Patents
Literature
324 results about "Mechanical resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mechanical resonance is the tendency of a mechanical system to respond at greater amplitude when the frequency of its oscillations matches the system's natural frequency of vibration (its resonance frequency or resonant frequency) than it does at other frequencies. It may cause violent swaying motions and even catastrophic failure in improperly constructed structures including bridges, buildings and airplanes. This is a phenomenon known as resonance disaster.
Tuning mechanical resonators for electrical filter
InactiveUS6307447B1Multiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyHelical resonatorPhysics
The present invention is a method for adjusting different resonant frequencies of a plurality of mechanical resonators formed on a common substrate, in a case where the resonant frequencies of the resonators are a function of each resonator thickness. According to this method the resonators are each formed with an etchable top electrode layer which includes a material having different etching properties as a topmost layer for each of the resonators having different resonant frequencies. By selectively etching these etchable layers one at a time in the presence of the others, one may adjust the resonant frequencies of each of the resonators without need to mask the resonators during the etching process. Associated with this method there is a resonator structure having a top electrode structure having a topmost layer having different etching characteristics for different resonators.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
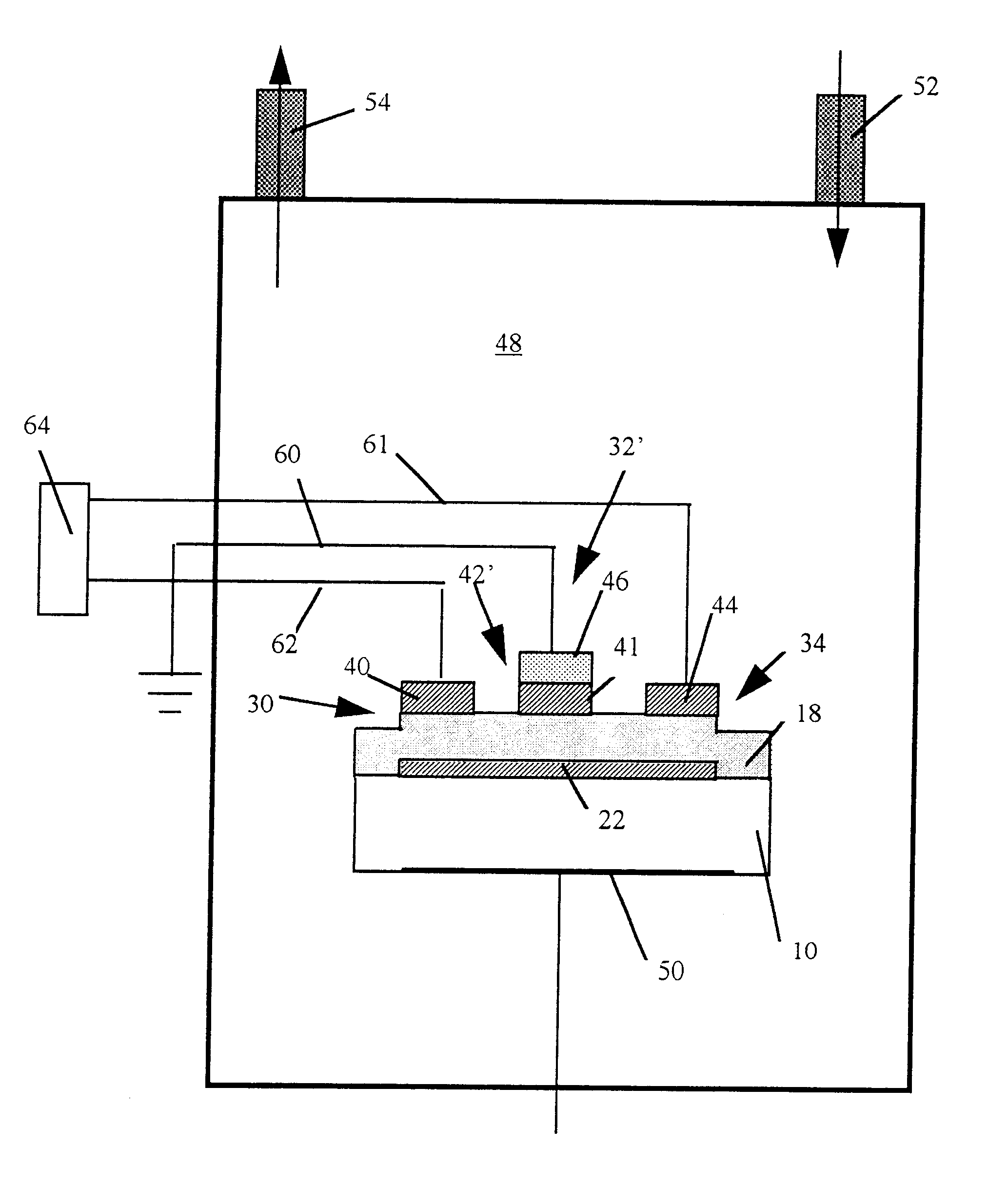
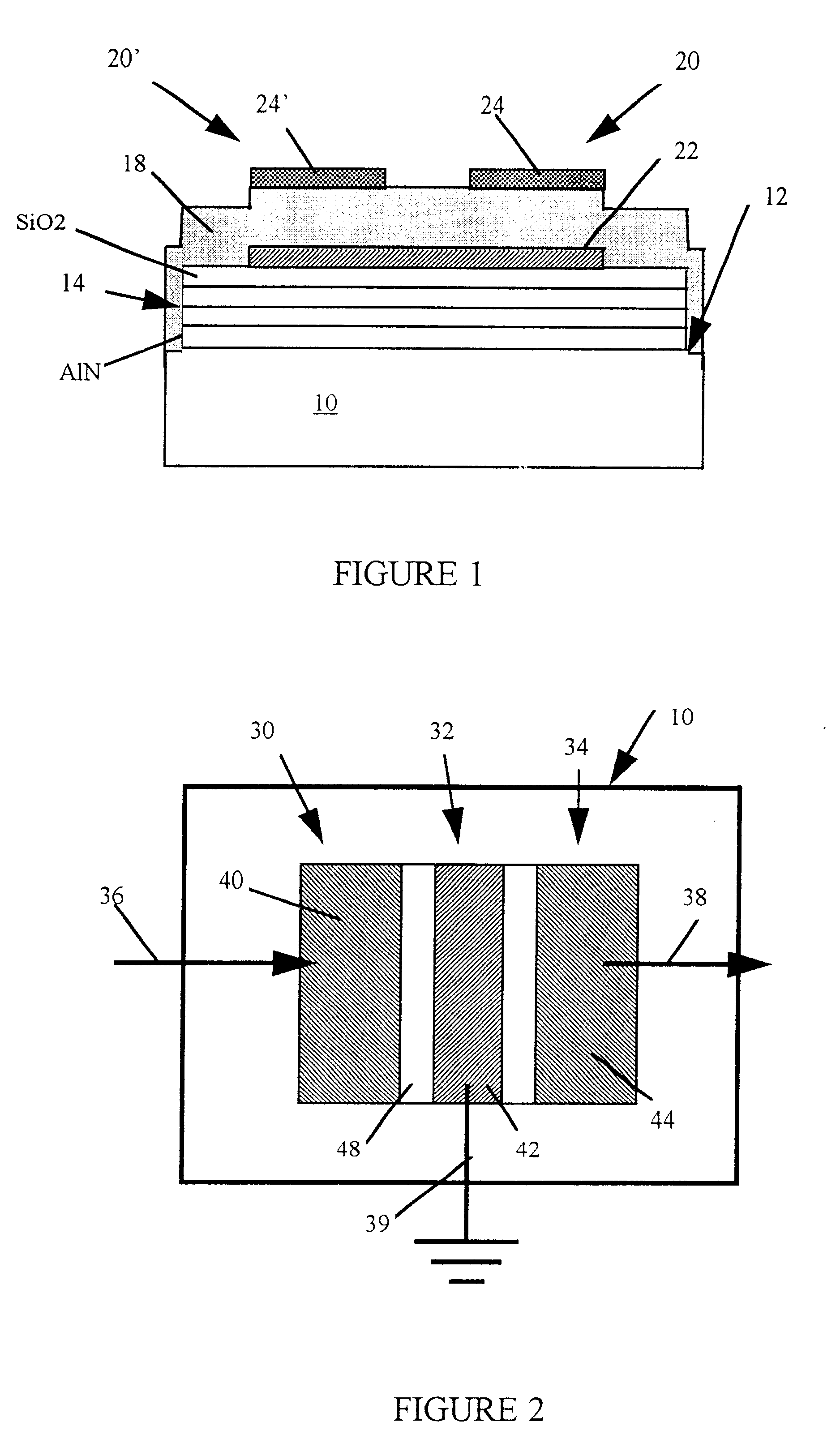
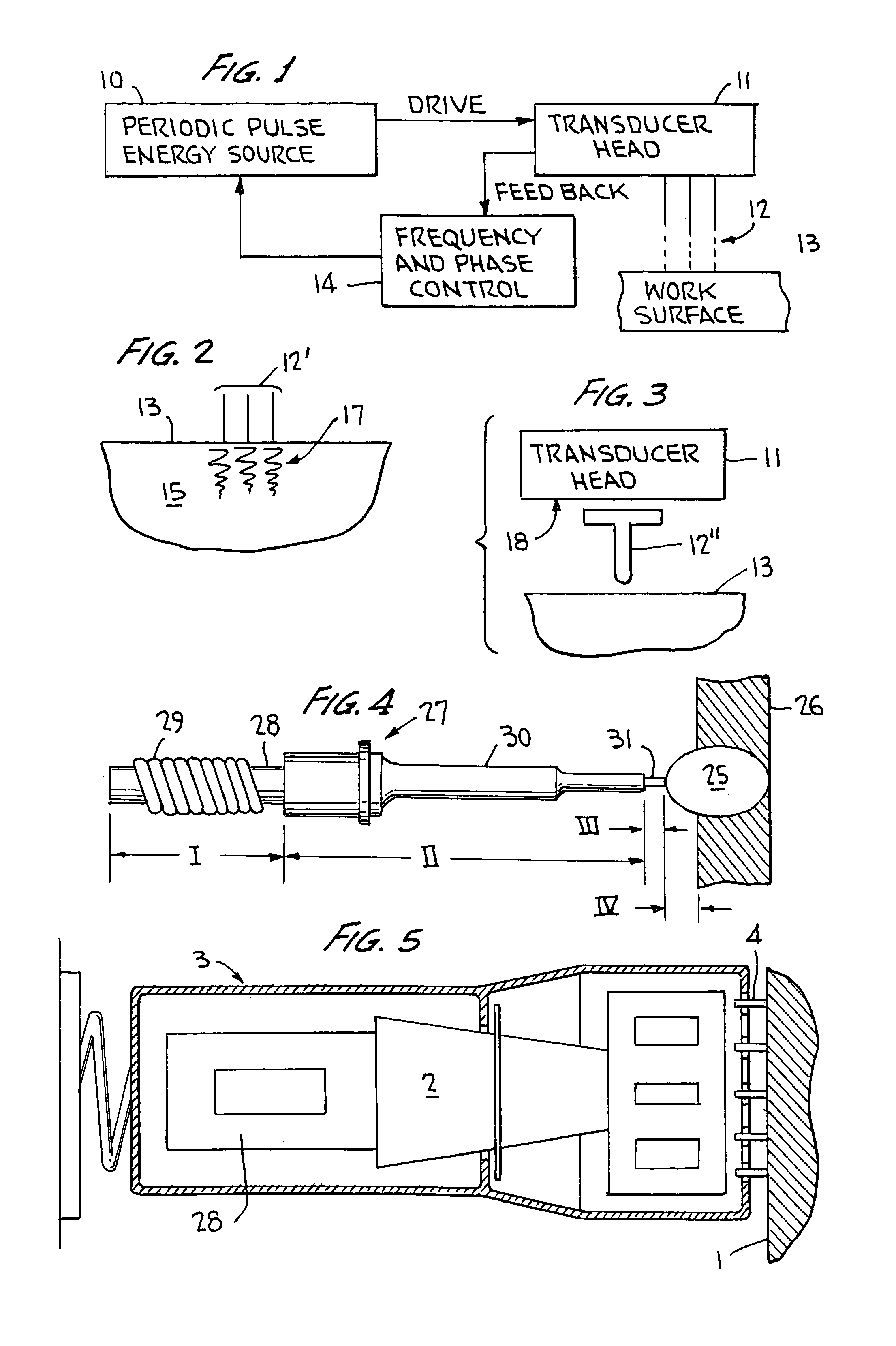
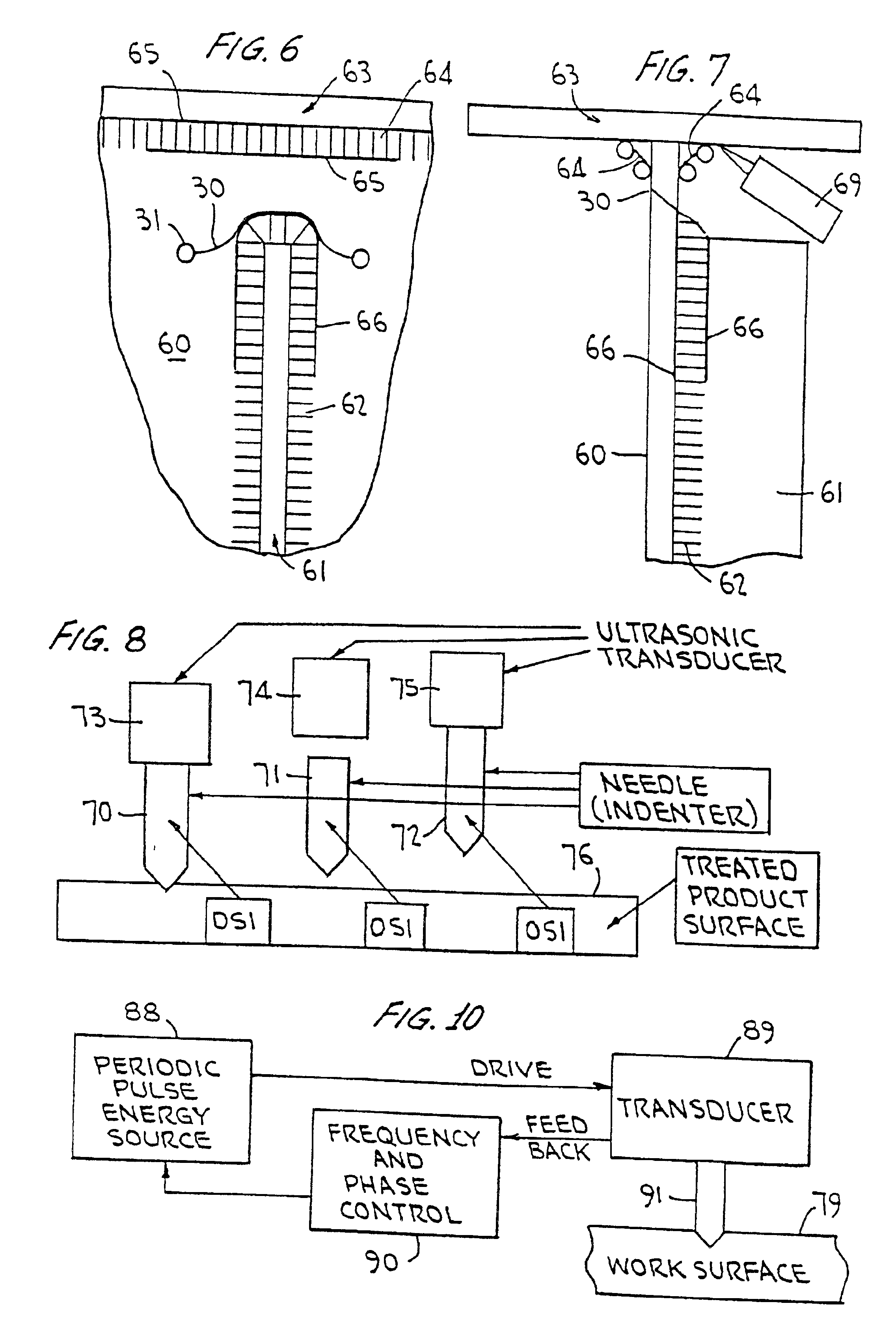
Ultrasonic impact machining of body surfaces to correct defects and strengthen work surfaces
InactiveUS6932876B1Improve power transfer efficiencyEfficient transferMechanical vibrations separationFurnace typesUltrasonic sensorPeriodic oscillation
Metallic workpieces of diverse shapes having work surfaces which are deformed at the surface and adjacent sub-surface layers by surface impact from ultrasonic transducers employing freely axially moving impacting elements propelled and energized by a transducer oscillating surface vibrating periodically at an ultrasonic frequency. The impacting elements are propelled in a random aperiodic and controlled impact mode at different phases of the periodic oscillation cycles. The transducer may be portable and provides a series of mechanically interconnected stages having mechanical resonances harmonically related as a multiple of the primary ultrasonic frequency and have matched stage resistances under instantaneous loading when the impact elements are driven by the transducer oscillating surface into the surface of the workpiece. This mode of operation produces Q-factor amplification of the input ultrasonic power oscillator energy at the impact needles and high propulsion velocities making it possible to machine metallic workpiece bodies to greater depths for compressing the metal to increase compressive strength of the workpiece work surfaces to substantially the ultimate material strength. The impact machining is done at ambient temperatures.
Owner:PROGRESS RAIL SERVICES
System for adjusting resonance frequencies in a linear compressor
InactiveUS20060110259A1Low costIncreased energy lossFluid parameterPositive displacement pump componentsReciprocating motionLinear compressor
A system for adjusting resonant frequencies in a linear compressor comprising, in the interior of a shell: a linear motor: a cylinder; a piston reciprocating inside the cylinder; and an actuating means operatively coupling the piston to the linear motor, said system comprising: a detecting means to detect a load imposed to the linear motor, in an operational condition of the latter related to the gas pressure in the discharge thereof; and a frequency adjusting means operatively associated with the detecting means and with the resonant assembly, in order to define, as a function of said operational condition, a frequency adjustment, by varying at least one of the values related to the mass of the resonant assembly and to the average stroke of the piston, to a value of the mechanical resonance frequency corresponding to the electrical supply frequency.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE COMPRESSORES SA (EMBRACO)
Energy Harvester with Adjustable Resonant Frequency
ActiveUS20080129147A1Facilitates great functionalityLess limitationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTyre measurementsCapacitanceElectricity
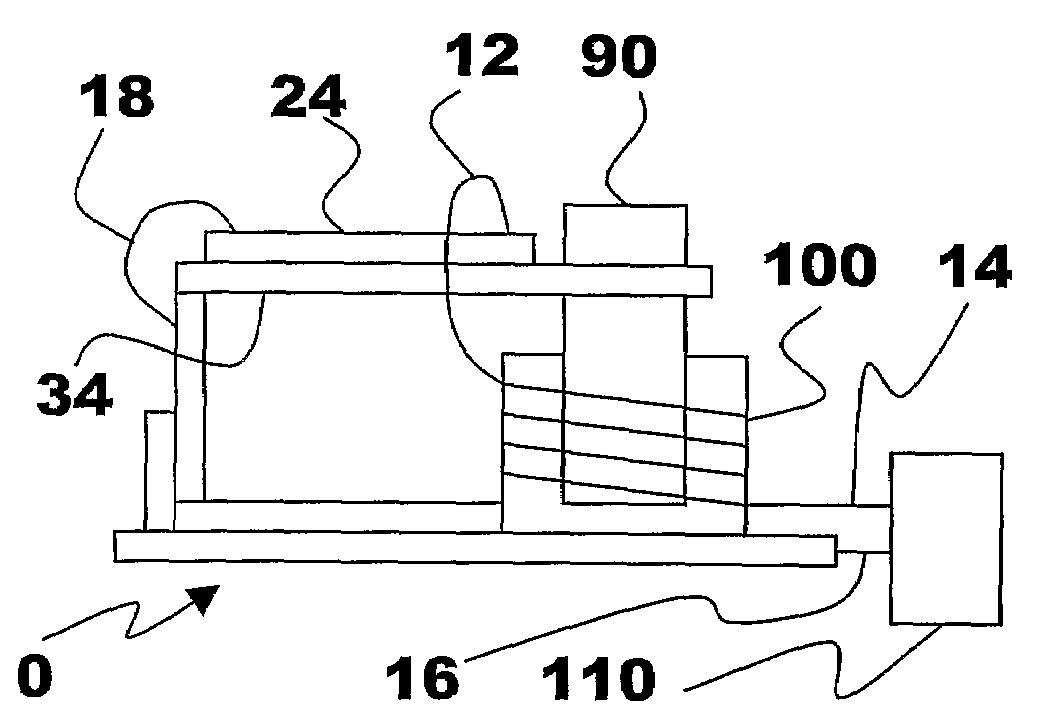
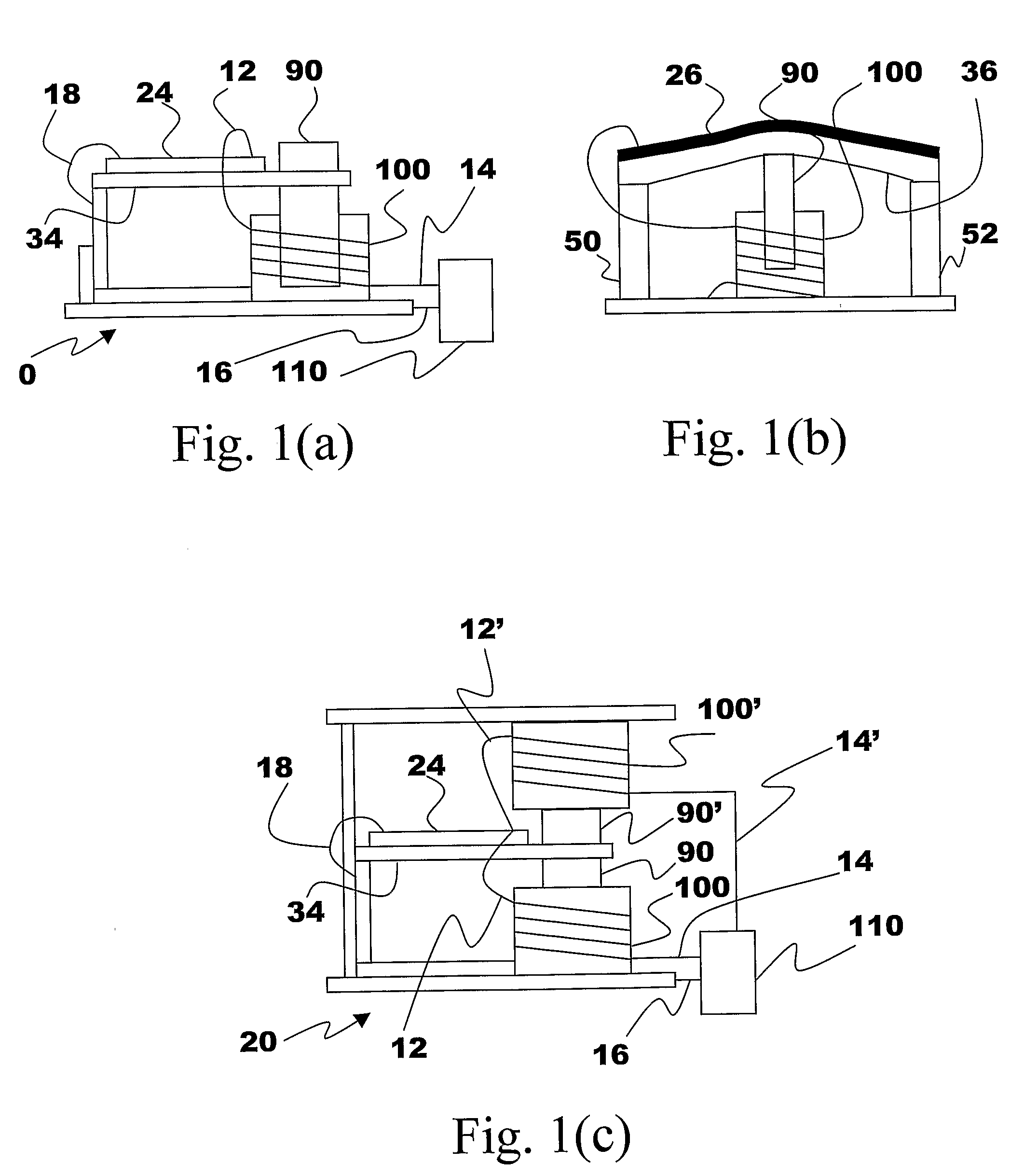
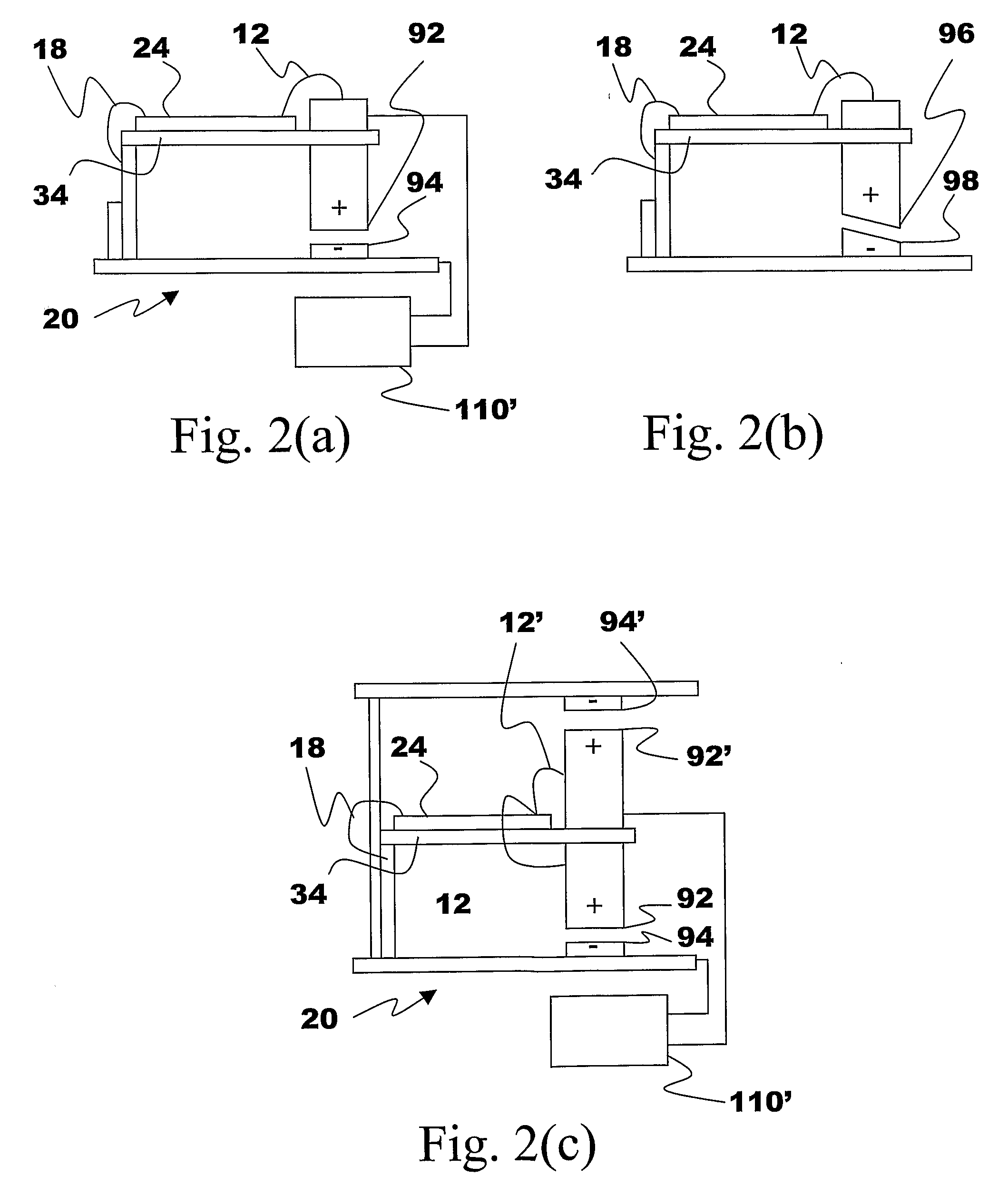
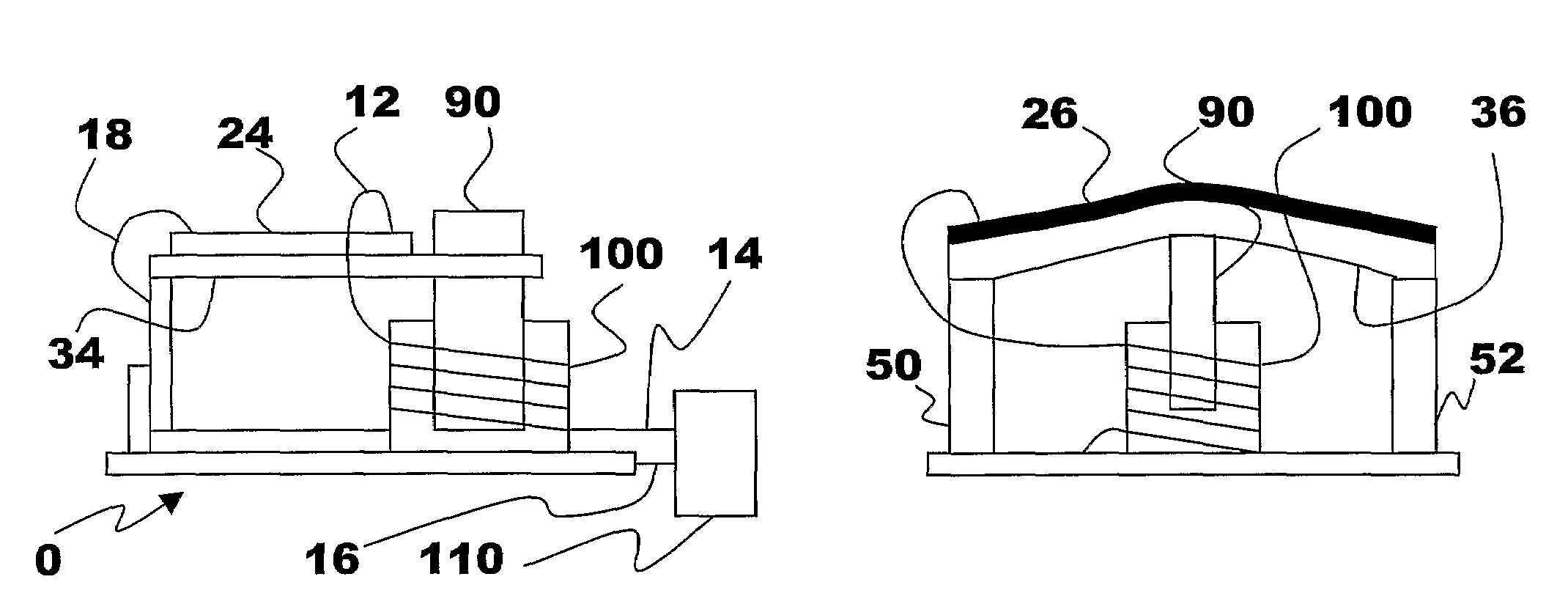
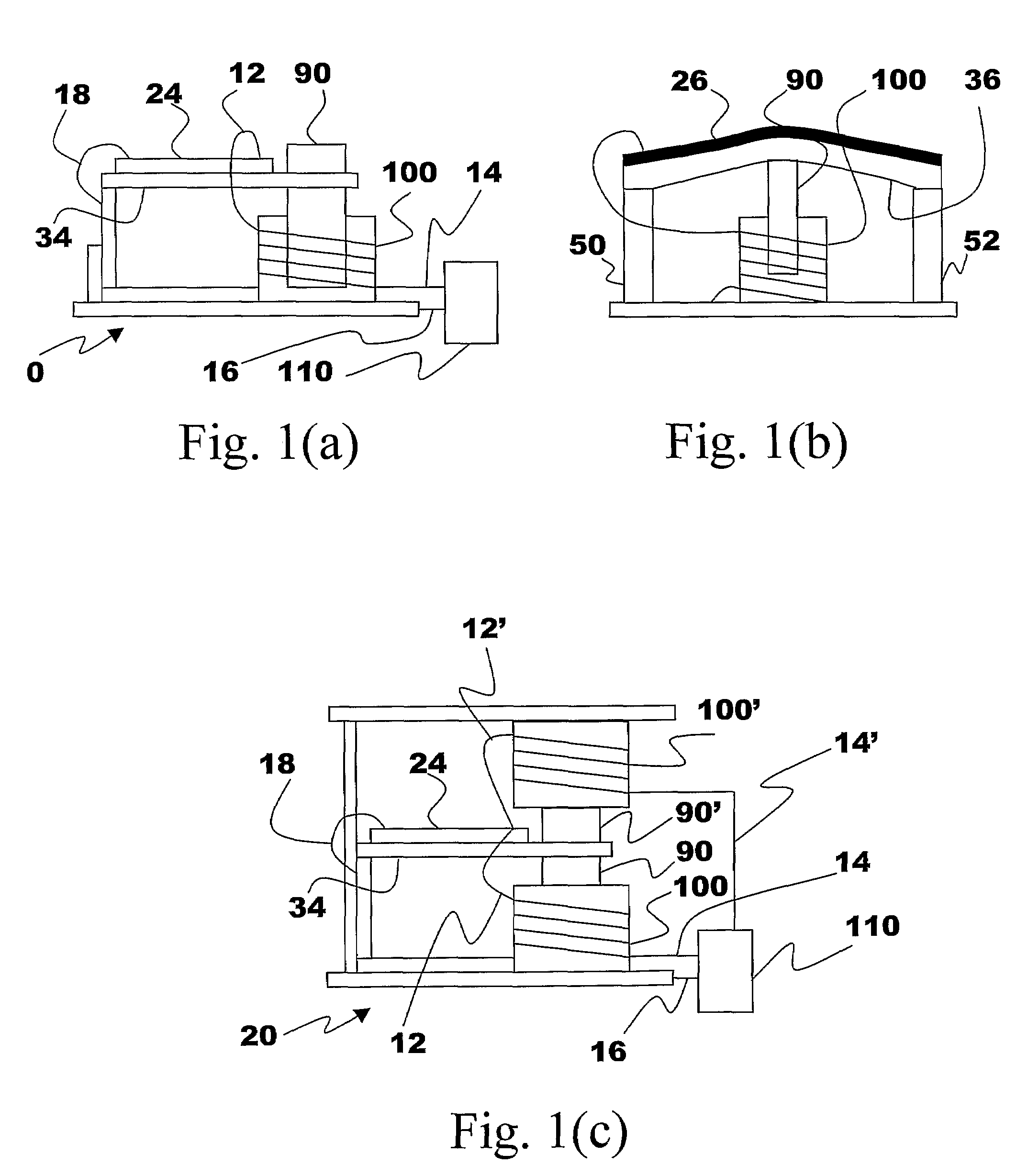
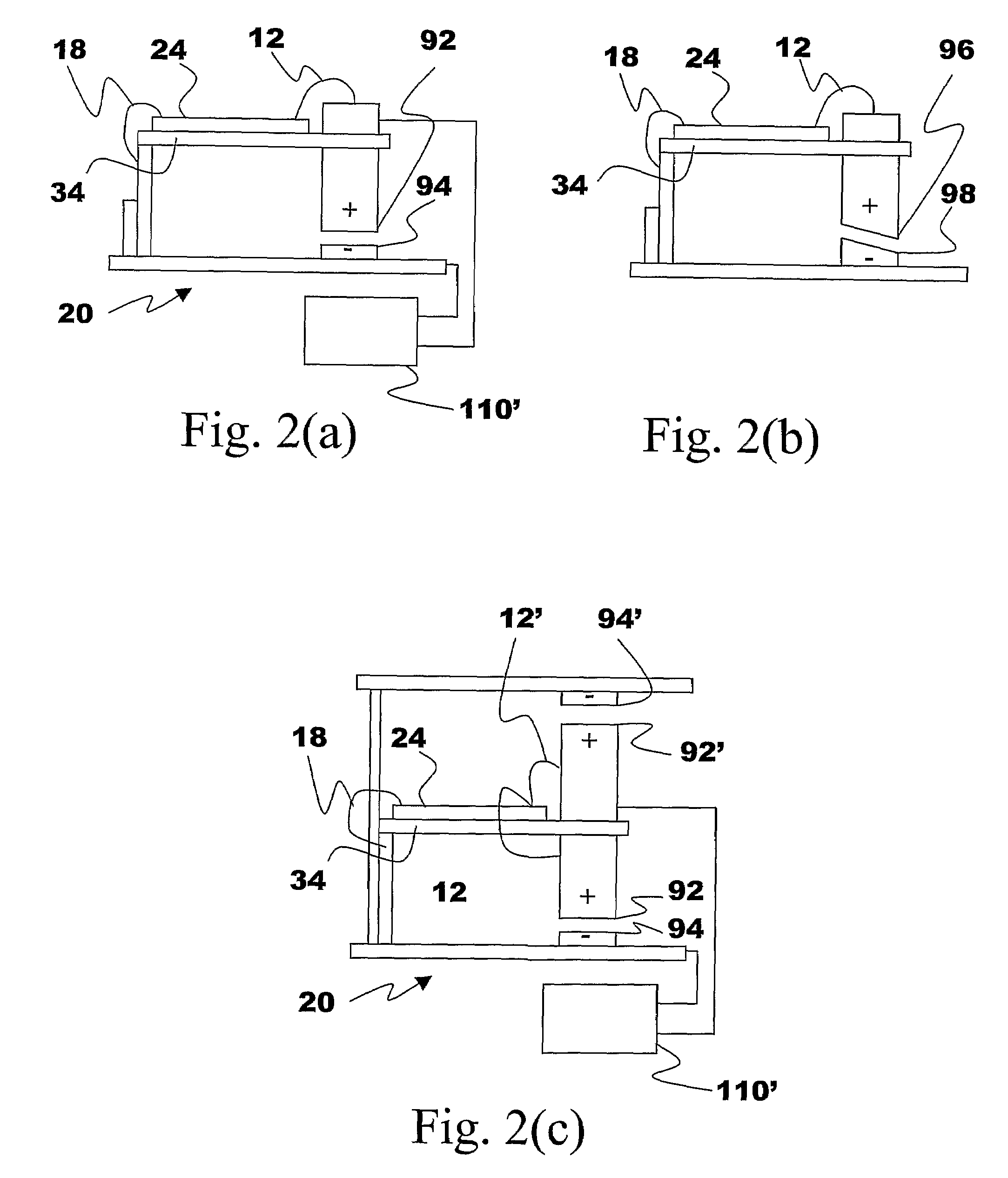
The present subject matter discloses devices, systems, and methodologies for harvesting power from environmentally induced vibrations. Piezoelectric devices (24) and structures are disclosed that may be employed in combination with electro-magnetic (100) or capacitive (92, 94) elements to enhance the power harvesting capabilities of the piezoelectric devices (24). The electromagnetic (100) and capacitive (92, 94) elements may be used to assist in maintaining system mechanical resonance in order to maximize energy harvesting capabilities. Power harvesting devices and systems in accordance with the subject technology may concurrently operate as sensors in motion sensitive applications thus providing self-powered monitoring capabilities.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
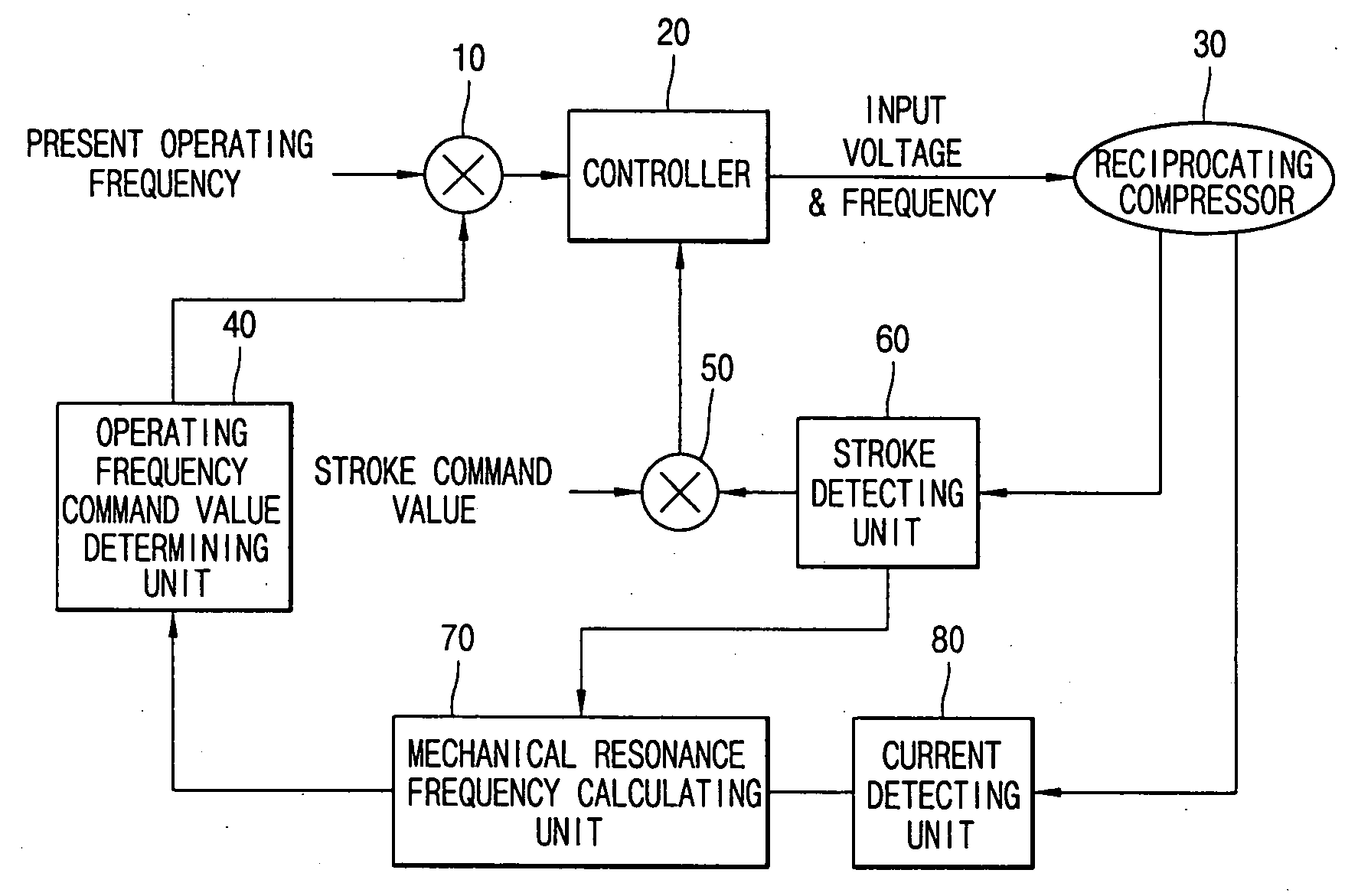
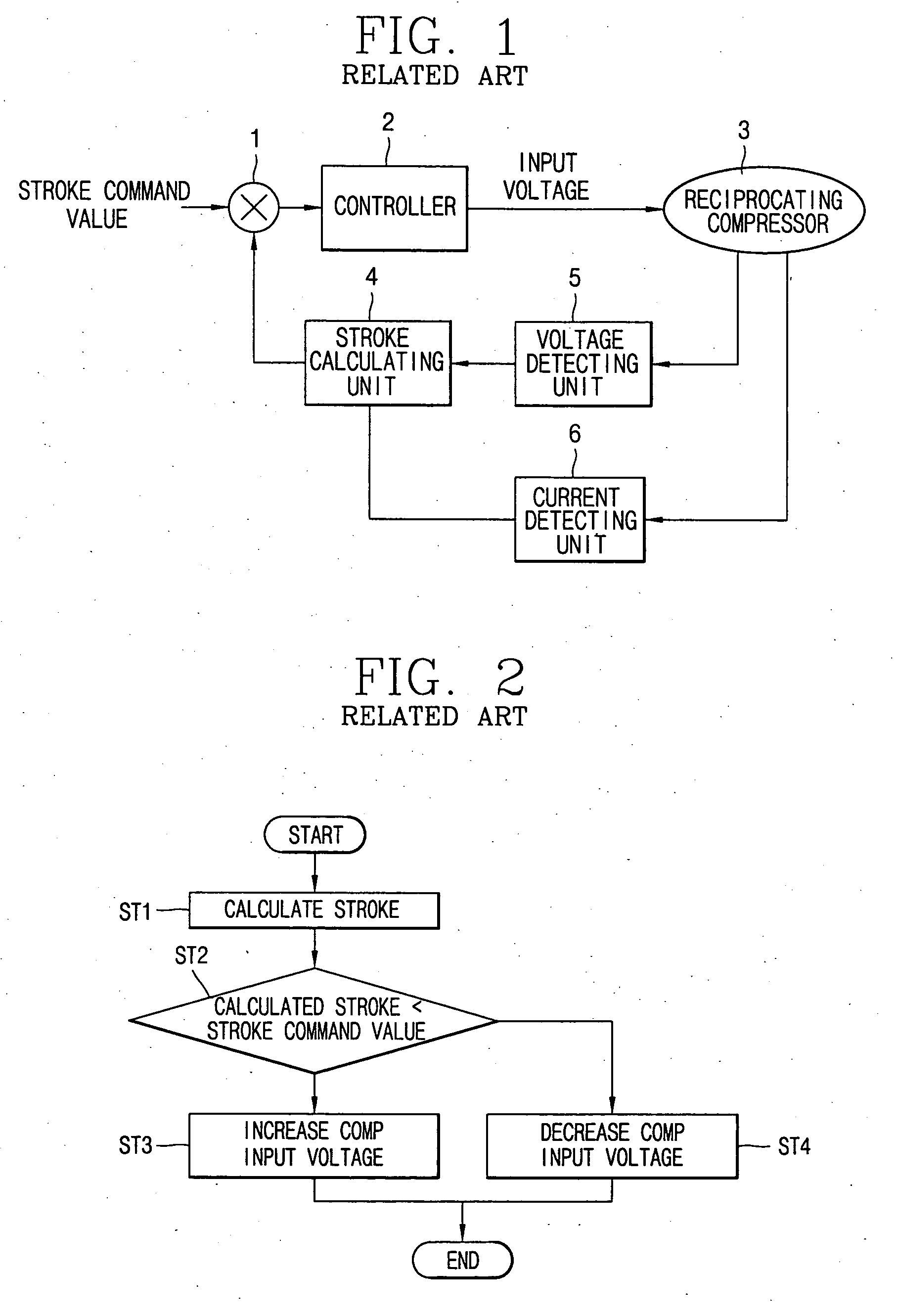
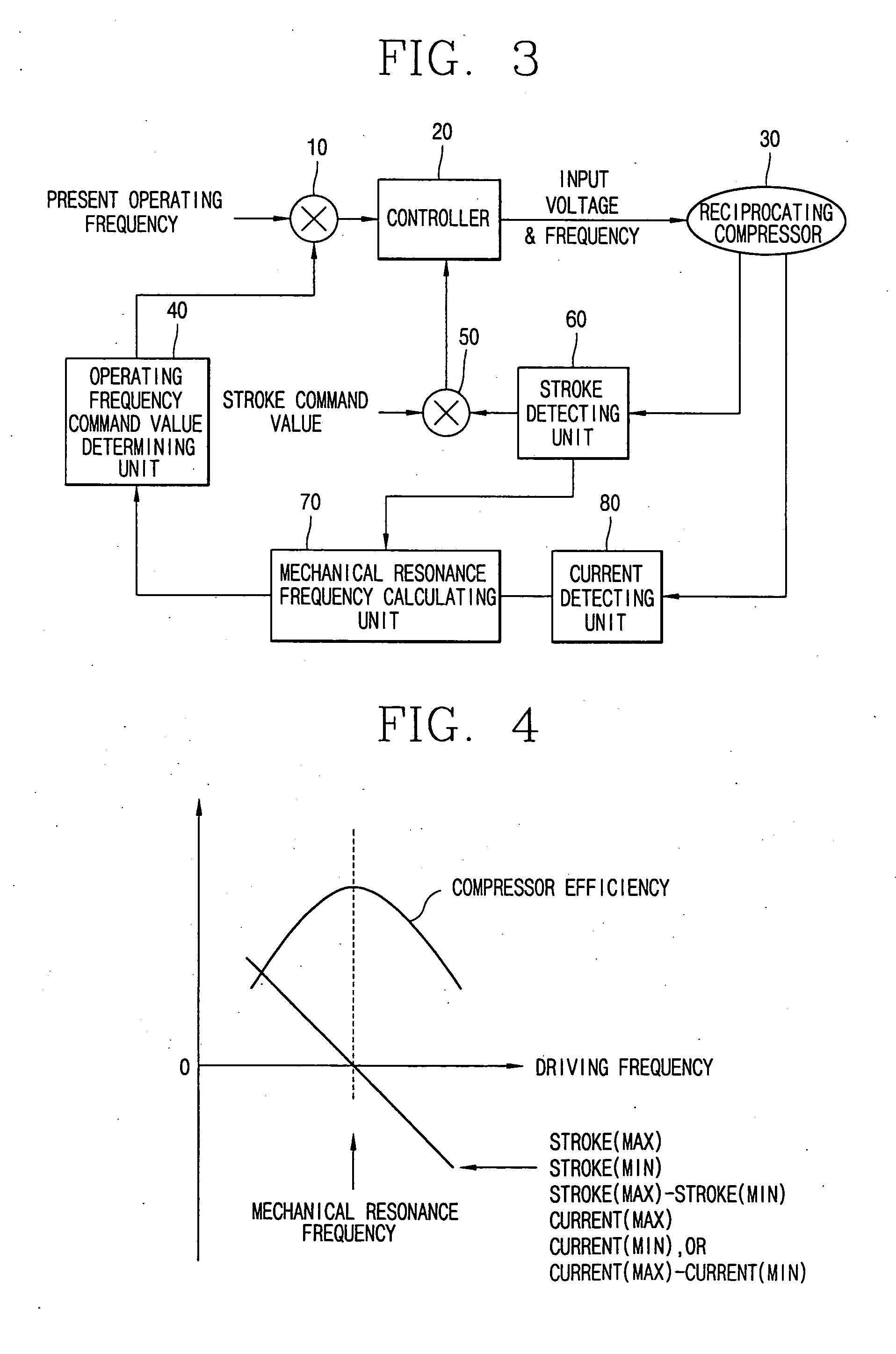
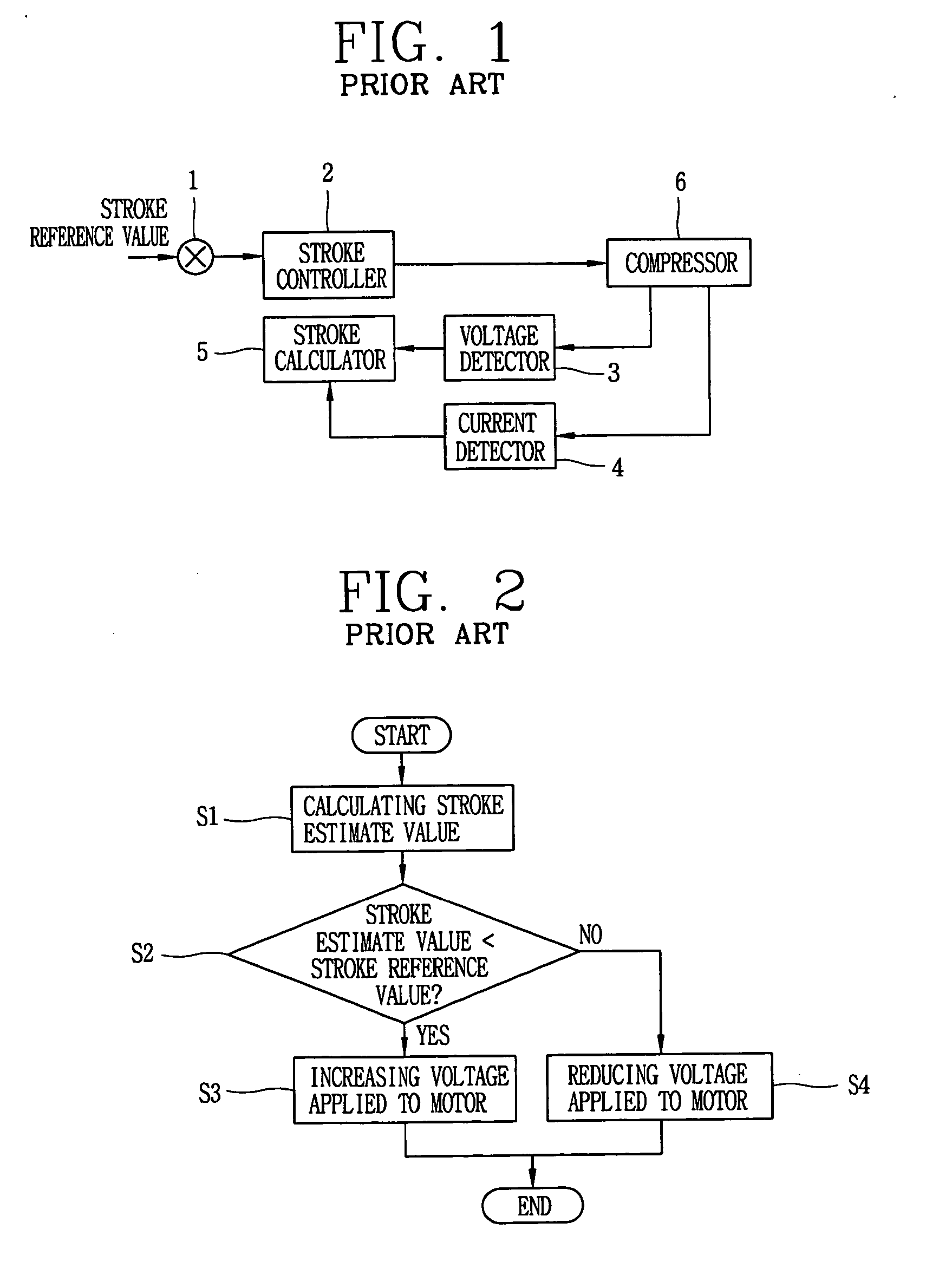
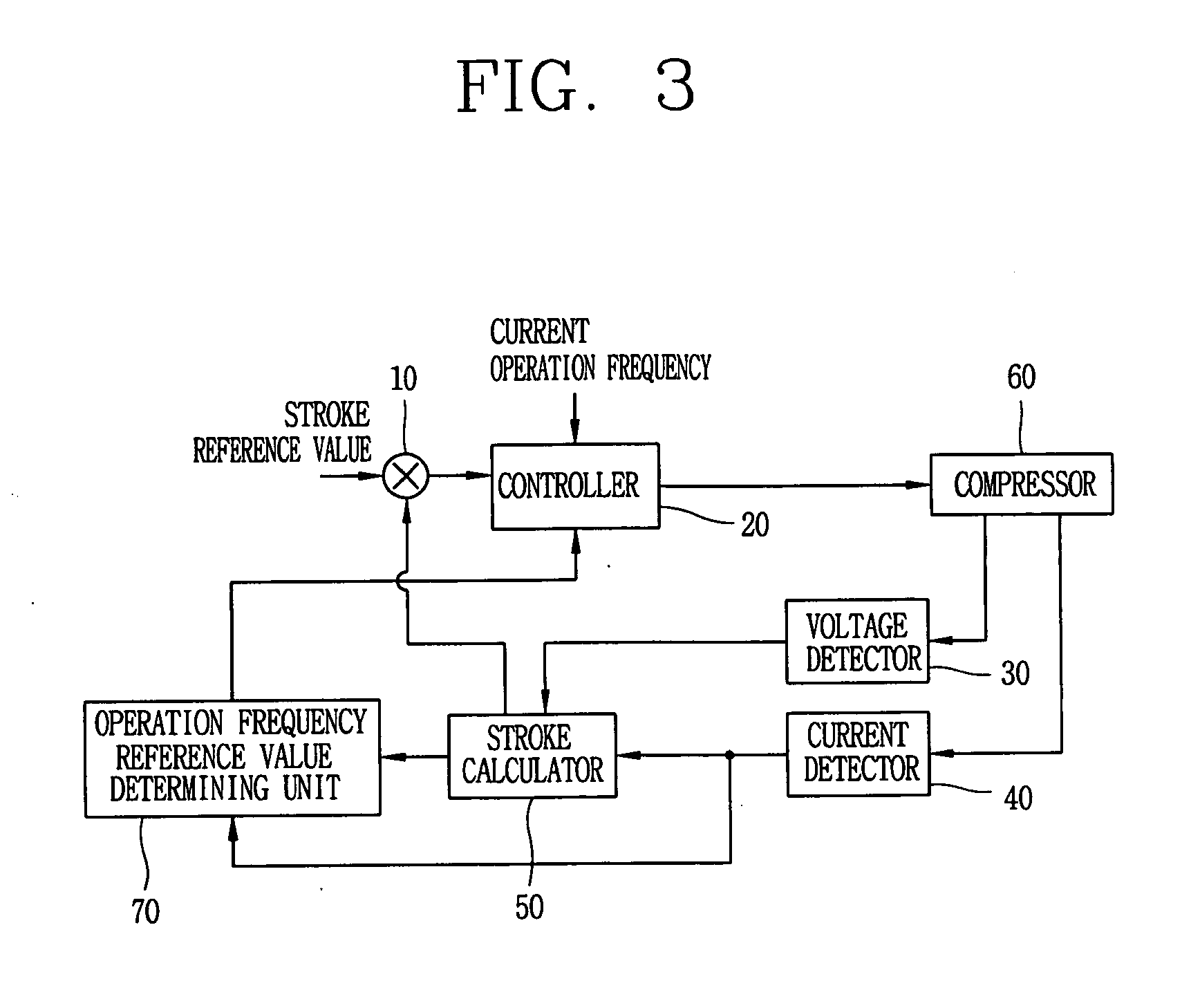
Apparatus and method for controlling operation of reciprocating compressor
ActiveUS20050111987A1Easy to operateAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlEngineeringMechanical resonance
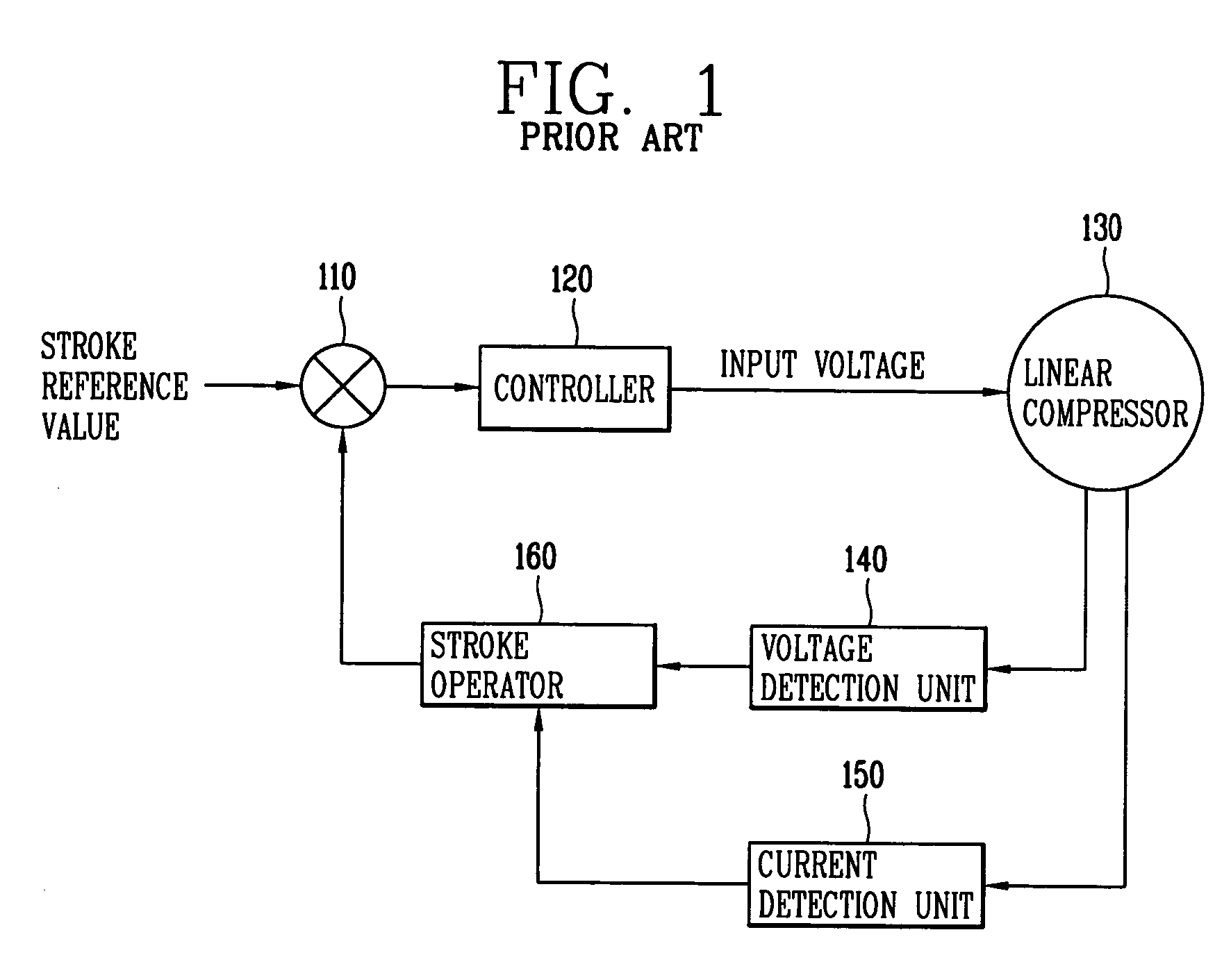
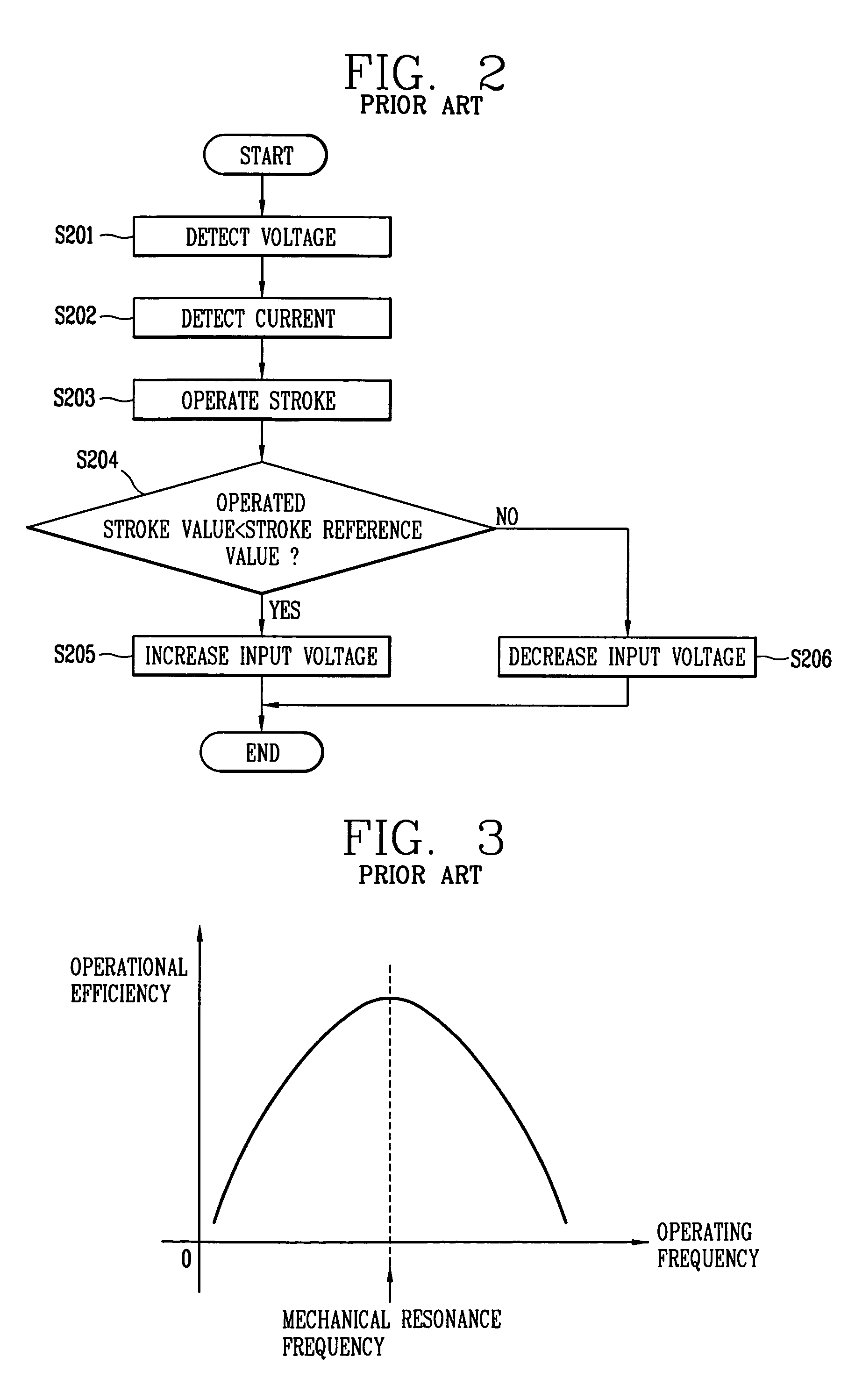
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for controlling operation of a reciprocating compressor. The operating efficiency of the compressor can be improved by performing the steps of: detecting a current and a stroke applied a compressor; a calculating a mechanical resonance frequency by using the detected current and stroke; and determining an operating frequency command value by adding or subtracting the present operating frequency so as to be within a predetermined range of the calculated mechanical resonance frequency and then driving the compressor by the operating frequency command value.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Flow detectors having mechanical oscillators, and use thereof in flow characterization systems
ActiveUS20030000291A1Ability to useNormalize signalAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComponent separationTuning forkEngineering
An improved system, device and method for characterizing a fluid sample that includes injecting a fluid sample into a mobile phase of a flow characterization system, and detecting a property of the fluid sample or of a component thereof with a flow detector comprising a mechanical resonator, preferably one that is operated at a frequency less than about 1 MHz, such as a tuning fork resonator.
Owner:MEAS FRANCE
Method and apparatus for acoustic logging of fluid density and wet cement plugs in boreholes
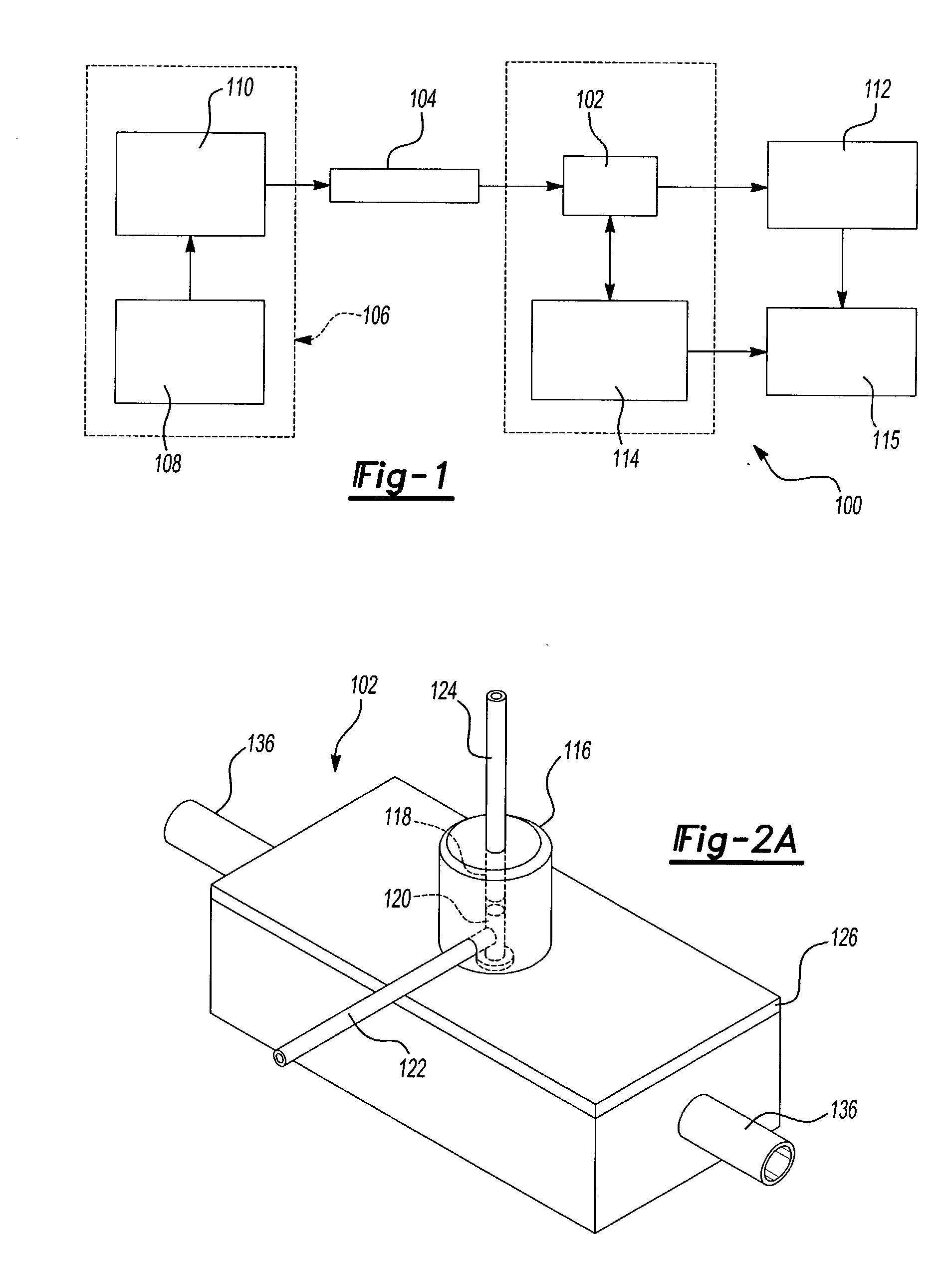
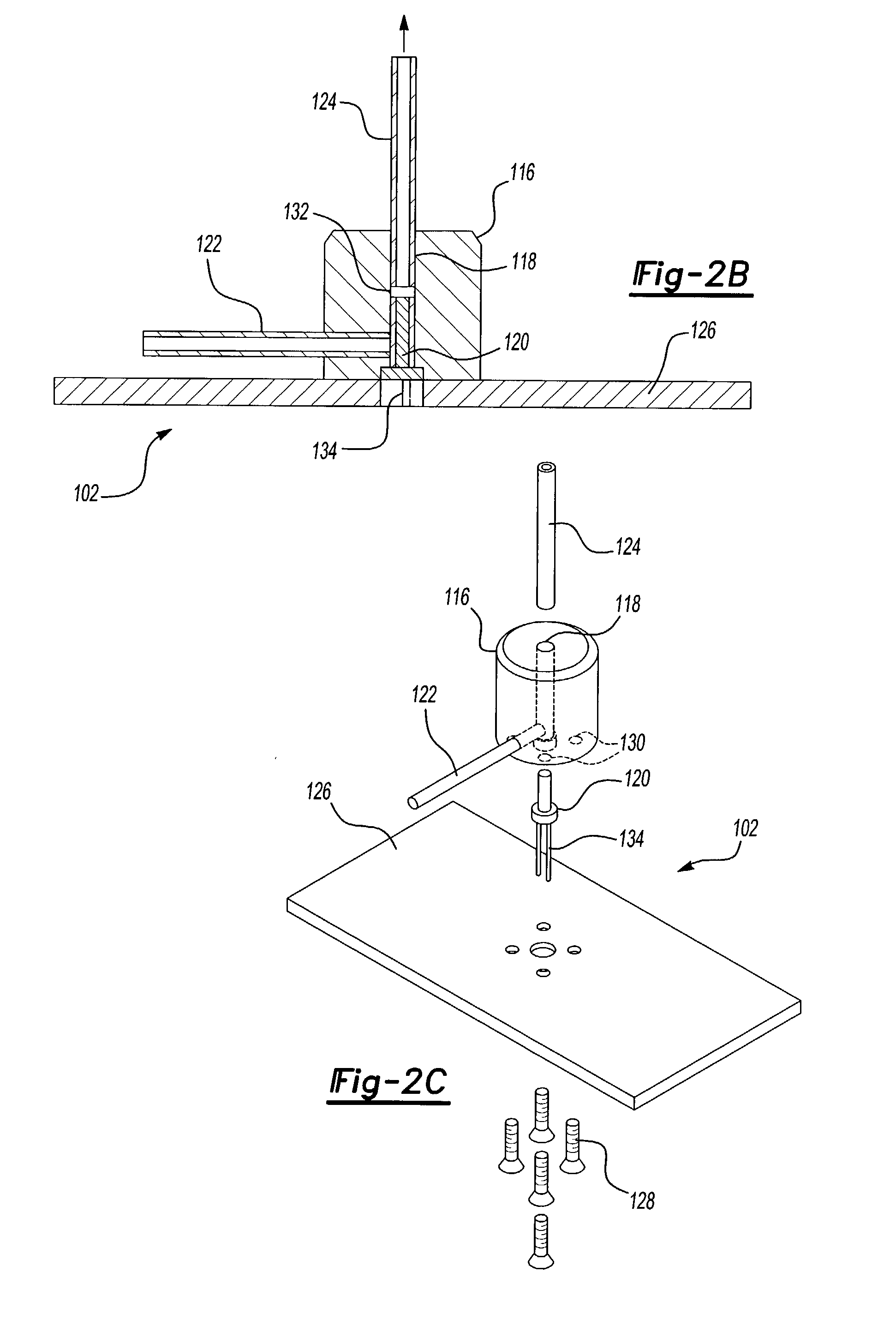
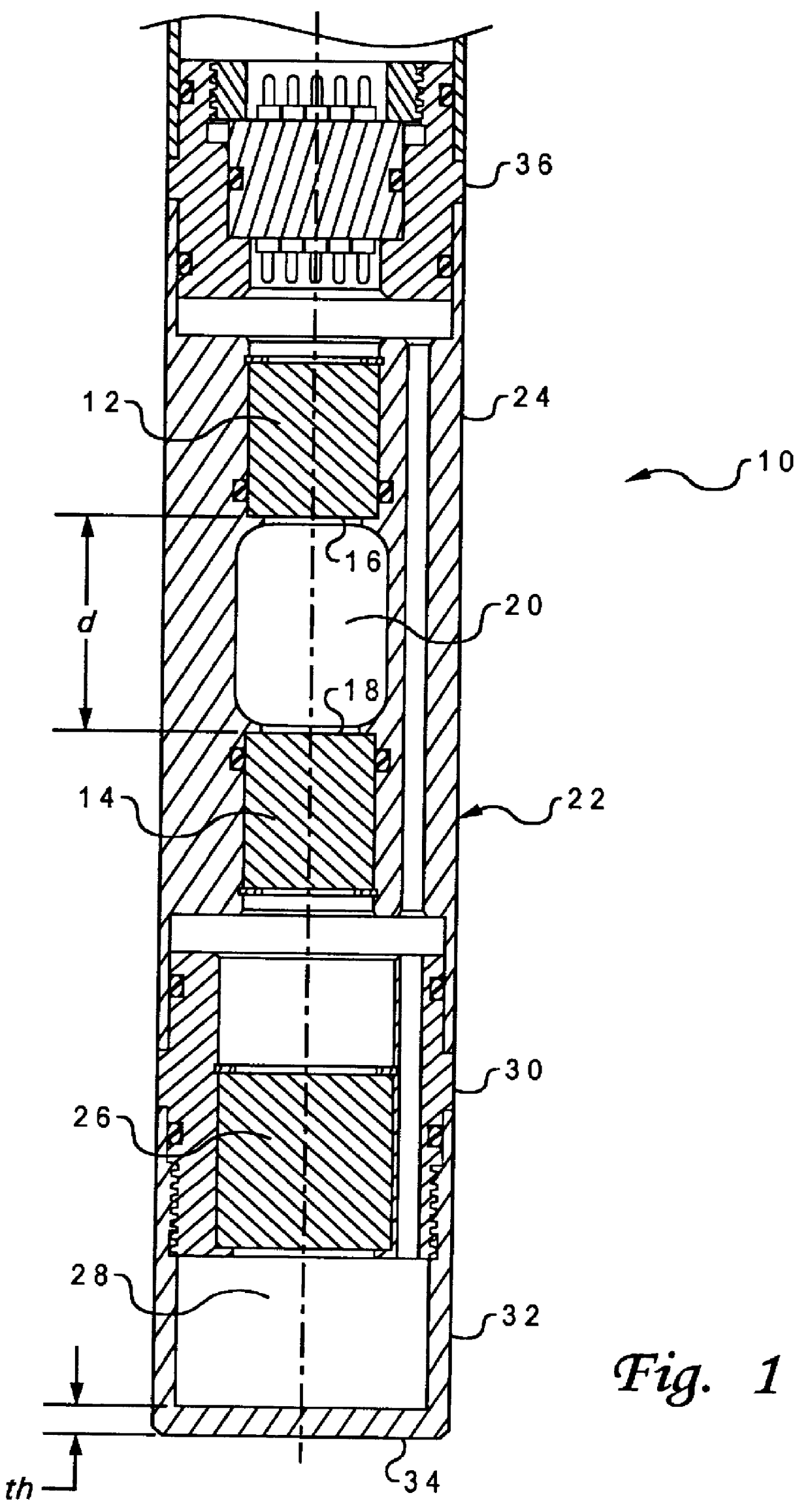
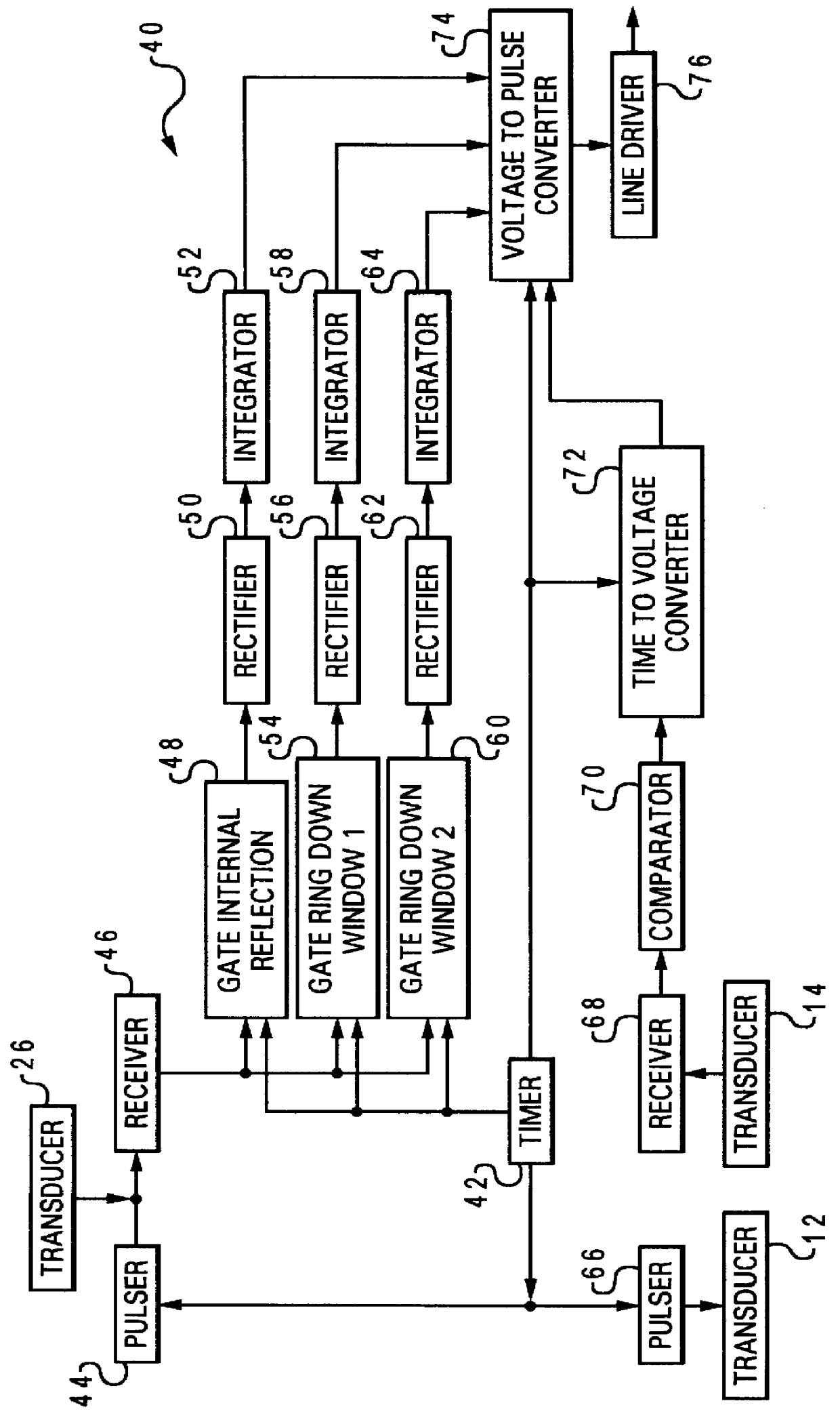
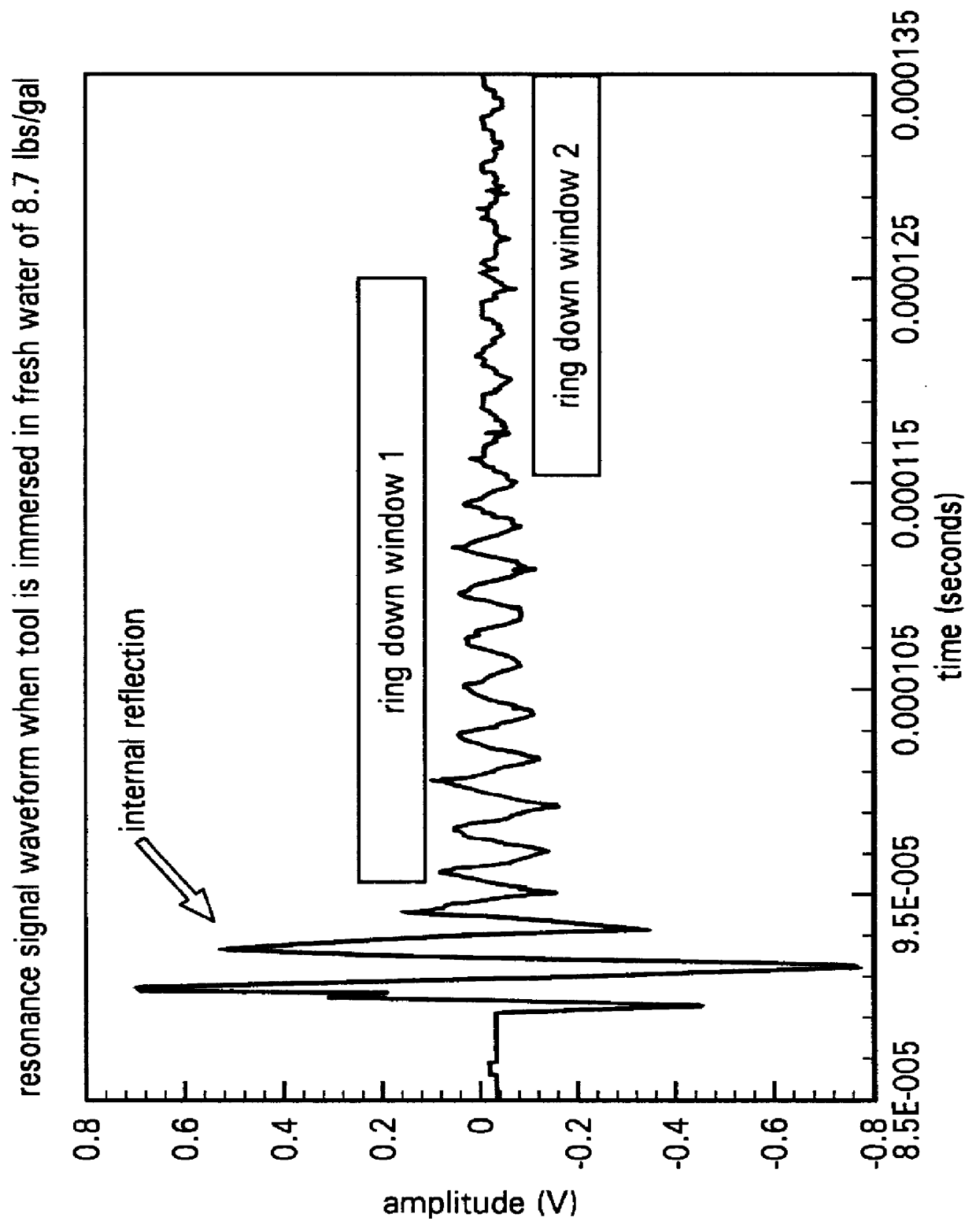
A method of determining the acoustic impedance of a fluid in a borehole, by gating a reflected acoustic signal into a plurality of time slots, and comparing received energies of the signal for the time slots to obtain a value indicative of the acoustic impedance of the fluid. The value may be normalized to yield the acoustic impedance of the fluid using the acoustic impedance of, e.g., water as a calibration point. The comparison is performed by comparing a ratio of an integration of a first ring down time slot and a second ring down time slot, to an integration of an internal reflection time slot. The acoustic pulse may be generated using a transducer immersed in an intermediate fluid contained within a chamber defined in part by a plate in contact with the borehole fluid and having a thickness such that a mechanical resonance frequency of the plate in a thickness mode is substantially equal to a resonance frequency of the transducer. The sonic velocity of the fluid is also measured and, when combined with the acoustic impedance, is used to determine the fluid density.
Owner:WEATHERFORD CANADA PARTNERSHIP +1
Acoustic attenuation materials
Acoustic attenuation materials are described that comprise outer layers of a stiff material sandwiching a relatively soft elastic material therebetween, with means such as spheres, discs or wire mesh being provided within the elastic material for generating local mechanical resonances that function to absorb sound energy at tunable wavelengths.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Energy harvester with adjustable resonant frequency
ActiveUS7471033B2Compact manufacturingProcess compatiblePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTyre measurementsCapacitanceElectricity
The present subject matter discloses devices, systems, and methodologies for harvesting power from environmentally induced vibrations. Piezoelectric devices (24) and structures are disclosed that may be employed in combination with electro-magnetic (100) or capacitive (92, 94) elements to enhance the power harvesting capabilities of the piezoelectric devices (24). The electromagnetic (100) and capacitive (92, 94) elements may be used to assist in maintaining system mechanical resonance in order to maximize energy harvesting capabilities. Power harvesting devices and systems in accordance with the subject technology may concurrently operate as sensors in motion sensitive applications thus providing self-powered monitoring capabilities.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
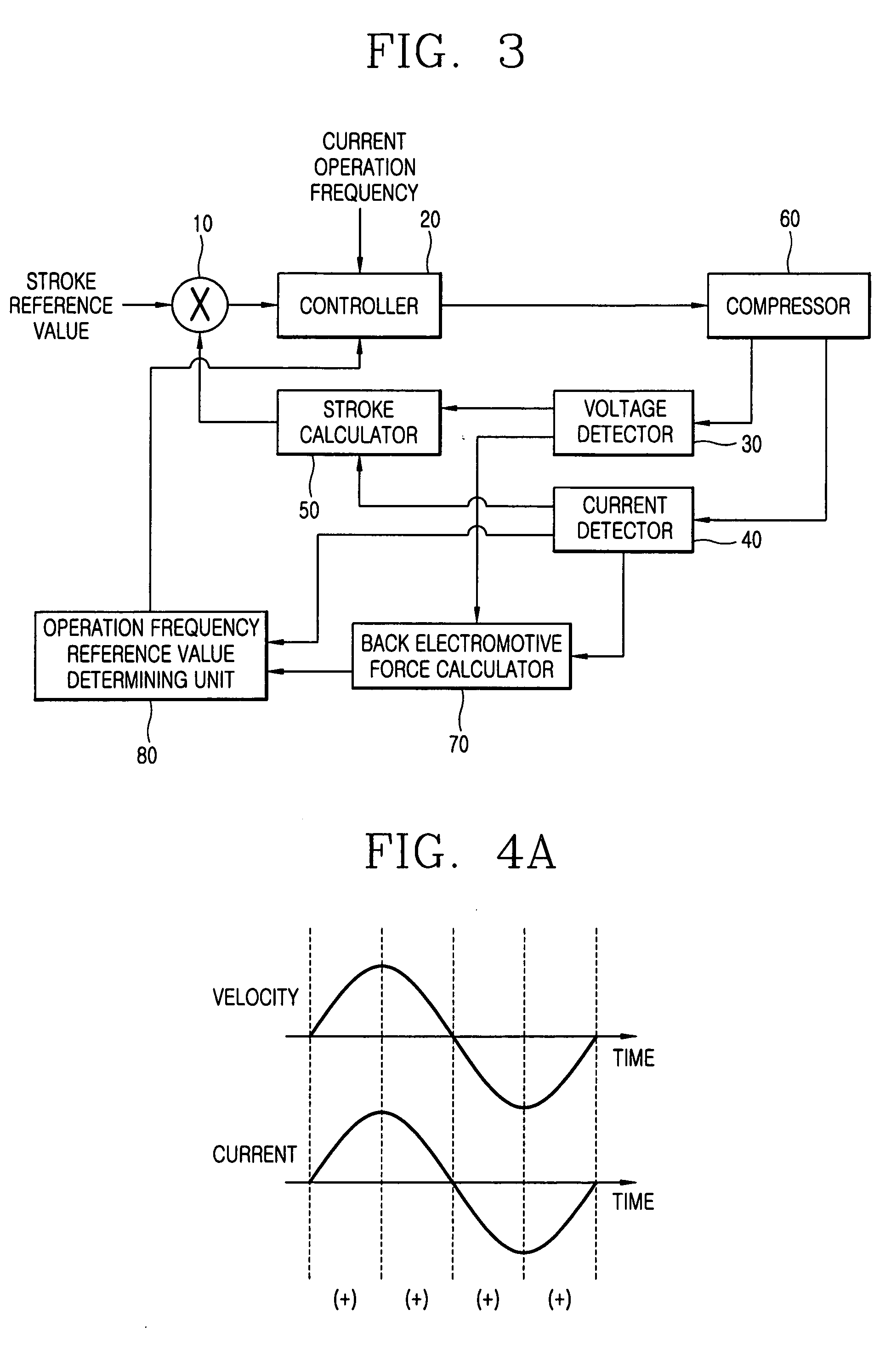
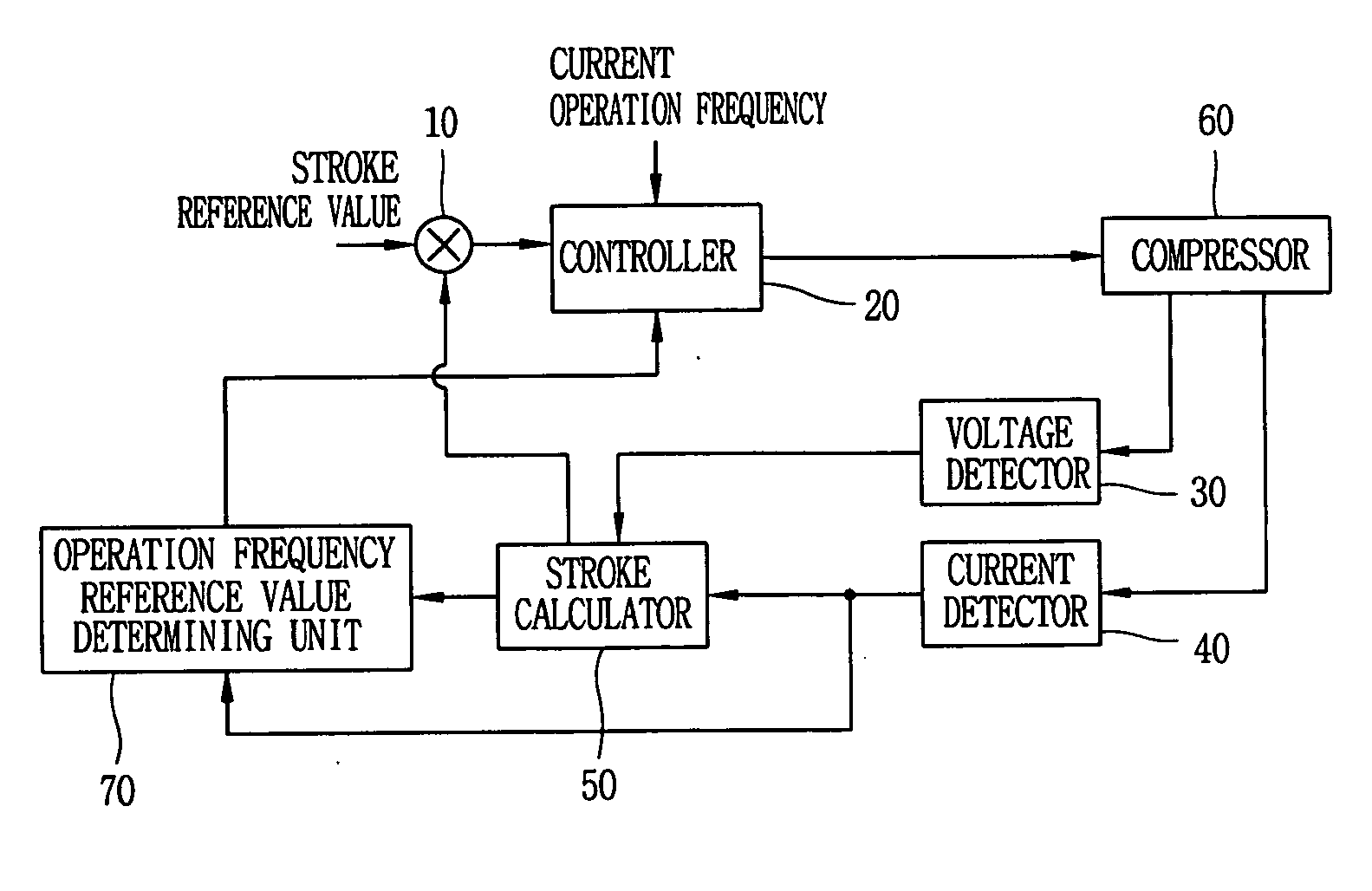
Apparatus and method for controlling operation of compressor
ActiveUS20060056980A1Easy to operateCompressorDC motor speed/torque controlMechanical resonanceElectromotive force
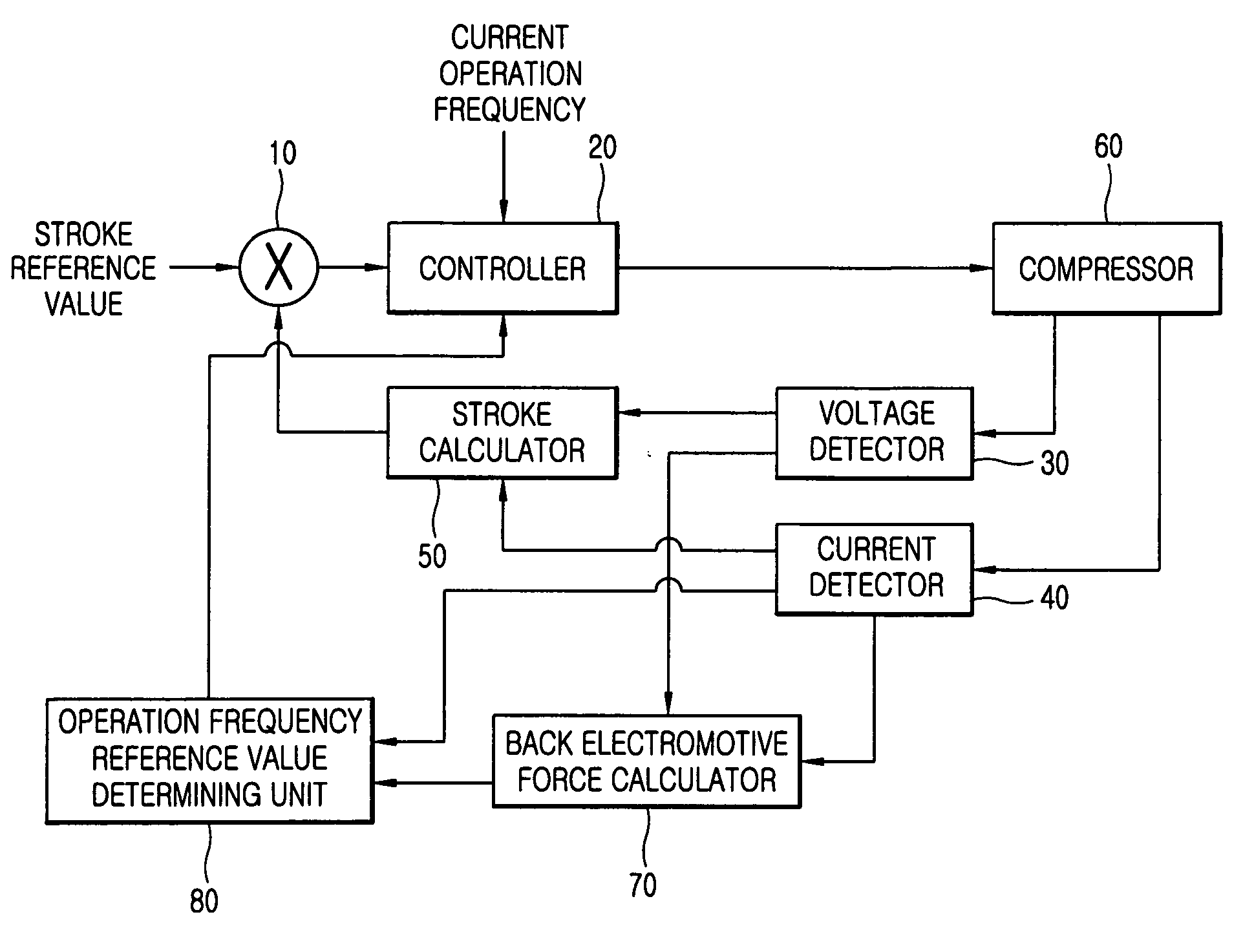
An apparatus for controlling an operation of a compressor includes: a back electromotive force calculator for calculating a back electromotive force of a compressor based on a value of a current applied to a motor of the compressor and a value of a voltage applied to the motor of the compressor; an operation frequency reference value determining unit for detecting a mechanical resonance frequency of the compressor based on the back electromotive force value and the current value and determining the detected mechanical resonance frequency as an operation frequency reference value; and a controller for varying an operation frequency of the compressor according to the determined operation frequency reference value.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
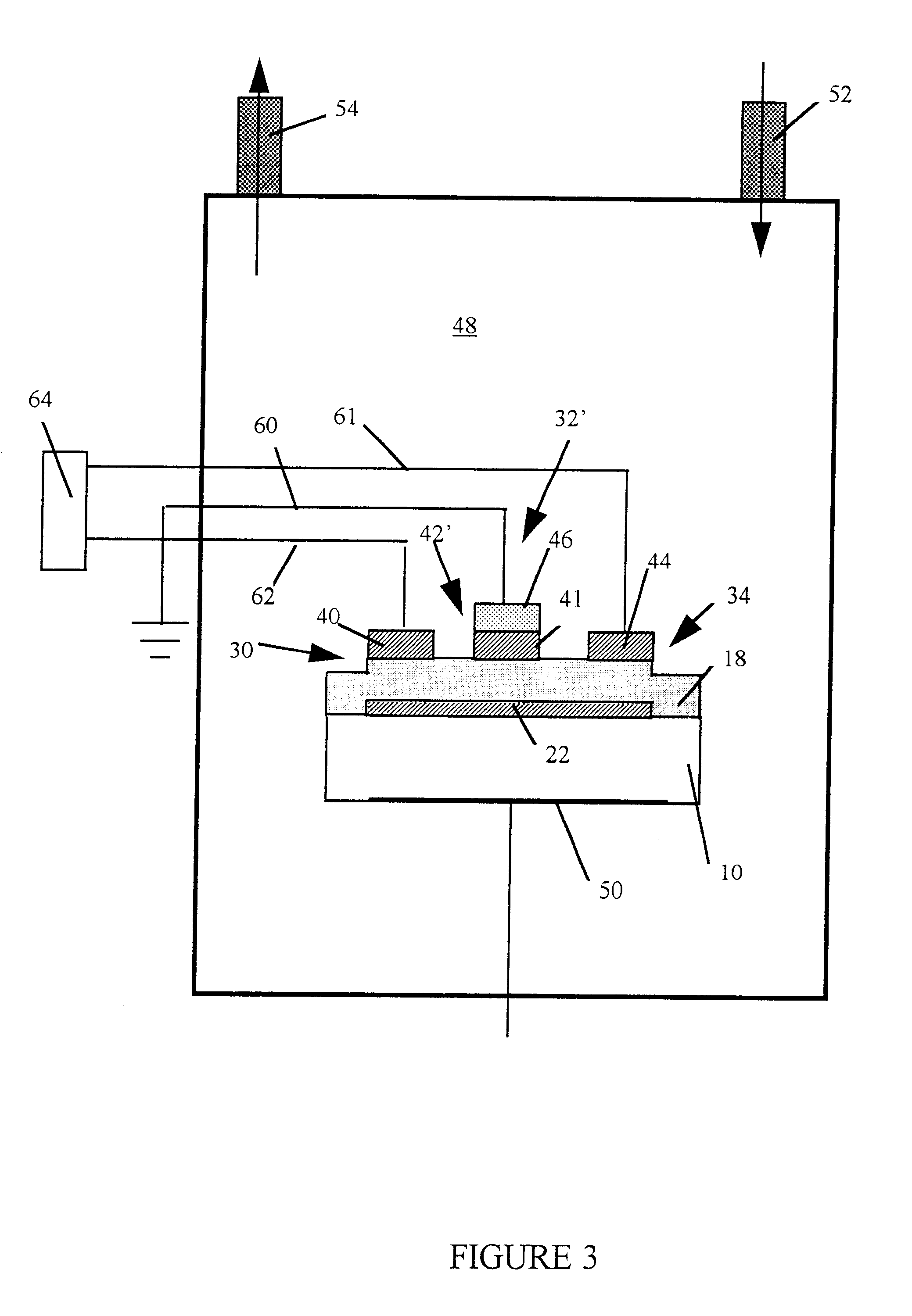
Ultrasonic impact methods for treatment of welded structures
InactiveUS6843957B2Improve corrosion fatigue strengthIncreased durabilityBlast furnace detailsHigh frequency current welding apparatusUltrasonic sensorEngineering
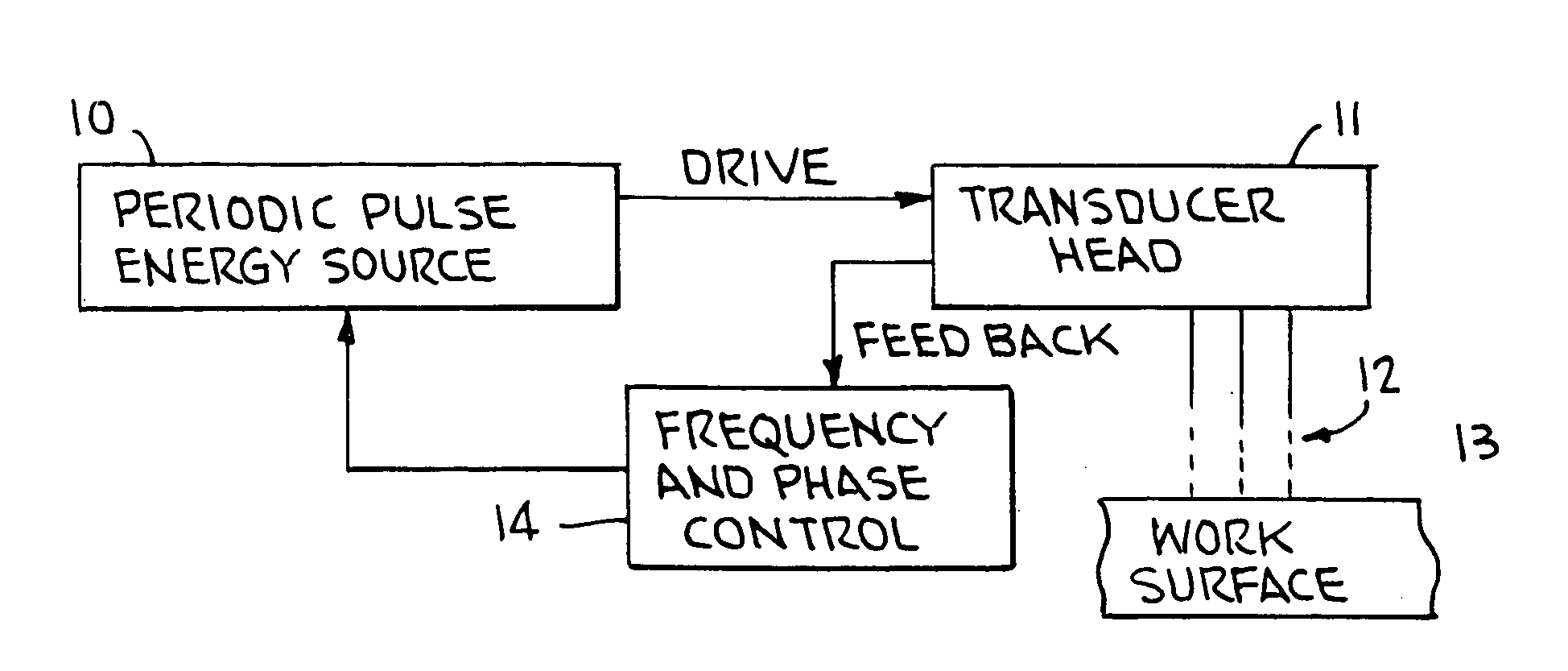
This invention provides methods of treatment for work products of materials such as steel, bronze, plastic, etc. and particularly welded steel bodies by pulse impact energy, preferably ultrasonic, to relax fatigue and aging and extend expectant life. The treatment may occur (a) at original production, (b) during the active life period for maintenance or (c) after failure in a repair stage. The ultrasonic treatment improves the work product strength. In welded products residual stress patterns near the weld sites are relaxed and micro-stress defects such as voids and unusual grain boundaries are reduced. The basic method steps are non-destructive in nature, inducing interior pulse compression waves with ultrasonic transducers and accessory tools impacting an external product surface with enough impulse energy to heat and temporarily plasticize the metal interior and relax stresses. The nature of the work product interior structure being treated is determined by sensing the mechanical movement at the impact surface of the work body to produce feedback frequency and phase signals responsive to input impact signals. These signals automatically conform driving pulse energy frequency and phase to the input transducers to match the mechanical resonance frequency of the working transducers and increase efficiency of energy transfer. Such feedback signals also are available for automated procedures which can improve product quality and consistency.
Owner:PROGRESS RAIL SERVICES
Apparatus and method for controlling operation of compressor
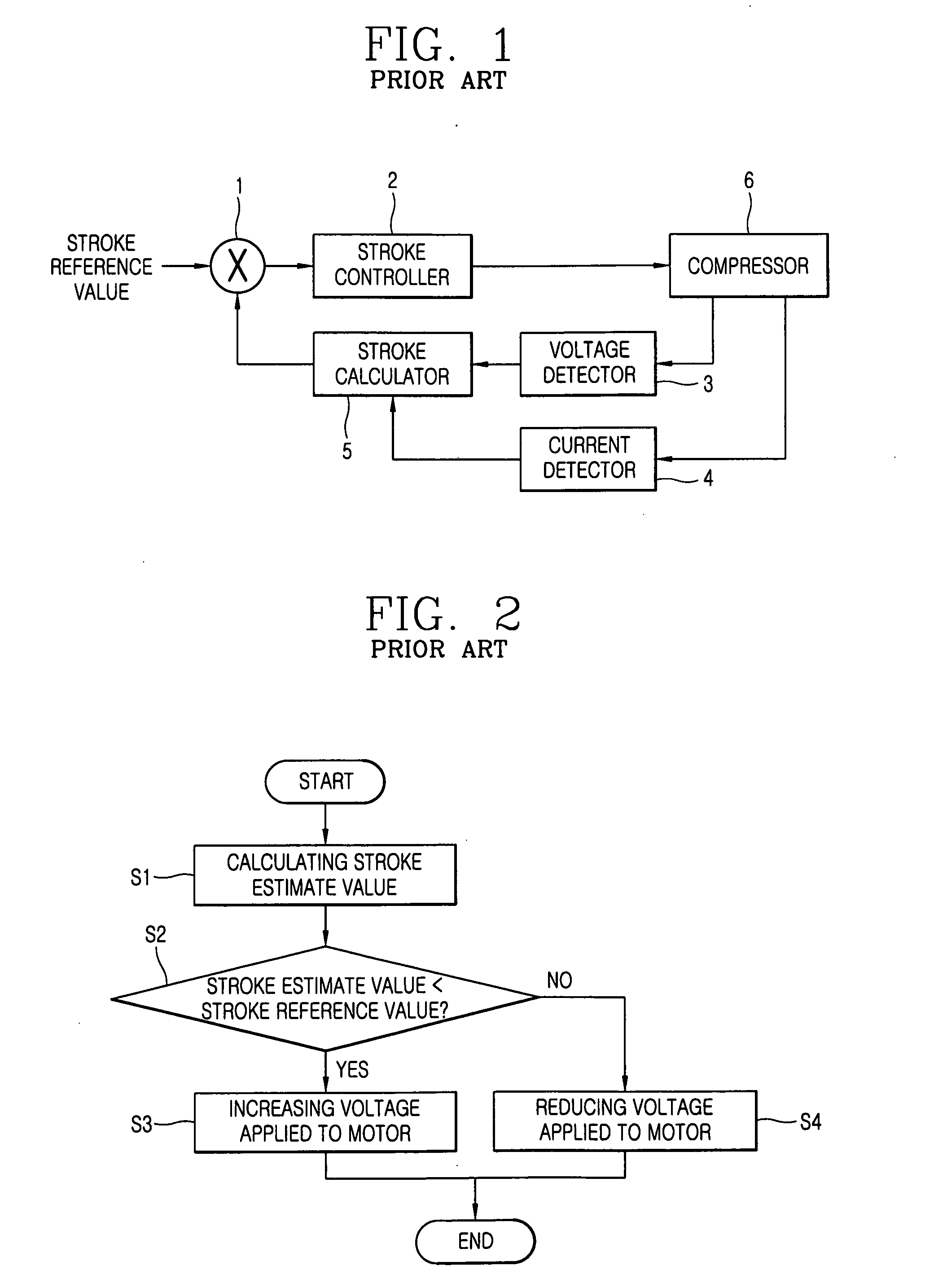
InactiveUS20060056979A1Easy to operateExternal parameterFlexible member pumpsEngineeringMechanical resonance
An apparatus for controlling a compressor includes a stroke calculator for calculating a stroke estimate value of a compressor based on a value of a current applied to a motor of the compressor and a value of a voltage applied to the motor of the compressor; an operation frequency reference determining unit for integrating the stroke estimate value to output an integrated stroke value, detecting a mechanical resonance frequency of the compressor based on the integrated stroke estimate value and the current value, and determining the detected mechanical resonance frequency as an operation frequency reference value; and a controller for varying a current operation frequency of the compressor according to the determined operation frequency reference value.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
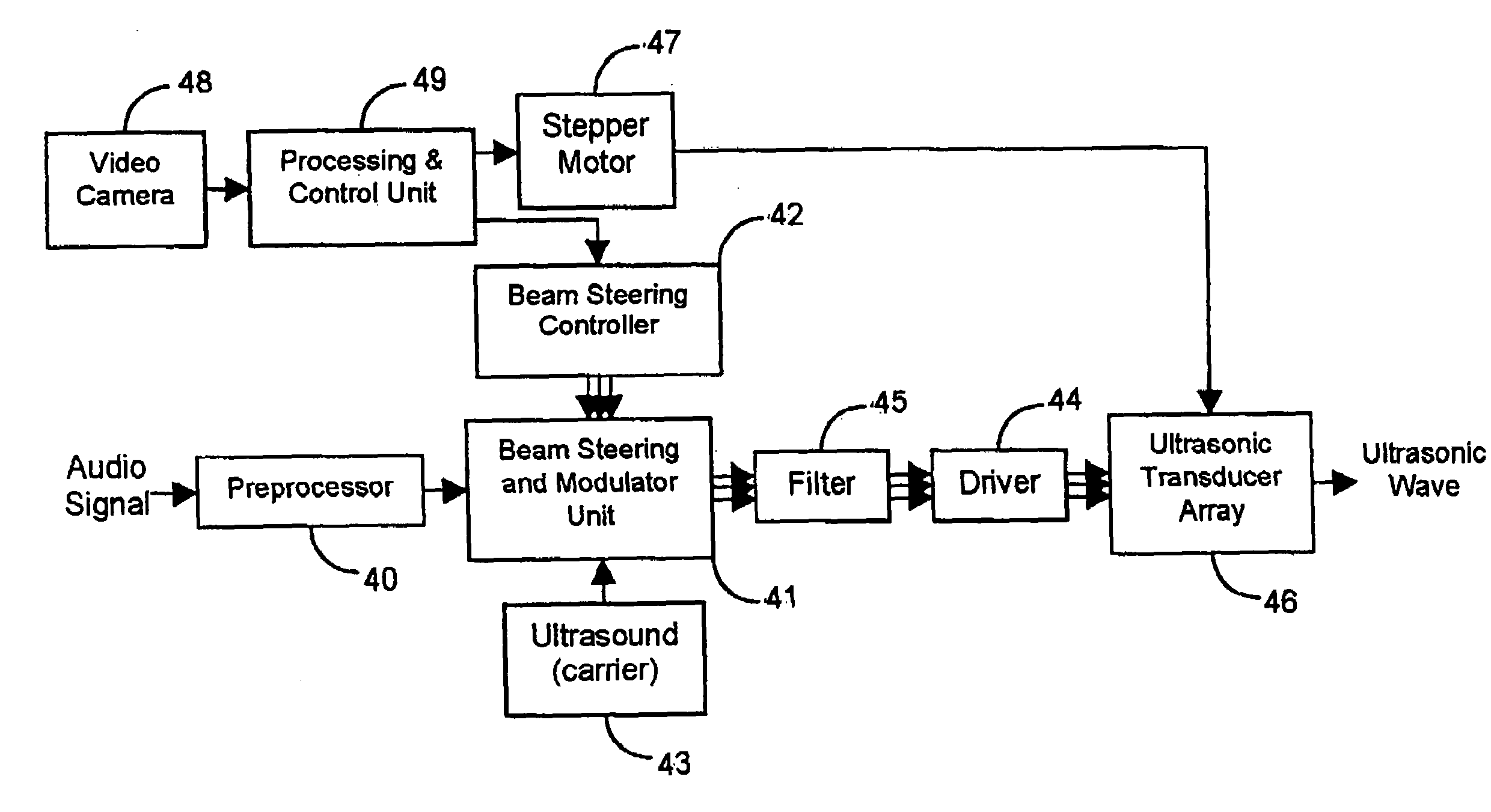
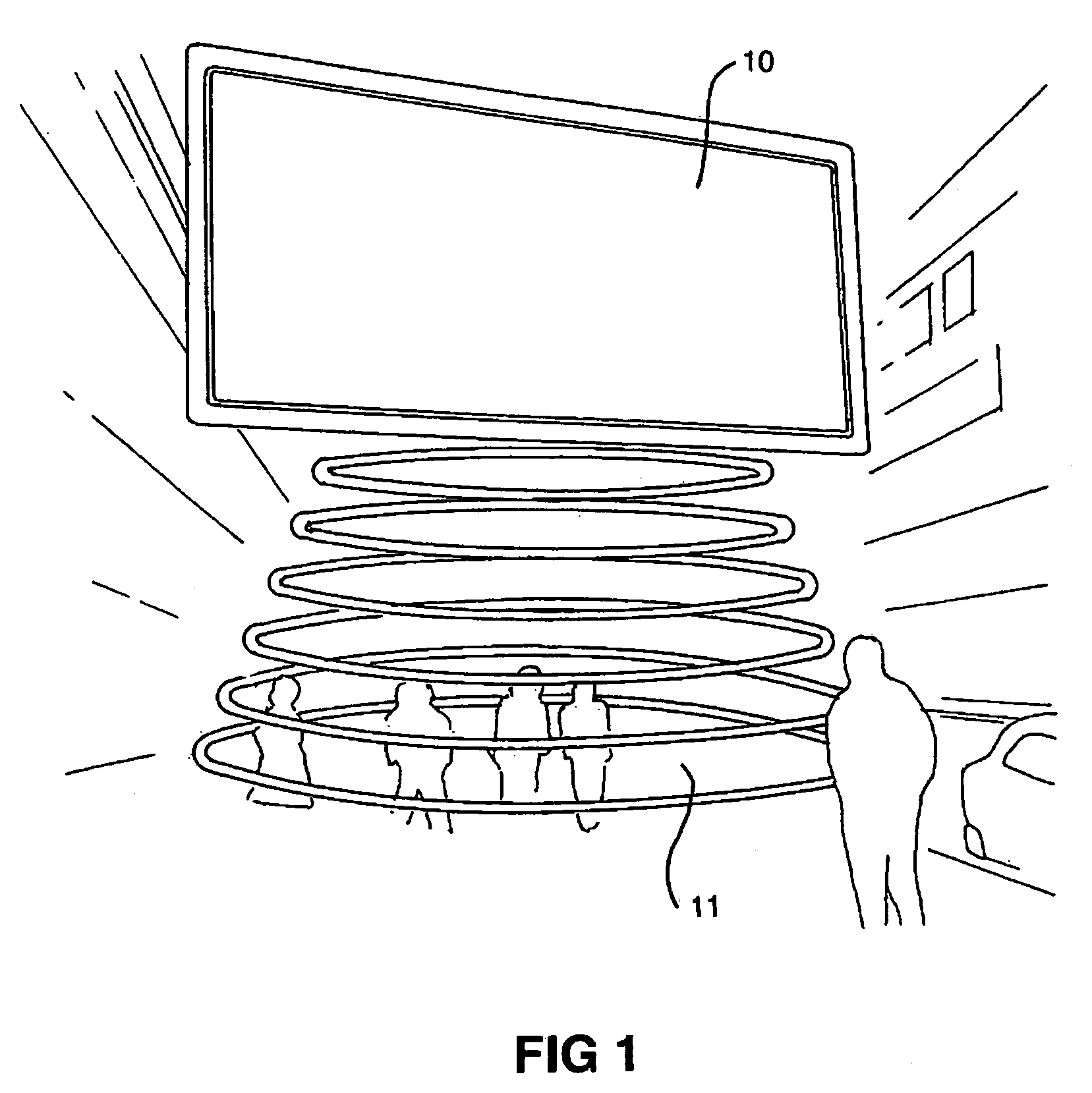
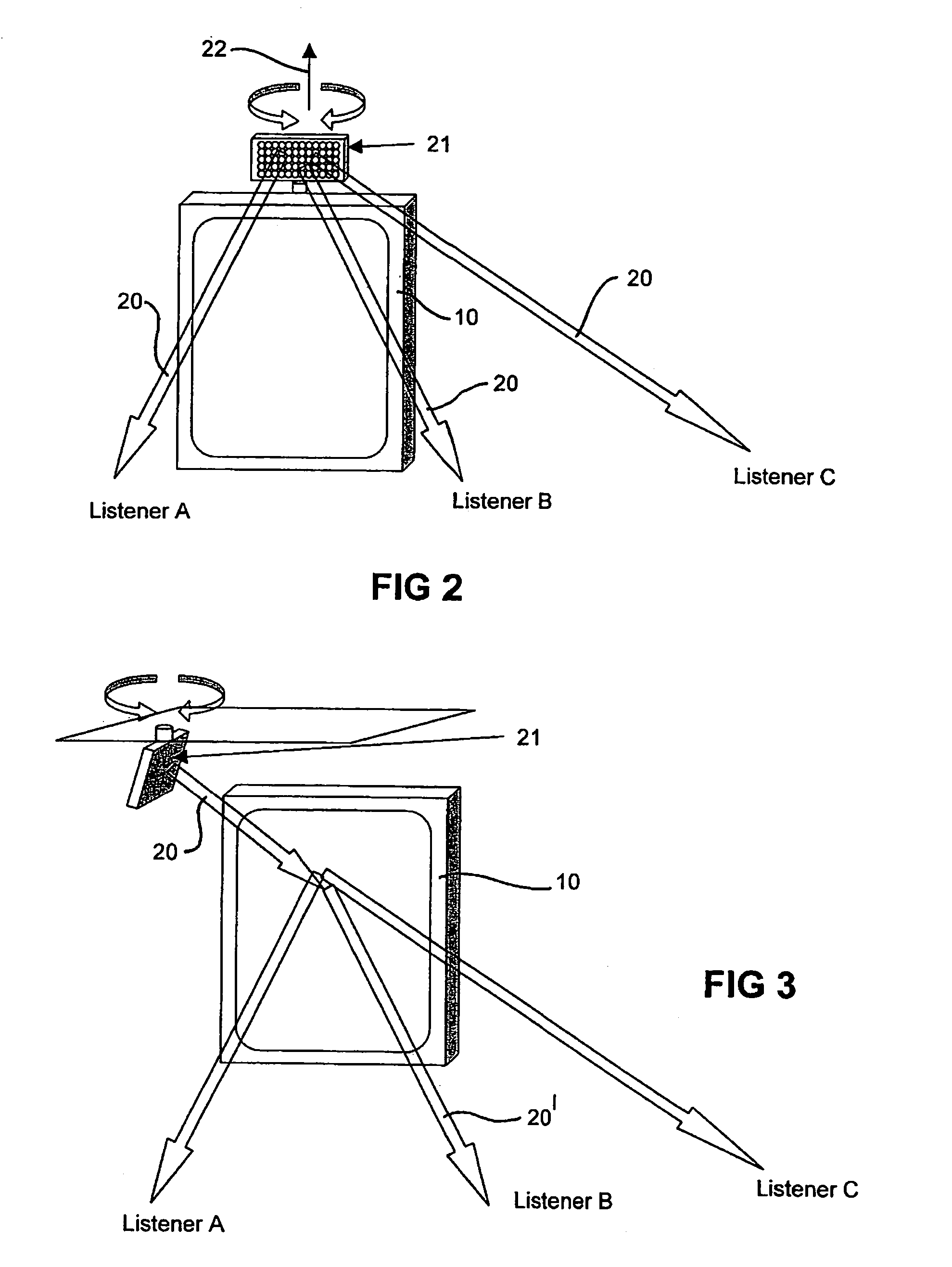
Steering of directional sound beams
InactiveUS7146011B2Contributing to noise pollutionEasy to adjustNear-field transmissionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersSonificationUltrasonic sensor
Apparatus is disclosed for steering a directional audio beam that is self-demodulated from an ultrasound carrier. The apparatus includes means for modulating a carrier signal with an audio signal and means for adjusting the amplitude and phase of at least one of the audio signal and / or the carrier signal to steer the audio beam to a desired direction. The apparatus also includes means for generating an ultrasound beam in the desired direction driven by the modulated carrier signal. The apparatus may include means for weighting the audio and / or carrier signal by a zeroth order Bessel function to synthesize a Bessel distribution source. A corresponding method for steering a directional audio beam is also disclosed. A harmonic generator may be used to generate harmonics of low frequencies in the audio signal. The harmonics may provide (upon demodulation) a psycho-acoustic impression of improved perception of low frequencies. Further, a modulated ultrasonic signal or an unmodulated audio signal may be band-passed into two or more different band-limited signals. The band-limited signals may be amplified and transmitted by ultrasonic transducers having mechanical resonance frequencies substantially equal to a characteristic frequency of the band-limited signals. Ultrasonic processing of the audio signal may include square root methods without generating large numbers of harmonics.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Mechanical resonating structures including a temperature compensation structure
ActiveUS20100182102A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksEngineeringMechanical resonance
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
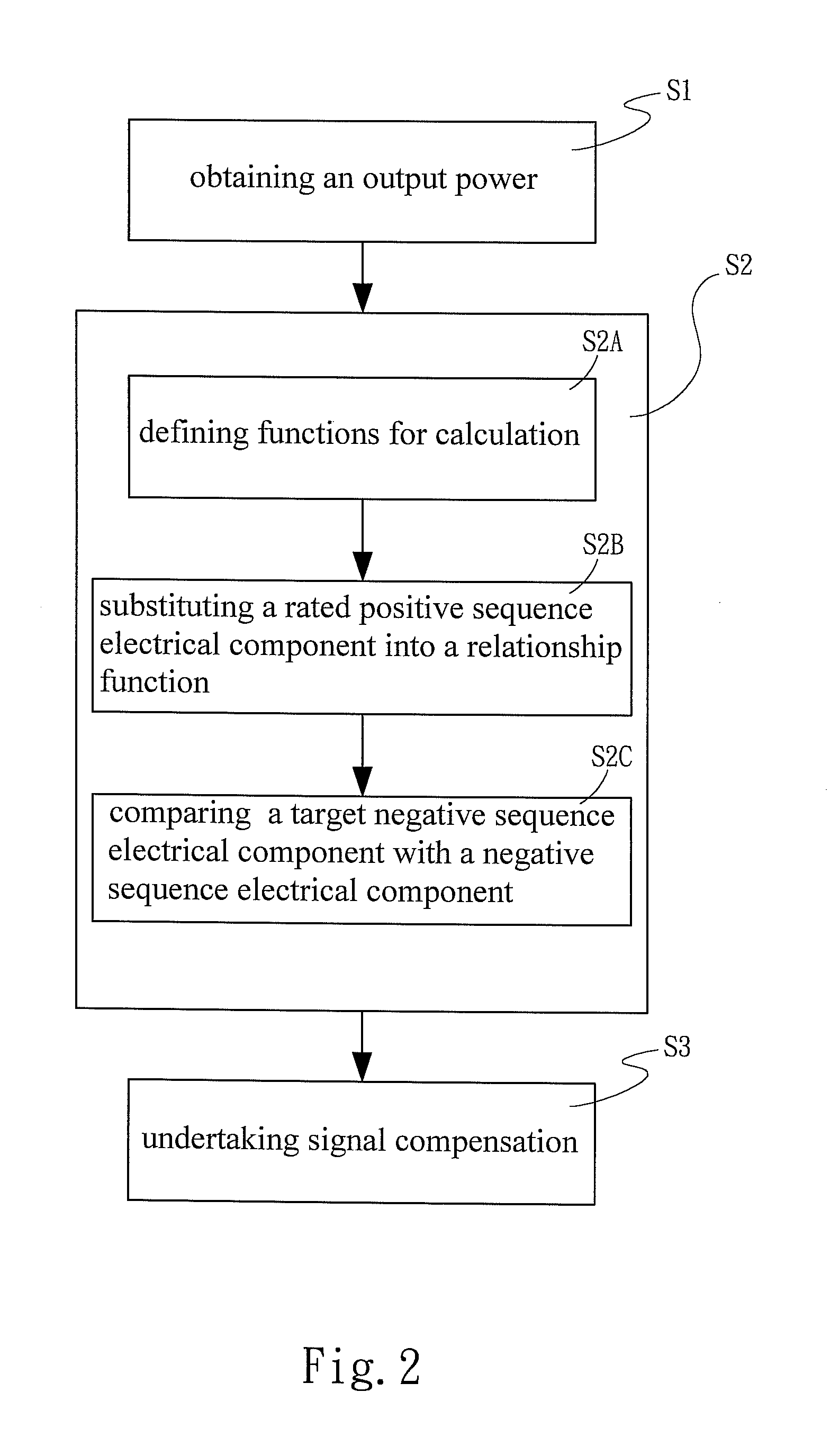
Low voltage ride-through control method for grid-connected converter of distributed energy resources
InactiveUS20130057236A1Improve balanceImprove stabilityWind energy generationPhotovoltaic energy generationPower compensationPower flow
An LVRT control method for a grid-connected converter of distributed energy resources comprises steps of: obtain a positive sequence electrical component and a negative sequence electrical component during an LVRT period; outputting a compensation signal according to a power threshold withstood by a grid-connected converter to undertake reactive power compensation; and constraining the output power lower than the power threshold. The present invention uses the positive and negative sequence electrical components to undertake reactive power compensation, whereby to improve balance and stability of voltage during the LVRT period, avoid reverse torque and mechanical resonance, and prolong the service life of the power generator. Moreover, the present invention constrains the sum of the compensation currents below the power threshold to prevent the circuit of the power generator from being overloaded and damaged, whereby is prolonged the service life of the power system.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
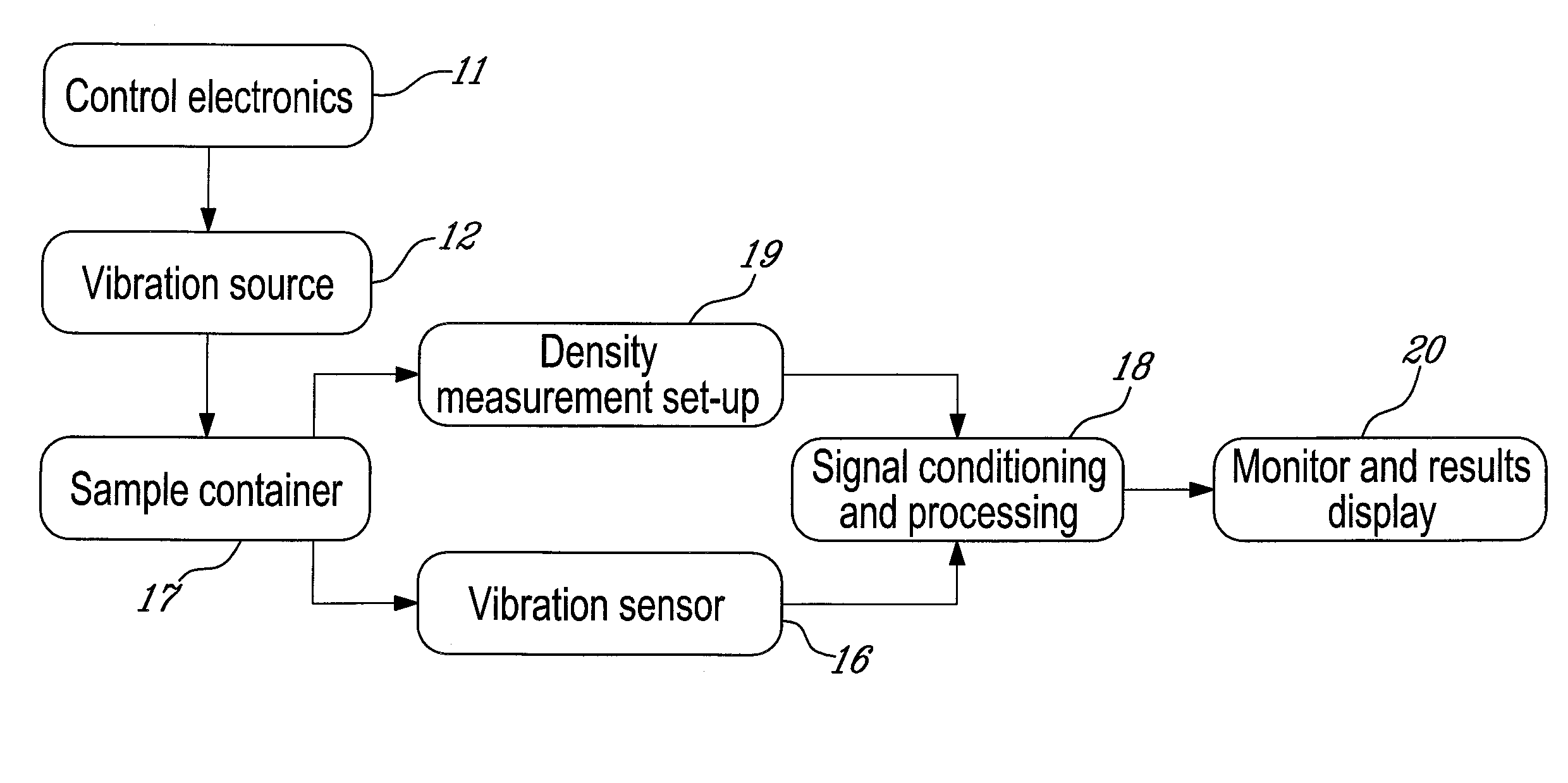
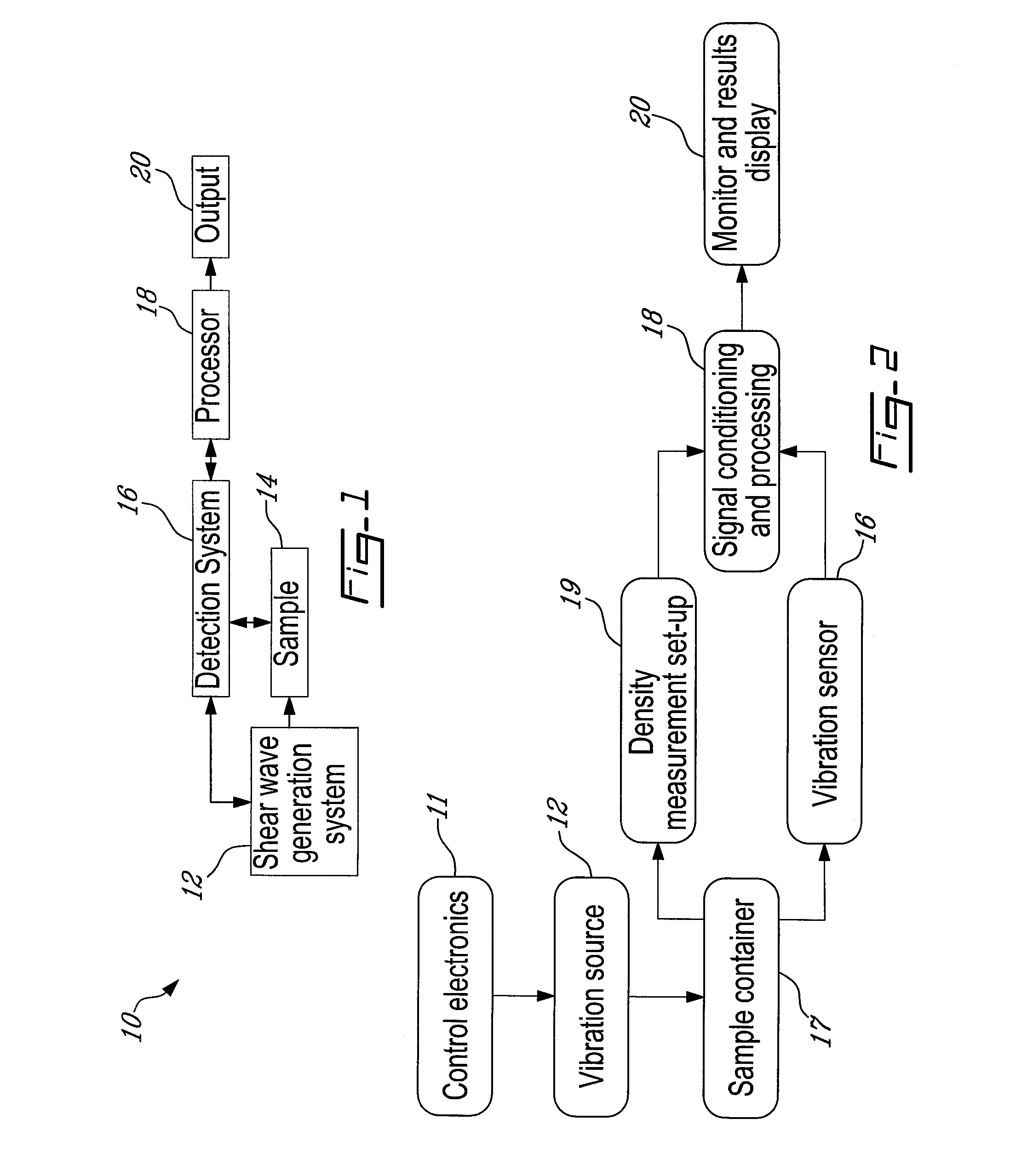
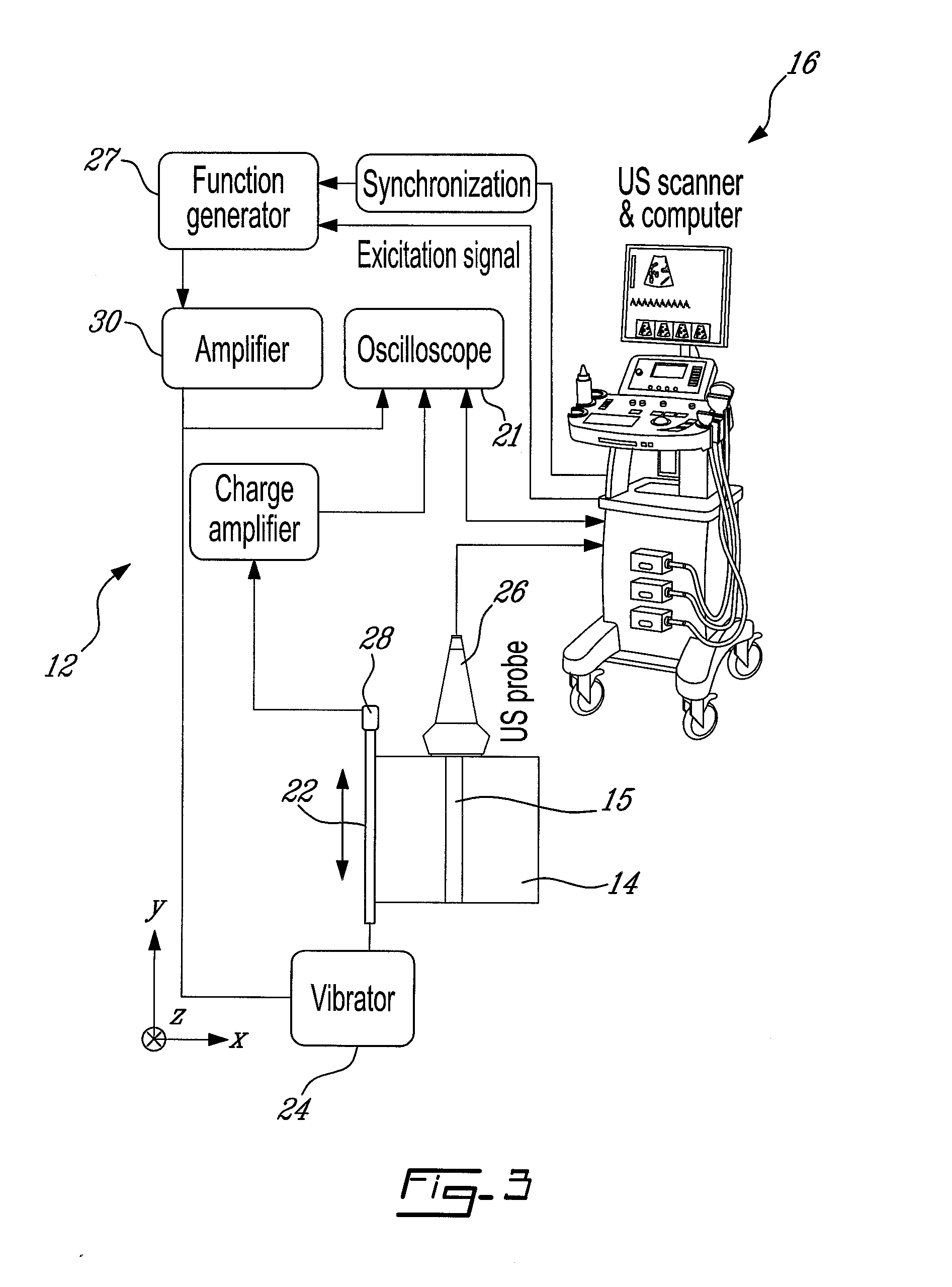
System and method for detection, characterization and imaging of heterogeneity using shear wave induced resonance
InactiveUS20110130660A1Ultrasound therapyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical resonanceAcoustics
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
Fluid Powered Oscillator
InactiveUS20070176430A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngine fuctionsEngineeringMechanical resonance
A method and device for converting fluidic kinetic energy into oscillatory mechanical motion is disclosed. A mechanical structure of finite stiffness is coupled to a fluid-dynamical control surface the thrust from which is oscillated in direction. The coupling thereby induces oscillations in the structure, the magnitude of which can be controlled by the degree of mechanical resonance between the oscillation rate of the fluidic thrusting and the structure's resonance frequency. The resulting mechanical energy can be converted into electrical energy using either piezo-electric or electromagnetic means.
Owner:HAMMIG MARK D
Metallic glass alloys for mechanically resonant marker surveillance systems
InactiveUS6093261AImprove magnetic propertiesAvoid interferenceInorganic material magnetismElectric/magnetic detectionVoltage amplitudeRadiance
A glassy metal alloy consists essentially of the formula FeaCobNicMdBeSifCg, where "M" is at least one member selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, chromium and manganese, "a-g" are in atom percent, "a" ranges from about 30 to about 45, "b" ranges from about 8 to about 18, "c" ranges from about 20 to about 45, "d" ranges from about 0 to about 3, "e" ranges from about 12 to about 20, "f" ranges from about 0 to about 5 and "g" ranges from about 0 to about 2. The alloy can be cast by rapid solidification into ribbon, cross-field annealed to enhance magnetic properties, and formed into a marker that is especially suited for use in magneto-mechanically actuated article surveillance systems. Advantageously, the marker is characterized by substantially linear magnetization response in the frequency regime wherein harmonic marker systems operate magnetically. Voltage amplitudes detected for the marker are high, and interference between surveillance systems based on mechanical resonance and harmonic re-radiance is virtually eliminated.
Owner:TYCO FIRE & SECURITY GMBH
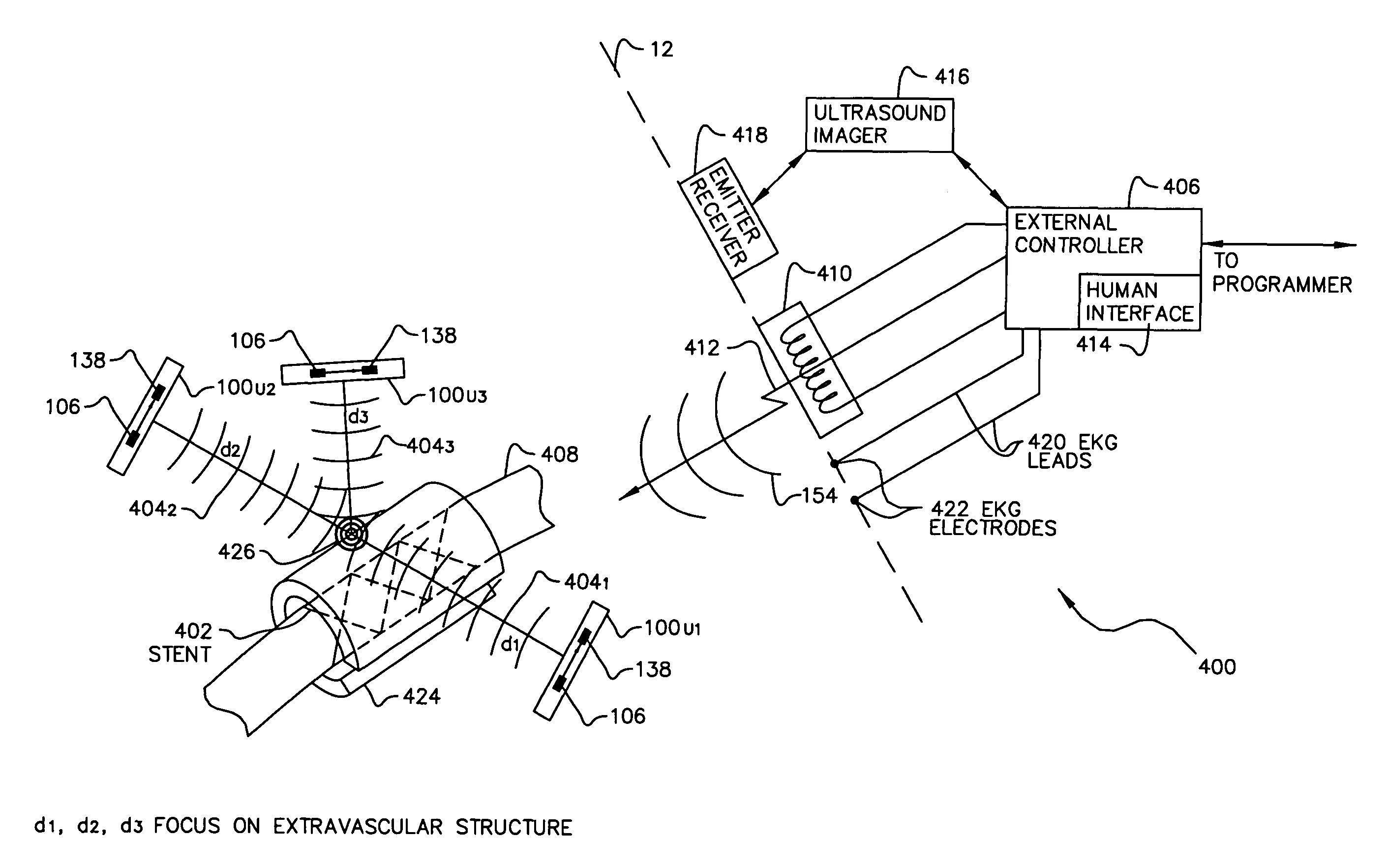
System of implantable ultrasonic emitters for preventing restenosis following a stent procedure
A system and method that minimizes plaque accumulation on a stent and thereby restenosis that could require a subsequent invasive medical procedure following implantation of the stent in a patient. A plurality of electrically-powered, biocompatible devices, implantable via injection, are positioned within the patient proximate to the stent and under control of a externally-placed controller are commanded to emit ultrasonic waves corresponding to the mechanical resonance of the stent. By controlling the frequency and the relative phases of the ultrasonic waves, the accumulation of plaque on the stent can thus be minimized.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Miniature magnetomechanical tag for detecting surgical sponges and implements
InactiveUS7464713B2Serious consequenceEasy to operateDiagnosticsSurgeryEngineeringMechanical resonance
Externally detectable electronic article surveillance markers are attached to surgical implements, such as sponges and surgical instruments, appointed for use in a surgical wound. The attachment mechanism facilitates detection by an external interrogating field before the wound has been closed and the patient has left the operating table. The markers are responsive to the imposition of an interrogating field produced by an electronic article surveillance system. Markers contain one or more magnetomechanically responsive elements that are urged into mechanical resonance by the interrogating field. The ring-down of the resonance and the associated dipolar electromagnetic field provide a signal-identifying characteristic detected by a detection system. Upon detection, an audible or visible signal is triggered to alert relevant medical personnel to the need for follow-up care and removal of the offending item. The resonance occurs at a frequency ranging from about 70 to 300 kHz. Misadventures during operative procedures—especially those wherein implements remain undiscovered at the time of surgery and are retained indefinitely within the surgical cavity, often entailing dire consequences to the patient—are virtually eliminated. The attachment mechanism and markers assure that surgical implements are reliably detected and removed before completion of the surgical procedure.
Owner:FABIAN CARL E +2
Apparatus and method for controlling operation of reciprocating compressor
InactiveUS20050158178A1Operation efficiency can be improvedCompressorExternal parameterMechanical resonanceOperating frequency
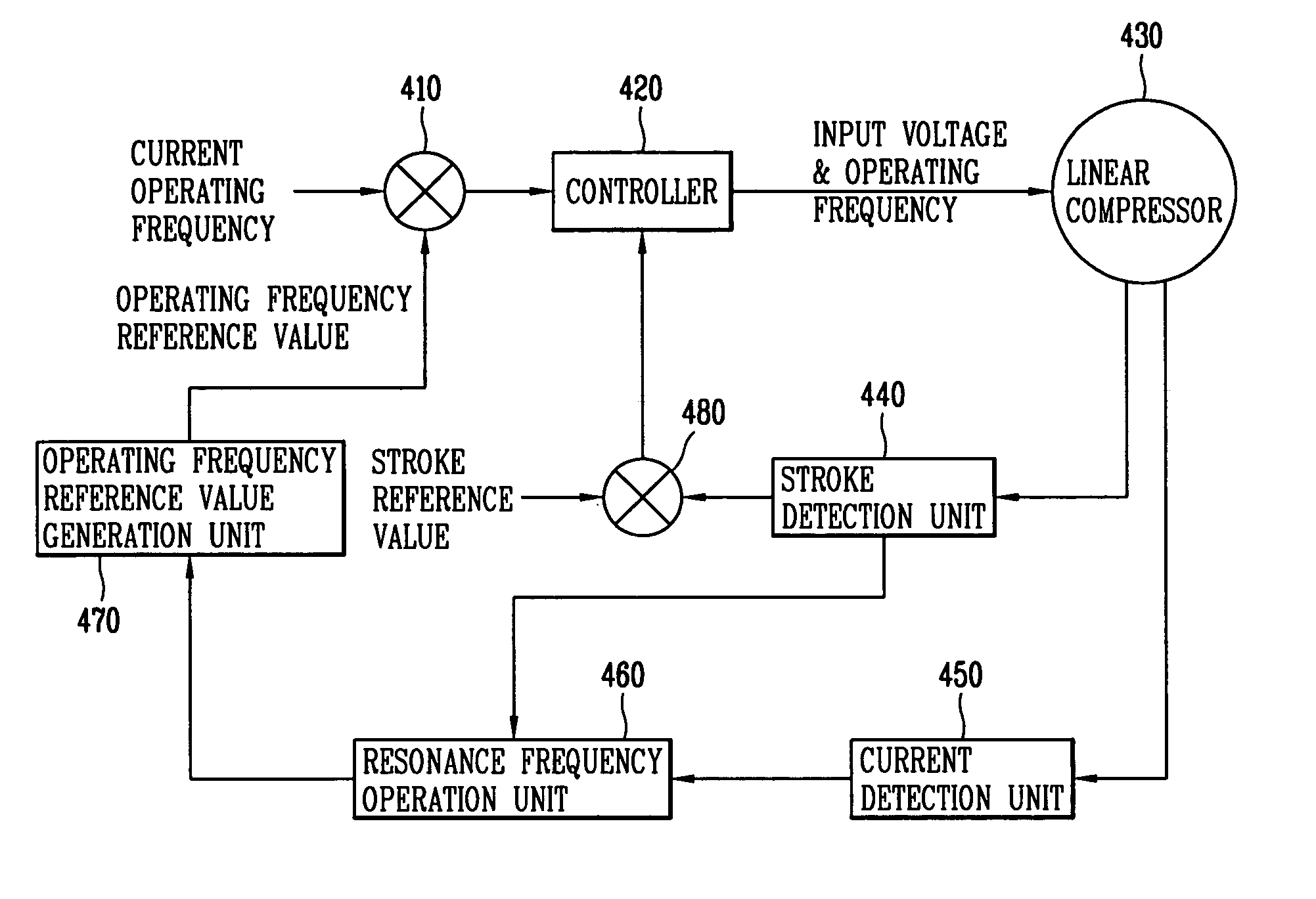
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for controlling an operation of a reciprocating compressor which can improve operational efficiency of the reciprocating compressor. The apparatus for controlling the operation of the reciprocating compressor includes a resonance frequency operation unit for operating a mechanical resonance frequency of the reciprocating compressor, an operating frequency reference value generation unit for comparing the operated mechanical resonance frequency with a current operating frequency of the reciprocating compressor, and generating an operating frequency reference value according to the comparison result, and a controller for controlling a motor of the reciprocating compressor according to the generated operating frequency reference value.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
Method, device and system for suppressing shaking of electric automobile
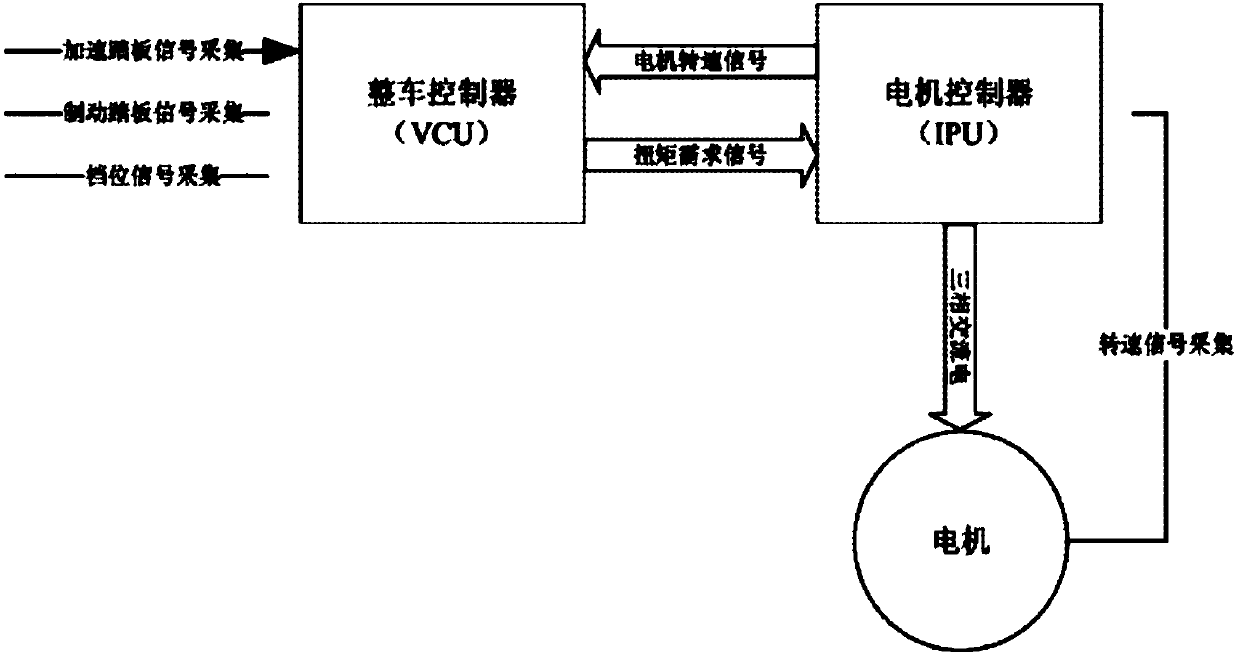
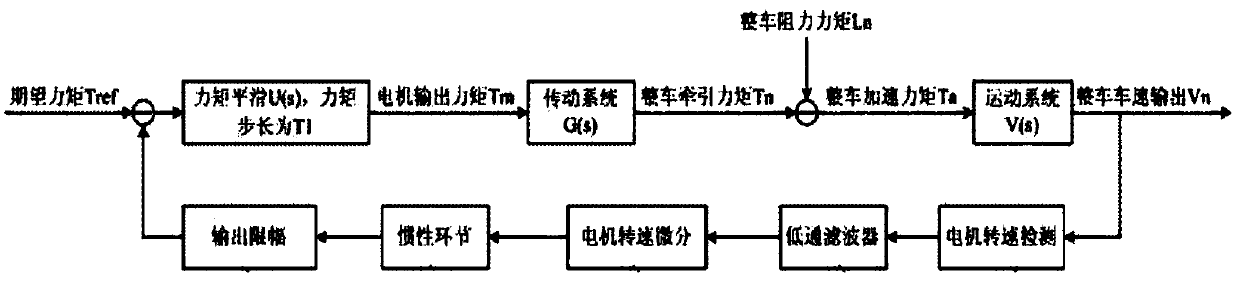
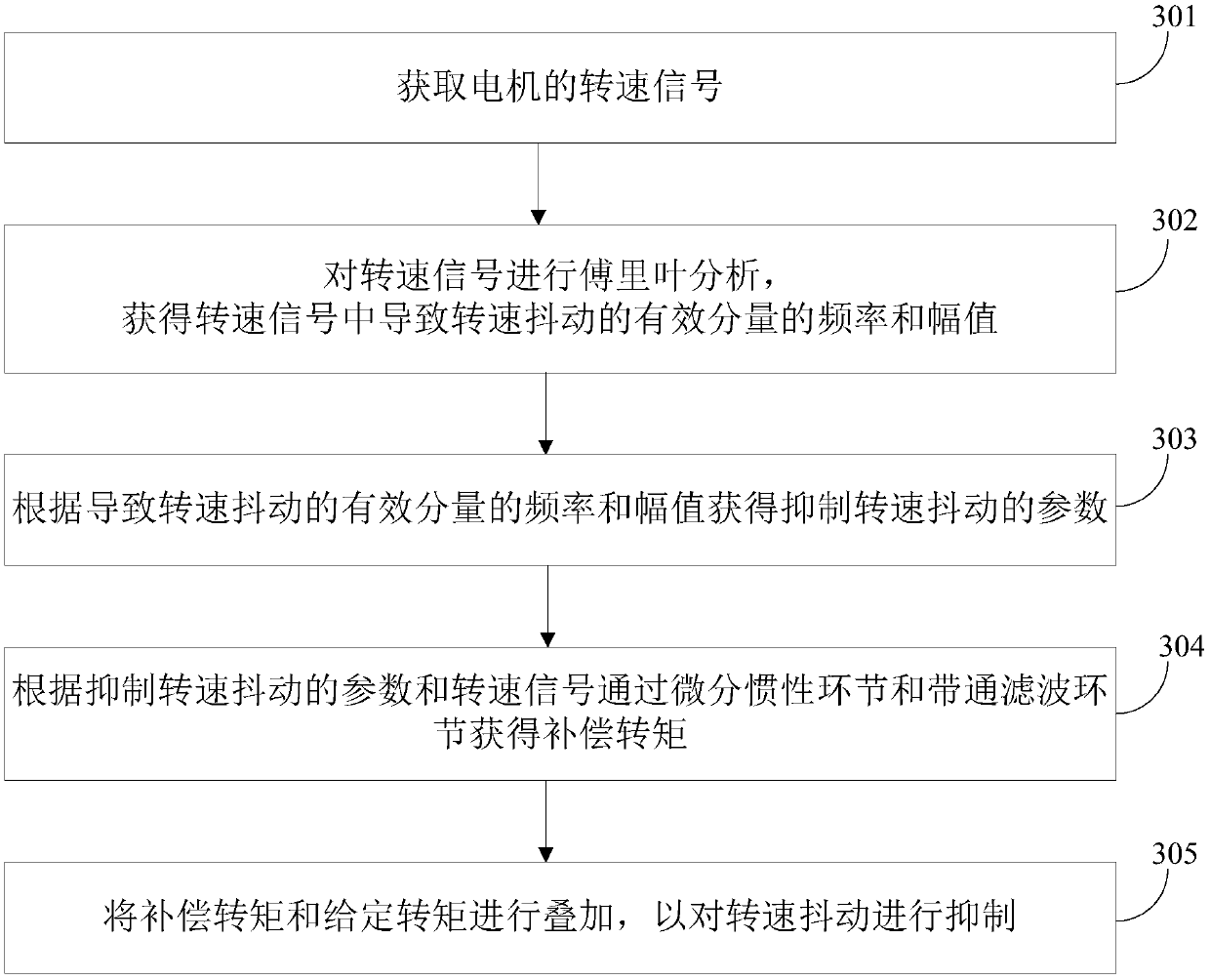
ActiveCN108068659ASuppress jitterSolve the problem of direct deviation in the extraction of rotational speed fluctuationsSpeed controllerElectric machinesBand-pass filterLinear relationship
The invention discloses a method, device and system for suppressing shaking of an electric automobile. The method, device and system are used for suppressing the shaking of the electric automobile andimproving the driving comfort level. The method includes the steps that a rotation speed signal of a motor is obtained; Fourier analysis is conducted on the rotation speed signal, and the frequency and the amplitude of an effective component, causing rotation speed shaking, in the rotation speed signal are obtained, wherein rotation speed shaking is shaking caused by the non-linear relationship between traction torque and the resistance moment of the electric automobile; according to the frequency and the amplitude of the effective component causing rotation speed shaking, a parameter for suppressing rotation speed shaking is obtained; according to the parameter for suppressing rotation speed shaking and the rotation speed signal, compensation torque is obtained through a differential inertial element and a band-pass filtering element; and the compensation torque and given torque are superposed so as to suppress the rotation speed shaking. Due to the fact that the shaking of the electric automobile is suppressed, mechanical resonance generated in the shaking process is reduced, and therefore hardware wear of the electric automobile is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Electrostatic ultrasonic transducer drive control method, electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic speaker using the same, audio signal reproduction method, ultra-directional acoustic system, and display device
InactiveUS20070154036A1High strengthImprove energy conversion efficiencyMicrophonesSignal processingSonificationUltrasonic sensor
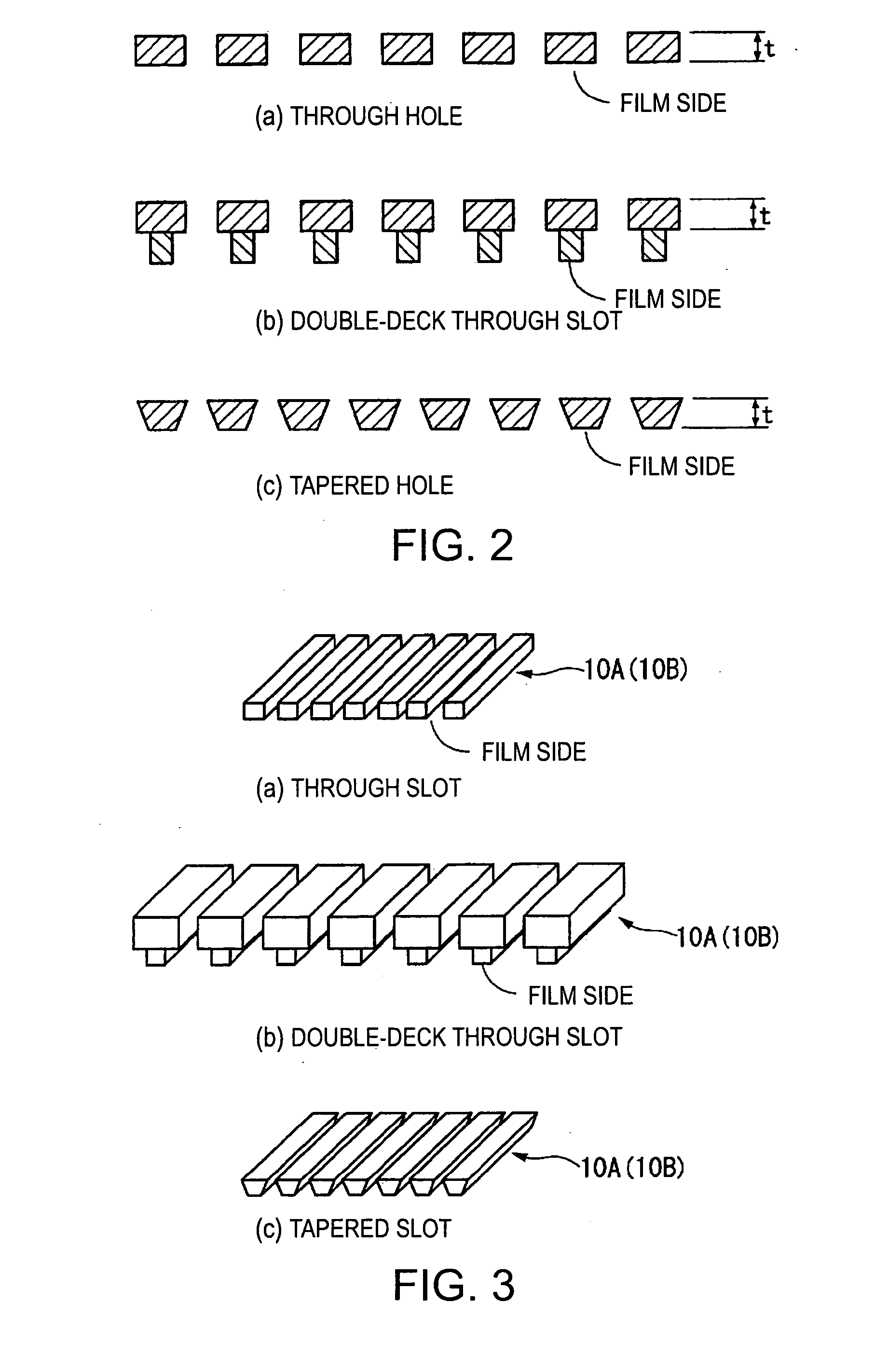
A Push-Pull-type electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a first electrode having a through hole, a second electrode having a through hole making a pair with the through hole of the first electrode, and a vibration film held between a pair of electrodes composed of the first and the second electrodes and having a conductive layer to which a direct-current bias voltage is applied, and holds the pair of electrodes and the vibration film. Assuming that λ is the wavelength of the carrier wave having a frequency shifted as a predetermined amount of frequency from the resonance frequency, which is the mechanical resonance frequency of the vibration film, the thickness t of each of the pair of electrodes is set to (λ / 4)·n or roughly (λ / 4)·n (where, λ is the wavelength of the ultrasonic wave, n is a positive odd number), and an alternating-current signal, which is a modulated wave obtained by modulating the carrier wave in the ultrasonic frequency band with a signal wave in an audible frequency band, is applied between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Seabed seismic station packaging
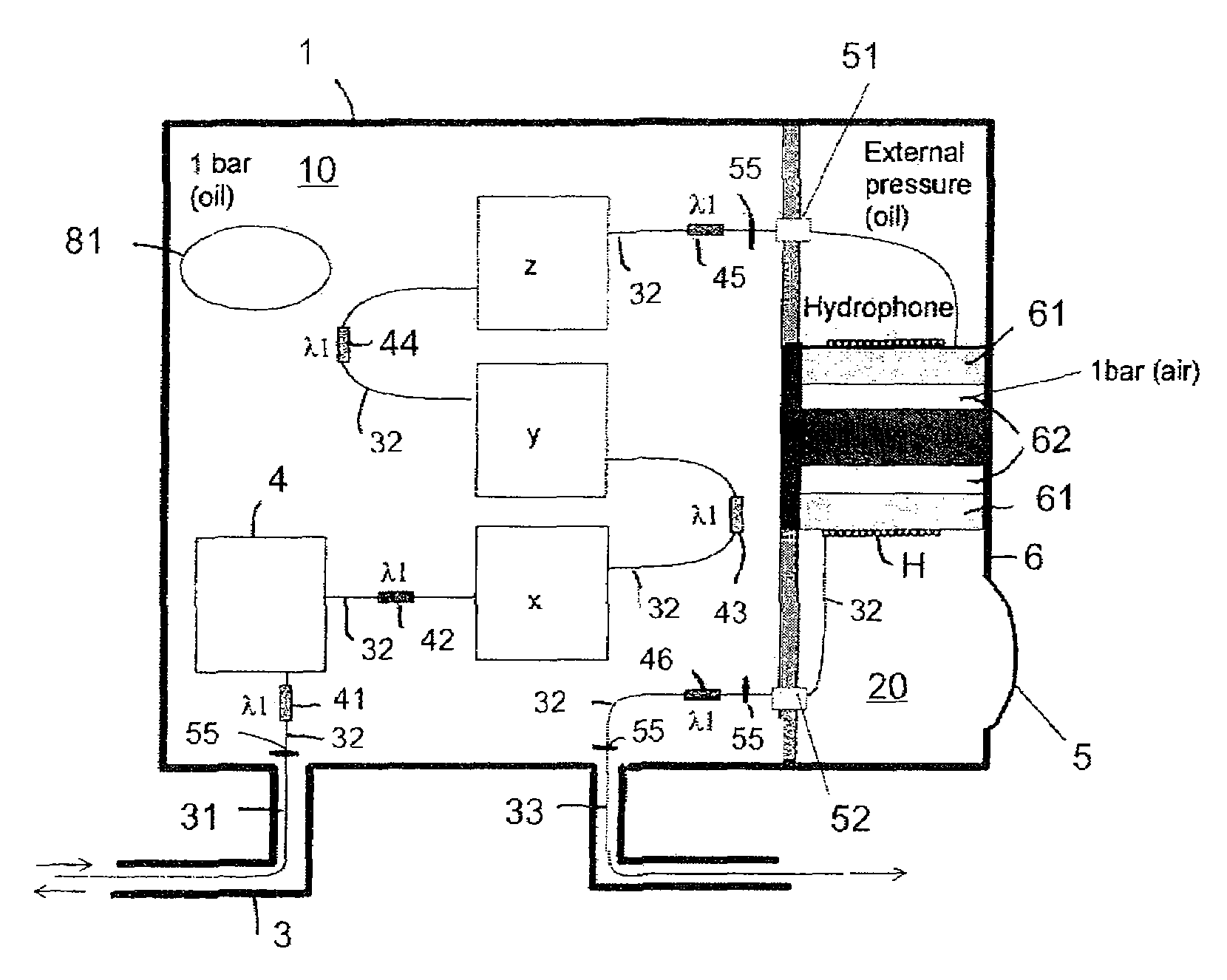
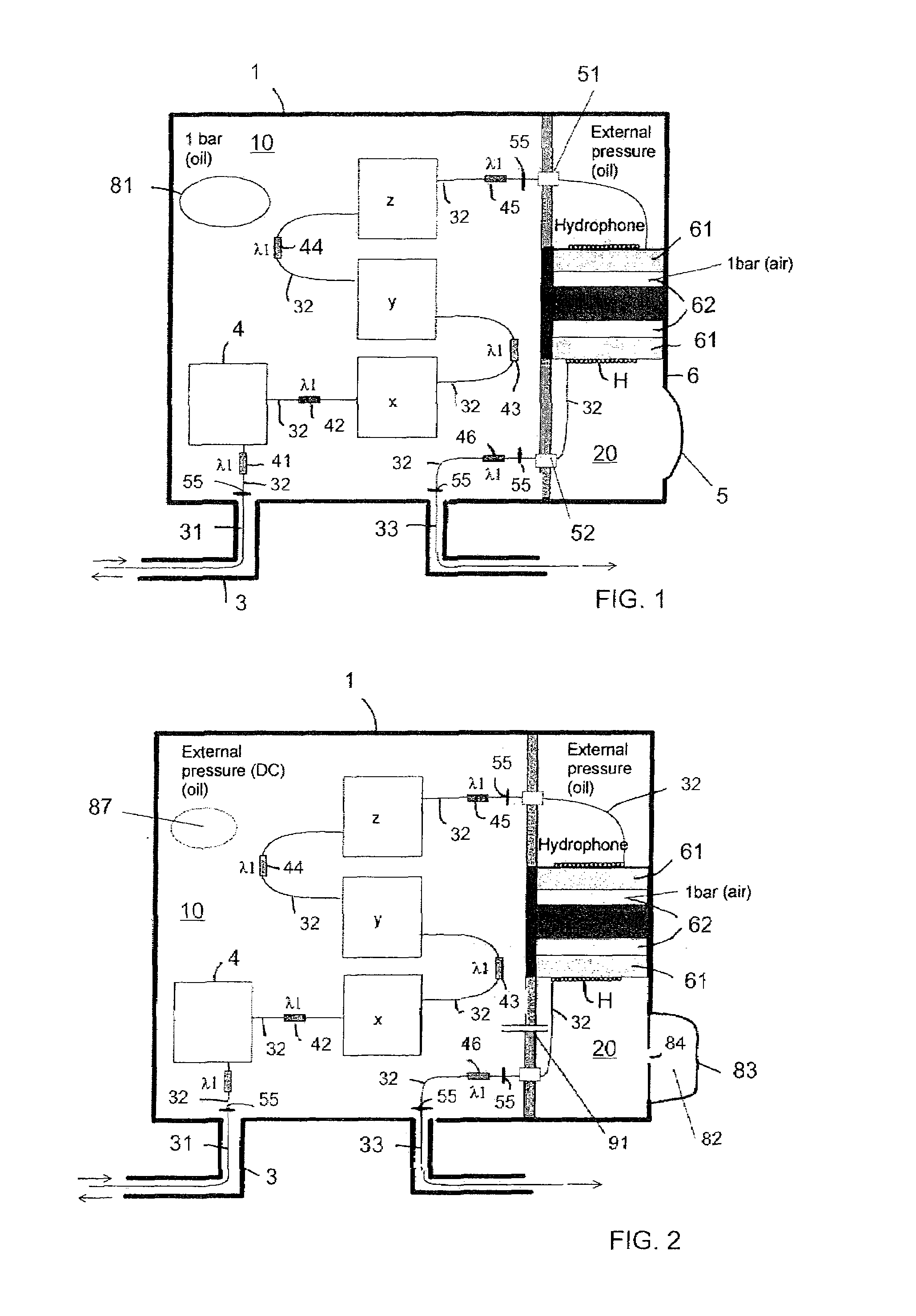
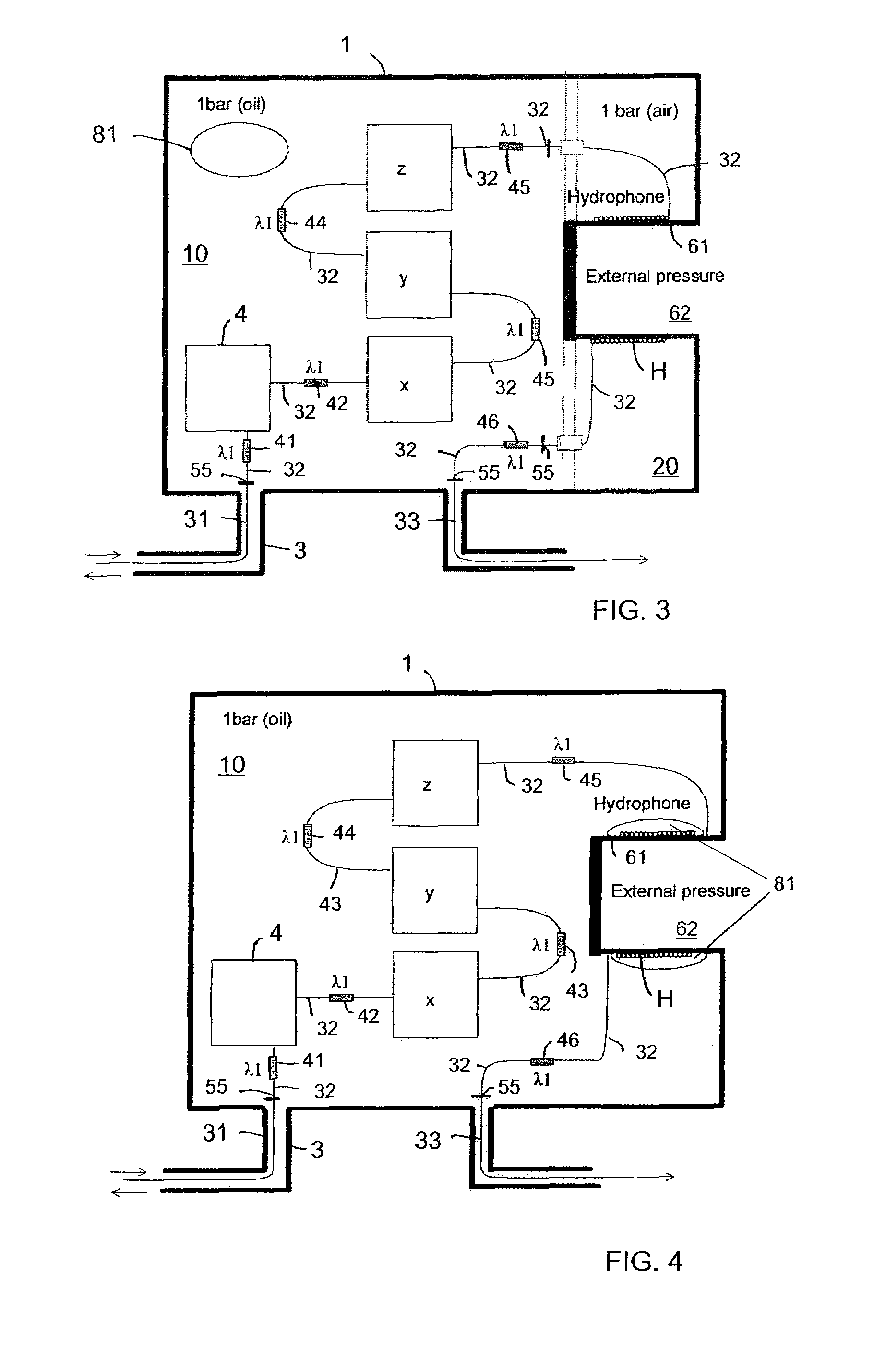
ActiveUS7551517B2Stable internal pressureSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementOptical detectionHydrophoneOcean bottom
A seismic sensor station includes a housing containing a fiber optic hydrophone and a fiber optic accelerometer that can both be made from a single length of optical fiber arranged inside the housing. The fiber optic accelerometer is arranged in a liquid / oil filled compartment of the housing for dampening of mechanical resonances in the accelerometer due to mechanical disturbances and pressure fluctuations.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
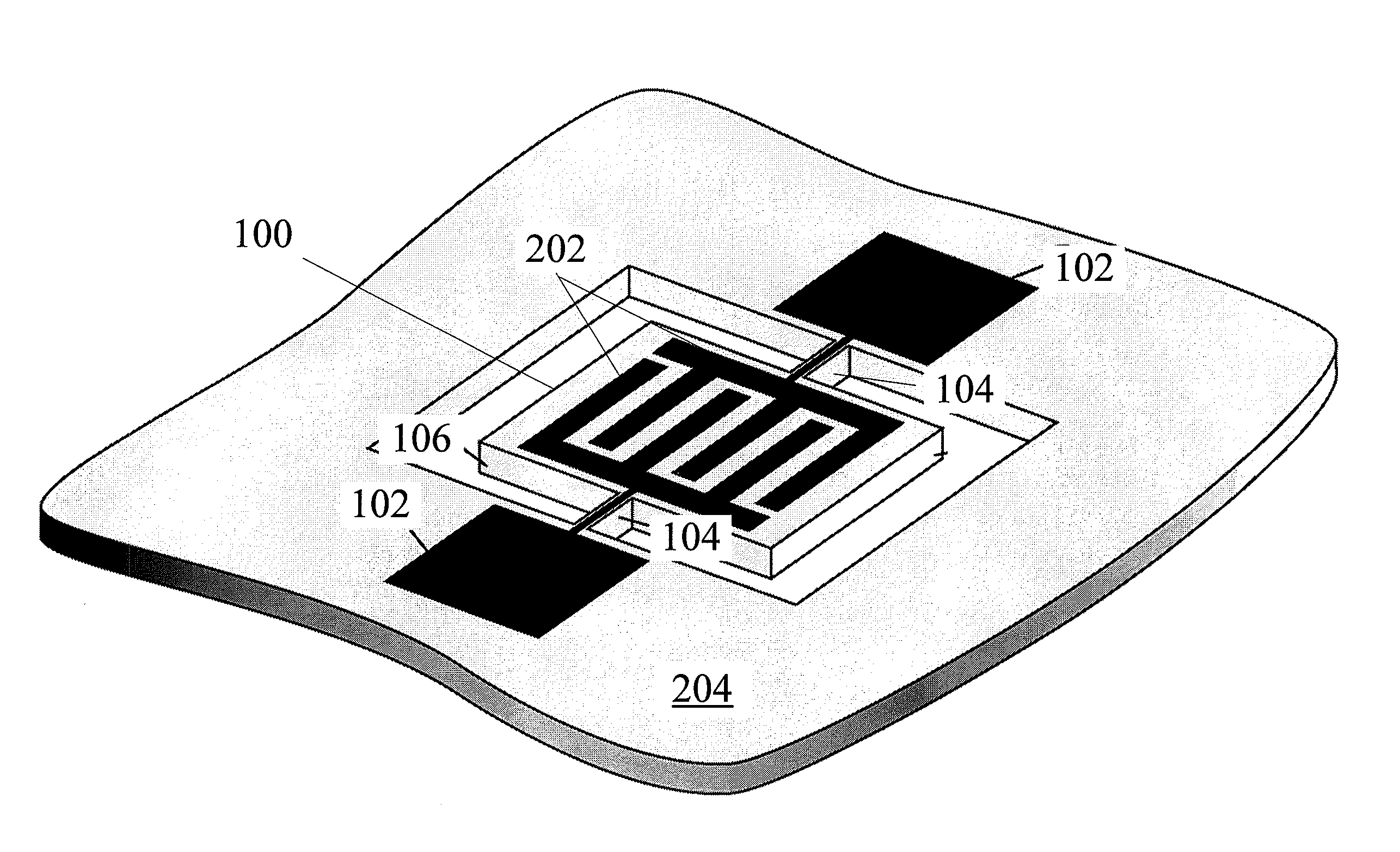
Mechanical resonator having a variable resonance frequency
InactiveUS6134964AStiffness of spring can be increasedReduce the spring rateAcceleration measurement using interia forcesImpedence networksElectricityInertial mass
A mechanical resonator has an electronically adjustable resonance frequency and is especially adapted to be used as a tunable vibration absorber. The mechanical resonator includes an inertial mass mounted on a free end of a spring, which is secured at its other end to the structure that is to be vibrationally damped. In order to vary the resonant frequency of the resonator, an electromechanical converter such as a piezoelectric element is connected to the spring and / or the inertial mass, and a displacement and / or acceleration sensor provides a sensor signal that is dependent on the respective displacement and / or acceleration of the spring and / or the inertial mass. An electronic control circuit generates an actuating signal based on the sensor signal. The actuating signal is applied to the electro-mechanical converter, which responsively exerts an adjusting force onto the spring and / or the inertial mass. The control circuit may include one or more variable amplifiers, inverters, and phase shifters, to control the actuating signal such that the adjusting force exerted by the electromechanical converter either counteracts or reinforces the bending force exerted by the inertial mass on the spring. In this manner, the effective total spring constant of the resonator can be increased or decreased relative to the inherent spring constant of the spring, whereby the resonant frequency is adjusted.
Owner:AIRBUS HELICOPTERS DEUT GMBH
Piezoelectric vibration energy collecting apparatus with resonance frequency adjustable
InactiveCN101359882AEasy to adjustOvercoming the inability to precisely adjust the resonance frequencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesElectricityAmbient vibration
The invention discloses a piezoelectric vibration energy-harvesting device with adjustable resonance frequency, which belongs to the technique field of energy conversion and collection. The device adopts a supporting substrate as a vibration structure, and collects vibration energy through a piezoelectric material fixed thereon. The device combines a fixed mass block and a movable mass block, and adjusts the resonance frequency of the device simply and accurately in a rather large range, so as to keep the mechanical resonance with the ambient vibration for maximizing the vibration energy collecting capability. The energy-harvesting device can be applied to different vibration conditions in rather large frequency range, and can be combined with a sensor for making the sensor have the self-powered capability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Hearing aid and method for adjusting a hearing aid
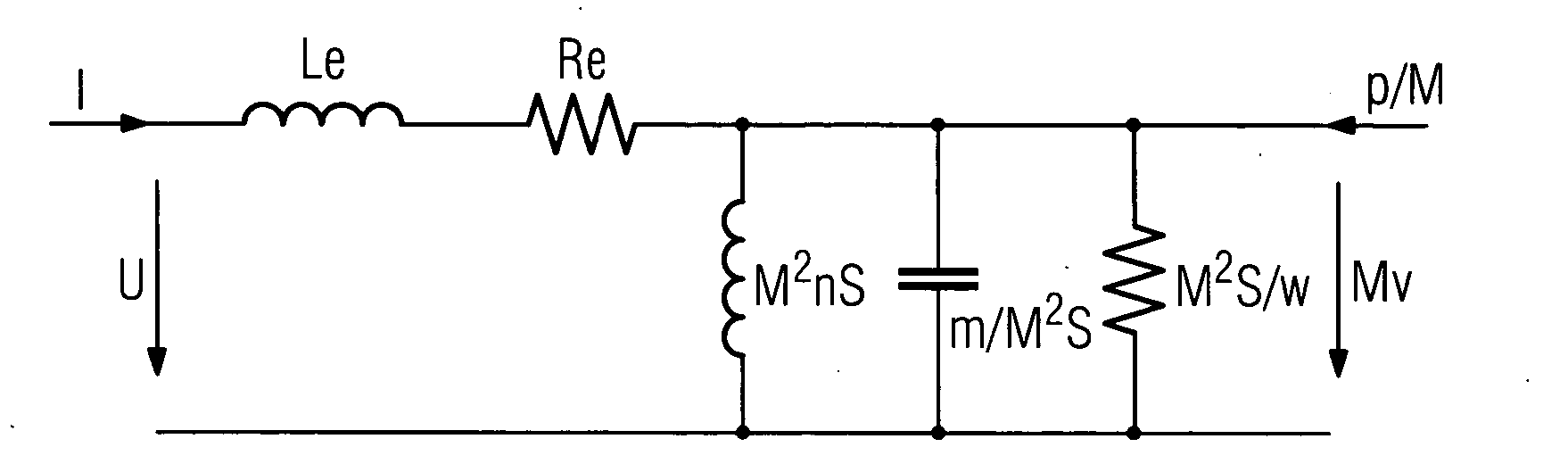
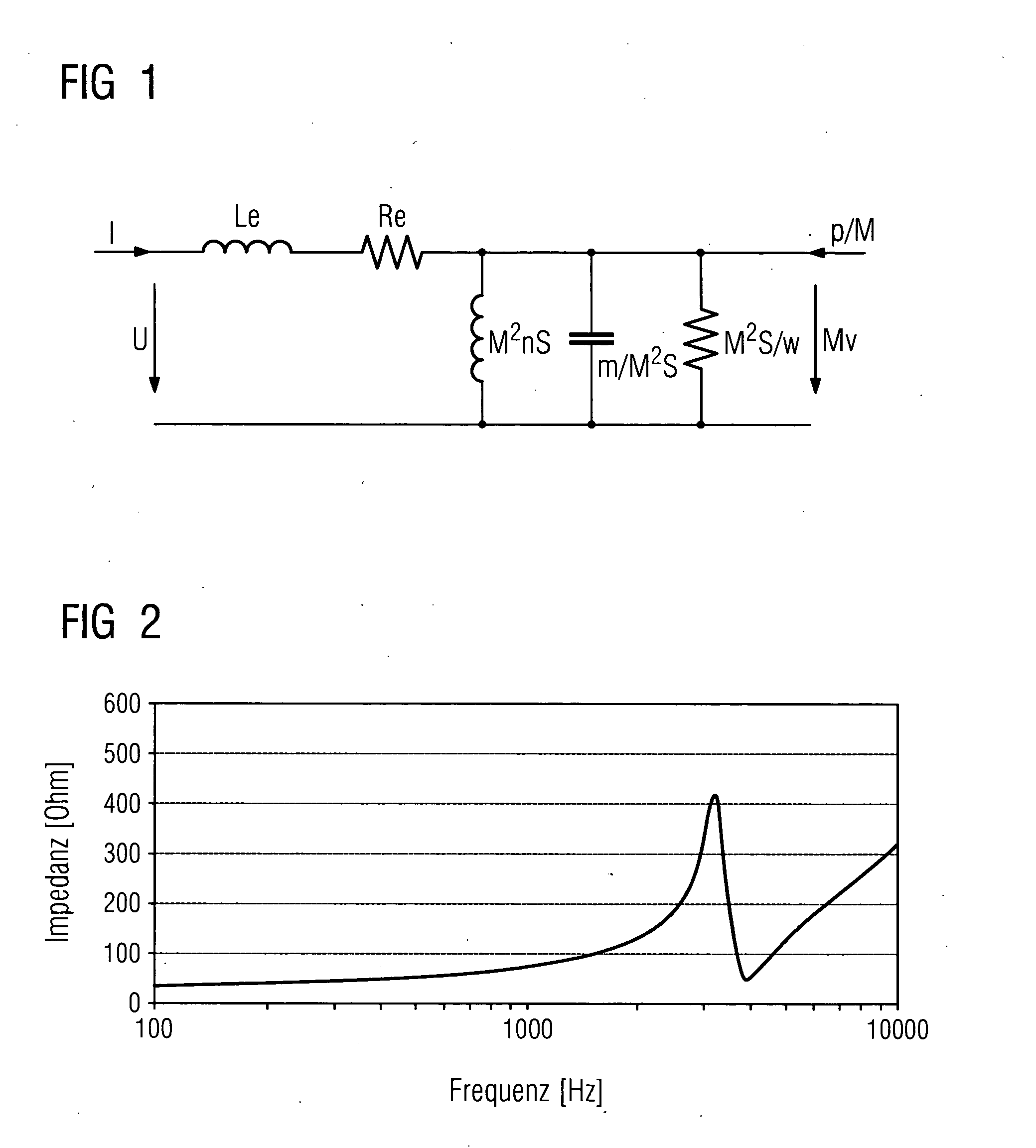
The process of adapting a hearing aid to its wearer is to be simp lified. To this end the acoustic conditions in the auditory canal, especially the acoustic impedance, are estimated by measuring the input impedance of the earpiece on the hearing aid. For adjusting the hearing aid it is worthwhile using the mechanical resonance of the system of hearing aid and auditory canal which can be detected with the aid of the input impedance. This is produced by a simplified equivalent circuit diagram from which the corresponding acoustic variables can be obtained.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Active double or multi gate micro-electro-mechanical device with built-in transistor
InactiveUS20100171569A1Multiple-port networksFrequency selective two-port networksMechanical resonanceDc ac converter
The present invention exploits the combination of the amplification, provided by the integration of a FET (or any other active device with two or more terminals), with the signal modulation, provided by the MEM resonator, to build a MEM resonator with built-in transistor (hereafter called active MEM resonator). In these devices, a mechanical displacement is converted into a current modulation and depending on the active MEM resonator geometry, number of gates and bias conditions it is possible to selectively amplify an applied signal. This invention integrates proposes to integrate transistor and micro-electro-mechanical resonator operation in a device with a single body and multiple surrounding gates for improved performance, control and functionality. Moreover, under certain conditions, an active resonator can serve as DC-AC converter and provide at the output an AC signal corresponding to its mechanical resonance frequency.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Electro-mechanical resonance loop
ActiveUS20140300425A1Reduce startup timeImprove immunityOscillations generatorsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesEngineeringMechanical resonance
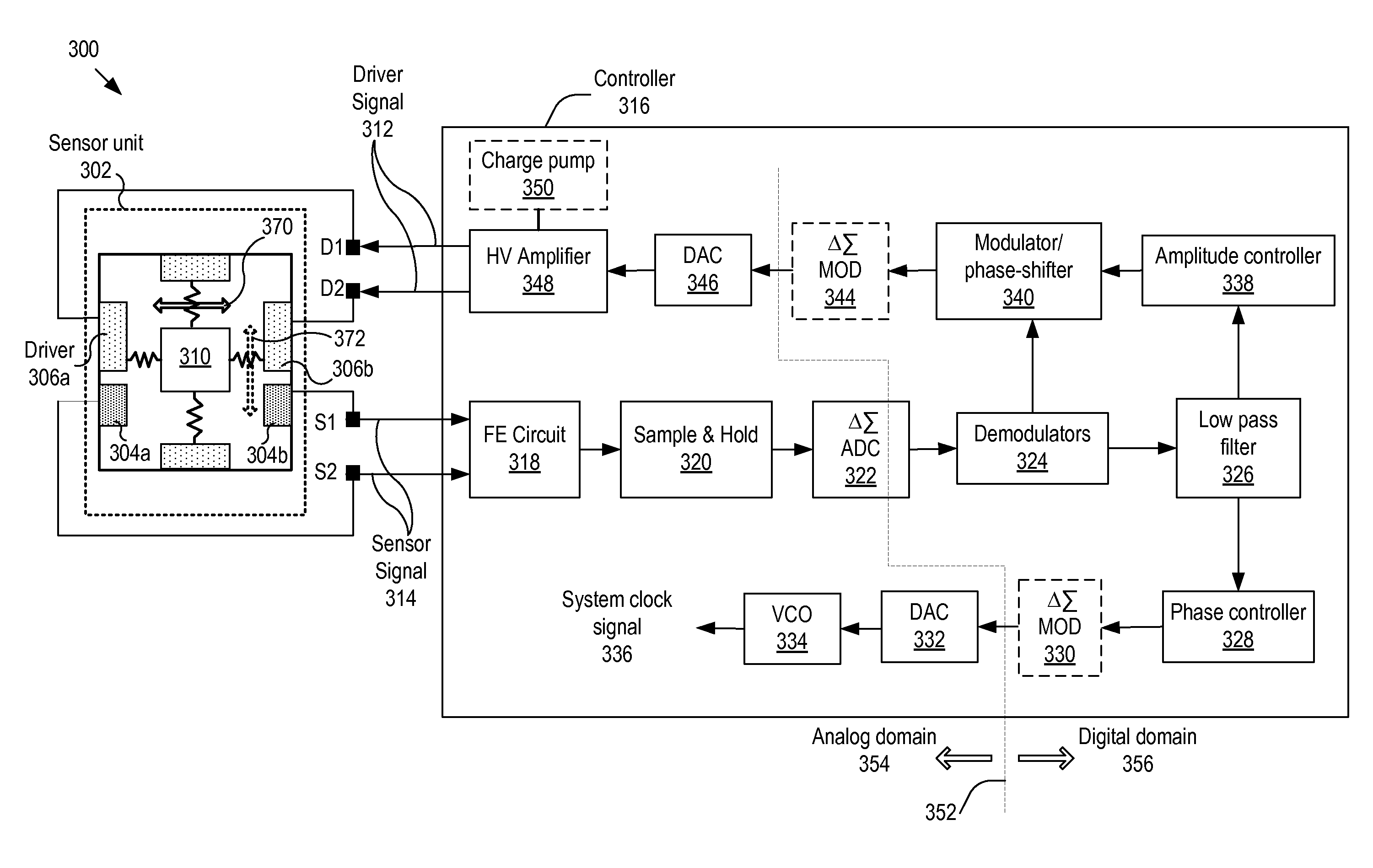
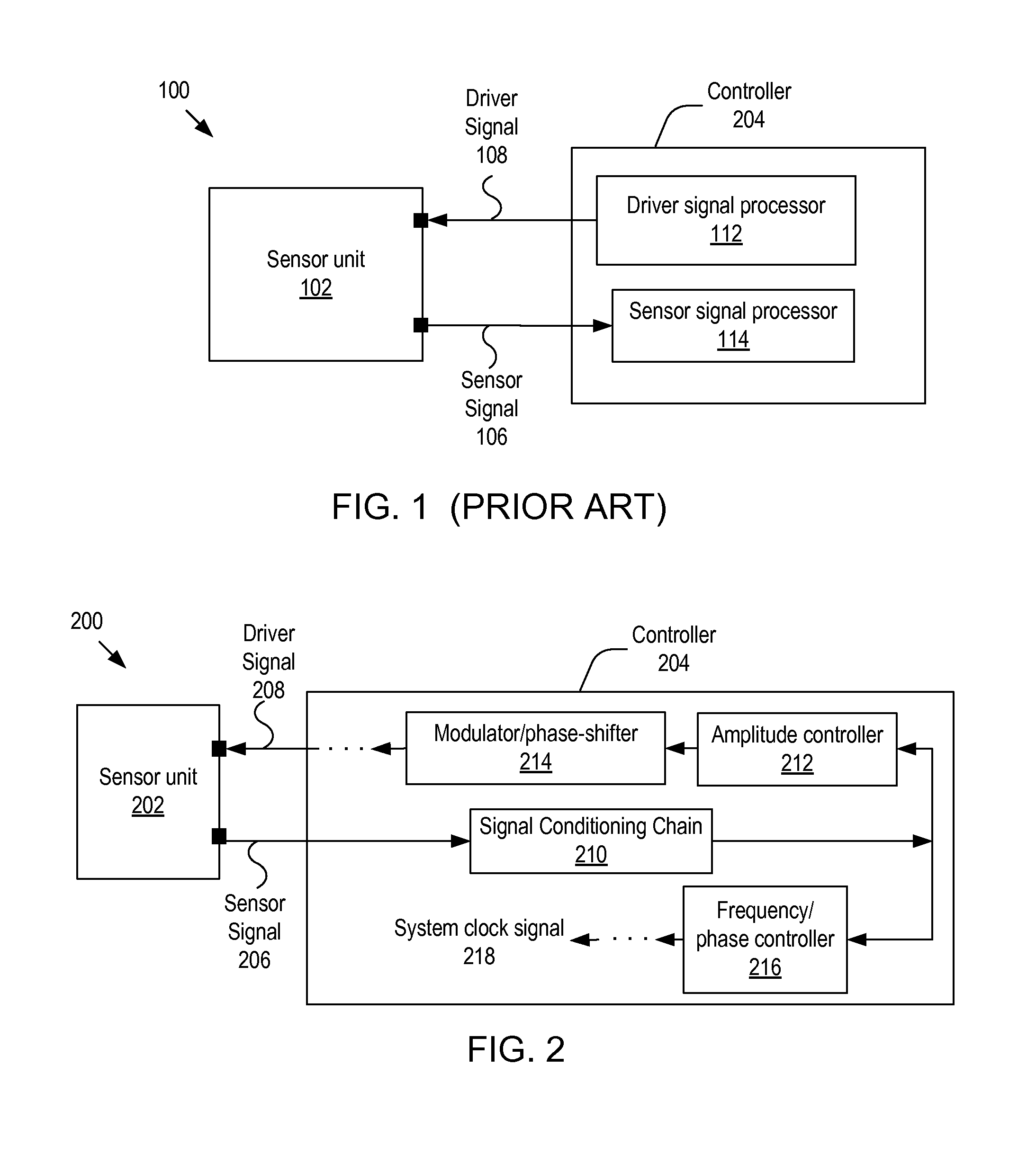
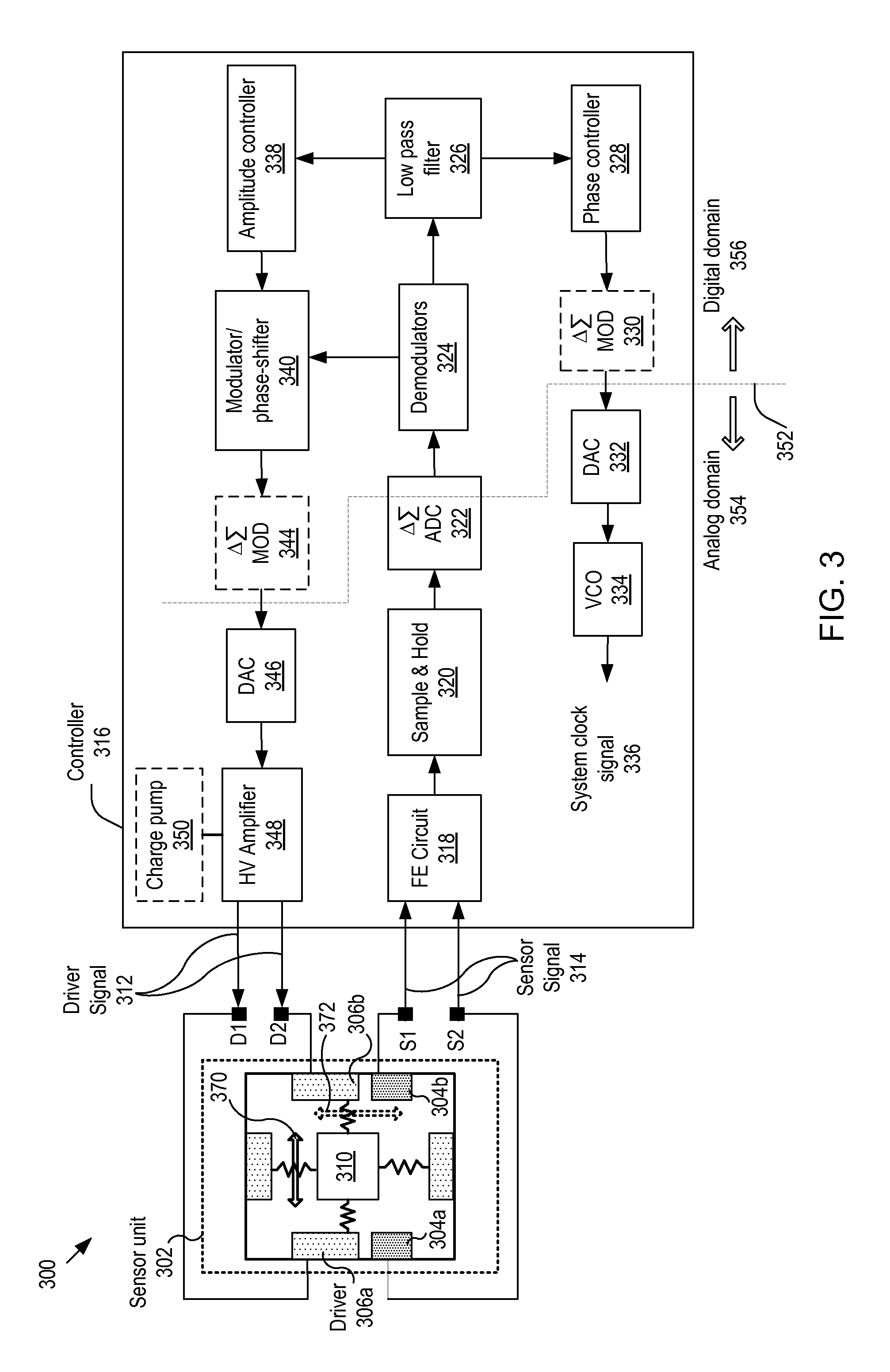
The invention relates to a controller, and more particularly, to systems, devices and methods of controlling a sensor having a resonating mass. The controller includes: an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) unit for extracting a digitized sensor signal from the sensor signal; a phase controller for generating, based on the digitized sensor signal, a phase-controlled signal that is locked in phase with the digitized sensor signal; an amplitude controller for applying a gain to the digitized sensor signal to thereby generate an amplitude-adjusted signal; a modulator for modulating the amplitude-adjusted signal to thereby generate a modulated signal; and a phase shifter for shifting the phase of the modulated signal by 90 degrees. The output signal from the phase shifter is amplified and input to the drive for exciting the resonating mass, to thereby form a closed resonance loop for controlling the oscillation amplitude of the resonating mass.
Owner:HANKING ELECTRONICS LTD
Robot joint vibration analyzing and inhibiting method based on flexible dynamical model
InactiveCN108638056AExperimental modal analysis method is simple and easySatisfied with the test resultsProgramme-controlled manipulatorExperimental methodsMechanical resonance
The invention discloses a robot joint vibration analyzing and inhibiting method based on a flexible dynamical model. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing the flexible dynamical model of a robot joint and analyzing the reason that the robot joint vibrates; (2) acquiring vibrating model information of the joint by means of ABAQUS finite element software, acquiring monitoring point arrangement of a force hammer excitation experimental method based on the vibrating model information of ABAQUS, acquiring modal information of the robot joint and further analyzing the control influence of resonant frequency on the robot; (3) adopting a double T-shaped trapped wave filter with an adjustable trapped wave depth and a width parameter; (4) solving the optimum trapped wave depth of the double T-shaped trapped wave filter by simulation; and (5) setting proper parameters on an alternating current servo system of the robot joint, and starting the rapped wave function of the double T-shaped trapped wave filter so as to inhibit the vibration of the robot joint. The invention provides the robot joint vibration analyzing and inhibiting method based on the flexible dynamical modelfor solving the problem of mechanical resonance often caused by a flexible transmission link in a transmission system of an industrial robot.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com