Patents
Literature
746results about "Logic circuits using opto-electronic devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plasmonic nanophotonics methods, materials, and apparatuses
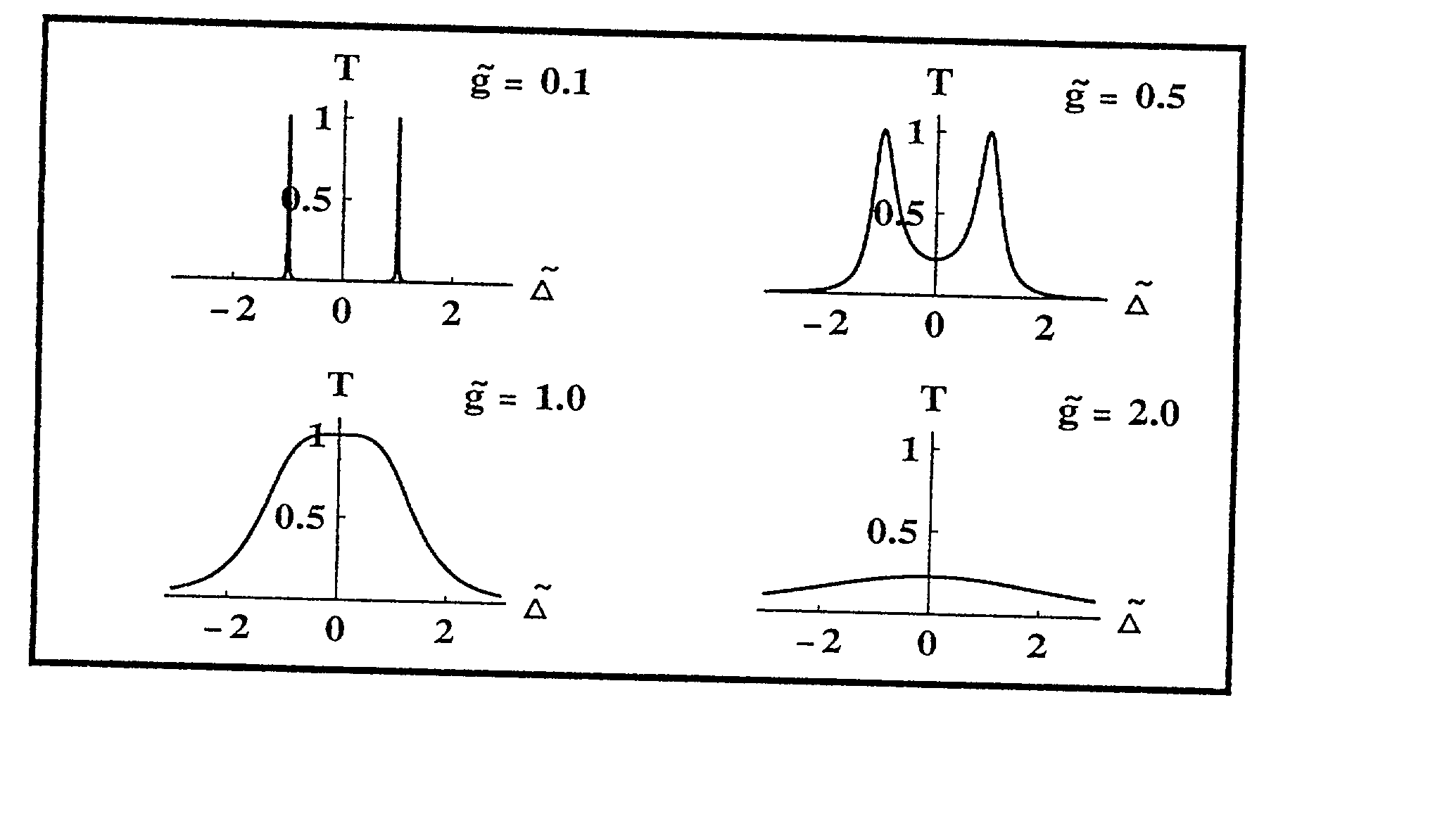
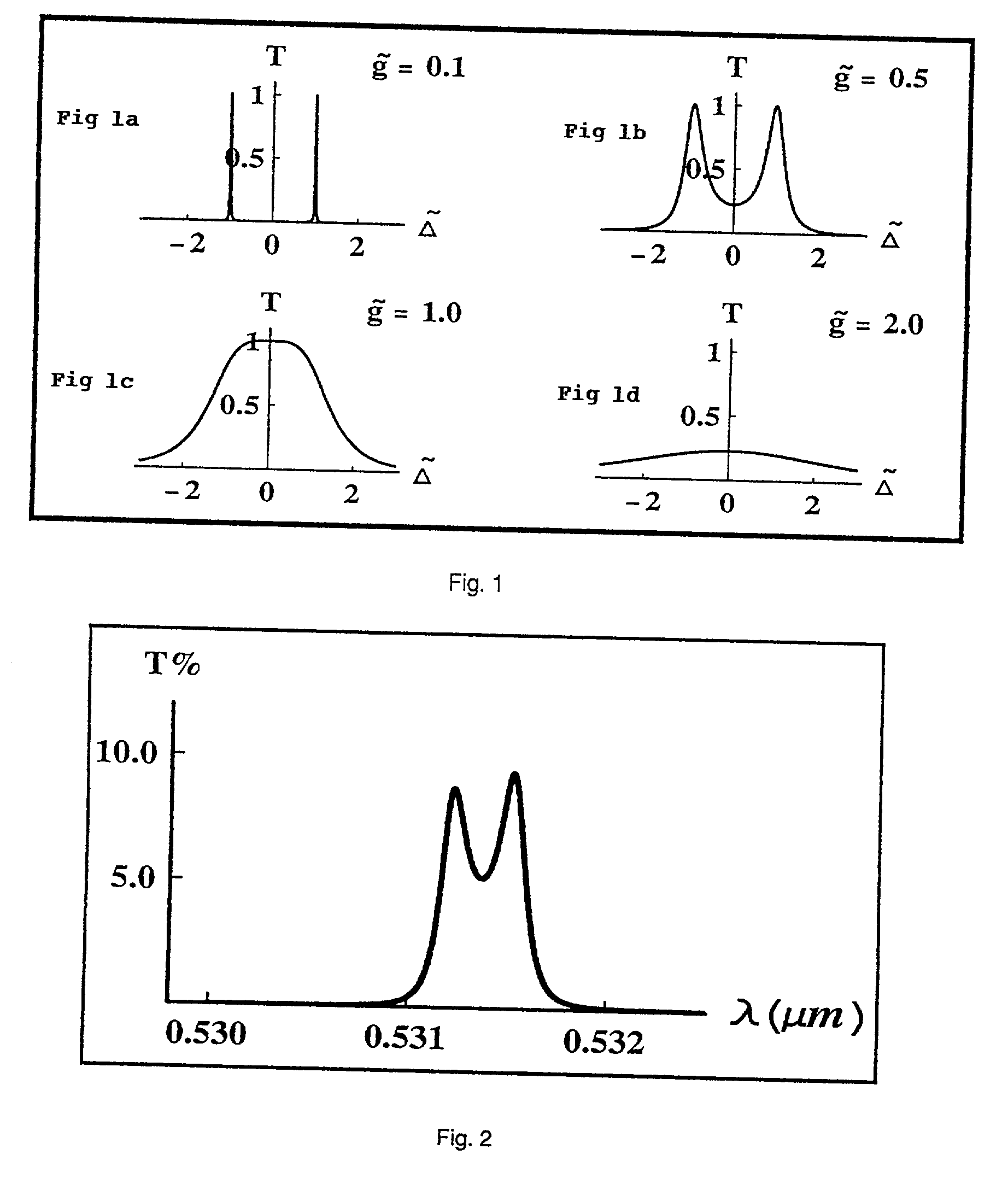
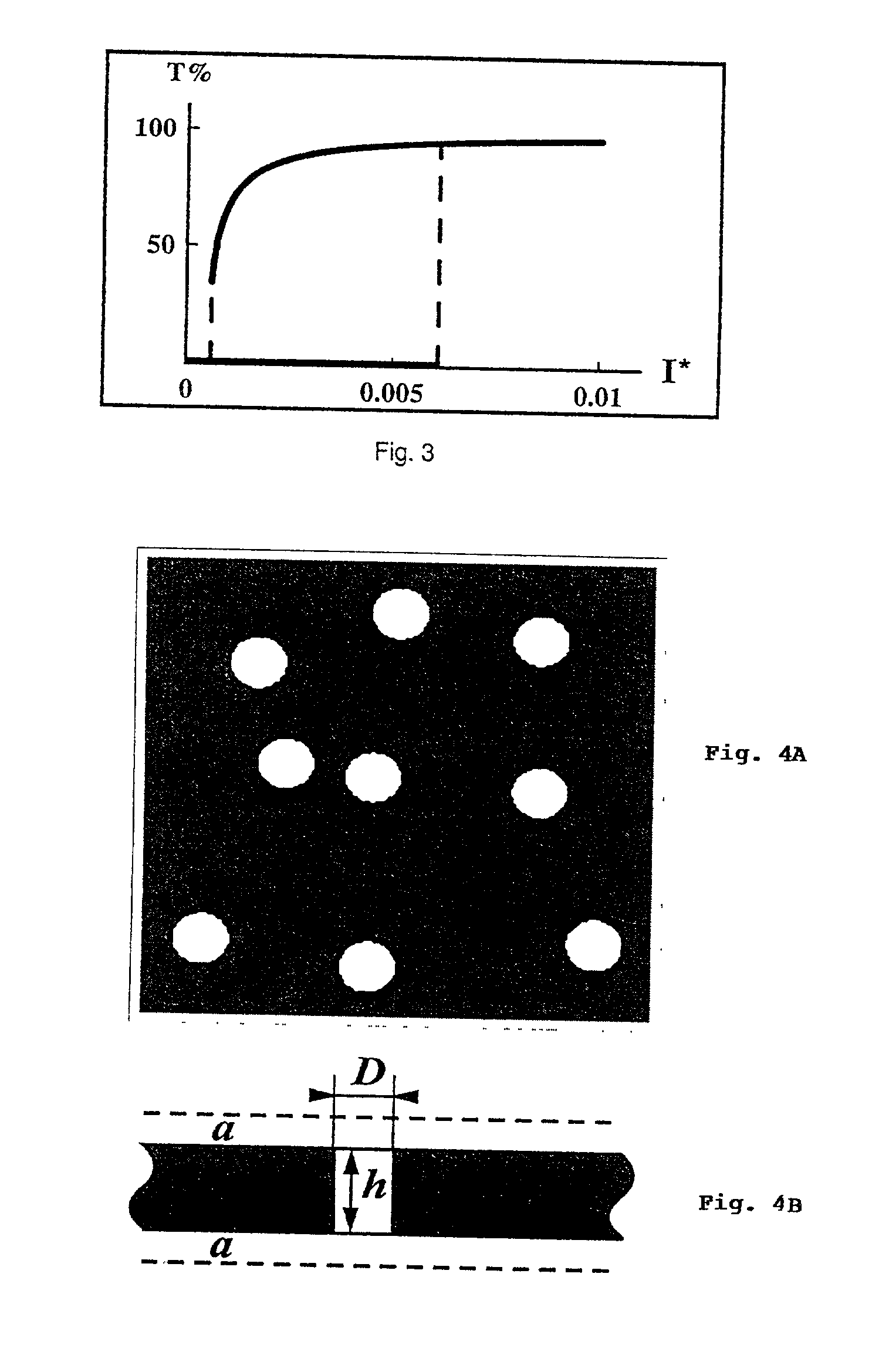
Controlling, guiding, manipulating, and circuiting light and performing surface-enhanced spectroscopy in a medium comprising plasmonic nanomaterials via the excitation of plasmon modes in the materials. The plasmonic nanomaterials are based on metal films with or without arrays of nanoholes and / or on metal nanowires and / or spheroids. Also devices and methods employing such plasmonic nanomaterials.
Owner:NEW MEXICO STATE UNIV TECH TRANSFER
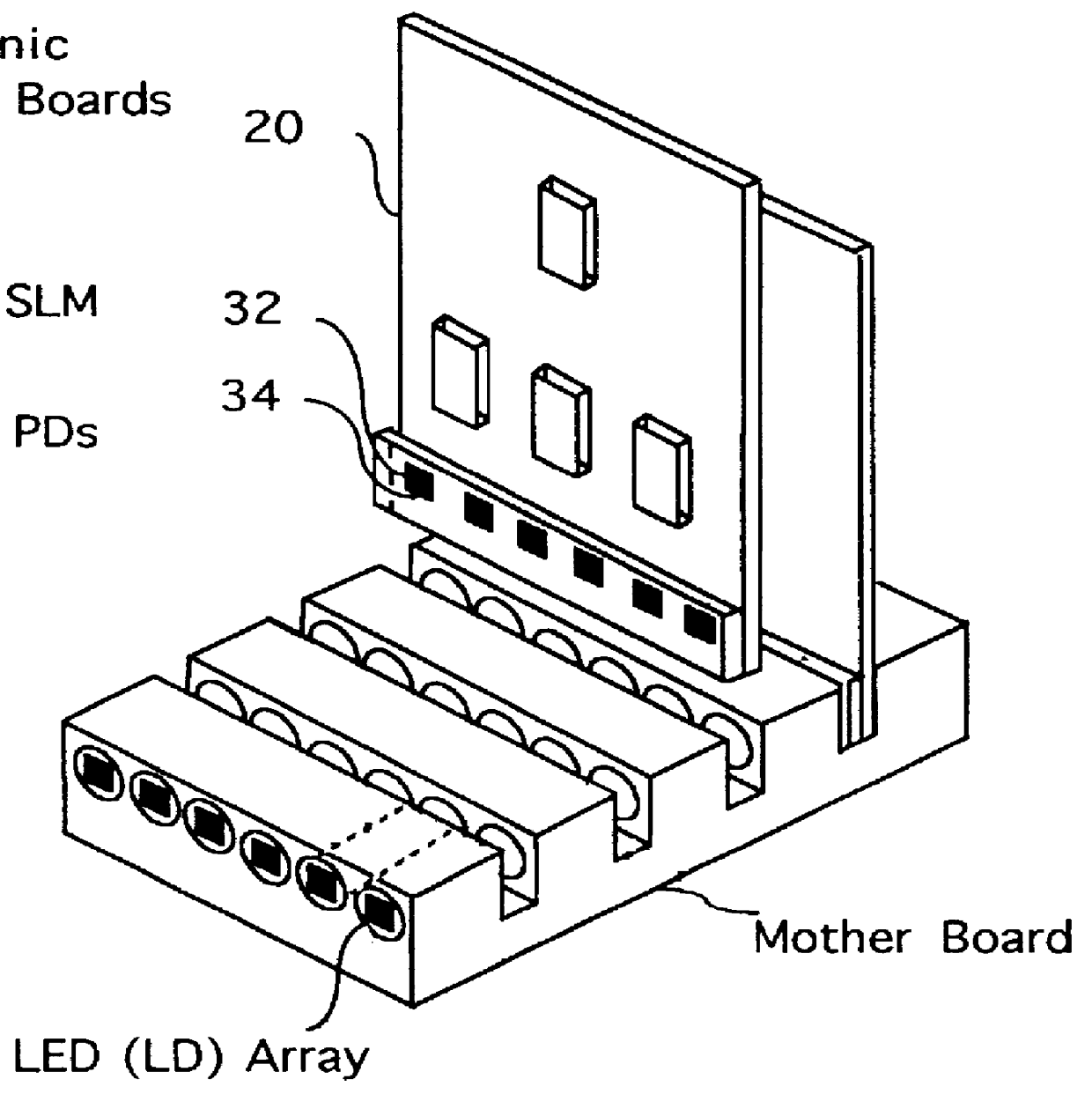
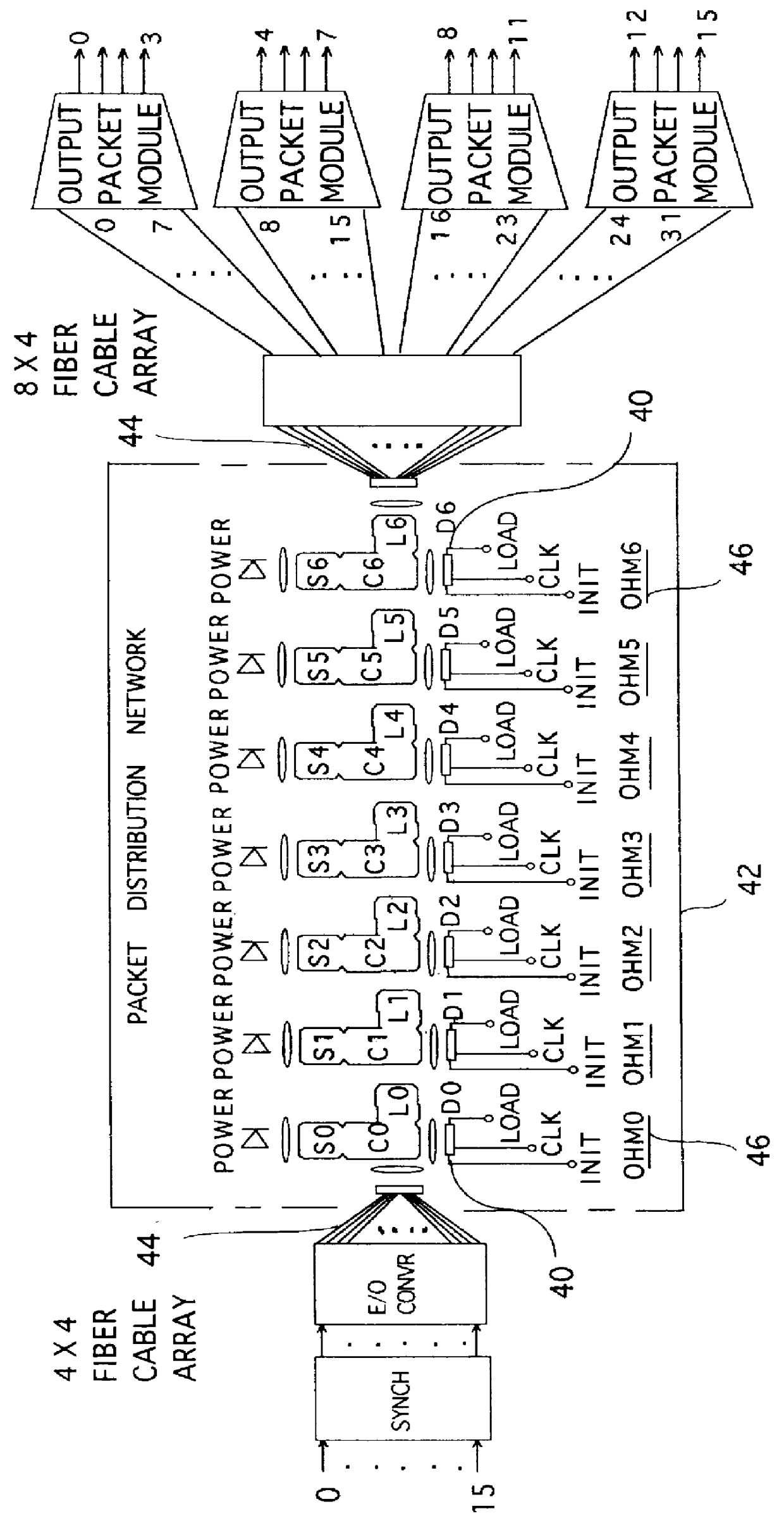
Optoelectronic smart pixel array for a reconfigurable intelligent optical interconnect
InactiveUS6016211APowerful and flexibleHigh bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsEngineeringOptical communication
A packaged smart pixel array for a reconfigurable intelligent optical interconnect is described. The smart pixel array (298) comprises an optical-to-electronic optical I / O channel 68 input means, an electronic-to-optical optical I / O channel 68 output means, an electrical channel input means (134), an electrical channel output means (114), a data switching means (110) for switching data from optical channel input means to electrical channel output means, a data switching means (130) for switching data from electrical channel input means and optical channel input means to optical channel output means and a packaging means (300) which packages all these means onto a single package with identifiable input and output port means. The smart pixel array makes possible the realization of a reconfigurable optical interconnect which implements multiple reconfigurable optical communication channels.
Owner:SZYMANSKI TED +1
MEMS optical switch with thermal actuator
InactiveUS6853765B1Minimize adverse temperature effectAdverse temperature effectCoupling light guidesLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesEngineeringActuator
A MEMS type optical switch includes a substrate, the substrate including at least one groove formed therein; first and second optical fibers disposed in the at least one groove, the at least one groove including a widened portion for movement of at least one of the first and second optical fibers; a thermal actuator disposed adjacent one of the first and second optical fibers, the thermal actuator comprising at least one v-beam, a pair of anchors connected to ends of the v-beam, and a yoke disposed in a central portion of the v-beam.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Optical semiconductor device
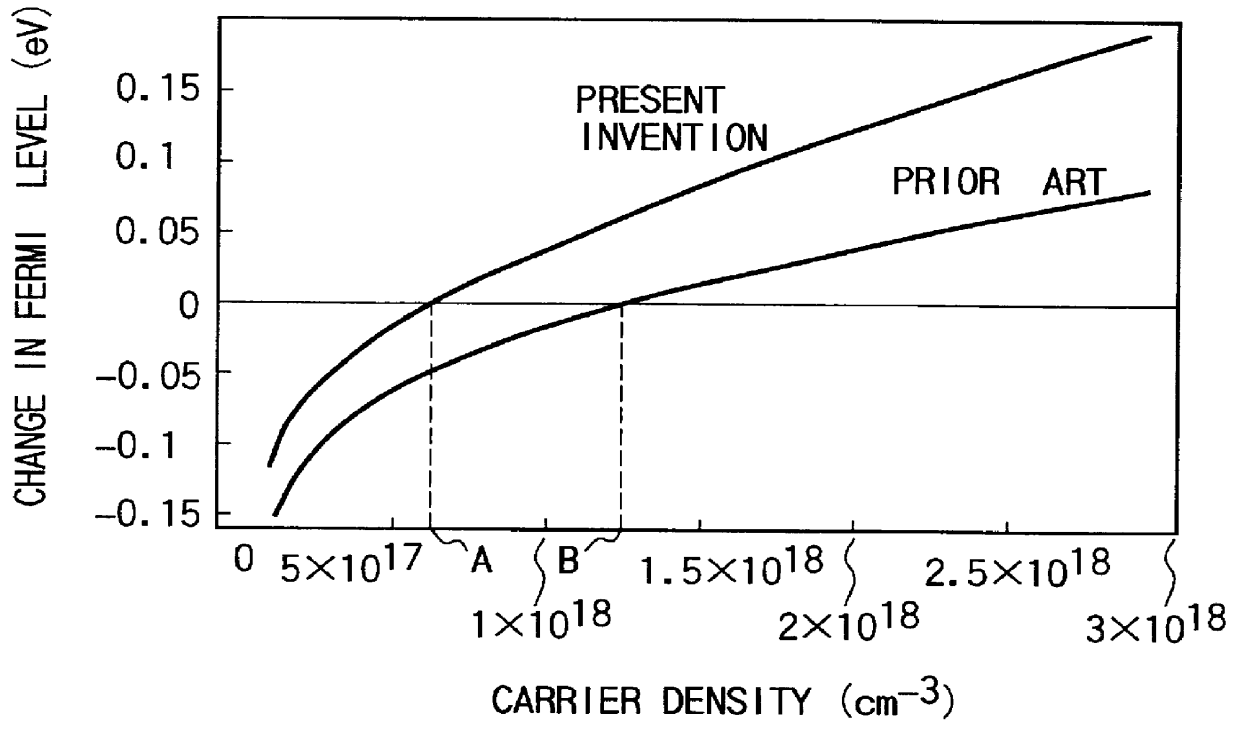
InactiveUS6043515AEasy population inversionImprove featuresExcitation process/apparatusSolid-state devicesMagnetizationContact layer
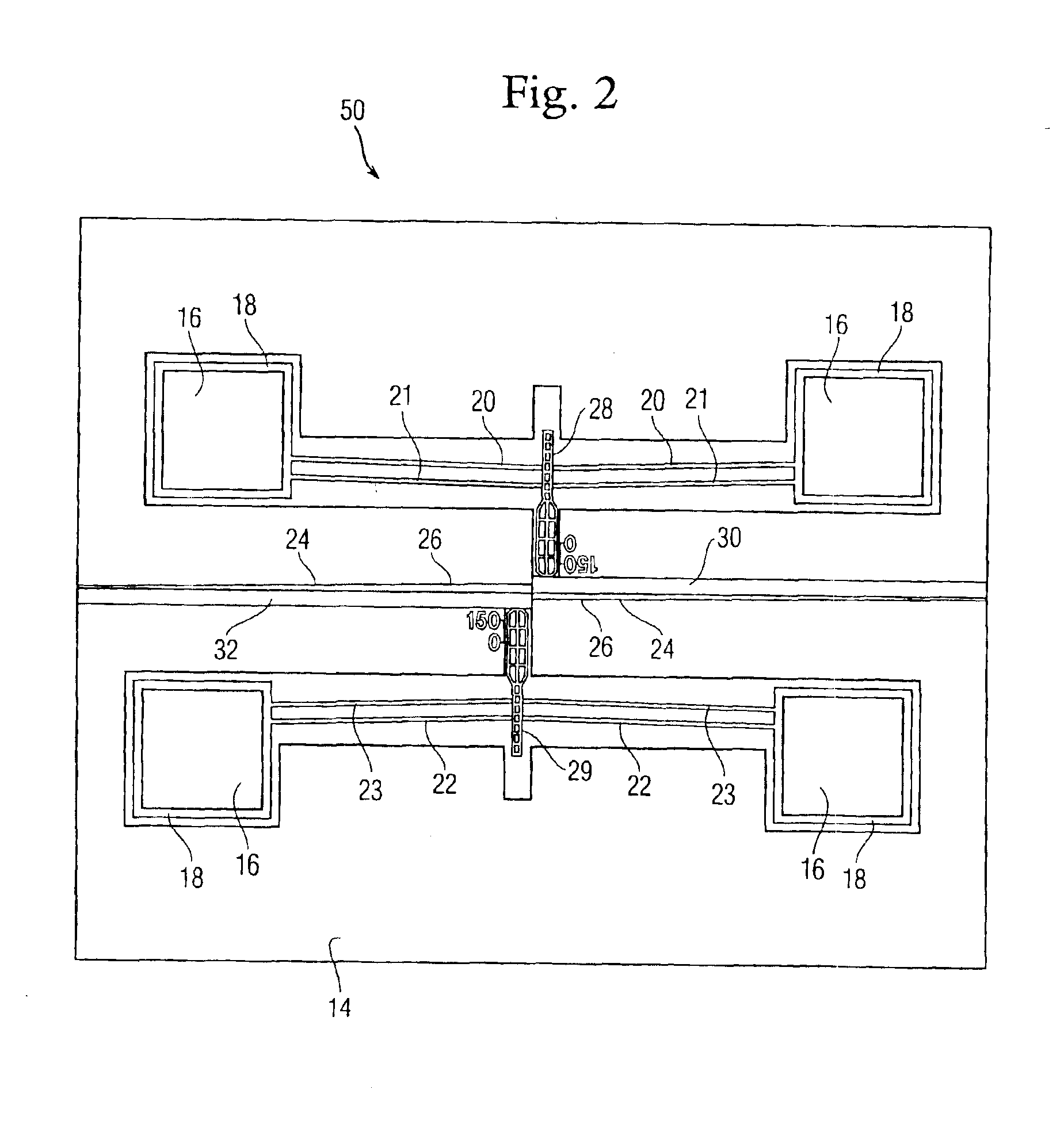
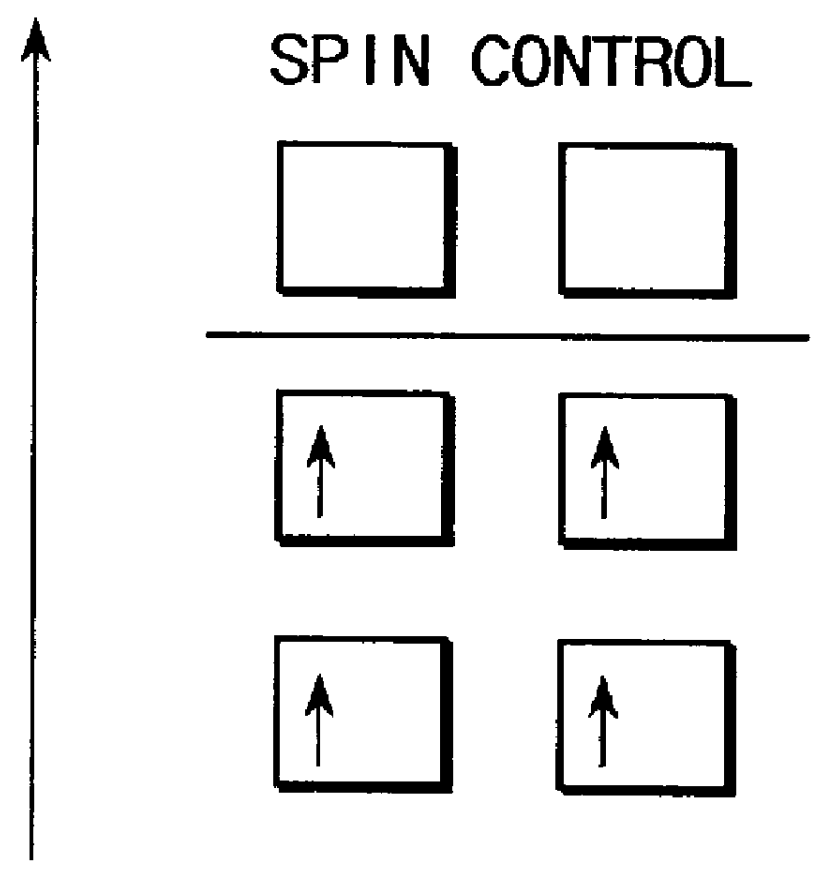
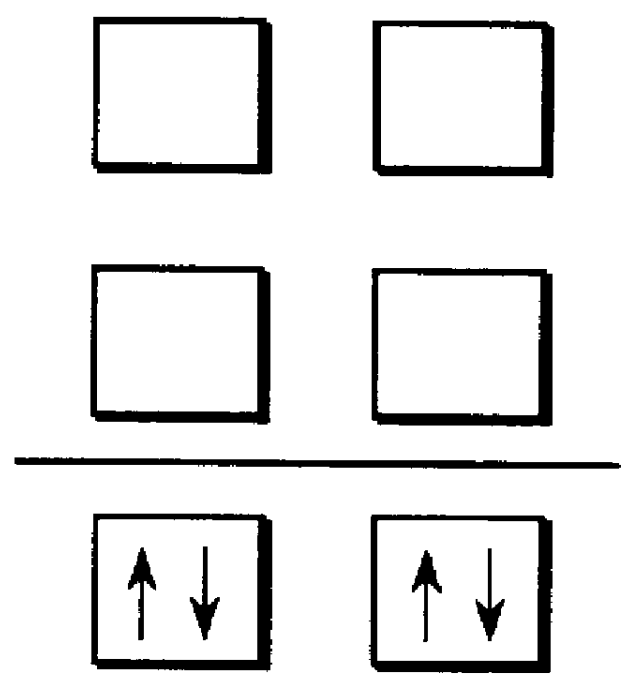
An optical semiconductor device has a structure in which a semiconductor active layer is sandwiched by a p-type semiconductor cladding layer and an n-type semiconductor cladding layer and a p-type contact layer is formed on the p-type semiconductor cladding layer side and an n-type contact layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor cladding layer side, wherein two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the n-type contact layer and two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the p-type contact layer. Magnetization directions of a pair of ferromagnetic layers vertically opposed to each other are set to be parallel to each other, and the magnetization directions of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are inverted to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
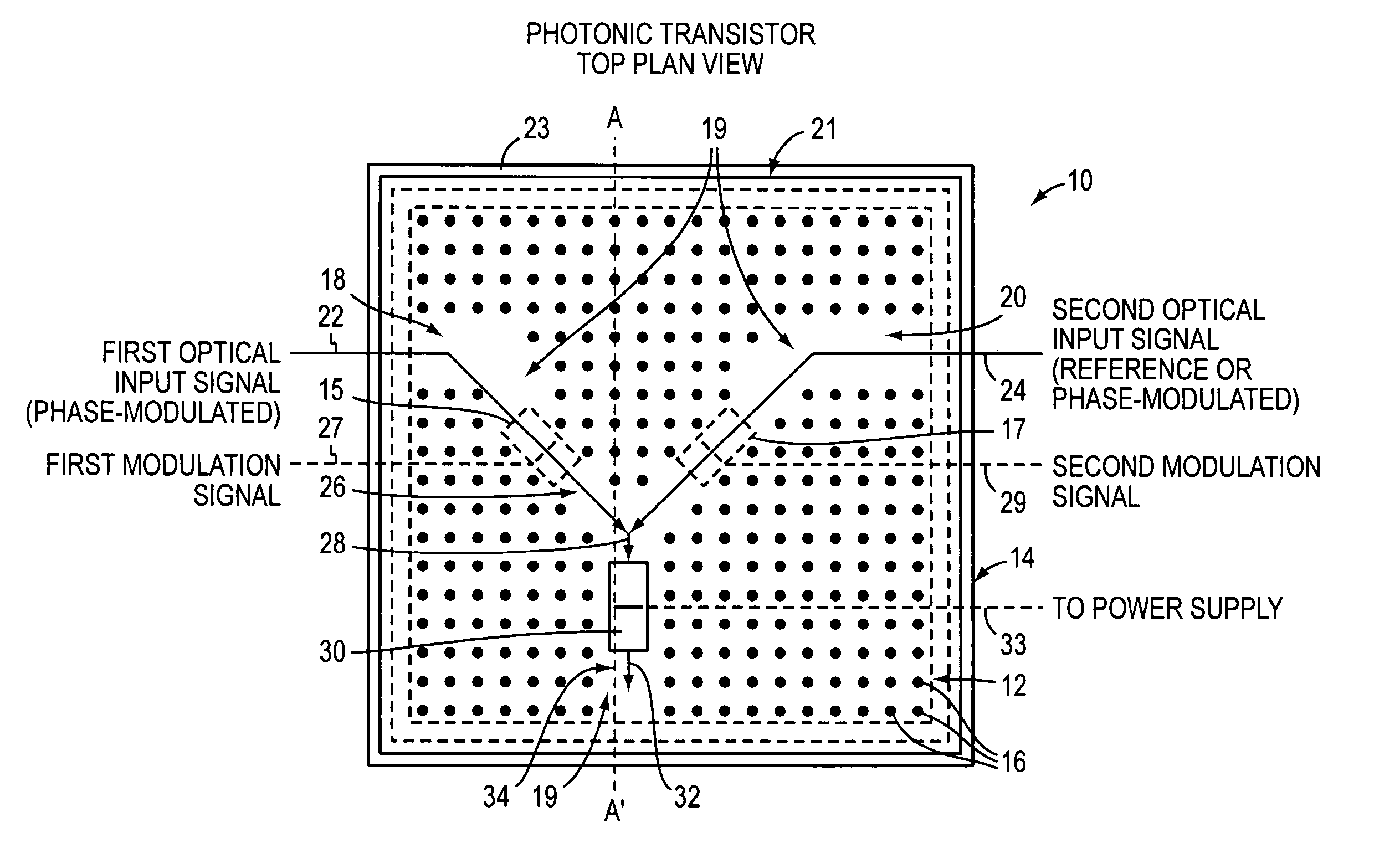
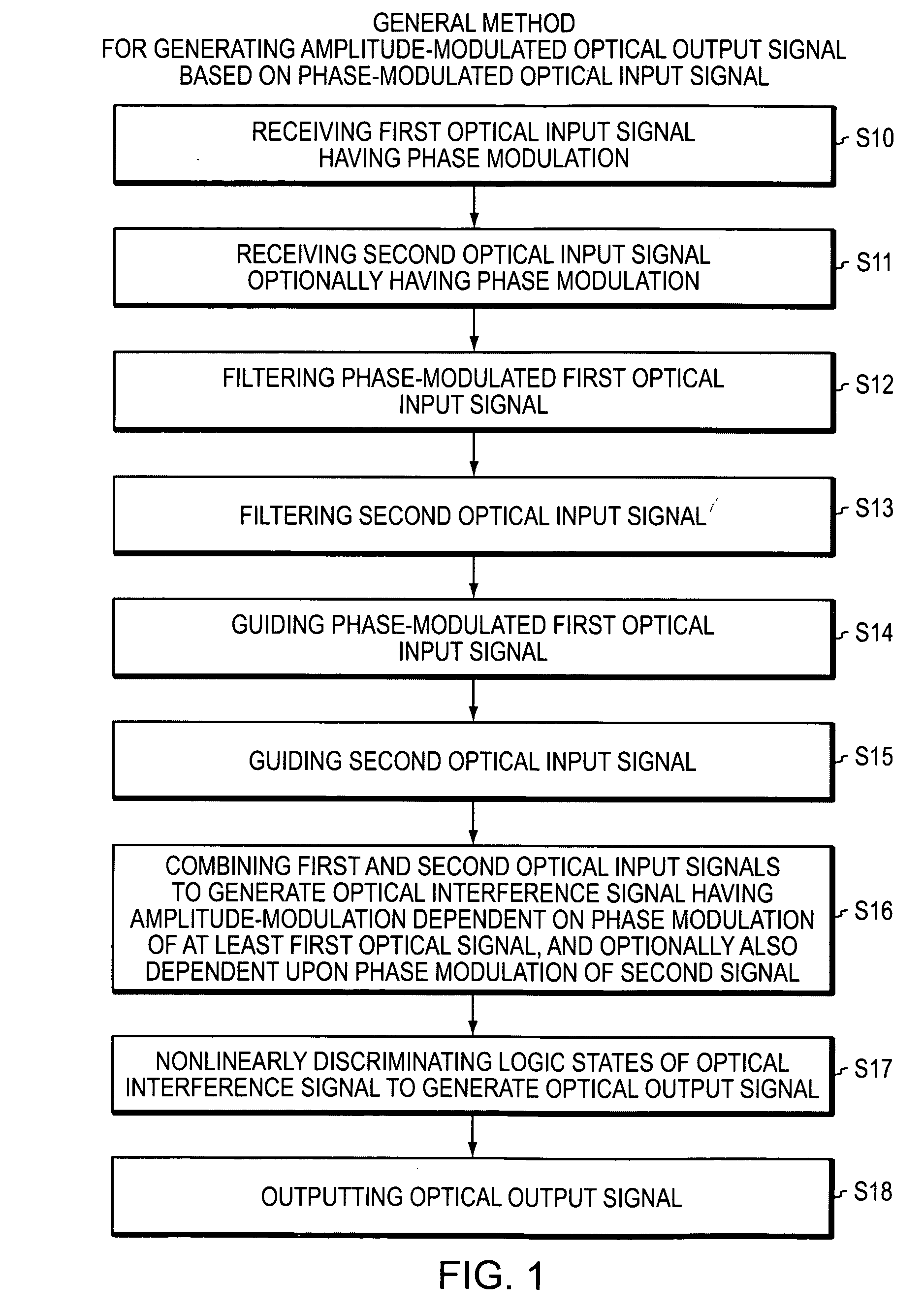
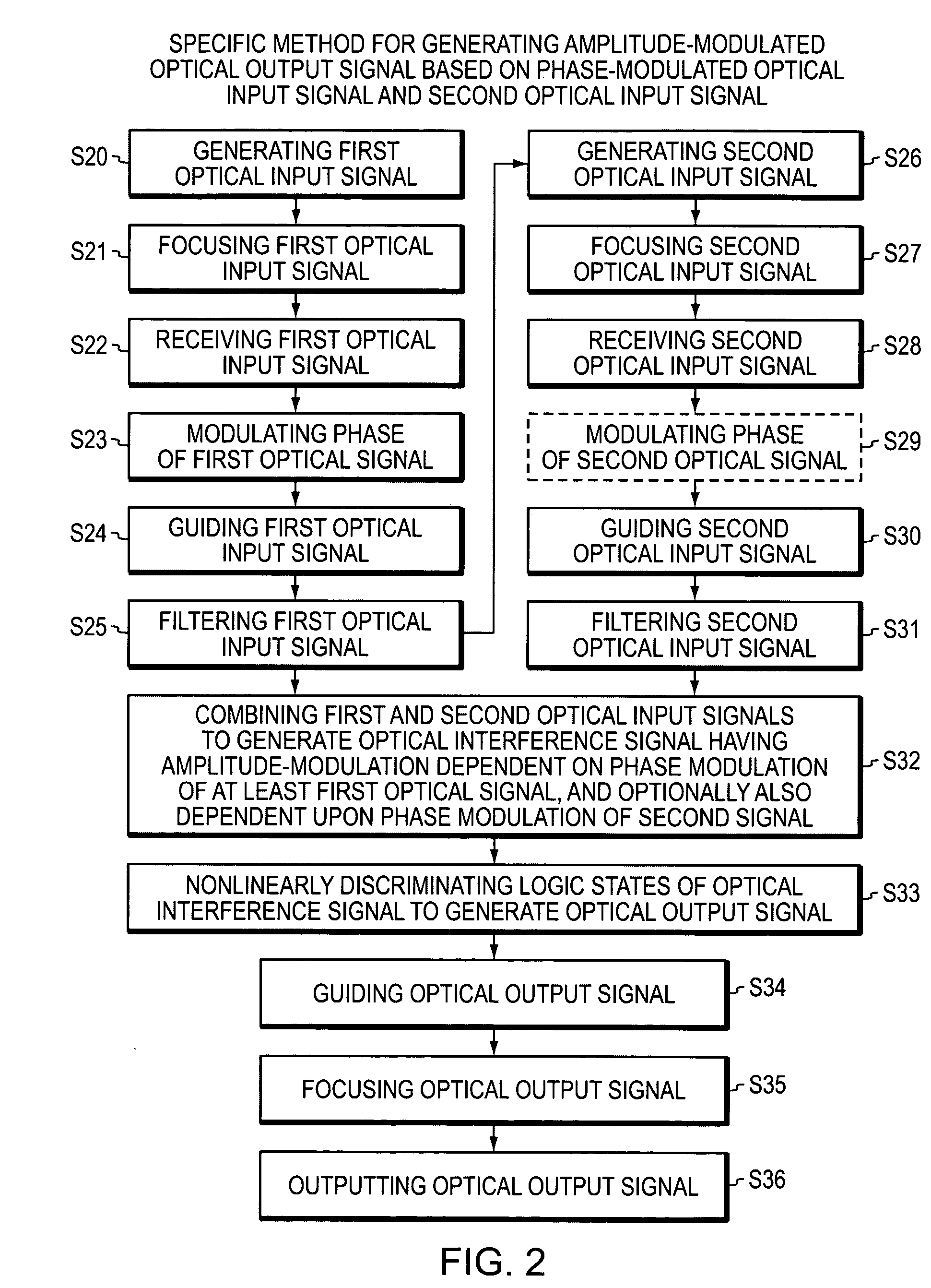
Optical device and circuit using phase modulation and related methods
InactiveUS20050259999A1Logic circuits using opto-electronic devicesElectromagnetic transmittersNonlinear elementLogic gate
A disclosed apparatus comprises a guiding element and a nonlinear element. The guiding element guides optical input signals, at least one of which is phase-modulated, to an interference area where such signals meet and interfere. The resulting interference signal is nonlinearly discriminated by the nonlinear element to produce an optical output signal that can be amplitude- or phase-modulated according to the phase modulation of the input signals. The invention also includes related methods and photonic logic gates.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
Quantum processing device
ActiveUS20140291490A1High efficiency in photon collectionAttenuation bandwidthQuantum computersNanoinformaticsPhoton emissionPhoton detection
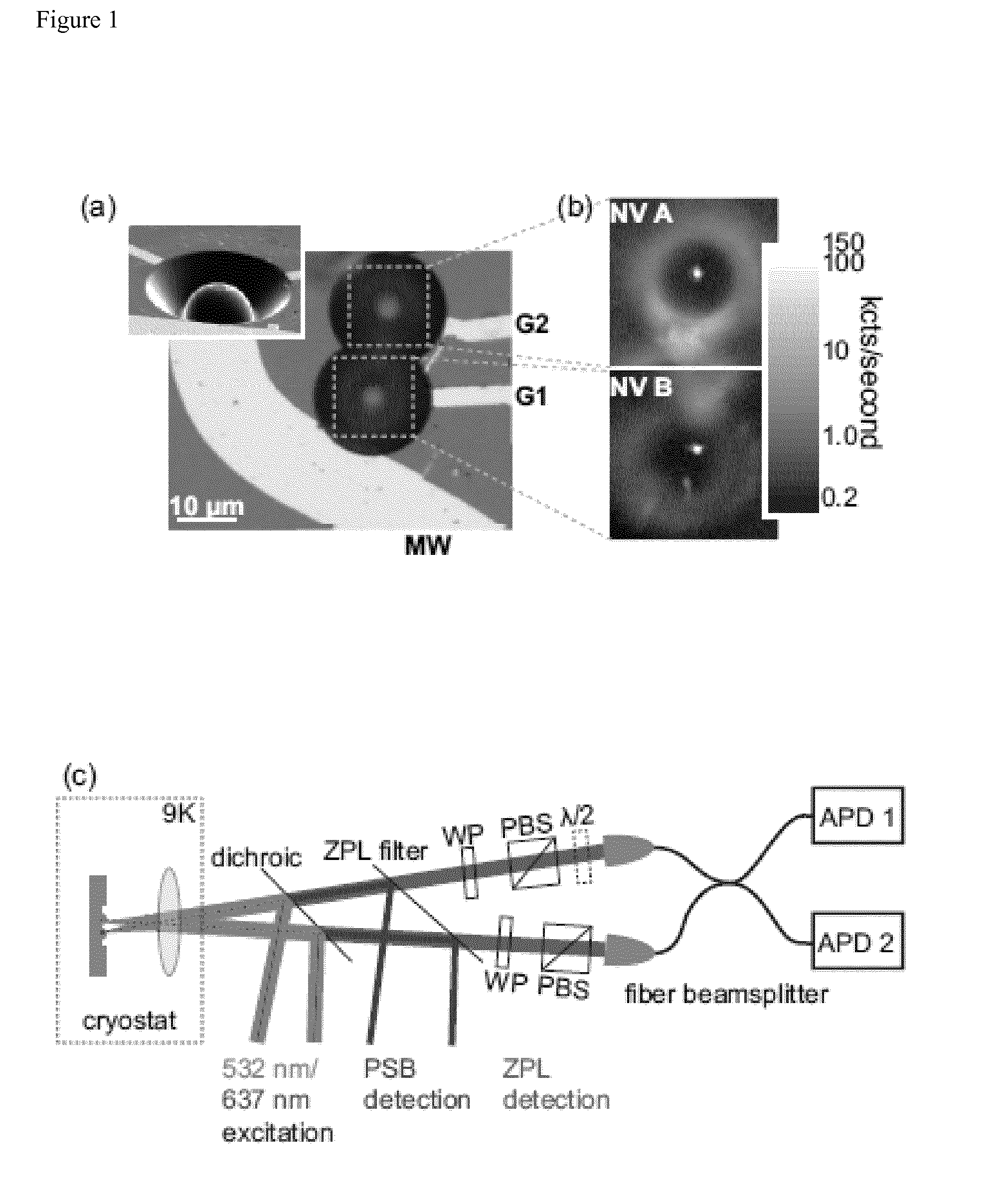
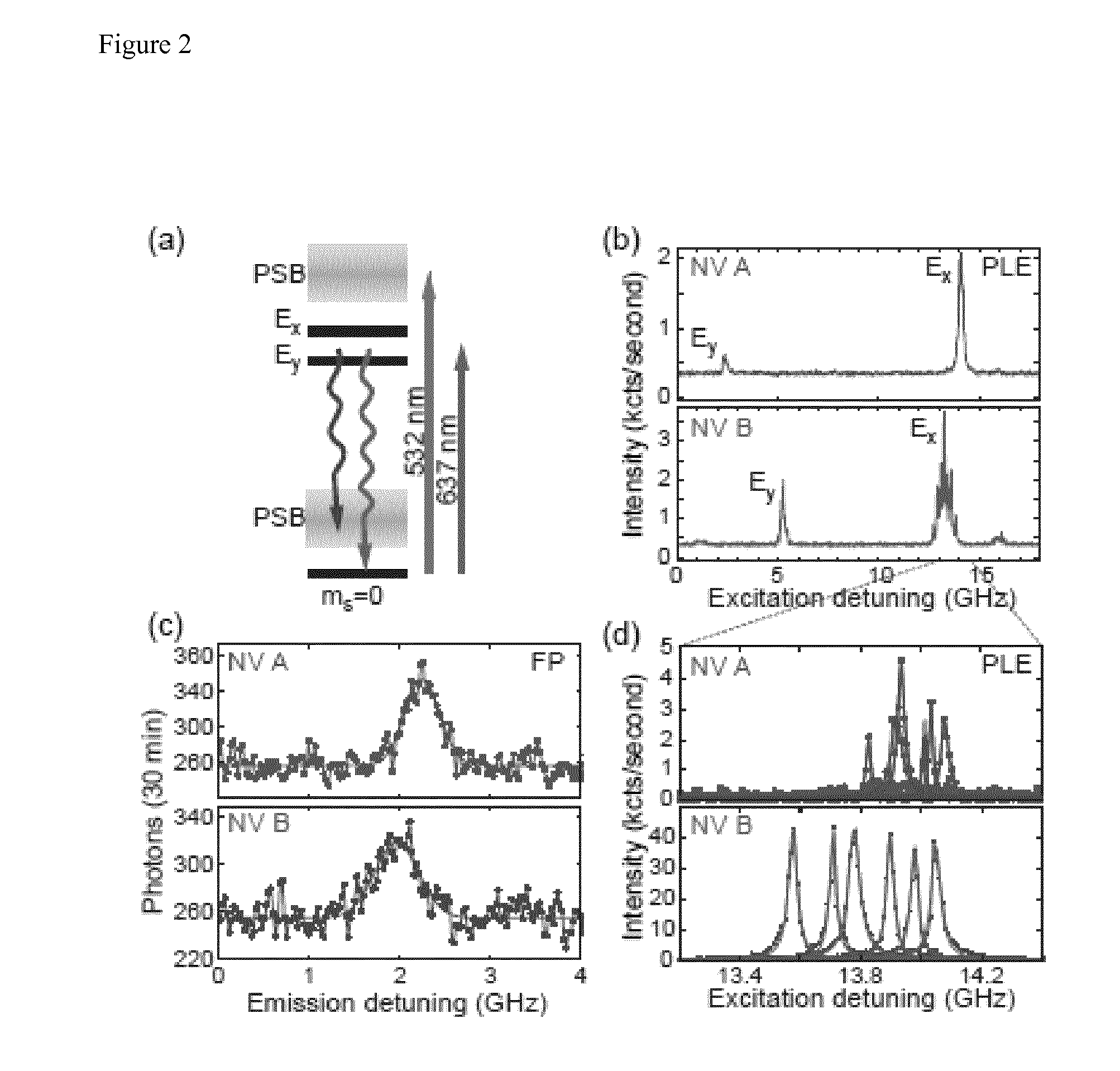
A device for achieving multi-photon interference, said device comprising: at least two solid state photon emitters, each solid state photon emitter comprising nuclear and electron spin states coupled together, each solid state photon emitter being configured to produce photon emission comprising a photon emission peak, wherein the photon emission peaks from different solid state photon emitters have a first frequency difference between peak intensities, and wherein the electron spin states of each solid state photon emitter are resolvable; an excitation arrangement configured to individually address the at least two solid state photon emitters; a plurality of optical out coupling structures wherein each solid state photon emitter is provided with an associated optical out coupling structure; a tuning arrangement configured to reduce the first frequency difference between the peak intensities of the photon emission peaks from the at least two solid state photon emitters to a second frequency difference which is smaller than the first frequency difference; a photon interference arrangement configured to overlap photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning; and a detector arrangement configured to detect photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning and passing through the photon interference arrangement, wherein the detector arrangement is configured to resolve sufficiently small differences in photon detection times that tuned photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters are quantum mechanically indistinguishable resulting in quantum interference between indistinguishable photon emissions from different solid state photon emitters.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
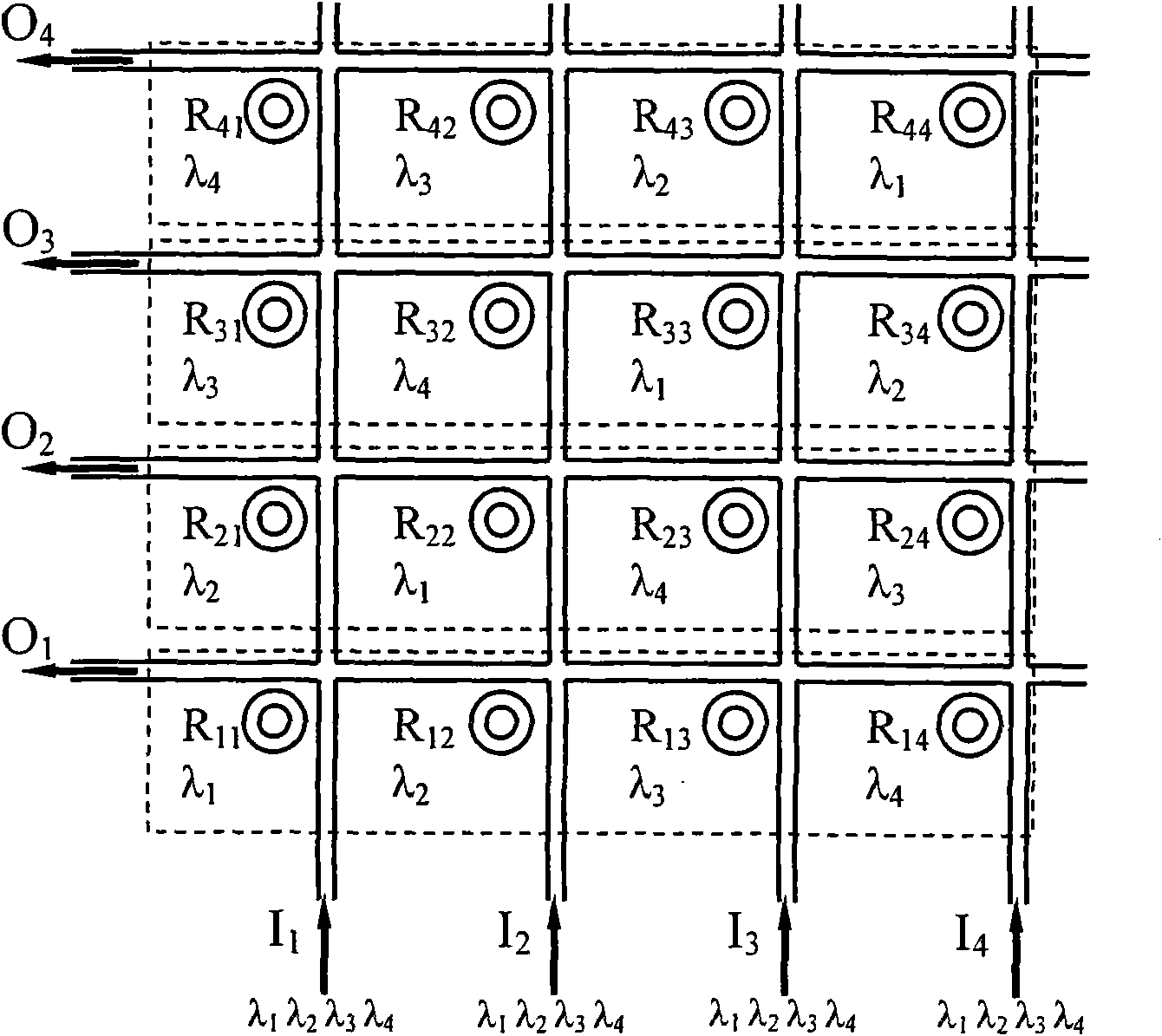
Silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier
ActiveCN101630178AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesNon-linear opticsNanowireMatrix multiplier
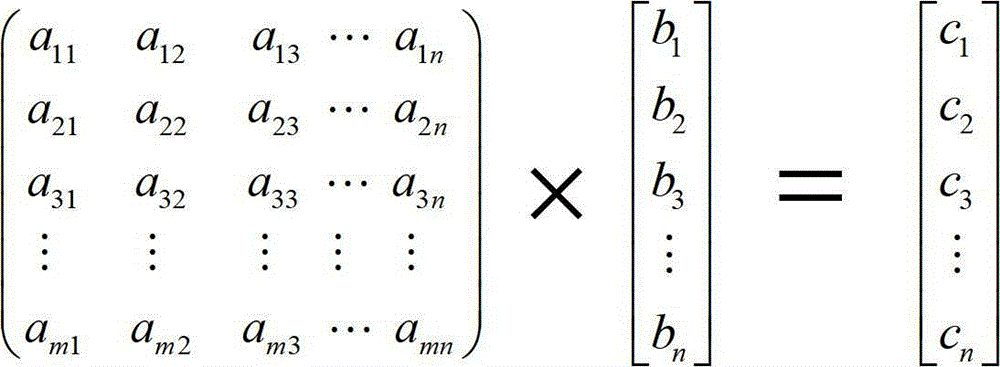
The invention discloses a silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier, which consists of nano-wire micro-ring resonators arranged periodically, and is used for realizing the multiplication of an N*N matrix and an N*1 vector, wherein elements in the N*N matrix and the N*1 vector are all 0 or 1. The optical vector-matrix multiplier is prepared from a silicon-on-insulator material, the basic units of the multiplier are the nano-wire micro-ring resonators (MRR), and the basic structure is the MRRs which are arranged in N*N and are provided with a thermal modulation mechanism respectively. The silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier adopts the prior art, so that the device has small volume, low power consumption and good expansibility and is convenient to be integrated with an electrical element; the silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier adopts laser pulses to transmit information, so the speed is high and the delay is short; a digital mode is utilized for processing signals, so the defect that an analog optical computing system has low accuracy and poor programmable capacity is avoided; and waveguides with a great refractive index difference are utilized to transmit light, so the problem that the space diversity efficiency of the conventional optical vector-matrix multiplier is low is avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
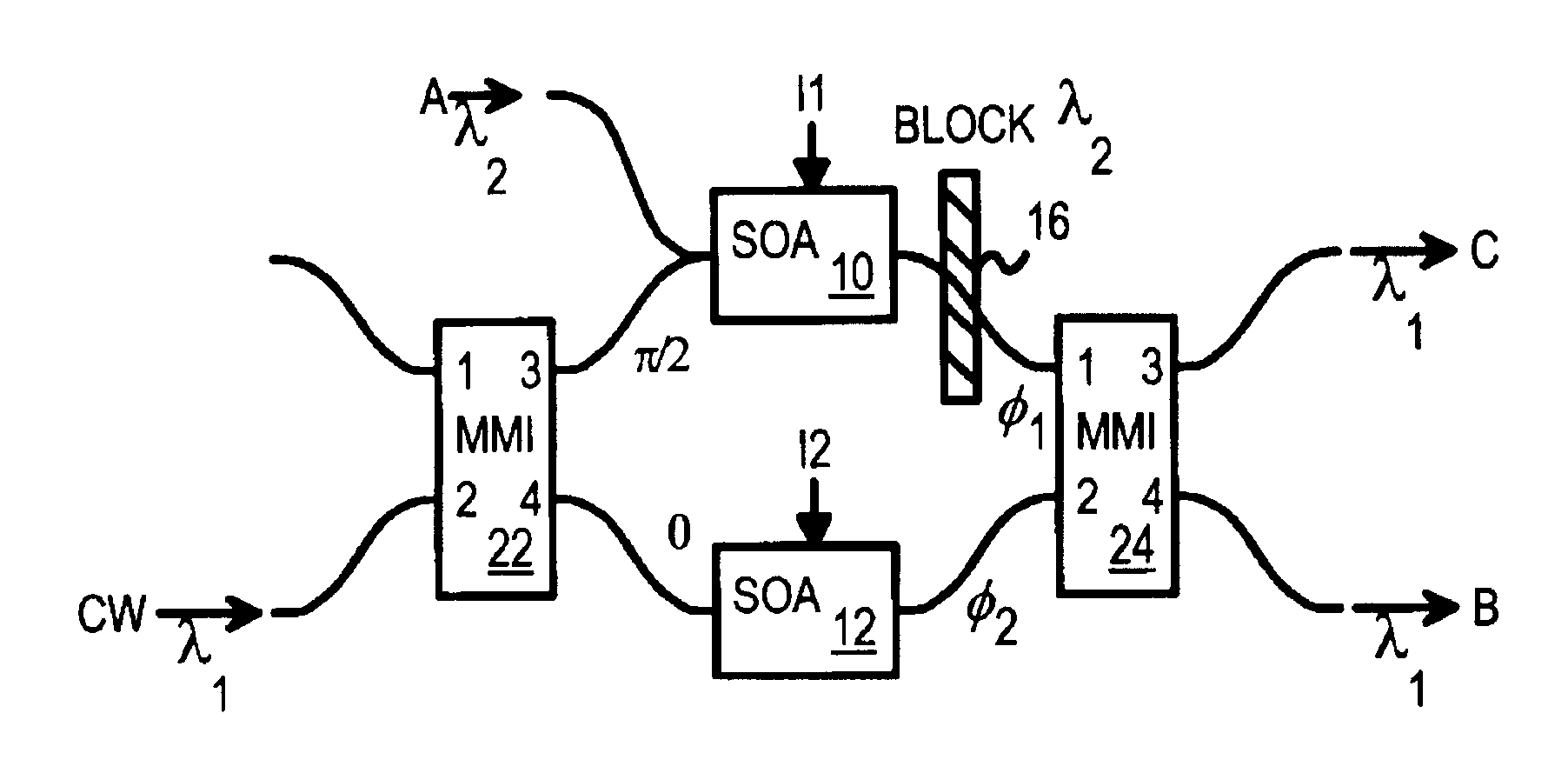
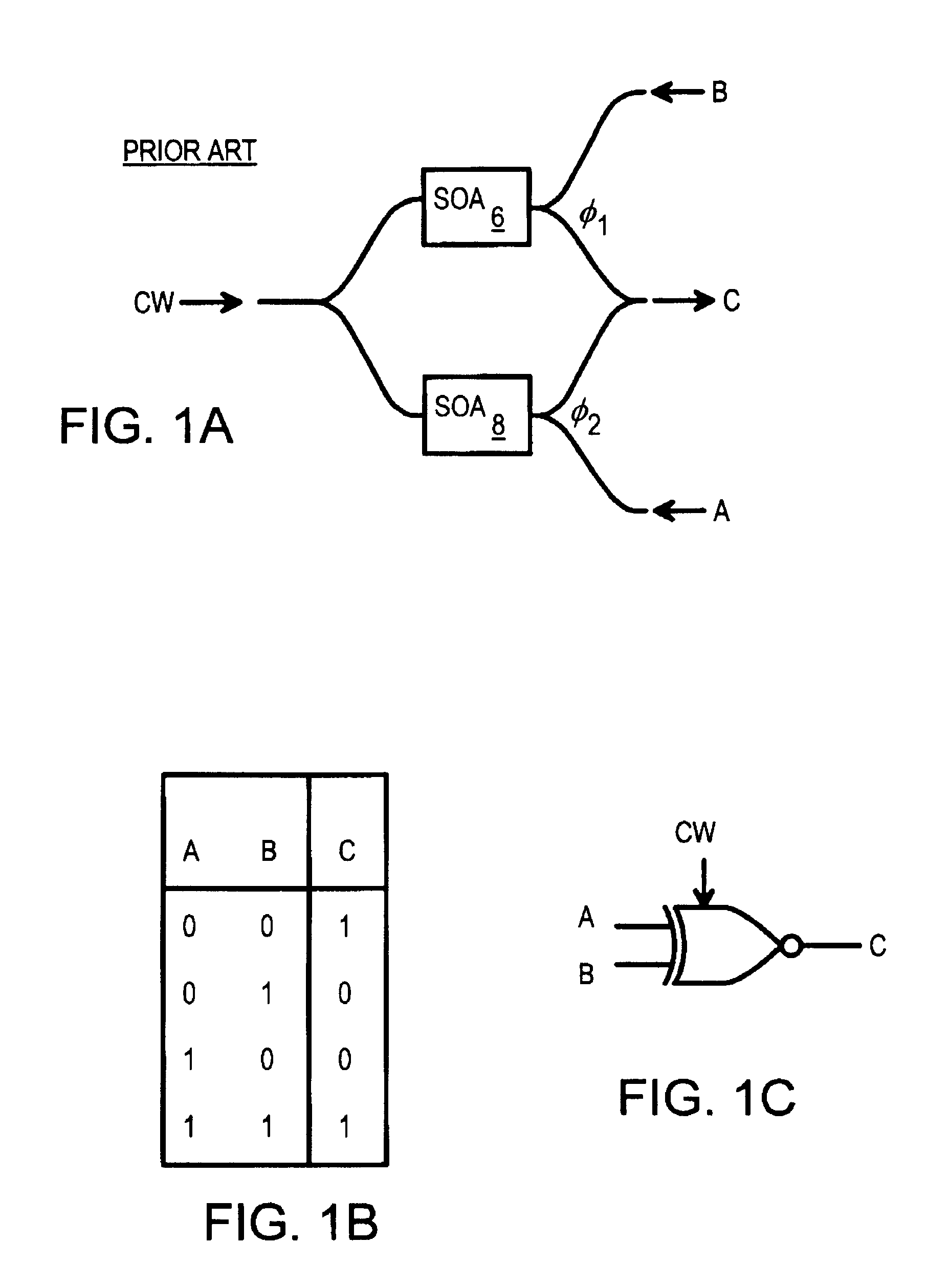
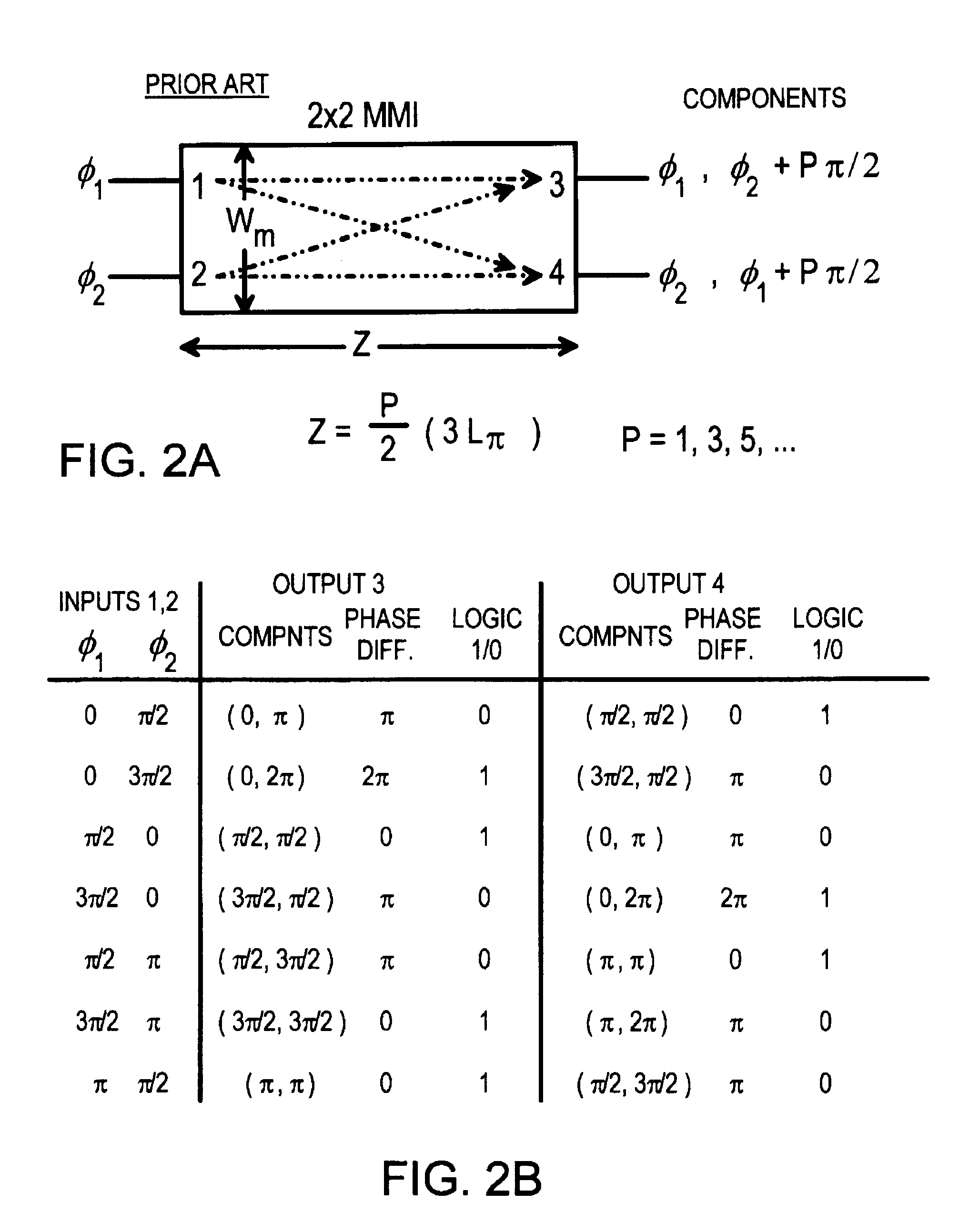
All optical logic using cross-phase modulation amplifiers and mach-zehnder interferometers with phase-shift devices
Optical logic gates are constructed from Mach-Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) optical circuits. A multi-mode interference (MMI) splitter divides a continuous-wave input into two branches of the interferometer. Each branch has a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA). When a logic input having a logic-high power level is applied to one of the SOA's, cross-phase modulation occurs in the SOA. The phase shift increases through the SOA. The branch coupled to the logic input has a relative phase shift of pi compared with the other branch. When two branches with the pi phase difference are combined, destructive interference occurs, producing a logic low. An MMI combiner or an equivalent phase shifter is used to combine the two branches. The MMI splitter adds a phase shift of pi / 2 to the upper branch but not to the lower branch, while the MMI combiner also adds pi / 2 shifts.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
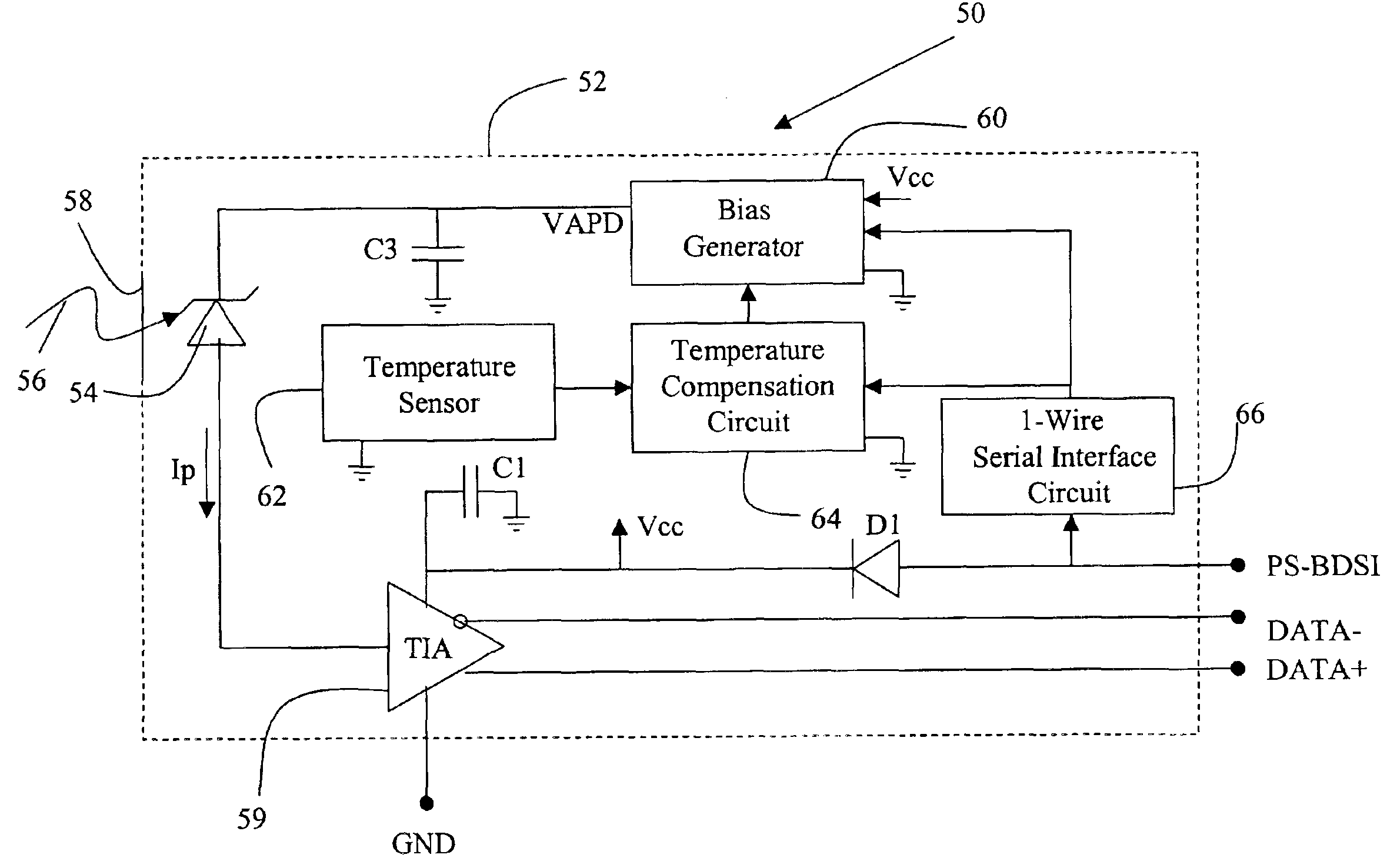
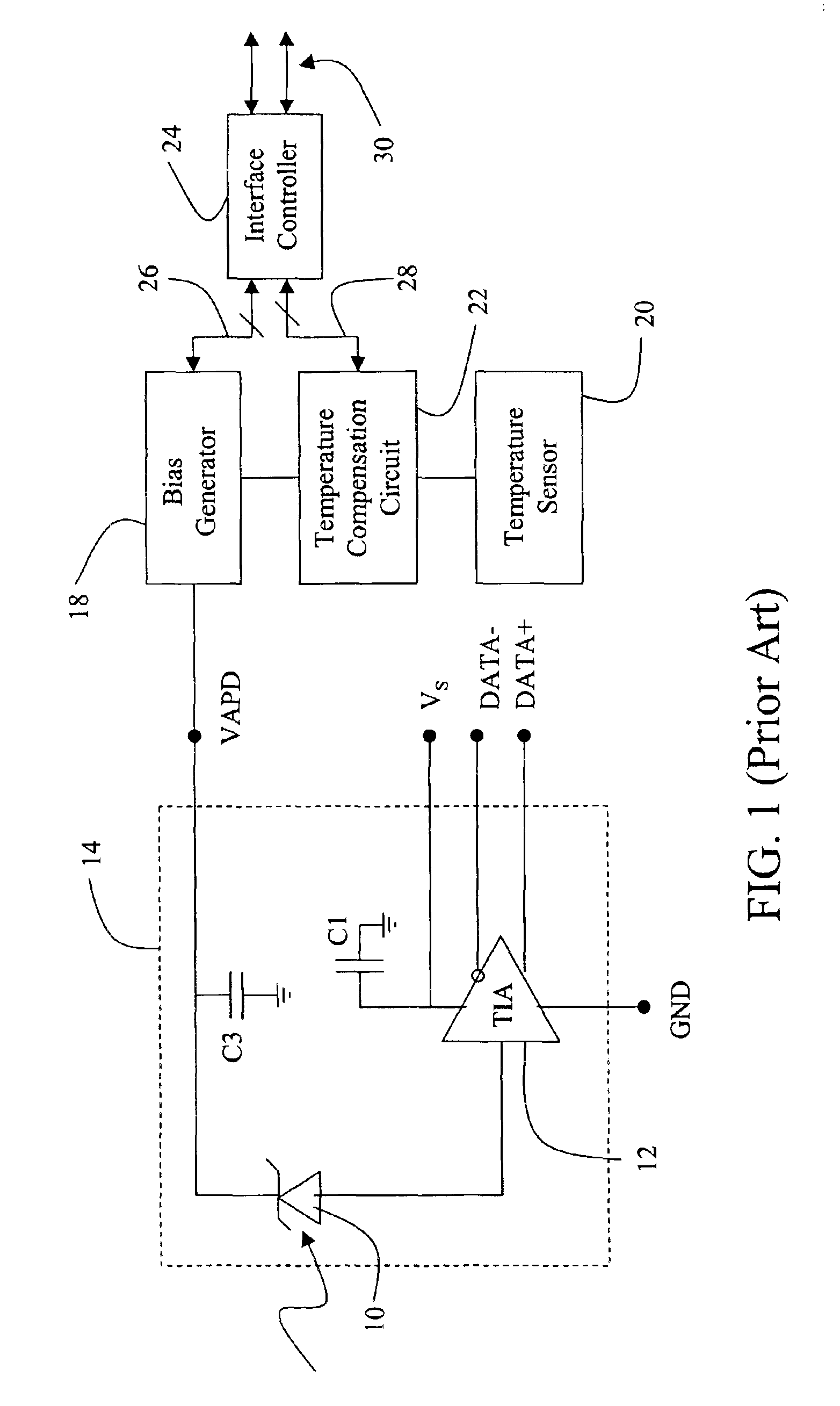
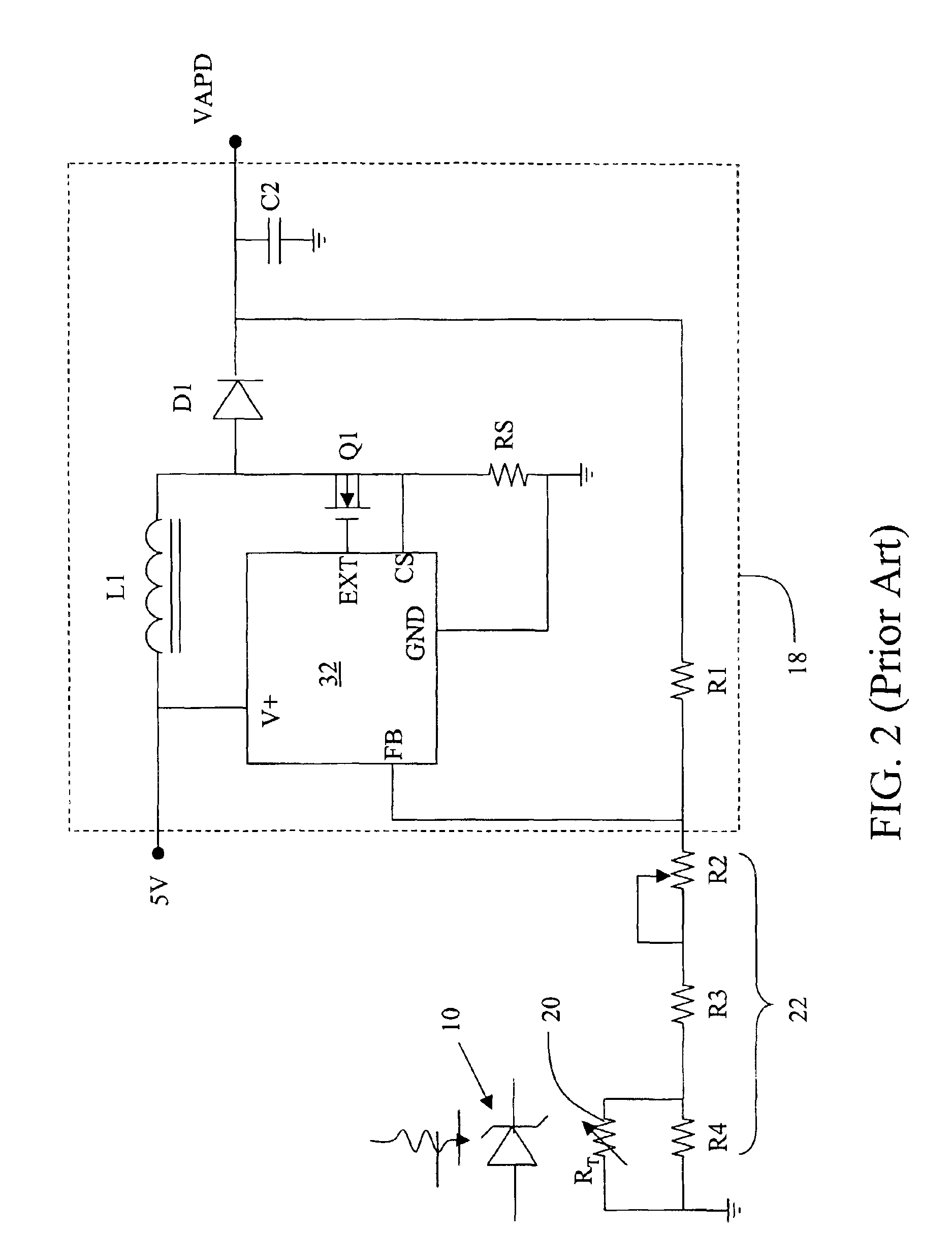
Single chip ASIC and compact packaging solution for an avalanche photodiode (APD) and bias circuit
ActiveUS6894266B2Few partsSmall sizeMultiplier circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringOperating frequency
A compact integrated APD device integrates the bias voltage and temperature compensation functions inside a standard 4-pin PIN package. The active components of the bias and temperature compensation circuits are integrated into a single ASIC using a high-voltage CMOS process and operated at frequencies of at least 1 MHz to greatly reduce the size of the passive components. To mount the relatively large ASIC chip inside the package with the APD chip, TIA chip and passives, the 4-pin package may be modified by either recessing the pins inside the can to facilitate surface mounting the ASIC or adding a spacer inside the can to facilitate three-dimensional packaging. Communication with the bias and temperature circuits is accomplished using a unique bi-directional 1-wire serial interface via the power supply pin. A clock signal is preferably embedded in the control data to synchronize the APD with an external controller.
Owner:OPLINK COMM
Plasmonic nanophotonics methods, materials, and apparatuses
Controlling, guiding, manipulating, and circuiting light and performing surface-enhanced spectroscopy in a medium comprising plasmonic nanomaterials via the excitation of plasmon modes in the materials. The plasmonic nanomaterials are based on metal films with or without arrays of nanoholes and / or on metal nanowires and / or spheroids. Also devices and methods employing such plasmonic nanomaterials.
Owner:NEW MEXICO STATE UNIV TECH TRANSFER
Quantum computing method and quantum computer
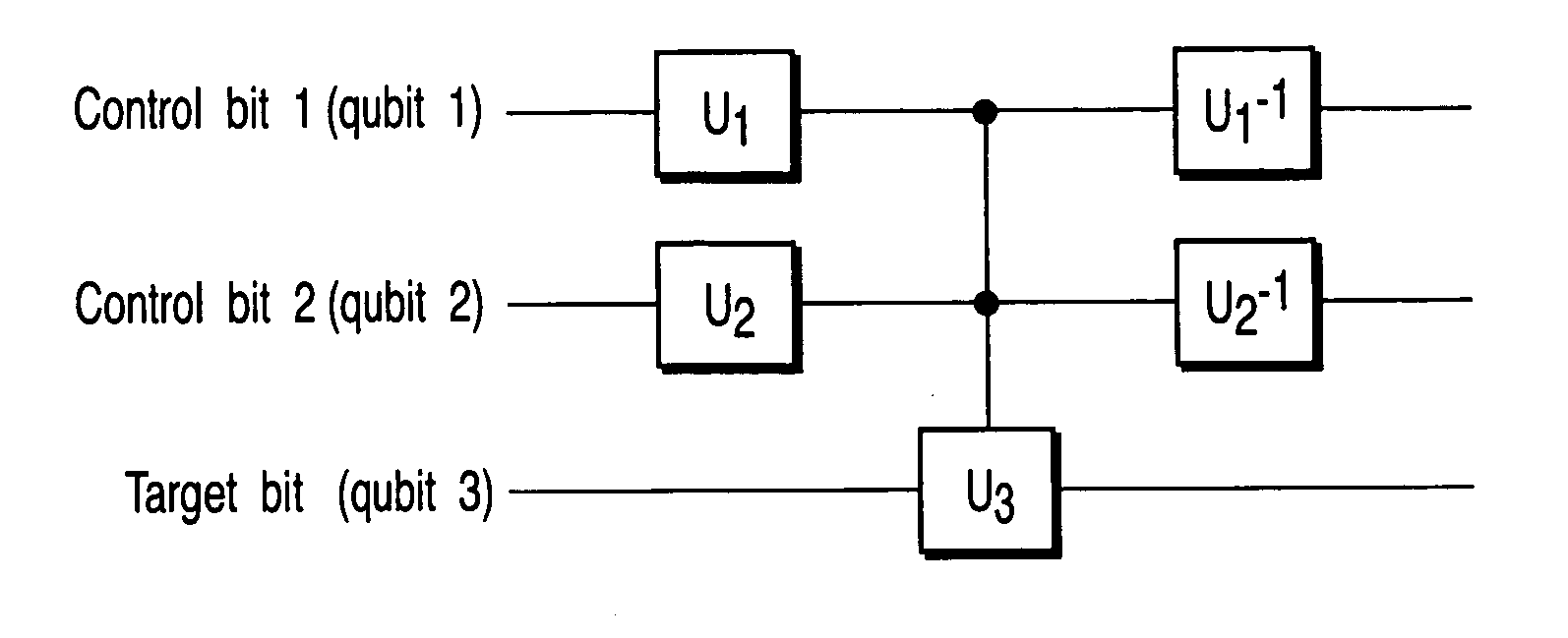
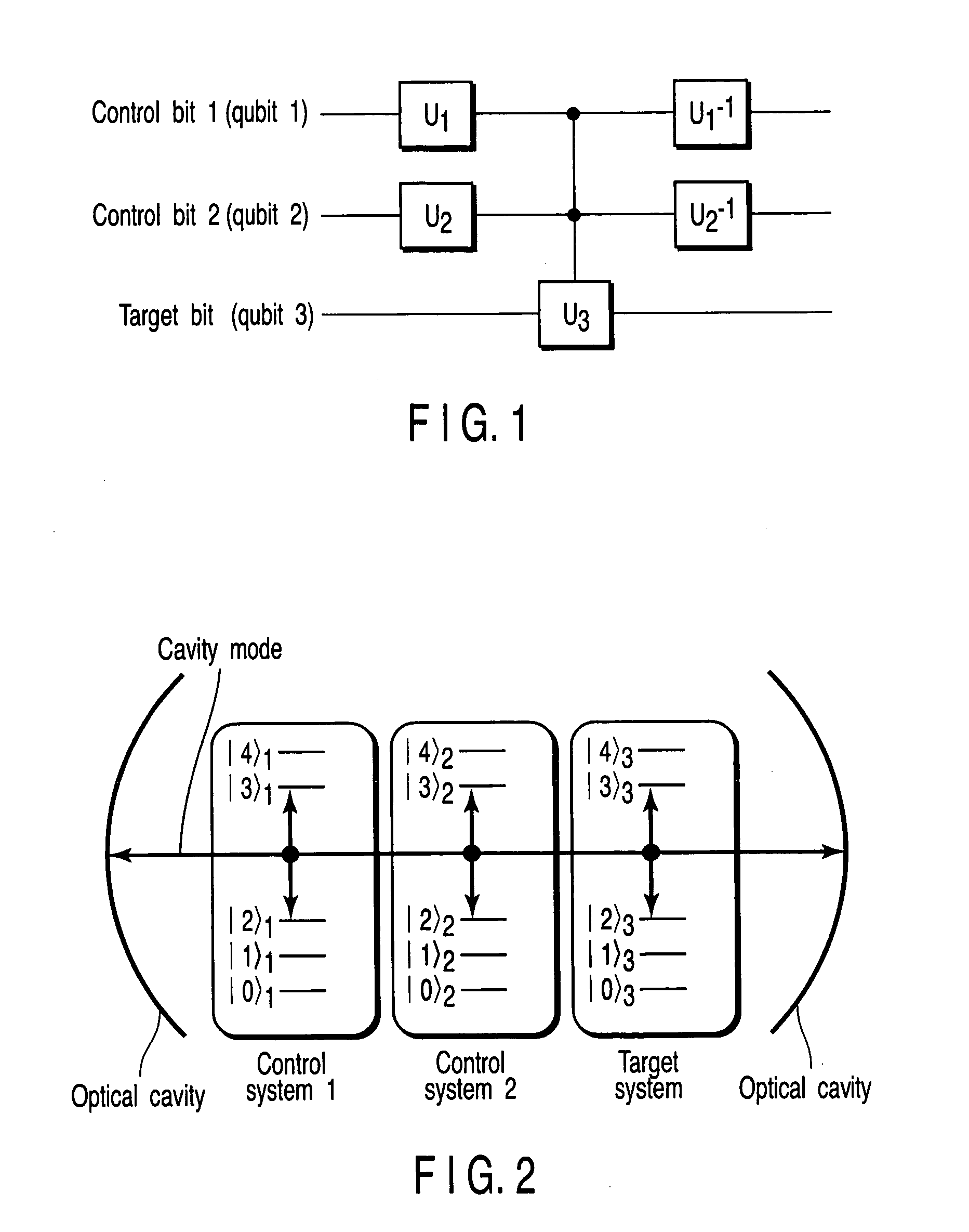
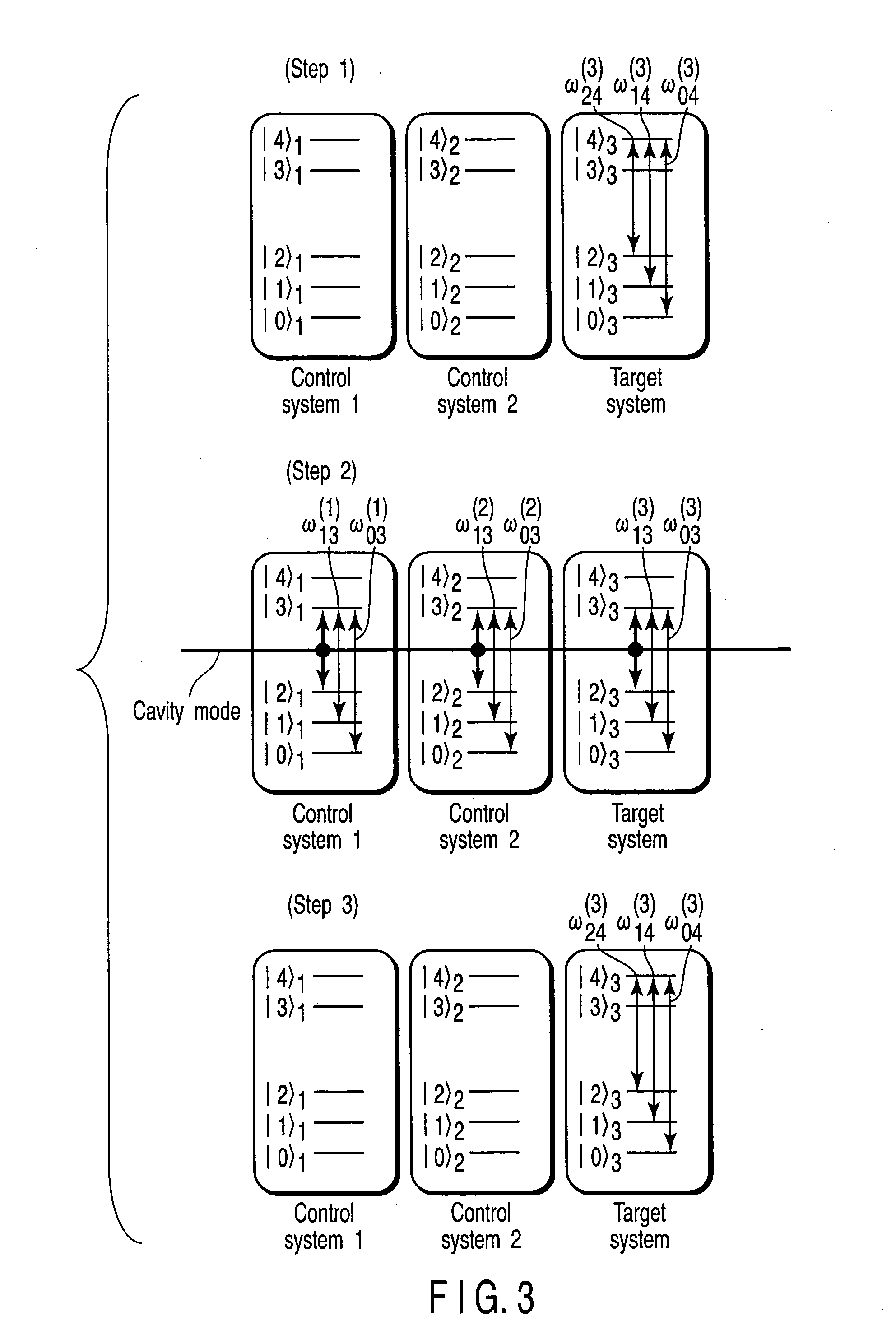
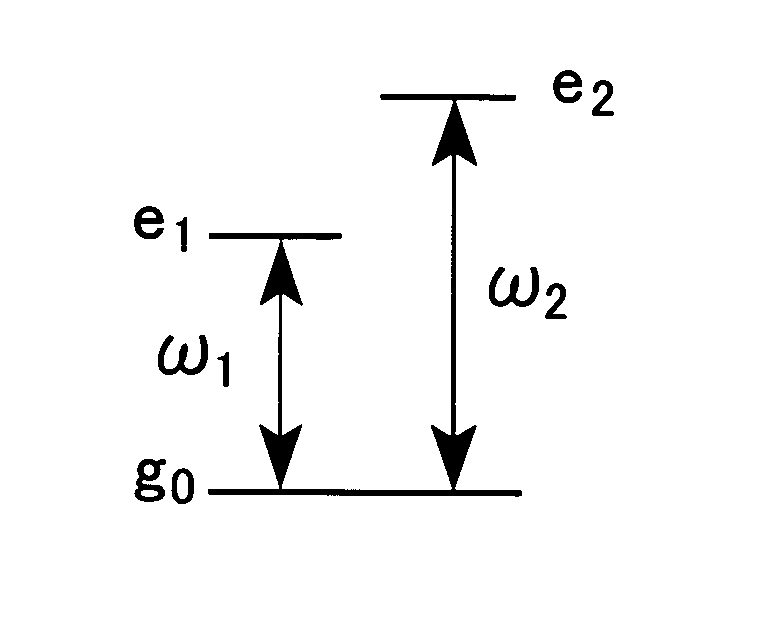
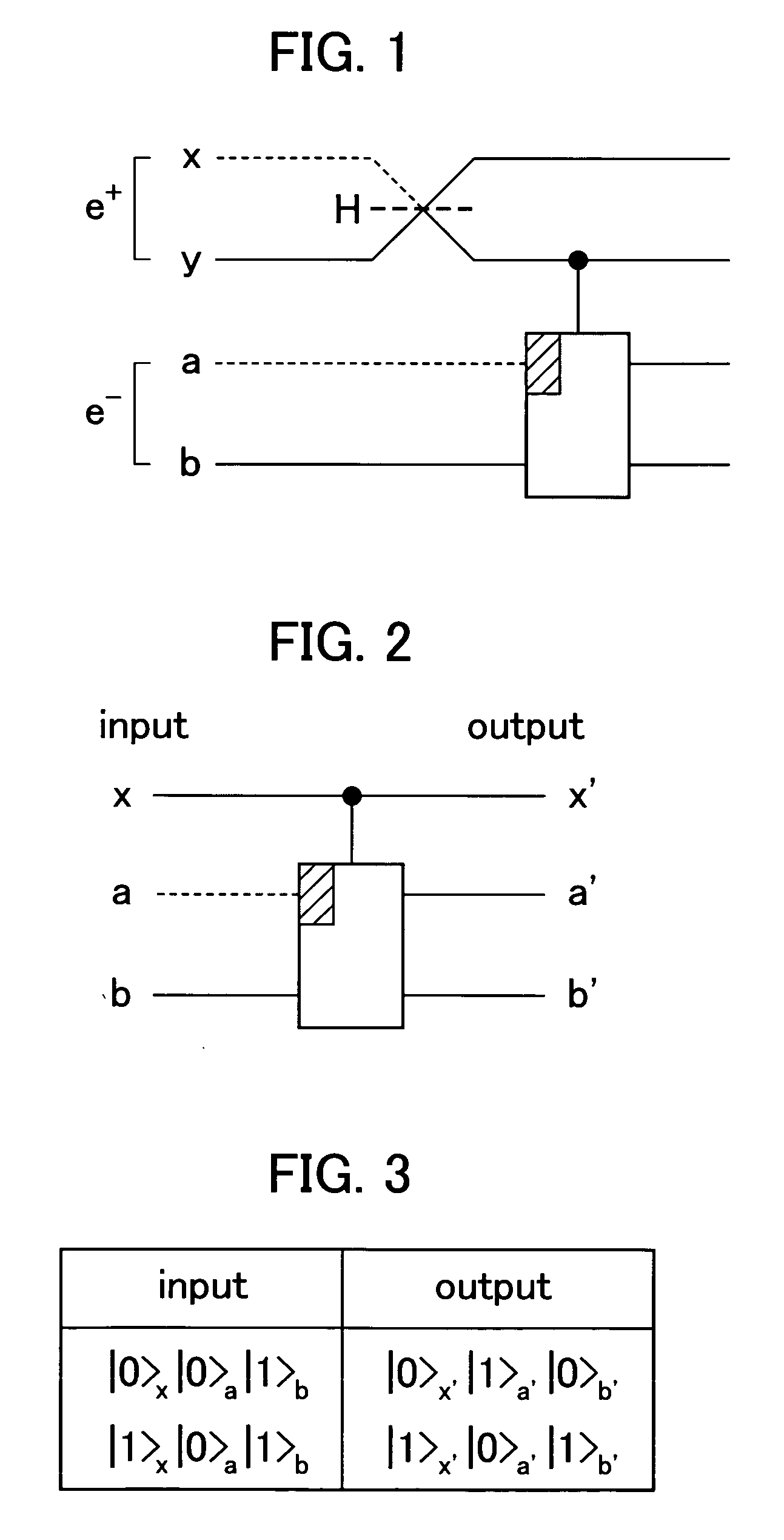
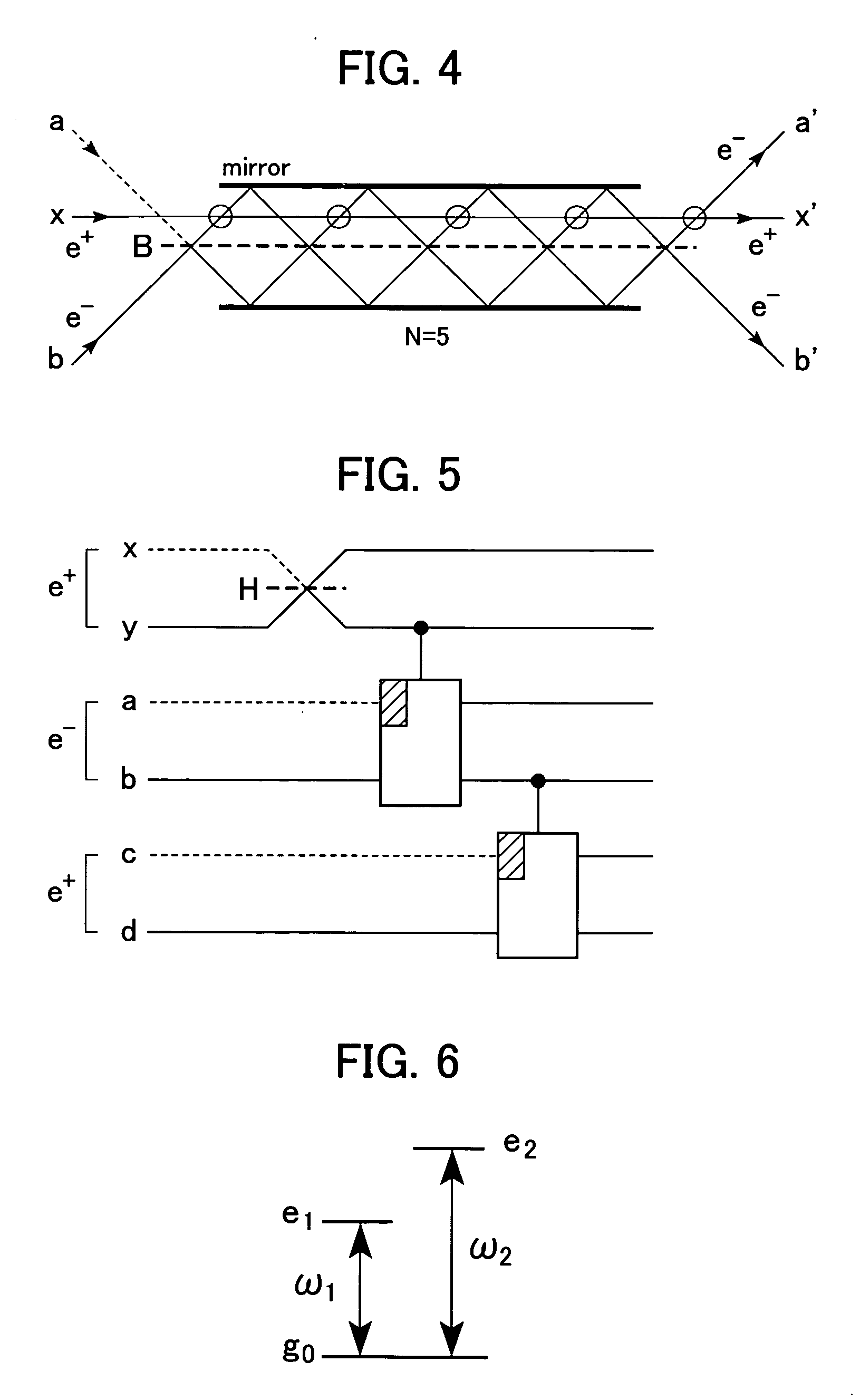
An (N+1) number of physical systems each having five energy levels |0>, |1>, |2>, |3>, and |4>, a qubit being expressed by |0> and |1>, are provided in an optical cavity having a cavity mode resonant with |2>-|3>, such that an N number of control systems and a target system are prepared. The target system is irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|4>, |1>-|4>, and |2>-|4> to change a superposed state |c> to |2>. All of the physical systems are irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|3> and |1>-|3>, and a phase of the light pulse resonant with the target system is shifted by a specific value dependent on a unitary transformation U. The target system is irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|4>, |1>-|4>, and |2>-|4>, with a phase difference between them being set to a specific value dependent on the unitary transformation U, to return |2> to |c>.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical CDMA system using sub-band coding
InactiveUS6236483B1Polarisation multiplex systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical cdmaCommunications system
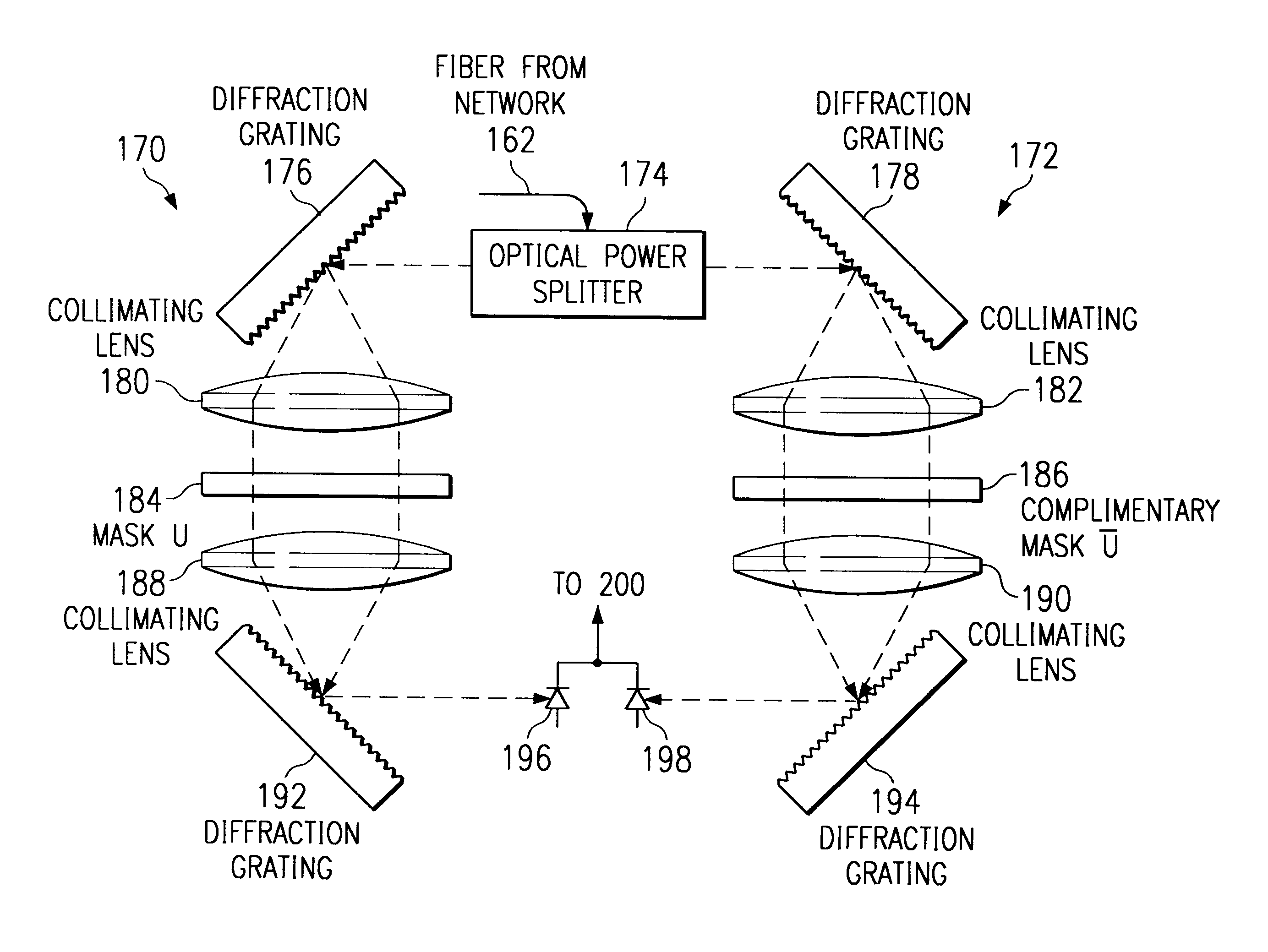
An optical fiber communications system using spread spectrum code division multiple access techniques to achieve better bandwidth utilization. A transmitting user in the system encodes the optical signal using a first coding mask, and a receiving user decodes the received signal using two decoding masks, all of the masks having lengths N. The first mask is divided into two sections of lengths N / 2 each, one of the sections defining a first sub-code of length N / 2, while the other section blocks light. Each of the second and third masks is also divided into two sections, which correspond to the two sections of the first mask. The section of the second mask corresponding to the coded section of the first mask has a second code that is identical to the first code, and the section of the second mask corresponding to the blocked section of the first mask is also blocked. The section of the third mask corresponding to coded section of the first mask has a third code that is complementary to the first code, and the section of the third mask corresponding to the blocked section of the first mask is also blocked. Some users on the system have masks in which the first of the two sections are blocked and the second of the two sections are coded, while other users have masks in which the second of the two sections are blocked and the first of the two sections are coded. The first codes used to code the encoding masks are selected from a set of unipolar codes that are derived from a set of balanced bipolar orthogonal codes.
Owner:CODESTREAM TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for single-photon source and quantum memory
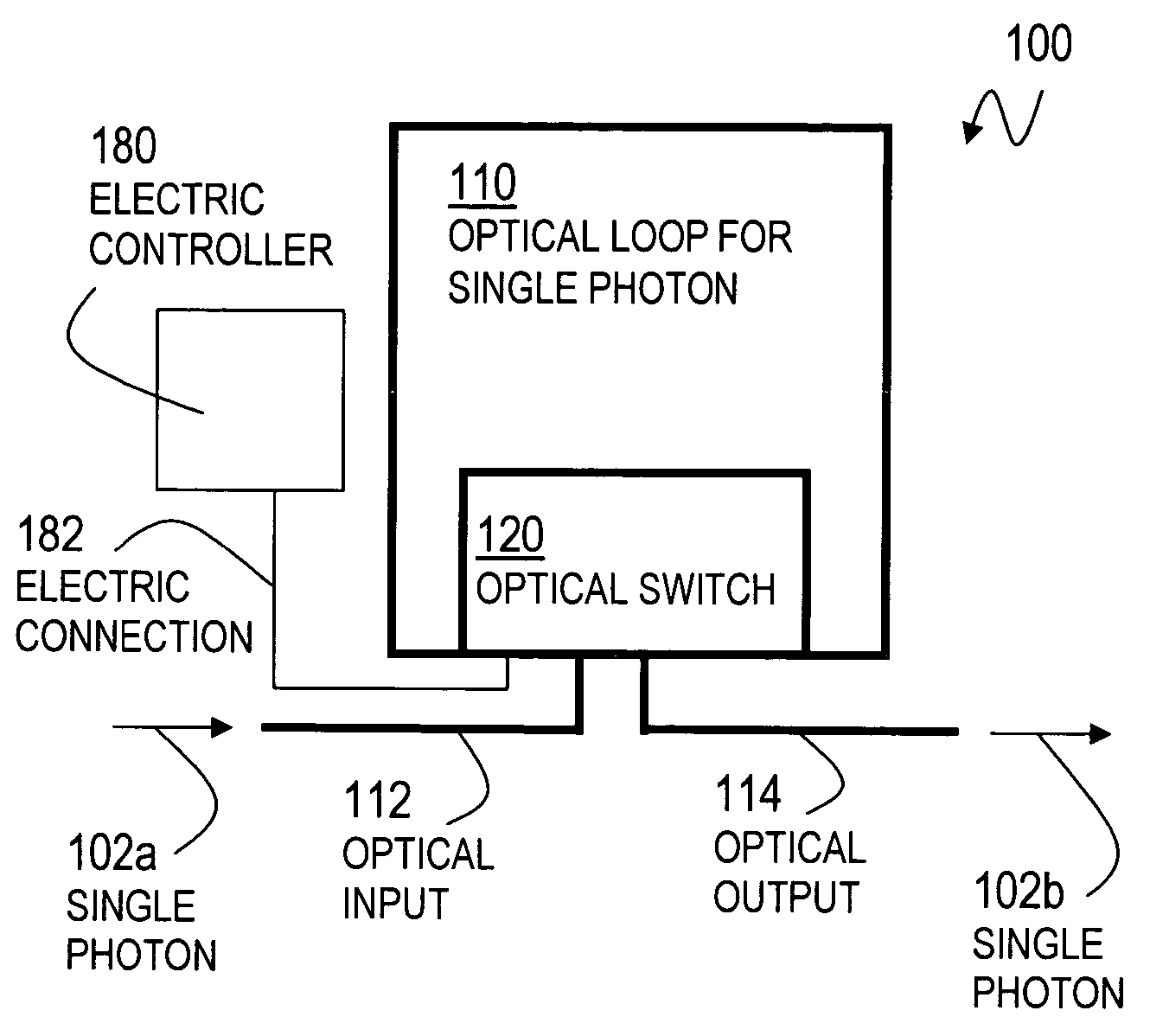
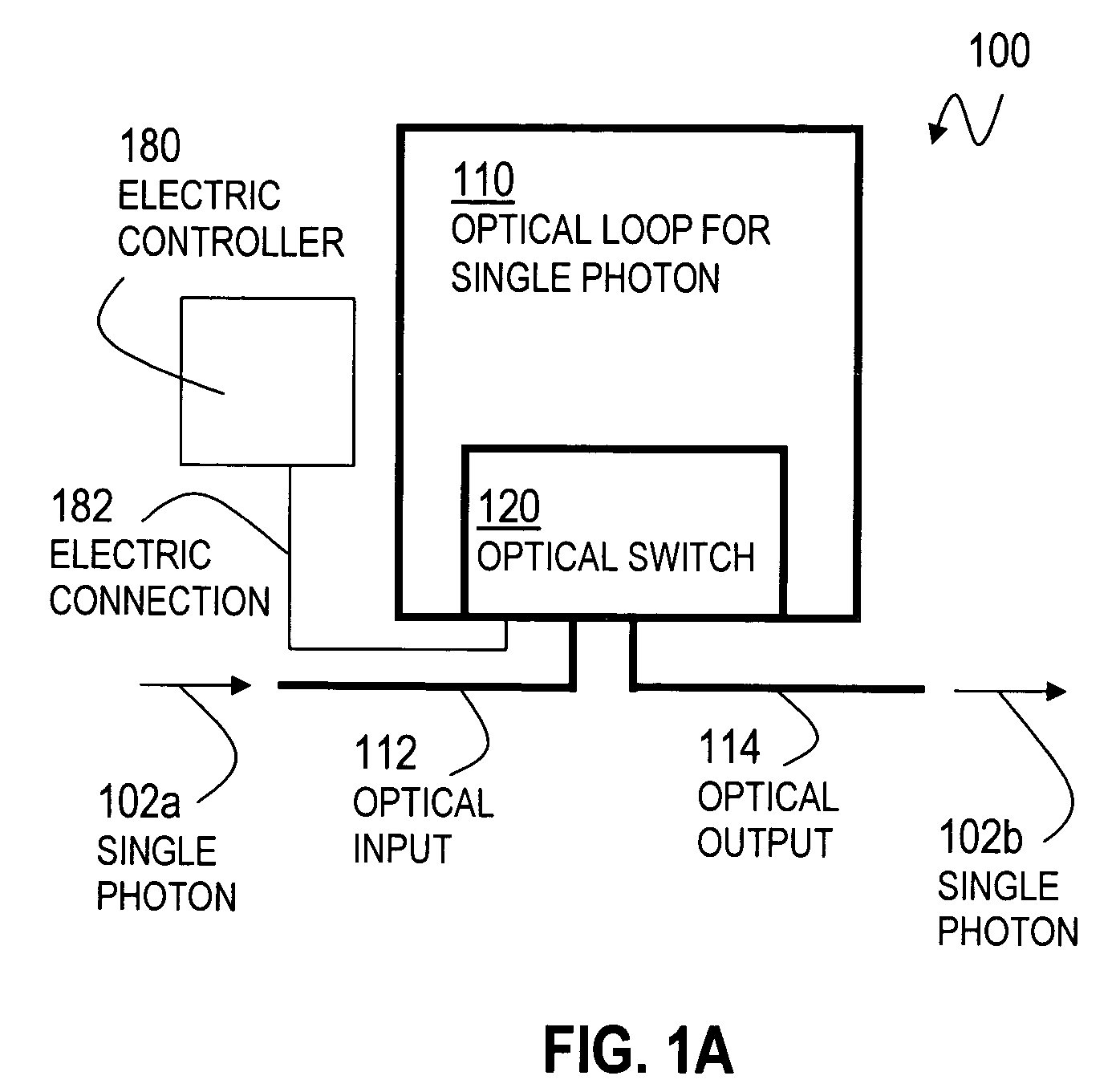
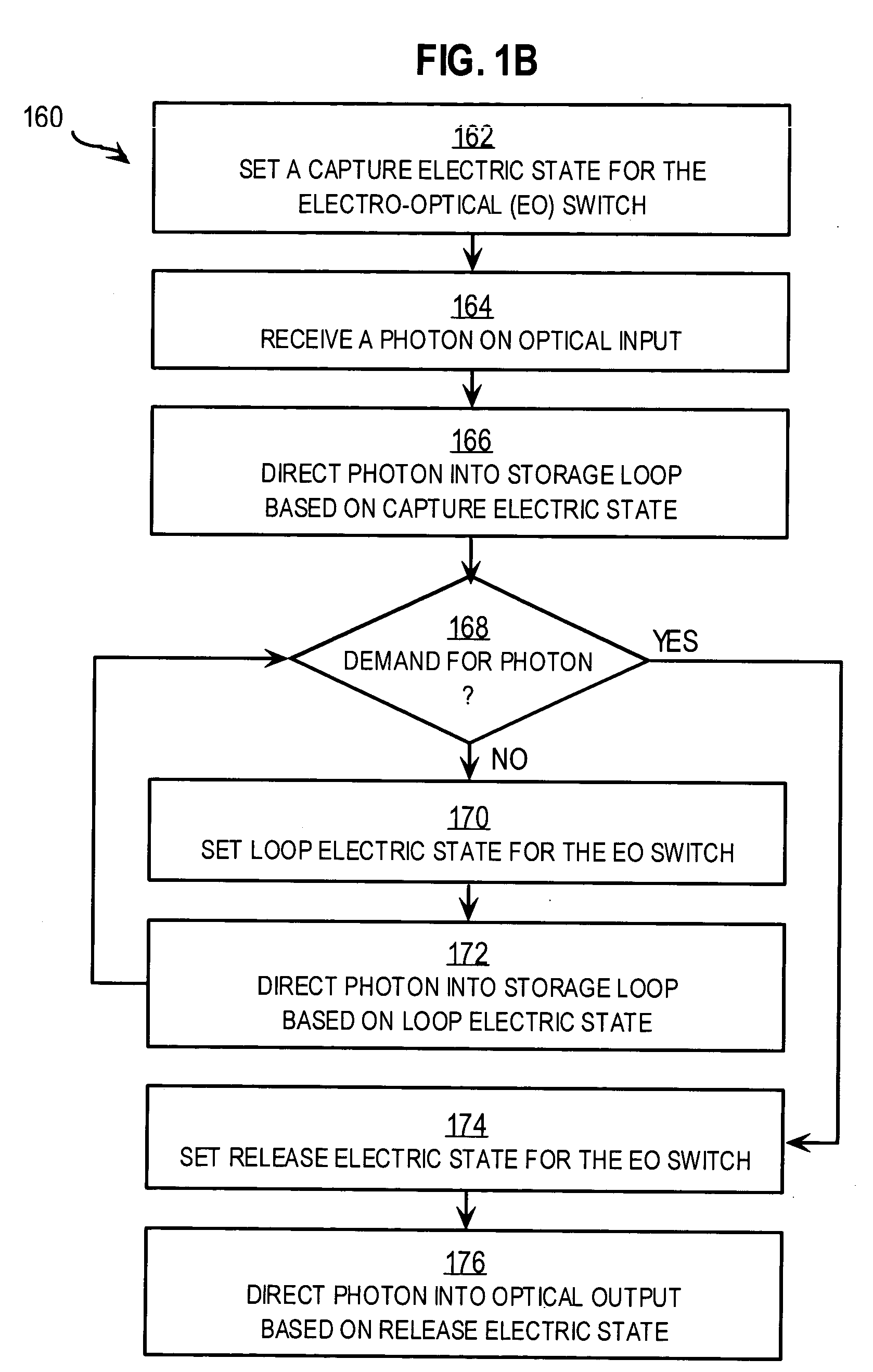
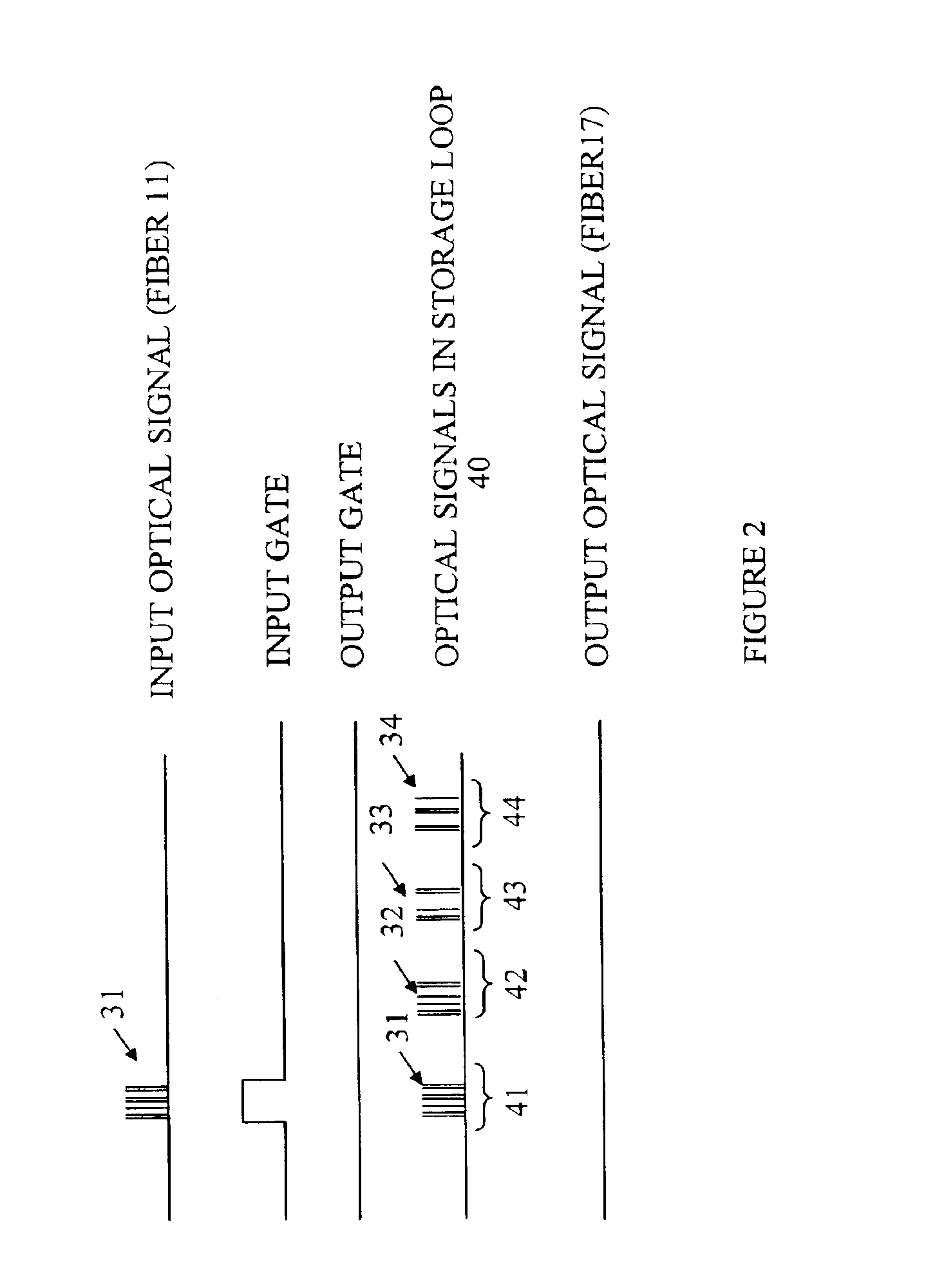
An optical switch and optical storage loop are used as the basis of a single-photon source and a quantum memory for photonic qubits. To operate as a single-photon source, the techniques include a source of a pair of photons, such as a parametric down-conversion crystal, which is known to emit photons in pairs. The detection of one member of the pair activates the switch, which re-routes the other member into the storage loop. The stored photon is then known to be circulating in the loop, and can be switched out of the loop at a later time chosen by the user, providing a single photon for potential use in a variety of quantum information processing applications. To operate as a quantum memory for photonic qubits, a single-photon in an arbitrary initial polarization state is coherently stored in the loop, and coherently switched out of the loop when needed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
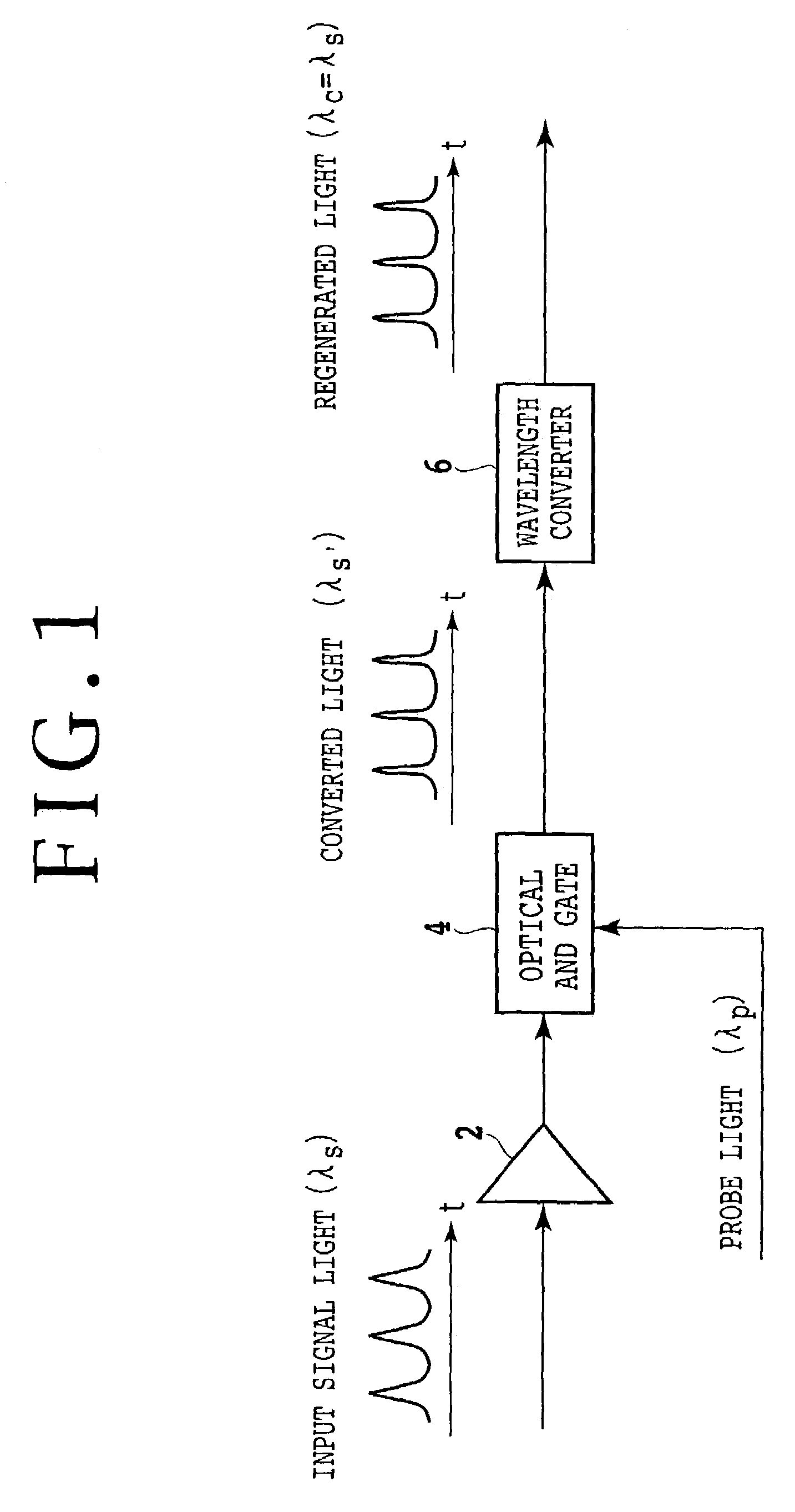
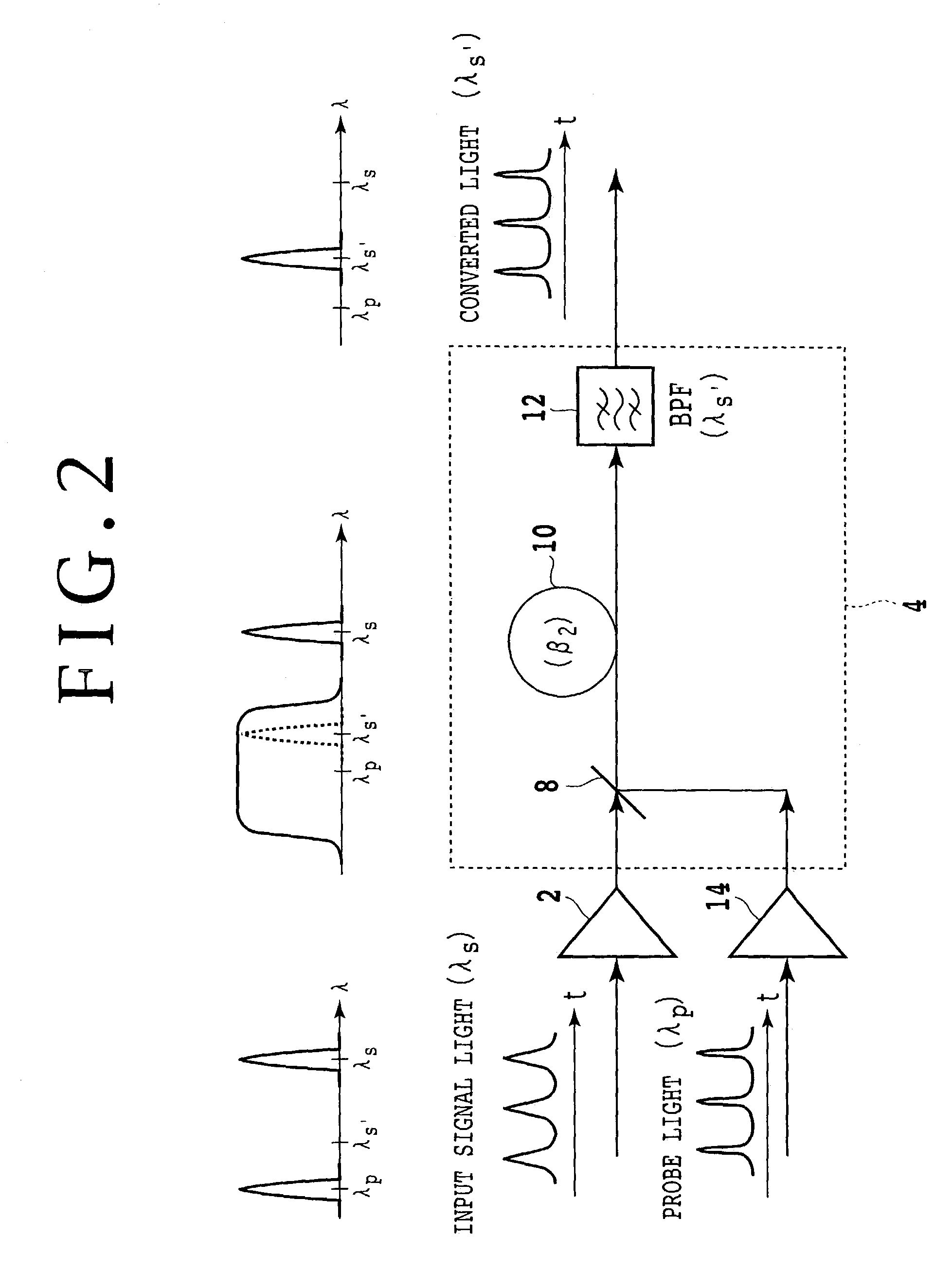
Optical AND gate and waveform shaping device
InactiveUS6987607B2Promote conversionLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesElectromagnetic transmissionWaveform shapingSignal light
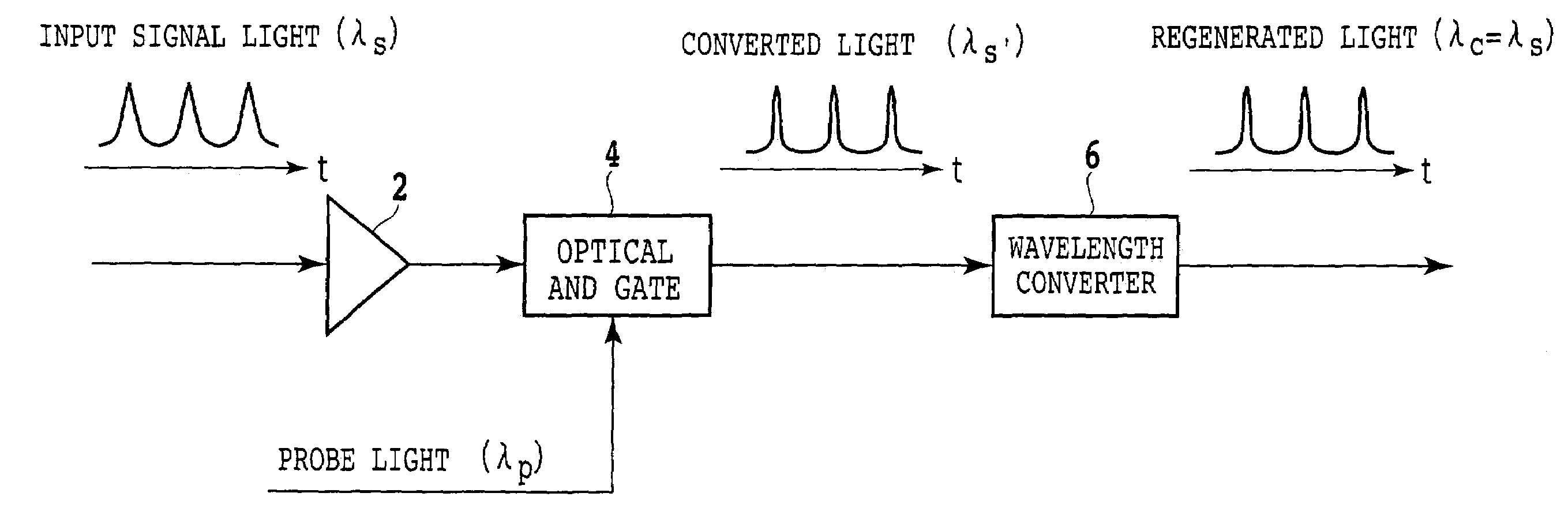
The method according to the present invention includes the steps of inputting an optical signal having a first wavelength and probe light having a second wavelength different from the first wavelength into a nonlinear optical medium, broadening the spectrum of the probe light through cross phase modulation between the optical signal and the probe light inside the nonlinear optical medium, and extracting a signal component including a modulated component of the optical signal and having a band narrower than the band of the spectrum broadened. According to the present invention it can be possible to provide a method and device which can easily convert the wavelength of signal light into an arbitrary wavelength in performing optical 3R functions.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical cache memory
An optical memory having an input port for receiving an input optical signal to be stored in the optical memory is disclosed. A portion of the optical signal is coupled to a storage loop for storing optical signals by a coupler that transfers a portion of the input optical signal to the storage loop. An optical signal stored in the storage loop is output by coupling a portion of that optical signal to a first external optical waveguide. The storage loop includes a semiconductor optical amplifier for amplifying the signals stored in the storage loop to compensate for losses incurred by those signals in traversing the storage loop. A plurality of such optical memories can be combined to form a larger memory that includes a reconditioning circuit that resets the amplitude of the optical signals to a value that depends on the amplitude of the optical signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
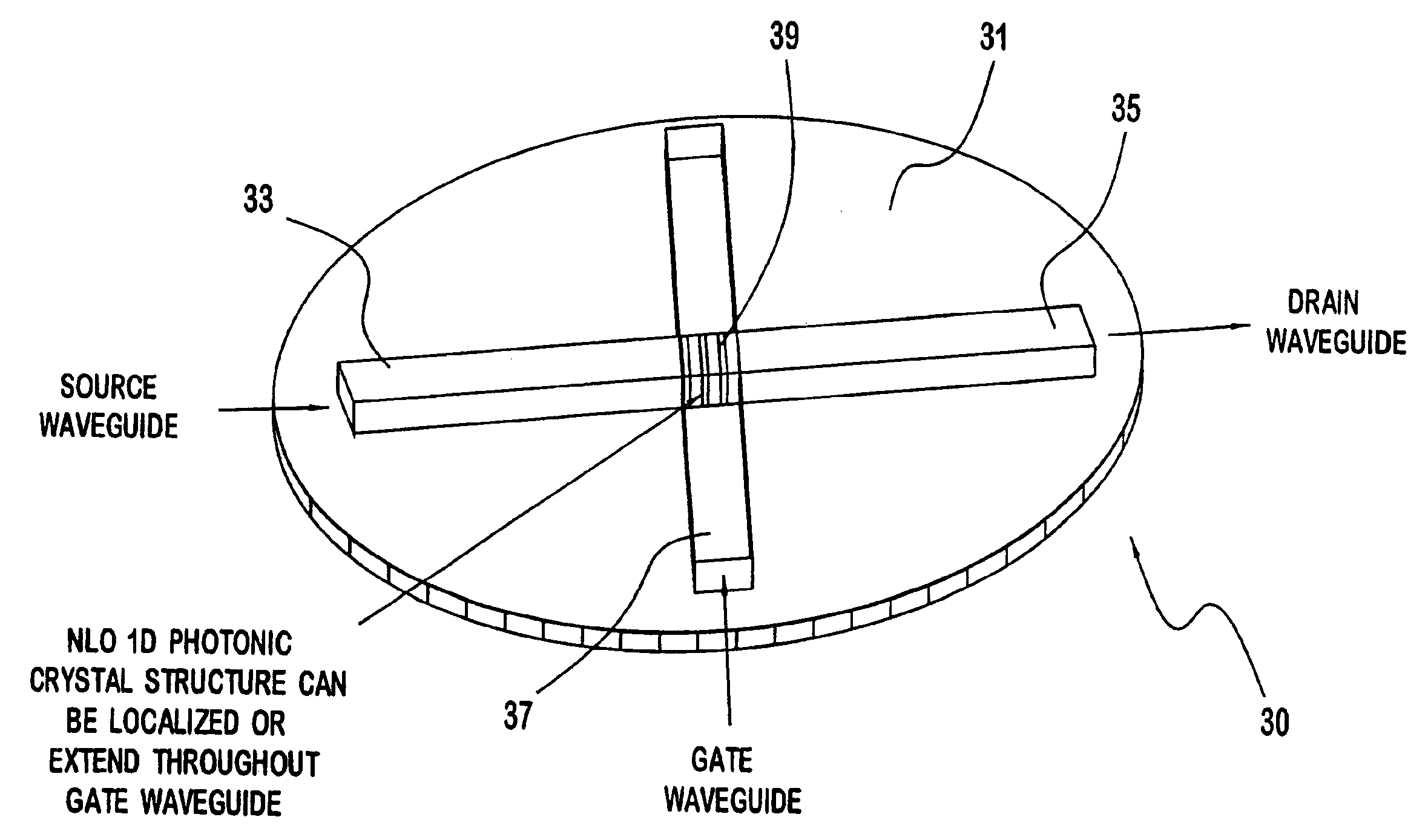
Non-linear photonic switch and method of making the same
InactiveUS6937804B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrocontact printingPhotonics
A photonic switch according to the present invention may be formed using one of a selected group of non-linear optical materials. Each of the materials within this group has a refractive index that demonstrates a substantial peak as a function of wavelength, where the peak occurs at a wavelength distinct from the wavelength of the input signal. A method of producing a photonic switch according to the present invention includes fabricating source and drain waveguides using micro-molding or micro-contact printing processes, or MIMIC (micro-molding in capillaries) of a UV-curable polymer. If desired, a gate waveguide may also be formed in part by these processes. The photonic switch also includes a photonic crystal formed from non-linear optical material, which may be formed, for example, using a block copolymer and nanoparticle composite in a MIMIC or μfluidics process. Such a process may employ a functionalized mold material to align the blocks.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
Single chip integrated optical matrix-vector multiplier
InactiveCN102866876ASmall sizeReduce in quantityDigital data processing detailsLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesSelective modulationBeam splitting
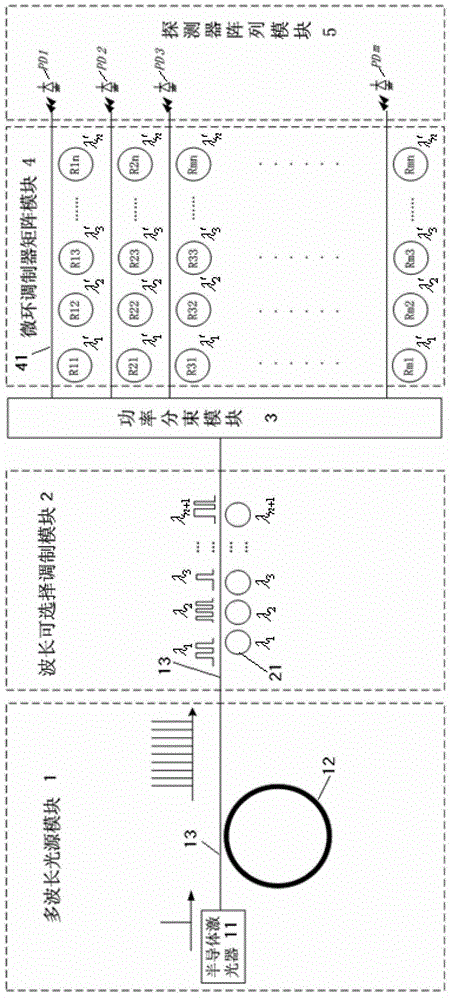
The invention relates to a single chip integrated optical matrix-vector multiplier which is characterized by comprising a silicon base, wherein a multi-wavelength light source module, a wavelength selecting modulating module, a power beam splitting module, a micro-ring modulator matrix module and a detector array module are integrated on the silicon base; the multi-wavelength light source module is used for outputting multi-wavelength optical signals with n+1different wavelengths to the wavelength selecting modulating module; the wavelength selecting modulating module is used for selectively modulating each wavelength optical signal in the multi-wavelength optical signals and then sending to the power beam splitting module; the power beam splitting module is used for performing 1:m equal power beam splitting on the multi-wavelength optical signals and sending the multi-wavelength optical signals after being subjected to the beam splitting to the micro-ring modulator matrix module; the micro-ring modulator matrix module is used for processing m paths of multi-wavelength optical signals and sending a processing result to the detector array module; and the detector array module is used for detecting the outputted optical signals. The single chip integrated optical matrix-vector multiplier can be widely applied to the processing process of mass data.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Reservoir Computing Using Passive Optical Systems
ActiveUS20150009548A1Improve efficiencyLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesPhysical realisationPhotonicsInterconnection
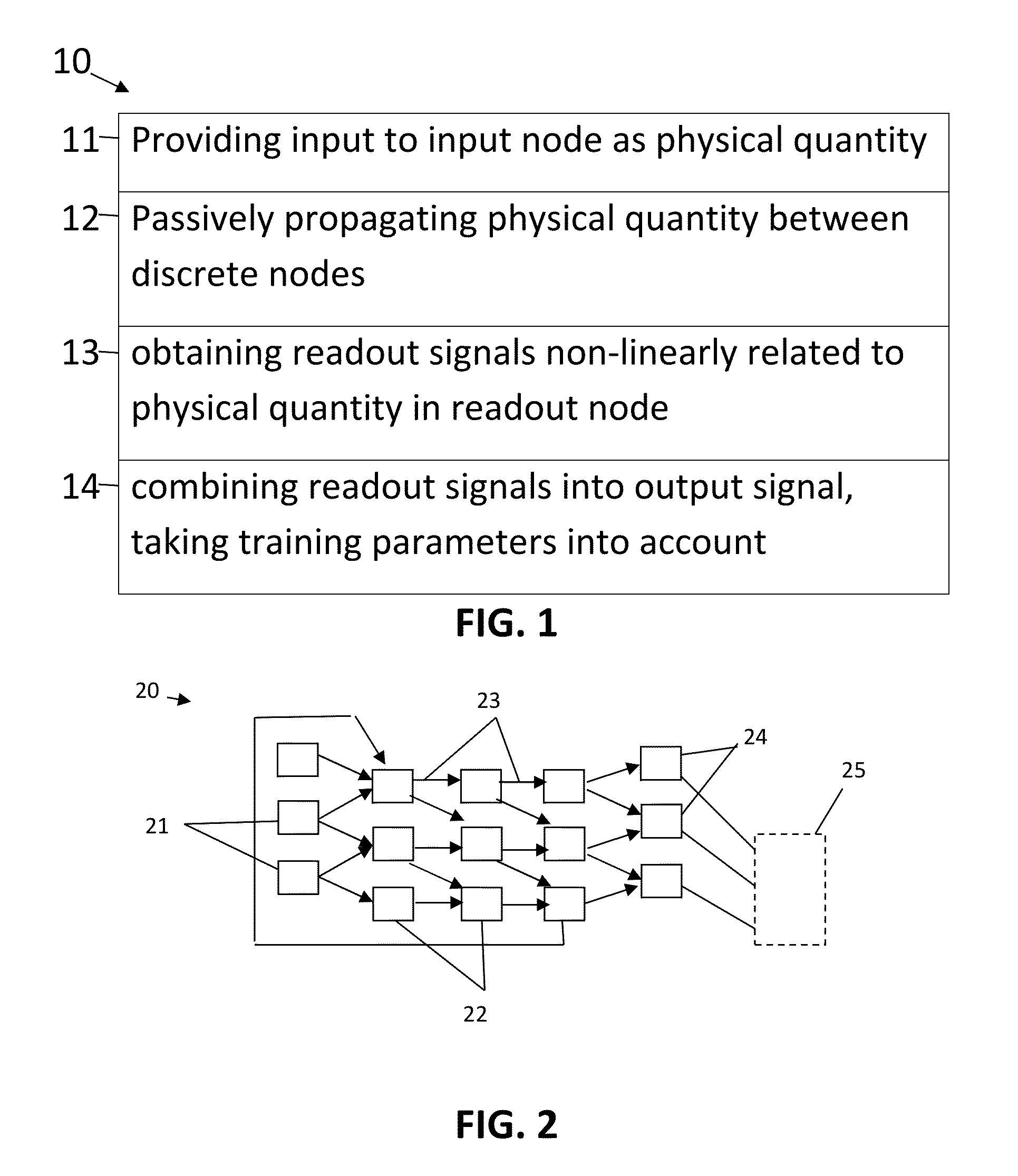
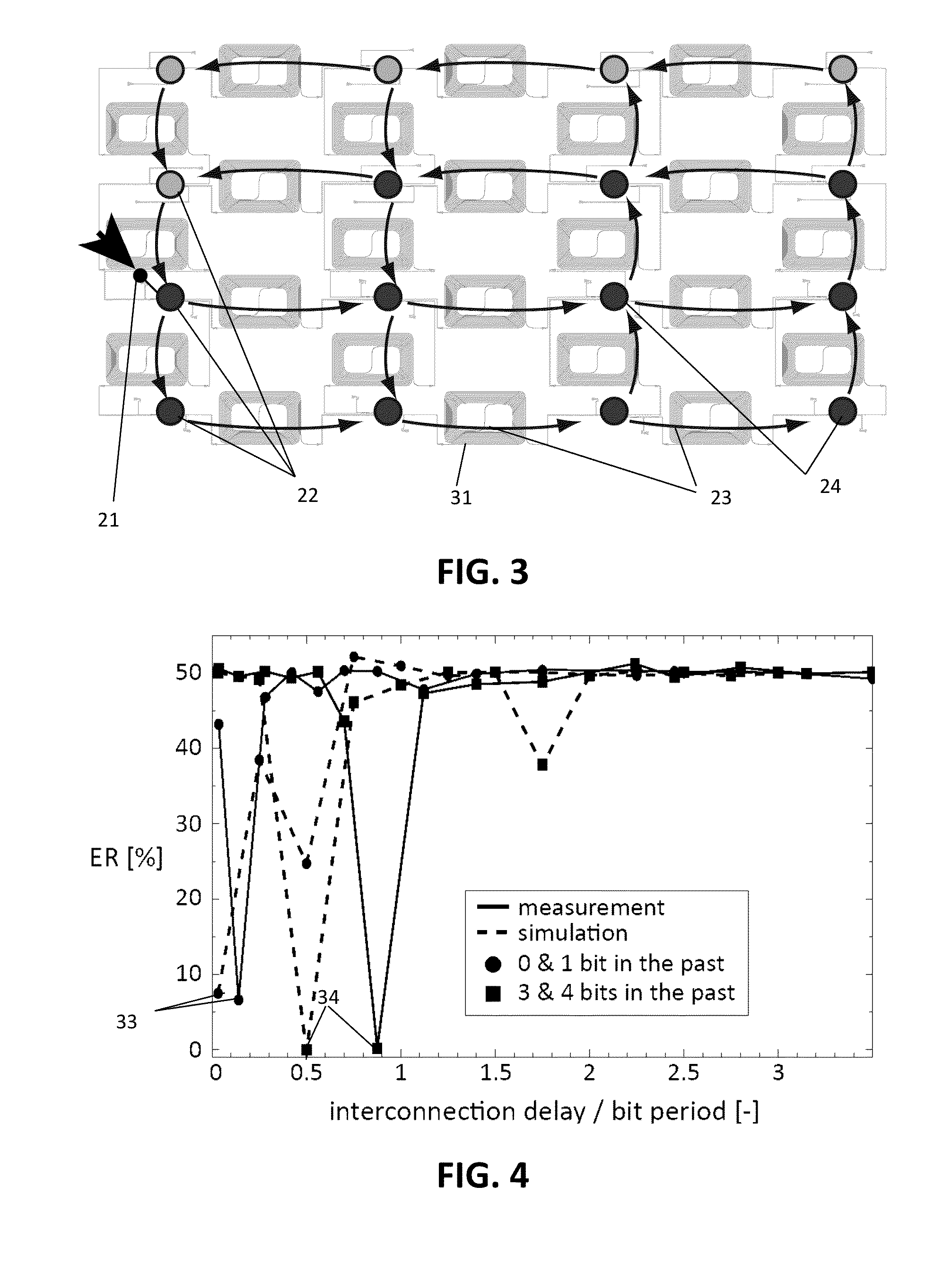
A method comprising providing an input signal to at least one input node of a computing reservoir by temporally encoding the input signal by modulating the at least one photonic wave as function of the input signal is described. The method further comprises propagating the at least one photonic wave via passive guided or unguided propagation between discrete nodes of the computing reservoir, in which each discrete node is adapted for passively relaying the at least one photonic wave over the passive interconnections connected thereto. The method also comprises obtaining a plurality of readout signals, in which each readout signal is determined by a non-linear relation to the at least one photonic wave in at least one readout node of the computing reservoir, and combining this plurality of readout signals into an output signal by taking into account a plurality of training parameters.
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
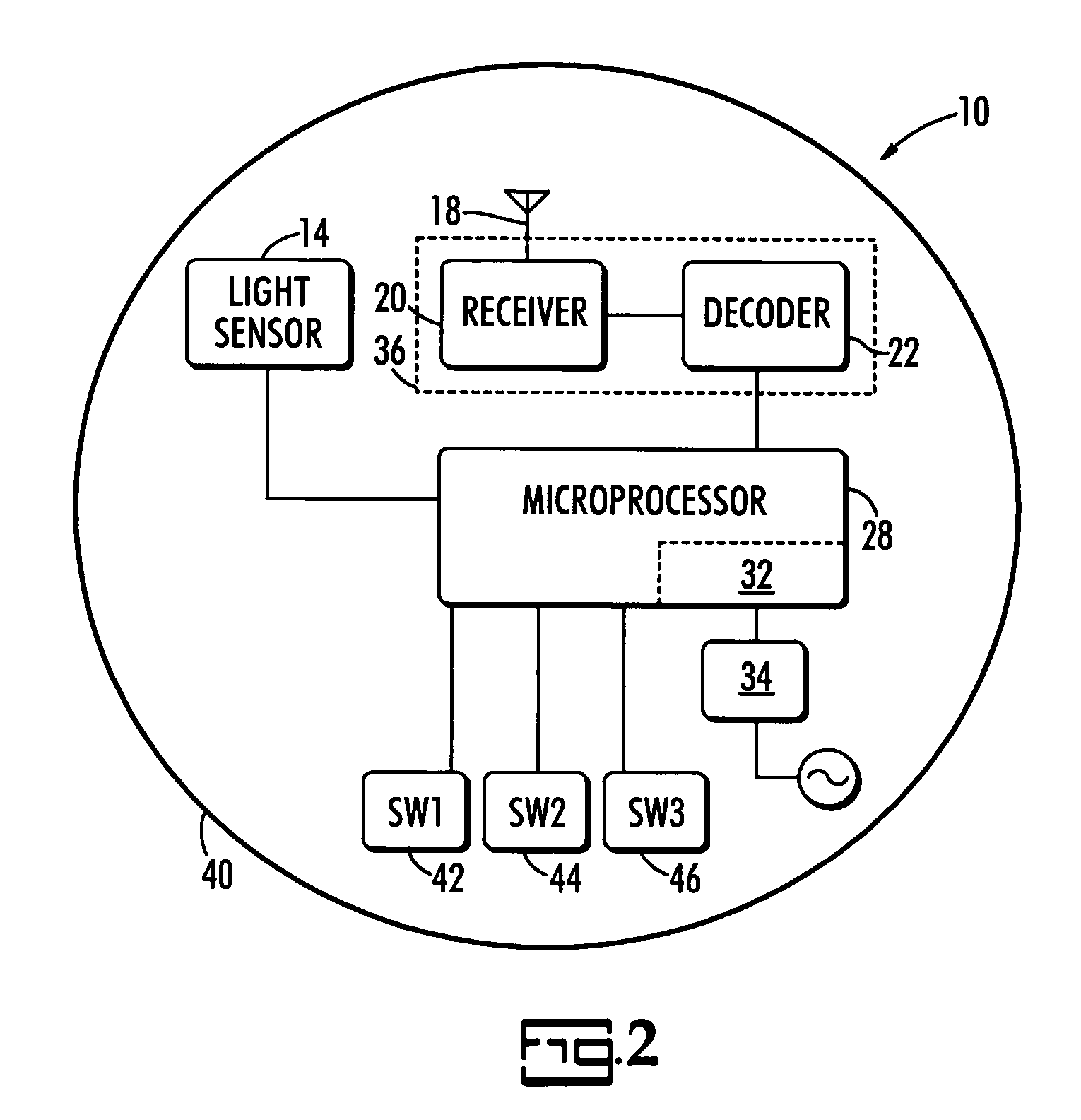
Photocontrol with radio-controlled timer and a decoder
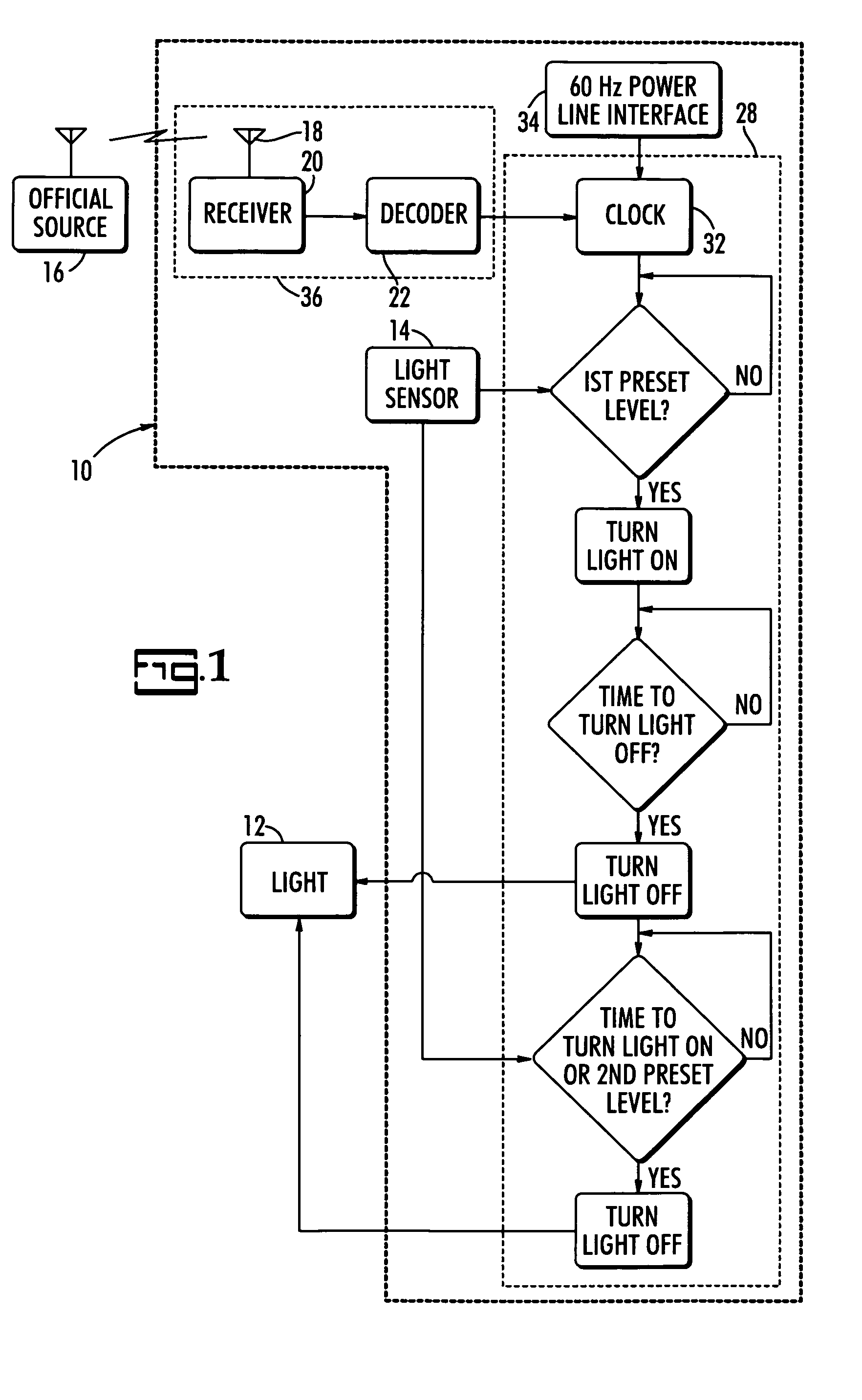
ActiveUS7345270B1Material analysis by optical meansElectronic switchingTime informationBiological activation
A photocontrol controls the activation of lighting based on ambient light and the time of day using a radio-controlled timer. Radio signals from a particular source of correct time, such as the National Institute for Science and Technology's WWVB radio broadcast, carry encoded time information that can be decoded by the photocontrol to ascertain the current time on start up and periodically during operation. The correct date and time information is used to synchronize the photocontrol's internal clock so that it can turn the lighting load off or on at specific times of the day in accordance with the user's needs. Thus area, business signage, and security lighting, for example, can be turned off late at night and then back on early in the morning to reduce energy consumption by the lighting during those hours when the lighting is not needed.
Owner:ELECTRO SWITCH
Optical processing
InactiveUS7012749B1Reduce speckle effectReduce complexityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical processingComputational physics
A method of performing a DFT (discrete Fourier transform) or a DFT derived transform on data, comprising: providing spatially modulated light having spatial coherence, said spatially modulated light representing the data to be transformed; Fourier transforming said spatially modulated light, using an at least one optical element; and compensating for at least one of a scaling effect and a dispersion effect of said at least one optical element, using an at least one dispersive optical element.
Owner:LENSLET
Quantum-state-generating apparatus, Bell measurement apparatus, quantum gate apparatus, and method for evaluating fidelity of quantum gate
InactiveUS20050133780A1Promote generationQuantum computersComputing operations for integration/differentiationBell stateBeam splitter
An apparatus for generating a quantum state of a two-qubit system including two qubits, each qubit being represented by a particle which invariably travels through one of two paths, includes a quantum gate composed of an interferometer for implementing an-interaction-free measurement. The apparatus receives two particles having no correlation and generates a Bell state with asymptotic probability 1. A Bell measurement of a state of a two-qubit system is performed by observing a quantum gate composed of the interferometer after the quantum gate has processed the state and selecting the state from the Bell bases. An approximate fidelity of a quantum gate composed of the interferometer is calculated, if an absorption probability with which a first particle absorbs a second particle in the interferometer is less than 1, under the condition that the number of times the second particle hits beam splitters in the interferometer is sufficiently large.
Owner:CANON KK
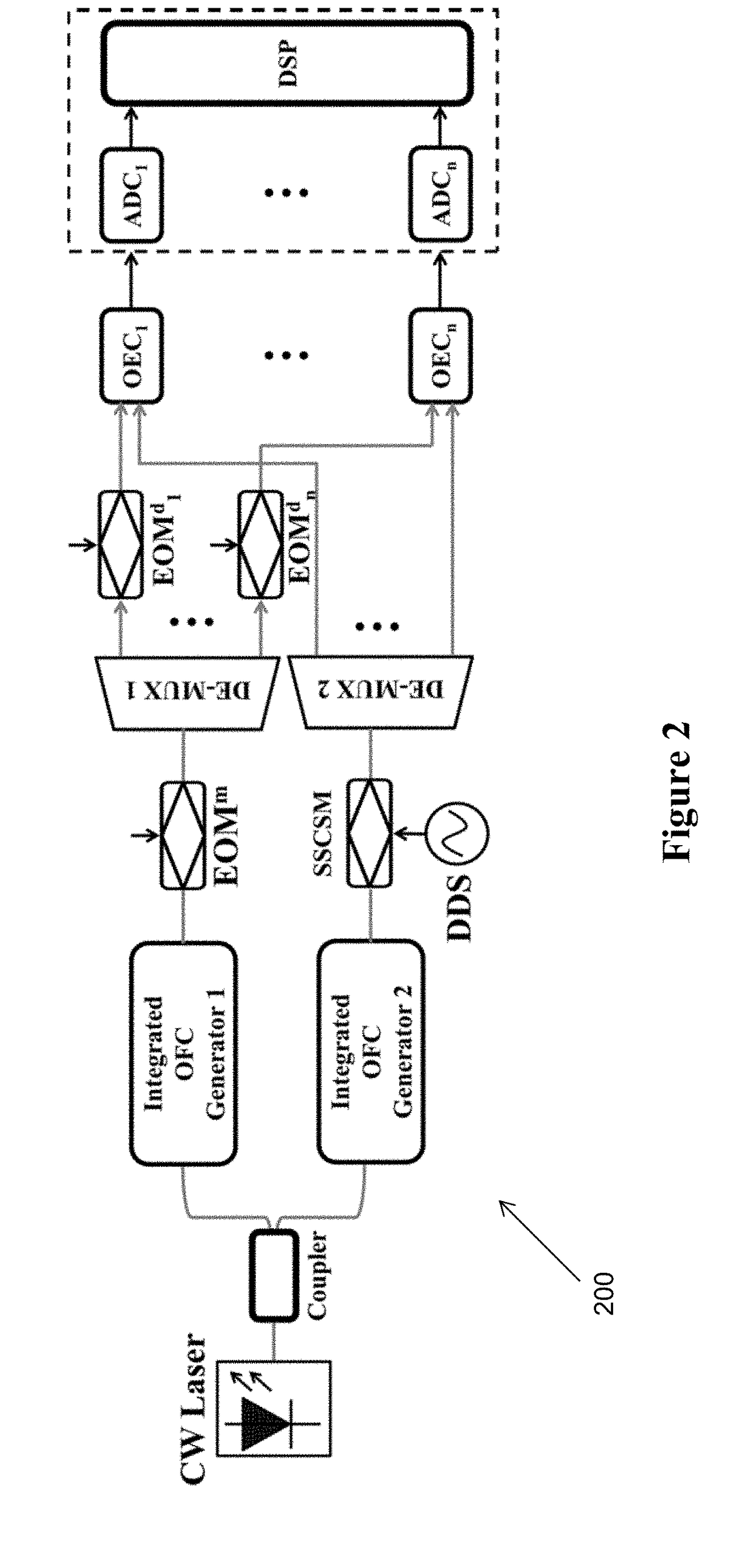
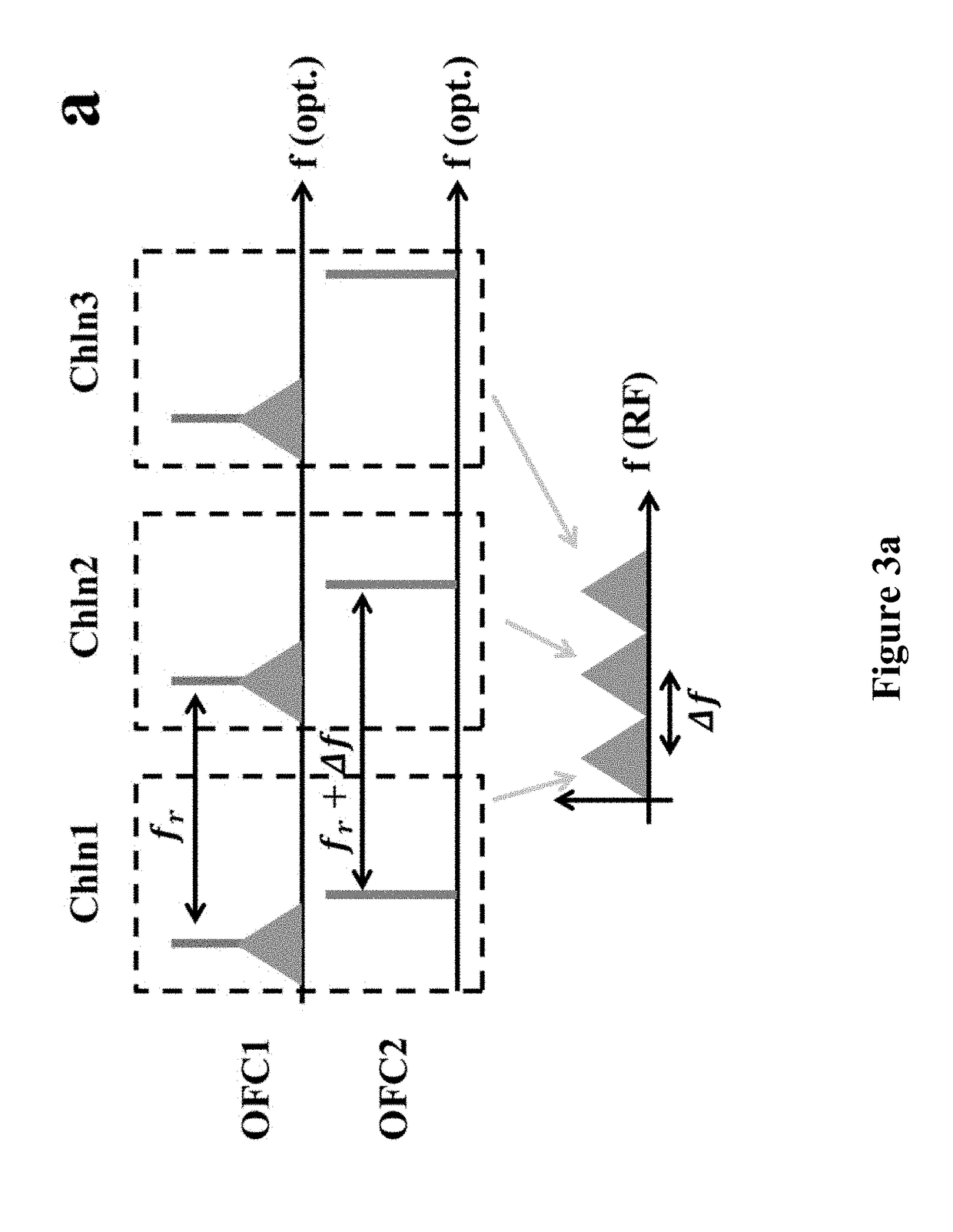
Integrated photonic microwave transceiver system
ActiveUS20190028203A1Enable detectionReduce system footprintWavelength-division multiplex systemsOpticsFrequency spectrumTransceiver
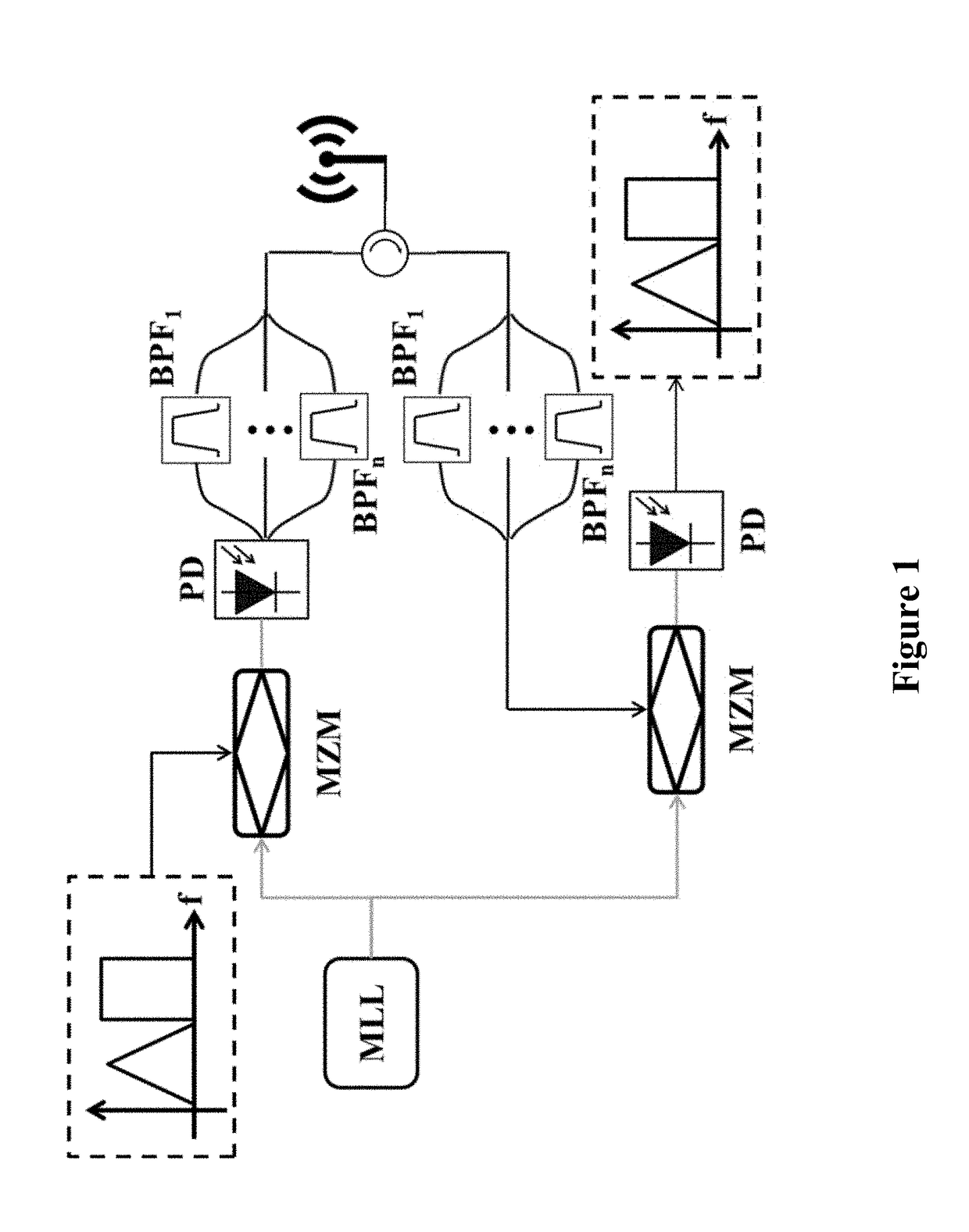
Examples of systems and methods for integrated photonic broadband microwave transceivers are disclosed based on integrated coherent dual optical frequency combs. In some cases, when the system is configured as a transmitter, multiple radio frequency (RF) carriers can be generated, which can either be encoded independently, or used for broadcasting the same information into different bands. In some cases, when the system is configured as a receiver, the spectrum of the input signal can be sliced into several spectral segments for low-bandwidth detection and analysis. In some systems, the optics-related functionalities can be achieved via integrated optic technology, for example based on silicon photonics, providing tremendous possibilities for mass-production with significantly reduced system footprint.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
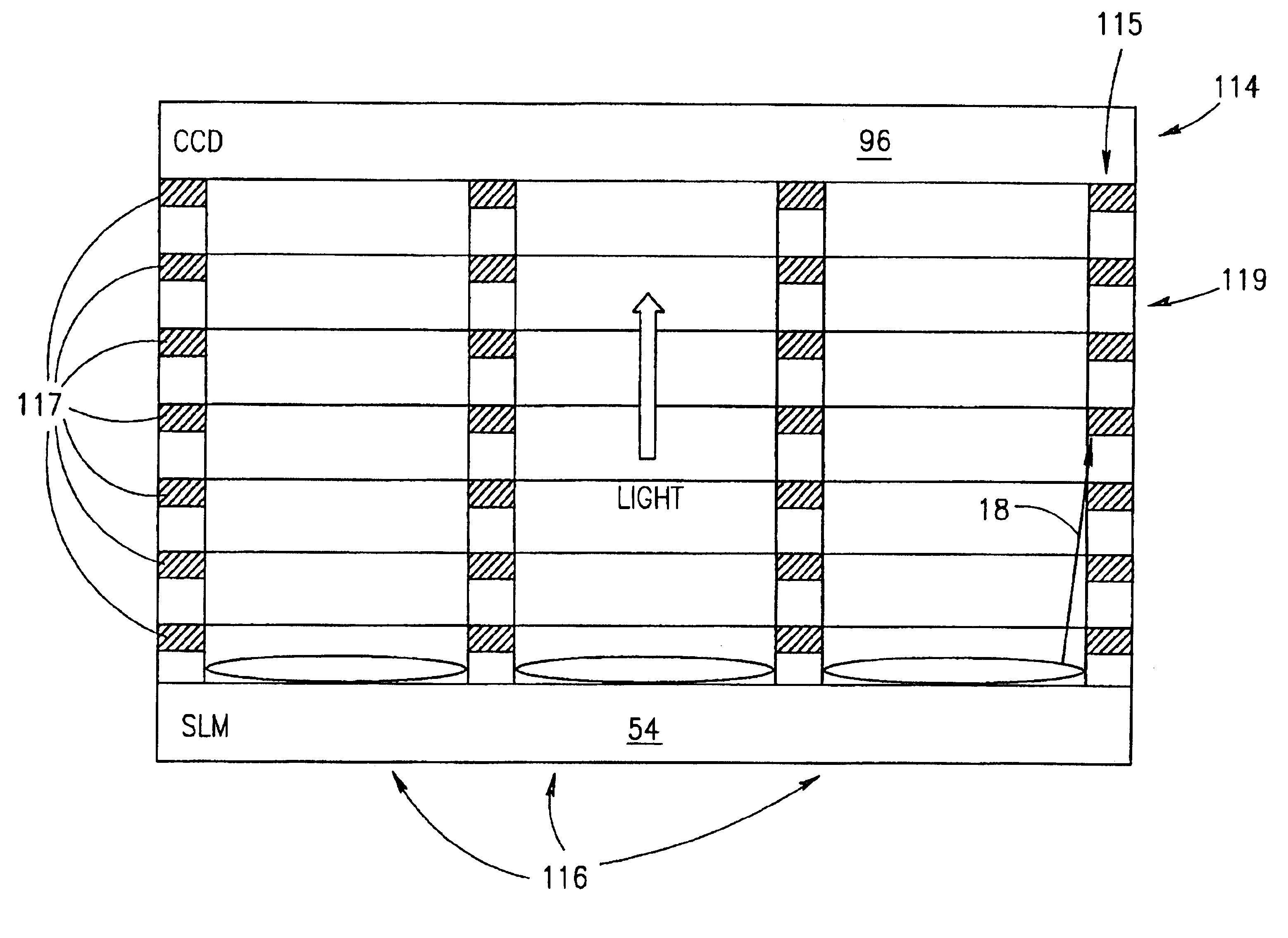
Light-receiving device and image sensor
InactiveUS6740807B2Increase ratingsAccurate informationLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor electrodeEngineering
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Optical processing
InactiveUS20050149598A1Reduce interactionReduce speckle effectImage analysisImage codingOptical processingComputational physics
A method of performing a DFT (discrete Fourier transform) or a DFT derived transform on data, comprising: providing spatially modulated light having spatial coherence, said spatially modulated light representing the data to be transformed; Fourier transforming said spatially modulated light, using an at least one optical element; and compensating for at least one of a scaling effect and a dispersion effect of said at least one optical element, using an at least one dispersive optical element.
Owner:LENSLET
Integrated optics logic gate for polarization-encoded quantum qubits and a method for the production and use thereof
InactiveUS20140126030A1Increased complexityAdd dimensionQuantum computersNanoinformaticsBeam splitterRefractive index contrast
A quantum logic gate for qubits, suitable for receiving as inputs at least two polarization-encoded qubits, includes at least one partially polarizing beam splitter (PPBS), the beam splitter comprising a first waveguide and a second waveguide which are constructed in integrated optics, the first and second waveguides having a refractive index contrast of between 0.1% and 6% and a birefringence of between 10−6 and 6*10−5.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE +1
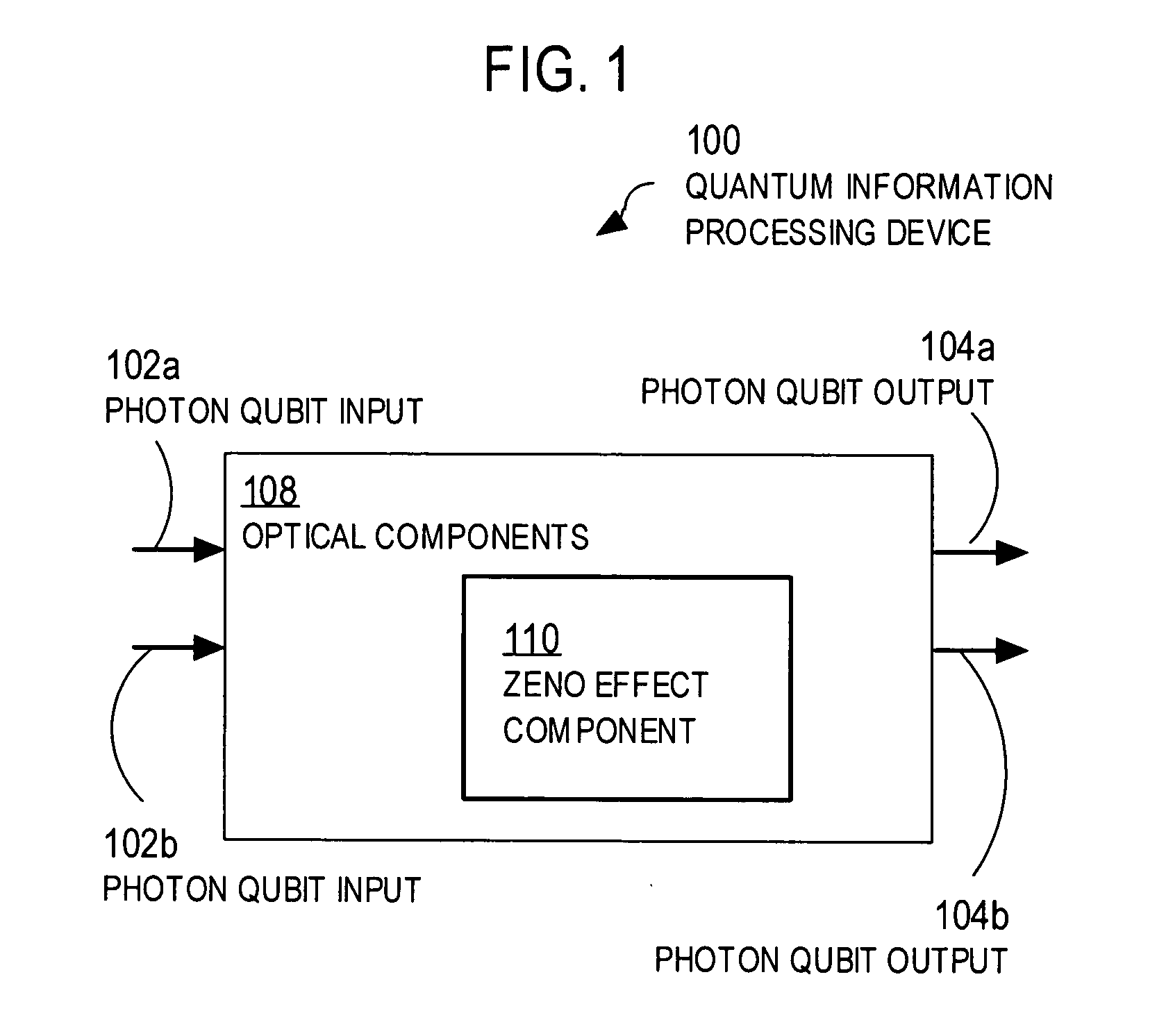
Techniques for quantum processing with photons and the Zeno effect
ActiveUS20050117836A1Small spacingReduce error rateQuantum computersComputing operations for integration/differentiationInformation processingQuantum Zeno effect
Techniques are provided that use the quantum Zeno effect to implement practical devices that use single photons as the qubits for quantum information processing. In the quantum Zeno effect, a randomly-occurring event is suppressed by frequent measurements to determine whether the event has occurred. The same results can be obtained by using atoms or molecules or ions to react to the occurrence of the event. Techniques include directing one or more input qubits onto a device and applying a quantum Zeno effect in the device. The quantum Zeno effect is applied by consuming one or more photons in the device under conditions in which photons, that would otherwise be output by the device, do not represent a result of a particular quantum information processing operation. Devices implemented using the quantum Zeno effect can operate with low error rates without the need for high efficiency detectors and large number of ancilla.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Coloring matter sensitization type photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20050224112A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyIncreased durabilityLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesSolar lightPorphyrin structure
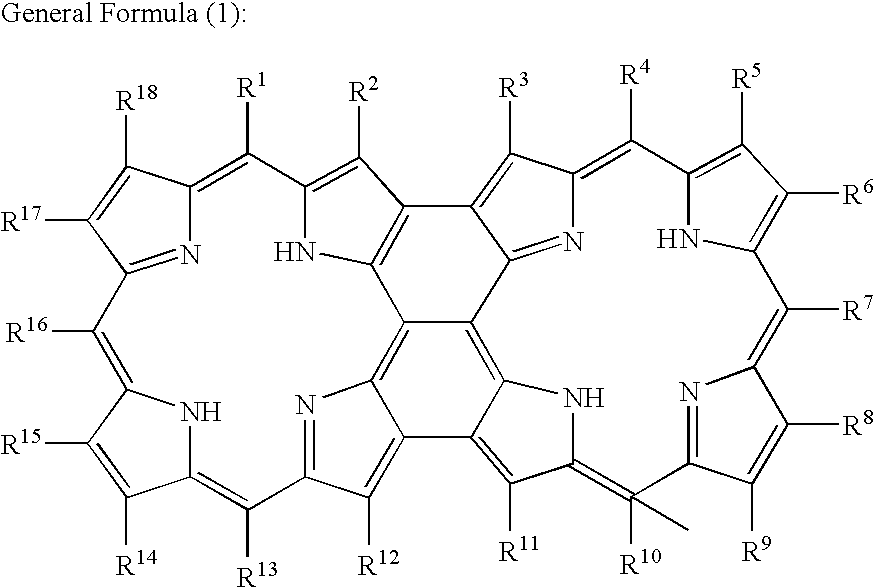
The present invention relates to a dye-sensitized type photoelectric conversion device for generating electric power by using solar light. The dye-sensitized type photoelectric conversion device includes a semiconductor layer on which a sensitizing dye having an acidic group-containing porphyrin polymer expressed by a below-described general formula (1) is carried and an electrolyte layer. (Here, in the above-described general formula (1), R1 to R18 indicate substituents such as hydrogen atoms, halogen atoms and at least one of R1 to R18 is an acidic substituent such as 4-carboxyphenyl group.)
Owner:SONY CORP
Fast quantum gates with ultrafast chirped pulses
ActiveUS7899092B2Laser using scattering effectsLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesTime domainPulse shaper
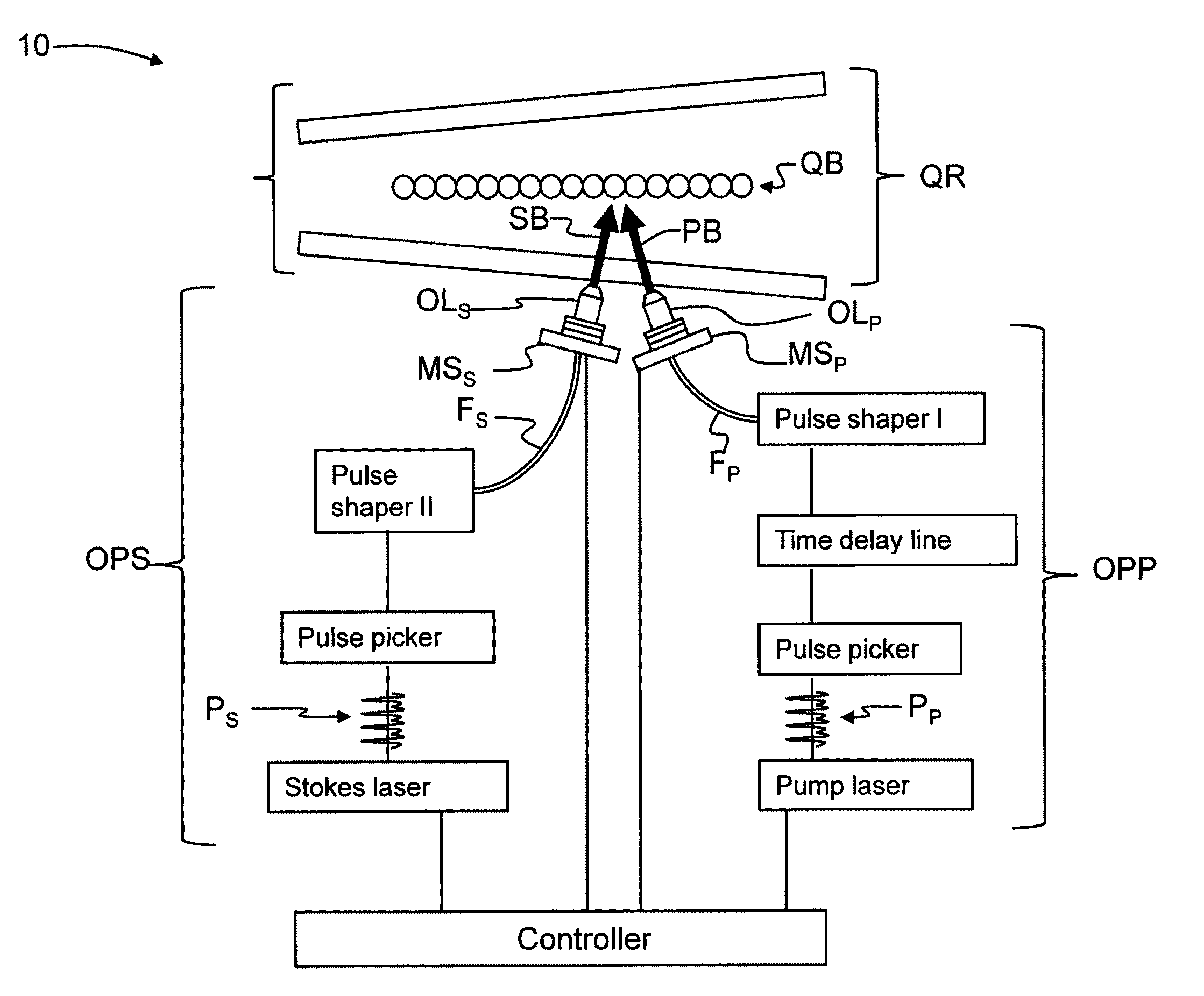
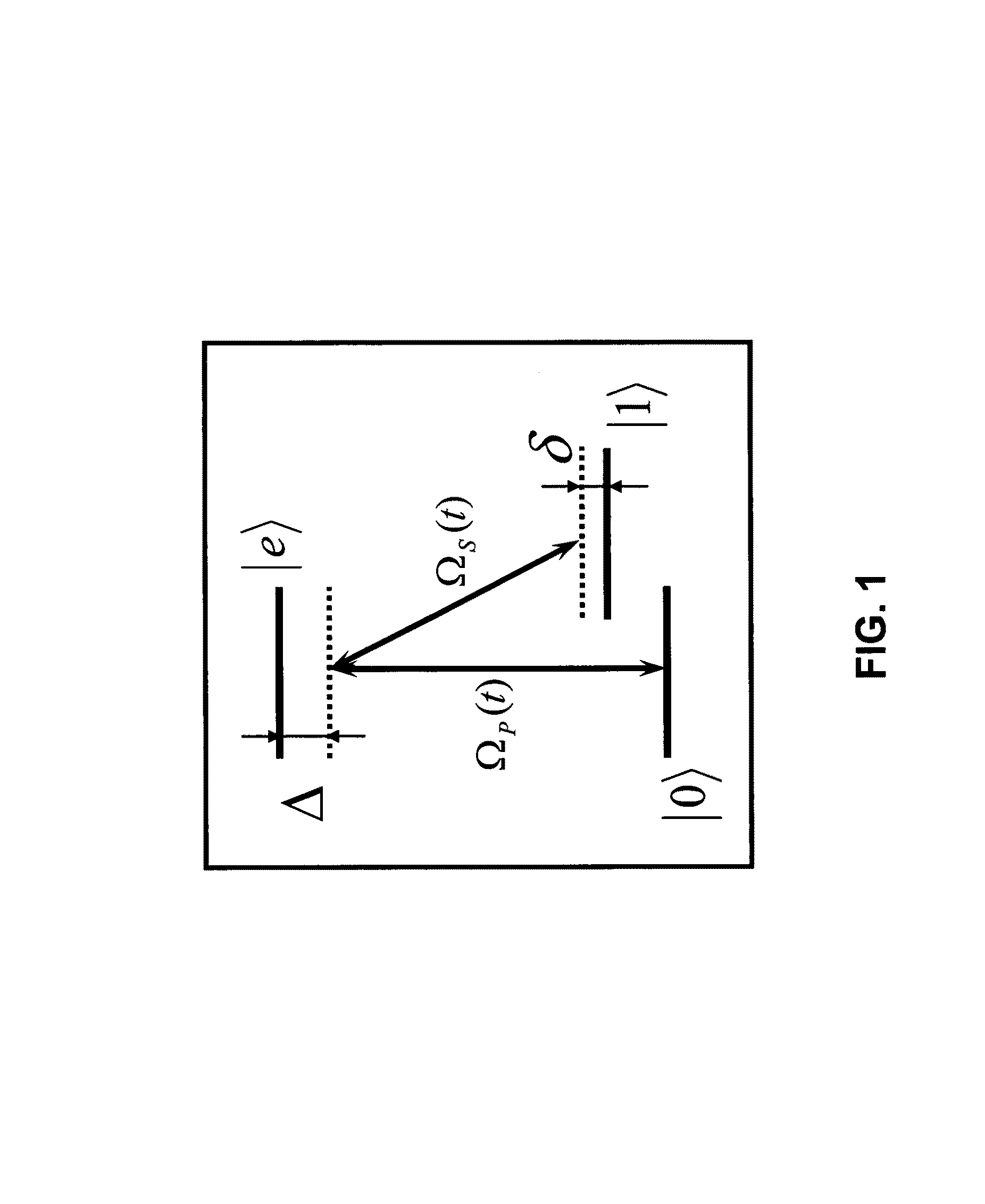
Apparatus and methods of performing fast single-qubit quantum gates using ultrafast femtosecond frequency chirped laser pulses are disclosed. The use of chirped pulses removes the demanding restrictions of prior art approaches and allows for the construction of fast quantum gates that operate at speeds on the of order several picoseconds. The apparatus includes two synchronized lasers (pump and Stokes) used to manipulate a qubit wave function in a select manner. Each laser system generates a train of optical pulses. Pulse pickers choose pump and Stokes pulses, which propagate though respective pulse shapers that apply necessary time-dependent phases. To achieve complete overlap between the pulses in time domain, necessary adjustments can be made by using an additional time delay line, which can be located in any path or in both paths.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
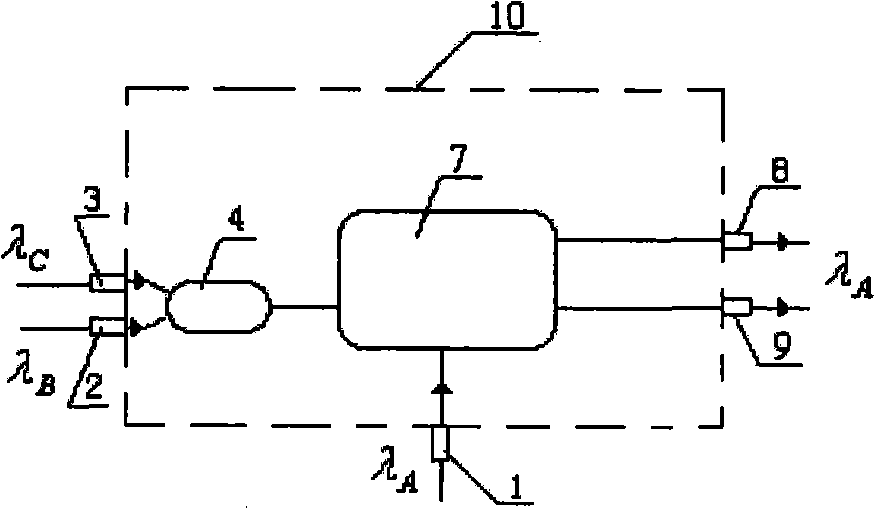
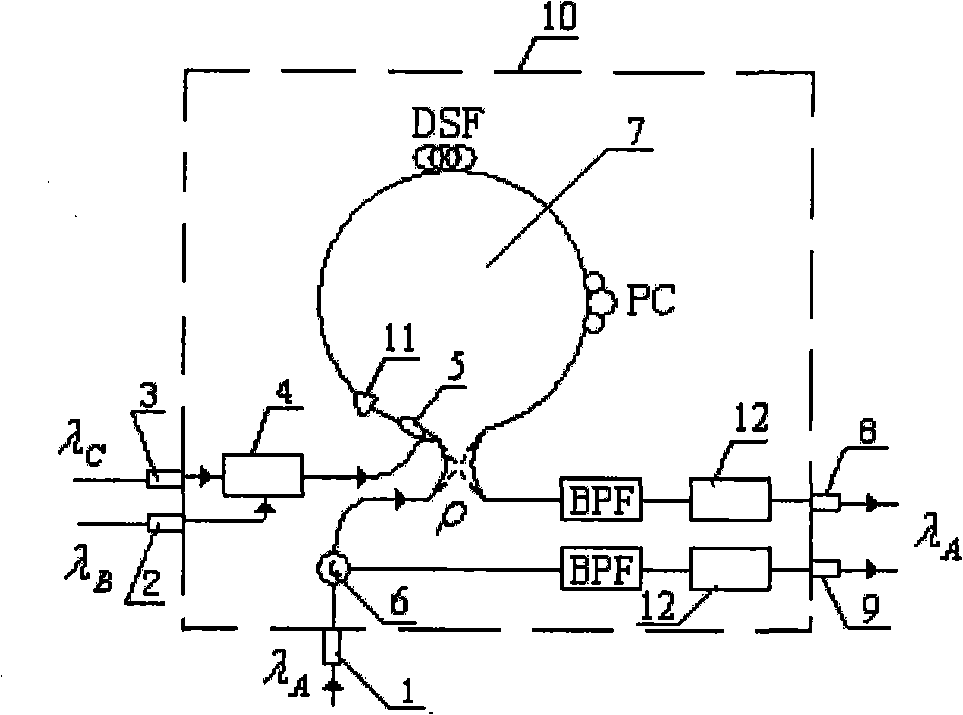
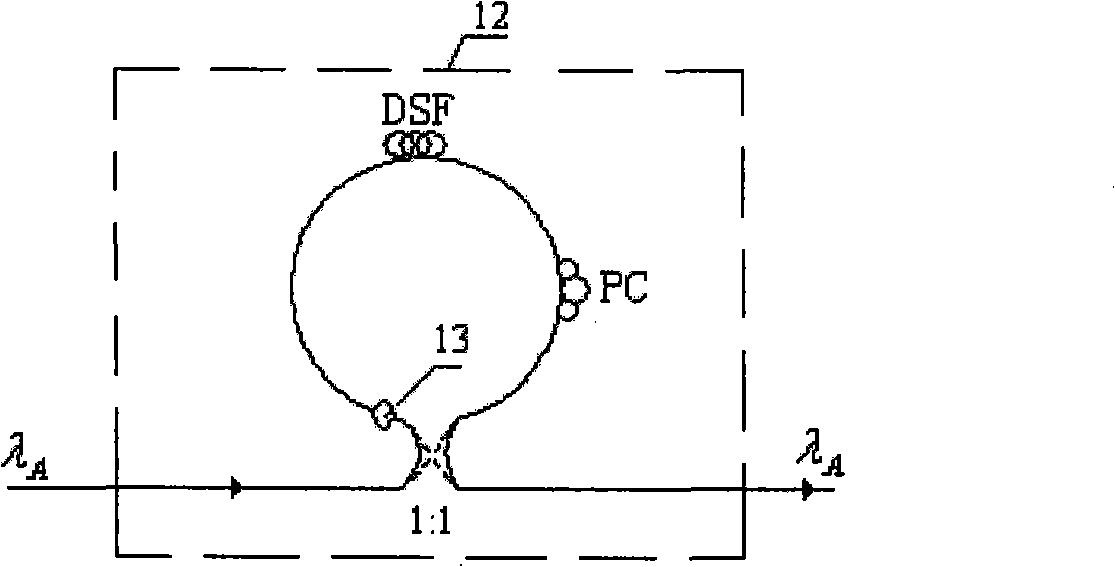
Full-optical logic gate
InactiveCN101526715AReduce the incident light powerReduce Sagnac loop lengthLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesNon-linear opticsControl signalNOR gate
The invention relates to a full-optical logic gate (10), which can be reused to achieve opposite phase operations of an AND gate, an OR gate, an NOT gate, an NAND gate, an NOR gate, an XOR gate, an XNOR gate and combination thereof, and can also achieve a half adder. The full-optical logic gate comprises light input ports (2, 3) for receiving two control light signals respectively, a light input port (1) for receiving a synchronous light clock signal, a light output port (8) for outputting the result for expressing logic application, and a light output port (9) for outputting opposite phase operation. The full-optical logic gate is characterized by comprising a light combination device (4) and a nonlinear optical device (7), wherein the light combination device (4) is used for combining the two control light signals to generate corresponding combined signals with a wavelength division multiplexer or a polarization beam combiner; and the nonlinear optical device (7) is used for receiving the combined signals and the synchronous light clock signal and emitting two paths of light output signals mutual in opposite phase operations. The full-optical logic function depends on the characteristic of the nonlinear optical device, wherein the characteristic is selected so that the power of the output signals and the light power of the clock signal are redistributed and associated through the selected logic function.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
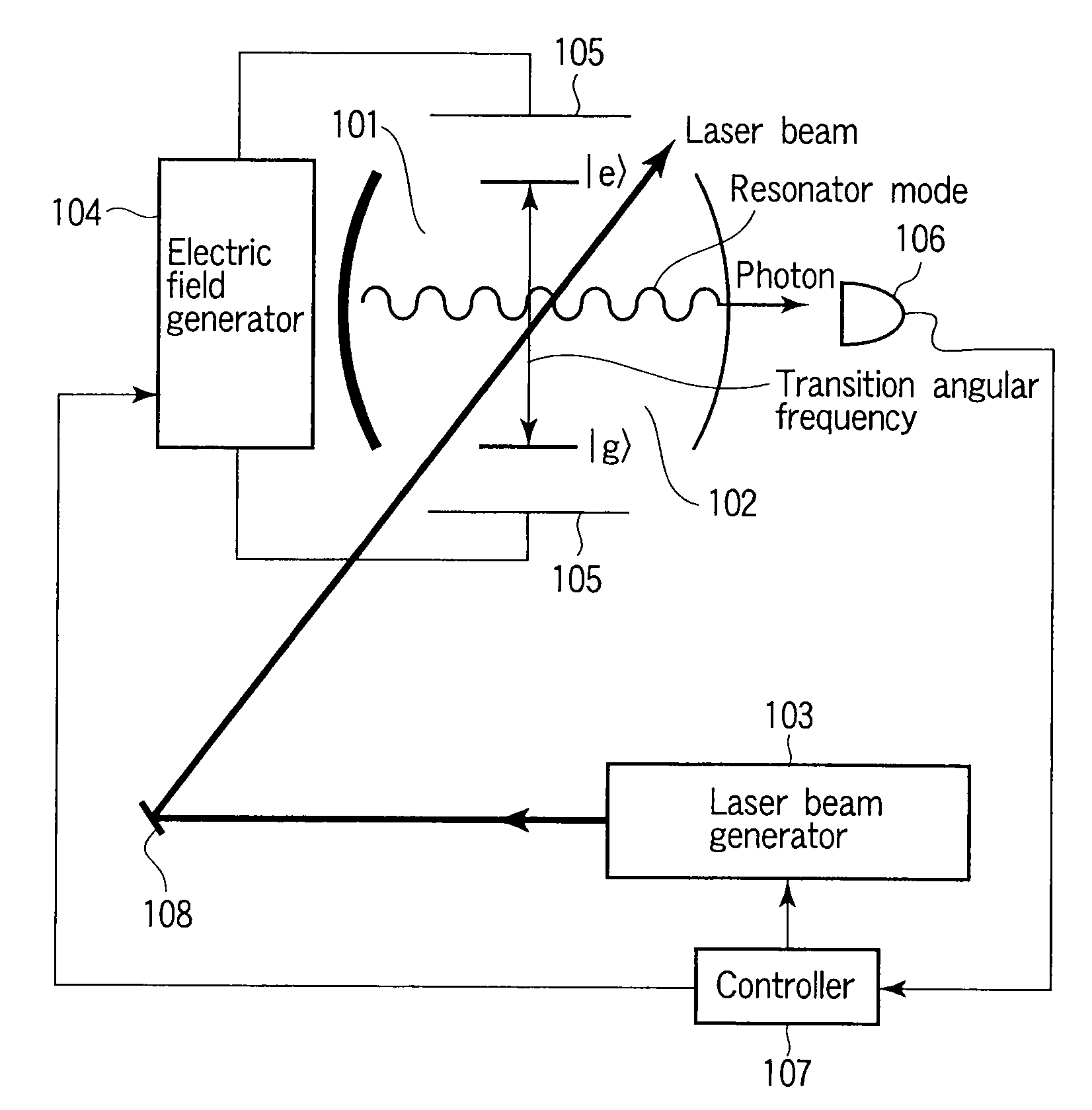
Single-photon generation apparatus and quantum bit reading apparatus and method
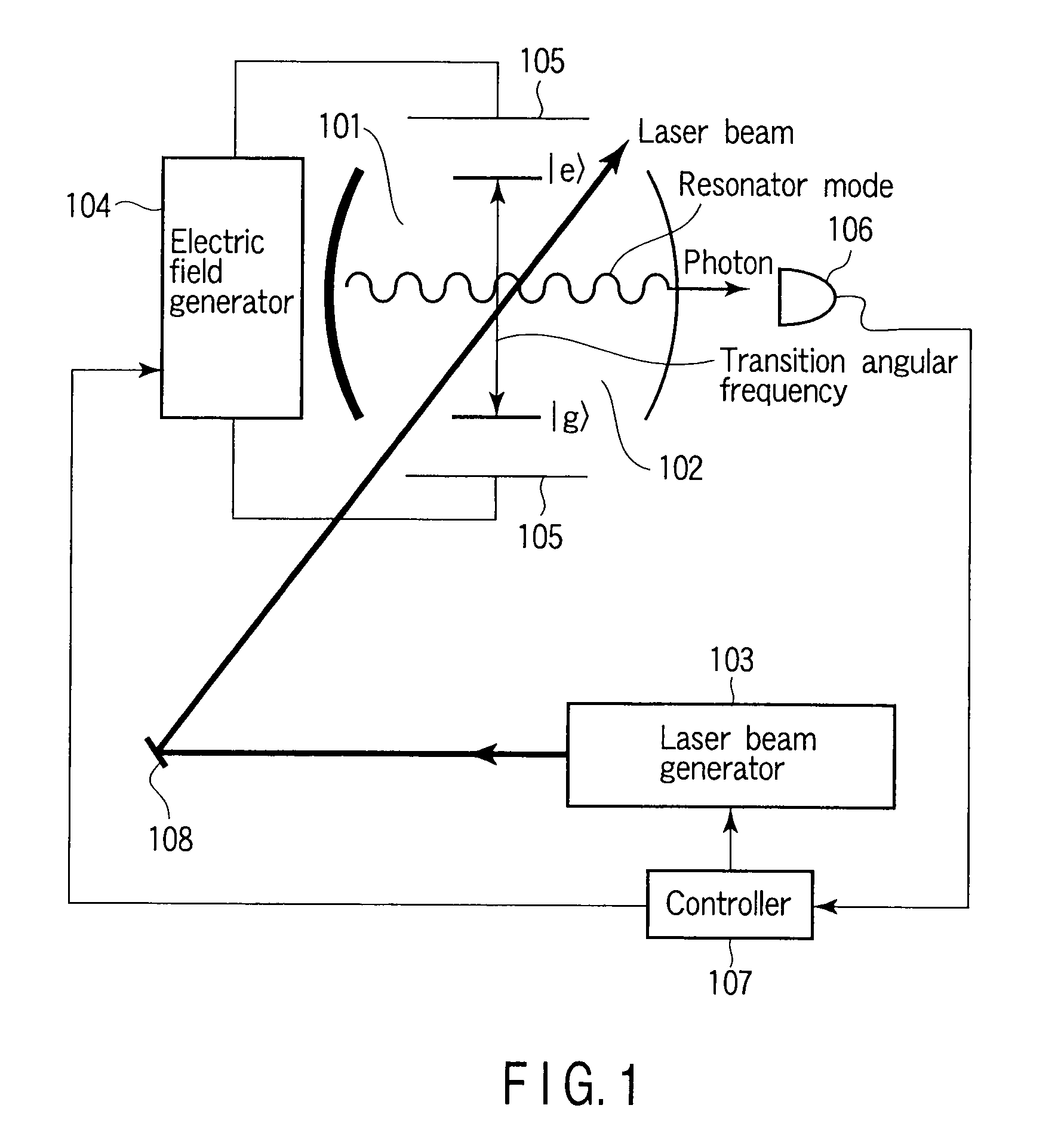
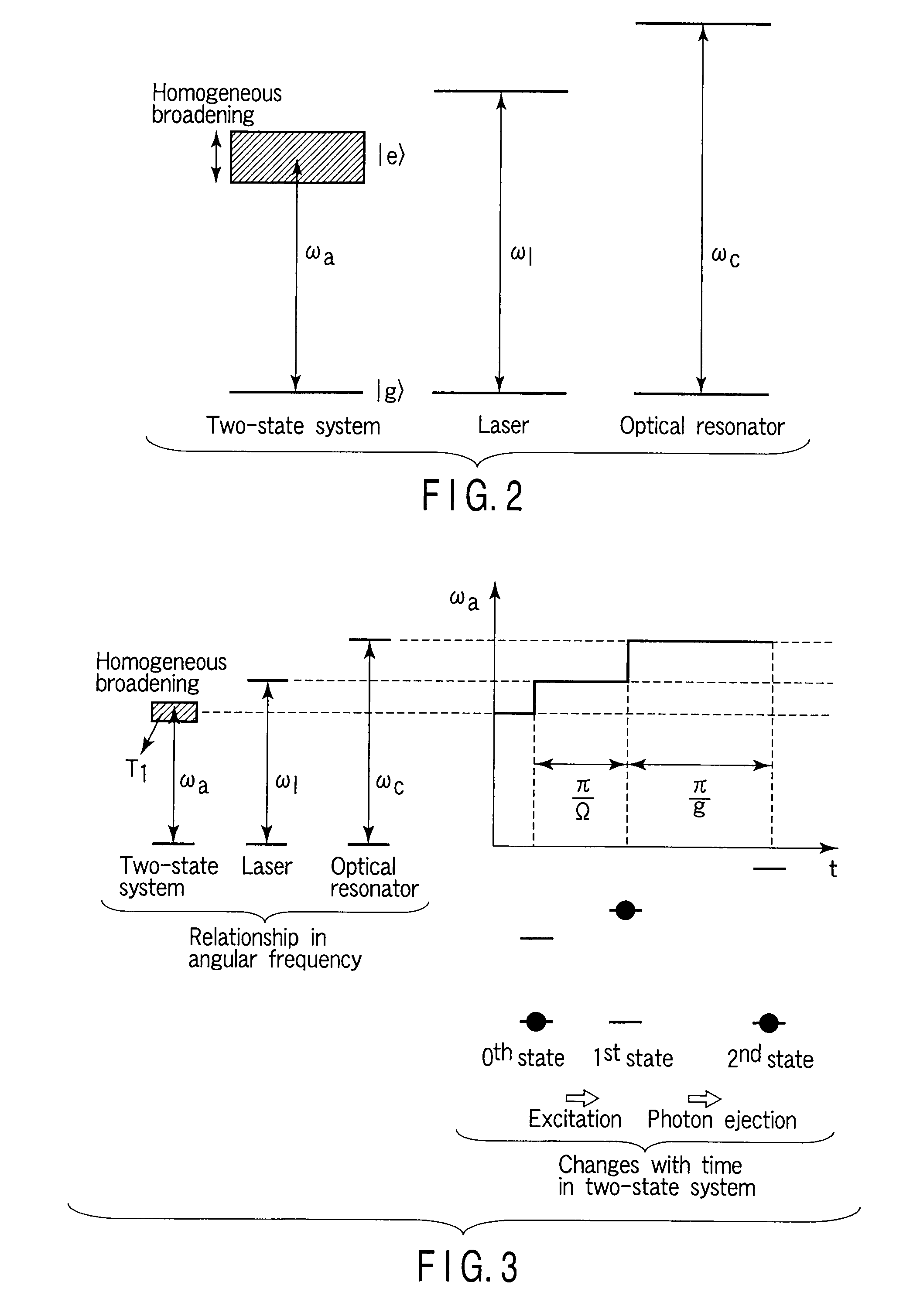
A method of generating a single photon, includes preparing an optical resonator including a resonator mode of a resonance angular frequency ωc, preparing a material contained in the optical resonator, including a low energy state |g> and a high energy state |e>, and including a transition angular frequency ωa between |g>−|e> that is varied by an external field, applying, to the material, light of an angular frequency ωl different from the resonance angular frequency ωc, and applying a first external field to the material to vary the transition angular frequency ωa to resonate with the angular frequency ωl, such that a state of the material is changed to |e>, and then applying a second external field to the material to vary the transition angular frequency ωa to resonate with the resonance angular frequency ωc, such that the state of the material is restored to |g>.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com