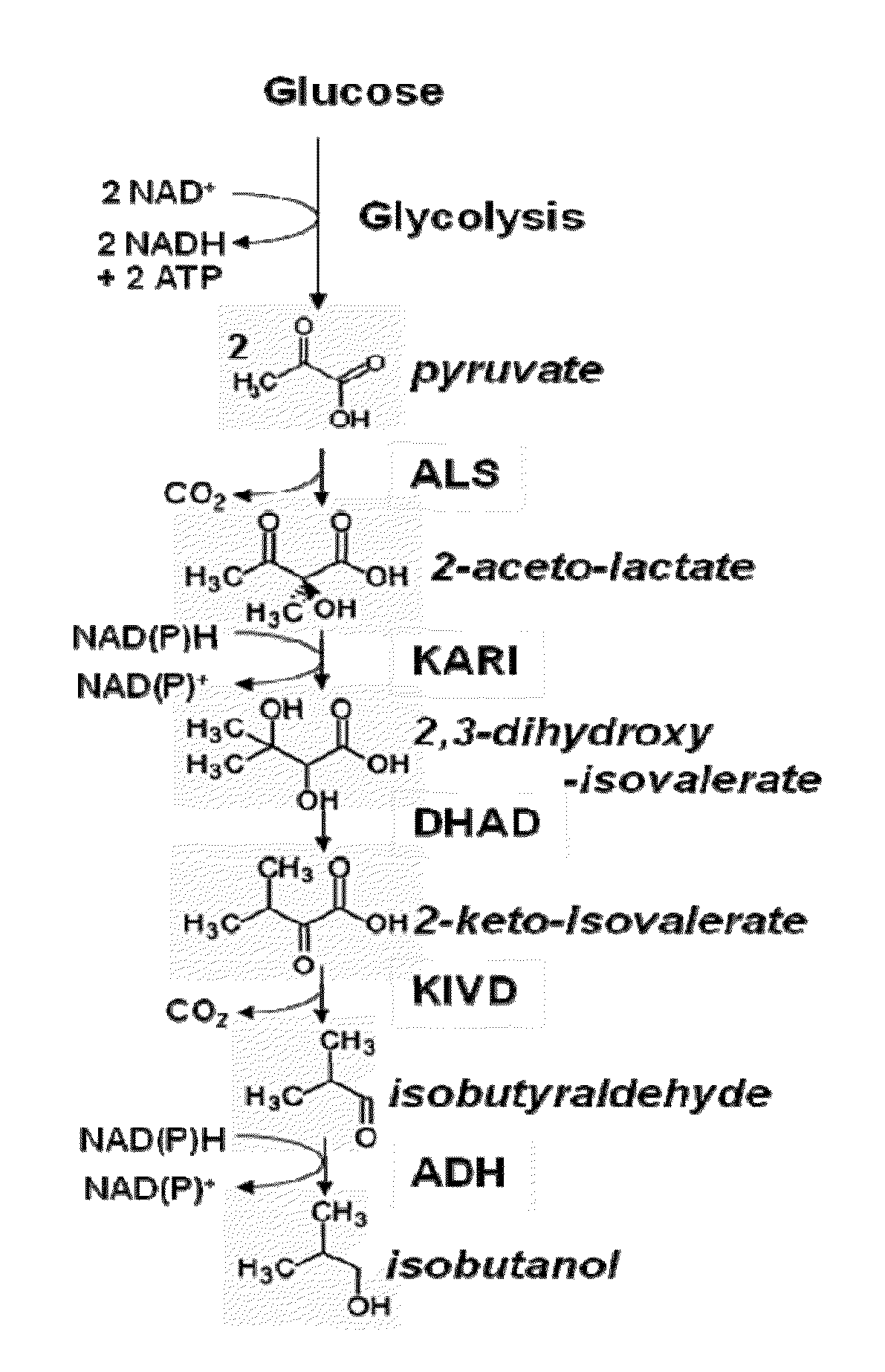
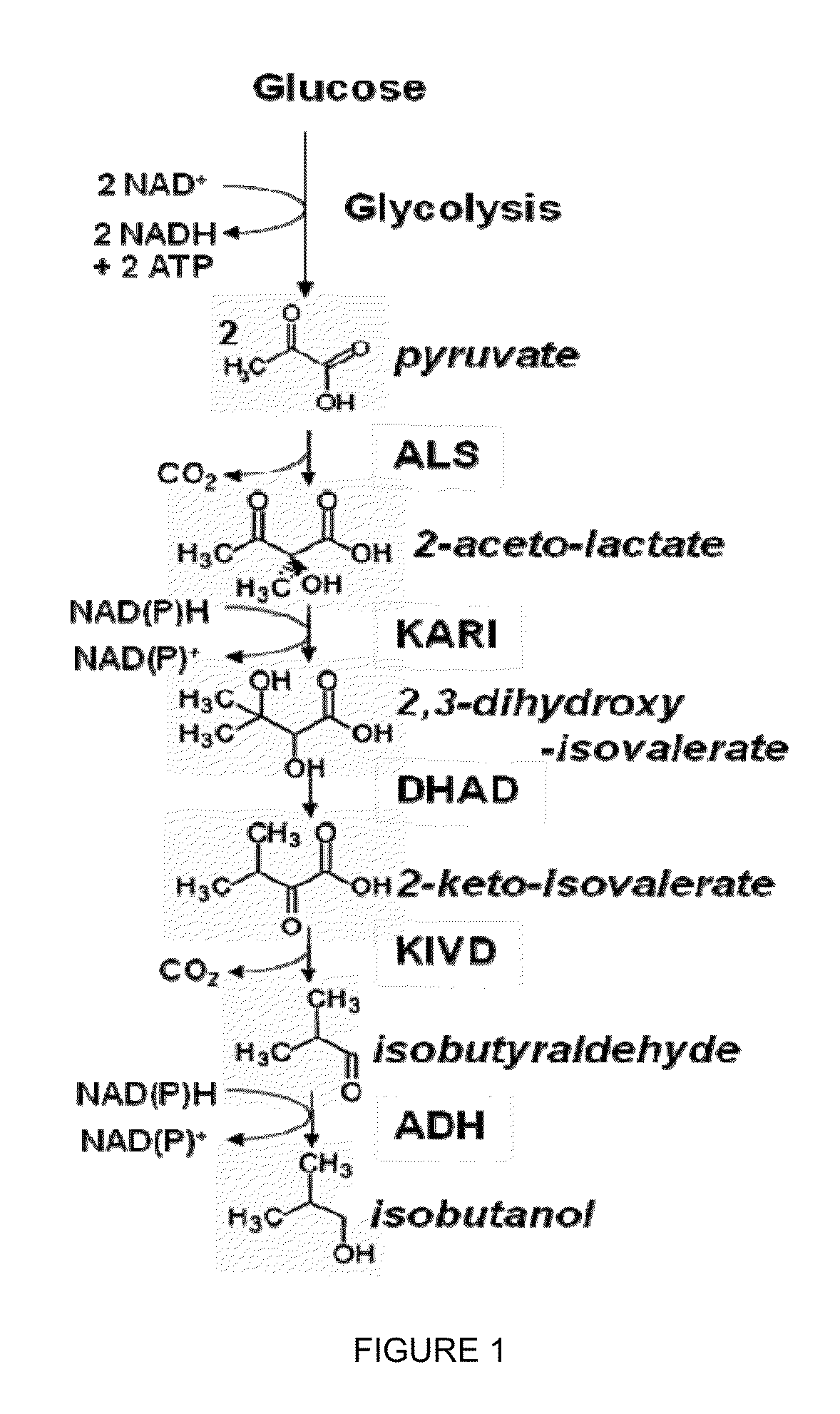
Yeast microorganisms with reduced by-product accumulation for improved production of fuels, chemicals, and amino acids
InactiveUS20110201090A1Improve abilitiesHigh catalytic efficiencyFungiBiofuelsBiotechnologyMetabolite
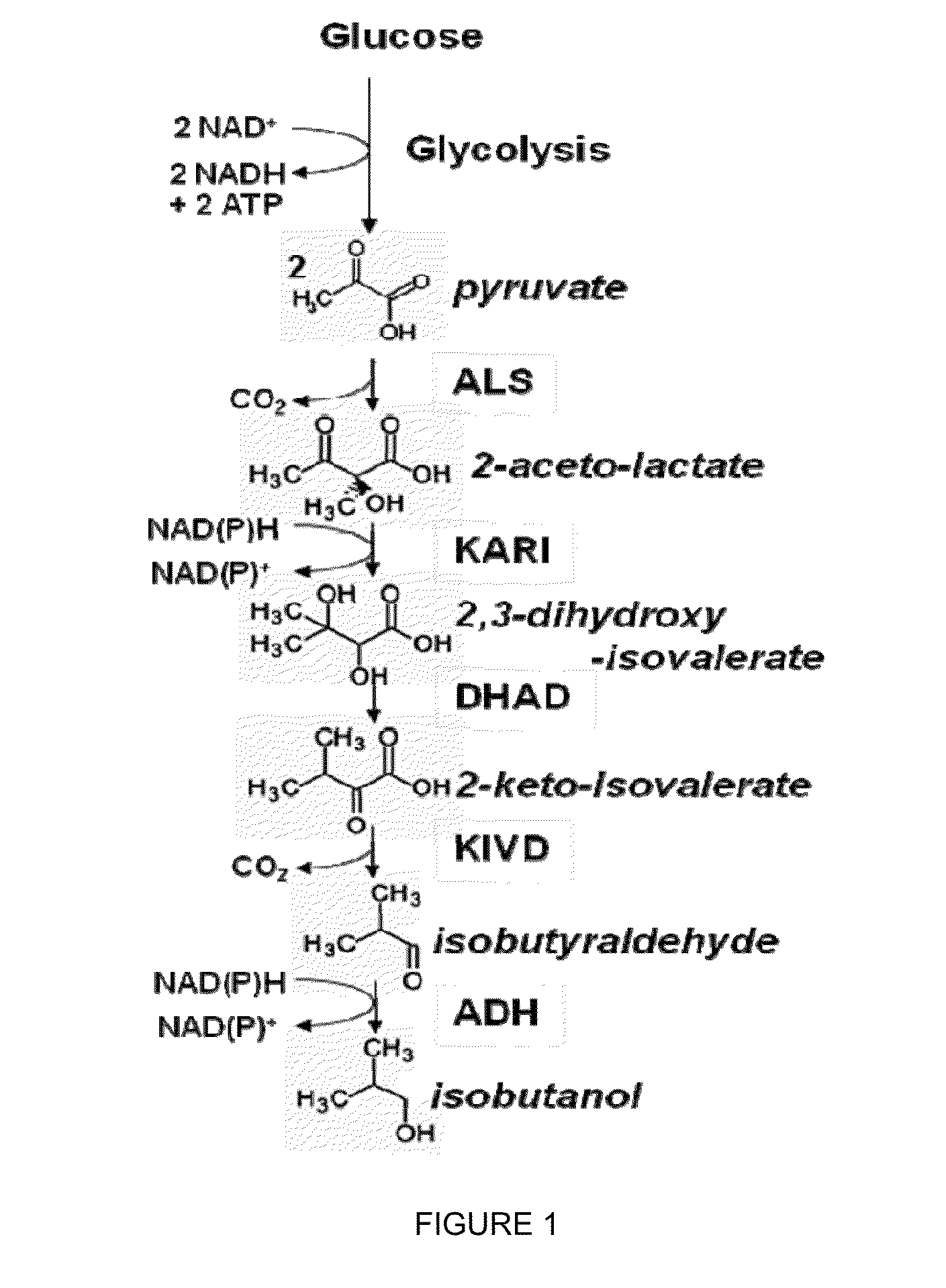
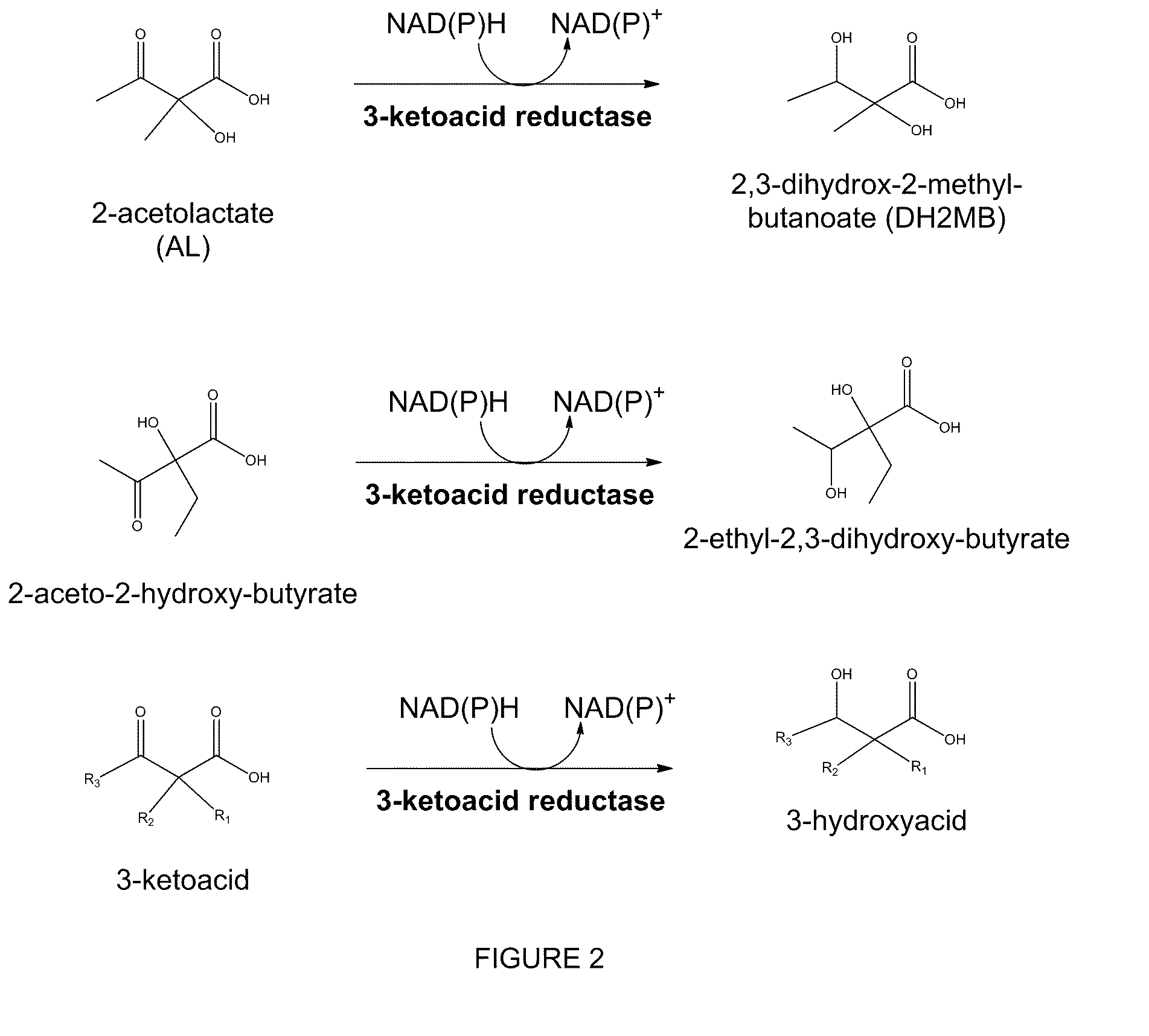
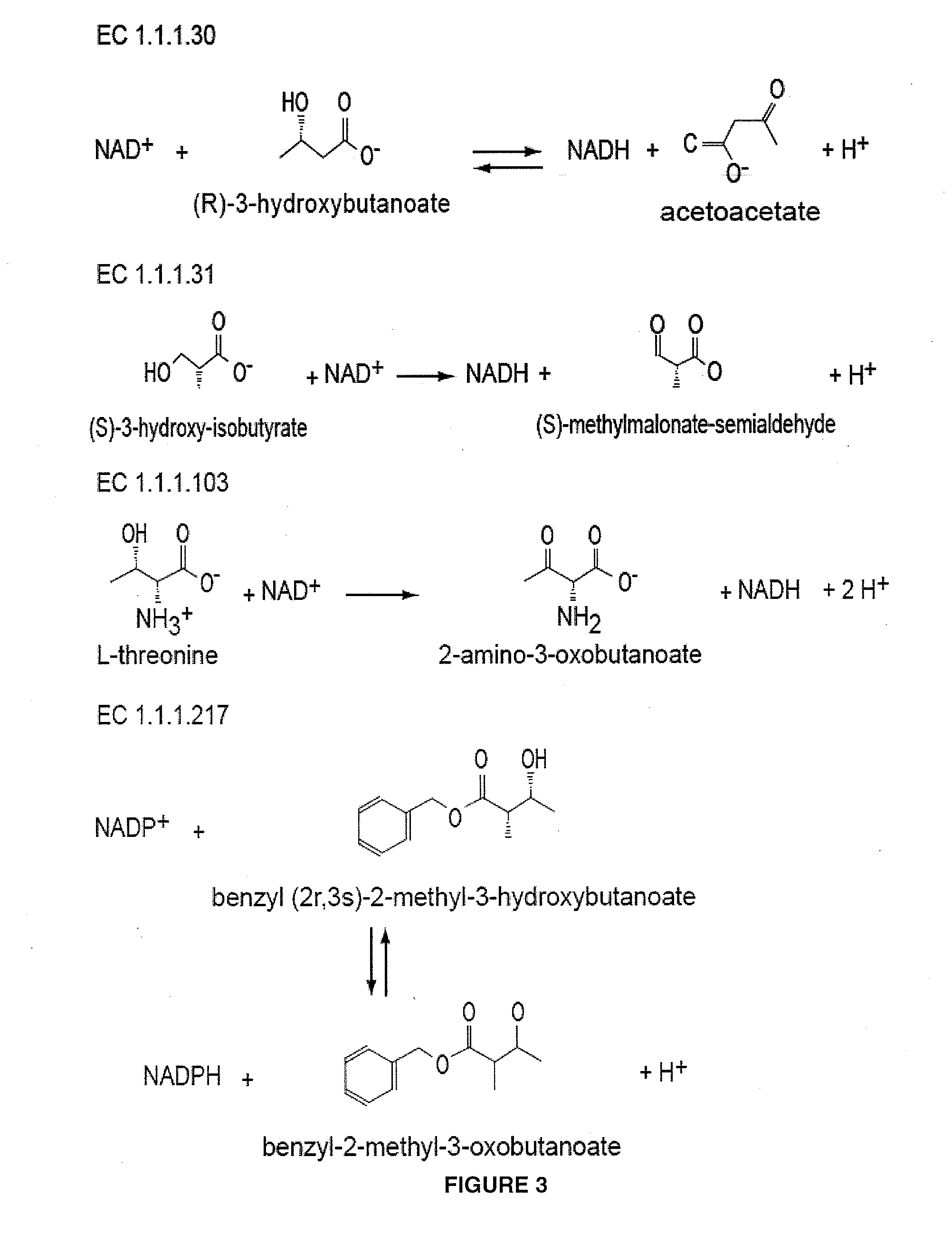
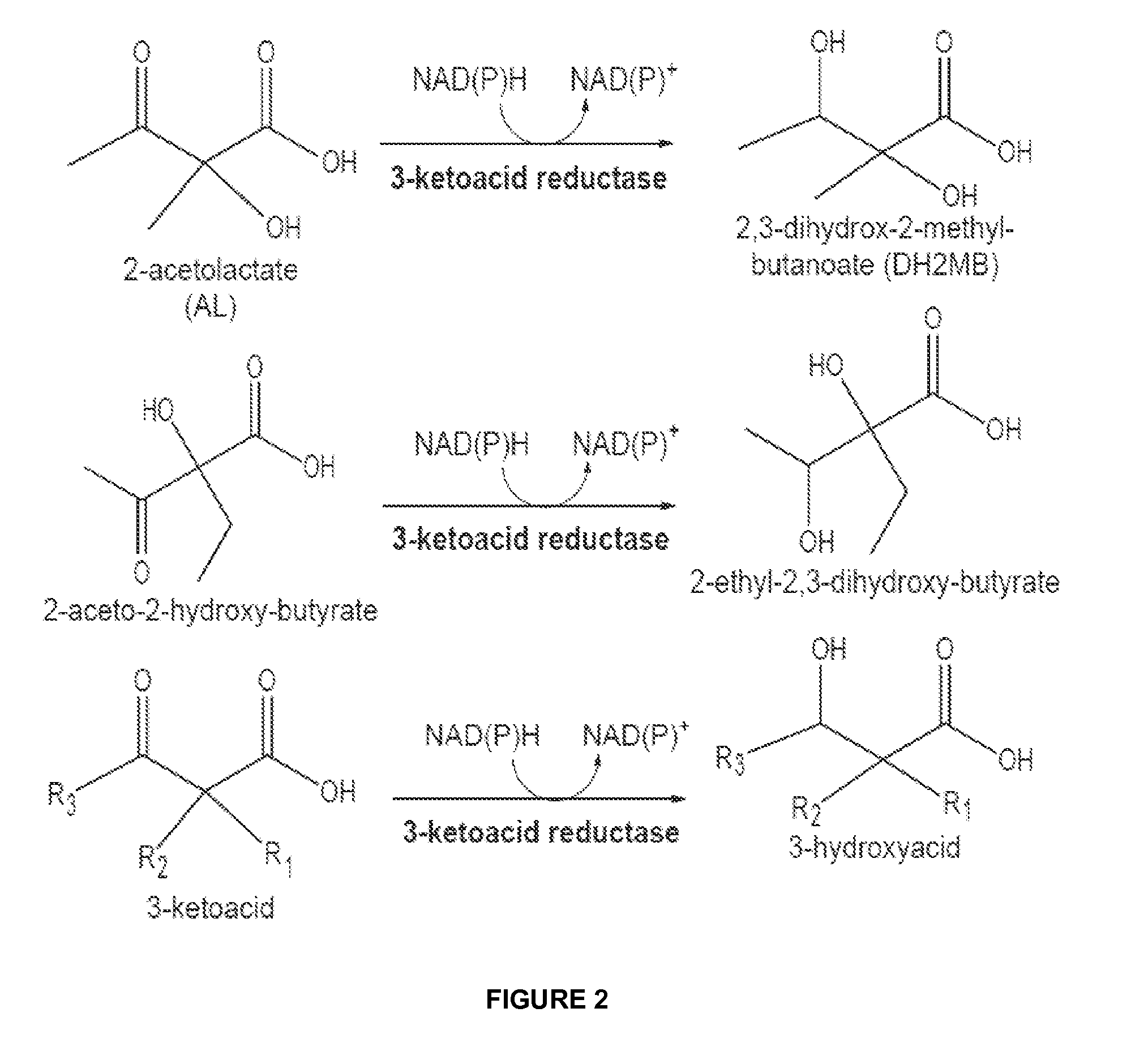
The present invention relates to recombinant microorganisms comprising biosynthetic pathways and methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce various beneficial metabolites. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may further comprise one or more modifications resulting in the reduction or elimination of 3 keto-acid (e.g., acetolactate and 2-aceto-2-hydroxybutyrate) and / or aldehyde-derived by-products. In various embodiments described herein, the recombinant microorganisms may be microorganisms of the Saccharomyces clade, Crabtree-negative yeast microorganisms, Crabtree-positive yeast microorganisms, post-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, pre-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, and non-fermenting yeast microorganisms.
Owner:GEVO INC
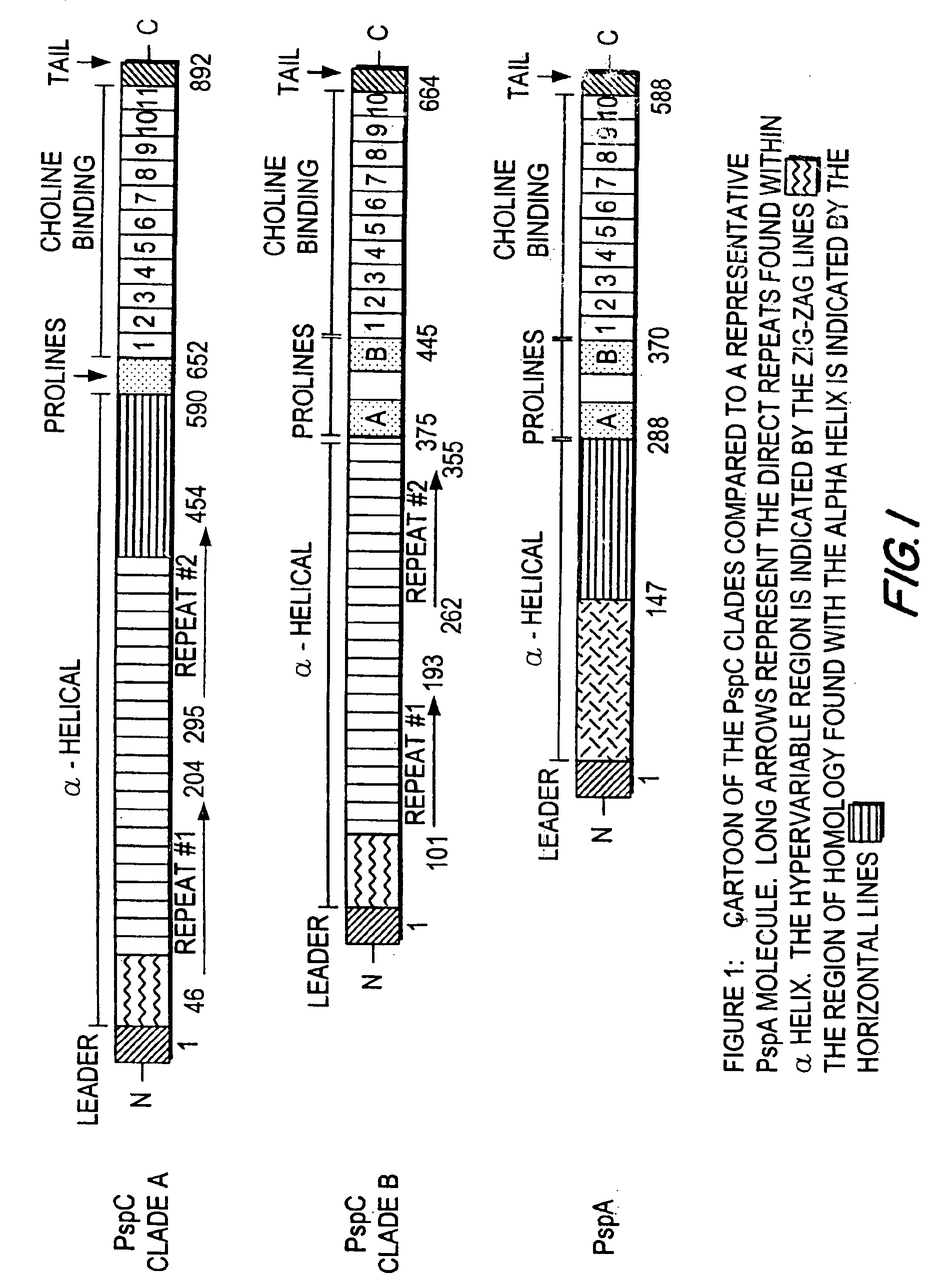
Pneumococcal surface protein C (PspC), epitopic regions and strain selection thereof, and uses therefor
InactiveUS7078042B2Improving immunogenicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEukaryotic plasmidsIn vivo
Owner:ALABAMA AT BIRMINGHAM UNIVERISTY OF +1
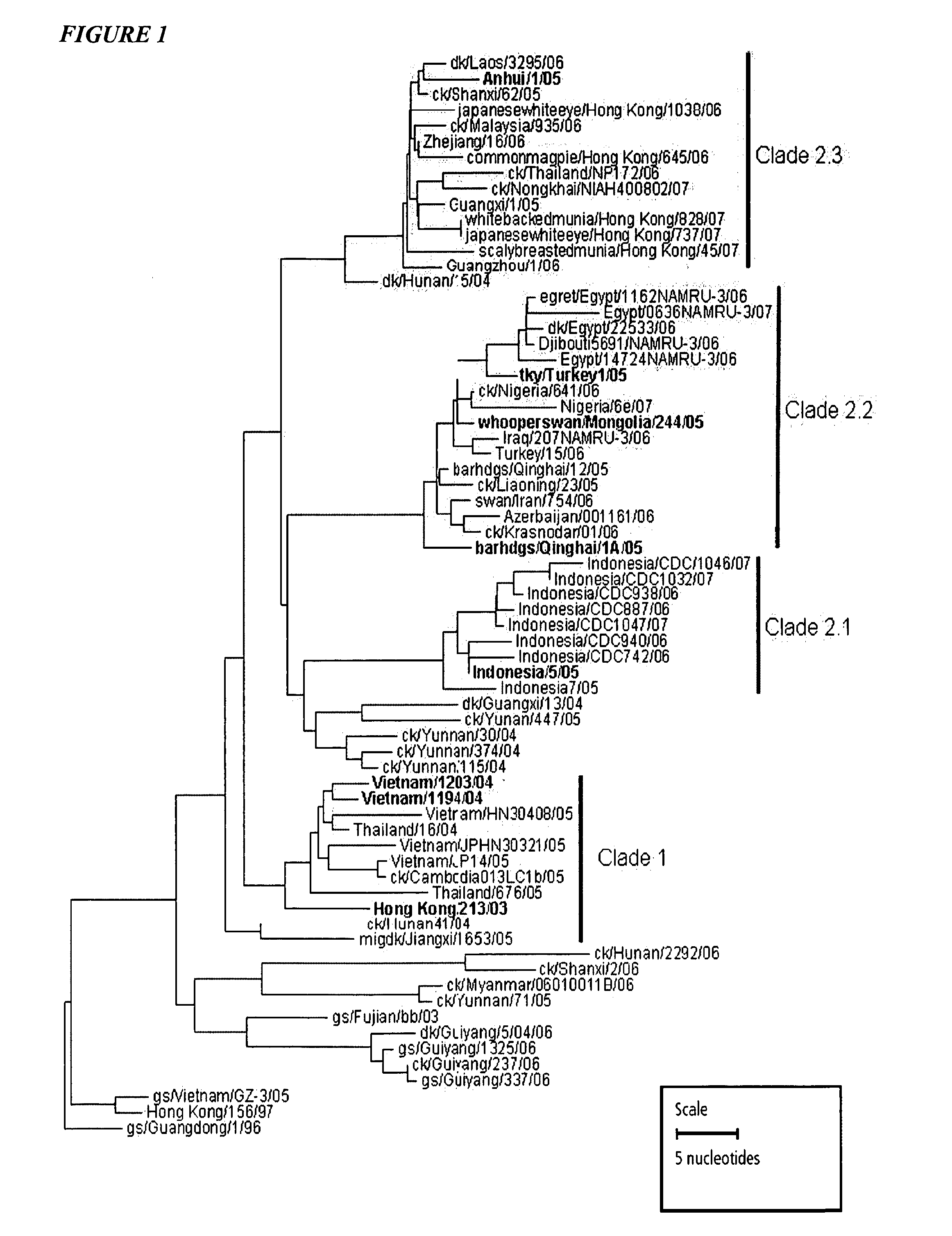
Rapid, Informative Diagnostic Assay For Influenza Viruses Including H5N1
InactiveUS20090123909A1Reduce needMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHemagglutininSequon
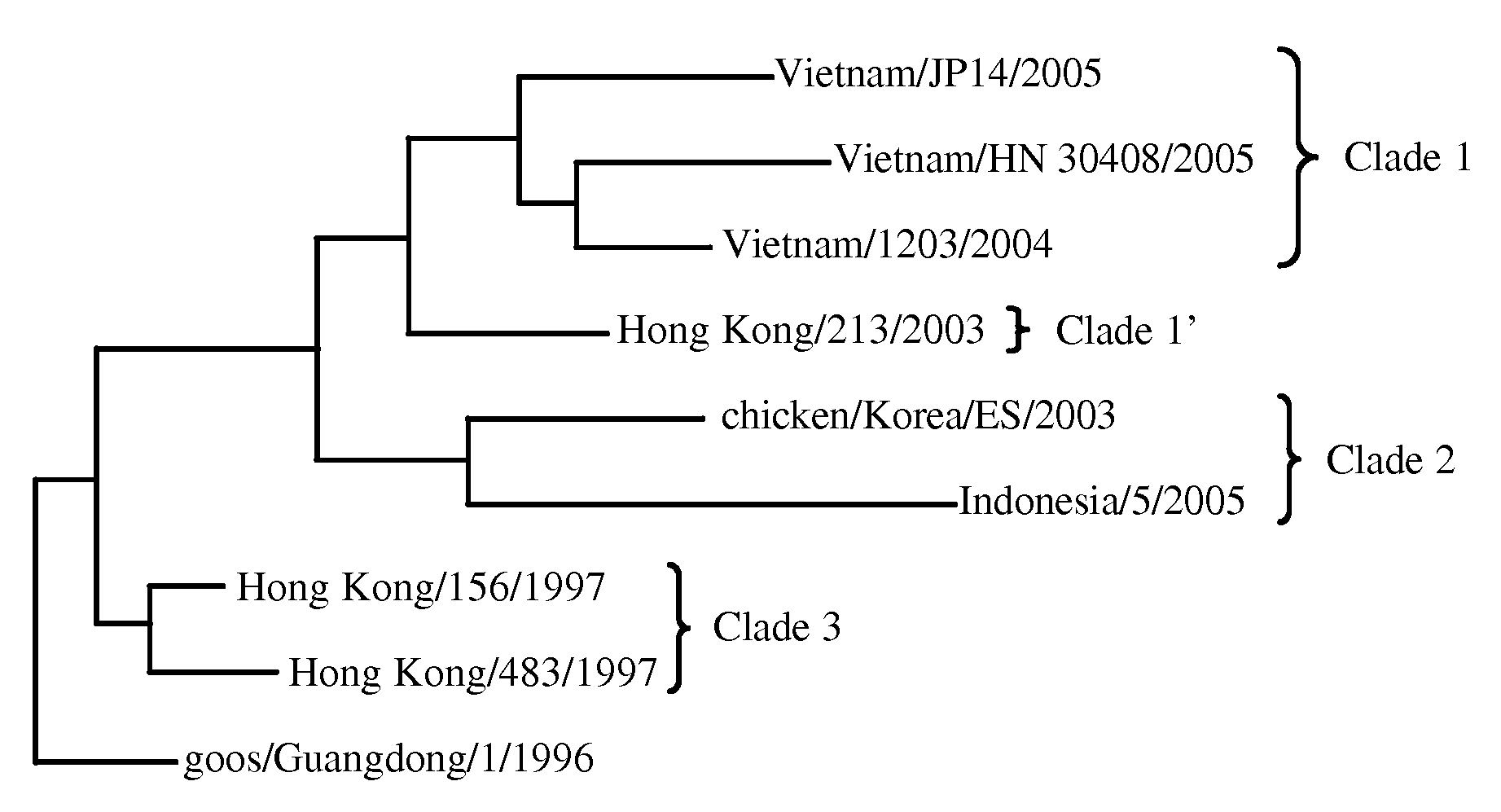
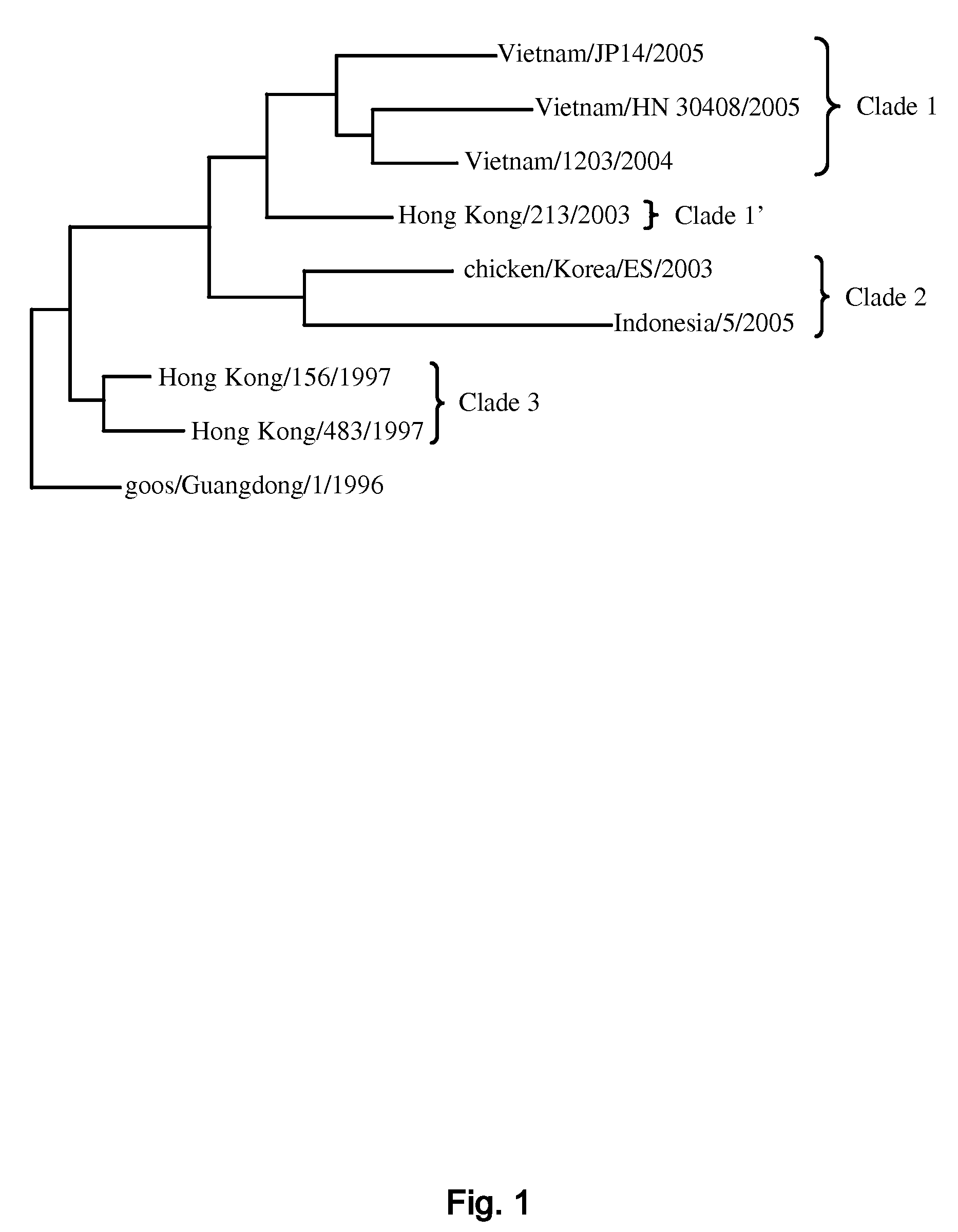
A rapid diagnostic assay for influenza virus, particularly avian influenza and more particularly H5N1, is described. The assay is based on amplification of a significant portion of the hemagglutinin (HA) gene and sequencing of several loci within the HA gene, using techniques which can obtain real time sequence information from multiple sites of a target DNA, in particular pyrosequencing and bioluminescence regenerative cycle. The assay contemplates the use of information-rich subsequences within the HA gene, e.g., (1) a glycosylation sequon; (2) receptor binding site; and (3) HA1 / HA2 cleavage site. Other subsequences for sequencing include strain and clade markers, which vary among H5N1 strains.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Multiplex DNA identification of clinical yeasts using flow cytometry
InactiveUS7465543B1Readily apparentMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementAscomycetous yeastPathogenic yeast
Oligonucleotide probes that are specific for pathogenic yeasts and which may be used for the detection of such yeasts in biological samples are described. These probes are specific for yeast species within the clade of Candida albicans and other pathogenic ascomycetous yeasts, and may be used singly or in a multiplex hybridization assay system.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Rapid, informative diagnostic assay for influenza viruses including H5N1
InactiveUS7989185B2Reduce needMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHemagglutininReceptor binding site
A rapid diagnostic assay for influenza virus, particularly avian influenza and more particularly H5N1, is described. The assay is based on amplification of a significant portion of the hemagglutinin (HA) gene and sequencing of several loci within the HA gene, using techniques which can obtain real time sequence information from multiple sites of a target DNA, in particular pyrosequencing and bioluminescence regenerative cycle. The assay contemplates the use of information-rich subsequences within the HA gene, e.g., (1) a glycosylation sequon; (2) receptor binding site; and (3) HA1 / HA2 cleavage site. Other subsequences for sequencing include strain and clade markers, which vary among H5N1 strains.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Therapeutic Peptides and Vaccines
Compositions are disclosed that induce broadly HIV theraputic and vaccine inducing antibodies against diverse HIV clades and relate to the ability to identify HIV gp120-derived short peptide sequence immunogens and various therapeutic compositions made from the identified peptides which compose CCR5 binding sites. Also disclosed are methods of selecting peptide sequences that are likely candidates for drugs which will offer effective treatment in such areas as Alzheimer's disease, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis and other diseases associated with the human inflammatory cascade as well as related retroviruses such as HTLV-1, the cause of tropical spastic paraparesis.
Owner:PEPTIDE ACCOUNT LLC
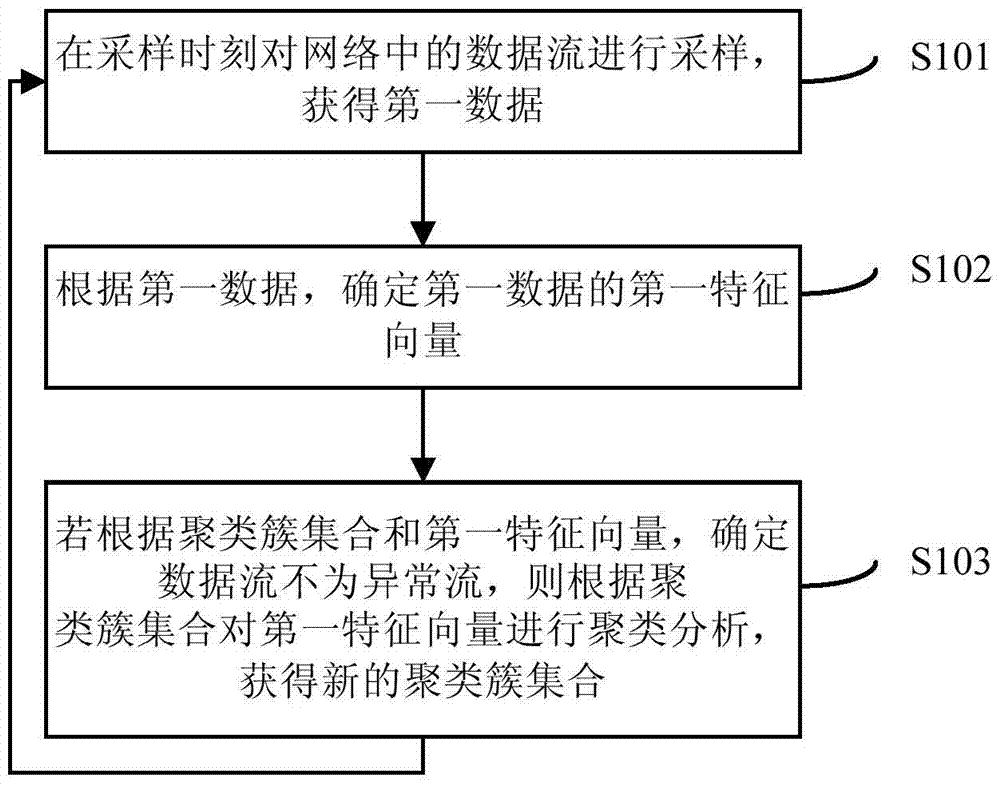
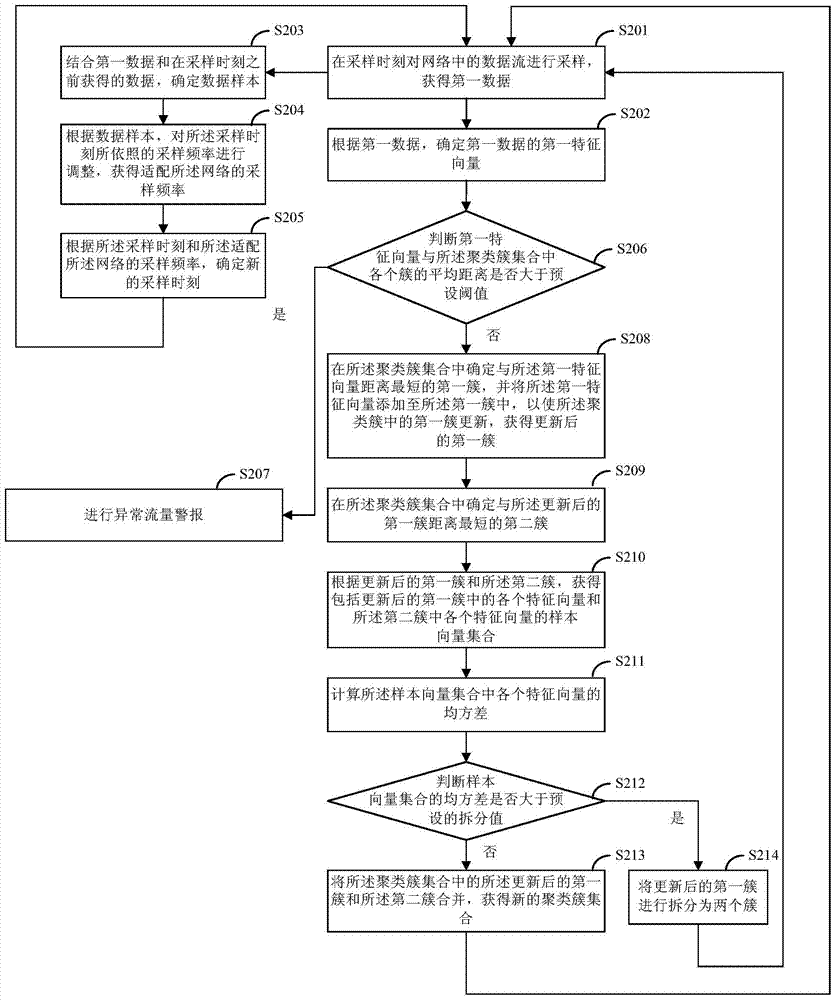
Data stream processing method and device
Embodiments of the present invention provide a data flow processing method and device, the processing method includes: sampling the data flow in the network at the sampling moment to obtain the first data; according to the first data, determining the first characteristic of the first data vector; if according to the cluster set and the first eigenvector, it is determined that the data flow is not an abnormal flow, then perform cluster analysis on the first eigenvector according to the cluster set, obtain a new cluster set, and return to the executed The data flow in the network is sampled at the sampling moment; wherein, the number of clusters in the cluster cluster set is different from the number of clusters in the new cluster cluster set; the processing method of the data stream provided by the embodiment of the present invention And the device, since the clustering cluster set used to determine whether the data stream is an abnormal stream is updated in real time, and the number of clusters in the clustering cluster set is also changed in real time, the accuracy of judging the data stream can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Compositions and methods for generating an immune response
InactiveUS20150004132A1Easy to produceImprove stabilityGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesAntigenViral vector
We have developed DNA and viral vectors that can be used, alone or in combination, as a vaccine against one HIV clade, subtype, or recombinant form of HIV or against multiple HIV clades, subtypes, or recombinant forms. Moreover, the vectors can encode a variety of antigens, which may be obtained from one clade or from two or more different clades, and the antigens selected and / or the manner in which the vectors are formulated (e.g., mixed) can be manipulated to generate a protective immune response against a variety of clades (e.g., the clades to which a patient is most likely to be exposed; with the proportions of the components of the vaccine tailored to the extent of the patient's risk to a particular clade or clades).
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
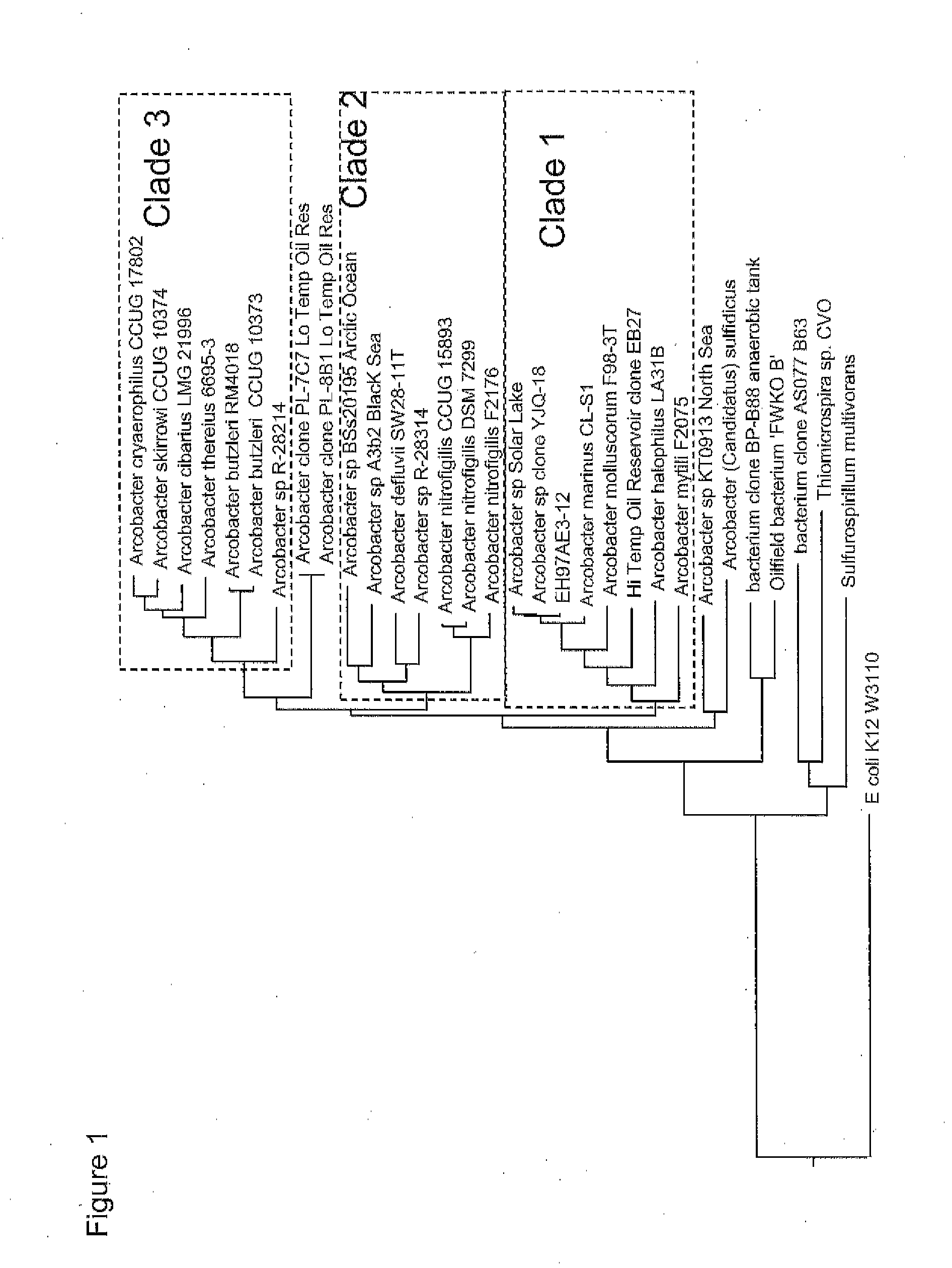
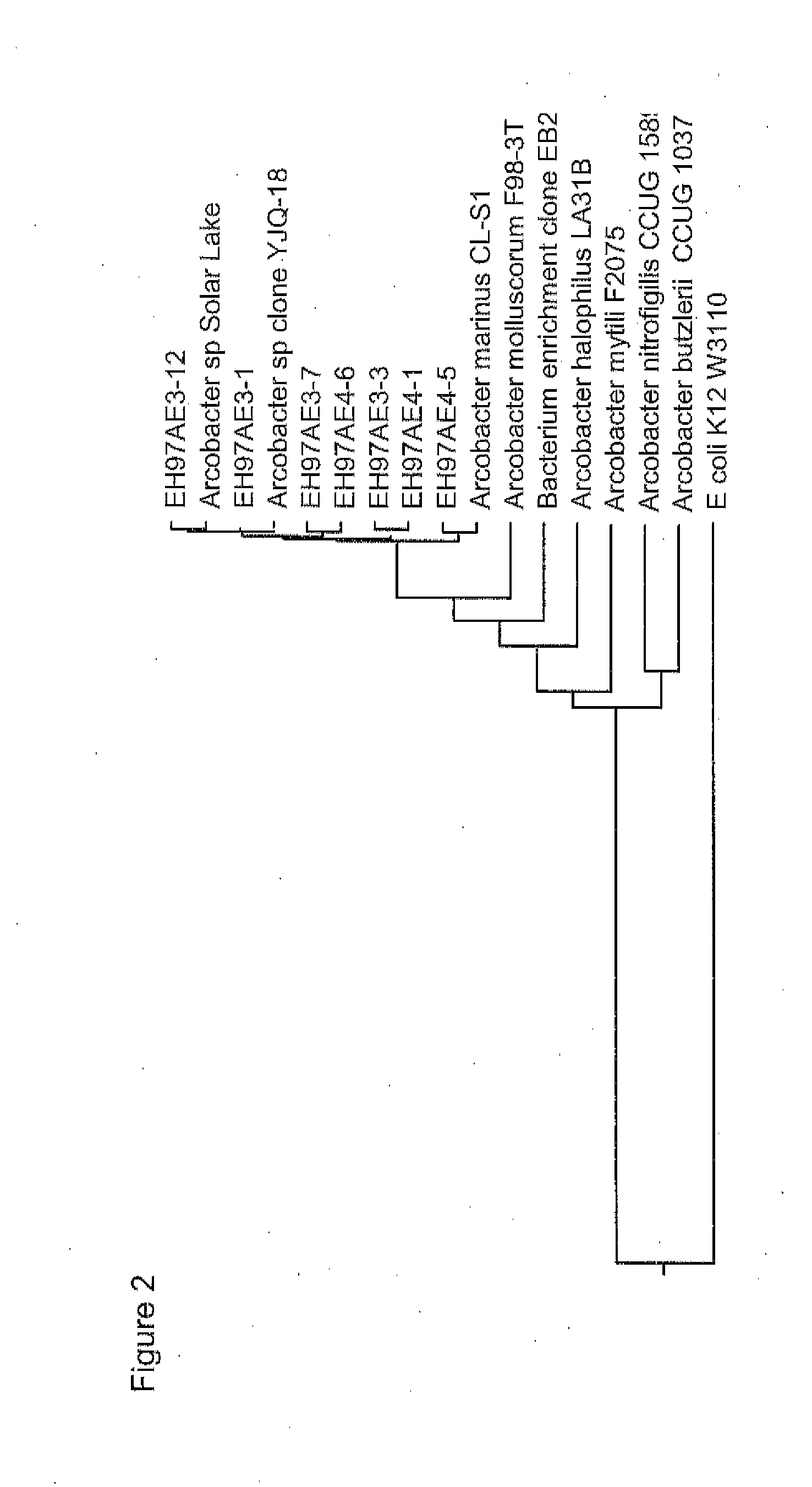
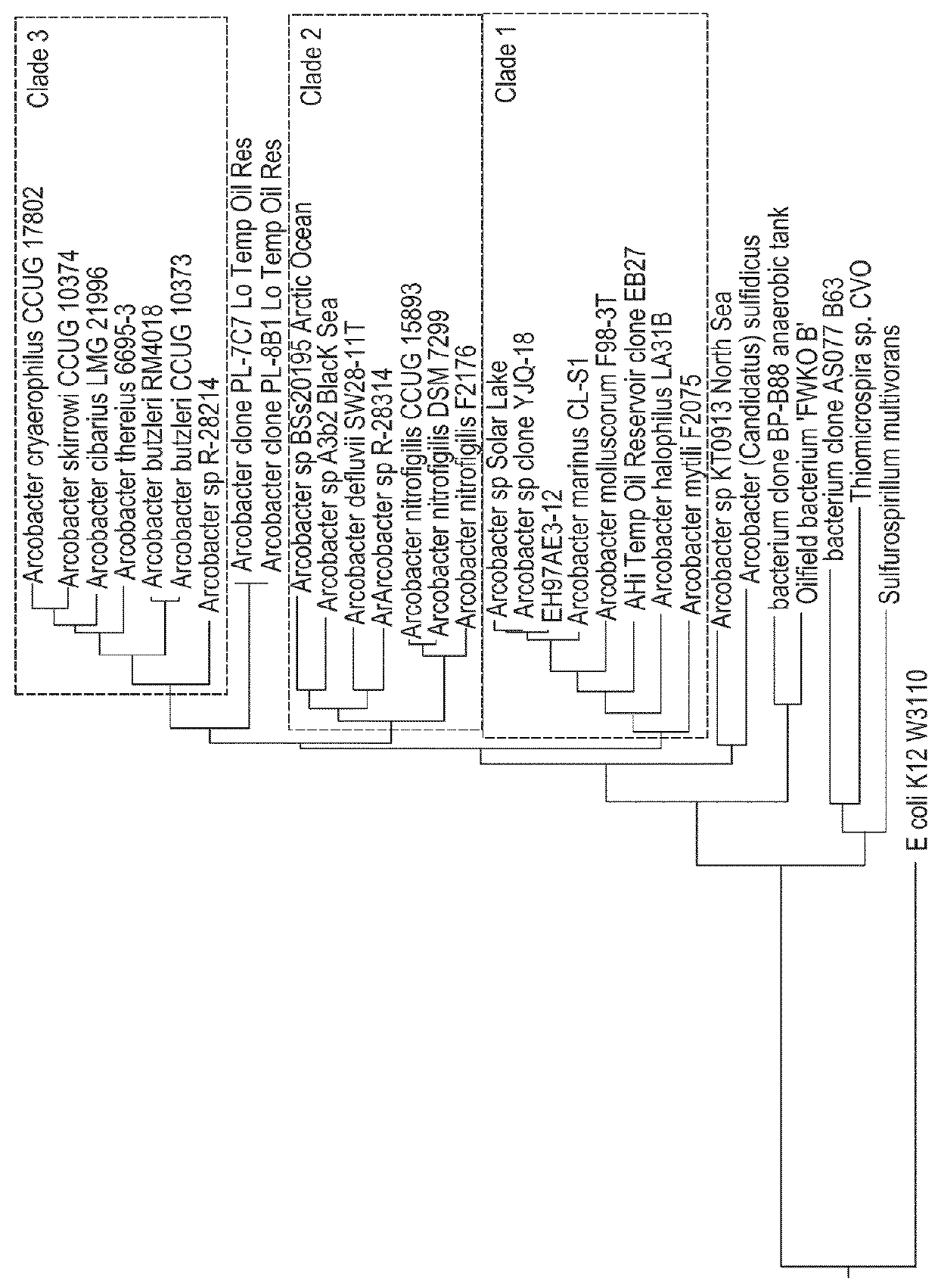
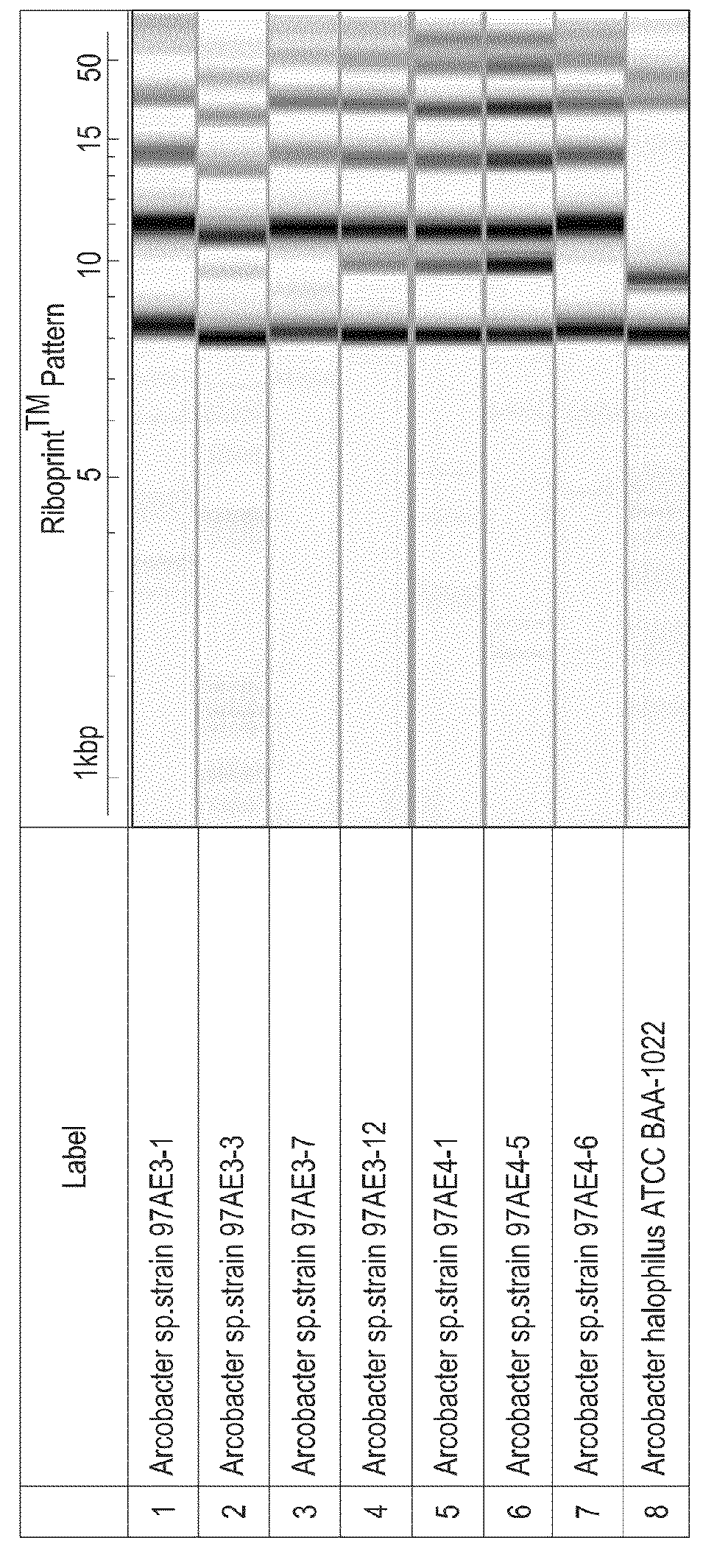
Methods, strains, and compositions useful for microbially enhanced oil recovery: arcobacter clade 1
Methods, microorganisms, and compositions are provided wherein oil reservoirs are inoculated with microorganisms belonging to Arcobacter clade 1 and medium including an electron acceptor. The Arcobacter strains grow in the oil reservoir to form plugging biofilms that reduce permeability in areas of subterranean formations thereby increasing sweep efficiency, and thereby enhancing oil recovery.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Vaccination with multiple clades of h5 influenza a virus
ActiveUS20110189230A1Eliminate needAvoid the needSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininPrime boost
H5N1 influenza viruses isolated from animals and humans since 2003 separate into distinct clades based on hemagglutinin amino acid sequences. According to the invention, multiple clades are used in influenza immunization. Thus there is a prime-boost immunization schedule where a subject receives a priming dose of a first clade of H5 influenza A virus and a boosting dose of a second clade of H5 influenza A virus. There is also an immunogenic composition comprising hemagglutinin antigens from more than one clade of H5 influenza A virus.
Owner:SEQIRUS UK LTD
Multivalent HIV immunogenic compositions comprising a pool of lipidated and nonlipidated peptides representing Gag and Env variable regions
An anti-HIV vaccine composition is disclosed. The vaccine comprises an combination of immunogenic peptide mixtures, which mixtures may be prepared in a single synthesis. The composition collectively represents the in vivo variability seen in immunogenic epitopes from highly variable regions of HIV. Immunization with the vaccine elicits broadly reactive immunity (CTL and T helper cell responses) against the divergent strains of HIV upon which it is based. The vaccine may be formulated to target regionally distinct variability based on an HIV clade predominant in a geographical region.
Owner:VARIATION BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Therapeutic peptides and vaccines
The present invention discloses compositions of vaccines that broadly induce HIV therapeutics and antibodies that induce antibodies to different HIV clades, and also relates to the identification of HIV gp120-derived short peptide sequence immunogens and the generation of various The capacity of the therapeutic composition. The invention also discloses methods for selecting candidate peptide sequences that may be effective drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis and the cascade of inflammation associated with humans and related retroviruses such as the tropical Other HTLV-1-associated diseases with spastic paralysis.
Owner:拉皮德医药股份公司
System and method for detection of hiv-1 clades and recombinants of the reverse transcriptase and protease regions
InactiveUS20120322665A1Reduce frequencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseProtease
A method for detecting low frequency occurrence of one or more HIV sequence variants associated with reverse transcriptase and / or protease is described that comprises the steps of: (a) generating a cDNA species from a plurality of RNA molecules in an HIV sample population; (b) amplifying a plurality of first amplicons from the cDNA species, wherein each first amplicon is amplified with a pair of nucleic acid primers capable of generating amplicons from an HIV clade comprising clade A, clade B, clade C, clade D, clade F, and clade G; (c) clonally amplifying the amplified copies of the first amplicons to produce a plurality of second amplicons; (d) determining a nucleic acid sequence composition of the second amplicons; and (e) detecting one or more sequence variants in the nucleic acid sequence composition of the second amplicons.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Methods, strains, and compositions useful for microbially enhanced oil recovery: Arcobacter clade 1
Methods, microorganisms, and compositions are provided wherein oil reservoirs are inoculated with microorganisms belonging to Arcobacter clade 1 and medium including an electron acceptor. The Arcobacter strains grow in the oil reservoir to form plugging biofilms that reduce permeability in areas of subterranean formations thereby increasing sweep efficiency, and thereby enhancing oil recovery.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Methods of screening for causative agents of onychodystrophy
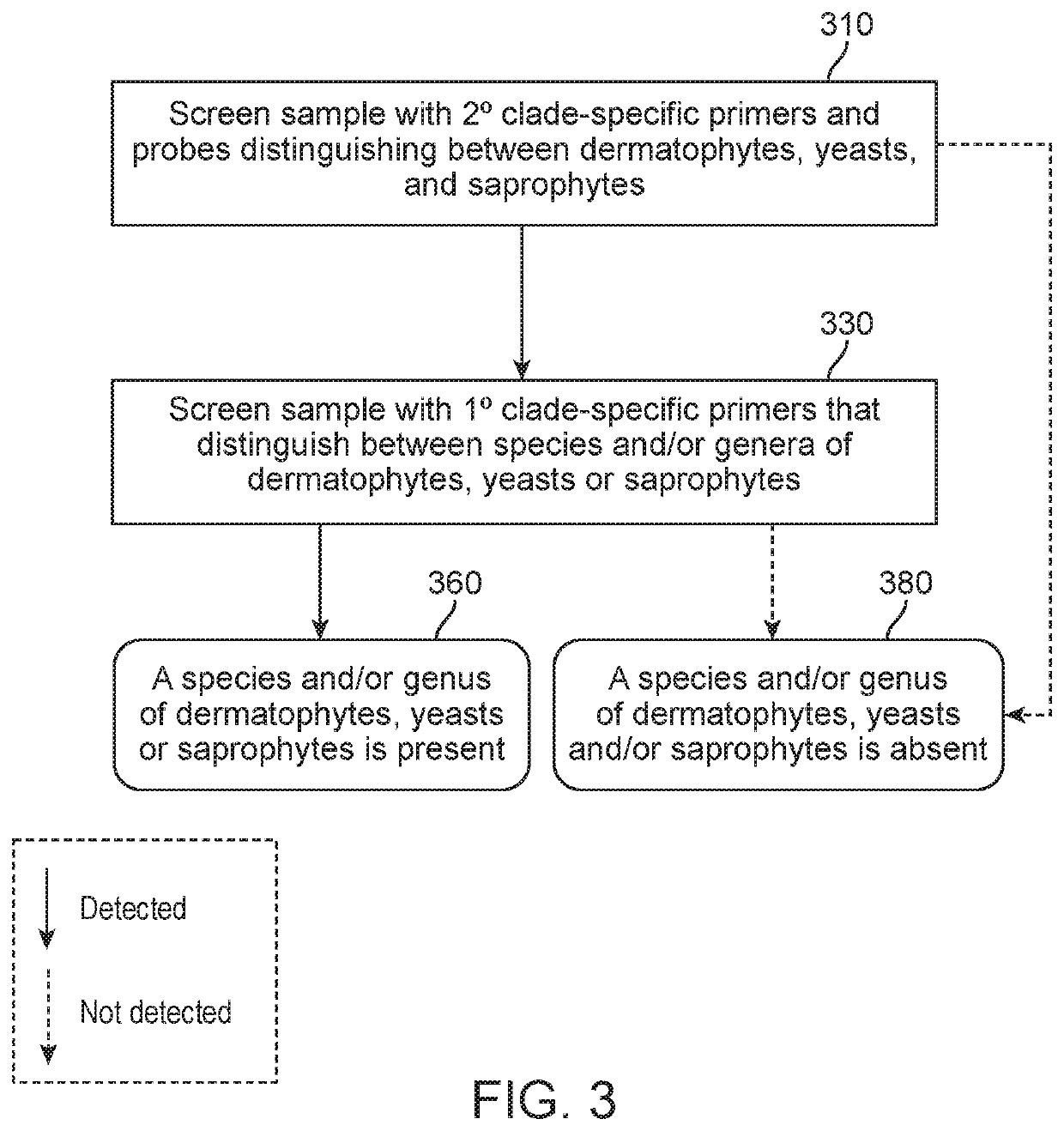
Provided herein is a real-time PCR-based method of detecting, in a sample, an agent causing onychodystrophy, wherein the agent causing onychodystrophy belongs to a secondary clade member including one or more primary clade members. Also provided are compositions and kits that finds use in implementing the present method.
Owner:BAKOTIC PATHOLOGY ASSOC LLC
Recombinant HIV-1 gp120 Immunogen with Three Different V3 Loops from Viruses of Different Clades
InactiveUS20080095791A1Increase breadthMinimize potentialSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA constructMammal
A novel immunogenic HIV-1 Env, particularly gp120, DNA construct is disclosed in which either the V1 / V2 loop and the V4 loop, or all three variable loops, including V3, are replaced with a V3 sequence each of which is from a different viral isolate. Preferably, each replacement V3 loop is a consensus sequence of V3 of a different clade. Such constructs are useful as immunogens as each presents three independent V3 epitopes, so that the immunized subject generates a more broadly reactive neutralizing antibody response than with conventional gp120 or V3 DNA or polypeptide immunogens. Also disclosed are methods of using the DNA construct to immunize a mammal, preferably a human, particularly in a priming regiment in which the DNA immunogen is followed by administration of a V3 fusion protein boosting immunogen.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com