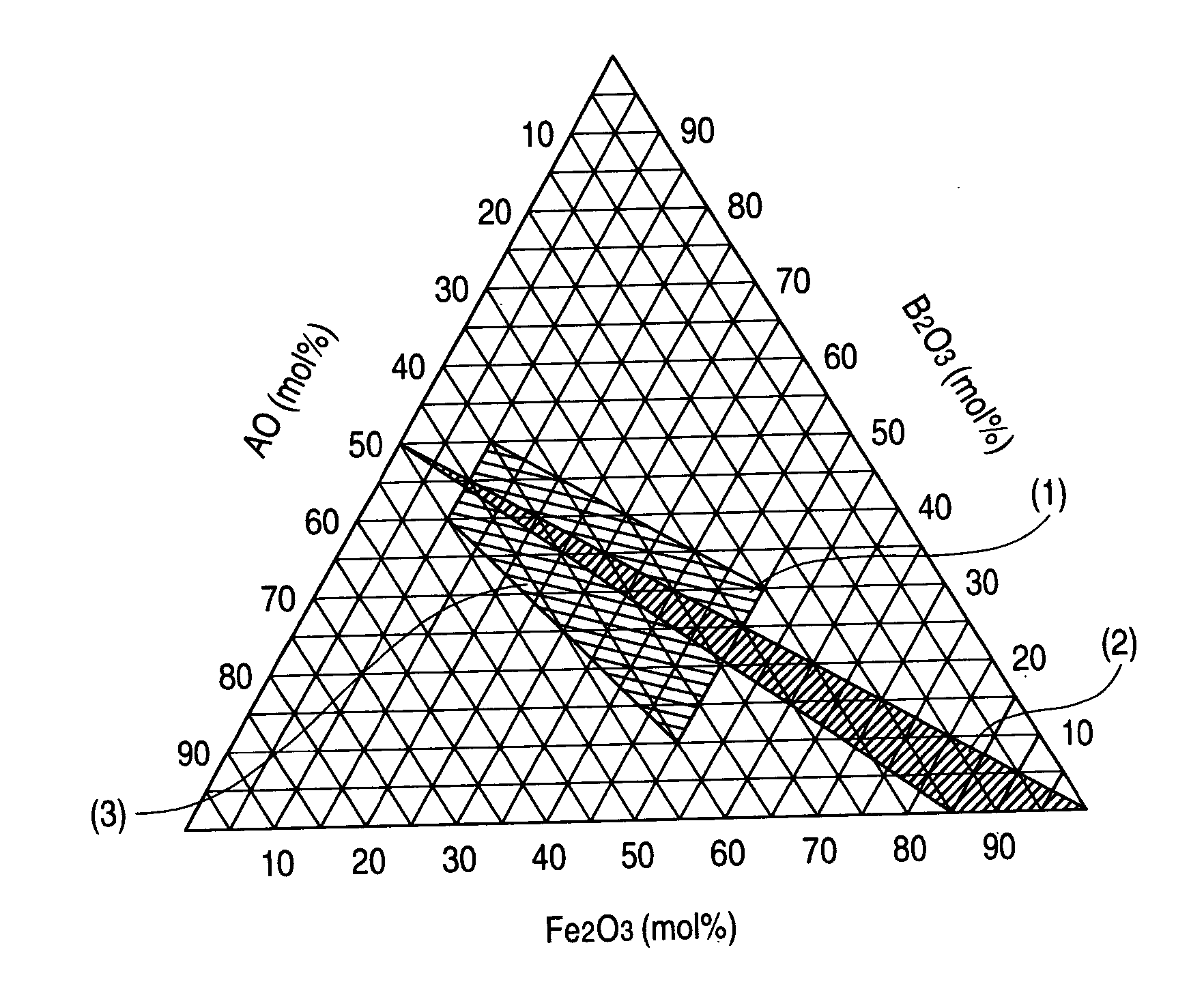
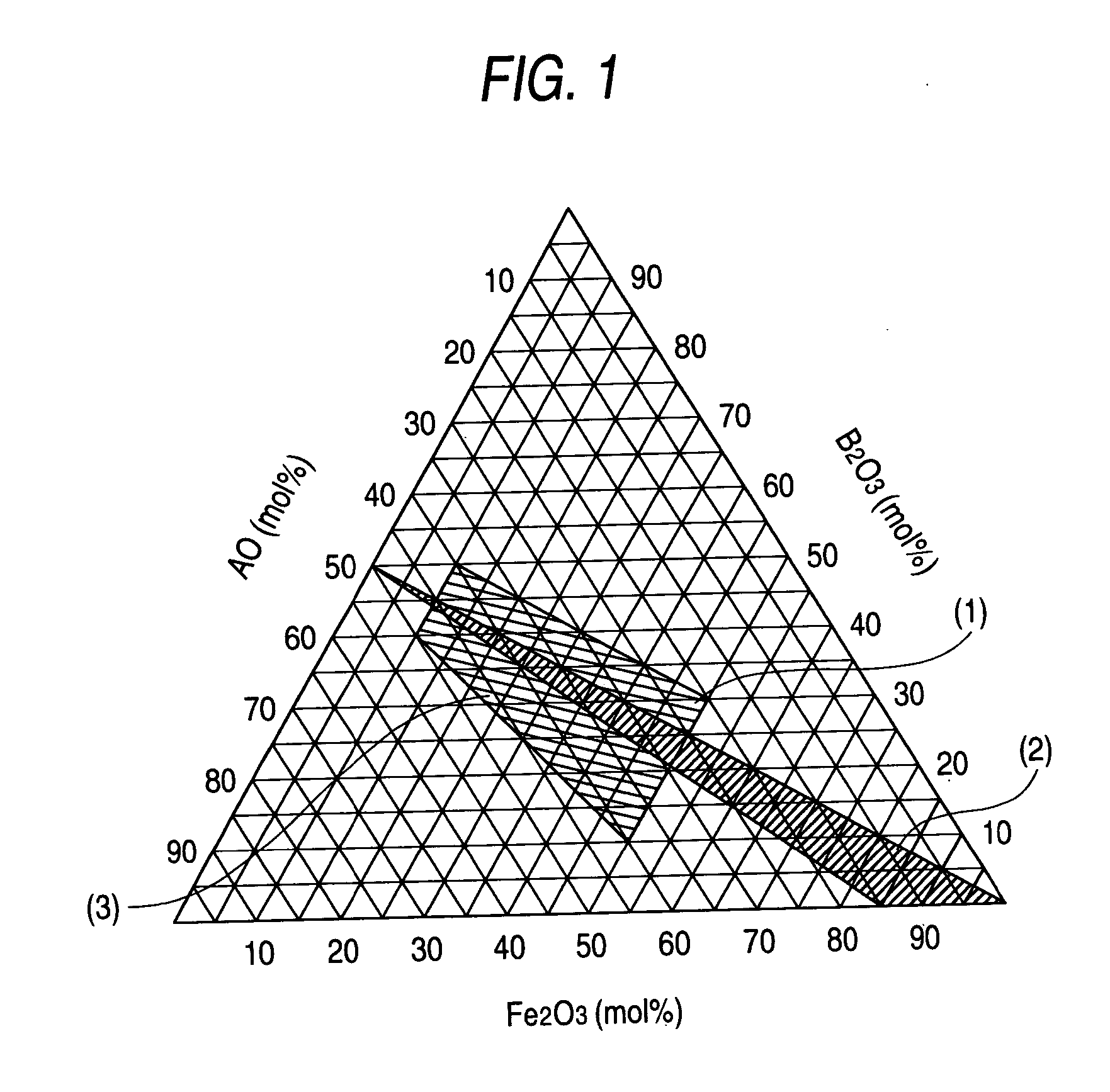
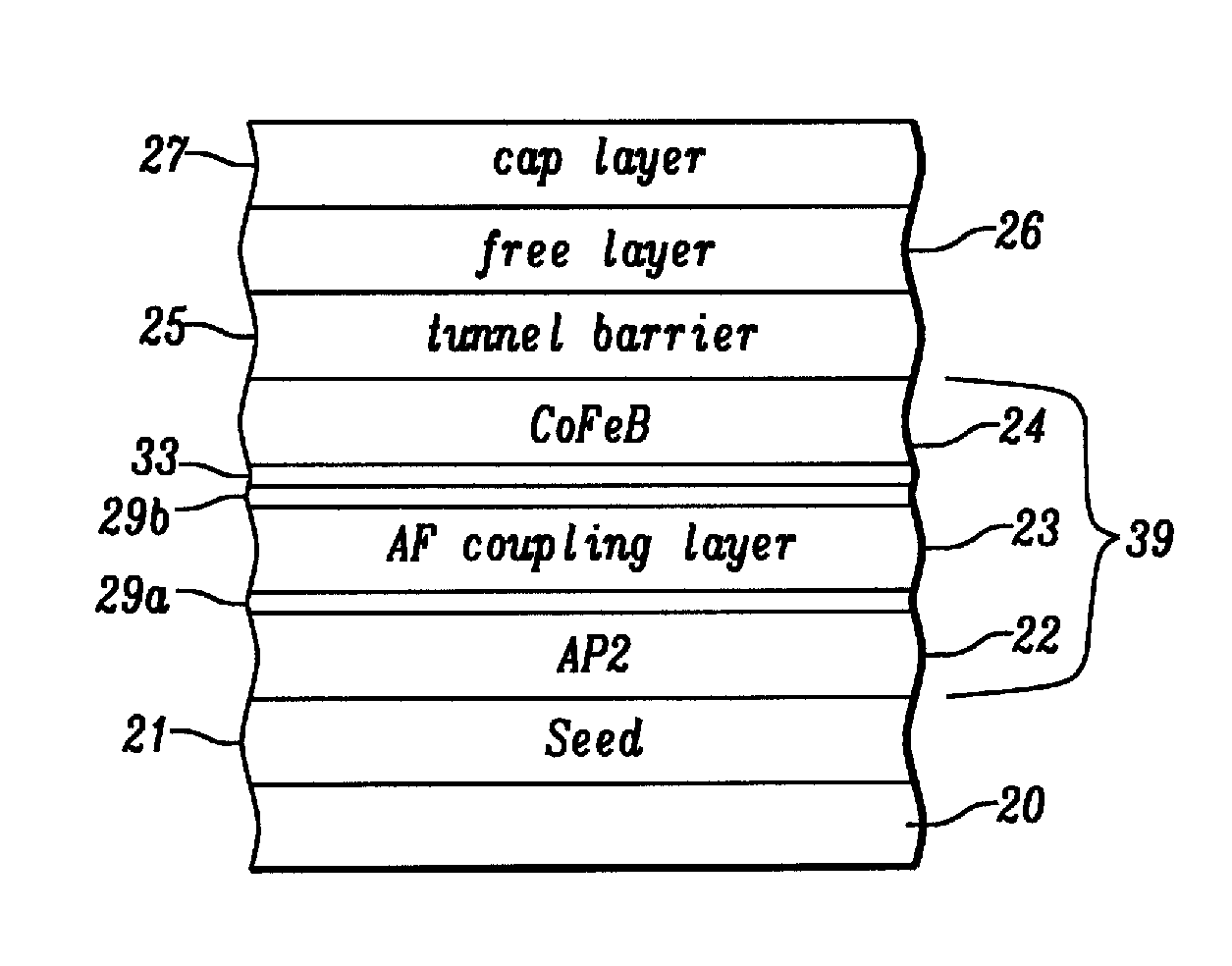
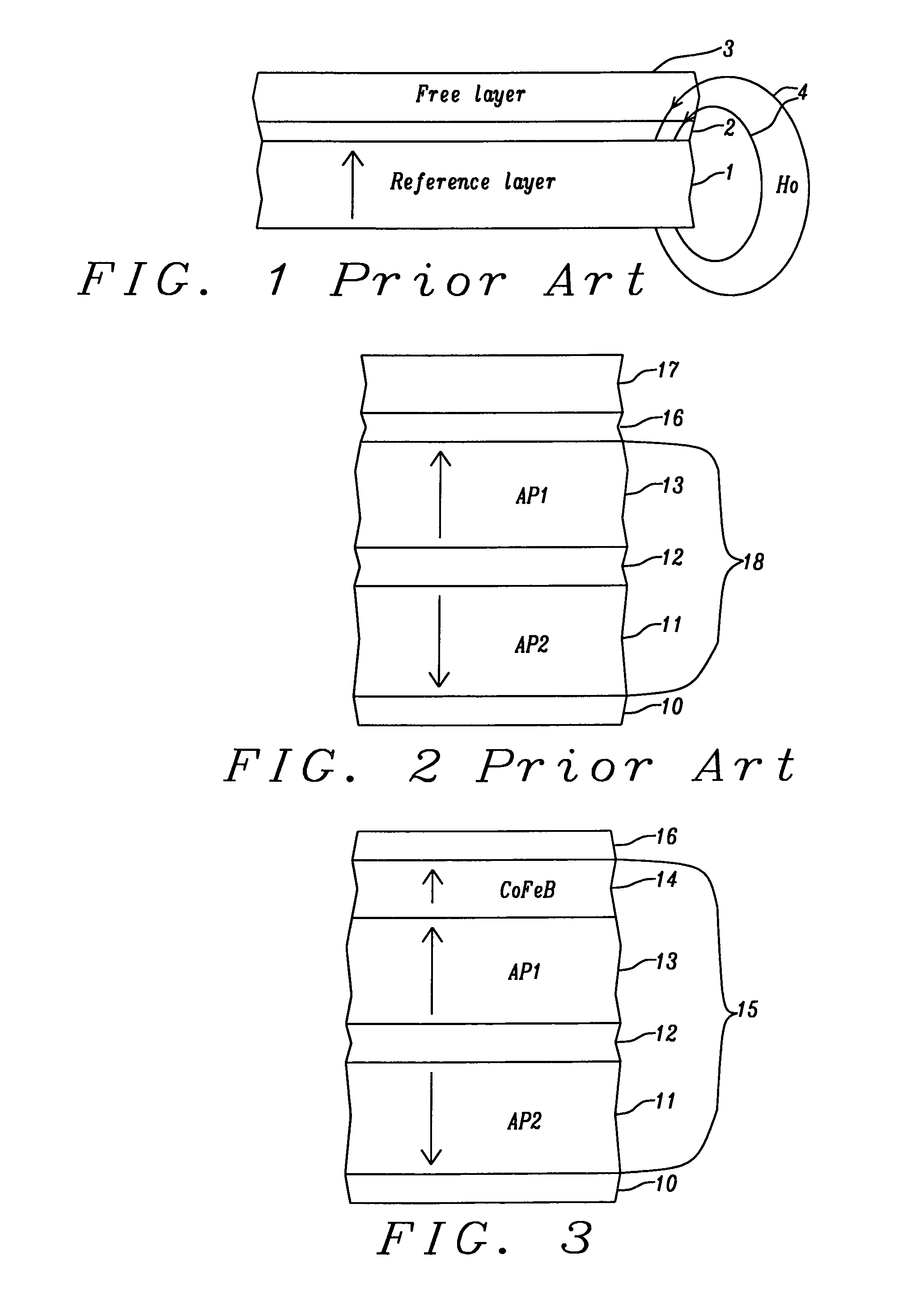
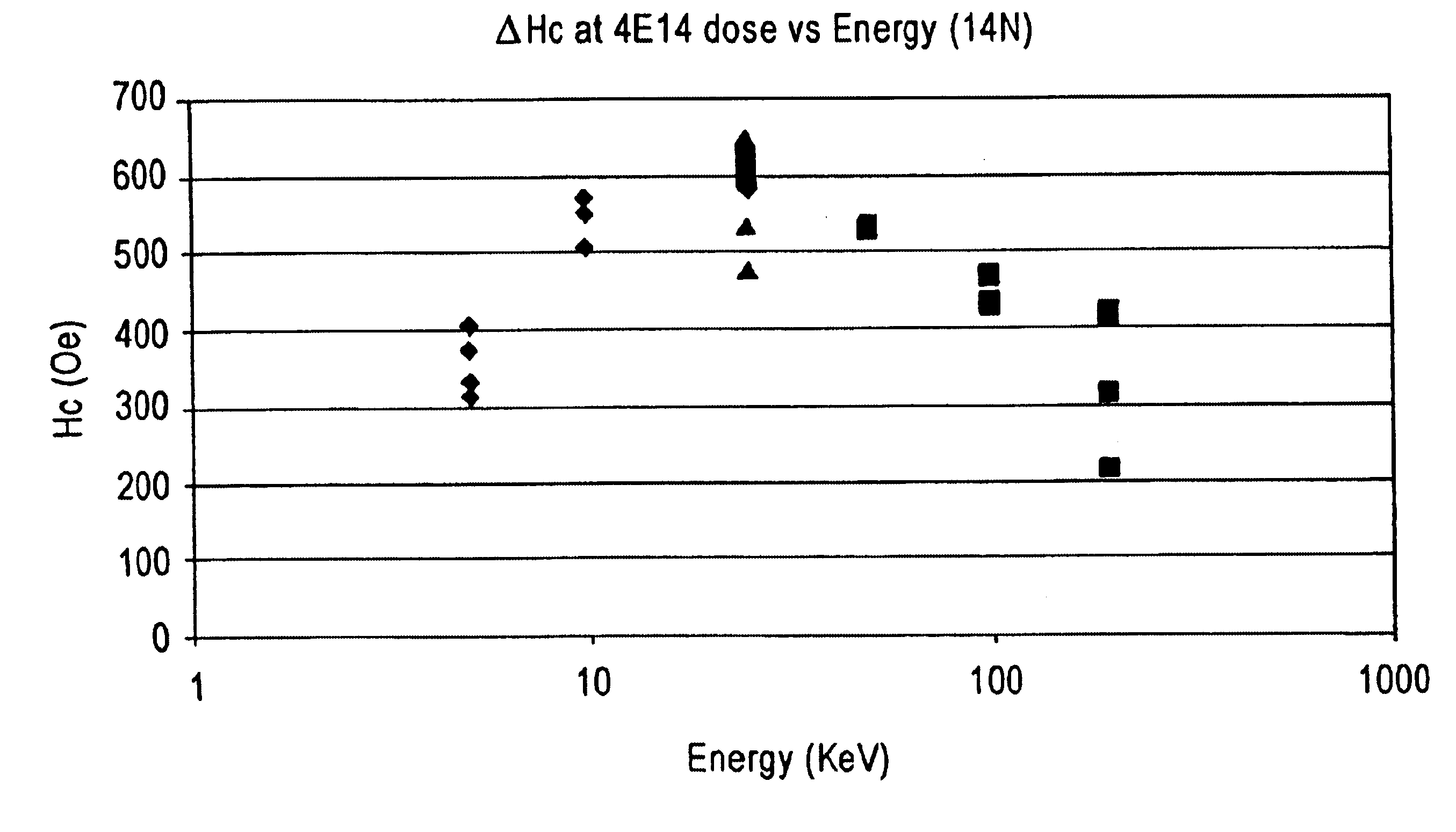
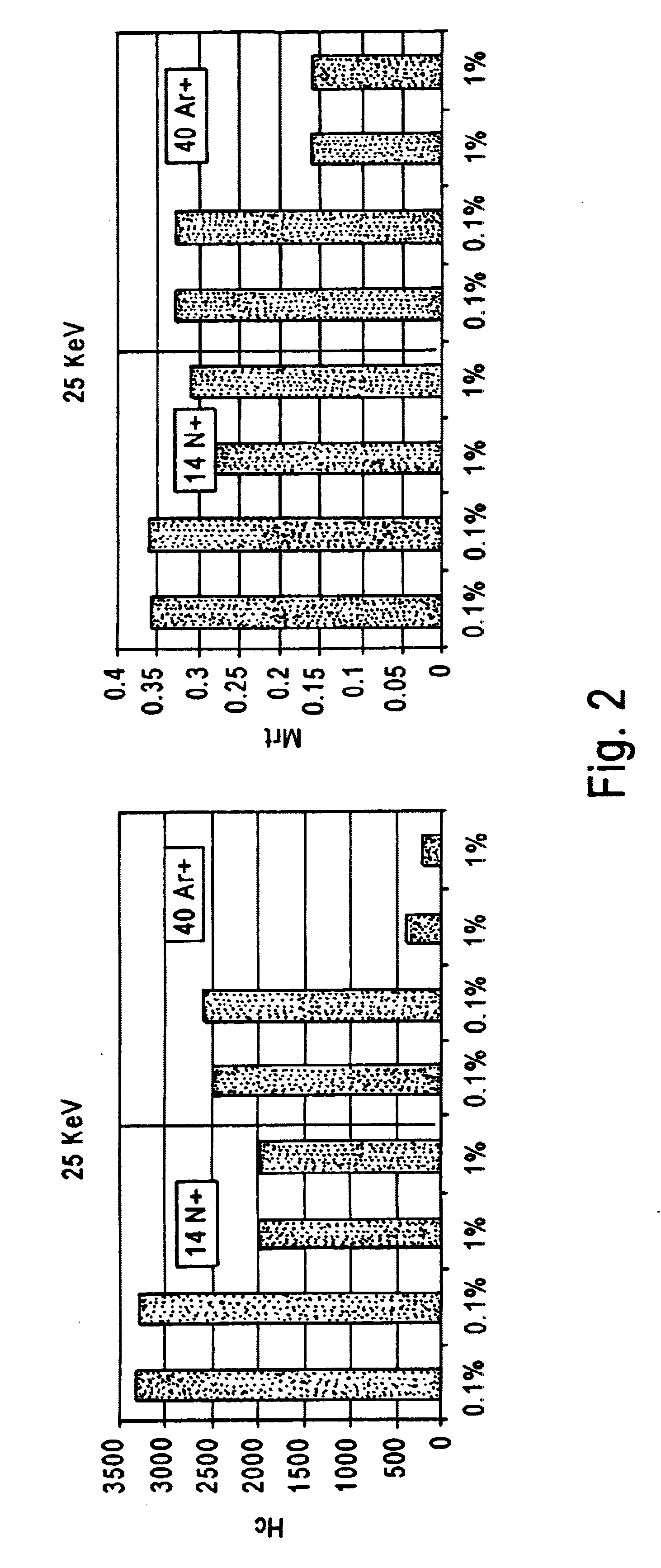
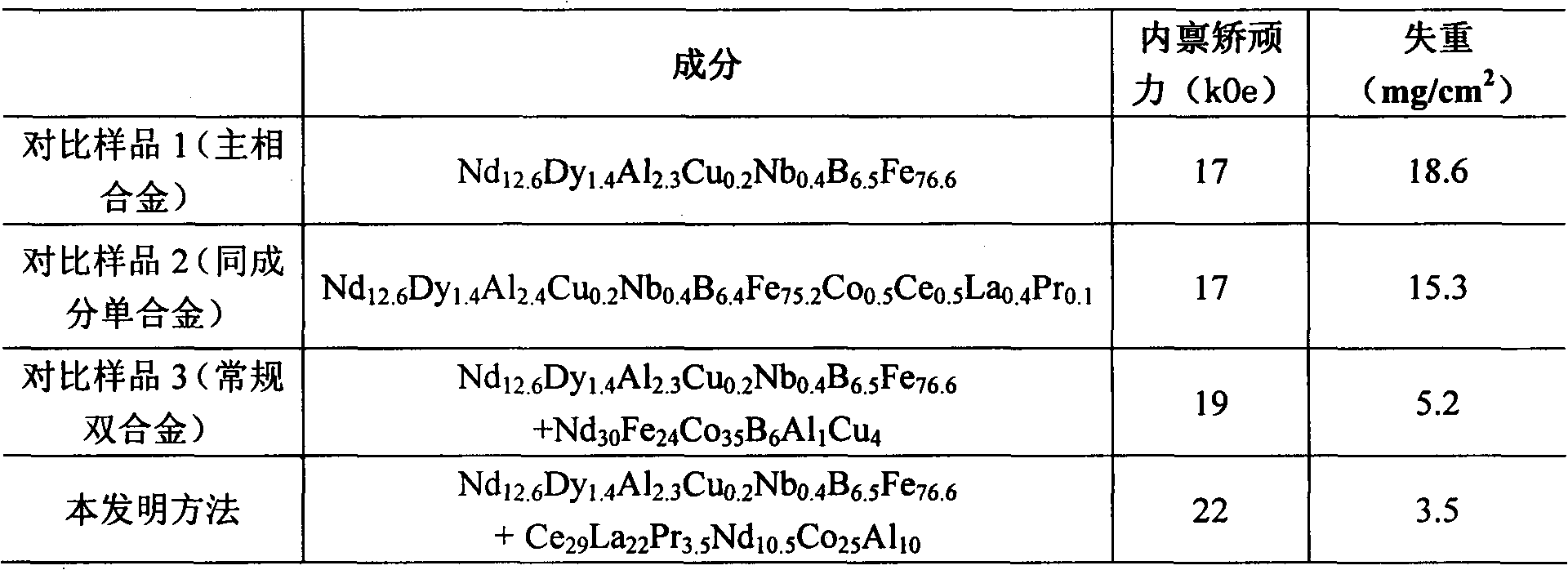Patents
Literature
2543 results about "Coercivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electrical engineering and materials science, the coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming demagnetized. An analogous property, electric coercivity, is the ability of a ferroelectric material to withstand an external electric field without becoming depolarized.
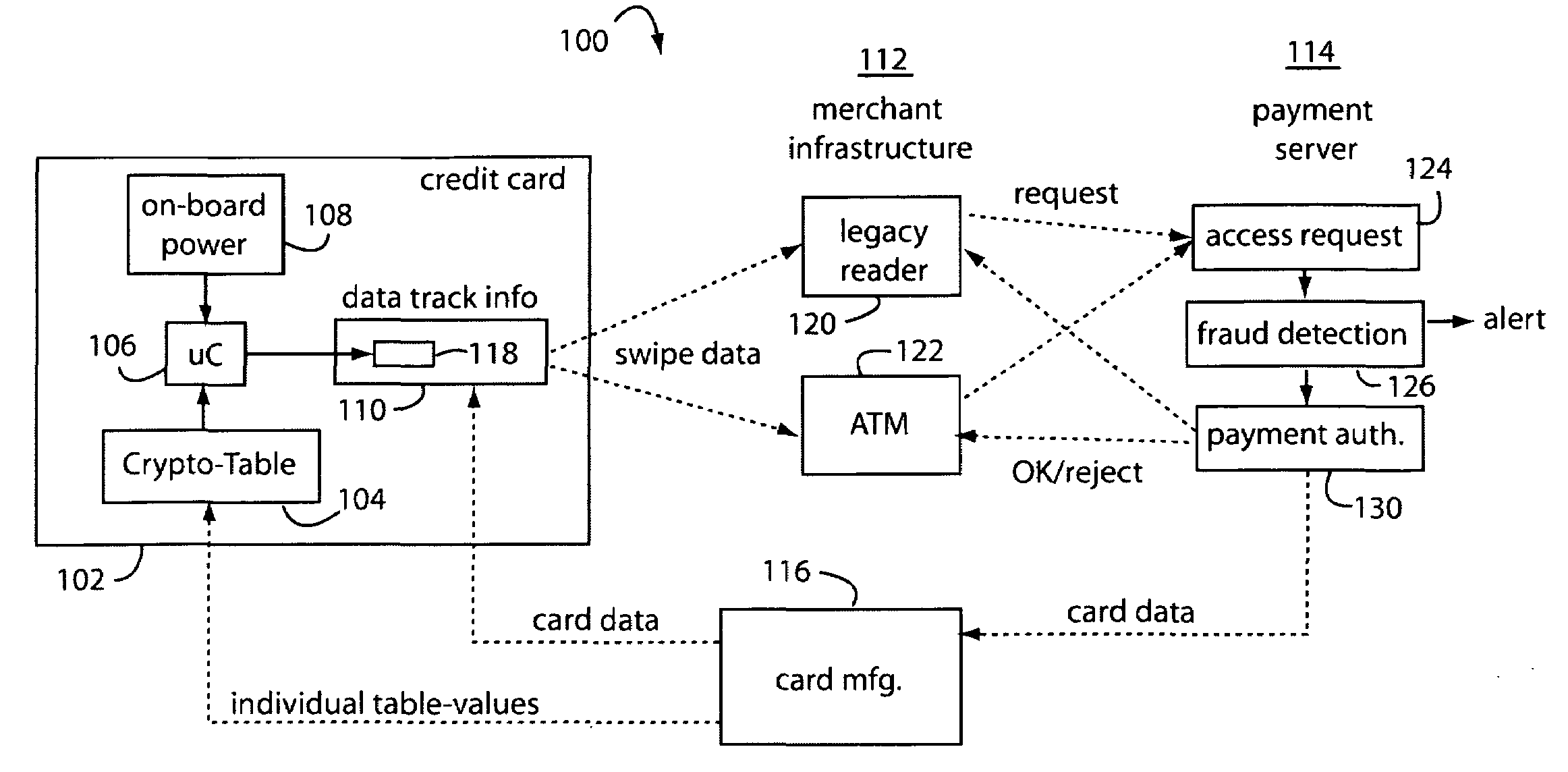
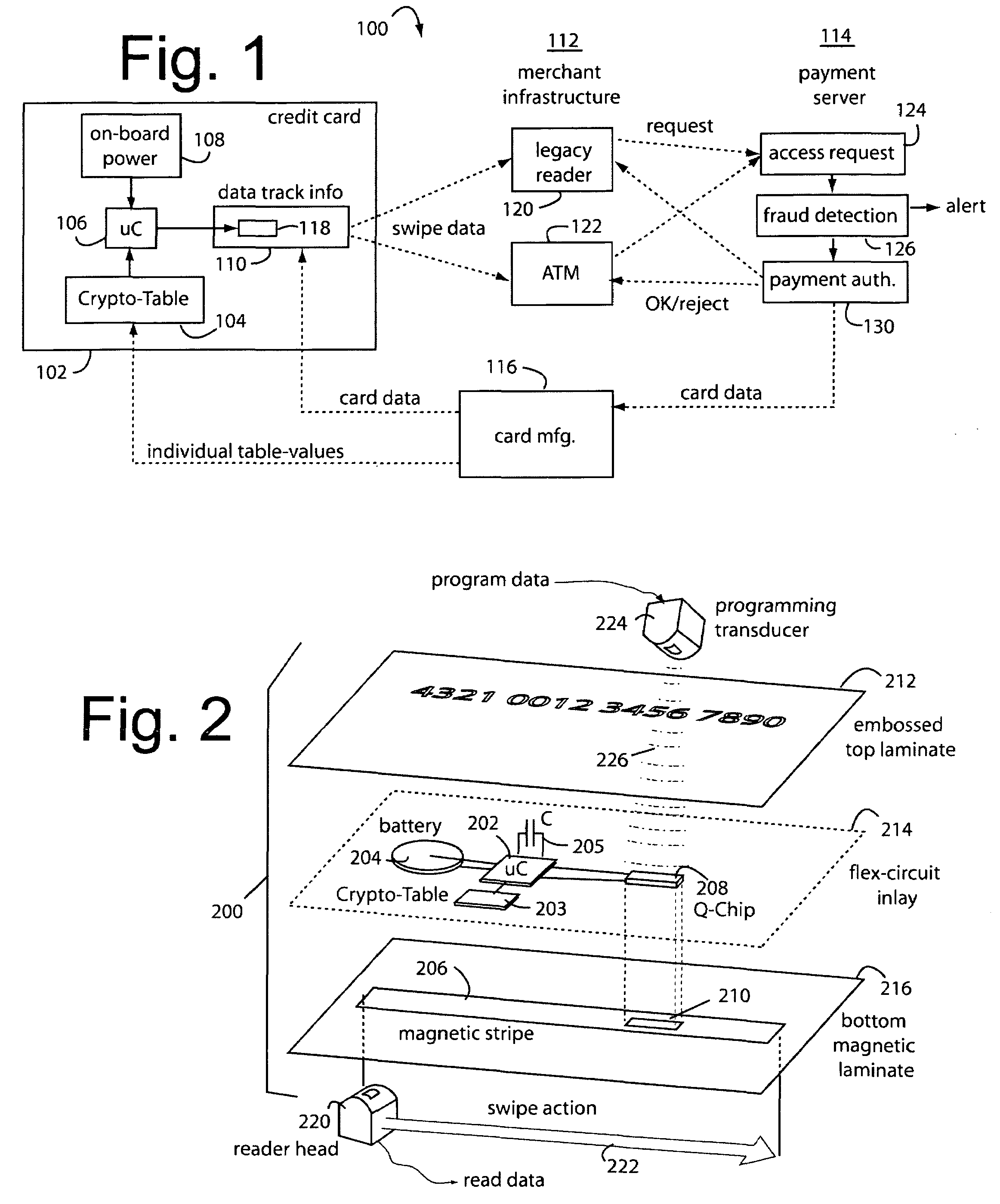
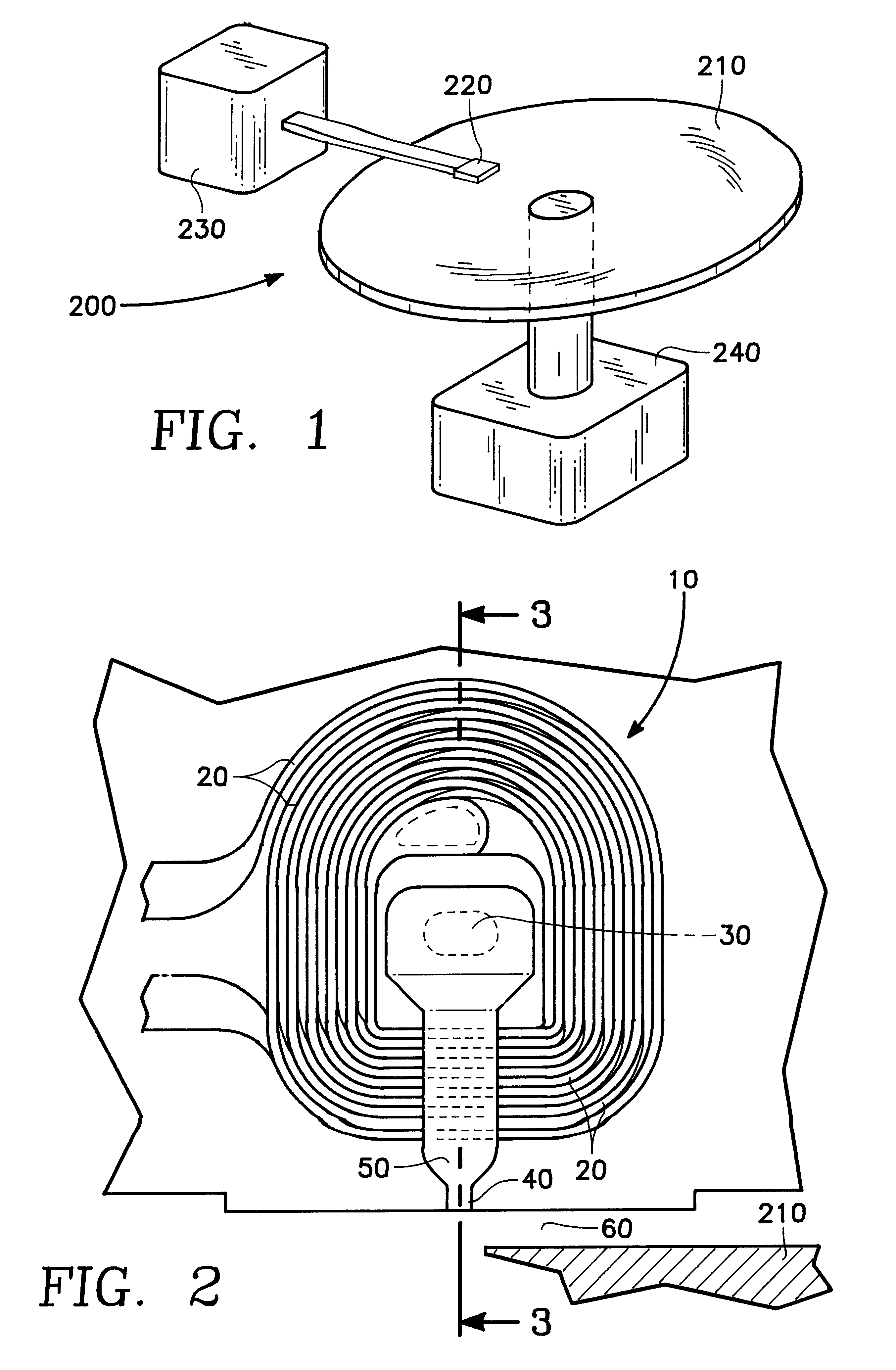
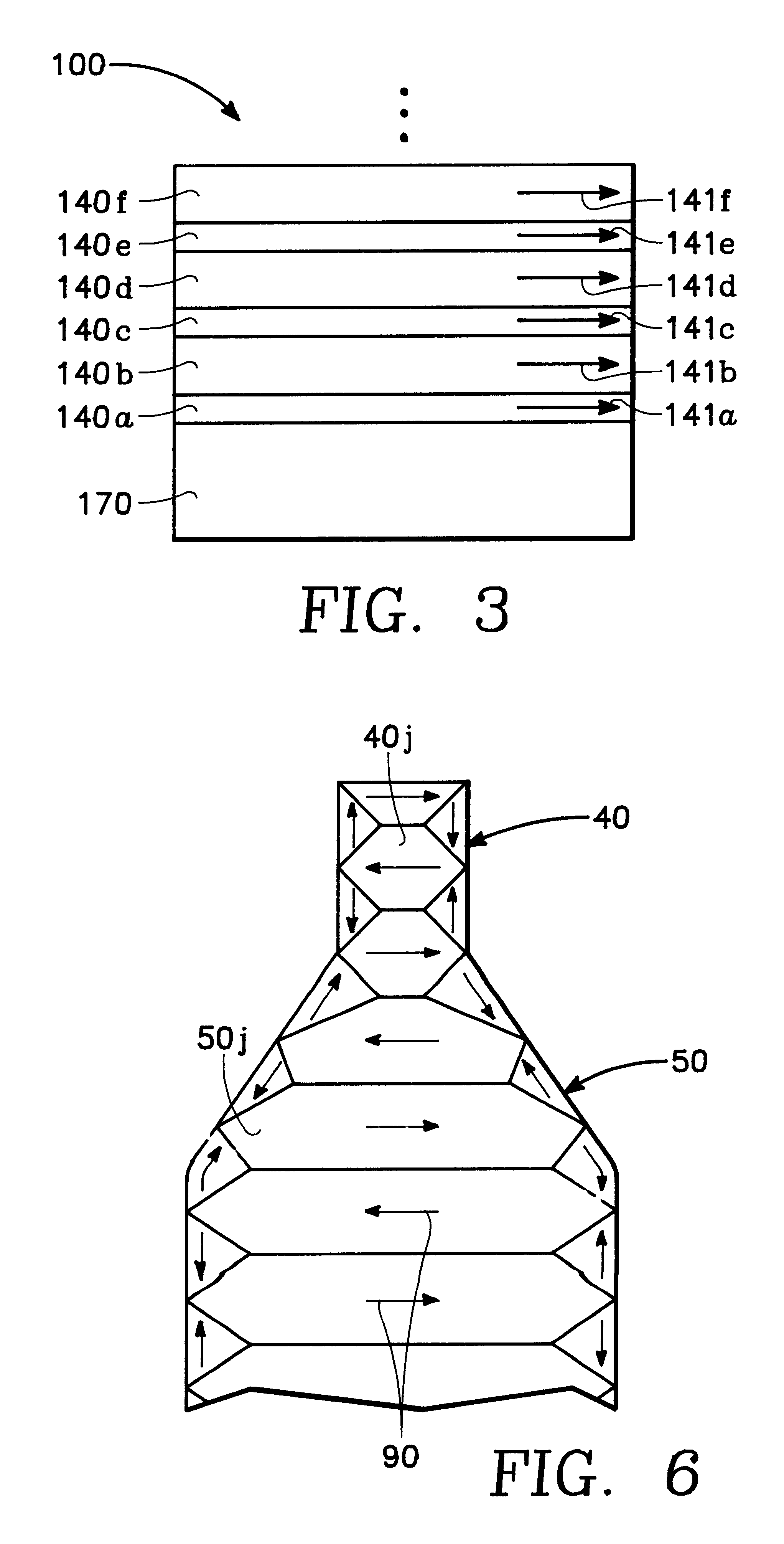
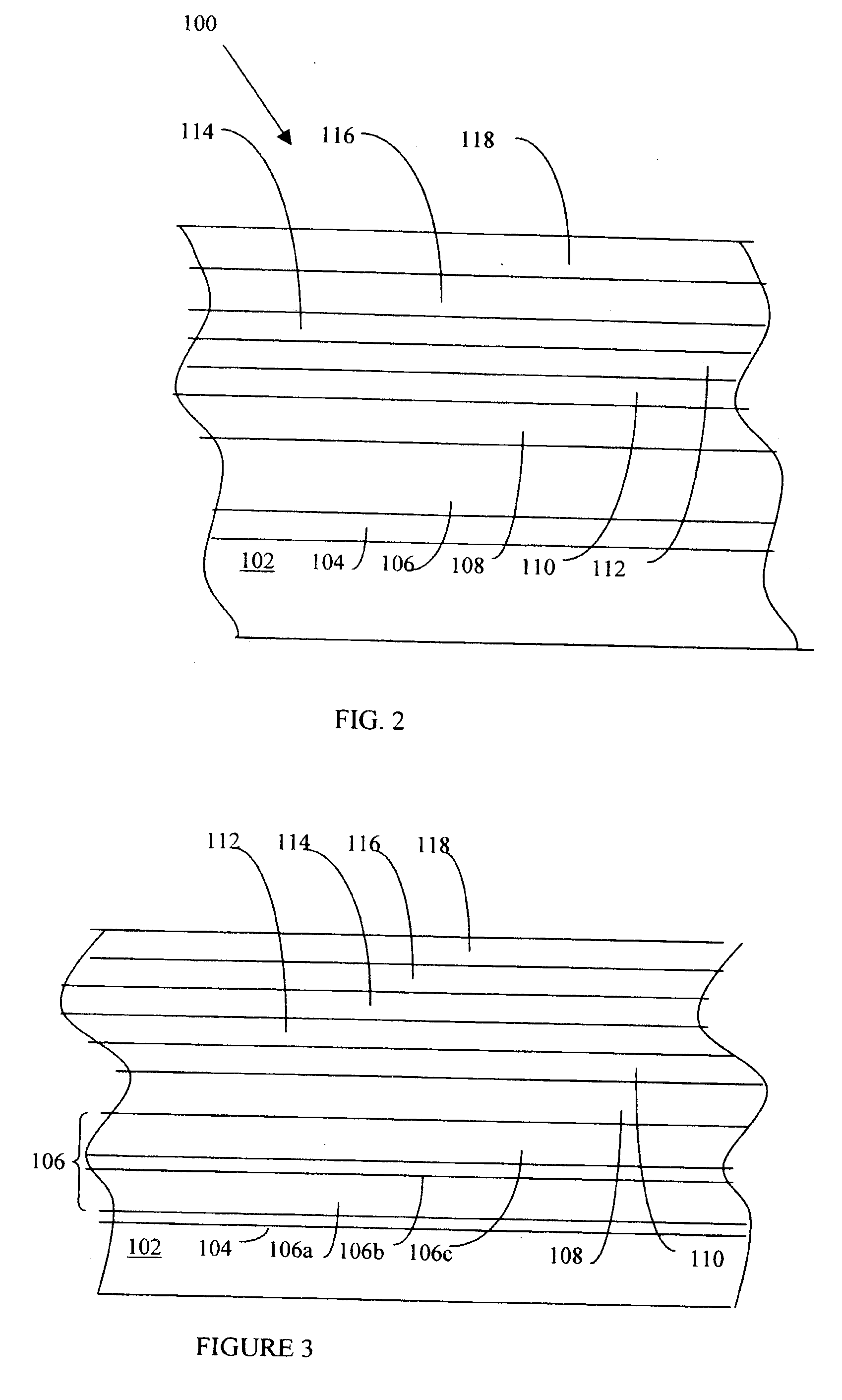
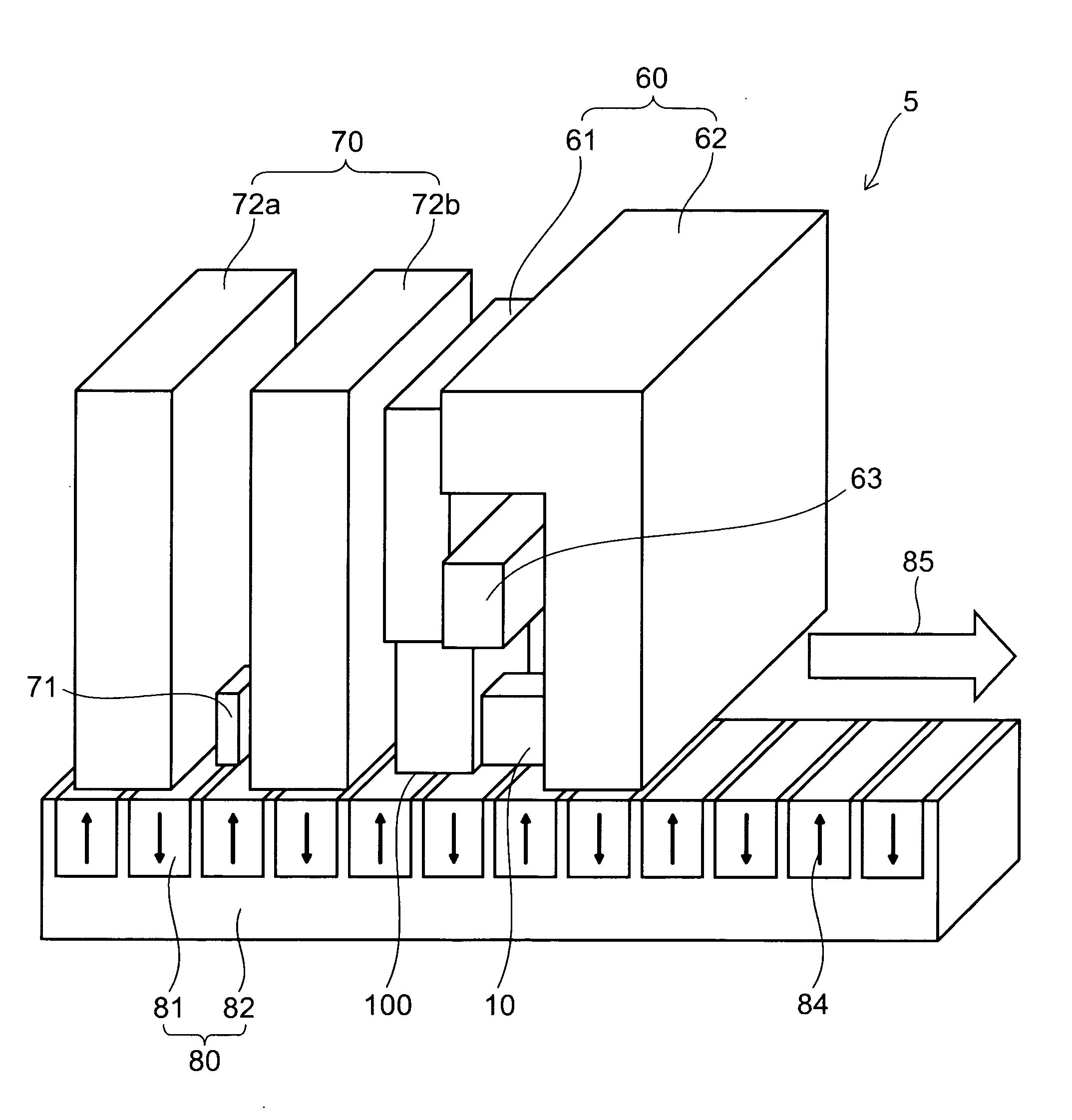
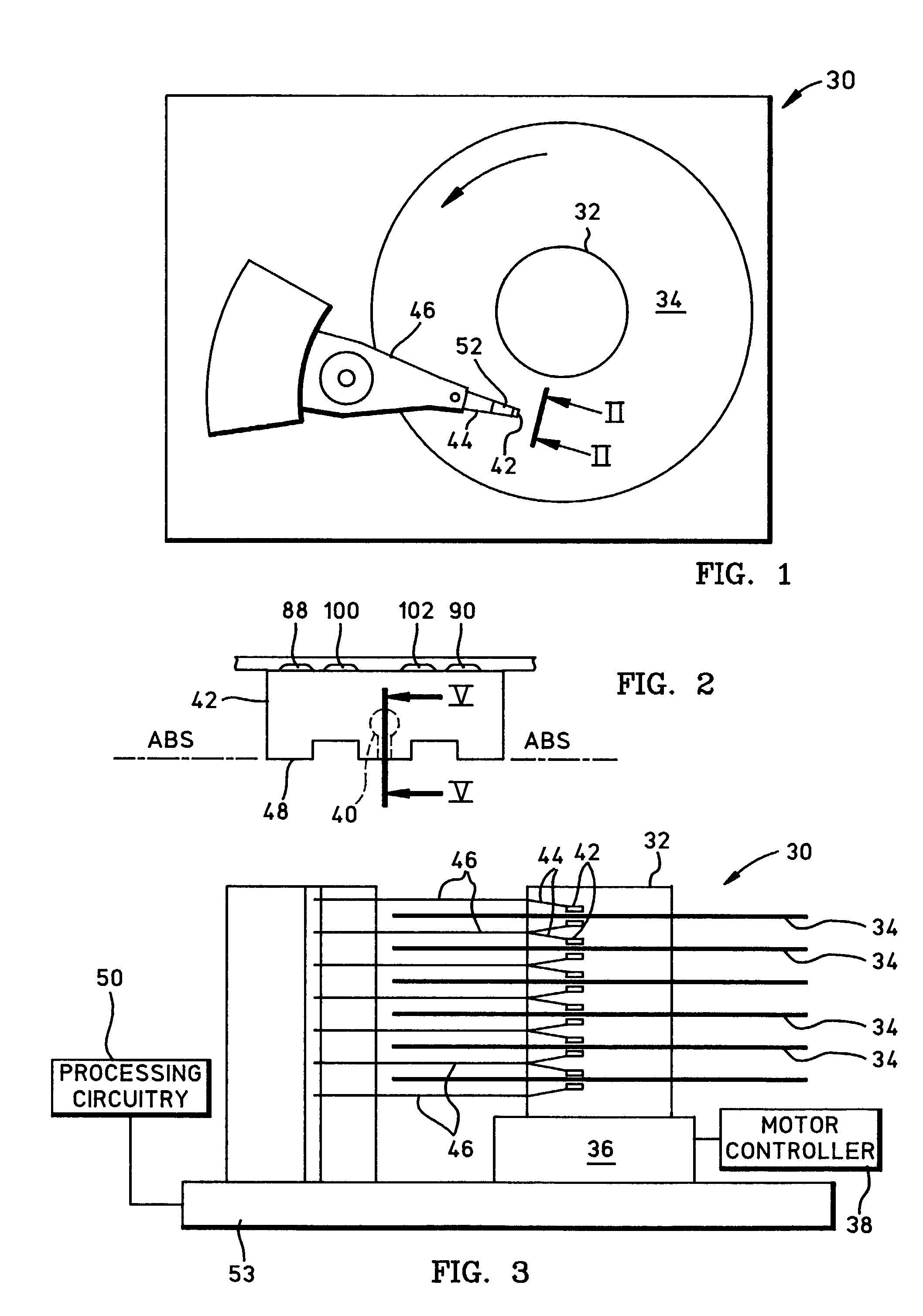
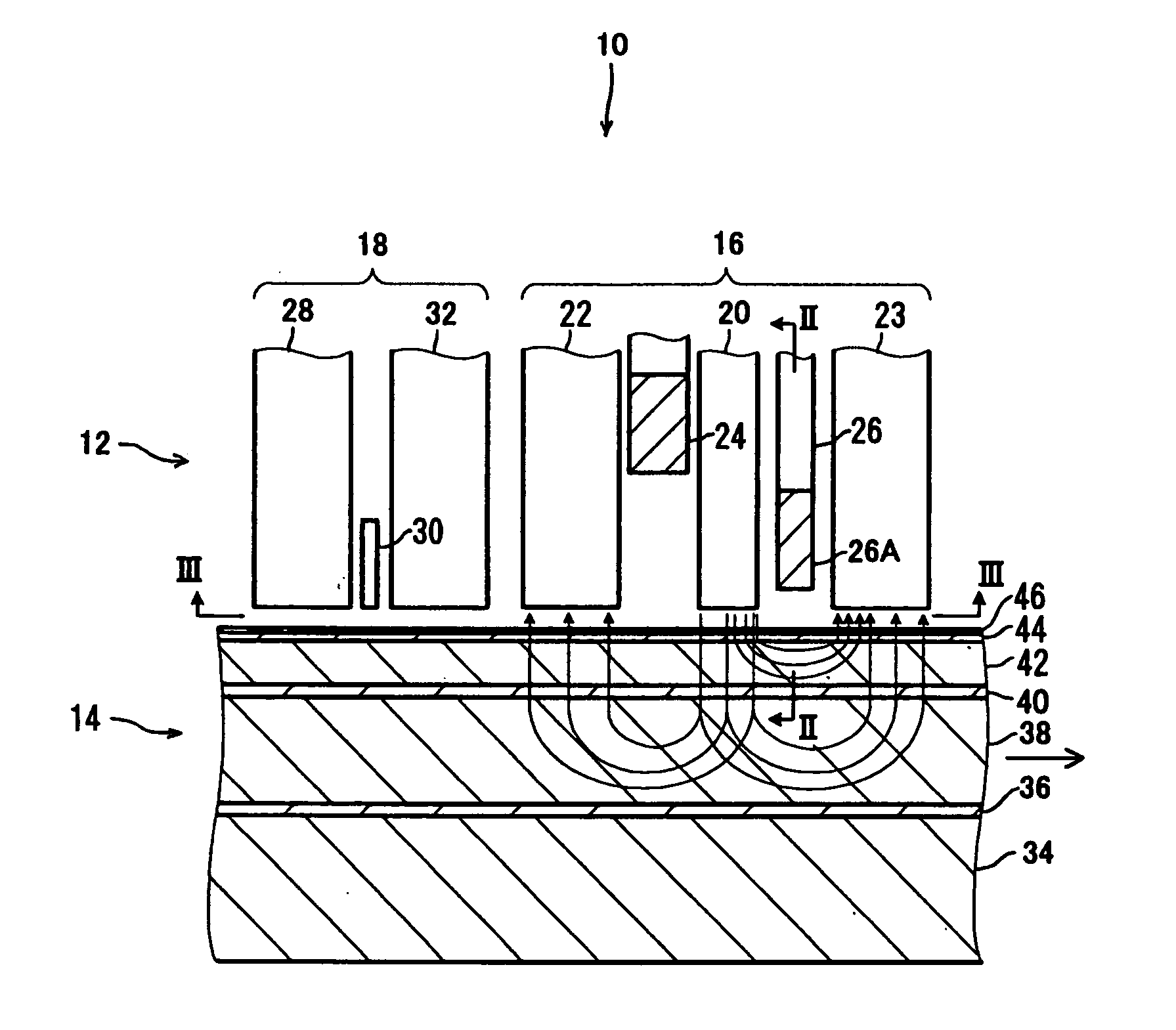
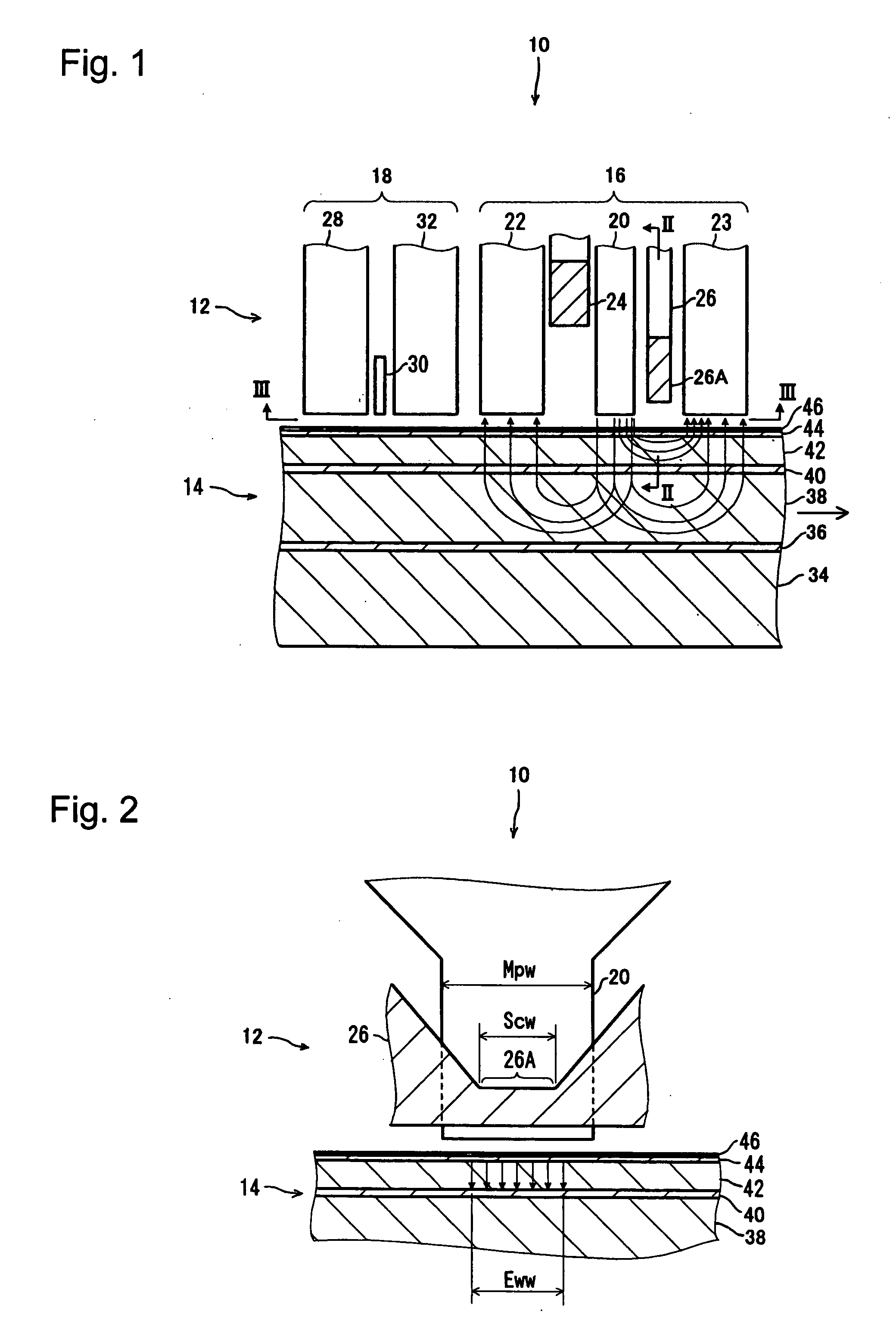
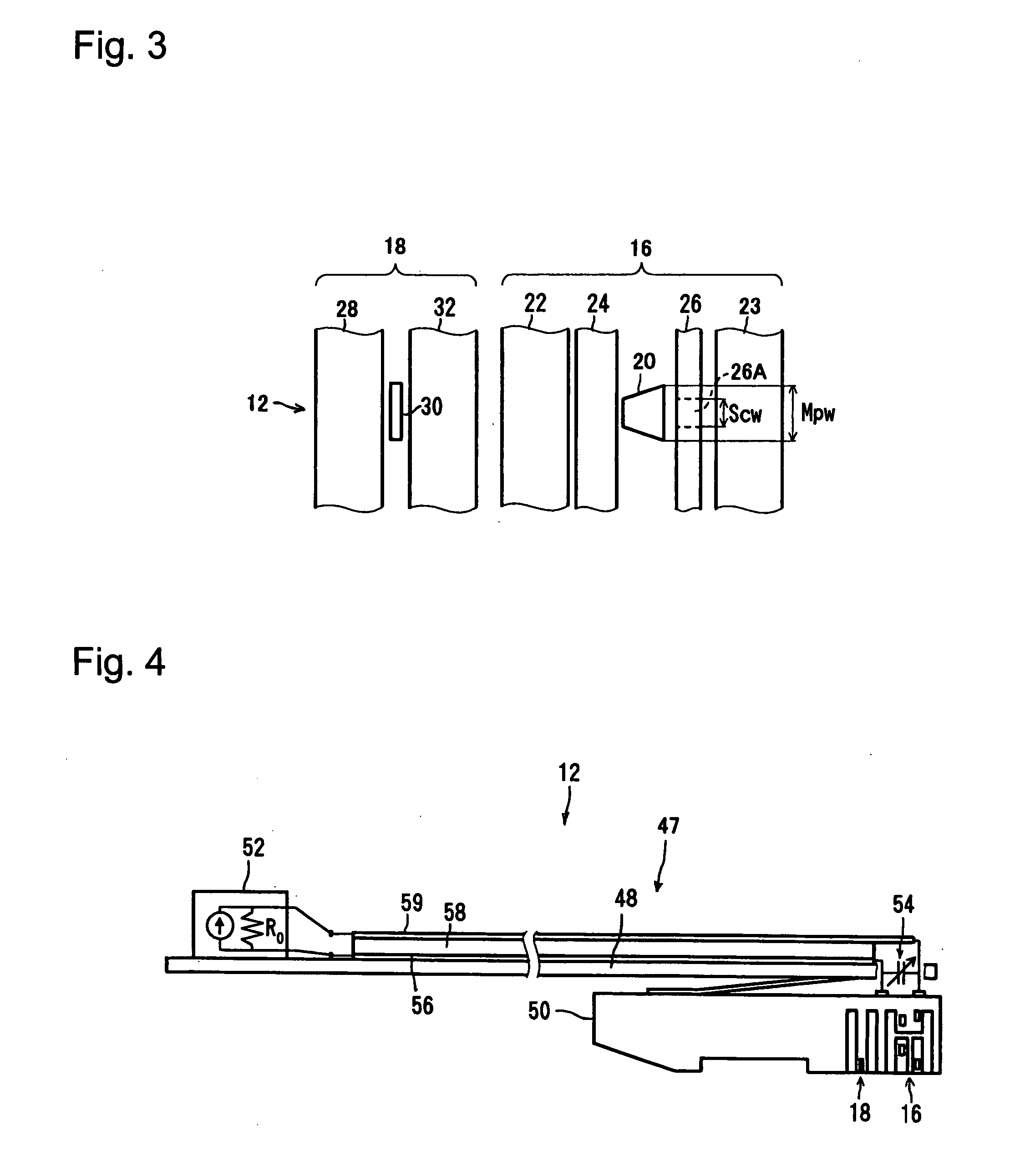
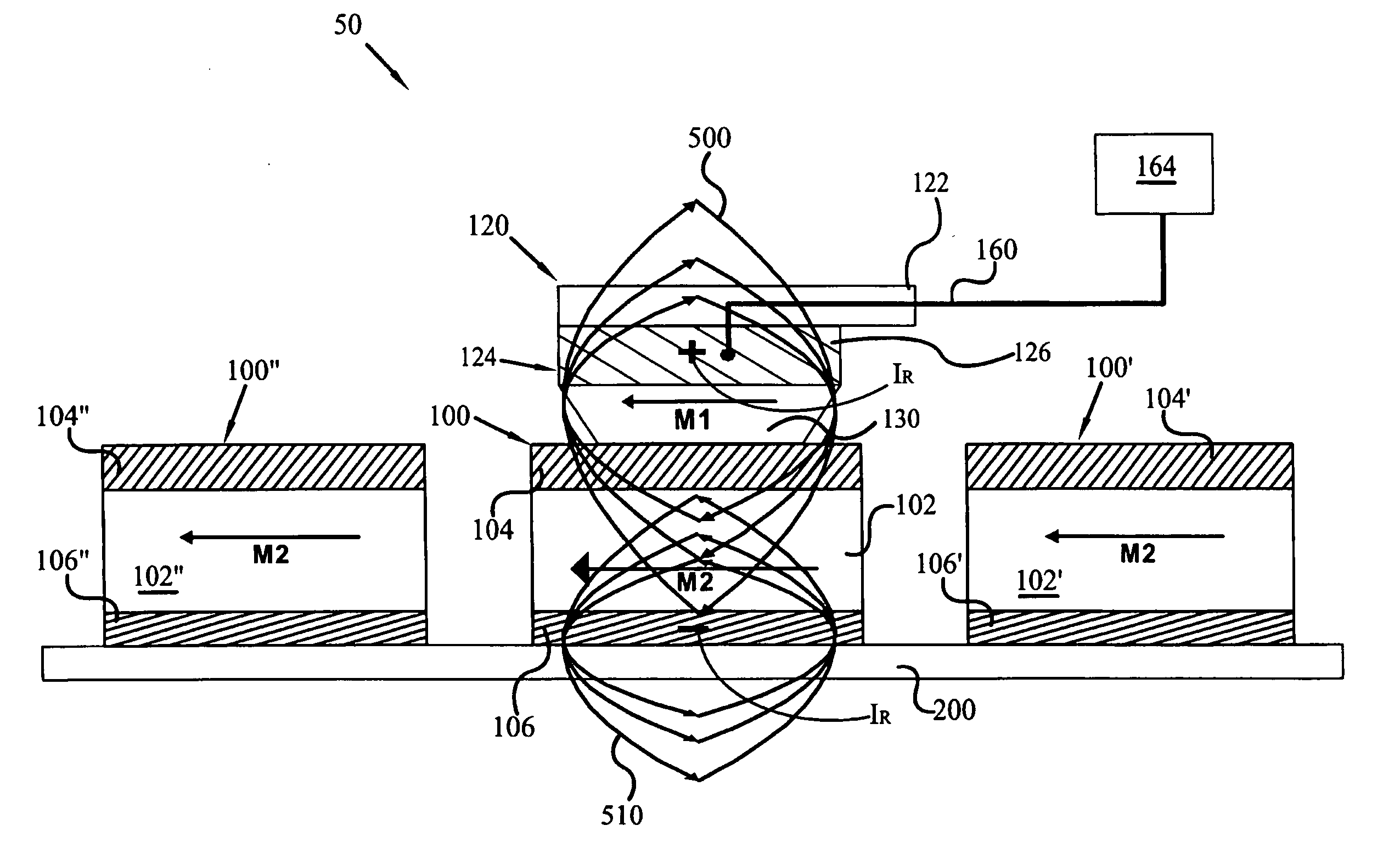
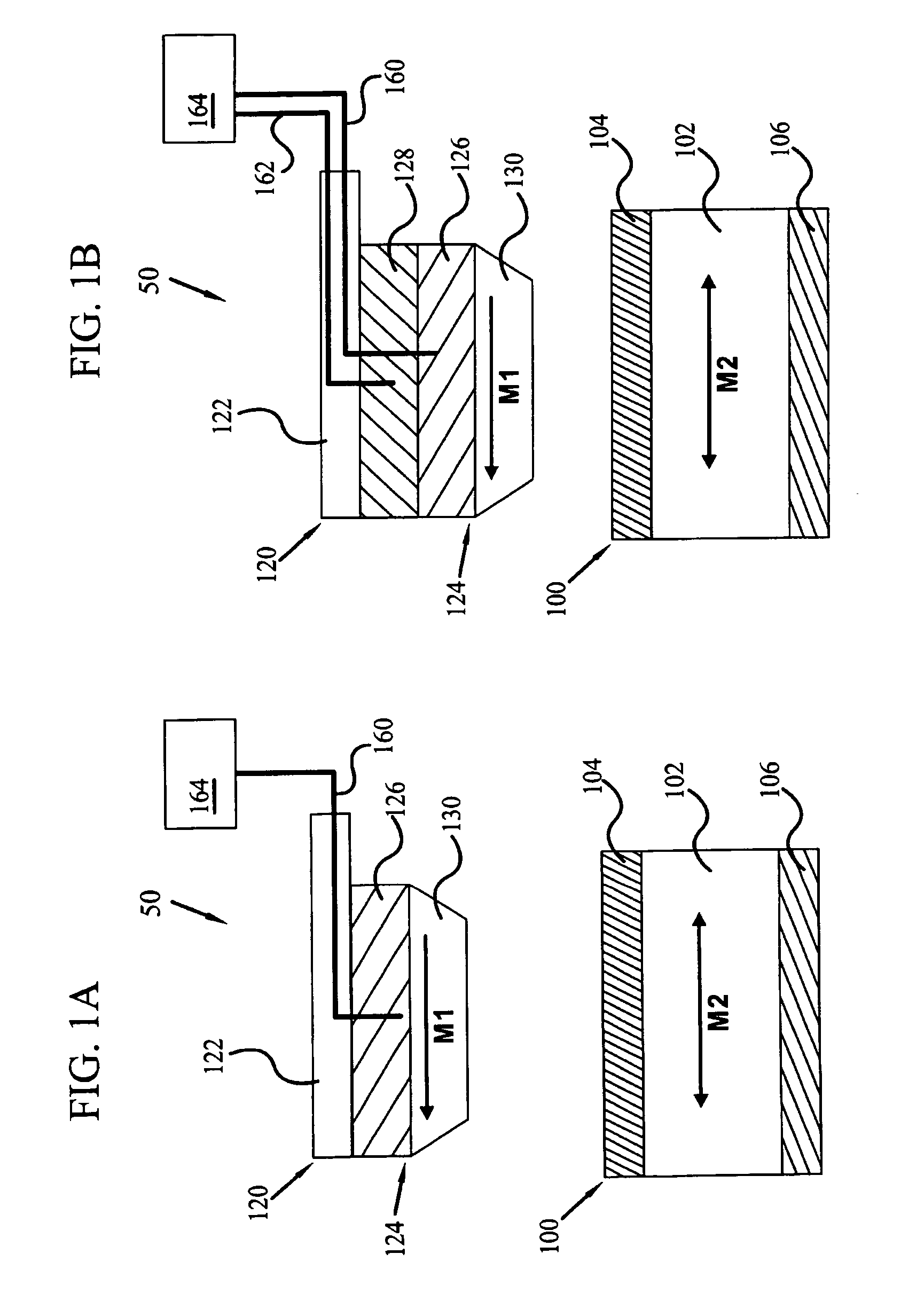
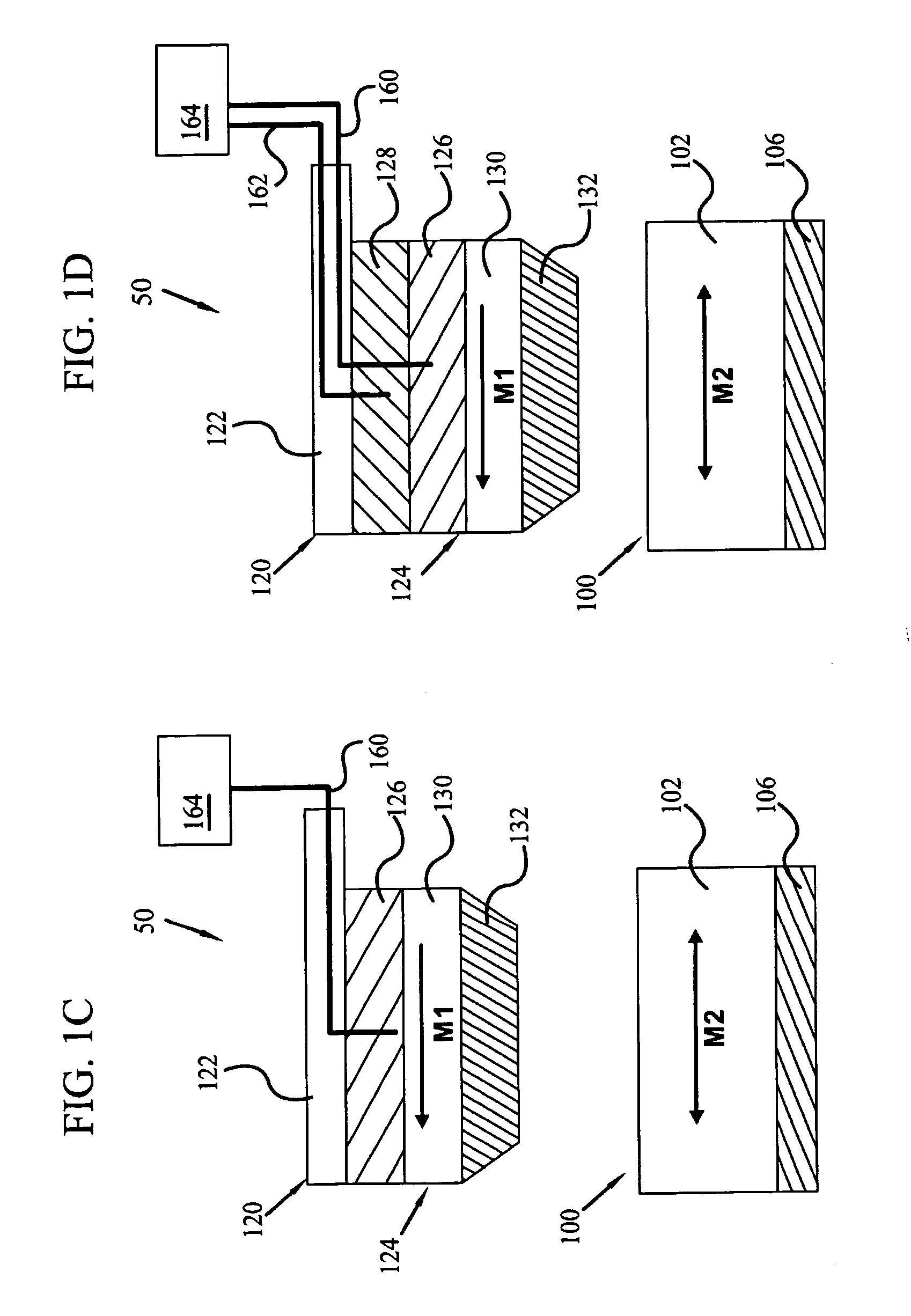
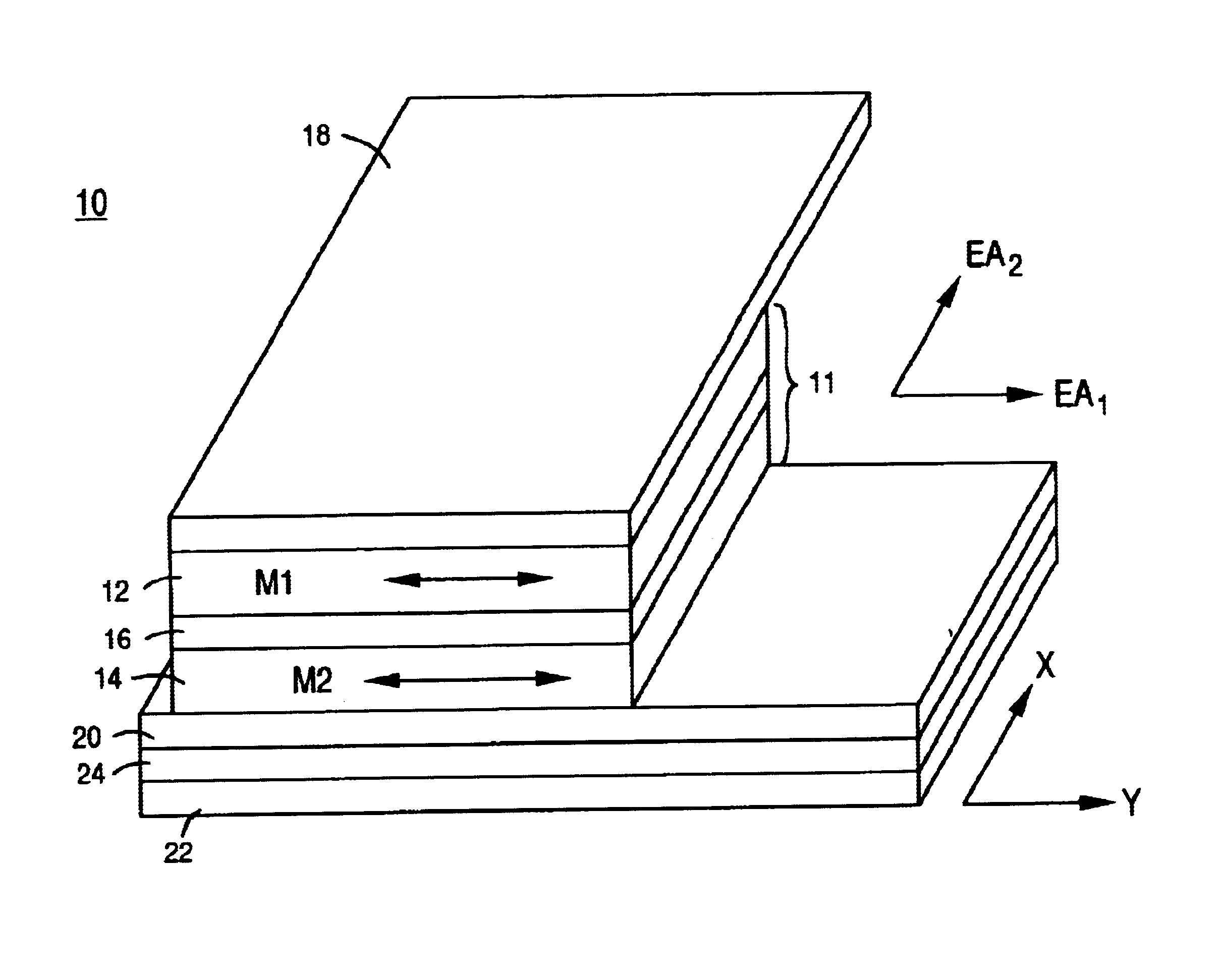
Magnetic data recording device
Owner:FITBIT INC
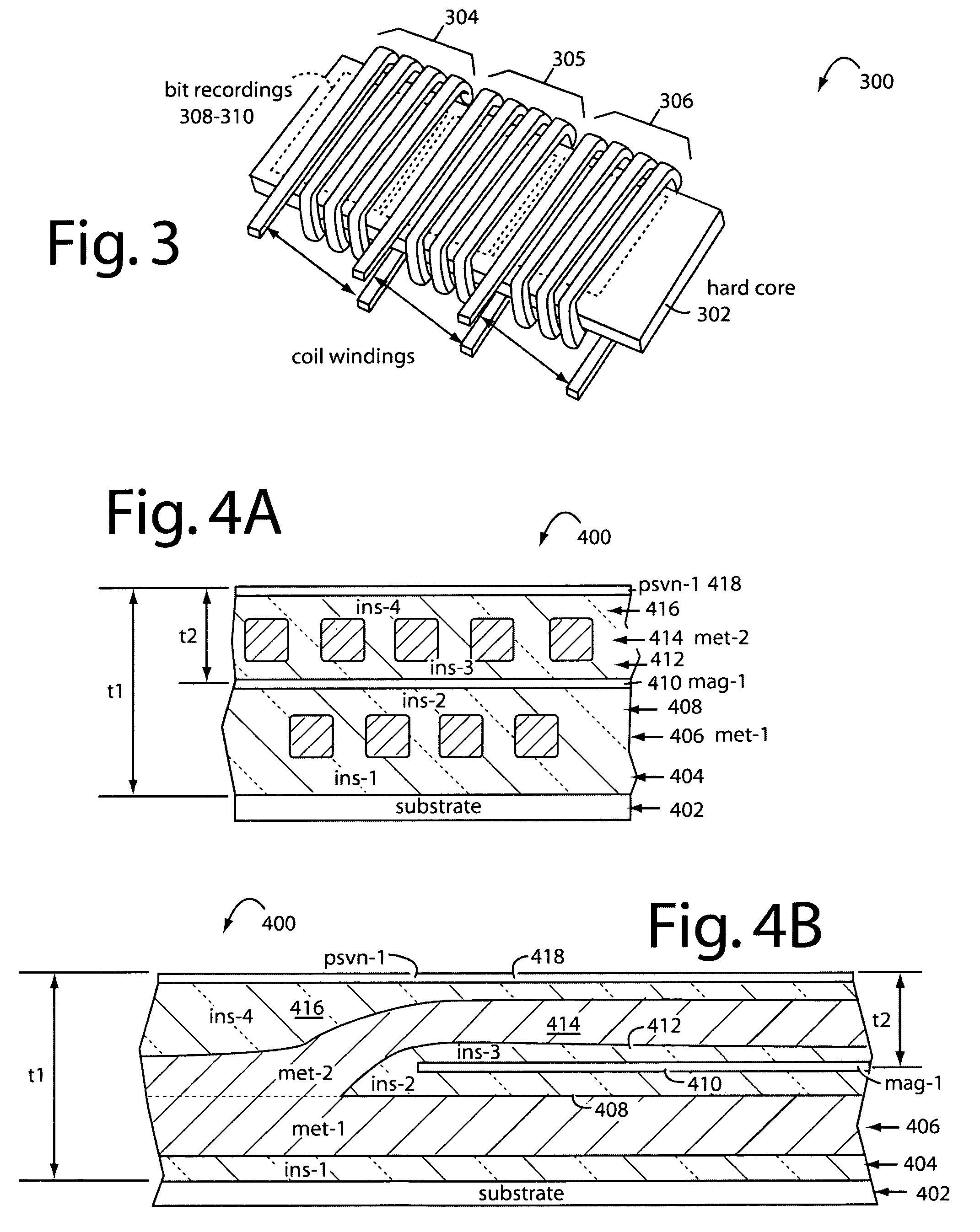
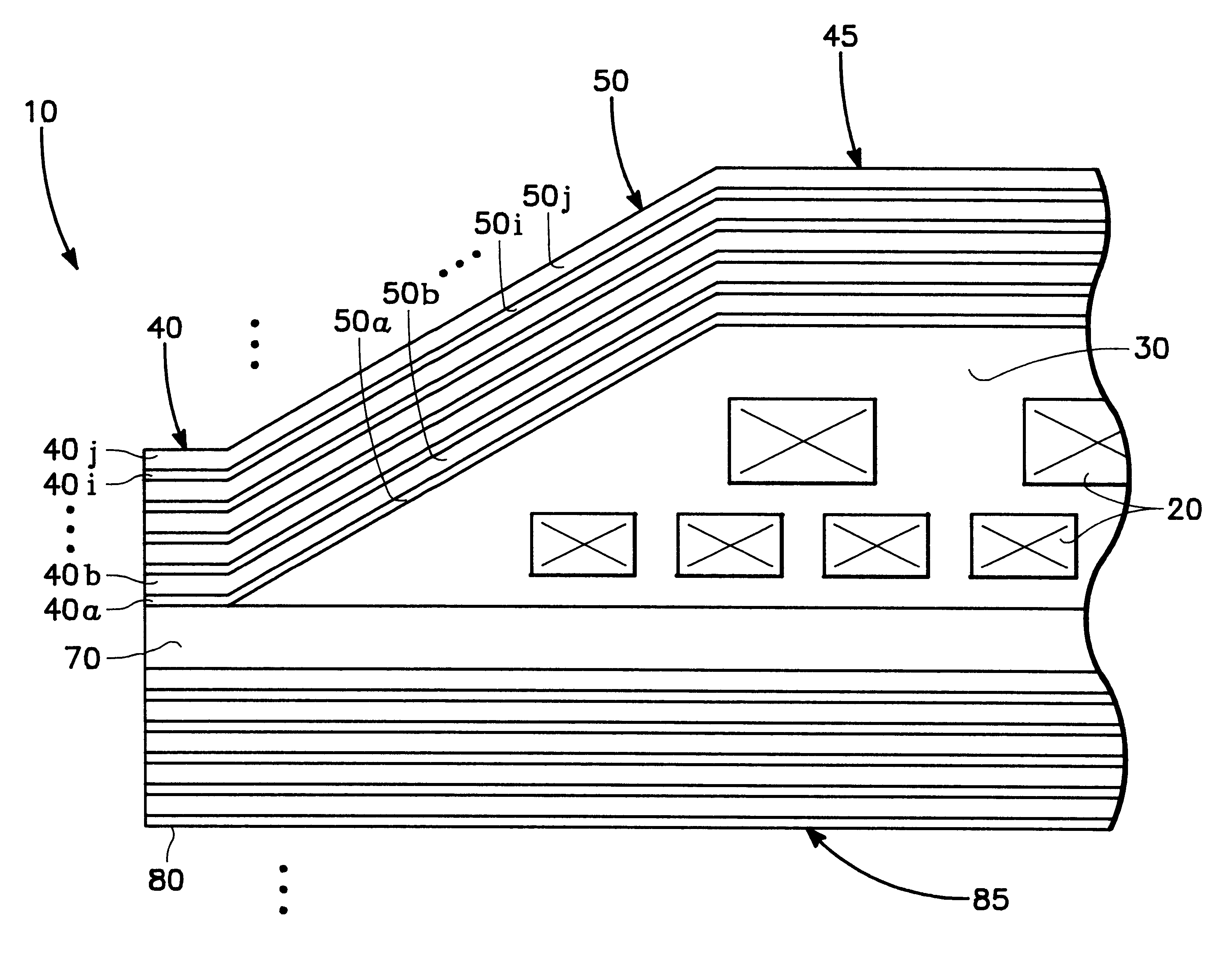
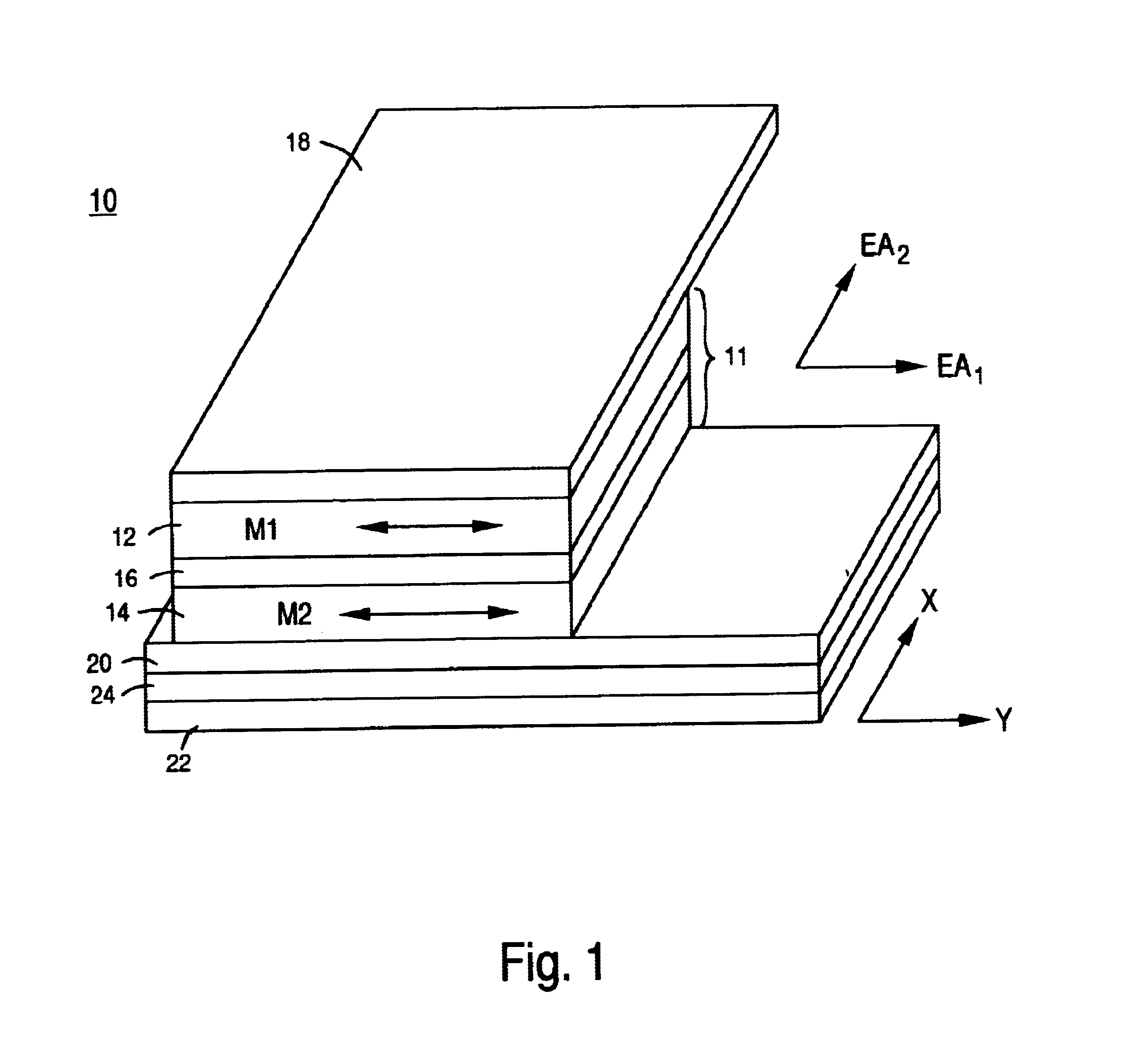
Thin film write head with improved laminated flux carrying structure and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6233116B1High resistivityExcellent soft magnetic propertiesConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsLower poleHigh resistivity
The present invention provides a thin film write head having an improved laminated flux carrying structure and method of fabrication. The preferred embodiment provides laminated layers of: high moment magnetic material, and easily aligned high resistivity magnetic material. In the preferred embodiment, the easily aligned laminating layer induces uniaxial anisotropy, by exchange coupling, to improve uniaxial anisotropy in the high moment material. This allows deposition induced uniaxial anisotropy by DC magnetron sputtering and also provides improved post deposition annealing, if desired. It is preferred to laminate FeXN, such as FeRhN, or other crystalline structure material, with an amorphous alloy material, preferably Co based, such as CoZrCr. In the preferred embodiment, upper and lower pole structures may both be laminated as discussed above. Such laminated structures have higher Bs than structures with insulative laminates, and yokes and pole tips and may be integrally formed, if desired, because flux may travel along or across the laminating layers. The preferred embodiment of the present invention improves soft magnetic properties, reduces eddy currents, improves hard axis alignment while not deleteriously affecting the coercivity, permeability, and magnetostriction of the structure, thus allowing for improved high frequency operation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC +1
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium with improved magnetic anisotropy field
InactiveUS20100035085A1High HcExcellent crystallographic C axis orientationMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic anisotropyAlloy
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium comprising a substrate, a soft underlayer, a seed layer, a non-magnetic FCC NiW alloy underlayer, a non-magnetic HCP underlayer, and a magnetic layer. We have discovered that the combination of a seed layer comprising Ta and a NiW alloy underlayer uniquely improves media recording performance and thermal stability by achieving excellent coercivity of the thin bottom magnetic recording layer and narrow C axis orientation distribution.
Owner:WD MEDIA
Magnetic recording head and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20090052095A1Construction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceInter layerMagnetic poles
A magnetic recording head includes:a main magnetic pole; a laminated body; and a pair of electrodes. The laminated body includes a first magnetic layer having a coercivity lower than magnetic field applied by the main magnetic pole, a second magnetic layer having a coercivity lower than the magnetic field applied by the main magnetic pole, and an intermediate layer provided between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The pair of electrodes are operable to pass a current through the laminated body.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder, method for producing the same and magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20070020489A1High strengthHigh specific gravityMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsMagnetic powderThermal treatment
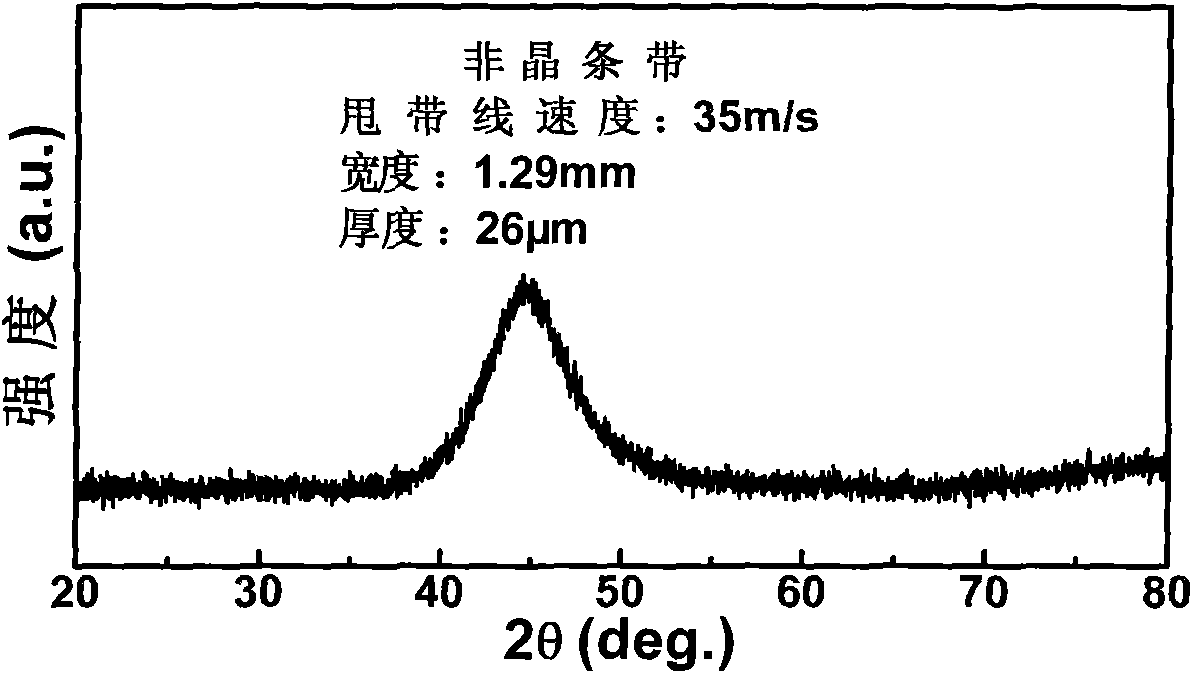
A hexagonal ferrite magnetic powder having an average tabular diameter of from 15 to 28 nm, a coercive force (Hc) of from 2,000 to 5,000 Oe (from 160 to 400 kA / m), a switching field distribution (SFD) of from 0.3 to 0.7 and a D70 / D50 of from 1.05 to 1.25. This magnetic powder can be obtained by melting and quenching starting materials to obtain an amorphous product, and thermally treating the product, which comprises increasing a temperature at a rate of 300 to 500° C. / hr in a temperature range of 550 to 600° C. in the thermal treatment before the temperature reaches the thermally treating temperature.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Minimal thickness synthetic antiferromagnetic (SAF) structure with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for STT-MRAM
ActiveUS8860156B2Raise the ratioTransformersGalvano-magnetic material selectionCouplingMagnetization
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Rare earth - iron - bron based magnet and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20070034299A1High energyImprove resolutionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementTrace element
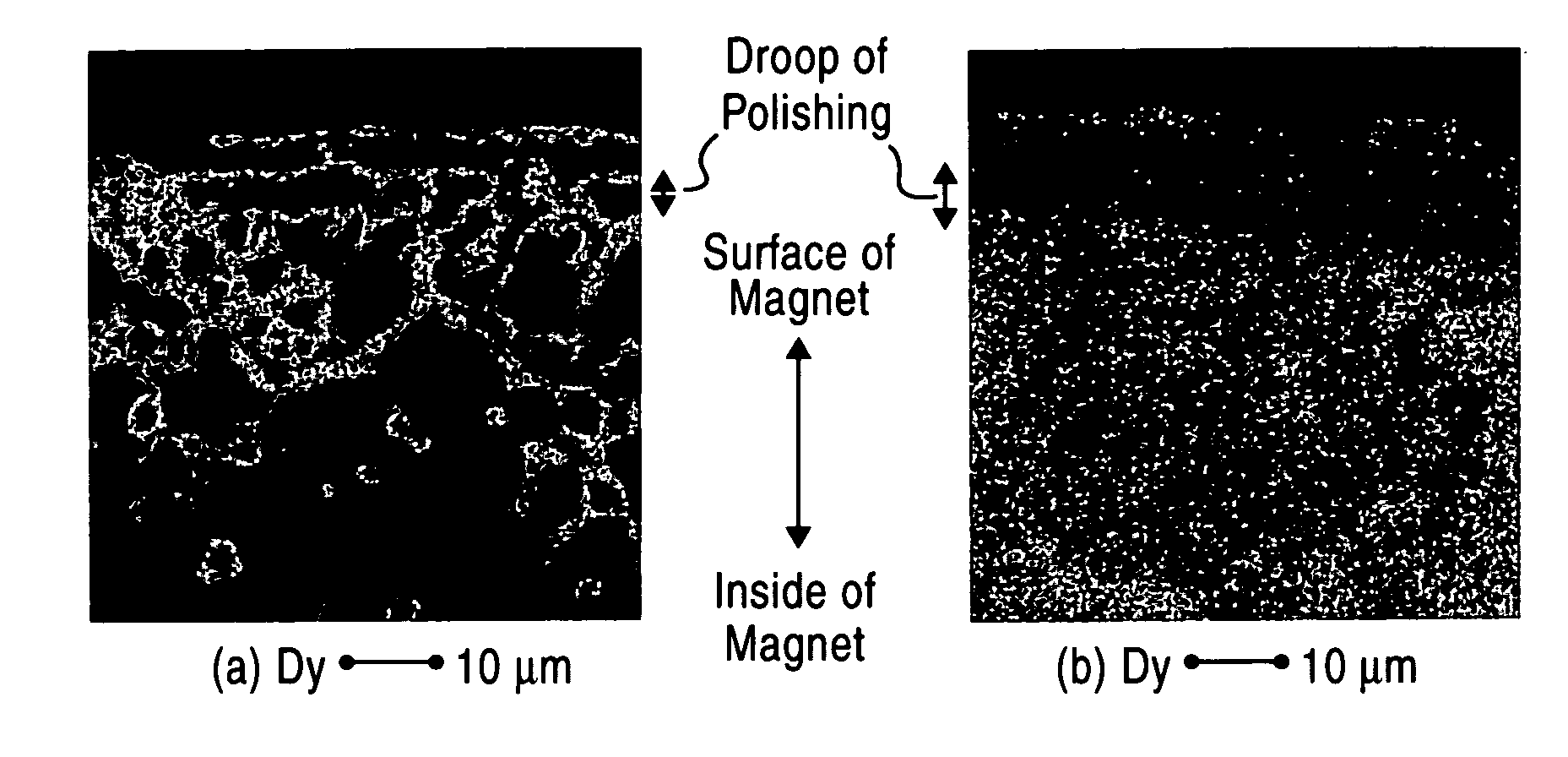
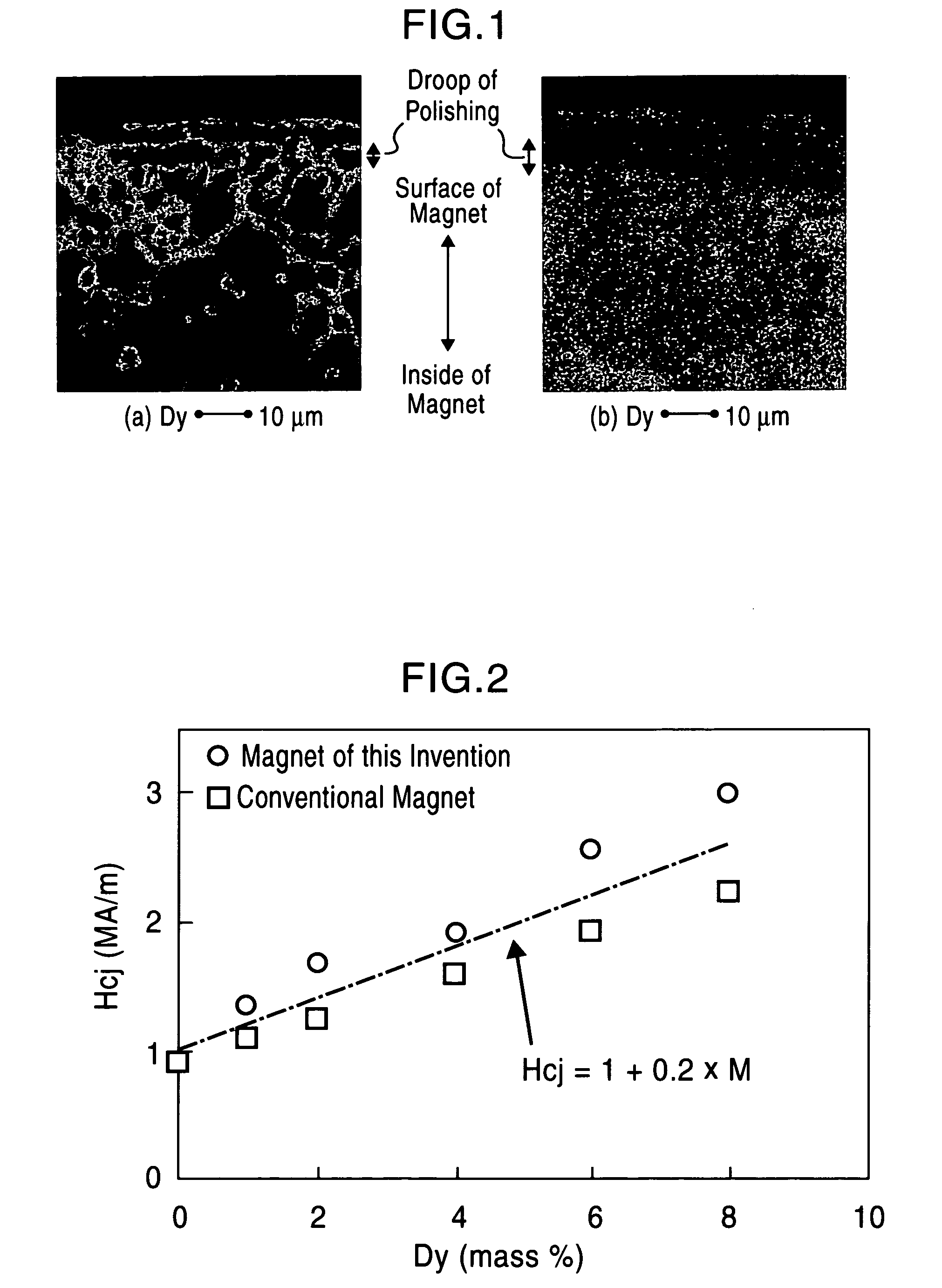
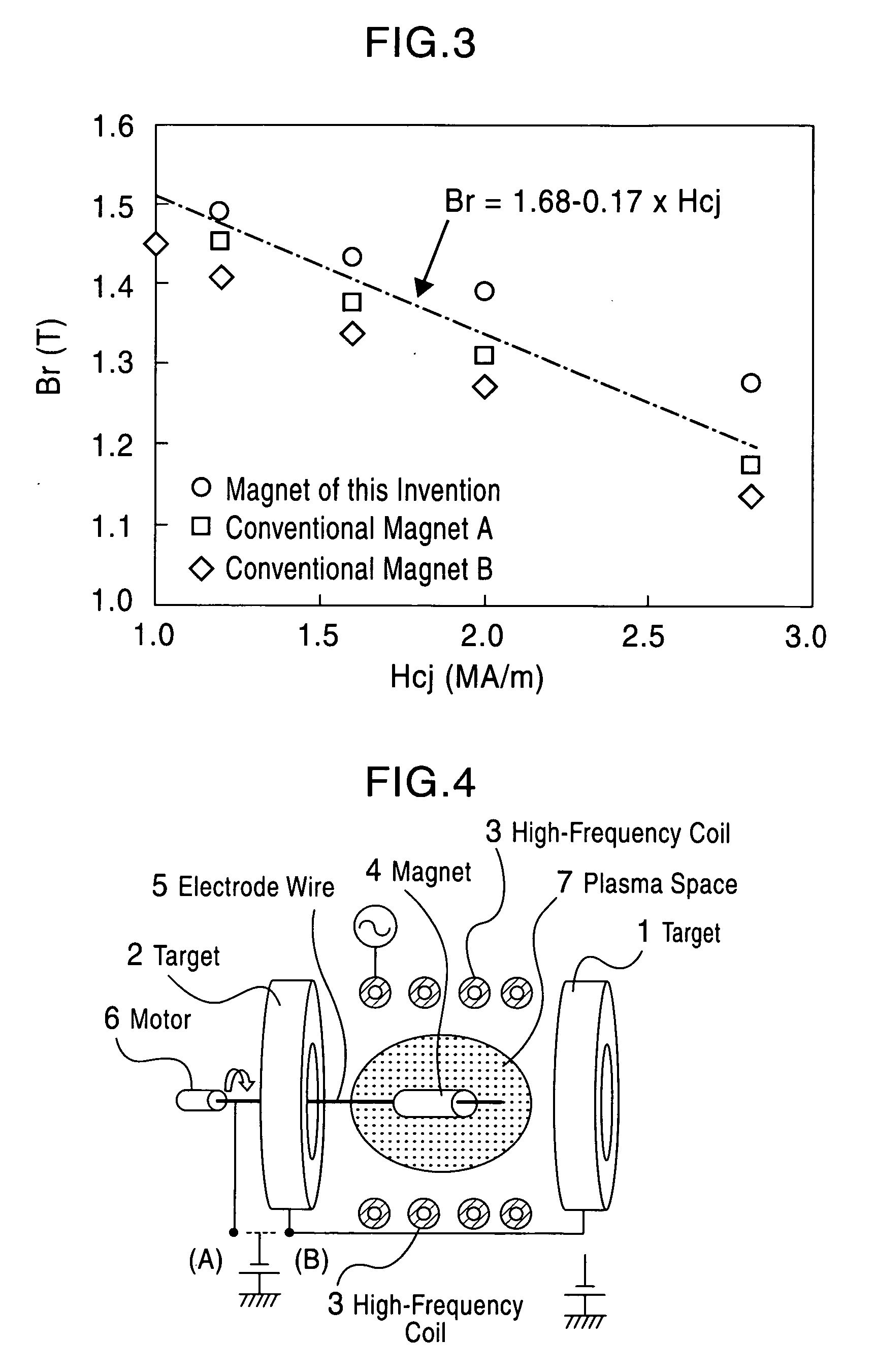
[Object] To provide a high-performance rare earth-based magnet exhibiting a high coercive force or a high residual magnetic flux density even when the content of a rare earth element such as Dy or the like which is scarce is reduced. [Construction] A rare earth-iron-boron based magnet includes a crystal grain boundary layer enriched in element M (M is at least one rare earth element selected from Pr, Dy, Tb, and Ho) by diffusion of the element M from the surface of the magnet, wherein the relation between the coercive force Hcj and the content of the element M in the whole of the magnet is represented by the following expression: Hcj≧1+0.2×M (wherein 0.05≦M≦10) wherein Hcj is the coercive force (unit: MA / m), and M is the content of the element M in the whole of the magnet (% by mass). Furthermore, the magnet satisfies the following expression: Br≧1.68−0.17×Hcj wherein Br is the residual magnetic flux density (unit: T).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
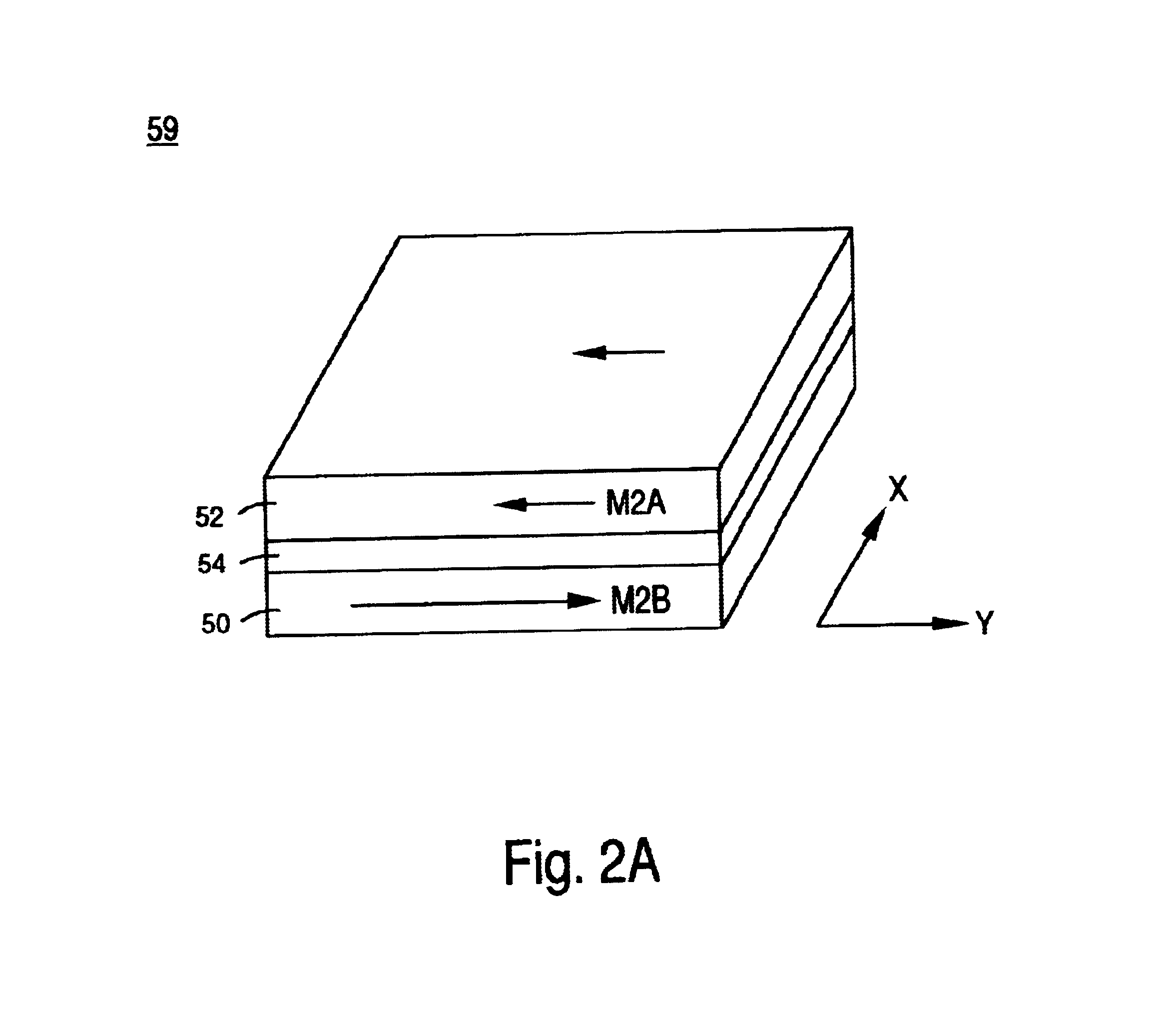
Magnetic media with improved exchange coupling
InactiveUS6899959B2Easy and fast switchingImprove thermal stabilityDifferent record carrier formsRecord information storageInter layerMagnetic media
A magnetic recording medium includes a substrate, an underlayer, a lower magnetic layer formed on the underlayer, an intermediate layer, and an upper magnetic layer formed on the intermediate layer. The intermediate layer is typically Ru, and promotes antiferromagnetic coupling between the upper and lower magnetic layers. The upper and lower magnetic layers are typically Co alloys. The lower magnetic layer has a high saturation magnetization Ms to promote high exchange coupling between the upper and lower magnetic layers. The dynamic coercivity of the lower magnetic layer is lower than the exchange field to ensure rapid switching of the lower magnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
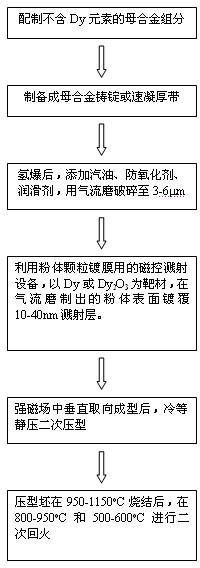
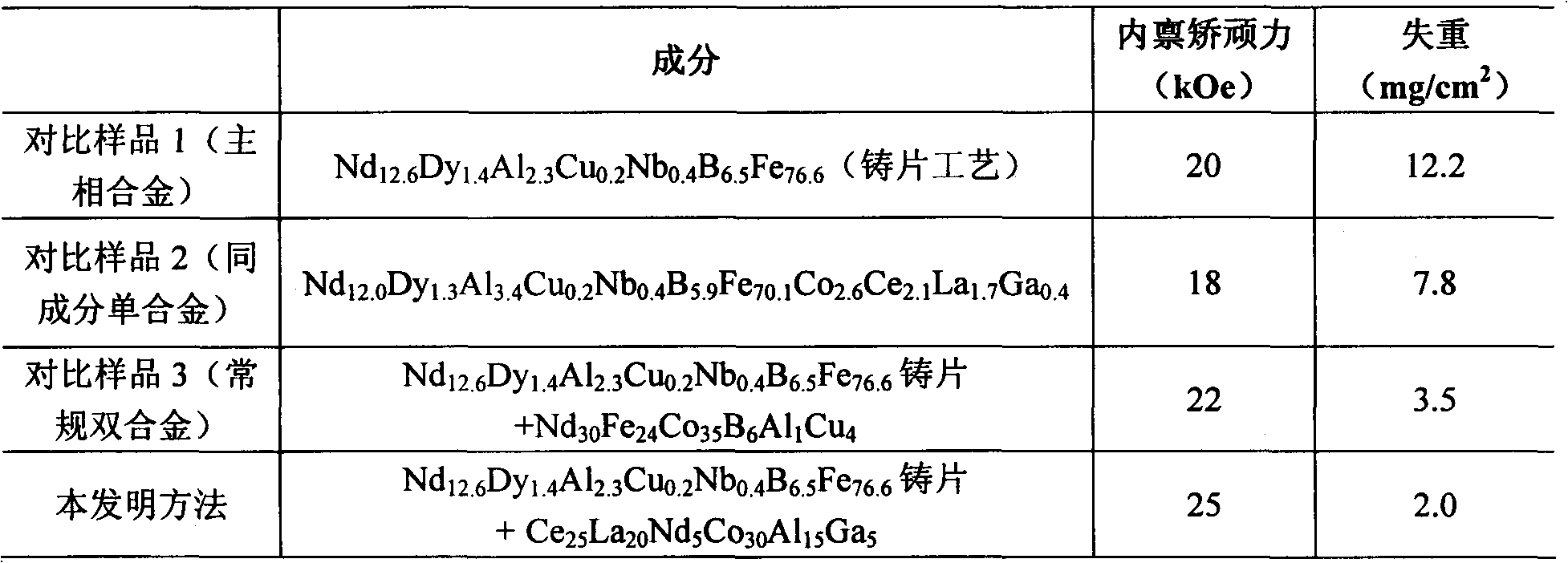
A preparation method of high-performance sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium (Dy) content and high performance; the method comprises the following steps of: sputtering and plating the Dy element on the surface of jet mill powder by using the powder plate technology based on magnetron sputtering on the basis of preparing NdFeB powder, and then sufficiently dispersing the Dy element to micron-sized NdFeB crystal particles by dispersing the Dy element at high temperature in the sintering and tempering process, thereby achieving the effect of improving magnetic performance of the sintered NdFeB. Compared with the introduction of the Dy element in the proportioning process of the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages: the low dysprosium content and high performance is limited in the nano-size by adopting the physical gas-phase deposition, the consumption quantity of the Dy element during the production process is controlled effectively and the preparationof sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content and high performance is realized. Compared with the sintered NdFeB of the same components prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, both the intrinsic coercivity and the maximum magnetic energy product of the sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnetic material obtained according to the invention are improved obviously; compared with the sintered NdFeB with the same performance prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, the dosage of the dysprosium element is reduced remarkably. The method can be widely applicable to producing and manufacturing sintered NdFeB with high performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20110223446A1Improve recording densityImprove signal-to-noise ratioRecord information storageMagnetic recordingRecording layerRecording density
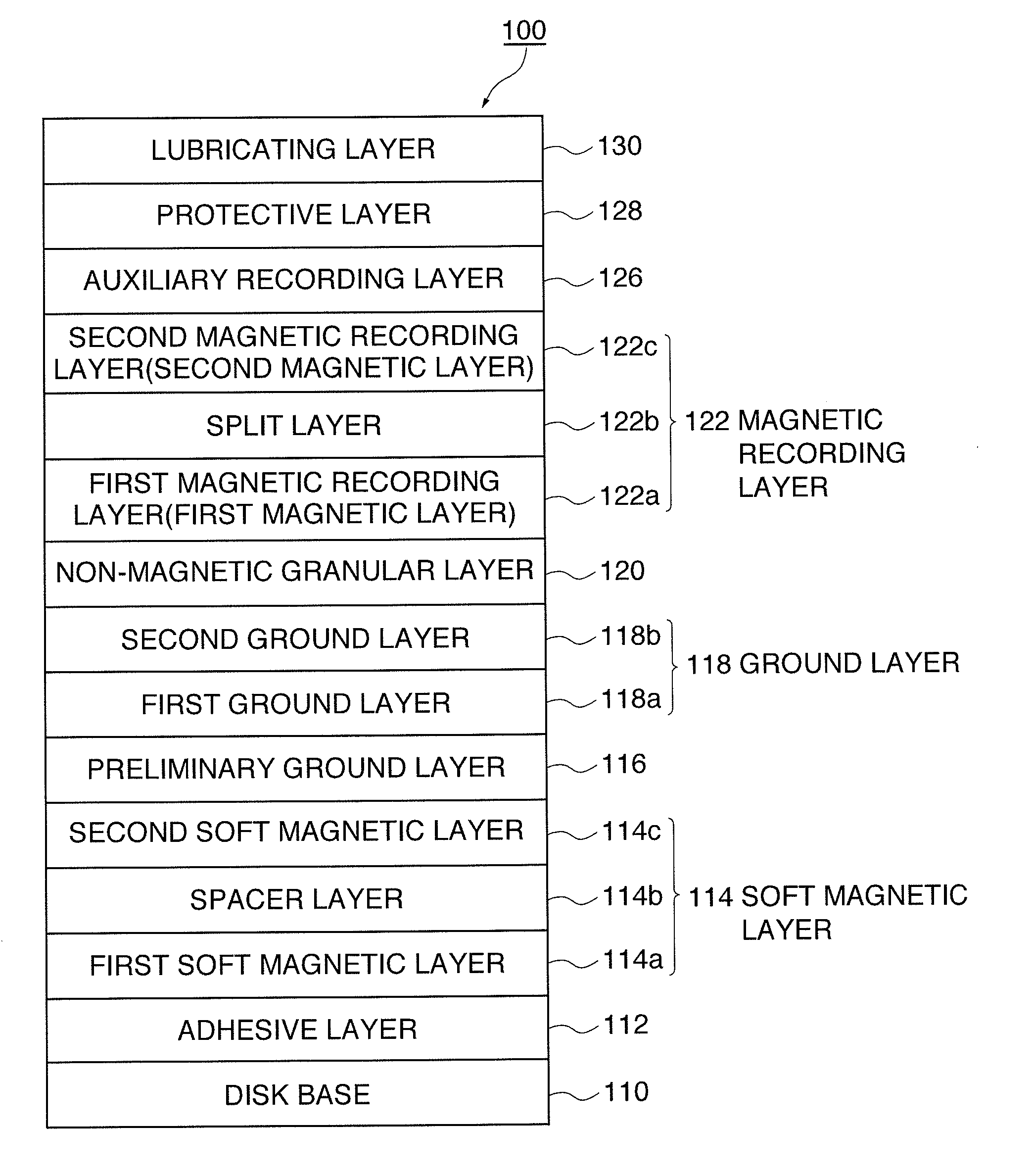
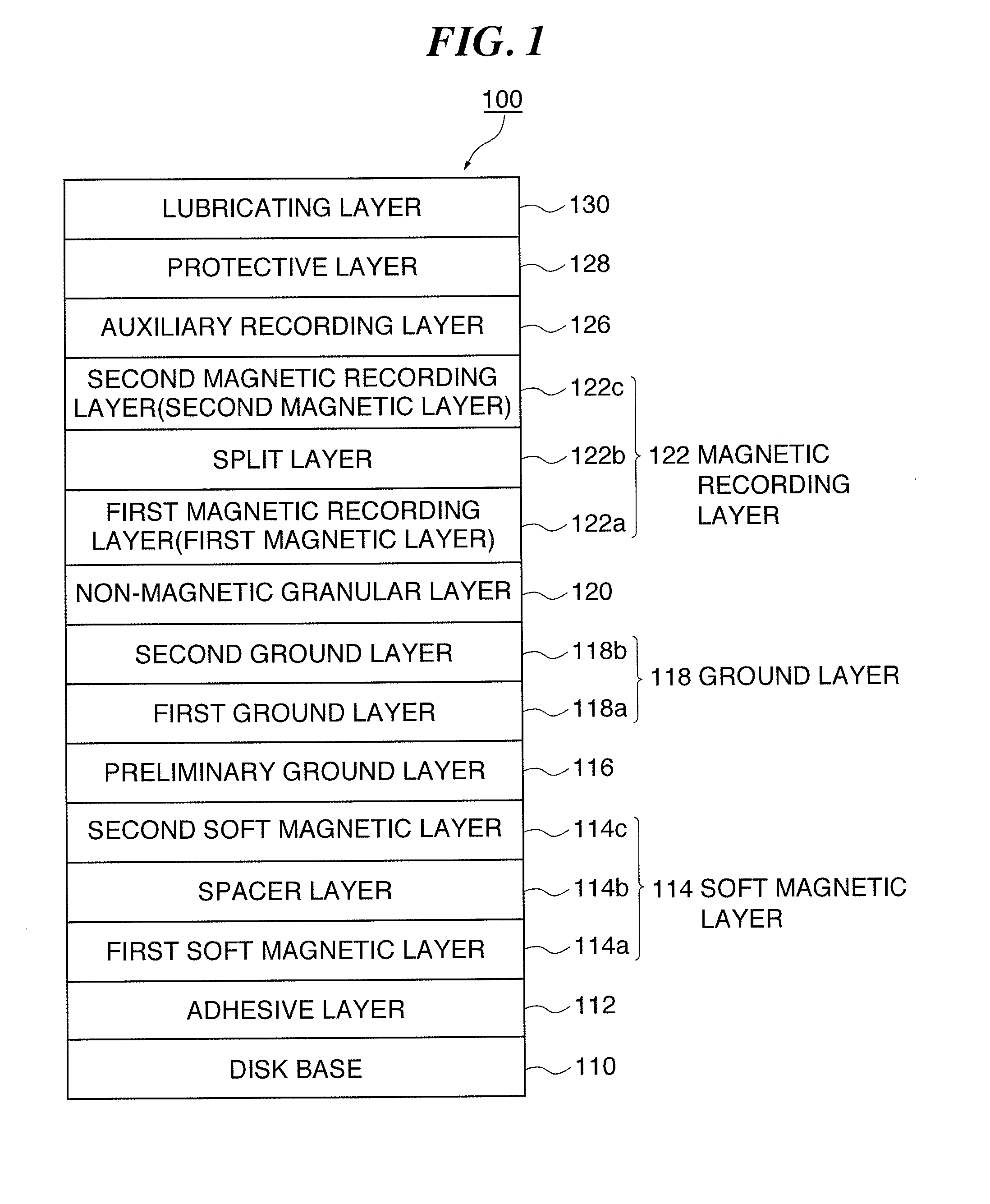
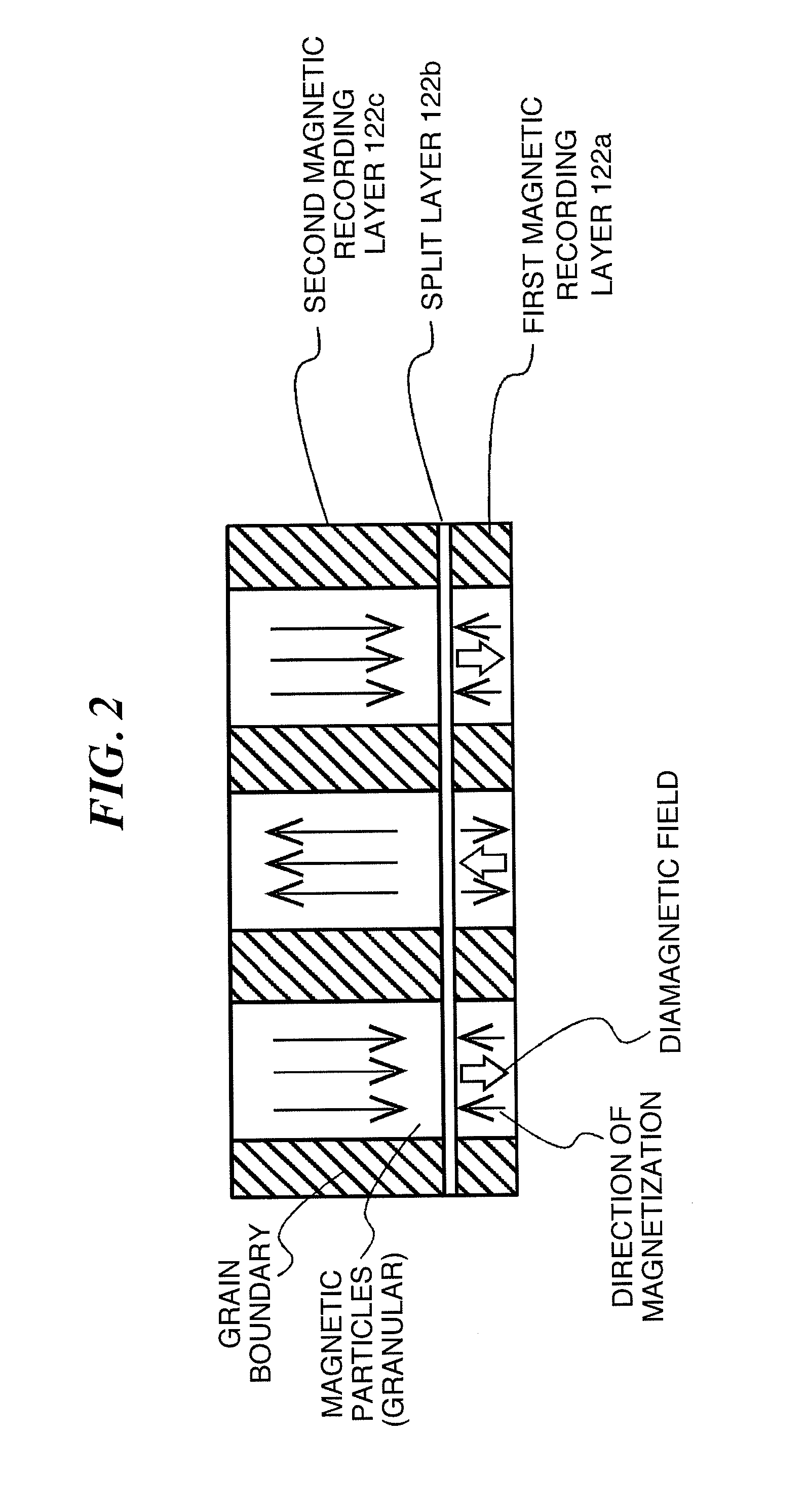
An object of the present invention is to provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium the SNR of which is further improved while a high coercive force Hc is secured so that a higher recoding density can be achieved.The structure of a perpendicular magnetic recording medium 100 according to the present invention includes, on a base, at least a first magnetic recording layer 122a having a granular structure in which a non-magnetic grain boundary portion is formed between crystal particles grown in a columnar shape; a non-magnetic split layer 122b containing Ru disposed on the first magnetic layer; and a second magnetic recording layer 122c that is disposed on the split layer and that has a granular structure in which a non-magnetic grain boundary portion is formed between crystal particles grown in a columnar shape, wherein the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer contain oxides that form the grain boundary, and when an oxide content of the first magnetic layer is represented by A and an oxide content of the second magnetic layer is represented by B, a relationship between the oxide contents A / B is in the range of 0.5<A / B<1.0.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for increasing sintering Nd-Fe-B coercive force by adding nano-oxide in crystal boundary phase
InactiveCN1688000ANot easily oxidizedIncrease the coercive force of the magnetInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureIngotGrain boundary
This invention discloses a method for increasing sintered Nd FeB coercive force by adding nm oxide in grain-boundary phase including the following steps: 1,applying casting technology to produce NdFeB ingot alloy or applying rapid hardening film technology to produce NdFeB rapid hardening film of with host phase alloy, applying casting technology to produce ingot alloy or rapid hardening film technology to get rapid hardening film or rapid quench technology to manufacture a rapid quench strip with the grain boundary phase alloy, 2, processing powder with the two alloys, 3, adding a nm oxide to the grain boundary phase alloy powder, 4, pressing the mixed powder into formation, 5, producing sintered magnetic body in a vacuum sintering oven.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Magnet for a dynamoelectric machine, dynamoelectric machine and method
InactiveUS20070284960A1Improve electrical performanceImprove the level ofMagnetic circuit stationary partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnet
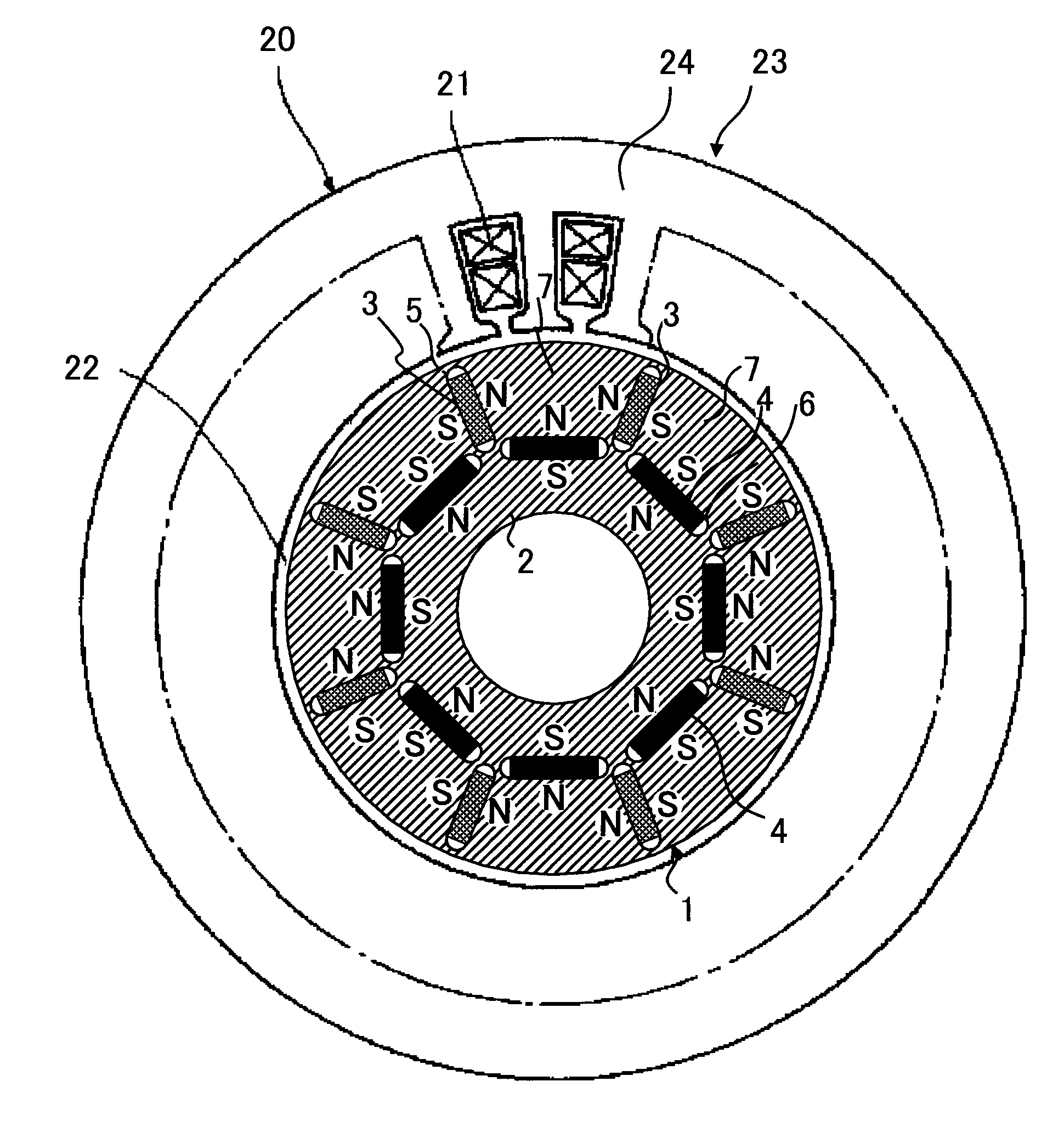
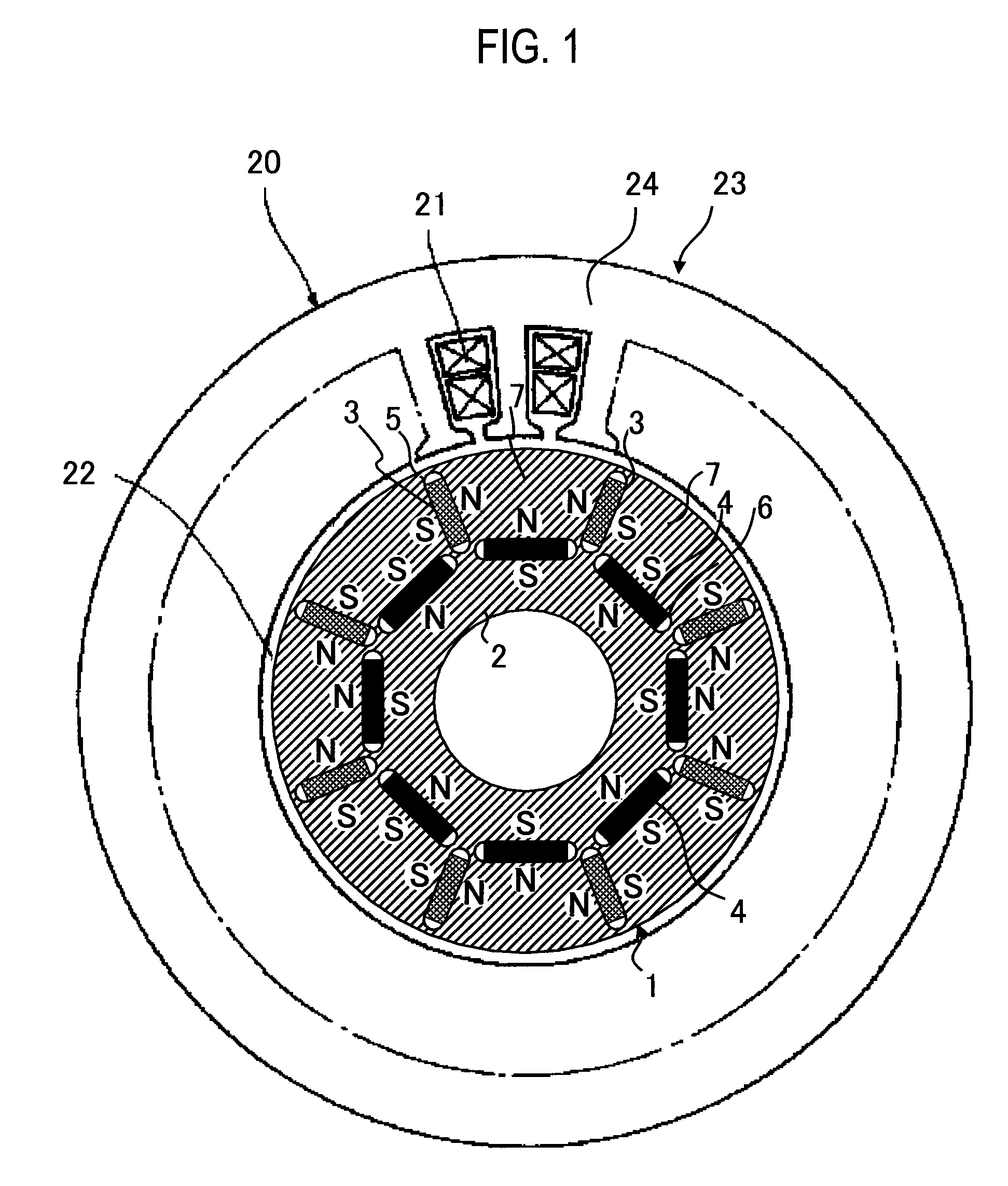
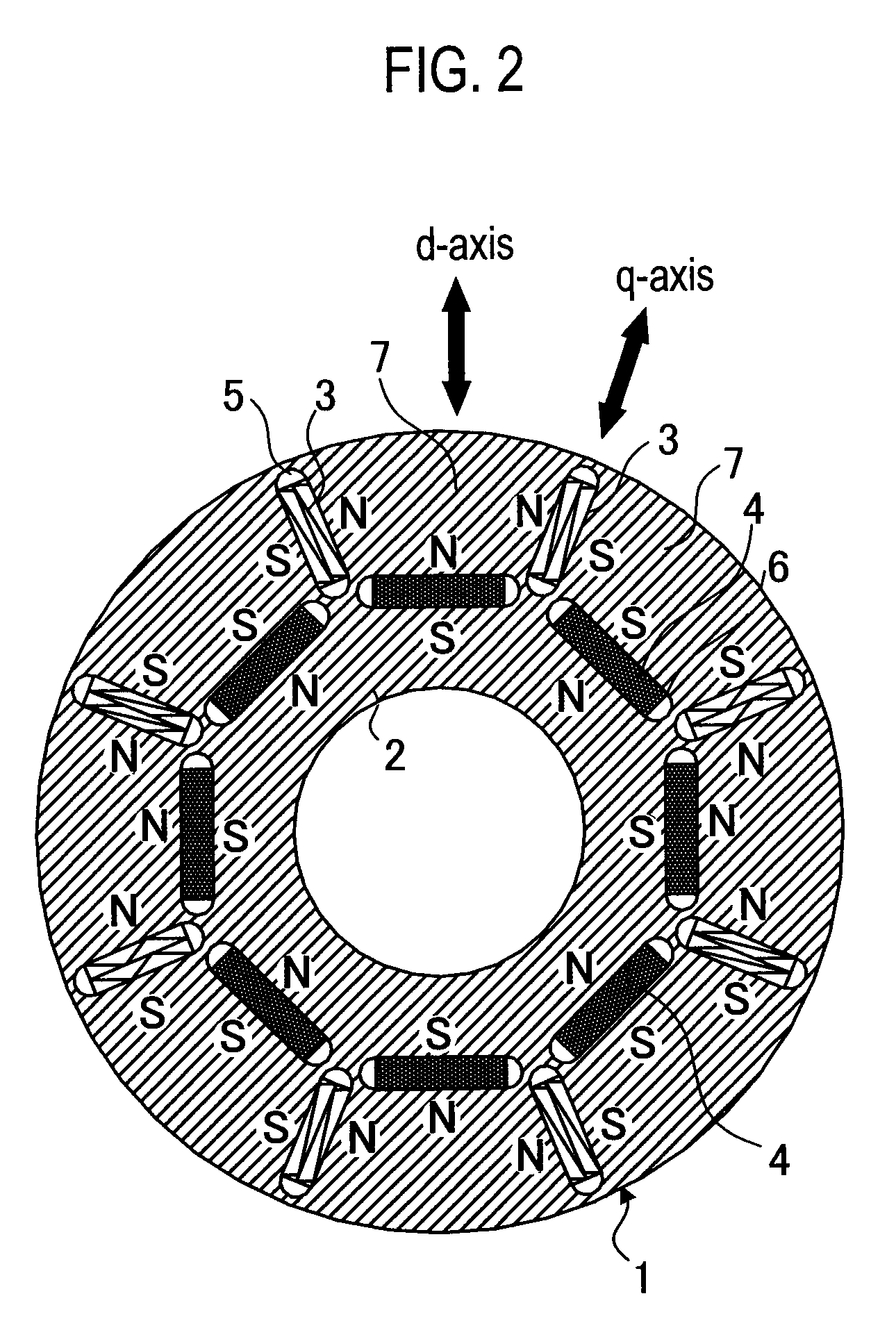
Disclosed herein is an apparatus relating to a magnet member for a dynamoelectric machine comprising, a first portion of the magnet member made of a first magnetic material and a second portion of the magnet member made of a second magnetic material. Further disclosed is a method that relates to increasing performance of an electric machine comprising, determining locations of high demagnetization fields at the dynamoelectric machine, and positioning a magnetic member having a first portion having a higher level of coercivity and a second portion having a lower level of coercivity in the machine such that the portion having a higher level of coercivity is more proximate the location of high demagnetization fields than the portion having the lower level of coercivity.
Owner:REMY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Method for improving performance of sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic material
ActiveCN101615459AEvenly distributed and orderlySolve bad problems such as α-Fe segregationInorganic material magnetismHigh energyPositive pressure
The invention relates to a method for improving performance of sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic property by a rapid-hardening flake grain boundary diffusion heavy rare earth compound in rare earth material technical field, which comprises the following steps: 1) rapid-hardening technology is adopted to prepare an Nd-Fe-B alloy rapid-hardening flake; 2) a high-energy ball mill is used to prepare the heavy rare earth compound into powder particles with diameter being smaller than 1mu m; 3) the rapid-hardening flake is put into heavy rare earth compound turbid liquid to carry out ultrasonic coating; 4) the coated rapid-hardening flake is put into a sintered furnace filled with Ar2 to carry out positive pressure thermal diffusion; 5) ball milling, powder processing, orientation shaping, isostatic pressing and vacuum sintering are adopted to prepare the strip-casting flake after the heat treatment into a magnet. The chemical formula of the Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic material is NdxFe(100-x-y-z-xl)ByCozCuxl, and the mass percent is as follows: x is 30-31.5, y is 0.95-1, z is 1-1.2, and xl is 0-0.06. The magnet prepared by the invention improves the intrinsic coercivity on the basis of keeping the current magnetic energy product.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
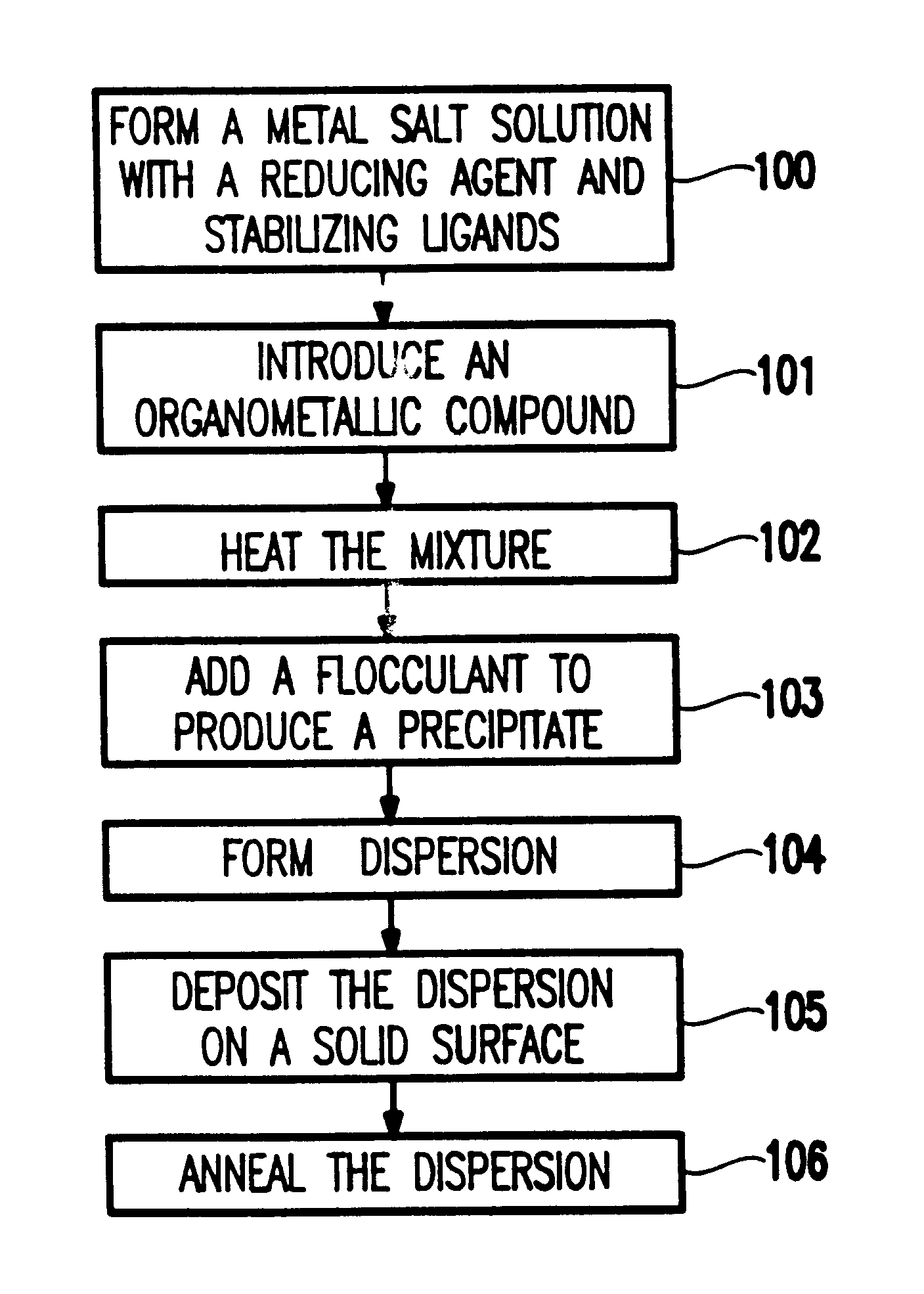
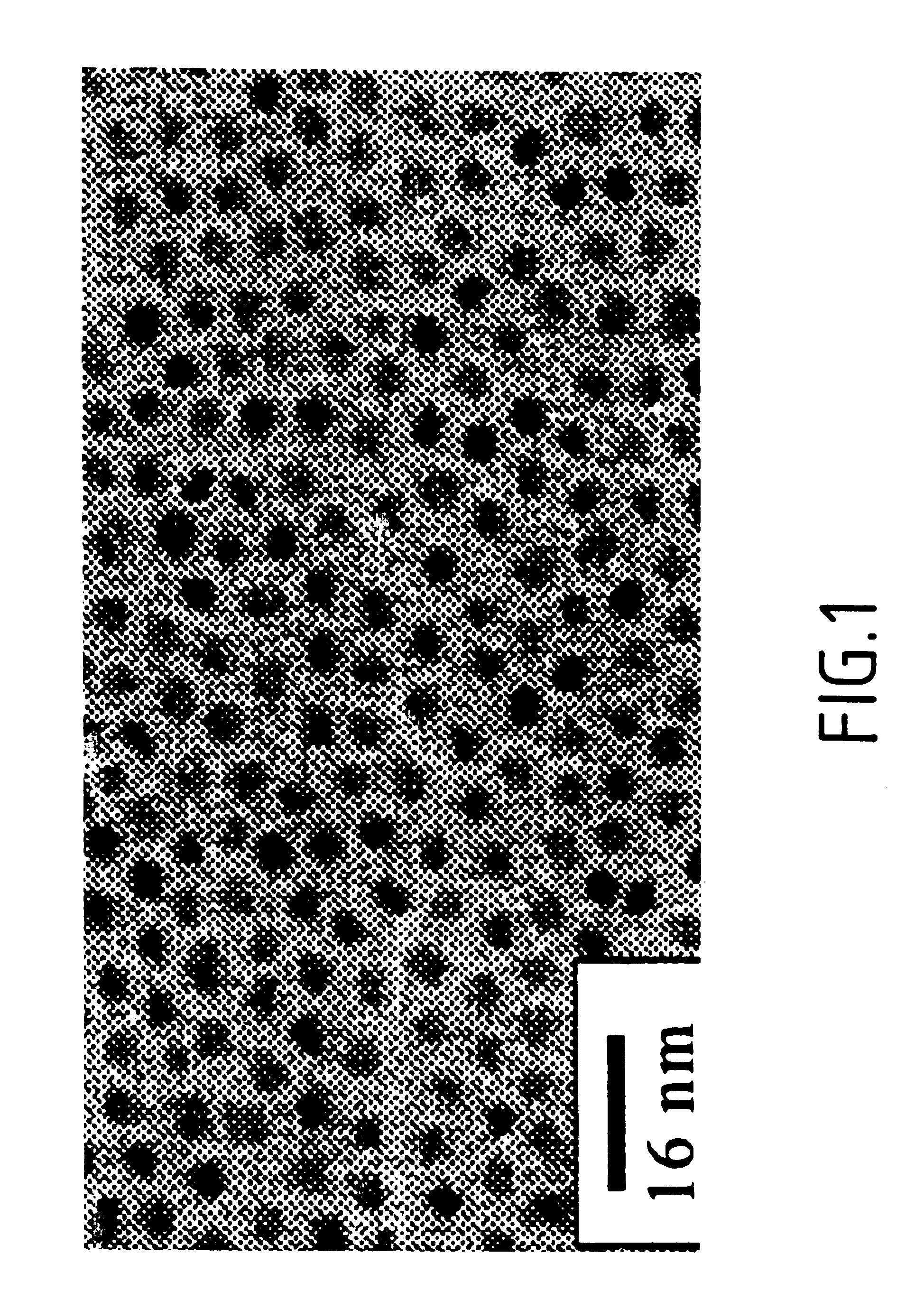
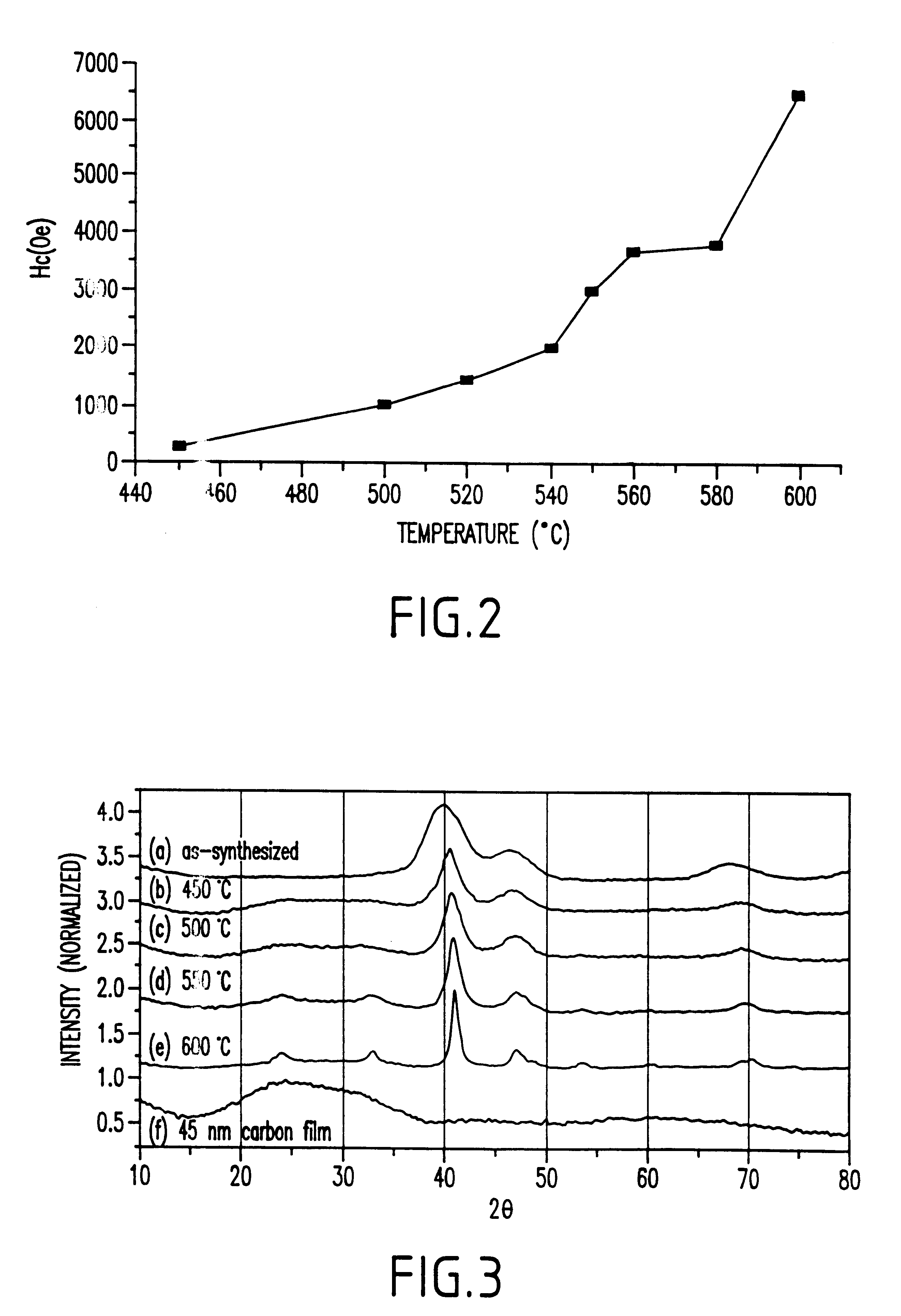
Chemical synthesis of monodisperse and magnetic alloy nanocrystal containing thin films
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
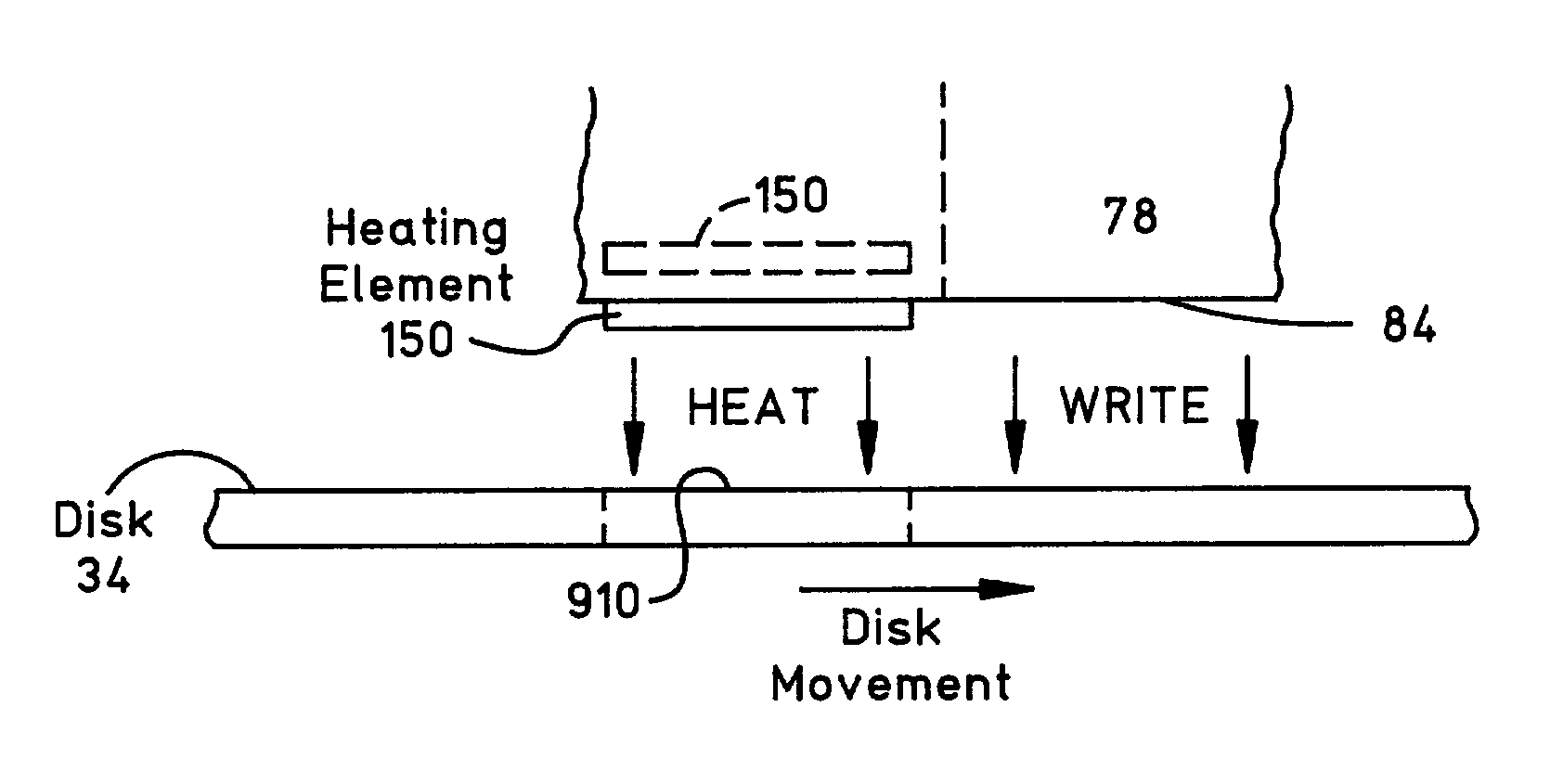
Magnetic head having a heater circuit for thermally-assisted writing
InactiveUS7006336B2Facilitates writing of dataImprove coercive forceConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsEngineeringHeating element
A magnetic head for thermally-assisted writing of data to a disk is disclosed. In one illustrative example, the magnetic head includes a write head element and a heating element which is a resistive infared radiator. The heating element is coupled to at least one via pad which is exposed on an outer surface of the magnetic head. This via pad may be the same pad utilized for the write head element or for a read sensor. The heating element is formed beneath or within the pole tip such that it is able to transfer heat to a portion of the disk before the write head element can write data to it Advantageously, the heater facilitates the writing of data to high coercivity media.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
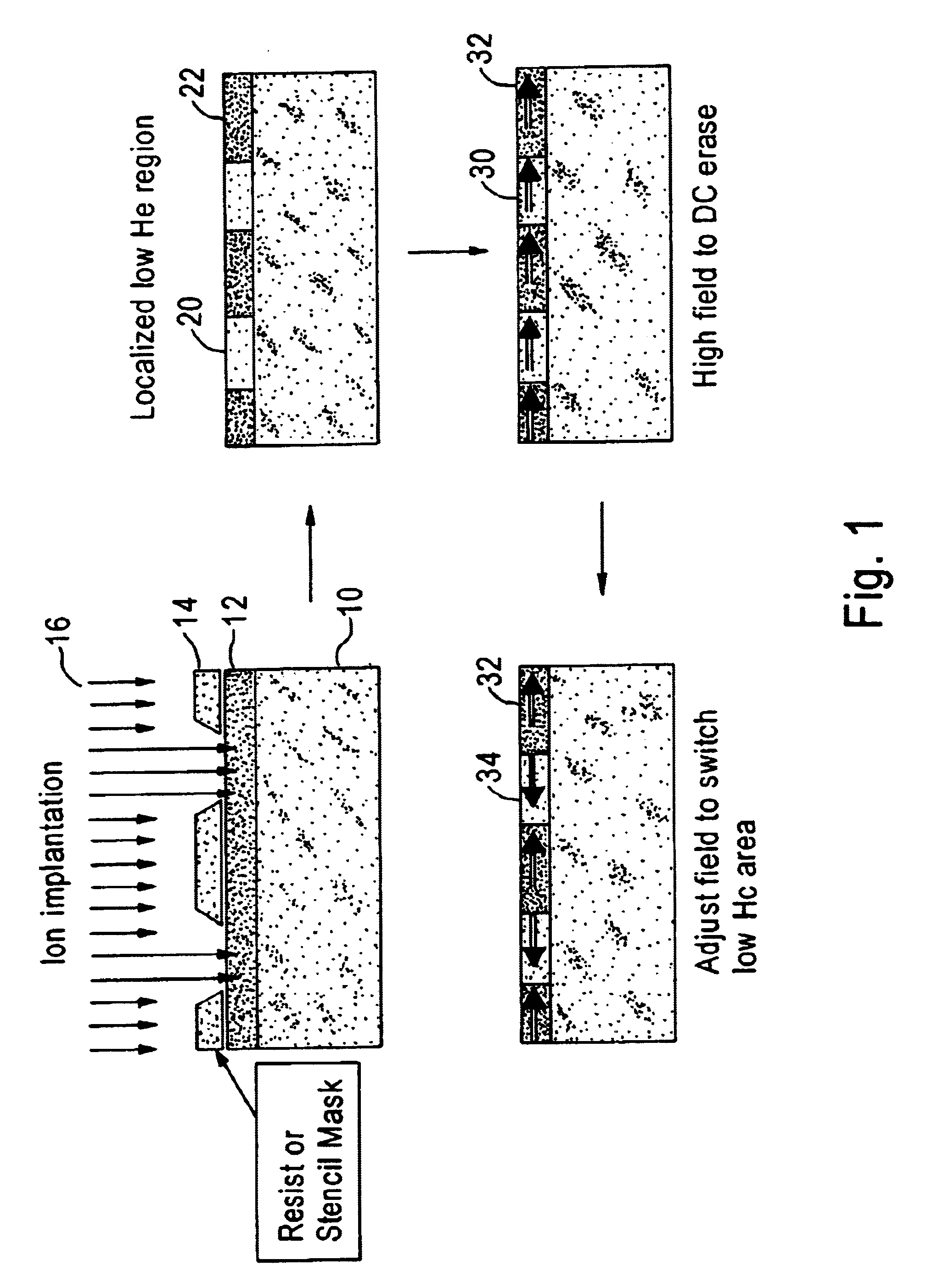
Patterning longitudinal magnetic recording media with ion implantation
InactiveUS6864042B1Increased areal recording densityUniform surfaceNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersIon bombardmentTopography
A magnetic recording medium is formed with a distribution of low coercivity regions functioning as a transition pattern for servo information capable of being sensed by a read / write head by exposing a masked magnetic layer to ions to change the coercivity of the exposed magnetic layer without substantially affecting the topography of the magnetic layer.Embodiments of the present invention include forming a series of substantially radially extending low coercivity regions used to divide the magnetic layer into a plurality of sectors comprising substantially concentric circumferentially extending data tracks by exposing a masked magnetic layer having a high coercivity, i.e. from about 2000 Oe to about 10000 Oe, to one or more heavy atom ion bombardments of gaseous ions, e.g. argon ions, at a dose of about 1×1013 atoms / cm2 to about 9×1015 atoms / cm2 having an implantation energy of about 10 KeV to about 50 KeV.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic head apparatus and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20070253106A1Improve coercive forceImprove recording accuracyConstruction of head windingsRecord information storageMagnetic polesEngineering
A magnetic head apparatus is provided which is capable of recording data in a recoding layer having high coercive force with high accuracy without heating. A magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus is also provided which has the magnetic head apparatus. A recording head has: a main magnetic pole; a recording-side front-end shield (a return magnetic pole); a recording-side rear-end shield (a return magnetic pole); a main coil for generating a perpendicular recording magnetic field at the main magnetic pole; and an auxiliary coil for generating a longitudinal alternating current magnetic field having a frequency in the microwave band at the main magnetic pole.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
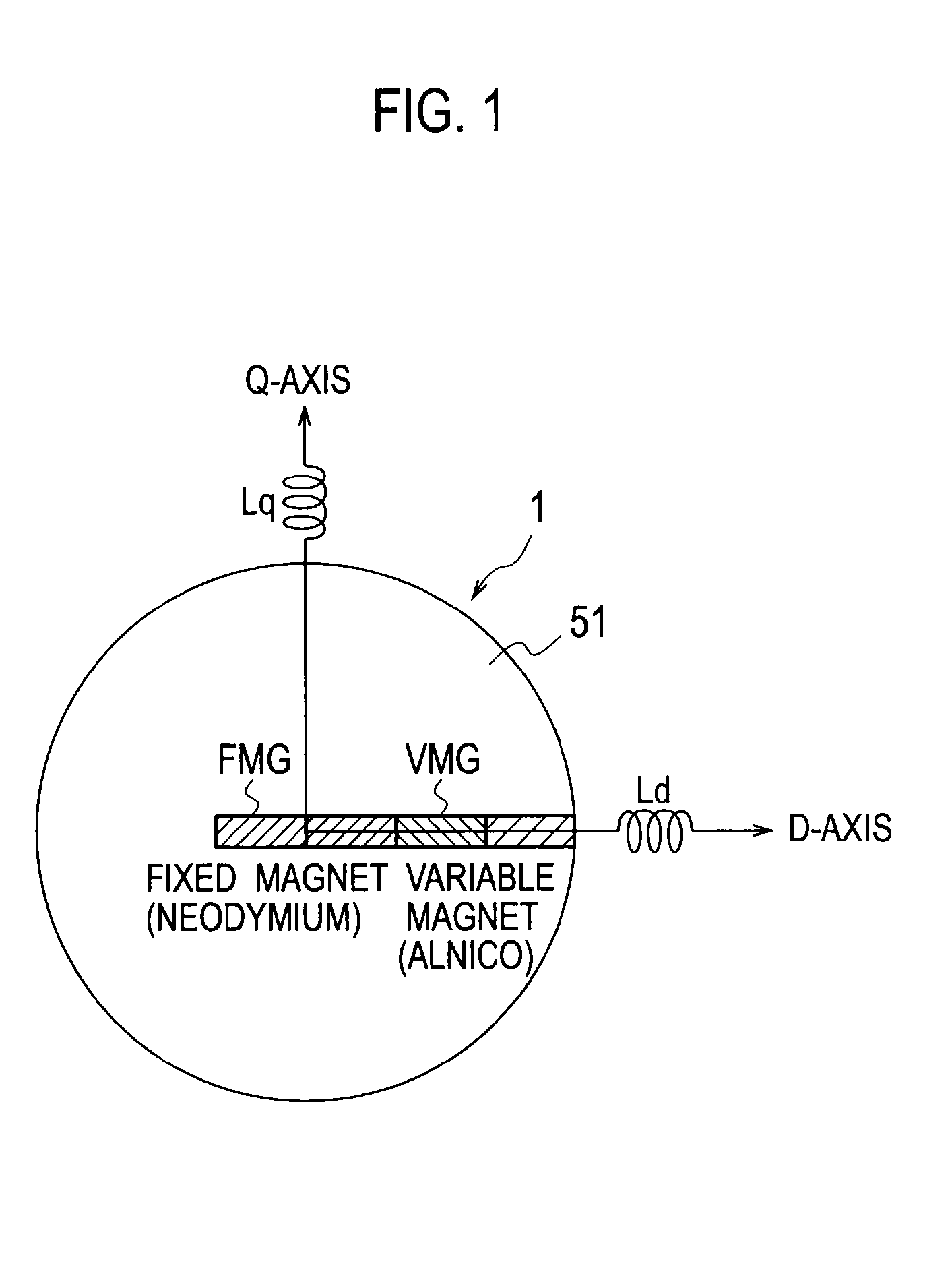
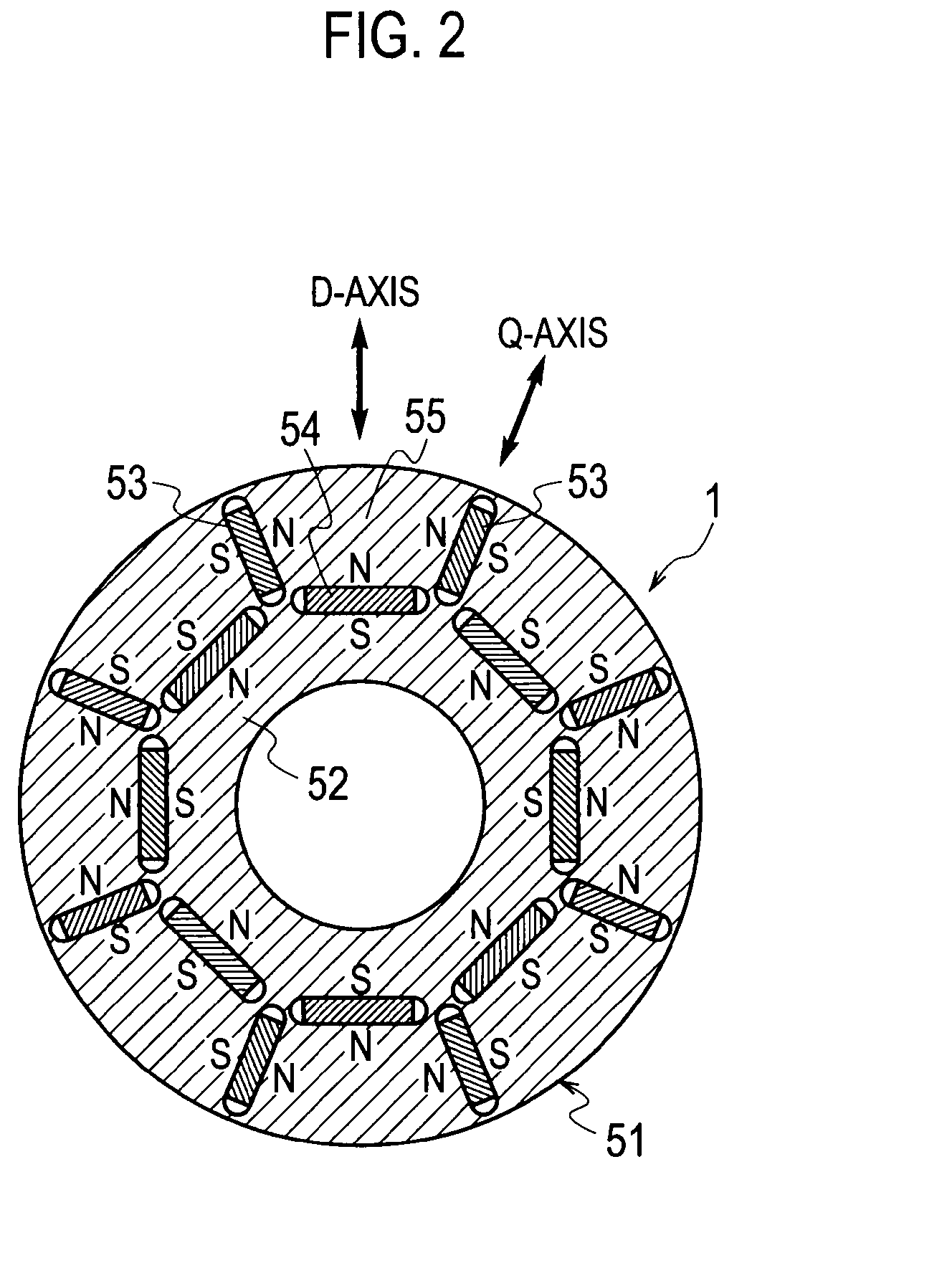
Variable magnetic flux drive system
ActiveUS20100201294A1Improve efficiencyMinimize induced voltageAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersMotor driveMagnetization
A variable magnetic flux motor drive system includes: a variable magnetic flux motor having a variable magnet which is a low-coercive permanent magnet; an inverter that drives the variable magnetic flux motor 1; an inverter as a magnetization unit which supplies a magnetization current for controlling a magnetic flux of the variable magnet; and a boosting unit boosting an input DC voltage to a predetermined target value to output it to the inverter. The variable magnetic flux motor drive system makes it possible to achieve size reduction and high efficiency, while securing a voltage required for supplying a magnetization current when controlling the magnetic flux of the variable magnet.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
R-T-B series permanent magnet material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110853855AImprove coercive forceImprove remanenceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementComposite material
The invention discloses an R-T-B series permanent magnet material and a preparation method and application thereof. The R-T-B series permanent magnet material comprises components of 29.5-33.0 wt.% ofR', N, B and Te, wherein the R' comprises R, Pr, Nd, the R is a rare earth element except Pr and Nd, the content of Pr is greater than or equal to 8.85 wt.%, a mass ratio of Nd to R' is less than 0.5, the N is greater than 0.05 wt.% and is not greater than 4.1 wt.%, the N is Ti, Zr or Nb, the B is 0.90-1.2wt.%, and the Fe is 62.0-68.0wt.%. The R-T-B series permanent magnet material is advantagedin that a sintered permanent magnet product with high coercive force and a stable temperature coefficient is prepared by adopting a formula with high Pr content, advantages of Pr can be exerted to themaximum extent by adopting the formula disclosed by the invention, and production cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Low-loss magnetic powder core, and switching power supply, active filter, filter, and amplifying device using the same
InactiveUS6897718B2Reduced core lossLess distortionDc-dc conversionInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyAlloy
A magnetic powder core comprises a molded article of a mixture of a glassy alloy powder and an insulating material. The glassy alloy comprises Fe and at least one element selected from Al, P, C, Si, and B, and has a texture primarily composed of an amorphous phase. The glassy alloy exhibits a temperature difference ΔTx, which is represented by the equation ΔTx=Tx−Tg, of at least 20 K in a supercooled liquid, wherein Tx indicates the crystallization temperature and Tg indicates the glass transition temperature. The magnetic core precursor is produced mixing the glassy alloy powder with the insulating material, compacting the mixture to form a magnetic core precursor, and annealing the magnetic core precursor at a temperature in the range between (Tg−170) K and Tg K to relieve the internal stress of the magnetic core precursor. The glassy alloy exhibits low coercive force and low core loss.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
High-coercivity and high-stability neodymium iron boron magnet and preparation method based on crystal boundary reconstruction
ActiveCN103106991AImprove organizationImprove distributionPermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementAlloy
The invention discloses a high-coercivity and high-stability neodymium iron boron magnet and a preparation method based on crystal boundary reconstruction. The preparation method comprises the steps of separating design and preparation of main alloy and crystal boundary phase alloy powder, nano-modification of crystal boundary phase, powder mixing, magnetic field profiling, isostatic pressing, sintering and thermal treatment. According to the high-coercivity and high-stability neodymium iron boron magnet and the preparation method is based on crystal boundary reconstruction and combines with a rich heavy rear earth novel crystal boundary phase and nano-modification technology, namely the rich heavy rare earth novel crystal boundary phase is redesigned and synthesized, in the process of magnetic sintering and tempering, magnetic hardening is achieved through spread of the heavy rare earth element to the boundary layers of the principle phase crystal grain, and thus a high-coercivity magnetic is prepared under the condition that no or less heavy rear earth is added in the principle phase. Meanwhile the distribution of the crystal boundary and the form of the crystal grain boundary are optimized through a nano-modification method, a pinning domain wall restrains counter magnetic field nucleation and crystal grain growth, and thus high coercivity and high stability of the neodymium iron boron is achieved. The high-coercivity and high-stability neodymium iron boron magnet and preparation method based on crystal boundary reconstruction is simple in process, low in cost and suitable for large-scale volume production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
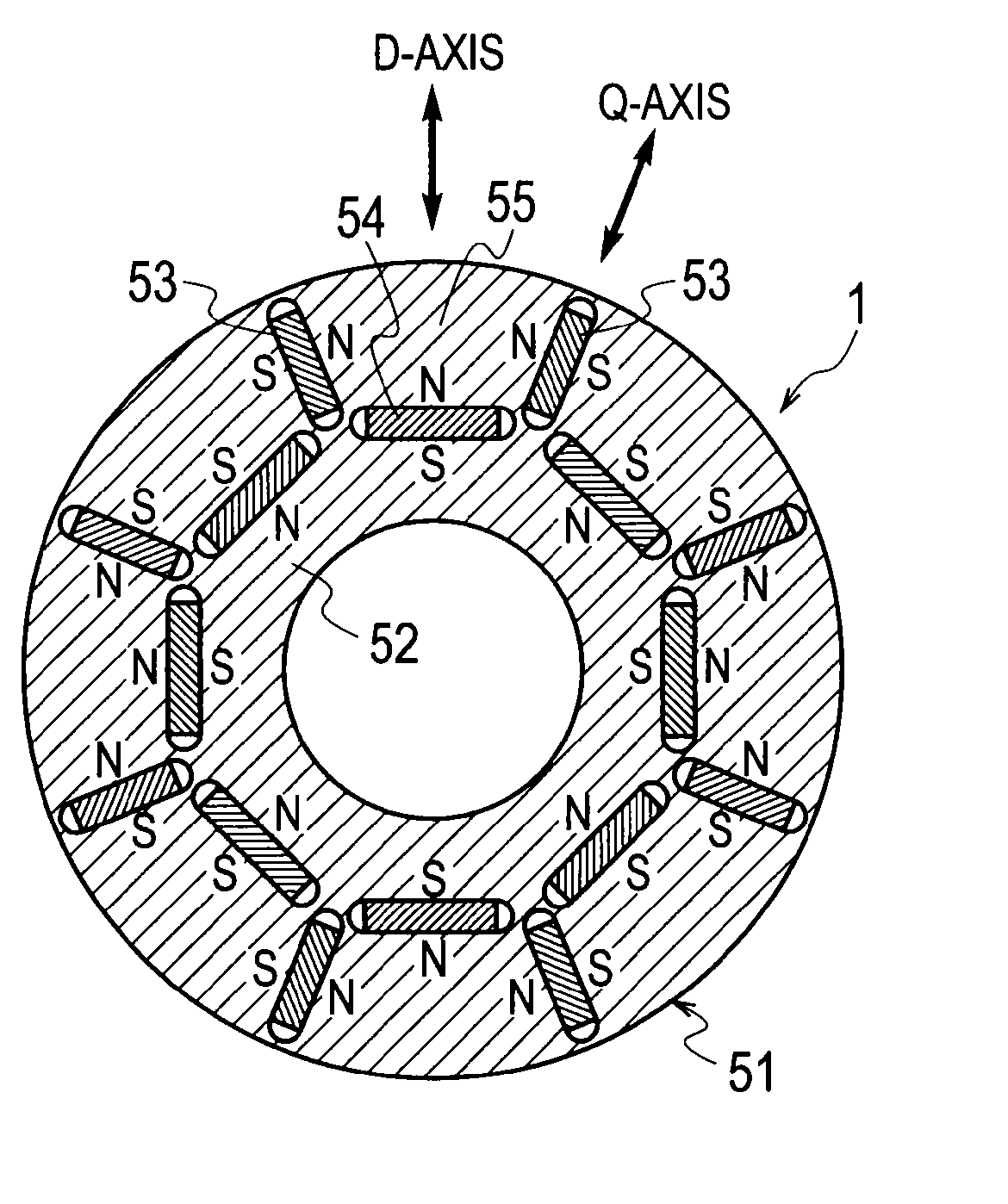
Permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine
ActiveUS20090236923A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLow speedElectric machine
An object of the present invention is to provide a permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine capable of realizing a variable-speed operation at high output in a wide range from low speed to high speed and improving efficiency and reliability. The permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine of the present invention includes a stator provided with a coil and a rotor in which there are arranged a low-coercive-force permanent magnet whose coercive force is of such a level that a magnetic field created by a current of the stator coil may irreversibly change the flux density of the magnet and a high-coercive-force permanent magnet whose coercive force is equal to or larger than twice that of the low-coercive-force permanent magnet. At the time of high-speed rotation with a voltage of the permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine being around or over a power source maximum voltage, the low-coercive-force permanent magnet is magnetized with a magnetic field created by a current in such a way as to decrease total linkage flux of the low- and high-coercive-force permanent magnets, thereby adjusting a total linkage flux amount.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High saturation magnetization intensity Fe-based nanocrystalline magnetically soft alloy material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101834046AHigh saturation magnetizationReduce contentMagnetic materialsMagnetizationMicrostructure
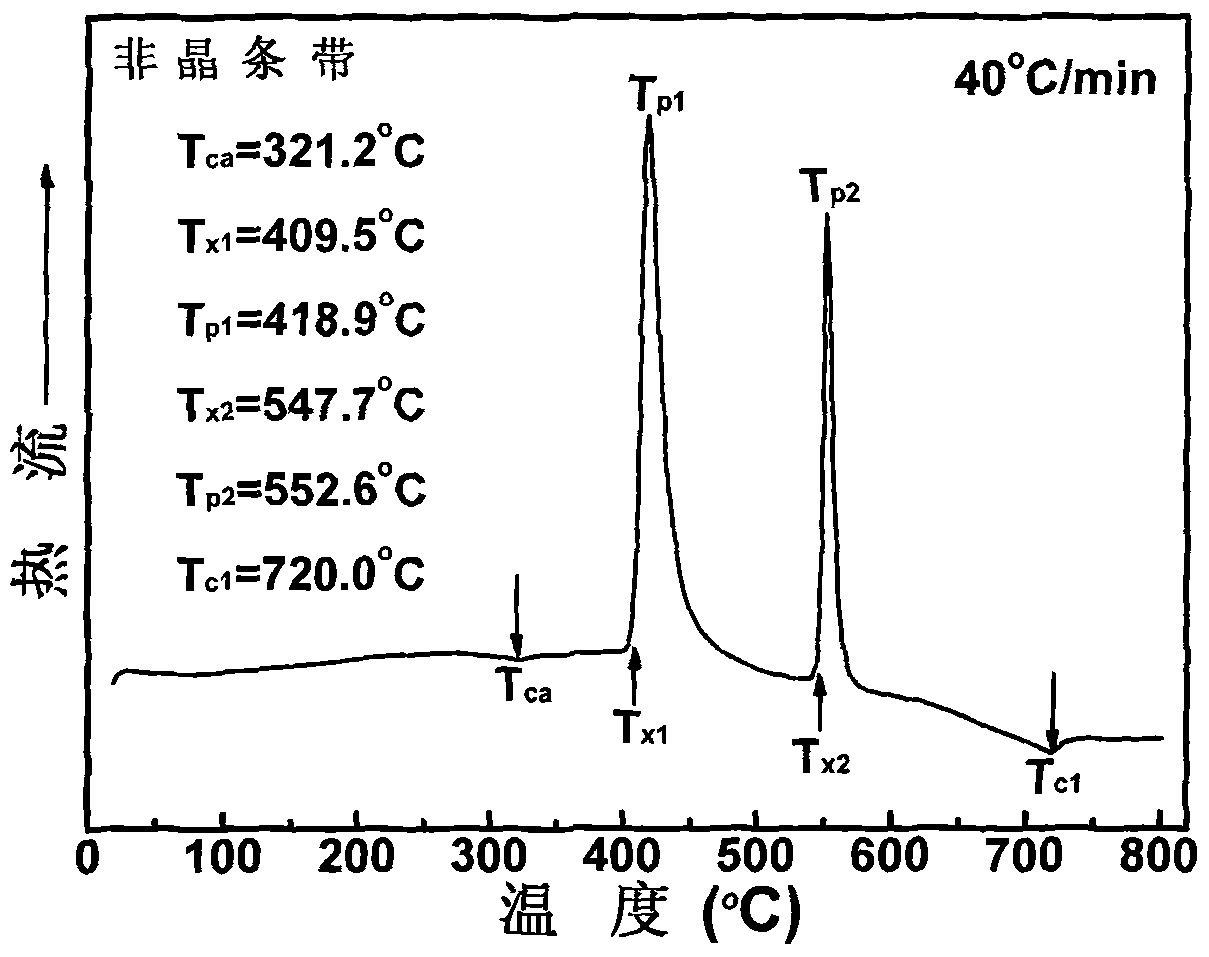
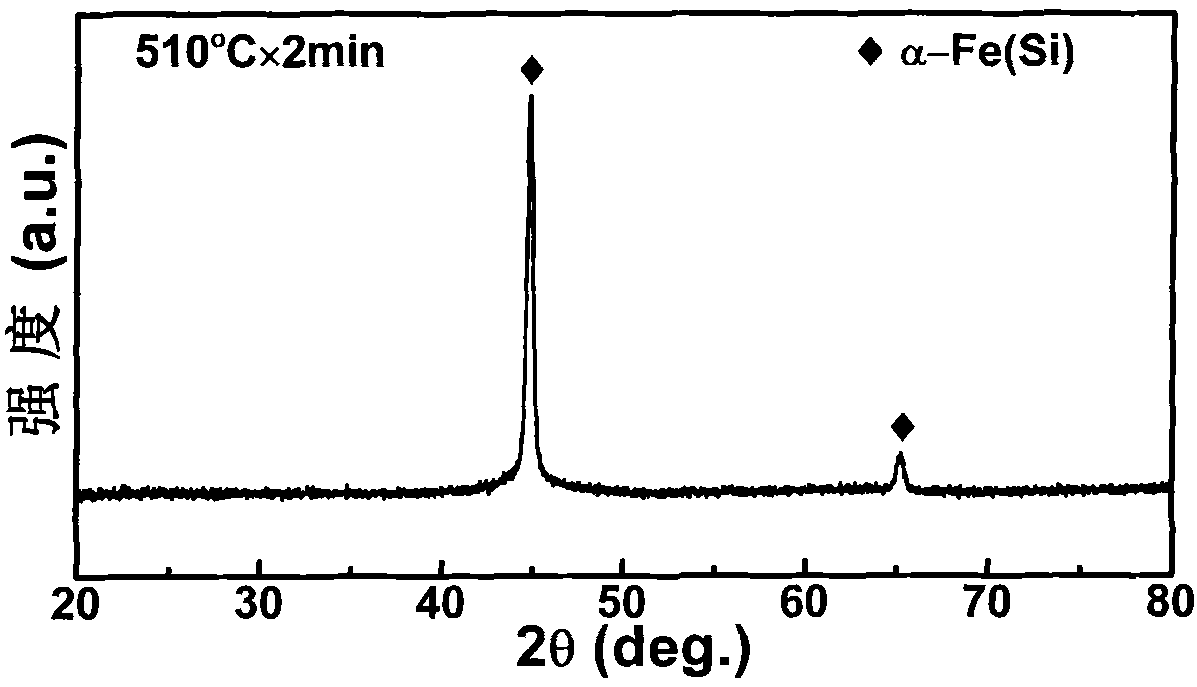
The invention relates to a high saturation magnetization intensity Fe-based nanocrystalline magnetically soft alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The high saturation magnetization intensity Fe-based nanocrystalline magnetically soft alloy material is a FexSiyBzPaCub alloy comprising ferrum, silicon, boron, phosphorus and copper, wherein x, y, z, a and b in the formula respectively represent atom percentage content of each corresponding component, x=70-90%, y=1-15%, z=1-20 %, a=1-20% and b=0.1-1%, and x+y+z+a+b=100%; the microstructure of the Fe-based nanocrystalline magnetically soft alloy is as follows: a body-centered cubic Alpha-Fe(Si) nanocrystalline phase with the size of 1-35nm and an amorphous phase rich in phosphorus and boron coexist, and the amorphous phase is the basic phase. The preparation method comprises steps of: preparing proportioned raw materials into an alloy ingot, preparing into amorphous alloy and carrying out other procedures to obtain the high saturation magnetization intensity Fe-based nanocrystalline magnetically soft alloy. The invention can greatly enhance the saturation magnetization intensity of the nanocrystalline magnetically soft alloy, maintain lower coercivity and effectively reduce cost of raw materials simultaneously.
Owner:朗峰新材料启东有限公司
Sintered neodymium-iron-boron preparation method capable of improving intrinsic coercivity and anticorrosive performance
ActiveCN102220538ALow cooling rate requirementsEnhanced Amorphous Formation AbilityInorganic material magnetismAlloyGas quenching
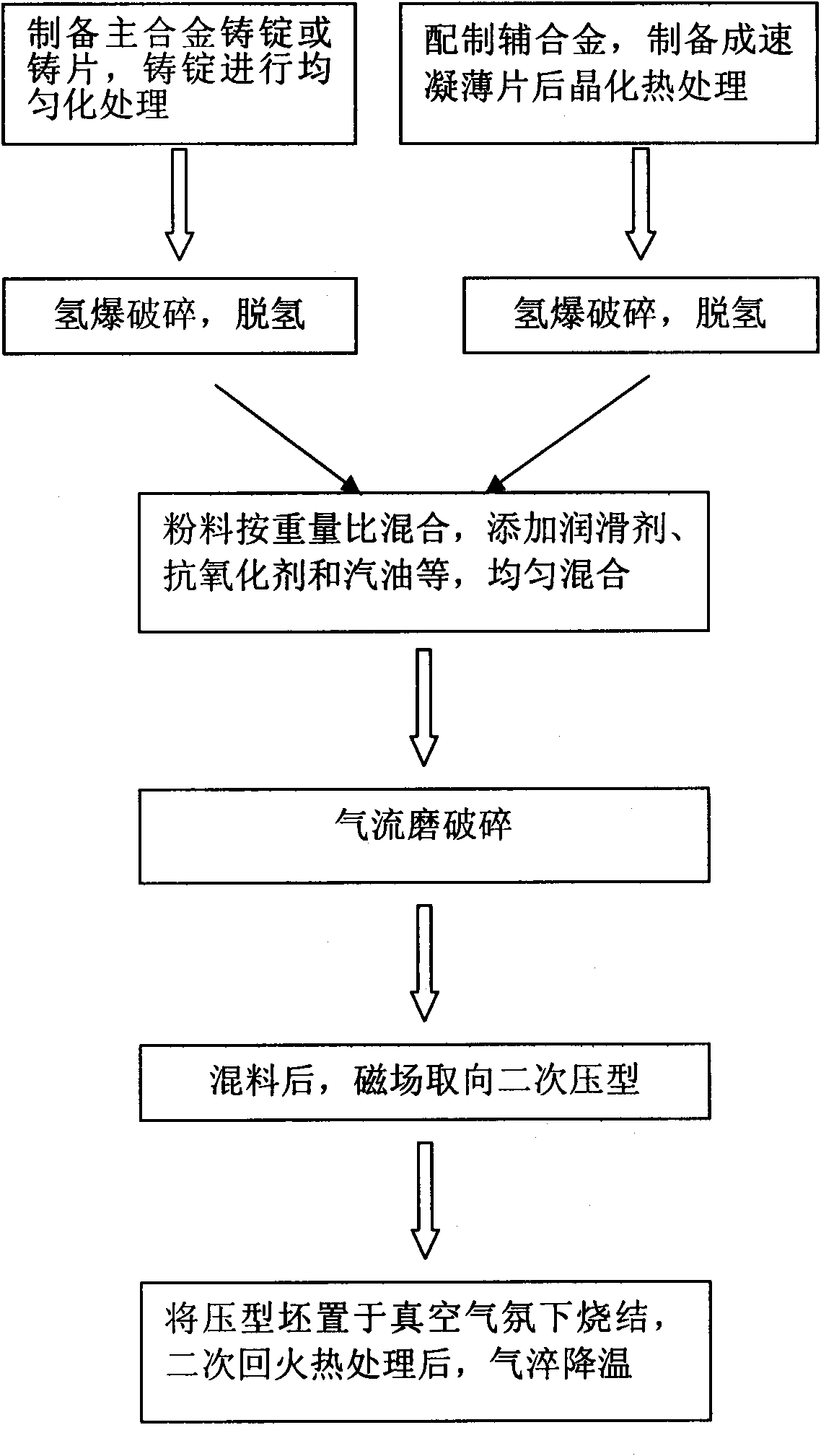
The invention discloses a sintered neodymium-iron-boron preparation method capable of improving intrinsic coercivity and anticorrosive performance. On the basis of a double-alloy preparation process, Ce-enriched multicomponent rare-based alloy with high amorphous forming ability is used as an auxiliary alloy, and the decrystallizatoin of crystal boundary phase structure is realized by gas quenching cooling in a sintering tempering process. In the invention, the intrinsic coercivity is obviously improved, the anticorrosive weight loss is greatly reduced, the magnetic performance and anticorrosive performance are high, and the method can be widely used in the field of production of high-performance anticorrosive sintered neodymium-iron-boron material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
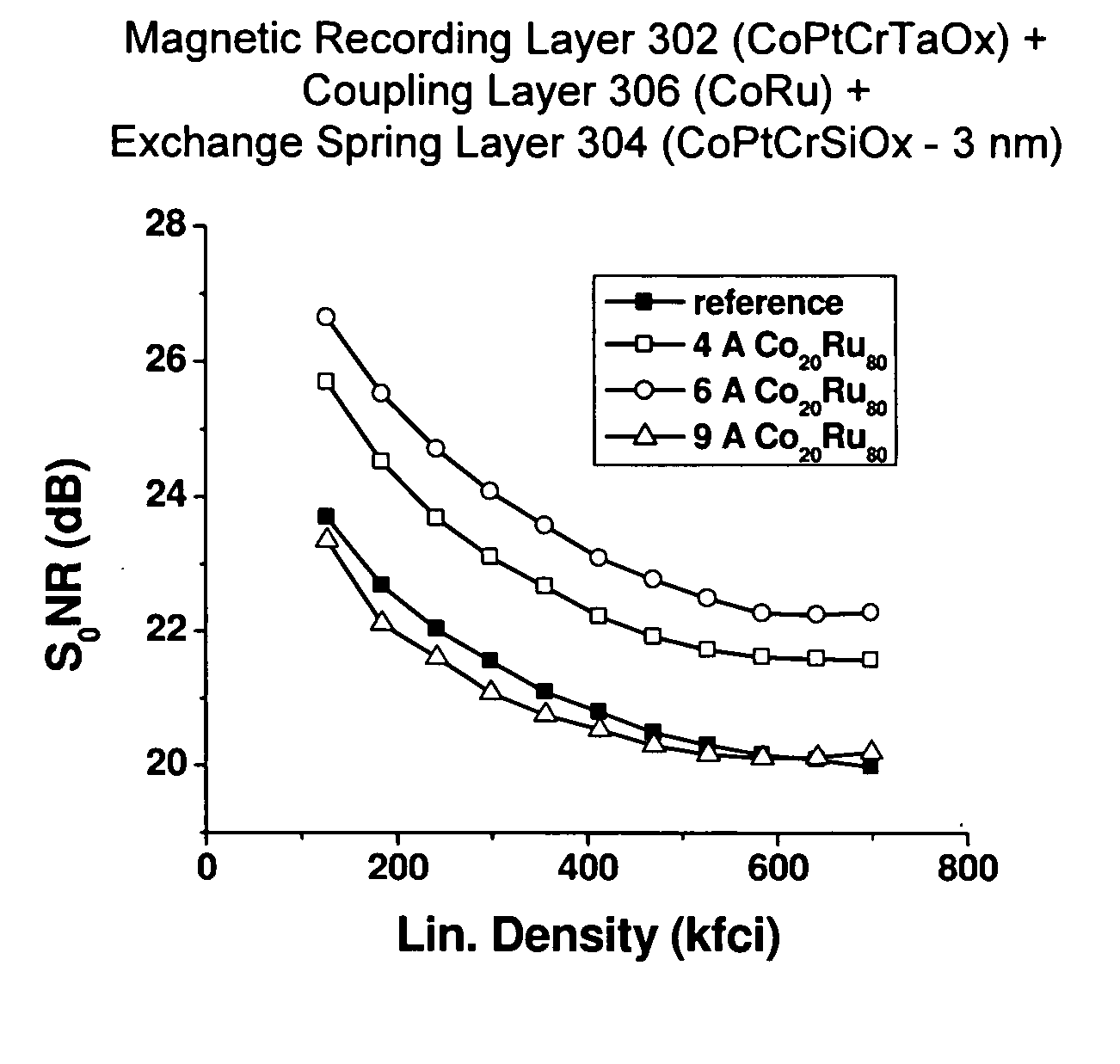
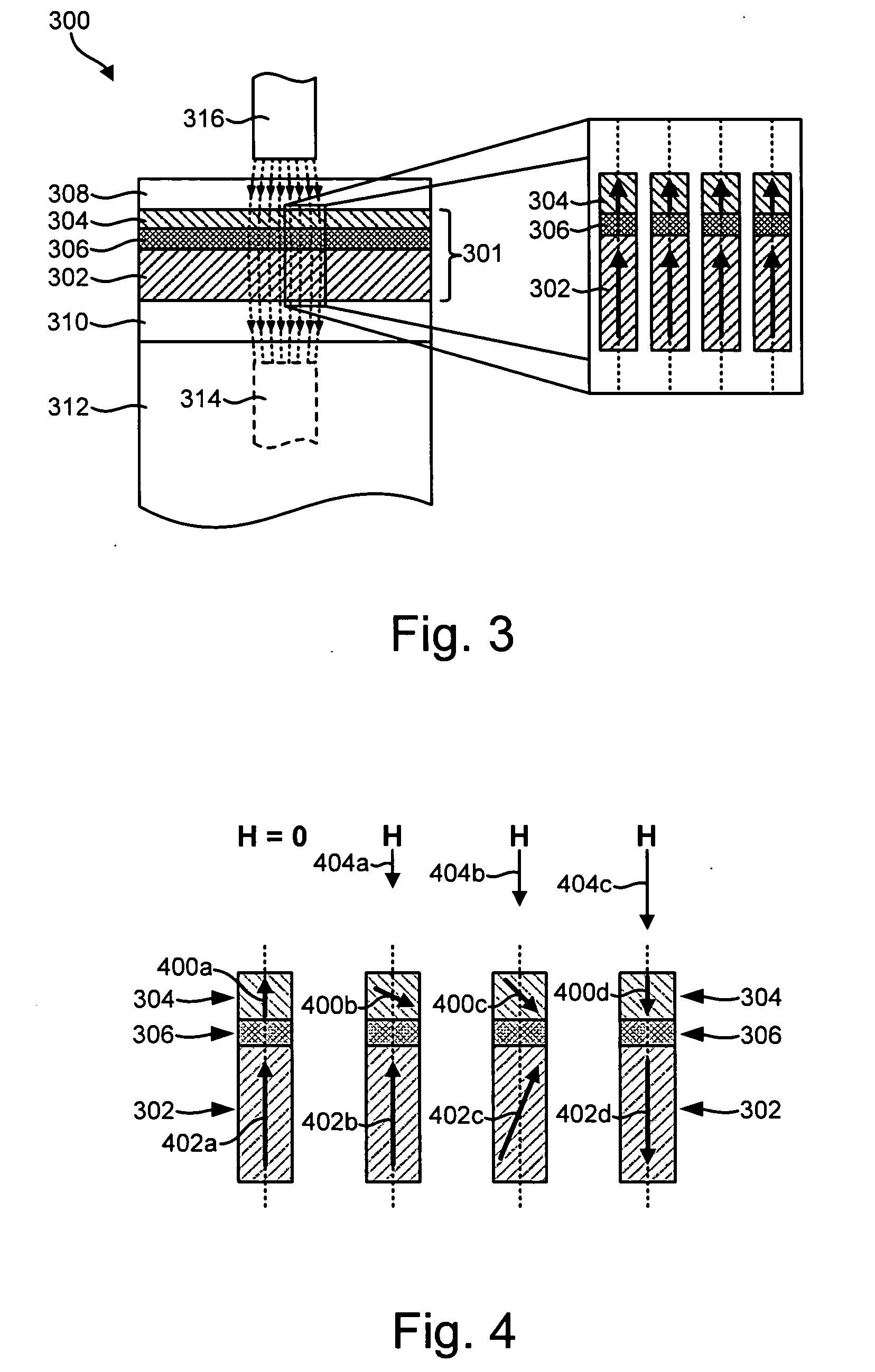
Perpendicular recording media having an exchange-spring structure
InactiveUS20060177704A1Writeability is improvedRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMagnetic anisotropyCoupling
A recording medium providing improved writeability in perpendicular recording applications includes a magnetic recording layer having an axis of magnetic anisotropy substantially perpendicular to the surface thereof, an exchange-spring layer ferromagnetically exchange coupled to the magnetic recording layer and having a coercivity less than the magnetic recording layer coercivity, and a coupling layer between the magnetic recording layer and the exchange-spring layer. The coupling layer regulates the ferromagnetic exchange coupling between the magnetic recording layer and the exchange-spring layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic memory storage device
This invention provides a probe based magnetic memory storage device. In a particular embodiment, magnetic memory cells are provided in an array. Each cell provides a magnetic data layer and a conductor. At least one movable probe having a tip characterized by a conductor and a soft reference layer is also provided. In addition, an intermediate layer joined to either the movable probe or each memory cell is provided. The movable probe may be placed in contact with a given memory cell, the probe and cell thereby forming a tunnel junction memory cell with the intermediate layer serving as the tunnel junction. The magnetic field provided by the probe conductor may be combined with a field provided by the cell conductor to produce a switching field to alter the orientation of the data layer. The memory cells may include a material wherein the coercivity is decreased upon an increase in temperature. The probe may also include a heat generator. The magnetic field provided by the probe connector will not alter the orientation of an unheated cell, but may alter the orientation of a heated cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic memory device and method
InactiveUS6850433B2Low coercivityNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic memorySoft reference
A magnetic memory device can include a synthetic ferrimagnetic data, a soft reference layer and a tunneling layer. The synthetic ferrimagnetic data layer has a magnetic moment directable to a first orientation and a second orientation. The soft reference layer has a lower coercivity than the synthetic ferrimagnetic data layer. The tunneling layer has electrical resistance qualities which are influenced by magnetic moment orientations of the synthetic ferrimagnetic data layer and the soft reference layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Preparation method of neodymium iron boron magnet
ActiveCN102103916AReduce usageUniformity controllableInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare earthImpurity
A preparation method of neodymium iron boron magnet is disclosed. The composition general formula of the magnet provided by the invention is R1R2FeMB, wherein R1 is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Nd, Pr, La, Ce, Sm, Sc, Y and Eu, having a content of 23 to 35 wt%; R2 is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Tb, Dy, Gd, and Ho, having a content of 0.1 to 5 wt%; M represents transition group metal with the exception of Fe, having the content of 0.01 to 5 wt%; B represents simple substance boron, having the content of 0.8 to 1.2 wt%; the balance isFe and the other inevitable impurities. The preparation method of neodymium iron boron magnet provided by the invention works in such a manner that: one or more elements in the R2 are plated to the surface of the magnet, the metal R2 is diffused into the interior of the magnet by primary high temperature heat treatment, and imbalance organization and internal stress brought by the high temperature treatment are eliminated through secondary low temperature tempering. Low temperature molten salt electrodeposition method is employed to plate films. The present invention is advantageous in greatly improving the production efficiency, reducing the dosage of the heavy rare earth during preparation process of magnet, saving rare earth resource, and obtaining high coercivity without reducing remanent magnetism and magnetic energy product of a magnet.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Rare earth permanent magnet alloy material and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN102610347AImprove coercive forceImprove high temperature resistanceMagnetic materialsRare earthAlloy
The invention relates to a rare earth permanent magnet alloy material and a preparation process thereof. The rare earth permanent magnet alloy material is a high-coercivity and high-temperature-resistant magnet prepared by mixing two types of alloy. The alloy S is mainly used as the growth foundation of the R2Fe14B phase of crystal grains and used for increasing proportion of the main phase in the magnet and magnetic energy product of the magnet. Part of the alloy T is used for generating the R2Fe14B phase and part of the alloy T is used for generating crystal boundary phase to cover around the main phase of the crystal grains. The coercivity and the high-temperature resistance of the magnet prepared by the preparation process can be improved, heavy rare earth such as Tb, Dy and the like can be saved, more cost can be saved, and competitiveness of products can be improved.
Owner:ORIENT MAGNET TECH OMT
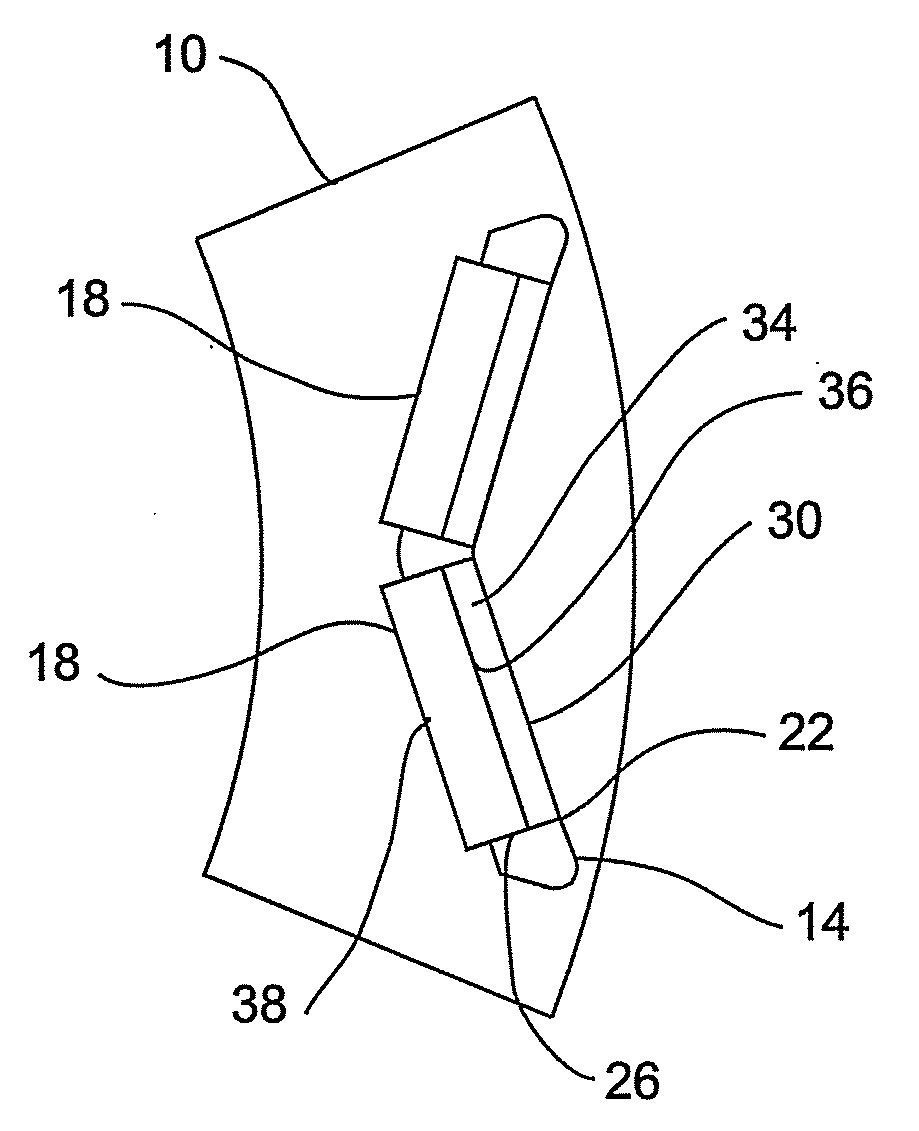
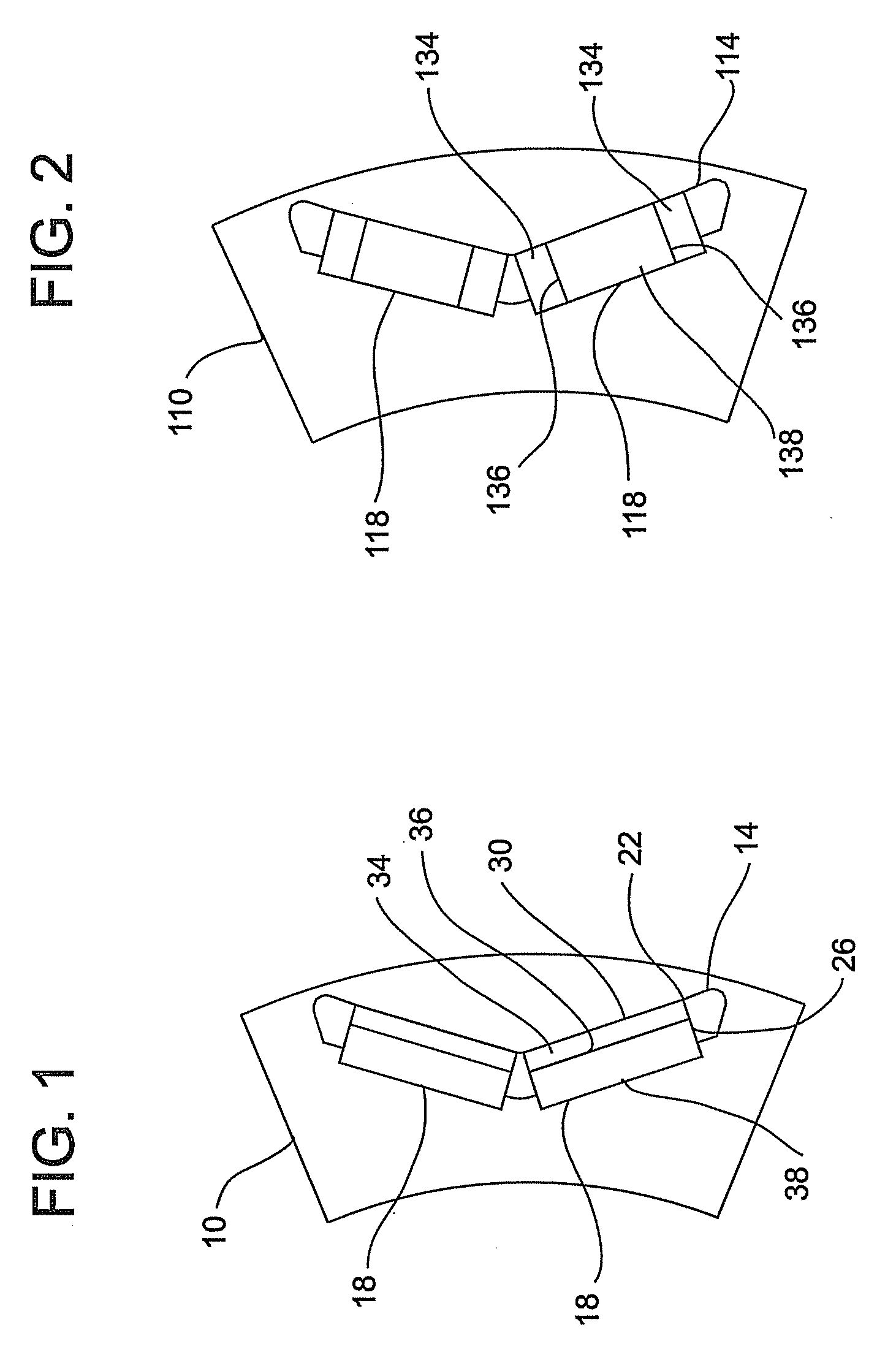
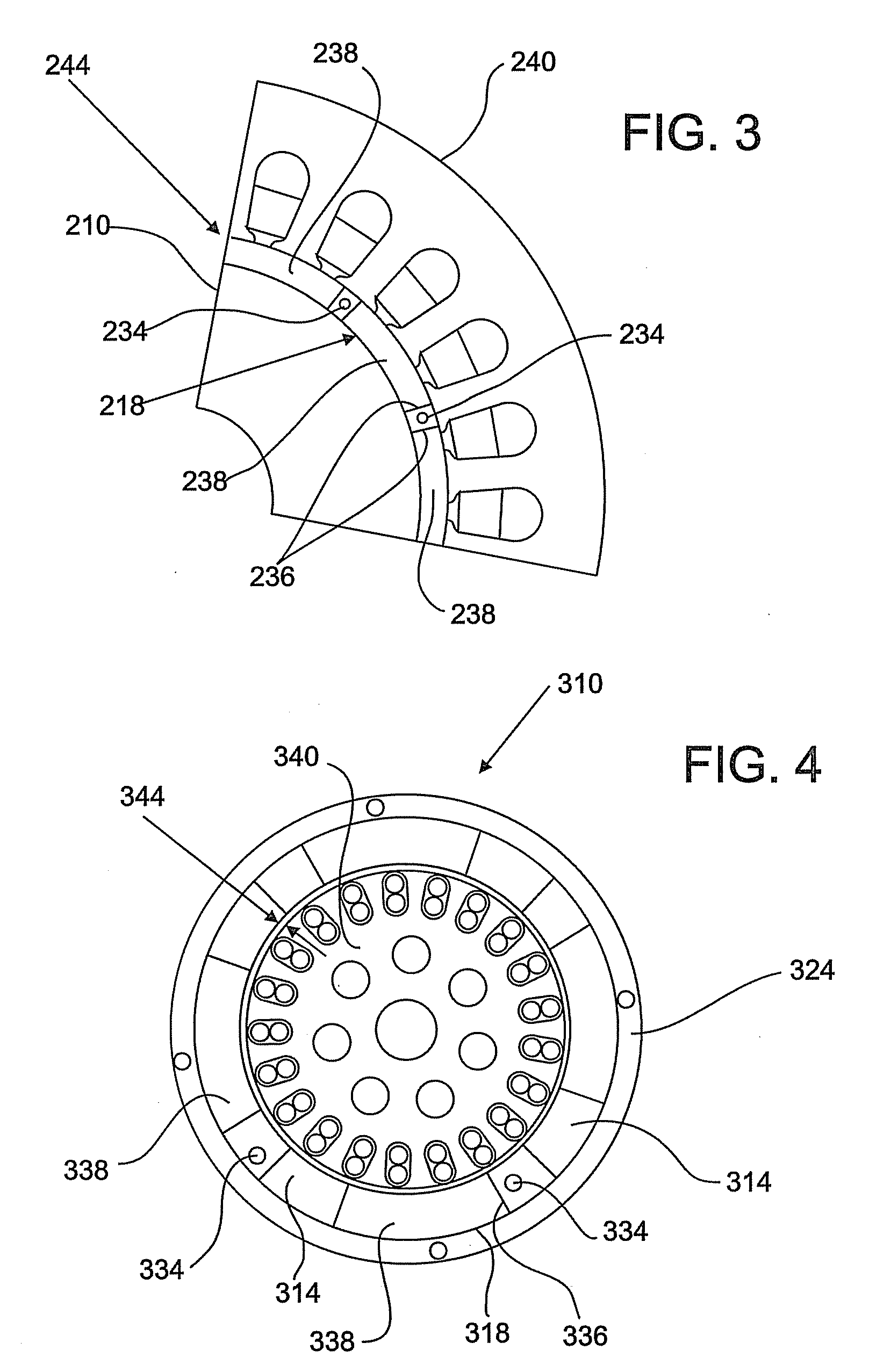
Flux focusing arrangement for permanent magnets, methods of fabricating such arrangements, and machines including such arrangements
ActiveUS8400038B2Improve effective coercivityImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetsConductor CoilDynamo
Numerous arrangements for permanent magnets are disclosed that can focus the flux produced by the magnets. Depending on the particular application in which the disclosed designs and techniques are used, efficiency and reliability may be increased by minimizing flux leakage, increasing peak flux density, and shaping the flux fields to improve the effective coercivity of the flux focusing permanent magnet arrangement when loaded, and to achieve customized voltage and current waveforms. The disclosed magnet assemblies may be incorporated into a machine, such as a motor / generator, having windings and may be disposed for movement relative to the windings. The magnet assembly may be mounted on a support formed of one or more ferromagnetic materials, such as a back iron The disclosed flux focusing magnet assemblies may be formed using a variety of manufacturing methods.
Owner:BWP GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com