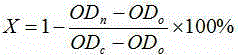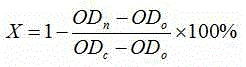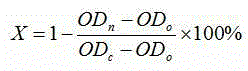Patents
Literature
121 results about "Lethal dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In toxicology, the lethal dose (LD) is an indication of the lethal toxicity of a given substance or type of radiation. Because resistance varies from one individual to another, the "lethal dose" represents a dose (usually recorded as dose per kilogram of subject body weight) at which a given percentage of subjects will die. The lethal concentration is a lethal dose measurement used for gases or particulates. The LD may be based on the standard person concept, a theoretical individual that has perfectly "normal" characteristics, and thus not apply to all sub-populations.
Non-lethal conditioning methods for the treatment of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
InactiveUS6039684AGood conditionPromote resultsPeptide/protein ingredientsEnergy modified materialsAcquired immunodeficiencyImmunodeficiency virus
The present invention relates to the use of a non-lethal preparative regimen for the treatment of a patient with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease. In a clinical trial, an HIV-positive patient was conditioned by non-lethal doses of irradiation and a chemotherapeutic drug prior to receiving donor bone marrow cells from a baboon. While long-term engraftment of donor cells was not observed, the non-lethal preparative conditioning regimen was able to reduce the viral burden and improved the clinical outcome. Such method is useful for treatment of patients with advanced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Owner:ALLEGHENY UNIV OF THE HEALTH SCI +1
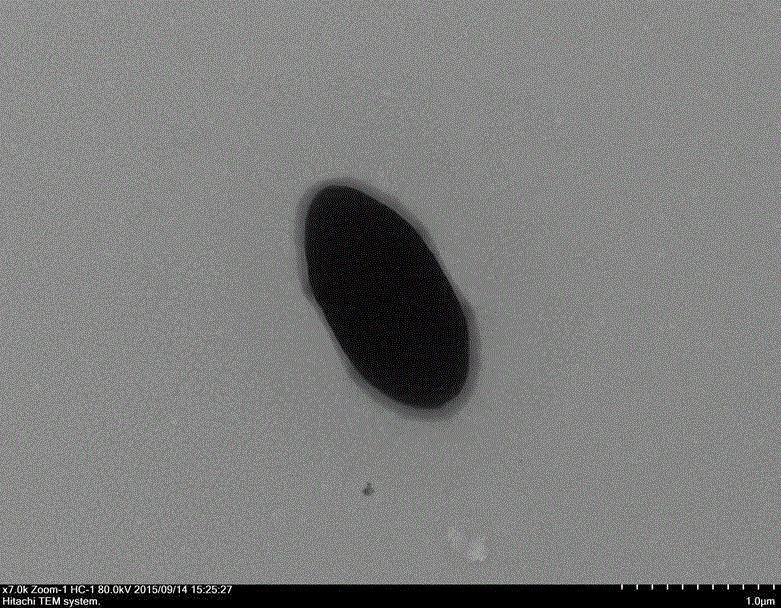
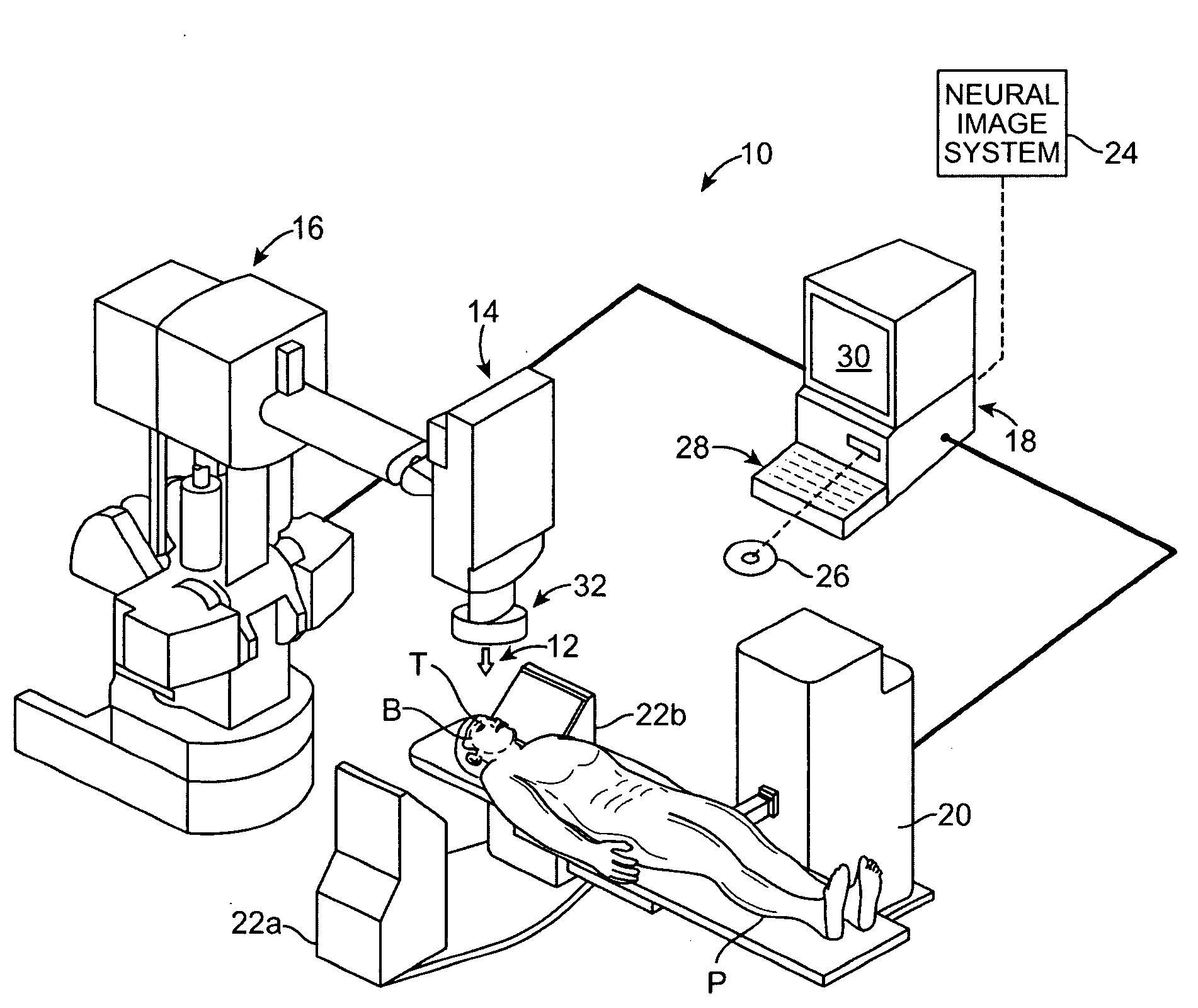
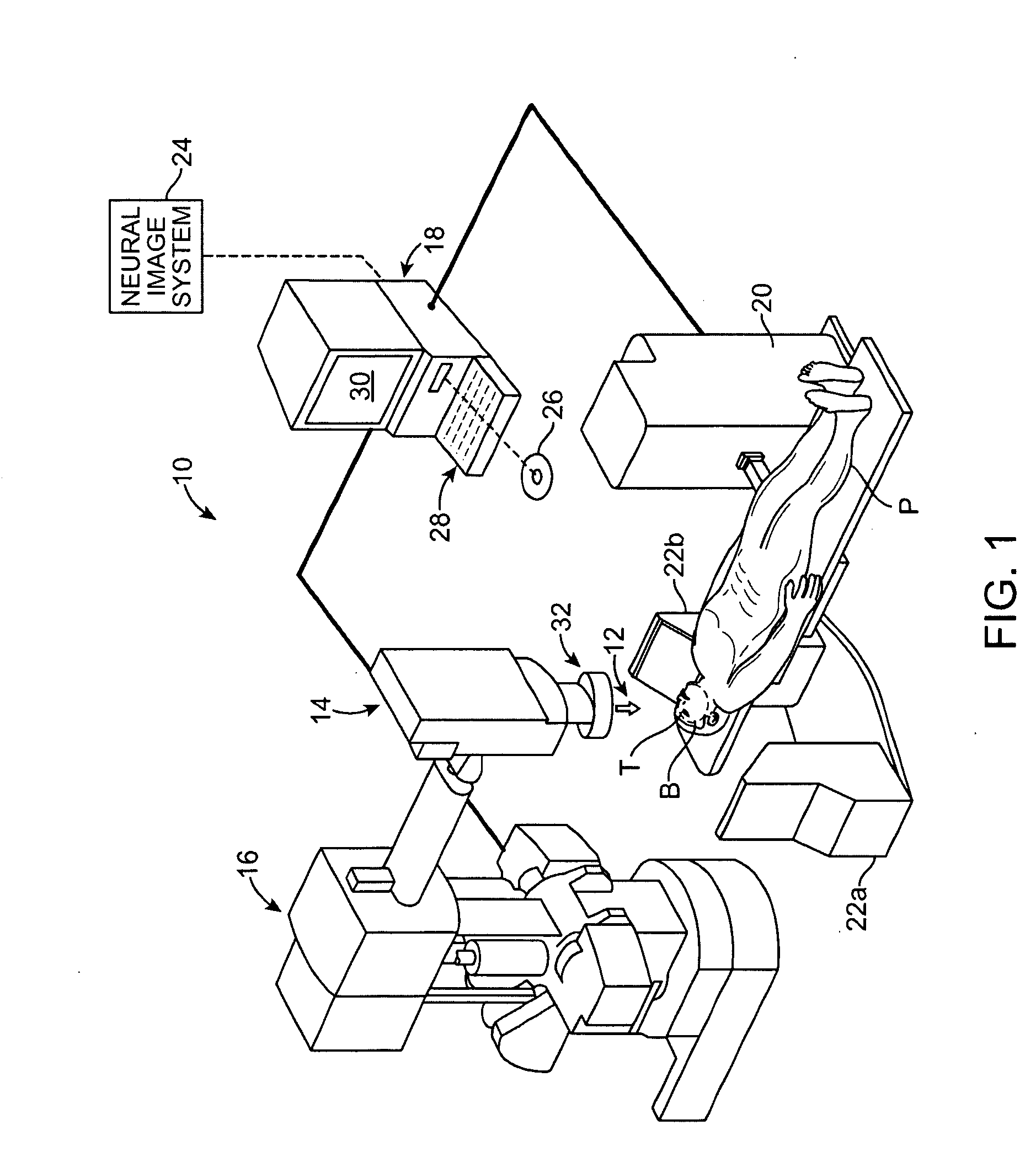
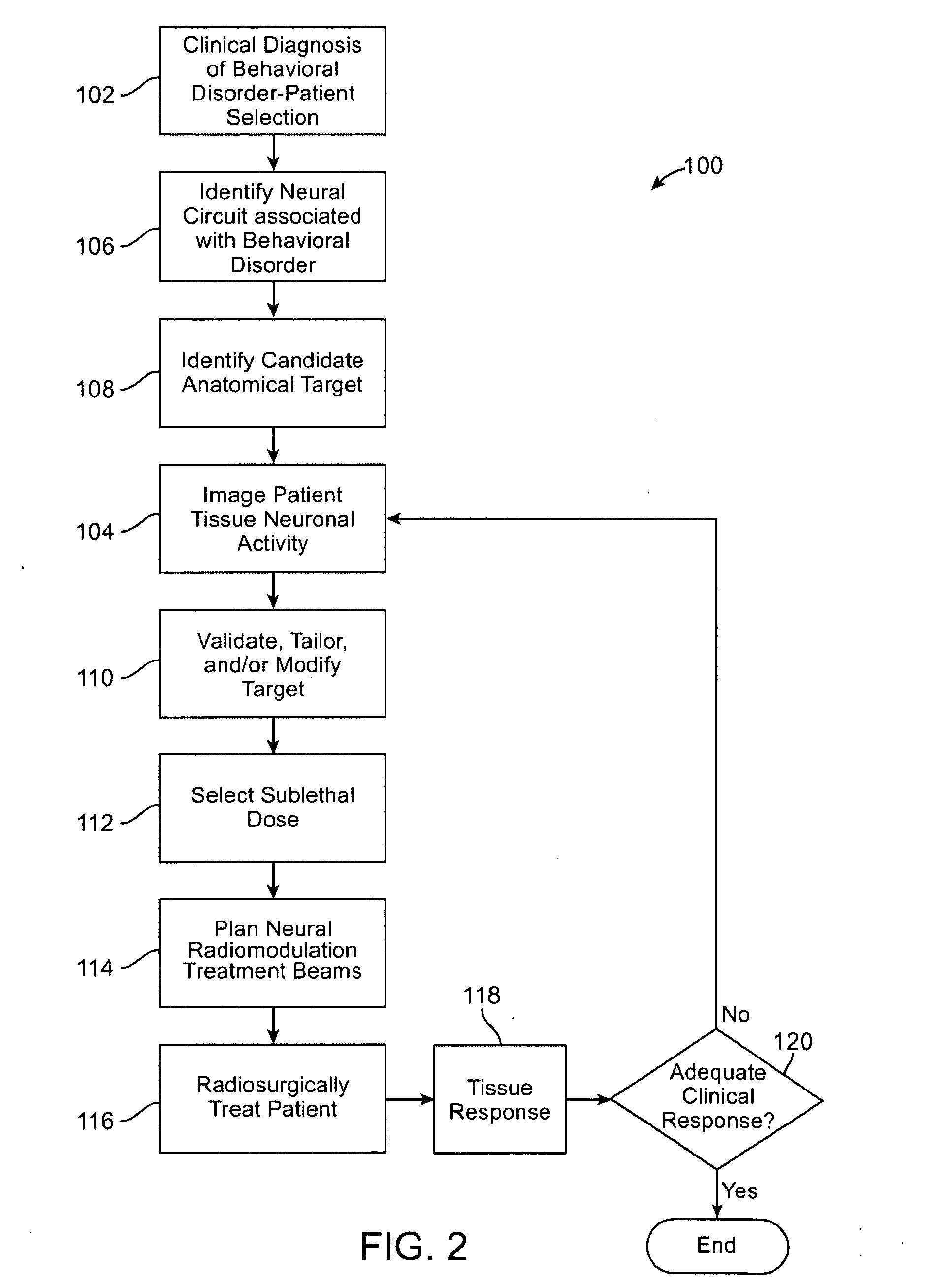
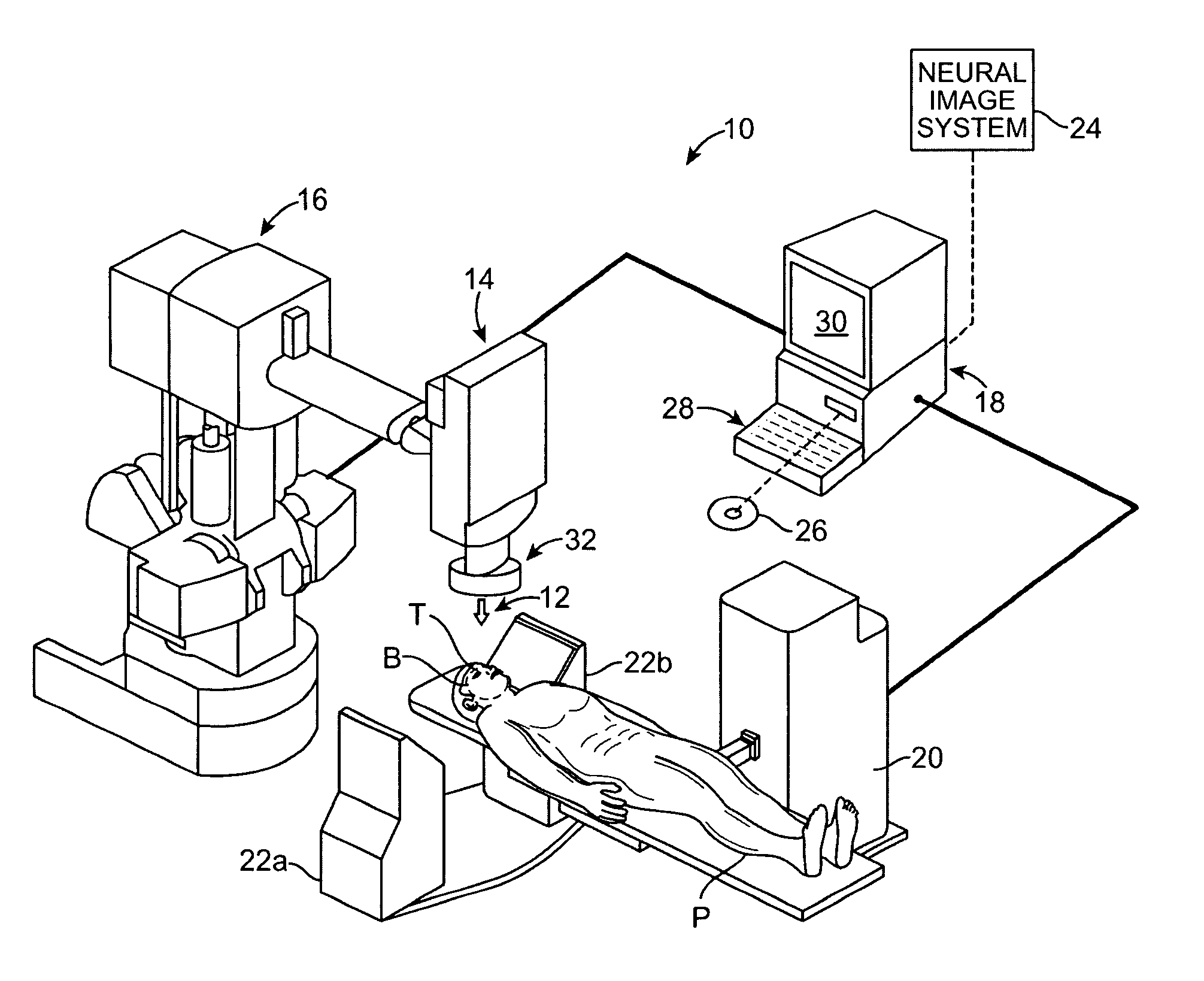
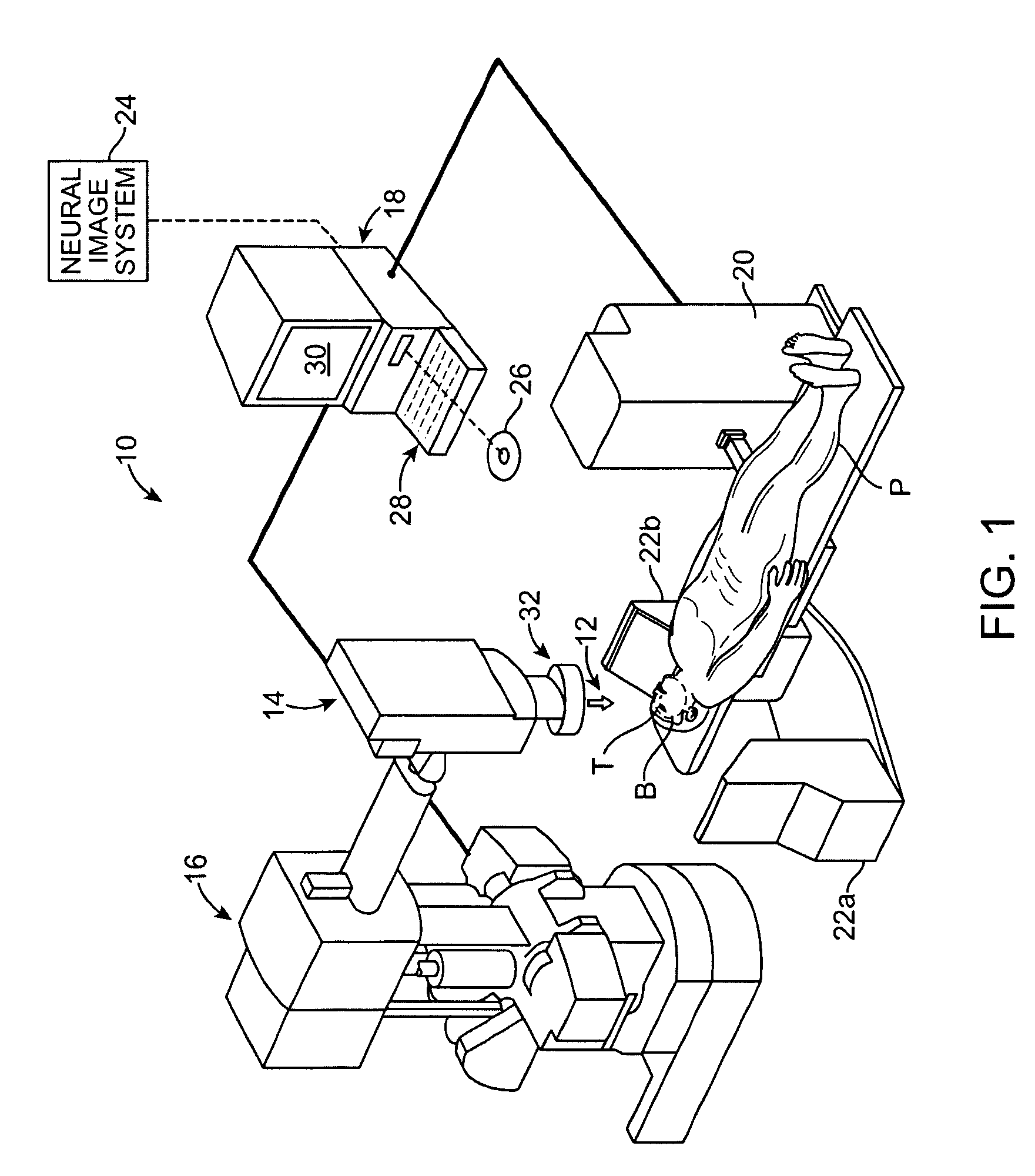
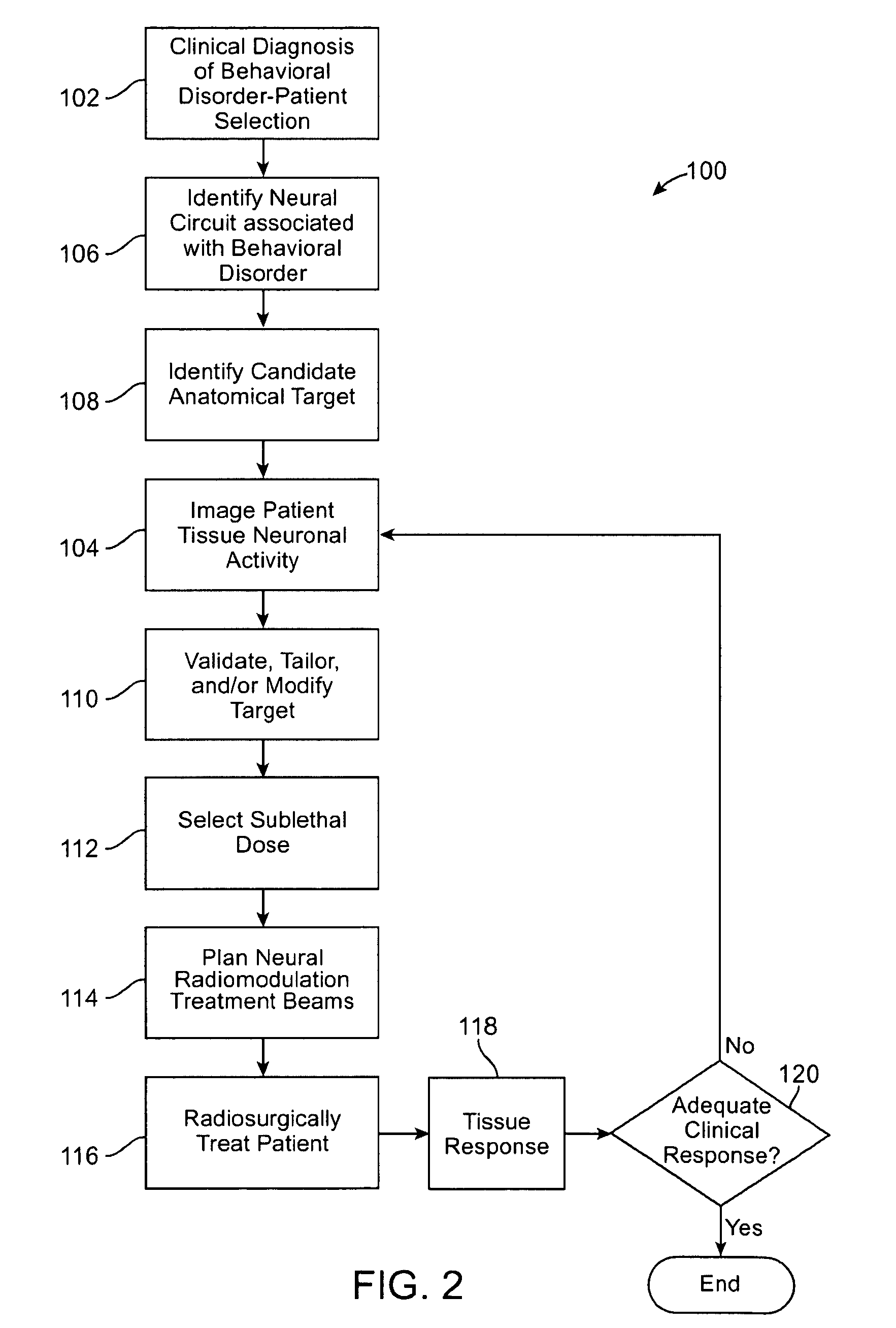
Radiosurgical neuromodulation devices, systems, and methods for treatment of behavioral disorders by external application of ionizing radiation
ActiveUS20090114849A1Reduce obesityModulate levelChemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapeutic ACTHLethal dose
Radiosurgical techniques and systems treat behavioral disorders (such as depression, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (“OCD”), addiction, hyperphagia, and the like) by directing radiation from outside the patient toward a target tissue within the patient's brain, typically without imposing surgical trauma. The target will often be included in a neural circuit associated with the behavioral disorder. A cellularly sub-lethal dose of the radiation may be applied and the radiation can mitigate the behavioral disorder, obesity, or the like, by modulating the level of neural activity within the target and in associated tissues. Hypersensitive and / or hyperactive neuronal tissue may be targeted, with the radiation downwardly modulating hyperactive neuronal activity. By down-regulating the activity of a target that normally exerts negative feedback or a limiting effect on a relevant neural circuit, the activity of the circuit may be increased.
Owner:ADLER JR JOHN R M D +1
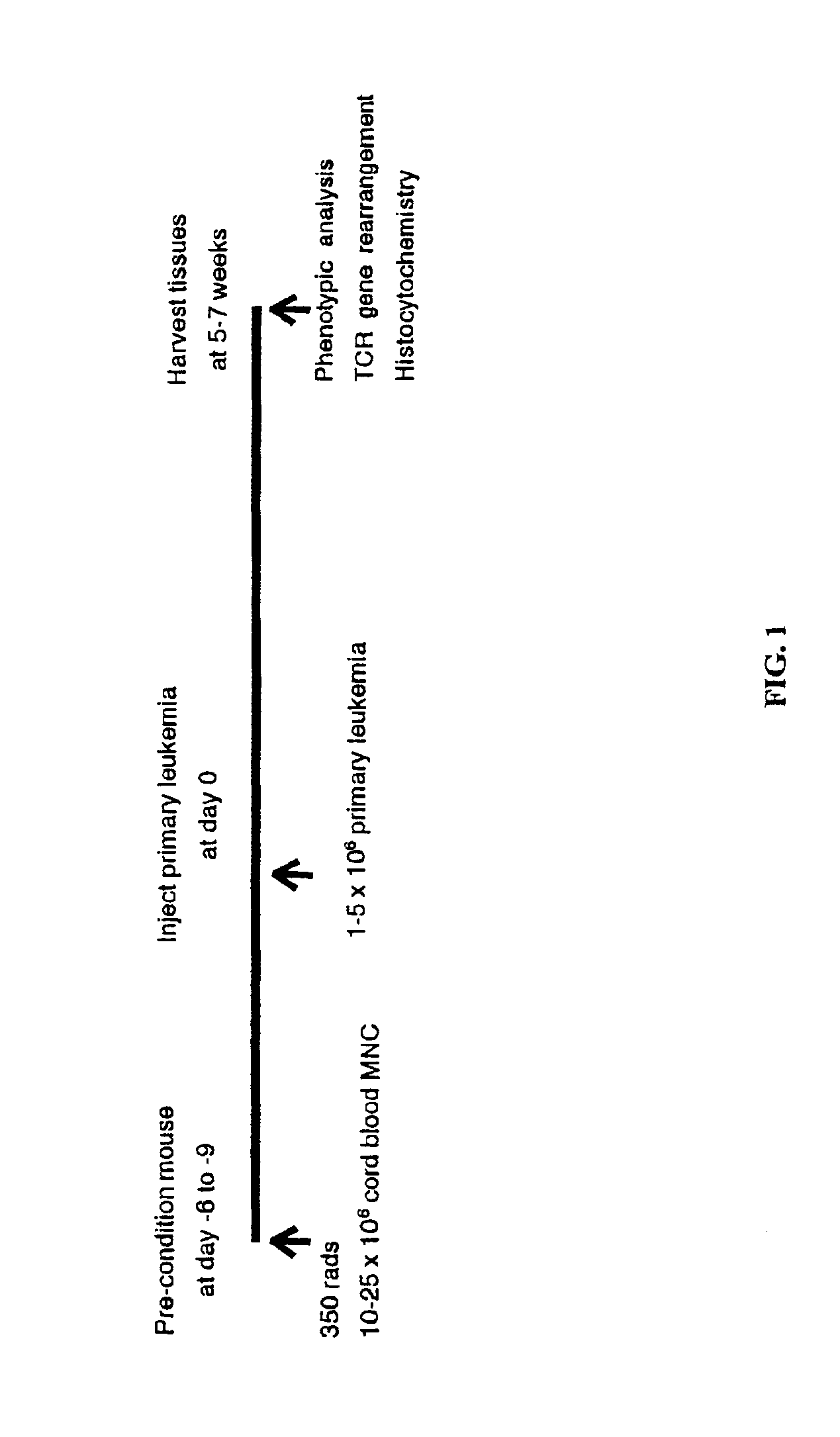
In vivo animal model of human leukemia
InactiveUS6930222B2Improve the level ofIncrease the number ofAnimal husbandryCord blood stem cellHuman leukemia
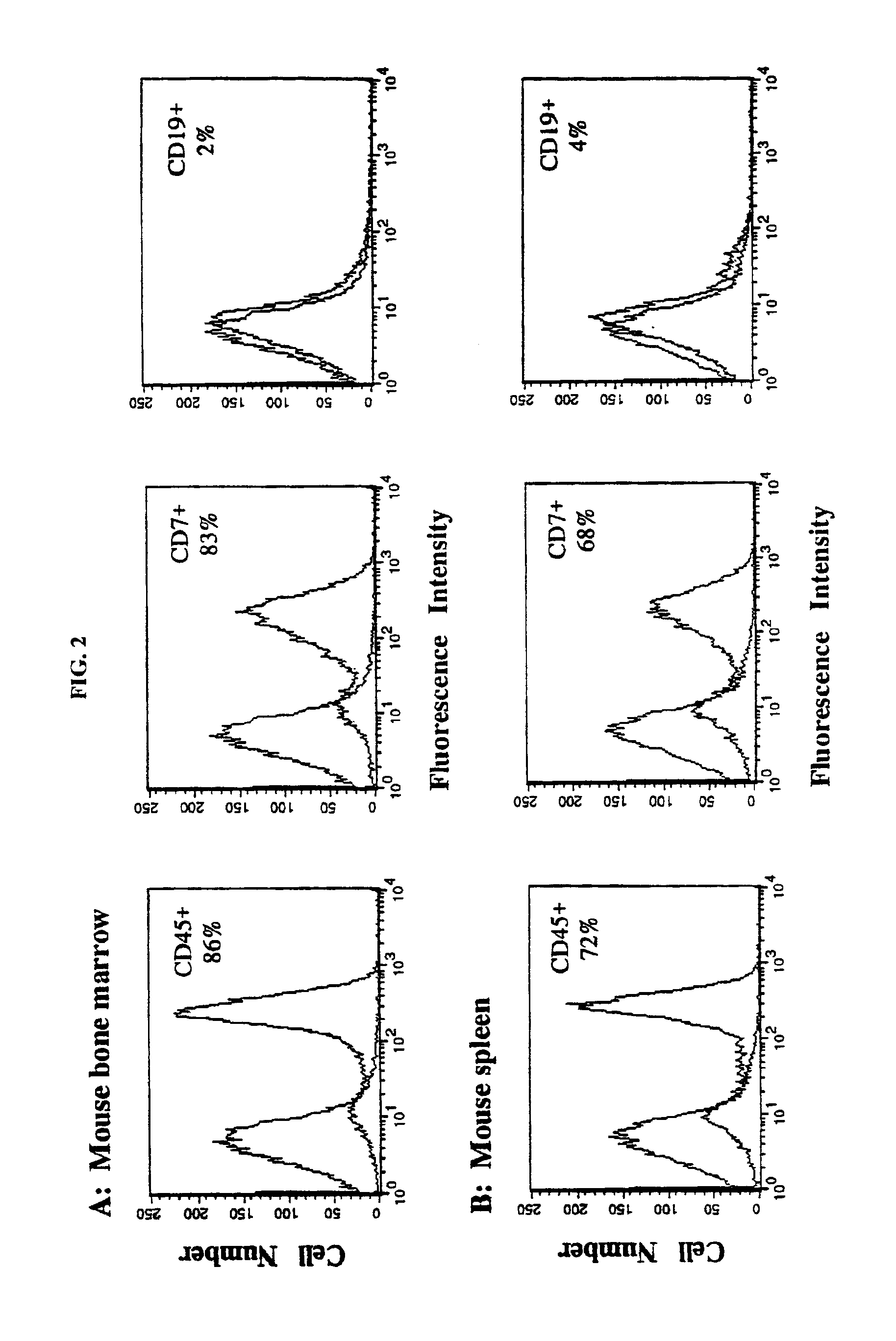
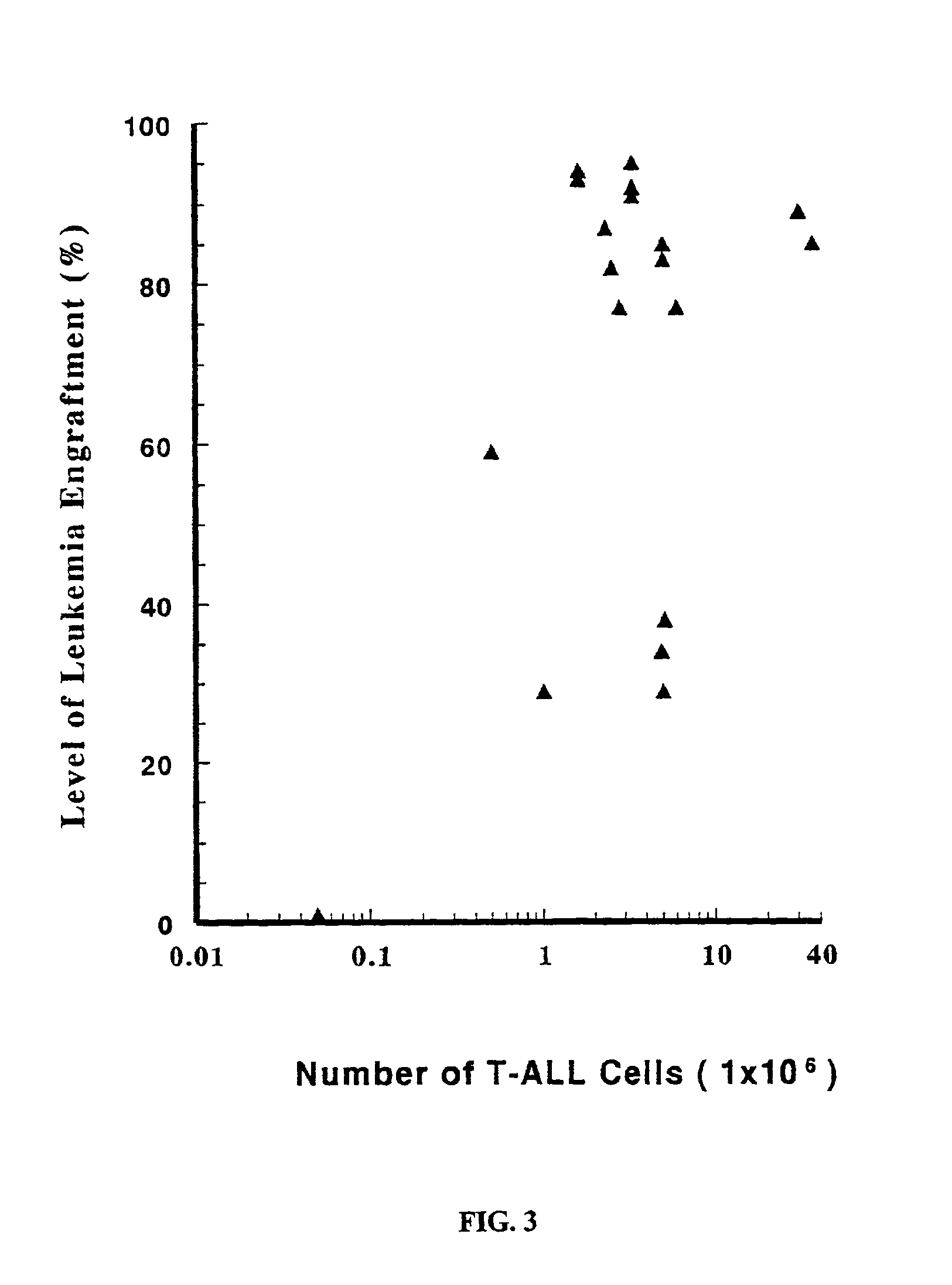
The present invention provides a process for making an in vivo model of human leukemia. The process includes the steps of: pre-conditioning an immunodeficient rodent by administering to the rodent a sub-lethal dose of irradiation and injecting the rodent with an effective pre-conditioning amount of human fetal cord blood mononuclear cells; maintaining the rodent for from about 5 to 10 days; and injecting the rodent with an effective engrafting amount of primary human leukemia cells. An in vivo and in vitro model of human leukemia are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Targeted system for removing tumor cells from cell populations
InactiveUS7129070B2Microbiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsLethal doseViable cell
A method is presented for killing a first population of cells within a mixture of viable cells by providing the mixture of viable cells, contacting the cells with a label, illuminating a portion of the mixture, capturing an image of multiple cells in the illuminated portion of the mixture, determining at least two dimensional coordinates of one or more cells of the first population of cells using the first captured image, and applying a lethal dose of energy to said dimensional coordinates of the one or more cells at a first focal plane.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
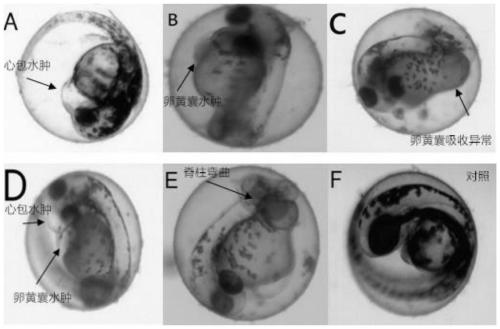
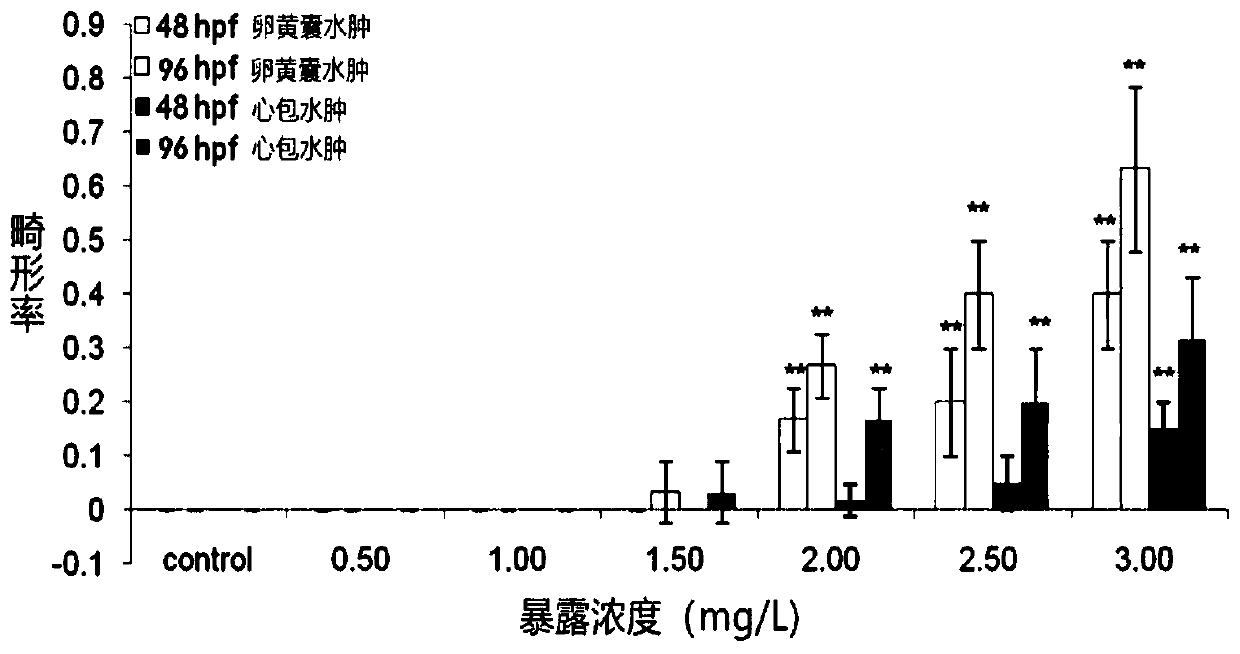
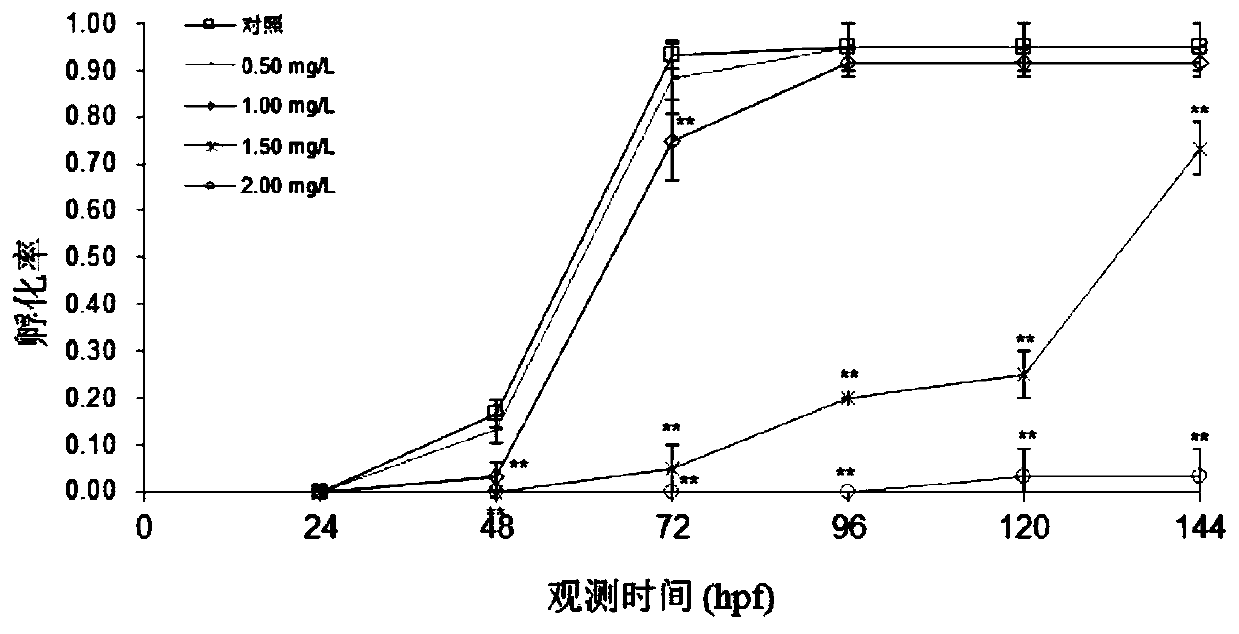
Method for evaluating influence of pollutants on zebra fish biotoxicity
The invention provides a method for evaluating the influence of pollutants on zebra fish biotoxicity. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively carrying out toxicity tests on zebra fish embryos, larva zebra fish and adult zebra fish to respectively obtain LC50 values and / or sub-lethal doses of zebra fish in different growth stages; selecting the zebra fish at a growth stage with the lowest LC50 value and / or sub-lethal dose as the most sensitive stage zebra fish; evaluating the toxicity strength of pollutants by adopting the LC50 value and / or the sub-lethal dose of the most sensitive stage zebra fish; according to the evaluation method, toxicity tests are carried out on zebra fish at different growth stages respectively, the most sensitive stage zebra fish can be determinedaccording to the biotoxicity difference of pollutants to zebra fish at different stages, and important guiding significance is achieved on zebra fish protection work by determining the most sensitivestage of zebra fish; in addition, the toxicity strength of pollutants is evaluated by the biotoxicity of zebra fish at the most sensitive stage, and the accuracy of pollutant toxicity evaluation is improved.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Test method for detecting cytotoxicity of buccal tobacco products
ActiveCN104789633AEasy to handleAccurate and effective detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFiberPretreatment method
The invention provides a test method for detecting cytotoxicity of buccal tobacco products. The test method comprises the following steps: sample pretreatment, single-cell suspension preparation, cell concentration calculation, cell inoculation, test substance addition, test substance incubation, dye incubation, light absorption value measurement, cell inhibition rate calculation and cell half lethal dose calculation. According to the test method provided by the invention, the exposure means and action manners of the buccal tobacco products are comprehensively surveyed, a sample pretreatment method of the buccal tobacco products is established, human oral mucosa fibroblasts hoMF are selected as the cells for cytotoxicity test of the buccal tobacco products according to the acting target cells, the sample detection dosage is determined and a cytotoxicity test method suitable for the buccal tobacco products is formed.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Colloidal gold test paper for fast detecting residual of kelengtelu hydrochloride
InactiveCN1725013AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLethal doseHigh doses
The invention is a colloid gold test paper for rapidly detecting clenbutero HCl residual, composed of bottom plate, water absorbing plate, pyroxylen film, clenbutero HCl monoclonal antibody gold label pad, and sample liquor absorbing layer. The establishment of paired monoclonal antibodies is implemented by regulating immunizing dose, where the high dose is 50% of lethal dose, i.e. immunizing in 10-60 mug; the low dose is below 5 mug and the low-dose immunization is easy to induce highly selective and highly affine antibodies; but on the contrary, the high-dose immunization paired- screens the antibodies produced in low and high dose to obtain the paired monoclonal antibodies in lager probability. The method for establishing colloid gold double antibody sandwich by this theory screens antibodies to make test paper for detecting if there is the clenbutero HCl remained in animal products and has the advantages of strong peculiarity, high sensitivity, operating simplicity, and being easy to store and transport, etc.
Owner:万积成
Acrylate combined casting filling material as well as preparation method and application thereof
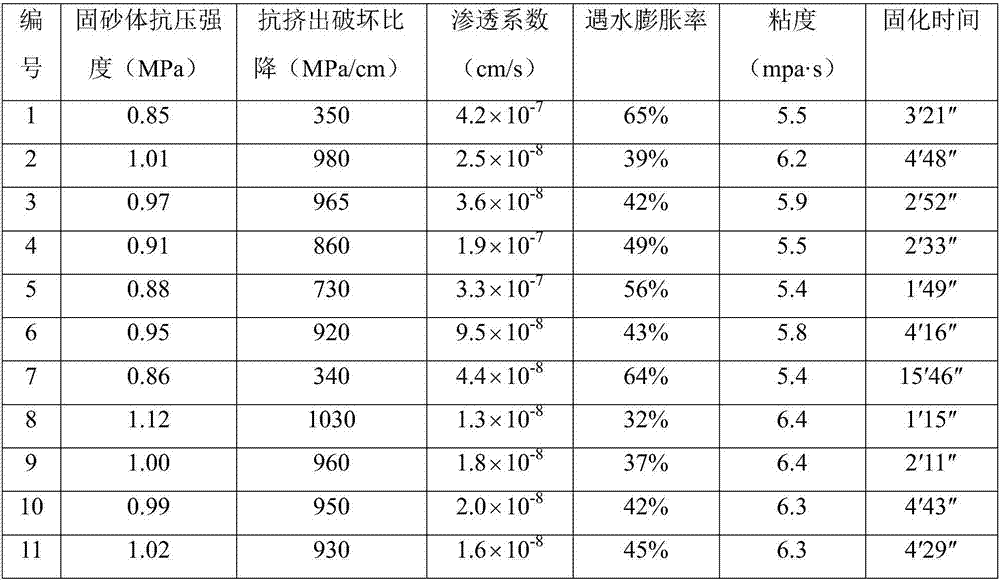
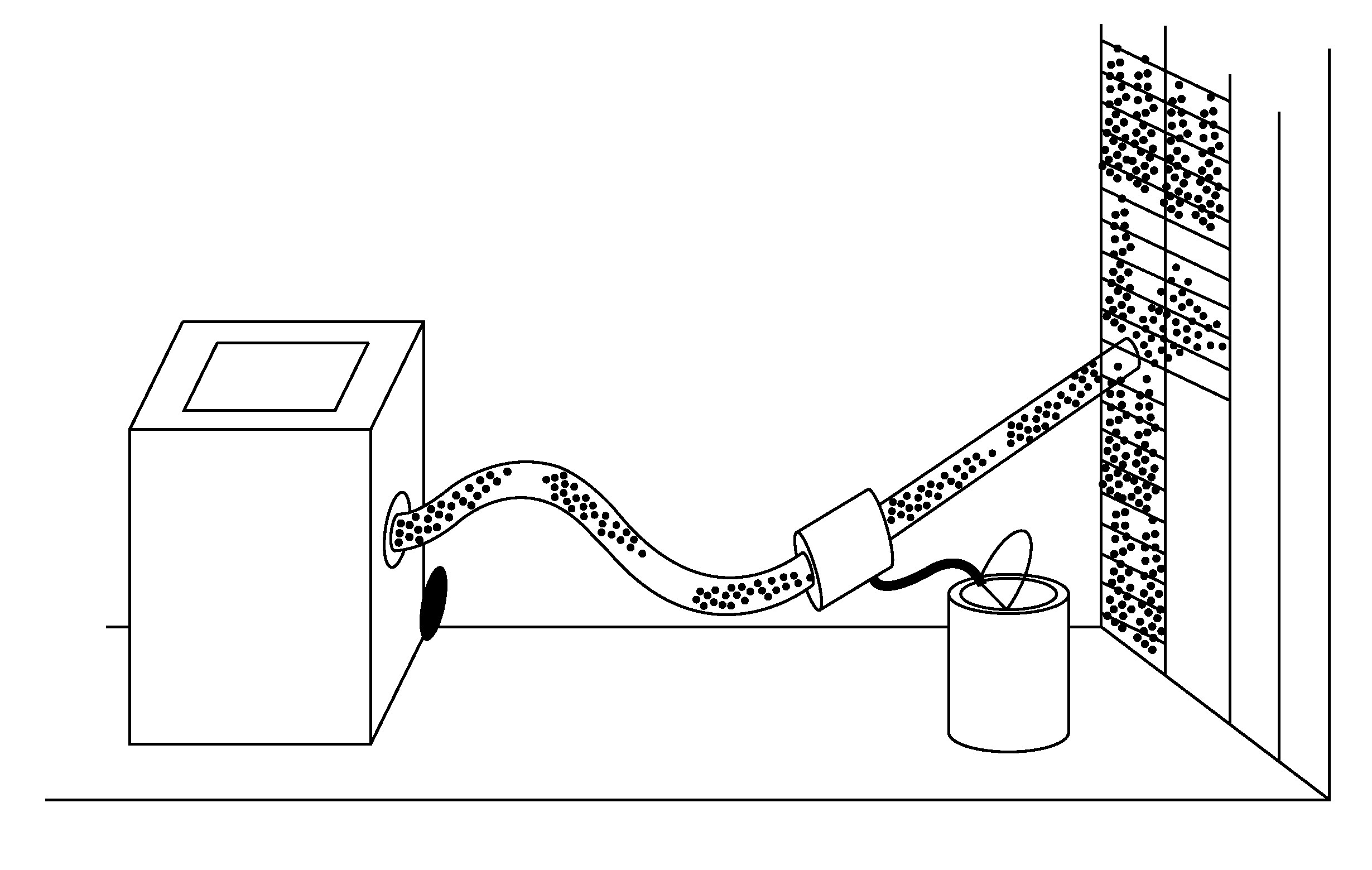
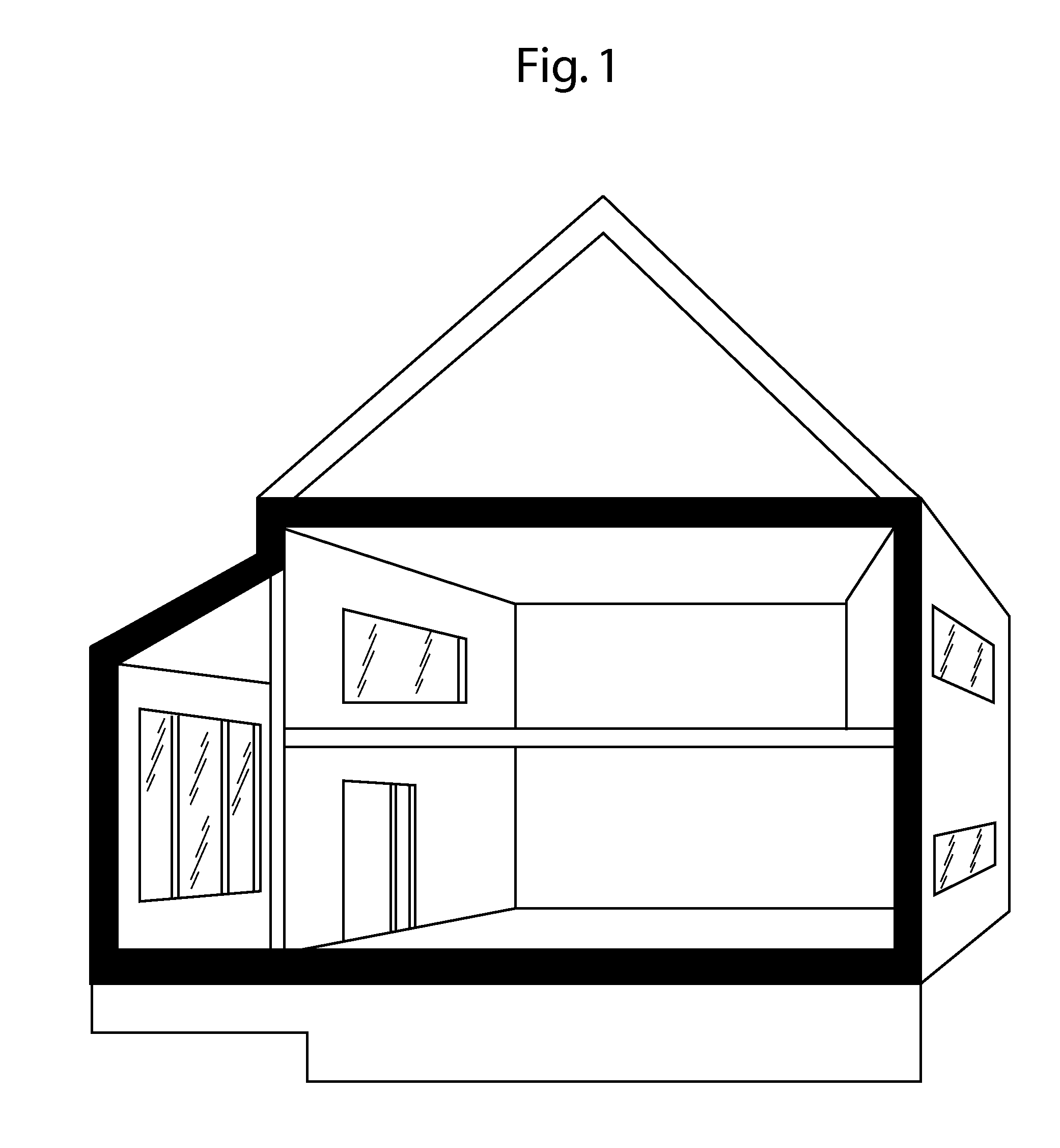
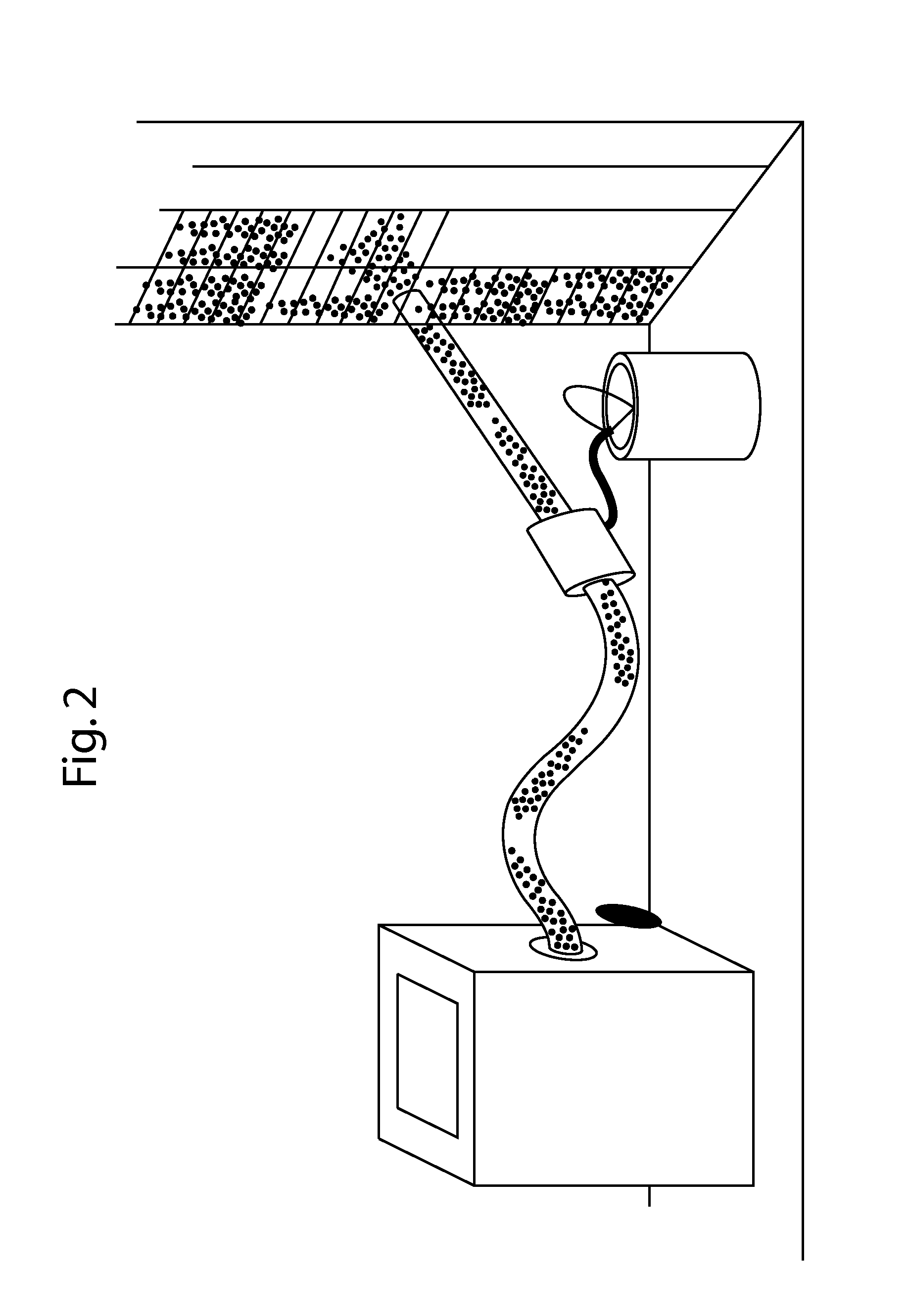
ActiveCN106927719AReduce the impactImprove fill curing strengthBuilding constructionsOrganic fertilisersCross-linkPolymer science
The invention discloses an acrylate combined casting filling material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The acrylate combined casting filling material comprises the following components: a main agent and a cross-linking agent, wherein the main agent is a mixture of acrylate; the cross-linking agent is one or a mixture of two of polyethylene glycol diallyl ether and oxidized bisphenol A diallyl ether. As the non-toxic polyethylene glycol diallyl ether and / or oxidized bisphenol A diallyl ether are adopted as the cross-linking agent, the rat oral half lethal dose of the casting material is greater than or equal to 6500mg / kg, the material is actually non-toxic, then a safe operation environment can be provided for construction operators, and the influence on the environment can be reduced to the maximum extent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Fiberglass insulation treated with a pesticide
A system including fiberglass insulation that is treated with a pesticide is disclosed. The system can provide pest control for structures in which it is installed. The pesticide is applied to the fiberglass insulation in sufficient quantities to provide pest control. The pesticide is also applied to the insulation such that it is bioavailable, yet remains on the insulation during manufacturing, transportation, installation, and a significant period thereafter. The pesticide is applied such that it is bioavailable, i.e., a lethal dose of pesticide is provided to pests that come into contact with the insulation.
Owner:PEST CONTROL INSULATION
Taxol/DNA tetrahedral drug loading system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107496931AGood water solubilityReverse drug resistanceOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityLethal dose
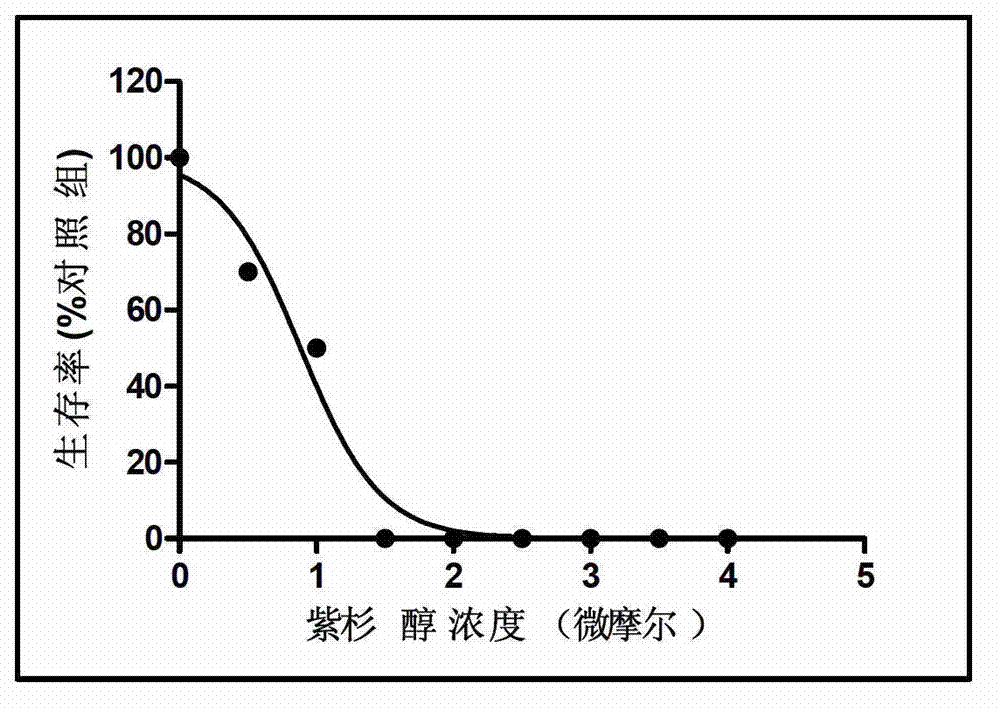
The invention discloses a preparation method of a taxol / DNA tetrahedral drug loading system and belongs to the field of biological drugs. The preparation method includes: mixing a taxol solution with a DNA tetrahedral solution, hatching, then centrifuging, and removing supernate to obtain the taxol / DNA tetrahedral drug loading system. The preparation method has the advantages that the water solubility of PTX is increased, the anaphylactic reaction of an existing PTX solvent which is the mixture of polyoxyethylated castor oil and anhydrous ethanol, lethal dose of 50% is lowered, the resource limitation problem is relieved effectively, the drug tolerance of the PTX can be reversed, and lethality to drug-tolerant tumors is increased.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method and composition for the treatment of cancer by the enzymatic conversion of soluble radioactive toxic precipitates in the cancer
InactiveUS20050058652A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCancer cellMedicine
Owner:ROSE DAVID STUART
Methods for purification of cells based on product secretion
The invention provides methods for purifying one or more cells based on the level of one or more products secreted by the cells. In one embodiment, the method involves (a) contacting a plurality of cells immobilized in proximity to a capture matrix, the capture matrix capable of localizing a product secreted by one or more of the cells, with an agent that selectively binds to the product, the agent capable of generating a signal detectable as a property of light; (b) illuminating a population of the cells, the population contained in a frame; (c) detecting two or more properties of light directed from the frame, wherein a first property of light identifies substantially all cells of the population, and the second property of light identifies product localized to the capture matrix; (d) locating (i) substantially all cells of the population with reference to the detected first property of light, and (ii) one or more selected cells with reference to the detected second property of light, and (e) irradiating the non-selected cells, wherein each non-selected cell receives a substantially lethal dose of radiation, whereby one or more selected cells having a desired product secretion profile are purified.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Medicine for preventing and treating radiative damage
InactiveCN1421227AReduce mortalityImprove the quality of lifeUnknown materialsDrug compositionsMedicineLethal dose
The present invention relates to one kind of medicine for preparing and treating radiative damage. It is prepared with figwort, rehmannia root, ophiopogon root, isatis root, oldenlandia, astragalus root, privet fruit, glossy ganoderma and green tea in certain proportion. It can reduce the death rate of mouse irradiated with the lethal dose, improve the survival quality and raise the immune of mouse with tumor, and has the same anti-tumor effect as radiative ray.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Anti-tumor activating fuling scloerotium glucan sulfate and its preparation and use
InactiveCN1583800AGood antitumor activitySimple production processOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSolubilityChlorosulfuric acid
An anti-tumour activated Tuckahoe sclerotium glucan sulfuric is prepared by: taking fresh Tuckahoe sclerotium, extracting non-water soluble (1->3)-beta- D- glucan with NaOH, solving them in anhydrous dimethylsulfoxide, adding pyridine and chloro-sulfonic acid to react to get glucan sulfuric ester. The glucan sulfuric ester's substituted reaction is of non-selective substitution, occurred at C-6 position of hydroxy, the substitution value of sulfuric ester is 0.66- 1.21, weight-average molecular weight is 0.8X104-16.4X104, and has well water solubility. Testing in vivo and in vitro showed that, the glucan sulfuric ester has obvious inhibit effect for Sarcoma 180 and proliferation of adenocarcinoma of stomach. The toxic testing in small rat prove that half lethal dose of glucan sulfuric ester (LD50)>1600 mg / kg, and without toxic or side effects. The Tuckahoe sclerotium glucan sulfuric ester is capable of use in preparing anti-tumour pharmaceuticals or health food with function of increasing body immunological competence.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
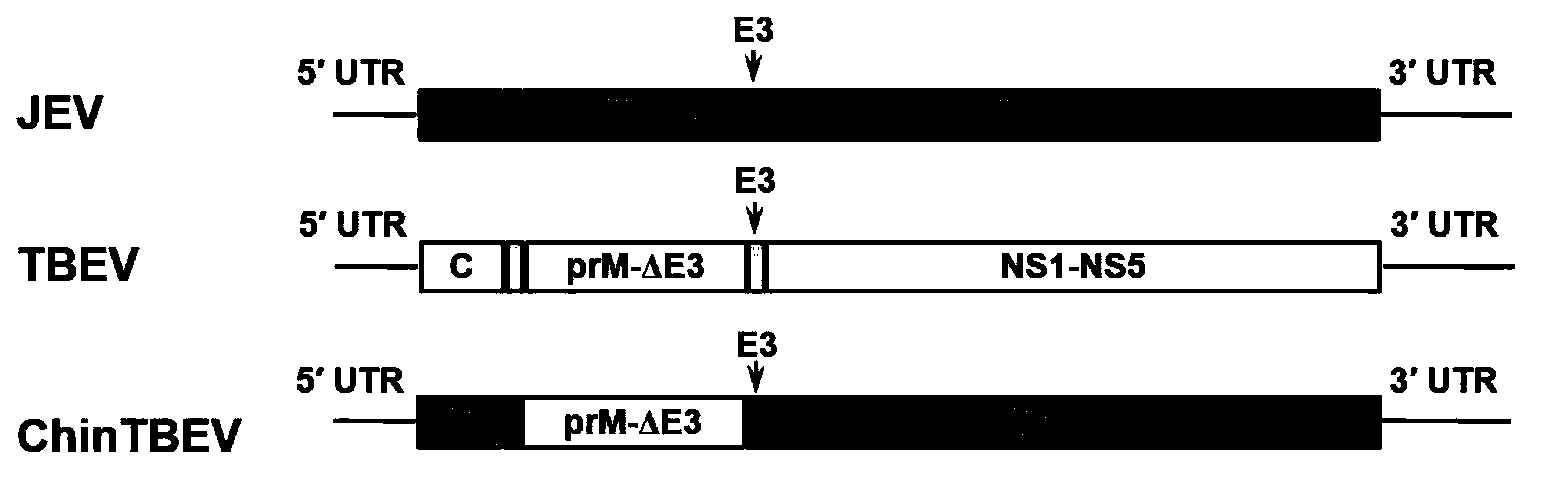
Epidemic encephalitis B/forest encephalitis hybrid virus and application of virus
InactiveCN103352029AImprove securityStable attenuation characteristicsViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLethal doseEncephalitis Viruses
The invention discloses an epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus and an application of the virus. The epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus takes an epidemic encephalitis virus attenuated strain as a gene skeleton, and is a recombinant virus obtained by replacing a deoxyribonucleotide fragment of an encoded epidemic encephalitis virus prM-E delta 3 protein in epidemic encephalitis virus genome RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) with a deoxyribonucleotide fragment of an encoded forest encephalitis virus prM-E delta 3 protein in forest encephalitis virus genome RNA. The epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus has the advantages that the virus is high in safety, and strong in stability, and can be induced to generate a good immune response to a forest encephalitis virus envelope protein, and protect an animal from being attacked by the exogenous forest encephalitis virus of lethal dose. The epidemic encephalitis B / forest encephalitis hybrid virus has a good application prospect in preventing and / or treating forest encephalitis virus infection as a vaccine.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Radioprotective agents
InactiveCN1447689AReduce severitySeverity eliminated or reducedEnergy modified materialsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsLethal doseMedicine
Owner:阿拉·夏皮罗
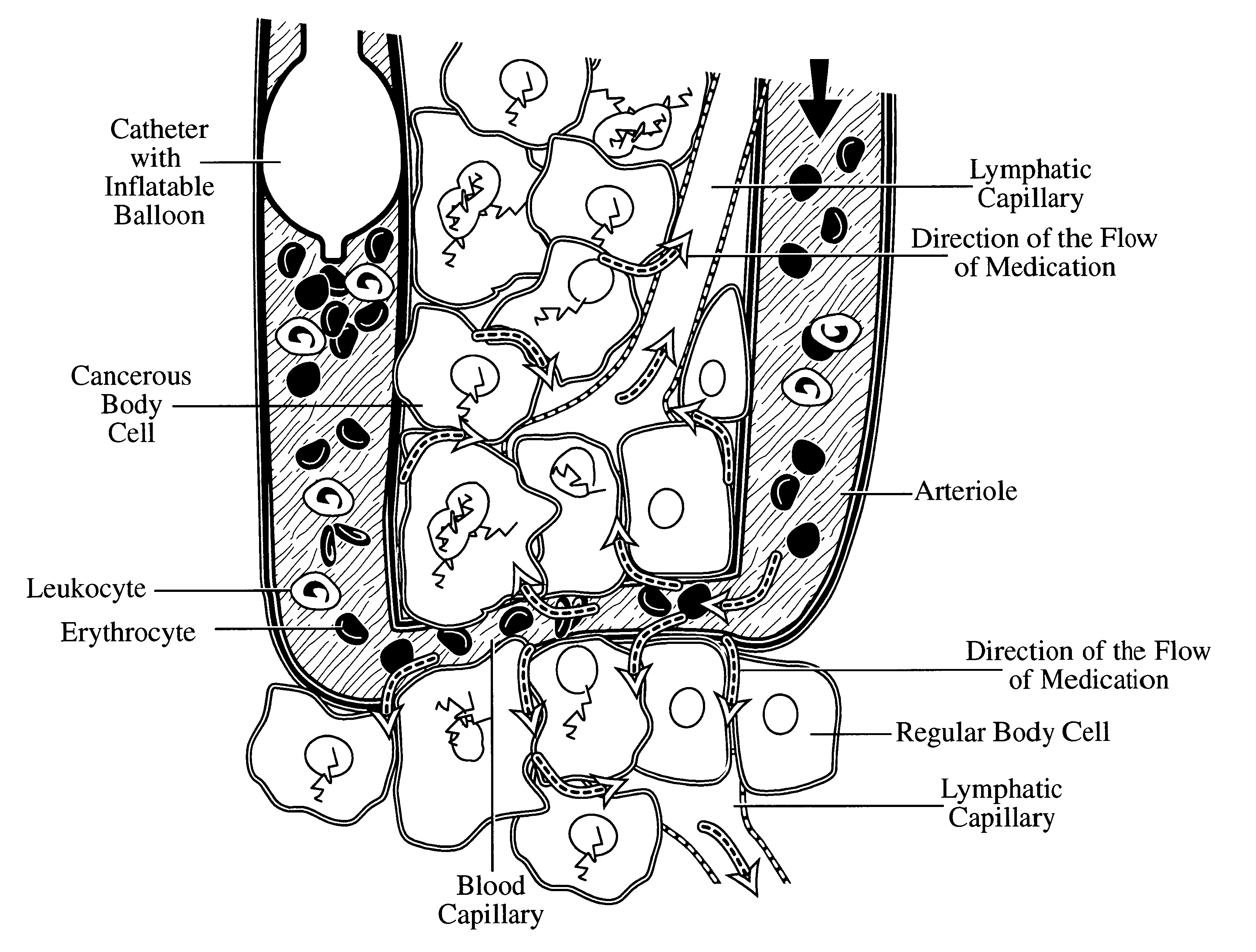
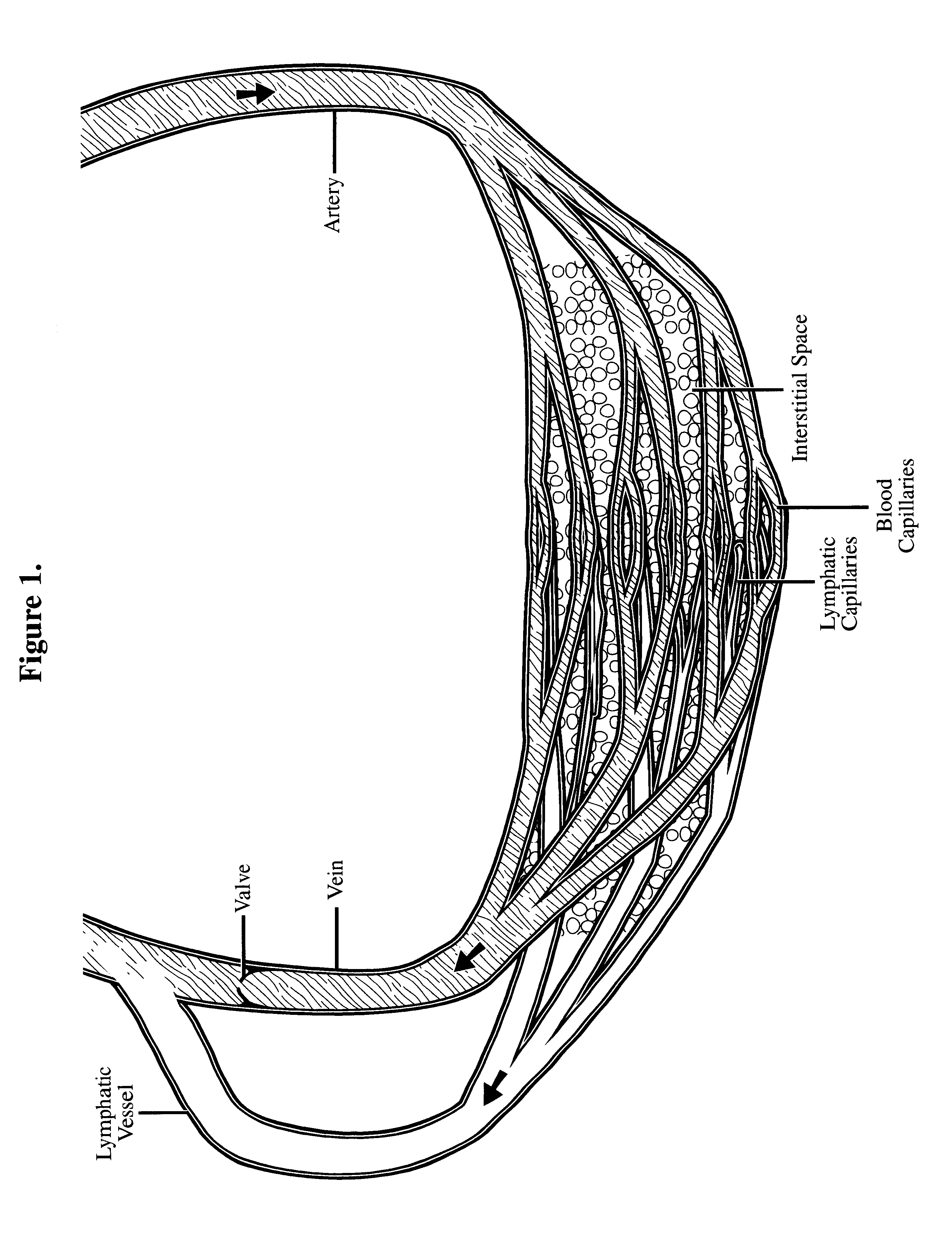
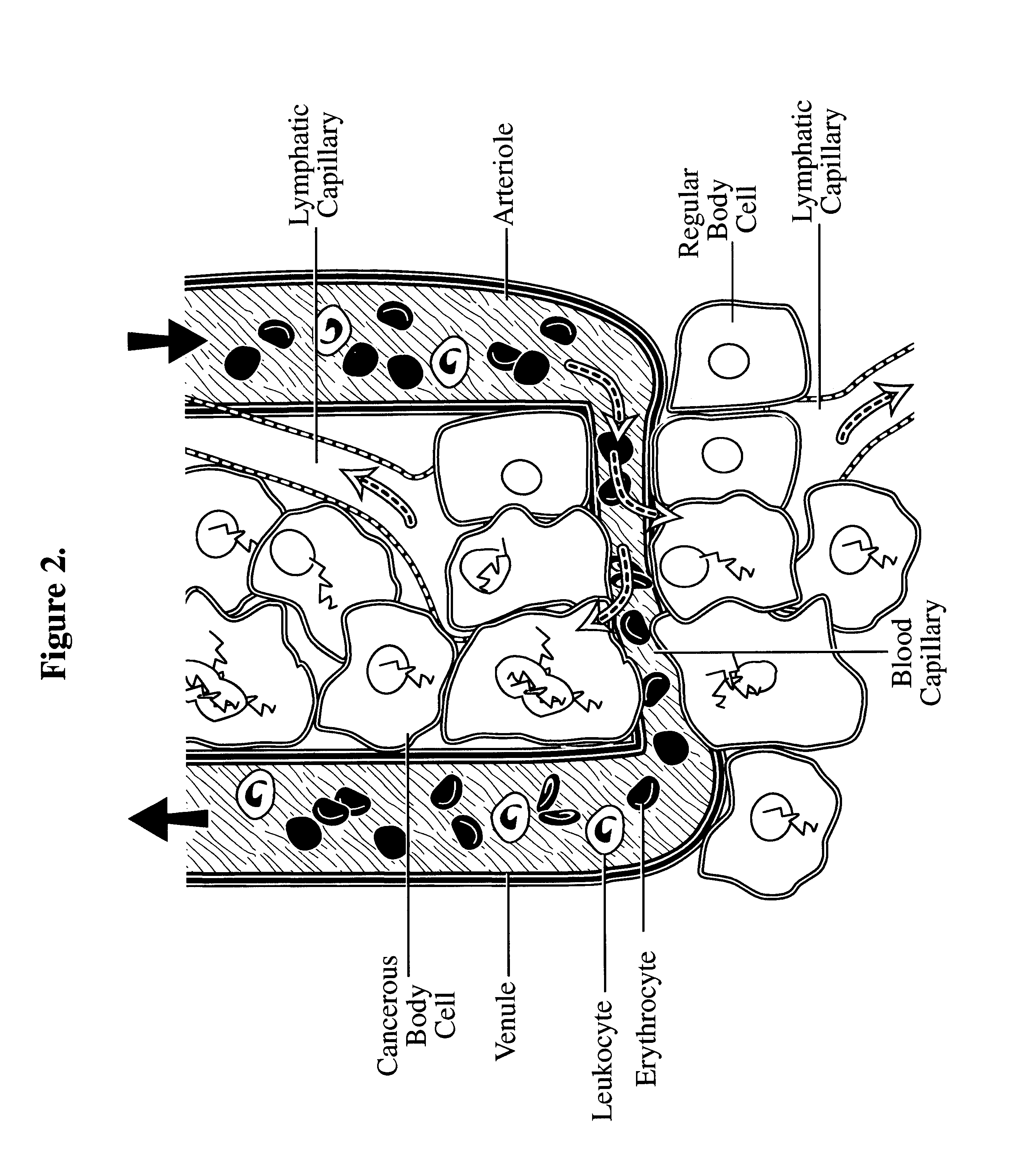
Interstitial space saturation
Providing a means for perfusing a high concentration of medication to treat a lesion, specifically cancer, infection, or autoimmune process, while averting the leakage of a substantial quantity of medication into the general blood stream. The process prevents toxic levels of the agent from entering the body's general circulation while delivering lethal doses of the agent to the lesion.
Owner:CHERKASSKY MICHAEL
Method for producing mutant of hemerocallis middendorffii by in vitro mutagenesis of ethyl methane sulfonate
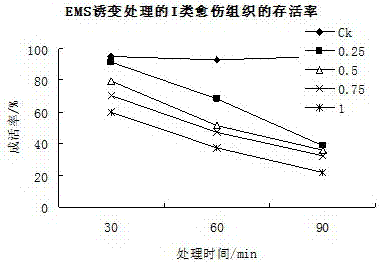
InactiveCN106973791AImprove seedling efficiencyImprove the level of breeding technologyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLethal doseNormal growth
Owner:INST OF DRY LAND FARMING SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Neutralizing monoclonal antibody resisting to tetanus toxin and application thereof
ActiveCN105542004AStrong specificityProlonged deathAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaLethal doseComplete antibody
The invention discloses a neutralizing monoclonal antibody resisting to tetanus toxin. Hybridoma cells are obtained from tetanus toxin heavy chain C fragment immune mice, light chain and heavy chain variable region genes of the antibody are taken, human-mouse chimeric complete antibody expression vectors are built, CHO cell transfection is carried out, purification is carried out, and then the antibody is obtained. The antibody has the activity of specific binding to tetanus toxin, the monoclonal antibody can partially protect mice against attack of tetanus toxin, and four antibodies can completely protect mice against a twofold lethal dose of tetanus toxin in combination.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
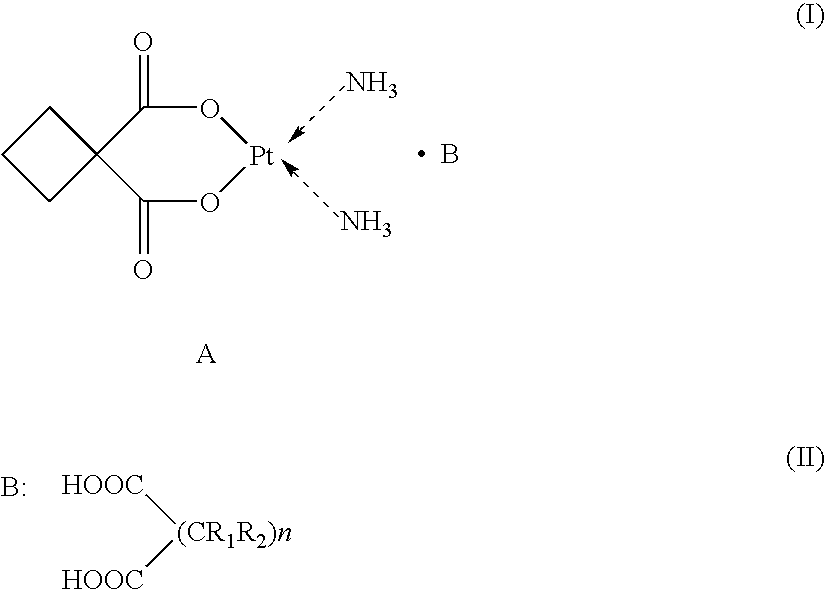
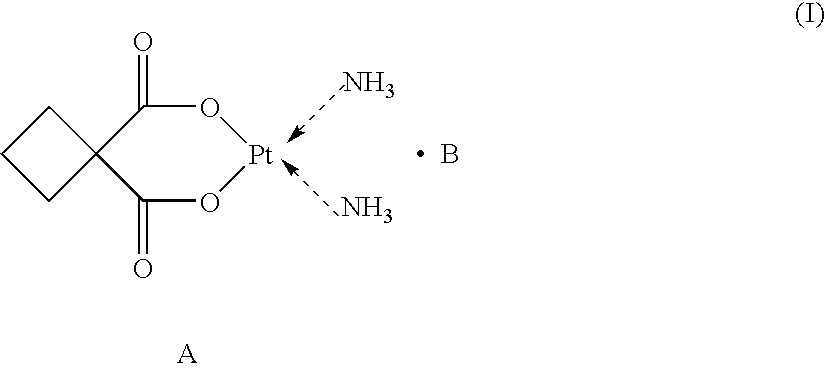
Supermolecular carboplatinum derivatives, their preparation and pharmaceutical composition containing tem as active ingredient and applications of the compositions
The present invention relates to a novel class of supermolecular carboplatin derivatives represented by general formula (I), wherein B is a polycarboxylic acid represented by general formula (II), wherein R1, R2 and n are defined as in the description. The present invention also relates to a process for preparing the same, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same as active ingredient and the use of the derivatives in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions which are useful in treating various cellular cancers including hepatoma, stomach cancer, lung cancer and the like. The derivatives have stable cage-like chemical structures and constitutions in solid and in aqueous solution. The derivatives can not only kill cancer cells at a rate significantly higher than that by carboplatin, in particular, in the case of hepatoma cells, at a rate one to two times higher than that by carboplatin, but also produce little side effects such as vomit, baldness, decreases of leucocytes and platelets, and the like, which can be induced by administration of other chemotherapeutics. In the acute toxicity tests on mice, the lethal dose (LD50) of the present derivatives is about 300 mg / kg and 260 mg / kg body weight for a subcutaneous(sc) and an intraperitoneal(ip) administration, respectively. Therefore, the present derivatives are a novel class of cis-platium which can be widely used as anticancer agents.
Owner:WANG JINGZUN +3
Uv liquid steriliser
InactiveCN102427830AImprove reliabilityConstant and thorough mixingWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFood preservationLethal doseEngineering
Owner:STERIFLOW
Defective interfering virus
ActiveUS20090191158A1Shorten the progressFaster rateSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideLethal doseWild type
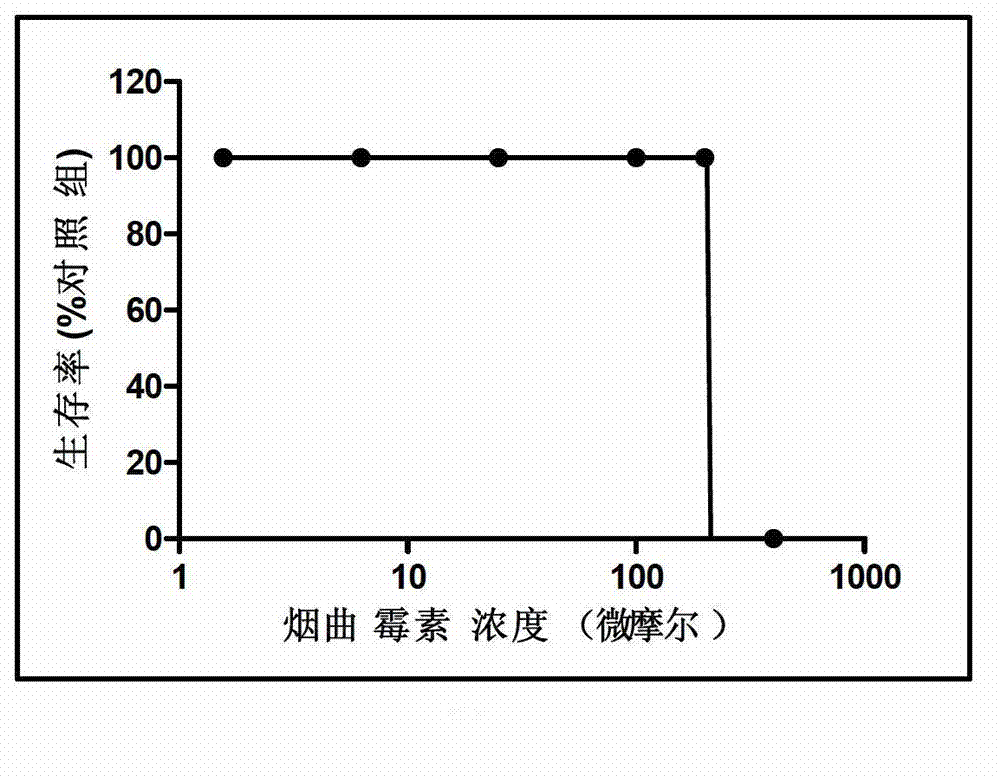
Cloned, i.e. defined, defective interfering (DI) influenza A virus is produced in embryonated hens eggs using a method which generates large quantities of DI virus material. Cloned DI virus is then used in tests on mice and ferrets given a lethal challenge of wild-type influenza A virus. When cloned DI influenza A virus is co-administered with a lethal dose of virulent influenza A virus, mice are protected compared to a control of inactivated cloned DI influenza A virus. Mice which survived the administration of cloned DI influenza A virus and infective challenge virus are three weeks later still protected against lethal challenge with infective virus. Control mice which received only cloned DI influenza A virus and no lethal challenge are not protected three weeks later on lethal challenge with infective virus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
Recombinant adenovirus expressing E0, E2 gene of classical swine fever virus
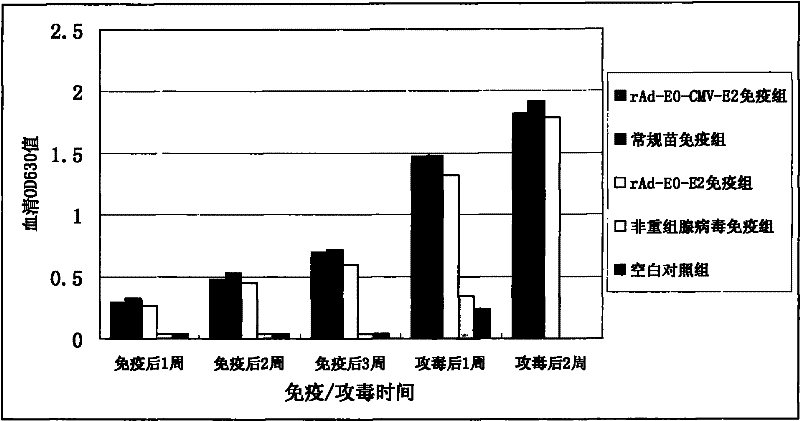
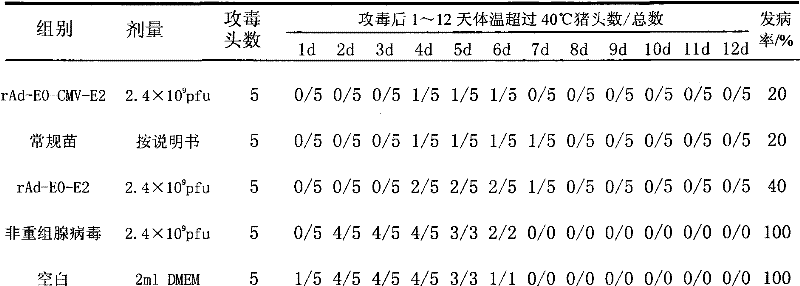
ActiveCN102181404AStrong resistanceSolve the phenomenon of returning to ancestors and increasing virulenceMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsVirulent characteristicsLethal dose
The invention provides recombinant adenovirus expressing E0, E2 genes of classical swine fever virus, which is characterized in that the E0 gene of classical swine fever virus is inserted into Bgl II and Kpn I enzyme sites of a multiple cloning site at downstream of adenovirus CMV promoter, and a adenovirus CMV promoter and a CMV-E2 segment of the E2 gene of classical swine fever virus are inserted into Xho I and Xba I enzyme sites. The invention solves the problems of low yield and weak protective effect of the fusion tandem expression of the E0, E2 genes, allows an immunized swine to obtainan antibody against classical swine fever virus only by immunization once, and the production cost is half of that of conventional vaccines; the recombinant adenovirus belongs to non-replicative virus, and does not propagate in swine; the phenomenons of virus atavism and virulence enhancement due to the long-term inoculation of attenuated vaccine are solved. The recombinant adenovirus only comprises main protective genes of classical swine fever virus and does not comprises other genes of the virus, so no recombination with field strains occurs. After a swine is immunized by vaccine prepared by the recombinant adenovirus, the protective effect against live virus infection of classical swine fever virus with a lethal dose of 100 times of TCID 50 is 100%.
Owner:孙永科
Radiosurgical neuromodulation devices, systems, and methods for treatment of behavioral disorders by external application of ionizing radiation
ActiveUS8337382B2Reduce obesityModulate levelChemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLethal doseDirect radiation
Radiosurgical techniques and systems treat behavioral disorders (such as depression, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (“OCD”), addiction, hyperphagia, and the like) by directing radiation from outside the patient toward a target tissue within the patient's brain, typically without imposing surgical trauma. The target will often be included in a neural circuit associated with the behavioral disorder. A cellularly sub-lethal dose of the radiation may be applied and the radiation can mitigate the behavioral disorder, obesity, or the like, by modulating the level of neural activity within the target and in associated tissues. Hypersensitive and / or hyperactive neuronal tissue may be targeted, with the radiation downwardly modulating hyperactive neuronal activity. By down-regulating the activity of a target that normally exerts negative feedback or a limiting effect on a relevant neural circuit, the activity of the circuit may be increased.
Owner:ADLER JR JOHN R M D +1
Neovison vison klebsiella peneumoniae
InactiveCN105199991AStrong toxicityIncreased toxicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a neovison vison klebsiella peneumoniae, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The neovison vison klebsiella peneumoniae is named as a WMOK strain with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.11222, belongs to the K2 type, and is gram-negative (G-), facultative anaerobic, atrichous and asporous, has an obvious capsule, and besides, most strains have fimbriae and are rod-shaped with finely rounded ends; the WMOK strain has relatively high toxicity, has a half lethal dose (HLD) of 1.8 CFU to mice, and further has an HLD of 15 CFU to neovison vison. According to the neovison vison klebsiella peneumoniae, provided by the invention, separation and identification of the strain provide a certain foundation for further deep development of correlational studies on and control over neovison vison klebsiella peneumoniae.
Owner:王贵升
Method for constructing pepper mutant library from ethylmethane sulfonate
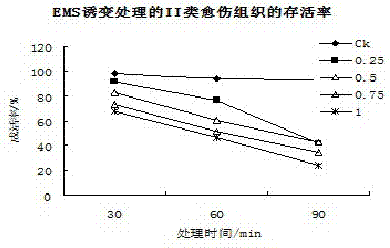
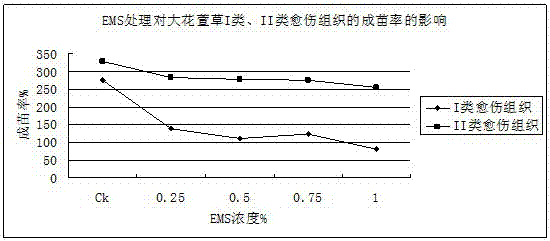
PendingCN108617502AImprove anti-aphid performanceHigh yieldPlant genotype modificationGenomicsEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention discloses a method for constructing a pepper mutant library from ethylmethane sulfonate. The method is characterized in that a Zunla 1 is used as a mutagenesis object; on the premise ofpointing out the influence of treating fluid dose and excluding space of each seed on germination percentage, semi-lethal dose is determined by comparing the germination percentage of pepper seeds with EMS treating fluid with different concentrations at different mutagenesis time; the pepper seeds are treated by mutagenesis of the semi-lethal dose; mutation frequency and mutation types of M2 generation are investigated, a mutant capable of stably inheriting of M4 generation is identified and a mutant library is constructed; the mutation types of leaves, stems, fruits, growth period, flower organs, fertility and the like are obtained and create abundant materials for functional genomics reach of pepper; and meanwhile, partial beneficial mutation can be directly applied to breeding practice.
Owner:GUIZHOU SERICULTURE RES INST GUIZHOU PEPPER RES INST
Method for assessing acute toxicity of medicament by using model animal zebrafish fries
ActiveCN103301479AReduce dosageEasy to operateIn-vivo testing preparationsAcute toxicity testingAlcohol
The invention aims to provide a method for assessing the acute toxicity of a medicament by using model animal zebrafish fries. The method is easy to operate, rapid and high in accuracy. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of preparing the medicament into solutions to be tested with various concentrations by using dimethyl sulfoxide or ethyl alcohol, selecting the zebrafish fries normal in development 72 hours after fertilization, randomly distributing the zebrafish fries into perforated plates, adding the medicament to be tested with various concentrations, observing under a microscope 96 hours after the fertilization, judging that the fries are dead after the hearts of the fries stop beating, counting the survival rate of each group of the zebrafish fries and carrying out statistics, counting the half lethal dose (LD50) value through fitting curve by using GraphPad Prism software and responding the acute toxicity of the medicament by using the LD50 value. The method has the advantages that the method is simple in operation, rapid and high in accuracy and the acute toxicity of the medicament to be tested can be judged preliminarily.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods of using thrombin peptide derivatives
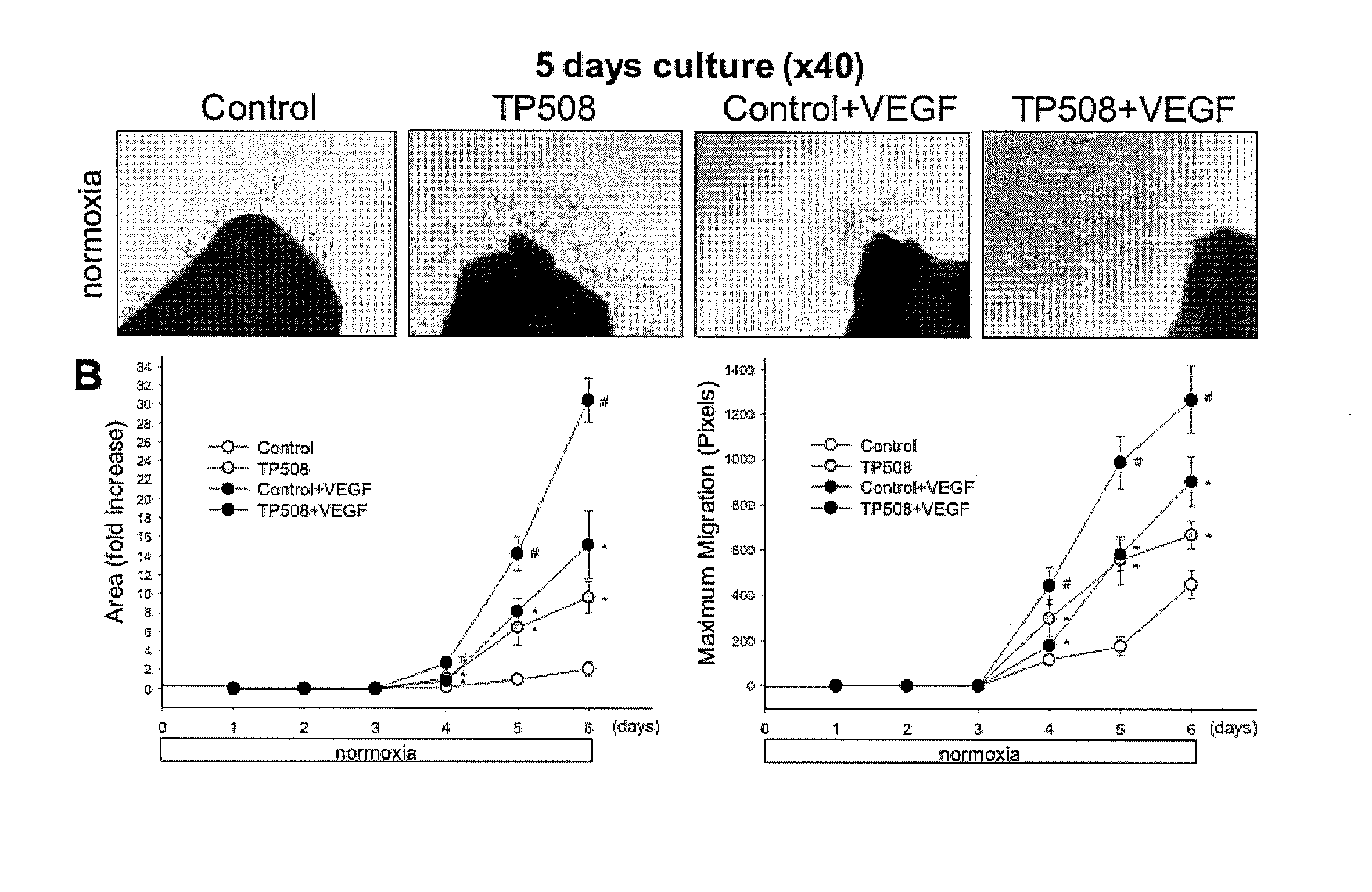
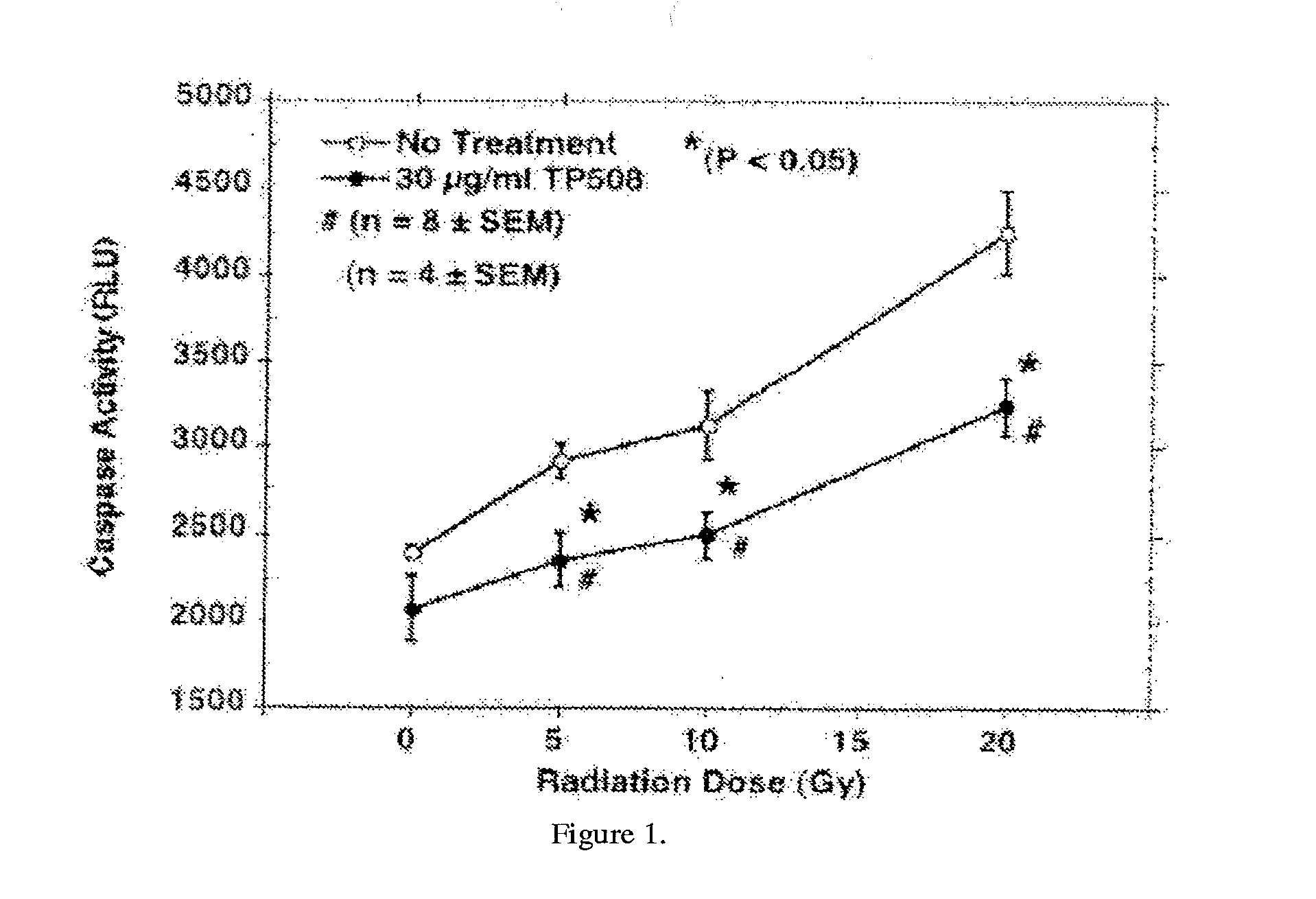
InactiveUS20130101574A1Prolong survival timeSlow onsetPeptide/protein ingredientsArterial ulcerLethal dose
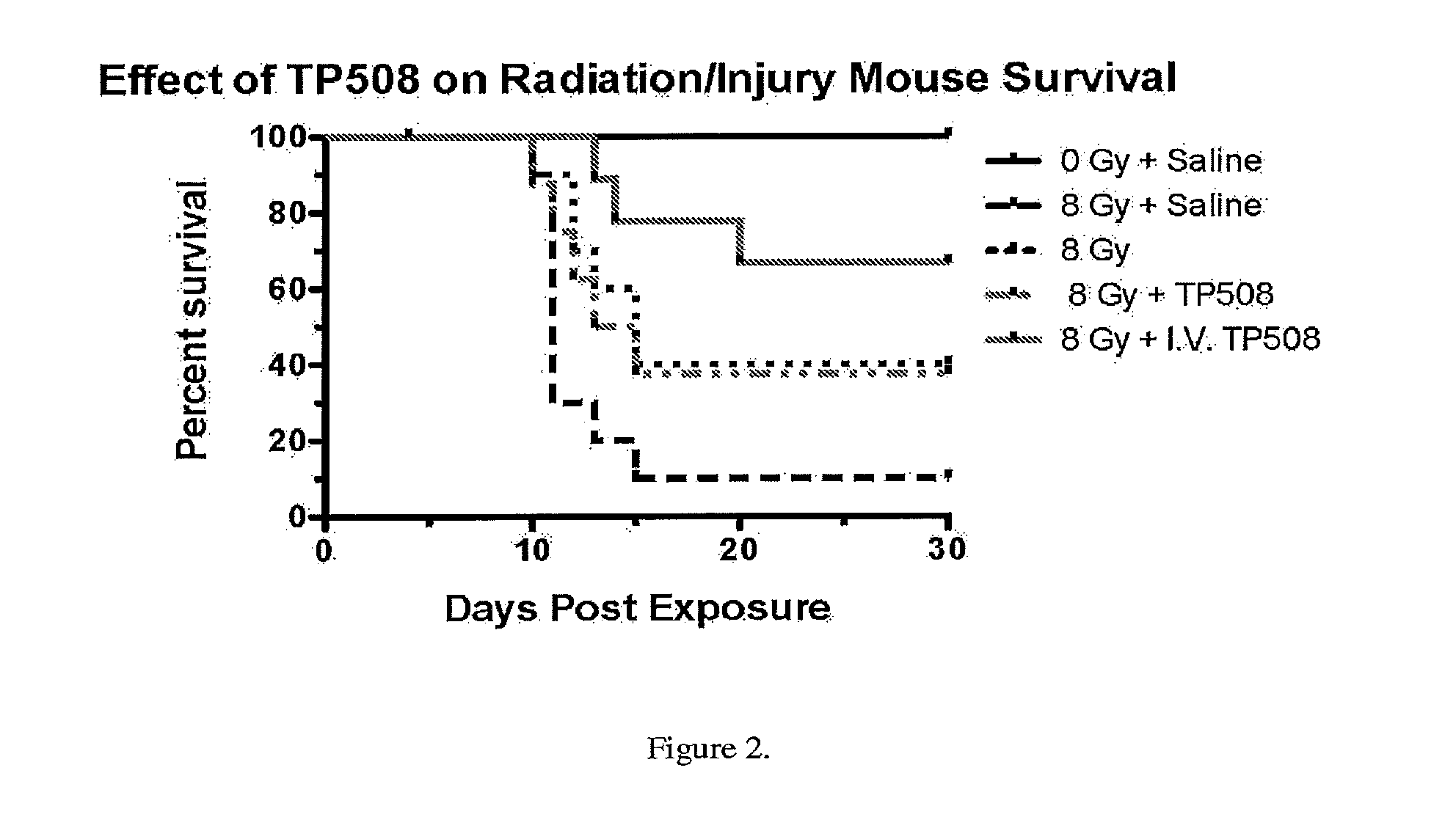
The present invention provides methods of reducing mortality in a subject exposed to a lethal dose of radiation, methods of reducing the risk of developing bacterial, fungal or viral systemic infection in a subject who is exposed or not exposed to radiation, methods of prevention and treatment of oral complications, particularly oral complications as a result of treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy, methods of treating dermal ulcers, particularly diabetic dermal ulcers, pressure dermal ulcers, venous stasis ulcers, and arterial ulcers, methods of promoting bone growth, and methods of promoting cartilage growth and repair in a subject in need thereof, by administering a thrombin peptide derivative to a subject. The administration may be local or systemic.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Broad Spectrum of Streptococcus Lyase and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20180104316A1High activityIncrease enzyme activityAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationEscherichia coliBacteroides
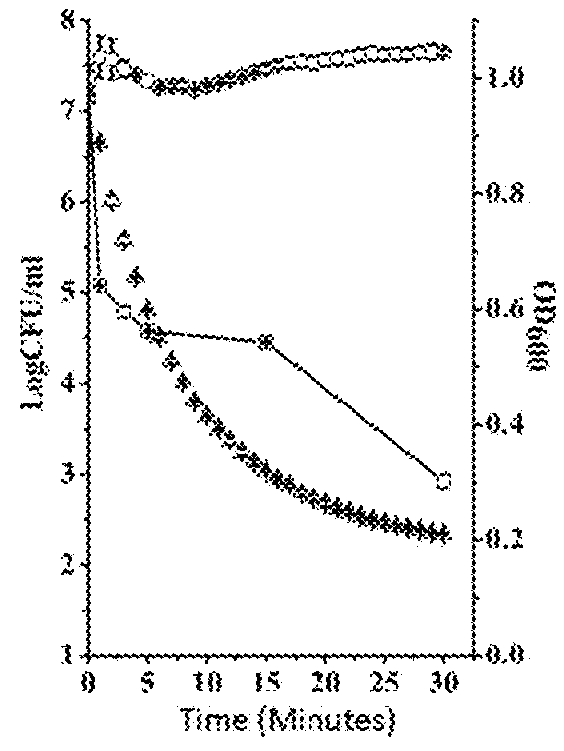
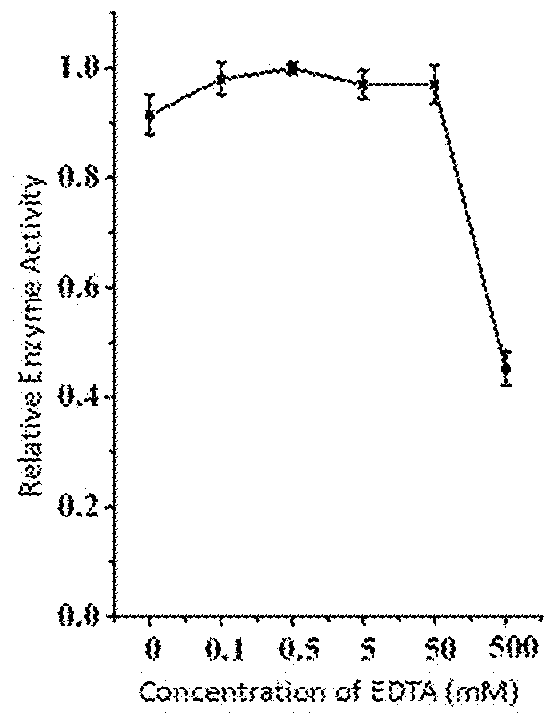
This invention discloses a lysin that can kill many species of Streptococci. A new lysin, ClyR, was constructed by the gene splicing method. The ClyR can effectively kill different species of Streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus equi, and various Enterococci and Staphylococcus aureus. ClyR shows good stability and is not sensitive to EDTA and high concentration of NaCl. Moreover, the ClyR is active in a wide range of pH and maintains high activity in pH 5-11. Recombinant protein ClyR is well expressed in E. coli stain BL21 (DE3). High doses of ClyR showed no apparent toxicity in mice. Furthermore, administration of 0.8 mg per mouse once is able to completely protect the mouse infected with lethal doses of Group B Streptococci. The ClyR can be used alone or in combination with different forms of reagents and solutions, for the control of a variety of Streptococci and for the treatment of infections caused by these bacteria. It has a broad application prospect.
Owner:PHAGELUX INC
Method for separating lethal toxin protein from cyanea nozakii nematocyst toxin
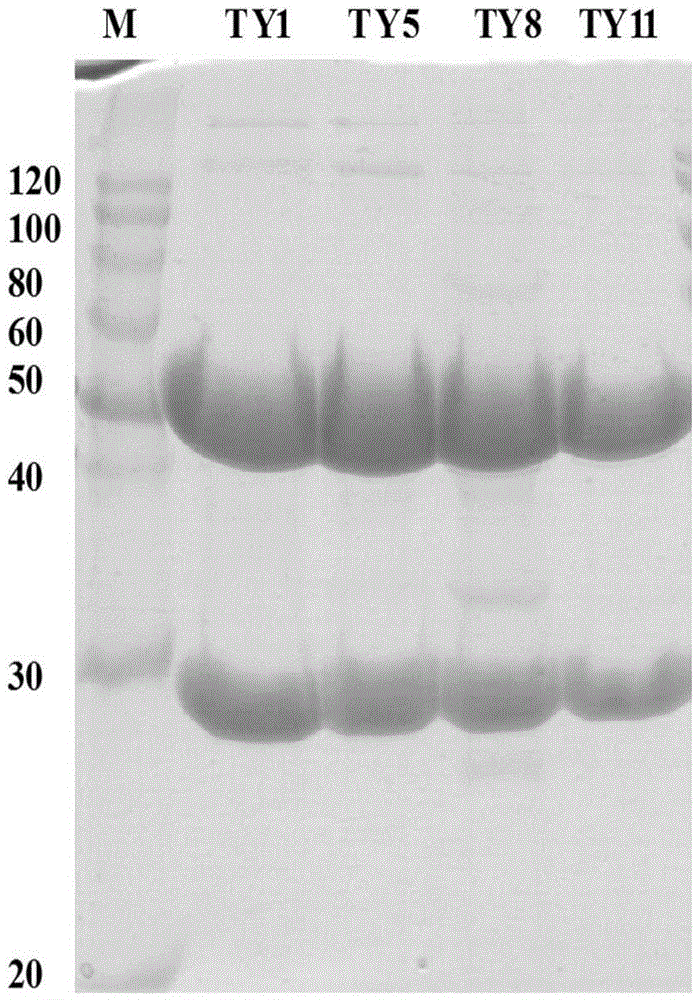
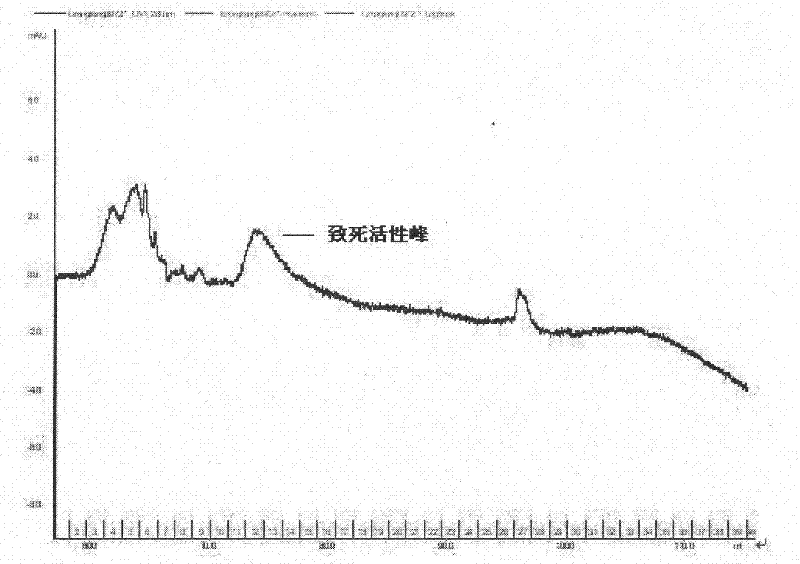
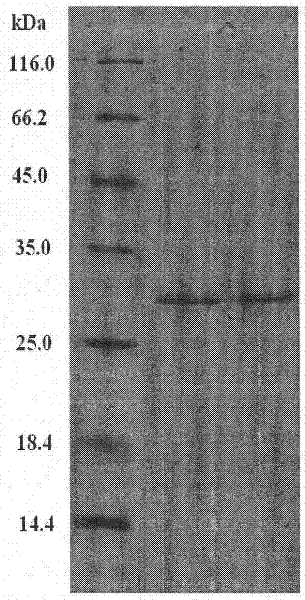
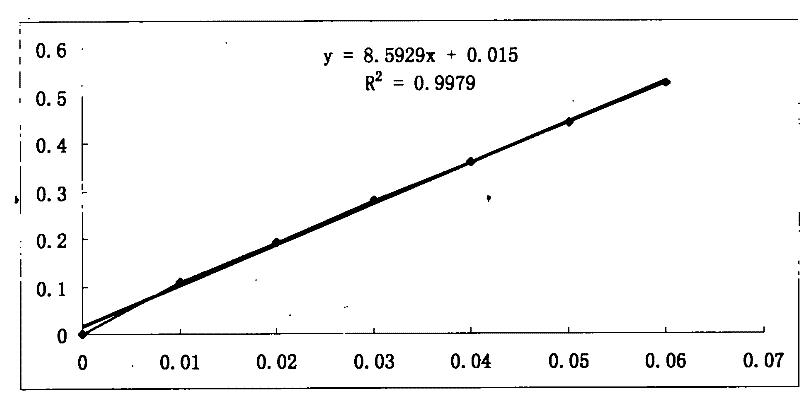
ActiveCN102174098ALittle loss of activityFast flowPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesChromatographic separationLethal dose
The invention relates to the technical field of marine organisms, in particular to a method for separating and purifying a cyanea nozakii lethal toxin protein. The method comprises the following steps of: ultrasonically crushing cyanea nozakii nematocyst cells to extract a jellyfish crude toxin, dialyzing and desalting, and separating and purifying by affinity chromatographic separation and an anion exchange chromatographic technology in turn to obtain a jellyfish toxin protein with lethal activity, wherein through measurement, the molecular weight of the toxin protein is 30kDa, and the lethal dose 50 (LD50) of the toxin protein to 1g of zebra fish is 0.56mu g. The method has the characteristics that: the method is quick, simple and convenient and provides important guidance for obtainingthe cyanea nozakii lethal toxin protein.
Owner:水母娘娘海洋生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com