Patents
Literature
15009 results about "Dynamo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundation upon which many other later electric-power conversion devices were based, including the electric motor, the alternating-current alternator, and the rotary converter. Today, the simpler alternator dominates large scale power generation, for efficiency, reliability and cost reasons. A dynamo has the disadvantages of a mechanical commutator. Also, converting alternating to direct current using power rectification devices (such as vacuum tubes or more recently via solid state technology) is effective and usually economical.
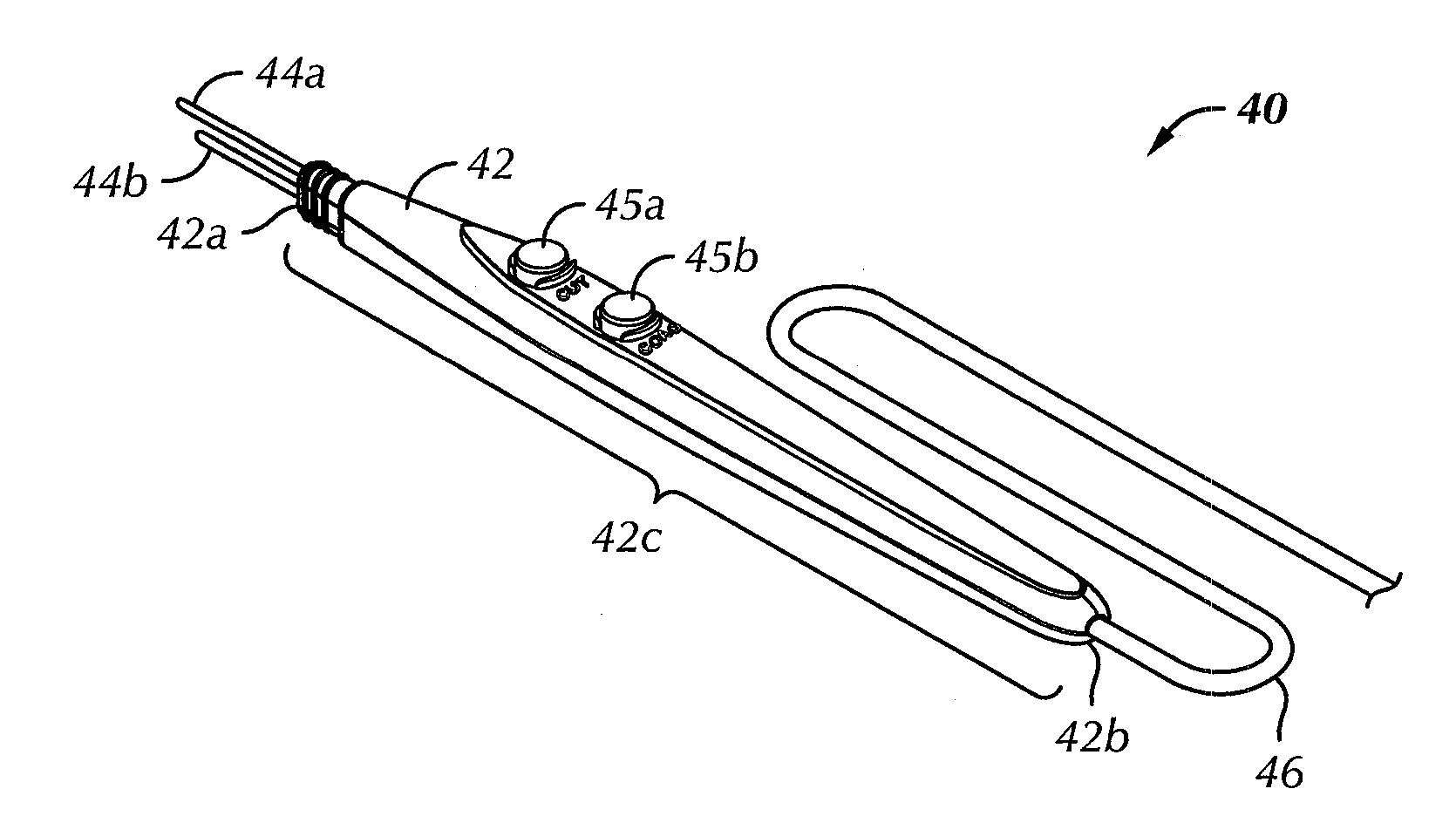
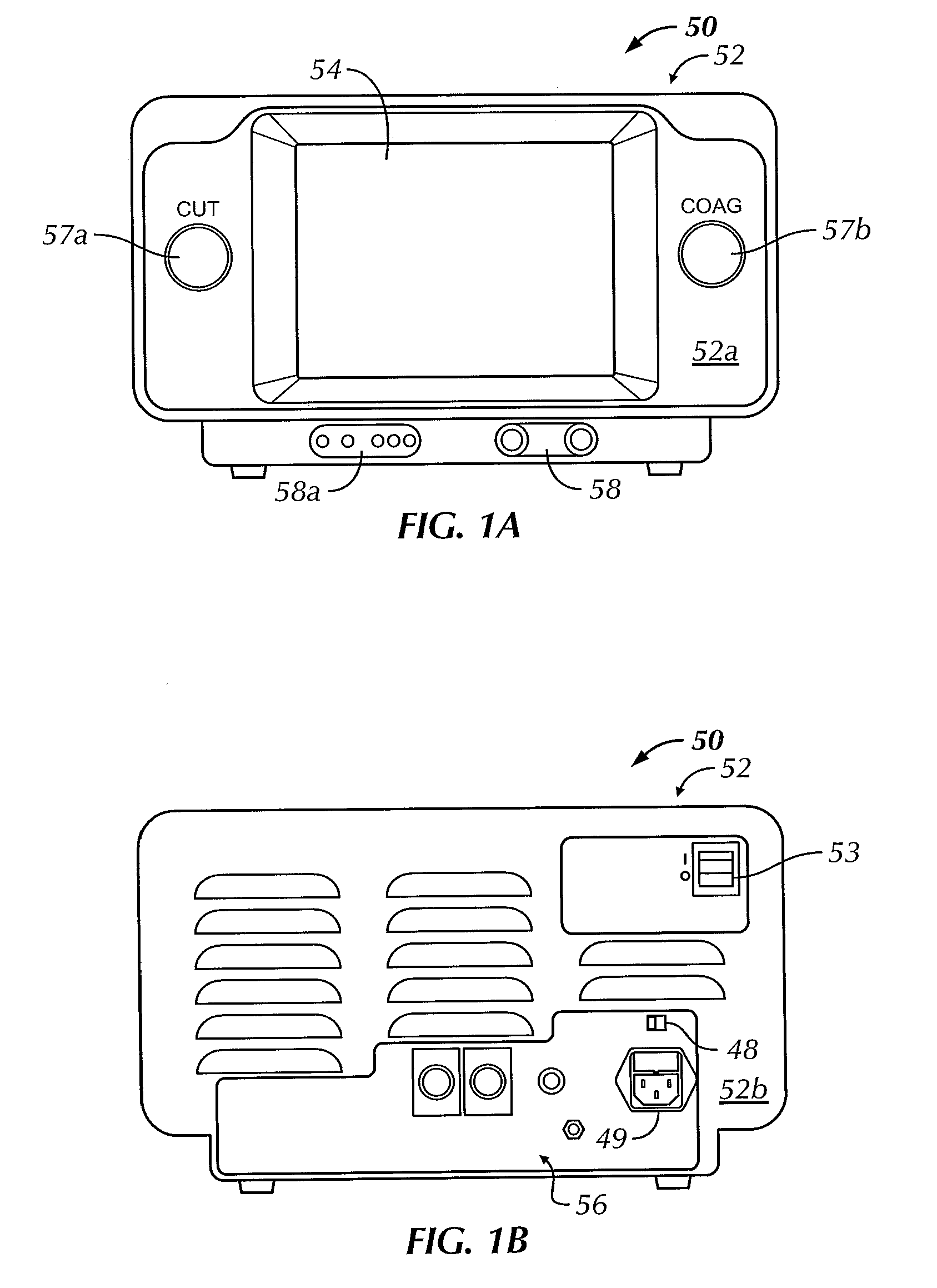
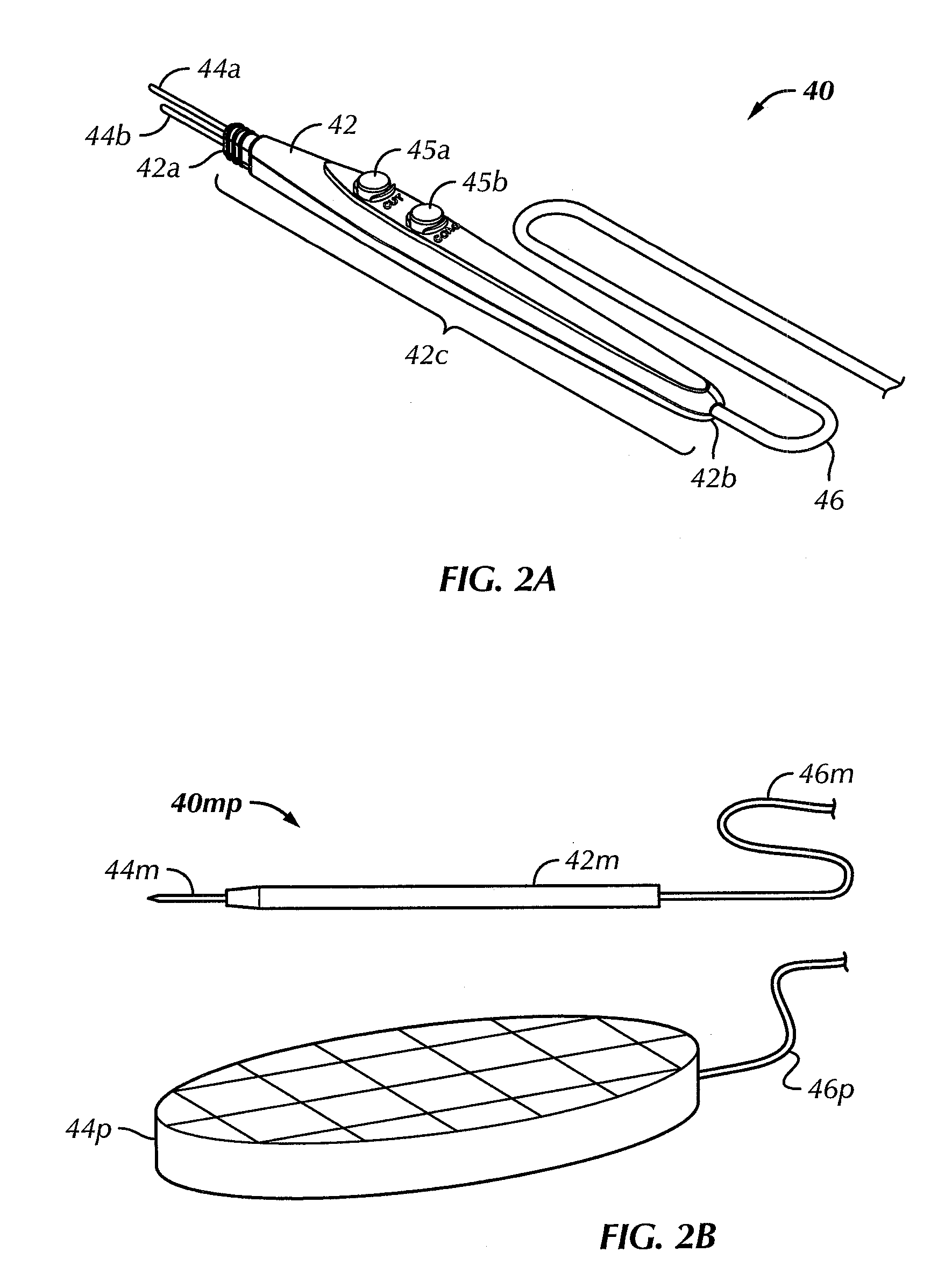
Electrosurgical generator
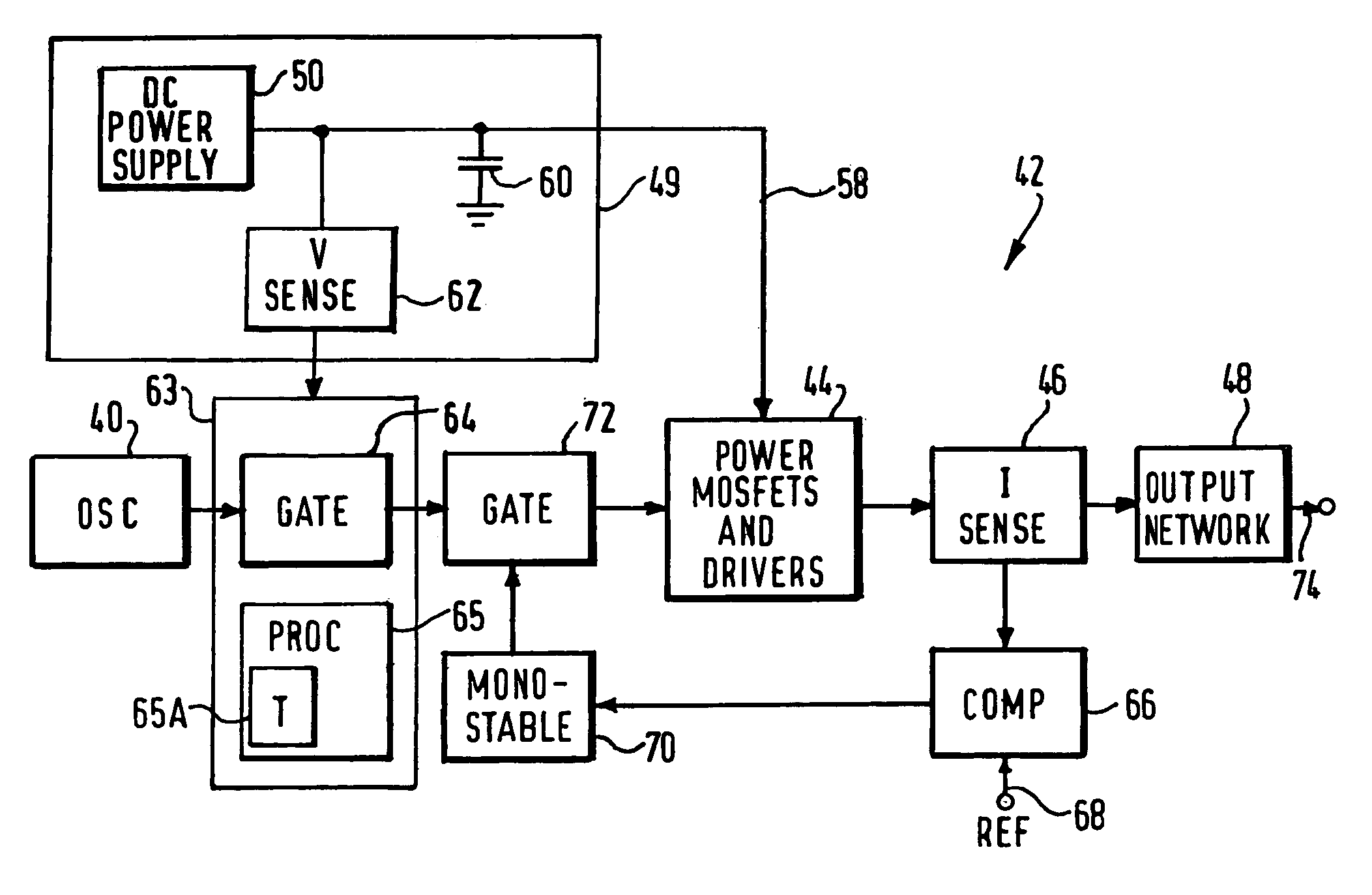
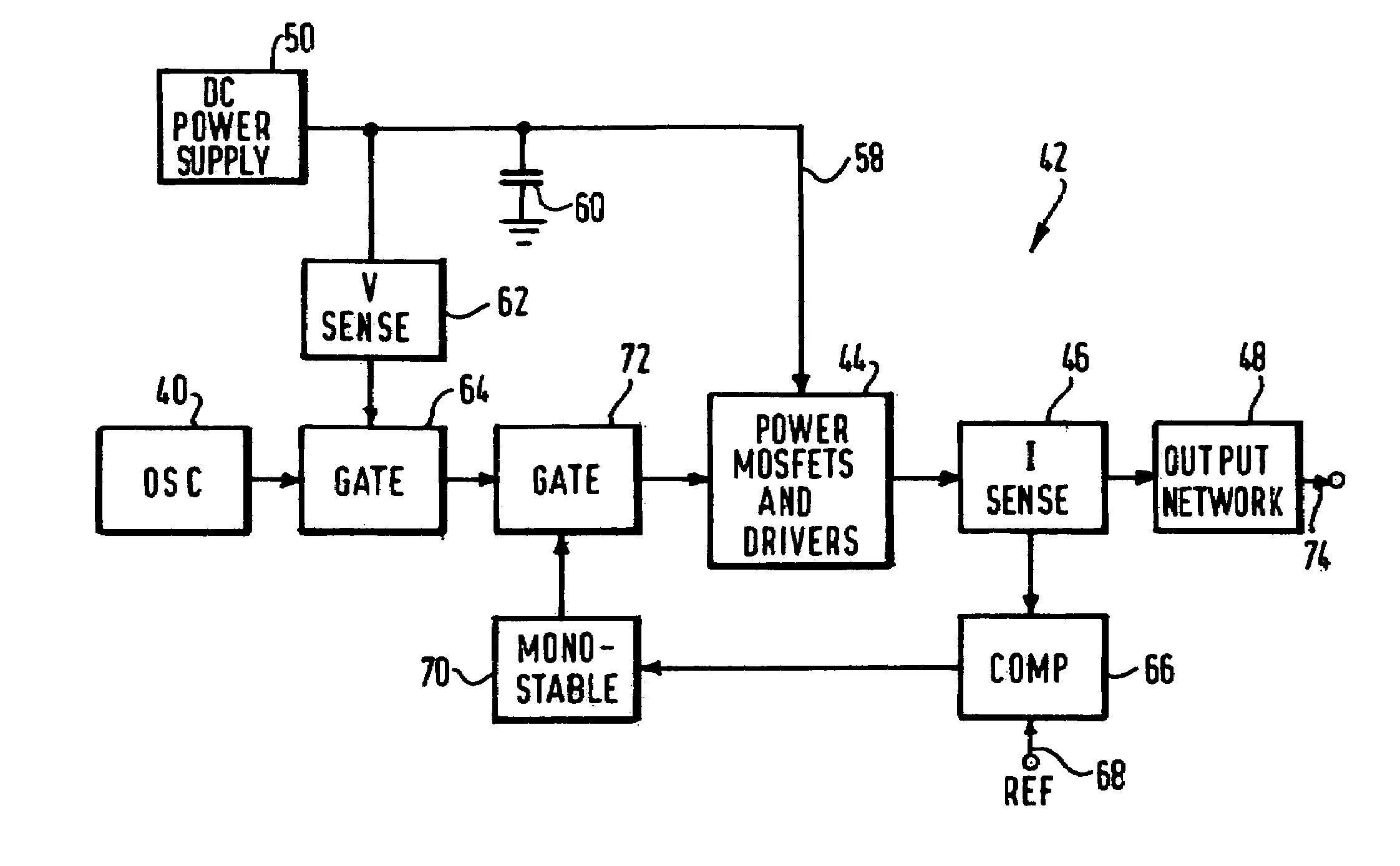
ActiveUS7195627B2High peak power capabilityReduces delay and unwanted coagulation effectSurgical instruments for heatingPeak valueContinuous wave
An electrosurgical generator for supplying RF power to an electrosurgical instrument for cutting or vaporising tissue has an RF output stage with RF output devices, a series-resonant output network and an RF output. The generator offers improved cutting and vaporising performance, especially in relation to the reliability with which an arc can be struck when presented with an initial load impedance load. This is achieved by virtue of the output stage being capable of maintaining output pulses of at least 1 kW peak by supplying the RF output devices from a large reservoir capacitor. An appropriate combination of cutting performance and haemostasis is provided by allowing for pulsed or continuous wave operation once an arc has been established, according to whether or not a surplus energy condition exists, as indicated by the voltage across the reservoir capacitor.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Electrosurgical generator
ActiveUS7211081B2Reducing switching transientPromote resultsSurgical instruments for heatingCapacitor voltageEngineering
An electrosurgical generator for supplying RF power to an electrosurgical instrument for cutting or vaporising tissue has an RF output stage (42) with an RF power bridge (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4), a pair of output lines (74) and a series-resonant output network (48). The output impedance of the output stage (42) at the output lines (74) is less than 200 / √P ohms, where P is the maximum continuous RF output power of the generator. The generator offers improved cutting and vaporising performance, especially in relation to the reliability with which an arc can be struck when presented with an initial low impedance load. Overloading of the output stage is prevented by rapidly operating protection circuitry responsive to a predetermined electrical condition such as a substantial short-circuit across the output lines. In the preferred embodiment, the output stage is capable of maintaining output pulses at least 1kW peak by supplying the power bridge from a large reservoir capacitor (60). Pulsing is dynamically variable in response to load conditions by controlling the maximum energy per pulse in response to the reservoir capacitor voltage.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Method for calculating transducer capacitance to determine transducer temperature
InactiveUS7077853B2Improve performanceImprove securitySurgical instrument detailsFrequency analysisCapacitanceExact resonance
A method for calculating the capacitance of a transducer (C0) without knowing the exact resonance frequency of a transducer / blade combination is achieved by sweeping across a broad frequency range which contains resonant and non-resonant frequencies where C0 can be measured. A pre-defined frequency range is set independently of the resonance frequency of a specific transducer / blade combination. C0 of the transducer / blade is measured at several different frequencies within the pre-defined frequency range to ensure that invalid C0 measurements are disregarded, and the temperature of the transducer is calculated based on valid C0 measurements. The determined transducer temperature, based on C0 measurements, can be used to optimize performance and / or provide a safety shutdown mechanism for the generator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Method of Sensing Speed of Electric Motors and Generators
InactiveUS20080298784A1Simple and inexpensiveLow costMotor/generator/converter stoppersField or armature current controlMotor speedMotor control
A method and circuit for determining the speed and / or counting the revolutions of brush and commutator motors is described. The method and circuitry detects signals present on the windings of the motor due to commutation that occurs at the brushes and commutator of the motor. This method can be used to simply monitor & indicate the motor speed and revolutions or to form the basis of a motor control.
Owner:KASTNER MARK ALLEN
Implantable generator having current steering means
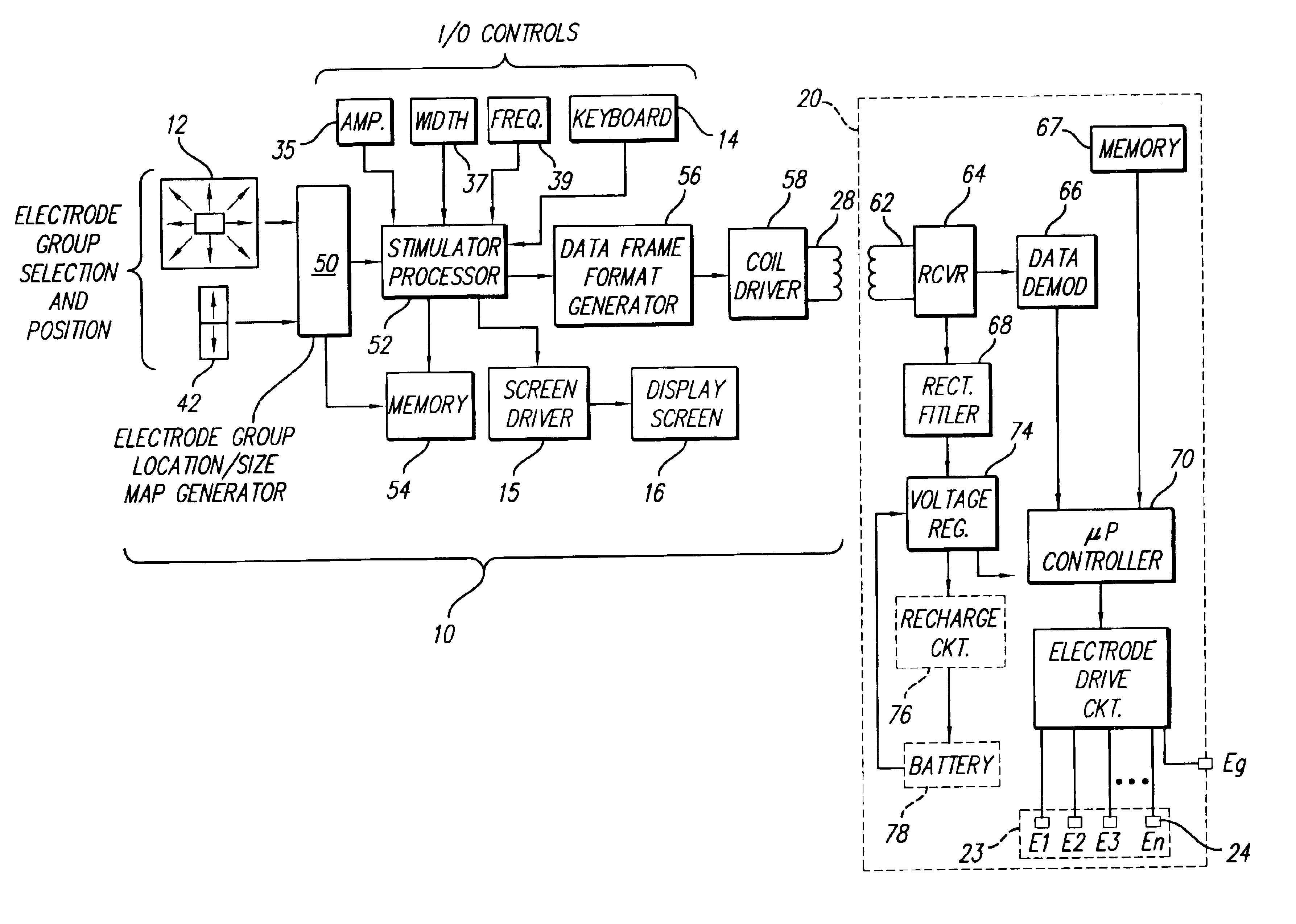
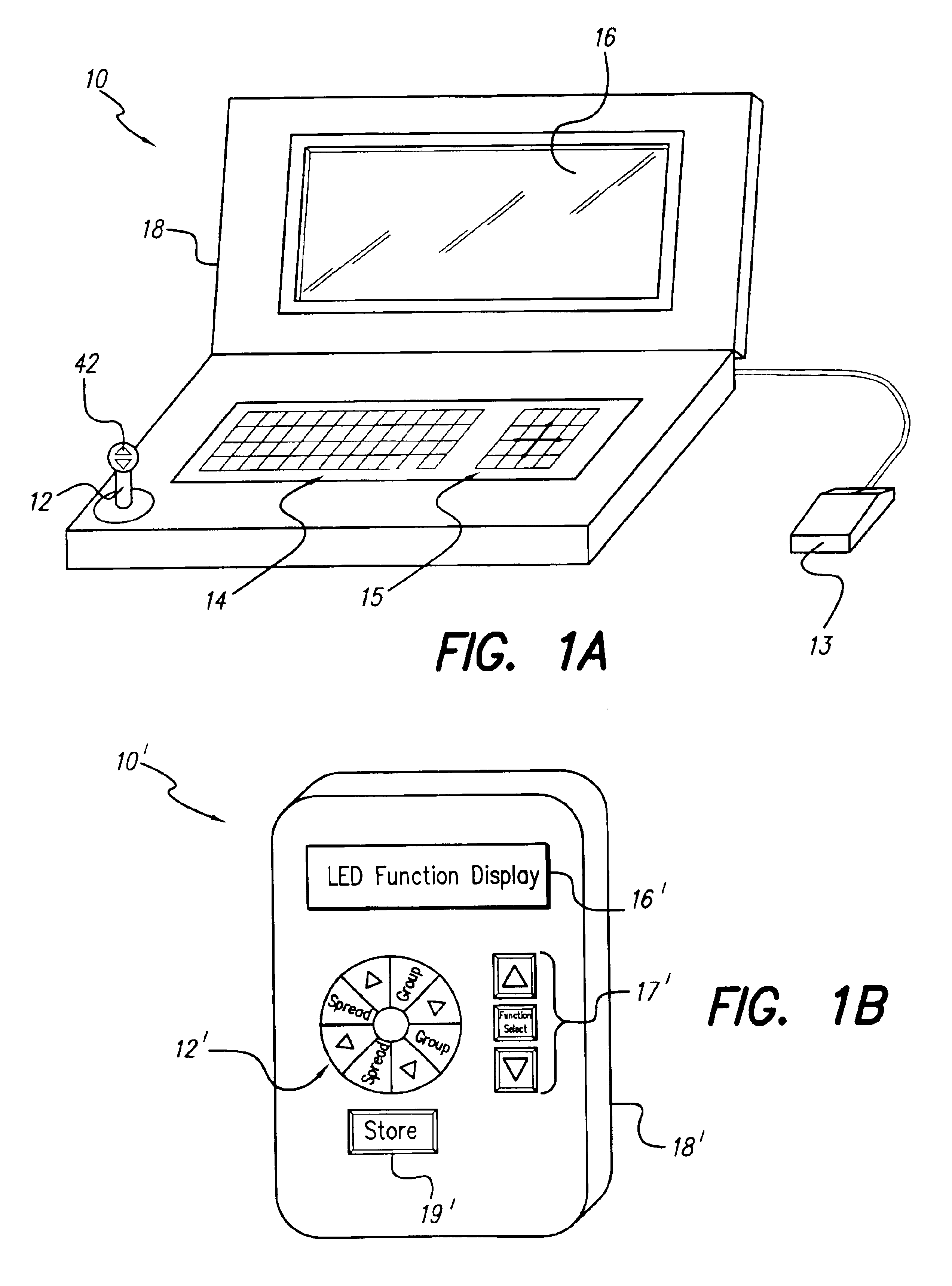
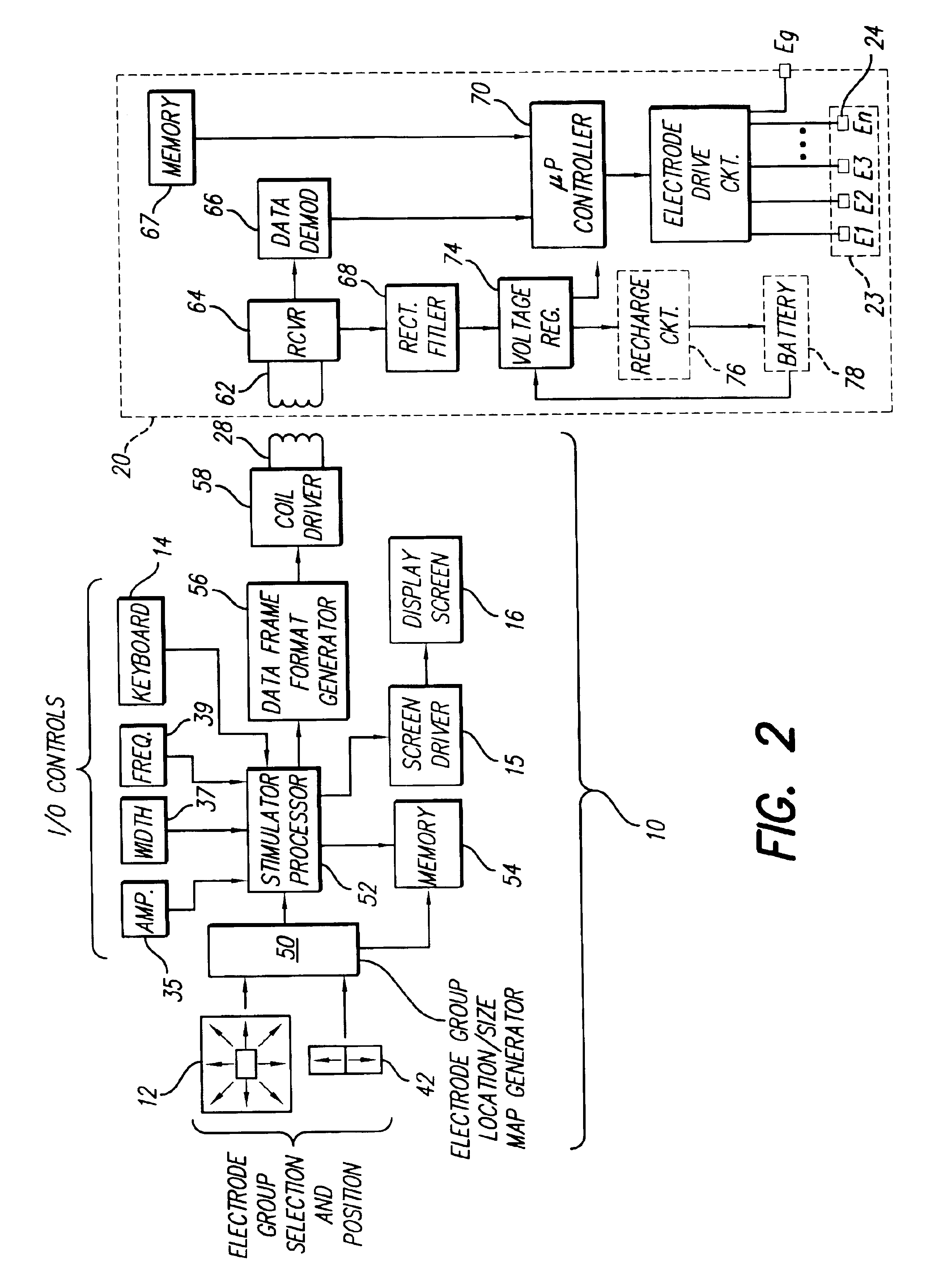
An implantable pulse generator includes a current steering capability that allows a clinician or patient to quickly determine a desired electrode stimulation pattern, including which electrodes of a group of electrodes within an electrode array should receive a stimulation current, including the amplitude, width and pulse repetition rate of such current. Movement of the selected group of electrodes is facilitated through the use of remotely generated directional signals, generated by a pointing device, such as a joystick. As movement of the selected group of electrodes occurs, current redistribution amongst the various electrode contacts takes place. The redistribution of stimulus amplitudes utilizes re-normalization of amplitudes so that the perceptual level remains fairly constant. This prevents the resulting paresthesia from falling below the perceptual threshold or above the comfort threshold.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Circuit for controlling arc energy from an electrosurgical generator
ActiveUS7044948B2Quantity minimizationLimit thermal spreadSurgical instruments for heatingElectrosurgeryEngineering
A circuit is disclosed which minimizes the amount of tissue vaporized during a first half (positive half cycle) of an electrosurgical current cycle and minimizes the amount of current applied to tissue during a second half (negative half cycle) of the electrosurgical current cycle to control thermal spread. The circuit is preferably provided within an electrosurgical generator which is capable of controlling the amount of energy delivered to a patient during electrosurgery on a per arc basis.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
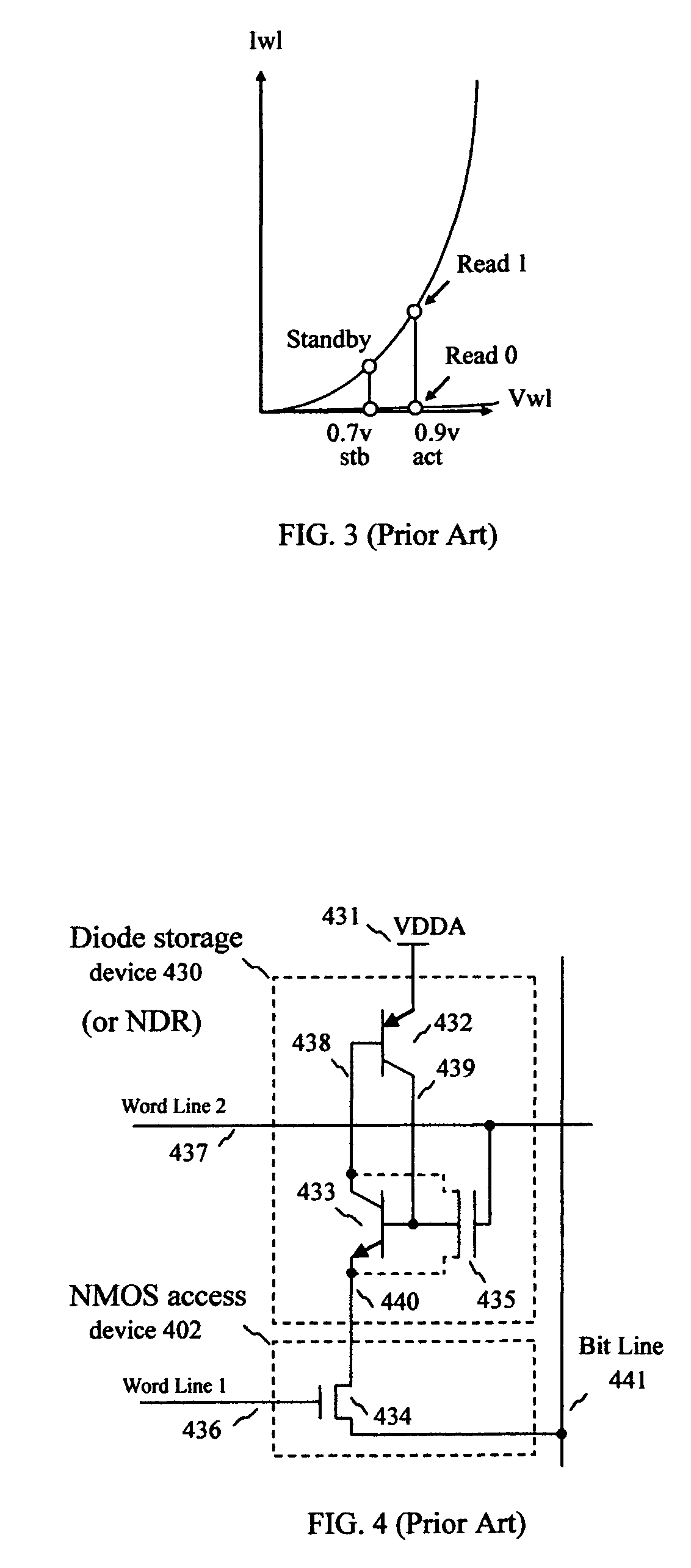
Planar capacitor memory cell and its applications
InactiveUS7209384B1Less complicated to fabricateImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
A capacitor memory is realized, wherein a capacitor stores data and a diode controls to store data “1” or “0”. Diode has four terminals wherein first terminal serves as word line, second terminal serves as storage node, third terminal is floating, and fourth terminal serves as bit line, wherein back channel effect is suppressed adding additional ions in the bottom side of third terminal or applying negative voltage in the well or substrate. A capacitor plate couples to second terminal, which plate has no coupling region to first, third and fourth terminal. With no coupling, the inversion layer of plate in the storage node is isolated from the adjacent nodes. In doing so, the plate can swing ground level to positive supply level to write. As a result, no negative generator is required for controlling plate. Word line and bit line keep ground level during standby, and rise to supply level for read or write operation. In this manner, no holding current is required during standby, and operating current is dramatically reduced with no negative generator. Write has a sequence to clear the state of cell before writing to store data regardless of previous state. Refresh cycle is periodically asserted to sustain data. The present invention can be applied for destructive read, or for nondestructive read adding pull-down device to bit line. The height of cell is almost same as control circuit on the bulk or SOI wafer.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
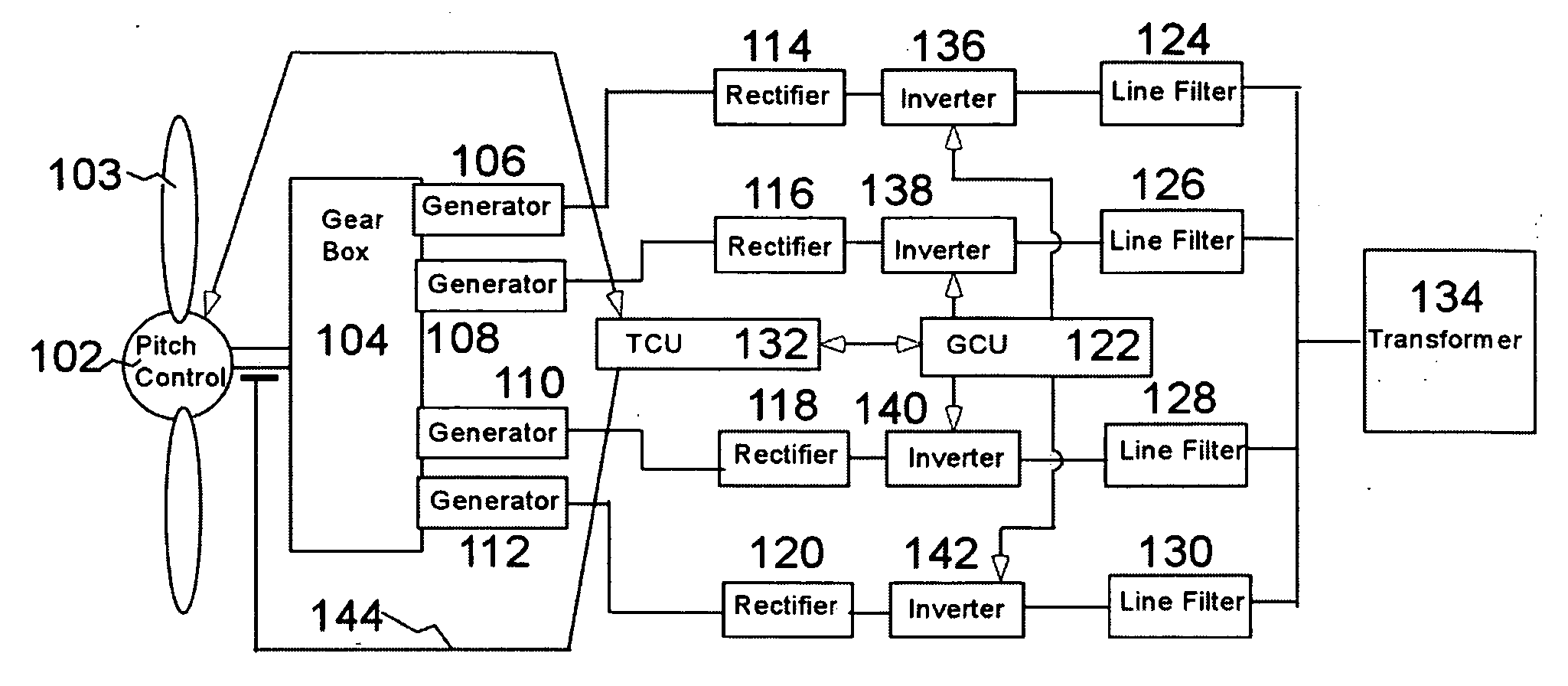
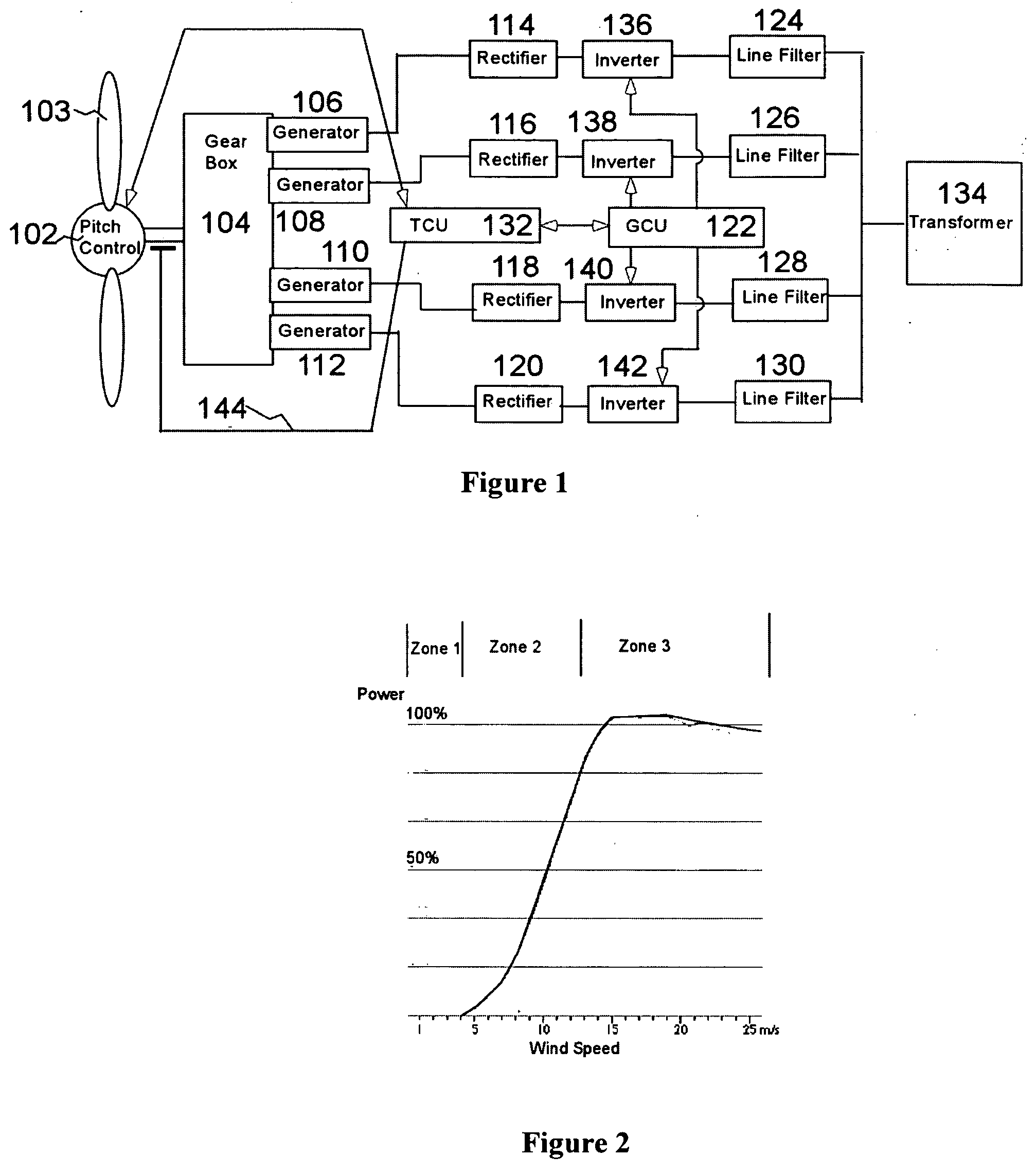
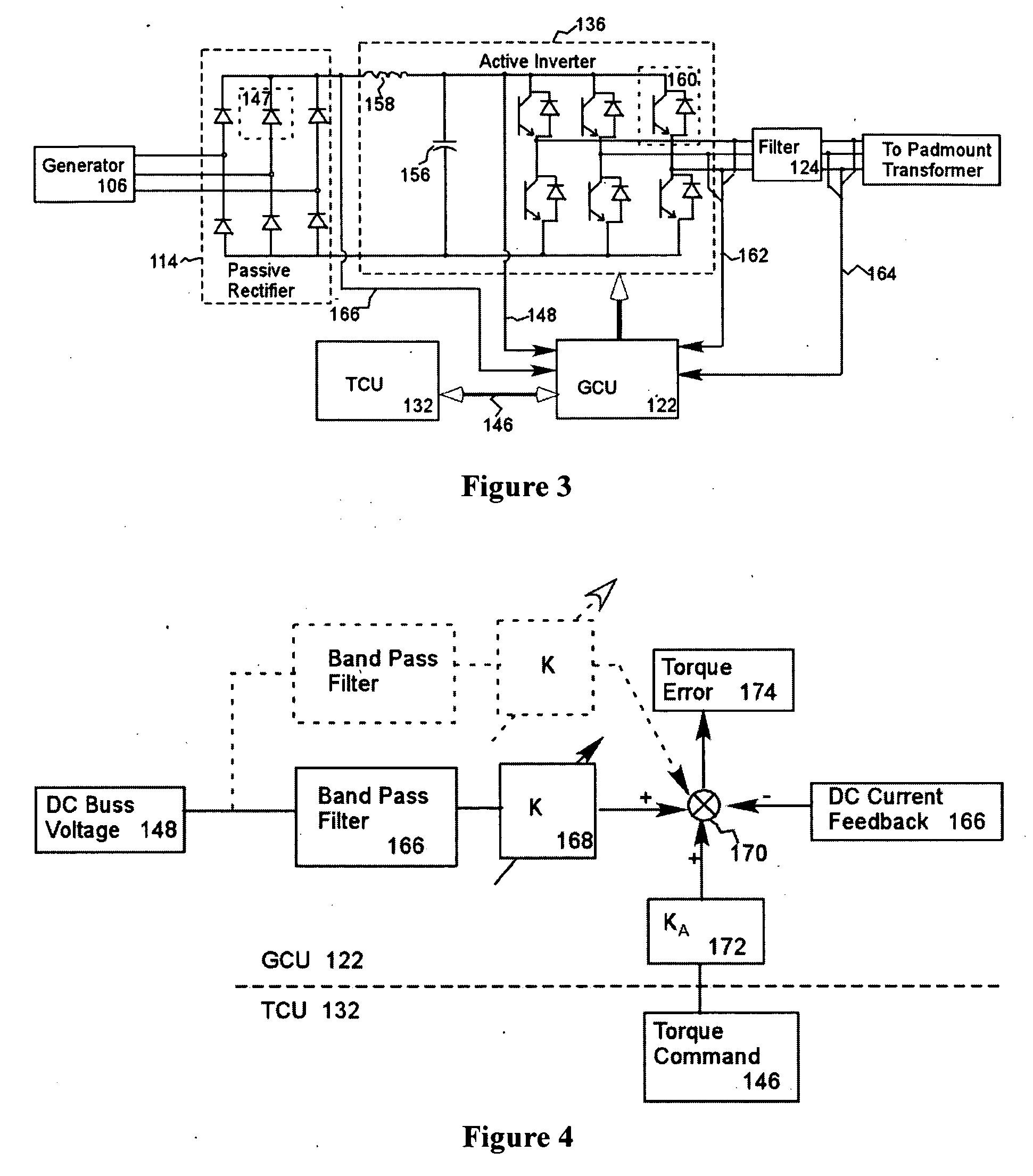
InactiveUS20050012339A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectric power transmissionPermanent magnet rotor
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Self-powered resonant leadless pacemaker
InactiveUS20070293904A1Increases natural velocity and acceleration of heart muscleExtended durationElectrotherapyCardiac cycleCardiac pacemaker electrode
A self-powered medical device, for example a pacemaker uses the variations of blood pressure inside the heart or a major artery to create a mechanical resonance in an electromagnetic or piezoelectric generator. The resonance extends the time power is generated during the cardiac cycle. The pressure variations compress a bellows carrying the resonant generator. The inside of the bellows may be evacuated to a partial or full vacuum, and a spring restores the bellows to the desired equilibrium point, acting against the blood pressure. The current pulses are stored in a capacitor. Eliminating the battery allows dramatic miniaturization of the medical device to the point it can be implanted at the point of desired stimulation via a catheter.
Owner:LG RES PARTNERSHIP
System for pumping hydraulic fracturing fluid using electric pumps
A system for hydraulically fracturing an underground formation in an oil or gas well to extract oil or gas from the formation, the oil or gas well having a wellbore that permits passage of fluid from the wellbore into the formation. The system includes a plurality of electric pumps fluidly connected to the well, and configured to pump fluid into the wellbore at high pressure so that the fluid passes from the wellbore into the and fractures the formation. The system can also include a plurality of natural gas powered generators electrically connected to the plurality of electric pumps to provide electrical power to the pumps.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
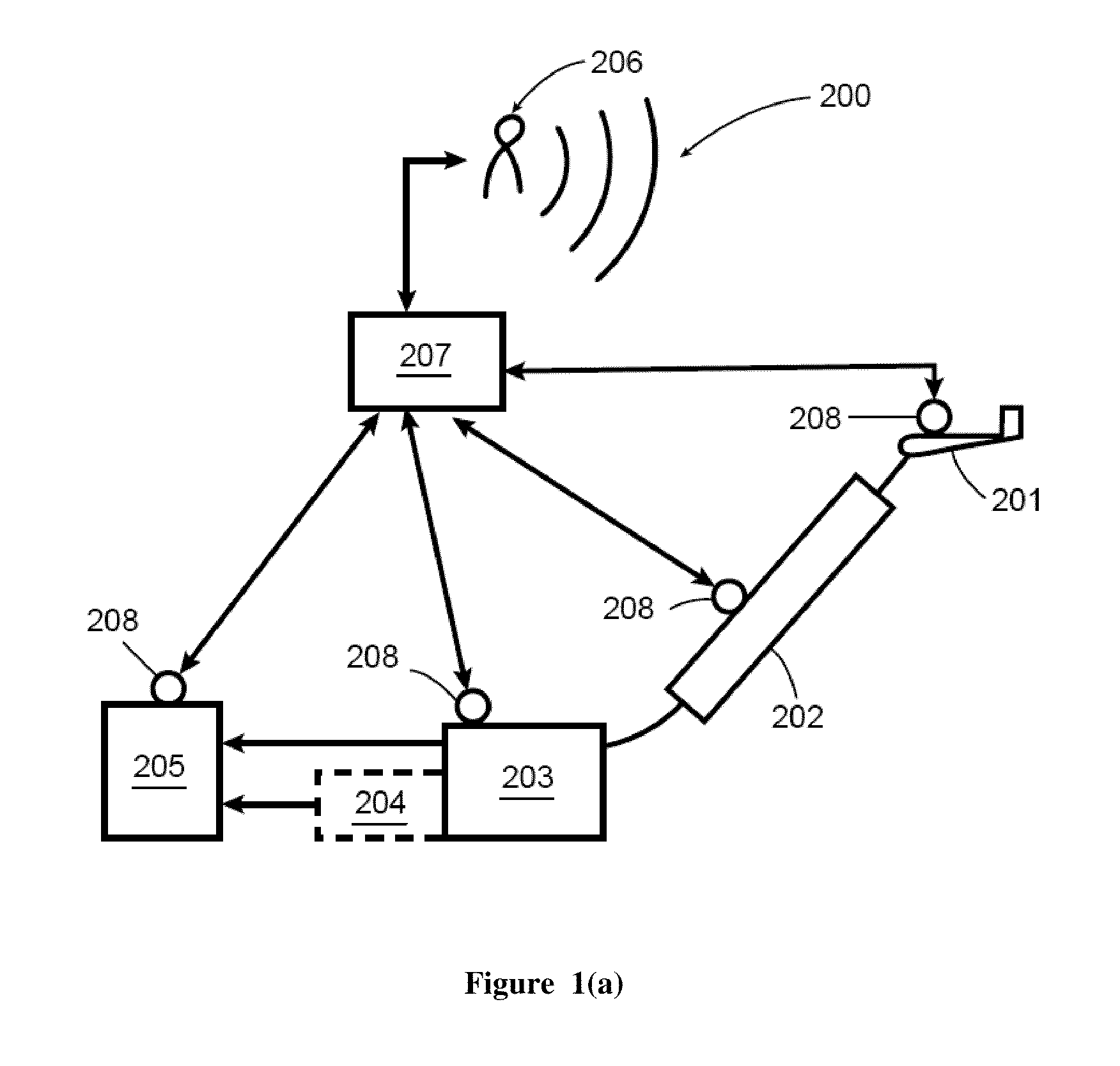
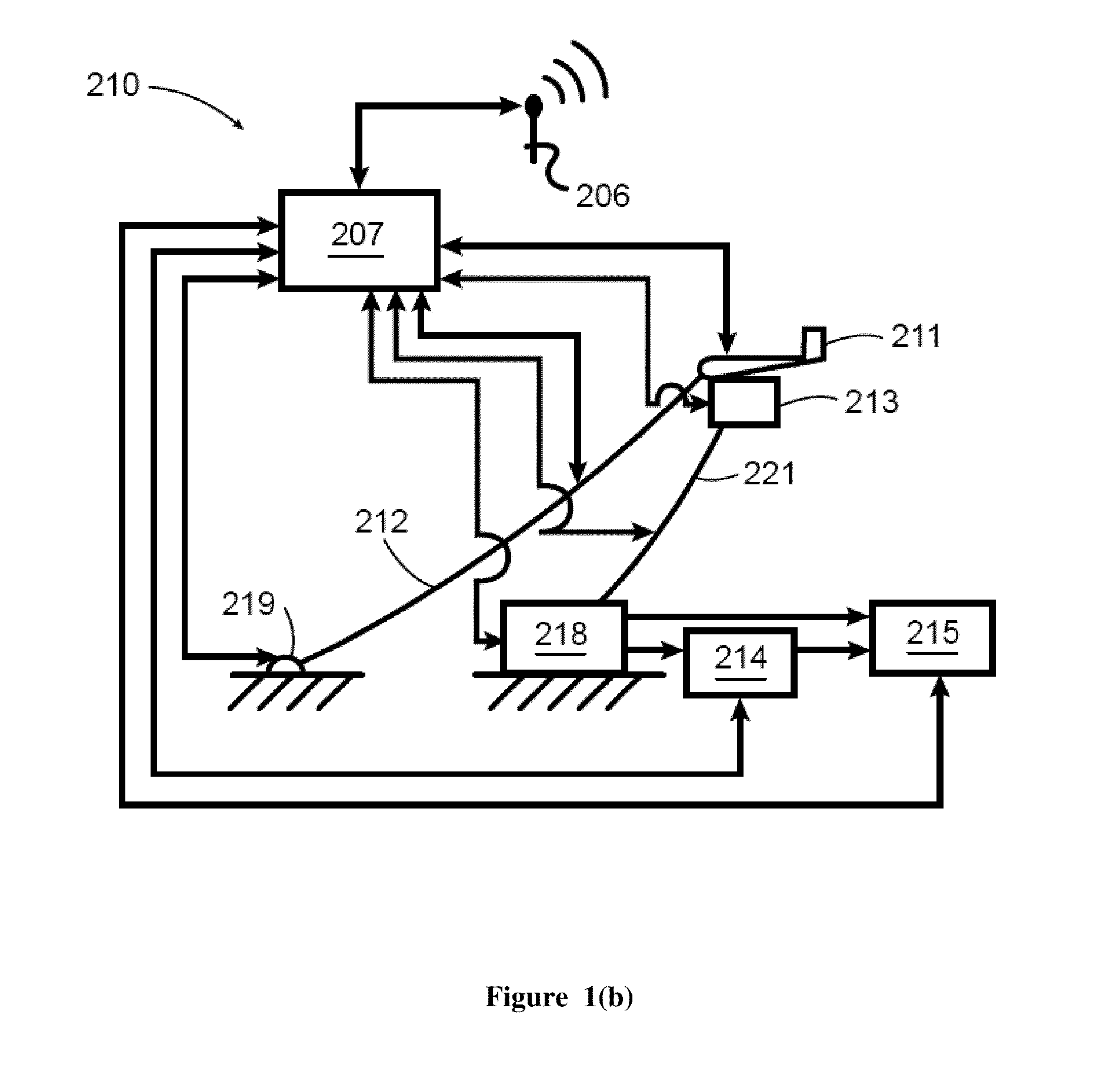
Magnetic tracking system
InactiveUS6980921B2Improve accuracyEliminates patchingSurgical navigation systemsDigital computer detailsMagnetic trackingSignal conditioning
The present invention provides an electromagnetic tracking system that includes a field generator and a field sensor arranged to generate and detect, respectively, an electromagnetic field. Both the transmitter and receiver coils are connected to signal conditioning and processing circuitry to provide outputs indicative of the coil signals. A processor operates on the signals to determine the coordinates of the sensing assembly relative to the generator assembly. The signal processor produces ratiometric outputs, and applies a mutual inductance model to solve for position / orientation coordinates. In some embodiments, a disturber in the form of a conductive ring or a sheath is disposed about an interfering piece of equipment to moderate and standardize disturbances due to eddy currents.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
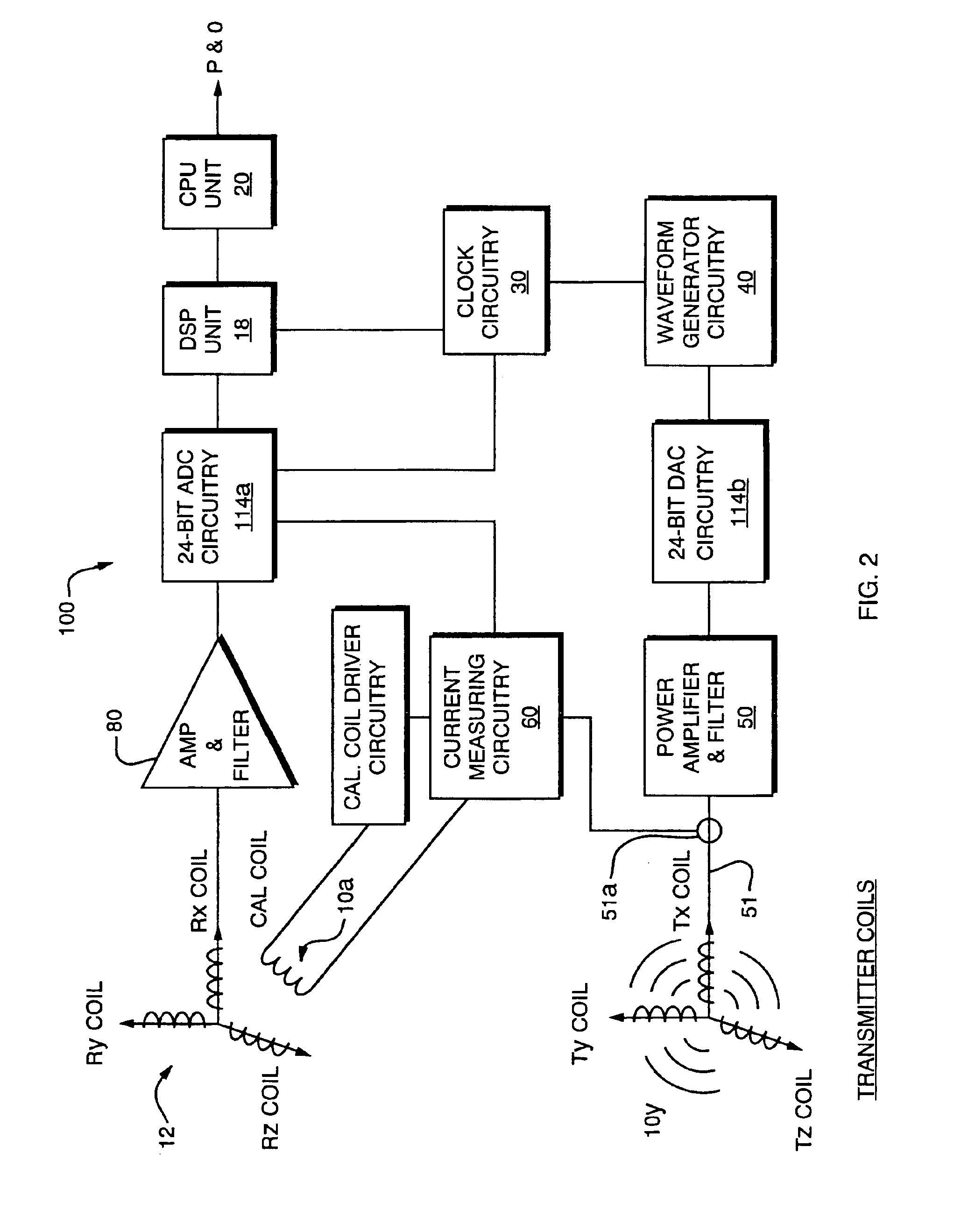
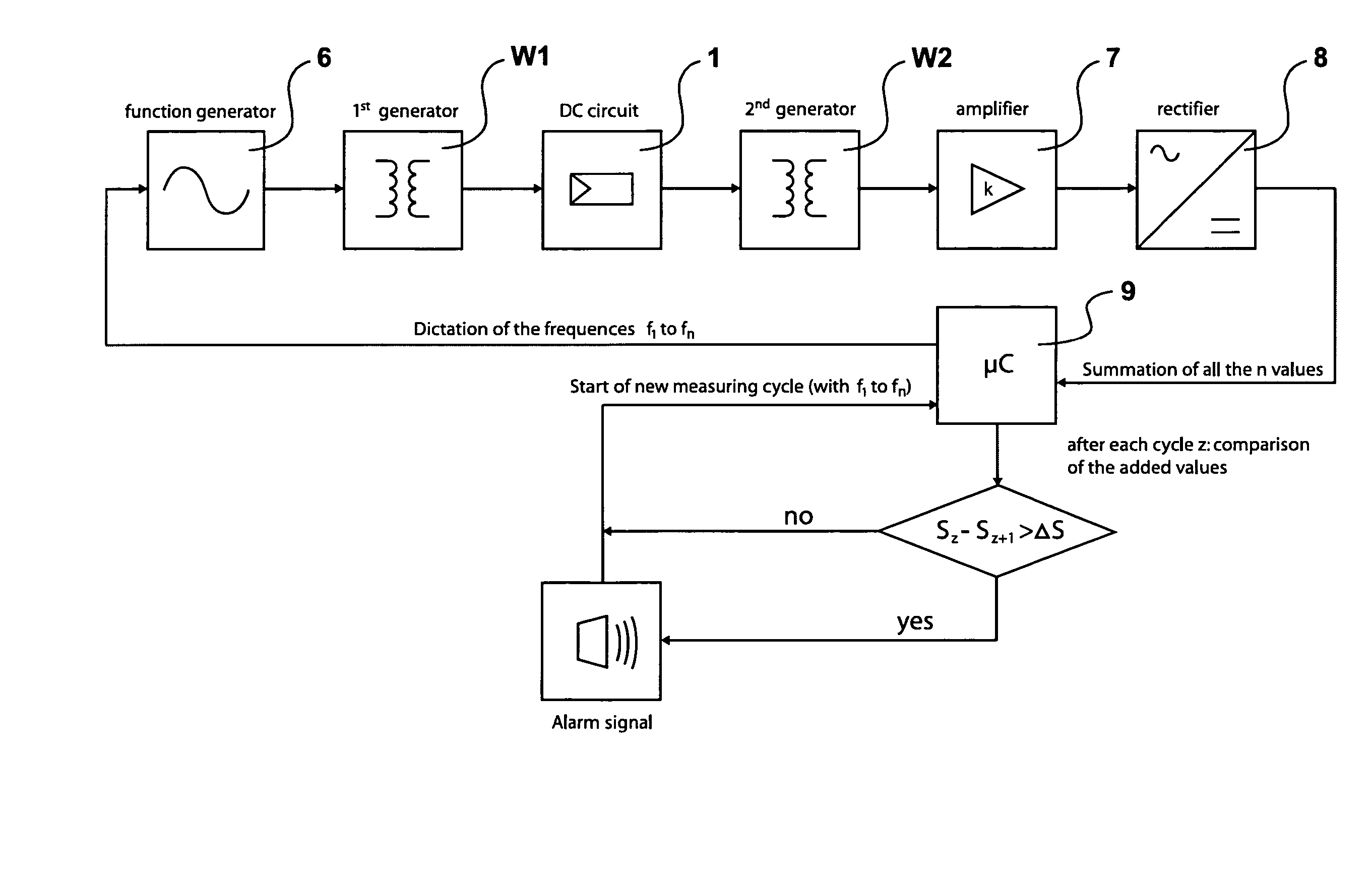
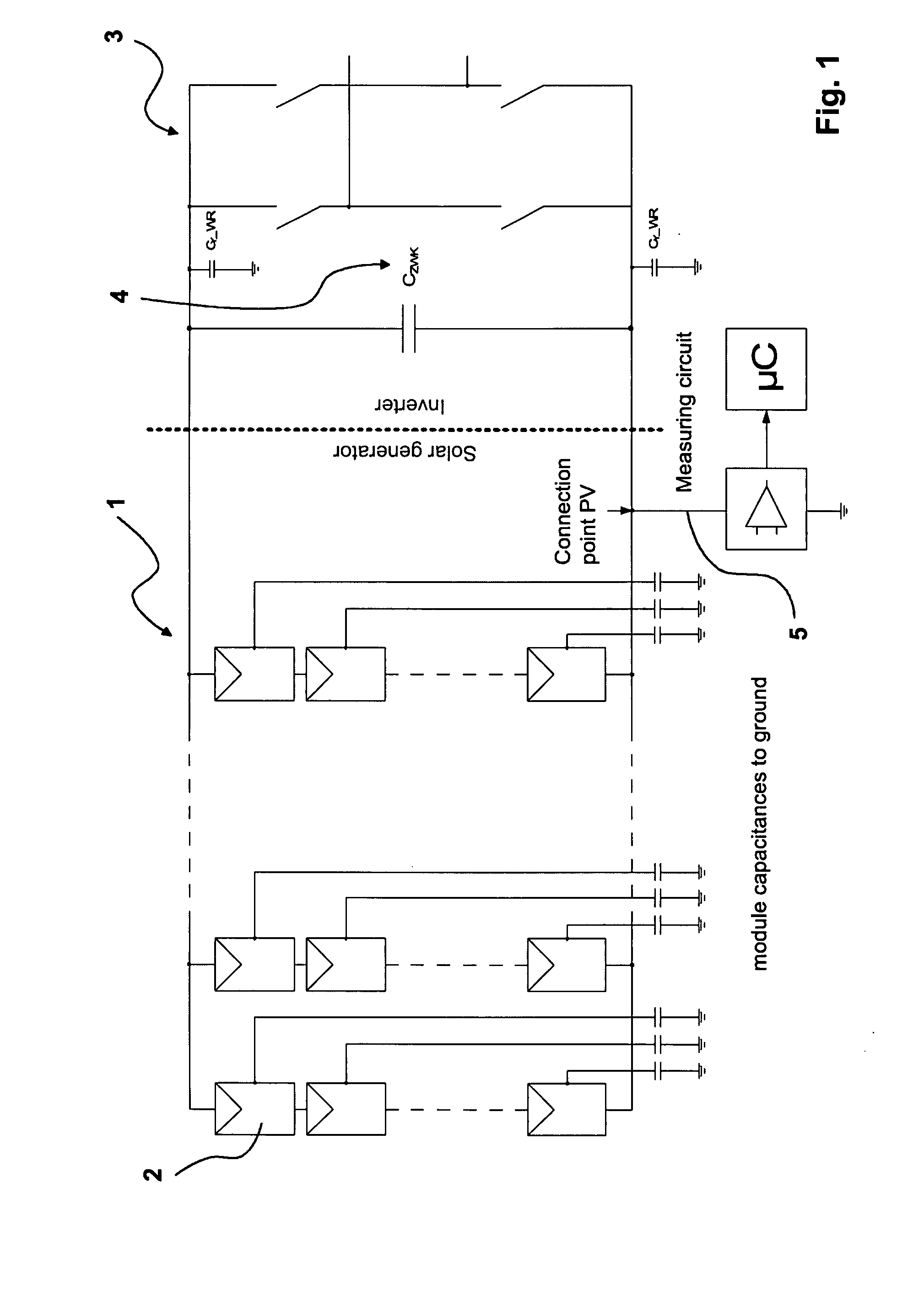
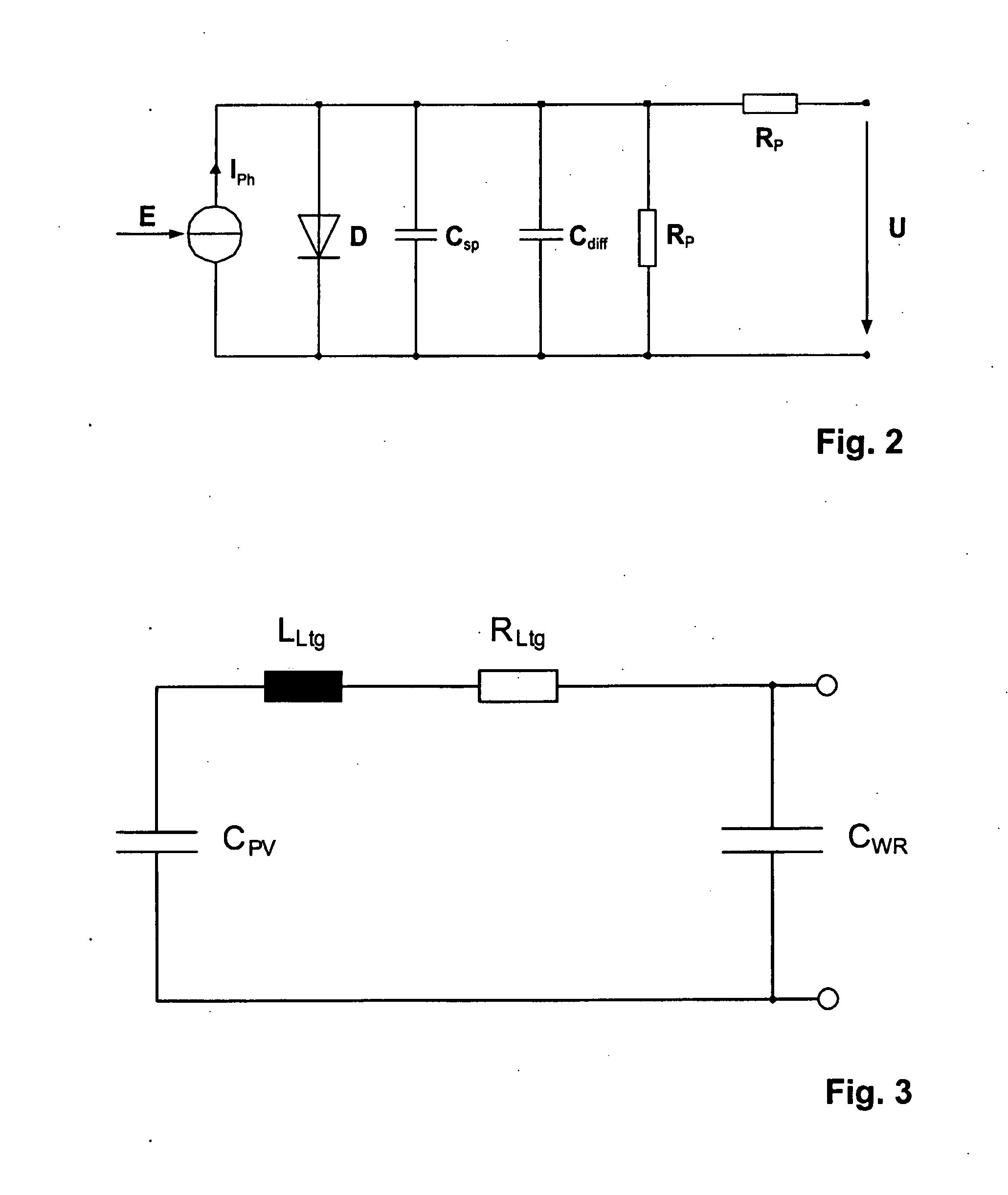
Method of monitoring a photvoltaic generator
ActiveUS20080106250A1Cost advantageOptimal theft securityPhotovoltaic monitoringPV power plantsFrequency spectrumElectrical battery
The subject matter of the present invention is a method for monitoring a photovoltaic generator (1) for generating current with a number of solar cells connected between two external connections by repeated feeding of a current with a frequency spectrum into the generator current circuit, detecting thereby a respective frequency response in the frequency spectrum with the supplied current as the input variable and an electric variable of the generator as the output variable, and detecting a change in the frequency response for monitoring the photovoltaic generator (1) in the event of a change during repeated feeding.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
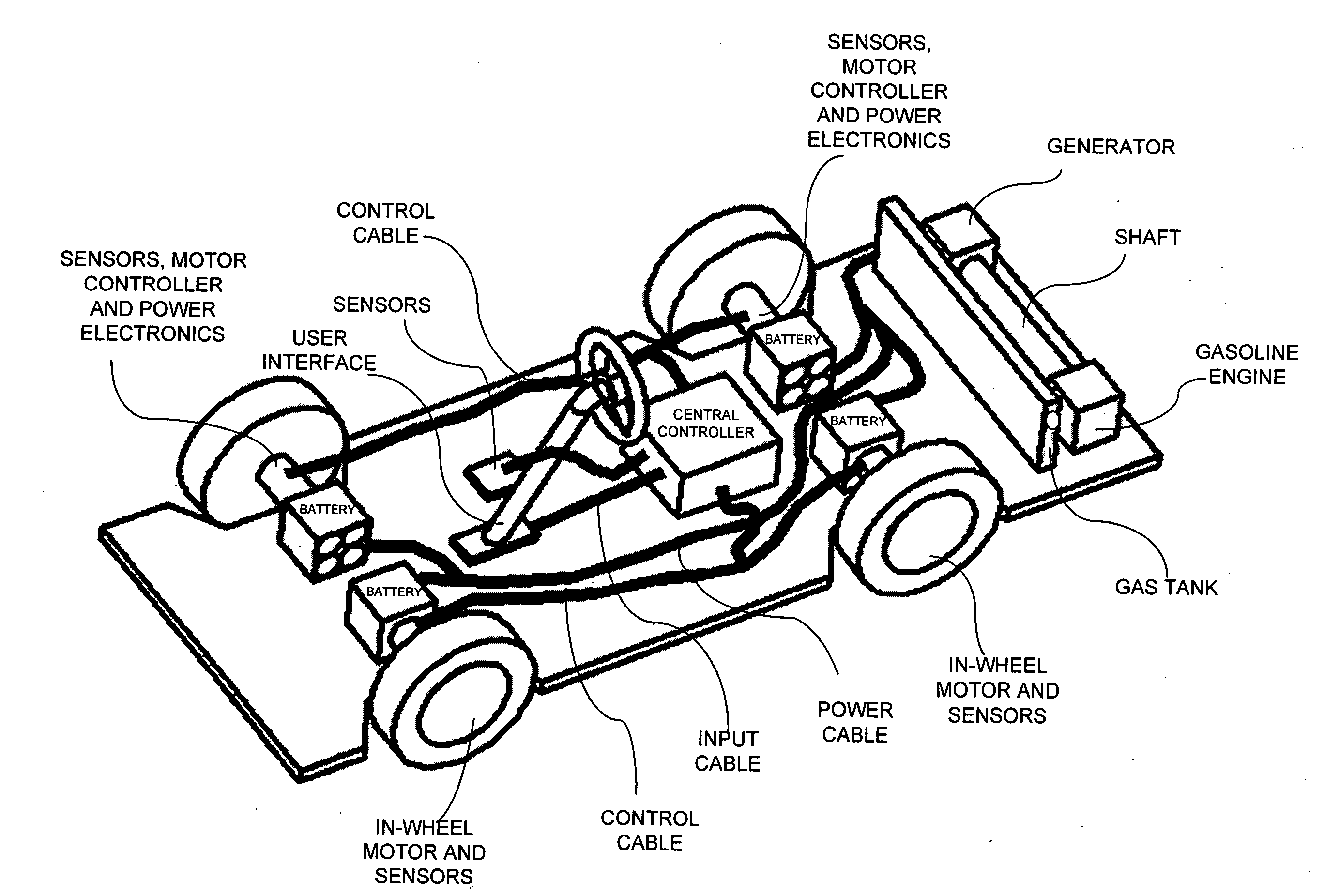
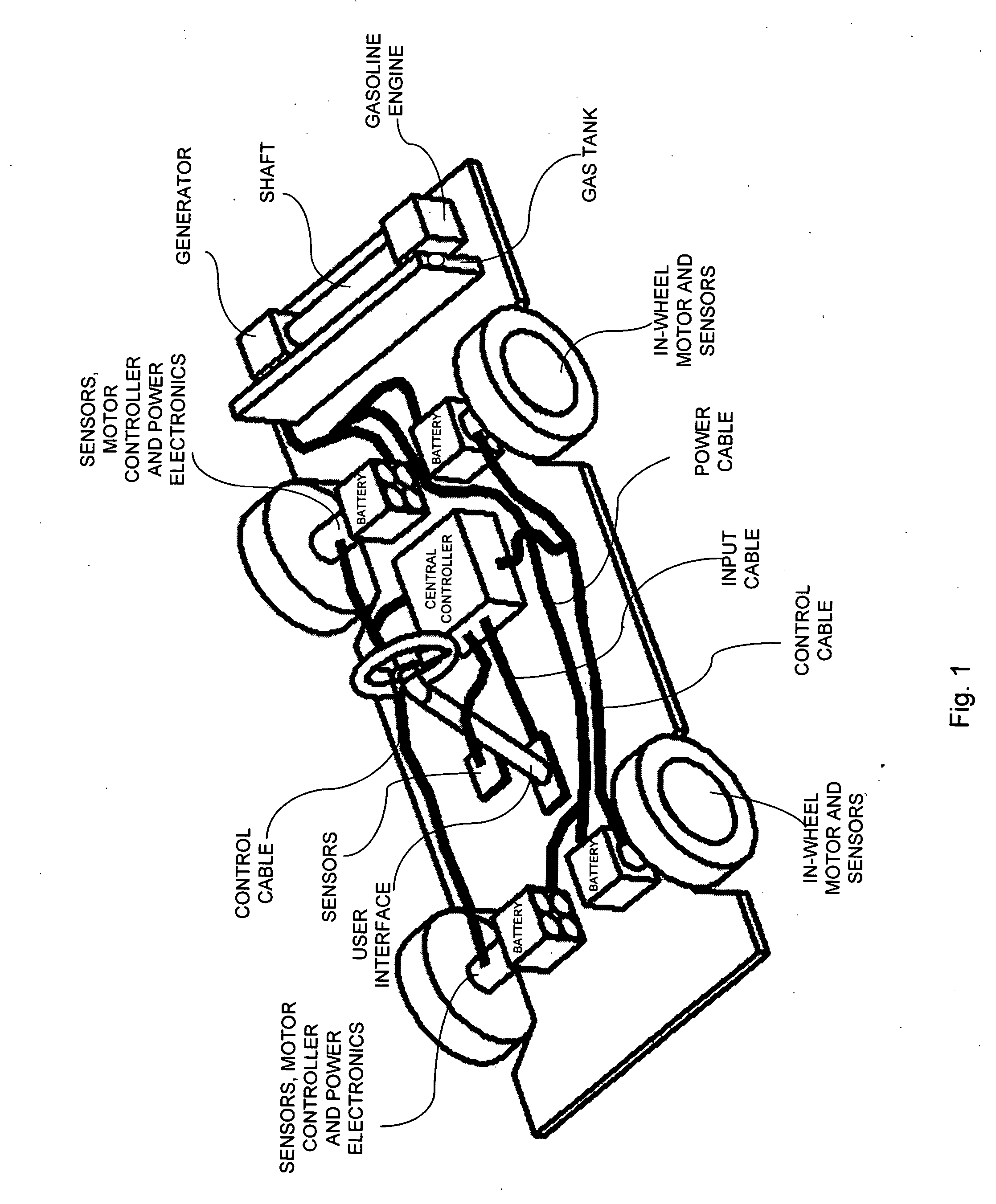
Adaptive electric car
InactiveUS20050052080A1Eliminate electromagneticEliminate electrical interferenceRailway vehiclesAc-dc conversionGasolineMotor control
An adaptive electric car or other vehicle with potentially better performance—power, efficiency, range—than a gasoline vehicle, at a competitive cost. The motor control system can dynamically adapt to the vehicle's operating conditions (starting, accelerating, turning, braking, cruising at high speeds) and other inputs and parameters. That consistently provides better performance. Isolating the vehicle's motor or generator electromagnetic circuits allows effective control of more independent parameters. That gives great freedom to optimize. Adaptive motors and generators for an electric vehicle are cheaper, smaller, lighter, more powerful, and more efficient than conventional designs. An electric vehicle with in-wheel adaptive motors delivers high power with low unsprung mass and high torque and power-density. Total energy management of the vehicles entire electrical system allows for large-scale optimization. An adaptive architecture improves performance of a wide variety of vehicles, particularly those that need optimal efficiency over a range of operating conditions.
Owner:BLUWAV SYST LLC
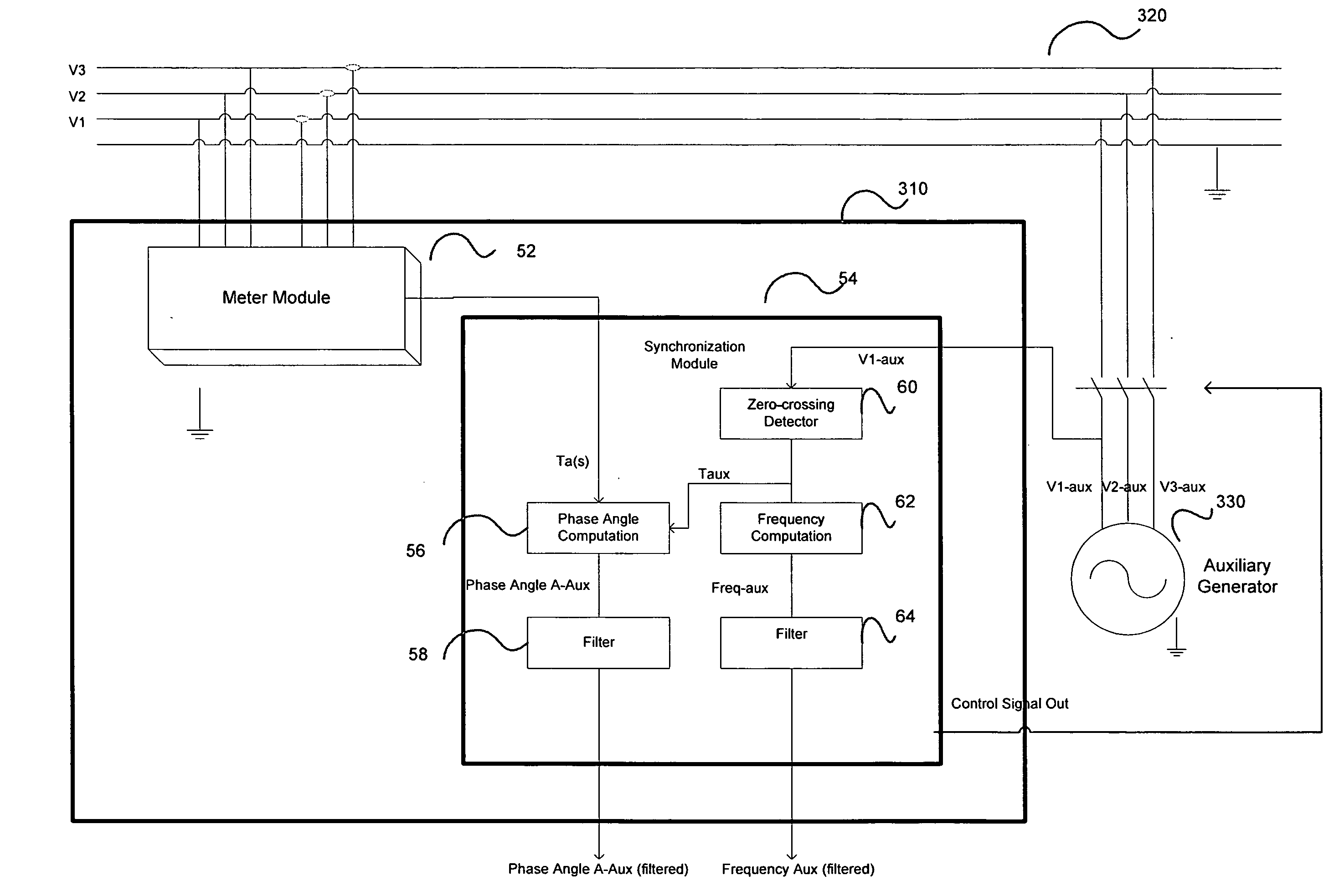
System and method for synchronizing an auxiliary electrical generator to an electrical system
There is provided herein methods and apparatus for apparatus for controlling the interconnection of an auxiliary AC generator with an electrical system, such as an electrical distribution system, e.g., a utility grid. A measuring circuit measures the frequency of an auxiliary AC generator and the phase angle between one voltage phase of the generator and the correspondent voltage phase of the electric utility's electricity supply lines, i.e., the grid, each of which are averaged and filtered. The measured frequency of the auxiliary AC generator is matched to the frequency of the electrical system and the measured phase angle of the generator is matched to the electric utility's electricity supply lines. Once matching is achieved to within a defined tolerance, interconnecting contactors are closed.
Owner:ELECTRO INDUSTRIES GAUGE TECH
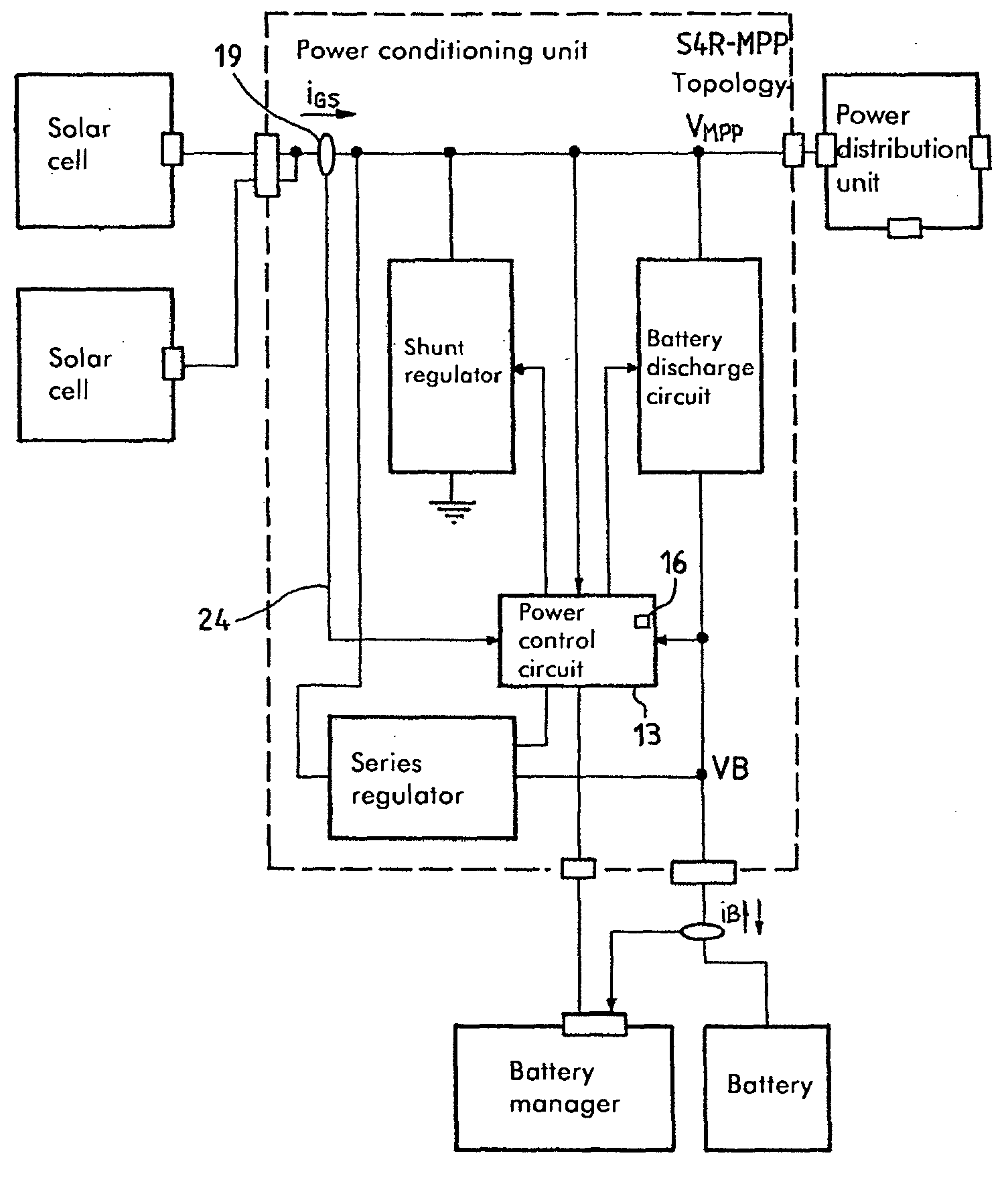
Conditioning circuit for a power supply at the maximum power point, a solar generator, and a conditioning method
InactiveUS20050017697A1Batteries circuit arrangementsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSolar generatorOperating point
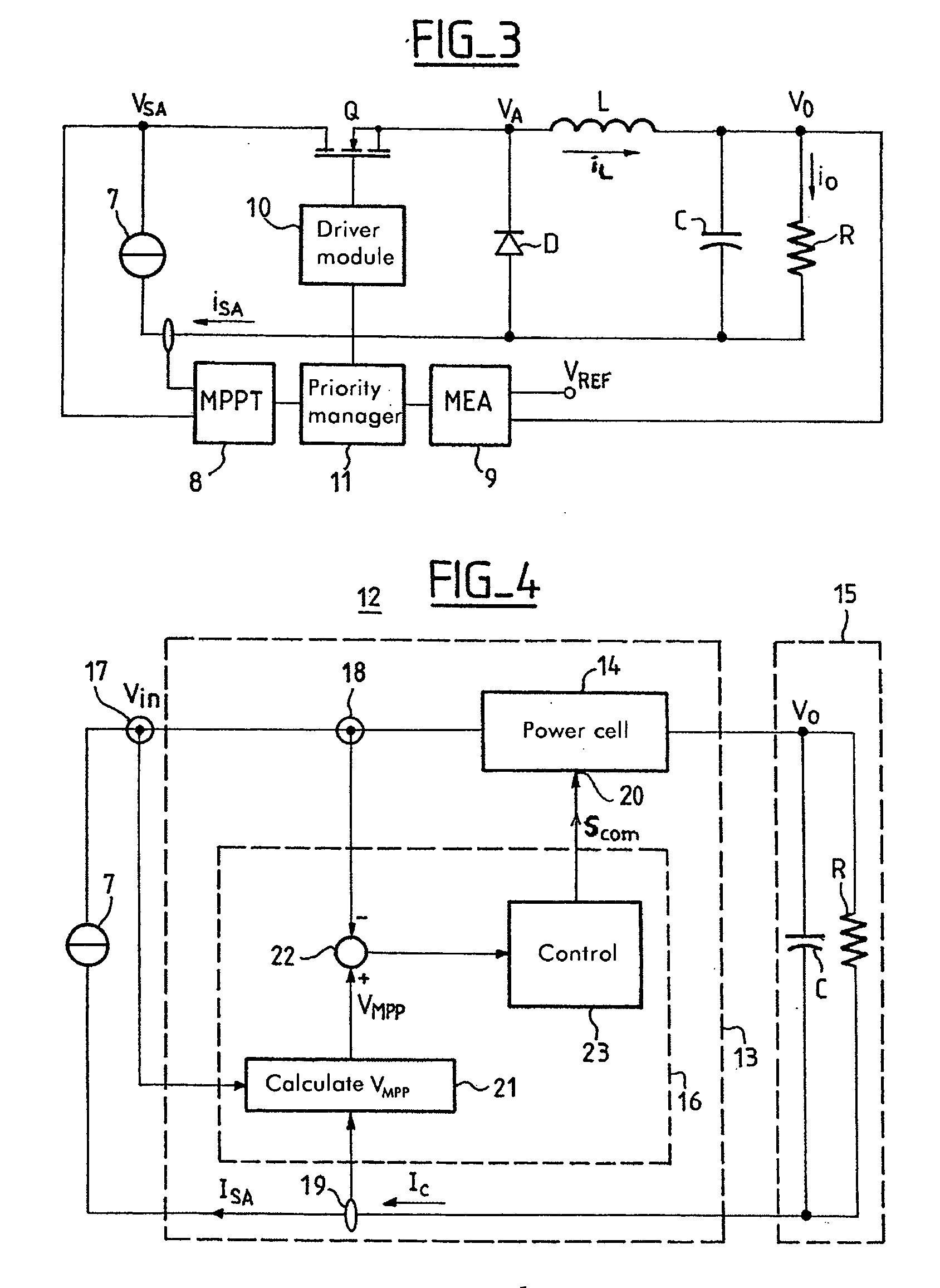
The invention relates to a conditioning circuit that measures operating points of a power supply to deduce therefrom the current-voltage characteristic thereof and to determine directly the voltage corresponding to its maximum power point, without using any kind of tracking algorithm that causes the operating point of the power unit to oscillate about the maximum power point. The maximum power point voltage VMPP is supplied to a controller which regulates a power cell by slaving it to the input voltage until the output voltage of the supply is equal to the maximum power point voltage VMPP. The invention also relates to a solar generator and an associated conditioning method. One particular application is to high-power satellites.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Device for non-dissipative measurement of the current in an inductor
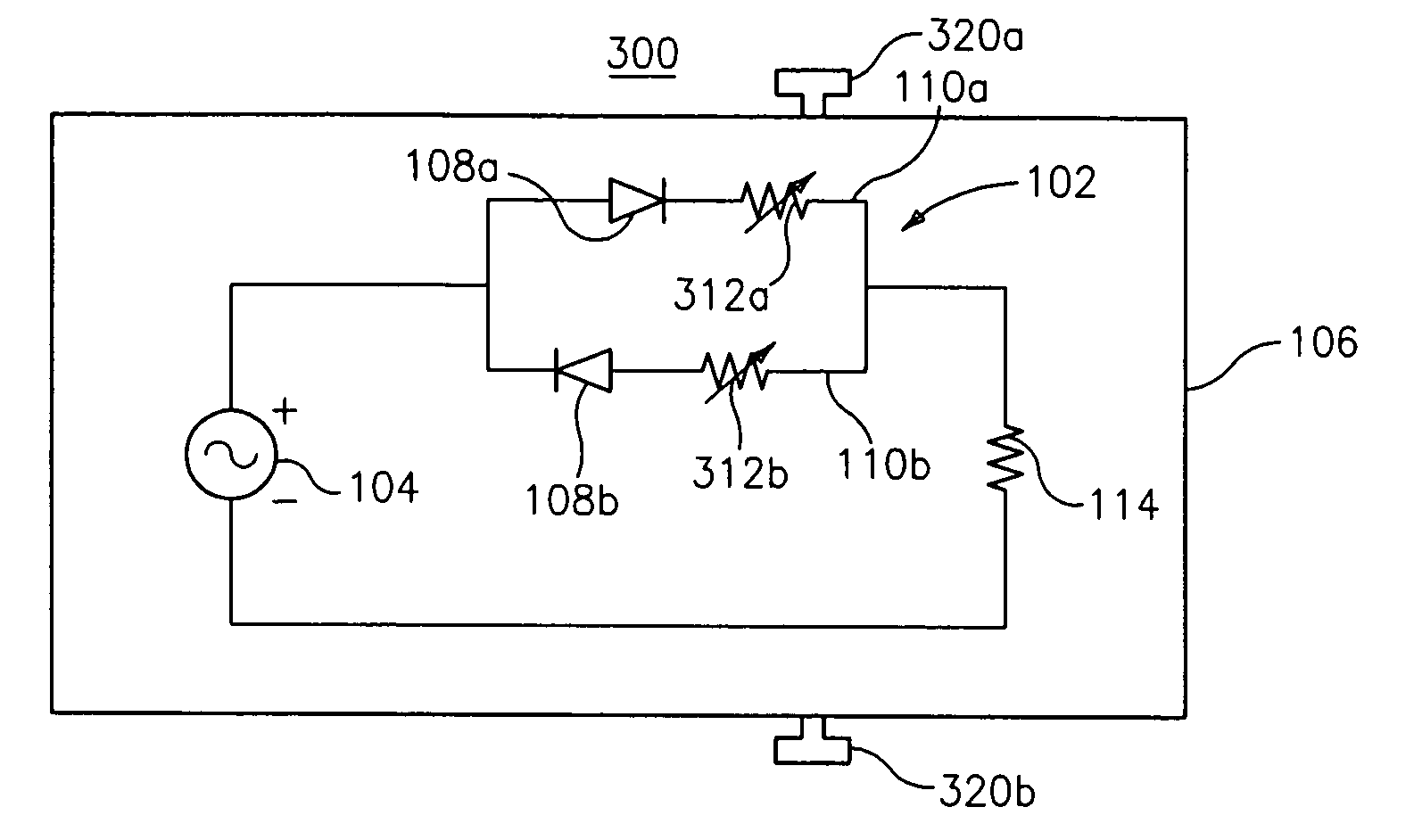
ActiveUS20070075711A1The equipment is easy to operateHigh precisionResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsMeasurement deviceInductor
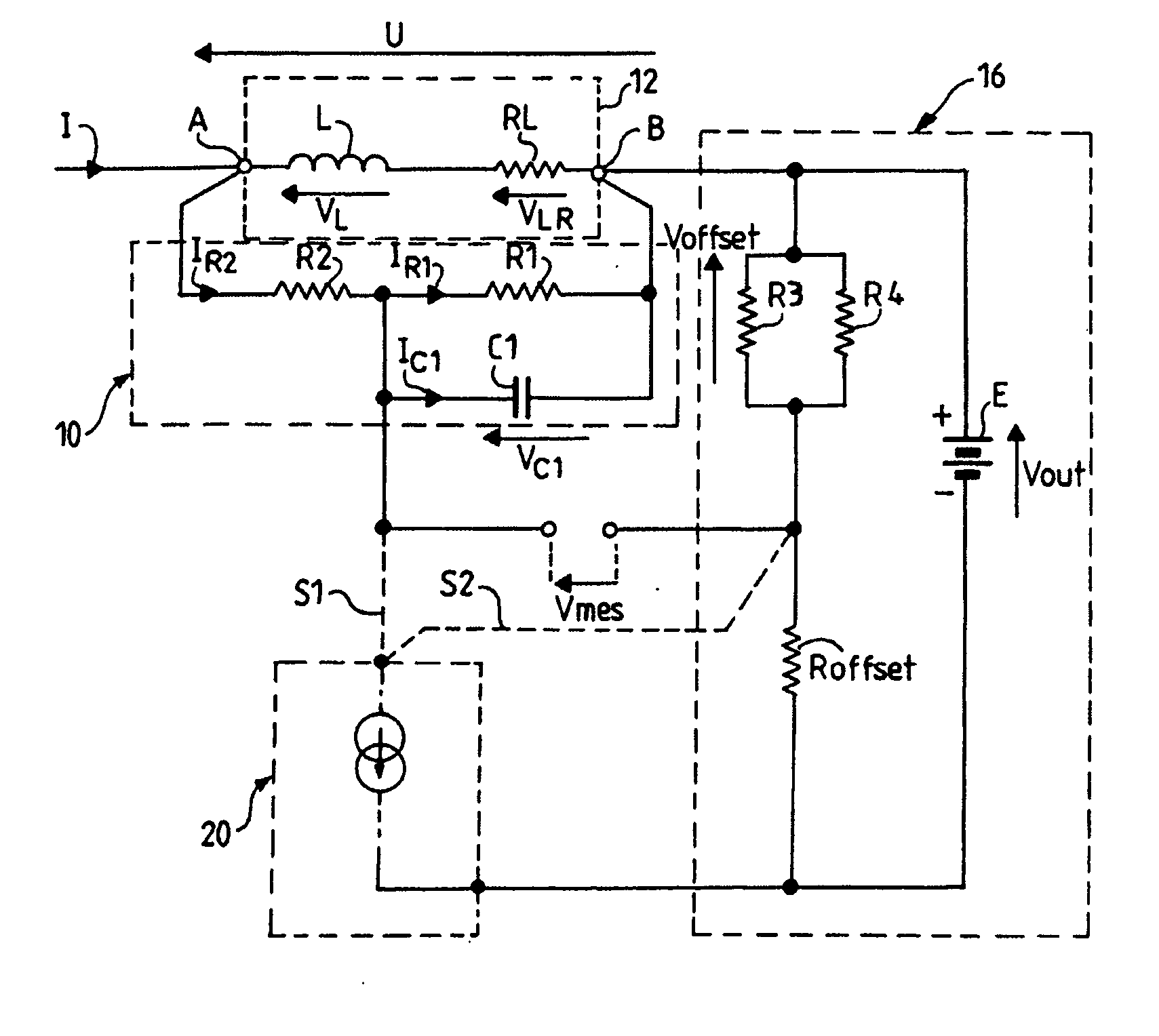
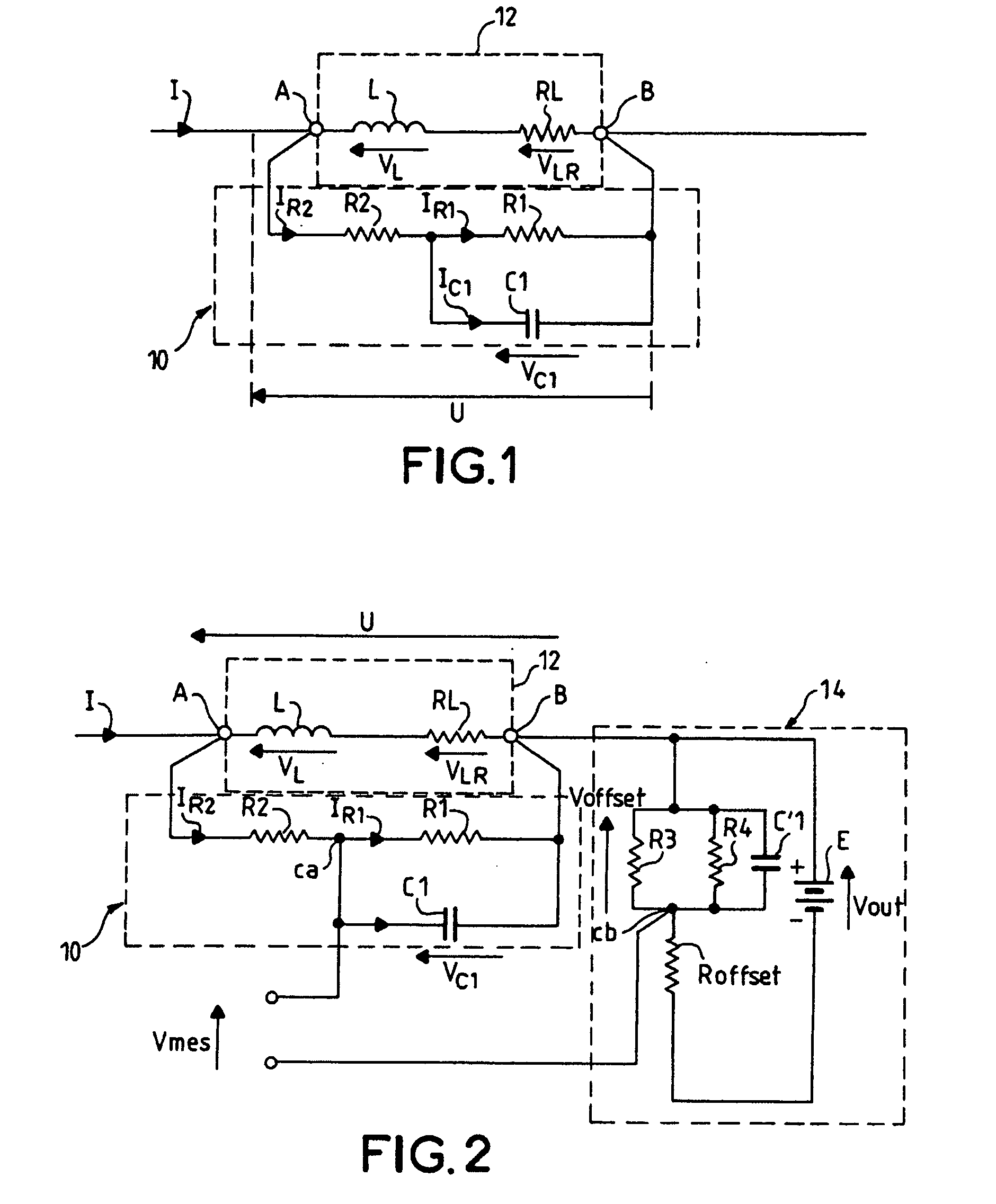
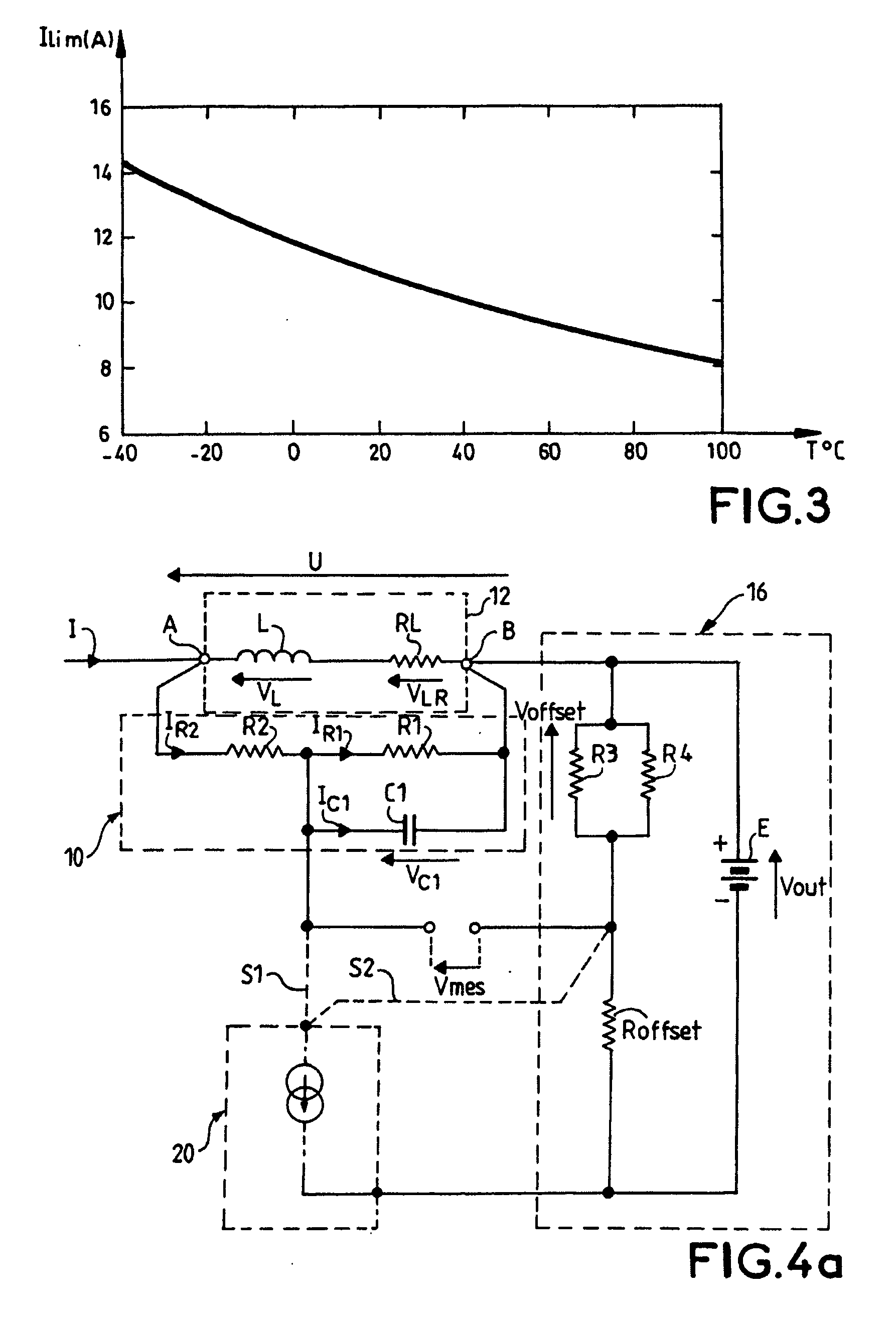
The invention relates to a device for measuring current in an inductor, which device is intended to be connected in parallel with said inductor, comprising two terminals A and B. The device comprises: a network in parallel with the inductor and connected to the terminals A and B having a resistor R2 in series with a resistor R1 in parallel with a capacitor C1; a voltage offset circuit having a DC voltage generator E connected in parallel with an offset resistor (Roffset) in series with two resistors in parallel R3 and R4, the positive pole of this voltage source being connected to terminal B of the inductor; a temperature compensation circuit comprising a current source controlled as a function of the temperature, one of the two terminals of the current source being connected to the negative pole of the generator E, the other terminal of the current source being connected to different points of the measurement device according to the direction of variation of the current of the source as a function of the temperature. The measurement of voltage Vmes, the image of the current I in the inductor 12, is performed between the common point between the resistors R1, R2 of the network and the common point between the offset resistor and the two resistors R3 and R4.
Owner:THALES SA
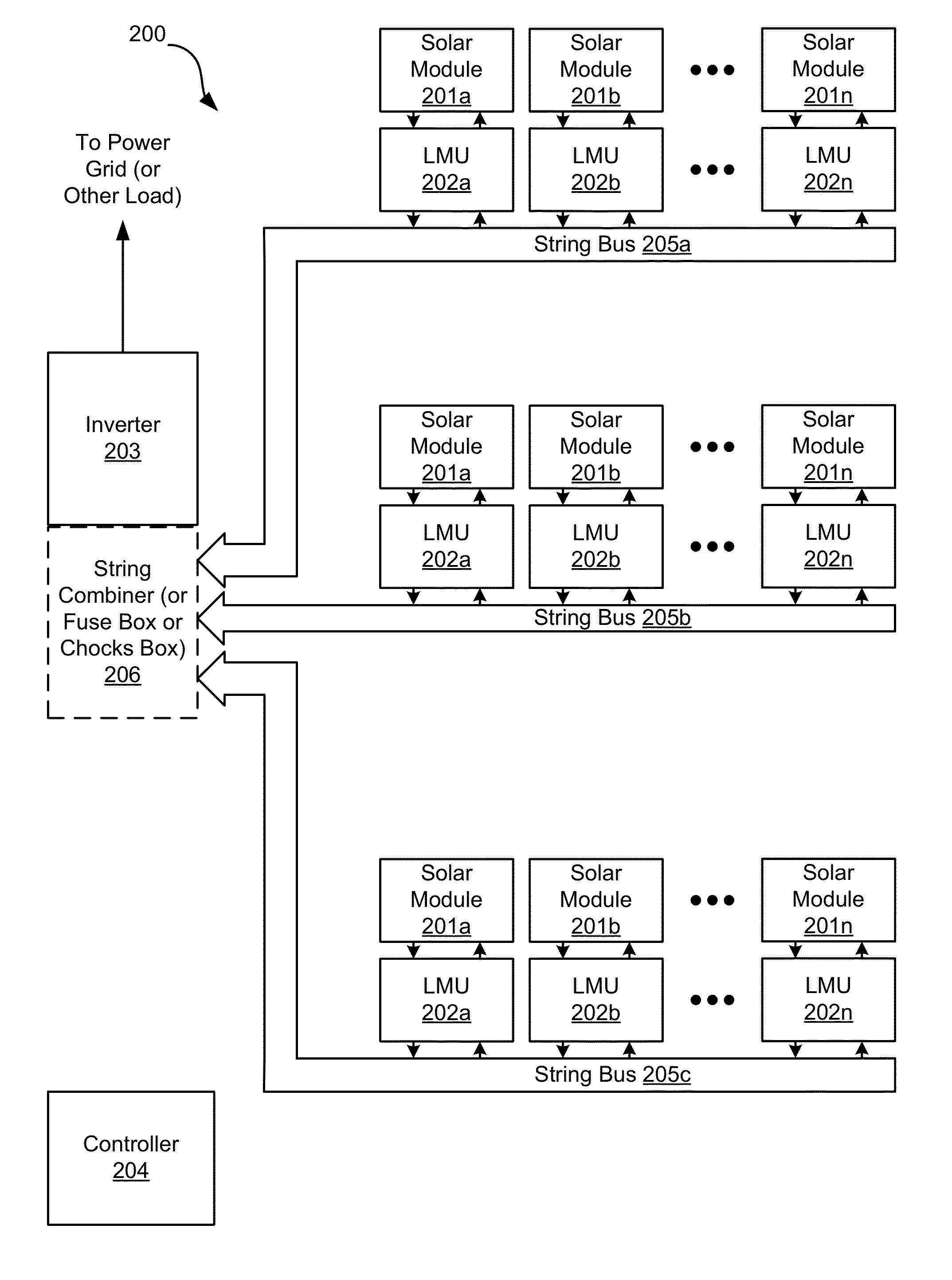
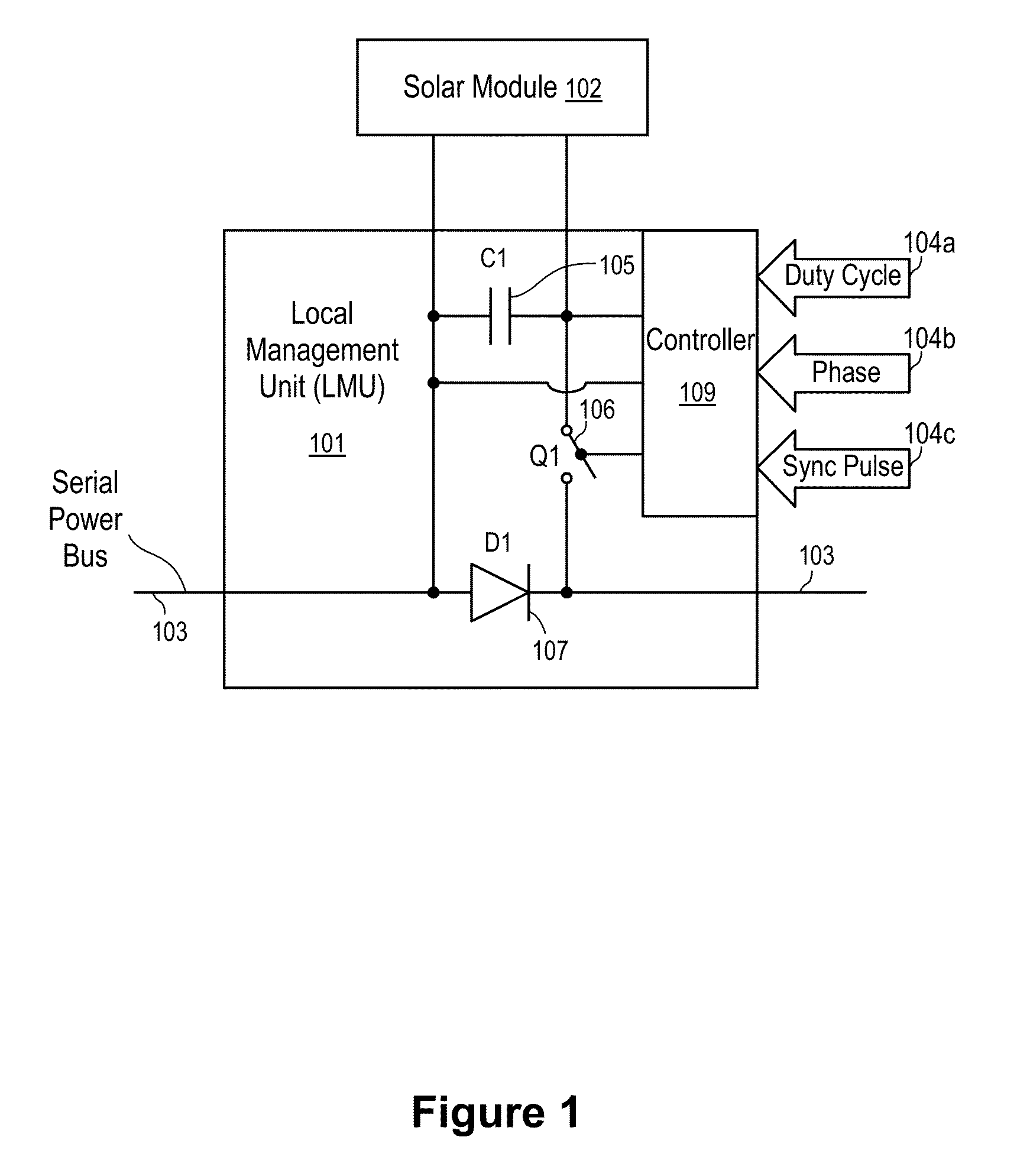
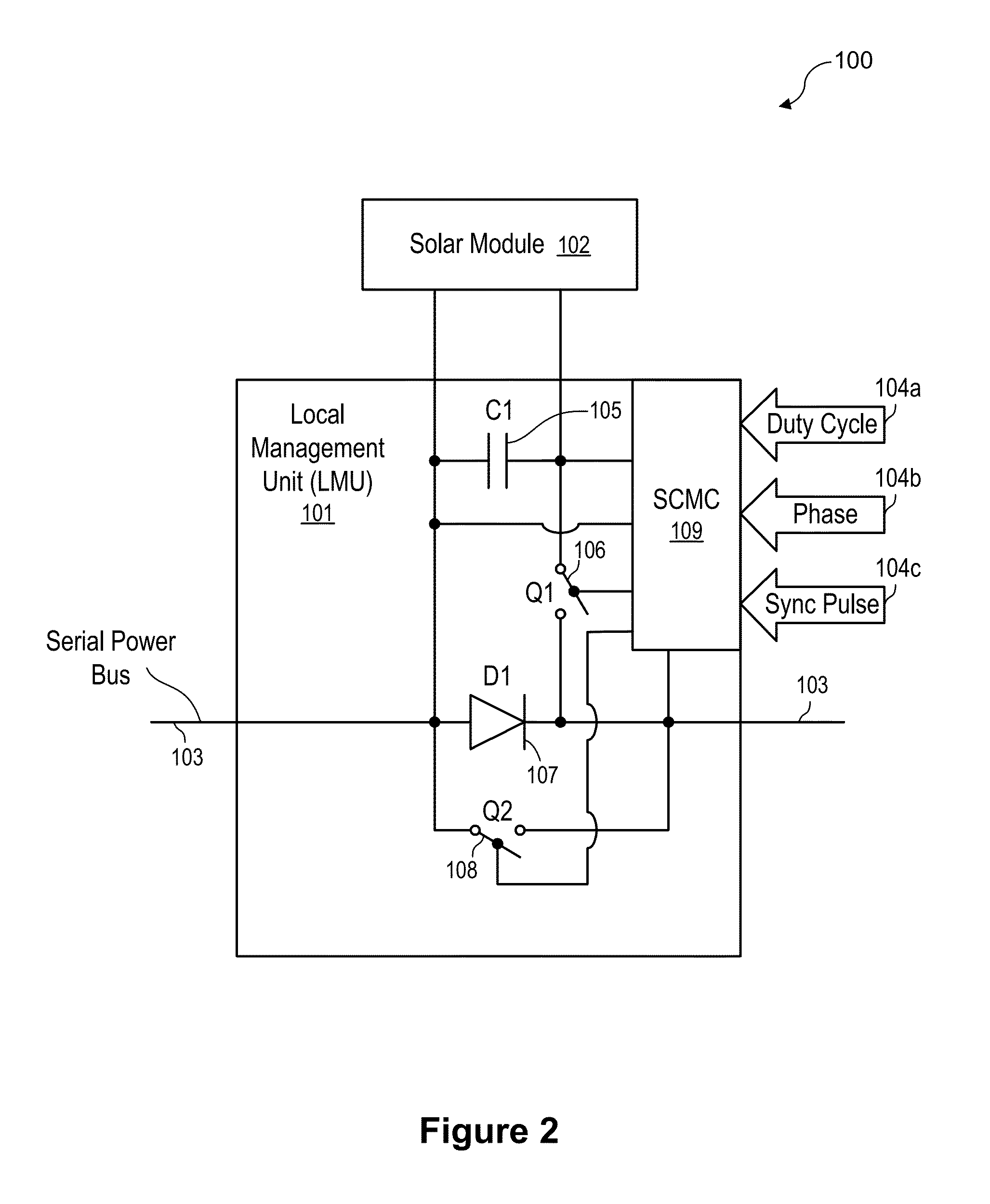
Systems and Methods to Reduce the Number and Cost of Management Units of Distributed Power Generators
ActiveUS20130026840A1Low costSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc source parallel operationManagement unitCommunication unit
Apparatuses and methods for configuring and managing solar panels to form strings of photovoltaic energy generators with improved performance and reduced cost. The photovoltaic energy generators are connected via one or more combined local management units (CLMUs), each having a plurality of direct current converters connected to and configured to receive direct current power from a respective solar panel. A controller unit shared by the CLMU's direct current converters is utilized to separately control the operation of each converter such that the power extracted from the solar panels is maximized. A communications unit coupled with the controller unit is utilized to facilitate communications between the controller unit and a system unit remote from the CLMU to report measurements and receive control signals.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
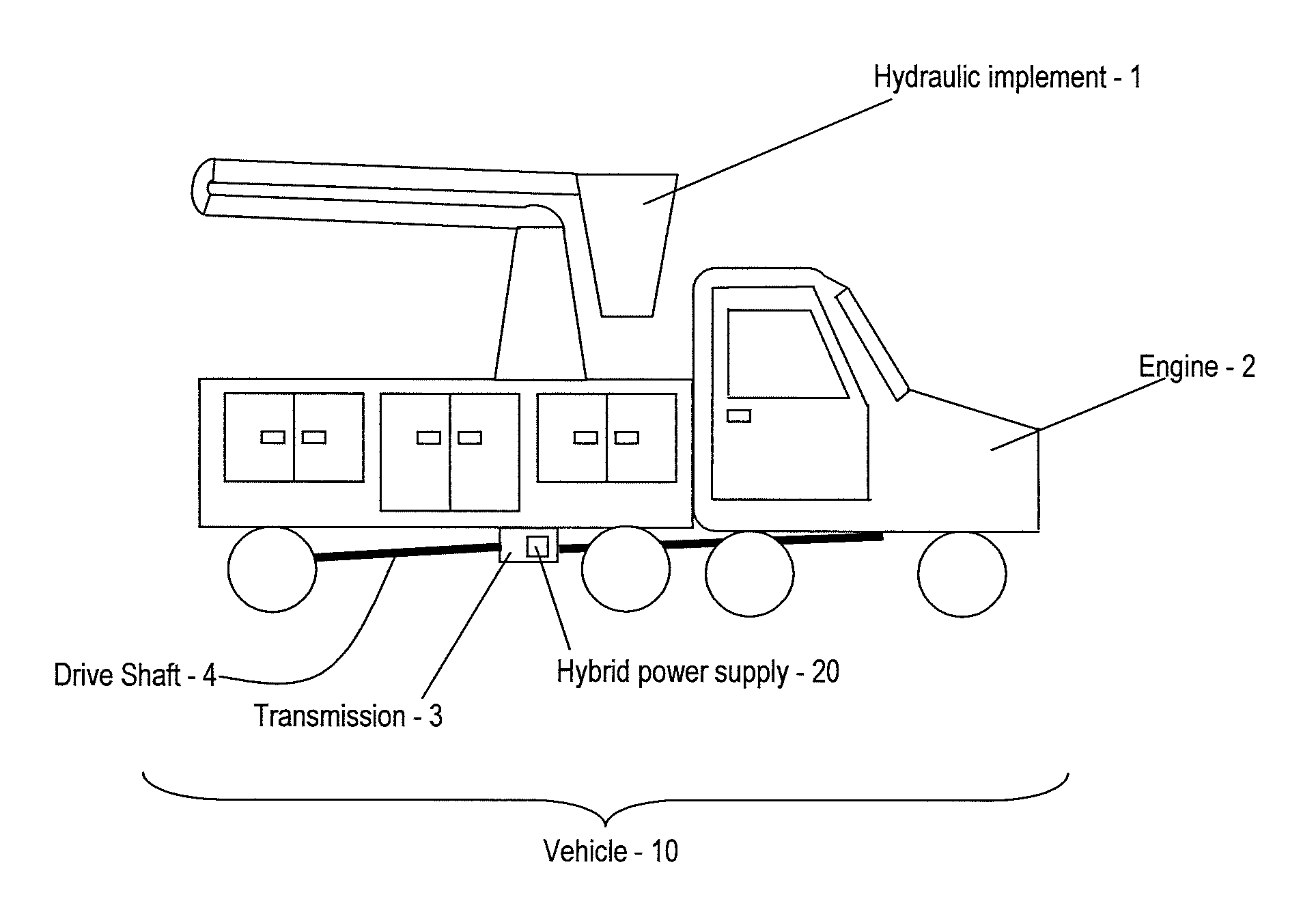
Hybrid drive for hydraulic power
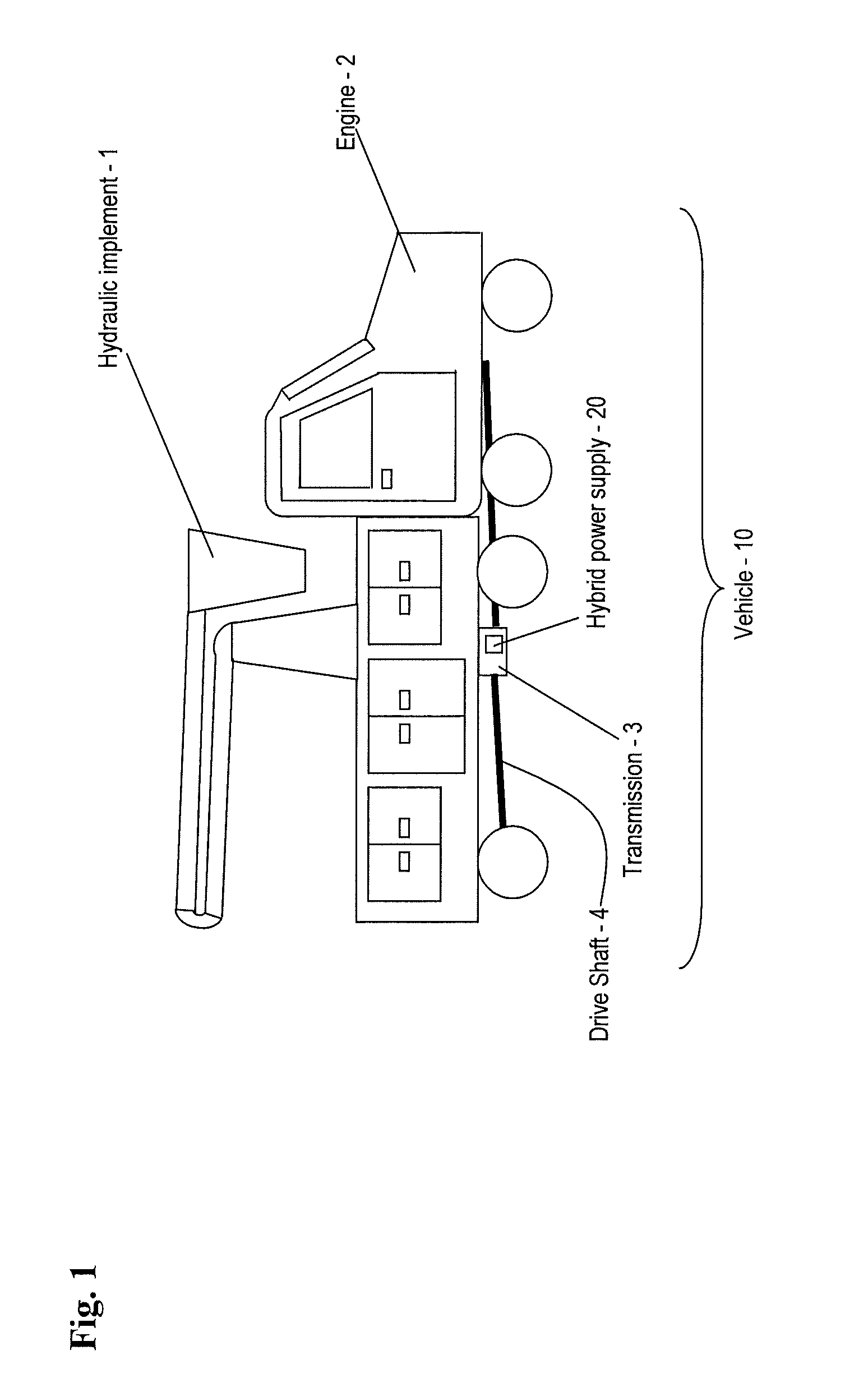
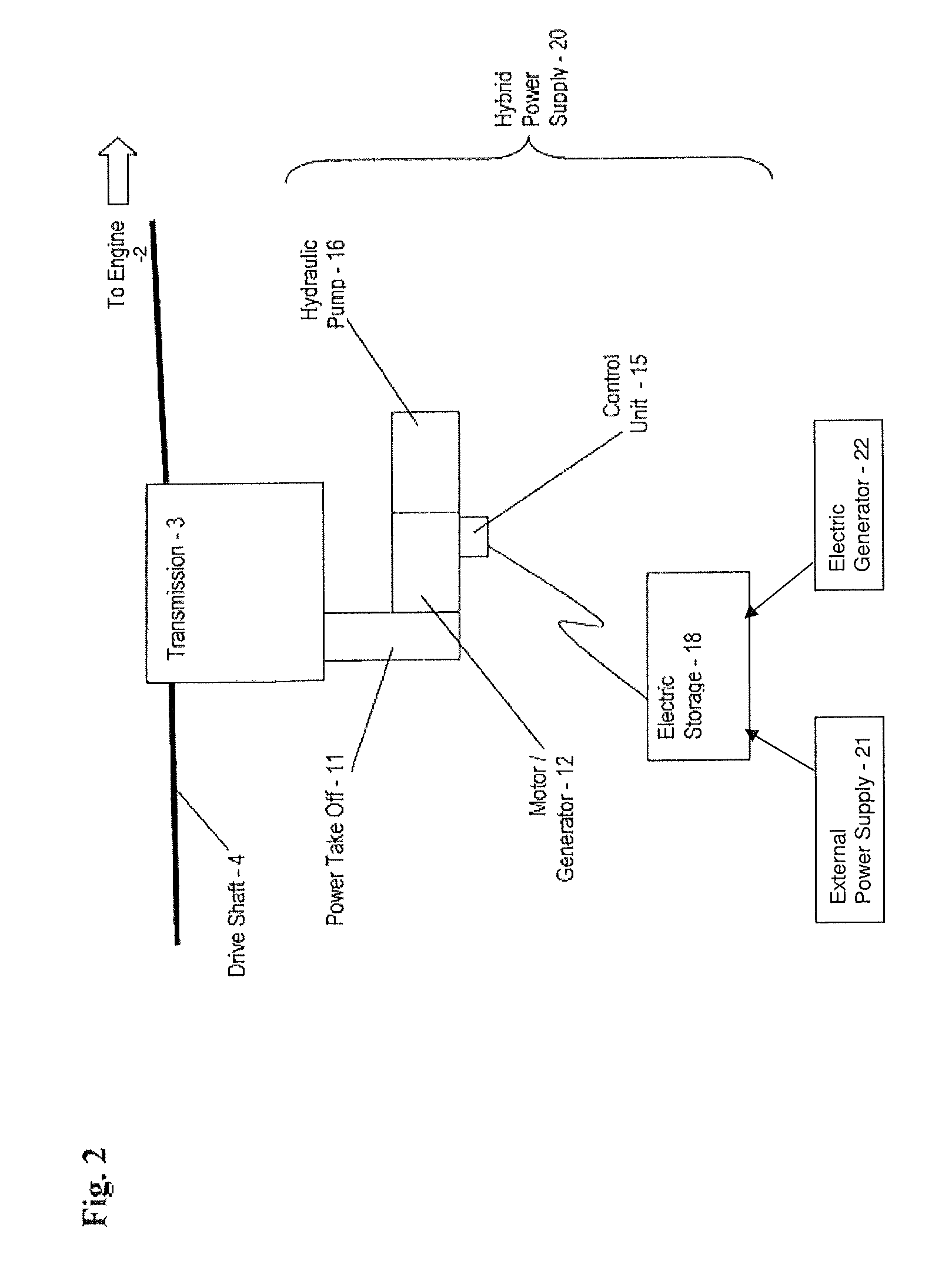
A power supply for powering a hydraulic implement includes: an electric storage unit; an electric motor, an electric generator, a hydraulic pump and a control unit; the electric motor adapted for receiving electric power and driving the hydraulic pump to power the hydraulic implement; the electric generator adapted for translating mechanical energy into the electric power; the electric storage unit also being adapted for providing the electric power; and the control unit for selecting a source of the electric power from one of the generator and the electric storage unit. A method for operating the power supply and a vehicle are also provided.
Owner:TEREX SOUTH DAKOTA
Distributed energy neural network integration system
Owner:ORION ENG
AC generator for vehicles
InactiveUS6137201ASynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsDynamoElectrical and Electronics engineering
An AC generator for a vehicle including a rotor with a fan, a stator disposed around the outer periphery of the rotor, and a frame. The stator includes a laminated core having a plurality of slots, a plurality of electric conductors in the slots, and an insulator. There is a gap between the electric conductors and the insulator in a diametrical section of the slots, and an area ratio of the gap with respect to the sectional area of the slots is not more than 25%. A portion of the electric conductor positioned within the slot has a substantially rectangular shape along the shape of the slot.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Mobile power generation system including dual voltage generator
InactiveUS20190067991A1Reduce system weightEliminate needSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMechanical energy handlingElectricityVoltage generator
Mobile power generation system and methods for dual-voltage generation include providing a trailer including a rear end, a front end, a bottom end, and a top end, a gas turbine housed inside the trailer, and an electrical generator coupled to the gas turbine to generate electricity and housed inside the trailer. The electrical generator is at least a dual-voltage generator configured to provide an auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads and a main primary load output power and comprising one or more taps configured to provide the auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads. The electrical generator is at least a dual-voltage generator comprising three-phase circuitry including three lines and one or more taps configured to provide auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads, ends of the three lines configure to provide a main primary load output power.
Owner:ON POWER INC
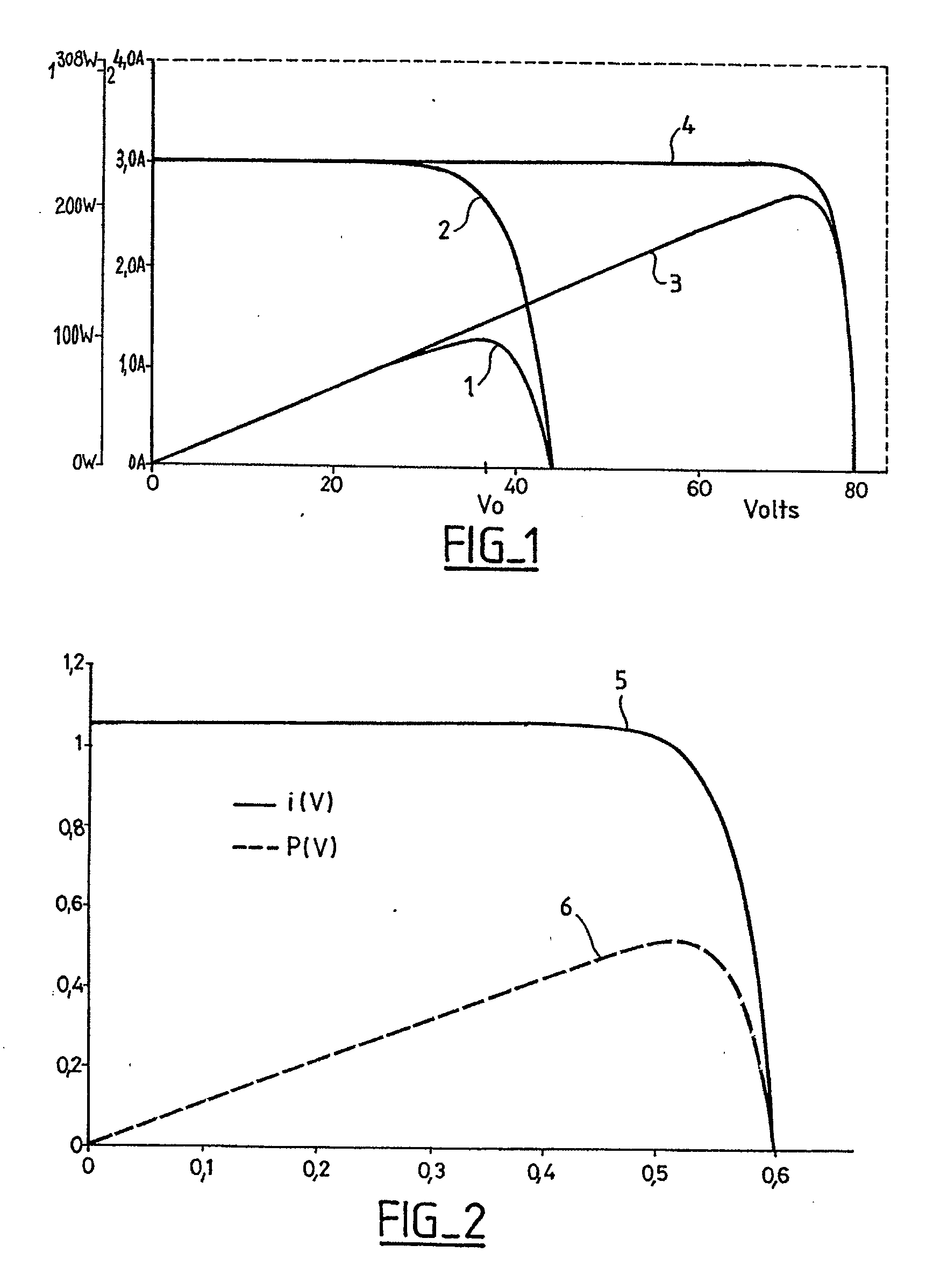
Method of finding a maximum power of a photovoltaic generator
ActiveUS20070027644A1Reduce the required powerImprove energy efficiencyBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsElectric devicesOperating pointPhotovoltaic generator
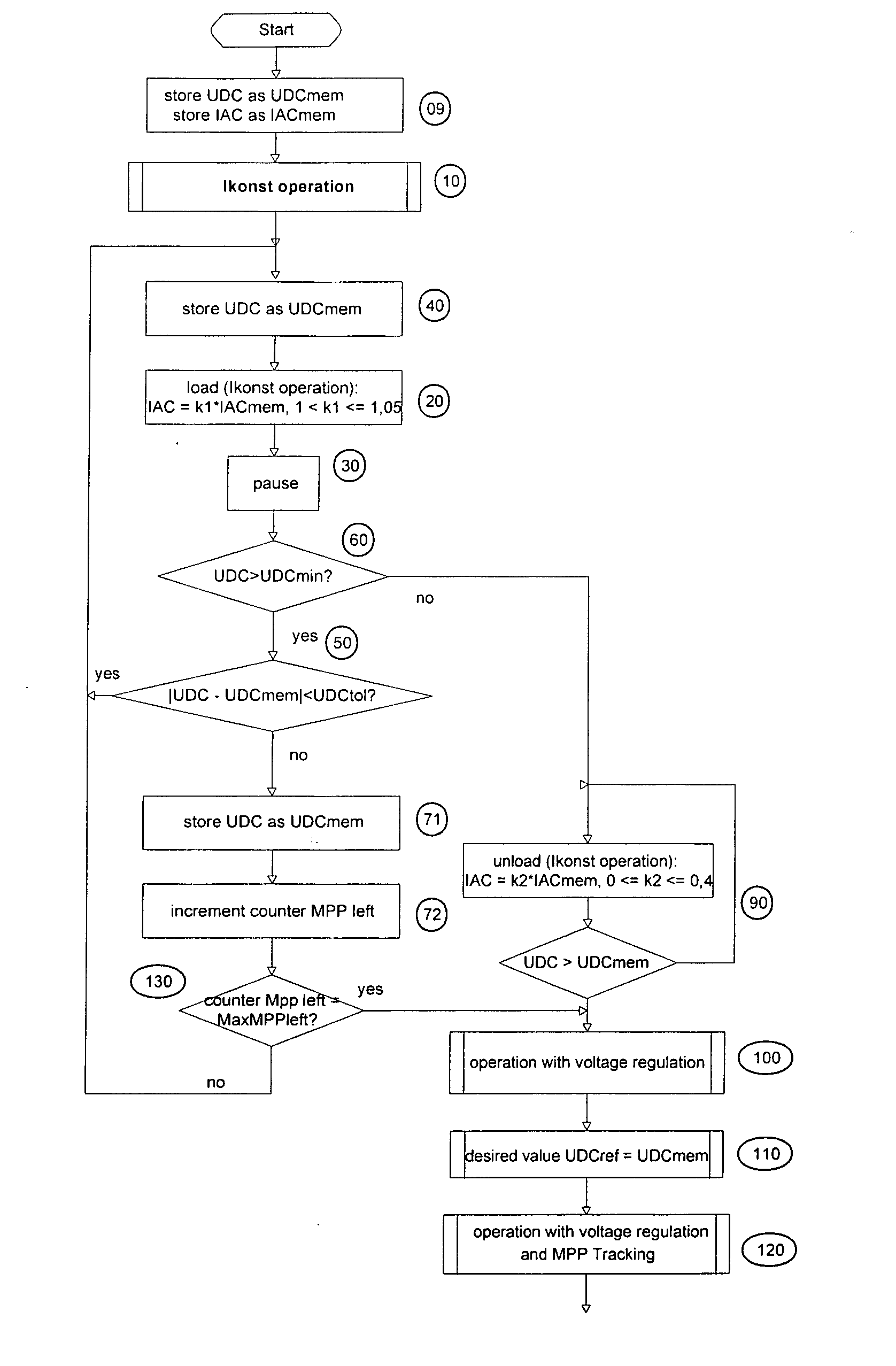
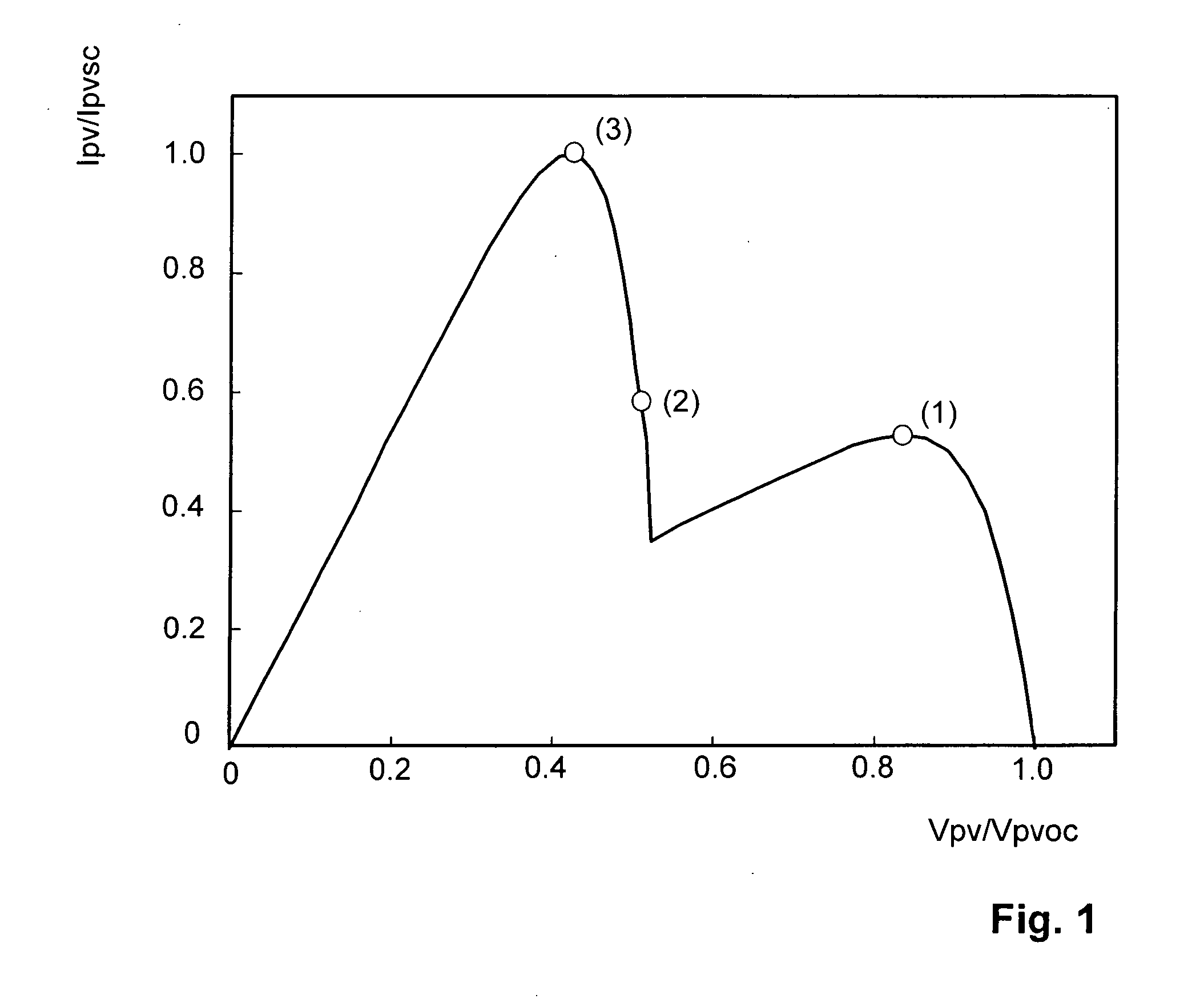
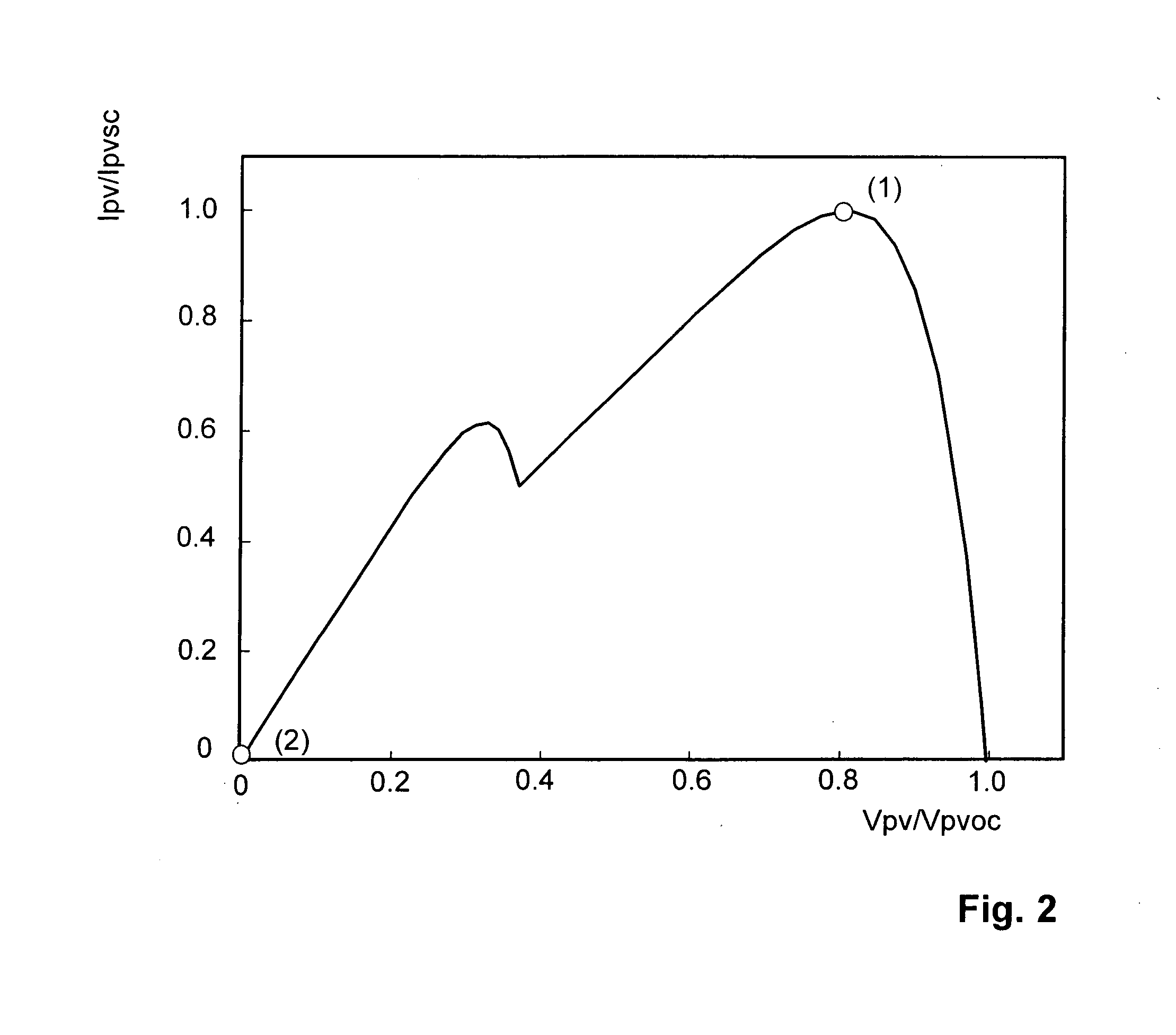
A method of finding a power maximum of a photovoltaic generator using an MPP regulator of a photovoltaic current converter by means of which a maximum generator power is set at an operating point of the generator's characteristic curve is intended to supply improved efficiency when the generator is partially shadowed. This is achieved by switching the MPP regulator off in order to next load and / or unload the generator to allow a new operating point of the generator's characteristic curve to set and by next switching the MPP regulator on again.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Method for activating a multi-string inverter for photovoltaic plants
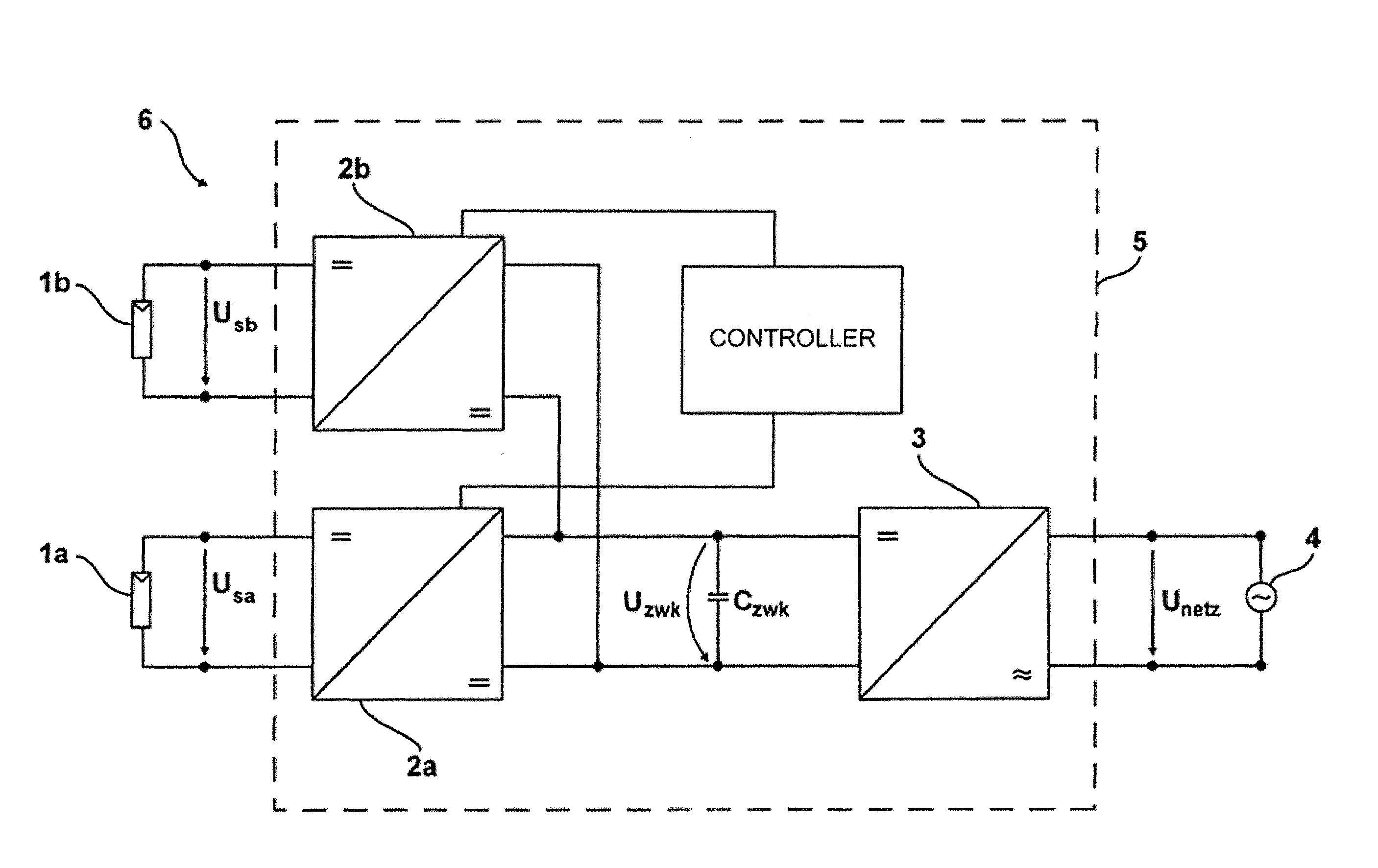
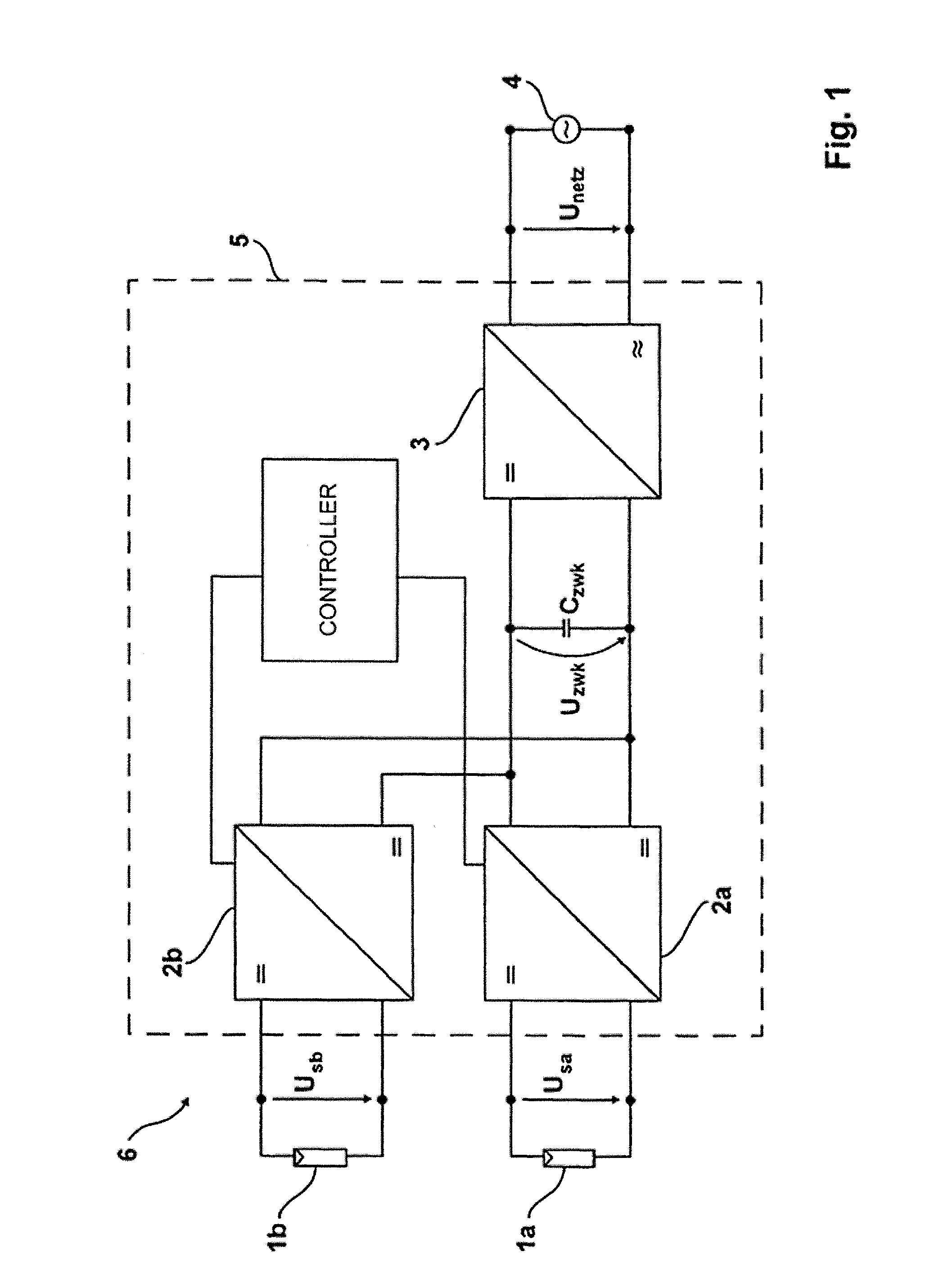
ActiveUS8212409B2Improve photovoltaic efficiencyImprove efficiencyDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionDc dc converterPhotovoltaic power station
A method of activating a Multi-String inverter for photovoltaic generators (1a, 1b) of a photovoltaic plant (6), the Multi-String inverter incorporating on the input side a separate DC-DC converter (2a, 2b) for each generator string (photovoltaic generator) (1a, 1b) and each output of the DC-DC converters (2a, 2b) being connected in parallel and to an input of a DC-AC converter (3) and the DC-AC converter (3) being connected with an alternating current mains (4) for feeding into the mains aims at improving efficiency. This is achieved in that one or several electrical variables, namely input current, input voltage and / or input power are measured at each DC-DC converter (2a, 2b) and at least one of the DC-DC converters (2a, 2b) changing its operating condition as a function of this measurement when a limit value and / or a range is exceeded in such a manner that its power loss is reduced so that the energy yield of the photovoltaic plant (6) is increased.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
HEV charger/generator unit
The present invention provides an apparatus, system, and method of utilizing a Home Power Unit ("HPU") which functions as a battery charger for a Hybrid Electric Vehicle ("HEV") or as a generator, utilizing the HEV's electrical power to operate external electrical devices. In its simplest form, the HPU comprises a Transformer, inverter means, rectifier means, a control unit, connection means to the HEV and external electrical loads or sources and switching means to change operation between charger and generator function. Alternative embodiments of the present invention utilize the HEV's existing components thereby avoiding component redundancy within the HPU. Specifically, in the first alternative embodiment, the inverter means are utilized within the vehicle, therefore, requiring only filter and transformer to be added to the vehicle. In the second alternative embodiment, the vehicle's DC-to-DC Converter is utilized as opposed to implementing a transformer. Therefore, only an inverter and filter are added to the system.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
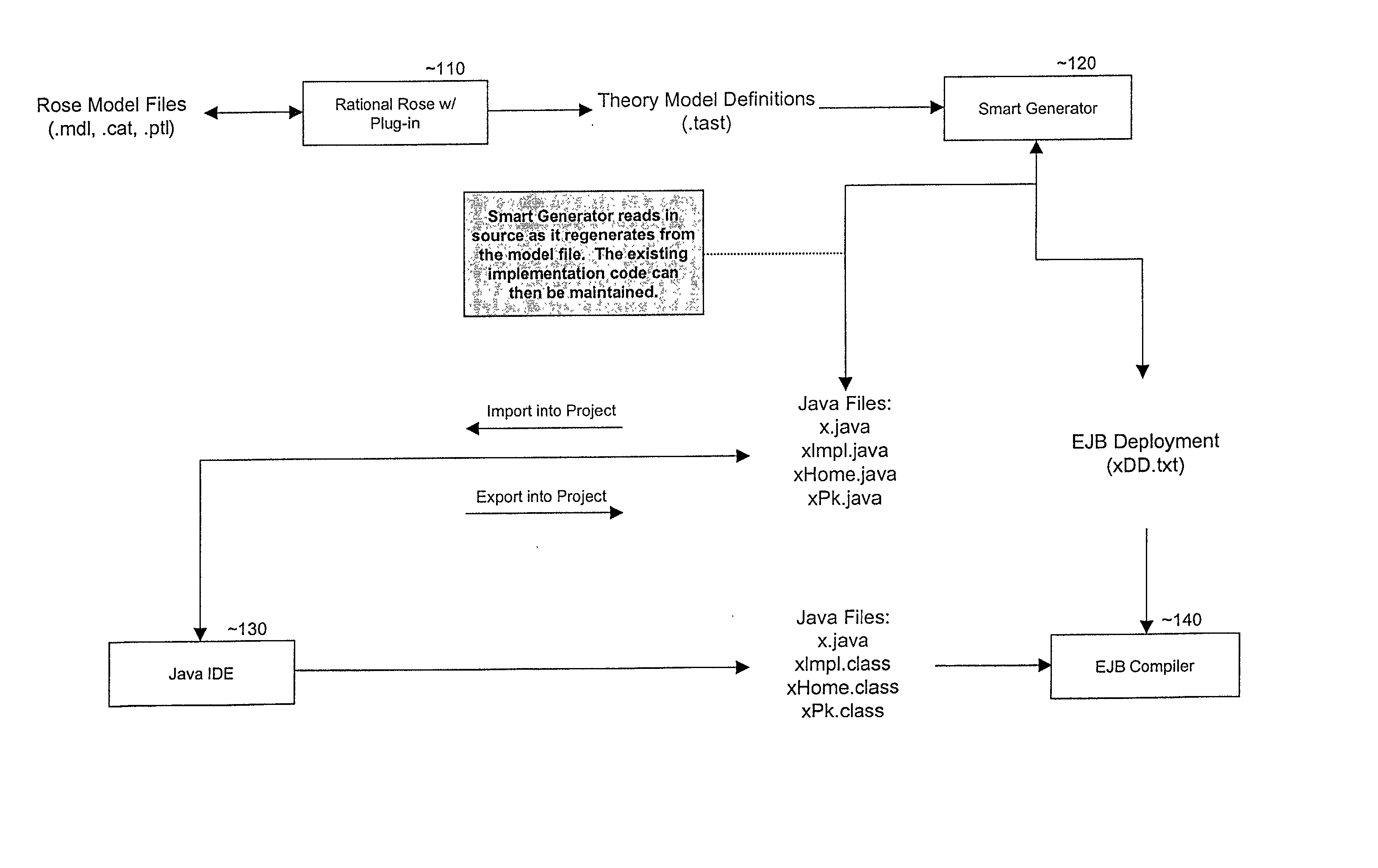
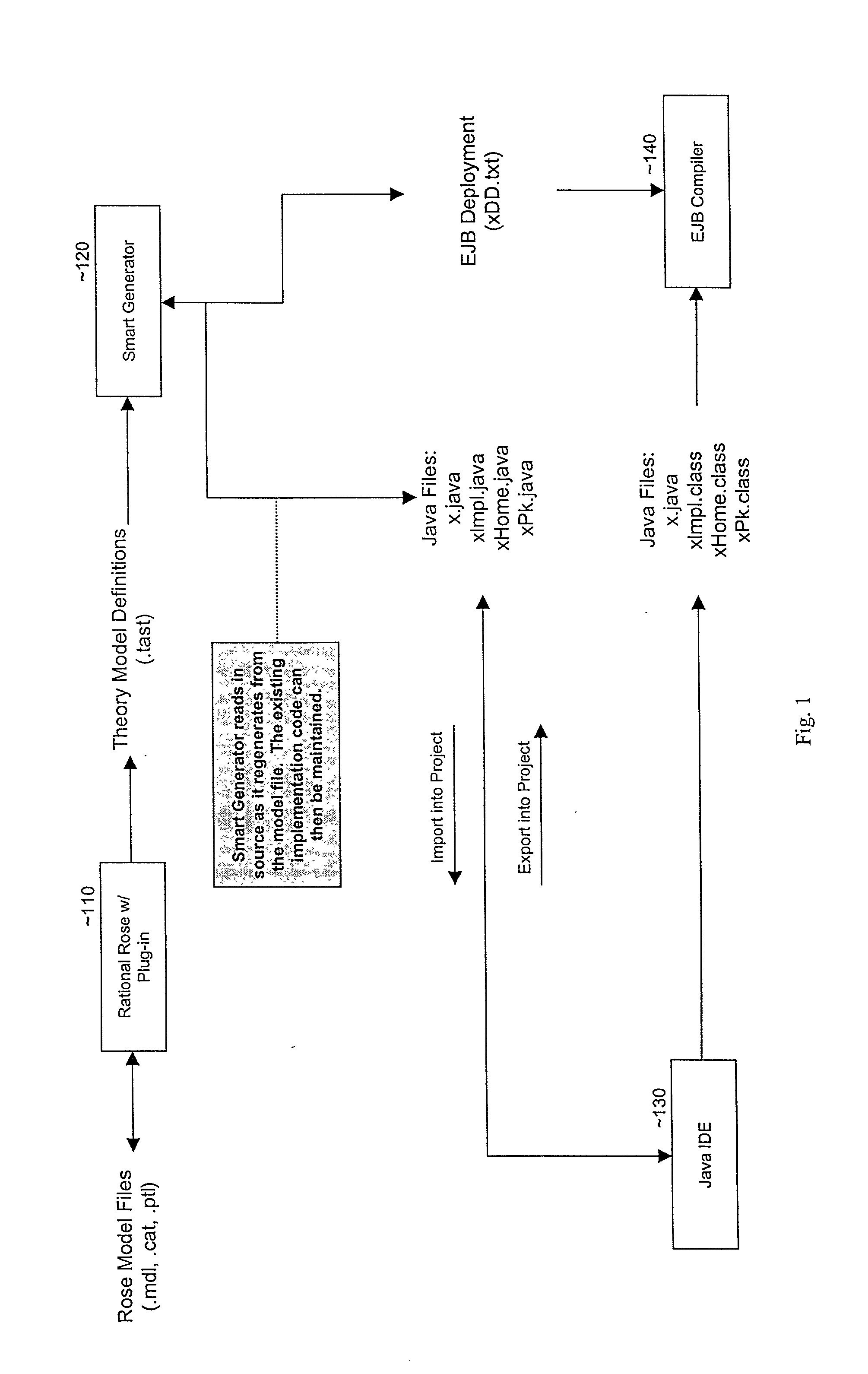
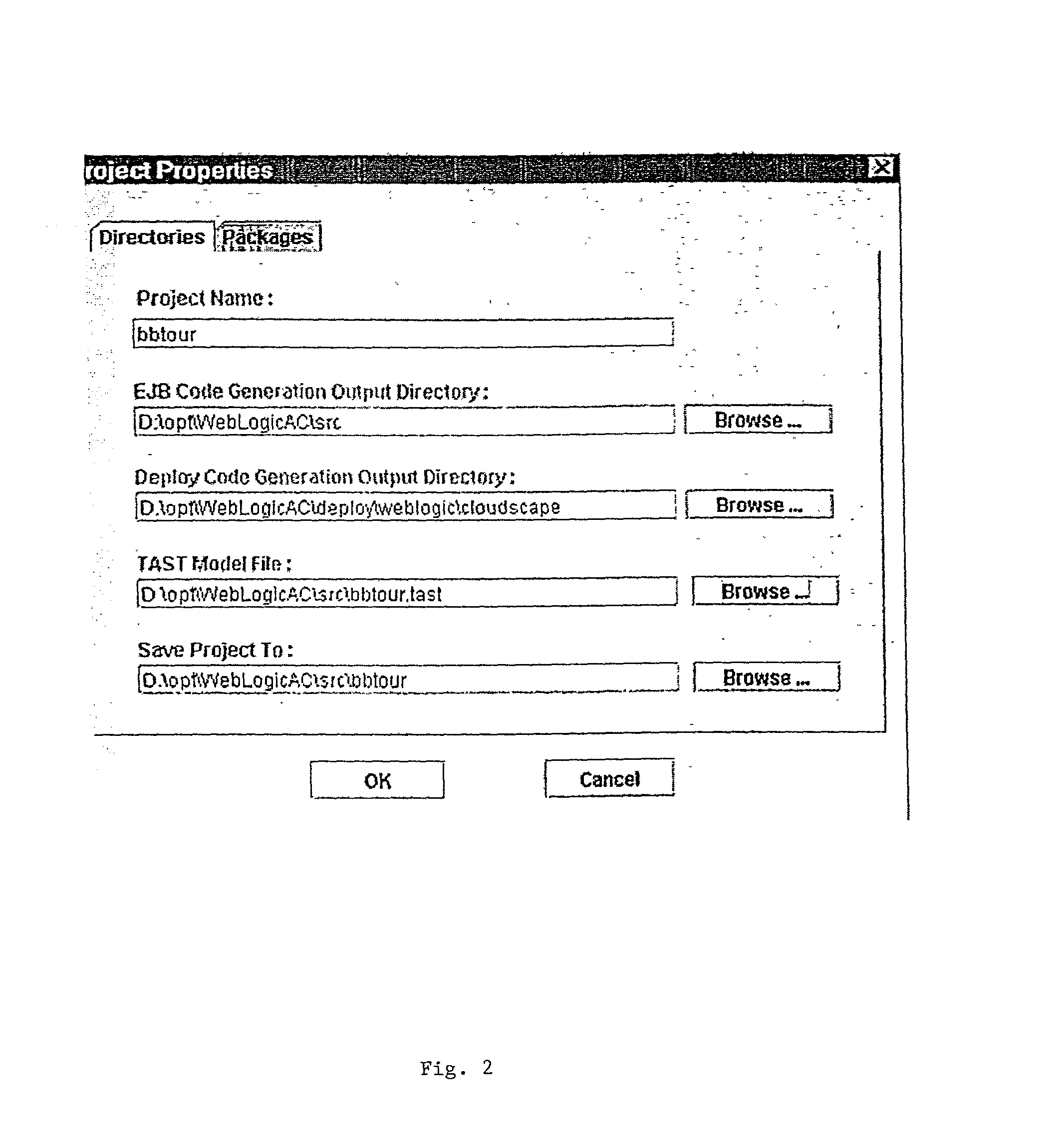
Smart generator
ActiveUS20020147763A1Laborious taskDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess methodDEVS
The Smart Generator of the present invention allows the designer / developer / user to model the EJB components in a natural way without being concerned with implementation-specific details. The developer models the business objects using a UML drawing tool and the Smart Generator creates a set of classes that implements these objects with reference to the Enterprise JavaBeans specification. That is, the Smart Generator automatically create access methods and handling containment of references from the UML diagram.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
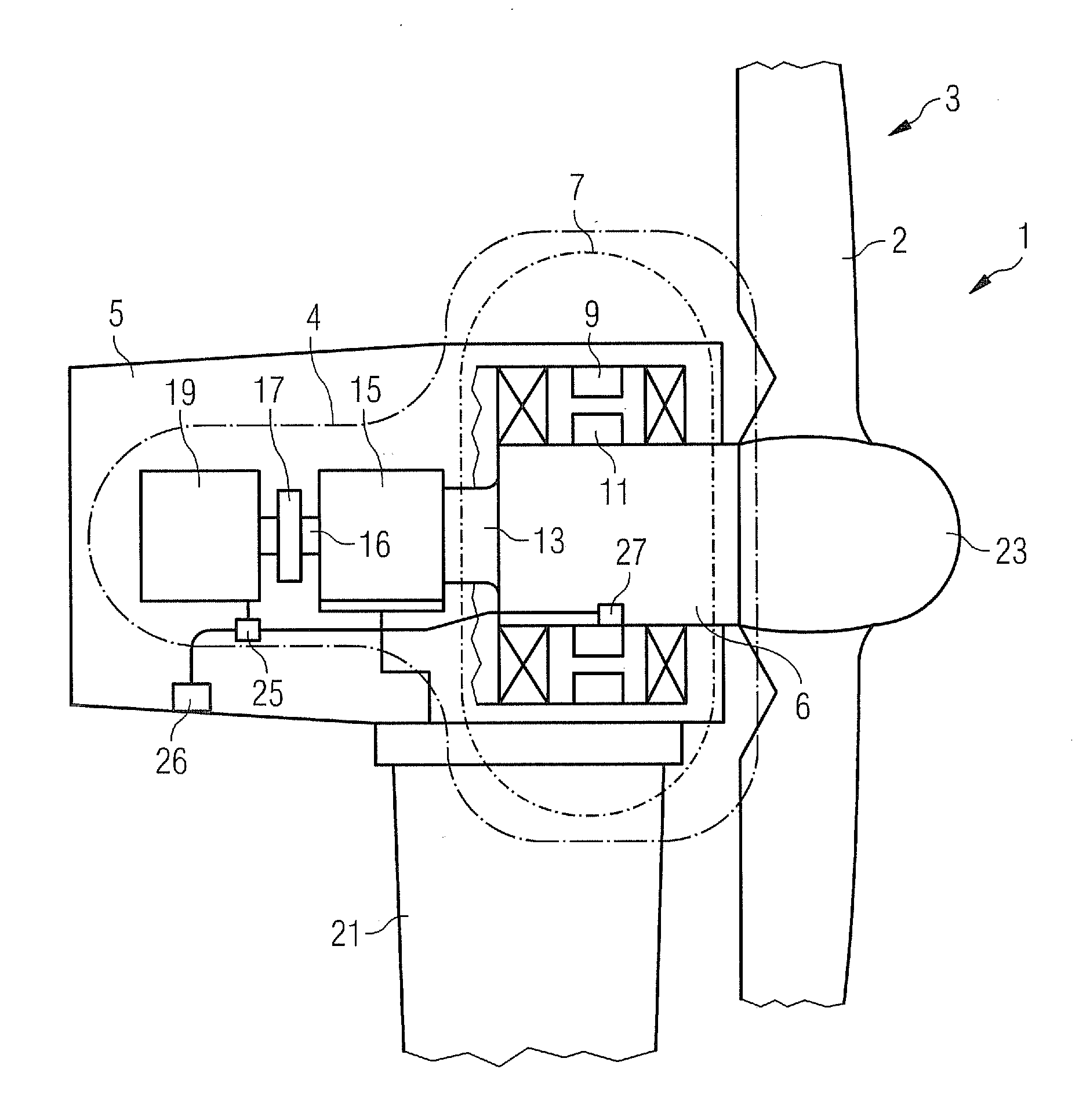
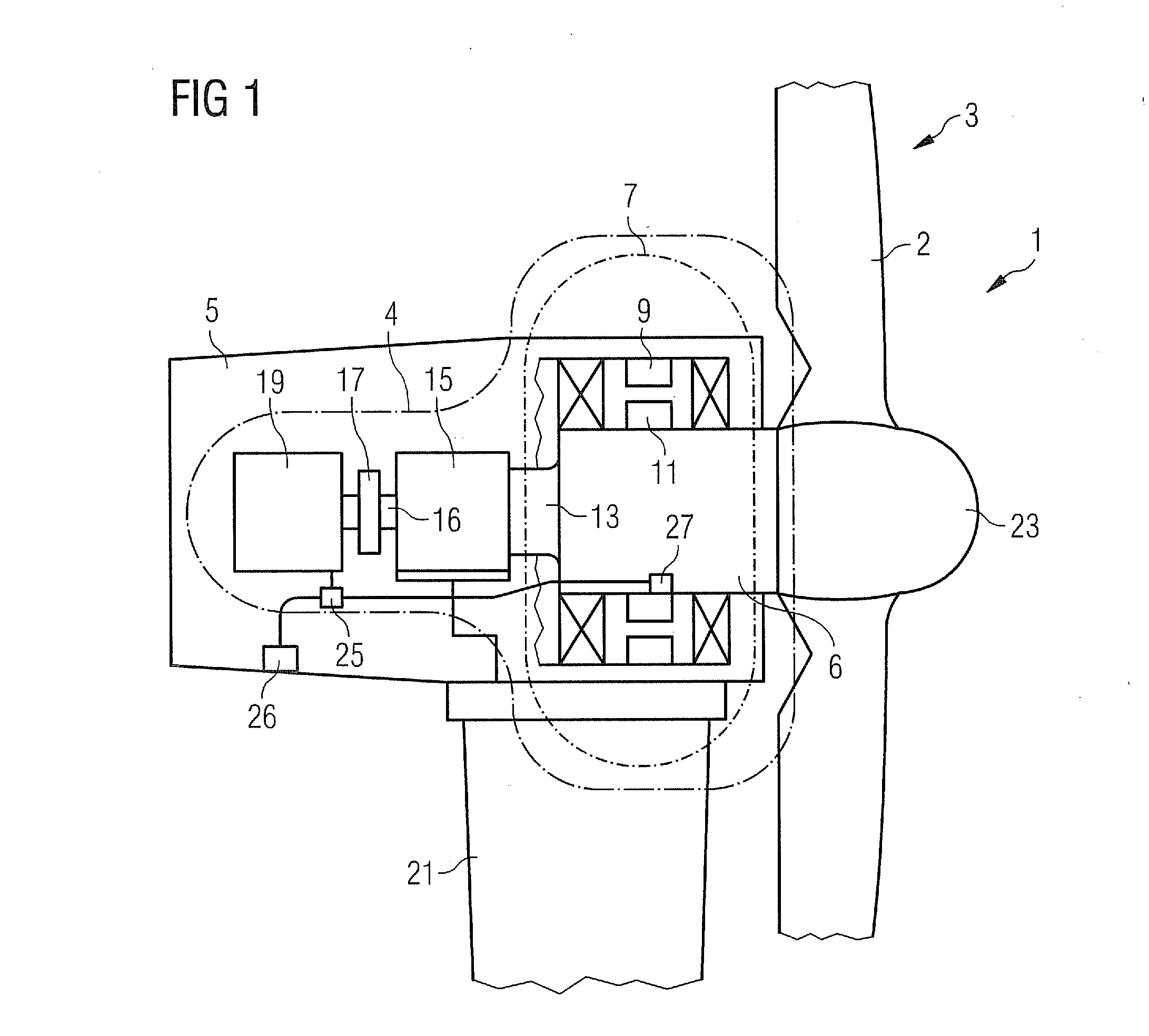
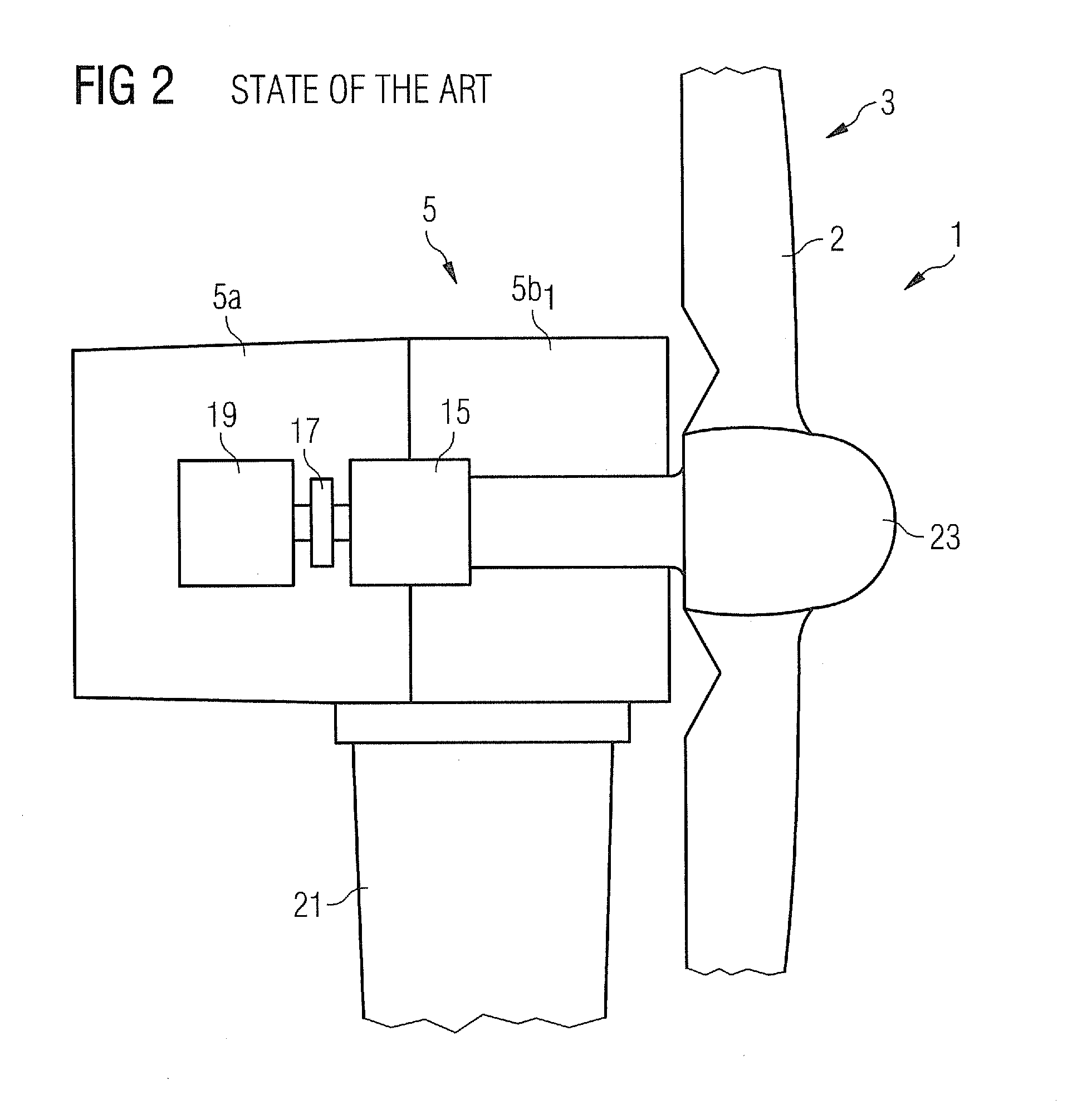
Wind turbine, drive train assembly, wind turbine nacelle system, methods for converting rotational energy and methods for building a nacelle and for re-equipping a wind turbine
InactiveUS20120019001A1Mitigate such drawbackSmall sizeWind motor controlWind motor combinationsNacelleRotational energy
A wind turbine with a drive train connecting a drive unit with a generator assembly is provided. The generator assembly includes a first generator with a first stator and a first rotor, the first rotor being directly connected to the drive train, and at least a second generator indirectly coupled to the drive train via a gear box. Further, a drive train assembly, a wind turbine nacelle system, a method for converting rotational energy into electrical energy, a method of building a nacelle and methods of re-equipping a wind turbine are provided.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
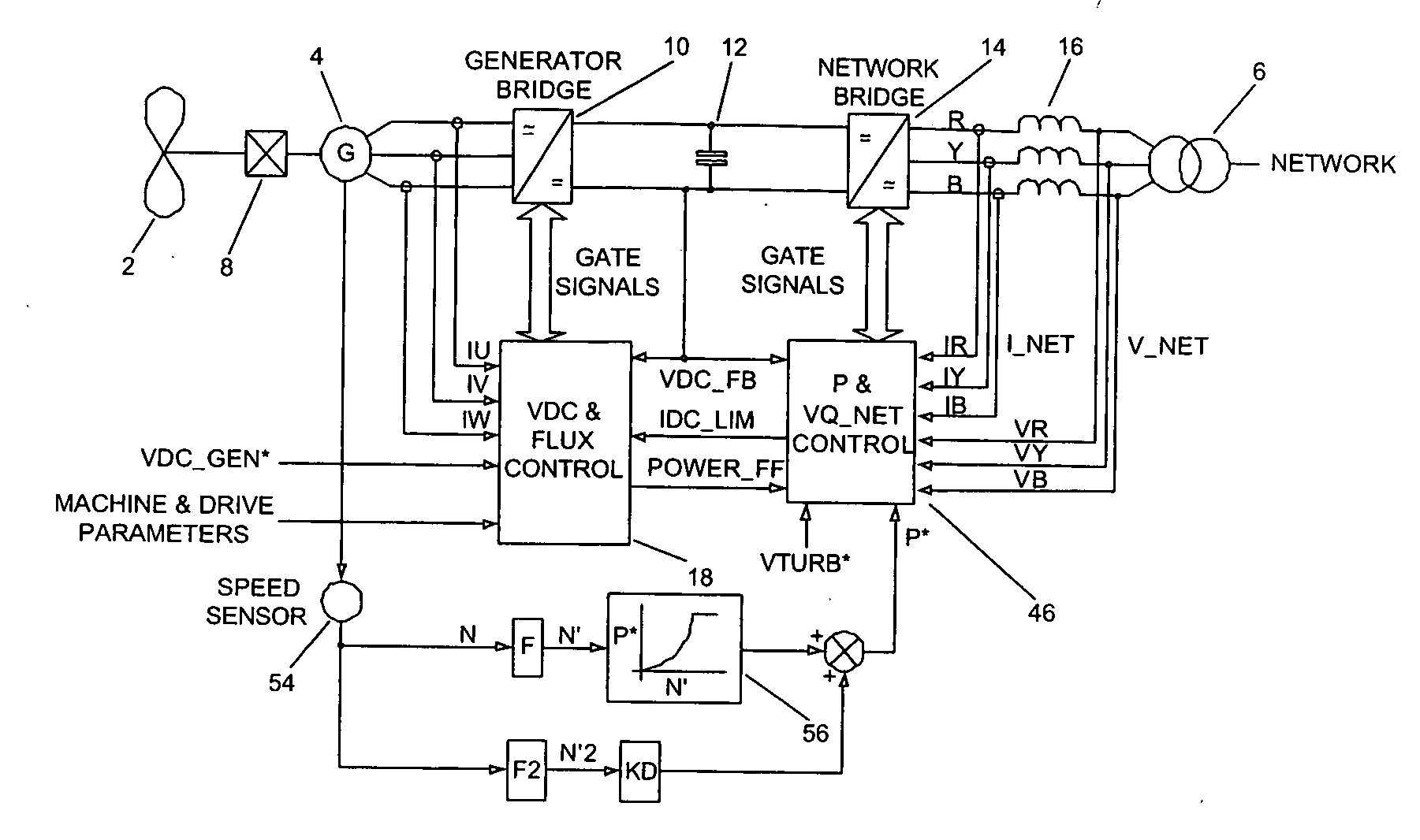
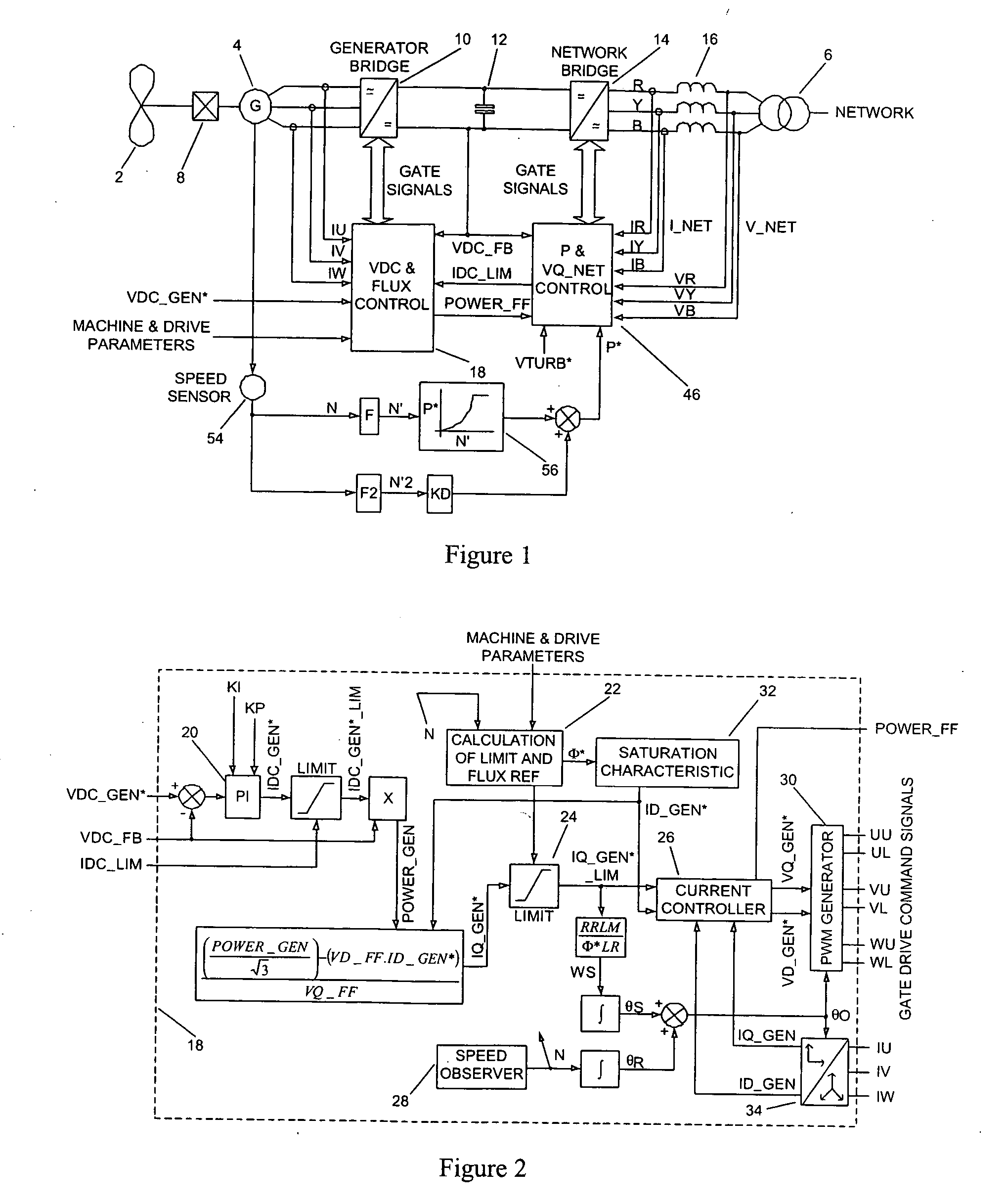
Power converters
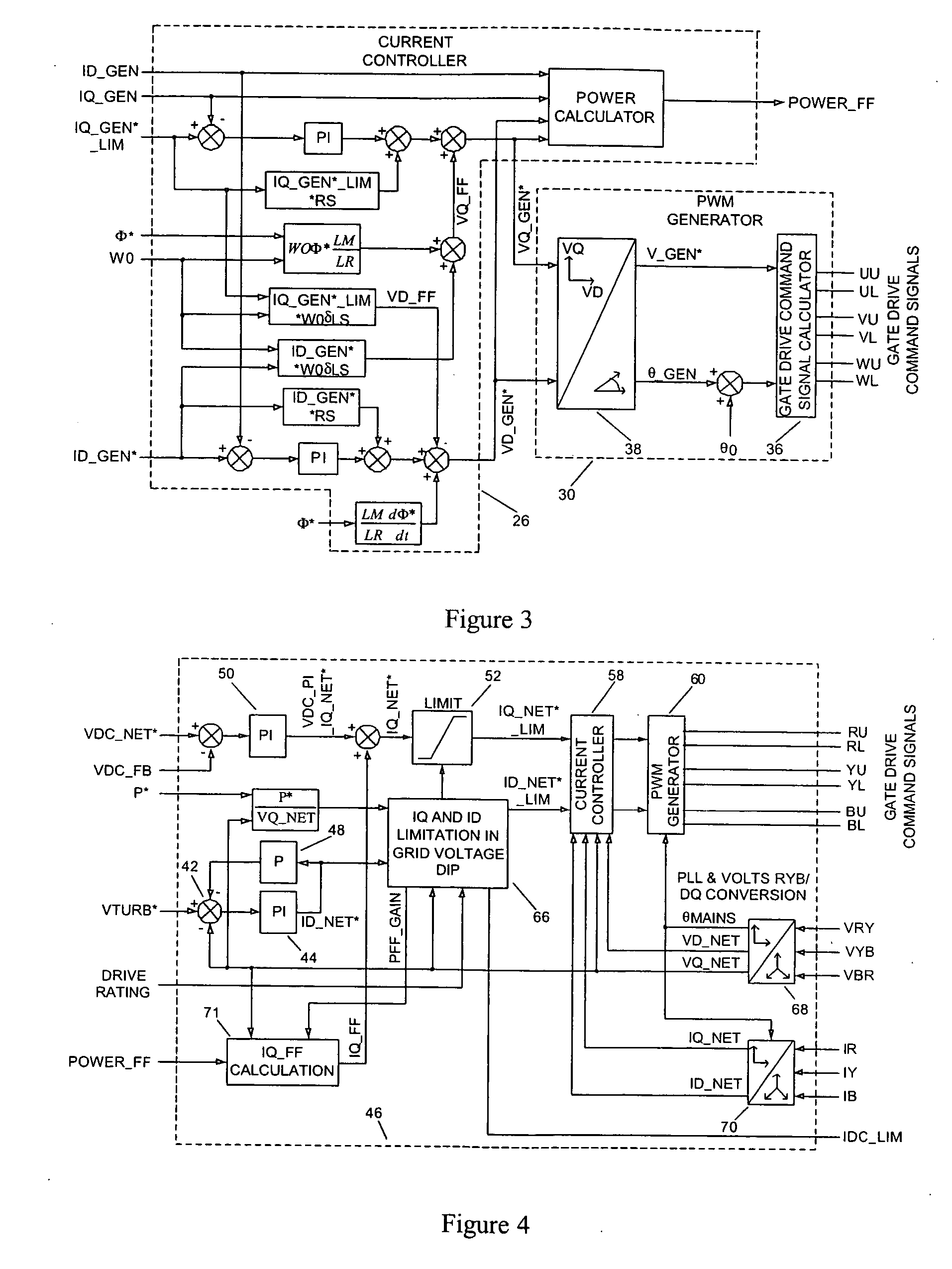
ActiveUS20070108771A1Eliminate effectEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlDc link voltageStator
The present invention provides a power converter that can be used to interface a generator that provides variable voltage at variable frequency to a supply network operating at nominally fixed voltage and nominally fixed frequency and including features that allow the power converter to remain connected to the supply network and retain control during supply network fault and transient conditions. The power converter includes a generator bridge electrically connected to the stator of the generator and a network bridge. A dc link is connected between the generator bridge and the network bridge. A filter having network terminals is connected between the network bridge and the supply network. A first controller is provided for controlling the operation of the semiconductor power switching devices of the generator bridge. Similarly, a second controller is provided for controlling the operation of the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge. The first controller uses a dc link voltage demand signal VDC_NET* indicative of a desired dc link voltage to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge to achieve the desired level of dc link voltage that corresponds to the dc link voltage demand signal VDC_NET*. The second controller uses a power demand signal P* indicative of the level of power to be transferred from the dc link to the supply network through the network bridge, and a voltage demand signal VTURB* indicative of the voltage to be achieved at the network terminals of the filter to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the network bridge to achieve the desired levels of power and voltage that correspond to the power and voltage demand signals P* and VTURB*.
Owner:GE POWER CONVERSION
Low inductance electrical machine
A low inductance electrical machine that may be used as an alternator or motor with low armature inductance is disclosed. Arrangements of complementary armature windings are presented in which the fluxes induced by currents in the armature windings effectively cancel leading to low magnetic energy storage within the machine. This leads to low net flux levels, low core losses, low inductance and reduced tendency toward magnetic saturation. The inclusion of additional gaps in the magnetic circuit allows for independent adjustment of air gap geometry and armature inductance. Separately excited field arrangements are disclosed that allow rotor motion to effect brush-less alternator or brush-less motor operation. An exemplary geometry includes a stator including two annular rings and a concentric field coil together with a rotor structure separated from the stator by four air gaps.
Owner:RAVEN TECH
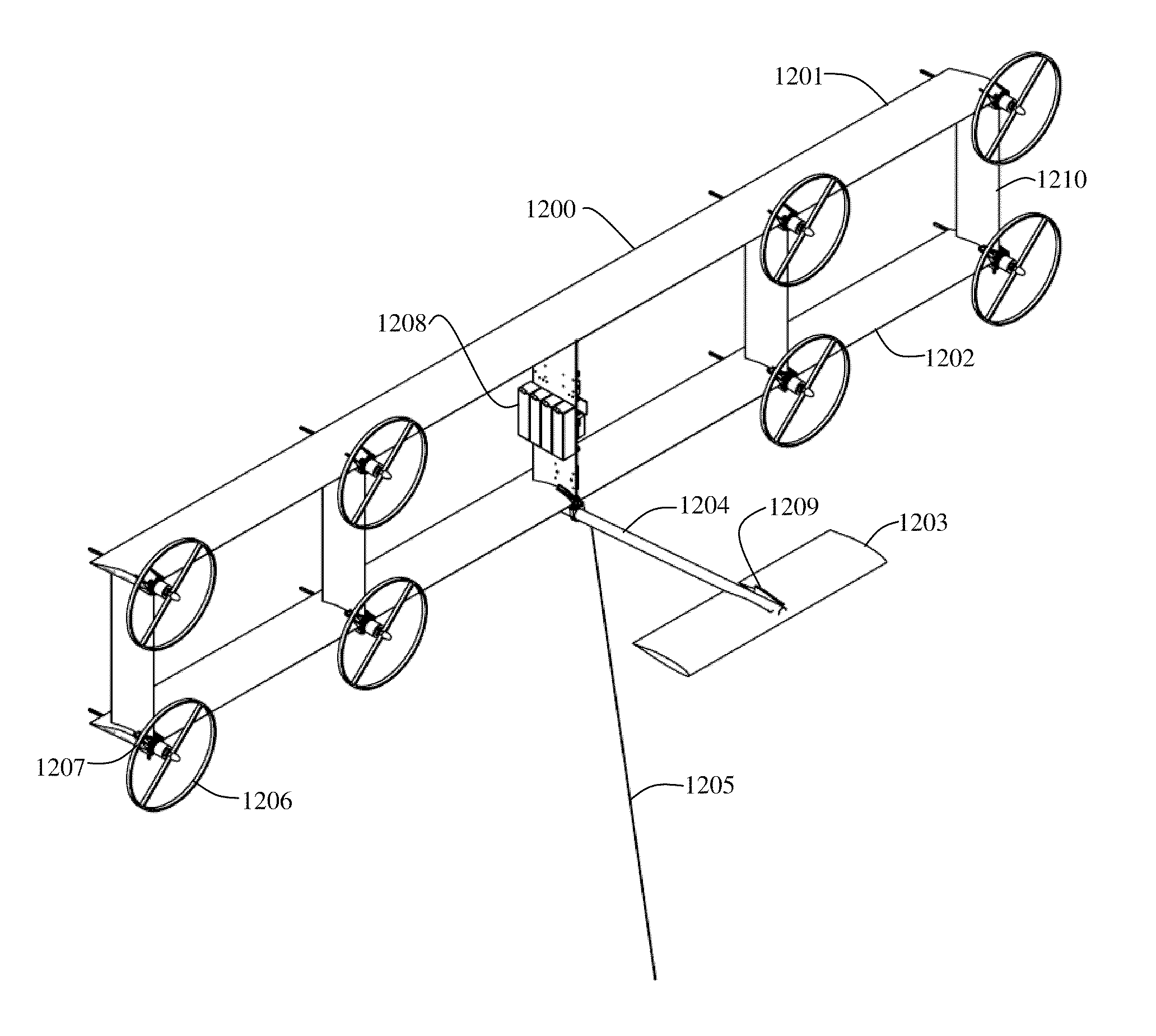
System and method for controlling a tethered flying craft using tether attachment point manipulation
InactiveUS20110121570A1Increase speedIncrease loadWind motor controlWind motor combinationsPrevailing windsTurbine
A tethered airborne electrical power generation system which may utilize a strutted frame structure with airfoils built into the frame to keep wind turbine driven generators which are within the structure airborne. The primary rotors utilize the prevailing wind to generate rotational velocity. Electrical power generated is returned to ground using a tether that is also adapted to fasten the flying system to the ground. The flying system is adapted to be able to use electrical energy to provide power to the primary turbines which are used as motors to raise the system from the ground, or mounting support, into the air. The system may use an attachment mechanism for the tether adapted to move the tether attachment point relative to the flying craft.
Owner:BEVIRT JOEBEN +1
Electrosurgical Generator Having Boost Mode Control Based on Impedance
A method of controlling output power of an electrosurgical generator apparatus that controls a variable output signal to a pair of electrodes includes setting the output power of the generator apparatus to a selected power output level. An impedance is measured across the electrodes when the electrodes are applied to an area of tissue. The output power of the generator apparatus is changed to a boost power output level greater than the selected power output level. The boost power output level corresponds to a calculation based at least in part on the measured impedance. The method further includes applying the output signal to the electrodes at the boost power output level for a first time duration and changing the power output to the selected power output level after the first time duration. An electrosurgical generator apparatus operating in accordance with the method is also described.
Owner:SYNERGETICS USA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com