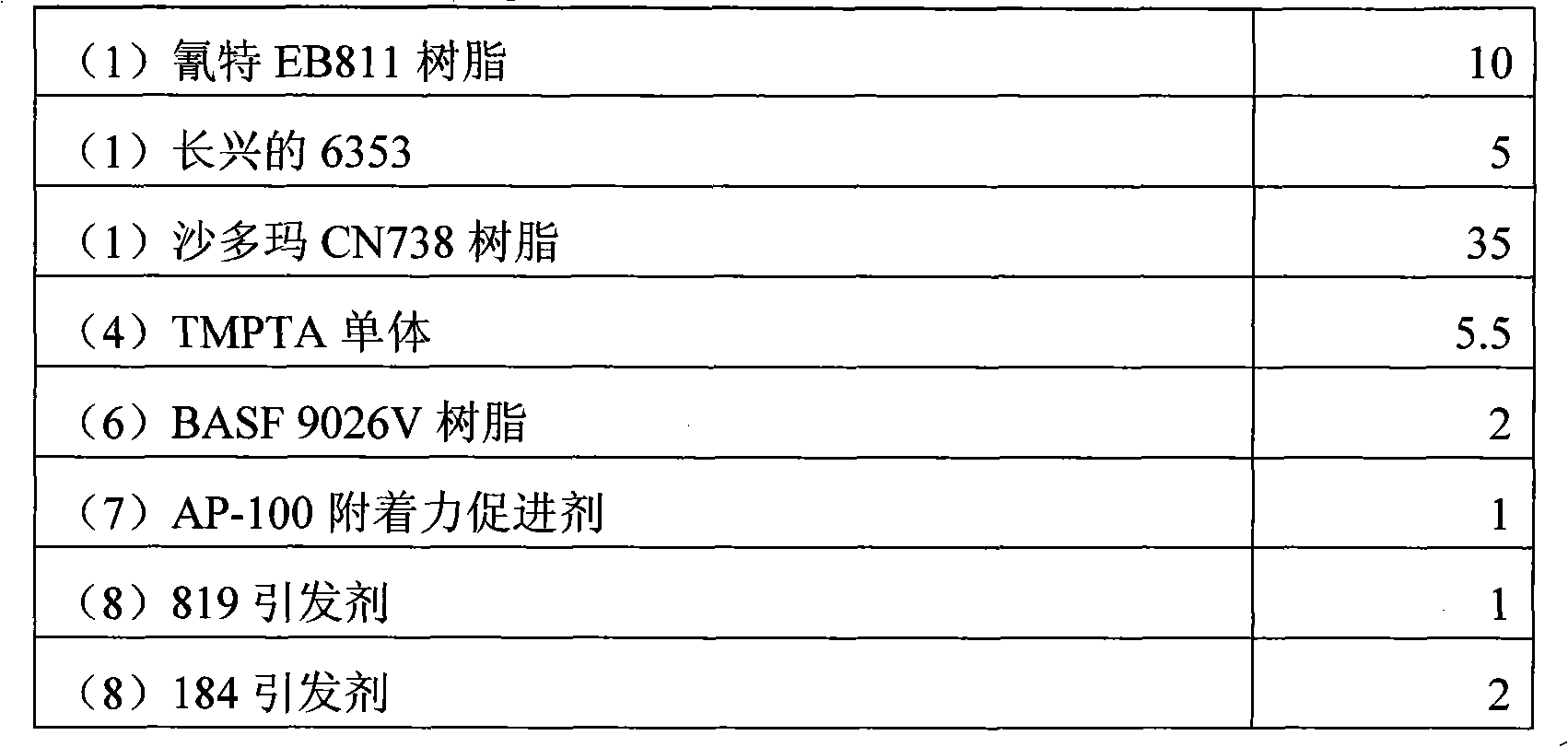
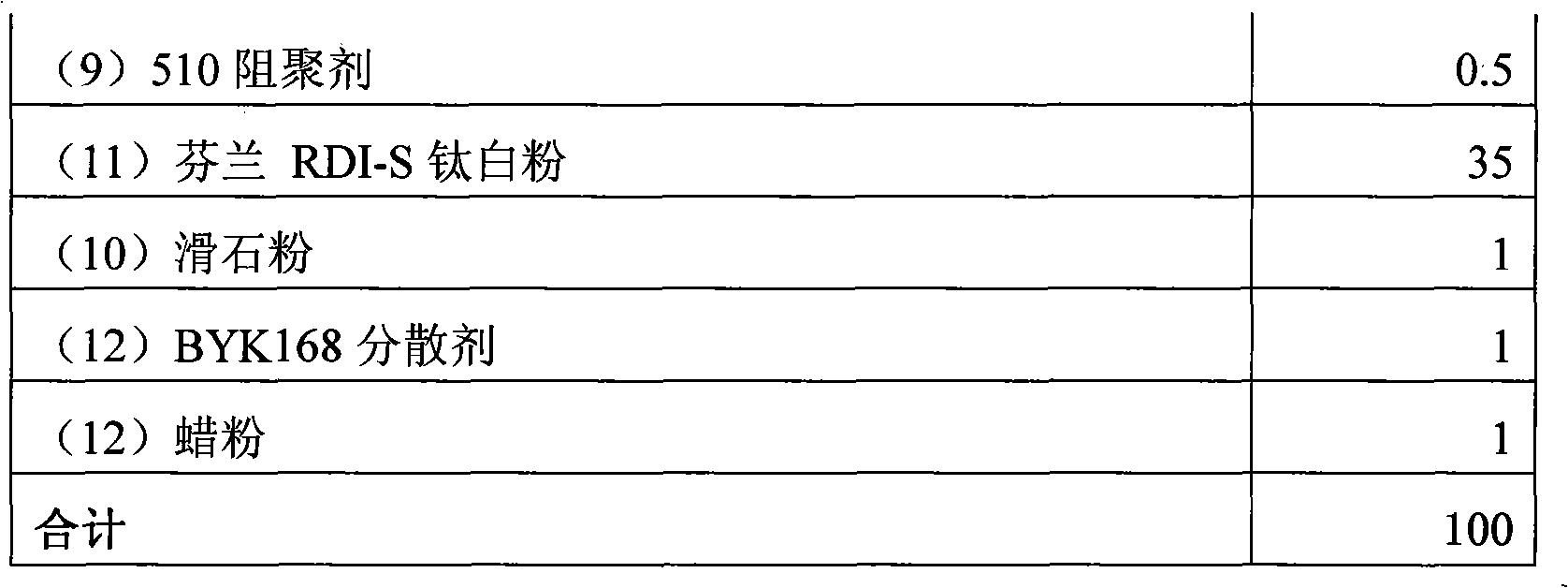
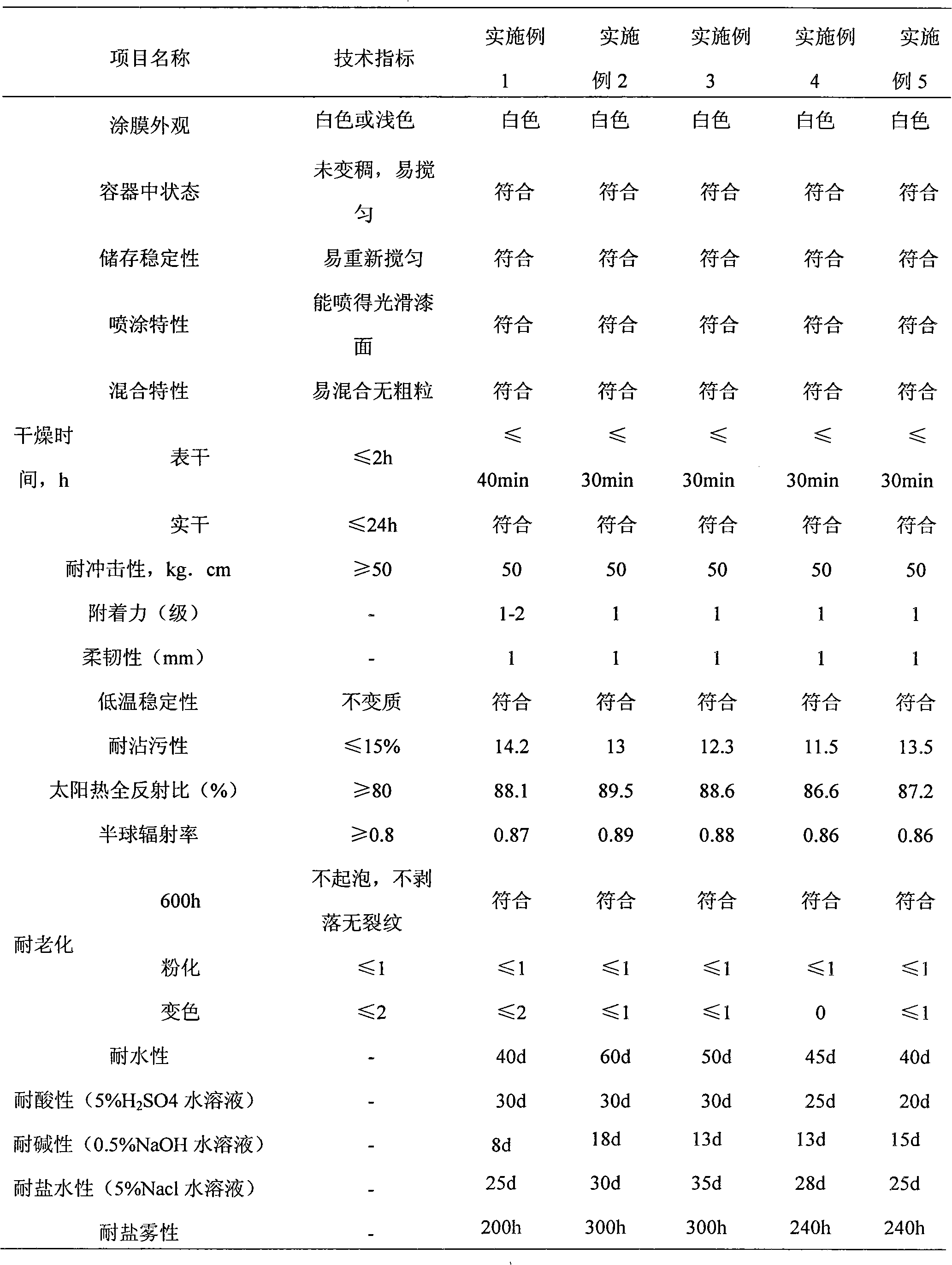
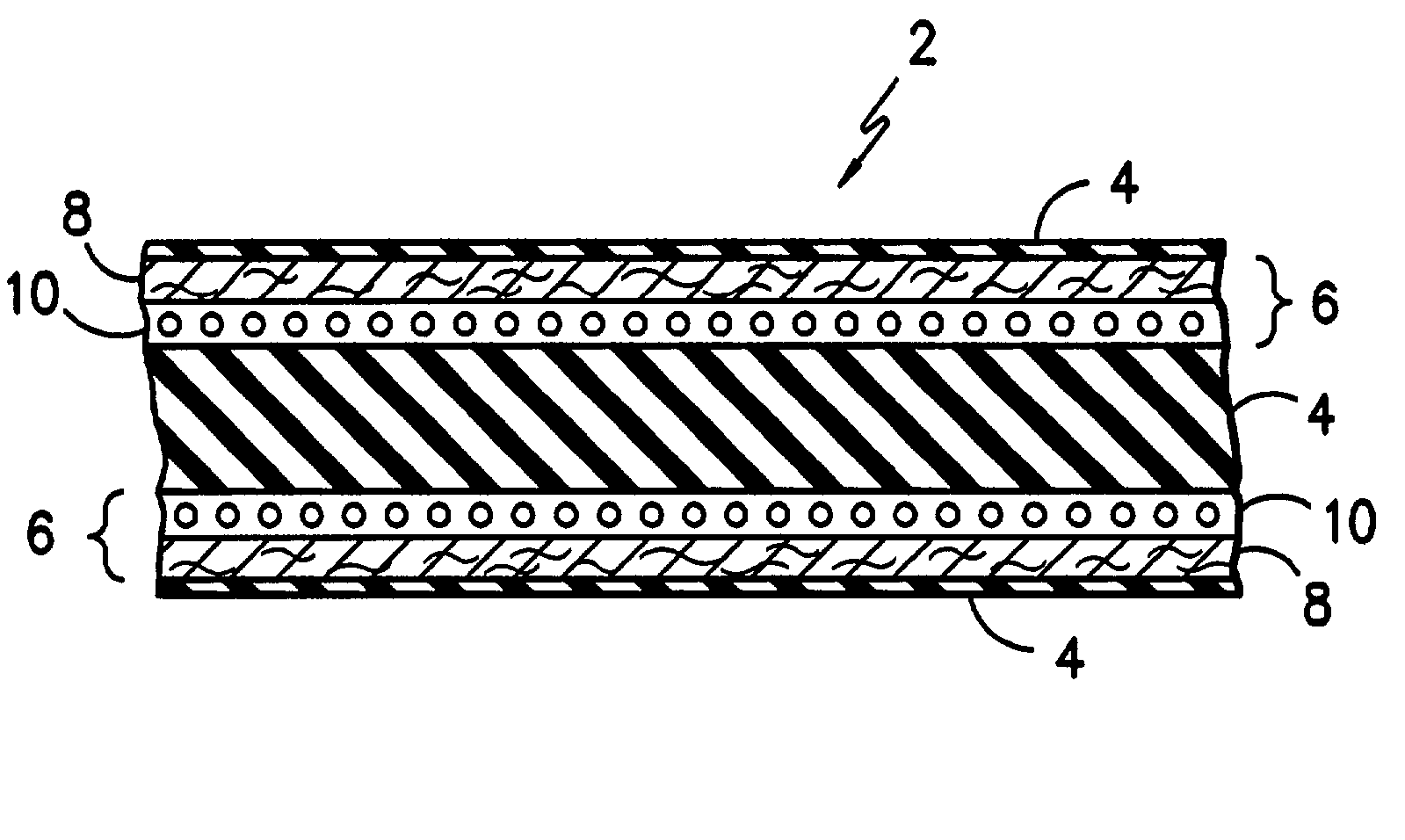
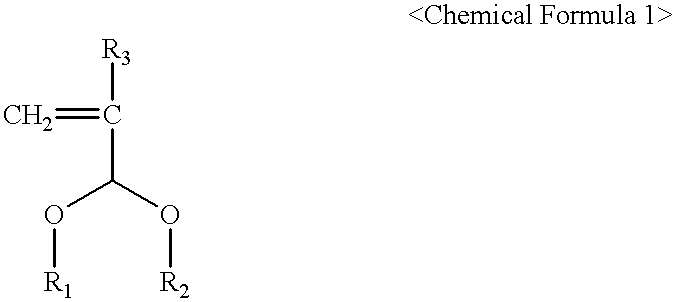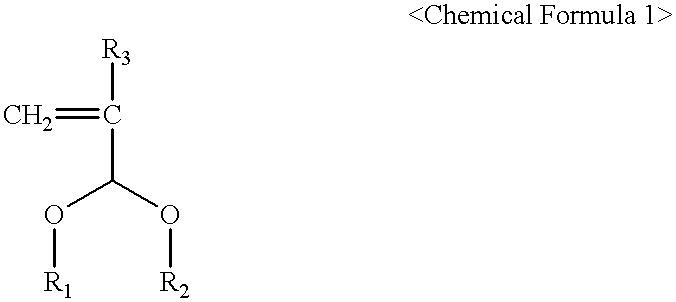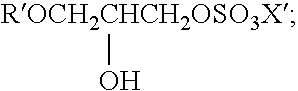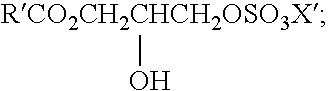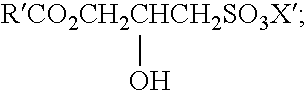Patents
Literature
46378 results about "Acrylic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: propenoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH₂=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually.
Acrylic microchannels and their use in electrophoretic applications
Microchannels having at least an acrylic inner surface and methods of their use in electrophoretic applications are provided. The subject microchannels may be in the form of a variety of configurations suitable for holding an electrophoretic medium. The subject microchannels give rise to substantially reduced EOF and / or adsorption as compared to fused silica under conditions of electrophoresis and find use in a variety of electrophoretic applications in which charged entities are moved through a medium under the influence of the an applied electric field.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Compositions with Improved Adhesion to Low Surface Energy Substrates
InactiveUS20080113094A1Excellent low surface energyImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic dyesOligomerEnd-group
Acrylic-based pressure sensitive adhesives are modified with a telechelic hydrocarbon oligomer. The oligomer comprises a hydrocarbon polymer chain or backbone and a functional end group, e.g., an oligomer prepared from a mono hydroxyl polybutadiene polymer and toluene diisocyanate. The oligomer attaches to the acrylic backbone of the polymer as a pendant group and in a preferred embodiment, the oligomer is mixed with the PSA shortly before the PSA is coated.
Owner:BRADY WORLDWIDE INC
Photoresist cross-linker and photoresist composition comprising the same
InactiveUS6368773B1Enhance the imageAdequate resultOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsCarboxylic acidKetone
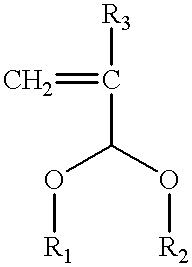
The present invention relates to a cross-linker for photoresist compositions which is suitable for a photolithography process using KrF (248 mn), ArF (193 mn), E-beam, ion beam or EUV light sources. Preferred cross-linkers, according to the present invention, comprise a copolymer of (i) a compound represented by following Chemical Formula 1 and / or (ii) one or more compound(s) selected from the group consisting of acrylic acid, methacrylic acid and maleic anhydride. ##STR1## wherein, R.sub.1 and R.sub.2 individually represent straight or branched C.sub.1-10 alkyl, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 ester, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 ketone, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 carboxylic acid, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 acetal, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 alkyl including at least one hydroxyl group, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 ester including at least one hydroxyl group, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 ketone including at least one hydroxyl group, straight or branched C.sub.1-10 carboxylic acid including at least one hydroxyl group, and straight or branched C.sub.1-10 acetal including at least one hydroxyl group; and R.sub.3 represents hydrogen or methyl.
Owner:HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS IND CO LTD
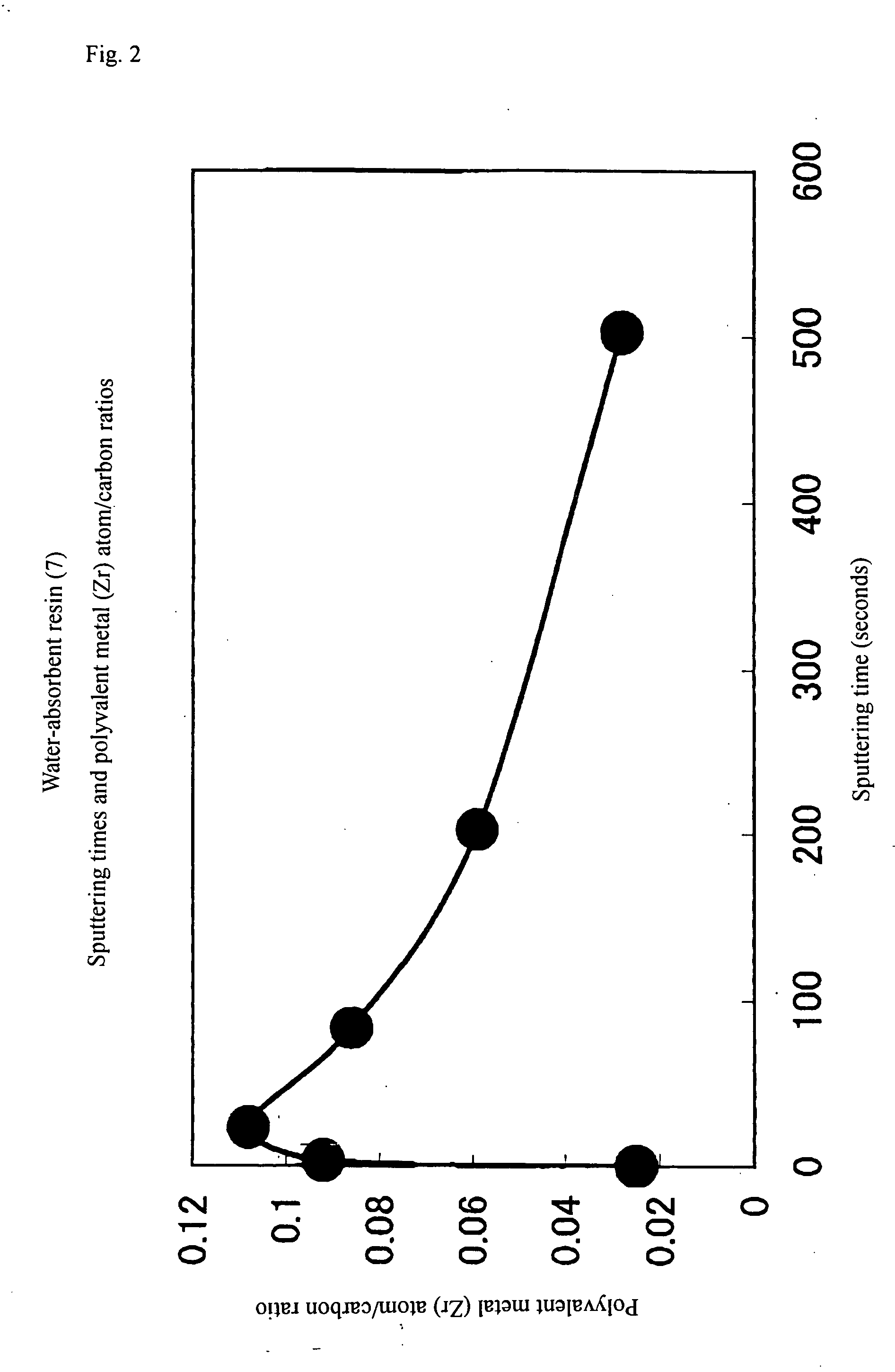
Vater-absorbent resin composition and its production process
ActiveUS20060073969A1Little gel-blockingGood liquid permeabilityNon-fibrous pulp additionOther chemical processesLiquid diffusionCompound (substance)
There are disclosed a water-absorbent resin composition and its production process, wherein the water-absorbent resin composition causes little gel-blocking and is excellent in the liquid permeability and liquid diffusibility and is high also in the absorption performances and further is strong also against the physical damage; and there are further disclosed a water-absorbent resin composition and its production process, wherein the water-absorbent resin composition has the following further advantages, in addition to the above, of involving little segregation of the metal compound and further having a dust prevention effect. One of water-absorbent resin compositions according to the present invention is a water-absorbent resin composition comprising water-absorbent resin particles obtained by polymerizing a monomer including acrylic acid and / or its salt, with the composition having a mass-average particle diameter of 100 to 600 μm and comprising water-soluble polyvalent metal salt particles and the water-absorbent resin particles that have been surface-crosslinked.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Walter-absorbing agent
There is disclosed a water-absorbing agent which combines both performances of the capillary suction force and the liquid permeability. This water-absorbing agent is a particulate water-absorbing agent comprising water-absorbent resin particles (α) and a liquid-permeability-enhancing agent (β), wherein the water-absorbent resin particles (α) are surface-crosslink-treated particles of a crosslinked polymer of a monomer including acrylic acid and / or its salt; with the water-absorbing agent being characterized in that the particulate water-absorbing agent has: a mass-average particle diameter (D50) in the range of 234 to 394 gm, a logarithmic standard deviation (σξY) of a particle diameter distribution in the range of 0.25 to 0.45, an absorption capacity without load (CRC) of not less than 15 g / g, and a water-extractable component content of not higher than 15 mass %; and further a liquid-permeability-enhancing agent (β) content in the range of 0.01 to 5 mass parts per 100 mass parts of the water-absorbent resin particles (α).
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
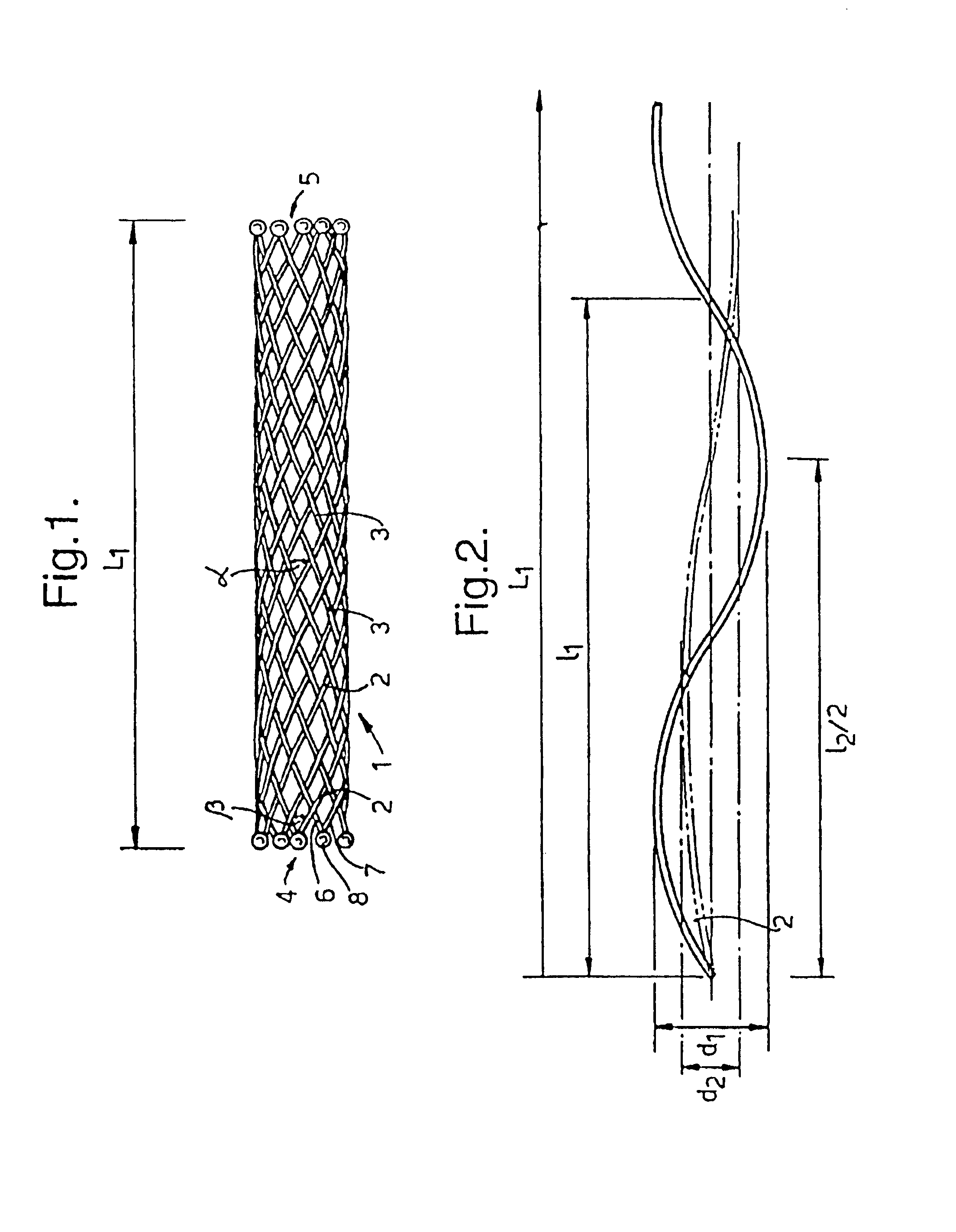
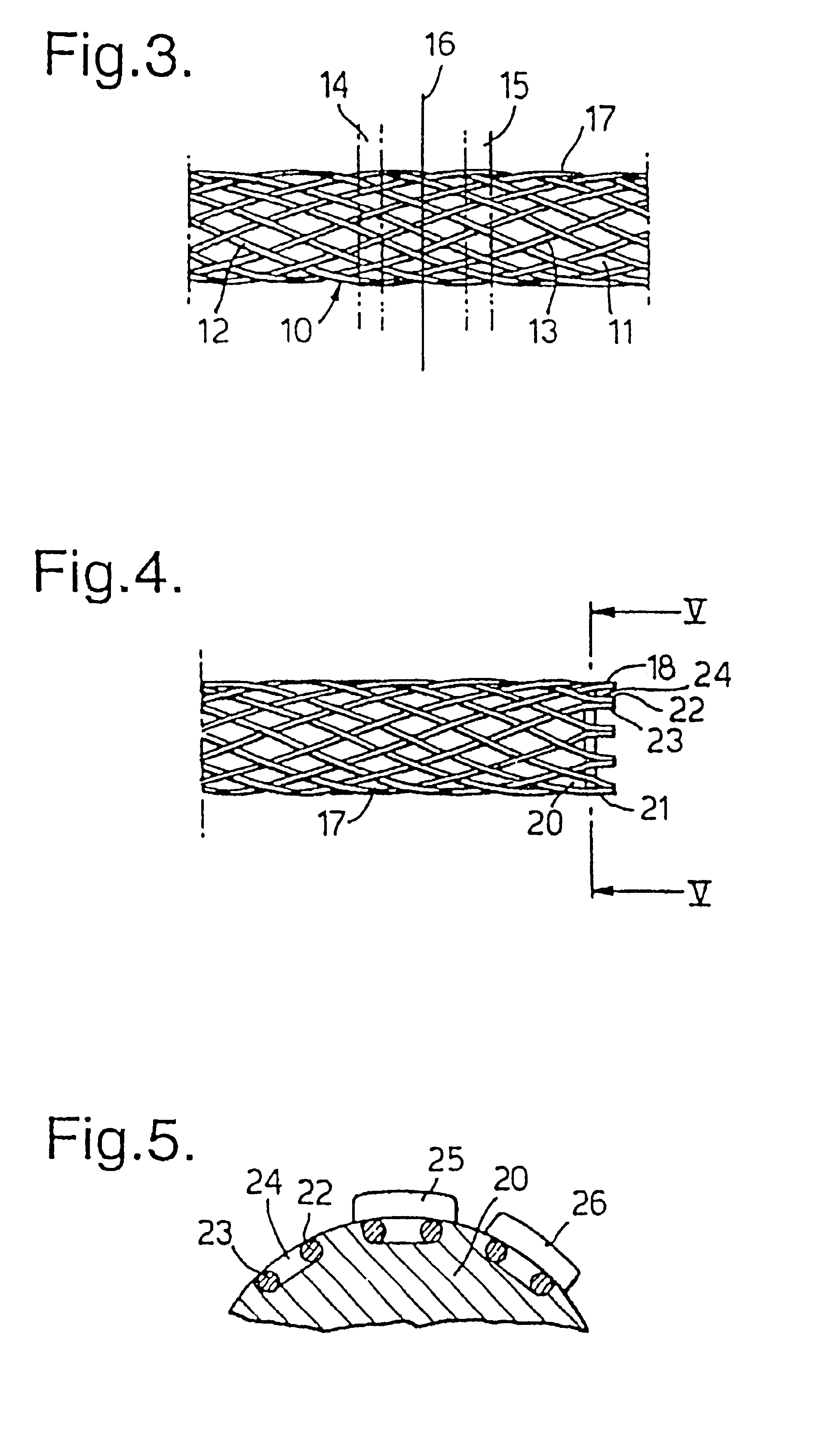
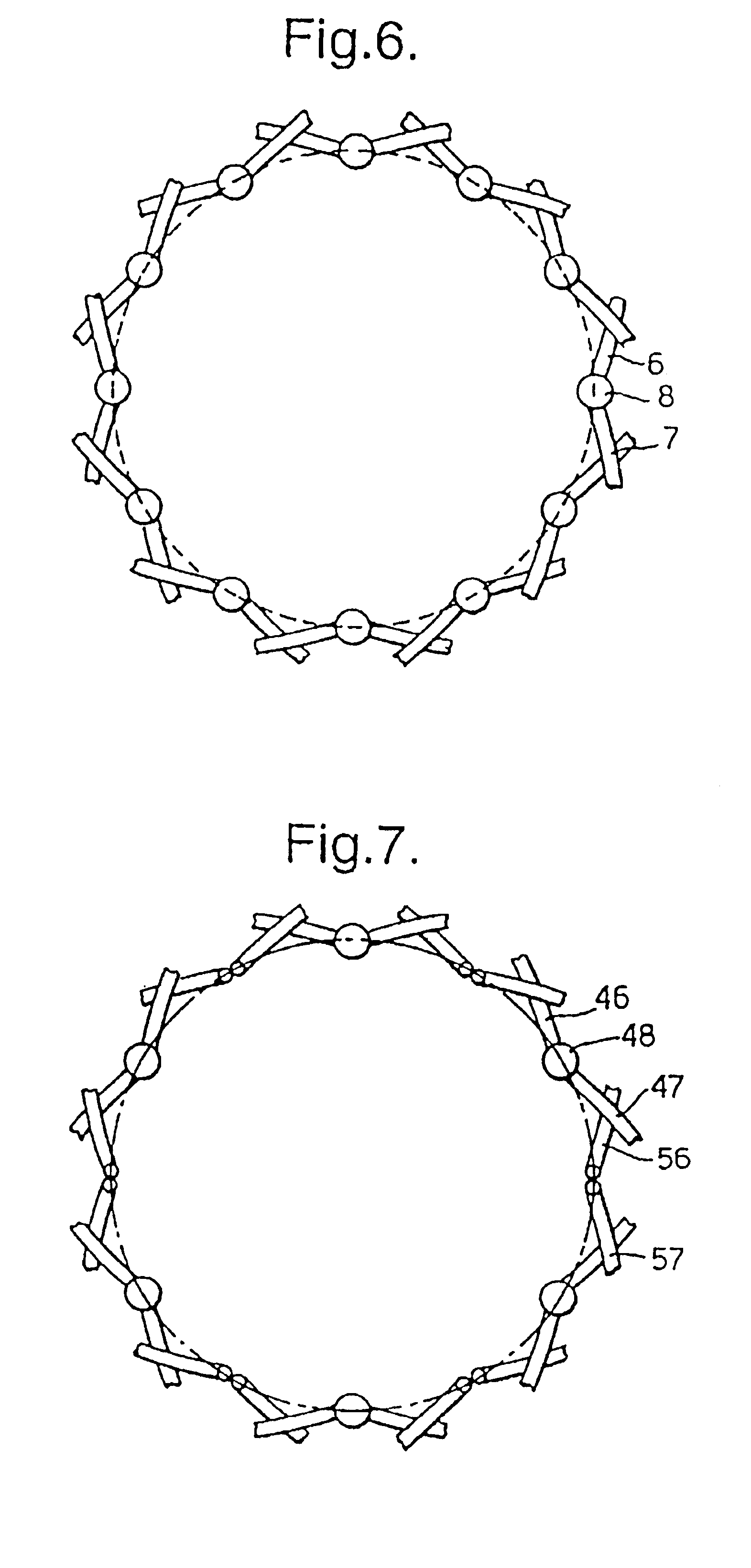
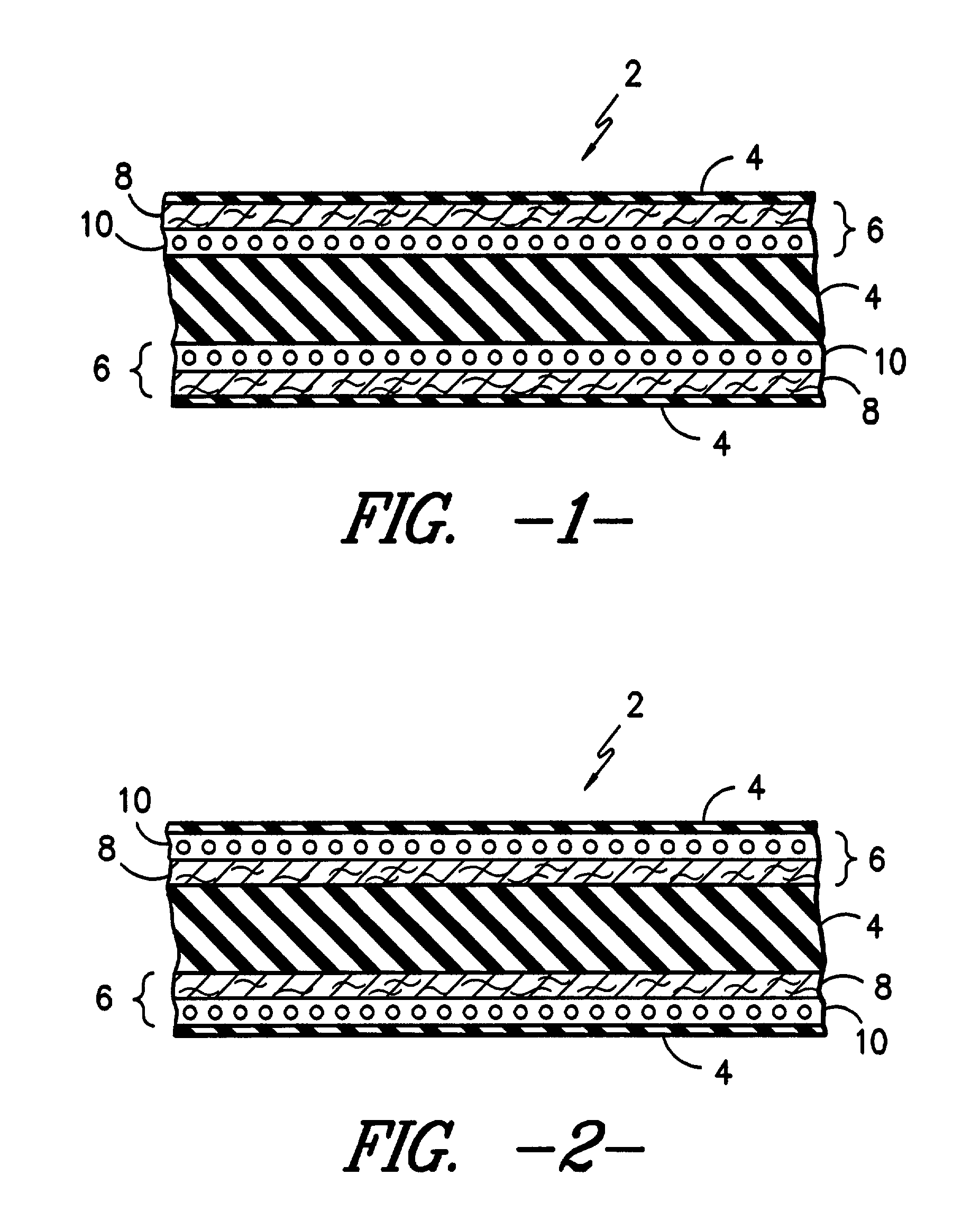
Biocompatible crosslinked coating and crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating
A braided stent (1) for transluminal implantation in body lumens is self-expanding and has a radial expanded configuration in which the angle α between filaments is acute. Some or all of filaments (6,7) are welded together in pairs at each end (4,5) of the stent to provide beads (8), thereby strengthening the stent and assisting its deployment from a delivery device. The stent is preferably completely coated using a biocompatible polymeric coating, said polymer preferably having pendant phosphoryl choline groups. A method of making the stent by braiding and welding is described as well as a delivery device for deploying the device.The present invention provides a biocompatible crosslinked coating and a crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating. The biocompatible crosslinked coating may be formed by curing a polymer of 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate. The crosslinkable coating polymer may include 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate.<?insert-end id="INS-S-00001" ?>
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Water-absorbing agent
There is disclosed a water-absorbing agent which combines both performances of the capillary suction force and the liquid permeability. This water-absorbing agent is a particulate water-absorbing agent comprising water-absorbent resin particles (α) and a liquid-permeability-enhancing agent (β), wherein the water-absorbent resin particles (α) are surface-crosslink-treated particles of a crosslinked polymer of a monomer including acrylic acid and / or its salt; with the water-absorbing agent being characterized in that the particulate water-absorbing agent has: a mass-average particle diameter (D50) in the range of 234 to 394 gm, a logarithmic standard deviation (σζ) of a particle diameter distribution in the range of 0.25 to 0.45, an absorption capacity without load (CRC) of not less than 15 g / g, and a water-extractable component content of not higher than 15 mass %; and further a liquid-permeability-enhancing agent (β) content in the range of 0.01 to 5 mass parts per 100 mass parts of the water-absorbent resin particles (α).
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Water-absorbing agent and production process therefor, and water-absorbent structure
InactiveUS7098284B2Promote absorptionMaintain good propertiesOther chemical processesAbsorbent padsBursting strengthAbsorption capacity
The present invention provides: a novel water-absorbing agent, which exhibits an excellent absorption capacity under a load (AAP), gel layer liquid permeation rate under a load (FRUP), saline flow conductivity (SFC), and shape-maintaining property and ball burst strength (BBS) of a swollen water-absorbing agent aggregate, and excellent persistency of these effects for a long time. The water-absorbing agent, which comprises a polymer obtained by a process including the steps of polymerizing and then crosslinking a monomer including acrylic acid and / or a salt thereof, with the water-absorbing agent being characterized by: (1) exhibiting a free swelling capacity of not less than 23 g / g (GV), a gel deformation of not more than 12.5 cm under a short-time load (0.5 hrPT), and a gel deformation deterioration of not more than 3.5 cm under a load with the passage of time (ΔPT); (2) exhibiting a free swelling capacity of not less than 23 g / g (GV), a ball burst strength of not less than 80 gf (BBS), and a deterioration of ball burst strength of not more than 40% (DBBS); or (3) exhibiting a free swelling capacity of not less than 23 g / g (GV), an absorption capacity of not less than 20 g / g under a load of 4.9 kPa (AAP), and a gel deformation of not more than 12.5 cm under a load (16 hrPT).
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Novel Polymers
ActiveUS20080015315A1Sufficient amountReduce the amount requiredOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention relates to novel crosslinkable copolymers which are obtainable by (a) copolymerizing at least two different hydrophilic monomers selected from the group consisting of N,N-dimethyl acrylamide (DMA), 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA), glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP), acrylic acid (AA) and a C1-C4-alkoxy polyethylene glycol (meth)acrylate having a weight average molecular weight of from 200 to 1500, and at least one crosslinker comprising two or more ethylenically unsaturated double bonds in the presence of a chain transfer agent having a functional group; and (b) reacting one or more functional groups of the resulting copolymer with an organic compound having an ethylenically unsaturated group.
Owner:ALCON INC
Controlled release formulations coated with aqueous dispersions of acrylic polymers
InactiveUS6143353ADissolution stabilityIncrease weight gainPretreated surfacesMedical devicesWater insolubleActive agent
A stable solid controlled release formulation having a coating derived from an aqueous dispersion of a hydrophobic acrylic polymer includes a substrate including an active agent selected from the group consisting of a systemically active therapeutic agent, a locally active therapeutic agent, a disinfecting and sanitizing agent, a cleansing agent, a fragrance agent and a fertilizing agent, overcoated with an aqueous dispersion of the plasticized water-insoluble acrylic polymer. The formulation provides a stable dissolution of the active agent which is unchanged after exposure to accelerated storage conditions.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
Microstructure-bearing articles of high refractive index
InactiveUS6844950B2High refractive indexLiquid crystal compositionsImpression capsPolymer scienceMeth-
Blends of oligomeric urethane multi(meth)acrylate; optionally at least one other monomer selected from the group consisting of acrylic monomers, styrenic monomers and ethylenically unsaturated nitrogen heterocycles, preferably a polyol multi(meth)acrylate; and nanoparticles of an ethylenically unsaturated, preferably (meth)acrylic-functionalized, titanium or zirconium compound can be cured by ultraviolet radiation in contact with a photoinitiator to produce optical resinous articles having high refractive indices, haze ratings of at most 5% and other properties which may be tailored according to the desired use.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Cross-linkable, photoactive polymer materials
InactiveUS6107427AAvoid problemsReverse twist can beLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryActive polymerAryl
The invention is concerned with novel cross-linkable, photoactive polymer materials with 3-aryl-acrylic acid esters and amides as well as their use as orienting layers for liquid crystals and for the production of non-structured or structured optical elements and multi-layer systems.
Owner:ROLIC AG
Water-absorbent resin having treated surface and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20050070671A1Easy to operateSufficient absorption capacityAbsorbent padsBandagesAbsorption capacityMetal
An object of the present invention is to provide: a water-absorbent resin which can sufficiently overcome the problem of the gel blocking, can manifest sufficient absorption capacity without load and sufficient absorption capacity under load and, at the same time, can also exert excellent liquid permeability under load; and a process for producing the same. As a means of achieving this object, a first production process among the processes according to the present invention for producing a water-absorbent resin having a treated surface is a process comprising: a step of mixing a water-absorbent resin having an internal crosslinked structure obtained by polymerizing a monomer containing acrylic acid and / or a salt thereof as a main component, a complex containing a polyvalent metal atom as a central atom and an organic secondary crosslinking agent in the presence of an aqueous liquid; and a step of crosslinking a surface of the water-absorbent resin with the organic secondary crosslinking agent. And a second production process is a process comprising a step of mixing a water-absorbent resin having an internal crosslinked structure and a crosslinked surface obtained by polymerizing a monomer containing acrylic acid and / or a salt thereof as a main component, and a complex containing a polyvalent metal atom as a central atom in the presence of an aqueous liquid.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
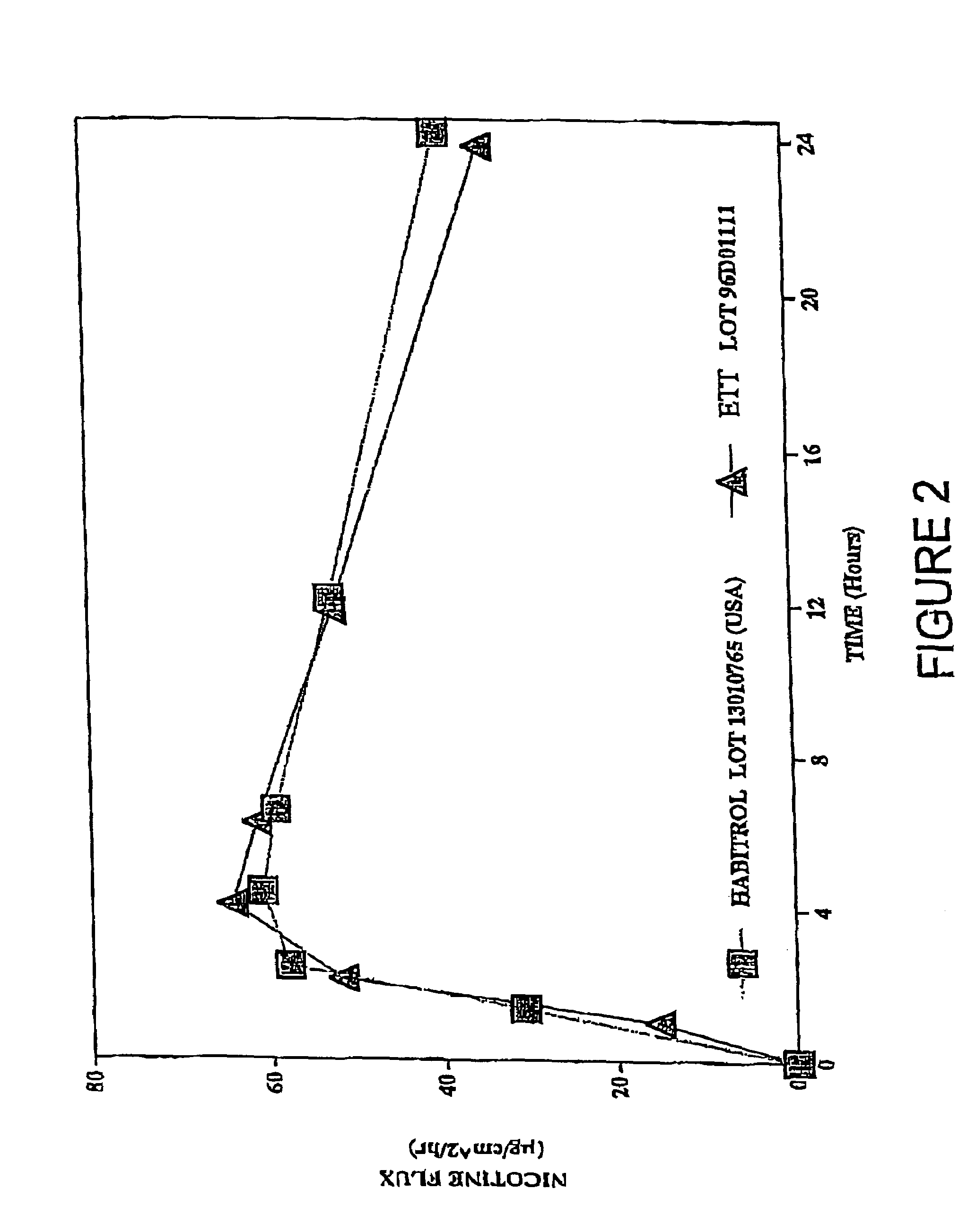
Transdermal patch for delivering volatile liquid drugs
A transdermal patch for administering a volatile liquid drug, such as nicotine, transdermally to a patient comprising a four-layer laminated composite of: a top drug impermeable backing layer; a pressure sensitive silicone adhesive layer containing the drug; a pressure sensitive acrylic adhesive layer also containing the drug; and a removable siliconized release liner layer. Also disclosed is a method for treating a person for nicotine dependence and particularly for treating a woman for nicotine dependence.
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD +1
Silicone hydrogels comprising n-vinyl amides and hydroxyalkyl (meth)acrylates or (meth)acrylamides
The present invention relates to a process comprising the steps of reacting a reactive mixture comprising at least one silicone-containing component, at least one hydrophilic component, and at least one diluent to form an ophthalmic device having an advancing contact angle of less than about 80°; and contacting the ophthalmic device with an aqueous extraction solution at an elevated extraction temperature, wherein said at least one diluent has a boiling point at least about 10° higher than said extraction temperature.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Medical electrode
An electrode providing electrical contact with a patient's skin includes a conductive member adapted for connection to an external electrical apparatus and a non-liquid film for electrically interfacing to said patient's skin, the liquid film being electrically and mechanically connected to said conductive member. The non-liquid film includes an electrically conductive organic polymer plasticized with a polyhydric alcohol with said organic polymer being derived from a monomeric mixture comprising from about 15 to 30 pph acrylic acid, 0.5 to 30 pph N-vinylpyrrolidone and 0.01 to 2 pph of a crosslinking agent. The monomeric mixture may further comprise from about 0.5 to 8 pph of a thickening agent selected from the group consisting of N-vinylpyrrolidone / acrylic acid copolymers, N-vinylpyrrolidone / vinylacetate copolymers, and N-vinylpyrrolidone / vinylimidazole copolymers.
Owner:AXELGAARD MANUFACTURING COMPANY INC
Self adaptive cement systems
InactiveUS20070137528A1Avoid seizuresInhibit migrationSolid waste managementDrilling compositionSelf-healingChemical products
A self-adaptive cement system includes cement, water and at least one additive that reacts or and expands in contact with oil and gas. Several chemical products have been identified including rubber alkylstyrene, polynorbornene, resins such precrosslinked substituted vinyl acrylate copolymers and diatomaceous earth. These additives have the effect of making the cement self-healing in the event of physical failure or damage such as micro-annuli. The self healing property is produced by the contact with subterranean hydrocarbon fluids, the potential repair mechanism is thus activated if and when needed in case of start of loss of zonal isolation. In another embodiment, the expansion is deliberately induced by pumping a hydrocarbon fluid in the vicinity of the set cement.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Medical electrode
An electrode providing electrical contact with a patient's skin includes a conductive member adapted for connection to an external electrical apparatus and a non-liquid water containing film for electrically interfacing to said patient's skin, the non-liquid film being electrically and mechanically connected to said conductive member. The non-liquid water containing film includes an electrically conductive organic polymer plasticized with a polyhydric alcohol with said organic polymer being derived from a monomeric mixture comprising from about 2 to 30 pph acrylic acid, 2 to 30 pph of a glycolvinylether and 0.01 to 1.5 pph of a crosslinking agent. Preferably the polyhydric alcohol is glycerol.
Owner:AXELGAARD MANUFACTURING COMPANY INC
Composite metal oxide for unsaturated aldehyde selective oxidation and preparing method thereof
A composite metallic oxide as catalyst for selective oxidization of unsaturated aldehyde, especially the acrylaldehyde or methyl acrylaldehyde to obtain acrylic acid or methyl acrylic acid, is composed of active components (Mo, V and Cu), stabilizer (at least Sb and Ti) and the composite oxide of Ni, Fe, Si, Al, alkali metal and alkali-earth metal. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:兰州金润宏成新材料科技有限公司
Intumescent, flame retardant pressure sensitive adhesive composition for EMI shielding applications
InactiveUS6410137B1Readily apparentGood physical propertiesScreening gaskets/sealsSynthetic resin layered productsDecabromodiphenyl etherPolybrominated Biphenyls
A flame retardant, intumescent pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) composition for EMI shielding gaskets, tapes, wraps, and the like. The composition is formulated as an admixture of: (a) a PSA component; (b) a halogenated first flame retardant component; (c) a metal-based second flame retardant component; and (d) a filler component of expandable, intercalated graphite particles. In a representative embodiment the PSA component (a) is acrylic-based, the halogenated first flame retardant component (b) is a polybrominated diphenyl compound such as decabromodiphenyl oxide or decabromodiphenyl ether, the metal oxide-based second flame retardant component (c) is antimony oxide, antimony trioxide, or antimony pentoxide, and the filler component (d) is graphite flake.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
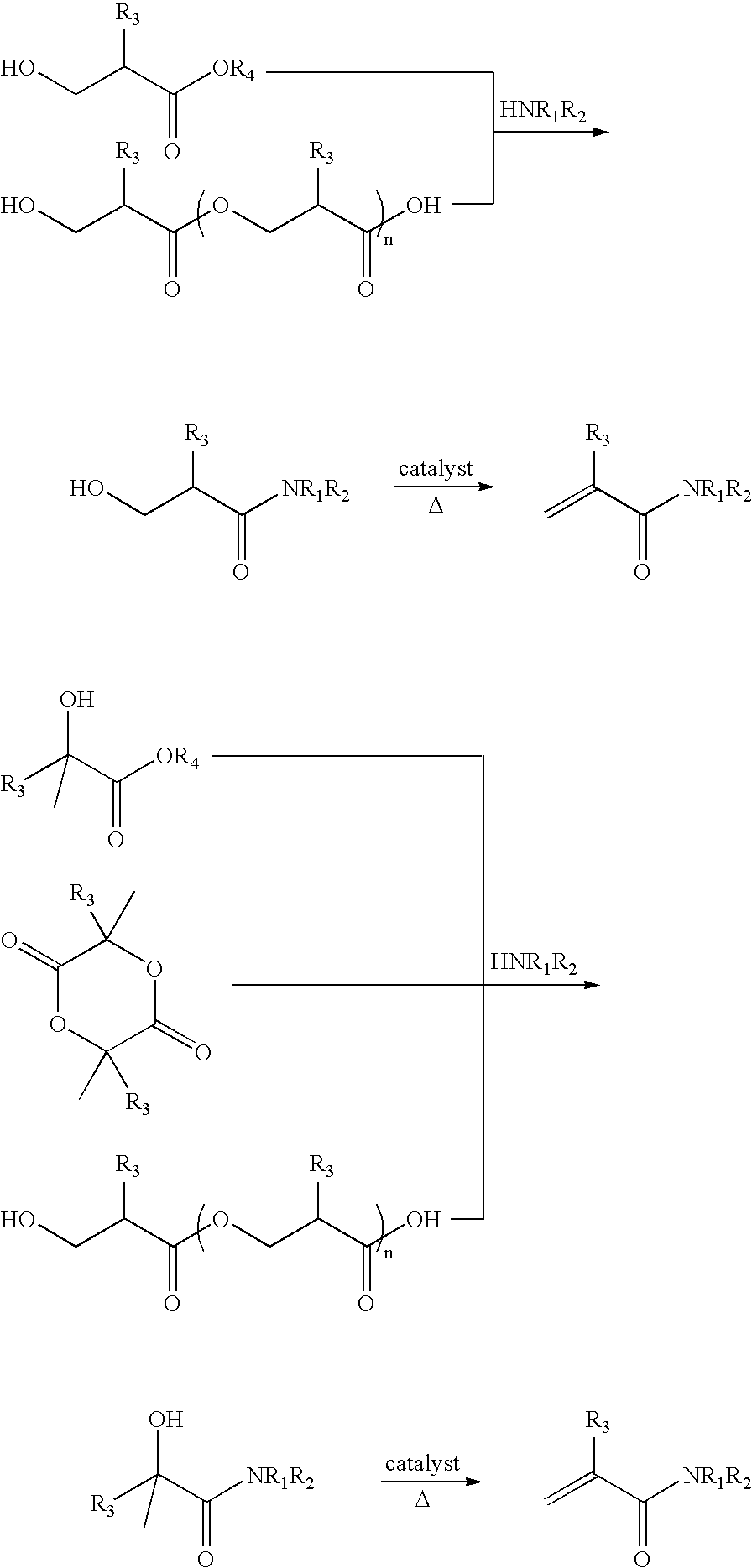
Preparation of acrylic acid derivatives from alpha-or beta-hydroxy carboxylic acids
InactiveUS20050222458A1Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCarboxylic acidMedicinal chemistry
The invention is directed to a process for the preparation of α,β-unsaturated acids, esters and amides from α- or β-hydroxycarboxylic acids or esters or precursors in high yields and high selectivity. The α,β-unsaturated acids or esters are optionally prepared in the presence of specific dehydration and / or esterification catalysts. The α,β-unsaturated amides or substituted amides are prepared optionally in the presence of a dehydration and / or amidation catalyst. The source of α- or β-hydroxycarboxylic acids or precusor is preferably from a renewable resource. The precursor is defined herein.
Owner:CIBA SPECIALTY CHEM WATER TRATMENTS
Mild and effective cleansing compositions
InactiveUS7084104B2Reducing skin and eye irritancyInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsPolymer scienceActive agent
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Composite materials comprising polar polymers and single-wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6936653B2Improve conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationPolyesterPolymer science
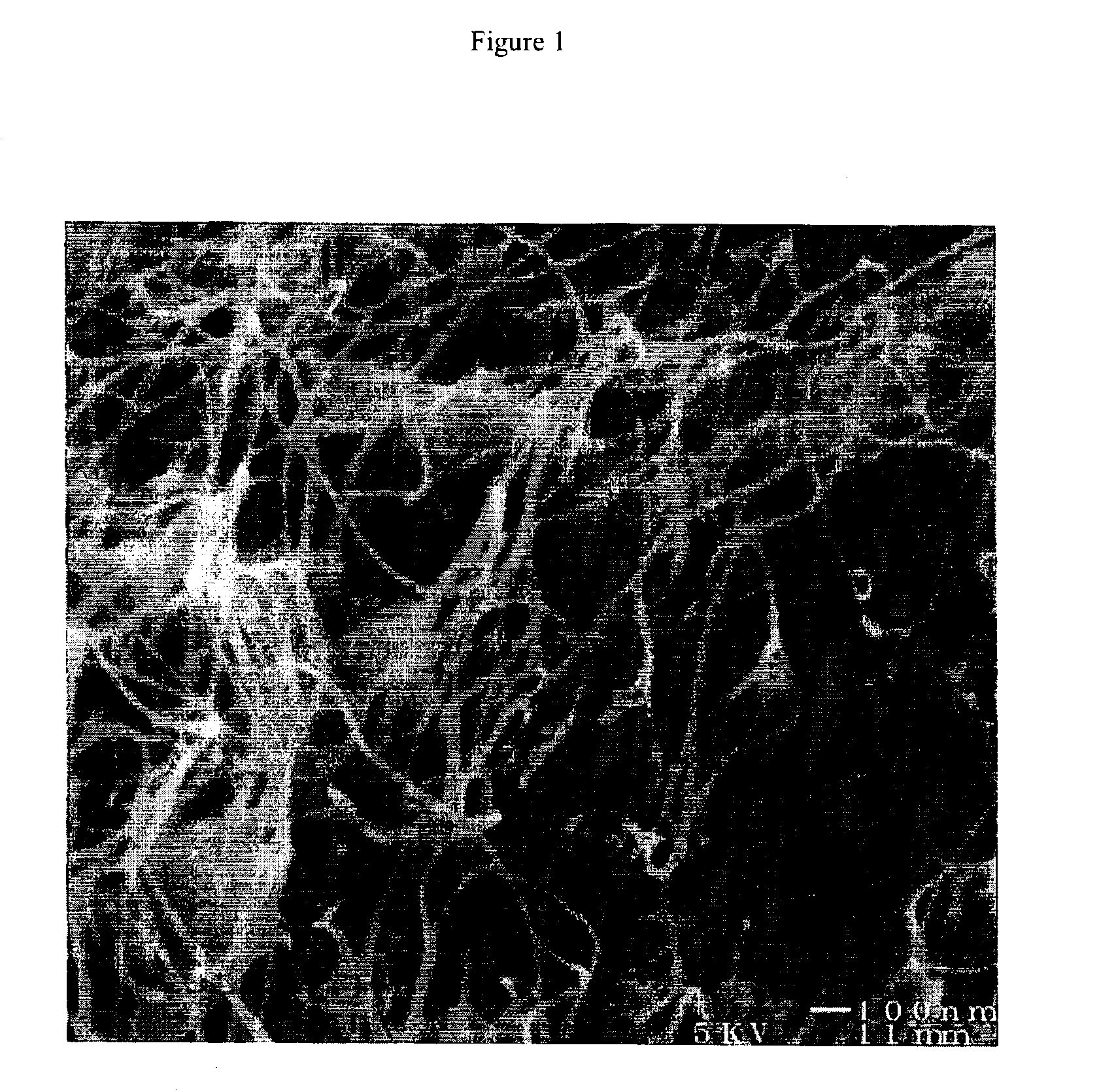
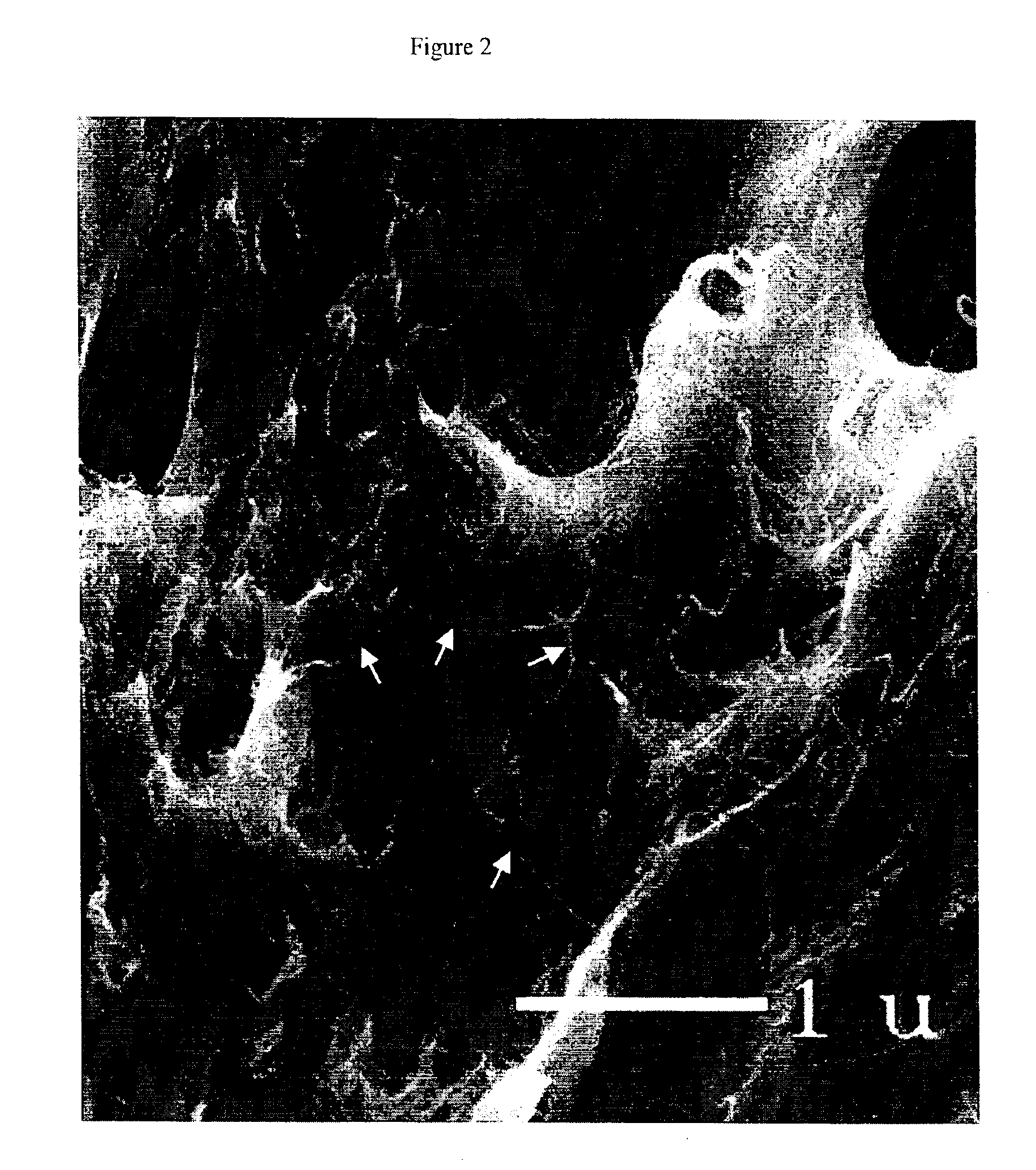
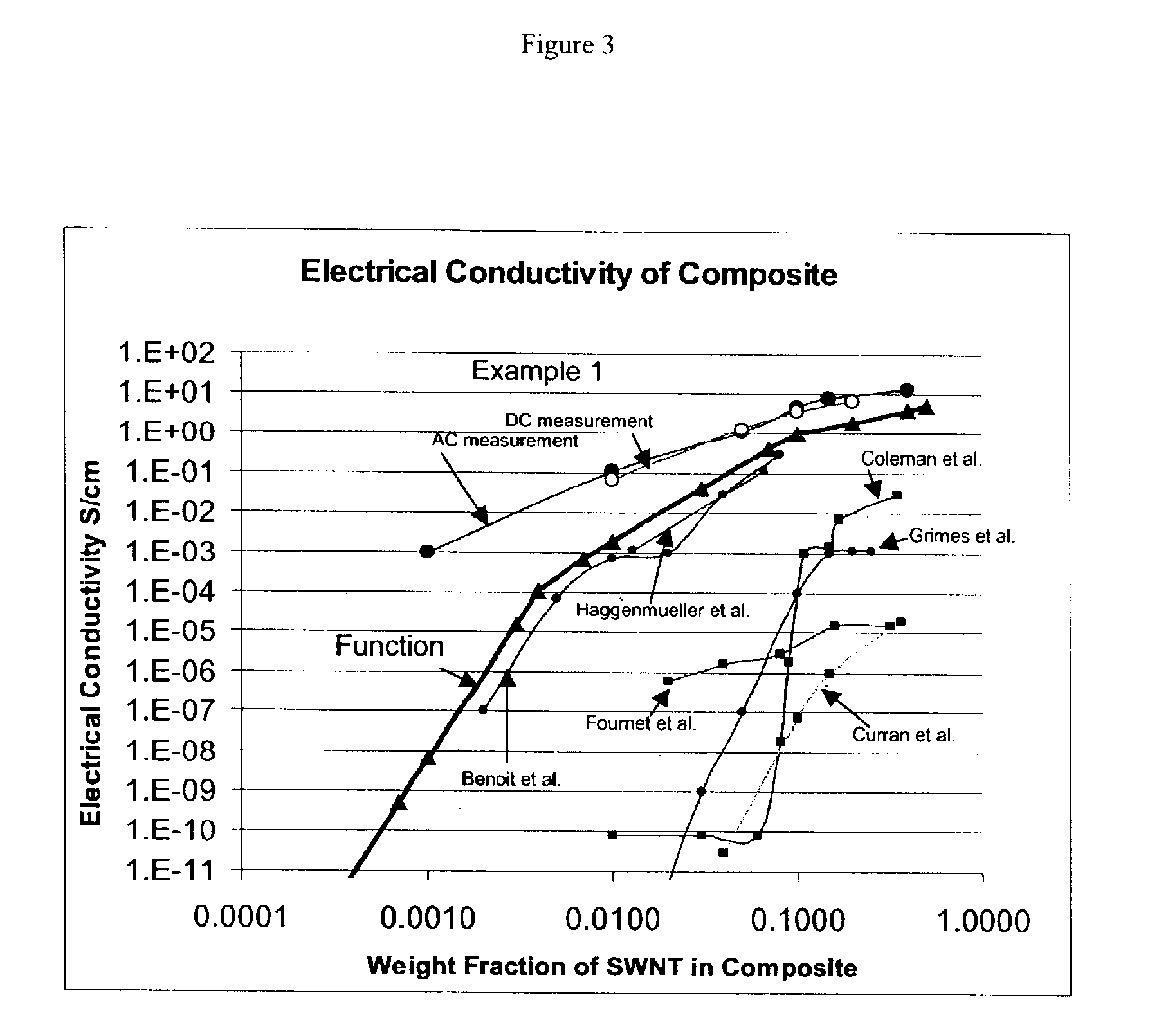
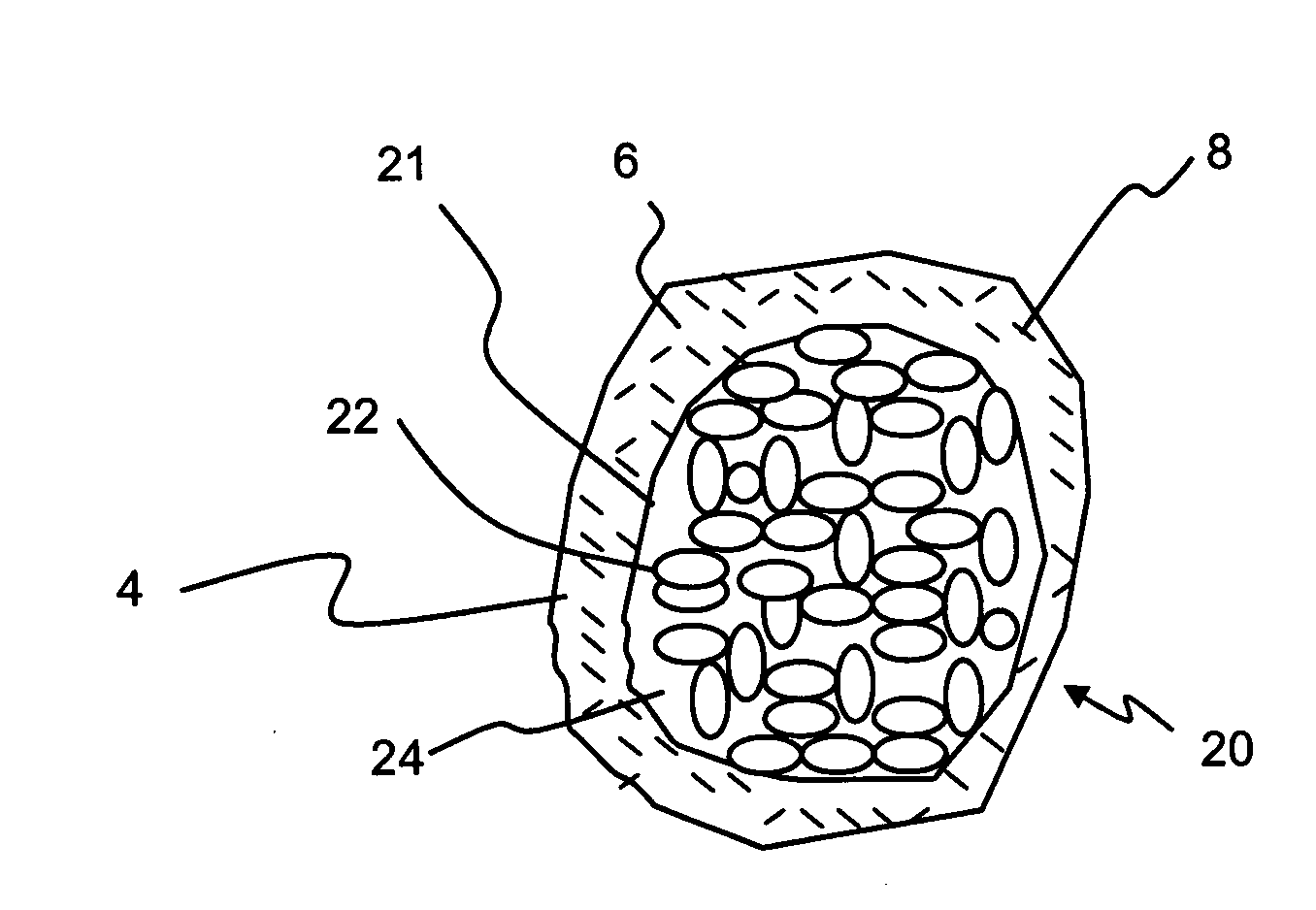
The invention relates to a composite comprising a weight fraction of single-wall carbon nanotubes and at least one polar polymer wherein the composite has an electrical and / or thermal conductivity enhanced over that of the polymer alone. The invention also comprises a method for making this polymer composition. The present application provides composite compositions that, over a wide range of single-wall carbon nanotube loading, have electrical conductivities exceeding those known in the art by more than one order of magnitude. The electrical conductivity enhancement depends on the weight fraction (F) of the single-wall carbon nanotubes in the composite. The electrical conductivity of the composite of this invention is at least 5 Siemens per centimeter (S / cm) at (F) of 0.5 (i.e. where single-wall carbon nanotube loading weight represents half of the total composite weight), at least 1 S / cm at a F of 0.1, at least 1×10−4 S / cm at (F) of 0.004, at least 6×10−9 S / cm at (F) of 0.001 and at least 3×10−16 S / cm (F) plus the intrinsic conductivity of the polymer matrix material at of 0.0001. The thermal conductivity enhancement is in excess of 1 Watt / m-° K. The polar polymer can be polycarbonate, poly(acrylic acid), poly(acrylic acid), poly(methacrylic acid), polyoxide, polysulfide, polysulfone, polyamides, polyester, polyurethane, polyimide, poly(vinyl acetate), poly(vinyl alcohol), poly(vinyl chloride), poly(vinyl pyridine), poly(vinyl pyrrolidone), copolymers thereof and combinations thereof. The composite can further comprise a nonpolar polymer, such as, a polyolefin polymer, polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutene, polyisobutene, polyisoprene, polystyrene, copolymers thereof and combinations thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low temperature coated particles for use as proppants or in gravel packs, methods for making and using the same
ActiveUS20080230223A1Improves unconfined compressive strength propertyImprove performanceLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterParticulates
Disclosed herein are free flowing coated particles and low temperature methods of making same. Each particle has a curable coating disposed upon a substrate. The substrate is a particulate substrate including an inorganic material, a particulate substrate including an organic material, a composite substantially homogeneous formed particle including a first portion of an at least partly cured binder and filler particles, or a hybrid particle having an inorganic particle as a core and a composite coating including at least partially cured resin and filler. The curable coating includes a continuous phase including resole resin and reactive powder particles embedded or adhered to the continuous phase. The reactive powder particles typically include resole resin, novolak resin, polyester, acrylic and / or urethane. A method including applying a coating including the continuous phase including resole resin and reactive or non-reactive powder particles embedded or adhered to the continuous phase.
Owner:HEXION INC
Use of an acrylic type polymer as disintegrating agent
InactiveUS6696085B2Appreciable performancePowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer chemistryPolymer
The present invention provides for the use of a polymer of the acrylic type as a disintegration agent.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA IPL
Fluorochemical sulfonamide surfactants
InactiveUS6852781B2High yieldLow costNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPhotosensitive materialsSide chainSulfonyl fluoride
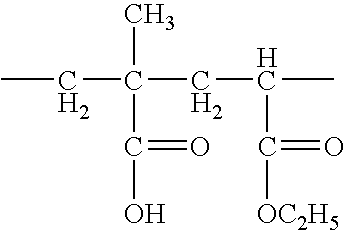
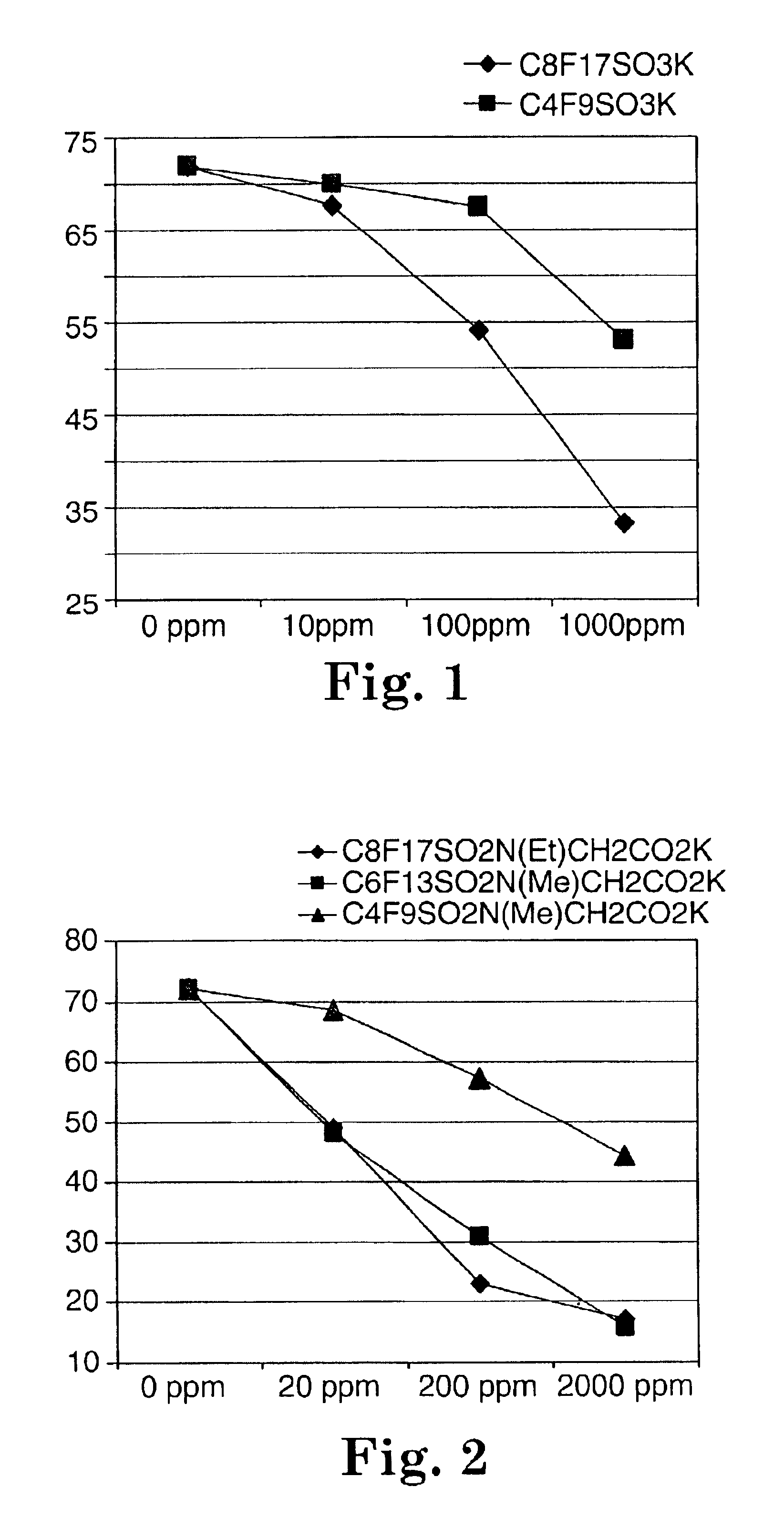
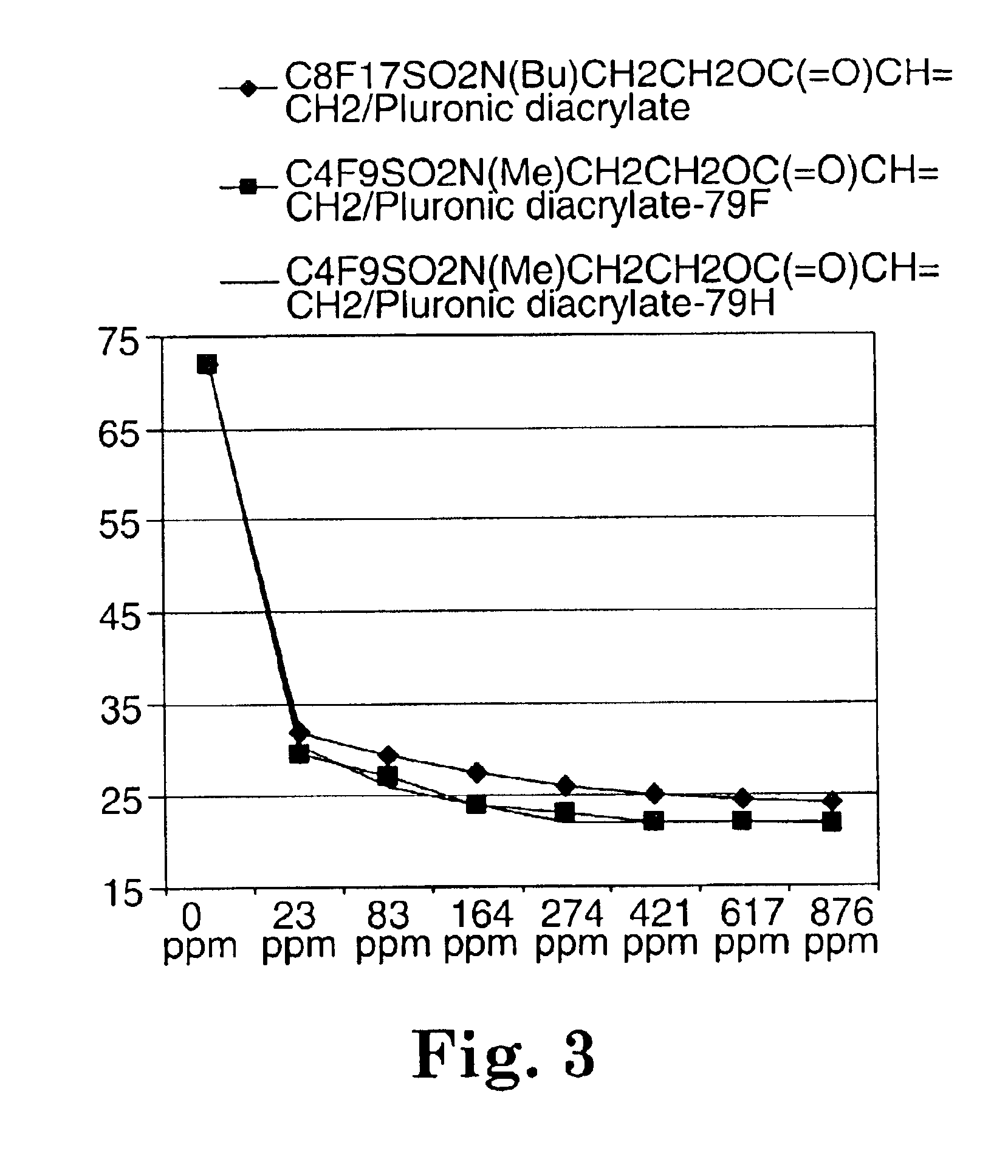
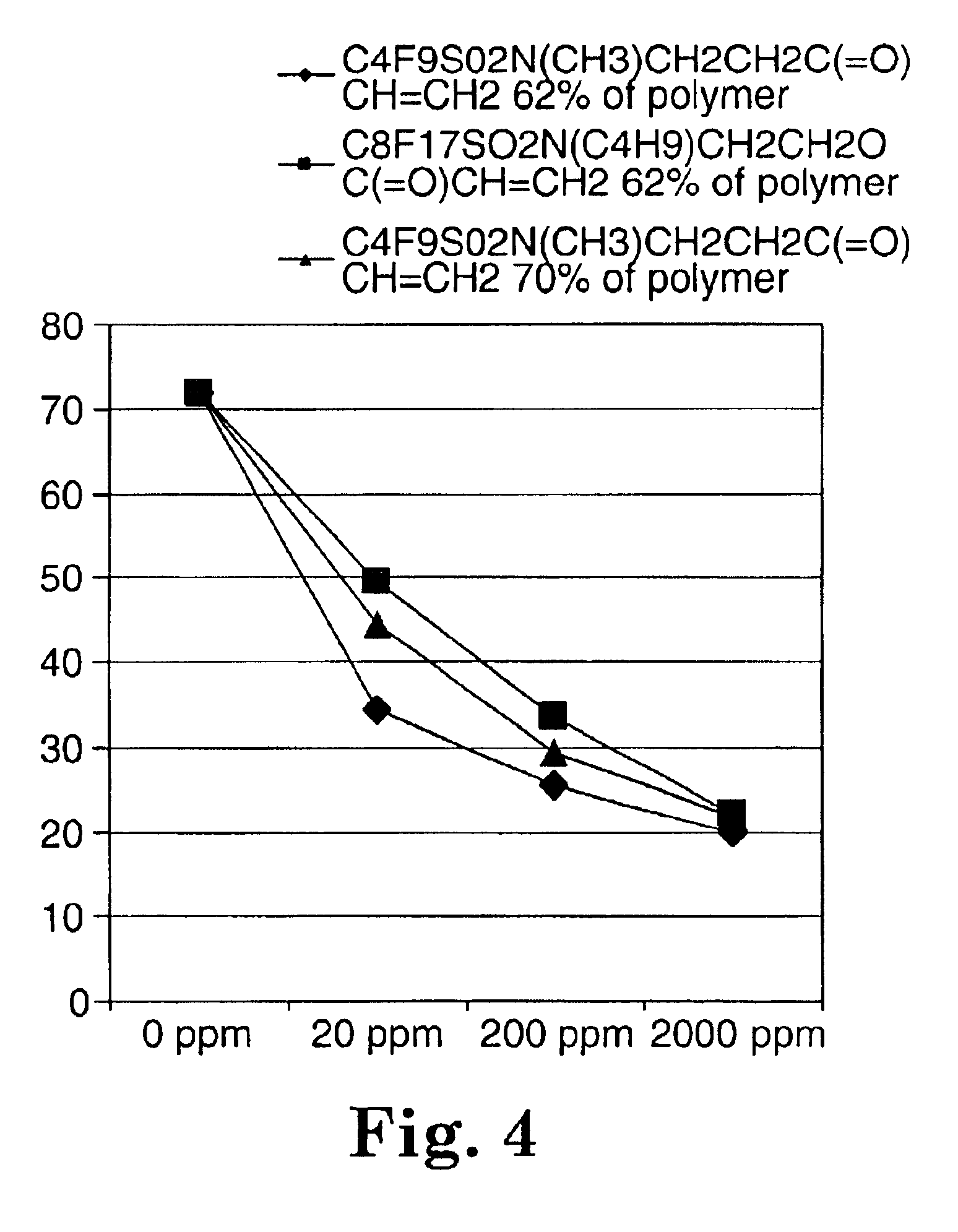
Described are fluorochemical surfactants derived from nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride that contain polyalkyleneoxy side chains and may be copolymerized with acrylic acid or methacrylic acid to form polyacrylates or polymethacrylates. The surfactants surprisingly lower the surface tension of water and other liquids in the same or similar low values achieved by premier surfactants such as those derived from perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Pigment ink jet ink composition
An ink jet ink composition comprising an aqueous media and a pigment dispersion comprising a pigment and a polymeric dispersant wherein said polymeric dispersant is a copolymer comprising at least a hydrophobic methacrylate or acrylate monomer containing an aliphatic chain having greater than or equal to 12 carbons; and a hydrophilic methacrylic or acrylic acid monomer; wherein said copolymer comprises at least 10% by weight of the methacrylate or acrylate monomer and at least 5% by weight of the methacrylic or acrylic acid monomer; and wherein the copolymer comprises, in total, 20 to 95 weight % of hydrophobic monomer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Ultraviolet light curing offset printing ink and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an ultraviolet light curing offset printing ink and a preparation method thereof. The ultraviolet light curing offset printing ink is made of 25.0-50.0% of polyfunctional polyester acrylic resin or polyfunctional chlorinated polyester acrylate, 0.0-15.0% of epoxy acrylate oligopolymer, 0.0-20.0% of polyfunctional urethane acrylate, 0.0-15.0% of difunctional or polyfunctional acrylic monomer, 0.0-20.0% of grinding-type resin, 2.0-10.0% of polyether acrylate modified by nano silicon dioxide, 0.0-5.0% of adhesion promoter, 3.0-5.0% of photoinitiator, 0.1-2.0% of polymerization inhibitor, 0.0-10.0% of filler, 16.0-55.0% of paint or dye and 0.2-5.0% of accessory ingredient. The prepared offset printing ink has high transparency as well as good adhesive attraction and flexility, and can be widely applied to packages printing industry and the printing of various transfer paper.
Owner:CHUZHOU JINQIAO TEXAS NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Nanometer compound water-based heat insulation anticorrosion paint used for metal and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101665645AGood heat insulationImprove corrosion resistanceAnti-corrosive paintsReflecting/signal paintsWater basedAcrylic resin
The invention discloses a nanometer compound water-based heat insulation anticorrosion paint used for metal and a preparation method thereof. The raw materials of the paint consists of the following components: tap water, watercraft acrylic resin, rustproofing pigment, reflection pigment and filler, hollow micro-beads, watercraft nanometer size, anti-settling agent, wetting and dispersing agent A,wetting and dispersing agent B, film-forming assistant, defoaming agent, flatting agent, anti-flash rustproofing agent and thickening agent. Watercraft polyacrylic emulsion is styrene-crylic acid copolymerization emulsion, pure crylic acid polymerization emulsion or organic silicon-crylic acid copolymerization emulsion. The wetting and dispersing agent A is block macromolecule copolymer, multivalence carboxylate polymer and / or synthetic macromolecule copolymer, and the wetting and dispersing agent B is anion wetting agent and / or nonionic wetting agnet. The product contains no organic solvent,heavy metal and other harmful substances, is extremely excellent in environmental conservation, integrates the functions of anticorrosion and heat insulation as a whole and is simple and convenient for construction, safe in storage and stable in performance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JOINTAS CHEM
Composite facer for wallboards
InactiveUS20020151240A1Easy to foldReduce the possibilityMedical devicesPressure infusionSecondary layerPolyester
A composite facer material for use with cementitious wallboards, where the composite facer is embedded in a top and bottom face thereof. The composite facer material, in a most preferred embodiment, comprises two layers. The first layer is preferably a carded polyester nonwoven mat, which is bonded to a second layer comprising preferably a tri-directional laid scrim fabric reinforcement layer made of continuous glass fibers. The two layers are preferably bonded together using an acrylic adhesive, which offers superior adhesion between the layers as well as superior adhesion between the composite facing material and the cementitious core.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com