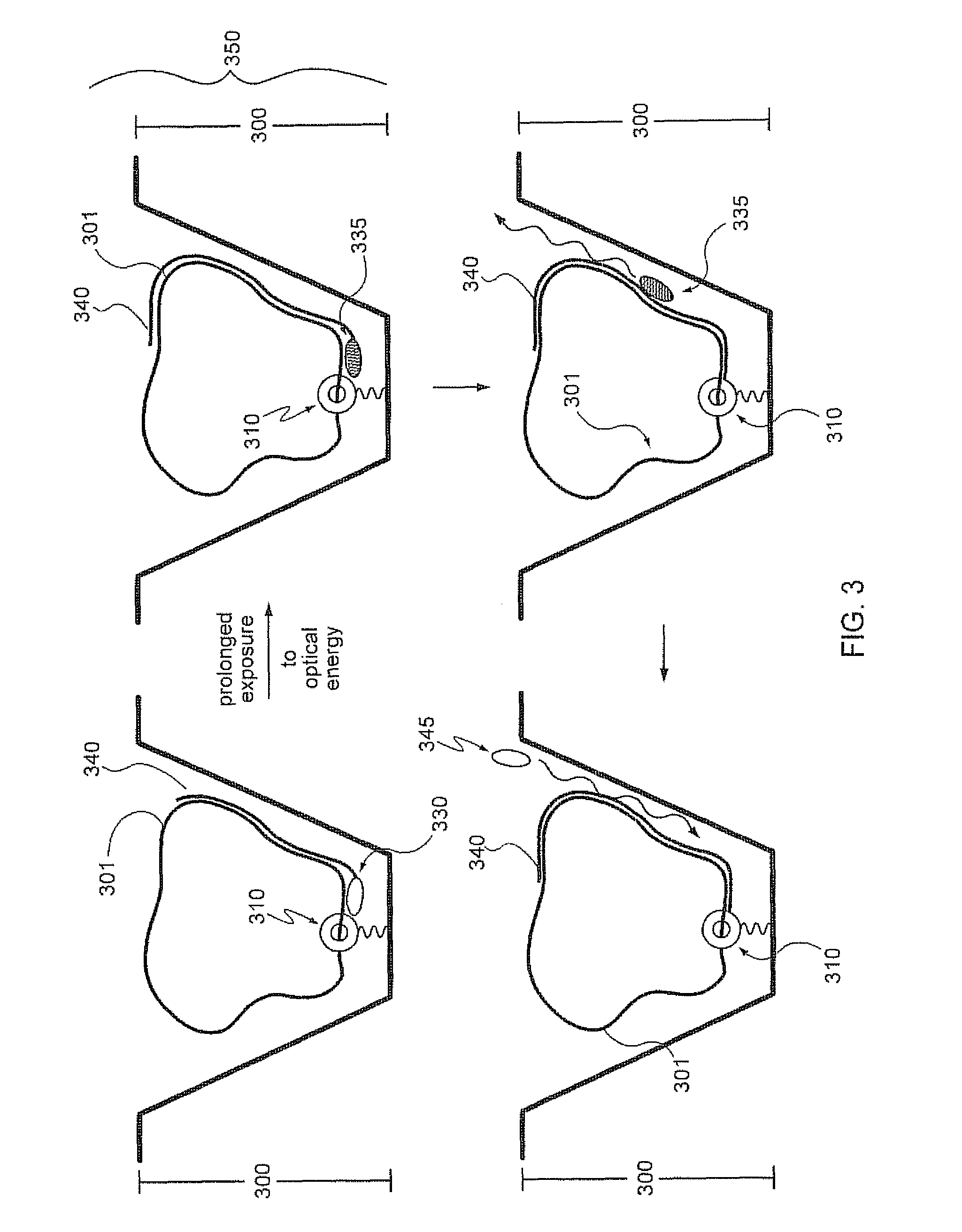
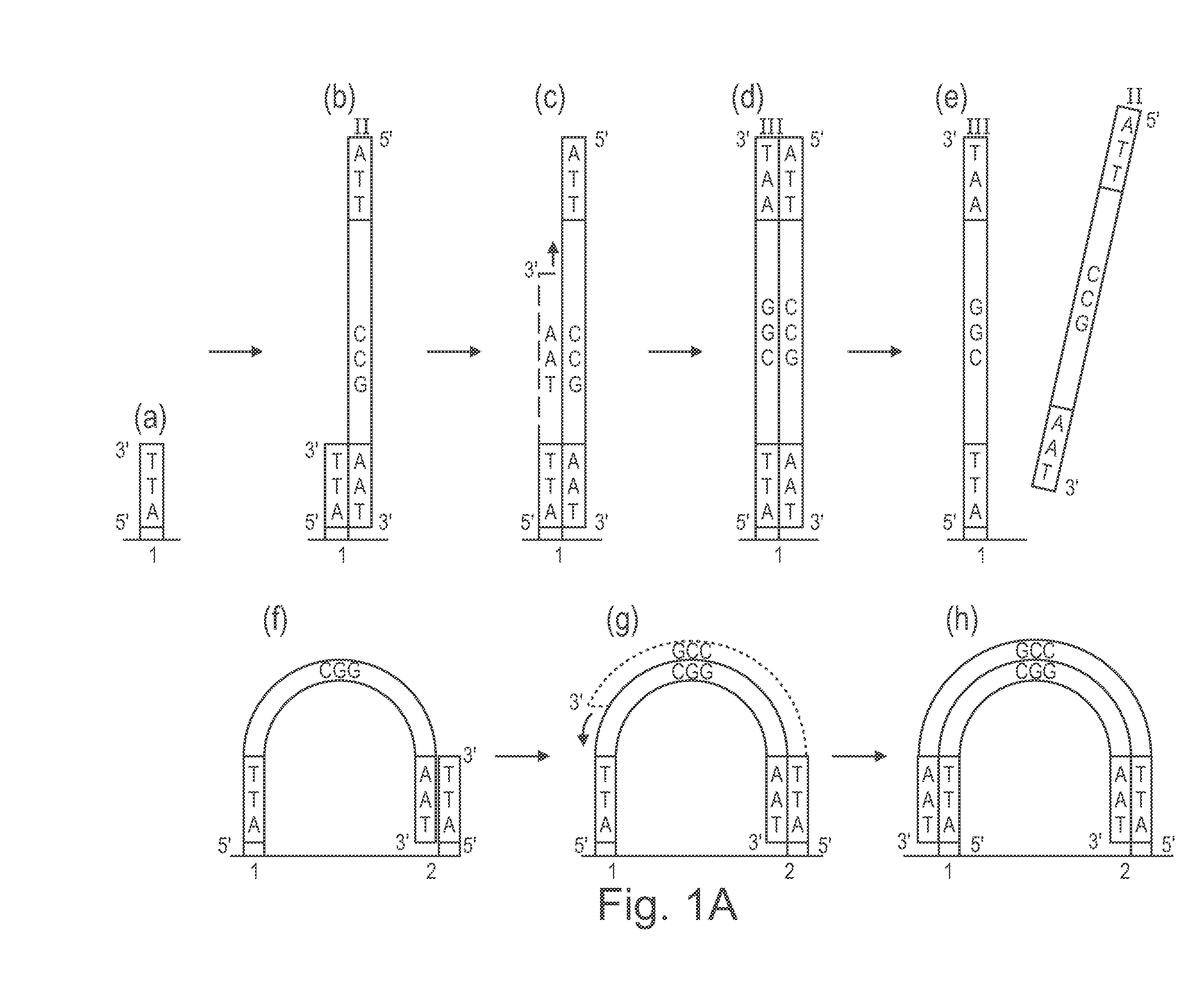
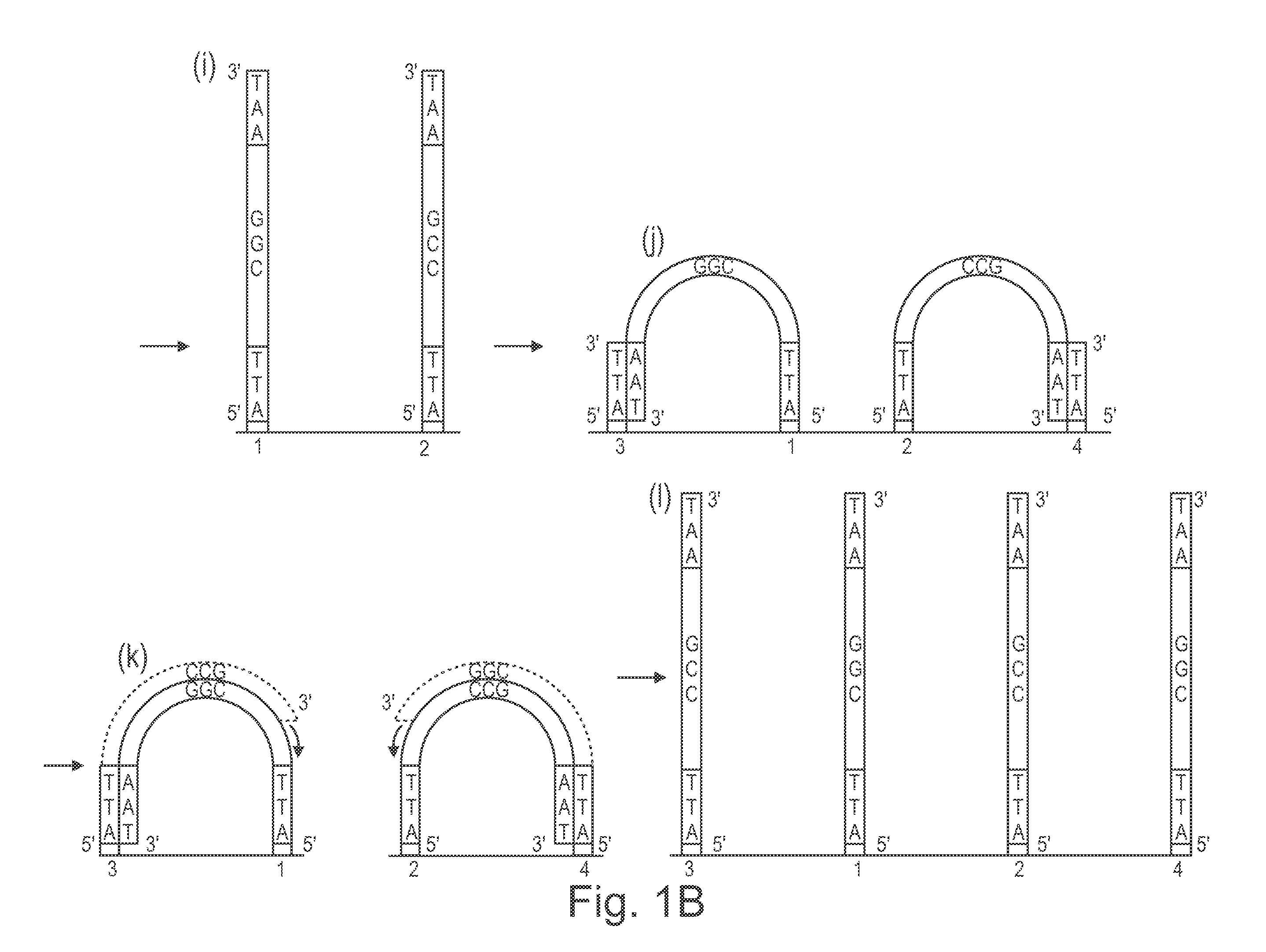
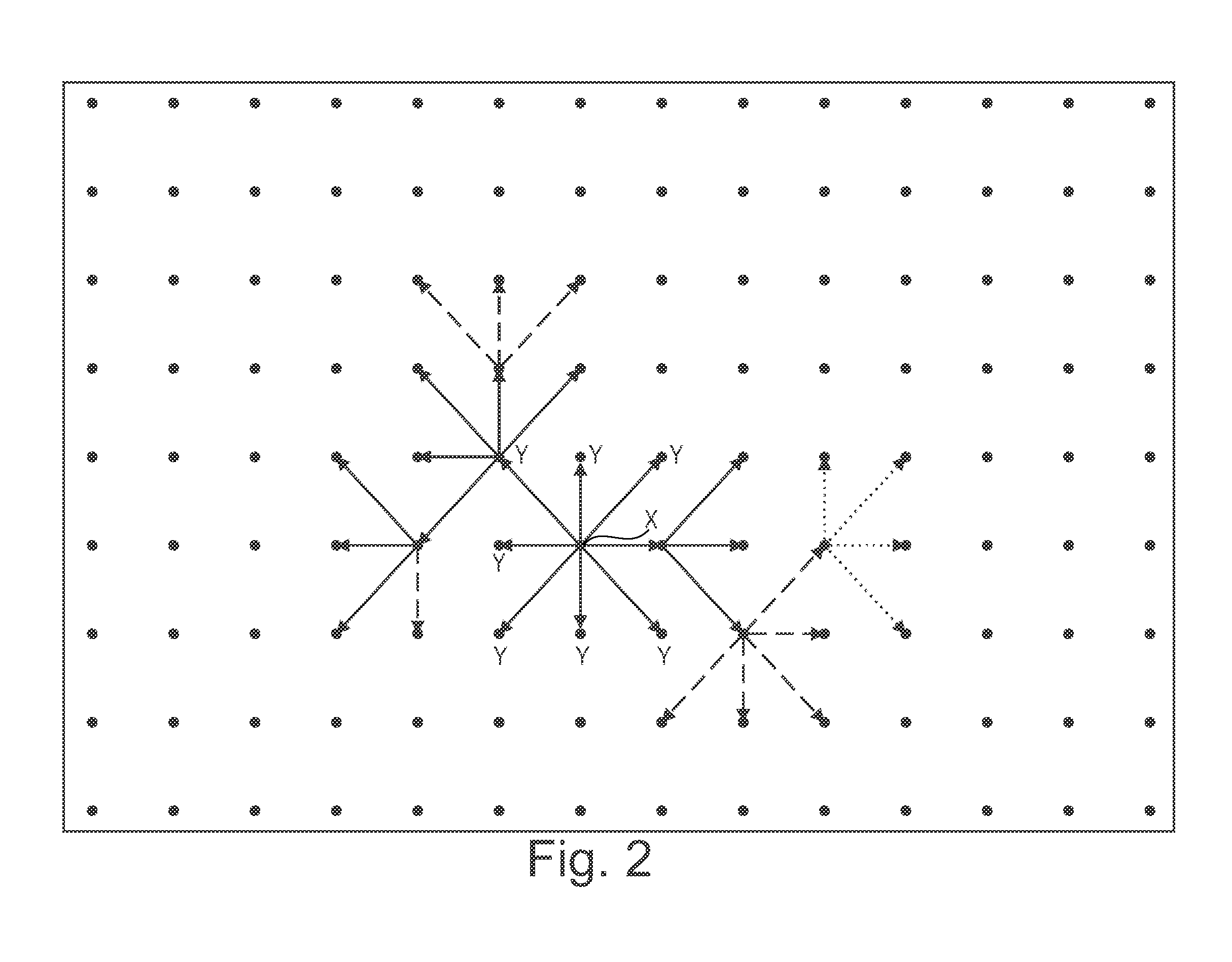
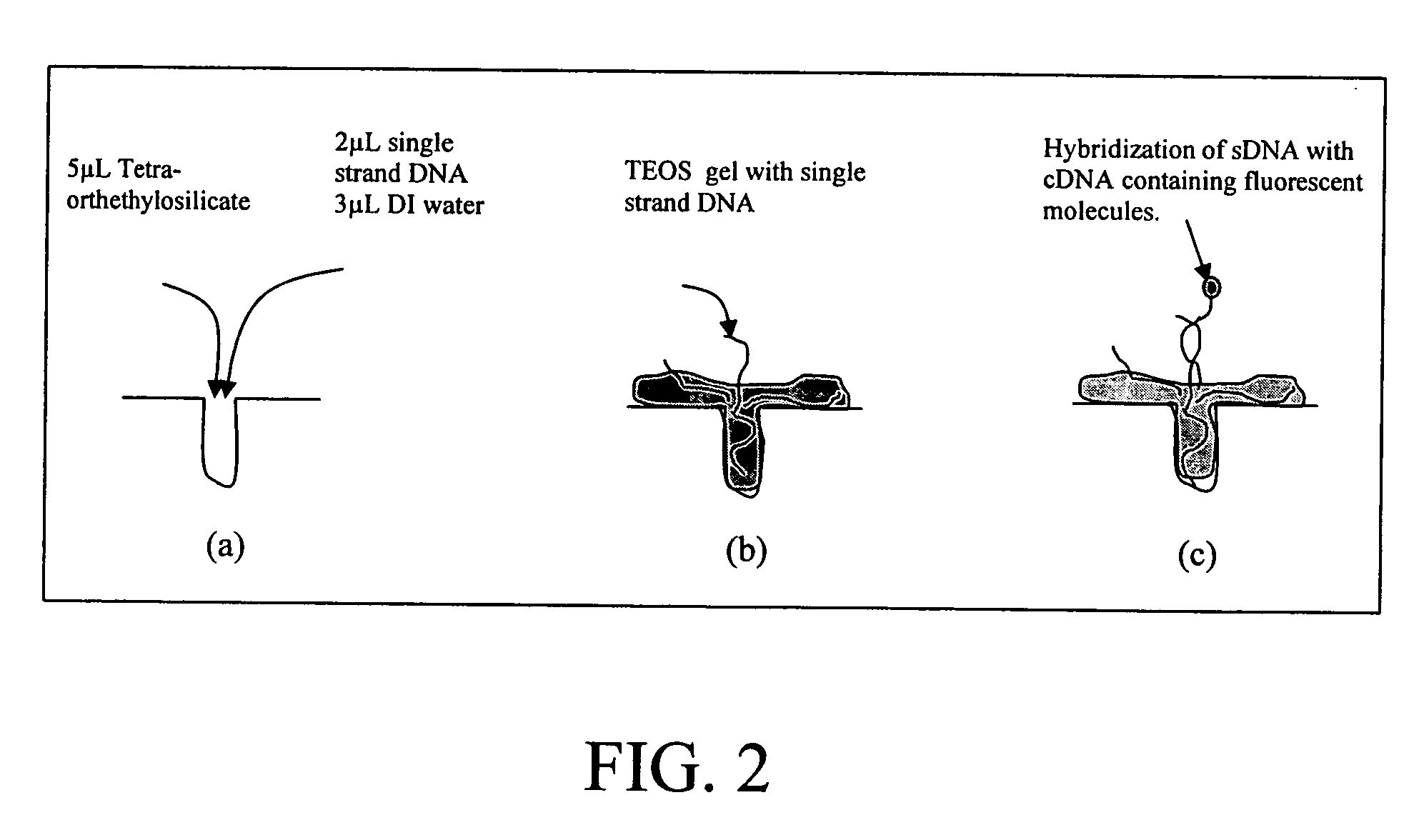
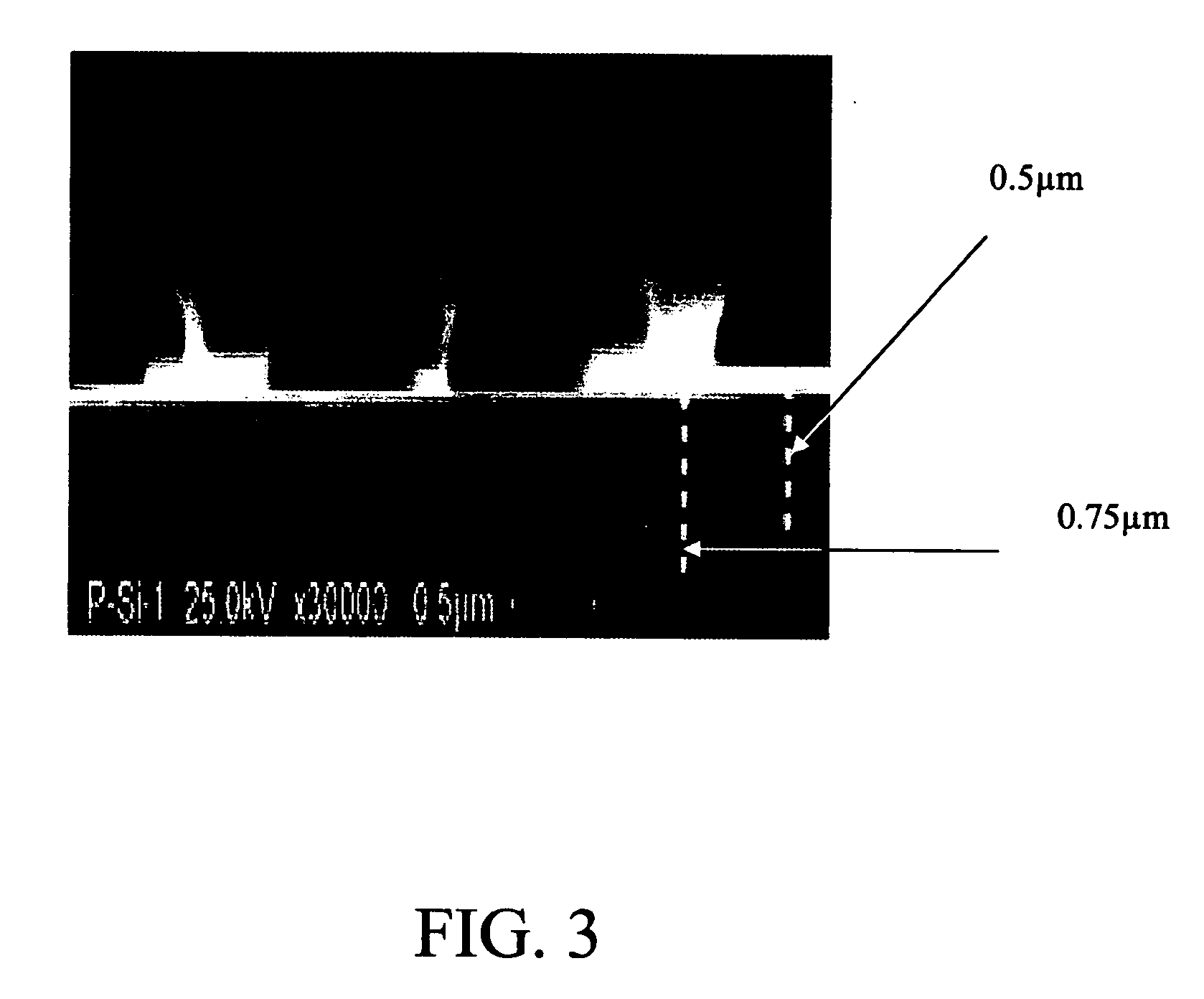
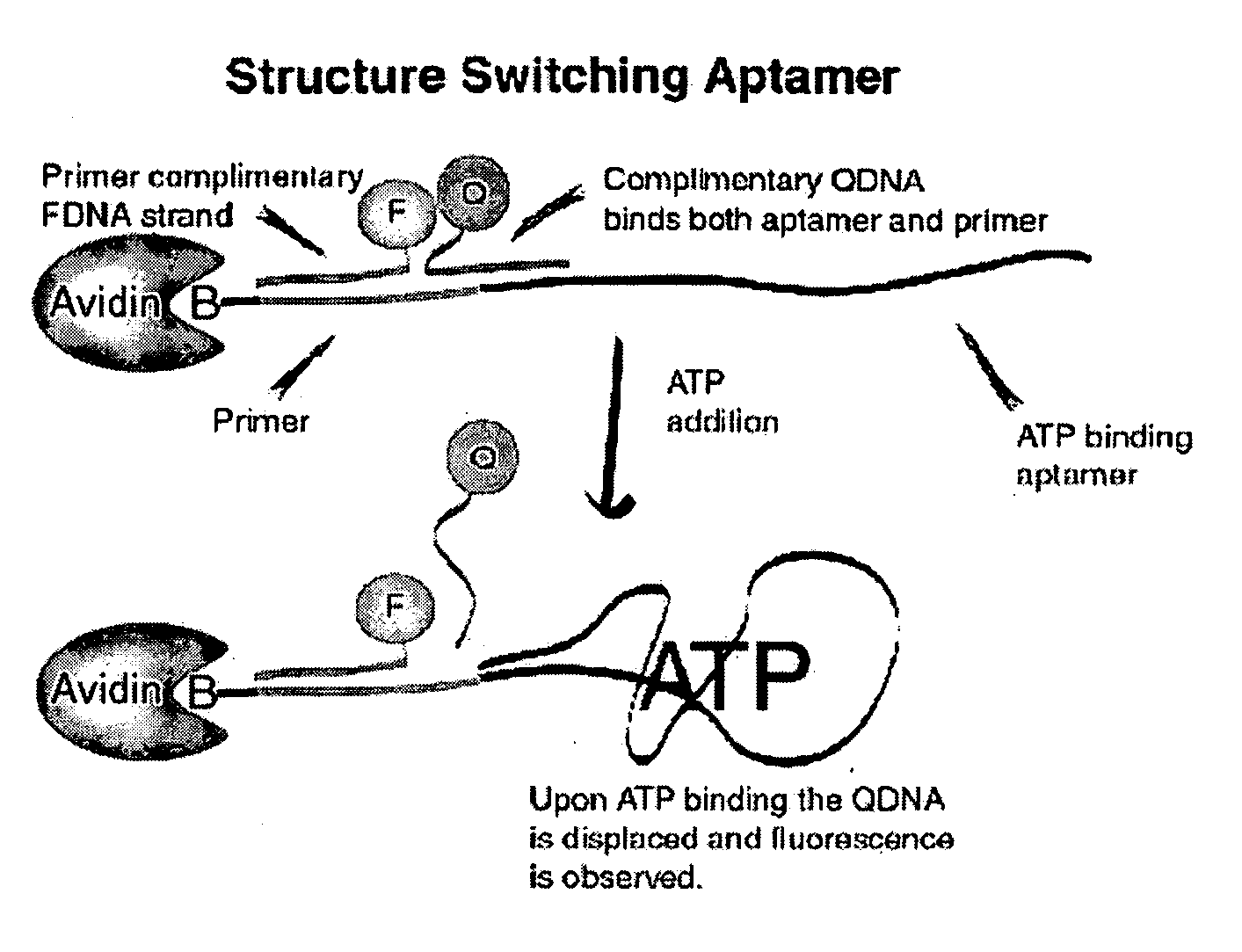
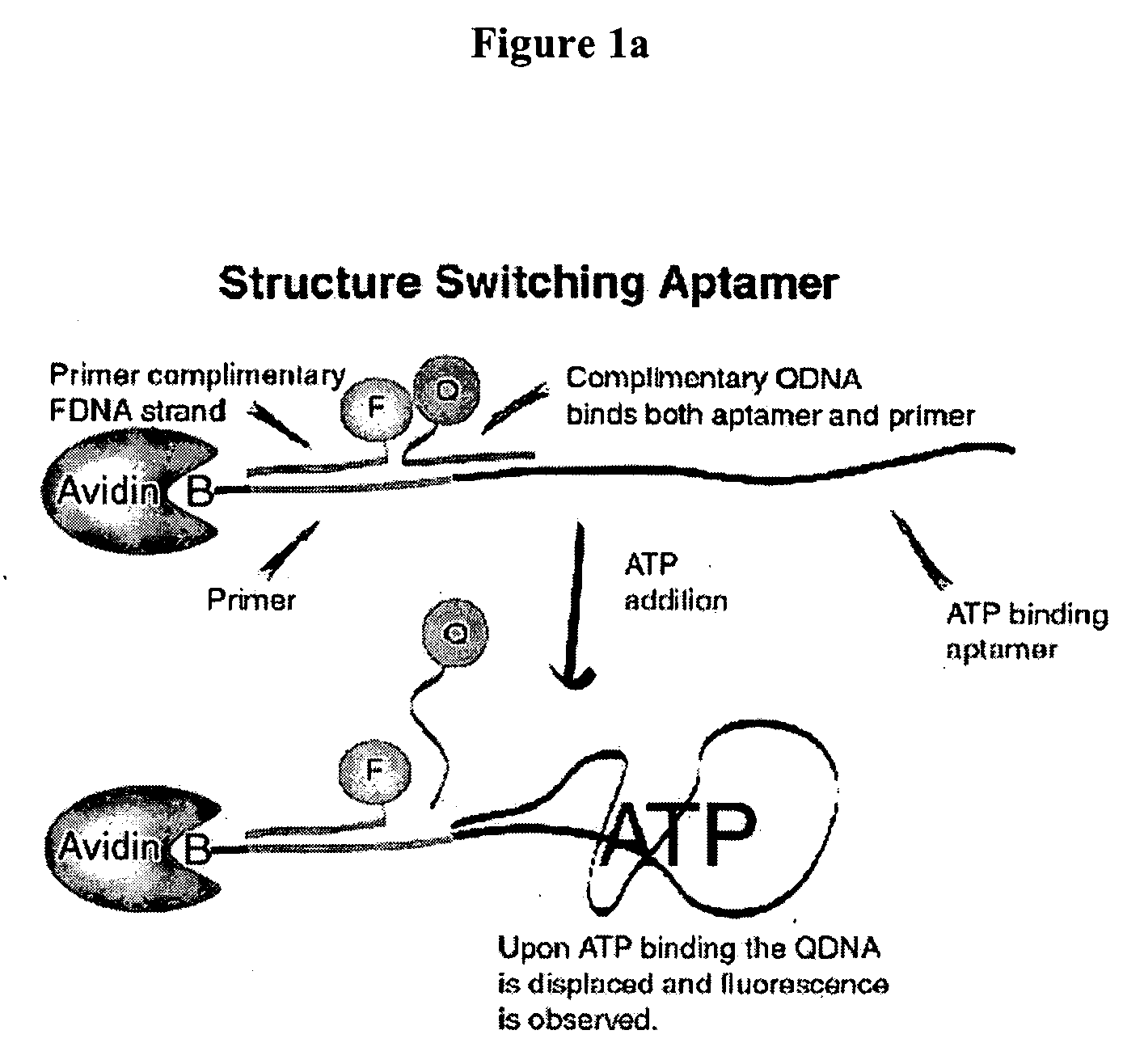
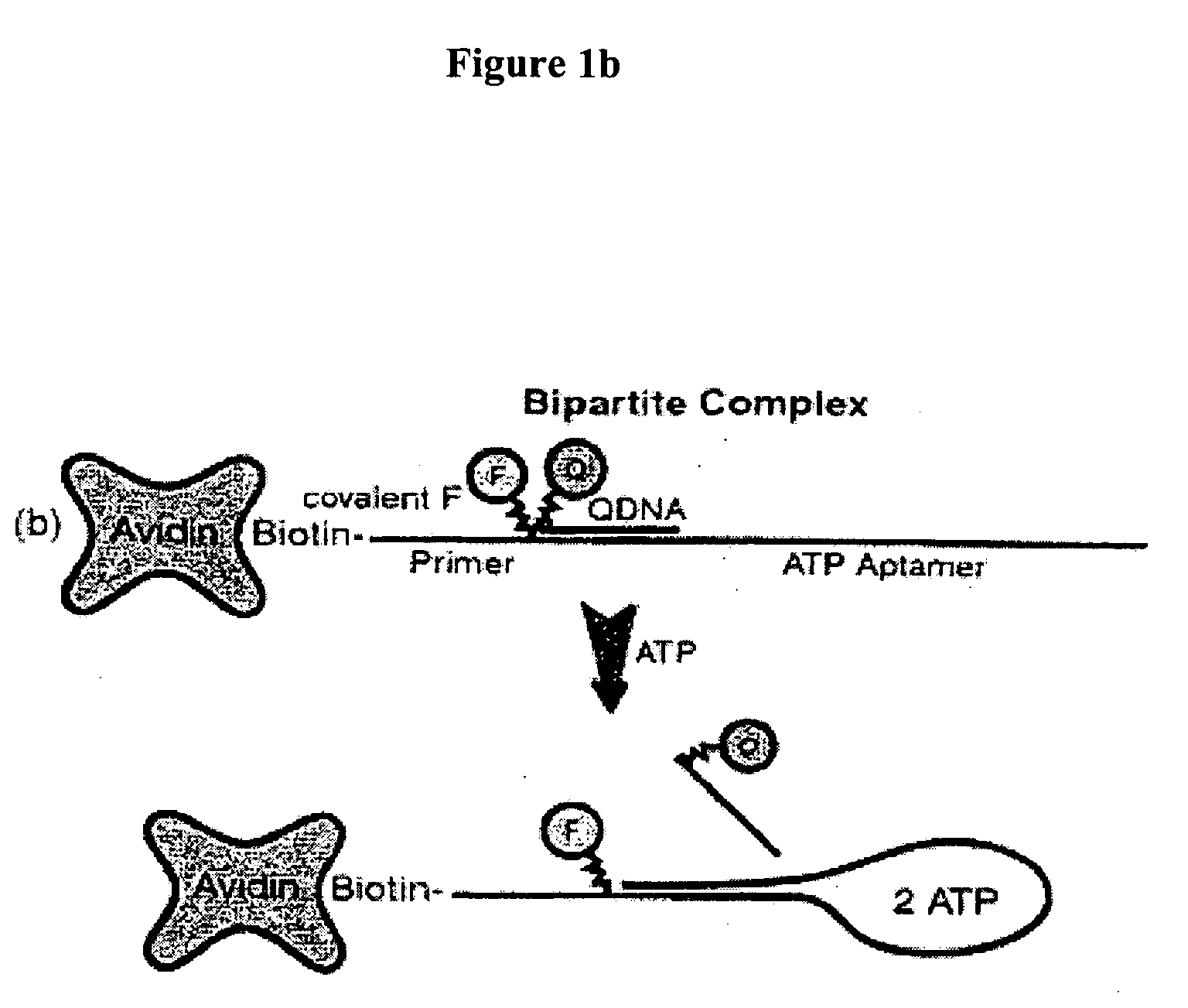
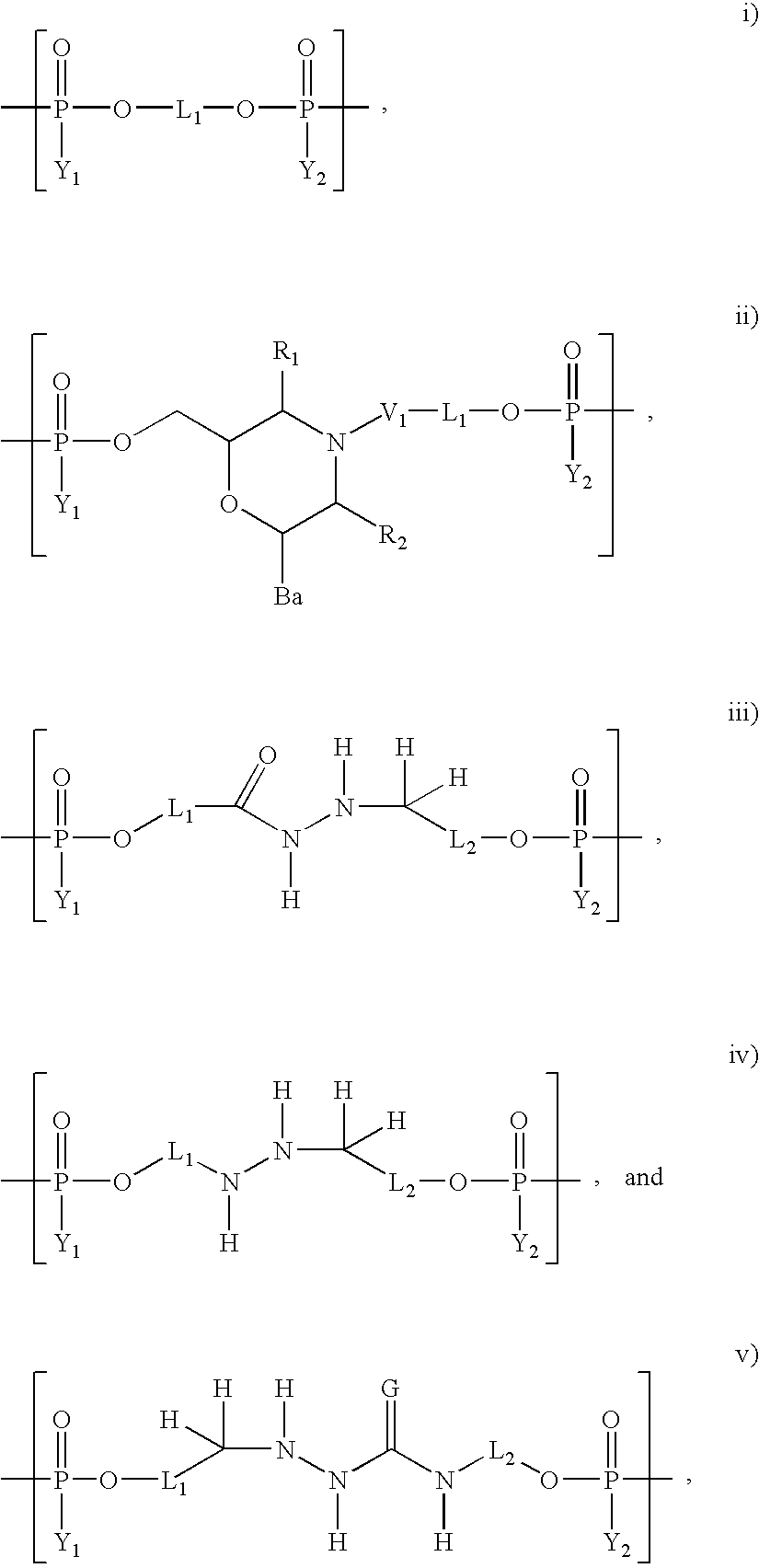
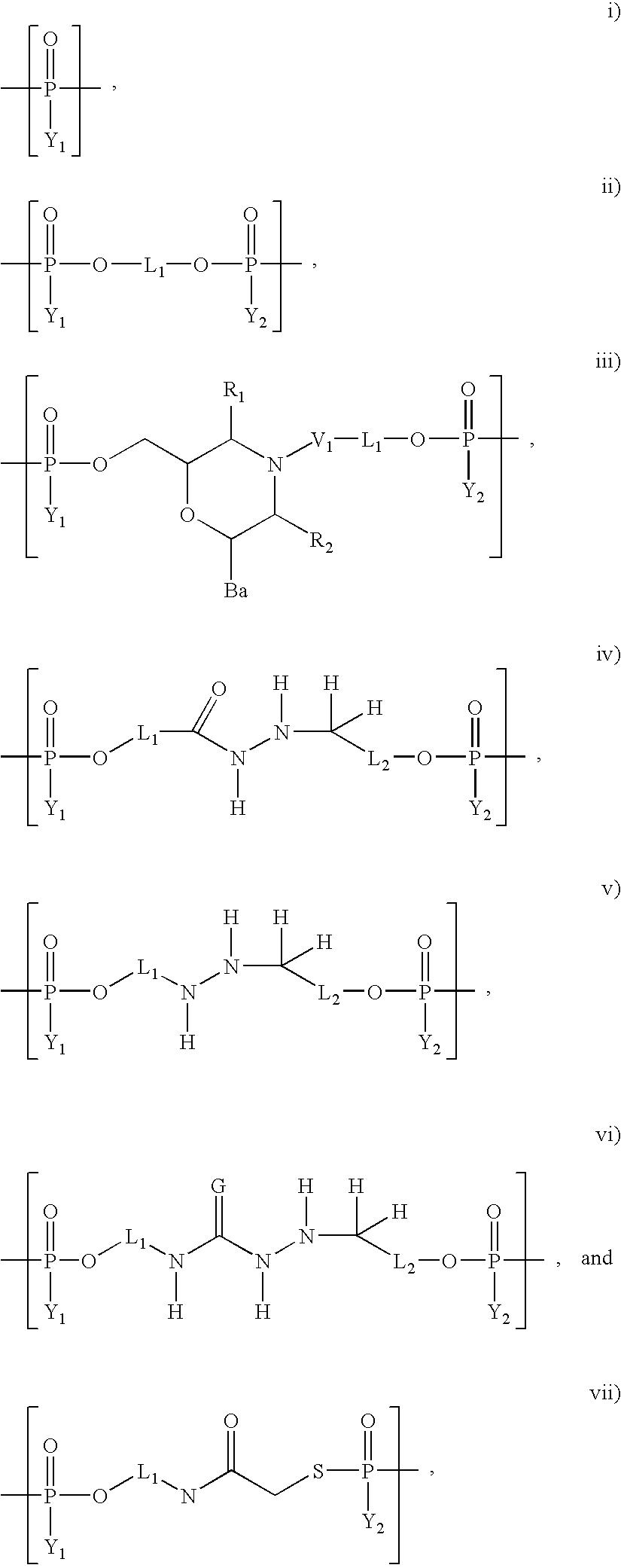
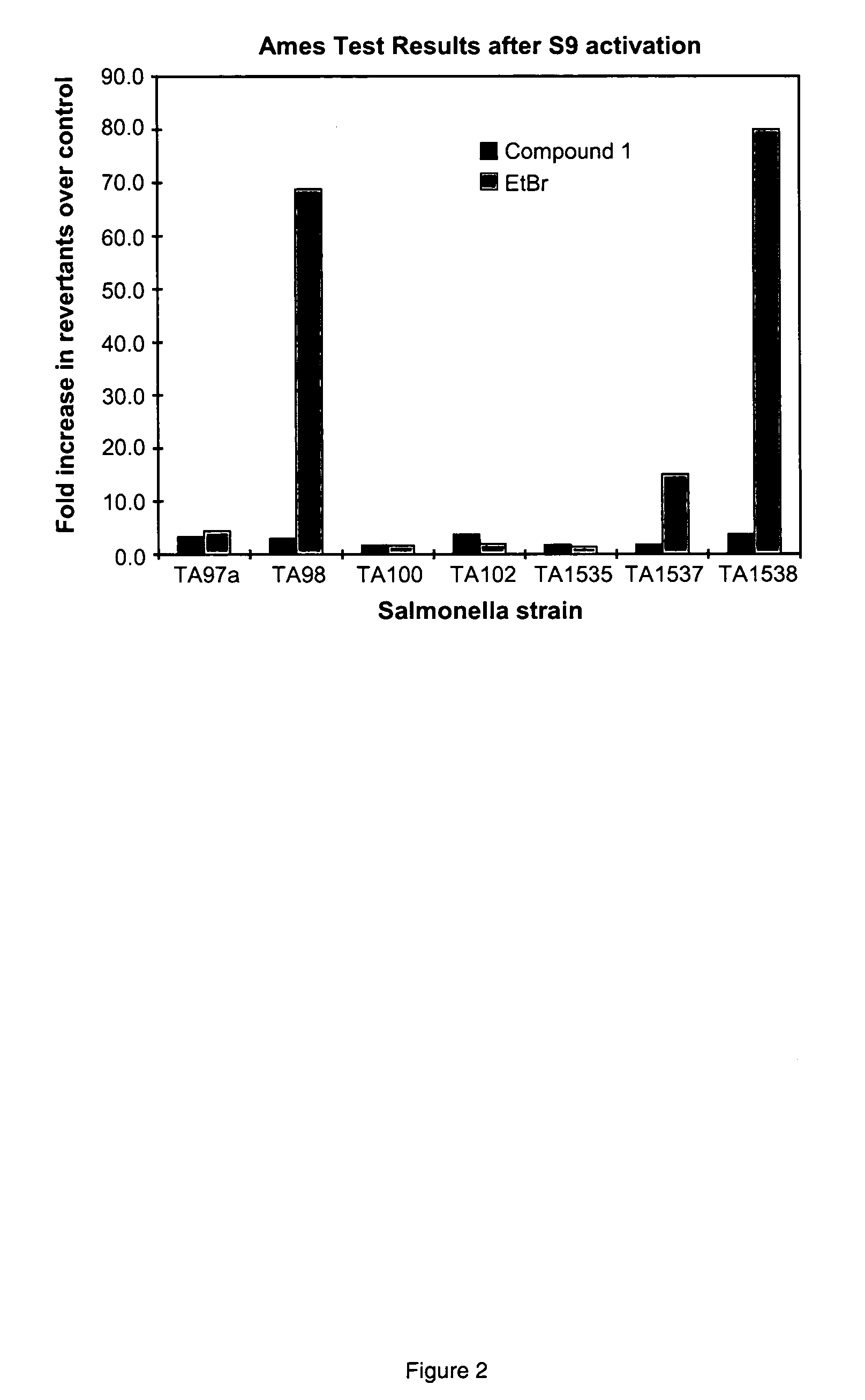
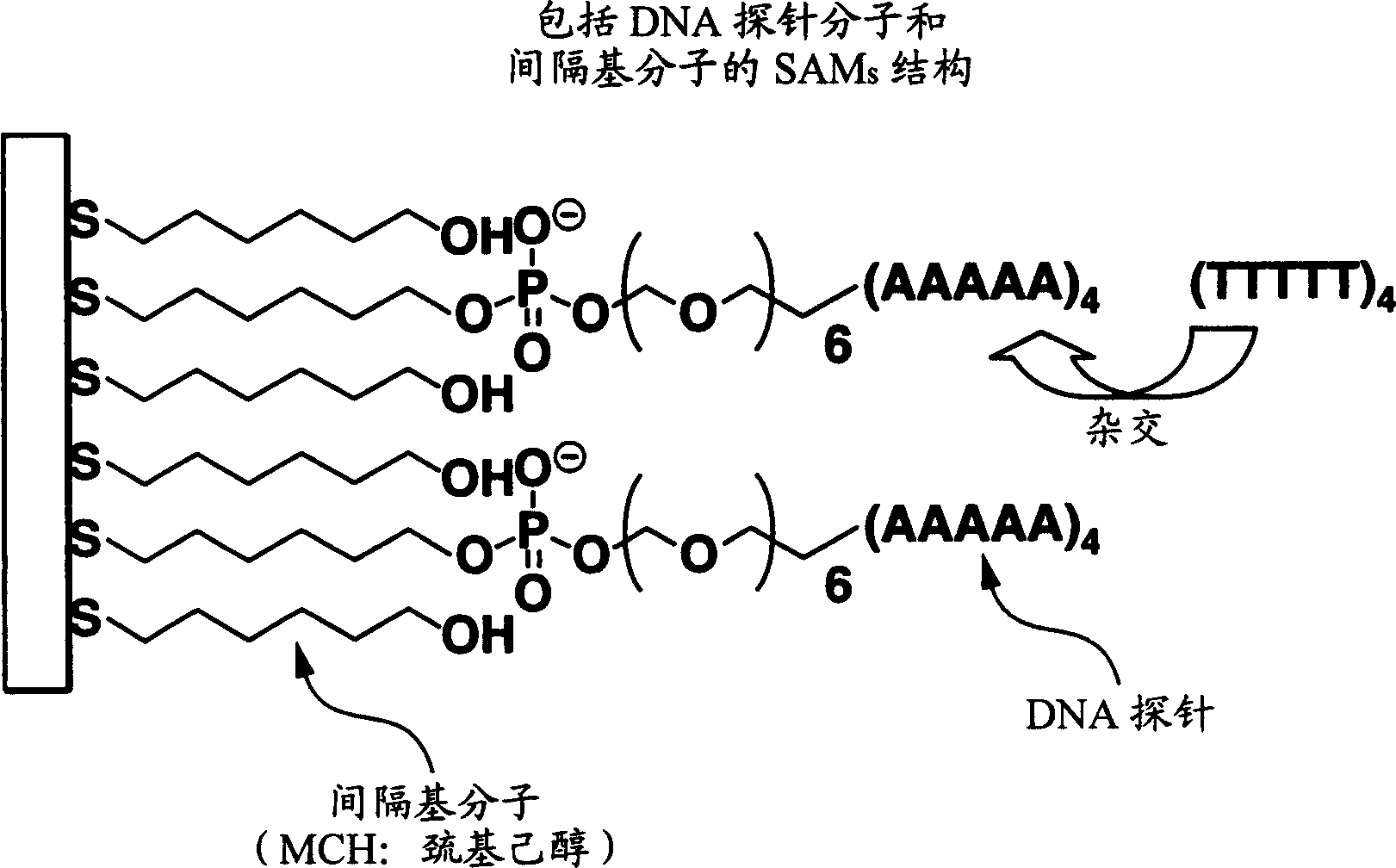
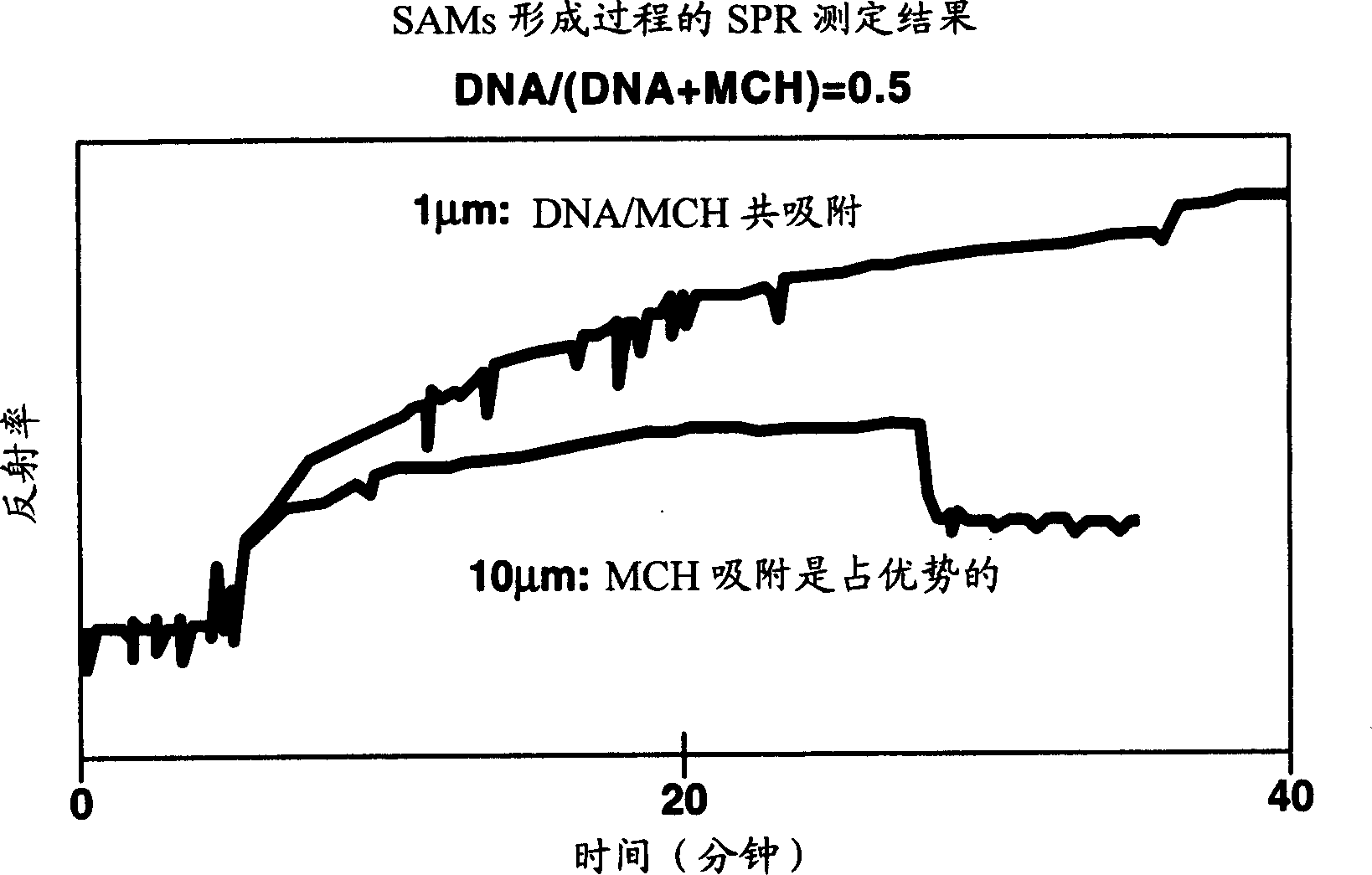
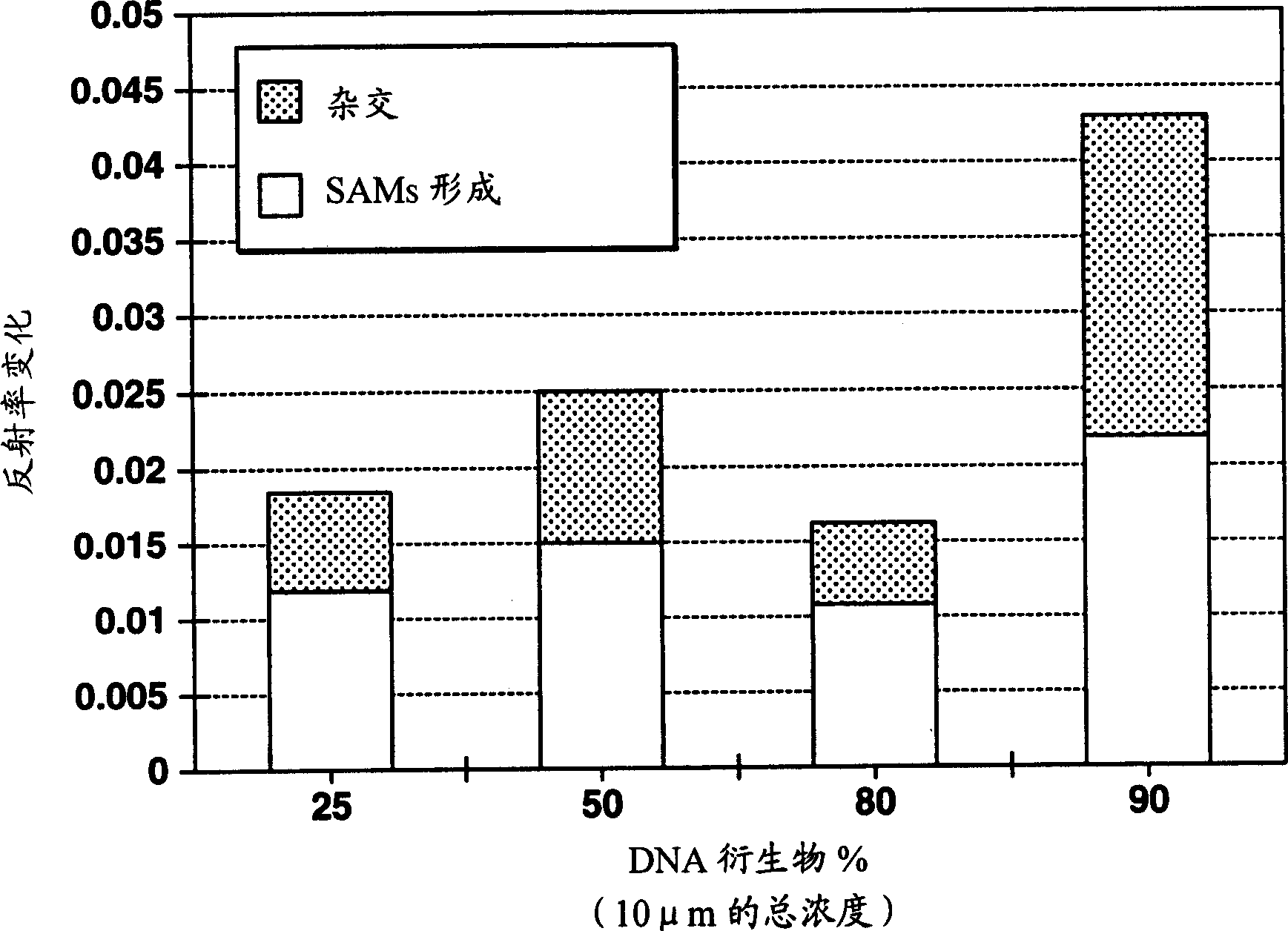
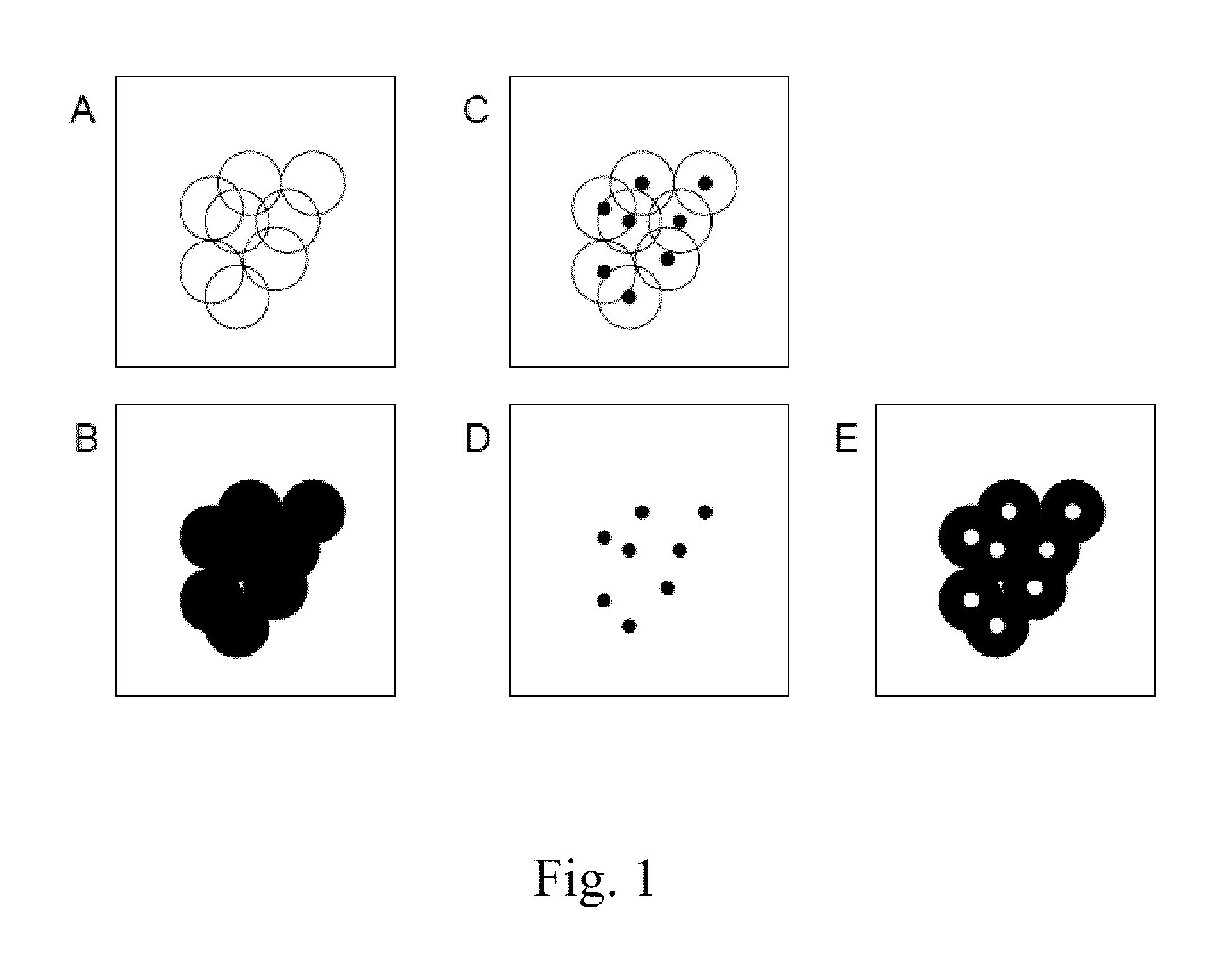
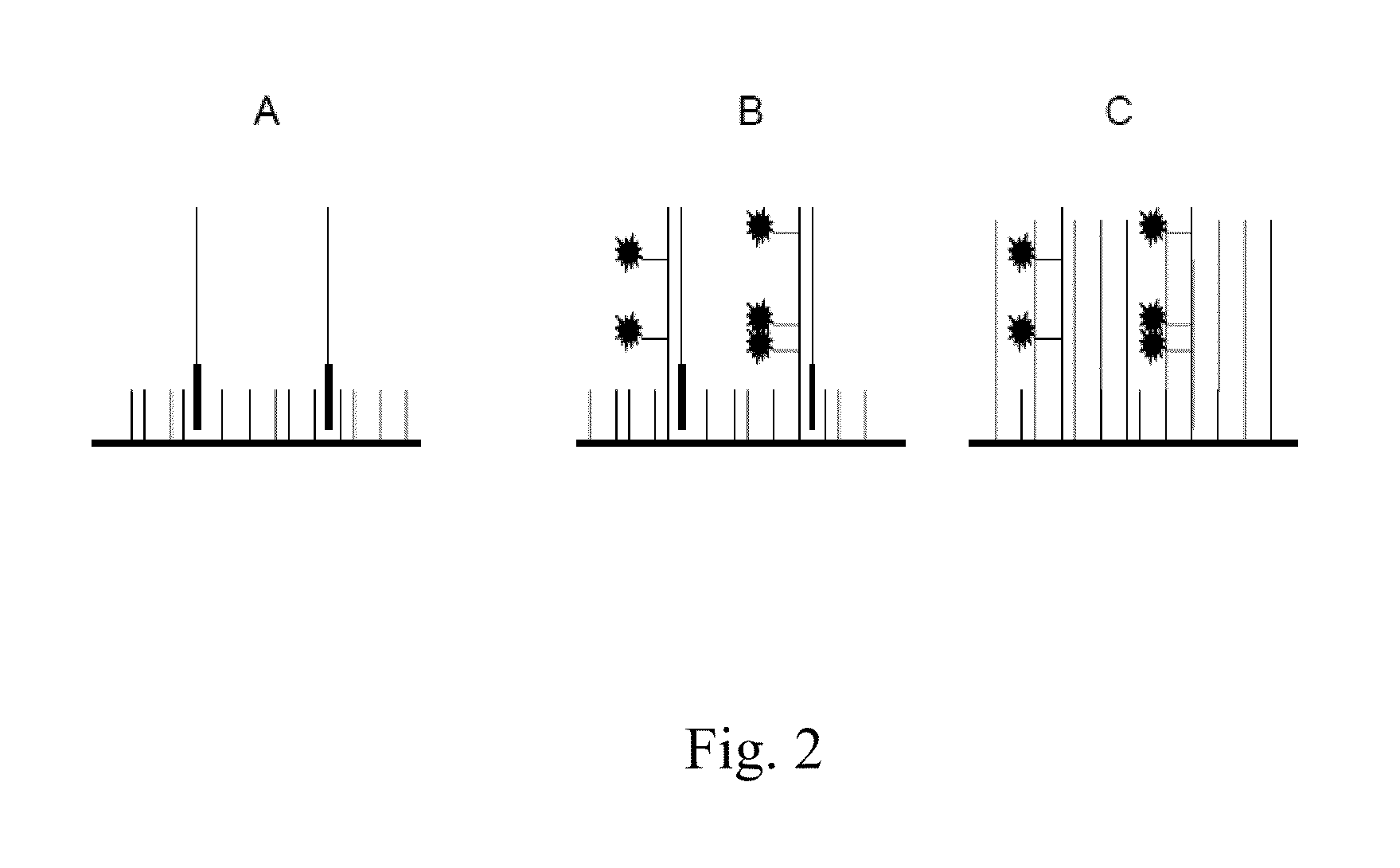
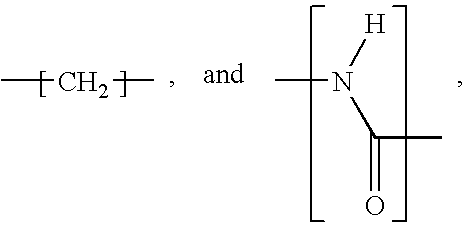Patents
Literature
63 results about "Immobilized Nucleic Acids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
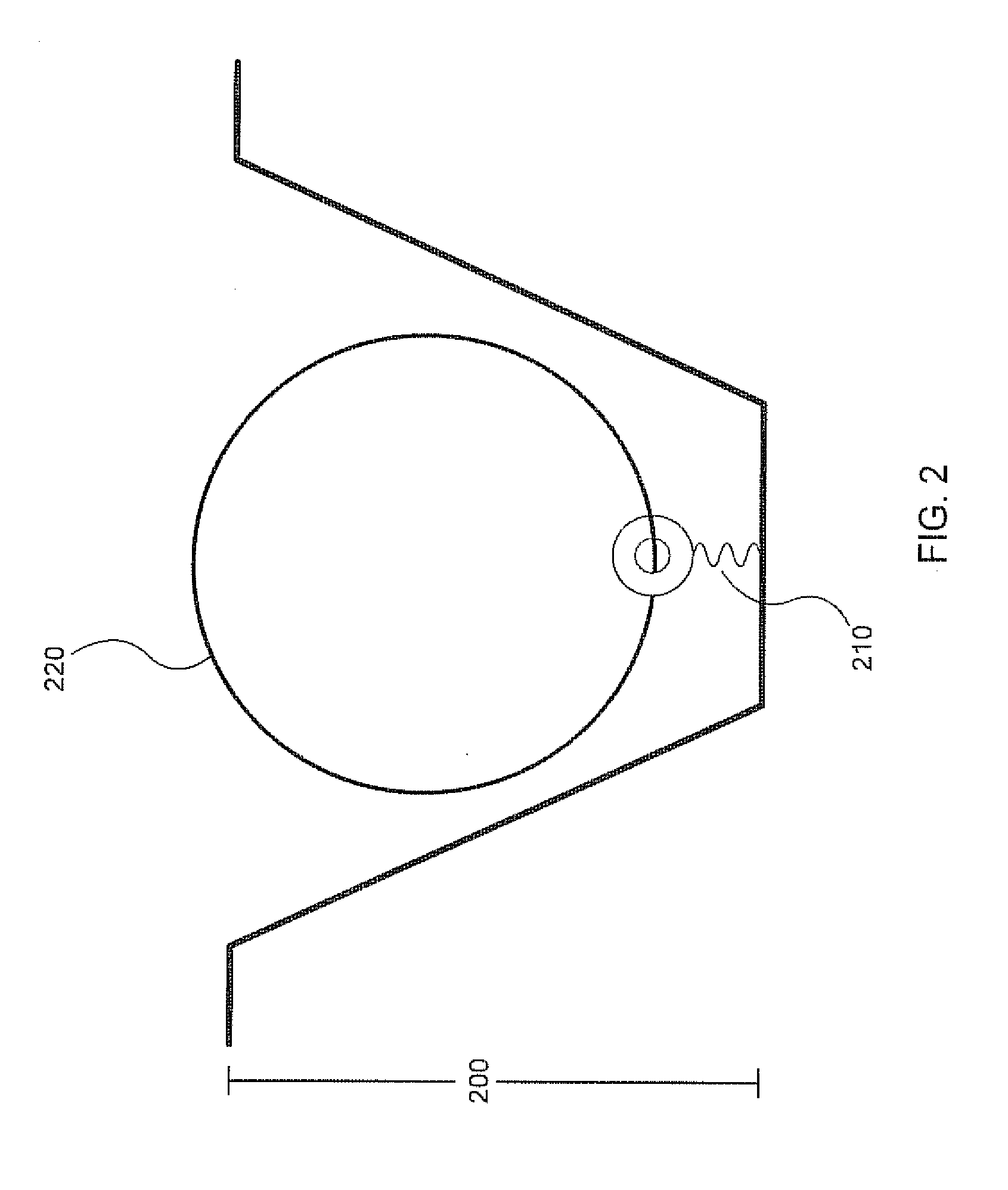
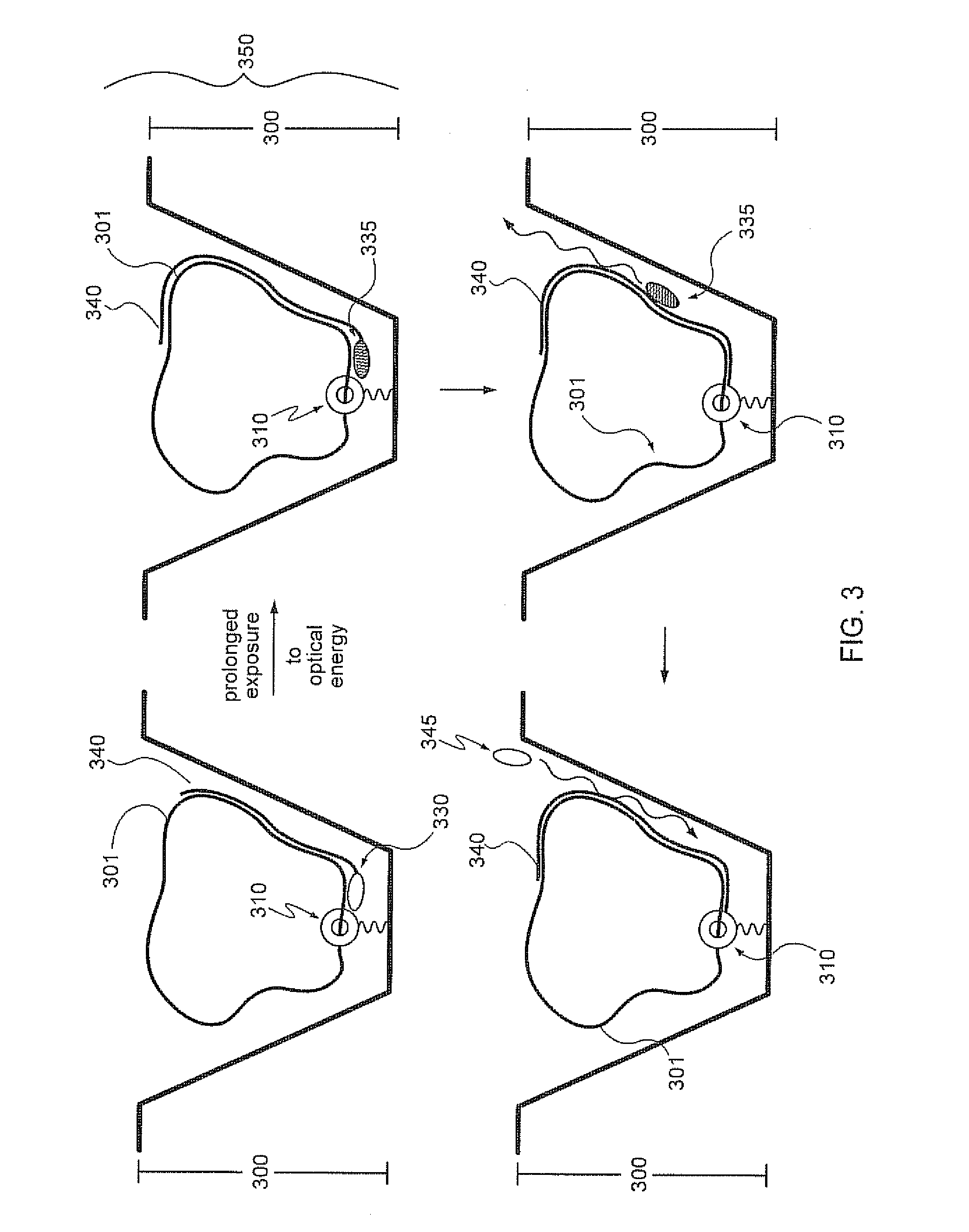
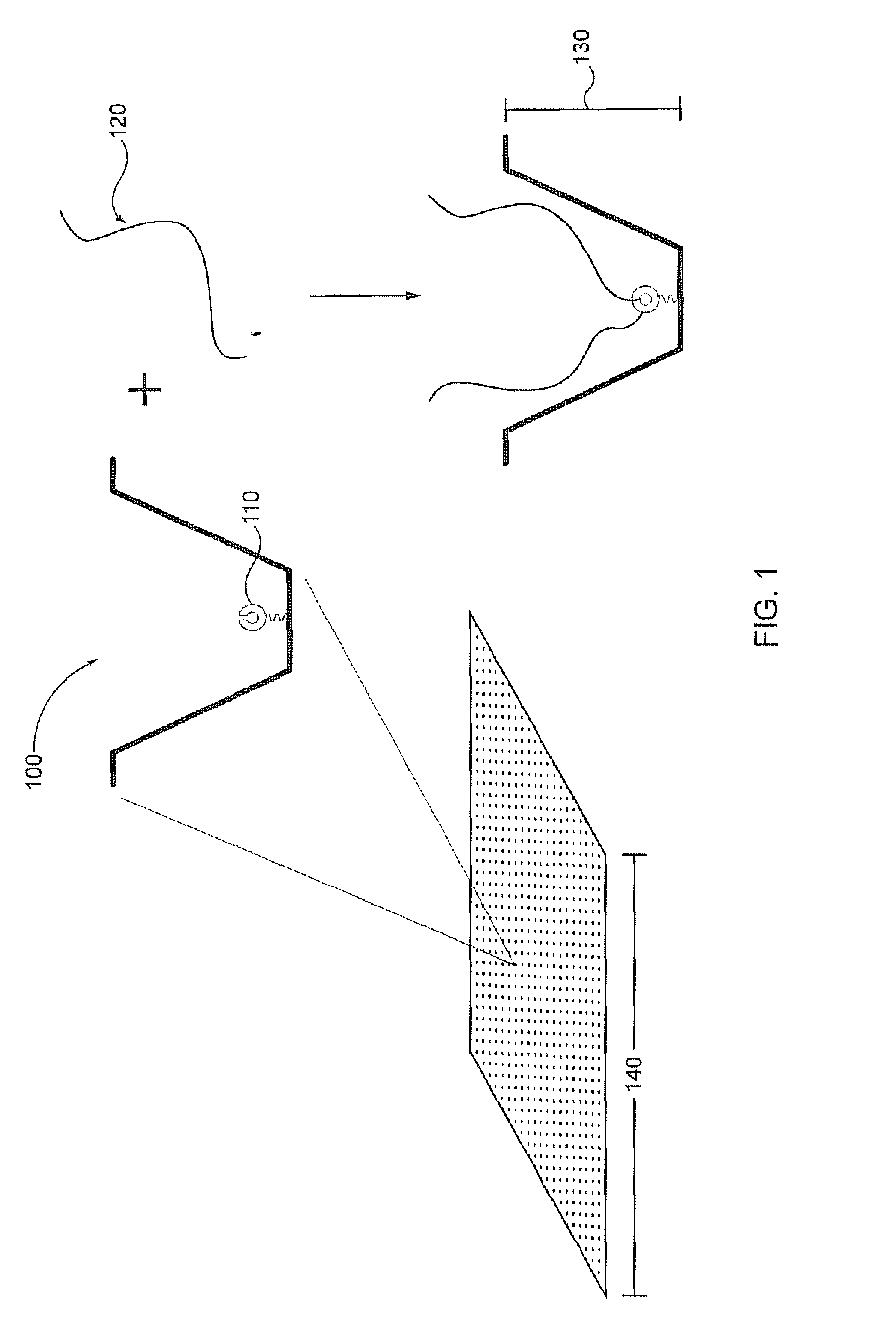
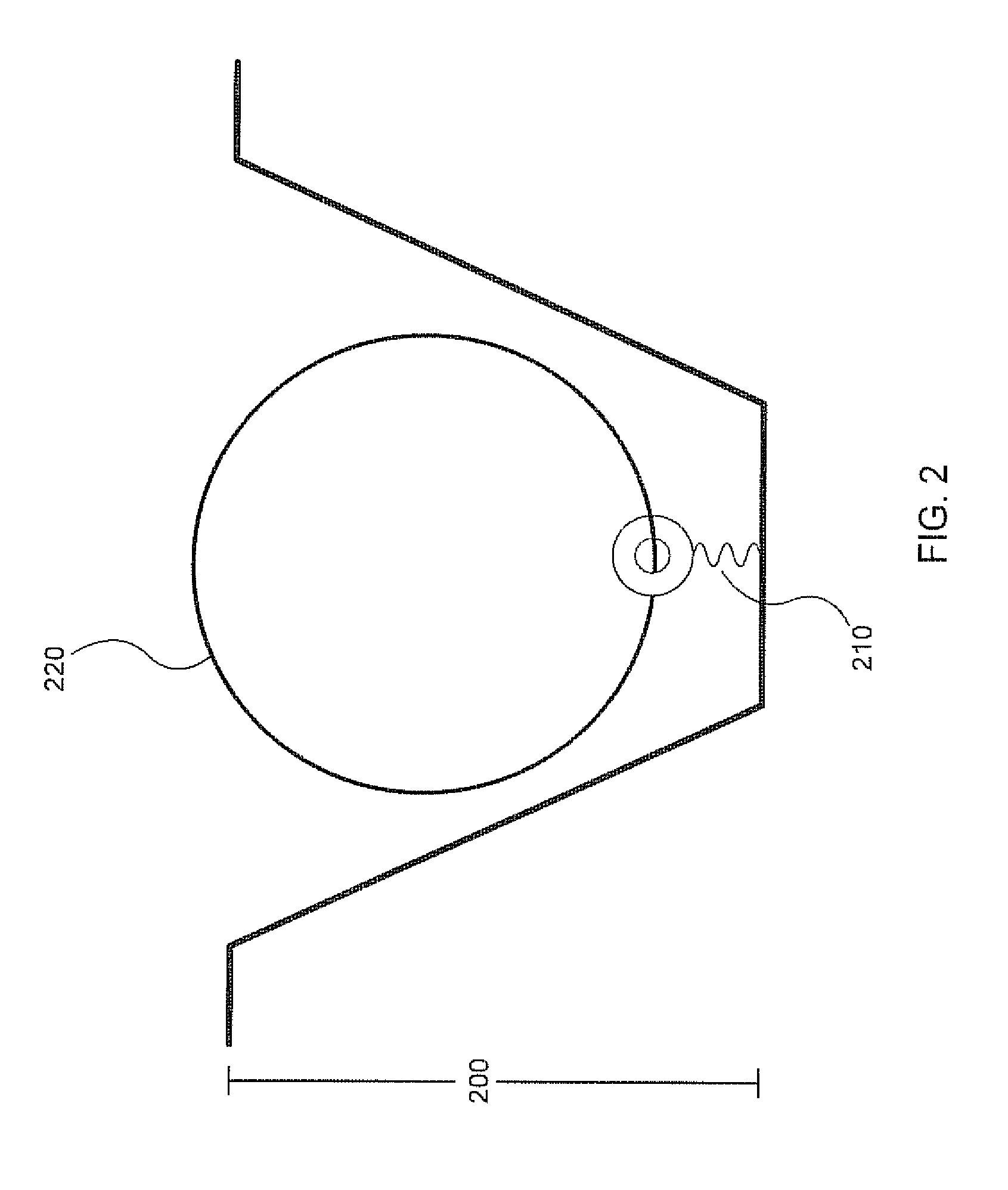
Replica amplification of nucleic acid arrays
InactiveUS7785790B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityImage resolution
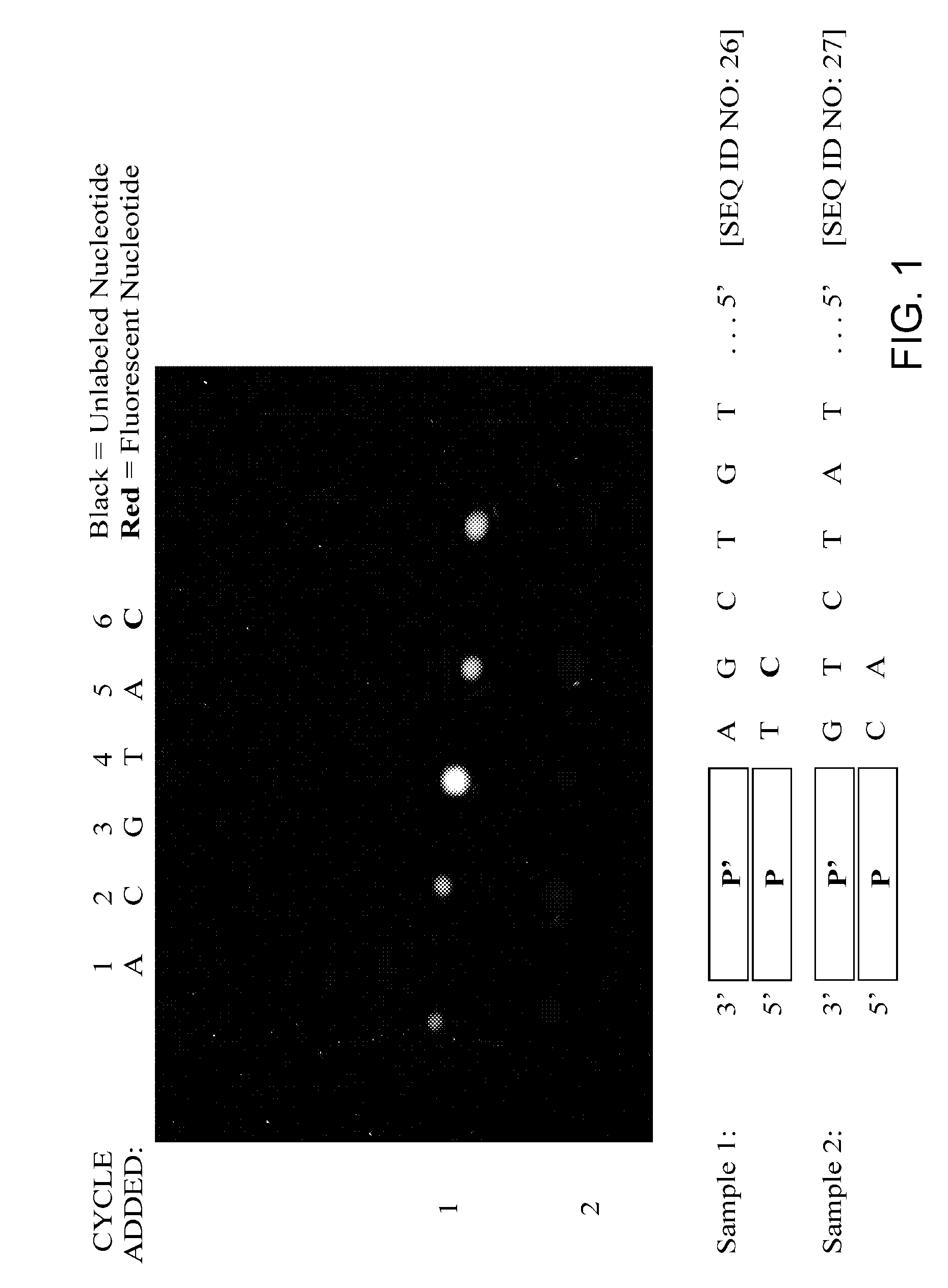
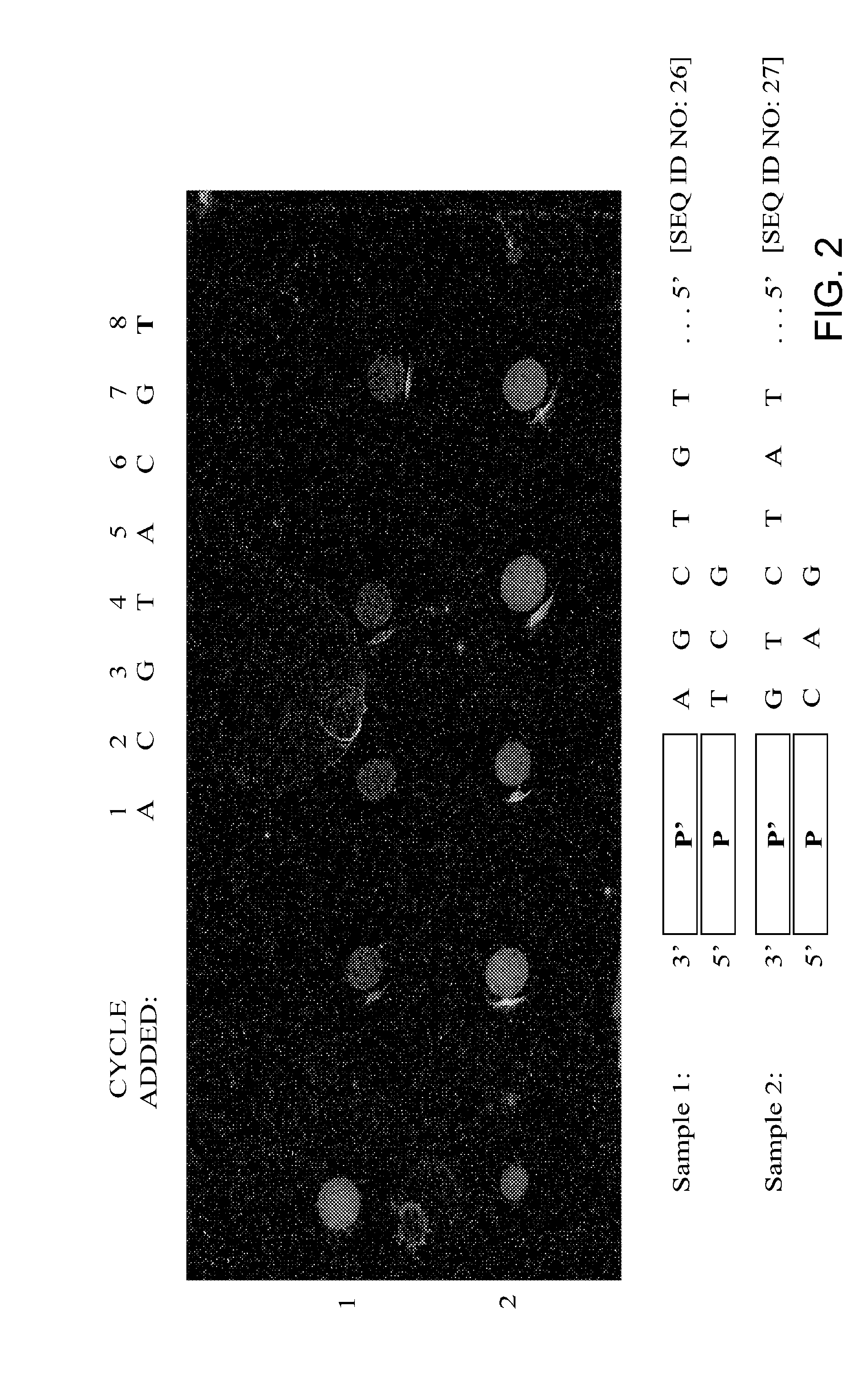
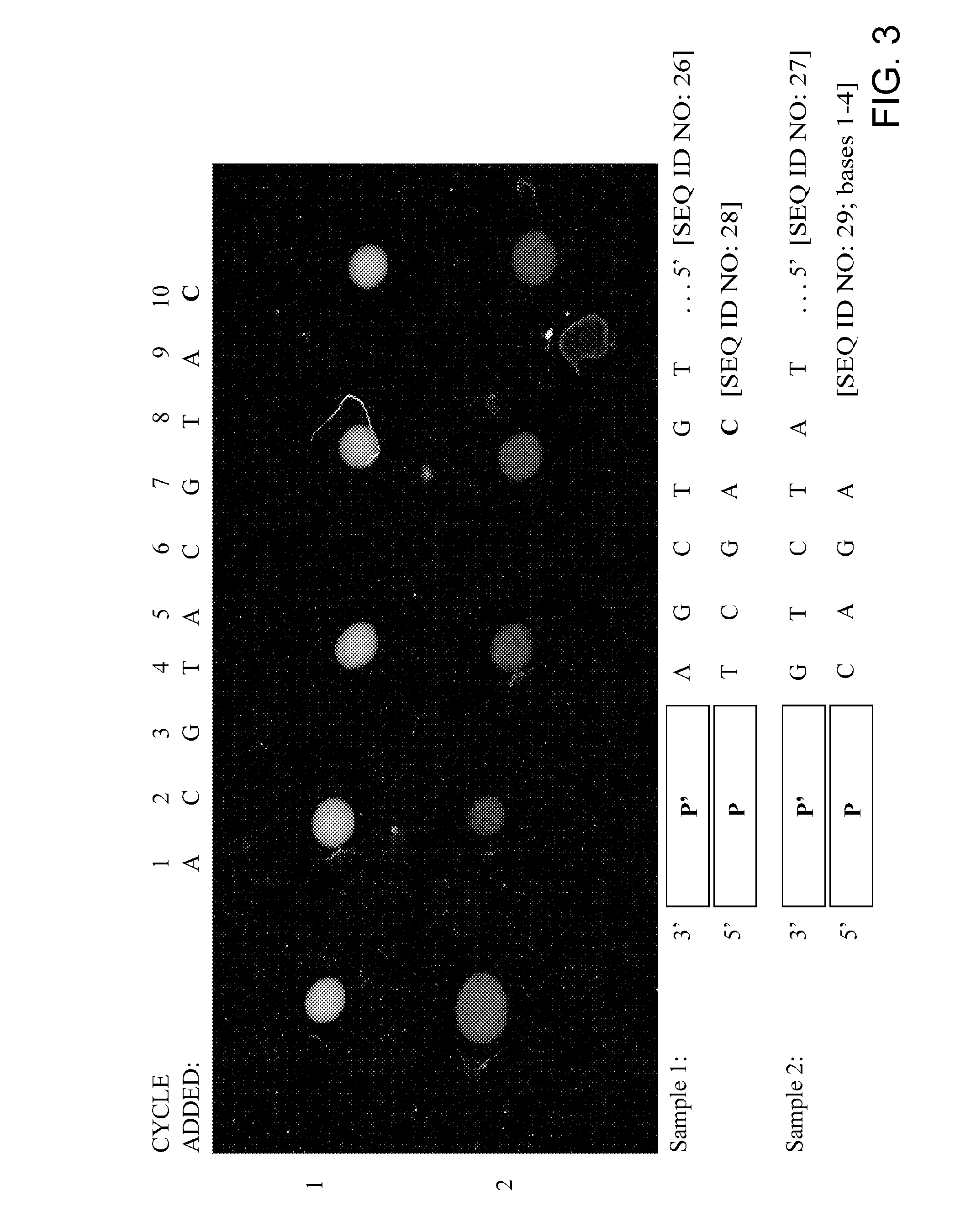
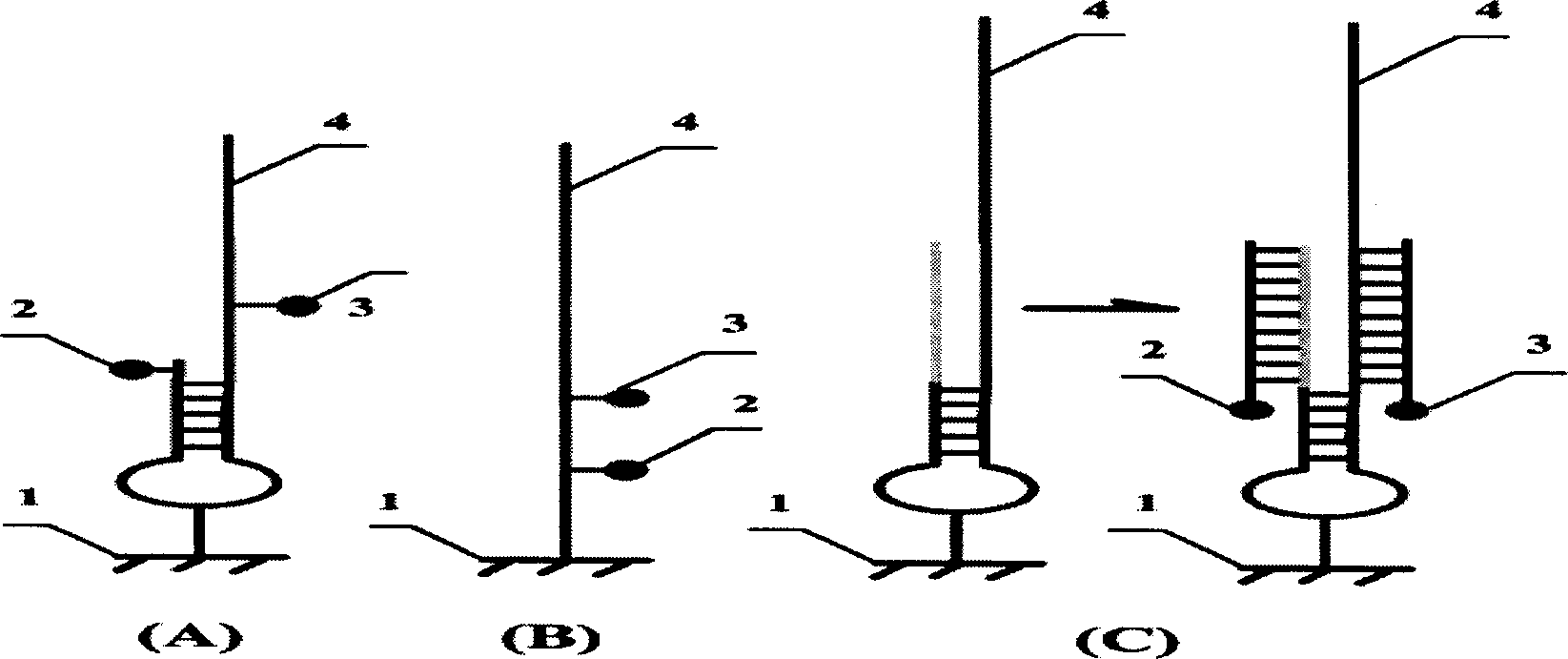
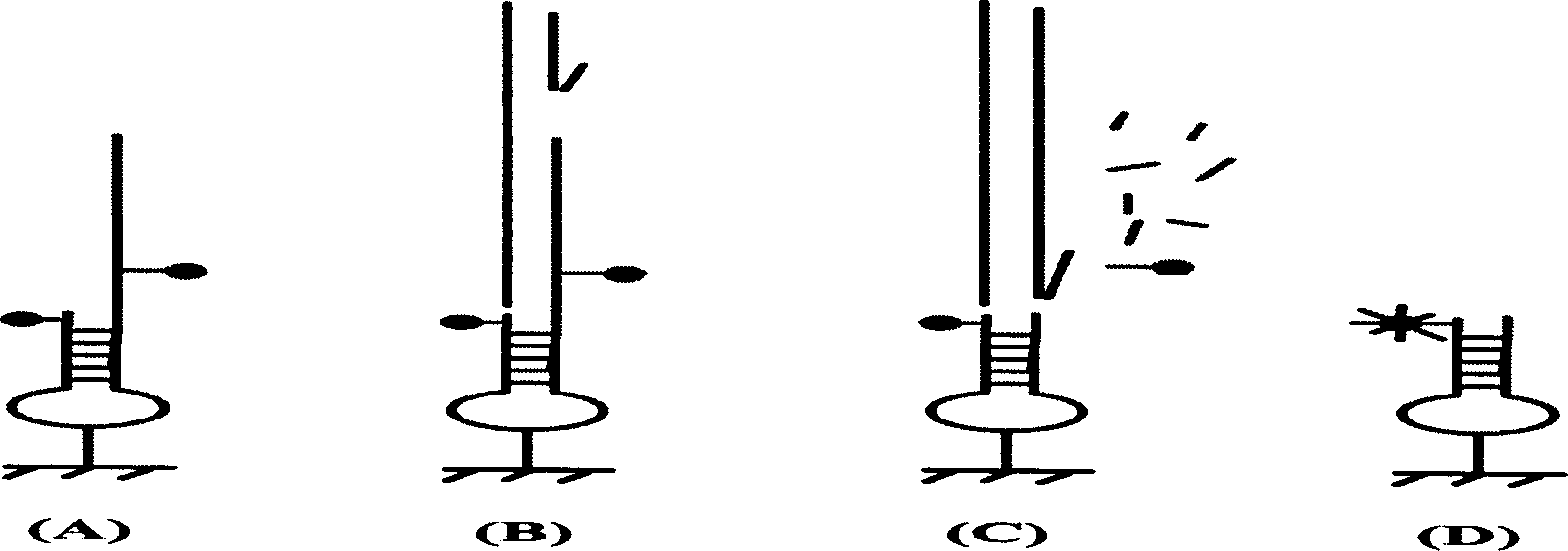
Disclosed are improved methods of making and using immobilized arrays of nucleic acids, particularly methods for producing replicas of such arrays. Included are methods for producing high density arrays of nucleic acids and replicas of such arrays, as well as methods for preserving the resolution of arrays through rounds of replication. Also included are methods which take advantage of the availability of replicas of arrays for increased sensitivity in detection of sequences on arrays. Improved methods of sequencing nucleic acids immobilized on arrays utilizing single copies of arrays and methods taking further advantage of the availability of replicas of arrays are disclosed. The improvements lead to higher fidelity and longer read lengths of sequences immobilized on arrays. Methods are also disclosed which improve the efficiency of multiplex PCR using arrays of immobilized nucleic acids.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
System, array and non-porous solid support comprising fixed or immobilized nucleic acids
InactiveUS7064197B1Easy to quantifyPromote repairSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementImmobilized Nucleic AcidsDouble strand
Nucleic acids are fixed or immobilized to non-porous solid supports (substrates), and include systems containing such supports and arrays with fixed or immobilized nucleic acids. These compositions are useful for nucleic acid analyses and a host of applications, including, for example, detection, mutational analysis and quantification. The non-porous solid supports can be transparent or translucent, and the surfaces can be treated with agents to fix or immobilize the nucleic acids. Such agents include, for example, amine providing compounds, epoxy compounds and acid solutions. The fixed or immobilized nucleic acids can be unlabeled, or labeled with at least one non-radioactive signaling moiety, such as the case when the nucleic acids are double-stranded.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Immobilized nucleic acid complexes for sequence analysis
ActiveUS20100075328A1Use performanceImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPolymerase L
Provided are methods for sequencing a nucleic acid that include fixing a template to a surface through a template localizing moiety and sequencing the nucleic acid with a sequencing enzyme, e.g. a polymerase or exonuclease. The sequencing enzyme can optionally be exchanged with a second sequencing enzyme, which continues the sequencing of the nucleic acid. The template localizing moiety can optionally anneal with the nucleic acid and / or associate with the sequencing enzyme. Also provided are compositions comprising a nucleic acid fixed to a surface via a template localizing moiety, and a first sequencing enzyme, which can sequence the nucleic acid and optionally exchange with a second sequencing enzyme present in the composition. Compositions in which a template localizing moiety is immobilized on a surface are provided. Compositions for sequencing reactions are provided. Also provided are sequencing systems comprising reaction regions in which or near which template localizing moieties are immobilized.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Immobilized nucleic acid complexes for sequence analysis
ActiveUS8481264B2Use performanceImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisExonuclease I
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method of nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS20130231254A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmobilized Nucleic AcidsGene expression
A nucleic acid molecule can be annealed to an appropriate immobilized primer. The primer can then be extended and the molecule and the primer can be separated from one another. The extended primer can then be annealed to another immobilized primer and the other primer can be extended. Both extended primers can then be separated from one another and can be used to provide further extended primers. The process can be repeated to provide amplified, immobilized nucleic acid molecules. These can be used for many different purposes, including sequencing, screening, diagnosis, in situ nucleic acid synthesis, monitoring gene expression, nucleic acid fingerprinting, etc.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods for preparing nucleic acid samples useful for screening dna arrays
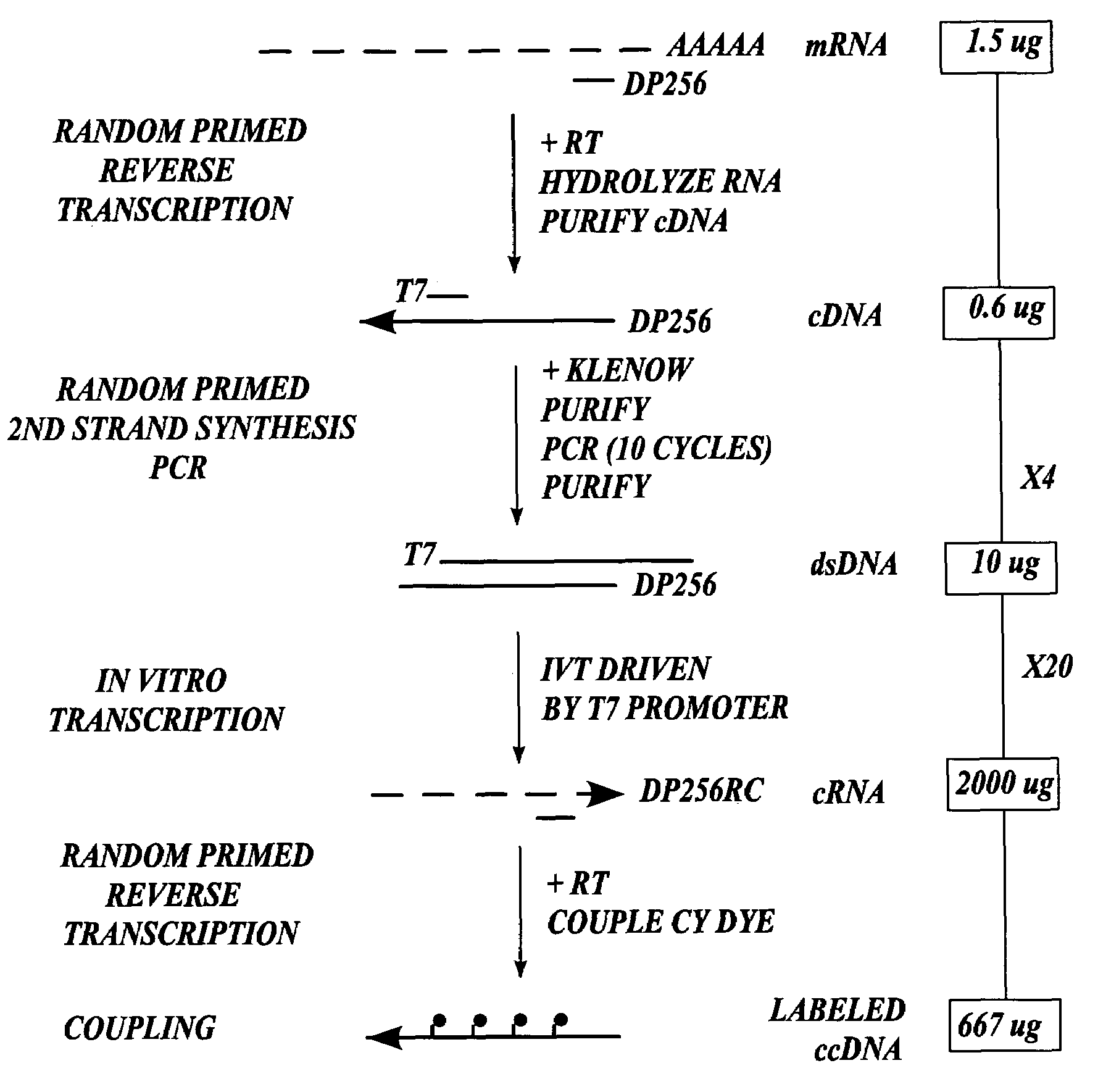
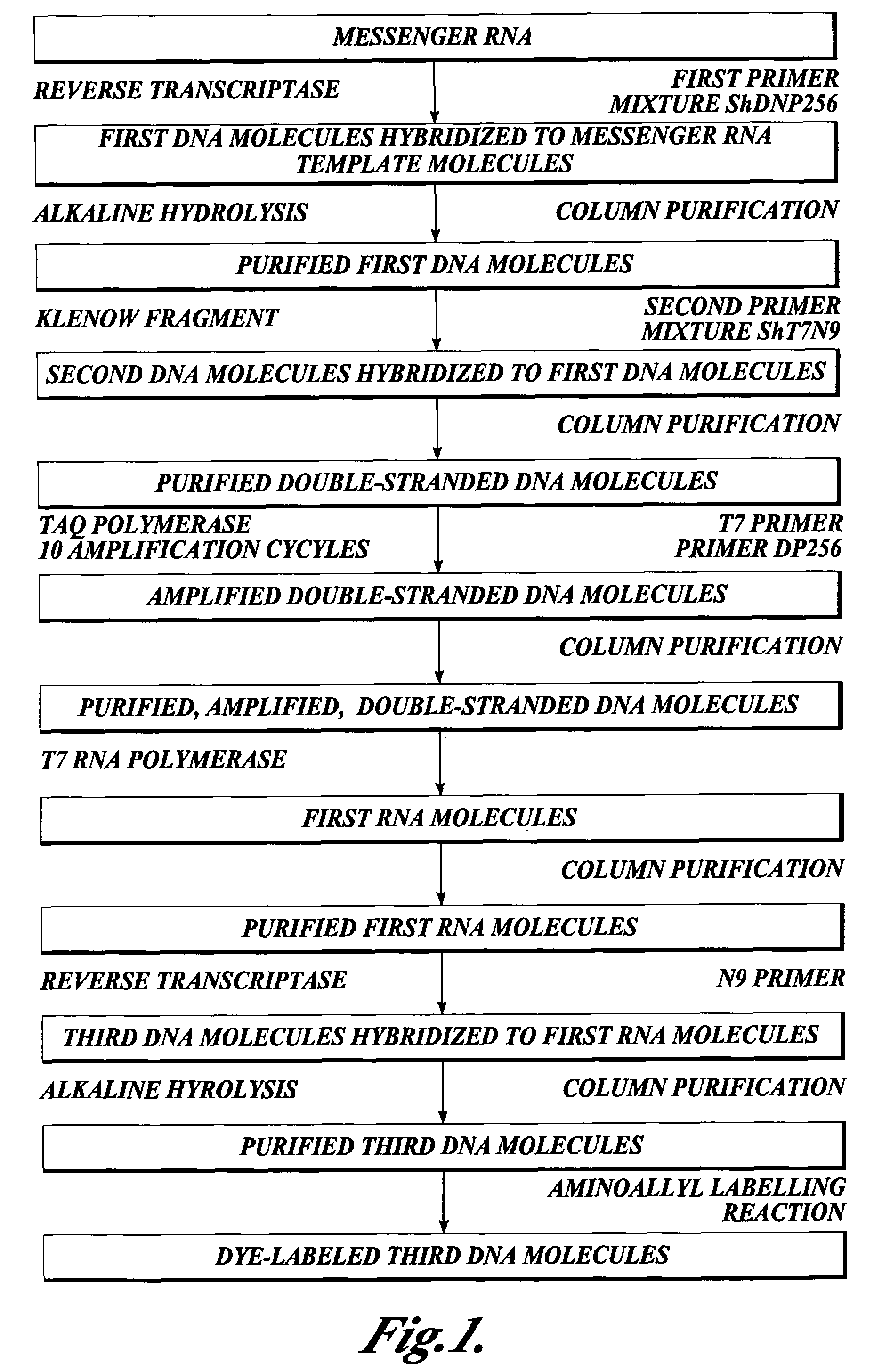
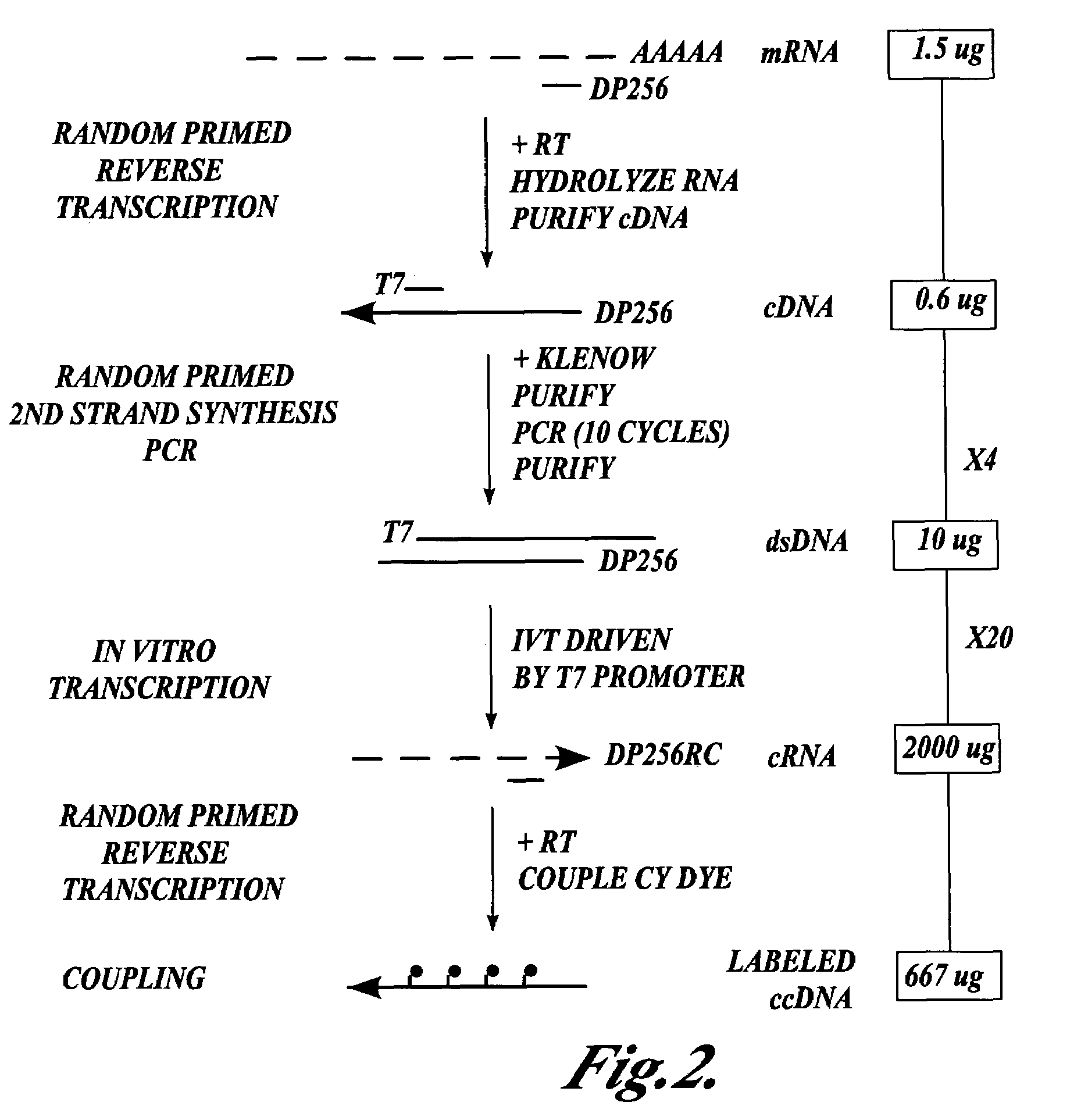
InactiveUS7432084B2High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationEnzymatic synthesisImmobilized Nucleic Acids
In one aspect the present invention provides methods of synthesizing a preparation of nucleic acid molecules, the methods comprising the steps of: (a) utilizing an RNA template to enzymatically synthesize a first DNA molecule that is complementary to at least 50 contiguous bases of the RNA template; (b) utilizing the first DNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a second DNA molecule, thereby forming a double-stranded DNA molecule wherein the first DNA molecule is hybridized to the second DNA molecule; (c) utilizing the first or second DNA molecule of the double-stranded DNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a first RNA molecule that is complementary to either the first DNA molecule or to the second DNA molecule; and (d) utilizing the first RNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a third DNA molecule that is complementary to the first RNA molecule. In another aspect, the present invention provides processed DNA samples prepared by a method of the invention for synthesizing a preparation of nucleic acid molecules. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods for hybridizing a processed DNA sample to a population of immobilized nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Replica amplification of nucleic acid arrays
InactiveUS20020127552A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityImage resolution
Disclosed are improved methods of making and using immobilized arrays of nucleic acids, particularly methods for producing replicas of such arrays. Included are methods for producing high density arrays of nucleic acids and replicas of such arrays, as well as methods for preserving the resolution of arrays through rounds of replication. Also included are methods which take advantage of the availability of replicas of arrays for increased sensitivity in detection of sequences on arrays. Improved methods of sequencing nucleic acids immobilized on arrays utilizing single copies of arrays and methods taking further advantage of the availability of replicas of arrays are disclosed. The improvements lead to higher fidelity and longer read lengths of sequences immobilized on arrays. Methods are also disclosed which improve the efficiency of multiplex PCR using arrays of immobilized nucleic acids.
Owner:CHURCH GEORGE M +1
Amplified nucleic acids and immobilized products thereof
InactiveUS20050118578A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationImmobilized Nucleic AcidsOligonucleotide Primer
A nucleic acid, which is provided in a large amount through a nucleic acid amplification reaction with the use of chimeric oligonucleotide primers, is constructed in a state of containing a modified deoxyribonucleotide for immobilizing the nucleic acid to a solid phase and then immobilized to a solid phase at a high efficiency, thereby giving an immobilized nucleic acid product with excellent qualities.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
DNA biochip and methods of use
ActiveUS20070015175A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceNucleic acid sequencing
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for detecting nucleic acid sequences. One aspect of the invention concerns a silicon-based “biochip” comprising nucleic acid immobilized thereon. In one embodiment, the silicon comprises microcavities. The nucleic acid to be assayed for the presence of one or more target nucleic acid sequences is immobilized on the silicon. A nucleic acid, such as an oligonucleotide probe, having a sequence substantially complementary to the target nucleic acid sequence can be used to detect the immobilized nucleic acid on the silicon. If the nucleic acid used for detection hybridizes with a target nucleic acid sequence, the hybridized sequences can be detected directly or indirectly. In an exemplified embodiment, the oligonucleotide probe can be labeled with a detectable label, for example, a fluorescent molecule. The subject invention also concerns methods for detecting a target nucleic acid using a silicon-based biochip of the invention.
Owner:ALABAMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Detection of immobilized nucleic acid
The present invention provides methods for determining the presence of immobilized nucleic acid employing unsymmetrical cyanine dyes that are derivatives of thiazole orange, a staining solution and select fluorogenic compounds that are characterized as being essentially non-genotoxic. The methods comprise immobilizing nucleic acid, single or double stranded DNA, RNA or a combination thereof, on a solid or semi solid support, contacting the immobilized nucleic acid with an unsymmetrical cyanine dye compound and then illuminating the immobilized nucleic acid with an appropriate wavelength whereby the presence of the nucleic acid is determined. The cyanine dye compounds are typically present in an aqueous staining solution comprising the dye compound and a tris acetate or tris borate buffer wherein the solution facilitates the contact of the dye compound and the immobilized nucleic acid. Typically the solid or semi-solid support is selected from the group consisting of a polymeric gel, a membrane, an array, a glass bead, a glass slide, and a polymeric microparticle. Preferably, the polymeric gel is agarose or polyacrylamide. The methods employing the non-genotoxic compounds represent an improvement over commonly used methods employing ethidium bromide wherein the present methods retain the advantages of ethidium bromide, ease of use and low cost, but without the disadvantageous, known mutagen requiring special handling and waste procedures.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for determining the methylation pattern of a polynucleic acid
InactiveUS20060204988A1Reduce complexityEffective and powerfulMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBase JNucleotide
Particular aspects relate to a method for determining the methylation pattern of a polynucleic acid, comprising: a) preparing a solution comprising a mixture of fragments of the polynucleic acid; b) coupling the fragments with a substance being detectable with a detection method; c) contacting a solution comprising the fragments of b) with a DNA microarray having a plurality of different immobilized oligonucleotides, each comprising at least one methylation site, at respectively assigned different locations thereon, the contacing under conditions affording hybridization of fragments with correlated immobilized oligonucleotides under defined stringency, and wherein the immobilized oligonucleotides have a length of less than 200 bases; d) optionally performing a a washing step; and e) detecting, using the physical detection method, such immobilized nucleic acids to which solution fragments are hybridized and / or to which solution fragments are not hybridized.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
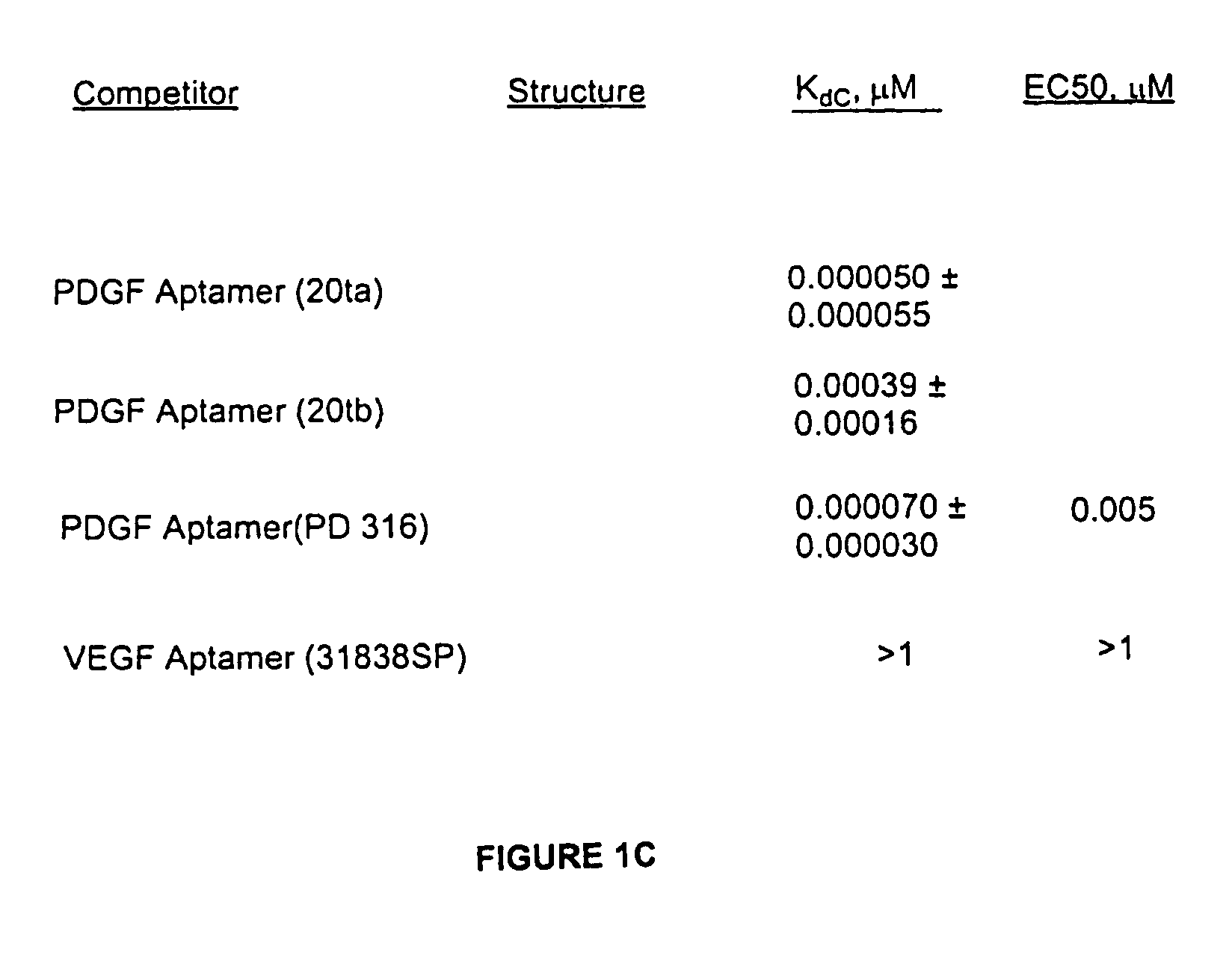
Determining non-nucleic acid molecule binding to target by competition with nucleic acid ligands
InactiveUS7258980B2Easy to identifyQuick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsCompetitive binding
A competitive binding assay is used to determine whether a non-nucleic acid molecule from a library of non-nucleic acid molecules binds to a target. The non-nucleic acid molecule competes with a labeled nucleic acid ligand for binding to the target which may be immobilized. Detecting displacement of labeled nucleic acid ligand from a complex of the labeled nucleic acid ligand and the target determines binding of the non-nucleic acid molecule to the target. The nucleic acid ligand may be immobilized and contacted with a labeled target to form a complex. Adding a non-nucleic acid molecule to the complex displaces labeled target from the complex, and detecting displacement of the labeled target determines binding of the non-nucleic acid molecule to the target. Labeled nucleic acid ligand or labeled target displaced from or remaining in the complex can be detected for detecting displacement. Nucleic acid ligands that bind to the target are identified by the SELEX method. The assay provides a high throughput screening method for determining whether a non-nucleic acid molecule binds to a target.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
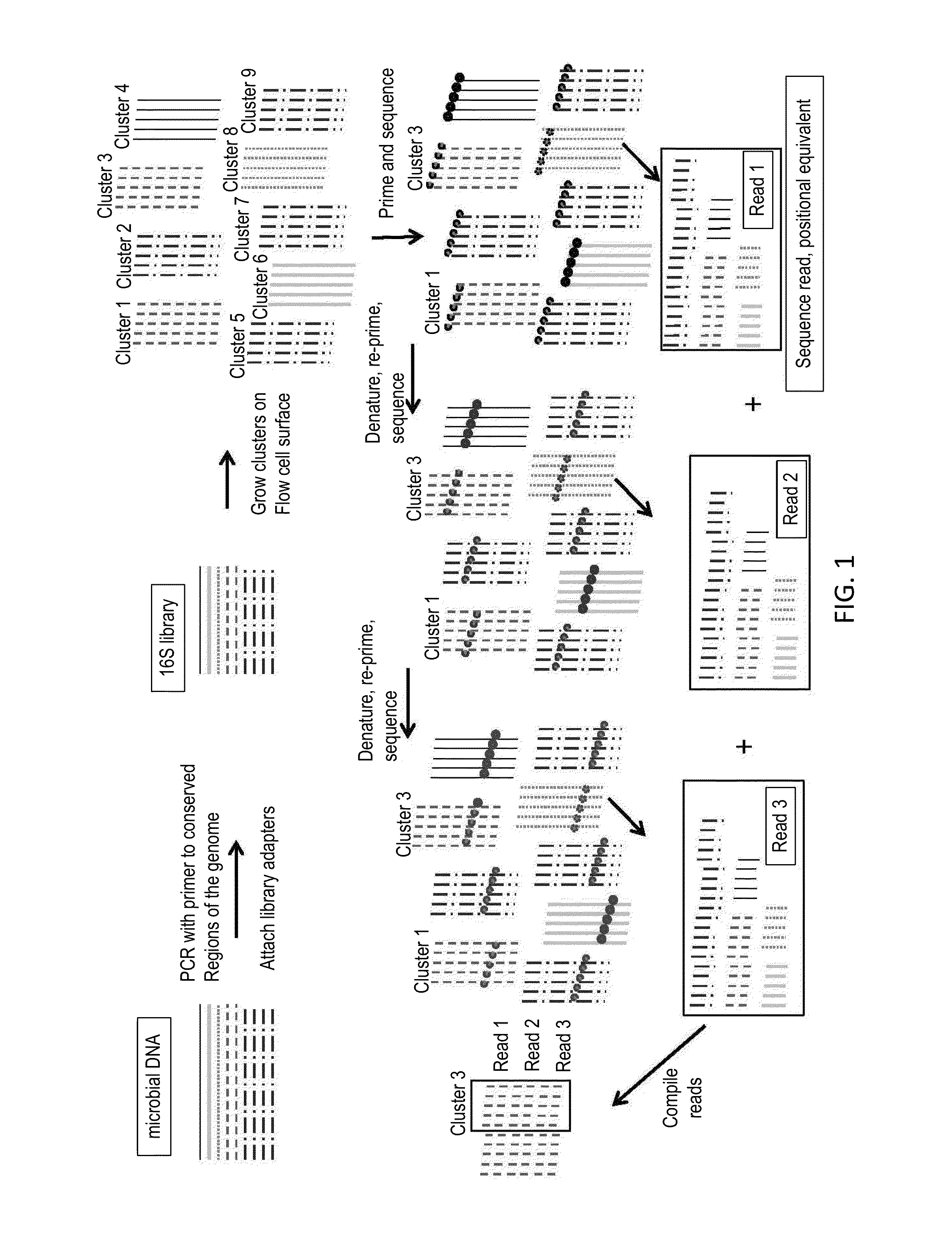
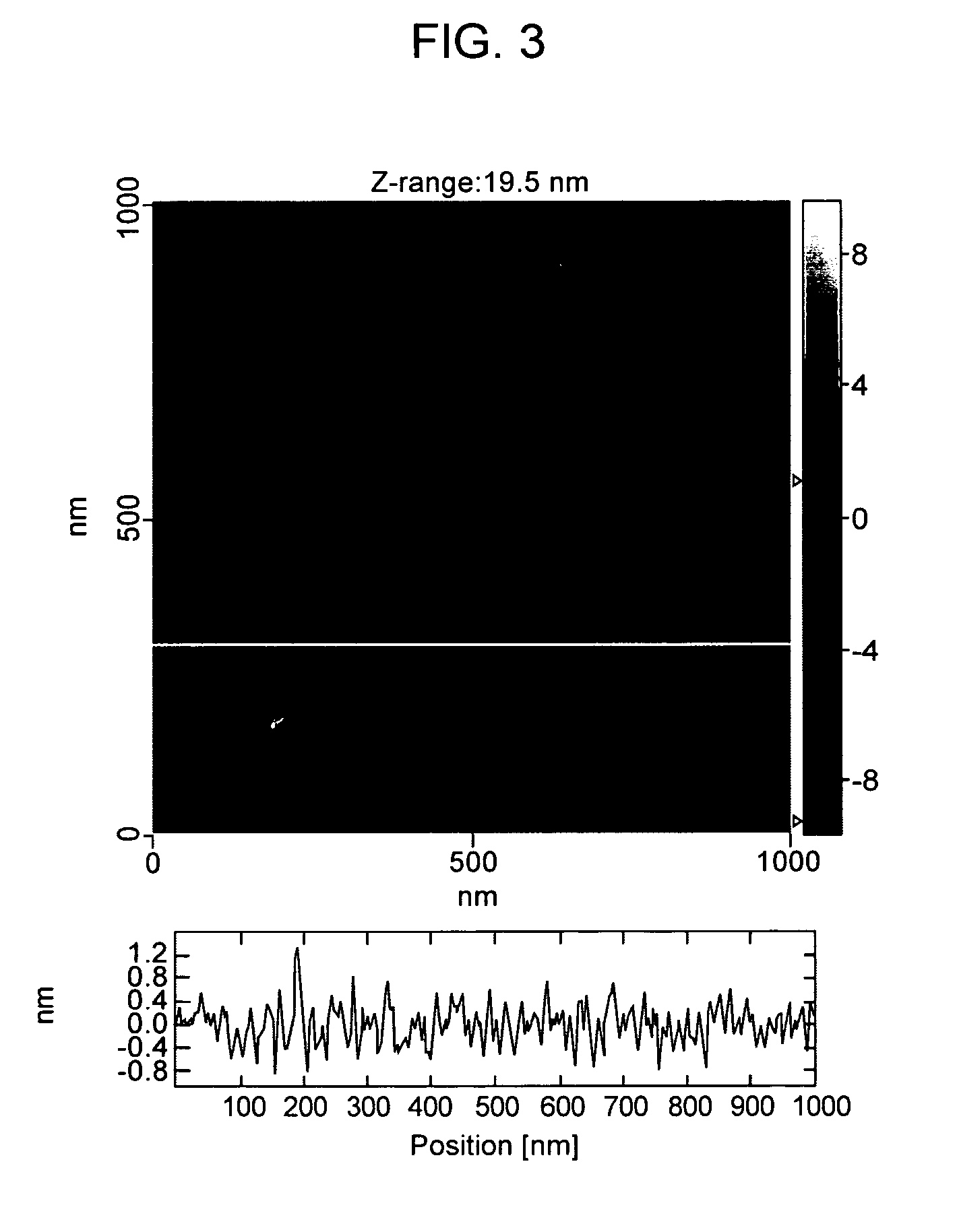
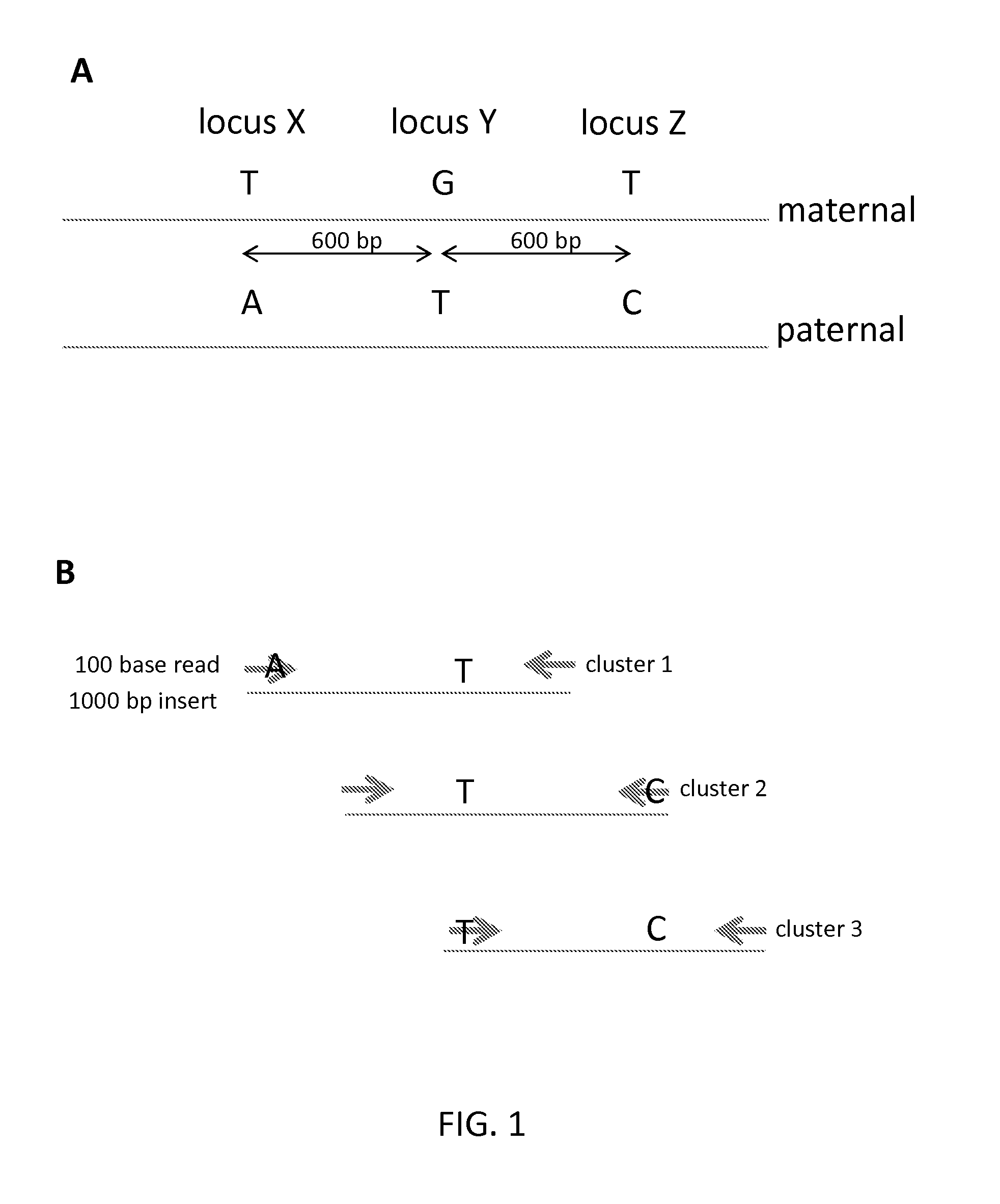
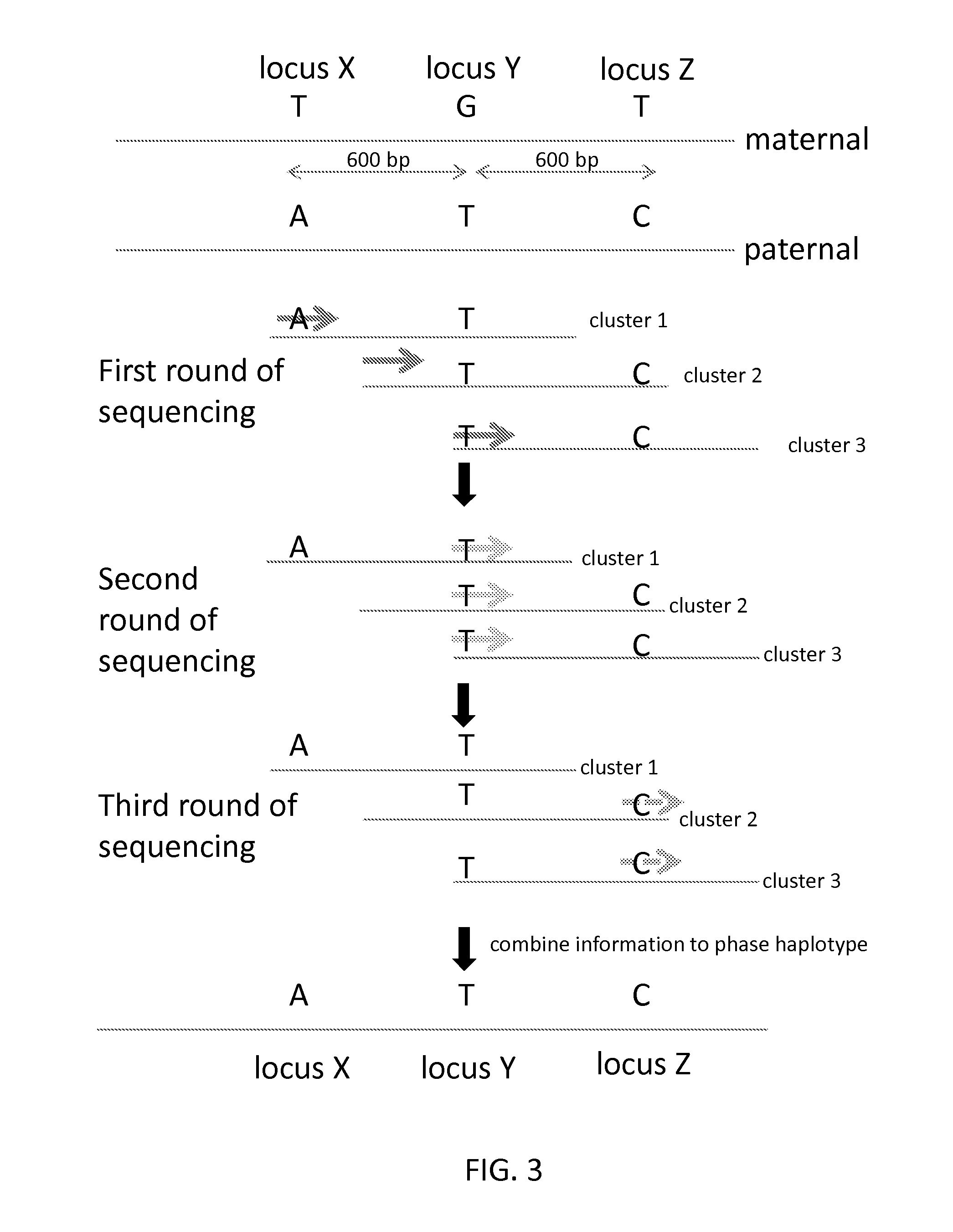
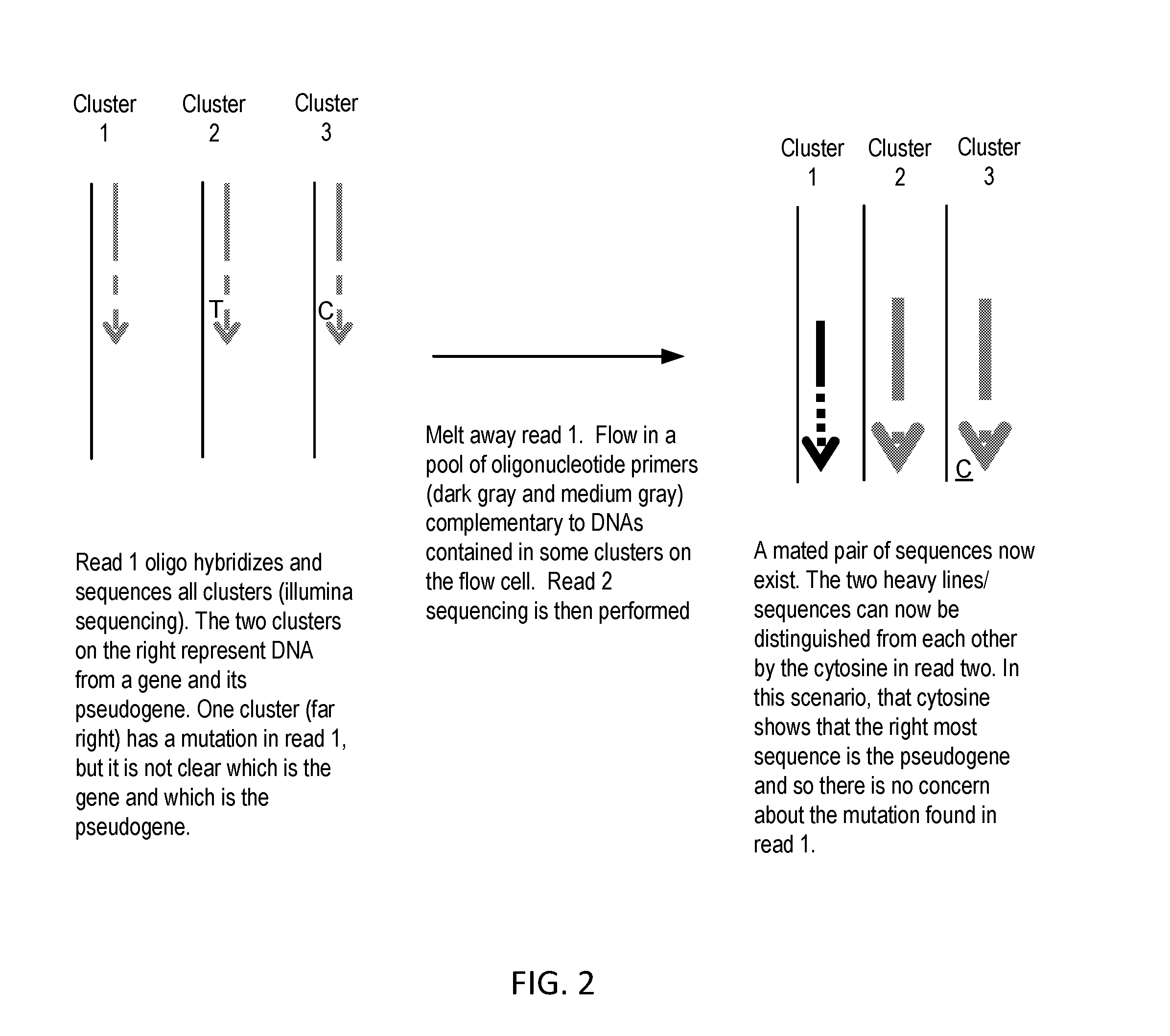
Sequential sequencing
InactiveUS20140274738A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleic acid sequencingExon
The present invention provides improved methods, compositions and kits for short read next generation sequencing (NGS). The methods, compositions and kits of the present invention enable phasing of two or more nucleic acid sequences in a sample, i.e. determining whether the nucleic acid sequences (typically comprising regions of sequence variation) are located on the same chromosome and / or the same chromosomal fragment. Phasing information is obtained by performing multiple, successive sequencing reactions from the same immobilized nucleic acid template. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein are useful, for example, for haplotyping, SNP phasing, or for determining downstream exons in RNA-seq.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
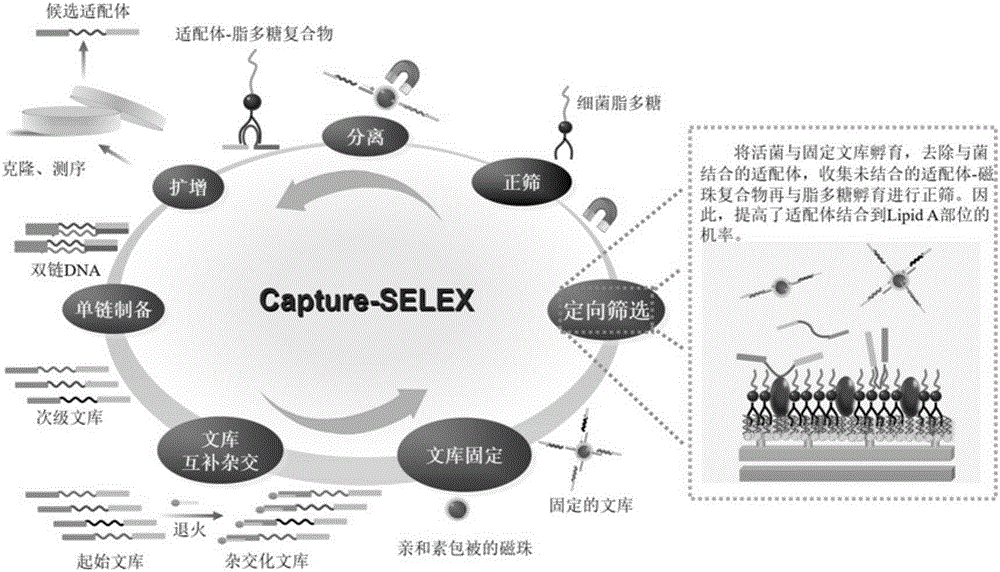
Broad-spectrum nucleic acid aptamer capable of specifically identifying lipopolysaccharides and directed screening method of broad-spectrum nucleic acid aptamer
The invention provides a broad-spectrum nucleic acid aptamer capable of identifying lipopolysaccharides of different Gram-negative bacterium sources. The broad-spectrum nucleic acid aptamer is obtained by directed screening on the basis of the capture-SELEX technology of label-free target molecules and immobilized nucleic acid libraries. A directed screening method of the broad-spectrum nucleic acid aptamer includes: using mouse salmonella typhi lipopolysaccharides as the unique target, using a biotin-avidin effect to fix random oligonucleotide libraries to Fe3O4 magnetic nano particles wrapped by avidin through biotinylated short complementary chains, performing incubation, separation, amplification, digestion single chain preparation, cloning sequencing and the like, adding complete active bacteria of salmonella and escherichia coli to serve as directed molecules to perform directed screening when the libraries are enriched to a certain degree, and one broad-spectrum nucleic acid aptamer capable of identifying four kinds of lipopolysaccharides is obtained through 15 rounds of repeated screening. The nucleic acid aptamer is applicable to the analysis and detection, separation and enriching, toxicity neutralizing and the like of the lipopolysaccharides in aspects of drinking water, food or clinical medicine and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for analyzing immobilized nucleic acids
ActiveUS20070092905A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteScanning probe microscopy
The present invention provides methods of detecting a nucleic acid analyte in a sample. The methods generally involve modifying immobilized nucleic acids from a sample onto an insoluble support in a substantially elongated configuration, where modification generates an identifying feature that identifies the analyte; and detecting the identifying feature(s) using scanning probe microscopy, to detect the analyte. The present invention further provides a method for assigning a profile of a feature to a nucleic acid. The present invention further provides a computer program product for use in a subject method. The present invention further provides a system for detecting a nucleic acid in a sample; and a system for assigning a profile of a feature to a nucleic acid. The present invention further provides a method for immobilizing a nucleic acid onto an insoluble support; and further provides insoluble support having nucleic acid(s) immobilized thereon. The present invention further provides a method of diagnosing a disorder or condition in an individual, where the method involves use of a subject method for detecting a nucleic acid analyte.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Sequential sequencing
ActiveUS20160251711A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingExon
Described herein are improved methods, compositions and kits for next generation sequencing (NGS). The methods, compositions and kits described herein enable phasing of two or more nucleic acid sequences in a sample, i.e. determining whether the nucleic acid sequences (which can comprise regions of sequence variation) are located on the same chromosome and / or the same chromosomal fragment. Phasing information can be obtained by performing multiple, successive sequencing reactions from the same immobilized nucleic acid template. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein can be useful, for example, for haplotyping, SNP phasing, or for determining downstream exons in RNA-seq.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Method of immobilizing nucleic acid aptamers
InactiveUS20060068407A1Efficient fluorescence quenchingHigh fluorescence intensitySequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesSilanesImmobilized Nucleic Acids
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Sorting and immobilization system for nucleic acids using synthetic binding systems
InactiveUS20050208576A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsImmobilized Nucleic AcidsChemistry
Methods are provided for producing an array of immobilized nucleic acids on an array device. The array device has a plurality of microlocations each having an electrode. At least one of the microlocations has a synthetic addressing unit coupled to the microlocation. The microlocation is the activated, usually by electronically biasing the electrode of the microlocation. The at least one microlocation is then contacted by a conjugate which has a nucleic acid and a synthetic binding unit. The conjugate is then coupled to the microlocation through an interaction between the synthetic binding unit and the synthetic addressing unit. In one embodiment, the synthetic binding unit and synthetic addressing unit may be pRNA, pDNA, or CNA.
Owner:NANOGEN RECOGNOMICS
Temperature gradient nucleic acid hybridization method
InactiveUS20050221367A1Efficient responseEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementCross linked membraneImmobilized Nucleic Acids
A novel method of nucleic acid hybridization placing immobilized nucleic acid at the lower end of a temperature gradient to achieve more efficient and more completed hybridization. Immobilized nucleic acids such as DNA array or cross-linked membrane for Northern blotting is anchored on a surface with a heat sink, while within the same hybridization chamber a heat source is place the furthest possible distance away from the array or membrane. The invention also teaches different ways to construct such a hybridization chamber and additional optional improvement features.
Owner:TRAN NATHANIEL TUE
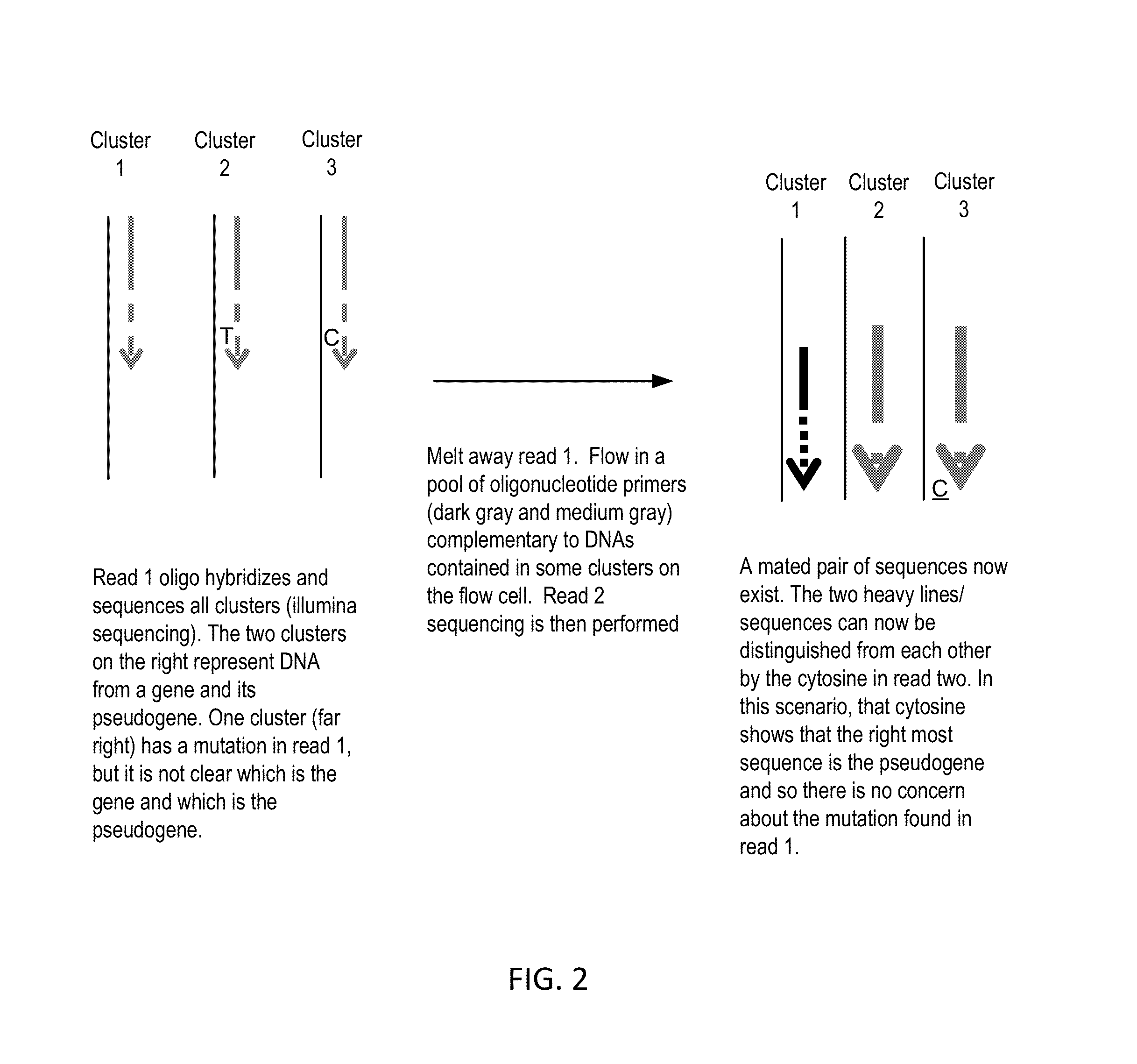
Centroid markers for image analysis of high density clusters in complex polynucleotide sequencing
ActiveUS20110065607A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityNucleotide
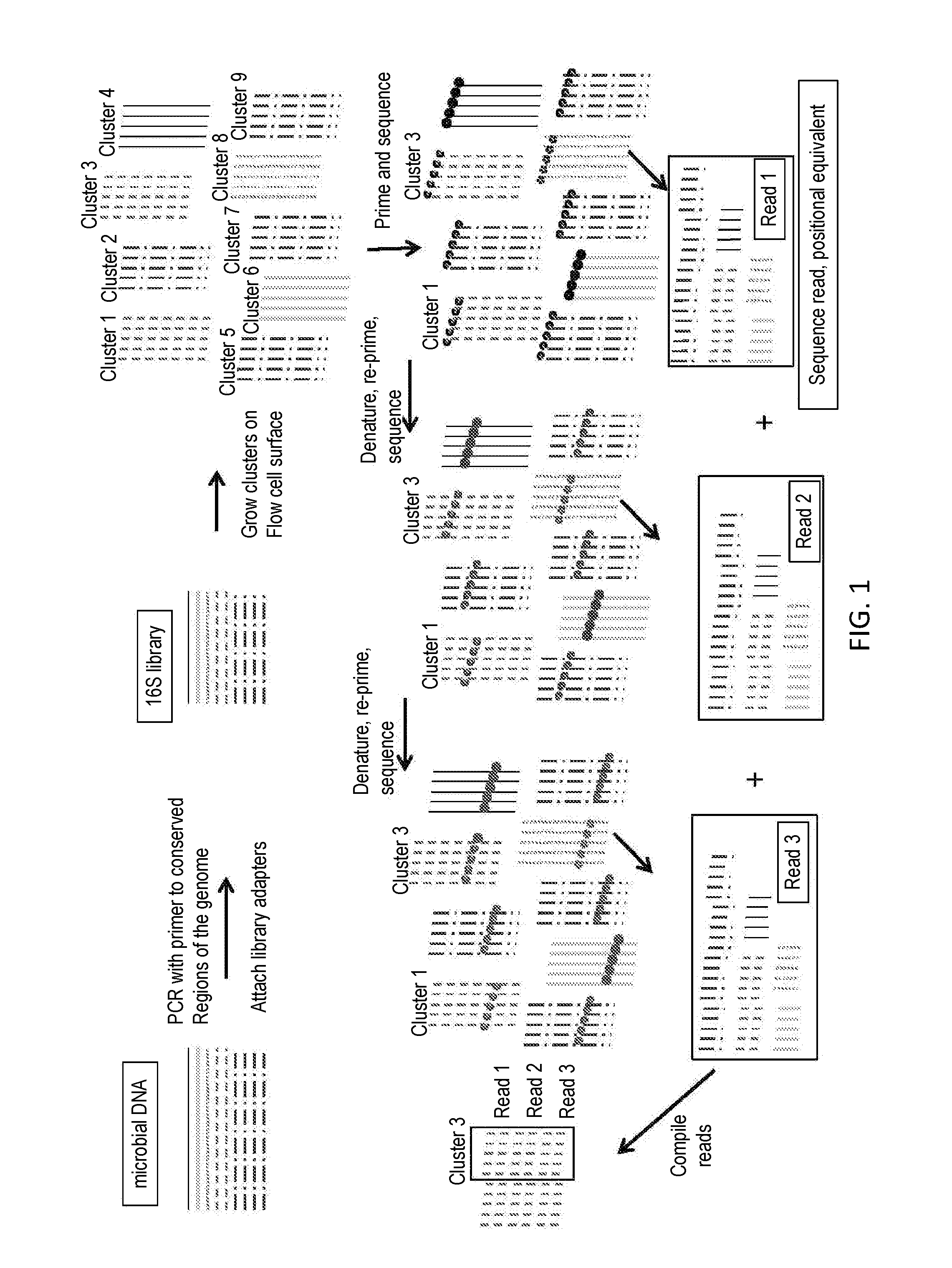
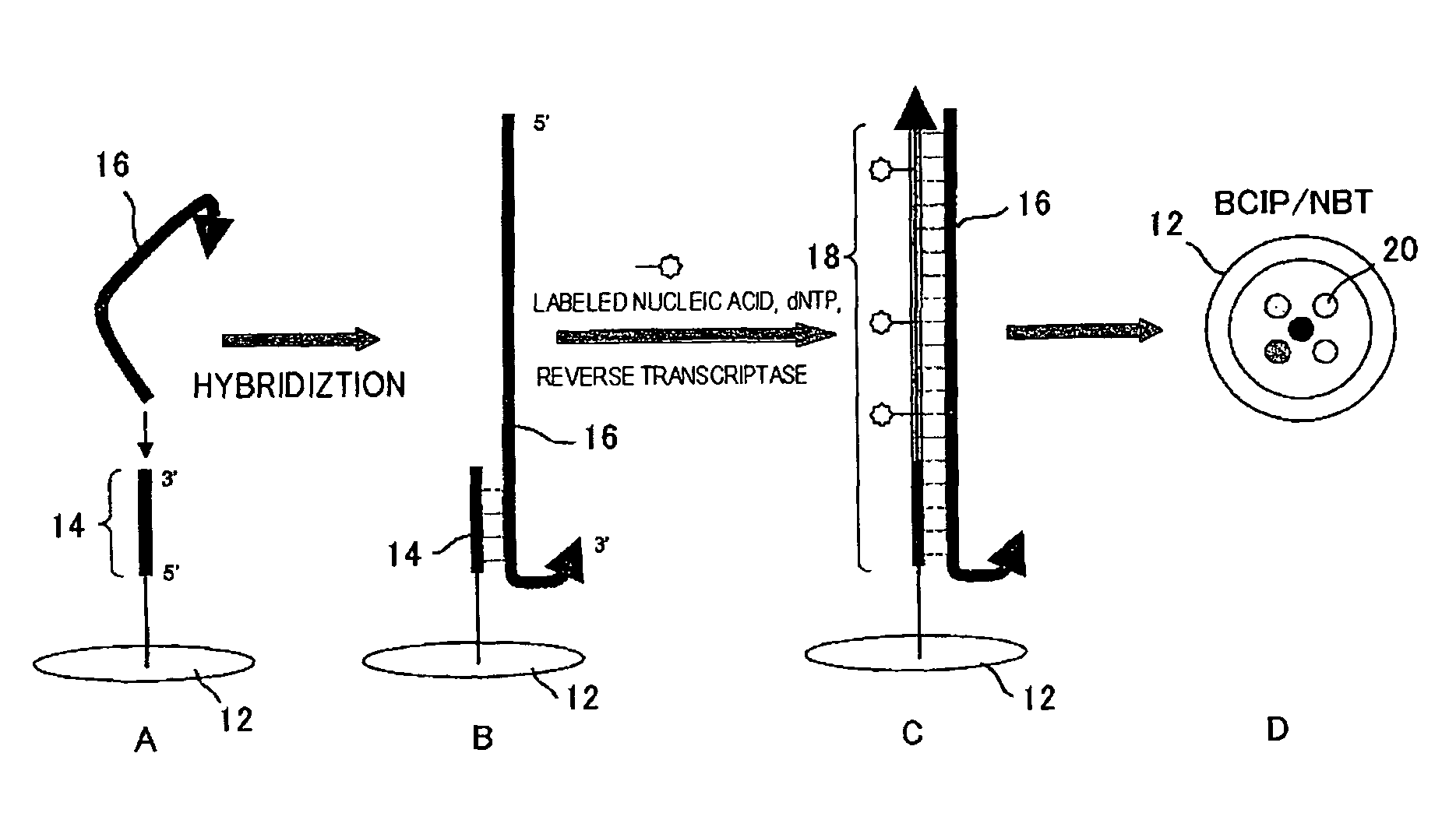
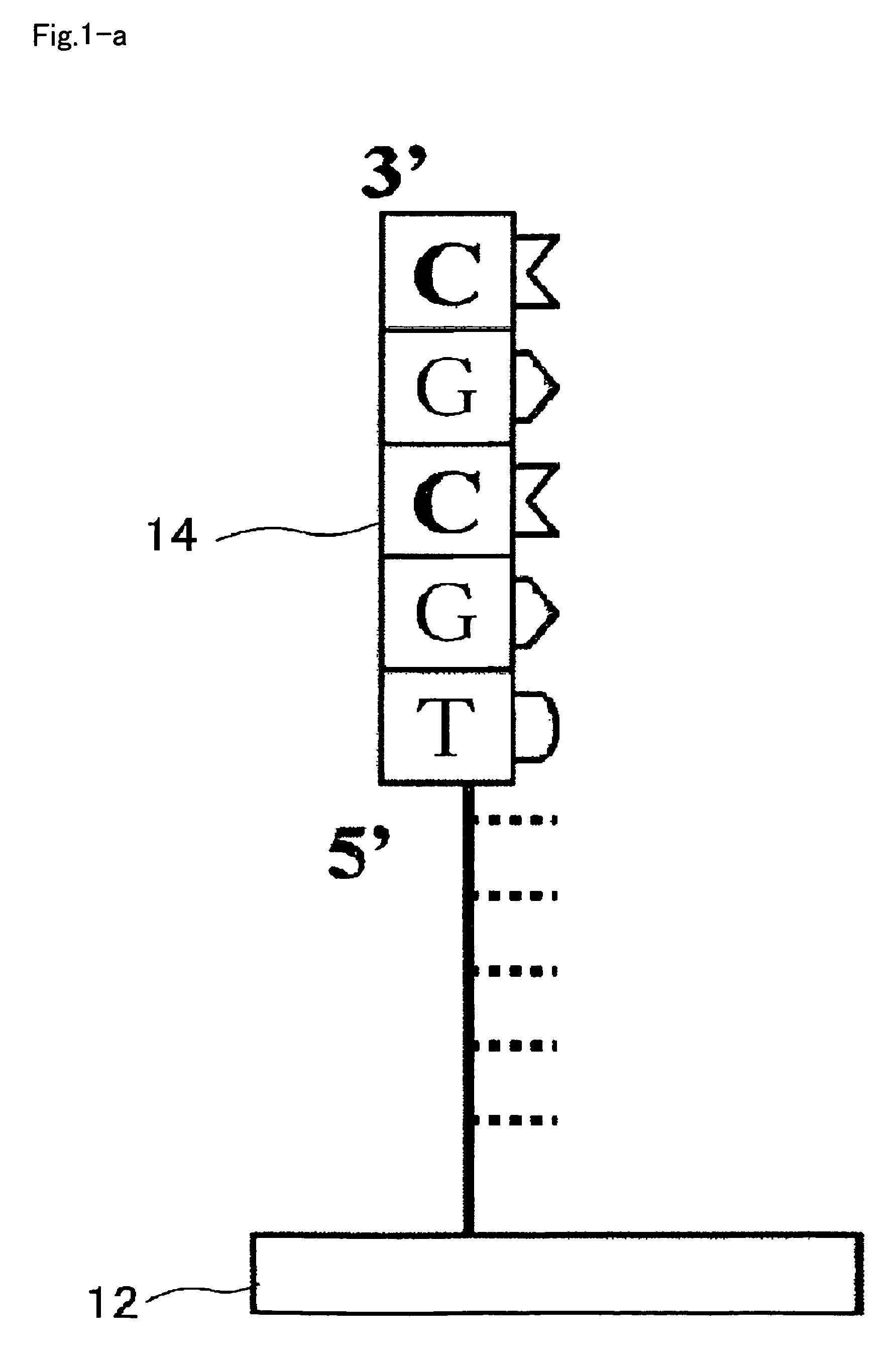
Improved compositions, methods, apparatus, and kits for high-throughput nucleic acid amplification, detection and sequencing are disclosed. A nucleic acid cluster having an identifiable center is produced by generating on a solid support an immobilized nucleic acid complement from a template, one of which comprises a detectable label; and amplifying the complement and the template to obtain a nucleic acid cluster on the support, the cluster having a substantially central location marked by the detectable label and a surrounding region comprising immobilized copies. Also disclosed are nucleotide sequence determination in nucleic acid clusters so produced, center position annotation in the clusters, assignment of sequence information to overlapping clusters, and related compositions and methods.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
RNA Detection Method
InactiveUS20090137406A1The way is simple and fastRapid multi-sample treatmentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPOLYMER SUBSTANCEPhosphate
The present invention provides an RNA detection method detecting, from a reaction system containing a target sample, a target RNA chain originated from the target sample, using a surface having on the surface thereof a polymer substance which contains a first unit having a group derived from a phosphate ester composing the hydrophilic portion of a phospholipid and a second unit having a carboxylic acid derivative group composed of an electron-attractive substitutional group bound to a carbonyl group, while being provided with at least one reaction space, the reaction space having an immobilized nucleic acid primer immobilized therein.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Nucleic acid detection device
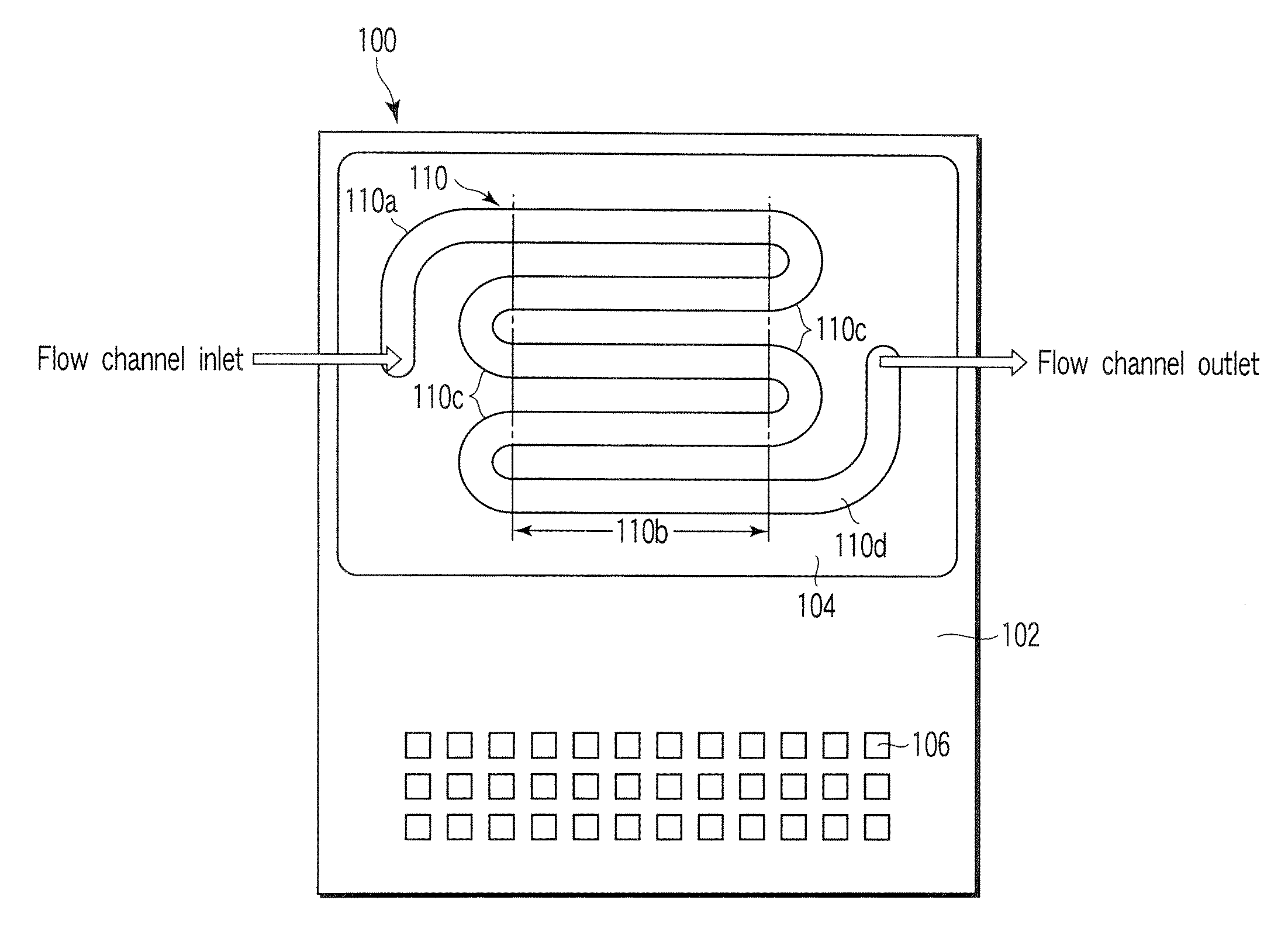
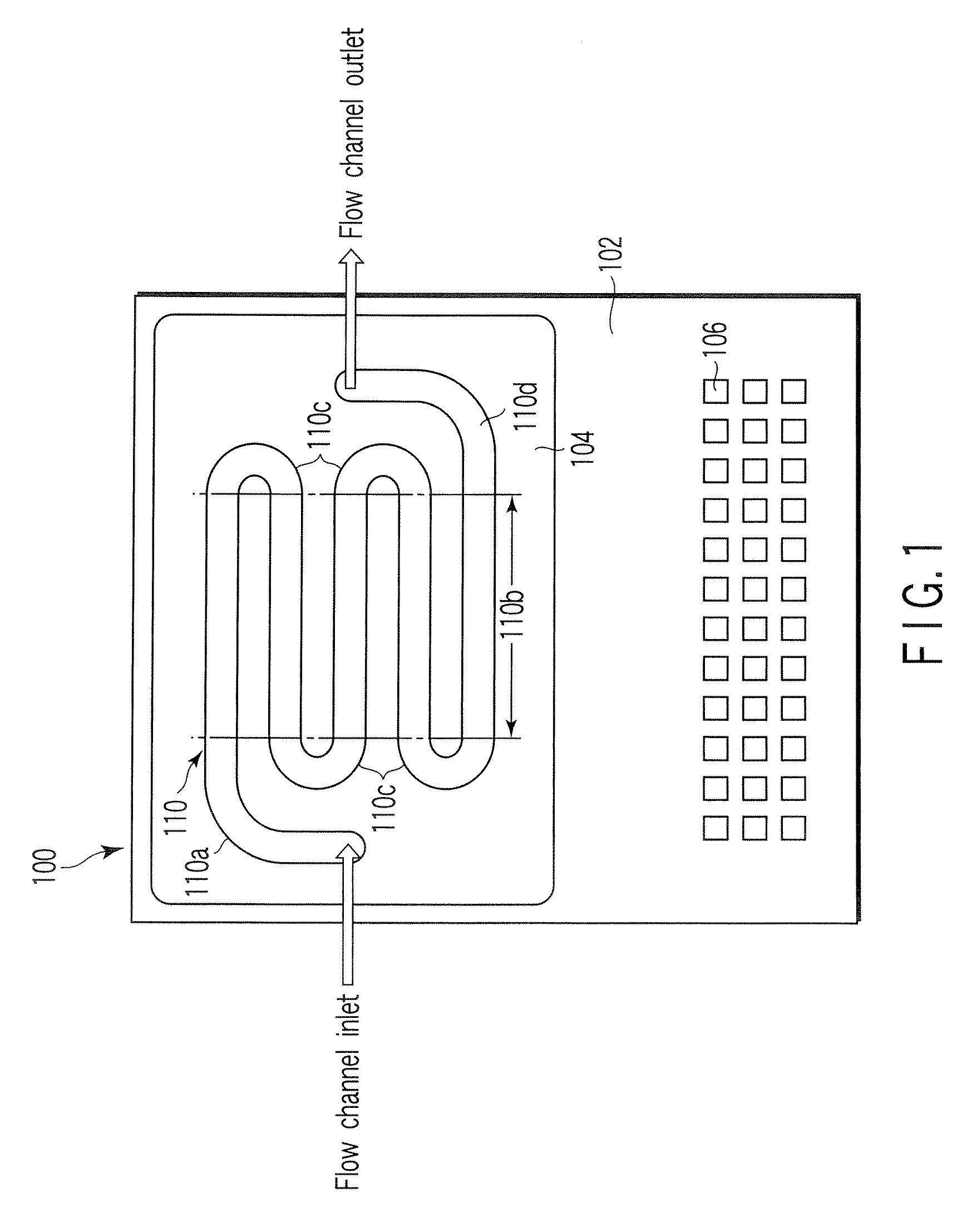
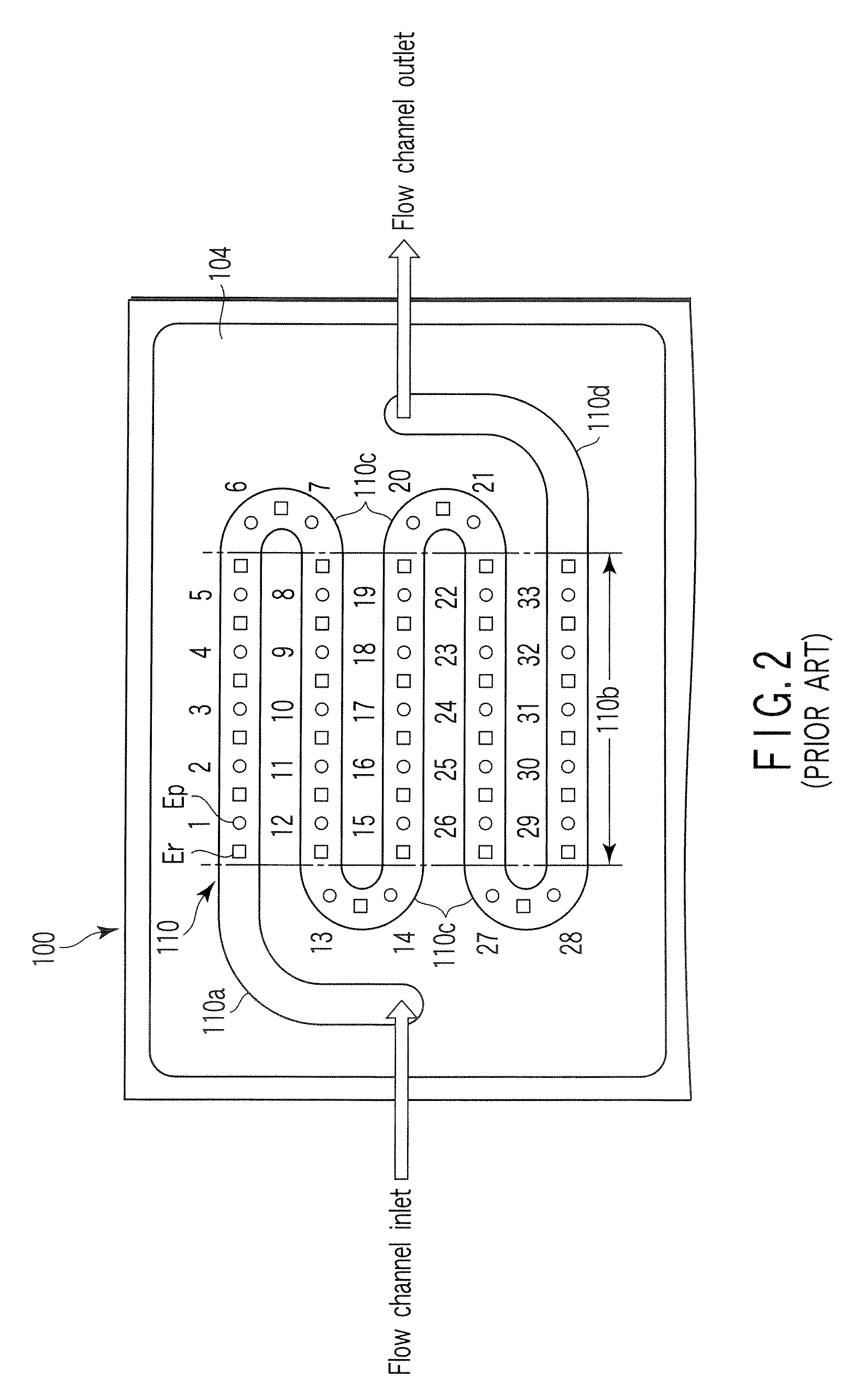
ActiveUS20070227885A1Inhibitory responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseNucleic acid detection
A nucleic acid detection device includes a flow channel through which a solution containing a nucleic acid recognition body flows, probe electrodes having immobilized nucleic acid probes, and a counter electrode used to measure an electrochemical response of the nucleic acid recognition body. The flow channel includes a curved portion and a straight portion continued from and located downstream of the curved portion. The probe electrodes are arranged at intervals along the straight portion, avoiding an upstream end of the straight portion that is located within a distance L from the curved portion. The distance L is given by L=0.065×Re×D, Re=ρuD / μ, and D=4 S / Lp where ρ, u, and μ are a concentration, a flow velocity, and a viscosity of the solution, and S and Lp are a sectional area and a wall peripheral perimeter of the flow channel, respectively.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Sequential Sequencing
ActiveUS20160251712A1Microbiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingExon
Owner:NUGEN TECH
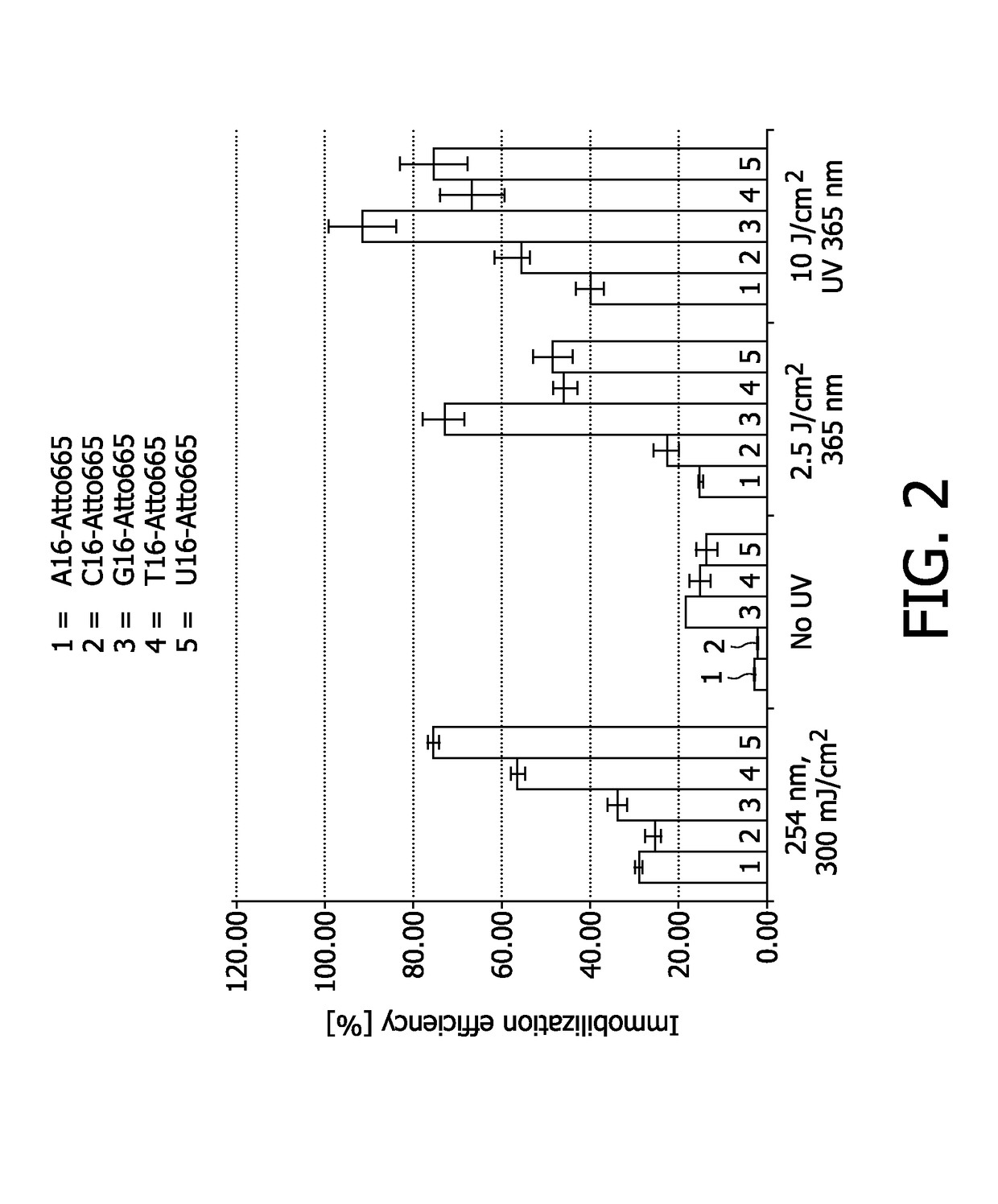
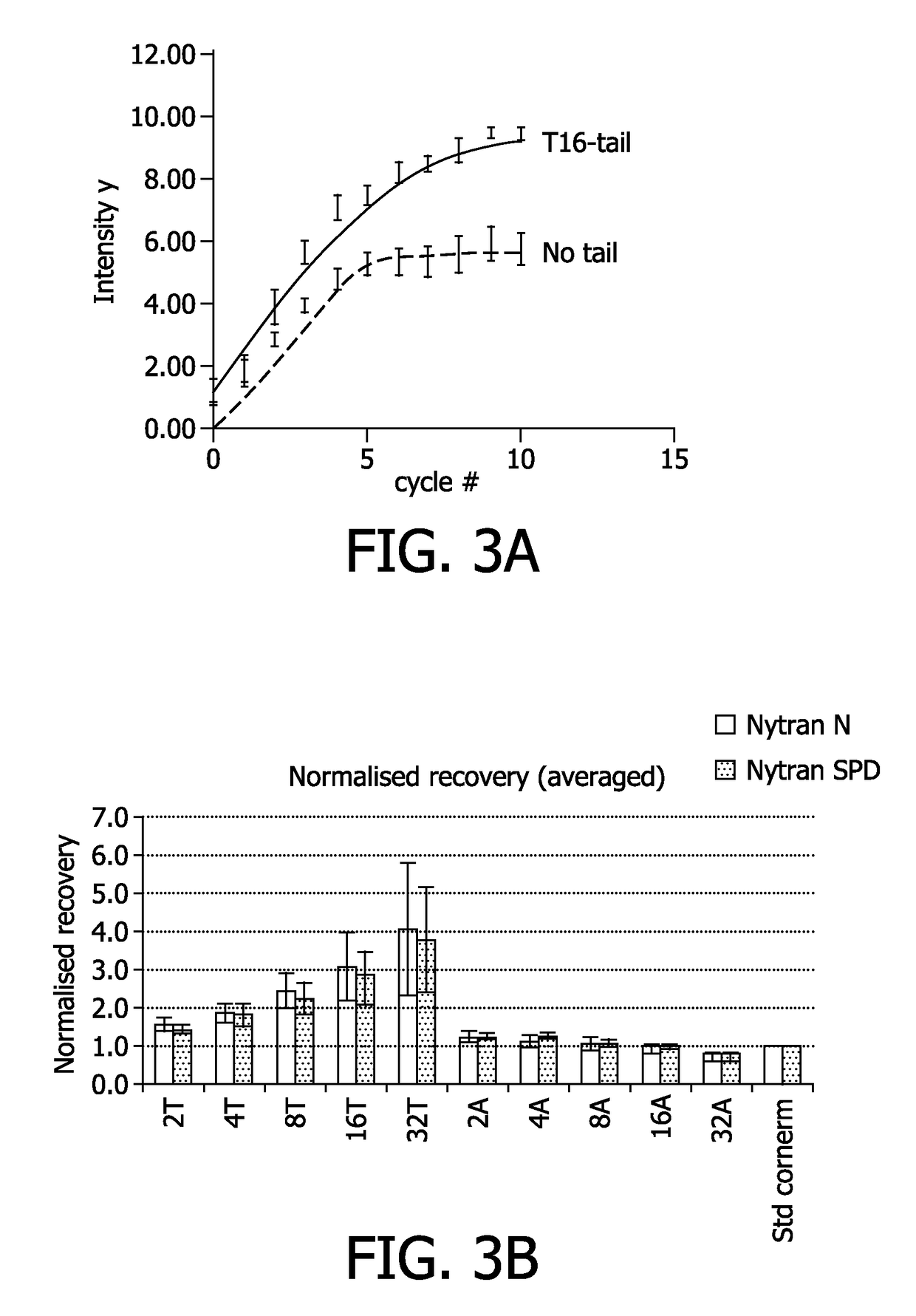
Method for immobilizing nucleic acids on a support
ActiveUS9657338B2Effectively fixedMinimize damageSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesNucleotideImmobilized Nucleic Acids
The present invention relates to a method for immobilizing nucleic acids on a support, comprising the provision of a nucleic acid with a stretch of nucleotides of only one basetype and the immobilization of said nucleic acid on a support by crosslinking by light, wherein said crosslinking by light is performed at a wavelength of about 300-500 nm, preferably at a wavelength of 365 nm. The present invention further relates to a method for the analysis of nucleic acids immobilized according to the invention, which comprises the hybridization of the immobilized nucleic acid with complementary and mismatch segments. Furthermore, the present invention relates to immobilized nucleic acids obtainable by the method of the invention, the use of accordingly immobilized nucleic acids for the production of nucleic acid arrays and a diagnostic kit, comprising an array of nucleic acids which are immobilized according to the present invention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Detection of immobilized nucleic acid
The present invention provides methods for determining the presence of immobilized nucleic acid employing unsymmetrical cyanine dyes that are derivatives of thiazole orange, a staining solution and select fluorogenic compounds that are characterized as being essentially non-genotoxic. The methods comprise immobilizing nucleic acid, single or double stranded DNA, RNA or a combination thereof, on a solid or semi solid support, contacting the immobilized nucleic acid with an unsymmetrical cyanine dye compound and then illuminating the immobilized nucleic acid with an appropriate wavelength whereby the presence of the nucleic acid is determined. The cyanine dye compounds are typically present in an aqueous staining solution comprising the dye compound and a tris acetate or tris borate buffer wherein the solution facilitates the contact of the dye compound and the immobilized nucleic acid. Typically the solid or semi-solid support is selected from the group consisting of a polymeric gel, a membrane, an array, a glass bead, a glass slide, and a polymeric microparticle. Preferably, the polymeric gel is agarose or polyacrylamide. The methods employing the non-genotoxic compounds represent an improvement over commonly used methods employing ethidium bromide wherein the present methods retain the advantages of ethidium bromide, ease of use and low cost, but without the disadvantageous, known mutagen requiring special handling and waste procedures.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Nuclein acid fixing method and method for producing biosensor by said method
InactiveCN1532293ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical compoundNucleic Acid Probes
A superior adsorption method for immobilizing nucleic acid probe on the surface of a solid phase substrate is provided. A nucleic acid immobilization method for immobilizing nucleic acid on a solid phase substrate comprising: bringing the above-mentioned solid phase substrate into contact with a composition comprising a total concentration of 0.1 to 2 mu M of a nucleic acid as a probe and a compound or a salt thereof, the compound being represented by the following formula: HS-L<1>-L<2>-R wherein L<1> is a single bond or a C1-15 alkylene group; L<2> is a single bond, nucleic acid, a polyethylene glycol group, -CO-NH-, or -NH-CO-; R is a hydroxyl group, an amino group, a ferrocenyl group, or a carboxyl group; provided that neither L<1> nor L<2> is a single bond, and incubating the composition in contact with a surface of the solid phase substrate.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Centroid markers for image analysis of high density clusters in complex polynucleotide sequencing
ActiveUS8182994B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityNucleotide
Improved compositions, methods, apparatus, and kits for high-throughput nucleic acid amplification, detection and sequencing are disclosed. A nucleic acid cluster having an identifiable center is produced by generating on a solid support an immobilized nucleic acid complement from a template, one of which comprises a detectable label; and amplifying the complement and the template to obtain a nucleic acid cluster on the support, the cluster having a substantially central location marked by the detectable label and a surrounding region comprising immobilized copies. Also disclosed are nucleotide sequence determination in nucleic acid clusters so produced, center position annotation in the clusters, assignment of sequence information to overlapping clusters, and related compositions and methods.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Immobilized nucleic acid probe for non-labeling detection
InactiveCN1434286AAvoid the problem of selection being limited to the excitation wavelength rangeEnable label-free detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPhysical spaceFluorescence
The invention discloses a solid-phase nucleic acid probe used to non-marking detection, including solid carrier, on which the scant nucleotide probe, with the fluorescence group, the fluorescence cancellation group and the identification sequence snippet of the peculiar nucleic acid is fixed, and the fluorescence cancellation group can be cancel the fluorescence; after intercrossing the group andthe snippet in the scant nucleotide probe, by the biochemical reaction, separate the two groups in the scant nucleotide probe to make the probe emit the fluorescence.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Amplified nucleic acids and immobilized products thereof
InactiveCN1500144AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationImmobilized Nucleic AcidsOligonucleotide Primer
A nucleic acid, which is provided in a large amount through a nucleic acid amplification reaction with the use of chimeric oligonucleotide primers, is constructed in a state of containing a modified deoxyribonucleotide for immobilizing the nucleic acid to a solid phase and then immobilized to a solid phase at a high efficiency, thereby giving an immobilized nucleic acid product with excellent qualities.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
RNA detection method
InactiveUS8088580B2Rapid multi-sample treatmentThe process is simple and fastSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPOLYMER SUBSTANCEPhosphate
The present invention provides an RNA detection method detecting, from a reaction system containing a target sample, a target RNA chain originated from the target sample, using a surface having on the surface thereof a polymer substance which contains a first unit having a group derived from a phosphate ester composing the hydrophilic portion of a phospholipid and a second unit having a carboxylic acid derivative group composed of an electron-attractive substitutional group bound to a carbonyl group, while being provided with at least one reaction space, the reaction space having an immobilized nucleic acid primer immobilized therein.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com