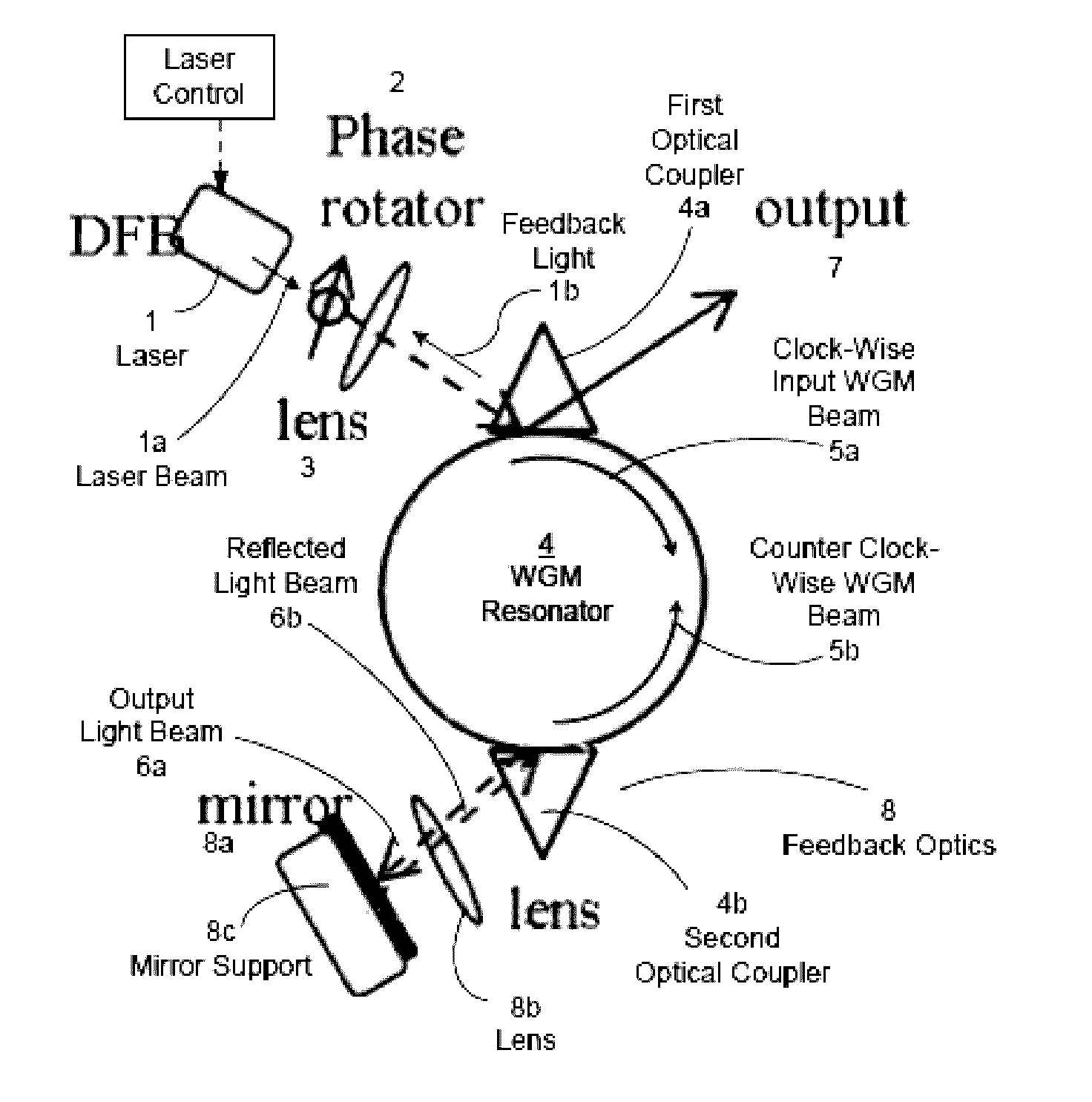
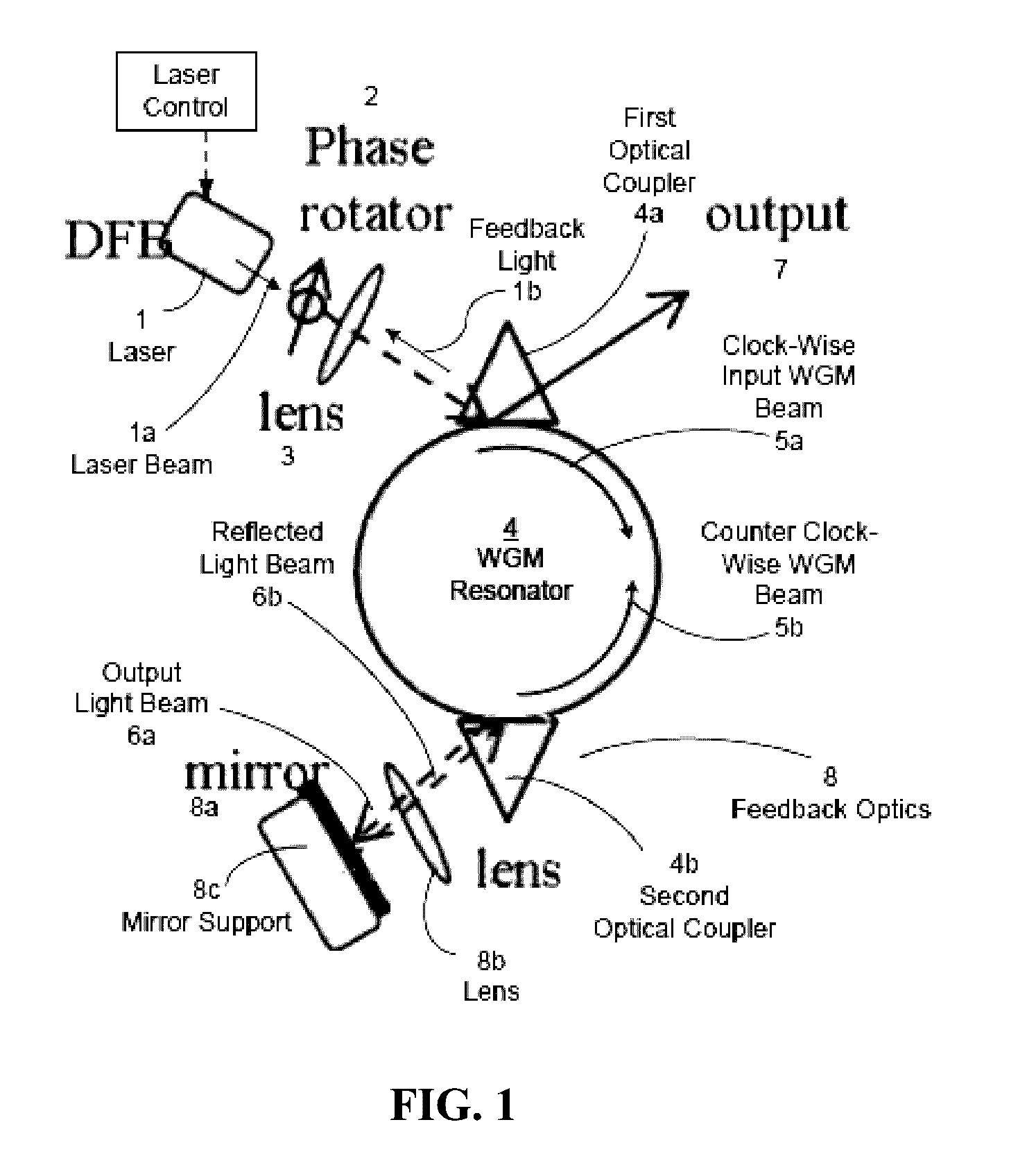
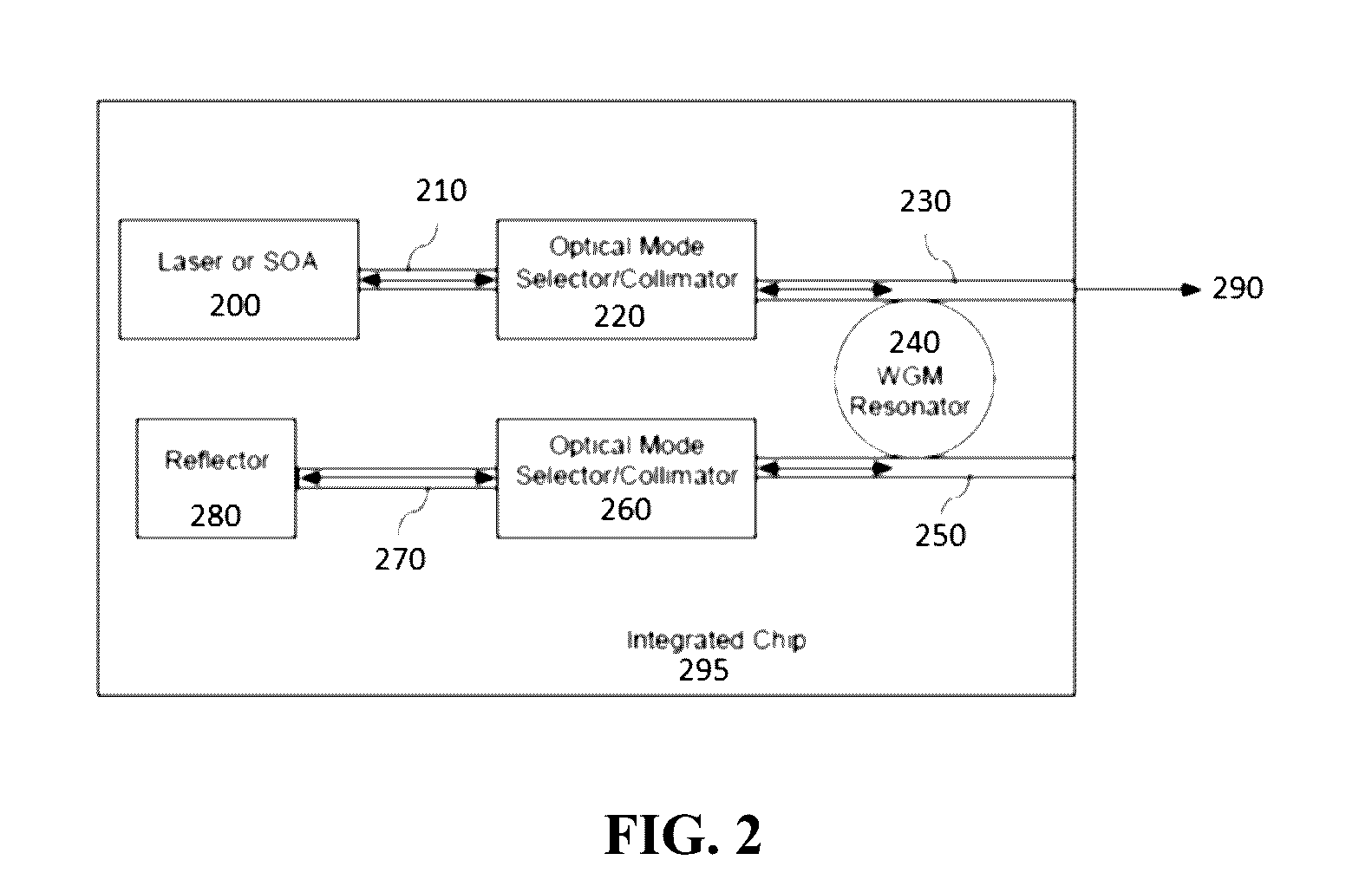
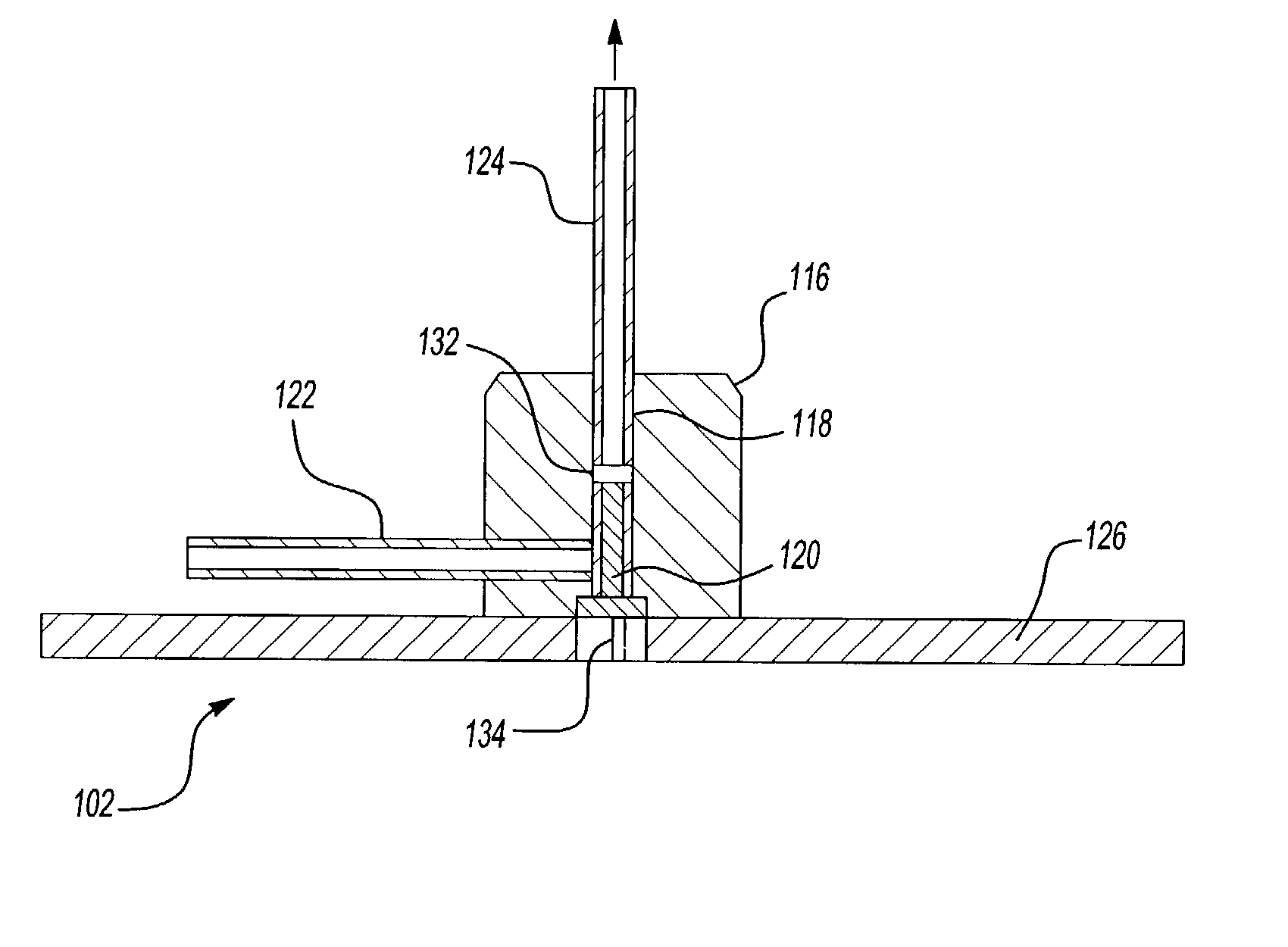
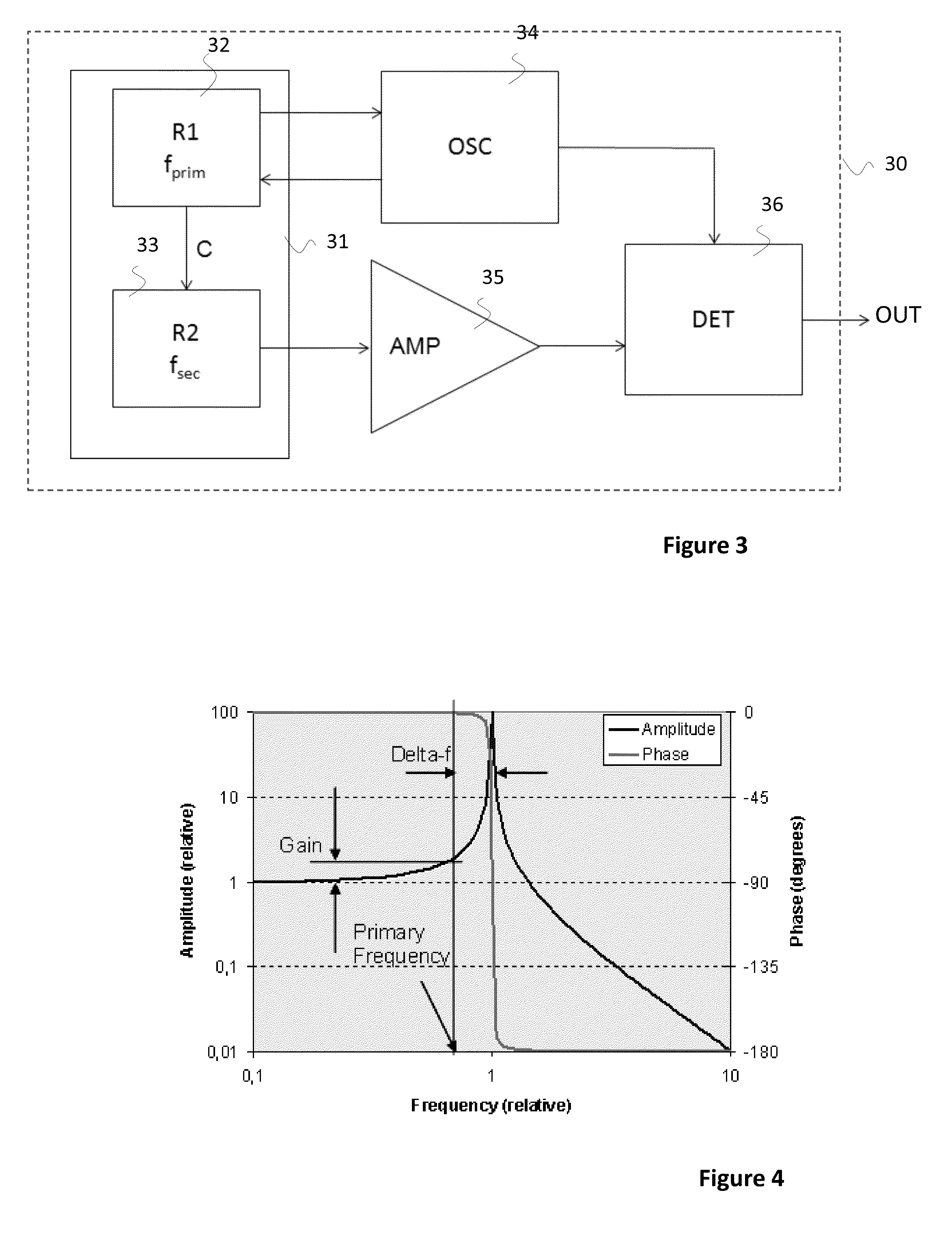
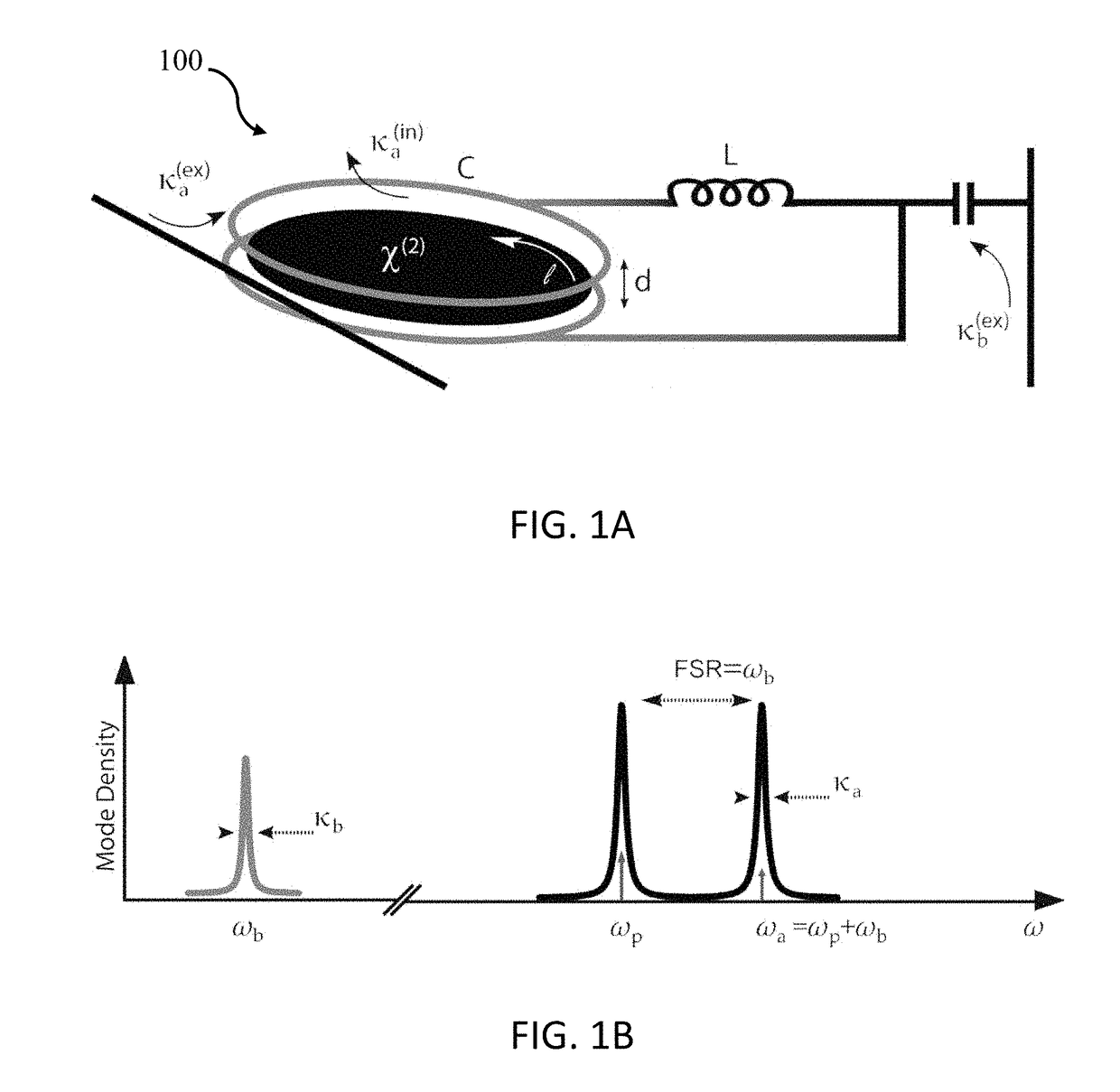
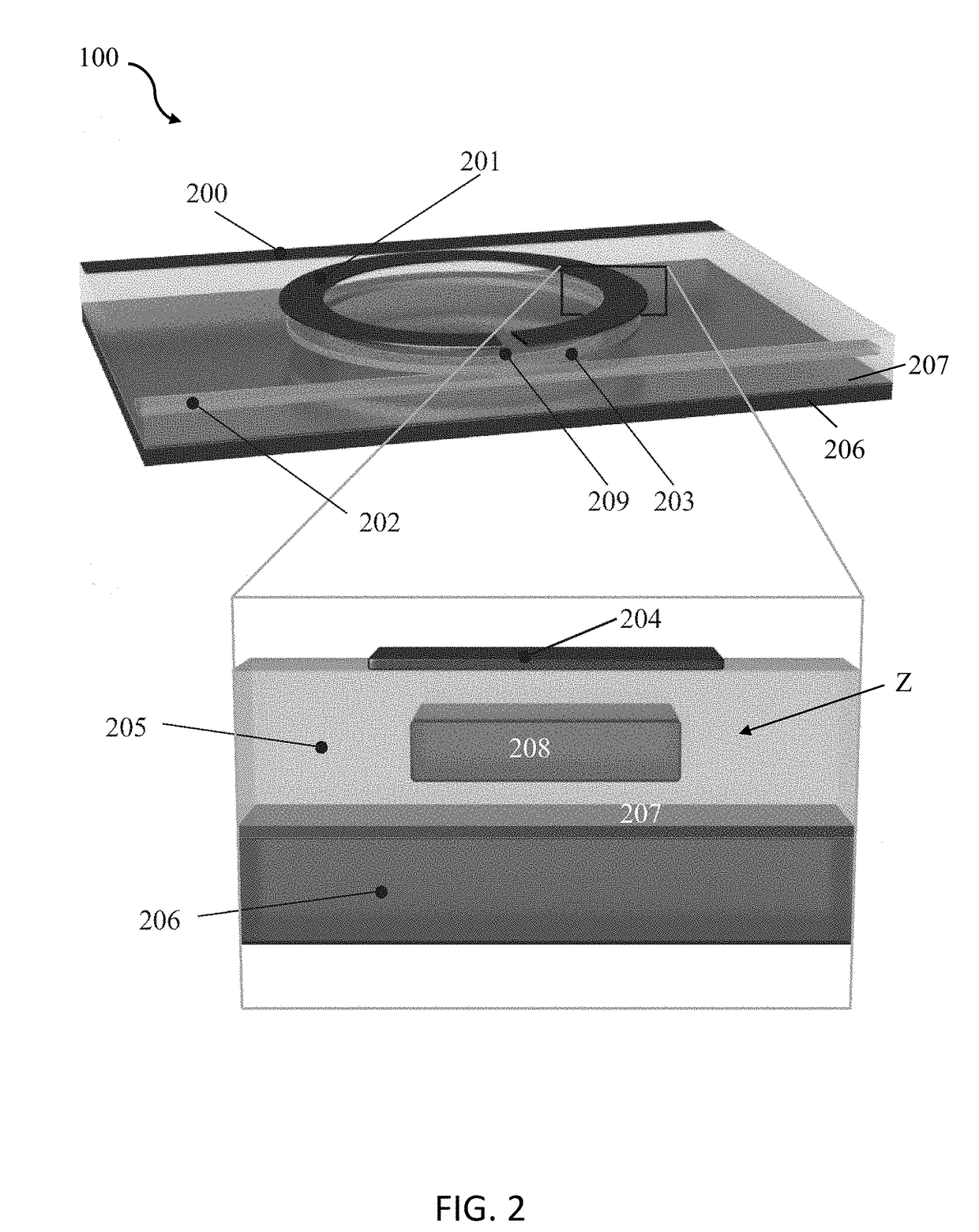
Patents
Literature
278 results about "Helical resonator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A helical resonator is a passive electrical component that can be used as a filter resonator. Physically, a helical resonator is a wire helix surrounded by a square or cylindrical conductive shield. One end of the helix is connected to the shield and the other end is left open (Weston, 2001, p. 660). The device works like a coaxial resonator, but it is much shorter because the helical inner conductor reduces the velocity of wave propagation (Lancaster, 2006, p. 99).
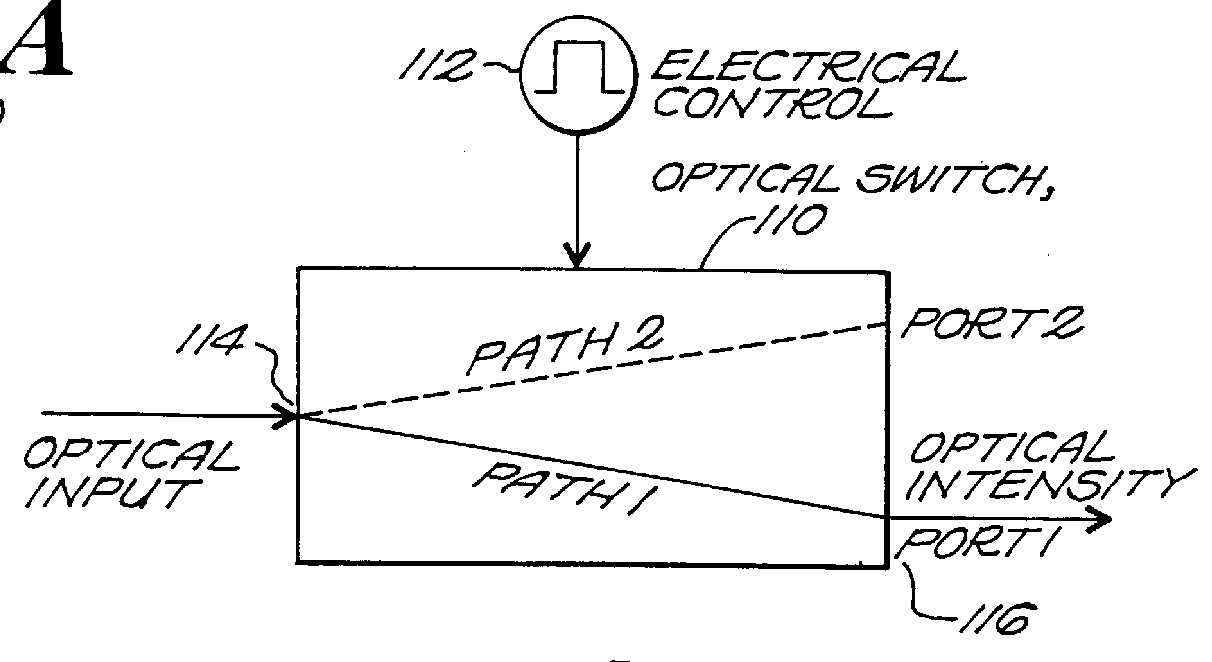
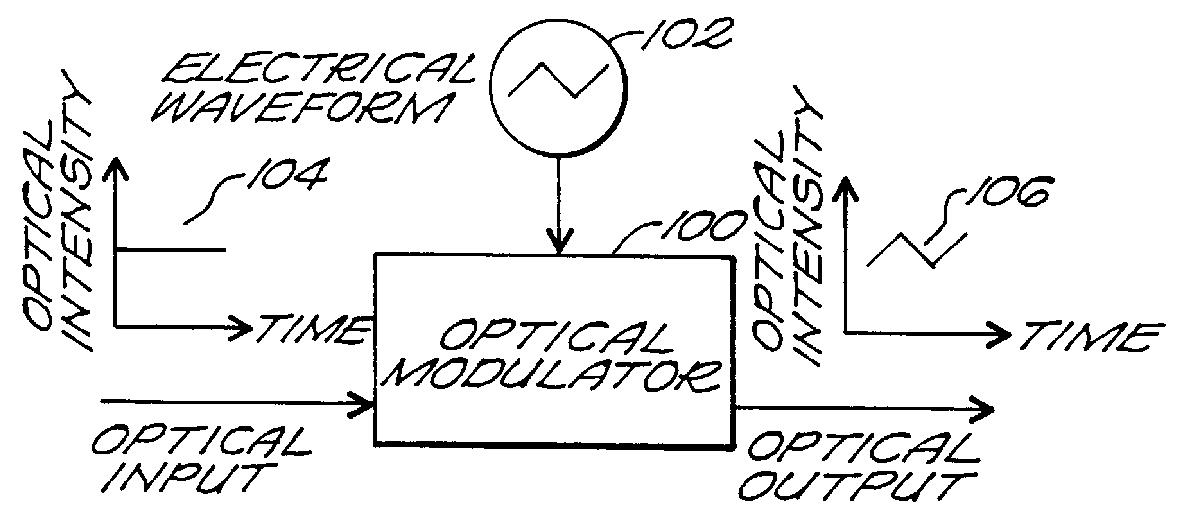
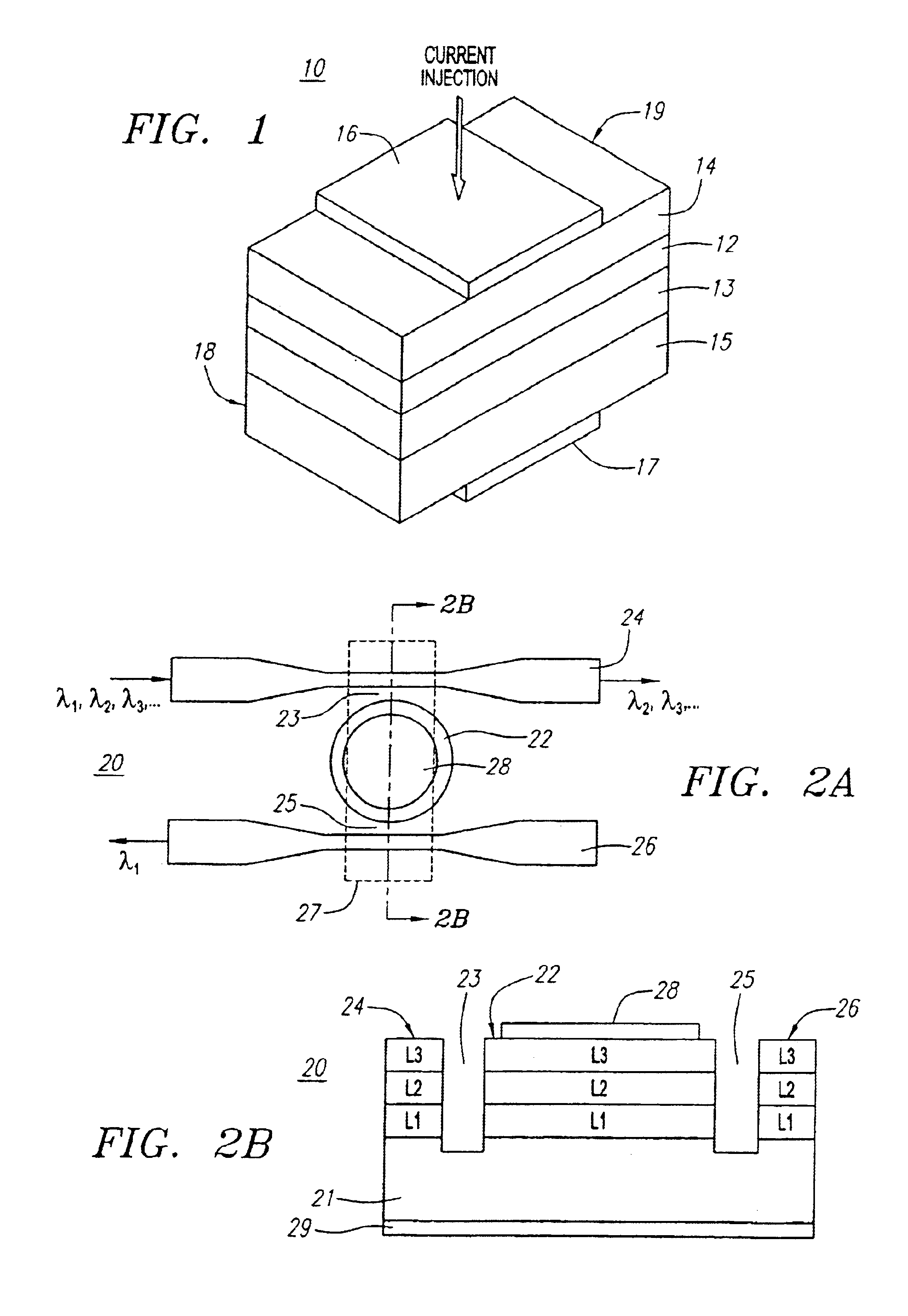
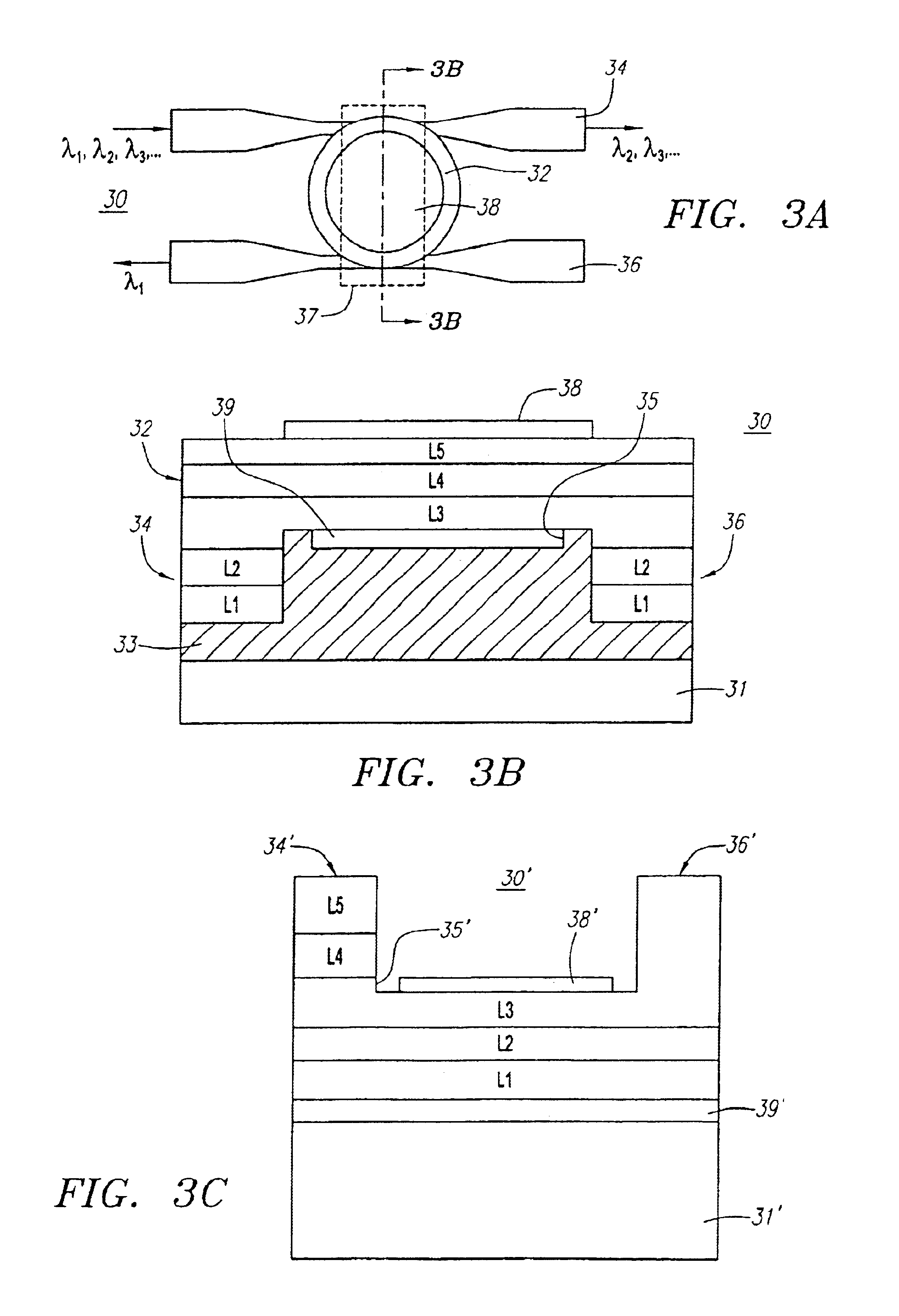
Resonator modulators and wavelength routing switches
InactiveUS6052495ASmall sizeImprove responseCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsClosed loopRefractive index
The invention provides an optical switch and modulator which uses a closed loop optical resonator. The optical resonator is a dielectric cavity whose primary function is to store optical power. Various structures are possible, and a particularly advantageous one is a ring shaped cavity. The wavelength response at the output port of a ring resonator side coupled to two waveguides is determined by the details of the resonator, and the coupling between the resonator and the waveguides. By coupling to adjacent resonators, the modulator response can be improved over that of a single resonator. One such improvement is in modulator efficiency, which is defined as the ratio of the change in optical intensity at the output, to a change in absorption in the ring waveguides. Absorption is used for switching and modulation without incurring significant optical attenuation. Another improvement involves making the resonance insensitive to small deviations in wavelength or index change. The latter improves fabrication tolerances and compensates for possible drift of the signal wavelength. Collectively, the behavior of multiple coupled resonators yields higher order responses.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Wireless power transmission apparatus
ActiveUS20130221757A1Lower resonance frequencySmall sizeElectromagnetic wave systemCharging stationsElectric power transmissionResonance
A wireless power transmission apparatus includes: a transmission resonator installed in one side wall within a specific space and configured to comprise a transmission feeding loop for transmitting impedance matching and power and receive and transmit the impedance matching and power using the transmission feeding loop. Further, the wireless power transmission apparatus includes a relay resonator installed in another side wall within the specific space and configured to have a resonant frequency identical with that of the transmission resonator and store energy in the specific space by generating mutual resonance through a resonance characteristic with the transmission resonator; and one or more reception resonators installed within the specific space and configured to have a resonant frequency identical with that of the transmission resonator and receive the energy stored in the specific space.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Tuning mechanical resonators for electrical filter
InactiveUS6307447B1Multiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyHelical resonatorPhysics
The present invention is a method for adjusting different resonant frequencies of a plurality of mechanical resonators formed on a common substrate, in a case where the resonant frequencies of the resonators are a function of each resonator thickness. According to this method the resonators are each formed with an etchable top electrode layer which includes a material having different etching properties as a topmost layer for each of the resonators having different resonant frequencies. By selectively etching these etchable layers one at a time in the presence of the others, one may adjust the resonant frequencies of each of the resonators without need to mask the resonators during the etching process. Associated with this method there is a resonator structure having a top electrode structure having a topmost layer having different etching characteristics for different resonators.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tunable piezoelectric micro-mechanical resonator
InactiveUS6943484B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksResonanceEngineering
One aspect of the invention relates to a composite member for a resonator having an active piezoelectric element and a passive piezoelectric element. The active piezoelectric element causes the resonator to vibrate and detects the frequency of the vibration. The passive piezoelectric element changes the frequency of the vibration. Another aspect of the invention relates to a method for controlling a resonator with composite member having a substrate carrying a composite piezoelectric element. The composite piezoelectric element includes an actuator element, a sensor element and a passive element. The method comprises inducing a resonance within the composite member with the actuator element, detecting the resonance with the sensor element, and altering the resonance by altering the electromechanical coupling of the passive element. Additional aspects and benefits of the invention are also given.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF THE
Compact LIDAR System
ActiveUS20160299228A1Linewidth also decreaseImprove linearityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersOptical propertyWhispering gallery
An FM LIDAR system is described that includes a frequency modulated LIDAR system that incorporates a laser source that is optically coupled to a whispering gallery mode optical resonator. Light from the laser that is coupled into the whispering gallery mode optical resonator is coupled back out as a returning counterpropagating wave having a frequency characteristic of a whispering gallery mode of the optical resonator. This returning wave is used to reduce the linewidth of the source laser by optical injection. Modulation of the optical properties of the whispering gallery mode optical resonator results in modulation of the frequency of the frequencies supported by whispering gallery modes of the resonator, and provides a method for producing highly linear and reproducible optical chirps that are highly suited for use in a LIDAR system. Methods of using such an FM LIDAR system and vehicle assisting systems that incorporate such FM LIDAR systems are also described.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Flow detectors having mechanical oscillators, and use thereof in flow characterization systems
ActiveUS20030000291A1Ability to useNormalize signalAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComponent separationTuning forkEngineering
An improved system, device and method for characterizing a fluid sample that includes injecting a fluid sample into a mobile phase of a flow characterization system, and detecting a property of the fluid sample or of a component thereof with a flow detector comprising a mechanical resonator, preferably one that is operated at a frequency less than about 1 MHz, such as a tuning fork resonator.
Owner:MEAS FRANCE
Low noise figure radiofrequency device
InactiveUS7738853B2Small sizeMinimizing volume of cavityResonant long antennasSubstation equipmentLow noiseCoaxial resonators
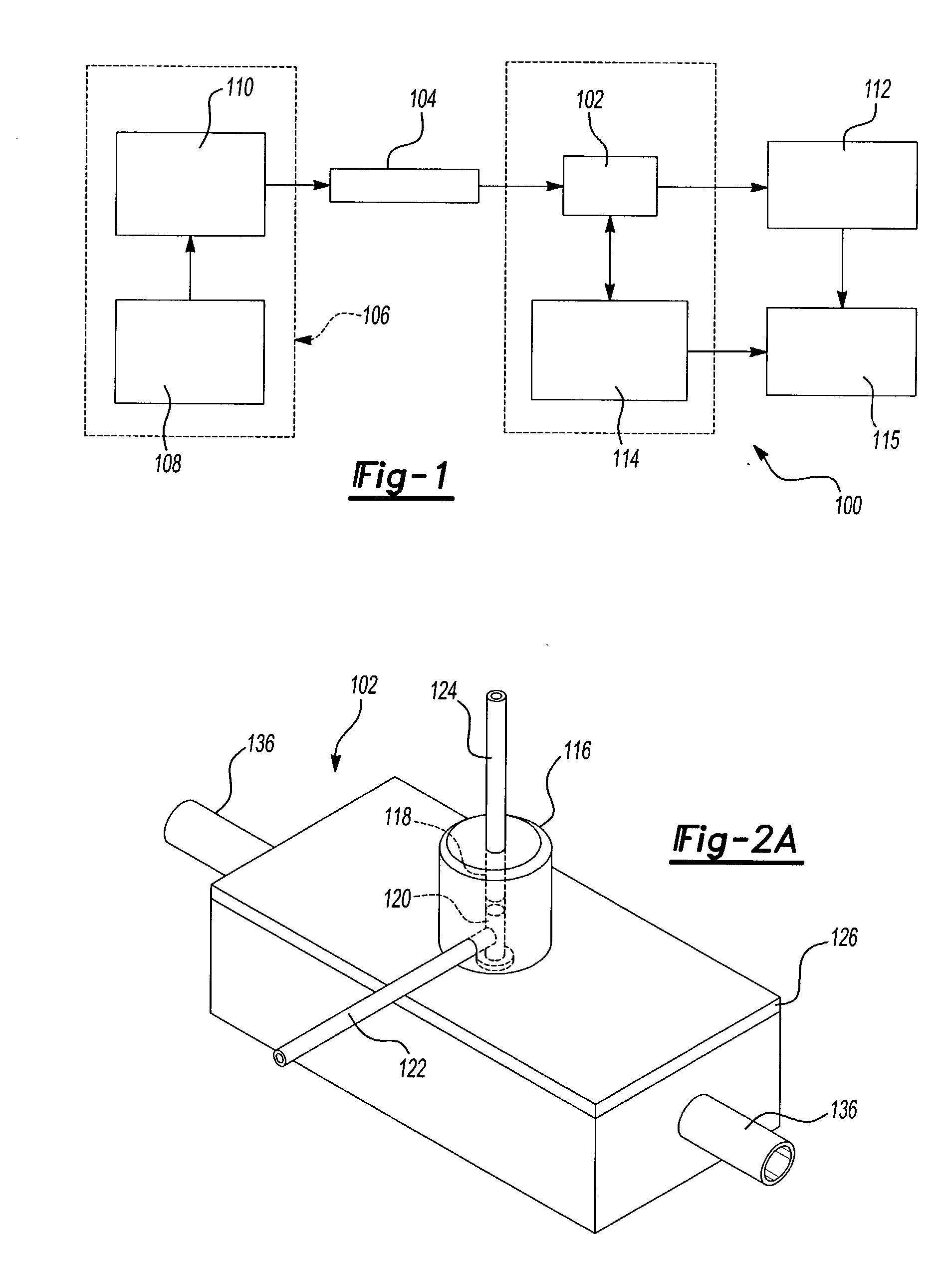
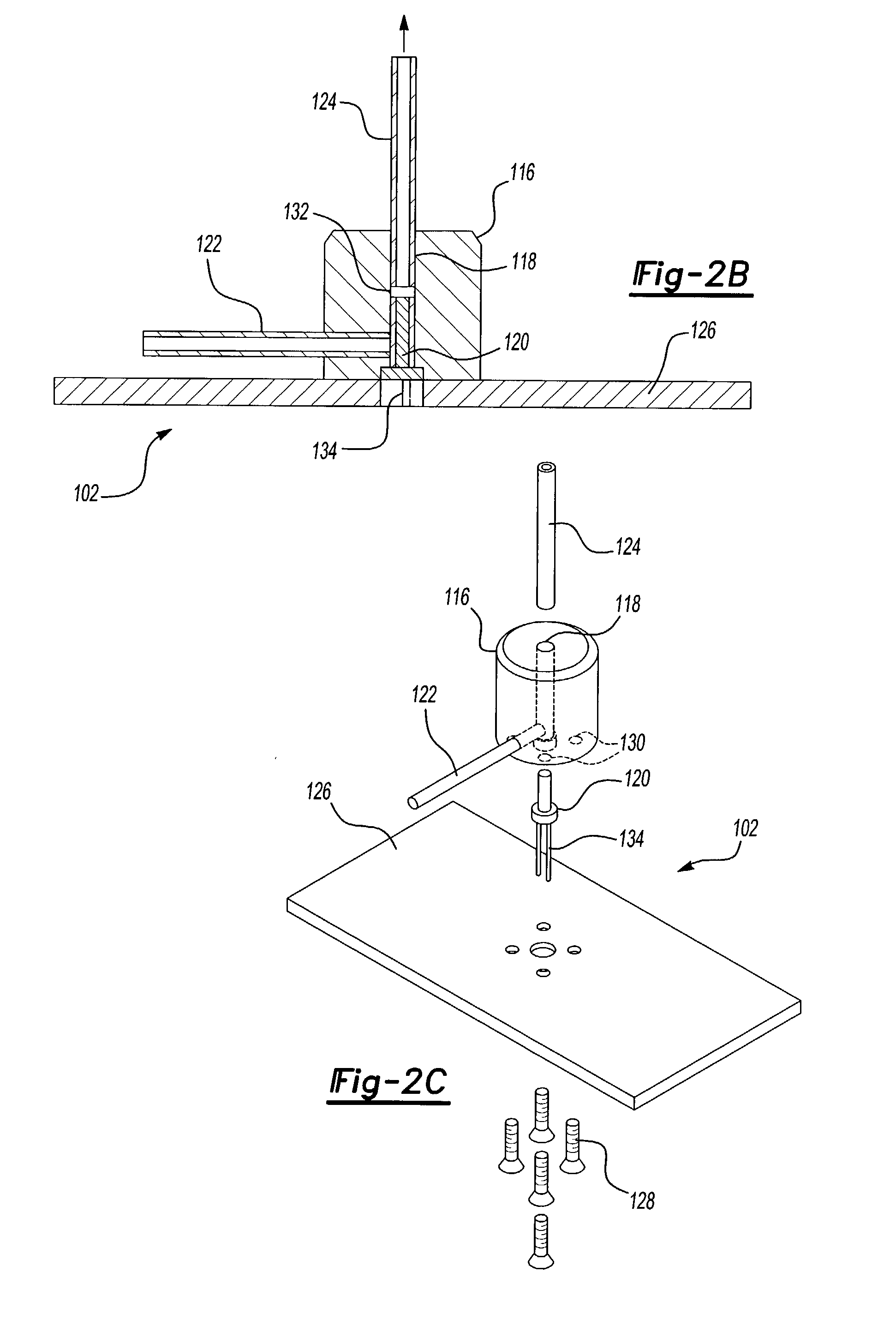
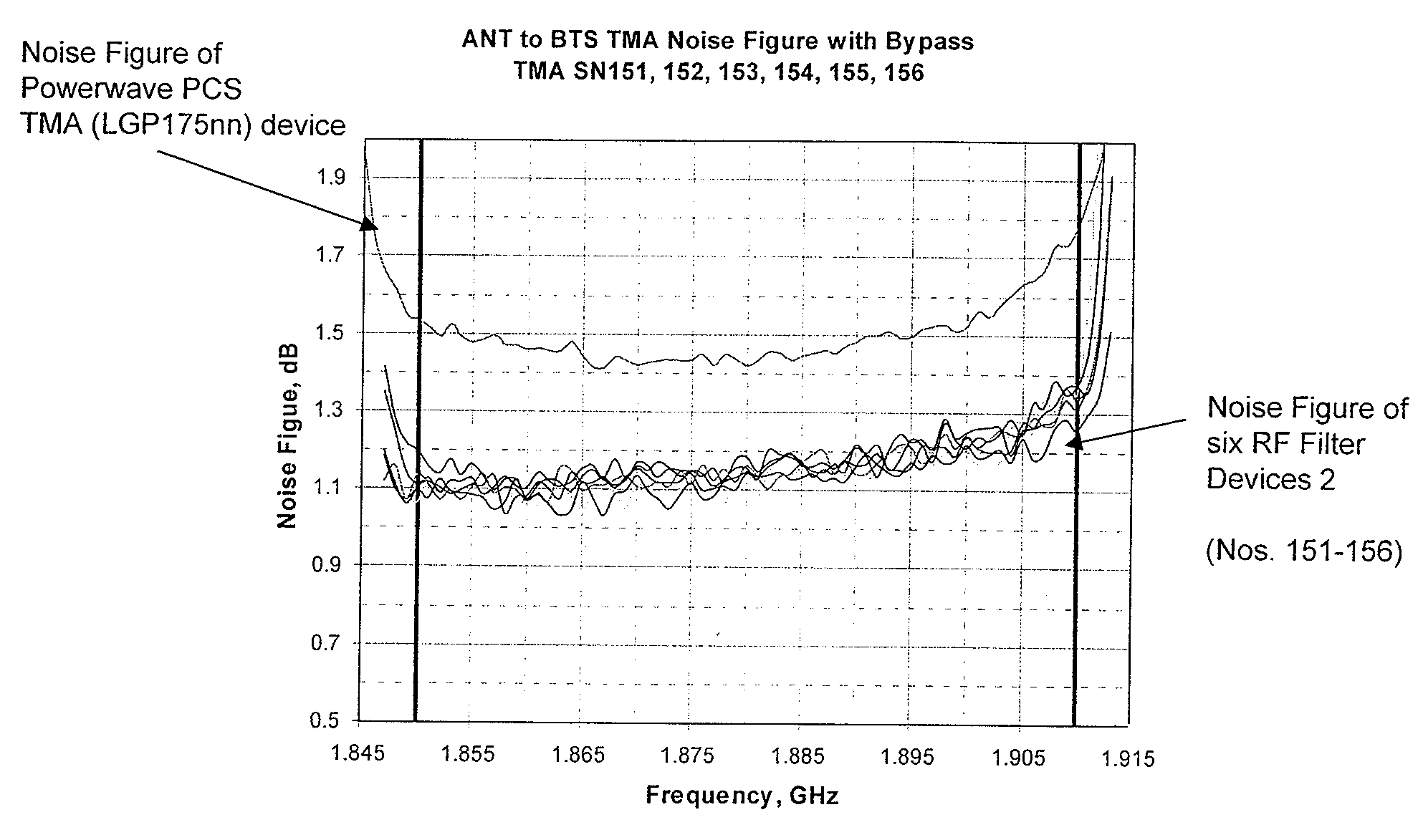
A RF device such as a tower mounted amplifier (TMA), mast-head amplifier (MHA), or Tower Mounted Boosters (TMB) includes a housing having a plurality of cavities and an input and an output, the input being coupled to the antenna and the output being coupled to a base station. The housing includes a transmission path holding multiple coaxial resonators. The housing further includes multiple receive paths including at least one path having a plurality of cavities, each cavity containing a dielectric resonator. The metallic transmit resonator nearest the antenna input is coupled to the first dielectric resonator via a common resonant wire. The last dielectric resonator in the receive path is coupled to a first metallic resonator of a downstream clean-up filter via another common resonant wire.
Owner:ANTONE WIRELESS CORP
Incremental tuning process for electrical resonators based on mechanical motion
InactiveUS6339276B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksEtchingHelical resonator
The present invention is a method for adjusting the resonant frequency of a mechanical resonator whose frequency is dependent on the overall resonator thickness. Alternating selective etching is used to remove distinct adjustment layers from a top electrode. One of the electrodes is structured with a plurality of stacked adjustment layers, each of which has distinct etching properties from any adjacent adjustment layers. Also as part of the same invention is a resonator structure in which at least one electrode has a plurality of stacked layers of a material having different etching properties from any adjacent adjustment layers, and each layer has a thickness corresponding to a calculated frequency increment in the resonant frequency of the resonator.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
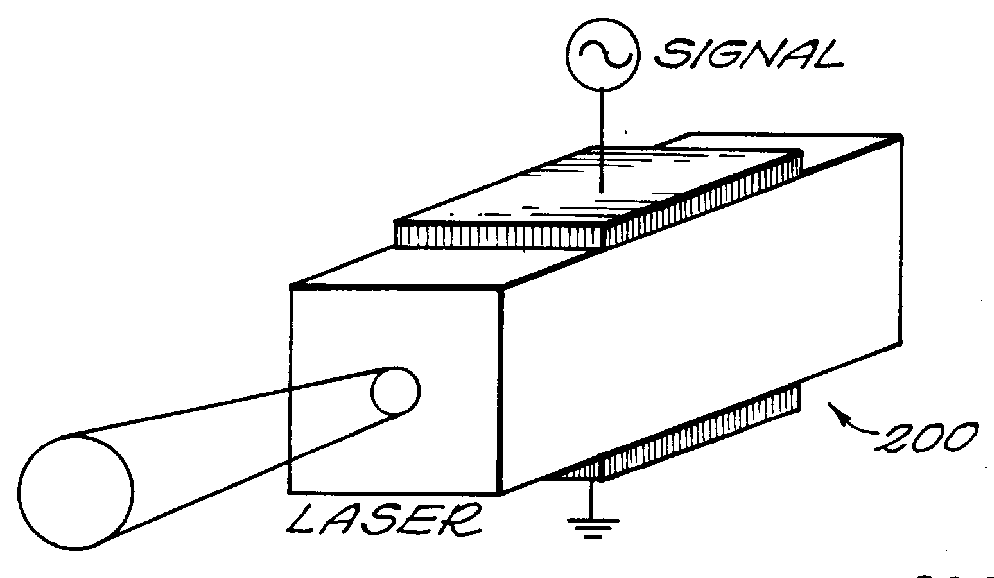
Wavelength tunable laser
InactiveUS6891865B1Increase speedBroad band wavelength tuningLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsResonance wavelengthWaveguide
A wavelength tunable laser comprising a laser diode and a closed external cavity formed by one or more optical resonators either horizontally or vertically coupled to adjacent waveguides. The optical resonator primarily functions as a wavelength selector and may be in the form of disk, ring or other closed cavity geometries. The emission from one end of the laser diode is coupled into the first waveguide using optical lens or butt-joint method and transferred to the second waveguide through evanescent coupling between the waveguides and optical resonator. A mirror system or high reflection coating at the end of the second waveguide reflects the light backwards into the system resulting in a closed optical cavity. Lasing can be achieved when the optical gain overcomes the optical loss in this closed cavity for a certain resonance wavelength which is tunable by changing the resonance condition of the optical resonator through reversed biased voltage or current injection. Multiple optical resonators may be used to reduce the lasing threshold and provide higher power output. With monolithic integration, more optical devices can be integrated with the tunable laser into the same substrate to produce optical devices that are capable of more complex functions, such as tunable transmitters or waveguide buses.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC +1
Variable wavelength laser light source
InactiveUS6047008ALaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical reflectionImage resolution
A variable wavelength laser light source to improve the resolution of the outgoing light and output only pure laser light without the natural emitted light has an optical amplification element (laser) 11, a first optical reflector 12 at one end surface 11a of the optical amplification element 11, and a wavelength selection element (diffraction grating) 13 at the other end surface 11b of the optical amplification element 11 which selects and outputs the desired wavelength light emitted by the optical amplification element 11. A second optical reflector 14 receives the outgoing light from the wavelength selection element 13 to form the optical resonator with the first optical reflector 12. A first rotating mechanism 15 rotates the second optical reflector 14 around its axis, and a second rotating mechanism 16 connected to the first rotating mechanism 15 rotates the second optical reflector 14 around a second axis 16a remote from the second optical reflector 14 by rotating the first rotating mechanism.
Owner:ANDO ELECTRIC CO LTD
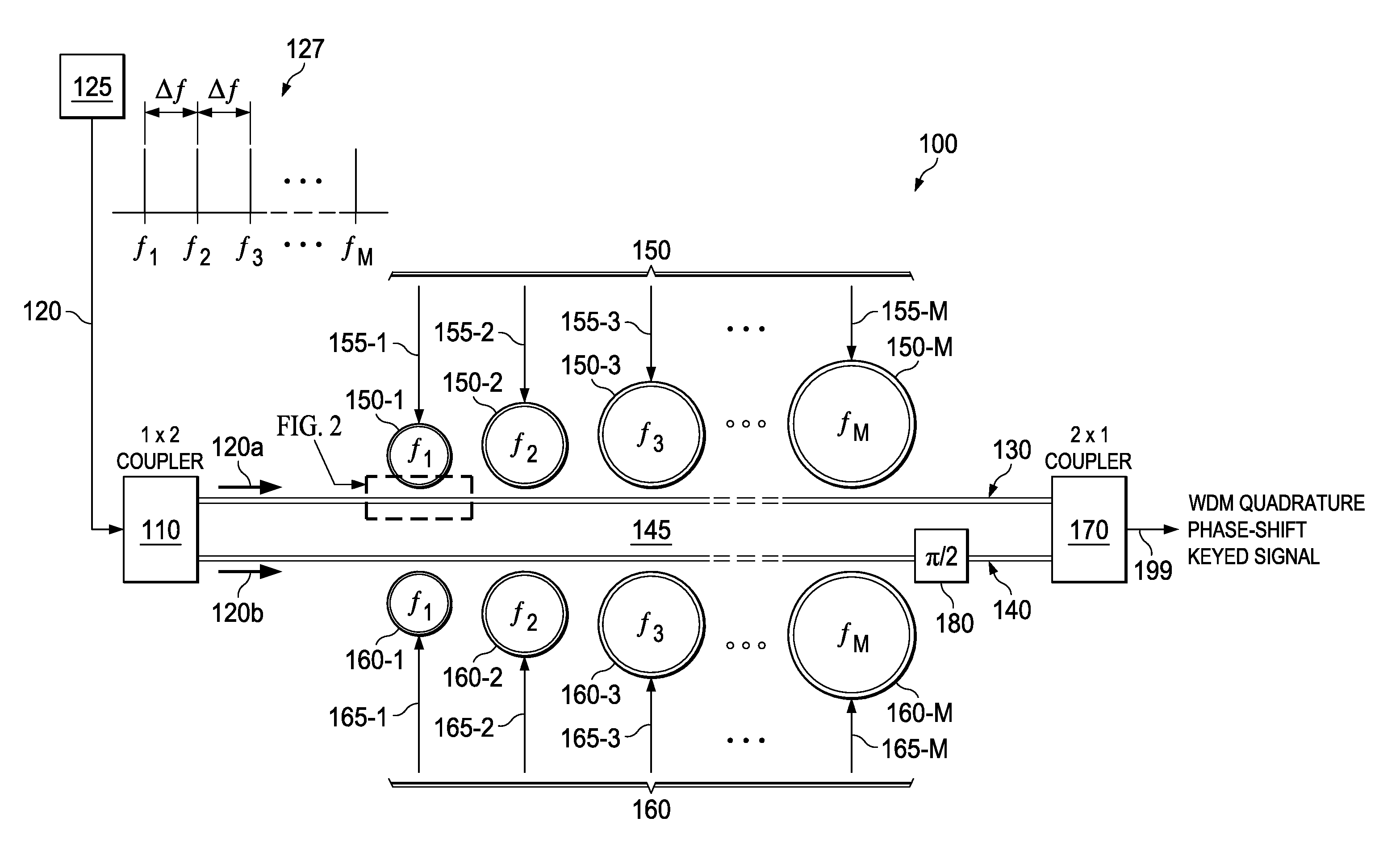
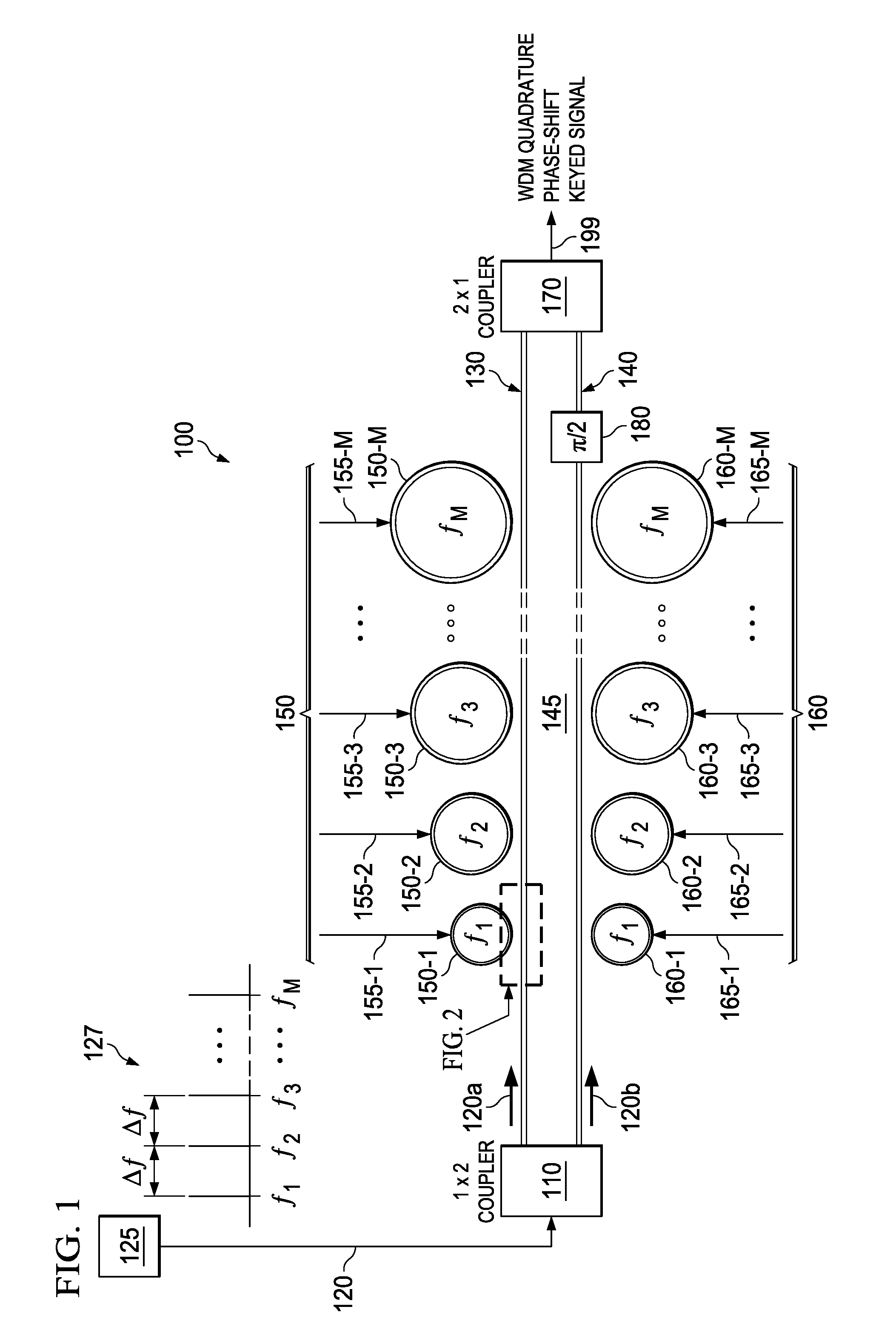
Advanced modulation formats using optical modulators
ActiveUS20140003761A1Wave amplification devicesOptical light guidesOptical frequenciesPlanar substrate
A system, e.g. an optical modulator, includes an optical waveguide and a plurality of optical resonators. The optical waveguide is located along a surface of a planar substrate. The plurality of optical resonators is also located along the surface and coupled to the optical waveguide. Each of said optical resonators is configured to resonantly couple to the optical waveguide at a different optical frequency.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Hybrid triple-mode ceramic/metallic coaxial filter assembly
A hybrid filter assembly is provided having a first ceramic triple-mode mono-block resonator, a second ceramic triple-mode mono-block resonator and at least one metallic resonator coupled to at least one of the first and second mono-block resonators. Each triple-mode mono-block resonator supports three resonant modes and each metallic resonator supports an additional mode, thereby providing a hybrid filter assembly of reduced size having more than six poles.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Thermal microphotonic sensor and sensor array
ActiveUS7667200B1Promote absorptionImprove insulation performanceRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansResonant cavitySensor array
A thermal microphotonic sensor is disclosed for detecting infrared radiation using heat generated by the infrared radiation to shift the resonant frequency of an optical resonator (e.g. a ring resonator) to which the heat is coupled. The shift in the resonant frequency can be determined from light in an optical waveguide which is evanescently coupled to the optical resonator. An infrared absorber can be provided on the optical waveguide either as a coating or as a plate to aid in absorption of the infrared radiation. In some cases, a vertical resonant cavity can be formed about the infrared absorber to further increase the absorption of the infrared radiation. The sensor can be formed as a single device, or as an array for imaging the infrared radiation.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
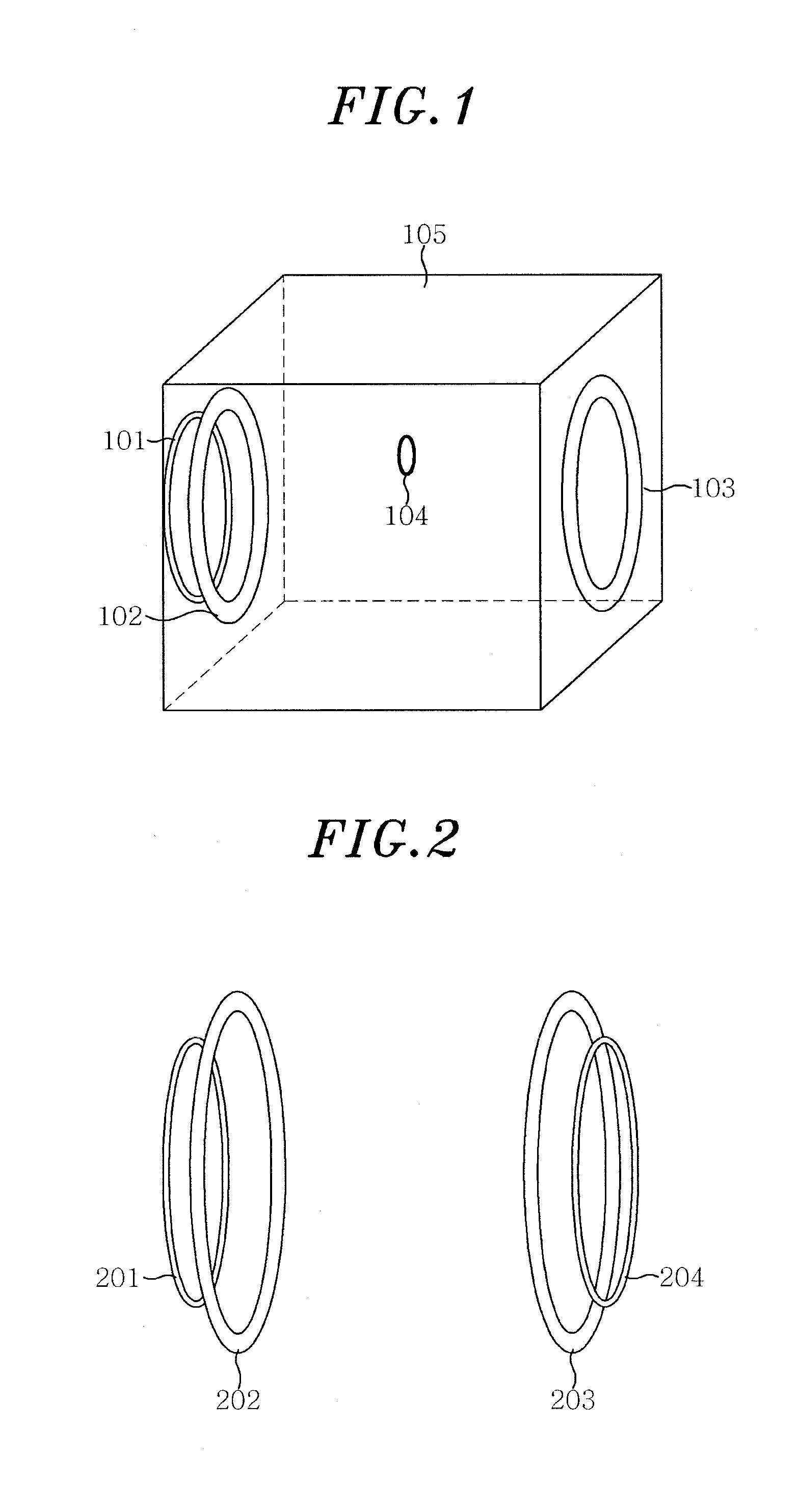
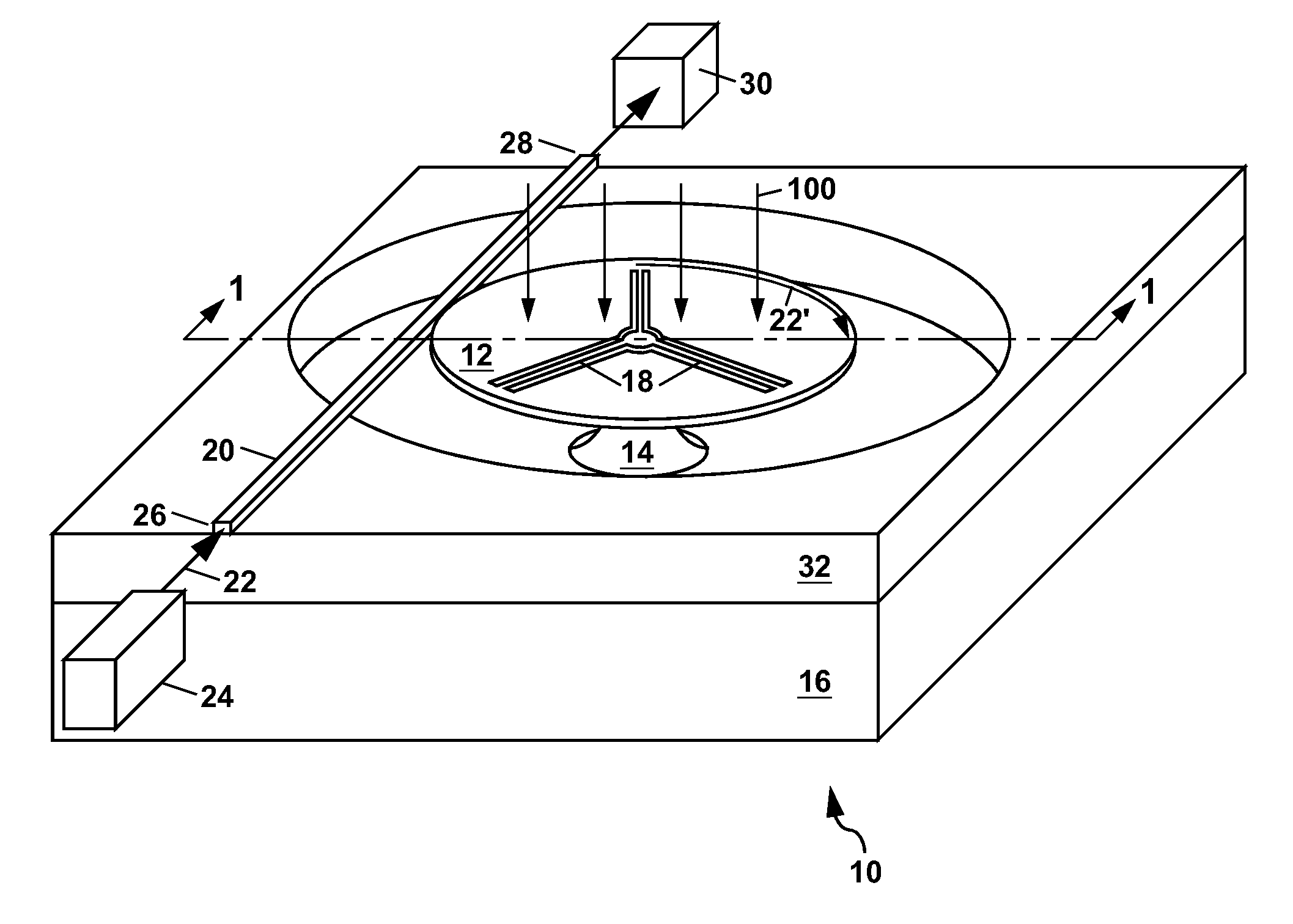
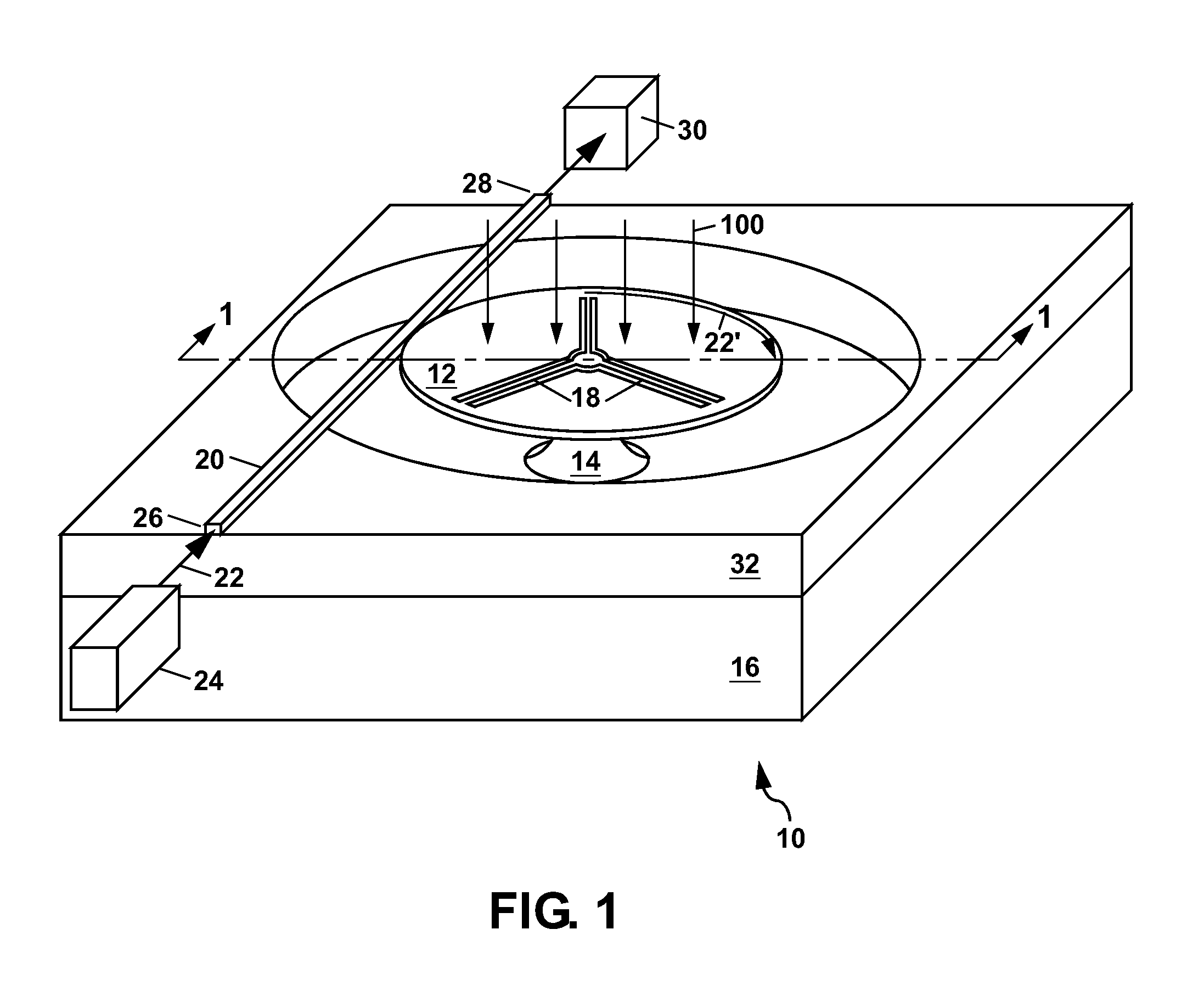
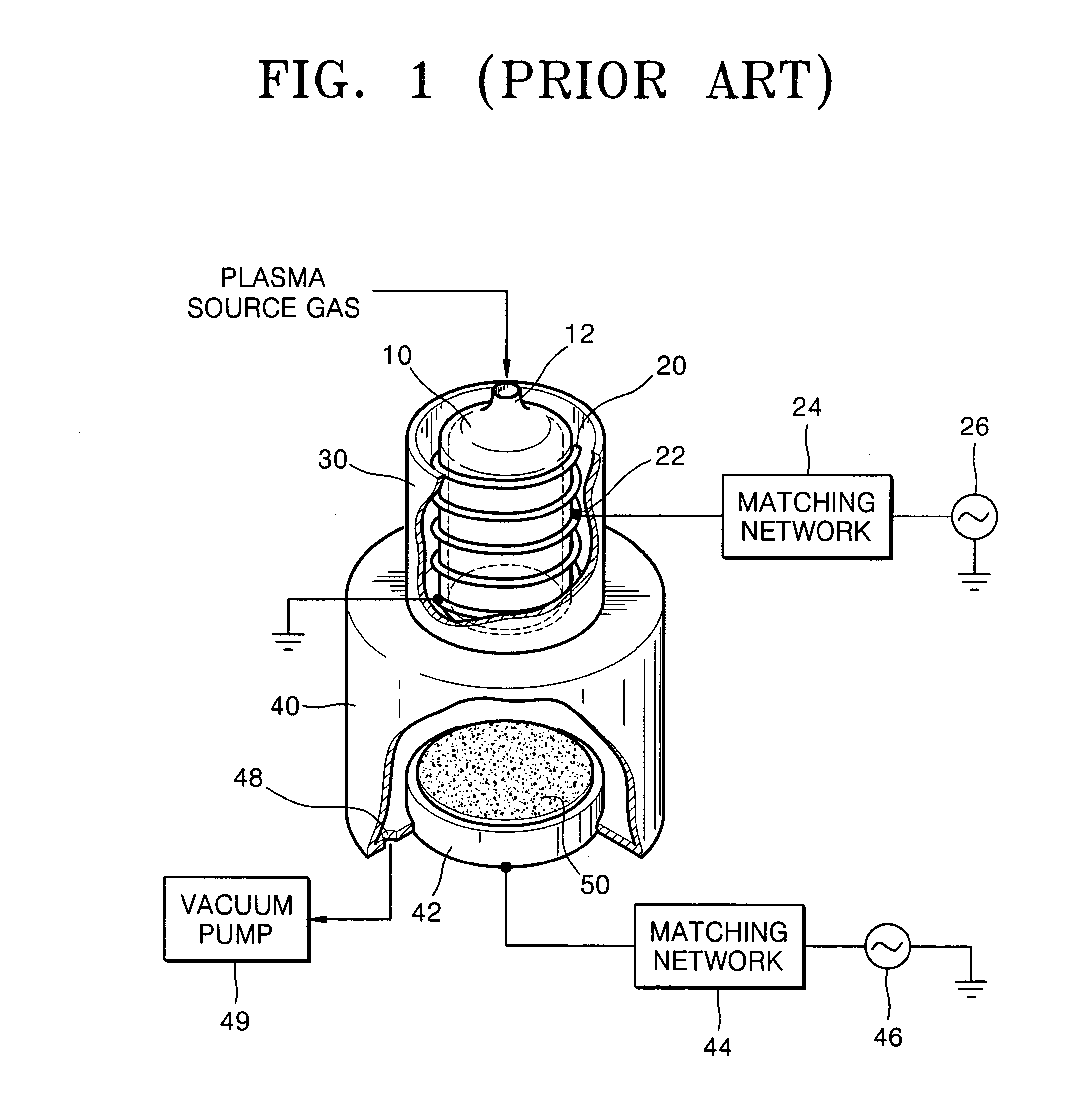
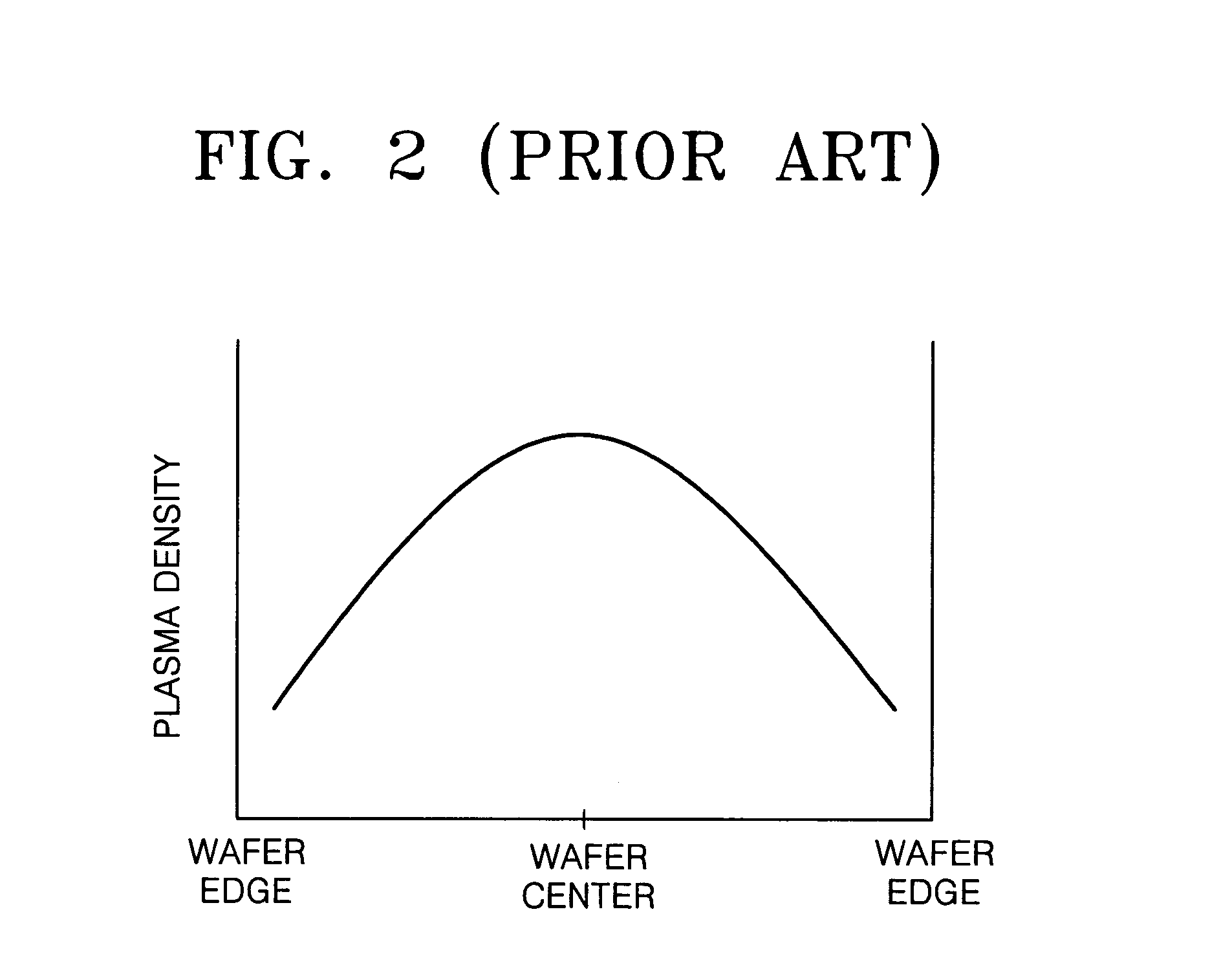
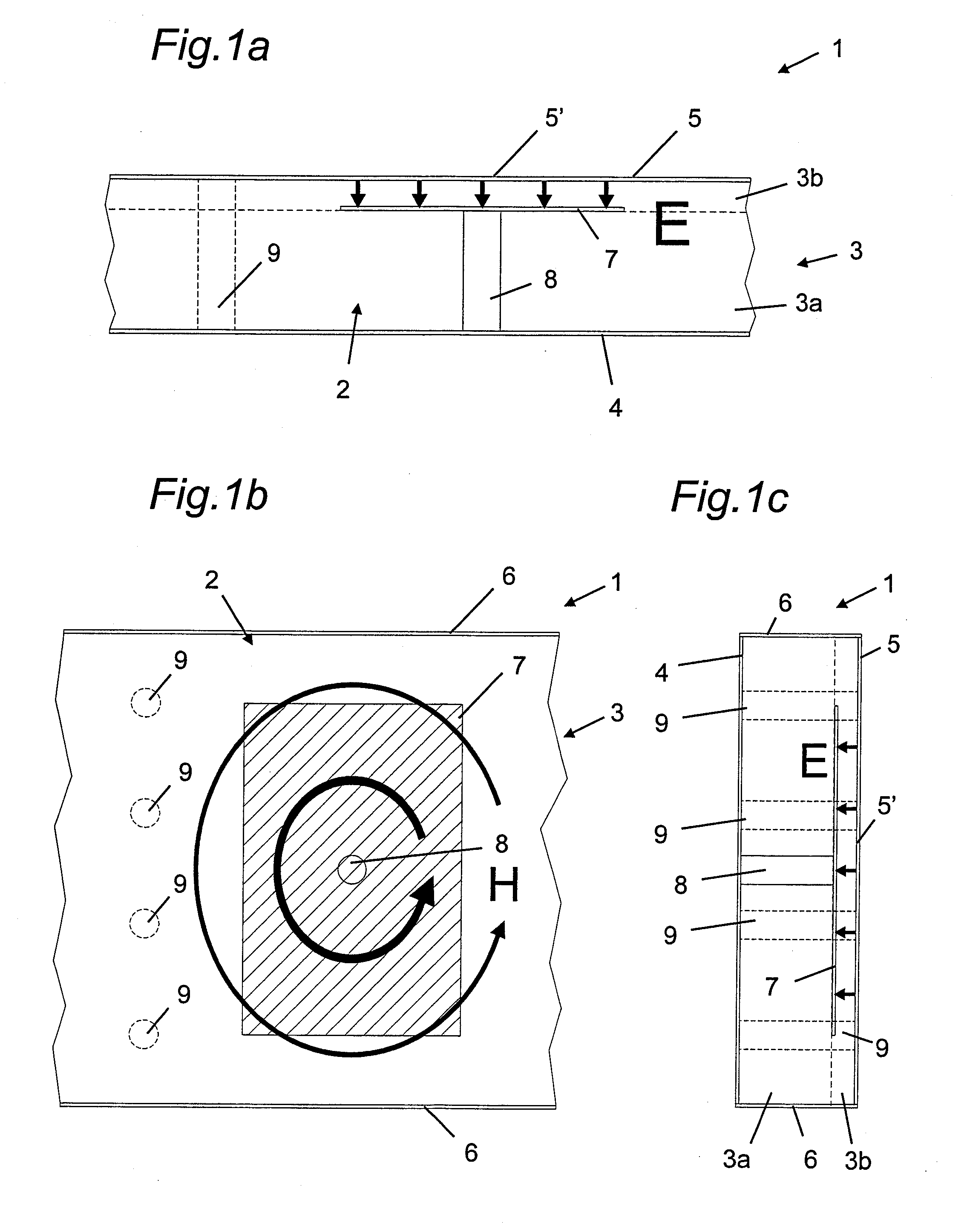
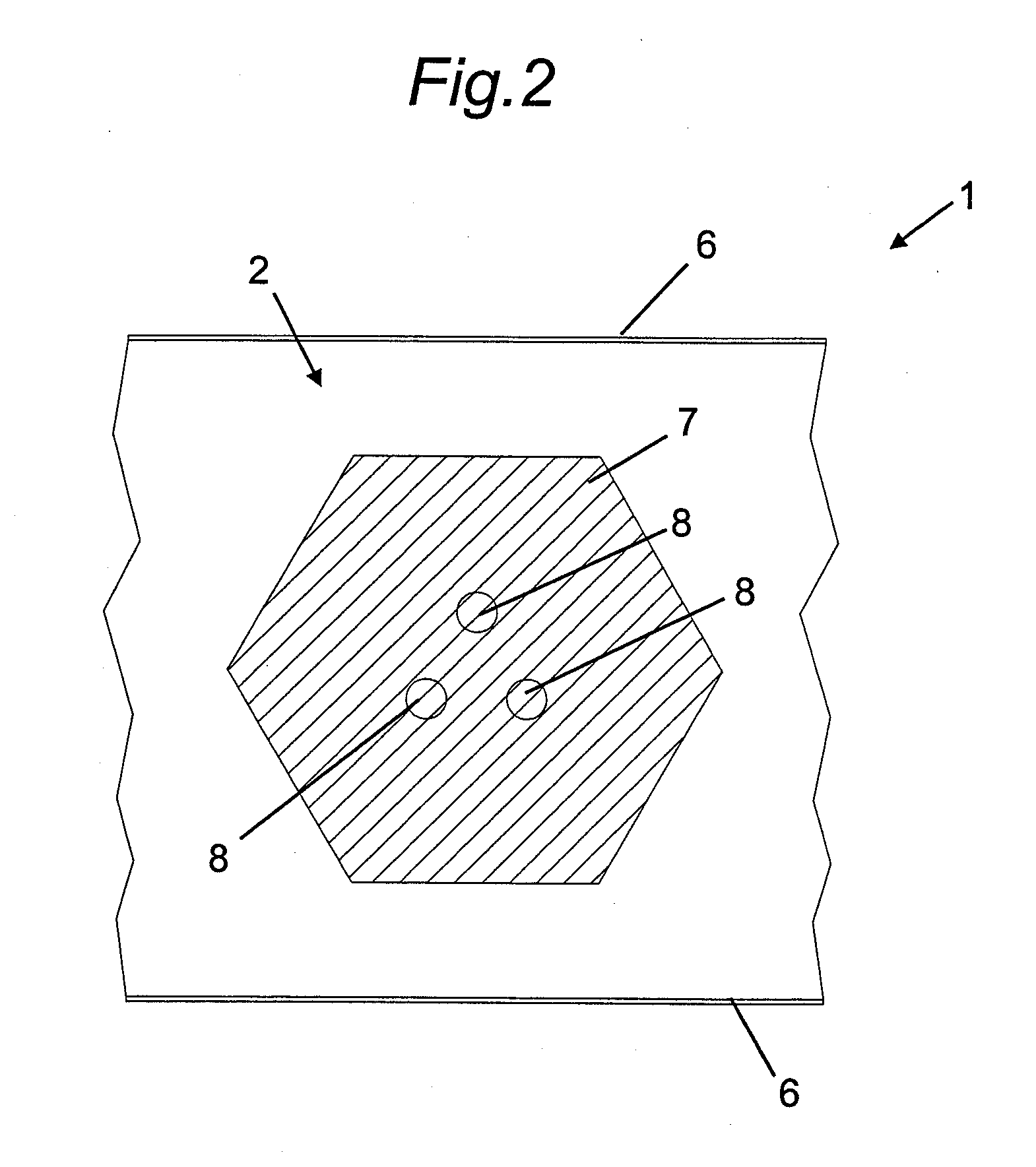
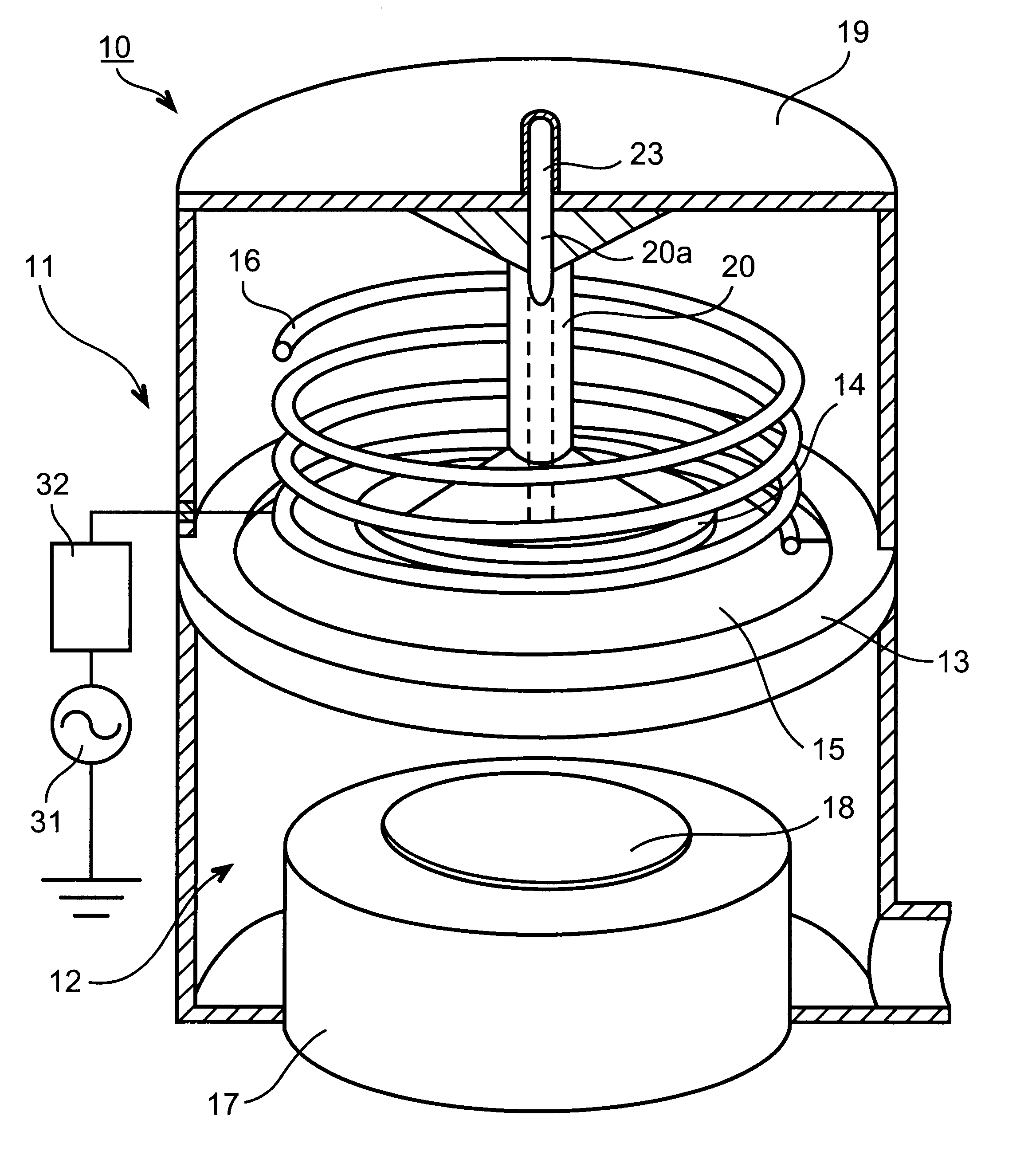
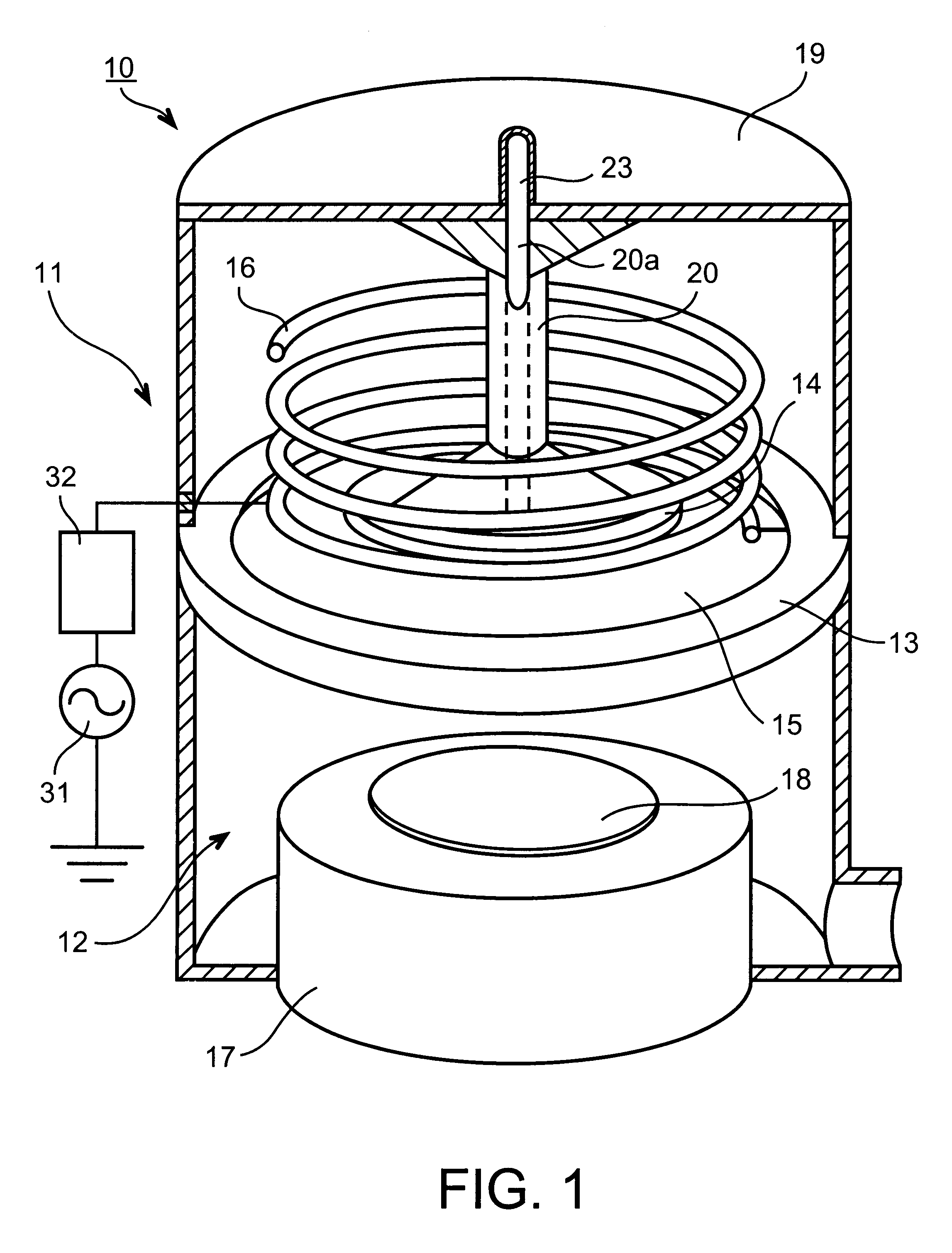
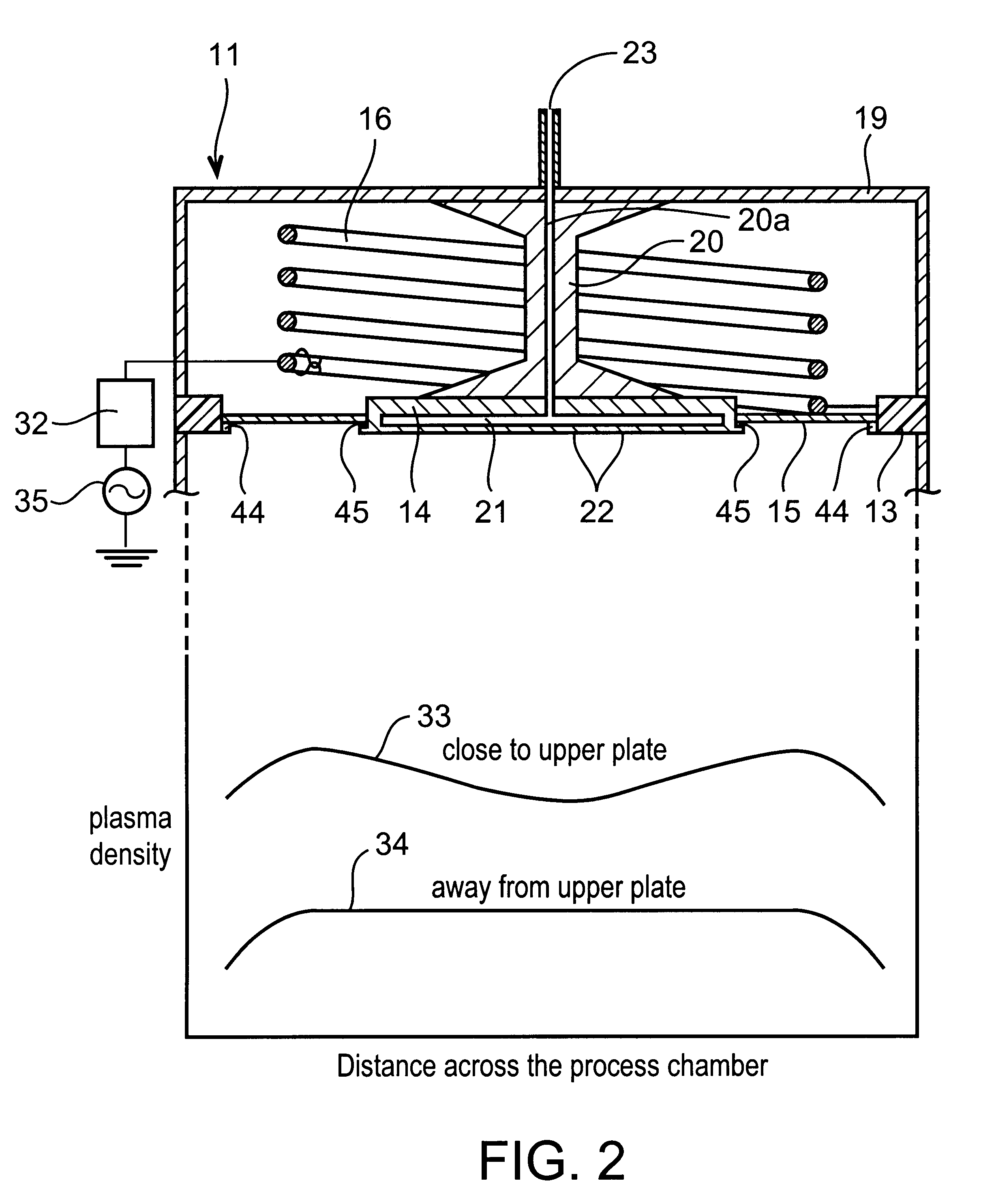
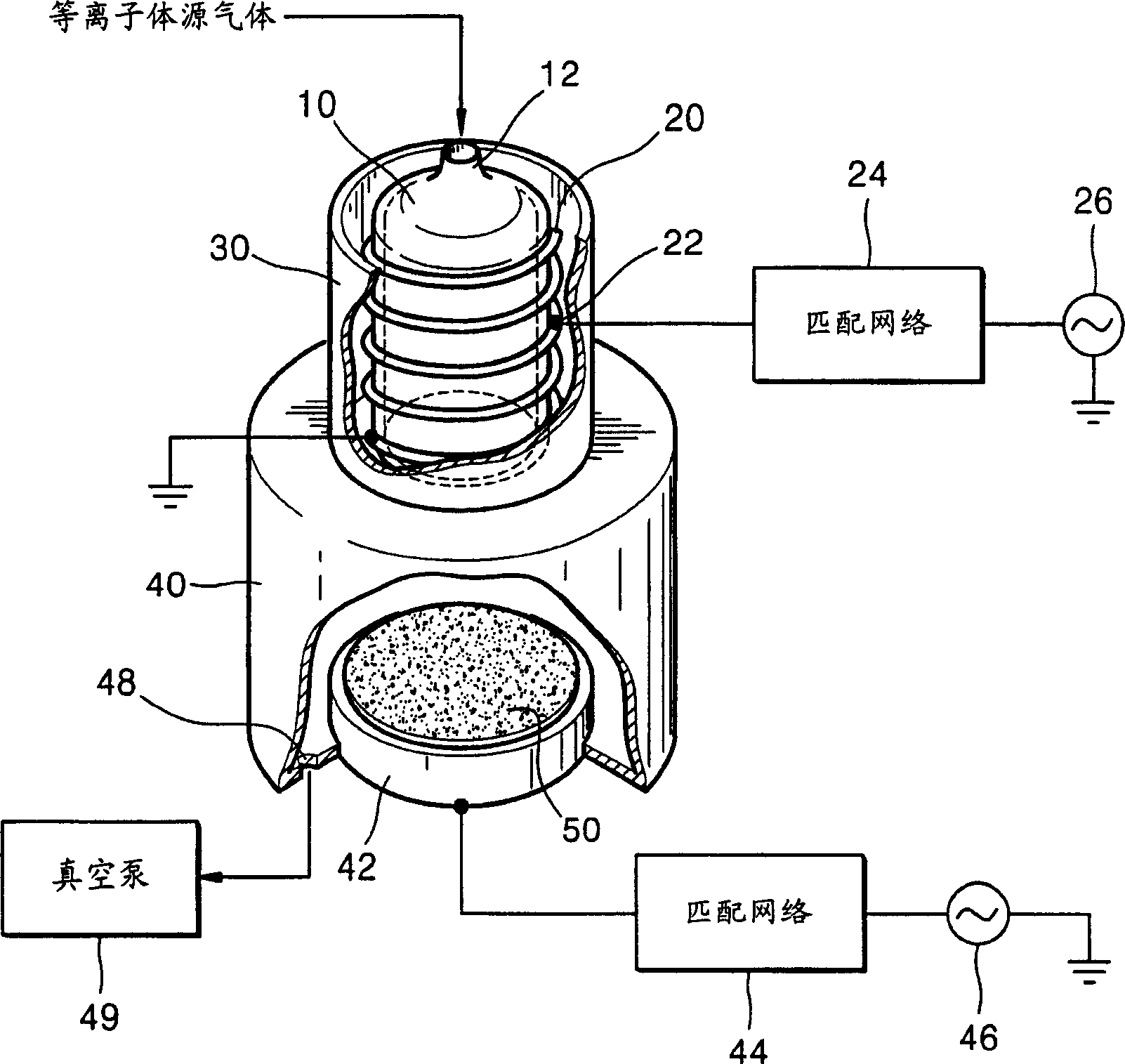
Helical resonator type plasma processing apparatus
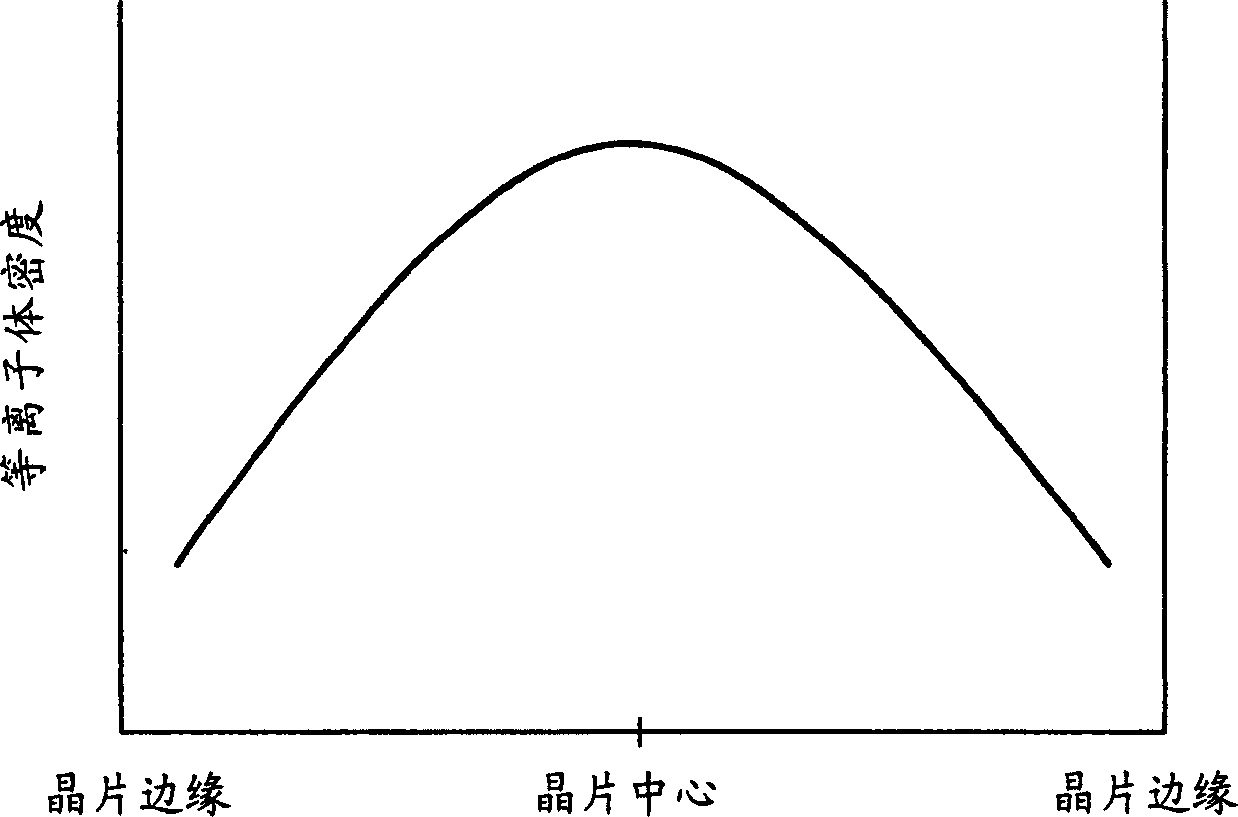
InactiveUS20050093460A1Improve density uniformityEasy to controlElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsDouble tubeHelical resonator
Provided is helical resonator plasma processing apparatus. The plasma processing apparatus comprises a process chamber having a substrate holder for supporting a substrate, a dielectric tube disposed on the process chamber to communicate with the process chamber, a helix coil wounded around the dielectric tube, and an RF power source to supply RF power to the helix coil. The dielectric tube has a double tube shape and comprises an inner tube and an outer tube, and a plasma source gas inlet port to supply plasma source gas into a space between the inner tube and the outer tube is disposed in the outer tube. A control electrode to control plasma potential is disposed in the dielectric tube. This plasma processing apparatus provides a uniform plasma density distribution along a radial direction of a wafer, and easy control of the plasma potential in the process chamber.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optoelectronic fiber photodetector
ActiveUS7292758B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The invention provides an optical fiber photodetector including a photoconductive element, such as a semiconducting element, having a fiber length. The semiconducting element is characterized as a non-composite material in at least one fiber direction. At least one pair of conducting electrodes is in contact with the semiconducting element along the fiber length, and an insulator is provided along the fiber length. An optical resonator can be disposed along the fiber length and along a path of illumination to the semiconducting element. The resonator is dimensioned to substantially reflect all illumination wavelengths except for a prescribed range of wavelengths transmitted to the semiconducting element. The fiber photodetector can be arranged in a photodetecting fiber grid, photodetecting fiber fabric, or other configuration for detecting incident illumination.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
All-optical logic gates using nonlinear elements-claim set VI
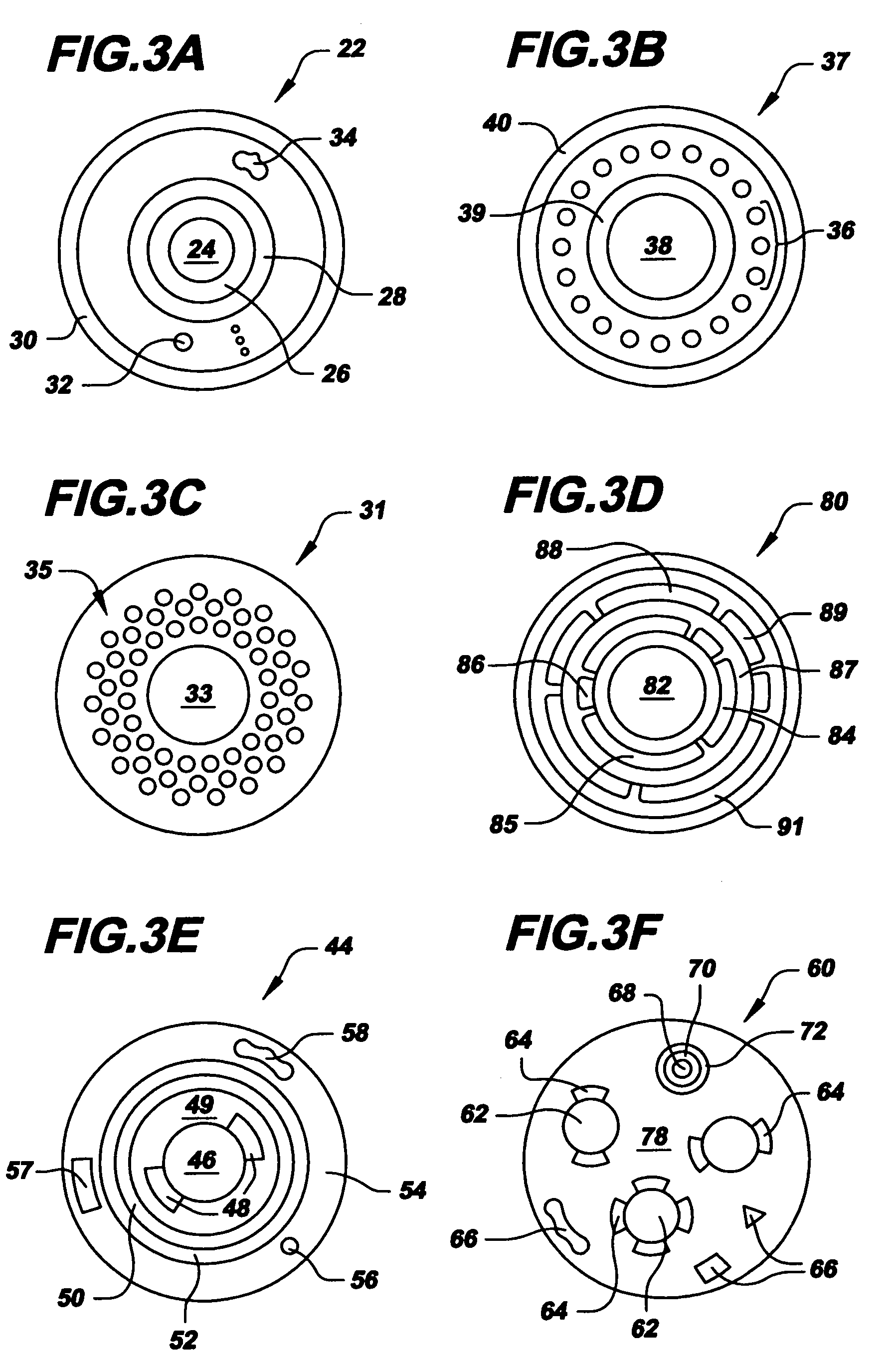
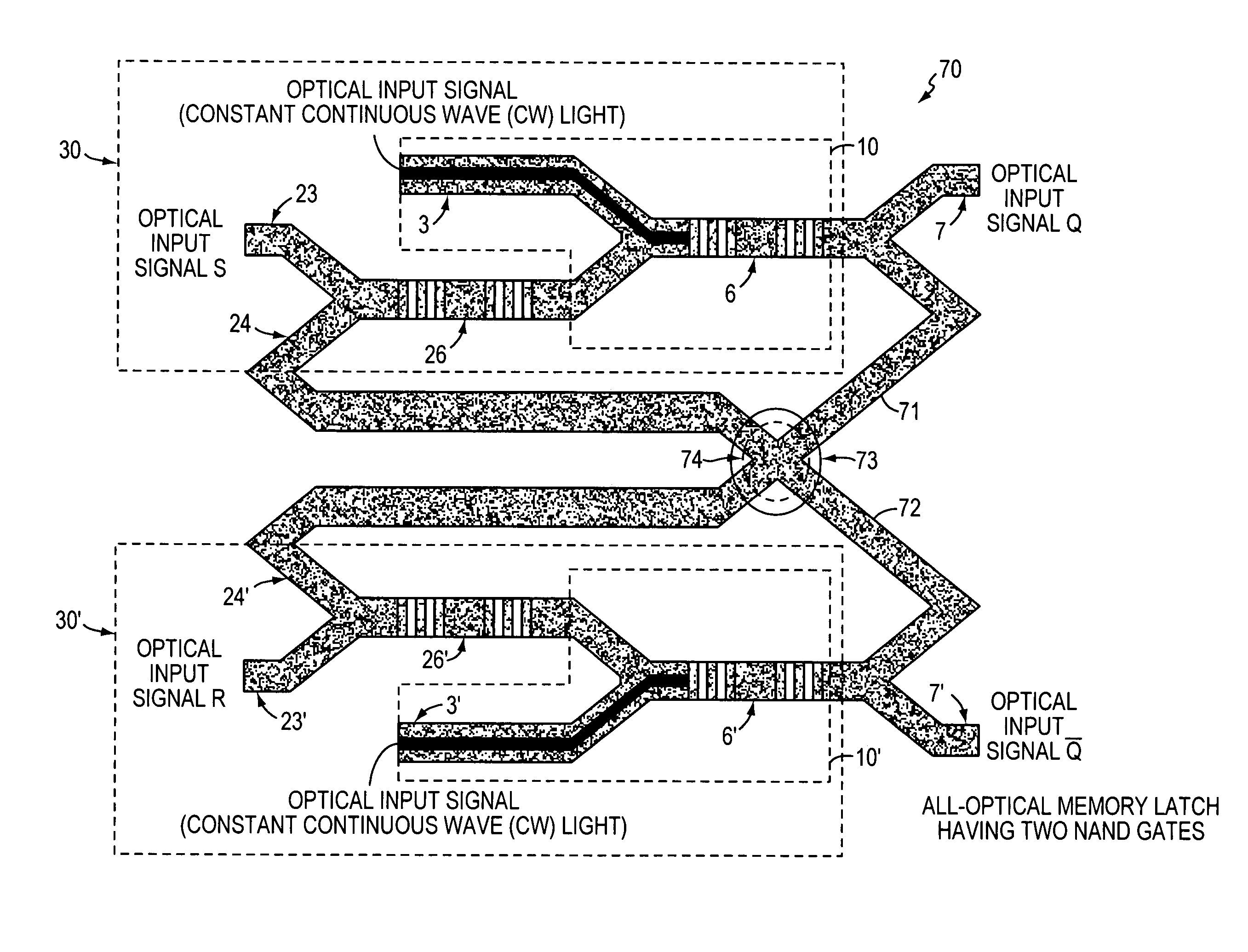
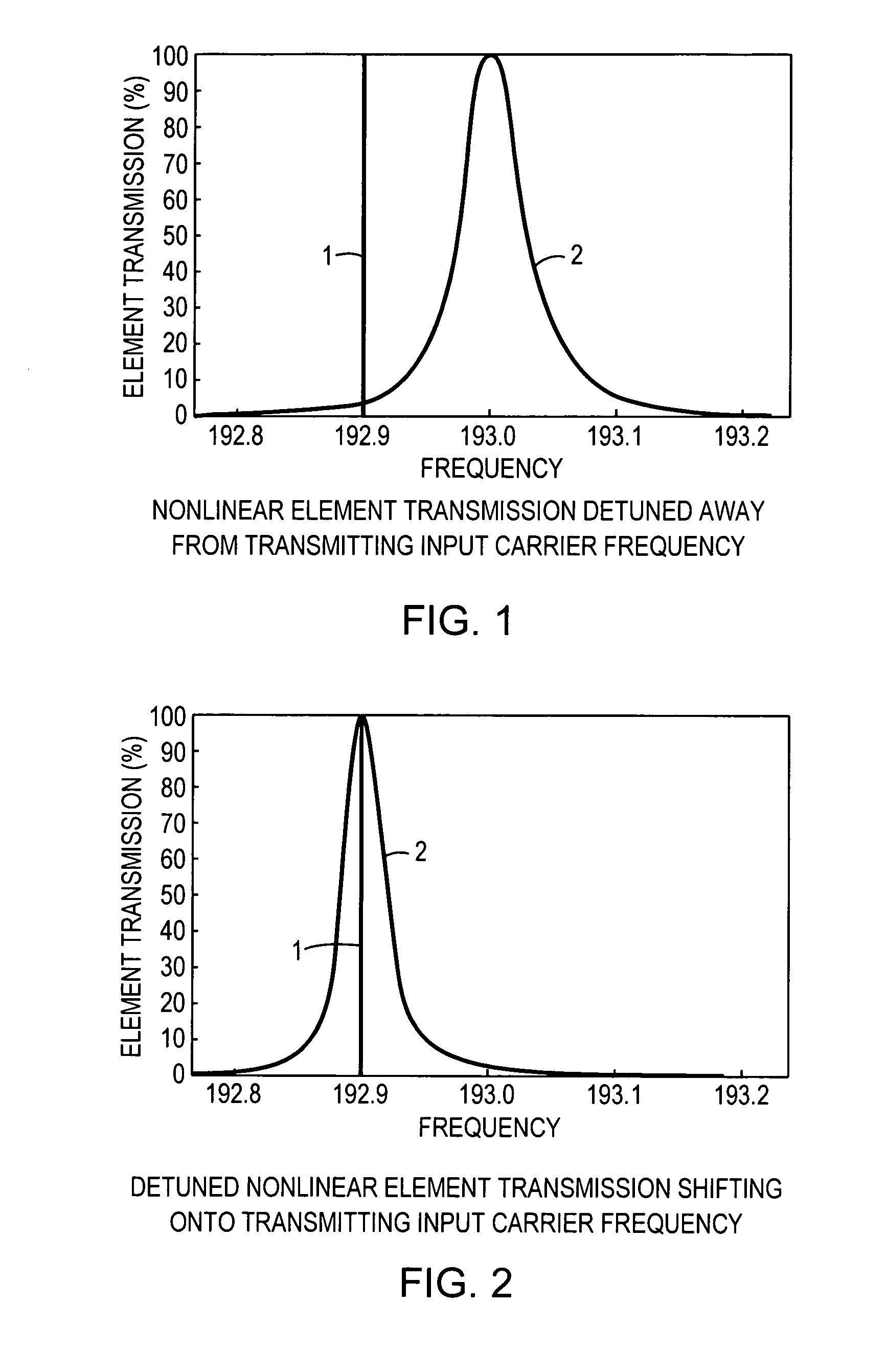
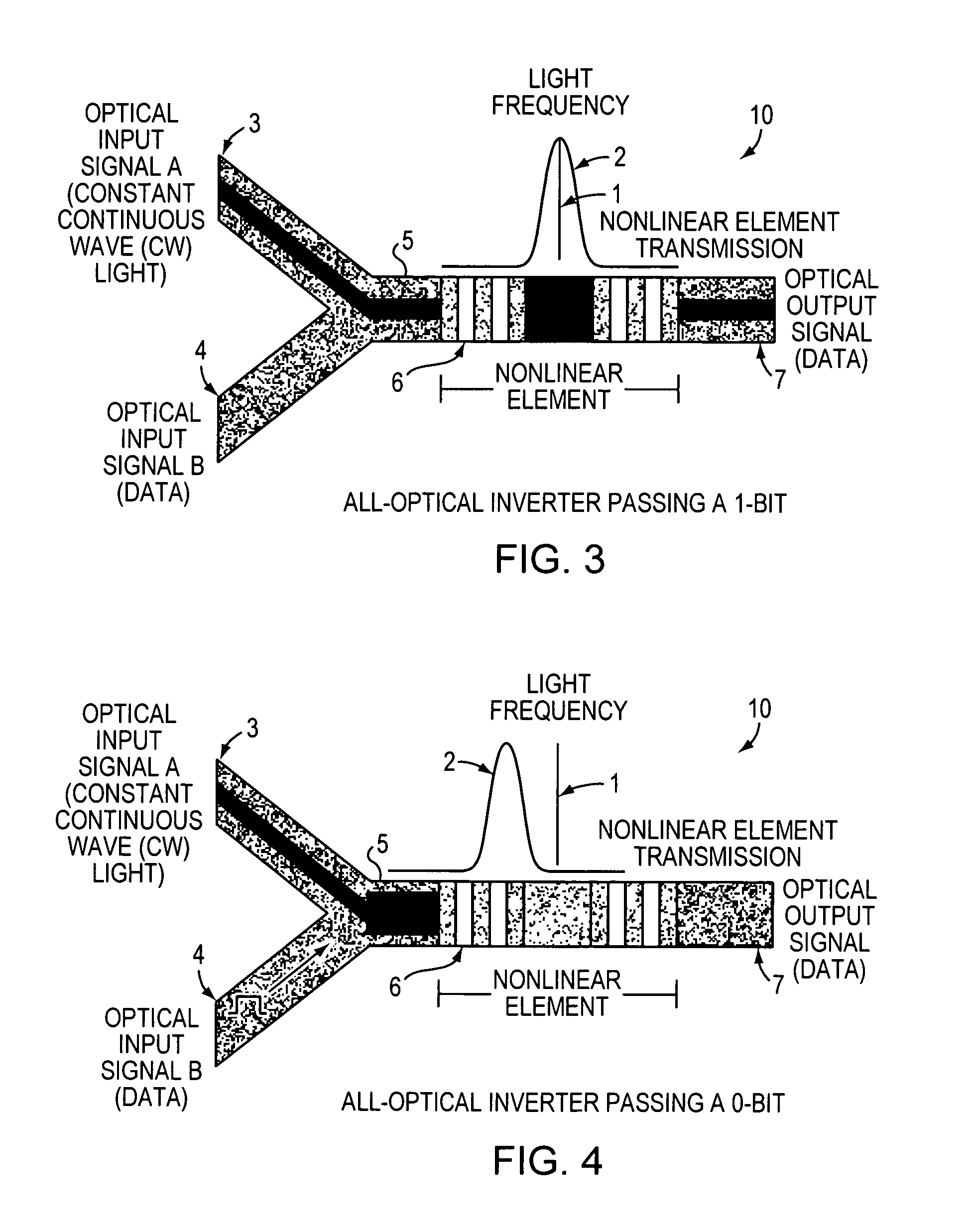
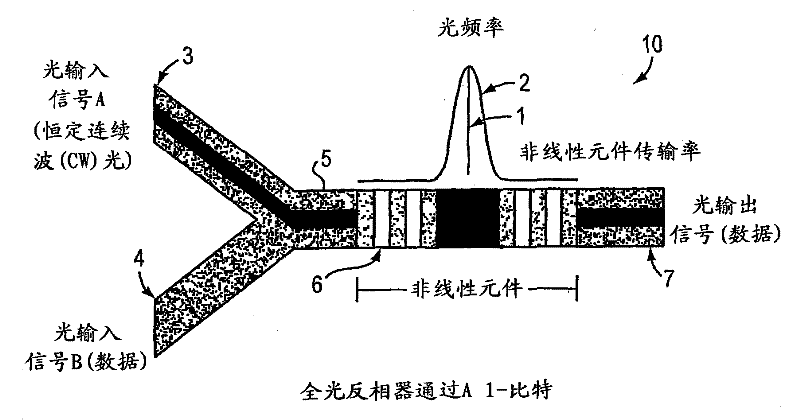
InactiveUS7263262B1Change quantityPrecise arrangementCoupling light guidesOptical bistable devicesNonlinear elementLogic gate
An all-optical logic gates comprises a nonlinear element such as an optical resonator configured to receive optical input signals, at least one of which is amplitude-modulated to include data. The nonlinear element is configured in relation to the carrier frequency of the optical input signals to perform a logic operation based on the resonant frequency of the nonlinear element in relation to the carrier frequency. Based on the optical input signals, the nonlinear element generates an optical output signal having a binary logic level. A combining medium can be used to combine the optical input signals for discrimination by the nonlinear element to generate the optical output signal. Various embodiments include all-optical AND, NOT, NAND, NOR, OR, XOR, and XNOR gates and memory latch.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
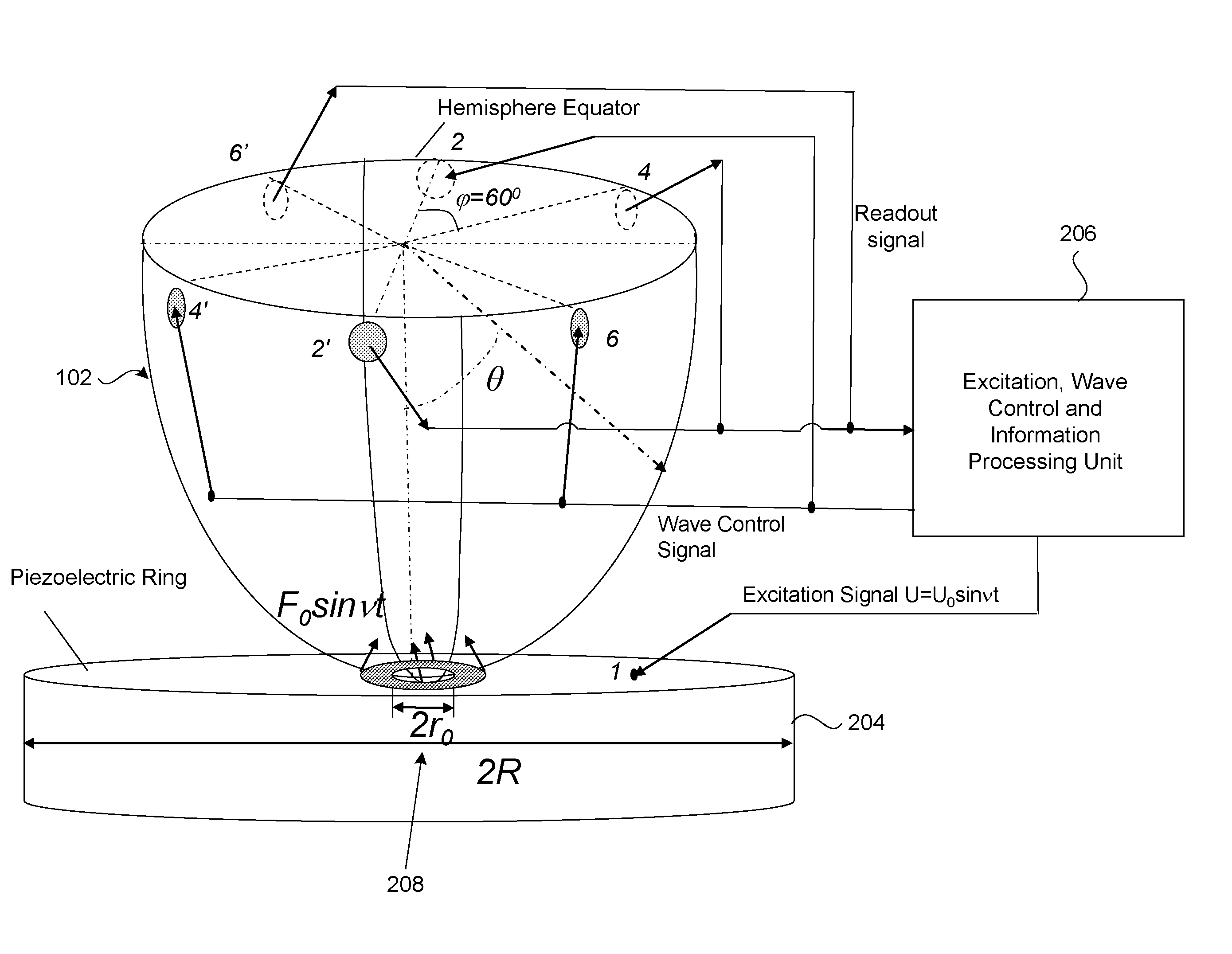
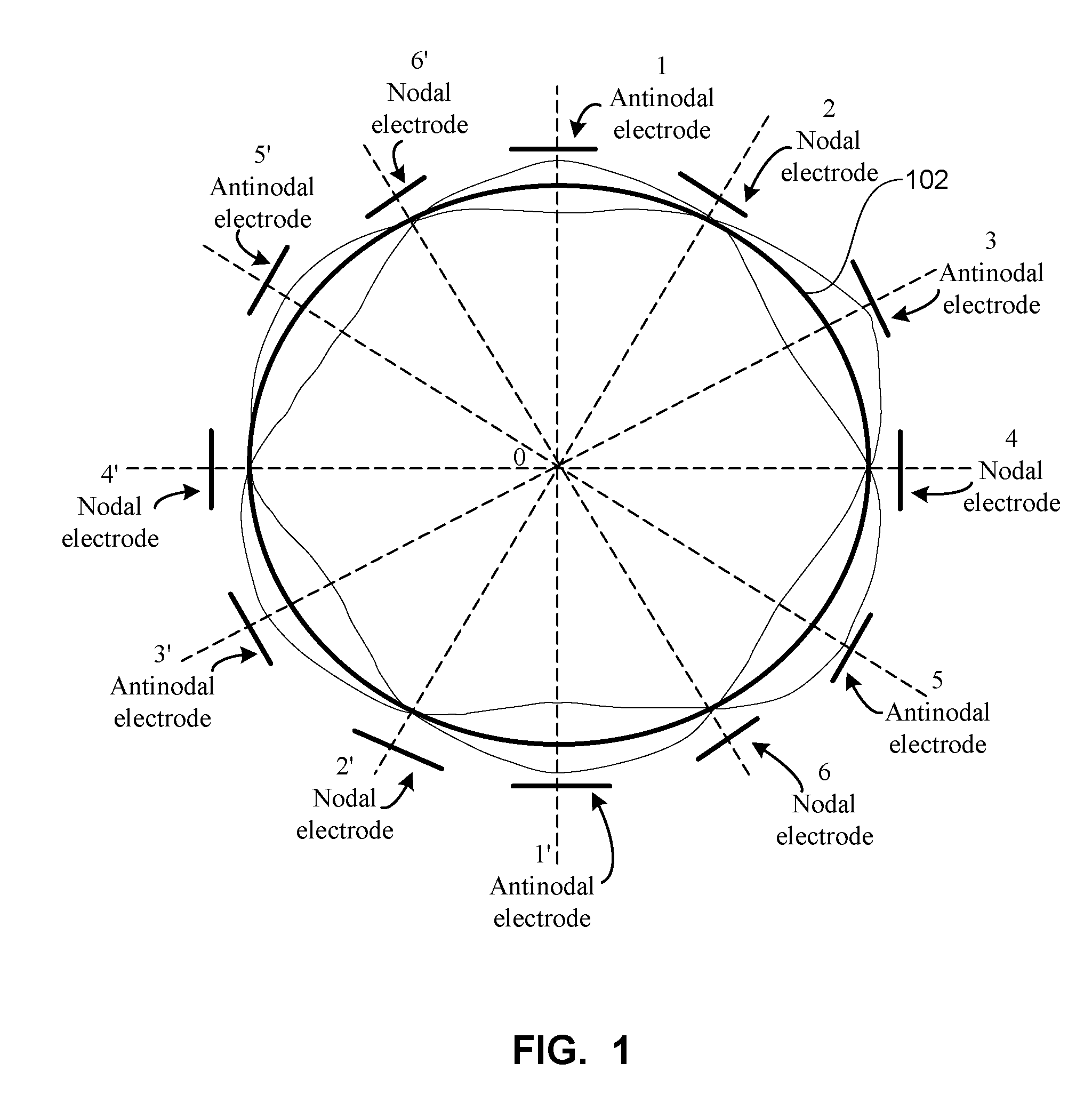
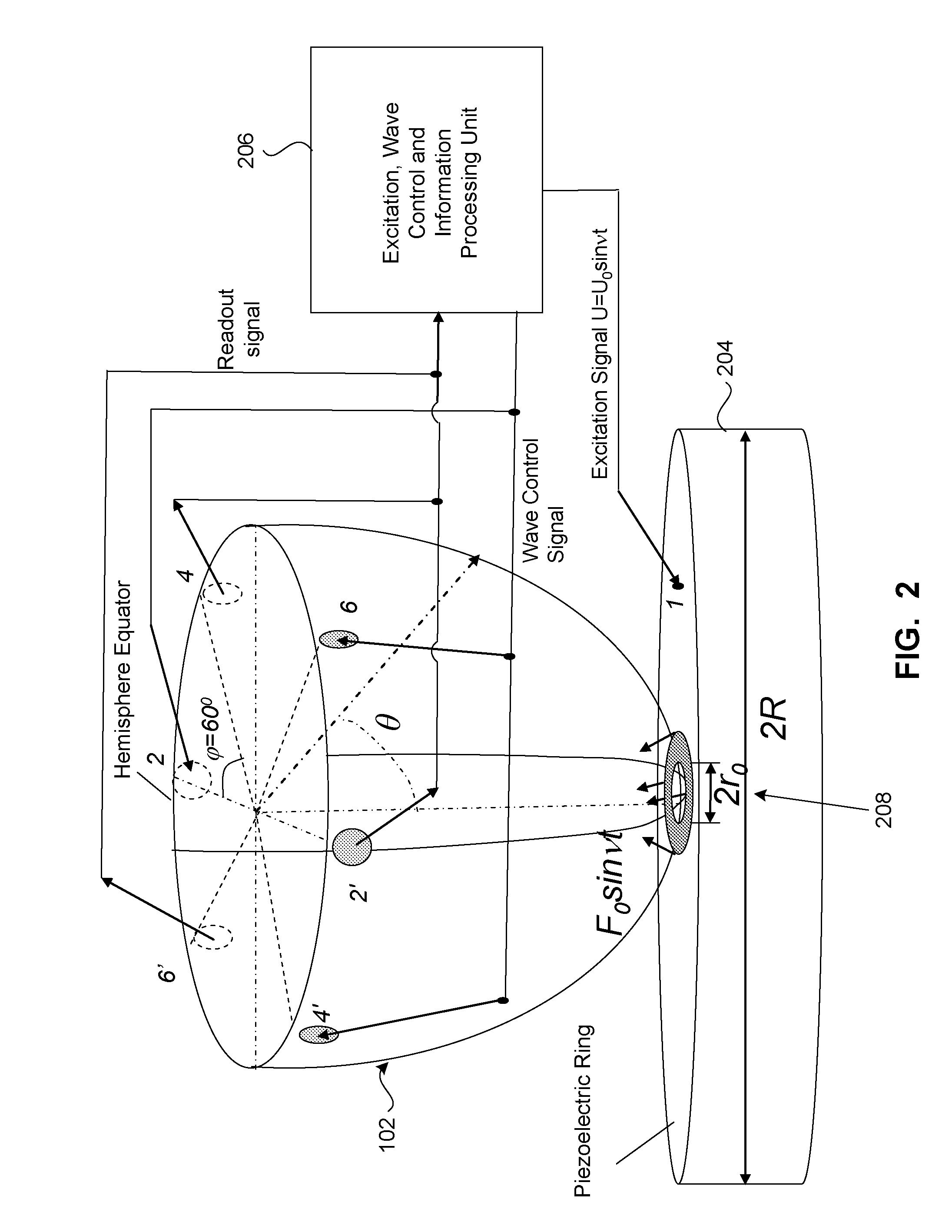
Stemless hemispherical resonator gyroscope
InactiveUS7281426B1Improve accuracyEliminate disadvantagesAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsConductive coatingAngular velocity
A vibrational gyroscope includes a piezoelectric ring having a central opening, and a hemispherical resonator having a central opening and mounted over the opening of the central opening of the piezoelectric ring. A plurality of electrodes delivers a voltage to the piezoelectric ring. A plurality of electrodes provides signal readout that corresponds to angular velocity. The hemispherical resonator can be glued to the piezoelectric ring. The hemispherical resonator preferably vibrates in the third vibration mode. A plurality of capacitive electrodes can be located at nodes and at antinodes of the vibration of the hemispherical resonator, and provide a signal readout that corresponds to the angular velocity. The piezoelectric ring is segmented, non-segmented, or includes an outer segmented portion and an inner non-segmented portion. The inner non-segmented portion can be used to excite the resonator into a vibration mode, and the outer segmented portion provides a readout signal and is used to adjust the vibration of the resonator. The piezoelectric ring includes a conductive coating used to conduct excitation voltage to the piezoelectric ring.
Owner:INNALABS
Laminated RF device with vertical resonators
InactiveUS20100265015A1To offer comfortCompact structureMultiple-port networksResonatorsElectrical connectionConductive materials
The present invention relates to a resonator device having a stacked arrangement of laminated layers including a plurality of dielectric layers, and at least one resonator comprising a short-circuit electrode, a first capacitor electrode and a second capacitor electrode. Each electrode comprises at least a portion of a layer of electrically conductive material provided on a surface of one of the dielectric layers. The second capacitor electrode is disposed spaced, in the stacking direction, from the short-circuit electrode and the first capacitor electrode. The short-circuit electrode and the second capacitor electrode are electrically interconnected by a first electrical connection comprising at least one via hole penetrating one or more of the dielectric layers.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High Frequency Ultrasound Detection Using Polymer Optical-Ring Resonator
ActiveUS20080095490A1Detection noise increaseIncreased signal noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationUltrasound pulse
A polymer waveguide resonator device for high-frequency ultrasound detection having a optical resonator coupled to a straight optical waveguide which serves as input and output ports. Acoustic waves irradiating the waveguide induce strain modifying the waveguide cross-section or other design property. As a consequence, the effective refractive index of optical waves propagating along the ring is modified. The sharp wavelength dependence of the high Q-factor resonator enhances the optical response to acoustic strain. High sensitivity is demonstrated experimentally in detecting broadband ultrasound pulses from a 10 MHz transducer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
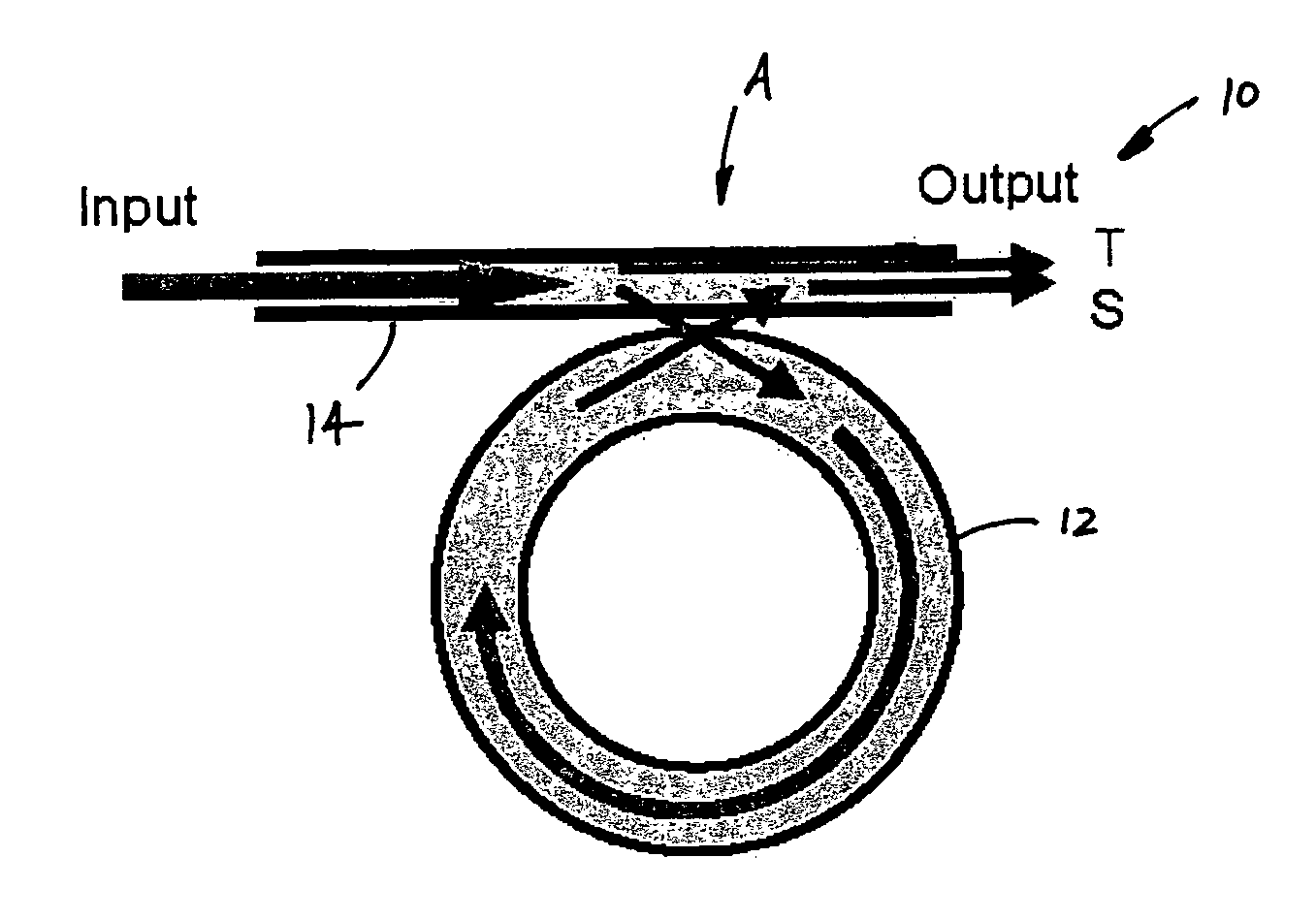
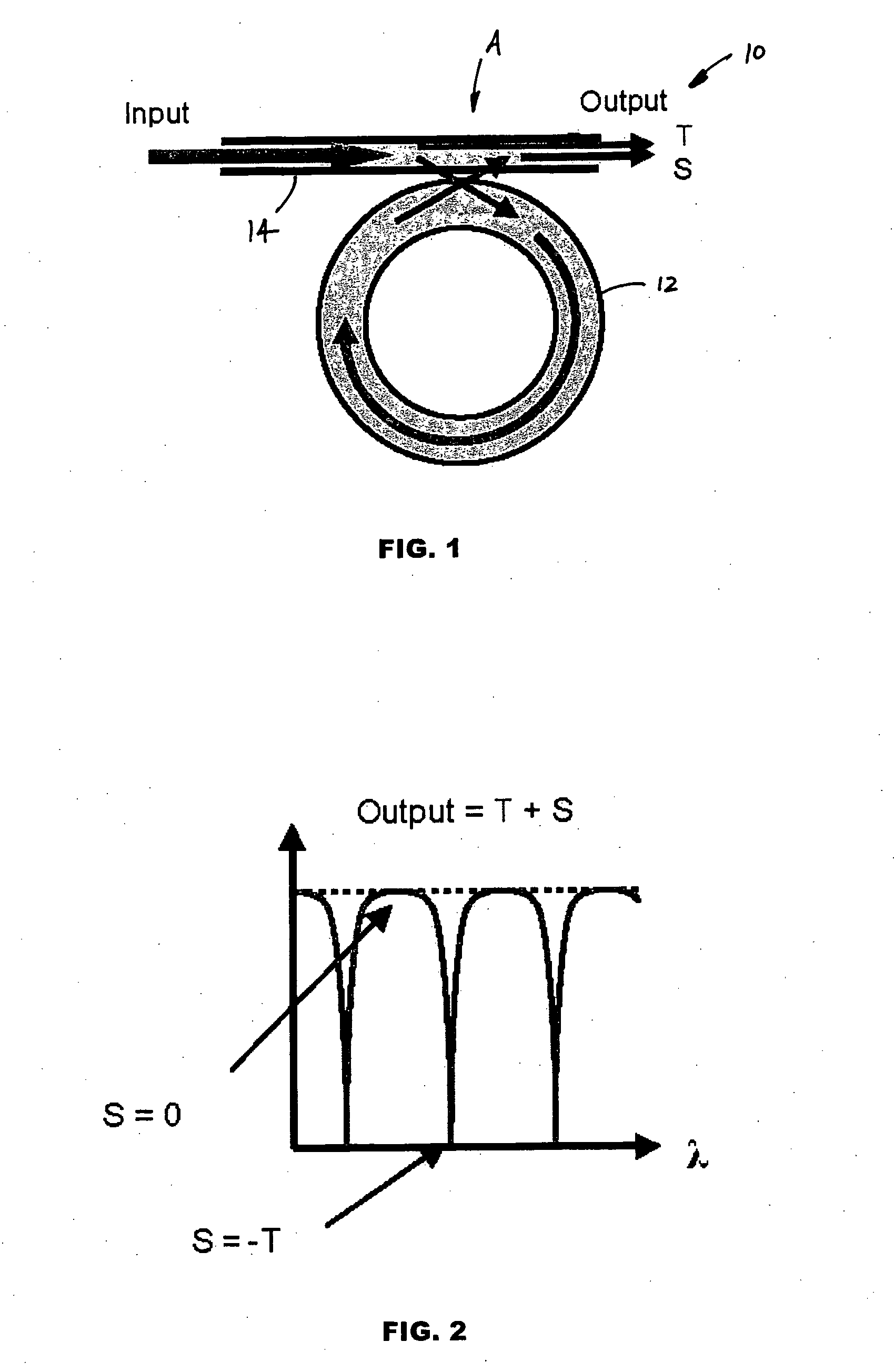
Optical waveguide ring resonator with an intracavity active element
An optical resonator, a photonic system and a method of optical resonance employ optical waveguide segments connected together with total internal reflection (TIR) mirrors to form a closed loop. The optical resonator includes the optical waveguide segments, an intracavity active element coupled to a designated one of the optical waveguide segments, the TIR mirrors and a photo-tunneling input / output (I / O) port. The photo-tunneling I / O port includes one of the TIR mirrors. The method includes propagating and reflecting the optical signal, or a portion thereof, in the optical resonator, transmitting a portion of the optical signal through the I / O port, and influencing the optical signal. The photonic system includes the optical resonator with optical gain and a source of an optical signal.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Planar optical waveguide element, chromatic dispersion compensator, optical filter, optical resonator and methods for designing the element, chromatic dispersion compensator, optical filter and optical resonator
InactiveUS20100322559A1Inhibition effectReduced polarization dependenceComputation using non-denominational number representationCoupling light guidesPhysicsHelical resonator
There is provided a planar optical waveguide element in which an optical waveguide comprises a core, and a gap portion that is positioned in a center of a width direction of the core so as to extend in a propagation direction of guided light, and that has a lower refractive index than that of the core; and wherein the core comprises two areas that are separated by the gap portion, and a single mode optical waveguide, in which a single mode is propagated span crossing these two areas, is formed.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Tunable light source apparatus, and adjustment method and control program of the same
InactiveUS7565045B2Great magnitudeOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesResonance wavelengthLaser beams
The present invention aims to provide a tuning light source apparatus including a multiple-optical resonator, where the resonance frequencies of the respective optical resonators in a multiple-optical resonator are exactly coincided with the set frequency, and the frequency of the output laser beam is locked within a range of about 1 GHz from the set frequency. Current is flowed to TO phase shifters based on lights detected by light receiving elements, and the resonance wavelengths of resonators are adjusted in an aim of obtaining a state in which an intensity of an oscillation light becomes a maximum and at the same time an intensity of a light from a through port becomes a minimum.
Owner:NEC CORP
All-optical logic gates using nonlinear elements
InactiveCN102226862ALogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesOptical waveguide light guideNonlinear elementHelical resonator
An all-optical logic gates comprises a nonlinear element such as an optical resonator configured to receive optical input signals, at least one of which is amplitude-modulated to include data. The nonlinear element is configured in relation to the carrier frequency of the optical input signals to perform a logic operation based on the resonant frequency of the nonlinear element in relation to the carrier frequency. Based on the optical input signals, the nonlinear element generates an optical output signal having a binary logic level. A combining medium can be used to combine the optical input signals for discrimination by the nonlinear element to generate the optical output signal. Various embodiments include all-optical AND, NOT, NAND, NOR, OR, XOR, and XNOR gates and memory latch.
Owner:COVEYTECH LLC
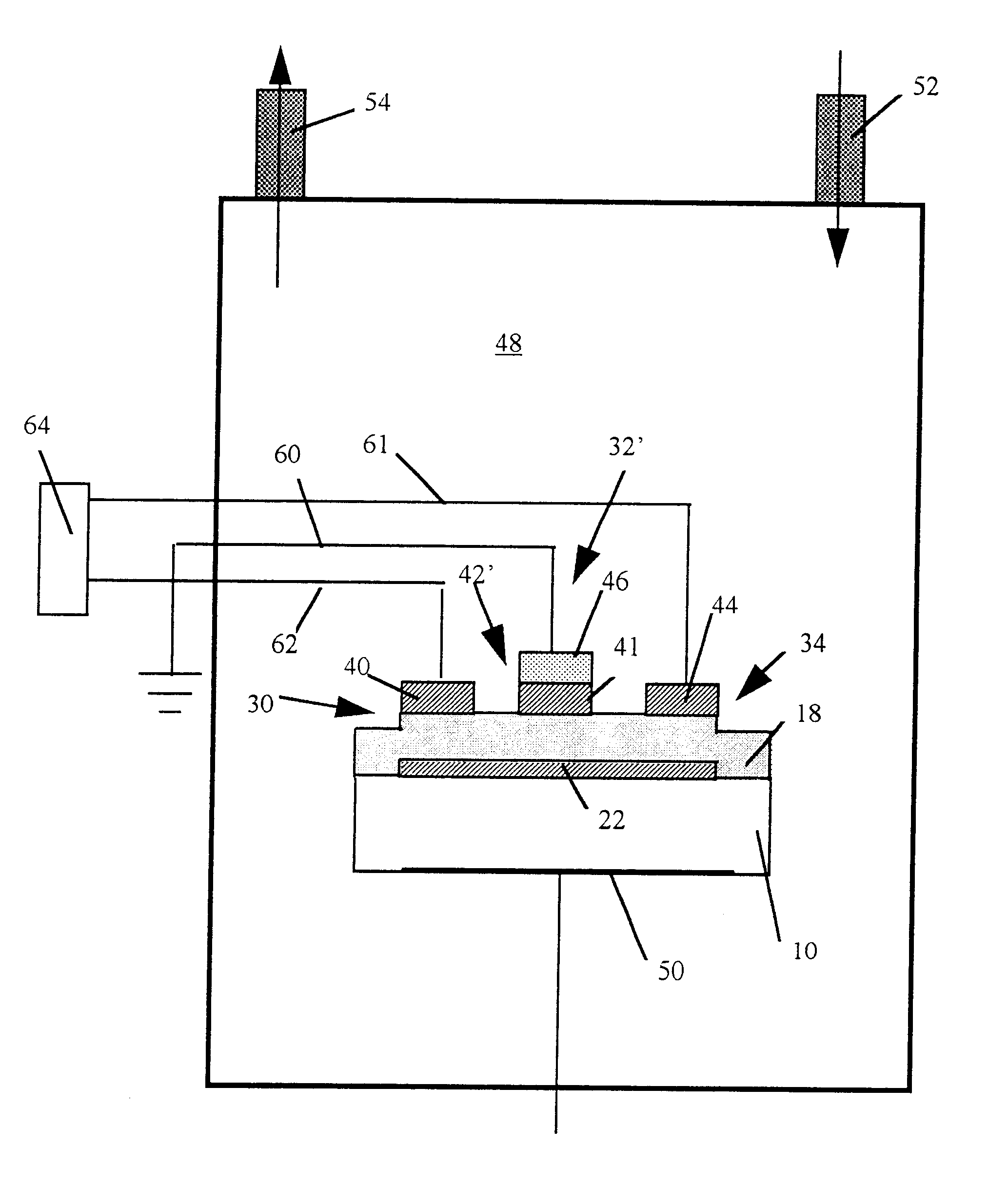
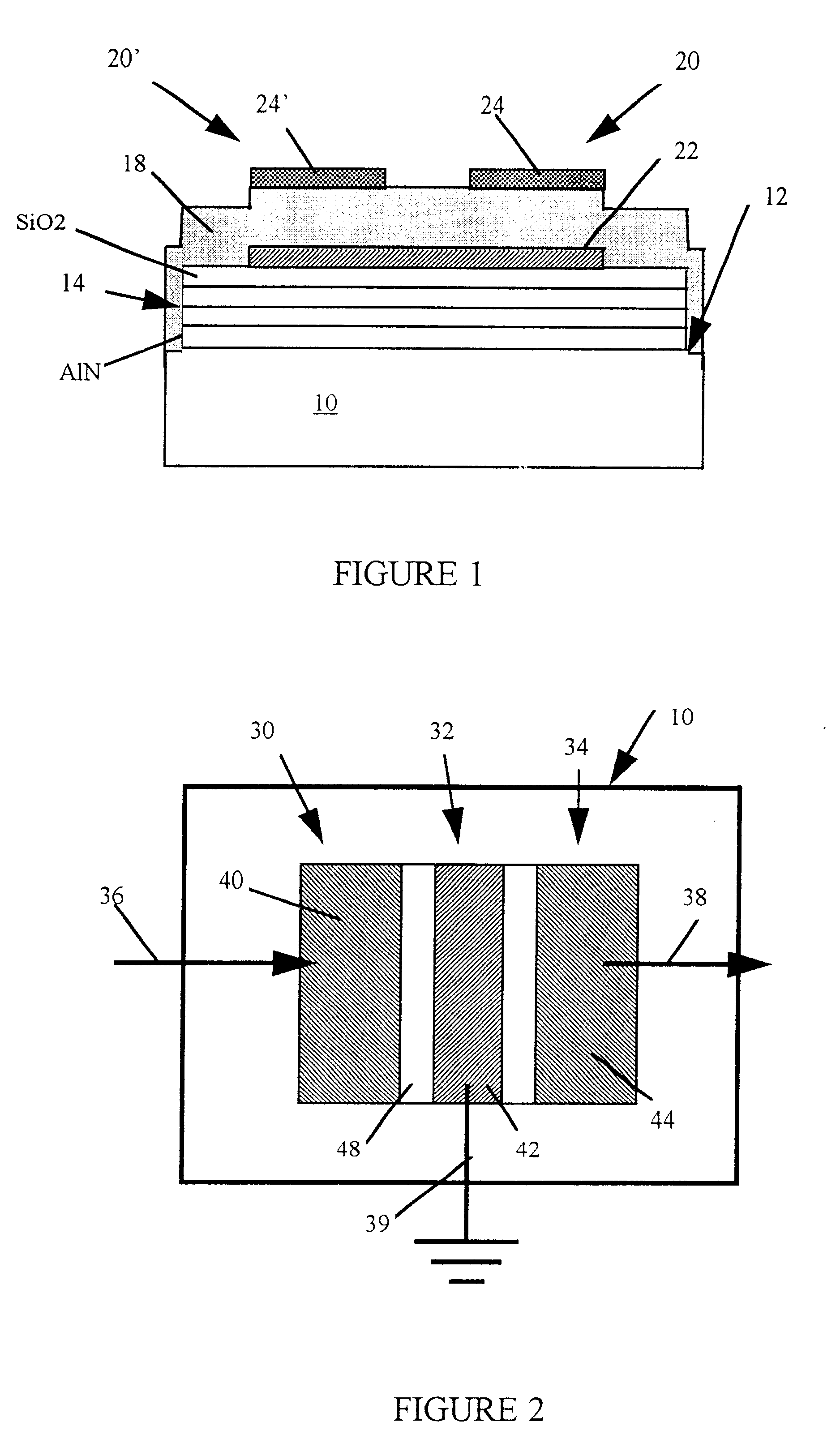
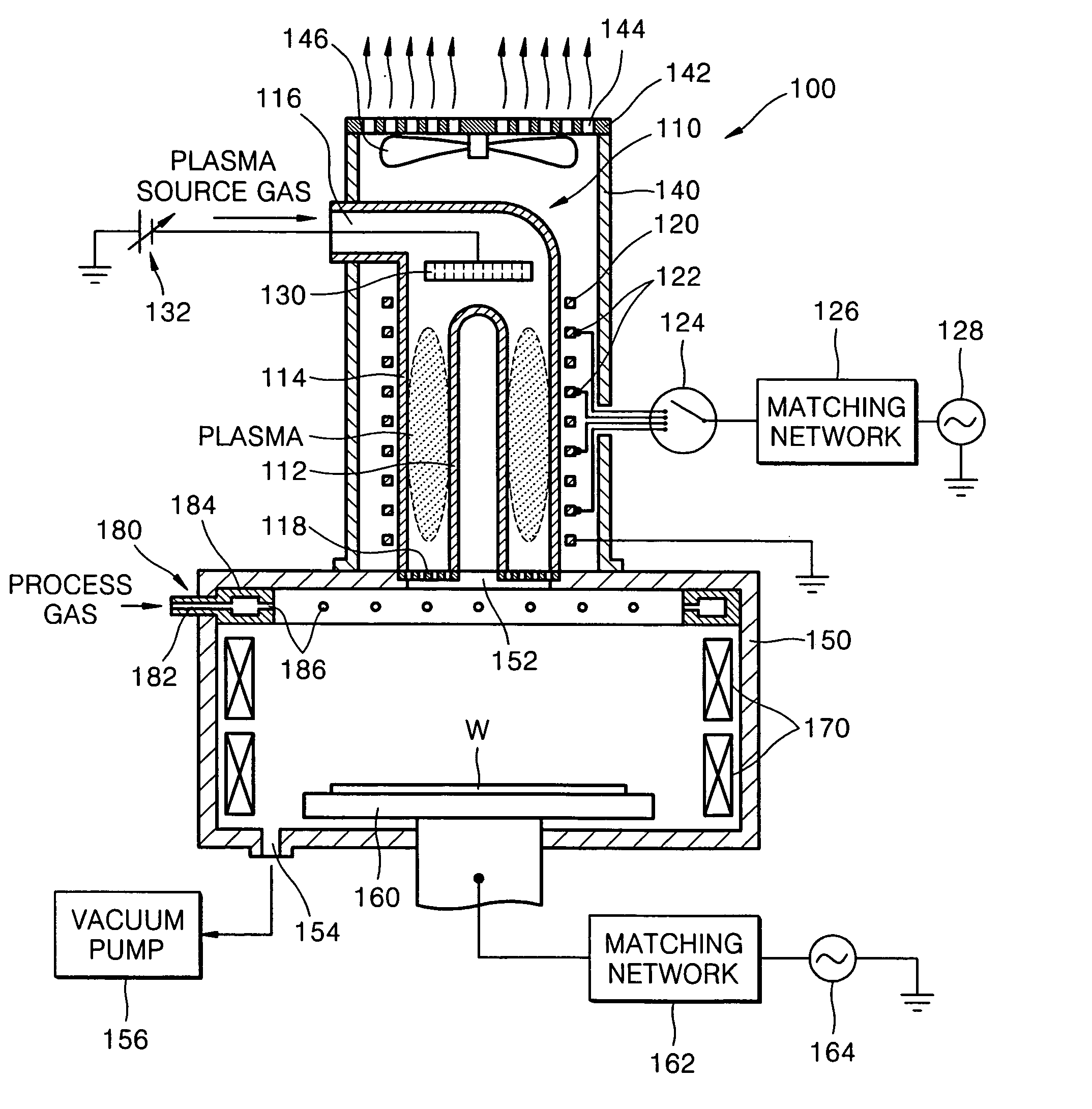
Plasma processing system
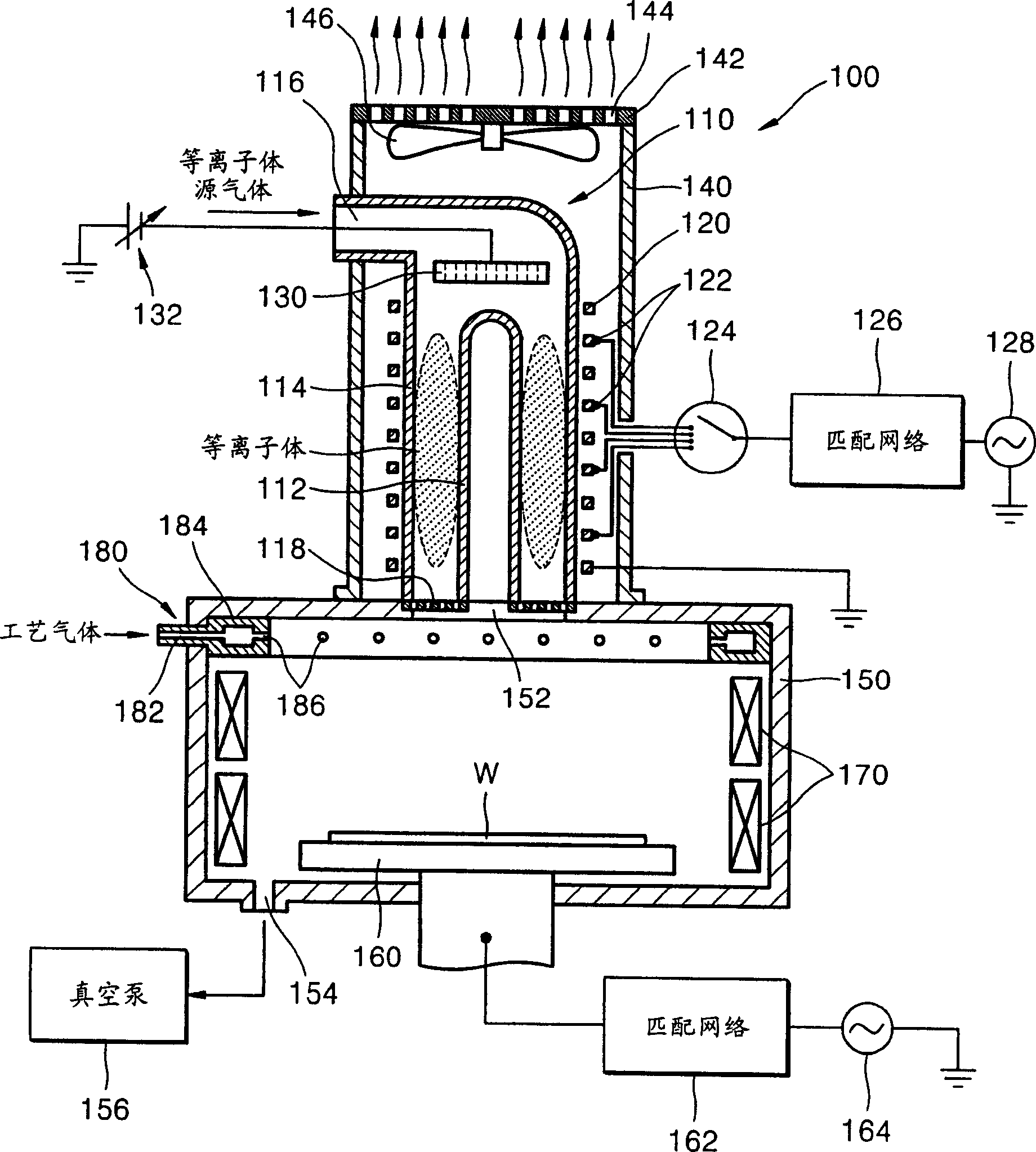
InactiveUS6225746B1High densityElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsVertical barDielectric plate
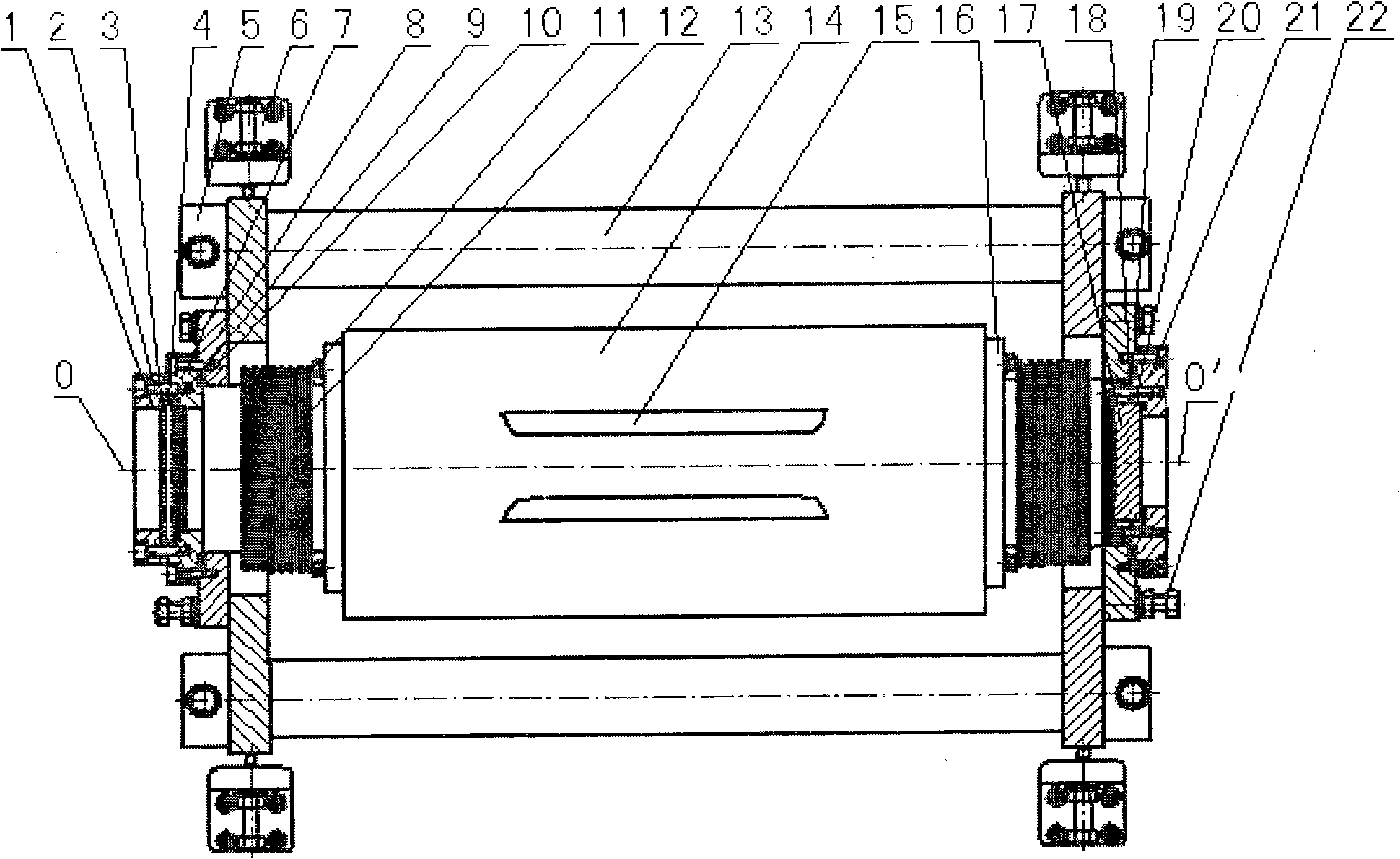
A plasma processing reactor includes a helical resonator including a top plate and a helical coil, the helical coil is made of a metal with a length of lambd / 4, wherein n is an integer and lambd is a wavelength of rf frequency applied to the helical coil. The reactor also includes a plasma process chamber including a wafer holder arranged at a lower position therein and a wafer to be processed is loaded on the wafer holder. The helical resonator has a vertical bar for introducing a gas, the vertical bar is fixed to the top plate of the helical resonator and is connected to a gas inlet port. A partition wall separates the helical resonator and the plasma process chamber. The partition wall includes an outer metal ring, a circular central metal plate, and a doughnut-shaped dielectric plate between the outer metal ring and the central metal plate, the doughnut-shaped dielectric plate having an inner diameter and an outer diameter. The central metal plate is fixed to the top plate using the vertical bar and includes a gas reservoir and a plurality of gas inlet ports. The helical coil is placed around the vertical bar, and the helical coil has a diameter that is greater than the inner diameter of the doughnut-shaped dielectric plate and is smaller than the outer diameter of the doughnut-shaped dielectric plate.
Owner:ANELVA CORP
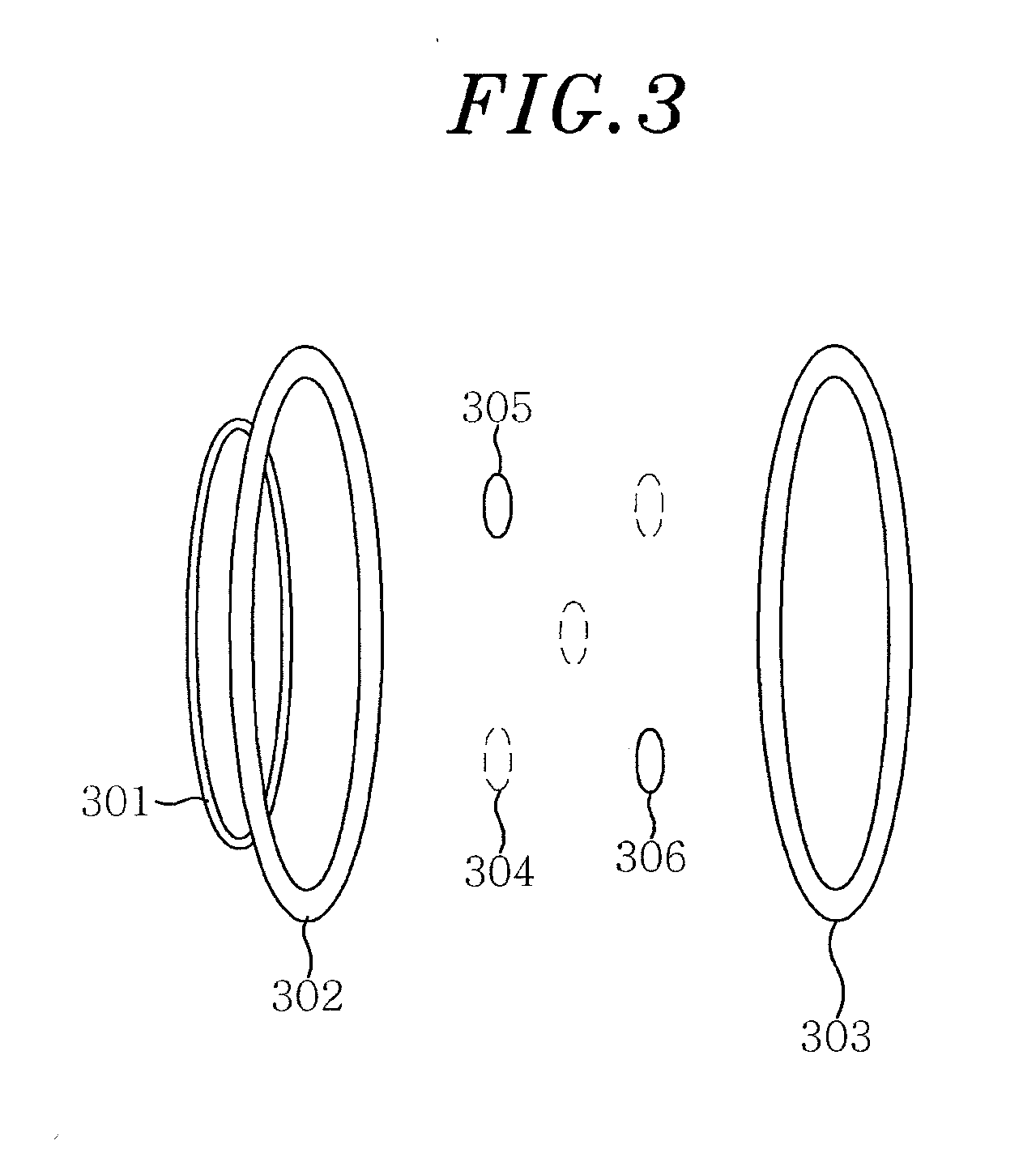
Helical resonator type plasma processing apparatus
InactiveCN1614746AImprove density uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDouble tubeHelical coil
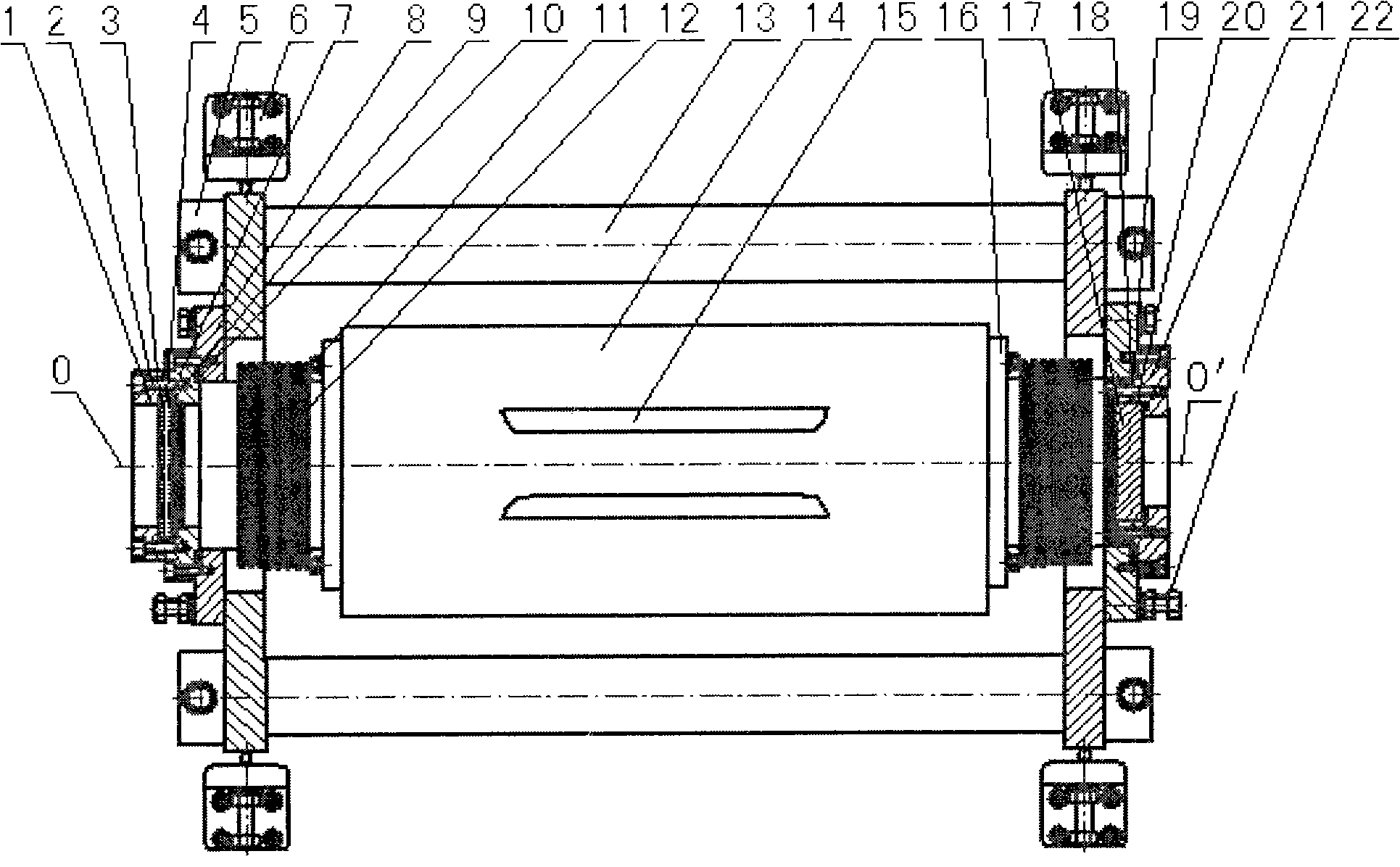
The invention discloses a spiral resonator plasma processing equipment. The plasma processing apparatus includes: a processing chamber having a substrate holder supporting a substrate to be processed; a dielectric tube disposed on the processing chamber so as to communicate with an interior space of the processing chamber; a helical coil wound around the outer tube of the dielectric tube; and an RF power supply that supplies RF power to the helical coil. The dielectric tube is in the form of a double tube, including an inner tube and an outer tube. A plasma source gas inlet is arranged in the outer tube to supply the plasma source gas into the space between the inner tube and the outer tube. A control electrode is arranged in the dielectric tube to control the plasma potential. This plasma processing apparatus provides a uniform plasma density distribution along the radial direction of the wafer and facilitates control of the plasma potential within the processing chamber.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
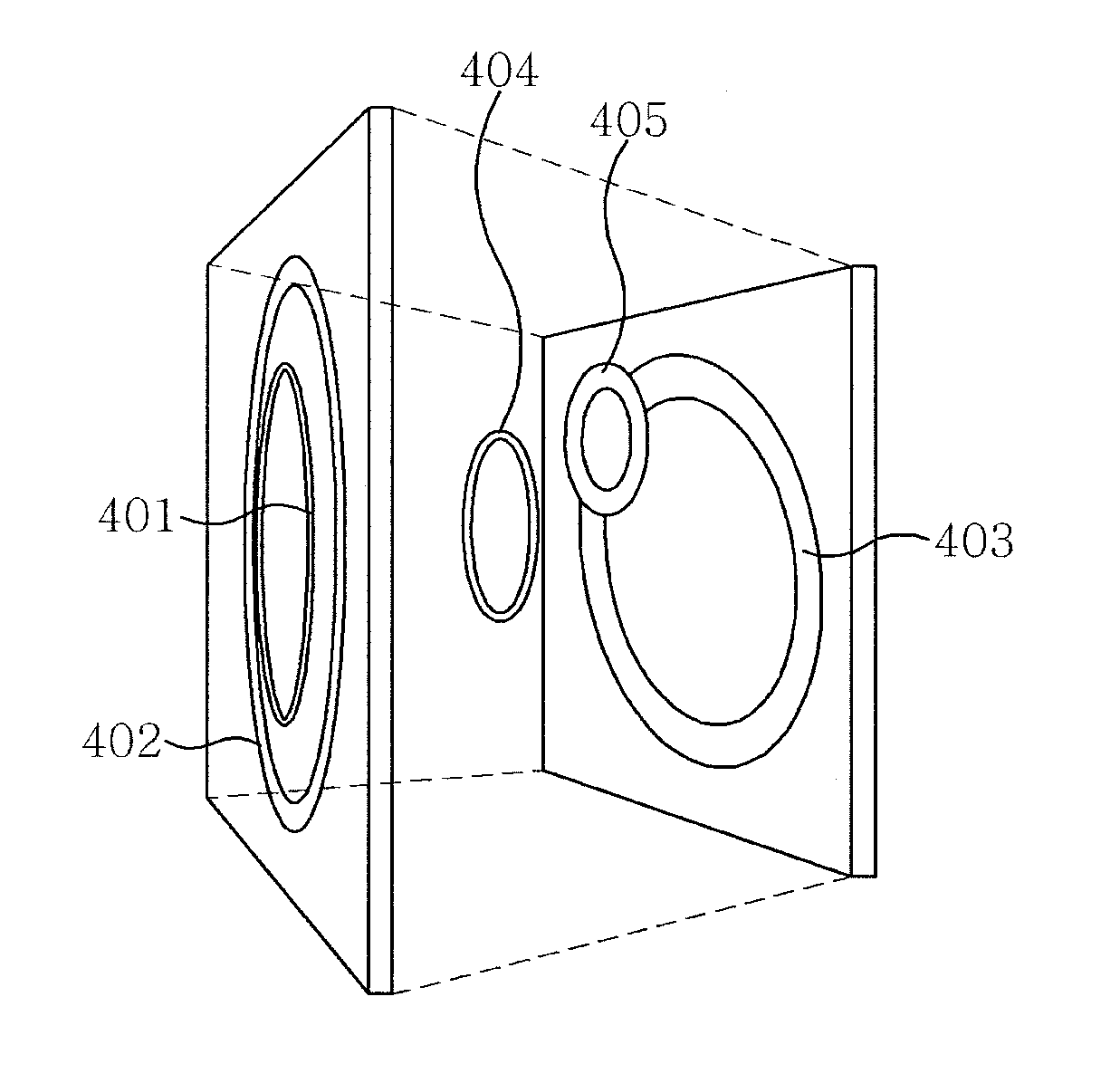
Coupled optical waveguide resonators with heaters for thermo-optic control of wavelength and compound filter shape
An integrated optical device is disclosed comprising a substrate, optical waveguide, and compound optical resonator having a temperature sensor, at least two coupled optical resonators, and a heater localized to each optical resonator. An optical input signal is coupled to one of the resonators making up the compound resonator to form an optical output signal. The center wavelength and shape of the output signal is optimized with a feedback loop using the temperature sensor to control the power dissipated in at least one of the localized heaters. The power dissipated in the remaining resonator heaters is set according to a predetermined function having as an input variable the power dissipated in the resonant heater under control of the said feedback loop.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Vibratory gyroscope
ActiveUS20140000366A1Improve signal level outputIncrease signal levelAcceleration measurement using interia forcesWave amplification devicesGyroscopeResonance
A sensing device comprising a micromechanical gyroscope, the gyroscope comprising an improved sensing device with a micromechanical gyroscope, where the resonance frequency of the first mechanical resonator and the resonance frequency of the second mechanical resonator are adjusted to essentially coincide. The device comprises a feed-back loop connected to the second mechanical resonator, the quality factor of the combination of the feed-back loop and the second mechanical resonator being less than 10. More accurate sensing is achieved without essentially adding complexity to the sensor device configuration.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Microwave to Optical Conversion Device and Method for Converting a Microwave Photon to an Optical Photon
InactiveUS20170248832A1Enhanced interactionLight demodulationNon-linear opticsOptical photonHelical resonator
A microwave to optical conversion device comprising:a superconducting microwave resonator, andan optical resonator including an electro-optical material,the superconducting microwave resonator and the optical resonator being arranged one with respect to the other so as to be electro-magnetically coupled.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Optical resonator of high-power CO2 gas laser
InactiveCN101854023ASolve the output stability problemReduce volumeLaser detailsOptical axisEffect light
The invention relates to an optical resonator of a high-power CO2 gas laser. The optical resonator comprises a total reflecting mirror, a total reflecting mirror base, a total reflecting mirror gland cover, an output reflecting mirror, an output reflecting mirror base and an output reflecting mirror gland cover. The connection relationship is as follows: the optical resonator is installed and fixed on two end plates of a high-stability optical support and is fixedly connected with both ends of a chamber passage of a working gas circularly flowing in a closed mode through elastic adjustable bellows. The axle centers of the total reflecting mirror and the output reflecting mirror are adjusted through a calibration lighting source and are coaxial with the space optical axis 0 of a laser discharge chamber. After an energy storing charge and discharge circuit supplies electrical energy, one pair of discharge electrodes of the laser discharge chamber glow discharges evenly to a large area. After multiple times of actuating resonation through the total reflecting mirror and the output reflecting mirror, pulse signals repeat multiple times and become stronger and stronger to form laser light, and the laser light is transmitted through an output window so as to form the optical resonator of the laser. The invention has high stability and reliability and compact structure, and is applicable to high-power gas lasers and pulsed gas lasers.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for making low-OH glass articles and low-OH optical resonator
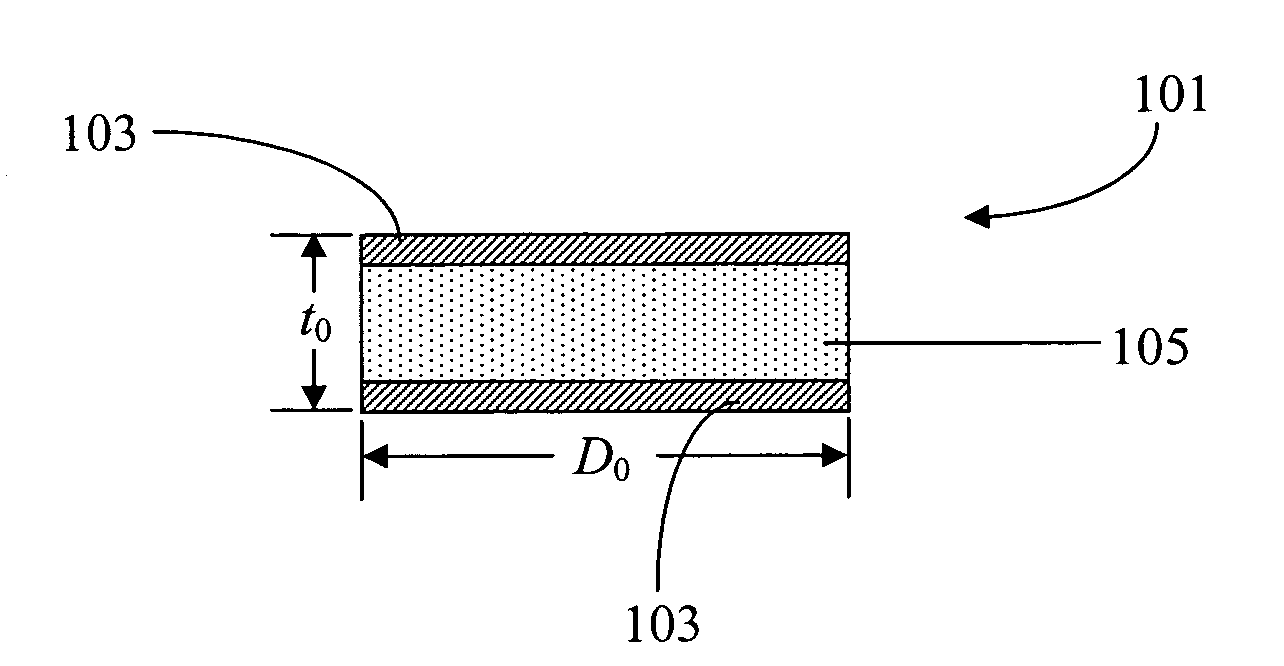
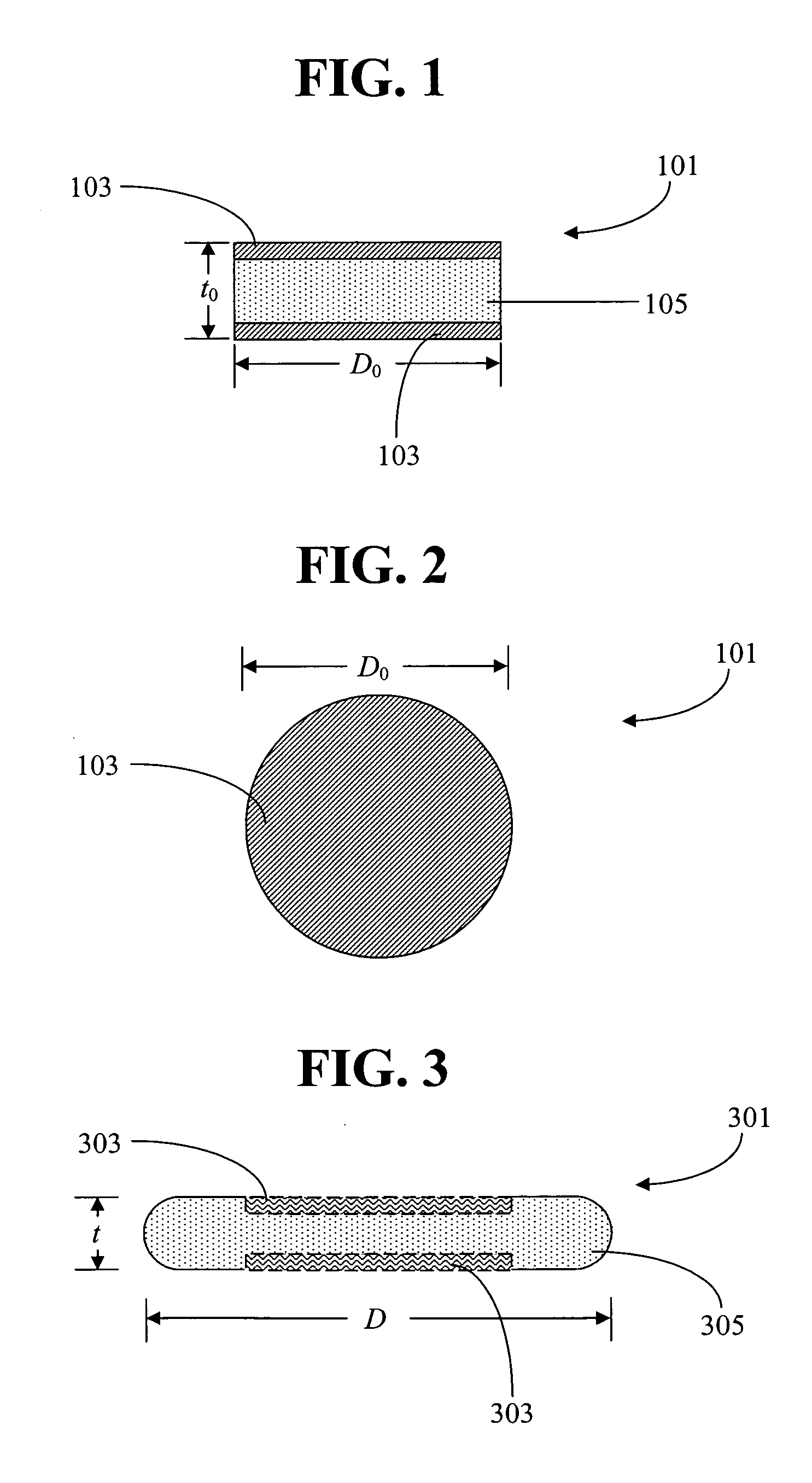
InactiveUS20050044893A1Lower levelReduce defectsLaser detailsGlass shaping apparatusProduct gasHelical resonator
Disclosed are optical resonators having low OH content in at least the near-surface region and a process for making low OH glass article by chlorine treatment of consolidated glass of the article. Cl2 gas was used to remove OH from depth as deep as 350 μm from the surface of the consolidated glass. The process can be used for treating flame-polished preformed optical resonator disks. A new process involving hot pressing or thermal reflowing for making planar optical resonator disks without the use of flame polishing is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com