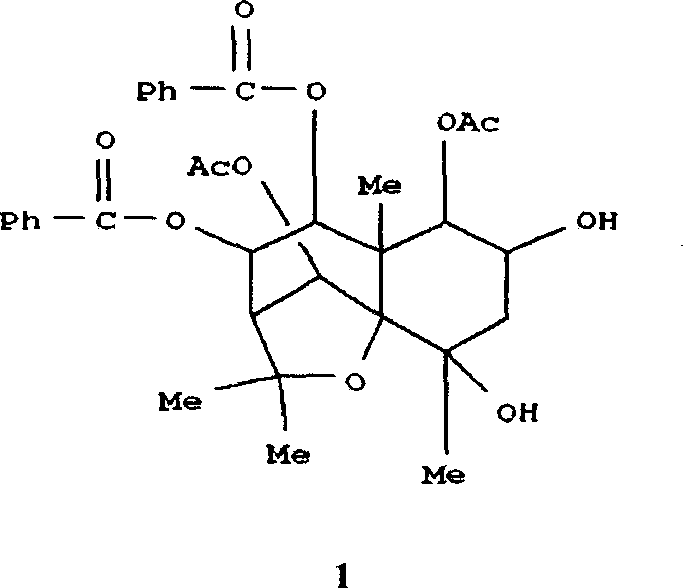
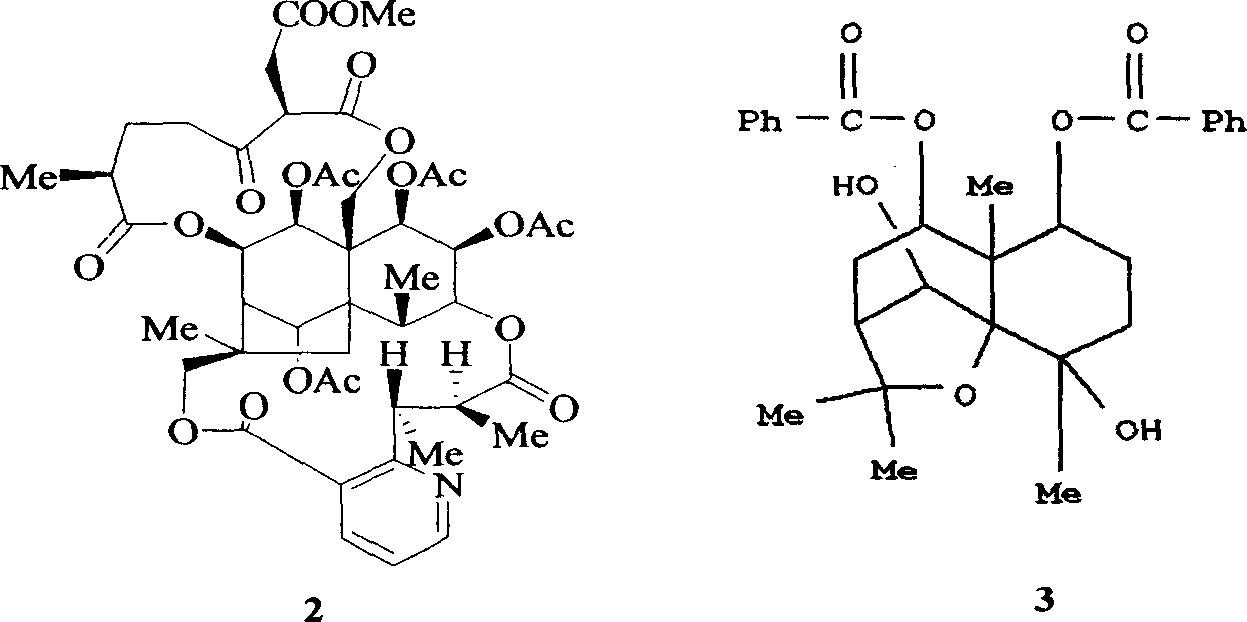
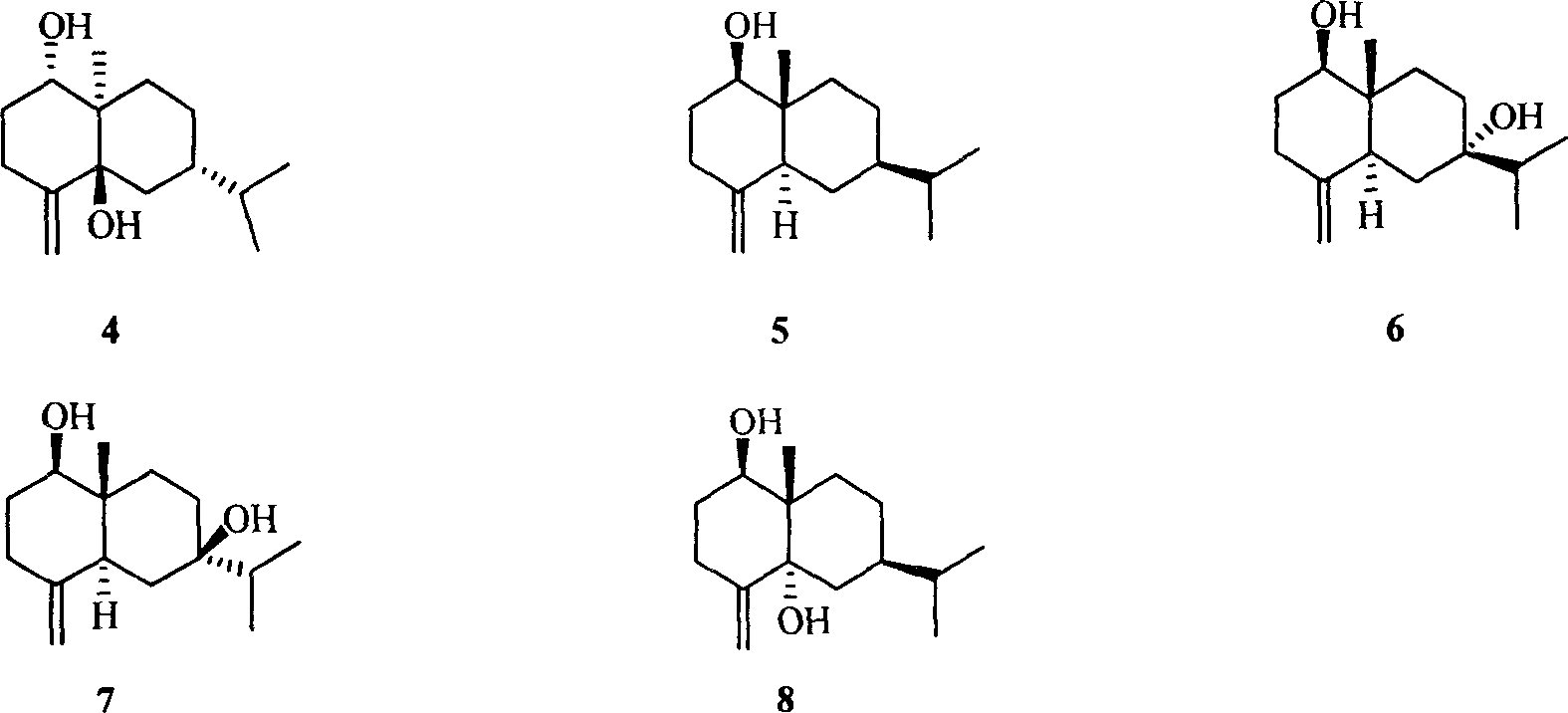
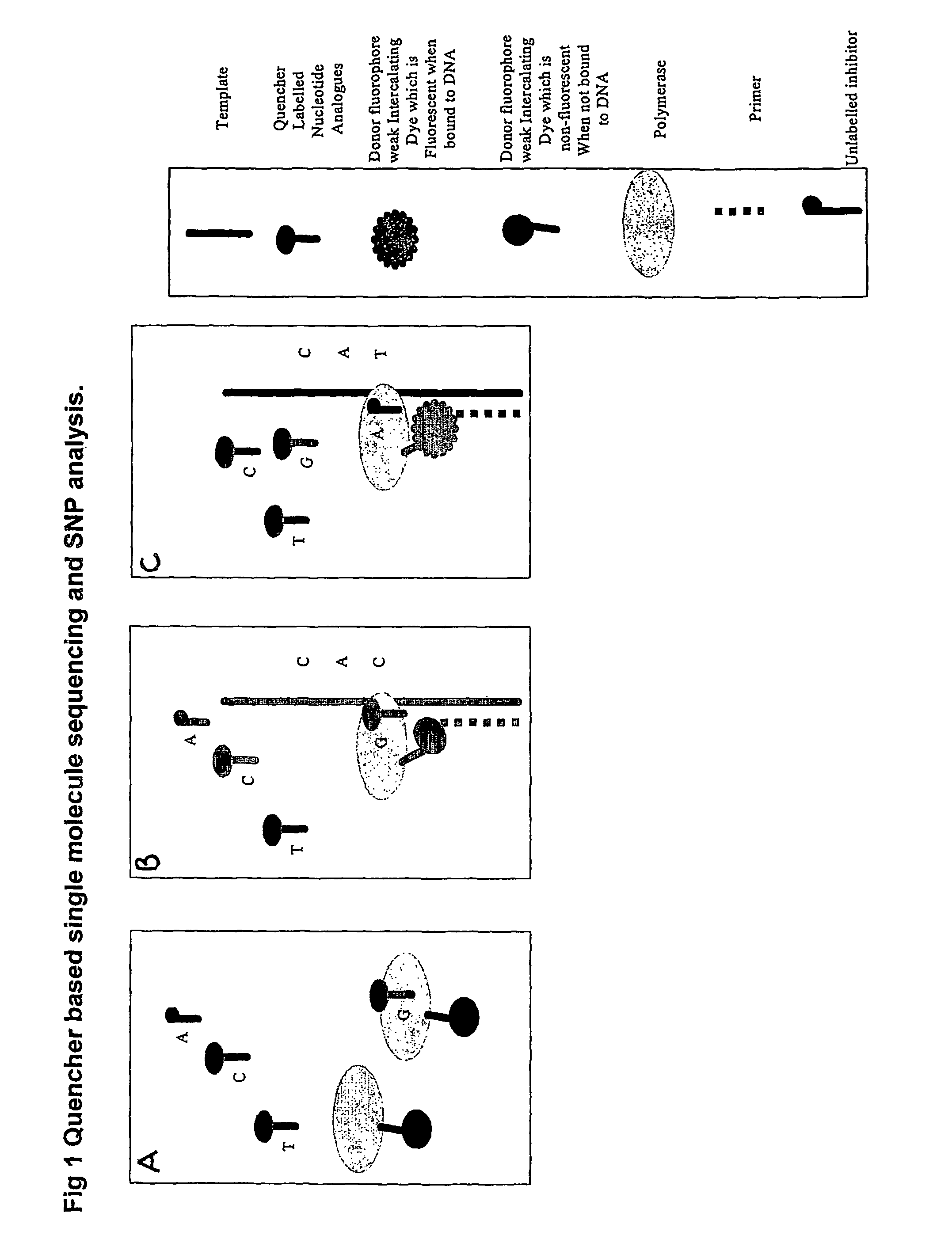
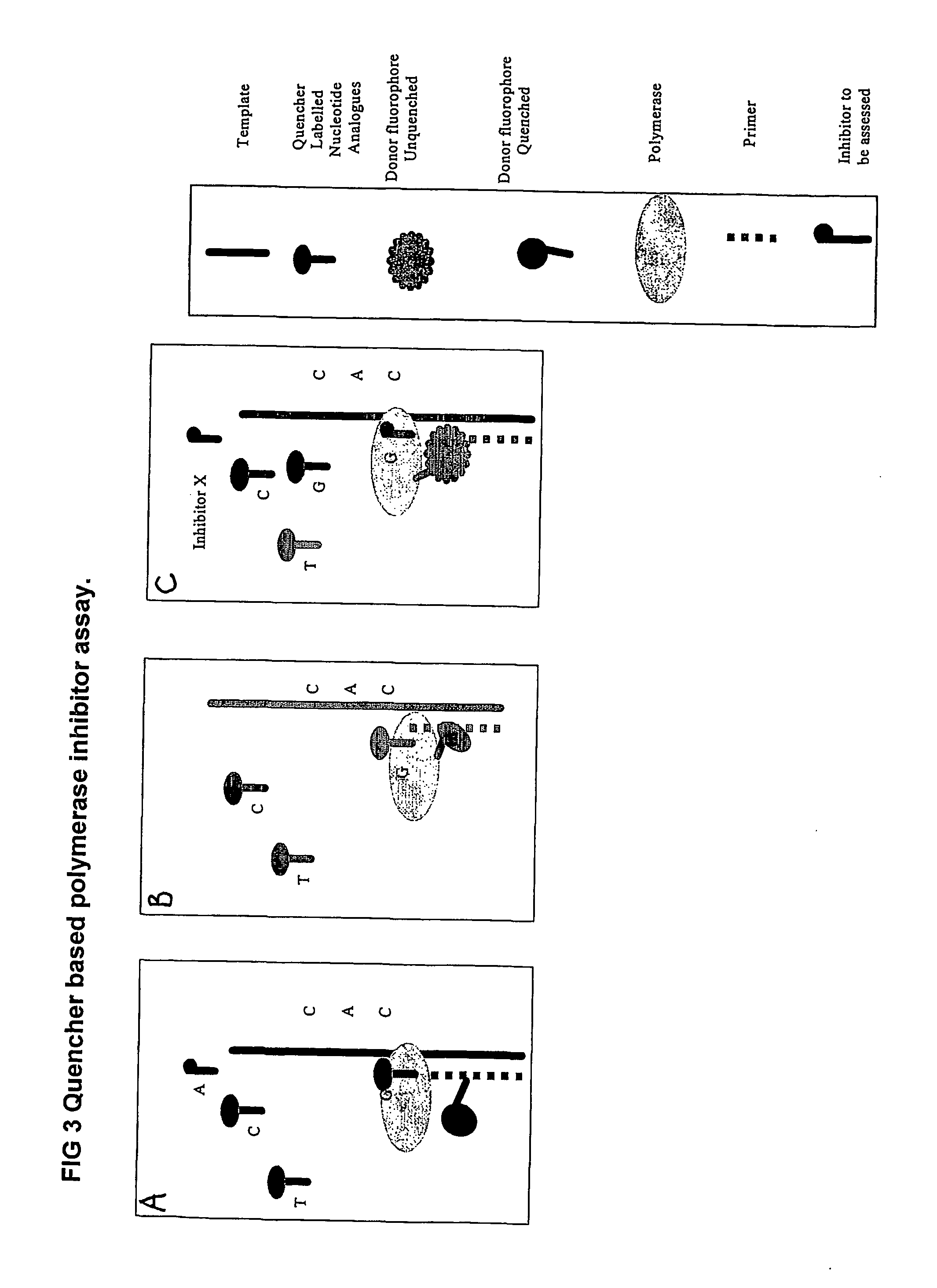
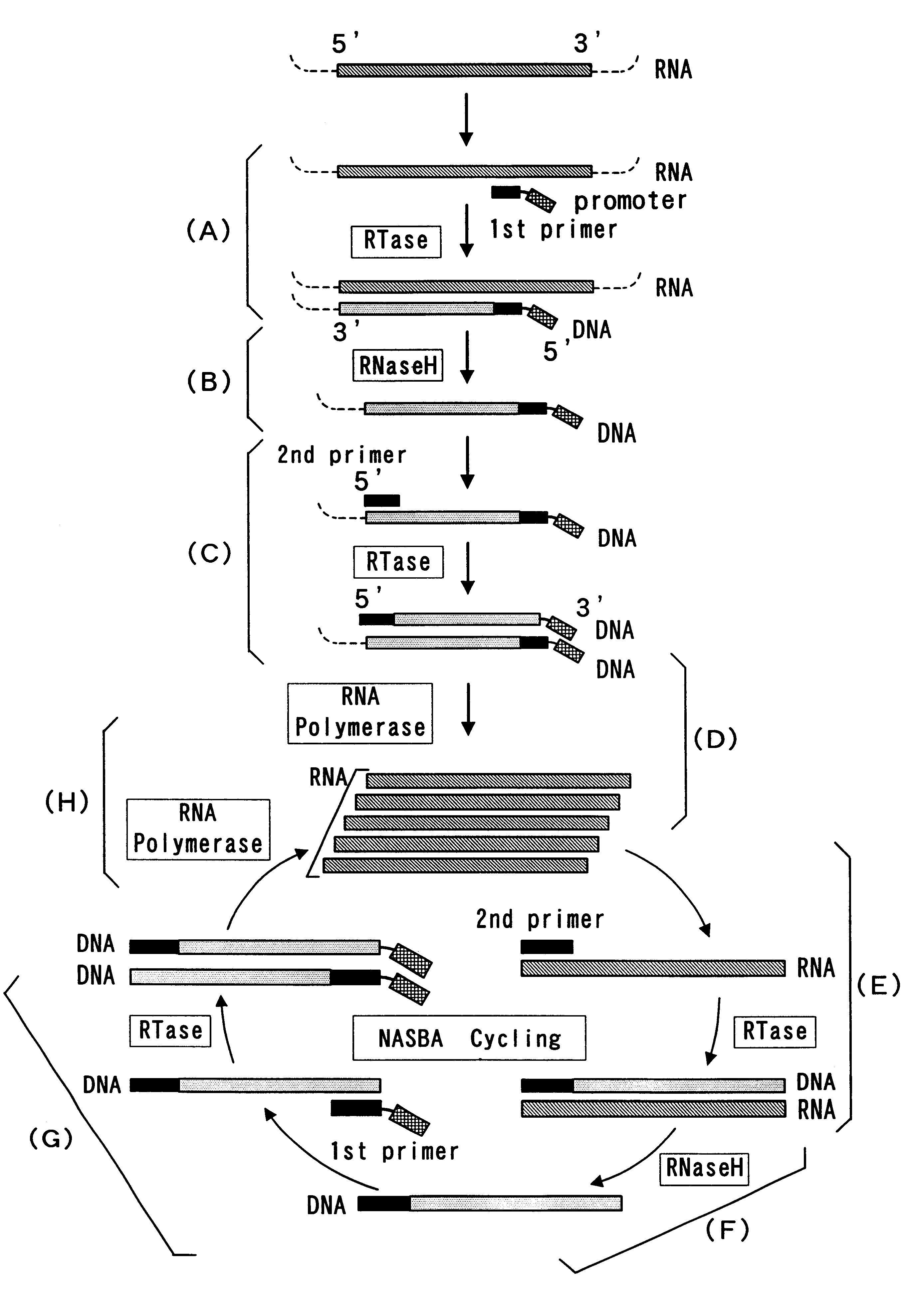
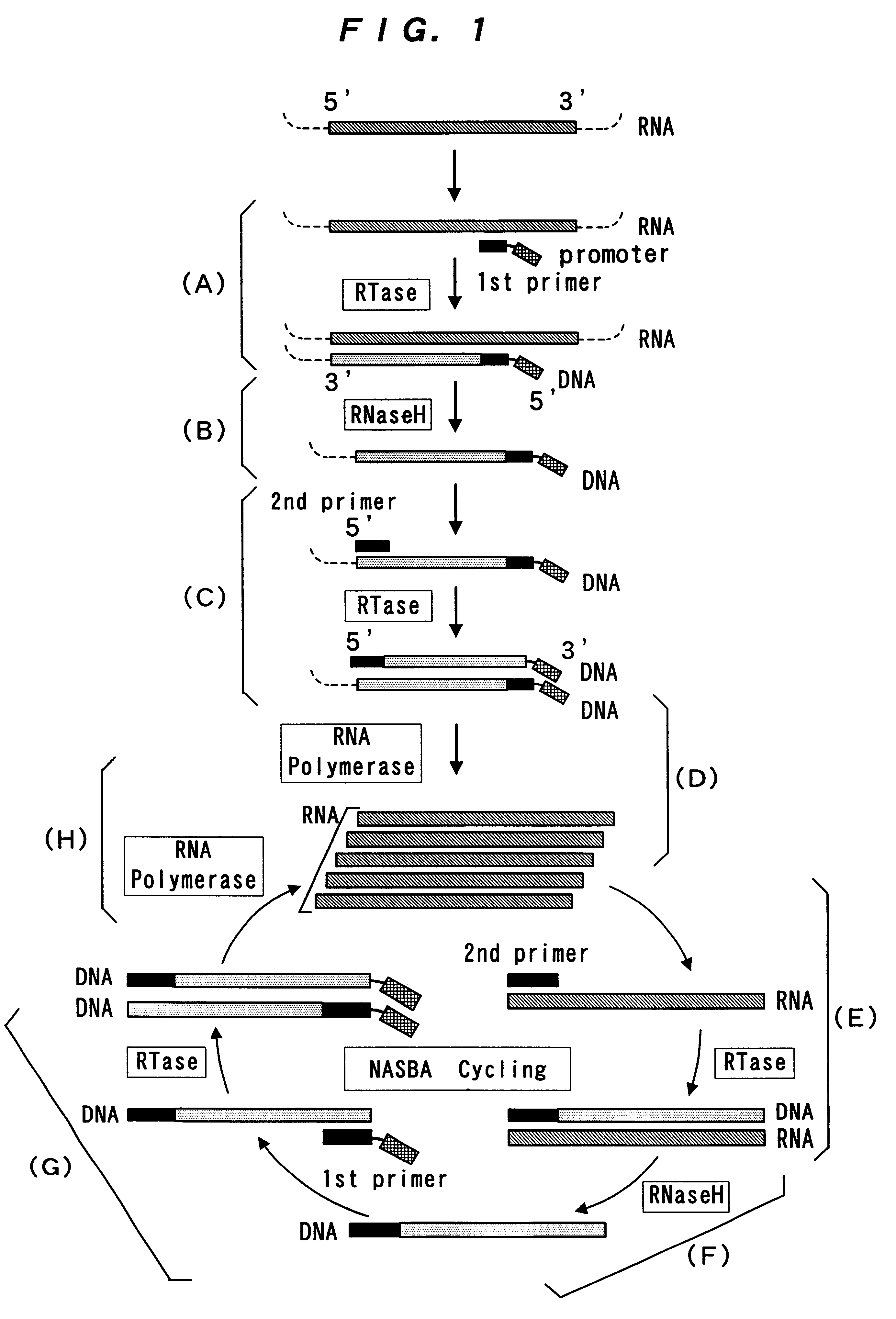
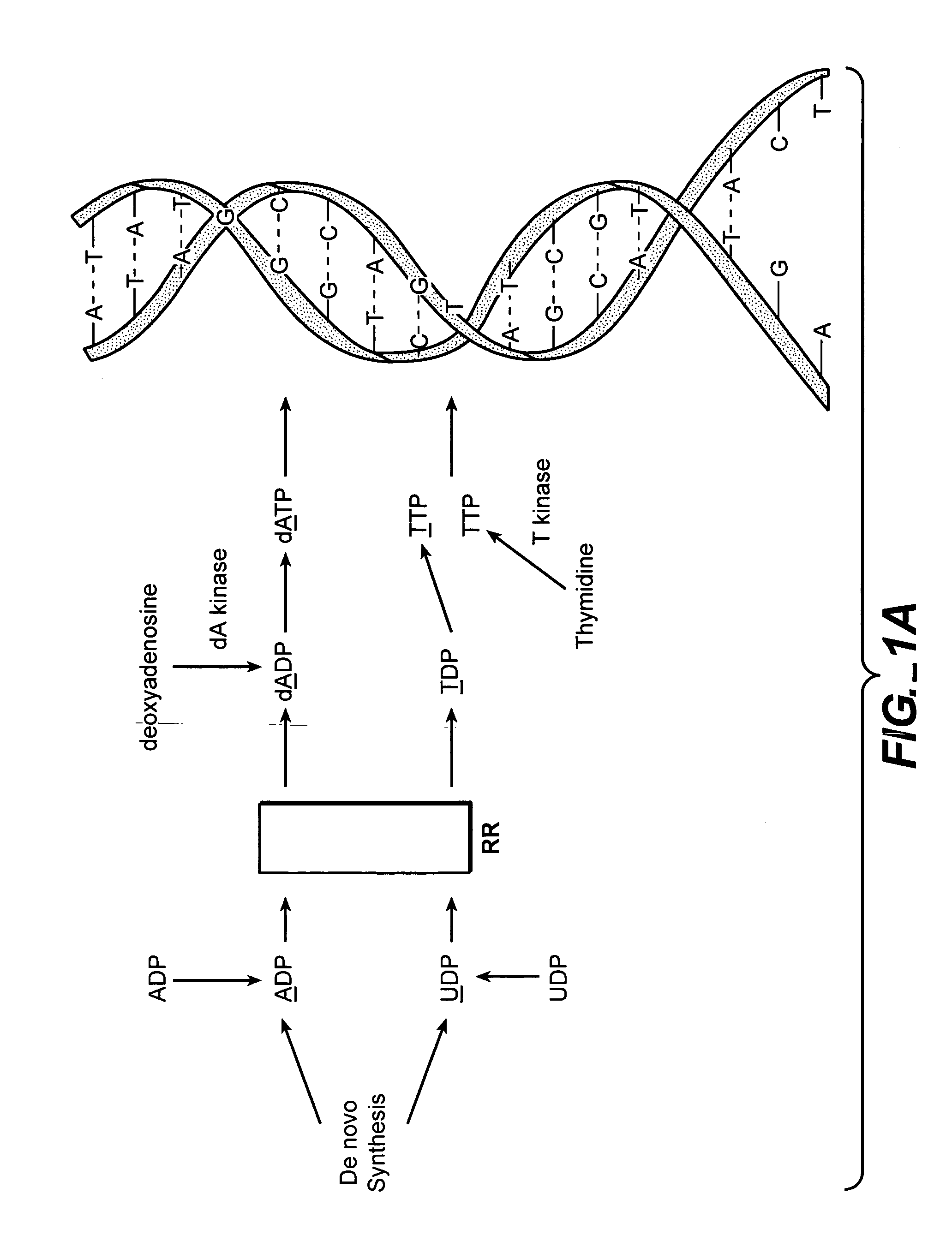
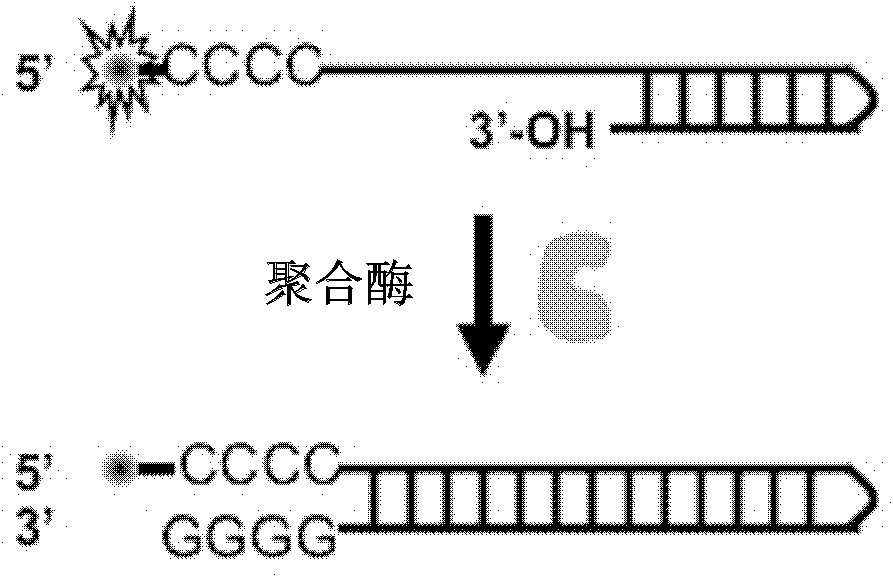
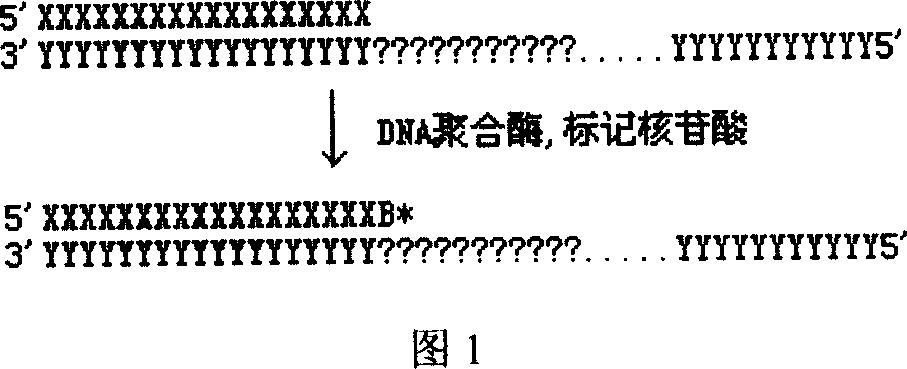
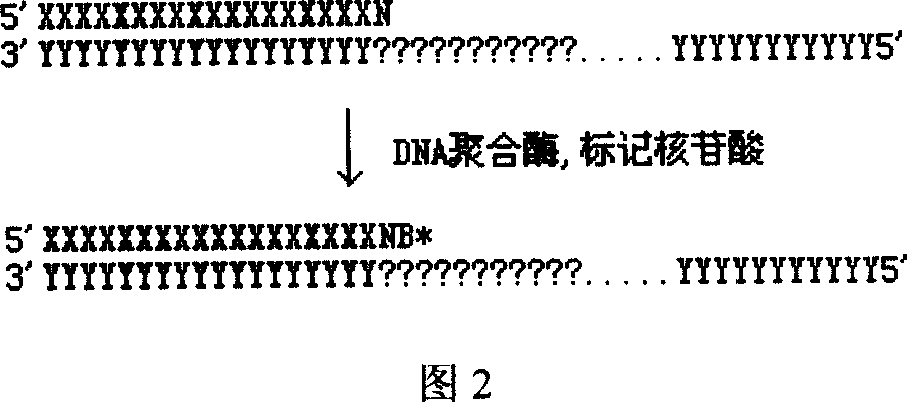
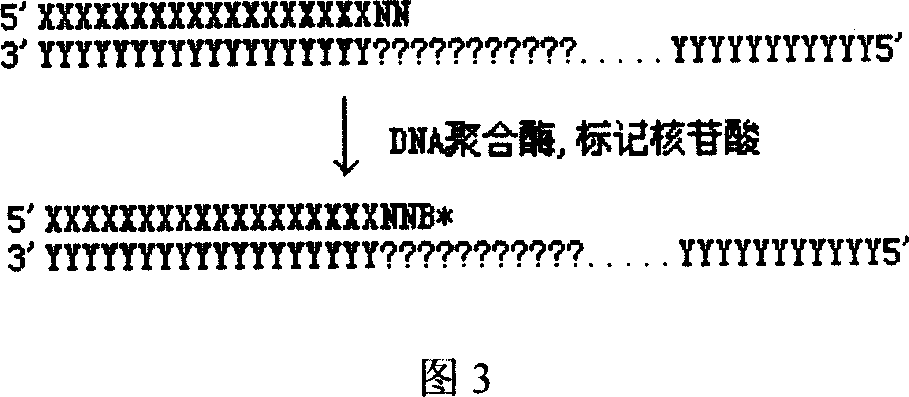
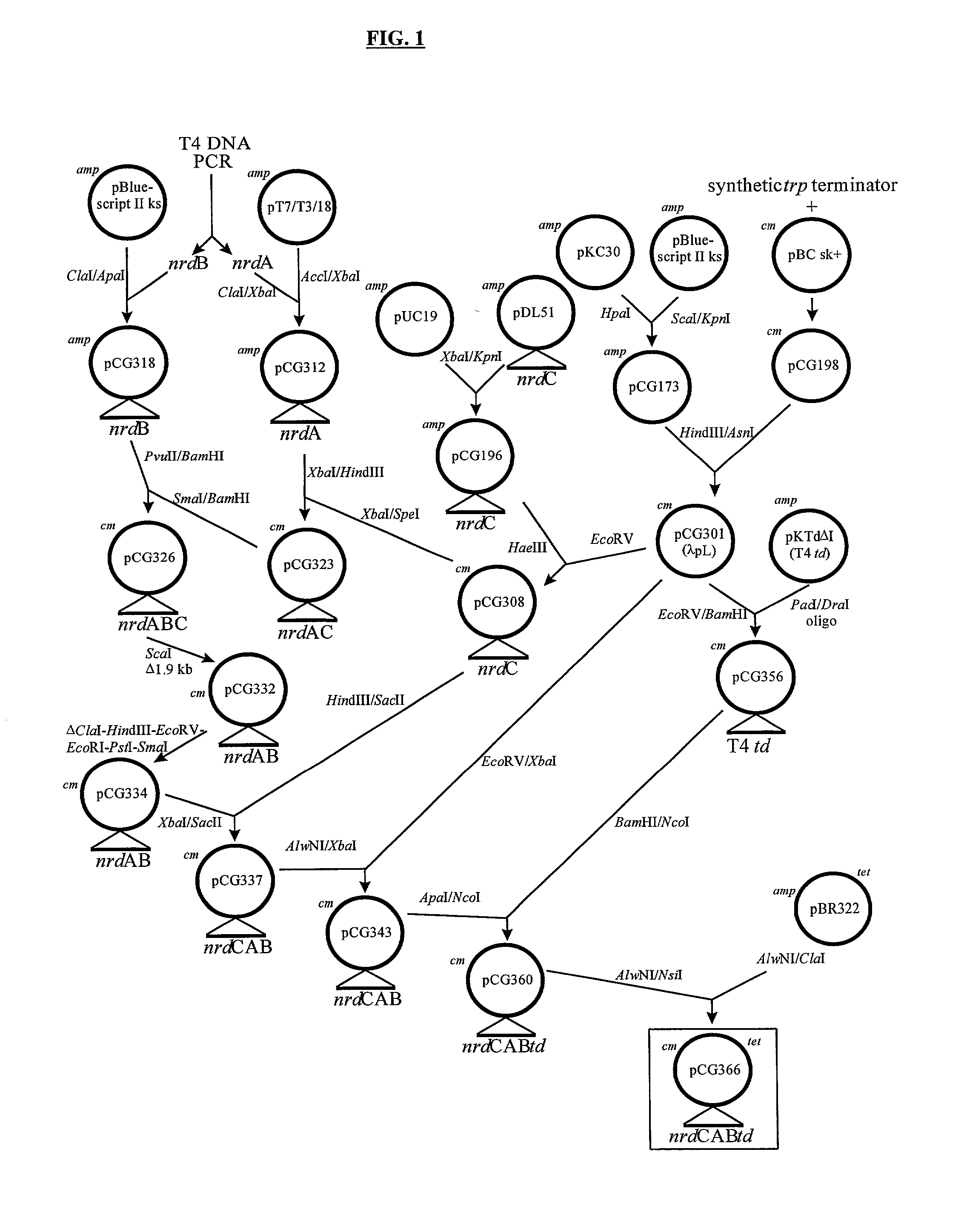
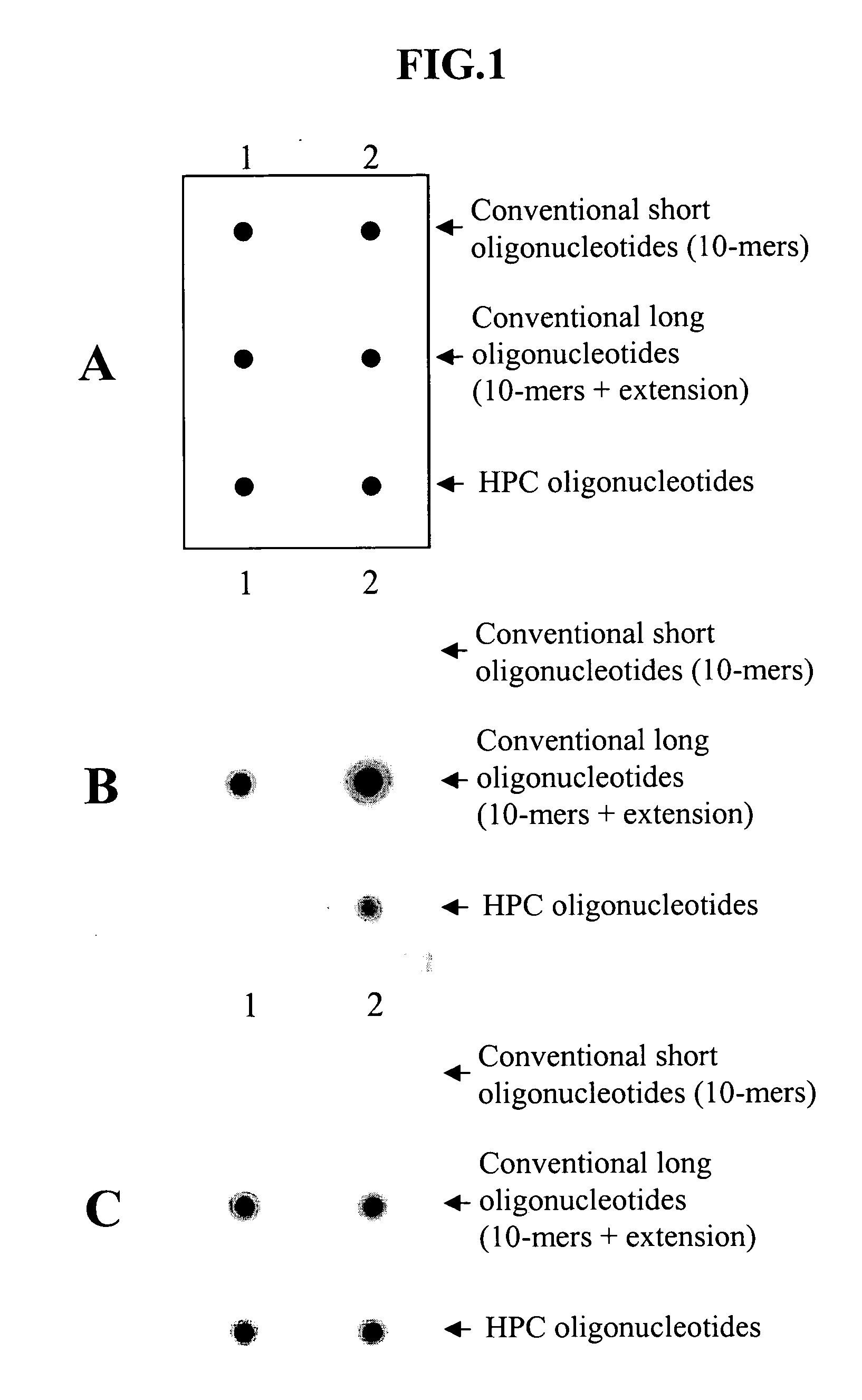
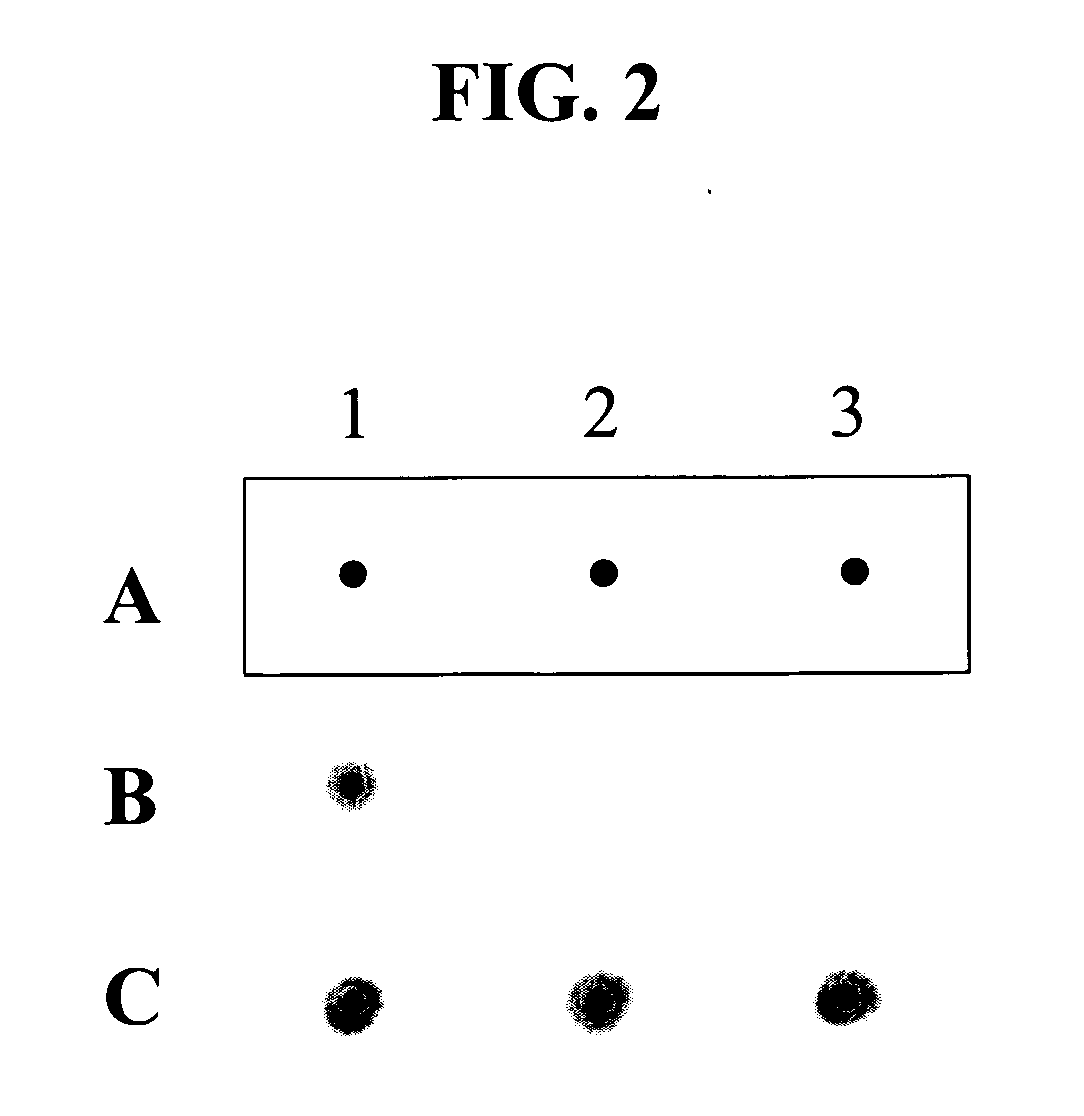
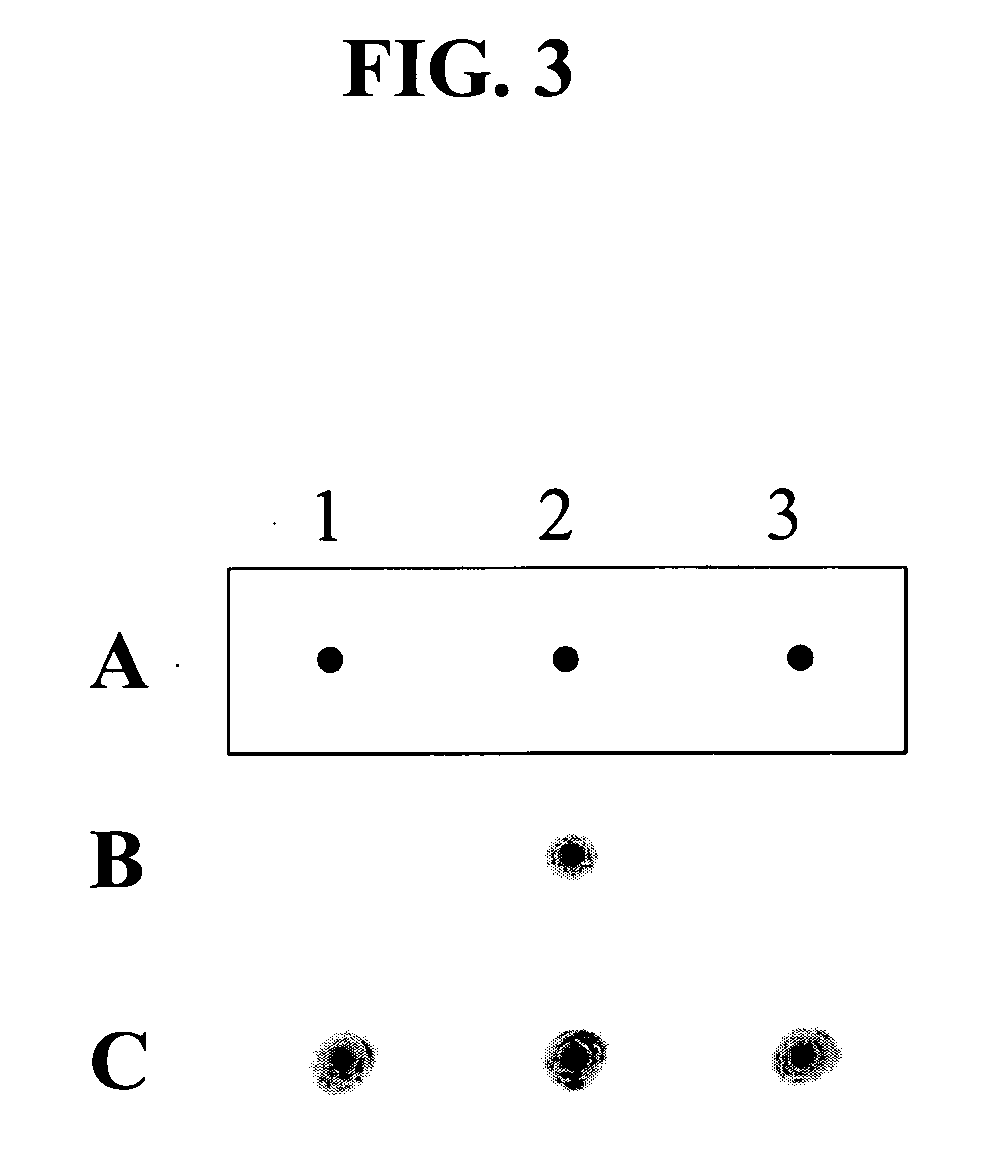
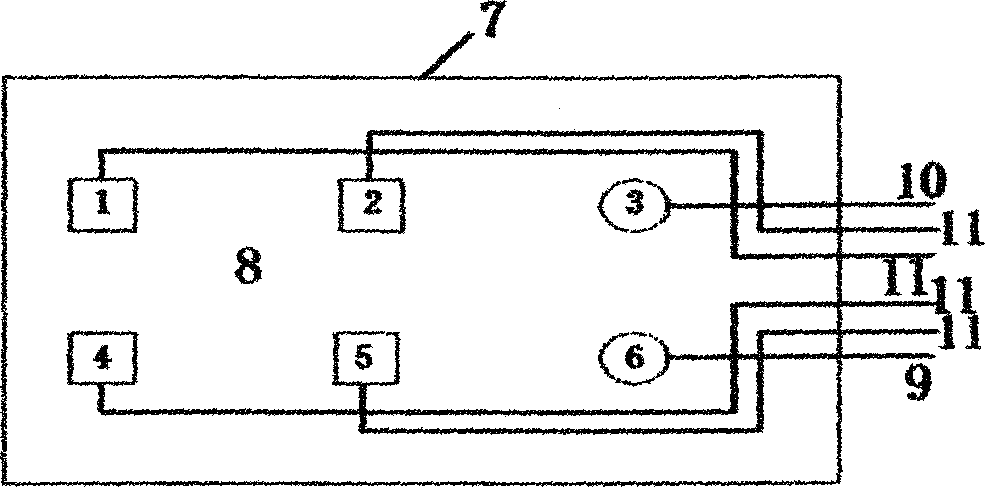
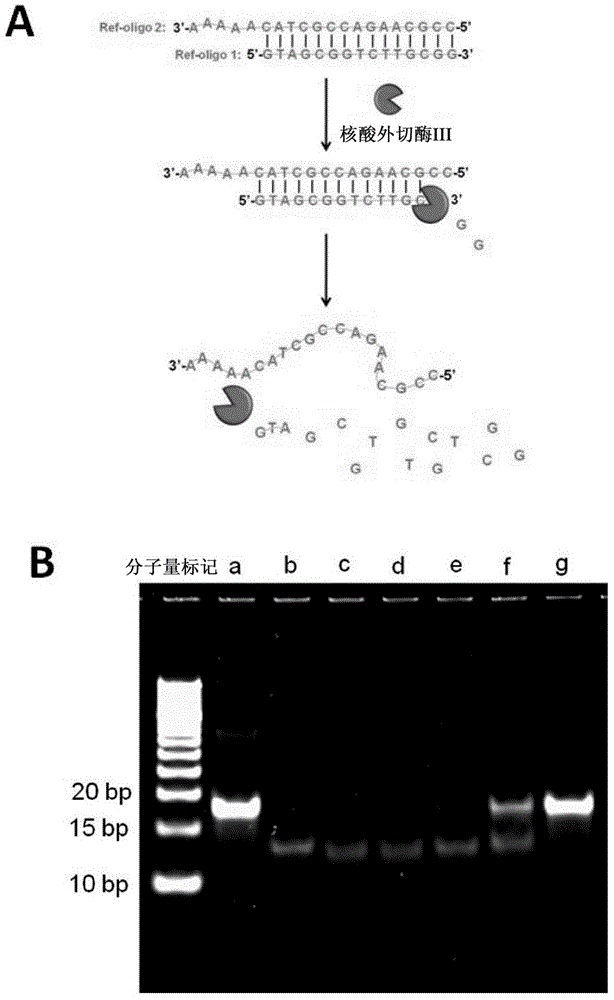
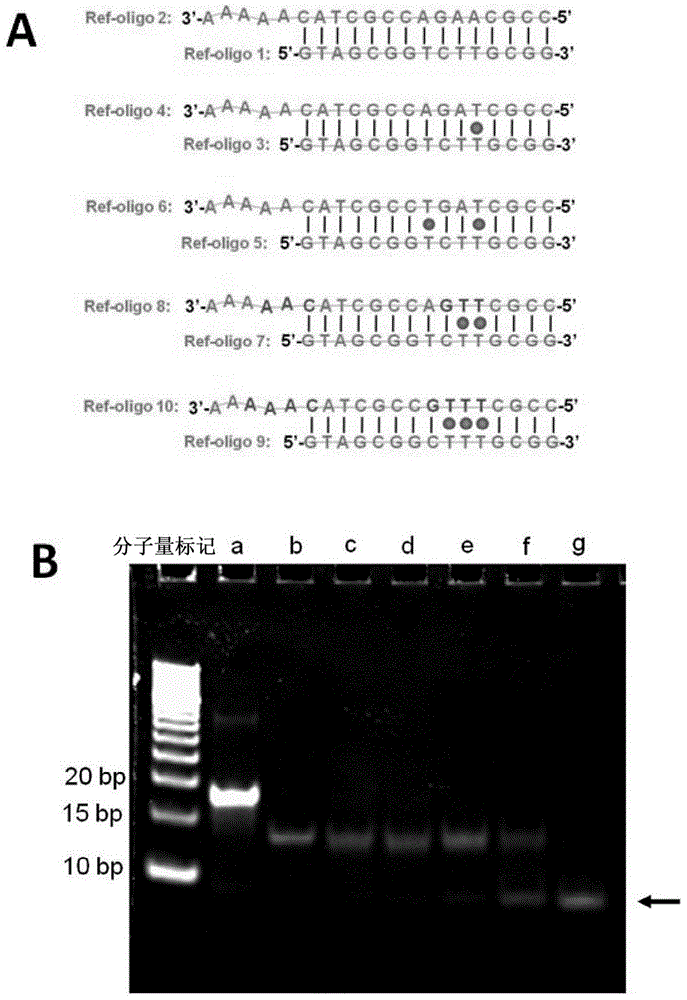
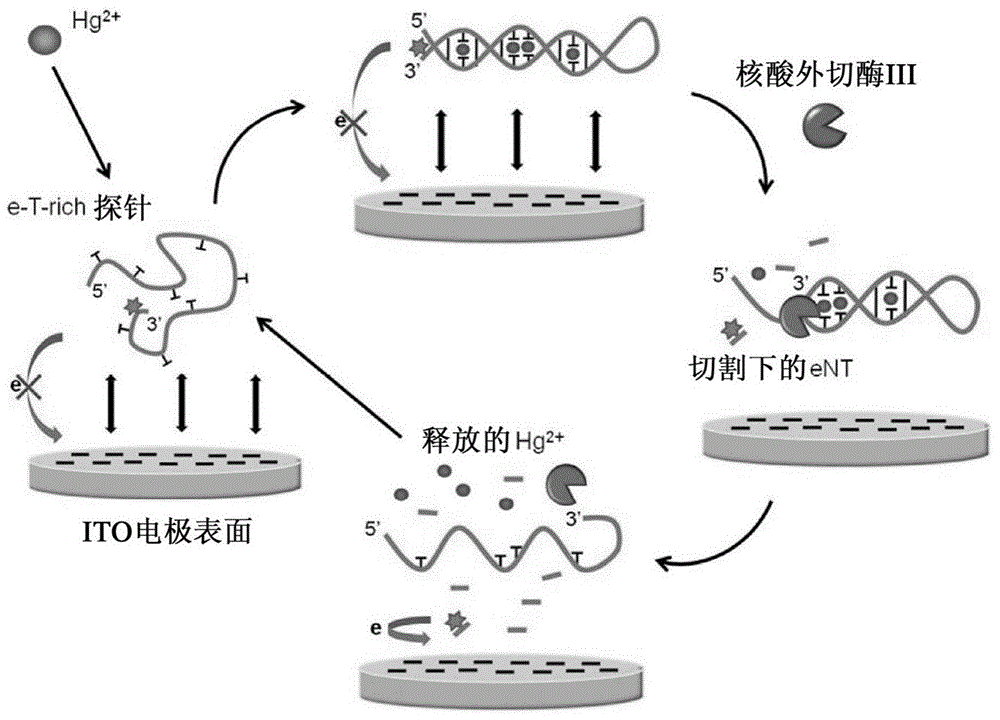
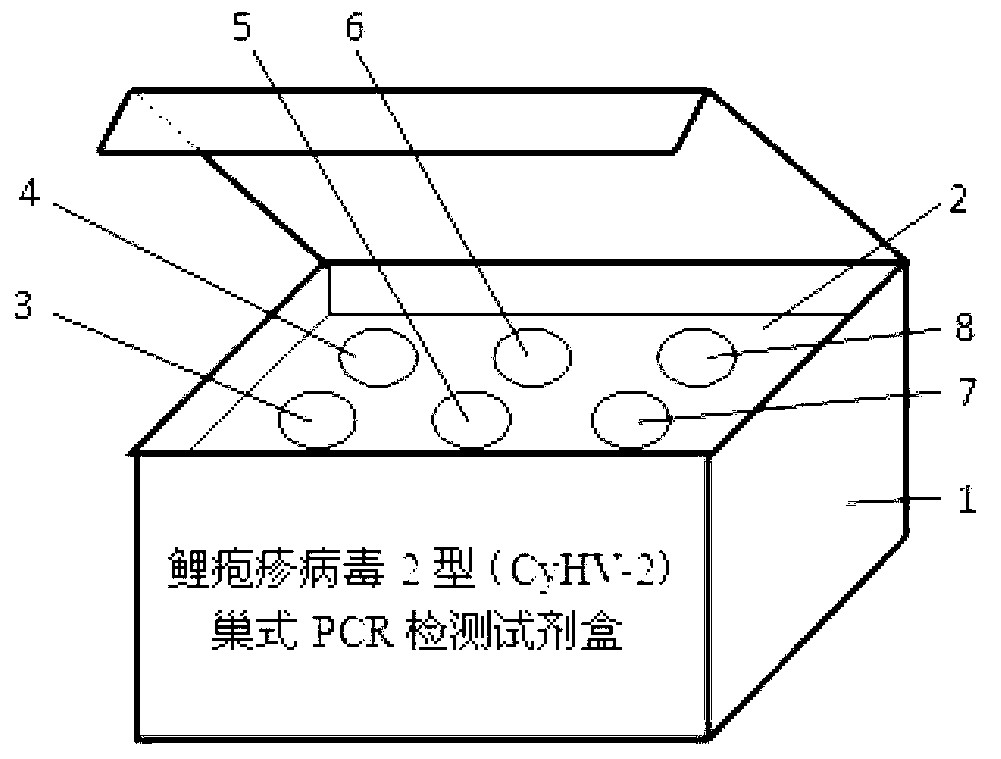
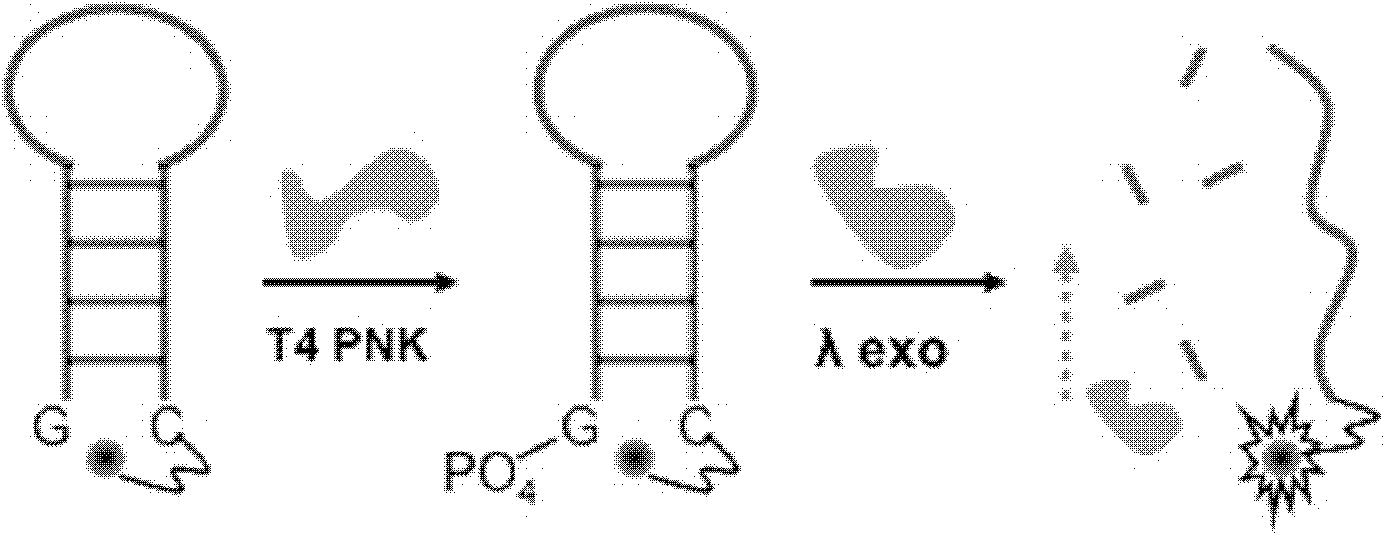Patents
Literature
245 results about "Deoxyribonucleotide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
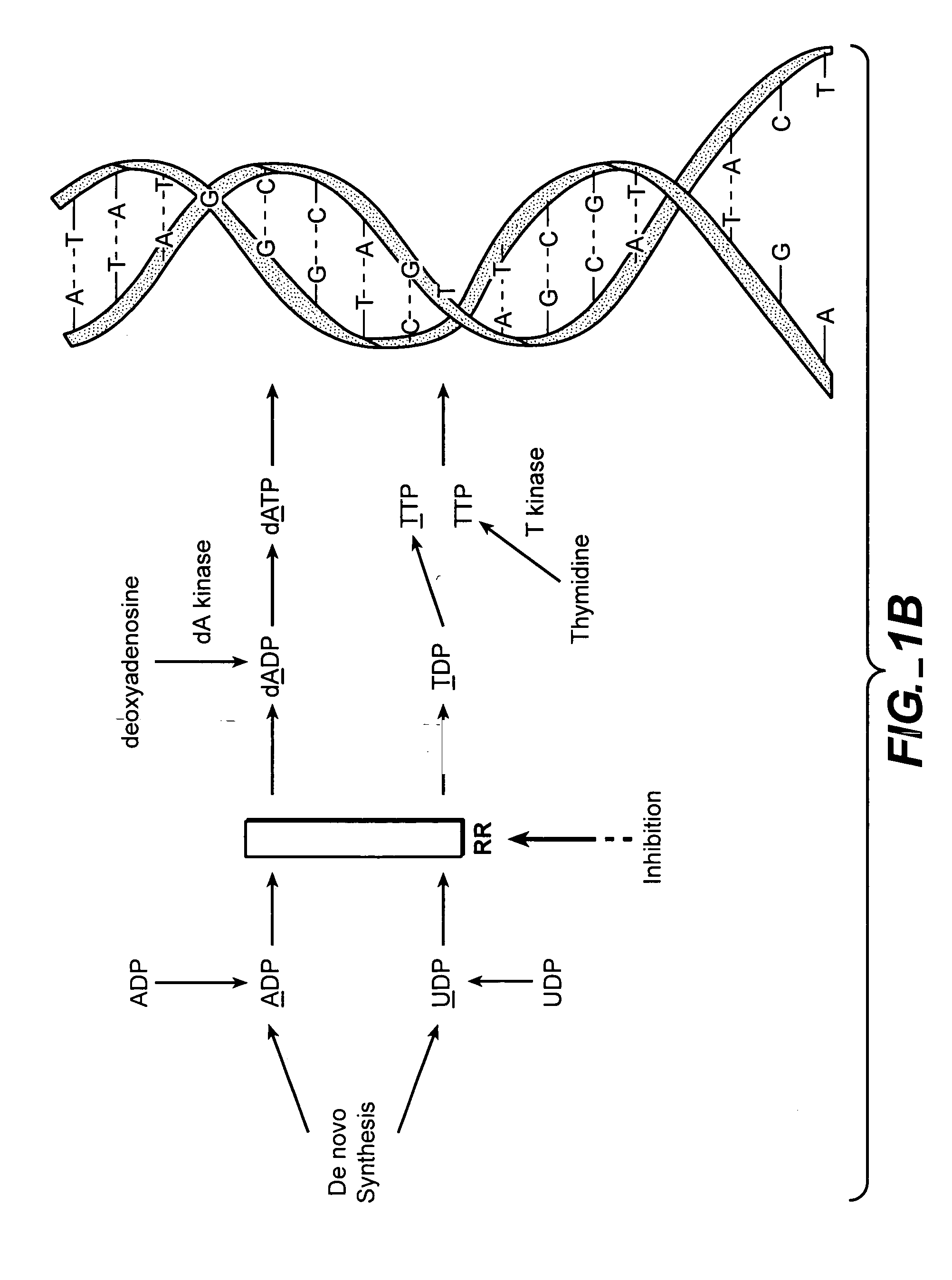
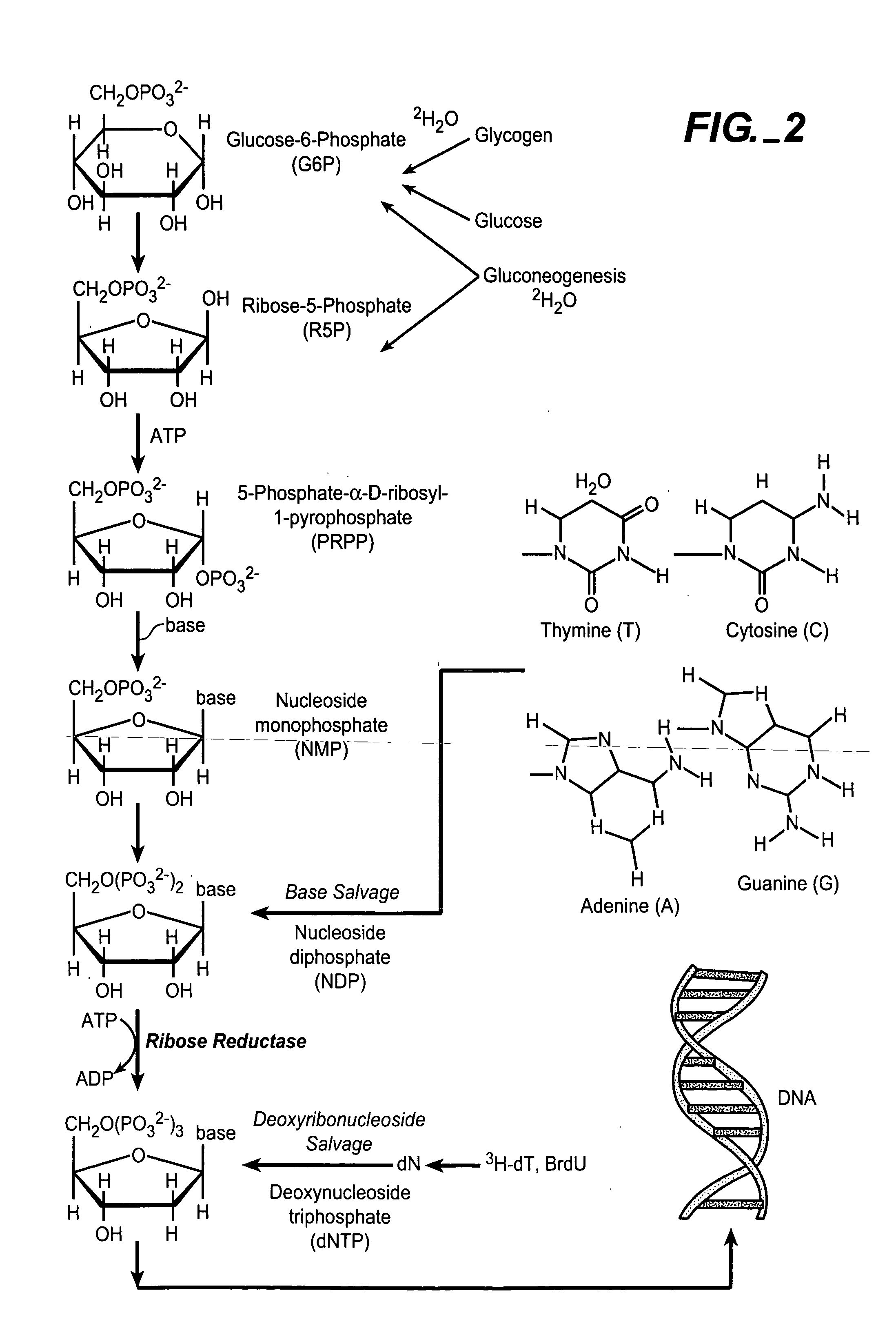
A deoxyribonucleotide is the monomer, or single unit, of DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid. Each deoxyribonucleotide comprises three parts: a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and one phosphate group. The nitrogenous base is always bonded to the 1' carbon of the deoxyribose, which is distinguished from ribose by the presence of a proton on the 2' carbon rather than an -OH group. The phosphate groups bind to the 5' carbon of the sugar.
Medical use of 1beta-keto-5, 11(13)-diene eudesmane-12-acid for inhibiting hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN1927197APrevention and treatment of viral hepatitis BHBsAg reductionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseasePositive control
The invention involves A 1- beta-keto-5, 11(13)-diene eudesmane-12-acidum who has the structure as formula (1) shows and its medical salt, or solvate and its drug combinations and its medical usage in reducing hepatitis B surface antgien and inhibiting replication activity of aethyl- hepatovirus HBV-DNA medicinal. The invention compounds has strong inhibitory action in hepatitis B surface antgien (HBsAg) externalized by HepG2.2.15 cells and replication of aethyl- hepatovirus deoxyribonucleotide (HBV-DNA) in vitro, its inhibiting ability against HBsAg surpasses that of positive control Lamivudine in the same dose; it has obvious inhibiting ability against replication of aethyl- hepatovirus HBV-DNA under the concentration of 100 mu g / mL,20 mug / mL and 4 mug / mL DNA, it belongs to anti- aethyl- hepatovirus natural products of superactive non-nucleoside, can be expected for producing drugs for treating aethyl- hepatovirus infected disease.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents
ActiveUS8399196B2Highly controllable homogeneousOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingProcessing enzymes
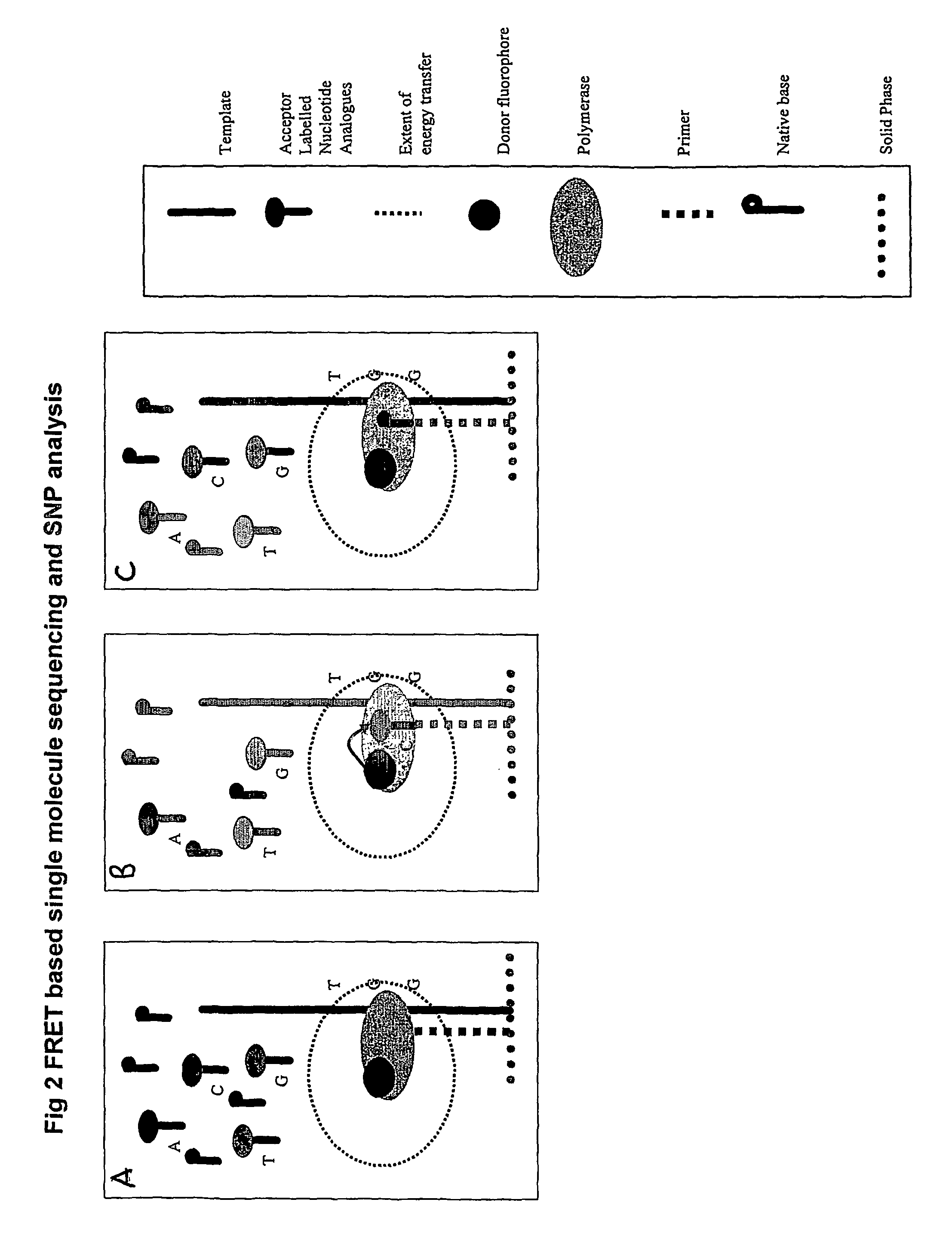
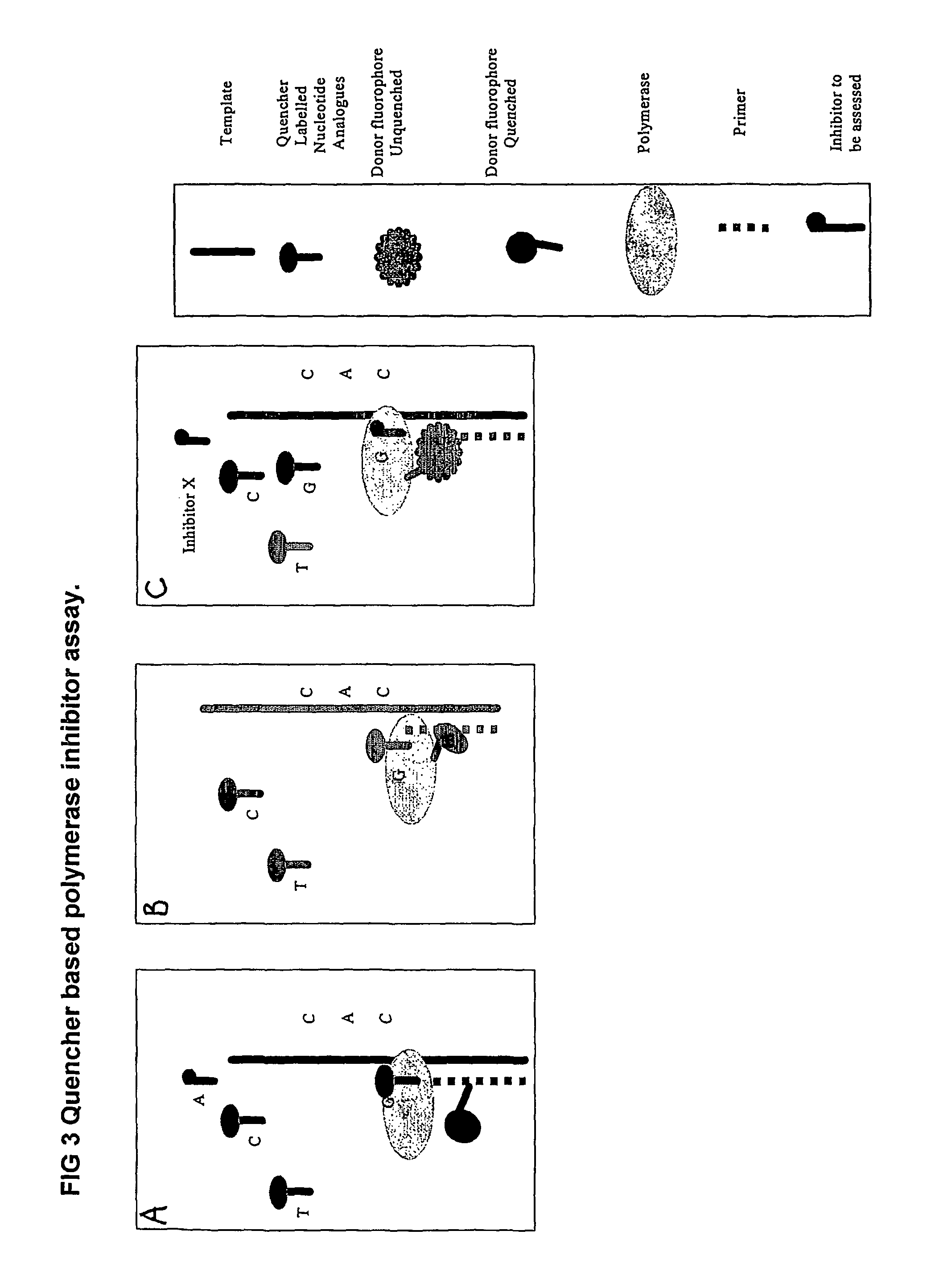
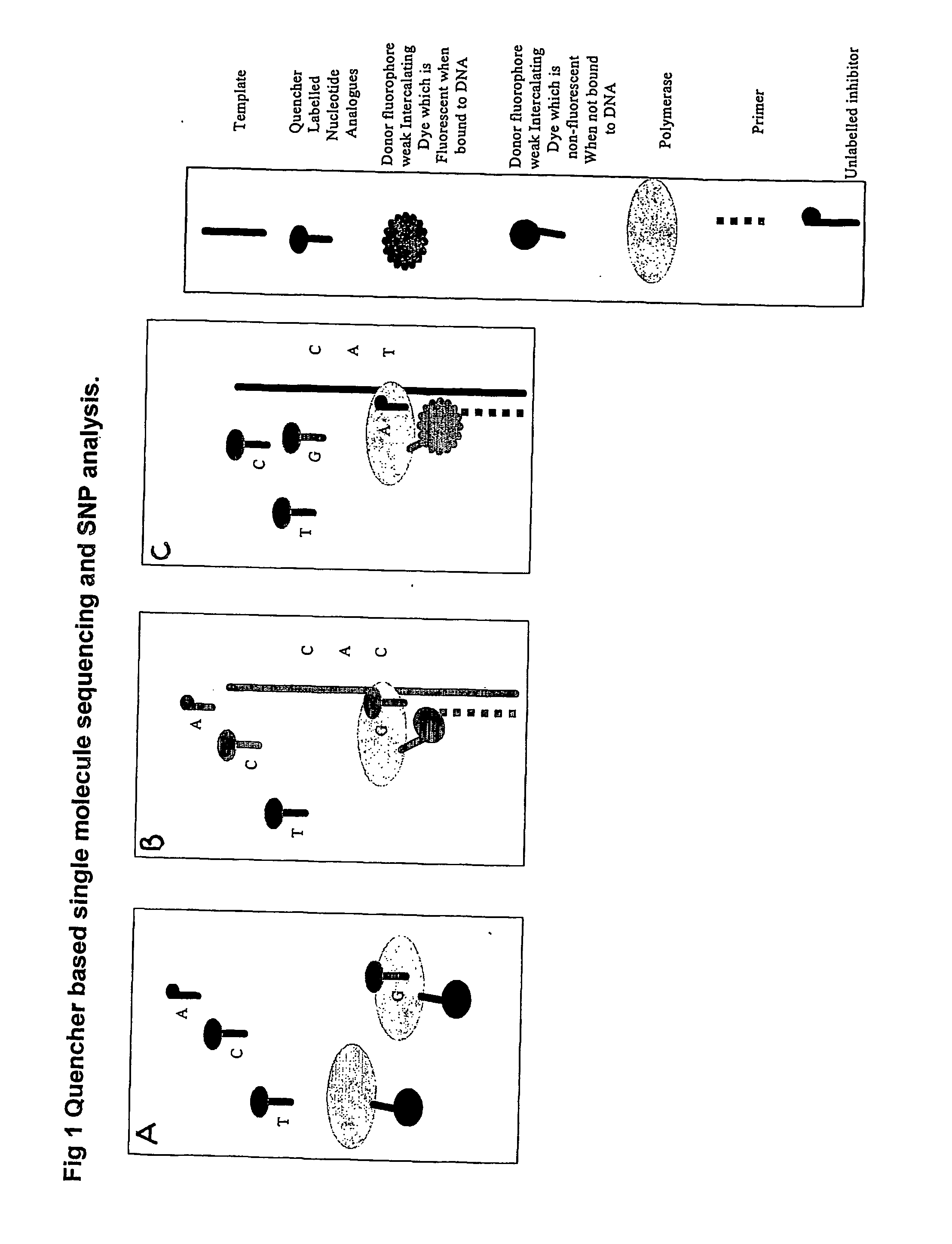
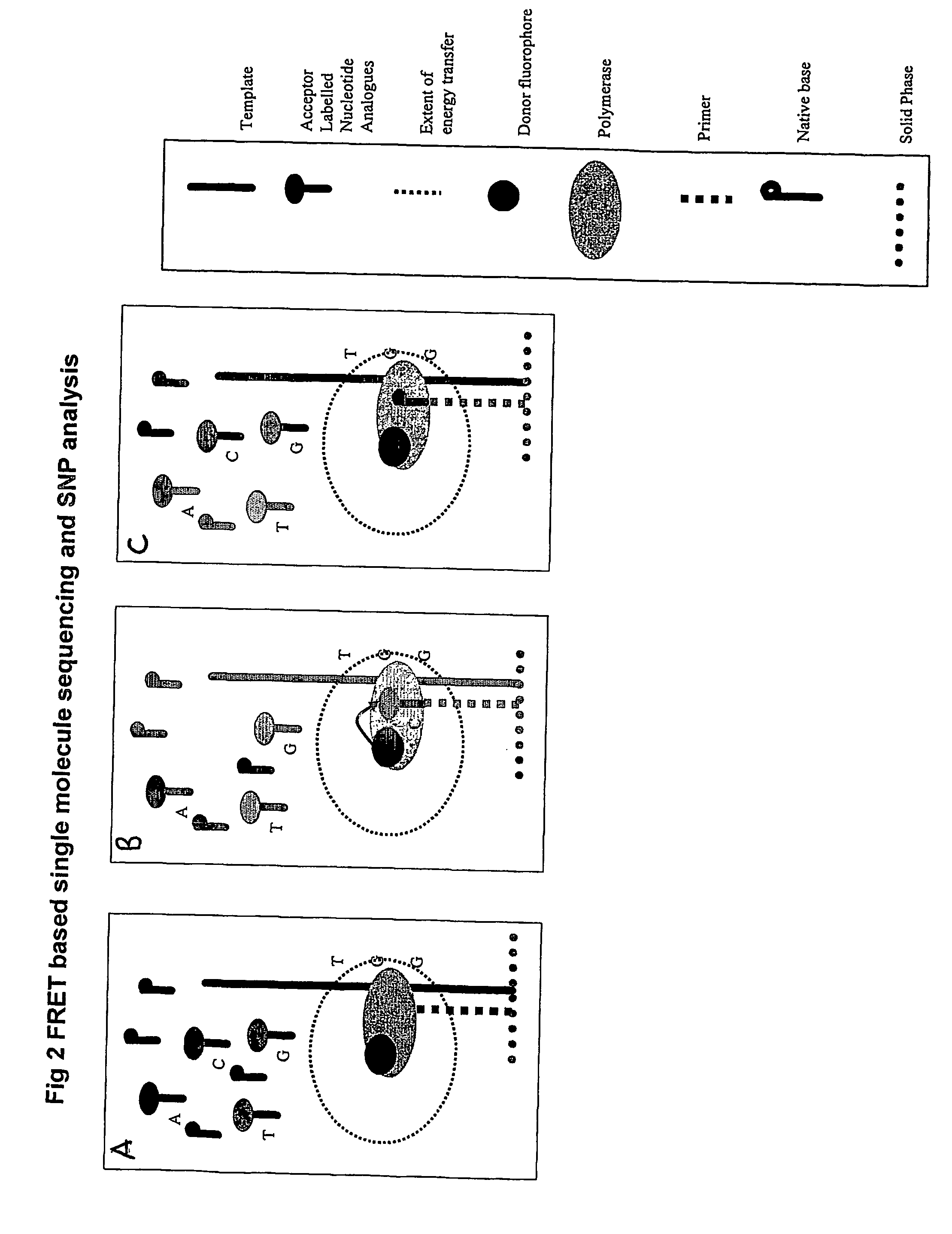
The present invention relates to nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents, and more particularly to methods of sequencing nucleic acid which employ a nucleic acid processing enzyme and one or more nucleotide analogues that are capable of binding to the active site of the enzyme and to complementary bases in the nucleic acid molecule being sequenced, but which are non-incorporable or inhibitors of the nucleic acid processing enzyme. In further aspects, the present invention relates to conjugates which comprise a deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (DNTPs) or an analogue thereof linked to an intercalating dye.
Owner:GENEFORM TECH LTD
Nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents
ActiveUS20070148645A1Conveniently preparedHighly controllable homogeneousSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReactive siteNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents, and more particularly to methods of sequencing nucleic acid which employ a nucleic acid processing enzyme and one or more nucleotide analogues that are capable of binding to the active site of the enzyme and to complementary bases in the nucleic acid molecule being sequenced, but which are non-incorporable or inhibitors of the nucleic acid processing enzyme. In further aspects, the present invention relates to conjugates which comprise a deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (DNTPs) or an analogue thereof linked to an intercalating dye.
Owner:GENEFORM TECH LTD
Reagent for nucleic acid amplification and process for nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS6261773B1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerPolymerase L
The present invention provide a process for sequence-specific nucleic acid amplification capable of improving the detection sensitivity and increasing the signal. In particular, the present invention provides a reagent for nucleic acid amplification containing at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts, specifically a reagent for nucleic acid amplification comprising, in addition to the at least one compound, a forward primer having a DNA sequence homologous to a sequence of a target RNA; a reverse primer having a DNA sequence complementary to a sequence of the target RNA and having a promoter for RNA polymerase attached to its 5' end; ribonucleotides; deoxyribonucleotides; a reverse transcriptase or RNA-directed DNA polymerase; a RNase H; a DNA polymerase or a reverse transcriptase having DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity; and a RNA polymerase. The present invention also provides a process for nucleic acid amplification characterized by carrying out a nucleic acid amplification reaction in the presence of at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
In vivo measurement of the relative fluxes through ribonucleotide reductase vs. deoxyribonucleoside pathways using isotopes
InactiveUS20050255509A1Increase salvageHigh activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionRate-determining stepDeoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis
The methods of the present invention allow for the measurement of ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity, an important enzyme in the de novo DNA synthesis pathway. Ribonucleotide reductase converts all four ribonucleotides to their deoxy form and is a rate-controlling step in this pathway. Biosynthetic pathways of deoxyribonucleotides (dN) have received considerable attention in the context of anti-proliferative chemotherapy. Inhibitors of various steps in dN biosynthesis, including inhibitors of RR are among the most useful chemotherapeutic agents in cancer, viral infections, and other therapeutic uses. DNA synthesis from the dN salvage pathway is also an important component to DNA replication. The relative contributions from RR vs. salvage pathways are critical to the actions and effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents that act on nucleoside metabolic pathways. Until now, however, it has not been possible to study these metabolic processes in vivo. Disclosed within are methods of measuring RR activity in vivo and in vitro which find use, among other things, in drug discovery, development, and approval.
Owner:KINEMED
Method for information storage with DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
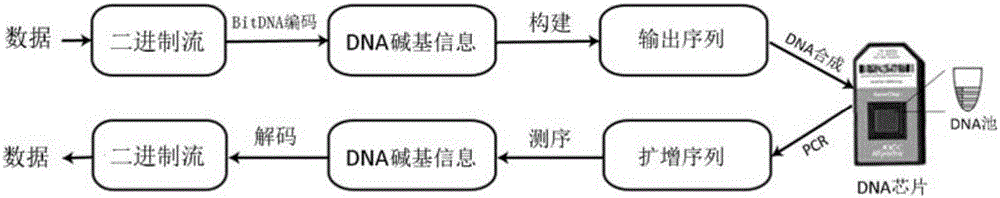
InactiveCN106845158ASimple structureImprove continuityBioinformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsBinary informationDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a method for information storage with DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). The method comprises the following steps: (1) converting binary information of an original document of a computer into quaternary information, encoding, converting into a DNA complete sequence, wherein binary codes 00, 01, 10 and 11 are respectively and correspondingly converted into four deoxyribonucleotides of A, T, C and G; (2) separating the DNA complete sequence into a plurality of DNA fragments, and organizing and establishing an output DNA sequence which is 90-110nt in length and comprises an interpolation nucleotide encoding sequence consisting of DNA fragments, side primer sequences at two ends, and index encoding sequences on the inner sides of the primer sequences; (3) according to the output DNA sequence, synthesizing an artificial DNA sequence, and storing the artificial DNA sequence. The method provided by the invention has the remarkable advantages of being good in universality, being capable of simplifying calculation, improving continuity, storage efficiency and density of DNA information storage, reducing fault rates, lowering sequence synthesis and detection cost, and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Amplified nucleic acids and immobilized products thereof
InactiveUS20050118578A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationImmobilized Nucleic AcidsOligonucleotide Primer
A nucleic acid, which is provided in a large amount through a nucleic acid amplification reaction with the use of chimeric oligonucleotide primers, is constructed in a state of containing a modified deoxyribonucleotide for immobilizing the nucleic acid to a solid phase and then immobilized to a solid phase at a high efficiency, thereby giving an immobilized nucleic acid product with excellent qualities.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe and method for detecting nuclease
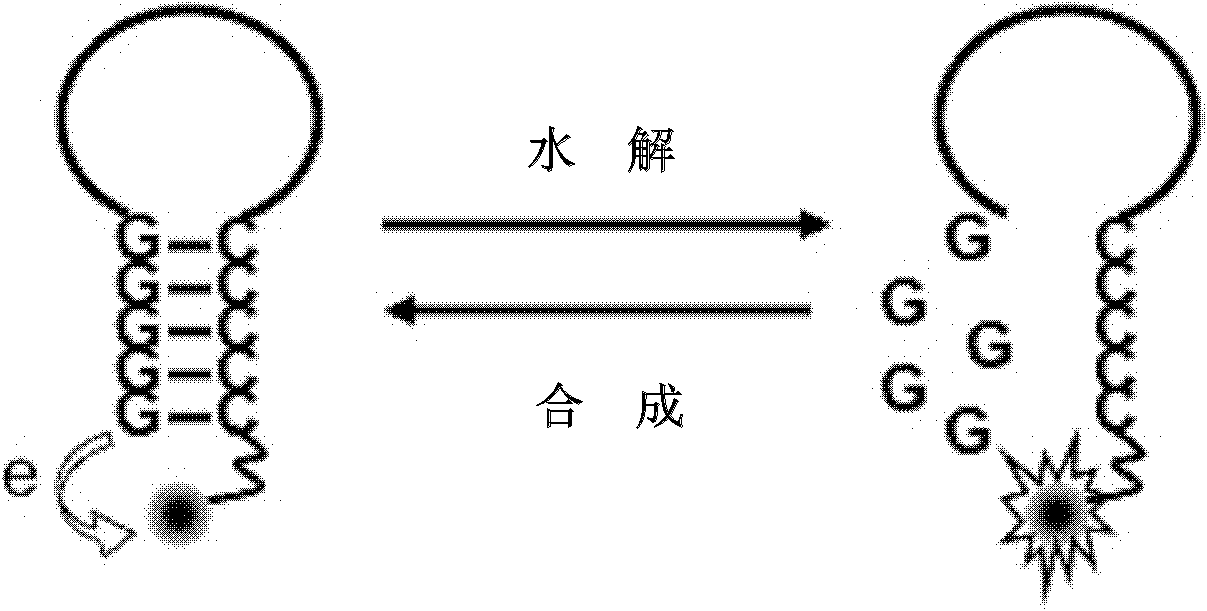
ActiveCN102154489ASimple and fast operationDesign and synthesis cost reductionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceSide chain
The invention discloses a singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe and a method for detecting nuclease. The singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe has a stem loop structure, wherein a loop part consists of 5-24 nucleotide residues; a stem part is in a hydrolysis mode or a synthesis mode according to the activity of nuclease to be detected; in the hydrolysis mode, the stem part has a double-chain structure, the tail end is provided with at least three continuous G-C base pairs, the C base ends are labeled with fluorescence groups, the G base ends have quenching effects, one chain of the stem part is hydrolyzed under the action of the nuclease to release a fluorescence signal; and in the synthesis mode, the stem part consists of a section of double chains and a 5'-(dC)4-8side chain, the 5'- end is labeled with a fluorescence group, the 3'- end reacts with the nuclease, 4-8 continuous guanine deoxyribonucleotides are produced by polymerization extension, the fluorescence group at the 5'- end is quenched, and the activity of the nuclease to be detected is analyzed according to the change condition of the fluorescence signal.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Lateral flow nucleic acid detector
InactiveUS20090305290A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibonucleotide synthesisNucleic acid sequencing
Point-of-care binding assays include at least one target nucleic acid binding in a multiplex structure with at least one sequence in a partner nucleic acid associated with a label, due to complementary base pairings between at least one sequence in the target nucleic acid and at least one sequence in the partner nucleic acid. The assays overcome the inherent deficiencies of antibody-protein antigen assays. In a preferred embodiment, color tagged nucleic acid sequences are used to bind a complementary target nucleic acid. The tagged nucleic acid sequences are preferably made from deoxyribonucleotides, ribonucleotides, or peptide nucleotides.
Owner:RAPID PATHOGEN SCREENING INC
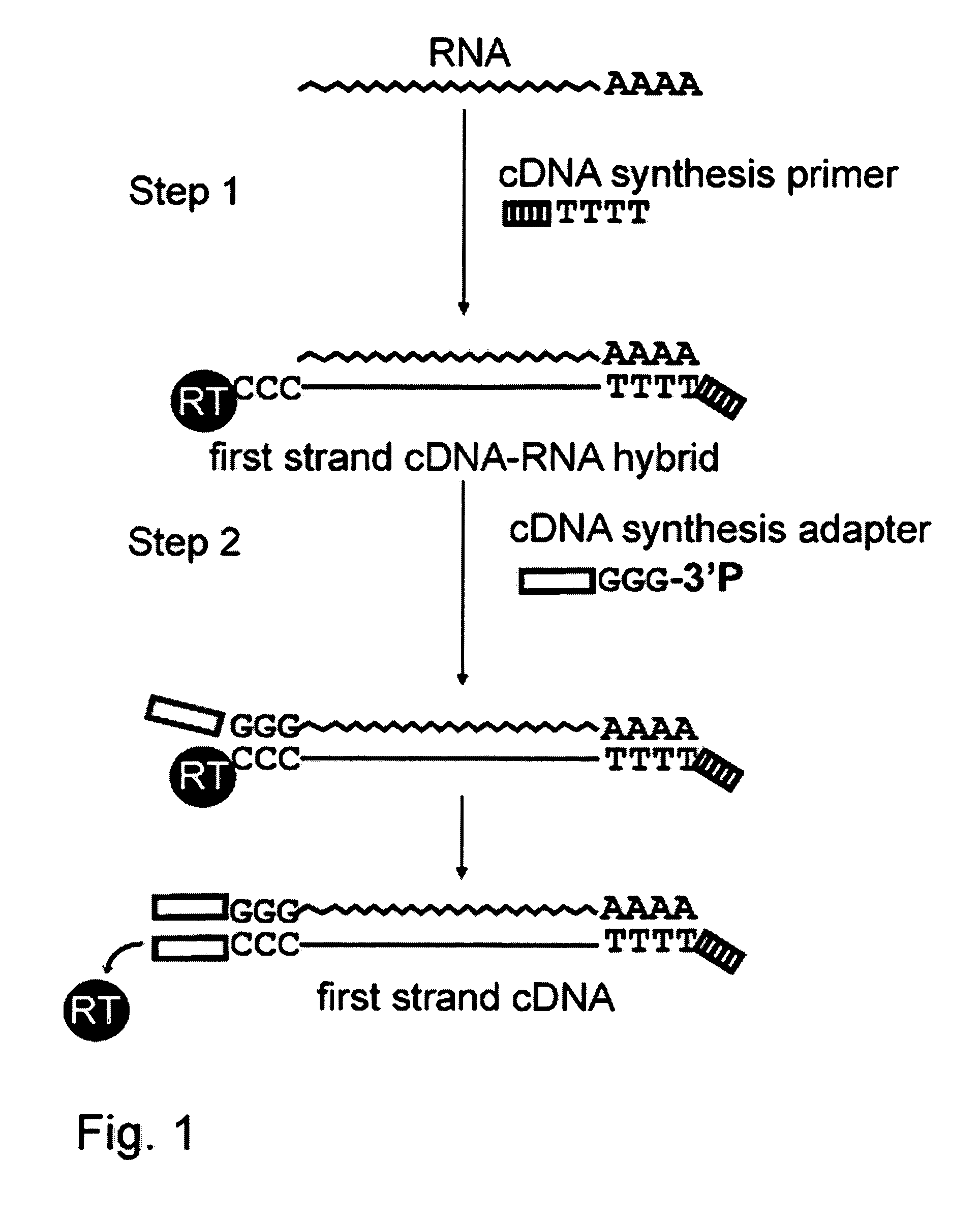
Methods of cDNA preparation
InactiveUS20080145844A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentation3-deoxyriboseReverse transcriptase activity
The present invention provides an improved method for cDNA preparation. The method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (1) contacting mRNA with a cDNA synthesis primer which can anneal to RNA and a suitable enzyme which possesses reverse transcriptase activity under conditions sufficient to permit the template-dependent extension of the primer to generate an mRNA-cDNA intermediates; (2) contacting a mixture from step 1 with a deoxyribonucleotide adapter in the presence of Mn2+-ions, wherein said oligonucleotide adapter has a pre-selected arbitrary nucleotide sequence at its 5′-end, and a short dG stretch at its 3′-end. The 3′-end nucleotide of the adapter is a terminator nucleotide, e.g., a nucleotide with a modified 3′-OH group of a deoxyribose residue.
Owner:EVROGEN
DNA sequence measurement based on primer extension
InactiveCN1940088AImprove throughputEasy detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
A method for measuring DNA sequence based on primer extension is carried out by inducing a section of DNA sequence on DNA template, fixing it onto solid-phase substrate, designing 1-15 oligonucleotide DNA primer combination to make it contain a section of DNA sequence, whose 3'end of 1-15 oligonucleotide DNA primer contains 0,1,2......14 degeneracy nucleic acid, selecting one primer from the primer combination by site position to be measured, hybridizing it with fixed DNA template, adhering site to primer 3'end, nucleic acid extending for primer by dideoxynucleic acid substrate or deoxyribonucleotide or dideoxyribonucleotide and inspecting extended nucleic acid type. The base type on DNA template is complementary with extended nucleic acid type.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
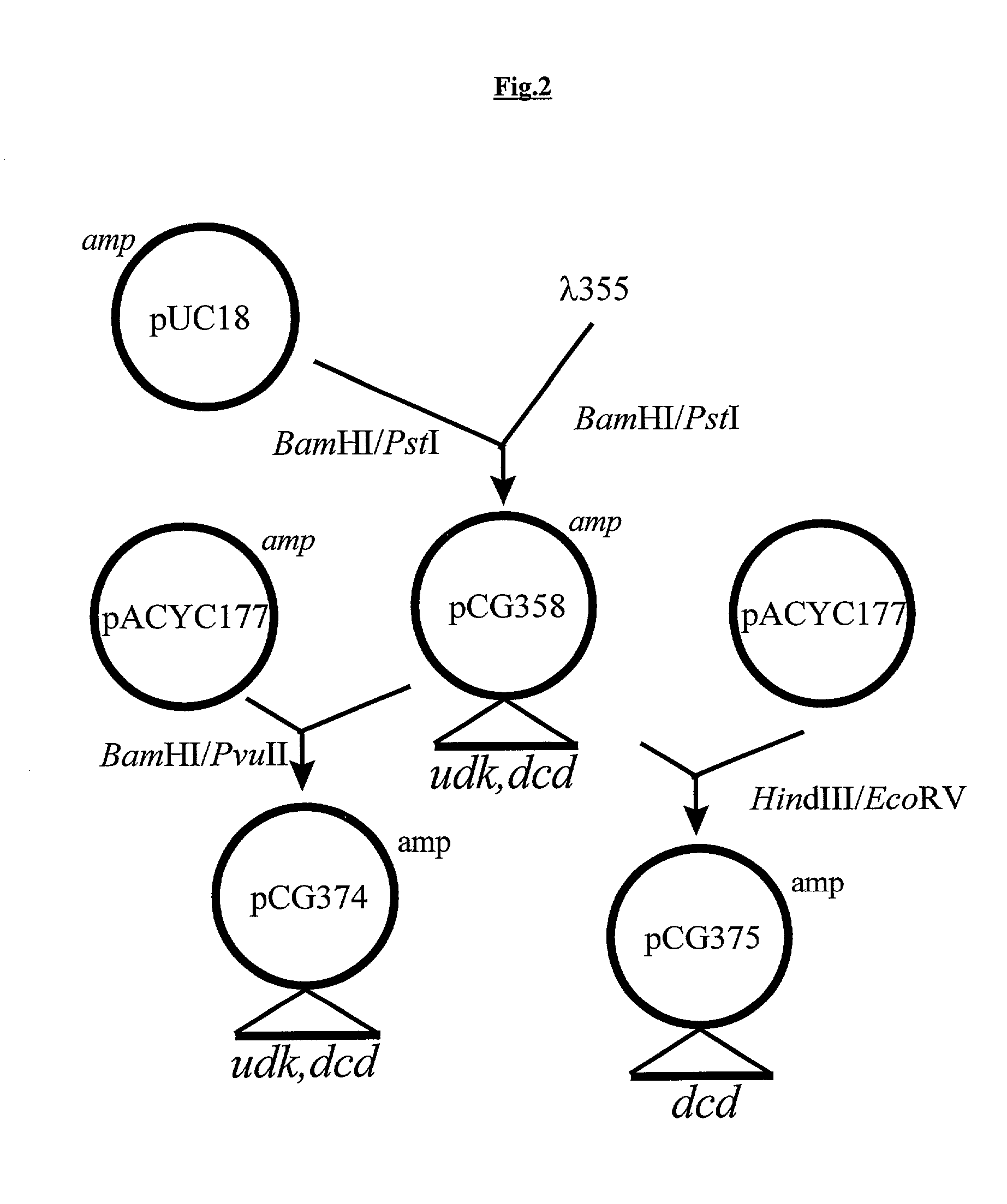
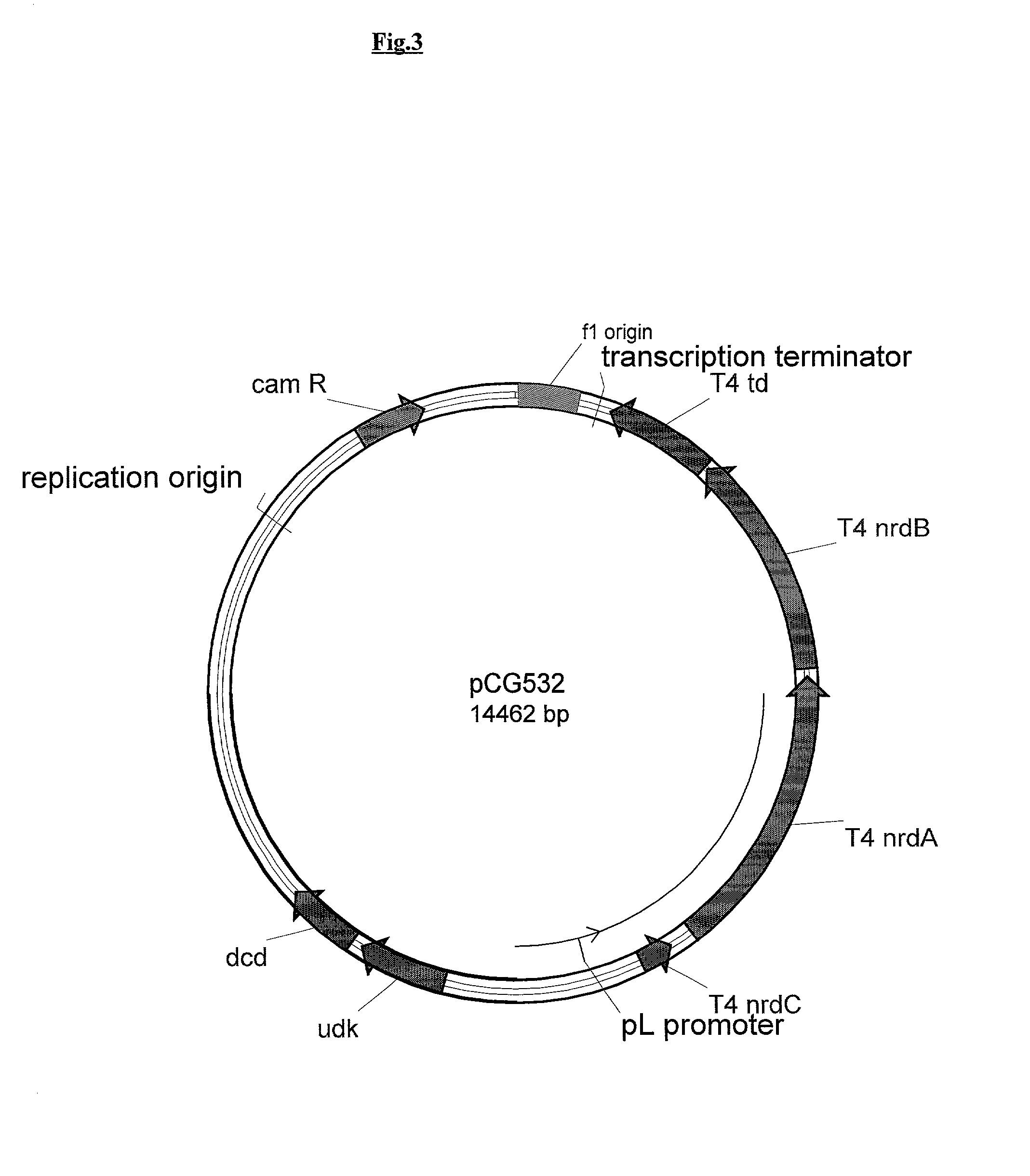
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin. In preferred embodiments, constructs further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, host cells comprising constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
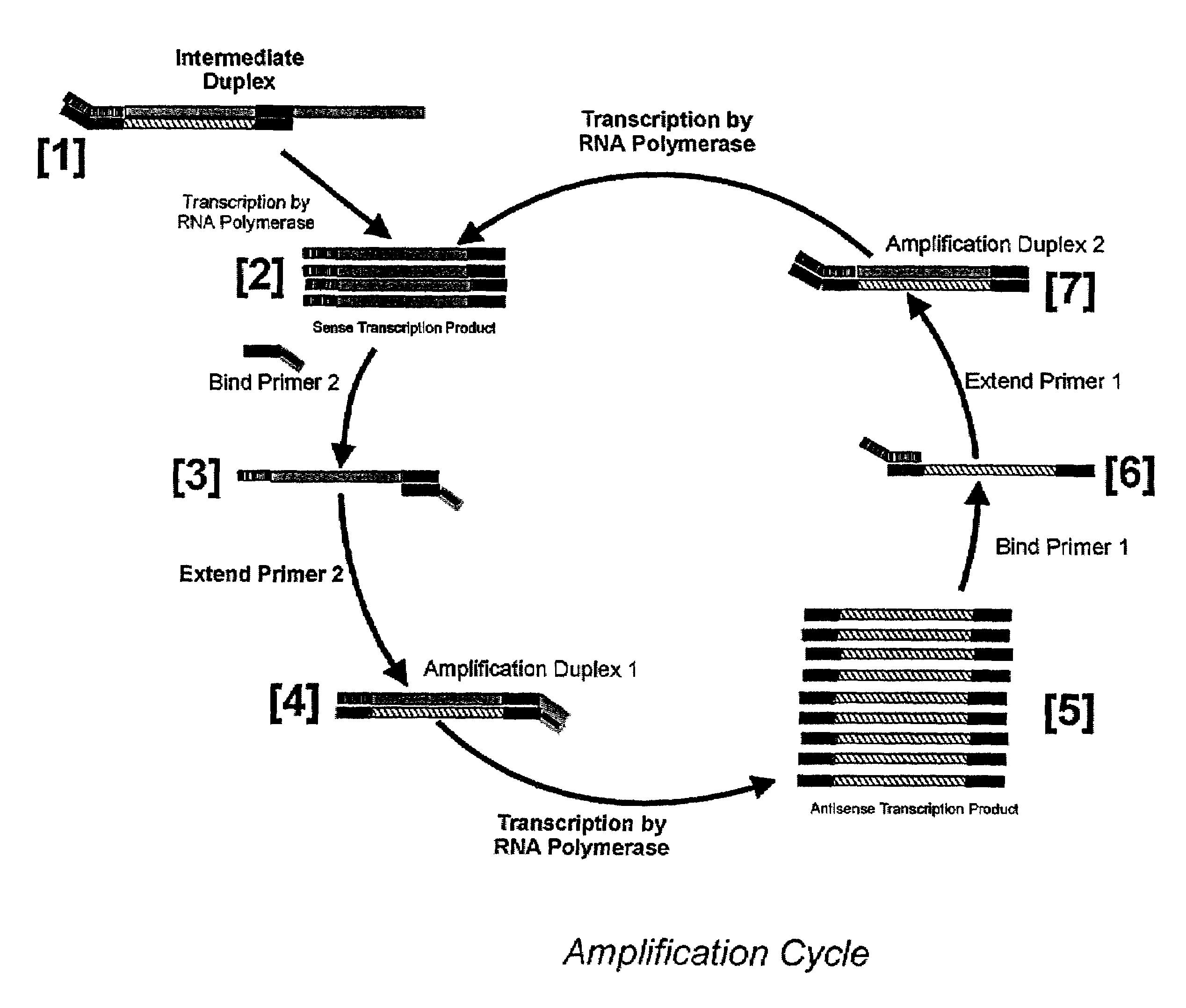
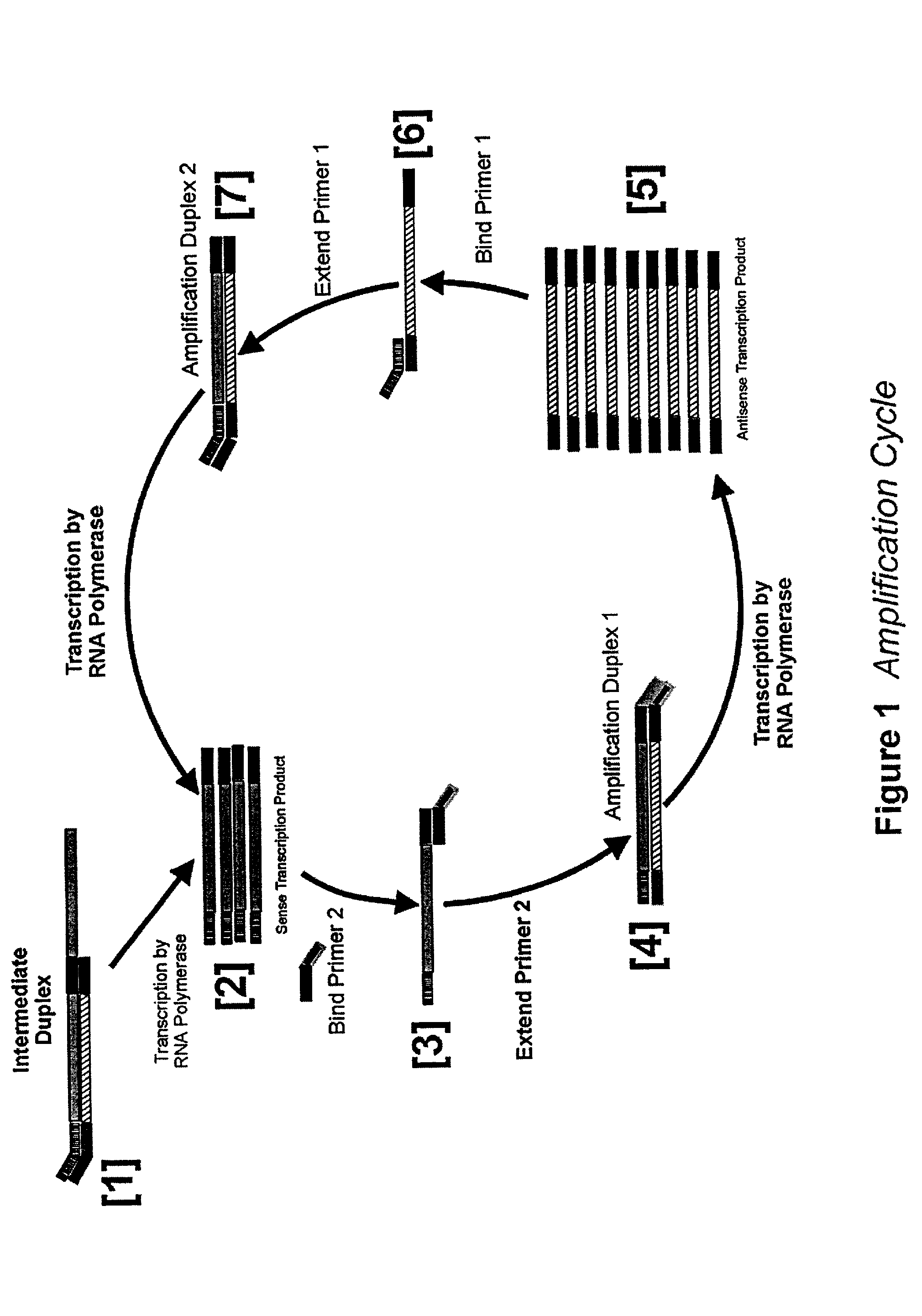
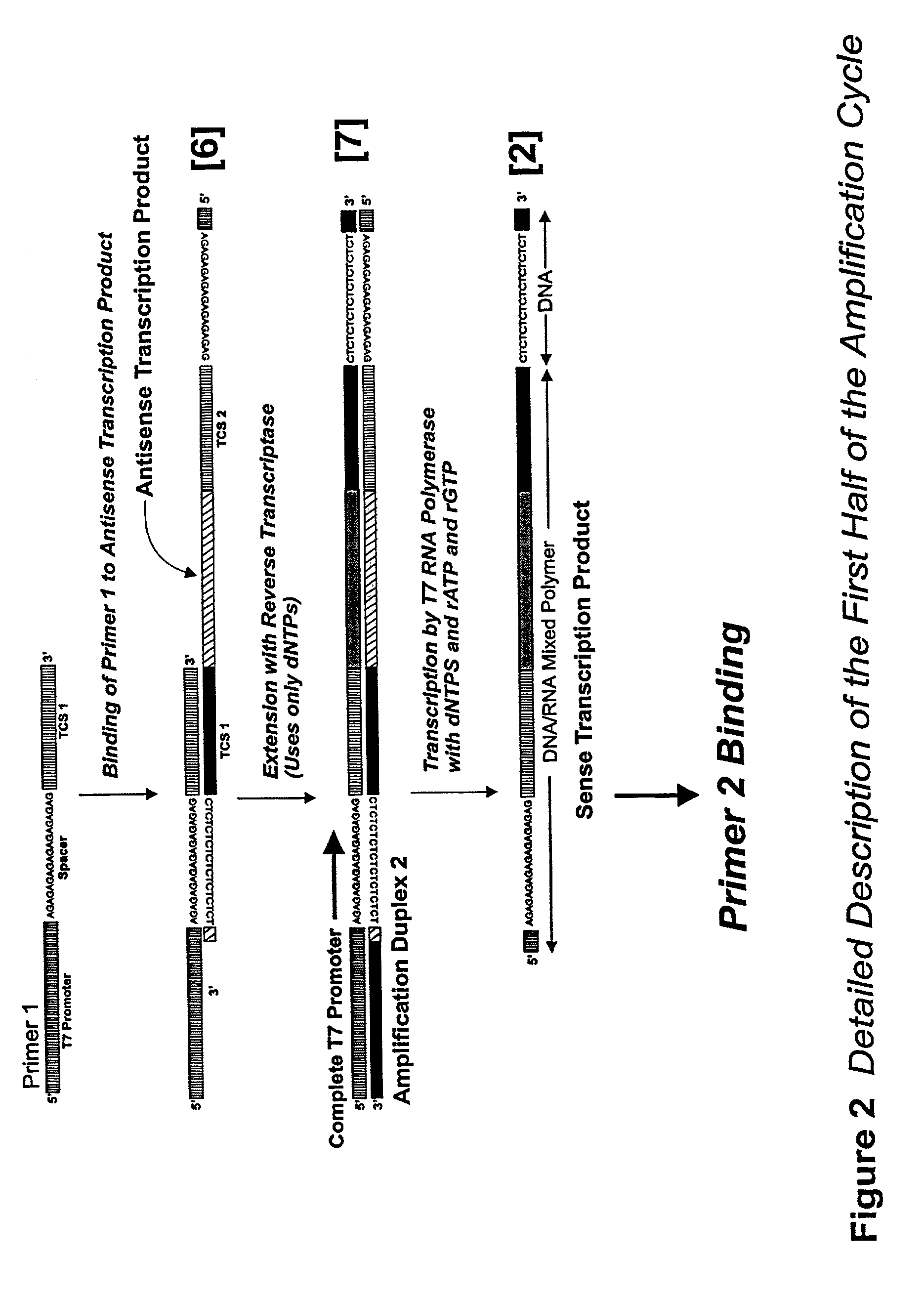
Nucleic acid amplification using an RNA polymerase and DNA/RNA mixed polymer intermediate products
InactiveUS7074558B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyRibonucleotide synthesis
This invention provides for a novel amplification procedure for nucleic acid. The method uses a wild type or mutant RNA polymerase designed to transcribe both deoxyribonucleotides and ribonucleotides.
Owner:PBI TECH
Root specific promoter and recombinant expression vector thereof
InactiveCN101280313AHigh expression activityIncrease inducible expression abilityFungiBacteriaPlant rootsA-DNA
The invention discloses a specific promoter of a root and a recombinant expression vector. The promoter adopts DNA molecular: a of following a) or b) or c) DNA molecular: a) is a DNA molecular which is composed of the deoxyribonucleotide shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence table; b) is a DNA molecular hybridized with a) defined DNA sequence under the strict condition; and c) is a specific expression DNA molecular in the root of the plant and has over 90 percents of homology and the gene with a adjusting and controlling purpose with a) defined DNA sequence. The invention also discloses a recombinant expression vector with the promoter, and the recombinant expression vector can be applied for cultivating the transgenic plant with a specific expressing target gene in the plant root.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
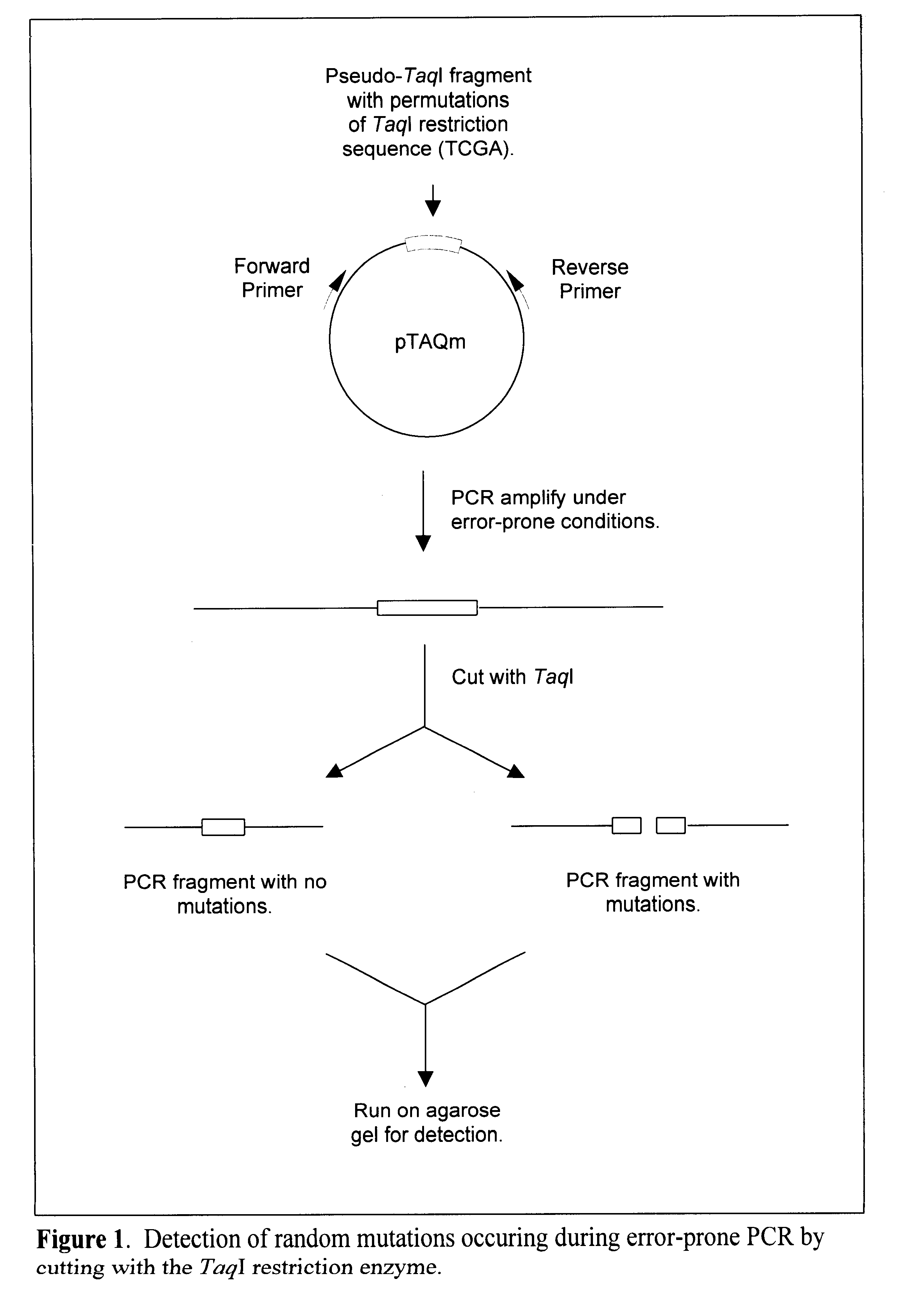
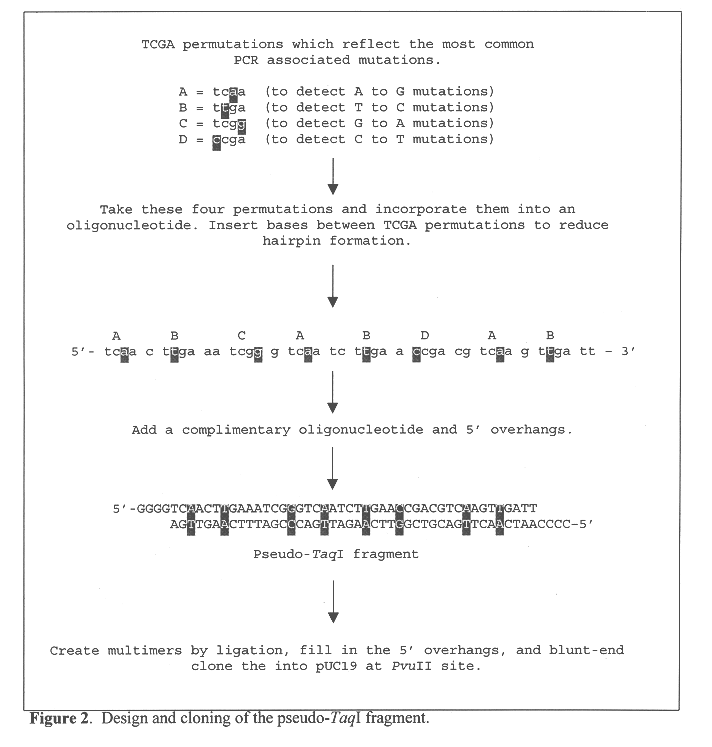
Methods and kits for determining the fidelity of polymerase chain reaction conditions
Methods are provided for evaluating the fidelity of a given set of polymerase chain reaction conditions. In the subject methods, a template polydeoxyribonucleotide is amplified under the to be evaluated polymerase chain reaction conditions, where the template polydeoxyribonucleotide includes a pseudo restriction endonuclease restriction site. The resultant amplified product population is then contacted with the corresponding restriction endonuclease and resultant cleavage products, if any, are detected. The fidelity of the polymerase chain reaction conditions is then derived from the detected cleavage products (or absence thereof). Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods are suited for determining the fidelity of a given polymerase under PCR conditions, and are particularly suited for determining the fidelity of a thermostable polymerase under PCR conditions.
Owner:CLONTECH LAB
Hybridization portion control oligonucleotide and its uses
InactiveUS20050164184A1Strong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleotide synthesisNucleotide sequencing
The present invention relates to an oligonucleotide for analyzing a target nucleotide sequence by hybridization and its applications. The oligonucleotide has the following general structure: 5′-Xp—Yq-Zr-3′ or 5′-Zr—Yq-Xp-3′ wherein Xp represents a first hybridization portion having a specific hybridizing nucleotide sequence substantially complementary to said target nucleotide sequence in said sample nucleic acid to hybridize therewith; Yq represents a regulator portion comprising at least two universal bases or non-discriminatory base analogs; Zr represents a second hybridization portion having a pre-selected arbitrary nucleotide sequence; p, q and r represent the number of nucleotides; and X, Y and Z is deoxyribonucleotide or ribonucleotide.
Owner:SEEGENE INC
Human miR-133a antisense nucleic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN102080086AGrowth inhibitionAbility to inhibit malignant proliferationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMicrorna 133aAntisense nucleic acid
The invention discloses an antisense oligonucleotide which can inhibit the expression of human microRNA-133a and application thereof. The antisense oligonucleotide specificity is combined with the human miR-133a and contains the consecutive nucleotide sequences complementary with the following nucleotide sequence: 5'-UUUGGUCCCCUUCAACCAGCUG-3', especially 5'-CAGCUGGUUGAAGGGGACCAAA-3'. The antisense oligonucleotide can be used as the chimera of ribonucleotides or deoxyribonucleotides or ribonucleotide with deoxyribonucleotide and can modify any nucleotide in the chains. The miR-133a antisense oligonucleotide can effectively inhibit the miR-133a expression in human brain glioma cells, and can inhibit the growth and proliferation of human brain glioma cells, thereby effectively treating braingliomas and other tumors with high miR-133a expression.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Preparation and detection method for electrochemical quantitative polymerase chain reaction detecting chip
InactiveCN1605861AThere will be no mutual contamination problemReduce testing costsMaterial electrochemical variablesActive matterElectrical wiring
The present invention is the electrochemical preparation process of quantitative PCR detection chip, and relates to the electrochemical detection technology for quantitative nucleic acid PCR chip. The preparation process includes preparing a micro electrode array on the surface of solid carrier; fixing nucleic acid capturing molecular probes on the electrodes of the micro electrode array; preparing closed micro cavity for carrying liquid in the electrode area of molecular probes; and connecting wires to the electrodes on the solid carrier. The detection process includes adding nucleic acid, enzyme, deoxyribonucleotide, electrochemically active matter and other reaction components into the micro cavity; setting the chip in large cavity for controlling temperature; detecting the current and voltage variance caused by reaction of the captured DNA probe molecule with constant potential instrument; and detecting the variance rule of PGR circulating process in different electrodes for PCR detection of genes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
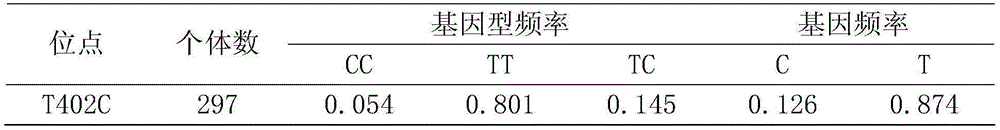
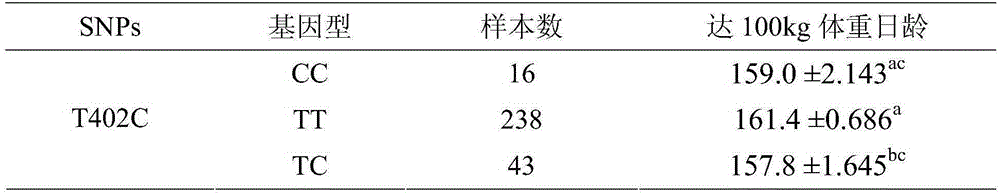
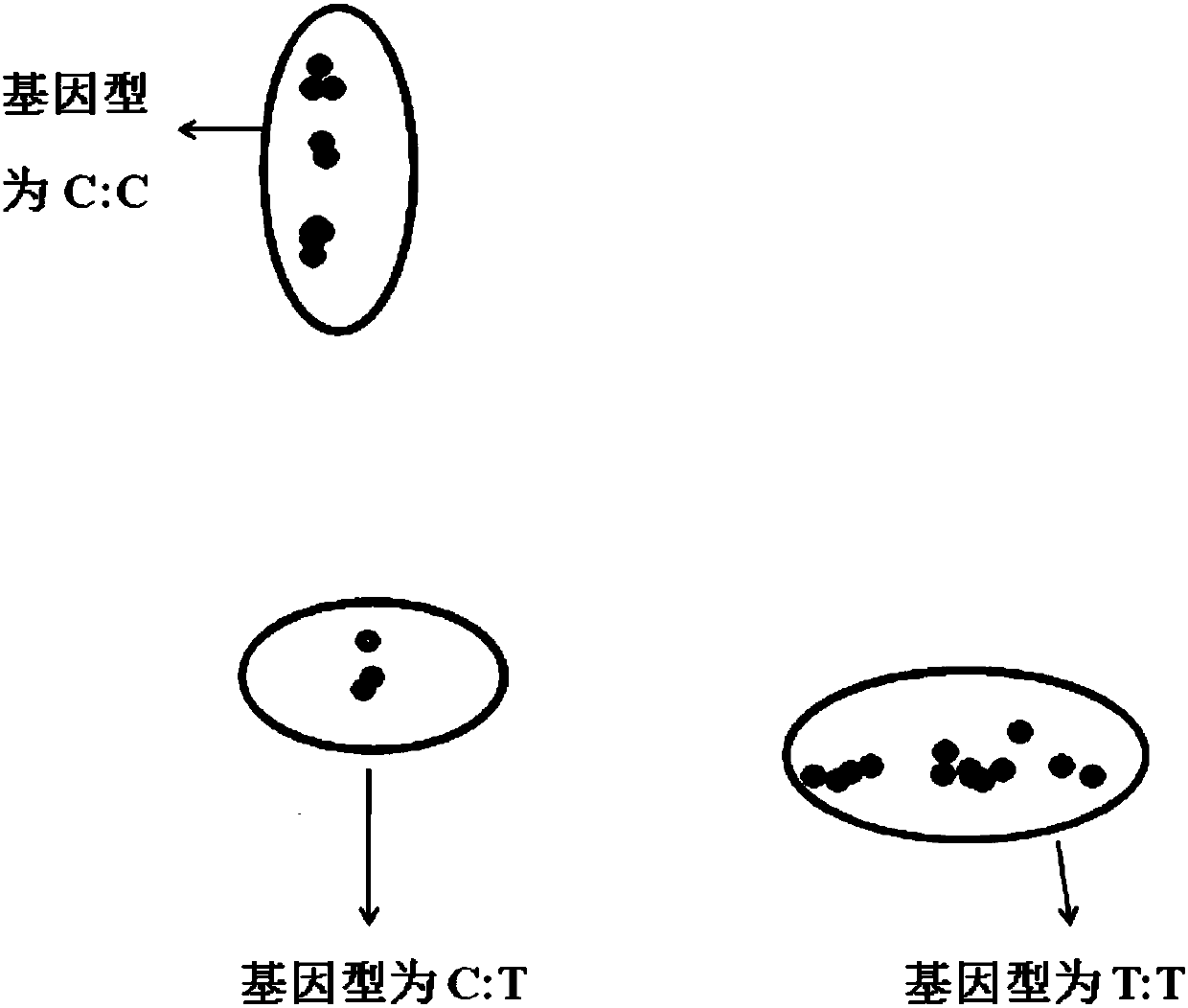
Method for identification or auxiliary identification of day age of pig at 100kg weight and special kit of method
ActiveCN105316412ABreeding for fast growthMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotype determinationBiology
The invention discloses a method for identification or auxiliary identification of day age of a pig at 100kg weight and a special kit of the method. The method comprises the following steps: detecting whether deoxyribonucleotide on the 402nd site of H19 gene of a pig individual is either C or T or both of them, so as to determine whether the genotype of the pig individual is TT or CC or TC; and determining the day age of the pig at 100kg weight according to the genotype of the pig individual: the day age of the pig individual of the TT genotype at 100kg weight is more than that of the pig individual of the CC genotype, and the day age of the pig individual of the CC genotype at 100kg weight is more than that of the pig individual of the TC genotype. Tests prove that the method disclosed by the invention, which is used for identifying the day age of the pig at 100kg weight through single nucleotide polymorphism on the 402nd site of the H19 gene, is consistent with an actual determination result of the day age of the pig at 100kg weight; therefore, the method is of great significance to the selection of excellent pigs.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Noval vaccine formulation consisting of dna vaccine and inactivated virus
Disclosed herein is a novel vaccine formulation for prophylatic or therapeutic immunization of vertebrates against infections caused by vertebrate viruses. The said vaccine contains a minimum of two components, one of which is a deoxyribonucleotide (DNA) vaccine comprising of a DNA molecule that encodes a polypeptide of the virus and the other component consisting of inactivated form of the virus. This invention can also be used to develop low cost inactivated virus-based vaccines that contain much lower amount of the said virus than that present in similar vaccines known in the prior art. This invention also relates to a process of producing that said novel vaccine formulation and the use of the said formulation.
Owner:THE REGISTRAR INDIAN INST OF SCI +1
Method for determining DNA nucleotide sequence
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 02254 Sec. 371 Date May 5, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date May 5, 1997 PCT Filed Nov. 6, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 14434 PCT Pub. Date May 17, 1996Disclosed is a method for determining a nucleotide sequence of DNA product amplified by polymerase chain reaction not requiring removal of primers and / or 2'-deoxyribonucleoside-5'-triphosphates and / or derivatives thereof, which comprises reacting ribonucleoside-5'-triphosphates comprising ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP and derivatives thereof and one or more of 3'-deoxyribonucleotide-5'-triphosphates comprising 3'-dATP, 3'-dGTP, 3'-dCTP, 3'-dUTP and derivatives thereof in the presence of an RNA polymerase and a DNA product which has been amplified by polymerase chain reaction and contains a promoter sequence for the RNA polymerase to afford a nucleic acid transcription product, separating the obtained nucleic acid transcription product and determining a nucleic acid sequence from the resluting separated fractions.
Owner:RIKEN
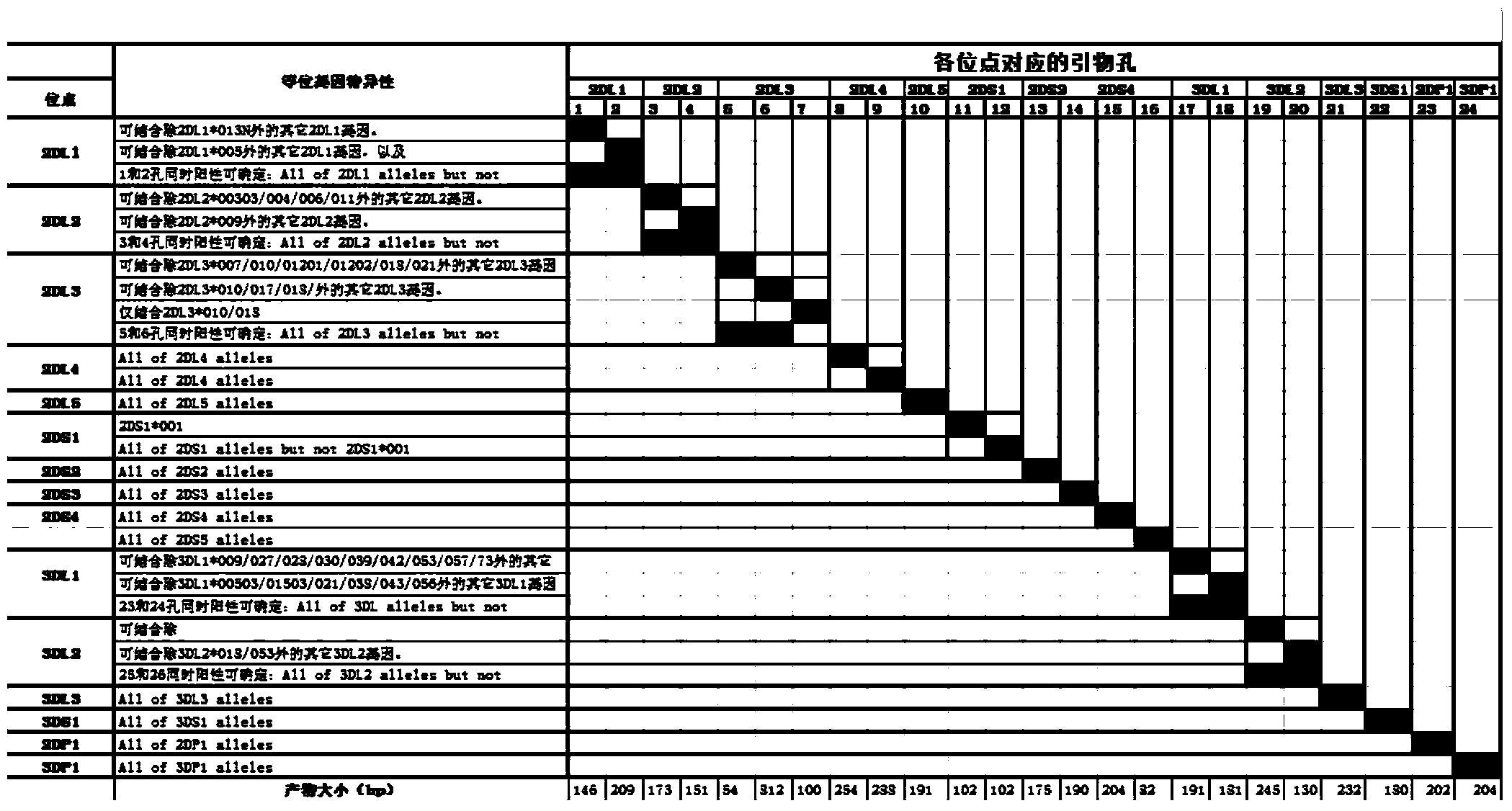
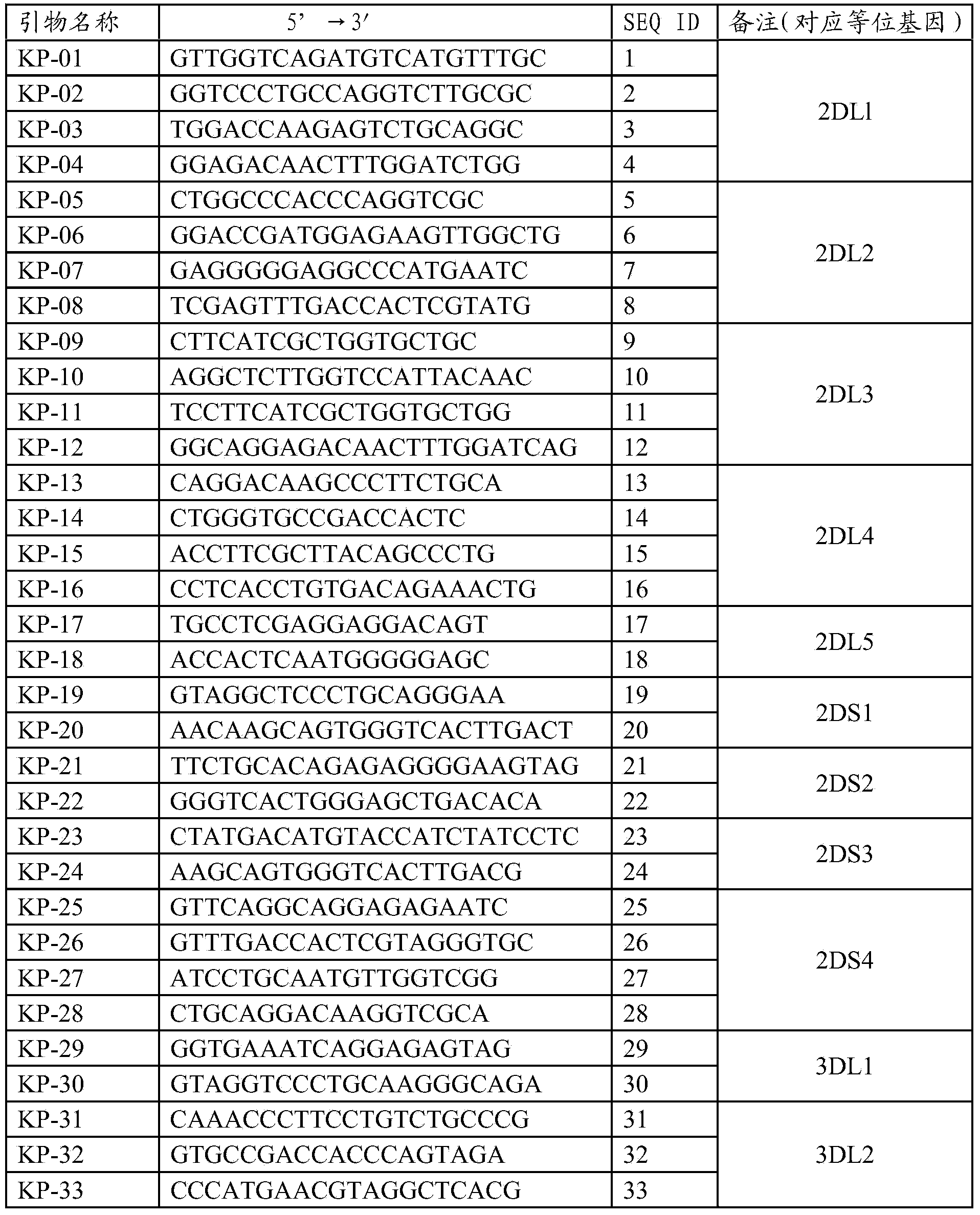
Primers, kit and method for quickly typing KIR (Killer Immunoglobulin-like Receptor) genes
ActiveCN104032025AReduce experiment costSave operating timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTypingToll-like receptor
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and discloses primers for quickly typing KIR (Killer Immunoglobulin-like Receptor) genes, a kit containing the primers and a method for quickly typing the KIR genes by adopting the primers. The specific primers of the KIR genes are used to enhance specific combination and can be fully used for detecting 16 known KIR allelic genes at present. In addition, the specific primers, dNTPs (Deoxyribonucleotide), a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) buffer liquid and dye are mixed in advance to greatly save the operating time and the workload, so that the method has the characteristics of quickness, simplicity and convenience, accuracy and intuitiveness. The typing experiment of the whole gene can be completed within 3 hours, so that the problem on quick typing of KIR genes is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TISSUEBANK BIOTECH +3
SPN locus in linkage with round or flat character of peach fruit shape, molecular marker based on locus and application thereof
ActiveCN104962627AAccurate distinctionReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationThymineMolecular marker
The invention discloses an SPN locus in linkage with the round or flat character of a peach fruit shape, a molecular marker based on the locus and application thereof. The SPN locus is located on the position of 2453bp of gene PPa003772 mg, and the sequence coding direction is in the 5'-3' direction. The SPN locus is exactly located on the position of the last 3' end basic group of downstream R primer marked down by an AS-PCR molecule, meanwhile, a 3' end secondary basic group is subjected to mispairing and changed into guanine deoxyribonucleotide G from thymine deoxyribonucleotide T. Through the method, in the flat peach and common peach seed selection work, the workload of peach tree seed breeding can be effectively reduced, the seed breeding time is shortened, and the seed breeding efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
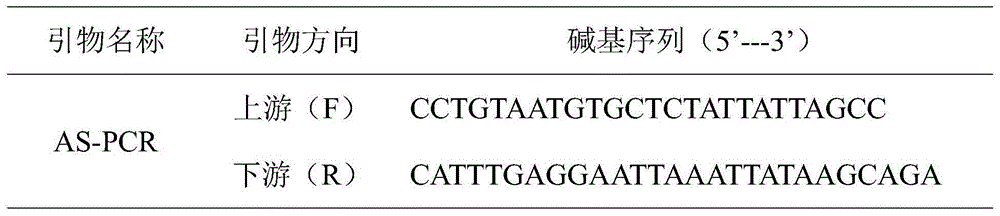
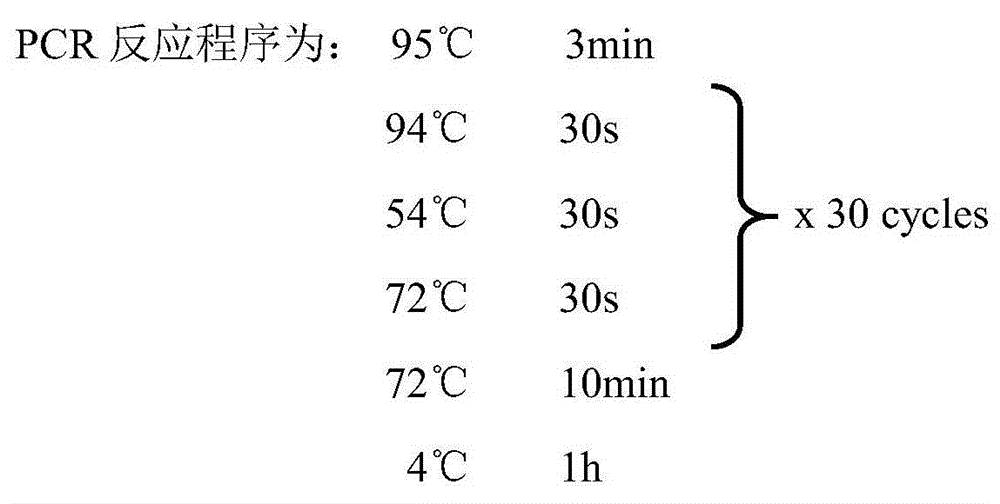
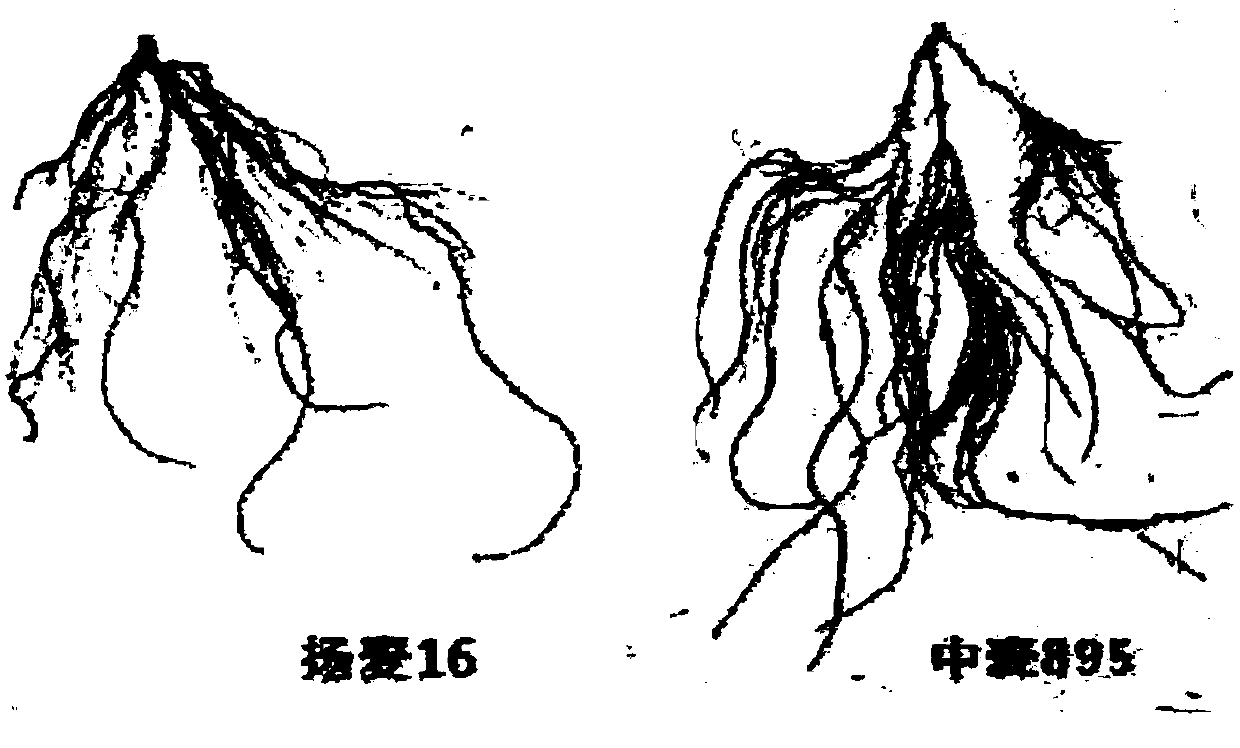
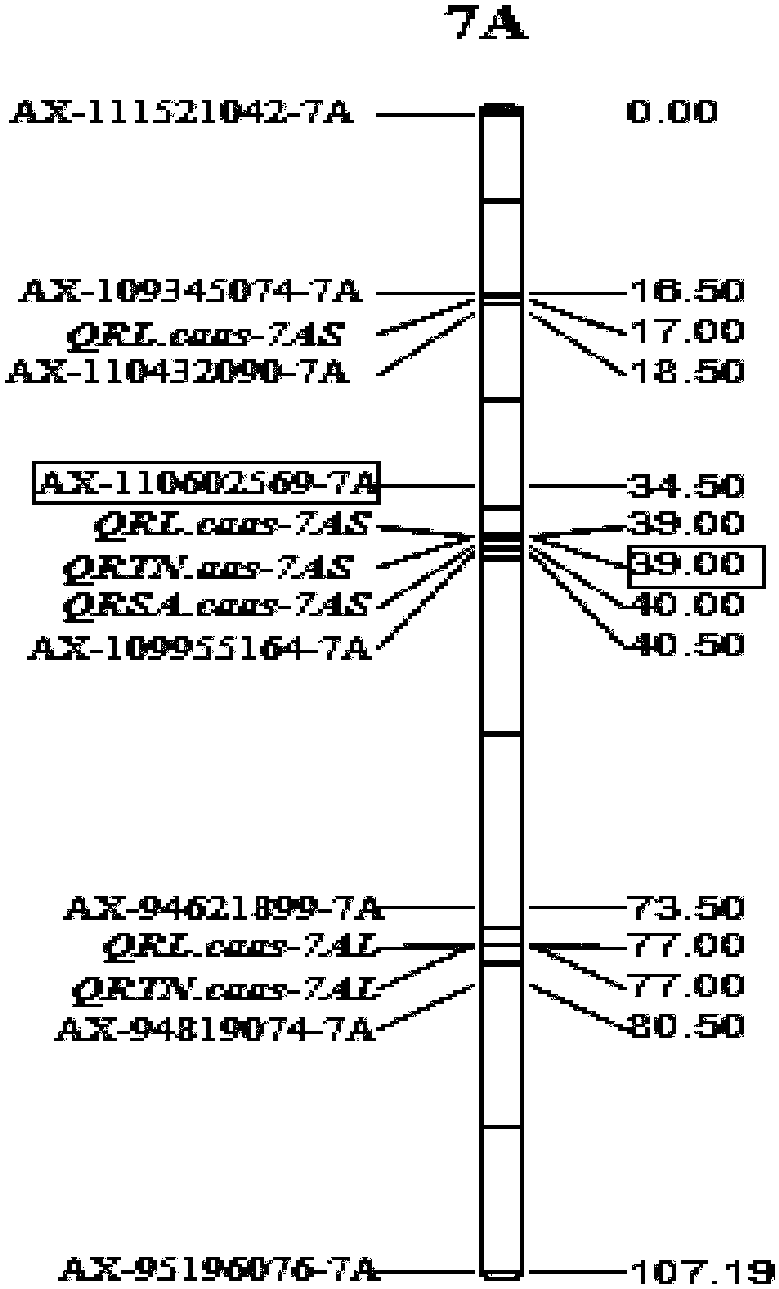
SNP label relevant to root characteristics in wheat seedling stage and application
The invention discloses an SNP label relevant to root characteristics in a wheat seedling stage and application. The invention provides a genotypic substance of 19-site deoxyribonucleotide of AX-110602569-7A gene in a detected wheat genome provided in the invention in application of authentication or auxiliary authentication for wheat root characteristics, and the 39cM position of the AX-110602569-7A gene in wheat chromosome 7AS. The invention provides a rated site QRL.caas-7A for root characteristics in the wheat seedling stage and the SNP site of the site for auxiliary sieving of the rated genes in the root system in the wheat seedling stage. Wheat with excellent related root characteristics can be sieved by using the SNP site, and the SNP plays an important role in cultivating water andfertilizer high-efficiency wheat varieties.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for synthesizing short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe
ActiveCN103276074AWide range of usesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDiseaseEnzyme digestion
The invention belongs to the field of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) biosynthesis, and in particular relates to a method for synthesizing a short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe and application thereof. The short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe can be used for detecting small non-coding ribonucleic acid (RNA) such as micro ribonucleic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing plasmids recombined with template DNA; (2) cutting and connecting the template DNA, performing enzyme digestion on the recombined plasmids to obtain the template DNA, and connecting the template DNA end to end to form a ring; (3) cutting a single strand, performing rolling-circle replication, cutting one strand of the template DNA by using nickase, adding polymerase to perform rolling-circle replication by taking annular DNA with a nick as a template, and amplifying to obtain a DNA single strand containing a neck ring-probe structure; and (4) preparing target short single strand DNA, cutting the product of the step (3) by using a type II incision enzyme to form a target single strand DNA probe and a byproduct DNA, and separating and purifying through PAGE (polyacylamide gel electrophoresis) to obtain a single strand DNA probe without mutation. The short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe has wide applications in the fields of detection of small non-coding RNA and diagnosis and treatment of small non-coding RNA related diseases.
Owner:深圳弸福科技有限公司
Method For Detecting Mercury Ions In Solution, And Kit
InactiveCN104059964AAmplify electrical signalsHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesExonuclease IThymine
The invention provides a method for detecting mercury ions in a solution, and a kit. The method comprises: 1) mixing the solution with single-stranded DNA containing thymine to form a mixture so that the single-stranded DNA containing the thymine forms double-stranded DNA through T-Hg2+-T base pairs wherein at least one deoxyribonucleotide of the single-stranded DNA containing the thymine is connected with a signal generating molecule; 2) contacting the double-stranded DNA obtained from the step 1) with exonuclease specifically different from the double-stranded DNA so that the exonuclease cuts the double-stranded DNA to release the deoxyribonucleotides connected with the signal generating molecules; and 3) detecting the signal generating molecules connected with the deoxyribonucleotides released in the detection step 2). The method has high specificity and sensitivity, does not need fixed DNA, is convenient to operate and can realize rapid detection.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cyprinidherpesvirus 2 (CyHV-2) nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit
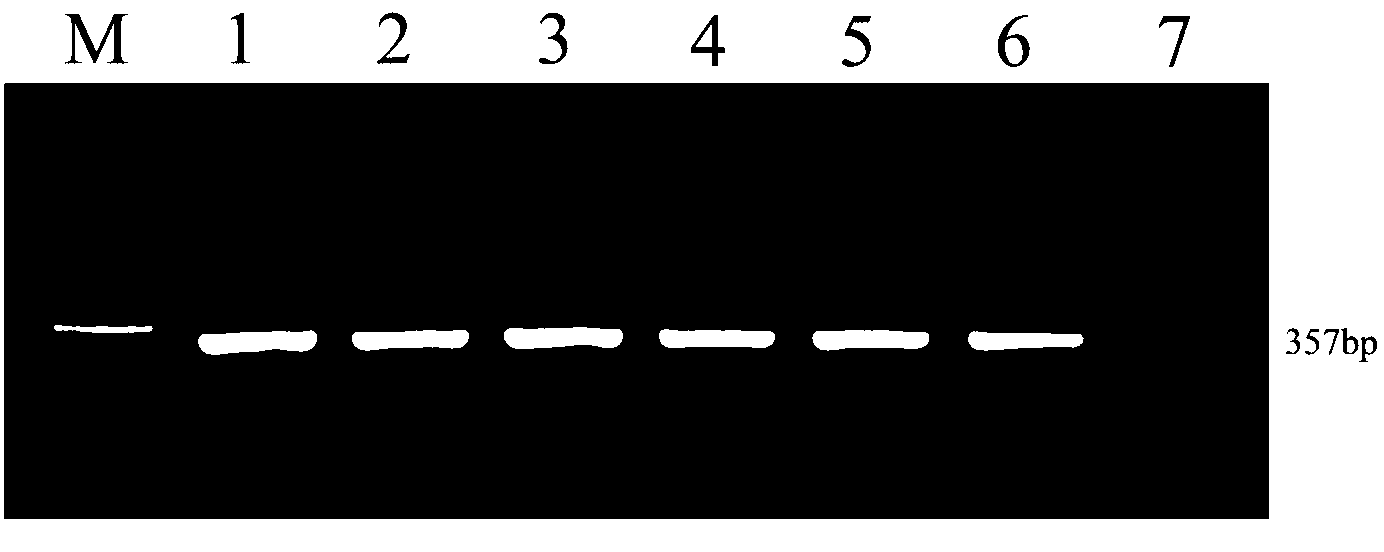
ActiveCN102851403AHigh detection sensitivityShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiologyDeoxyribonucleotide Triphosphate
The invention discloses a Cyprinidherpesvirus 2 (CyHV-2) nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit which is characterized in that six 1.5mL centrifuge tubes containing reagents are arranged on an inner pad (2) of a box body (1). The kit comprises a 10* reaction buffer, primers P1 and primers P2, wherein the 10* reaction buffer contains 100mM of Tris-HCL, 500mM of KCl, 15mM of MgCl2, 2mM of dNTPs (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates) (3), and 1U / mu L Taq enzyme (4); the primers P1 contain 10mu M of CyHV-2 P1F and 10mu M of CyHV-2 P1R (5); and the primers P2 contain 10mu M of CyHV-2 P2F and 10mu M of CyHV-2 P2R (6), pure water (7) and 10mu g / mL positive DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) (8). The sequences of the outer primers P1 are as follows: CyHV-2 P1F: TGAAATGTCAAAAGTGGATGG, and CyHV-2 P1R: TATTCCCAGACAGCCTTCAAA; and the sequences of the inner primers P2 are as follows: CyHV-2 P2F: GAACACCGCTGCTCATCATC, and CyHV-2 P2R: ACTCTTCGCAAGTCCTCACC. Two amplification processes are carried out by the inner and outer primers to finally obtain the DNA product of 357bp. The invention is simple to operate, is convenient and quick, and has the advantages of low detection limit, high sensitivity and accurate and reliable detection result.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Kit for loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection of Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae and preparation and usage methods thereof
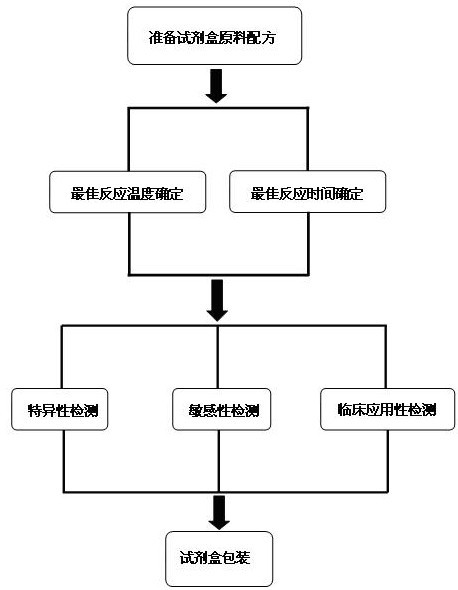
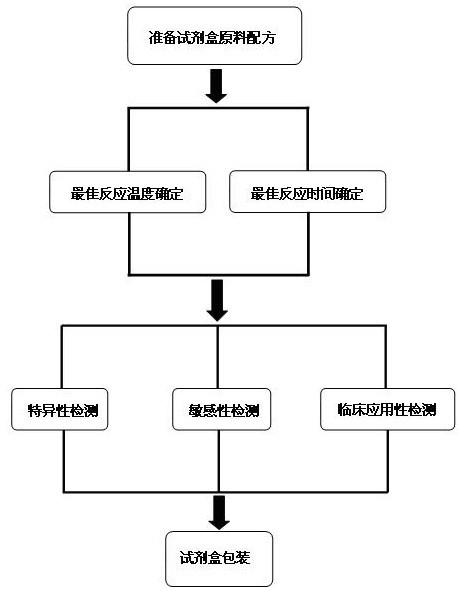
ActiveCN102634602AQuick checkReduce high costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlSpecific detection
The invention discloses a raw material composition of a kit for loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) detection of Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae and a preparation method and a usage method of the kit. The raw material composition comprises 1000-2000muL of reaction solution, 100-200muL of Bst (Bacillus stearothermophilus) DNA polymerase, 50-100muL of positive control, 50-100muL of negative control, 1-2mL of liquid paraffin and 1-2mL of ultrapure water. The reaction solution comprises an inner primer mixture solution, an outer primer mixture solution, an LAMP reaction buffer, Mg<2+> and dNTPs (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates), wherein the volume ratio of the five liquids in the reaction solution is 2:2:2.5:2:1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) determination of an optimum reaction temperature and an optimum reaction time; 2) specific detection, sensibility test and clinical application detection and 3) kit packaging. The kit disclosed by the invention has rapid, simple and accurate characteristics for pathogen detection of goat suspected cases of mycoplasma ovipneumoniae infection in goat farms.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Grain length gene marker based on genetic background of wheat variety Zhongmai 895 and its application
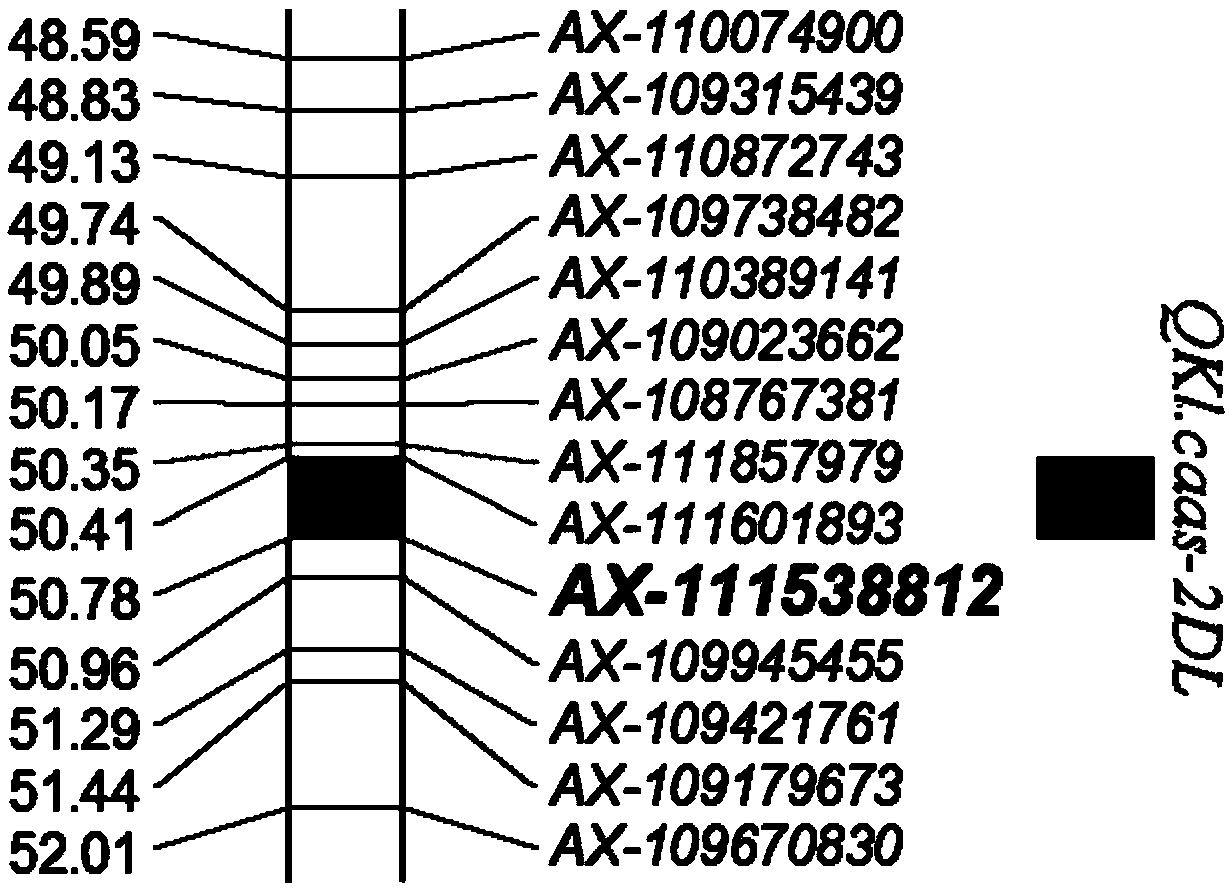
ActiveCN108998562ALow costReduce error rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLong armHigh density
The invention discloses a grain length gene marker based on the genetic background of the wheat variety Zhongmai 895 and its application. The invention provides any of the following applications of asubstance used for detecting whether a deoxyribonucleotide at the site 36 a gene segment shown in SEQ ID No. 4 and located on the chromosome 2D in a wheat genome is A, or G, or A and G: identificationor assisted identification of wheat grain length characters; comparison of the lengths of wheat grains to be tested; and breeding of a single wheat plant or wheat strain or wheat line or wheat variety with relatively long grain length. According to the invention, the 660K SNP high-density genetic map of Yangmai 16 / Zhongmai 895DH populations is utilized for QTL mapping of grain length, and a majorQTL is located on the long arm of the chromosome 2D; and based on the research, a KASP marker special primer set of the flanking marker AX-111538812 is developed, so a good tool is provided for utilization of the grain length QTL QKl. caas-2DL during breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primer, kit and method for quickly detecting HLA-B*5801 allele
ActiveCN104017898AImprove bindingAvoid it happening againMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHLA-BBiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a primer for quickly detecting HLA-B*5801 allele, a kit containing the primers and a method for quickly detecting HLA-B*5801 allele by using the primers and kit. By using the HLA-B*5801 gene specific primer and adopting the multiplex primer combination design, the SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) site of the HLA-B*5801 gene is completely covered, the specific combination is enhanced, and the generation of the false positive is prevented more effectively. Besides, the specific primer, dNTPs (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) buffer solution and dyes are mixed previously, thereby greatly saving the operation time and workload; and the method is quick, simple, accurate and visual, and can the screening and typing experiment of the whole gene within 3 hours, thereby solving the problem of safe application instructions of the HLA-B*5801 gene in drugs for treating gout and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI TISSUEBANK BIOTECH +3
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com