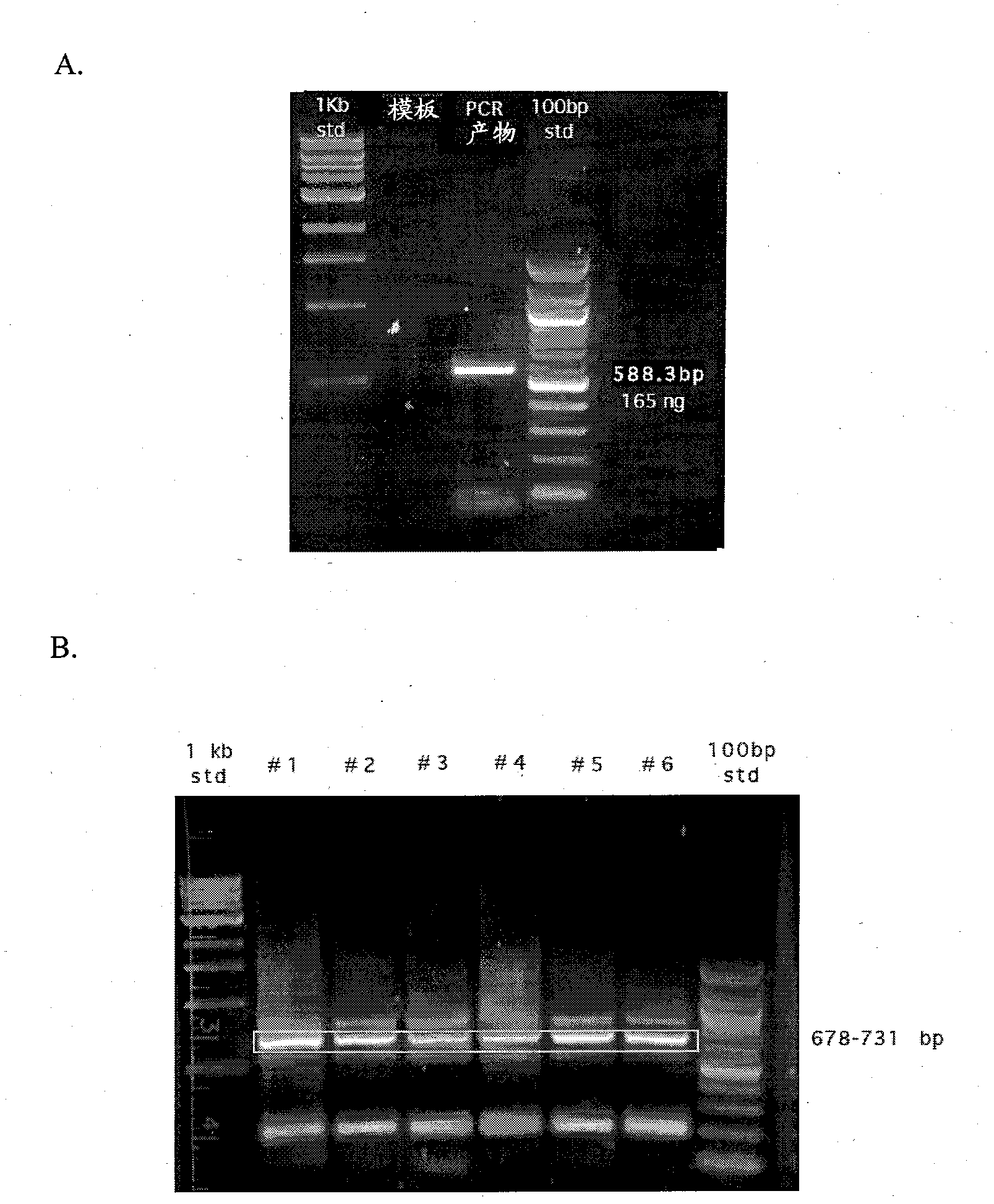
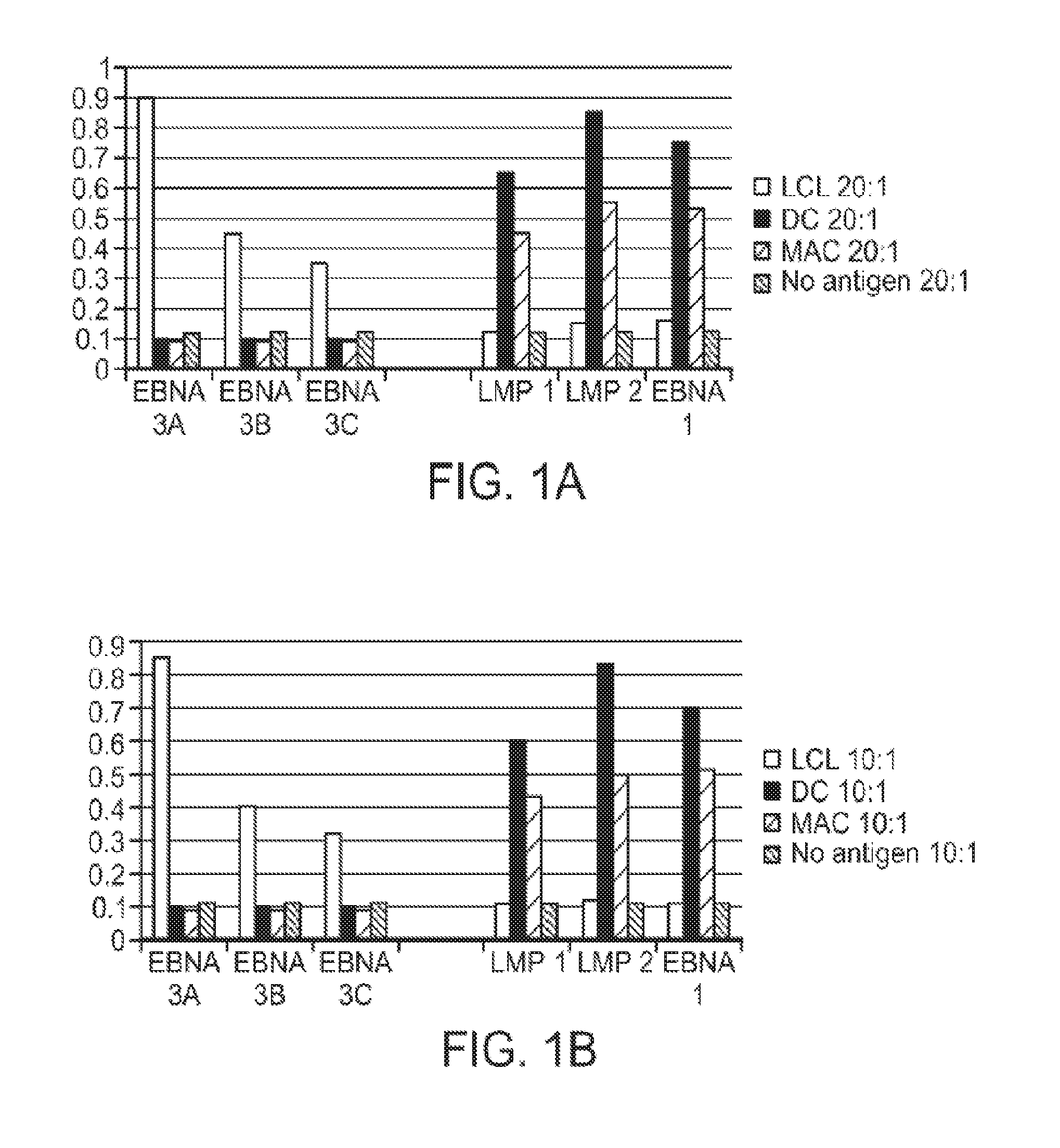
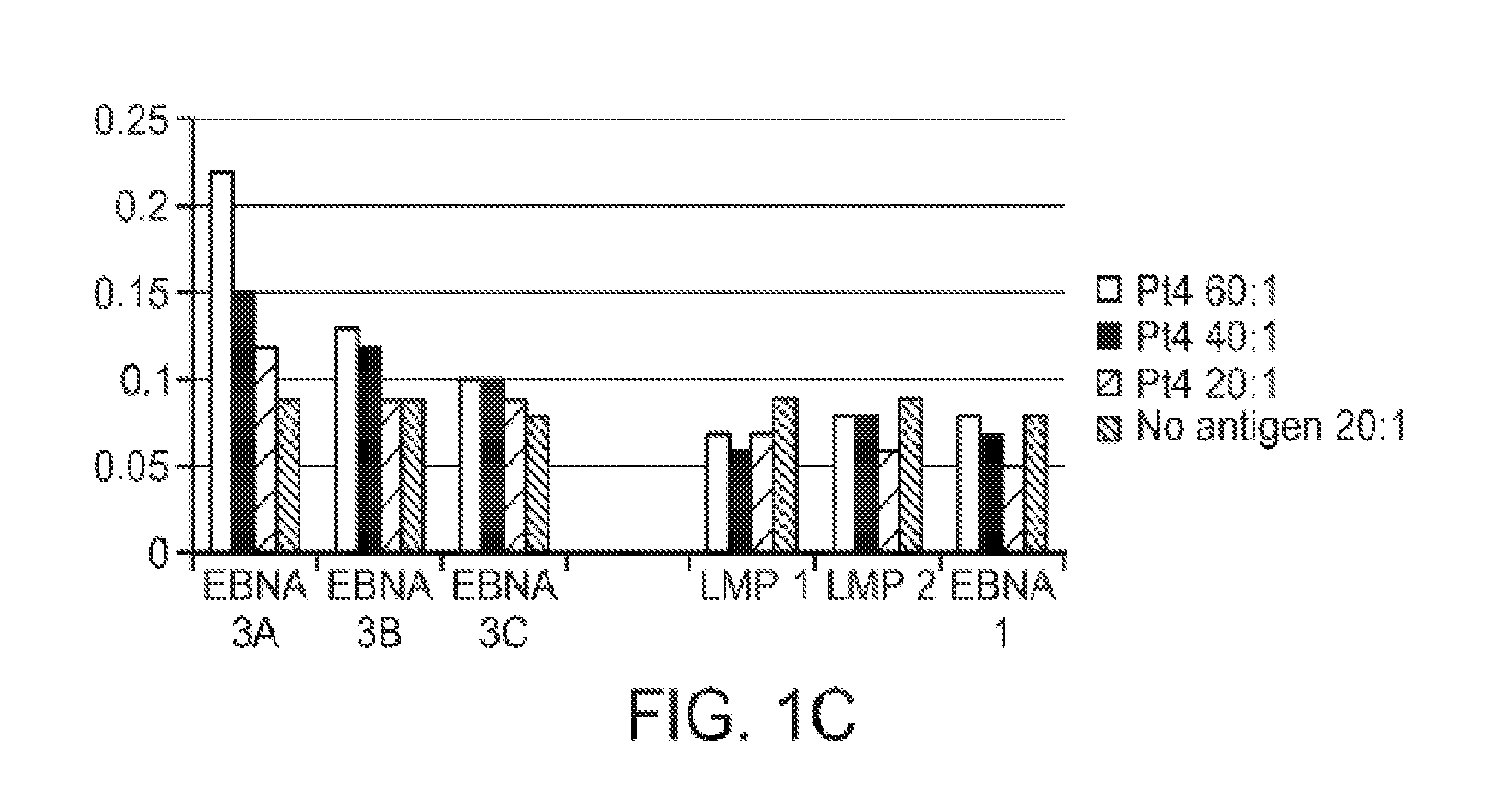
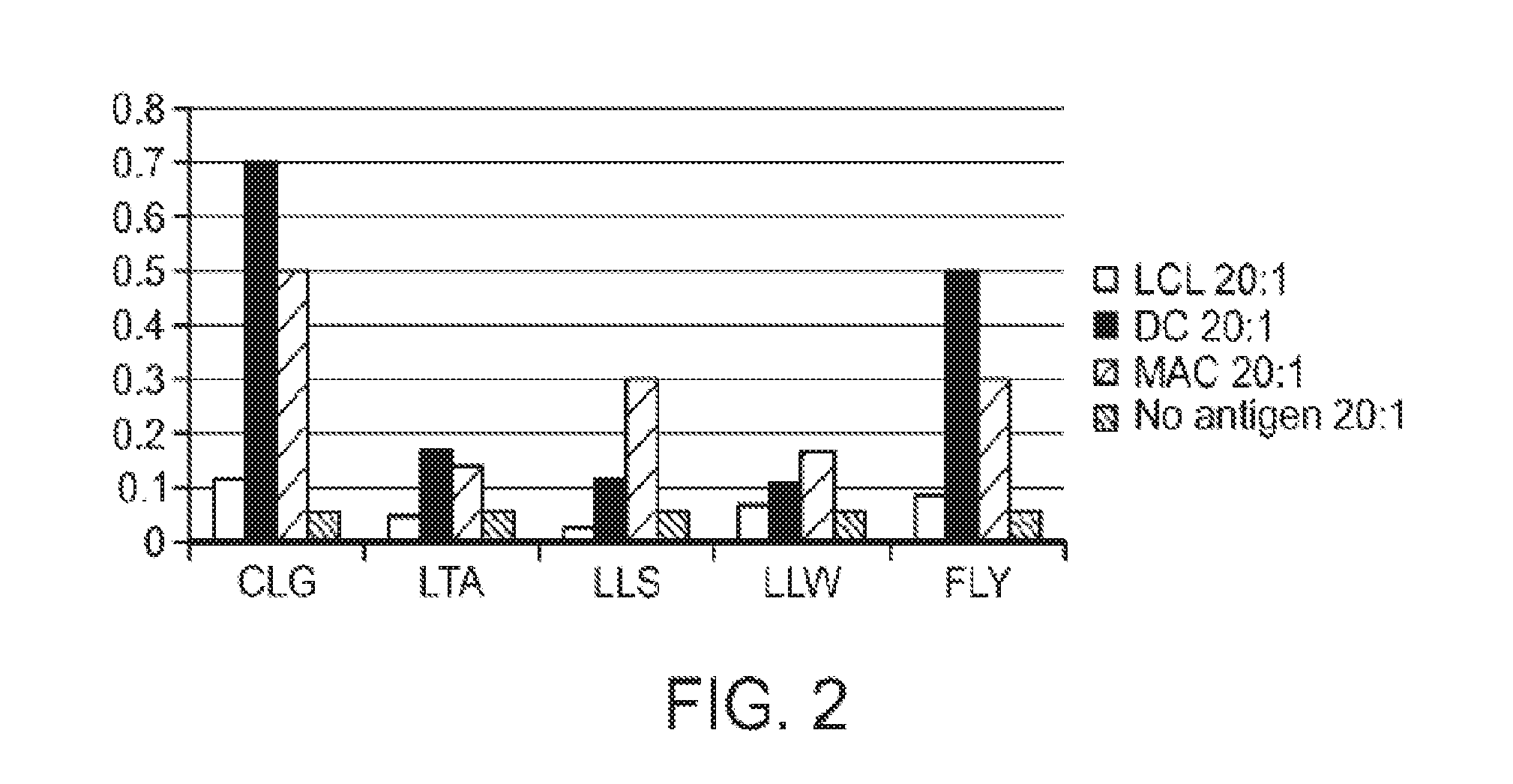
Patents
Literature
81 results about "Memory B cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Memory B cells are a B cell sub-type that are formed within germinal centers following primary infection and are important in generating an accelerated and more robust antibody-mediated immune response in the case of re-infection (also known as a secondary immune response).
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20110044994A1Sugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against virusesVaccinationImmunodeficiency virus
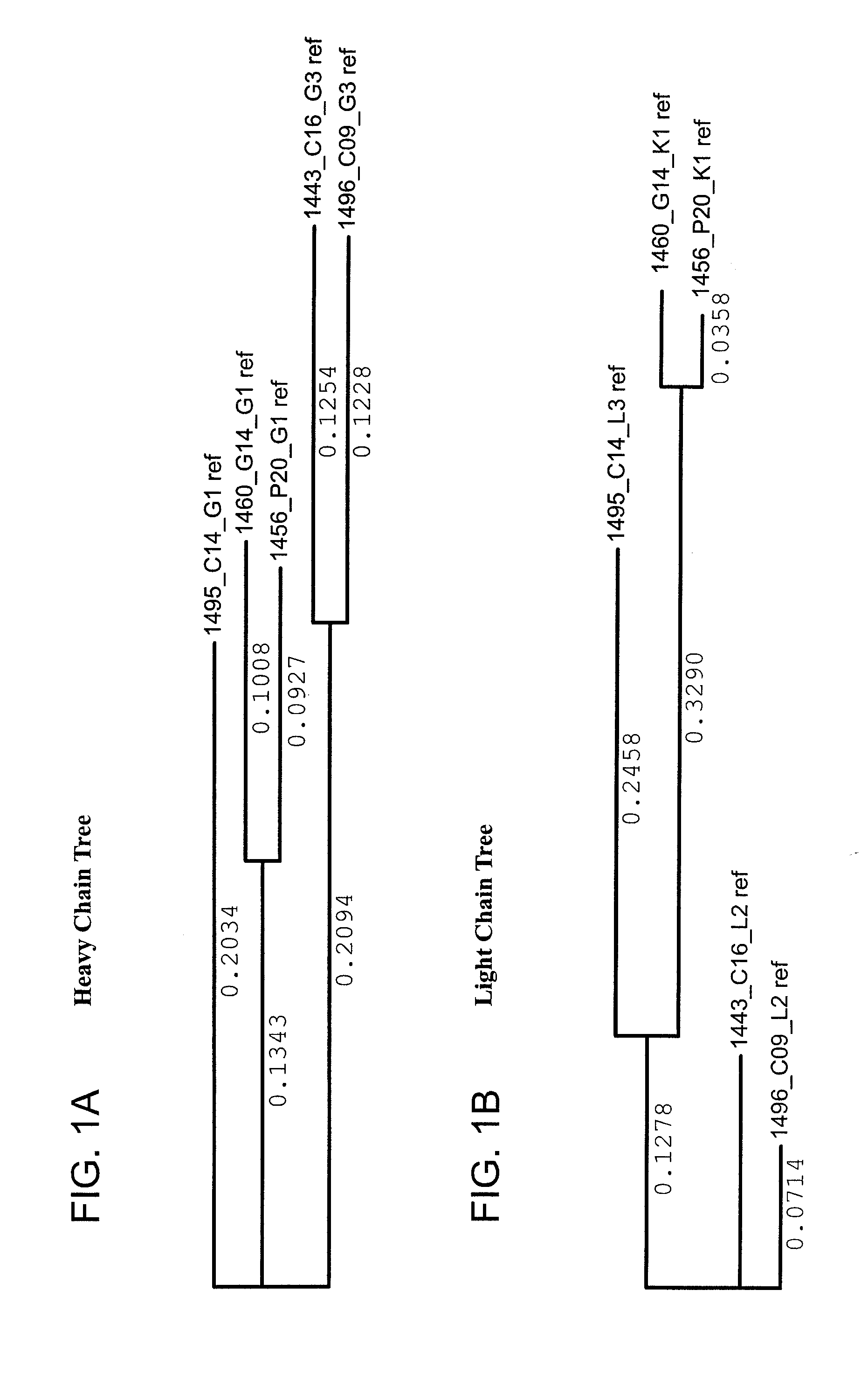
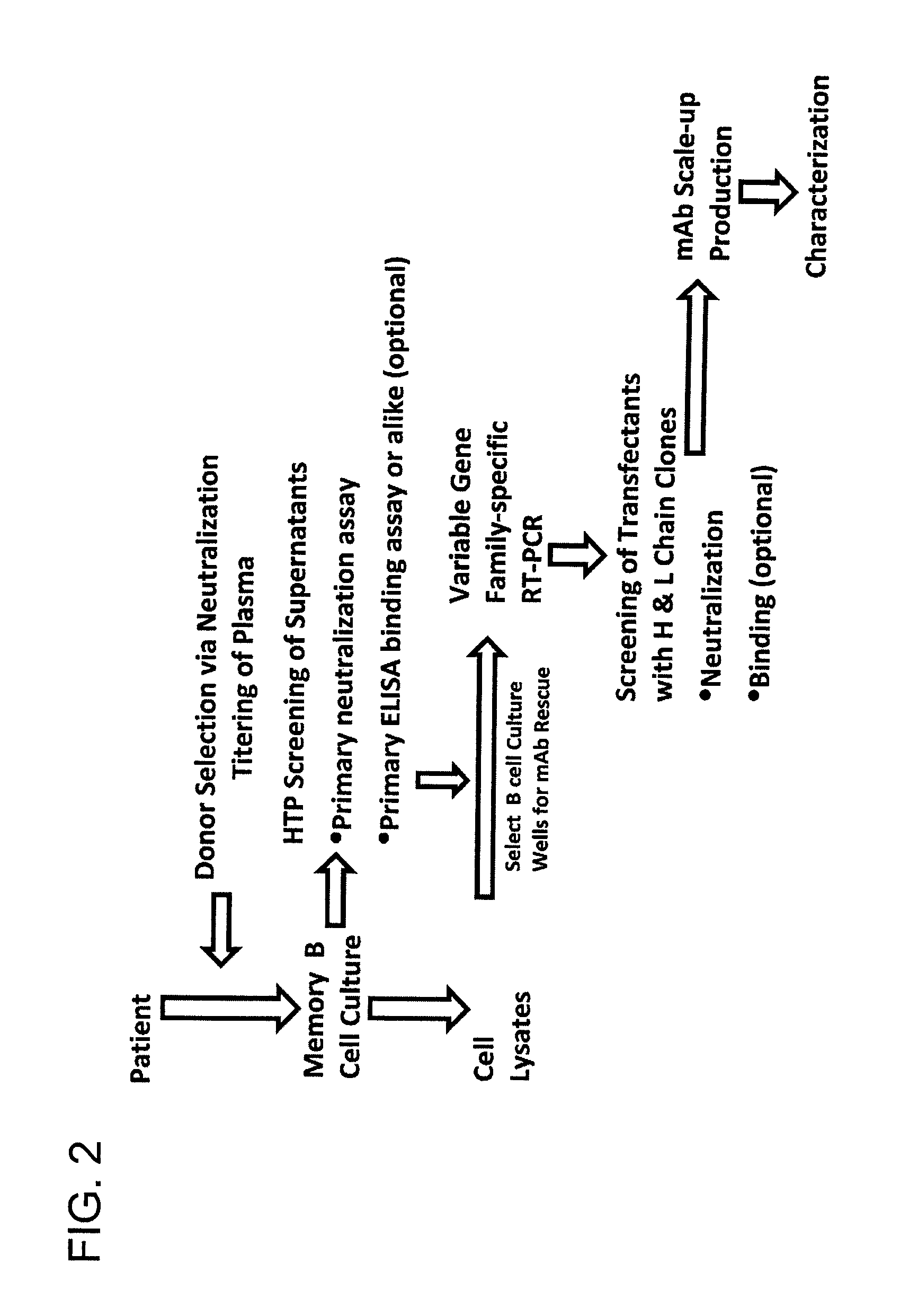
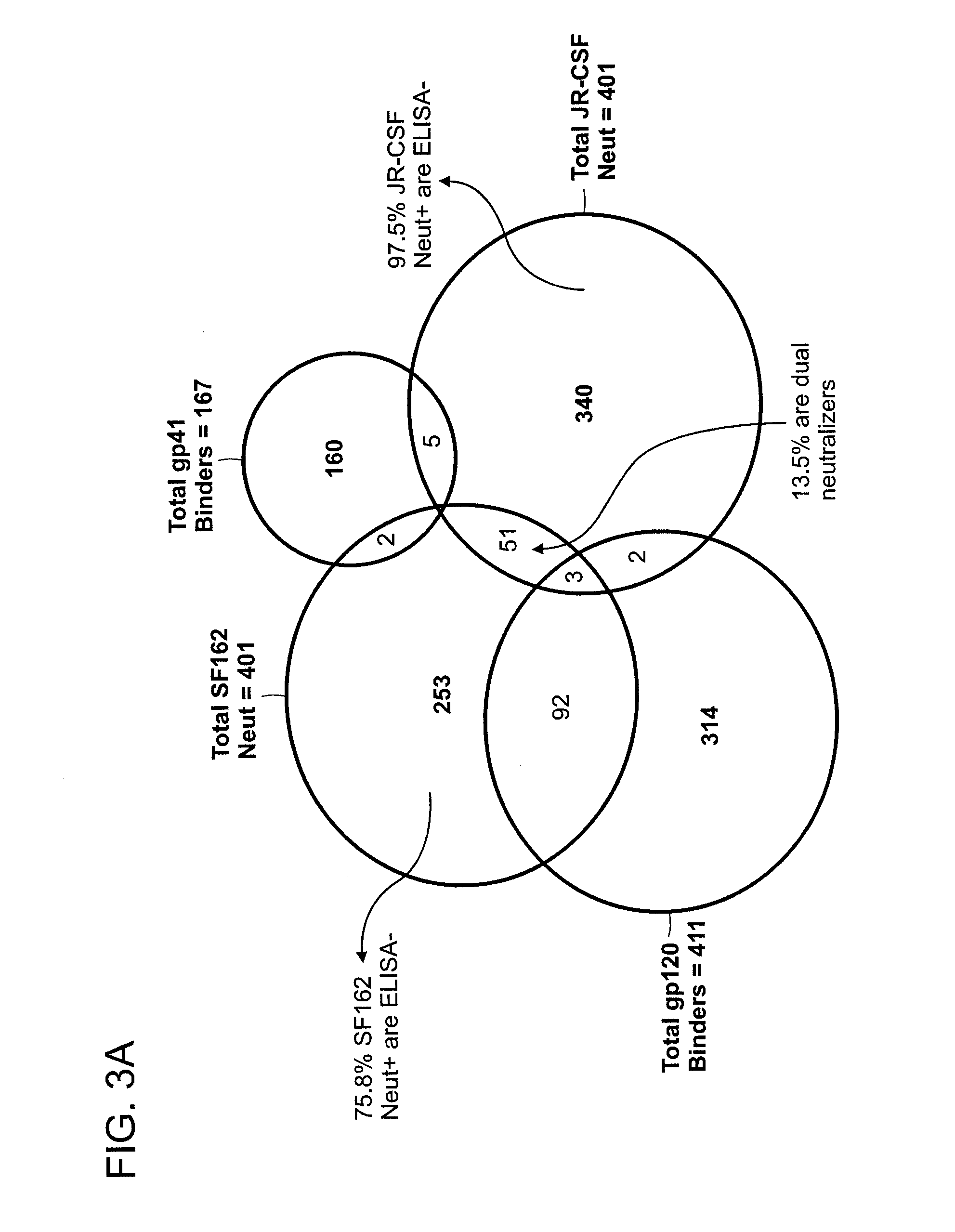
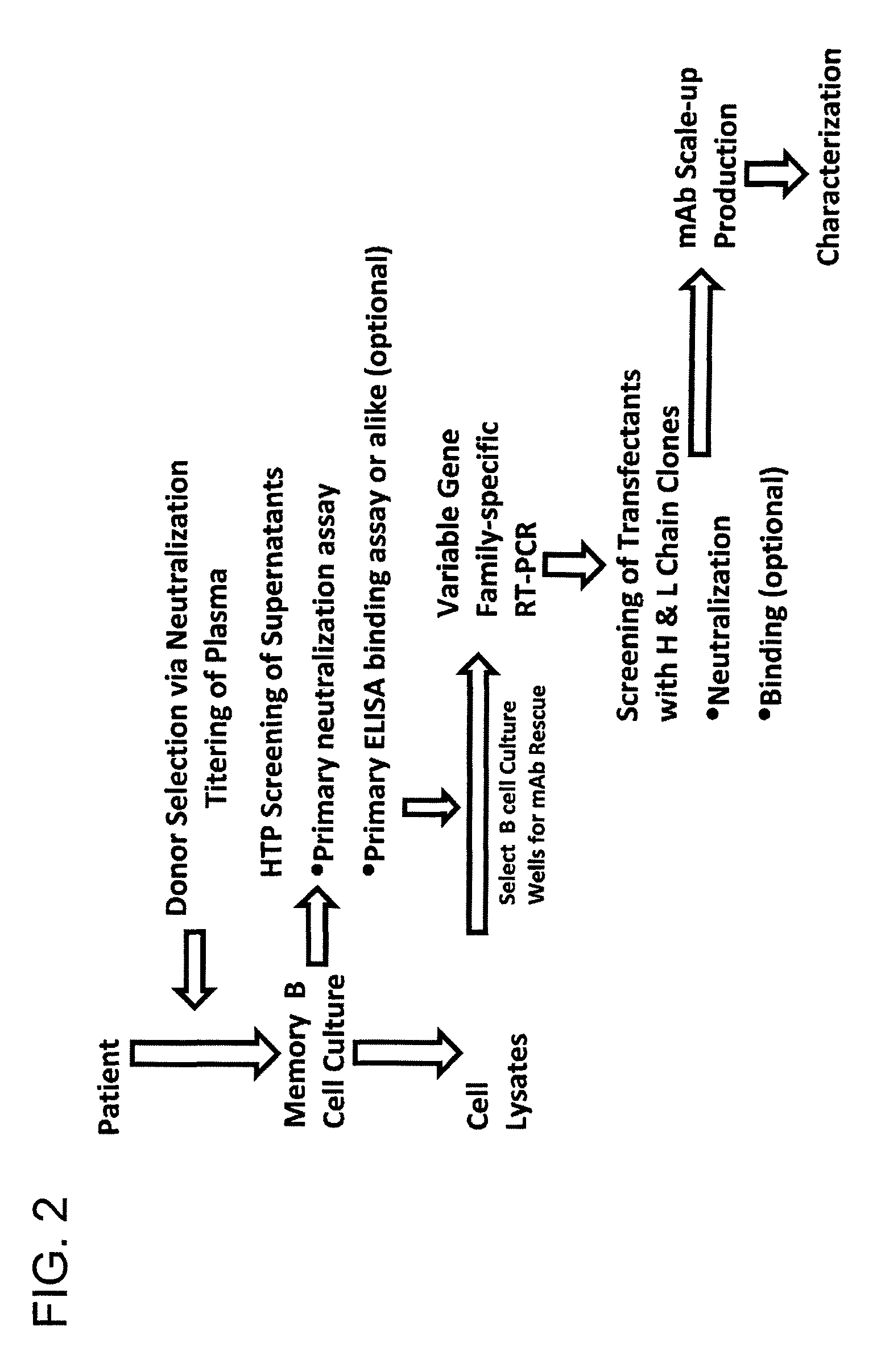
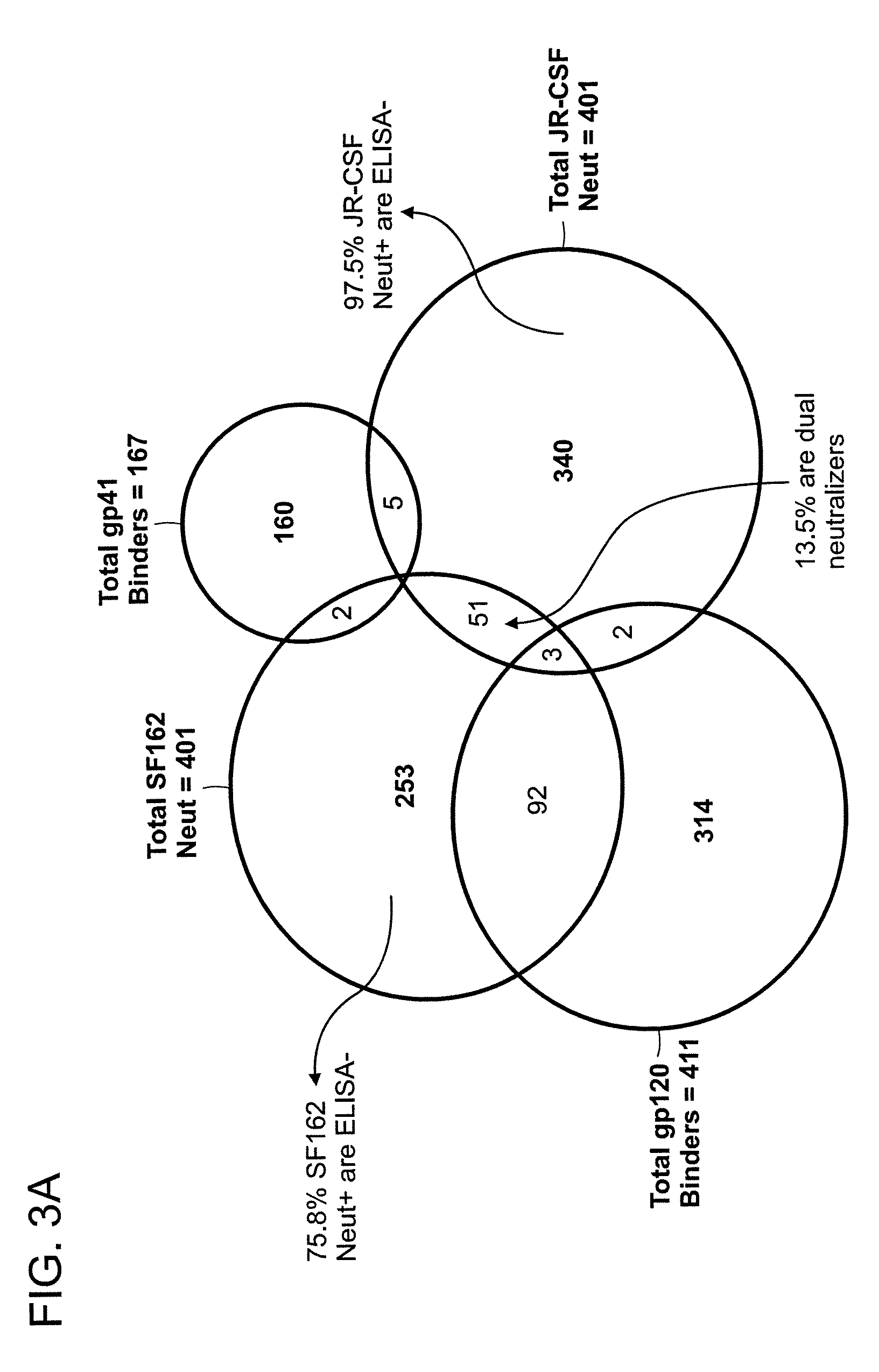
The invention provides a method for obtaining a broadly neutralizing antibody (bNab), including screening memory B cell cultures from a donor PBMC sample for neutralization activity against a plurality of HIV-1 species, cloning a memory B cell that exhibits broad neutralization activity; and rescuing a monoclonal antibody from that memory B cell culture. The resultant monoclonal antibodies are characterized by their ability to selectively bind epitopes from the Env proteins in native or monomeric form, as well as to inhibit infection of HIV-1 species from a plurality of clades. Compositions containing human monoclonal anti-HIV antibodies used for prophylaxis, diagnosis and treatment of HIV infection are provided. Methods for generating such antibodies by immunization using epitopes from conserved regions within the variable loops of gp120 are provided. Immunogens for generating anti-HIV1 bNAbs are also provided. Furthermore, methods for vaccination using suitable epitopes are provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +2
Anti-H7N9 full human derived monoclonal antibody hIg311 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110746503AGood neutralizing activityGood biocompatibilityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHemagglutininAntiendomysial antibodies
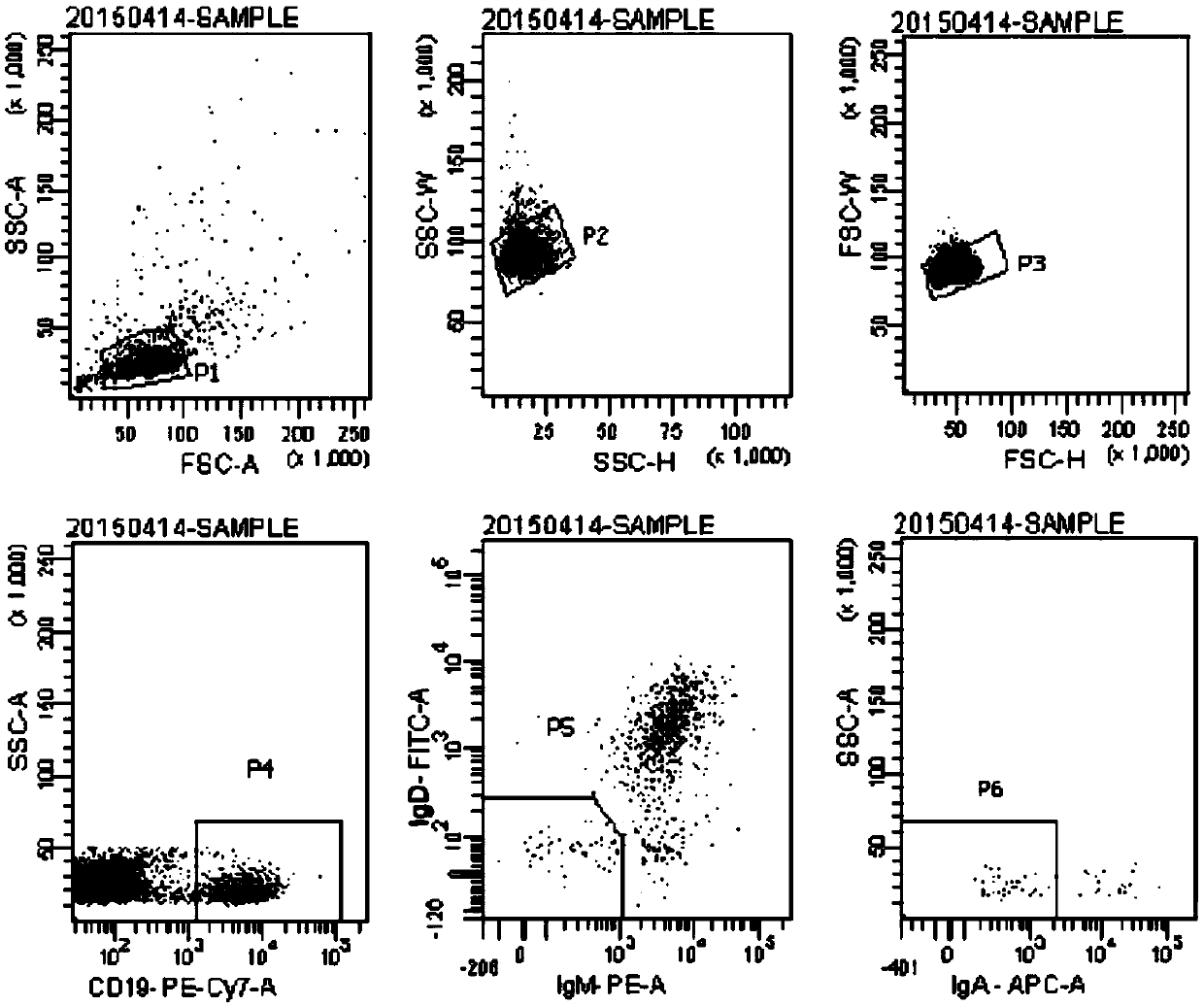
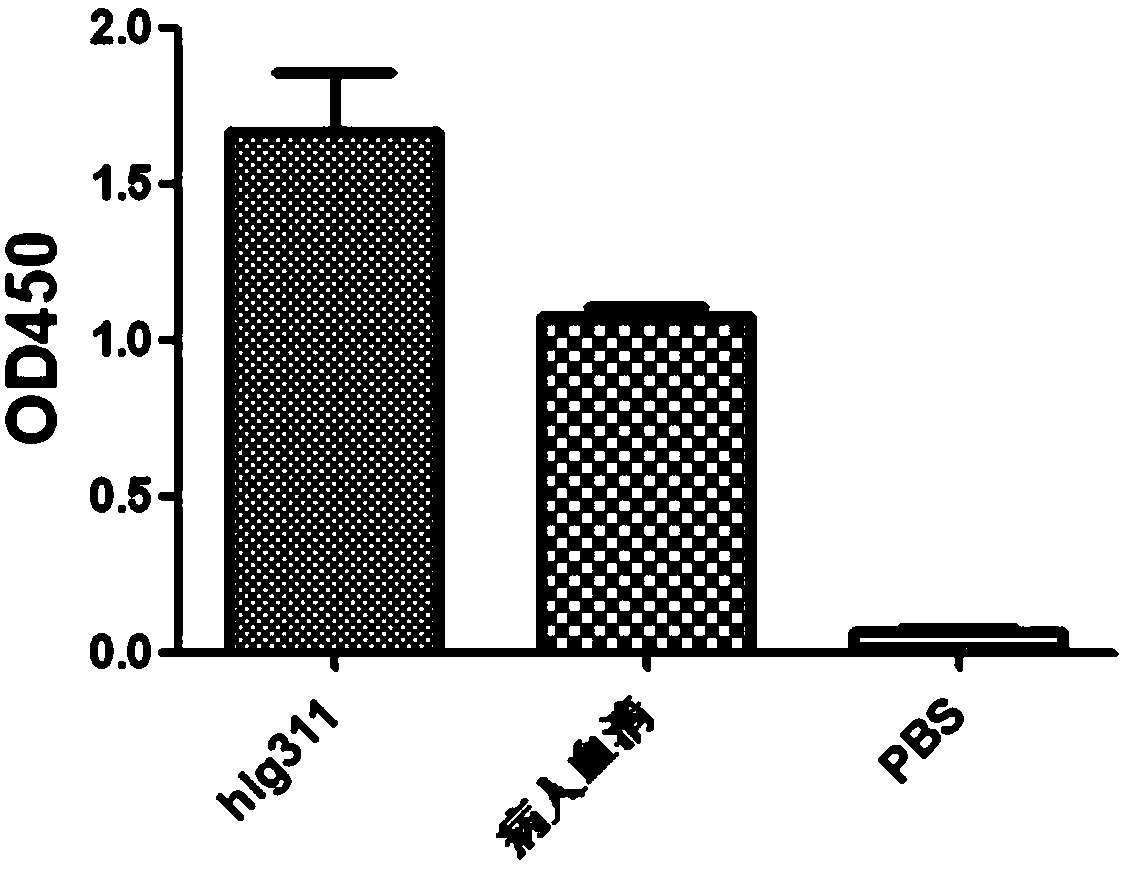
The application relates to an anti-H7N9 full human derived monoclonal antibody hIg311 and a preparation method and application thereof. A memory B cell PCR method is used for quickly screening a fullhuman derived monoclonal antibody hIg311, and the anti-H7N9 human derived monoclonal antibody hIg311 is free from any mouse derived components. The antibody disclosed by the application can realize target combination of hemagglutinin HA of H7N9 viruses, and has notable anti H7N9 viral infection neutralization activity. The antibody disclosed by the application does not generate toxic and side effects for resisting mouse resisting antibodies, has good biocompatibility, and is suitable for becoming and has potential to become macromolecular drugs for treating influenza viruses.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Monoclonal antibodies directed against trimeric forms of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein with broad and potent neutralizing activity
The invention provides a method for obtaining a broadly neutralizing antibody (bNab), including screening memory B cell cultures from a donor PBMC sample for neutralization activity against a plurality of HIV-1 species, cloning a memory B cell that exhibits broad neutralization activity; and rescuing a monoclonal antibody from that memory B cell culture. The resultant monoclonal antibodies are characterized by their ability to selectively bind epitopes from the Env proteins in native or monomeric form, as well as to inhibit infection of HIV-1 species from a plurality of clades. Compositions containing human monoclonal anti-HIV antibodies used for prophylaxis, diagnosis and treatment of HIV infection are provided. Methods for generating such antibodies by immunization using epitopes from conserved regions within the variable loops of gp120 are provided. Immunogens for generating anti-HIV1 bNAbs are also provided. Furthermore, methods for vaccination using suitable epitopes are provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +2
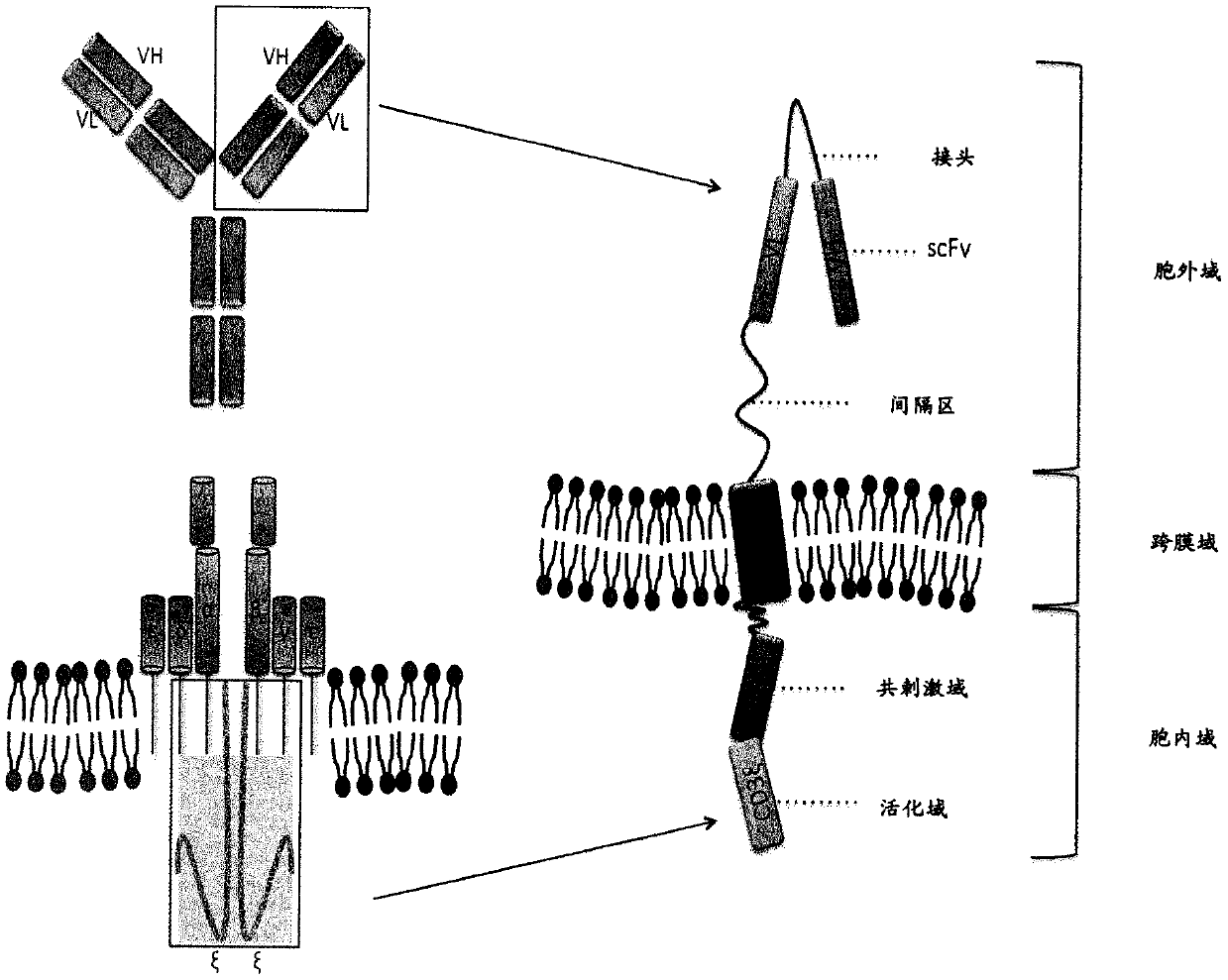
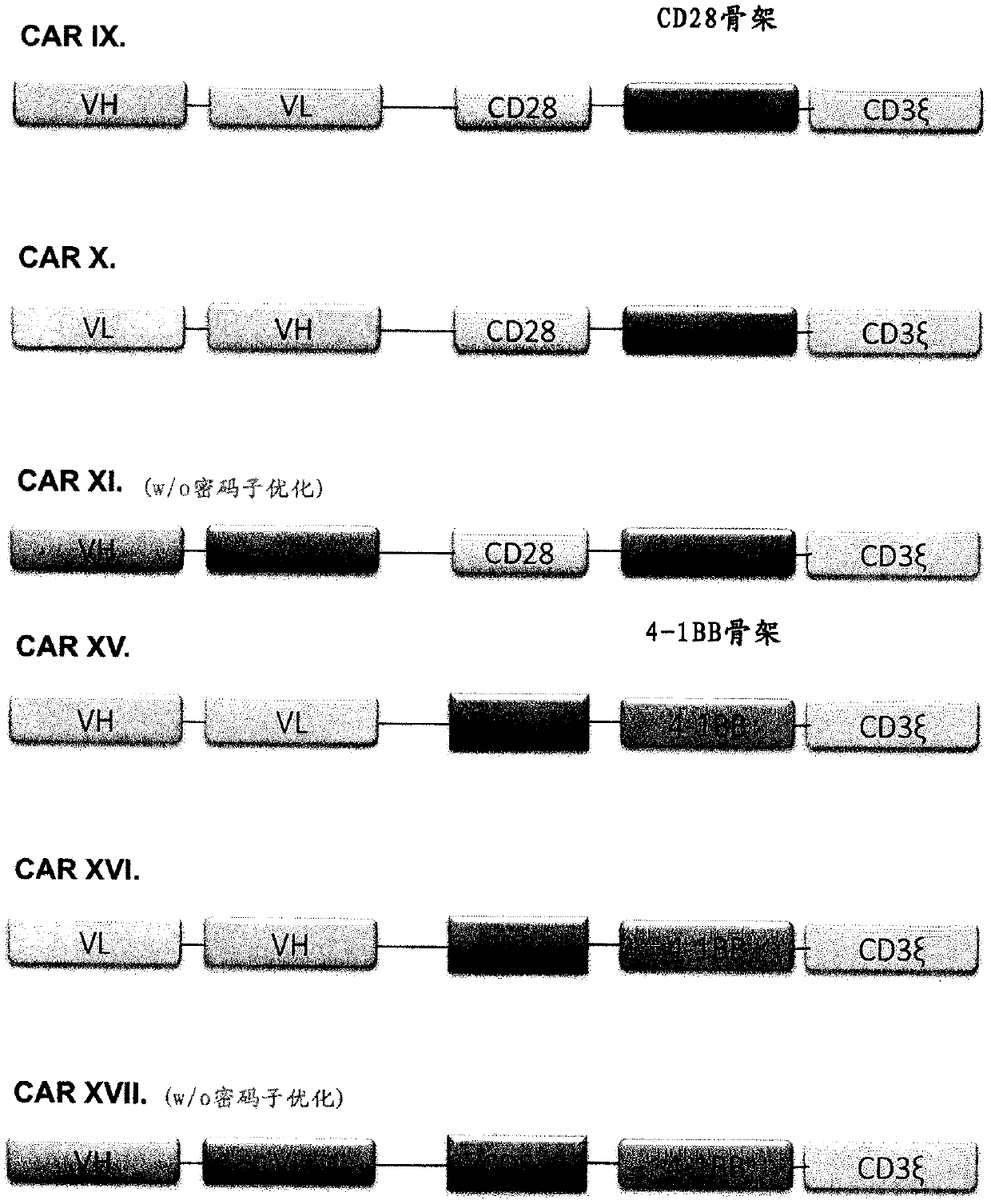
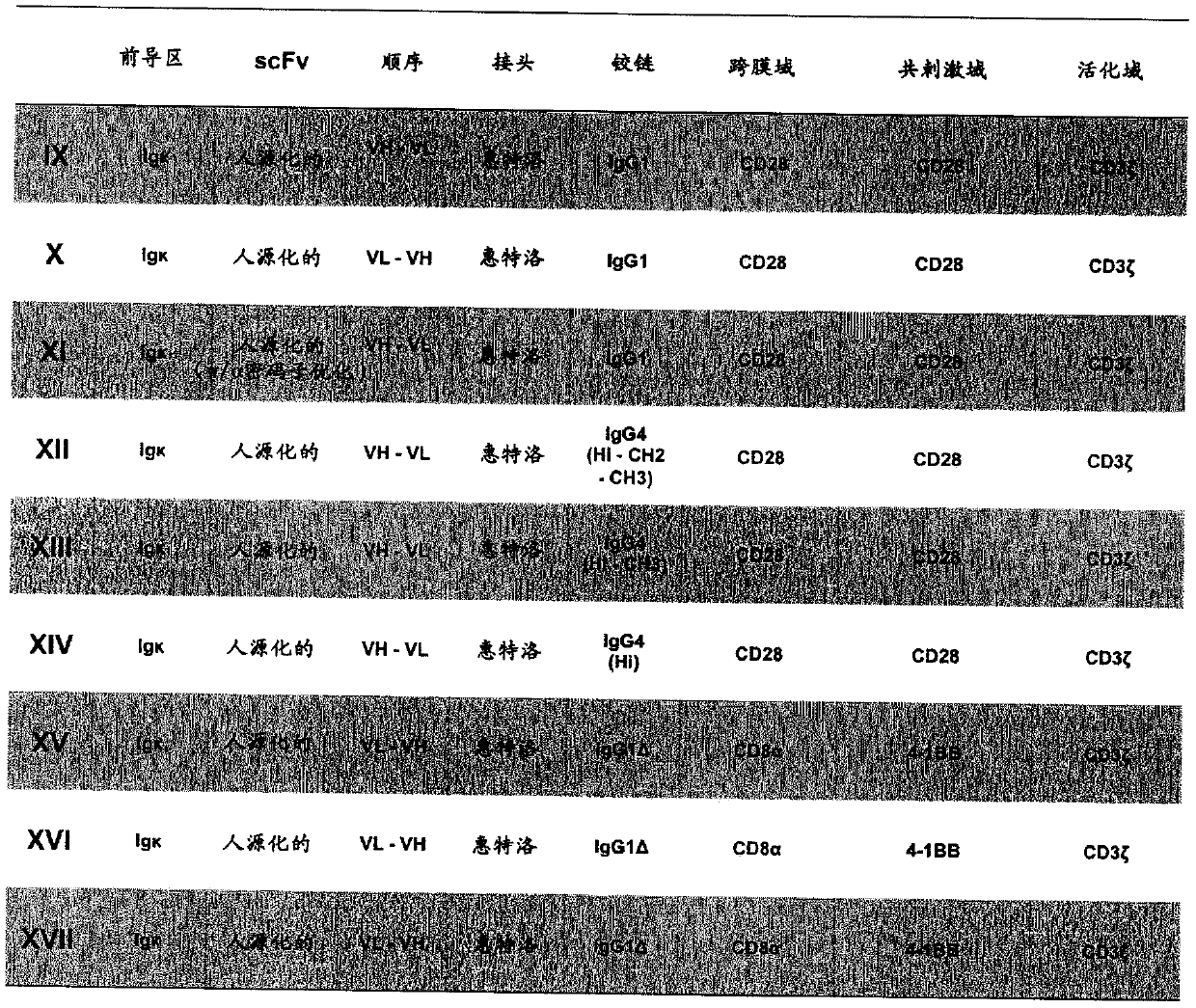
Chimeric antigen receptor and car-t cells that bind bcma
PendingCN109641012AHigh biosecurityNo off-target reactivityAntipyreticAnalgesicsAutoimmune conditionAutoantibody
Owner:MAX DELBRUECK CENT FUER MOLEKULARE MEDIZIN
Human monocolonal antibody with high neutralization activity for Zika virus and application thereof
ActiveCN110172095AFree from attackStrong neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAntigenEscherichia coli
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing memory T cells
InactiveCN109423478ASolve bottlenecksProlong survival timeMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellCentral Memory T-Cell
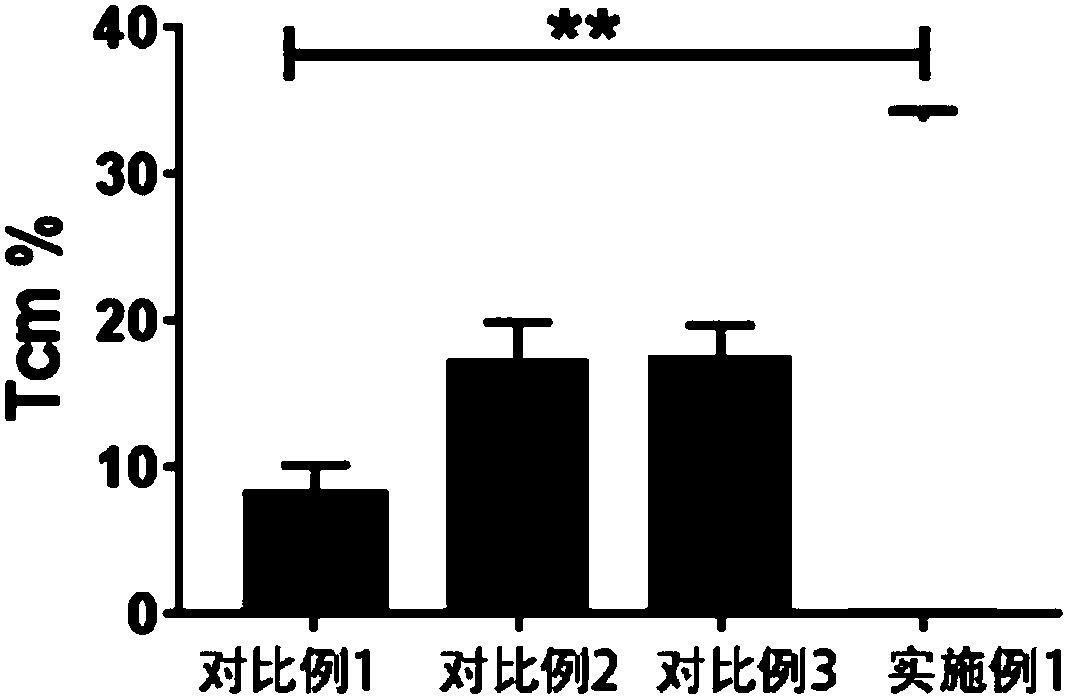
The present invention provides a method for efficiently preparing memory T cells by combining TWS119 and cytokines IL-7 and IL-21. The method includes collecting human peripheral blood; performing density gradient centrifugation to obtain human peripheral blood mononuclear cells; sorting CD8<+>T cells with a magnetic separation sorter; adding the CD8<+>T cells into a medium containing a stimulantCD3 / CD28 conjugated magnetic beads, cytokines IL-7and IL-21 and TWS119; and performing amplification so that a high number of CD8<+>T cells having Tcm and Tscm phenotypes can be obtained in the seventh day.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
IL-6 reorganization monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110655576ASolve the problem of low fusion efficiencySolve instability, there is a risk of antibody gene lossBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsTotal rnaPlasma cell
The invention provides a preparation method of an IL-6 reorganization monoclonal antibody. The preparation method comprises the following steps of performing immunization on a mouse with IL-6, after immunization, taking the spleen of the mouse, and preparing an unicellular suspension; screening memory B cells and pulp cells with a flow cytometry instrument; respectively culturing the obtained cells, adding the obtained culture supernatant in a culture device coated with the IL-6, continuing performing culturing, detecting cell strains secreting a specific antibody, and screening the antibody which can specially recognize antigen protein, and performing cloning; extracting total RNA on the obtained cells strains, performing reverse transcription to obtain cDNA, amplifying the variable regions of a heavy chain and a light chain of the antibody, and performing separate connection to a carrier; and then performing cell transfection, and producing the IL-6 reorganization monoclonal antibody. Through screening once, a large quantity of antibody sequences can be obtained, the gene information of the antibodies can be obtained, and the problems that cells in a hybridoma technique is low infusion rate and the antibody gene is lost, are solved.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
Bispecific antibody for hepatitis B surface protein, and use thereof
ActiveCN105061590AAvoid infectionCombined Application ExcellenceImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHepatitis a+b vaccineHumanized antibody
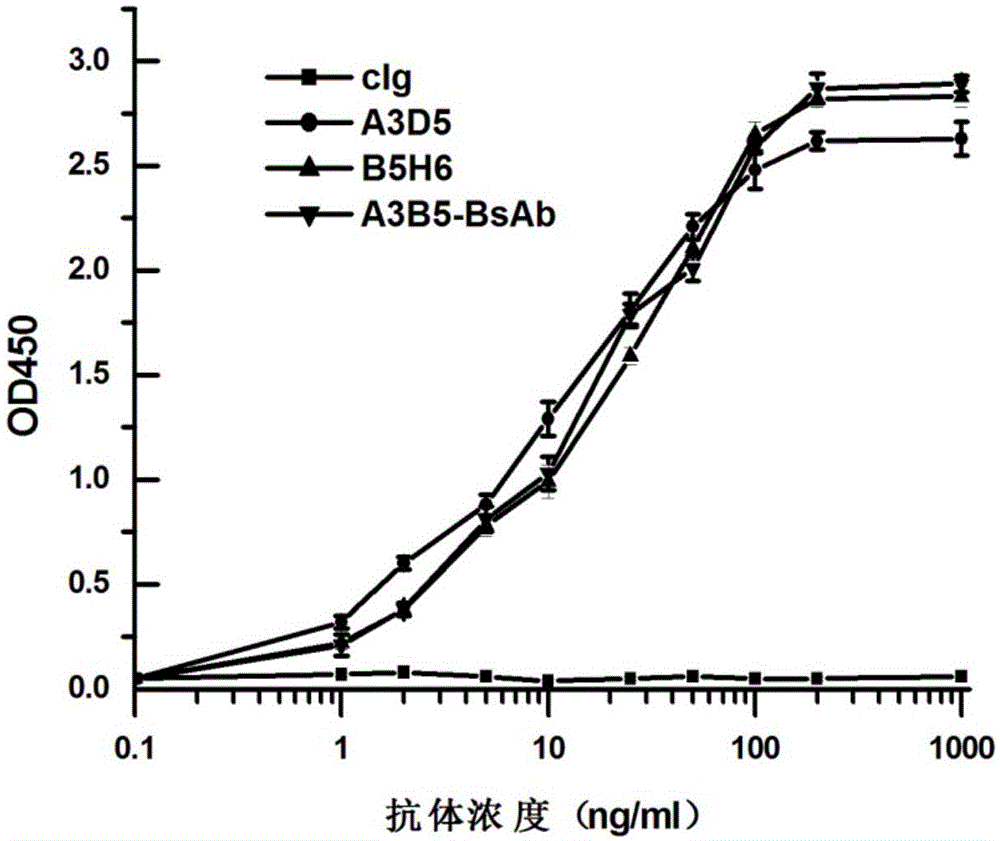
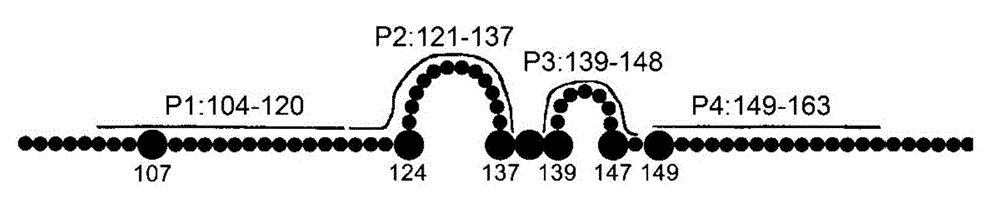
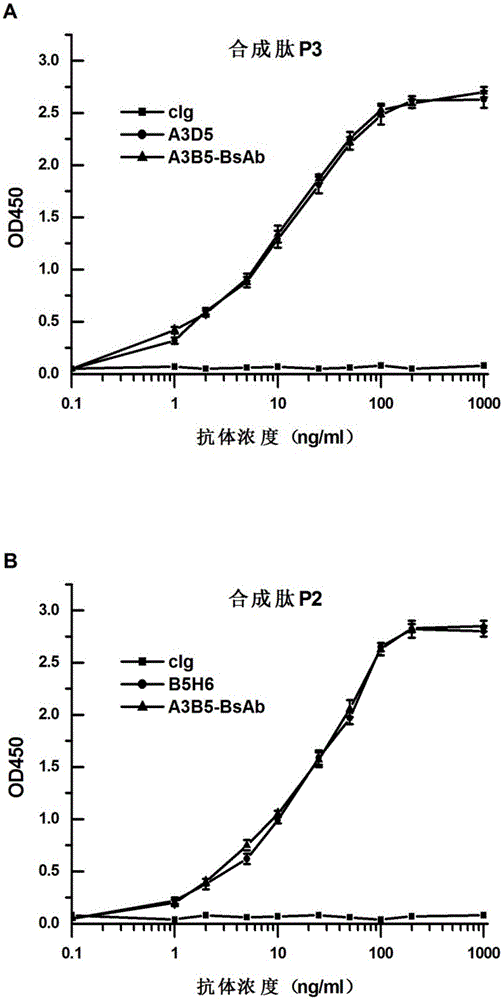
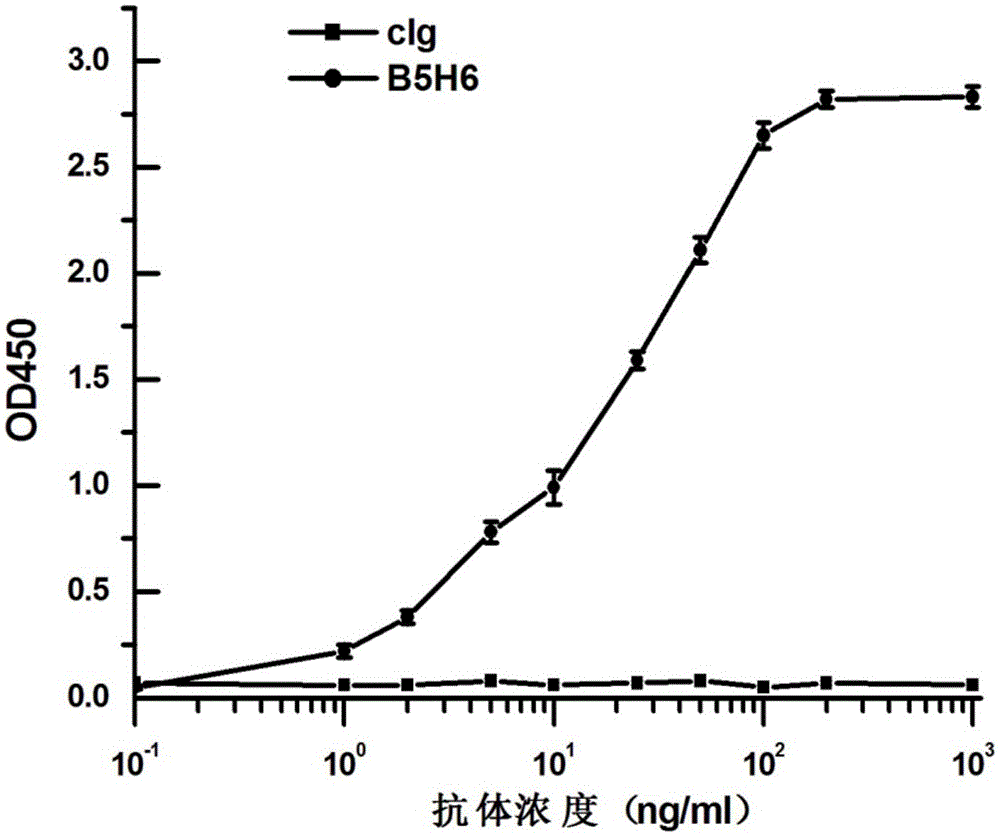
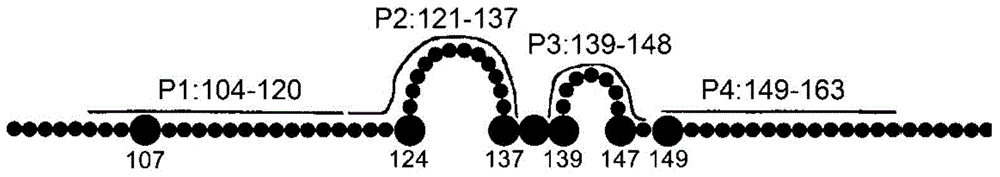
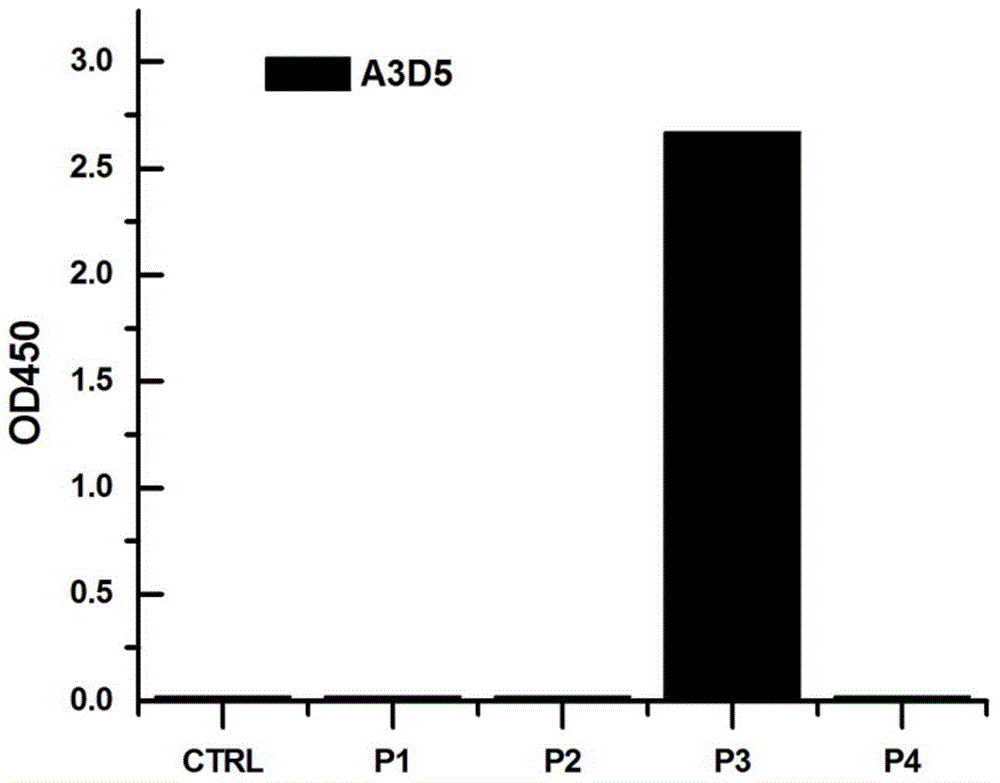
The invention provides a bispecific antibody A3B5-BsAb for a hepatitis B surface protein. The bispecific antibody is formed by combining an antibody A3D5 with an antibody B5H6. The bispecific antibody has better HBV virus neutralization ability and HBsAg release inhibition ability than single use of the antibody A3D5 and the antibody B5H6, and has strong synergistic effects, so the bispecific antibody is likely to prevent HBV infection related hepatitis, hepatic cirrhosis and liver cancer. The bispecific antibody is a completely humanized antibody obtained through cloning HBsAg specific memory B cells in the peripheral blood of hepatitis B vaccine inoculated volunteer, has lower immunogenicity than murine, chimeric and humanized antibodies, and can be used to prepare hepatitis B virus related hepatopathy prevention or treatment drugs or diagnose reagents.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Method for rapidly screening SARS-CoV-2 RBD specific fully humanized neutralizing monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN111925439ARBD-specificHas the effect of blocking virusesImmunoglobulins against virusesFermentationInfected cellViral infection
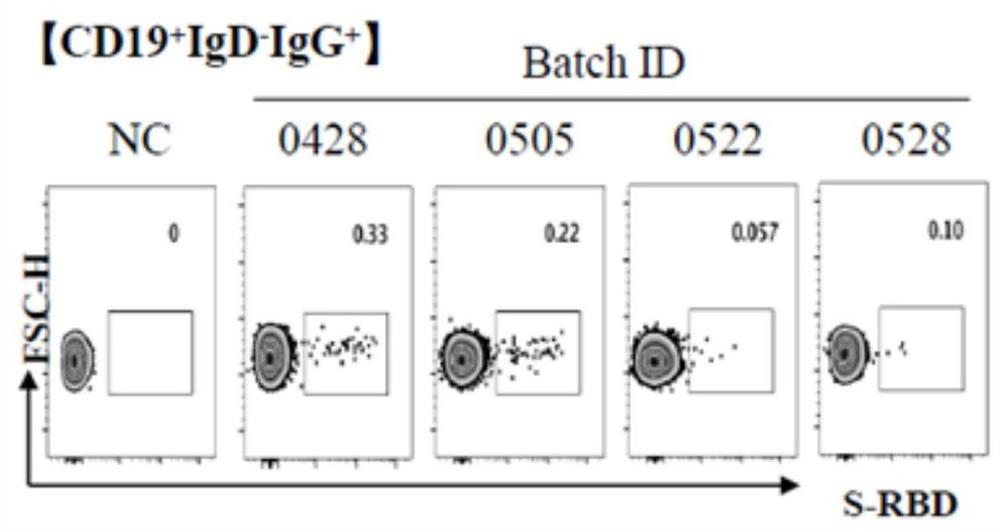
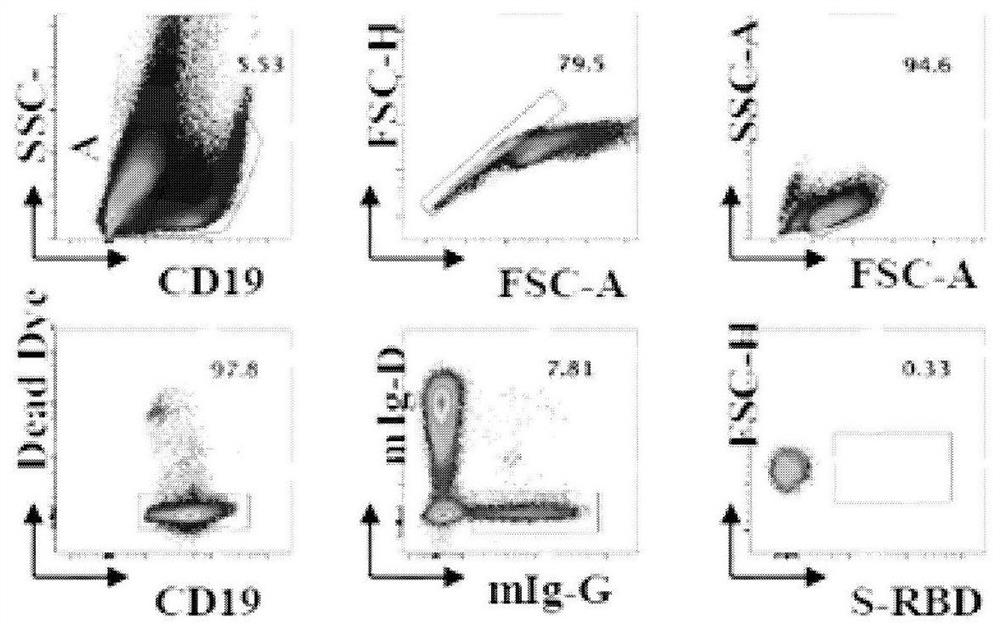
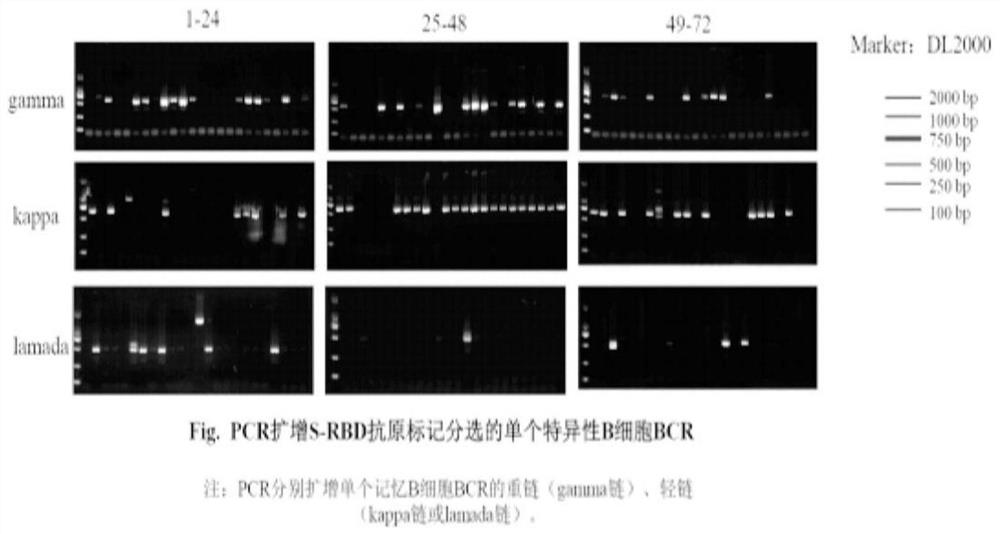
The invention belongs to the technical field of monoclone, and particularly discloses a method for rapidly screening SARS-CoV-2 RBD specific fully-humanized neutralizing monoclonal antibody, which comprises the following steps: S1-S3, collecting peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 rehabilitation patients, sorting RBD specific memory B cells, obtaining antibody variable region cDNA through RT-PCR amplification; S4, amplifying the antibody variable region cDNA obtained in the steps S1-S3 by adopting nested PCR, and constructing an antibody variable region gene expression box; s5, transferring the antibody variable region gene expression cassette obtained in the step S4 into a cell expression antibody, collecting supernate, and screening an RBD specific monoclonal antibody; and S6, detecting the activity of blocking pseudovirus infected cells by using the RBD specific antibody supernatant obtained in S5, detecting the binding capacity of the supernatant for blocking RBD and ACE2 by using ELISA, detecting the neutralizing capacity of the monoclonal antibody by using a dual method, and screening the RBD specific neutralizing monoclonal antibody. According to the invention, the SARS-CoV-2 RBDspecific fully humanized neutralizing monoclonal antibody can be rapidly and efficiently obtained.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Methods for treating infectious diseases and tumors
Disclosed herein are PD-1 antagonists useful for reducing PD-1 expression or activity in a subject. The use of such PD-1 antagonists in combination with antigens from infectious agents or tumors can enhance immune responses specific to infectious agents or tumor cells. Thus, subjects suffering from an infectious disease, such as a persistent infection, can be treated with a PD-1 antagonist. Additionally, subjects with tumors can be treated with PD-1 antagonists. In several embodiments, the subject can be treated by transplanting a therapeutically effective amount of activated T cells capable of recognizing an antigen of interest, and by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a PD-1 antagonist. Also disclosed herein are methods for testing the efficacy of a PD-1 antagonist in a subject administered the PD-1 antagonist. In some embodiments, the methods comprise measuring the proliferation of memory B cells in a sample from a subject administered a PD-1 antagonist.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
SARS-CoV-2 S protein specific antibody or fragment thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN113527472AClear structureHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHeavy chainReceptor
According to the invention, coronavirus spike protein RBD specific memory B cells are separated from PBMC of a rehabilitation person infected by a new coronavirus, amplification is carried out to obtain antibody light and heavy chain variable region sequences, a carrier is connected and introduced, recombinant expression is carried out to obtain a recombinant human monoclonal antibody, a monoclonal antibody which has high affinity with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD, strong blocking force on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD and a host receptor ACEII and strong neutralizing activity on virus infected cells is selected from the monoclonal antibody, further screening is performed the ADE effect of the monoclonal antibody, and finally an anti-SARS-CoV-2S protein specific antibody MW07 which does not generate an ADE phenomenon is obtained.
Owner:深圳市福田区格物智康病原研究所 +1
Methods for screening b cell lymphocytes
Methods are described herein for screening an antibody producing cell within a microfluidic environment. The antibody producing cell may be a B cell lymphocyte, which may be a memory B cell or a plasma cell. An antigen of interest may be brought into proximity with the antibody producing cell and binding of the antigen by an antibody produced by the antibody producing cell may be monitored. Methods of obtaining a sequencing library from an antibody producing cell are also described.
Owner:PHENOMEX INC
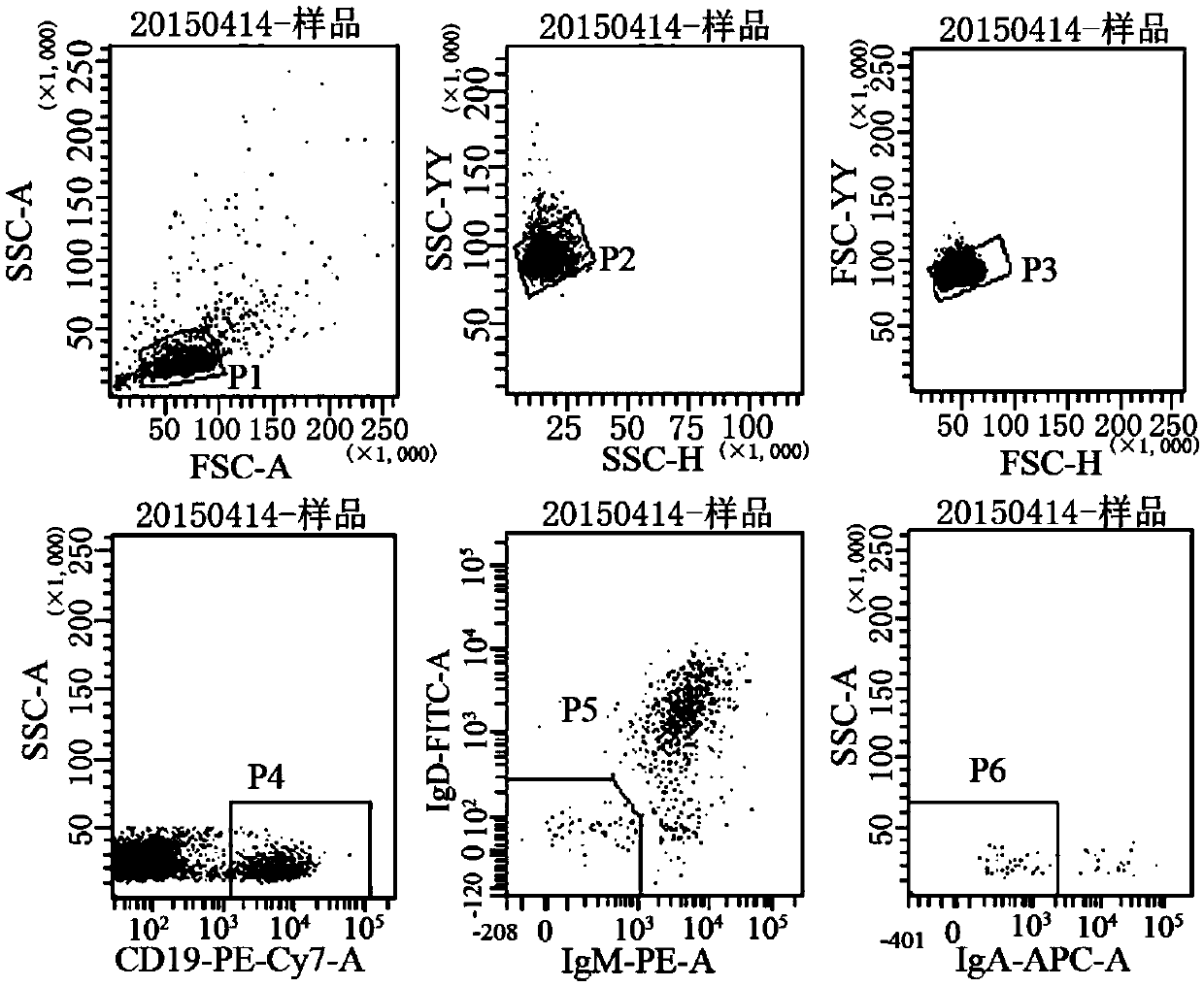
Cultivation method for activating human memory B cells into plasma cells in vitro
InactiveCN106222137AReduce in quantityEasy to operateSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBlood/immune system cellsPlasma cellBiological activation
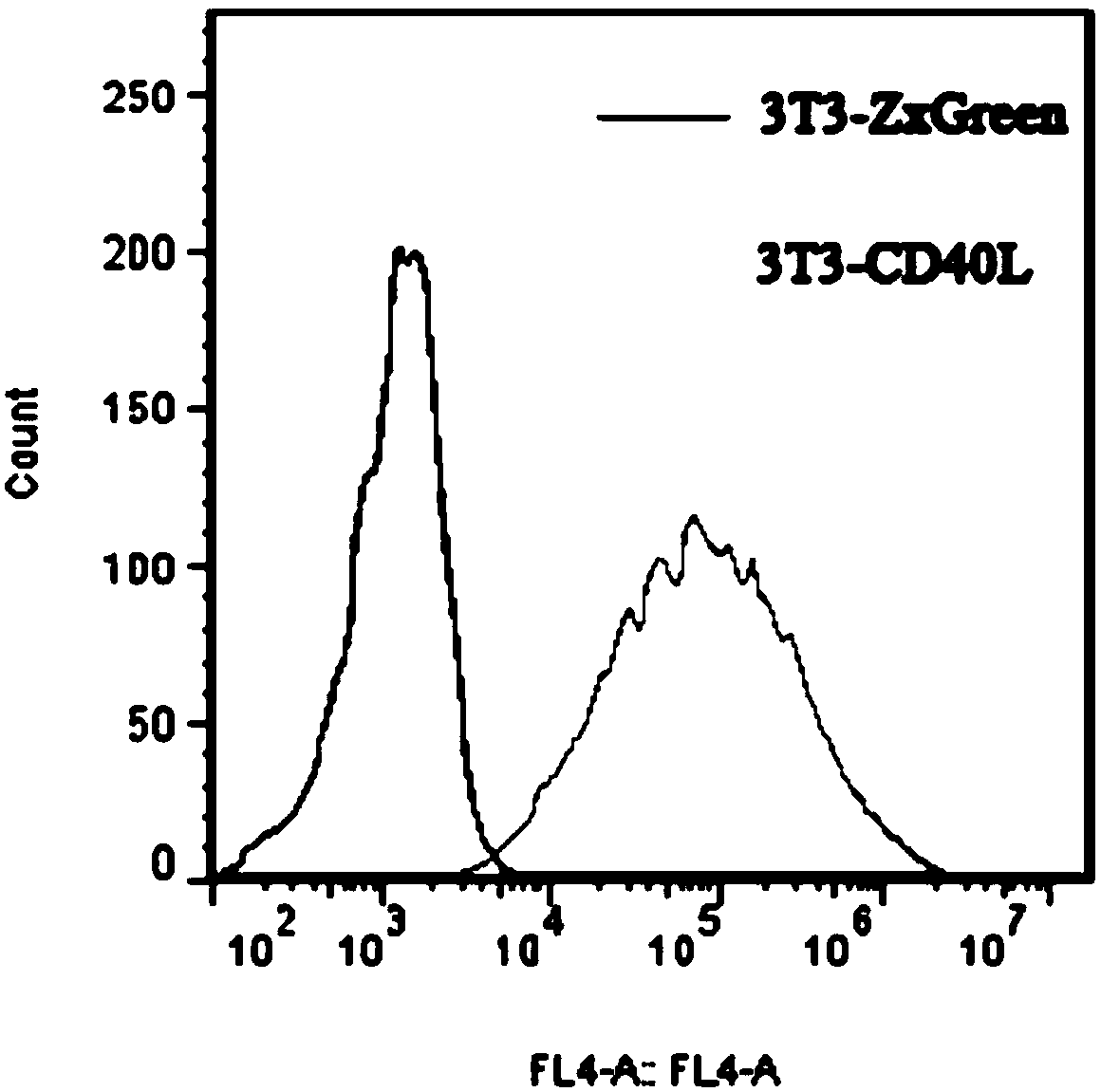
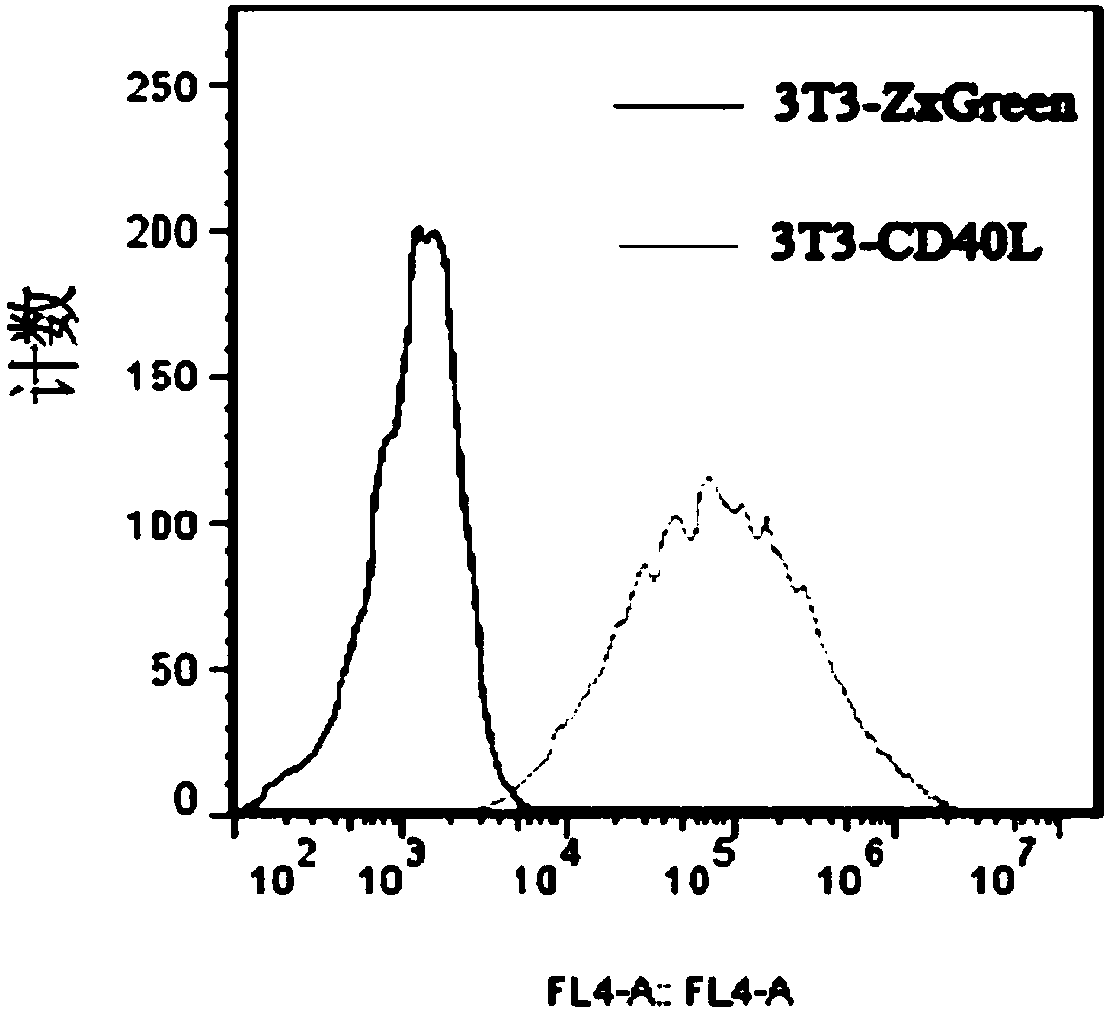
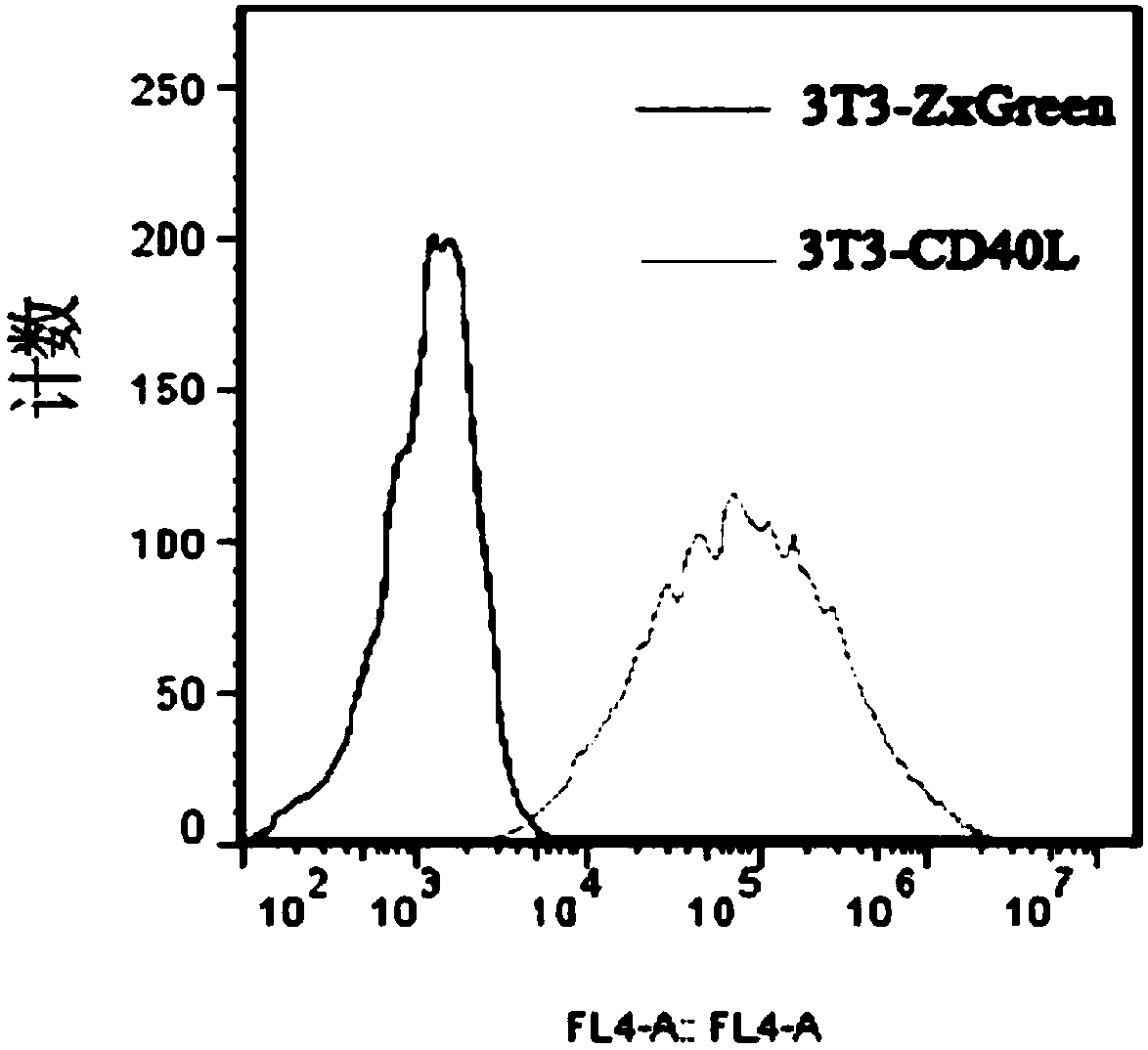
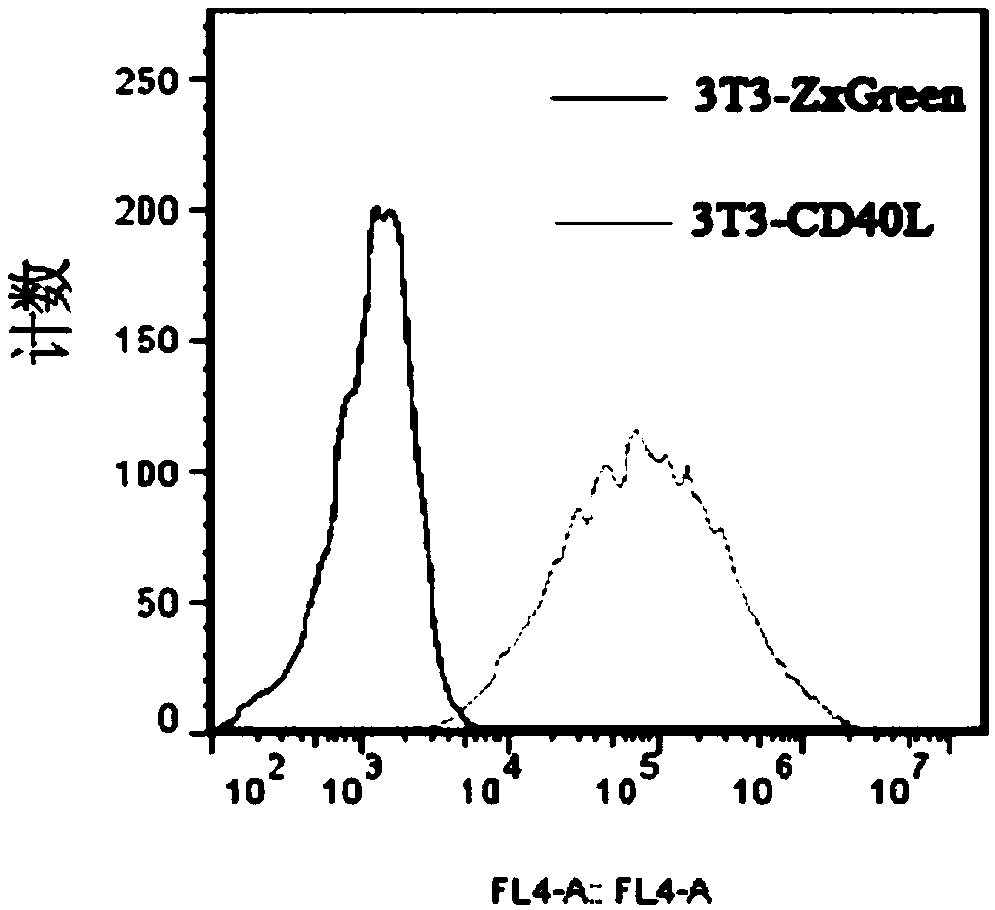
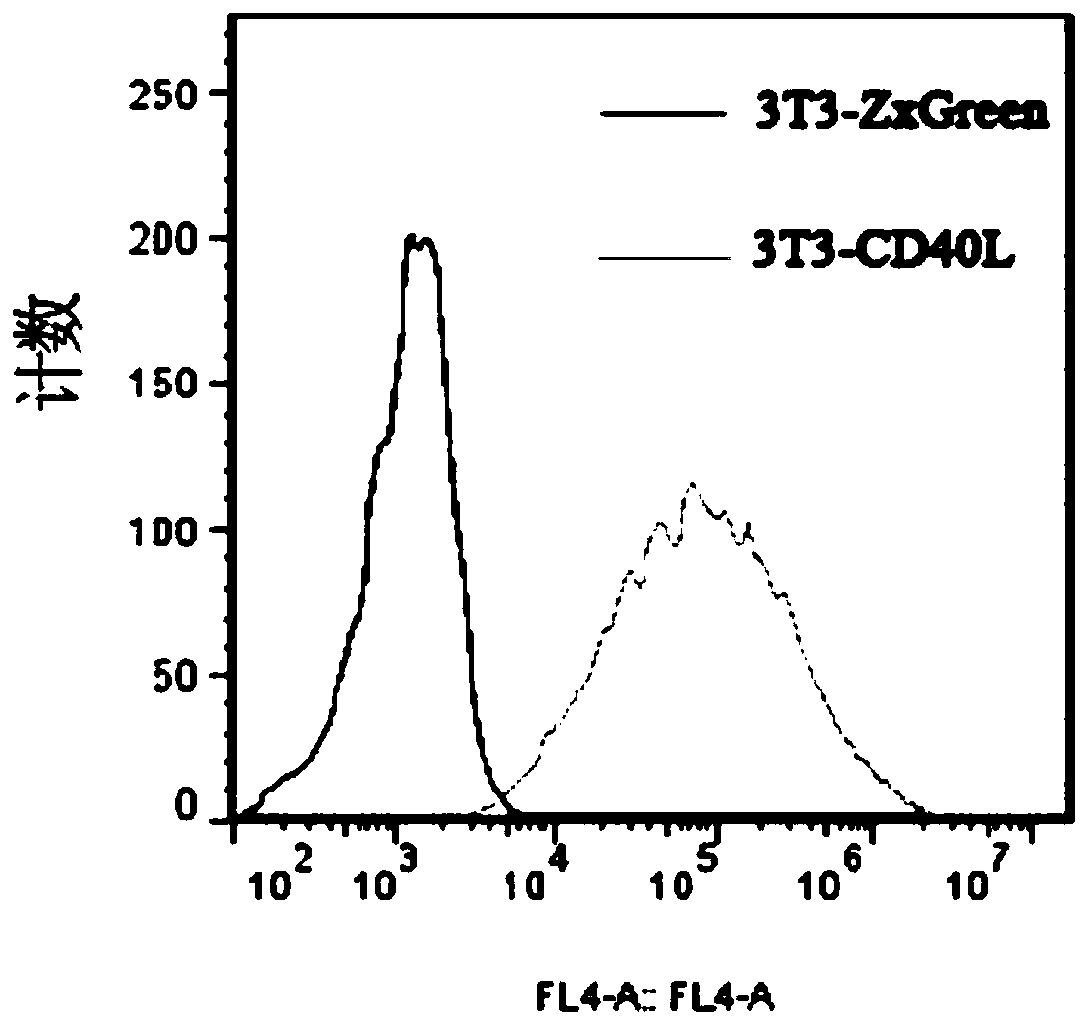
The invention discloses a cultivation method for activating human memory B cells into plasma cells in vitro. According to the method, irradiated 3T3-CD40L cells serve as feeder layer cells, IMDM of 10% FBS serves as basis culture solution, IL-2 and IL-21 serve as growth factors, and the memory B cells are induced in vitro to activate into the plasma cells and secrete antibodies. The cultivation method is simple to operate, low in cost, fewer in needed memory B cells and high in activation efficiency and activation quality.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Modulated Immunodominance Therapy
InactiveUS20140099341A1Substantial therapeutic benefitAlter immunodominance hierarchyAntipyreticAnalgesicsBiological bodyCellular homeostasis
The invention involves generating a T cell response to subdominant antigens and using the cells to therapeutically change the cellular homeostasis and nature of the immune response. In a preferred embodiment, the cells are generated outside of the patient avoiding the influence of the patient's immunologic milieu. By stimulating and growing the T cells from a patient in a tissue culture to one or more subdominant antigens and the transplanting them into the patient, if enough cells are expanded and transplanted, the transplanted cells overwhelm the endogenous dominant T cells in the response to either break or induce immune tolerance or otherwise modify the immune response to the cells or organism expressing that antigen. When the memory cells are established they are then reflective of this new immunodominance hierarchy so that the desired therapeutic effect is long lasting. In effect, the transplantation exogenously generated T cells reactive to the subdominant antigens is recapitulating priming and rebalancing the patient's immune response to target previously subdominant antigens in the cells or organism to produce a therapeutic benefit.
Owner:GENEIUS BIOTECH
Method for preparing monoclonal antibody to respiratory syncytial virus
InactiveCN106676113AReduce usageShorten the timeImmunoglobulins against virusesFermentationCompetent cellRespiratory syncytial virus antibody
The invention provides a method for preparing a monoclonal antibody to a respiratory syncytial virus. According to the method for preparing the monoclonal antibody to the respiratory syncytial virus provided by the invention, memory B cells are separated from peripheral blood of a patient who is infected with and recovered from the respiratory syncytial virus recently to further determine genes of a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region to express the antibody; murine typhia competent cell VNP20009 is utilized to directly transfect a 293T cell and enable expression of the monoclonal antibody to the respiratory syncytial virus in vitro; neutralization capacity and killing competence of the monoclonal antibody to the respiratory syncytial virus is evaluated after appraisal, so as to screen high-efficiency and scale production-available monoclonal antibodies to the respiratory syncytial virus. According to the method for preparing the monoclonal antibody to the respiratory syncytial virus provided by the invention, as the murine typhia competent cell VNP20009 is utilized to directly transfect the 293T cell, compared with the conventional methods, not only time is saved, but also the application a lot of transfection reagent can be avoided. As transfection of exogenous plasmids to an expression system is a key link of in-vitro expression of the monoclonal antibody, the invention provides a strong support to industrialized application of the technology.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
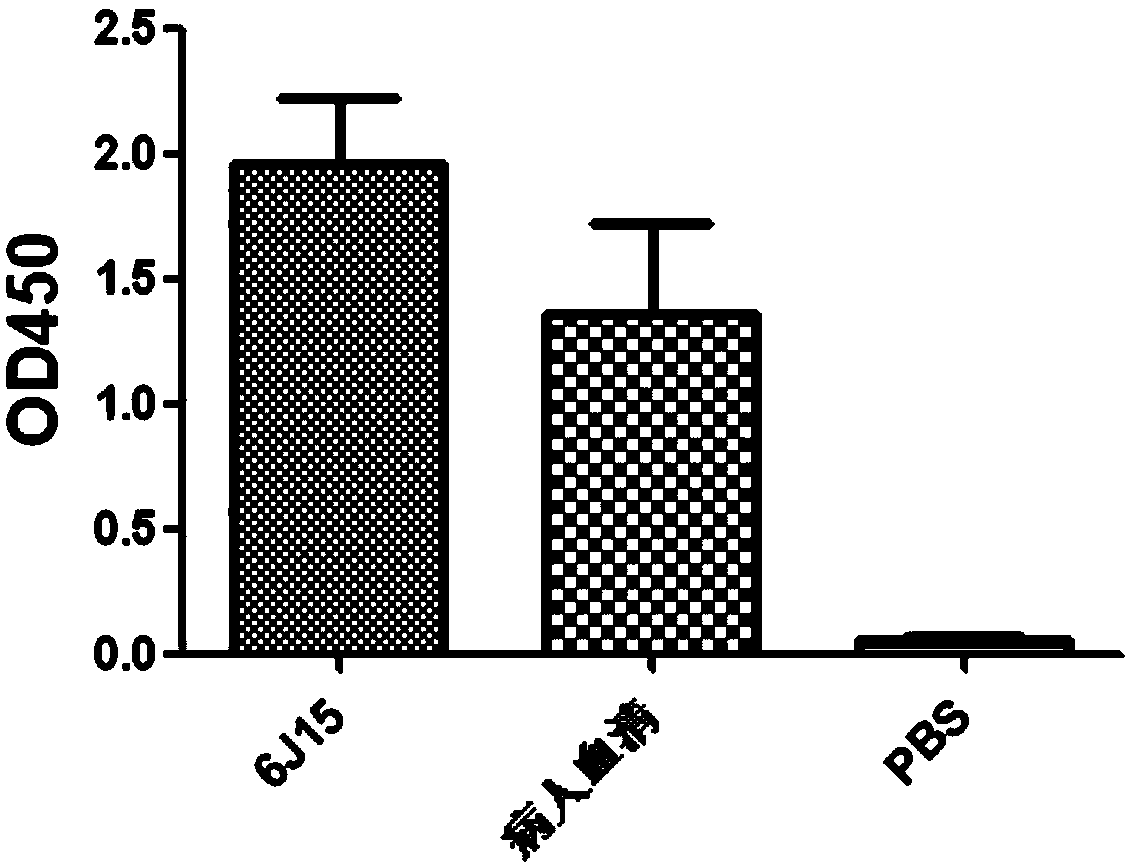
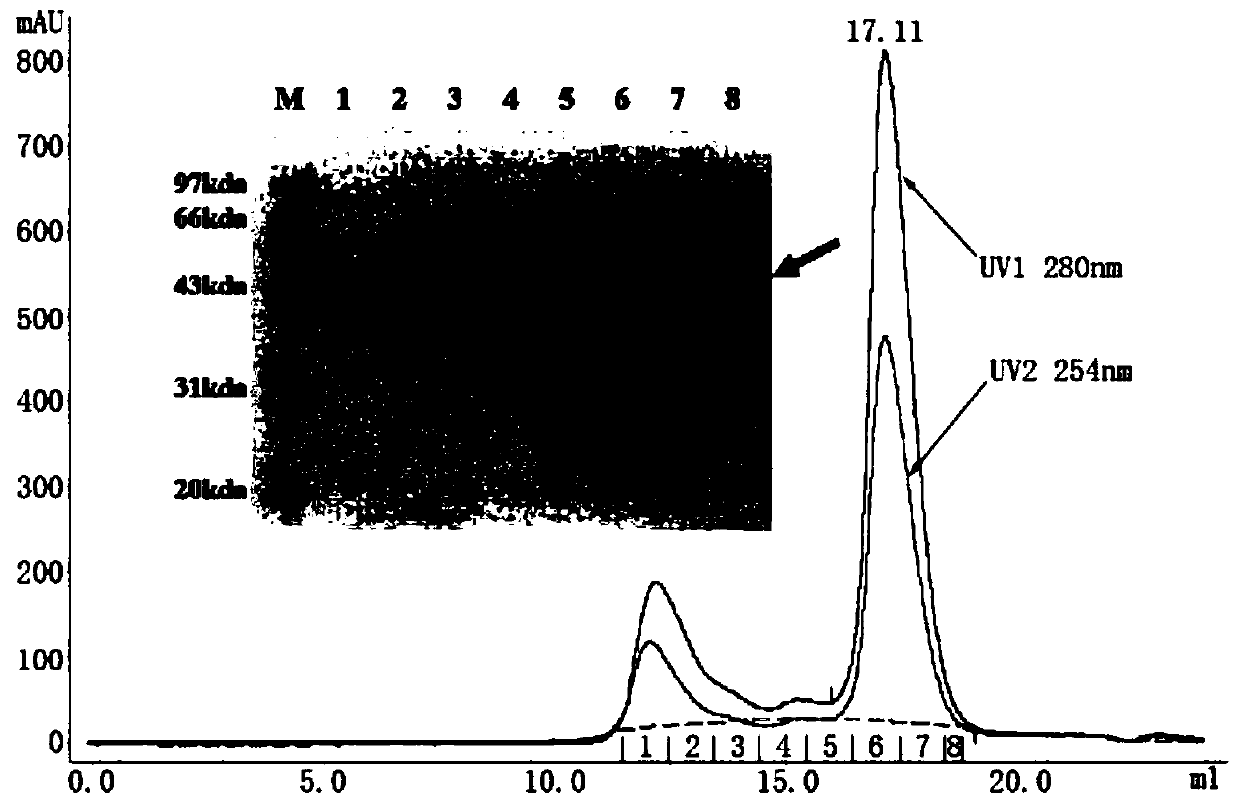
Anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 6J15 and preparation method therefor and application of anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 6J15
ActiveCN111434681AGood neutralizing activityGood biocompatibilityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHemagglutininAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to an anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 6J15 and a preparation method therefor and application of the anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 6J15. The whole-human monoclonal antibody 6J15 is quickly screened by utilizing a memory B cell polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, and does not include any murine component. The antibody disclosed by the invention can bebound to hemagglutinin HA of an H7N9 virus in a targeted manner, and has significant neutralizing activity of anti-H7N9 virus infection; and the antibody disclosed by the invention does not have toxicand side effects of anti-mouse anti-antibodies and the like, has better biocompatibility, and is more suitable and has more potential to become a macromolecular drug for treatment of influenza viruses.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rift valley fever virus humanized monoclonal antibodies and application thereof
ActiveCN109734800AHigh activityEffective treatmentImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAntigenBaculovirus expression
The invention discloses rift valley fever virus humanized monoclonal antibodies and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of medicine. According to the antibodies, RVFV glycoproteinsGn and Gc expressed by baculovirus are adopted as antigens, memory B cells which can be combined with the RVFV glycoproteins Gn and Gc are screened from PBMCs of a patient suffering from rift valley fever, and through experiments such as single B cell sequencing, in-vitro neutralization and in-vivo protection, eight Gn humanized monoclonal antibodies capable of efficiently neutralizing RVFV infection and one Gc humanized monoclonal antibody are identified. The humanized monoclonal antibodies have very high in-vitro neutralization activity (IC50 can be as low as 1.93 + / - 0.6 pM and reaches a pMlevel), can effectively treat mice infected with RVFV, prevents the mice from being infected with RVFV, and has an extremely high application value on clinical treatment and prevention of the infection of RVFV.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
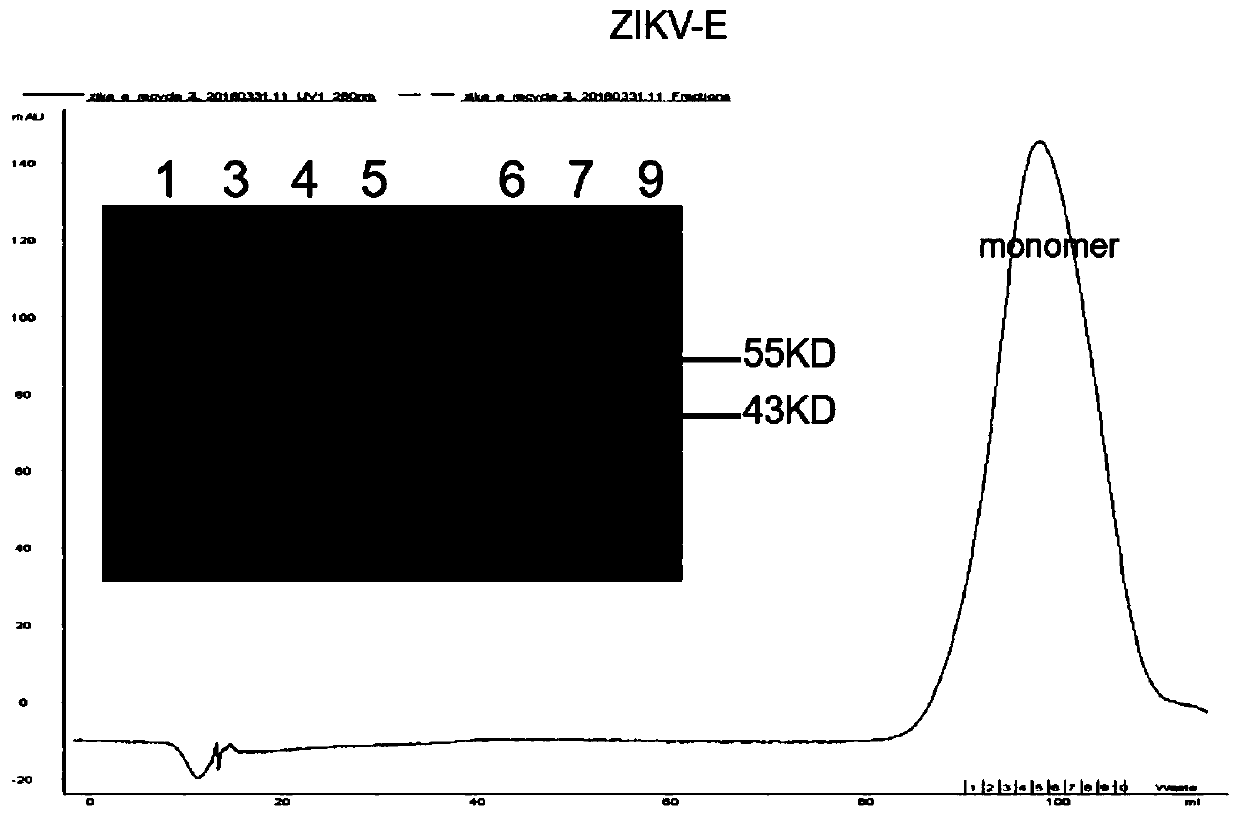
Specific Zika virus neutralizing antibodies and application thereof
ActiveCN110066333AFree from attackStrong neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsEscherichia coliAntigen
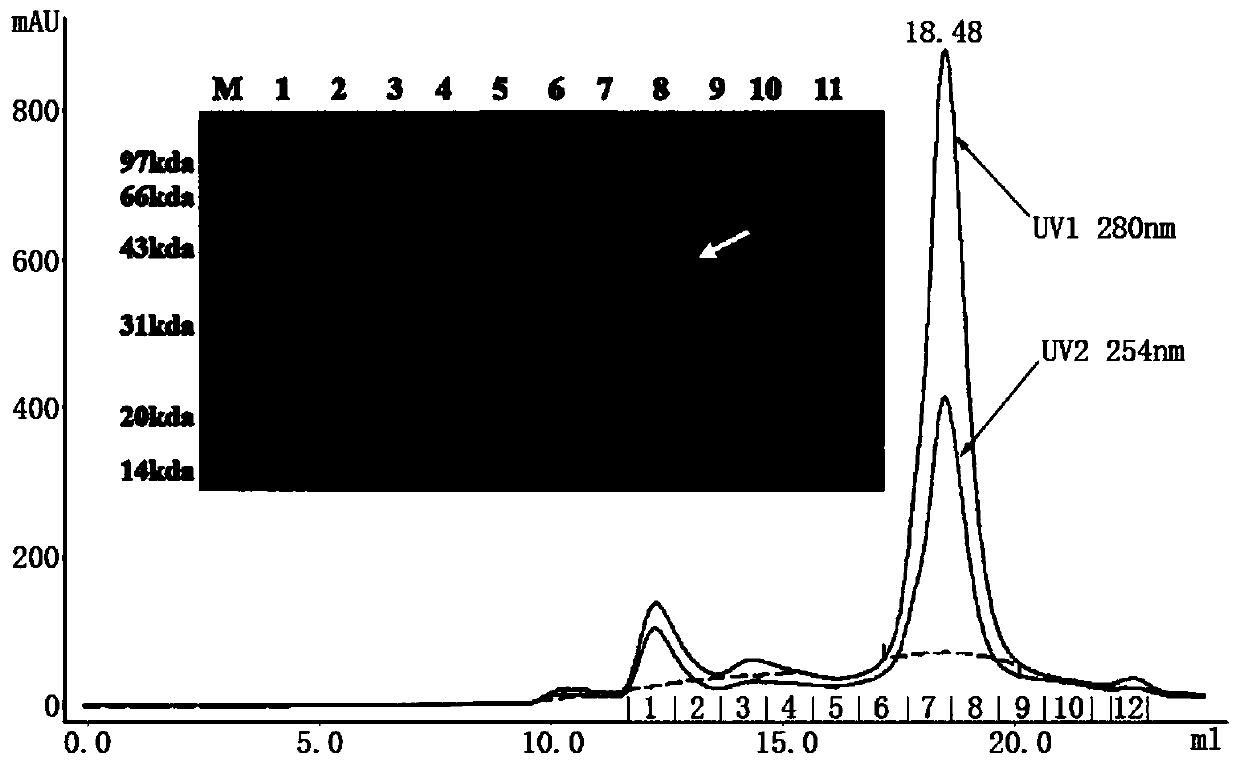
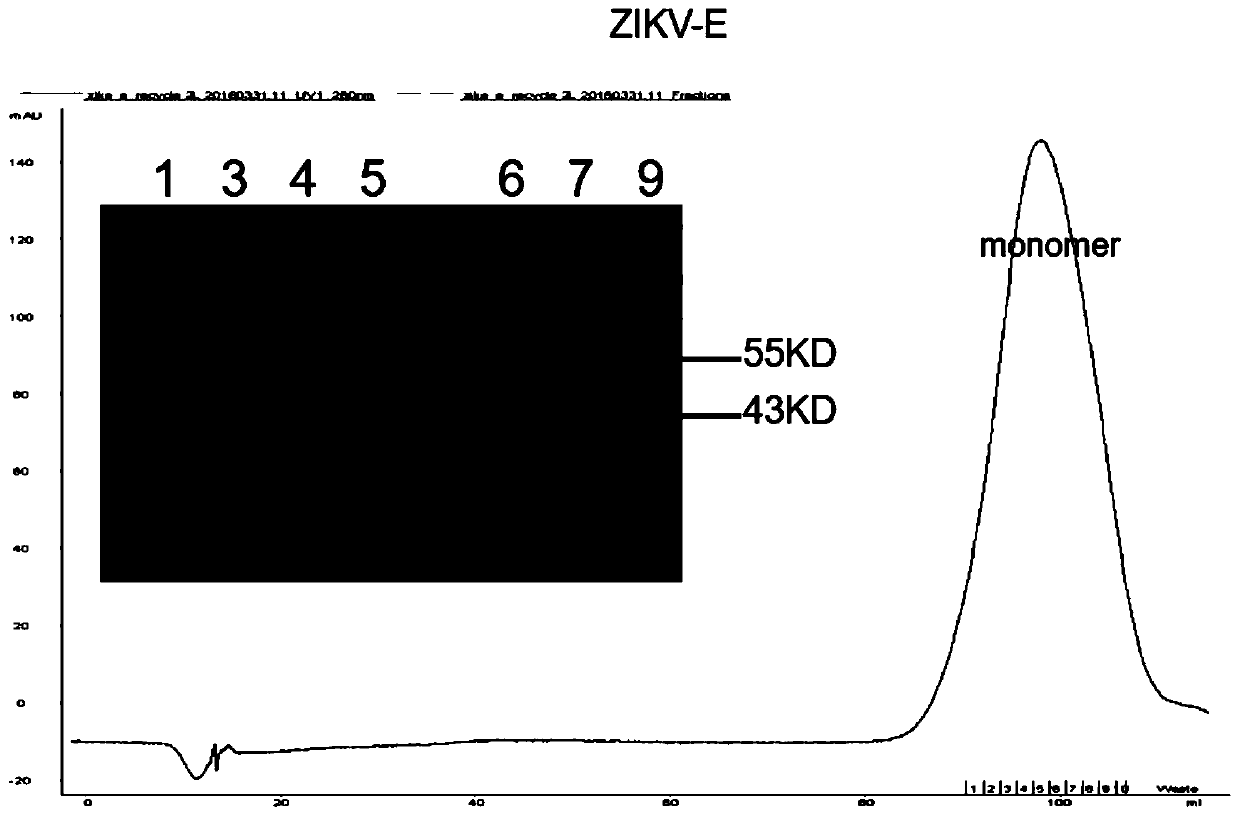
The invention discloses specific Zika virus neutralizing antibodies and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. Zika E protein expressed by colibacillus serves as an antigen, through fluorescence-activated cell sorting, memory B cells capable of being specifically bound with the Zika E protein are screened in PBMCs of a Zika patient in the rehabilitation stage, the screened single B cells are subjected to a RT-PCR, the sequence and segments of the variable region of the antibody are obtained, and the variable region and the constant region are connected in an expression vector. After mammalian cell expression and purification, a series of function detection is conducted, such as the binding force of the ZIKE-E protein, the in-vitro neutralizing effect and the in-vivo protection capacity, and the three human monoclonal antibodies capable of completely protecting Zika virus infection are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
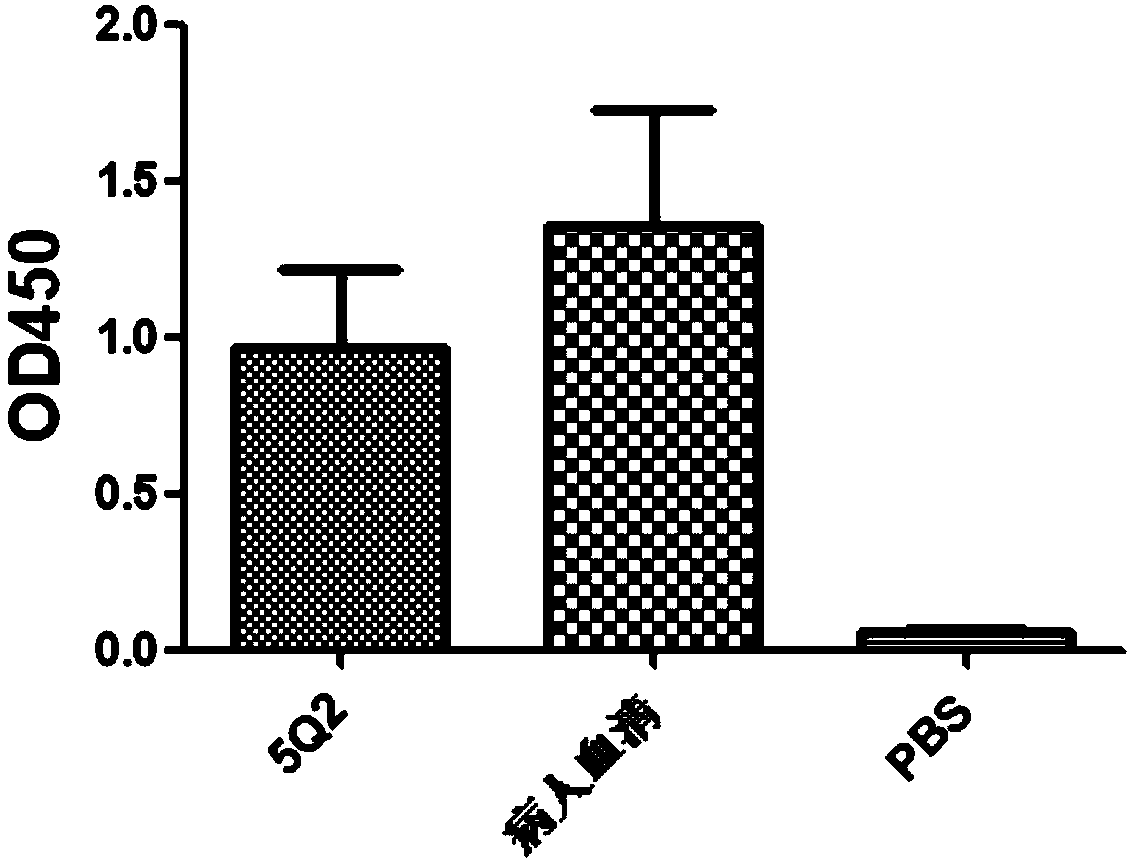
Anti-H7N9 fully-humanized monoclonal antibody 5Q2 as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111434684AGood neutralizing activityGood biocompatibilityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHemagglutininAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to an anti-H7N9 fully humanized monoclonal antibody 5Q2 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The fully humanized monoclonal antibody 5Q2 is rapidly screened by using a memory B cell PCR method, and does not contain any murine components. The antibody disclosed by the invention can be combined with hemagglutinin HA of an H7N9 virus in a targeted manner, andhas remarkable neutralizing activity for resisting H7N9 virus infection; the antibody does not have toxic or side effects such as anti-mouse antibody and the like, has better biocompatibility, and ismore suitable and more potential to become a macromolecular drug of treatment flu virus.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Peripheral blood memory T cell culture method
ActiveCN110093315AEfficient amplificationRaise the ratioBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsAntigenCytokine
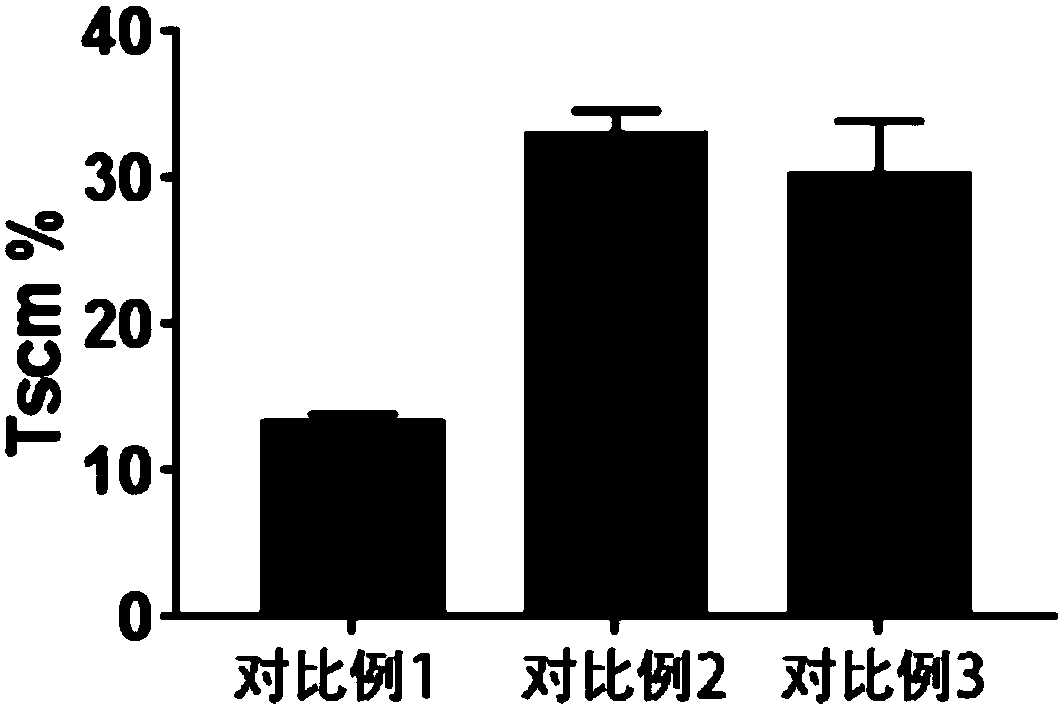
The invention relates to a peripheral blood memory T cell culture method. The method comprises: a) magnetically separating the PBMC isolated from the peripheral blood to obtain CD8<+> T cells; and inoculating the CD8<+> T cells in a culture container coated with a CD3 antibody and a CD28 antibody for culture; wherein a culture system contains autologous plasma, and the cytokine mainly includes IFN-gamma and IL-2; b) changing liquid for amplification culture, wherein a novel culture system contains autologous plasma and the cytokines mainly include IL-2, IL-1a, IL-7, and IL-15; and c) co-culturing the expanded T cells with DC cells; wherein the DC cells are previously co-cultured with an autologous tumor antigen. The method can effectively amplify memory T cells in vitro and effectively increase the proportion of active memory T cells.
Owner:新疆西部赛澳生物科技有限责任公司
Preparation method and application of completely humanized monoclonal antibody aiming at hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface protein
InactiveCN105017415AAvoid infectionBlock processImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHumanized antibodyA hepatitis b vaccine
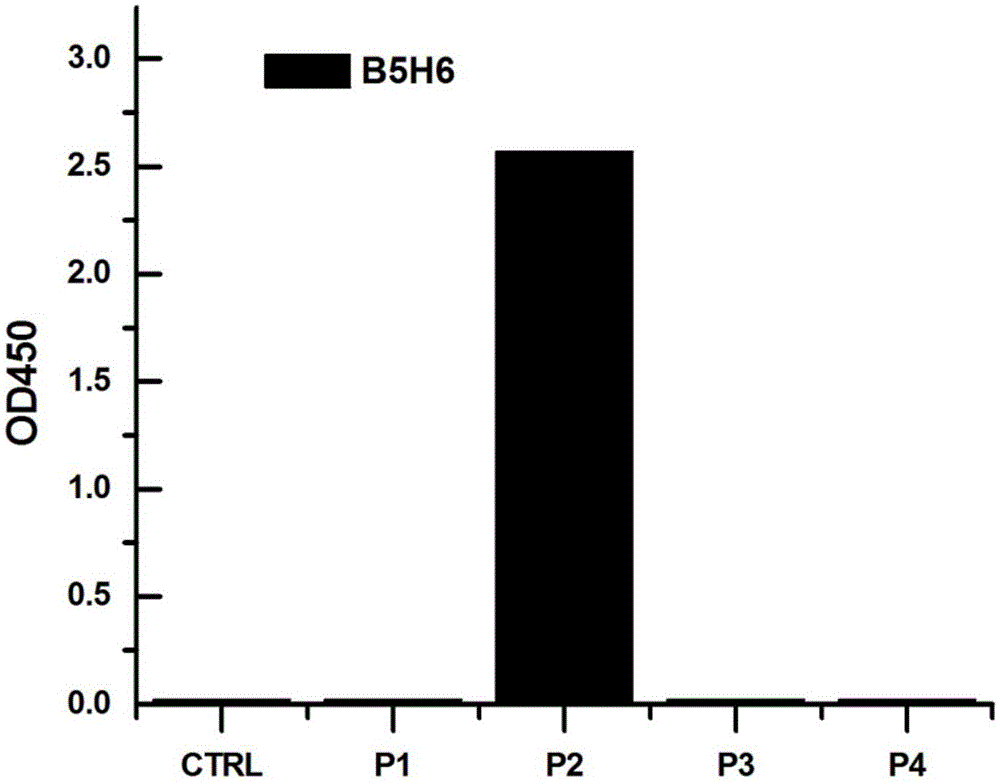
The invention provides a completely humanized monoclonal antibody B5H6 aiming at hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface protein and a gene for encoding the antibody. An experiment shows that the antibody B5H6 can be specifically combined with HBsAg protein, has relatively good HBV neutralization activity and then can resist the progresses of HBV infection related hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and liver cancers. Meanwhile, because the antibody is a completely humanized monoclonal antibody cloned from memory B cells with specific HBsAg in peripheral blood of a volunteer vaccinated with a hepatitis B vaccine, the antibody has immunogenicity lower than that of murine, chimeric and humanized antibodies, and can be used for preparing medicaments or diagnostic reagents for preventing or treating hepatitis B virus related hepatic diseases.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
High-affinity human monoclonal antibody against yellow fever virus and application thereof
ActiveCN110343174AFree from attackBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesEscherichia coliAntigen
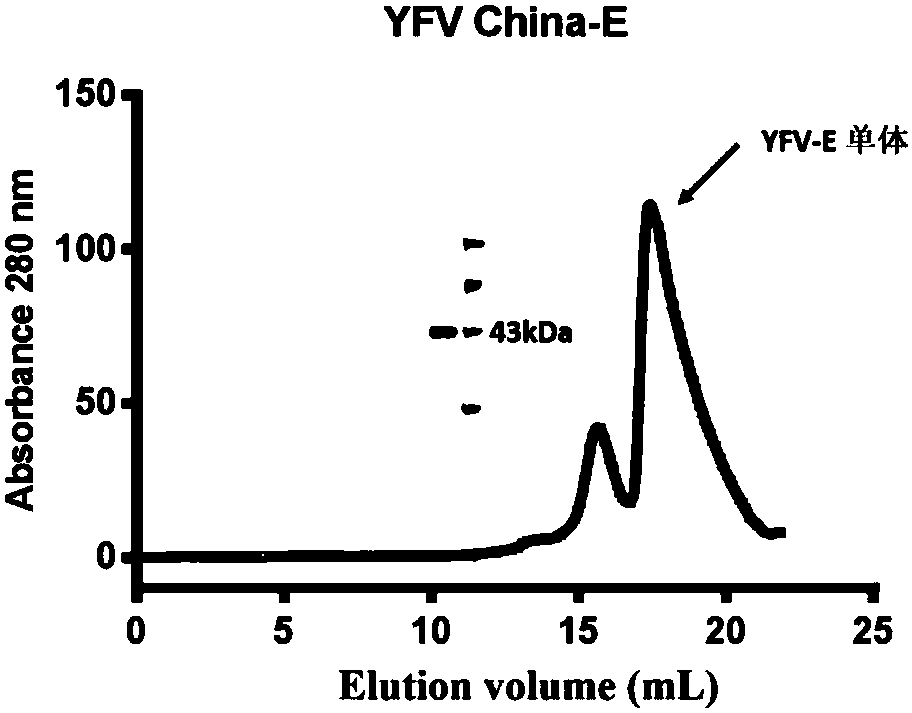
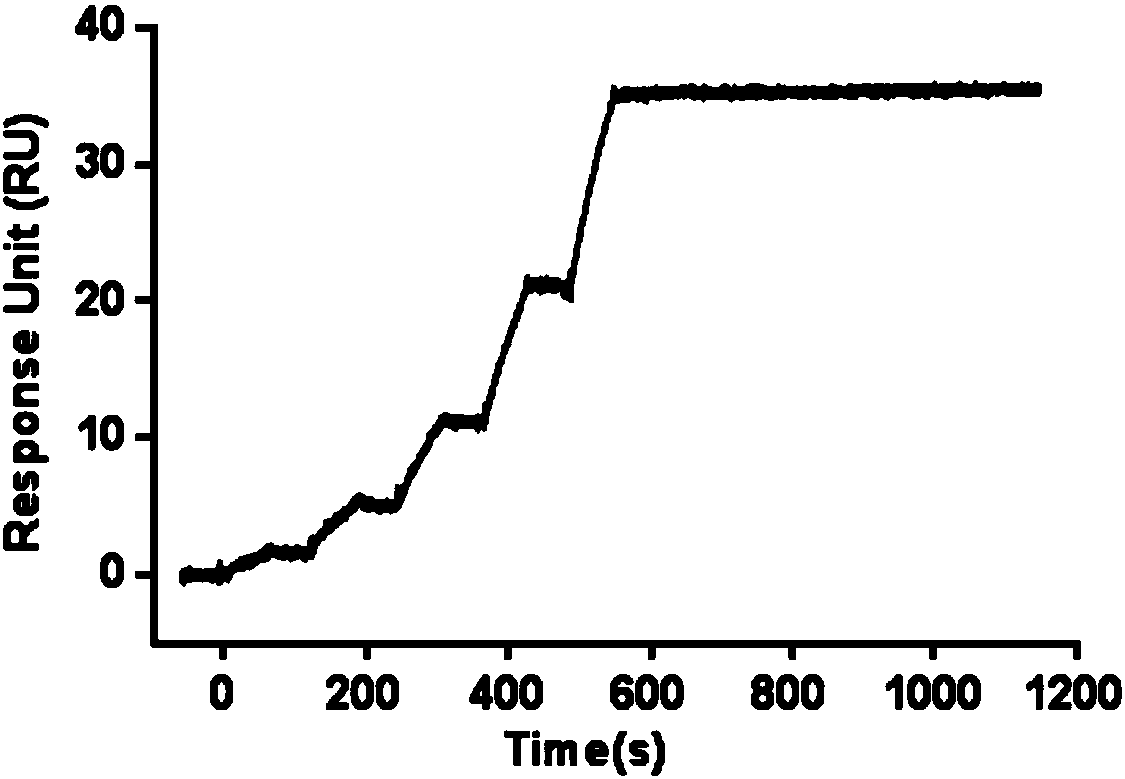
The invention discloses a high-affinity human monoclonal antibody against yellow fever virus and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The high-affinity human monoclonal antibody against yellow fever virus is prepared by the following steps: taking E protein of yellow fever virus expressed in Escherichia coli as an antigen; screening memory B cells which can specifically bind to the E protein of yellow fever virus from PBMCs of a convalescent patient by performing flow sorting, thereby further obtaining variable-region fragments of an antibody; connecting the variable-region fragments of the antibody with a constant region to an expression vector; carrying out expression in mammalian cells, and carrying out purification; and then, carrying out a series of function tests, thereby obtaining 1 strain of the high-affinity human monoclonal antibody against yellow fever virus. The affinity between the antibody and the antigen is 1.49pm; moreover, the antibodyhas very strong yellow fever virus neutralization activity and IC50 at 4ng / ml. In addition, the antibody is capable of completely protecting mice from yellow fever virus at lethal dose. Thus, the high-affinity human monoclonal antibody against yellow fever virus has application values in clinical treatment and prevention of yellow fever virus.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-hepatitis B virus surface antigen completely humanized human antibody and use thereof
InactiveCN105061591ALow immunogenicityAvoid infectionImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHumanized antibodyFhit gene
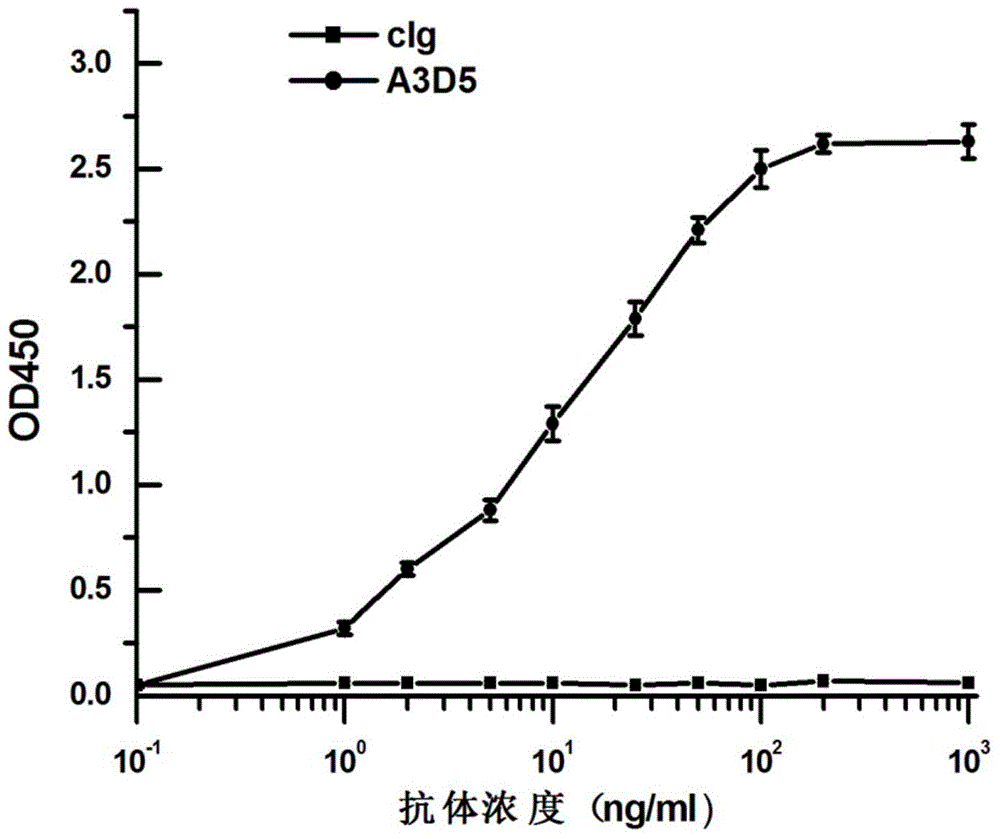
The invention provides an anti-hepatitis B virus surface antigen completely humanized human antibody A3D5 and a gene for encoding the antibody. Experiments show that the antibody A3D5 can specifically bind to an HBsAg protein, and has good HBV neutralization activity in order to possibly prevent HBV infection related hepatitis, hepatic cirrhosis and liver cancer. The antibody is a completely humanized human antibody obtained through cloning HBsAg specific memory B cells in the peripheral blood of hepatitis B vaccine inoculated volunteer, has lower immunogenicity than murine, chimeric and humanized antibodies, and can be used to prepare hepatitis B virus related hepatopathy prevention or treatment drugs or diagnose reagents.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
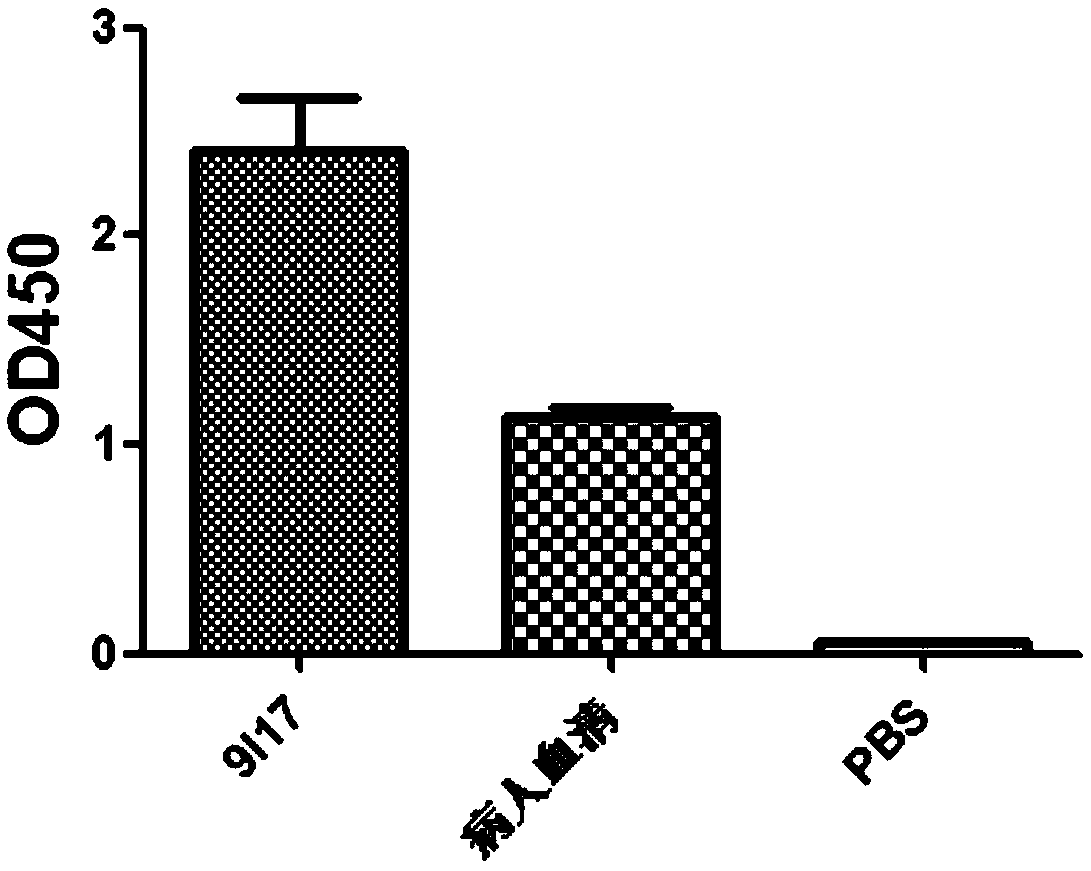
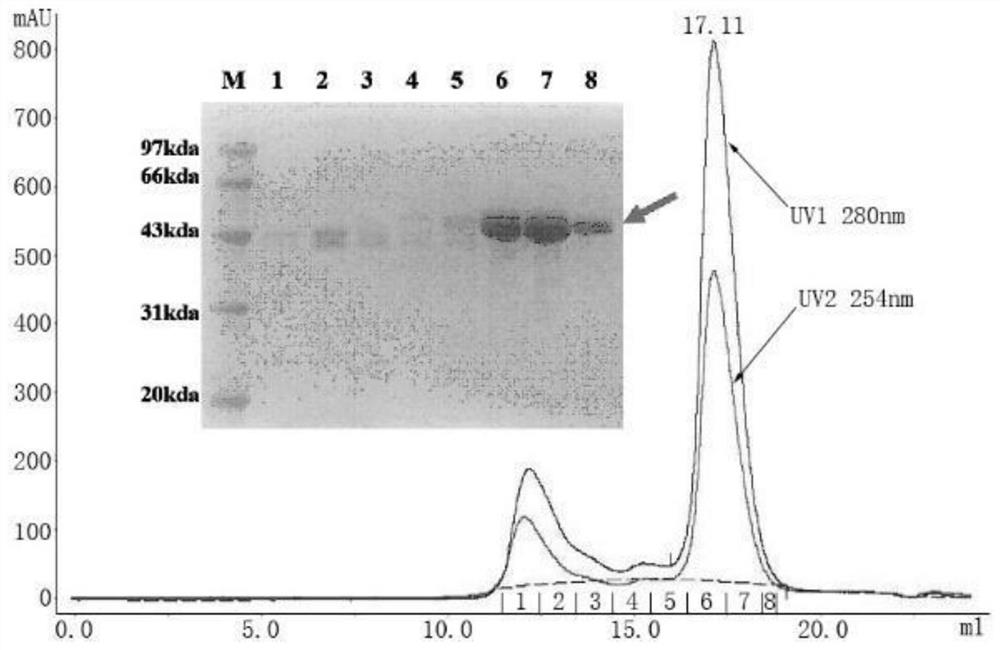
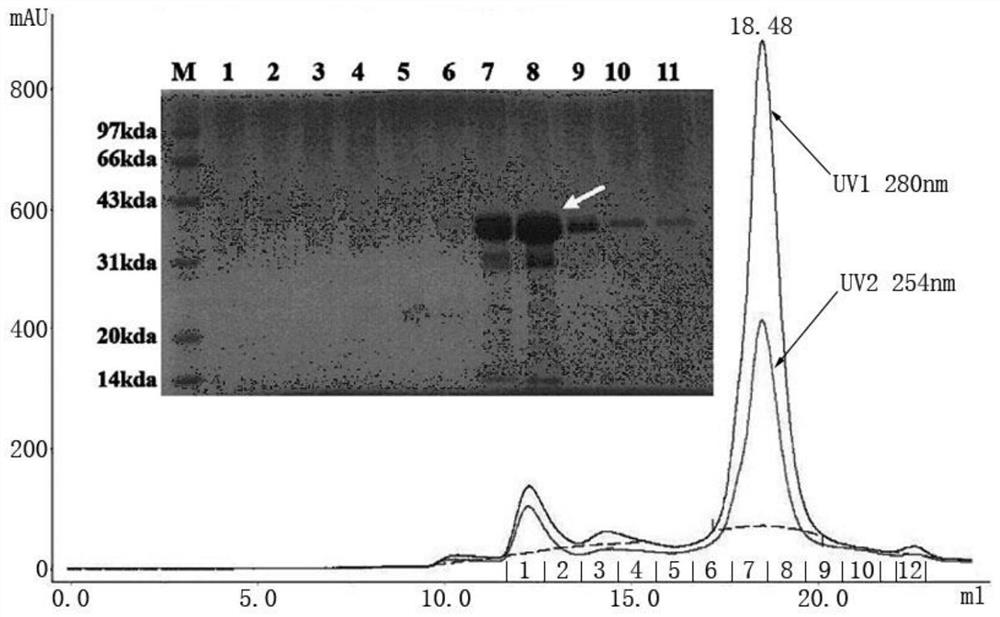
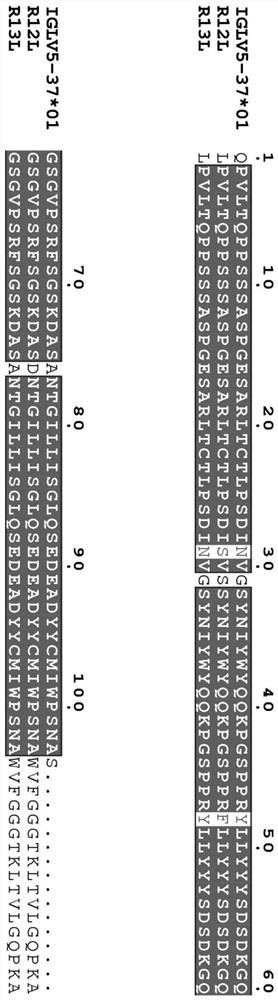
Anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 9I17 and a preparation method therefor and application of the anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 9I17
ActiveCN111434685AGood neutralizing activityGood biocompatibilityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHemagglutininAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to an anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 9I17 and a preparation method therefor and application of the anti-H7N9 whole-human monoclonal antibody 9I17. The whole-human monoclonal antibody 9I17 is quickly screened by utilizing a memory B cell polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, and does not include any murine component. The antibody disclosed by the invention can bebound to hemagglutinin HA of an H7N9 virus in a targeted manner, and has significant neutralizing activity of anti-H7N9 virus infection; and the antibody disclosed by the invention does not have toxicand side effects of anti-mouse anti-antibodies and the like, has better biocompatibility, and is more suitable and has more potential to become a macromolecular drug for treatment of influenza viruses.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rift valley fever virus humanized monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN111978400AHigh activityEffective treatmentImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAntigenBaculovirus expression
The invention discloses a rift valley fever virus humanized monoclonal antibody and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. According to the invention, RVFV glycoprotein Gn and Gc expressed by rod-shaped viruses are used as antigens; memory B cells capable of being combined with the RVFV glycoprotein Gn and Gc are screened from PBMCs of a rift valley fever rehabilitation patient; and through experiments of single B cell sequencing, in-vitro neutralization, in-vivo protection and the like, eight strains of Gn humanized monoclonal antibodies capable of efficiently neutralizing RVFV infection and a strain of a Gc humanized monoclonal antibody are identified. The humanized monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention has extremely high in-vitro neutralizationactivity (IC50 can be as low as 1.93 + / - 0.6 pM, reaching a pM level), can effectively treat mice infected by RVFV and prevent infection of RVFV on the mice, and has extremely high application valuein clinical treatment and prevention of RVFV infection.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Direct vaccination of the bone marrow
InactiveUS20090130144A1Enhance immune responseQuick activationSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseVaccination
The present invention provides methods for eliciting an effective immune response against a weakly immunogenic disease or for priming T cells to become memory T cells against a weakly immunogenic disease by directly vaccinating into the bone marrow of the patient an antigen associated with the weakly immunogenic disease. Also included in the present invention is an isolated population of human memory CD8+ T cells from the bone marrow which is in a heightened activation state with a unique effector phenotype.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Poxvirus human monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN113861285ALow heterogeneityHigh precisionImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsEscherichia coliAntigen
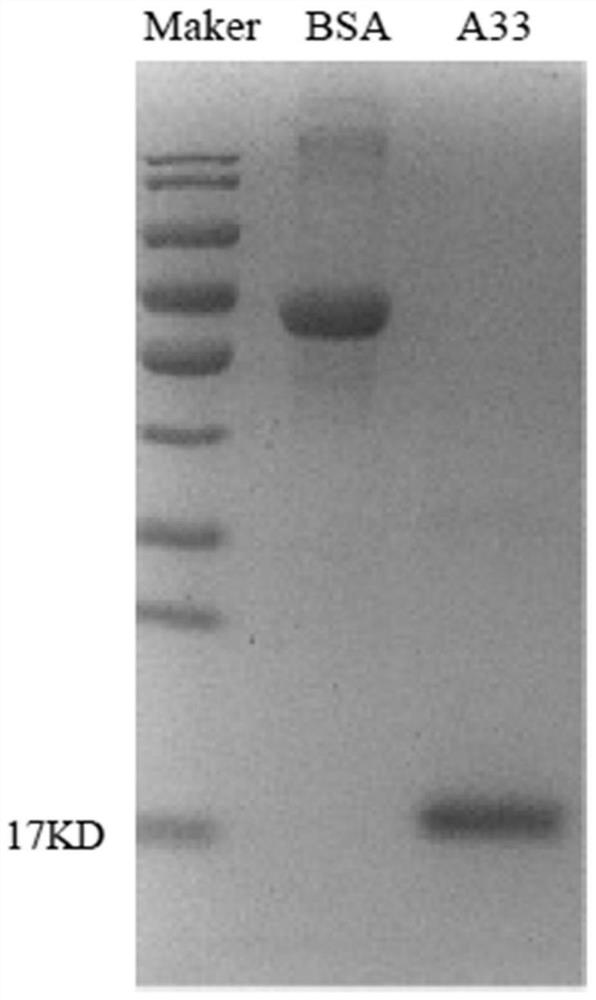
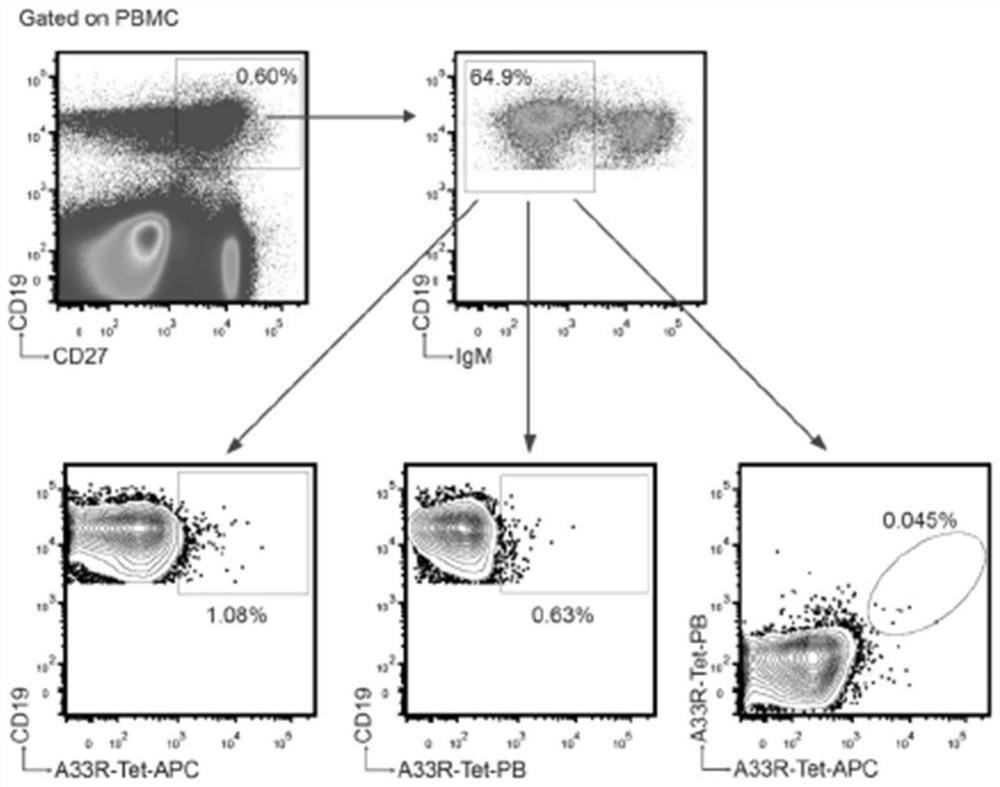
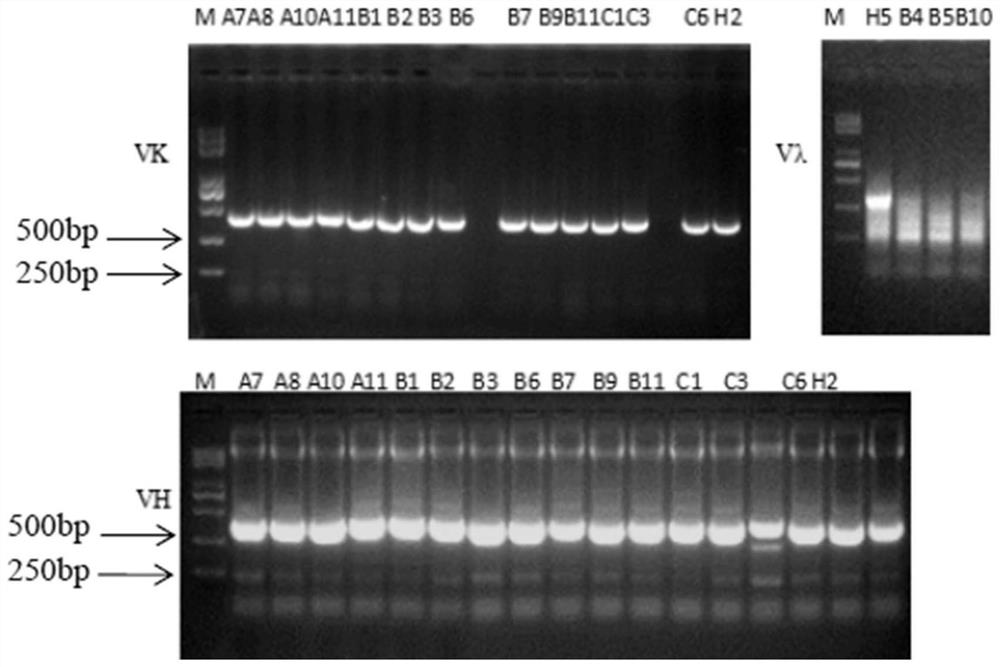
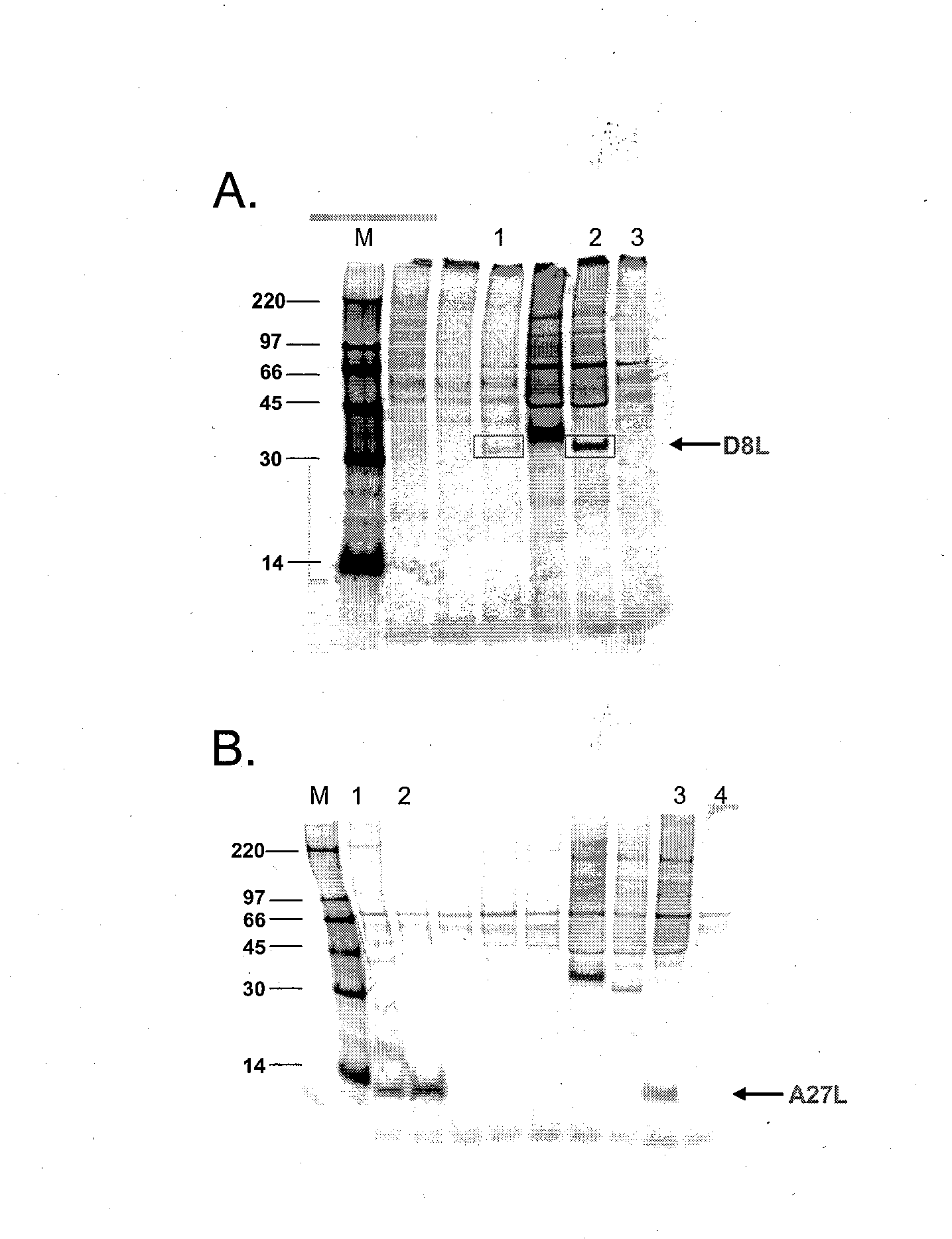
The invention discloses a poxvirus human monoclonal antibody and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. According to the invention, vaccinia virus surface film antigen A33 protein expressed by Escherichia coli is taken as an antigen; specific memory B cells of the A33 protein are screened from PBMCs of a volunteer inoculated with a ceiling vaccine; then, the specific B cells are reversed and amplified to obtain a variable region fragment of the antibody; and the variable region fragment and a constant region are further connected into an expression vector to obtain the human monoclonal antibody capable of protecting the pox virus through mammalian cell expression and purification and a series of function detections. Through ELISA detection, the antibody has good fixation capability with the antigen, and in addition, the high protection effect is achieved in the in vitro neutralization test and the mouse infection. The human antibody has an application value in clinical treatment and prevention of the pox virus.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Separation of antigen-specific memory b cells with a conjugated biopolymer surface
InactiveCN102439127ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellBiopolymer
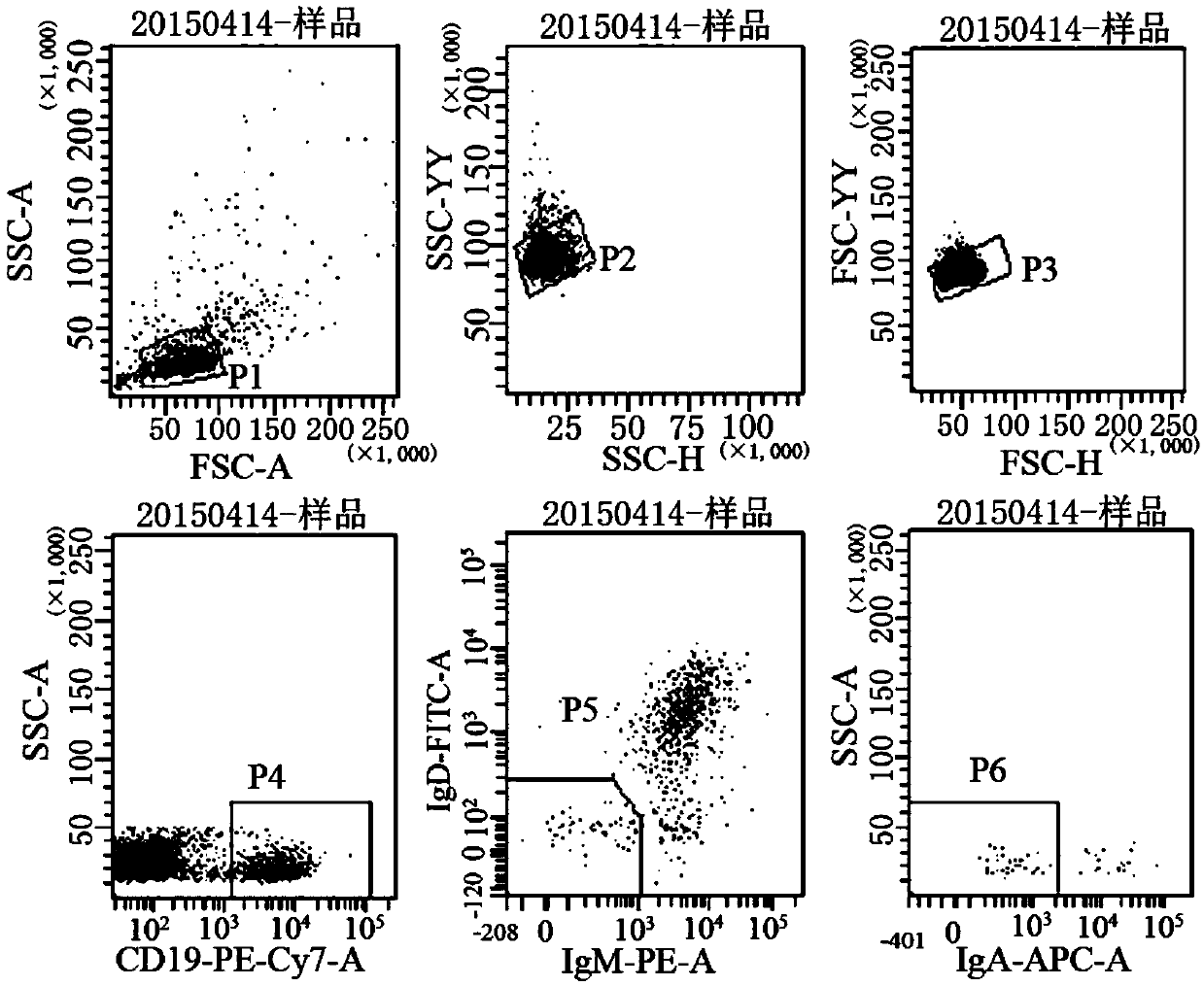
The present invention provides materials and methods for the isolation of immune cells. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a device for the isolation and separation of antigen-specific memory B cells. Immune cells will be separated by flowing the cells along a ligand-conjugated biopolymer surface. The ligand may be distributed in a concentration gradient along the z- axis of the biopolymer surface. Cells that display receptors specific for the ligands on the biopolymer will interact with the ligands and roll along the surface in the fashion of leukocyte rolling. Additive adhesive interactions will cause differential cell separation and eventual immobilization.
Owner:BIOFACTURA INC
Modulated immunodominance therapy
InactiveUS20170042998A1Altering the immunodominance hierarchy of a patientAntipyreticAnalgesicsBiological bodyCellular homeostasis
Owner:GENEIUS BIOTECH
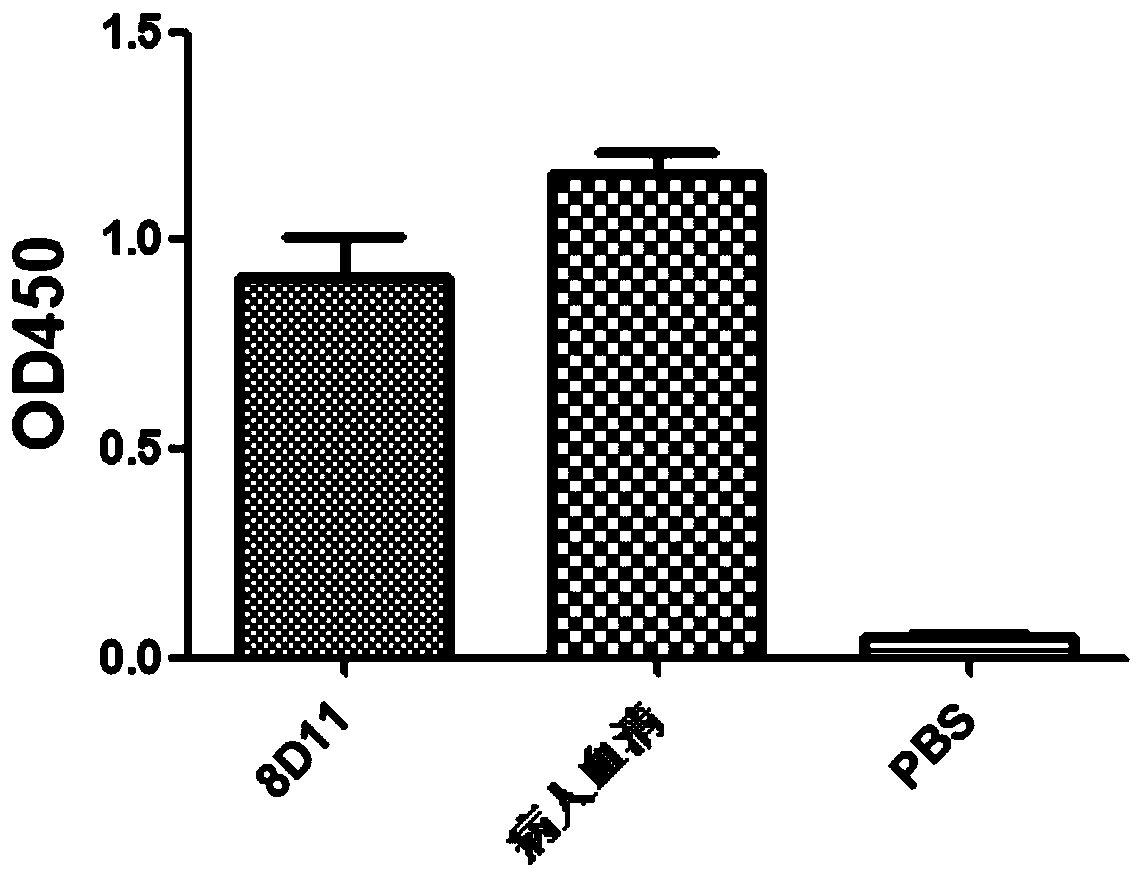
Anti-H7N9 fully-humanized monoclonal antibody 8D11 as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111434683AGood neutralizing activityGood biocompatibilityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsHemagglutininAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to an anti-H7N9 fully-humanized monoclonal antibody 8D11 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The fully humanized monoclonal antibody 8D11 is rapidly screenedby using a memory B cell PCR method, and does not contain any murine components. The antibody disclosed by the invention can be combined with hemagglutinin HA of an H7N9 virus in a targeted manner, and has remarkable neutralizing activity for resisting H7N9 virus infection; the antibody does not have toxic or side effects such as anti-mouse antibody and the like, has better biocompatibility, andis more suitable and more potential to become a macromolecular drug of treatment flu virus.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com