Improved homocysteine detection reagent and method
A homocysteine and detection reagent technology, applied in the field of improved homocysteine detection reagents, can solve problems such as poor stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: The effect of component exchange and concentration changes on the kit
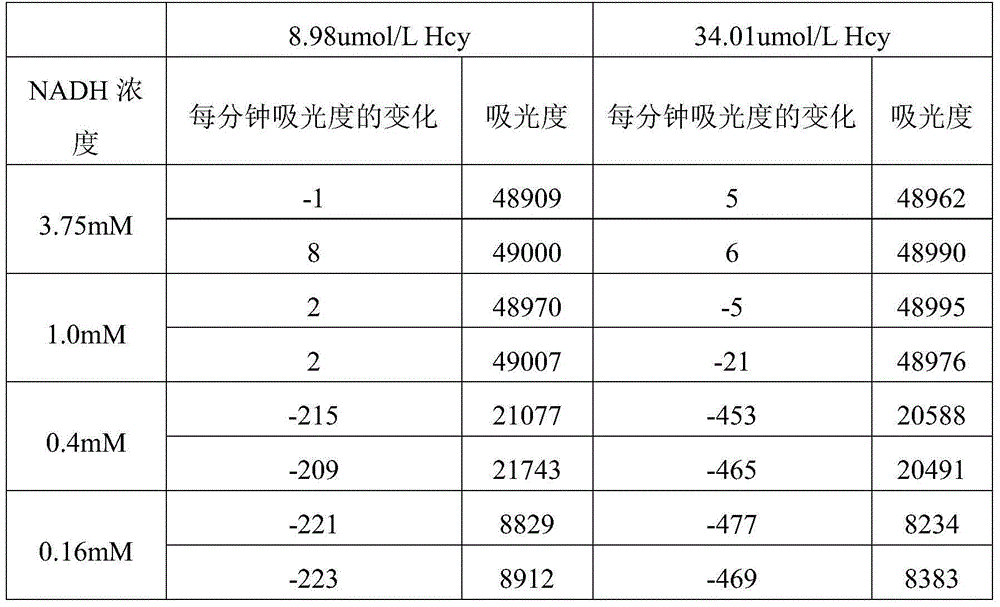
[0049] As a kit with clinical detection and diagnostic significance, the replacement of its reagent components, changes in concentration, and even changes in buffers and corresponding pH will change the performance of the kit, and these changes cannot be simple from the existing formula Derived from the ground, but it takes a lot of trials to get the ideal formula. The following content is several sets of examples involved in the development process of the kit of the present invention, which verify the influence of factors such as component exchange and concentration change on the efficacy and stability of the kit.
[0050] First, the formula of the kit 1 disclosed in the prior art is as follows:
[0051] Reagent 1 (R1: R2=3:1)
[0052] Reagent components
Final concentration
Good's buffer
15mM
NAD(P)H
5mM
GLDH
2KU / L
BSA
1.2g / L
0.2mM
ATP
10mM
alpha-ketoglutarate
30...
Embodiment 2
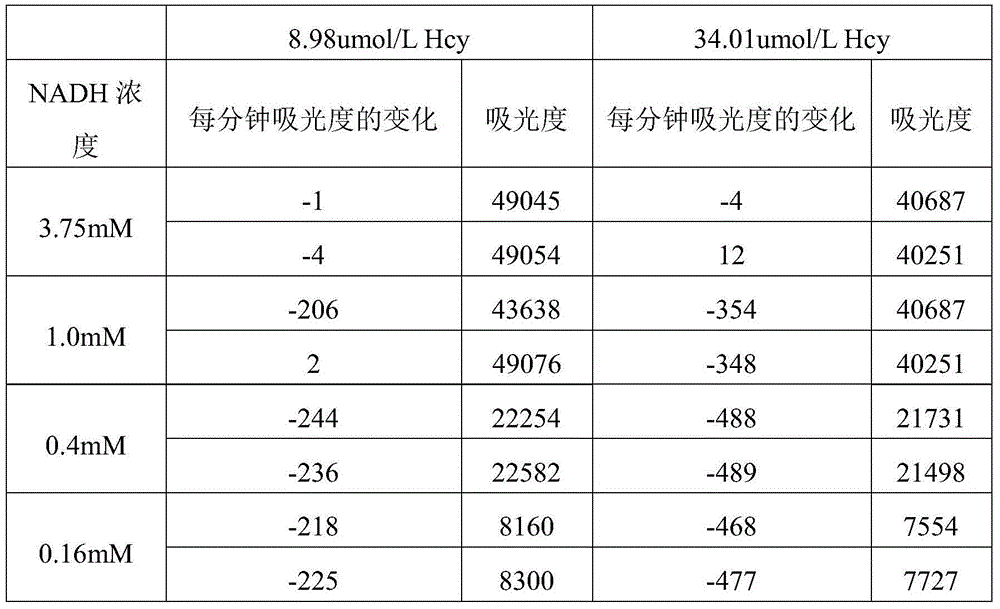
[0095] Example 2 Composition and method of use of the kit 1 of the present invention
[0096] After various attempts in the above-mentioned Example 1, the present invention adjusts part of the active enzyme to reagent 2, adds different stabilizers to reagent 2, adjusts the pH of reagents 1 and 2, and adjusts the content and position of reduced coenzymes. , Adjust the position and concentration of the reducing agent to obtain the kit of the present invention.
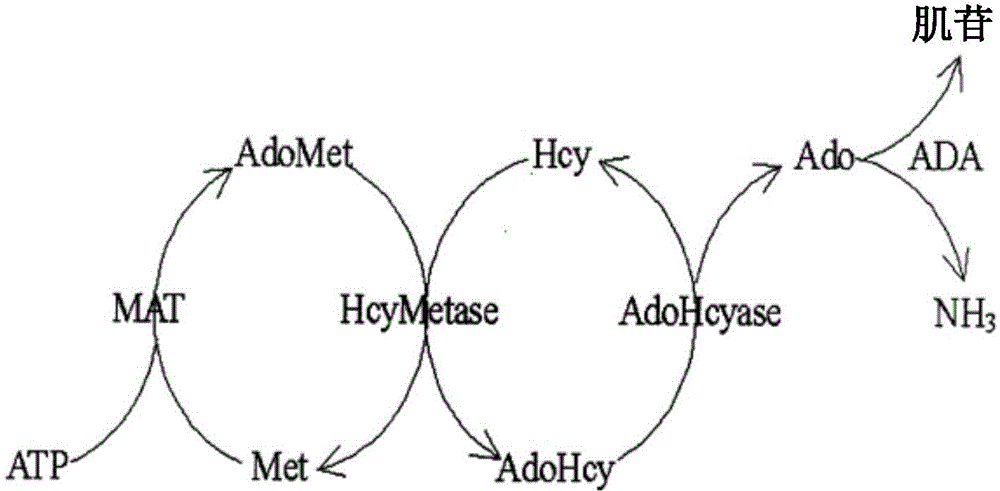
[0097] The following is a specific example of the kit of the present invention, called kit 1. The kit also adopts an enzyme cycle reaction consisting of homocysteine methyltransferase and adenosine homocysteine hydrolase, by using The method of detecting ammonia is to measure the rate of oxidation of reduced coenzyme within a fixed period of time to quantify the Hcy content in the sample.
[0098] Reagent 1: (R1:R2=3.75:1)
[0099] Reagent components
[0100] Reagent 2: (R1:R2=3.75:1)
[0101] Reagent components
[010...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3: Performance measurement of kit 1 of the present invention
[0105] Purpose: To evaluate the precision, accuracy, reportable range, sensitivity, and the appropriate range of the reference visible interval of the kit, to test whether it can meet the requirements of clinical testing and scientific research, and not cause obvious bias to clinical introduction.
[0106] Method: A Hitachi 7020 automatic biochemical analyzer was used to verify the following performance indicators of kit 1.
[0107] Conclusion: The test results of all performance indicators meet the requirements of clinical testing and scientific research.
[0108] 1 Test materials
[0109] 1.1 Instruments and reagents
[0110] 1.1.1 Instrument: Hitachi 7020 automatic biochemical analyzer
[0111] 1.2 Reagent: Beijing Aibixin batch number: 20130831
[0112] 1.3 The performance index requirements of the kit:
[0113] 1.3.1 Measuring range: within 3~50μmol / L, r≥0.990.
[0114] 1.3.2 Precision: intra-assay precision (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com