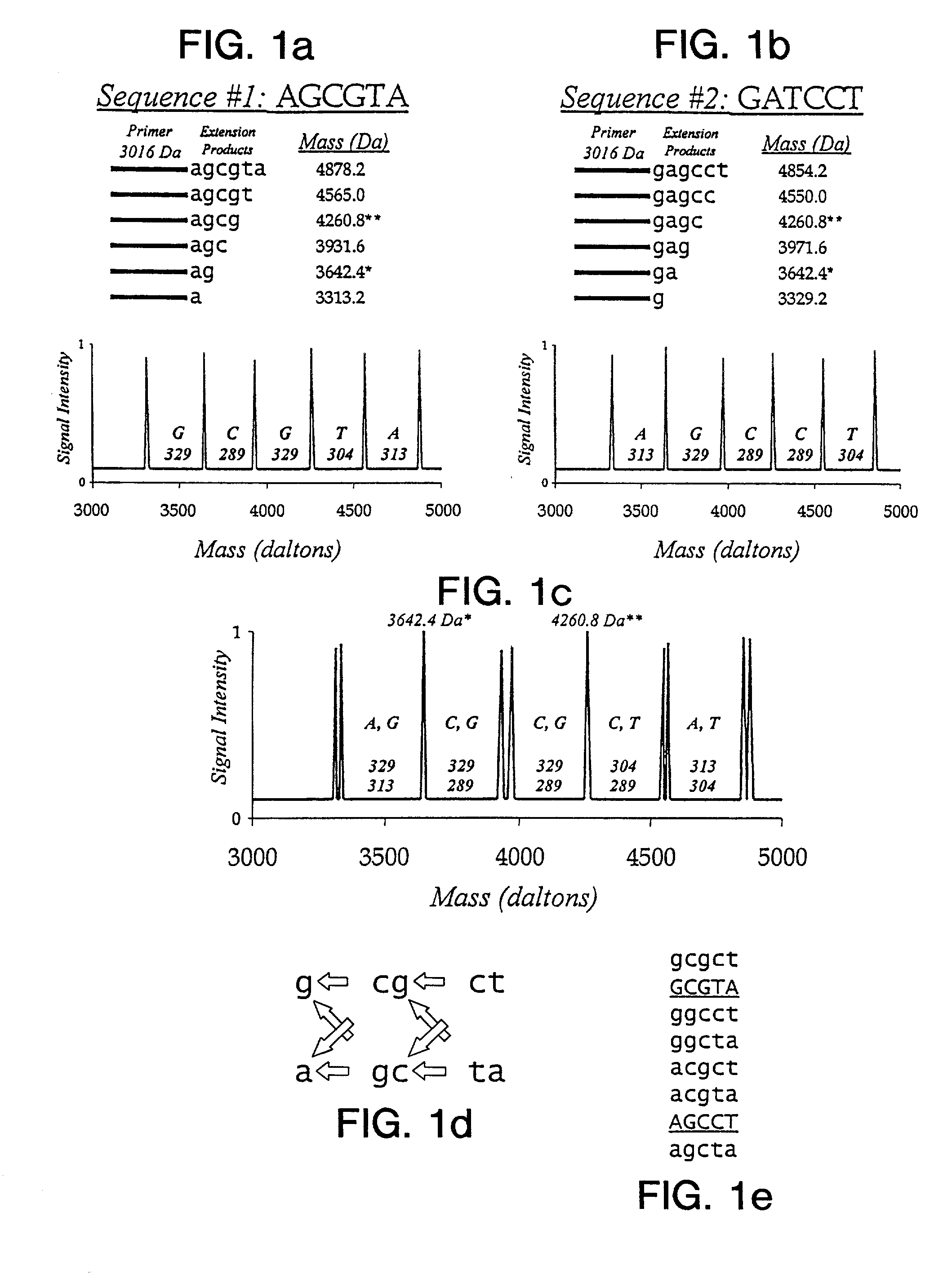
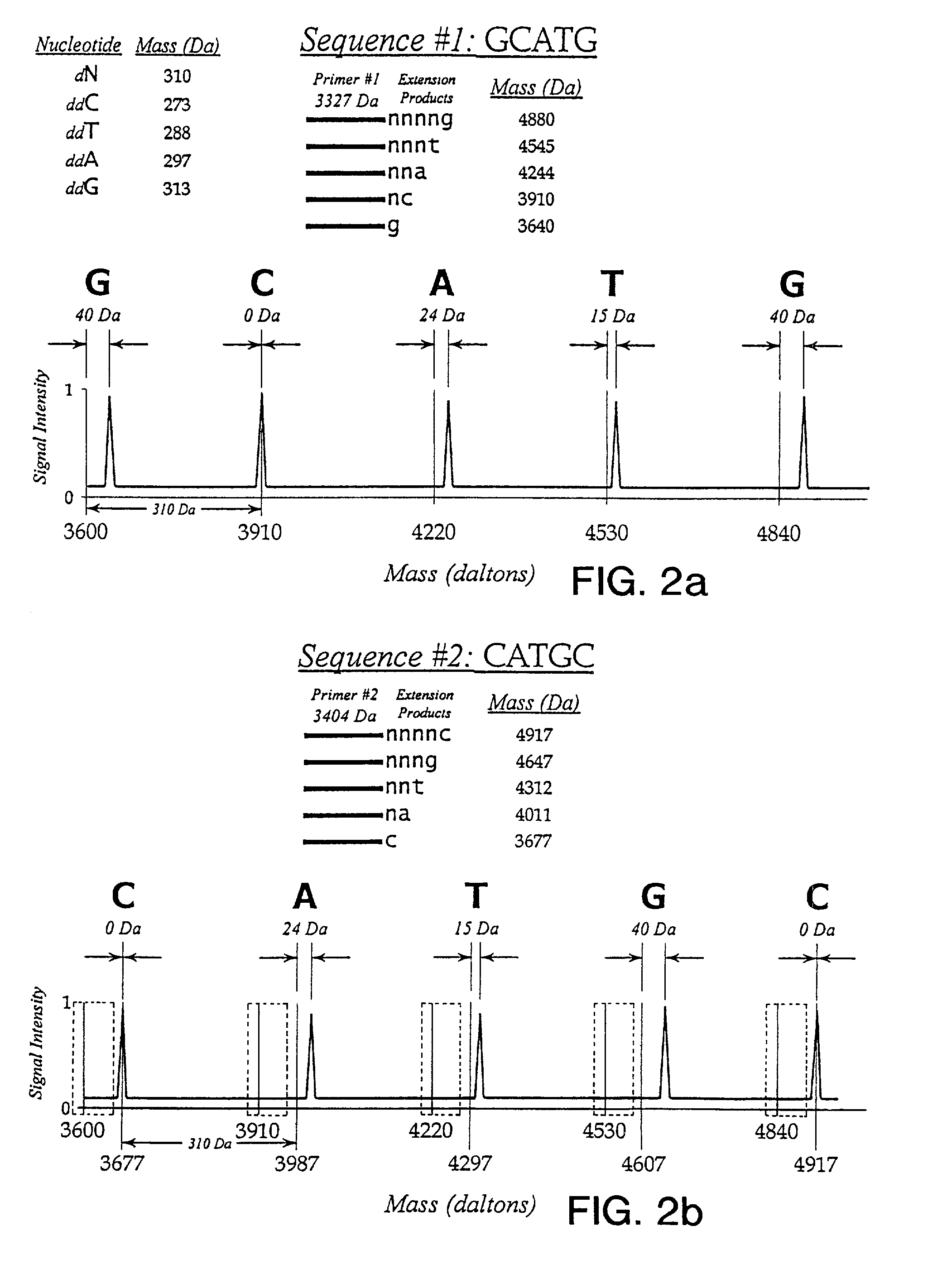
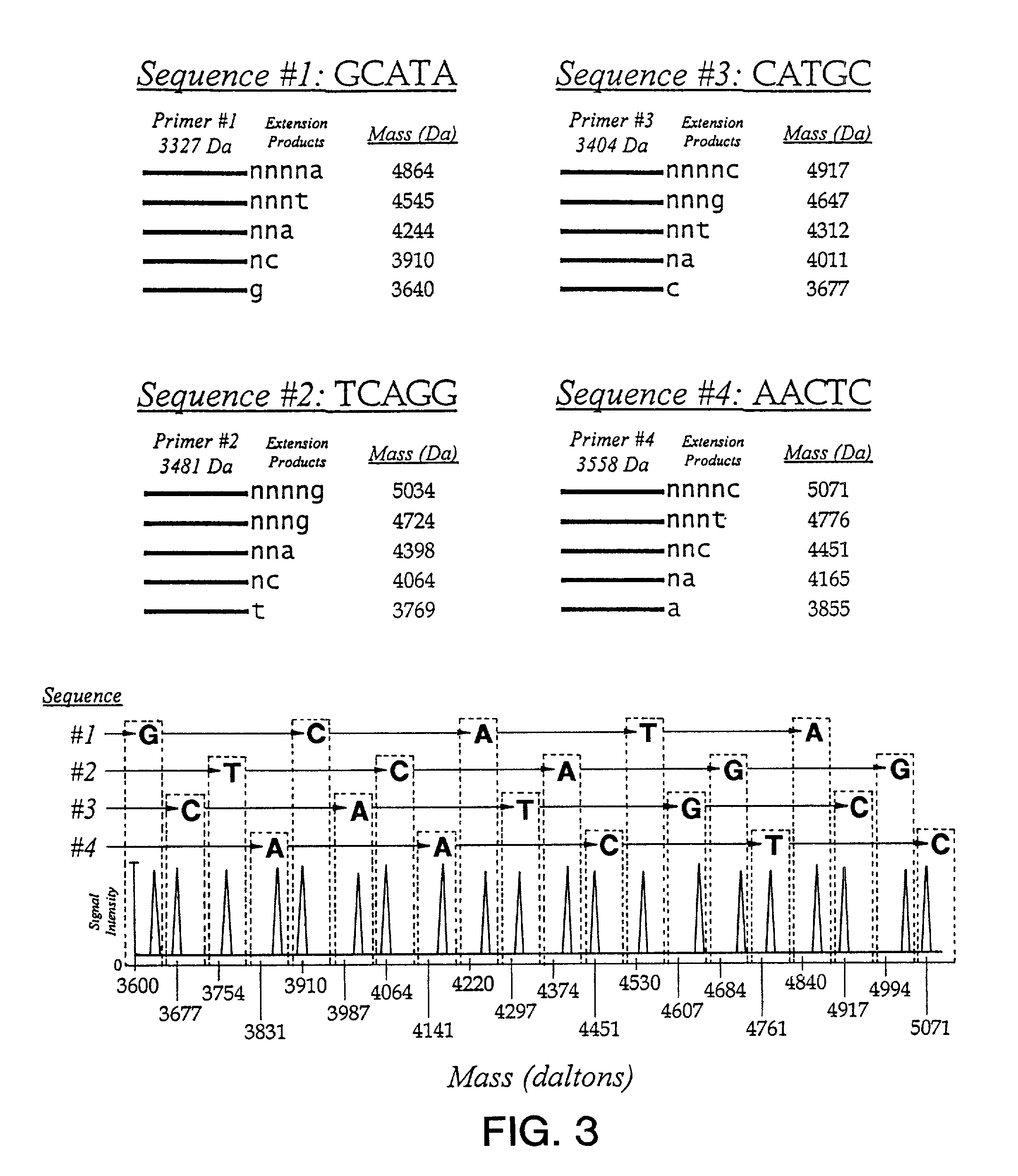
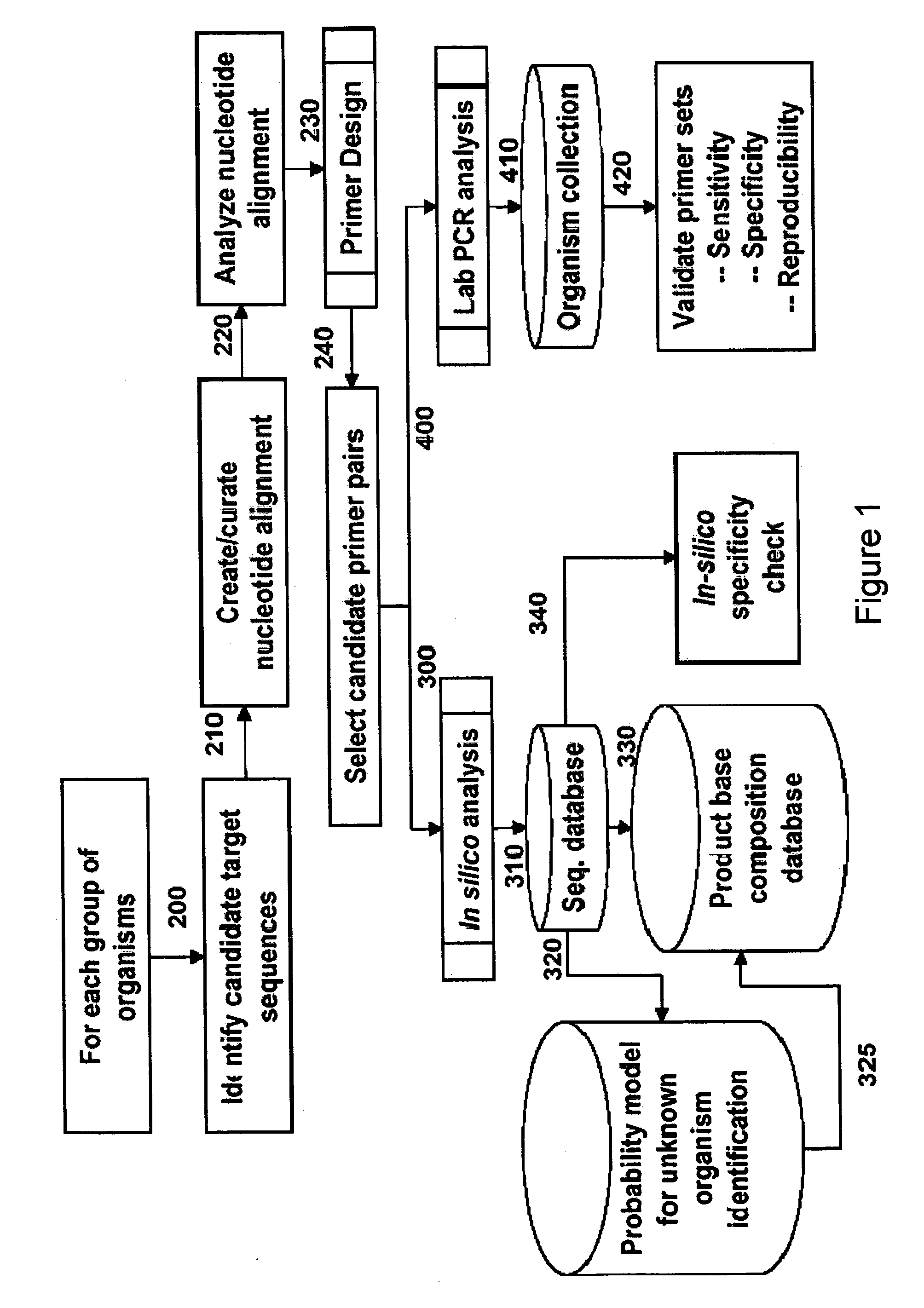
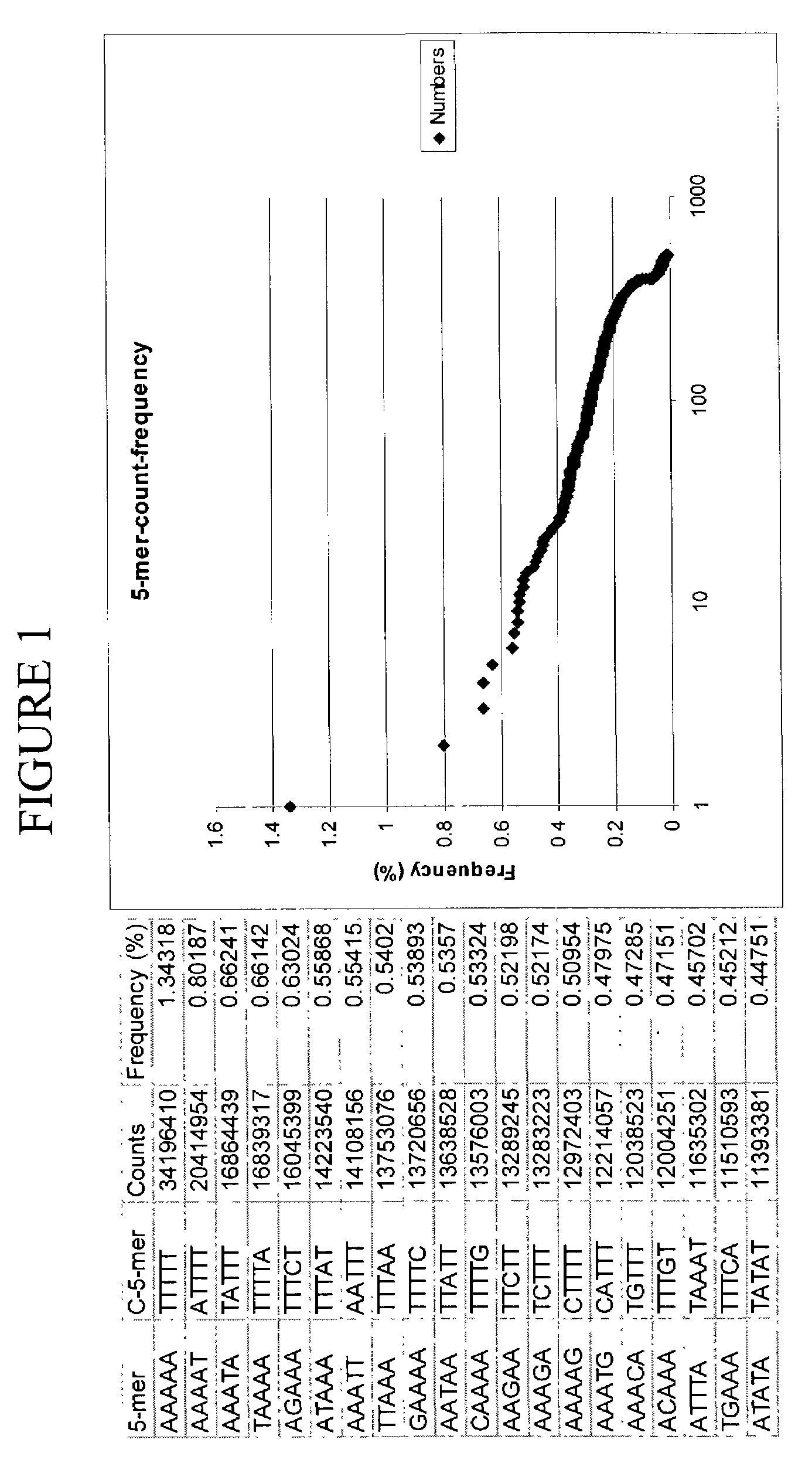
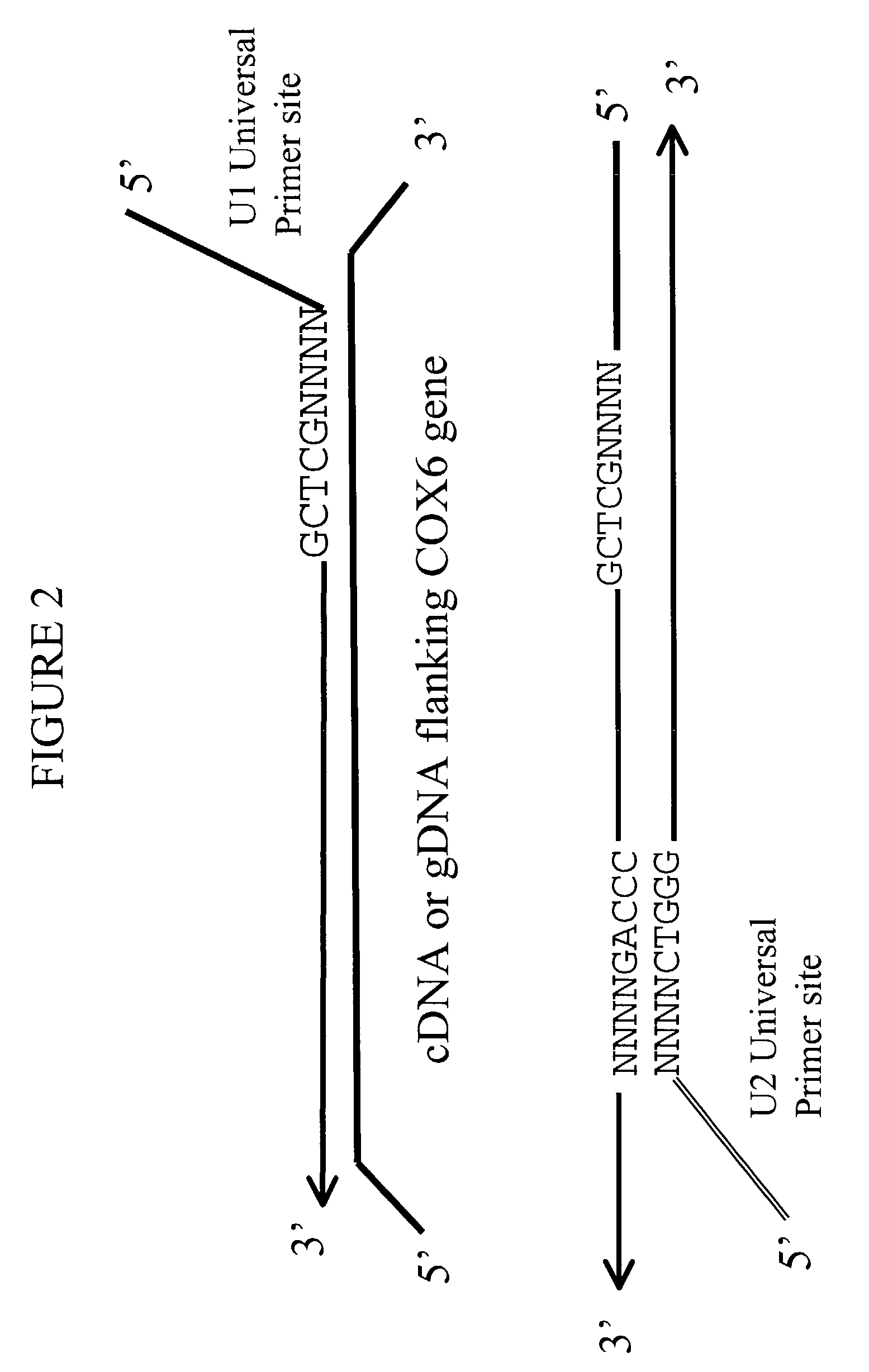
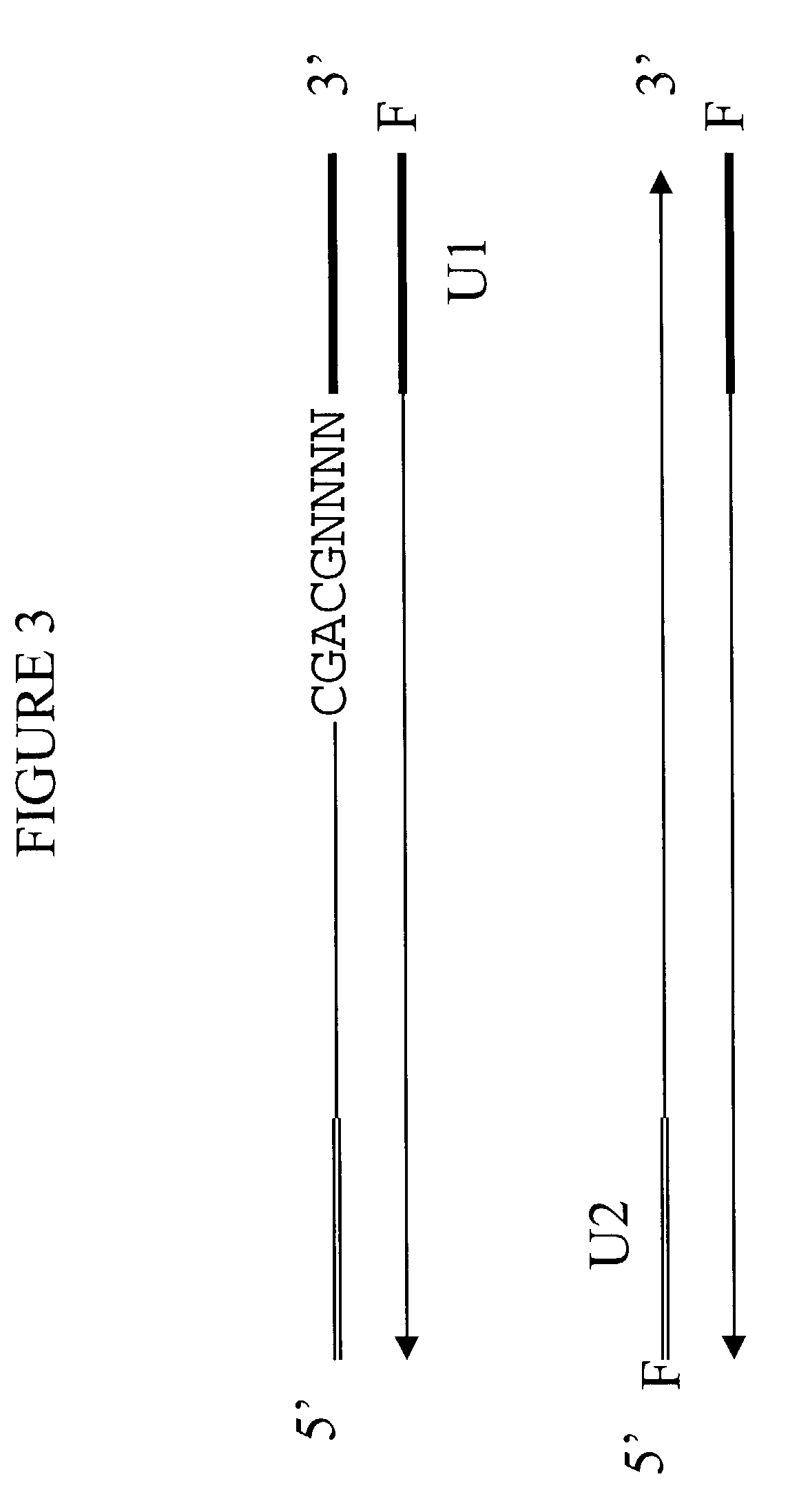
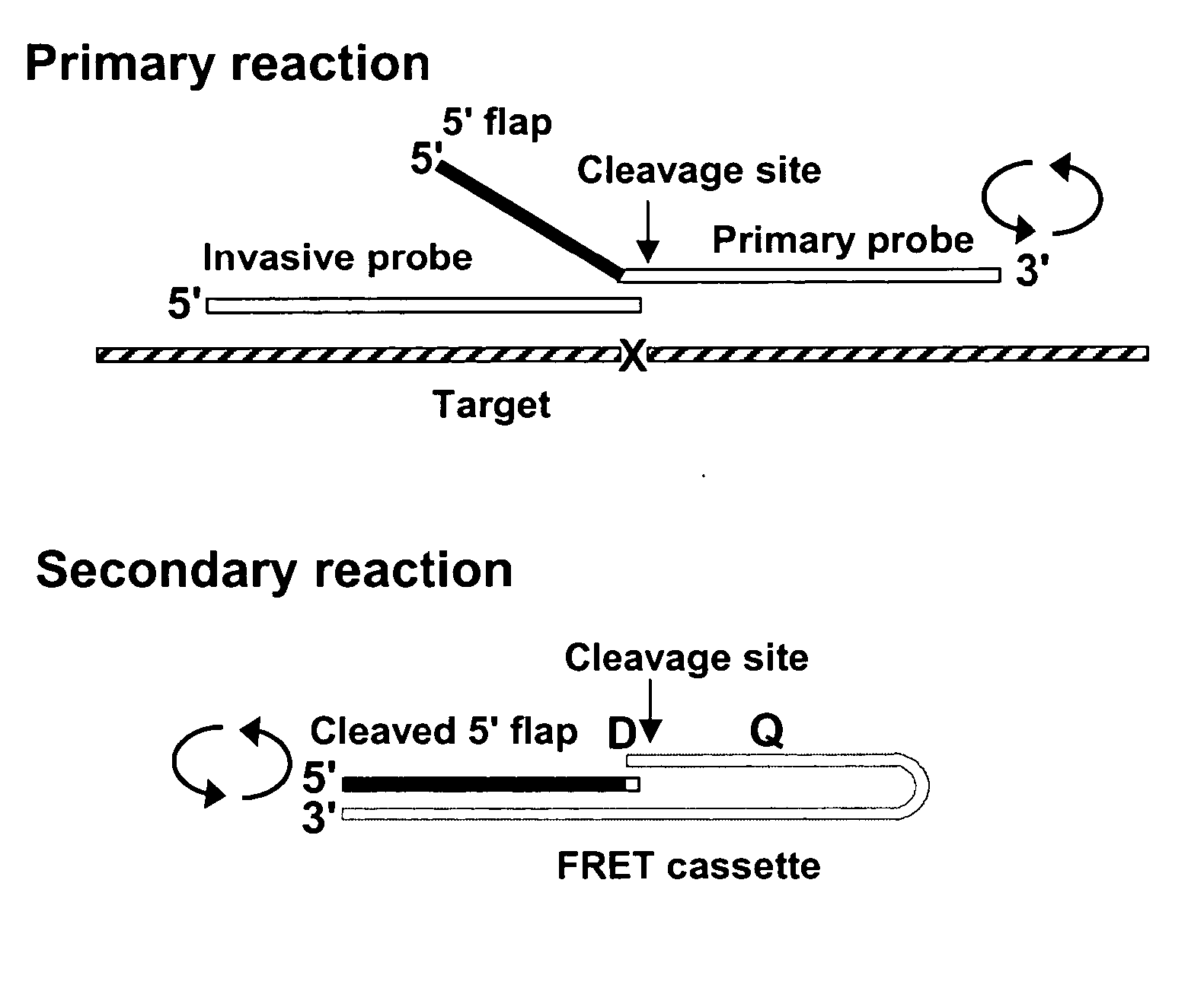
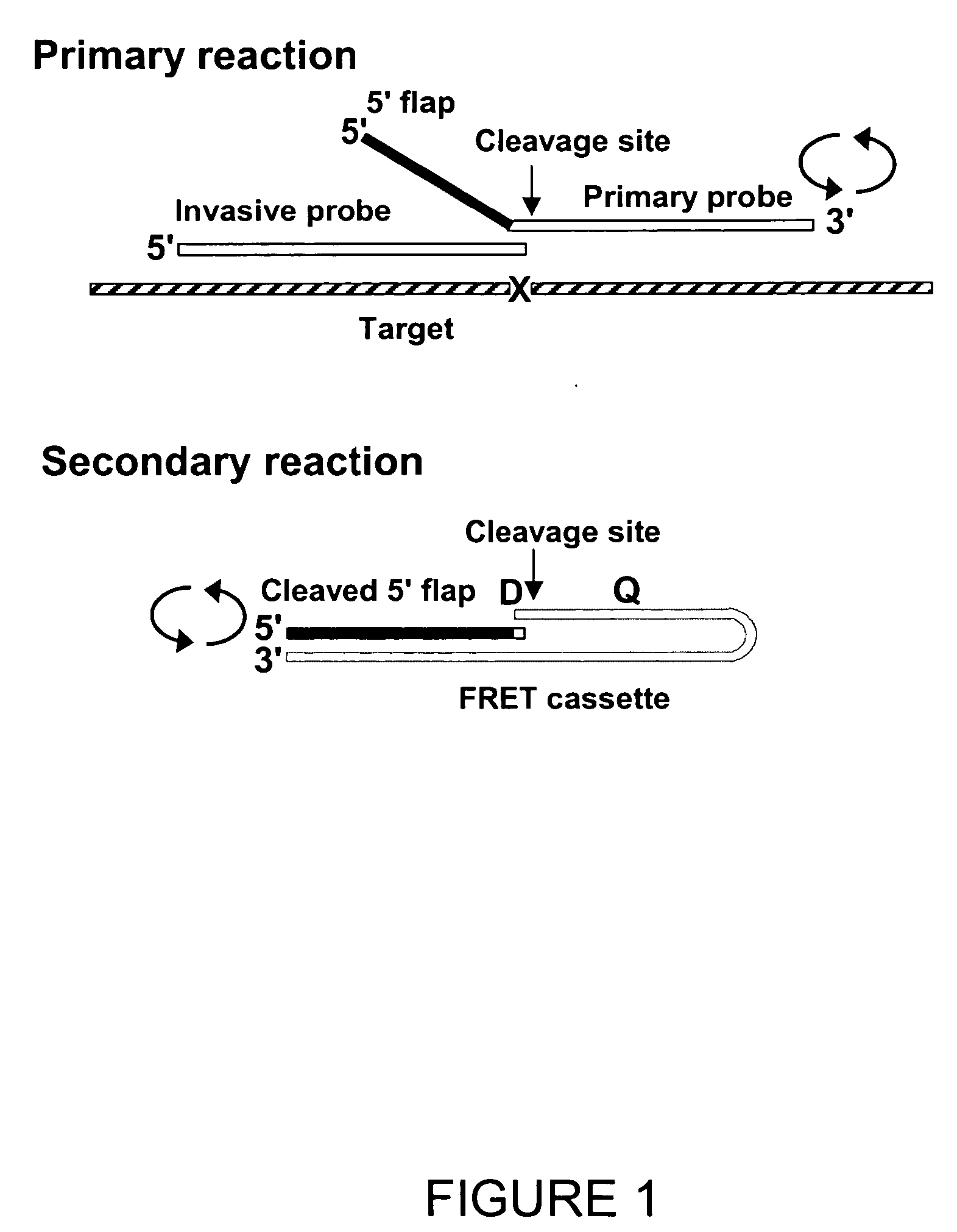
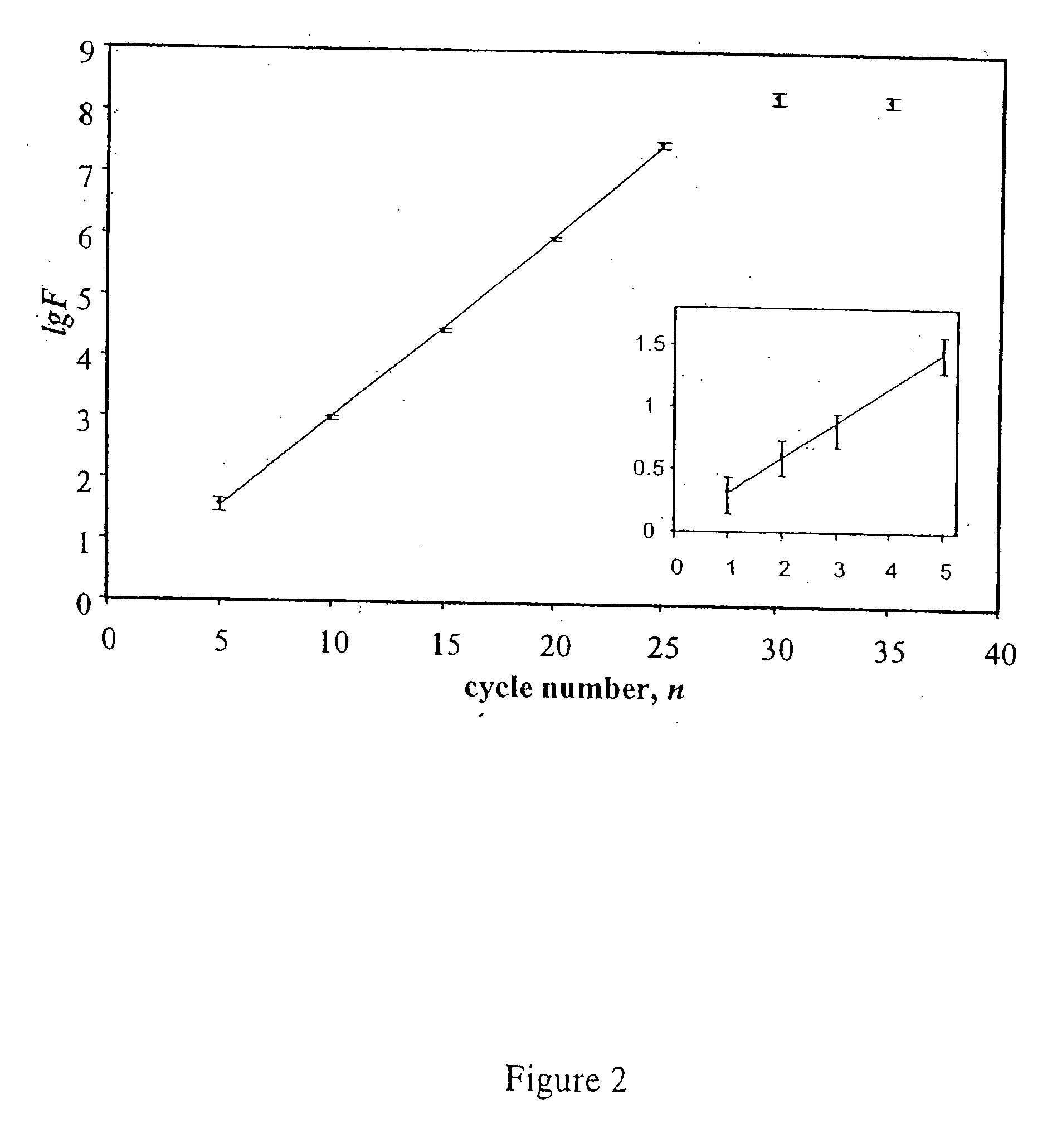
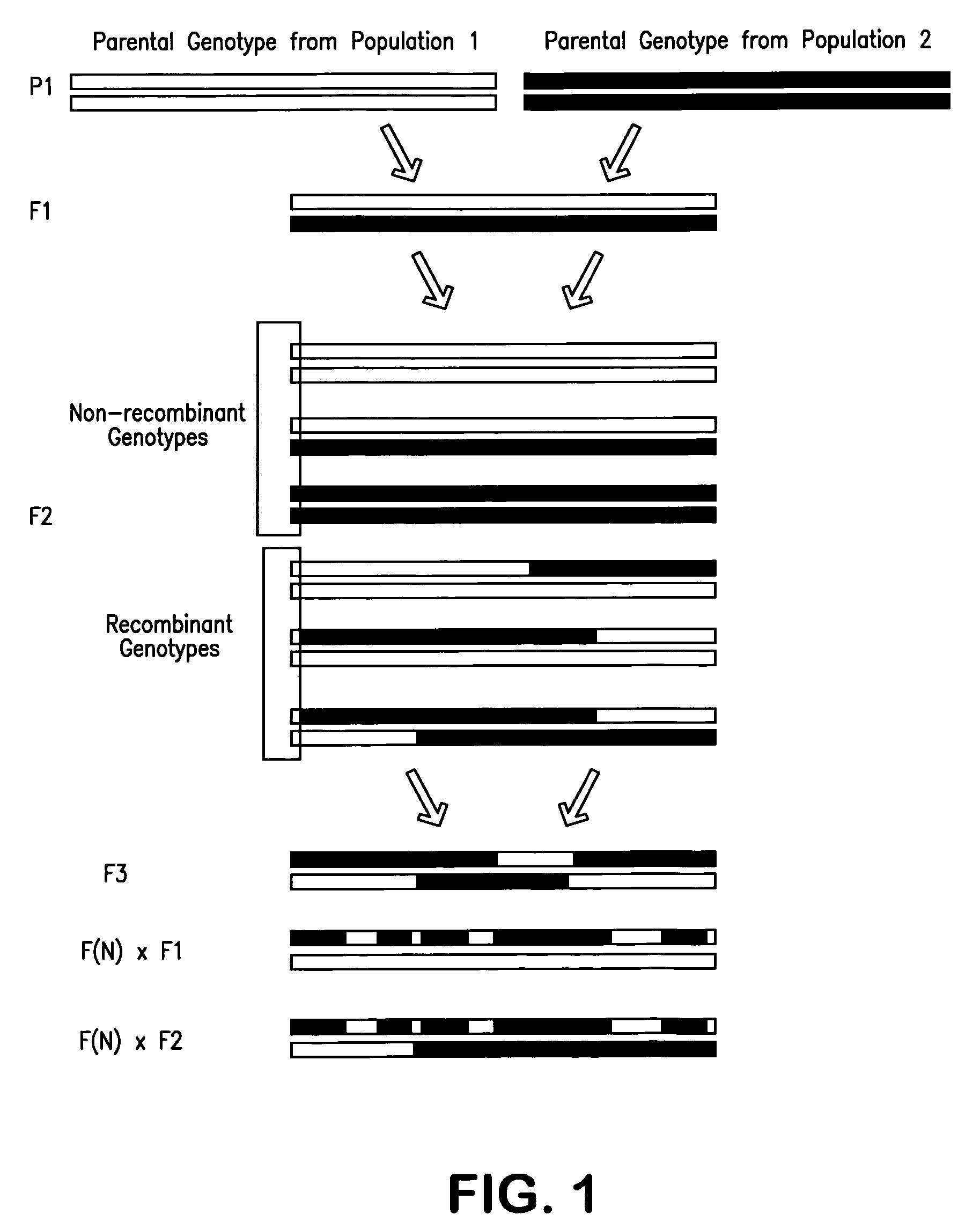
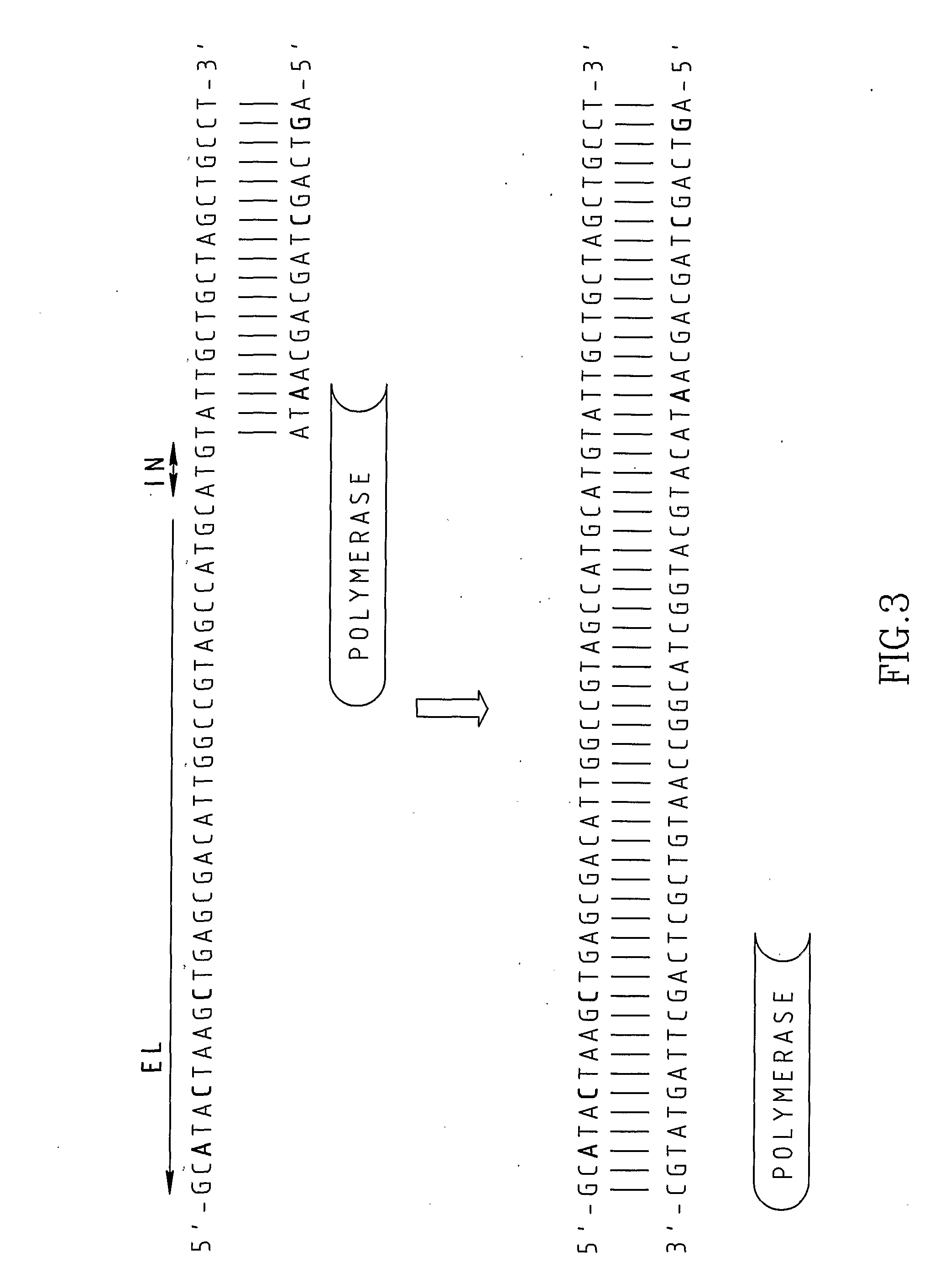
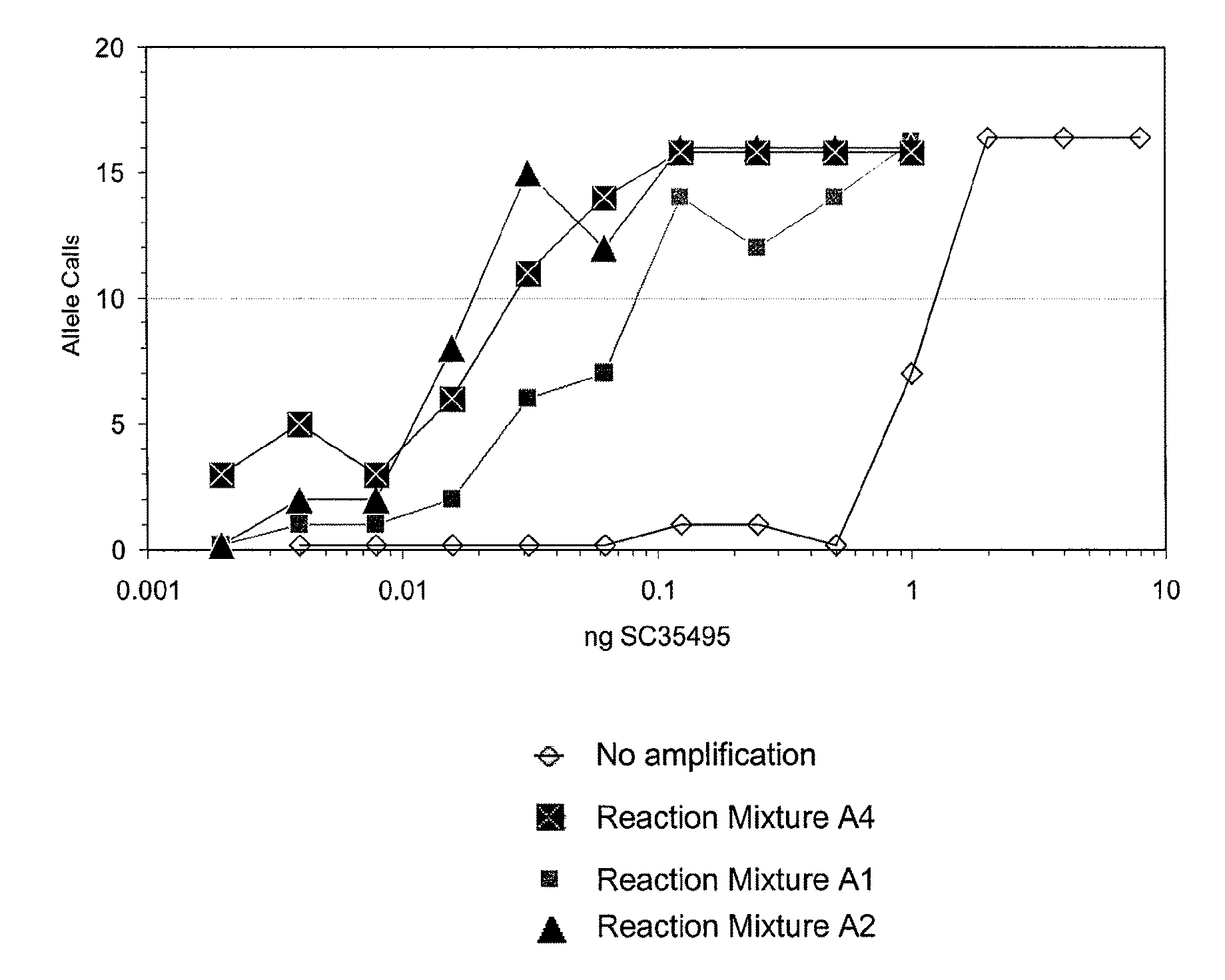
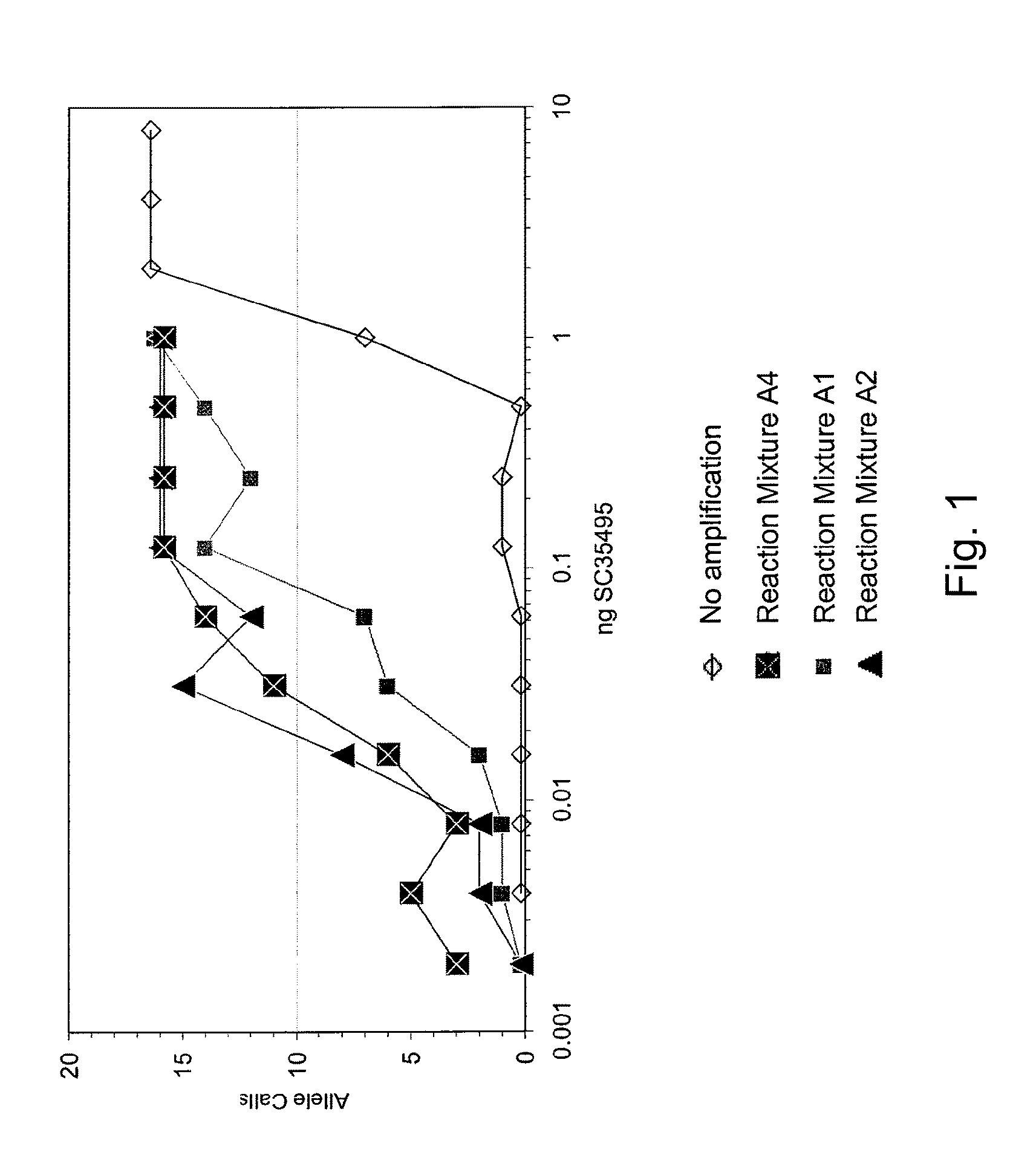
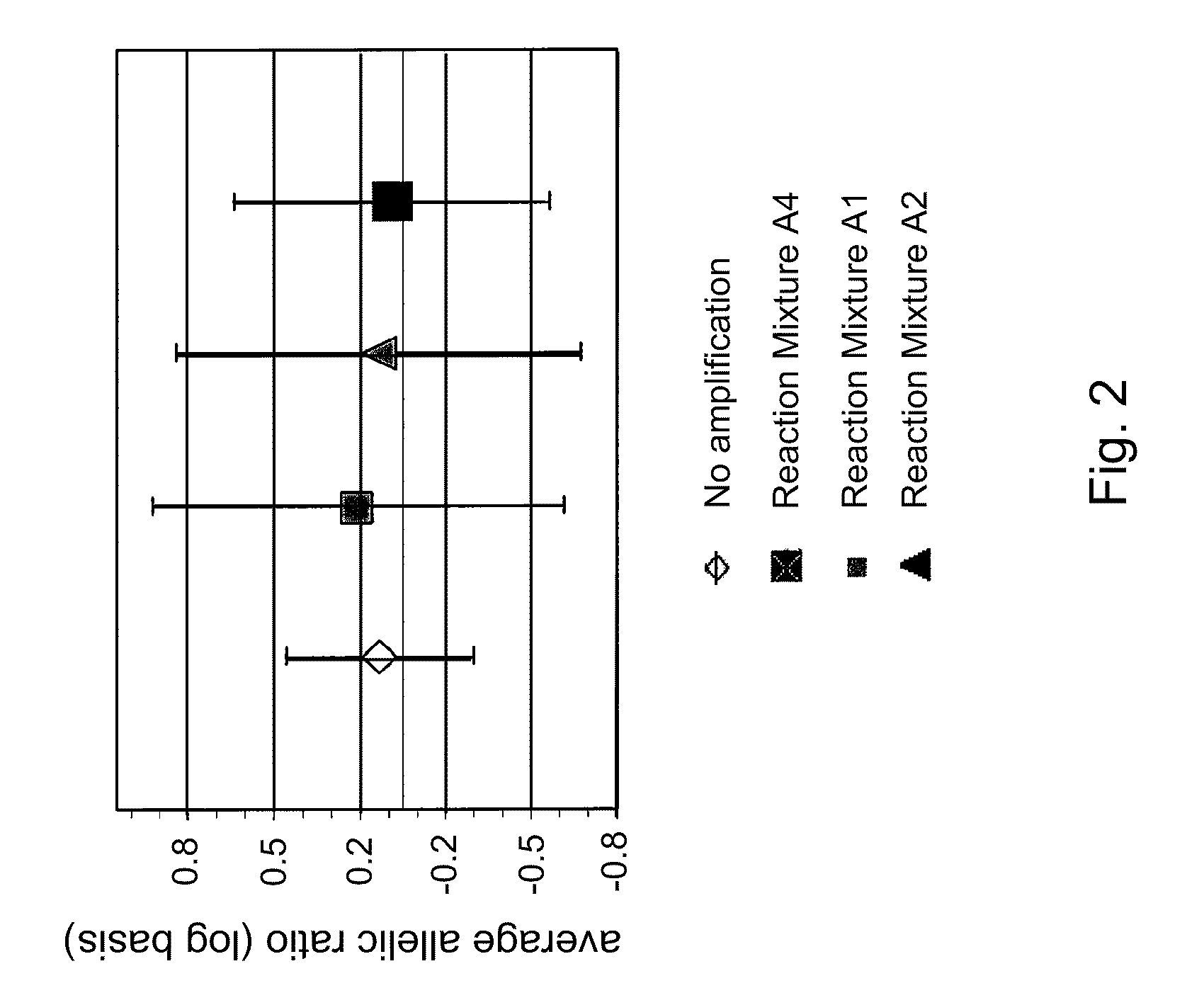
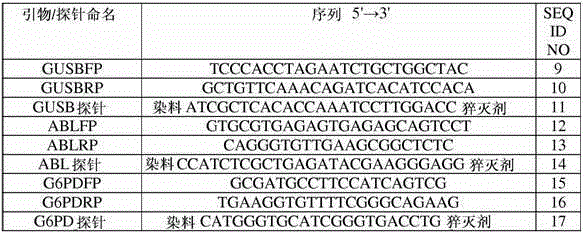
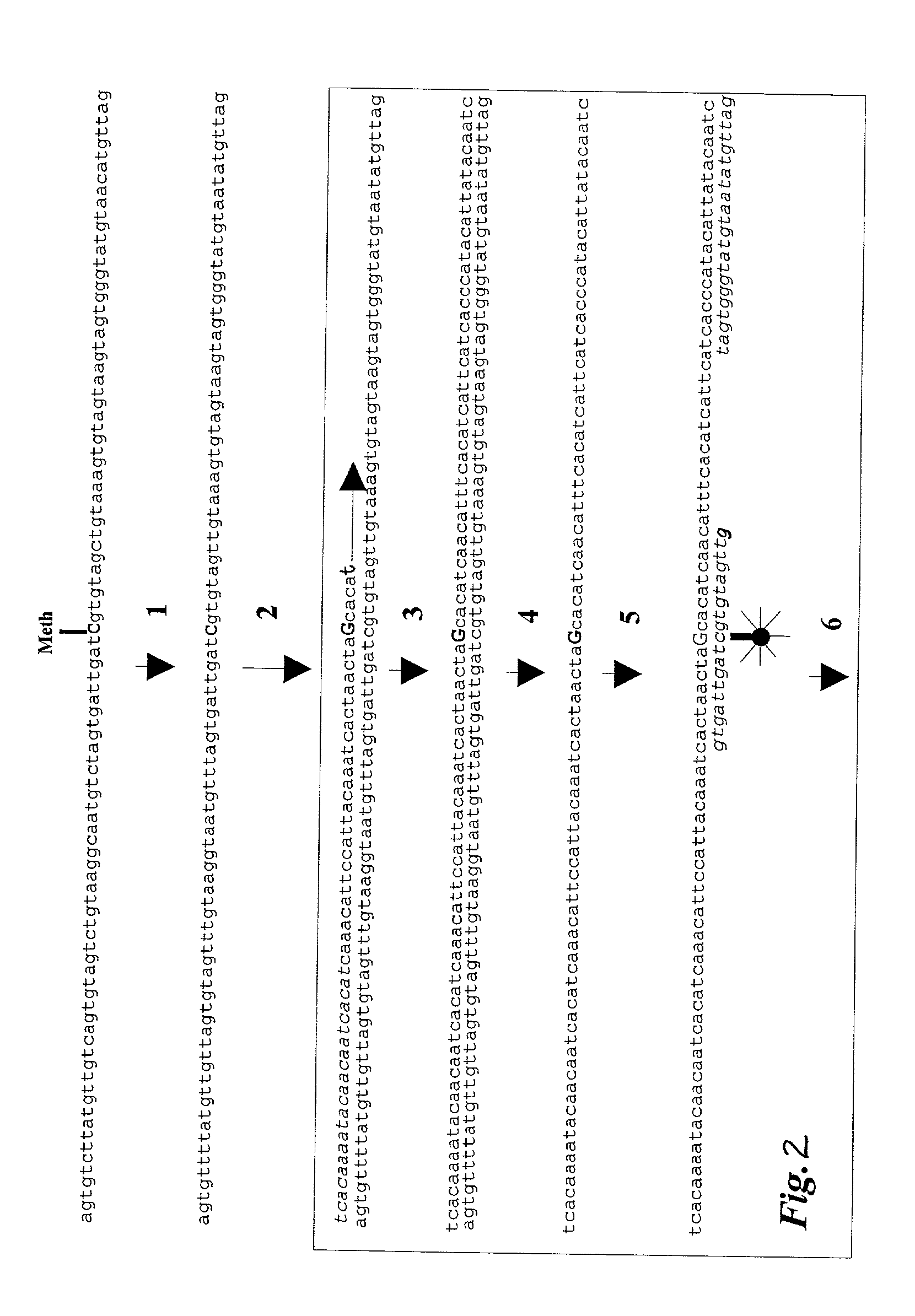
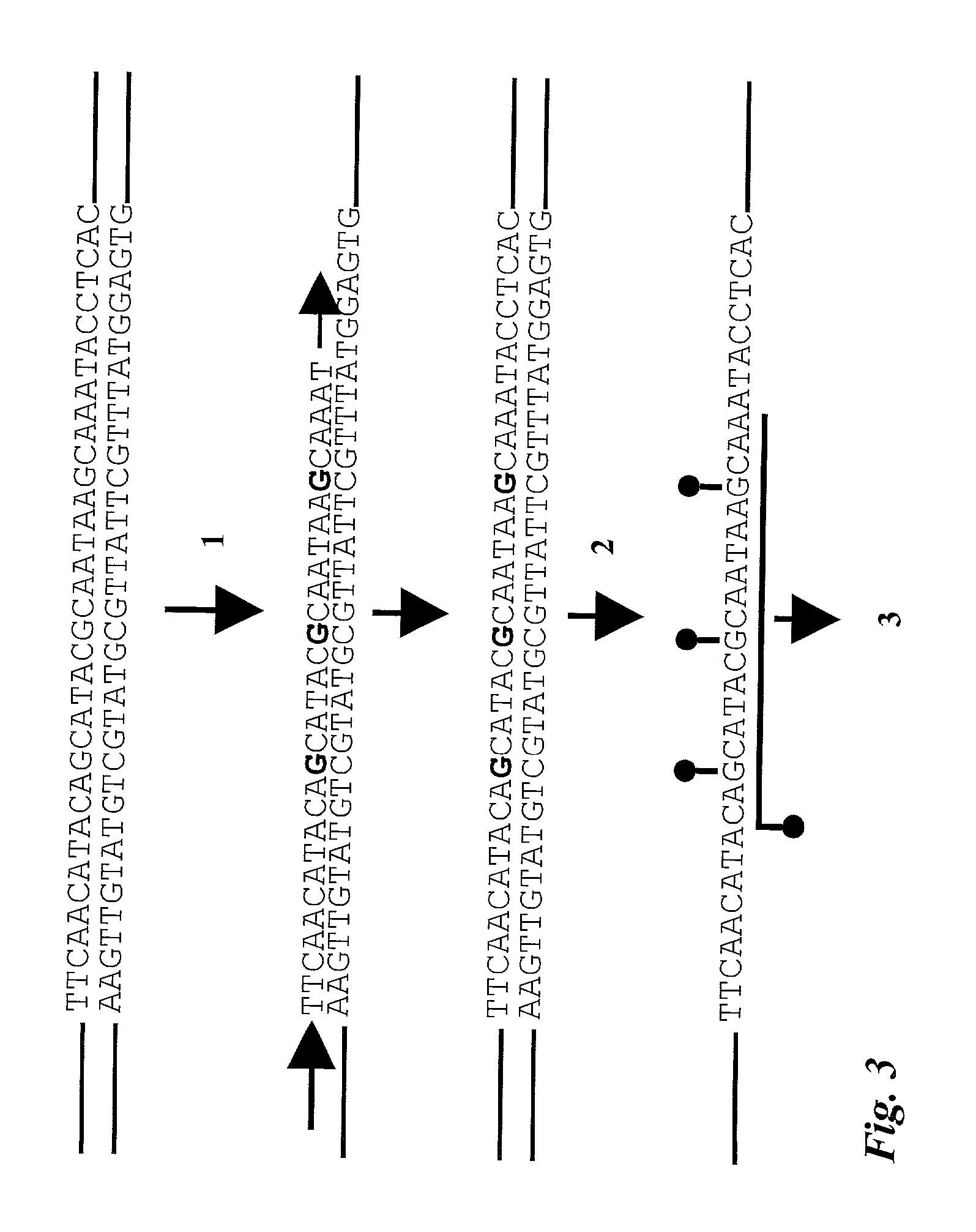
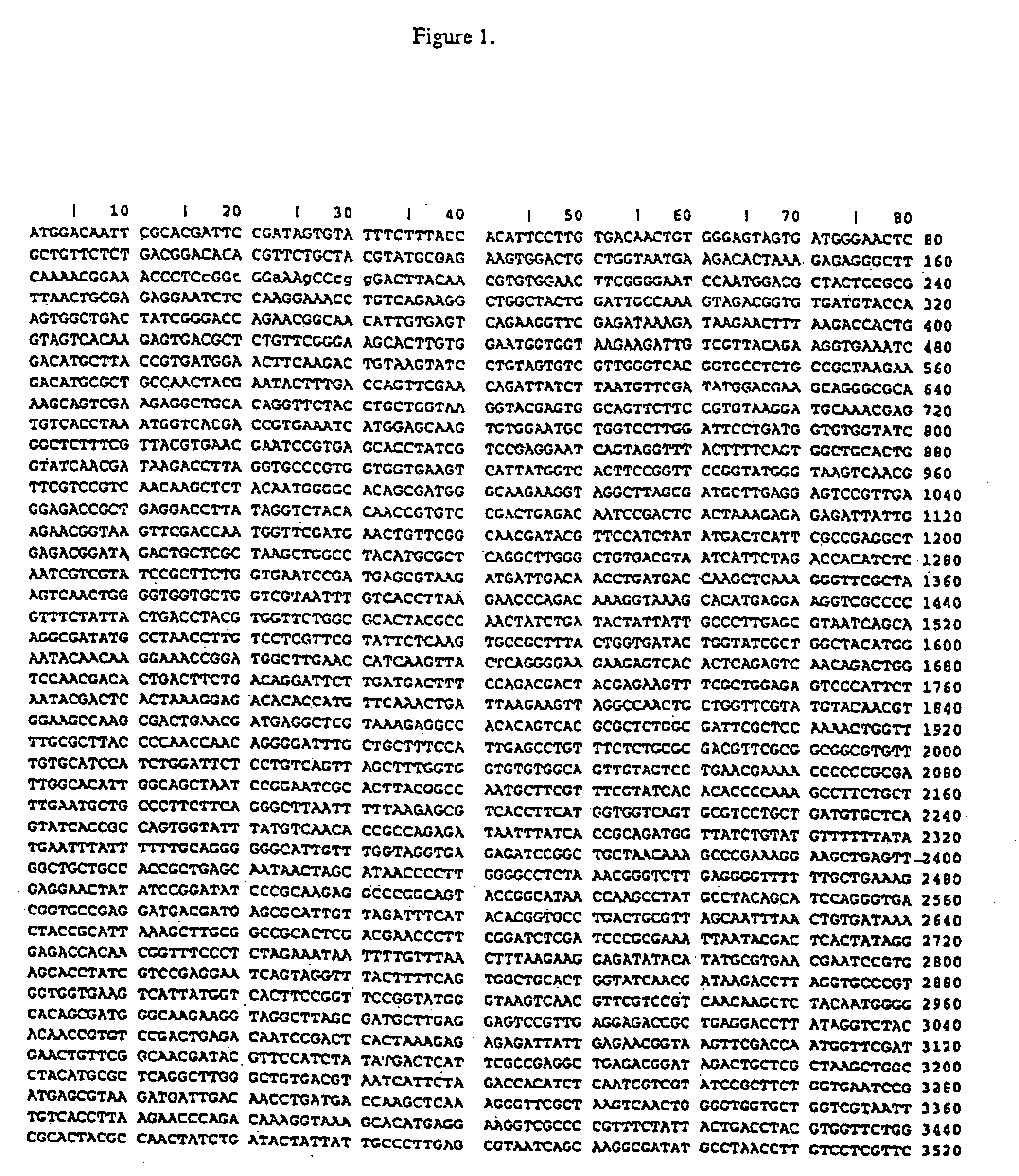
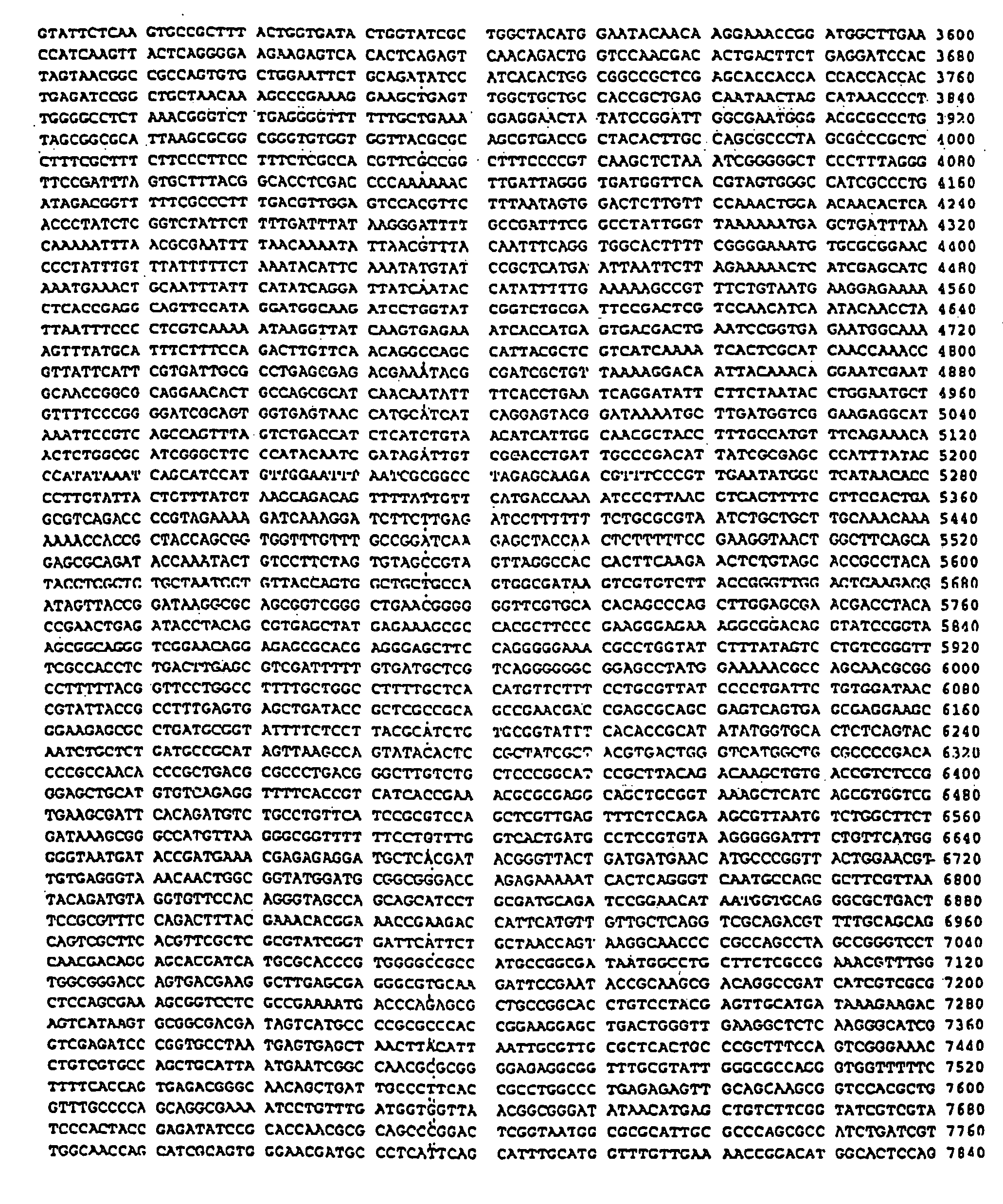
Patents
Literature
366 results about "Oligonucleotide Primer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Short DNA oligonucleotide chains used to prime DNA (and in some cases RNA) synthesis.
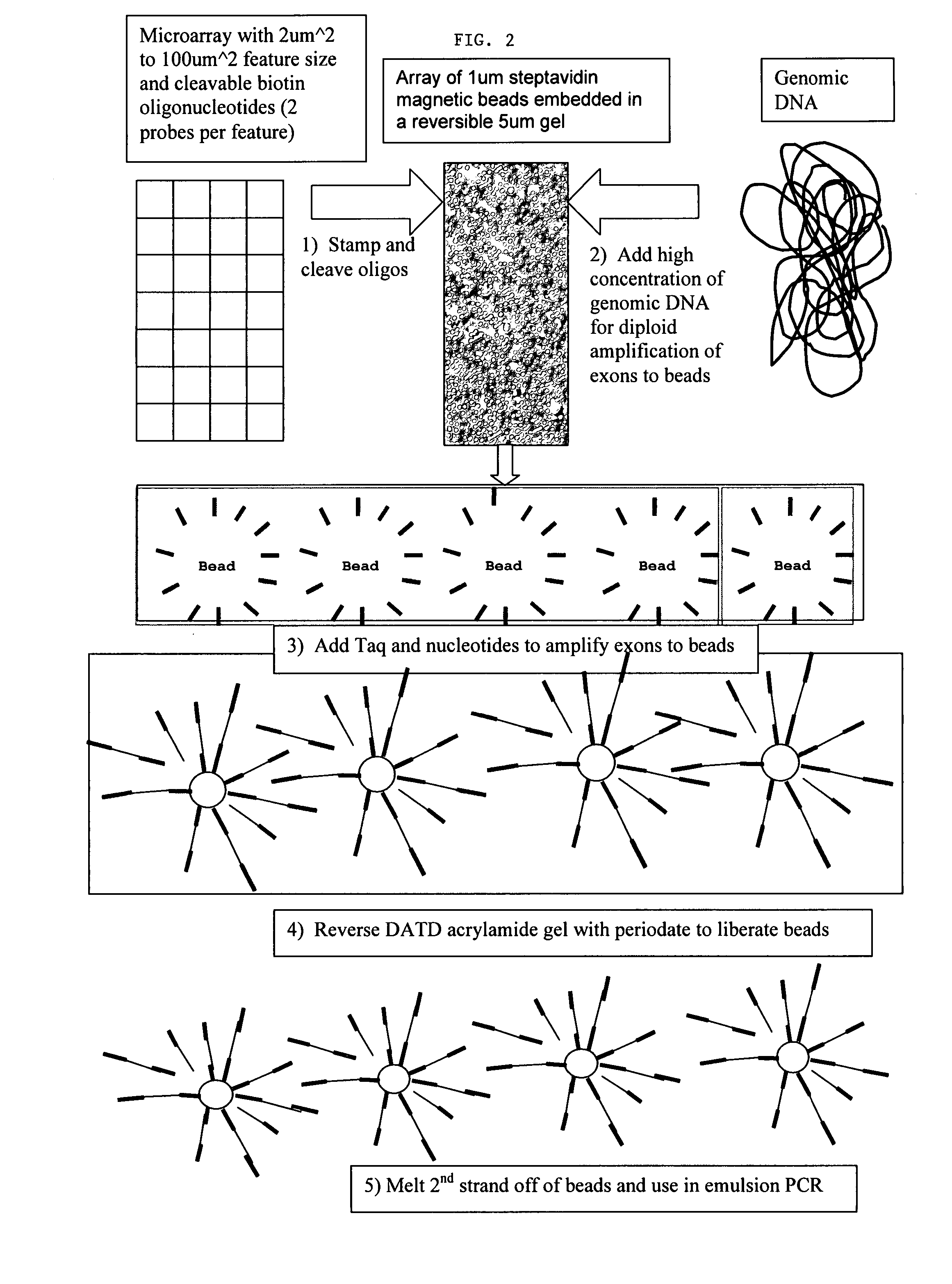
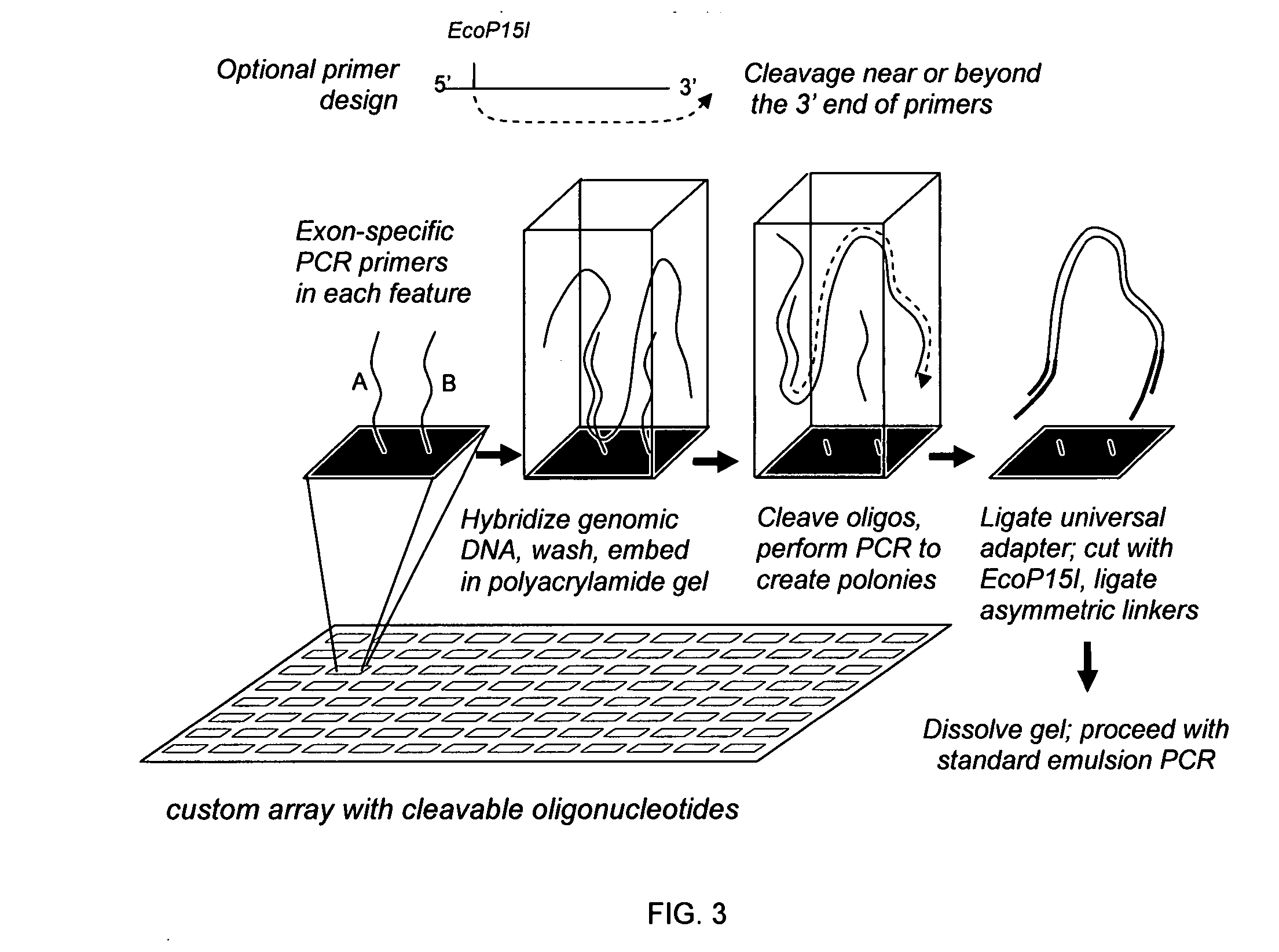
Directed enrichment of genomic DNA for high-throughput sequencing
InactiveUS20070231823A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNANucleotide
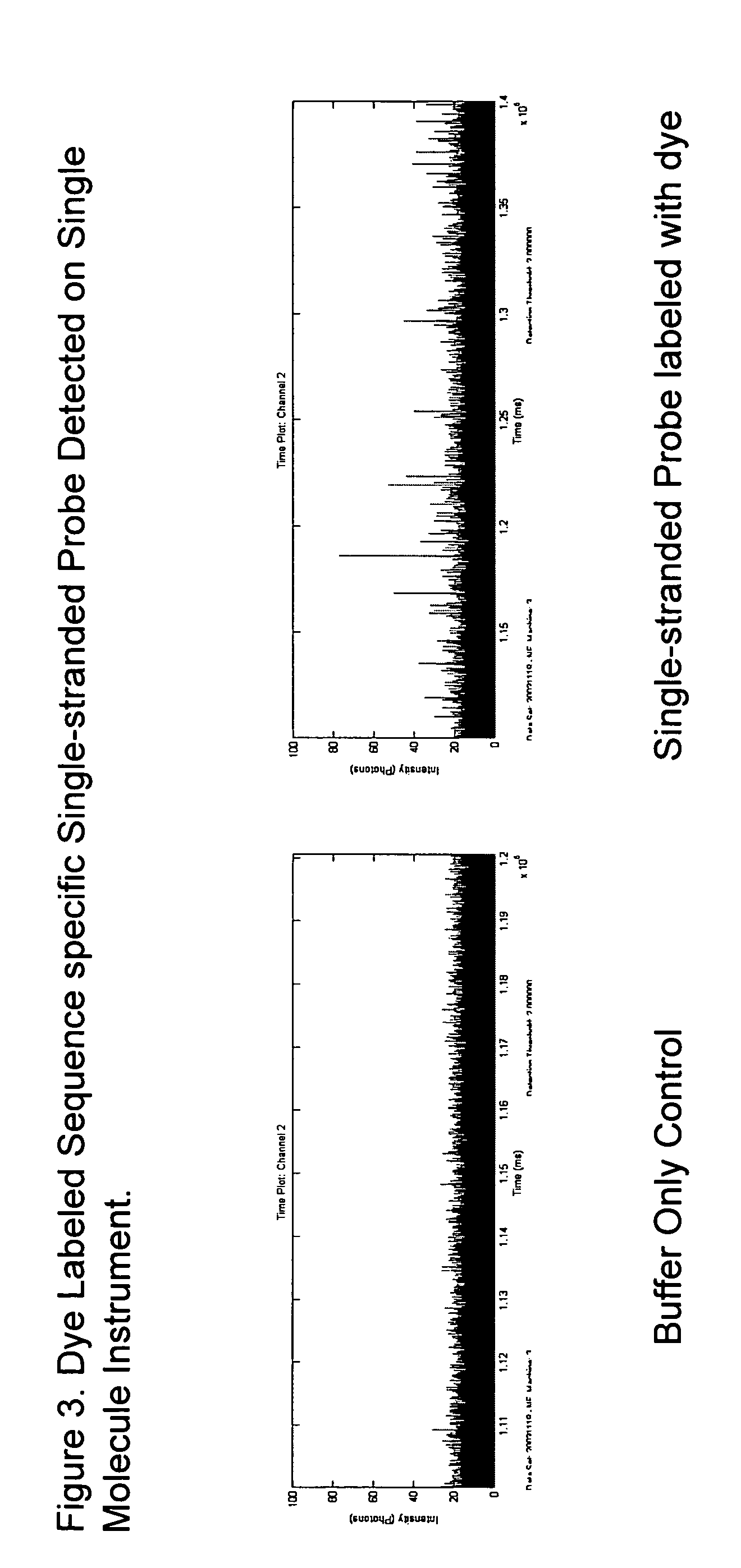
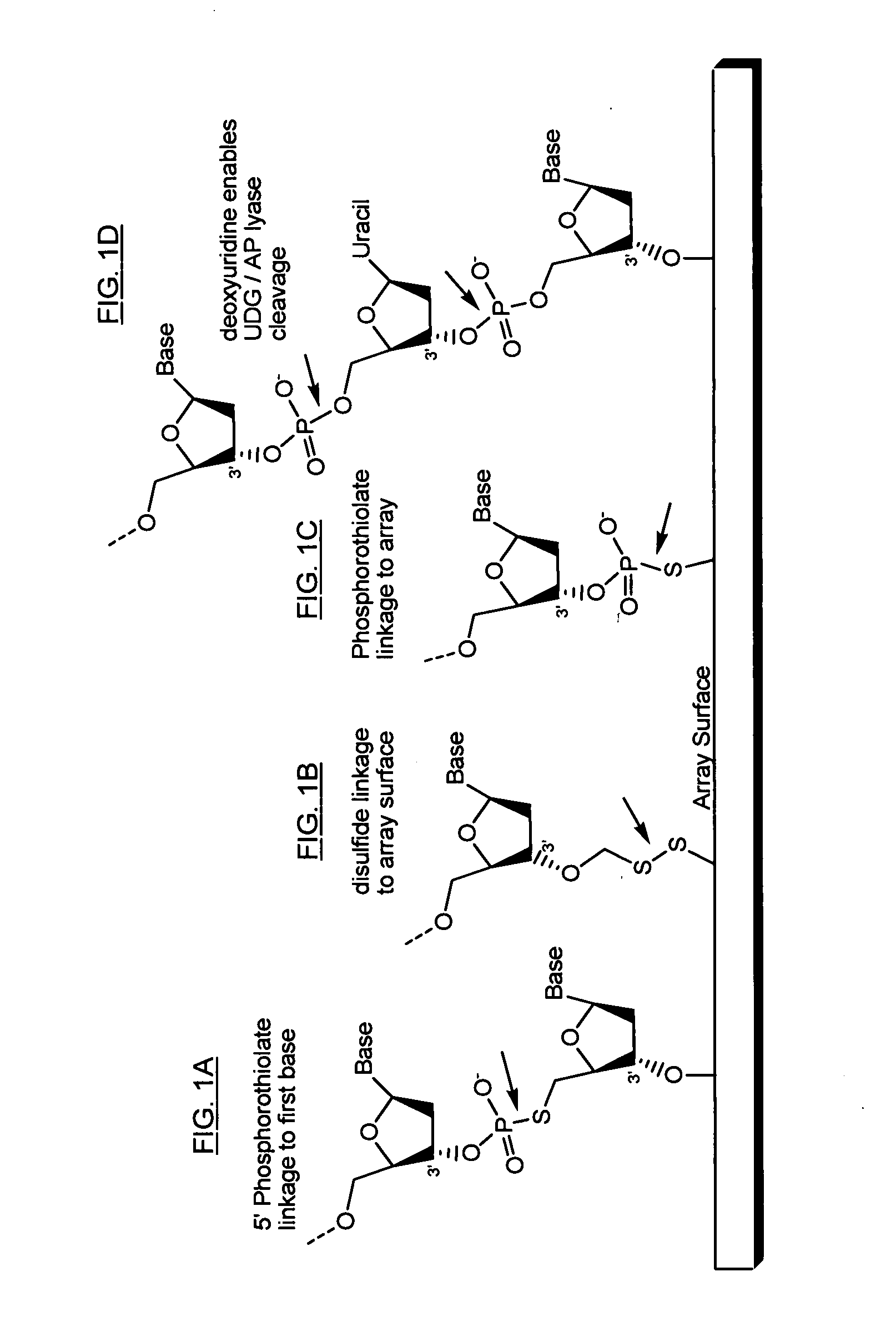
The present invention provides microarrays of oligonucleotide primer pairs, and in particular, microarrays of primers that comprise at least one cleavable linkage. Also provided are methods to capture oligonucleotide primer pairs from one or more microarrays, and methods to use the captured oligonucleotide primer pairs, such as for amplification of a target polynucleotide sequence. In addition, methods of using a microarray to isolate, purify and / or amplify a target polynucleotide are provided.
Owner:ADVANCED GENETIC ANALYSIS CORP
New sequencing method for sequencing rna molecules
InactiveUS20060166203A1Reduce decreaseMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseNucleotide
The present invention provides a method for determination of the identity of at least one nucleotide in a RNA-molecule comprising the steps of: (i) providing the RNA-molecule, an oligonucleotide primer binding to a predetermined position of the RNA molecule, a reverse transcriptase, deoxynucleotides and other necessary reagents, in a reaction vessel; (ii) performing a primer extension reaction, whereby the oligonucleotide primer is extended on the RNA-molecule through incorporation of at least one deoxynucleotide by the action of a reverse transcriptase, resulting in the release of a PPi molecule only upon incorporation of a deoxynucleotide; and (iii) detecting the presence or absence of incorporation, thereby indicating the nucleotide identity of the RNA molecule in the relevant position. In a preferred embodiment, the sequencing of the invention is coupled to the Pyrosequencing™ reaction. A variant of the method employs incorporation of modified nucleotides, with an optionally cleavable linker arm to which is attached a label.
Owner:TOOKE NIGEL
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS7875440B2Eliminate needHigh puritySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersFluorescence
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Single nucleotide detection using degradation of a fluorescent sequence
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms using a pair of oligonucleotides, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence hybridizes to the target DNA downstream from the primer and in the direction of primer extension. The snp detection sequence is characterized by having a nucleotide complementary to the snp and adjacent nucleotide complementary to adjacent nucleotides in the target and an electophoretic tag bonded to the 5'-nucleotide. The pair of oligonucleotides is combined with the target DNA under primer extension conditions, where the polymerase has 5'-3' exonuclease activity. When the snp is present, the electophoretic tag is released from the snp detection sequence, and can be detected by electrophoresis as indicative of the presence of the snp in the target DNA.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Use of nucleotide analogs in the analysis of oligonucleotide mixtures and in highly multiplexed nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20020045178A1Particle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
Methods and kits that use nucleotide analogs to confer increased accuracy and improved resolution in the analysis and sequencing of oligonucleotide mixtures are provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Compositions for use in identification of viral hemorrhagic fever viruses
InactiveUS7312036B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersRapid identification
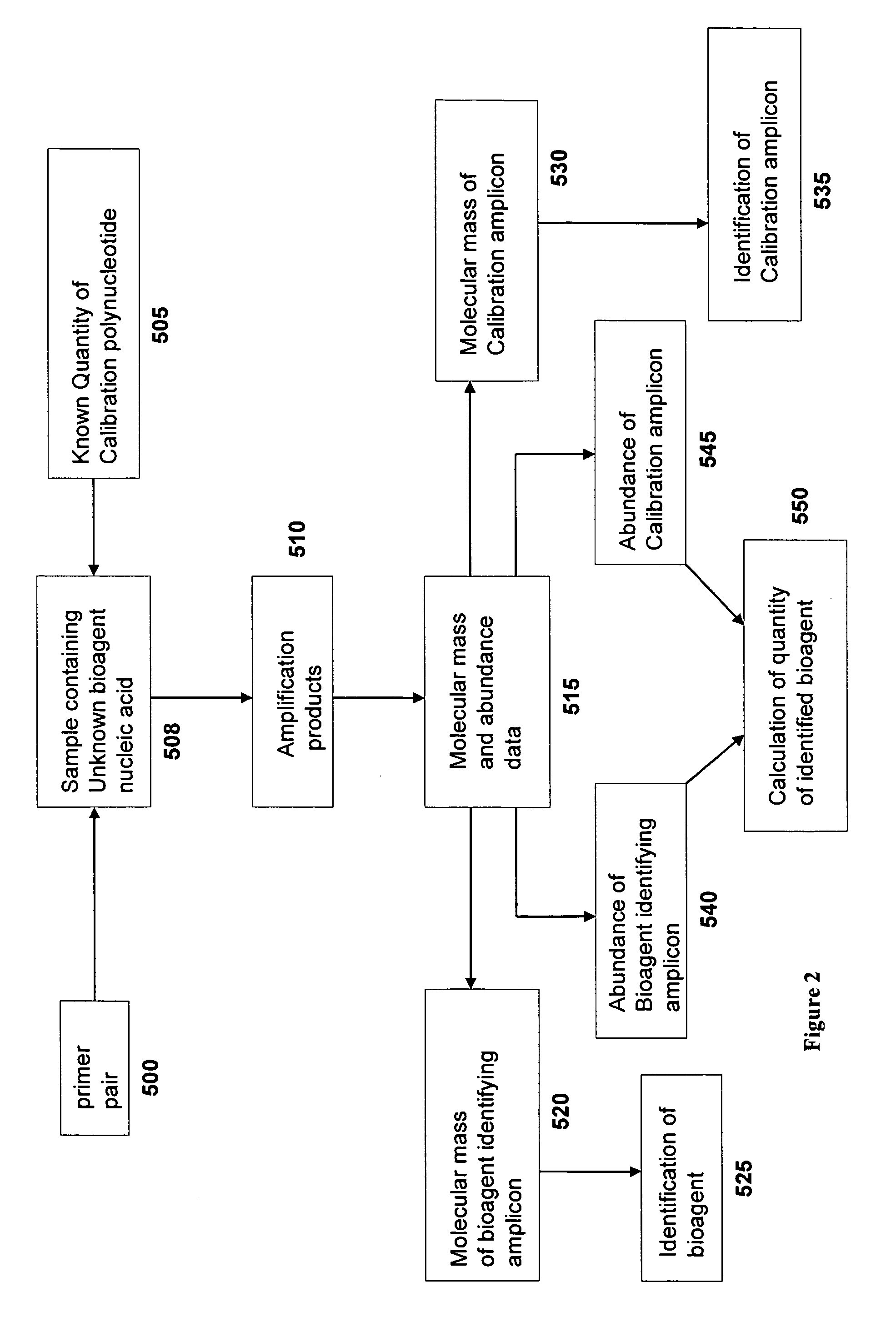
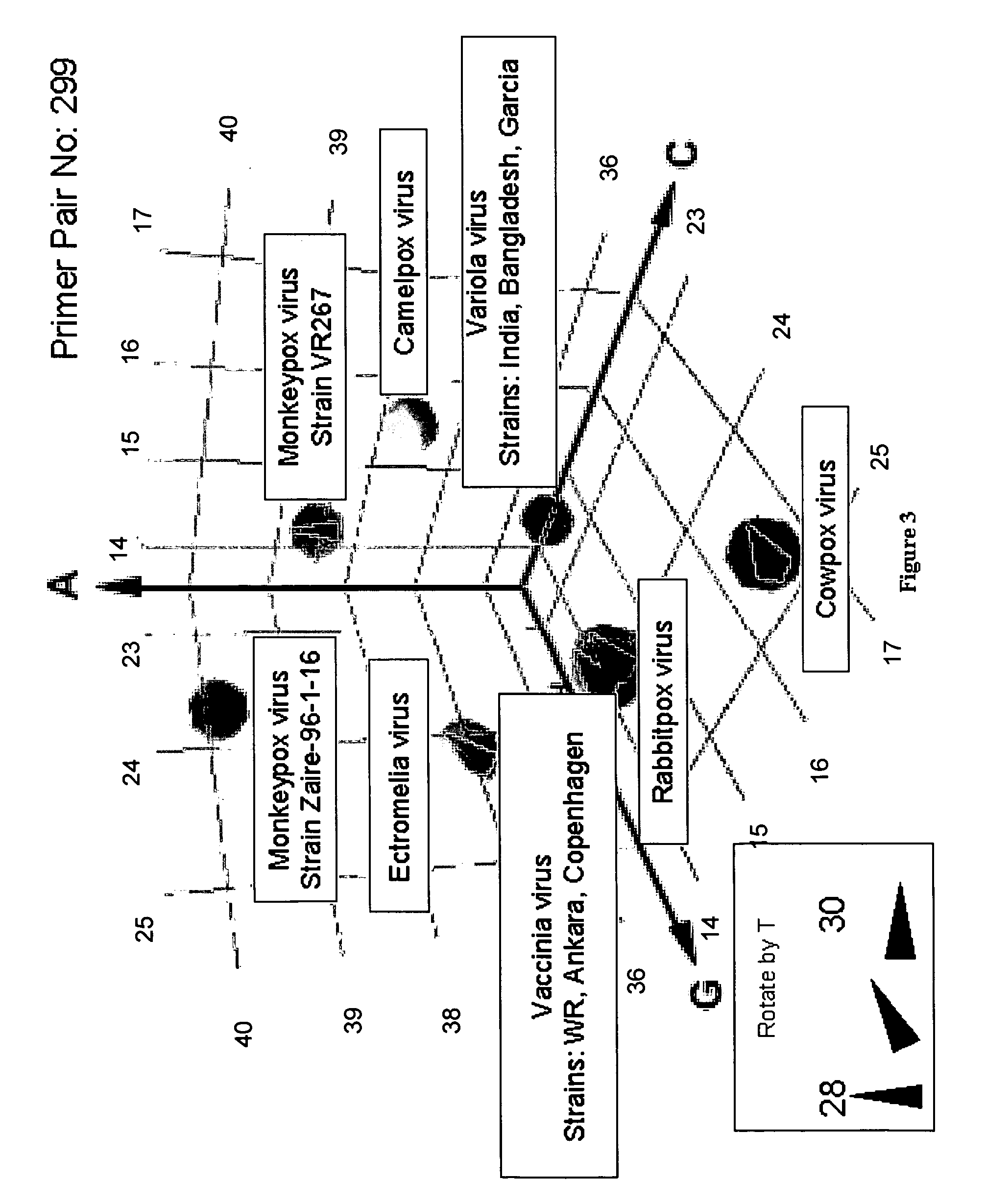
The present invention provides oligonucleotide primers, compositions, and kits containing the same for rapid identification of viruses that cause viral hemorrhagic fevers by amplification of a segment of viral nucleic acid followed by molecular mass analysis.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS20020137062A1Eliminate needHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyFluorescenceOligonucleotide primers
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Universal-tagged oligonucleotide primers and methods of use
InactiveUS7176002B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsOligonucleotide Primer
The present invention relates to universal-tagged oligonucleotide primers, and to methods of using the primers for amplifying the genome.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Single step detection assay
InactiveUS20060147955A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid detectionBasic research
The present invention provides methods and routines for developing and optimizing nucleic acid detection assays for use in basic research, clinical research, and for the development of clinical detection assays. In particular, the present invention provides methods for designing oligonucleotide primers to be used in multiplex amplification reactions. The present invention also provides methods to optimize multiplex amplification reactions. The present invention also provides methods for combined target and signal generation assays.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Multiplex assays for inferring ancestry
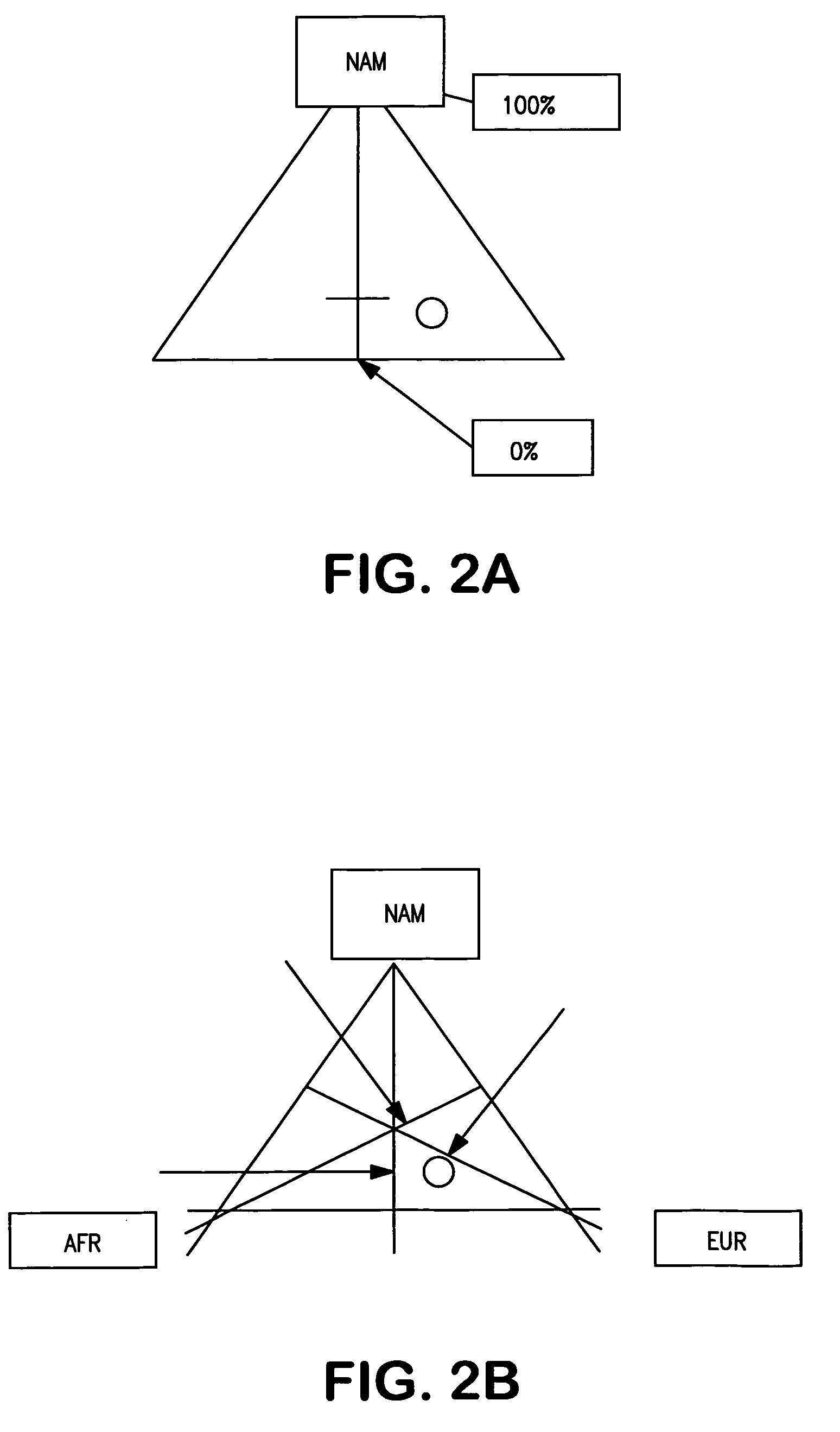
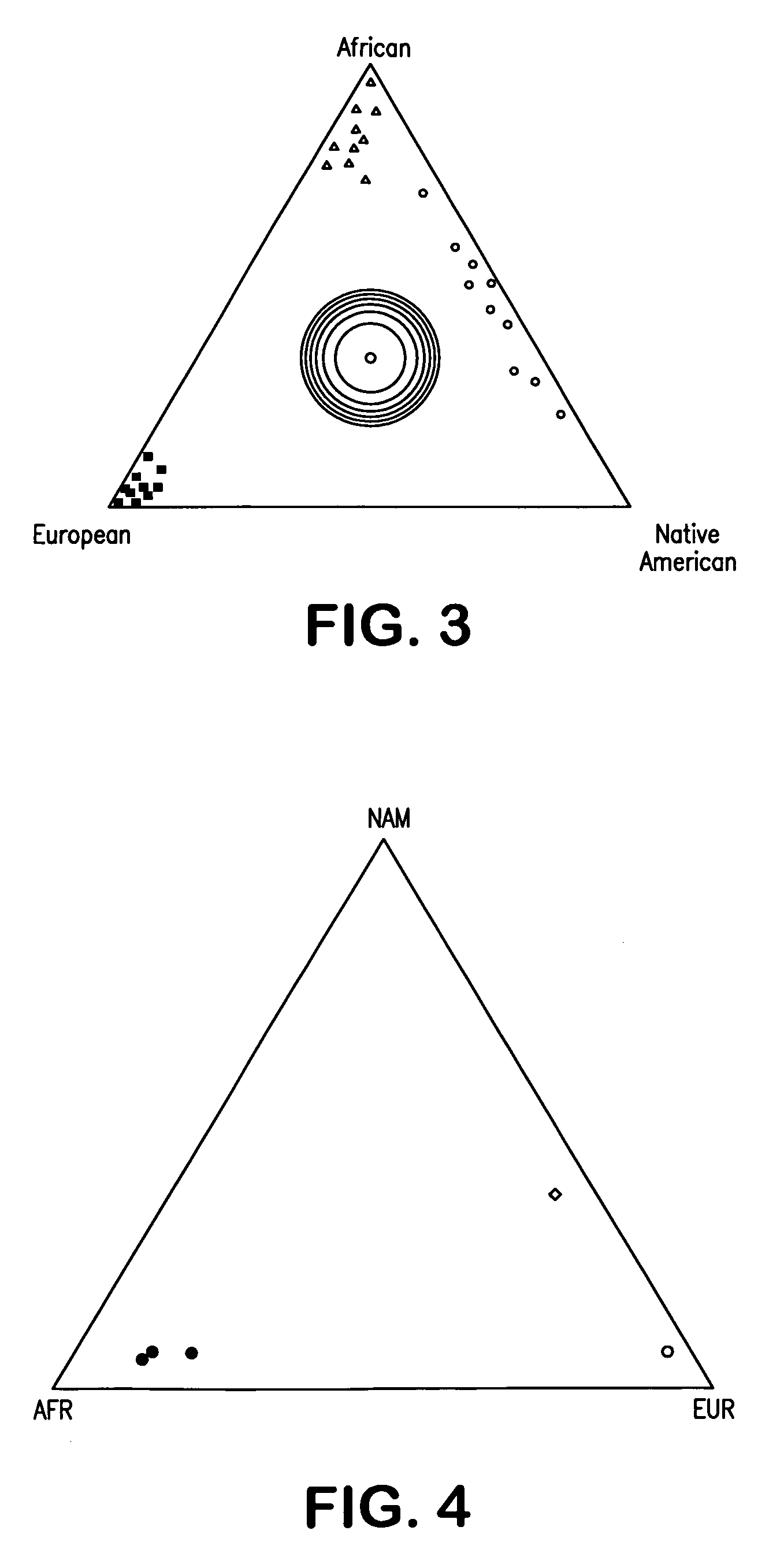
InactiveUS20070037182A1Improve the level ofLighter skinSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAncestry-informative markerOligonucleotide Primer
Oligonucleotide primers and probes for detecting Ancestry informative marker (AIMs) polynucleotides that contain a single nucleotide polymorphism or that contain an insertion or deletion, are provided, as are methods of using the oligonucleotide primers and probes to draw an inference as to a trait of an individual. The trait can be, for example, biogeographical ancestry, a pigmentation trait, responsiveness to a drug, or susceptibility to a disease. Also provided are methods of determining the proportional ancestry of an individual. Reagents and kits also are provided.
Owner:DNAPRINT GENOMICS
Circular chromosome conformation capture (4C)
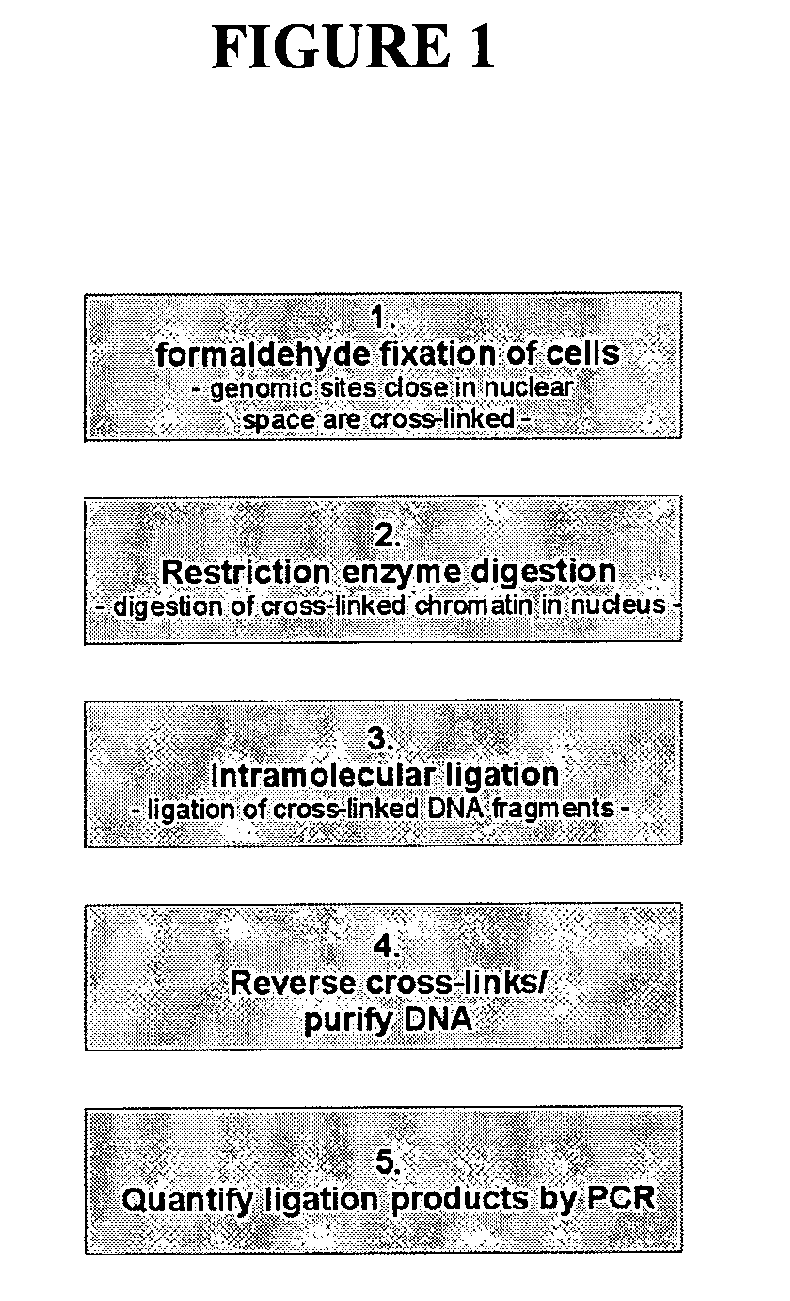
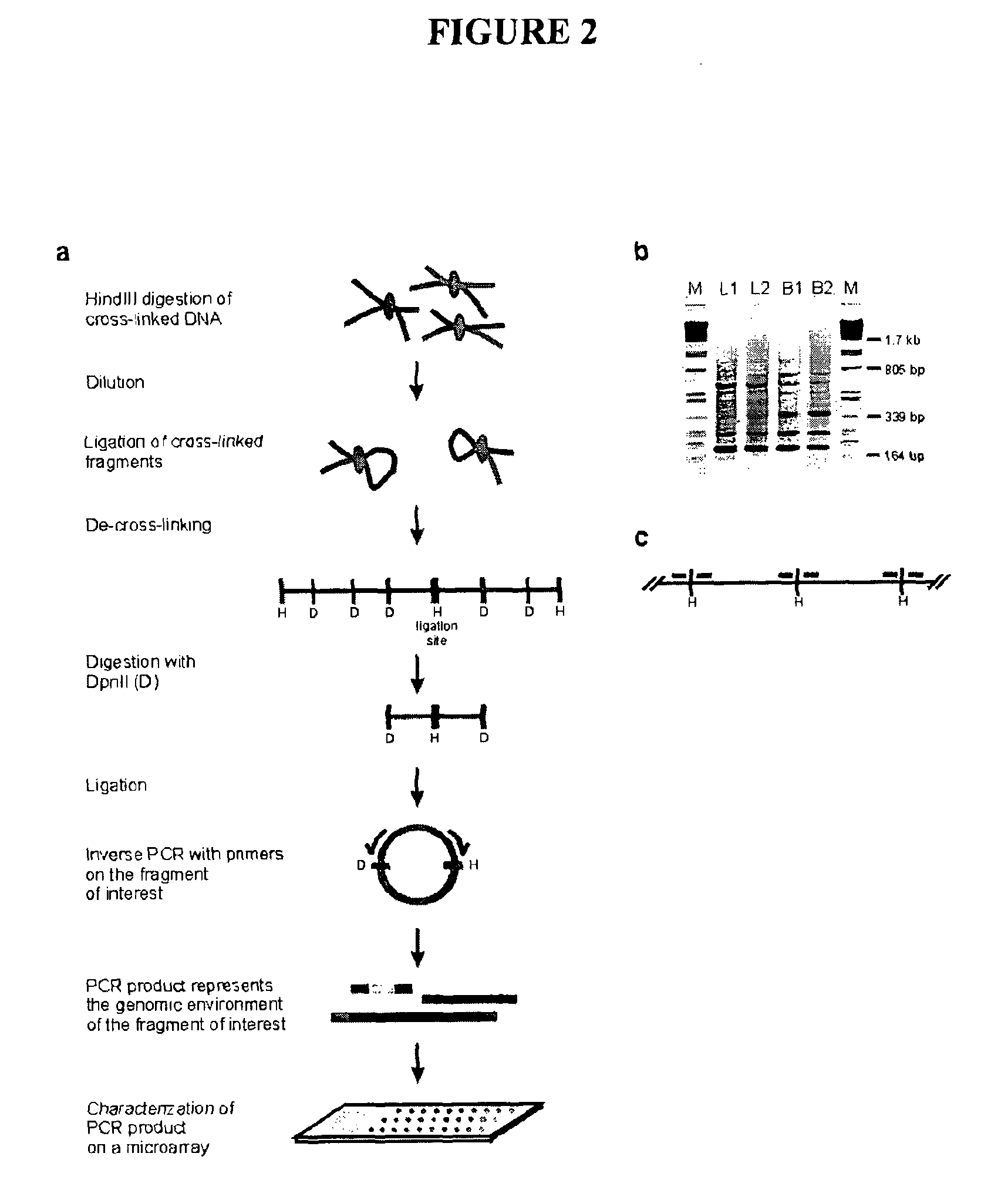
ActiveUS8642295B2High throughput analysisAccurate mappingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionRestriction enzyme digestion
The present invention relates in one aspect to a method for analyzing the frequency of interaction of a target nucleotide sequence with one or more nucleotide sequences of interest (eg. one or more genomic loci) comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample of cross-linked DNA; (b) digesting the cross-linked DNA with a primary restriction enzyme; (c) ligating the cross-linked nucleotide sequences; (d) reversing the cross linking; (e) optionally digesting the nucleotide sequences with a secondary restriction enzyme; (f) optionally ligating one or more DNA sequences of known nucleotide composition to the available secondary restriction enzyme digestion site(s) that flank the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest; (g) amplifying the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest using at least two oligonucleotide primers, wherein each primer hybridises to the DNA sequences that flank the nucleotide sequences of interest; (h) hybridising the amplified sequence(s) to an array; and (i) determining the frequency of interaction between the DNA sequences.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Chimeric primers for improved nucleic acid amplification reactions
ActiveUS20100291635A1Reduce formationLow efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesRibonucleotide synthesisNucleic acid sequencing
Methods are provided for amplification of a nucleic acid sequence. The method use RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotides as primers. The primers have RNA residues scattered along their length and no two ribonucleotides in the prime are adjacent to one another. The methods are useful for reducing non-specific amplification products, such as primer dimers. The invention also provides kits comprising RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotide primers for practicing the amplification methods.
Owner:INFINIPLEX LTD
Multiple displacement amplification
ActiveUS20110118151A1High sensitivityEfficient yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEmulsionHydrophobic polymer
The present invention provides methods kits and systems for performing multiple displacement amplification reactions. In one method a sample of nucleic acid is provided. The nucleic acid is contacted with a reaction mixture which includes a set of oligonucleotide primers, a one or more polymerase enzymes and a detergent. The reaction mixture is then subjected to conditions under which the nucleic acid sequence is amplified to produce an amplified product in a multiple displacement reaction. The method may also be carried out by contacting the nucleic acid with the reaction mixture in the form of an emulsion. A kit is also provided for carrying out either the methods described above. The kit includes one or more polymerases, a plurality of primers and a detergent. The kit may also include a hydrophobic polymer and may include instructions for performing a multiple displacement amplification reaction on a nucleic acid sample.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Chemically modified oligonucleotide primers for nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS20070281308A1Impairs DNA polymerase mediated oligonucleotide primer extensionMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorus organic compoundsOligonucleotide primersBiology
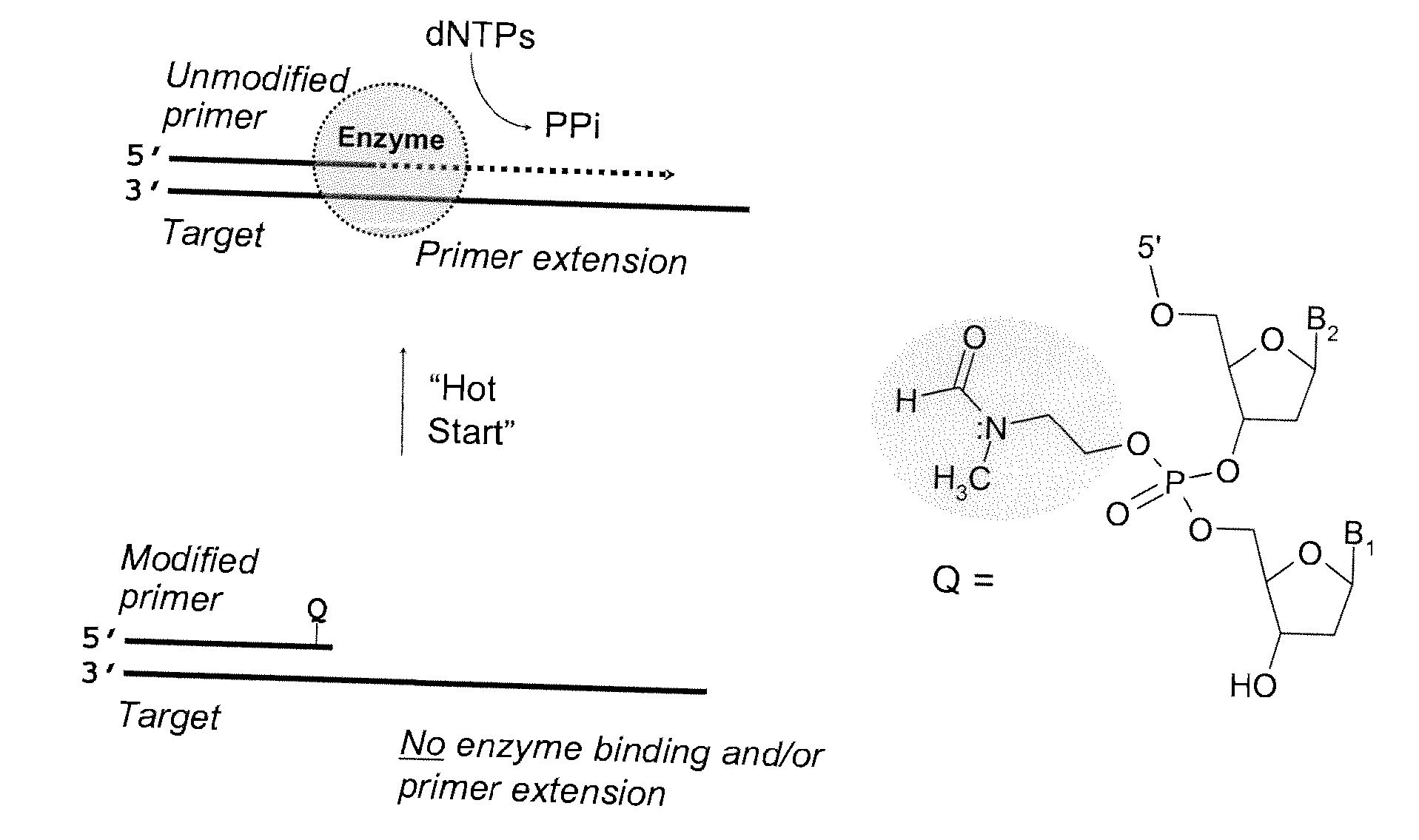
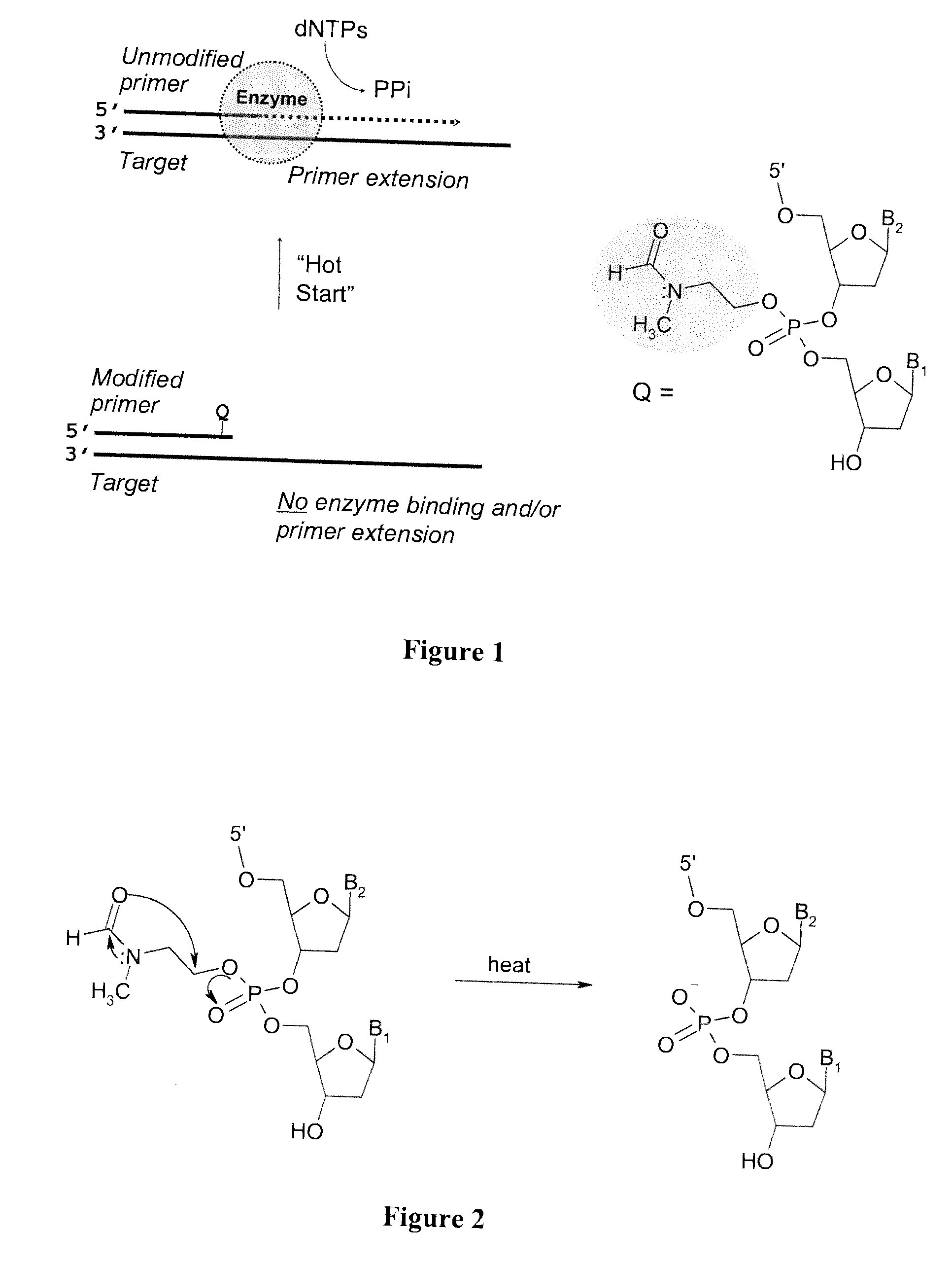
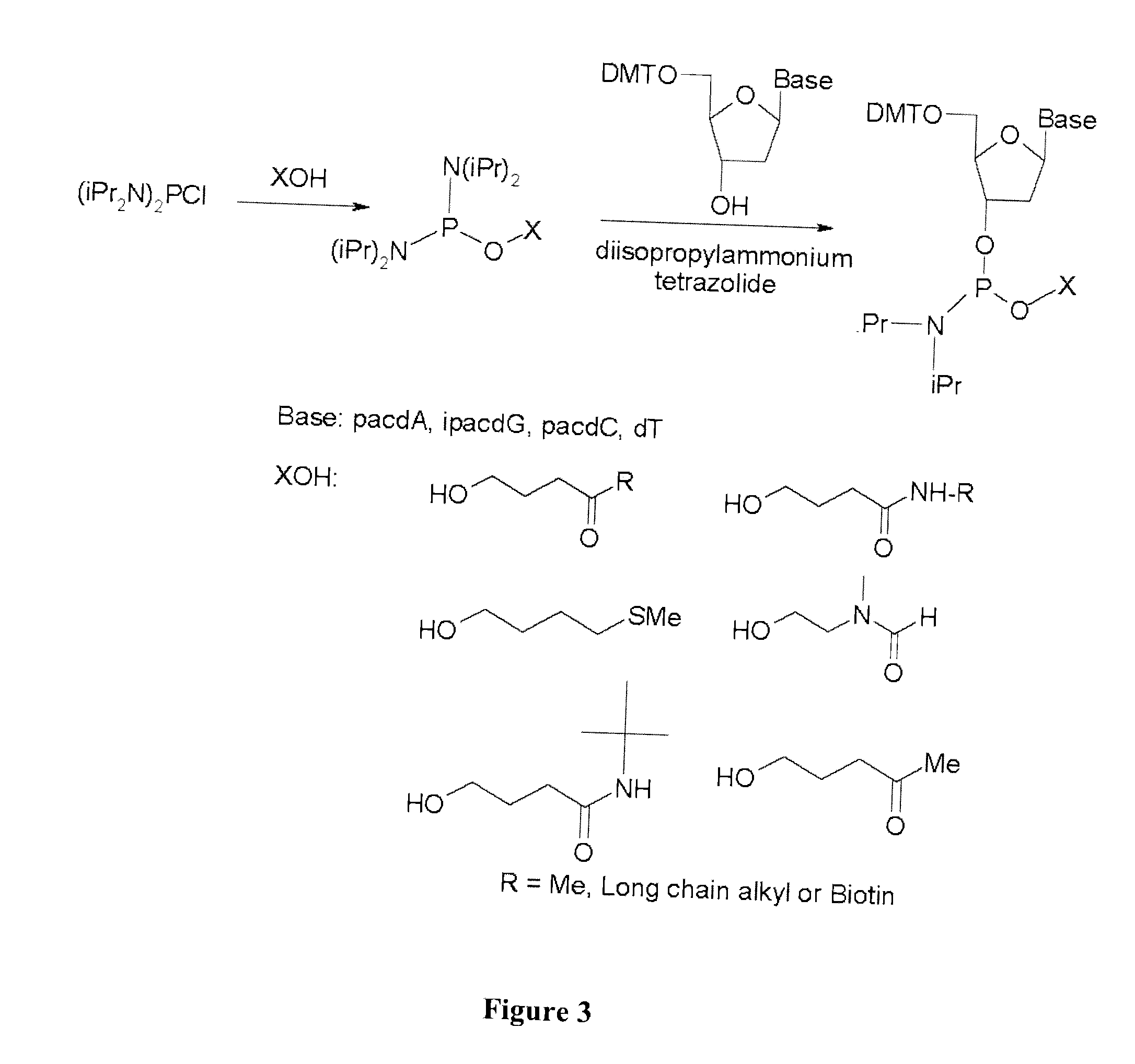
The present invention provides methods and compositions for nucleic acid amplification. These methods involve the use of oligonucleotide primers in temperature dependent nucleic acid amplification reactions. In certain aspects, the methods are accomplished by use of certain modified oligonucleotide primers which provide utility in nucleic acid amplification. In preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotide primers are modified with particular chemical groups such as esters.
Owner:TRILINK BIOTECH LLC
Quantitative methylation detection in DNA samples
InactiveUS6960436B2Quick fixFast and cost-effective and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LGenomic DNA
Described is a method for methylation detection in a DNA sample. An isolated genomic DNA sample is treated in a manner capable of distinguishing methylated from unmethylated cytosine bases. The pretreated DNA is amplified using at least one oligonucleotide primer, a polymerase and a set of nucleotides of which at least one is labeled with a first type of label. A sequence-specific oligonucleotide probe, marked with a second type of label, hybridizes to the amplification product and a FRET reaction occurs if a labeled oligonucleotide is present in close proximity in the amplification product. The method determines the level of methylation of a sample by measuring the extent of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between the donor and acceptor fluorophore.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Preparation of defined highly labeled probes
InactiveUS20060003333A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesSingle strand
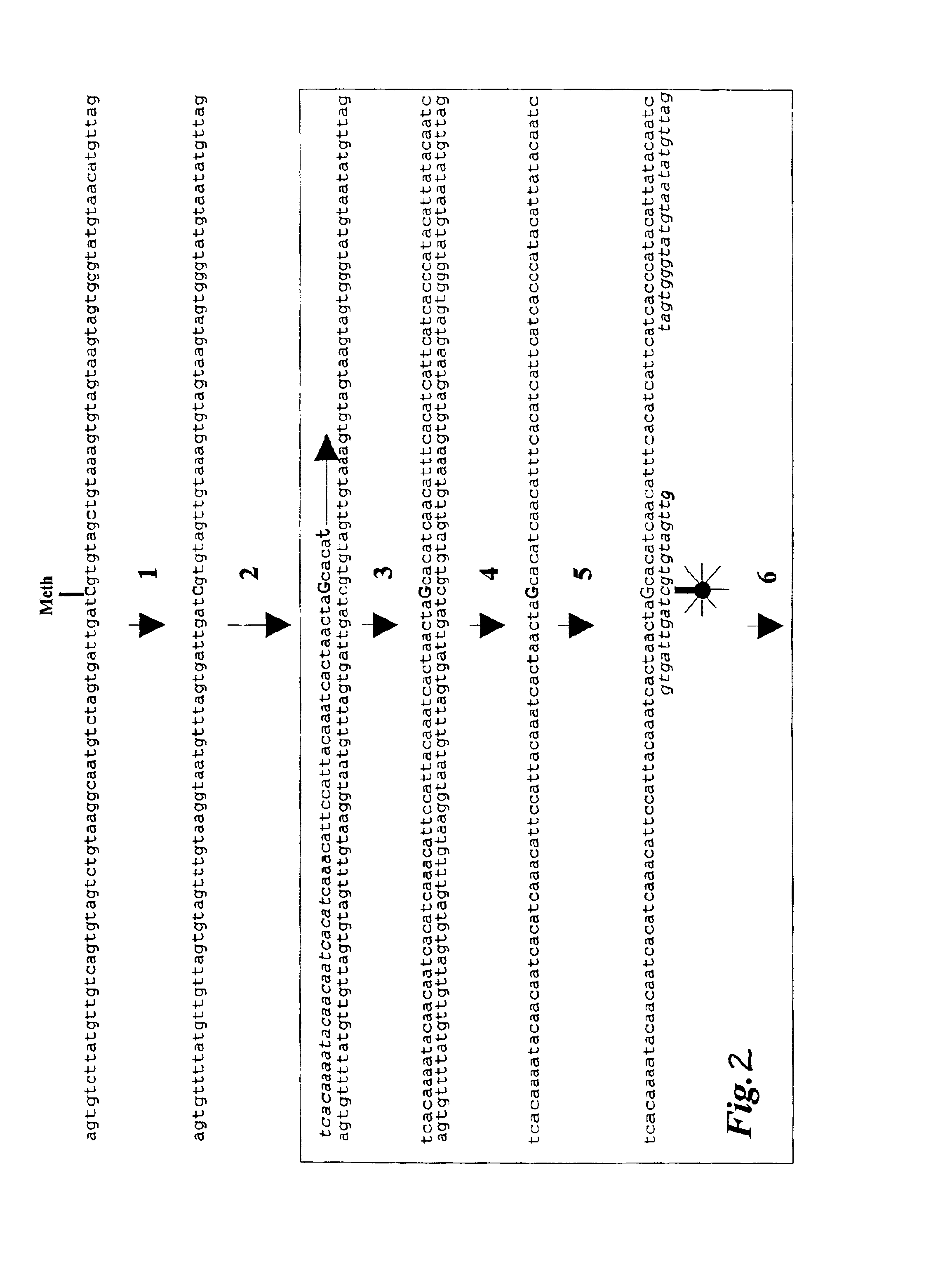
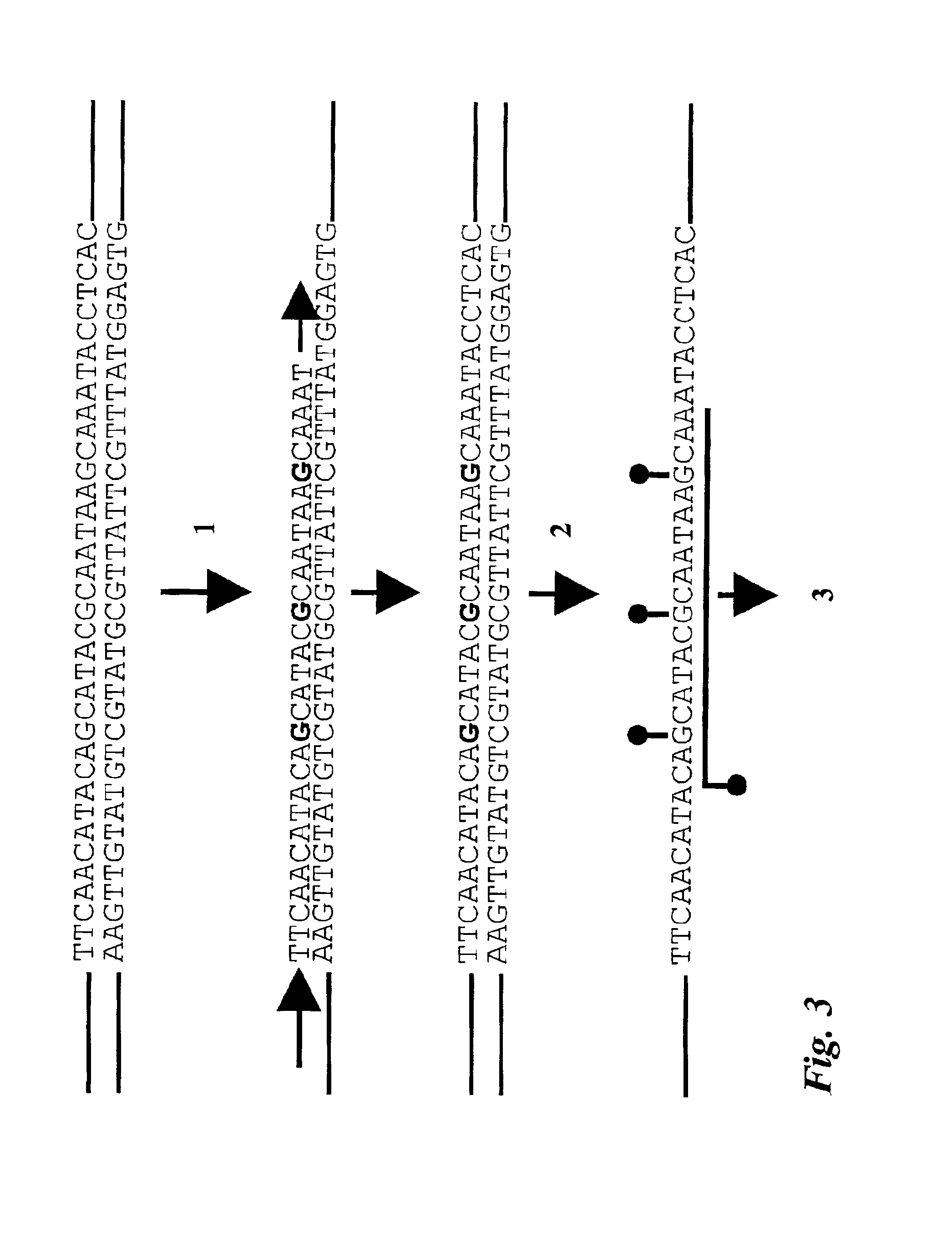
A method for producing a single-stranded unitized nucleic acid probe comprising the acts of: (a) contacting an oligonucleotide primer having a 5′ recognition end having a length of between about 6 to 50 nucleotides and having a 3′ priming end having a length of between about 6 to 50 nucleotides with a fixed-size template having a length between 101 and about 10,000 nucleotides under reaction conditions conducive to transcribing a unitized transcript from the fixed-size template; and (b) labeling the unitized transcript with at least one detectable molecule, thereby producing a unitized nucleic acid probe.
Owner:SINGULEX
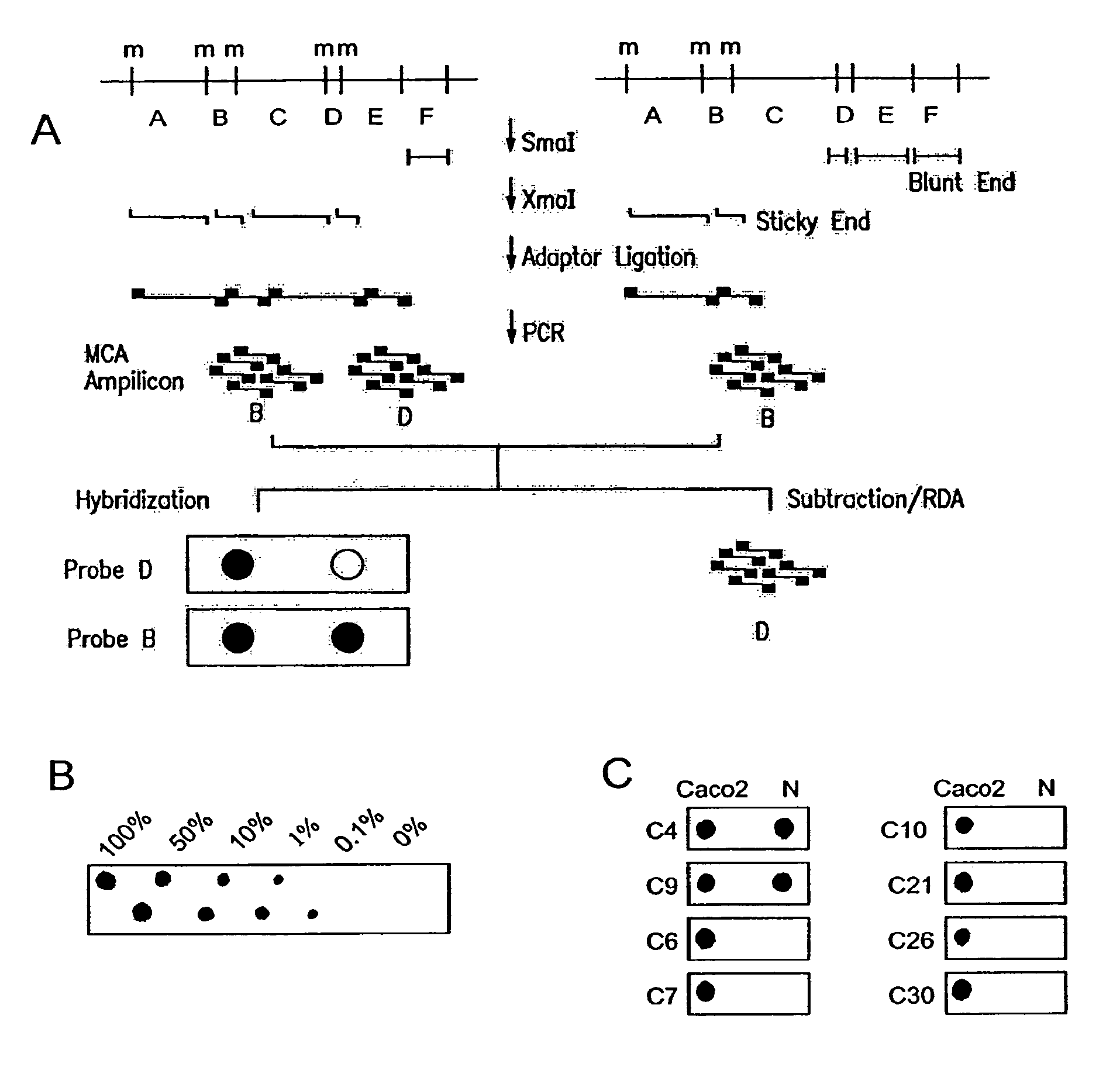
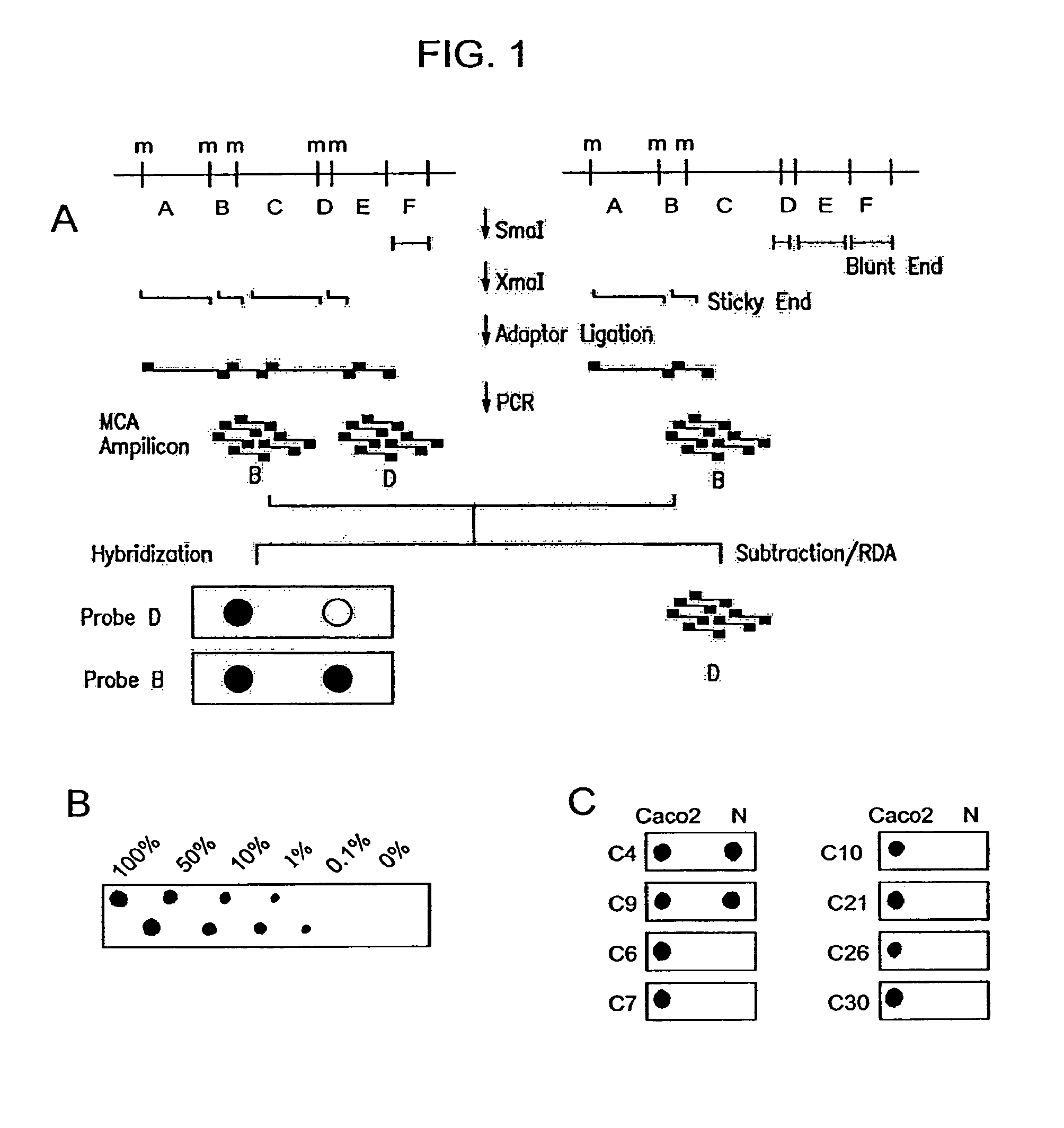
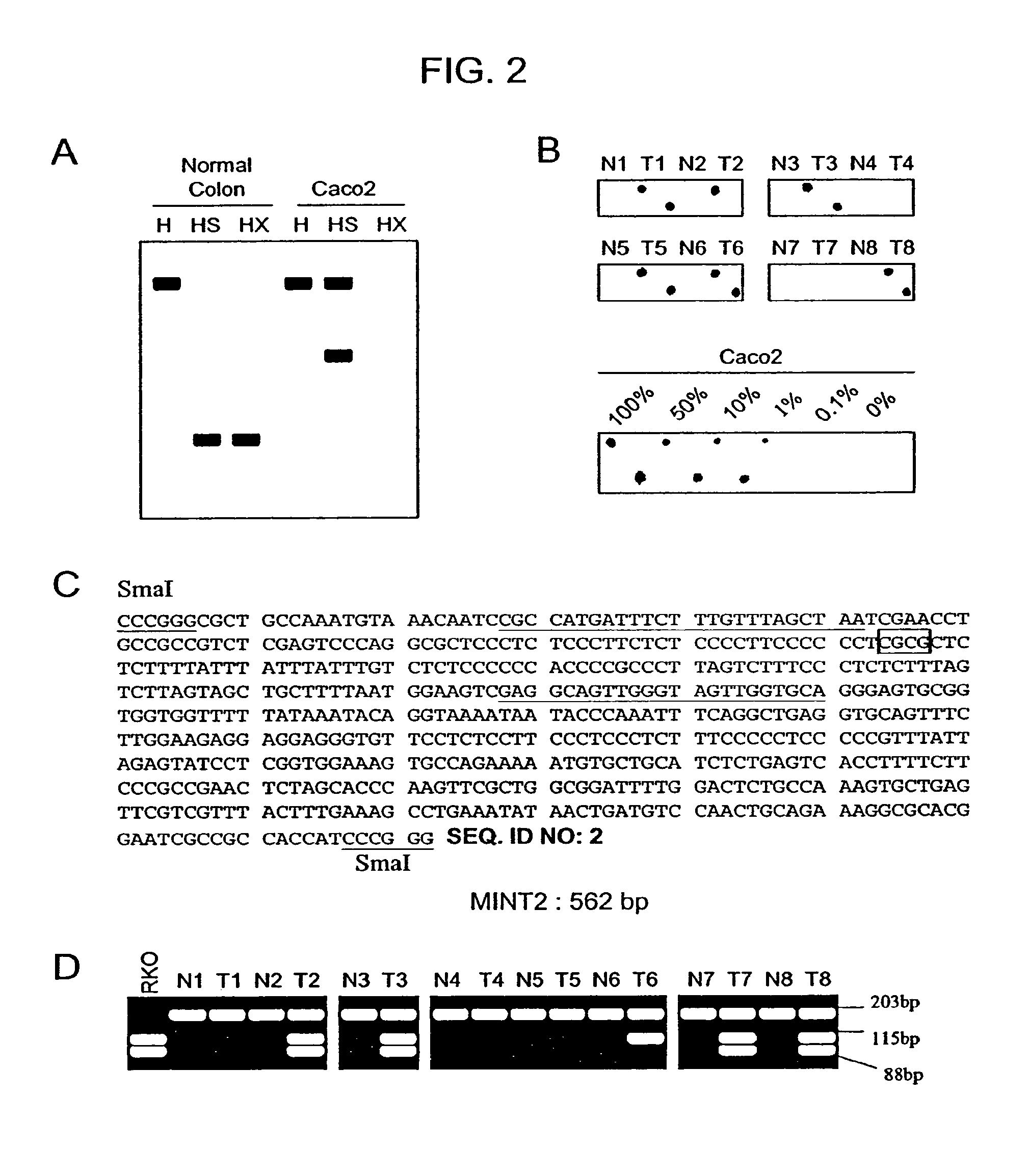
Methylated CpG island amplification (MCA)
The present invention provides a method for identifying a methylated CpG containing nucleic acid by contacting a nucleic acid with a methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease that cleaves unmethylated CpG sites and contacting the sample with an isoschizomer of the methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease, which cleaves both methylated and unmethylated CpG sites. The method also includes amplification of the CpG-containing nucleic acid using CpG-specific oligonucleotide primers A method is also provided for detecting an age associated disorder by identification of a methylated CpG containing nucleic acid. A method is further provided for evaluation the response of a cell to an agent A kit useful for detection of a CpG containing nucleic acid is also provided. Nucleic acid sequences encoding novel methylated clones.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
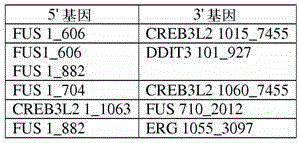
Method for amplification and assay of RNA fusion gene variants, method of distinguishing same and related primers, probes, and kits
Method for amplification, alone or in further combination with detection or detection and quantitation, of RNA from fusion gene variants, method of distinguishing same, and oligonucleotide primers and probes and kits for use in the methods.
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC A CORP ORGANISED & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF DELAWARE
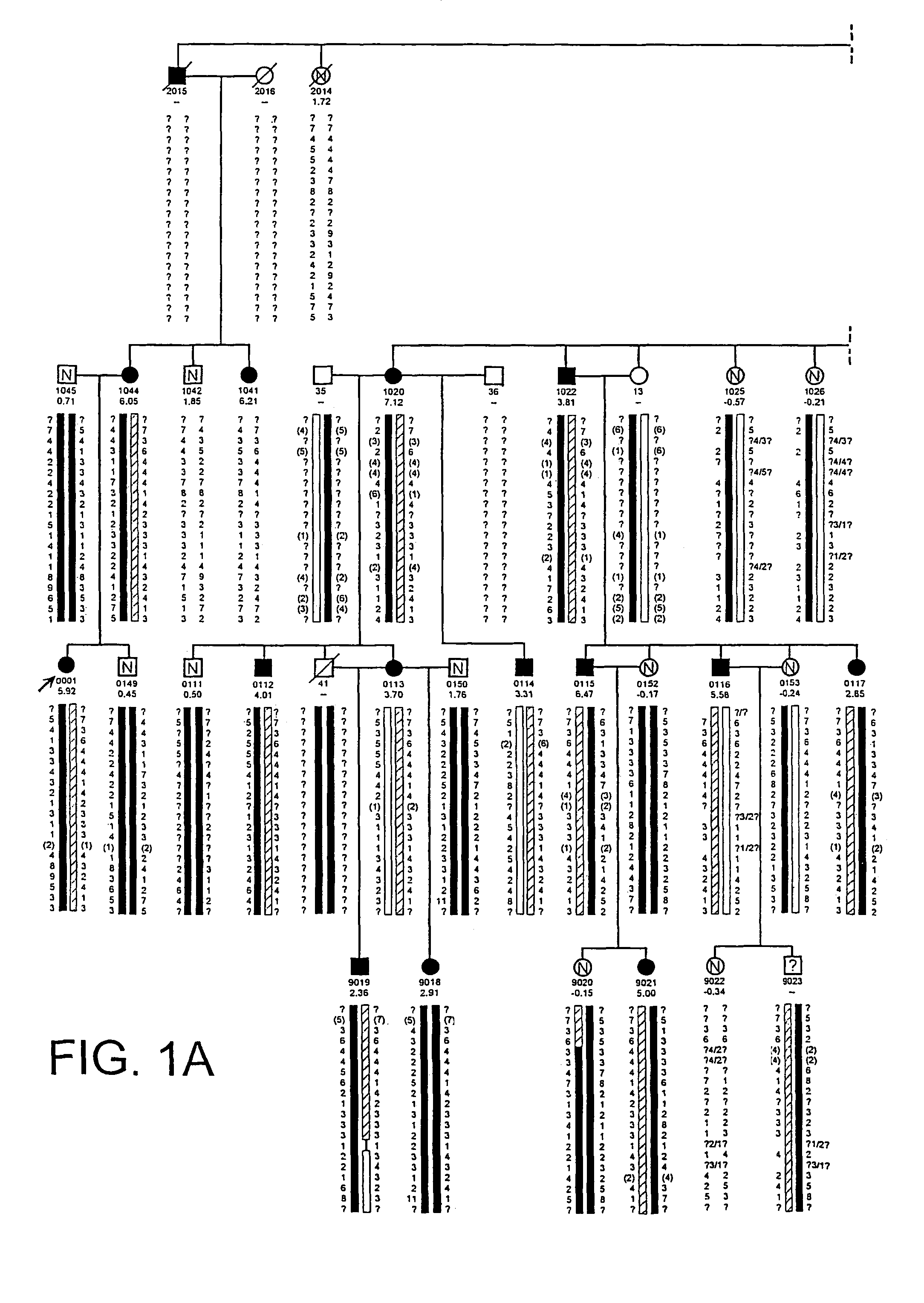
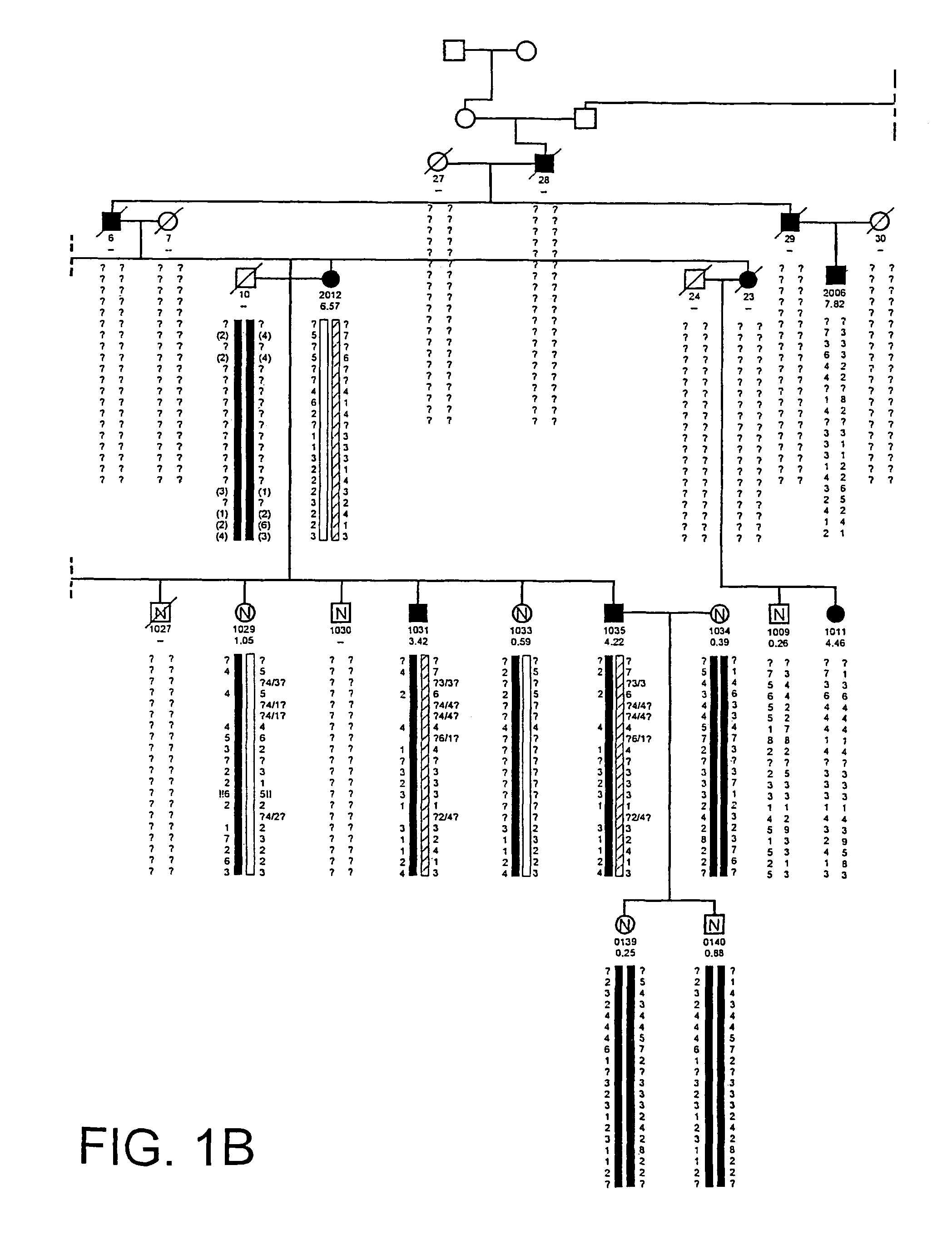
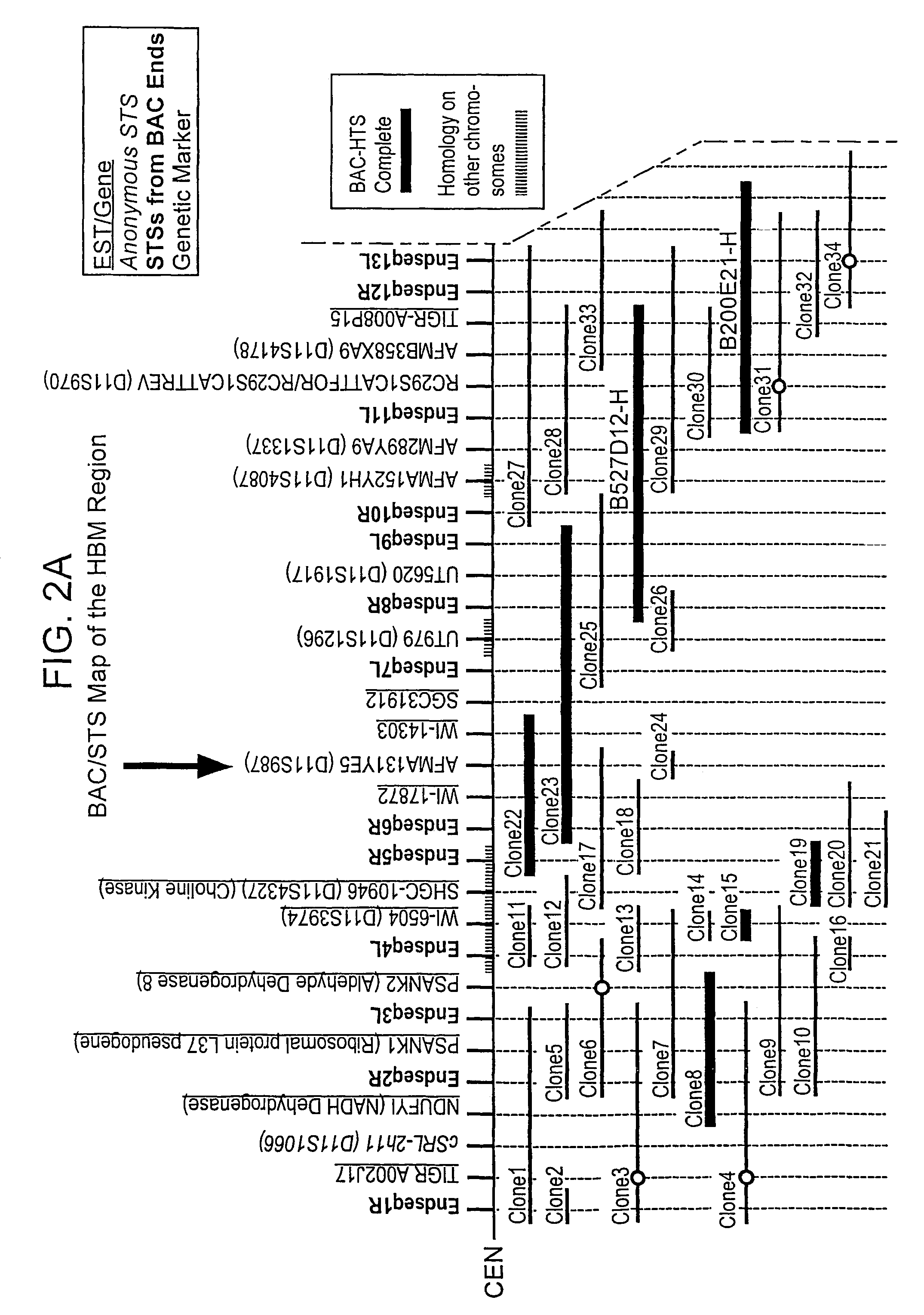
HBM variants that modulate bone mass and lipid levels
The present invention relates to methods and materials used to express an HBM-like polypeptide derived from HBM, LRP5 or LRP6 in animal cells and transgenic animals. The present invention also relates to transgenic animals expressing the HBM-like polypeptides. The invention provides nucleic acids, including coding sequences, oligonucleotide primers and probes, proteins, cloning vectors, expression vectors, transformed hosts, methods of developing pharmaceutical compositions, methods of identifying molecules involved in bone development, and methods of diagnosing and treating diseases involved in bone development and lipid modulation. In preferred embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods for treating, diagnosing and preventing osteoporosis.
Owner:WYETH +1
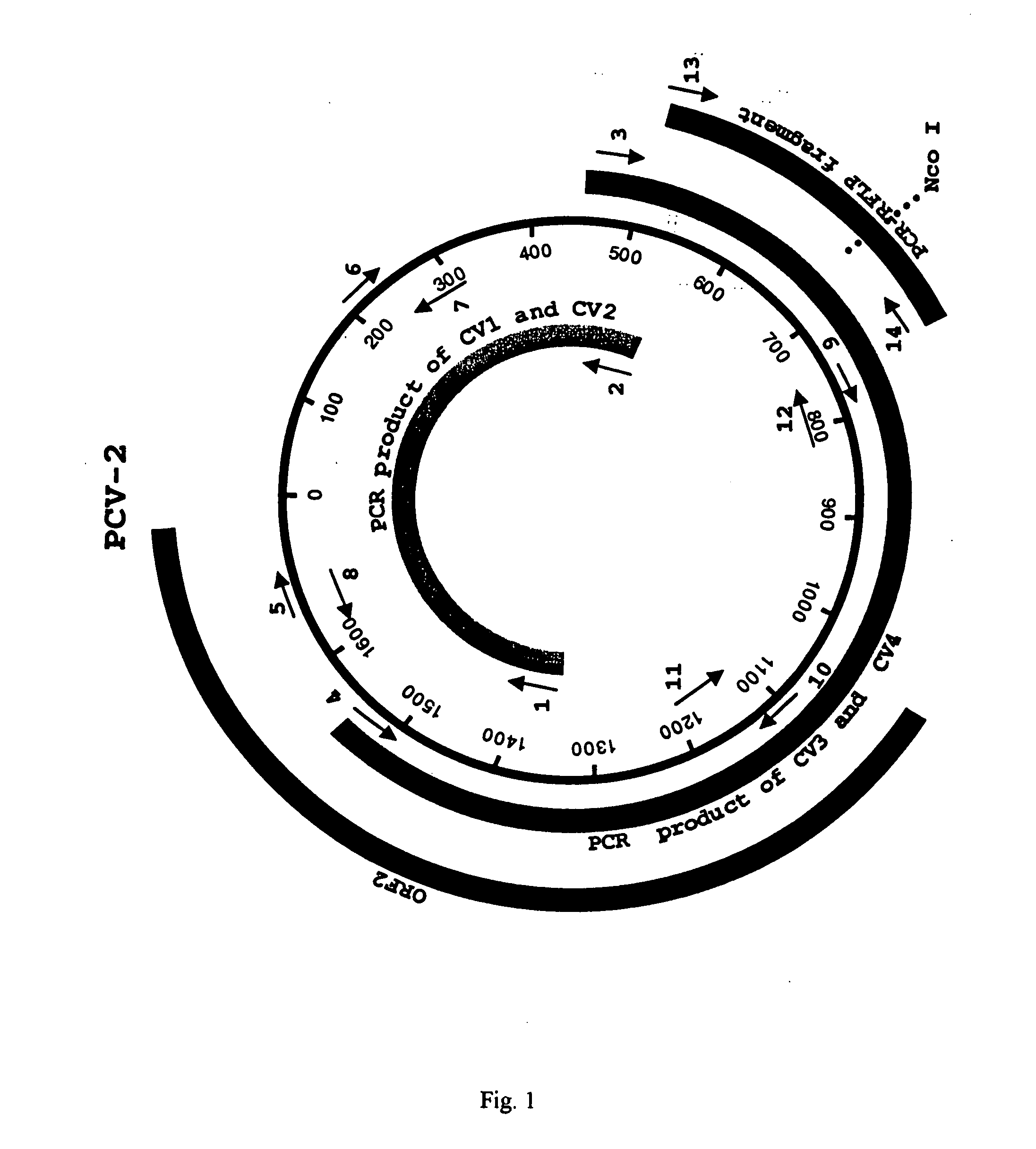
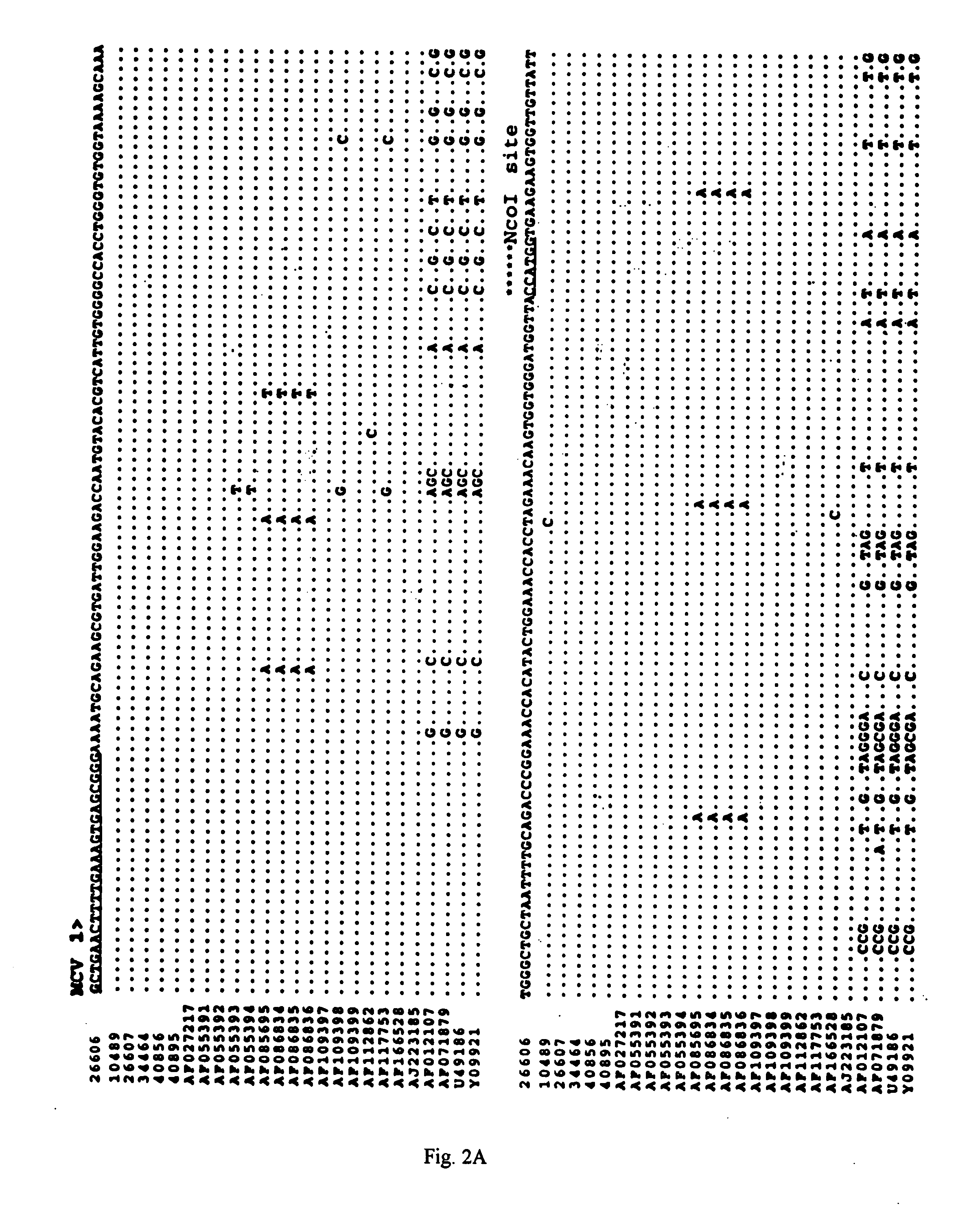
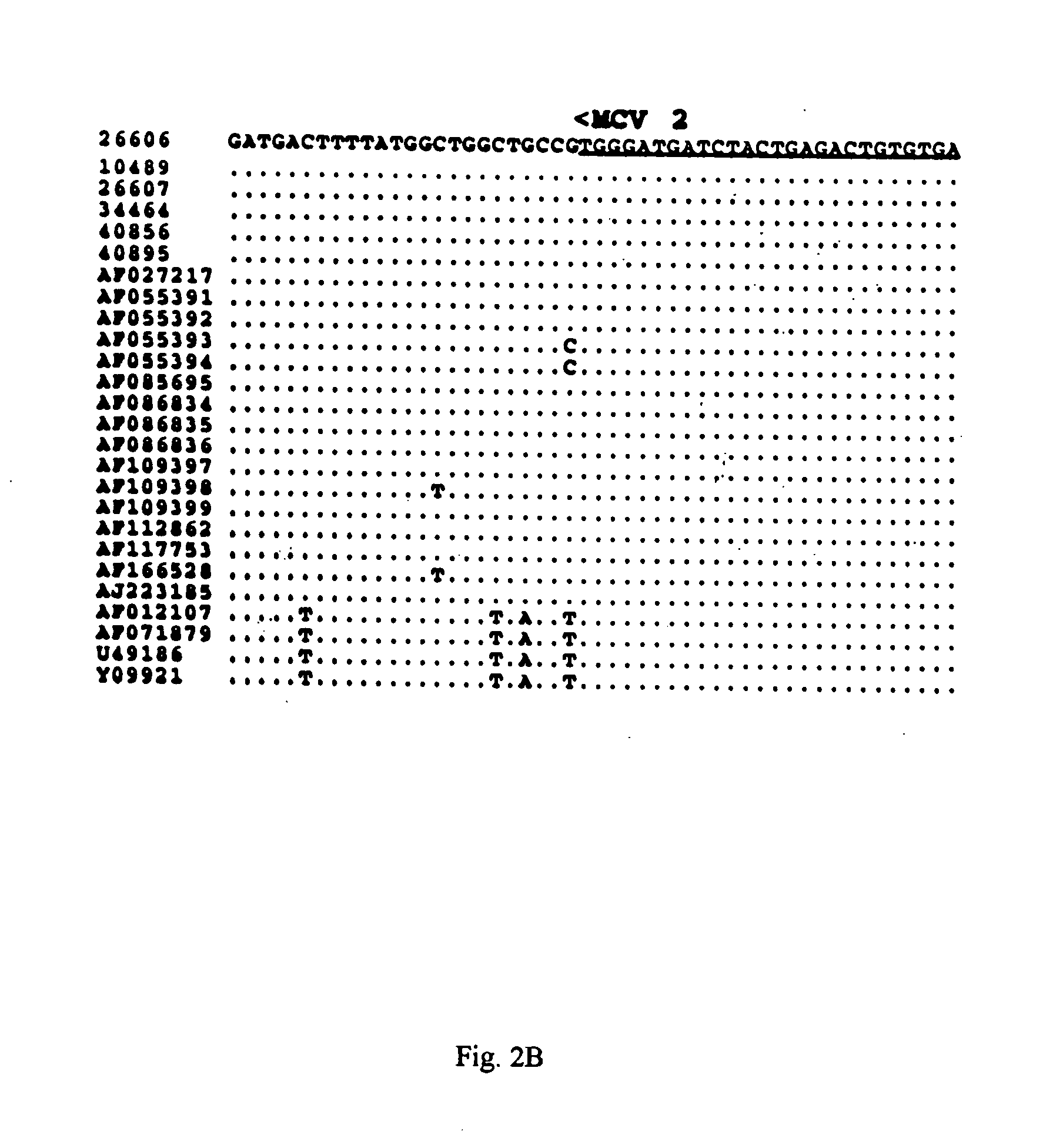
Differential PCR-RFLP assay for detecting and distinguishing between nonpathogenic PCV-1 and pathogenic PCV-2
InactiveUS20050147966A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for detecting and differentiating PCV infections in a biological sample taken from a pig which involves amplifying a fragment from an extracted nucleic acid; digesting the fragment with a suitable restriction enzyme such as the unique NcoI restriction enzyme; forming a restriction fragment length polymorphism pattern; and then detecting the presence or absence of a PCV isolate. The invention further concerns the new oligonucleotide primers for differentiating PCV infections comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of MCV1 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 and MCV2 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:2. Moreover, this invention provides a novel kit for detecting and distinguishing PCV infections that includes the new oligonucleotide primers and the suitable restriction enzyme.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Compositions for use in identification of orthopoxviruses
InactiveUS20060275749A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersRapid identification
Oligonucleotide primers and compositions and kits containing the same for rapid identification of orthopoxviruses by amplification of a segment of viral nucleic acid followed by molecular mass analysis are provided.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Isothermal chimeric primer nucleic acid amplification methods using blocking oglionucleotide
InactiveUS7056671B2Improve targeting efficiencyHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LRibonucleotide synthesis
Methods of amplifying a target nucleic acid whereby the target nucleic acid is amplified in the presence of a deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate, a DNA polymerase having strand displacement activity, at least one chimeric oligonucleotide primer, at least one upstream block oligonucleotide and a RNase H; wherein the chimeric oligonucleotide primer contains a ribonucleotide positioned at the 3′-terminus; wherein the upstream block oligonucleotide is capable of annealing to a region 3′ to a portion in the nucleic acid as the template to which the chimeric oligonucleotide primer anneals; and compositions and kits thereof.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Quantitative methylation detection in DNA samples
InactiveUS20030148290A1Quick fixFast and cost-effective and accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyPolymerase LGenomic DNA
Described is a method for methylation detection in a DNA sample. An isolated genomic DNA sample is treated in a manner capable of distinguishing methylated from unmethylated cytosine bases. The pretreated DNA is amplified using at least one oligonucleotide primer, a polymerase and a set of nucleotides of which at least one is labeled with a first type of label. A sequence-specific oligonucleotide probe, marked with a second type of label, hybridizes to the amplification product and a FRET reaction occurs if a labeled oligonucleotide is present in close proximity in the amplification product. The method determines the level of methylation of a sample by measuring the extent of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between the donor and acceptor fluorophore.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Isothermal amplification of DNA
InactiveUS20050164213A1Low toxicityImprove expression levelMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyOligonucleotide PrimerA-DNA
A method of amplifying a template DNA molecule comprising incubating the template DNA molecule in a reaction mixture comprising a DNA polymerase and at least one accessory protein at a constant temperature to produce amplified product, wherein production of amplified product does not require exogenously-added oligonucleotide primers and the template DNA molecule does not have have terminal protein covalently bound to either 5′ end.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for amplifying nucleic acid sequence
A convenient and effective method for amplifying a nucleic acid sequence characterized by effecting a DNA synthesis reaction in the presence of chimeric oligonucleotide primers; a method for supplying a large amount of DNA amplification fragments; an effective method for amplifying a nucleic acid sequence by combining the above method with another nucleic acid sequence amplification method; a method for detecting a nucleic acid sequence for detecting or quantitating a microorganism such as a virus, a bacterium, a fungus or a yeast; and a method for detecting a DNA amplification fragment obtained by the above method in situ.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
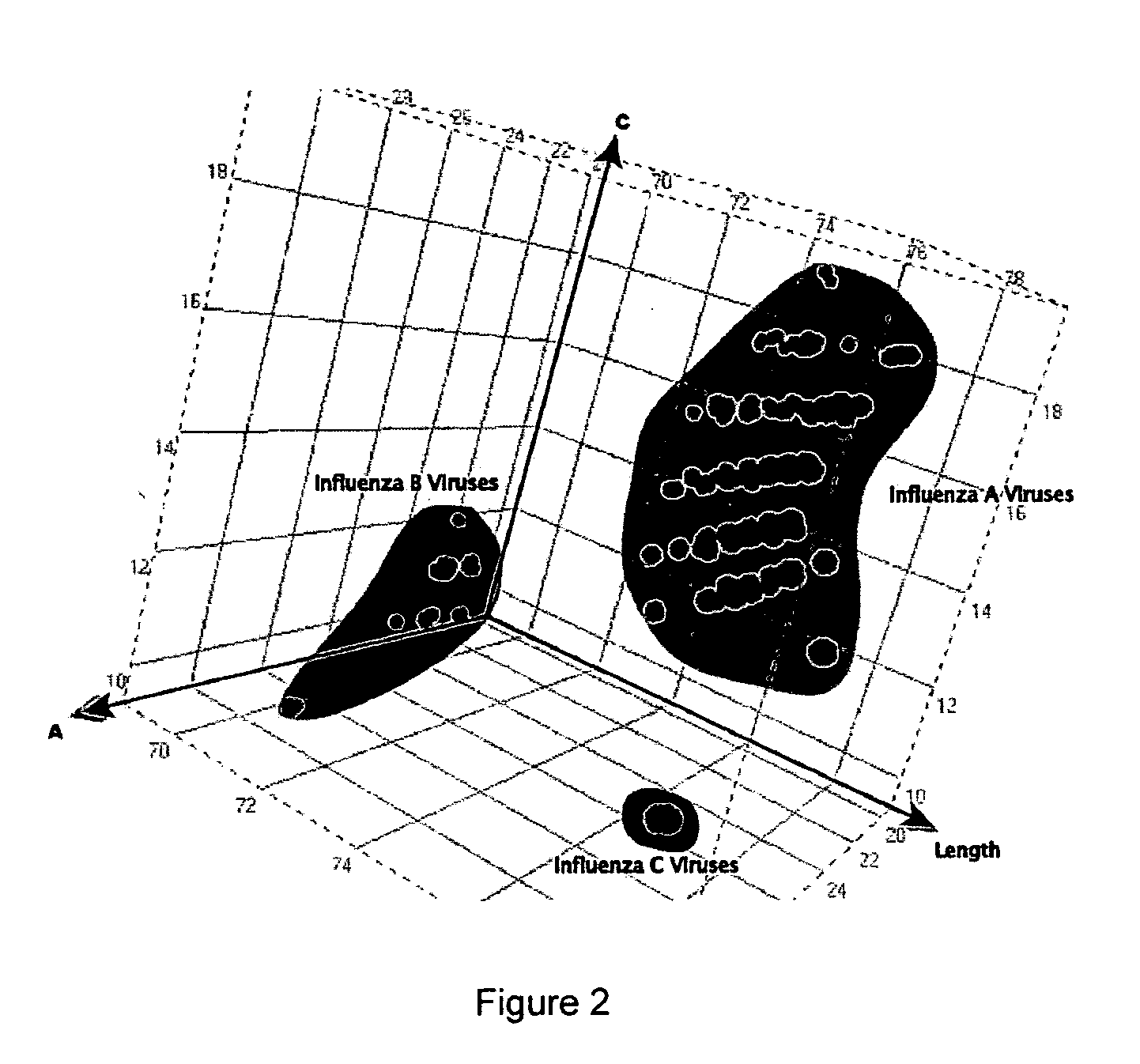
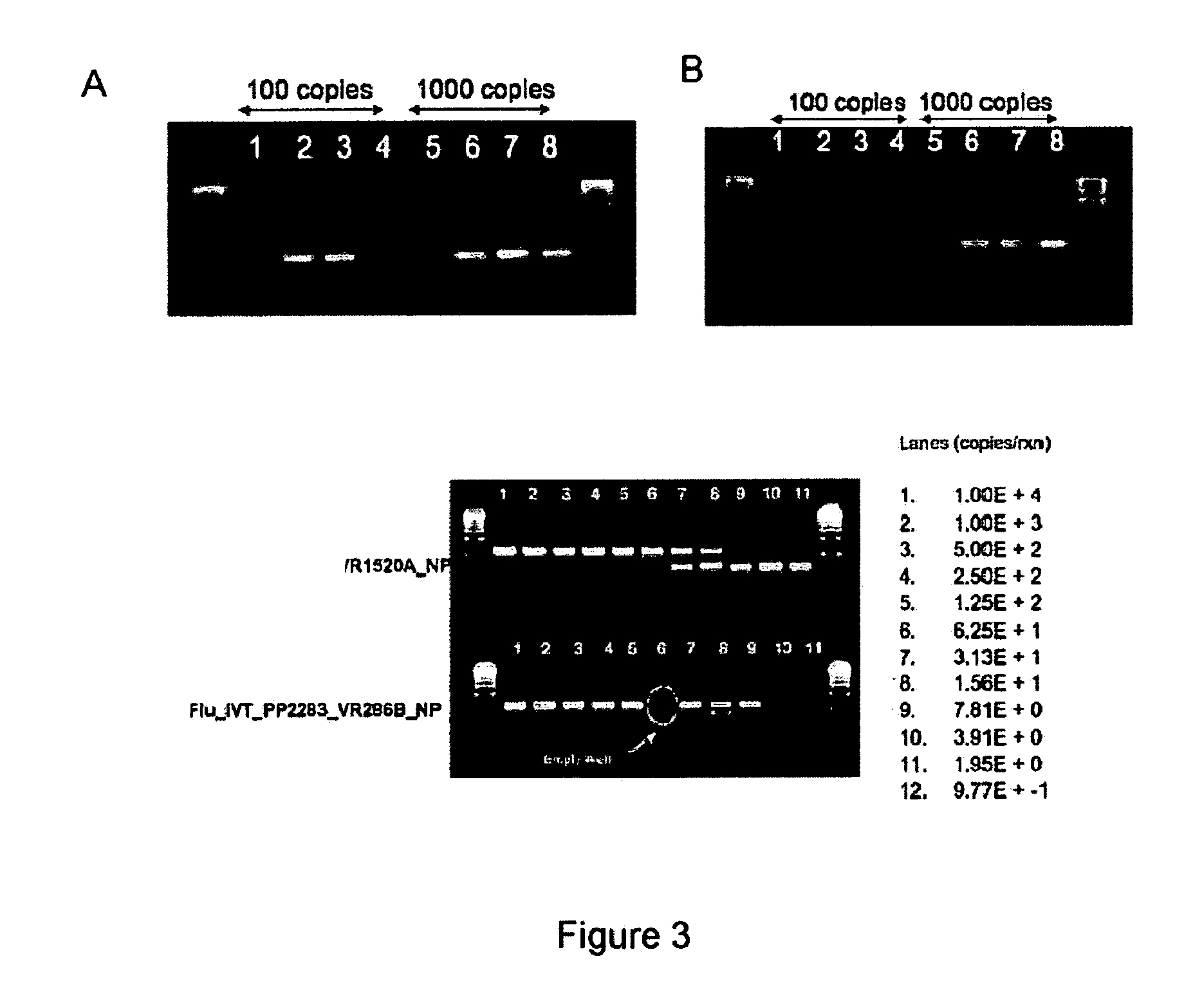
Compositions for use in identification of influenza viruses
InactiveUS20070184434A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersRapid identification
The present invention provides oligonucleotide primers, compositions, and kits containing the same for rapid identification of viruses which are members of the influenza virus family by amplification of a segment of viral nucleic acid followed by molecular mass analysis.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Nucleic acid amplification using nicking agents
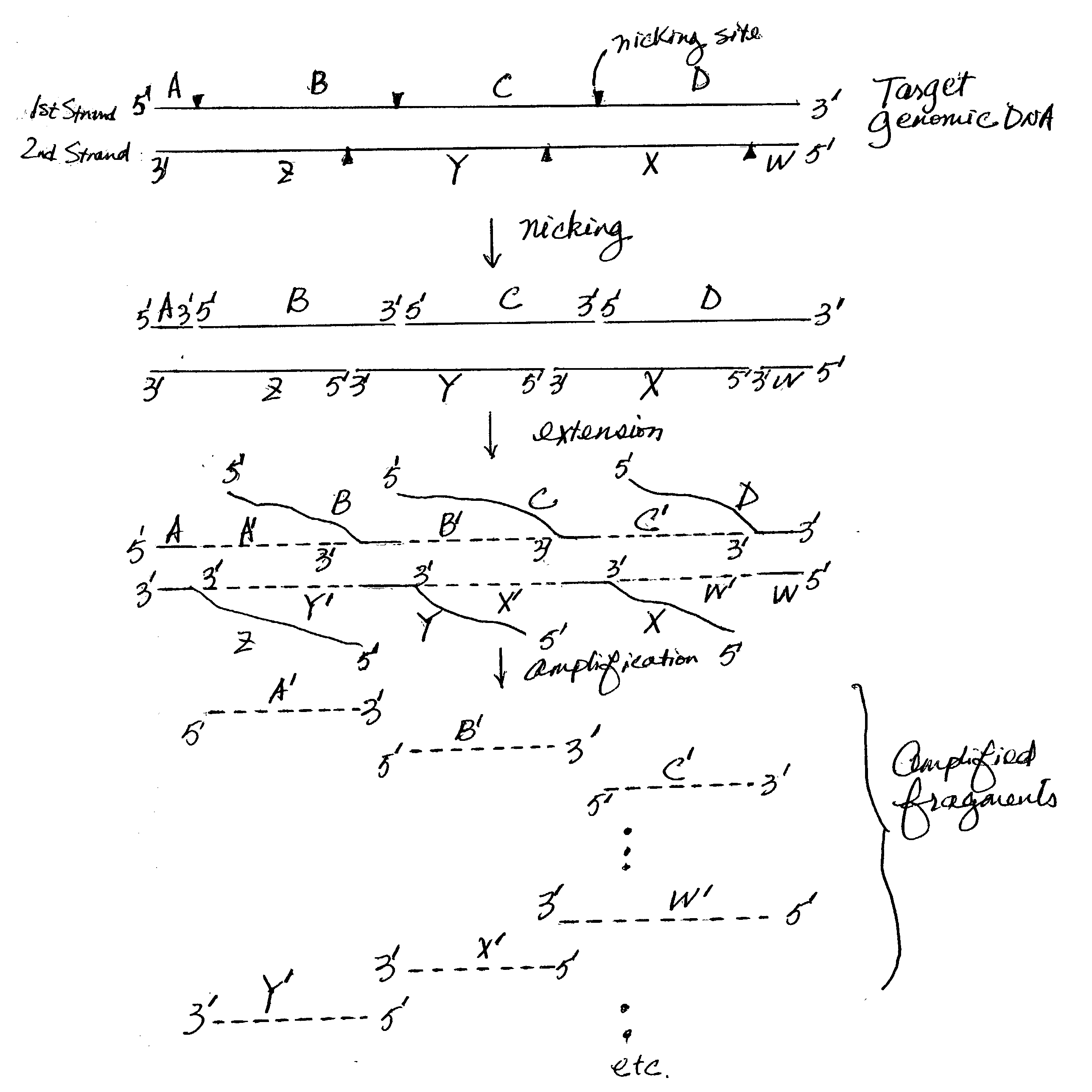
The present invention provides methods and kits for amplifying target nucleic acids (including whole genomes) using nicking agents. In certain aspects, the amplification does not require the use of any external oligonucleotide primers that are capable of annealing to a portion of the target nucleic acid. This invention is useful in many areas such as genetic disease diagnoses, forensic analyses and palcoarcheological studies.
Owner:KECK GRADUATE INST OF APPLIED LIFE SCI
Oligonucleotides for detection of Bacillus cereus group bacteria harmful to mammals, and method of detection with the oligonucleotides
A method of detection is provided that permits differentiation of each of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis from other microorganisms, using oligonucleotide primers for amplification of the target nucleotide sequences characteristic to Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis, consisting of the oligonucleotide (A) having a nucleotide sequence obtained from SEQ ID NO:1 and containing at least one site that can amplify a nucleotide sequence characteristic to Bacillus cereus, the oligonucleotide (B) having a nucleotide sequence obtained from SEQ ID NO:3 and containing at least one site that can amplify a nucleotide sequence characteristic to Bacillus thuringiensis, and the oligonucleotide (C) having a nucleotide sequence obtained from SEQ ID NO:5 and containing at least one site that can amplify a nucleotide sequence characteristic to Bacillus anthracis. Also provided are a method of detection of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a primer specific to the DNA gyrase sub-unit B (gyrB) gene and a method of detection of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis in a sample by differentiation on the genetic level.
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
Detection of fungal pathogens
Unique DNA sequences are provided which are useful in identifying different pathogenic fungi, such as those which infect grape plants. These unique DNA sequences can be used to provide oligonucleotide primers in PCR based analysis for the identification of fungal pathogens. The DNA sequences of the present invention include the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of the ribosomal RNA gene regions of particular fungal pathogens, as well as oligonucleotide primers which are derived from these regions which are capable of identifying the particular pathogen.
Owner:E & J GALLO WINERY
Detection of fermentation-related microorganisms
InactiveUS6248519B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismOligonucleotide primers
DNA sequences are provided which are useful in identifying different fermentation-related microorganisms, such as those involved in fermentations. These DNA sequences can be used to provide oligonucleotide primers in PCR based analysis for the identification of fermentation-related microorganisms. The DNA sequences of the present invention include the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of the ribosomal RNA gene regions of particular fermentation-related microorganisms, as well as oligonucleotide primers which are derived from these regions which are capable of identifying the particular microorganism.
Owner:E & J GALLO WINERY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com