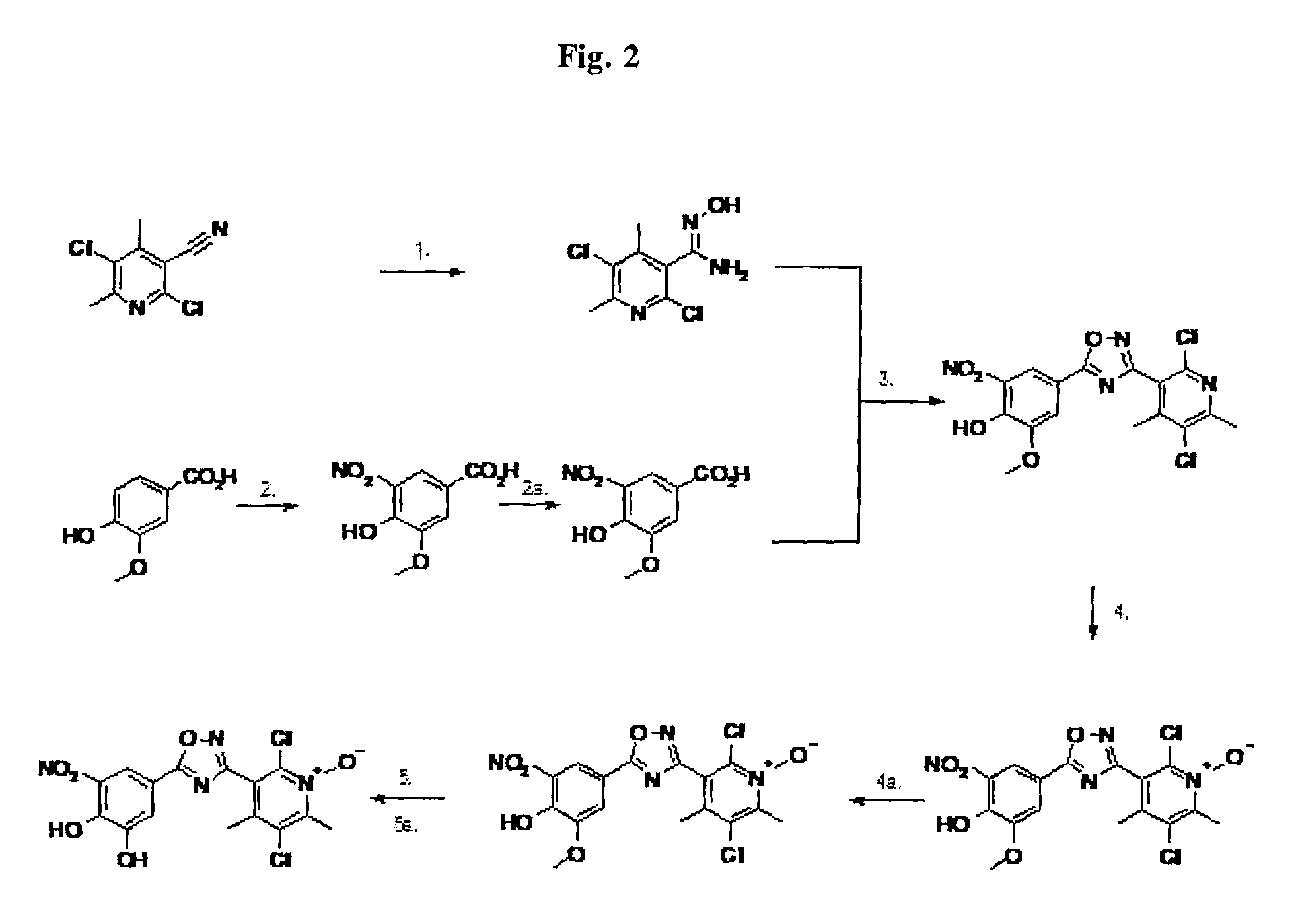
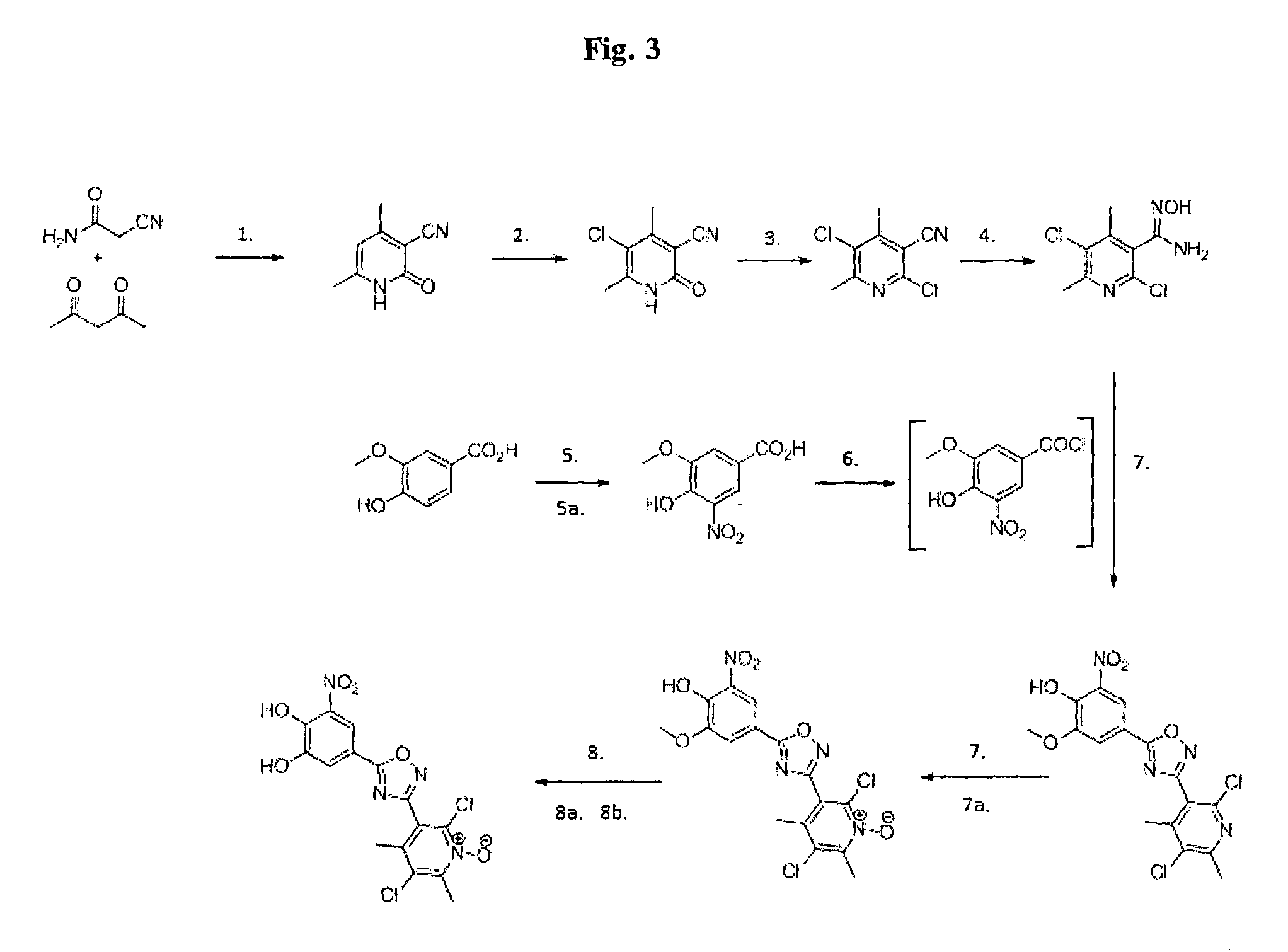
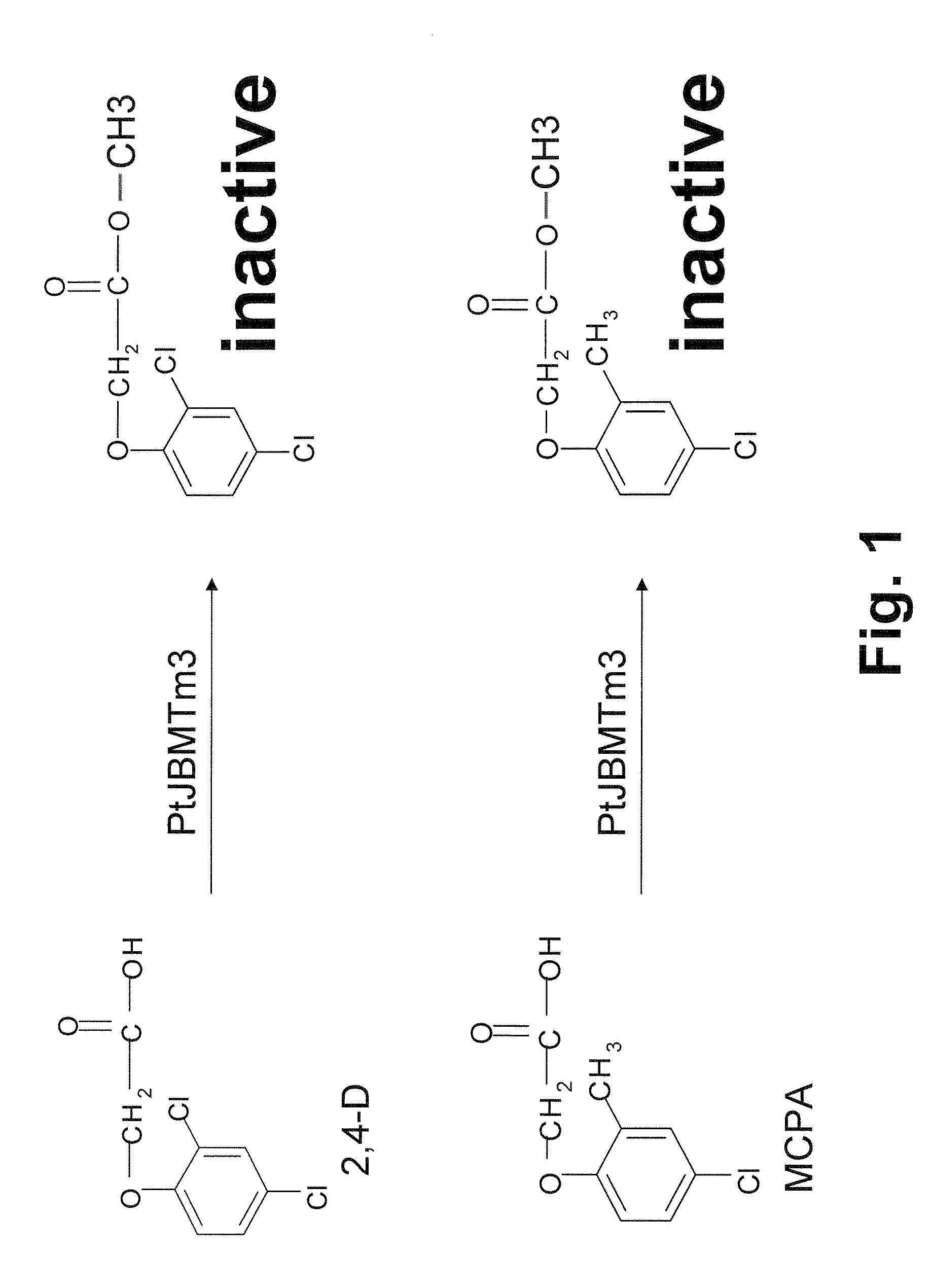
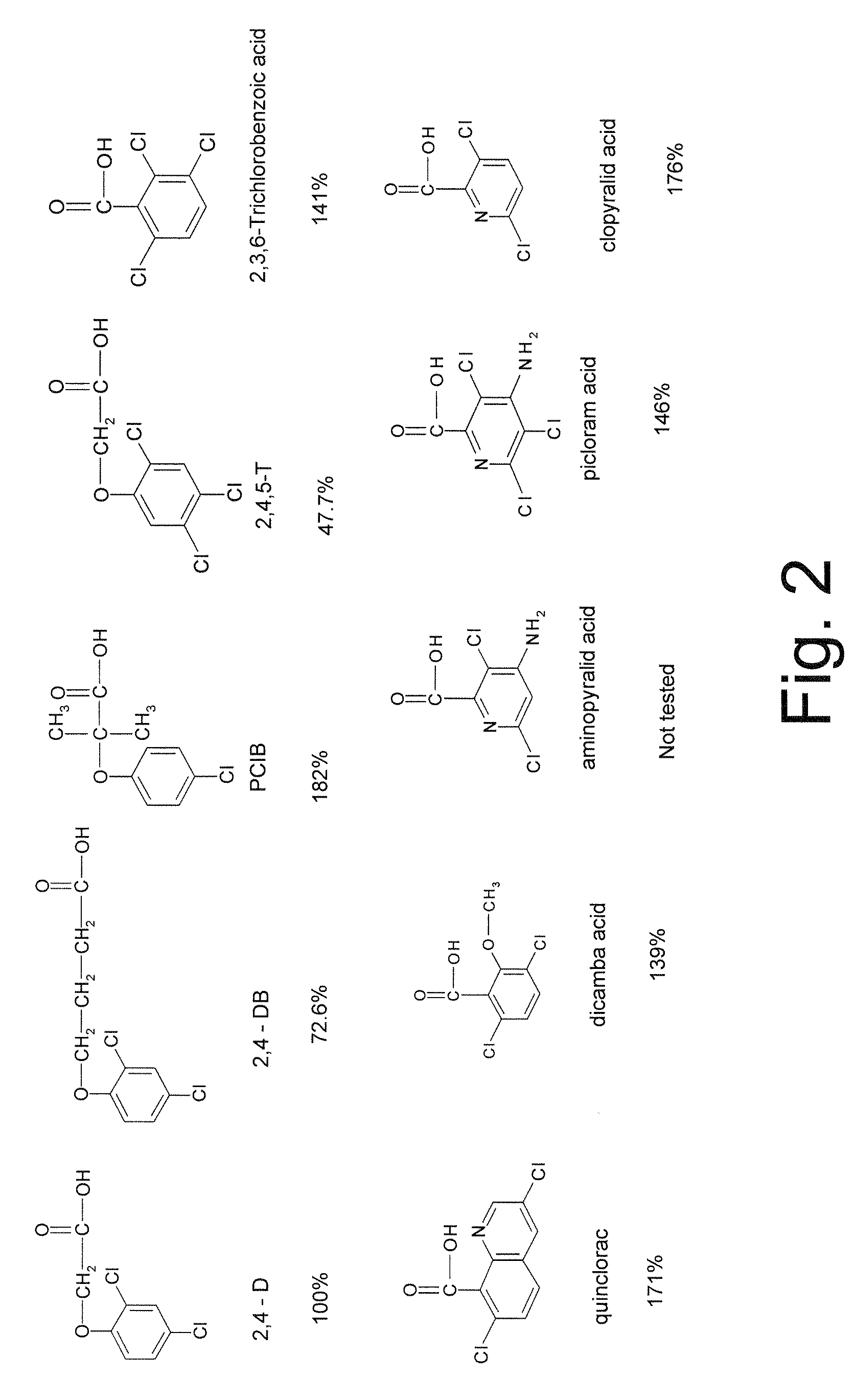
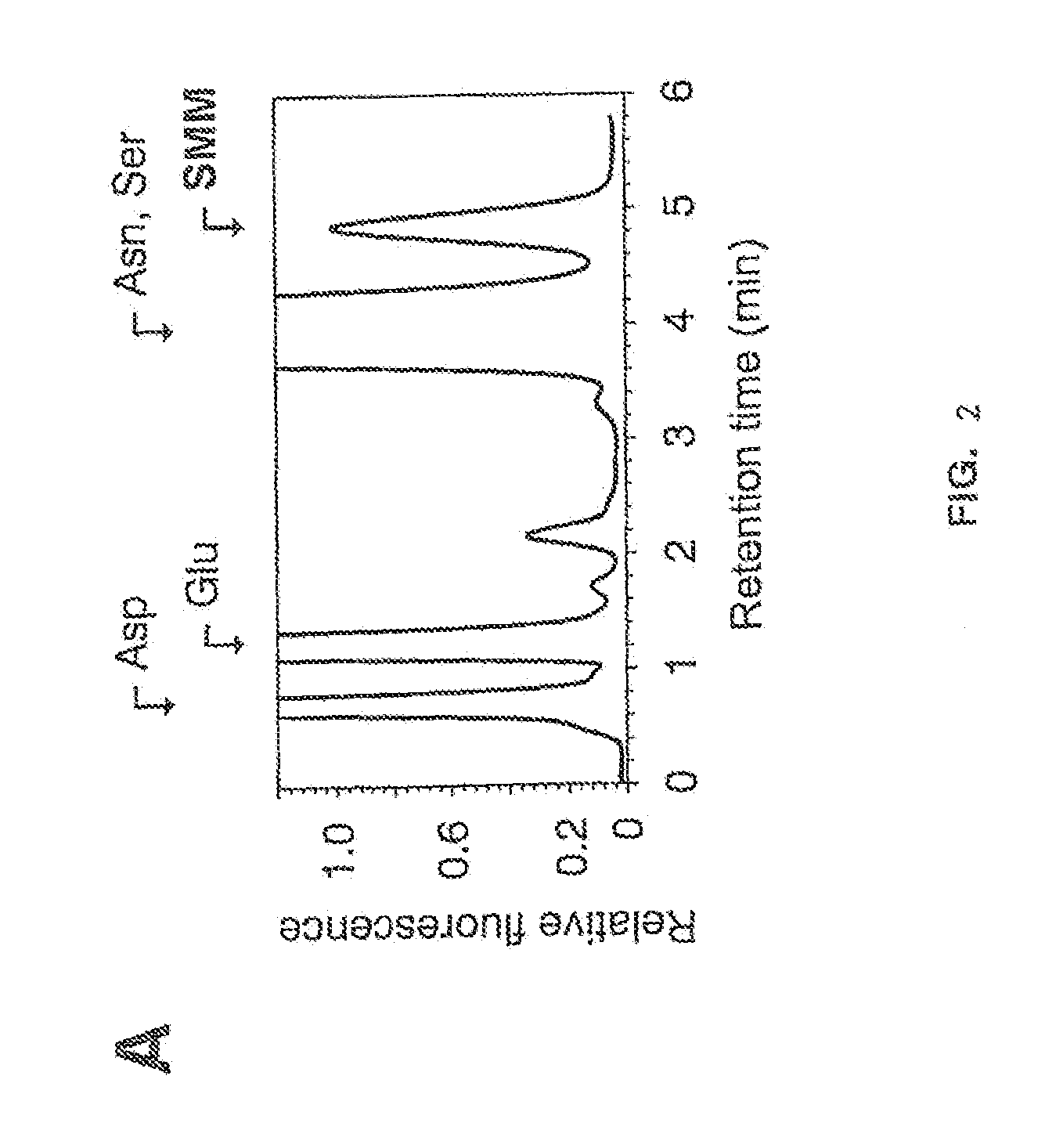
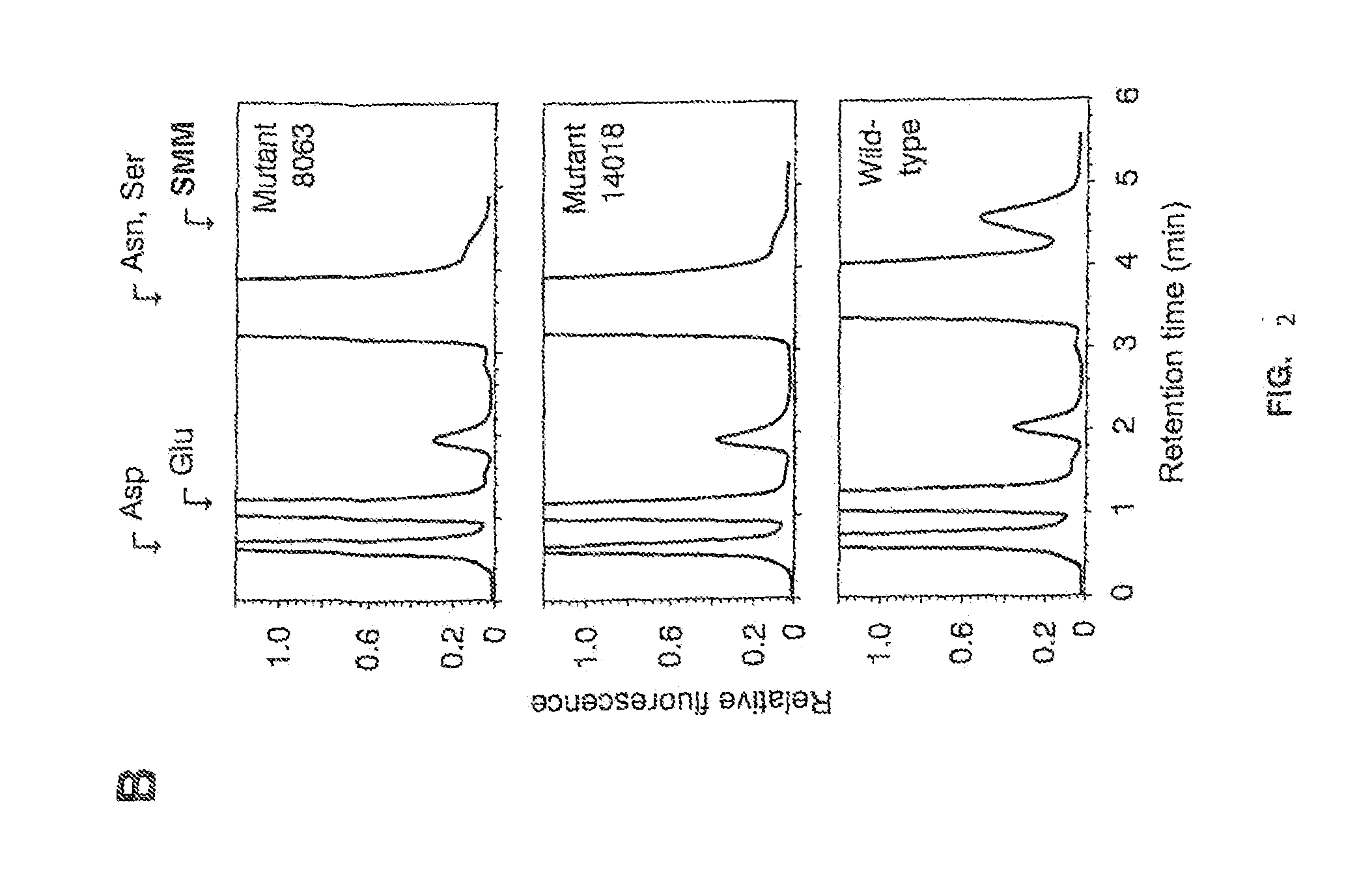
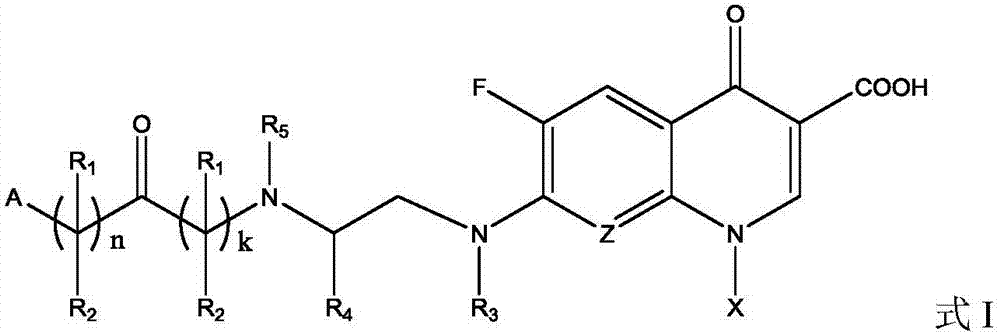
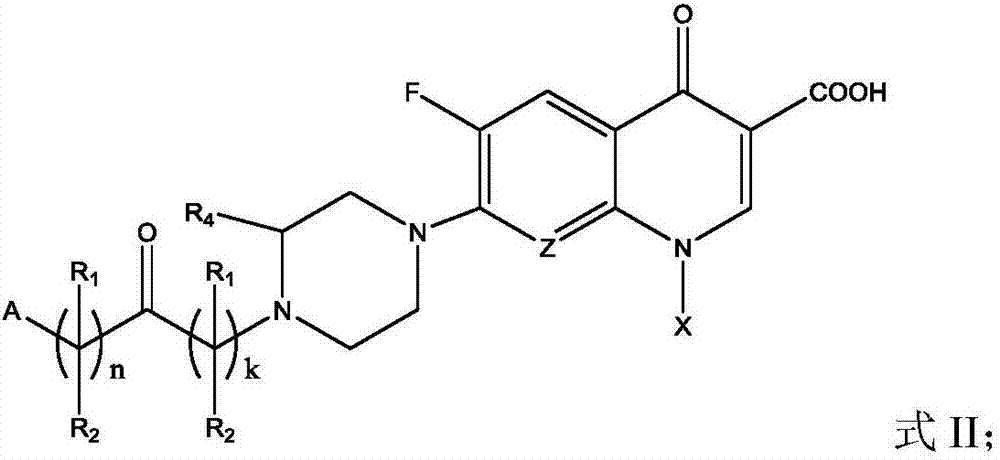
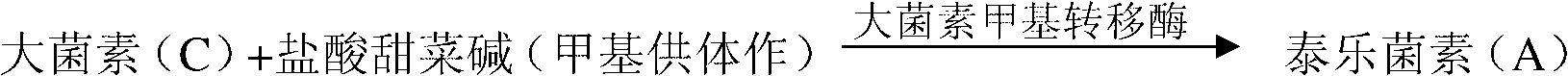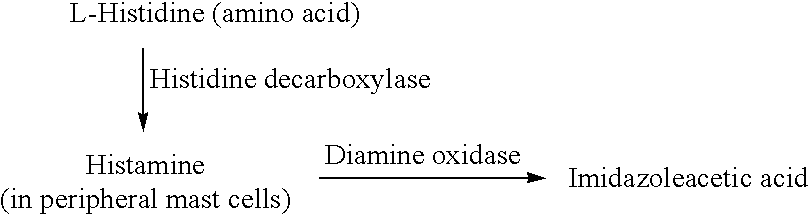Patents
Literature
329 results about "Methyltransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methyltransferases are a large group of enzymes that all methylate their substrates but can be split into several subclasses based on their structural features. The most common class of methyltransferases is class I, all of which contain a Rossman fold for binding S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM). Class II methyltransferases contain a SET domain, which are exemplified by SET domain histone methyltransferases, and class III methyltransferases, which are membrane associated. Methyltransferases can also be grouped as different types utilizing different substrates in methyl transfer reactions. These types include protein methyltransferases, DNA/RNA methyltransferases, natural product methyltransferases, and non-SAM dependent methyltransferases. SAM is the classical methyl donor for methyltrasferases, however, examples of other methyl donors are seen in nature. The general mechanism for methyl transfer is a SN2-like nucleophilic attack where the methionine sulfur serves as the nucleophile that transfers the methyl group to the enzyme substrate. SAM is converted to S-Adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) during this process. The breaking of the SAM-methyl bond and the formation of the substrate-methyl bond happen nearly simultaneously. These enzymatic reactions are found in many pathways and are implicated in genetic diseases, cancer, and metabolic diseases.
Analysis of methylation status using nucleic acid arrays
InactiveUS20050196792A1Efficient amplificationReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCytosineA-DNA
Methods for amplifying a nucleic acid sample while preserving the methylation status of cytosines are disclosed. In some aspects the amplified methylated sample is modified by methylation sensitive modification and analyzed by hybridization to an array to identify cytosines that were methylated in the starting material and cytosines that were not methylated in the starting material. Methods for detecting methylation status are also disclosed. In one embodiment a DNA methyltransferase activity is included in the amplification reaction and this activity methylates the newly synthesized DNA using the methylated genomic template strand as a guide.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
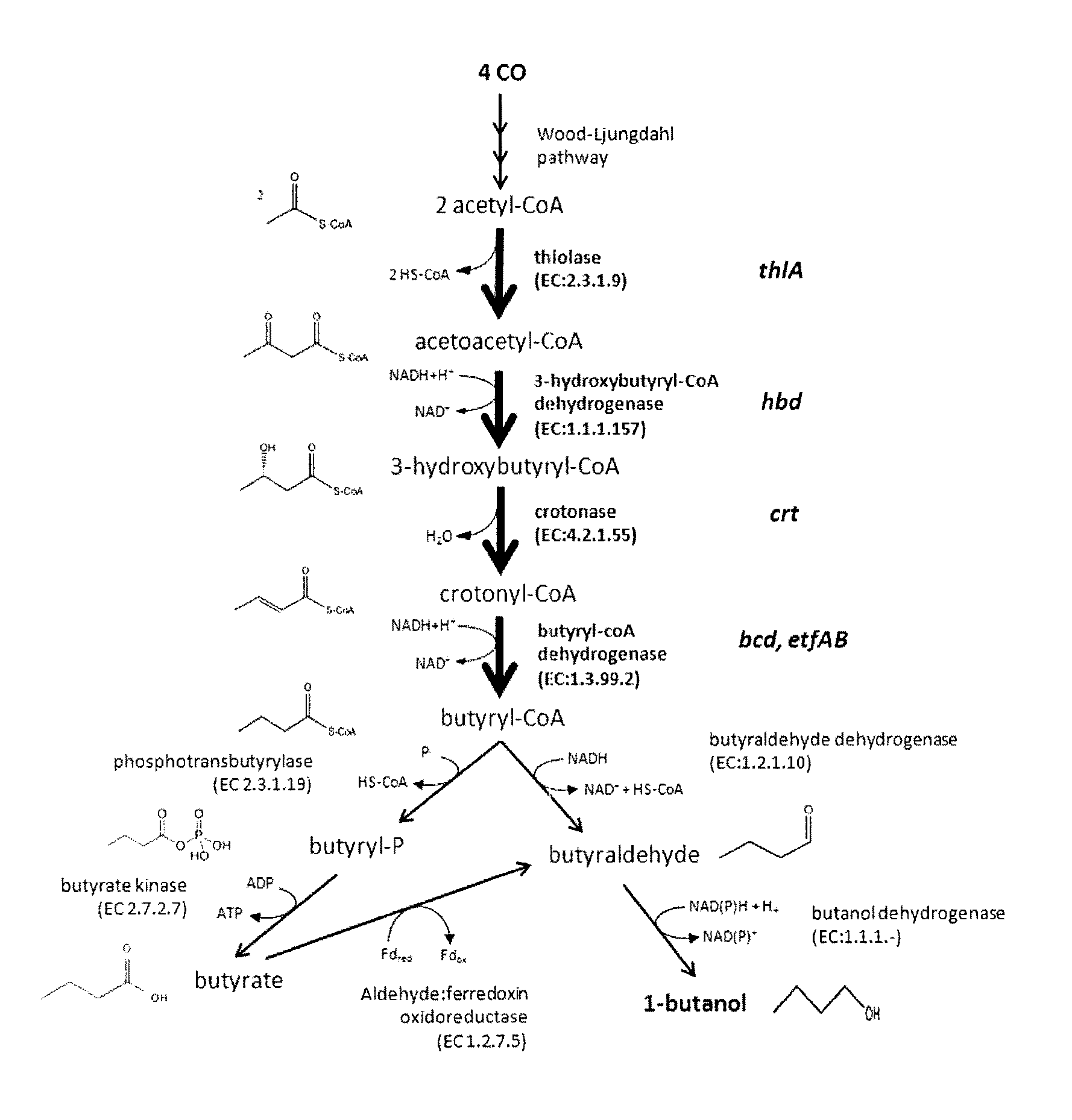
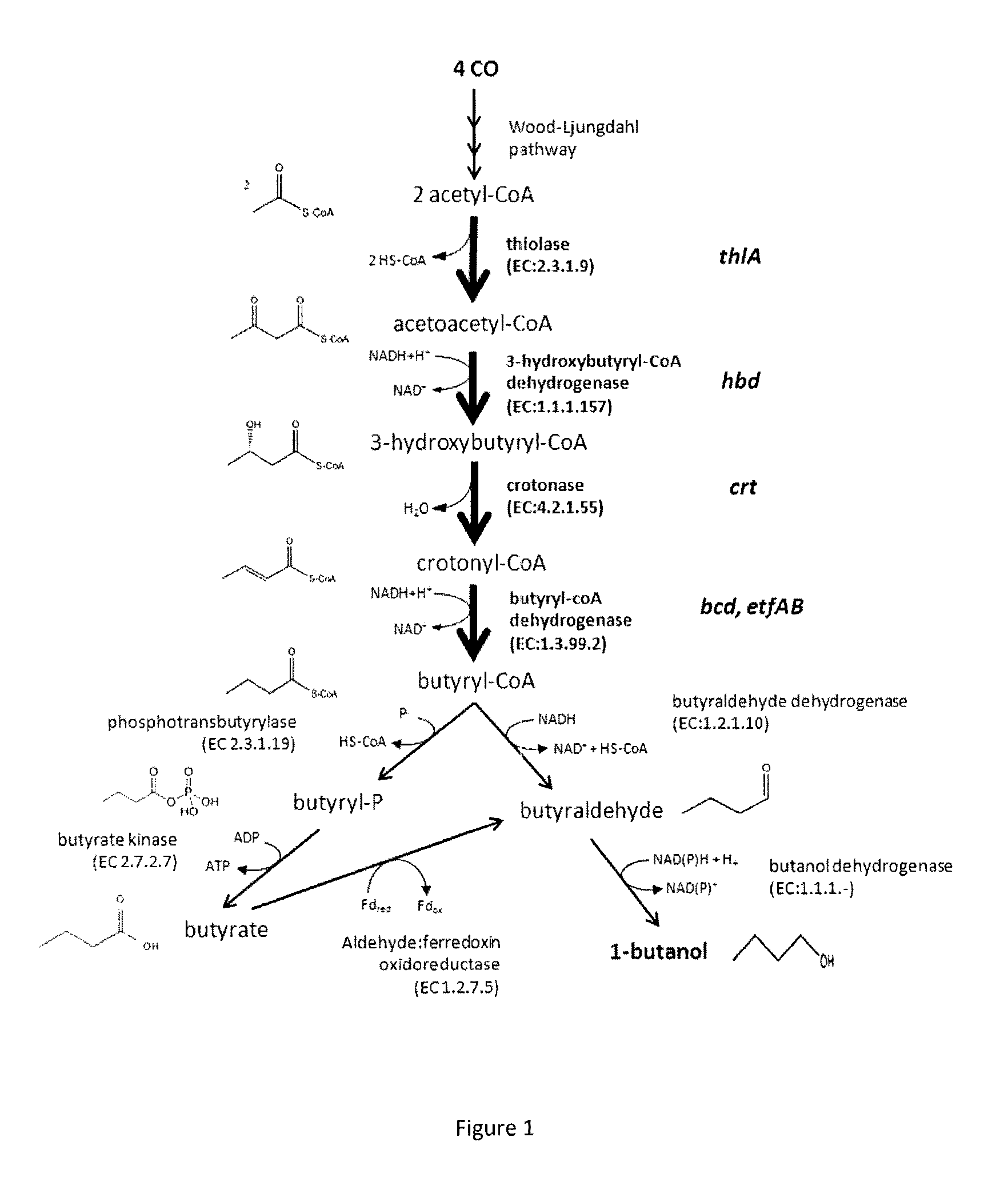
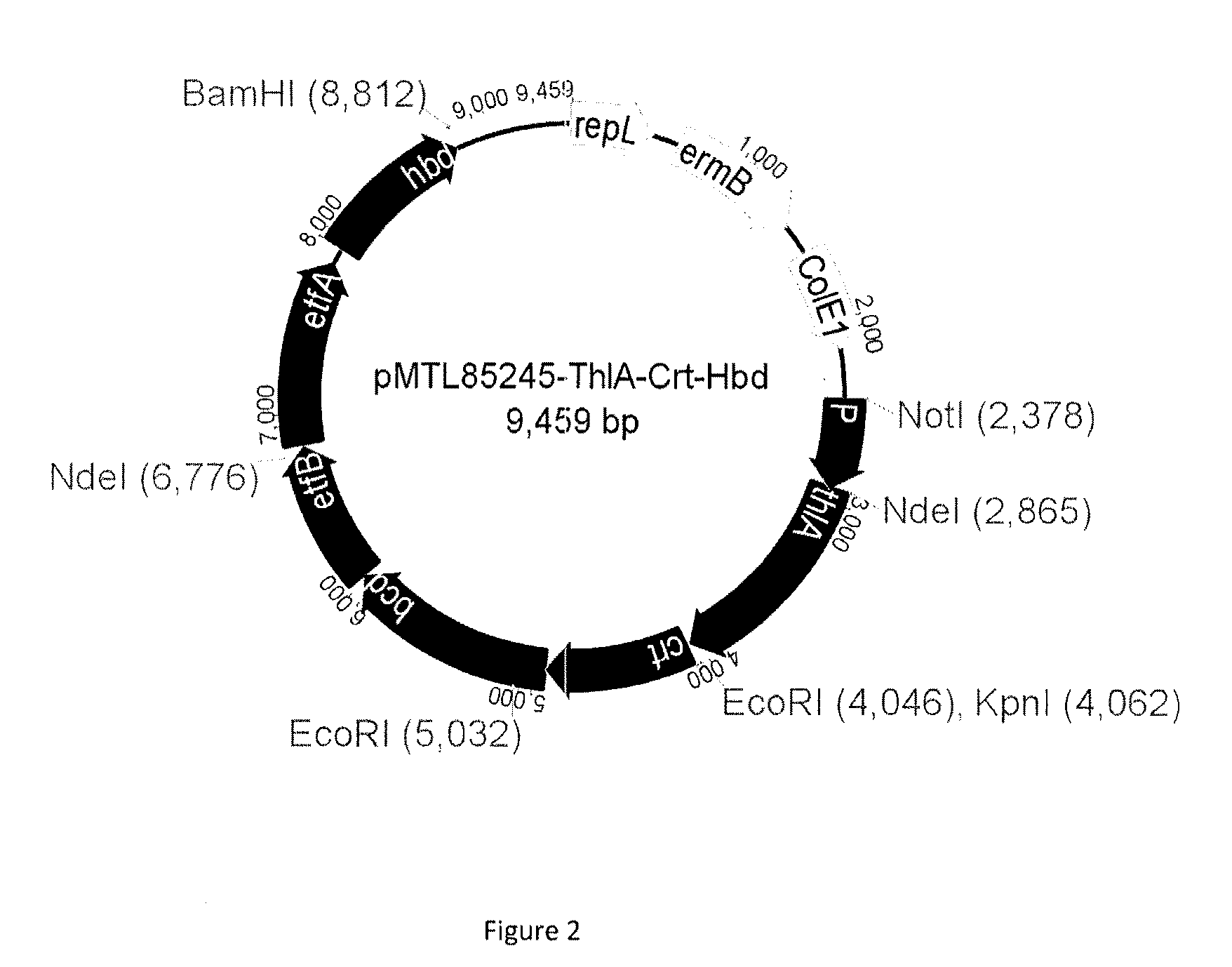
Recombinant microorganism and methods of production thereof
A novel genetically modified microorganisms capable of using CO to produce 1-butanol and / or a precursor thereof, novel methyltransferases and nucleic acids encoding same, methods for producing genetically modified microorganisms using said novel methyltransferases, and methods of producing 1-butanol and / or a precursor thereof by microbial fermentation.
Owner:LANZATECH NZ INC
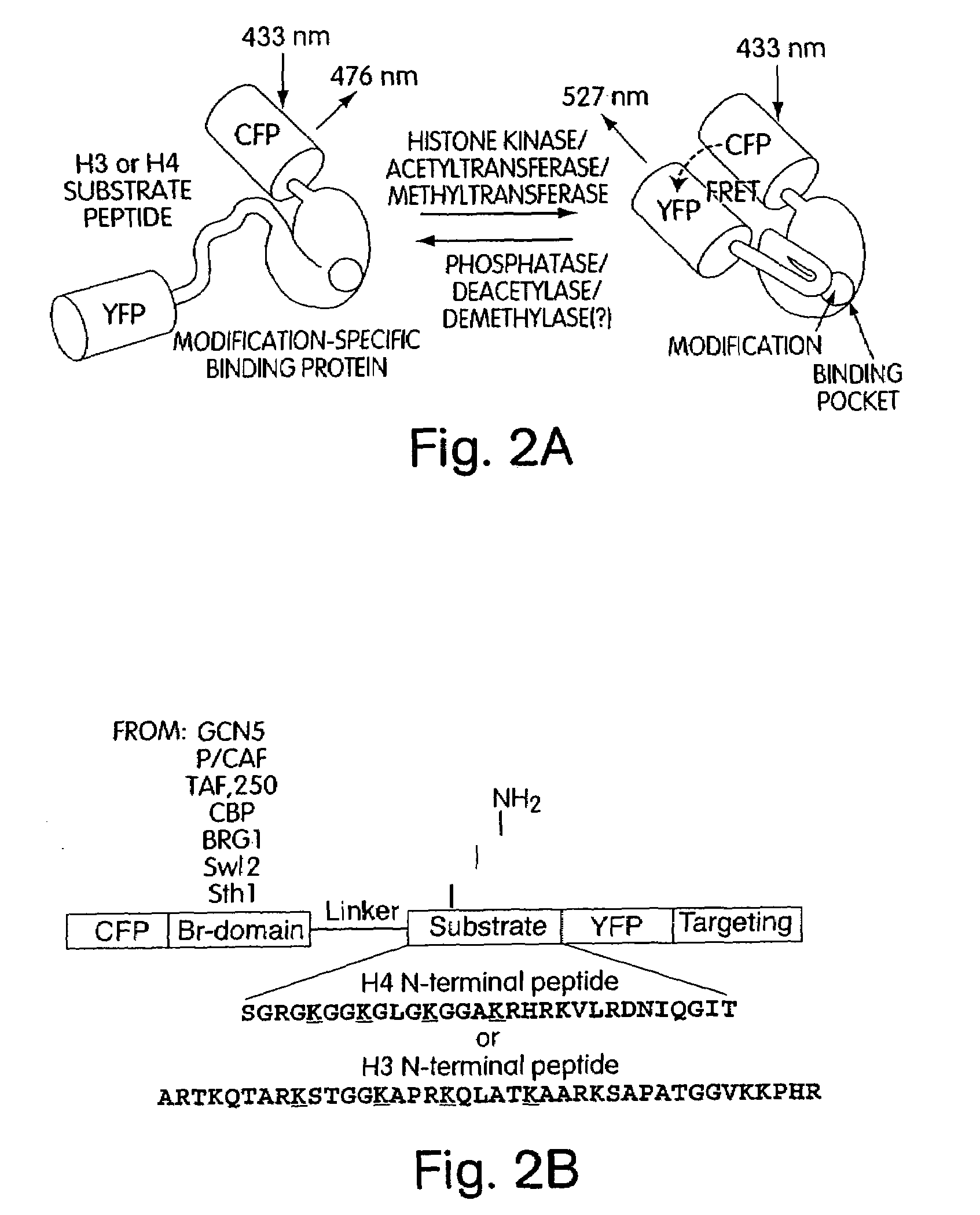
Genetically encoded fluorescent reporters of kinase, methyltransferase, and acetyl-transferase activities
InactiveUS7056683B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesMolecular diagnosticsFhit gene
The invention provides fusion protein reporter molecules that can be used to monitor protein modifications (e.g., histone modifications) in living cells, and methods of using the fusion reporter molecules for diagnosing protein-modification-associated disorders (e.g. histone-modification-associated disorders). The invention also provides methods of using the fusion protein reporters to identify candidate pharmaceutical agents that effect protein modification in cells and tissues, thus permitting identification of candidate pharmaceutical agents for treatment of protein-modification-associated disorders.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
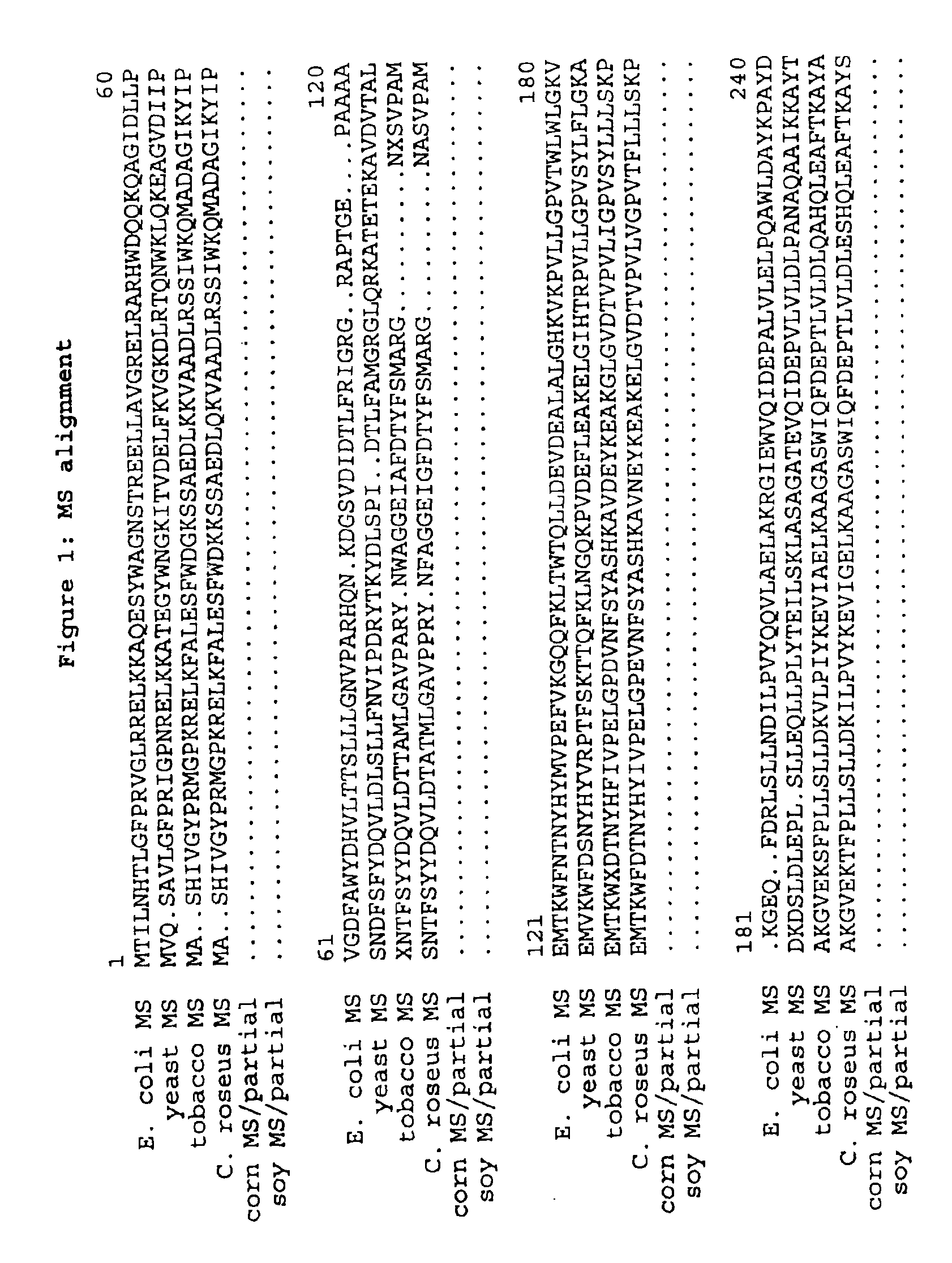
Plant methionine synthase gene and methods for increasing the methionine content of the seeds of plants
This invention relates to a nucleic acid fragment encoding a plant 5-methyltetra-hydropteroyltriglutamate-homocysteine methyltransferase or methionine synthase. The invention also includes chimeric genes, a first encoding a plant methionine synthase (MS) gene, a second encoding a plant cystathionine γ-synthase (CS) gene, a third encoding feedback-insensitive aspartokinase (AK) or bifunctional feedback-insensitive aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase (AK-HDH), which is operably linked to a plant chloroplast transit sequence, and a fourth encoding a methionine-rich protein, all operably linked to plant seed-specific regulatory sequences. Methods for their use to produce increased levels of methionine in the seeds of transformed plants are provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
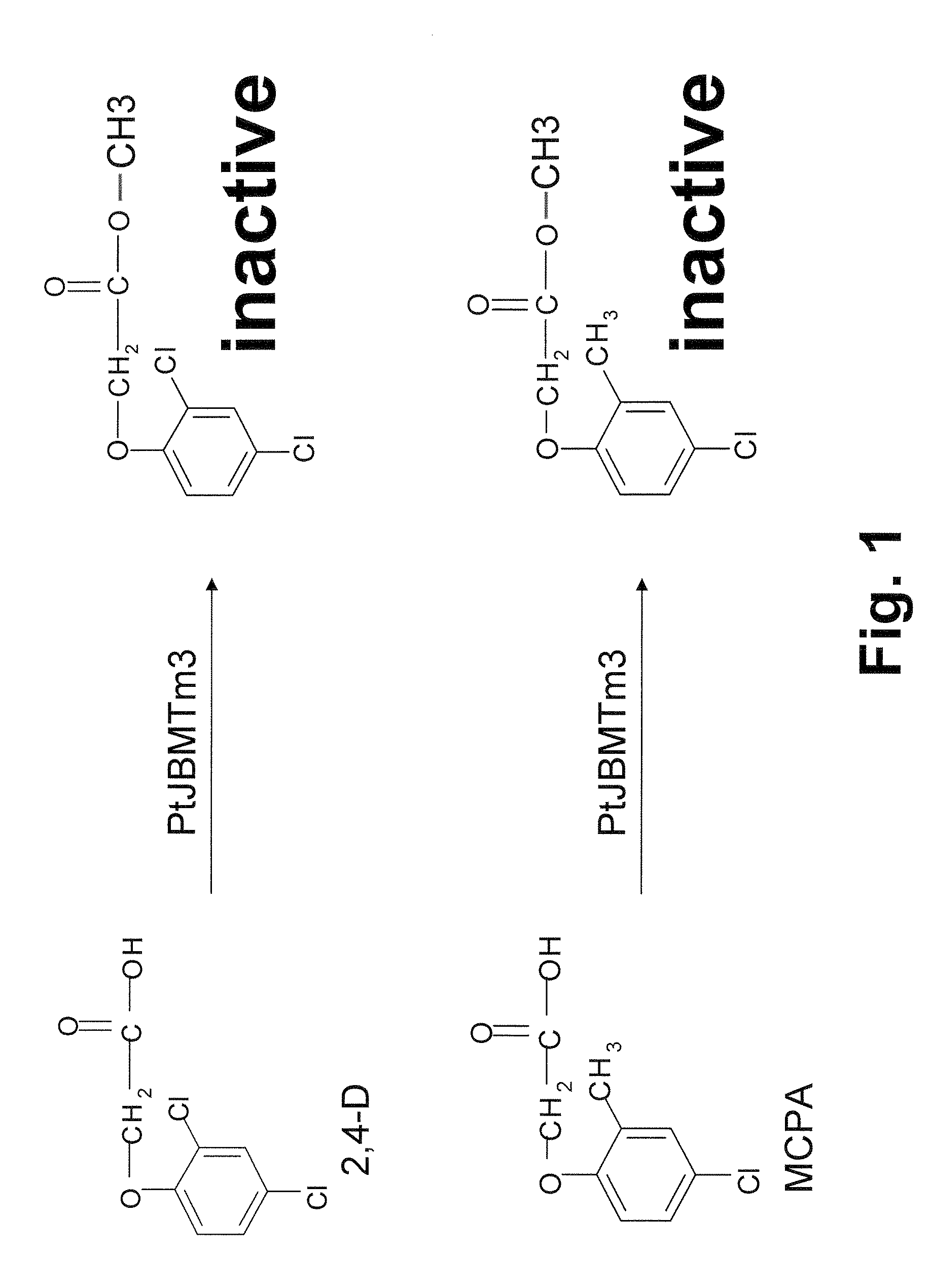
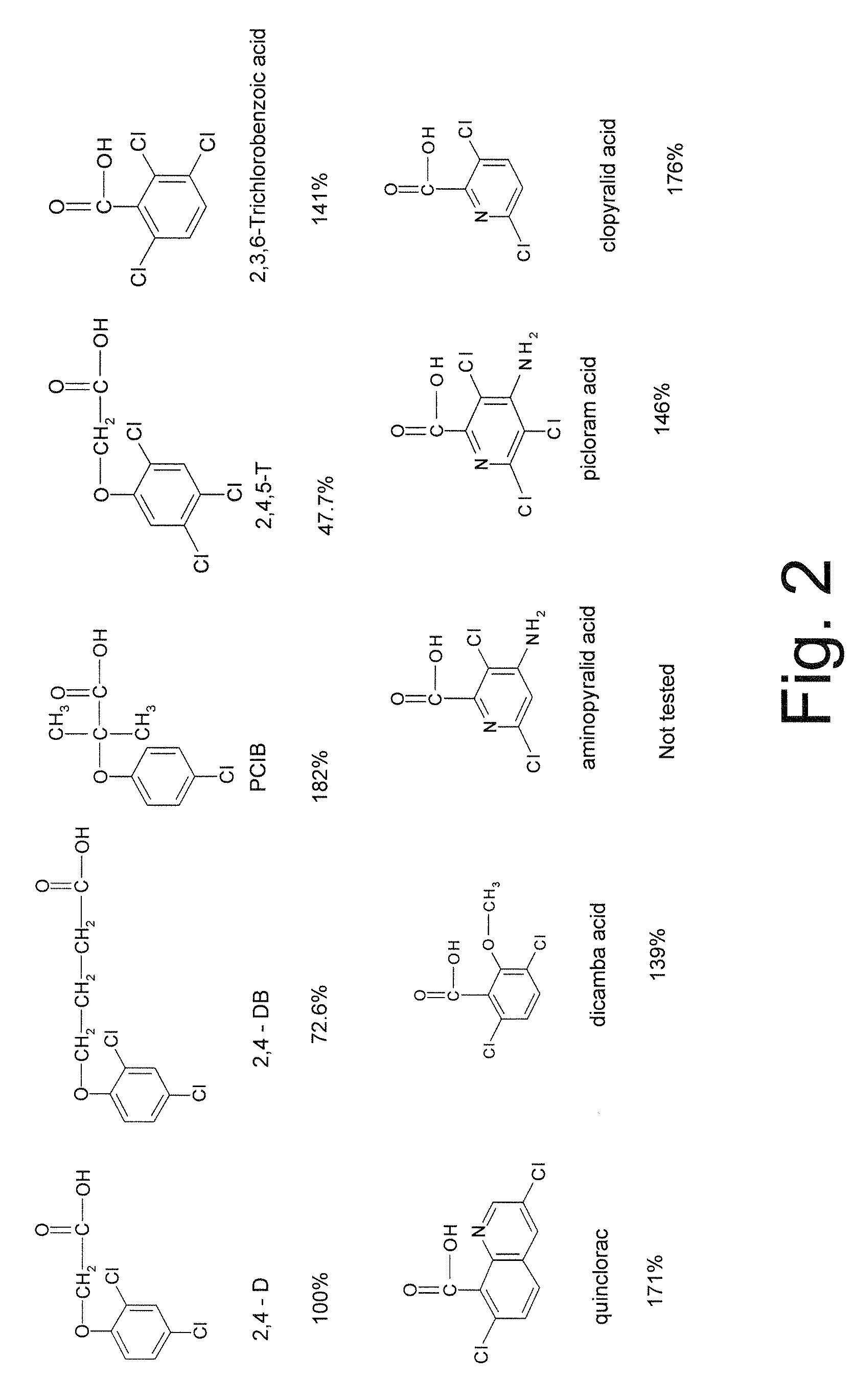
Novel herbicide resistance gene
The subject invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoding a methyltransferase. The subject invention provides novel plants that express the methyltrasferase disclosed herein and are resistant to auxin-based herbicides. The subject invention also provides transgenic plants have been transformed with one or more other herbicide resistance genes such that the plants are resistant to the application of auxin-based herbicides and one or more other herbicides.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
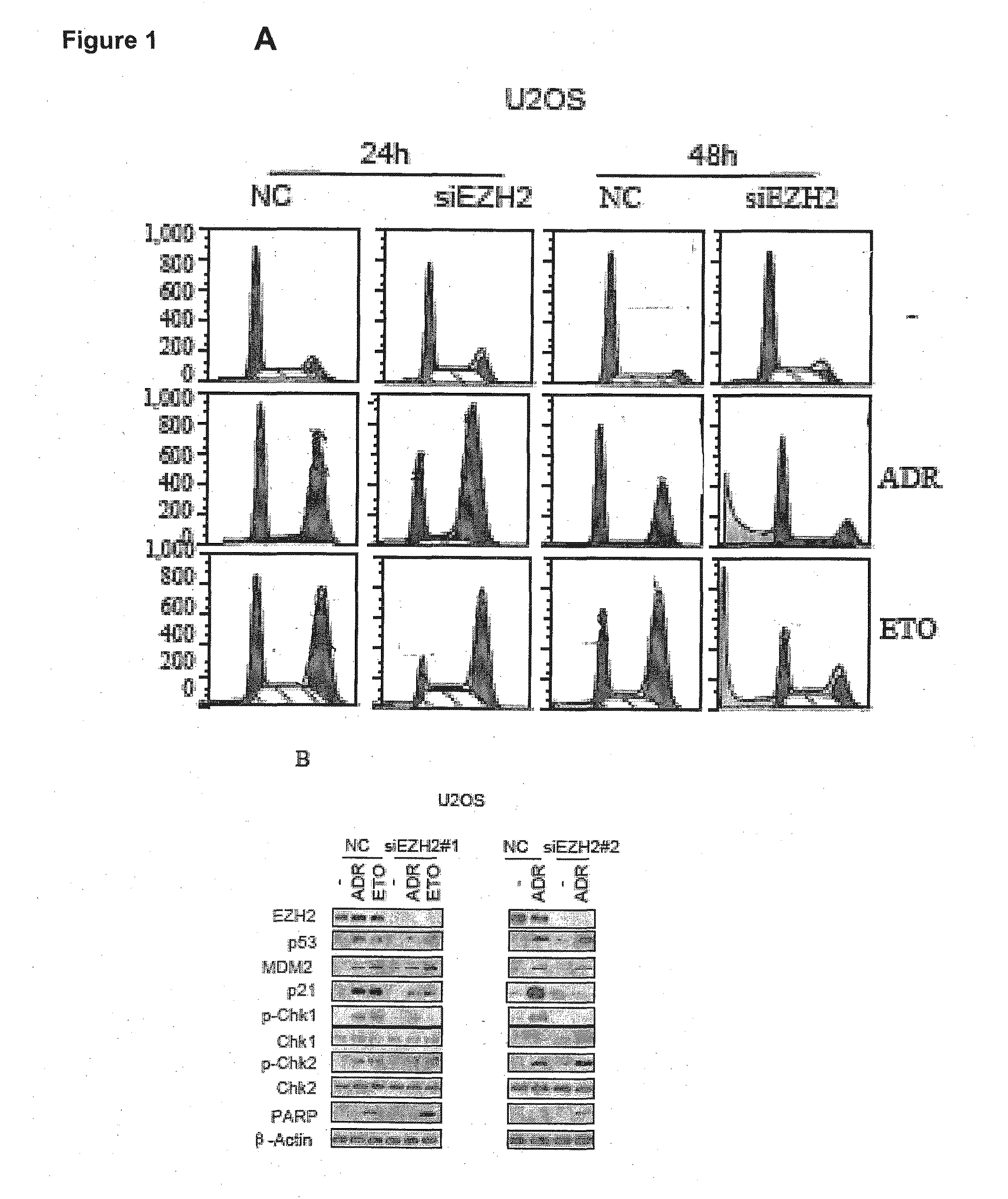
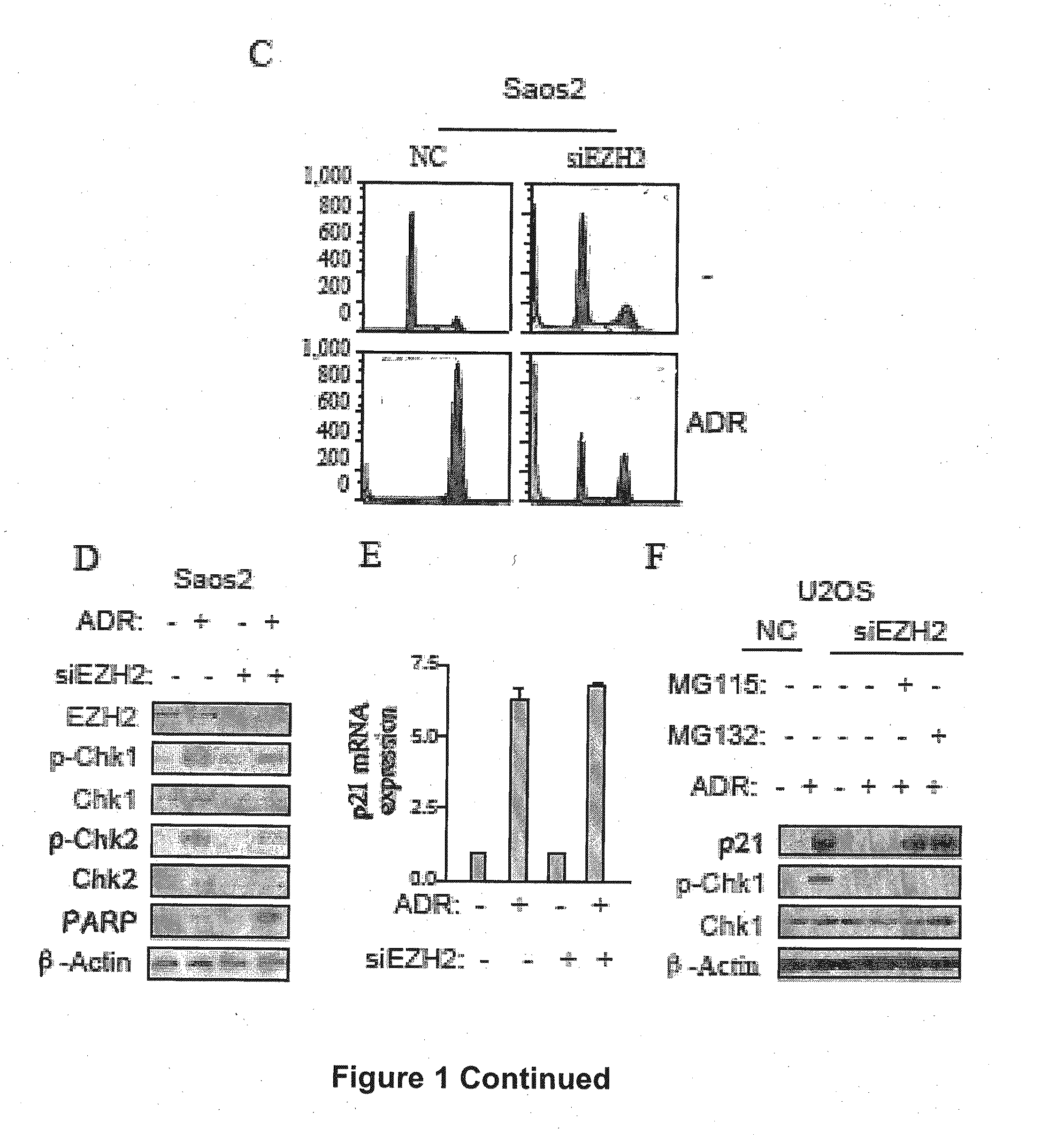
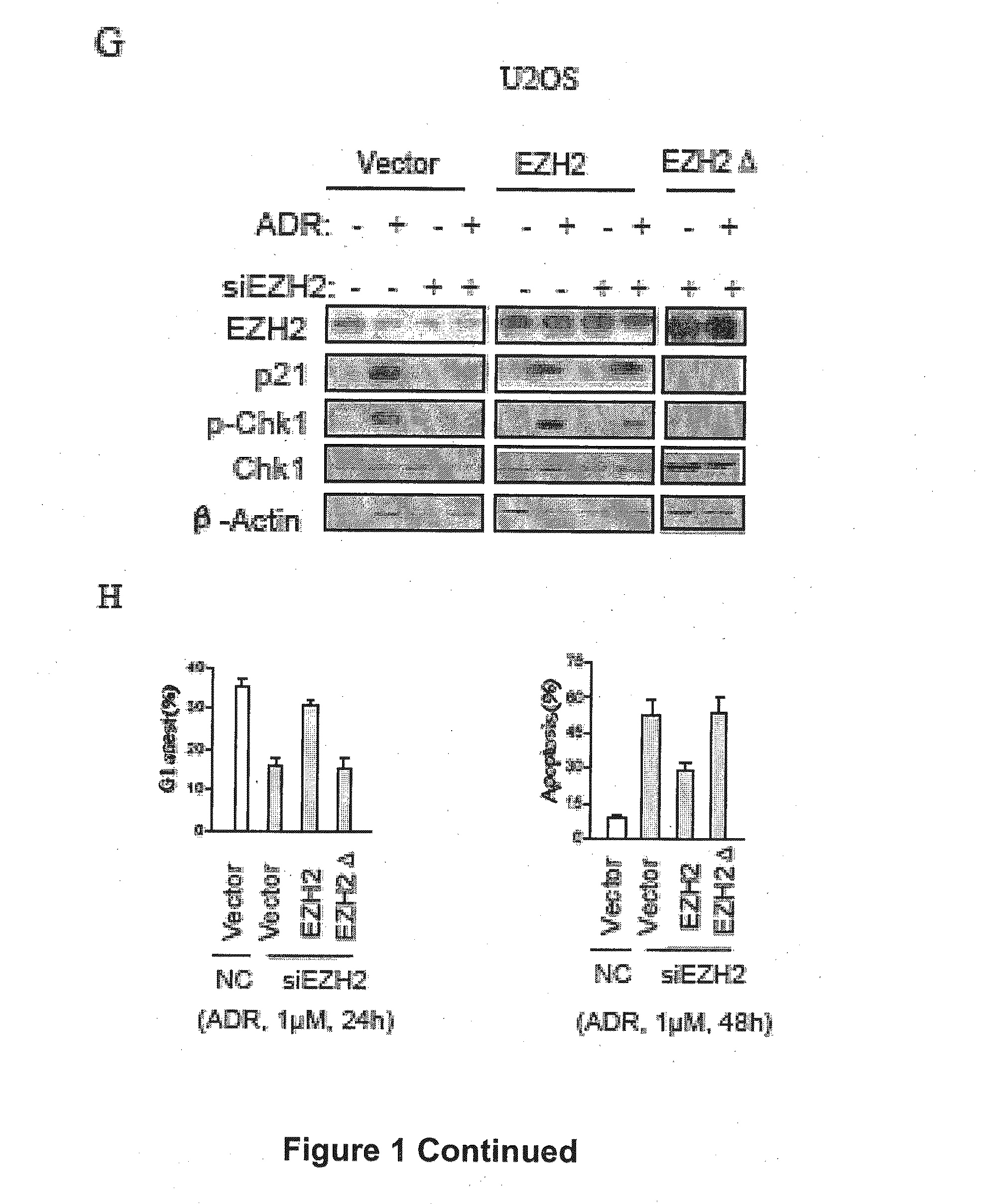
Combination treatment of cancer
The present technology relates to a method of treating cancer by sensitizing human tumours to DNA damaging therapies through activating FBXO32 expression. Transactivation of FBXO32 through the inhibition of EZH2, a histone methyltransferase, decreases p21 protein induction which results in the sensitization of human tumours to chemotherapy. The method further provides a prognostic method to determine if a combination treatment would be effective.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
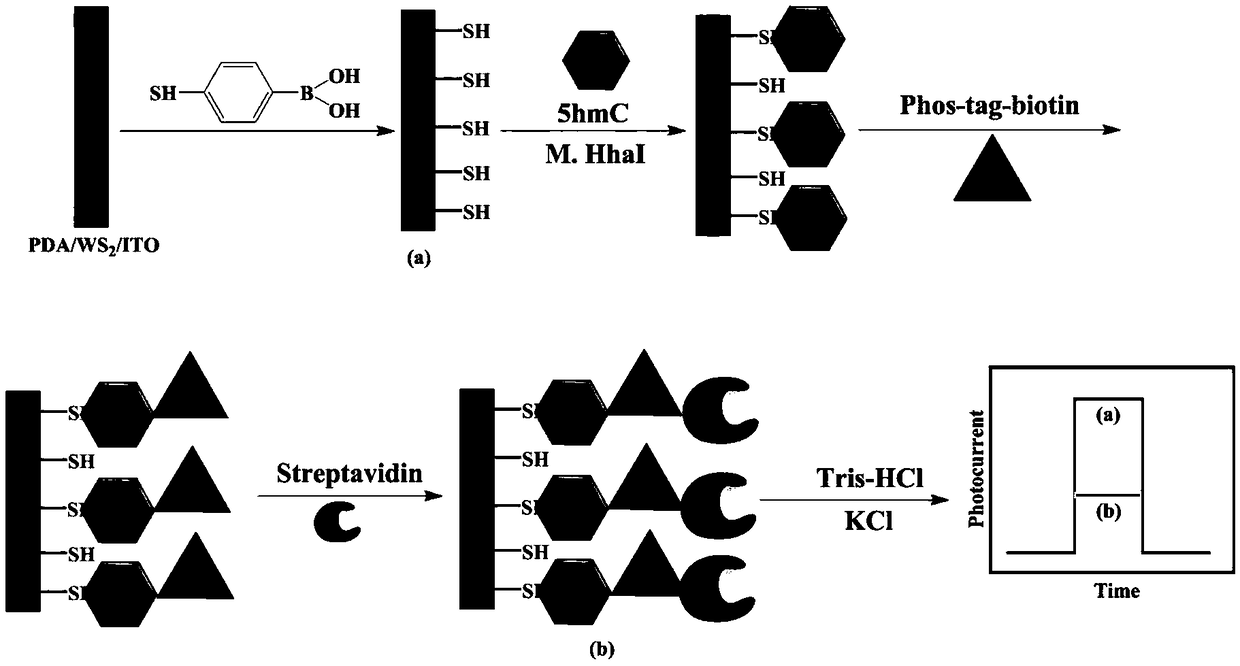
Photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) deoxyribonucleotide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108918622AExcellent electron donor propertiesAmplifyMaterial electrochemical variablesBiotin-streptavidin complexBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) deoxyribonucleotide and a preparation method thereof. The photoelectrochemical biosensor comprisesan electrode and tungsten sulfide, polydopamine, mercaptobenzoic acid, 5hmC, phos-tag-biotin and streptavidin which are sequentially modified on the surface of the electrode. High sensitivity and high specificity detection of 5 hmC can be realized by use of the good photoelectric activity and biocompatibility of the tungsten sulfide, the excellent electronic donor properties and biocompatibilityof the polydopamine, the specific recognition and binding properties of phos-tag-biotin to phosphoric acid groups, and the specific reaction of hydroxymethyl and sulfydryl groups on the 5hmC catalyzedby M.HhaI methyltransferase. The method can well eliminate the interference of 5mC to the detection of the 5hmC. The detection method is simple, instrument miniaturization is realized, the photoelectrochemical biosensor is easy to operate, and the detection of the 5hmC can be realized by simple treating of the surface of the electrode.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for generating pterostilbene by utilizing grape resveratrol-oxygen-methyl transferase to catalyze resveratrol
InactiveCN102120996AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRapid amplification of cDNA endsBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for generating pterostilbene by utilizing grape resveratrol-oxygen-methyltransferase to catalyze resveratrol, grape ROMT (resveratrol-oxygen-methyl transferase) genes are cloned by utilizing 5' and 3' RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) full-length gene cloning technology according to EST (expressed sequence tag) sequence of the ROMT genes of Chinese wild grapes in East China, and the full length of an open reading frame of the genes is 1074bp; and the cloned grape STS (steroid sulfatase) and ROMT genes can be simultaneously transferred into model plant tobacco, tobacco plant analysis is utilized for analyzing the biological synthesis path of generating the pterostilbene by utilizing the grape ROMT to catalyze the resveratrol, a grape ROMT gene sequence is obtained for orientation, and the ROMT genes can catalyze the resveratrol to generate the pterostilbene in the transgenic tobacco, thereby providing the sequence of the ROMT genes and the method for synthesizing the pterostilbene by utilizing plants and providing a basis for getting high-quality, disease-resistant and health care crops.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
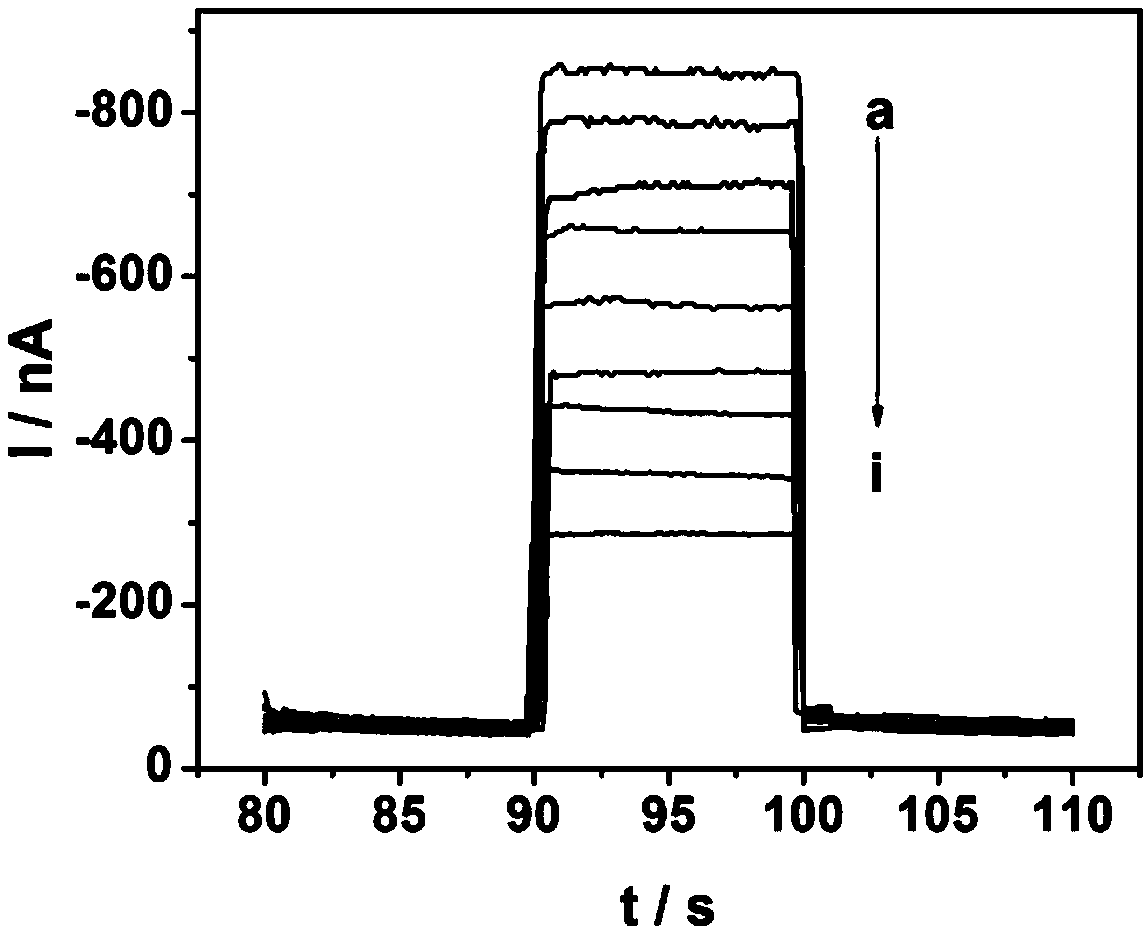
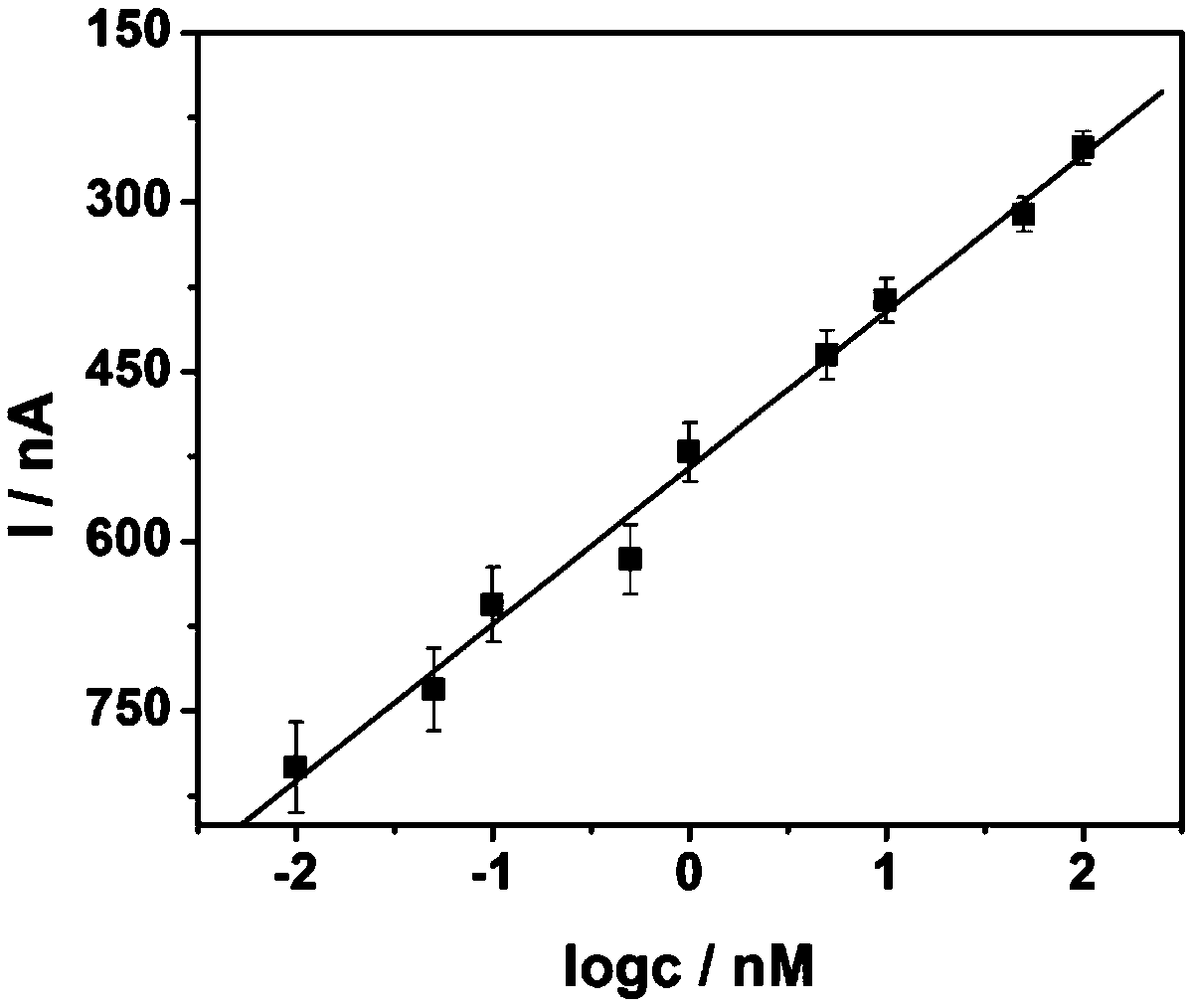
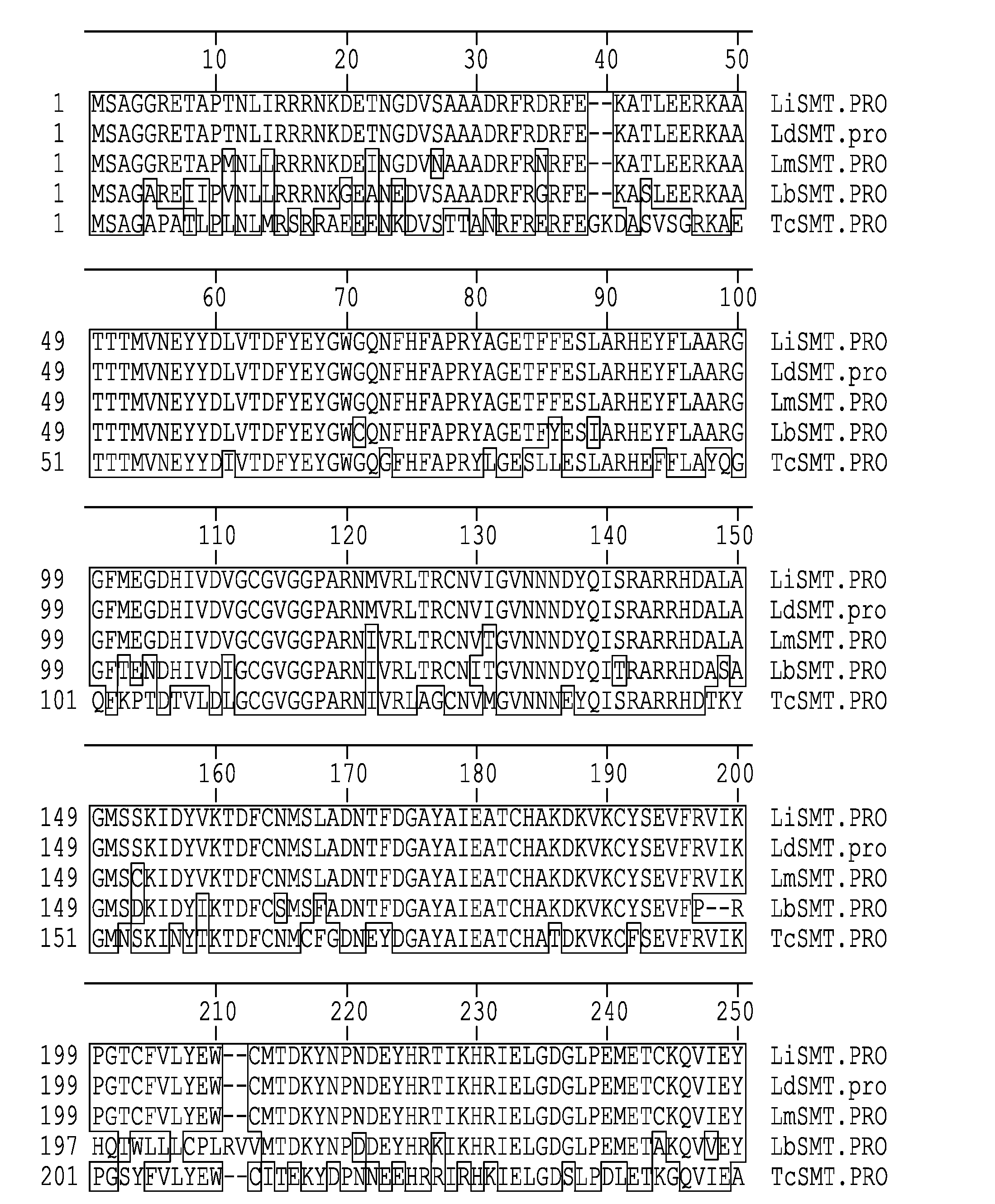
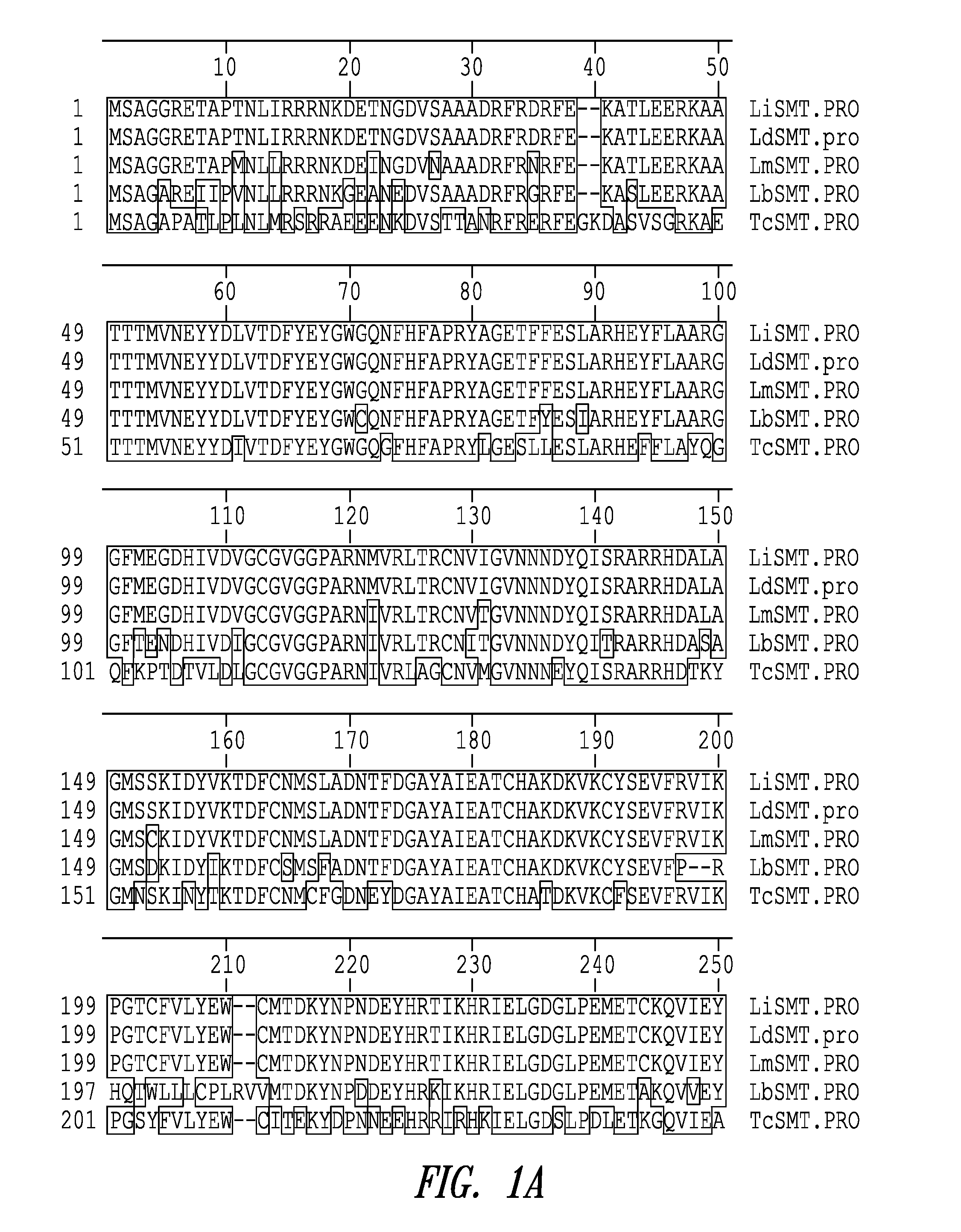
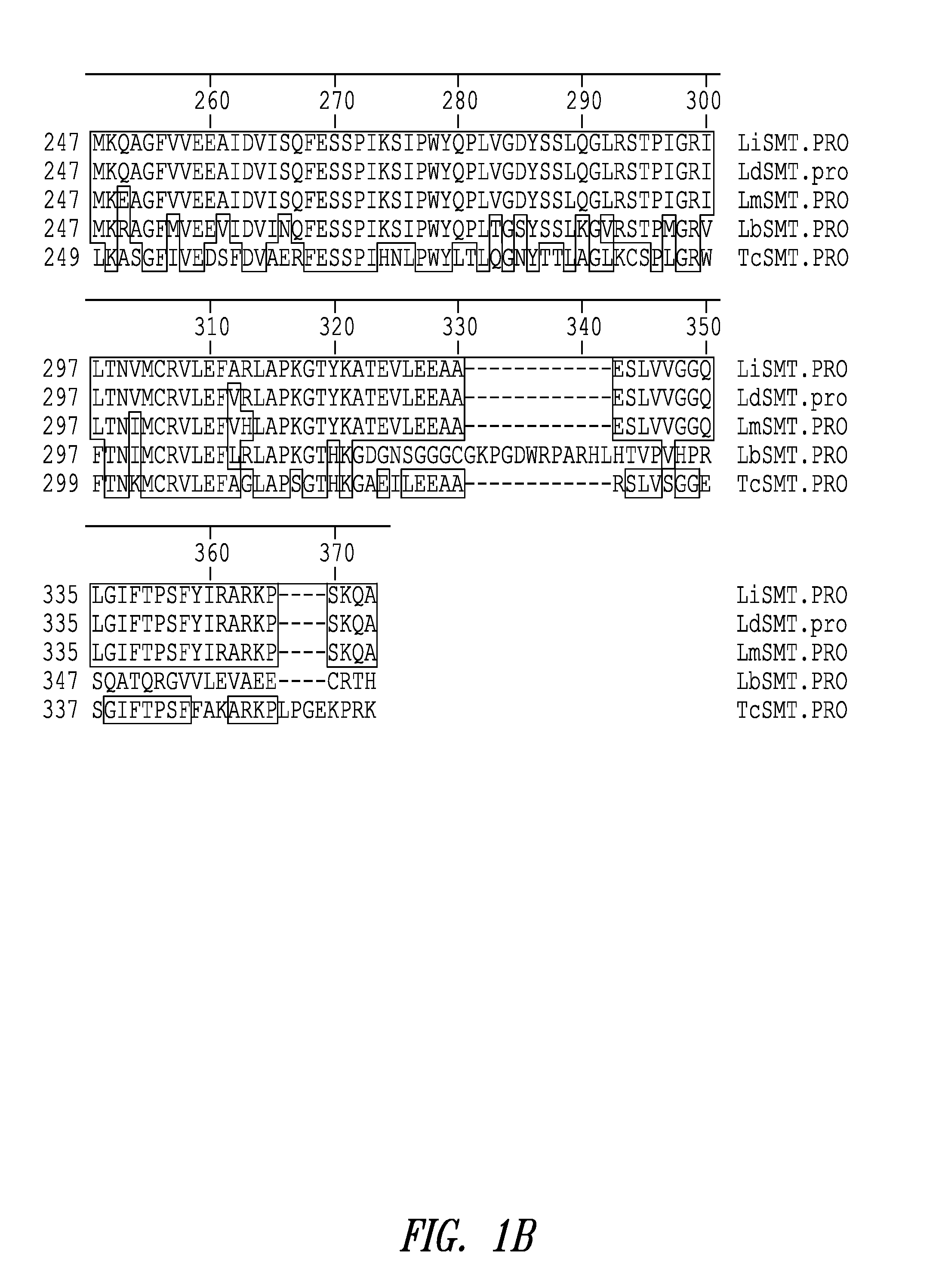
Leishmania sterol 24-c-methyltransferase compositions for the prevention, treatment and diagnosis of leishmaniasis
ActiveUS20090041798A1Preventing and treating and detecting leishmaniasisProtozoa antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLeishmaniasisSterol
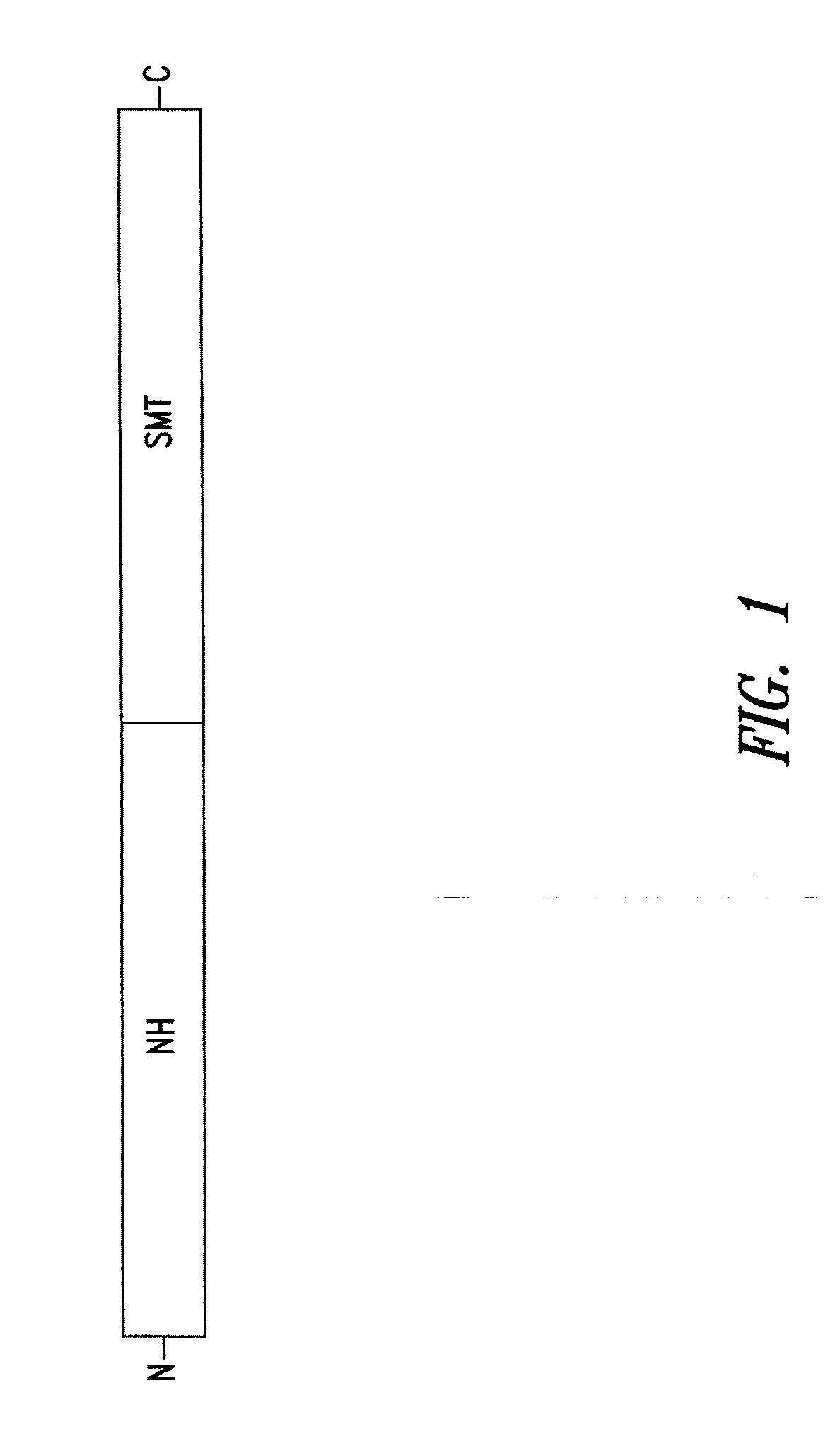
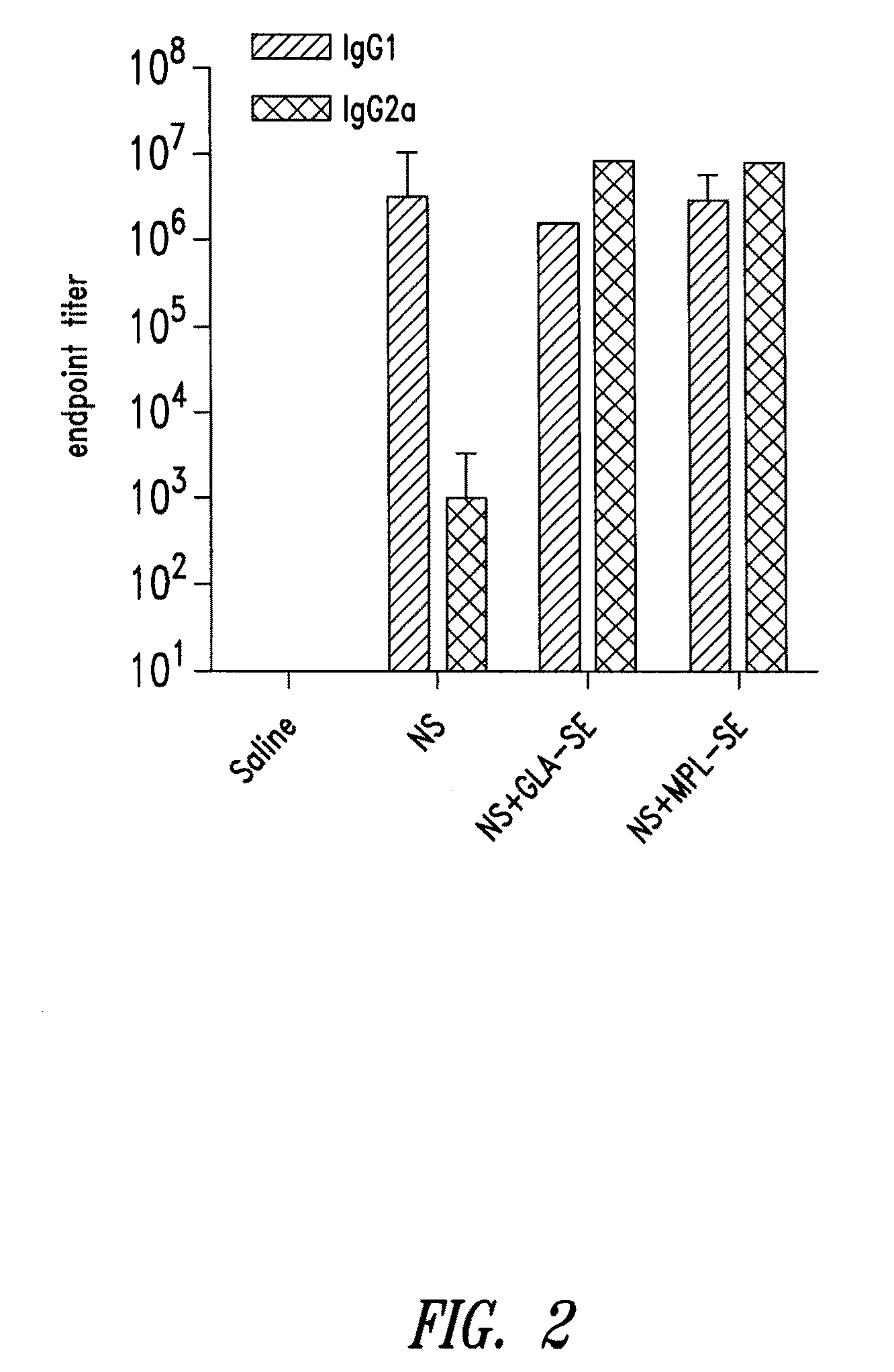
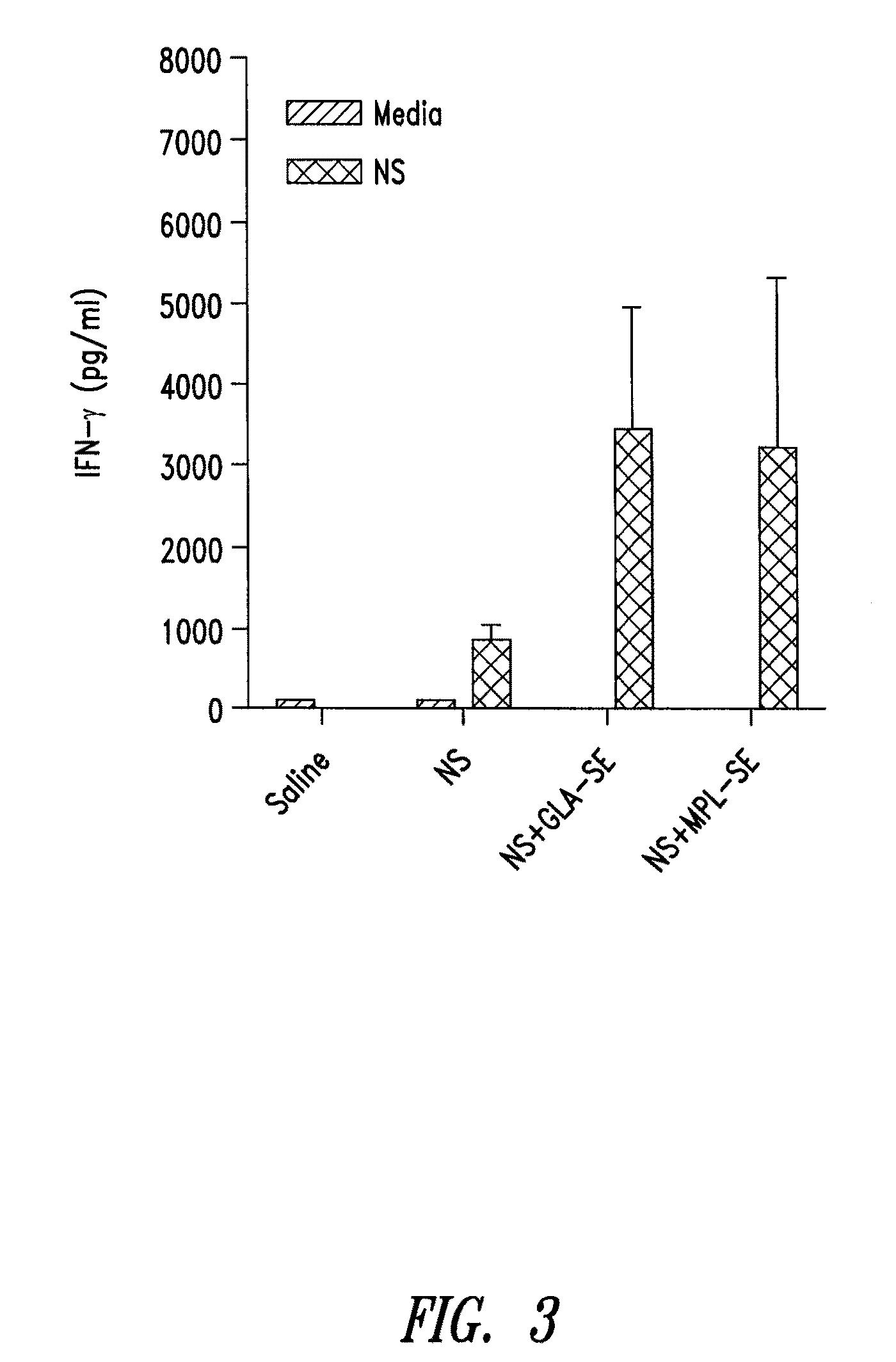
Compositions and methods for preventing, treating and detecting leishmaniasis are disclosed. The compositions generally comprise Leishmania sterol 24-c-methyltransferase (SMT) polypeptides, portions, variants and / or fusions, as well as polynucleotides encoding SMT polypeptides, portions, variants and / or fusions.
Owner:INFECTIOUS DISEASE RES INST
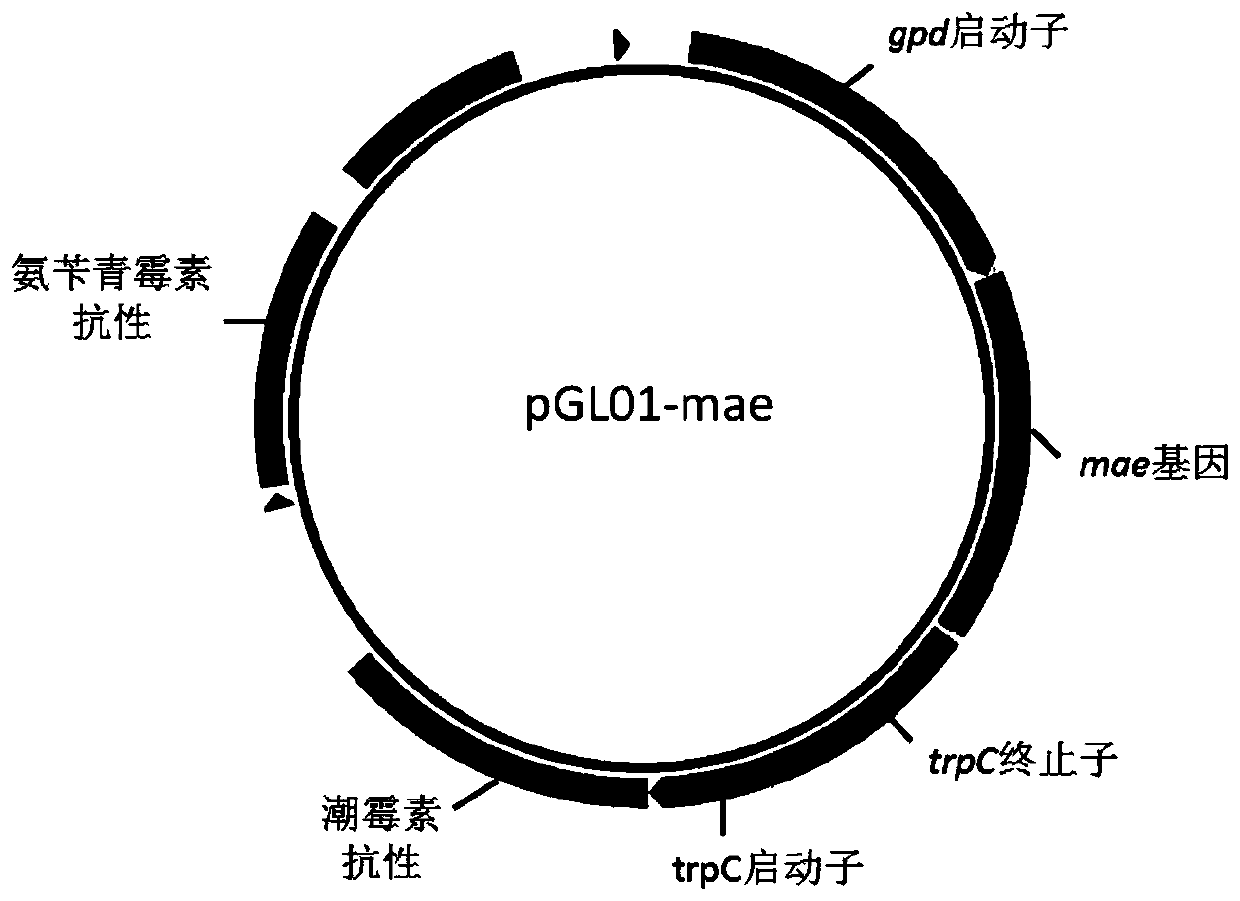
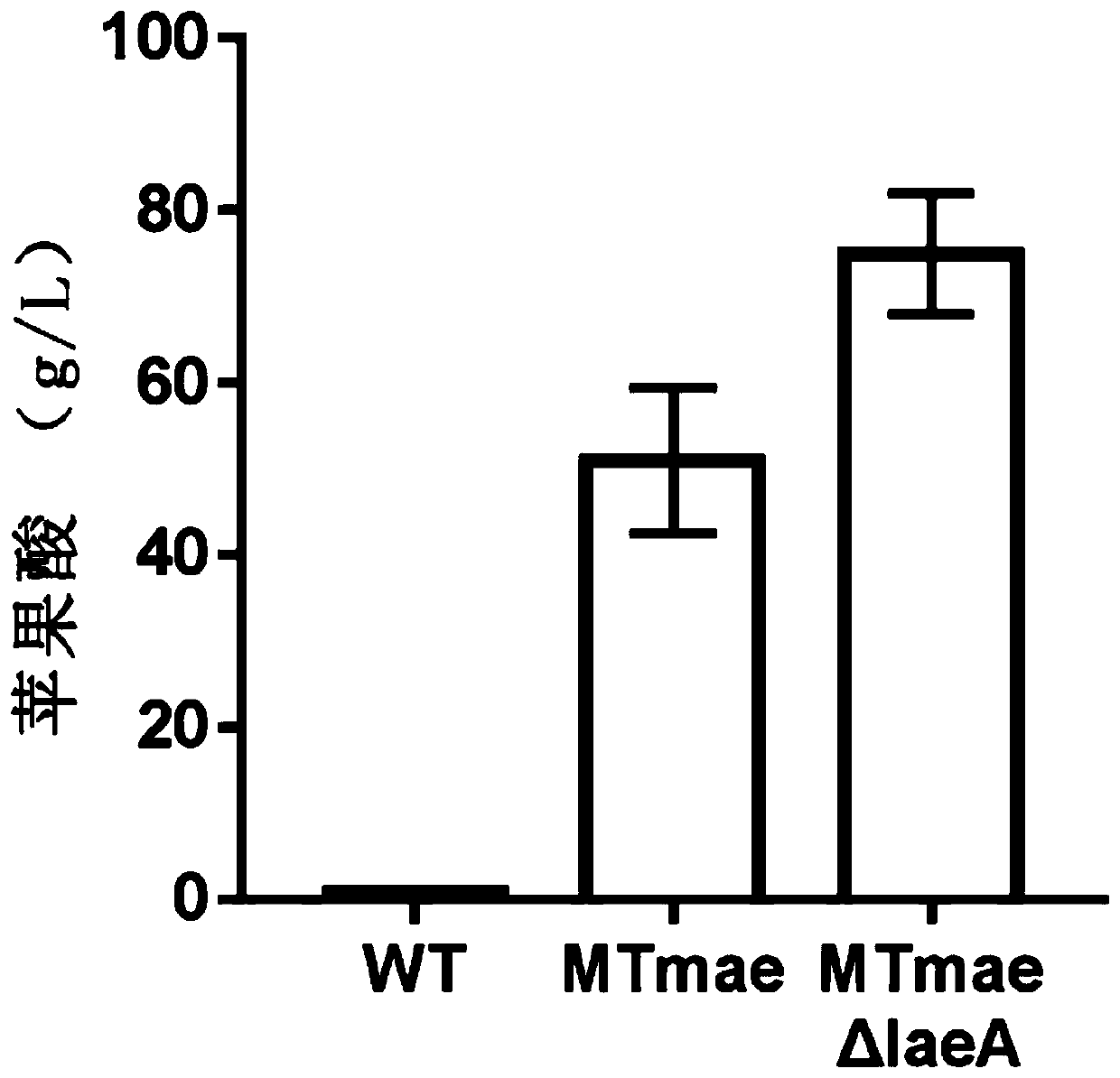
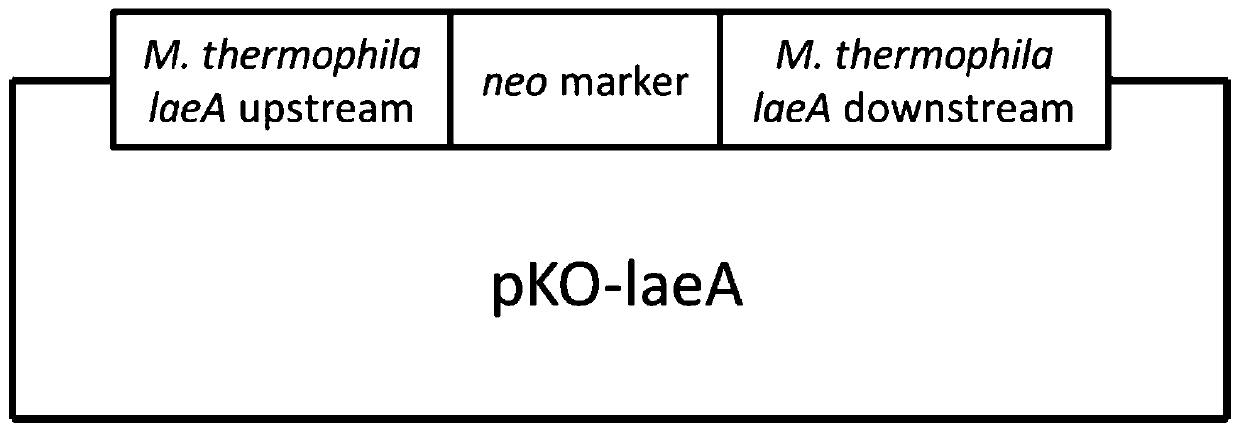
Genetically engineered bacterium producing malic acid and method for producing malic acid
ActiveCN109797111AIncrease productionHas acid resistanceFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyGenetically engineered
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium producing malic acid and a method for producing the malic acid. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by increasing the expressionor activity of diacid transporter in the recipient bacterium and decreasing the expression or activity of methyltransferase laeA in the recipient bacterium. By the arrangement, the yield of the malicacid is effectively increased, furthermore, use of a neutralizer is effectively avoided by introducing the acid-resistant engineered bacterium.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGGENG CHEM TECH CO LTD
Methyltransferase nucleic acids and polypeptides
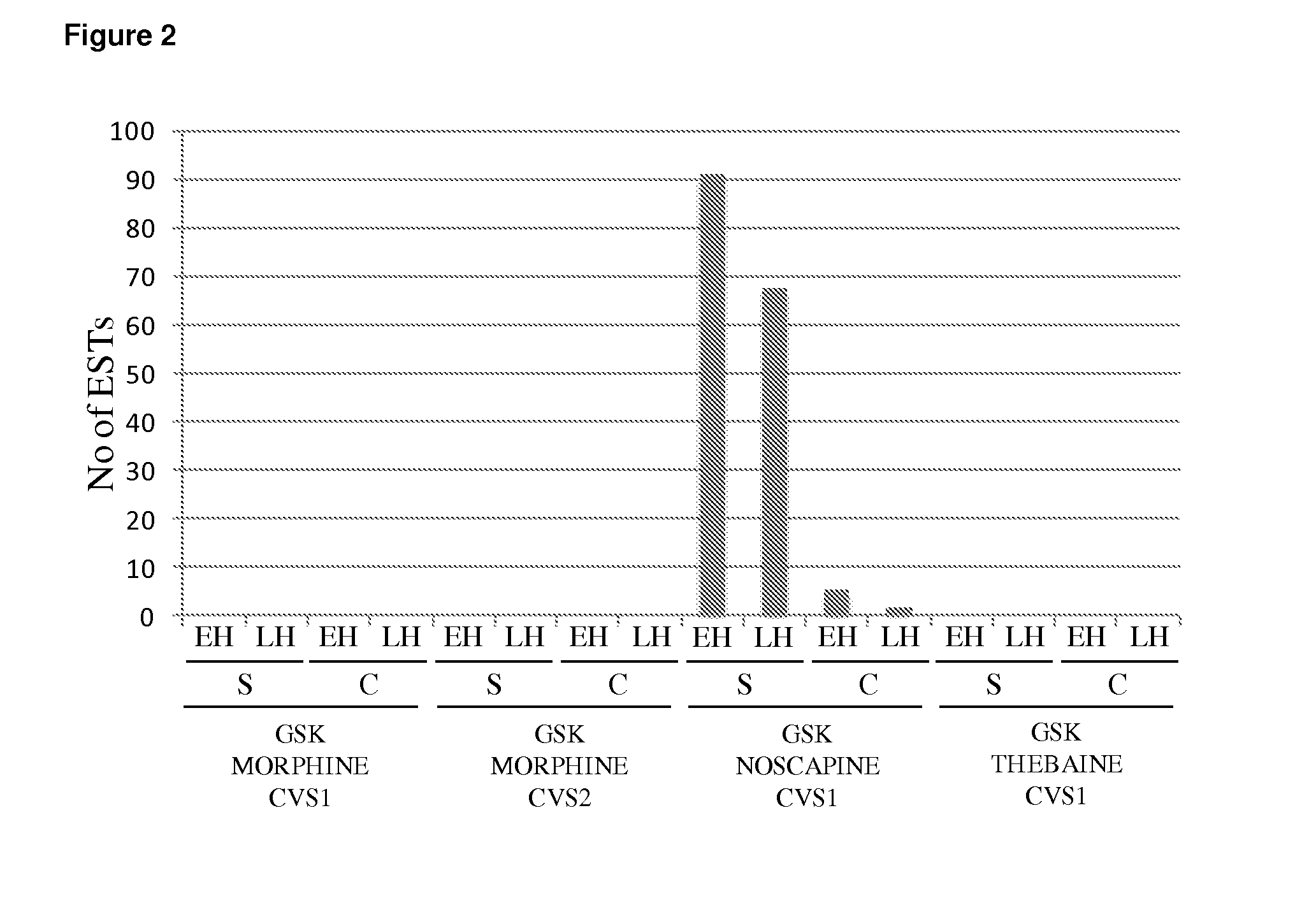
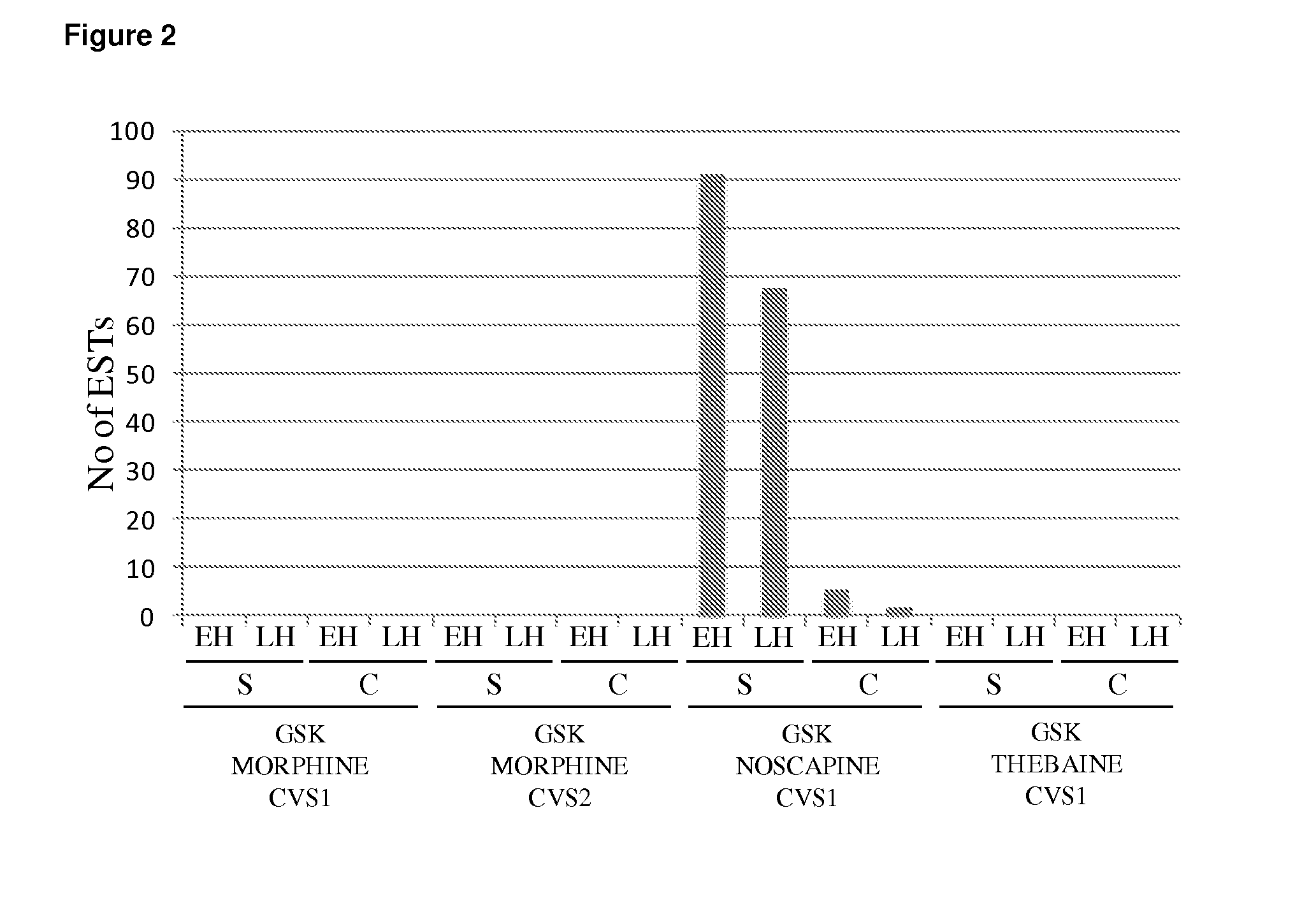
This disclosure relates to the isolation and sequencing of nucleic acid molecules that encode methyltransferase polypeptides from a Papaver somniferum cultivar; and uses in the production of noscapine and identification of poppy cultivars that include the genes that include these nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SUN PHARMA IND AUSTRALIA LTD
Method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash) using molecular markers
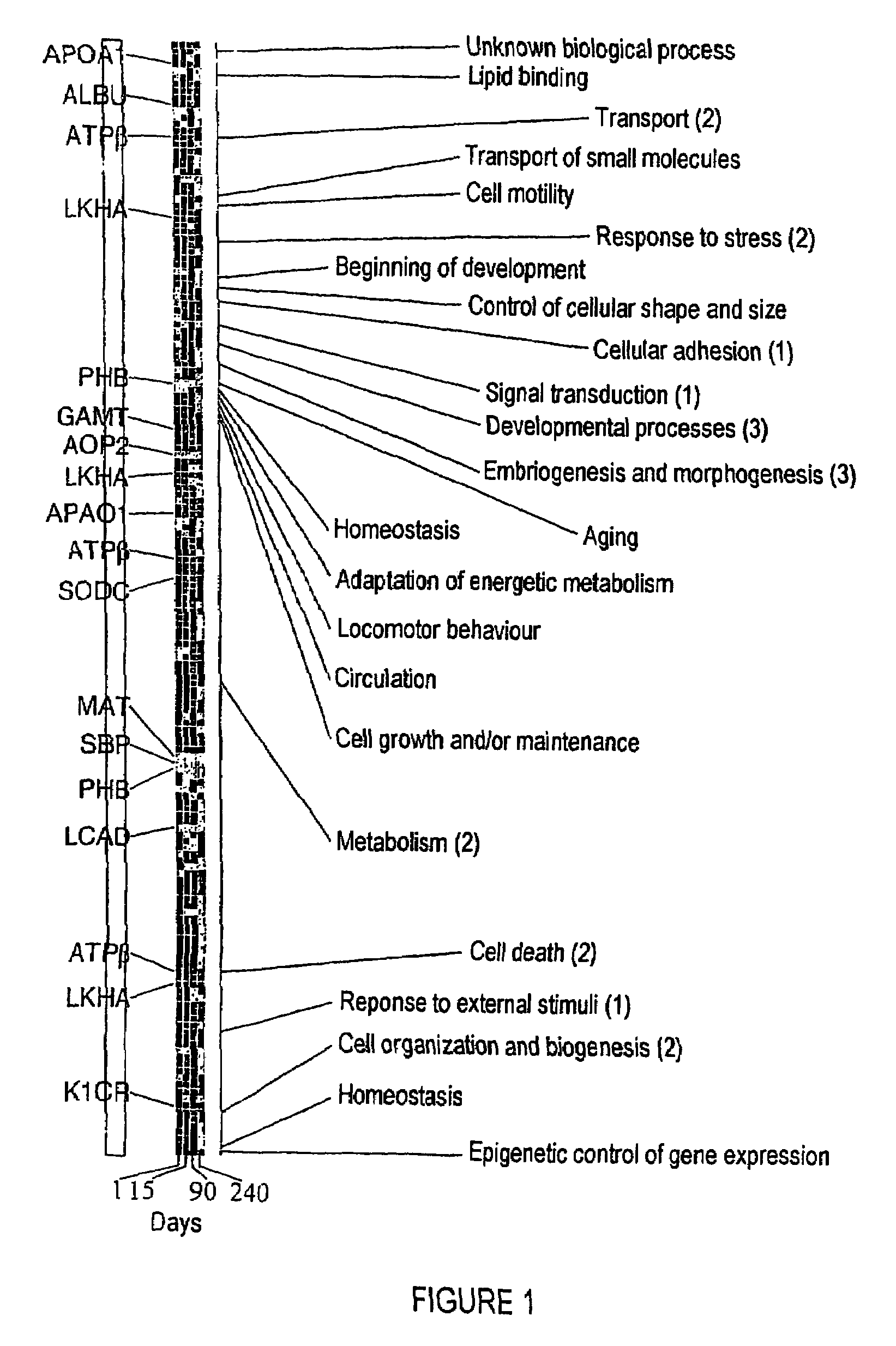
InactiveUS20060135420A1Easy and reliable evaluationEase of evaluationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntioxidant proteinSelenium-Binding Proteins
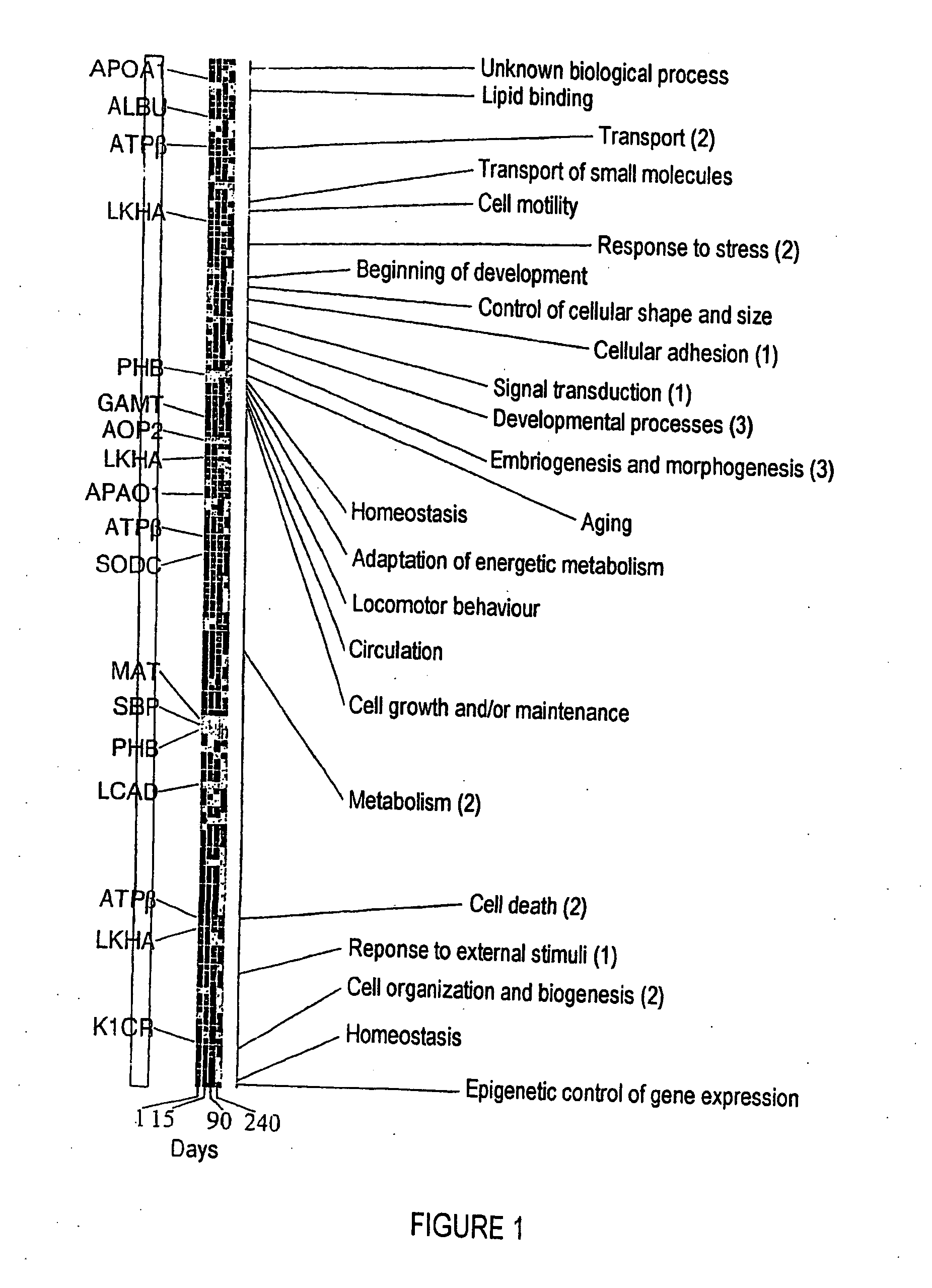
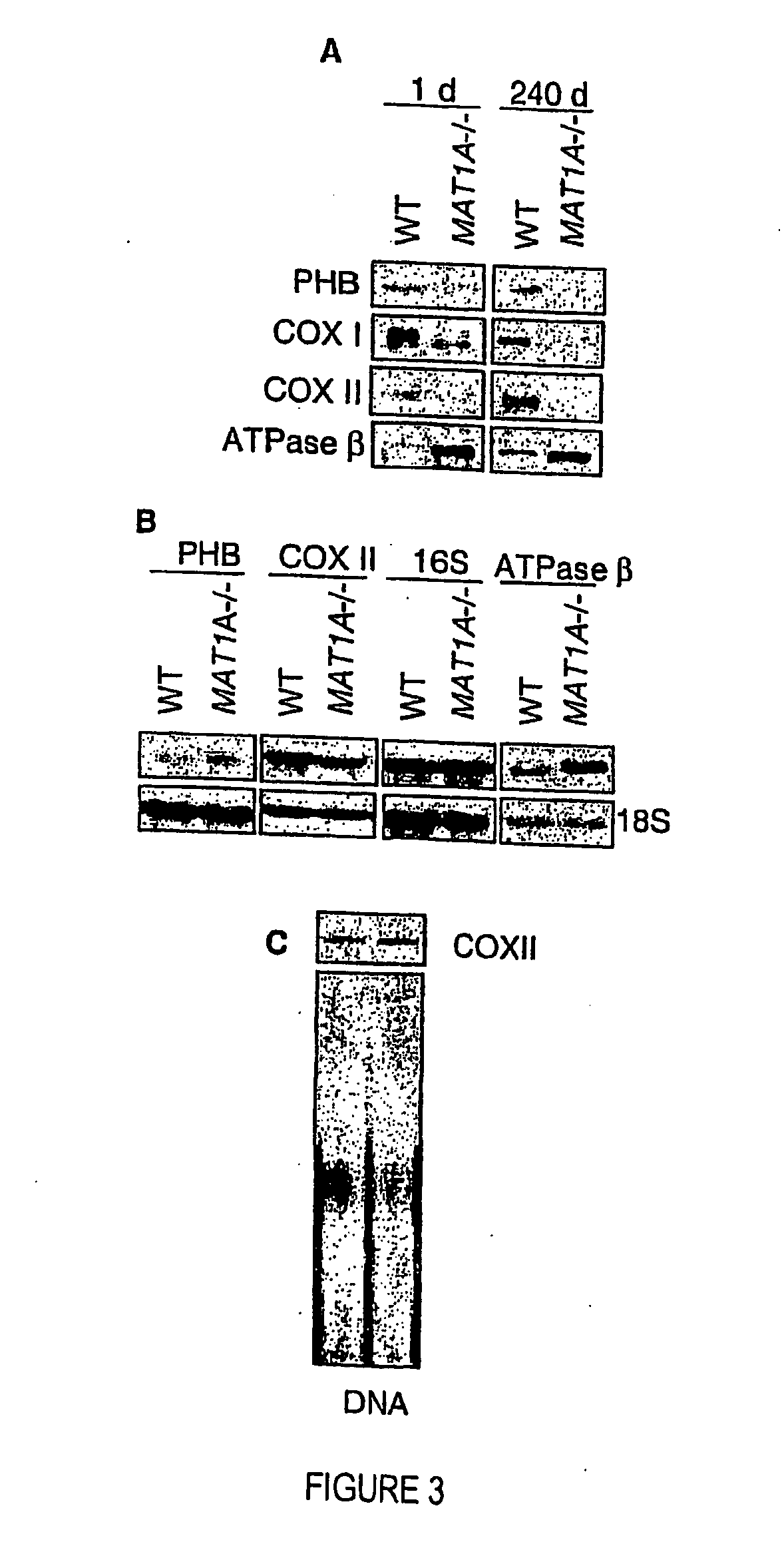
The invention relates to a method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) using molecular markers. The inventive method consists in detecting and quantifying, in vitro in a hepatic tissue sample, the levels of a protein which can be used as a NASH molecular marker and which is selected from apolipoprotein A1, sub-unit β of the mitochondrial ATPase, leukotriene A4 hydrolase, keratin 18, guanidine acetate N-methyltransferase, superoxide dismutase, albumin, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 1), prohibitin 1, methionine adenosyl transferase, long-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase, selenium binding protein, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 2), and combinations of same. The invention further consists in comparing the results obtained with the normal values of said proteins in healthy hepatic tissue. Said method can be used to diagnose NASH and / or to assess a patient's potential risk of developing NASH.
Owner:ONE WAY LIVER GENOMICS
Vaccines comprising non-specific nucleoside hydrolase and sterol 24-c-methyltransferase (SMT) polypeptides for the treatment and diagnosis of leishmaniasis
InactiveUS20120114688A1Preventing and treating and detecting leishmaniasisAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesLeishmaniaLeishmaniasis
Compositions and methods for preventing, treating and detecting leishmaniasis are disclosed. The compositions generally comprise fusion polypeptides comprising Leishmania antigens, in particular, SMT and NH antigens or immunogenic portions or variants thereof, as well as polynucleotides encoding such fusion polypeptides.
Owner:INFECTIOUS DISEASE RES INST
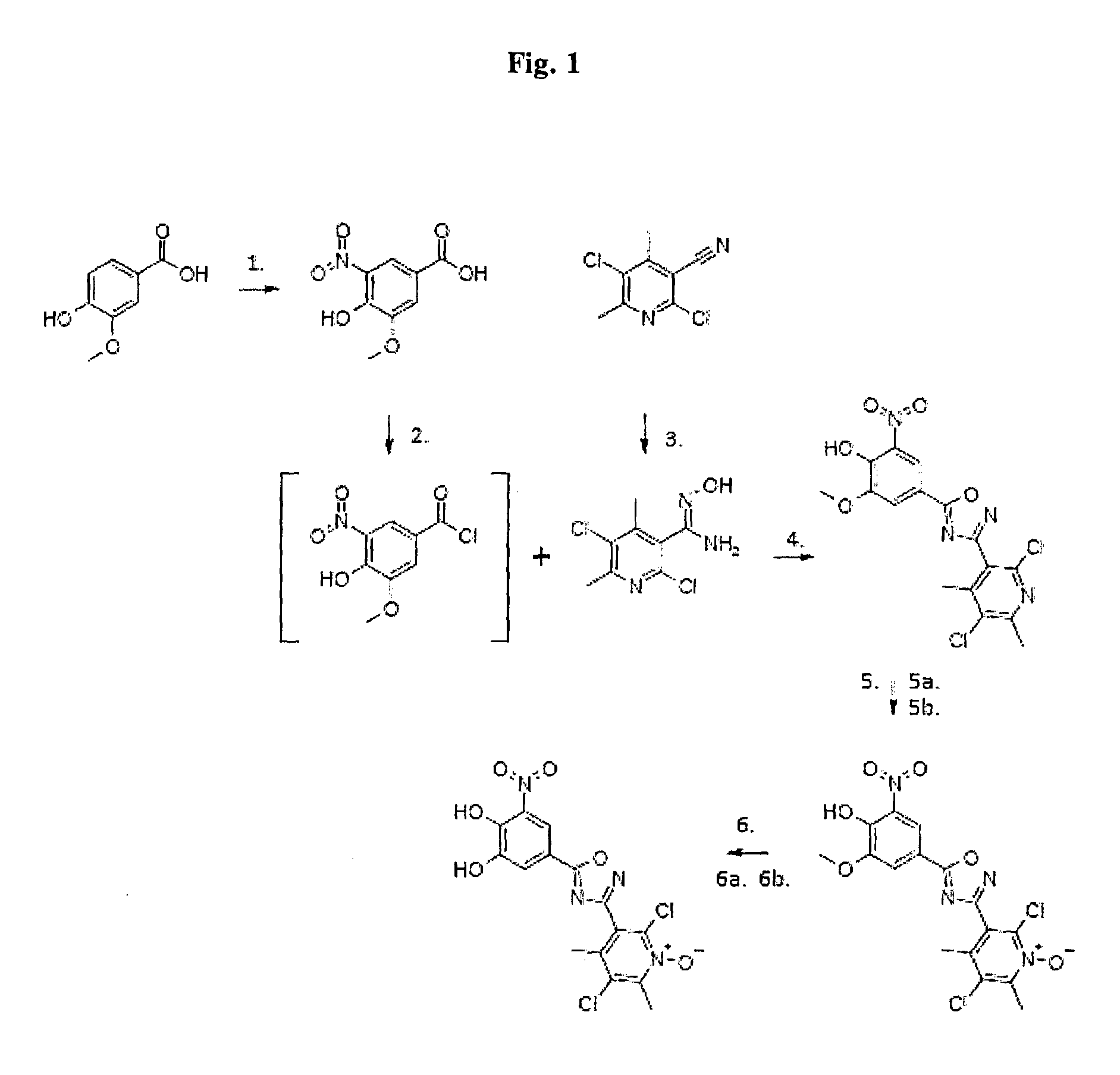
Intermediate for preparing a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor
ActiveUS9126988B2Improve securityExtension of timeNervous disorderOrganic chemistryParkinson's diseaseCatechol
There is disclosed a methylated intermediate which may be demethylated to provide an inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase useful in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Also disclosed are methods of making and using said intermediate.
Owner:BIAL PORTELA & CA SA
Herbicide resistance gene
The subject invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoding a methyltransferase. The subject invention provides novel plants that express the methyltrasferase disclosed herein and are resistant to auxin-based herbicides. The subject invention also provides transgenic plants have been transformed with one or more other herbicide resistance genes such that the plants are resistant to the application of auxin-based herbicides and one or more other herbicides.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Methods of detecting methyl transferase activity and methods of screening for methyl transferase activity modulators
The invention features a method for determining methyl transferase activity of a polypeptide and screening for modulators of methyl transferase activity. The invention further provides a method or pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treating of colorectal cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma using the modulator.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Method for improving percent conversion of tylosin component A
ActiveCN102703549AImprove permeabilityFacilitated releaseMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobiologyMethyltransferase
The invention relates to a method for improving the percent conversion of a tylosin component A. With the method, streptomyces fradiae is used as a producing strain and is fermented to produce the tylosin by first-level seed tank fermentation culture, second-level seed tank fermentation culture and fermentation tank fermentation culture. The method is characterized in that nonionic surfactant of which the mass concentration is 0.5-2.5% is added into a fermentation culture medium after the fermentation tank fermentation culture enters a stable period after a logarithmic growth phase is finished. The nonionic surfactant is added into the culture medium during a fermentation culture period to the stable period so as to enhance the permeability of a mycelium cell, so that a metabolin in a cell is accelerated to quickly release out of the cell to relieve the feedback inhibition of macrosin methyltransferase and improve the enzyme activity, and finally, a tylosin component C is accelerated to quickly covert into the tylosin component A. The tylosin component A in the current industrial production generally accounts for 80-85%, and the content of the tylosin component A can finally achieve 90-94% according to the method disclosed by the invention.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
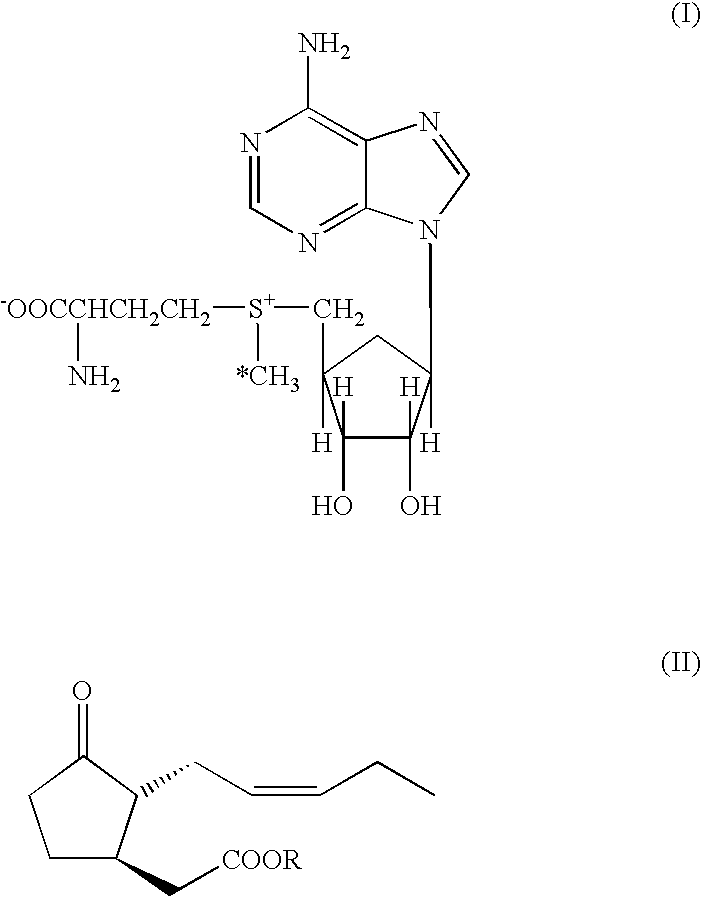
S-adenosyl-L-methionine analogs with extended activated groups for transfer by methyltransferases
ActiveUS8008007B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementS-Adenosyl-l-methionineAdenosine
S-Adenosyl-L-methionine analogs of formula (I):are disclosed wherein R comprises a carbon-carbon double bond, carbon-sulfur double bond, carbon-nitrogen double bond, -a carbon-carbon triple bond, carbon-nitrogen triple bond or an aromatic carbocyclic or heterocyclic system in β-position to the sulfonium center, X{circle around (−)} is an organic or inorganic anion carrying one or more negative charges, Z is —CR1R2—, —O—, —S— or —NR3— and R1, R2 and R3 are independently selected from H, D and C1—C alkyl; as well as complexes with a methyltransferase, pharmaceutical compositions, methods for modifying a biomolecule, and methods for detecting sequences specific methylation of biomolecules.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV +1
Method for increasing plant yields
InactiveUS20170016017A1Improved useful traitImprove toleranceHydrolasesClimate change adaptationProgenitorGenetics
The present invention provides methods for obtaining plants that exhibit useful traits by expression of a DNA methyltransferase fusion protein in progenitor plants. Methods for identifying genetic loci that provide for useful traits in plants and plants produced with those loci are also provided. In addition, plants that exhibit the useful traits, parts of the plants including seeds, and products of the plants are provided as well as methods of using the plants. Recombinant DNA vectors and transgenic plants comprising those vectors that express a DNA methyltransferase fusion protein are also provided.
Owner:FROMM MICHAEL E
Energy saving brewing method
ActiveUS20130095207A1Reduce energy inputReduce energy consumptionWort preparationBeer fermentationS-Adenosyl methionineS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
Barley based beverages are produced in large quantities, employing highly energy consuming methods, for example in the malting and brewhouse facilities for kiln drying and wort boiling operations, respectively. The present invention relates to energy saving methods for preparing barley based beverages, as well as to barley plants useful in such methods. In particular, the invention describes barley plants with combined traits of null-lipoxygenase-1 (null-LOX-1), null-lipoxygenase-2 (null-LOX-2) and null-S-adenosylmethionine:methionine S-methyltransferase in one plant, which is particularly useful for energy saving methods to prepare barley based beverages, such as beer.
Owner:CARLSBERG BREWERIES AS +1
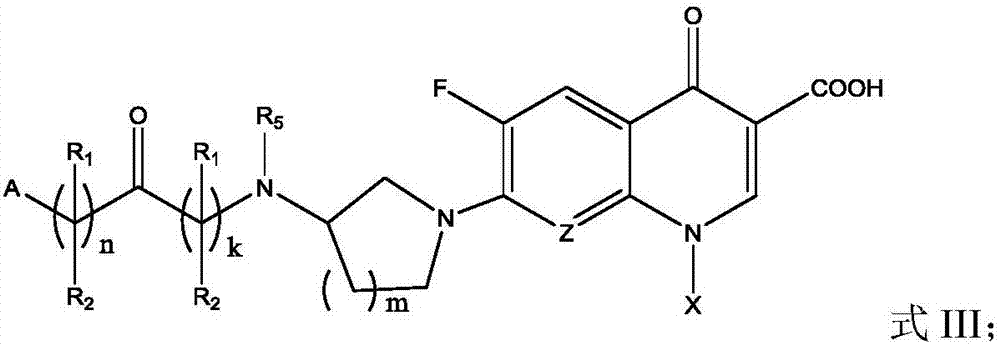
Fluoroquinolone amino derivatives and application thereof
ActiveCN107880023AHigh antibacterial activitySmall toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityDisease
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry, and in particular relates to fluoroquinolone derivatives and an application thereof. The compounds shown in a formula (I) are obtained by structural modification of fluoroquinolone medicines. The compounds provided by the invention can not only treat the infection caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis and common bacteria, but also can has activity inhibition effects on bacterial persister, citrus pathogenic bacteria, nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) and interleukin IL-17 PPI; and the compounds have a simple and easy preparation process and mild conditions, a plurality of the compounds with enhanced antibacterial activity, improved water solubility and reduced toxic and side effects are obtained, and the compounds are expectedto reduce the dosage, shorten the treatment cycle and improve patient compliance, thereby providing novel molecular types and research ideas for medicines of tuberculosis and other diseases.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
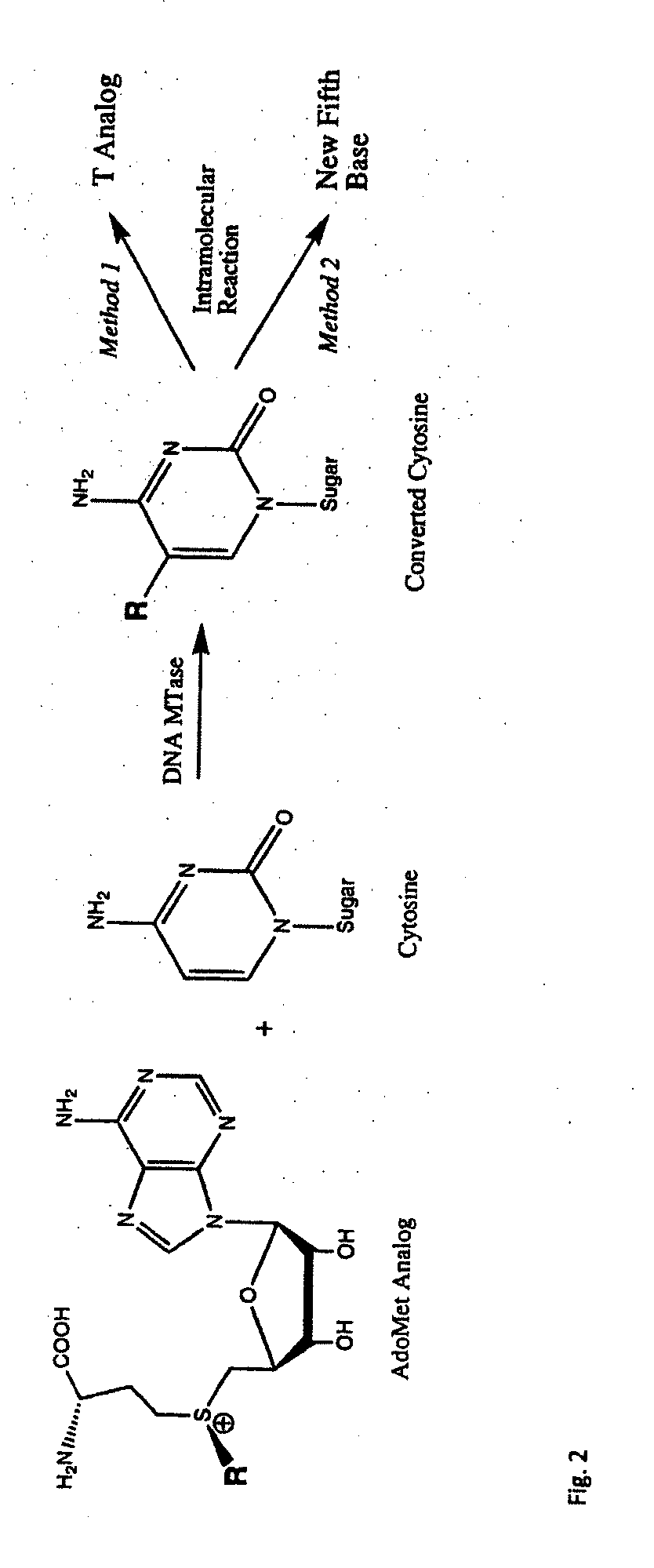
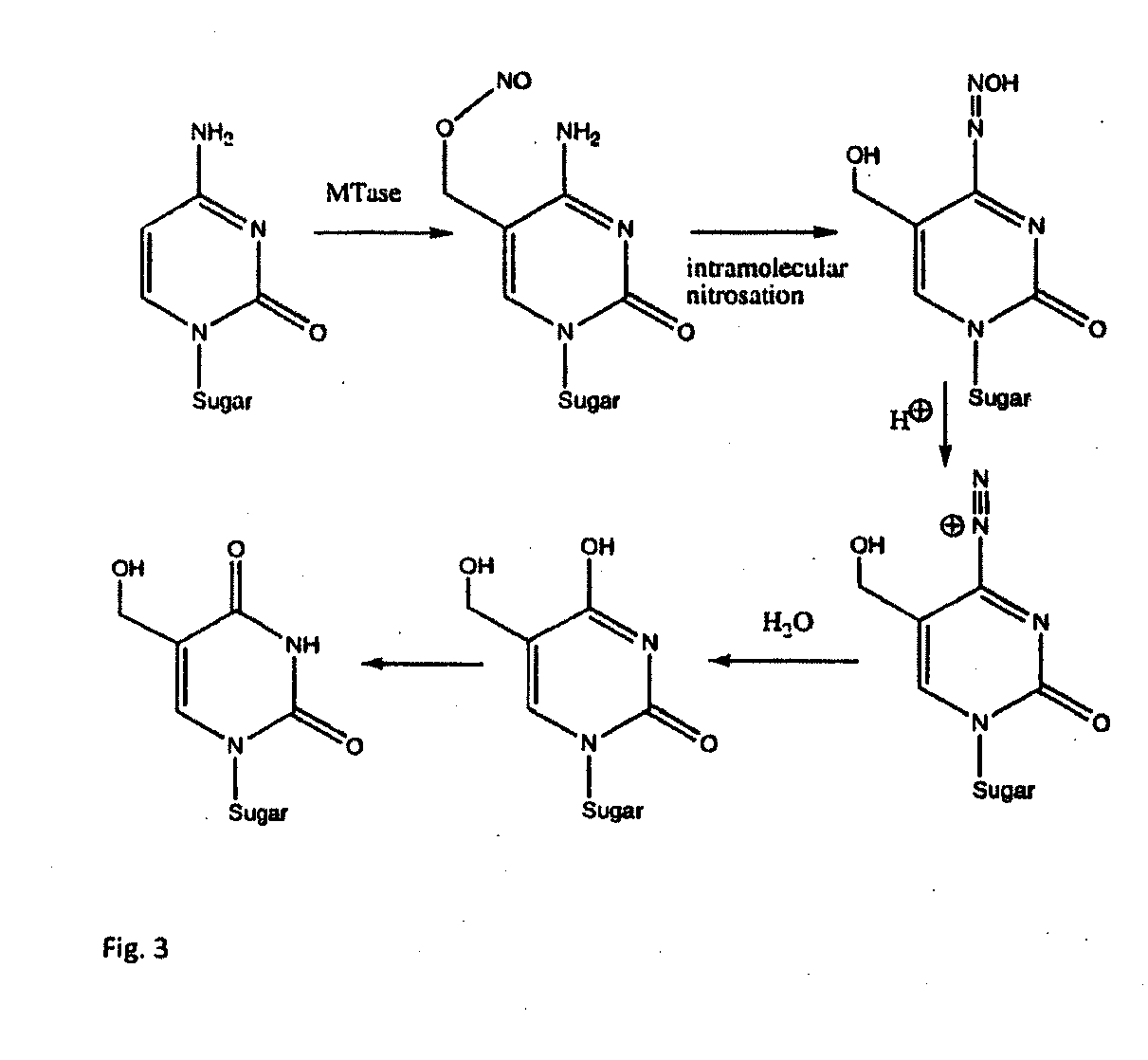
Universal methylation profiling methods
InactiveUS20110177508A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementS-Adenosyl methionineS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
This invention provides methods of derivatizing a double-stranded DNA comprising contacting double-stranded DNA with a CpG methyltransferase and an s-adenosylmethionine analog. This invention also provides methods of sequencing DNA to determine methylation patterns. This invention also provides neobases and methods of sequencing for methylation patterns using neobases.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
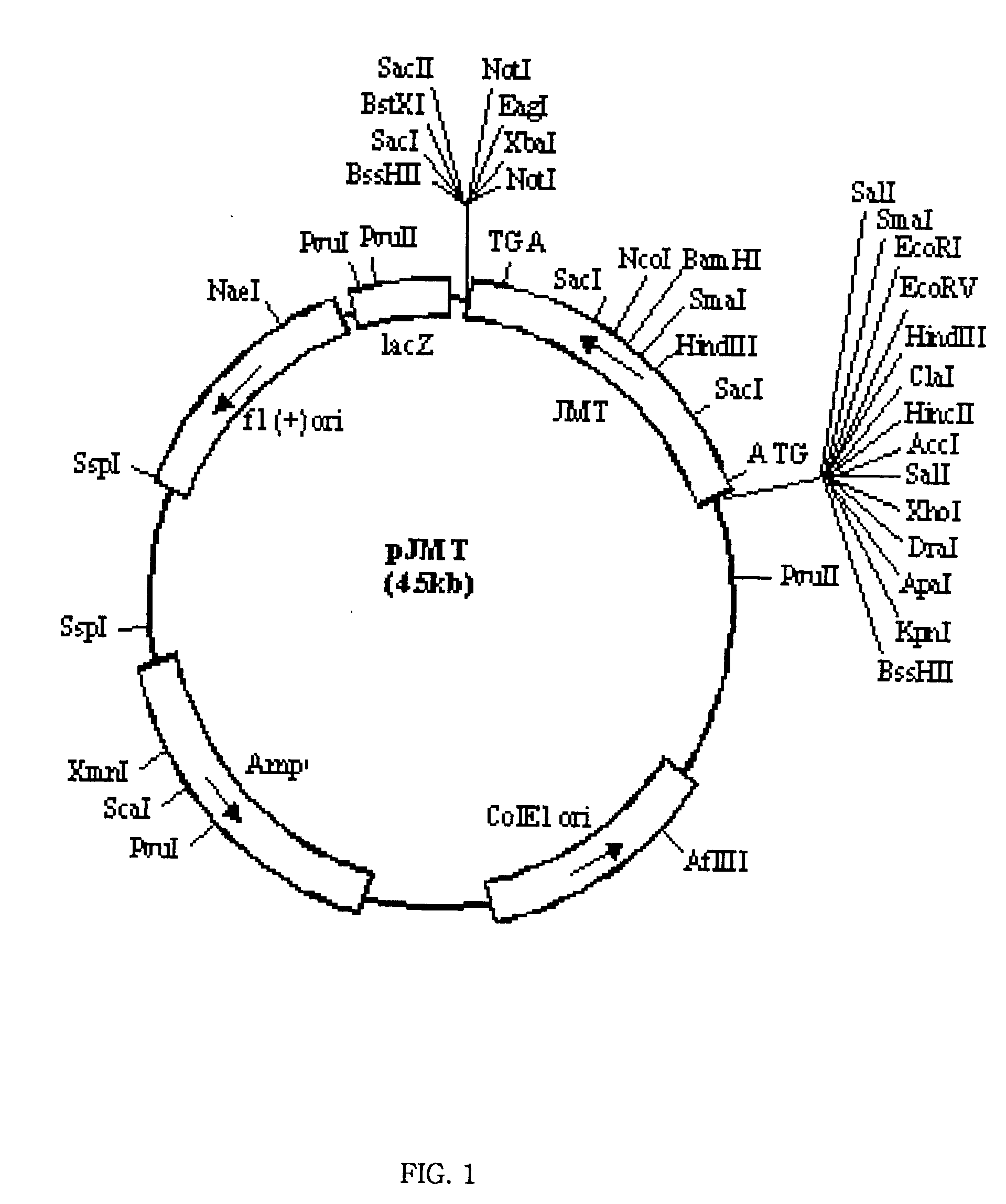
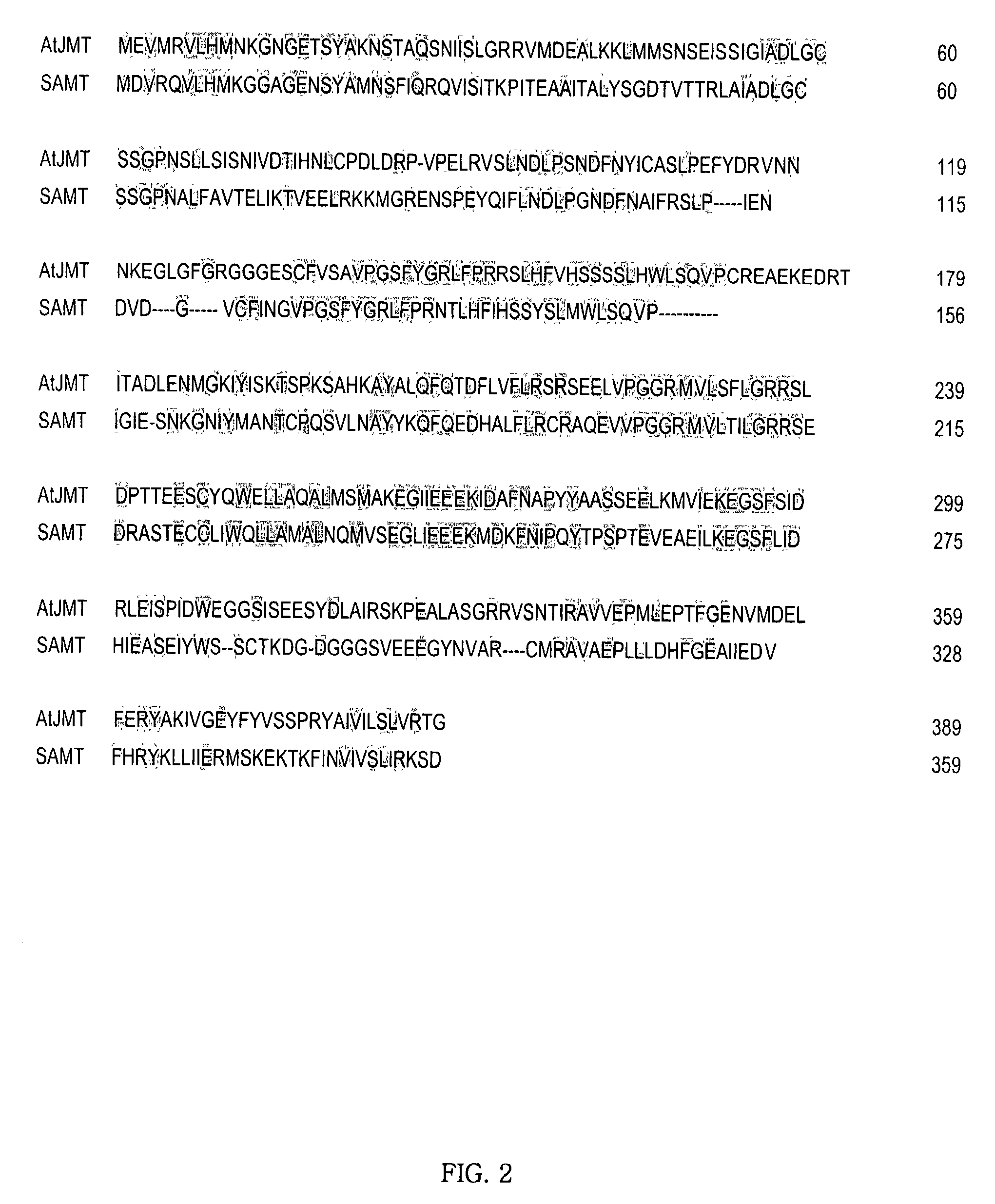
Genes for s-adenosyl l-methionine: jasmonic acid carboxyl methyltransferase and a method for the development of pathogen-and stress-resistant plants using the genes
InactiveUS20030064895A1Similar effectImprove resistance to damageBiocideClimate change adaptationNovel genePathogen
The present invention relates to a novel gene for S-adenosyl-L-methionine:jasmonic acid carboxyl methyltransferase, a novel jasmonic acid carboxyl methyltransferase protein synthesized therefrom, and a novel transgenic plant transformed with an expression vector containing said gene. It has been known that said enzyme synthesizes jasmonic acid methyl ester using jasmonic acid and S-adenosyl methionine as the substrate and jasmonic acid methyl ester is a compound mediating the defensive reactions upon invasion of phytopathogenic organisms and harmful insects as well as a compound for regulating the plant growth. By introducing said novel enzyme which is specifically expressed in flowers into the plant body, a transgenic plant which exhibits a resistance against phytopathogens, harmful insects and stresses without causing any adverse effect on the plant growth can be obtained.
Owner:SCIGEN HARVEST
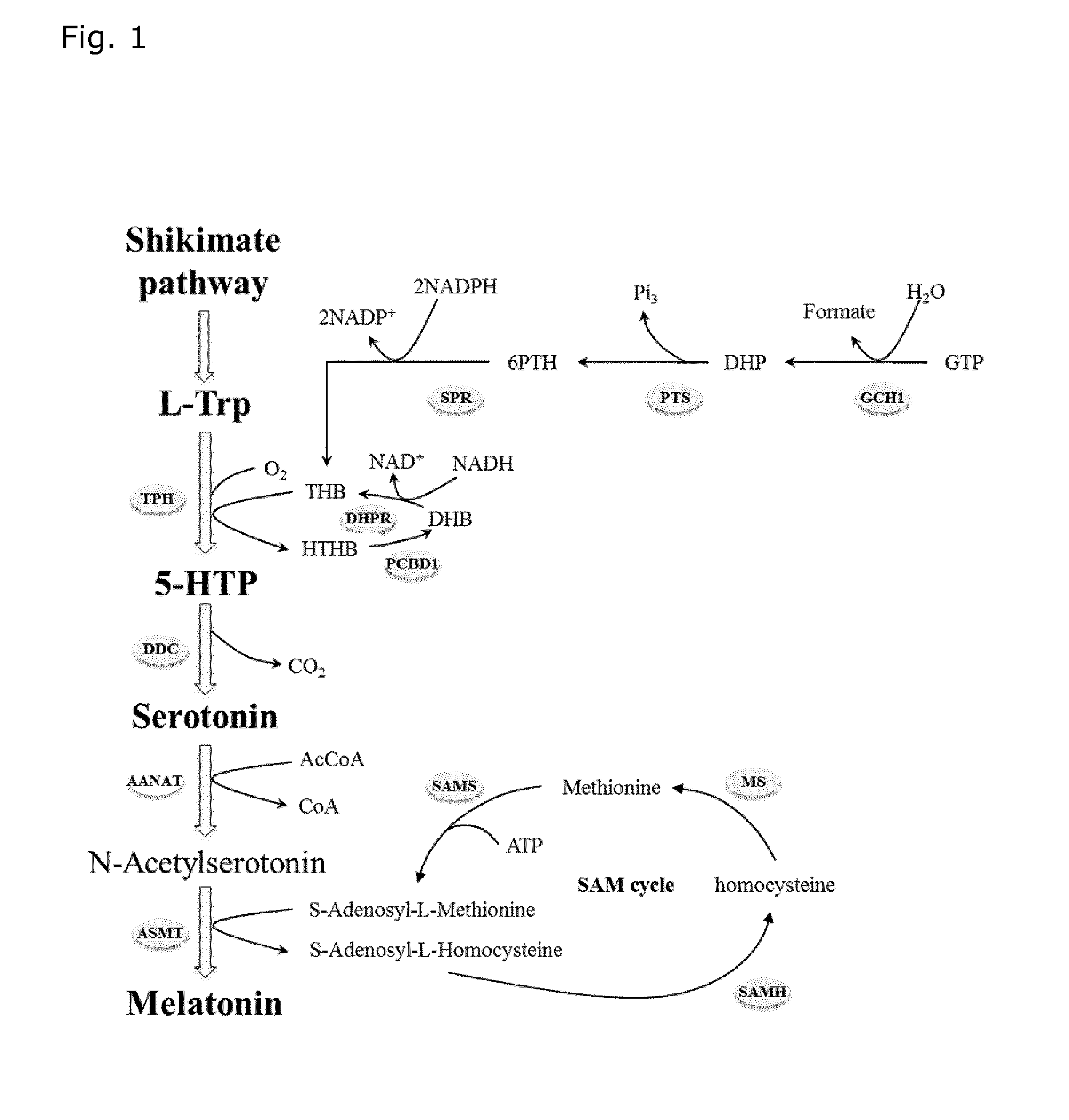
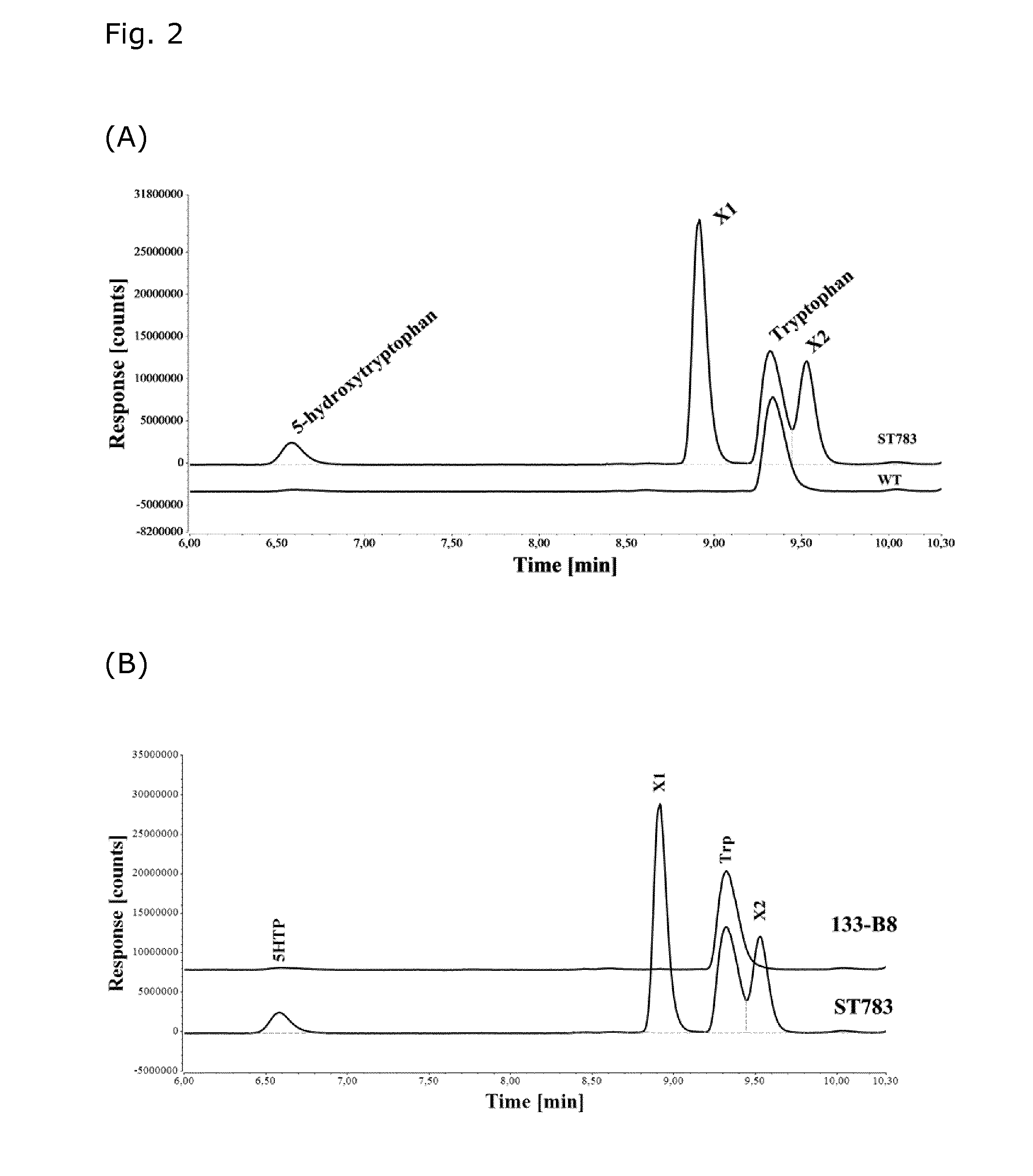
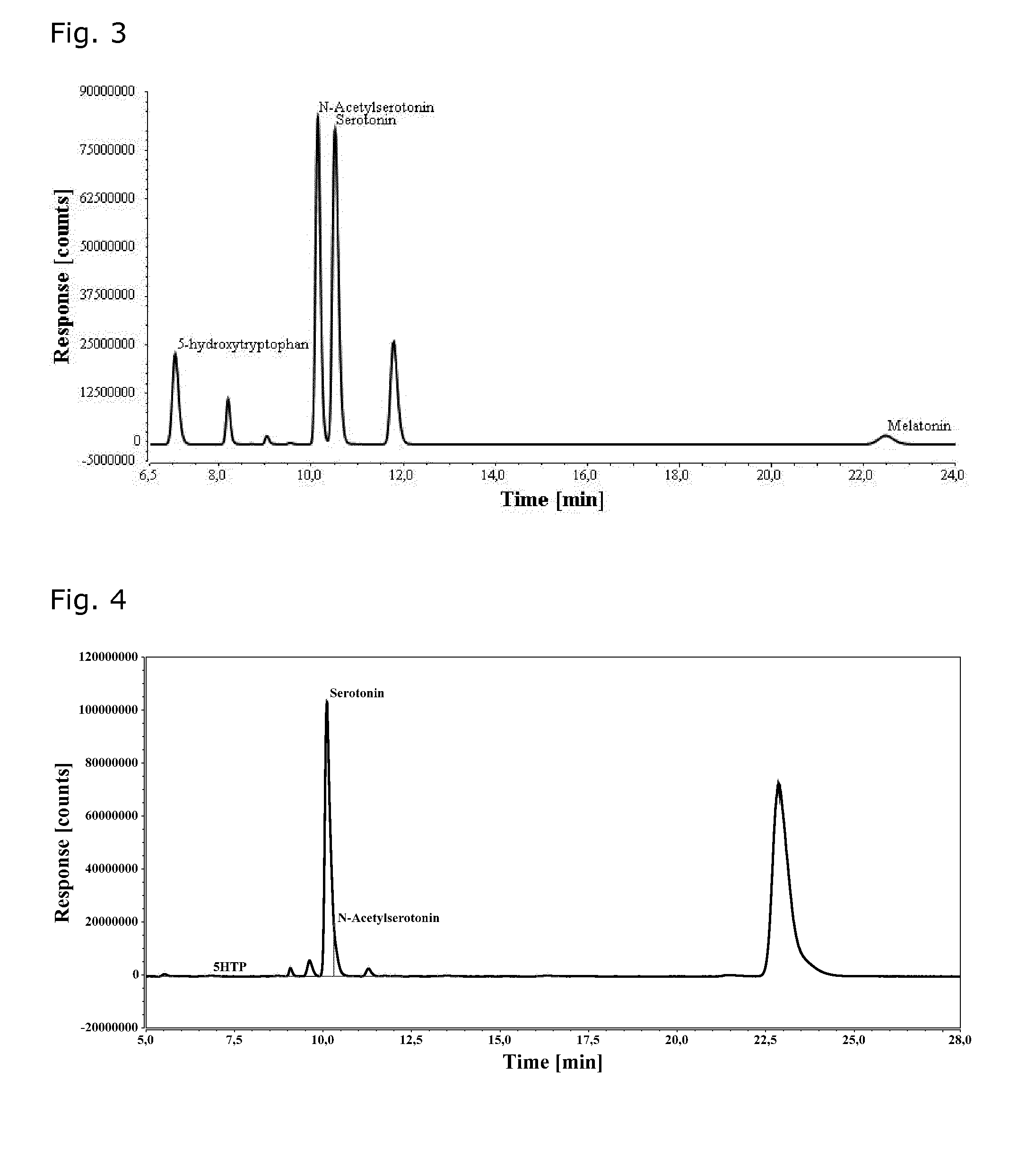
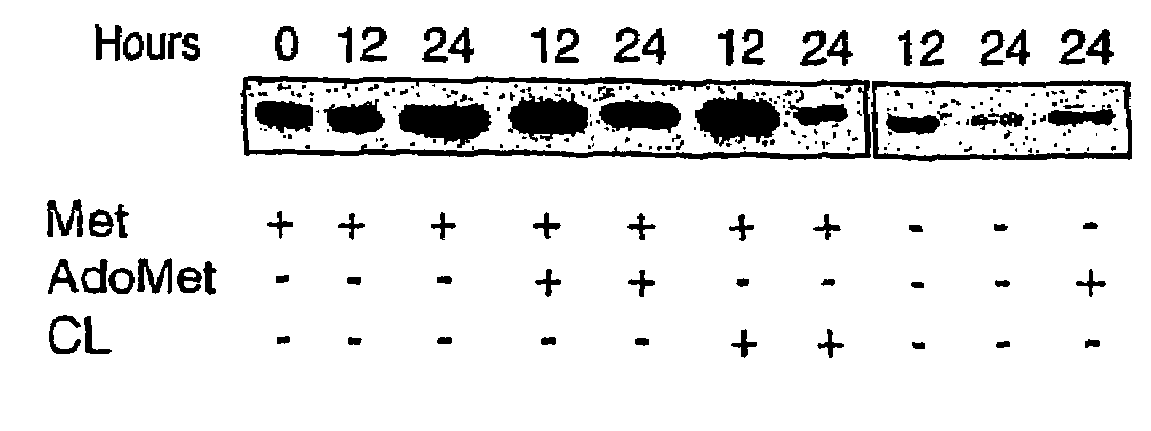
Microorganisms for efficient production of melatonin and related compounds
Recombinant microbial cells and methods for producing 5HTP, melatonin and related compounds using such cells are described. More specifically, the recombinant microbial cell may comprise exogenous genes encoding one or more of an L-tryptophan hydroxylase, a 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan decarboxylyase, a serotonin acetyltransferase, an acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase; and means for providing tetrahydrobiopterin (THB), and can be further genetically modified to enrich one or more of tryptophan, S-adenosyl-L-methinonine and acetyl coenzyme A. Related sequences and vectors for use in preparing such recombinant microbial cells are also described.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash) using molecular markers
InactiveUS7314720B2Ease of evaluationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntioxidant proteinMitochondrial ATPase
The invention relates to a method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) using molecular markers. The inventive method consists in detecting and quantifying, in vitro in a hepatic tissue sample, the levels of a protein which can be used as a NASH molecular marker and which is selected from apolipoprotein A1, sub-unit β of the mitochondrial ATPase, leukotriene A4 hydrolase, keratin 18, guanidine acetate N-methyltransferase, superoxide dismutase, albumin, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 1), prohibitin 1, methionine adenosyl transferase, long-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase, selenium binding protein, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 2), and combinations of same. The invention further consists in comparing the results obtained with the normal values of said proteins in healthy hepatic tissue. Said method can be used to diagnose NASH and / or to assess a patient's potential risk of developing NASH.
Owner:ONE WAY LIVER GENOMICS
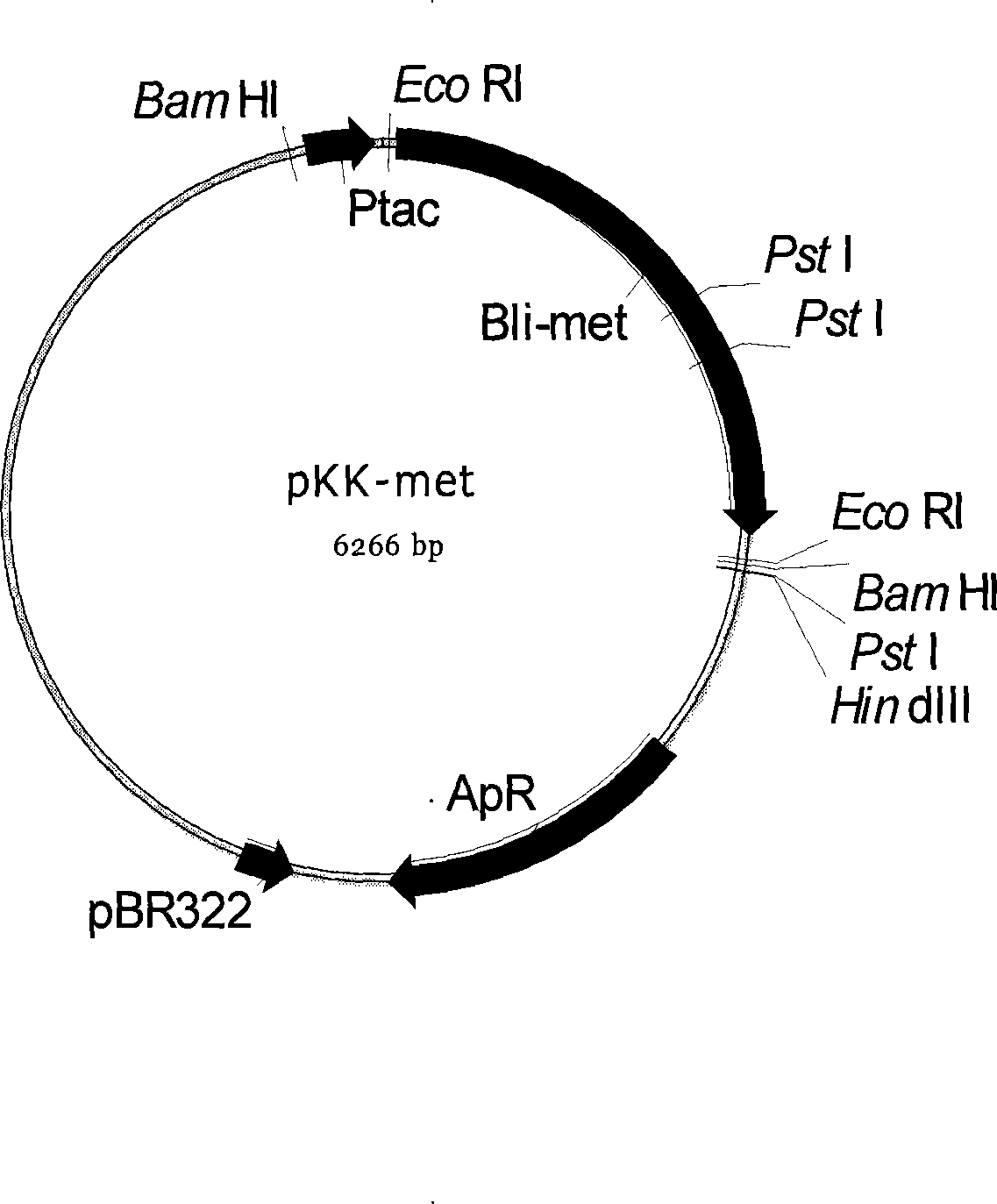
Bacillus licheniformis industrial production strain genetic transformation method
InactiveCN101230329AElimination of limitationsStable and efficient genetic transformationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisElectroporation
The invention provides a bacillus licheniformis industrially producing bacterial strain genetic transformation method, which belongs to microbial gene engineering and fermentation technology field. The invention provides a bacillus licheniformis industrially producing bacterial strain genetic transformation method; firstly DNA molecule which needs to be genetically transformed is methylated by the bacillus licheniformis specificity methyltransferase medium; specifically methylated DNA molecule adopts optimized electroporation method to realize the genetic transformation of bacillus licheniformis industrially producing bacterial strain. By the method, the genetic transformation rate can reach 25-1250 strains / microgram DNA. In particular, the invention can be used in the genetic transformation of bacillus licheniformis bacterial strain that the prior genetic transformation cannot be realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and effects of aging
InactiveUS7232830B2Increase neuronalIncrease neuronal metabolismBiocideNervous disorderAutoimmune diseaseMethyltransferase
A method for treatment of neurodegenerative disease conditions stemming from multiple sclerosis, aging, autoimmune diseases and fibromyalgia. A compound effective to increase neuronal metabolism of histamine to a histamine H2 agonist is administered in an amount sufficient to stimulate production of cyclic AMP at a level which is sufficient to maintain myelin against undergoing self-degeneration. The compound is selected from the group consisting of histamine M-methyltransferase, monoamineoxidase-A, monoamineoxidase-A agonists and histamine H3 antagonists. The histamine M-methyltransferase may be administered to increase neuronal metabolism of histamine to tele-methylhistamine, whereas the monoamineoxidase-A or monoamineoxidase-A agonist may be administered so as to increase neuronal metabolism of telemethylhistamine to an H2 agonist. Separately or in conjunction with the others, the histamine H3 antagonist may be administered so as to inhibit metabolism of the telemethylhistamine to an H3 agonist, thereby increasing metabolism of the telemethylhistamine to an H2 agonist. The increased histamine H2 agonist levels reduce demyelination and the symptoms that are associated with these conditions.
Owner:EAD
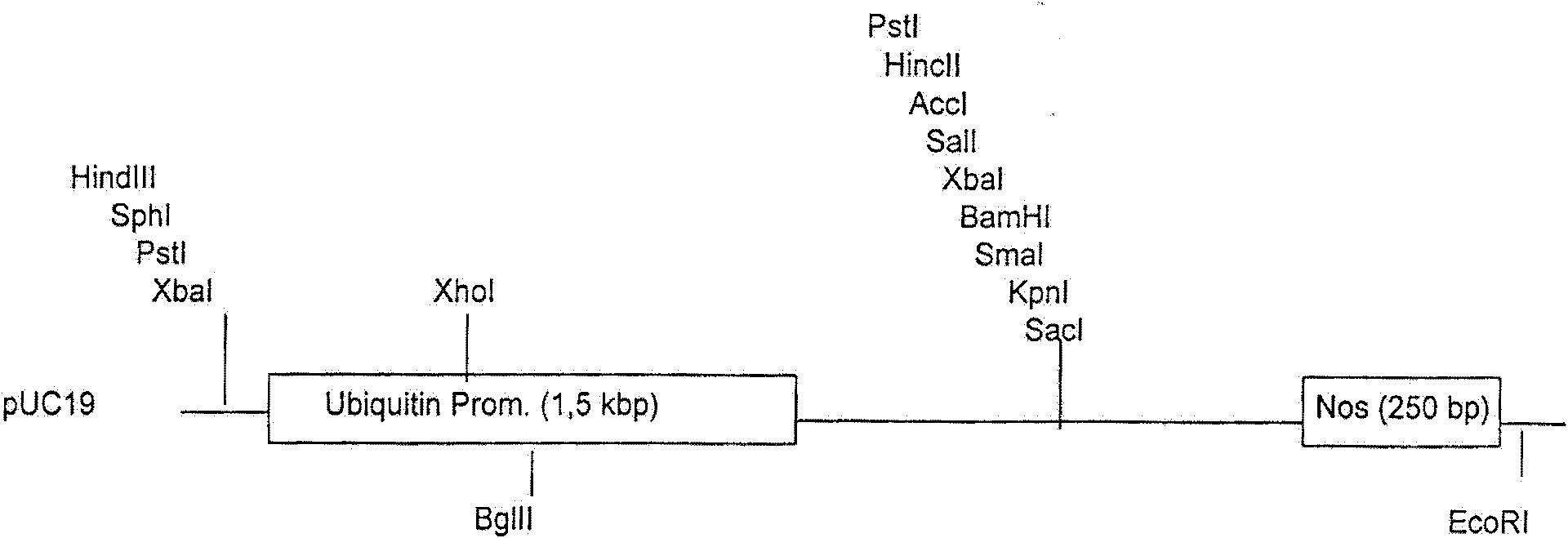
A plant transformation vector and its construction method and application
InactiveCN102286524AHigh expressionOvercoming the problem of preferenceVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsChloroplastMethyltransferase
The invention provides a plant transformation vector, and a construction method and application thereof. In the vector, a red fluorescent protein UPMT (uroporphyrinogen III methyltransferase) and a resistance screening alad gene are used as a reporter gene and a selected marker for plant transfection. The red fluorescent protein UPMT and the resistance screening alad gene have similar functions, are superior to antibiotic and a green fluorescent protein fusion marker for example, and can be used for screening and subcellular organelle positioning in rice chloroplast transformation. Thus, the two genes used as screening markers of a transgenic plant can indicate the positioning of the cytologic and tissue specificity of a target gene, and can also promote the photosynthesis efficiency of plants and the accumulation of nutrient substances. The invention has potential and broad application backgrounds in the transgenic plant research and marketing process, and is hopefully developed into a dominant selected marker system in plant transformation.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
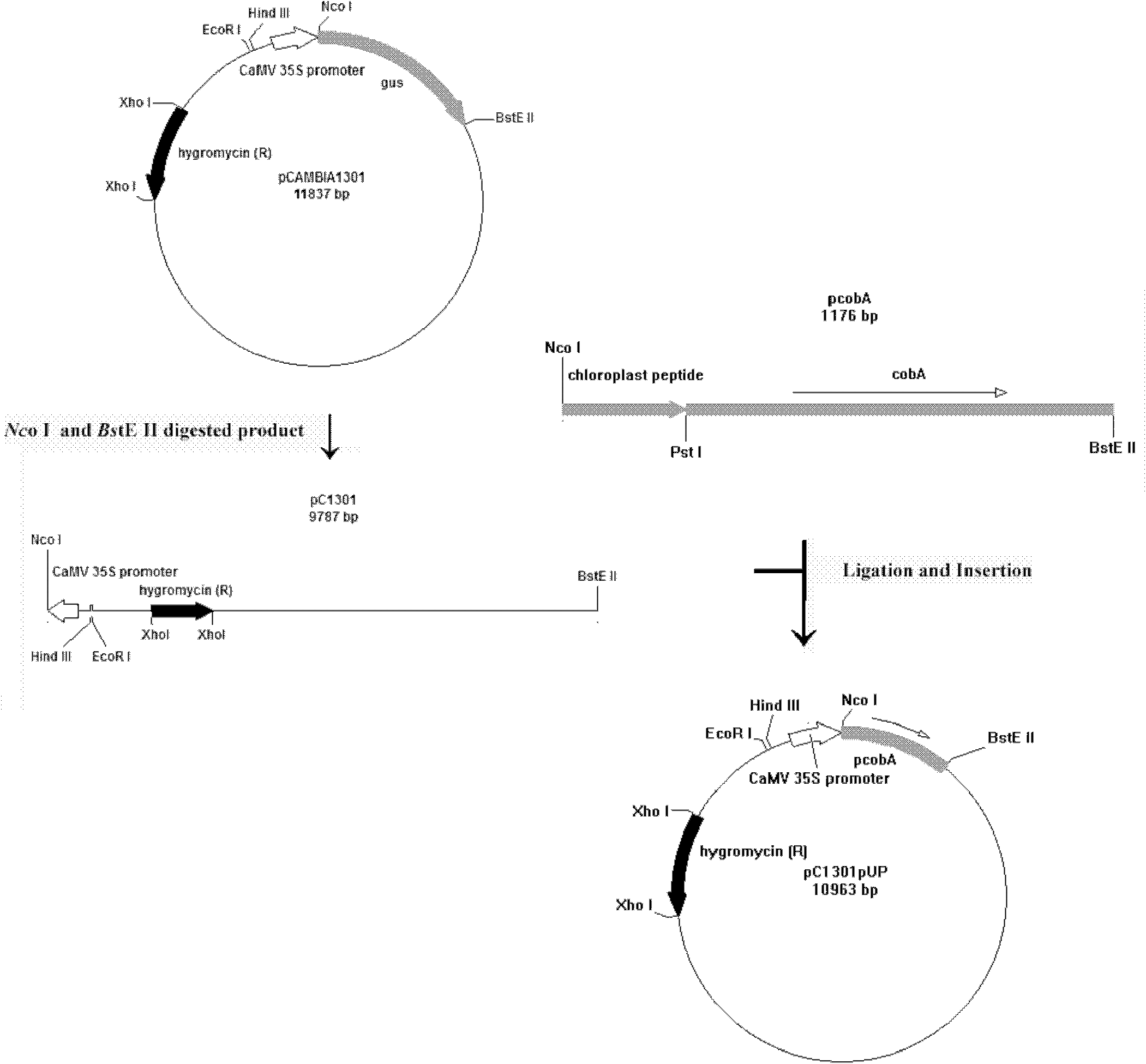
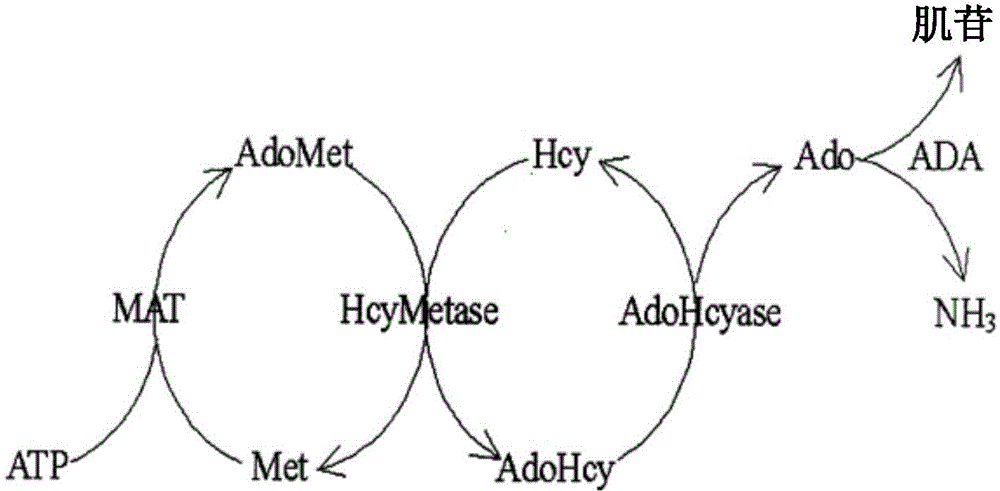
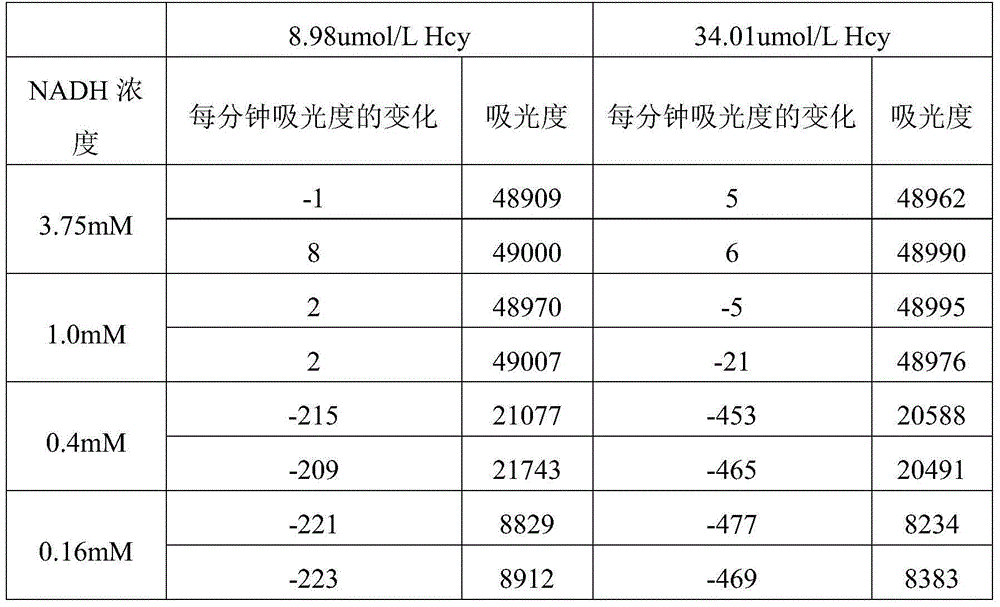
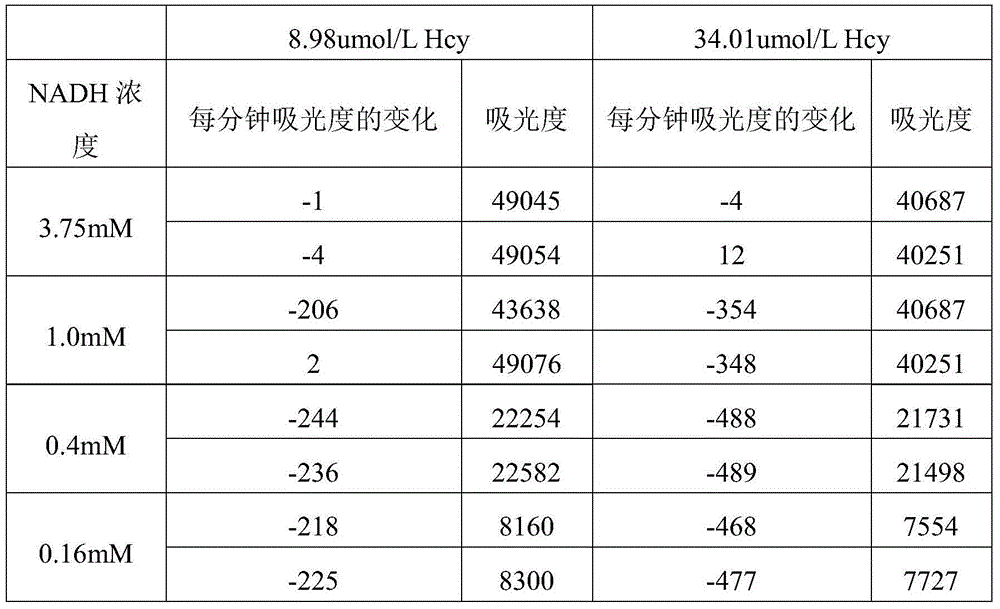
Improved homocysteine detection reagent and method
ActiveCN104630324AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementS-Adenosyl-l-methionineAdenosine
The invention relates to an improved homocysteine detection reagent and method. The method comprises the following steps: enabling homocysteine to perform repeated circular reaction with S-adenosylmethionine under the action of homocysteine methyltransferase and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase to produce adenosine, and determining the concentration of homocysteine in a sample by detecting the production rate of adenosine. According to the improved homocysteine detection reagent and method disclosed by the invention, by adopting measures of regulating positions and pH values of components in a kit and adding a stabilizing agent, a method and kit which have high specificity, high sensitivity and strong stability and can be used for automatically detecting homocysteine with extremely low content in body fluid can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING AMBITION BIOTECH
Methyltransferase nucleic acids and polypeptides
This disclosure relates to the isolation and sequencing of nucleic acid molecules that encode methyltransferase polypeptides from a Papaver somniferum cultivar; and uses in the production of noscapine and identification of poppy cultivars that include the genes that comprise said nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SUN PHARMA IND AUSTRALIA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com