Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Wide latitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel blue emitters for use in organic electroluminescence devices
ActiveUS20050175857A1Excellent thermal stabilityStrong thermal stabilitySilicon organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceHalogen
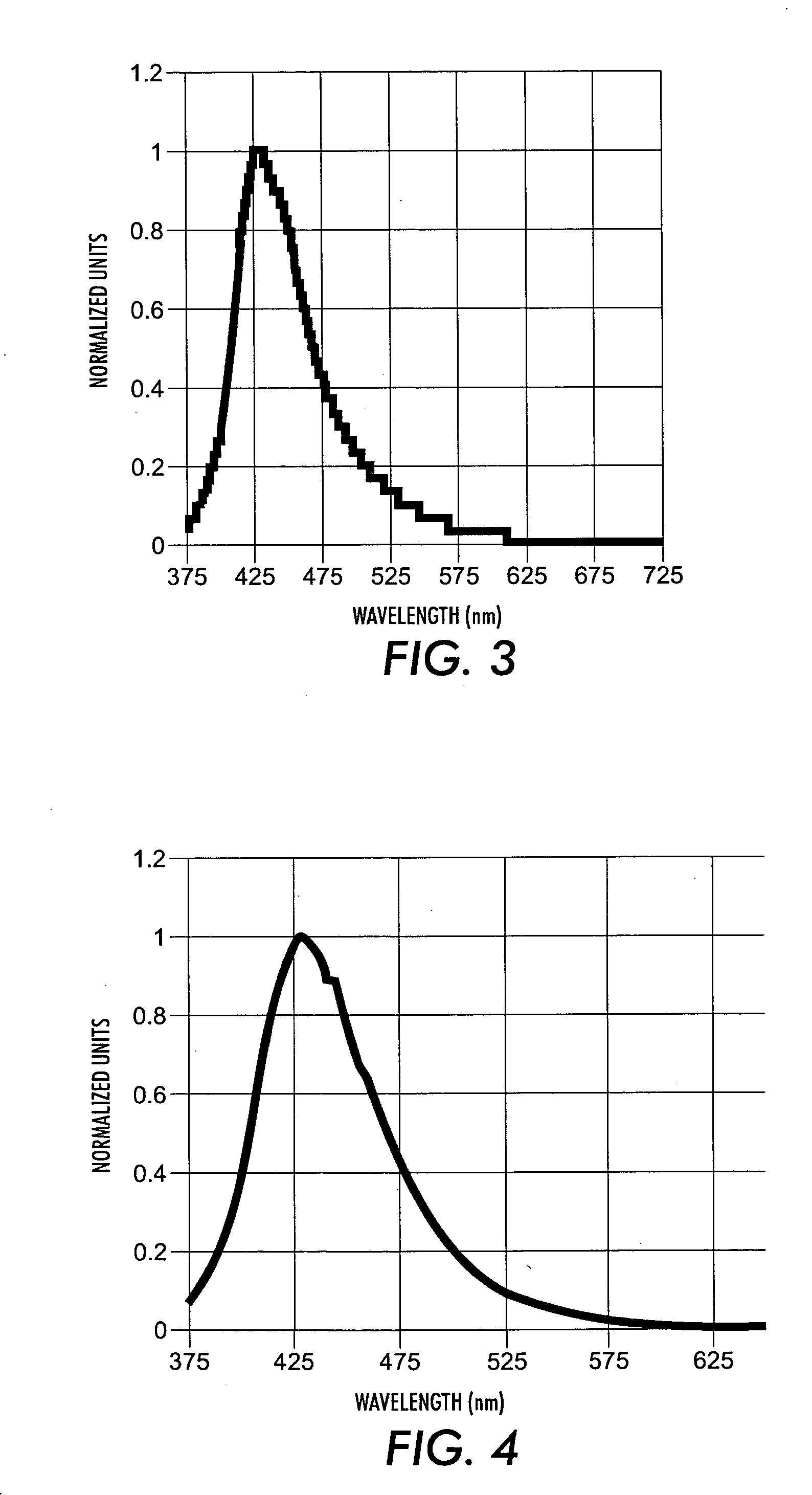
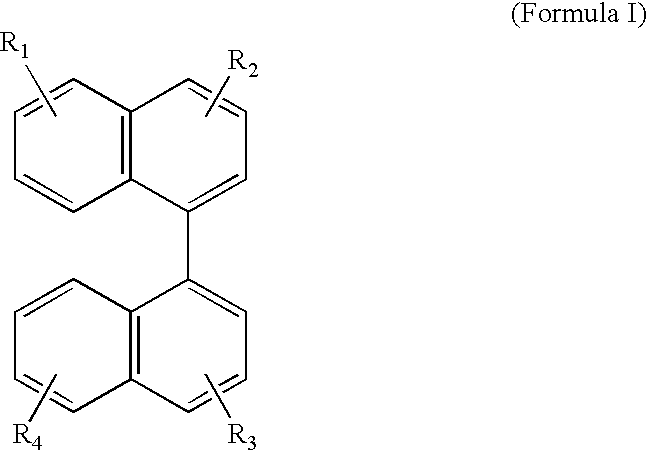
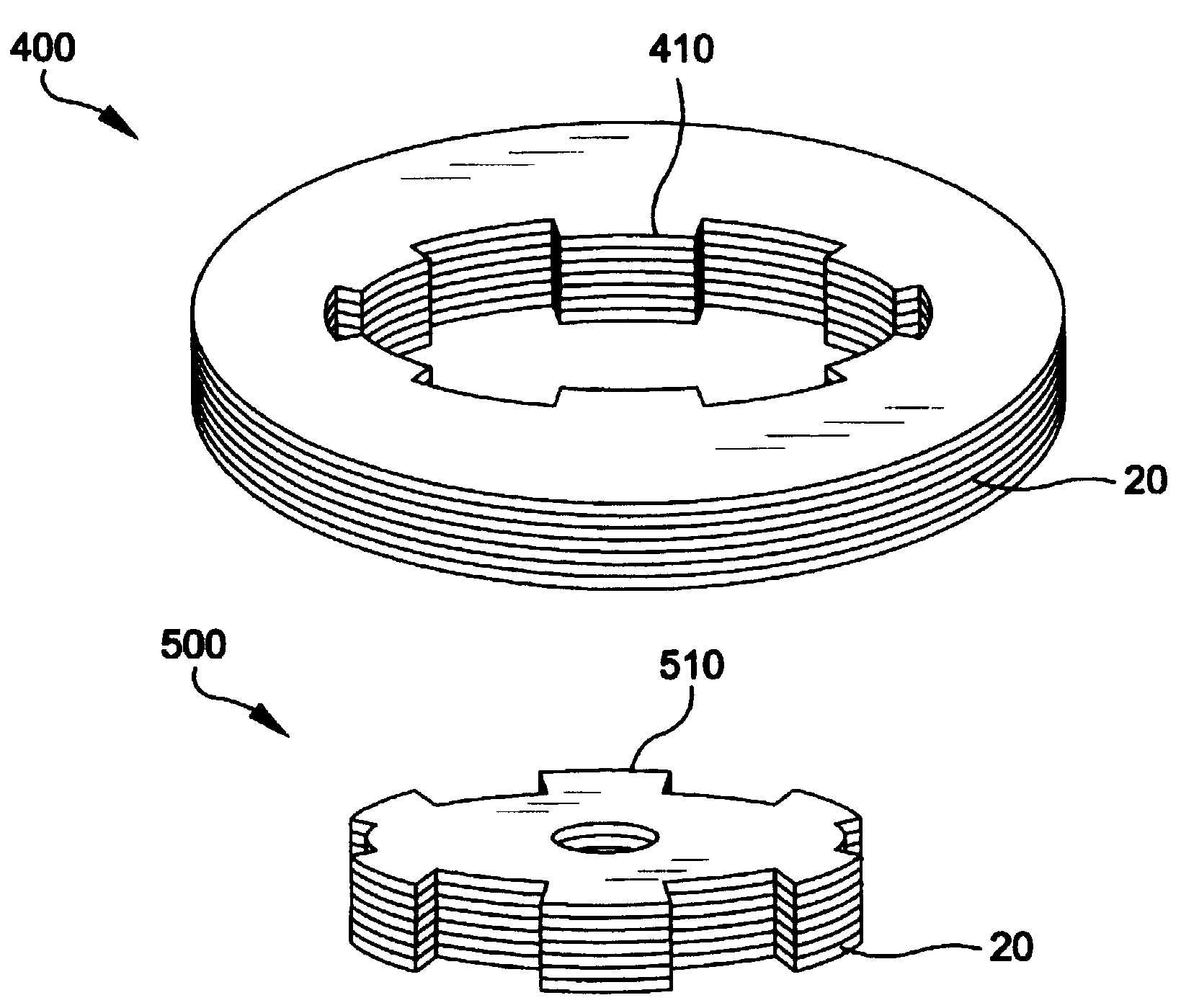
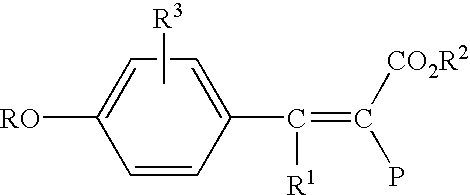
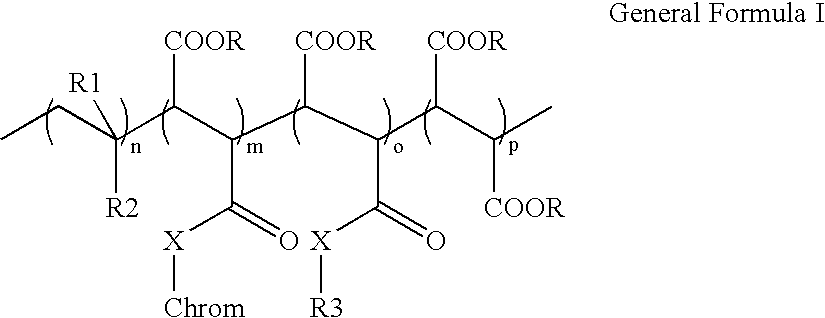
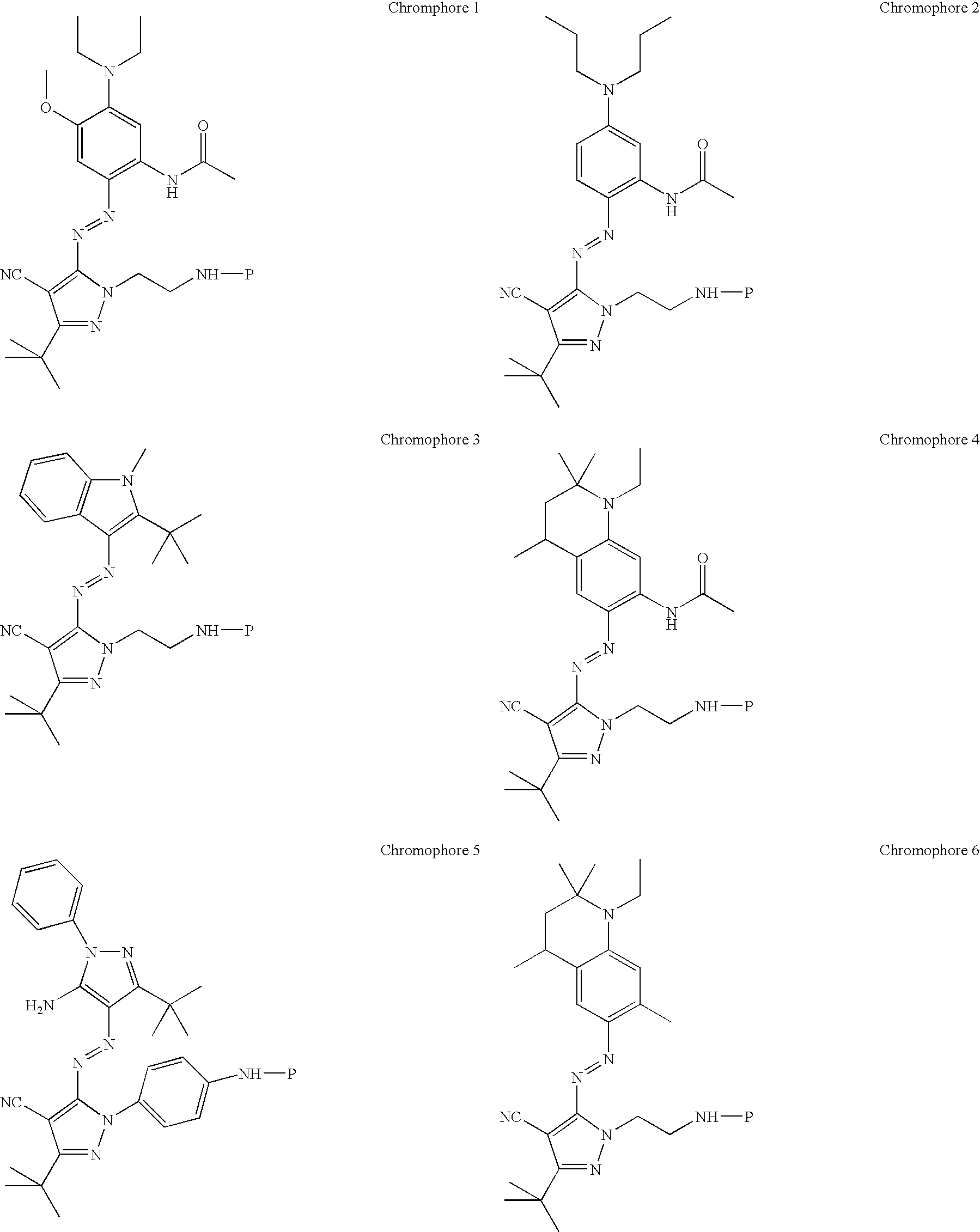
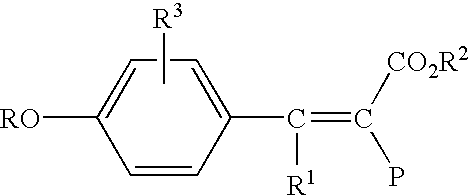
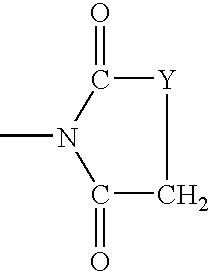
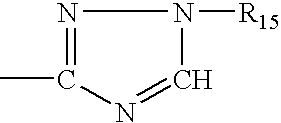
An electroluminescent (EL) is provided comprising an anode, an organic electroluminescent element, and a cathode wherein the electroluminescent element contains, for example, a fluorescent 1,1′-binaphthyl derivative component of Formula (I) wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are individual substituents or a group of substituents, each of which may be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, or alkyl of from 1 to about 25 carbon atoms; an alicyclic alkyl of from 3 to 15 carbon atoms; an aryl or substituted aryl with about 6 to about 30 carbon atoms; carbon atoms from 4 to 24 necessary to complete a fused aromatic ring of naphthalene, anthracene, perylene and the like; an alicyclic alkyl group with from about 3 to about 15 carbon atoms; a silicon atom which can be substituted with a trimethyl, diphenylmethyl, triphenyl group and the like; heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl of from 5 to 24 carbon atoms, carbon atoms necessary to complete a fused heteroaromatic ring of furyl, thienyl, pyridyl, quinolinyl and other heterocyclic systems; an alkoxy, amino, alkyl amino or aryl amino of from 1 to about 25 carbon atoms; a halogen, a cyano group, and the like.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Selective etching process for cutting amorphous metal shapes and components made thereof
InactiveUS7235910B2More size and shapeEasily accommodatedMaterial nanotechnologyInorganic material magnetismMagnetic corePeak value
A selective etching process cuts shapes from amorphous metal strip feedstock. The etching process comprises depositing a chemically resistant material to one side of the strip in a pattern that defines the requisite shape, mating the metal strip with a carrier strip, exposing at least one side of the metal strip to an etching agent to selectively etch the desired shape, and separating the shape from the strip feedstock. A plurality of layers of the shapes is assembled by adhesive lamination to form a generally polyhedrally shaped bulk amorphous metal magnetic component useful in high efficiency electric motors and inductive devices. The bulk amorphous metal magnetic component may include an arcuate surface, and preferably includes two arcuate surfaces that are disposed opposite to each other. The magnetic component is operable at frequencies ranging from about 50 Hz to about 20,000 Hz. When the component is operated at an excitation frequency “f” to a peak induction level Bmax, the component exhibits a core-loss less than about “L” wherein L is given by the formula L=0.005 f(Bmax)1.5+0.000012 f1.5(Bmax)1.6, said core loss, said excitation frequency and said peak induction level being measured in watts per kilogram, hertz, and teslas, respectively. Performance characteristics of the bulk amorphous metal magnetic component of the present invention are significantly better than those of silicon-steel components operated over the same frequency range.
Owner:METGLAS INC
Toner for developing electrostatic latent images, production method thereof, and electrostatic latent image developer using the same
ActiveUS7267920B2Maintain good propertiesDesirable particle shapeDevelopersLatent imageVolume average
The present invention provides a toner for developing an electrostatic latent image comprising of: toner particles containing at least a binder resin, a colorant and a releasing agent; wherein a volume-average particle diameter of the toner particles is in a range of about 5 to 8 μm; an average of shape factor SF1 of the toner particles is in a range of about 125 to 140; and an arithmetical mean undulation height of the surface of the toner particles at the 90% point on the cumulative distribution curve is in a range of about 0.15 to 0.25 μm. Further, the present invention provides an electrostatic latent image developer containing the toner. The invention also provides a method for producing the toner.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
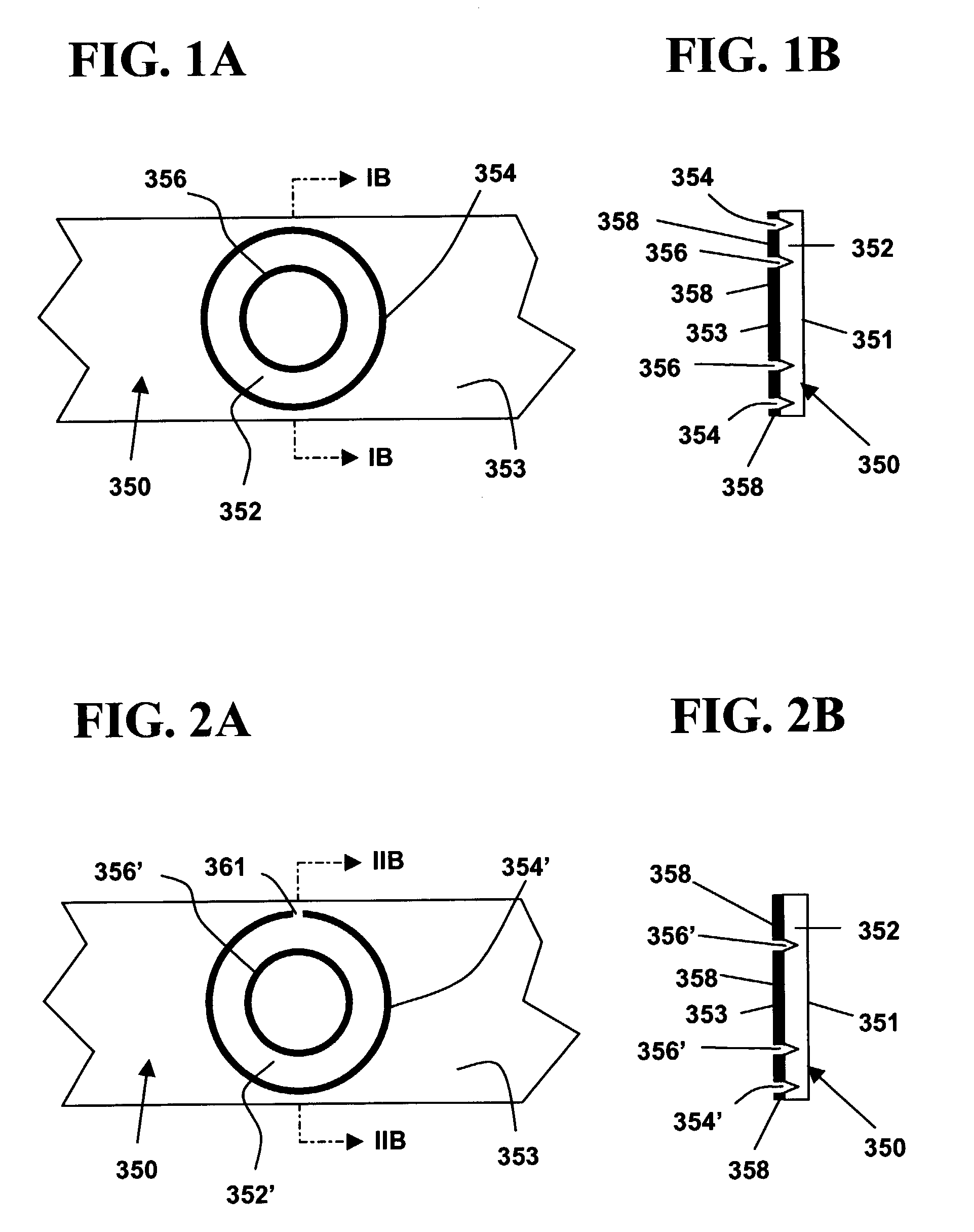
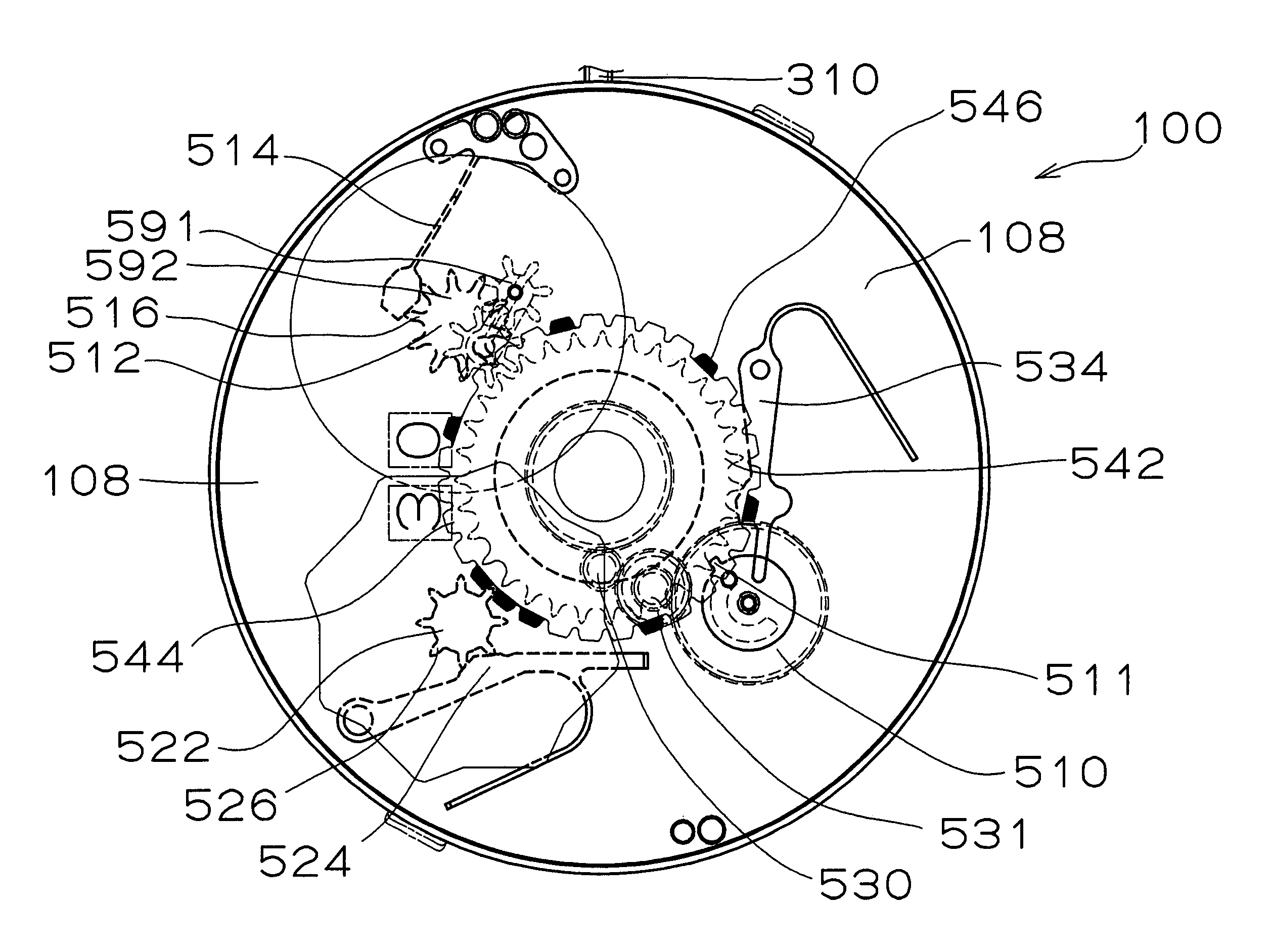
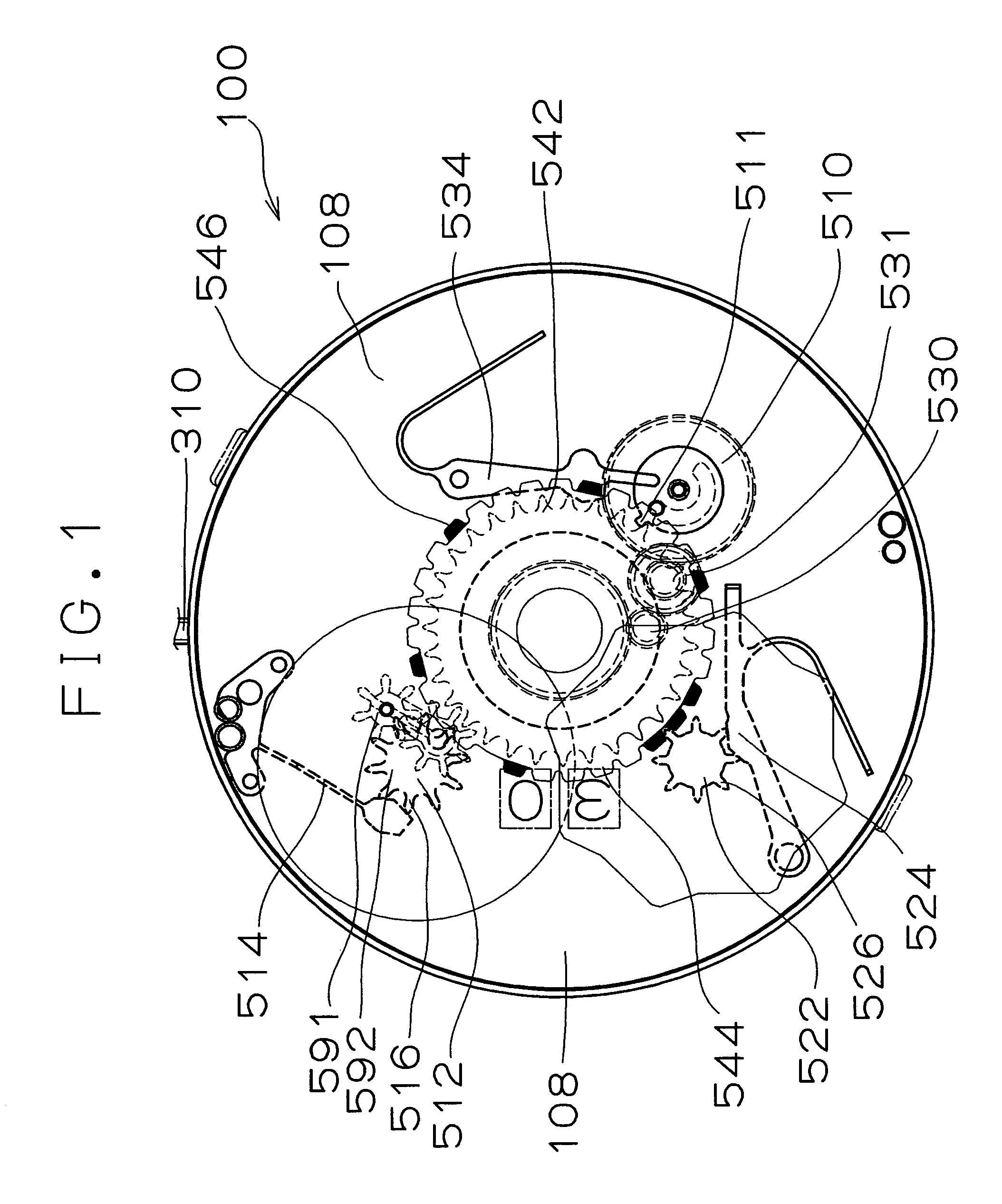
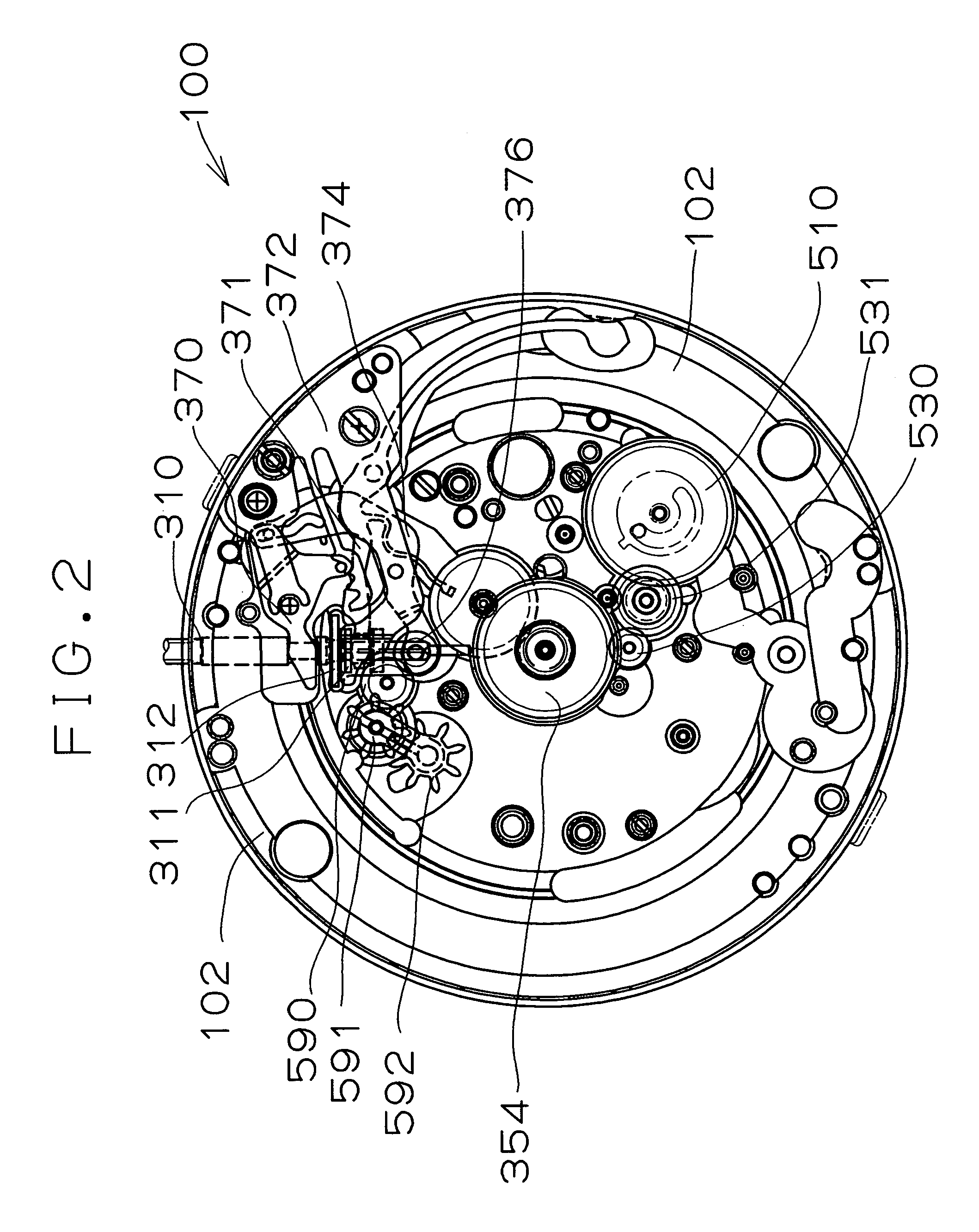
Timepiece equipped with calendar mechanism including first and second date indicators
InactiveUS7102962B2Wide latitudeSimple driving mechanismVisual indicationEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Bulk amorphous metal inductive device
InactiveUS20060066433A1Low reluctanceImprove energy storage performanceTransformers/inductances magnetic coresInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureTransformerPeak value
A bulk amorphous metal inductive device includes a magnetic core having at least one low-loss bulk ferromagnetic amorphous metal magnetic component forming a magnetic circuit having an air therein. The component has a plurality of similarly shaped layers of amorphous metal strips bonded together to form a polyhedrally shaped part. The device has one or more electrical windings and is easily customized for specialized magnetic applications, e.g. for use as a transformer or inductor in power conditioning electronic circuitry employing switch-mode circuit topologies and switching frequencies ranging from 1 kHz to 200 kHz or more. The low core losses of the device, e.g. a loss of at most about 12 W / kg when excited at a frequency of 5 kHz to a peak induction level of 0.3 T, make it especially useful at frequencies of 1 kHz or more.
Owner:METGLAS INC
Image-forming method and developer
InactiveUS20050026092A1Good developing propertiesReduce harmPhotoprinting processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDicarbonateRecording layer
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
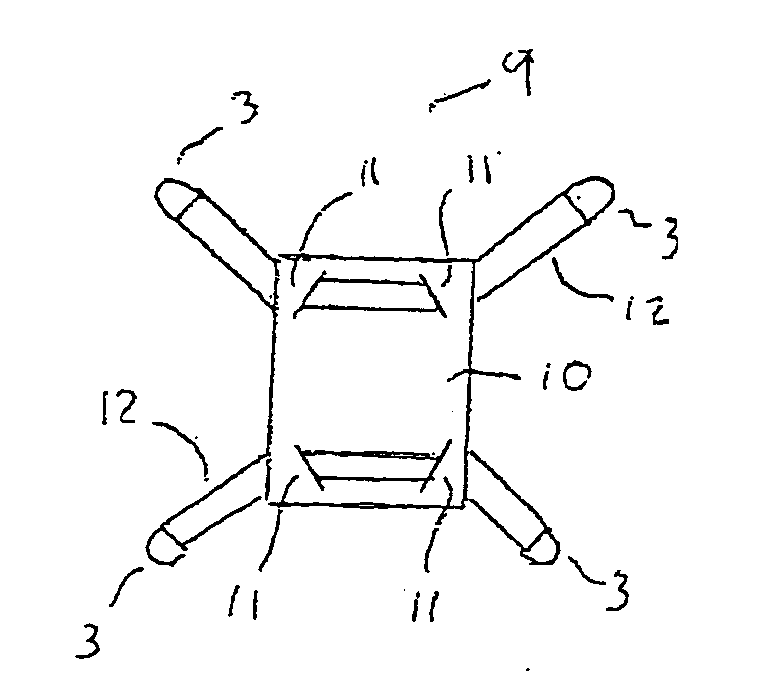
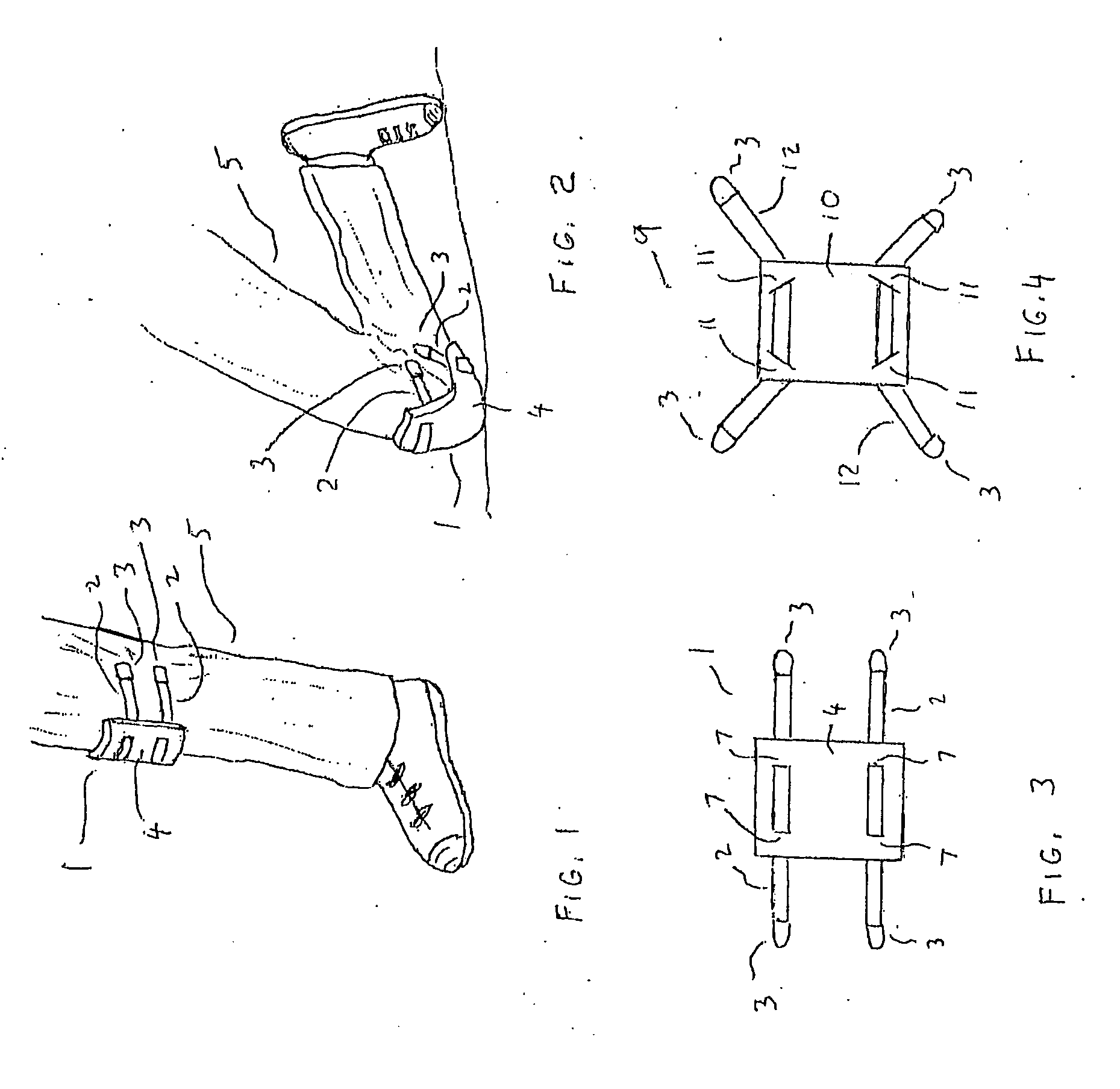
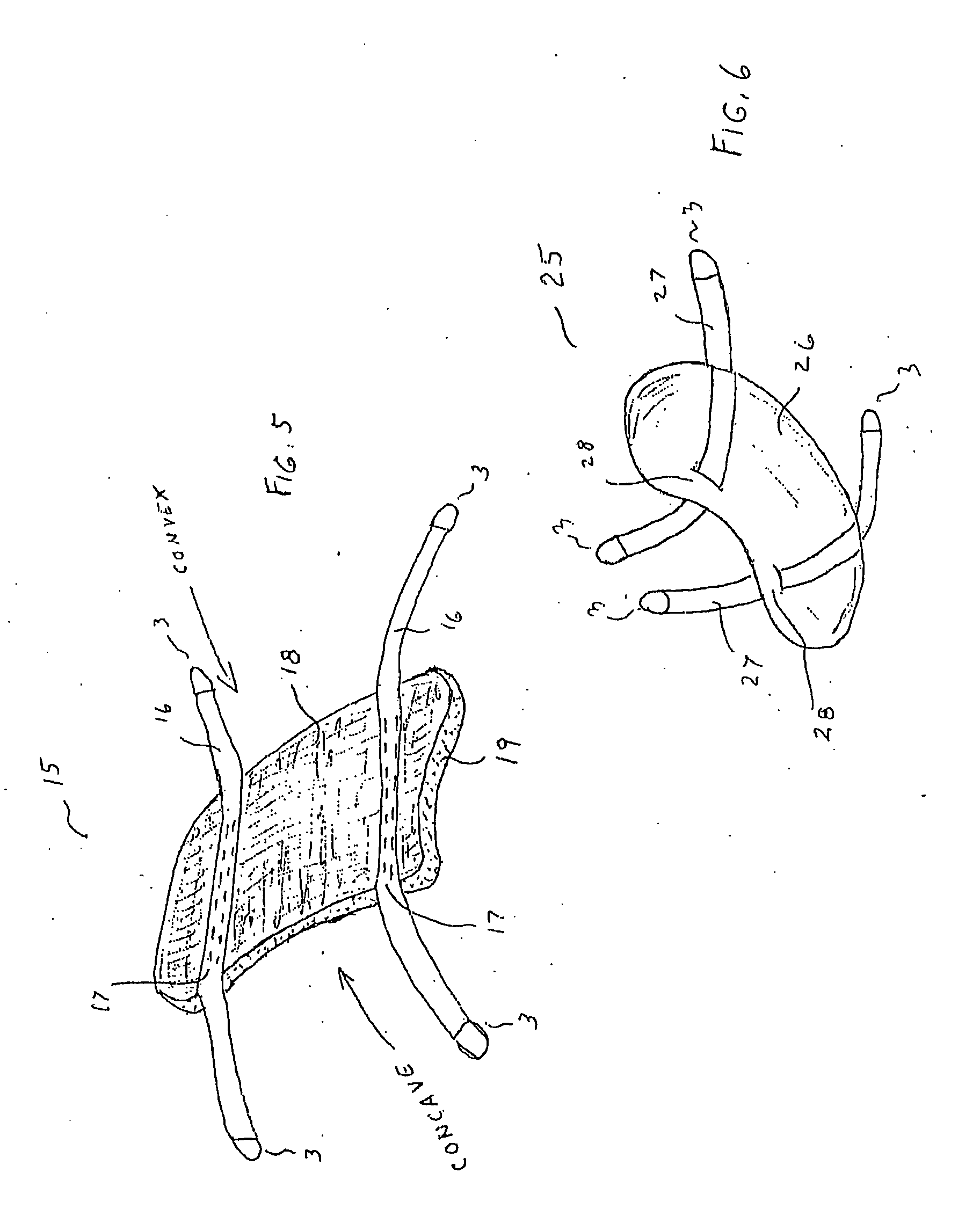
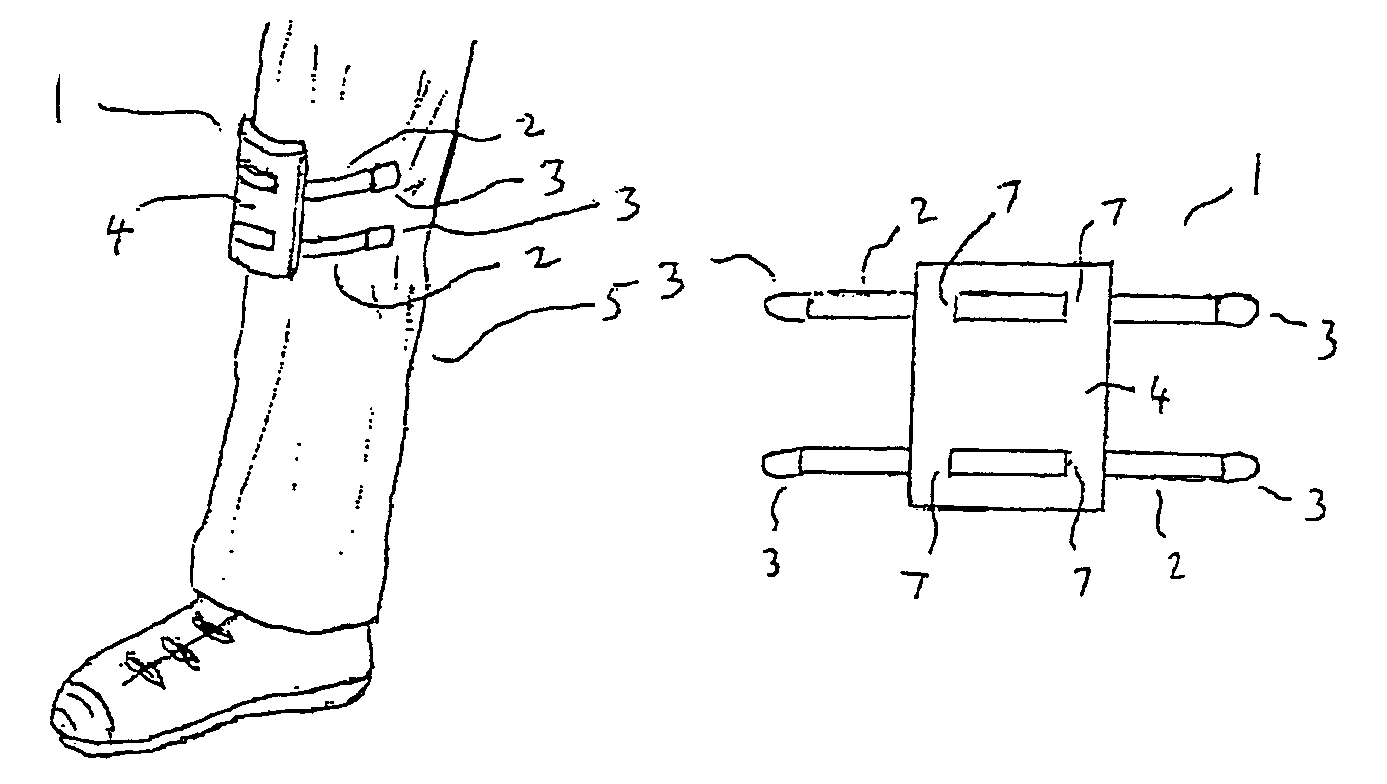
Clothing adherable knee pads
InactiveUS20060137071A1Easy to installAvoids uncomfortable encroachmentsProtective garmentKnee strapsEngineering
Owner:RAMPERSAD KENRICK
Clothing adherable knee pads
InactiveUS7415733B2Easy to installAvoids uncomfortable encroachmentsProtective garmentKnee strapsEngineering
Owner:RAMPERSAD KENRICK
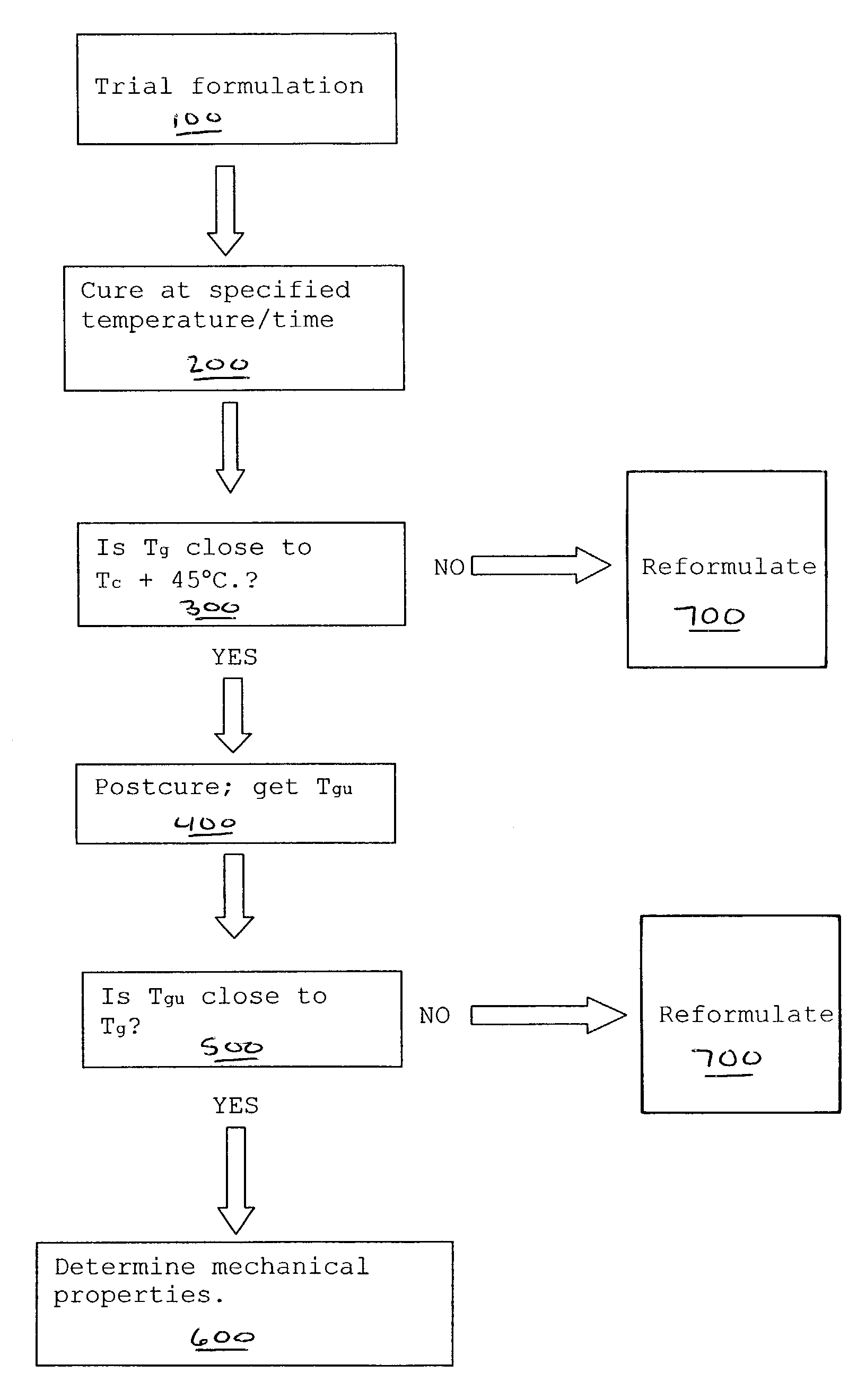
Epoxy hardeners for low temperature curing
Hardeners are provided for curing epoxies at lower temperatures than currently available hardeners while retaining superior mechanical and thermal properties. A first component is selected from imidazole, dicyandiamide, or a mixture of polyamines and tertiary amines. A poiyol mixture is then selected. The first component is combined with the polyol mixture to form a hardener. The hardener is combined with epoxy resin and is cured. A method for selecting a hardener to yield an epoxy-hardener system with good properties after curing at a specified temperature and time includes selecting components for the hardener so the glass transition temperature of the cured epoxy-hardener system is not significantly lower than 45° C. above the cure temperature. The method includes steps for adjusting and controlling the ultimate glass transition temperature to maximize the mechanical properties of the epoxy-hardener system. The method regularly produces hardened epoxy systems having about 90% or more epoxy groups reactect.
Owner:ARDES ENTERPRISES
Image processing method of digital images, digital camera and print system
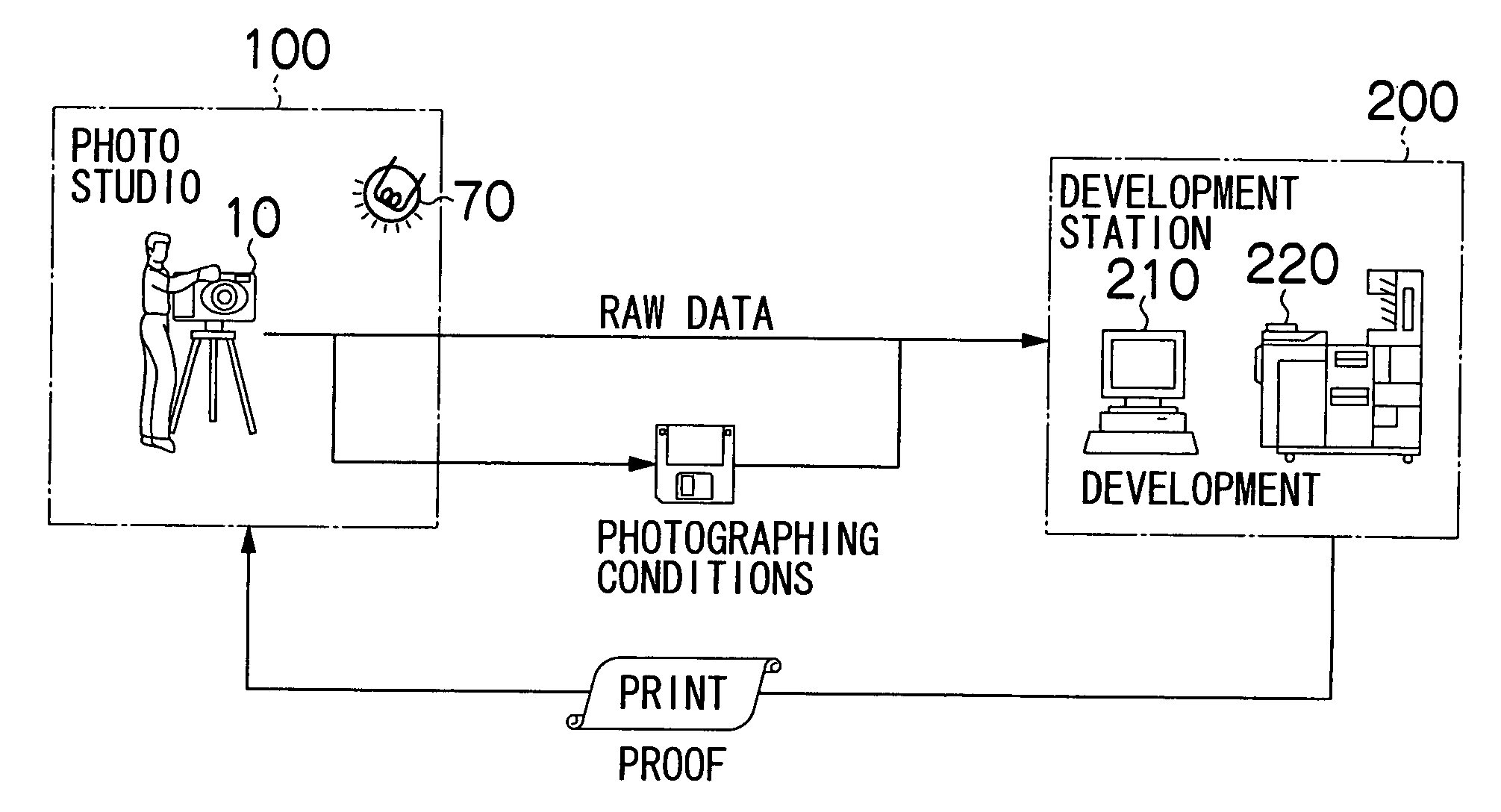
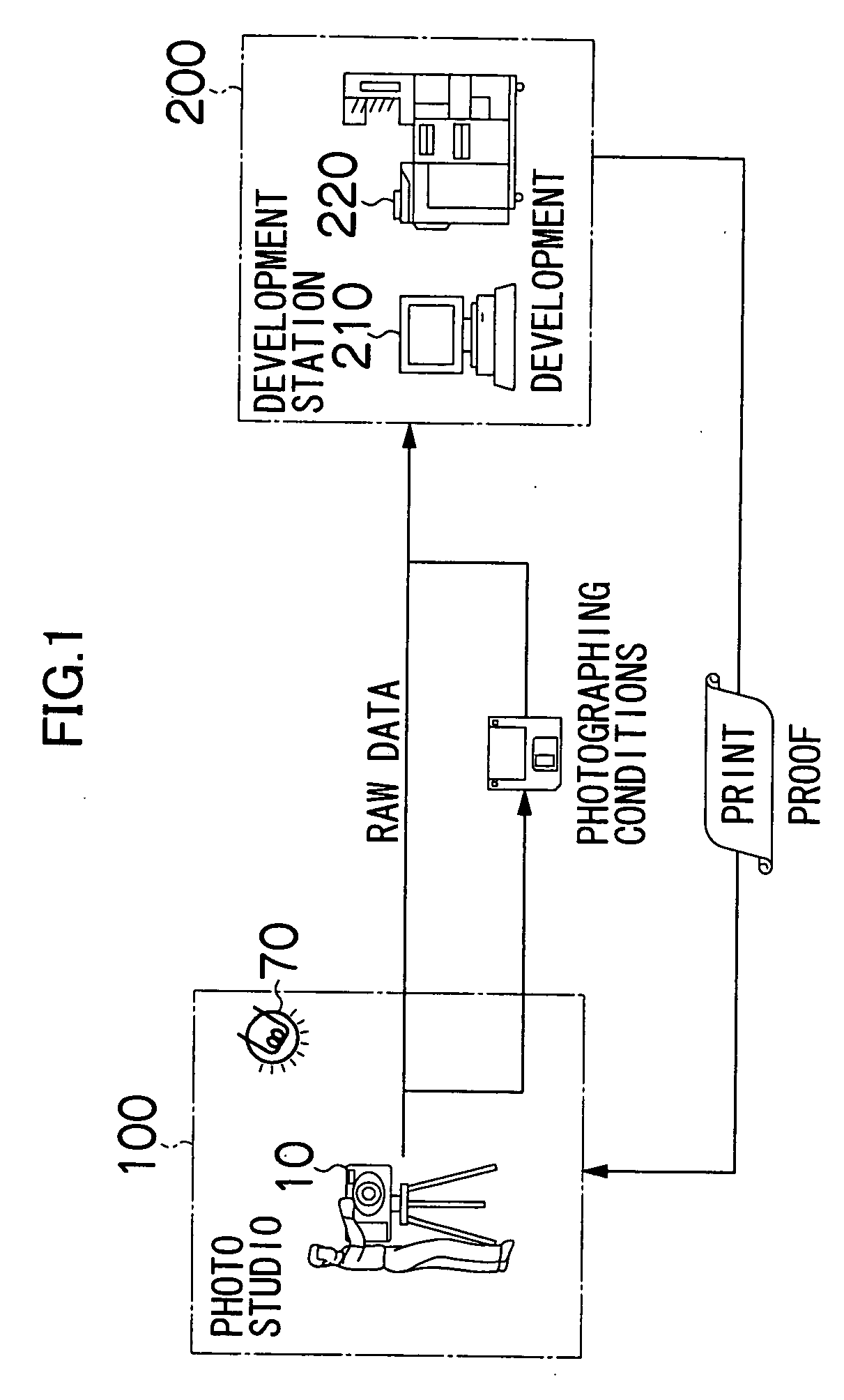
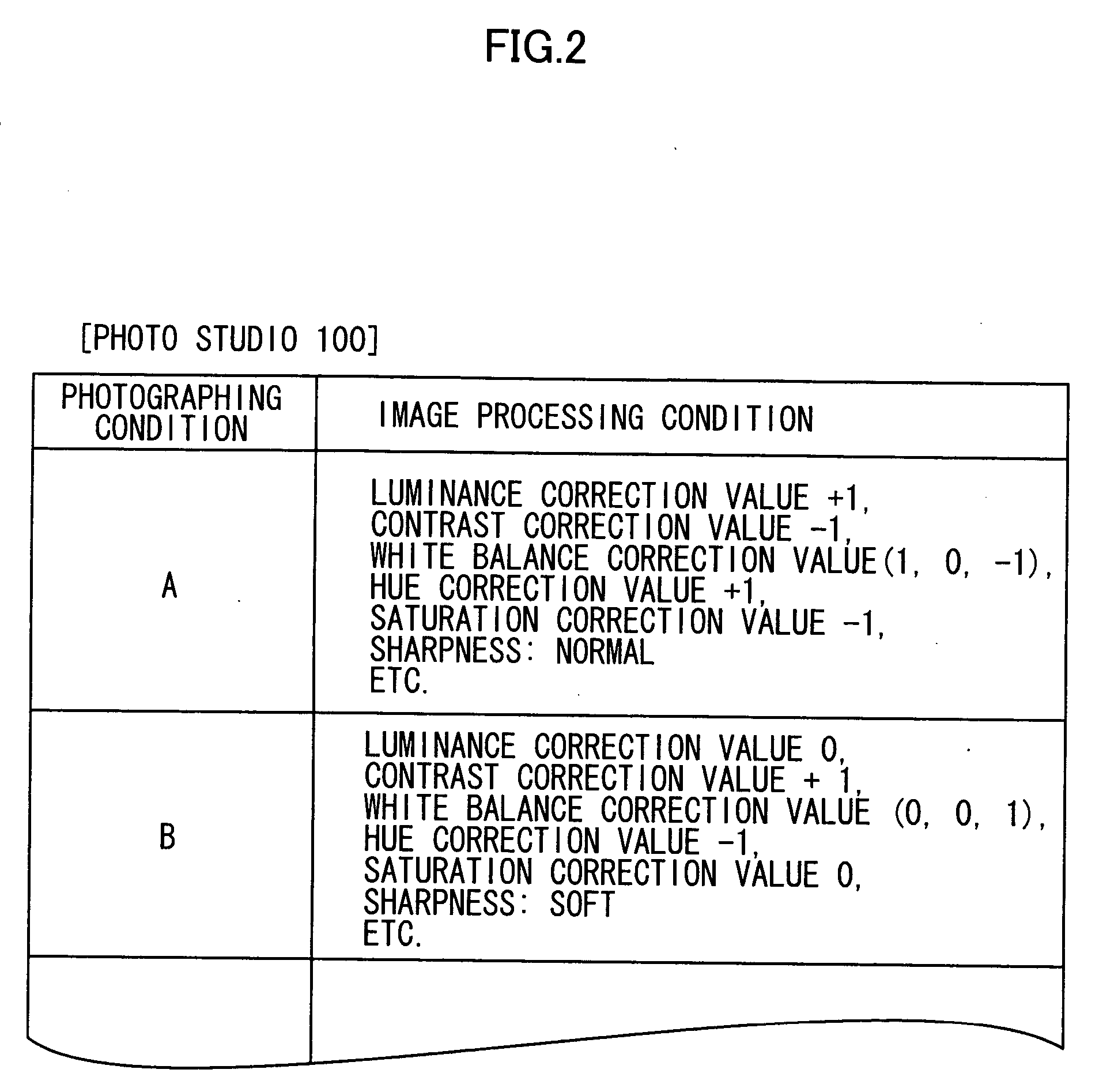
InactiveUS20050007610A1Reduce loadThe right amountTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing method of digital images comprising the steps of: loading photographic conditions on a photo studio when photographing objects with a digital camera of the photo studio and RAW data before image processing obtained under the photographic conditions; performing to the RAW data a development including the image processing according to image processing conditions and generating processed image data; and obtaining image processing conditions for the development so as to provide a color property and a gradation property intended by the photo studio for an output image based on the processed image data, and storing the image processing conditions and the photographic conditions loaded with the RAW data so as to link the image processing conditions to the photographic conditions.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Process and apparatus for drilling holes in the shell of a cylinder
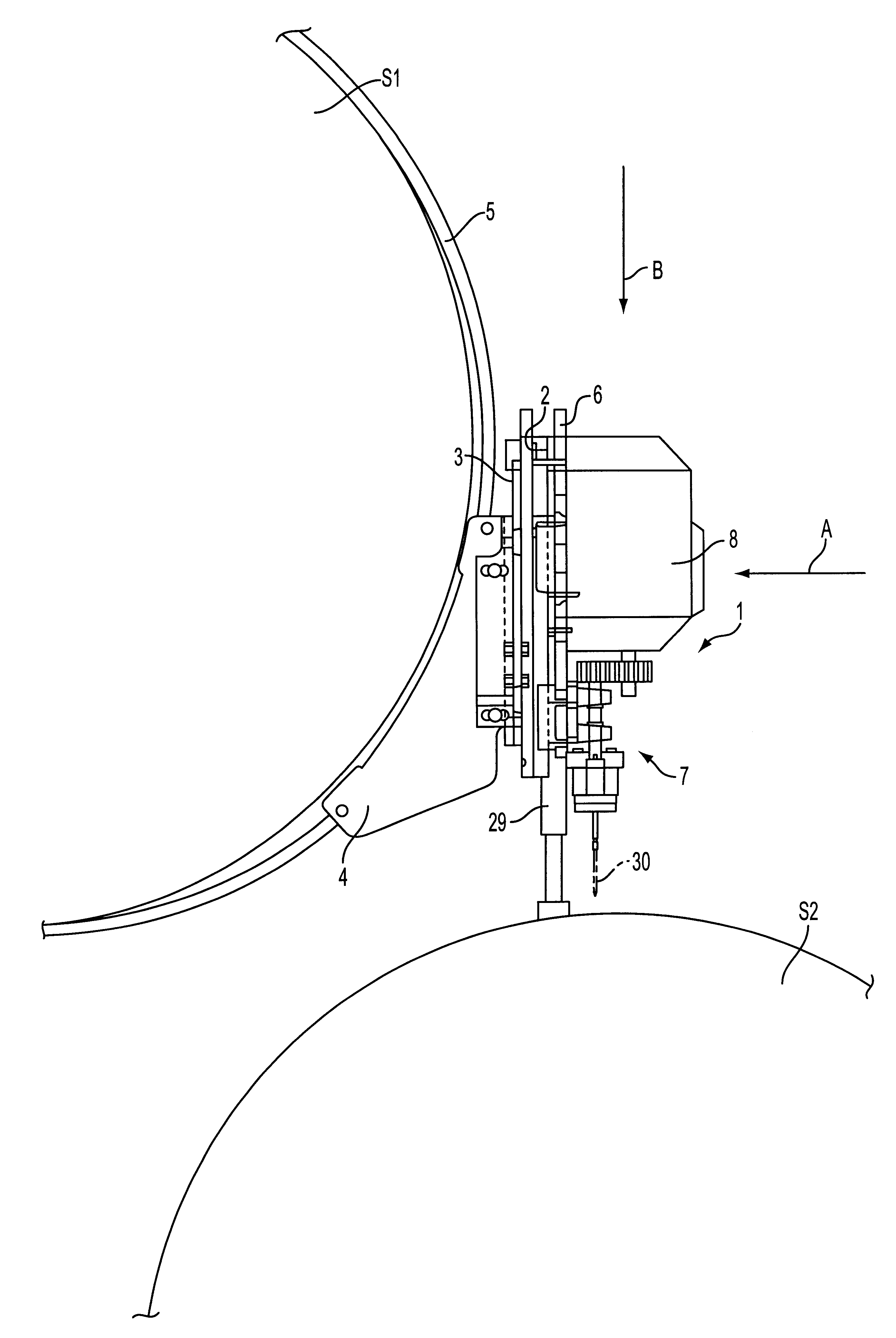
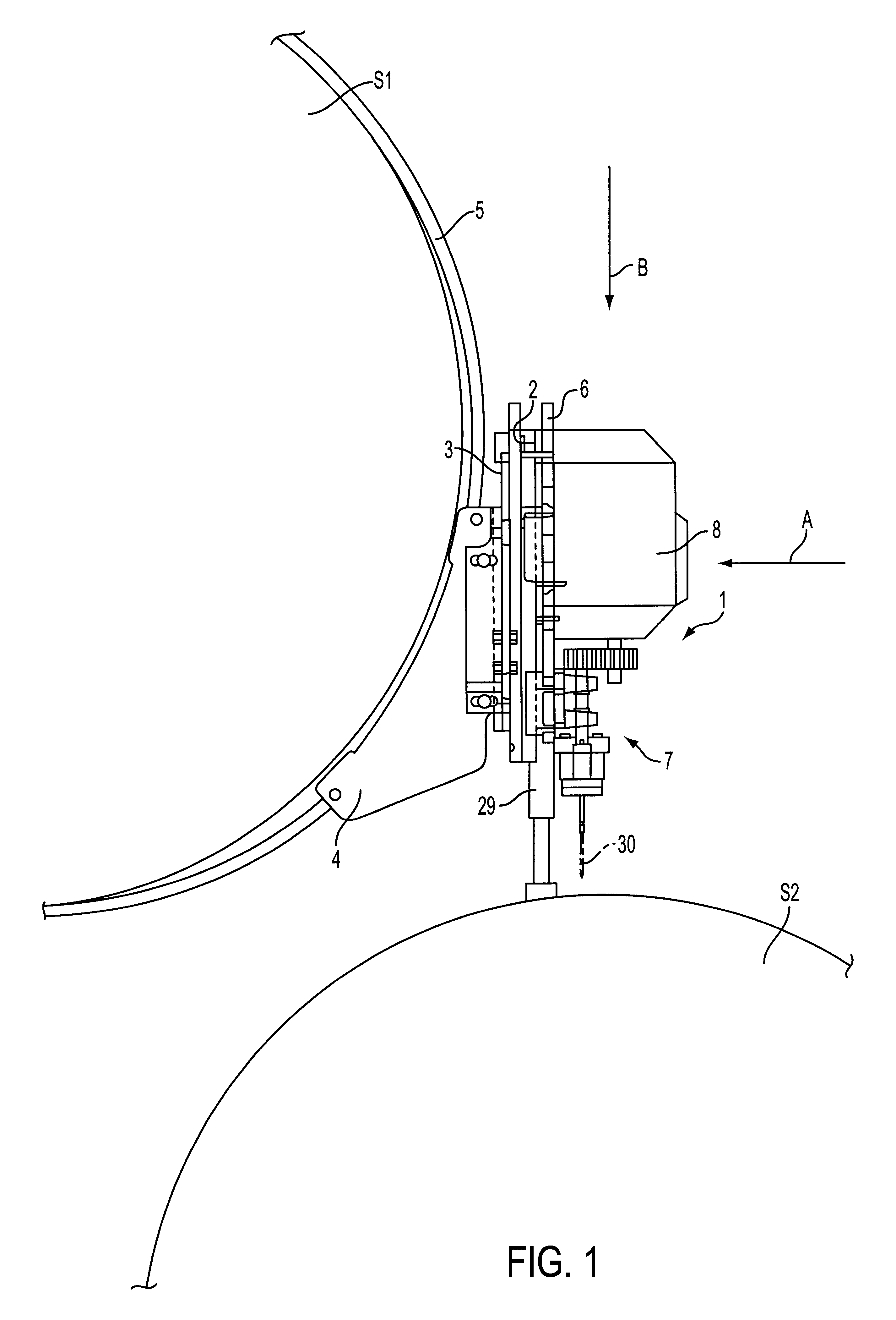
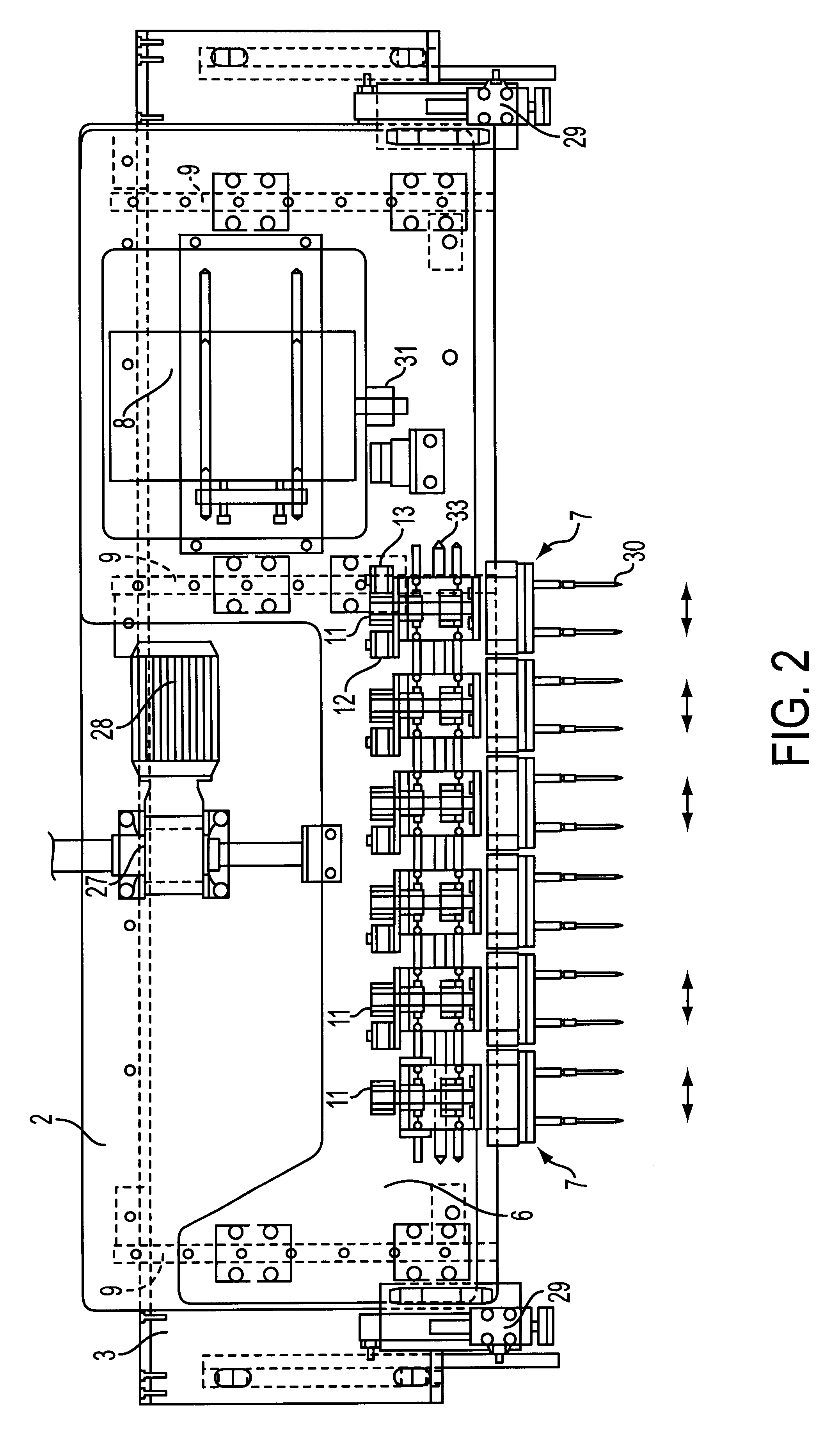
InactiveUS6361254B1Wide latitudeReduce the possibilityThread cutting machinesPrinted circuit manufactureDrive shaftFixed frame
Process and apparatus for operating an apparatus to drill holes in the shell of a paper machine cylinder. The apparatus includes a stationary framework supportable on the paper machine, a feed frame that is radially movable along the stationary framework relative to the shell, and a drive unit. A plurality of drilling modules are coupled to the feed frame, which are rotatable via the drive unit, and the drilling modules include a drive shaft, at least two spindle heads, and at least two intermediate shafts arranged between the drive shaft and the at least two spindle heads, in which at least one of the at least two spindle heads in each drilling module is rotatable about a respective intermediate shaft of the drilling modules. The process includes rotating at least one of the at least two spindle heads about a respective intermediate shaft of the drilling module arranged between a drive shaft and the at least one spindle head, such that a mutual distance between spindle shaft centers of the at least two spindle heads in the drilling modules is adjusted.
Owner:PIKOTEKNIK +1
Combined salt and pepper mill
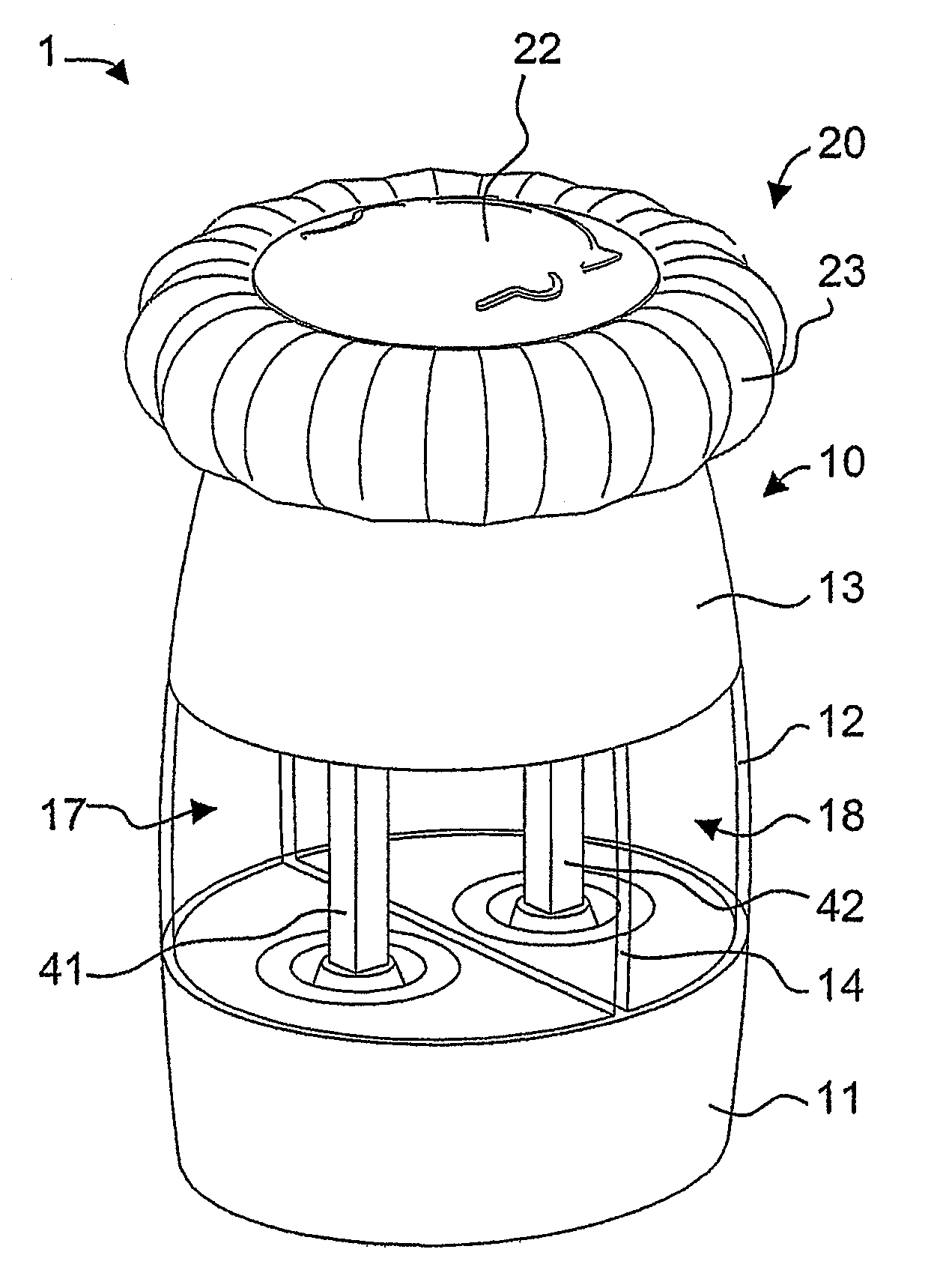
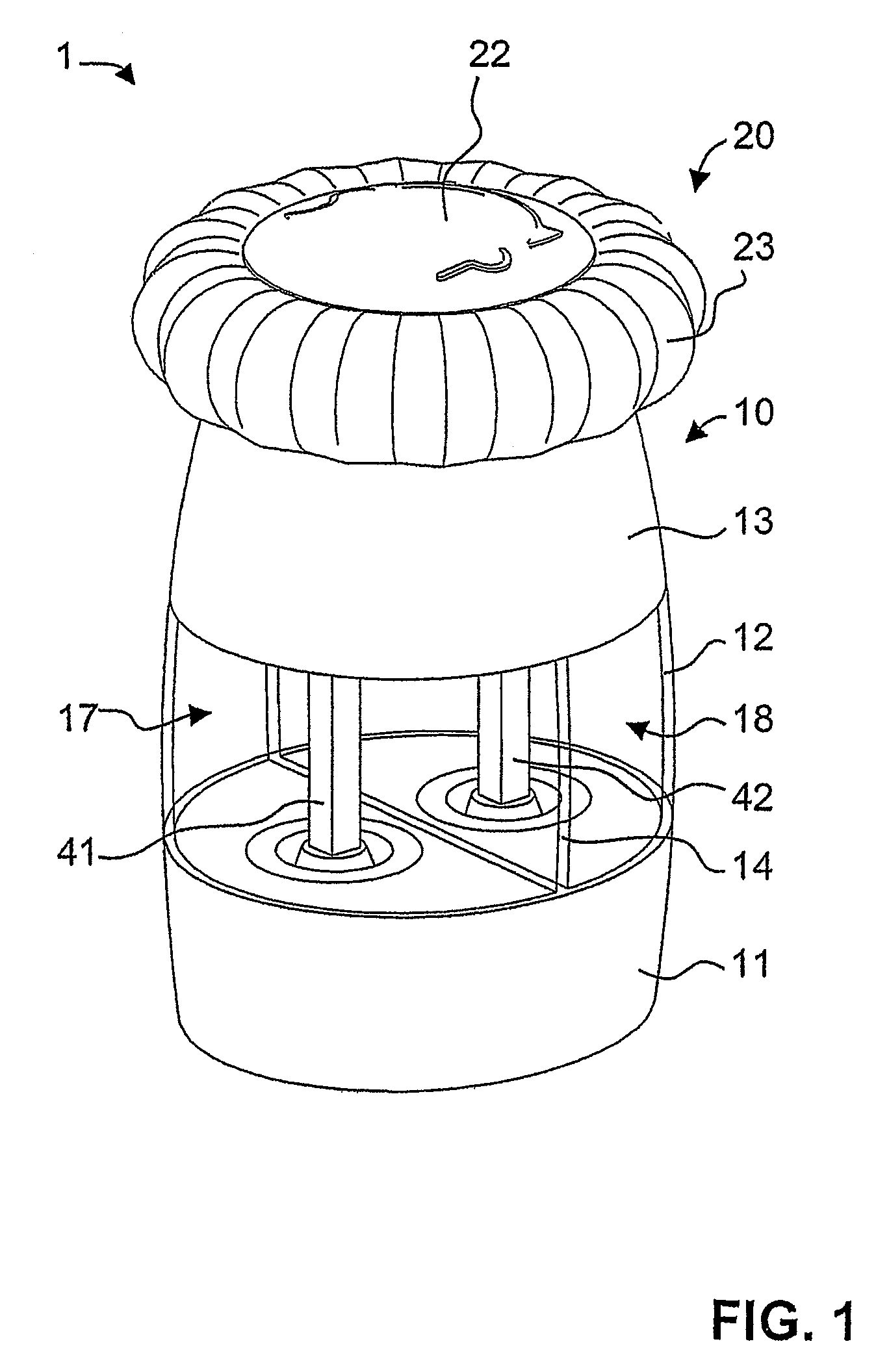
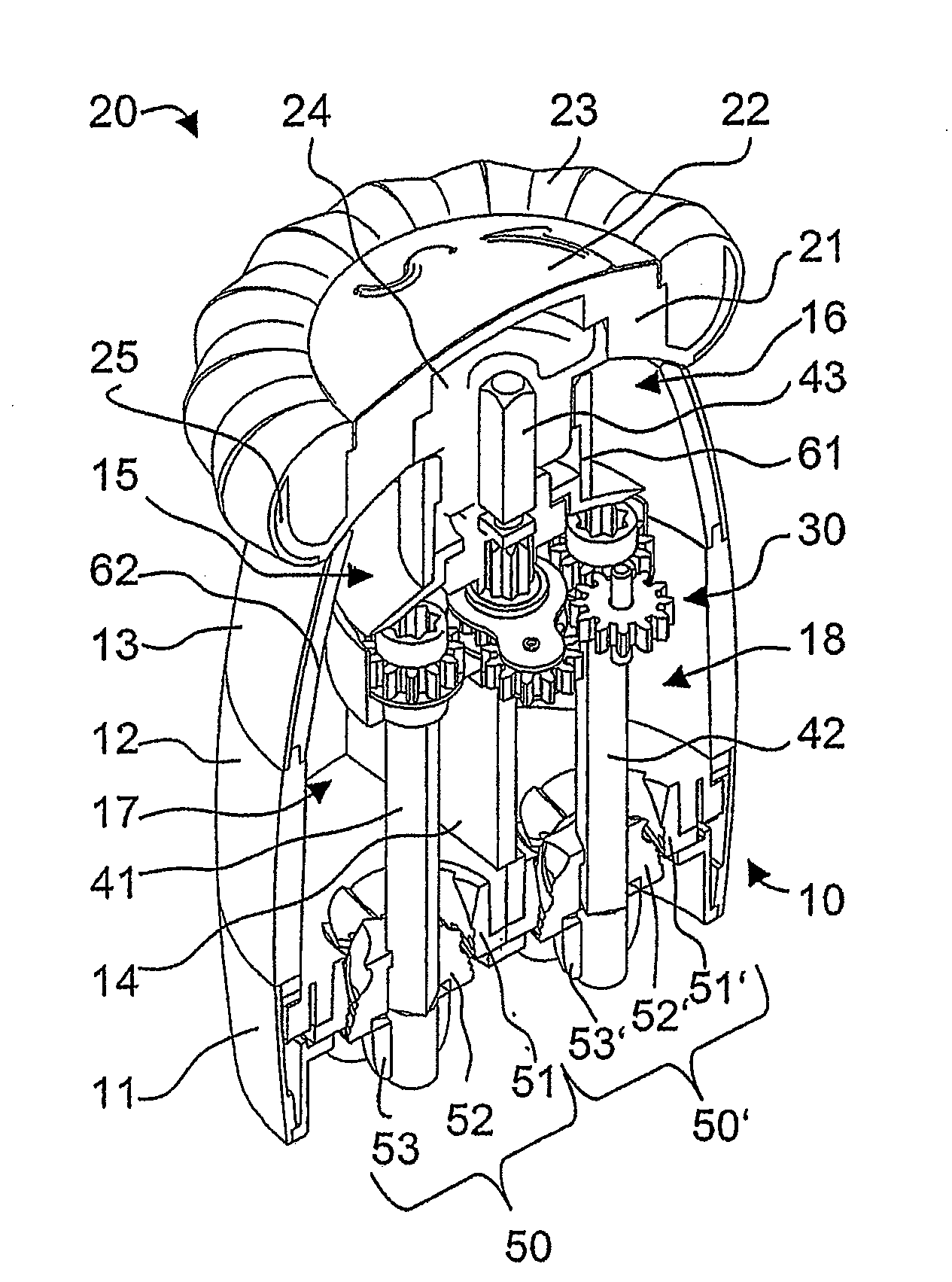
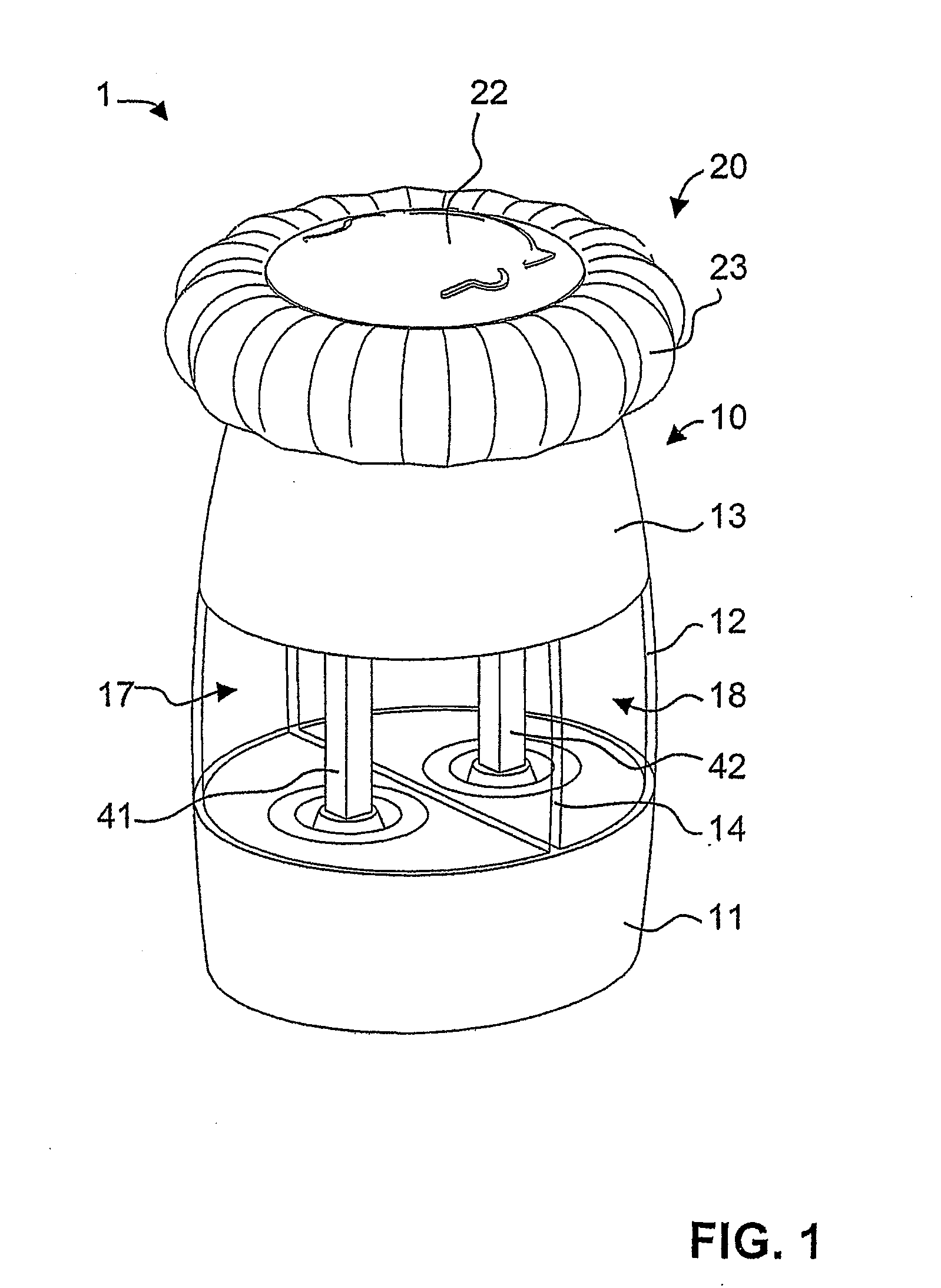
A spice mill for cutting up two different spices, in particular salt and pepper, is disclosed. Two spice containers (17, 18) and two grinding mechanisms (50, 50′) are arranged in a base part (10). A cover part (20) can be removed from the base part (10) and serves as a rotary handle. When the cover part (20) is removed, filling openings (15, 16) for the spice containers (17, 18) are opened up. An encapsulated gear mechanism (30) is arranged in the base part (10) between the cover part and the grinding mechanisms. When the cover part (20) is rotated in a first direction of rotation, the gear mechanism (30) drives the first grinding mechanism (50). By contrast, upon rotation in the opposite direction, the second grinding mechanism (50′) is driven. In a preferred embodiment, the gear mechanism is arranged in an upper region of the base part and, together with the base part, bounds the filling openings.
Owner:PI-DESIGN AG
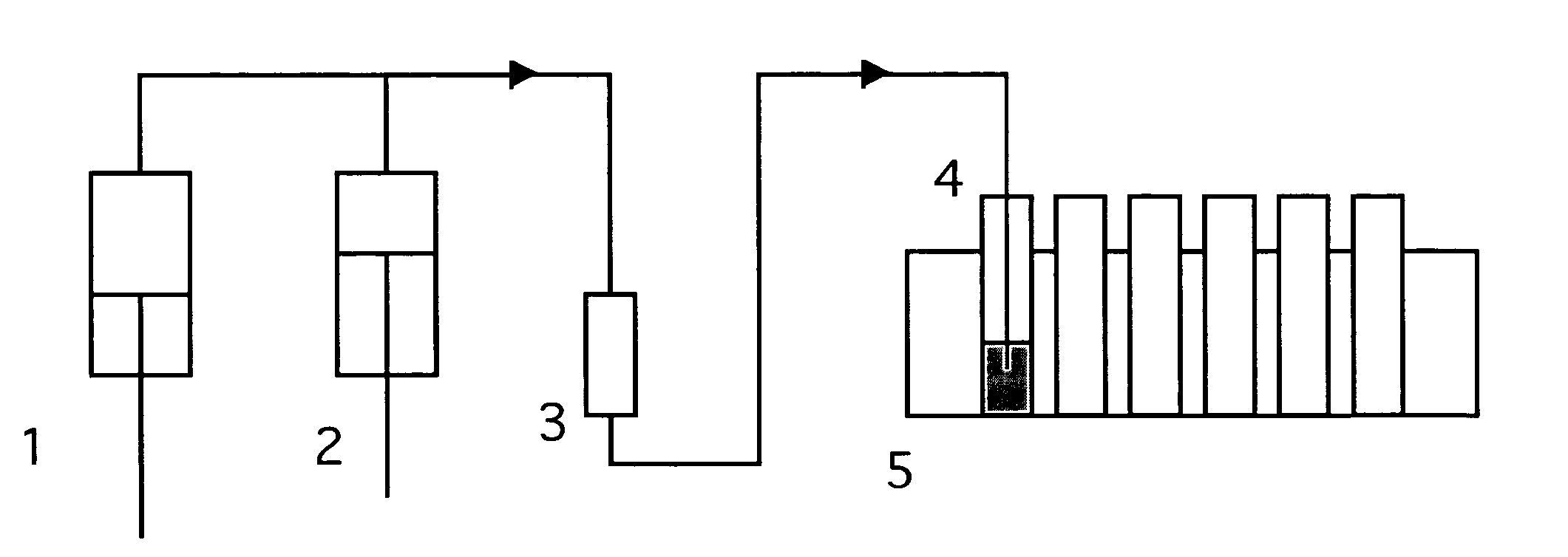
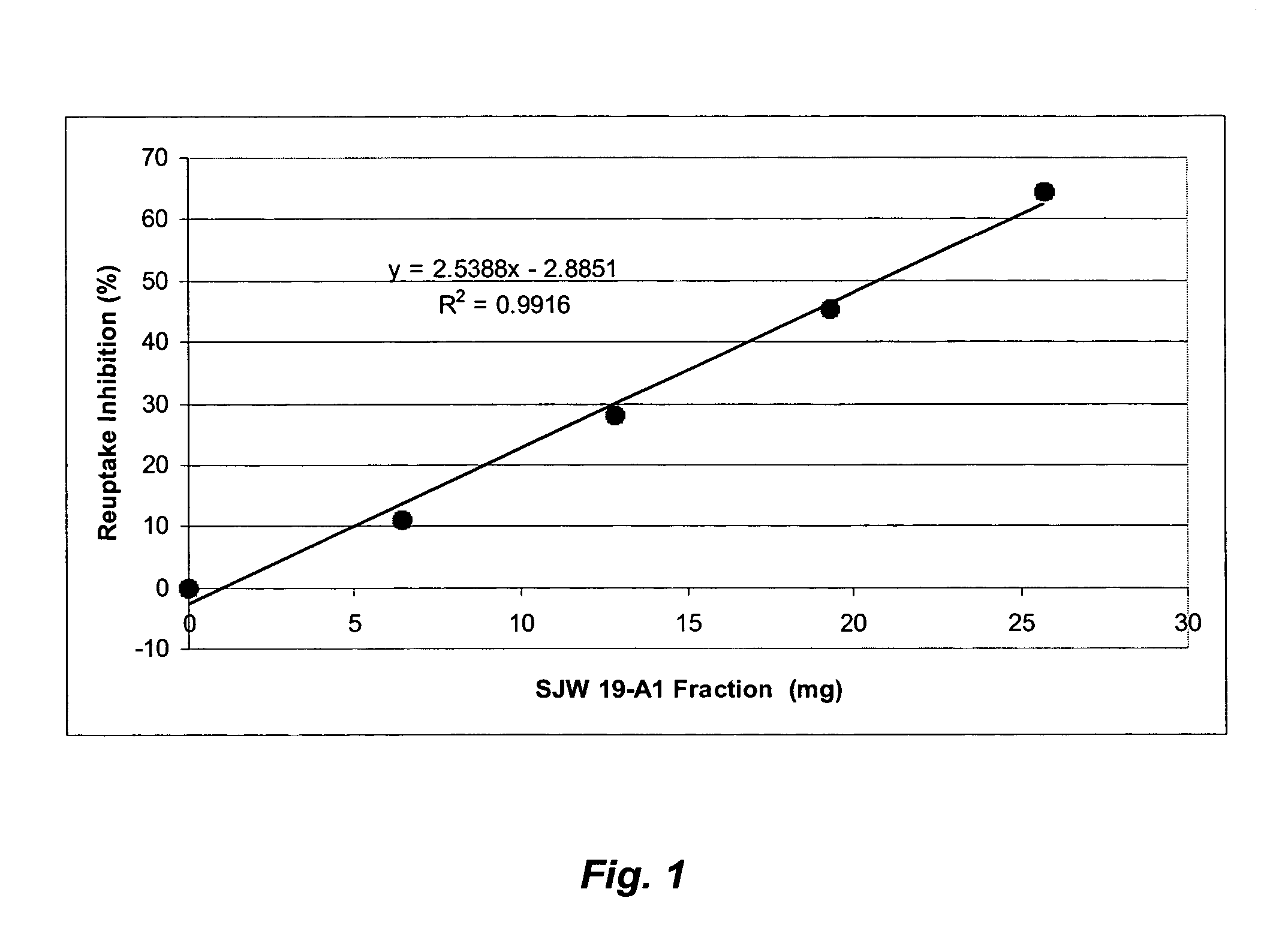
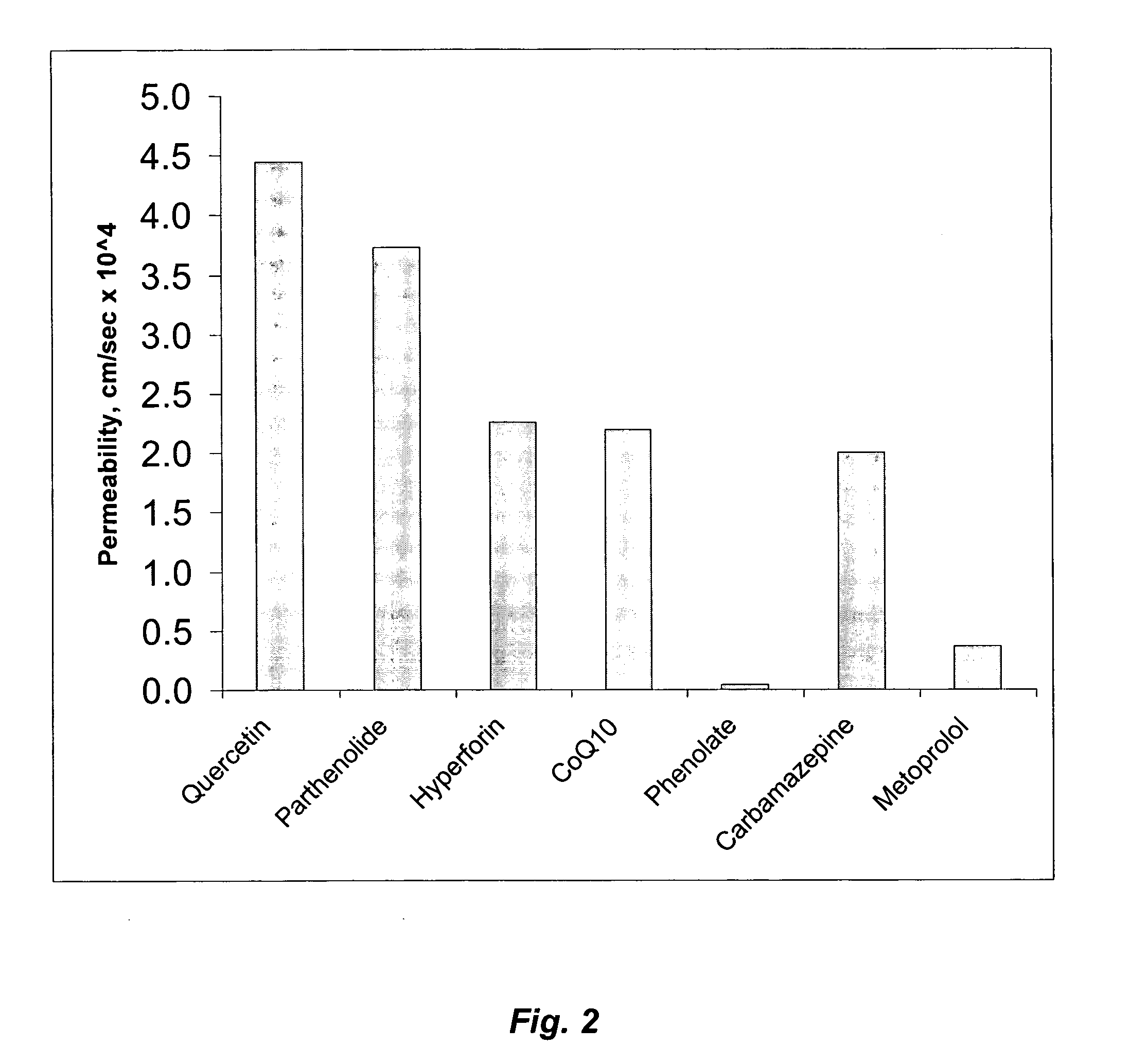
Formulations for hyperforin-enriched hypericum fractions
InactiveUS20060240098A1Improve stabilityNo reduction in nutritional benefitsBiocideCapsule deliverySerotoninAntioxidant
St. John's Wort products which have enhanced bioactivity in a serotonin re-uptake assay and enhanced stability and bioavailability are formulated and manufactured from hyperforin-enriched Hypericum fractions made by supercritical and near critical fluids with and without polar cosolvents. These fluids are used to fractionate the biomass materials in several sequential steps. In each step, the biomass is subjected to a multiplicity of supercritical or near critical fluid extraction steps, with different solvation conditions used for each fraction. Thus, fractionation of the biomass is effected and the St. John's Wort products are manufactured. In addition to excellent overall yield, the bioactivity and stability of the St. John's Wort products manufactured from Hypericum perforatum biomass with supercritical and near critical fluids with and without polar cosolvents are significantly higher than that obtained by conventional organic phase extraction. The advanced formulation of the hyperforin-enriched Hypericum fractions includes antioxidants as oxygen scavengers to improve stability and emulsifiers such as lecithin to improve bioavailability.
Owner:APHLOS
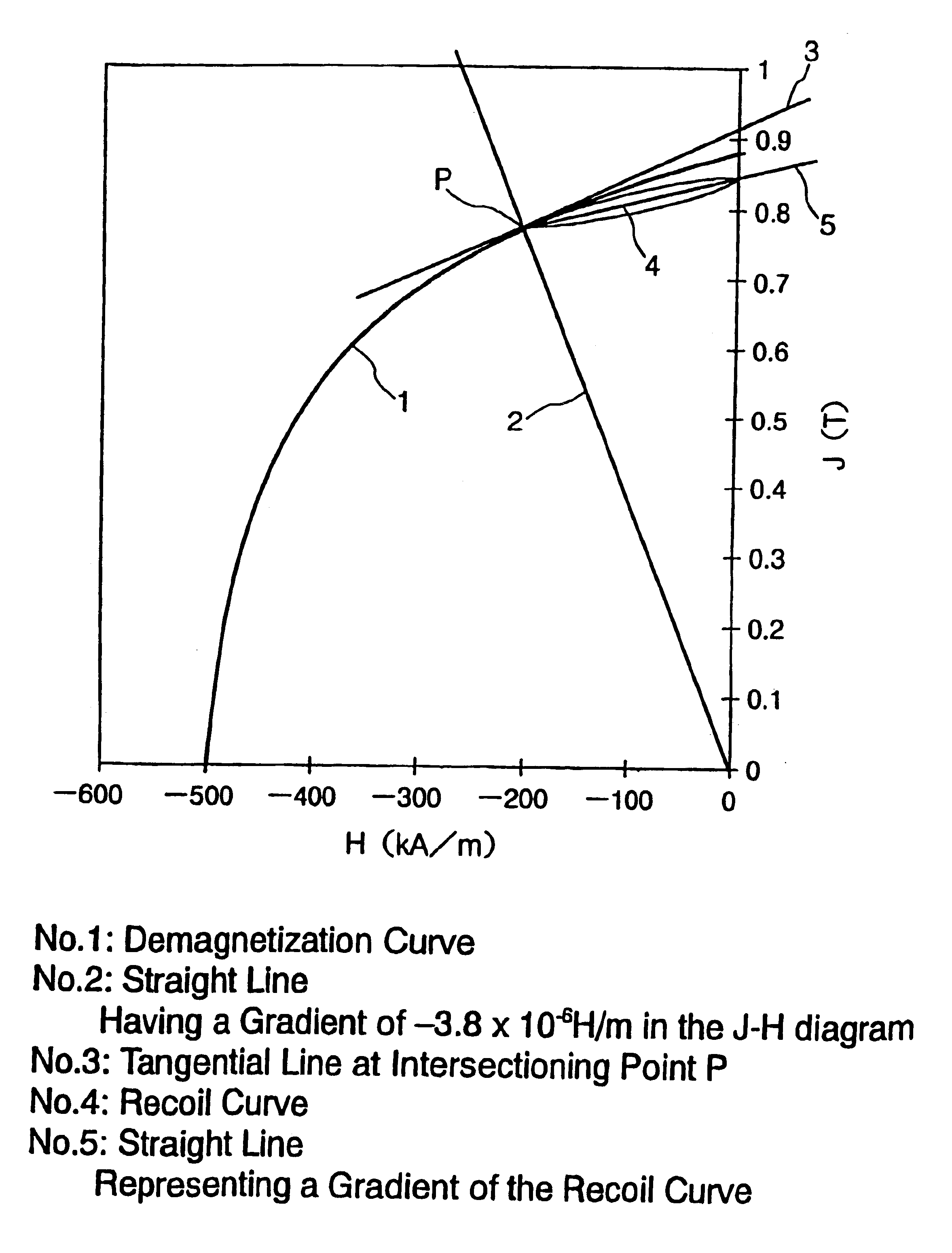
Magnetic powder and isotropic bonded magnet
InactiveUS6951625B2Improve magnetic propertiesHigher magnetic energyNanomagnetismInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementMagnetic phase
Disclosed herein is a magnetic powder which can provide magnet having excellent magnetic properties and having excellent reliability especially excellent heat stability. The magnetic powder is composed of an alloy composition represented by Rx(Fe1-aCoa)100-x-y-z-wByMz (where R is at least one kind of rare-earth element excepting Dy, M is at least one kind of element selected from Ti, Cr, Nb, V, Mo, Hf, W, Mn, Zr and Dy, x is 7.1-9.9at%, y is 4.6-8.0at%, z is 0.1-3.0at%, and a is 0-0.30), and the magnetic powder being constituted from a composite structure having a soft magnetic phase and a hard magnetic phase, wherein when the magnetic powder is mixed with a binding resin and then the mixture is subjected to injection molding or extrusion molding to form a bonded magnet having a density ρ[Mg / m3], the maximum magnetic energy product (BH)max[kJ / m3] of the bonded magnet at a room temperature satisfies the relationship represented by the formula (BH)max / ρ2[x10-9J·m3 / g2]≧ 2.10, and the intrinsic coercive force HCJ of the bonded magnet at the room temperature is in the range of 400-760 kA / m.
Owner:MAGNEQUENCH
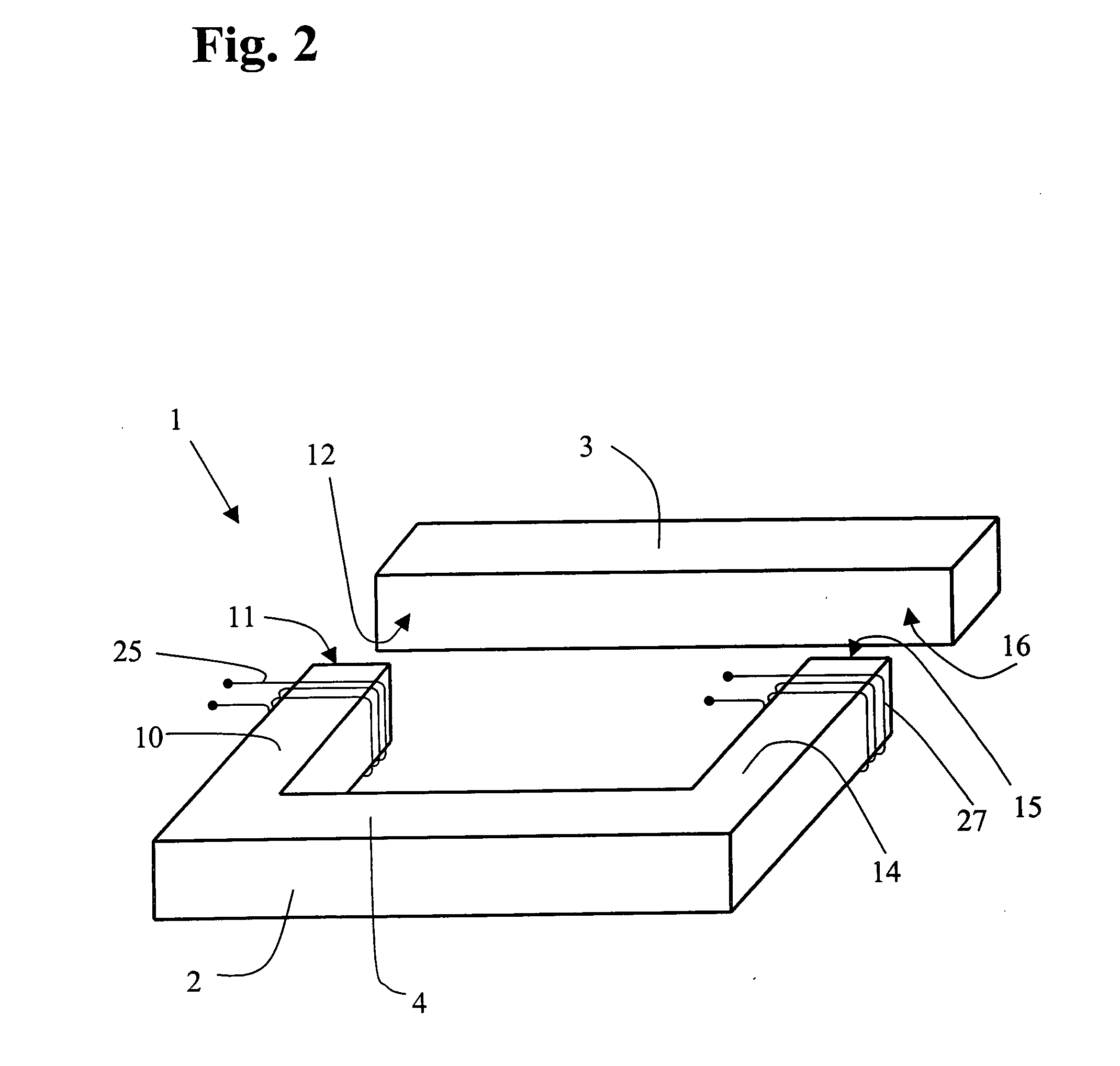
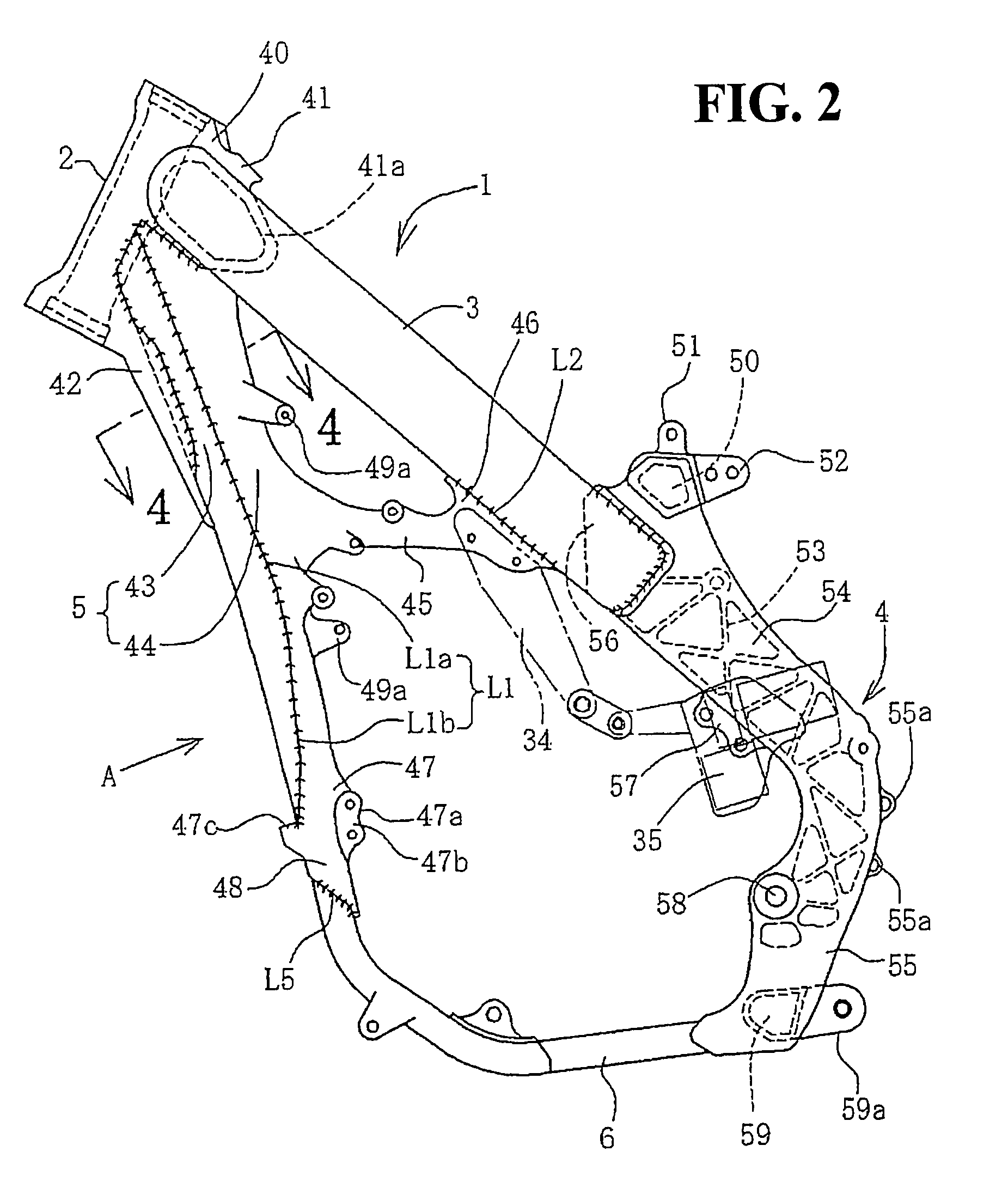
Motorcycle body frame structure
InactiveUS7699132B2Reduce weightWide latitudeExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusGusset plateVehicle frame
To ensure that a down frame in an off-road motorcycle body frame is lightweight, rigid and easy to weld, a down frame extending downward obliquely and backward from a main frame ahead of an engine is divided along its length into a down frame front portion and a down frame rear portion. Welding joins these portions, which abut each other in the longitudinal direction. The down frame front portion is a pipe wrought product formed by extrusion molding and the down frame rear portion is a casting. Since the down frame is welded along a straight welding line extending along its length, welding is easy. Since a main joint and a lower joint are provided integrally with the down frame rear portion as a casting, a separate gusset can be omitted.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Toner and image-forming method
InactiveUS6855471B2Easy to fixWide latitudeDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternPolymer scienceCross linker
Owner:CANON KK
High IV melt phase polyester polymer catalyzed with antimony containing compounds
ActiveUS20060149026A1Wide latitudeEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingMechanical apparatusPolyesterCompound a
A melt phase process for making a polyester polymer melt phase product by adding an antimony containing catalyst to the melt phase, polycondensing the melt containing said catalyst in the melt phase until the It.V. of the melt reaches at least 0.75 dL / g. Polyester polymer melt phase pellets containing antimony residues and having an It.V. of at least 0.75 dL / g are obtained without solid state polymerization. The polyester polymer pellets containing antimony residues and having an It.V. of at least 0.70 dL / g obtained without increasing the molecular weight of the melt phase product by solid state polymerization are fed to an extruder, melted to produce a molten polyester polymer, and extruded through a die to form shaped articles. The melt phase products and articles made thereby have low b* color and / or high L* brightness, and the reaction time to make the melt phase products is short.
Owner:ALPEK POLYESTER SA DE CV
Polymeric colorant-based ink compositions
InactiveUS20080122915A1High optical densityWide latitudeMeasurement apparatus componentsInksPolymer chemistryPolymer
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
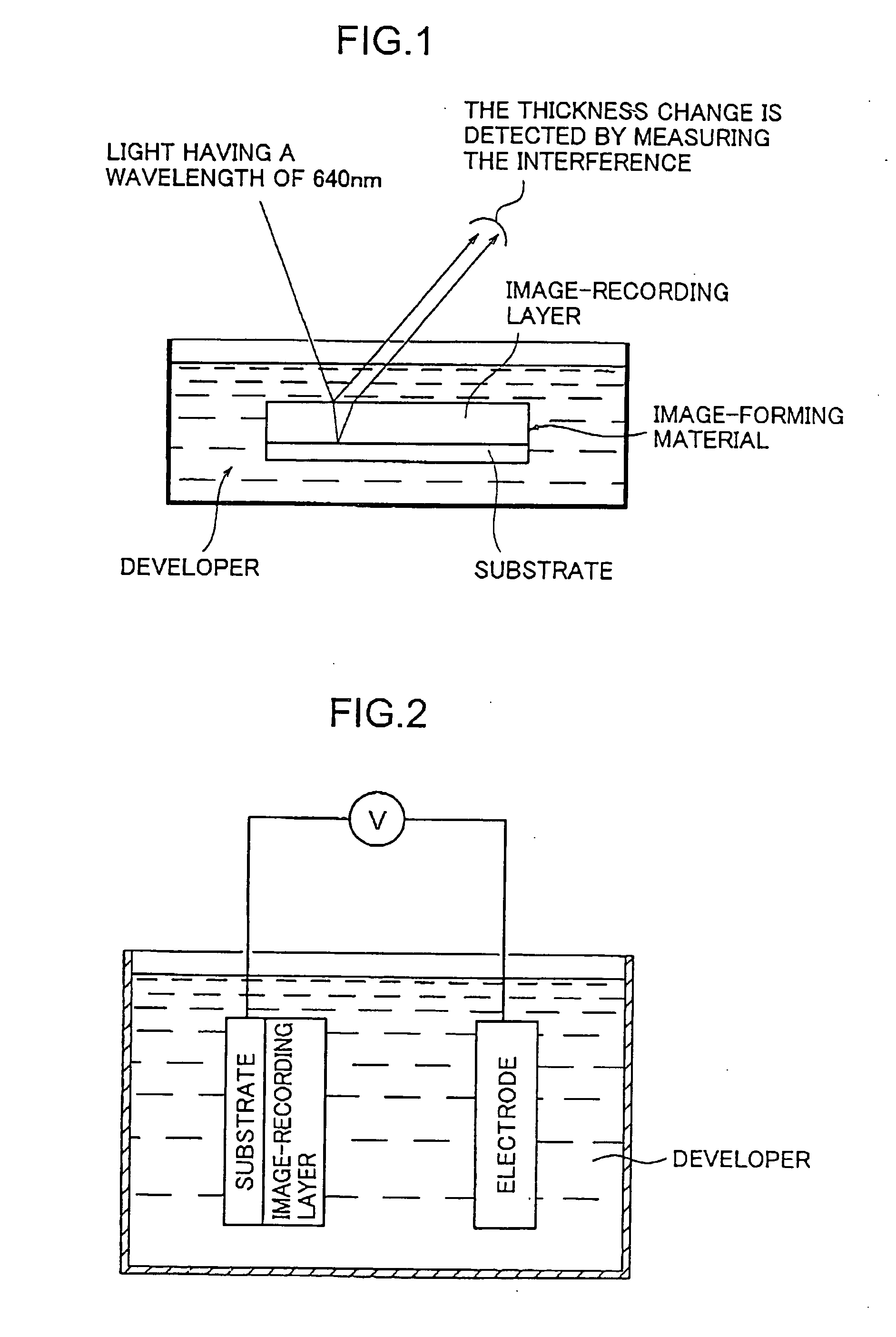
Photoelectric sensor, information recording method, and information recording system
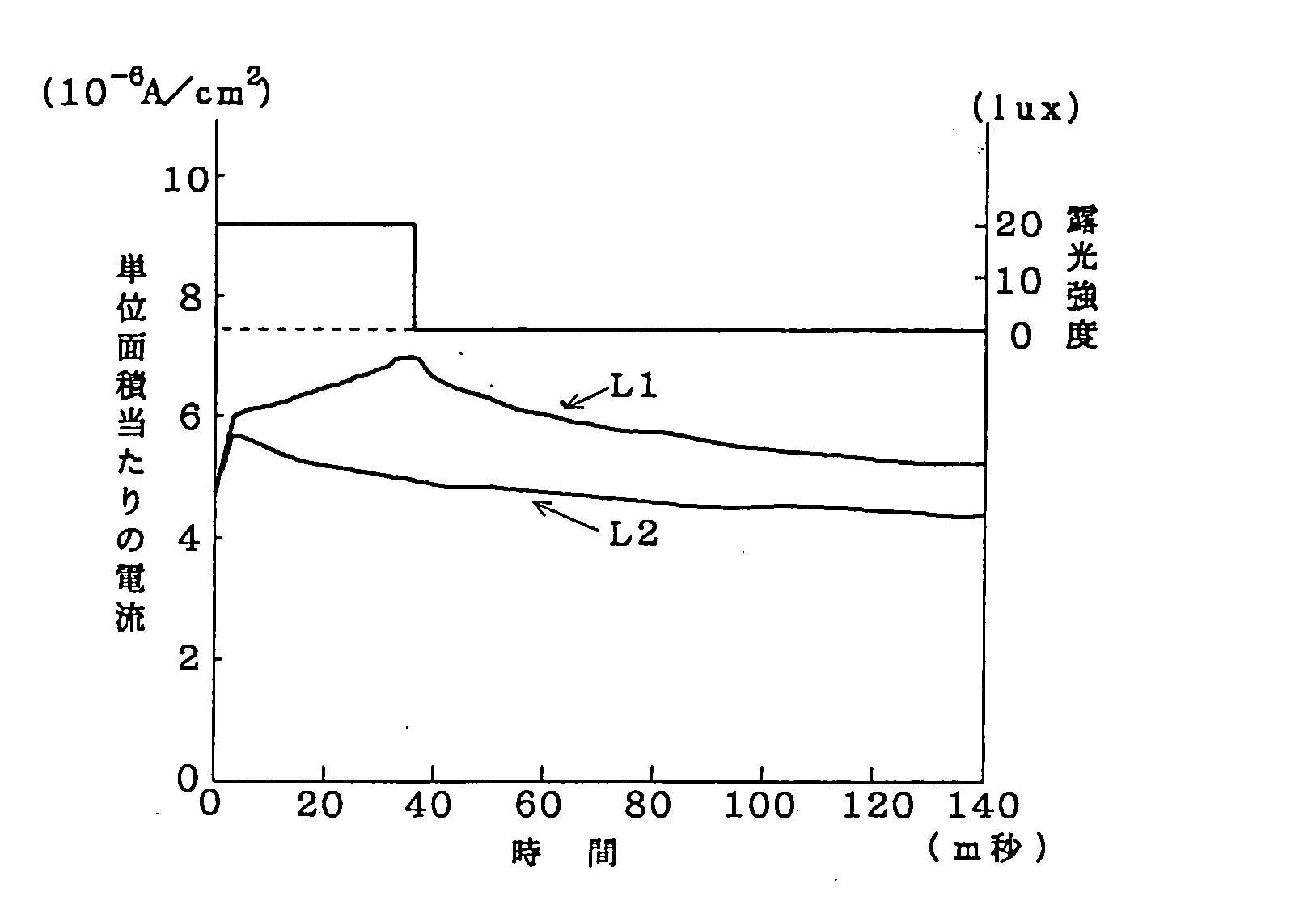
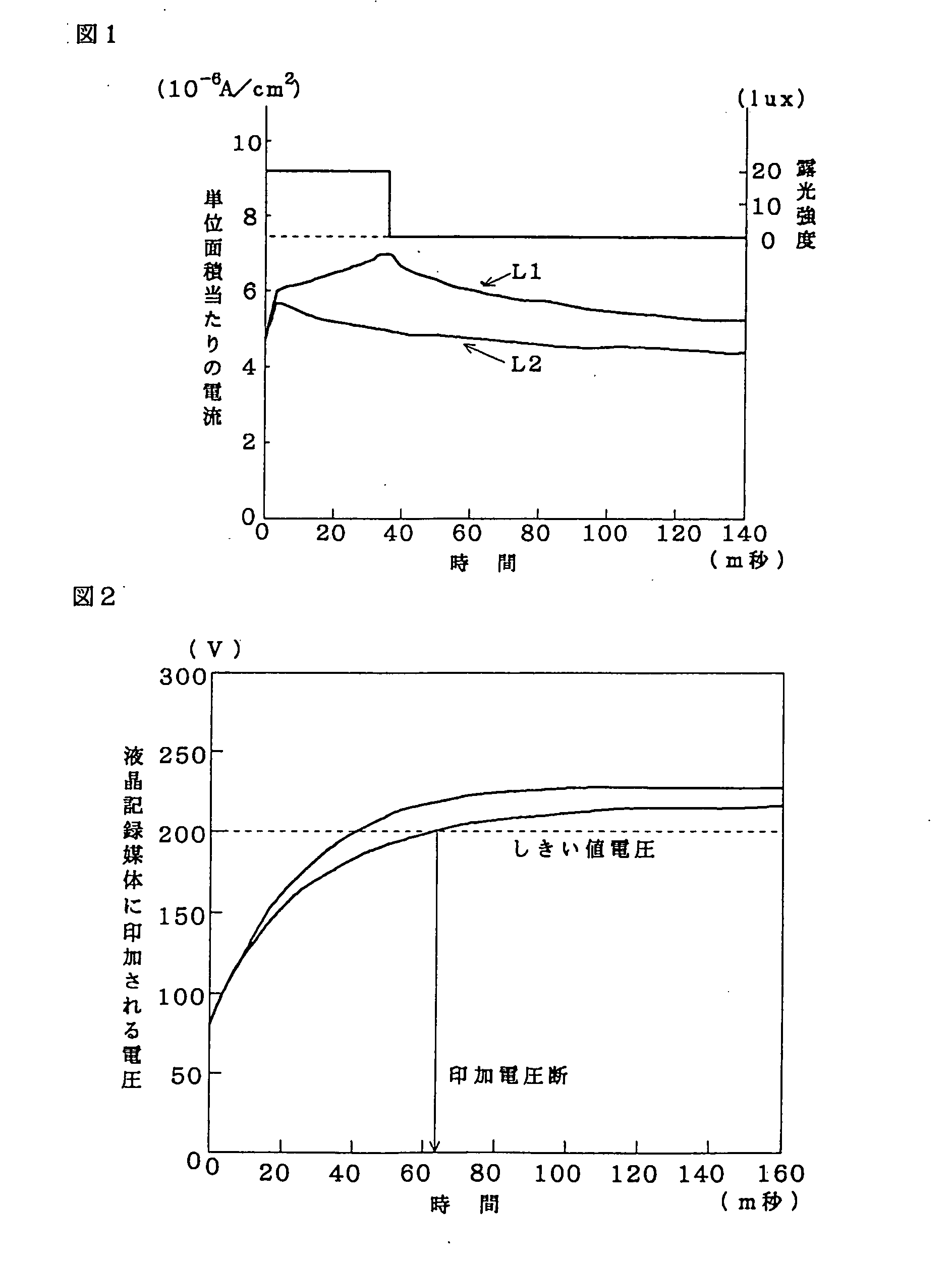
InactiveUS20080231768A1Wide latitudeRecord information storageRecording by electric charge/resistance/capacitanceComputer sciencePhotoelectric sensor
The present invention relates to an information recording system comprising an information recording medium and a photoelectric sensor capable of recording light information on the information recording medium in the form of visible information or electrostatic information, and to an information recording method wherein light information is recorded on an information recording medium utilizing an photoelectric sensor.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
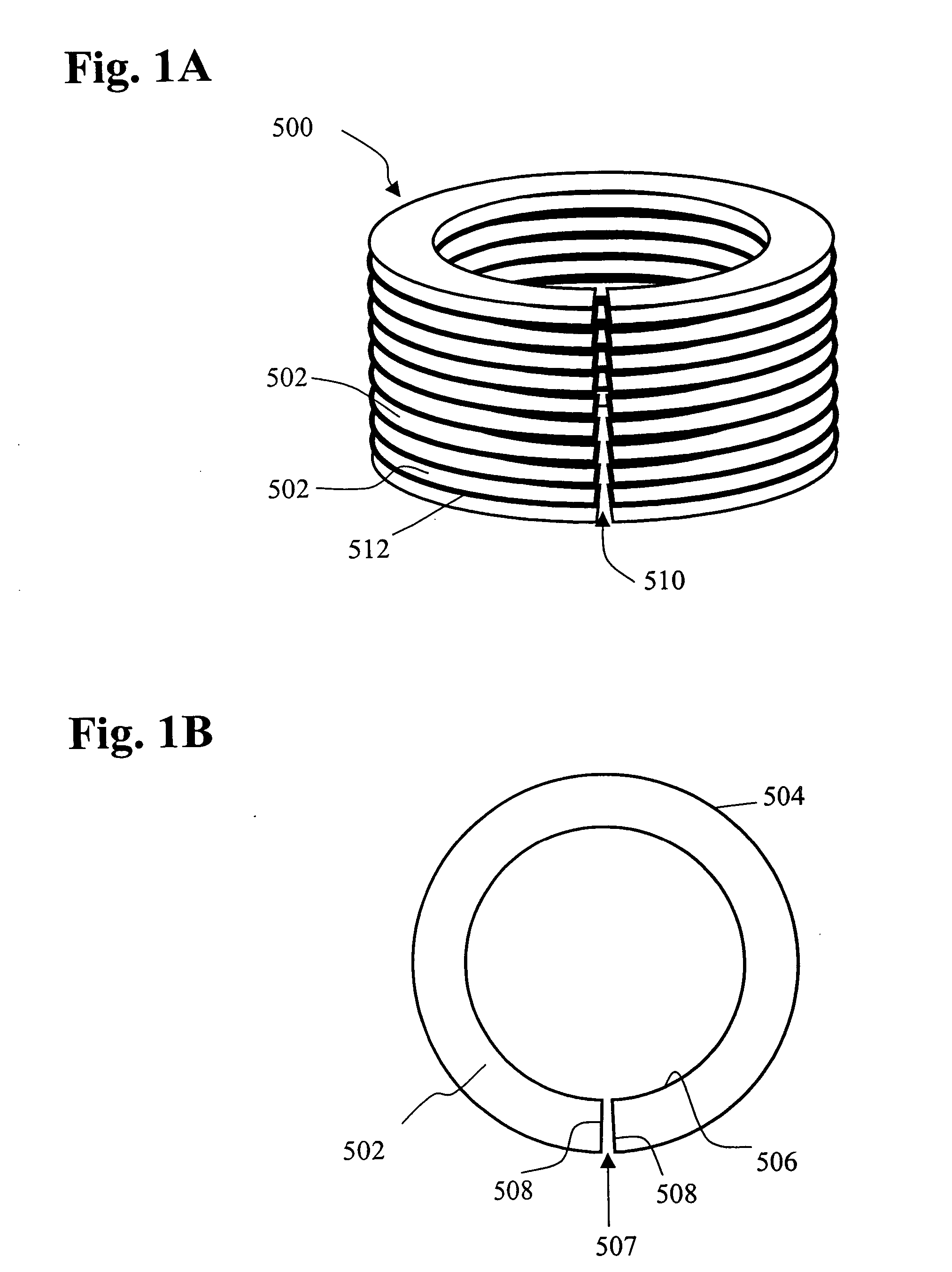
Method of manufacturing magnet material, ribbon-shaped magnet material, magnetic powder and bonded magnet
InactiveUS20030056933A1Improve liquidityHigh densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureSurface layerBand shape
A magnet material having excellent magnetic properties and a bonded magnet formed of the magnet material as well as a method of manufacturing the magnet material are disclosed. The method of manufacturing the magnet material is carried out by discharging a molten metal of the magnet material from a nozzle while rotating a cooling roll having a surface layer composed of ceramics on its outer periphery to be collided with the surface layer of the cooling roll and solidified by cooling, the method of manufacturing the magnet material being characterized in that the time during which the magnet material is in contact with the surface layer of the cooling roll is not less than 0.5 ms when the molten metal of said magnet material is discharged from directly above the center of rotation of the cooling roll toward an apex part of the cooling roll to be collided with the apex part.
Owner:ARAI AKIRA +1
Magnetic powder and isotropic bonded magnet
InactiveUS6855265B2Improve magnetic propertiesHigher magnetic energyNanomagnetismInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementMagnetic phase
Disclosed herein is a magnetic powder which can provide a bonded magnet having excellent magnetic properties and having excellent reliability especially excellent heat stability. The magnetic powder is composed of an alloy composition represented by Rx(Fe1-yCoy)100-x-z-wBzAlw (where R is at least one kind of rare-earth element, x is 7.1-9.9 at %, y is 0-0.30, z is 4.6-6.9 at %, and w is 0.02-1.5 at %), the magnetic powder being constituted from a composite structure having a soft magnetic phase and a hard magnetic phase, wherein the magnetic powder has magnetic properties in which, when the magnetic powder is formed into an isotropic bonded magnet having a density ρ[Mg / m3] by mixing with a binding resin and then molding it, the maximum magnetic energy product (BH)max[kJ / m3] of the bonded magnet at the room temperature satisfies the relationship represented by the formula (BH)max / ρ2[×10−9 J·m3 / g2]≧2.1, and the intrinsic coercive force (HCJ) of the bonded magnet at the room temperature is in the range of 320-720 kA / m.
Owner:MAGNEQUENCH
System for controlling an automatic transmission throttle valve
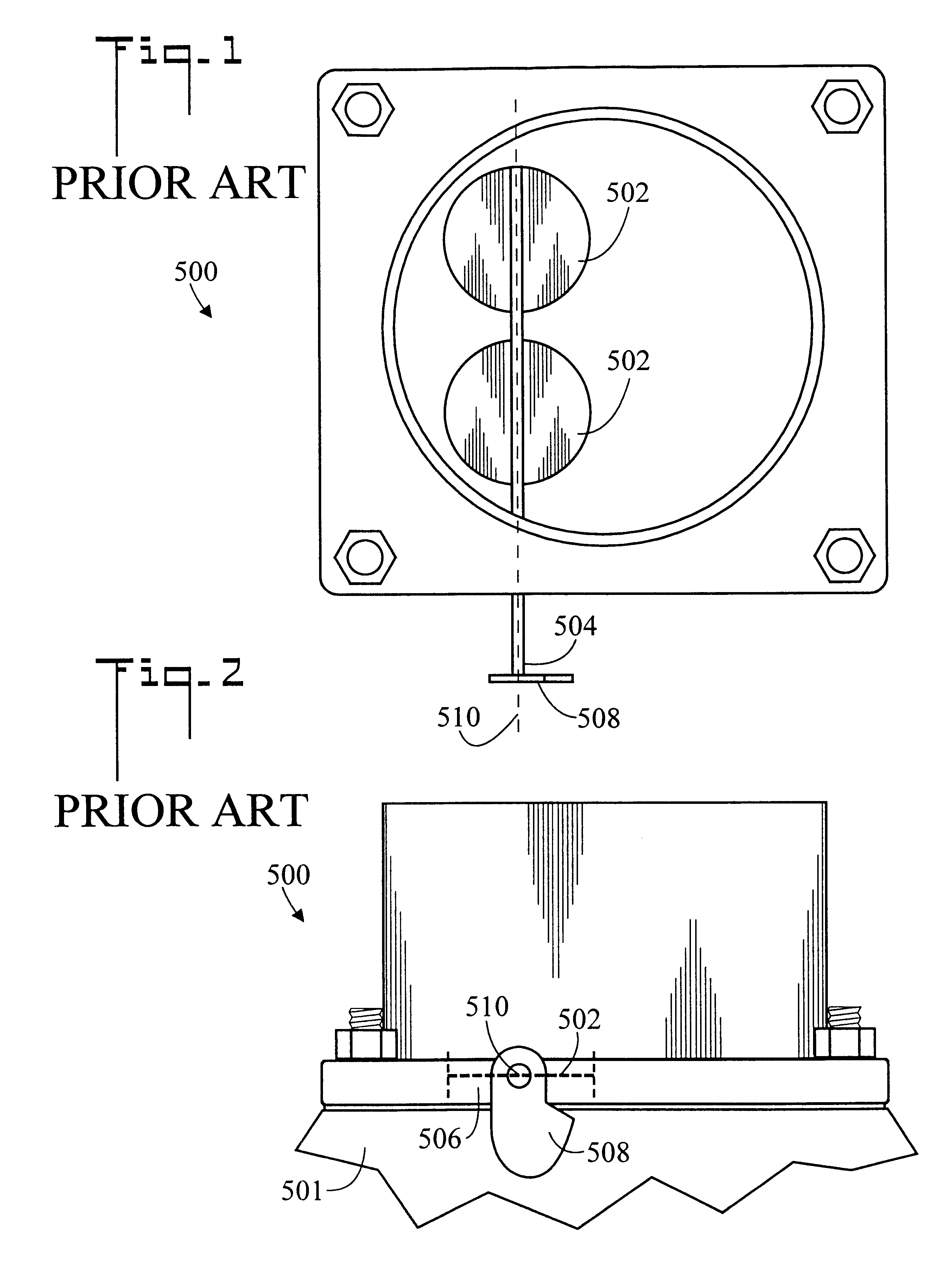
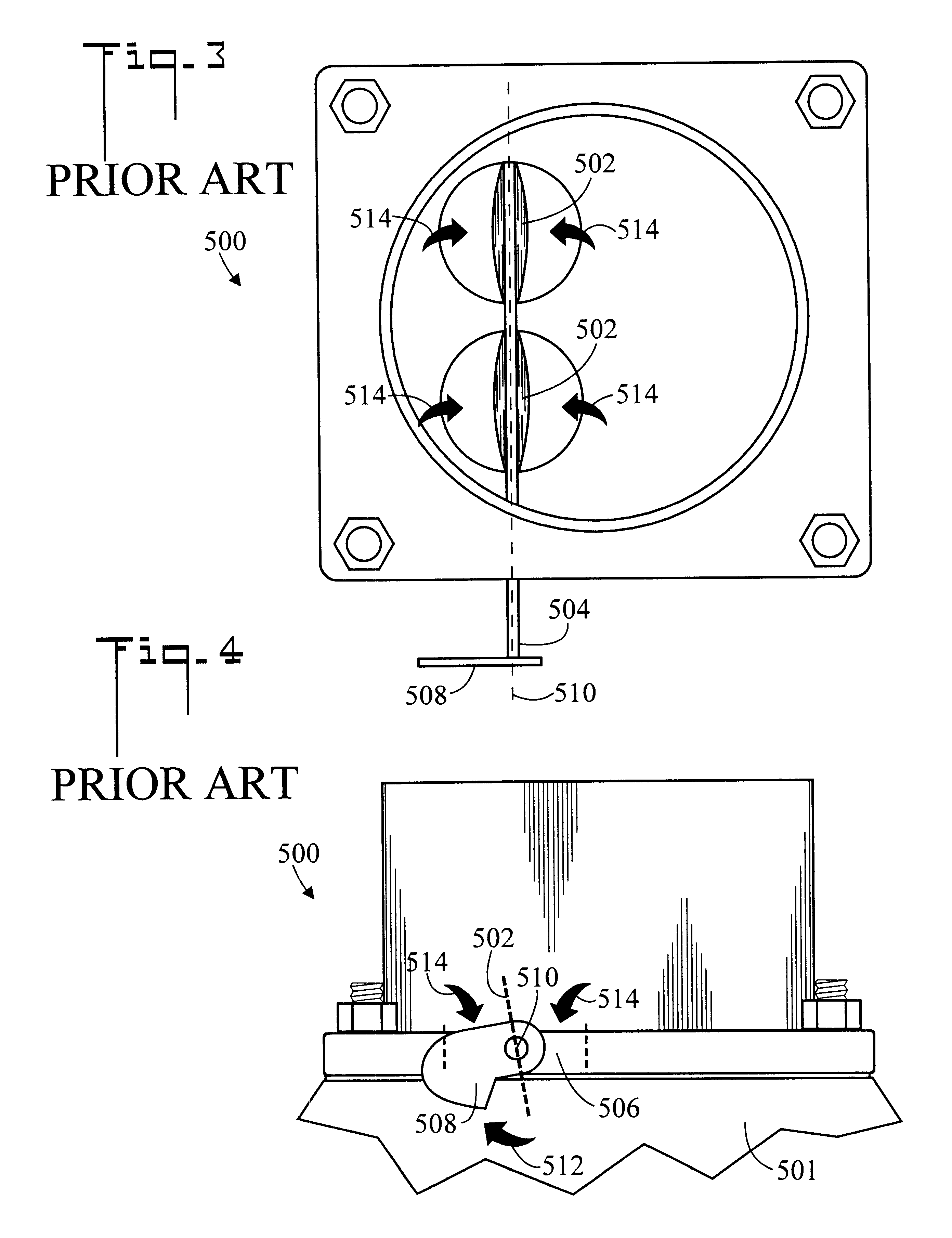
InactiveUS6575875B2Firmness and response aggressivenessWide latitudeGearing controlEngine controllersAutomatic transmissionEngineering
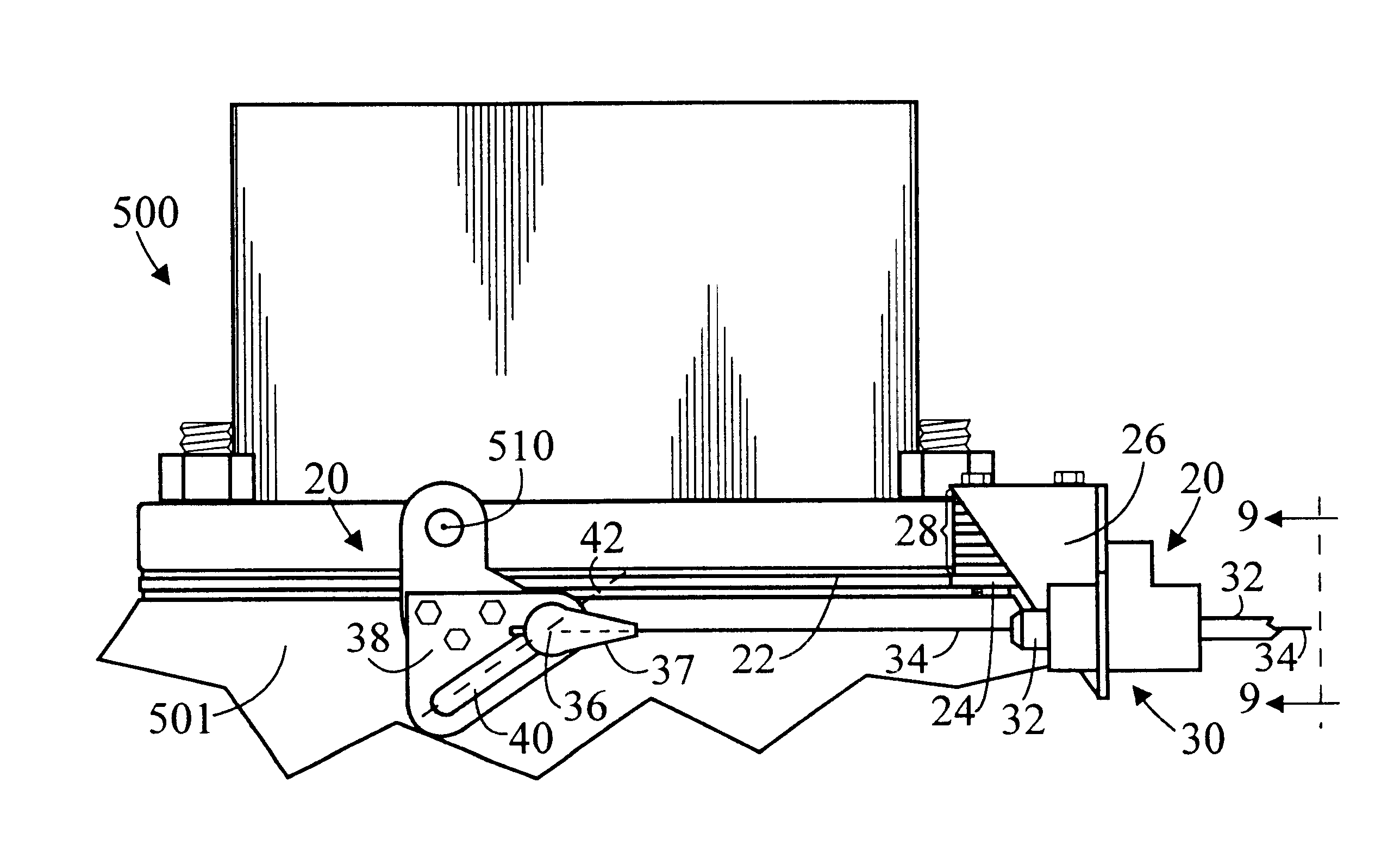
A system (20) for controlling a transmission throttle valve in a vehicle having a fuel management device (500) having a rotatable linkage member (508) includes an adapter plate (22) which is mountable beneath the fuel management device (500), a bracket (26) which is connectable to the adapter plate (22), and a throttle valve cable (30) which is connectable to the bracket (26). Throttle valve cable (30) has a tubular housing (32) which is fixedly connectable to bracket (26) and a cable (34) which is slidably disposed within tubular housing (32), the cable (34) having a first end (36) and an opposite second end connectable to the transmission throttle valve. First end (36) is selectively connectable along a slot (40. Different first end (36) connection positions along slot (40) result in correspondingly different rates of cable pull and therefore different transmission responses.
Owner:PAC INTERACTIVE TECH
Combined Salt and Pepper Mill
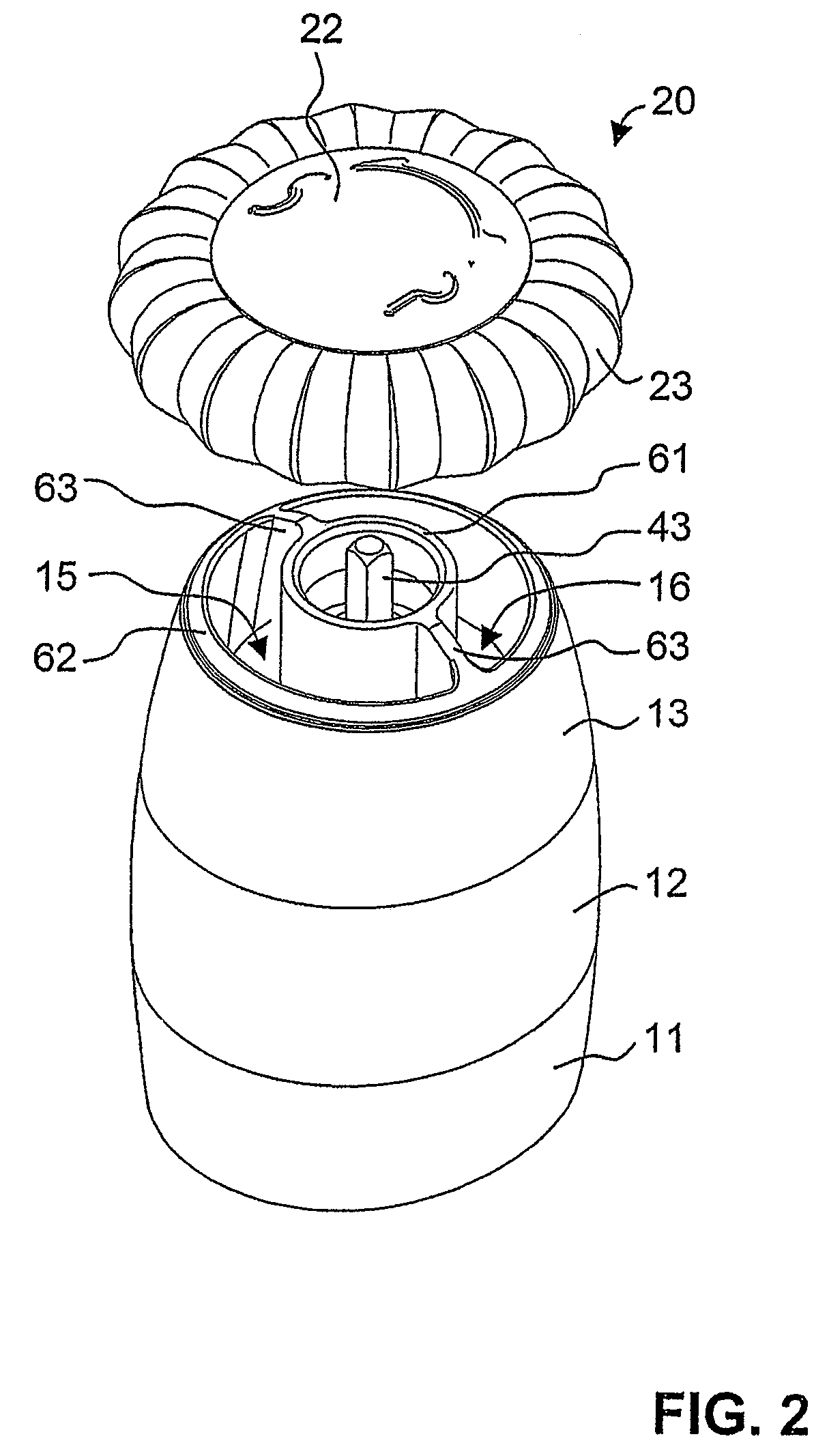
InactiveUS20090314867A1Easy constructionSimple wayCoffee millsSpice millsMechanical engineeringEngineering
A spice mill for cutting up two different spices, in particular salt and pepper, is disclosed. Two spice containers (17, 18) and two grinding mechanisms (50, 50′) are arranged in a base part (10). A cover part (20) can be removed from the base part (10) and serves as a rotary handle. When the cover part (20) is removed, filling openings (15, 16) for the spice containers (17, 18) are opened up. An encapsulated gear mechanism (30) is arranged in the base part (10) between the cover part and the grinding mechanisms. When the cover part (20) is rotated in a first direction of rotation, the gear mechanism (30) drives the first grinding mechanism (50). By contrast, upon rotation in the opposite direction, the second grinding mechanism (50′) is driven. In a preferred embodiment, the gear mechanism is arranged in an upper region of the base part and, together with the base part, bounds the filling openings.
Owner:PI-DESIGN AG
Negative dye-containing curable composition, color filter and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20050214660A1Easy to useWide latitudePhotosensitive materialsOptical filtersOrganic solventColor gel
There are provided a negative dye-containing curable composition comprising an alkali-soluble binder, an organic solvent-soluble dye, a photopolymerizable compound, a photopolymerization initiator, an organic solvent and at least one of higher fatty acids and derivatives thereof, a color filter produced by using the negative dye-containing curable composition and a method of producing the color filter.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Negative dye-containing curable composition, color filter and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20050214679A1Easy to useExcellent in rectangular profile of pattern shapePhotosensitive materialsOptical filtersOrganic solventColor gel
There is provided a negative dye-containing curable composition, comprising an alkali-soluble binder, an organic solvent-soluble dye, a photopolymerizable compound, a photopolymerization initiator and an organic solvent, wherein: the mass of the organic solvent-soluble dye is greater than the mass of the alkali-soluble binder; the mass of the organic solvent-soluble dye is greater than the mass of the photopolymerizable compound; the mass of the organic solvent-soluble dye is greater than the mass of the photopolymerization initiator; and the ratio of the mass of the photopolymerization initiator to the mass of the photopolymerizable compound is greater than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 7. Also provided are a color filter produced by using the negative dye-containing curable composition and a method of producing the color filter.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Polymeric colorant-based ink compositions
InactiveUS7732509B2High optical densityWide latitudeMeasurement apparatus componentsInksPolymer chemistryPolymer
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
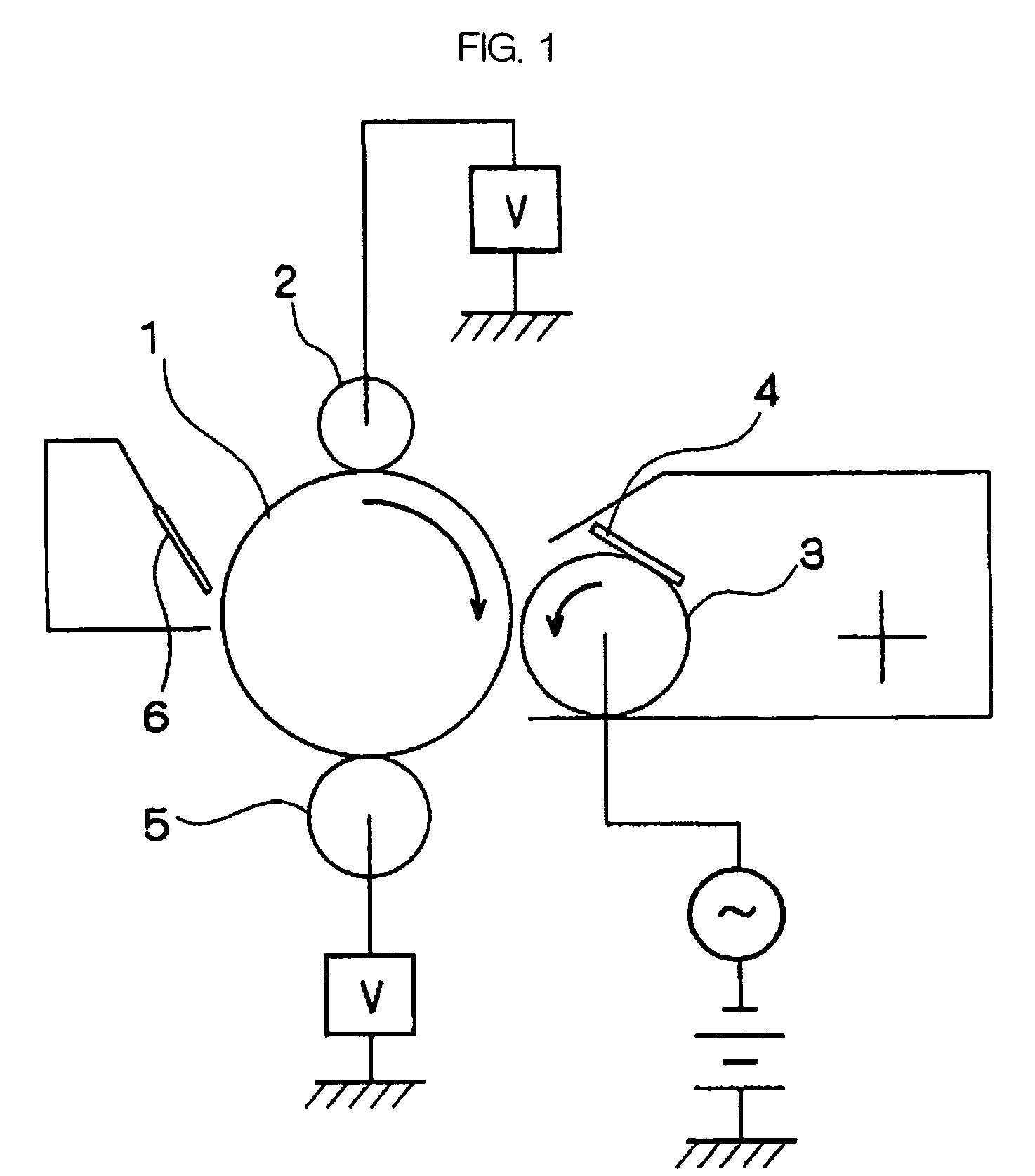
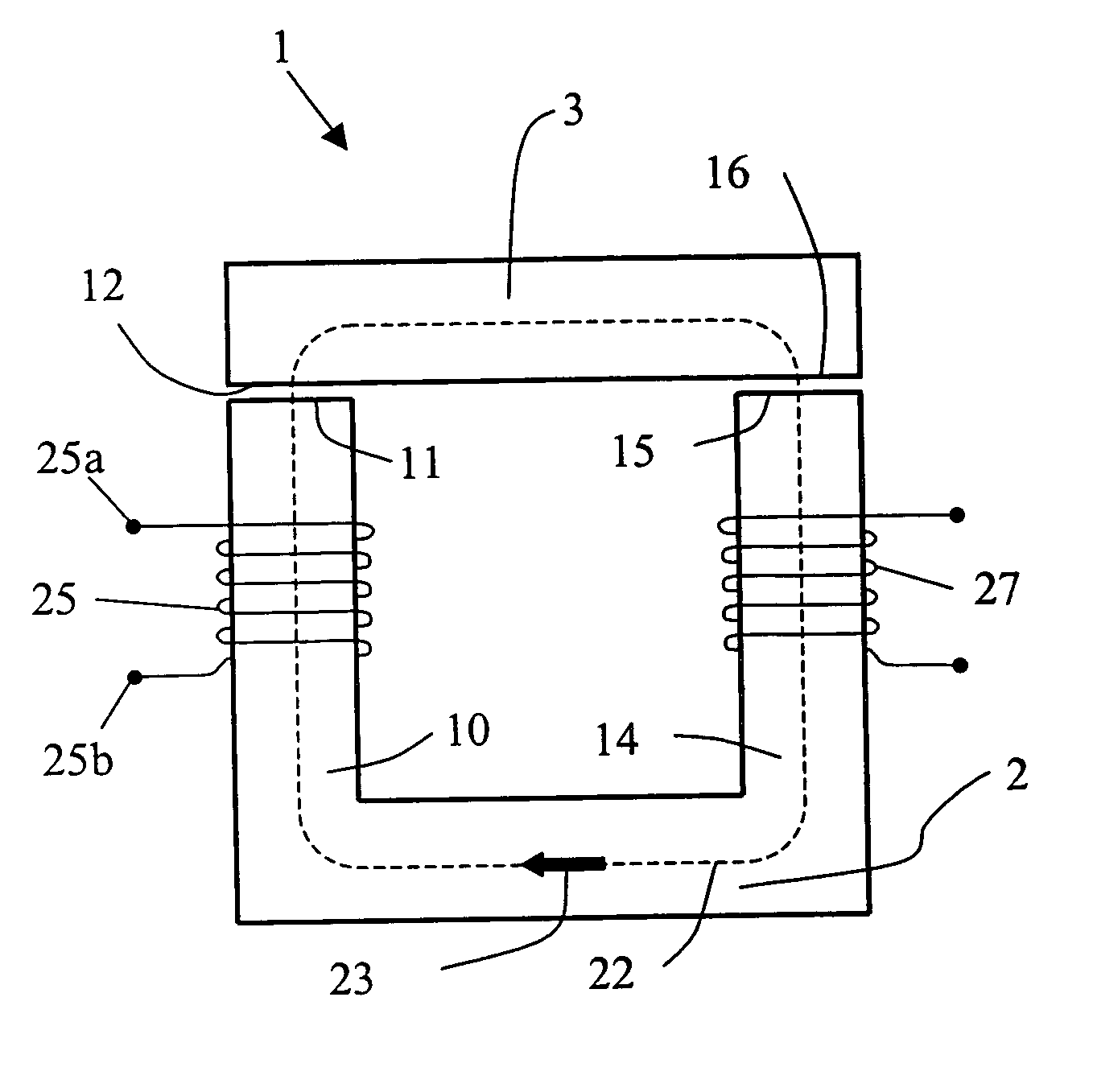
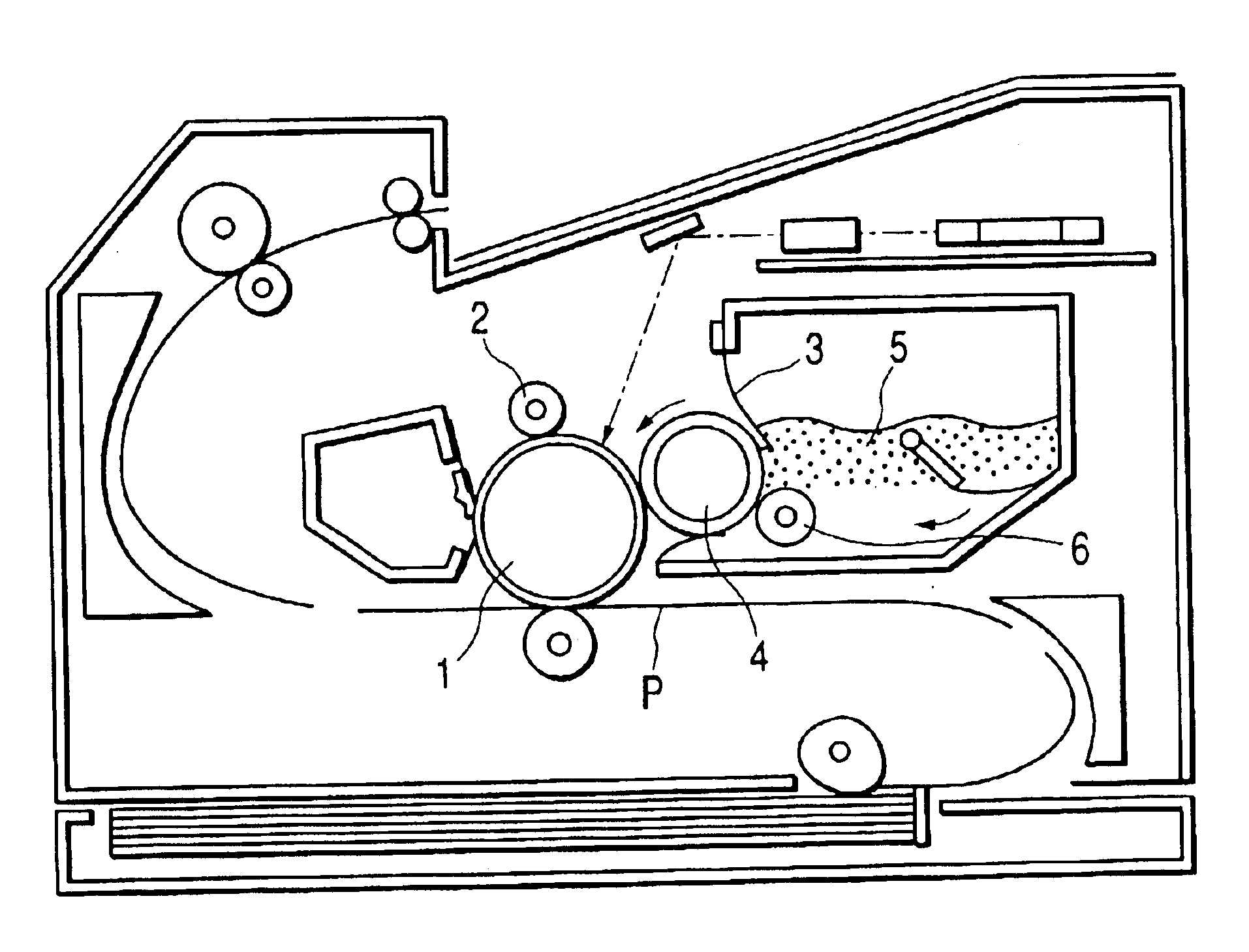
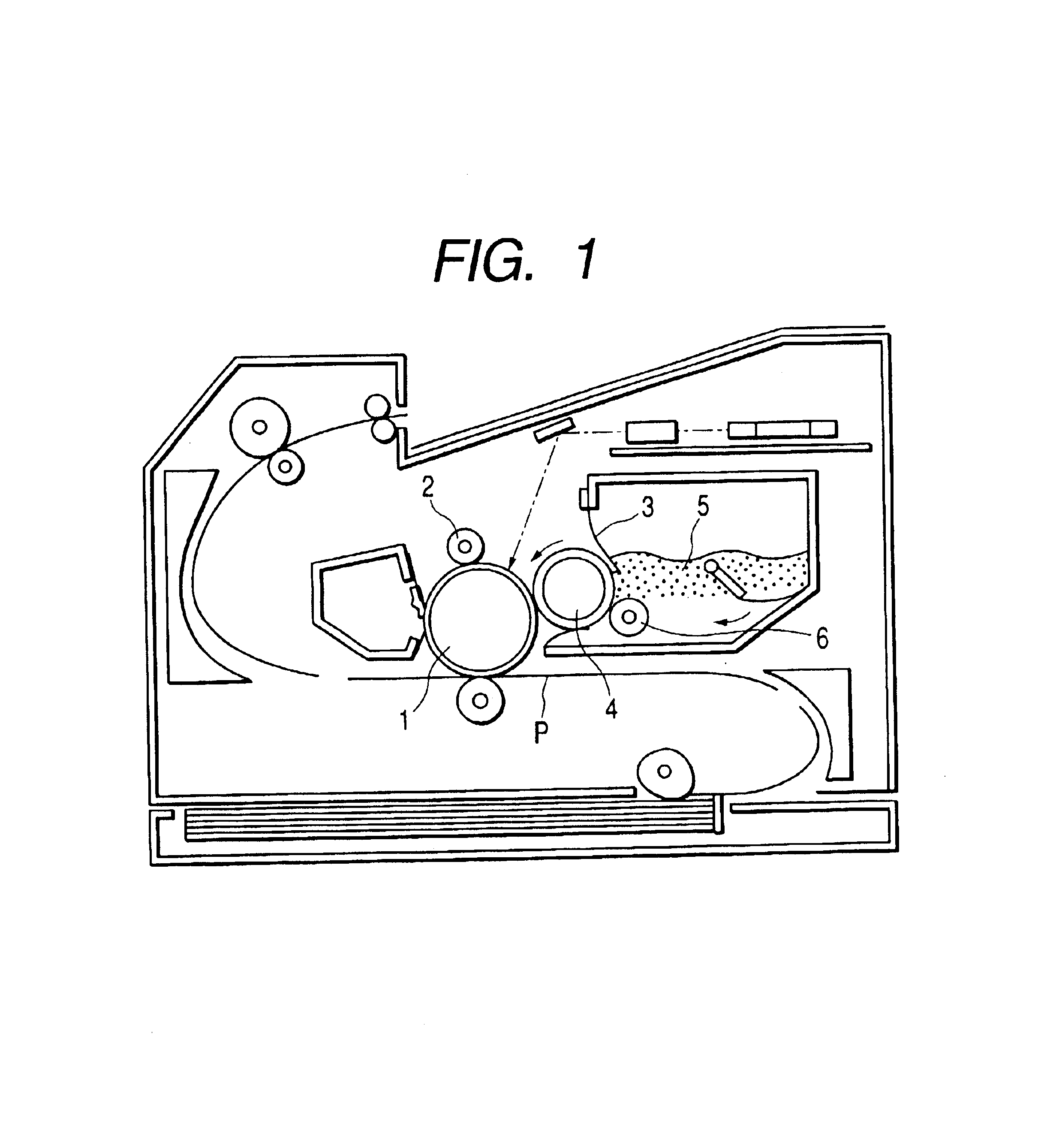
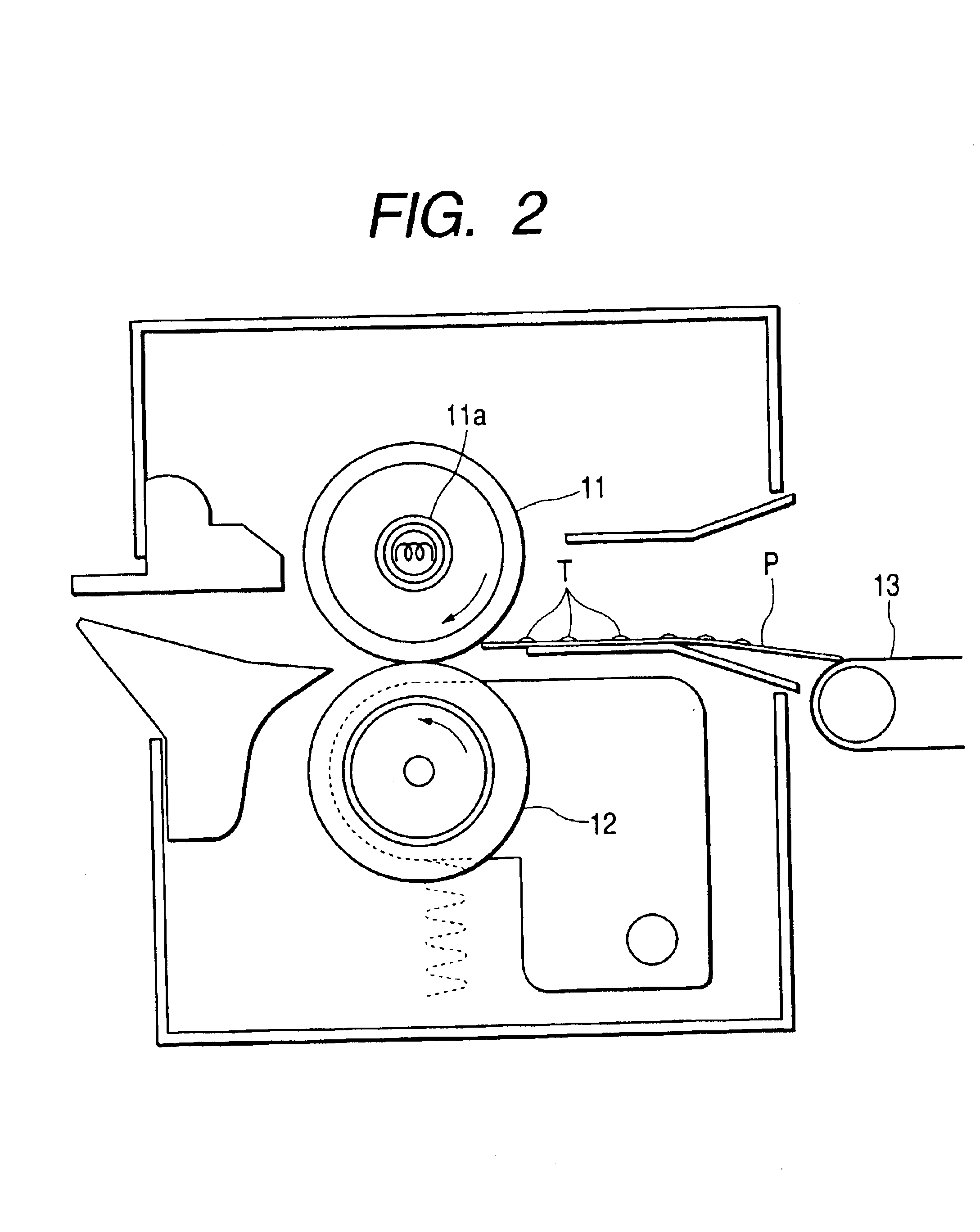
Cooling roll, ribbon-shaped magnetic materials, magnetic powders and bonded magnets
InactiveUS6892792B2Improve liquidityHigh magnetic flux densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMetallurgyBand shape
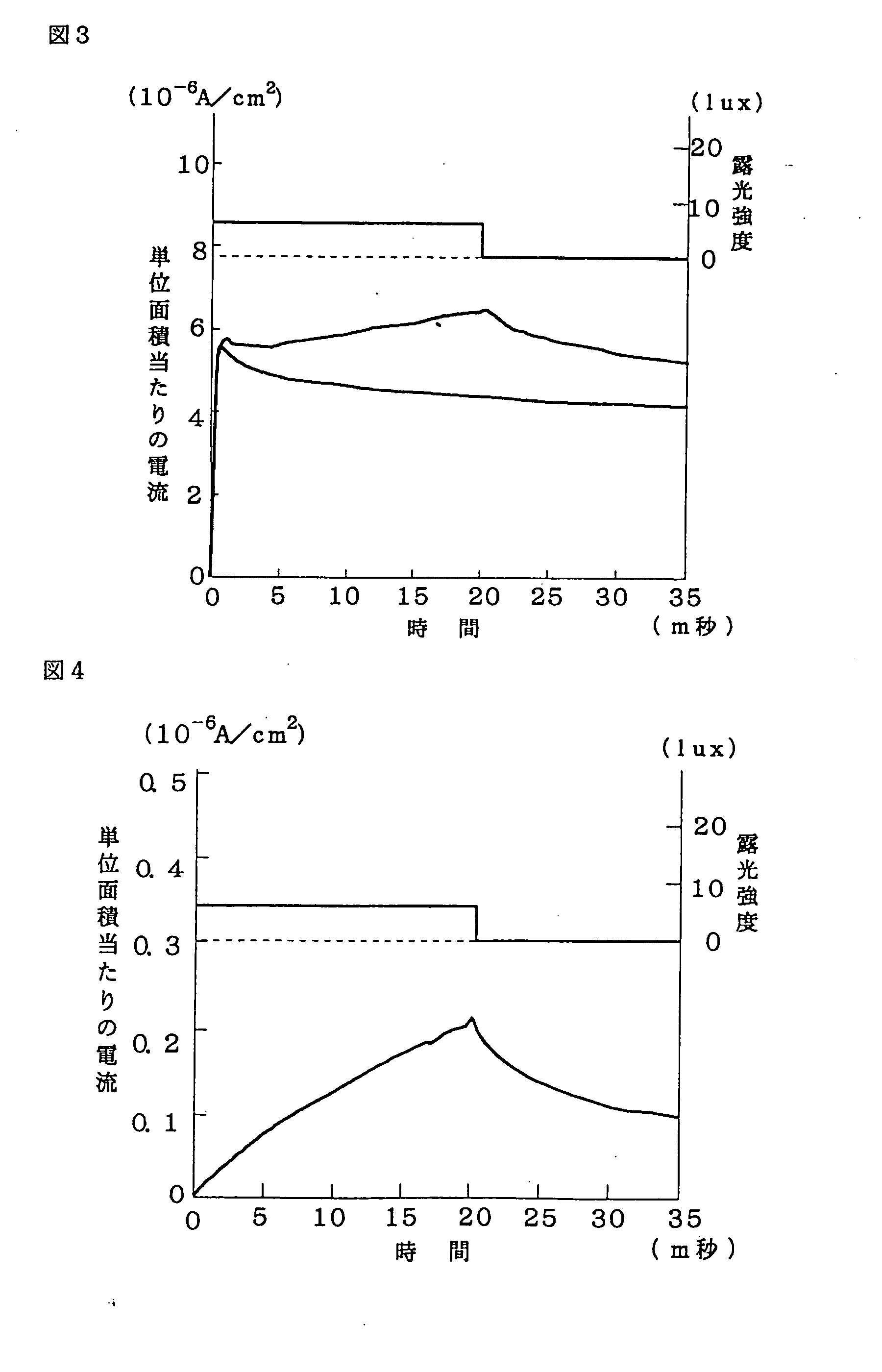
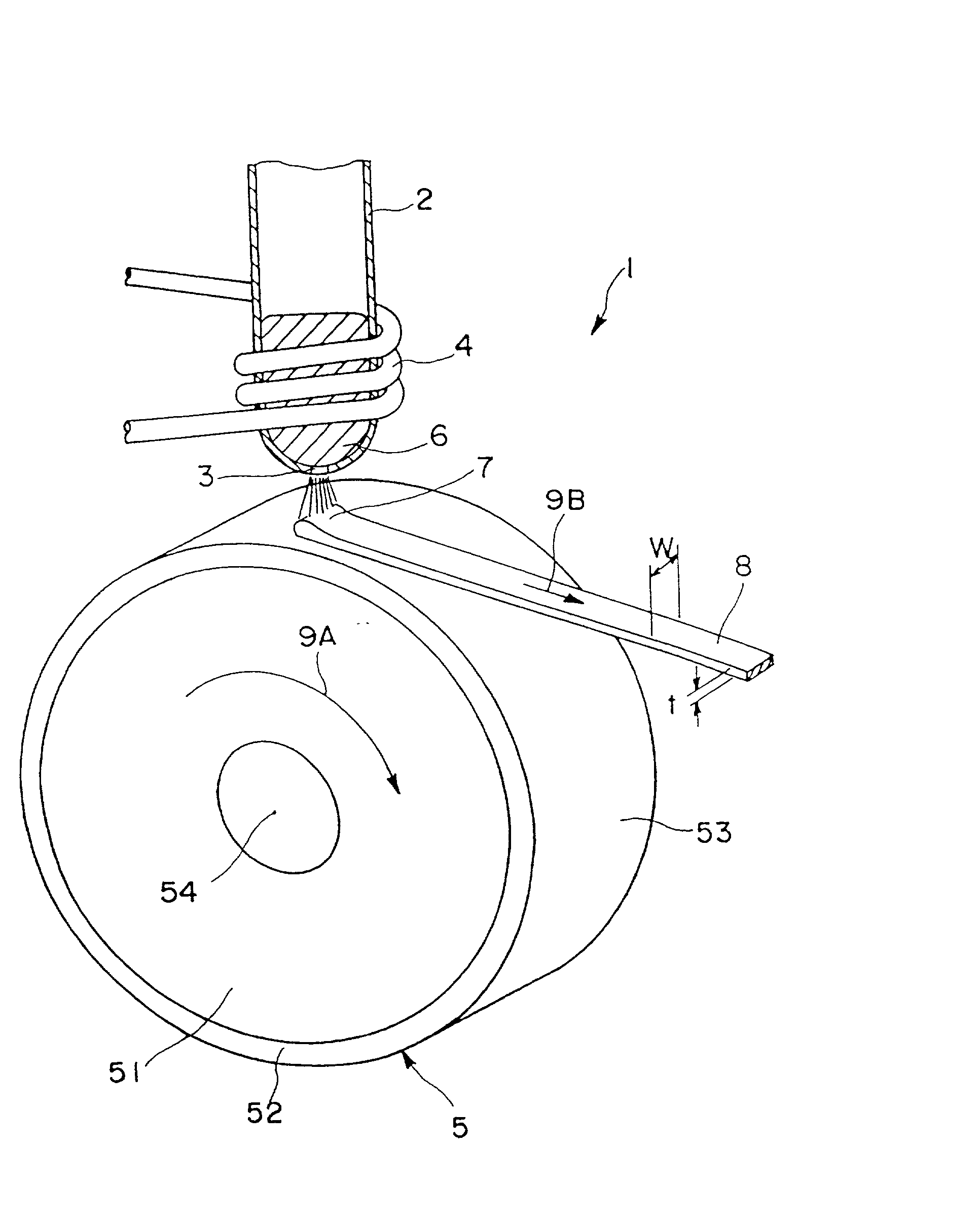
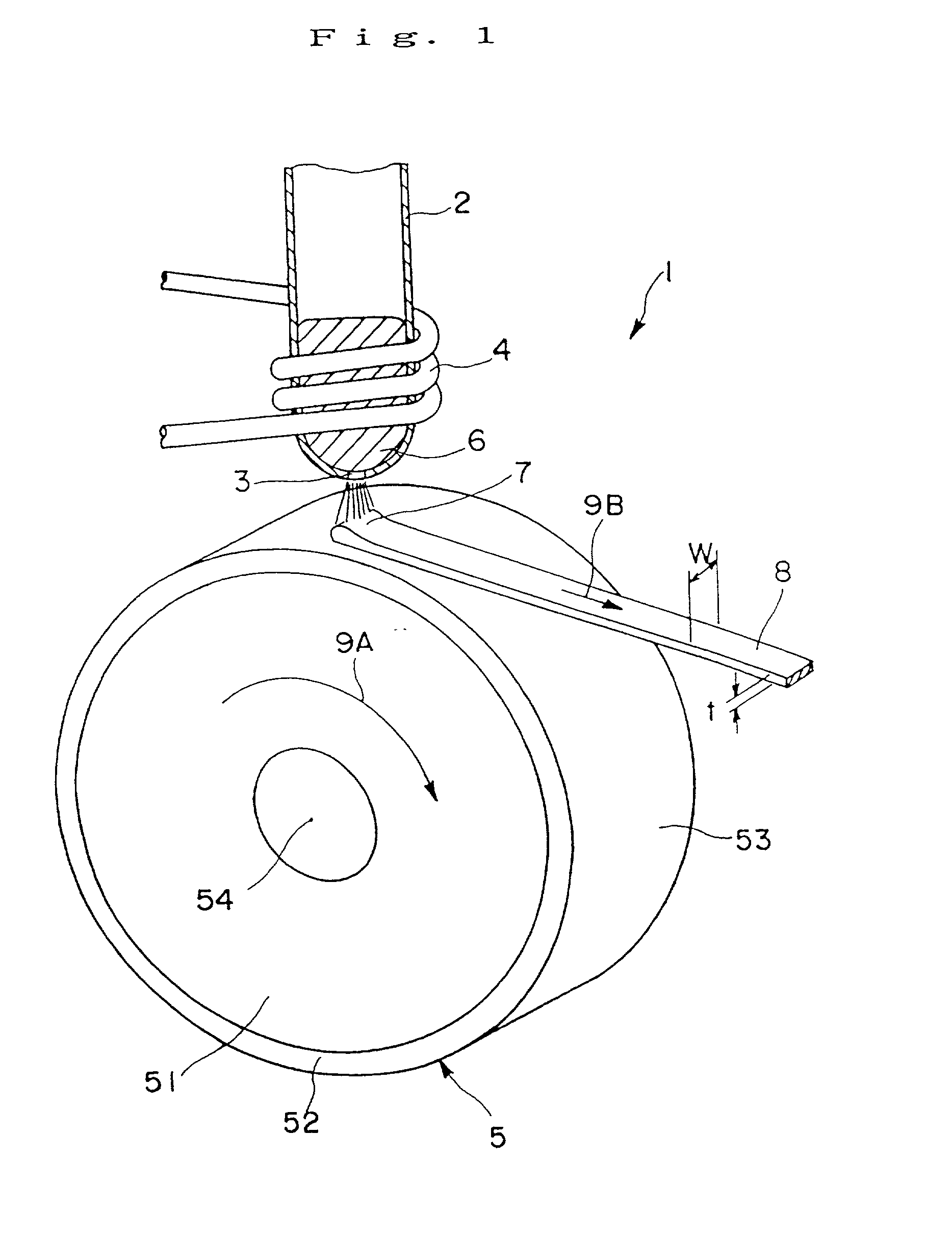
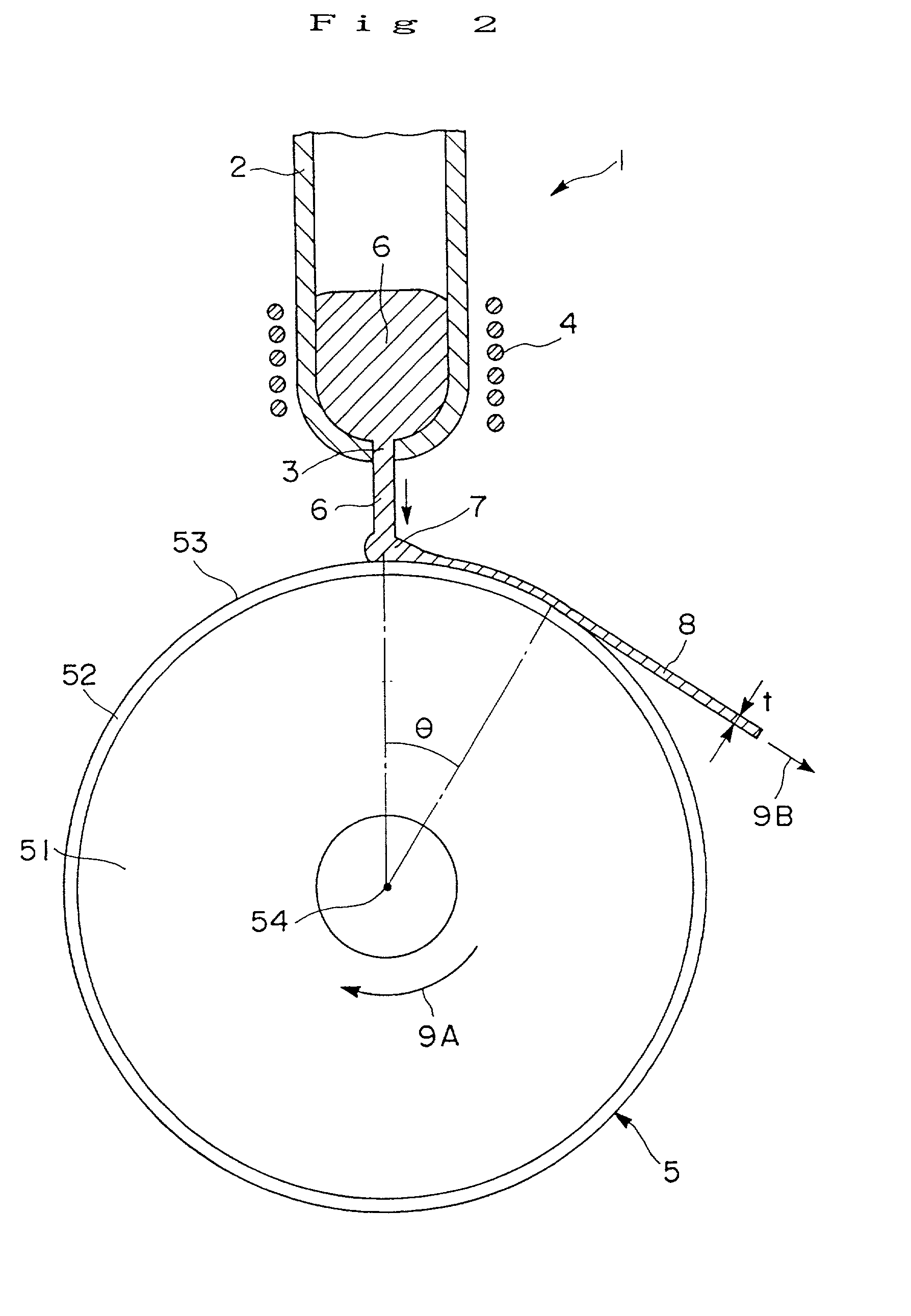
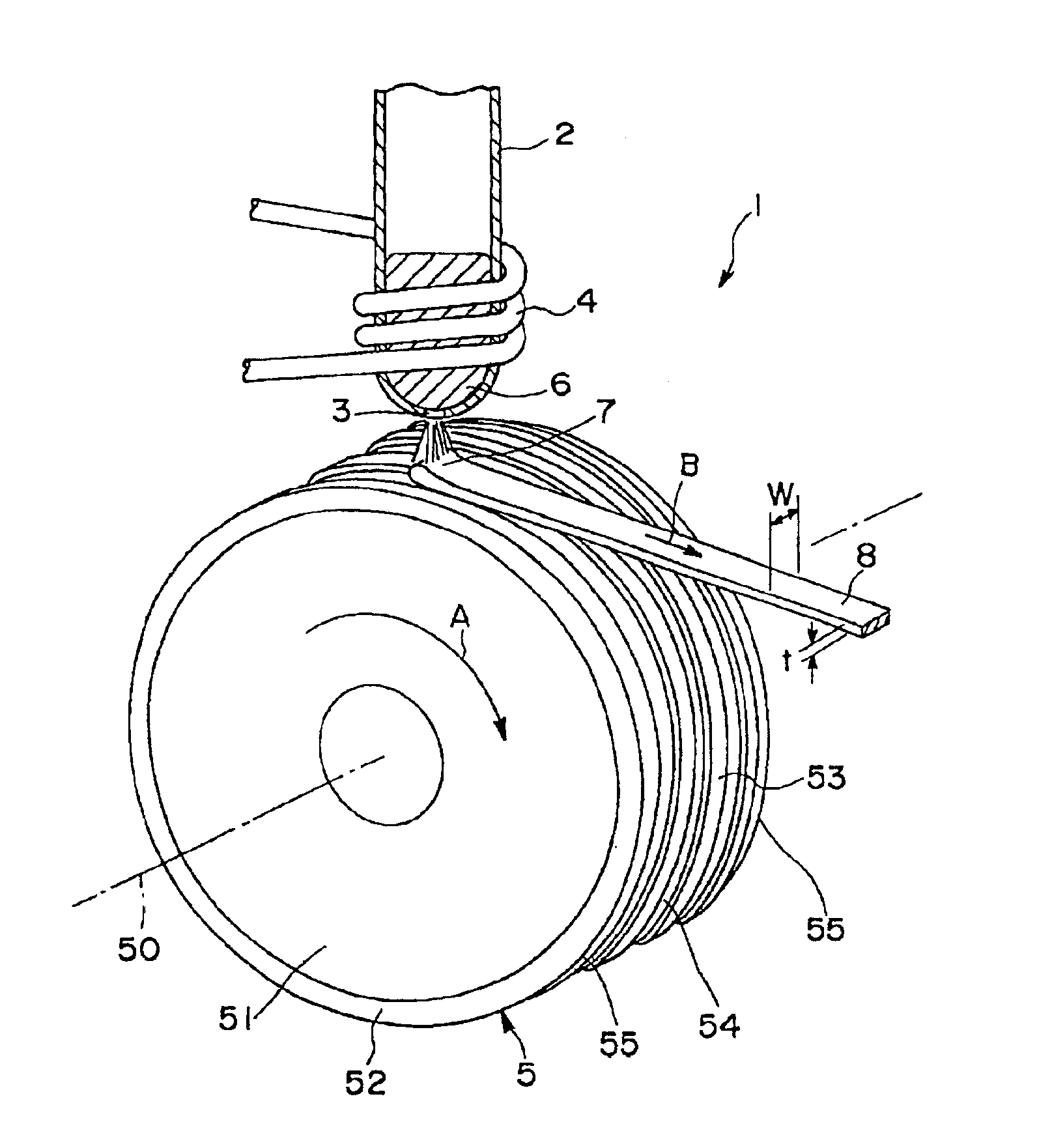
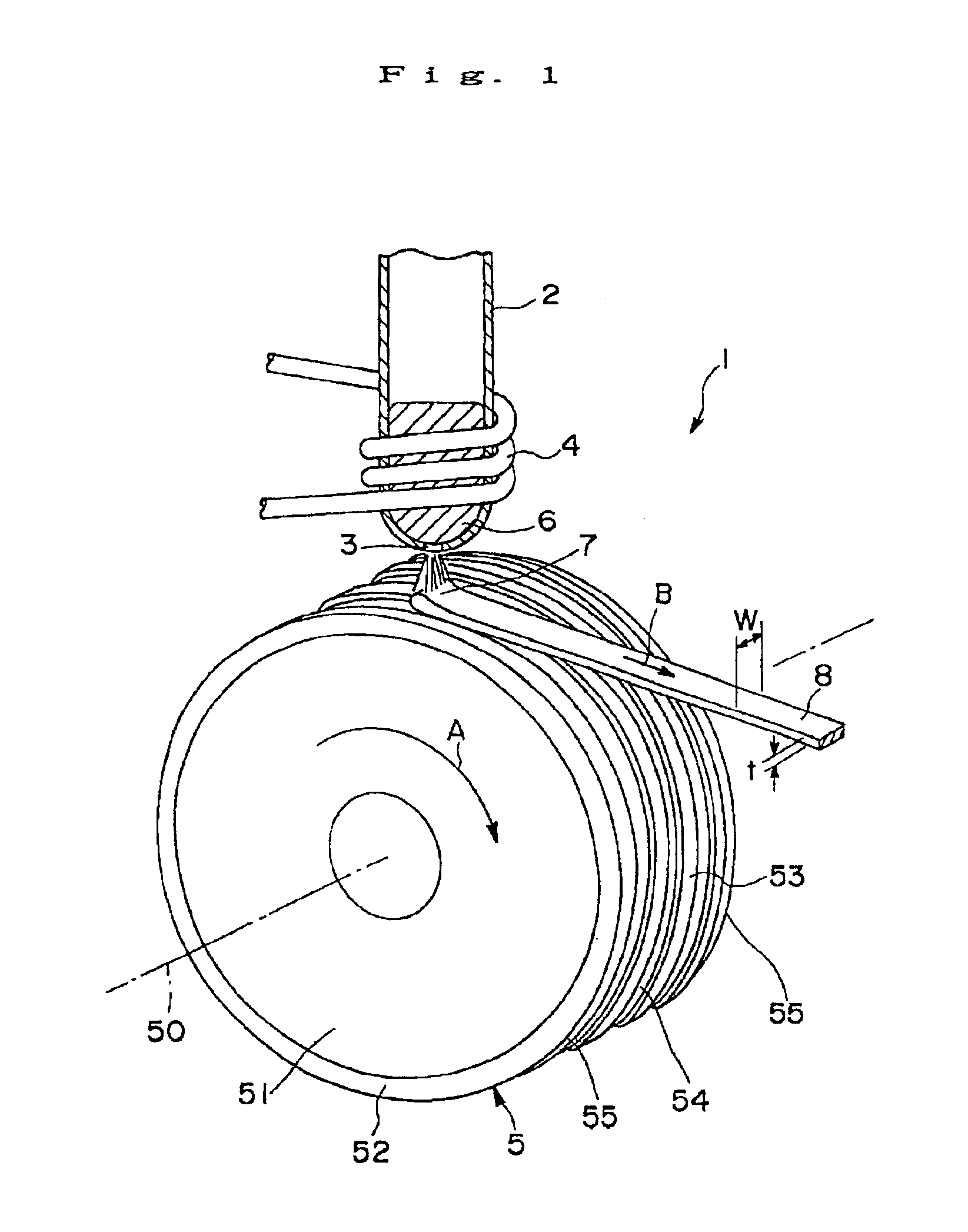
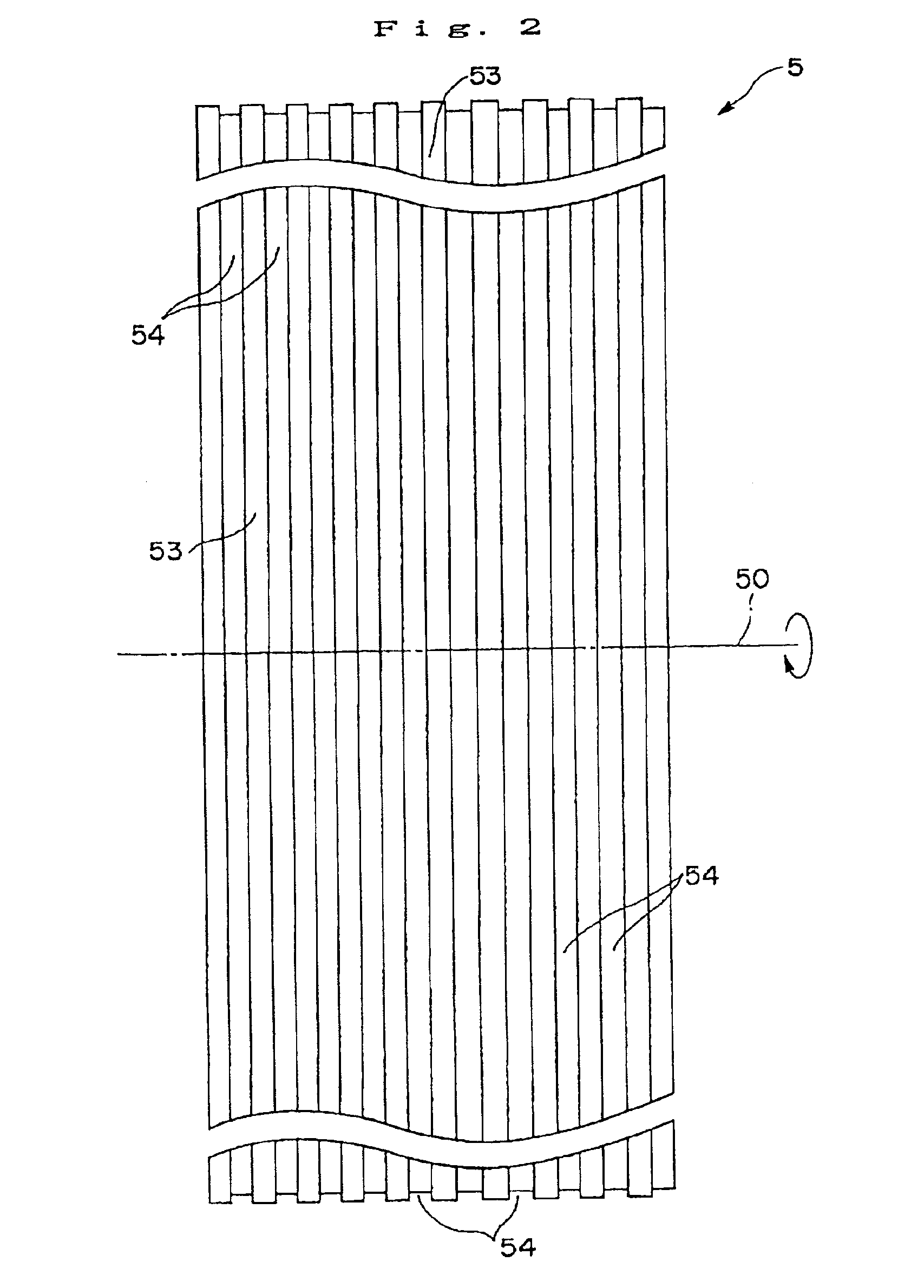
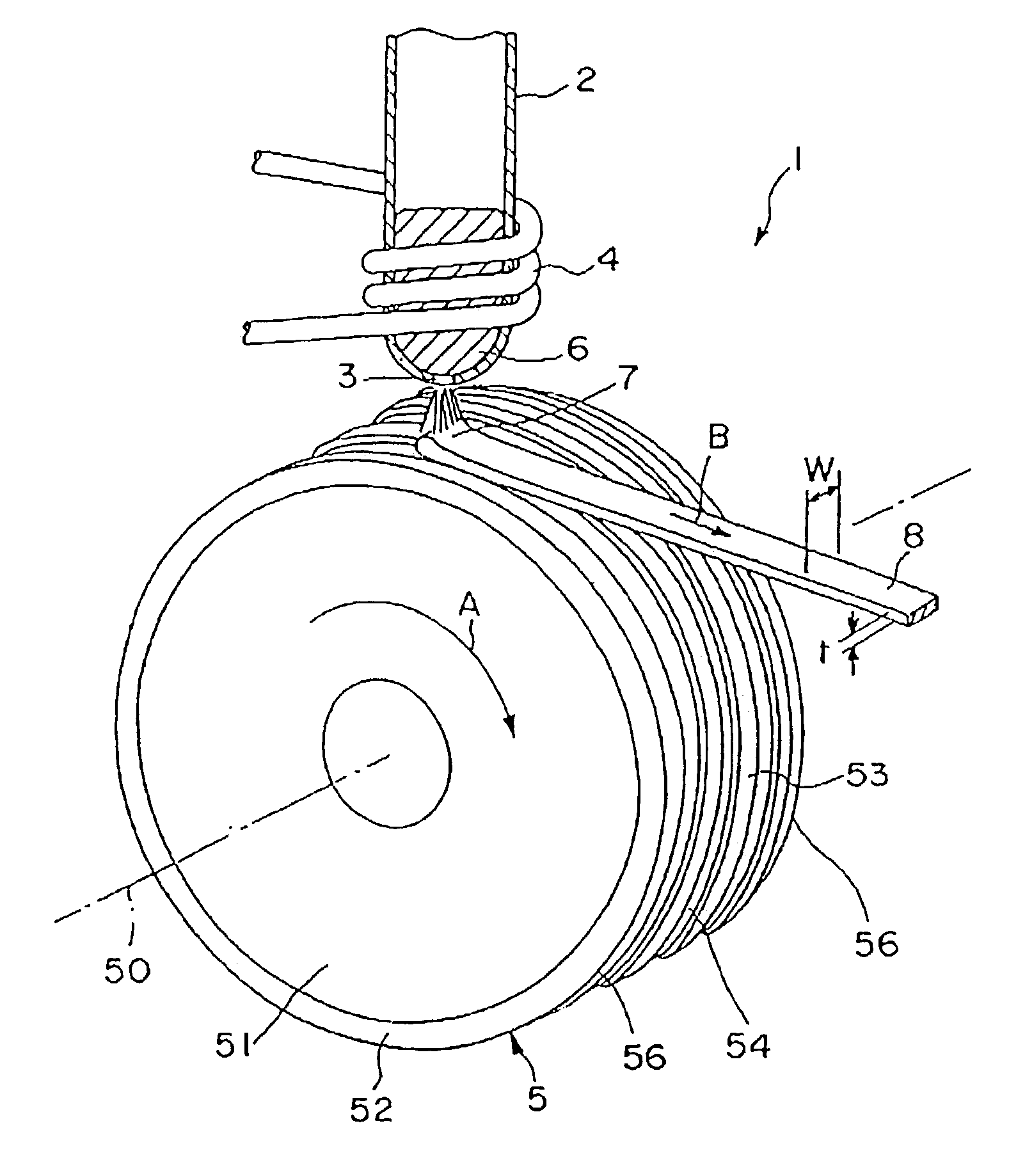
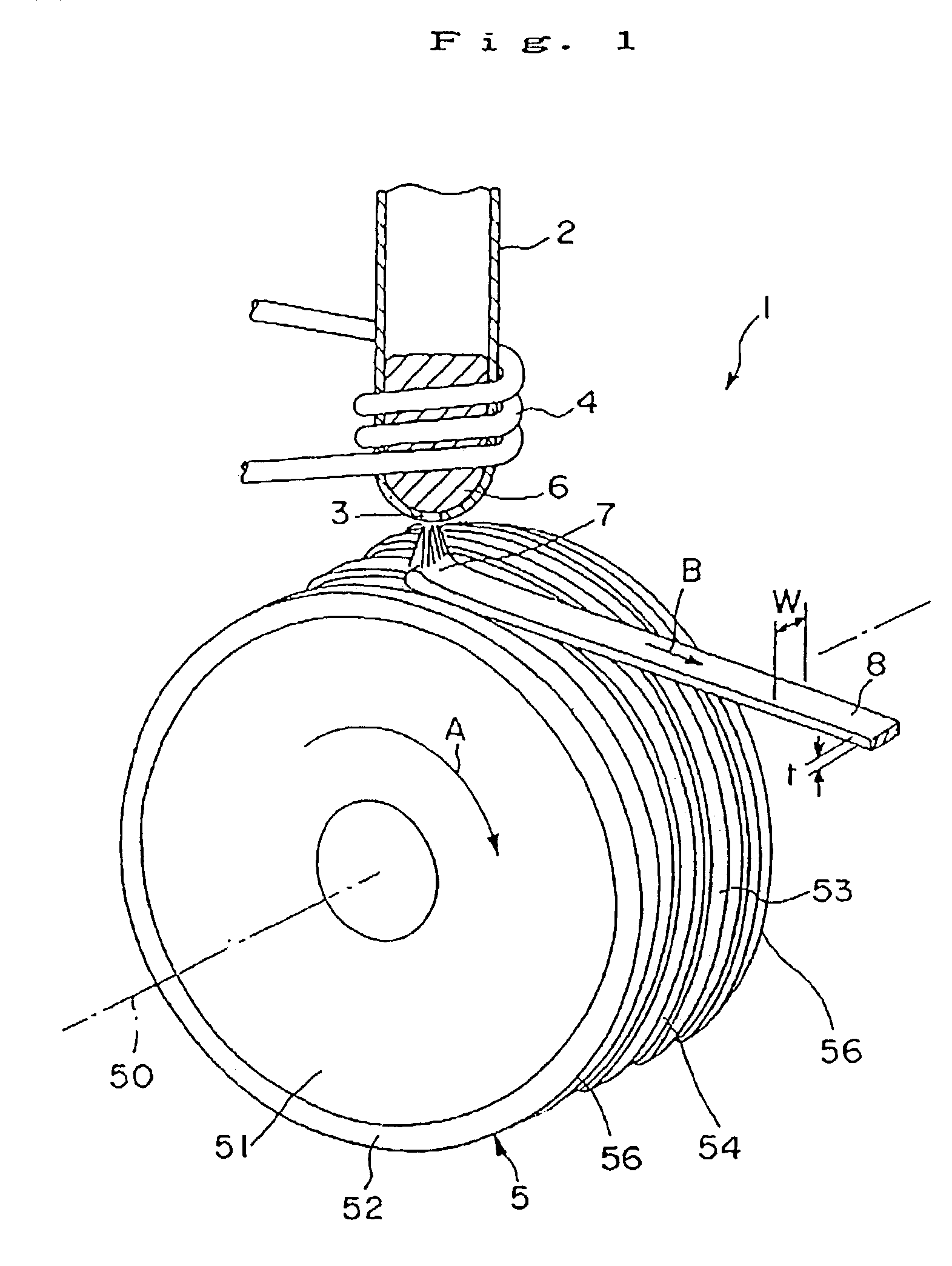
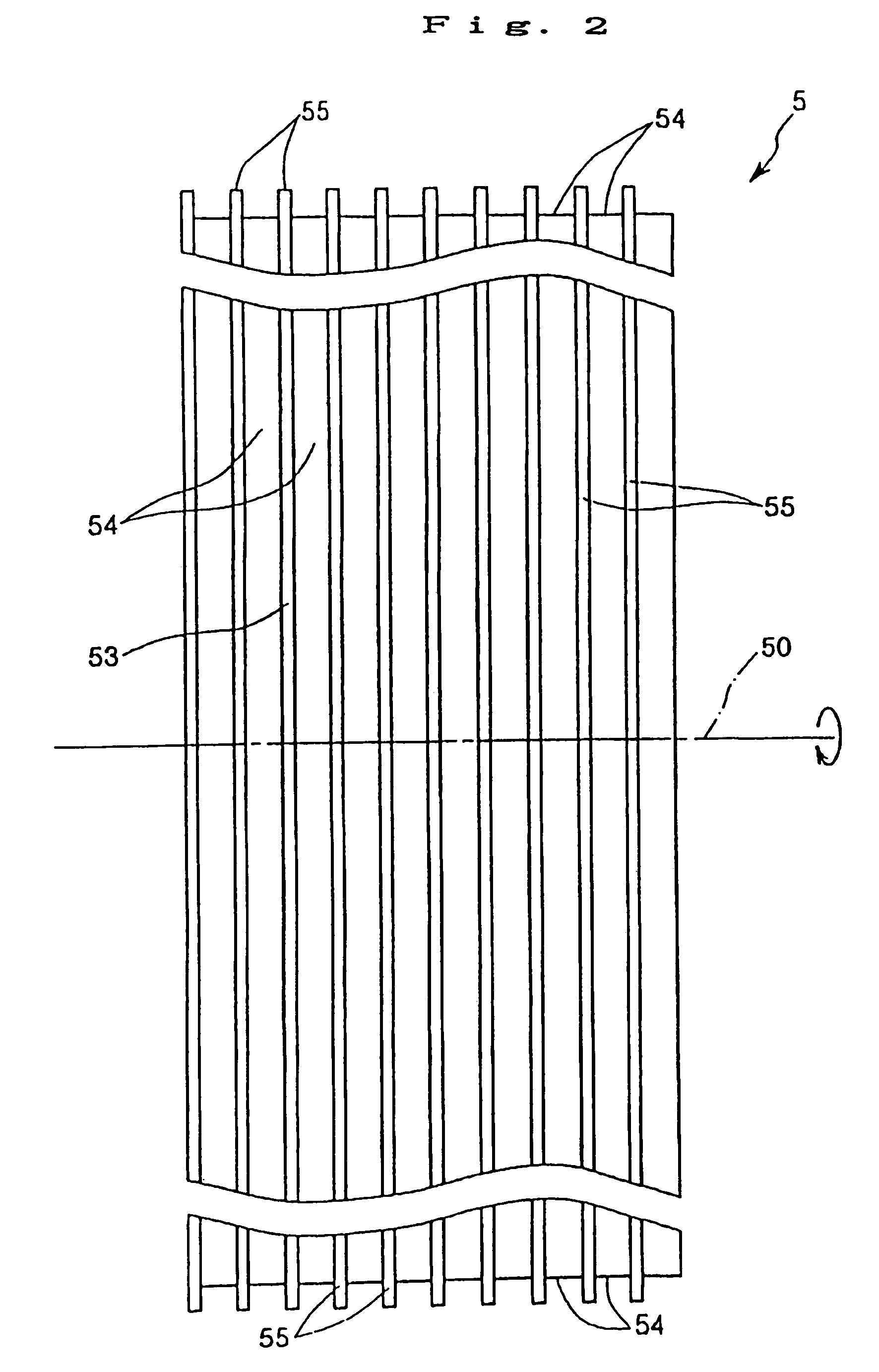
Disclosed herein is a cooling roll which can provide bonded a magnet having excellent magnetic properties and having excellent reliability. A melt spinning apparatus 1 is provided with a tube 2 having a nozzle 3 at the bottom thereof, a coil 4 for heating the tube and a cooling roll 5 having a circumferential surface 53 in which gas expelling grooves 54 are formed. A melt spun ribbon 8 is formed by injecting the molten alloy 6 from the nozzle 6 so as to be collided with the circumferential surface 53 of the cooling roll 5, so that the molten alloy 6 is cooled and then solidified. In this process, gas is likely to enter between a puddle 7 of the molten alloy 6 and the circumferential surface 53, but such gas is expelled by means of the gas expelling grooves 54.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
High IV melt phase polyester polymer catalyzed with antimony containing compounds
ActiveUS20060149027A1Wide latitudeEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingMechanical apparatusPolyesterCompound a
A melt phase process for making a polyester polymer melt phase product by adding an antimony containing catalyst to the melt phase, polycondensing the melt containing said catalyst in the melt phase until the It.V. of the melt reaches at least 0.75 dL / g. Polyester polymer melt phase pellets containing antimony residues and having an It.V. of at least 0.75 dL / g are obtained without solid state polymerization. The polyester polymer pellets containing antimony residues and having an It.V. of at least 0.70 dL / g obtained without increasing the molecular weight of the melt phase product by solid state polymerization are fed to an extruder, melted to produce a molten polyester polymer, and extruded through a die to form shaped articles. The melt phase products and articles made thereby have low b* color and / or high L* brightness, and the reaction time to make the melt phase products is short.
Owner:ALPEK POLYESTER SA DE CV
Freezer Cabinet
ActiveUS20170027338A1Easy to operateReliable functionShow cabinetsDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a freezer cabinet in which foods are stored frozen for sale in a shop, with a freezer space surrounded by solid walls at the front, at the rear, at the sides and at the bottom, which freezer space, at its upper end, is accessible via a housing opening from a user-side front edge, which opening, in the closed state, is covered by a cover unit with a cover part, adjoining the use-side edge and movable in a forwards / backwards direction, and a stationary rear cover part located away from the user-side edge. An advantageous embodiment is one in which, in order to open it, the front cover part is arranged in front of the rear cover part in the closed state or the central cover part can be pushed at least partially over the rear cover part.
Owner:AHT COOLING SYSTEMS GMBH
Magnetic material manufacturing method, ribbon-shaped magnetic materials, powdered magnetic material and bonded magnets
InactiveUS7138070B2Improve magnetic propertiesHigher magnetic energyNanomagnetismTransportation and packagingBand shapeMelt spinning
A magnetic material manufacturing method, a ribbon-shaped magnetic material manufactured by the method, a powdered magnetic material formed from the ribbon-shaped magnetic material and a bonded magnet manufactured using the powdered magnet material are disclosed. The method and the magnetic materials can provide magnets having excellent magnetic properties and reliability. A melt spinning apparatus 1 is provided with a tube 2 having a nozzle 3 at the bottom thereof, a coil 4 for heating the tube and a cooling roll 5 having a circumferential surface 53 on which dimple correcting means is provided. A melt spun ribbon 8 is formed by injecting the molten alloy 6 from the nozzle 3 so as to be collided with the circumferential surface 53 of the cooling roll 5 in an inert gas atmosphere (ambient gas) such as helium gas, so that the molten alloy 6 is cooled and then solidified. In this process, dimples to be produced on a roll contact surface of the melt spun ribbon are divided by the dimple correcting means, thereby preventing formation of huge dimples.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com