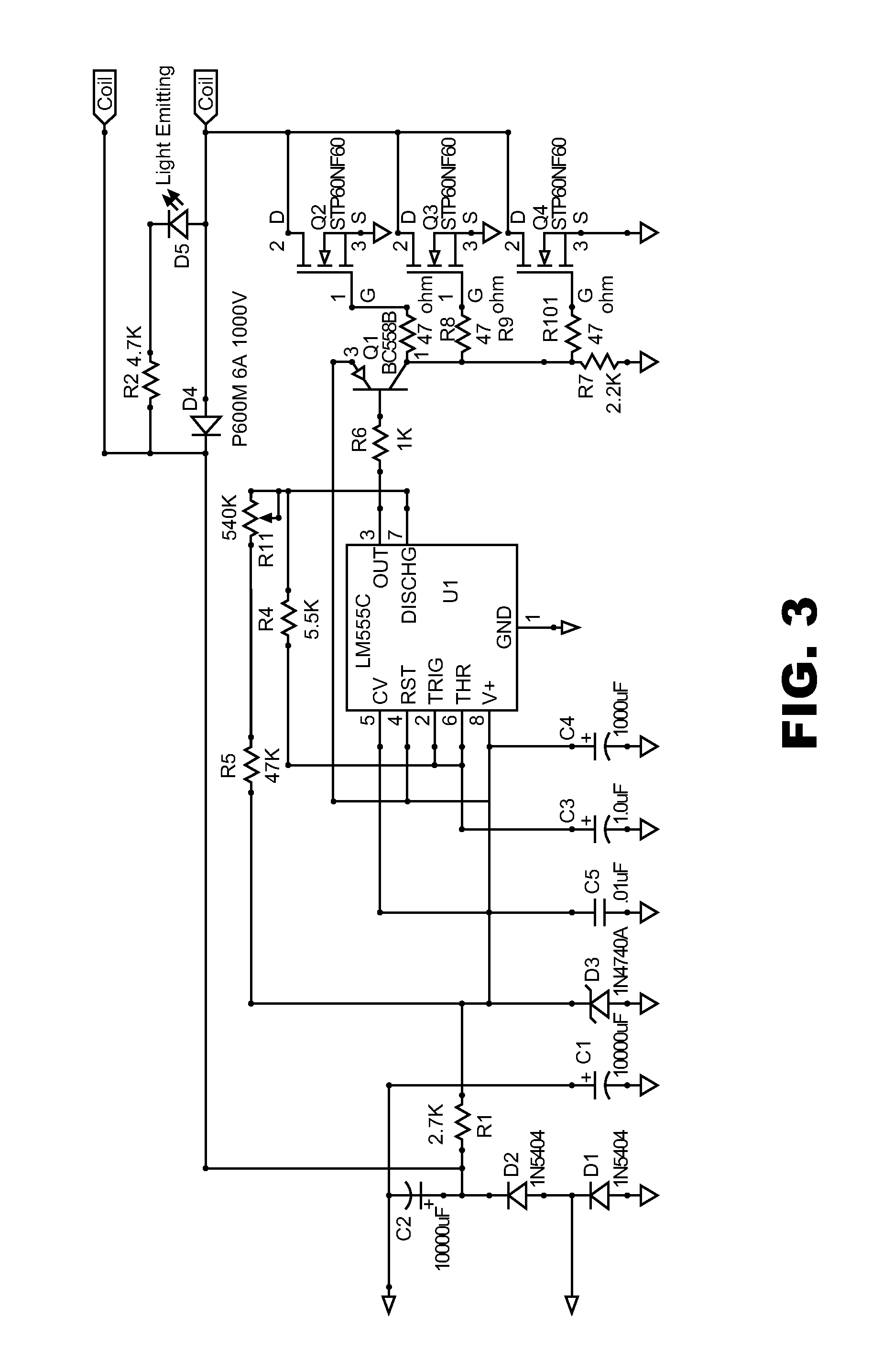
Patents
Literature
1833 results about "Magnetic energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
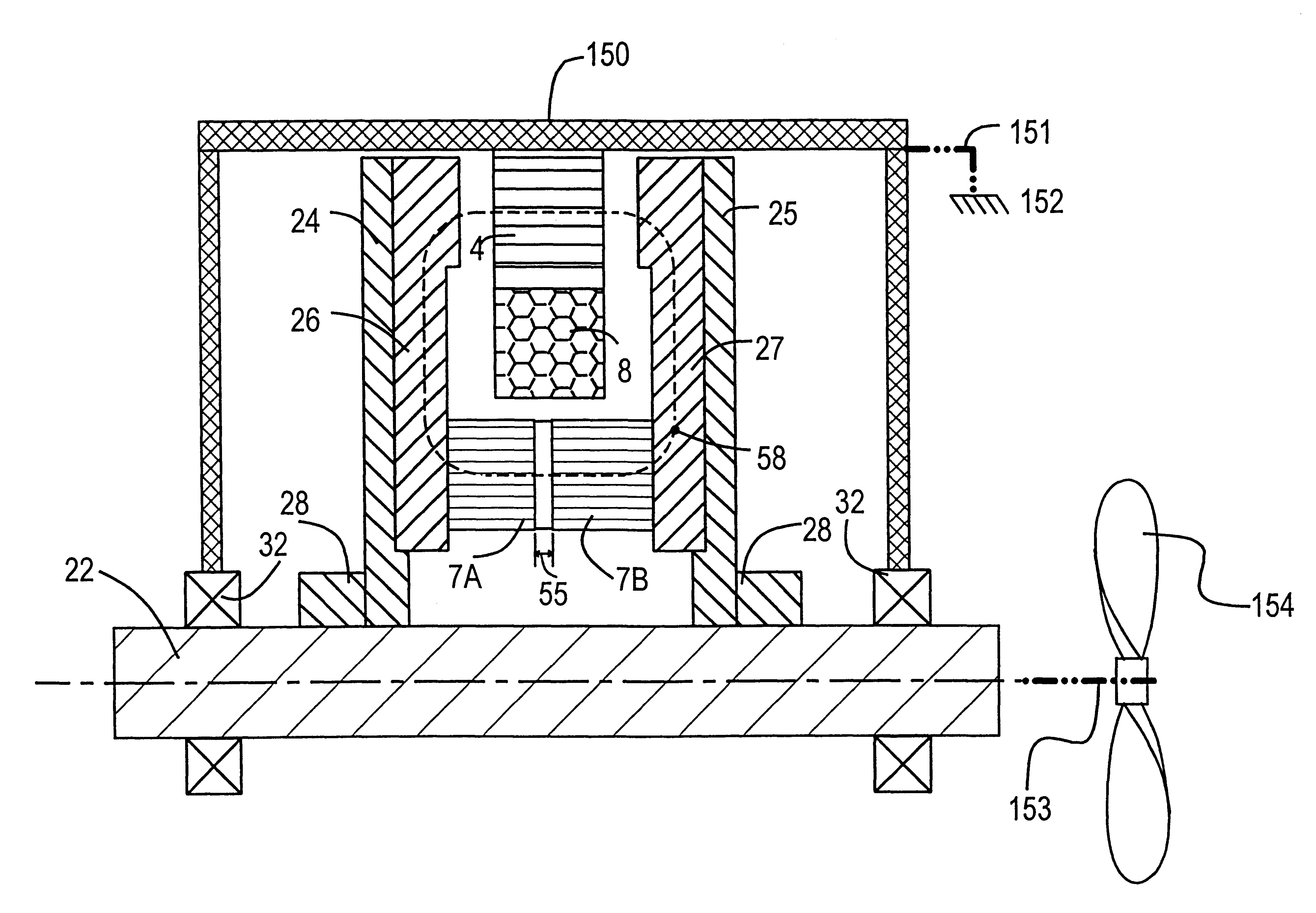
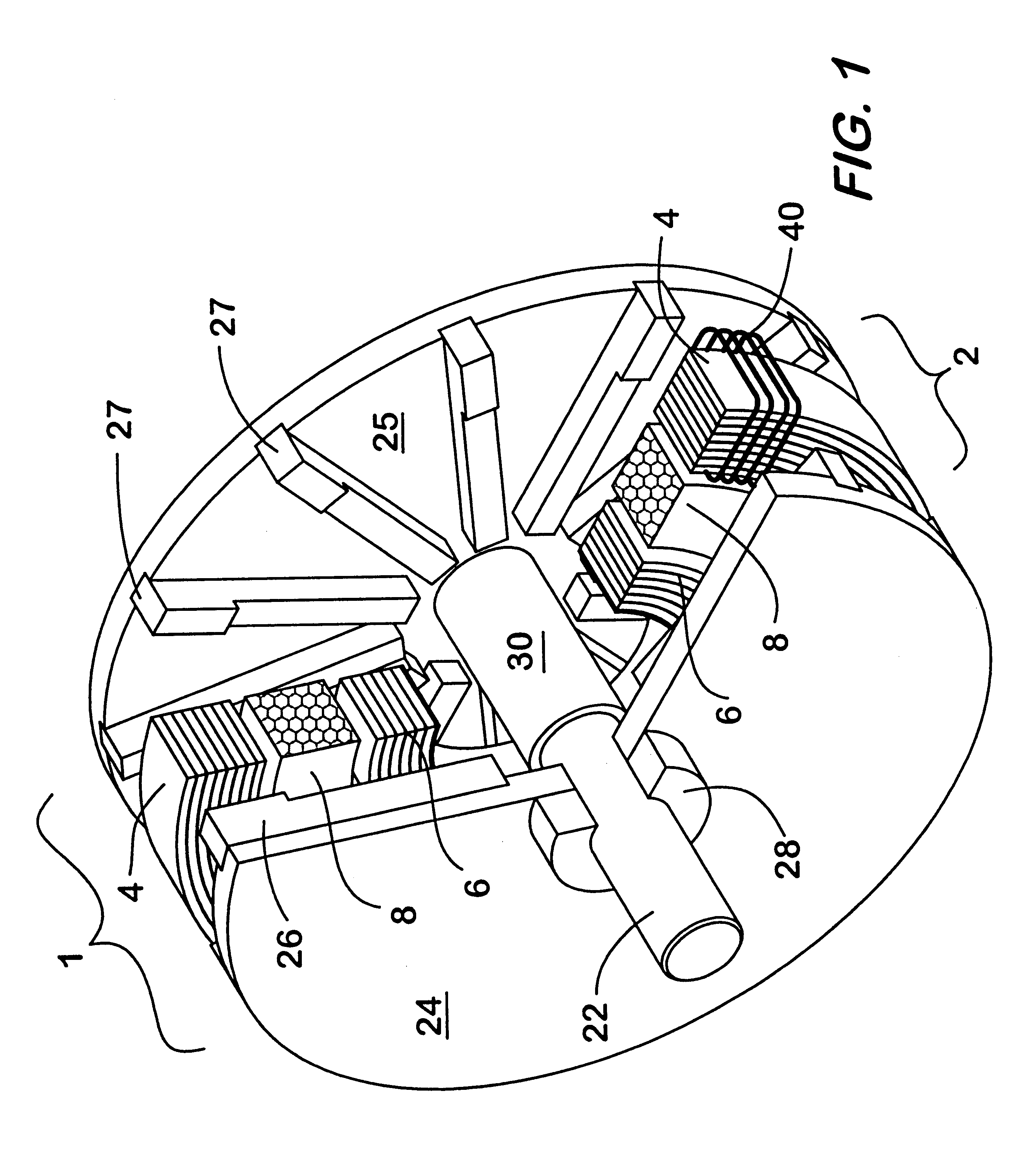
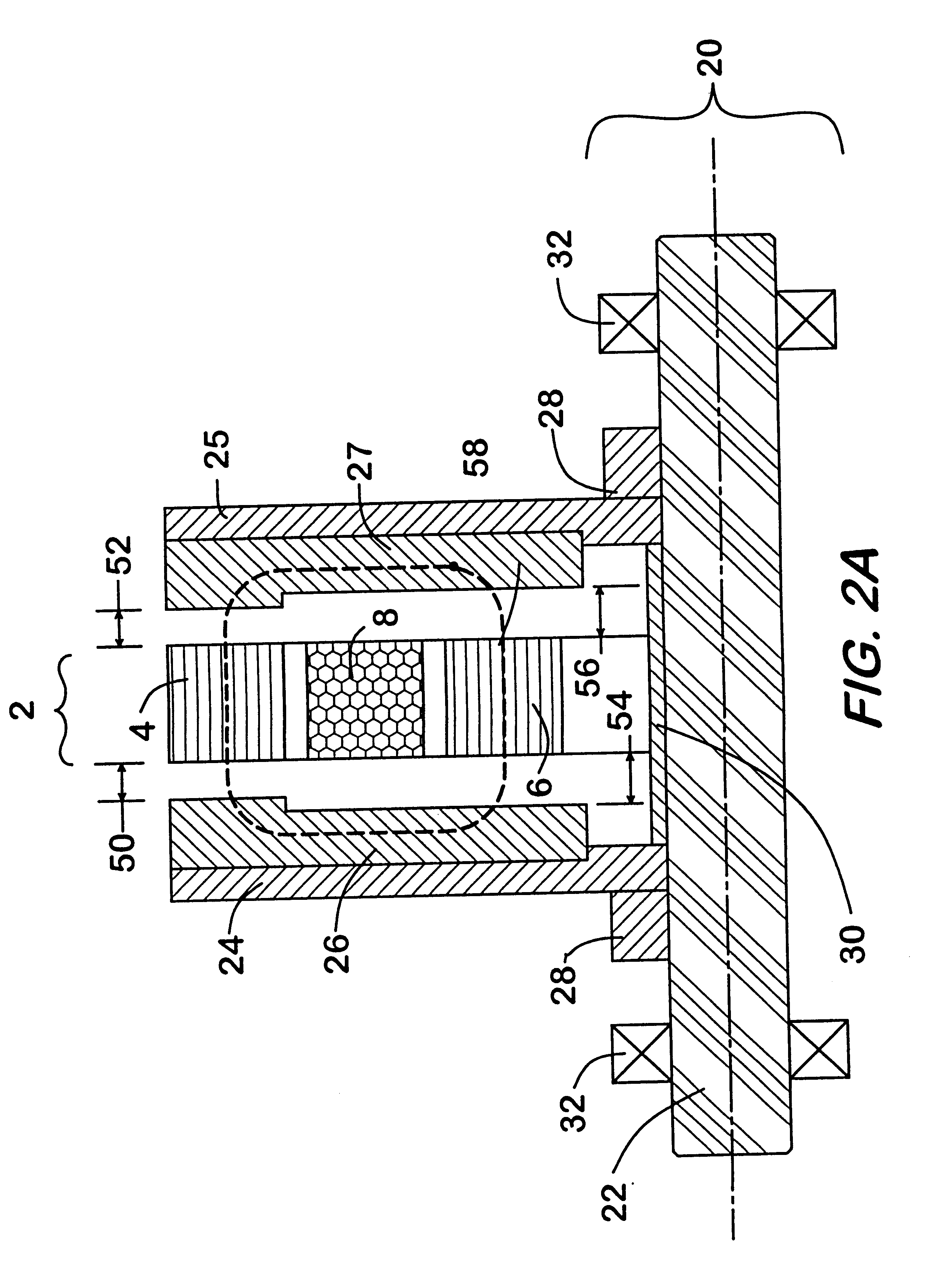
Magnetic energy and electrostatic potential energy are related by Maxwell's equations. The potential energy of a magnet of magnetic moment 𝐦 in a magnetic field 𝐁 is defined as the mechanical work of the magnetic force (actually magnetic torque) on the re-alignment of the vector of the Magnetic dipole moment and is equal to: Eₚ,ₘ=-𝐦·𝐁 while the energy stored in an inductor (of inductance L) when a current I flows through it is given by: Eₚ,ₘ=1/2LI².
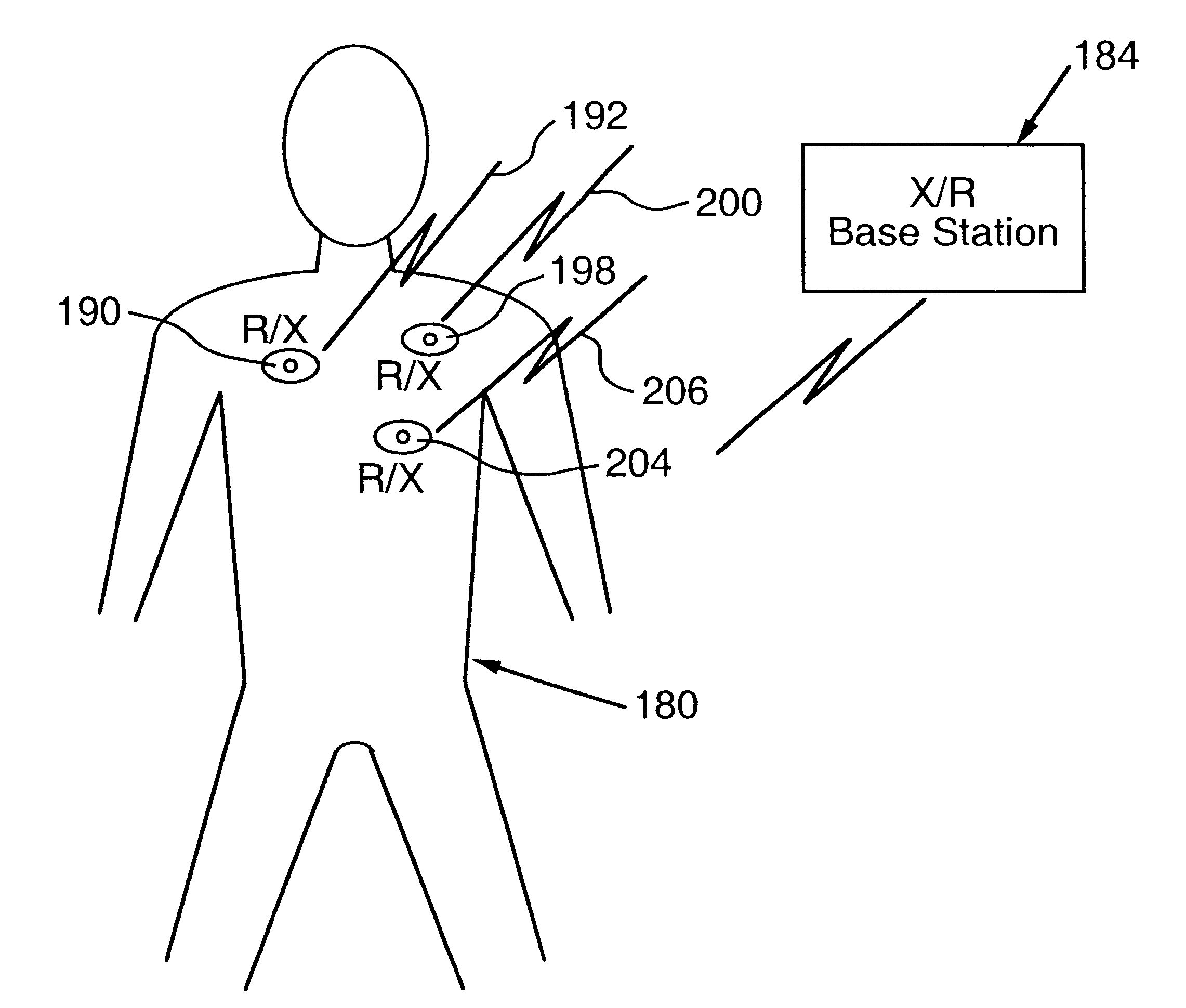
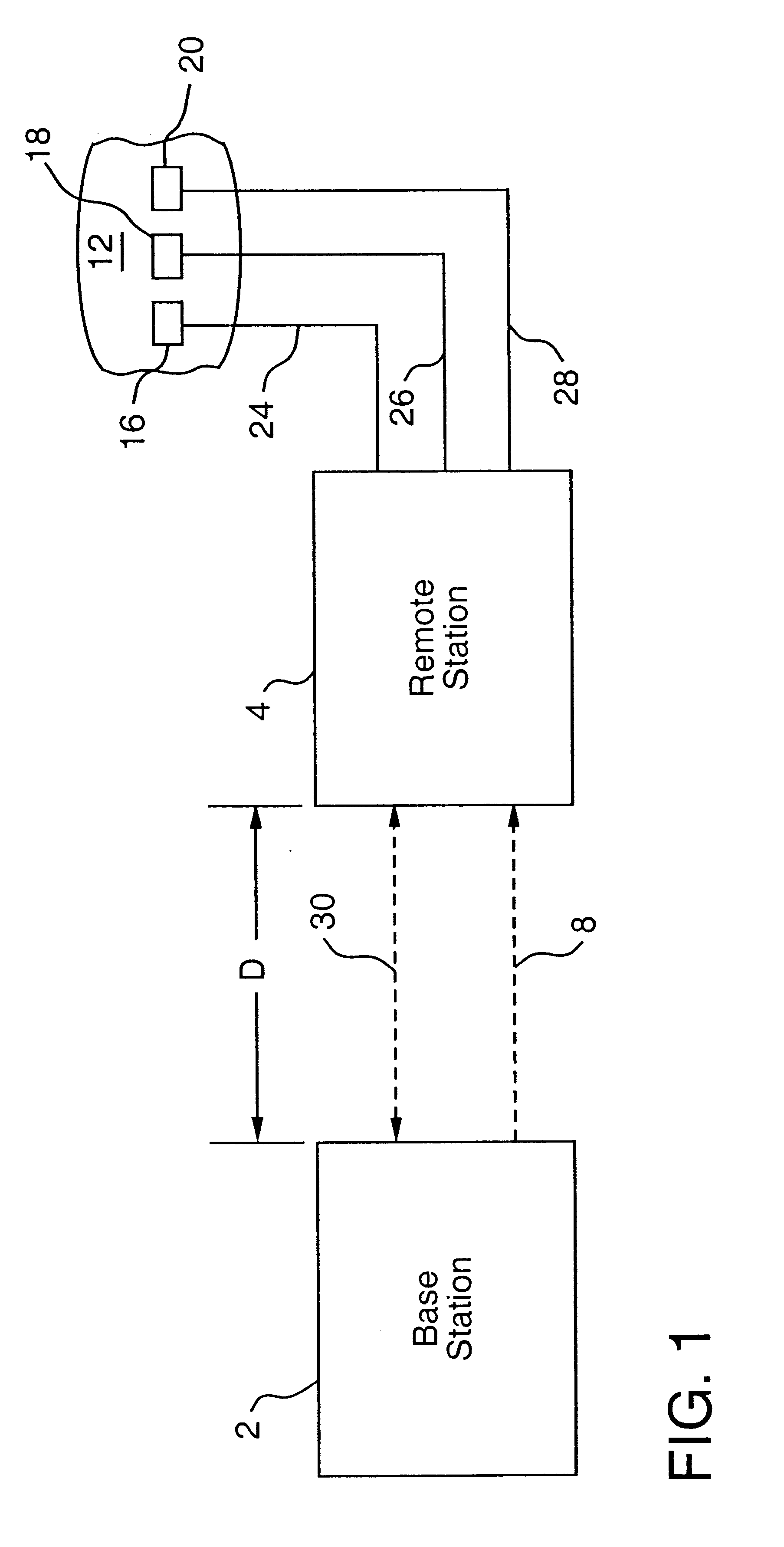
Apparatus for energizing a remote station and related method
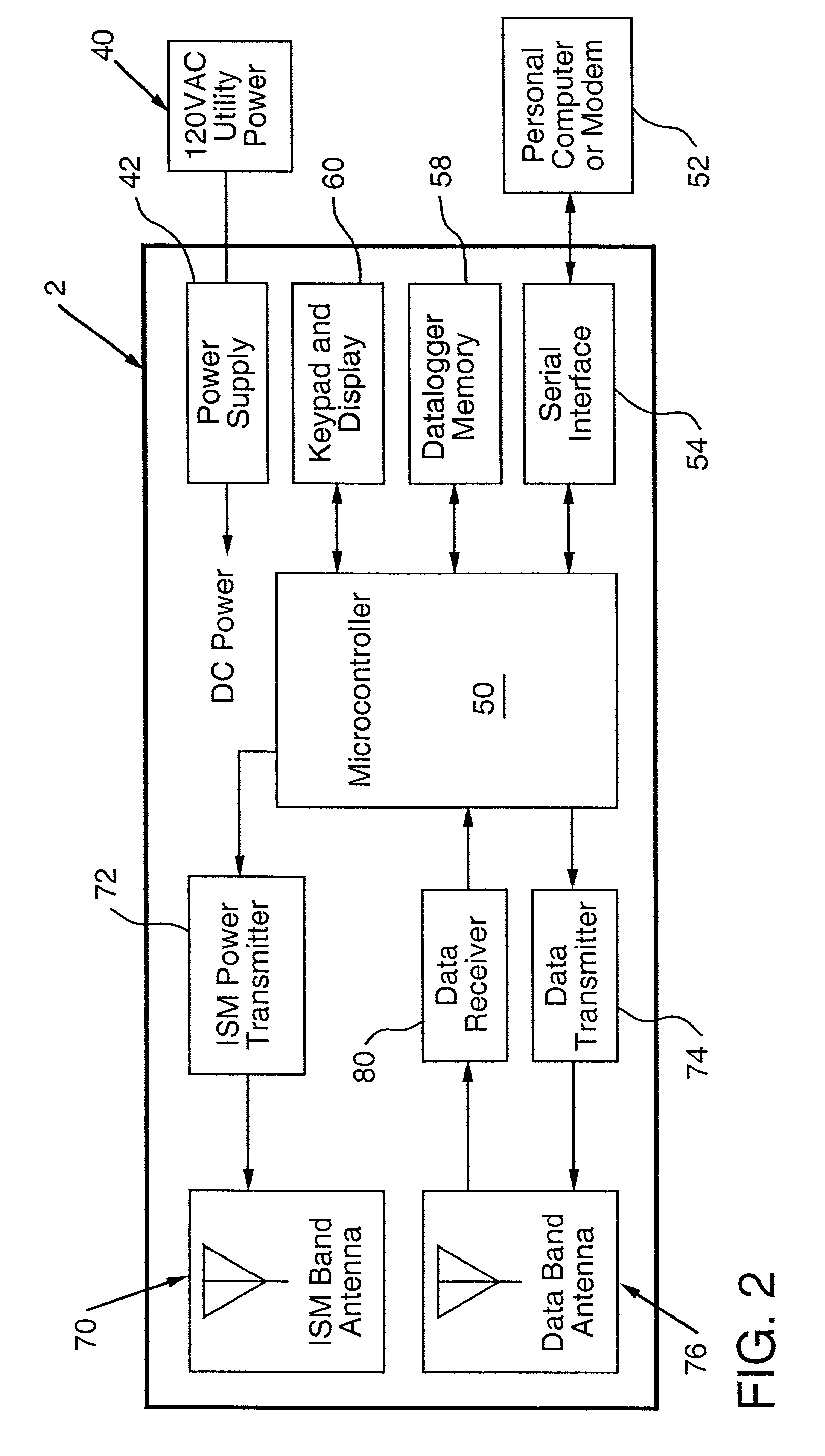
InactiveUS6615074B2Eliminate needEasy to useElectrotherapyTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsStored energyMiniaturization
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
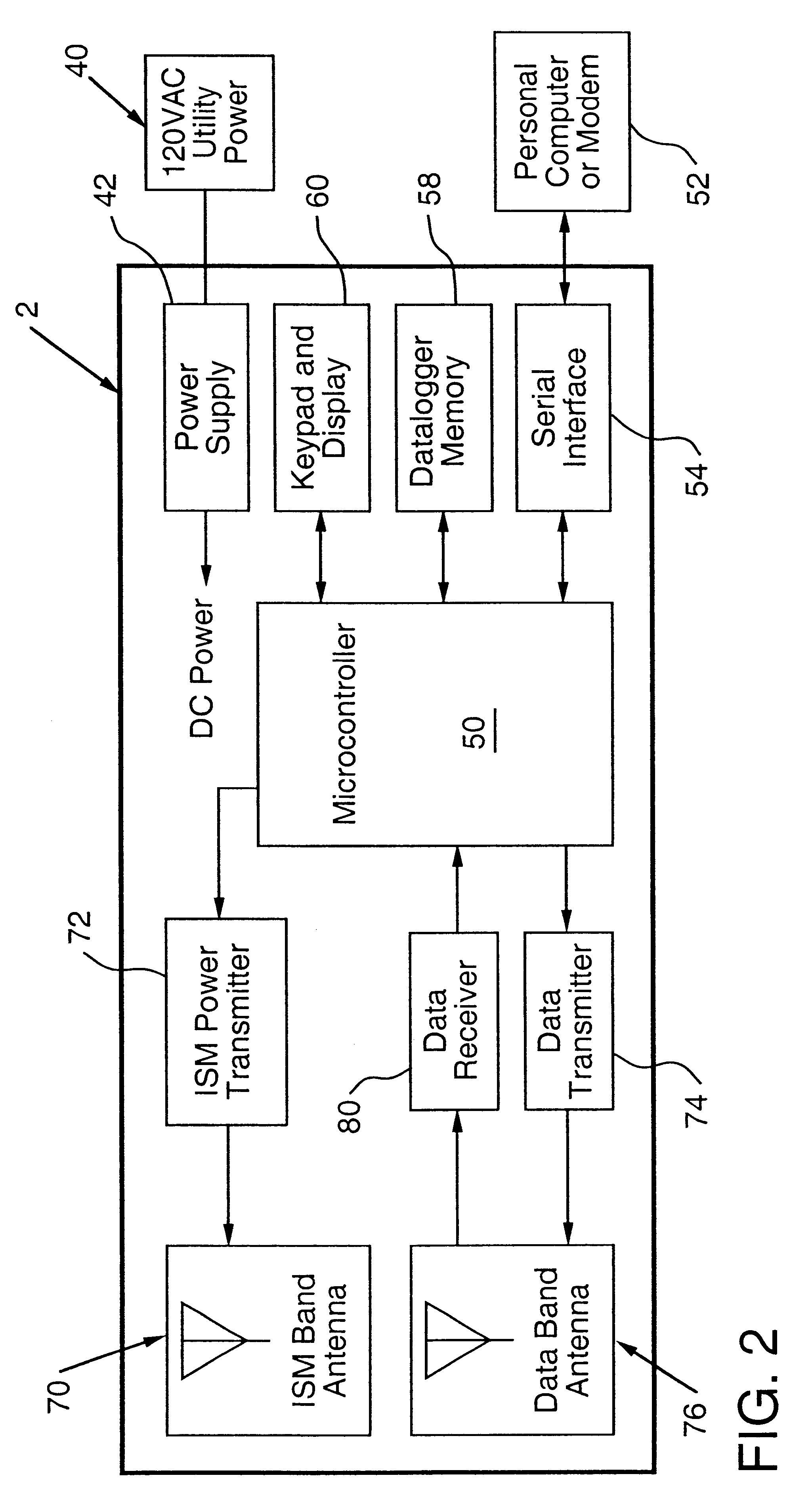
Apparatus for energizing a remote station and related method
InactiveUS6289237B1Eliminate needTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemStored energyMicroprocessor controller
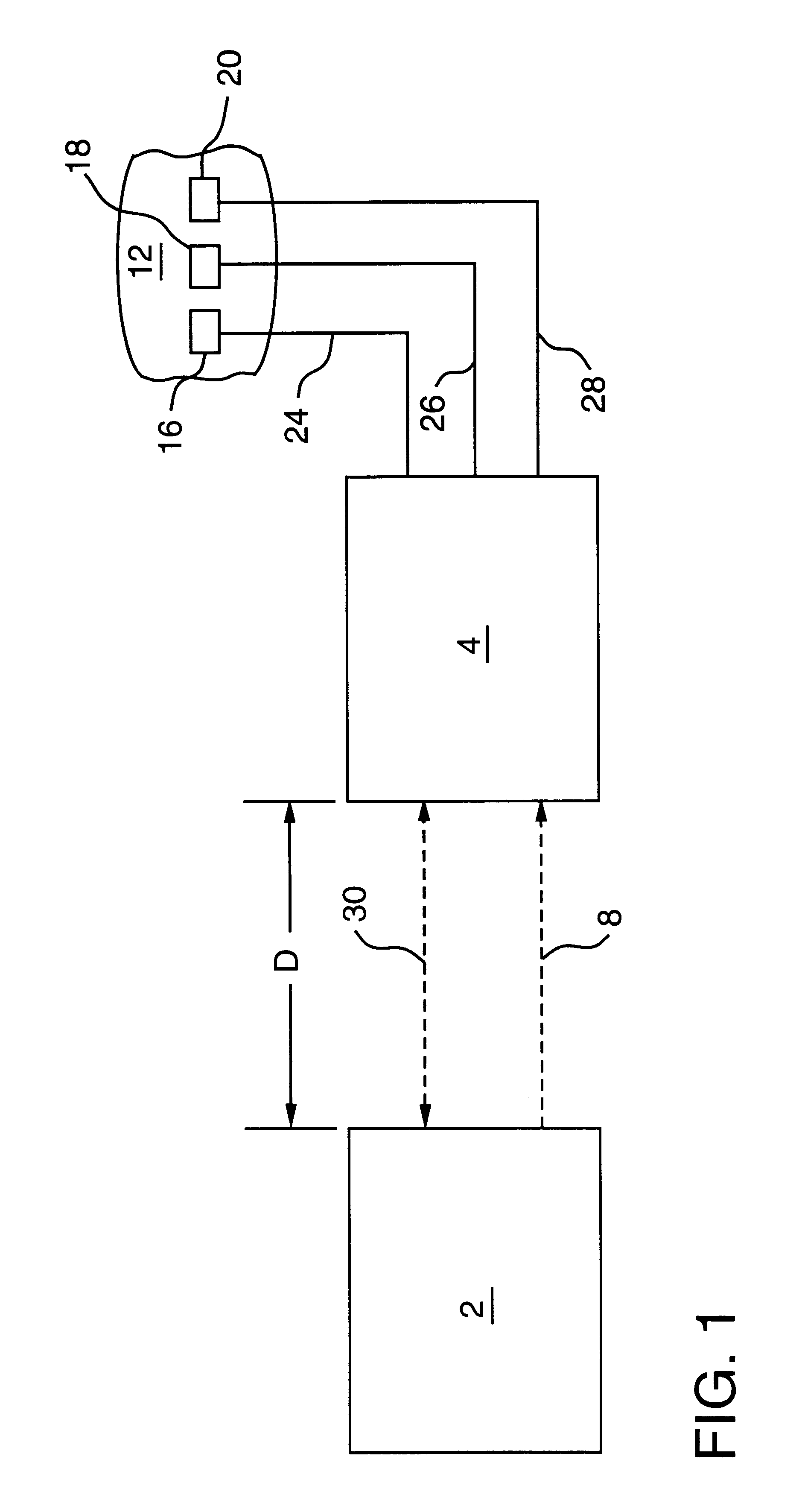
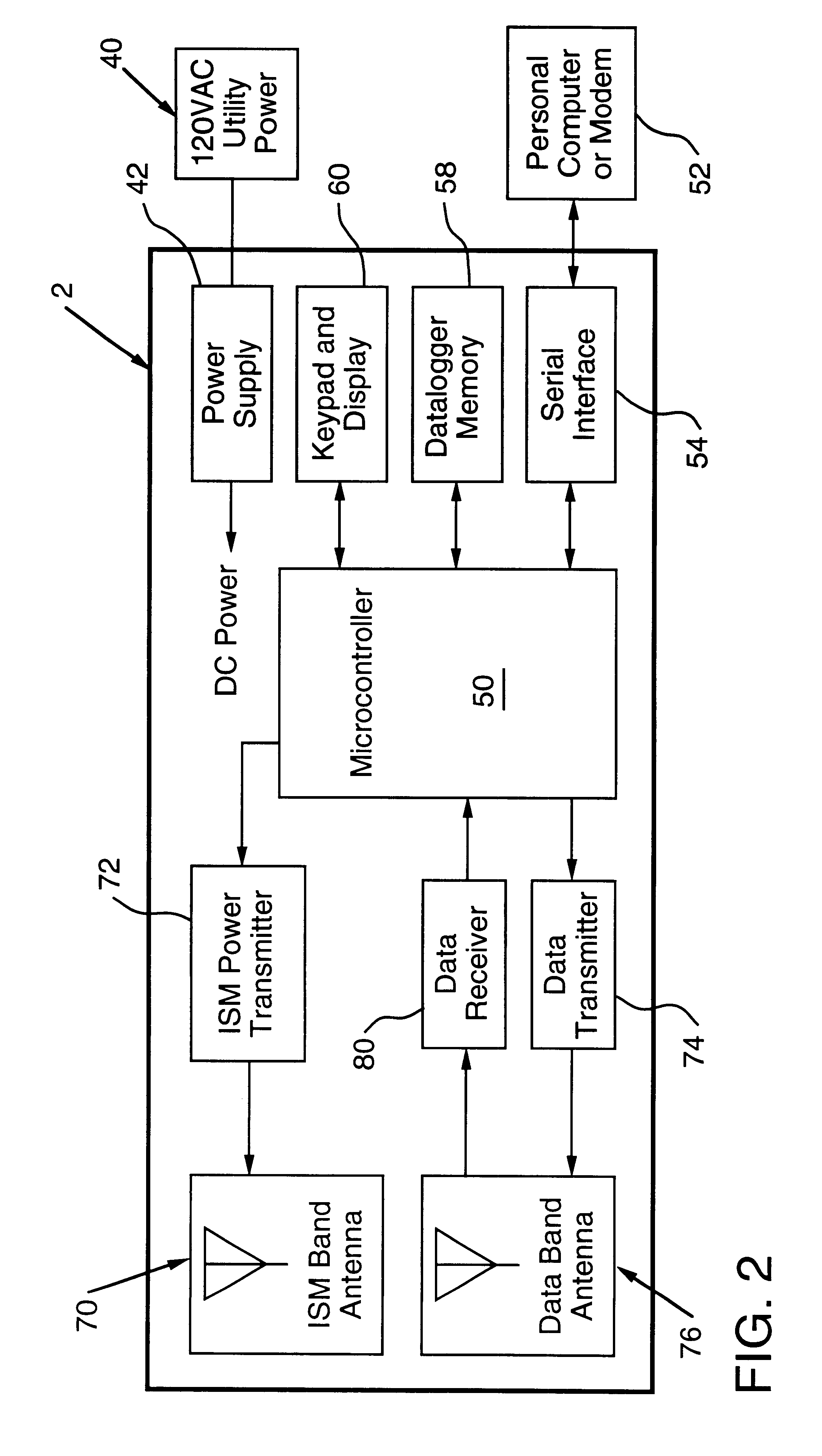
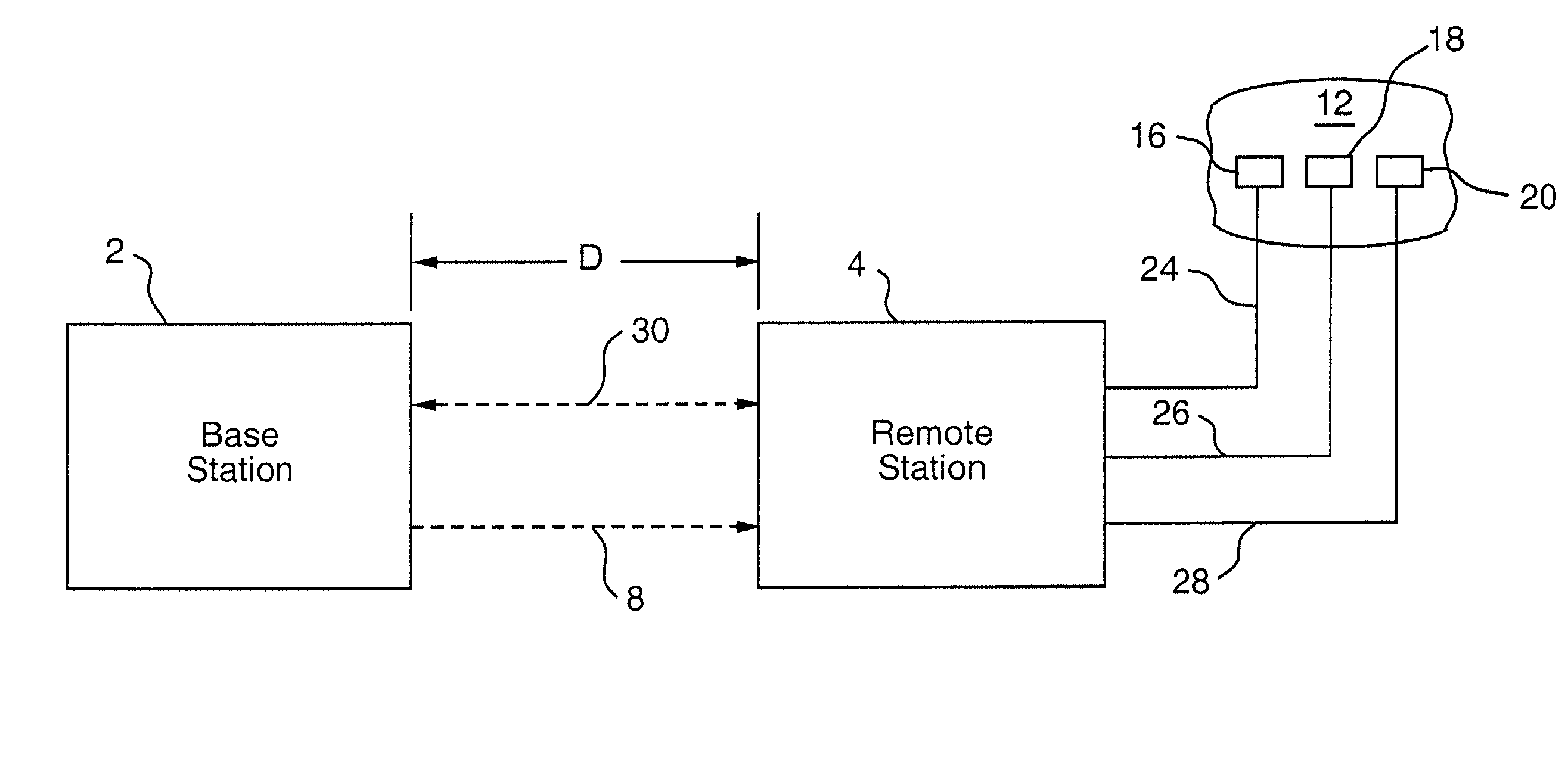
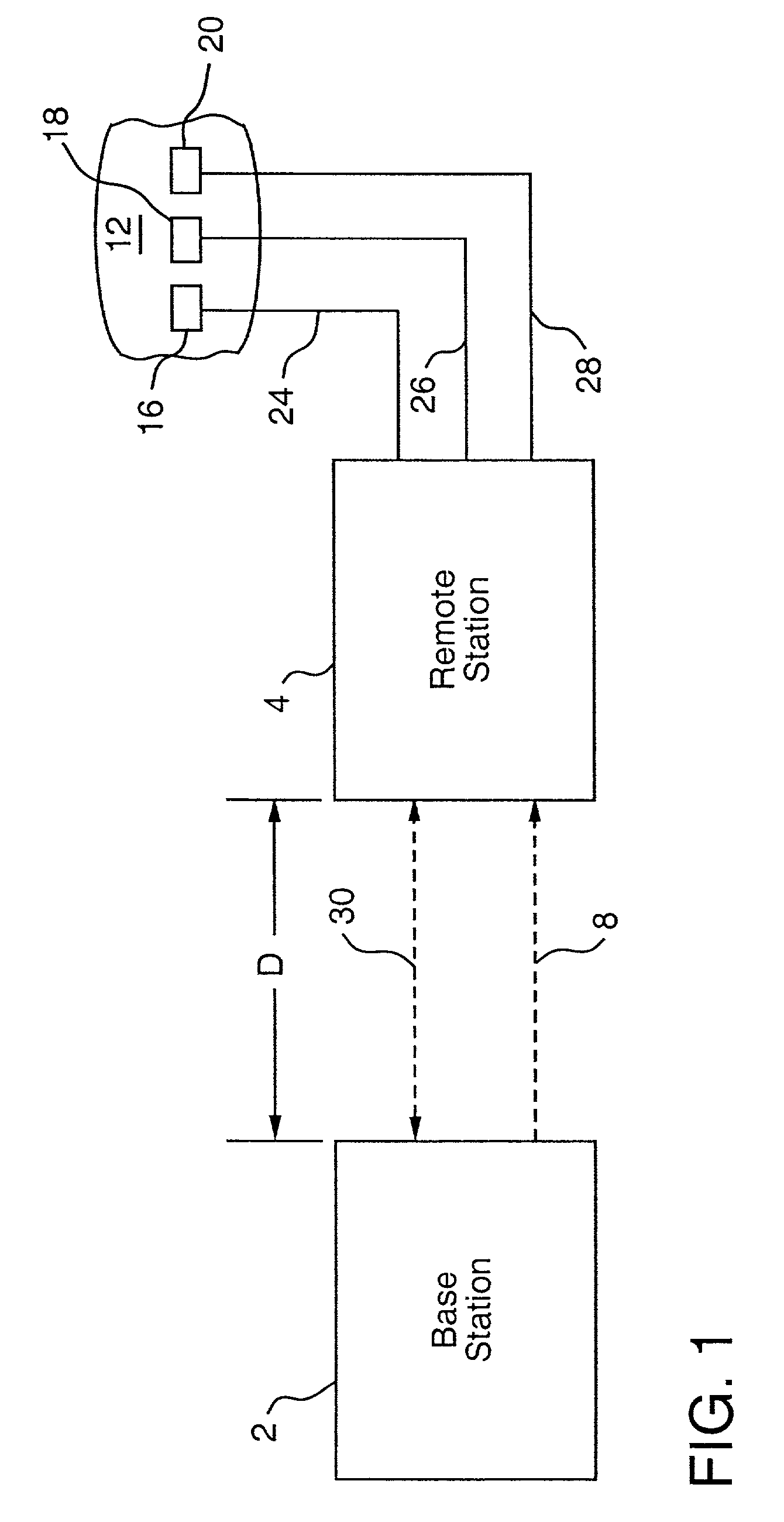
Apparatus for remote interaction with an object of interest includes a remote station for obtaining information from the object of interest, a base station for transmitting energy in space to and communicating with the remote station and the remote station having a conversion device for energizing the remote station responsive to receipt of the transmitted energy. The energy may be of any suitable type including RF power, light, acoustic, magnetic energy or other form of space transmitted or "radiant" energy. The remote station does not have to contain a source of stored energy or a wired connection to a source of energy. The remote station receives the energy transmission and data transmission from the base station and transmits data to the base station. Microprocessor controllers may be provided for the base station and the remote station. The remote station may receive information from sensors and through one or more transponders sequentially communicate information to the base station. An associated method is provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
Selectively adjustable cardiac valve implants
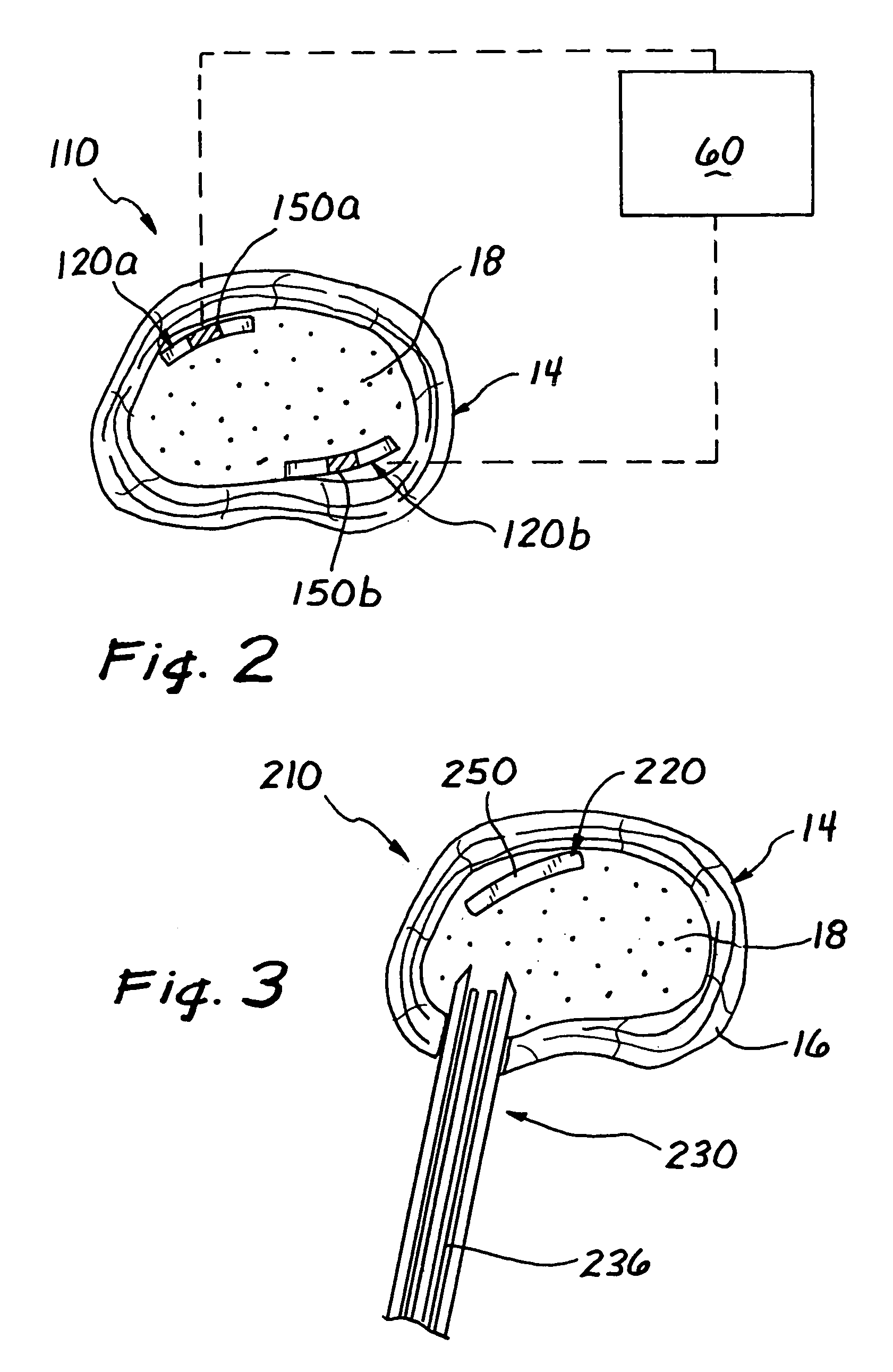
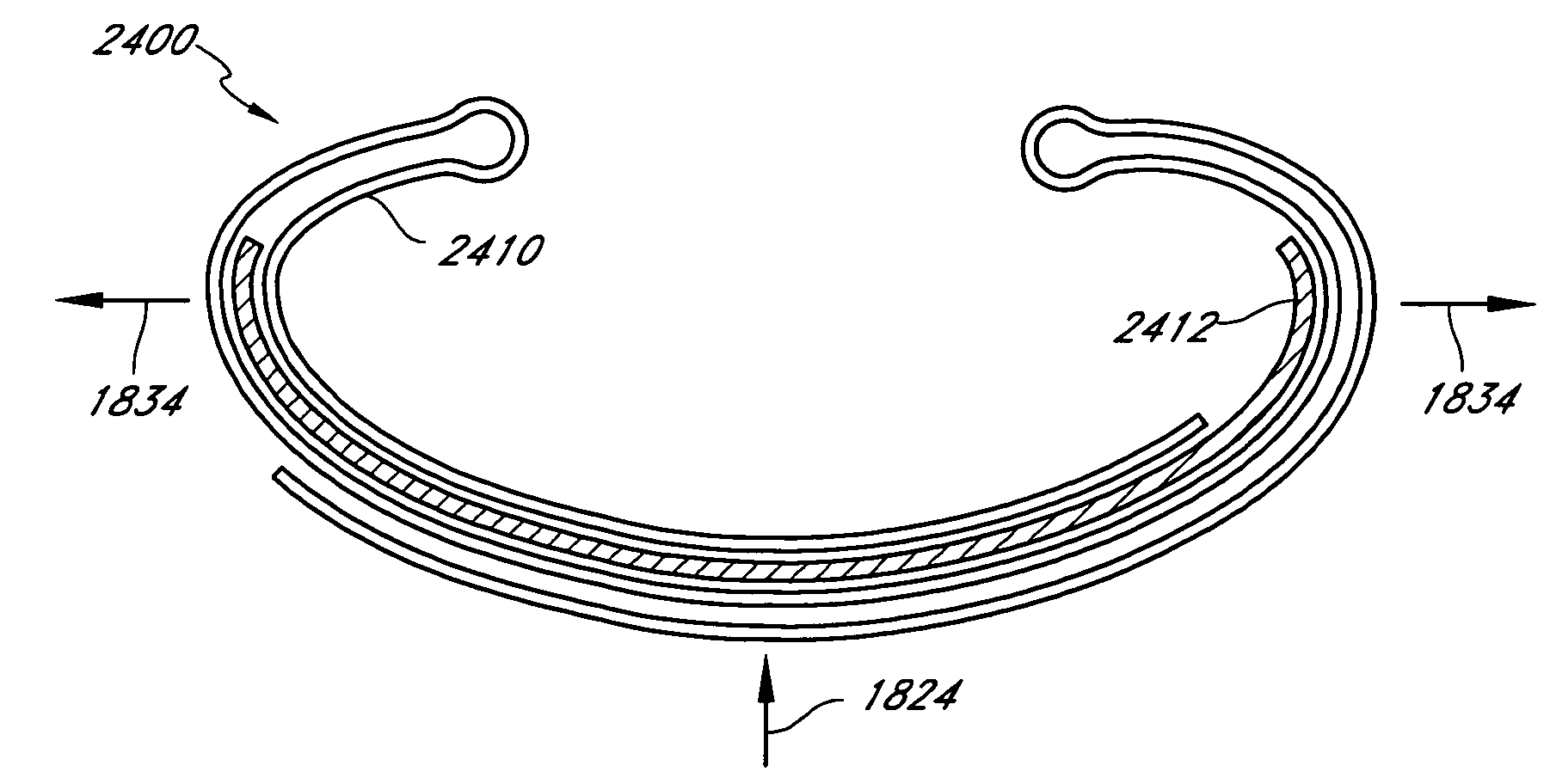
InactiveUS20050288778A1Improve heat transfer performanceEasy transferAnnuloplasty ringsRadio frequency energyLight energy
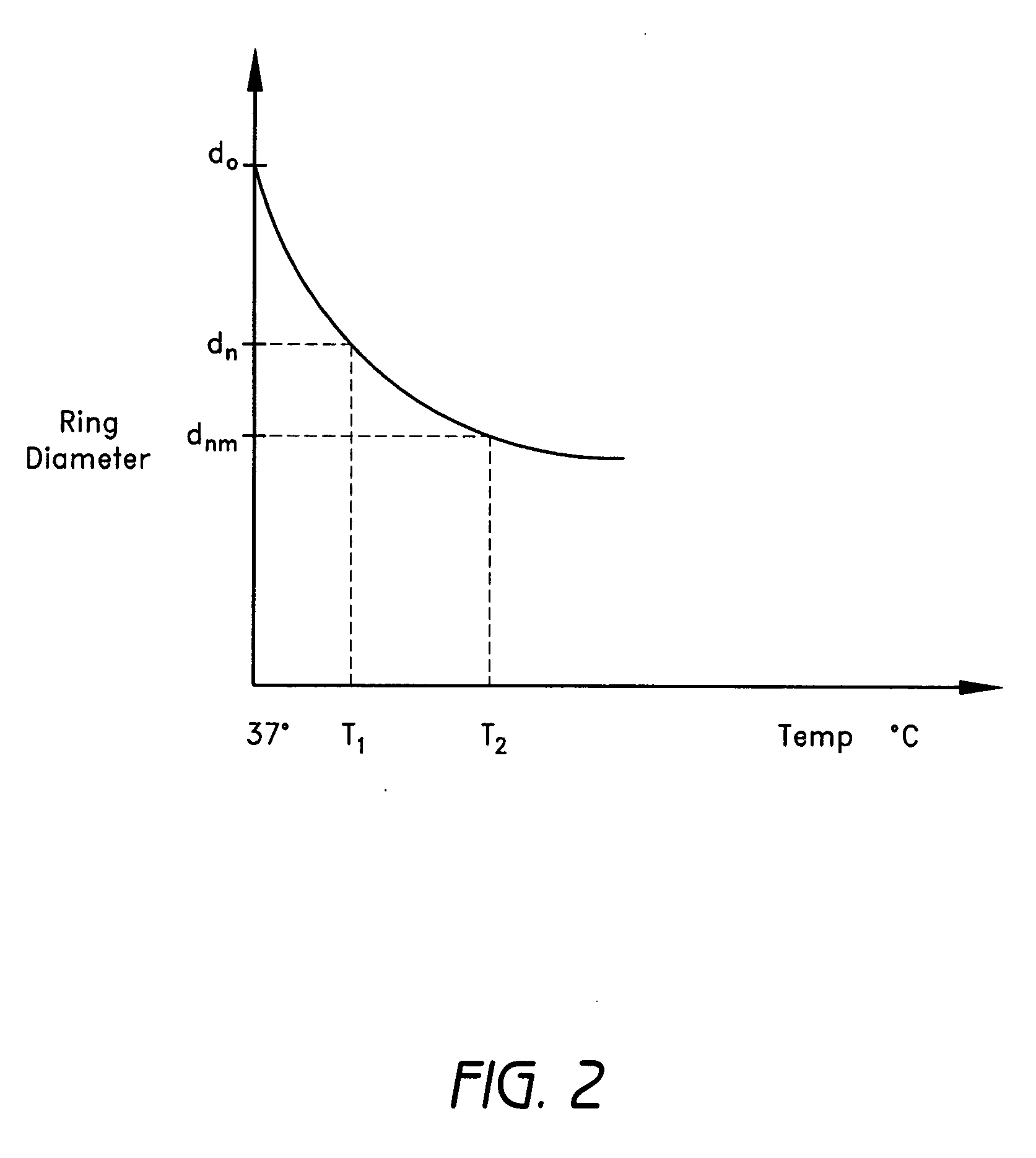
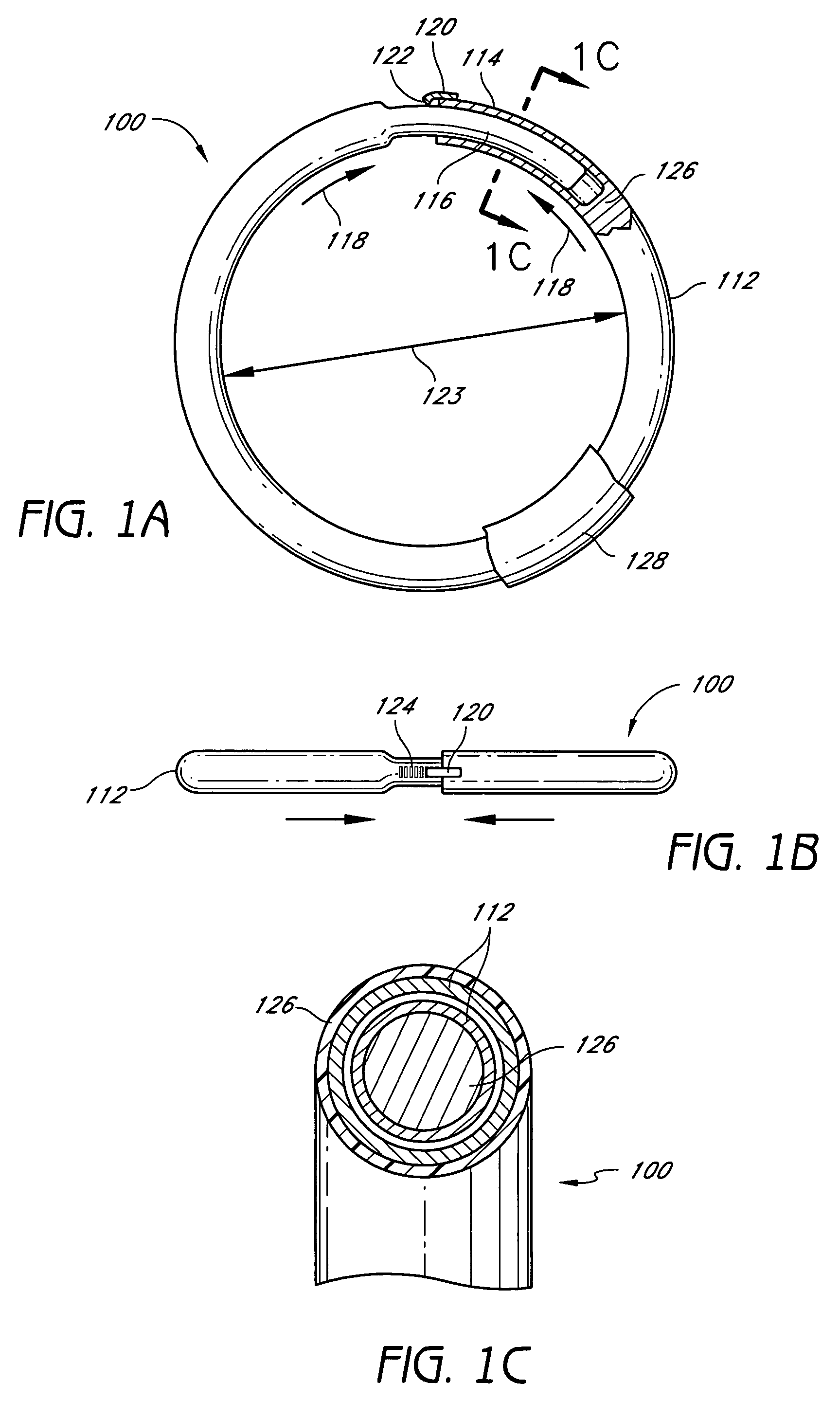
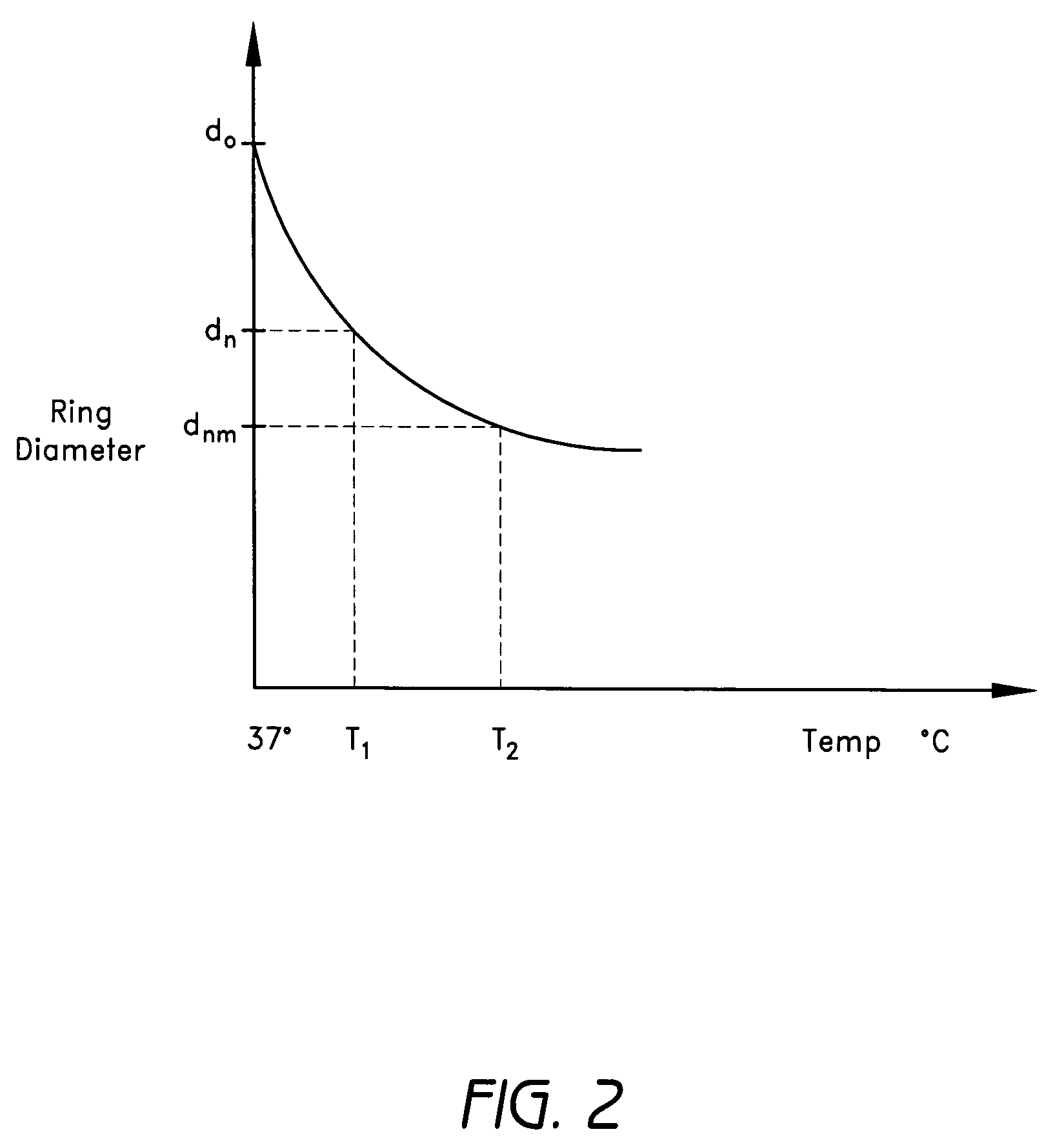
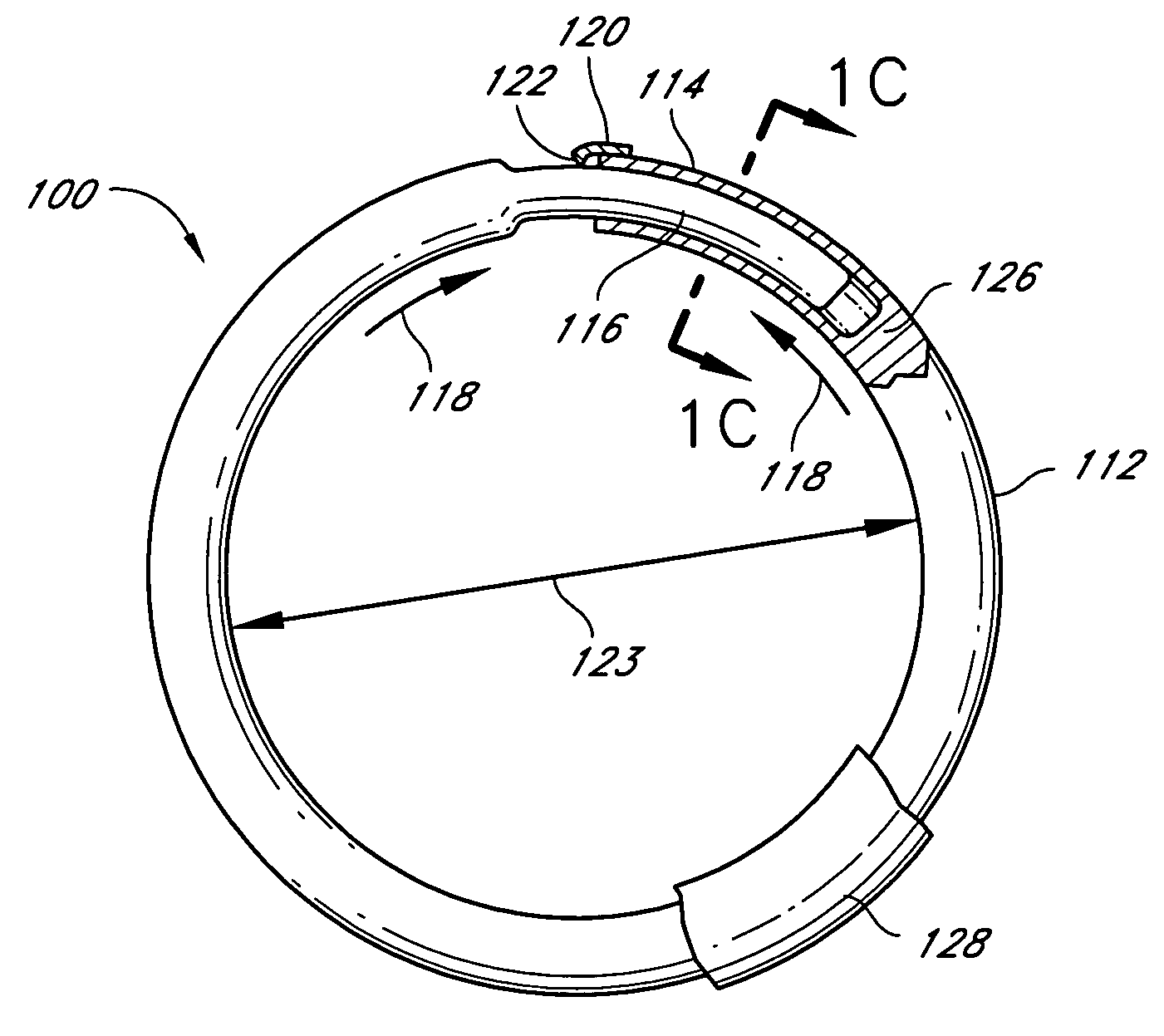
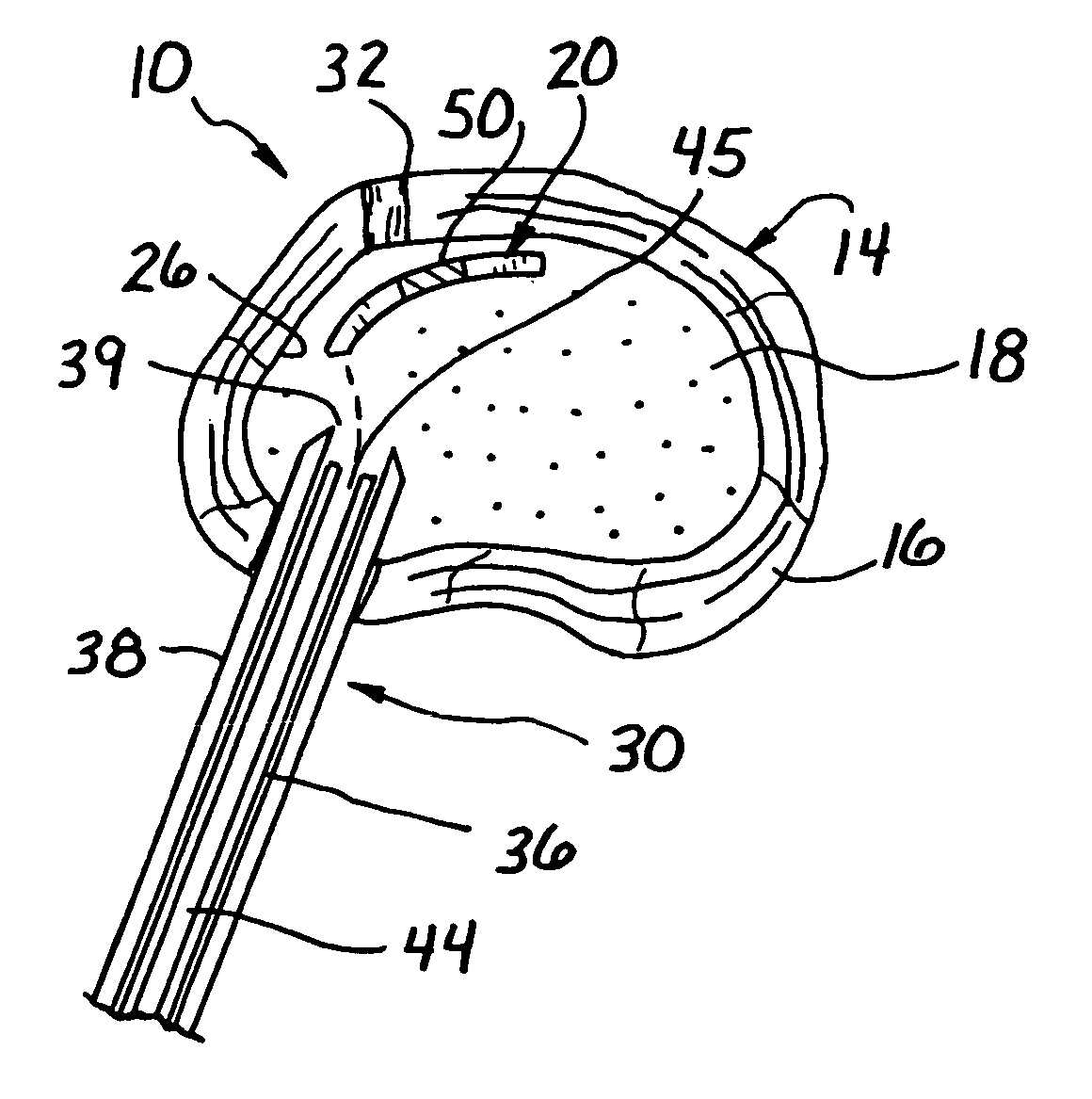
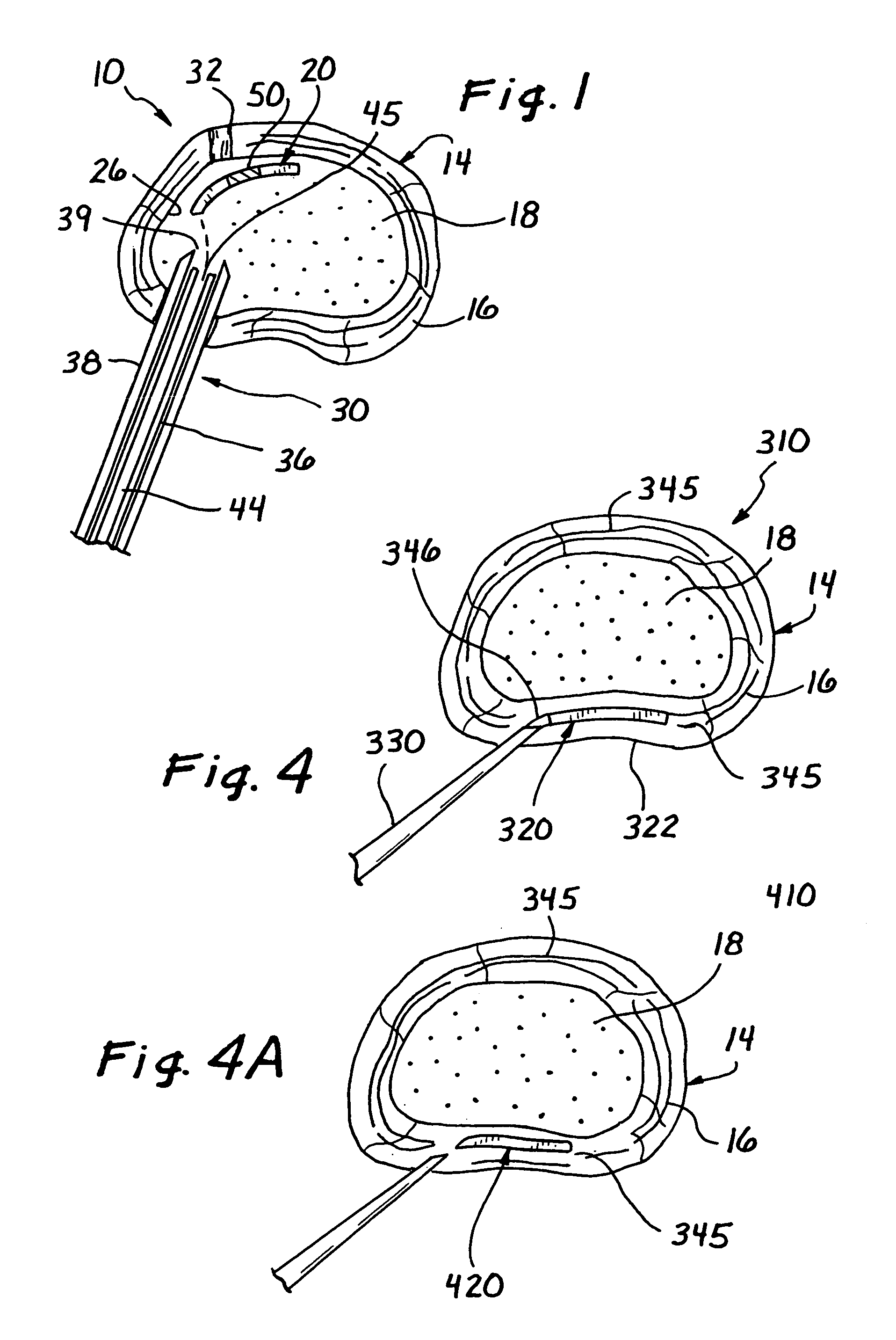
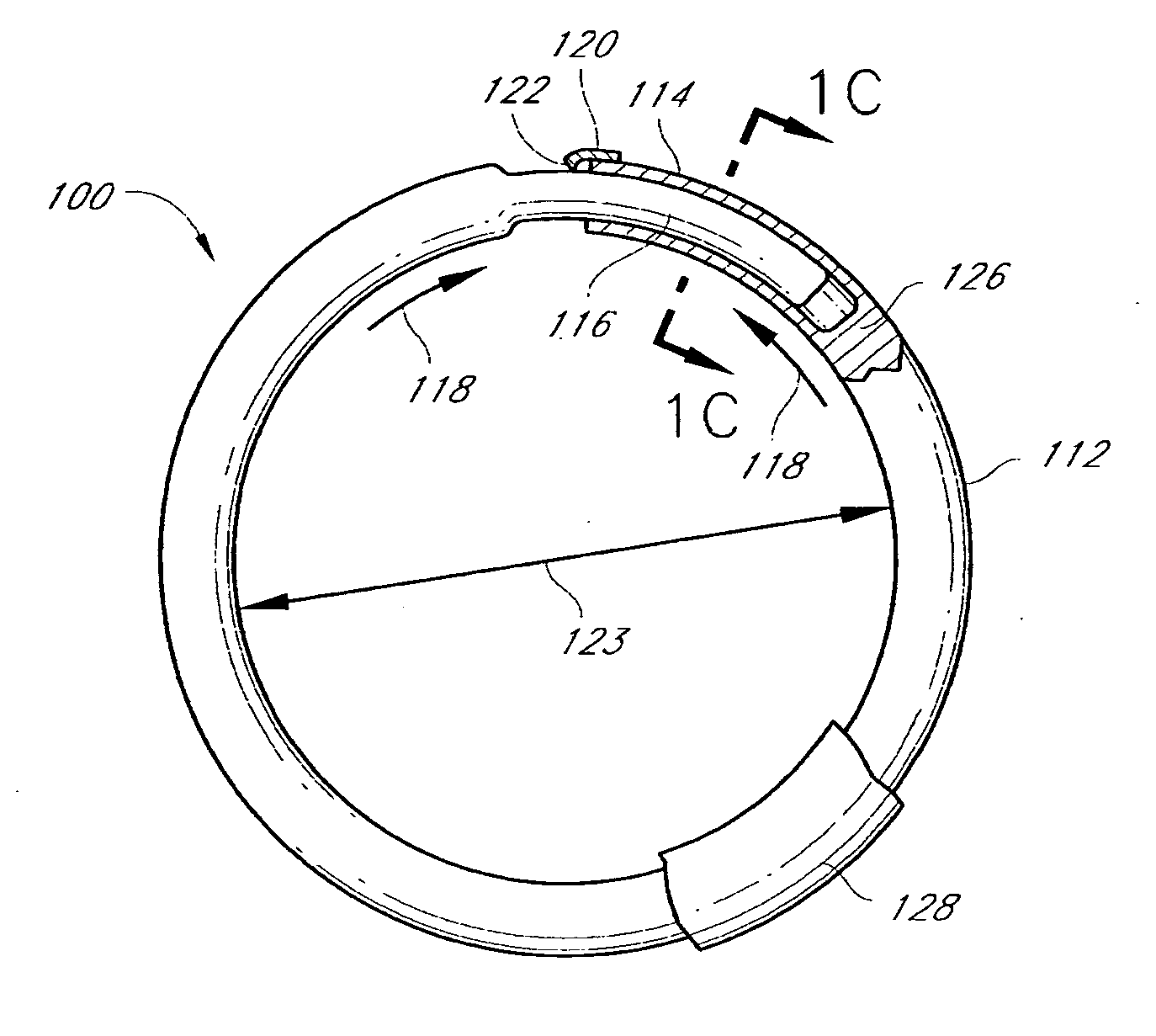
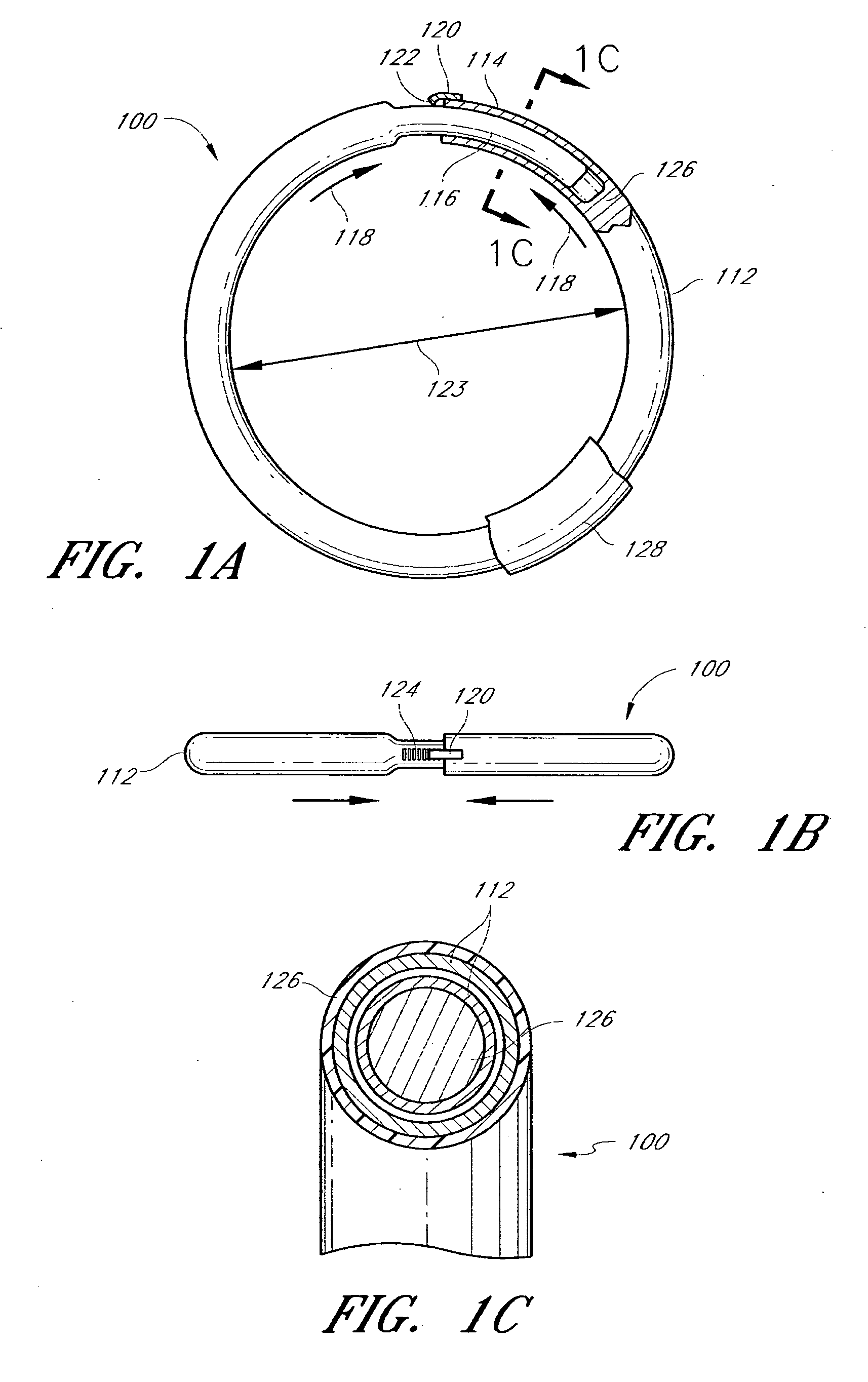
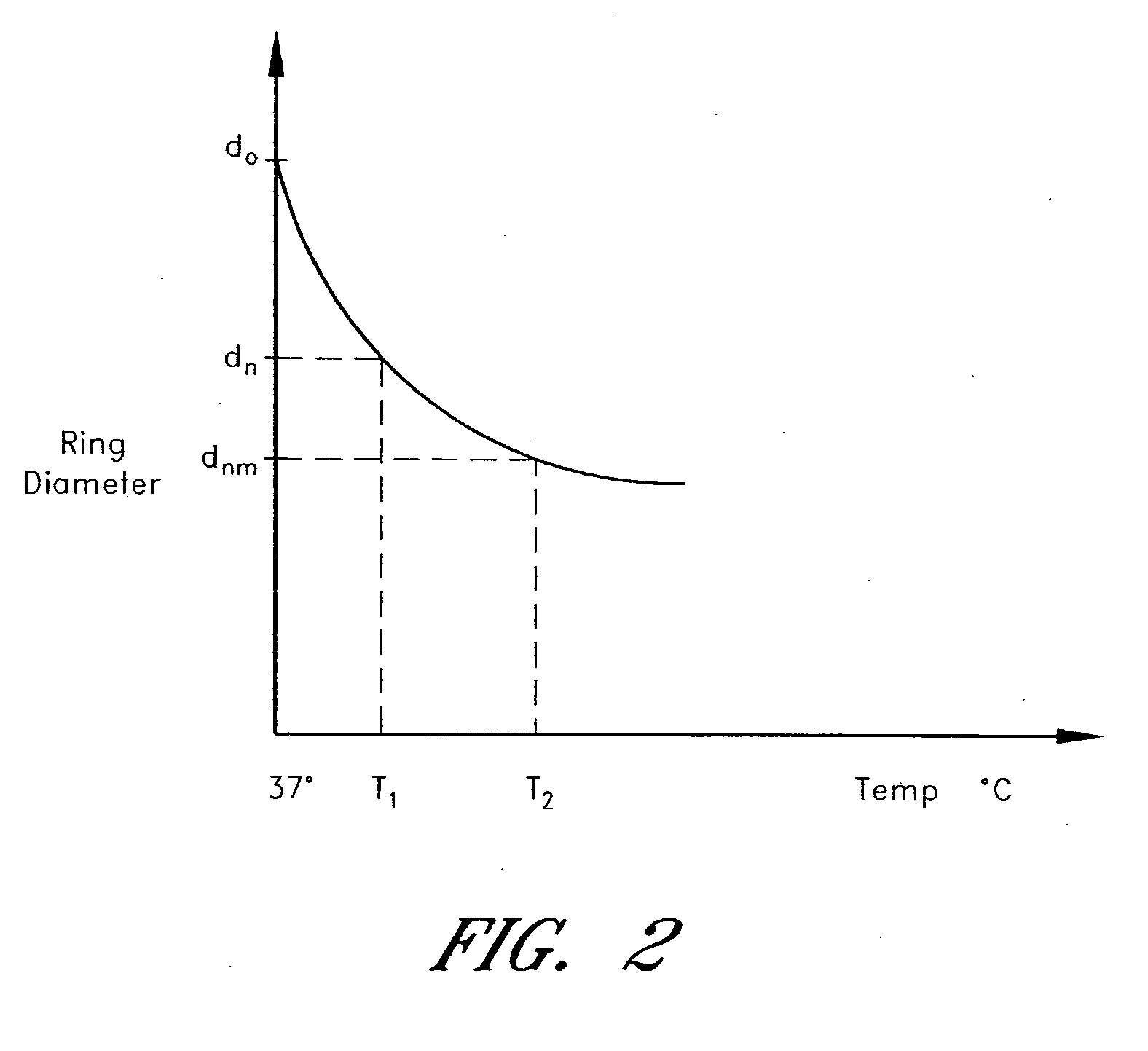
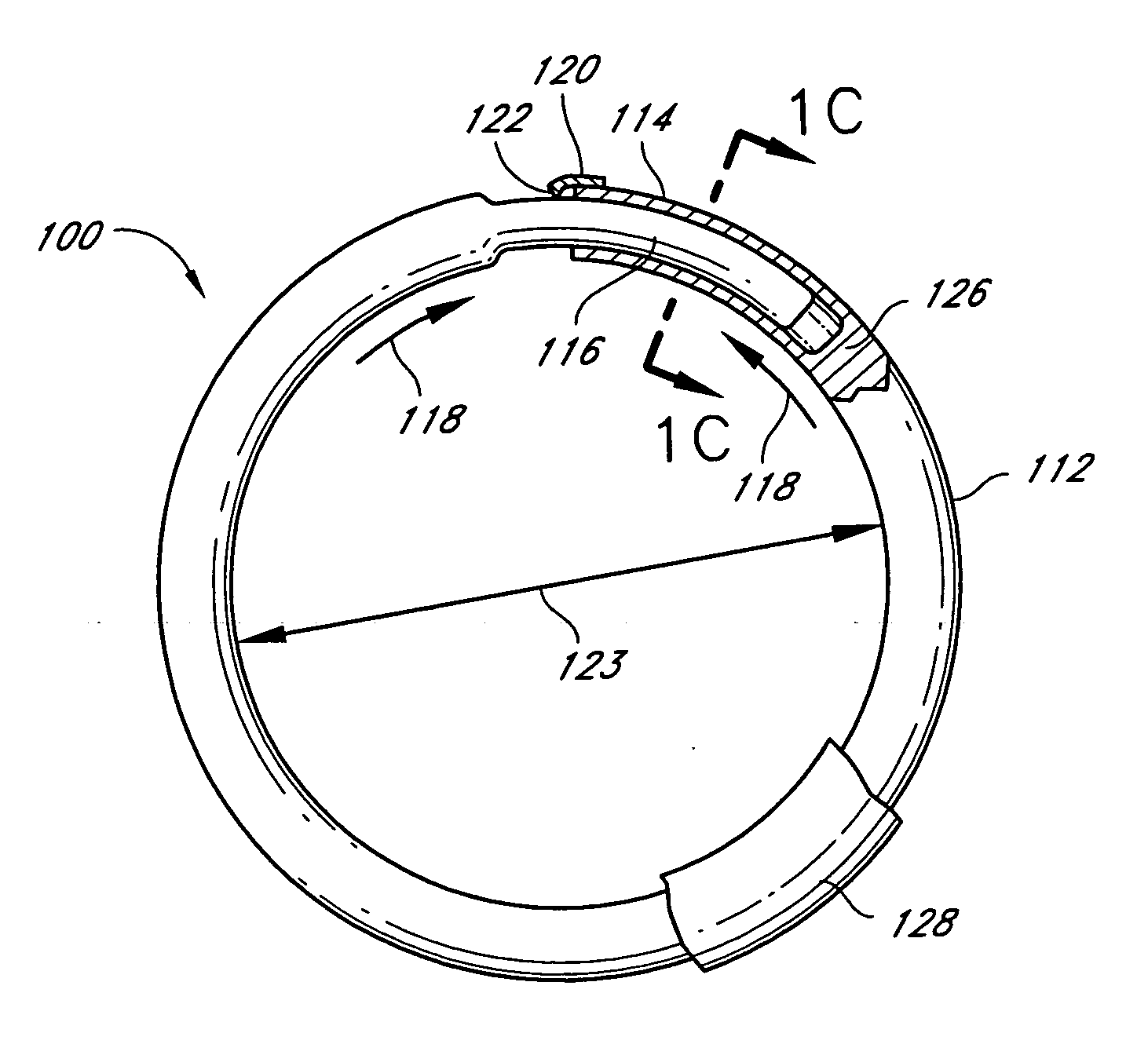
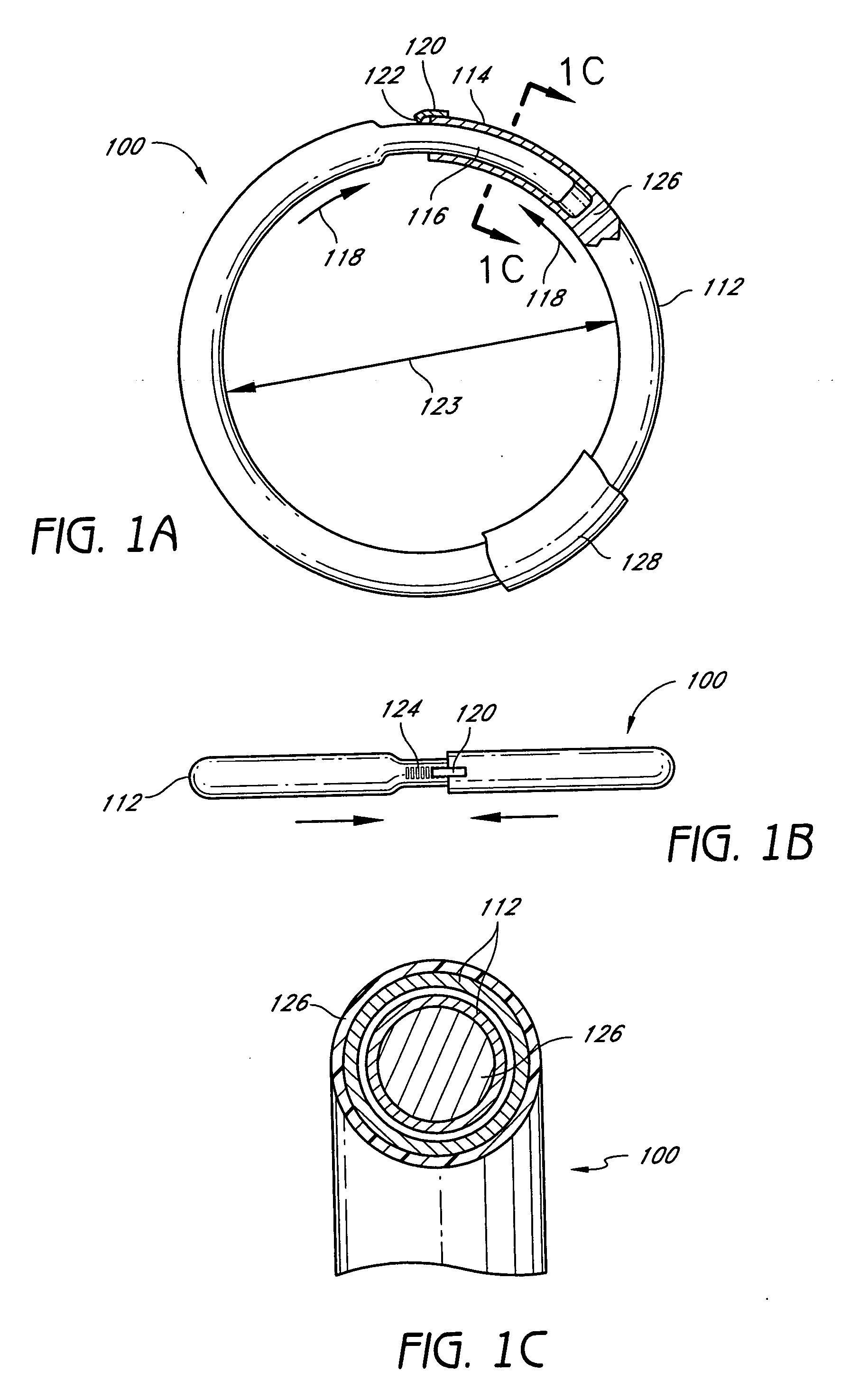
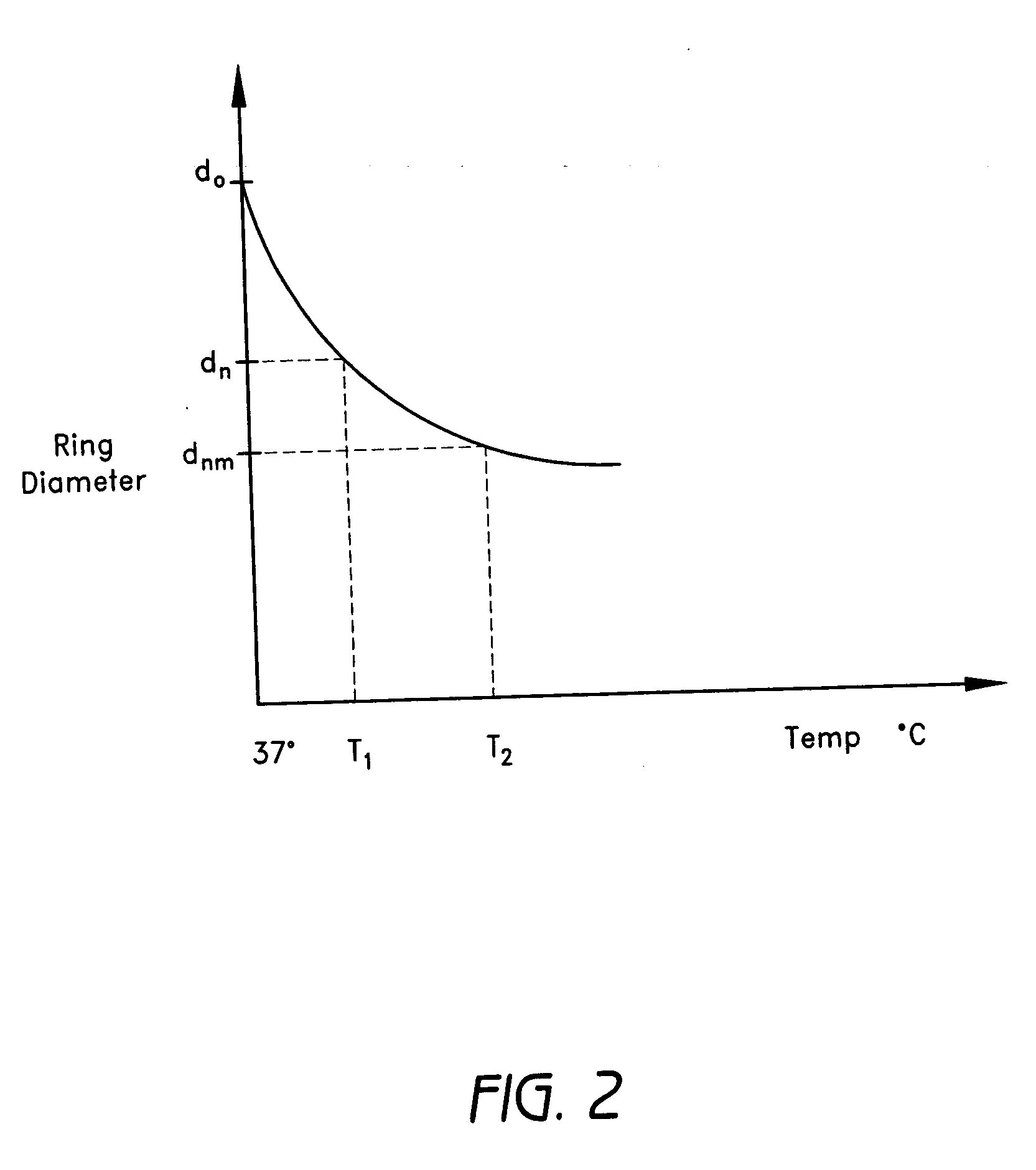
Methods and devices are provided for support of a body structure. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, as the body structure changes size and / or shape, the size and / or shape of the annuloplasty rings can be adjusted to provide continued reinforcement. In certain embodiments, the devices include a first body member including a first shape memory material configured to transform the annuloplasty ring from a first configuration having a first size of a dimension to a second configuration having a second size of the dimension. The second size is less than said first size in septal lateral distance. The devices also include a second body member including a second shape memory material configured to transform the annuloplasty ring from the second configuration to a third configuration having a third size of the dimension, wherein the second size is less than the third size in septal lateral distance.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Adjustable cardiac valve implant with coupling mechanism
InactiveUS7361190B2Improve heat transfer performanceEasy transferBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsRadio frequency energyAcoustic energy
Methods and devices are provided for support of a body structure. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, as the body structure changes size and / or shape, the size and / or shape of the annuloplasty rings can be adjusted to provide continued reinforcement. In certain embodiments, the devices include a tubular member configured to be attached to or near a cardiac valve annulus. The tubular member includes a receptacle end and an insert end configured to couple with the receptacle end of the tubular member such that the tubular member substantially forms a shape of a ring. The insert end is configured to move with respect to the receptacle end to change a circumference of the ring.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Adjustable cardiac valve implant with coupling mechanism
InactiveUS20050288776A1Improve heat transfer performanceEasy transferAnnuloplasty ringsRadio frequency energyAcoustic energy
Methods and devices are provided for support of a body structure. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, as the body structure changes size and / or shape, the size and / or shape of the annuloplasty rings can be adjusted to provide continued reinforcement. In certain embodiments, the devices include a tubular member configured to be attached to or near a cardiac valve annulus. The tubular member includes a receptacle end and an insert end configured to couple with the receptacle end of the tubular member such that the tubular member substantially forms a shape of a ring. The insert end is configured to move with respect to the receptacle end to change a circumference of the ring.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Spinal disc therapy system
InactiveUS7223227B2Simple structureEasy to placeElectrotherapyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSpinal columnTreatment effect
Spinal disc therapy systems in accordance with the present invention generally include an implant element structured to have a therapeutic effect on a human or animal body when implanted into an intervertebral disc annulus or intervertebral disc nucleus. The implant element may include a biochemically active agent that provides pain relief, inflammation relief or other benefit to the human or animal body. The implant element may be mechanically active or mechanically activatable in being effective in providing a therapeutic effect to the human or animal body when implanted in the intervertebral disc. For example, the implant element may include a mechanically active or mechanically activatable component that radiates wave energy, for example, in the form of electrical or magnetic energy, into the body.
Owner:PFLUEGER D RUSSELL
Adjustable cardiac valve implant with ferromagnetic material
InactiveUS20050288781A1Improve heat transfer performanceEasy transferAnnuloplasty ringsRadio frequency energyAcoustic energy
Methods and devices are provided for support of a body structure. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, as the body structure changes size and / or shape, the size and / or shape of the annuloplasty rings can be adjusted to provide continued reinforcement. In certain embodiments, the devices include a body member including a ferromagnetic shape memory material. The body member has a first size of a dimension in a first configuration and a second size of the dimension in a second configuration. The body member is configured to be implanted into a heart so as to reinforce a cardiac valve annulus in the first configuration. The body member is configured to transform from the first configuration to the second configuration in vivo in response to a magnetic field. The body member in the second configuration is configured to reduce a size of the cardiac valve annulus.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
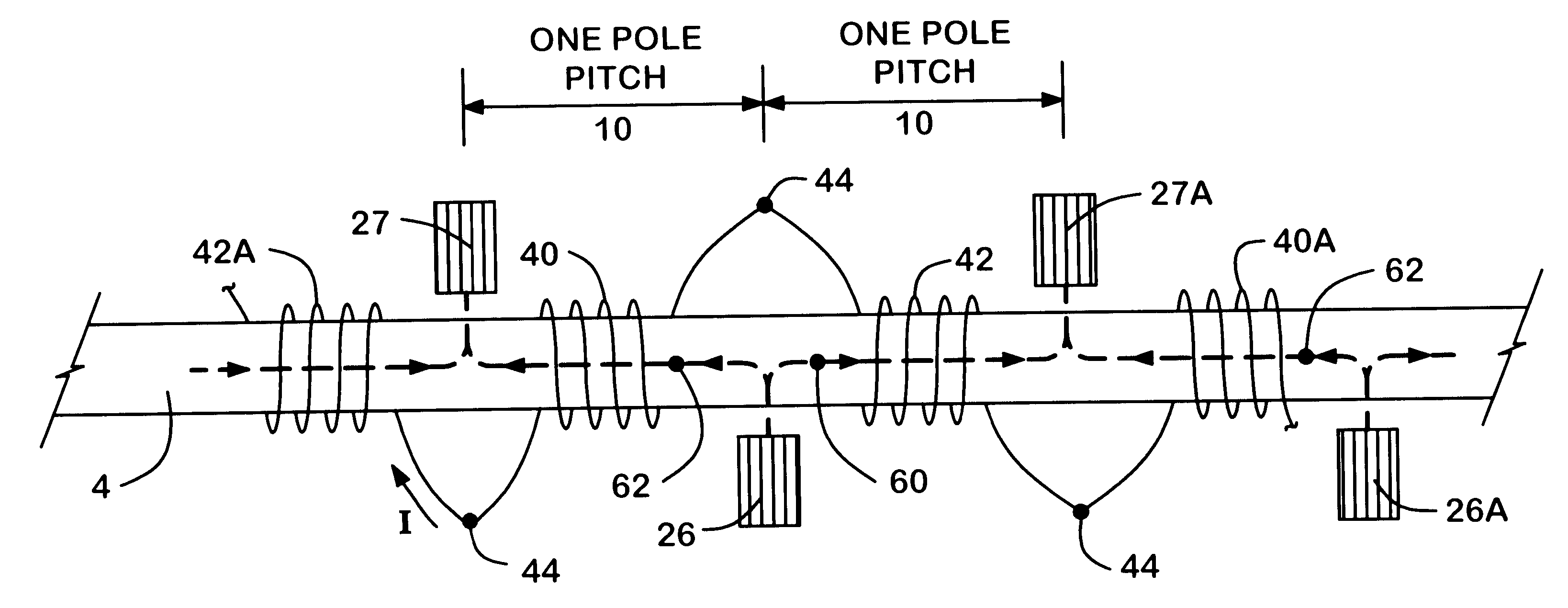
Low inductance electrical machine
A low inductance electrical machine that may be used as an alternator or motor with low armature inductance is disclosed. Arrangements of complementary armature windings are presented in which the fluxes induced by currents in the armature windings effectively cancel leading to low magnetic energy storage within the machine. This leads to low net flux levels, low core losses, low inductance and reduced tendency toward magnetic saturation. The inclusion of additional gaps in the magnetic circuit allows for independent adjustment of air gap geometry and armature inductance. Separately excited field arrangements are disclosed that allow rotor motion to effect brush-less alternator or brush-less motor operation. An exemplary geometry includes a stator including two annular rings and a concentric field coil together with a rotor structure separated from the stator by four air gaps.
Owner:RAVEN TECH
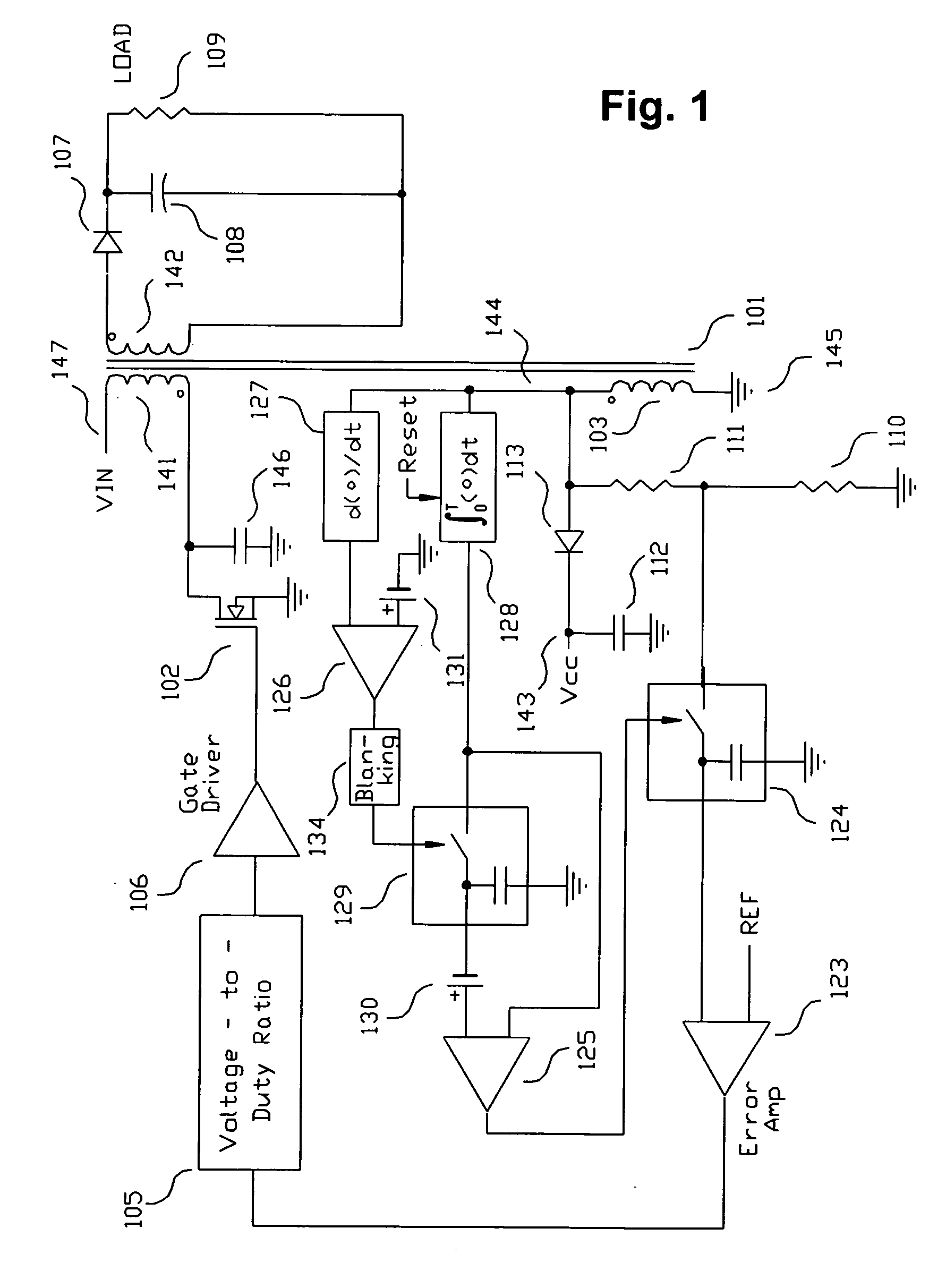
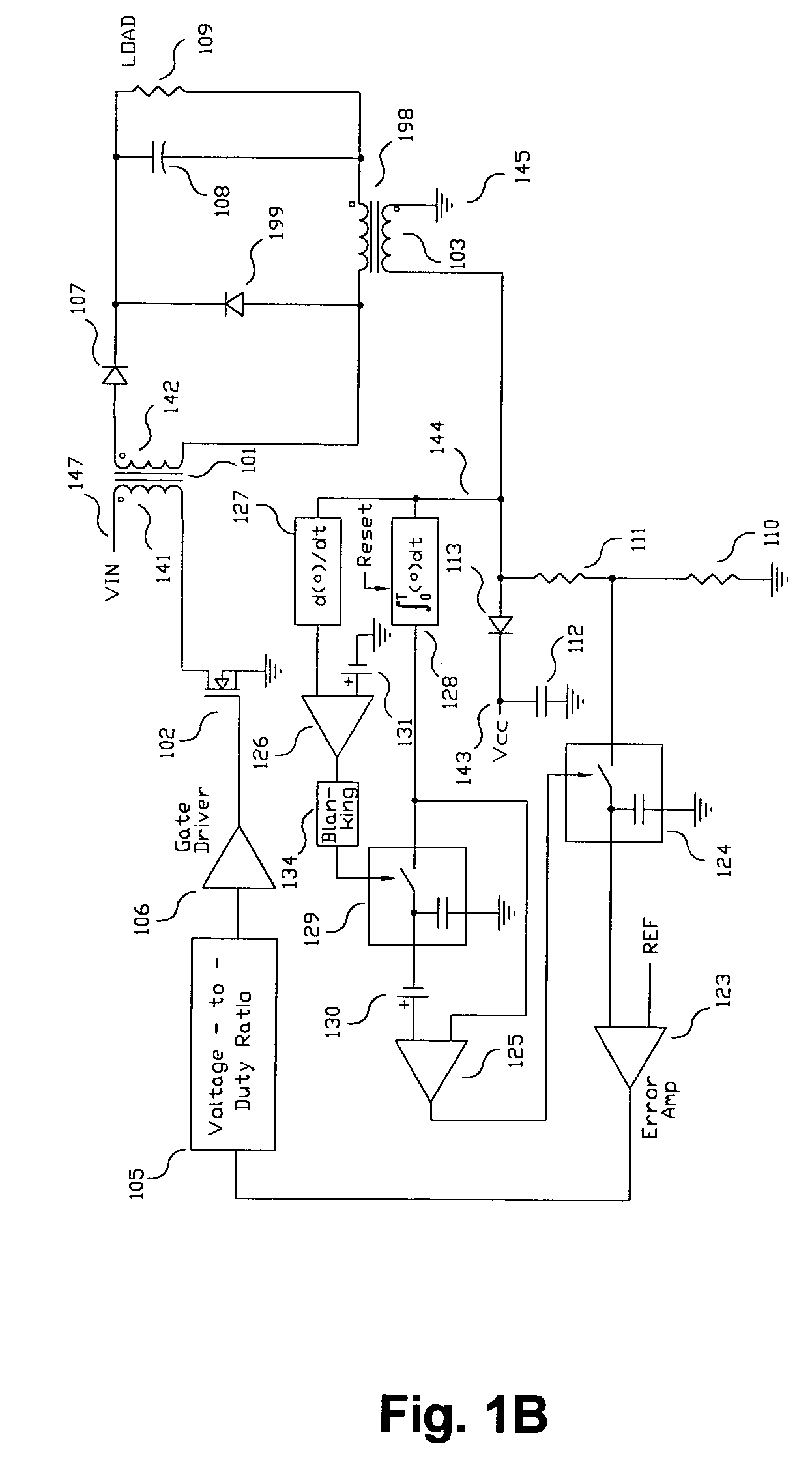
Switching power converter and method of controlling output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux
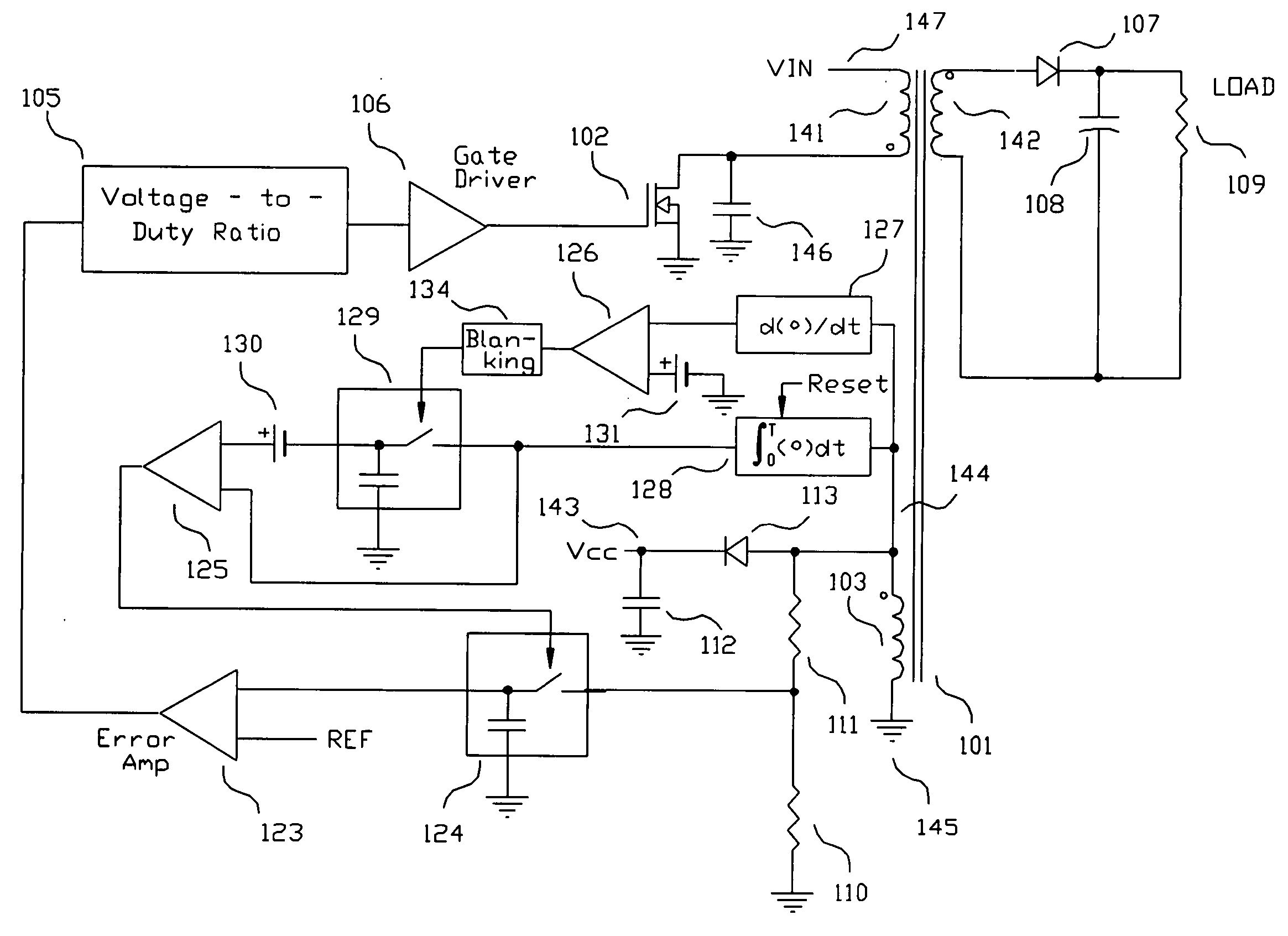
ActiveUS20050073862A1Improve immunityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationIntegratorSwitching cycle
A switching power converter and method of controlling an output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux provides a low-cost switching power converter via primary-side control using a primary-side winding. The power converter has improved immunity to parasitic phenomena and other variations within the power converter components. An integrator is used to generate a voltage analog that represents magnetic flux within a power magnetic element via an integration of a voltage on a primary-side winding of the power magnetic element. A detection circuit detects the end of a half-cycle of post-conduction resonance that occurs in the power magnetic element subsequent to the energy level in the power magnetic element reaching zero. The voltage of the integrator is stored at the end of the post-conduction resonance half-cycle and is used to determine a sampling point prior to or equal to the start of post-conduction resonance in a subsequent switching cycle of the power converter (which is the predicted zero-energy storage point of the power magnetic element). The primary-side winding voltage is then sampled at the sampling point, providing an indication of the output voltage of the power converter. By predicting the zero-magnetic-energy storage point, the output voltage of a power converter operating in discontinuous or boundary conduction mode can be accurately controlled without being affected by parasitic phenomena or variations in circuit performance over time, input voltage and temperature.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Non-contact magnetically adsorbed wall climbing robot
The present invention is non-contact magnetically adsorbed wall climbing robot, belongs to the field of robot design technology, and aims at providing robot with both high moving flexibility and great loading capacity. The non-contact magnetically adsorbed wall climbing robot includes wheeled moving mechanism and permanent adsorption mechanism. The wheeled moving mechanism includes chassis, driving mechanism and wheels, which are laid symmetrically, driven in differential mode, and turns on wall by means of the speed difference of the wheels. The permanent adsorption mechanism has no contact with the magnetically conducting wall surface, high magnetic energy utilization, and high adsorption capacity. The wall climbing robot has high loading capacity, high motion flexibility, especially high turning flexibility, and excellent application foreground.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
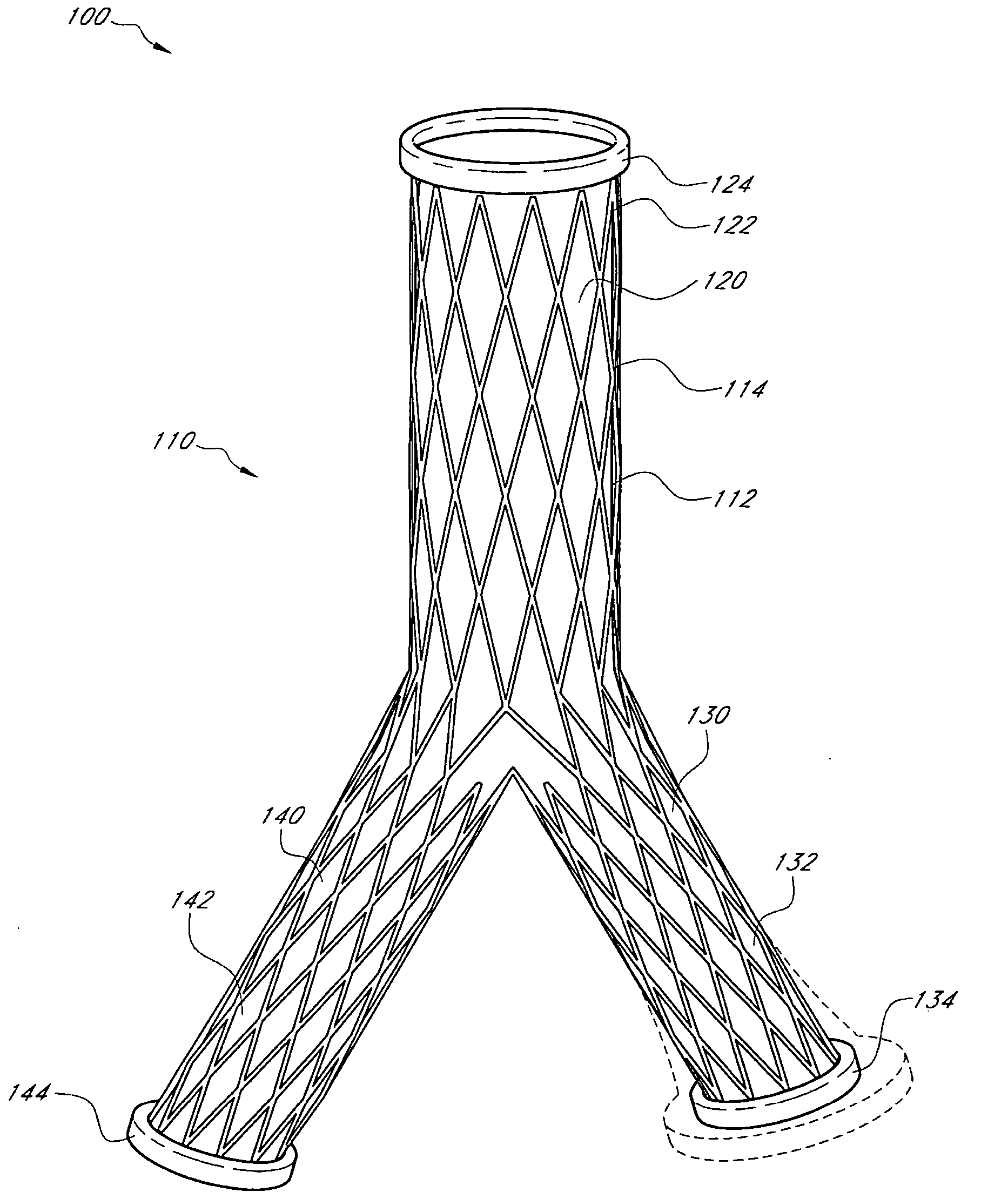
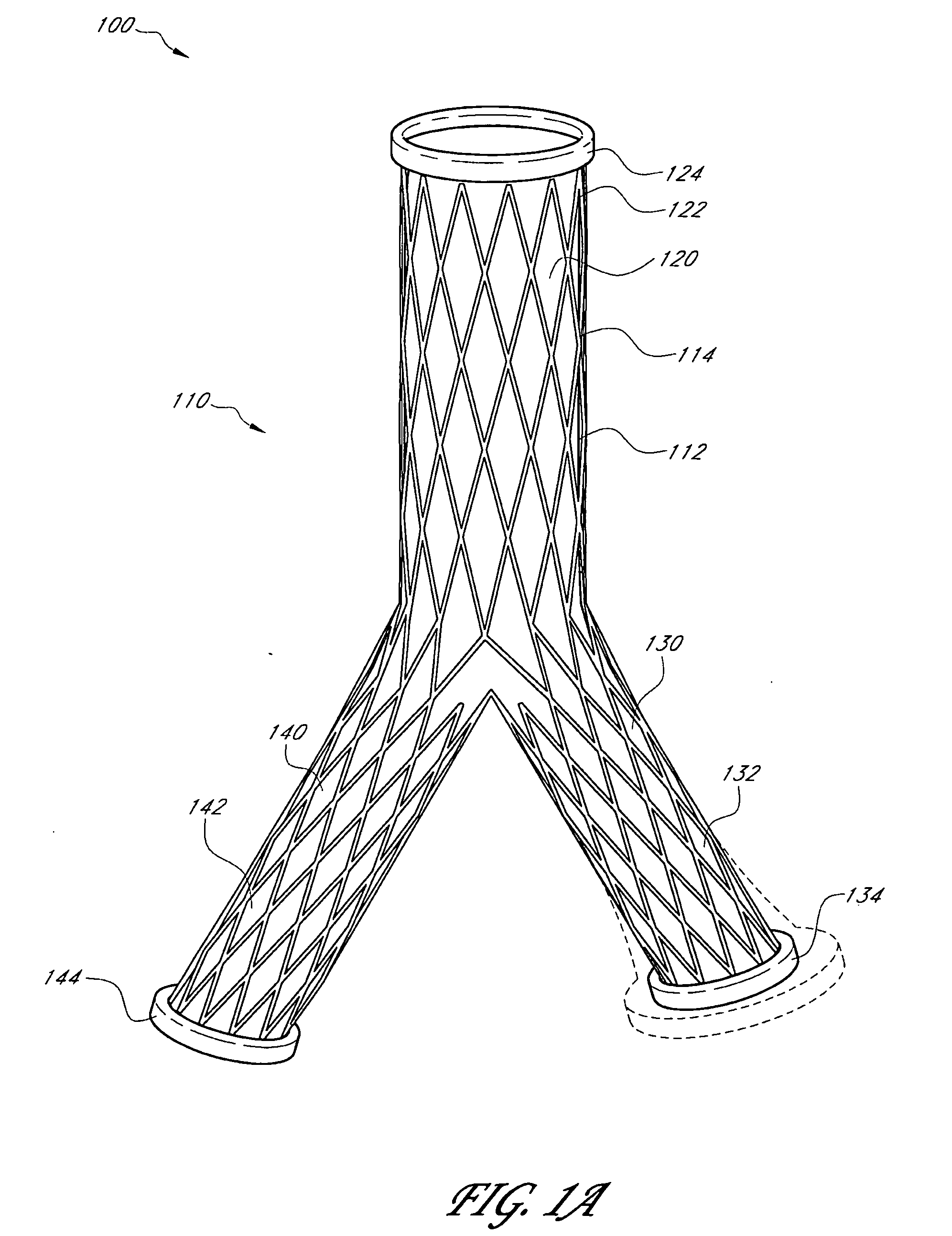
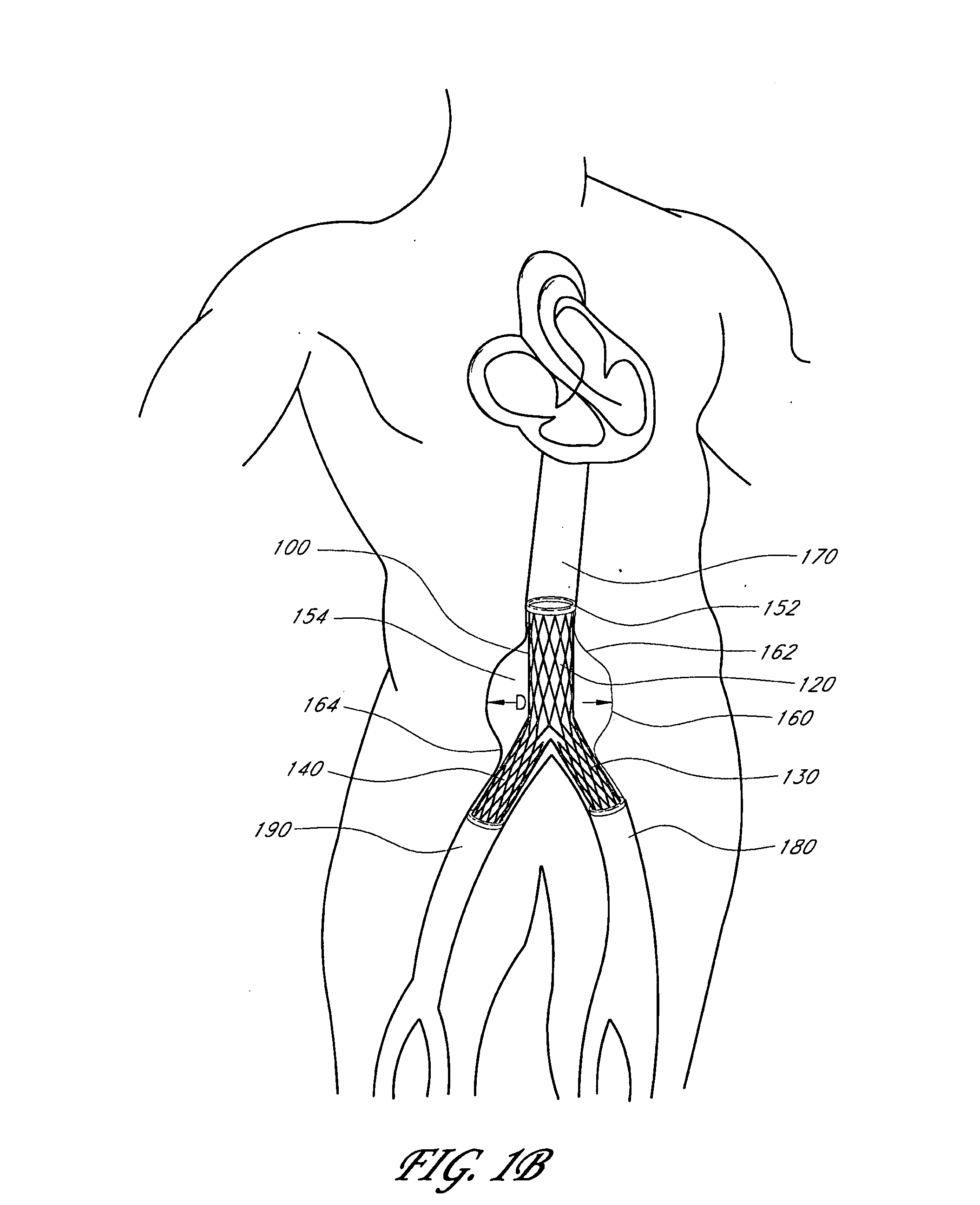
Externally adjustable endovascular graft implant
InactiveUS20060212113A1Improve performanceReduce leakageStentsBlood vesselsRadio frequency energyAcoustic energy
A device, method, and system for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms is described, where the device is an endovascular graft implant that one or more adjustable elements. The adjustable elements provide improved performance, for example, reduced leaking. The adjustable elements are adjustable within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. Examples of suitable types of energy include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy, and magnetic energy.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
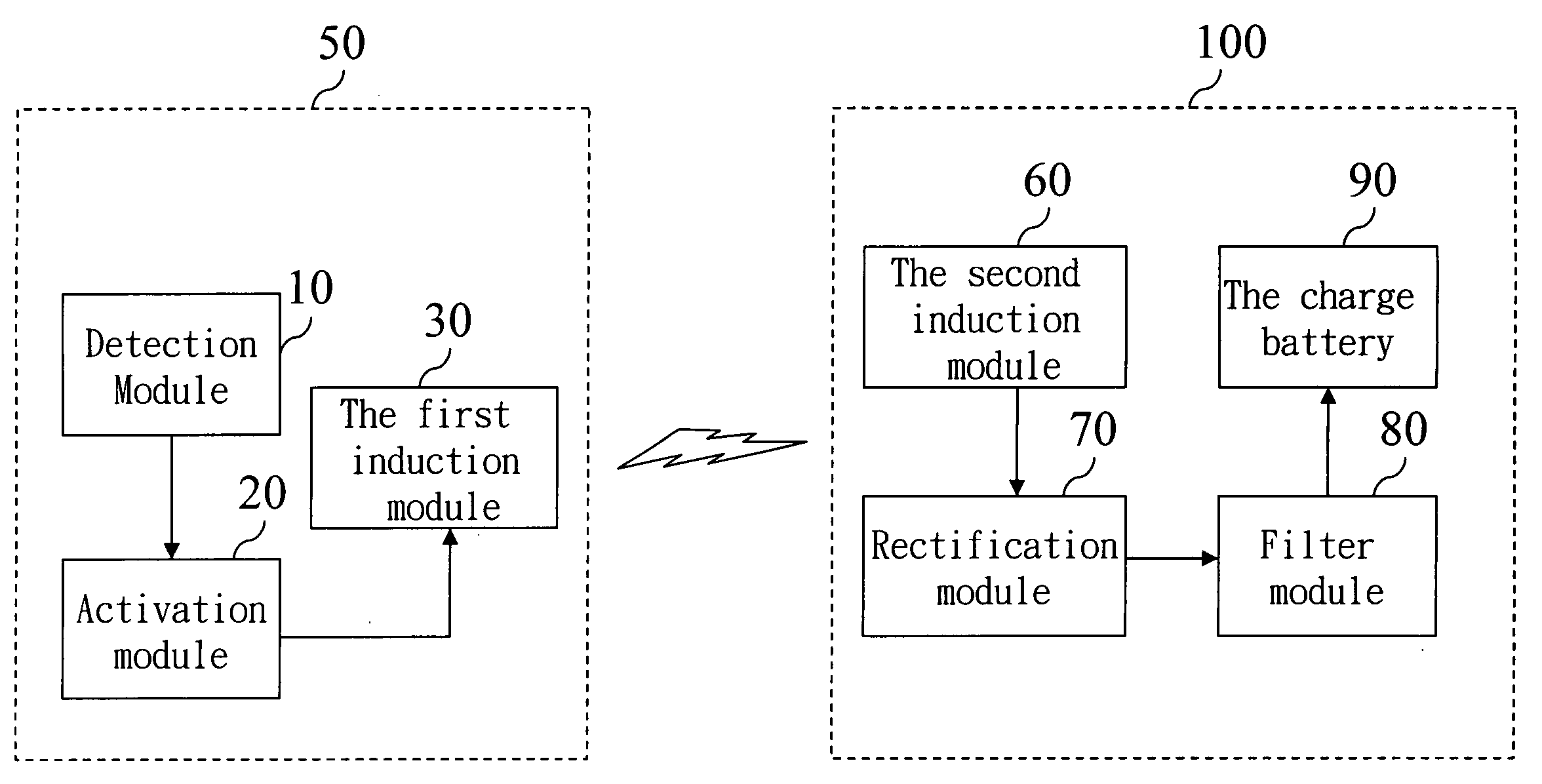
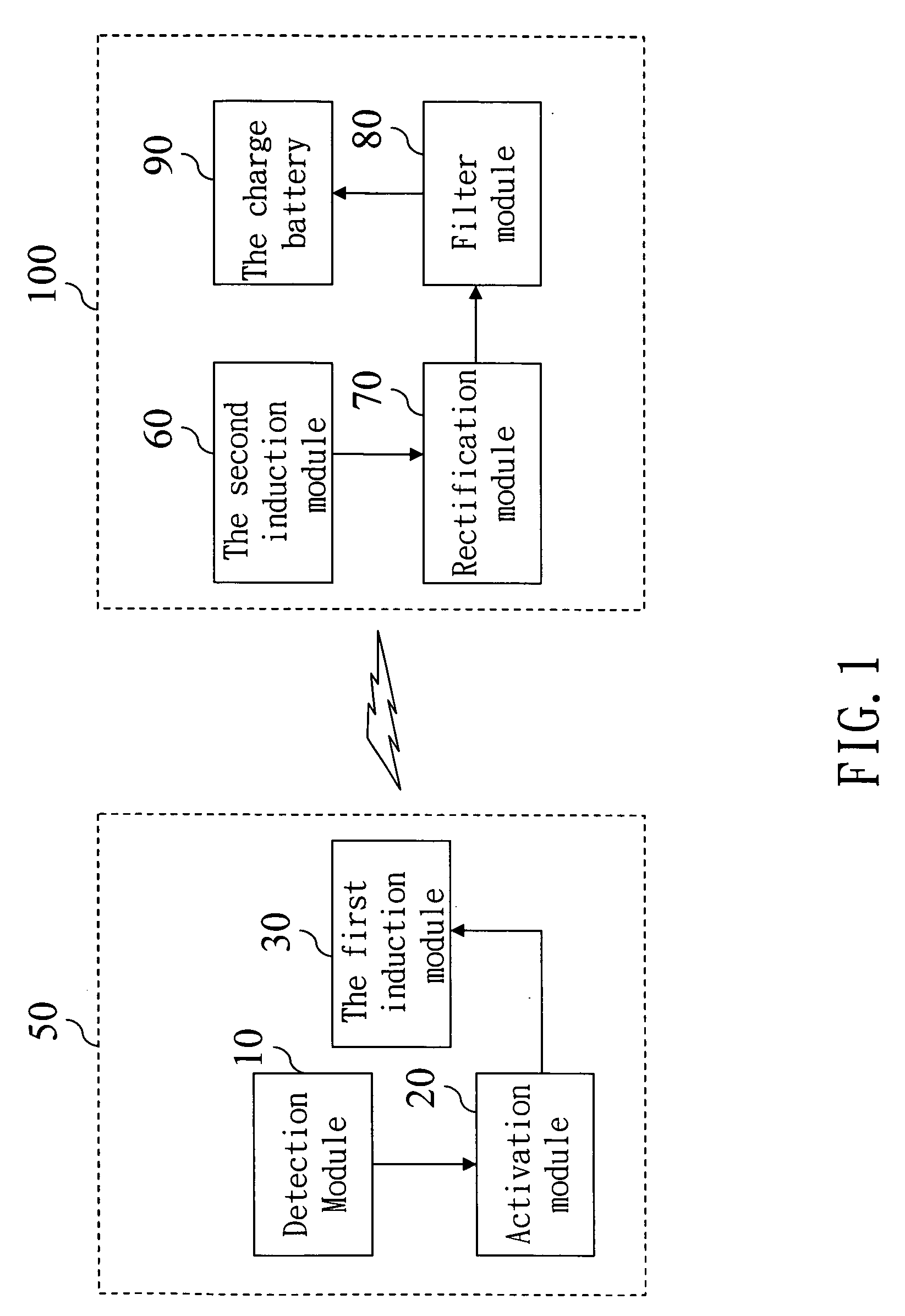
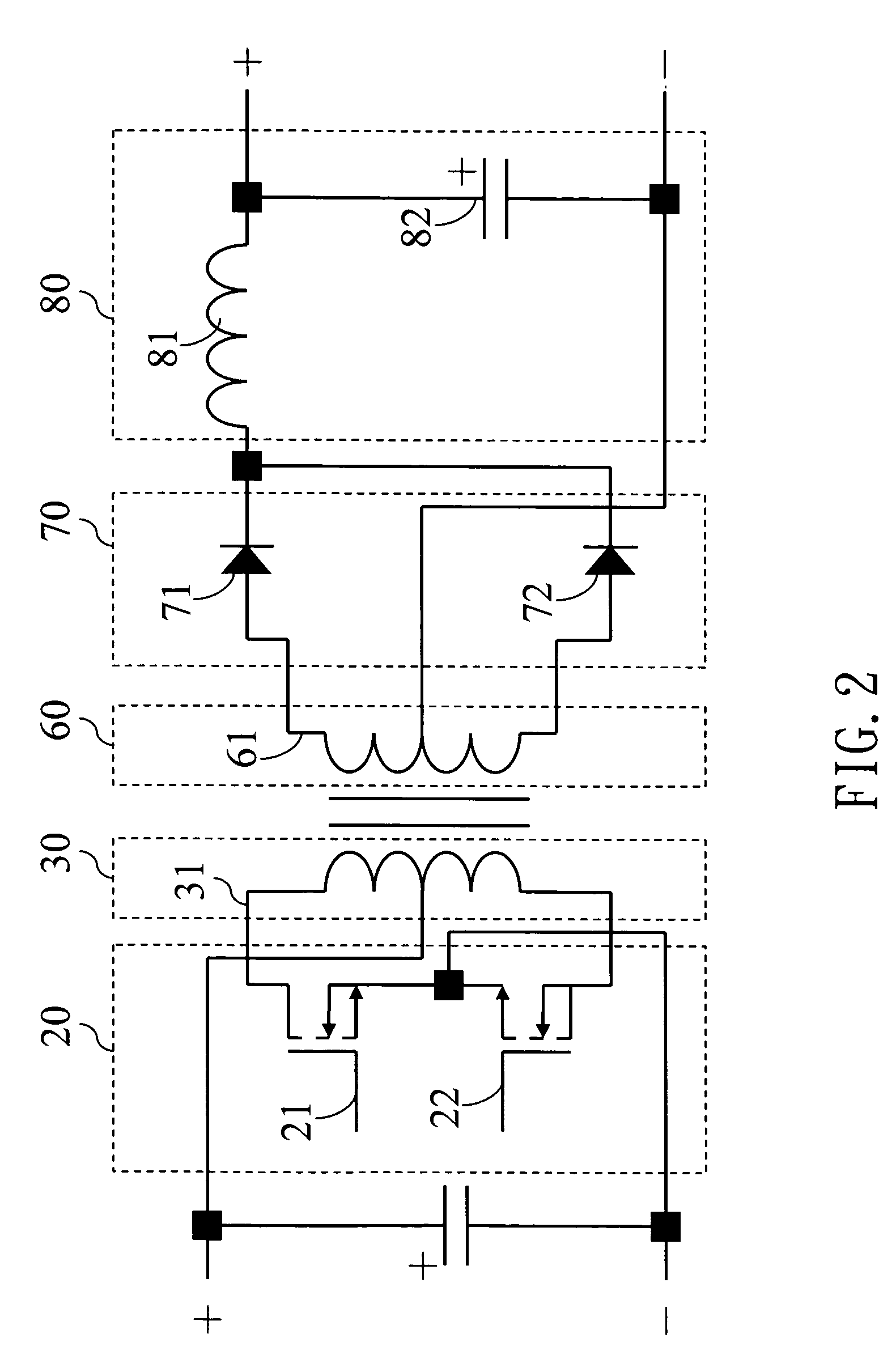
Integrated induction battery charge apparatus
An integrated induction battery charge apparatus transforms electric energy and magnetic energy according to electromagnetic induction principle to charge an induction charge battery. It integrates the conventional charge batteries to become an induction charge battery so that users may carry only one charge apparatus to charge the induction batteries of different specifications, thereby improve use convenience.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
Low inductance electrical machine for flywheel energy storage
InactiveUS6175178B1Synchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsBrushless motorsFlywheel energy storage
A low inductance electrical machine which may be used as an alternator or motor with low armature inductance is disclosed. Arrangements of complementary armature windings are presented in which the fluxes induced by currents in the armature windings effectively cancel leading to low magnetic energy storage within the machine. This leads to low net flux levels, low core losses, low inductance and reduced tendency toward magnetic saturation. Separately excited field arrangements are disclosed that allow rotor motion to effect brushless alternator or brushless motor operation. An exemplary geometry includes a stator including two toroidal rings and a concentric field coil together with a rotor structure separated from the stator by four air gaps. An alternate embodiment allows for counter-rotation of two rotor elements for use as a flywheel energy storage system in which the external gyroscopic effects cancel.
Owner:RAVEN TECH
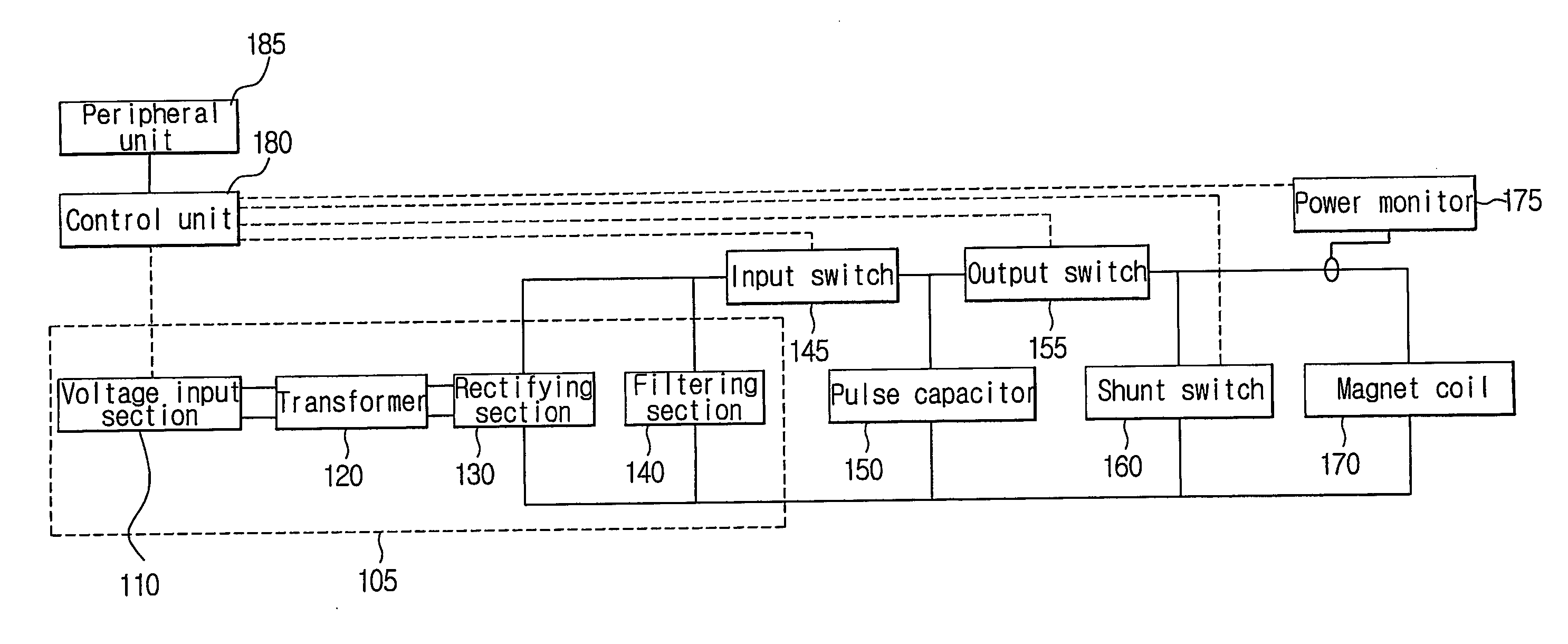
Apparatus and method for creating pulse magnetic stimulation having modulation function
InactiveUS20060187607A1Efficiently transferring energyEnergy efficiencyElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsModulation functionVoltage source
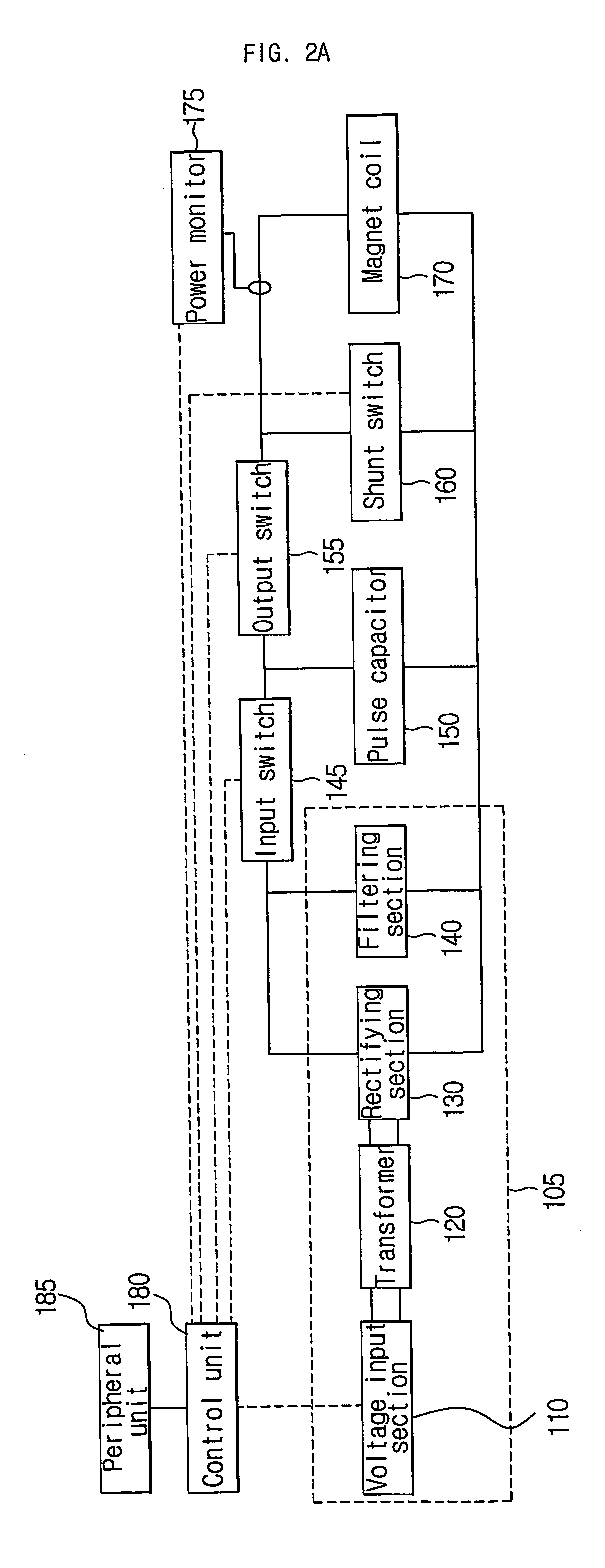
An apparatus for creating pulse magnetic stimulation, having a modulation function, according to the present invention, comprises: a driving voltage supplying section for converting AC voltage input from a voltage source into DC voltage having a predetermined magnitude; a capacitor section for accumulating electric charge in accordance with the DC voltage; an input switch section for controlling the accumulation of electric charge in the capacitor section; a coil for generating magnetic flux in accordance with current generated by both-end voltage corresponding to the electric charge accumulated in the capacitor section; an output switch section for controlling discharge of the electric charge accumulated in the capacitor section through the coil; and a shunt switch section for lowering magnetic energy stored in the coil and voltage stored in the capacitor section into a ground level to obtain a pulse magnetic field. In this pulse-magnetic-stimulation creating apparatus having a modulation function according to the present invention, it is possible to efficiently transfer energy on the basis of current compliance of a patient and impedance of biologic tissue for therapeutic applications.
Owner:MO SEUNG KEE
Adjustable embolic aneurysm coil
Methods and devices are provided for treatment of an aneurysm within a patient. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, the size and / or shape of the embolic coils can be adjusted to provide optimal filling of the aneurysm. In certain embodiments, the devices include a shape memory material that is responsive to changes in temperature and / or exposure to a magnetic field. A material having enhanced absorption characteristics with regard to a desired heating energy may be used in order to facilitate heating and adjustment of the embolic coil.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Boost converter utilizing bi-directional magnetic energy transfer of coupling inductor
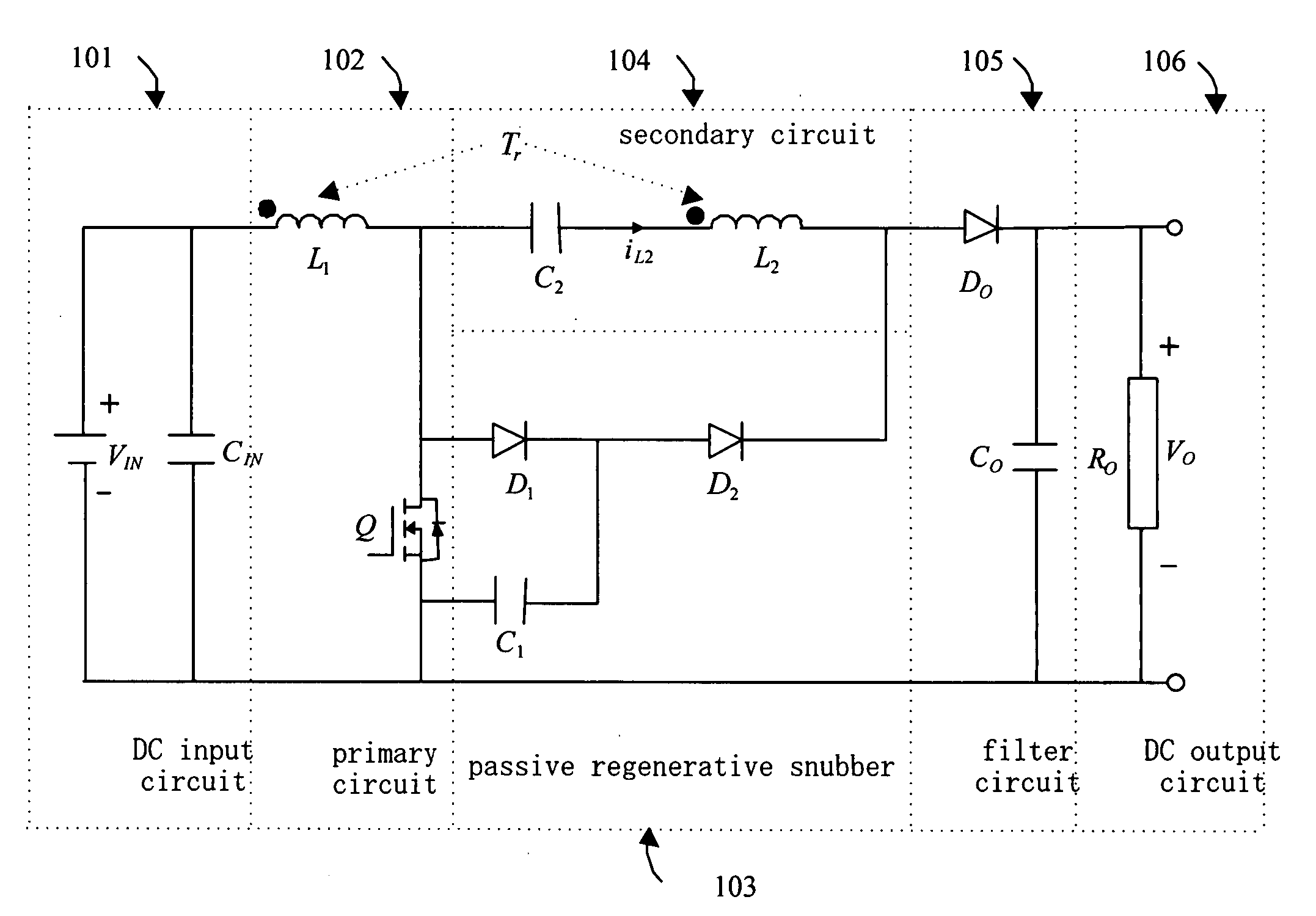
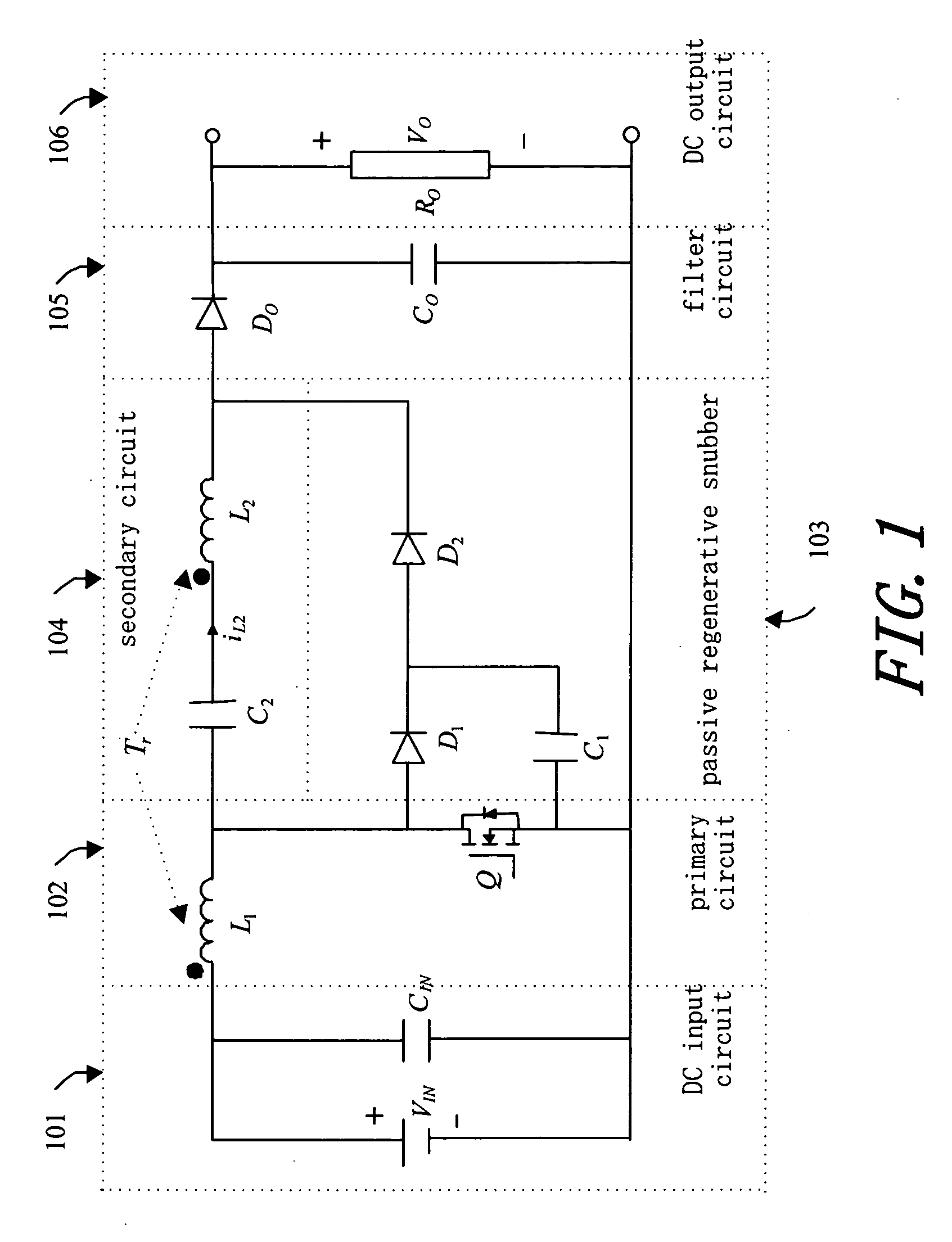
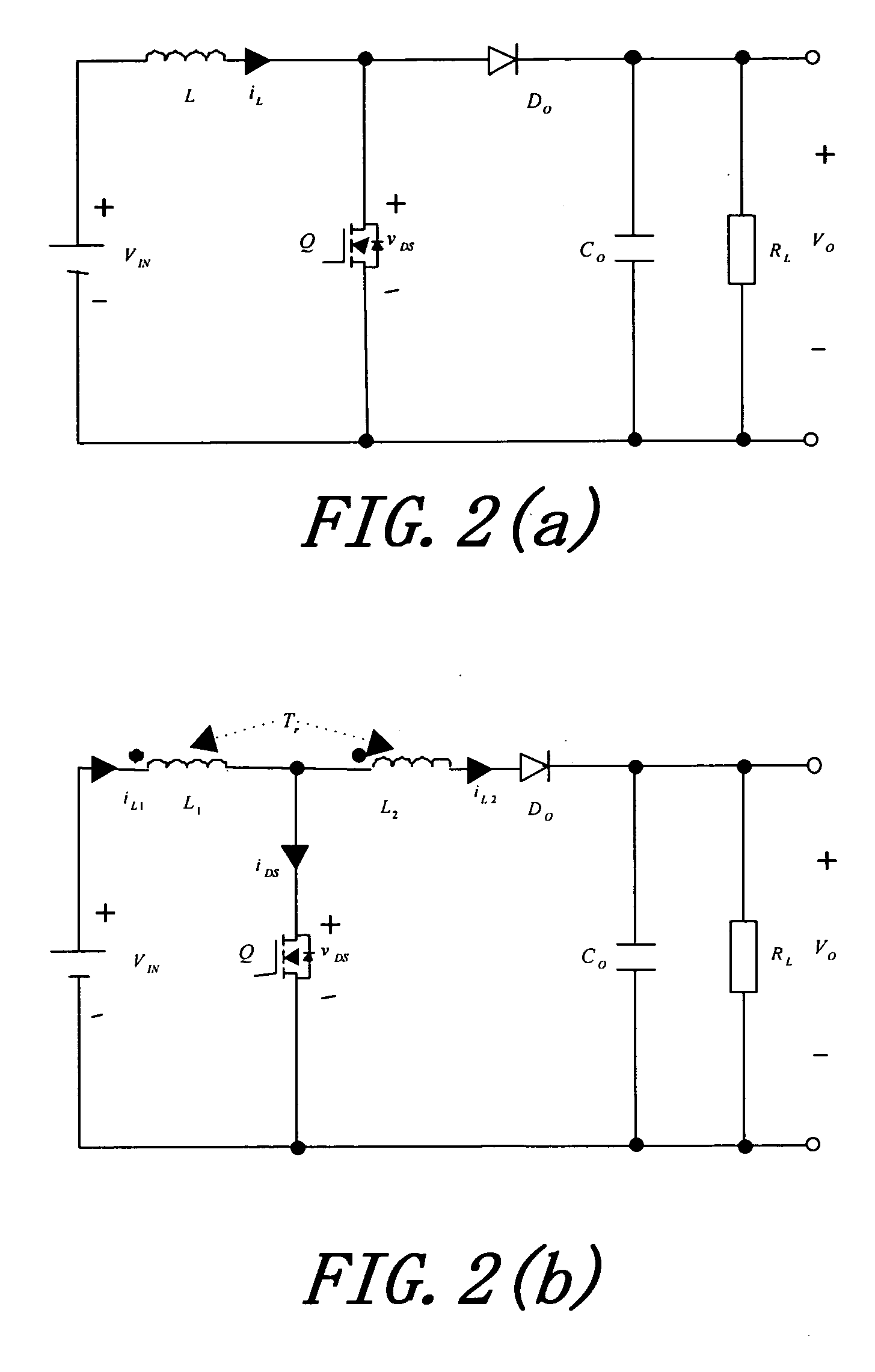
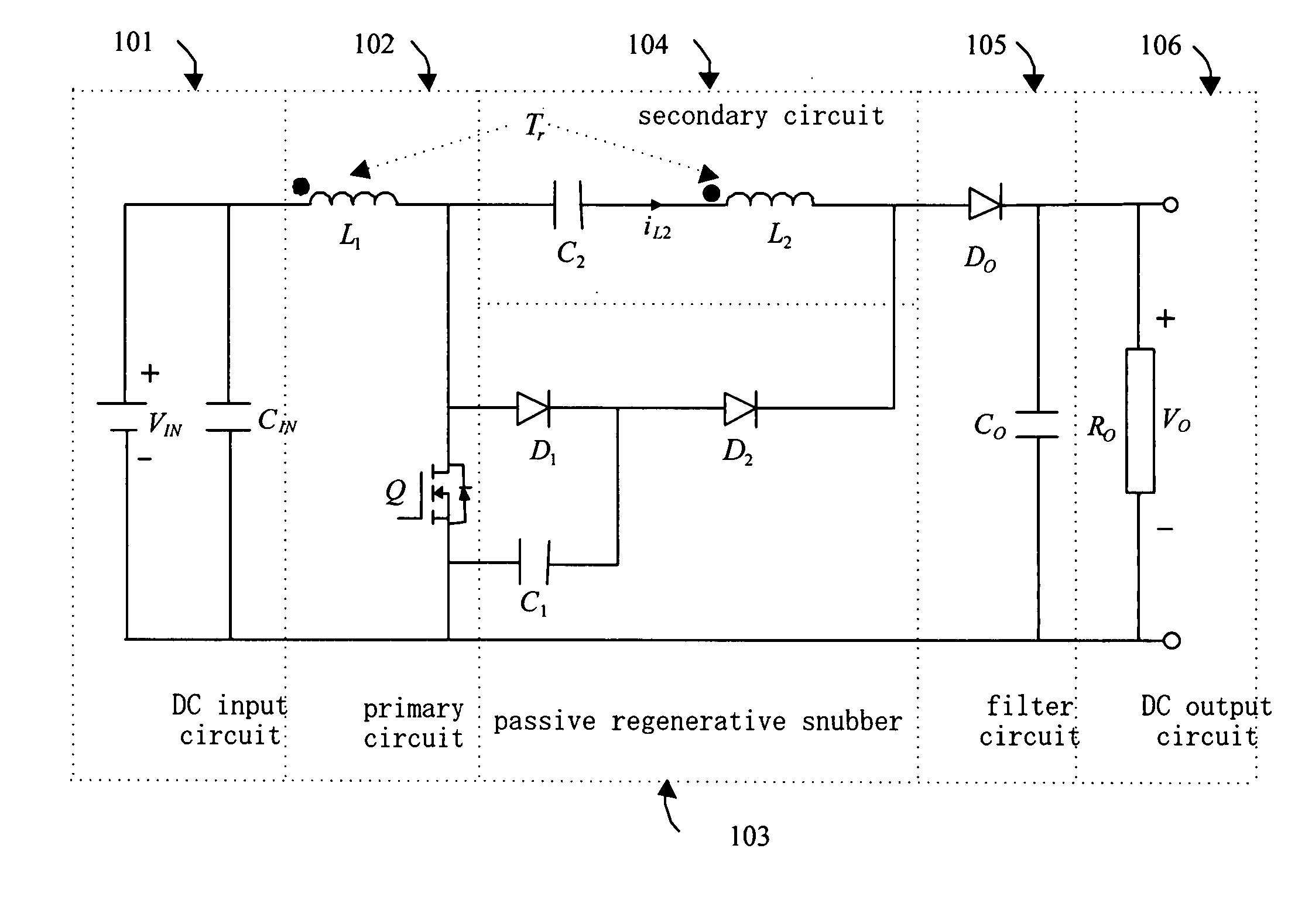
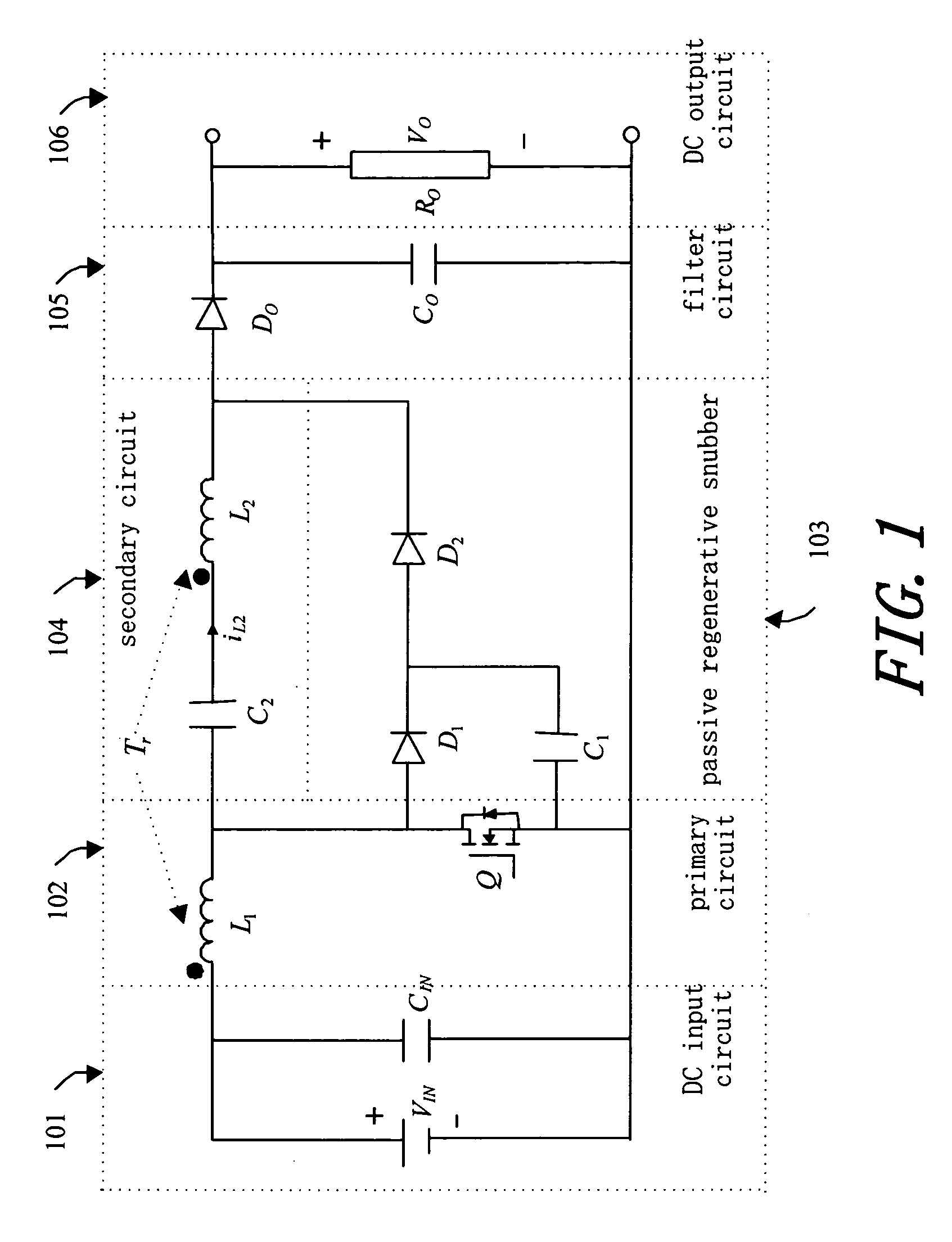
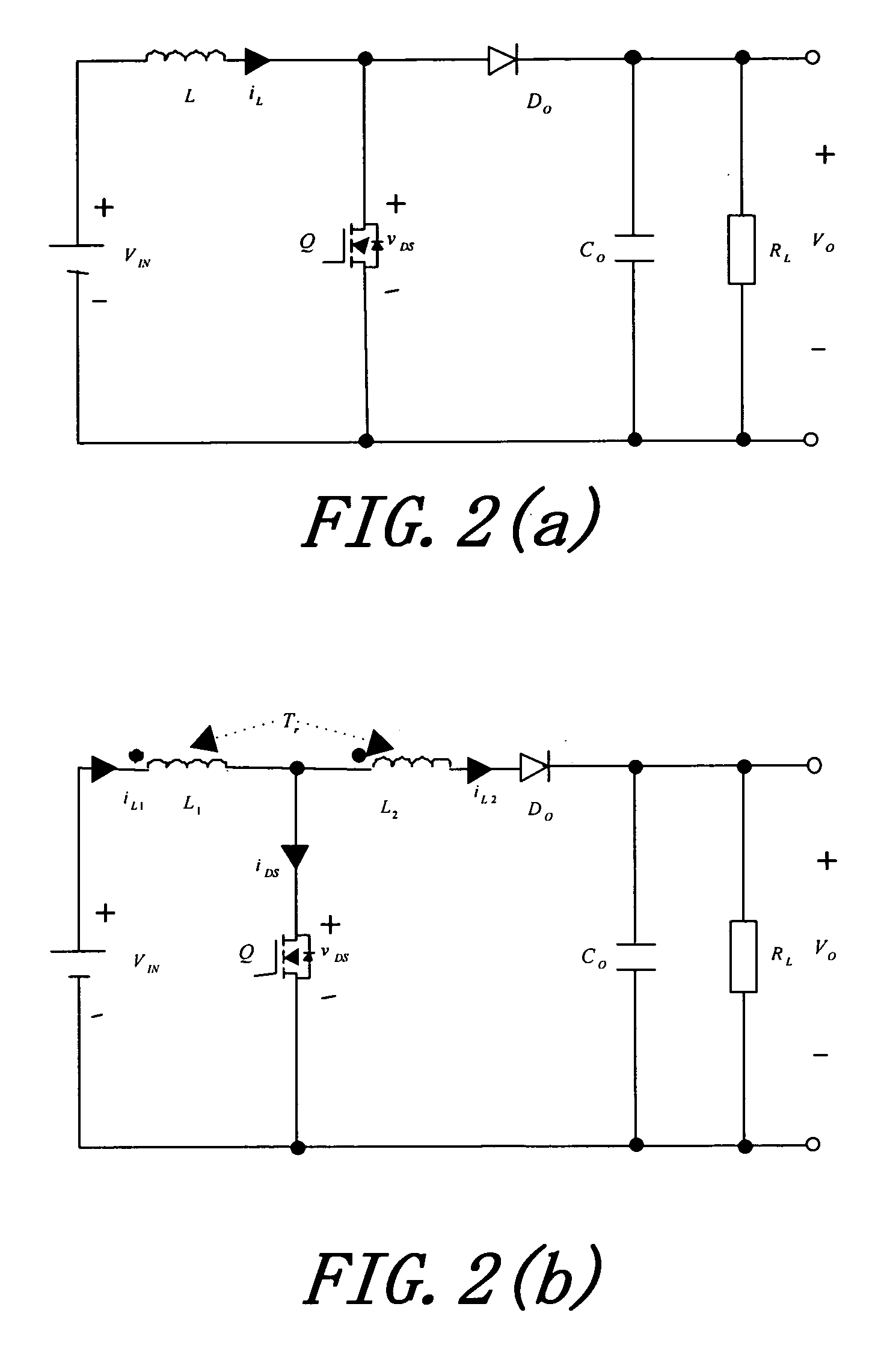
ActiveUS20060226816A1Reduce loadTotal current dropDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMagnetic currentTransformer
A boost converter utilizing bi-directional magnetic energy transfer of coupling inductor provides a high efficiency boost DC-DC converting with above 30 times voltage boost rate, which uses a coupling inductor and low voltage switch to absorb circuit induction voltage of a passive regenerative snubber no matter if switch is turned on or off. Such that, a much higher voltage boost rate than the turn rate of transformer and wider range of switching duty cycle is obtained. A bi-directional magnetic energy path is utilized, that is, when switch is turned on the first winding of coupling inductor stores magnetic excited high current energy, and opposite magnetic flux is induced on the second winding at the same time. When switch is turned off the magnetic excited current continues and increases the voltage on the second winding. The second winding has bi-directional magnetic current induced and fully utilizes capacity of transformer's iron core.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Boost converter utilizing bi-directional magnetic energy transfer of coupling inductor
ActiveUS7161331B2Low efficiencyImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMagnetic currentLow voltage
A boost converter utilizing bi-directional magnetic energy transfer of coupling inductor provides a high efficiency boost DC-DC converting with above 30 times voltage boost rate, which uses a coupling inductor and low voltage switch to absorb circuit induction voltage of a passive regenerative snubber no matter if switch is turned on or off. Such that, a much higher voltage boost rate than the turn rate of transformer and wider range of switching duty cycle is obtained. A bi-directional magnetic energy path is utilized, that is, when switch is turned on the first winding of coupling inductor stores magnetic excited high current energy, and opposite magnetic flux is induced on the second winding at the same time. When switch is turned off the magnetic excited current continues and increases the voltage on the second winding. The second winding has bi-directional magnetic current induced and fully utilizes capacity of transformer's iron core.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
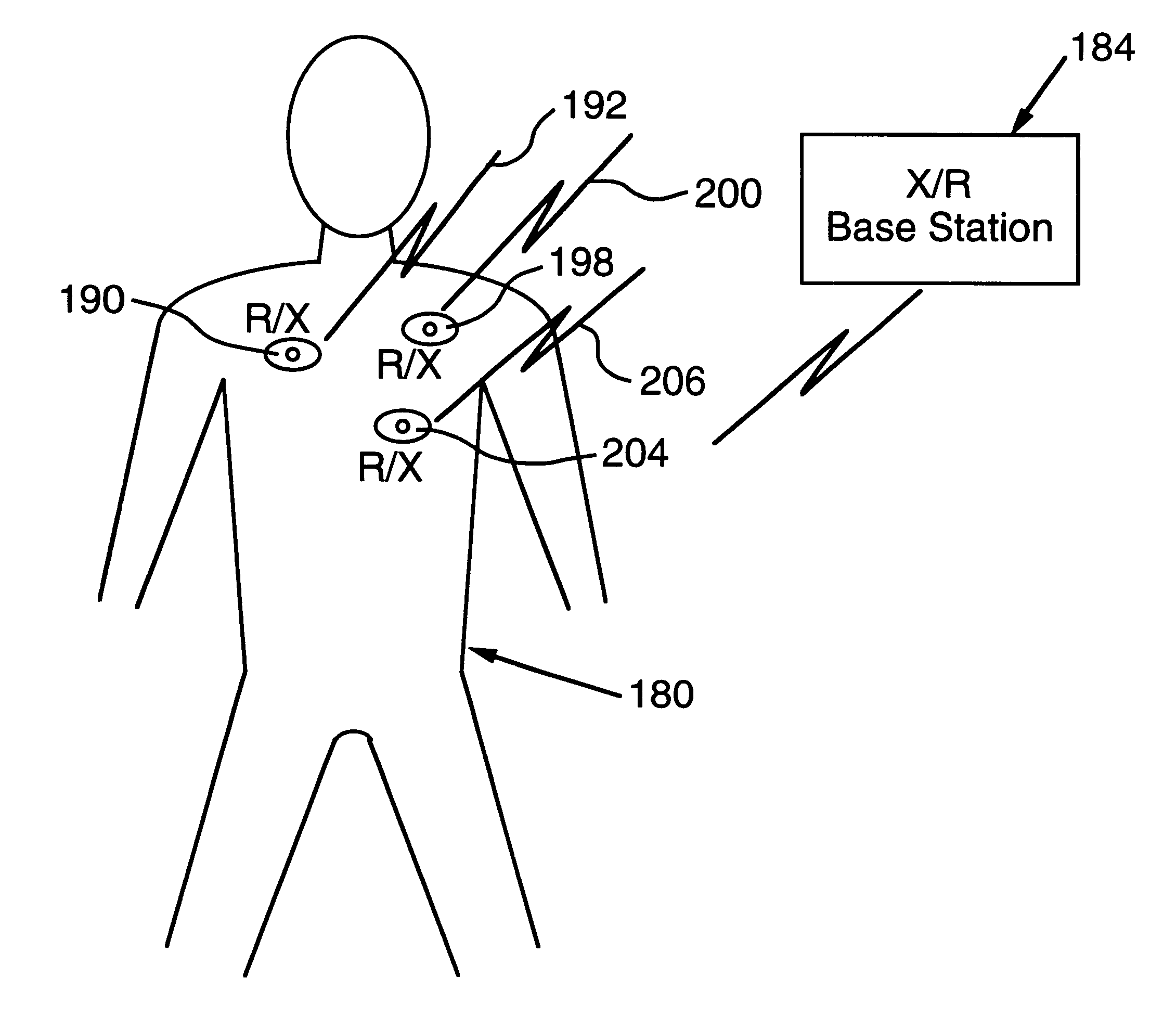
Apparatus for energizing a remote station and related method
InactiveUS20030032993A1Eliminate needEasy to useElectrotherapyTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsStored energyMiniaturization
Apparatus for remote interaction with an object of interest includes a remote station for obtaining information from the object of interest, a base station for transmitting energy in space to and communicating with the remote station and the remote station having conversion means for energizing the remote station responsive to receipt of the transmitted energy. The energy may be of any suitable type including RF power, light, acoustic, magnetic energy or other form of space transmitted or "radiant" energy. The remote station does not have to contain a source of stored energy or a wired connection to a source of energy. The remote station receives the energy transmission and data transmission from the base station and transmits data to the base station. Microprocessor controllers may be provided for the base station and the remote station. The remote station may receive information from sensors and through one or more transponders sequentially communicate information to the base station. An associated method is provided. In other embodiments which are suited for use in miniaturized electronic chip systems, power enhancement and increased effective antenna size are provided.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Thermal conductor for adjustable cardiac valve implant
InactiveUS20050288777A1Improve heat transfer performanceEasy transferAnnuloplasty ringsThermal energyRadio frequency energy
Methods and devices are provided for support of a body structure. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, as the body structure changes size and / or shape, the size and / or shape of the annuloplasty rings can be adjusted to provide continued reinforcement. In certain embodiments, the devices include a body member including a shape memory material. The shape memory material is configured to transform from a first shape to a second shape in response to being heated. The devices also include a thermally insulative material at least partially covering the body member and a thermally conductive material extending into the thermally insulative material. The thermally conductive material is configured to communicate thermal energy to the body member.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
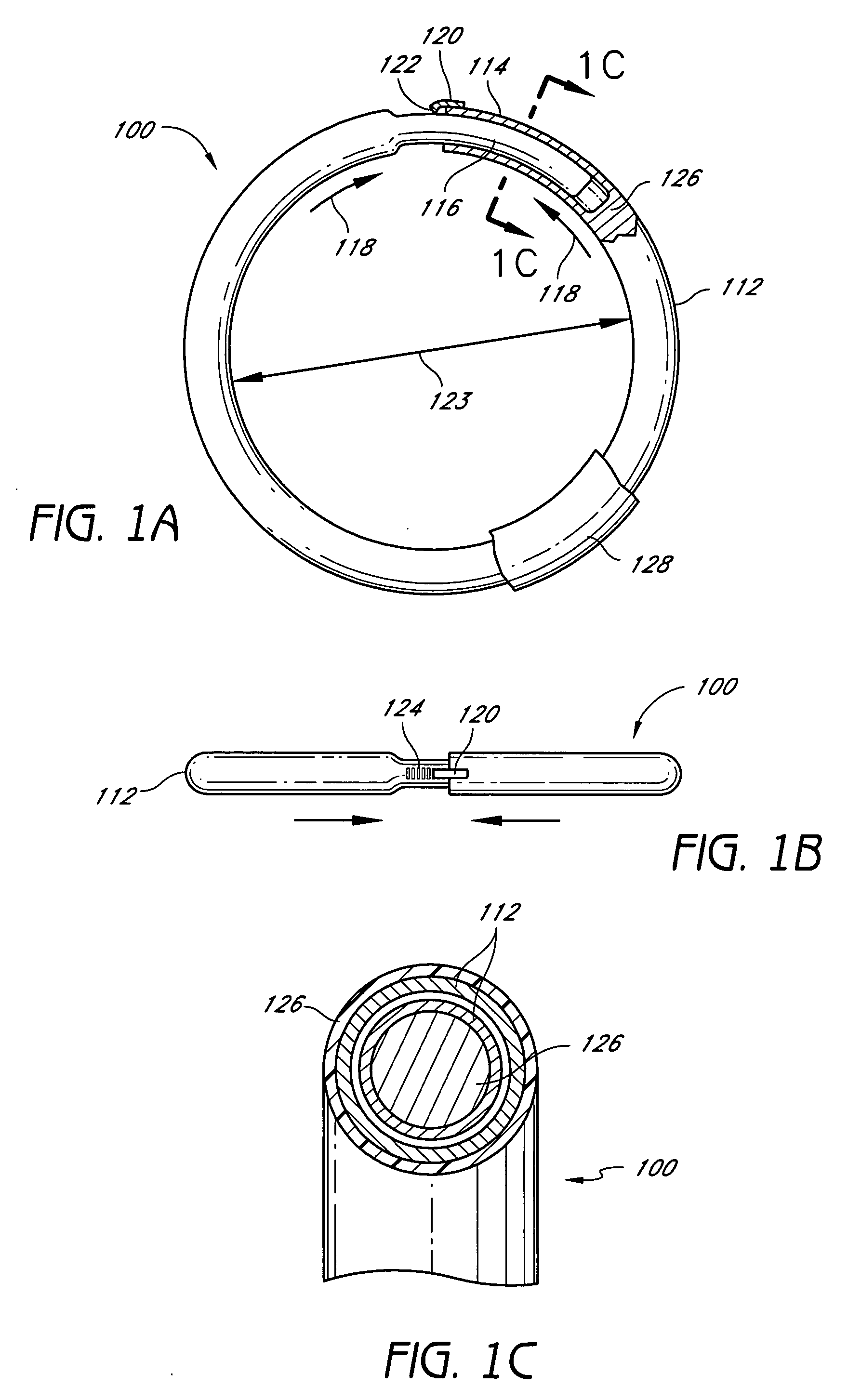
Slotted annuloplasty ring
InactiveUS20070055368A1Improve heat transfer performanceEasy transferAnnuloplasty ringsRadio frequency energyLight energy
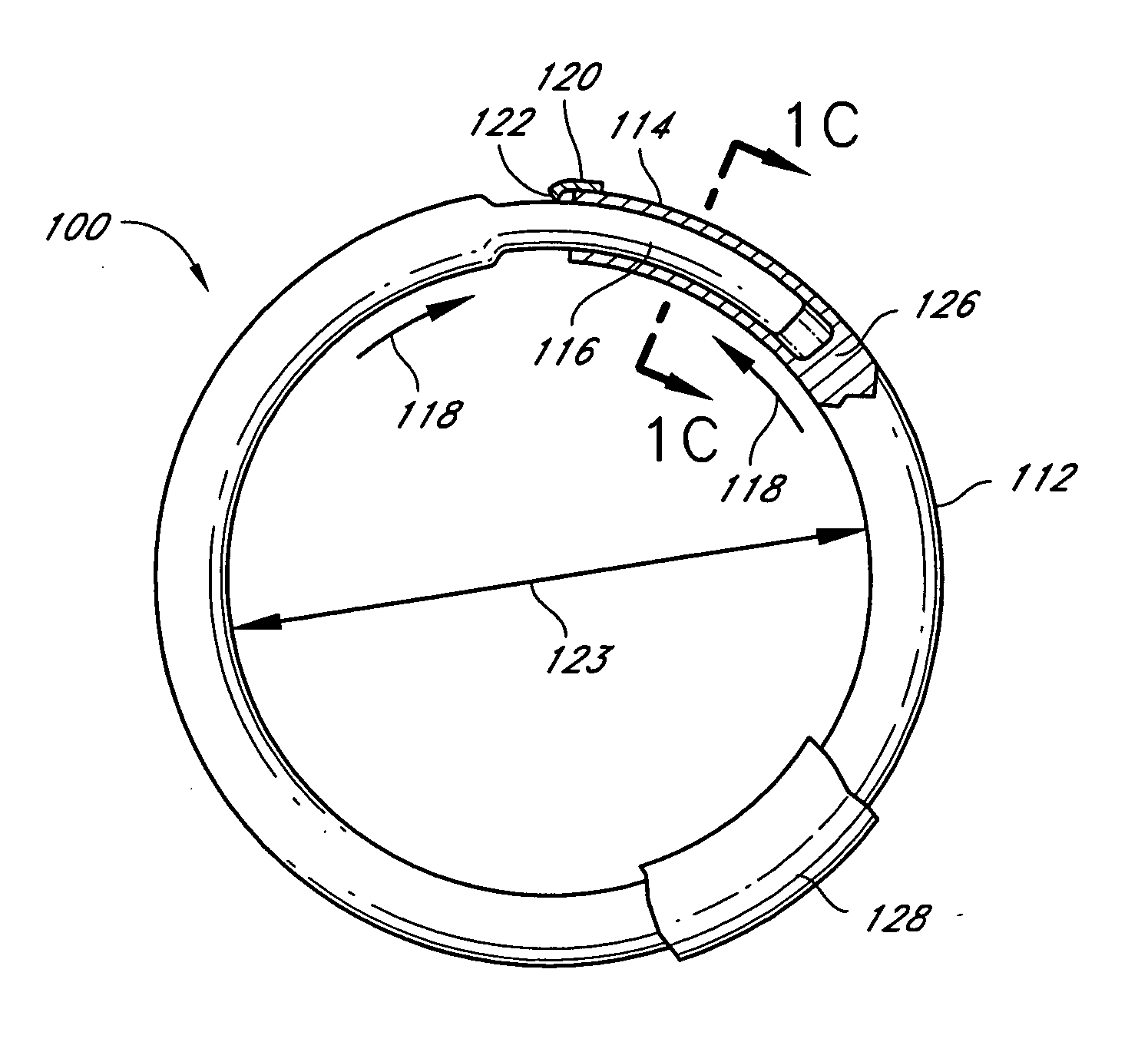
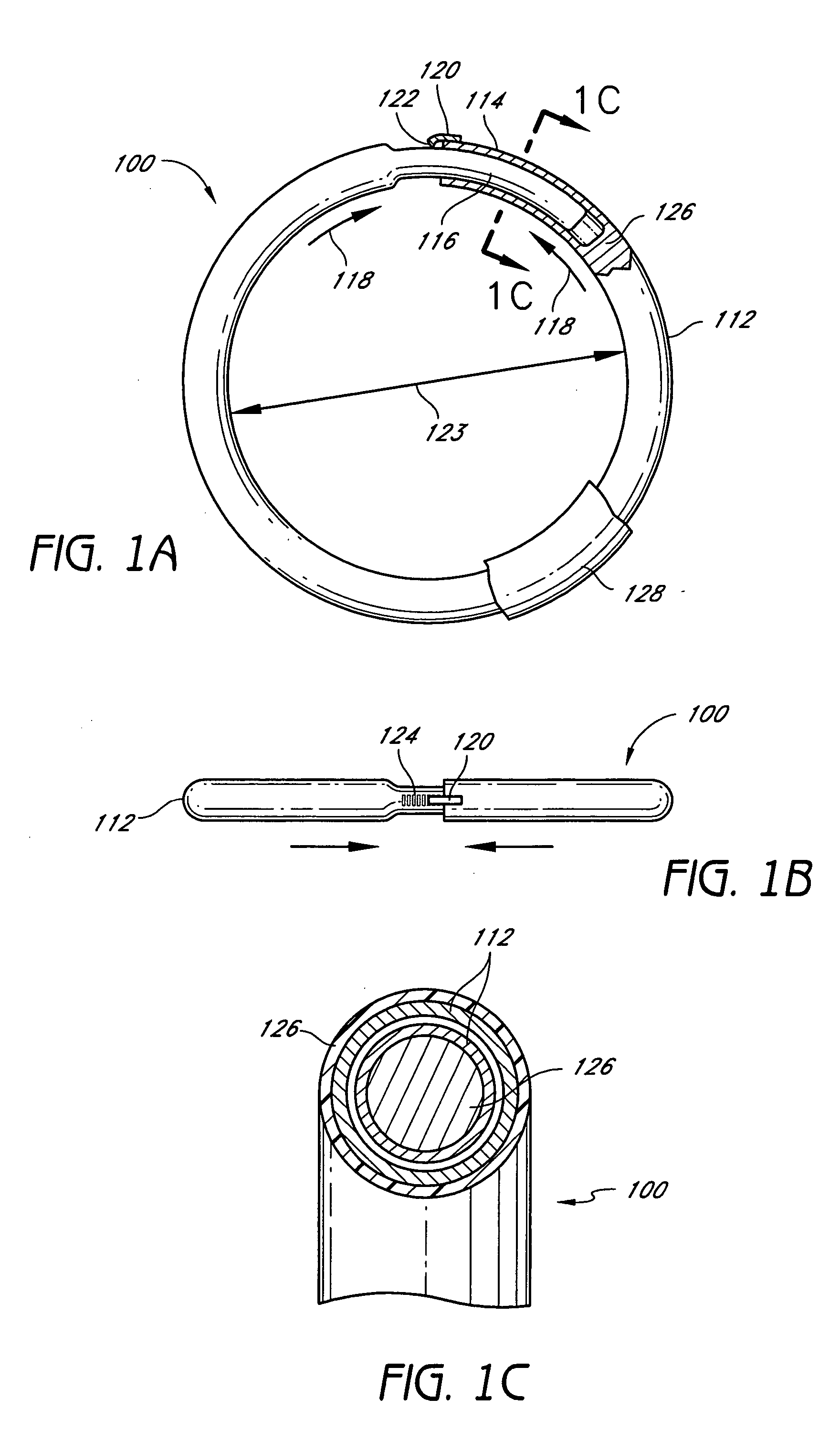
Methods and devices are provided for support of a body structure. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner, such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, as the body structure changes size and / or shape, the size and / or shape of the annuloplasty rings can be adjusted to provide continued reinforcement. In certain embodiments, the devices comprise a shape memory material, and further include a body member and an insert member. The body member has a circumference and a slot that extends at least partially along the circumference of the body. The insert member extends at least partially along the circumference of the body. The device has a first shape in a first configuration and a second shape in a second configuration, and is configured to transform from a first configuration to a second configuration in response to a first activation energy applied thereto.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
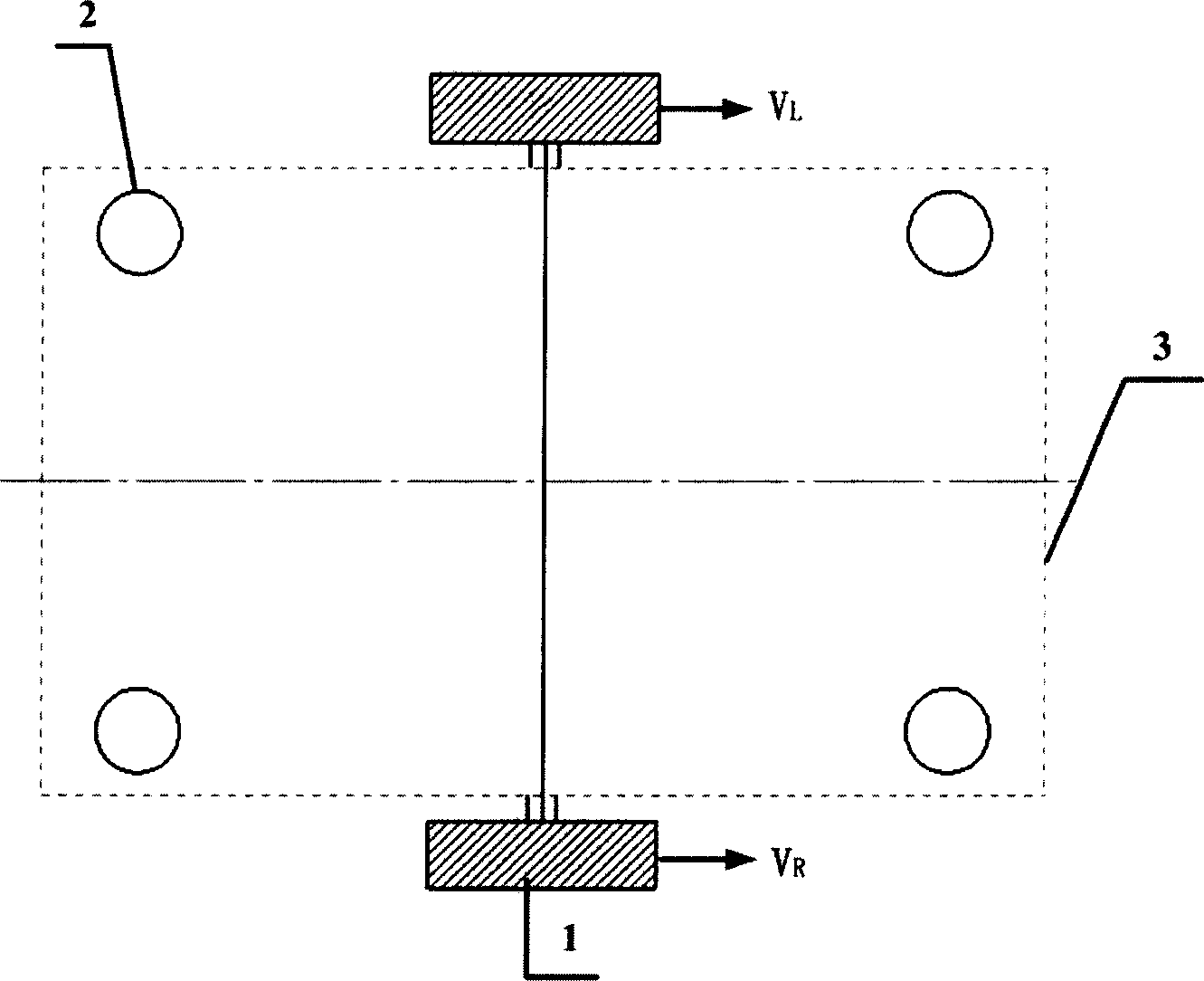
Methods for treating cardiac valves using magnetic fields
InactiveUS20050288783A1Improve heat transfer performanceEasy transferAnnuloplasty ringsRadio frequency energyAcoustic energy
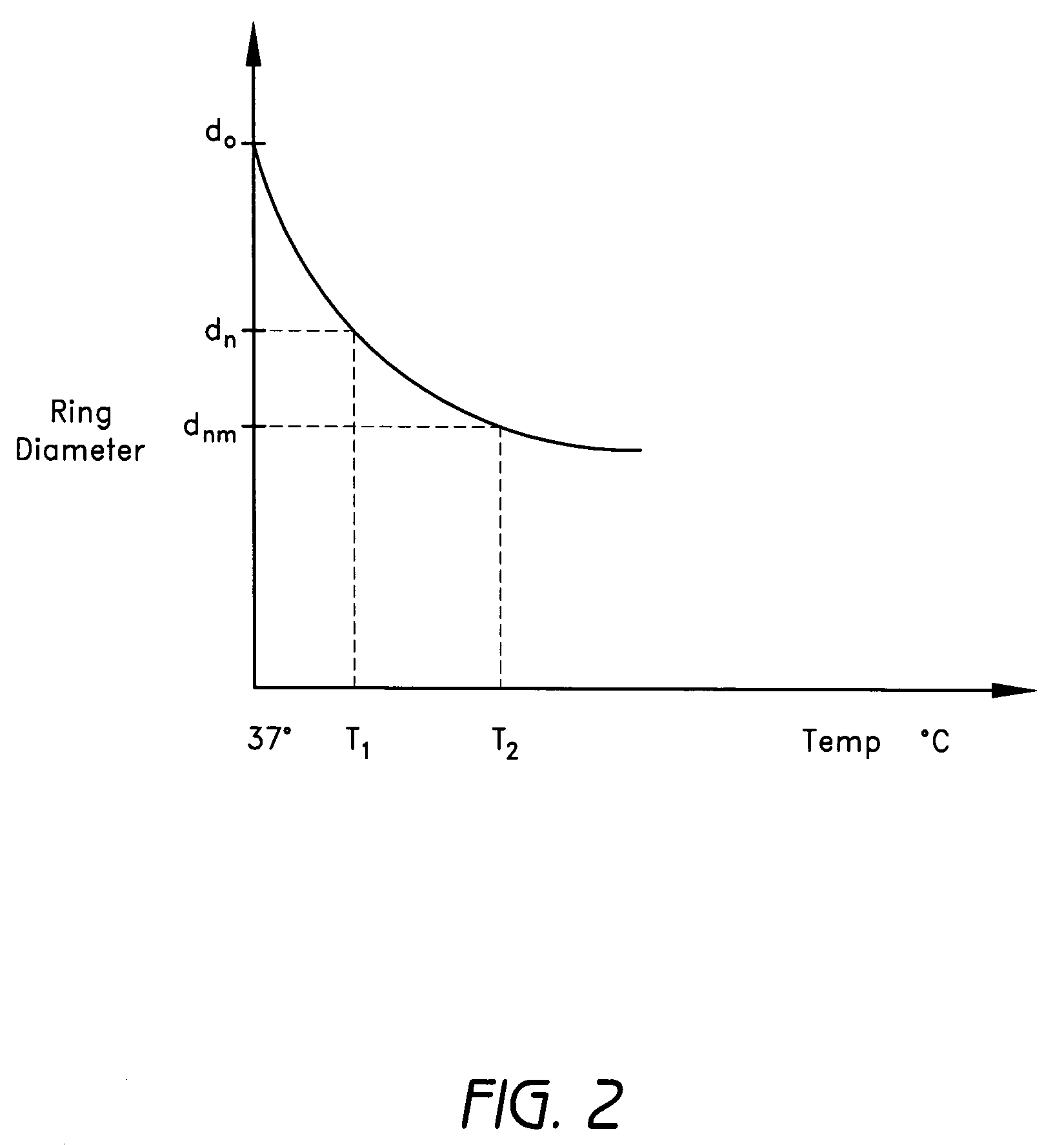
Methods and devices are provided for support of a body structure. The devices can be adjusted within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. Thus, as the body structure changes size and / or shape, the size and / or shape of the annuloplasty rings can be adjusted to provide continued reinforcement. In certain embodiments, a method for treating a cardiac valve includes providing an annuloplasty ring having a first size of a dimension in a first configuration and a second size of the dimension in a second configuration. In the first configuration, the method includes attaching the annuloplasty ring to or near a valve annulus in a heart. The method also includes applying energy from a magnetic resonance imaging device to the annuloplasty ring which responds to the energy by transforming from the first configuration to the second configuration.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
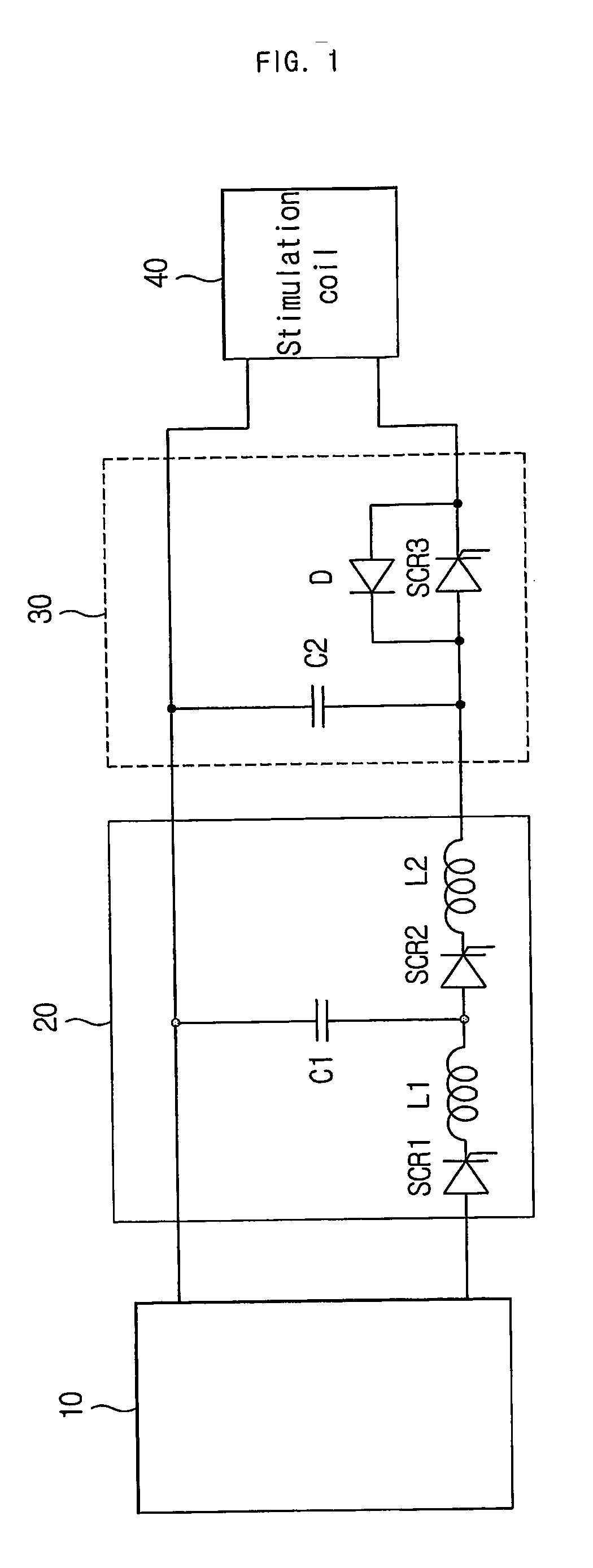
Pulsed Magnetic Therapy Device
InactiveUS20110263925A1Good for healthFunction increaseElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseHigh energy
A device for treating diseases and chronic ailments of the human body by inducing powerful, short duration magnetic pulses in close proximity to a region of the body. The device comprises an electromagnetic coil or inductor energized by an electric circuit and a power source, pulsed between 1 and 25 pulses per second for therapeutic means and use as an alternative medical treatment. The device comprises an electric circuit that transmits pulsating current to an induction coil placed within a handheld stylus device for introducing a high energy, pulsed magnetic field to target locations on the body. The stylus is placed against the human body and introduces the pulsating magnetic field into and through body tissue, bone and the bloodstream. The stylus is completely noninvasive and provides a means to direct magnetic energy to a specific part of the body. The device is an advancement in the art, and one that provides increased magnetic energy and pulse frequency without the use of Xenon flash tubes that consume large quantities of power.
Owner:BRATTON CHARLES
Arrangement for a charger
InactiveUS20130076308A1ChargingAccurate signalNear-field transmissionCircuit monitoring/indicationEngineeringMagnetic energy
The invention relates to an indication device, comprising means for receiving magnetic energy and means for transforming said received magnetic energy into light.
Owner:POWERMAT TECHNOLOGIES
Method for improving performance of sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic material
ActiveCN101615459AEvenly distributed and orderlySolve bad problems such as α-Fe segregationInorganic material magnetismHigh energyPositive pressure
The invention relates to a method for improving performance of sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic property by a rapid-hardening flake grain boundary diffusion heavy rare earth compound in rare earth material technical field, which comprises the following steps: 1) rapid-hardening technology is adopted to prepare an Nd-Fe-B alloy rapid-hardening flake; 2) a high-energy ball mill is used to prepare the heavy rare earth compound into powder particles with diameter being smaller than 1mu m; 3) the rapid-hardening flake is put into heavy rare earth compound turbid liquid to carry out ultrasonic coating; 4) the coated rapid-hardening flake is put into a sintered furnace filled with Ar2 to carry out positive pressure thermal diffusion; 5) ball milling, powder processing, orientation shaping, isostatic pressing and vacuum sintering are adopted to prepare the strip-casting flake after the heat treatment into a magnet. The chemical formula of the Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic material is NdxFe(100-x-y-z-xl)ByCozCuxl, and the mass percent is as follows: x is 30-31.5, y is 0.95-1, z is 1-1.2, and xl is 0-0.06. The magnet prepared by the invention improves the intrinsic coercivity on the basis of keeping the current magnetic energy product.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
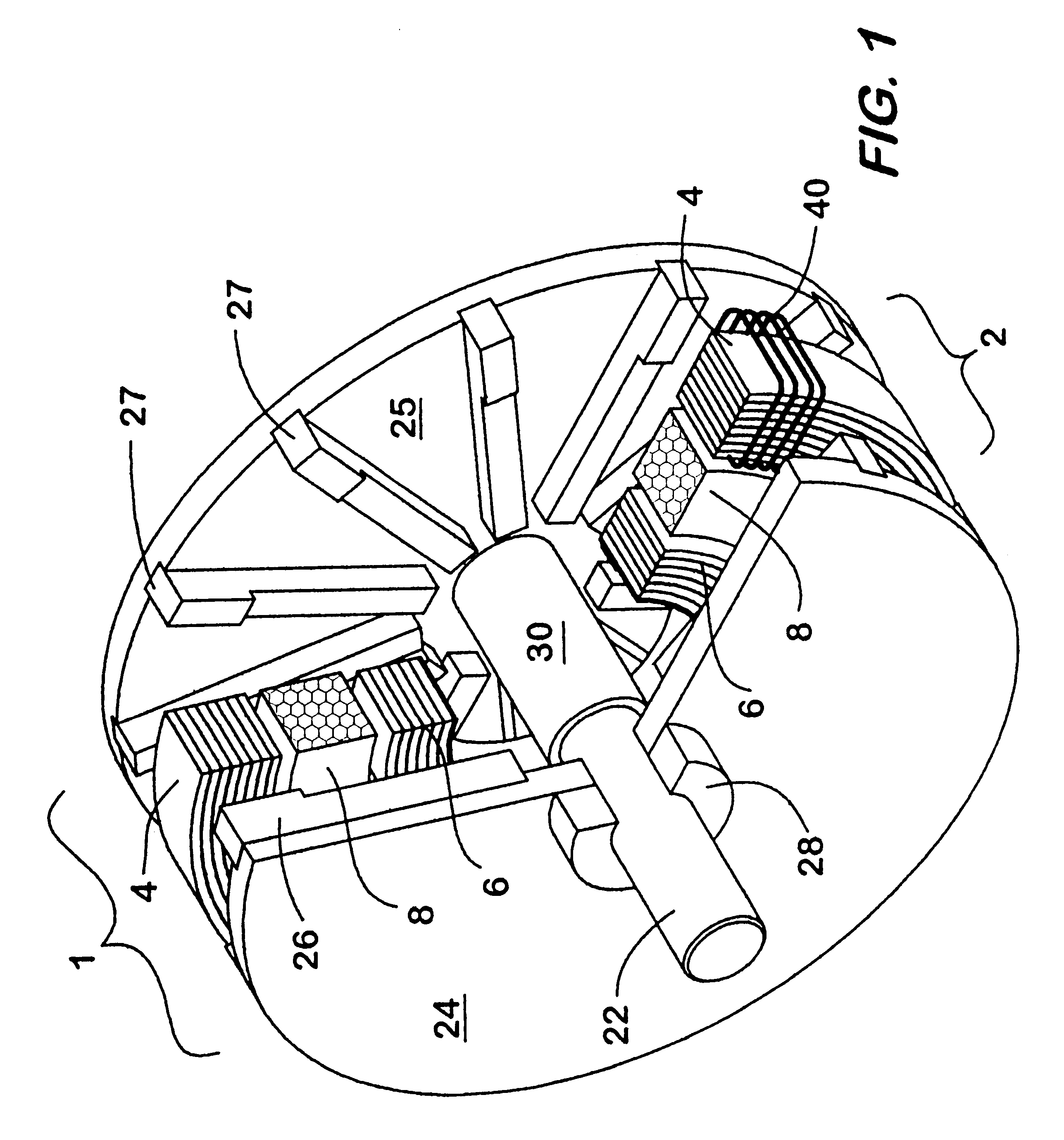
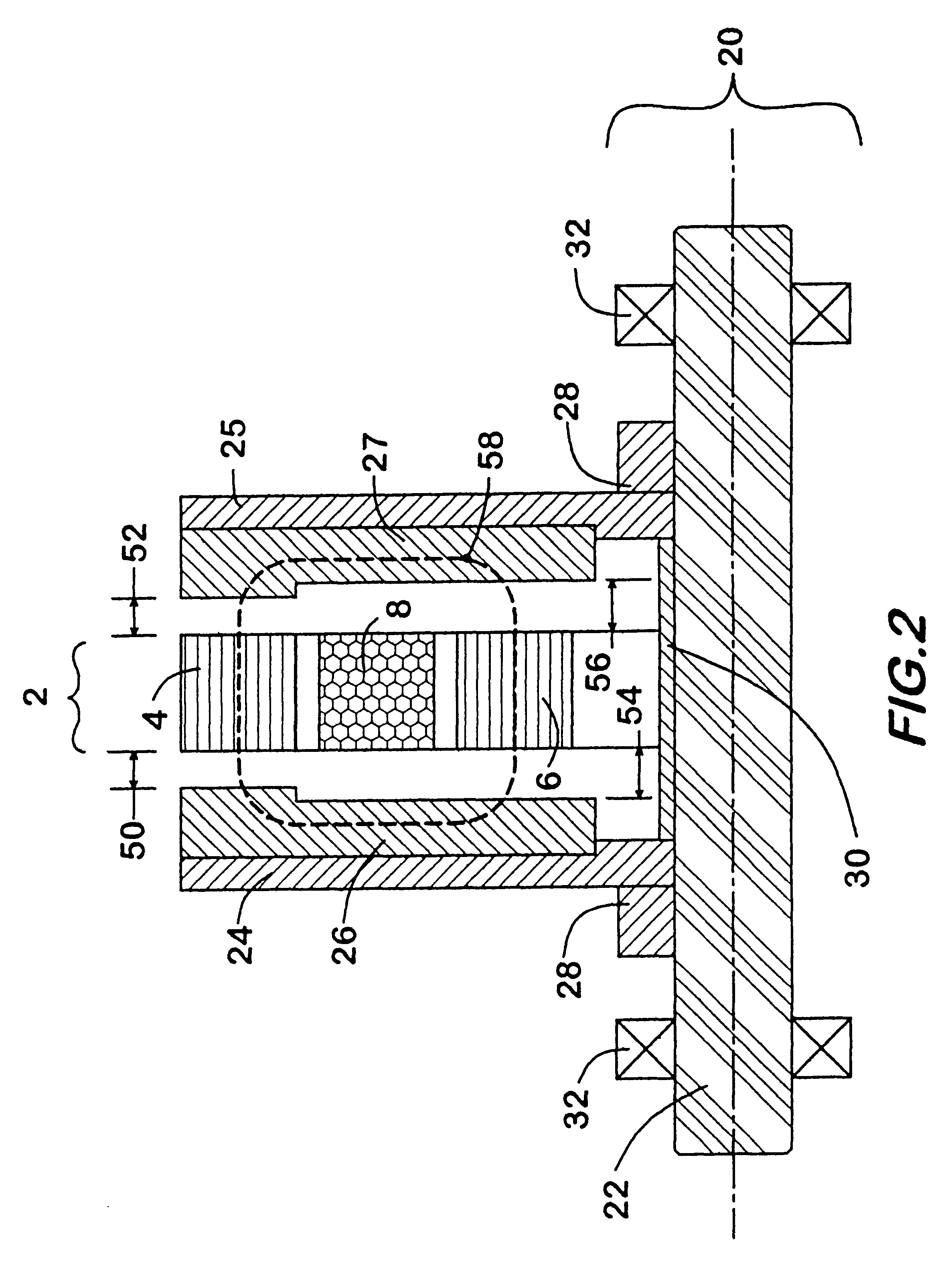
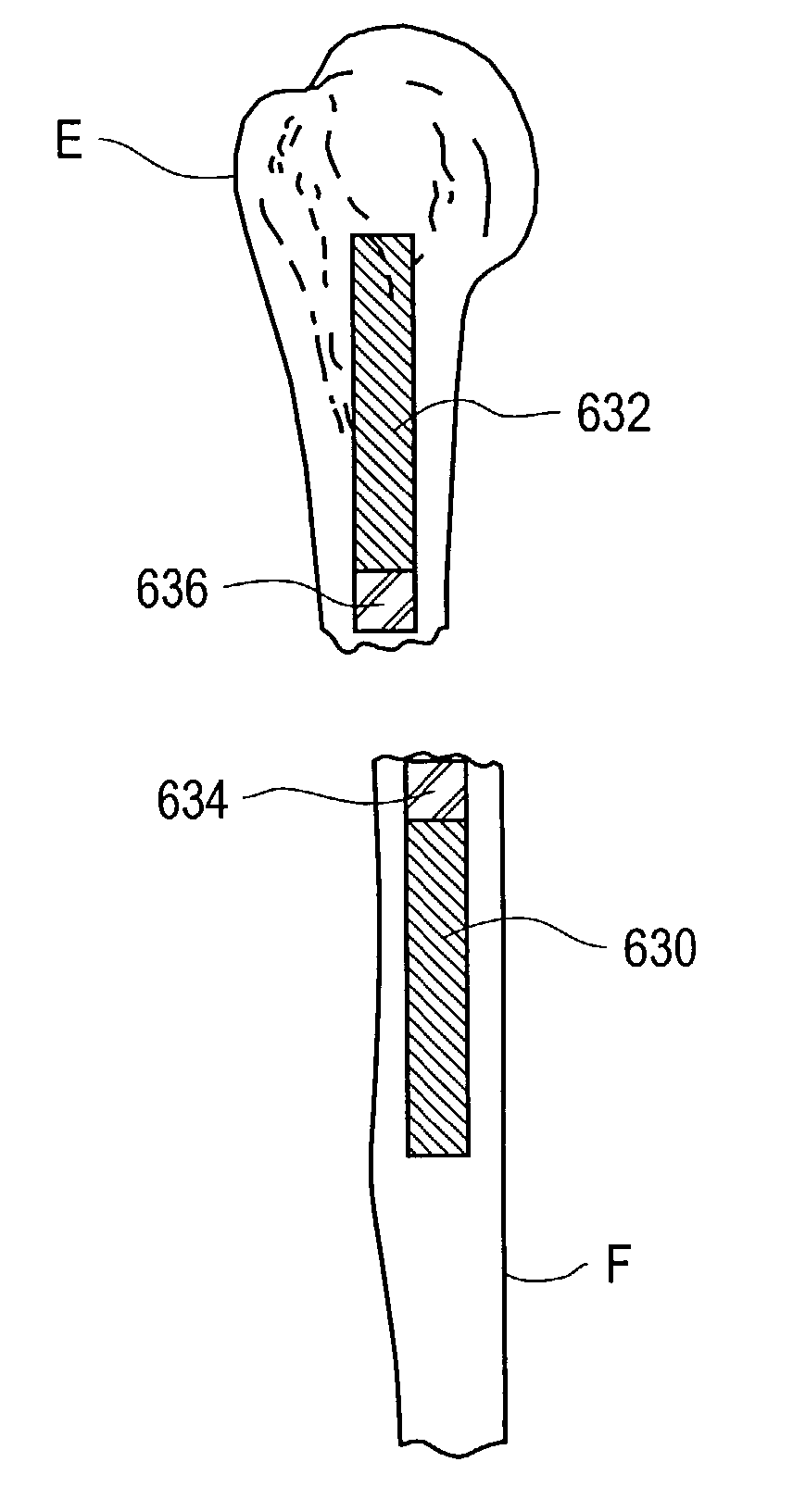
Magnetic array implant
InactiveUS7101374B2Easy to adaptAvoids potentially unpredictable implantationElectrotherapyInternal osteosythesisMechanical energyMagnetic energy
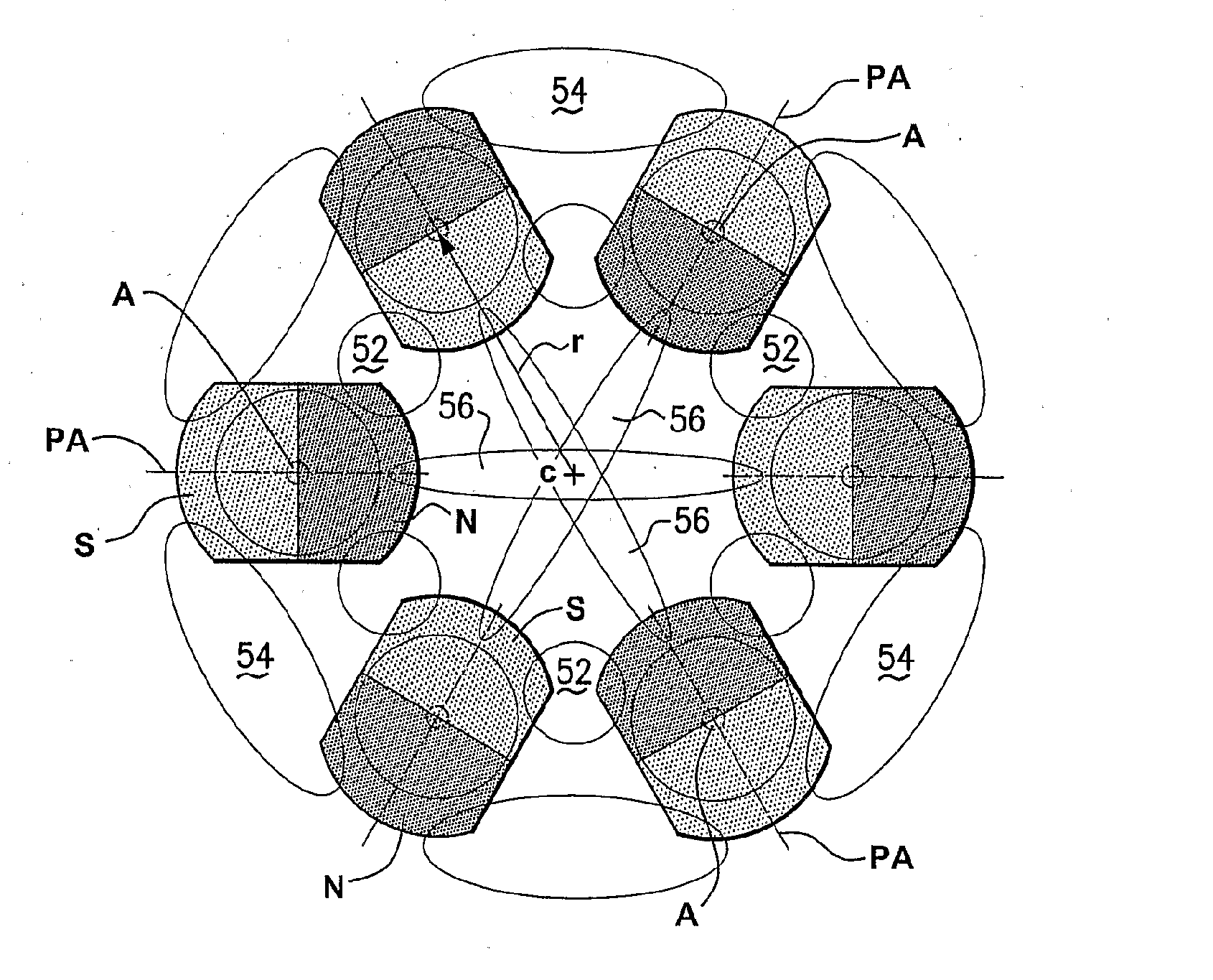
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for stabilizing and or maintaining adjacent bone portions in predetermined desired relationships and for constraining one, two or three-dimensional motion and / or rotation of the adjacent bone portions. More particularly, the present invention relates to a magnetic apparatus with at least two magnetic arrays, each of which may include any number of magnets arranged in a predetermined manner and each magnetic array generating a magnetic field therearound. Once implanted and secured to the adjacent bone portions, the apparatus provides interacting magnetic fields in the area of the bone portions and transduces magnetic energy into mechanical energy and mechanical energy into potential magnetic energy, thereby reproducing functionally anatomic and / or anatomically advantageous arrangement of the bone portions.
Owner:HYDE EDWARD R
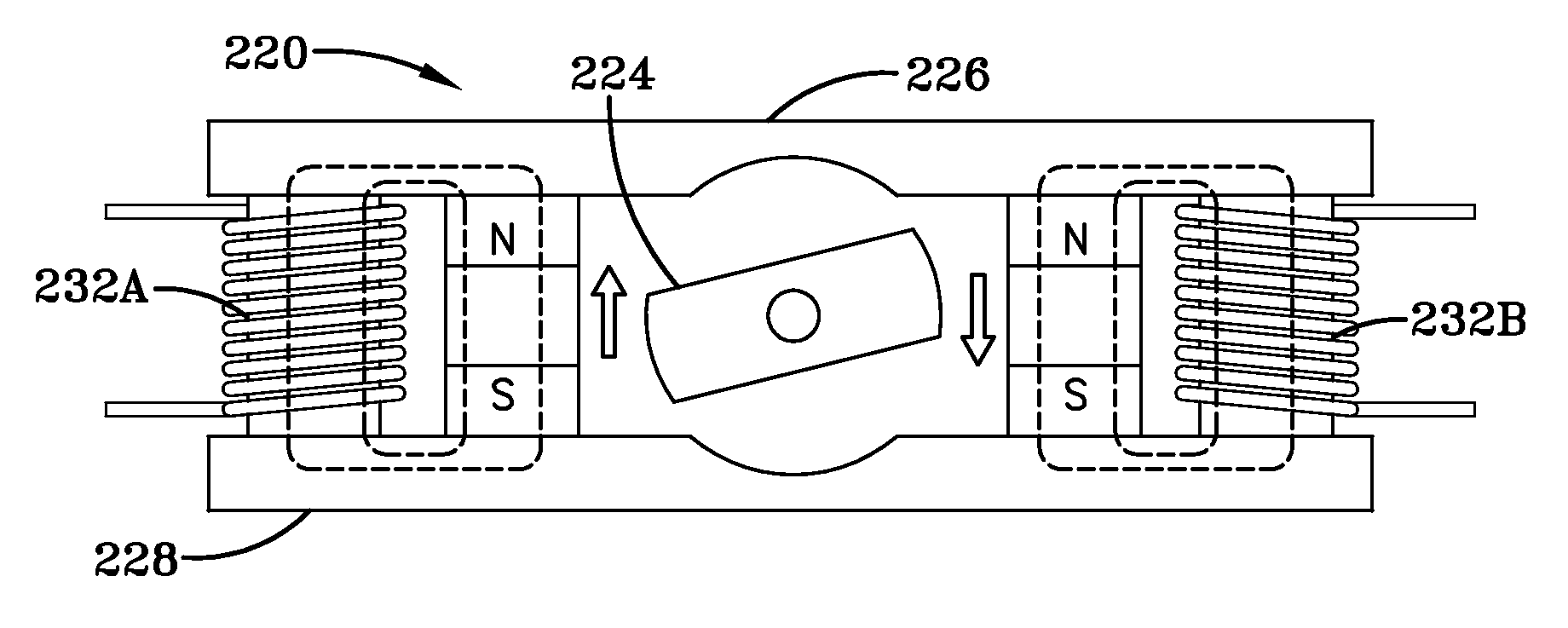
System and method for utilizing magnetic energy
InactiveUS7453341B1Improve energy efficiencyIncrease the magnetic fieldSynchronous generatorsWindingsEngineeringMagnetic energy
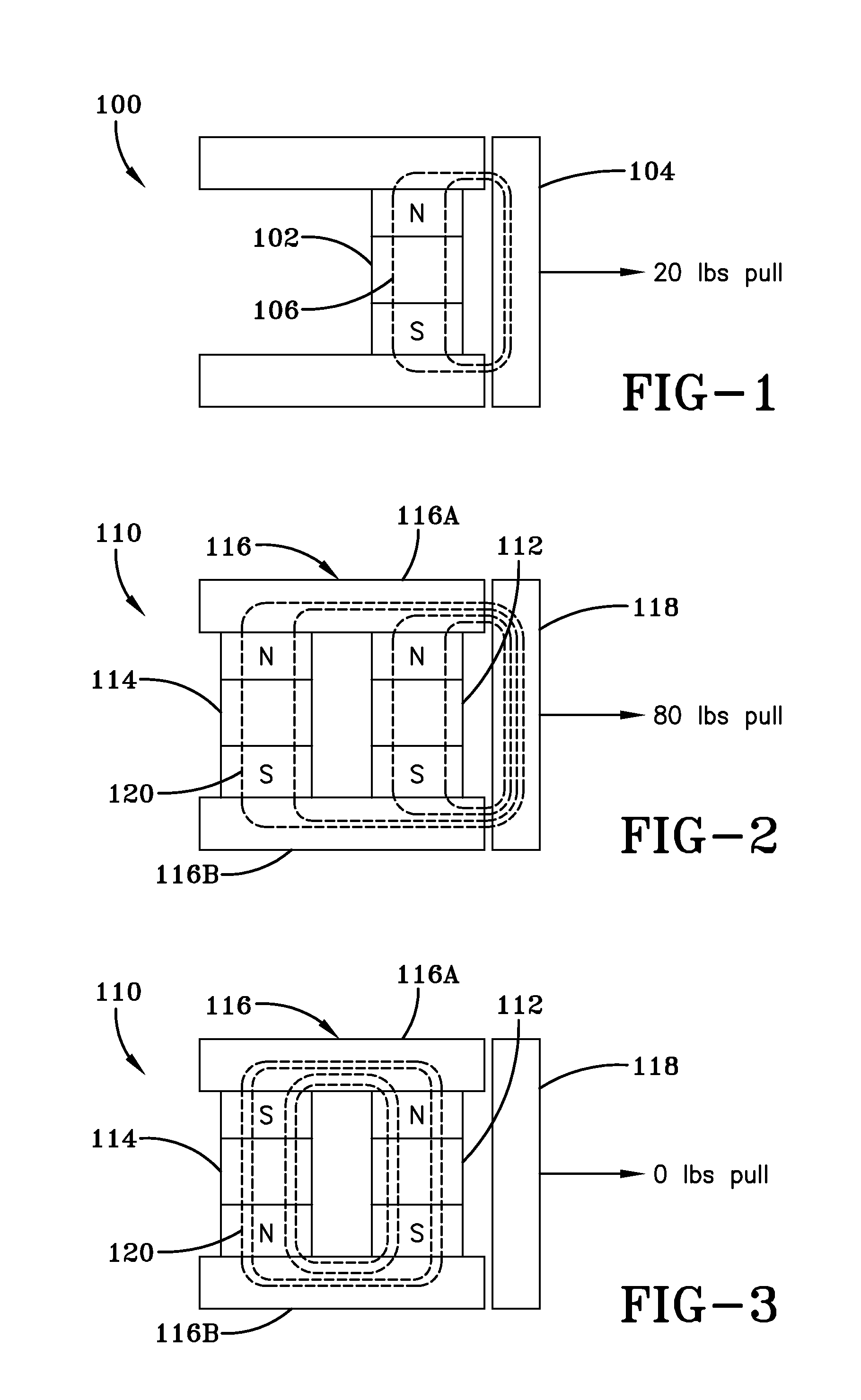
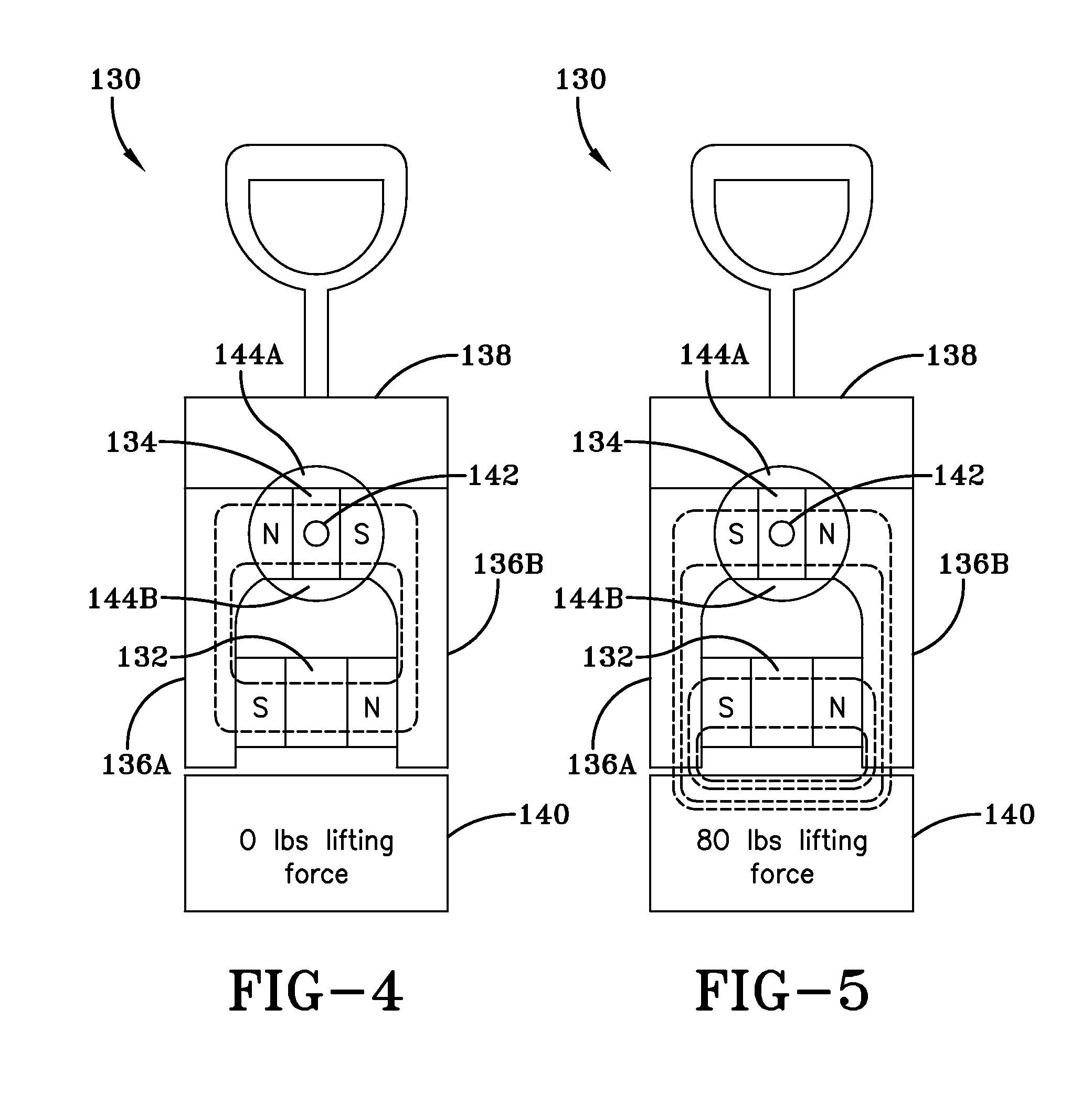
The present invention is a system and method for utilizing magnetic energy. The basic principles of the present invention may be implemented in a variety of systems and methods. A magnet may be rotated or an electromagnet may be controlled in order to control a magnetic field generated by a set of magnets. As a result, numerous, substantial benefits may be achieved by providing at least one set of multiple magnets. For example, the present invention may be used in systems and methods to perform a variety of functions including, but not limited to: (1) to control, manipulate, hold, and / or release a load; (2) to open and / or close a pathway; (3) to open and / or close a circuit; (4) to apply a magnetic field to a load and / or to remove a magnetic field from a load; (5) to intermittently apply and remove a magnetic field; (6) to increase the magnetic field that may be applied to a load; (7) to induce a load into motion; (8) to create energy; and (9) to improve the energy efficiency of a device or system.
Owner:HILDENBRAND JACK W
Quench protection of HTS superconducting magnets
InactiveUS20060291112A1Improved active protectionEffective quench protectionTransformers/inductances coolingSuperconducting magnets/coilsHigh-temperature superconductivitySuperconducting Coils
A method of constructing a superconducting coil. The method includes embedding a plurality of heater elements throughout a superconducting coil. The heater elements are positioned according to a predetermined distribution and substantially in thermal contact with the coil for heating the coil in response to a quench condition. Other aspects of the invention involve an active protection circuit and a high temperature superconductor magnet that includes such an active protection circuit for internally dissipating stored magnetic energy in the event of a quench.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Method and system for providing magnetic elements having enhanced magnetic anisotropy and memories using such magnetic elements
InactiveUS20100140726A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic anisotropyMagnetic energy
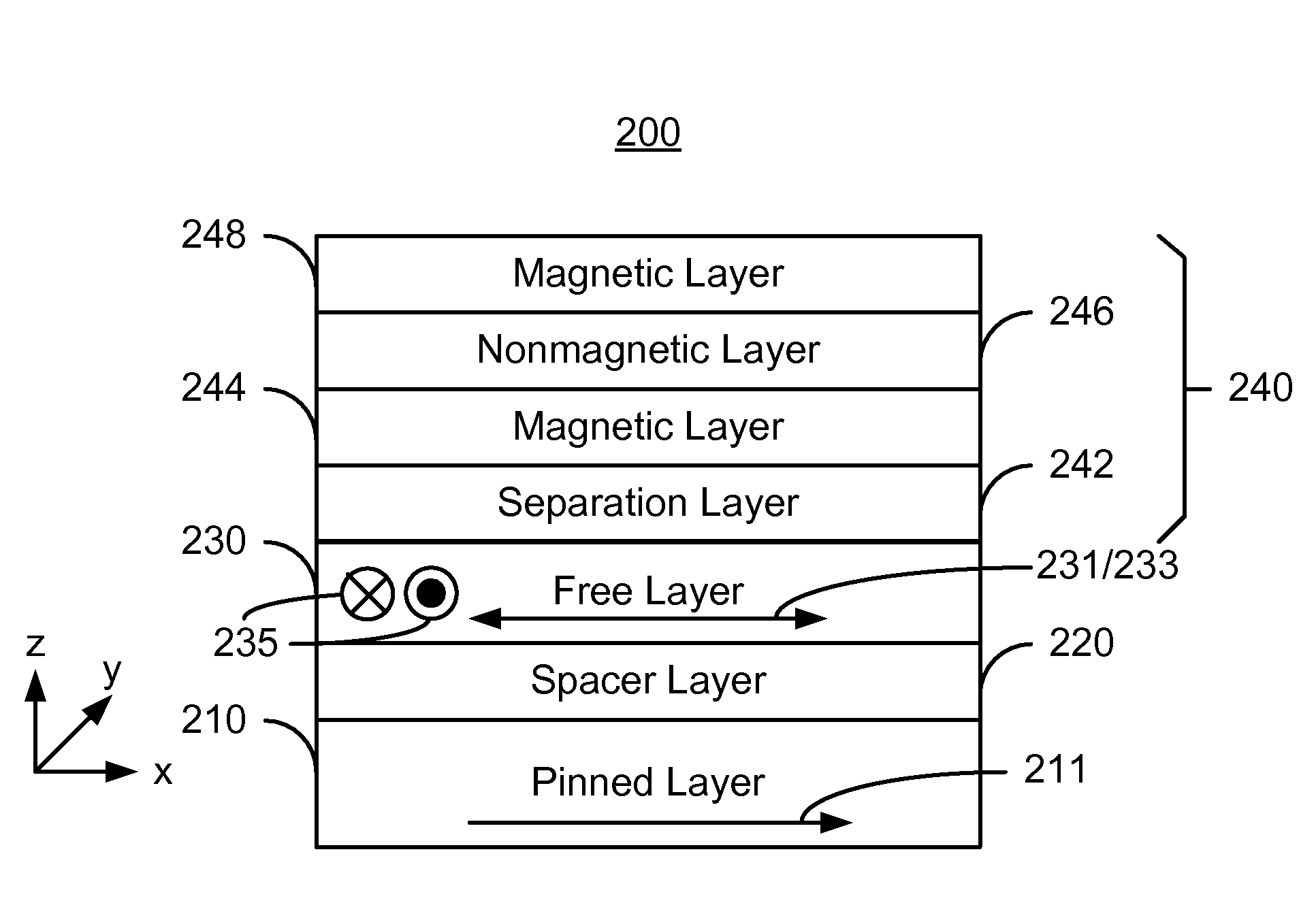
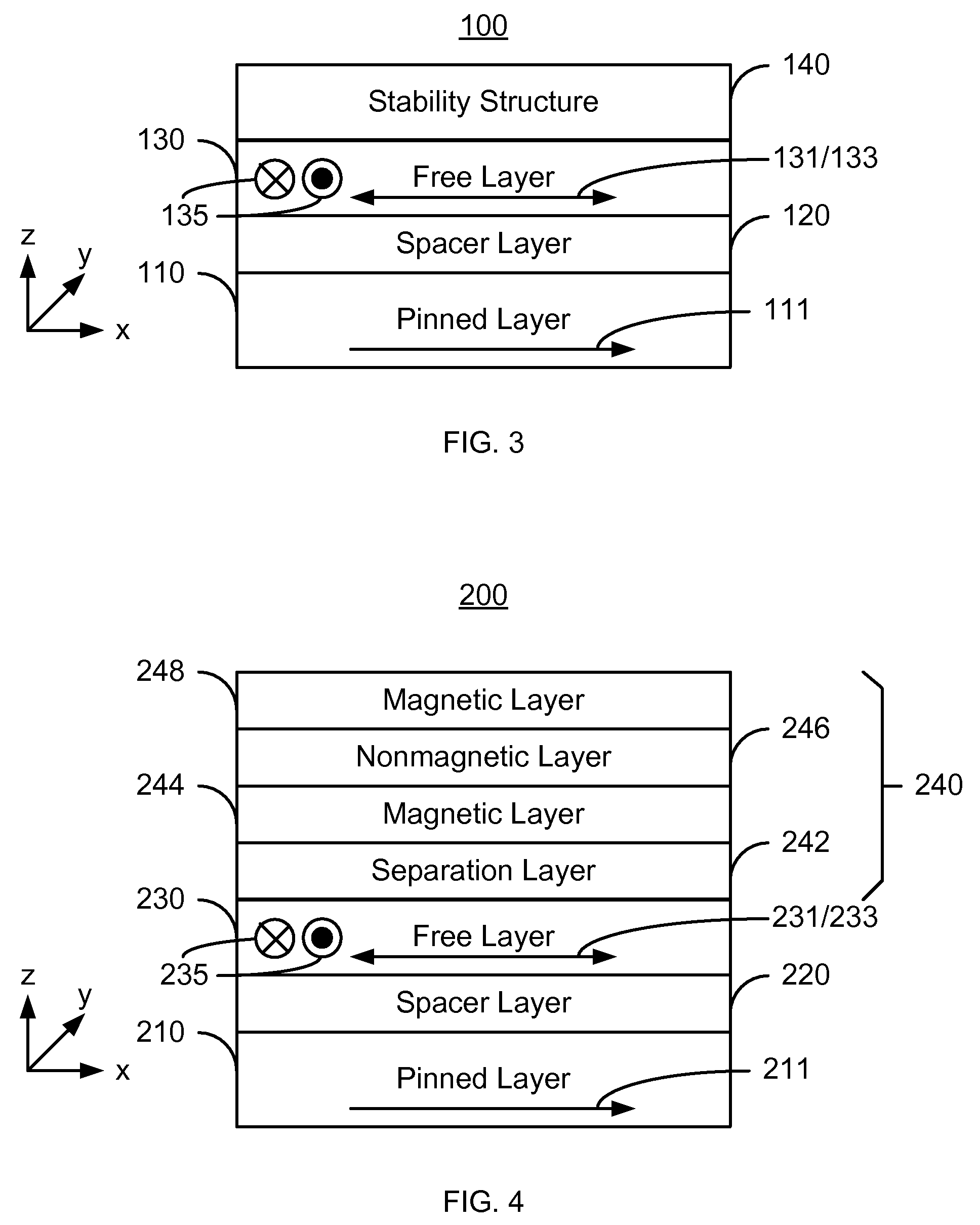
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are described. The magnetic element includes pinned and free layers, a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the free and pinned layers, and a stability structure. The free layer is between the spacer layer and the stability structure. The free layer has a free layer magnetization, at least one free layer easy axis, and at least one hard axis. The stability structure includes magnetic layers and is configured to decrease a first magnetic energy corresponding to the free layer magnetization being aligned with the at least one easy axis without decreasing a second magnetic energy corresponding to the free layer magnetization being aligned with the at least one hard axis. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer magnetization to be switched to between states when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
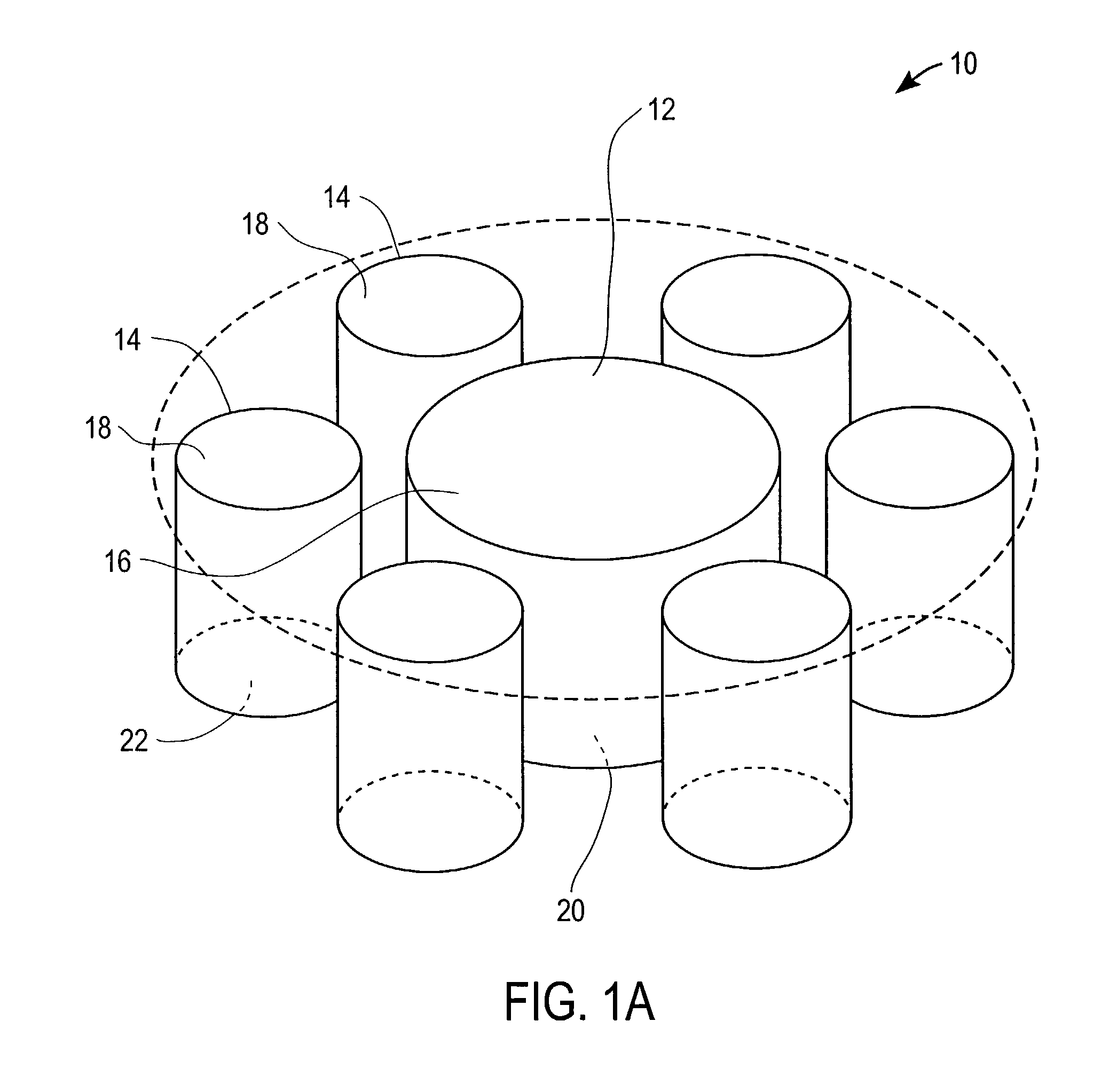
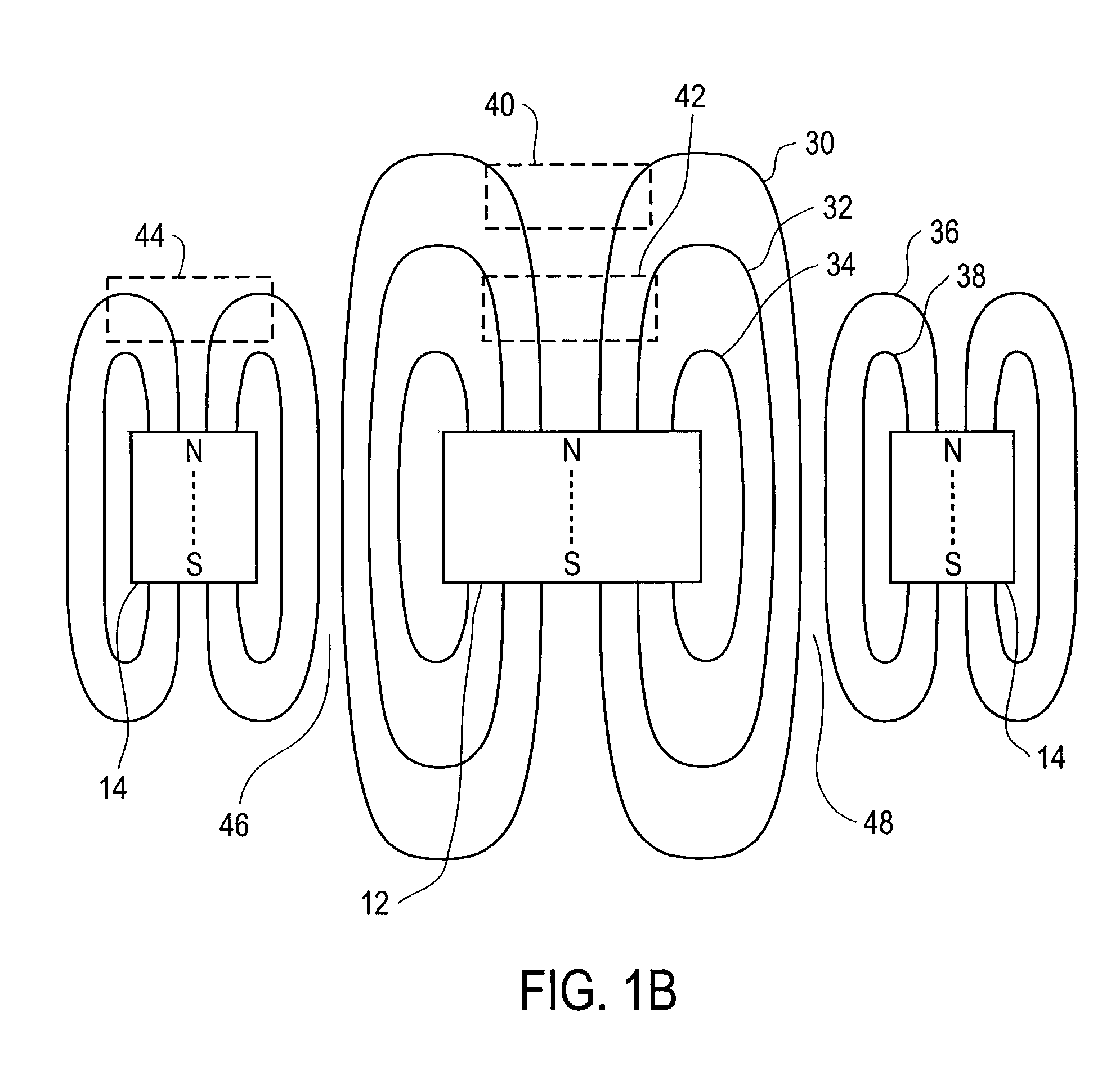
Magnet Arrays
InactiveUS20090027149A1Expand the field of viewDoubling numberElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsMagnetic reluctancePole piece
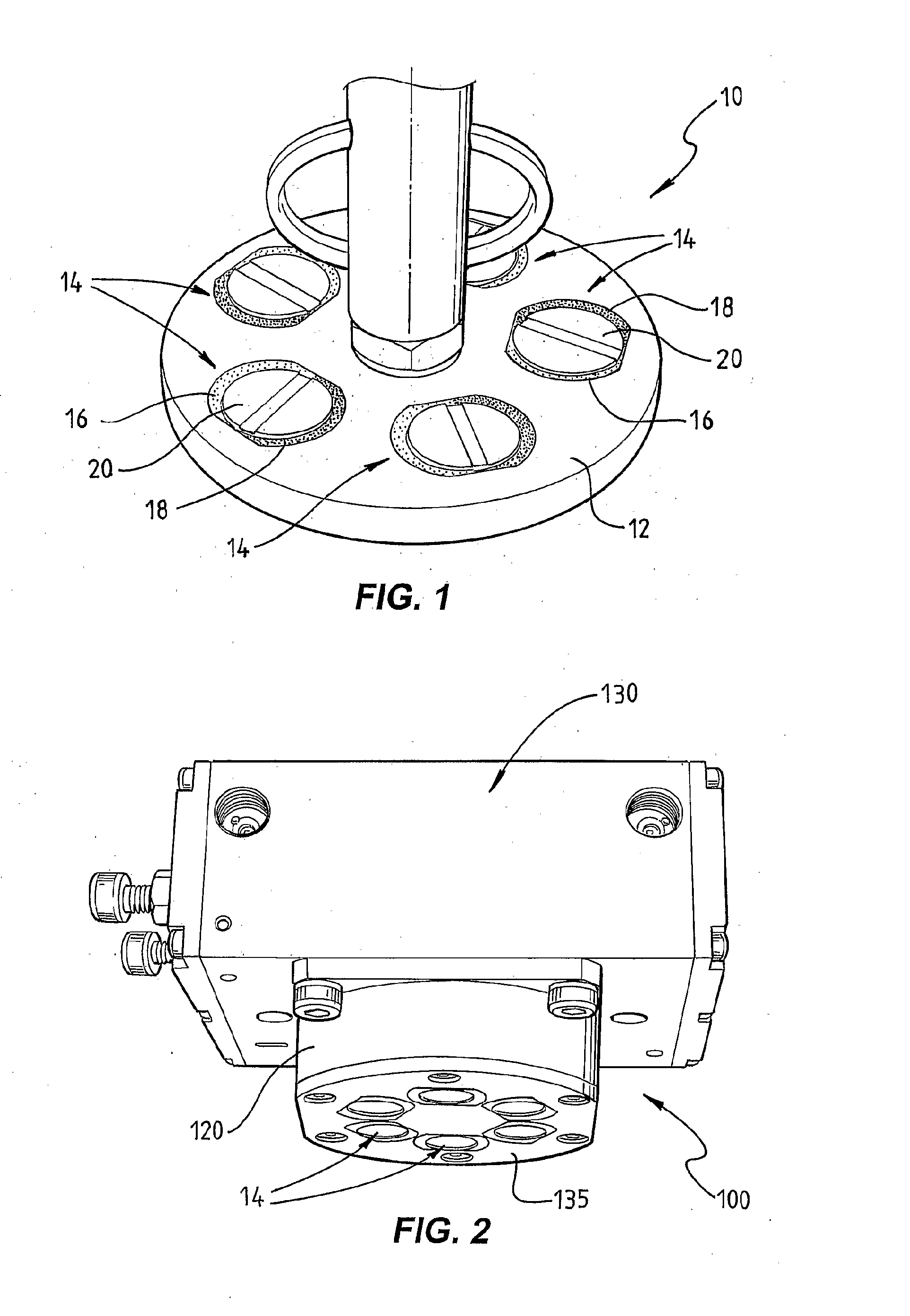
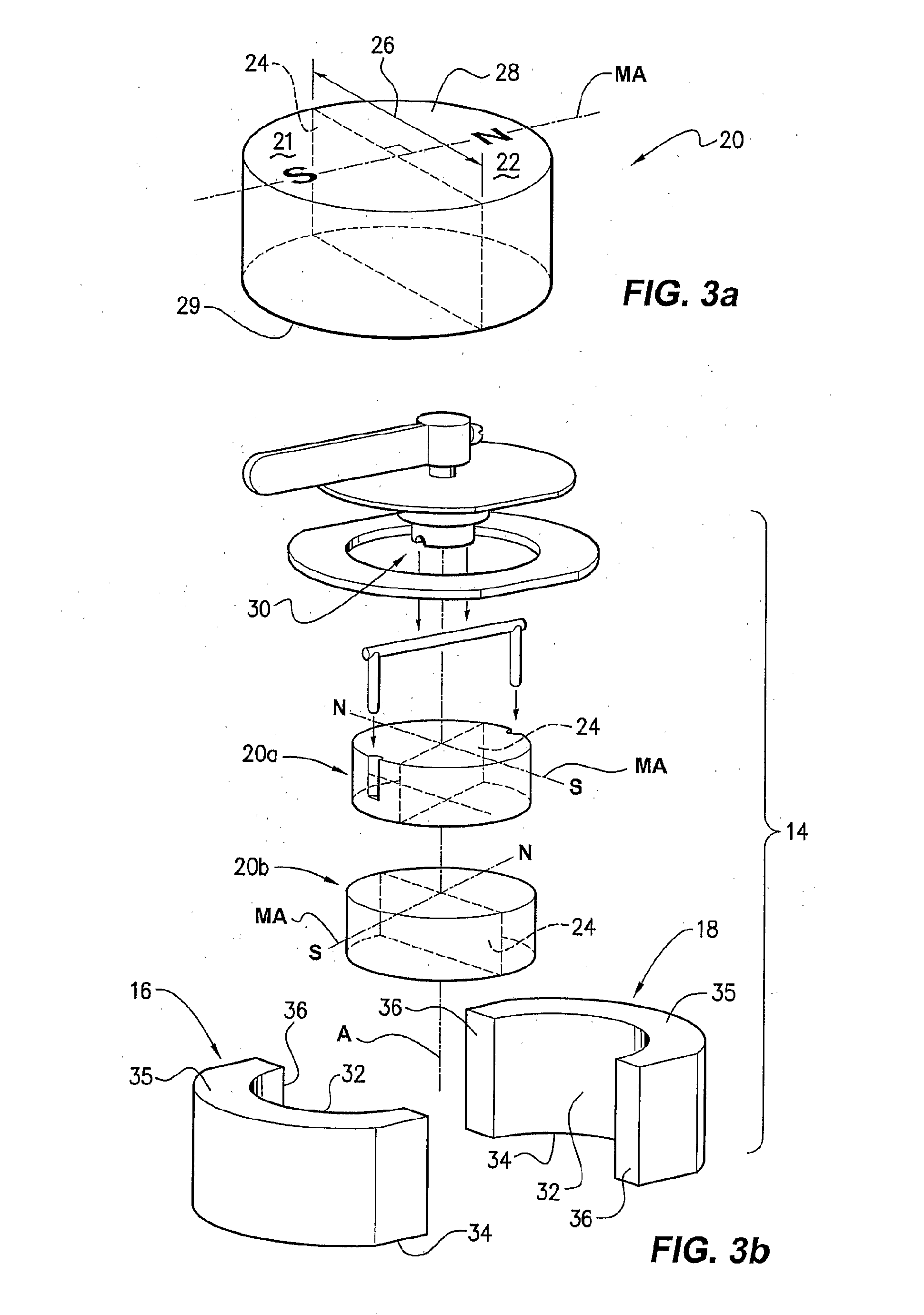
Method and device for self-regulated flux transfer from a source of magnetic energy into one or more ferromagnetic work pieces, wherein a plurality of magnets, each having at least one N-S pole pair defining a magnetization axis, are disposed in a medium having a first relative permeability, the magnets being arranged in an array in which gaps of predetermined distance are maintained between neighboring magnets in the array and in which the magnetization axes of the magnets are oriented such that immediately neighboring magnets face one another with opposite polarities, such arrangement representing a magnetic tank circuit in which internal flux paths through the medium exist between neighboring magnets and magnetic flux access portals are defined between oppositely polarized pole pieces of such neighboring magnets, and wherein at least one working circuit is created which has a reluctance that is lower than that of the magnetic tank circuit by bringing one or more of the magnetic flux access portals into close vicinity to or contact with a surface of a ferromagnetic body having a second relative permeability that is higher than the first relative permeability, whereby a limit of effective flux transfer from the magnetic tank circuit into the working circuit will be reached when the work piece approaches magnetic saturation and the reluctance of the work circuit substantially equals the reluctance of the tank circuit.
Owner:MAGSWITCH TECH WORLDWIDE PTY LTD
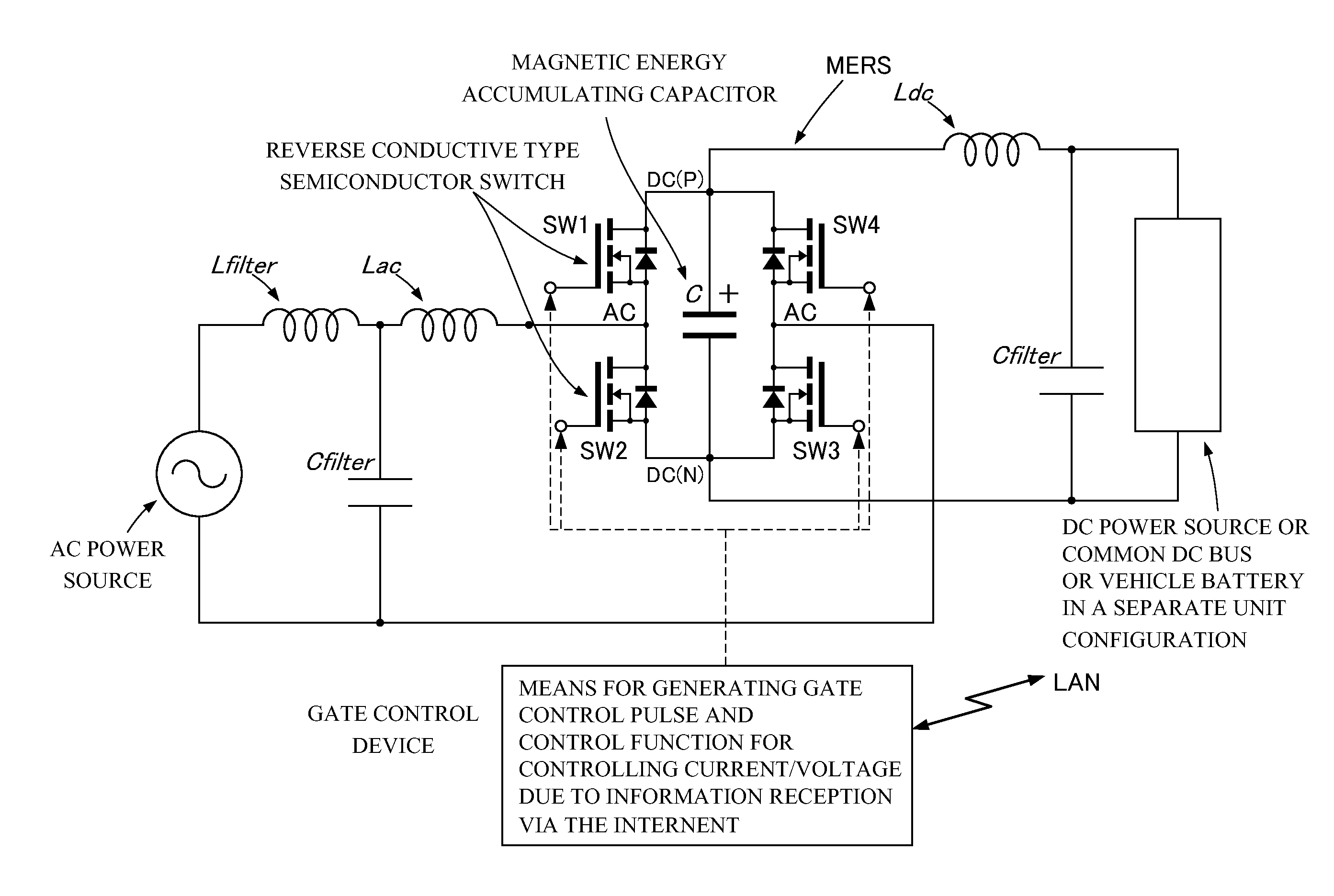
Power converting apparatus
InactiveUS20110176343A1Large capacityUtilization of power equipmentBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalBattery chargeElectrical battery
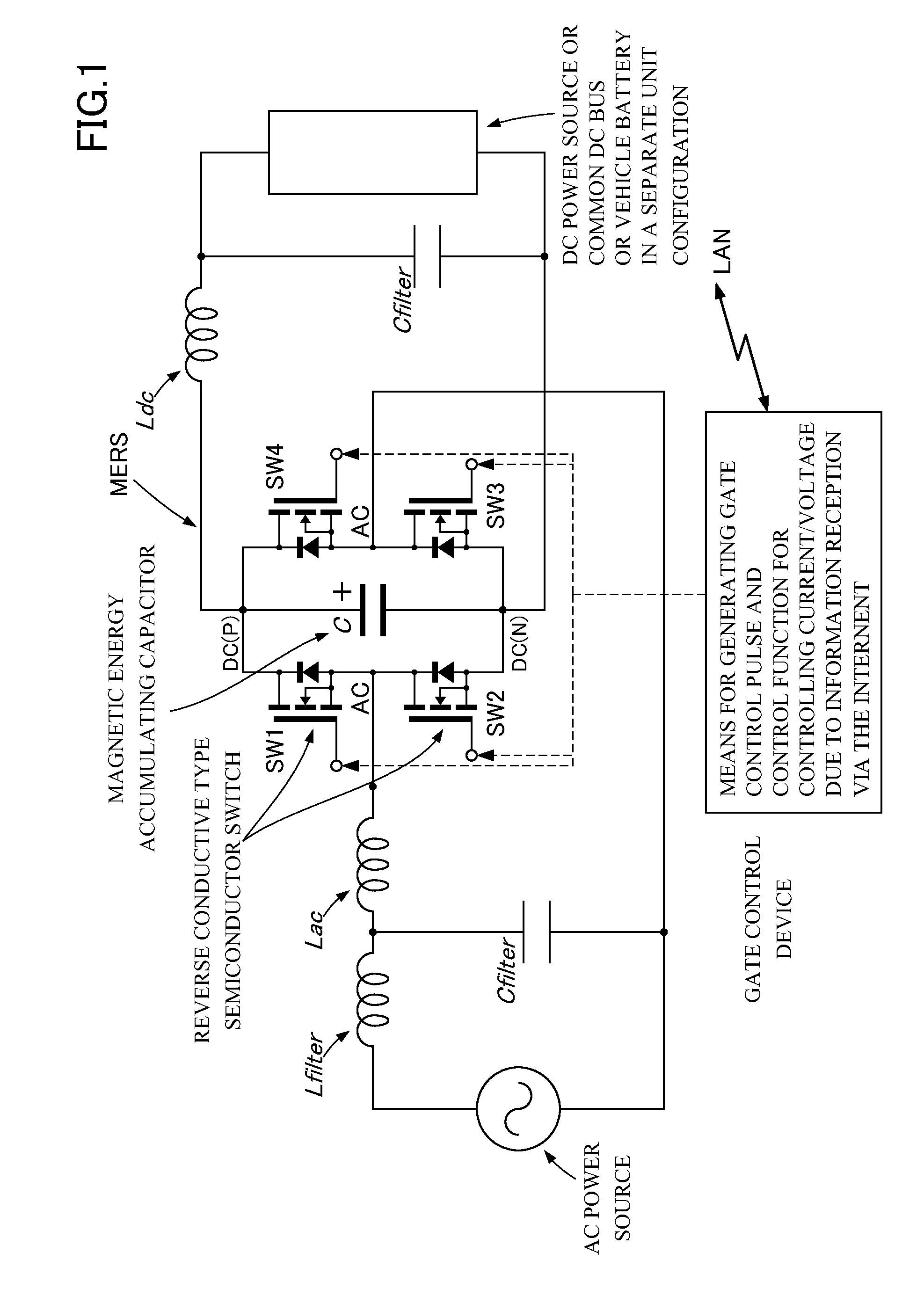
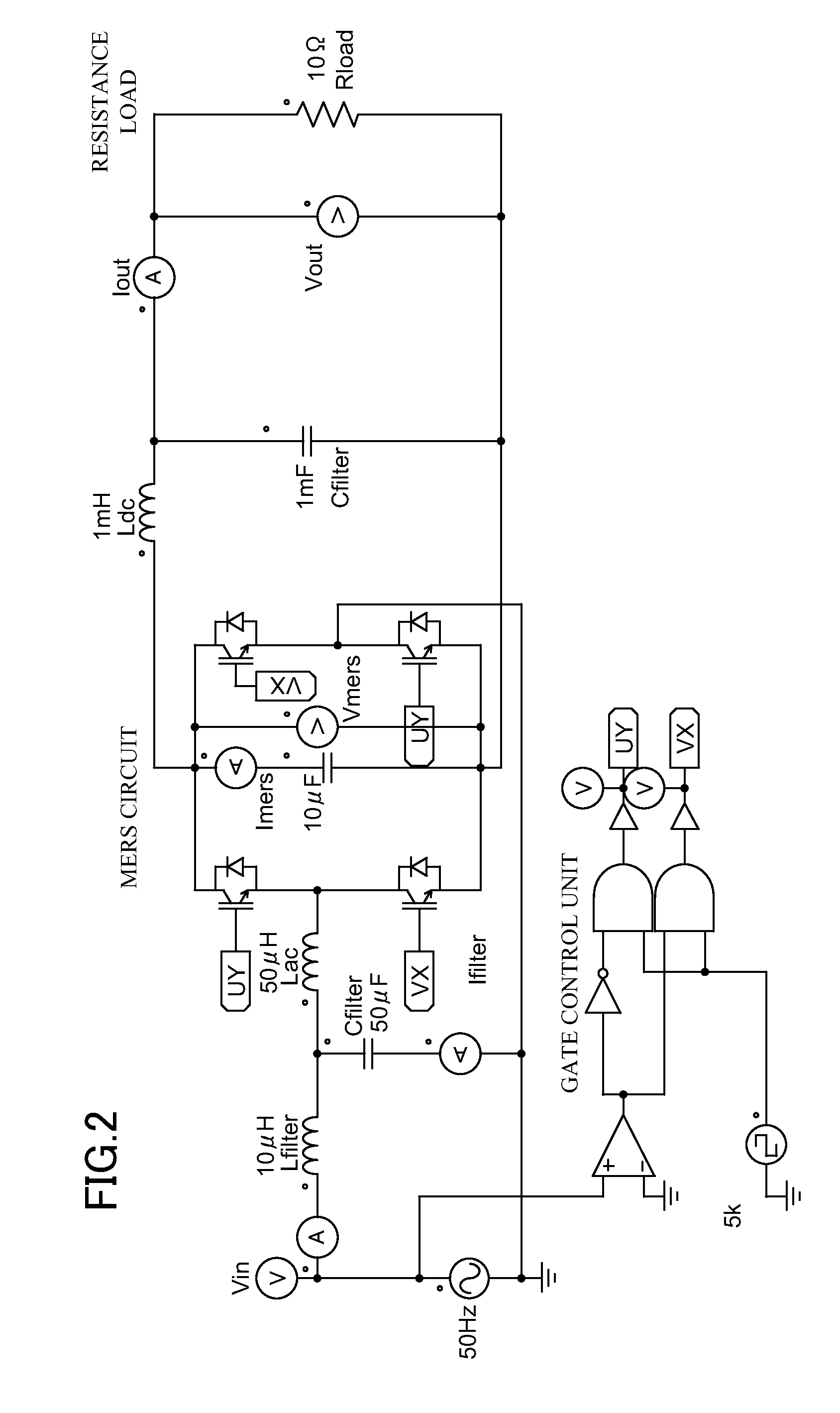
A power converter stabilizes a voltage by controlling leading of an AC current and performs maximum charging within contracted power reception amount when connected to a weak power system. The power converter comprises Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch comprising a bridge circuit including at least two reverse conductive type semiconductor switches and a magnetic energy accumulating capacitor with a small capacity connected between DC terminals of the bridge circuit. The power converter uses the Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch to perform power conversion from AC to DC or vise versa. Plurality of secondary battery charging devices each comprising the power converter have a DC part connected to a common DC bus bar, so that power is accommodated among the secondary battery charging devices.
Owner:MERSTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com