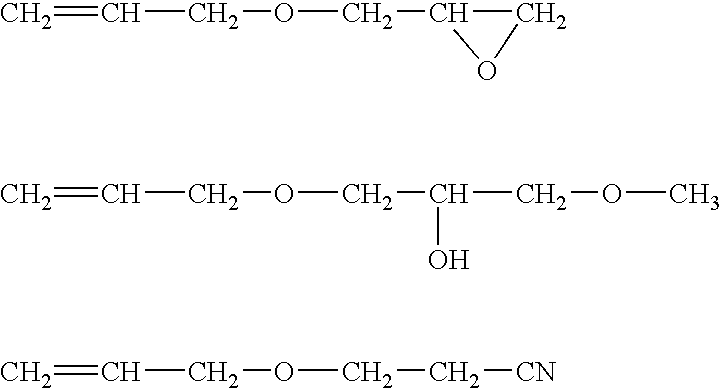
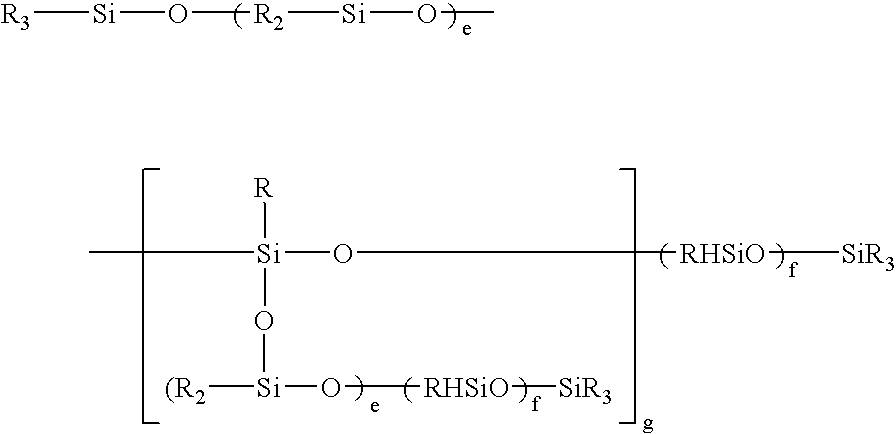
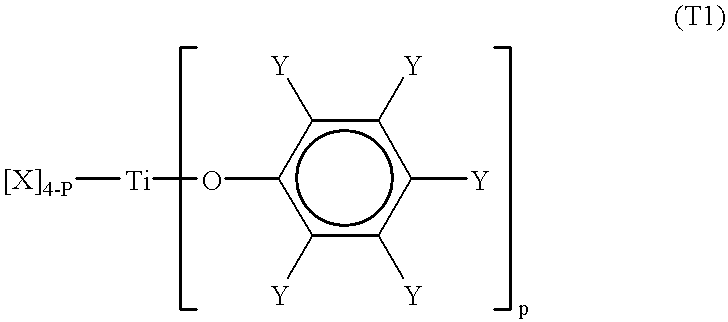
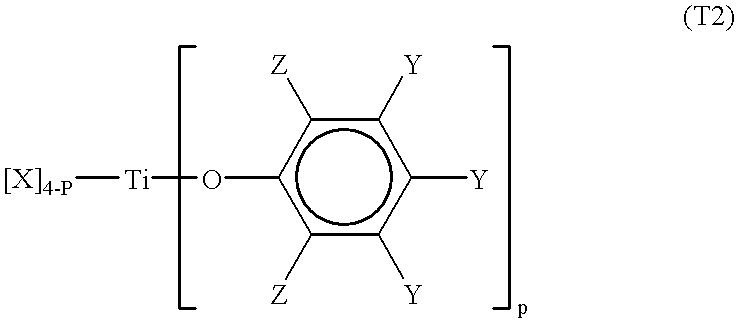
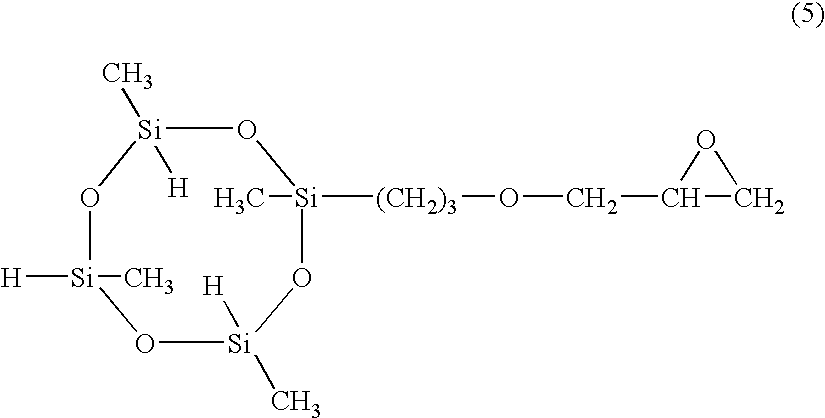
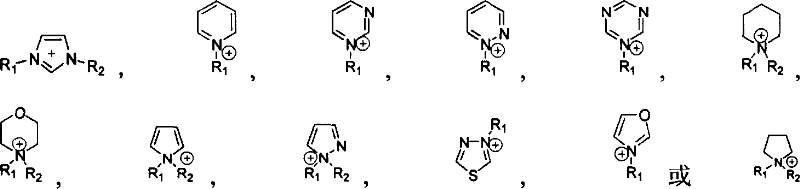
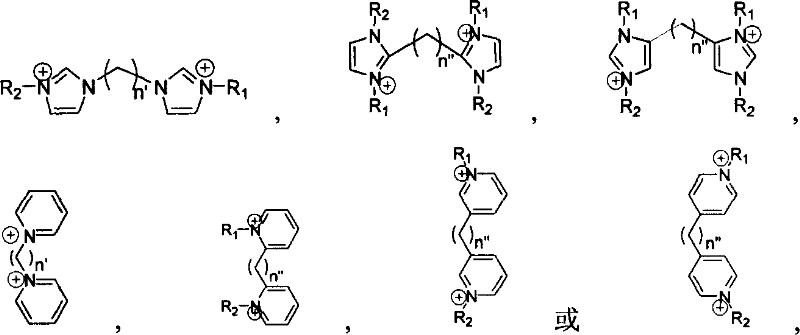
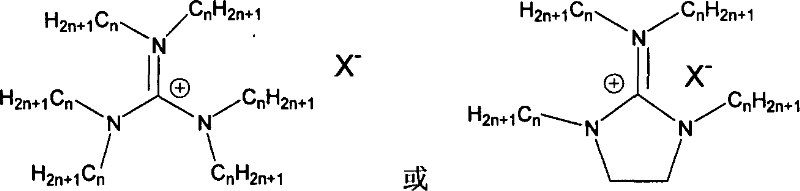
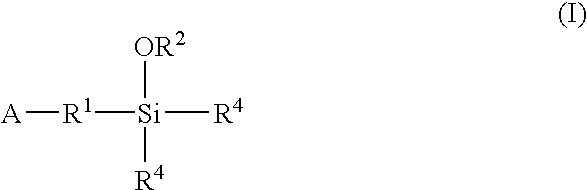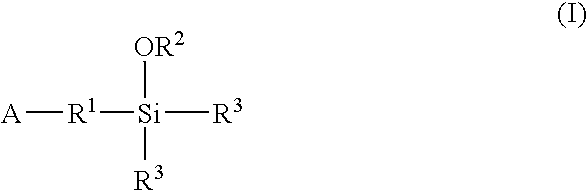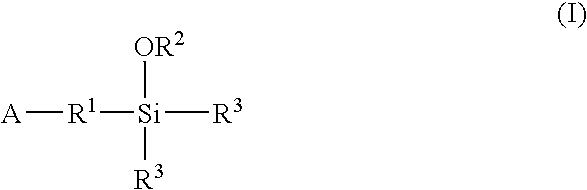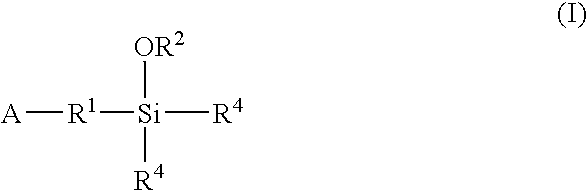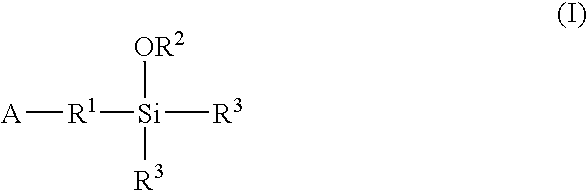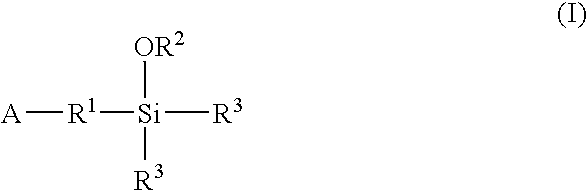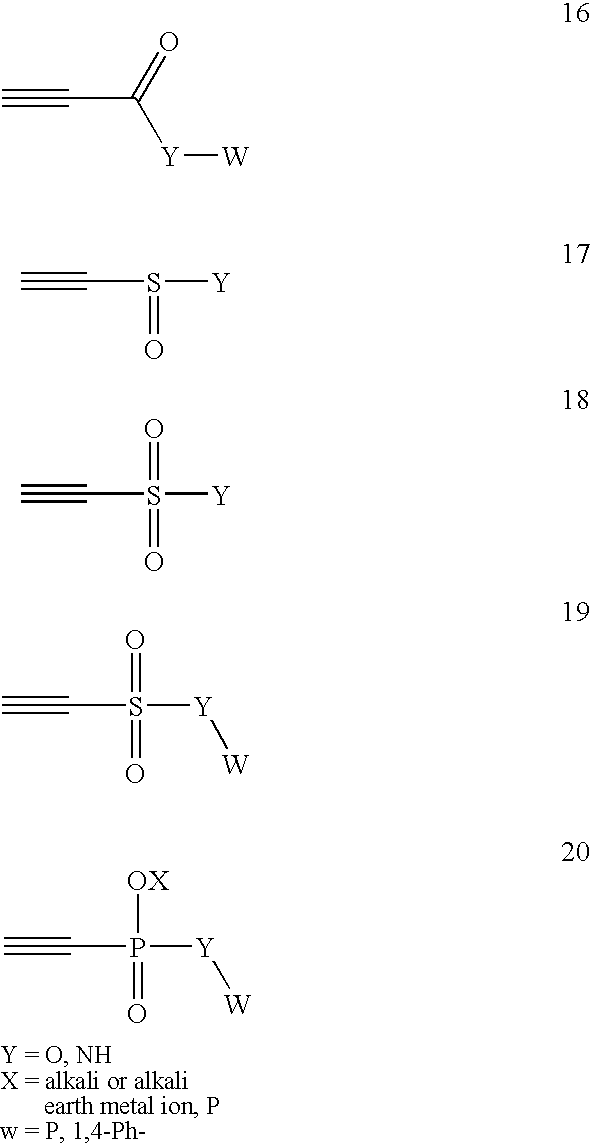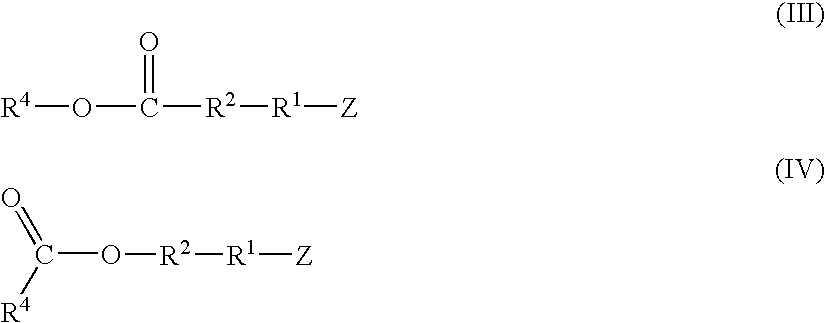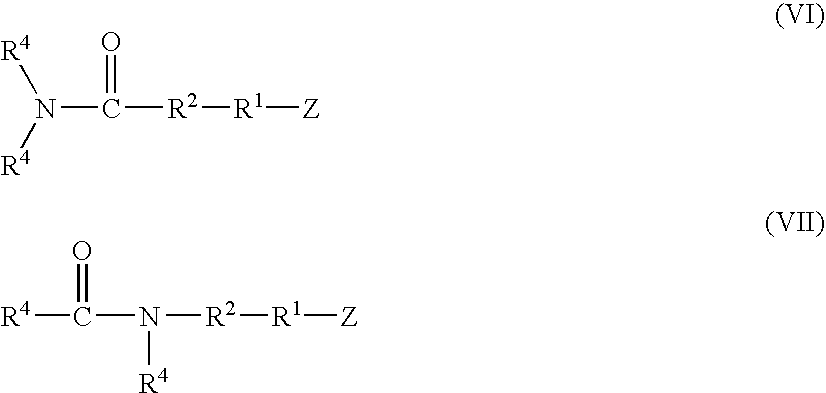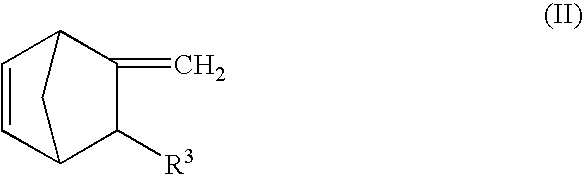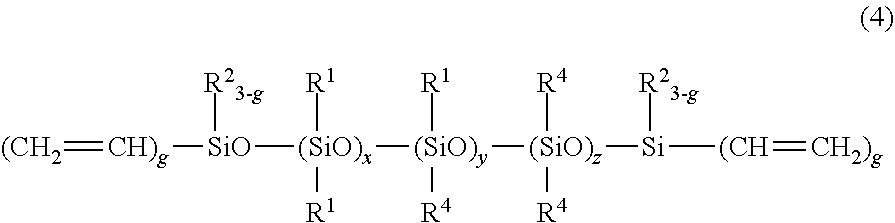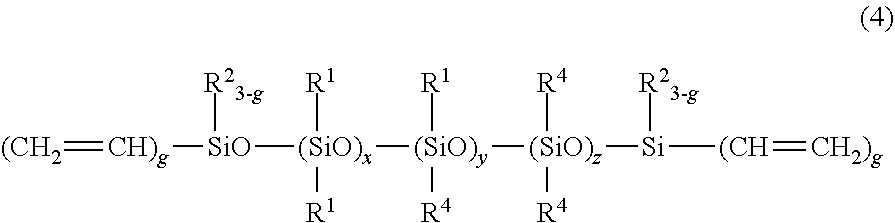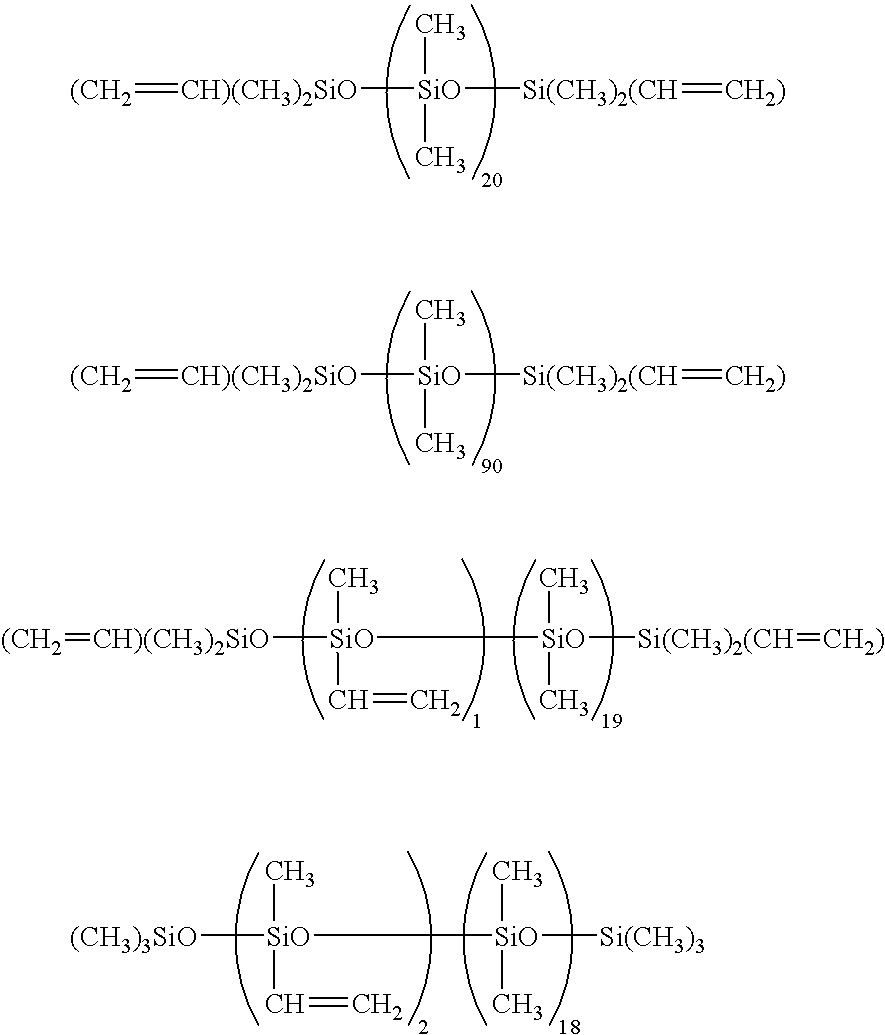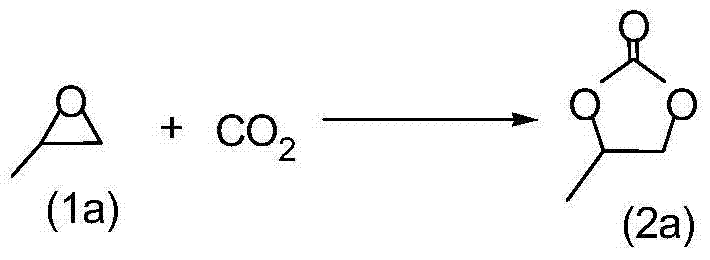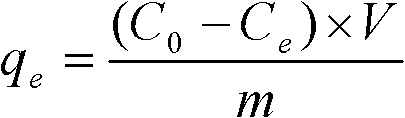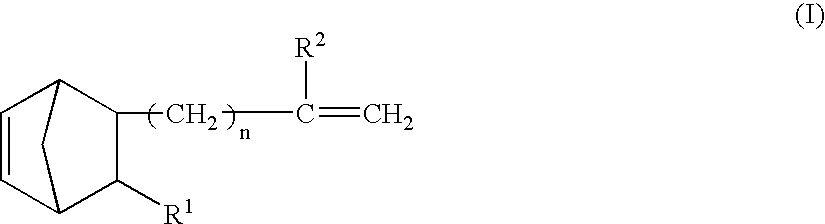Patents
Literature
5841 results about "Addition reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one (the adduct). Addition reactions are limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds, such as molecules with carbon–carbon double bonds (alkenes), or with triple bonds (alkynes). Molecules containing carbon—hetero double bonds like carbonyl (C=O) groups, or imine (C=N) groups, can undergo addition, as they too have double-bond character.
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
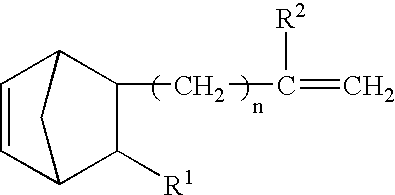
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) where A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, R1 is a divalent organic group, R2 is a monovalent organic group, and each R4, which may be the same or different, is a monovalent organic group or a substituent defined by —OR5 where R5 is a monovalent organic group, with the proviso that A, R1, R2, R4, and R5 are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer. Also, the functionalized polymer and a vulcanizable composition containing the polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) where A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, R1 is a divalent organic group, R2 is a monovalent organic group, and each R4, which may be the same or different, is a monovalent organic group or a substituent defined by —OR5 where R5 is a monovalent organic group, with the proviso that A, R1, R2, R4, and R5 are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer. Also, the functionalized polymer and a vulcanizable composition containing the polymer.
Owner:ENEOS MATERIALS CORP
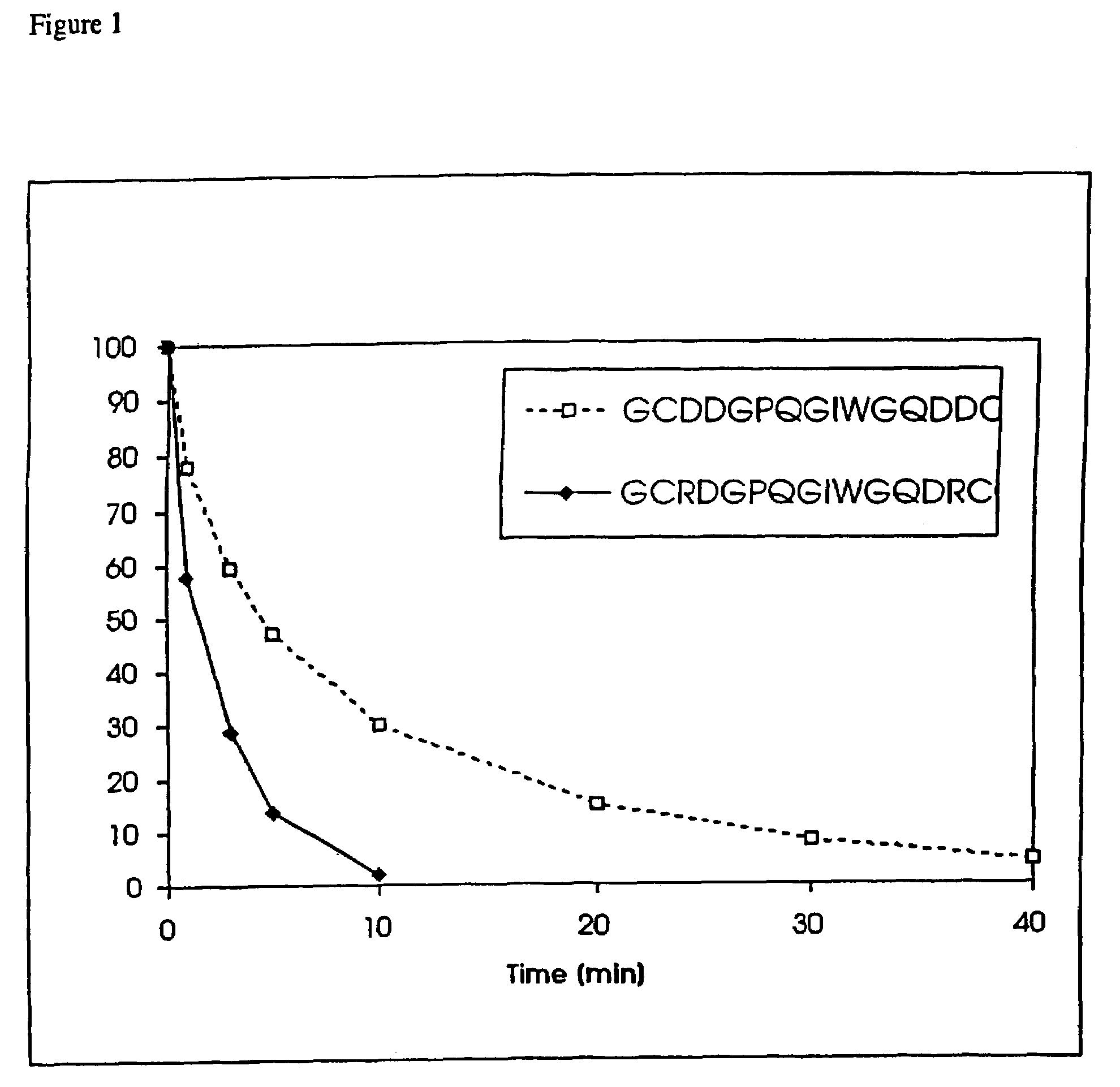
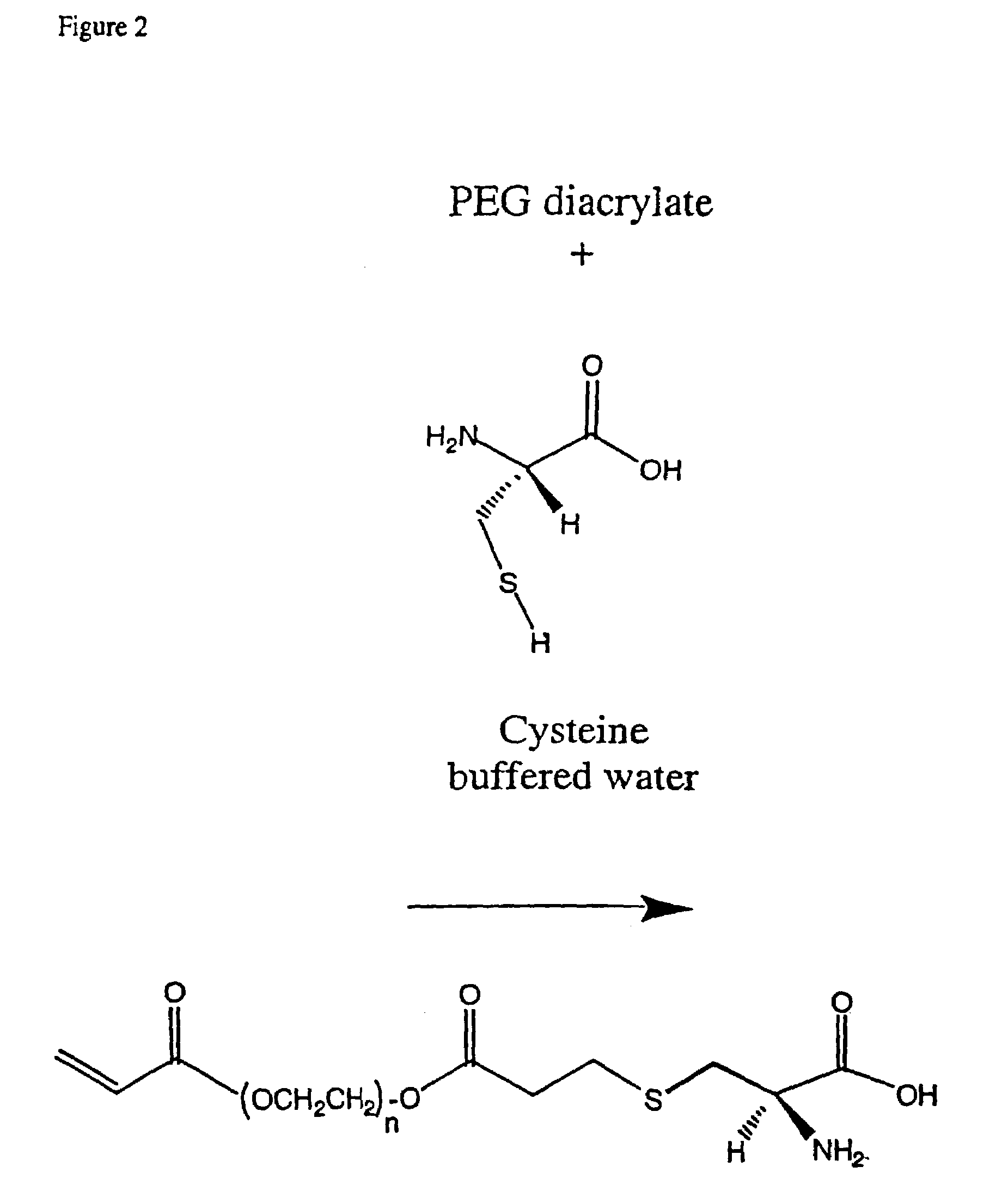
Conjugate addition reactions for the controlled delivery of pharmaceutically active compounds
InactiveUS6958212B1Reducing and delaying onsetGood water solubilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological materialsPolymer
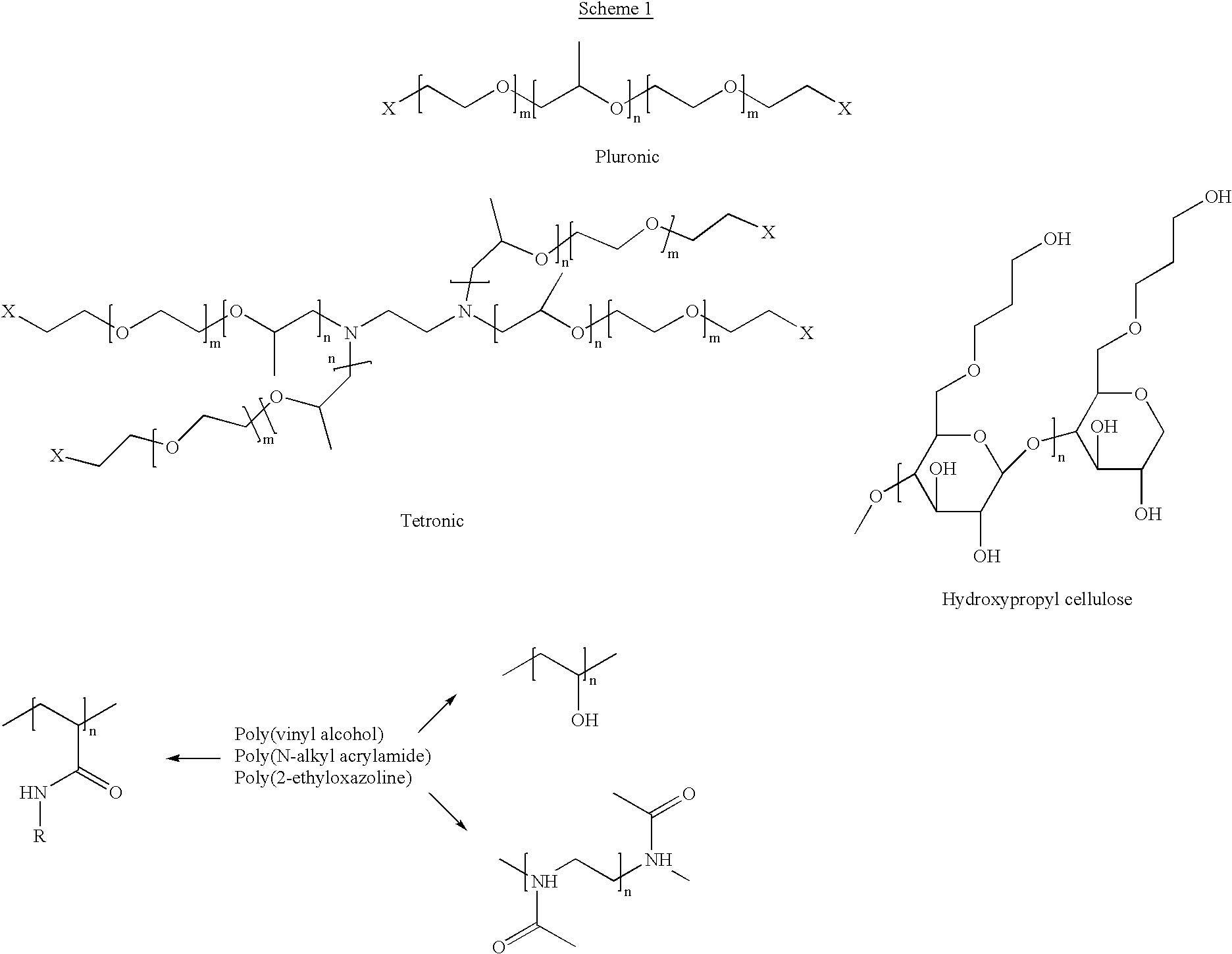
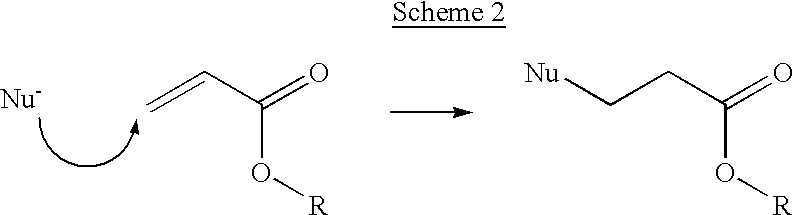
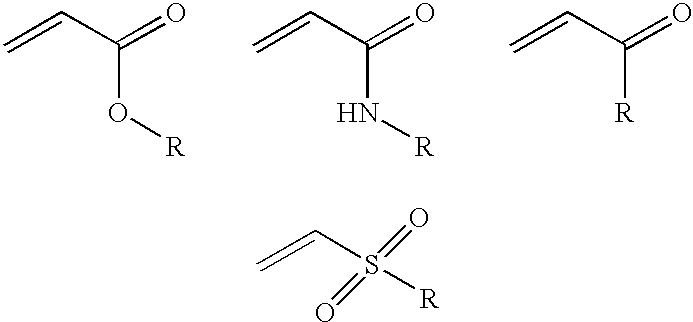
The invention features polymeric biomaterials formed by nucleophilic addition reactions to conjugated unsaturated groups. These biomaterials may be used for medical treatments.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
Functionalized high cis-1,4-polybutadiene prepared using novel functionalizing agents
InactiveUS20060004131A1High ci microstructureLower glass transition temperatureInksActive polymerPolymer science
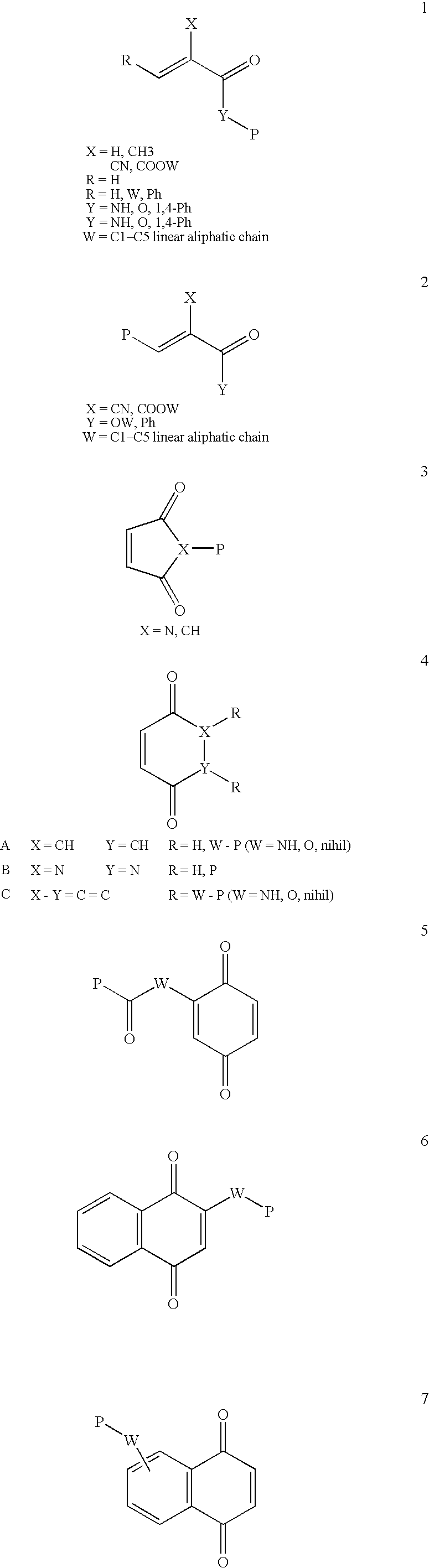
A functionalized polymer prepared by a process comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with a functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) A-R1-Z (I) where R1 is a divalent bond or divalent organic group comprising from 0 to about 20 carbon atoms, A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, and Z is a substituent that will react or interact with silica or carbon black reinforcing fillers, with the proviso that A, R1, and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
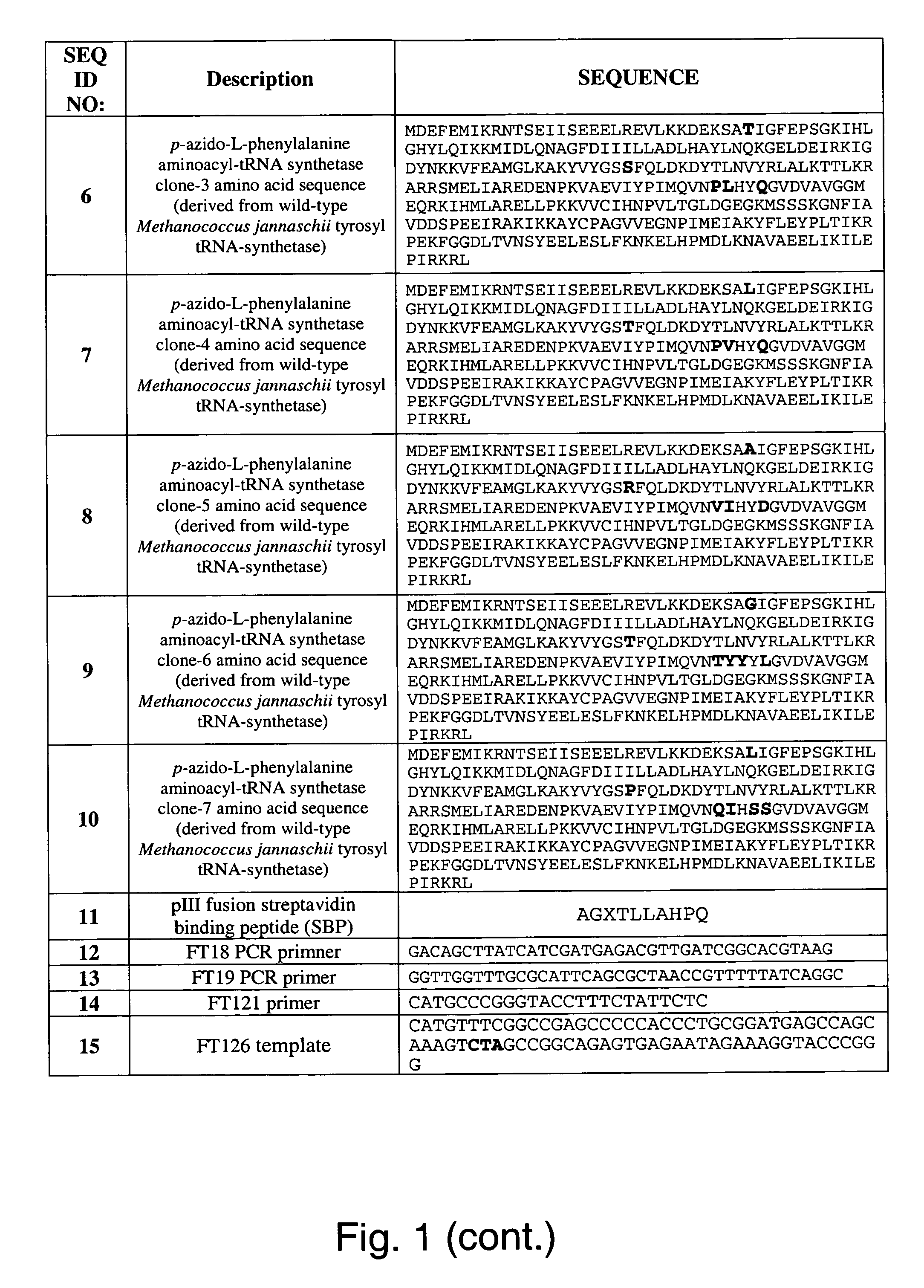
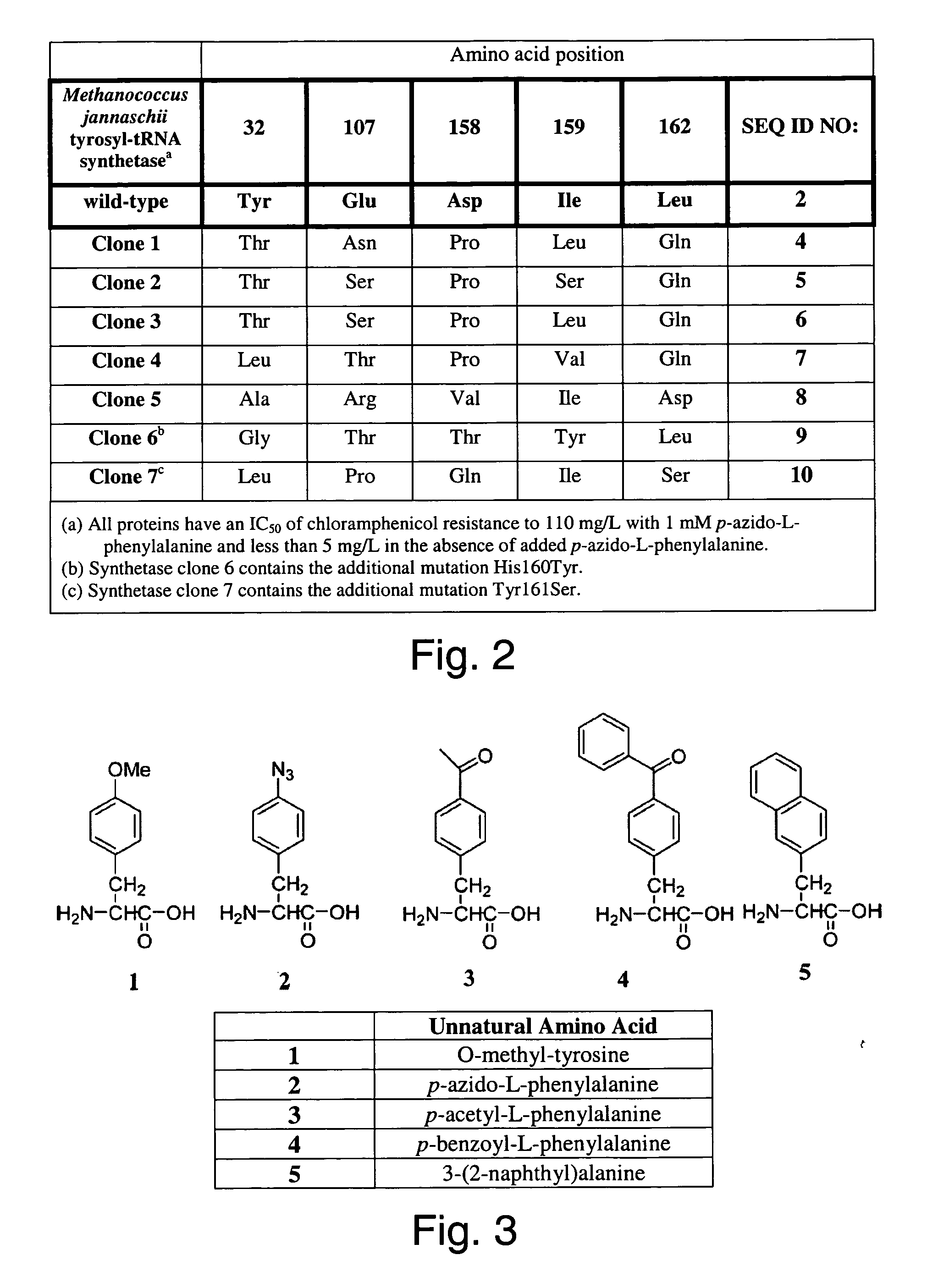
Selective posttranslational modification of phage-displayed polypeptides
ActiveUS20070178448A1Easy to detectEasy to quantifyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesArylCycloaddition
The invention relates to posttranslational modification of phage-displayed polypeptides. These displayed polypeptides comprise at least one unnatural amino acid, e.g., an aryl-azide amino acid such as p-azido-L-phenylalanine, or an alkynyl-amino acid such as para-propargyloxyphenylalanine, which are incorporated into the phage-displayed fusion polypeptide at a selected position by using an in vivo orthogonal translation system comprising a suitable orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and a suitable orthogonal tRNA species. These unnatural amino acids advantageously provide targets for posttranslational modifications such as azide-alkyne [3+2] cycloaddition reactions and Staudinger modifications.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
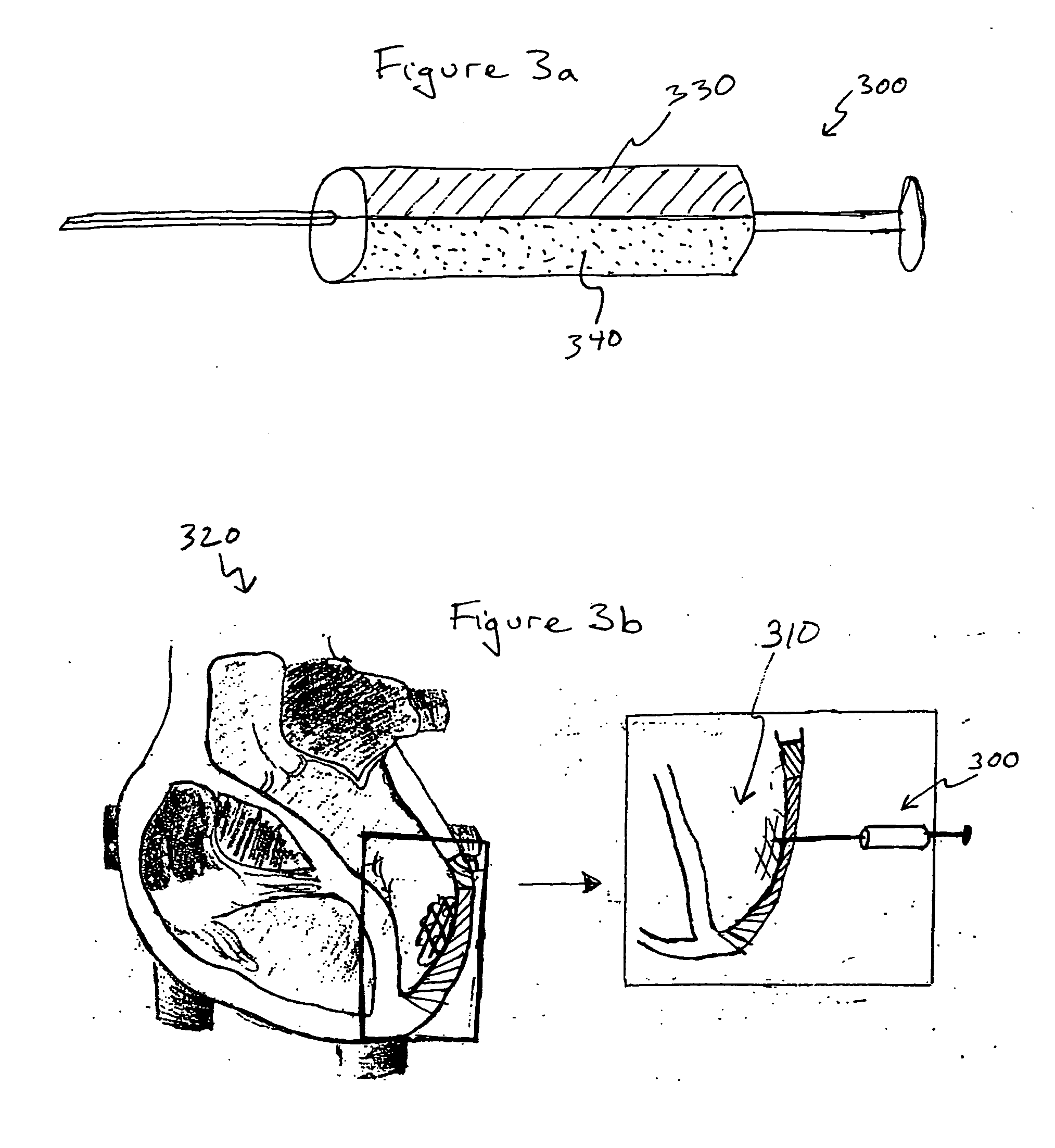
Hydrogel bioscaffoldings and biomedical device coatings
Bioscaffoldings formed of hydrogels that are crosslinked in situ in an infarcted region of the heart (myocardium) by a Michael's addition reaction or by a disulfide bond formed by an oxidative process are described. Each of the bioscaffoldings described includes hyaluronan as one of the hydrogel components and the other component is selected from collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, and fibrin. The bioscaffolding may further include an alginate component. The bioscaffoldings may have biofunctional groups such as angiogenic factors and stem cell homing factors bound to the collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, or fibrinogen hydrogel component. In particular, the biofunctional groups may be PR11, PR39, VEGF, bFGF, a polyarginine / DNA plasmid complex, or a DNA / polyethyleneimine (PEI) complex. Additionally, the hydrogel components may be injected into the infarct region along with stem cells and microspheres containing stem cell homing factors. The bioscaffolding may be formed on a stent or a cardiac medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Two-phase processing of thermosensitive polymers for use as biomaterials
InactiveUS20030044468A1Negligible cytotoxicityWithout adversely affecting the activity of these sensitive moleculesPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPolymer scienceThermosensitive polymer
A two-step system for preparing biomaterials from polymeric precursors is disclosed. The method involves (a) shaping the polymeric precursors by inducing thermal gelation of an aqueous solution of the polymeric precursors and (b) curing the polymeric precursors by cross-linking reactive groups on the polymeric precursors to produce a cured material. The curing reaction involves either a Michael-type addition reaction or a free radical photopolymerization reaction in order to cross-link the polymeric materials. The biomaterials produced by this method have a variety of biomedical uses, including drug delivery, microencapsulation, and implantation.
Owner:EIDGENOSSISCHE TECHN +1
Crosslinkable rubber compositions and use thereof
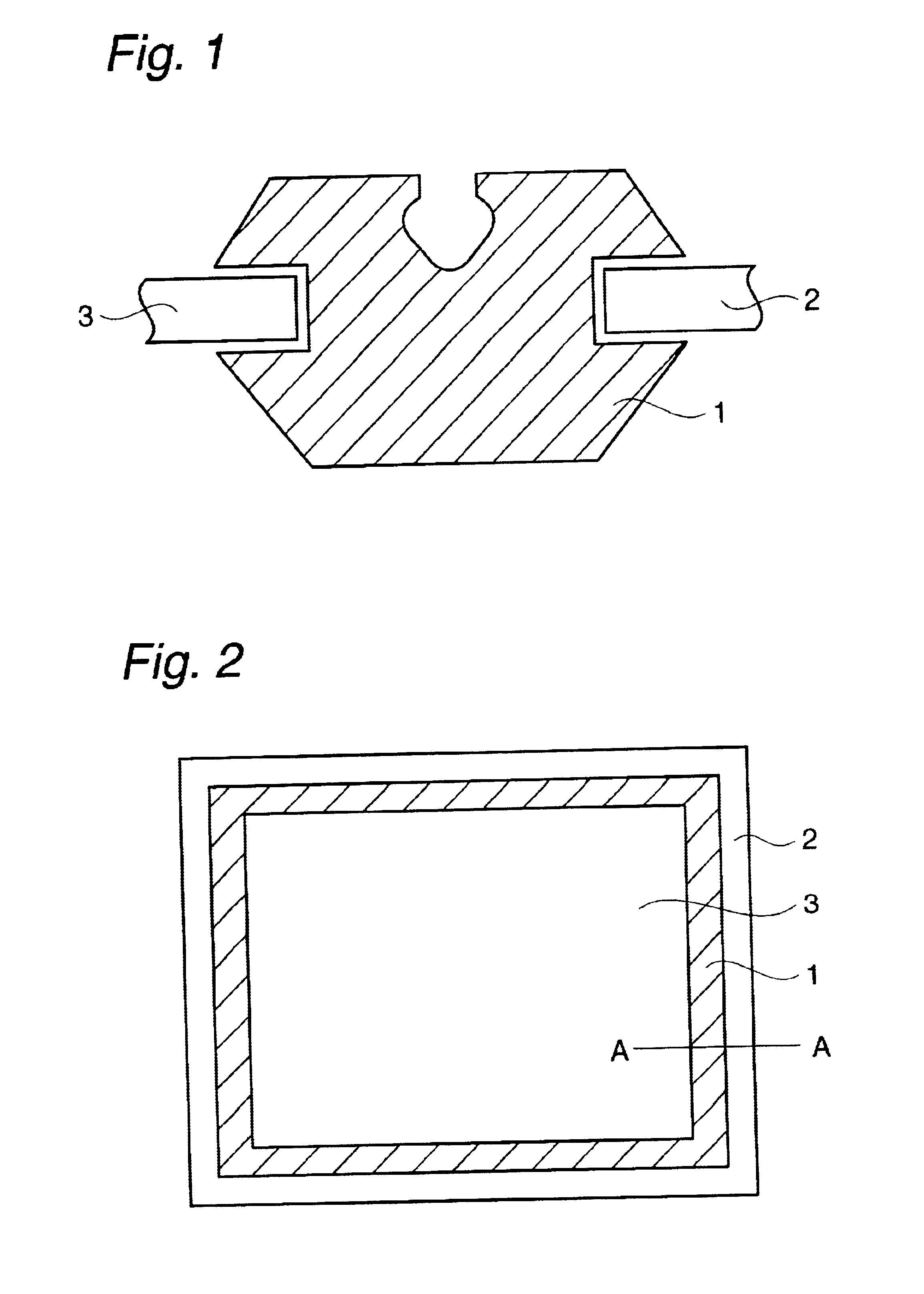
The crosslinkable rubber composition of the invention is crosslinkable by hot air, and a hot-air crosslinked rubber sheet thereof has no scratch on the surface in a hardness test using a pencil of HB and has a compression set of not more than 70% after a heat treatment at 150° C. for 22 hours. The rubber composition comprises an ethylene / α-olefin / non-conjugated polyene random copolymer rubber comprising a specific vinyl end group-containing norbornene compound, a SiH group-containing compound having at least two SiH groups in one molecule, and if necessary, an addition reaction catalyst comprising a platinum group element and a reaction inhibitor. The automobile weatherstrip, hose, rubber vibration insulator, belt, sealing material, expanded product, covered electric wire, electric wire joint, electric insulating part and household rubber product according to the invention comprise the above-mentioned rubber composition. The rubber composition has a high crosslinking rate and excellent productivity to produce crosslinked rubber molded products, is capable of undergoing hot-air crosslinking such as HAV or UHF and is capable of providing crosslinked rubber molded products having excellent compression set resistance, strength properties, heat resistance, weathering resistance and abrasion resistance.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC +1
Process for an addition reaction of organic silicon compounds having SiH groups with compounds having olefinic double bonds
ActiveUS7157541B2Silicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSilanesUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyorganosiloxanes and polyorganosilanes of high purity by an addition reaction of siloxanes and / or silanes which contain at least one H—Si group with compounds having olefinic double bonds in the presence of a platinum catalyst and optionally further additional components, wherein the reaction is carried out in the presence of a platinum(0) complex catalyst which was dissolved in a solvent before addition to the reaction medium and to whose solution an effective amount of at least one unsaturated hydrocarbon having 2 to 6 carbon atoms was added.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
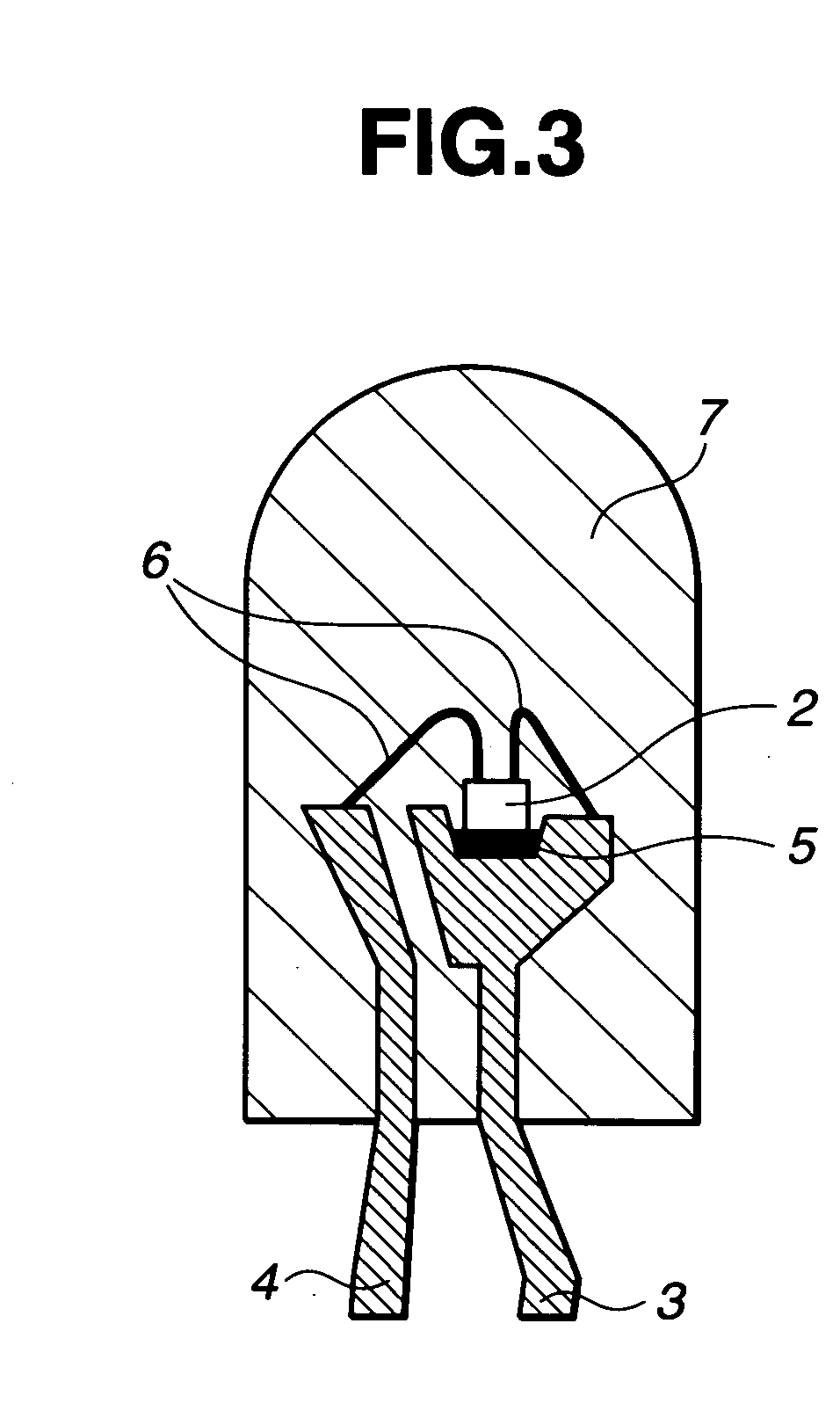
LED devices and silicone resin composition therefor
LED devices encapsulated with silicone resin compositions comprising (A) a silicone resin having at least two alkenyl groups bonded to silicon atoms in a molecule, (B) an organohydrogensilane and / or organohydrogenpolysiloxane having at least two hydrogen atoms bonded to silicon atoms in a molecule, and (C) an addition reaction catalyst which cure into transparent products having heat resistance and discoloration resistance.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
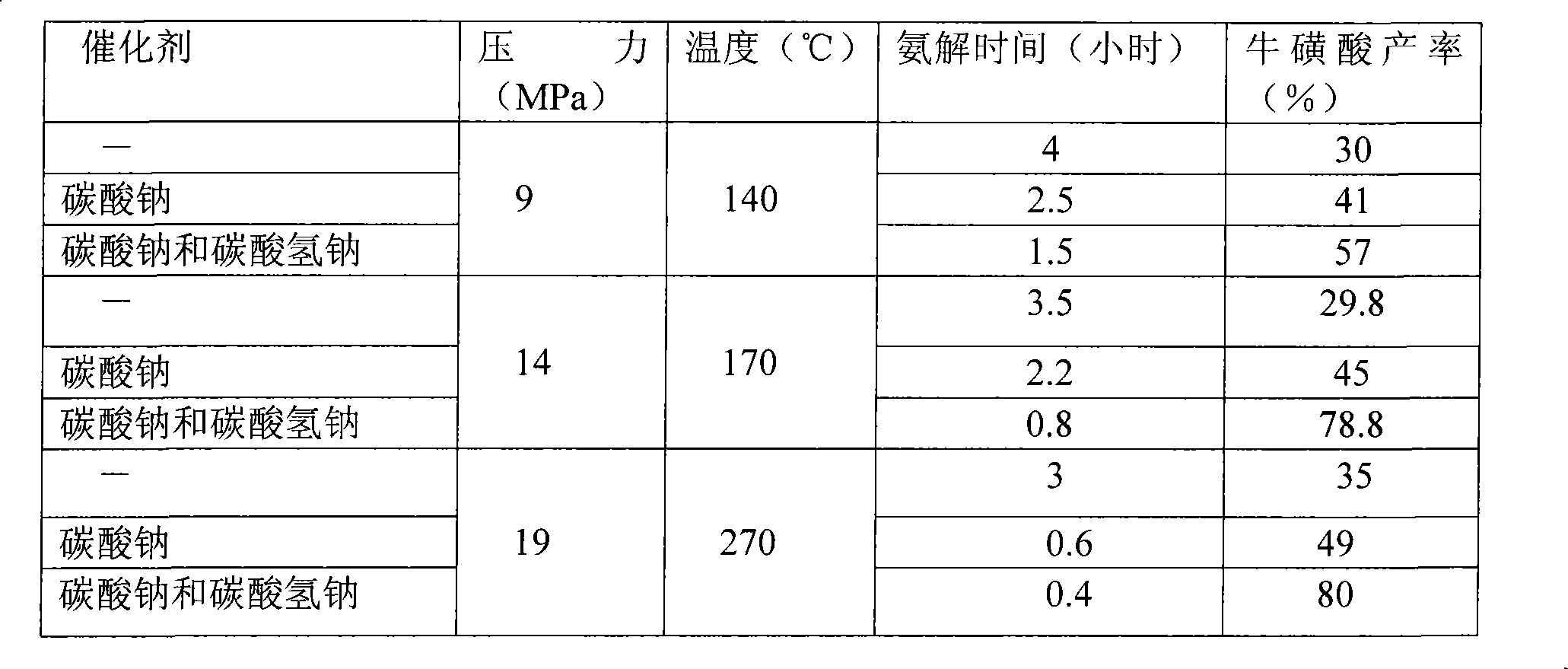
Synthesis of taurine
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing taurine, comprising the following steps: (1) according to the amount ratio of materials of 1:1 to 1:1.2, epoxy ethane and sodium bisulfite are subjected to addition reaction under 0.05 to 0.1MPa, with pH value of 6.5 to 7.5 and at a temperature between 75 and 85 DEG C to form hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate; (2) the hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate and liquid ammonia are subjected to ammonolysis reaction under 14 to 21MPa and at a temperature between 160 and 280 DEG C to generate sodium taurate, and the mass concentration of ammonia in the reaction liquid is 20 to 30 percent; and (3) neutralization: namely, the sodium taurate is neutralized by sulphuric acid to generate the taurine. The method for synthesizing the taurine has the advantages of short time, high yield and lower cost, and is easy for industrialized production.
Owner:王代龙 +1
Graphene/polysiloxane composite coating material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106752926AImprove scratch resistanceImprove wear resistanceFireproof paintsAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxyResin-Based Composite
The invention provides a graphene / polysiloxane composite coating material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: modifying the graphene surface with active groups by a chemical modification technique to obtain modified graphene, mixing the modified graphene with a silane compound, a dispersion medium, a non-essential comonomer and a non-essential accelerator, and carrying out hydrolytic condensation or hydrolytic condensation-free radical polymerization to generate a graphene / polysiloxane composite resin in situ; and mixing the resin with a non-essential blend resin, a non-essential curing agent, a non-essential solvent, a non-essential pigment and filler and a non-essential aid, and carrying out physical blending, amino epoxy addition reaction, Michael addition reaction and the like to form a film, thereby obtaining the graphene / polysiloxane composite coating material. The uniformly dispersed graphene lamellae and polysiloxane have strong interface effects, also have the gas / liquid barrier and heat shielding effects, and endow the coating with excellent corrosion resistance, flame retardancy and the like, thereby greatly enhancing the mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, scratch resistance, wear resistance and the like of the coating.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Toner, developer, image forming method, and toner container
ActiveUS20070015077A1Quality improvementHigh color reproductionDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternPolyesterParticulates
A toner is provided manufactured by a method having the steps: dispersing toner constituents including a resin, in an aqueous medium containing a particulate resin, wherein the resin has a polyester skeleton formed by a ring-opening addition reaction of a cyclic ester with a first compound having an active hydrogen group; and a developer and an image forming method using the toner, and a toner container containing the toner.
Owner:RICOH KK
Low gas permeable silicone resin composition and optoelectronic device
ActiveUS20120056236A1Low gas permeabilityLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsArylSilicon
A silicone resin composition comprising (A) an organopolysiloxane containing silicon-bonded aryl and alkenyl groups in a molecule, (B) an organohydrogenpolysiloxane, and (C) an addition reaction catalyst is low gas permeable. An optoelectronic device encapsulated therewith is highly reliable.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
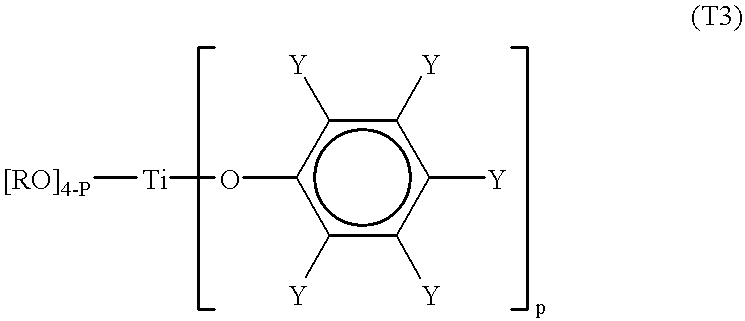
Processes for the preparation of a monodisperse polymers, processes for the continuous polymerization of cyclic monomers, and polymers prepared thereby
The present invention relates to a method for preparing lactone polymers, carbonate polymers, lactone-carbonate block copolymers and lactone-arbonate random copolymers via a ring-opening addition reaction of a lactone monomer, a cyclic carbonate monomer or a mixture thereof using an initiator and in the presence of a specific titanium-type Lewis acid catalyst. The resulting polymers have a molecular weight distribution (Mw / Mn) approximately equal to 1 or a extremely high purity of single-structure components. The polymer molecules range in an oligomer region to a molecular weight of approximately 200,000. The present invention also relates to a method for preparing lactone polymers, carbonate polymers and lactone-carbonate copolymers having a narrow molecular weight distribution and which can be obtained via a continuous polymerisation of a lactone monomer and / or a cyclic carbonate monomer using an initiator in an extruder in the presence of a specific titanium-type Lewis acid catalyst or an aluminium-type Lewis acid catalyst. The present invention also relates to these resulting polymers.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Low temperature curing acrylate and maleimide based formulations and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS20100063184A1Non-fibrous pulp additionFilm/foil adhesivesLow temperature curingElectronic packaging
The present invention is based on the discovery that certain electron poor olefins combined with nucleophiles and a base catalyst are useful as adhesive compositions for the electronic packaging industry. In particular, the adhesive formulations set forth herein are useful as low temperature curing formulations with high adhesion to a variety of substrates. Invention formulations typically cure at about 80° C. and have a potlife of about 24 hours. The formulations cure by the well-known Michael addition reaction.
Owner:DESIGNER MOLECULES
Self-photoinitiating multifunctional acrylates
Self-photoinitiating liquid oligomeric compositions having tertiary amine groups are provided by Michael Addition reaction of:A) an uncrosslinked Michael Addition reaction product of a multifunctional acrylate acceptor and a Michael Donor; andB) a primary and / or secondary amine. The compositions can be crosslinked to make coatings, laminates and adhesives.
Owner:ASHLAND LICENSING & INTPROP LLC
Conjugate addition reactions for the controlled delivery of pharmaceutically active compounds
InactiveUS7291673B2Reducing and delaying onsetGood water solubilityBiocideSurgical adhesivesPolymerControlled delivery
The invention features polymeric biomaterials formed by nucleophilic addition reactions to conjugated unsaturated groups. These biomaterials may be used for medical treatments.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
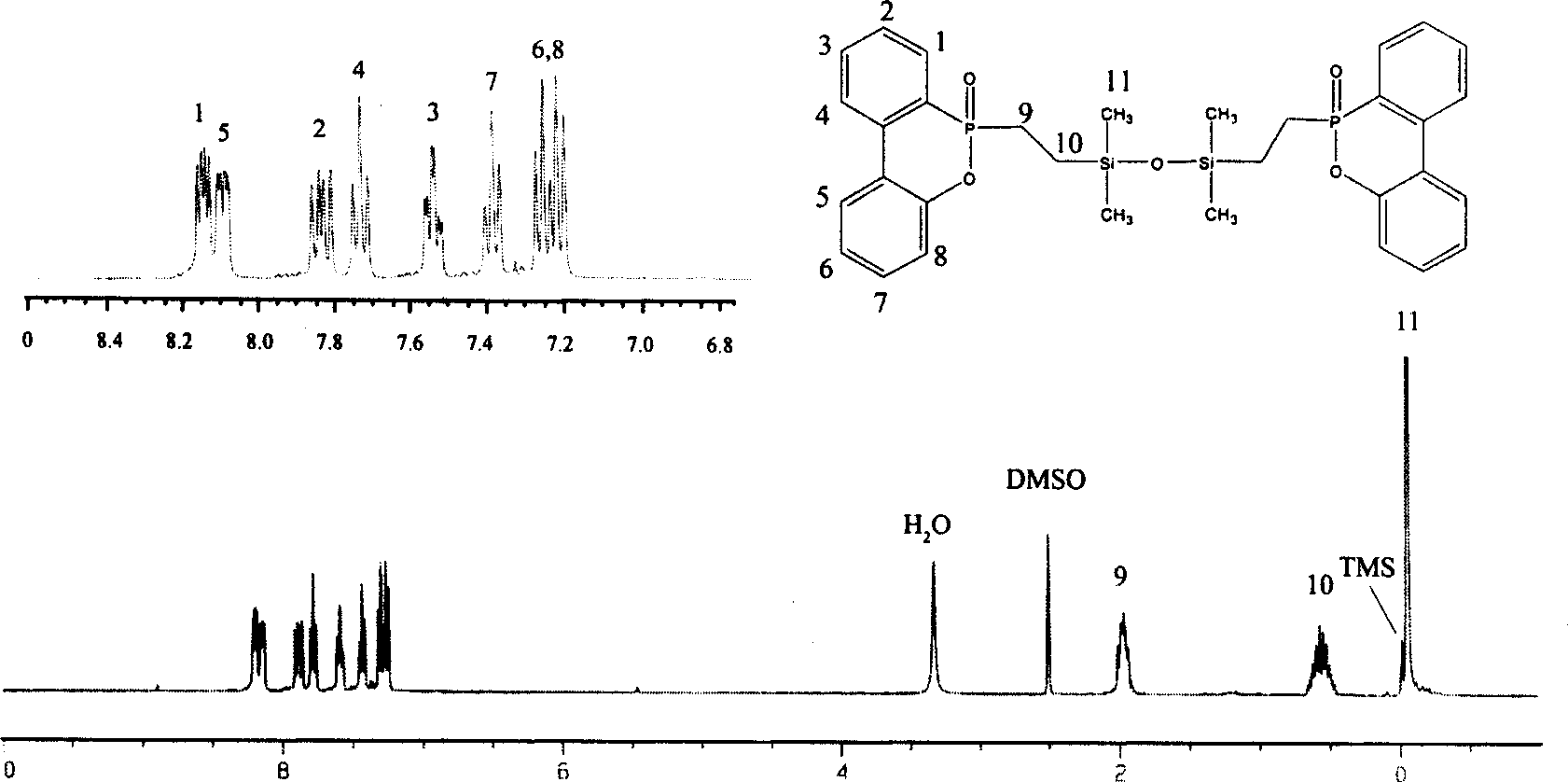
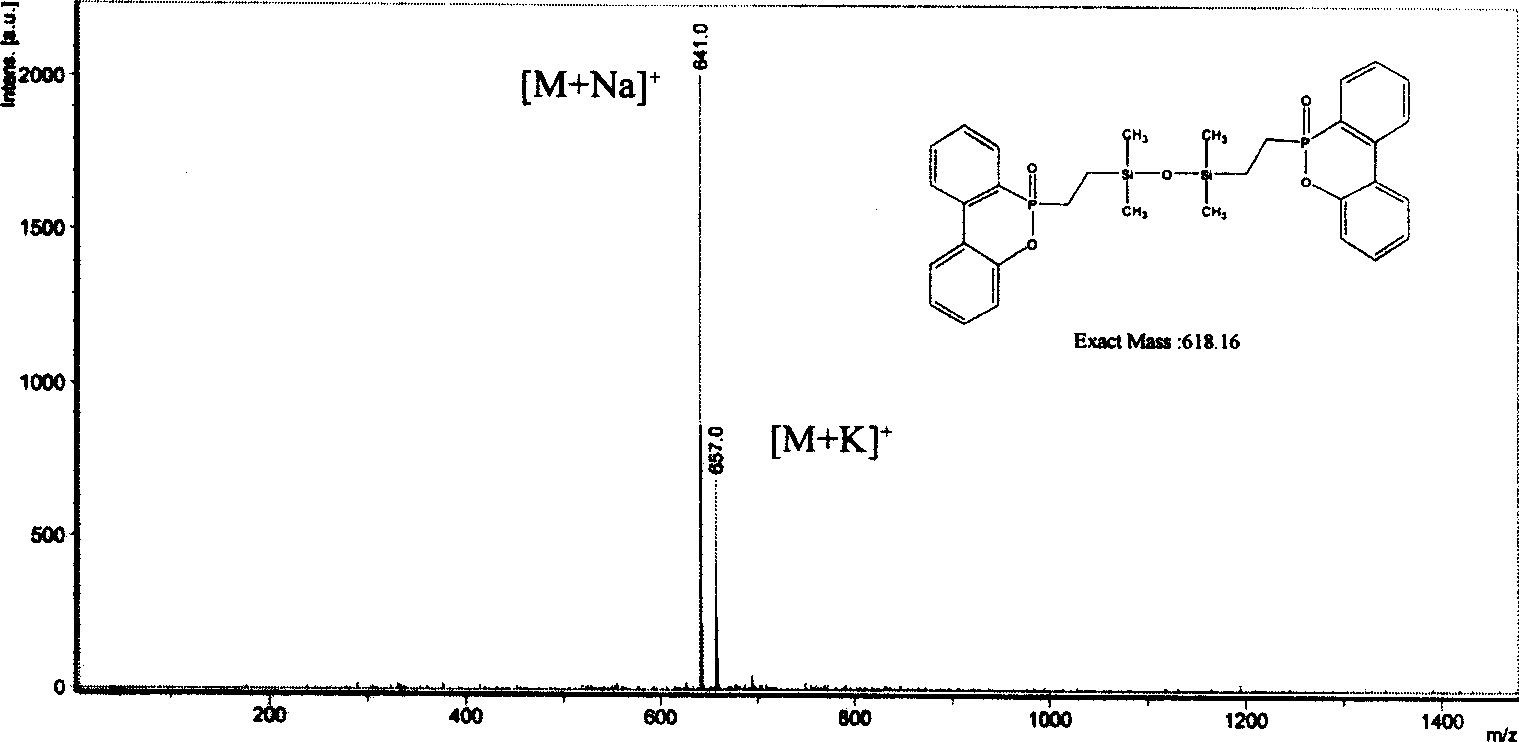
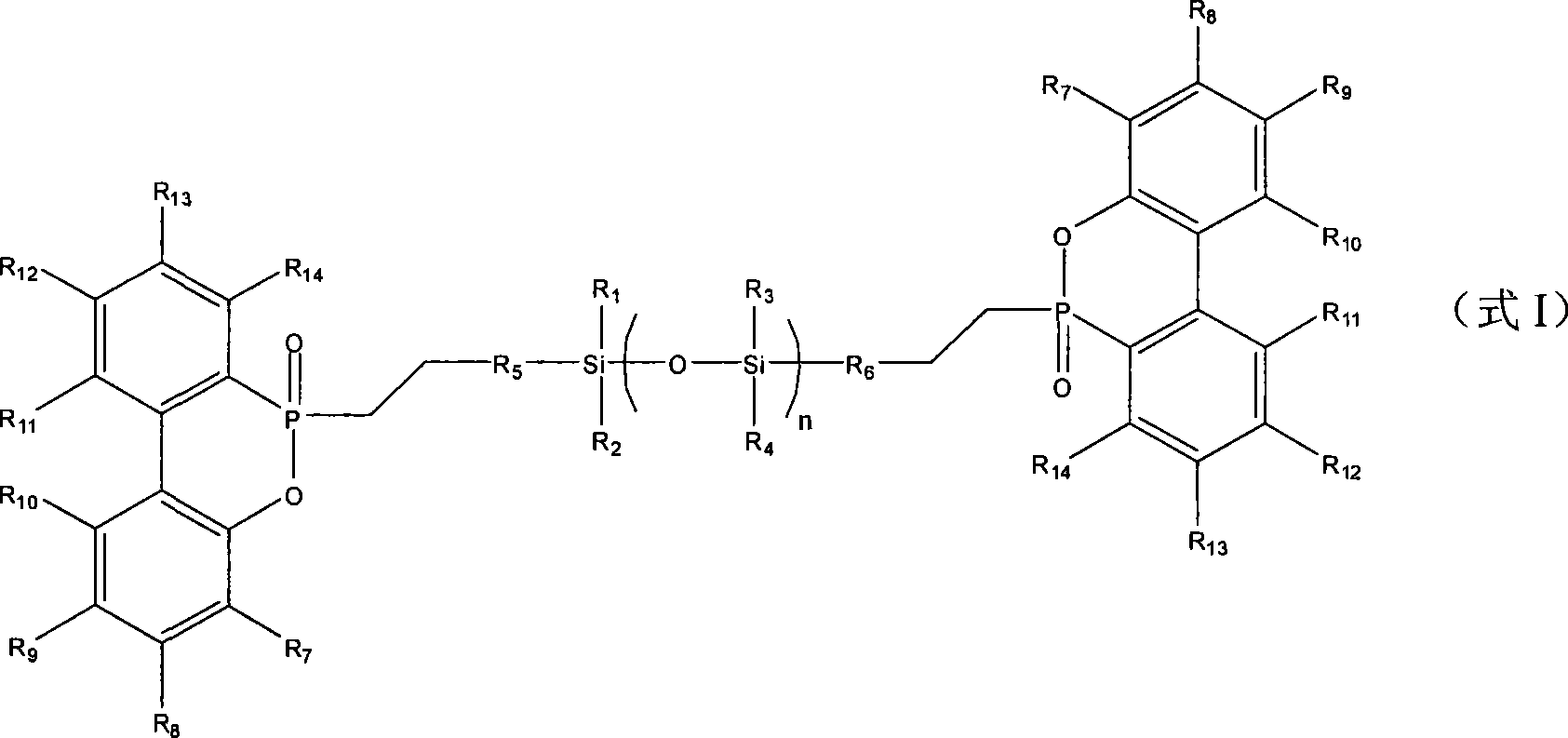
Phosphoric organic silicon compound, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a phosphoric organic silicon compound, a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the phosphoric organic silicon compound is shown as Figure 1, wherein, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are selected from C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, aryl, aryl substituted by halogen and aroxy; R5 and R6 are C0-C5 alkylidene groups; R7-R14 are selected from hydrogen atom, C1-C5 alkyl, nitro, the C1-C5 alkoxy, aryl, the aryl substituted by the halogen and the aroxy; and n is 1-10. The preparation method comprises performing an addition reaction of an active phosphorus-hydrogen bond in a 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide (DOPO) derivative and siloxane containing two carbon-carbon double bonds to produce the novel phosphoric organic silicon compound. The compound contains two elements namely phosphorus and silicon which have flame retardant property, and can be taken as an additive flame retardant for inflaming retarding of high molecular materials.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biological radical polyatomic alcohol prepared by Jatropha curcas oil
The present invention relates to a preparation method for a biological polybasic alcohol by using of an aleurites fordii. The preparation method is as follows: an alcohol-decomposing agent is added into the aleurites fordii to make the alcohol-decomposing reaction in the catalyzing environment to create a mixing ester of fatty acid; and then an epoxidizing agent is added into the mixing ester of fatty acid to make the epoxidizing reaction in the catalyzing environment to create a mixing epoxidizing ester of fatty acid; the mixing epoxidizing ester of fatty acid takes the opening reaction of epoxidizing key with an opening agent to create a mixing hydroxylic ester of fatty acid, i.e. a biological polybasic alcohol. The biological polybasic alcohol takes the addition reaction with an oxidation alkene in the catalyzing environment to create a biological polybasic alcohol with much higher molar weight. The preparation technics and operation of the present invention are more convenient; the adjustability for the product function is much better with much better performance. The aleurites fordii materials used in the present invention is a reproducible materials; so the cost is much lower and the material is abundant, which can replace the petrifaction polyether glycol to prepare the polyurethane foam plastic so that the dependence to the polyurethane product decreases.
Owner:HONGBAOLI GRP CO LTD
Preparation method of injectable natural polysaccharide self-healing hydrogel
ActiveCN103910894AGood biocompatibilityThe synthesis process is simple and greenSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSelf-healingPhosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method of injectable natural polysaccharide self-healing hydrogel. The preparation method of the injectable natural polysaccharide self-healing hydrogel comprises the following steps: firstly synthesizing water soluble N-carboxyethyl chitosan by carrying out a Michael addition reaction on acrylic acid and chitosan, carrying out an oxidization reaction on sodium periodate and sodium alginate to obtain oxidized sodium alginate, then carrying out a dehydration condensation reaction on N-carboxyethyl chitosan and oxidized sodium alginate and on adipic dihydrazide and oxidized sodium alginate in a phosphate buffer liquid at the temperature of 37 DEG C, so as to respectively generate invertible imine bond and acylhydrazone bond, and finally preparing injectable natural polysaccharide macromolecular hydrogel with self-healing property. The preparation method of the injectable natural polysaccharide self-healing hydrogel has the advantages that a synthetic process of the injectable self-healing hydrogel is simple and green, reaction conditions are mild, the injectable self-healing hydrogel can form gel in a physiological environment and has self-healing capability, and the injectable self-healing hydrogel has a good application prospect in the fields of drug sustained release and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Addition curing silicone rubber composition and pressure-sensitive adhesive rubber sheet
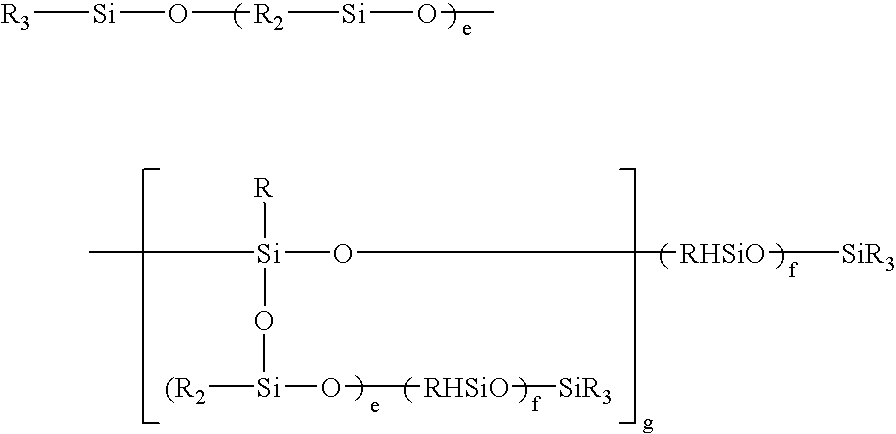
An addition curing silicone rubber composition comprising (A) an alkenyl-containing organopolysiloxane, (B) a resinous copolymer composed mainly of R3SiO1 / 2 units and SiO2 units in a molar ratio between 0.5 / 1 and 1.5 / 1 wherein R stands for a monovalent hydrocarbon group and is substantially free of alkenyl groups, (C) a resinous copolymer composed mainly of R'3SiO1 / 2 units and SiO2 units in a molar ratio between 0.5 / 1 and 1.5 / 1 wherein R' stands for a monovalent hydrocarbon group and includes an alkenyl group, and the total content of alkenyl groups is at least 0.0001 mol / g, (D) an organohydrogenpolysiloxane, and (E) an addition reaction catalyst cures into a silicone rubber sheet that has a satisfactory rubber strength and surface adhesive property.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
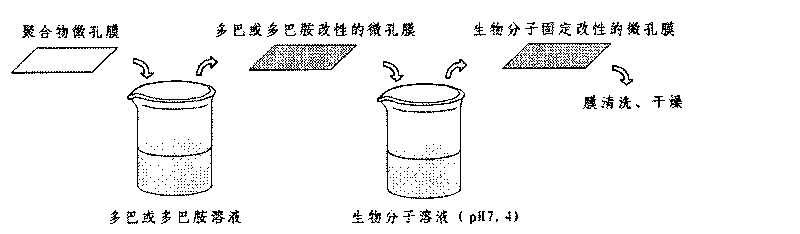
Method for fixing biological molecules on polymer microporous membrane surface
ActiveCN101745327ALow costEase of mass industrial productionSemi-permeable membranesBiocompatibility TestingPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for fixing biological molecules on a polymer microporous membrane surface, comprising the following steps: (1) respectively dissolving DOPA compounds and the biological molecules in a trihydroxymethyl aminomethane - muriatic acid buffer solution and a phosphoric acid buffer solution to prepare solutions; (2) immersing a polymer microporous membrane in a DOPA compound solution and oscillating to cause the DOPA compounds to be auto-polymerized-compounded on the membrane surface and to be closely attached to the membrane surface and a membrane pore wall; (3) immersing the polymer microporous membrane modified by the DOPA compounds in a biological molecule solution, and fixing the biological molecules on the polymer microporous membrane surface by the addition reaction between catechol groups of the membrane surface and amidogen in the biological molecules. The method for fixing biological molecules on the polymer microporous membrane surface has simple process, the prepared polymer microporous membrane has good hydrophilic property and biocompatibility, and the method has important meaning for improving the permeability and the biocompatibility of the polymer microporous membrane.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Silicone adhesive for semiconductor element
InactiveUS20090258216A1Improve concealmentEffective reflectionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesLayered productsPolymer scienceColored white
A silicone adhesive for a semiconductor element that is suitable as a die bonding material for fixing a light emitting diode chip to a substrate. The adhesive includes (a) an addition reaction-curable silicone resin composition having a viscosity at 25° C. of not more than 100 Pa·s, and yielding a cured product upon heating at 150° C. for 3 hours that has a type D hardness prescribed in JIS K6253 of at least 30, (b) a white pigment powder having an average particle size of less than 1 μm, and (c) a white or colorless and transparent powder having an average particle size of at least 1 μm but less than 10 μm. The adhesive exhibits high levels of concealment, effectively reflects light emitted from the LED chip, and also exhibits favorable chip positioning properties, superior adhesive strength, and excellent durability.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for synthesizing cricoid carbonate by addition reaction of carbon dioxide and epoxy compound ring
InactiveCN101037431AHigh activityHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEpoxyCycloaddition
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing cyclic carbonate by a cycloaddition reaction of carbon dioxide and epoxy-compound. The catalyzer is composed of metal-salt, ion liquid and quaternary ammonium salt. The cyclic carbonate is produced by catalyzing the carbon dioxide and epoxy-compound for a cycloaddition reaction under a reaction temperature of 30-200 DEG C, and a carbon dioxide pressure of 0.5-10 MPa. The reaction progress doesn't add any organic solvent. The purified cyclic carbonate by a simple purification may achieve a high purity more than 98%. The catalyzer can be reused and keeps an invariable activity. The catalyzer system has a high activity and low cost. The method can synthesize the cyclic carbonate quickly and highly selectively in a simple operation so than it will be a perfect industrial prospect.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
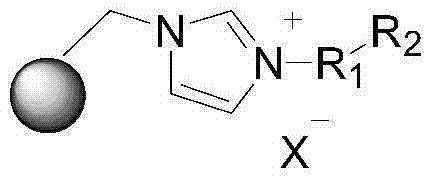
Supported ionic liquid catalyst, as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN103495437AChemical choice goodMild reaction conditionsProductsOrganic chemistryEpoxyCycloaddition
The invention discloses a supported ionic liquid catalyst. The supported ionic liquid catalyst is characterized in that imidazole is immobilized onto chloromethylated FDU mesoporous phenolic resin by nucleophilic reaction and reacts with halides containing different functional groups to prepare a mesoporous material supported functional imidazole type ionic liquid catalyst. The preparation of the catalyst comprises the following steps: chloromethylation of a mesoporous material, imidazolation and supporting of ionic liquid. The catalyst is used for synthesizing a cyclic carbonate by cyclic addition reaction of carbon dioxide and an epoxy compound, and the using quantity of the catalyst is 0.1-2mol% of the liquid content of the epoxy compound. Compared with the prior art, a large number of hydroxyl groups exist in the mesoporous material, and the supported ionic liquid catalyst has the double advantages of an inorganic mesoporous material and an organic polymer, as well as large specific surface area, adjustable pore structure, good hydrophobicity and chemical stability, high catalytic activity, good chemical selectivity, easiness in separation and recovery, mild reaction conditions, environmental friendliness and easiness in industrial implementation.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
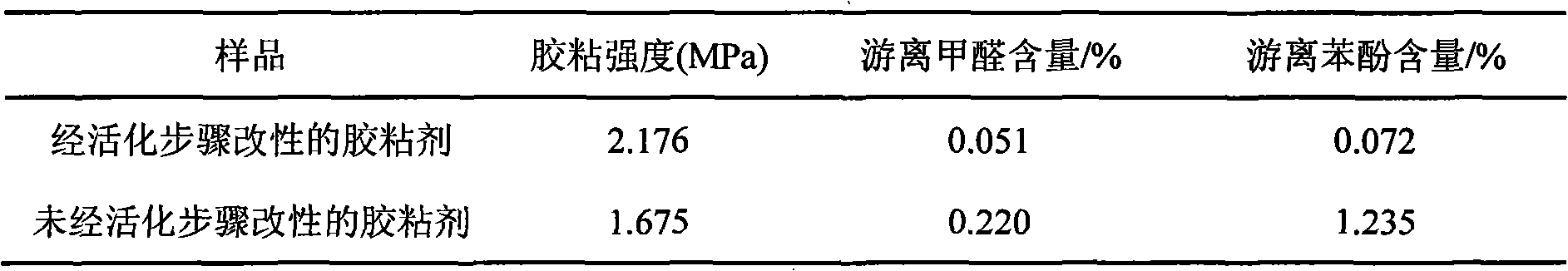
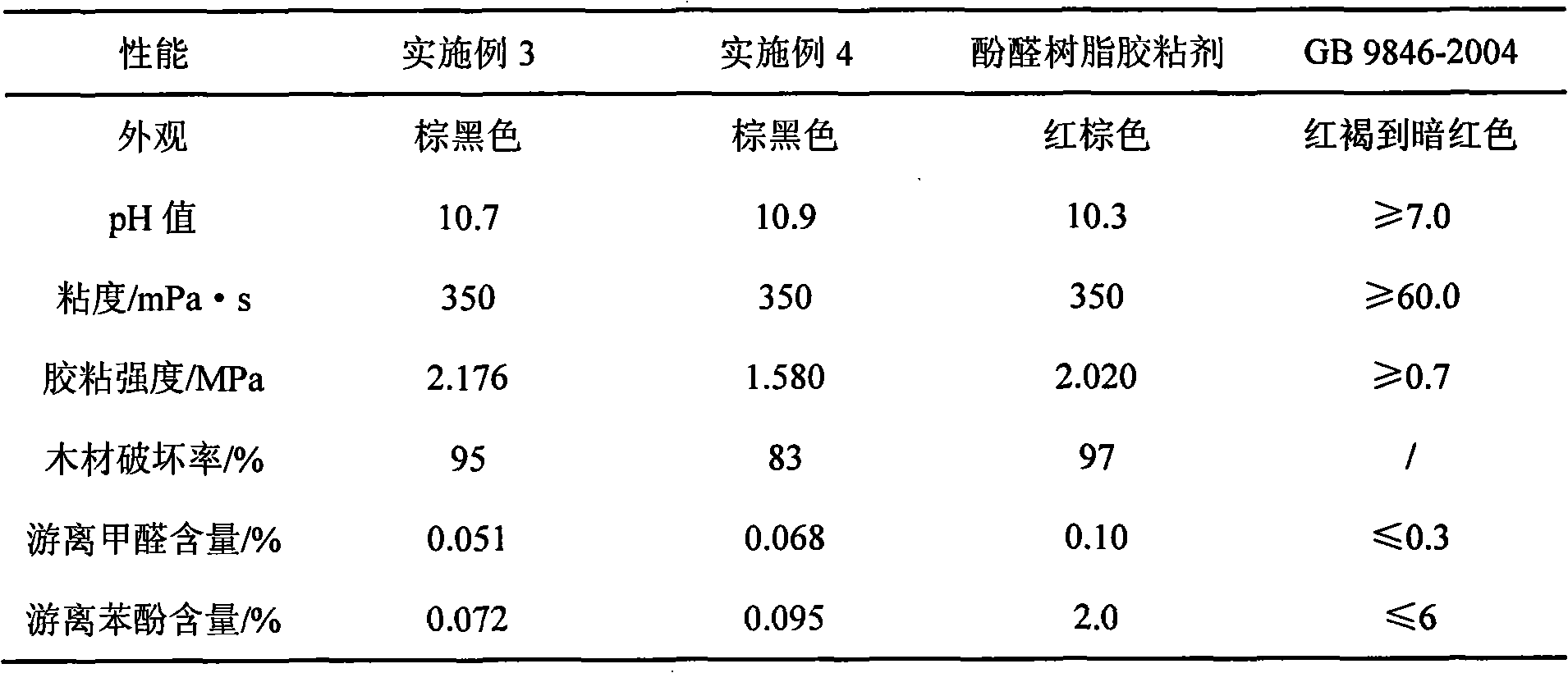
Environment-friendly type alkali lignin modified phenolic resin adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101358120AGood water resistanceLess phenolAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesProduct propertyPhenols
The present invention relates to an environment-friendly alkali-lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the following steps: water is added into alkali lignin powder, acid is then added, and under a temperature between 100 DEG C and 120 DEG C, acidolysis lasts for one to three hours; desugarized alkali lignin is obtained; the desugarized alkali lignin powder, sodium hydroxide and water are uniformly mixed, oxidant and 2-naphthol are added for reaction, the temperature is reduced to 45 DEG C to 50 DEG C, formaldehyde and phenol are added so that polycondensation reaction occurs, and the environment-friendly alkali-lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesive is prepared. The method adopts acidolysis desugarization to reduce a great deal of alcoholic hydroxyl content in the alkali lignin and modifies the alkali lignin by alkaline hydrolysis, degradation and nucleophilic addition reaction, thus greatly increasing the chemical reaction activity of the alkali lignin, the amount of toxic phenol required in the technique of preparing modified phenolic resin is little, and the residual phenol and formaldehyde are less, so the environment-friendly alkali-lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesive has the advantages of green production technique and product properties.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
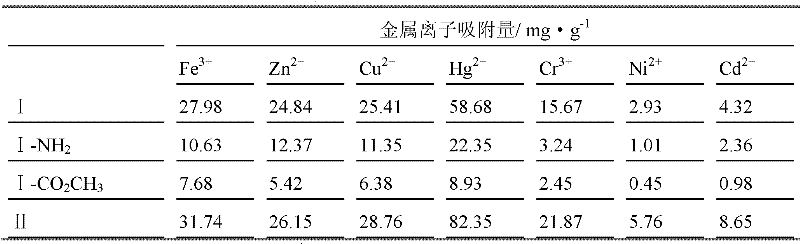
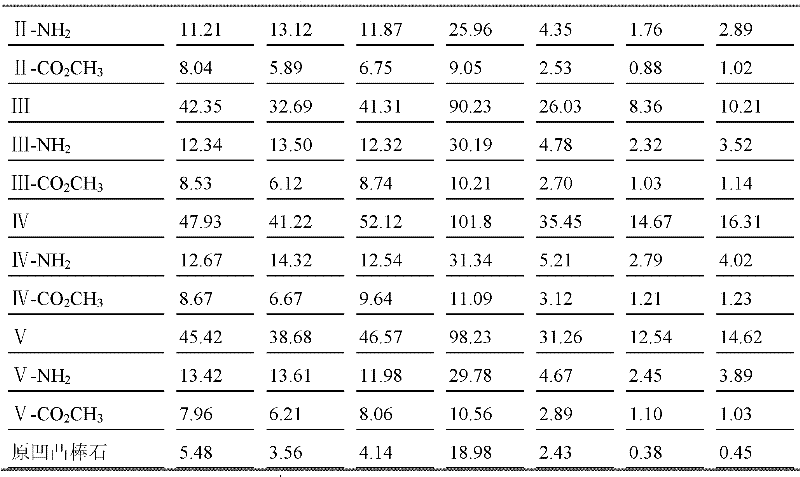
Preparation method and usage of modified attapulgite adsorption material
ActiveCN102247807AImprove adsorption capacityReduce process stepsOther chemical processesProcess efficiency improvementDistillationSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method and usage of a modified attapulgite adsorption material. The method comprises the following steps: modifying attapulgite which has undergone purification and acid activation with an amino-silane coupling agent so as to introduce amino onto the surface of attapulgite; subjecting amino and excess acrylic acid ester to a Michael addition reaction so as tointroduce ester groups, subjecting introduced ester groups and polyethylene polyamine to a Michael addition reaction, carrying out underpressure distillation to remove a solvent and excess reactants,and carrying out vacuum drying, grinding and sieving to obtain a finished product. According to the invention, polyethylene polyamine or alcamine compounds are bonded to the surface of attapulgite through covalent bonds, thereby substantially improving adsorption performance of attapulgite to metal ions.
Owner:江苏麦阁吸附剂有限公司
Heat conductive silicone grease composition and cured product thereof
InactiveCN101104738AImprove thermal conductivityImprove liquidityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialsContact resistance
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Crosslinkable rubber compositions and uses thereof
The crosslinkable rubber composition of the invention is crosslinkable by hot air, and a hot-air crosslinked rubber sheet thereof has no scratch on the surface in a hardness test using a pencil of HB and has a compression set of not more than 70% after a heat treatment at 150° C. for 22 hours. The rubber composition comprises an ethylene / α-olefin / non-conjugated polyene random copolymer rubber comprising a specific vinyl end group-containing norbornene compound, a SiH group-containing compound having at least two SiH groups in one molecule, and if necessary, an addition reaction catalyst comprising a platinum group element and a reaction inhibitor. The automobile weatherstrip, hose, rubber vibration insulator, belt, sealing material, expanded product, covered electric wire, electric wire joint, electric insulating part and household rubber product according to the invention comprise the above-mentioned rubber composition. The rubber composition has a high crosslinking rate and excellent productivity to produce crosslinked rubber molded products, is capable of undergoing hot-air crosslinking such as HAV or UHF and is capable of providing crosslinked rubber molded products having excellent compression set resistance, strength properties, heat resistance, weathering resistance and abrasion resistance.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com