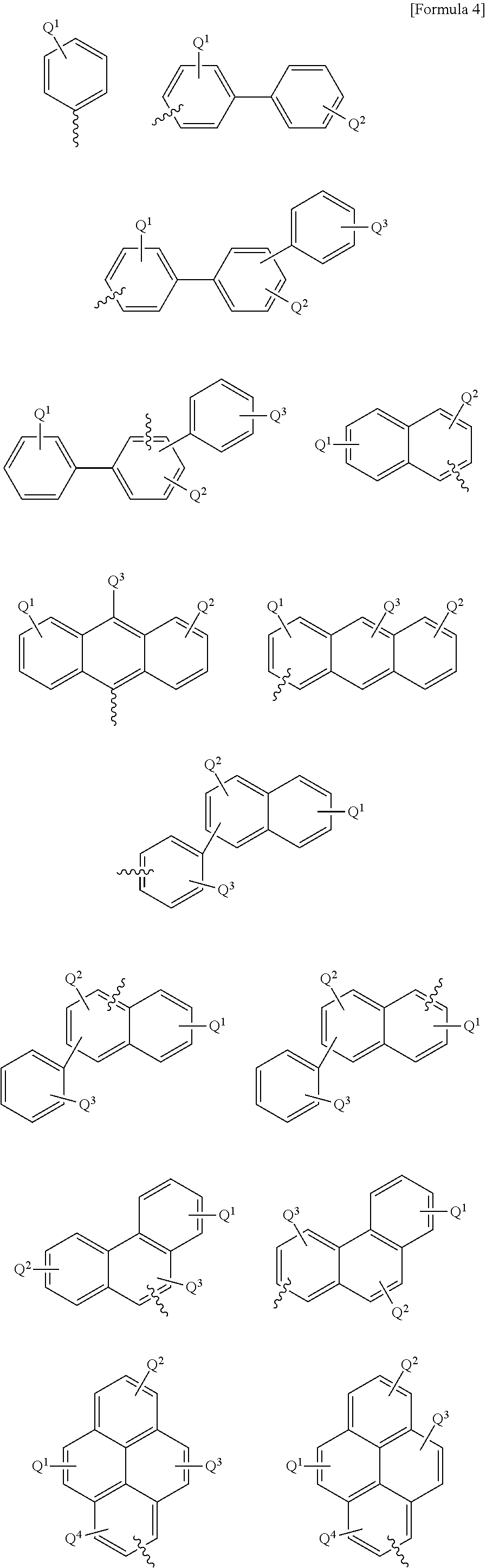
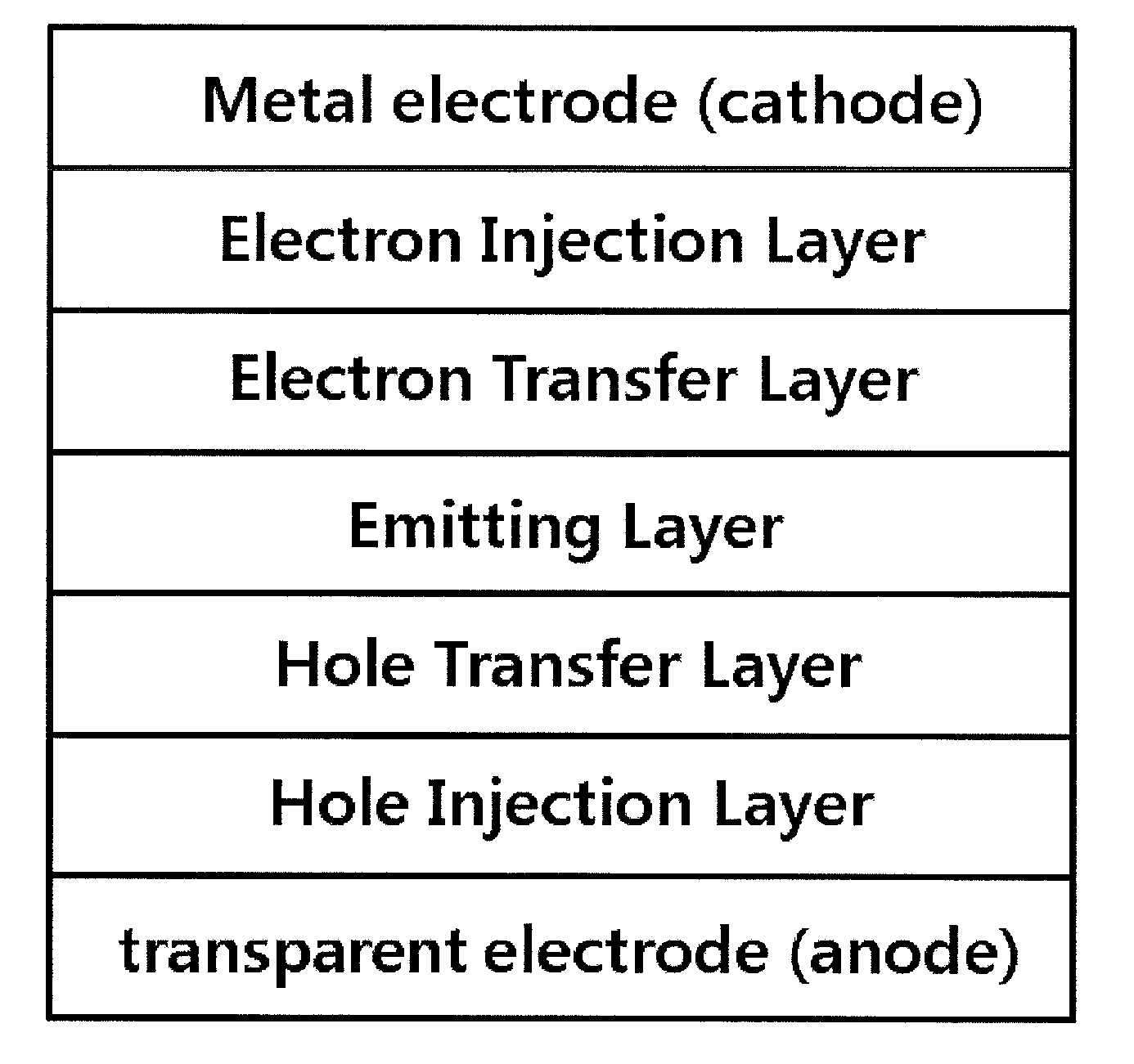
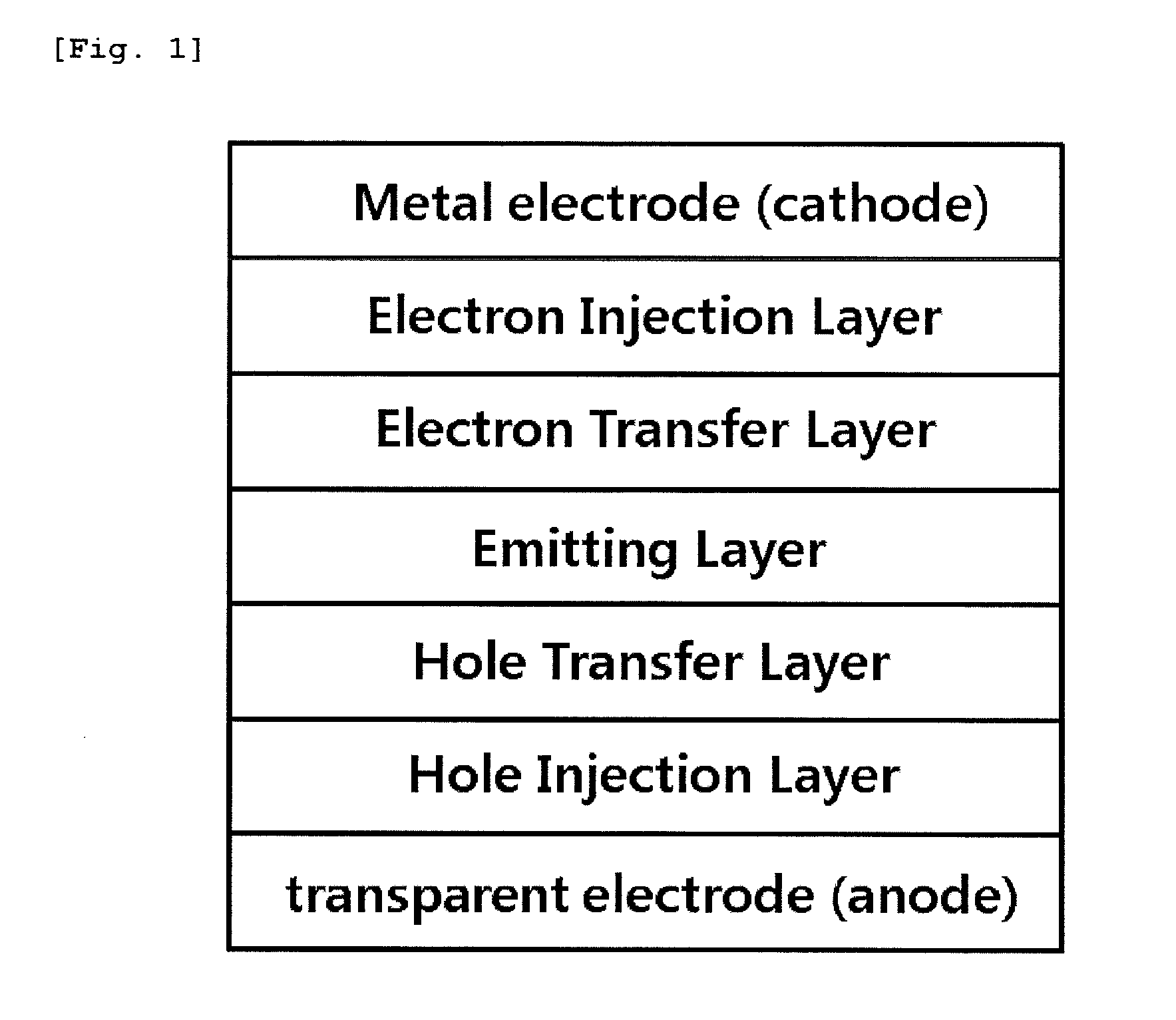
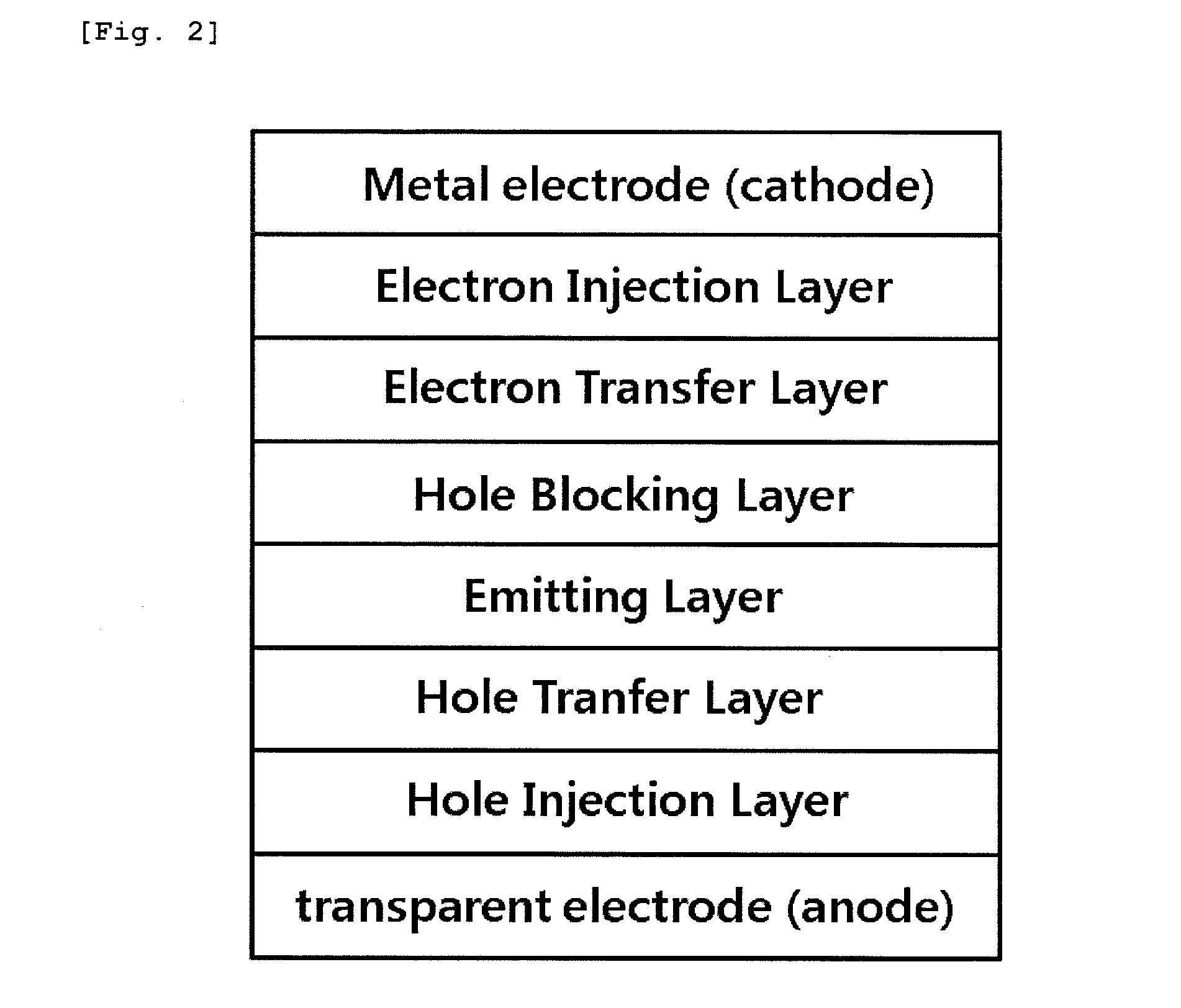
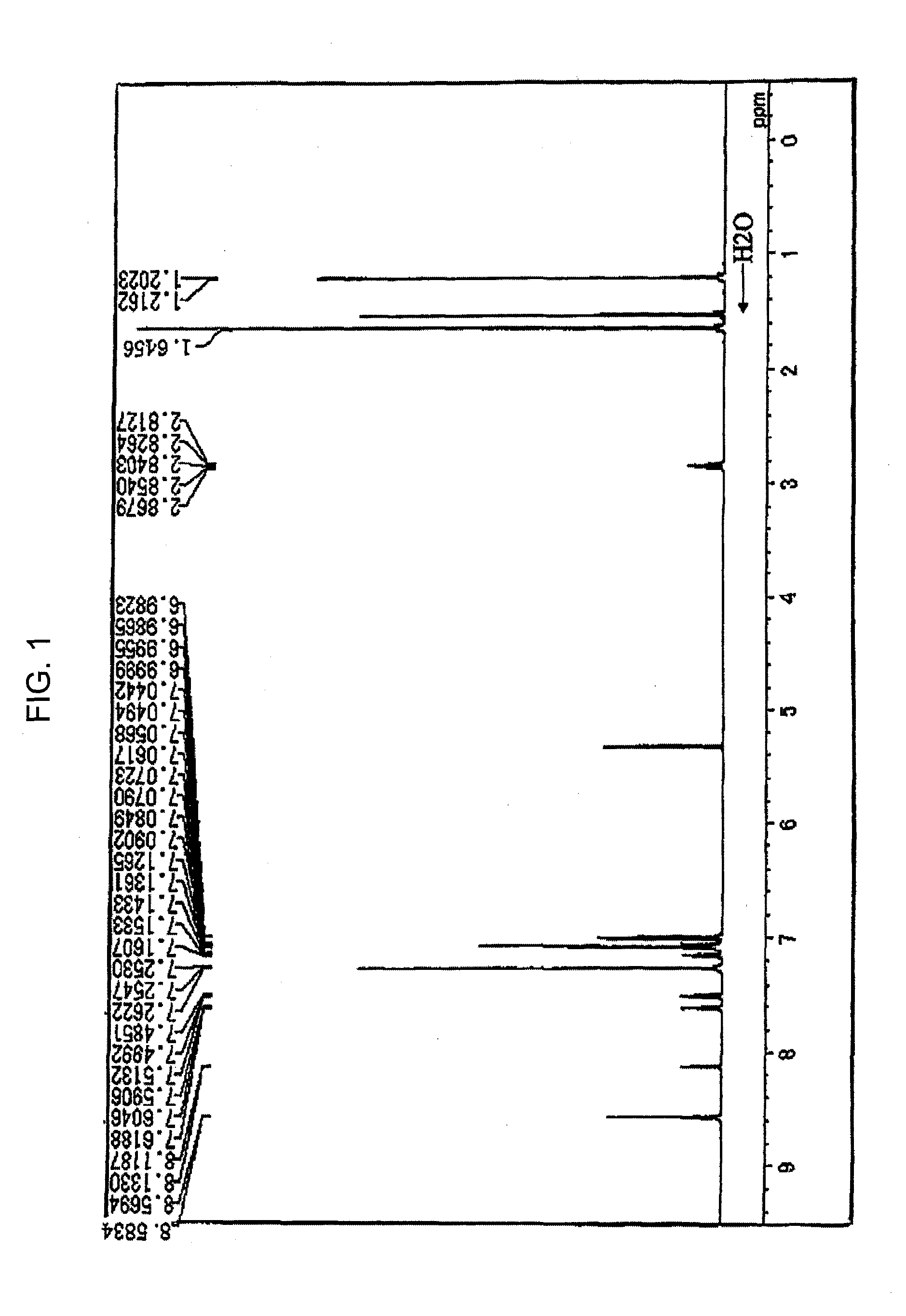
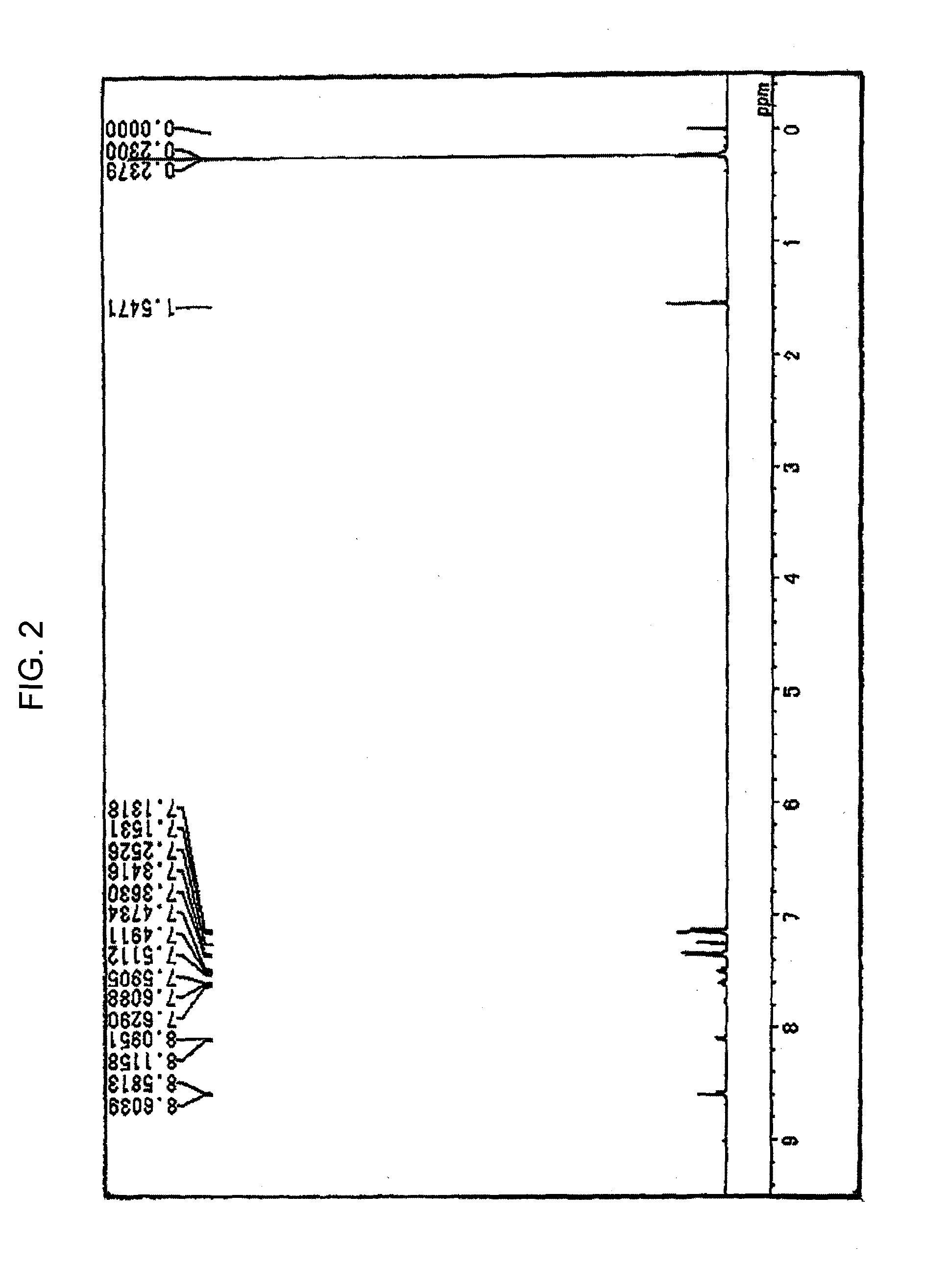
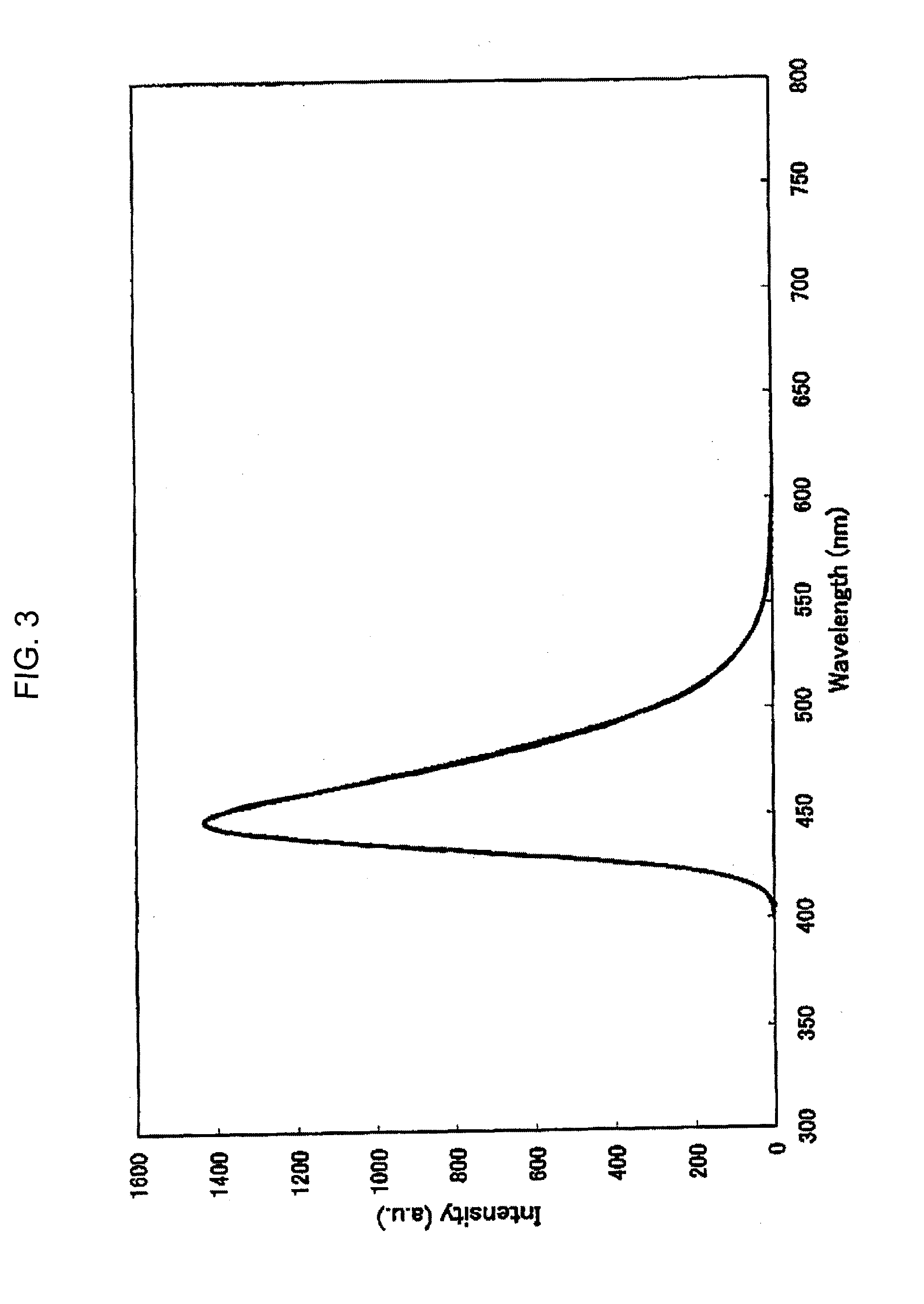
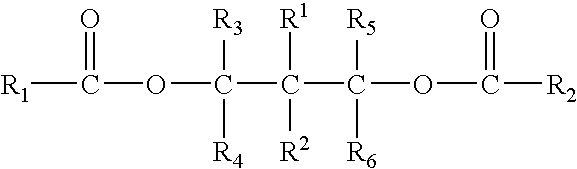
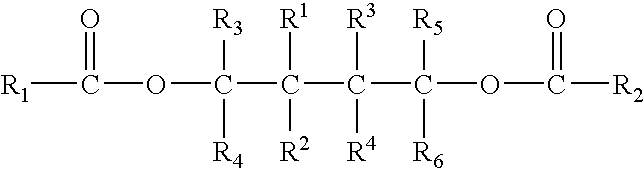
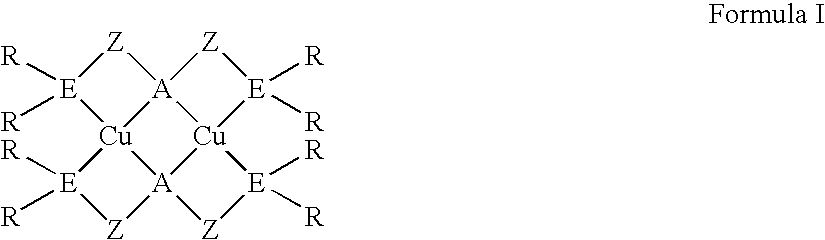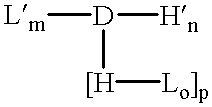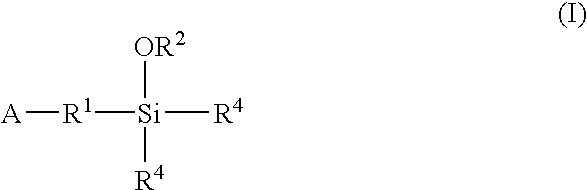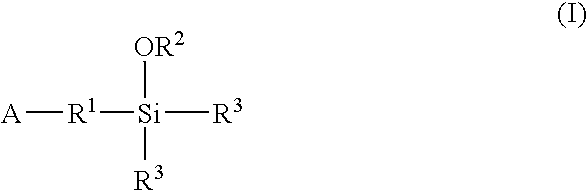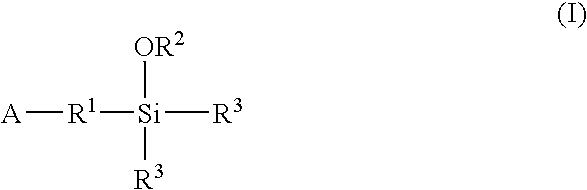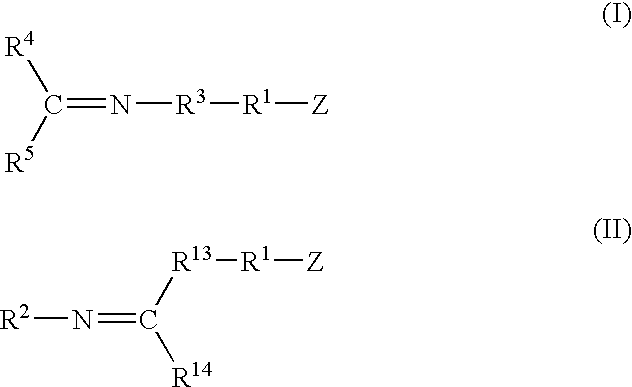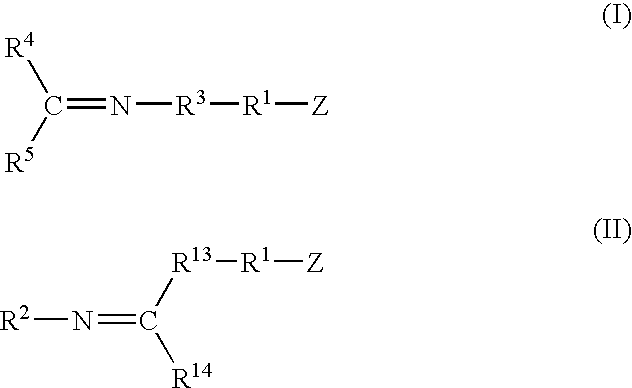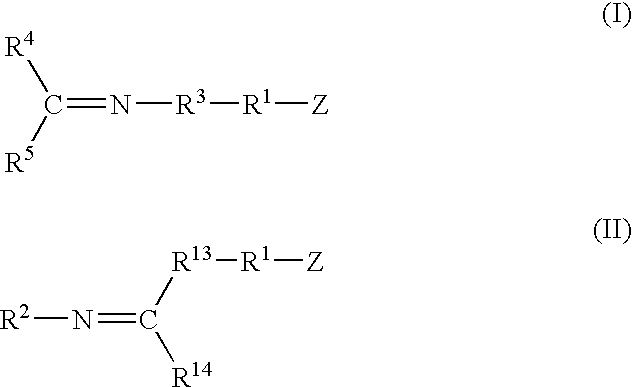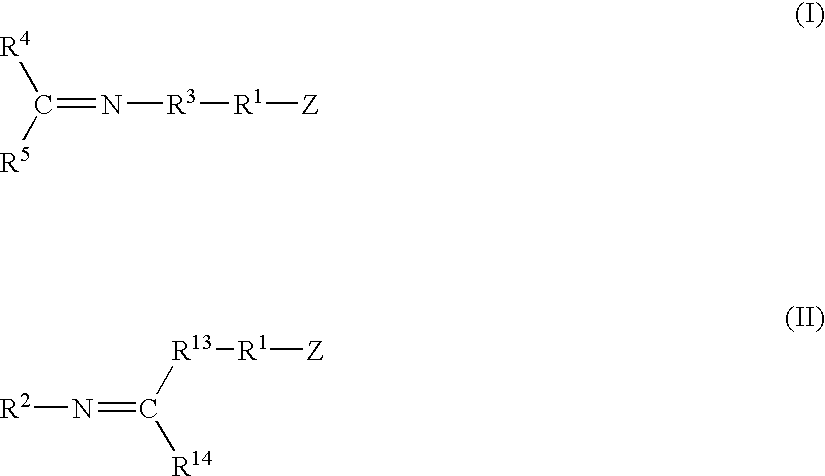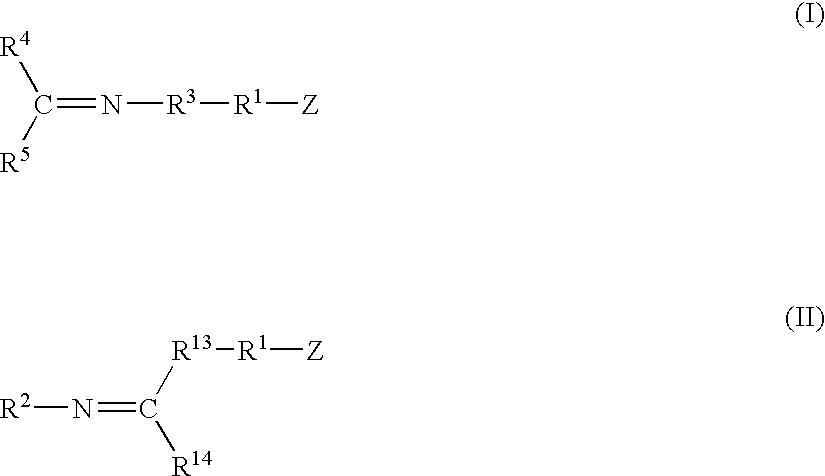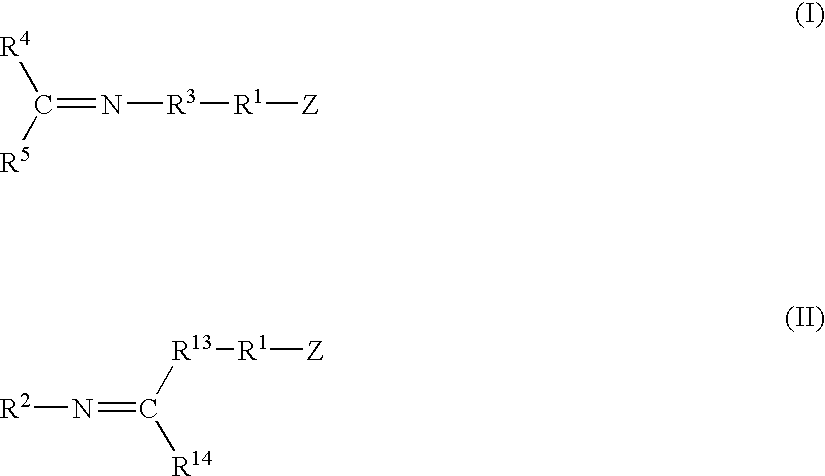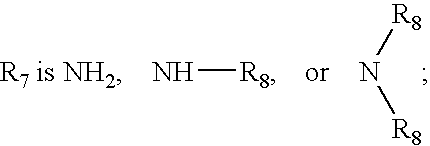Patents
Literature
10742 results about "Substituent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms which replaces one or more hydrogen atoms on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon, becoming a moiety of the resultant new molecule. The terms substituent and functional group, as well as other ones (e.g. side chain, pendant group) are used almost interchangeably to describe branches from a parent structure, though certain distinctions are made in the context of polymer chemistry. In polymers, side chains extend from a backbone structure. In proteins, side chains are attached to the alpha carbon atoms of the amino acid backbone.
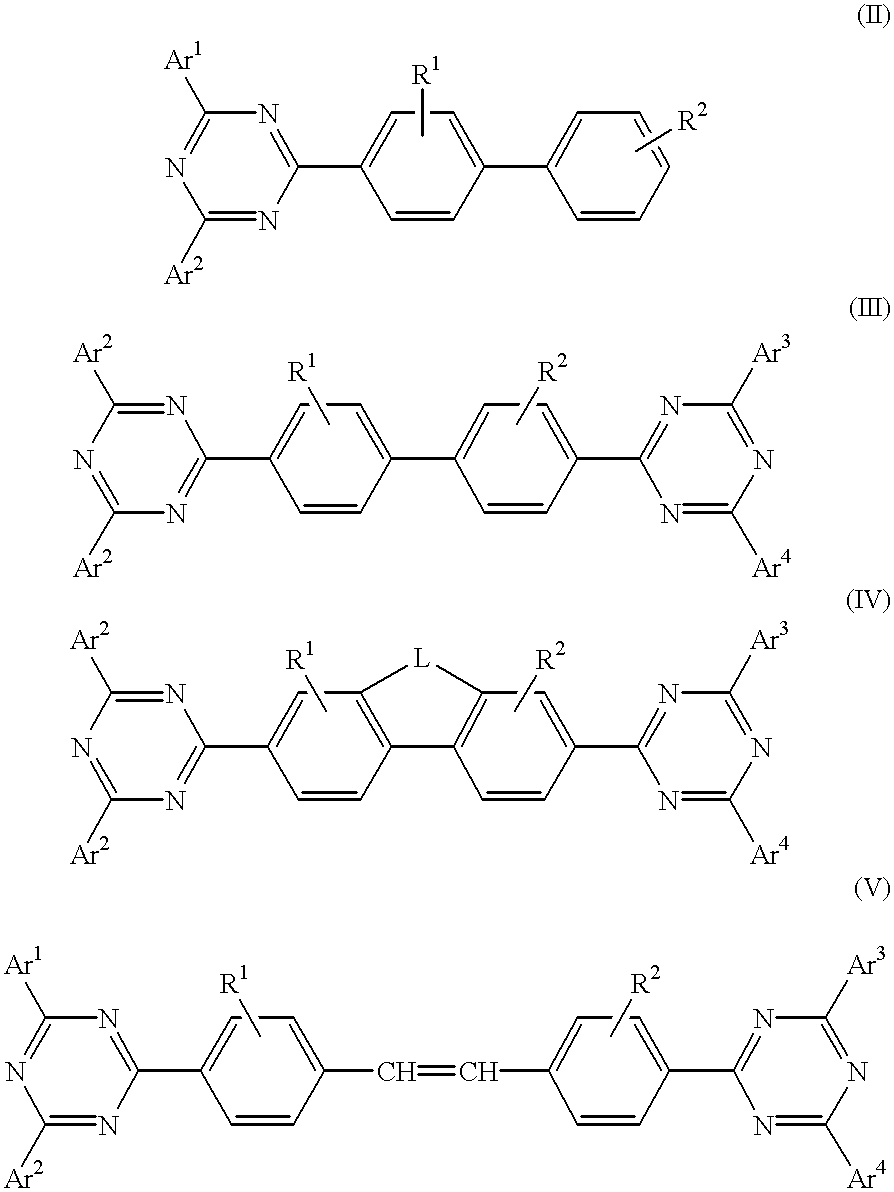
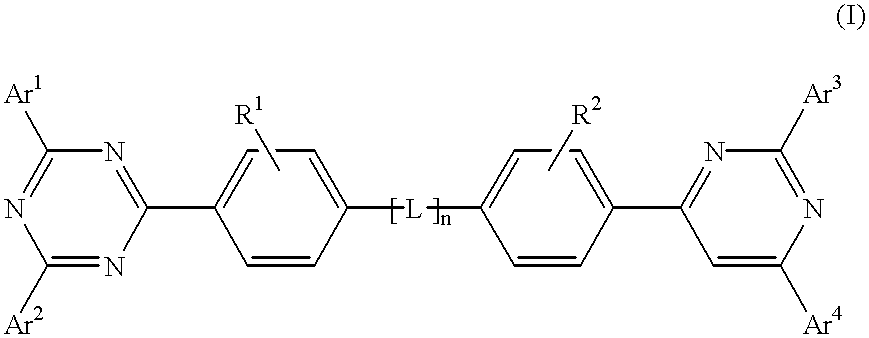
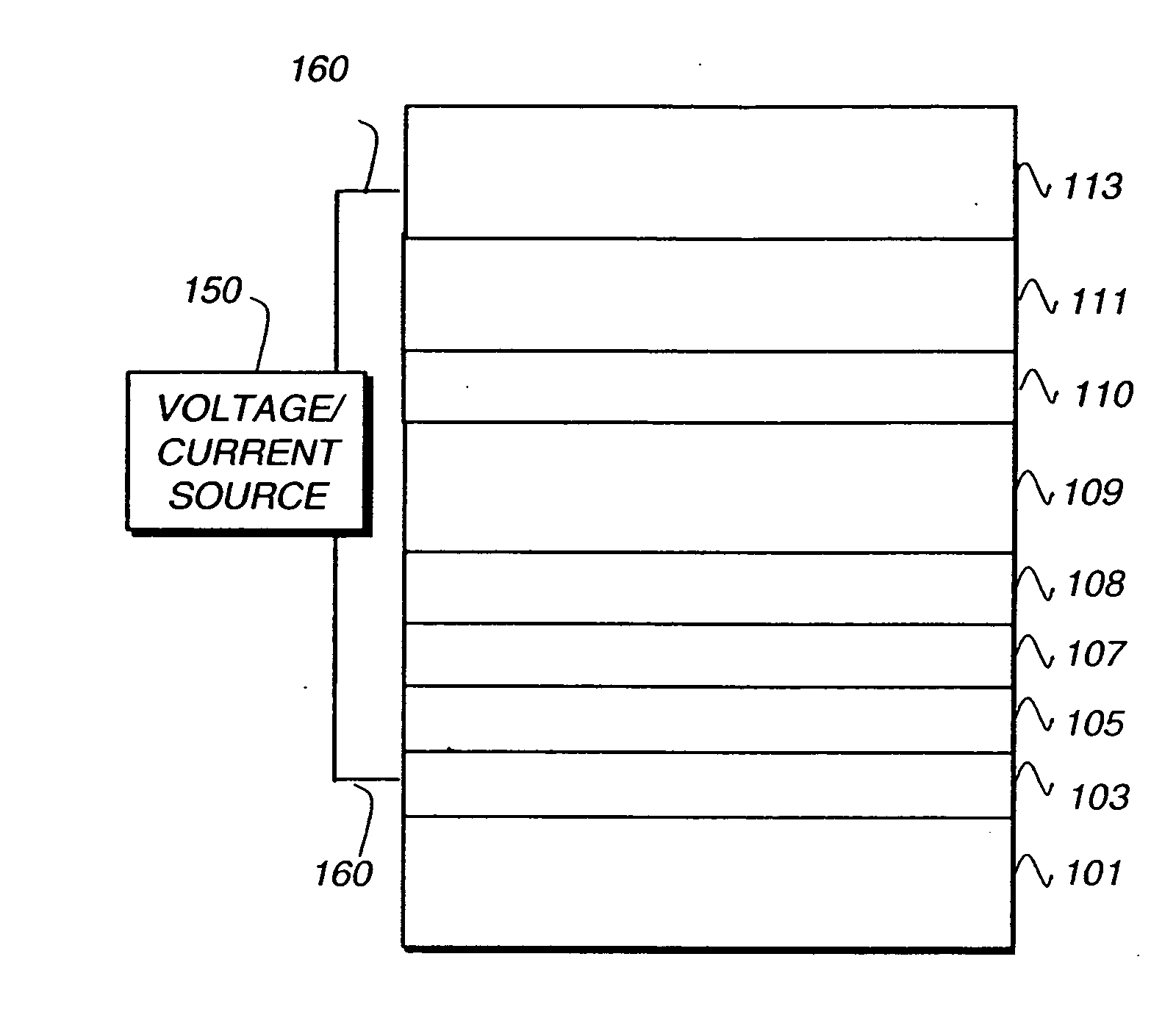
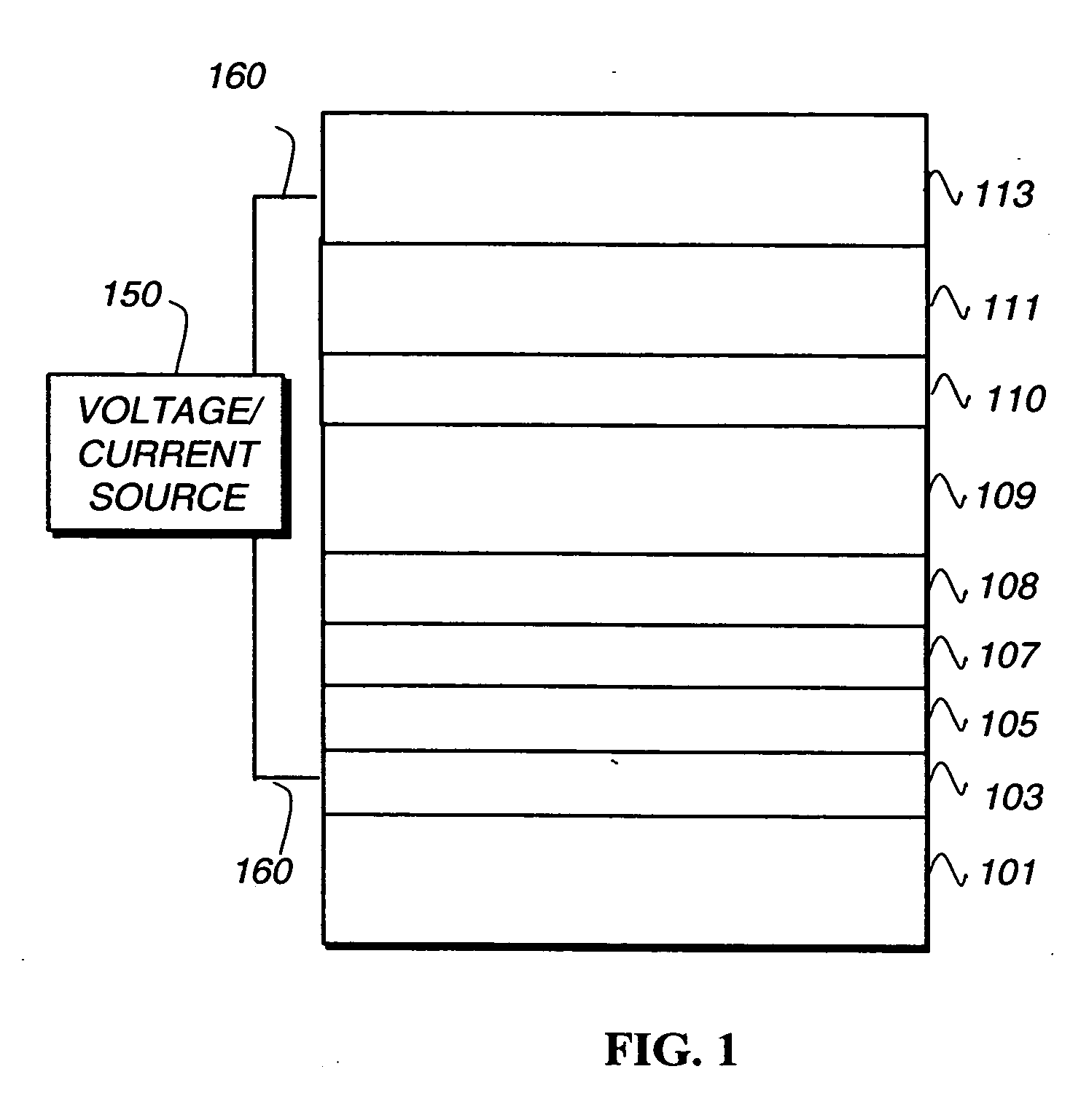
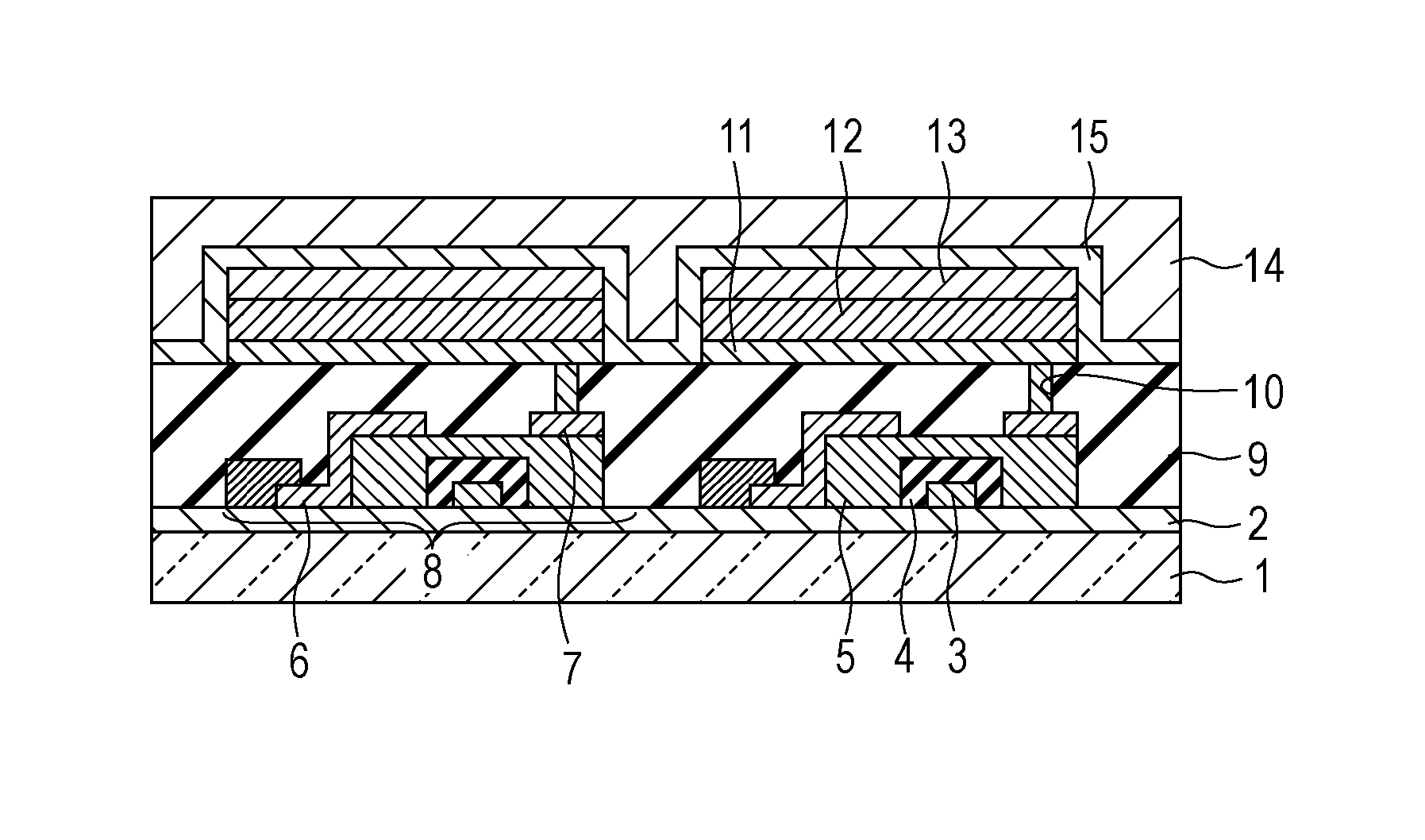
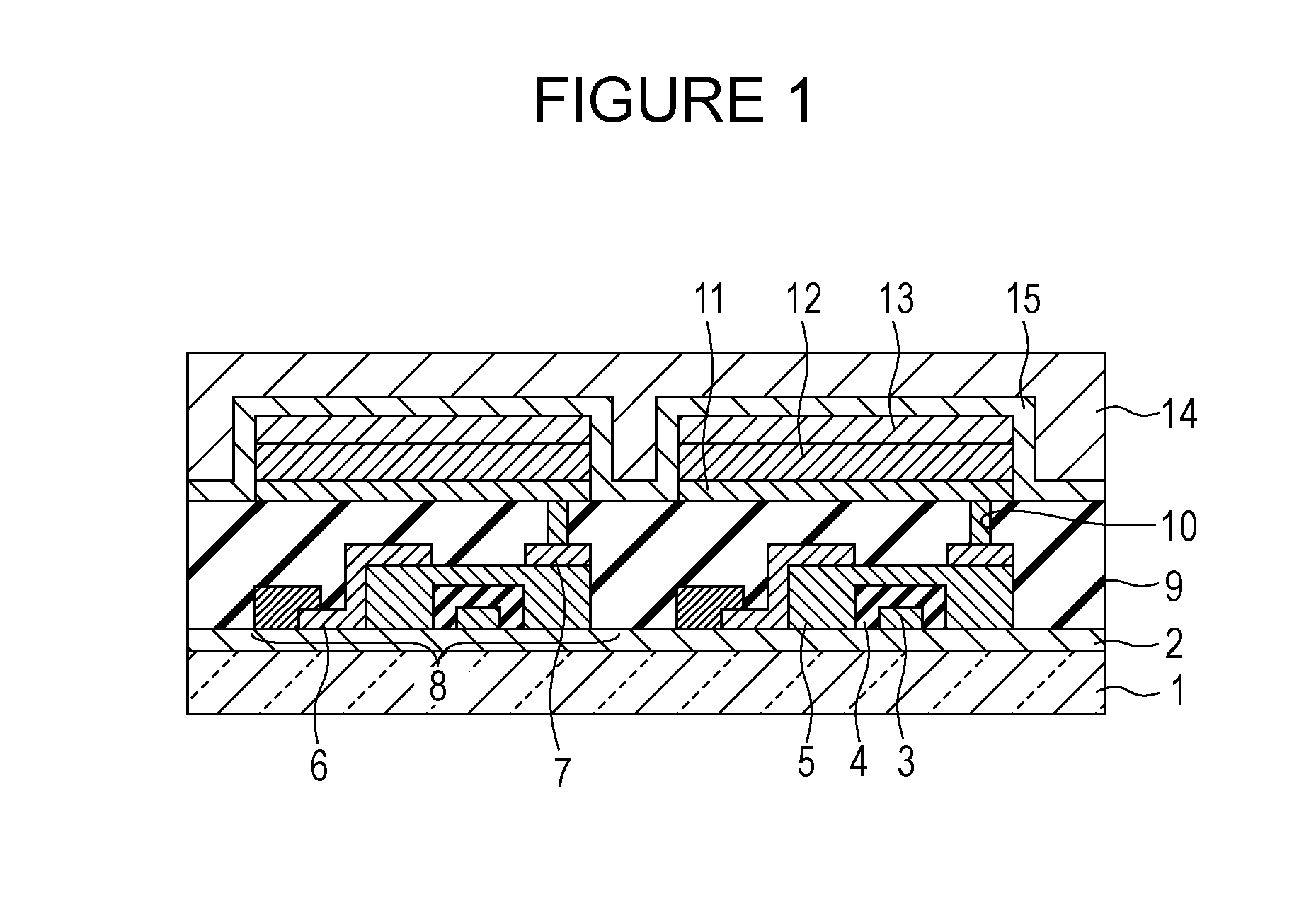
Metal coordination compound, luminescence device and display apparatus
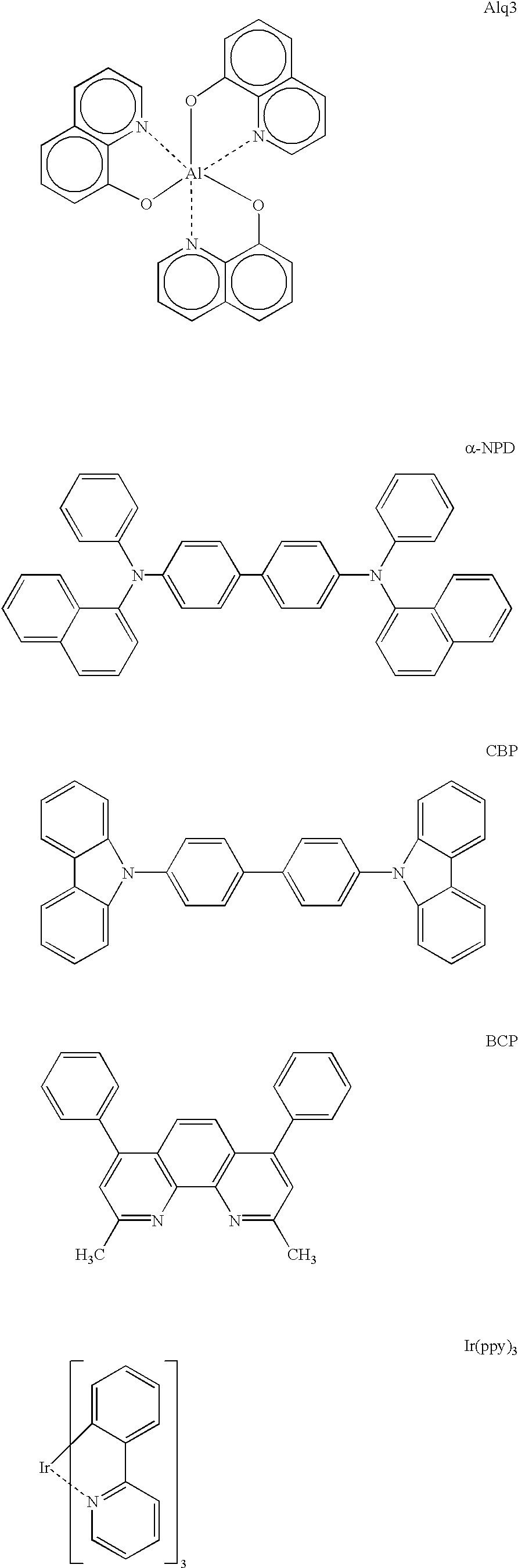
InactiveUS6921915B2High luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensLuminescenceHigh luminance
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
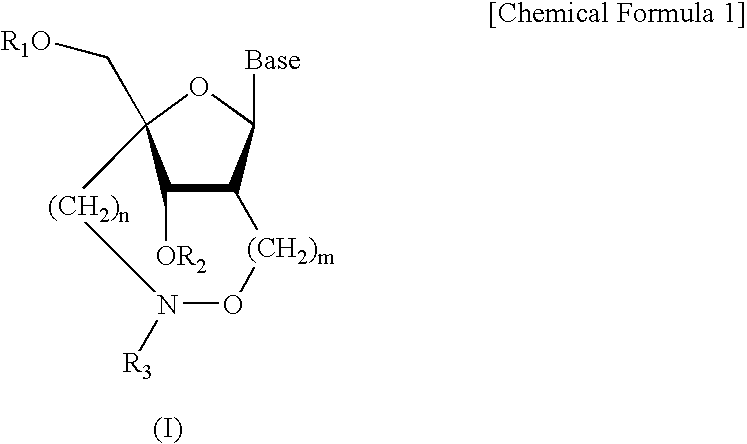
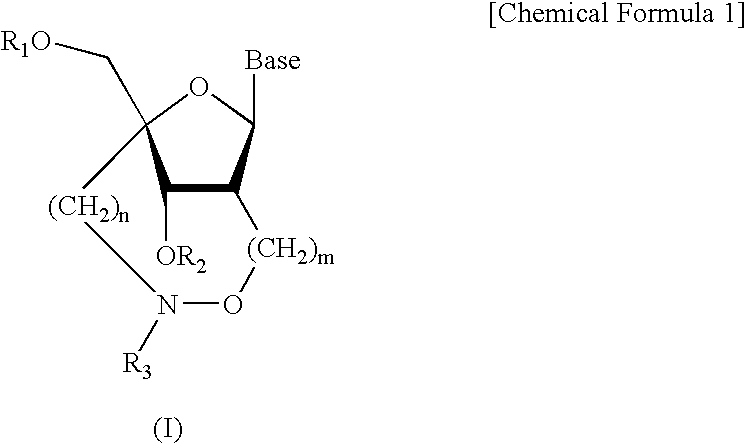
Artificial nucleic acids of n-o bond crosslinkage type
ActiveUS7427672B2High sensitivity analysisConfirmed its usefulnessBiocideSugar derivativesSingle strandDouble strand
Owner:RIKEN GENESIS
Electroluminescent (EL) devices
InactiveUS6225467B1Improve efficiencyIncreased durabilitySilicon organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesArylHalogen
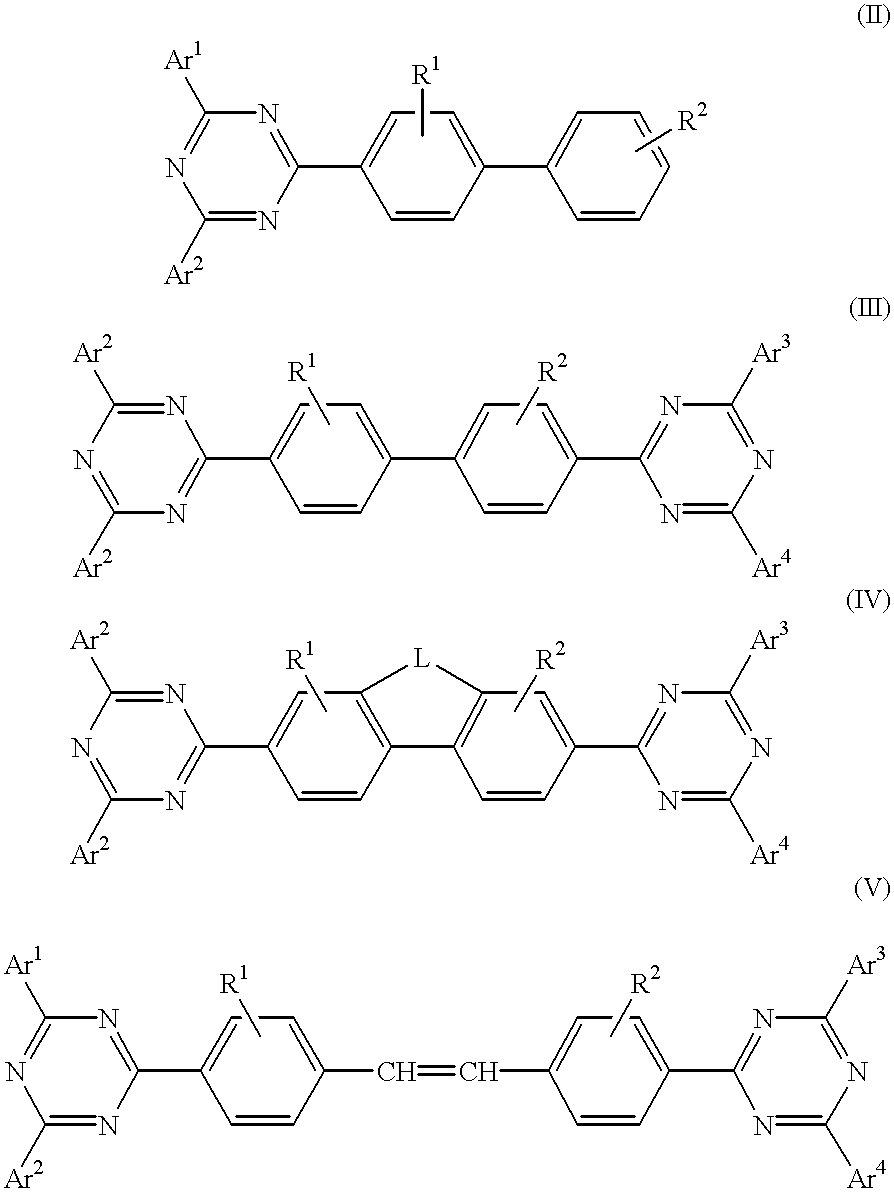
The triazinewherein Ar1, Ar2, Ar3, and Ar4 are each independently an aryl; R1 and R2 are substituents selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, an alkyl, an aryl, an alkoxy, a halogen atom, and a cyano; R3 and R4 are each a divalent group L selected from the group consisting of -C(R'R'')-, alkylene, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, and -Si(R'R'')-, wherein R' and R'' are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, and aryl.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Platinum complex and light emitting device
ActiveUS20070103060A1Enhanced glowSolve low luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOxygenLight emission
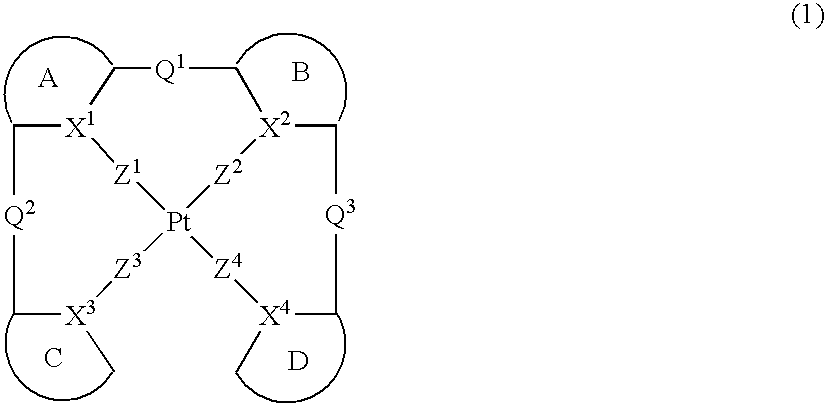
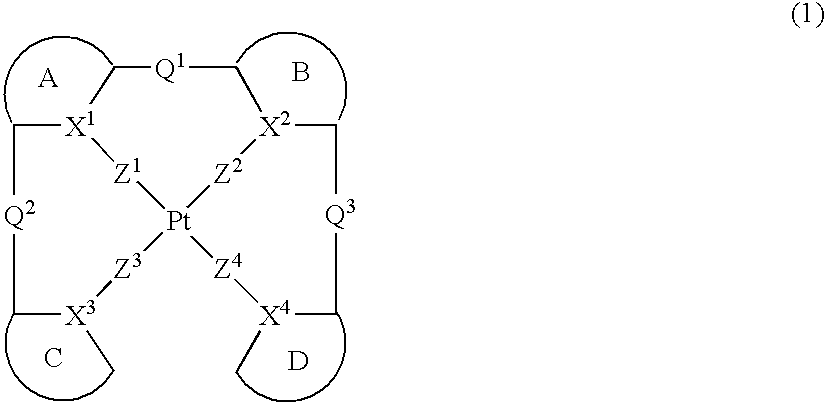
Provision of a novel platinum complex which is useful as a material for a light-emitting device of good light emission characteristic and light emission efficiency, and a novel light-emitting material that may be utilized in various fields. A platinum complex represented by the following general formula (1): (in which two rings of ring A, ring B, ring C, and ring D represent nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings which may have a substituent and the remaining two rings of them represent aryl rings or hetero aryl rings which may have a substituent, the ring A and the ring B, the ring A and the ring C or / and the ring B and the rind D may form condensed rings. Two of X1, X2, X3, and X4 represent nitrogen atoms coordination bonded to a platinum atom and the remaining two of them represent carbon atoms or nitrogen atoms. Q1, Q2, and Q3 each represents a bond, oxygen atom, sulfur atom or bivalent group, two of Z1, Z2, Z3, and Z4 represent coordination bonds, and the remaining two of them represent covalent bonds, oxygen atoms or sulfur atoms), and a light-emitting device containing the platinum complex.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Oled devices with dinuclear copper compounds
ActiveUS20070111026A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesCompound (substance)Copper
An OLED device comprises an anode, a cathode and therebetween a light emitting layer containing a compound represented by Formula I below: wherein: each A is independently selected from N and P; each E is independently selected from N, P, and As; each Z is a radical independently selected from each R is an independently selected substituent; and each R′ is independently selected from H and a substituent; provided that two substituent groups can join to form a ring.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
OLEDs with mixed-ligand cyclometallated complexes
InactiveUS20060134459A1Low sublimation temperatureGuaranteed uptimeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensPlatinumPyridine
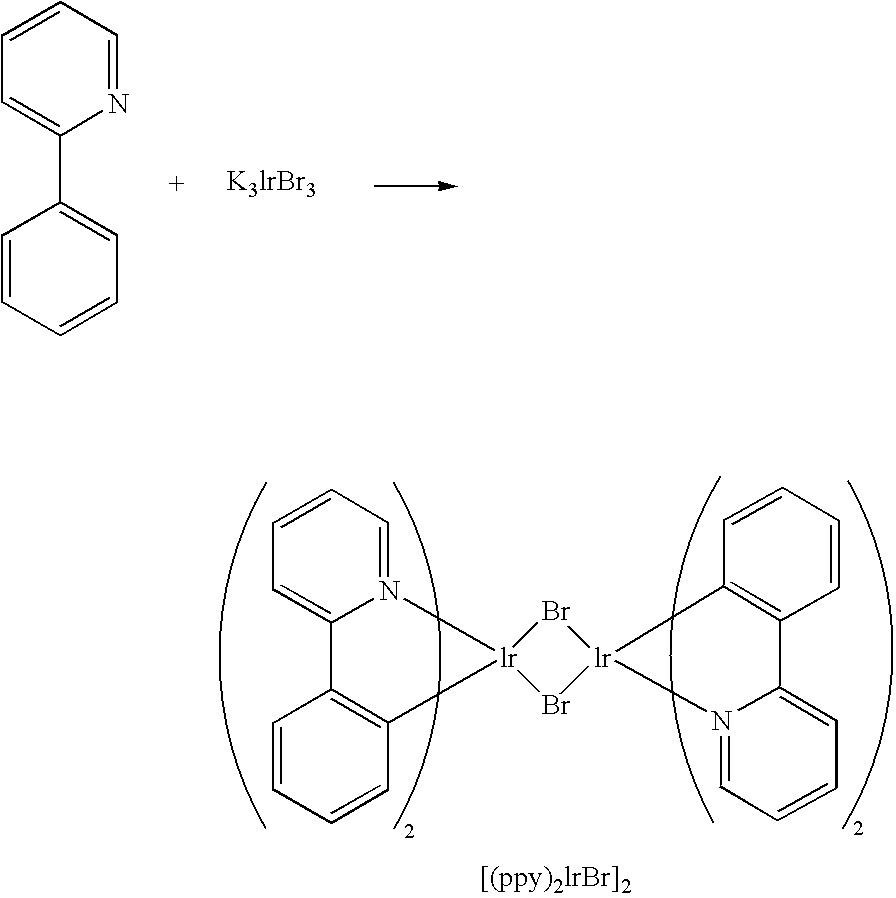
An OLED device comprising a cathode, an anode, and having located therebetween a light emitting layer containing an emitting compound having formula (I): (piq)b M ppy (I) wherein piq is a phenylisoquinoline group and ppy is a phenylpyridine group bearing at least one further substituent on the pyridine ring, wherein M is Ir, Rh, Pt, or Pd and b is 2 in the case of Ir and Rh and 1 in the case of Pt and Pd.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates with hydroyzable lipophile components and methods for making and using the same
InactiveUS6309633B1Reduce deliveryExtended durationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinCholesterol
The invention provides a drug-oligomer conjugate having the following general formula:wherein D is a therapeutic drug moiety; H and H' are each a hydrophilic moiety, independently selected from the group consisting of straight or branched PEG polymers having from 2 to 130 PEG subunits, and sugars; L is a lipophilic moiety selected from the group consisting of alkyl groups having 2-26 carbon atoms, cholesterol, adamantane and fatty acids; o is a number from 1 to the maximum number of covalent bonding sites on H; m+n+p together have a value of at least one and not exceeding the total number of covalent bonding sites on D for the -H', -L and -H-L substituents; the H-L bond(s) are hydrolyzable and the D-L' bond(s), when present, are hydrolyzable; the conjugate being further characterized by one of the following: (i) m is 0 and p is at least 1; (ii) n is 0 and p is at least 1; (iii) m and n are each 0 and p is at least 1; (iv) p is 0 and m and n are each at least 1. The therapeutic drug moiety is preferably a therapeutic protein or peptide, preferably insulin or a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20070092753A1Reduce the driving voltageIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsAnthraceneHydrogen
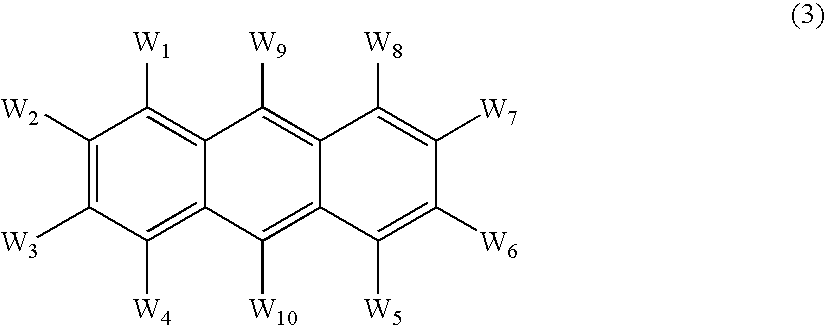
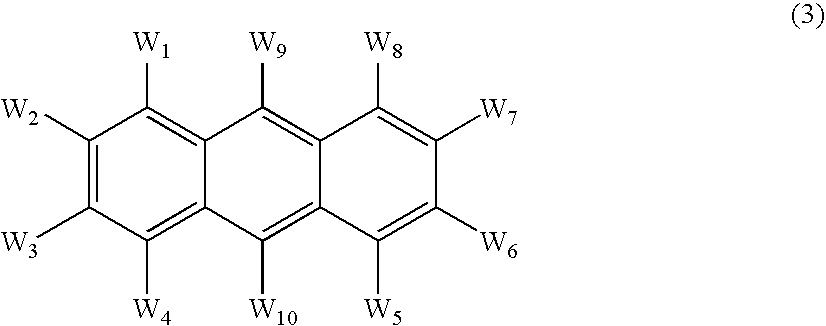
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, wherein (i) the light-emitting layer comprises up to 10 volume % of a light emitting compound and at least one anthracene host compound of Formula (3): wherein W1-W10 independently represents hydrogen or an independently selected substituent, and (ii) a further layer located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, contains (a) 10-volume % or more of an anthracene compound of Formula (3) and (b) at least one salt or complex of an element selected from Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB of the Periodic Table. Such devices exhibit reduced drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Anthracene derivative and organic electroluminescence element using the same
ActiveUS20110210320A1Enhanced electron transport capabilitiesImprove performanceOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesBenzoxazoleAnthracene
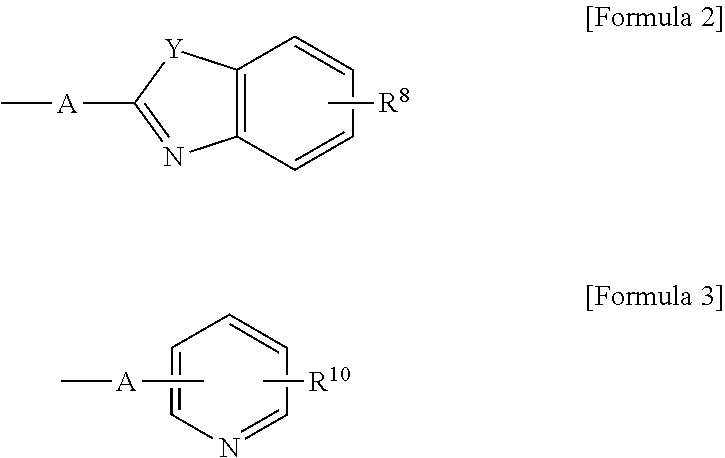
The present invention relates to an anthracene derivative and an organic electroluminescent device using the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to: a novel compound which has a core (for example, an indenoanthracene core) where both an anthracene moiety with excellent device characteristics and a fluorene moiety with excellent fluorescent properties are fused, wherein substituents (for example, a heterocyclic group such as a benzimidazole group, a benzothiazole group, a benzoxazole group, a pyridinyl group or a bipyridinyl group) with an electron transfer capacity are substituted to the core; and an organic electroluminescence element which has improved luminous efficiency, brightness, thermal stability, driving voltage, and lifetime, by comprising an organic layer which is positioned between a positive electrode and negative electrode and contains the novel compound.
Owner:SOLUS ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Novel organometallic compound, and organic light-emitting diode using same
ActiveUS20130334521A1Easy to useImprove emission efficiencyIndium organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesLight-emitting diodeOLED
The present invention relates to a novel organometallic compound, and more particularly, to a luminescent organometallic compound in which intermolecular interaction is inhibited by means of introducing a germanium substituent, thereby improving light-emitting characteristics. The present invention also relates to an organic electronic device, specifically, to an organic light-emitting diode using the compound. According to the present invention, a germanium substituent is introduced to the parent organometallic iridium compound, thus inhibiting an intermolecular interaction in the solid state and enabling the compound of the present invention to be effectively used in solution processing. When the compound of the present invention is used as part of a light-emitting layer of an organic light-emitting diode, the light-emitting efficiency of the light-emitting diode may be significantly improved. Therefore, the compound of the present invention may be effectively used as a material for an organic light-emitting diode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
New condensed polycyclic compound and organic light-emitting element using the same
InactiveUS20130175519A1Improve light emission efficiencyReduce the driving voltageOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPolycyclic compoundAryl
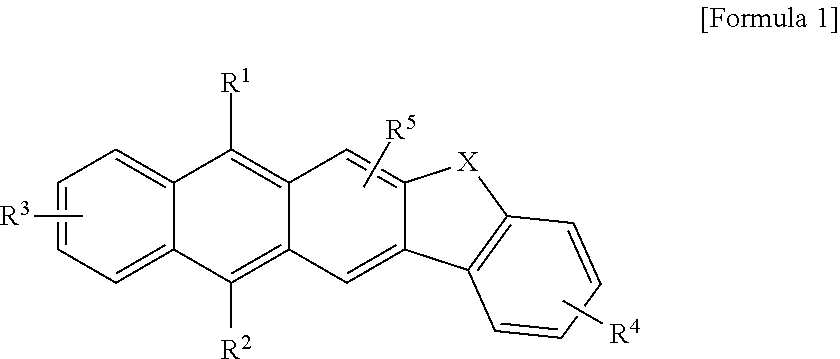
The present invention provides a stable new condensed polycyclic compound which is not likely to form a molecular association. In addition, the present invention also provides an organic light-emitting element having a high light-emitting efficiency and a low drive voltage. In the condensed polycyclic compound in Claim 1 represented by the general formula [1], R1, R2 and R5 are each independently selected from a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an aryl group, and a heterocyclic group. R3 and R4 each represent an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. The aryl group and the heterocyclic group each may have at least one of an alkyl group, an aralkyl group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, an amino group, and an alkoxy group as a substituent.
Owner:CANON KK
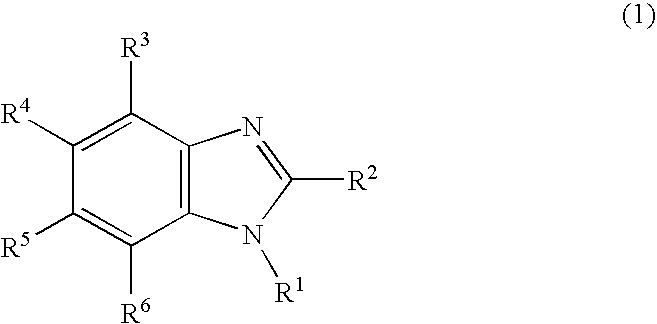
Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic derivative having electron-attracting substituent and organic electroluminescence element using the same
InactiveUS20090140637A1Improve efficiencyMaintain good propertiesOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensNitrogenous heterocyclic compoundNitrogen
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Synthesis of purine locked nucleic acid analogues
InactiveUS6998484B2Easy to convertEasy to liftSilicon organic compoundsSugar derivativesPurineLocked nucleic acid
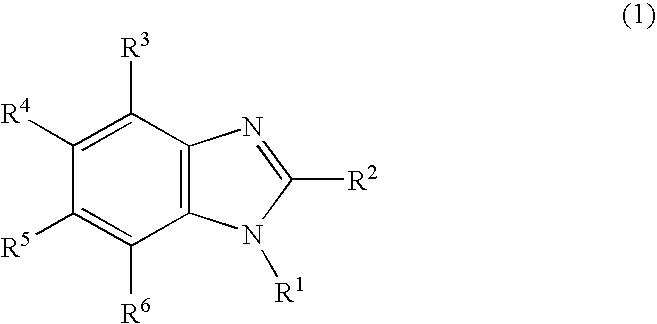
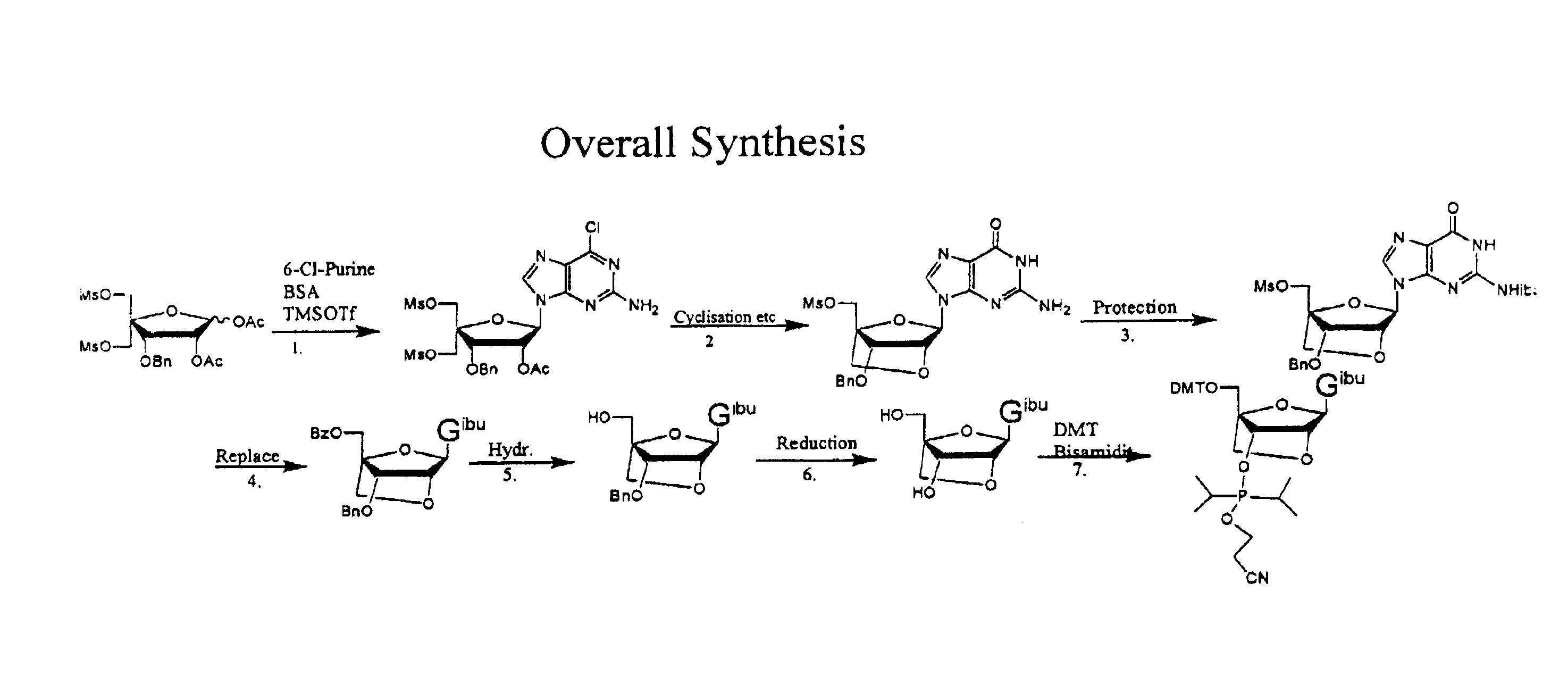
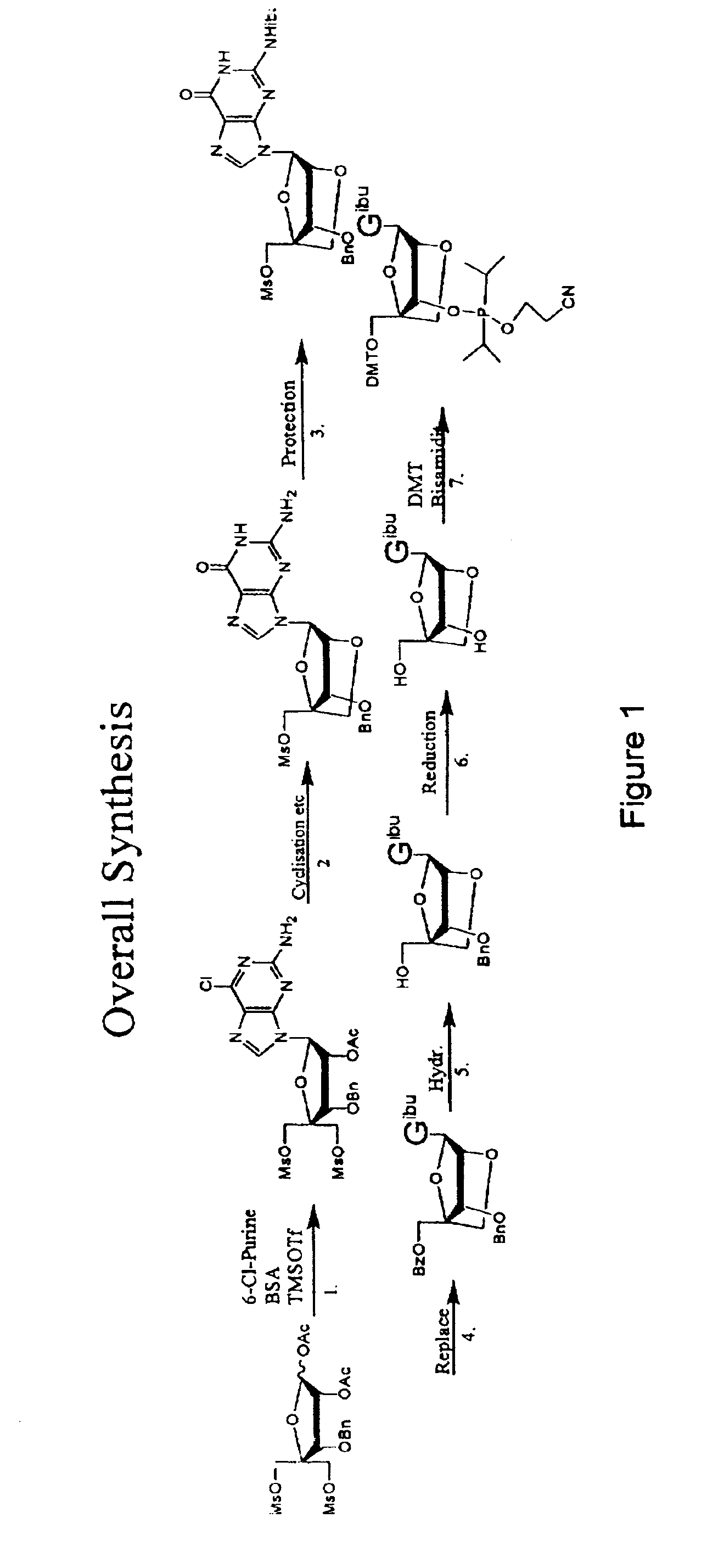
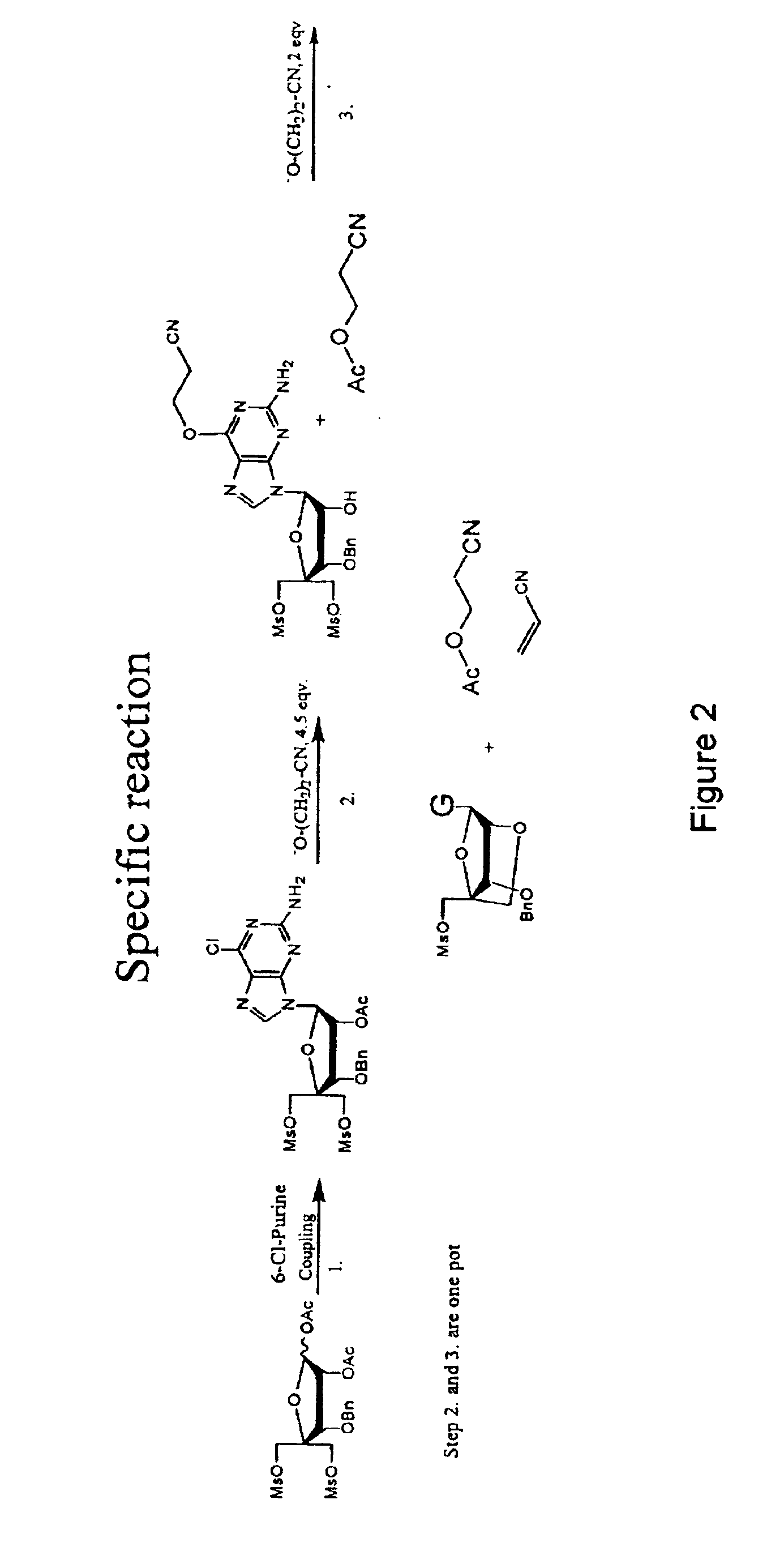
The present invention relates to a new method for the synthesis of purine LNA (Locked Nucleic Acid) analogues which provides a higher overall yield. The method comprising a regioselective 9-N purine glycosylation reaction followed by a one-pot nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction of the 6-substituent in the purine ring and simultaneous nucleophile-induced intramolecular ring closure of the C-branched carbohydrate to form novel purine LNA analogues. The novel strategy is illustrated by the synthesis of the novel compound (1S,3R,4R,7S)-7-benzyloxy-1-methanesulfonylmethyl-3-(guanin-9-yl)-2,5-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane which is easily converted into (1S,3R,4R,7S)-7-hydroxy-1-hydroxymethyl-3-((2-N-isobutyrylguanin-9-yl)-2,5-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane after isobutyryl protection of the 2-amino purine group and subsequent substitution of 1-methanesulfonyl with benzoate, debenzoylation and debenzylation.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Charge-transporting material and organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20120126221A1Improve light emission efficiencyIncreased durabilitySilicon organic compoundsSolid-state devicesHalogenOrganic layer
A charge-transporting material contains a compound represented by the following formula (1) in an organic layer, in which the contents of specific halogen-containing compounds are 0.1% or less to the compound represented by formula (1). In formula (1), each of A1 and A2 independently represents N, —CH or —CR; R represents a substituent; L represents a single bond, an arylene group, a cycloalkylene group or an aromatic heterocyclic group; each of R1 to R5 independently represents a substituent; each of n1, n2 and n3 independently represents an integer of 0 to 4; each of n4 and n5 independently represents an integer of 0 to 5; and each of p and q independently represents an integer of 1 to 4.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Light emitting element
InactiveUS20130105787A1Improve light emission efficiencySufficient durability lifeOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSilyleneAlkaline earth metal
Provided is an organic thin film light emitting element which has achieved all of improved luminous efficiency, improved driving voltage and improved durability life. Specifically provided is a light emitting element which comprises a hole transport layer and an electron transport layer between a positive electrode and a negative electrode and emits light by means of electrical energy. The light emitting element is characterized in that: the hole transport layer of the light emitting element contains a compound represented by general formula (1); the electron transport layer contains a donor compound; and the donor compound is an alkali metal, an inorganic salt containing an alkali metal, a complex of an alkali metal and an organic substance, an alkaline earth metal, an inorganic salt containing an alkaline earth metal, or a complex of an alkaline earth metal and an organic substance. (In the formula, R1-R20 each represents one group selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, deuterium, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an amino group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, a heteroaryl group, an alkenyl group, a cycloalkenyl group, an alkynyl group, analkoxy group, an alkylthio group, an arylether group, an arylthioether group, a halogen, a cyano group, a —P(═O)R24R25 group and a silyl group; R24 and R25 each represents an aryl group or a heteroaryl group; and these substituents may be further substituted, or adjacent two substituents may combine together to form a ring. Meanwhile, R21-R23 may be the same or different and each represents one group selected from the group consisting of an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an aryl group and a heteroaryl group; and these substituents maybe further substituted.)
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20070092755A1Reduce the driving voltageIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsHydrogenLow voltage
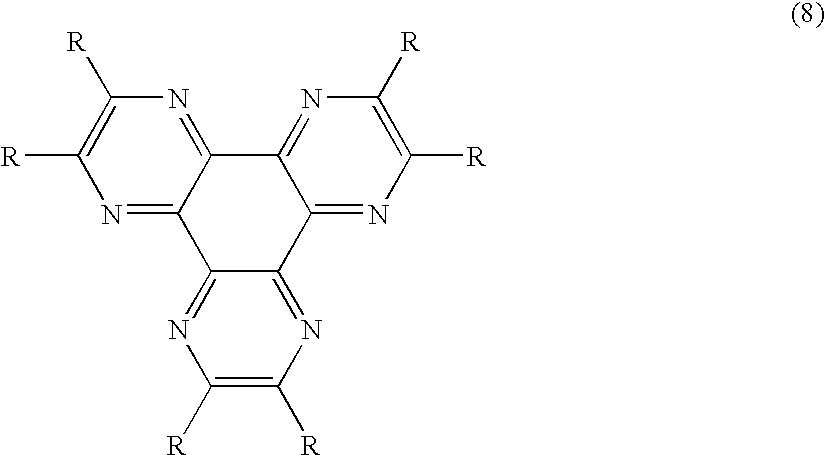
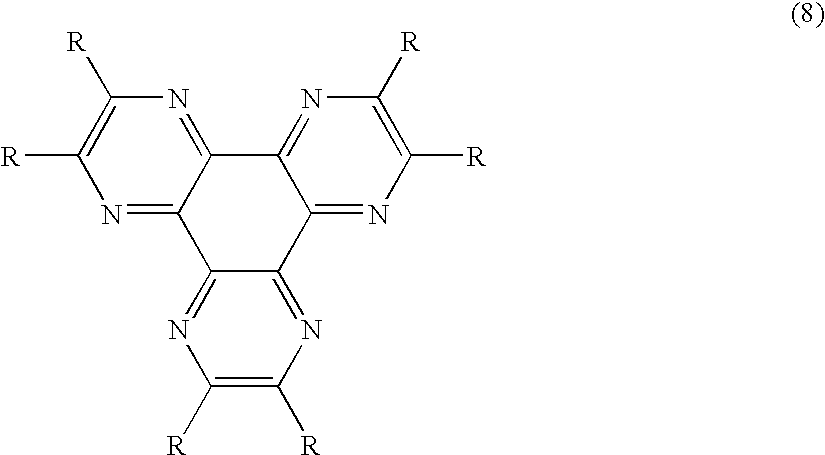
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, and comprises; (i) a further layer located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, containing (a) 10 vol % or more of a carbocyclic fused ring aromatic compound, and (b) at least one salt or complex of a Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB element of the Periodic Table, and (ii) an additional layer, located between the anode and the light emitting layer, containing a compound of Formula (8) wherein: each R independently represents hydrogen or an independently selected substituent, at least one R representing an electron-withdrawing substituent having a Hammett's sigma para value of at least 0.3. Such devices exhibit reduce drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) where A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, R1 is a divalent organic group, R2 is a monovalent organic group, and each R4, which may be the same or different, is a monovalent organic group or a substituent defined by —OR5 where R5 is a monovalent organic group, with the proviso that A, R1, R2, R4, and R5 are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer. Also, the functionalized polymer and a vulcanizable composition containing the polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, where said pseudo-living polymer is characterized by having greater than about 85 percent of the polymer in the cis microstructure and less than about 3 percent of the polymer is in the 1,2- or 3,4-microstructure, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) or (II) where Z is a substituent that will react or interact with organic or inorganic fillers; R1 is a single bond or a divalent organic group; R2 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R13 or R14; R3 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R4 or R5; R13 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R14; R4 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R5; R14 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R13; and R5 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R4; with the proviso that each group attached to the imino carbon is attached via a carbon atom and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R13, R14 and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
High-melting polyolefin copolymer elastomers, catalysts and methods of synthesis
InactiveUS6169151B1Property is limitedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElastomerPolymer science
This invention relates to high melting polyolefin copolymers suitable as thermoplastic elastomers and catalysts and methods for their synthesis. These elastomeric olefin copolymers are characterized by a mole fraction of crystallizable component Xc from about 30 to about 99%; low glass transition temperatures, below -20° C., and typically below -50° C.; melting points above about 90° C.; high molecular weights; a molecular weight distribution MW / Mn< / =10; and a narrow composition distribution between chains of < / =15%. The novel copolymers of the invention range from reactor blends to multiblock copolymers that can be sequentially fractionated into fractions of differing crystallinities, which fractions nevertheless show compositions of comonomers which differ by less than 15% from the parent polymer (reactor product). The invention also relates to a process for producing such copolymers by utilizing an unbridged, substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl metallocene catalyst that is capable of interconverting between states with different copolymerization characteristics, which interconversion is controlled by selecting the substituents of the cyclopentadienyl ligands so that the rate of interconversion of the two states is within several orders of magnitude of the rate of formation of a single polymer chain. Where ri>rf the polymer can be characterized as multiblock; where ri<rf, the result is a polymer blend and where ri / rf is close to 1, the resulting polymer is a mixture of blend and multiblock. The metallocene catalysts of the invention are able to interconvert between more than two states, with embodiments of four states being shown in FIG. 2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Nanoporous silicone resins having low dielectric constants
InactiveUS6541107B1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsDead plant preservationOrganic solventCarbon–carbon bond
Nanoporous silicone resins and silicone resin films having low dielectric constants and a method for preparing such nanoporous silicone resins. The silicone resin comprises the reaction product of a mixture comprising(A) 15-70 mol % of a tetraalkoxysilane described by formula where each R1 is an independently selected alkyl group comprising 1 to about 6 carbon atoms,(B) 12 to 60 mol % of a hydrosilane described by formula where each X is an independently selected hydrolyzable substituent,(C) 15 to 70 mole percent of an organotrialkoxysilane described by formula where R2 is a hydrocarbon group comprising about 8 to 24 carbon atoms or a substituted hydrocarbon group comprising a hydrocarbon chain having about 8 to 24 carbon atoms and each R3 is an independently selected alkyl group comprising 1 to about 6 carbon atoms; in the presence of(D) water,(E) hydrolysis catalyst, and(F) organic solvent for the reaction product.The silicone resin is cured and heated in an inert atmosphere at a temperature sufficient to effect thermolysis of carbon-carbon bonds of the R2 groups thereby forming a nanoporous silicone resin.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Method for producing aromatic amino compound
InactiveUS7250532B2High yieldEasy to eliminateOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationArylCompound a
A method for producing aromatic amino compound (V):by synthesizing intermediate compound (IV):by the reaction of compound (I): H2N—R1 with a mixture of halogenated aryl compounds (II): Ar1—X and (III): Ar2—X in the presence of a noble metal catalyst, followed by eliminating the substituent R1 from the nitrogen atom in compound (IV) under an acidic condition or an alkaline condition or by addition of a reducing agent or an oxidizing agent. (R1: a substituent having 2 to 50 carbon atoms; Ar1 and Ar2: a substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon group or heterocyclic group having 6 to 50 carbon atoms and the same with or different from each other; and X: a halogen group). The aromatic amino compound useful as the charge transporting material can be produced efficiently at a great yield without using highly toxic raw materials.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) where A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, R1 is a divalent organic group, R2 is a monovalent organic group, and each R4, which may be the same or different, is a monovalent organic group or a substituent defined by —OR5 where R5 is a monovalent organic group, with the proviso that A, R1, R2, R4, and R5 are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer. Also, the functionalized polymer and a vulcanizable composition containing the polymer.
Owner:ENEOS MATERIALS CORP
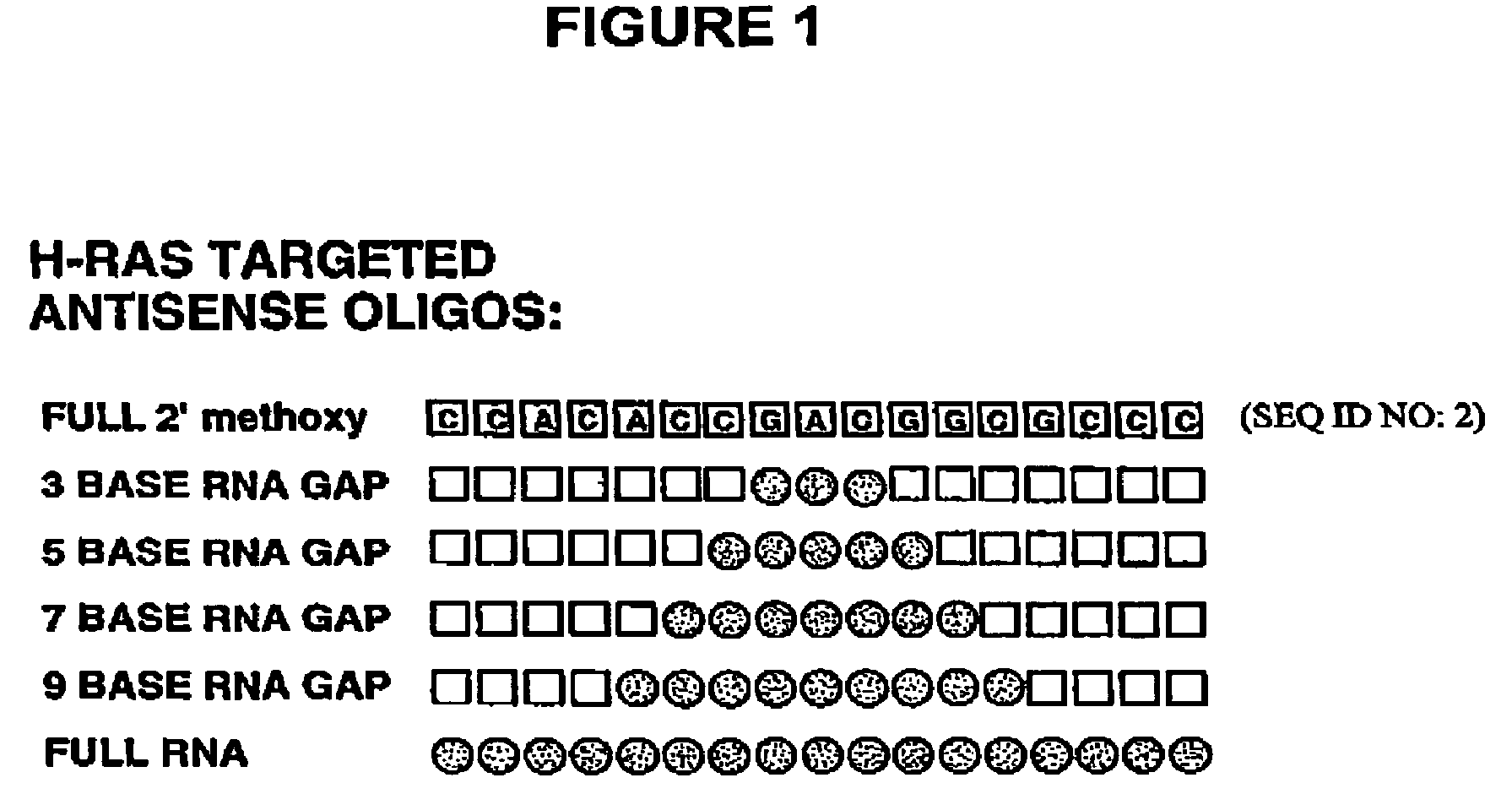
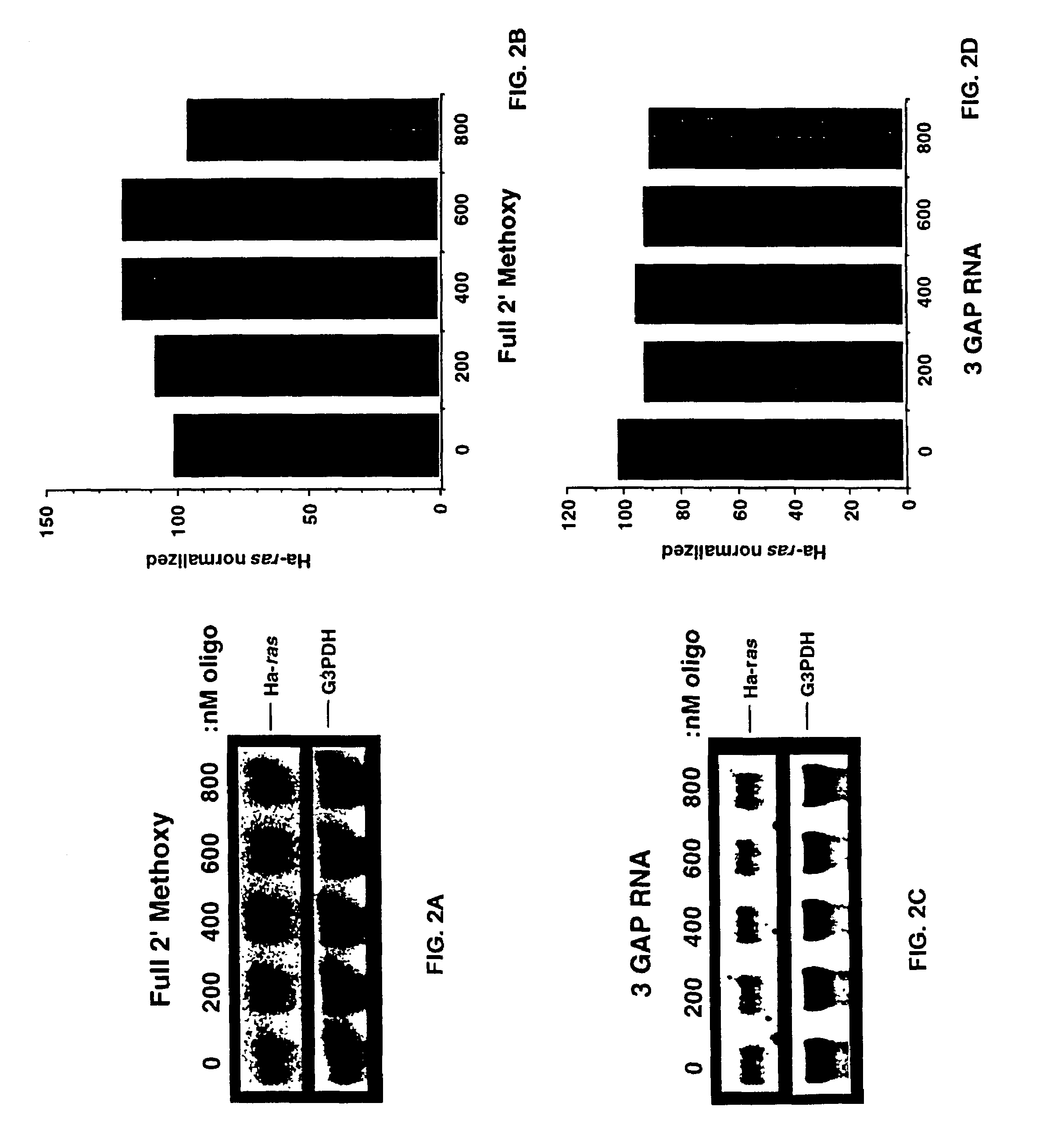
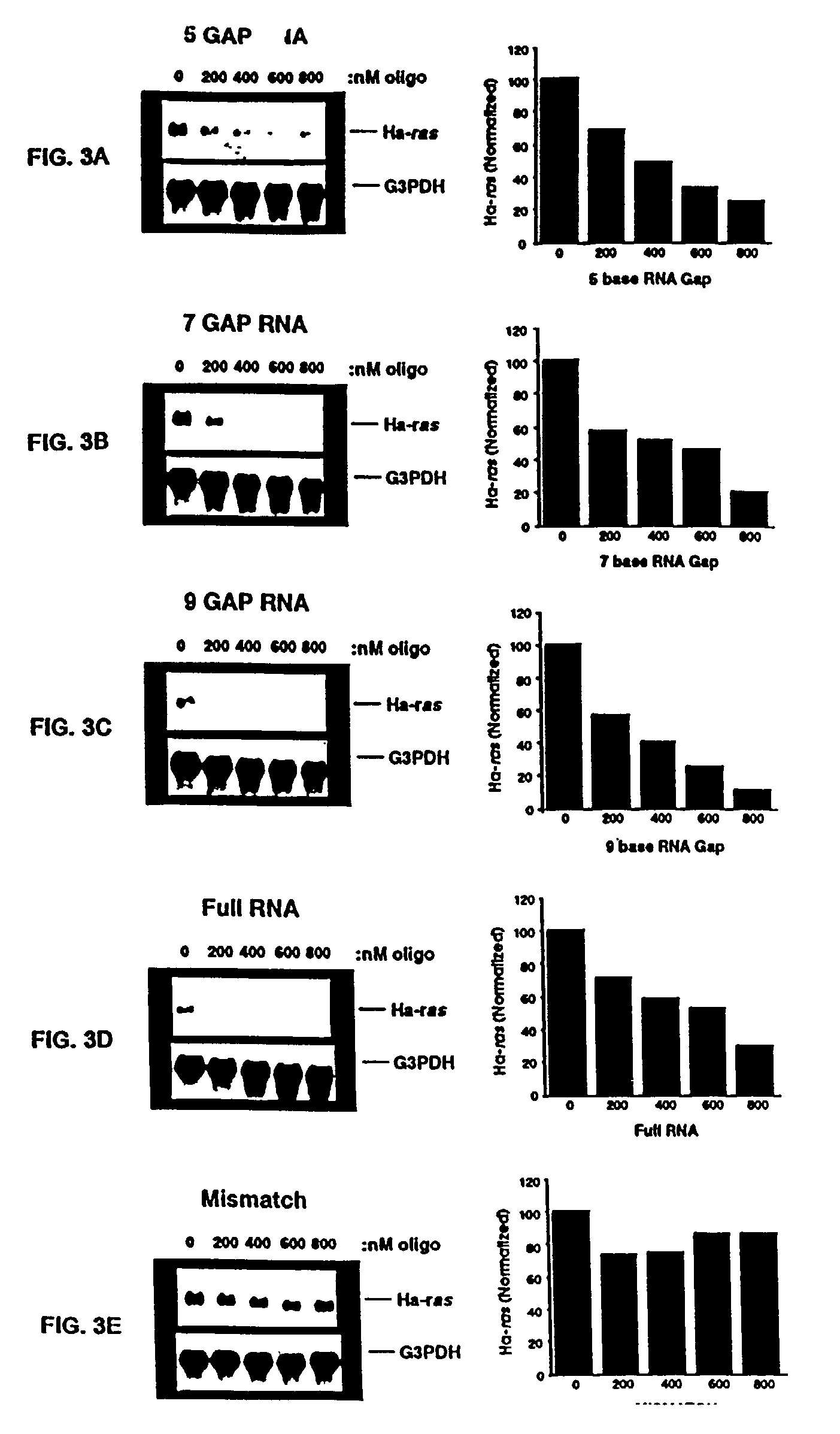
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432250B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, where said pseudo-living polymer is characterized by having greater than about 85 percent of the polymer in the cis microstructure and less than about 3 percent of the polymer is in the 1,2- or 3,4-microstructure, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) or (II) where Z is a substituent that will react or interact with organic or inorganic fillers; R1 is a single bond or a divalent organic group; R2 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R13 or R14; R3 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R4 or R5; R13 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R14; R4 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R5; R14 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R13; and R5 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R4; with the proviso that each group attached to the imino carbon is attached via a carbon atom and R1, R2 R3, R4, R5, R13, R14 and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Electrolyte composition, photoelectric conversion device and photo-electrochemical cell
InactiveUS6376765B1Improve rendering capabilitiesIncreased durabilityLight-sensitive devicesOrganic chemistryPhotoelectrochemical cellHydrogen atom
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Compound, liquid crystal composition, and anisotropic material
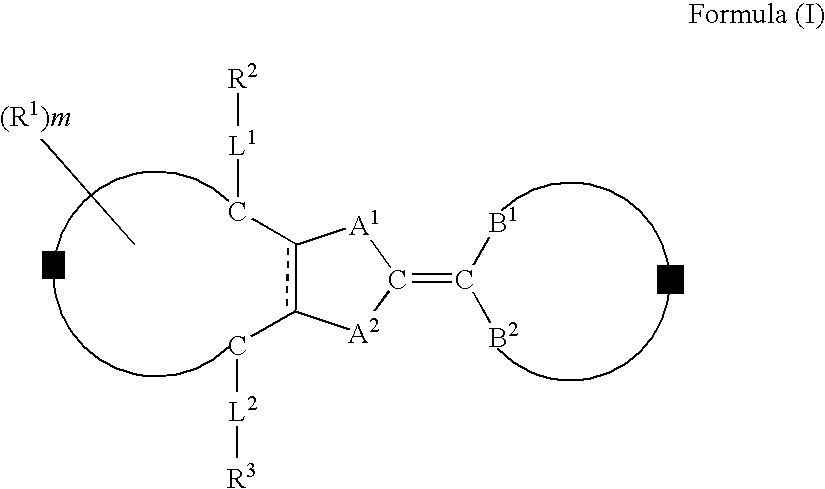
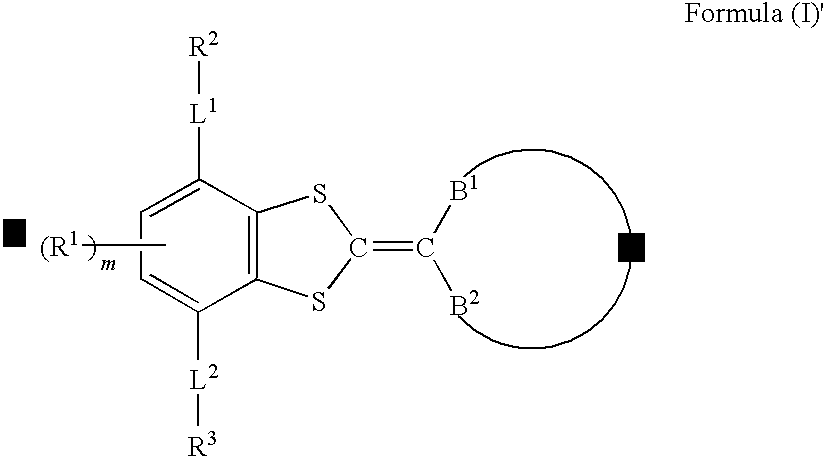
A compound represented by formula (I) below:where, each of A1 and A2 independently represents a group selected from the group consisting of —O—, —NR— (R represents a hydrogen atom or substituent), —S— and —CO—; Z forms a five- or six-membered ring together with C—C═C—C or C═C—C═C illustrated in the formula; Y forms a five- to seven-membered ring together with B1—C—B2 illustrated in the formula, provided that those having the same substituent for A1 and B1 and for A2 and B2 and those having the same substituent for A1 and B2 and for A2 and B1 are excluded, is disclosed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Luminescence device, display apparatus and metal coordination compound
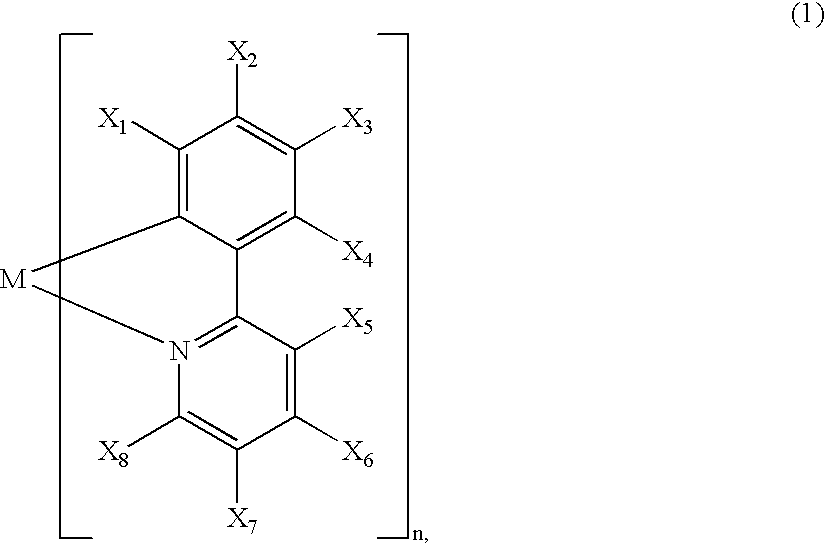
InactiveUS20020064681A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic compoundLuminescence
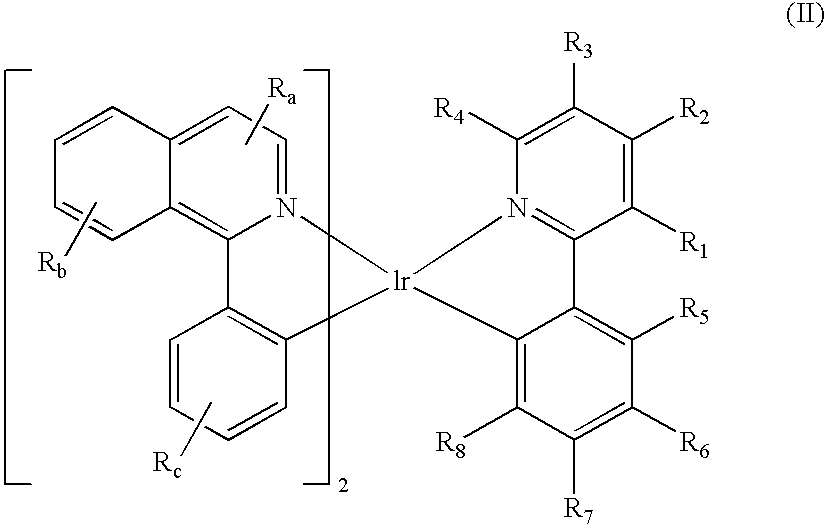
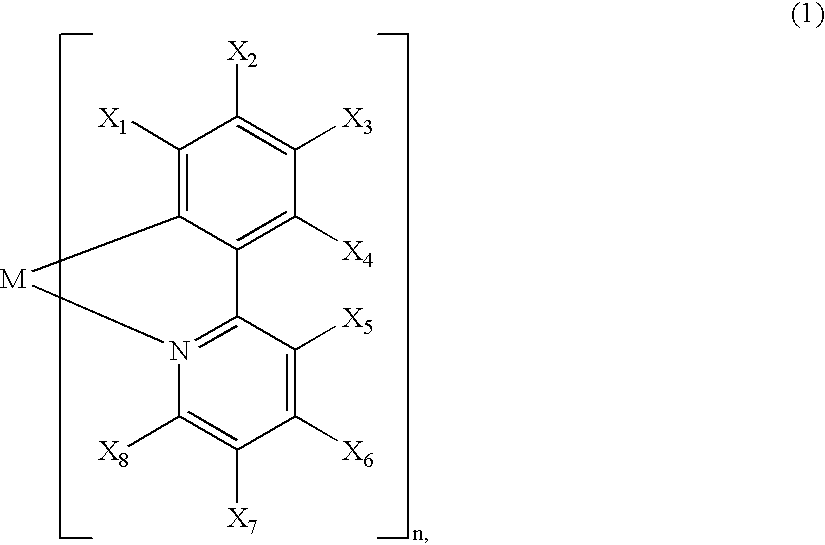
A luminescence device is principally constituted by a pair of electrodes and an organic compound layer disposed therebetween. The layer contains a metal coordination compound represented by the following formula (1): wherein M denotes Ir, Rh or Pd; n is 2 or 3; and X1 to X8 independently denote hydrogen atom or a substituent selected from the group consisting of halogen atom; nitro group; trifluoromethyl group trialkylsilyl group having three linear or branched alkyl groups each independently having 1-8 carbon atoms; and a linear or branched alkyl group having 2-20 carbon atoms capable of including one or at least two non-neighboring methylene groups which can be replaced with -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CO-O-, -O-CO-, -CH=CH- or -C=C- and capable of including hydrogen atom which can be replaced with fluorine atom; with the proviso that at least one of X1 to X8 is a substituent other than hydrogen atom, and X2 and X3 cannot be fluorine atom at the same time.
Owner:CANON KK
Substituted melanocortin receptor-specific piperazine compounds
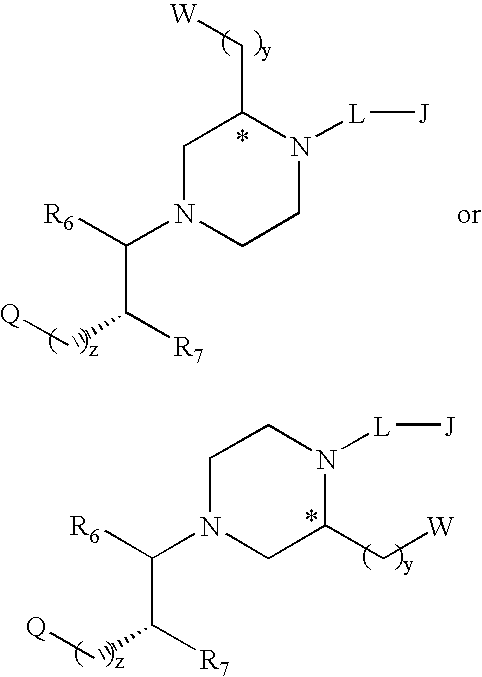
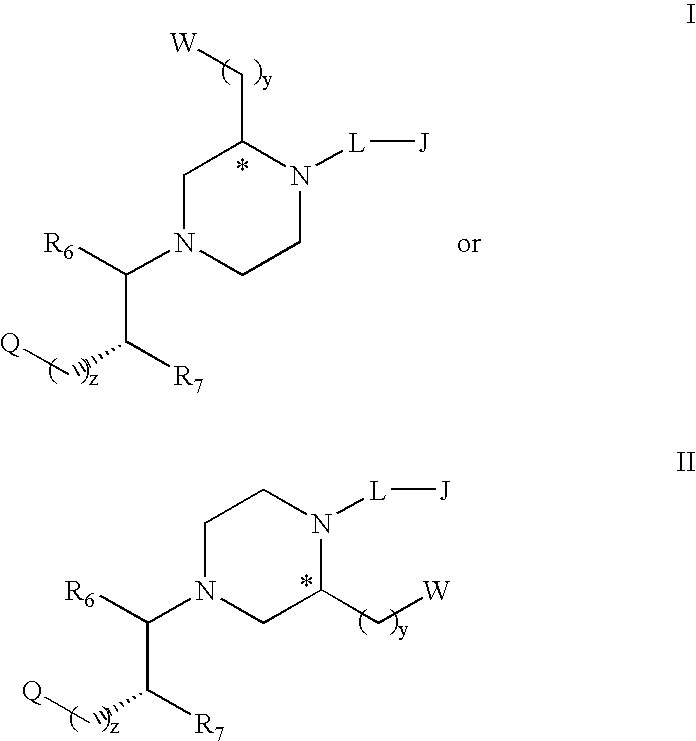
Melanocortin receptor-specific compounds of the general formulas and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, where J is a substituted or unsubstituted monocyclic or bicyclic ring structure, L is a linker, W is a heteroatom unit with at least one cationic center, hydrogen bond donor or hydrogen bond acceptor, Q includes a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic carbocyclic ring, R6, R7, y and z are as defined in the specification, and the carbon atom marked with an asterisk can have any stereochemical configuration, and optionally with one or two additional ring substituents as defined, which compounds bind to one or more melanocortin receptors and are optionally an agonist, a partial agonist, an antagonist, an inverse agonist or an antagonist of an inverse agonist, and may be employed for treatment of one or more melanocortin receptor-associated conditions or disorders, and methods for the use of the compounds of the invention.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
Material for organic electroluminescent element and organic electroluminescent element employing the same
InactiveUS20080102311A1Bright enoughImprove efficiencySilicon organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceLight emission
A material for electroluminescence devices comprising an aromatic amine derivative having a specific structure having bulky substituents at end portions and an organic electroluminescence device comprising an organic thin film layer which comprises a single layer or a plurality of layers comprising at least a light emitting layer and is disposed between an anode and a cathode, wherein at least one layer in the organic thin film layer comprises the material for organic electroluminescence devices singly or as a component of a mixture. The electroluminescence device having a long life and exhibiting a great luminance of emitted light and a great efficiency of light emission can be obtained by using the material.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
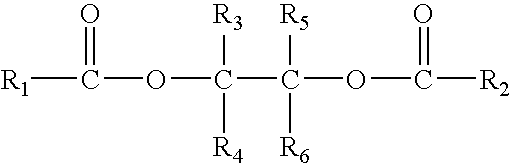
Solid catalyst component for polymerization of olefins, catalyst comprising the same and use thereof
InactiveUS7388061B2High stereospecificitySatisfactory polymerization yieldOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The present invention provides a solid catalyst component for the polymerization of olefins, comprising magnesium, titanium, a halogen and an electron donor, wherein said electron donor comprises at least one selected from the group consisting of ester of polyol of the formula (I):R1CO—O—CR3R4—A—CR5R6—O—CO—R2 (I)wherein, R1 and R2 groups, which may be identical or different, can be substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbyl having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, R3-R6 groups, which may be identical or different, can be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen or substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbyl having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, R1-R6 groups optionally contain one or more hetero-atoms replacing carbon, hydrogen atom or the both, said hetero-atom is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, silicon, phosphorus and halogen atom, two or more of R3-R6 groups can be linked to form saturated or unsaturated monocyclic or polycyclic ring A is a single bond or bivalent linking group with chain length between two free radicals being 1-10 atoms, wherein said bivalent linking group is selected from the group consisting of aliphatic, alicyclic and aromatic bivalent radicals, and can carry C1-C20 linear or branched substituents one or more of carbon atom and / or hydrogen atom on above-mentioned bivalent linking group and substituents can be replaced by a hetero-atom selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, silicon, phosphorus, and halogen atom, and two or more said substituents on the linking group as well as above-mentioned R3-R6 groups can be linked to form saturated or unsaturated monocyclic or polycyclic ring.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com