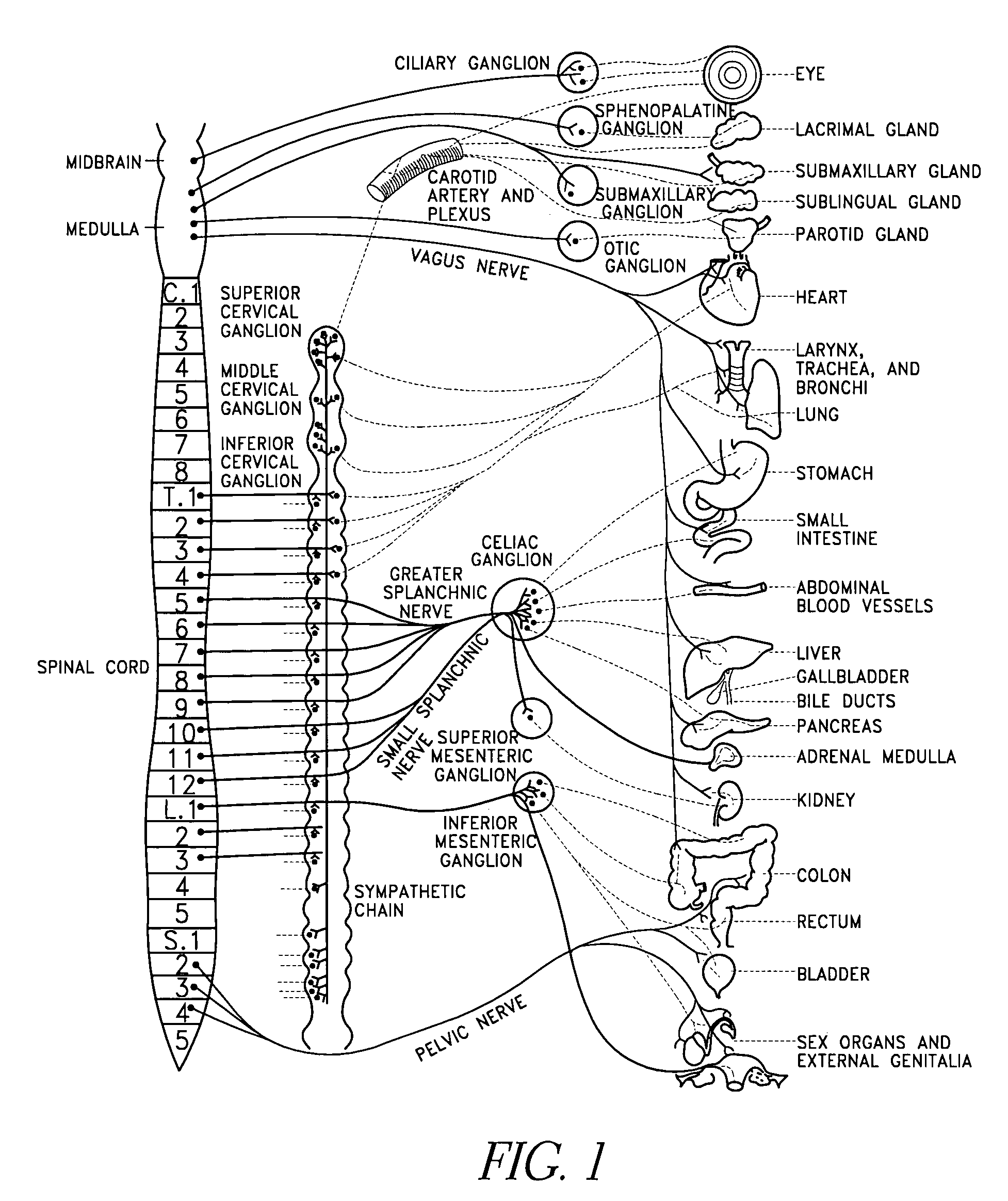
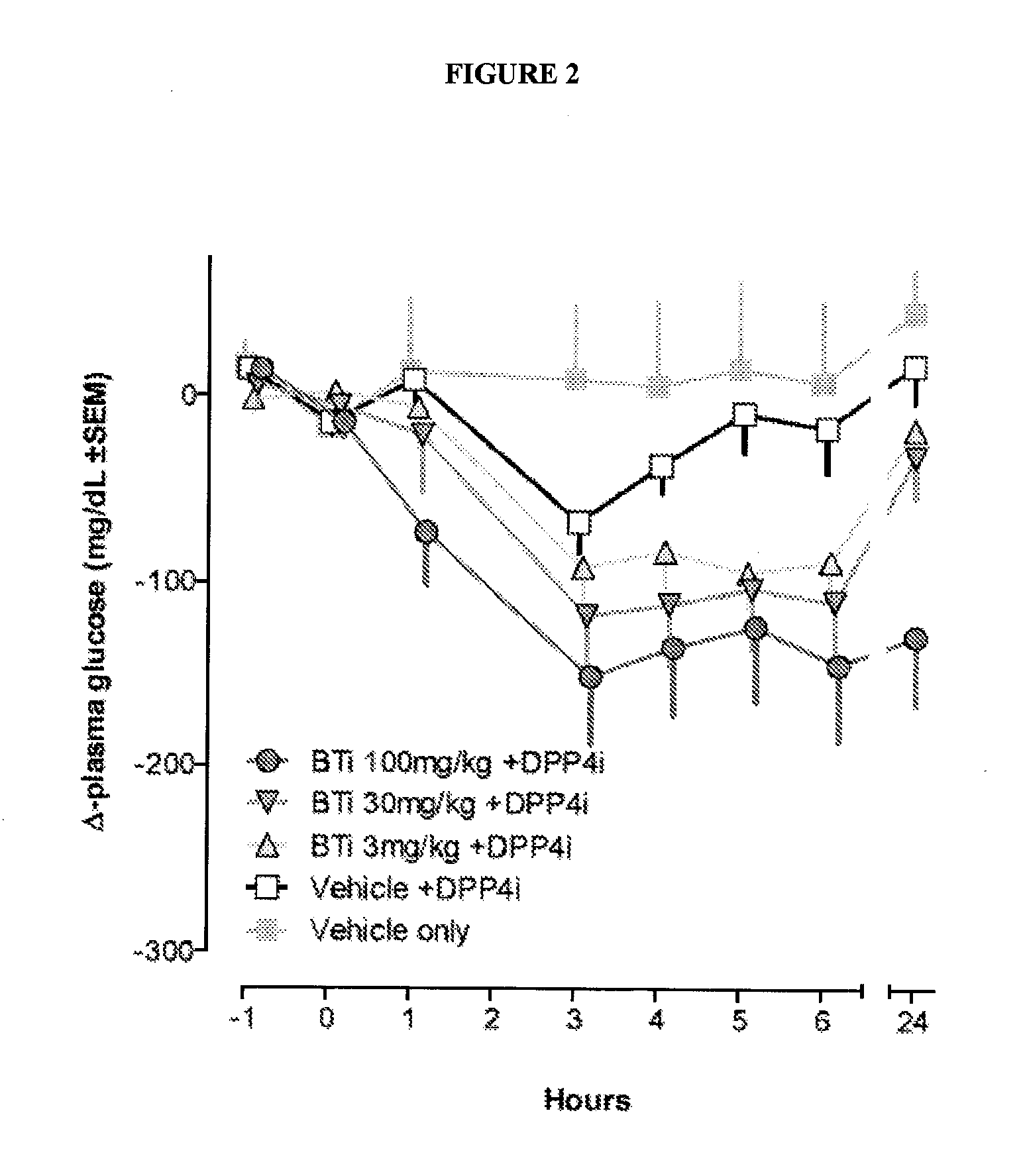
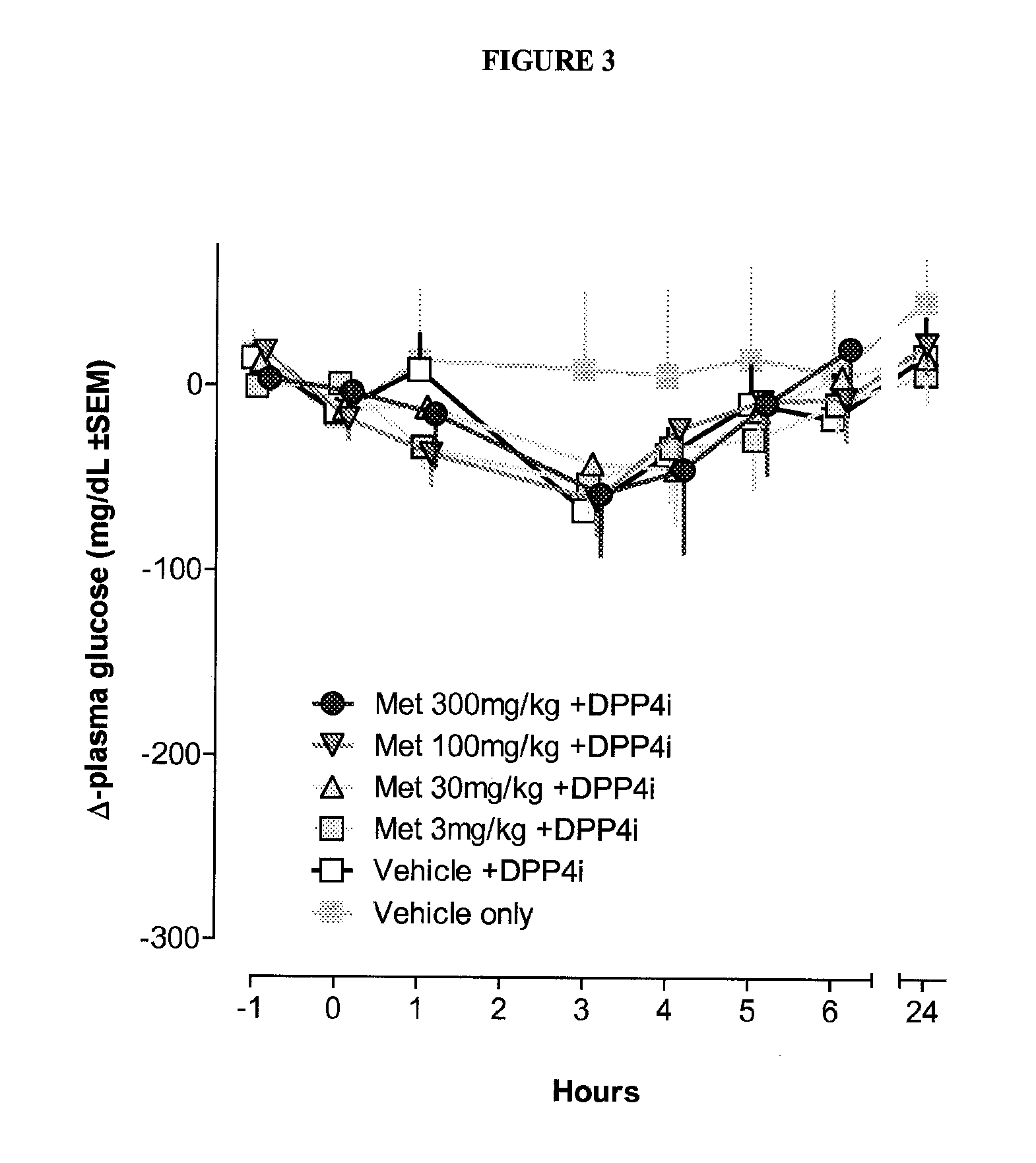
Patents
Literature
872results about How to "Increase secretion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
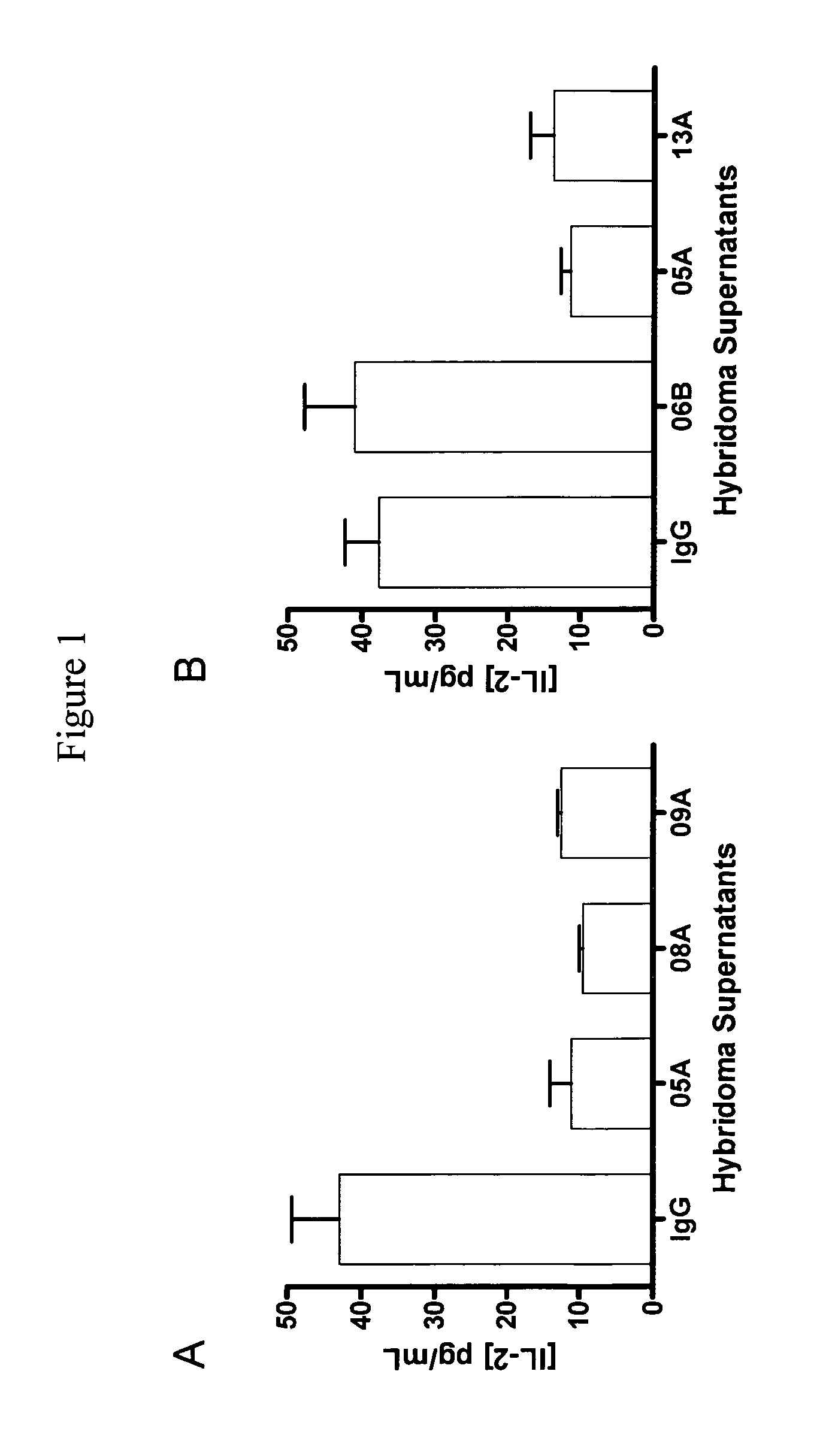
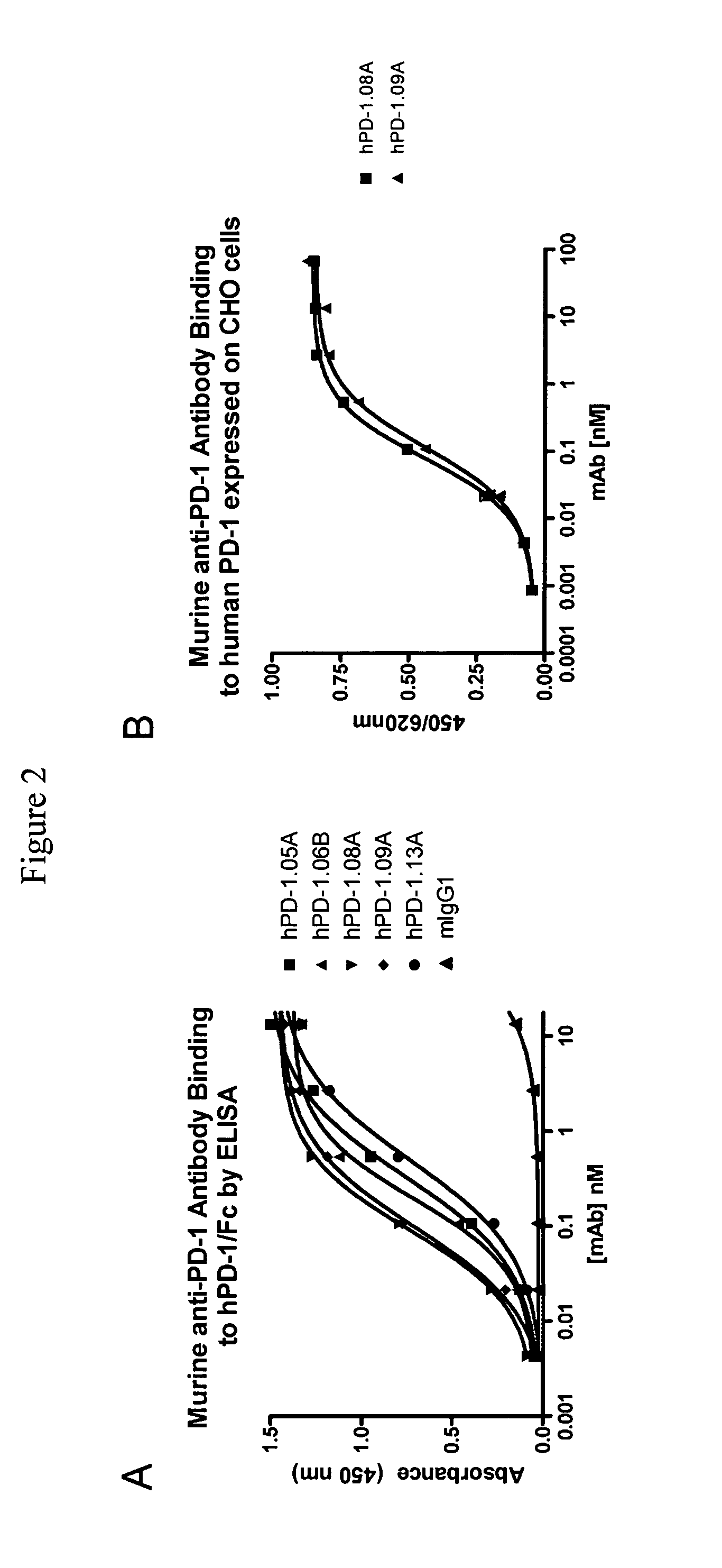
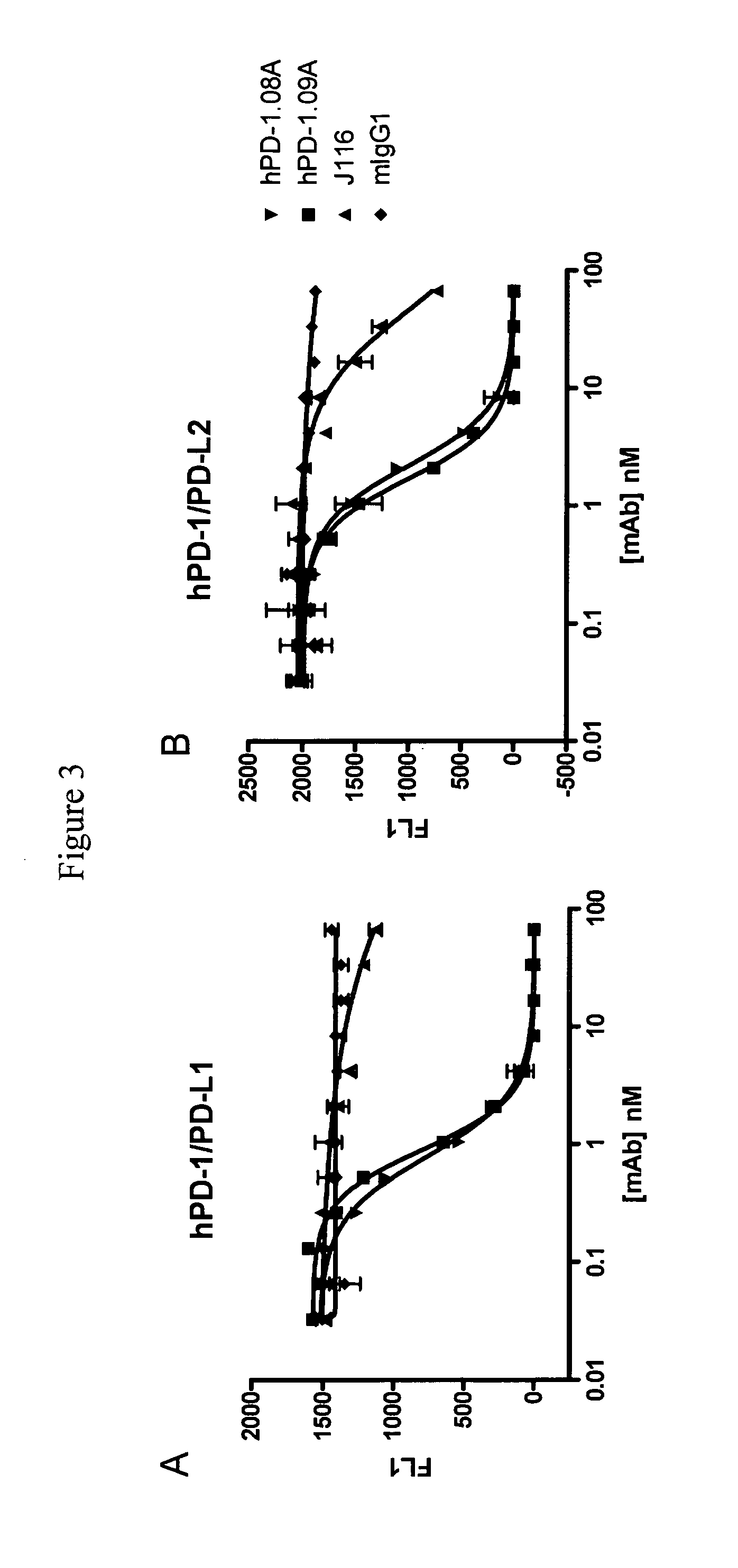
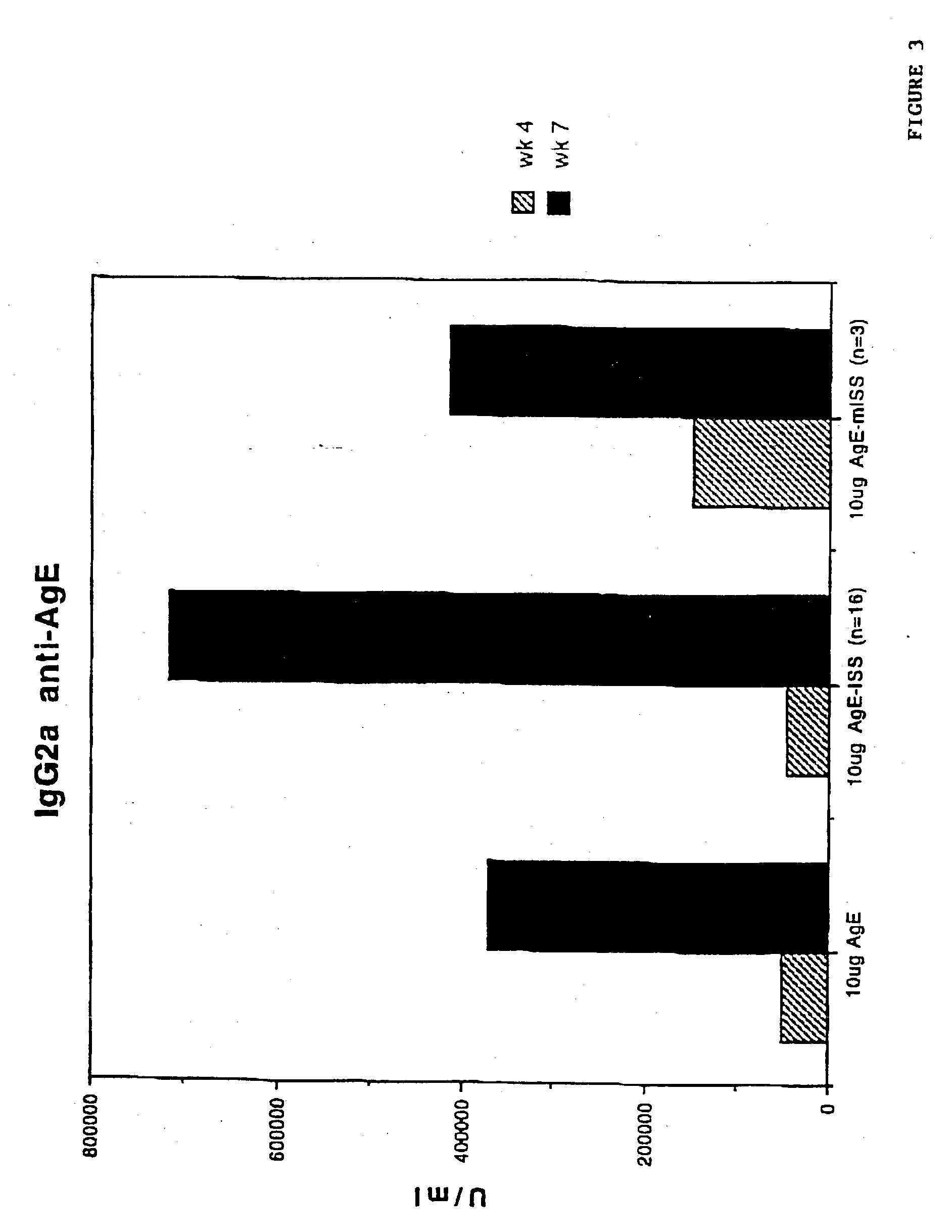
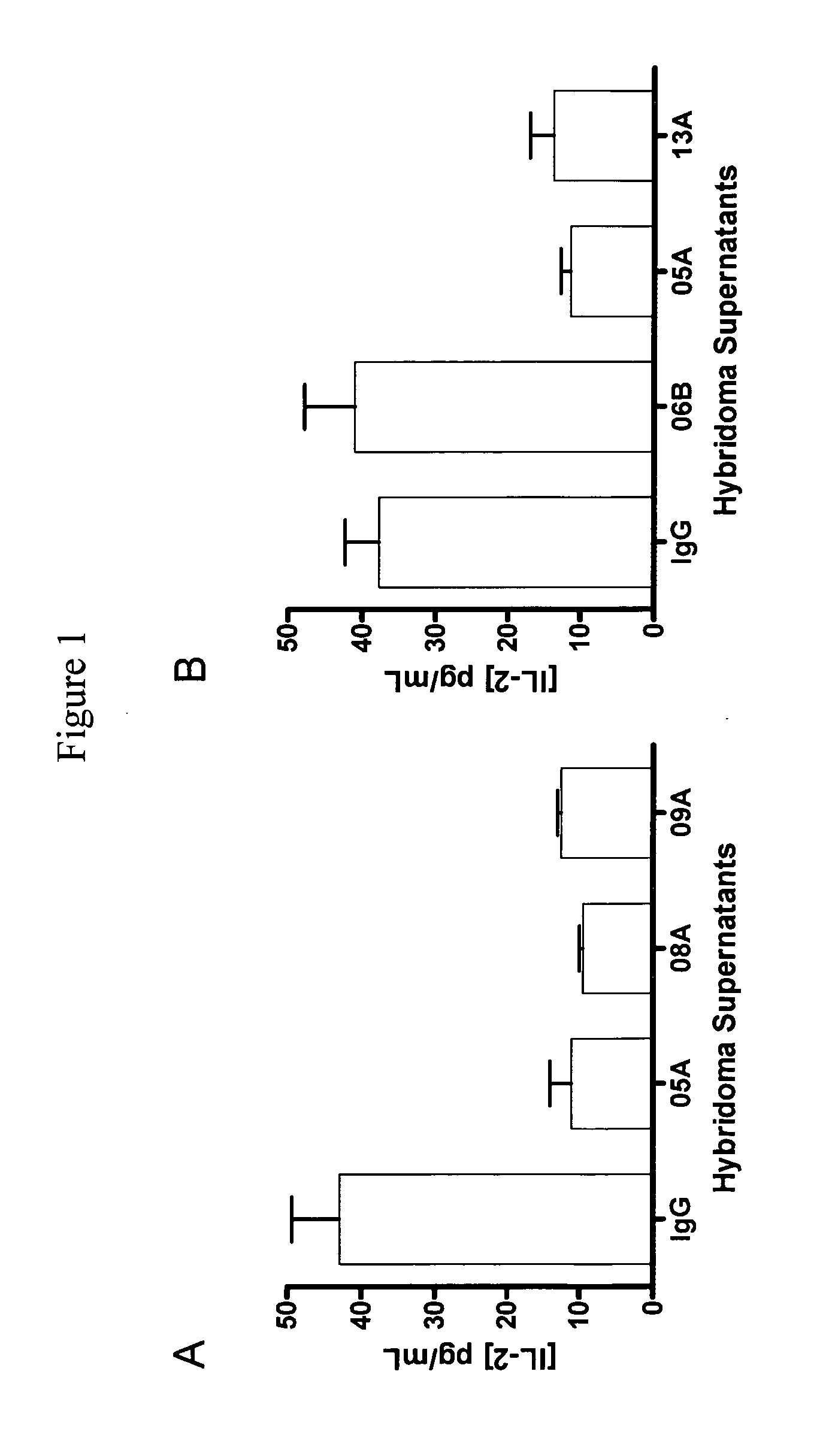
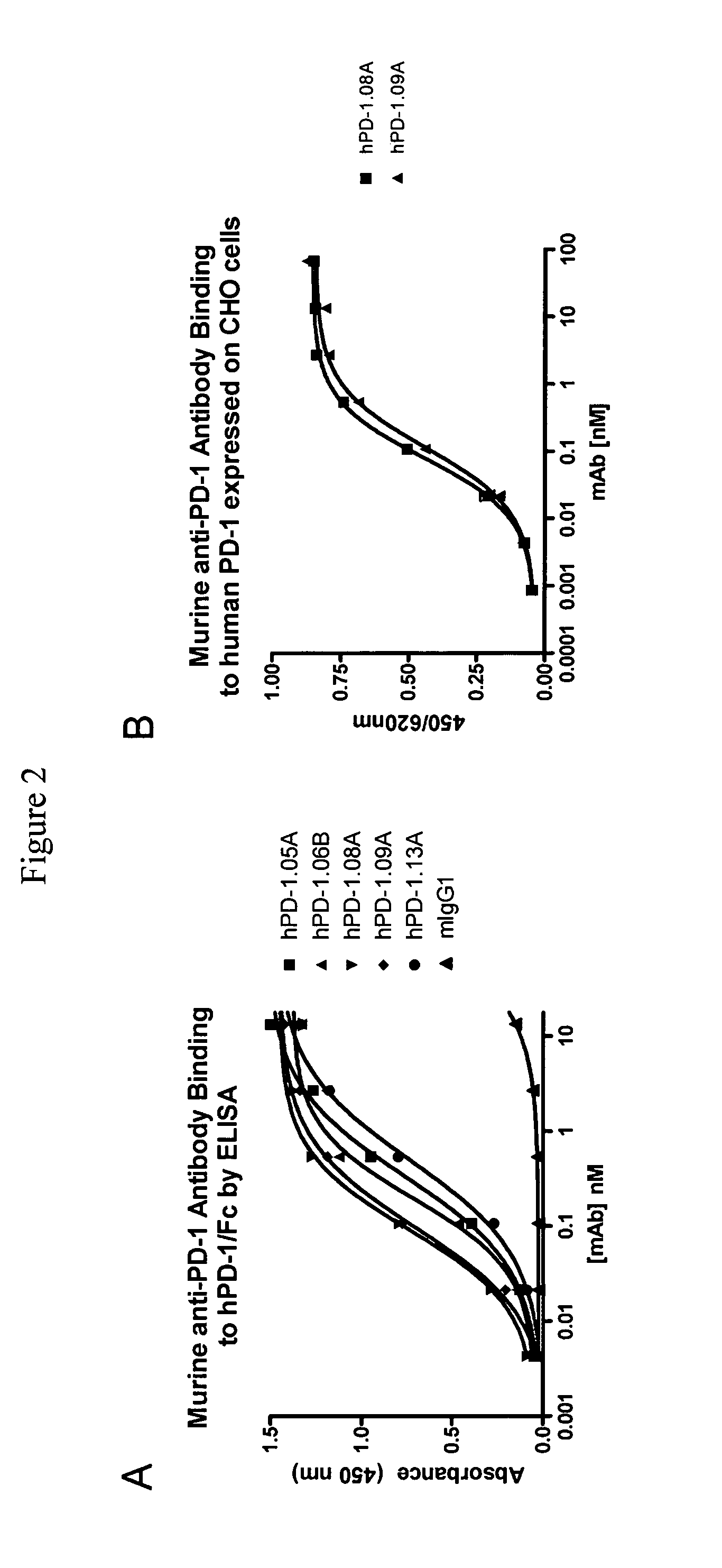
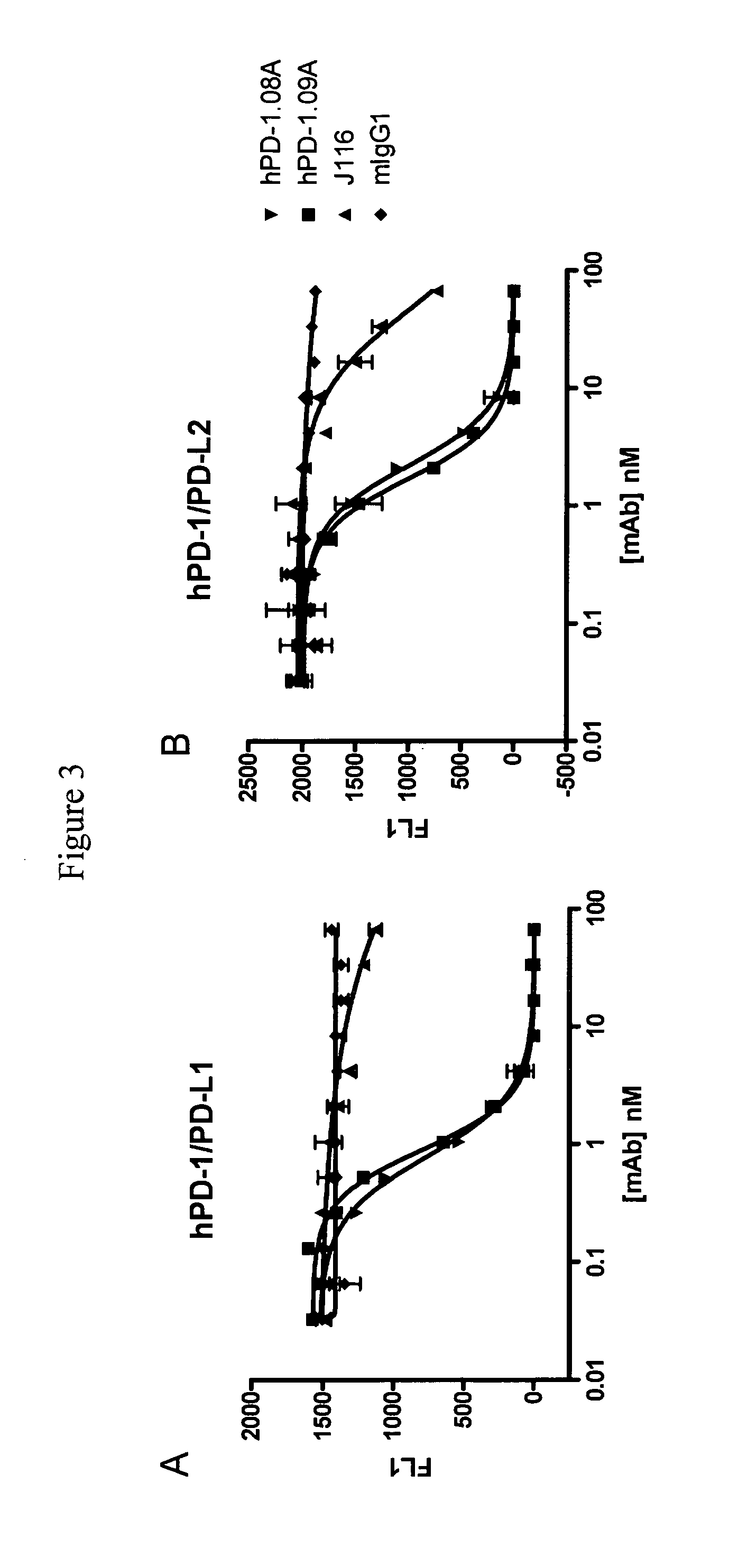
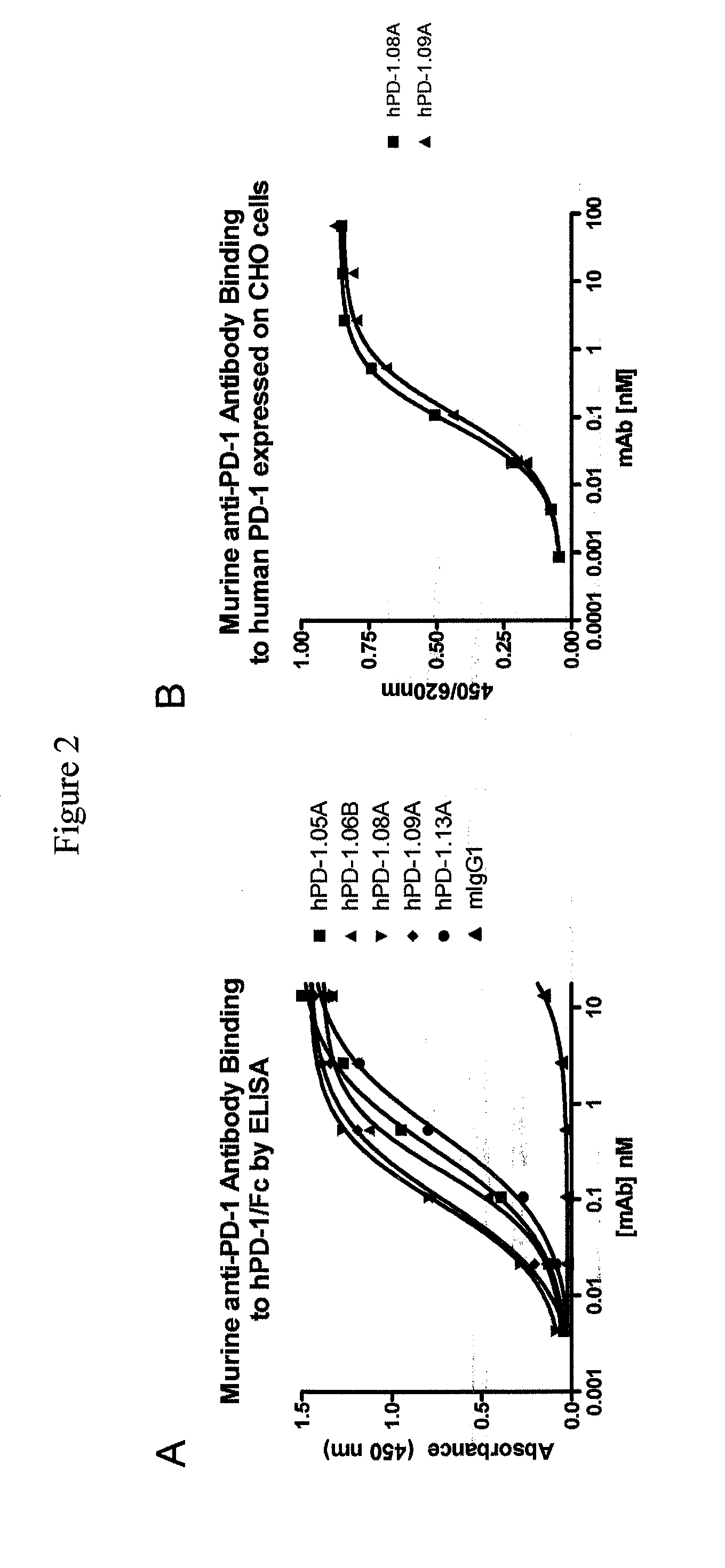
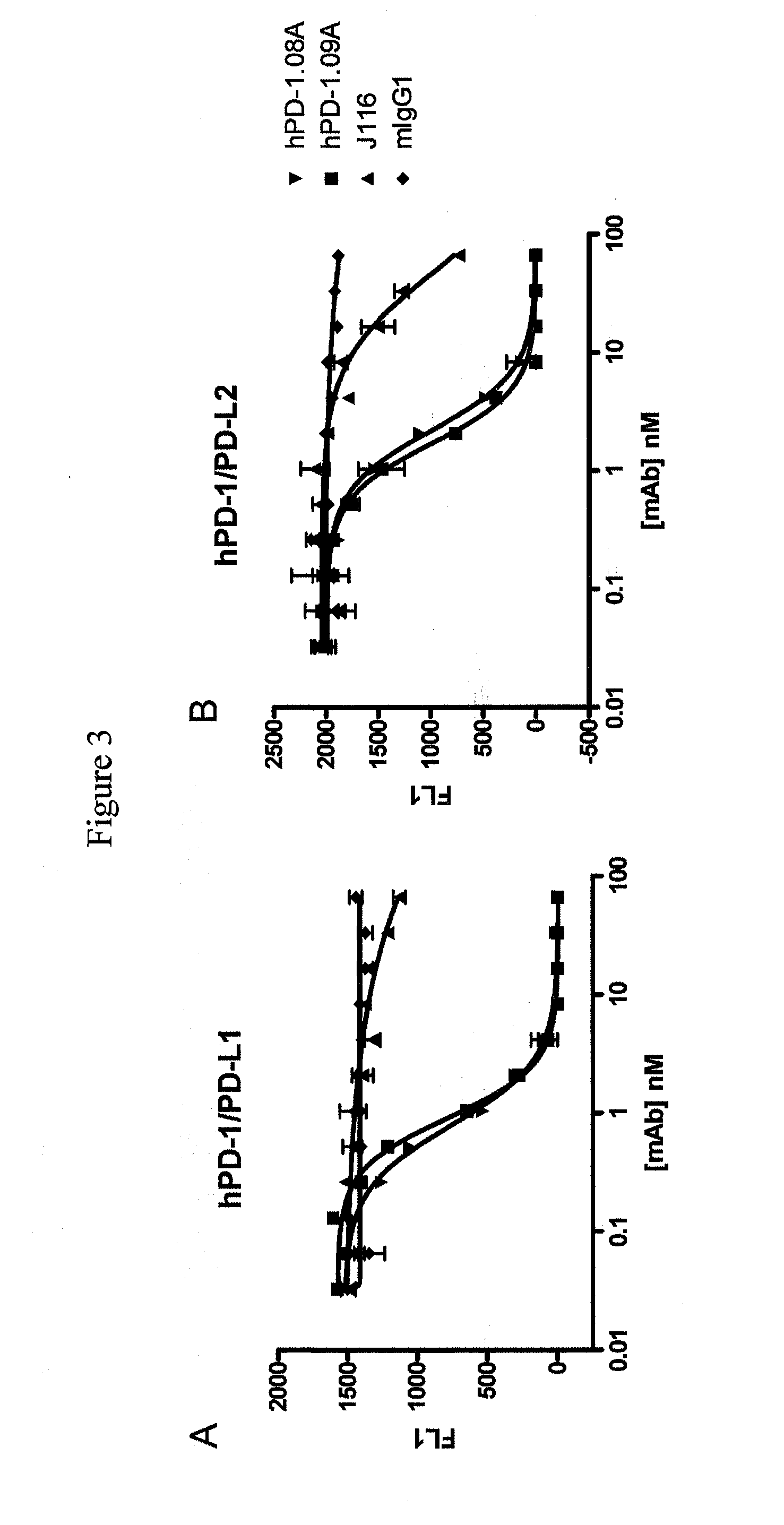
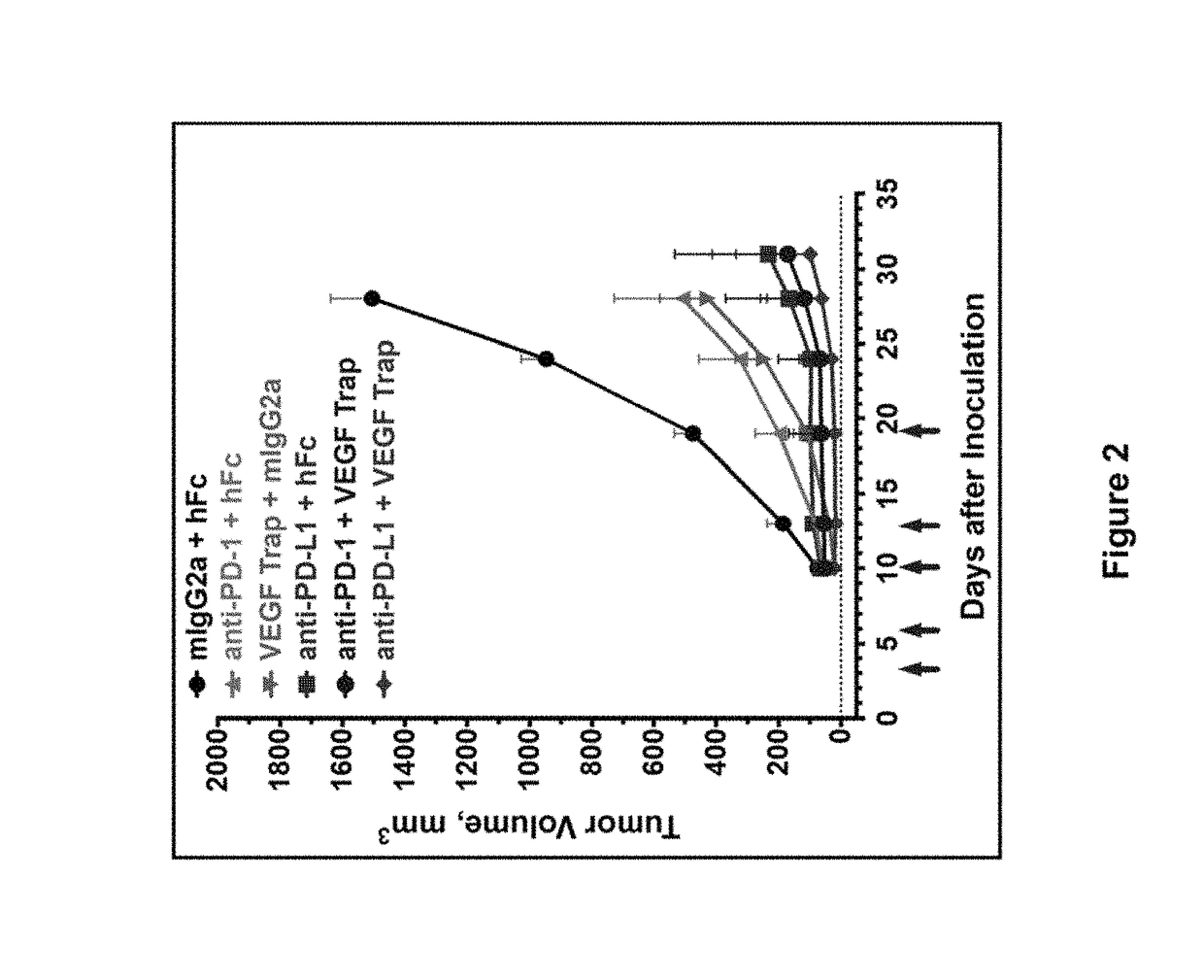
Antibodies to human programmed death receptor PD-1
ActiveUS8354509B2Increased activationIncreased proliferationSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsProgrammed deathReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Antibodies which block the binding of human Programmed Death Receptor 1 (hPD-1) to its ligands (hPD-L1 or hPD-L2) and their variable region sequences are disclosed. A method of increasing the activity (or reducing downmodulation) of an immune response through the PD-I pathway is also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME BV
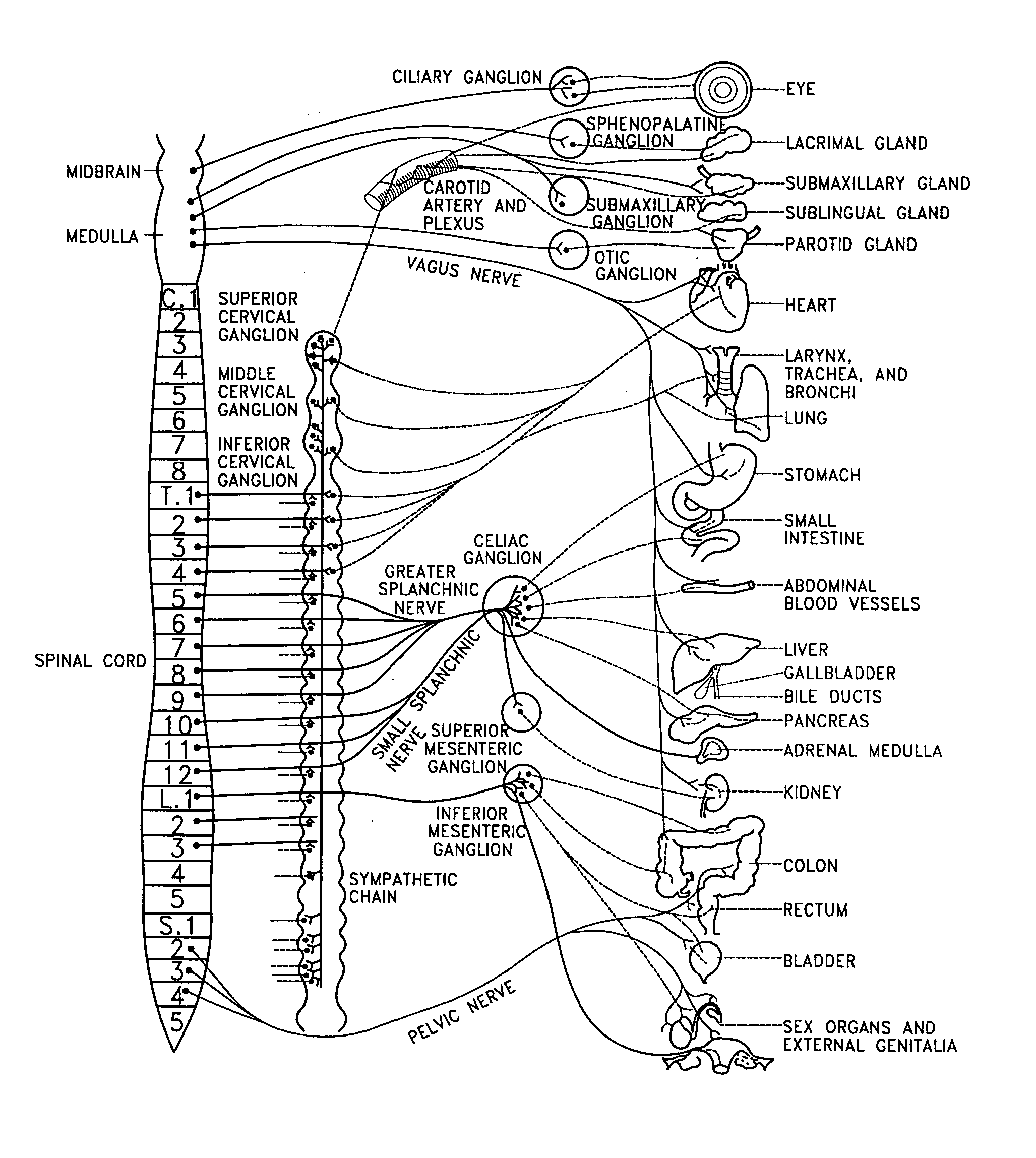
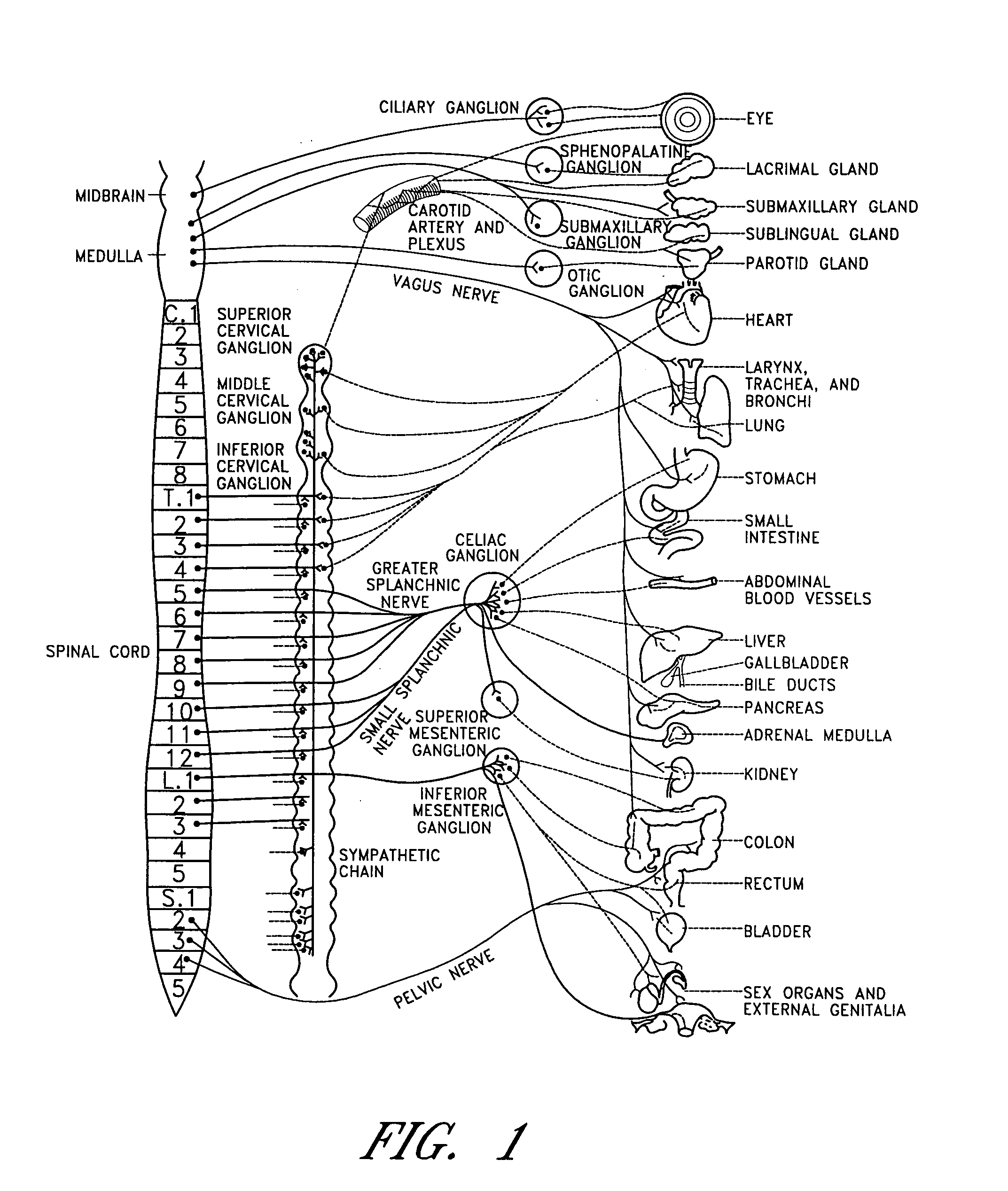
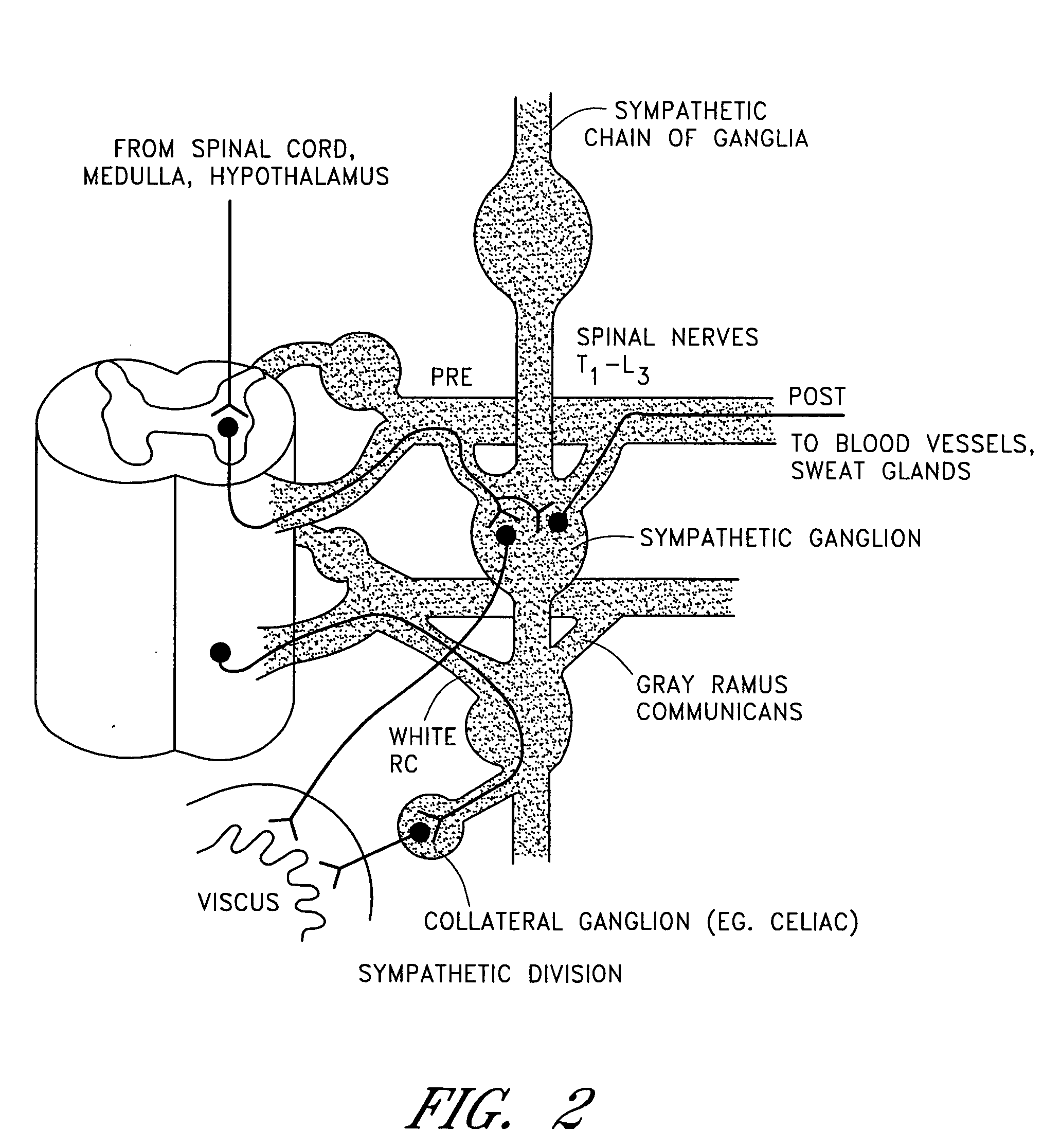
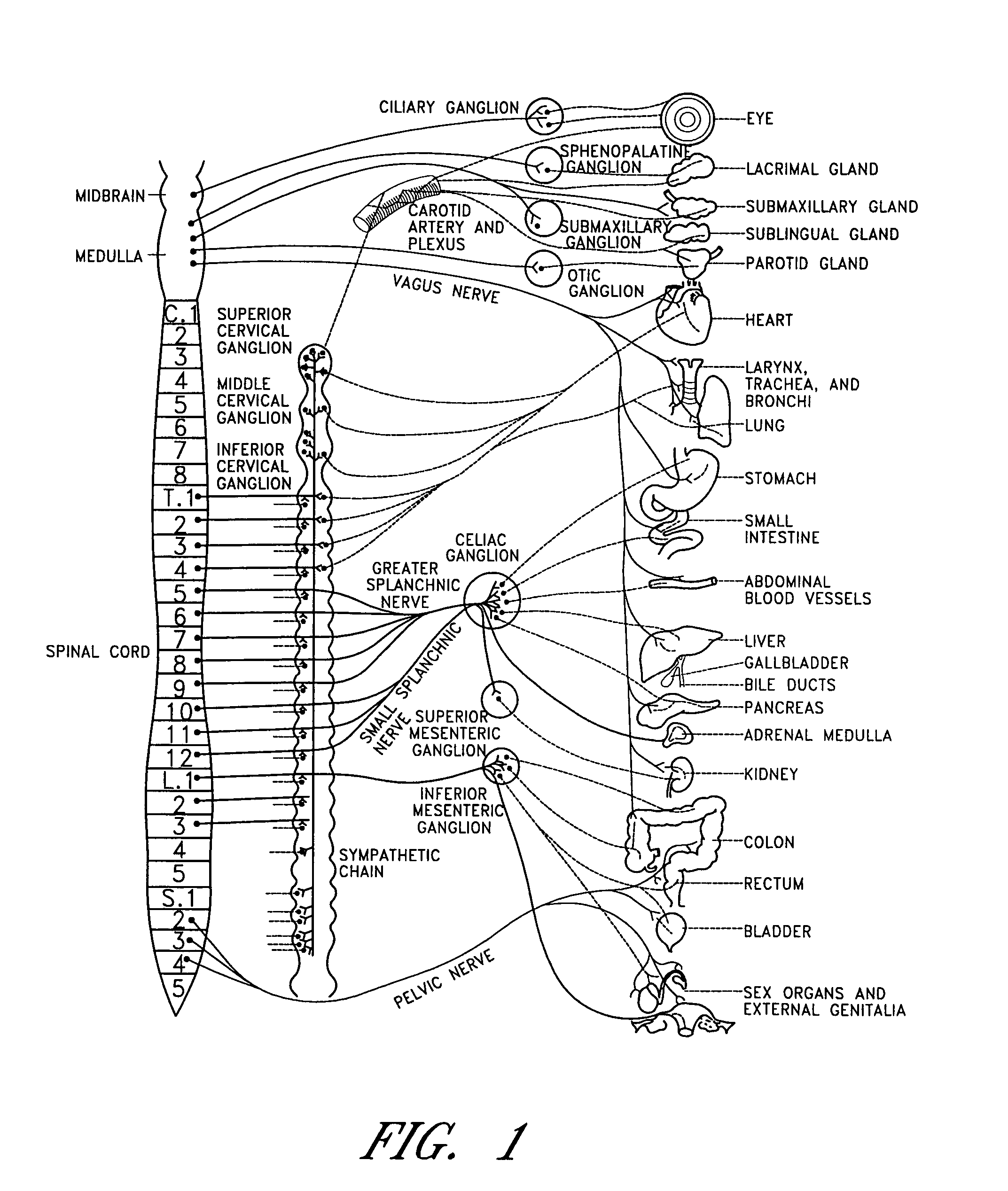
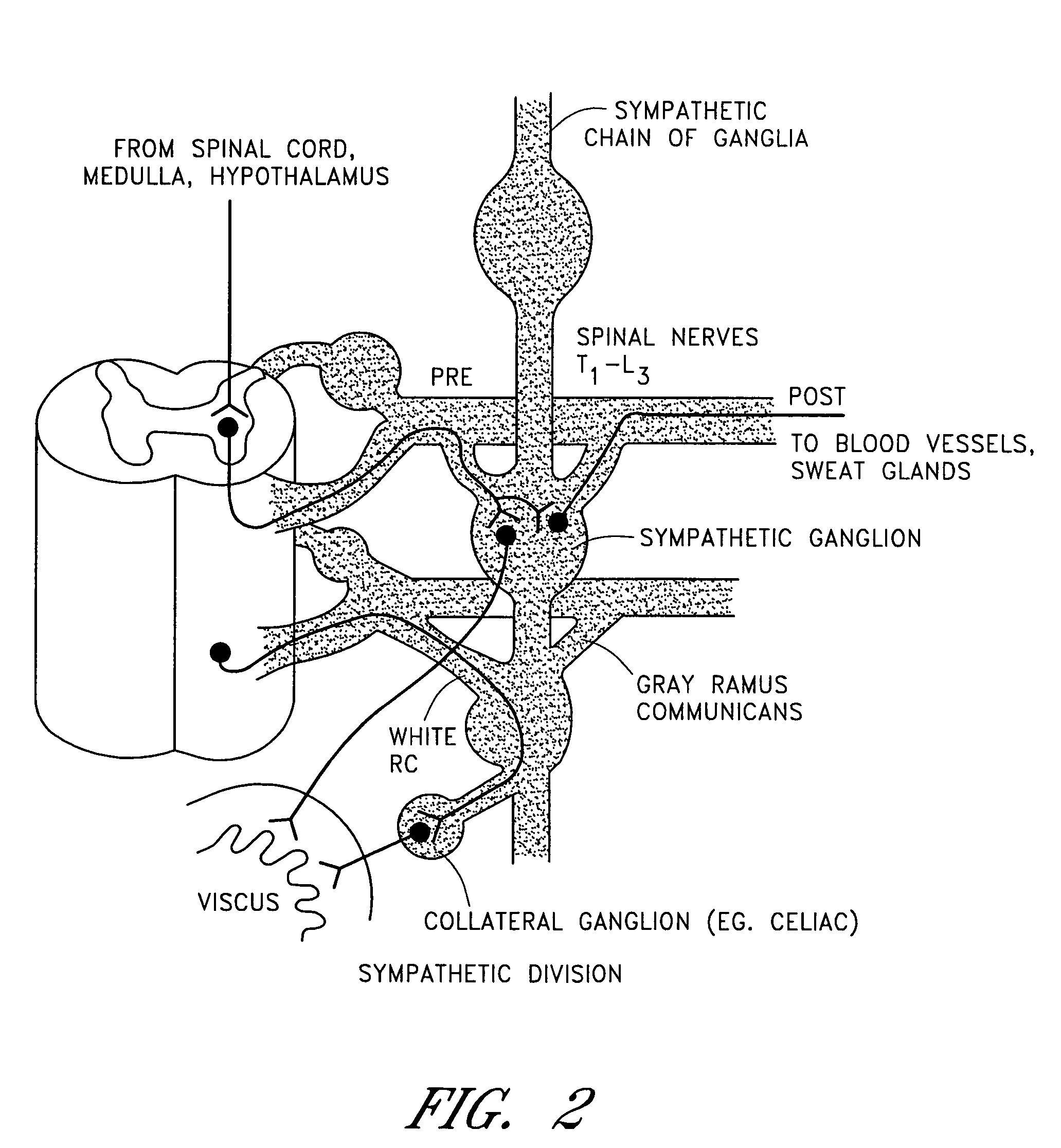
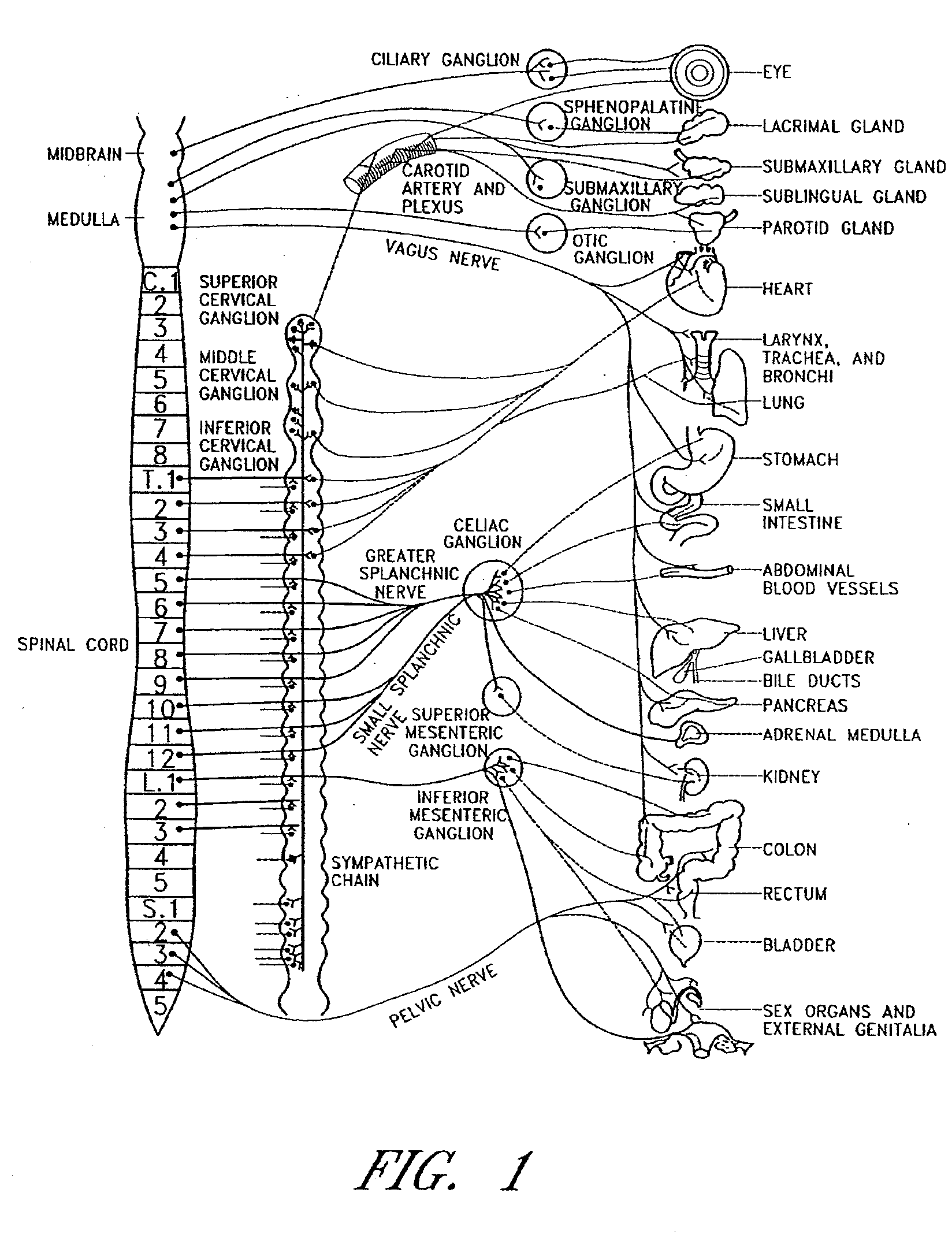
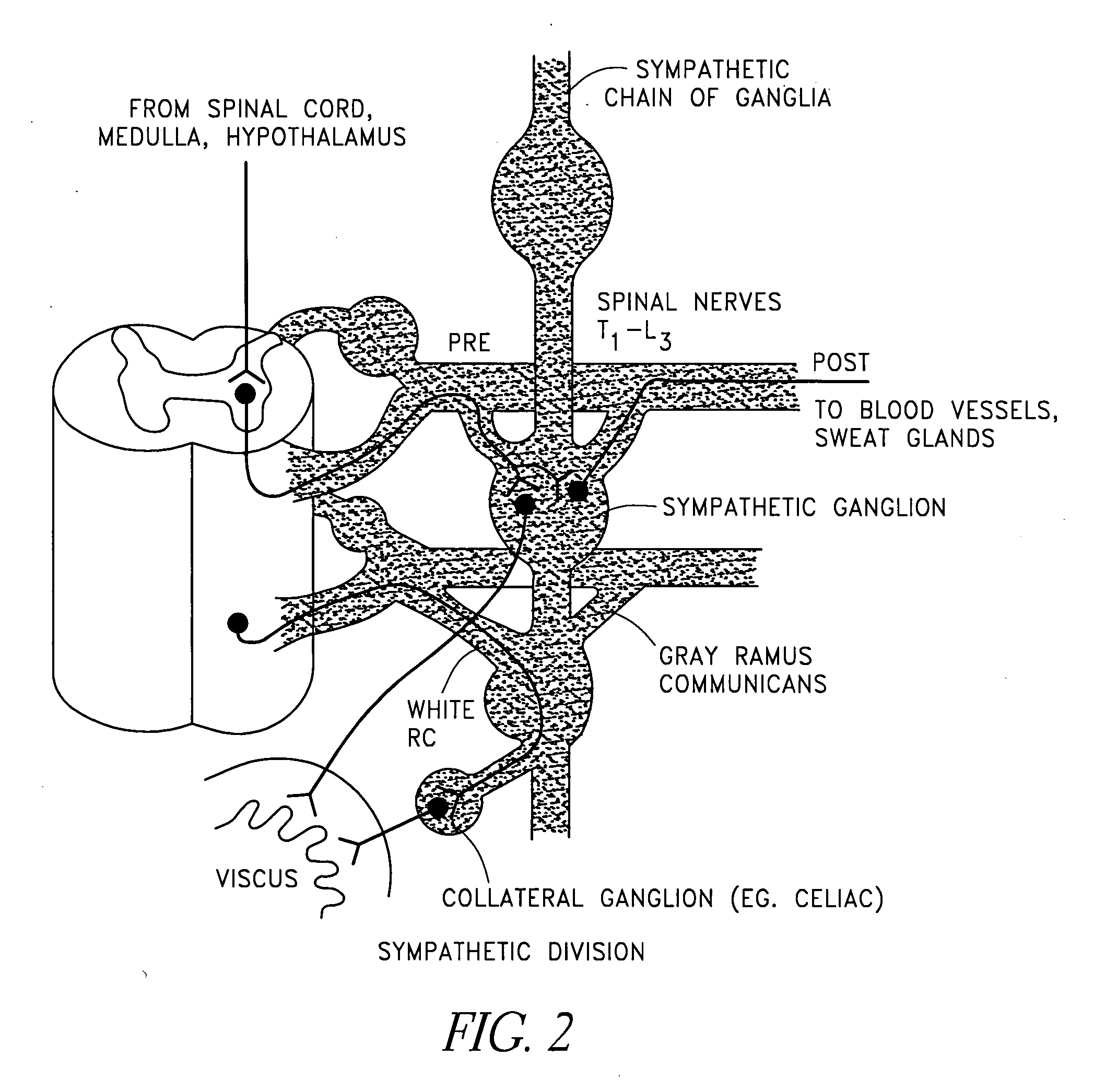
Dynamic nerve stimulation for treatment of disorders
ActiveUS20050065575A1Provide central nervous system satietyIncreased energy expenditureSpinal electrodesDiseasePhysical therapy
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders by electrical activation or inhibition of nerves is disclosed. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by stimulating a nerve using an electrode. Dynamic stimulation through ramped cycling of electrical stimulation, stimulation frequency alteration, and / or duty cycle variance can produce therapeutic benefits.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
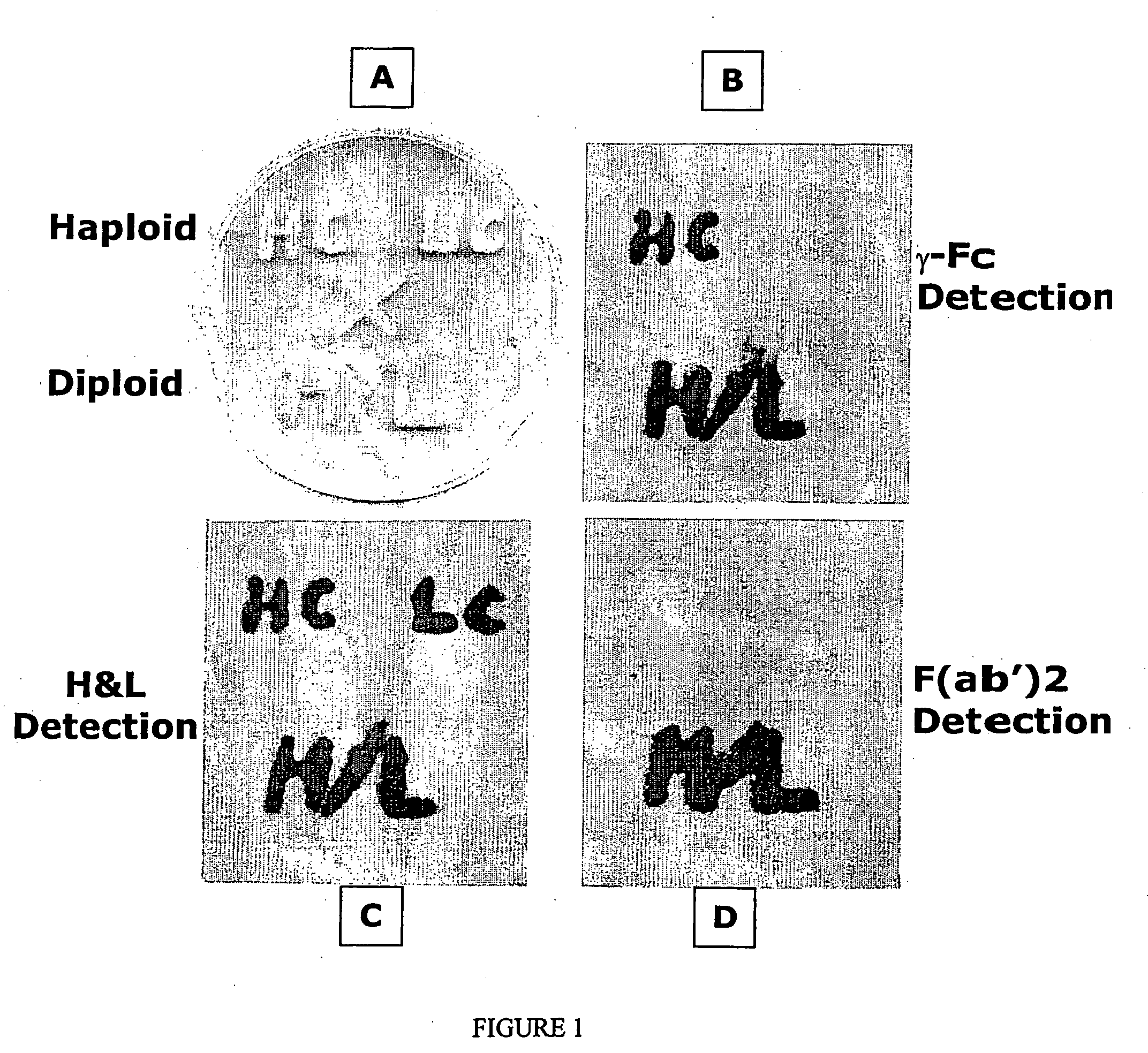
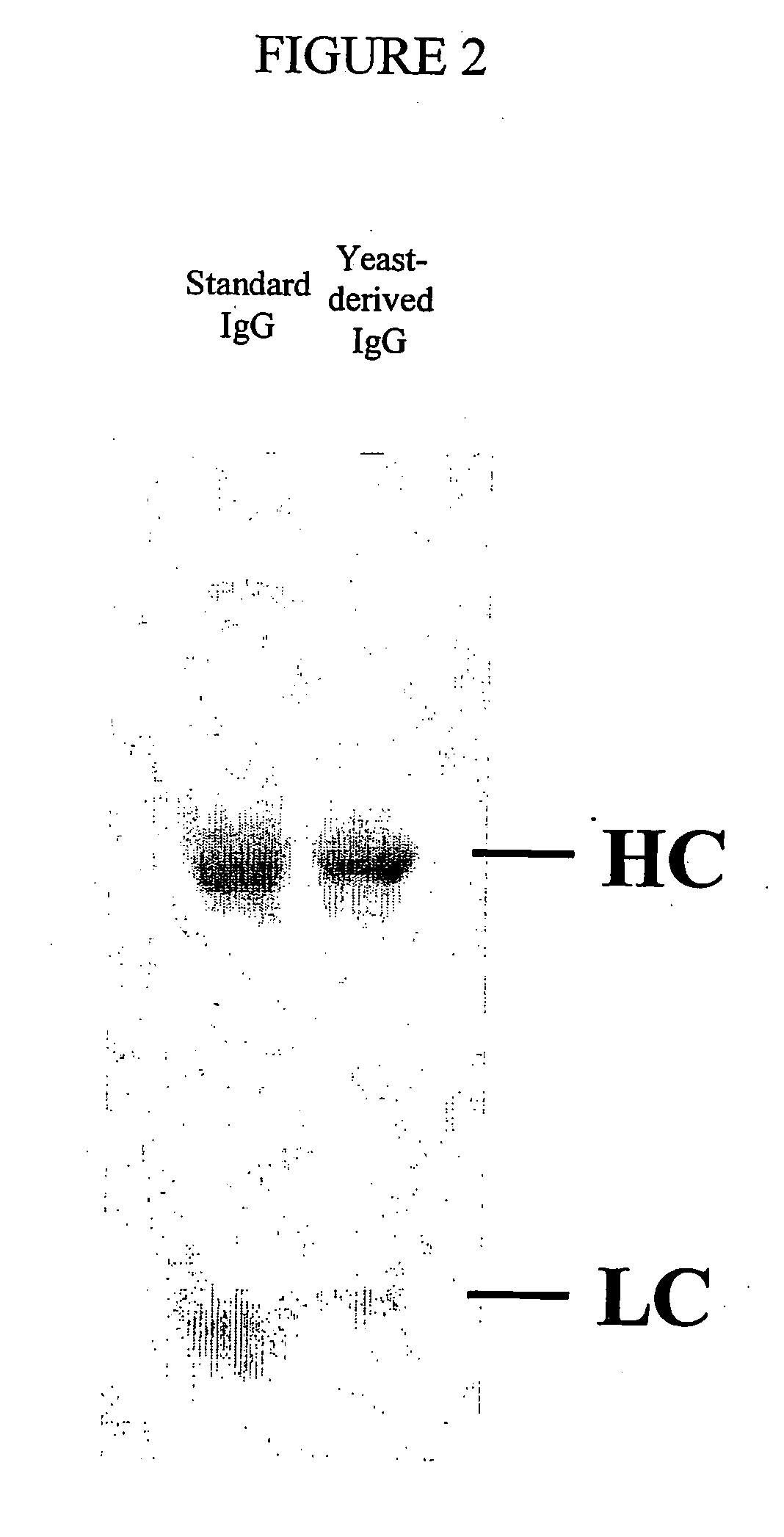
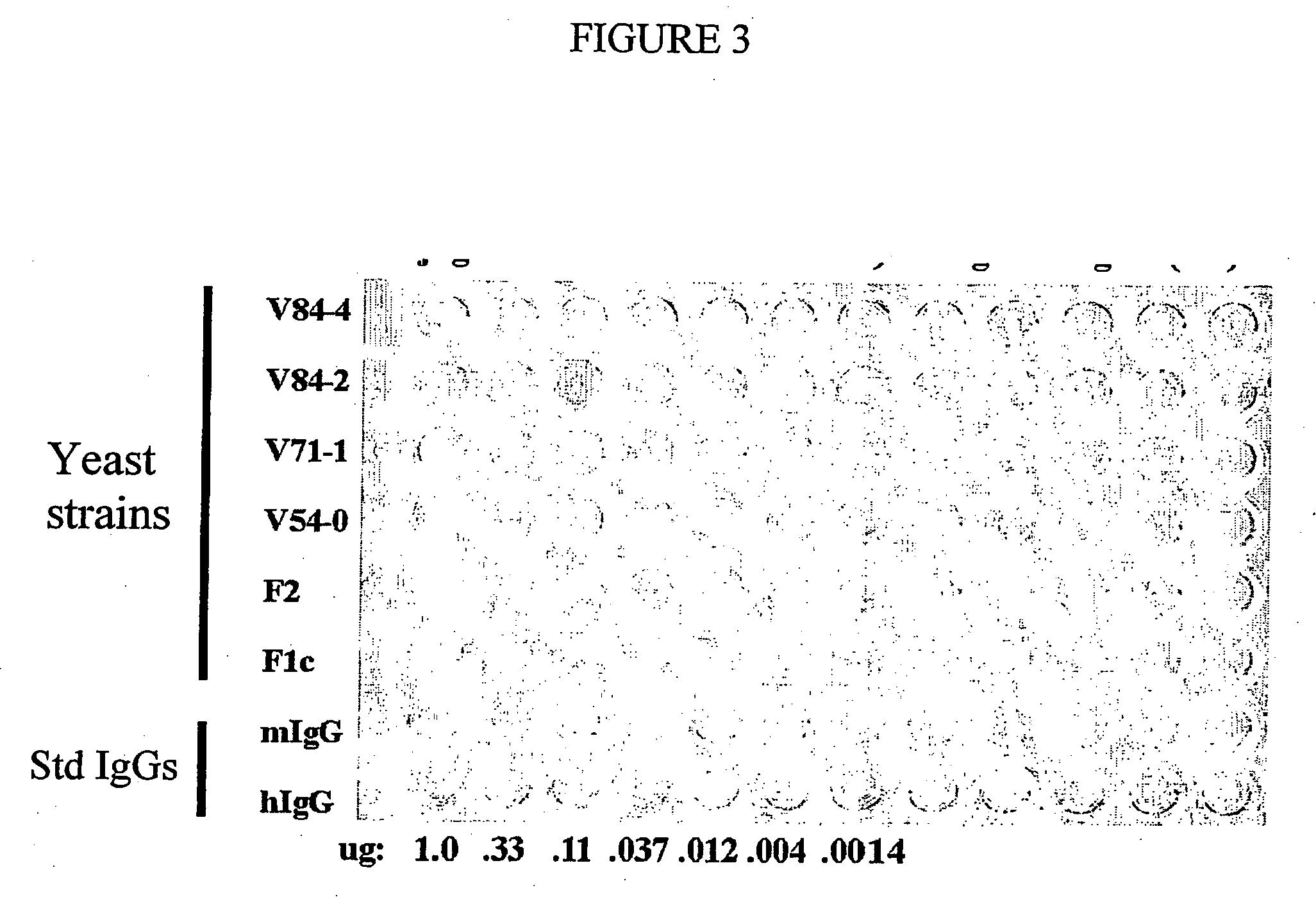
Methods of synthesizing heteromultimeric polypeptides in yeast using a haploid mating strategy
ActiveUS20060270045A1Enhance full-length product generationIncrease secretionFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMating
Methods are provided for the synthesis and secretion of recombinant proteins preferably large mammalian proteins or hetero-multimeric proteins at high levels and for prolonged time in polyploid, preferably diploid yeast. These methods use various mating competent yeast, including Pichia. In a preferred embodiment, a first expression vector is transformed into a first haploid cell; and a second expression vector is transformed into a second haploid cell. The transformed haploid cells, each individually synthesizing a non-identical polypeptide, are identified and then genetically crossed or fused. The resulting diploid strains are utilized to produce and secrete fully assembled and biologically functional hetero-multimeric protein.
Owner:KECK GRADUATE INST OF APPLIED LIFE SCI +1
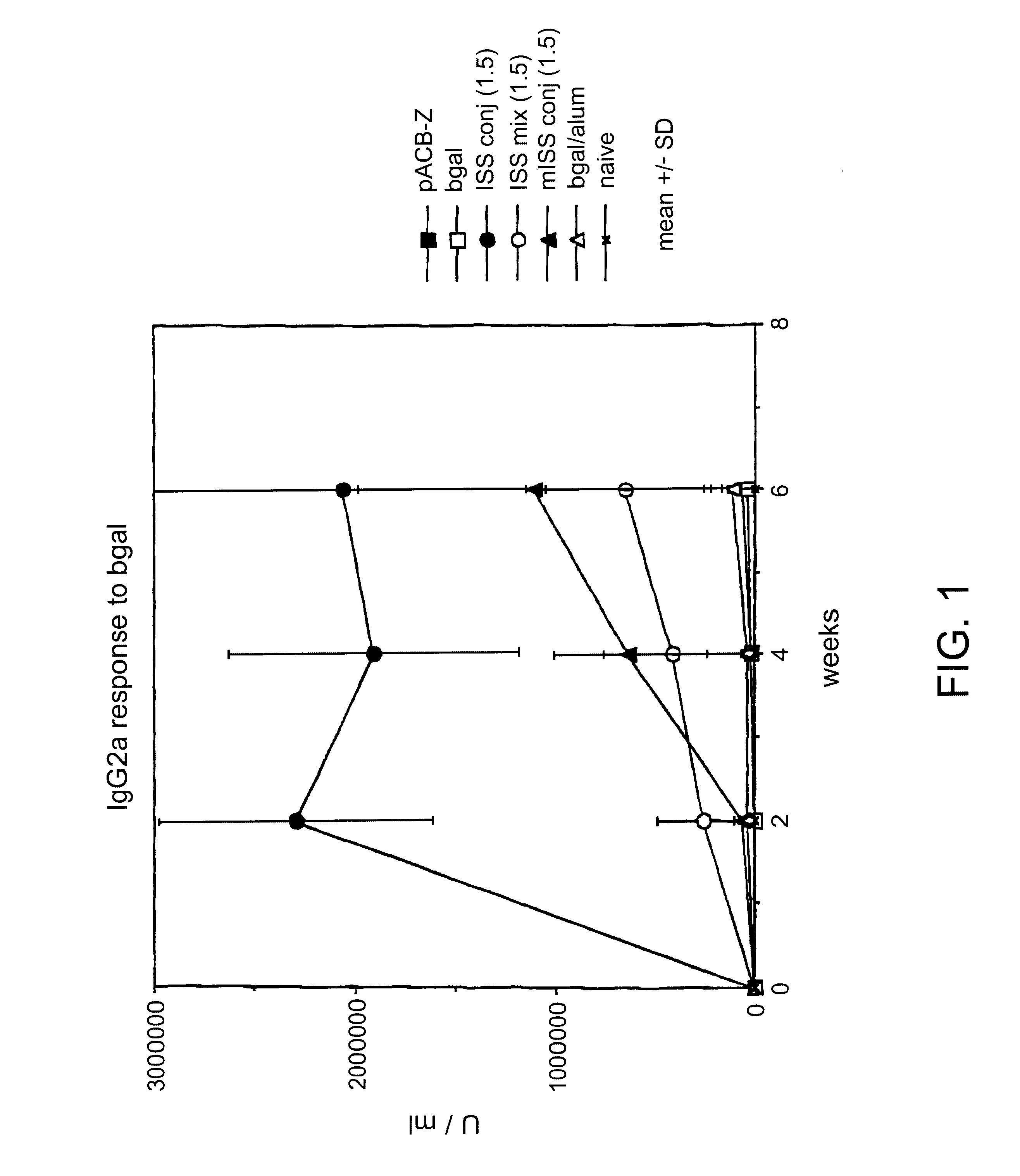
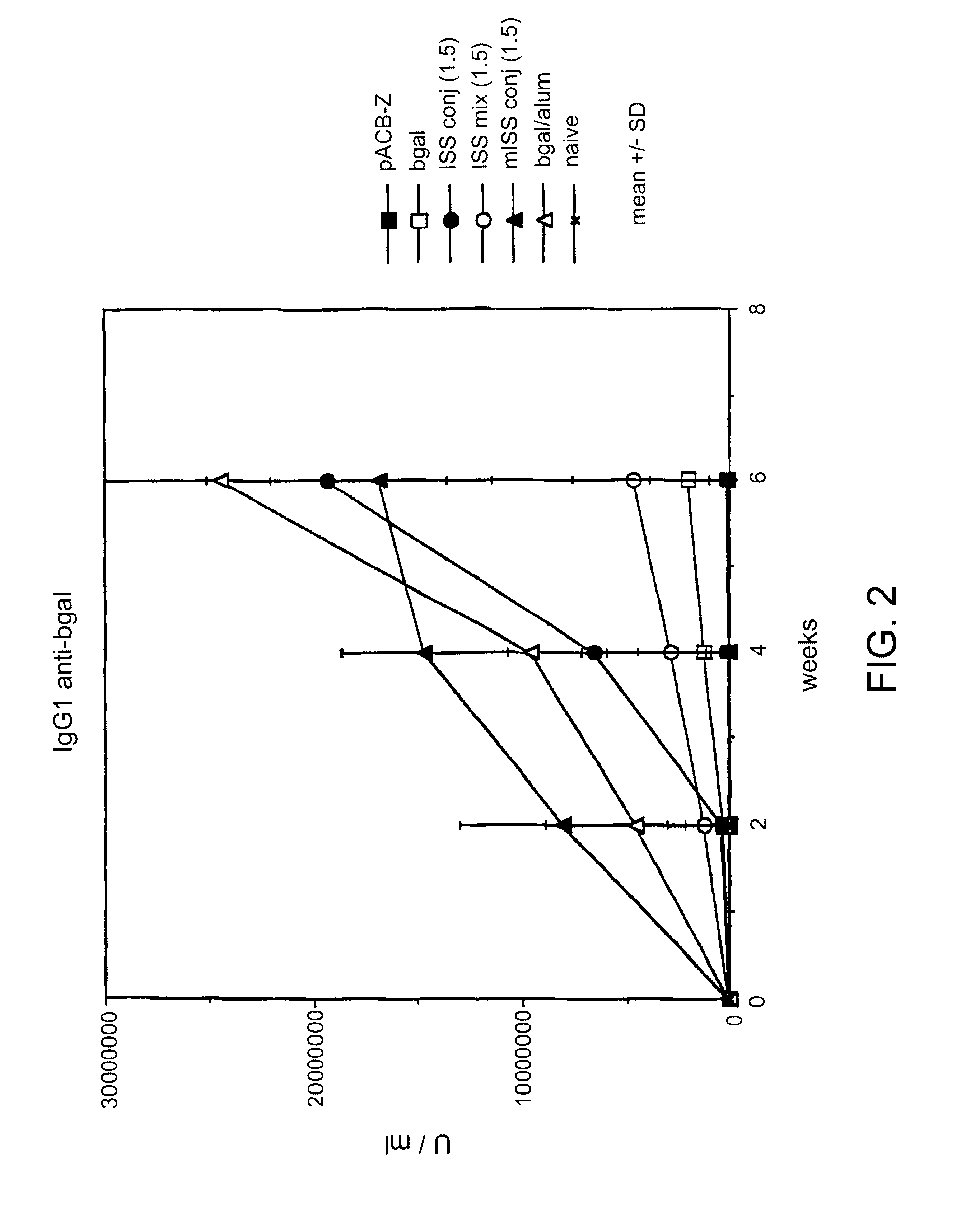
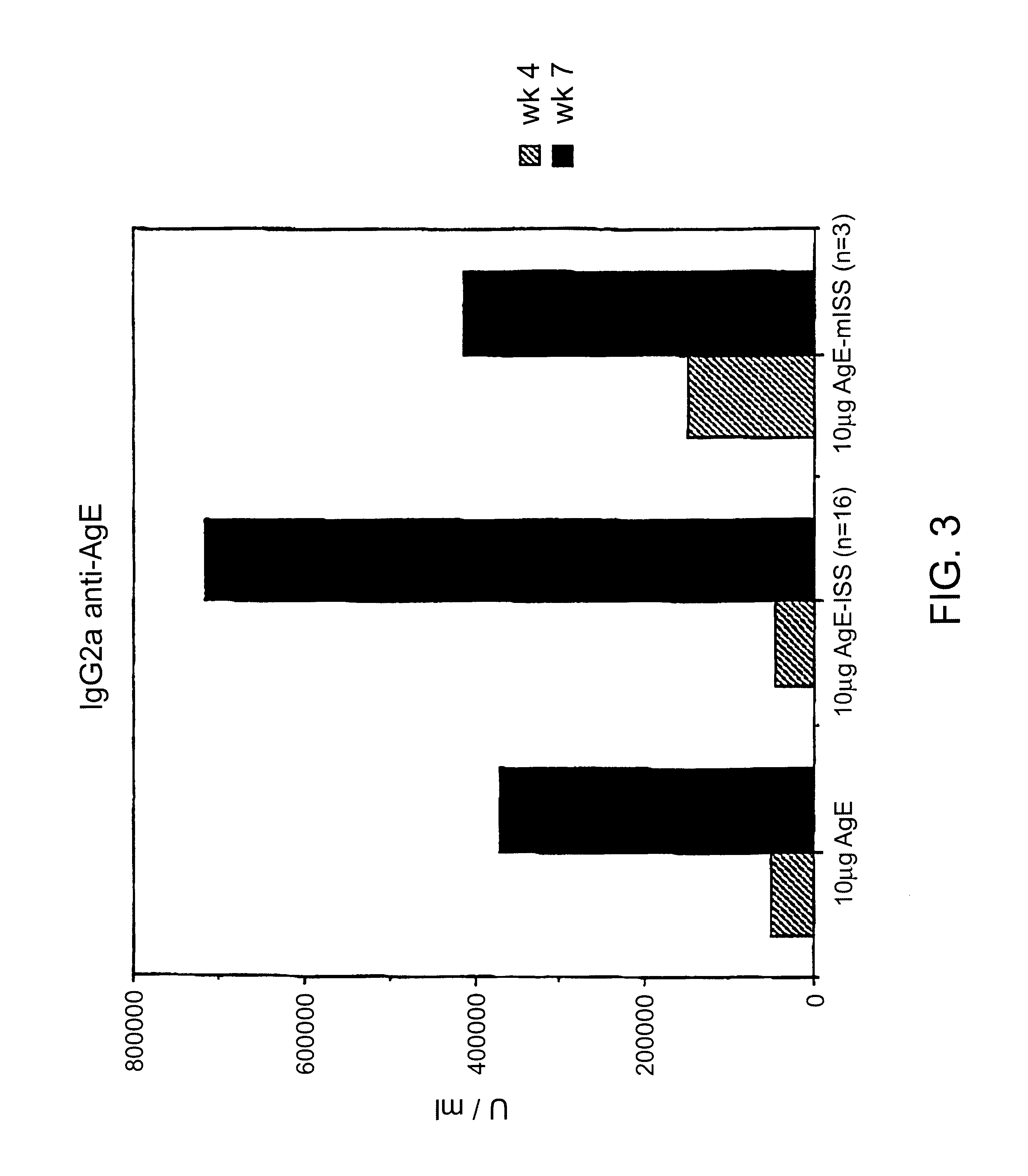
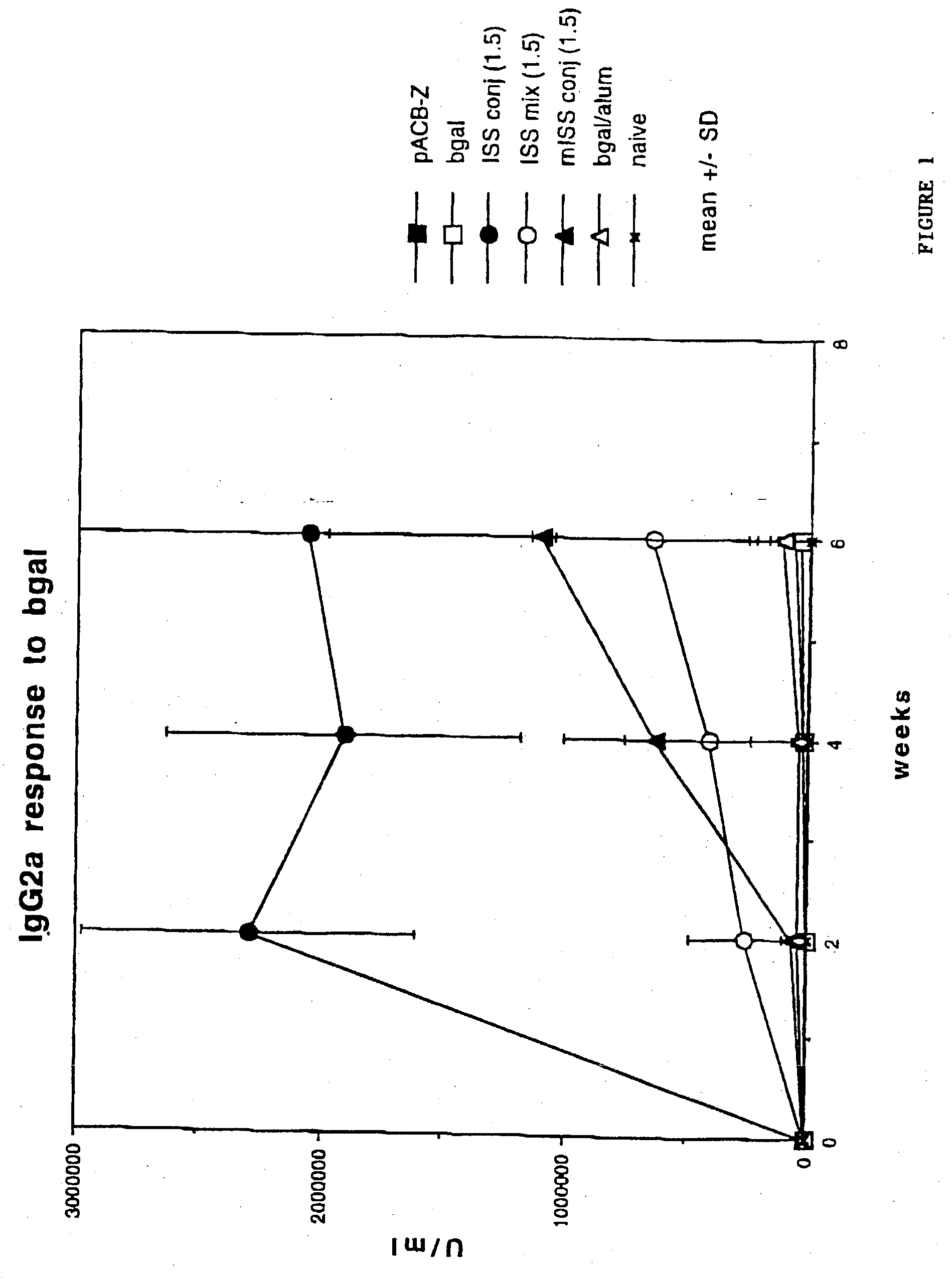
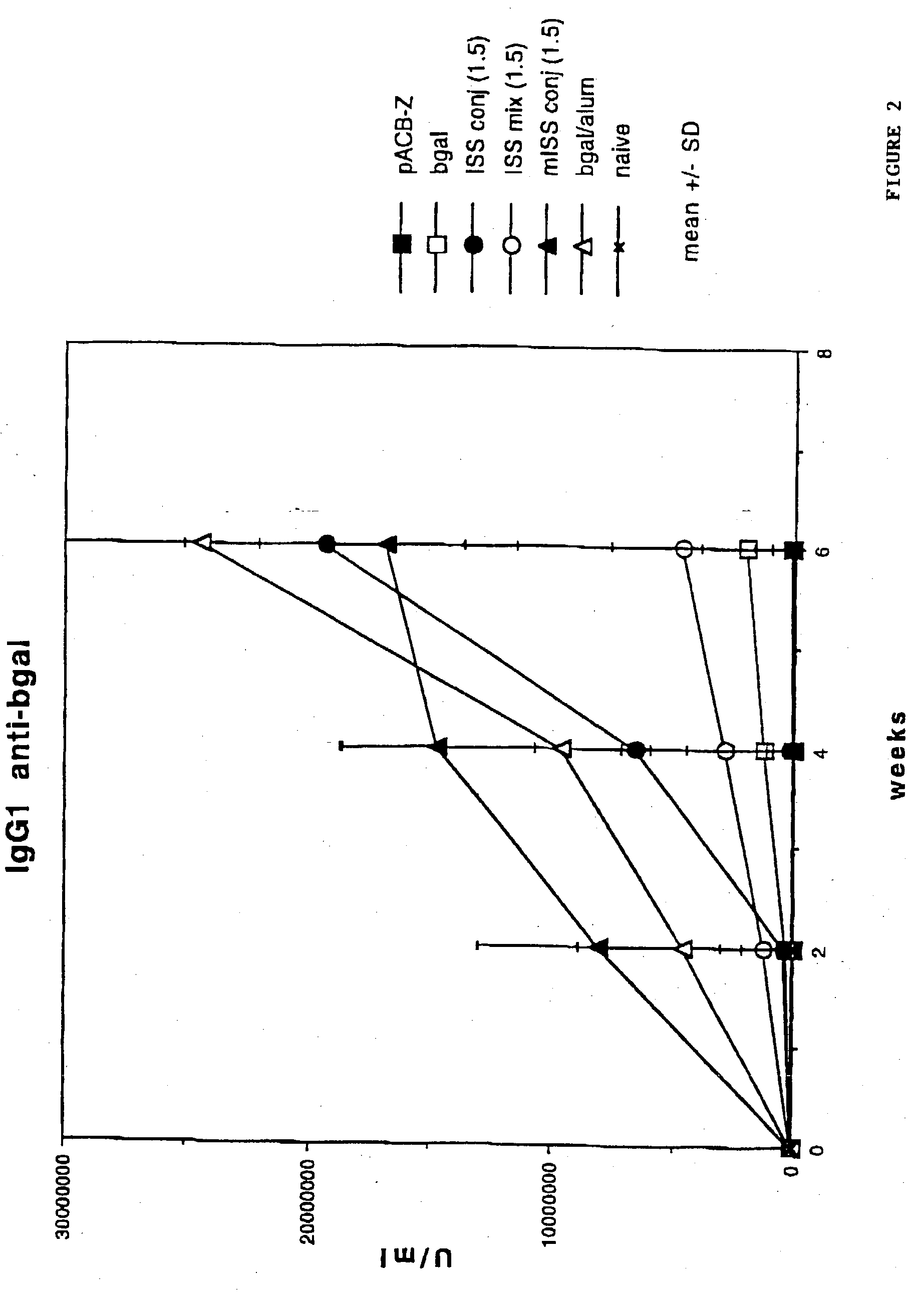
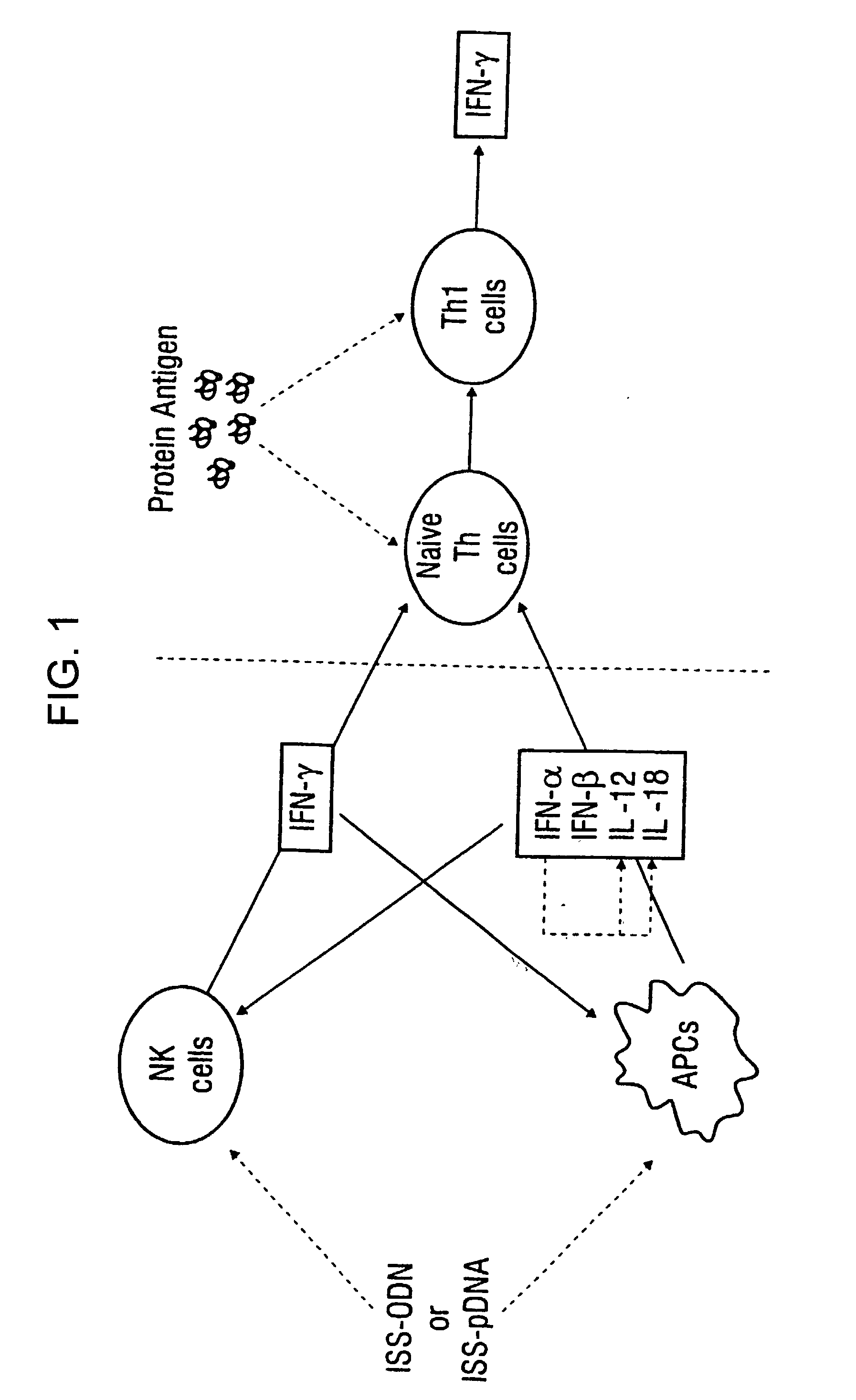
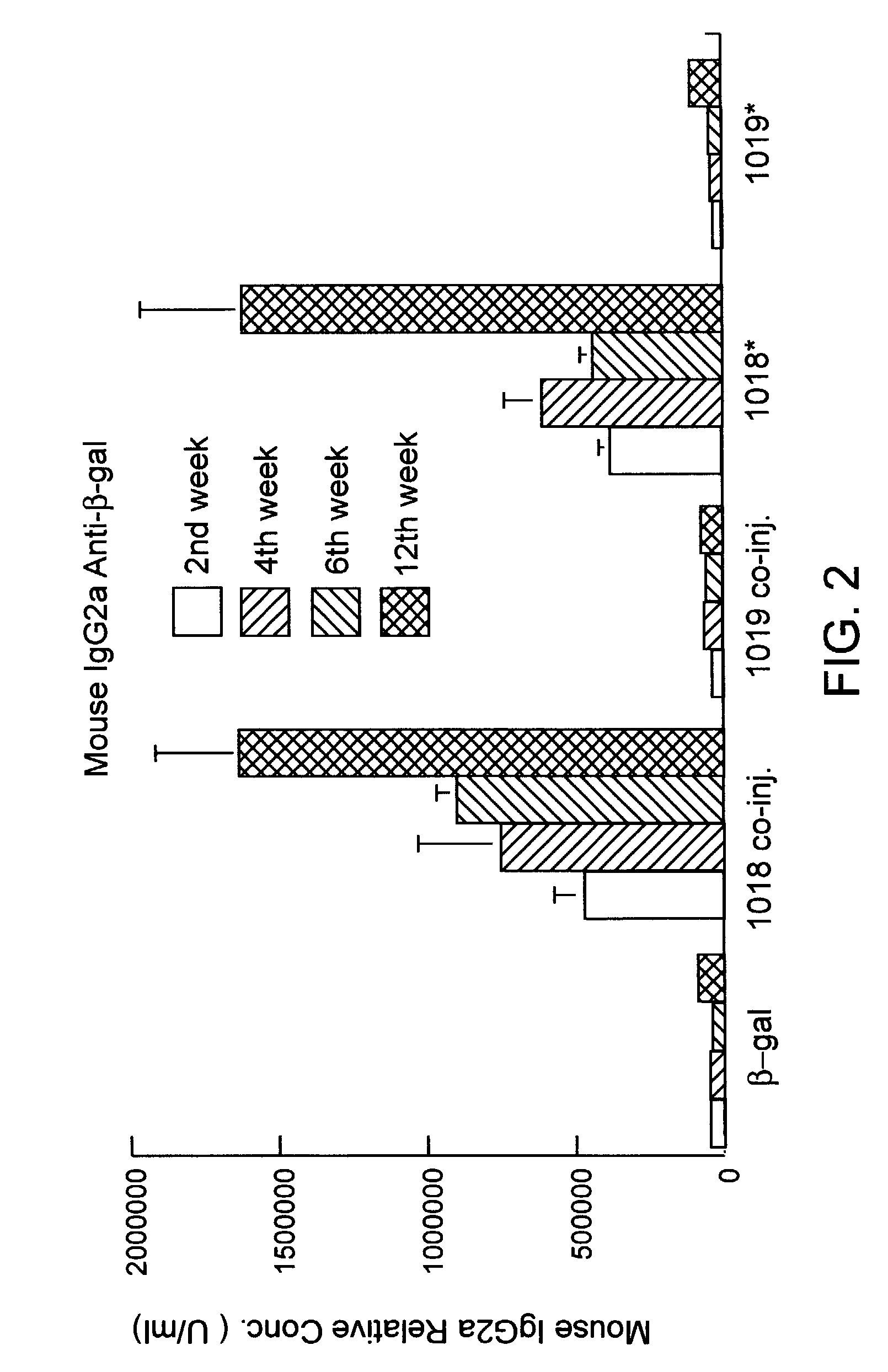
Immunostimulatory polynucleotide/immunomodulatory molecule conjugates
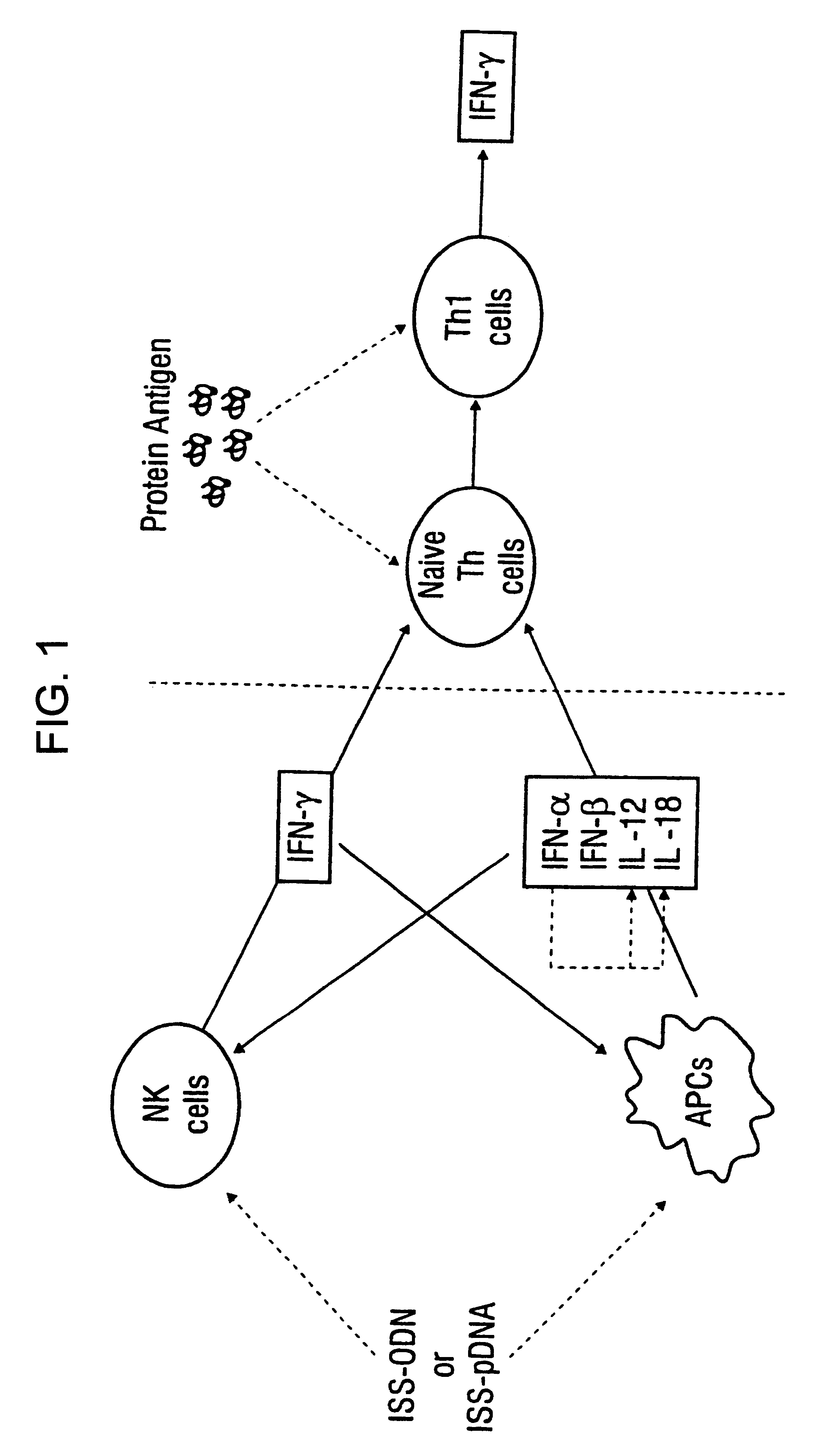
InactiveUS6610661B1Boost magnitudeBoost both humoral (antibody)Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
Immunostimulatory polynucleotide-immunomodulatory molecule conjugate compositions are disclosed. These compositions include a polynucleotide that is linked to an immunomodulatory molecule, which molecule comprises an antigen and may further comprise immunomodulators such as cytokines and adjuvants. The polynucleotide portion of the conjugate includes at least one immunostimulatory oligonucleotide nucleotide sequence (ISS). Methods of modulating an immune response upon administration of the polynucleotide-immunomodulatory conjugate preparation to a vertebrate host are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Blood glucose level control
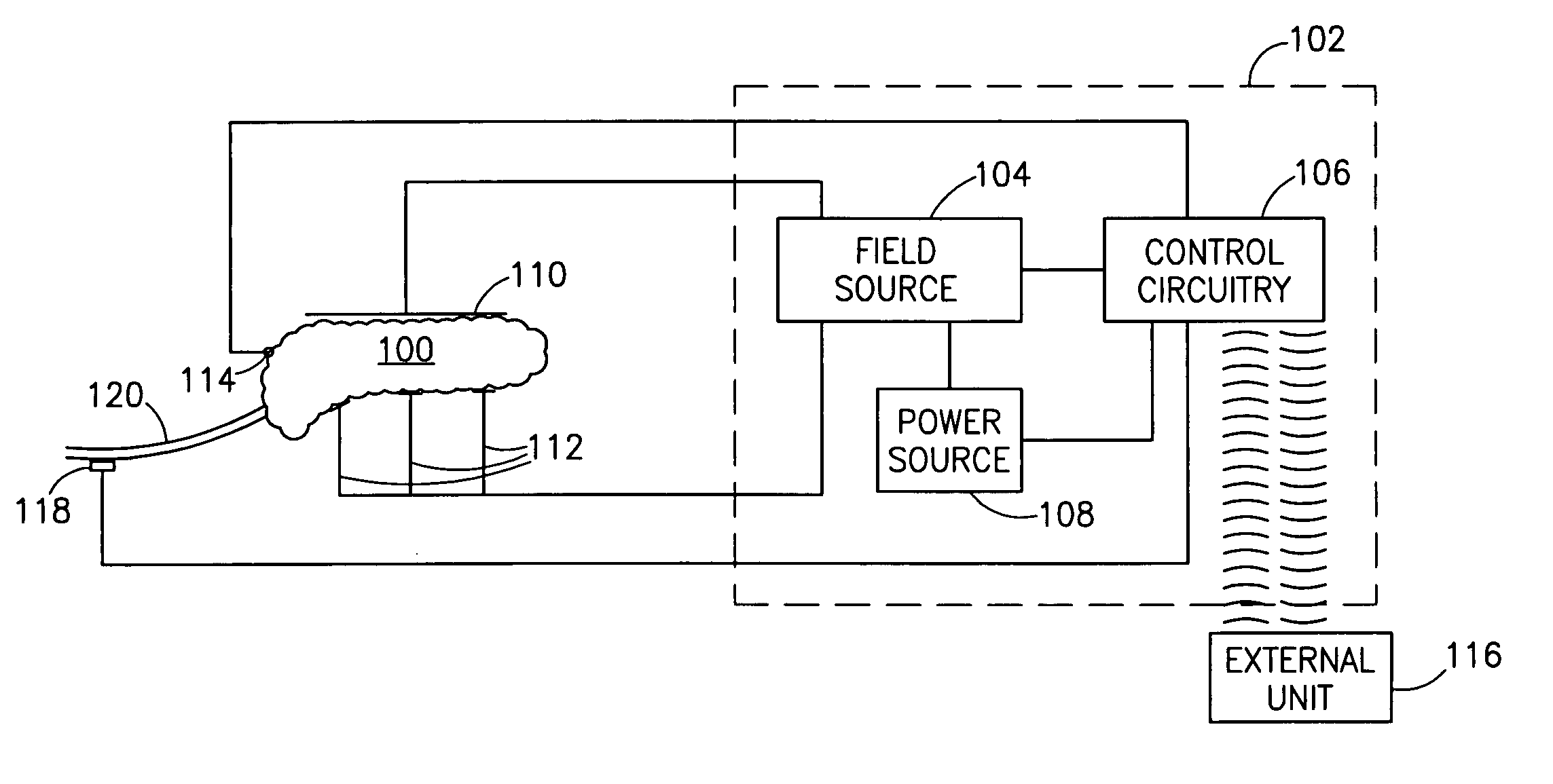
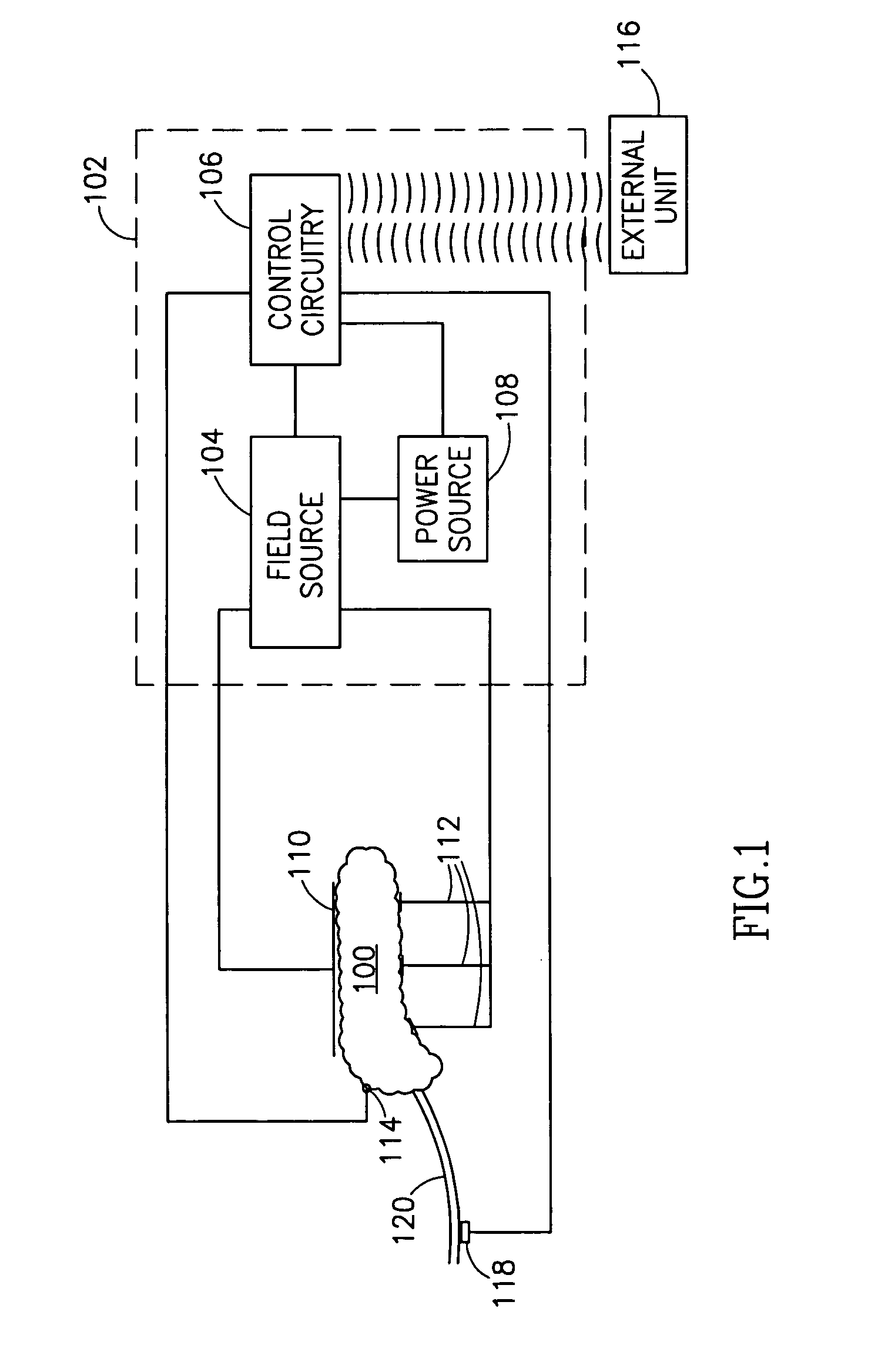
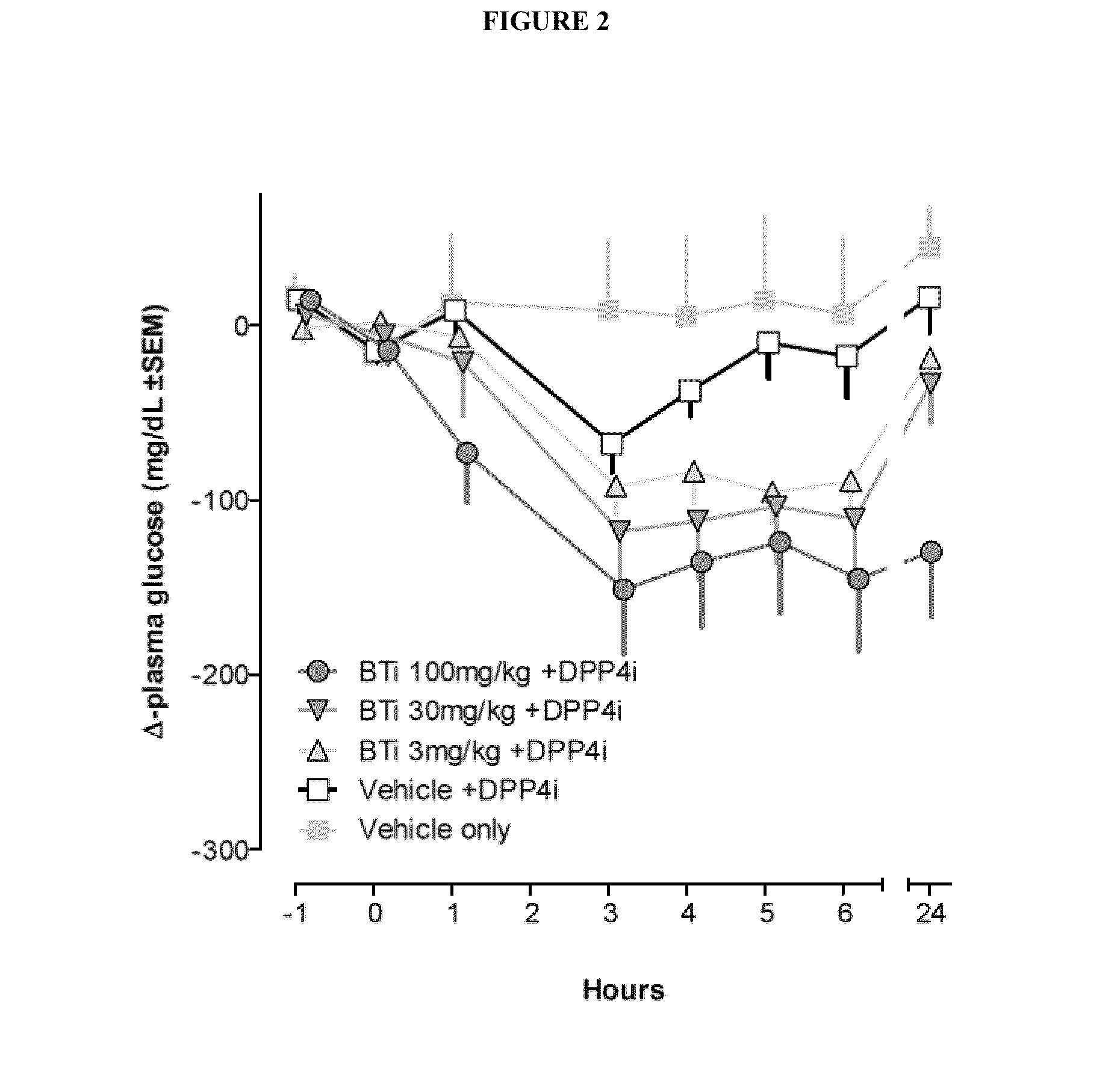
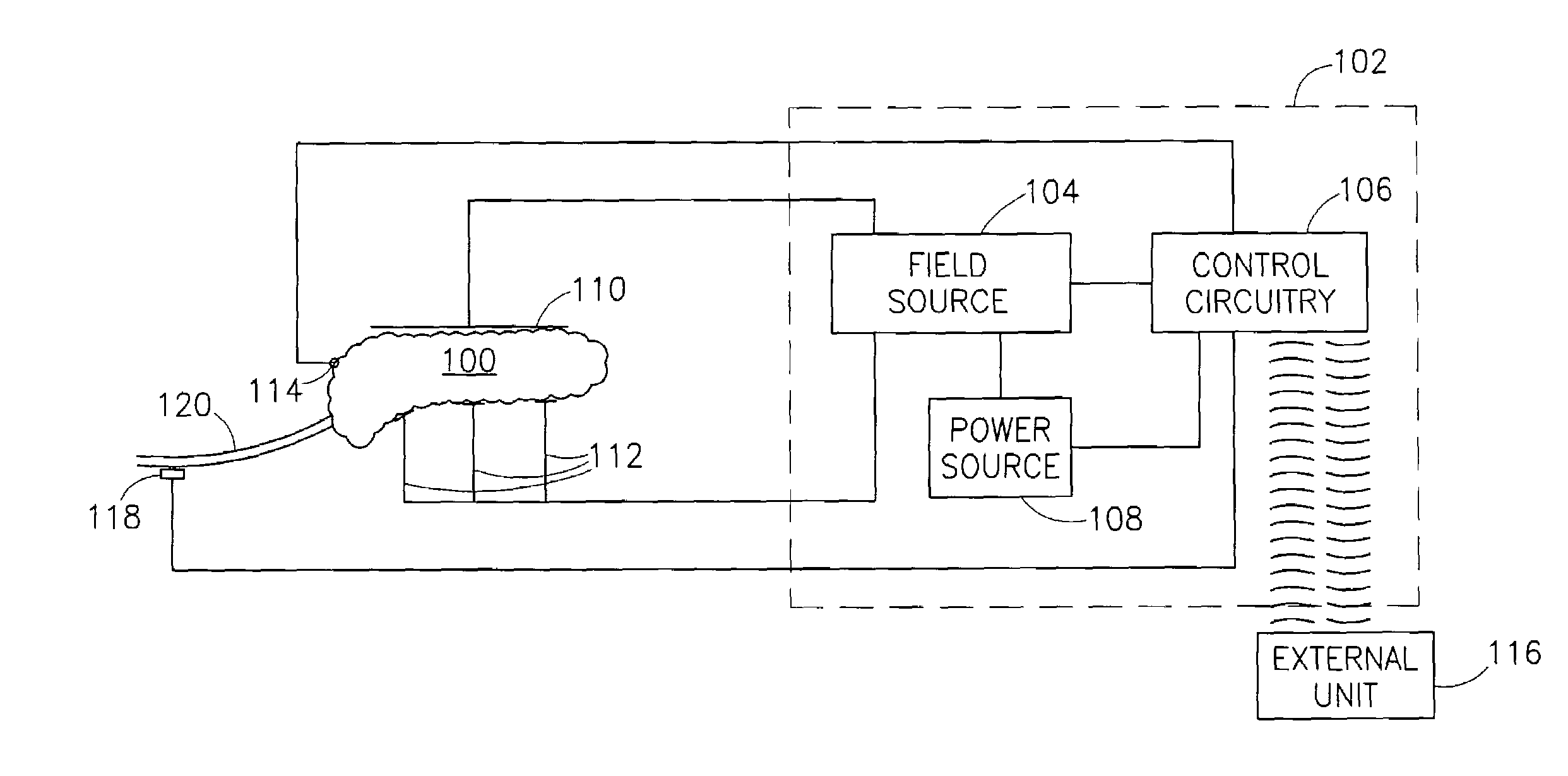
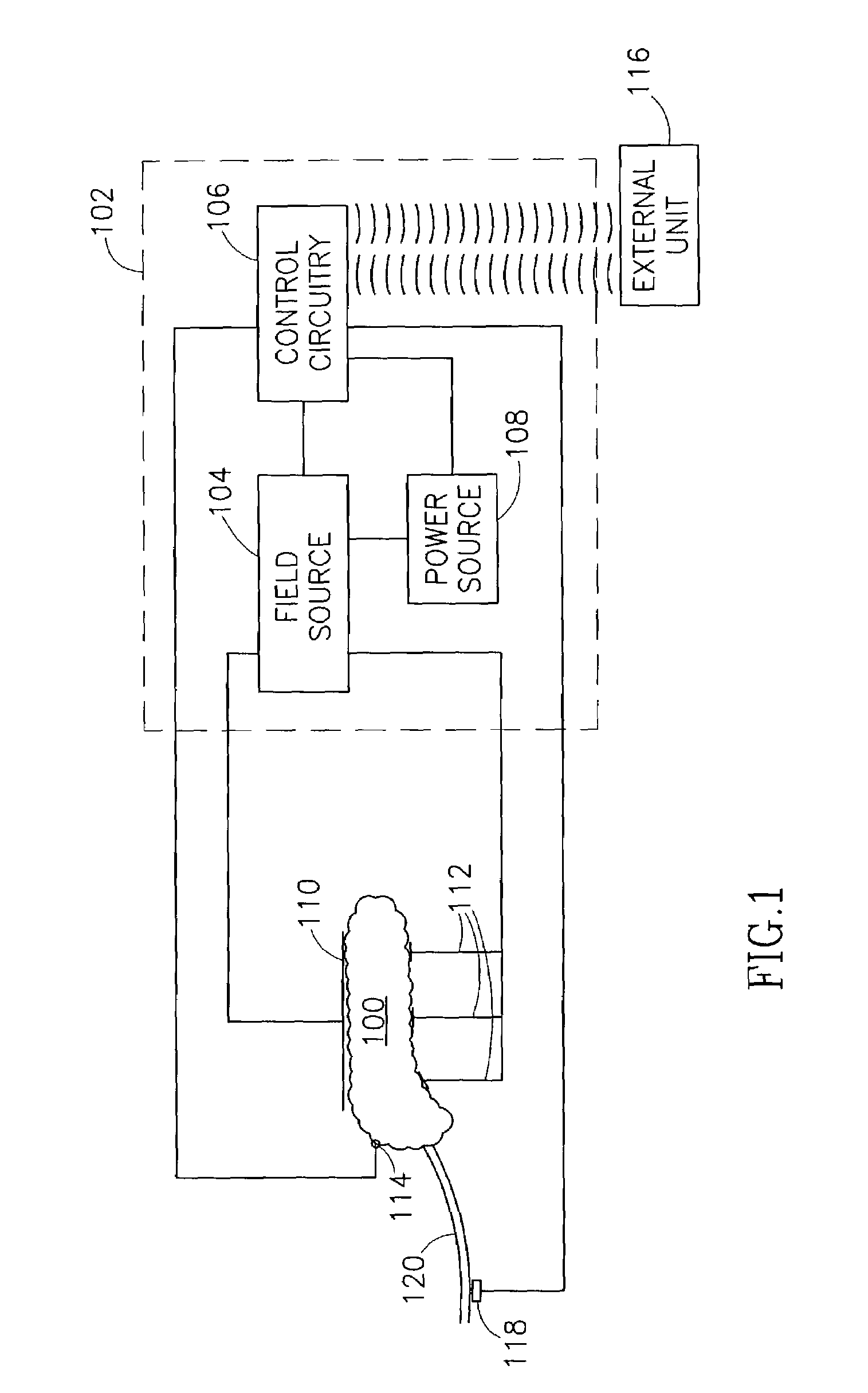
InactiveUS7006871B1Increased insulin secretionAvoiding unacceptable calcium level profileElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsLevel insulin
A pancreatic controller (102), comprising: a glucose sensor (118), for sensing a level of glucose or insulin in a body serum; at least one electrode (110, 112), for electrifying an insulin producing cell or group of cells; a power source (104) for electrifying said electrode with a pulse that does not initiate an action potential in said cell and has an effect of increasing insulin secretion; and a controller (106) which receives the sensed level and controls said power source to electrify said electrode to have a desired effect on said level.
Owner:METACURE
Immunization-free methods for treating antigen-stimulated inflammation in a mammalian host and shifting the host's antigen immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype
InactiveUS6498148B1Treatment and prevention of inflammationSuppresses antigen-stimulated granulocyte infiltrationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAntigen stimulationTherapeutic intent
The invention relates to methods for preventing or reducing antigen-stimulated, granulocyte-mediated inflammation in tissue of an antigen-sensitized mammal host by delivering an immunostimulatory oligonucleotide to the host. In addition, methods for using the immunostimulatory oligonucleotides to boost a mammal host's immune responsiveness to a sensitizing antigen (without immunization of the host by the antigen) and shifting the host's immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype to achieve various therapeutic ends are provided. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
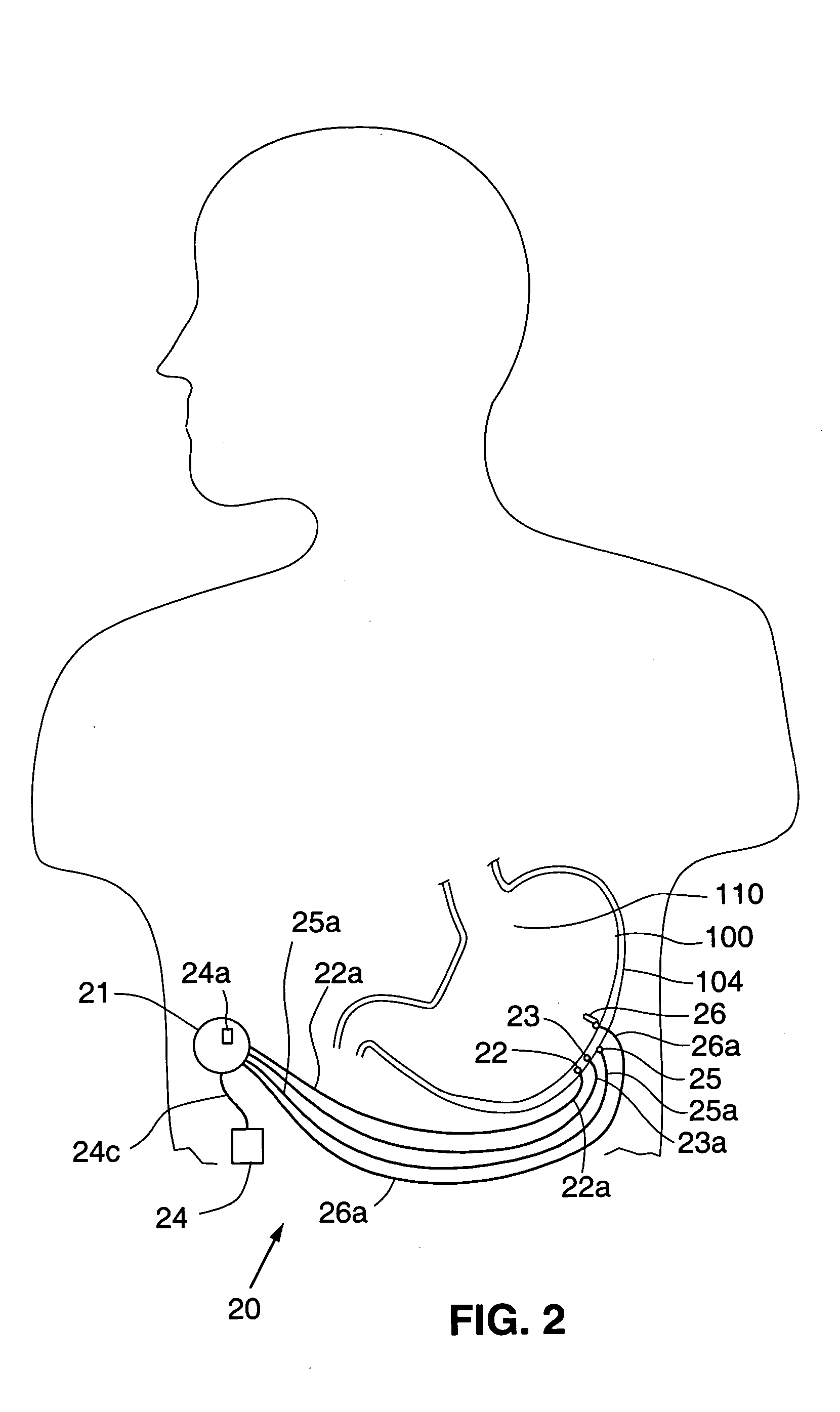
Responsive gastric stimulator
InactiveUS20050065571A1Decreased and increased respirationPrevent and reduce hungerElectrotherapySurgerySensing dataFood consumption
A responsive gastrointestinal stimulation device is provided where one or more sensors sense data corresponding to a subject or the gastrointestinal tract of a subject and responds to sensing the data by stimulating, adjusting stimulation, or stopping stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract. A stimulation device is also provided to stimulate the gastrointestinal tract to produce a sensation of satiety or to control hunger or food consumption.
Owner:INTRAPACE
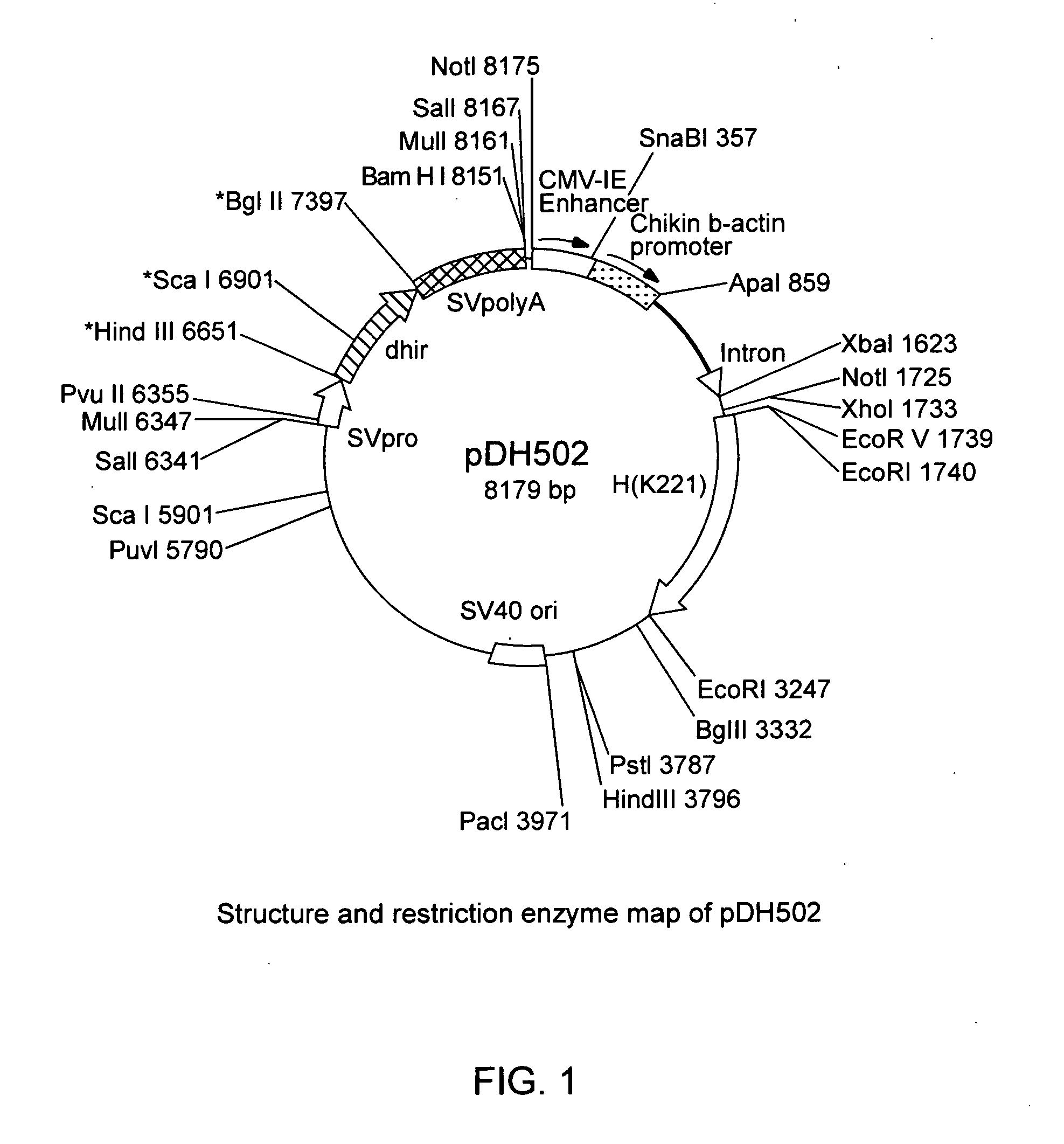
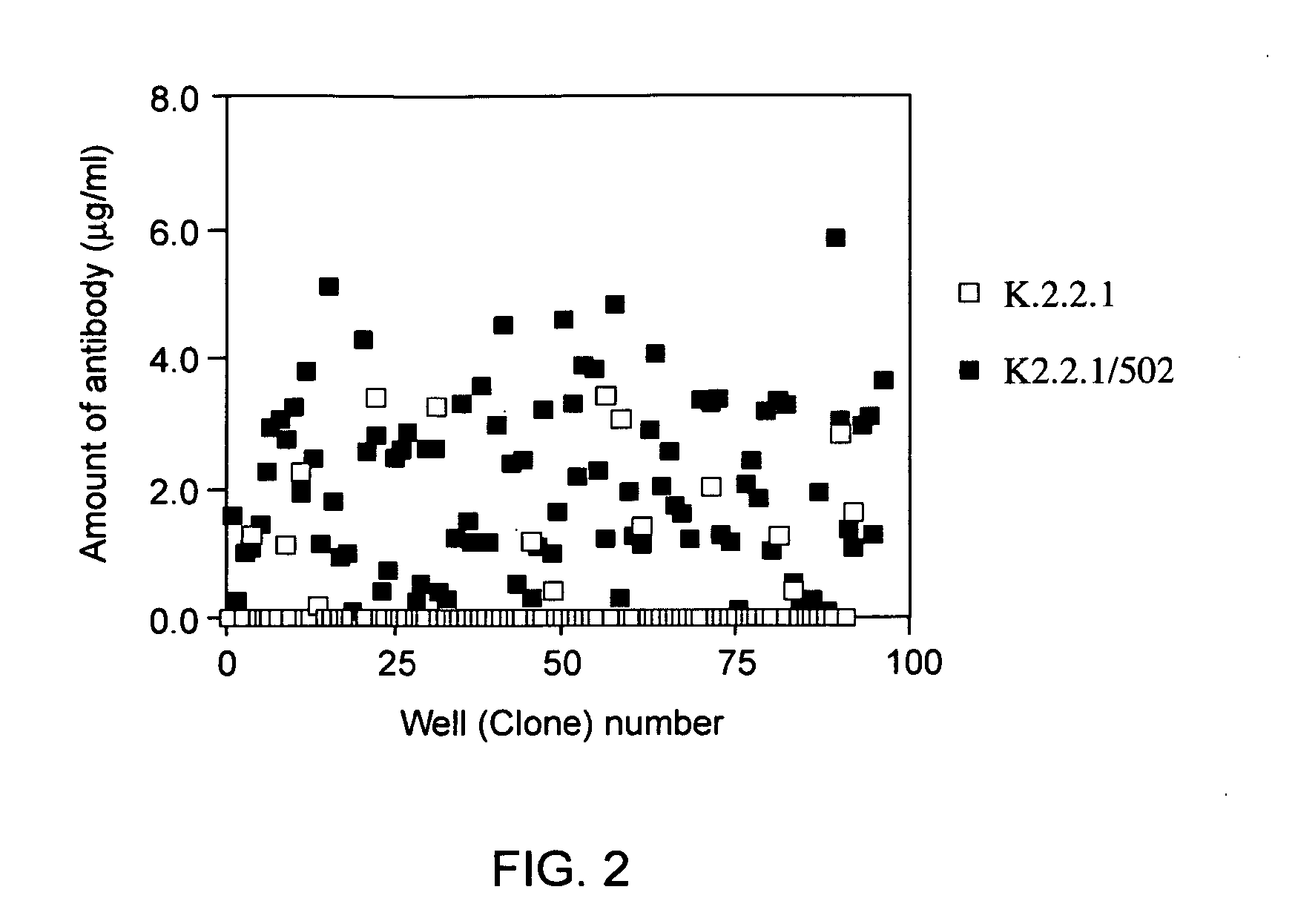
Method for preparing monoclonal antibody
ActiveUS20060059575A1Improve productivityImprove expression efficiencyNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin heavy chainMonoclonal antibody
A significantly increased amount of a monoclonal antibody is obtained from the culture medium of recombinant hybridoma prepared by introducing genes encoding a protein identical to the immunoglobulin heavy chain polypeptide of the specific monoclonal antibody into an immortalized B cell (hybridoma) producing the monoclonal antibody.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC +1
Dynamic nerve stimulation for treatment of disorders
ActiveUS7689276B2Increased energy expenditureReducing food intakeSpinal electrodesDiseasePhysical therapy
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders by electrical activation or inhibition of nerves is disclosed. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by stimulating a nerve using an electrode. Dynamic stimulation through ramped cycling of electrical stimulation, stimulation frequency alteration, and / or duty cycle variance can produce therapeutic benefits.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Immunostimulatory polynucleotide/immunomodulatory molecule conjugates
InactiveUS20040006010A1Boost magnitudeBoost both humoral (antibody)BiocideOrganic active ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
Immunostimulatory polynucleotide-immunomodulatory molecule conjugate compositions are disclosed. These compositions include a polynucleotide that is linked to an immunomodulatory molecule, which molecule comprises an antigen and may further comprise immunomodulators such as cytokines and adjuvants. The polynucleotide portion of the conjugate includes at least one immunostimulatory oligonucleotide nucleotide sequence (ISS). Methods of modulating an immune response upon administration of the polynucleotide-immunomodulatory conjugate preparation to a vertebrate host are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antibodies to human programmed death receptor pd-1
ActiveUS20100266617A1Increased activationIncreased proliferationSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProgrammed deathAntibody
Antibodies which block the binding of human Programmed Death Receptor 1(hPD-1) to its ligands (hPD-L1 or hPD-L2) and their variable region sequences are disclosed. A method of increasing the activity (or reducing downmodulation) of an immune response through the PD-I pathway is also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME BV
Methods and reagents for the treatment of metabolic disorders
InactiveUS20060069161A1Reduced glucose levelHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiabetes mellitusObesity
The invention features compositions, methods, and kits for the treatment of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity.
Owner:ZALICUS INC
Antibodies to human programmed death receptor pd-1
ActiveUS20130109843A1Increased activationIncreased proliferationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease diagnosisProgrammed deathAntibody
Antibodies which block binding of hPD-1 to hPD-L1 or hPD-L2 and their variable region sequences are disclosed. A method of increasing the activity (or reducing downmodulation) of an immune cell through the PD-1 pathway is also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME BV
Dynamic nerve stimulation in combination with other eating disorder treatment modalities
InactiveUS20080262411A1Provide central nervous system satietyIncreased energy expenditureBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseWeight-loss drugs
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders by electrical activation or inhibition of nerves is disclosed. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by stimulating a nerve using an electrode. The method further comprises performing a surgical procedure and / or administering a weight loss drug.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
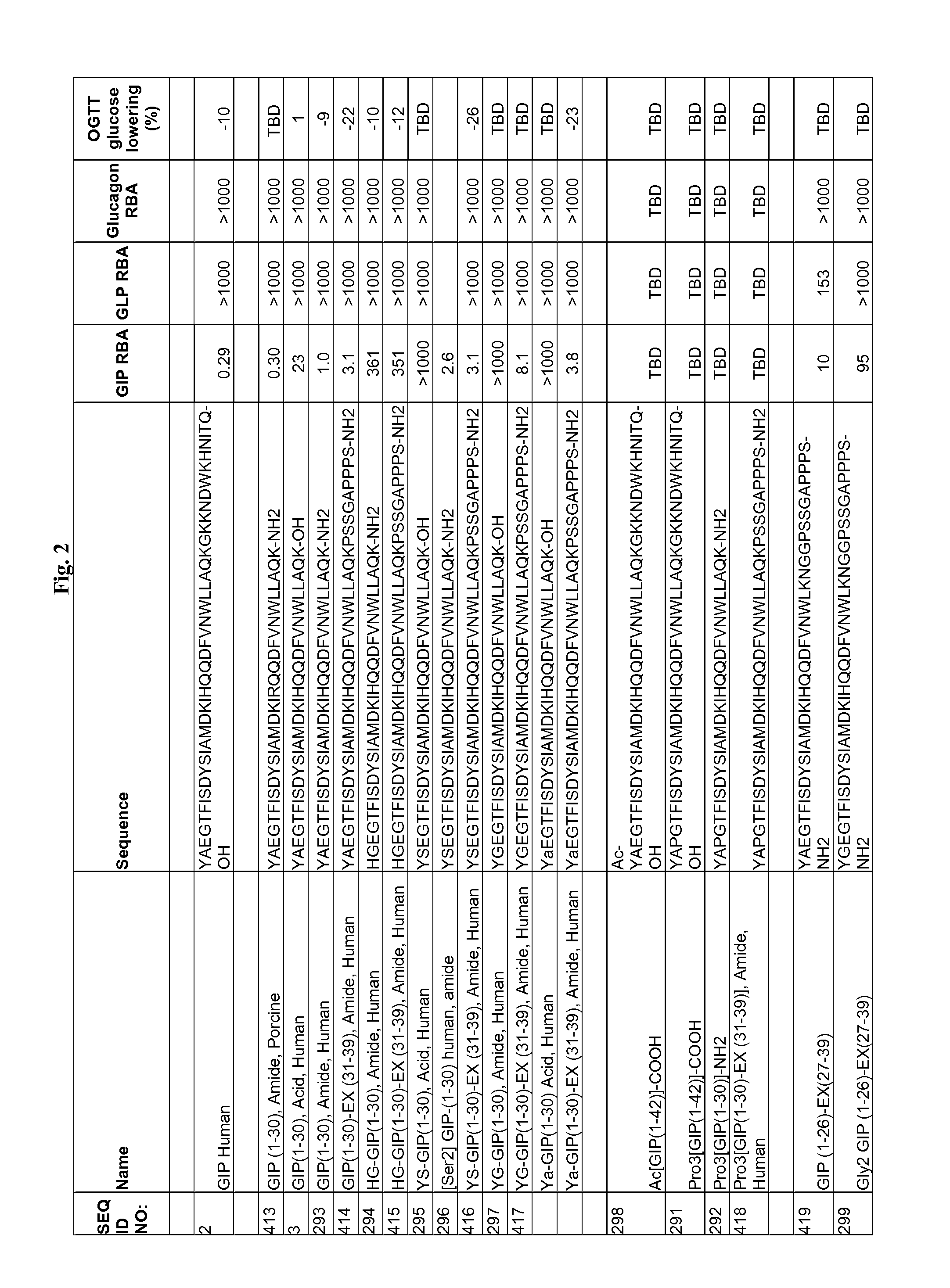
Gip analog and hybrid polypeptides with selectable properties
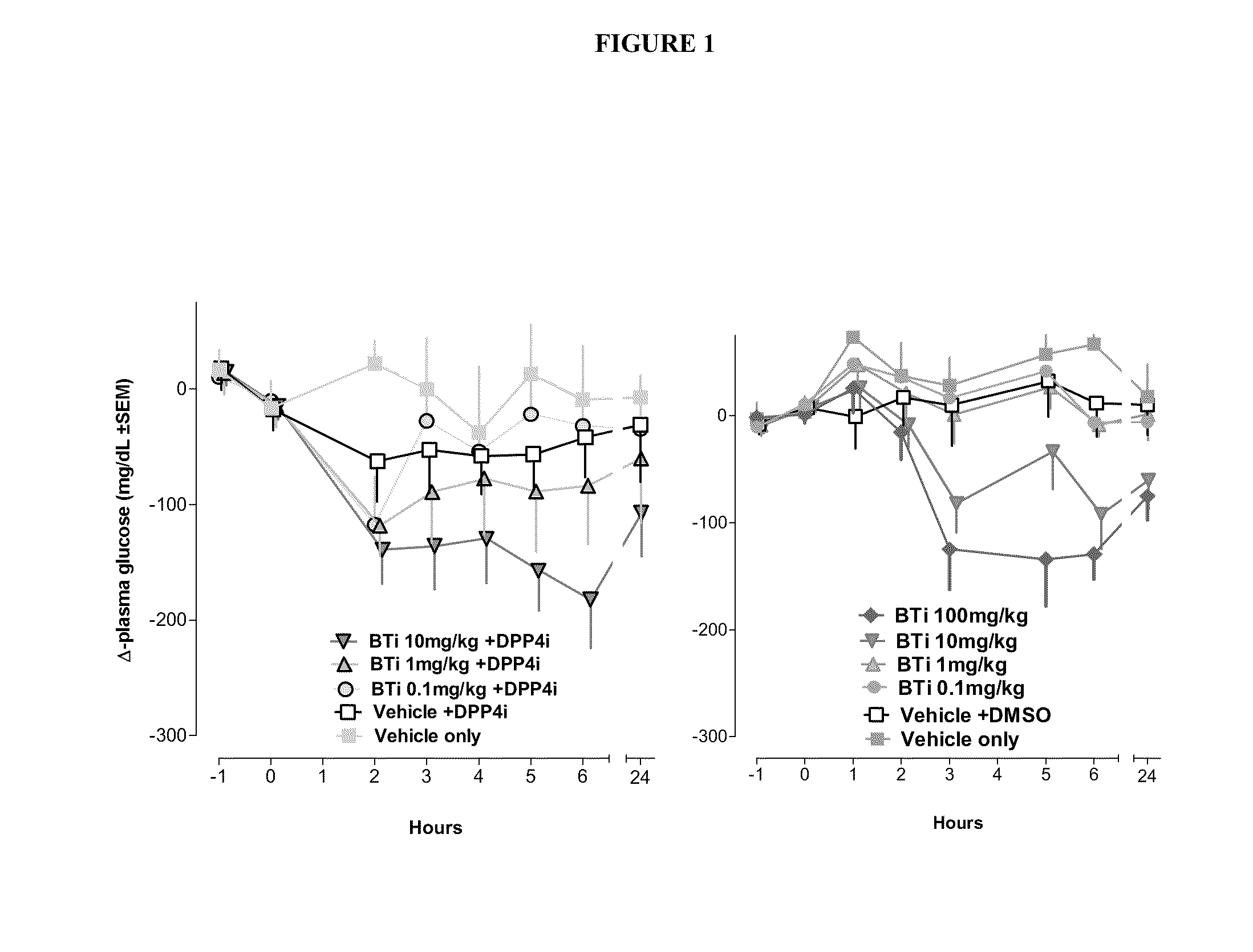
InactiveUS20090036364A1Increased insulin secretionDecreasing bone loss boneSenses disorderNervous disorderDyslipidemiaPhysiology
The present invention relates generally to novel GIP analogs and GIP hybrid polypeptides with selectable properties, useful as agents for the treatment and prevention of metabolic diseases and disorders, for example those which can be alleviated by control plasma glucose levels, insulin levels, and / or insulin secretion, positive inotropic effects, reduction of catabolic effects, slowing of gastric emptying. Such conditions and disorders include, but are not limited to, hypertension, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease, eating disorders, critical care, insulin-resistance, obesity, and diabetes mellitus of any kind, including type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Bile acid recycling inhibitors for treatment of obesity and diabetes
ActiveUS20100130472A1Reduces and inhibits recyclingIncreased L-cell secretionBiocideOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusObesity
Owner:SATIOGEN PHARMA
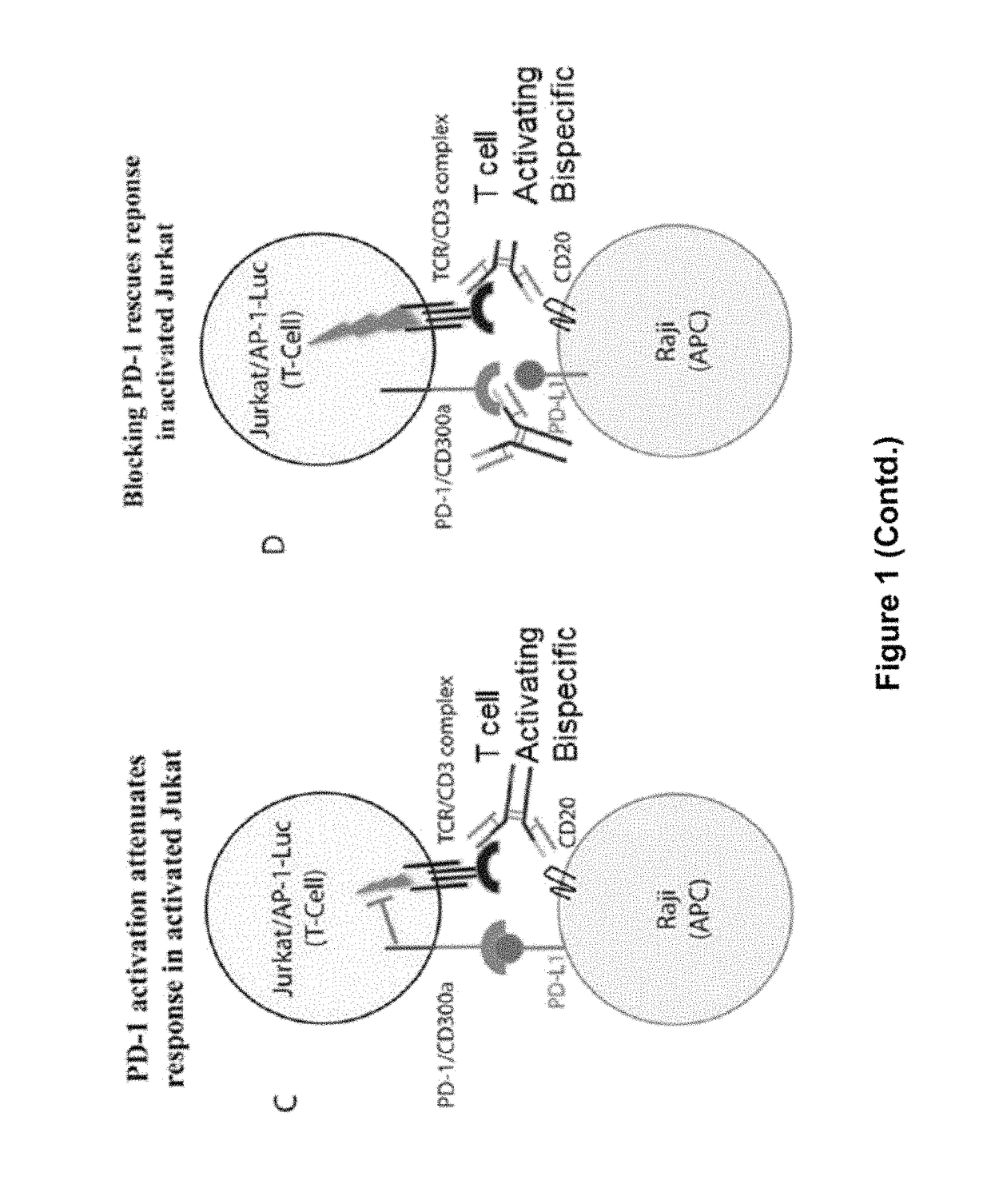
Human antibodies to PD-1
ActiveUS9987500B2Rescues T-cell signalingInhibit tumor growthNervous disorderAntipyreticFc(alpha) receptorDisease
The present invention provides antibodies that bind to the T-cell co-inhibitor programmed death-1 (PD-1) protein, and methods of use. In various embodiments of the invention, the antibodies are fully human antibodies that bind to PD-1. In certain embodiments, the present invention provides multi-specific antigen-binding molecules comprising a first binding specificity that binds to PD-1 and a second binding specificity that binds to an autoimmune tissue antigen, another T-cell co-inhibitor, an Fc receptor, or a T-cell receptor. In some embodiments, the antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing PD-1 activity, thus providing a means of treating a disease or disorder such as cancer or a chronic viral infection. In other embodiments, the antibodies are useful for enhancing or stimulating PD-1 activity, thus providing a means of treating, for example, an autoimmune disease or disorder.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Immunization-free methods for treating antigen-stimulated inflammation in a mammalian host and shifting the host's antigen immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype
InactiveUS20030092663A1Useful in treatment and prevention of inflammationSuppresses antigen-stimulated granulocyte infiltrationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAntigen stimulationTherapeutic intent
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Recombinant expression of proteins from secretory cell lines
InactiveUS6110707AIncrease productionIncrease secretionHormone peptidesRecombinant DNA-technologyHeterologousDisease
The present invention a provides methods for production of heterologous polypeptides, for example amylin, using recombinantly engineered cell lines. Also described are methods engineering cells for high level expression, methods of large scale heterologous protein production, methods for treatment of disease in vivo using viral delivery systems and recombinant cell lines, and methods for isolating novel amylin receptors.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Bile Acid Recycling Inhibitors for Treatment of Hypercholemia and Cholestatic Liver Disease
InactiveUS20130108573A1Relieve symptomsReduce recurrenceBiocideCyclic peptide ingredientsDiseaseHepatic bile
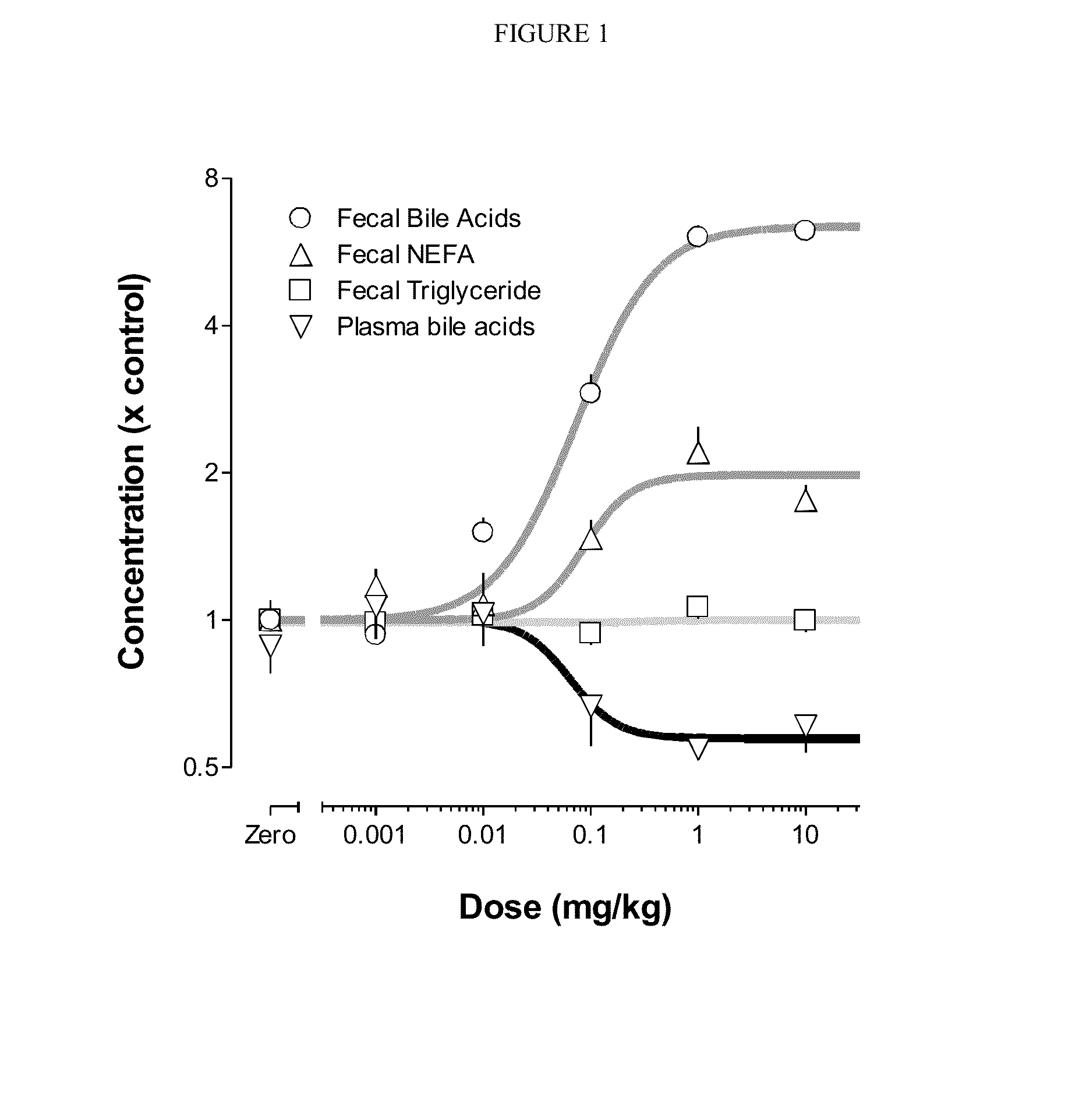
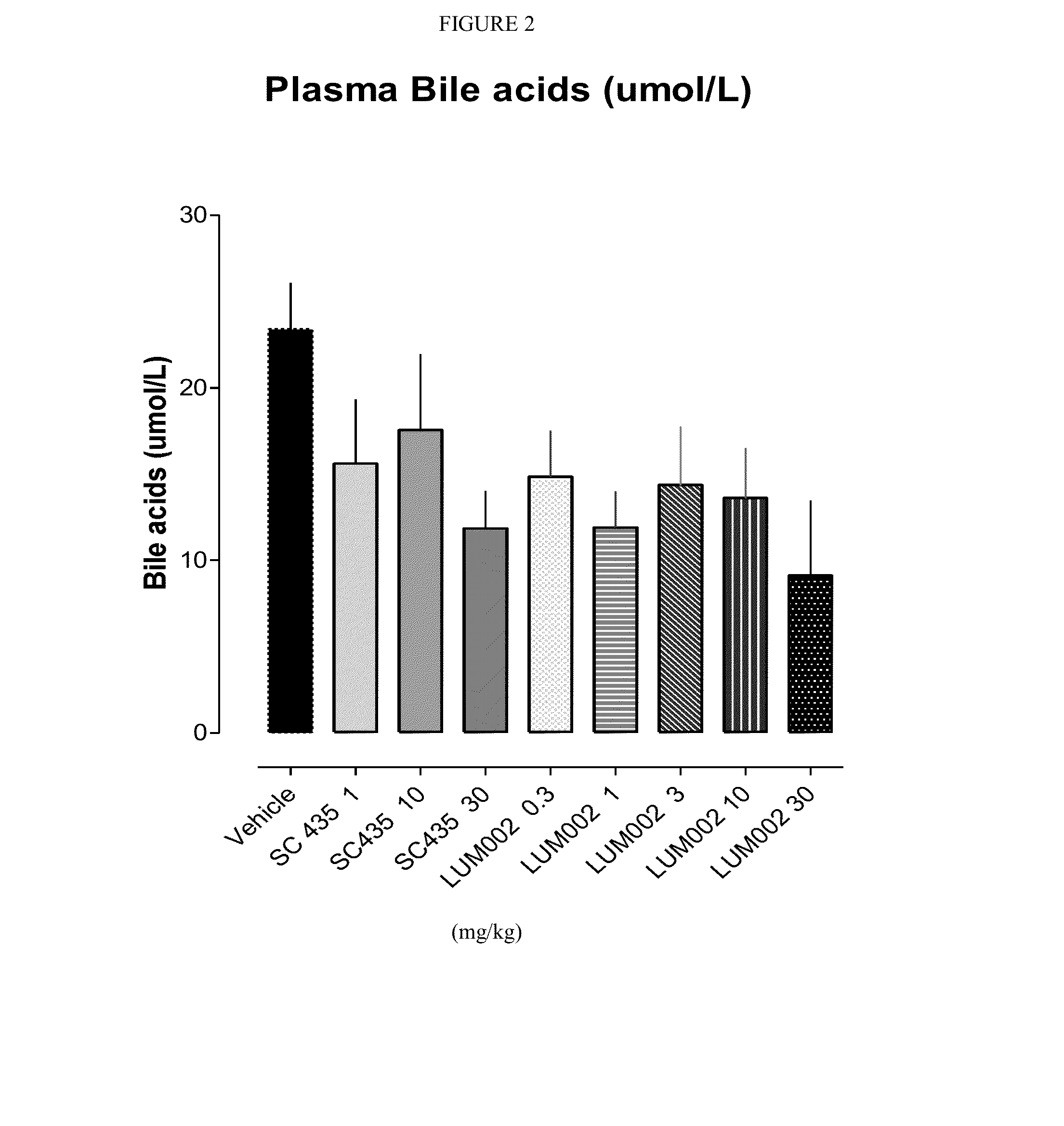
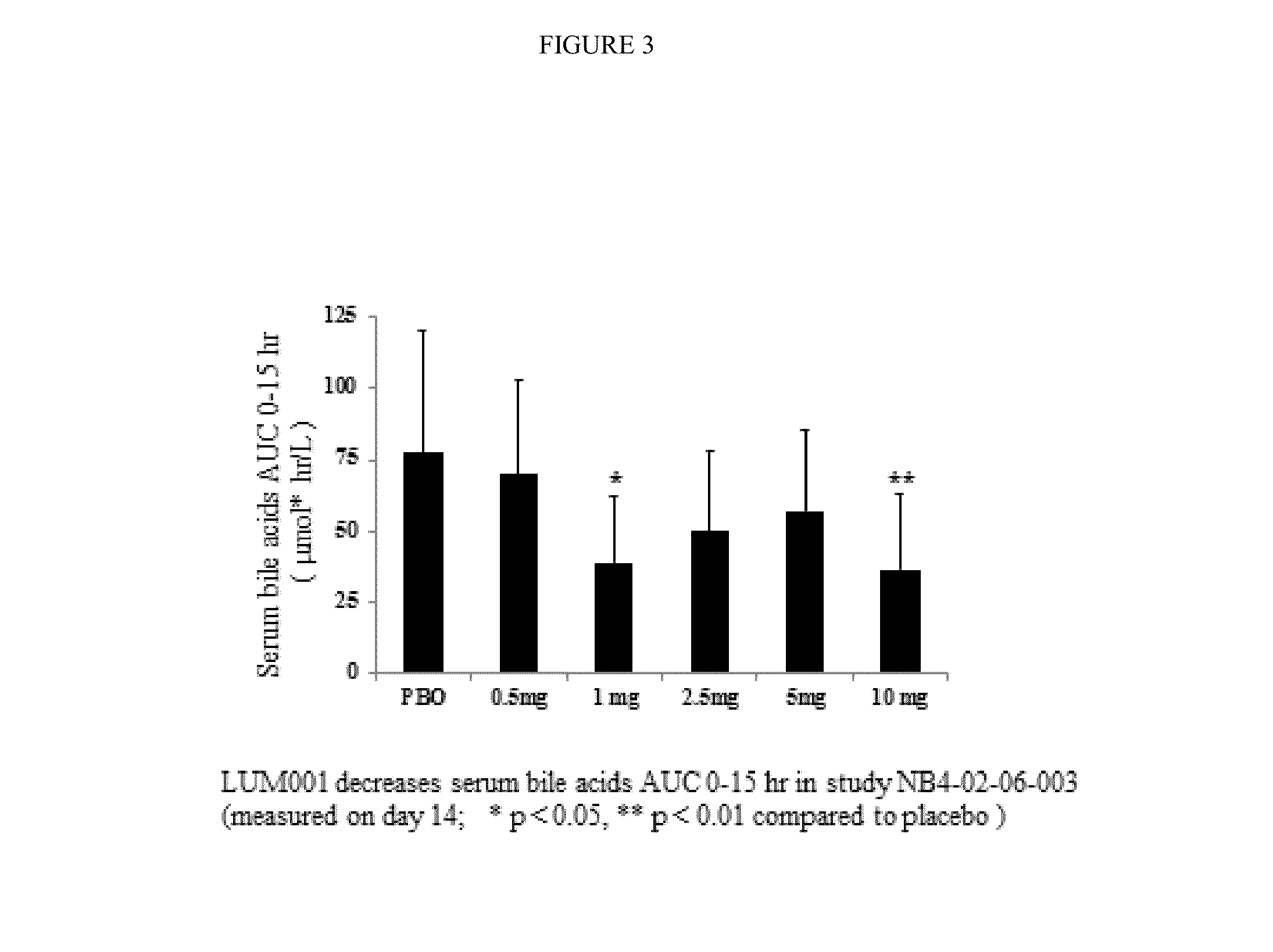
Provided herein are methods of treating or ameliorating hypercholemia or a cholestatic liver disease by administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of an Apical Sodium-dependent Bile Acid Transporter Inhibitor (ASBTI) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Also provided are methods for treating or ameliorating a liver disease, decreasing the levels of serum bile acids or hepatic bile acids, treating or ameliorating pruritis, reducing liver enzymes, or reducing bilirubin comprising administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of ASBTI or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:LUMENA PHARMA INC
Bile acid recycling inhibitors and satiogens for treatment of diabetes, obesity, and inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions
InactiveUS20110294767A1Reduces and inhibits recyclingIncreased L-cell secretionBiocideOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusObesity
Owner:SATIOGEN PHARMA
Blood glucose level control
InactiveUS8019421B2Reduced effectivenessOverworking pancreasInternal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsBlood levelBlood insulin
A pancreatic controller, comprising:at least one electrode adapted for electrifying at least a portion of a pancreas; anda controller programmed to electrify said electrode so as to positively control at least the effect of at least two members of a group consisting of blood glucose level, blood insulin level and blood level of another pancreatic hormone. In one example, the controller controls insulin, glucagon and / or glucose blood levels.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Vaginal health products
InactiveUS7485666B2Minor side effectsPromote cell growthBiocideEther/acetal active ingredientsCell turnoverMammal
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
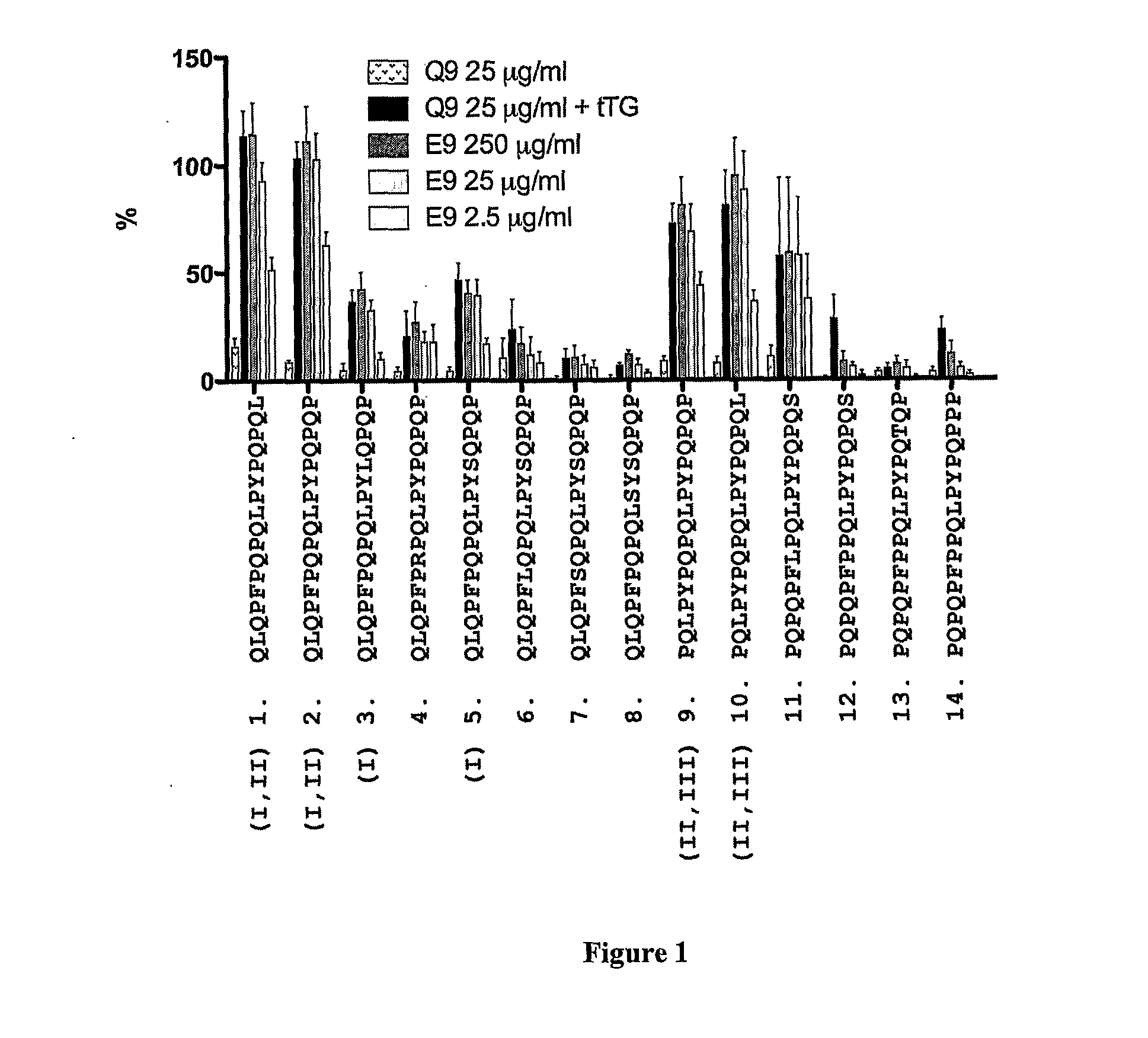
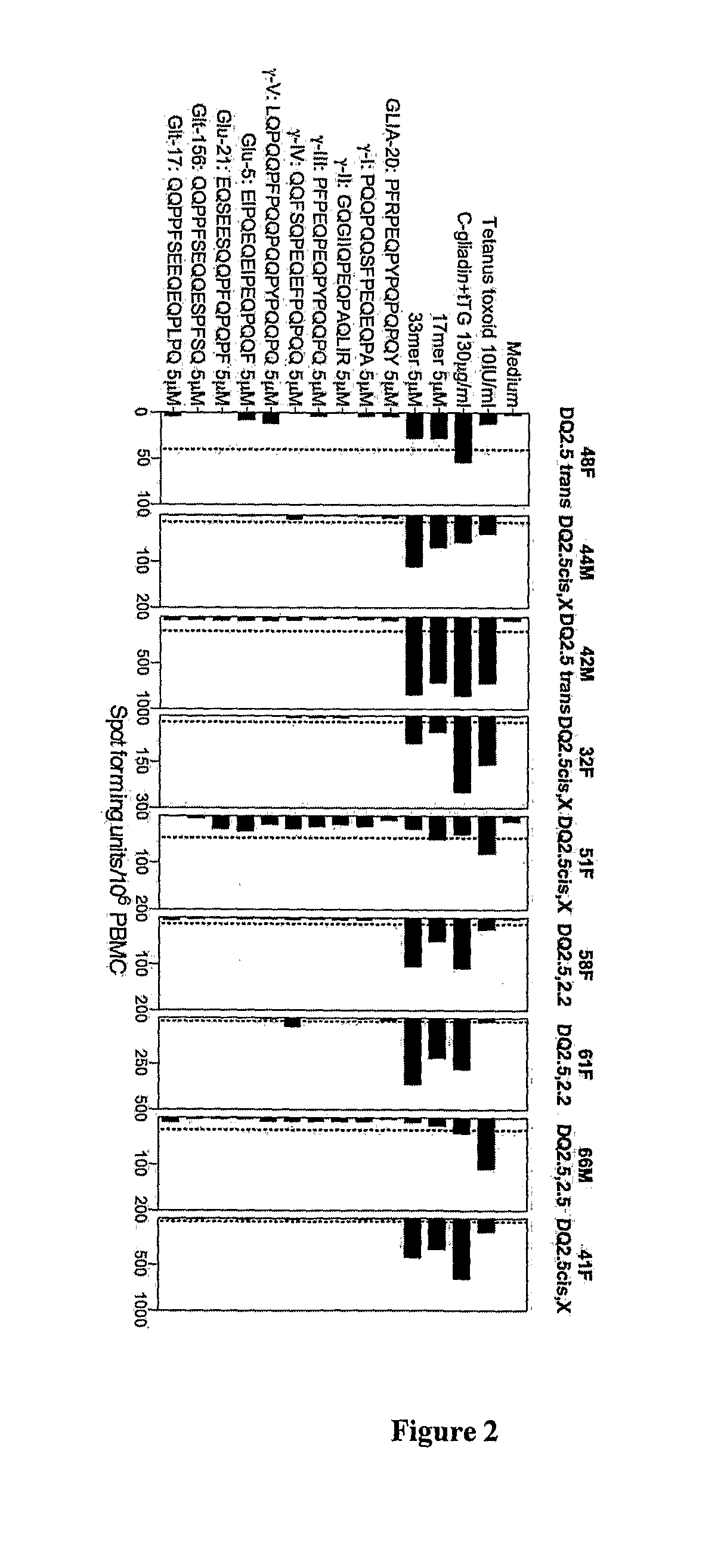
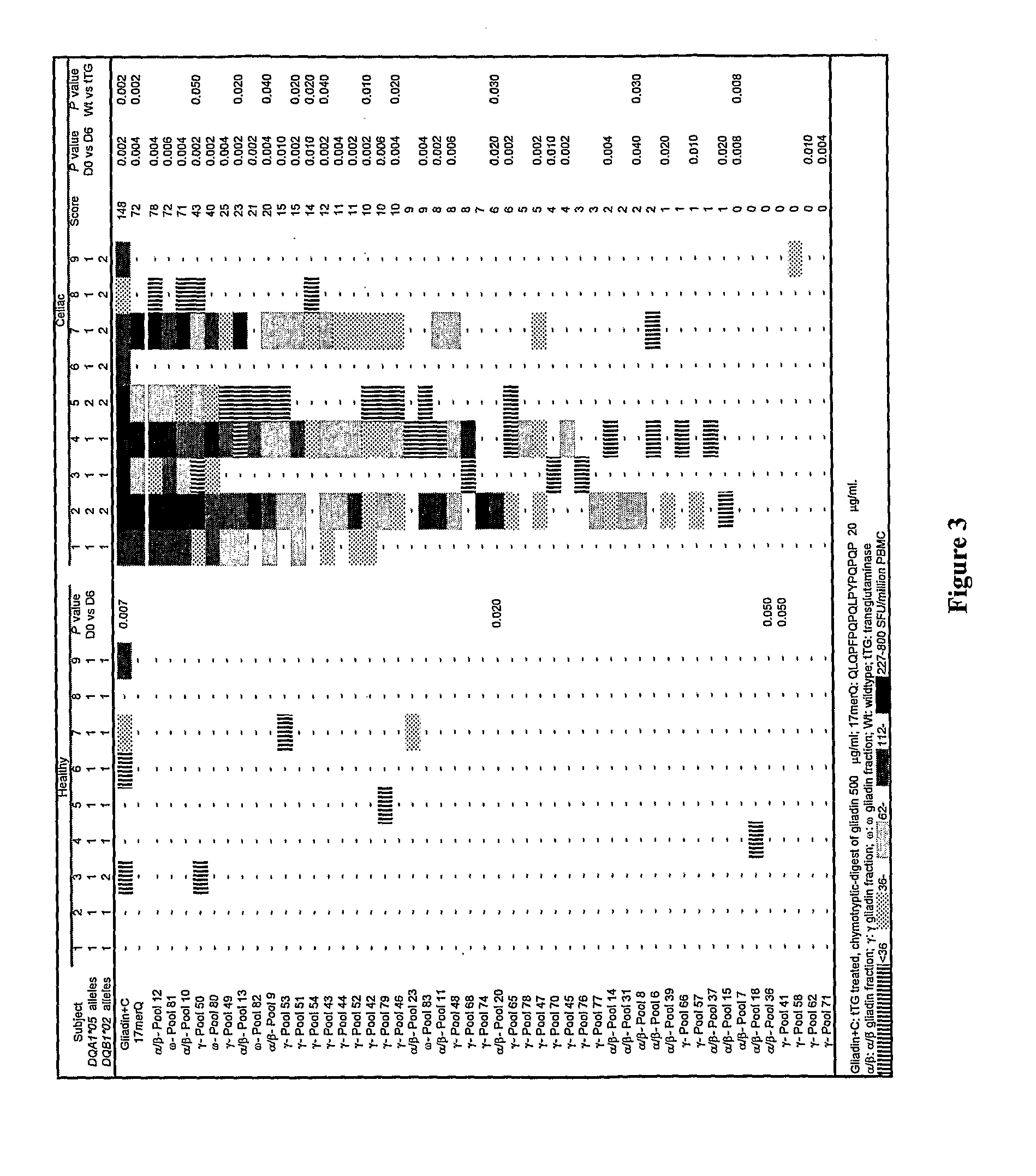
Compositions and methods for treatment of celiac disease
ActiveUS20110293644A1Improve bioavailabilityWider effectivePeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisPeptidePathology
Owner:IMMUSANT
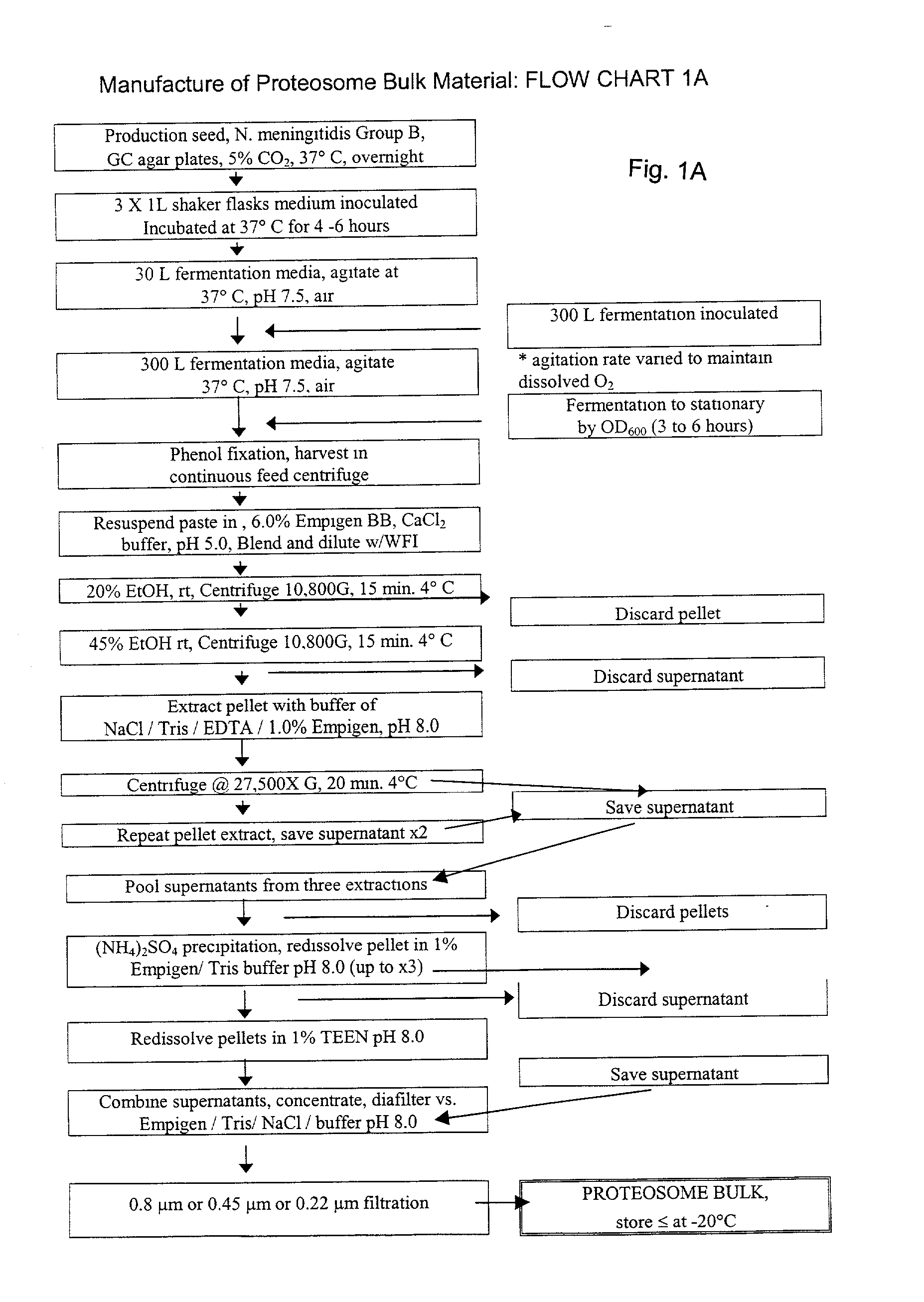
Novel proteosome-liposaccharide vaccine adjuvant
InactiveUS20030044425A1Increase secretionUniform processSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideImmunotherapeutic agentCytokine
An adjuvant complex composed of bacterial outer membrane protein proteosomes complexed to bacterial liposaccharide is prepared to contain the component parts under a variety of conditions. The complex can be formulated with antigenic material to form immunogenic compositions, vaccines and immunotherapeutics. An induced immune response includes protective antibodies and / or type 1 cytokines is shown for a variety of protocols.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL CORP LAVAL
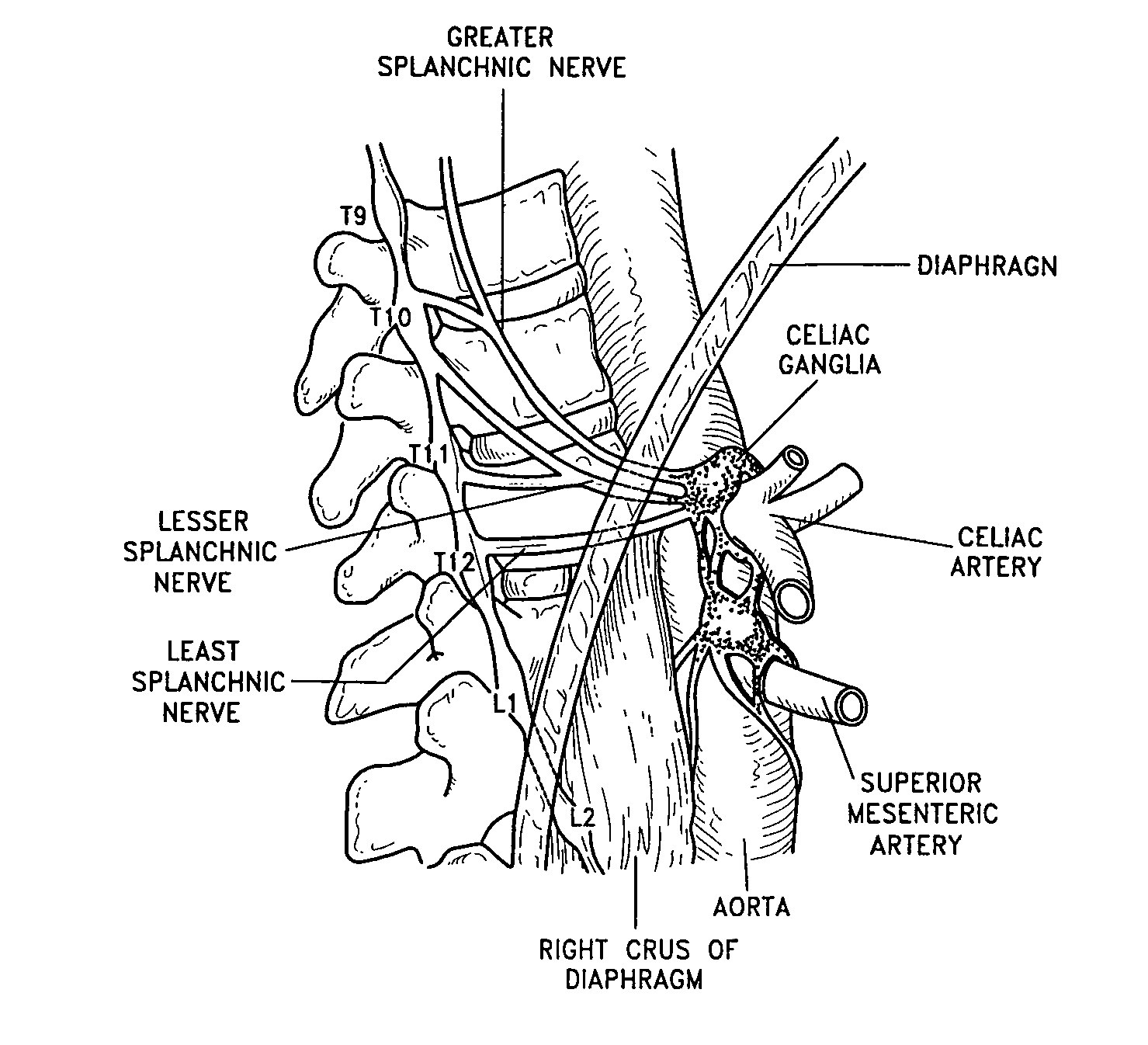
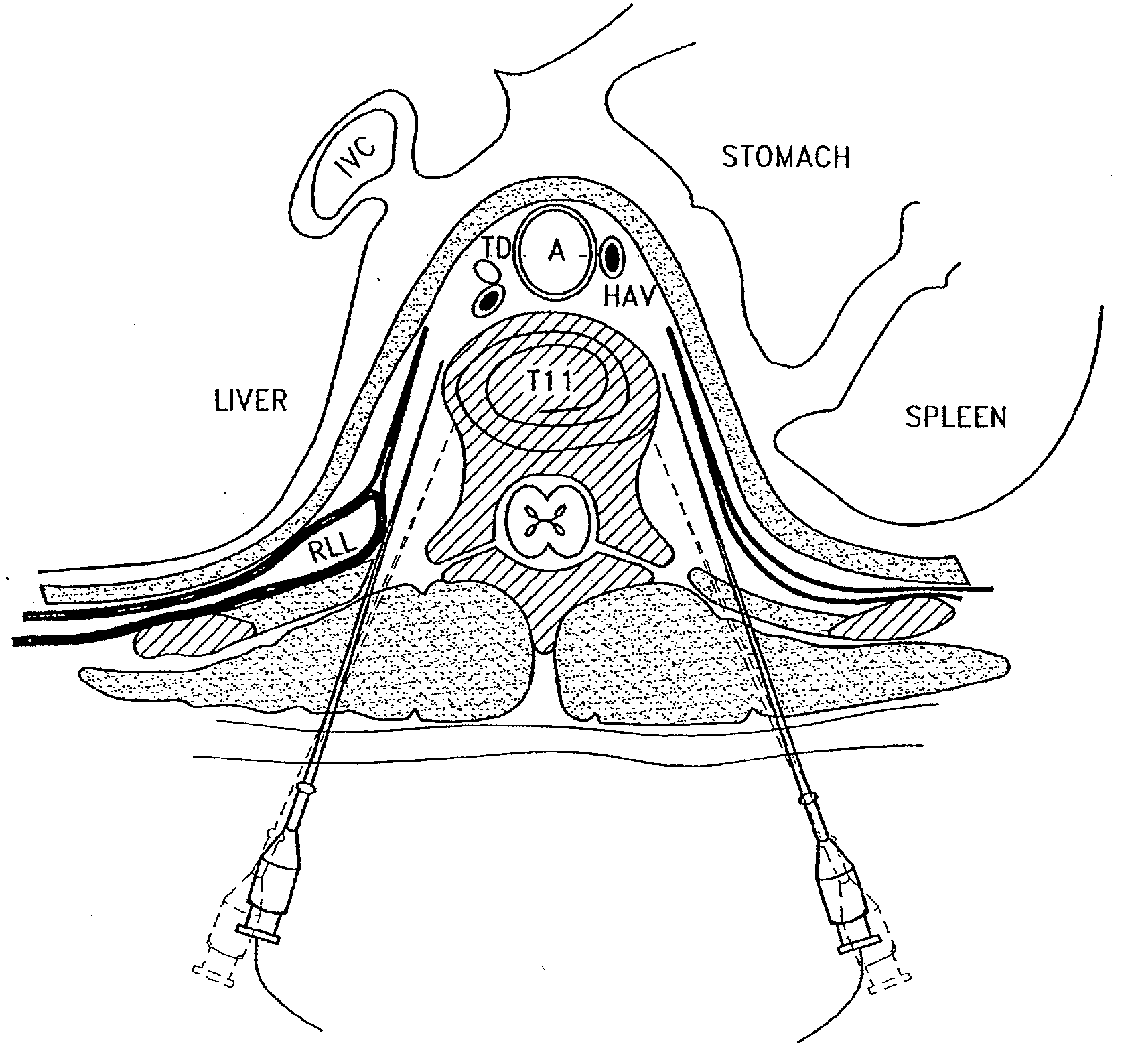
Splanchnic nerve stimulation for treatment of obesity
InactiveUS7551964B2Increased energy expenditureReducing food intakeElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseaseSplanchnic nerve stimulation
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders by electrical activation or inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system is disclosed. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by stimulating the greater splanchnic nerve or other portion of the sympathetic nervous system using an electrode. This nerve activation can result in reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Methods for suppressing the induction of nitric oxide synthase in a cell
InactiveUS7049058B2Increase ratingsIncrease volumeBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementAntioxidantSuppressor
Disclosed are methods for suppressing the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase in a cell comprising contacting said cell with an effective amount of at least one induction suppressor of inducible nitric oxide synthase or a cytokine are disclosed. The induction suppressor can be an inhibitor of mevalonate synthesis, an inhibitor of the farnesylation of Ras, an antioxidant, an enhancer of intracellular cAMP, an enhancer of protein kinase A (PKA), an inhibitor of NF-kβ activation, an inhibitor of Ras / Raf / MAP kinase pathway, an inhibitor of mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase or an inhibitor of farnesyl pyrophosphate.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Bile acid recycling inhibitors and satiogens for treatment of diabetes, obesity, and inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions
ActiveUS20130059807A1Reduces and inhibits recyclingIncrease secretionBiocideOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusObesity
Owner:SATIOGEN PHARMA
Extendin derivatives
InactiveUS7226990B2Good synergistic effectAdditional therapeutic advantageMetabolism disorderPeptide sourcesPeptideC-Terminal Amino Acid
The present invention relates to novel derivatives of exendin-4 or exendin-4 fragments, wherein the derivatives have a lipophilic substituent attached, optionally via a spacer, to an amino acid residue, which is not the N-terminal or C-terminal amino acid residue of the derivative.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
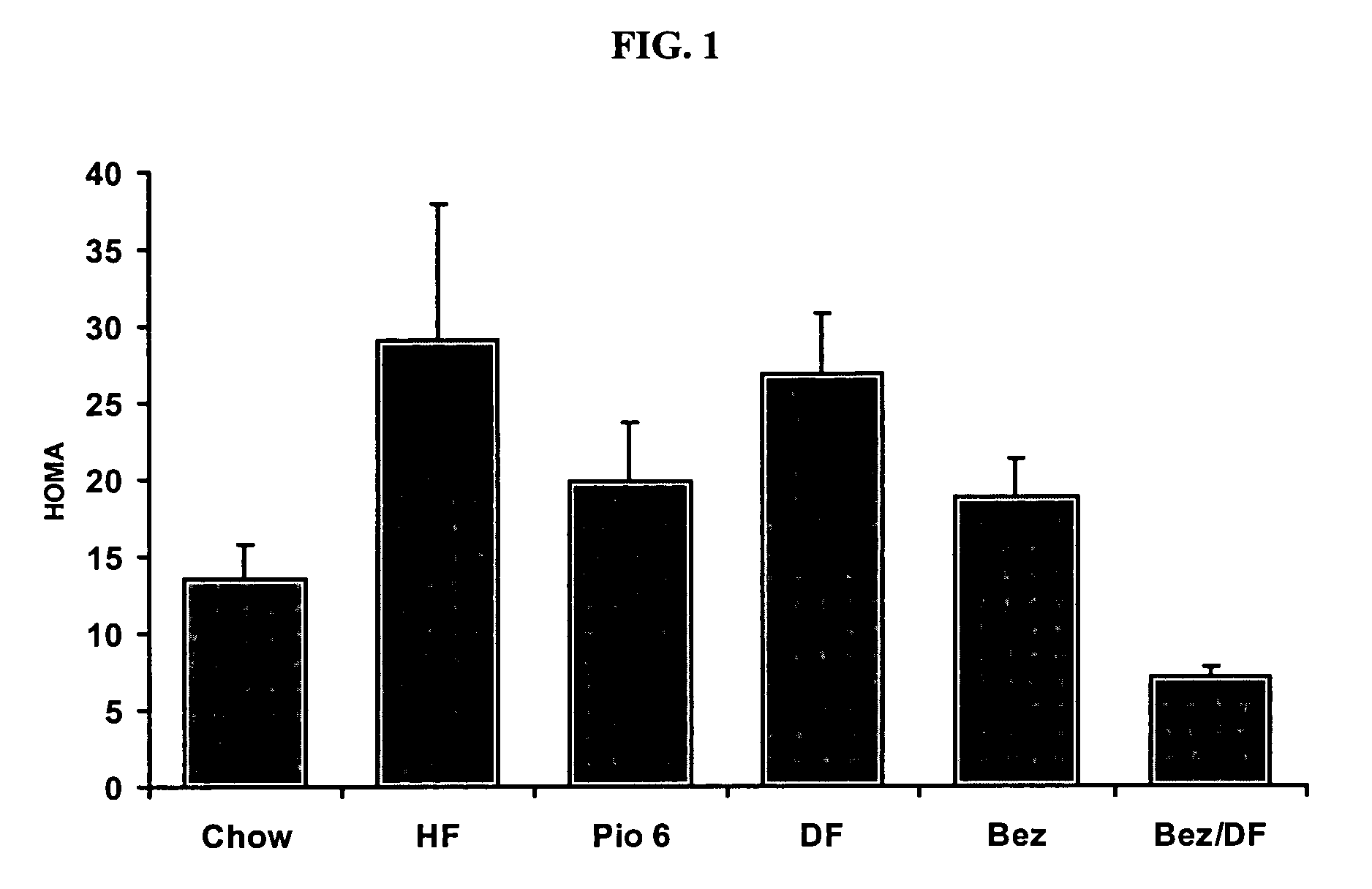
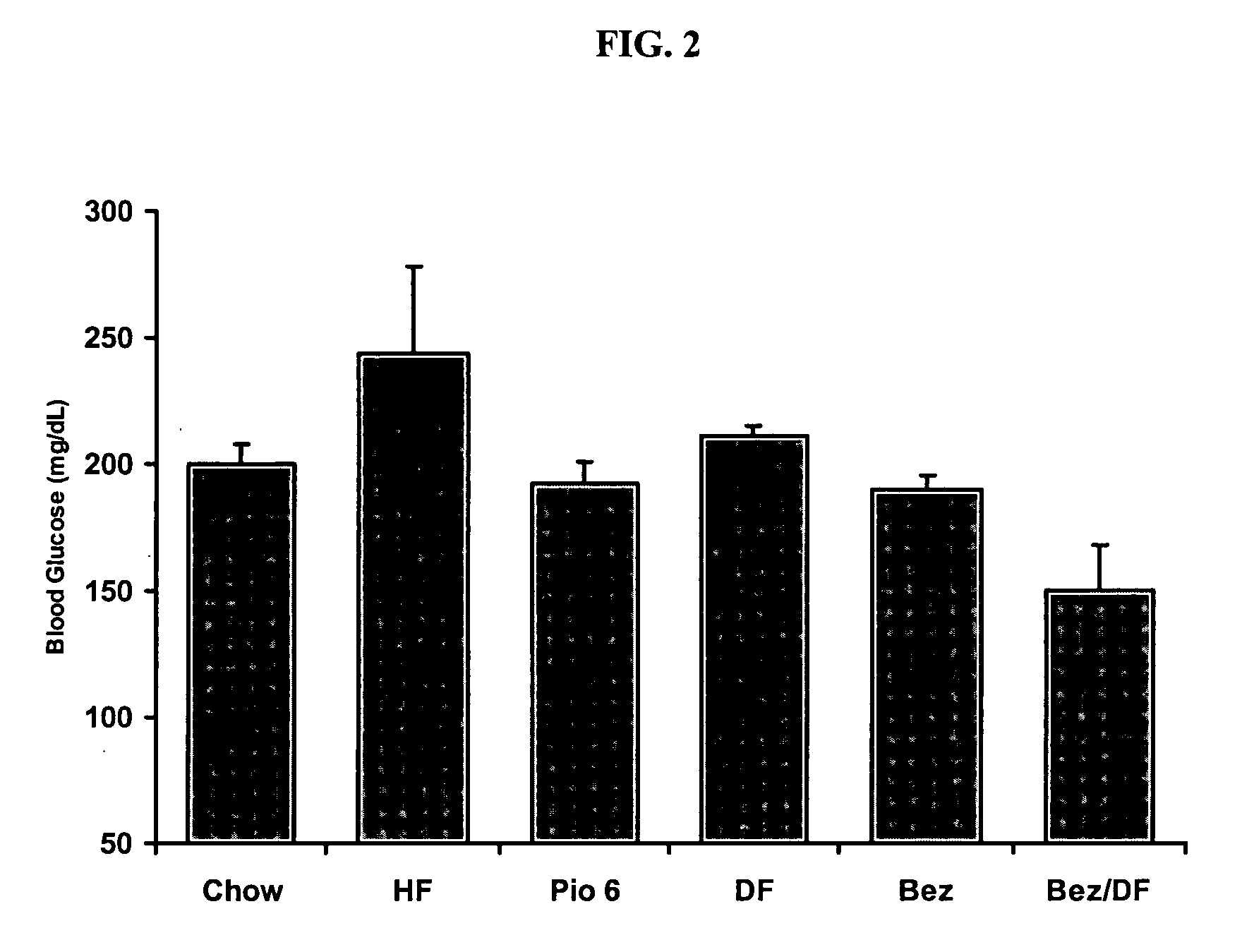
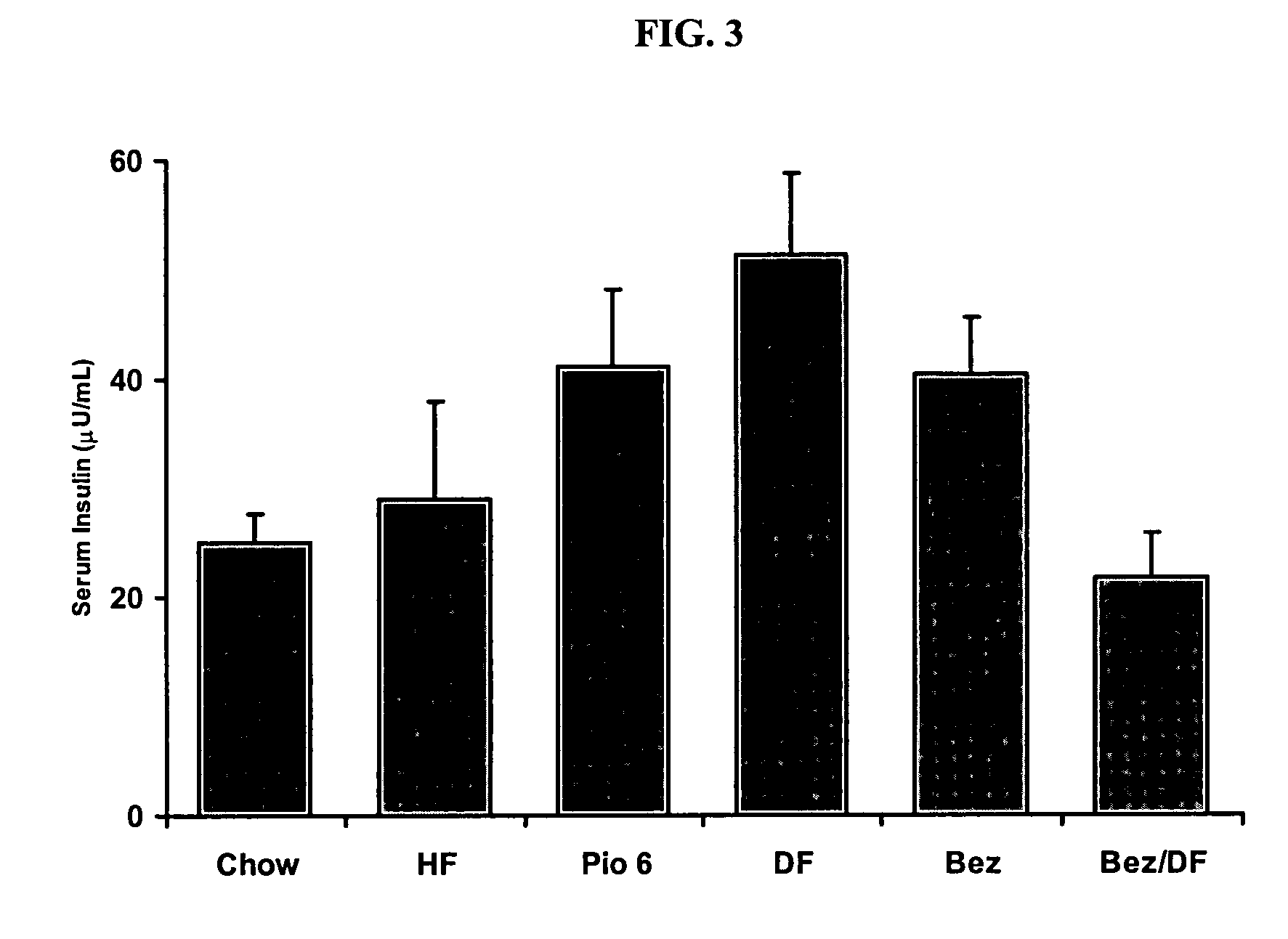
Synergistic use of thiazolidinediones with glucagon-like peptide-1 and agonists thereof to treat metabolic instability associated with non-insulin dependent diabetes
InactiveUS7223728B2Lower blood sugar levelsIncrease secretionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin dependent diabetesSide effect
Thiazolidinedione (TZD) and its pharmacologically active derivatives can be used, in combination with agonists of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), to treat non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, optionally with other therapies, by improving glycemic control while minimizing side effects, such as heart hypertrophy and elevated fed-state plasma glucose, which are associate with both TZD and GLP-1 monotherapies. Thus, the co-administration of TZD and GLP-1 helps regulate glucose homeostasis in Type II diabetic patients.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com