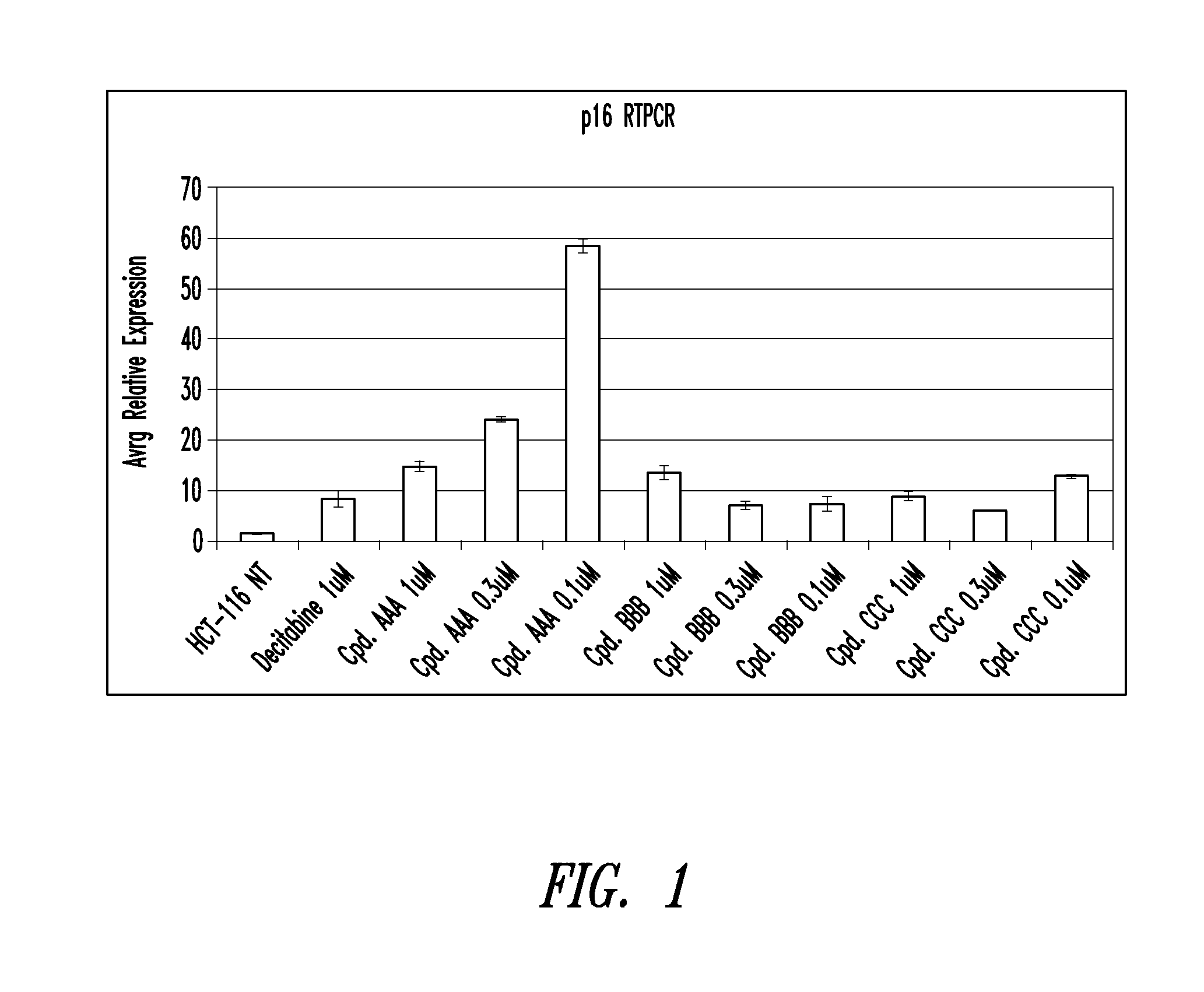
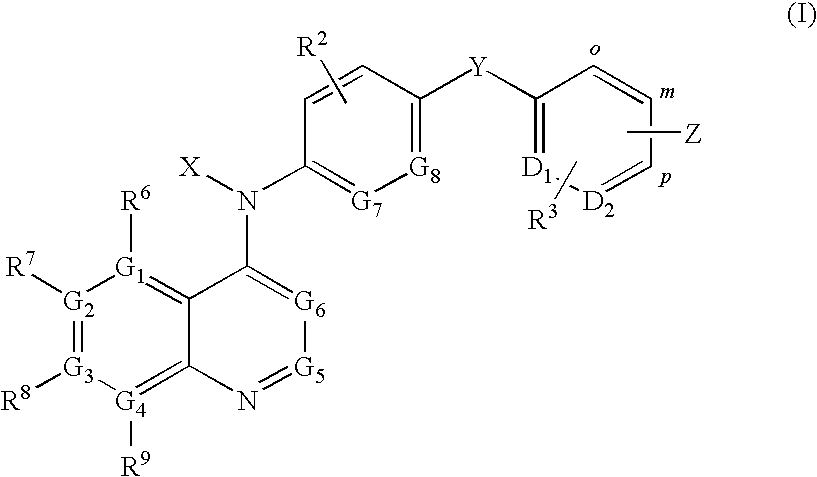
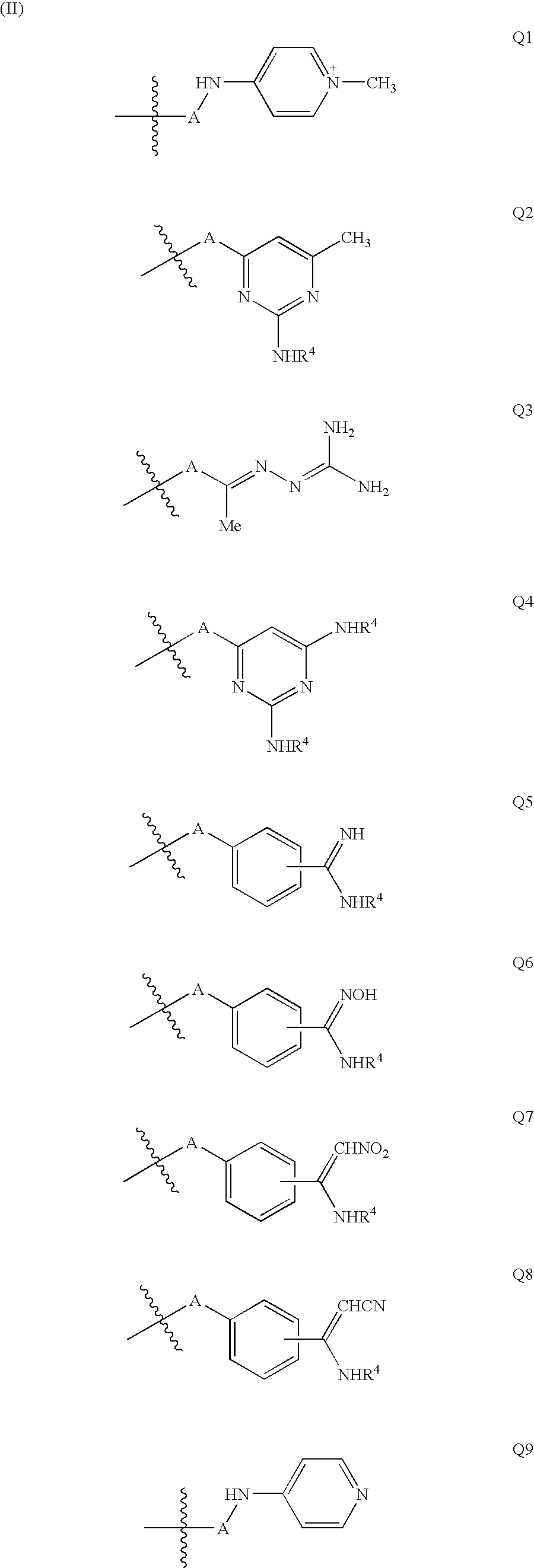
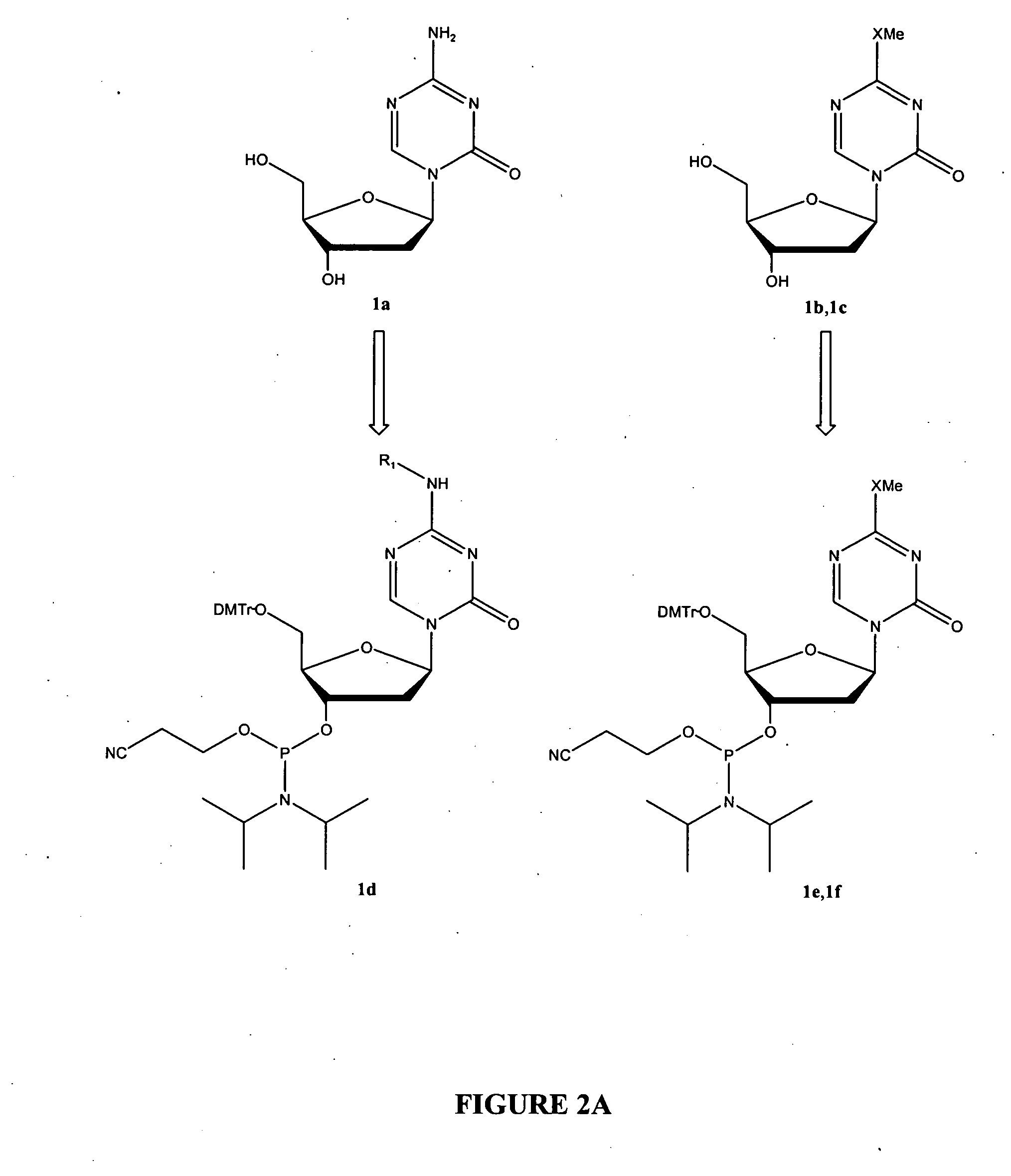
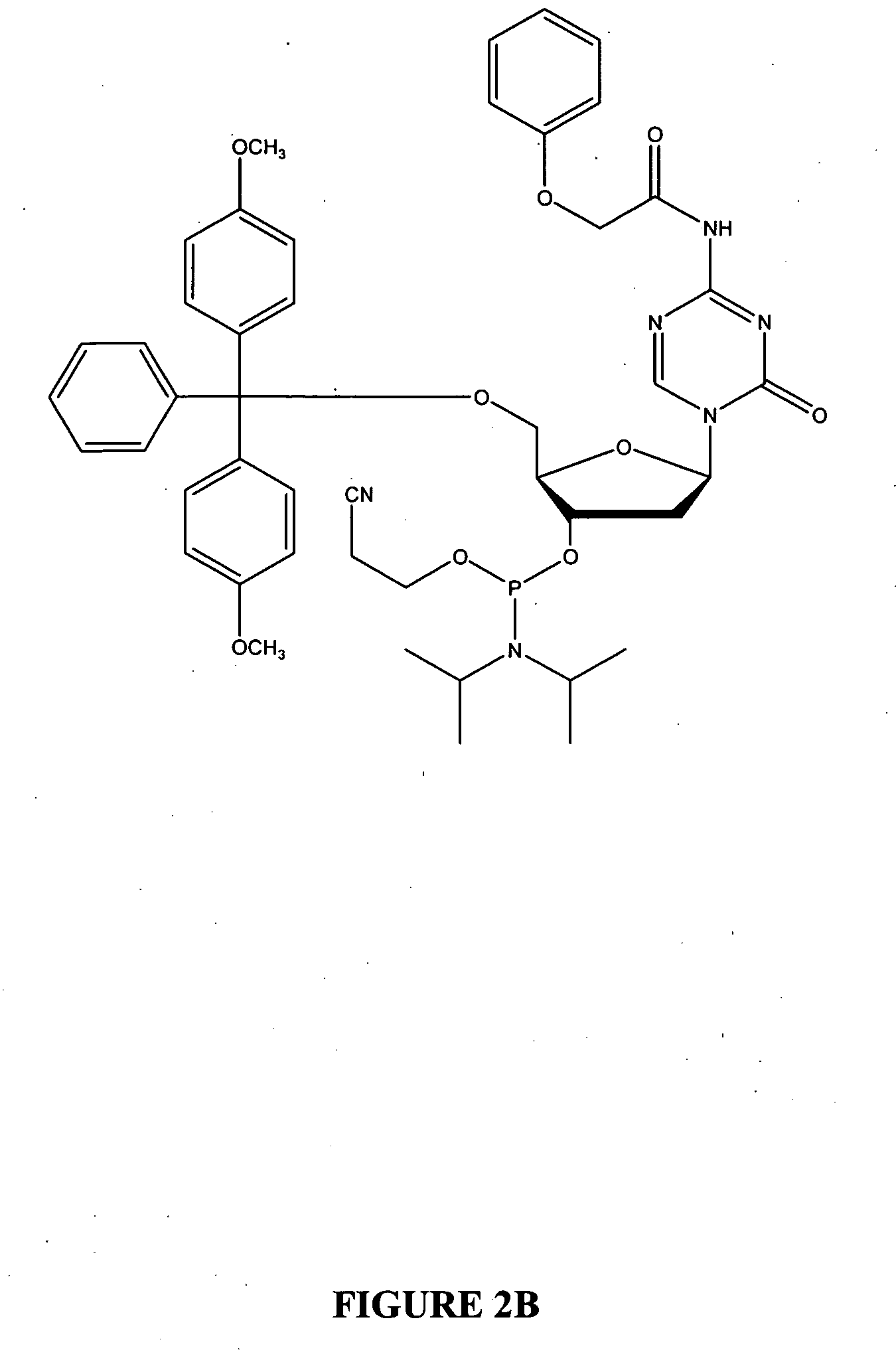
Patents
Literature
990 results about "Cytosine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
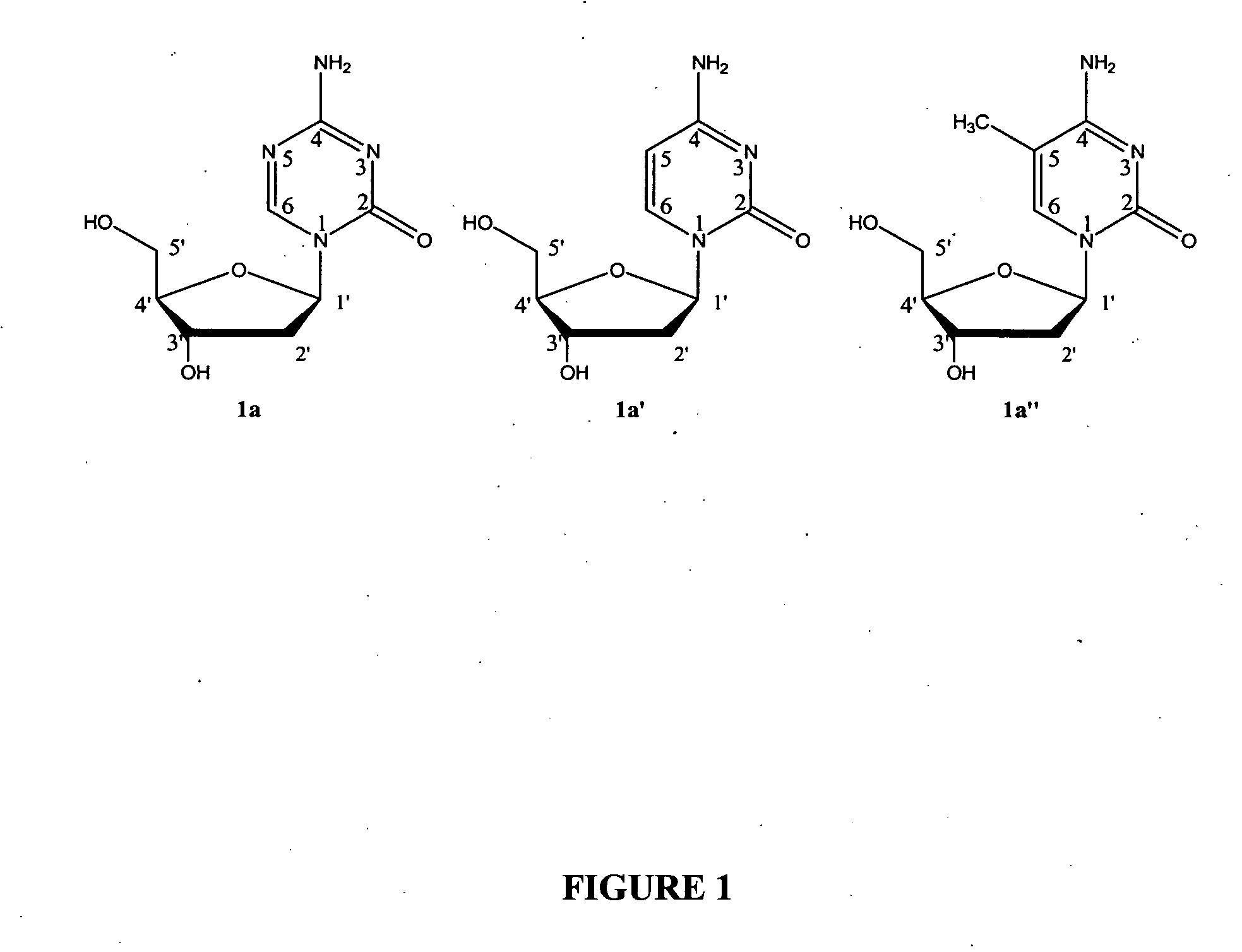
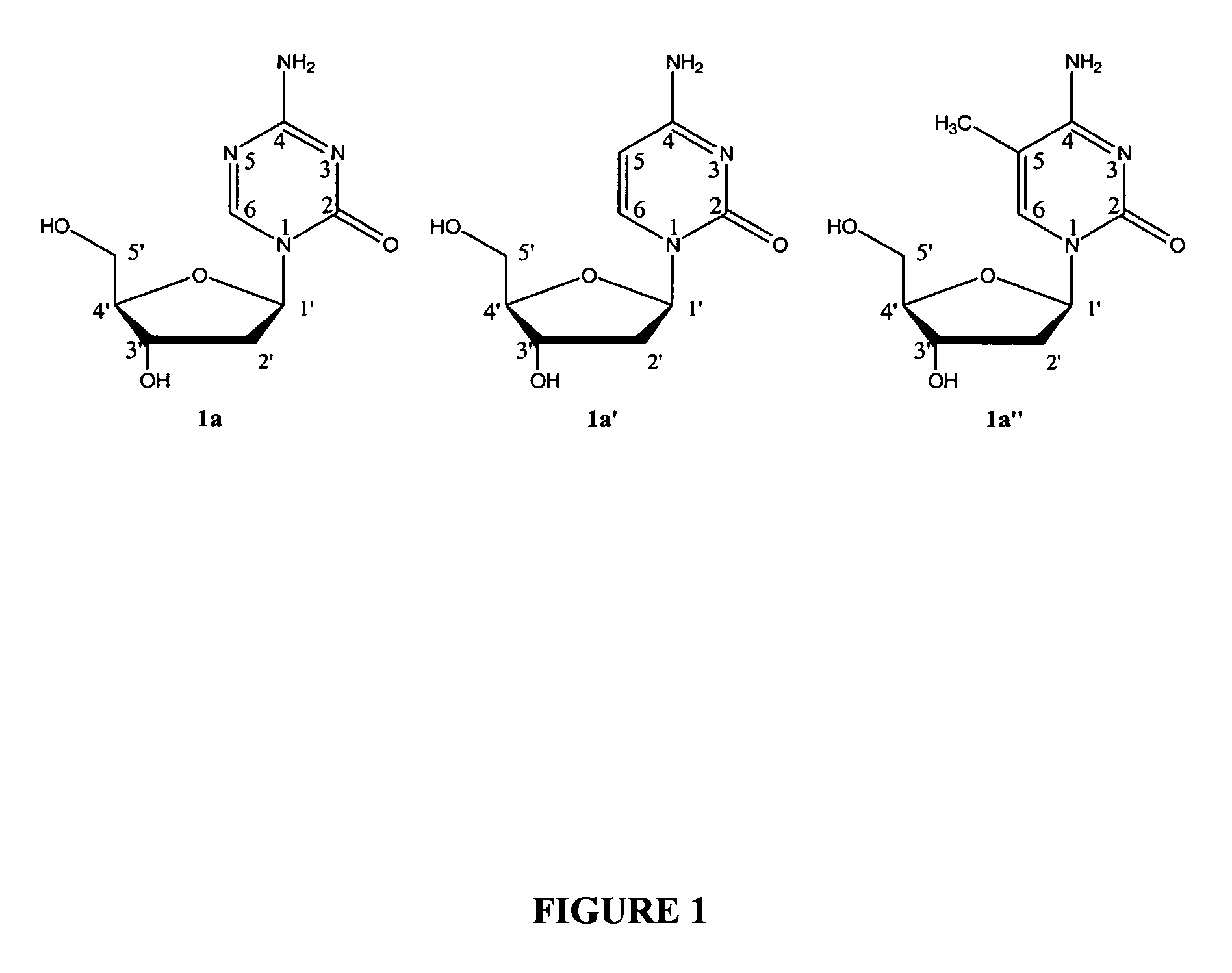
Cytosine (/ˈsaɪtəˌsiːn, -ˌziːn, -ˌsɪn/; C) is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached (an amine group at position 4 and a keto group at position 2). The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine.
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20080113351A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
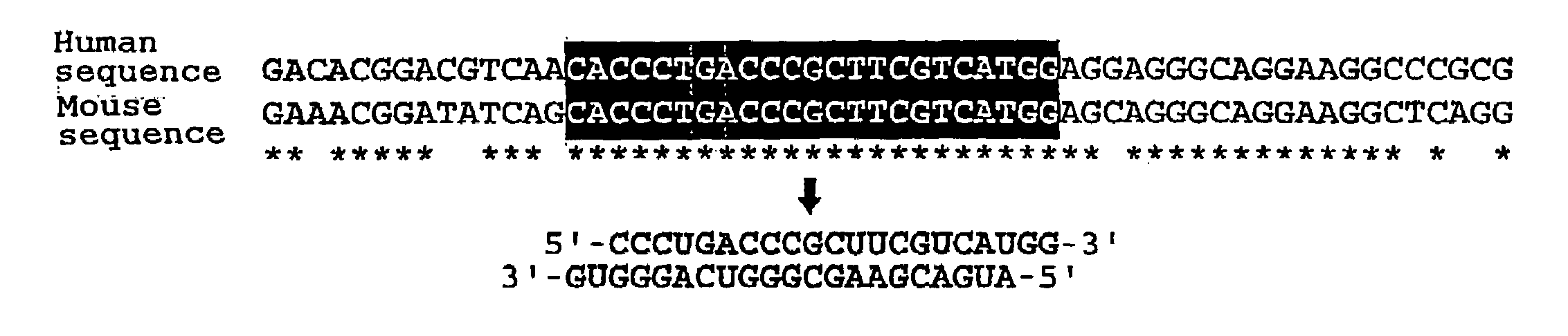
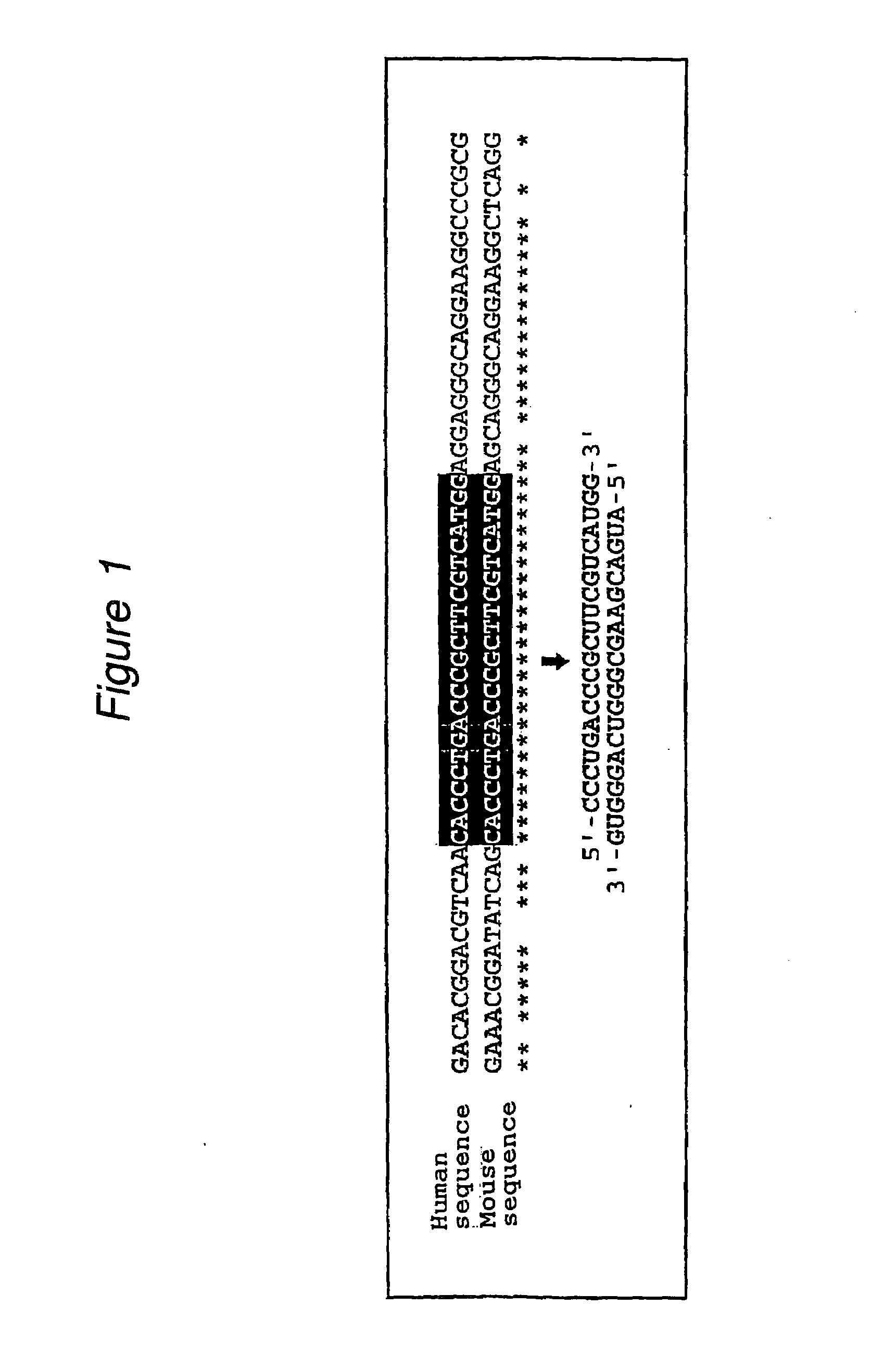
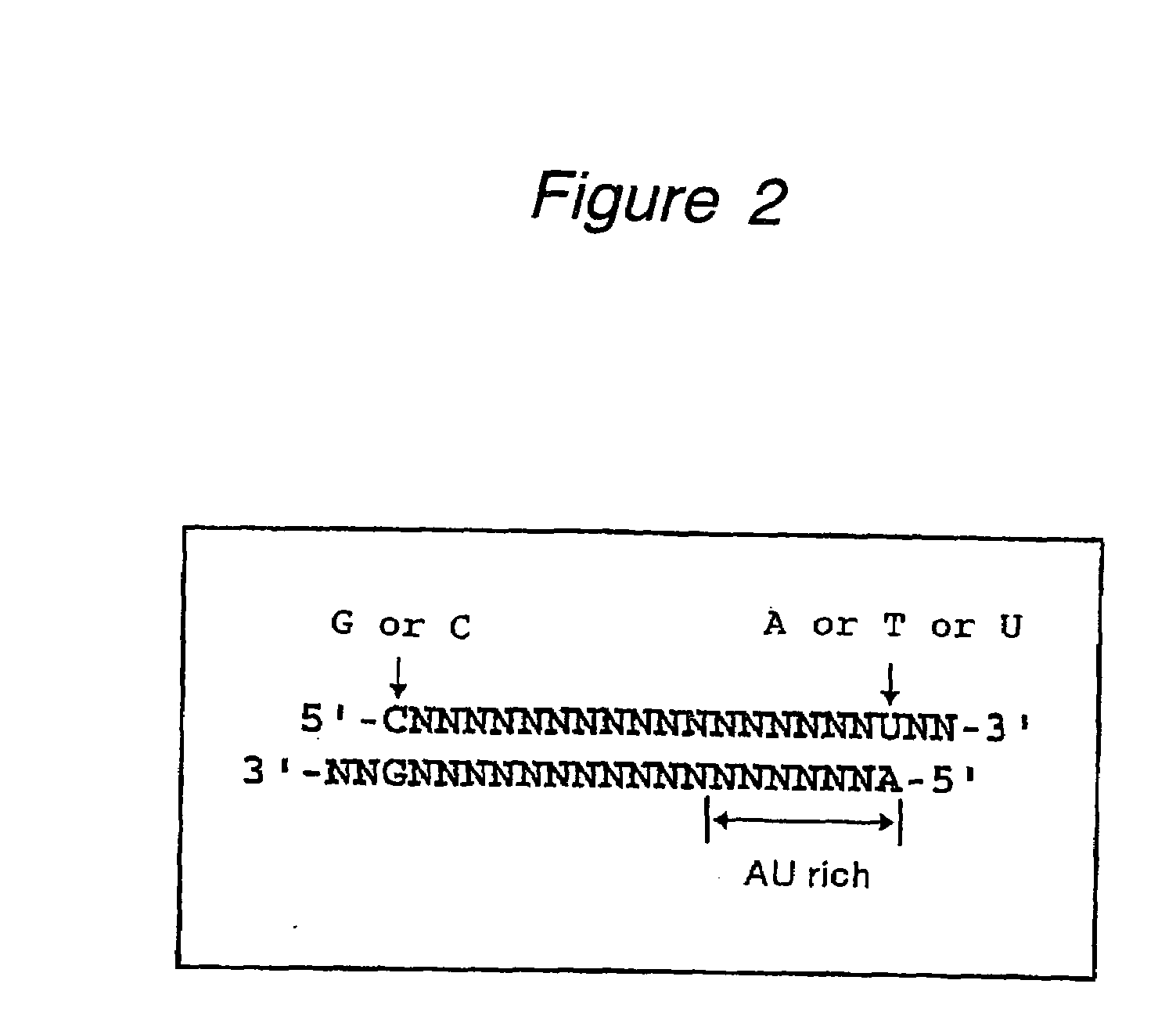
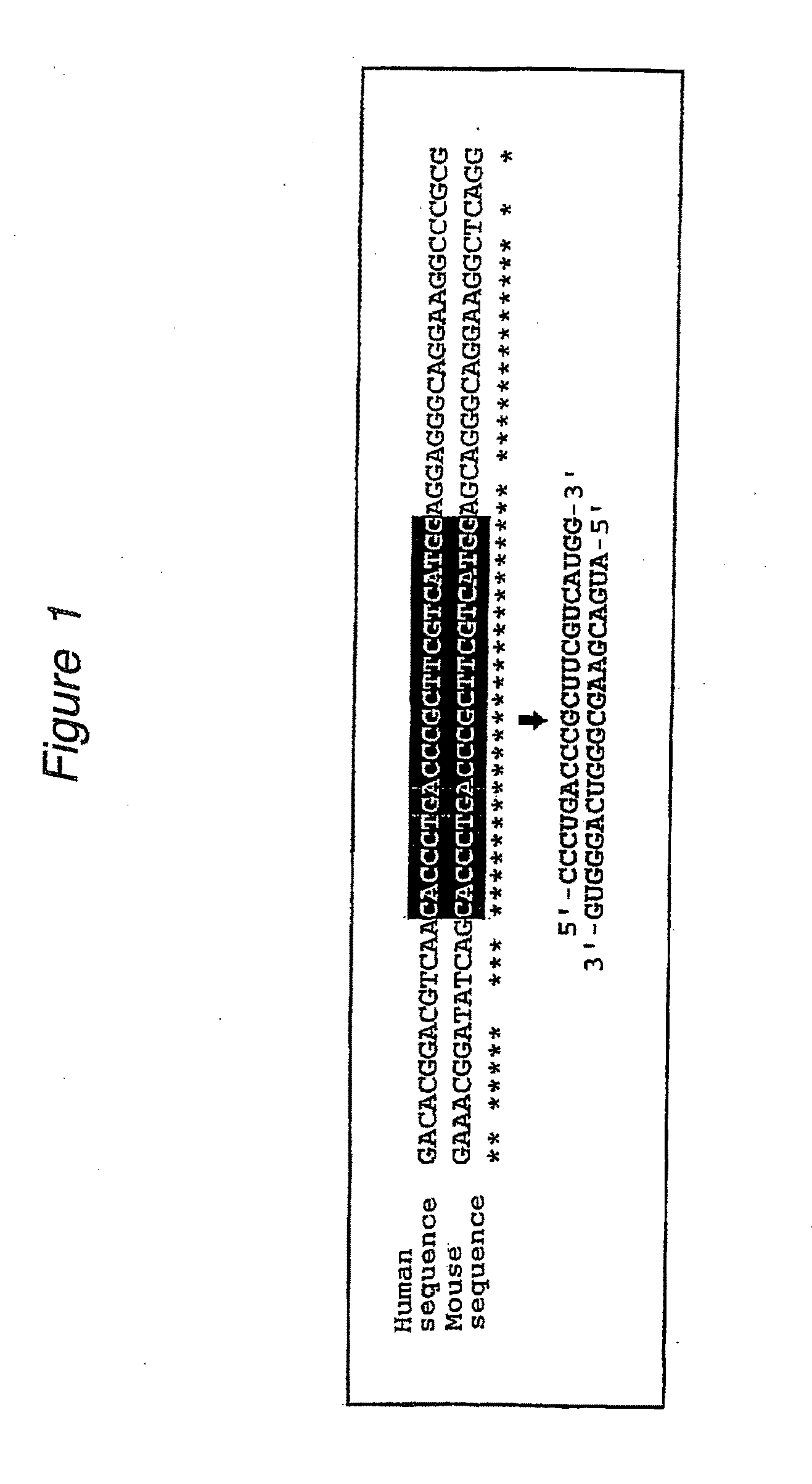
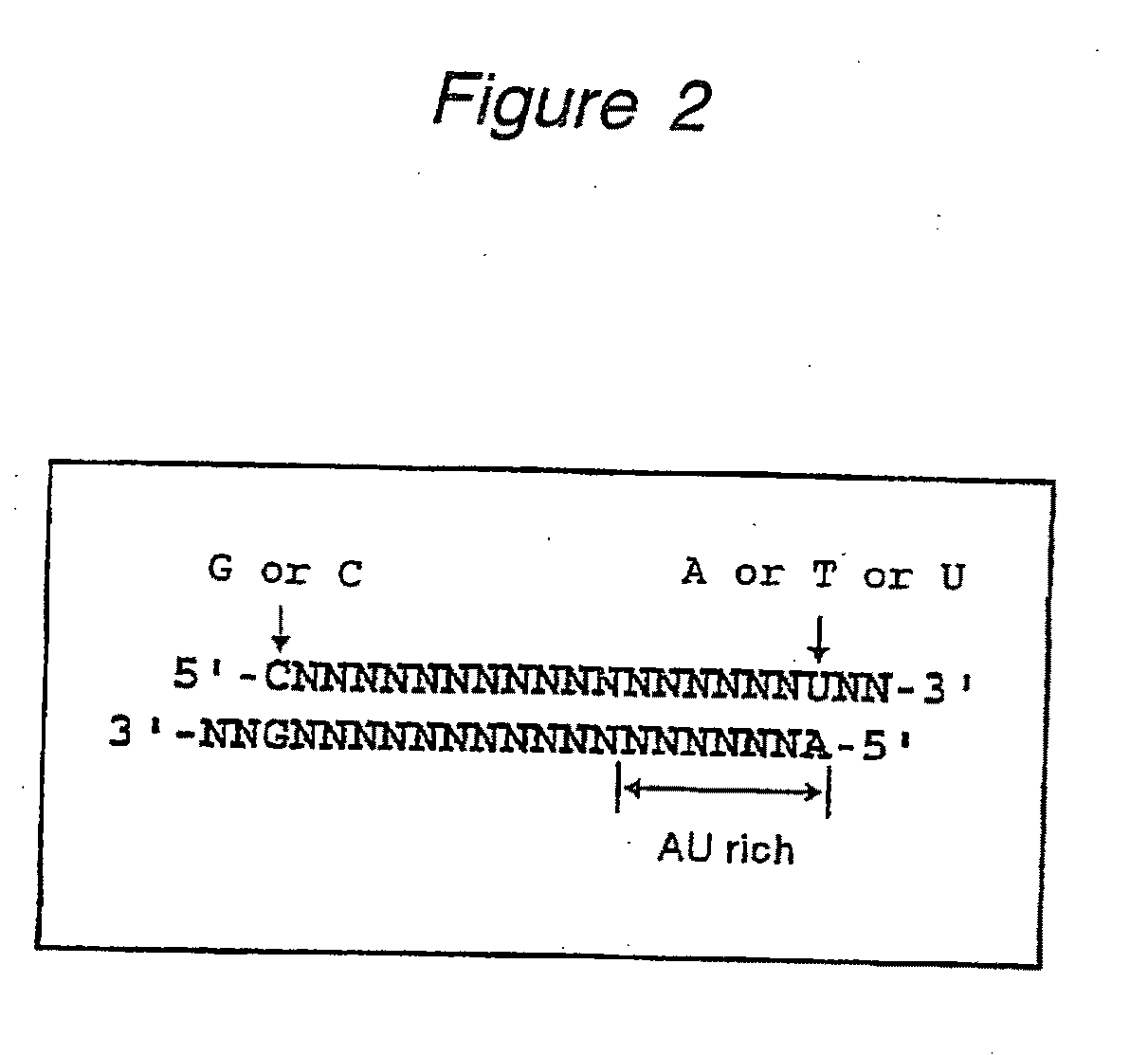
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:ALPHAGEN
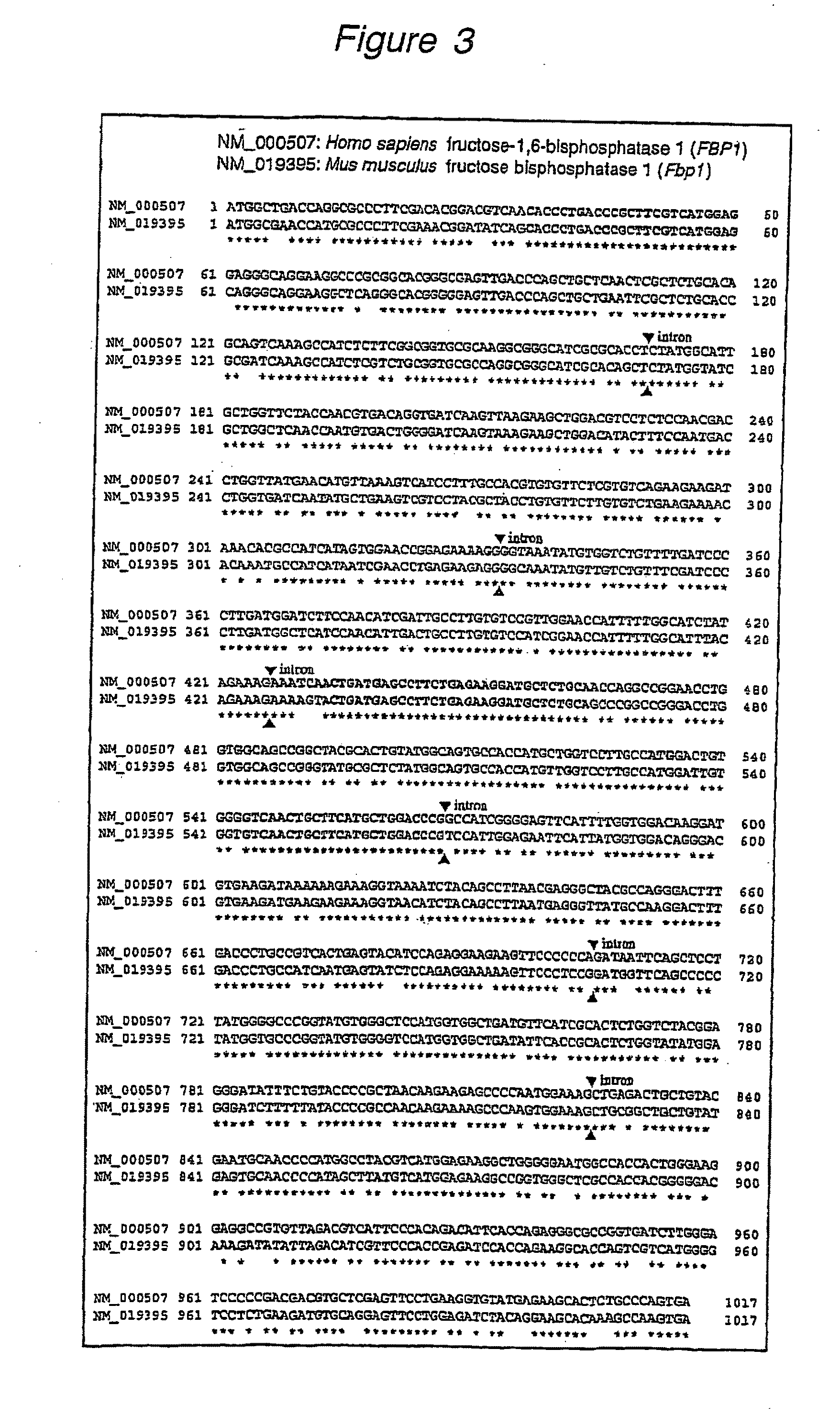
Method for the development of gene panels for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes based on the expression and methylation status of the genes
InactiveUS20020137086A1Fast and reliable diagnosis and therapyPowerful toolBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderCytosineTherapeutic intent
A method for the development of gene panels for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes comprising the steps of: (a) isolating at least one biological sample from each of at least two groups of biological material containing mRNA and / or proteins; (b) analyzing the expression level of at least one gene in the at least one biological sample; (c) selecting the gene(s) exhibiting a different expression level between the at least two groups of biological material, whereby a first knowledge base is generated; (d) analyzing the level of cytosine methylation in the methylation relevant regions of at least one gene of at least one of the biological samples of step (a), wherein the gene is selected on the basis of the first knowledge base; (e) selecting the gene(s) exhibiting a different level of cytosine methylation between the at least two groups of biological material, whereby a second knowledge base is generated; and (f) adding selected genes from the second knowledge base to a gene panel.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
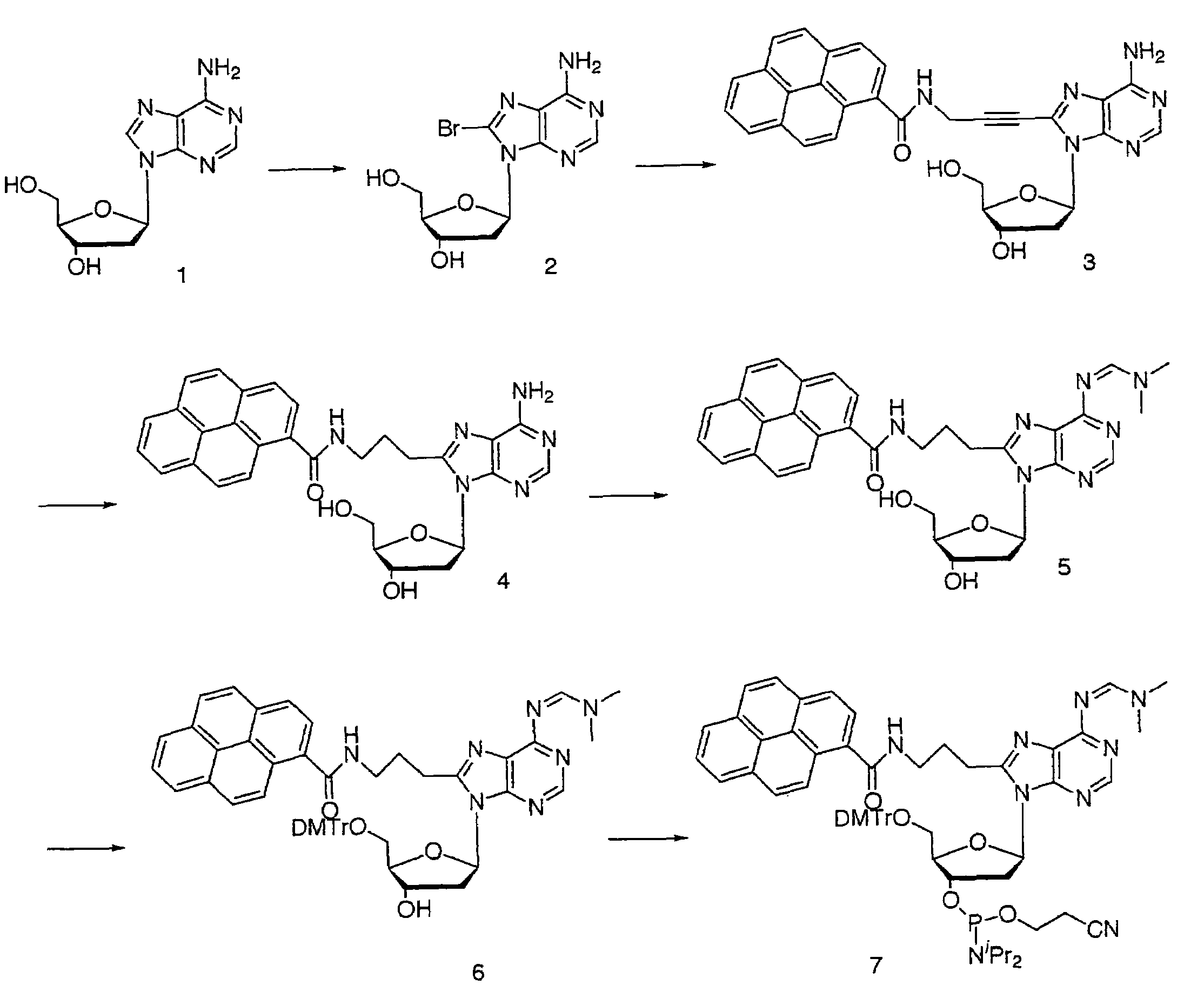
Substituted nucleosides, preparation thereof and use as inhibitors of RNA viral polymerases
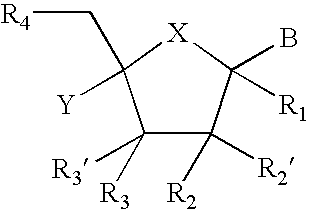
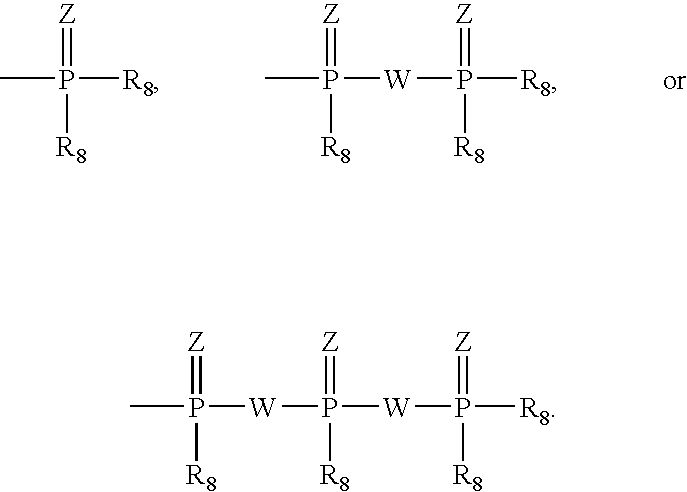
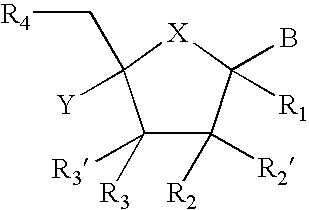
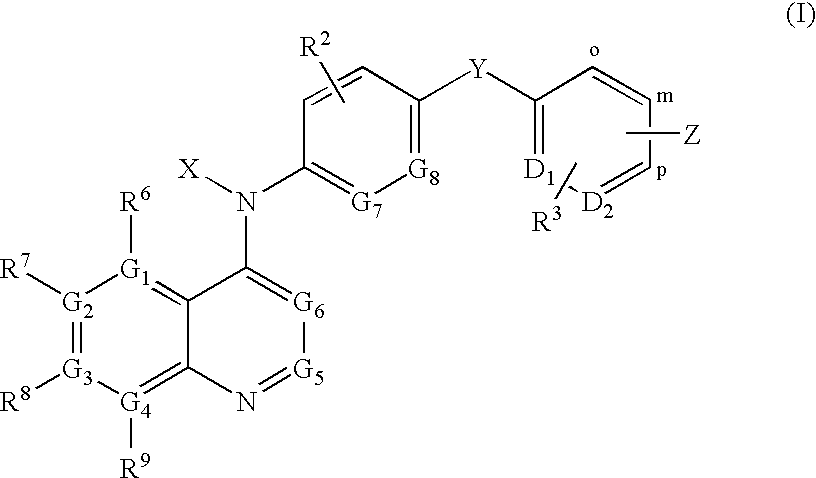
Provided are compounds represented by: X is O, S or NR6, R1 is H or (CH2)mR5, R2, R2', R3 and R3' are independently NO2, N3 or (CH2)mR5, OH R4 is H, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)nR7, R5 is H, halo, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)mR7, R6 and R6a are individually H, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, aryl or substituted aryl, R7 is: R8 is H, F, SR9 or OR9, R9 is H, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl or hydroxyprotecting group, Y is H, CH3 or (CH2)mR5, Z is O or S W is CH2, CF2, CHF or O, m is 0-4, B is adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, thymine, modified purines and pyrimidines substituted pyridines, five membered heterocycles substituted by at least one of amines, substituted amines, amides, substituted amides, esters, halogens, alkyls, ethers; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and prodrugs thereof. These ring systems may be substituted.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
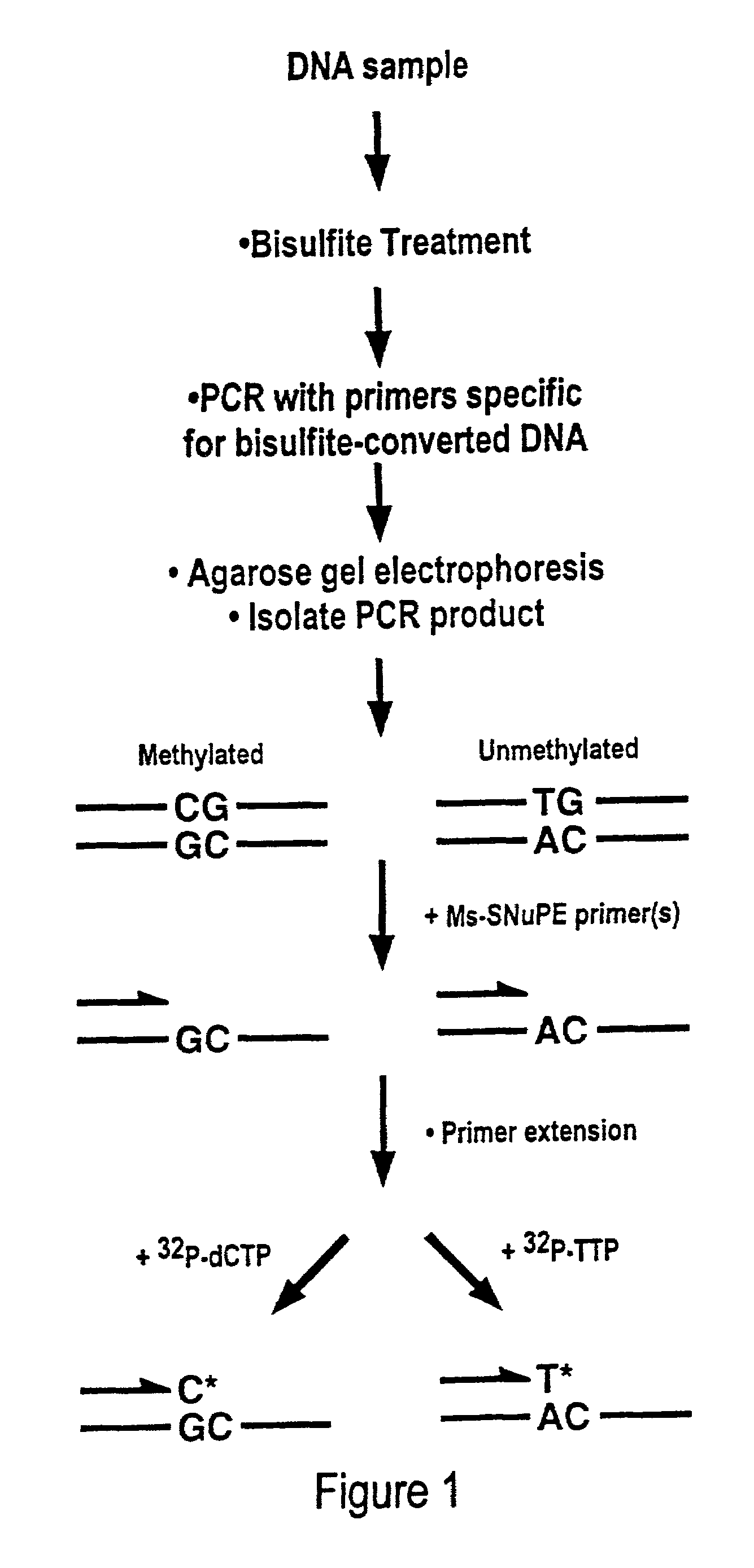
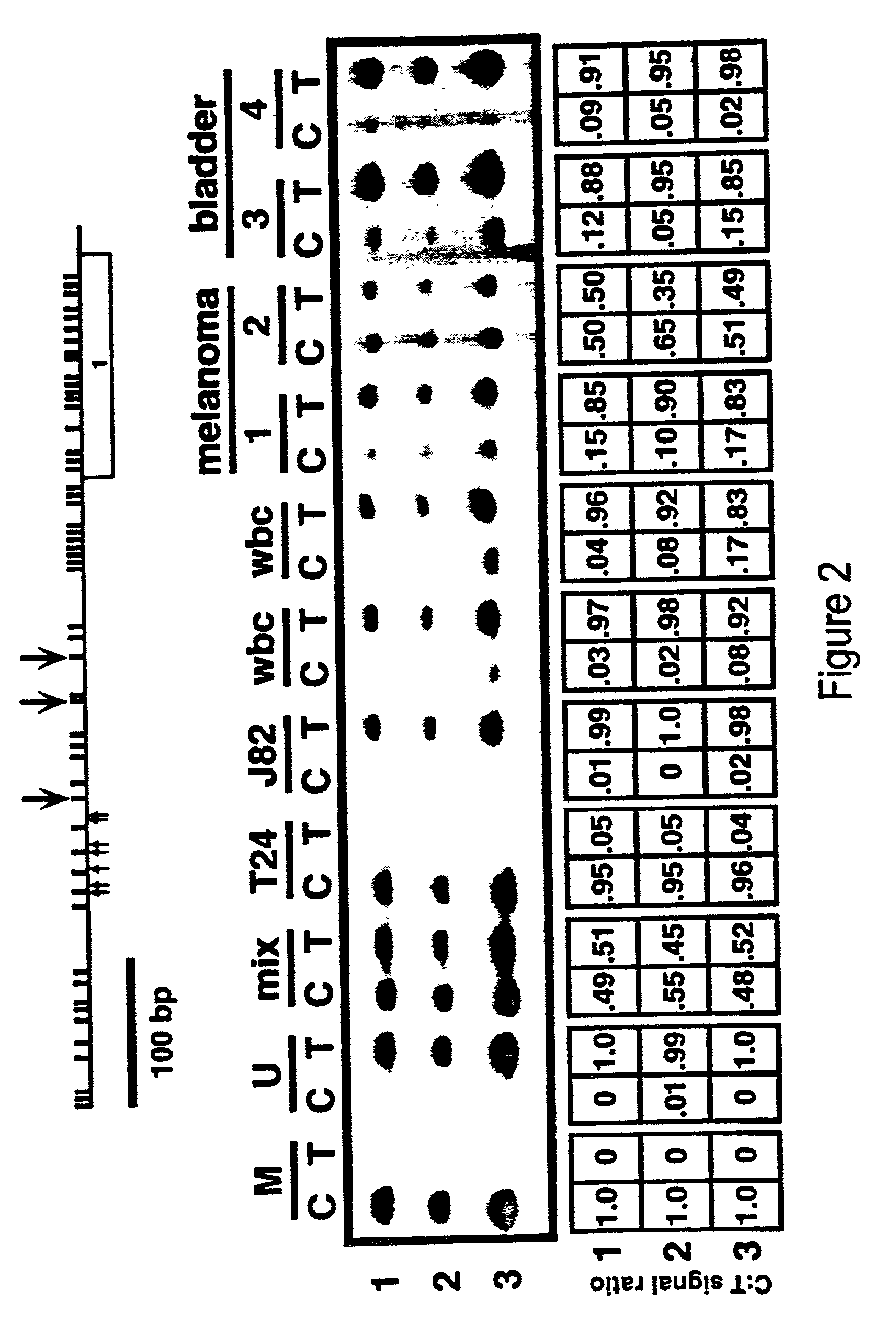
Cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences
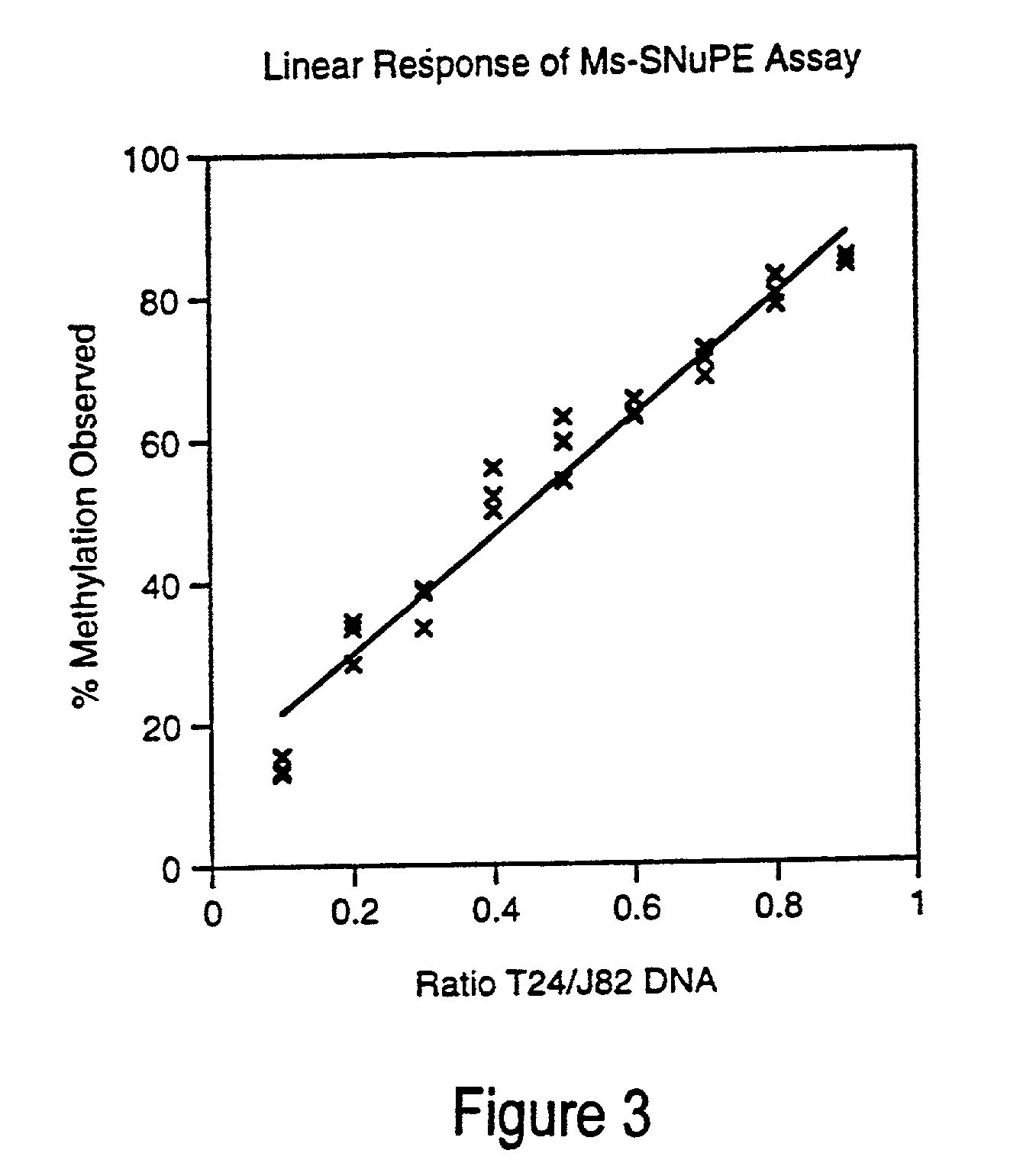
There is disclosed a cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences at specific CpG sites. Specifically, the inventive method provides for a bisulfite treatment of DNA, followed by methylation-sensitive single nucleotide primer extension (Ms-SNuPE), for determination of strand-specific methylation status at cytosine residues.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Diagnosis of diseases associated with the immune system by determining cytosine methylation
InactiveUS20030143606A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytosineOligomer
The present invention relates to chemically modified genomic sequences of genes associated with the immune system, to oligonucleotides and / or PNA-oligomers directed against the sequence, for the detection of the methylation status of genes, associated with the immune system as well as to a method for ascertaining genetic and / or epigentic parametres of genes, associated with the immune system.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Analysis of methylation status using nucleic acid arrays
InactiveUS20050196792A1Efficient amplificationReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCytosineA-DNA
Methods for amplifying a nucleic acid sample while preserving the methylation status of cytosines are disclosed. In some aspects the amplified methylated sample is modified by methylation sensitive modification and analyzed by hybridization to an array to identify cytosines that were methylated in the starting material and cytosines that were not methylated in the starting material. Methods for detecting methylation status are also disclosed. In one embodiment a DNA methyltransferase activity is included in the amplification reaction and this activity methylates the newly synthesized DNA using the methylated genomic template strand as a guide.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
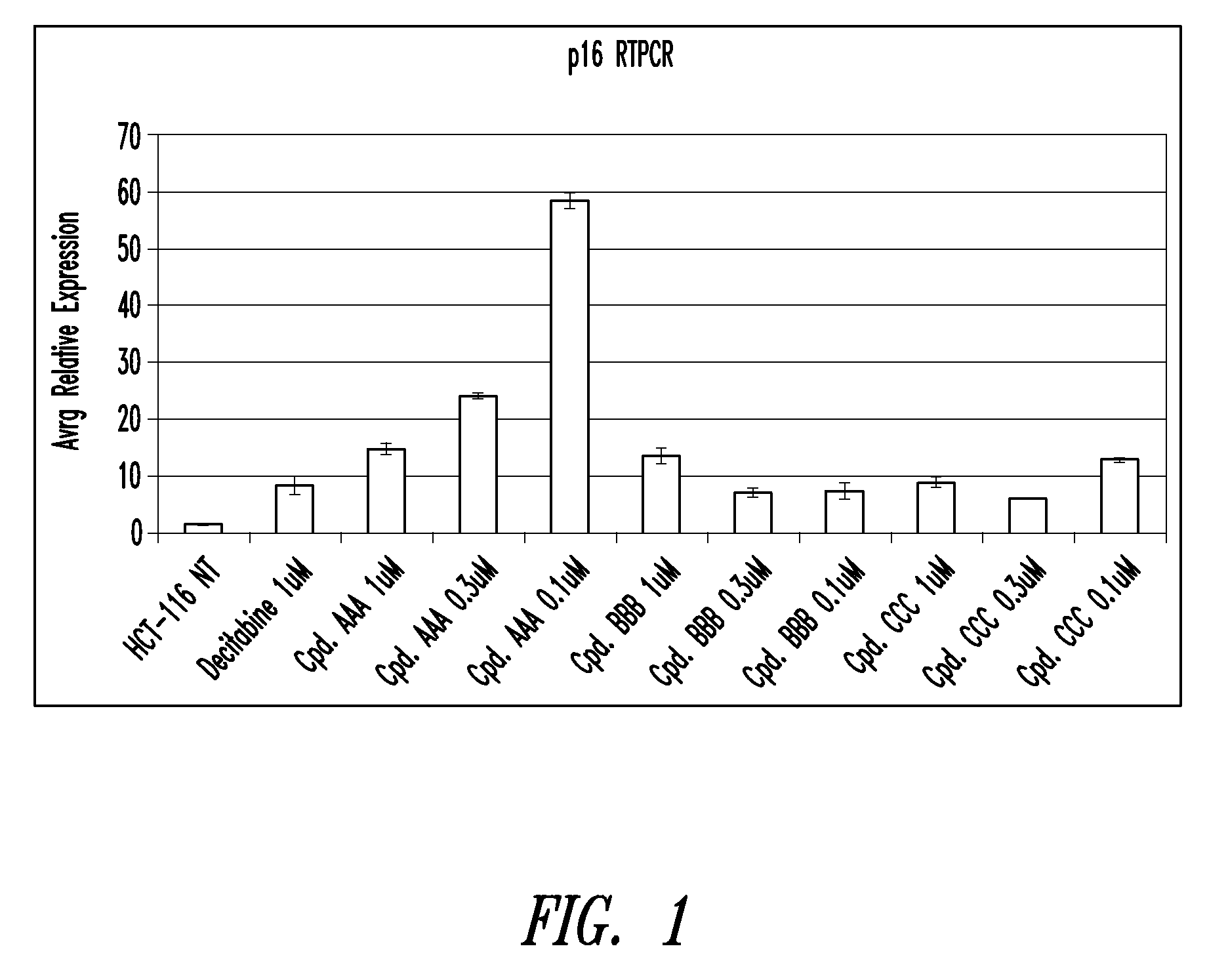
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
InactiveUS20090285772A1Reduction in function/activityReduced activityBiocideOrganic chemistryCytosineDNA methylation
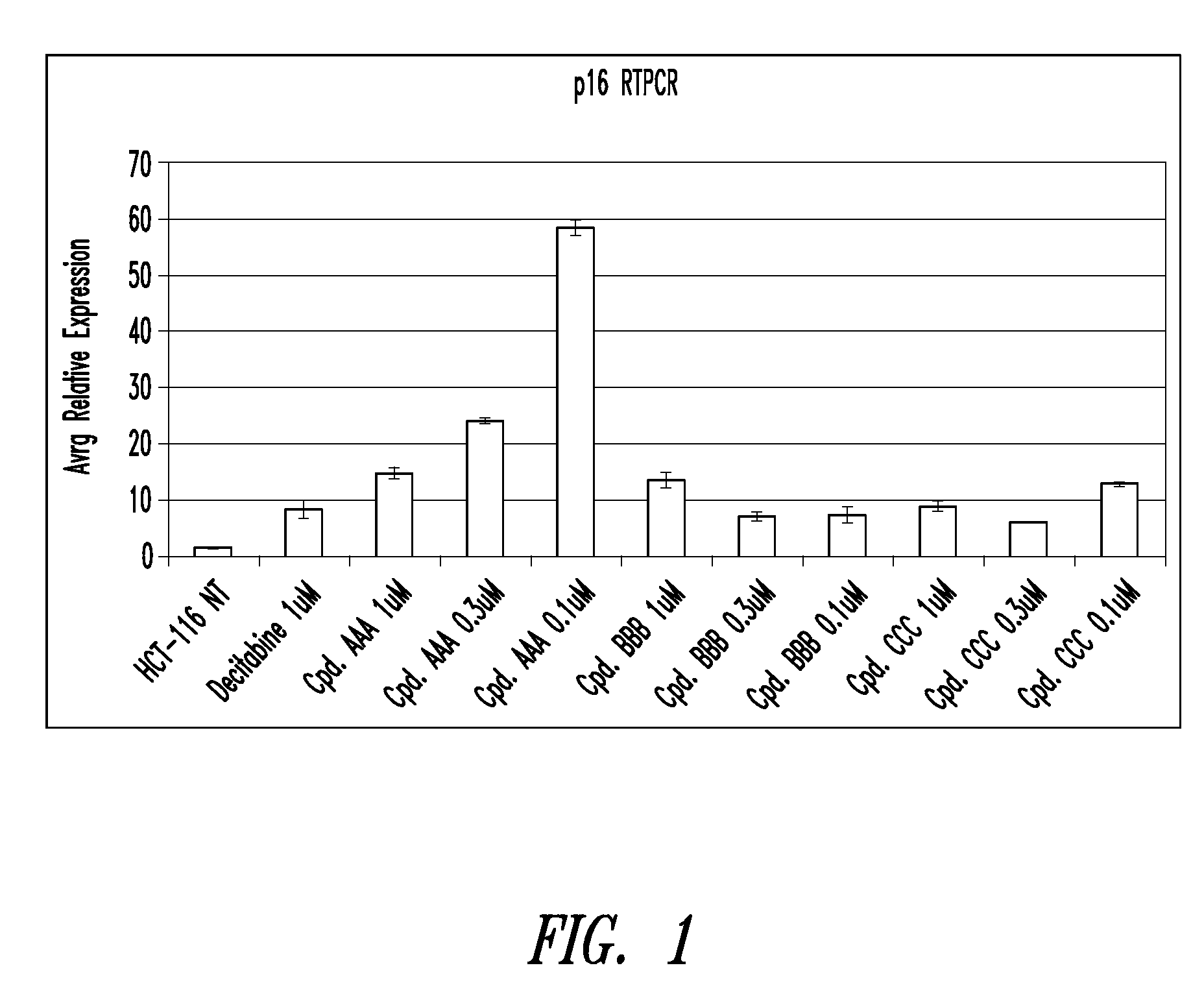
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20110054005A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:BIO THINKTANK
Nucleotide derivative and DNA microarray
ActiveUS7414117B2Easy to prepareSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineDNA microarray
A novel nucleotide derivative, in case of existing as a member of a single-stranded sequence, undergoing a change in the fluorescent signal intendity depending on the corresponding base type in the partner strand with which the single-stranded sequence is hybridized, and which is a thymin / uracil derivative (1) emitting light most intensely when a confronting base in the partner strand with which the single-stranded nucleotide sequence is hybridized is adenine; a cytosine derivative (2) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is guanine; an adenine derivative (3) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is cytosine; a guanine derivative (4) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is cytosine or thymine / uracil; and an adrnine derivative (5) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is thymine / uracil / .
Owner:SAITO ISAO +1
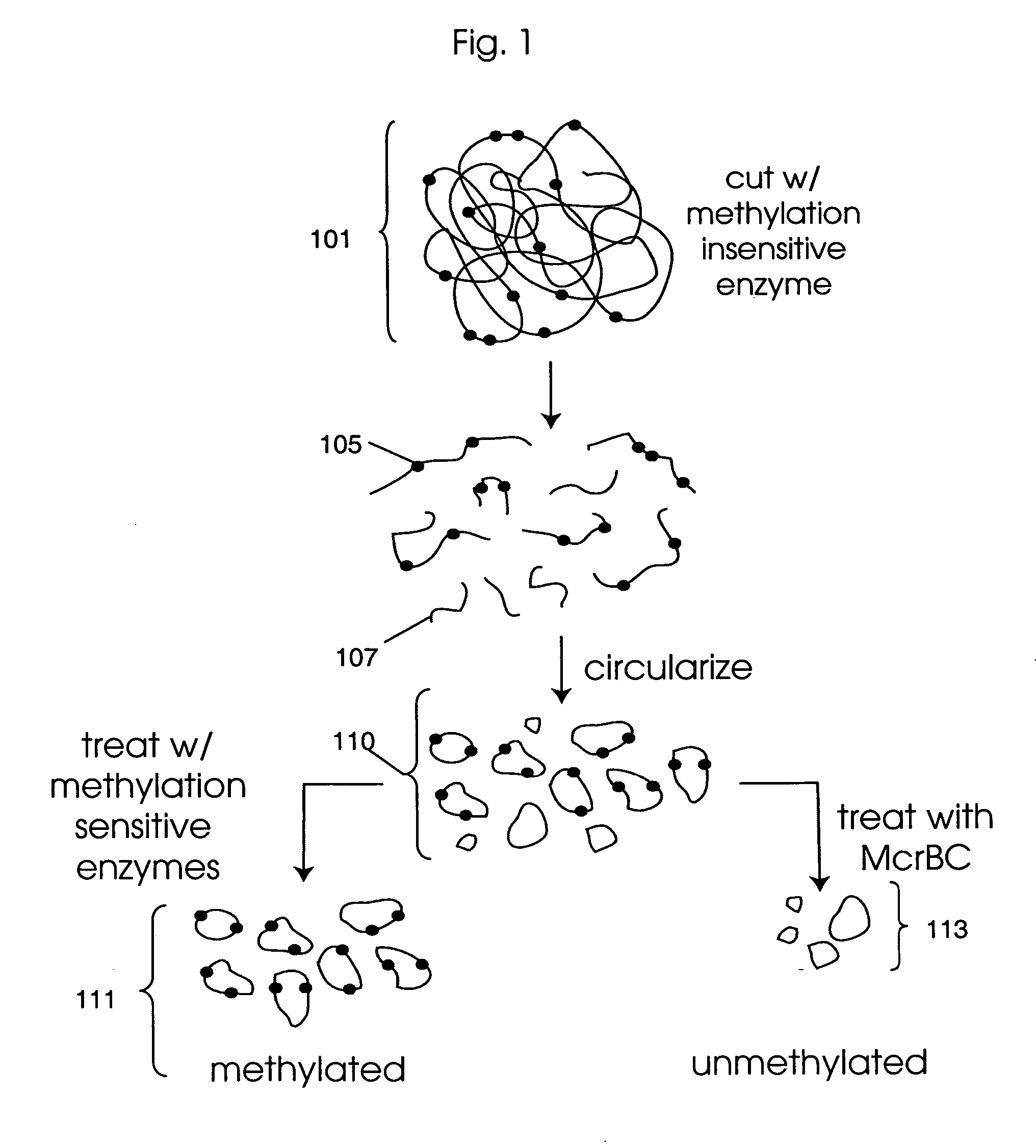
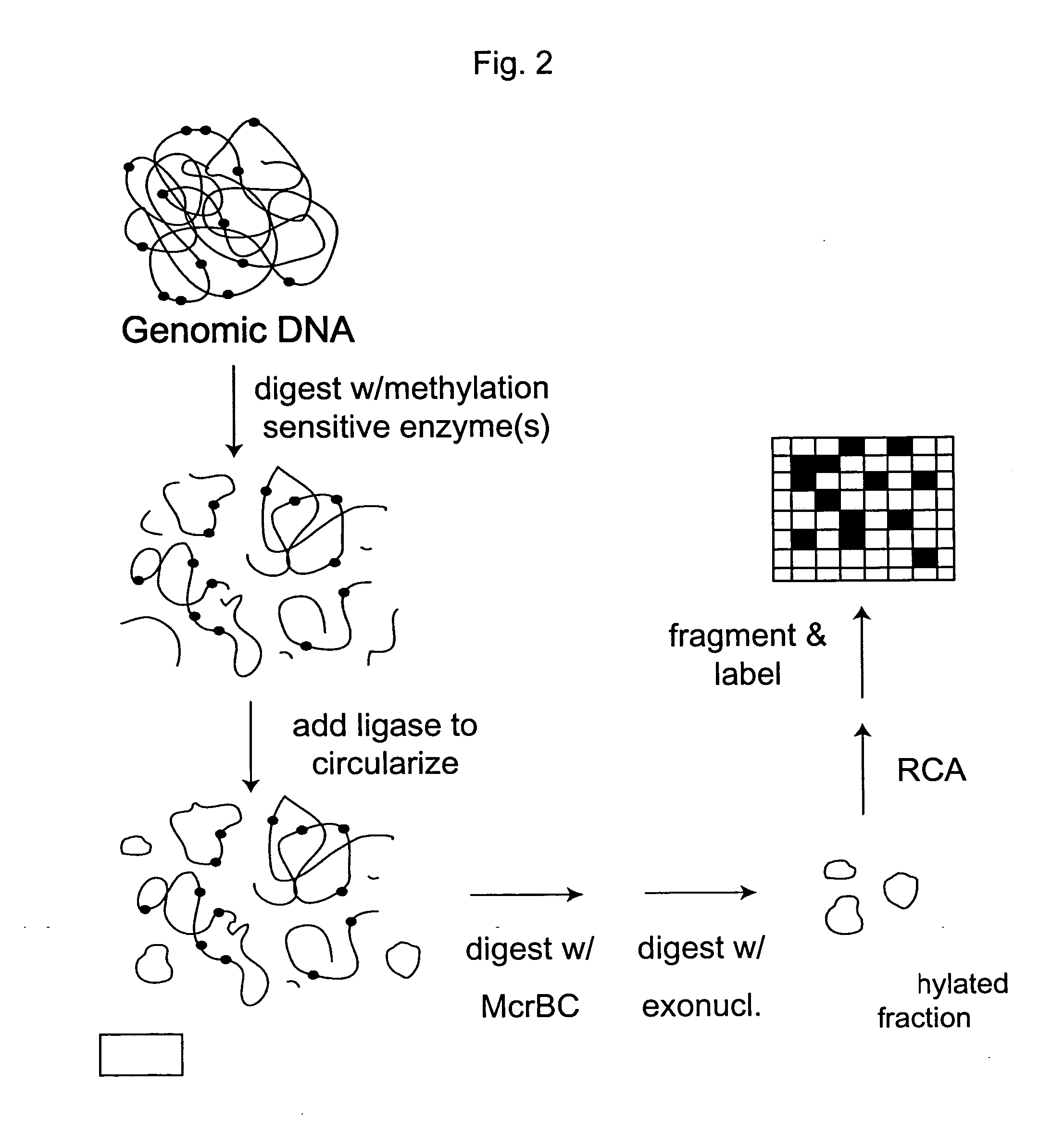
Analysis of methylation using nucleic acid arrays
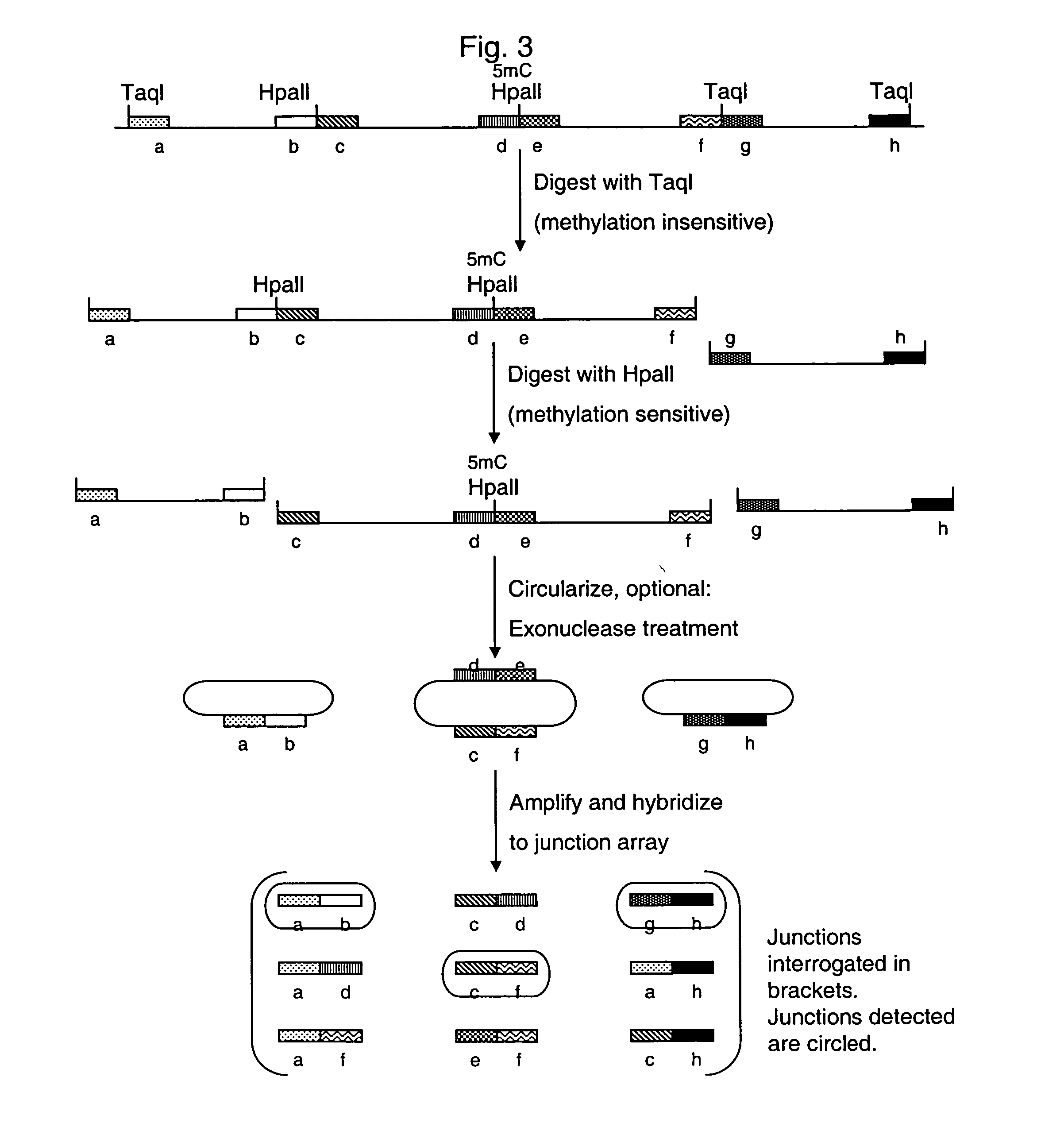
Methods of analyzing DNA to determine the methylation status of a plurality of cytosines are disclosed. In one aspect genomic DNA is fragmented, fragments are circularized, the circles are treated with a methylation sensitive enzyme to enrich for circles with methylated sites or with a methylation dependent enzyme to enrich for circles with unmethylated sites, and the circles are amplified. The amplified product is fragmented, labeled and hybridized to an array of probes. The array of probes may be a tiling array or an array of junction probes. The hybridization pattern is analyzed to determine methylation status of cytosines.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
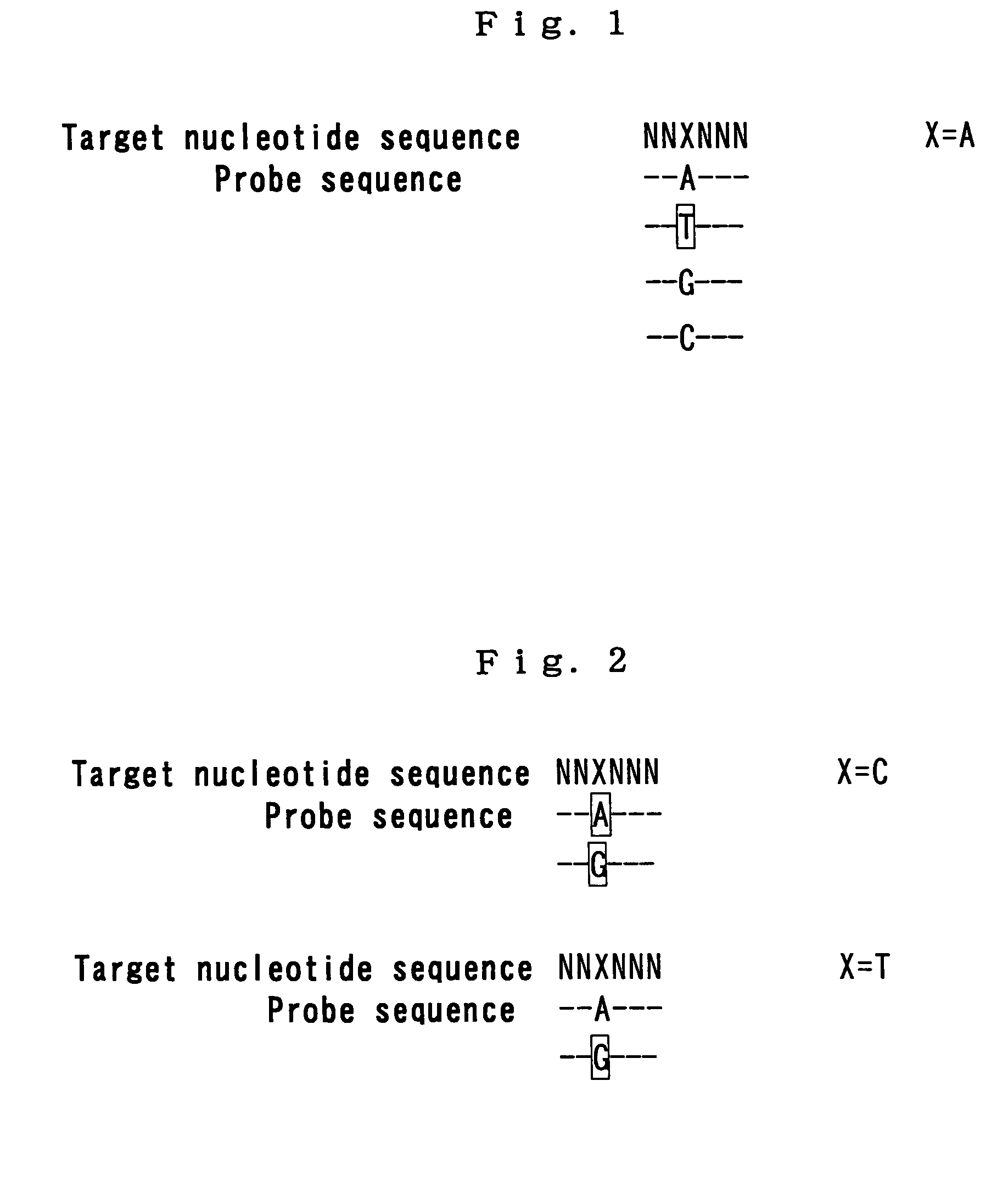
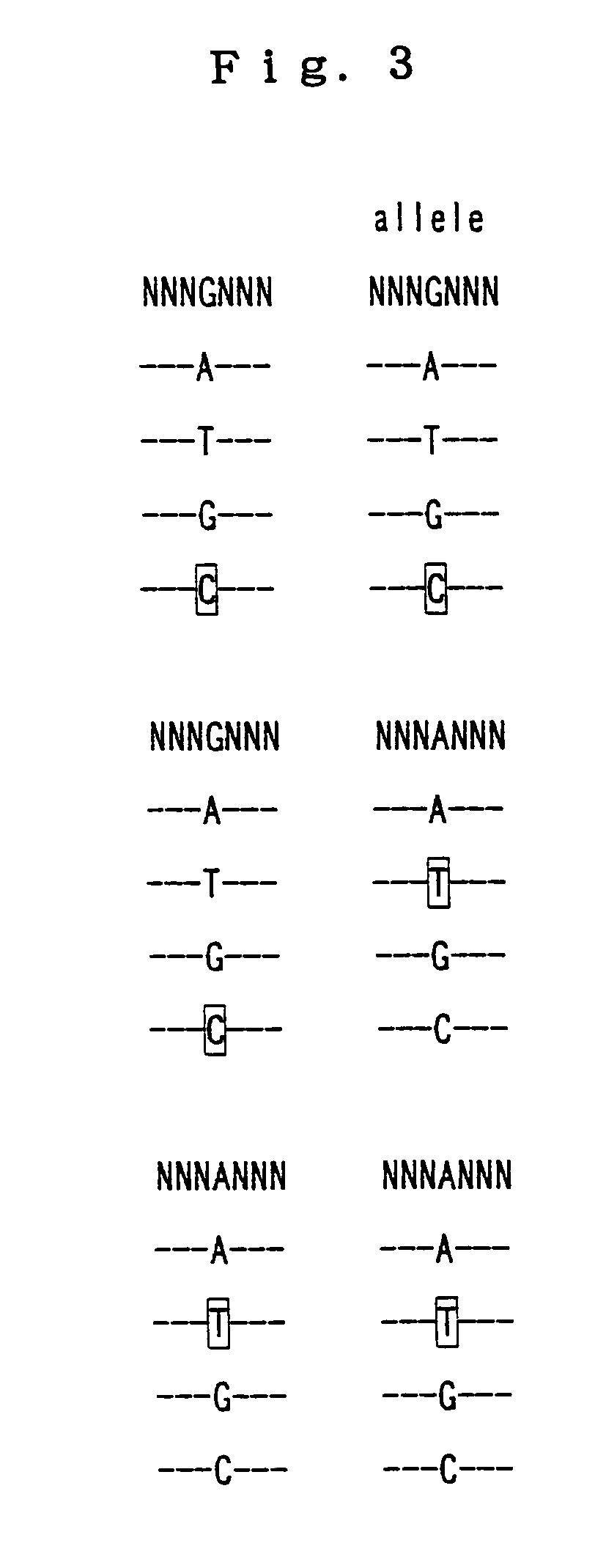
Method for detecting methylation status by using methylation-independent primers
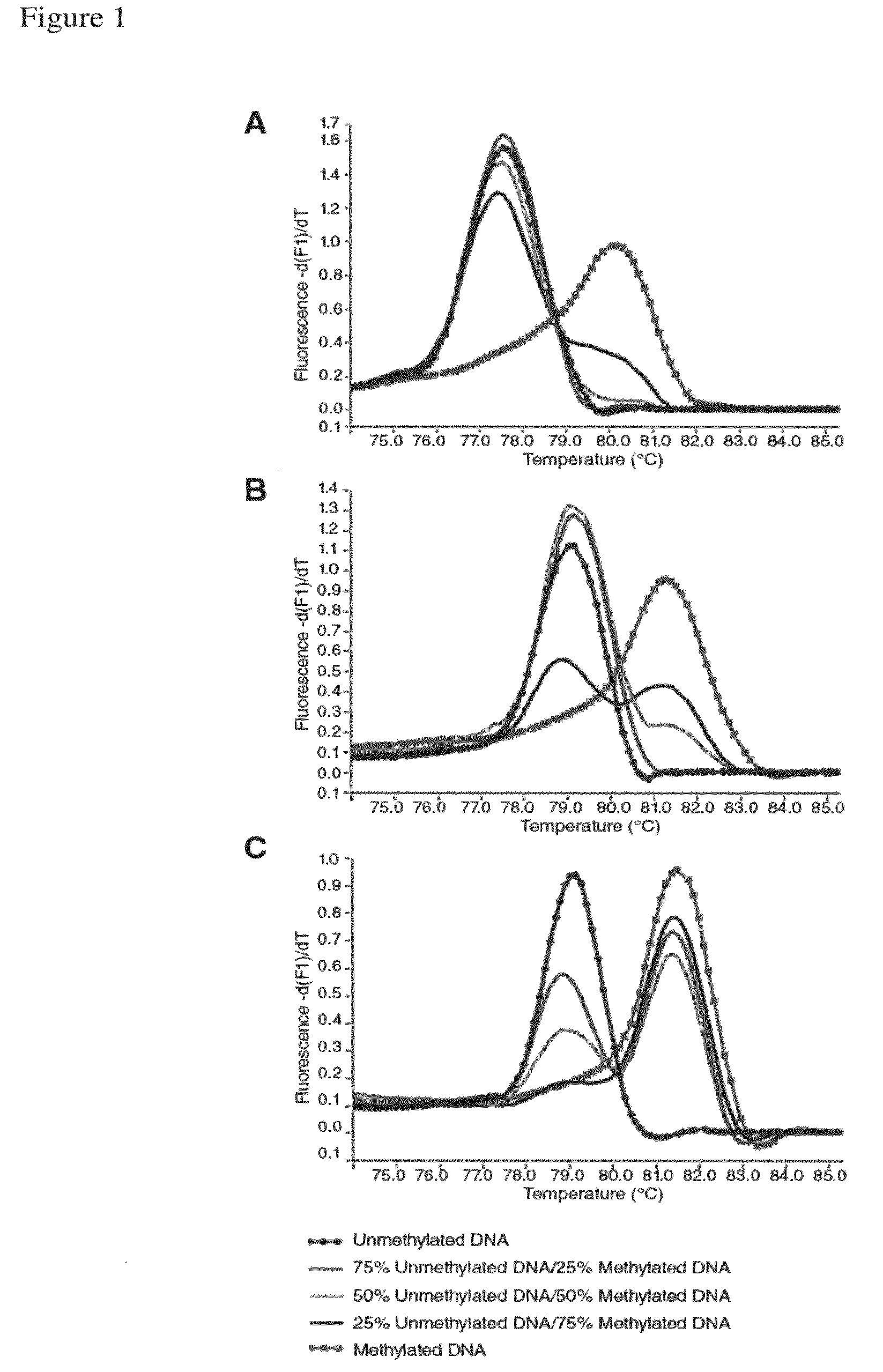
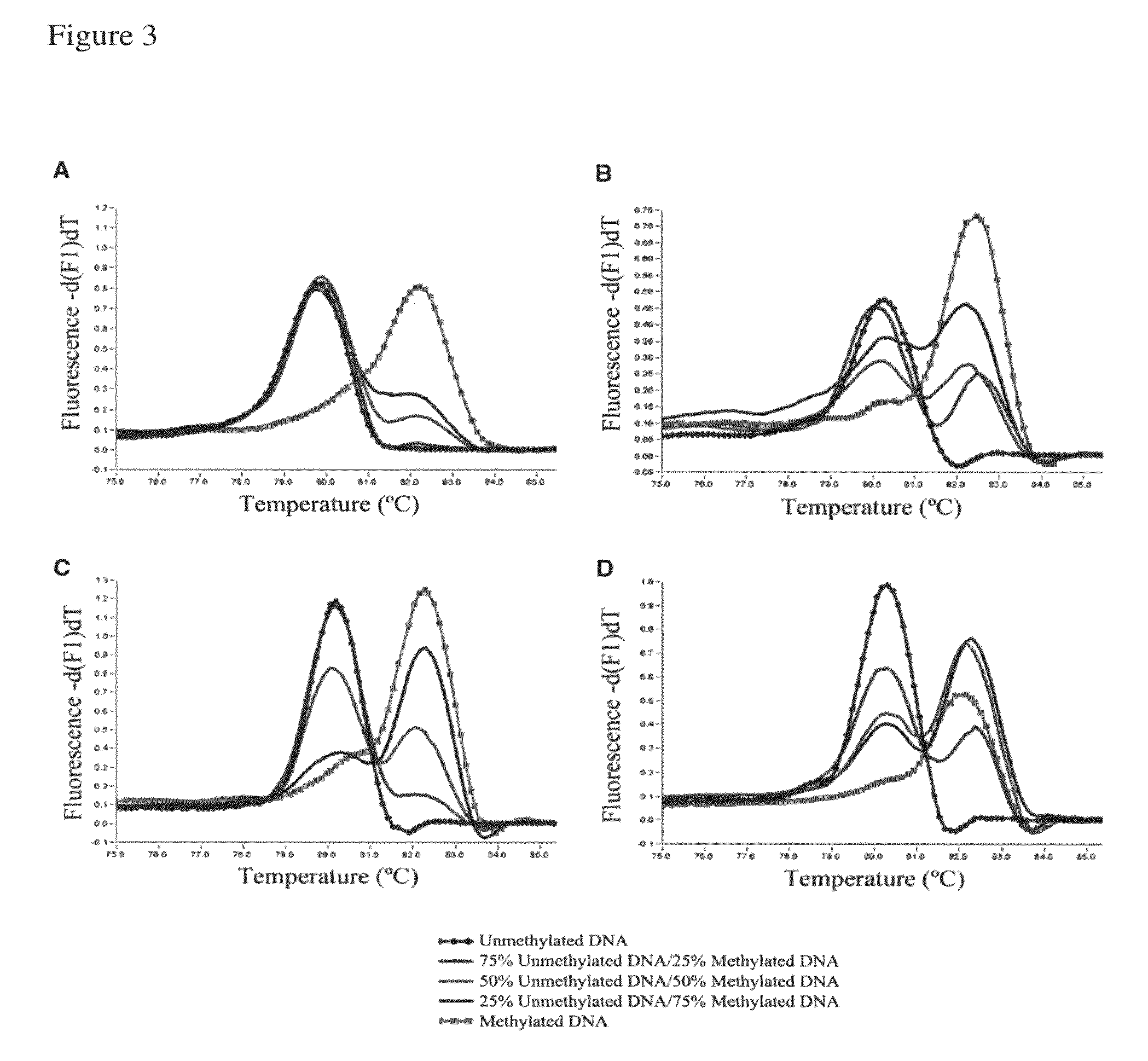
A reliable and highly sensitive method is provided for detecting methylation status of CpG-containing nucleic acids by nucleic acid amplification and melting curve analysis of amplification products. The methods and compositions employs a novel design of primers. CpG-containing methylation-independent oligonucleotide primers, wherein both unmethylated and methylated alleles of a CpG-containing nucleic acid can be detected by use of only one set of primers after the CpG-containing nucleic acid has been subjected to cytosine to thymine conversion of unmethylated Cytosine. The method is useful for detection of methylation status in for example cancer genes and other disease related genes, wherein methylation influences gene expression.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV +1
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
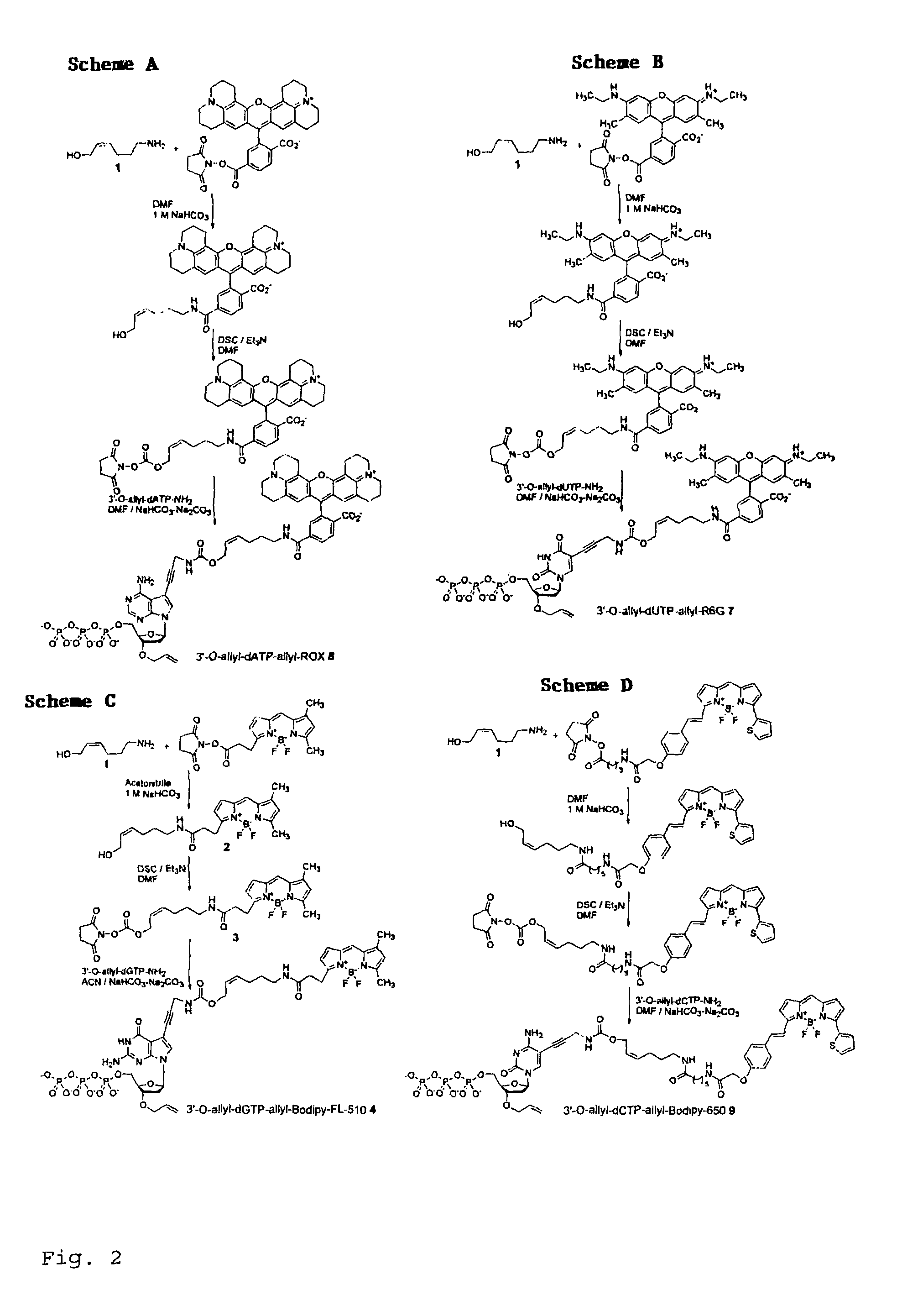
Chemically cleavable 3'-o-allyl-DNTP-allyl-fluorophore fluorescent nucleotide analogues and related methods
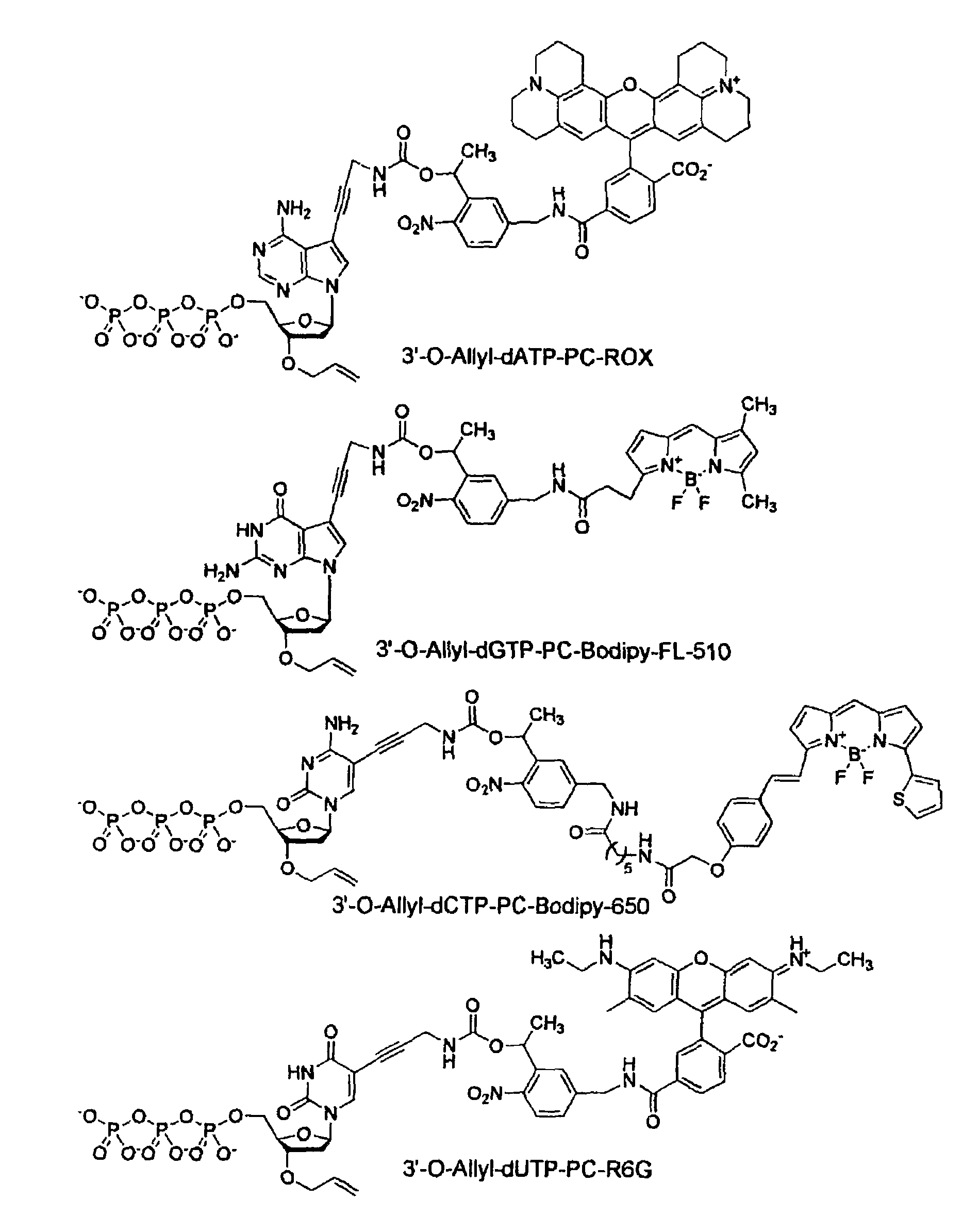
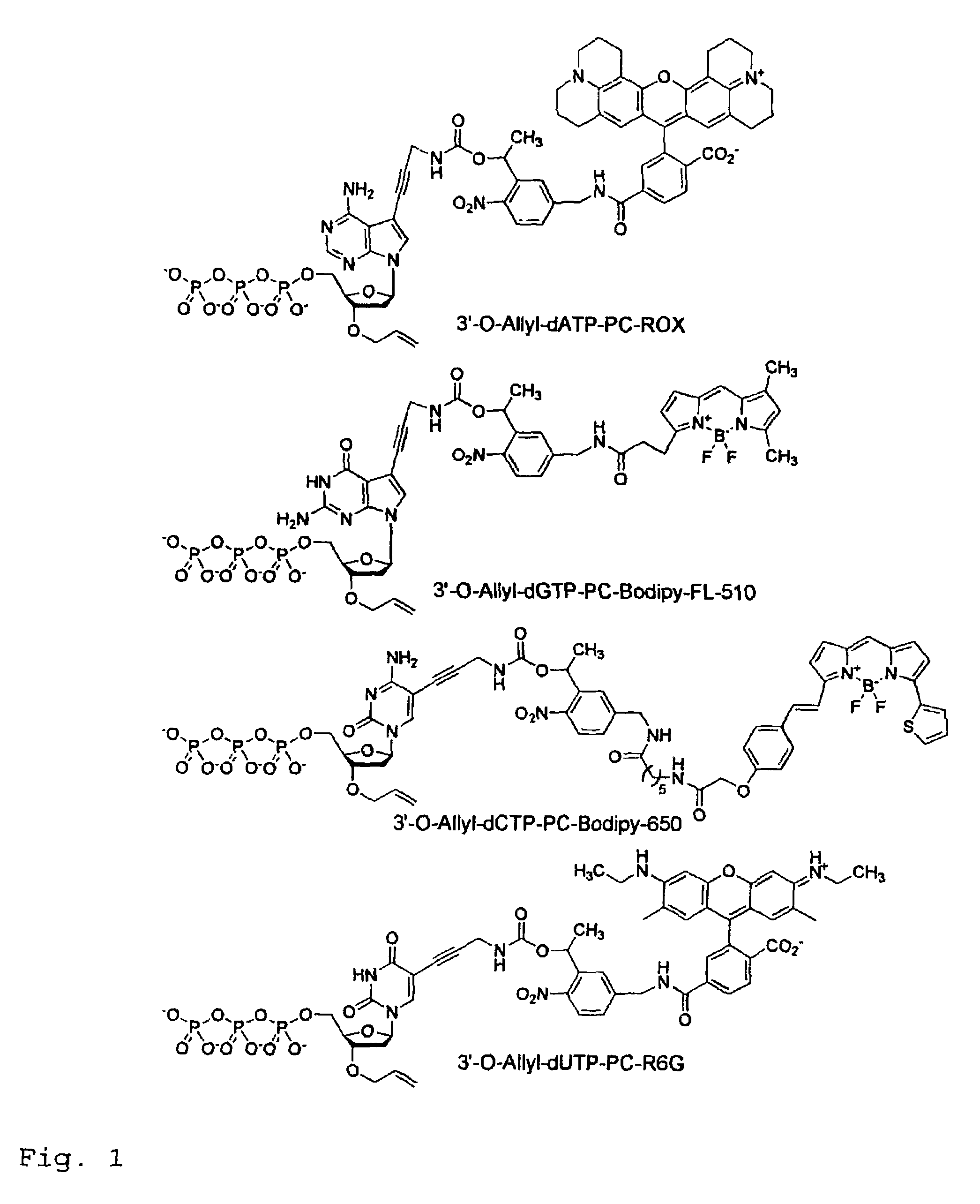
This invention provides a nucleotide analogue comprising (i) a base selected from the group consisting of adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine and uracil, (ii) a deoxyribose, (iii) an allyl moiety bound to the 3′-oxygen of the deoxyribose and (iv) a fluorophore bound to the base via an allyl linker, and methods of nucleic acid sequencing employing the nucleotide analogue.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
InactiveUS20080175814A1Reduction in function/activityReduced activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDNA methylationCytosine
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Quantitative methylation detection in DNA samples
InactiveUS6960436B2Quick fixFast and cost-effective and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LGenomic DNA
Described is a method for methylation detection in a DNA sample. An isolated genomic DNA sample is treated in a manner capable of distinguishing methylated from unmethylated cytosine bases. The pretreated DNA is amplified using at least one oligonucleotide primer, a polymerase and a set of nucleotides of which at least one is labeled with a first type of label. A sequence-specific oligonucleotide probe, marked with a second type of label, hybridizes to the amplification product and a FRET reaction occurs if a labeled oligonucleotide is present in close proximity in the amplification product. The method determines the level of methylation of a sample by measuring the extent of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between the donor and acceptor fluorophore.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
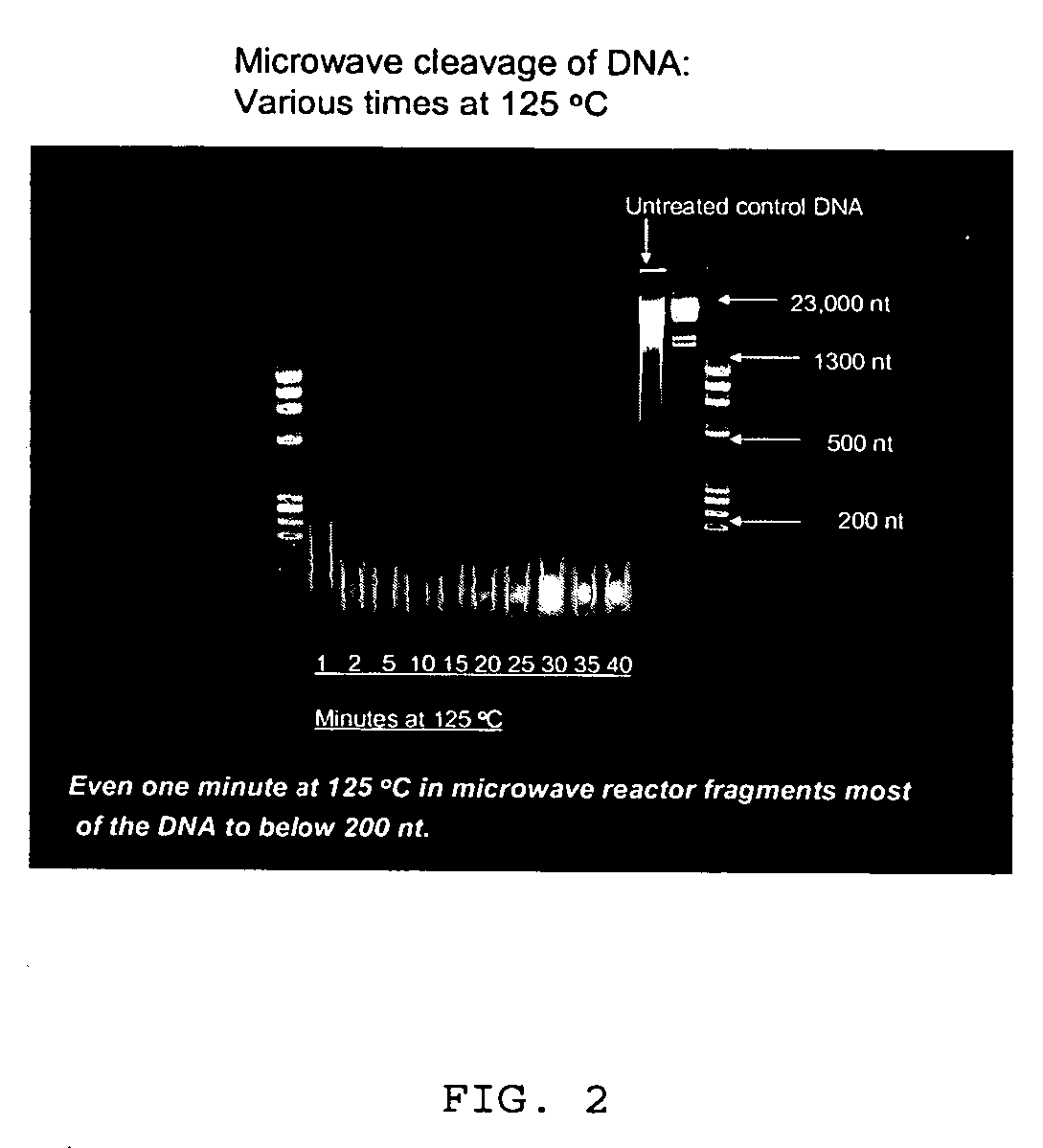
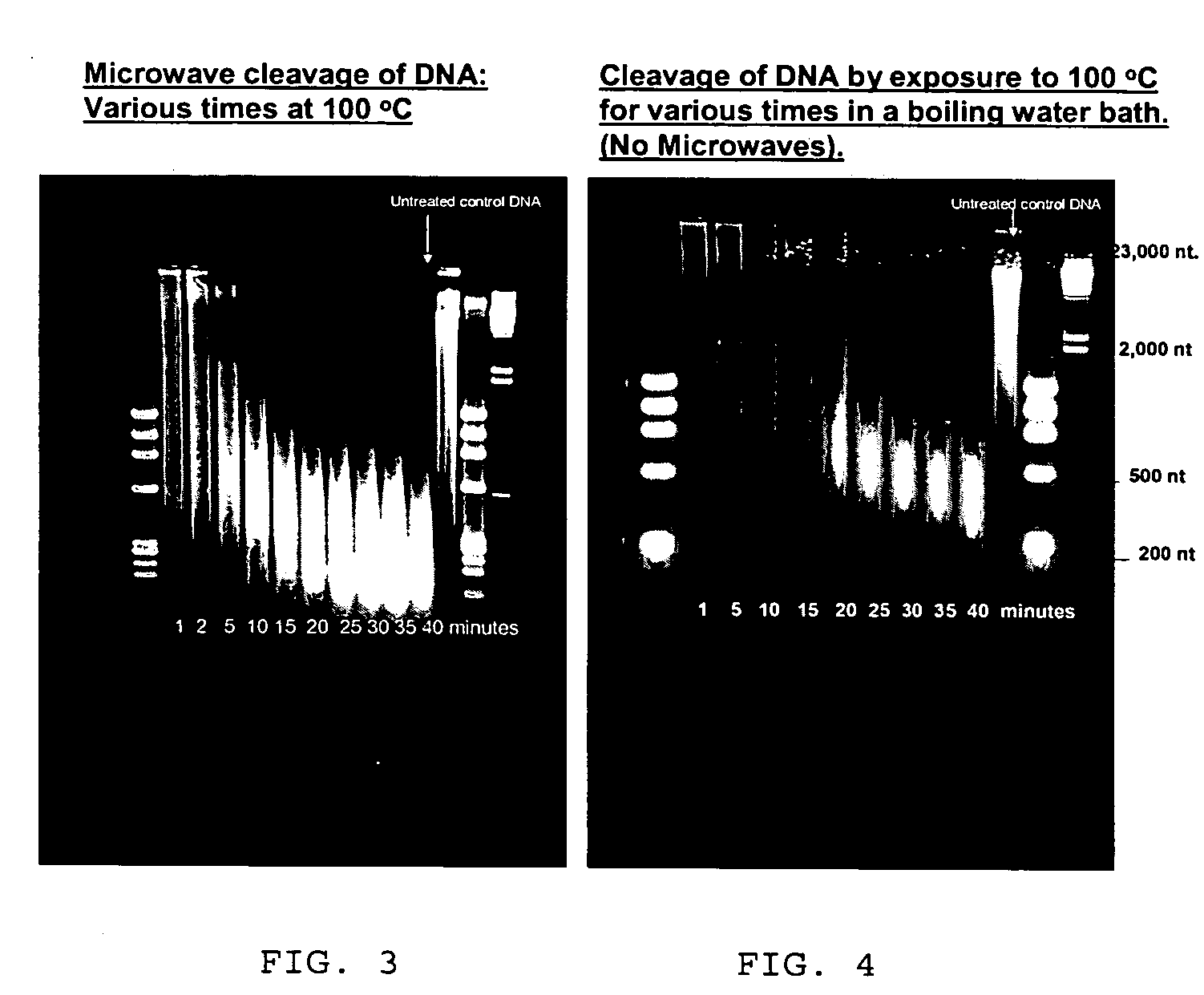
Microwave mediated synthesis of nucleic acid probes
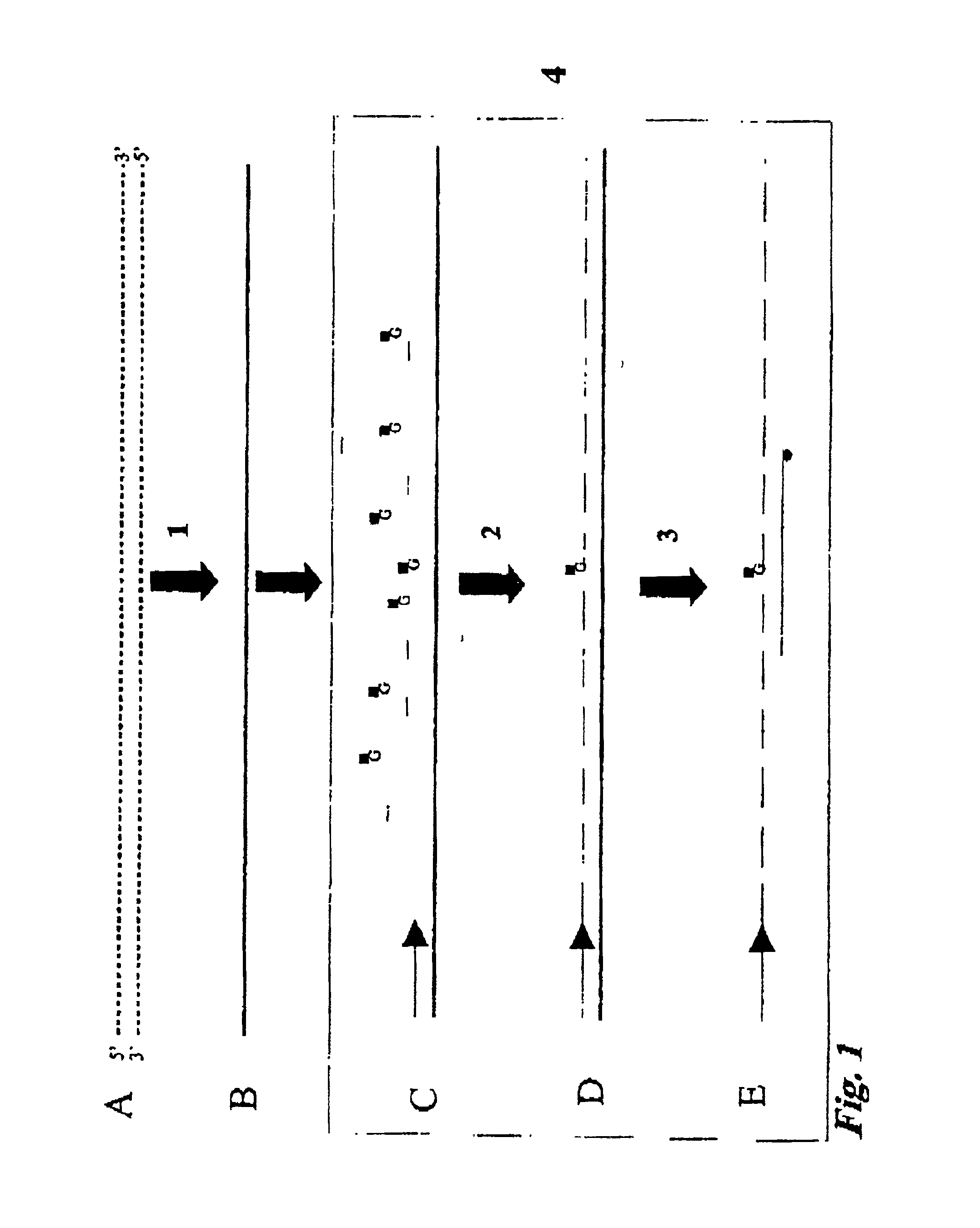
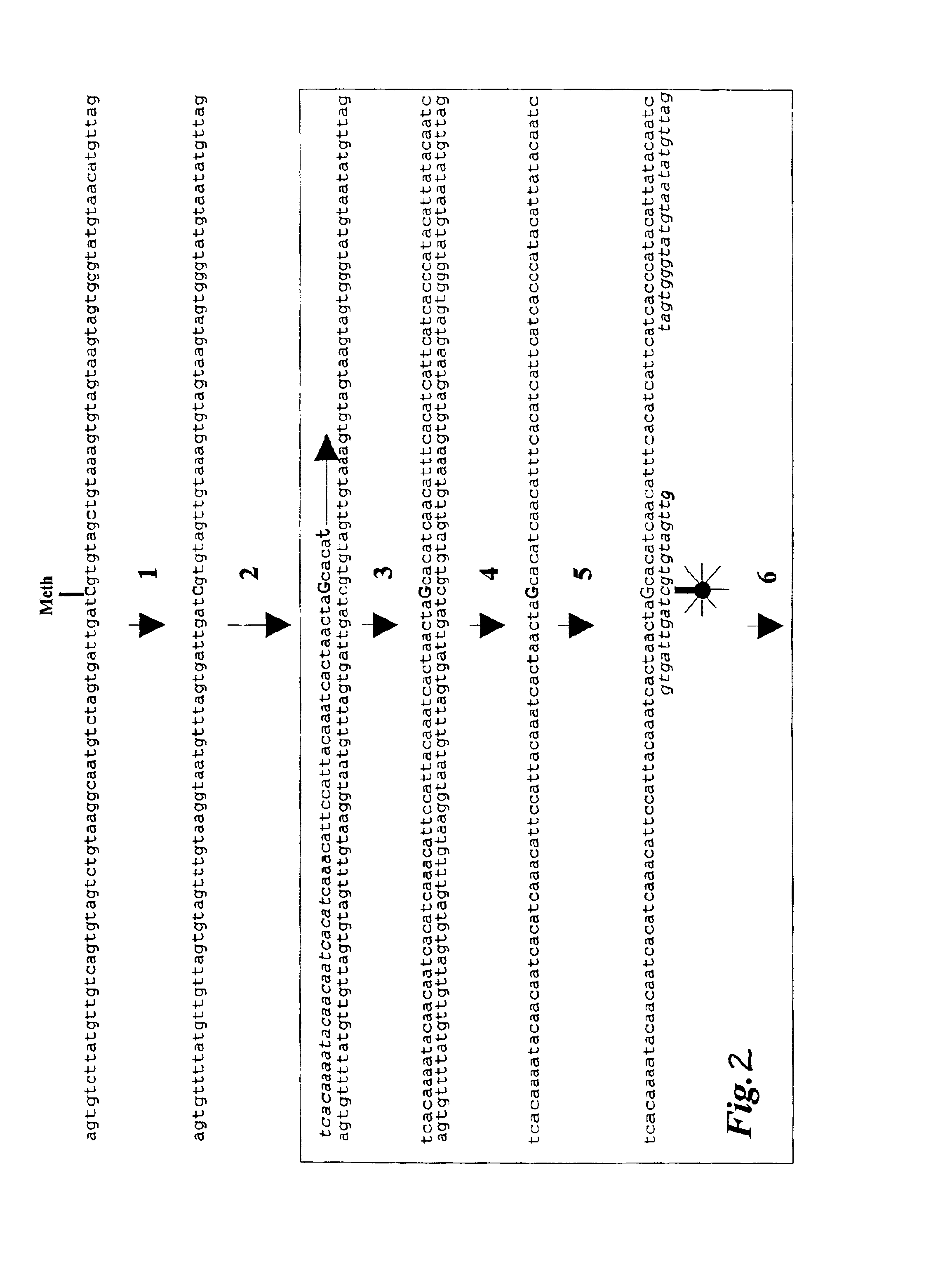
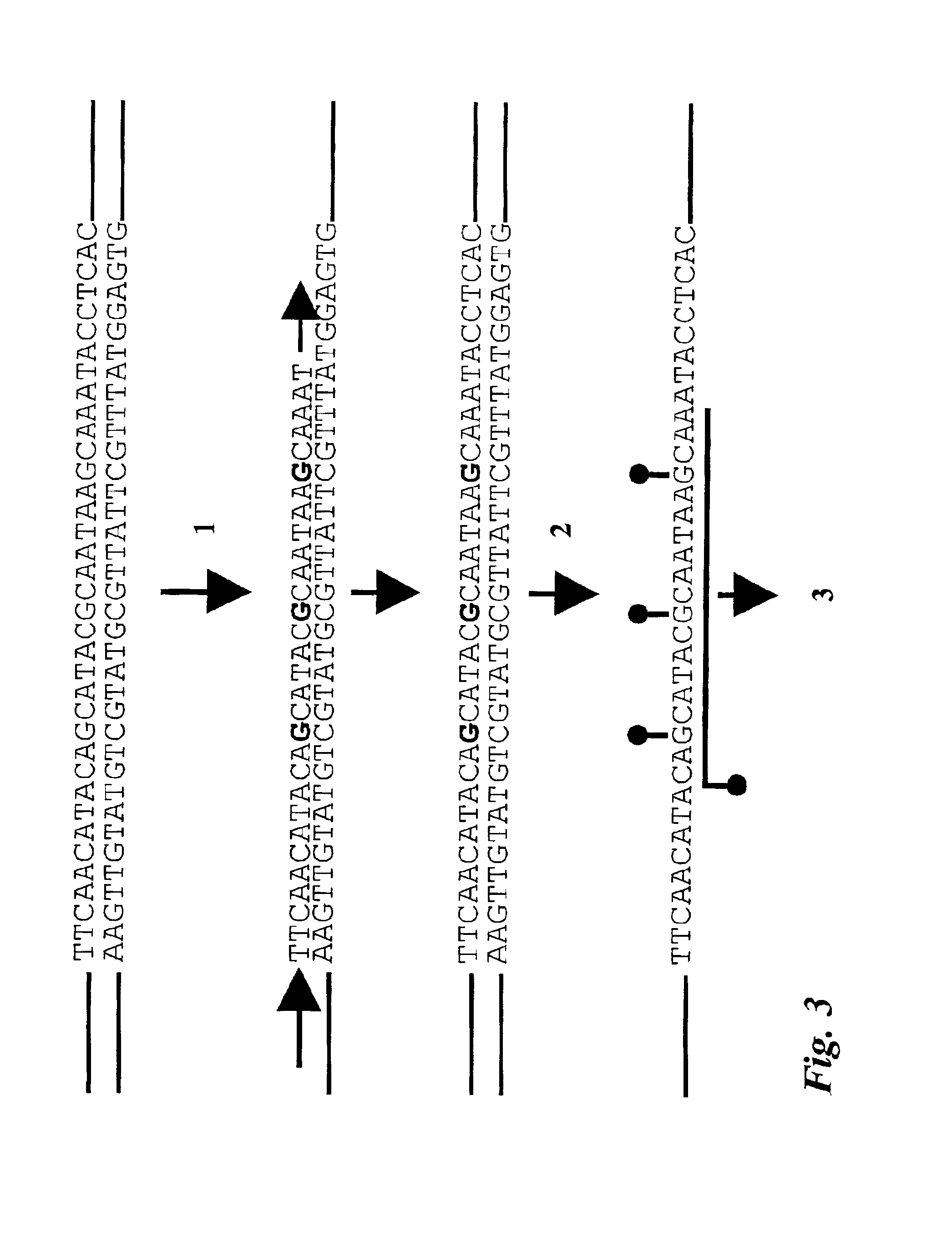
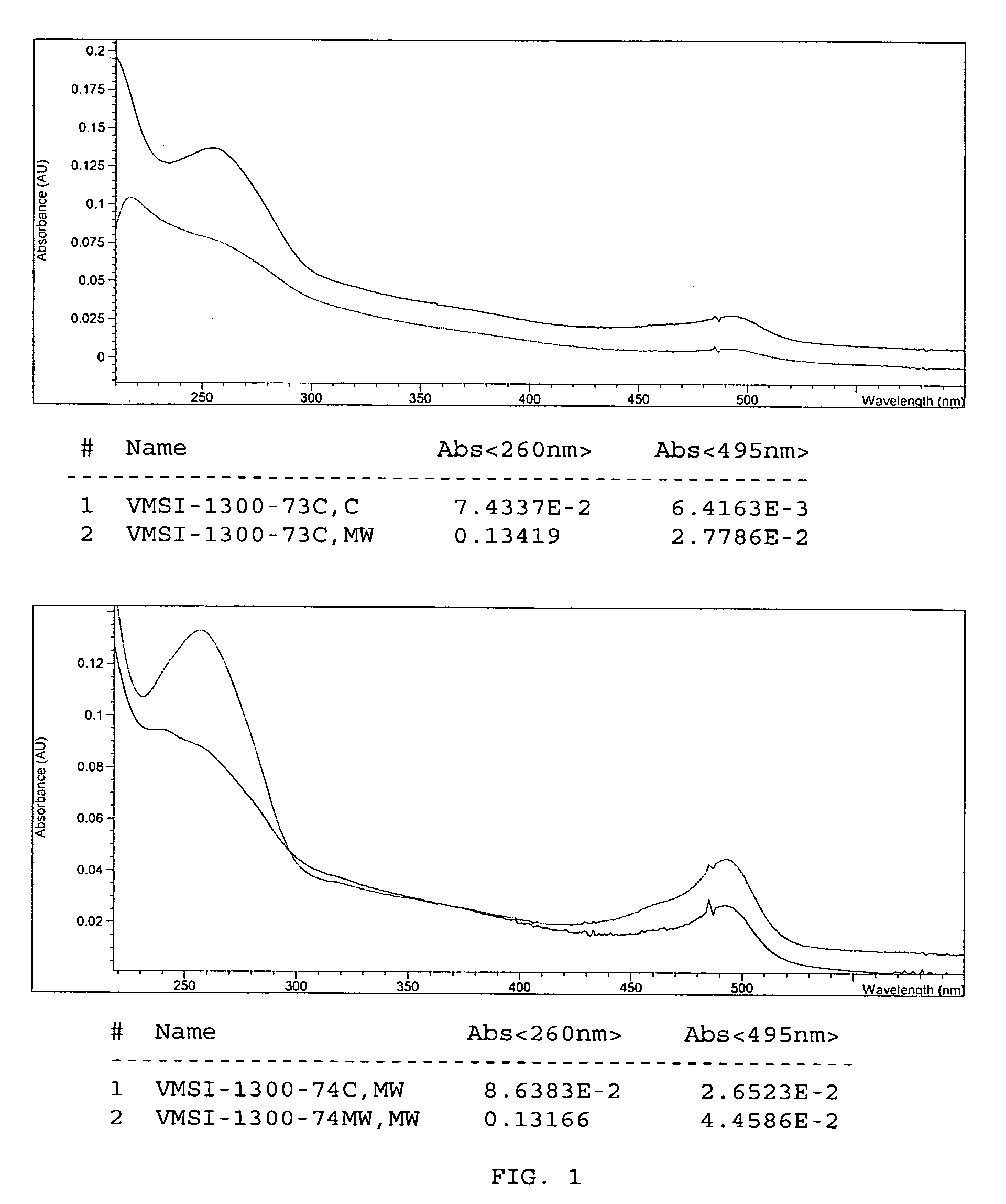
A method for preparing a nucleic acid probe is provided. The method comprises forming an activated cytosine or cytidine by a bisulfite catalyzed reaction; and covalently linking a reporter molecule to the activated cytosine or cytidine, wherein said activating step, said covalently linking step, or both are conducted in the presence of microwave energy. Also provided by the invention are nucleic acid probes.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
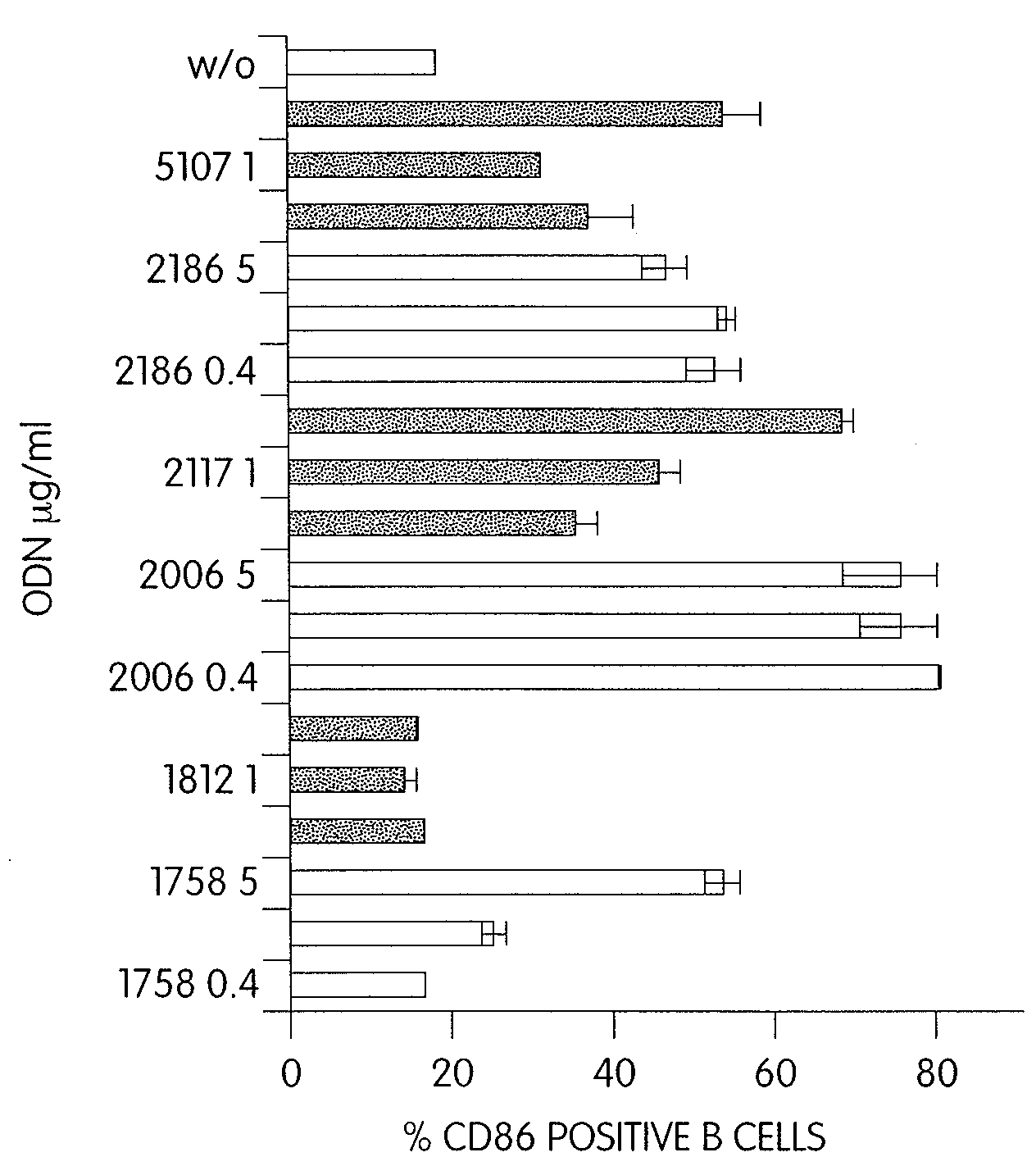
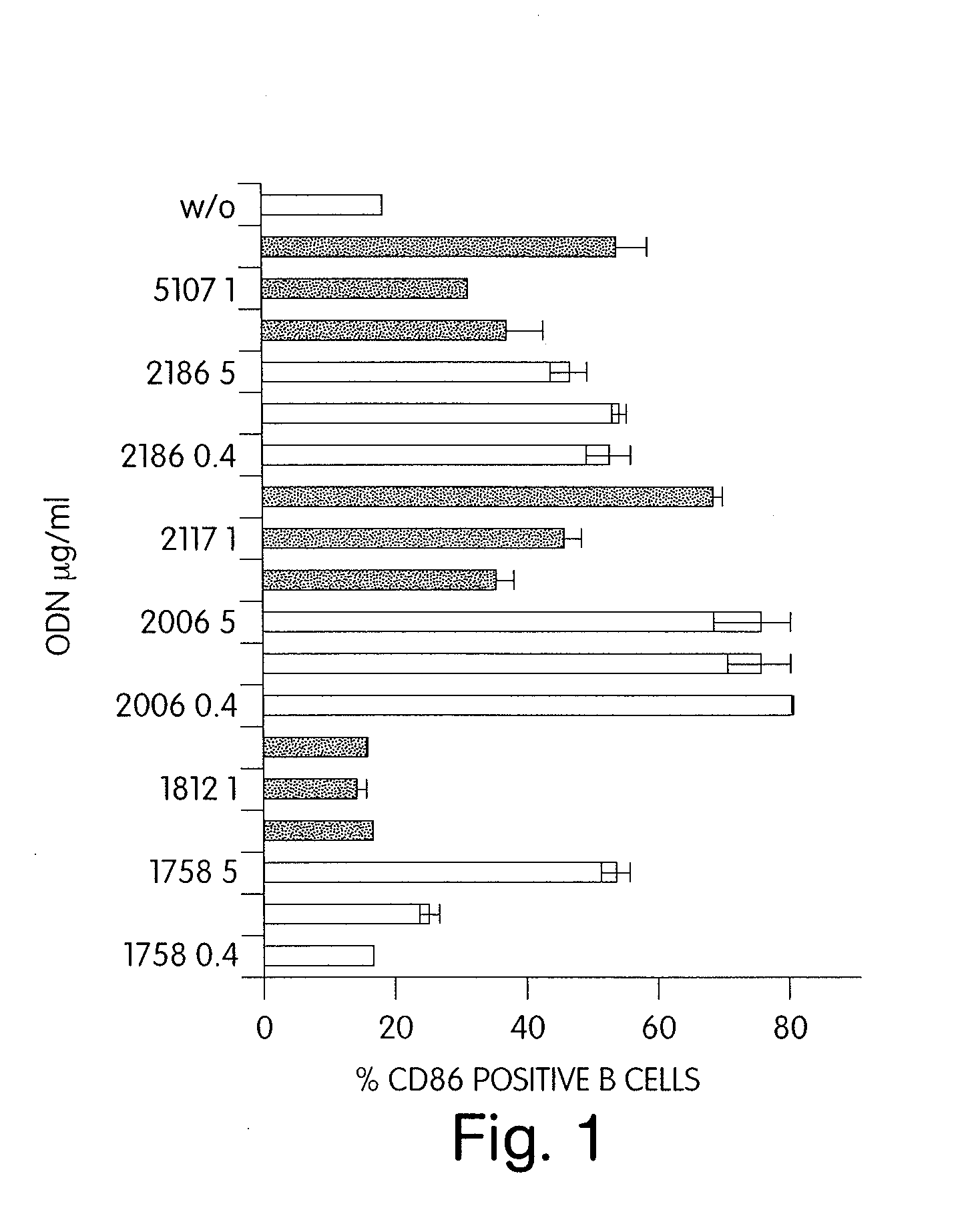
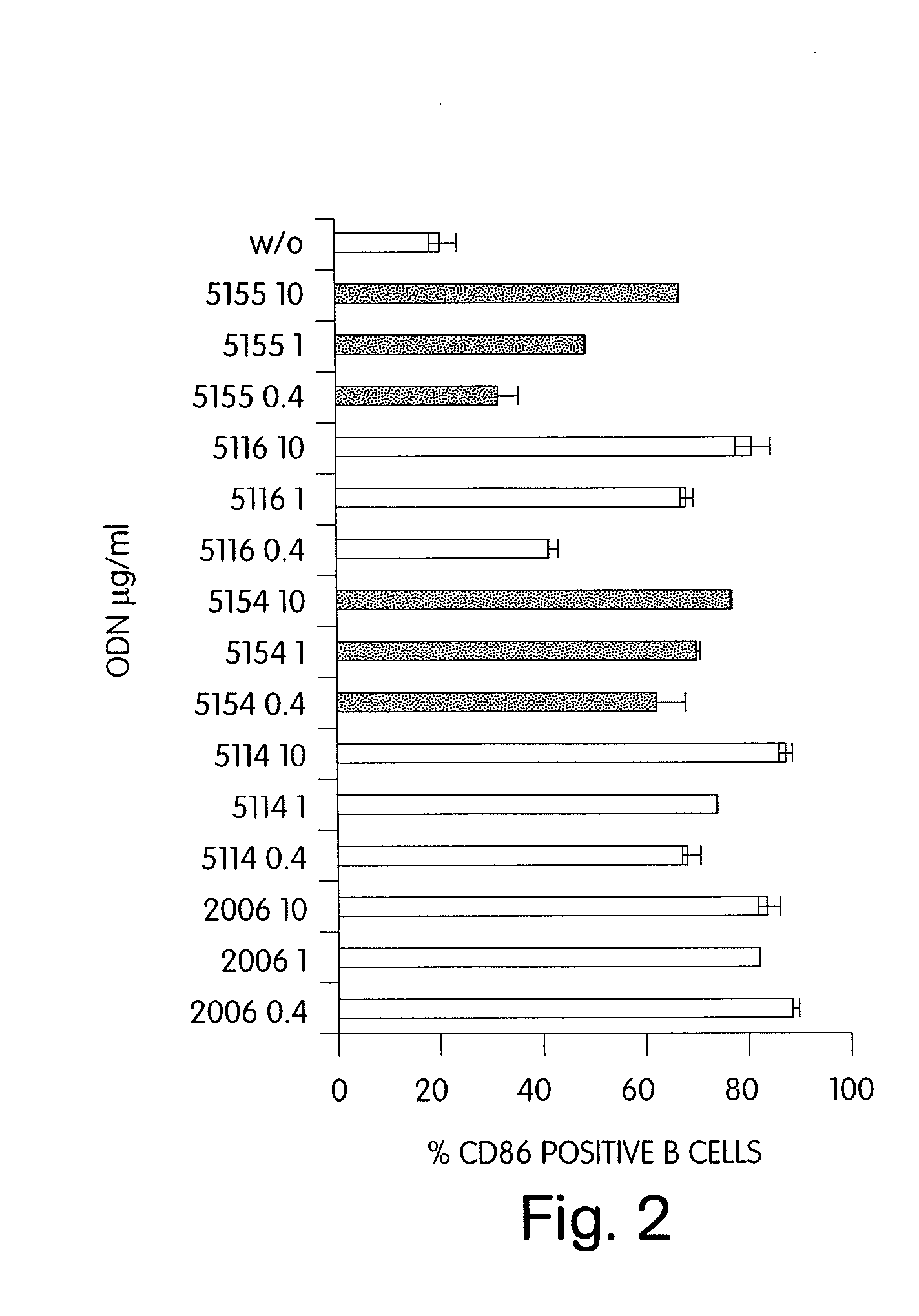
CPG-like nucleic acids and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080226649A1Enhancing neutrophil proliferationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAllergyPurine
Immunostimulatory compositions described as CpG-like nucleic acids are provided, including nucleic acids having immunostimulatory characteristics of CpG nucleic acid, despite certain substitutions of C, G, or C and G of the CpG dinucleotide. The substitutions can include, among others, exchange of methylated C for C, inosine for G, and ZpY for CpG, where Z is cytosine or dSpacer and Y is inosine, 2-aminopurine, nebularine, or dSpacer. Also provided are methods for inducing an immune response in a subject using the CpG-like nucleic acids. The methods are useful in the treatment of a subject that has or is at risk of developing an infectious disease, allergy, asthma, cancer, anemia, thrombocytopenia, or neutropenia.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GMBH
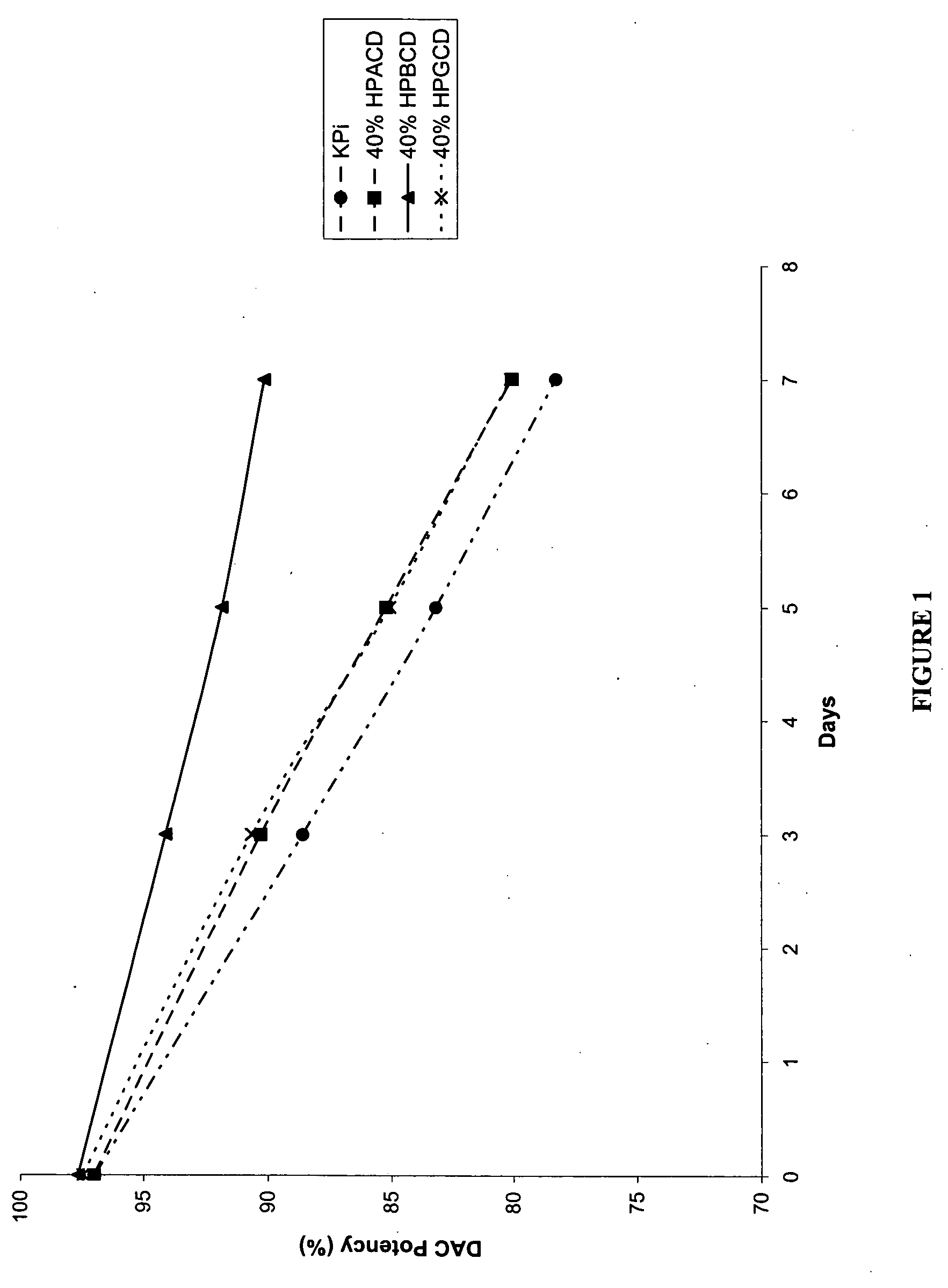
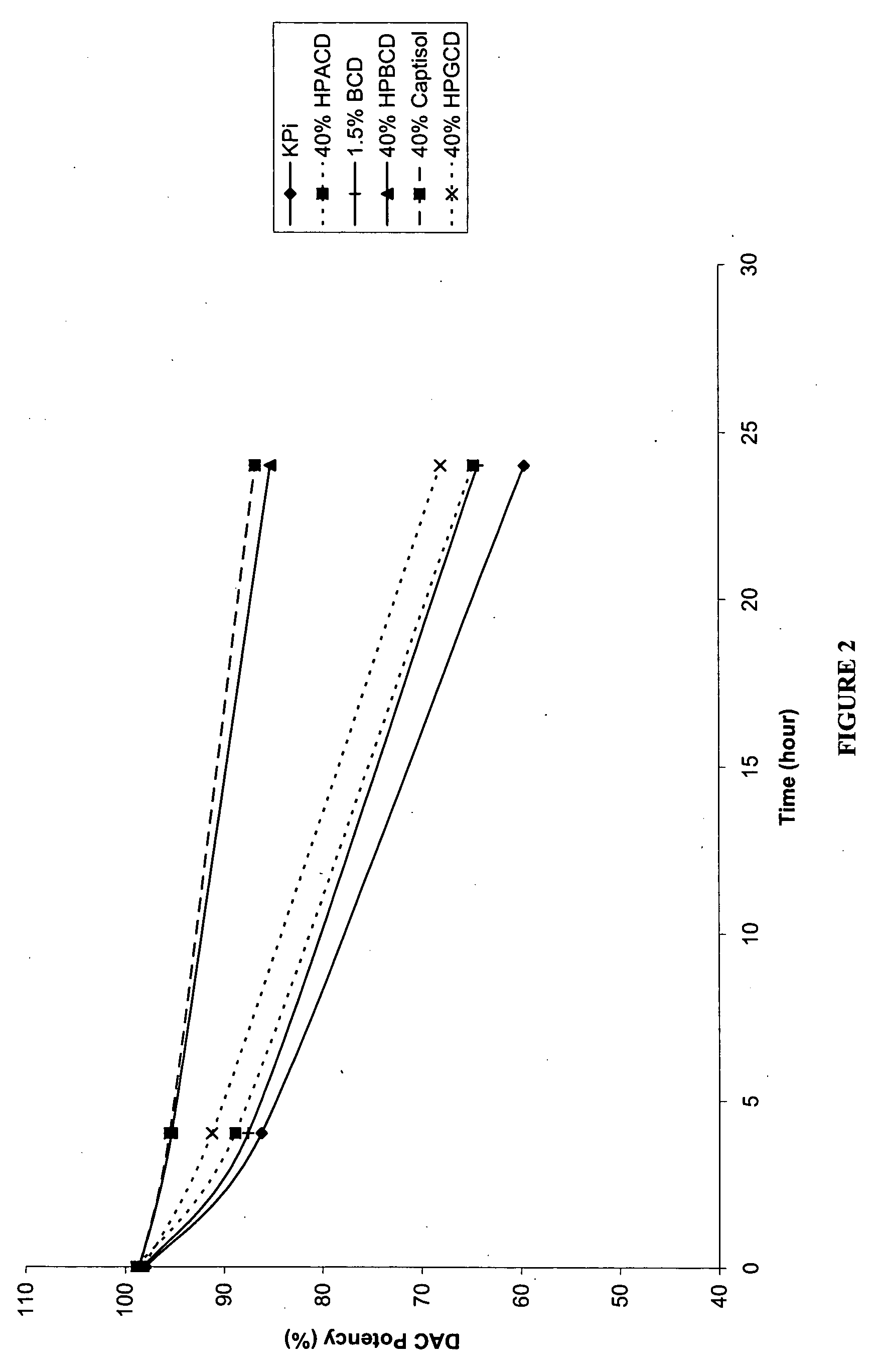
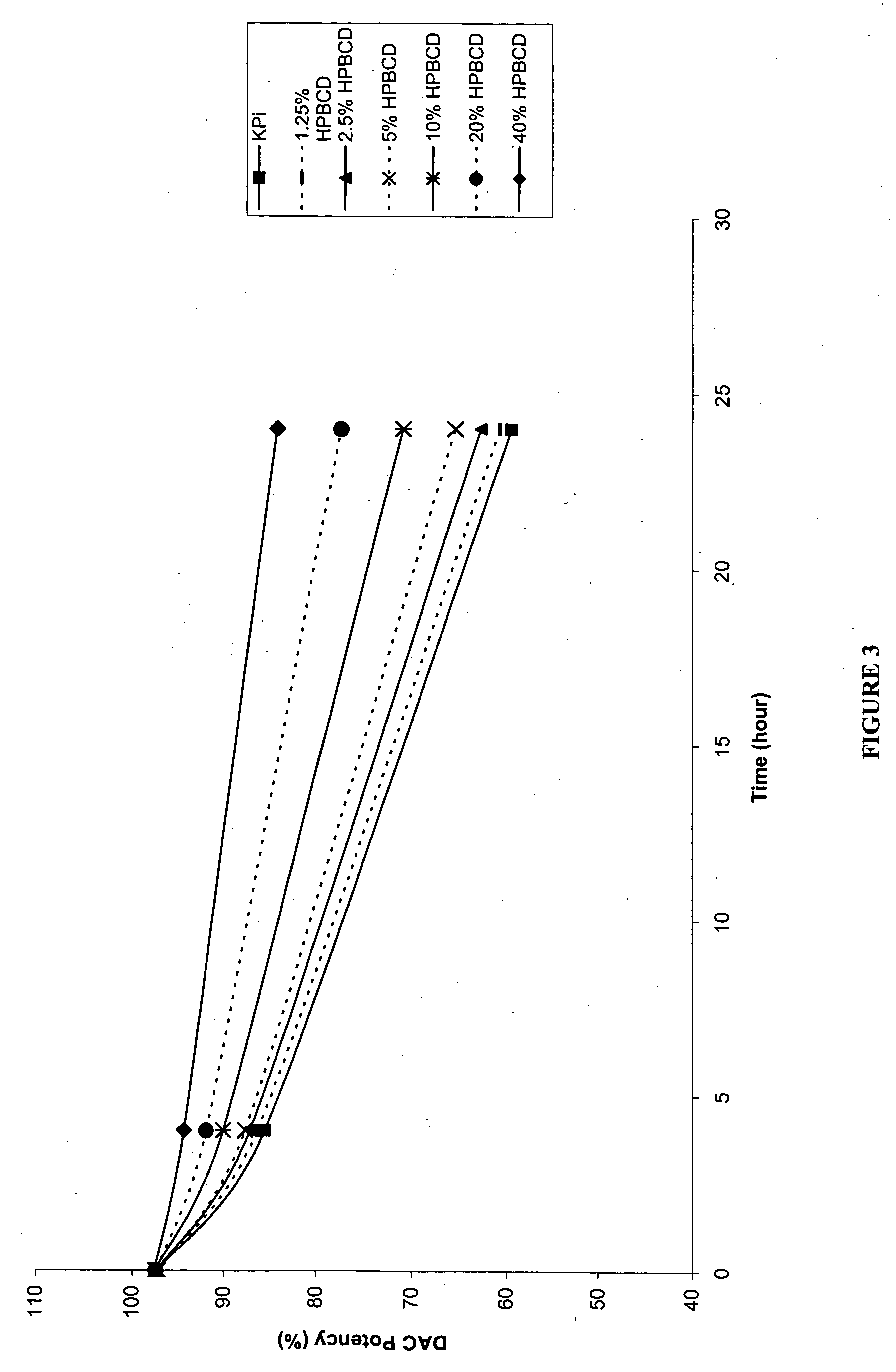
Pharmaceutical formulation of cytidine analogs and derivatives
InactiveUS20060128654A1Reduce decompositionImprove solubilityBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsSolubilityCytosine
The present invention provides pharmaceutical formulations of cytidine analogs and derivatives, such as 5-azacytidine, 5-aza-2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine, 5-aza-2′-deoxy-2′-fluorocytidine, 2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine, and cytosine 1-β-D-arabinofuranoside, as well as methods of manufacturing the formulations. In particular, the cytidine analog or derivative is formulated with a cyclodextrin compound to stabilize and / or enhance solubility of the drug. Kits and methods for using the pharmaceutical formulations are also provided, including methods of administering the cytidine analog or derivative to treat conditions or diseases, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Construction method and application of high-throughout sequencing library
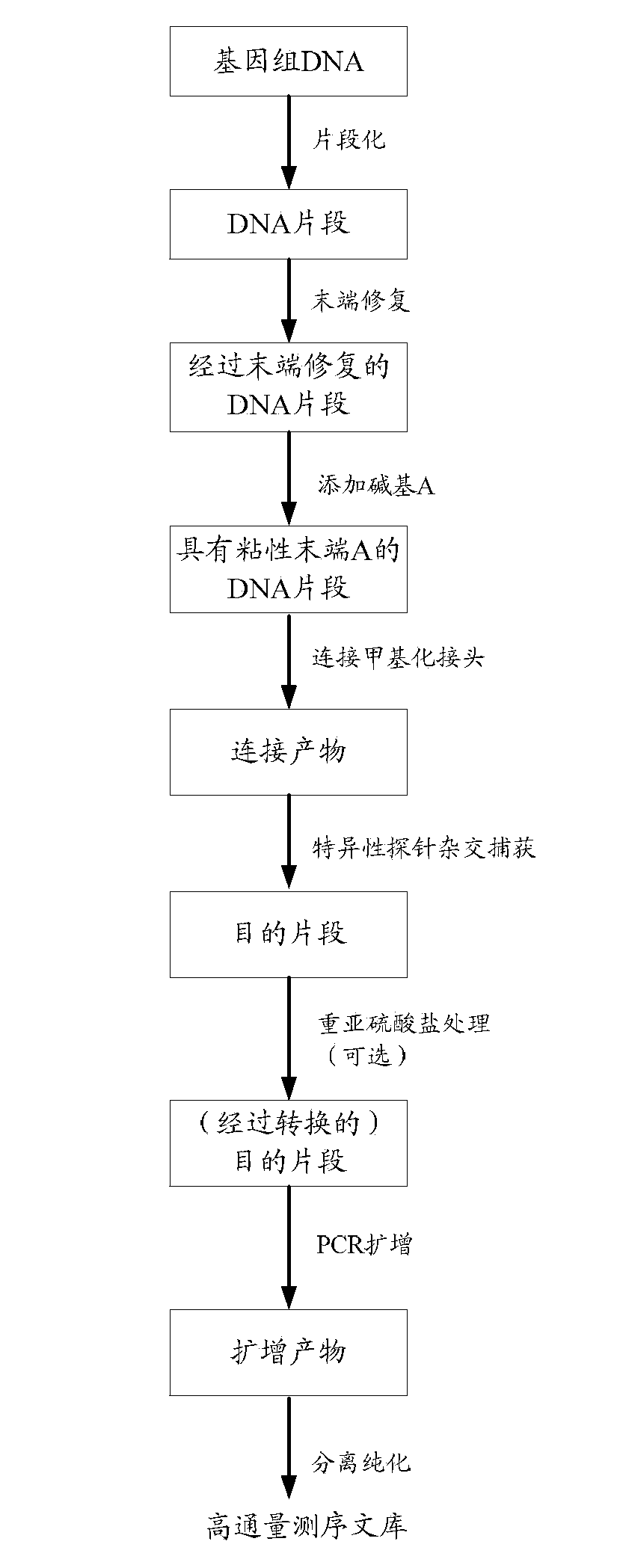
InactiveCN103806111AEfficient constructionEfficiently obtainedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytosineDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a high-throughout sequencing library. The construction method of the high-throughout sequencing library comprises the following steps: fragmenting genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); repairing terminals of DNA fragments; adding a base A to 3' terminals of the DNA fragments with the repaired terminals; connecting the DNA fragments with sticky ends A to methylation linkers; carrying out hybrid capture on connecting products by using a specificity probe so as to obtain target fragments; carrying out bisulfite treatment on the target fragments so as to convert non-methylated cytosine in the target fragments to uracil; carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the converted target fragments; separating and purifying amplification products which form the high-throughout sequencing library. According to the method and application of the high-throughout sequencing library, the high-throughout sequencing library of a genome specific zone of a sample can be conveniently and efficiently constructed.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Construction method and application of genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library and
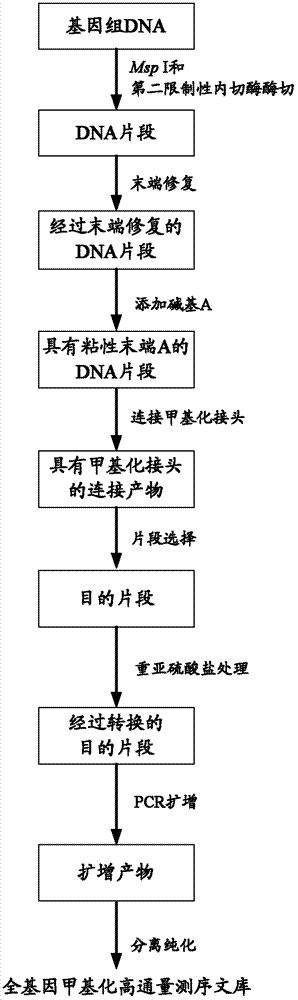
ActiveCN103088433AEfficient constructionEfficiently obtainedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytosineDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a construction method and application of a genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library. The construction method of the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library comprises steps of: conducting digestion on a genome DNA with Msp I and a second restriction endonuclease; conducting end repair on DNA fragments; adding a basic group A on a 3'terminal of the DNA fragment subjected to end repair; connecting a DNA fragment with a cohesive end A to a methylation joint; conducting fragment selection on the connect products with the methylation joint, in order to obtain a target fragment; subjecting the target fragment to a bisulfite treatment, in order to convert unmethylated cytosine in the target fragment to uracil; subjecting the converted target fragment to PCR amplification; and separating and purifying the amplification products, wherein the amplification products form the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library. The construction method and application of the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library provided by the invention can conveniently and effectively construct the genome-wide methylation high-throughput sequencing library of the genome DNA sample.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI
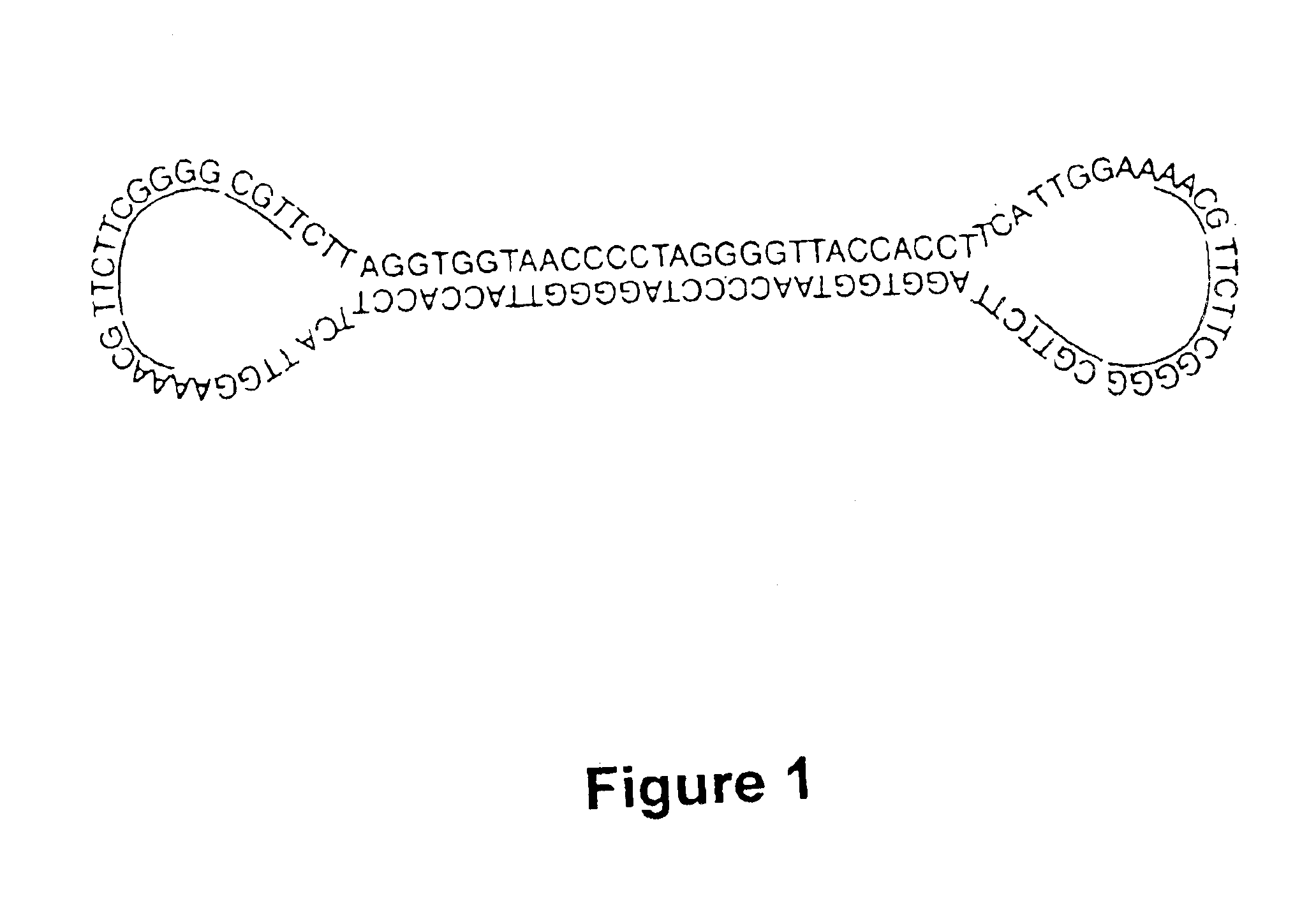
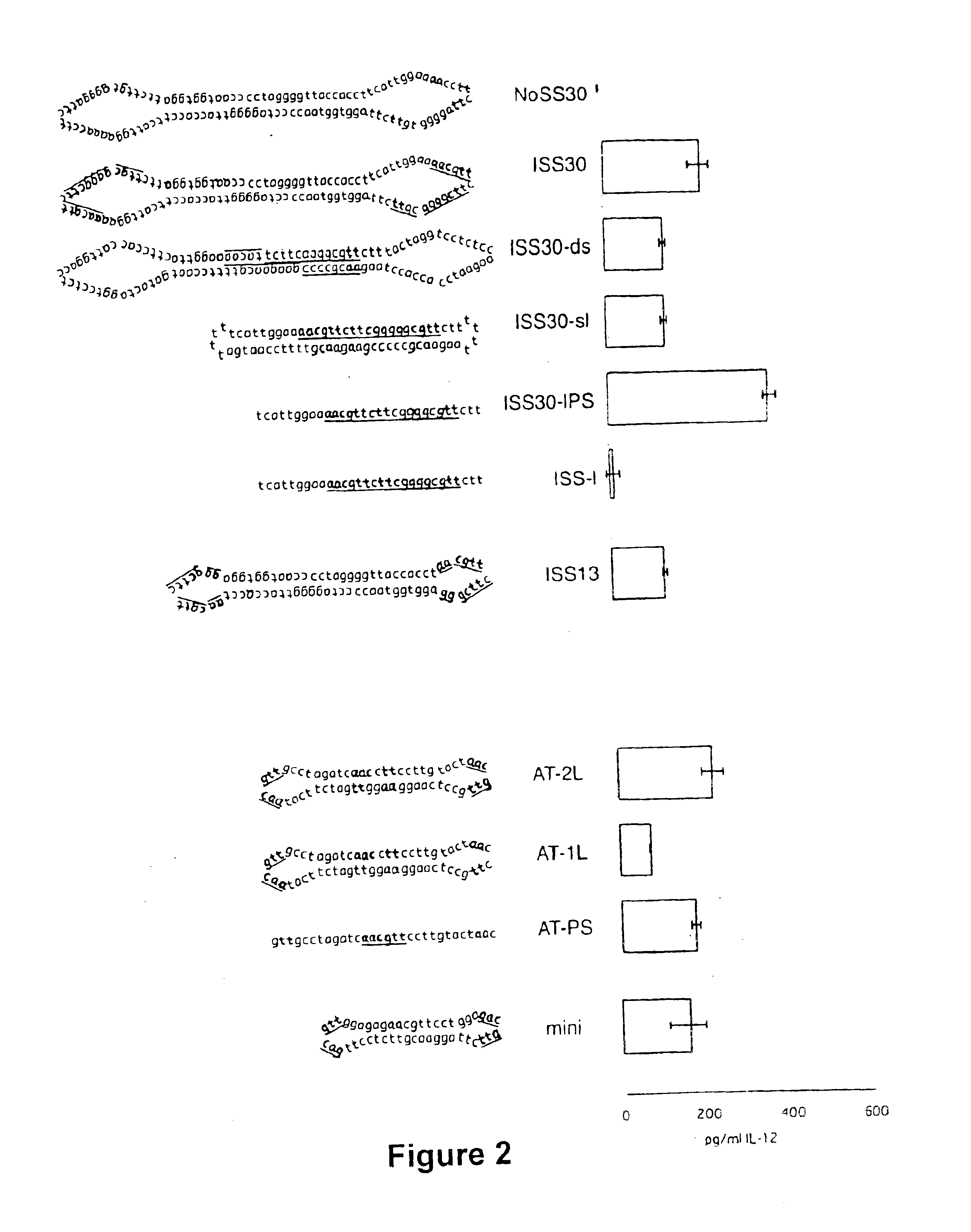
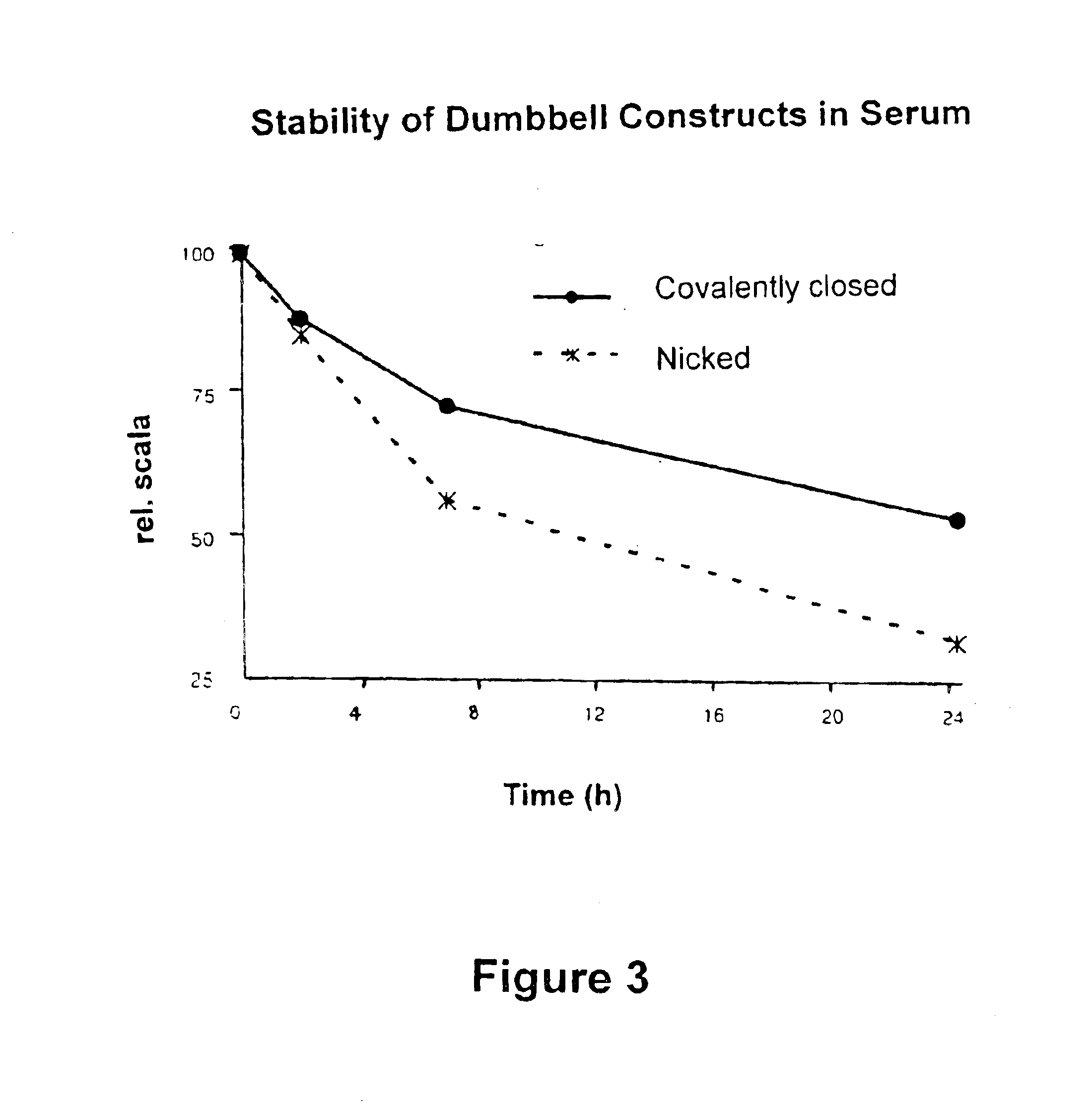
Covalently closed nucleic acid molecules for immunostimulation
InactiveUS6849725B2Improve the level ofIncrease irritationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCytosineSingle strand
Short deoxyribonucleic acid molecules that are partially single-stranded, dumbbell-shaped, and covalently closed, which contain one or more unmethylated cytosine guanosine motif (CpG motif) and exhibit immunomodifying effects. Such molecules can be used for immunostimulation applications in humans or vertebrates.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
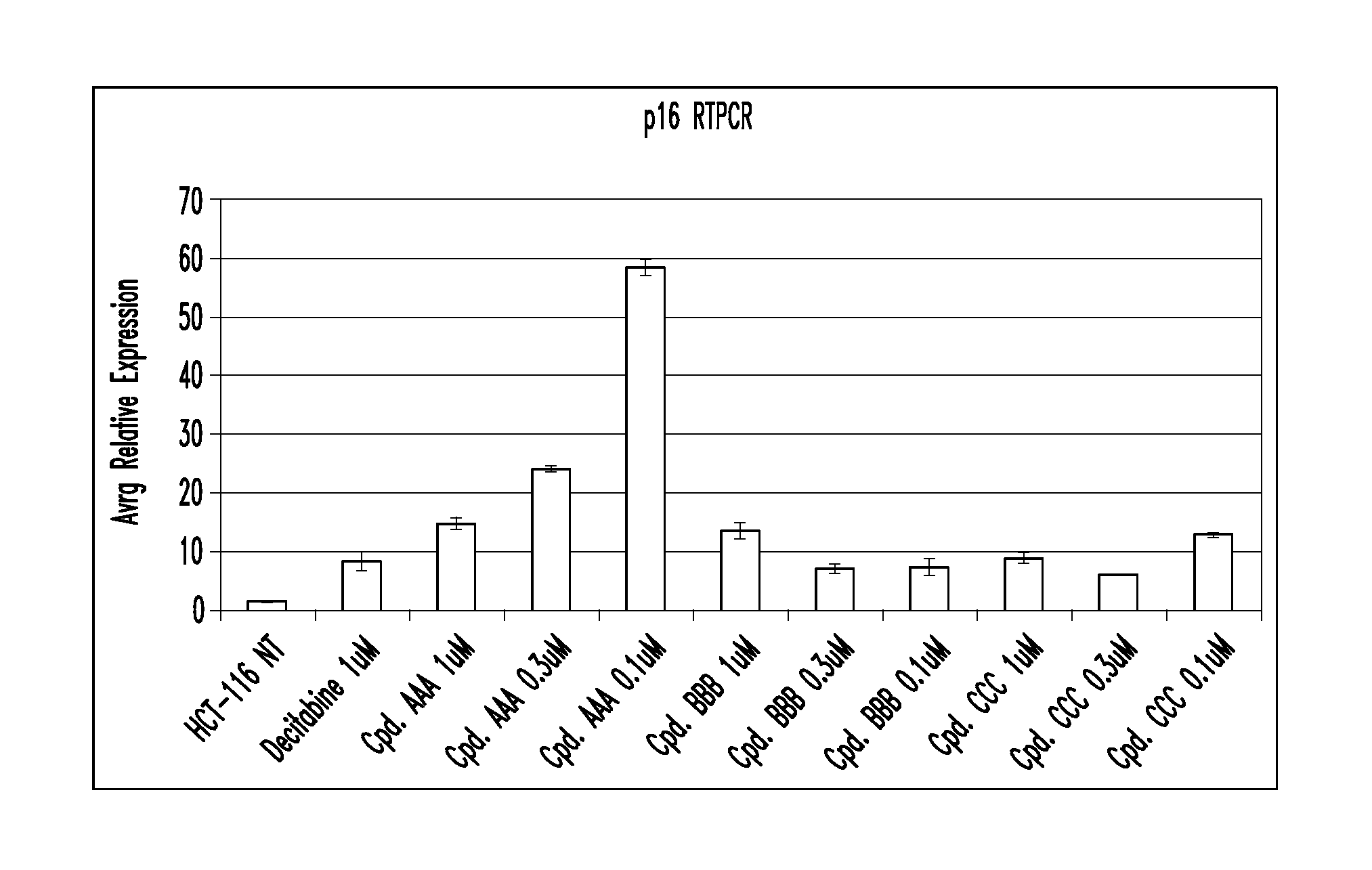
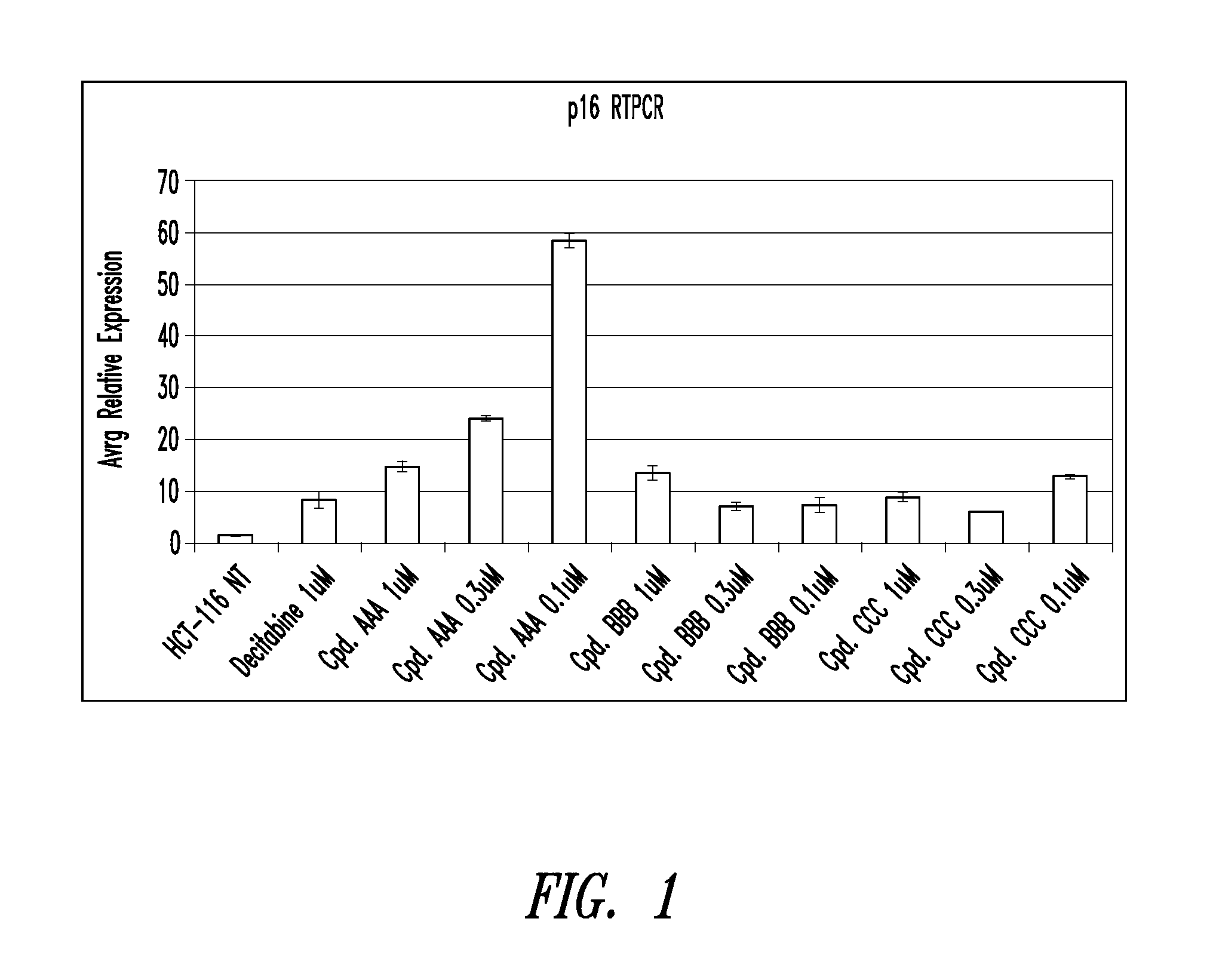
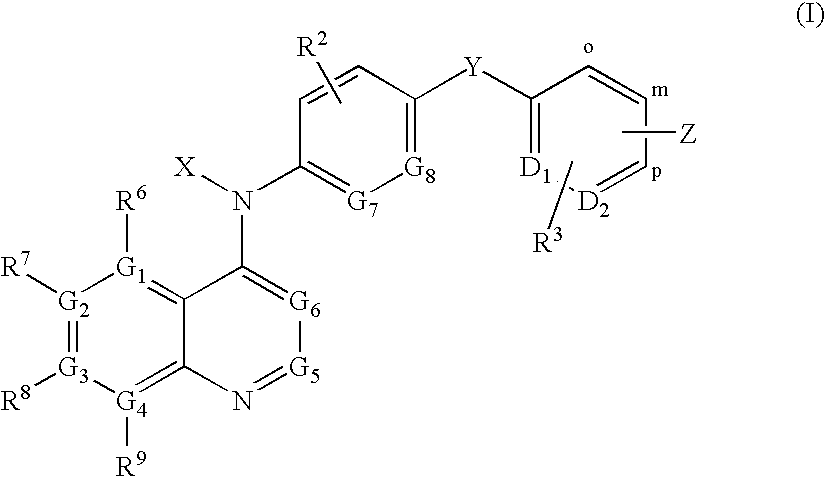
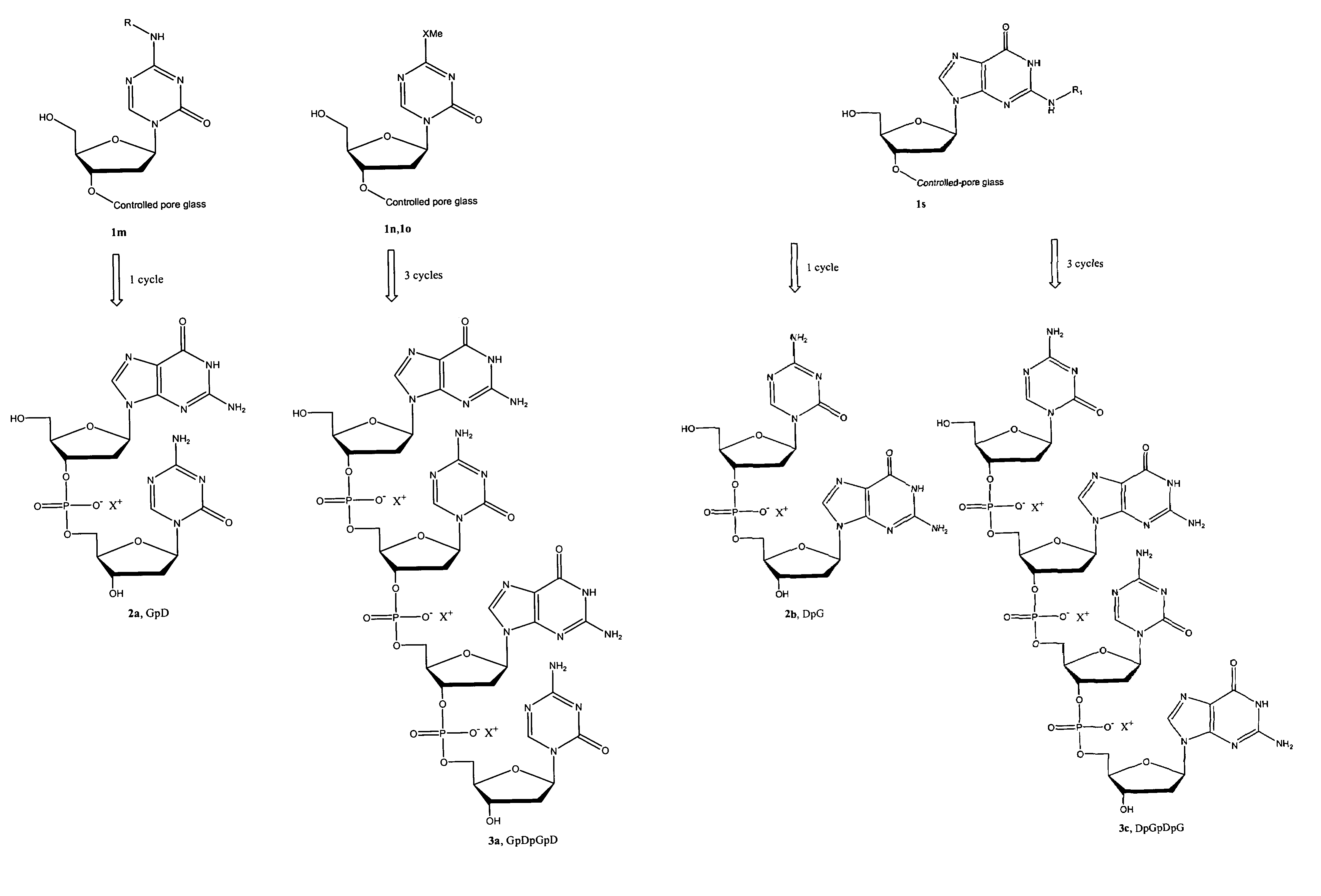
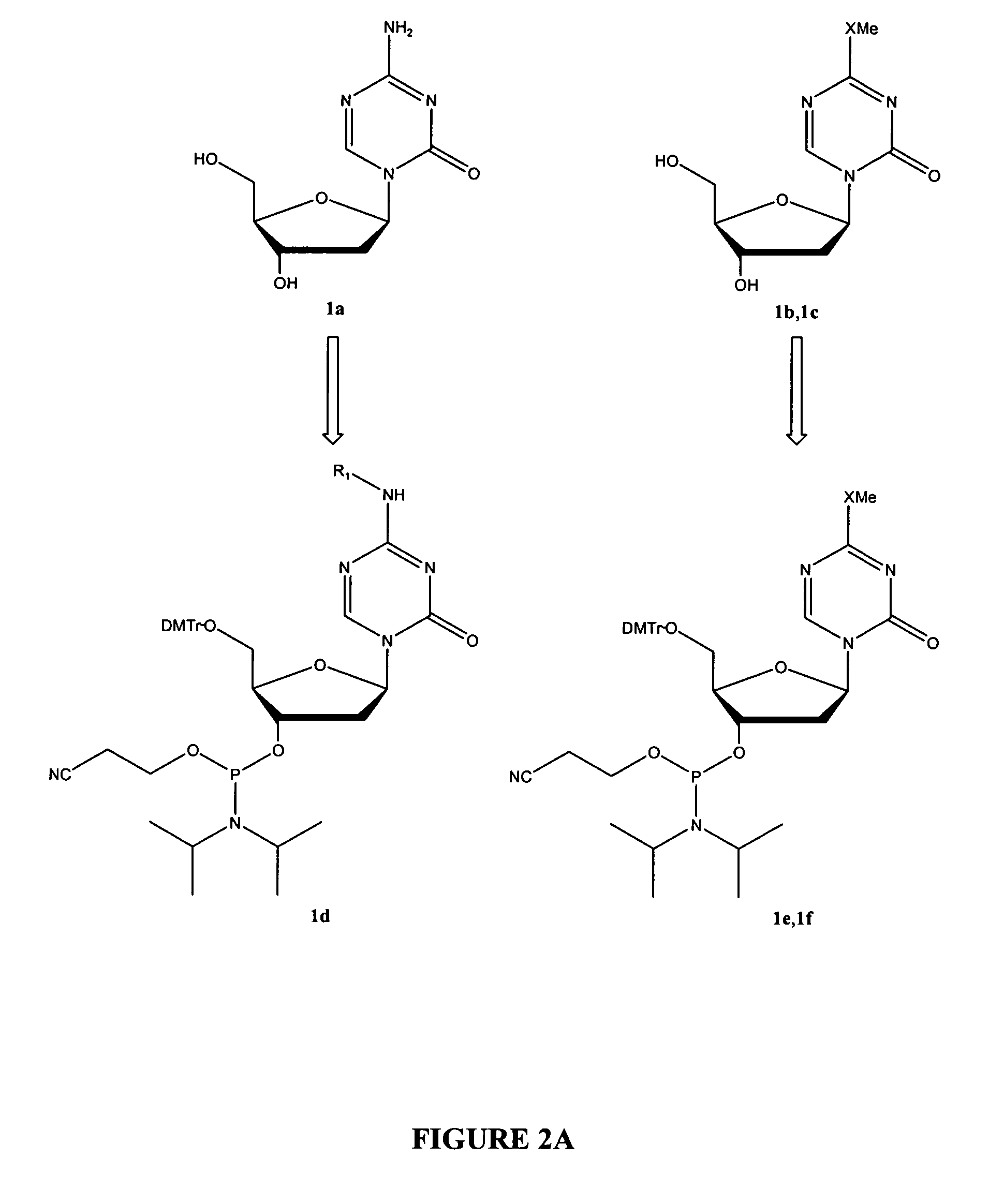
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Diagnosis of diseases associated with metastasis
The present invention relates to the chemically modified genomic sequences of genes associated with metastasis, to oligonucleotides and / or PNA-oligomers for detecting the cytosine methylation state of genes associated with metastasis which are directed against the sequence, as well as to a method for ascertaining genetic and / or epigenetic parameters of genes associated with metastasis.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
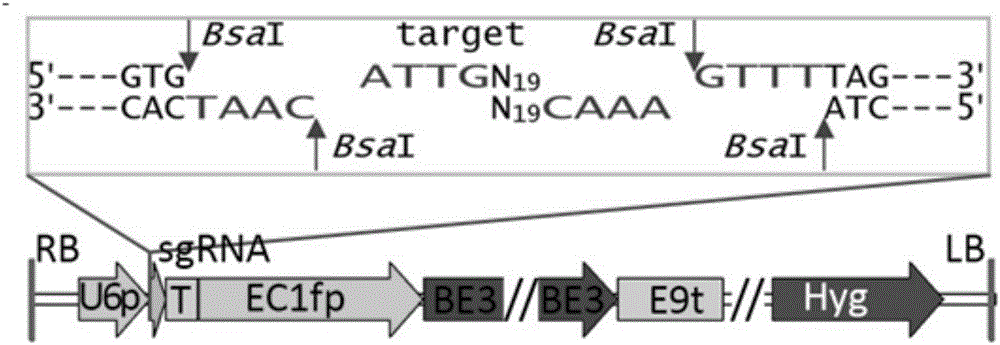
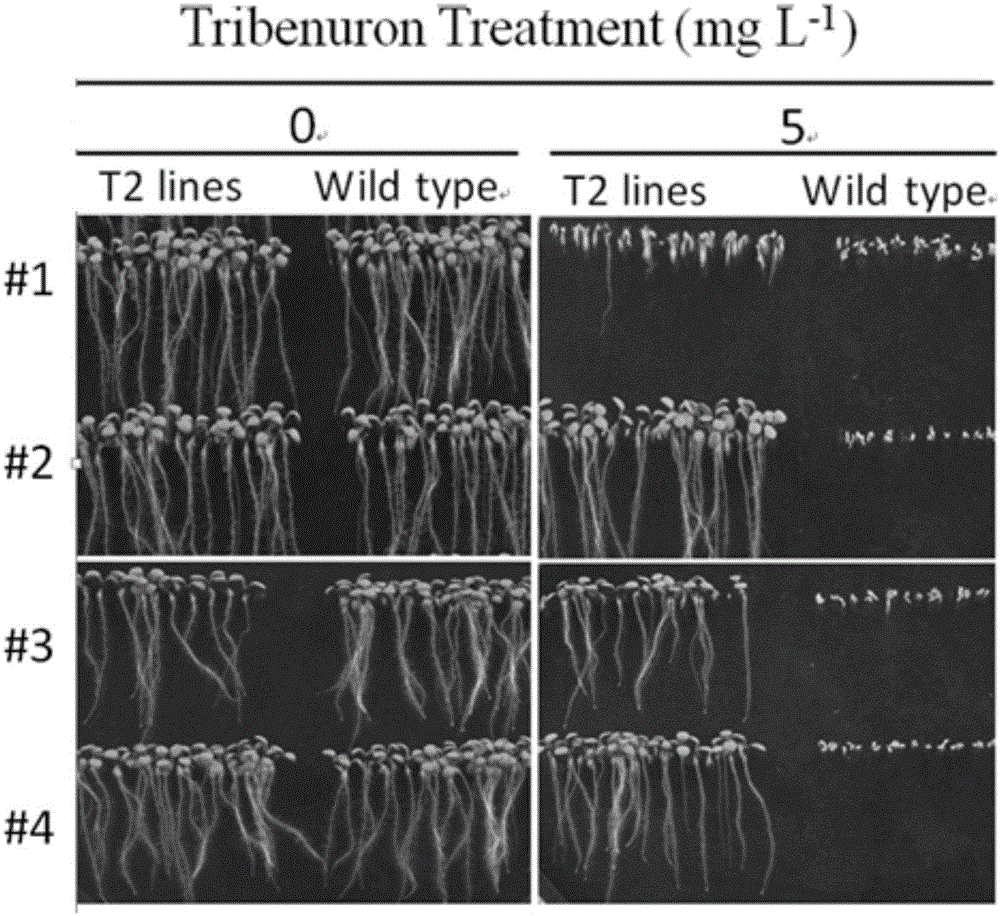
Gene site-directed mutation vector as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106834341ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionCytosine deaminaseCytosine
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and in particular relates to a gene site-directed mutation vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention provides the gene site-directed mutation vector due to lots of optimizations, cytosine deaminase is guided to be close to cytosine through a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system, the cytosine is changed into uracil, then uracil is changed into thymine through self-repair in plant cells, and finally, site-specific mutagenesis from C to T is realized in plants so as to generate resistance to herbicides. In addition, point mutation can be produced in a non-sgRNA targeted area, and novel herbicide-resistant great agronomic traits are brought.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fluorescently-labeled gene multiplex amplification method for identifying sources of goat, sheep, pig and duck meat simultaneously
ActiveCN103397101AAvoid cross interferenceHigh detection throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCytosineFluorescence
The invention provides a fluorescently-labeled gene multiplex amplification technology for detecting sources of goat, sheep, pig and duck meat simultaneously. A method comprises the steps that mitochondria 16S rRNA (ribosomal Robonucleic Acid) and Cyt (Cytosine) b genes of a goat, sheep, a pig and a duck serve as target genes, and are subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) multiplex amplification by two pairs of fluorescently-labeled primers; PCR amplification products are detected by a 3730xl full automatic gene analysis meter; and species identification is performed according to 16S rRNA gene amplified fragment length polymorphism. The method fills in a gap of a detection method of the four kinds of meat.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
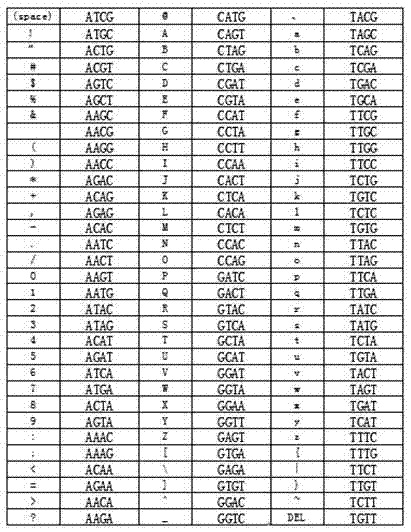
Artificially synthesized DNA storage medium with coding information, storage reading method for information, and applications
ActiveCN104850760AEasy to synthesizeLower Sequencing CostsSpecial data processing applicationsCytosineA-DNA
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, specifically belongs to the technical field of DNA storage, more specifically an artificially synthesized DNA storage medium with coding information, a storage reading method for the information, and applications. Discarding DNA storage technology depended on a mature binary code or a ternary code in the prior art, the invention creatively discloses a DNA storage mode capable of coding directly. Through using storage method capable of coding directly, especially tetragenous basic group coding, the obtained DNA chain storing digit information is short in entire sequence and average content of guanine and cytosine in the sequence is relatively balanced. The method of the invention is in favour of synthesizing, convenient for decoding, and could reduce error rate. The method of the invention can be used for covering a plurality of character types such as English, figure, Chinese and punctuation marks with wide application range.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
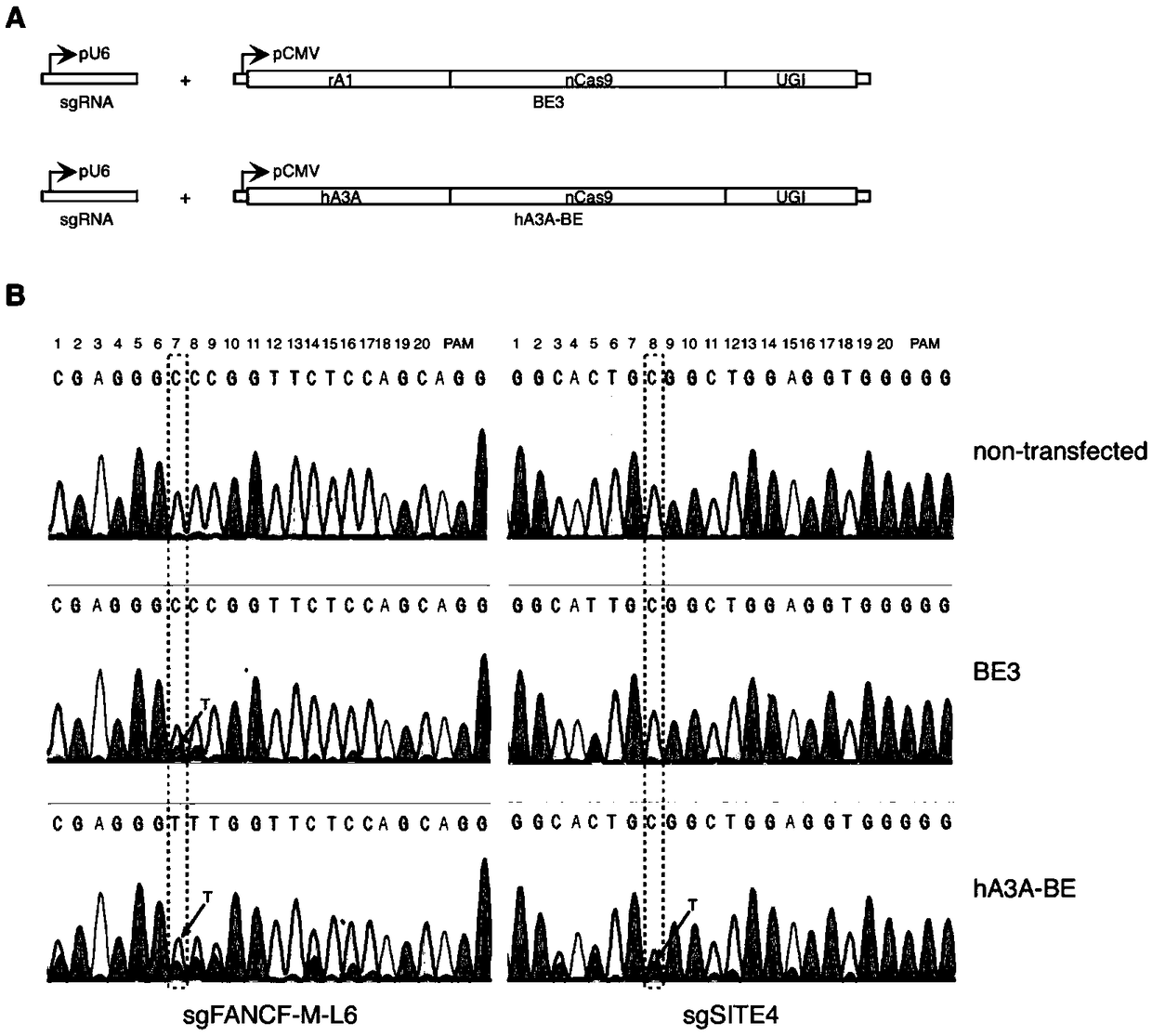
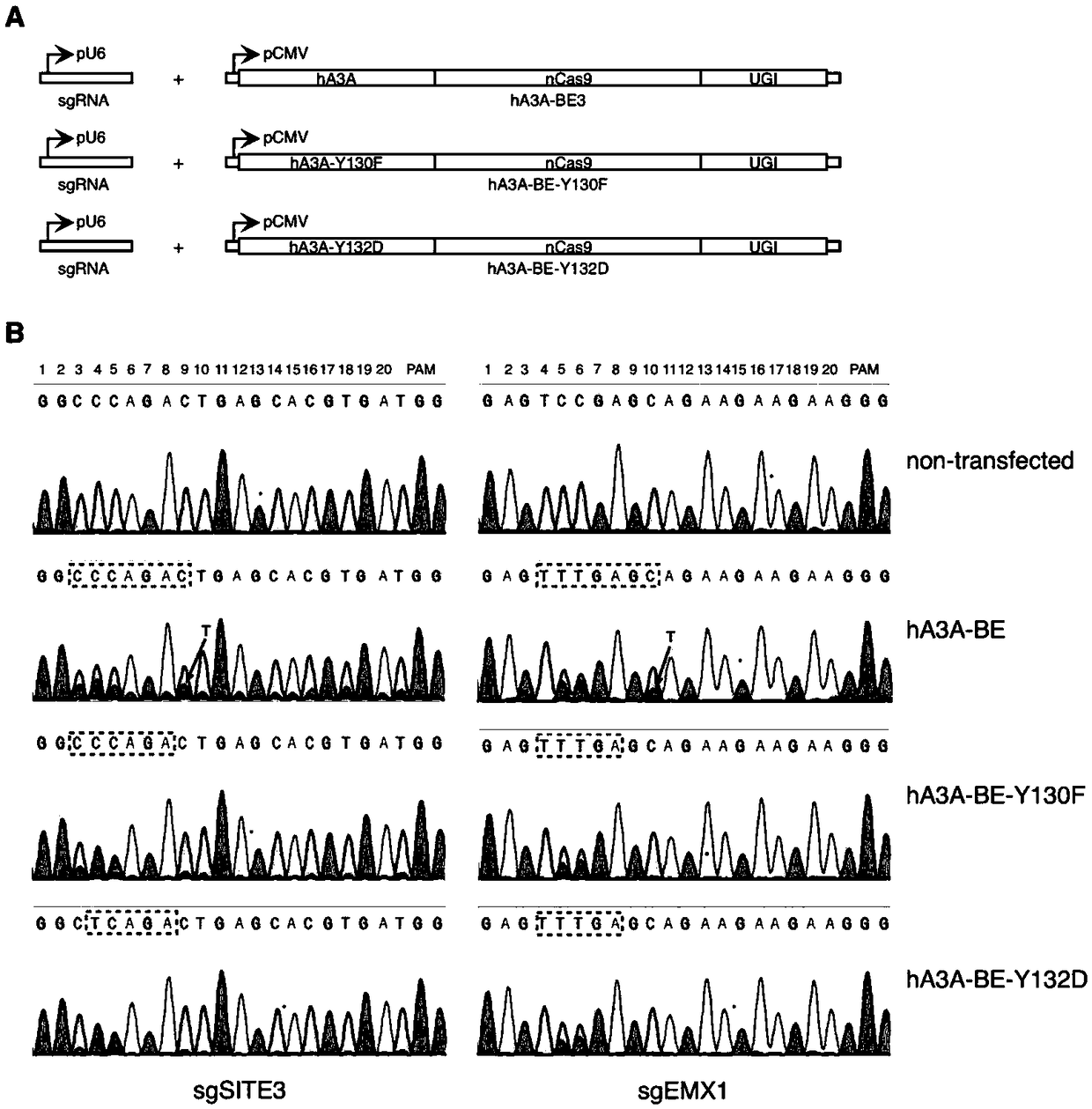
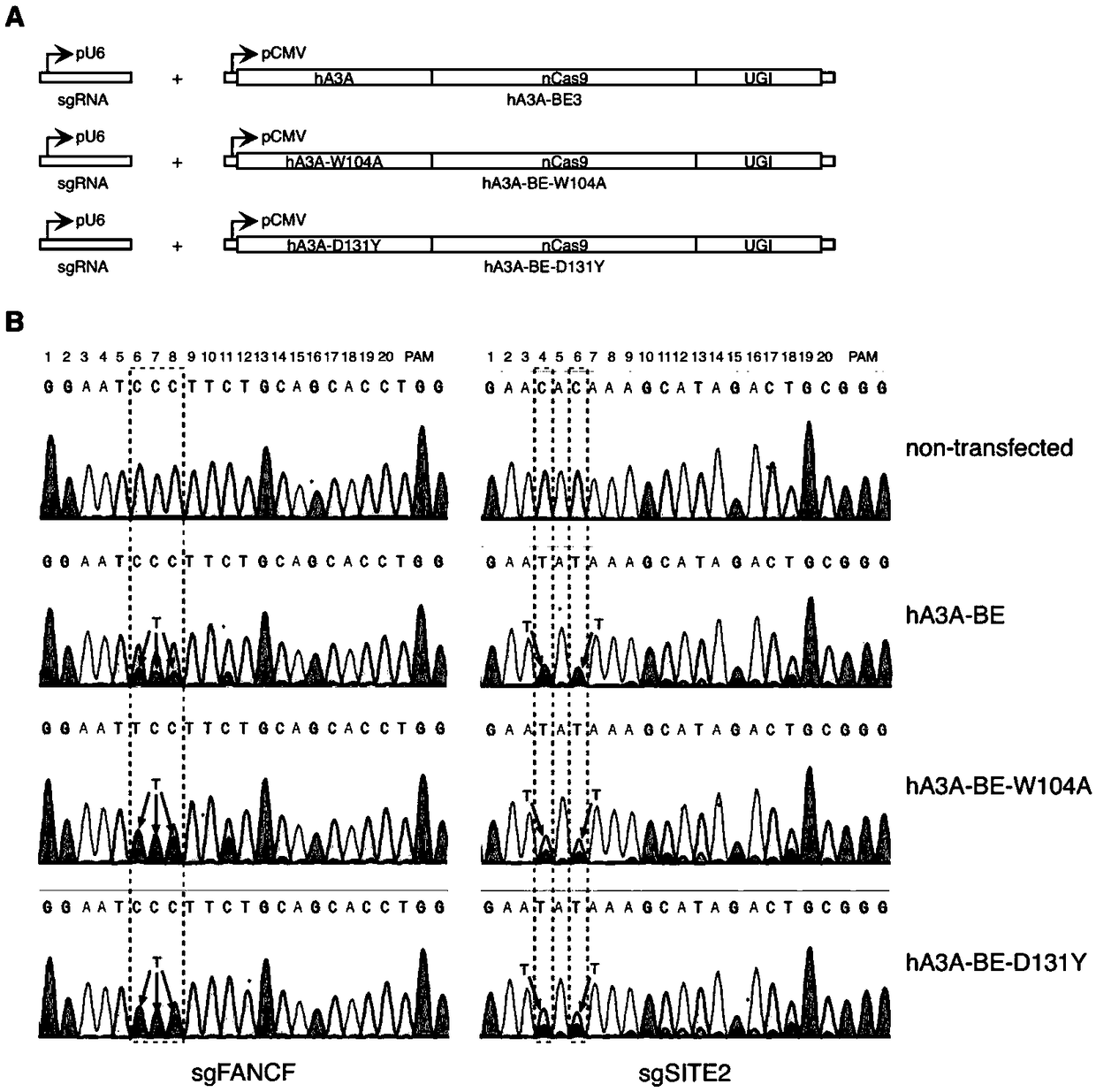
Gene base editor
The invention provides a gene base editor, in particular relates to fusion protein. The fusion protein is characterized by comprising two fragments. The first fragment comprises APOBEC3A and the second fragment comprises CRISPR-related Cas protein. The base editor is capable of performing base edition in DNA and performing deamination on cytosine to be uracil, and the base editor still has higherediting efficiency even if cytosine is located at a GpC site or in a hypermethylated state.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Methods and kits for characterizing GC-rich nucleic acid sequences
Methods and kits of characterizing a GC rich region of a nucleic acid of interest are provided. One method is effected by (a) contacting the nucleic acid of interest with an agent that modifies cytosine or guanine residues into residues complementary to adenine or thymine for obtaining a modified nucleic acid in which the cytosine or guanine residues are replaced by the residues complementary to adenine or thymine; (b) amplifying the modified nucleic acid by amplification primers being hybridizable with the modified nucleic acid and being designed for directing amplification of at least a portion of the modified nucleic acid, for obtaining an amplification product corresponding to the GC rich region; and (c) determining the size of the amplification product, thereby characterizing the GC rich region of the nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:GAMIDAGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com