Patents
Literature
7863results about How to "Improve photoelectric conversion efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
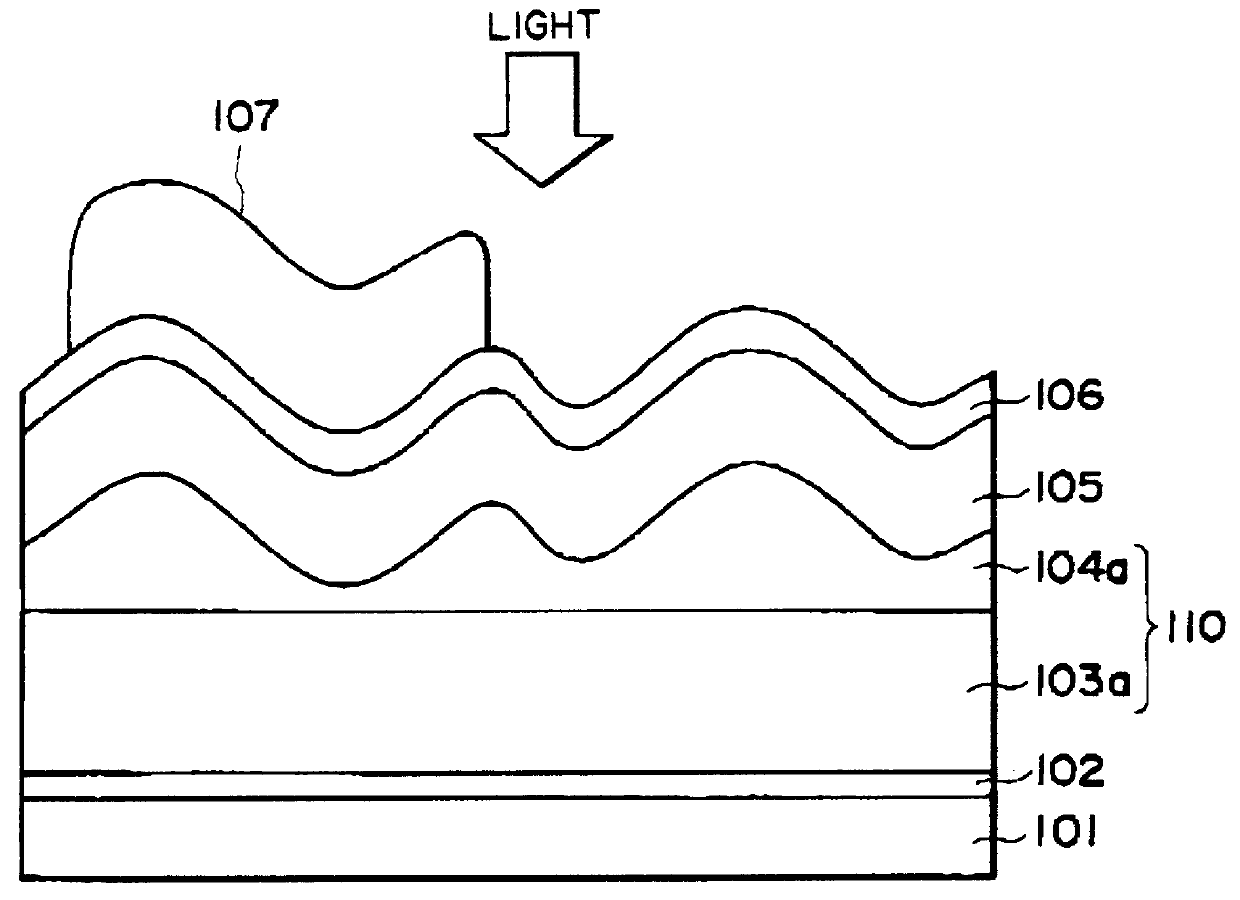
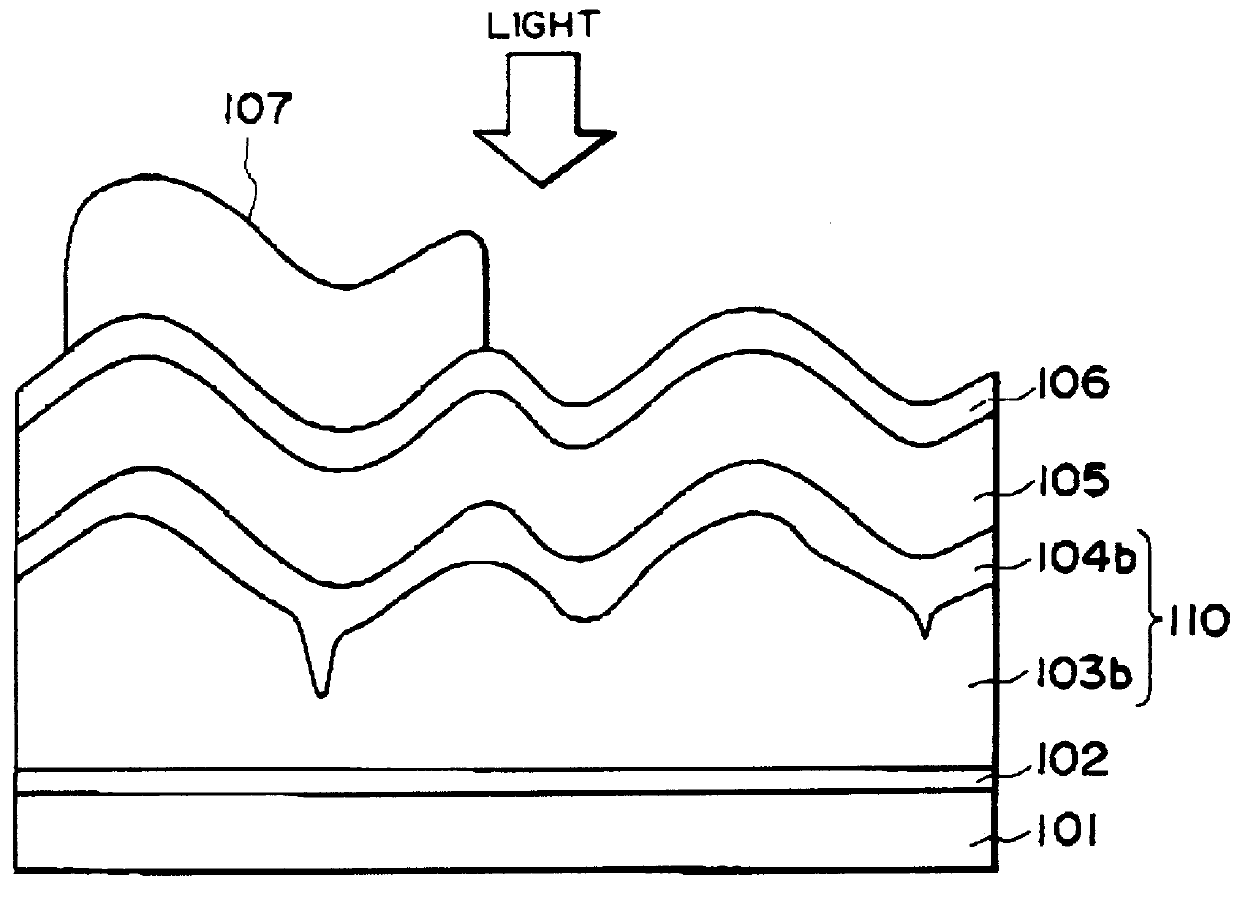
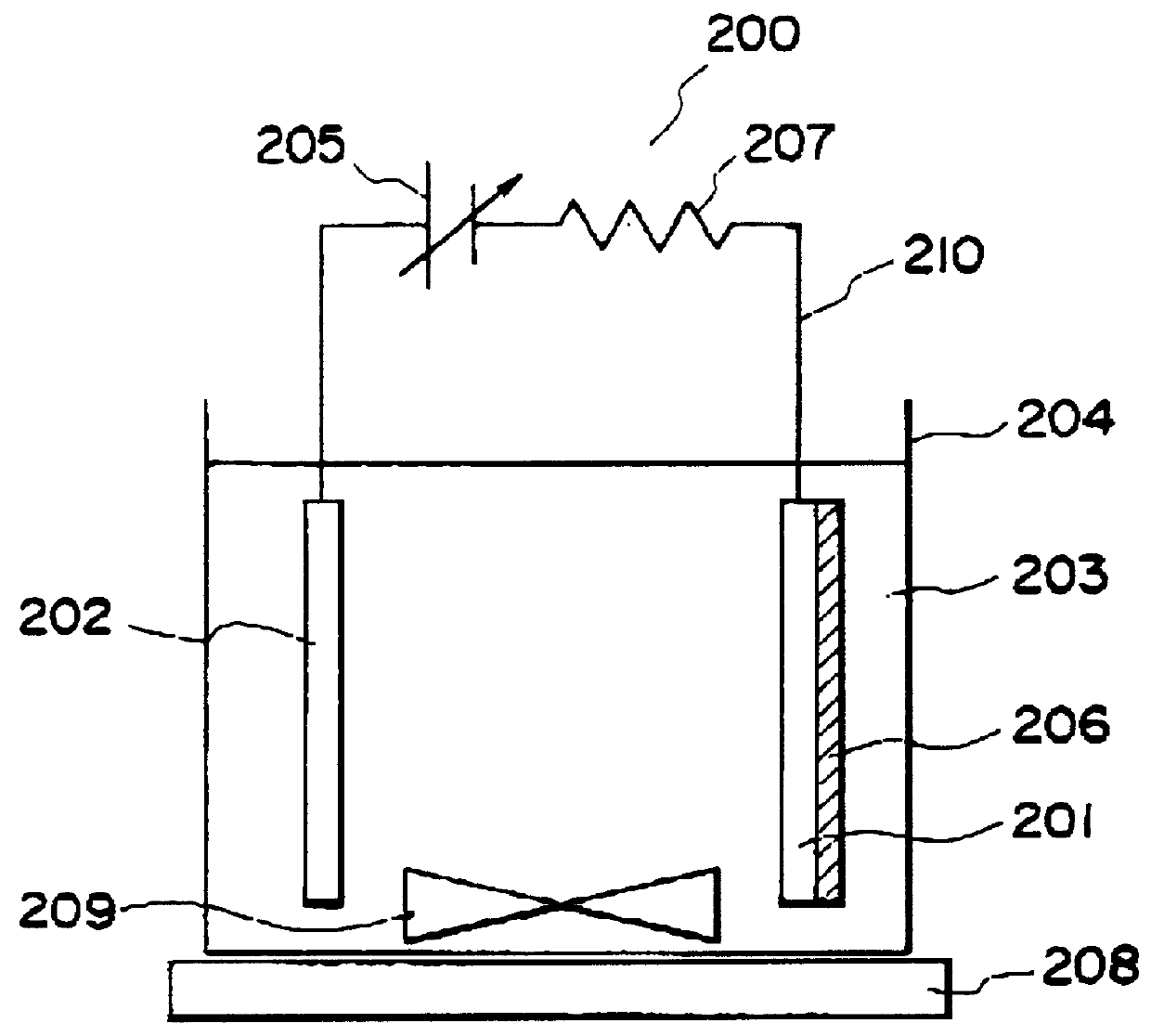
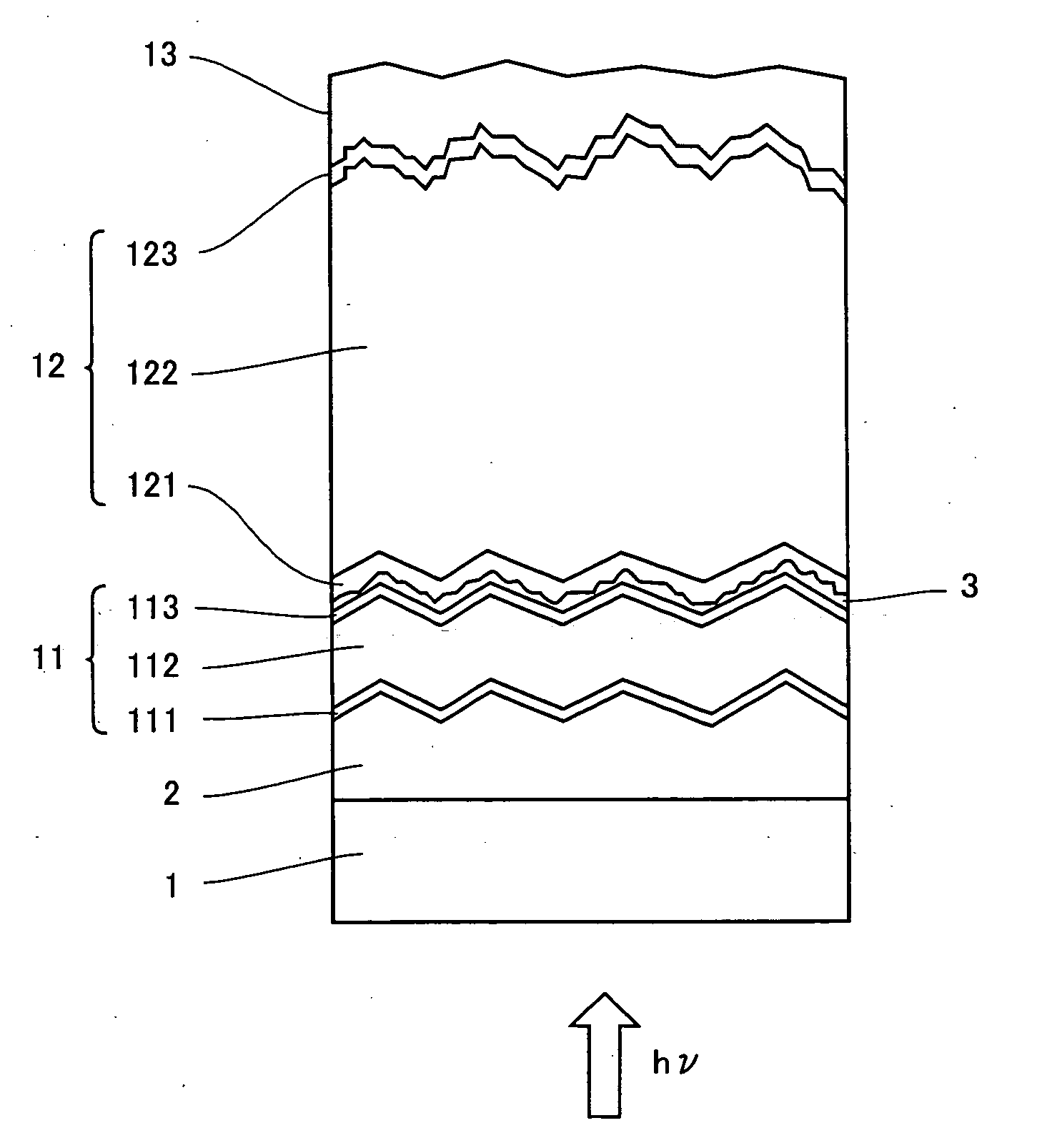
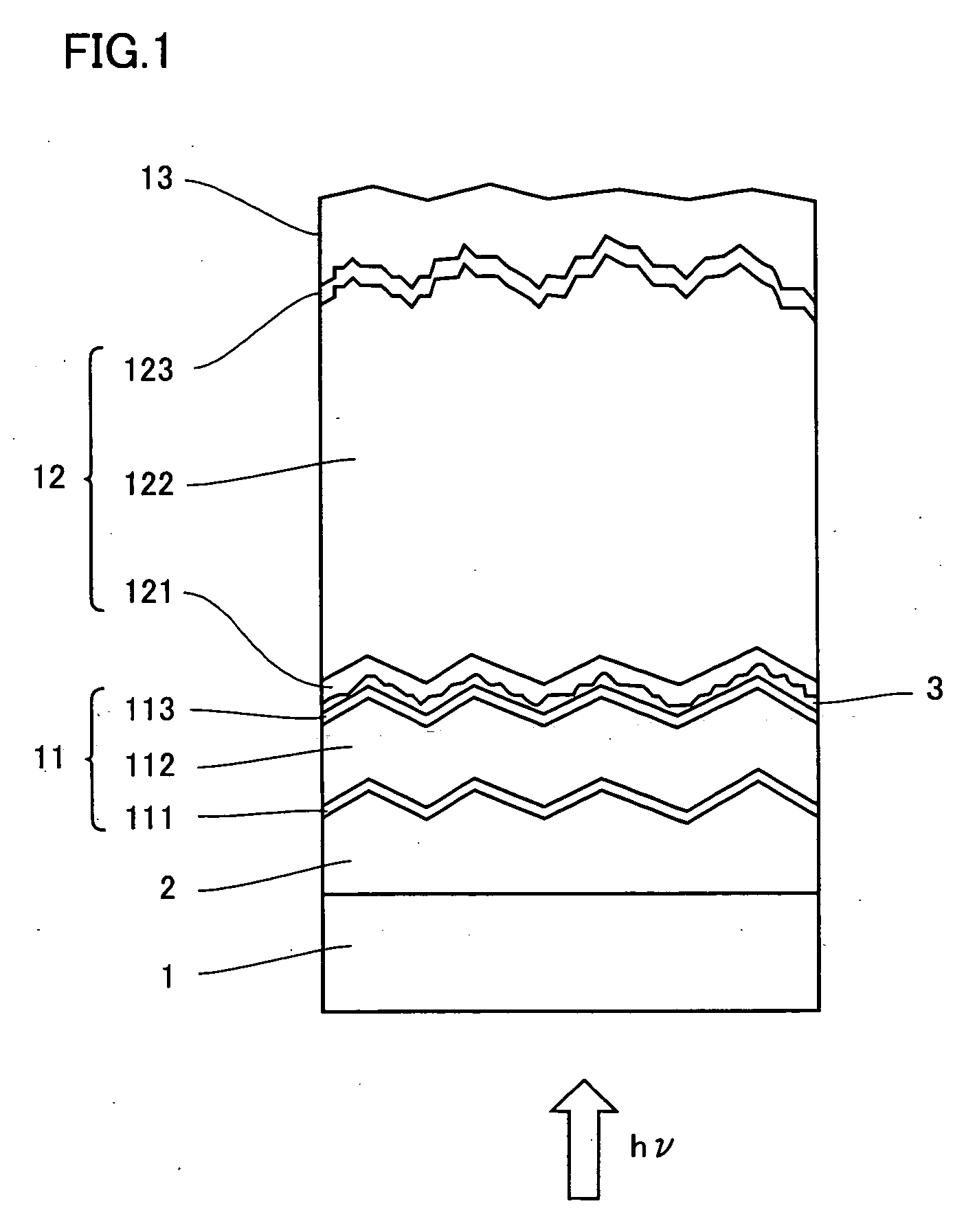
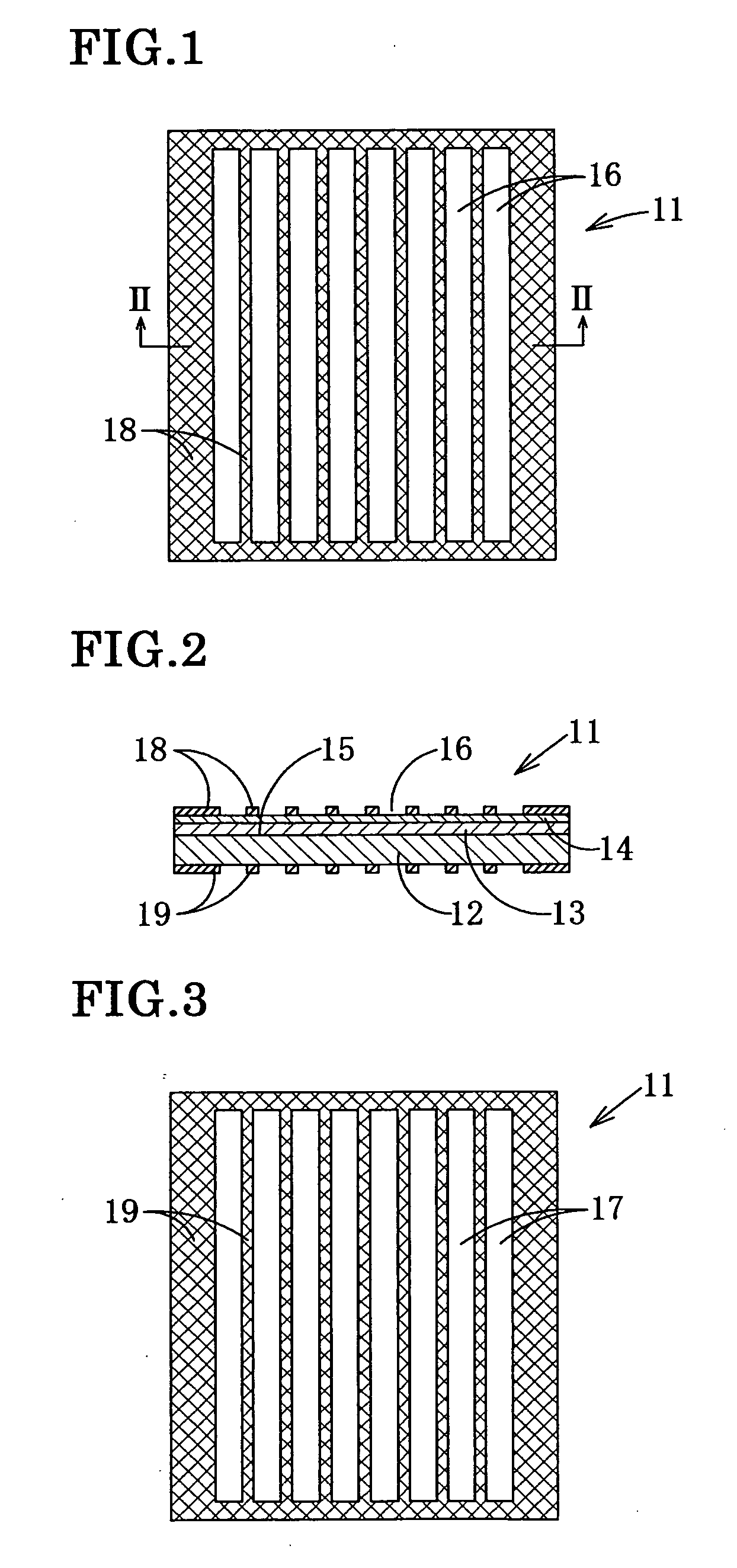
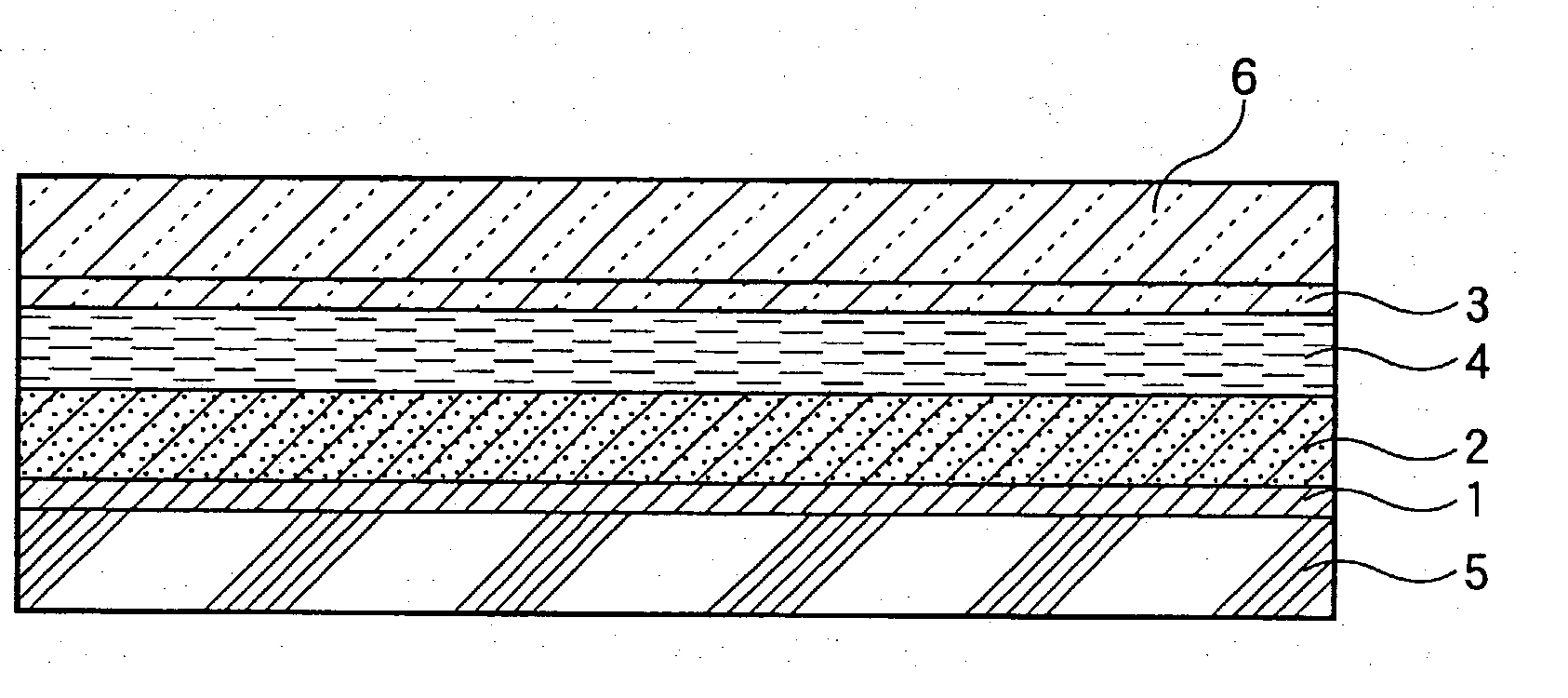
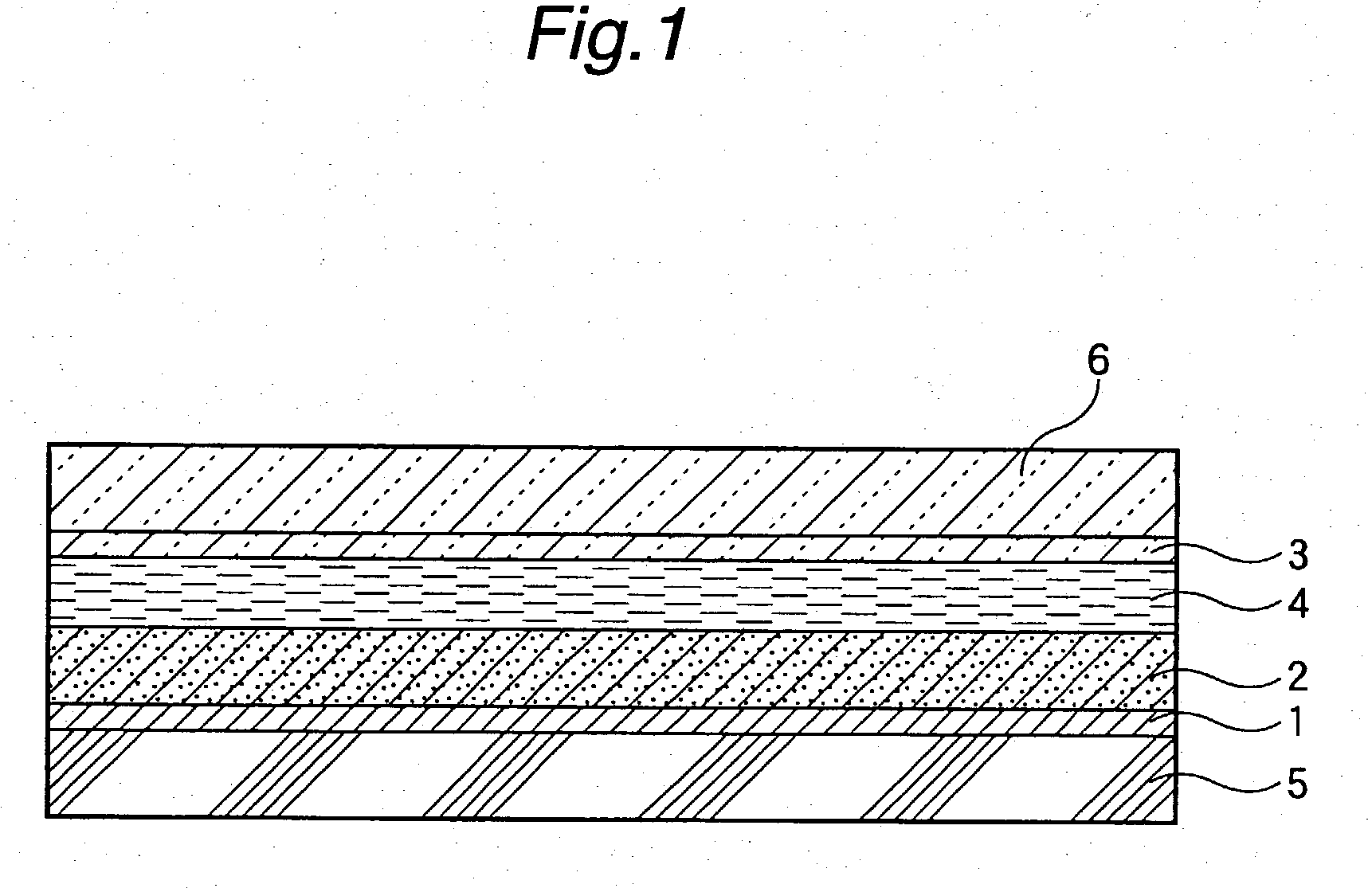
Process for producing photo-electricity generating device
InactiveUS6123824AInhibition of abnormal growthReduce leakage currentElectrolytic inorganic material coatingSurface reaction electrolytic coatingElectricityPower flow
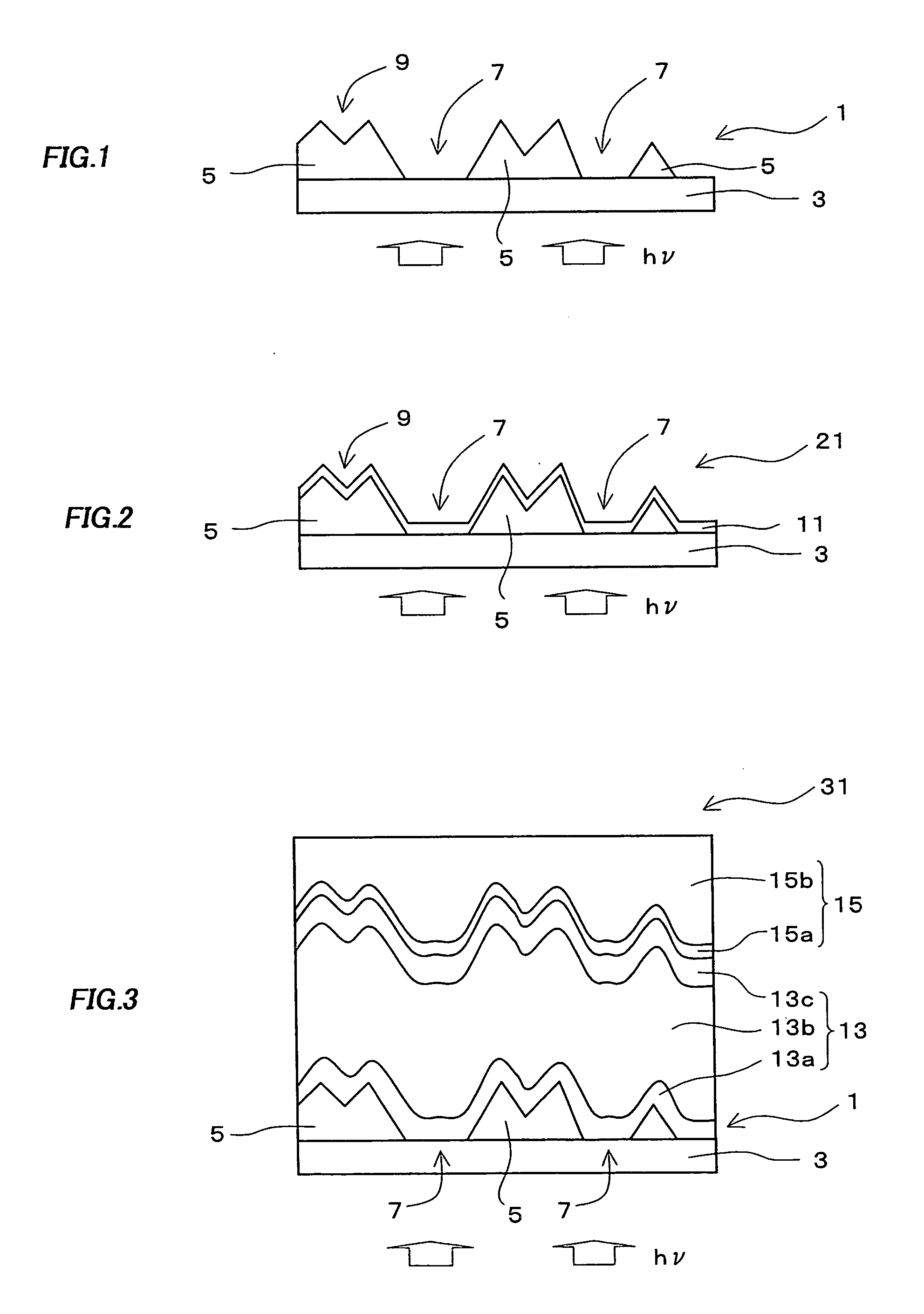
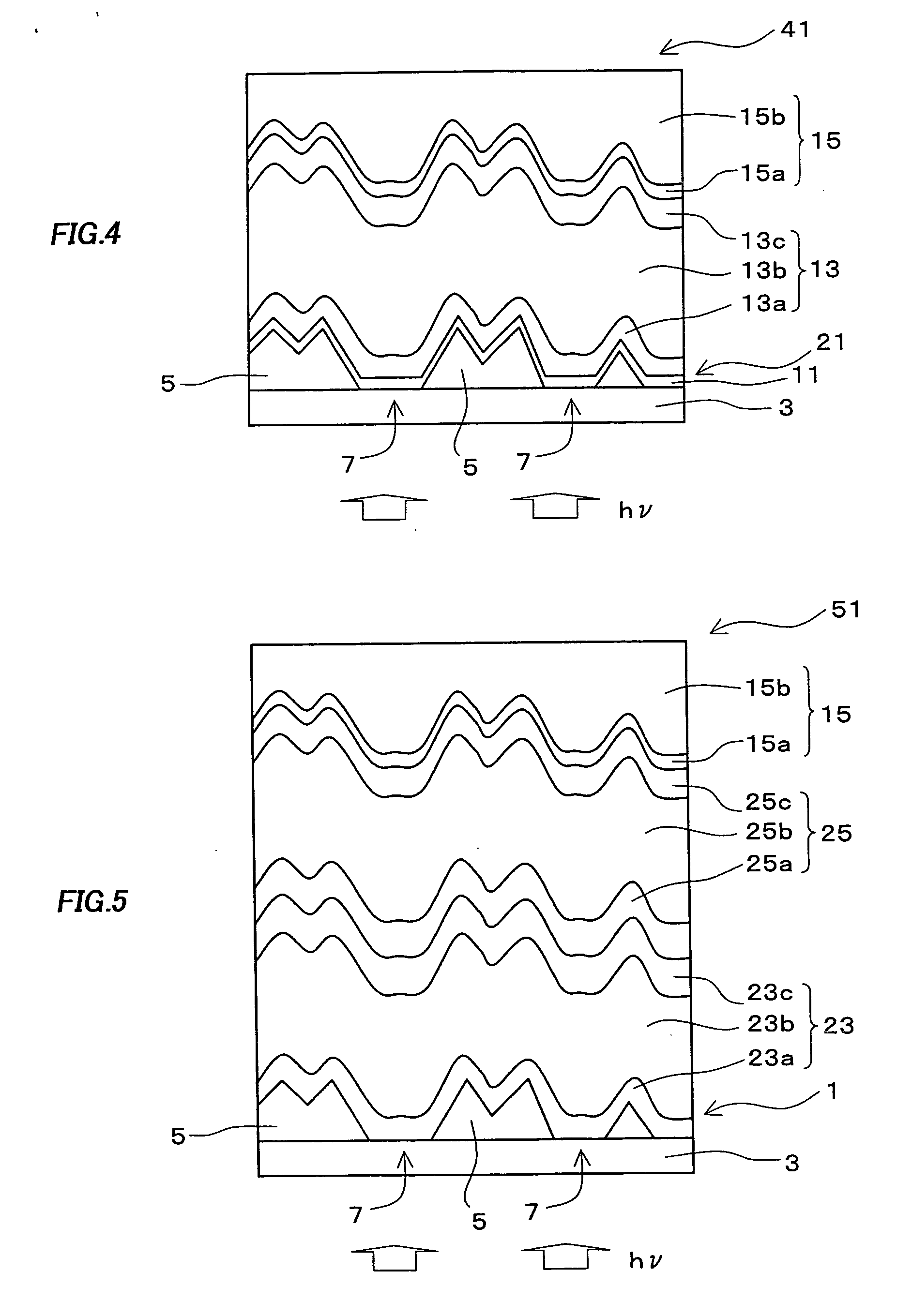
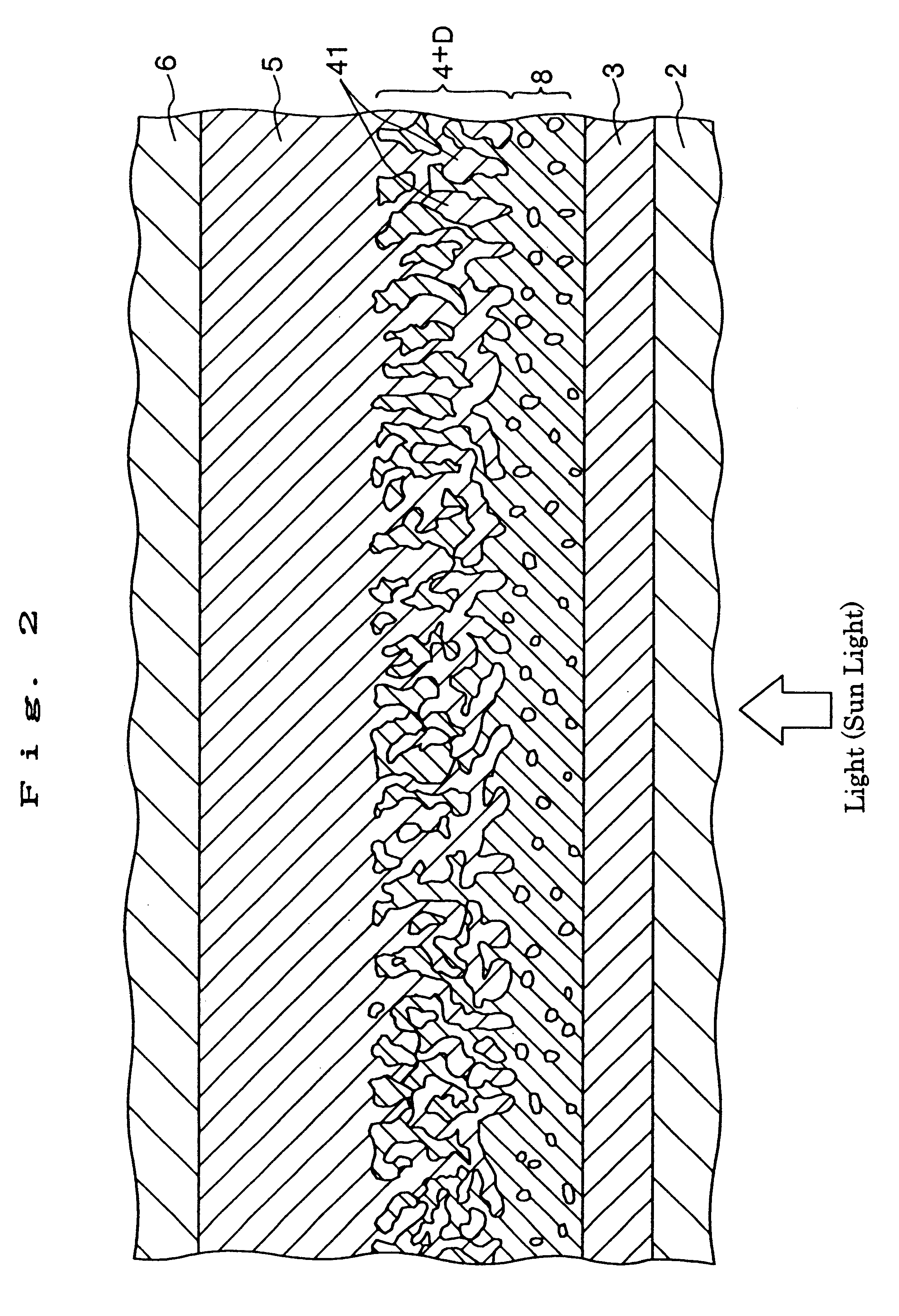
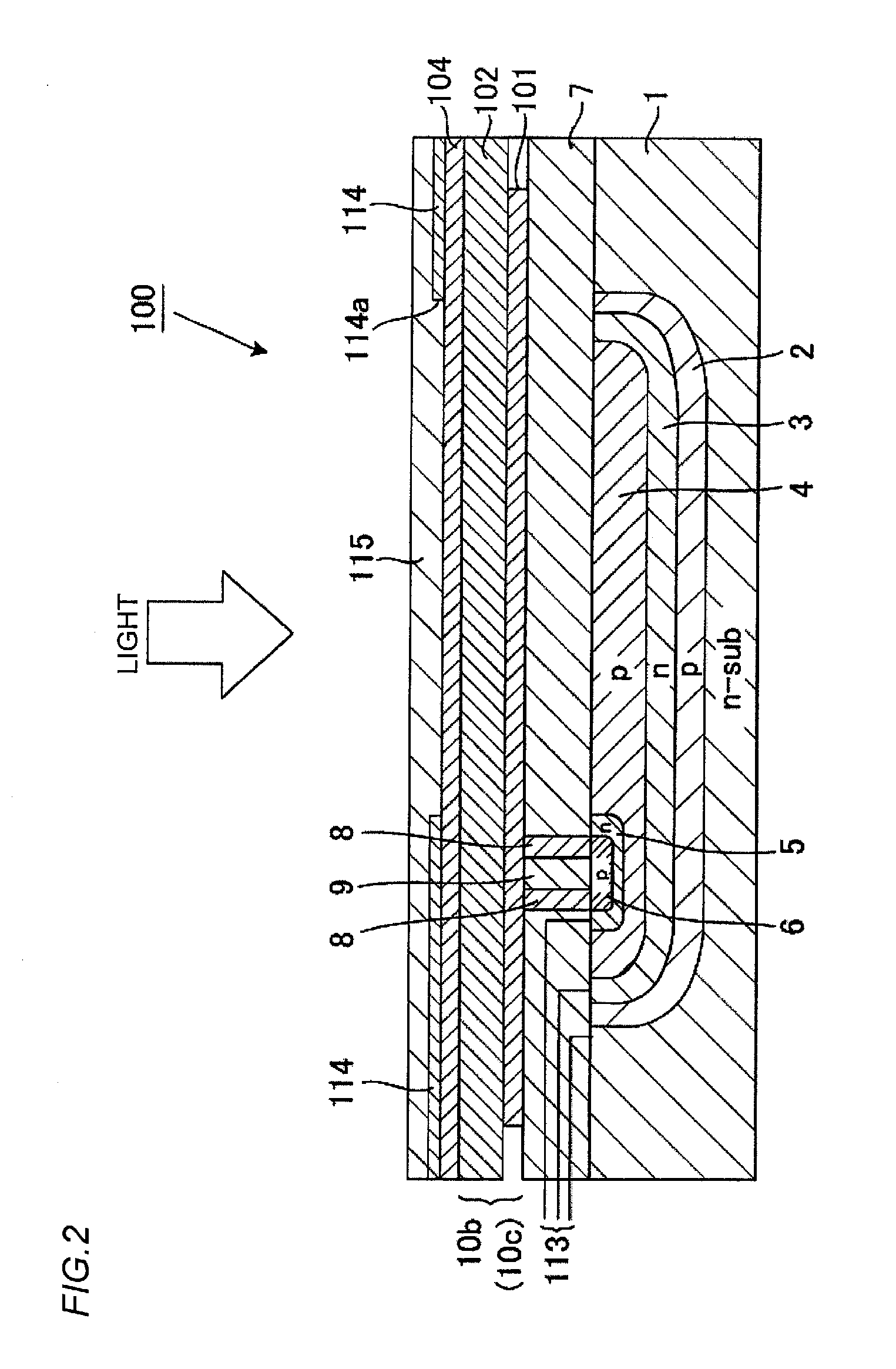
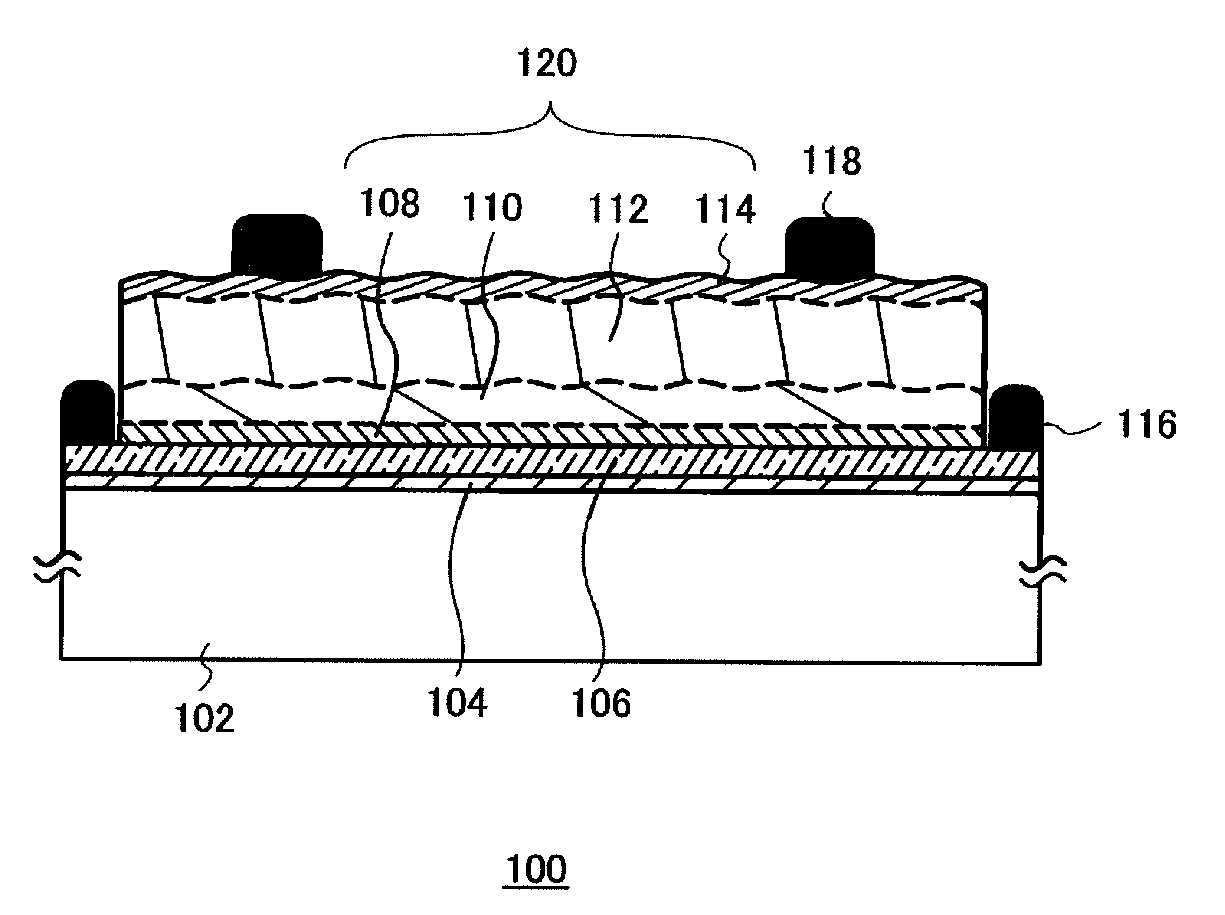
A photo-electricity generating device is produced through the steps of: immersing an electrode and an electroconductive substrate in an aqueous solution comprising nitrate ions and zinc ions, supplying a current passing through a gap between the electrode and the electroconductive substrate to form a first zinc oxide layer on the electroconductive substrate, etching the first zinc oxide layer, and forming a semiconductor layer on the zinc oxide layer. The zinc oxide layer may preferably be formed in two zinc oxide layers under different electrudeposition conditions. In this case, the etching step may preferably be performed between steps for forming these zinc oxide layers. The zinc oxide layer is provided with an unevenness at its surface suitable for constituting a light-confining layer of a resultant photo-electricity generating device.
Owner:CANON KK
Substrate for photoelectric conversion device, photoelectric conversion device, and stacked photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20070151596A1High light transmittanceSpeed up the conversion processPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPhotoelectric conversion
A substrate 1 for a photoelectric conversion device includes a first transparent conductive layer 5 formed on at least a part of the surface region of a transparent substrate 3, the first transparent conductive layer 5 having at least an opening portion 7 exposing the substrate 3.
Owner:SHARP KK
Photoelectric conversion element
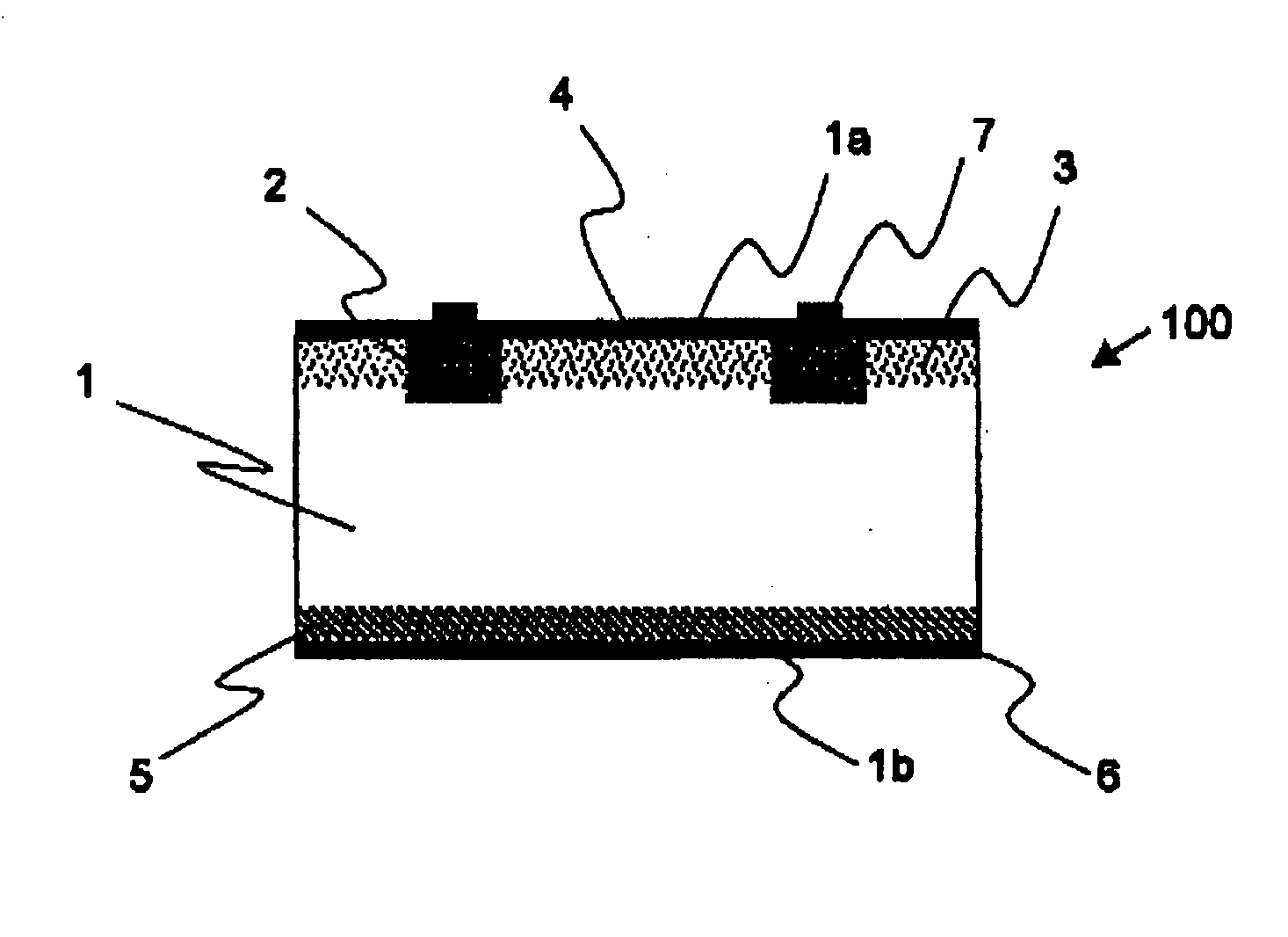
InactiveUS6683244B2Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyPrevent and suppressLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsPorosityPhotoelectric conversion
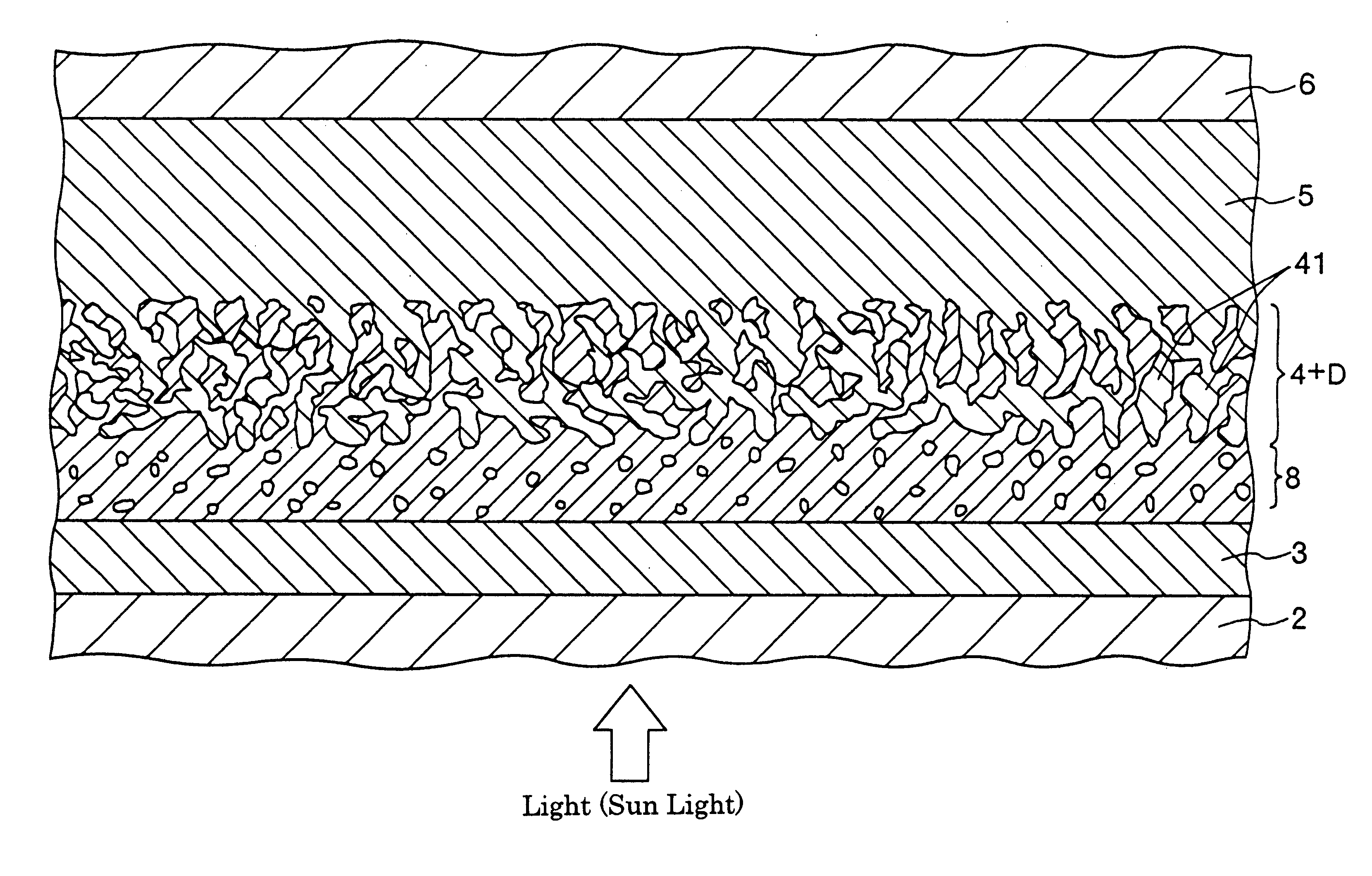
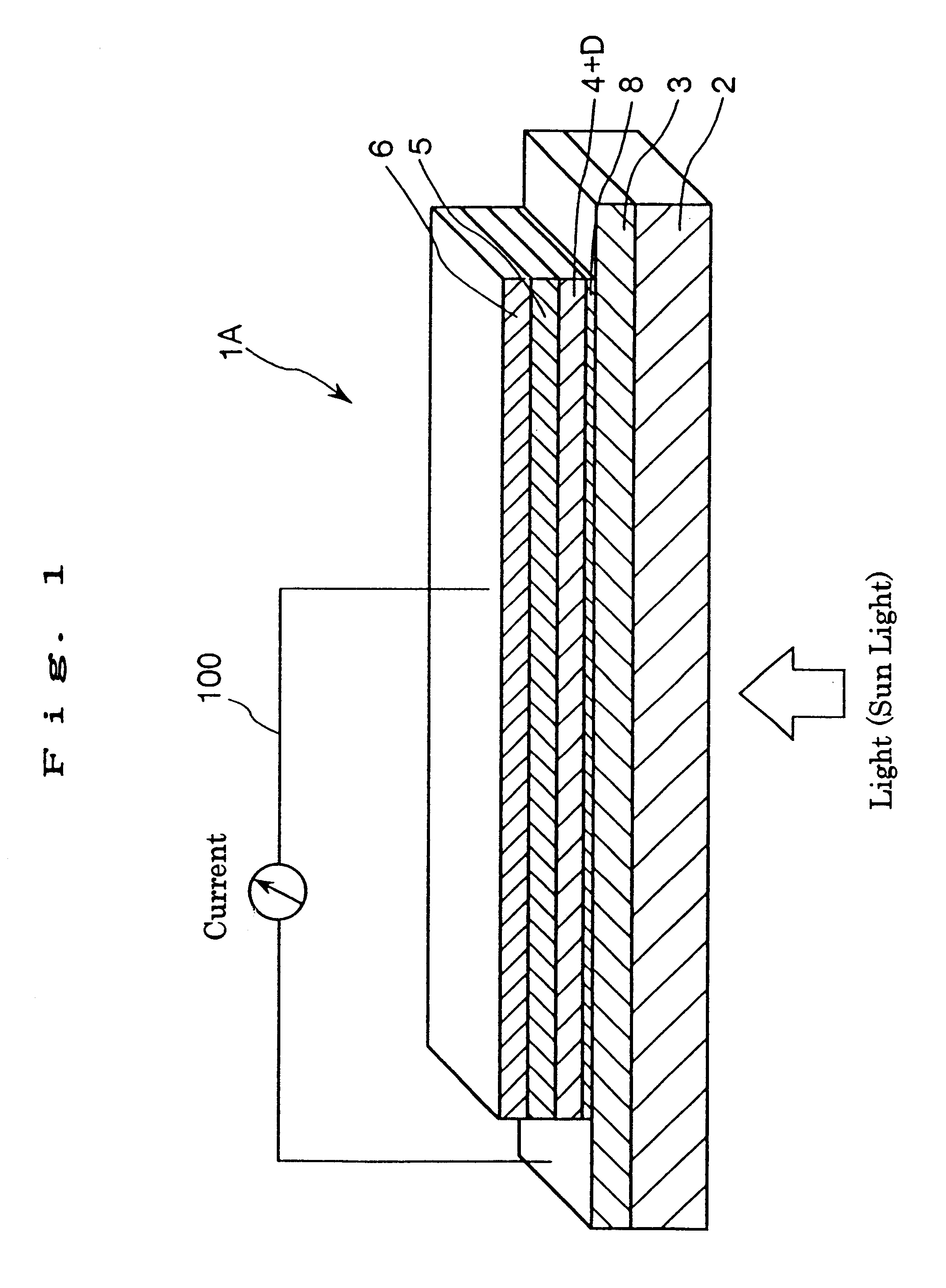
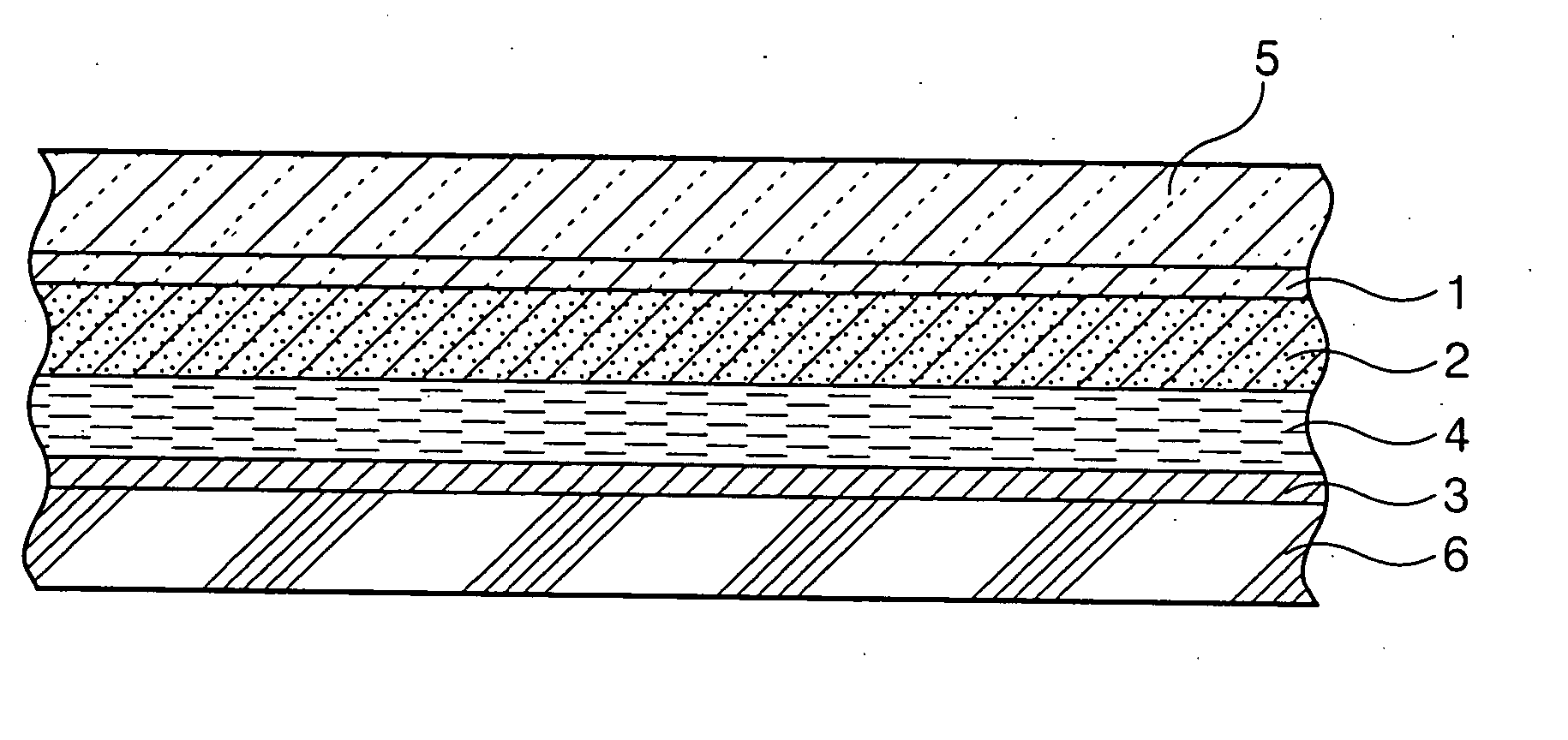
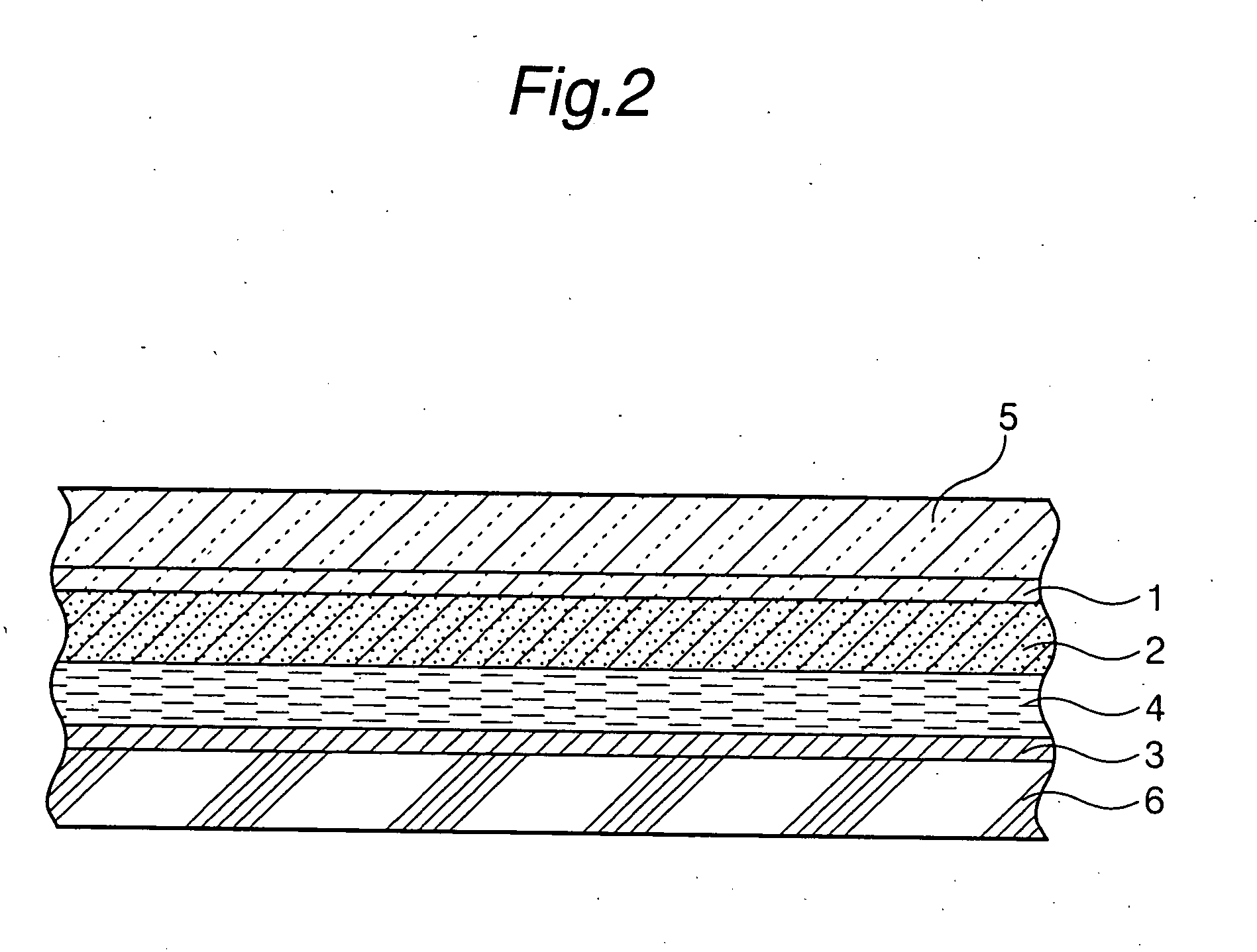
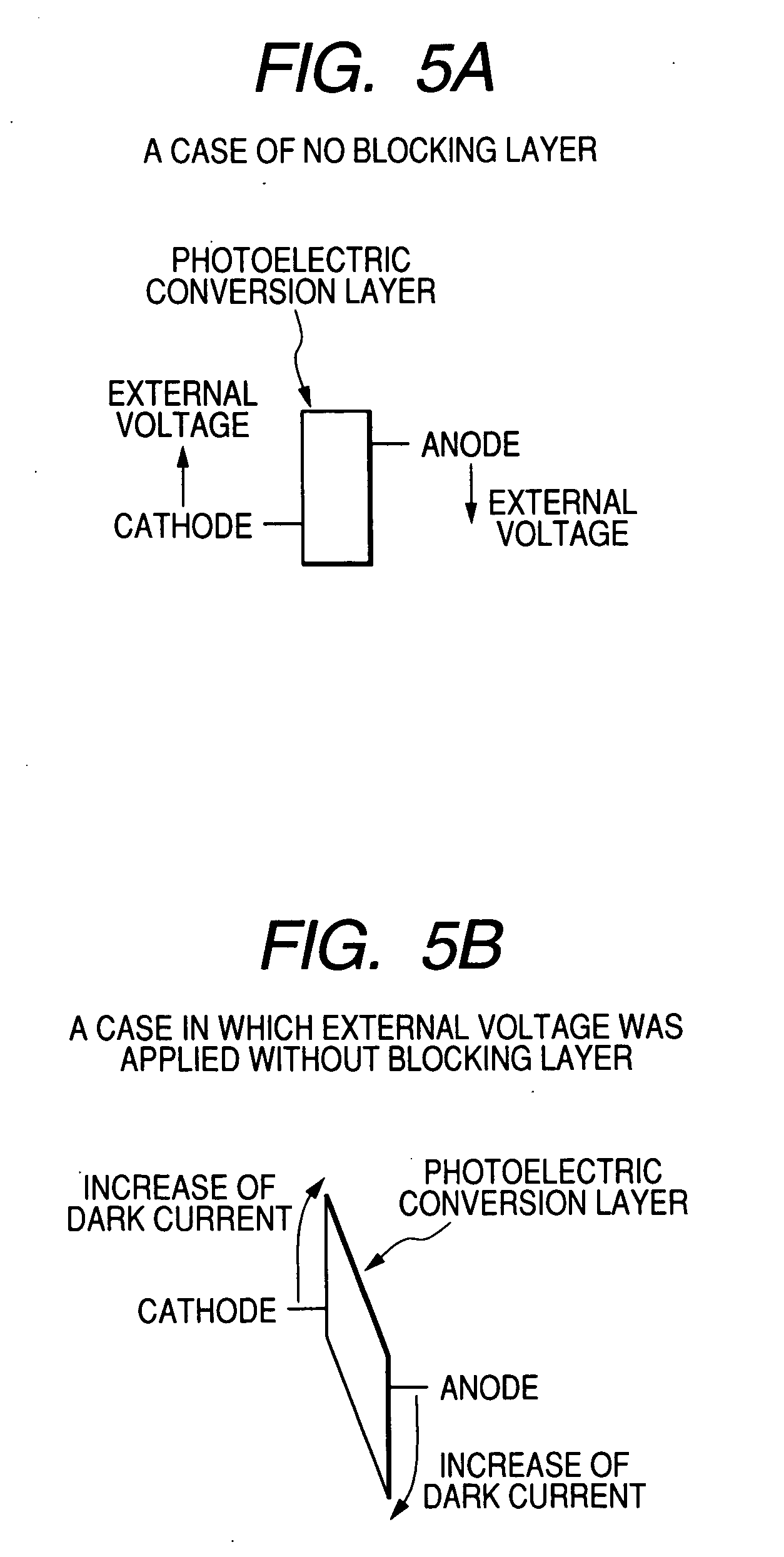
A solar cell including a first electrode, a second electrode arranged opposite to the first electrode, an electron transport layer arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode, a dye layer D which is in contact with the electron transport layer, a hole transport layer arranged between the electron transport layer and the second electrode and being in contact with the dye layer D, and a barrier layer, and these elements are provided on a substrate. The barrier layer prevents or suppresses short-circuit between the first electrode and the hole transport layer. The porosity of the barrier layer is made smaller than that of the electron transport layer. The barrier layer is formed into a film-like shape and arranged between the first electrode and the electron transport layer. The solar cell can accomplish excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency by the provision of such a barrier layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Tubular titanium oxide particles, method for preparing the same, and use of the same
InactiveUS20040265587A1Large specific surface areaImprove detection accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesReduction treatmentSorbent
The process for preparing tubular titanium oxide particles comprises subjecting a water dispersion sol, which is obtained by dispersing (i) titanium oxide particles and / or (ii) titanium oxide type composite oxide particles comprising titanium oxide and an oxide other than titanium oxide in water, said particles having an average particle diameter of 2 to 100 nm, to hydrothermal treatment in the presence of an alkali metal hydroxide. After the hydrothermal treatment, reduction treatment (including nitriding treatment) may be carried out. The tubular titanium oxide particles obtained in this process are useful as catalysts, catalyst carriers, adsorbents, photocatalysts, decorative materials, optical materials and photoelectric conversion materials. Especially when the particles are used for semiconductor films for photovoltaic cells or photocatalysts, prominently excellent effects are exhibited.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Organic photoelectric conversion element and image element
InactiveUS20070063156A1Photoelectric conversion efficiency is not reducedImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesInvestigating moving sheetsElectron holeWork function
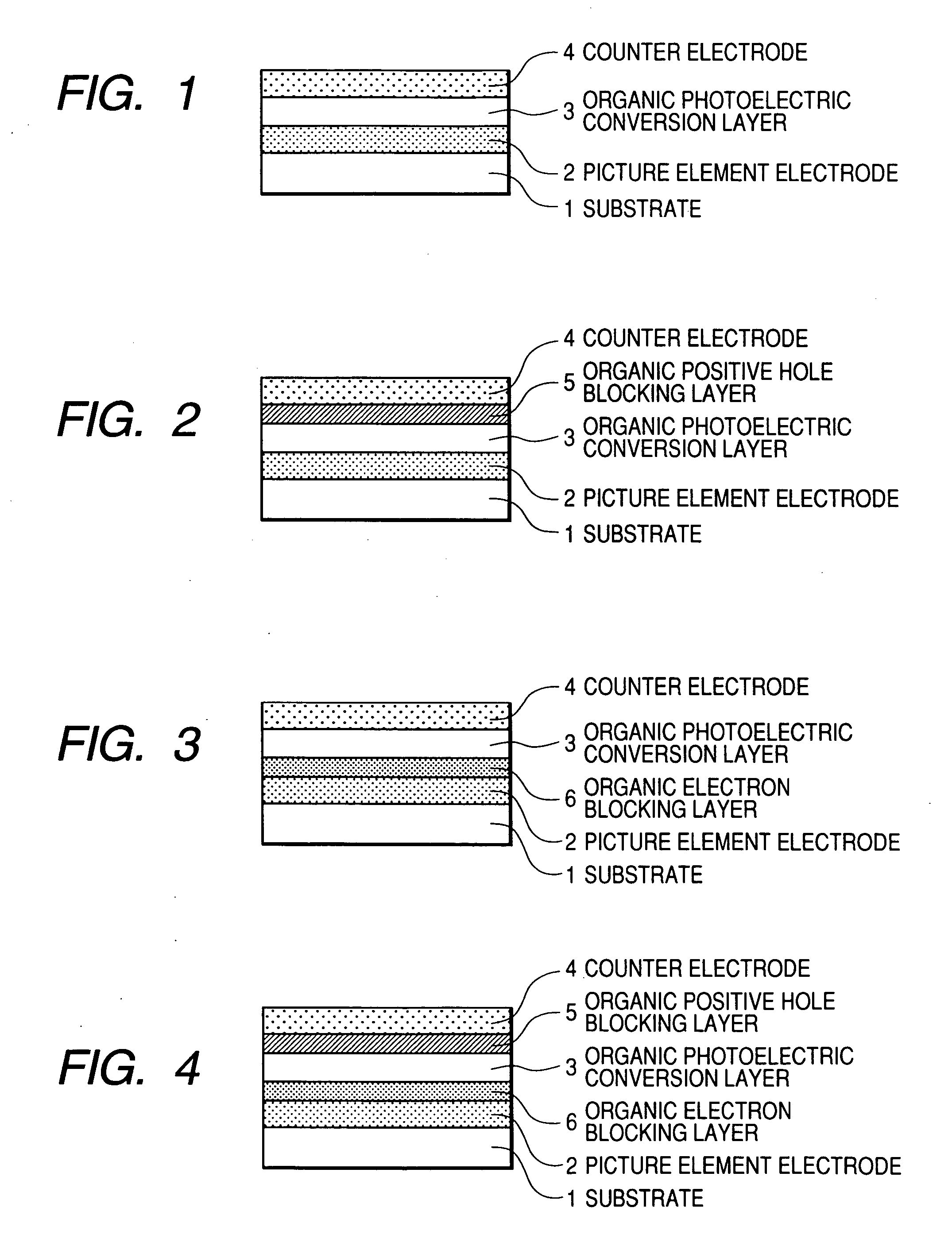
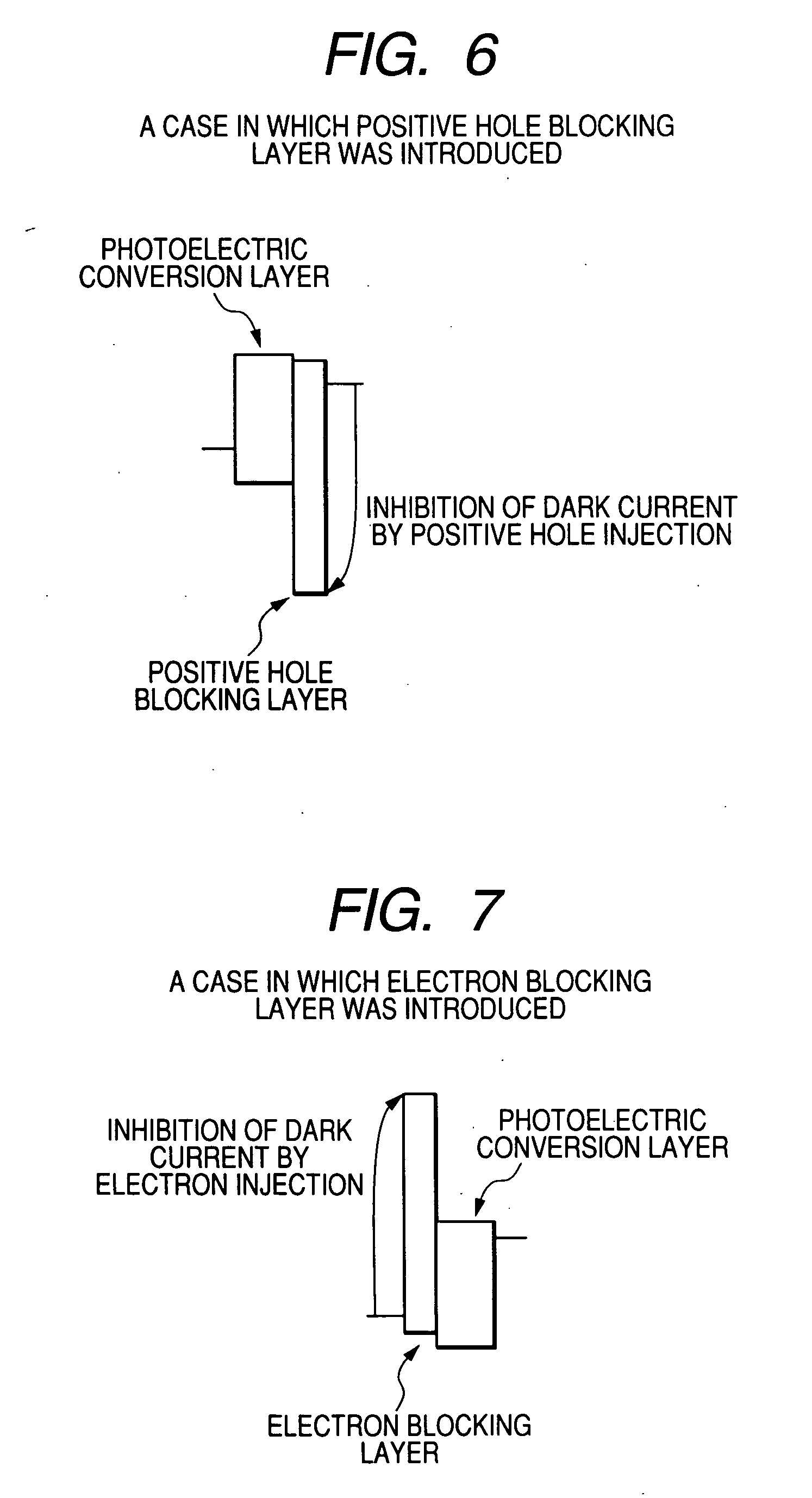
An organic photoelectric conversion element comprises: a pair of electrodes; an organic photoelectric conversion layer arranged between the pair of electrodes; and an positive hole blocking layer arranged between one of the pair of electrodes and the organic photoelectric conversion layer, wherein an ionization potential of the positive hole blocking layer is larger than a work function of the adjoining electrode by 1.3 eV or more, and wherein an electron affinity of the positive hole blocking layer is equal to or larger than that of the adjoining organic photoelectric conversion layer. An electron blocking layer may be arranged between the other one of the pair of electrodes and the organic photoelectric conversion layer, wherein its electron affinity is smaller than a work function of the adjoining electrode by 1.3 eV or more, and its ionization potential is equal to or smaller than that of the adjoining organic photoelectric conversion layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
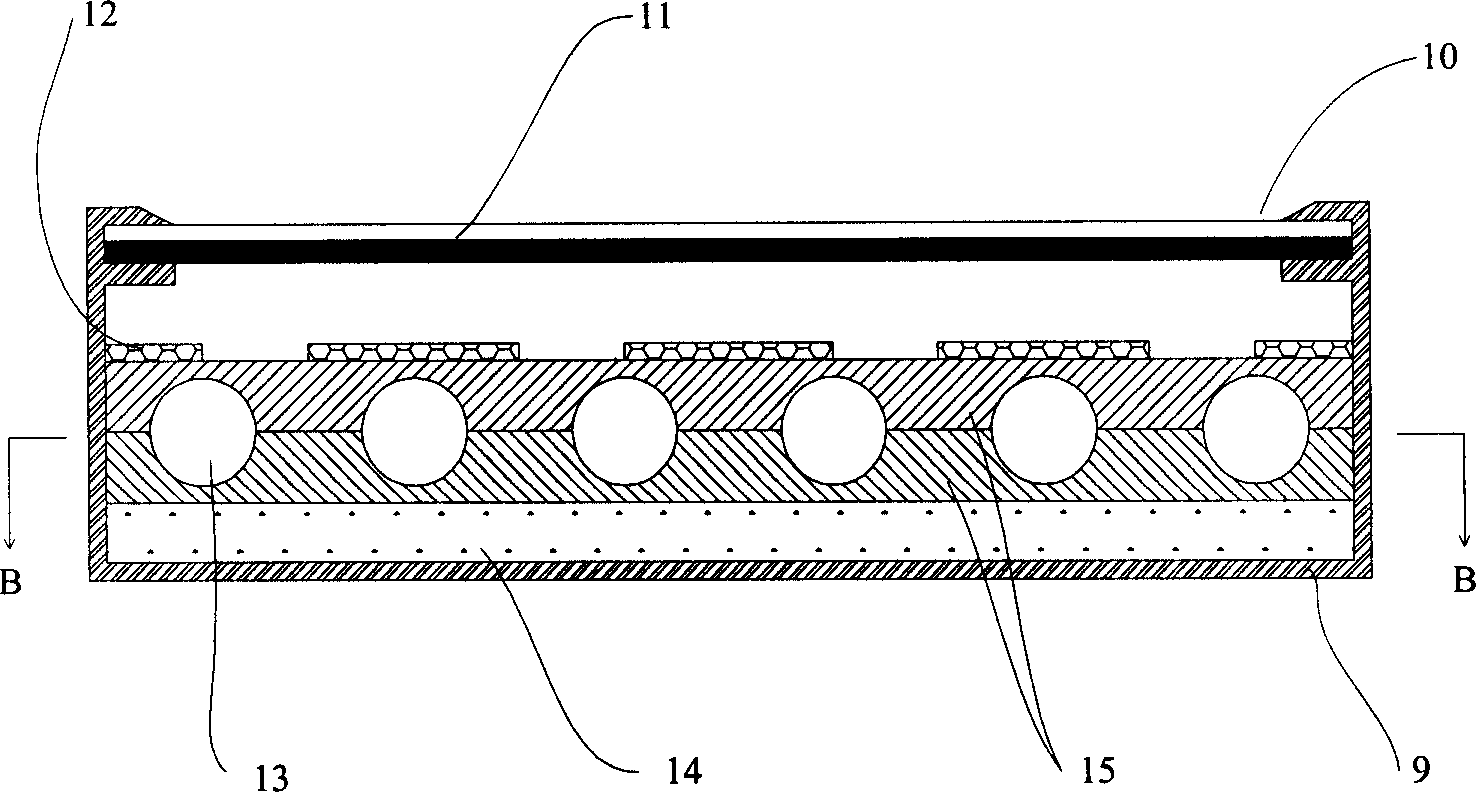
Conductive slurry for solar battery front side electrode and production method thereof
ActiveCN101295739AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyImprove adhesionFinal product manufactureNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialConductive pasteElectrical battery
The invention relates to a conductive paste for the surface electrode of a solar cell, which comprises conductive metal powders, organic carriers, adhesives, solvents and addition agent, wherein, the conductive paste also comprises additives which are selected from phosphorus pentachloride and one or more VIII group metal halide. The additive in the conductive paste of the invention can help improve the adhesive force between the conductive paste and silicon substrate, and lead adhesion between compounds obtained after electrode sintering and silicon substrate to be more firm; the formed compound does not have cracks and bubbles and the electrode surface is flat and smooth, thus providing the solar cell finally prepared with higher photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Electric conductive silver paste and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103258584AEnhanced interconnectionIncrease contact areaNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureSilver pasteMetal alloy
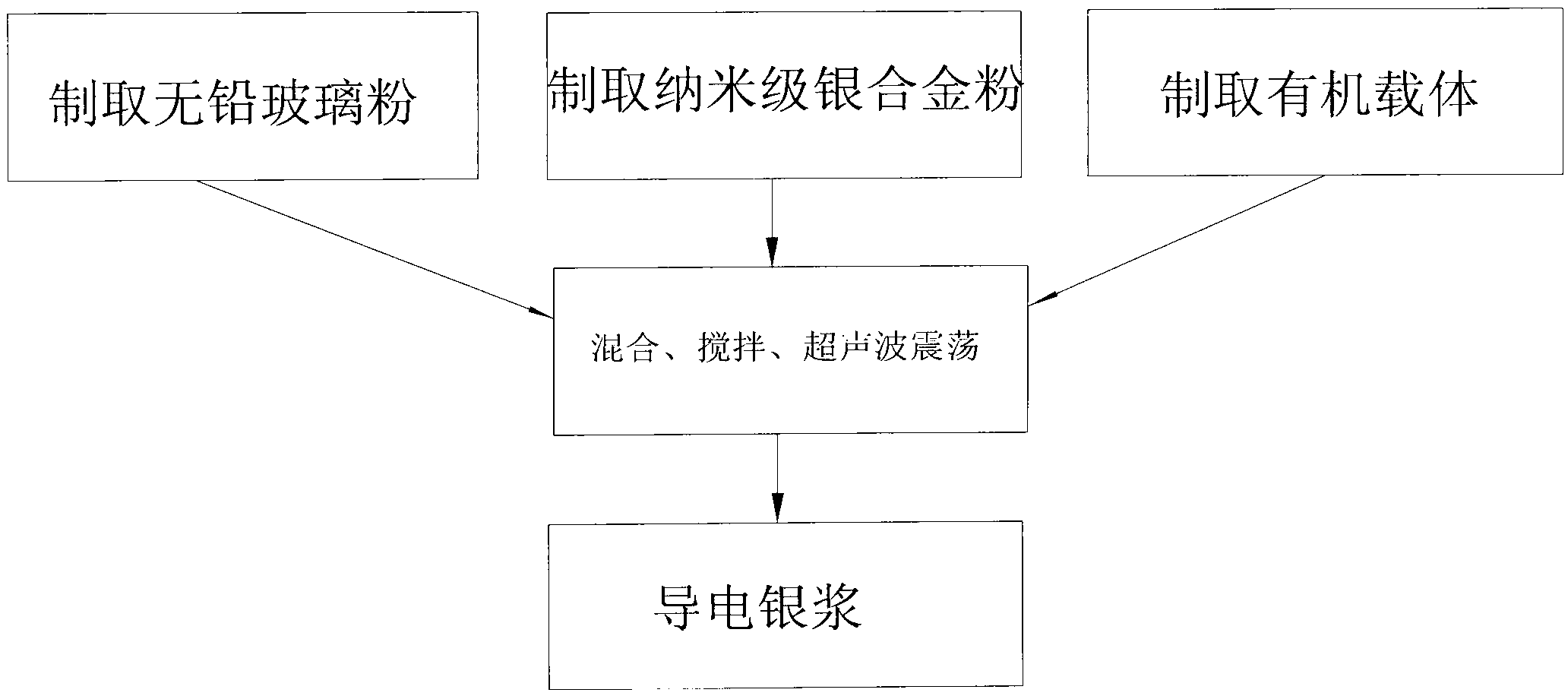
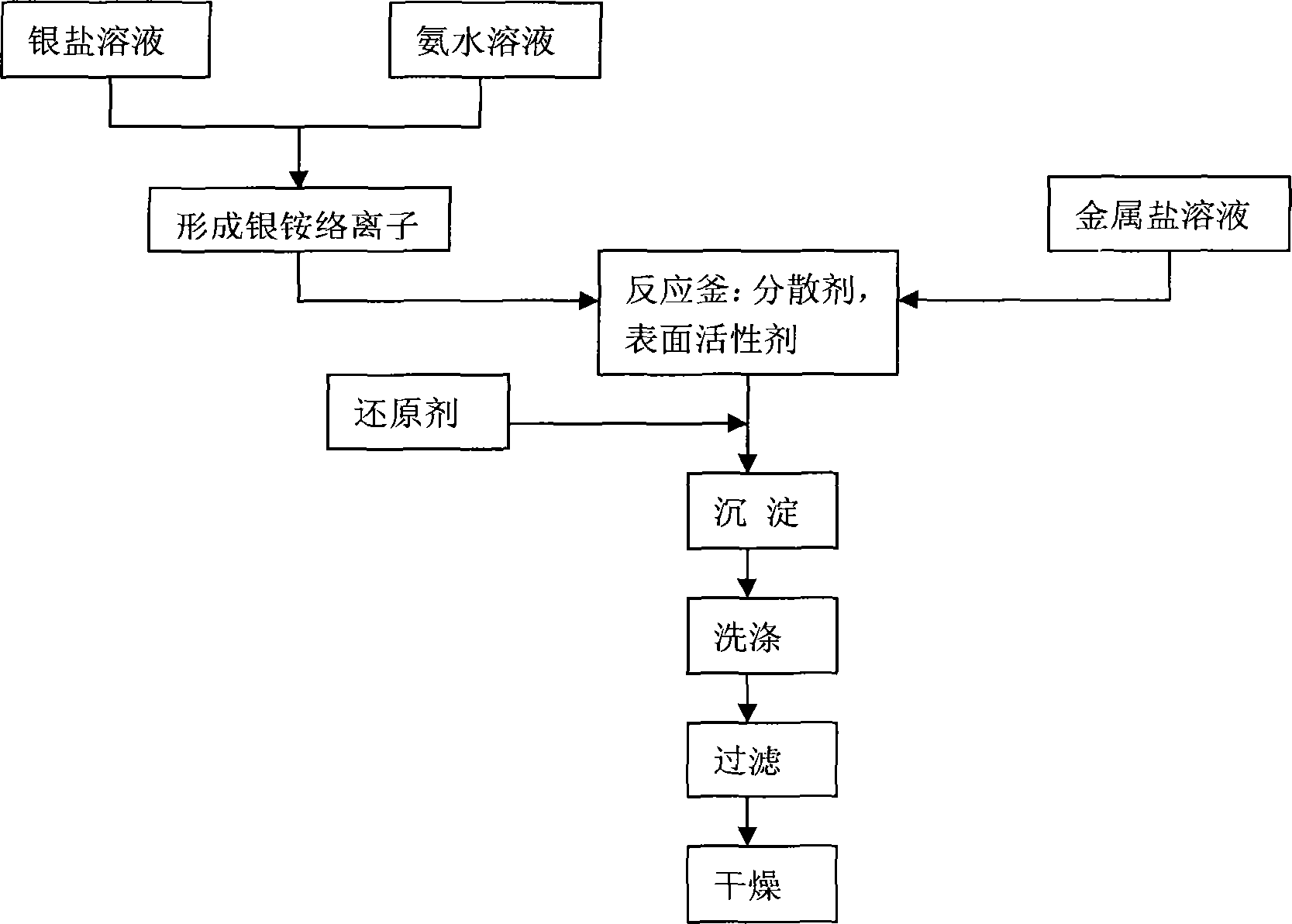
The invention discloses electric conductive silver paste and a manufacturing method of the electric conductive silver paste. The electric conductive silver paste comprises, by mass percentage, 35 - 65 % of micron-sized silver powder, 1-10 % of nanometer-sized silver powder of or 1-20 % of nanometer-sized silver and other metal alloy powder, and 1-10 % of an organic carrier; for ceramics, solar cell silver paste comprises 2-15 % of unleaded glass powder, each component is manufactured in parts, weighed, mixed and stirred or mixed and rapidly scattered, and ultrasonic-vibrated or fine adjusted of viscosity of solvent, and therefore the electric conductive silver paste is obtained. Due to the fact that the nanometer-sized silver powder or the nanometer-sized silver alloy powder is mixed with the micron-sized silver powder, intensity of conductivity and a circuit is improved, adhesive force of crushing resistance and a base plate is improved, at the same time unleaded slurry good in thixotropy, low in contacting resistance and low in piece-needed slurry amount replaces lead slurry materials, the electric conductive silver paste is used for manufacturing crystalline silicon solar cells, improves photoelectric conversion efficiency, accords with environmental-protection ideas, and can be produced in large scales continuously.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHENGGONG CHEM
Photoelectric conversion film, photoelectric conversion element, imaging element, method of applying electric field thereto and electric field-applied element
ActiveUS20050205903A1High color reproductionHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionOrganic dye
An imaging element having a photoelectric conversion film which has a laminated structure comprising a p-type semiconductor layer and an n-type semiconductor layer between a pair of electrodes, wherein at least one of the p-type semiconductor and the n-type semiconductor contains an organic compound with controlled orientation; a photoelectric conversion film having at least one organic dye compound, wherein the organic dye compound forms a J aggregate, or the angle between the spectral absorption transition dipolar moment of the organic dye compound and the photoelectric conversion film plane is 40° or less, a photoelectric conversion element and an imaging element; and a method of applying an electric field thereto, and an imaging element which comprises a photoelectric conversion film (a photosensitive layer) having a bulk heterojunction layer as an intermediate layer, or a photoelectric conversion film having two or more repeating structure units of a pn junction layer comprising a p-type semiconductor layer and an n-type semiconductor layer between a pair of electrodes.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Photoelectric conversion element and solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20080230123A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce noiseMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesElectricityPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion element comprises a first photoelectric conversion part, the first photoelectric conversion part comprising: a pair of electrodes; and a photoelectric conversion film between the pair of electrodes, wherein the photoelectric conversion film comprises an organic photoelectric conversion material having an absorption peak in an infrared region of an absorption spectrum within a combined range of a visible region and the infrared region and generating an electric charge according to light absorbed, and the first photoelectric conversion part as a whole transmits 50% or more of light in the visible region.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
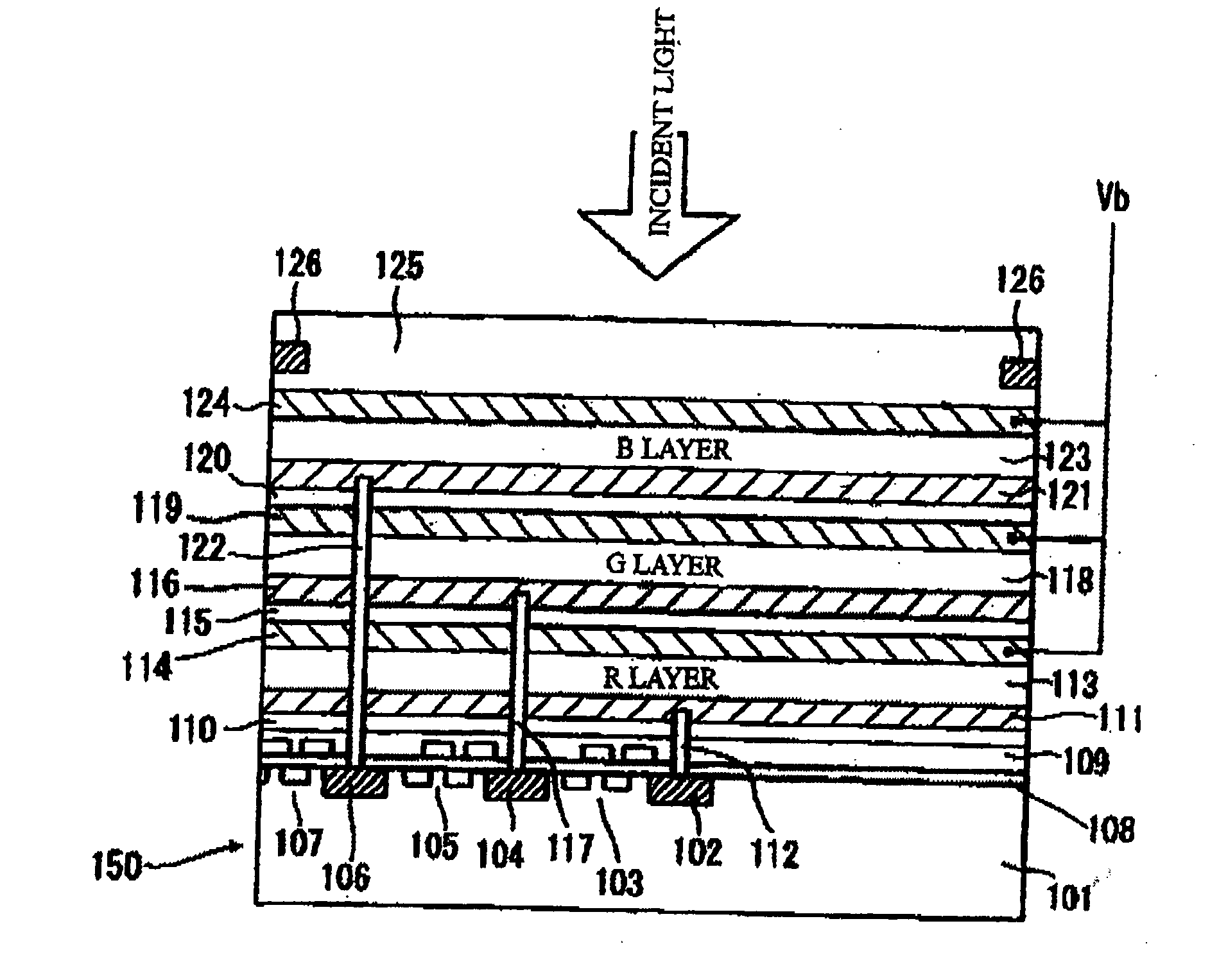
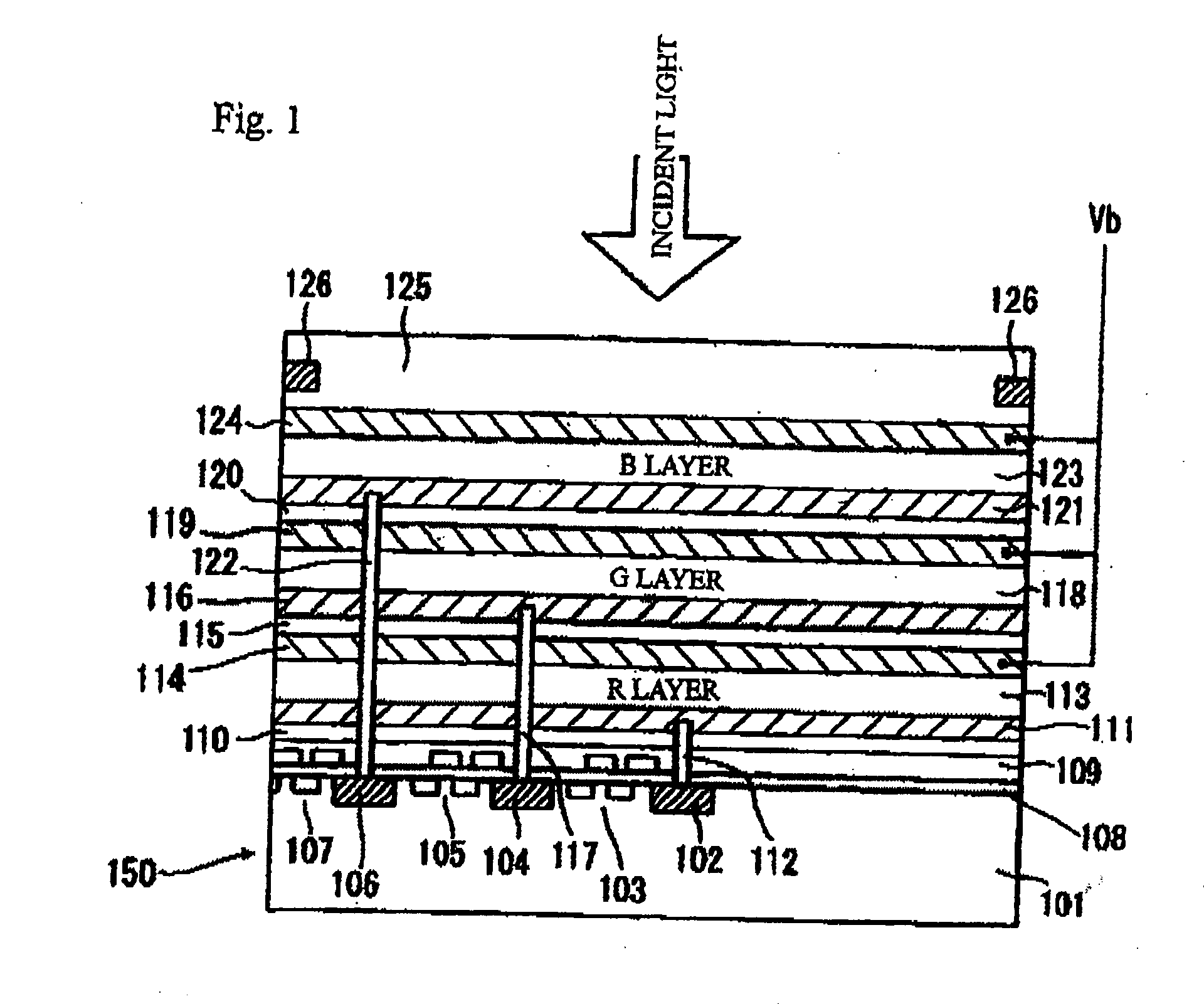
Multilayer deposition multipixel image pickup device and television camera
InactiveUS20050205958A1Improve stabilityHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
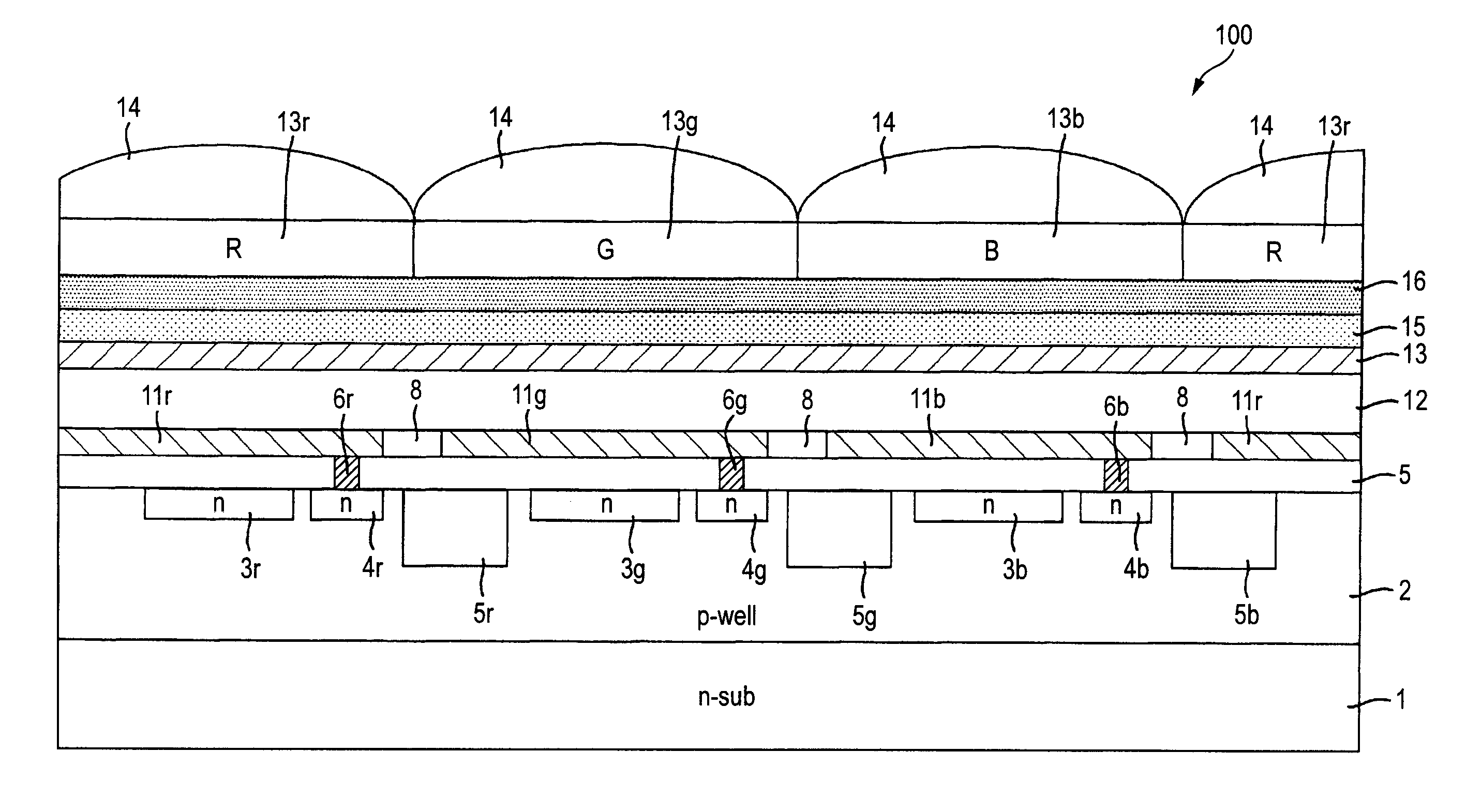
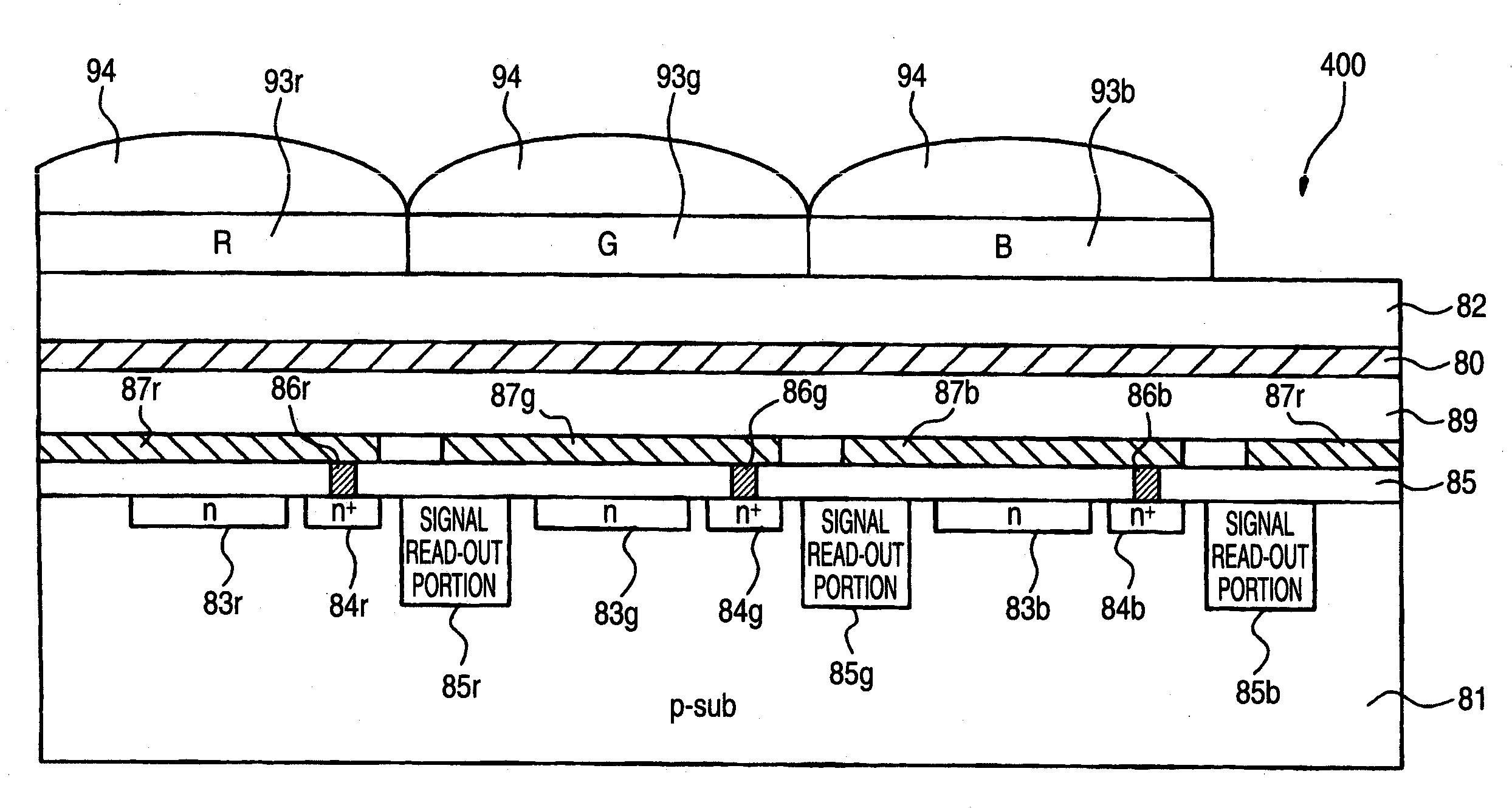
A multilayer deposition multipixel image pickup device comprising a pixel unit, wherein the pixel unit comprises: a plurality of electromagnetic absorption layers being capable of absorbing electromagnetic waves of different wavelengths and performing photoelectric conversion; at least one pair of electrodes that sandwich each of electromagnetic absorption layers; a charge transfer and charge read part; and a plurality of contact parts that couple at least one of the electrodes and the charge transfer and charge read part, wherein a length between outermost surfaces of ones among electrodes of the pixel unit is smaller than a pixel size that is a circle-equivalent diameter of the same area as a first electromagnetic absorption layer of the electromagnetic absorption layers, the first electromagnetic absorption layer having a largest area in said plurality of electromagnetic absorption layers.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
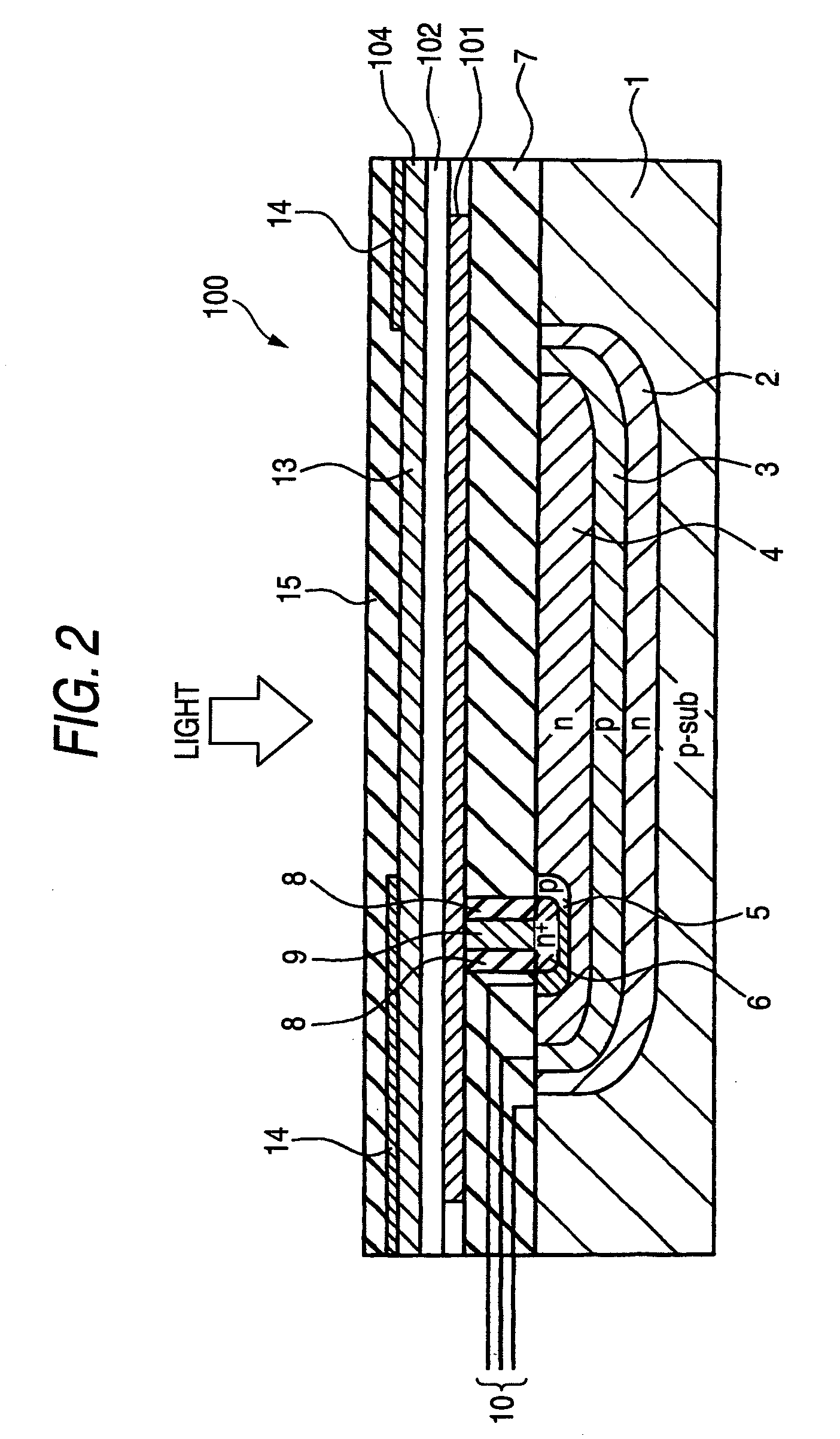
Photoelectric conversion element
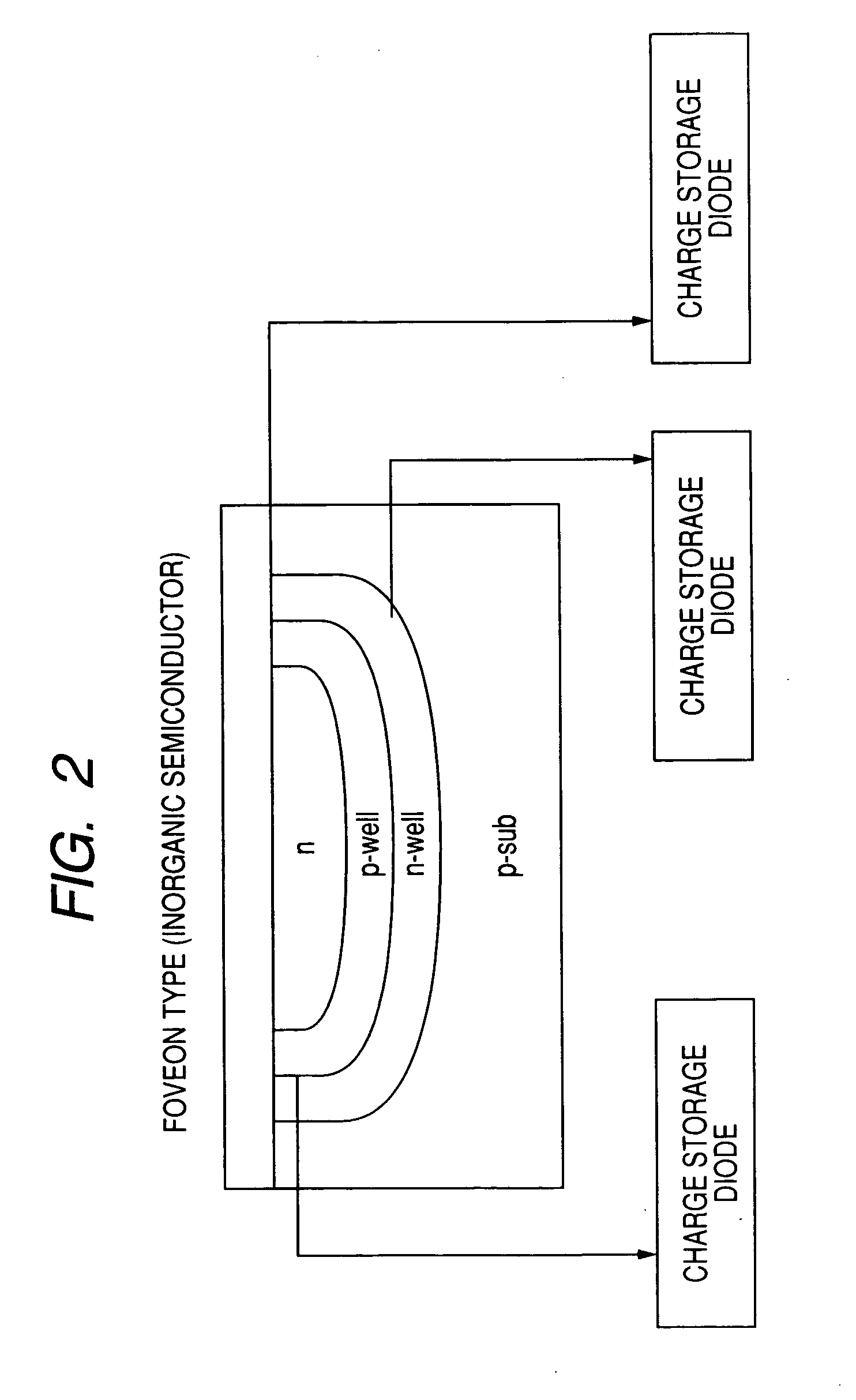
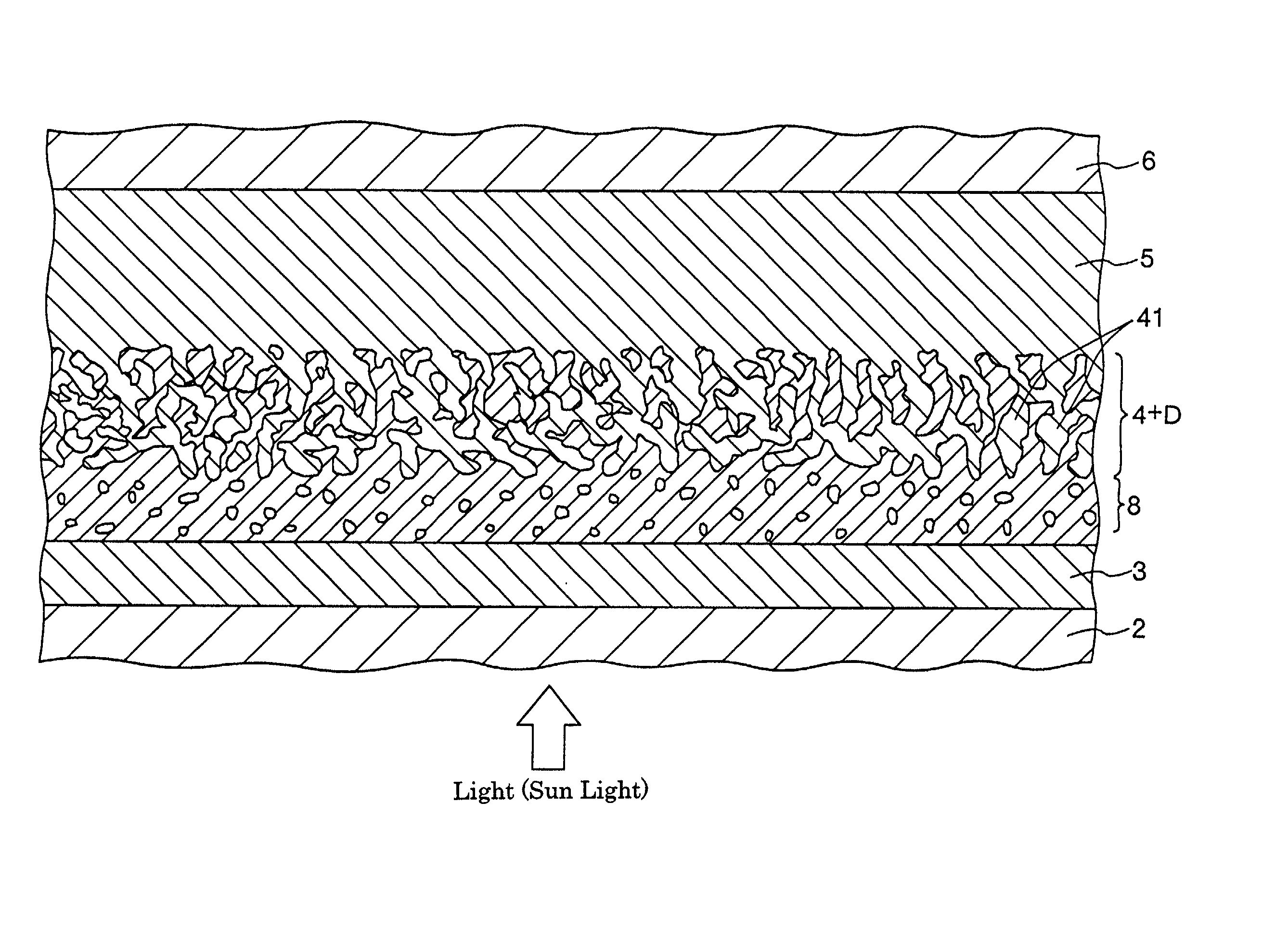
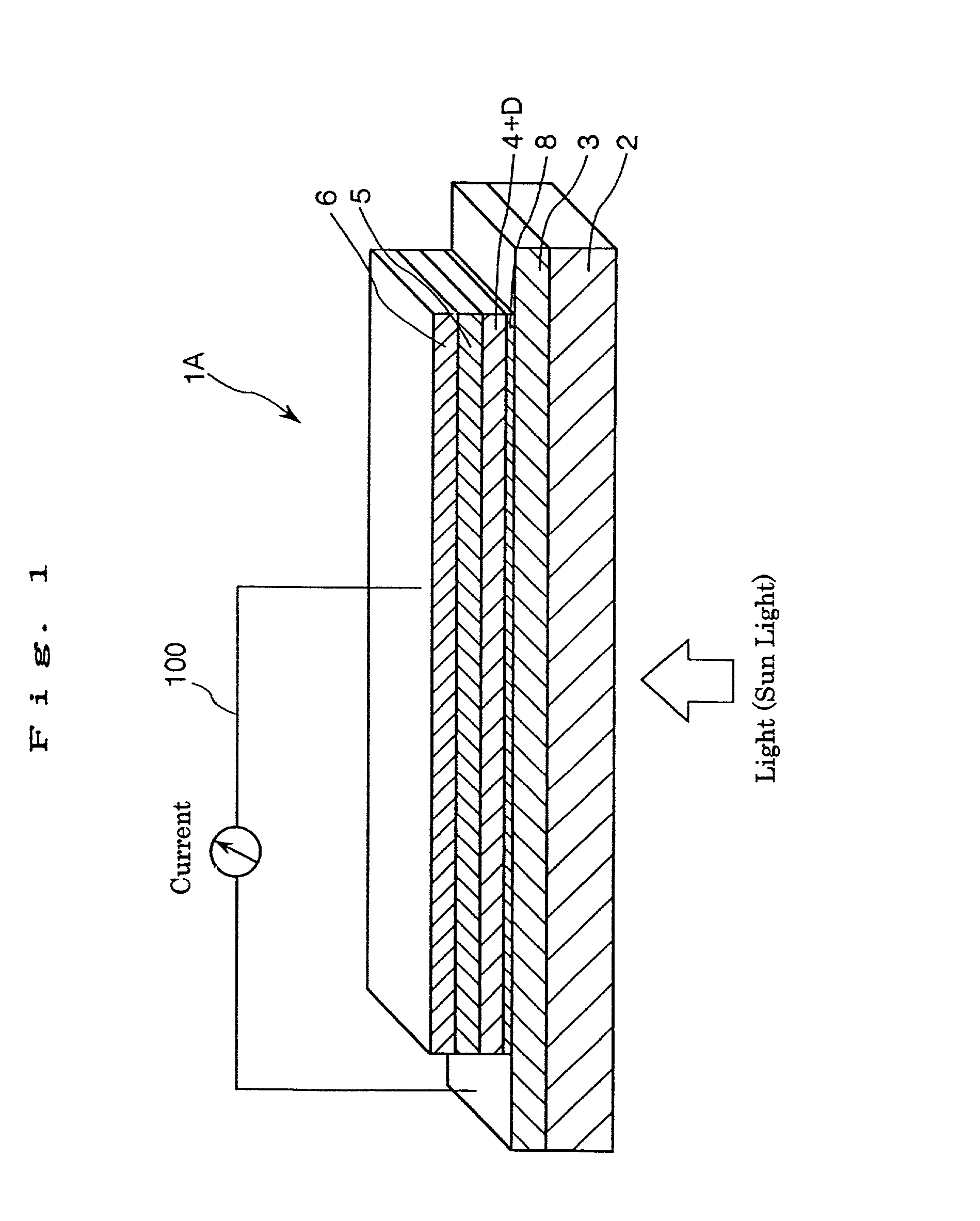
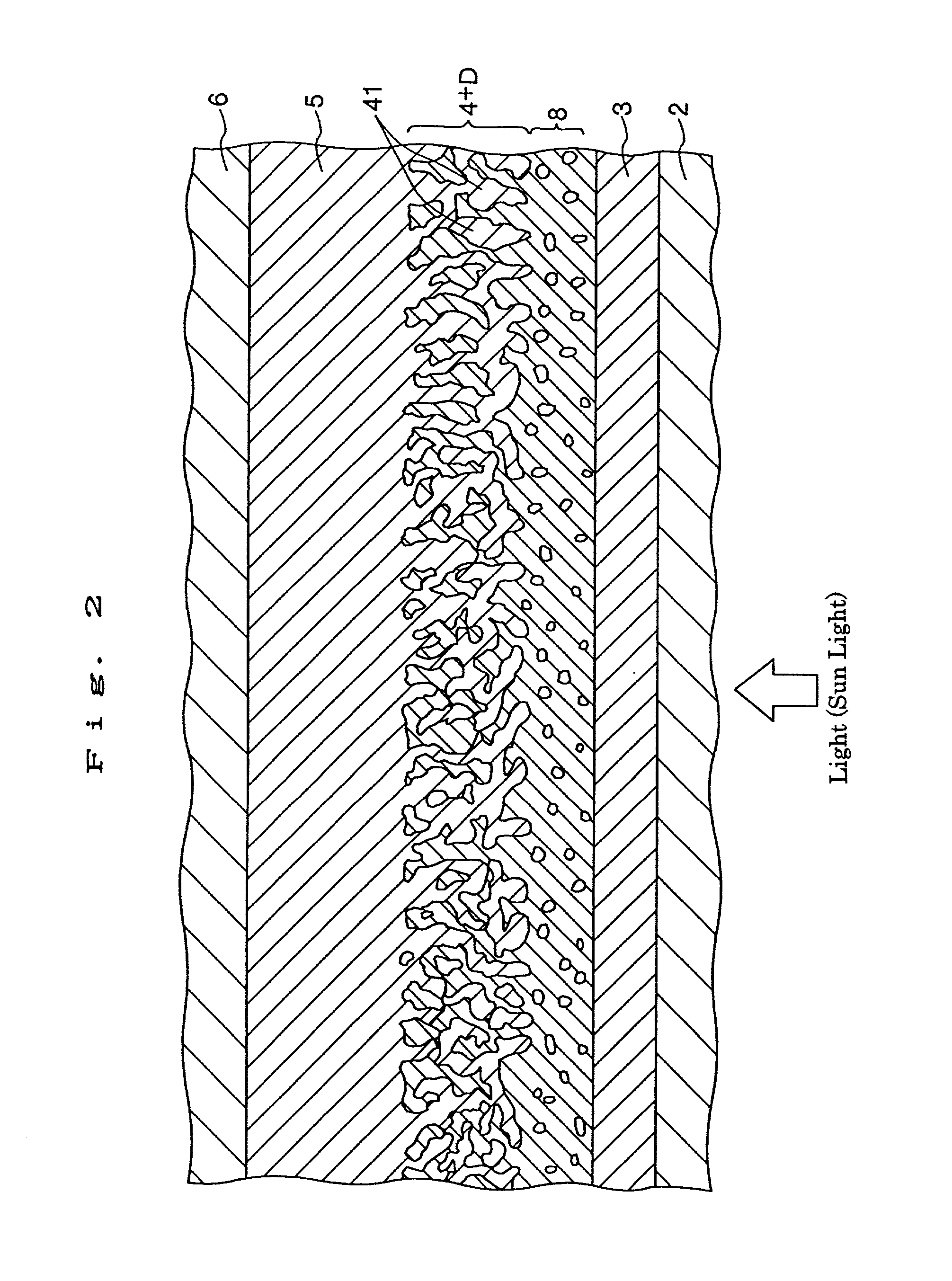
InactiveUS20020108649A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyPrevent and suppressLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesPorosityTransport layer
A solid type dye-sensitized photoelectric conversion element which is excellent in photoelectric conversion efficiency and which can be manufactured at a low cost is disclosed. The photoelectric conversion element can be applied to a so-called wet type solar cell which does not use any electrolyte. The solar cell comprises a first electrode 3, a second electrode 6 arranged opposite to the first electrode 3, an electron transport layer 4 arranged between the first electrode 3 and the second electrode 6, a dye layer D which is in contact with the electron transport layer 4, a hole transport layer 5 arranged between the electron transport layer 4 and the second electrode 6 and being in contact with the dye layer D, and a barrier layer 8, and these elements are provided on a substrate 2. The barrier layer 8 constitutes short-circuit preventing or suppressing means for preventing or suppressing short-circuit between the first electrode 3 and the hole transport layer 5. The porosity of the barrier layer is made smaller than that of the electron transport layer 4. The barrier layer is formed into a film-like shape and arranged between the fist electrode 4 and the electron transport layer 4. The solar cell can accomplish excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency by the provision of such a barrier layer 8.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
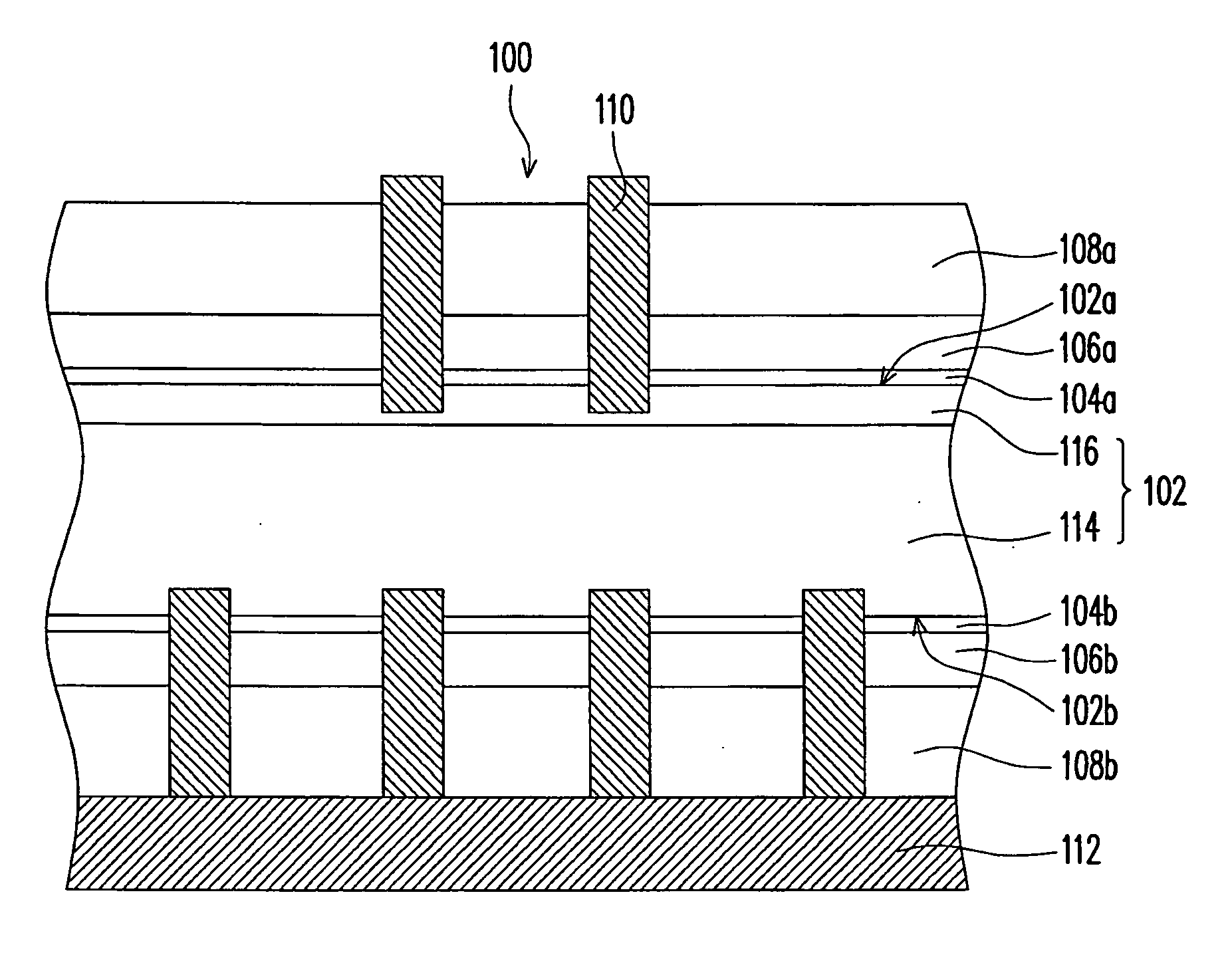
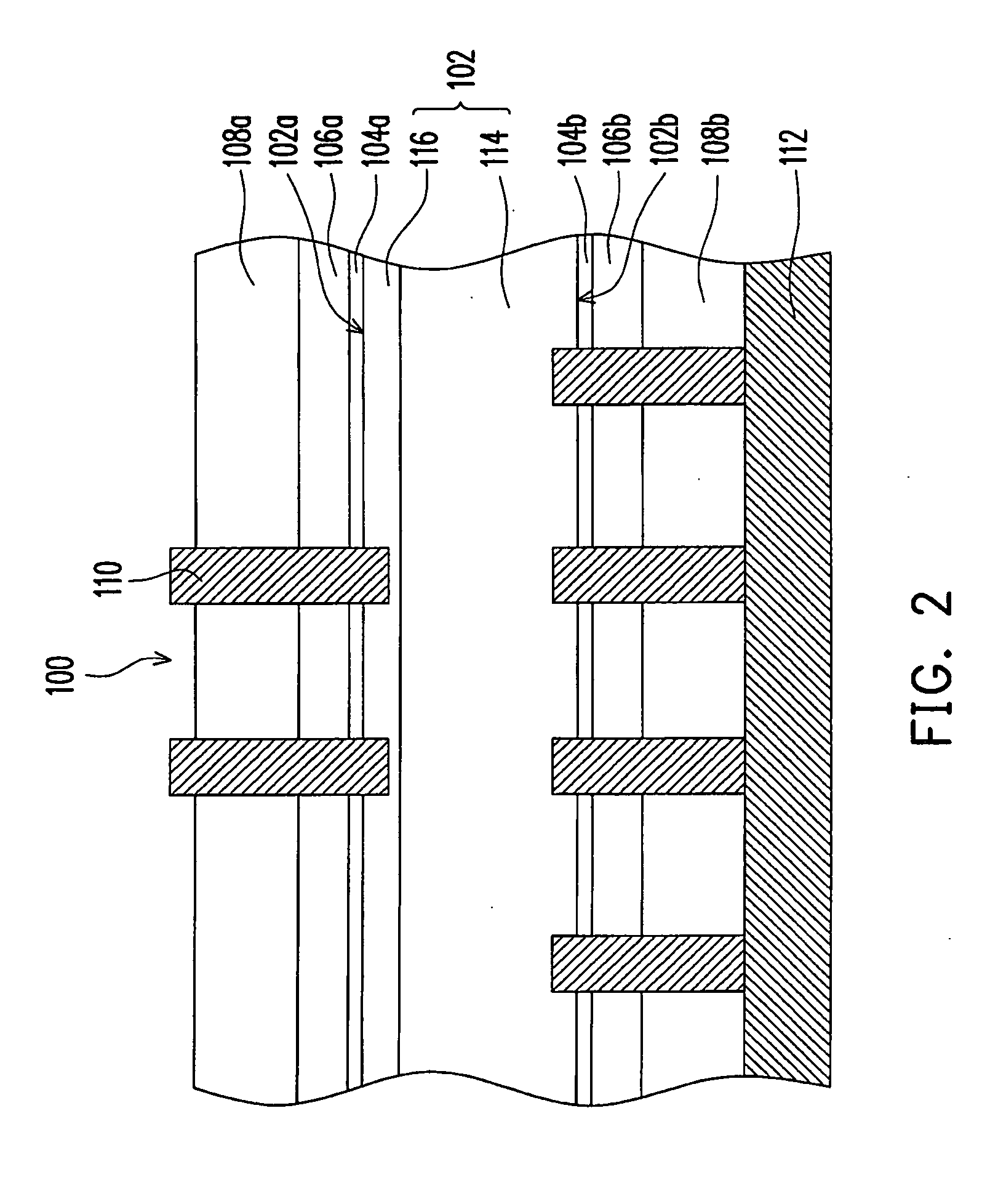
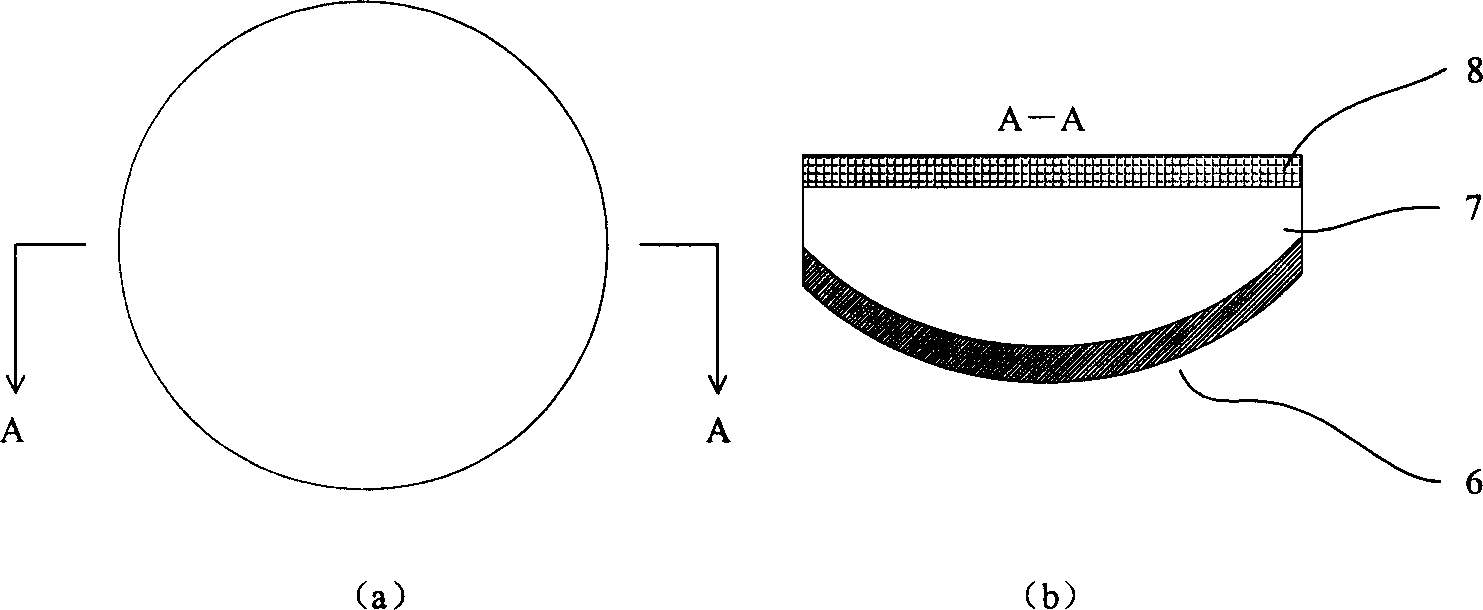
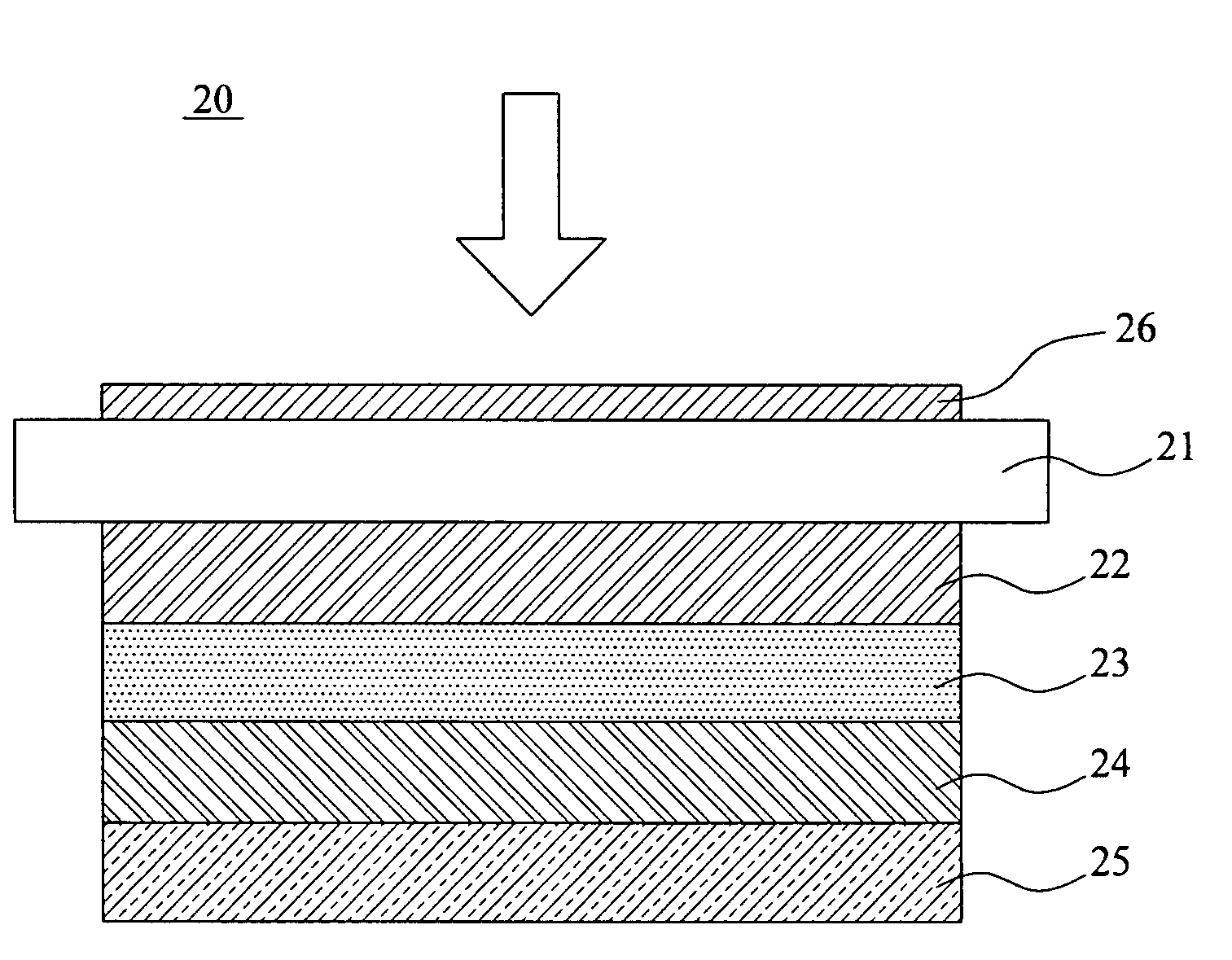
Passivation layer structure of solar cell and fabricating method thereof
InactiveUS20090165855A1Improve passivation effectImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureCoatingsCarrier lifetimePhotoelectric conversion efficiency
A passivation layer structure of a solar cell, disposed on a substrate, is provided. The passivation layer structure has a first passivation layer and a second passivation layer. The first passivation layer is disposed on the substrate. The second passivation layer is disposed between the substrate and the first passivation layer, and the material of the second passivation layer is an oxide of the material of the substrate. Since the second passivation layer is disposed between the substrate and the first passivation layer, the surface passivation effect and carrier lifetime of a photoelectric device are enhanced, and a photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell is increased as well.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Photoelectric conversion element and imaging device
ActiveUS20090223566A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce dark currentNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesAtomic groupThin layer
A photoelectric conversion element is provided and includes: an electrically conductive thin layer; an organic photoelectric conversion layer; and a transparent electrically conductive thin layer. The organic photoelectric conversion layer contains: a compound represented by formula (I); and a fullerene or a fullerene derivative.In the formula, Z1 represents an atomic group necessary for forming a 5- or 6-membered ring, L1, L2 and L3 each independently represents an unsubstituted methine group or a substituted methine group, D1 represents an atomic group, and n represents an integer of 0 or more.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photoelectric conversion device, imaging device, and method for driving photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20130087682A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce dark currentMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
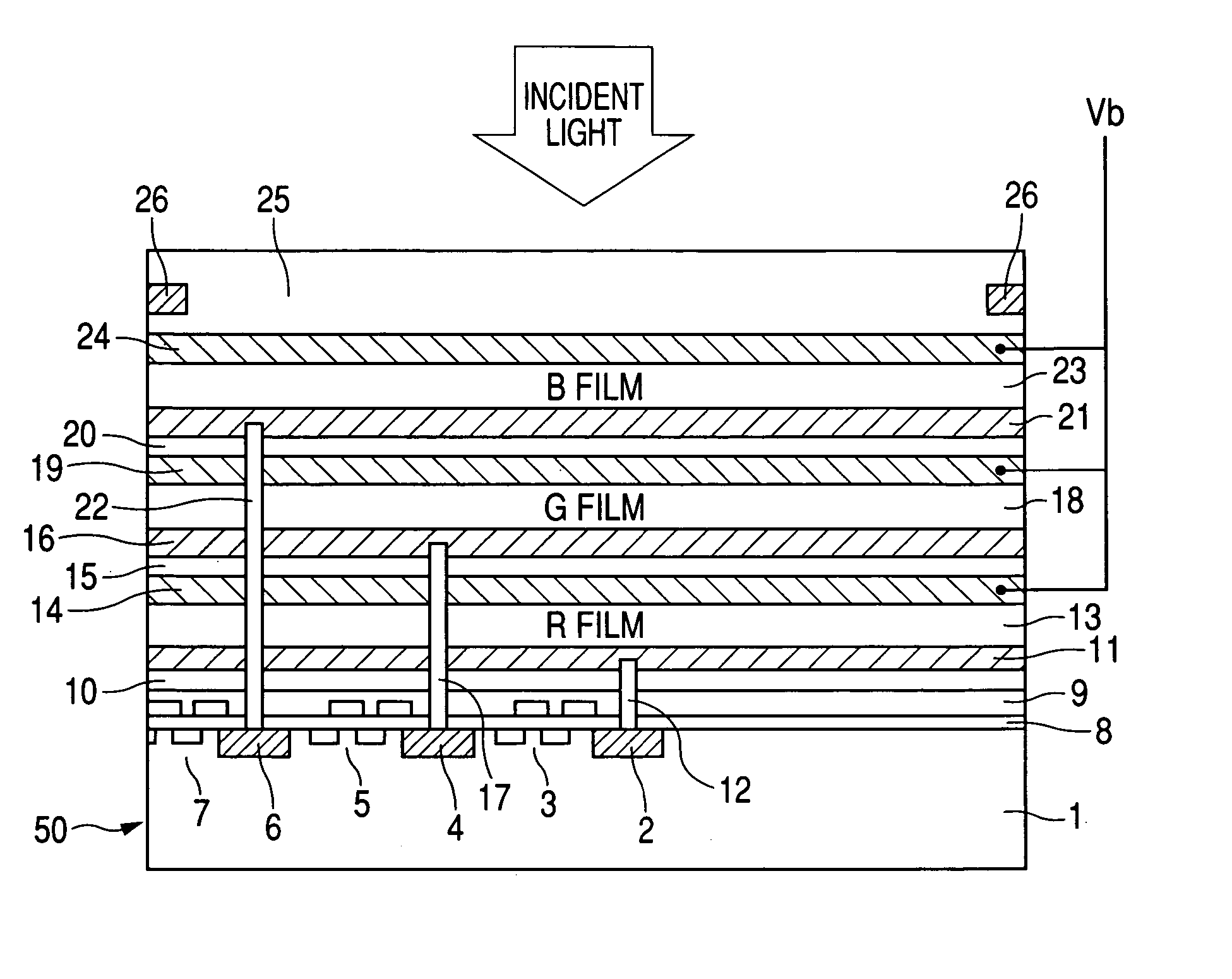
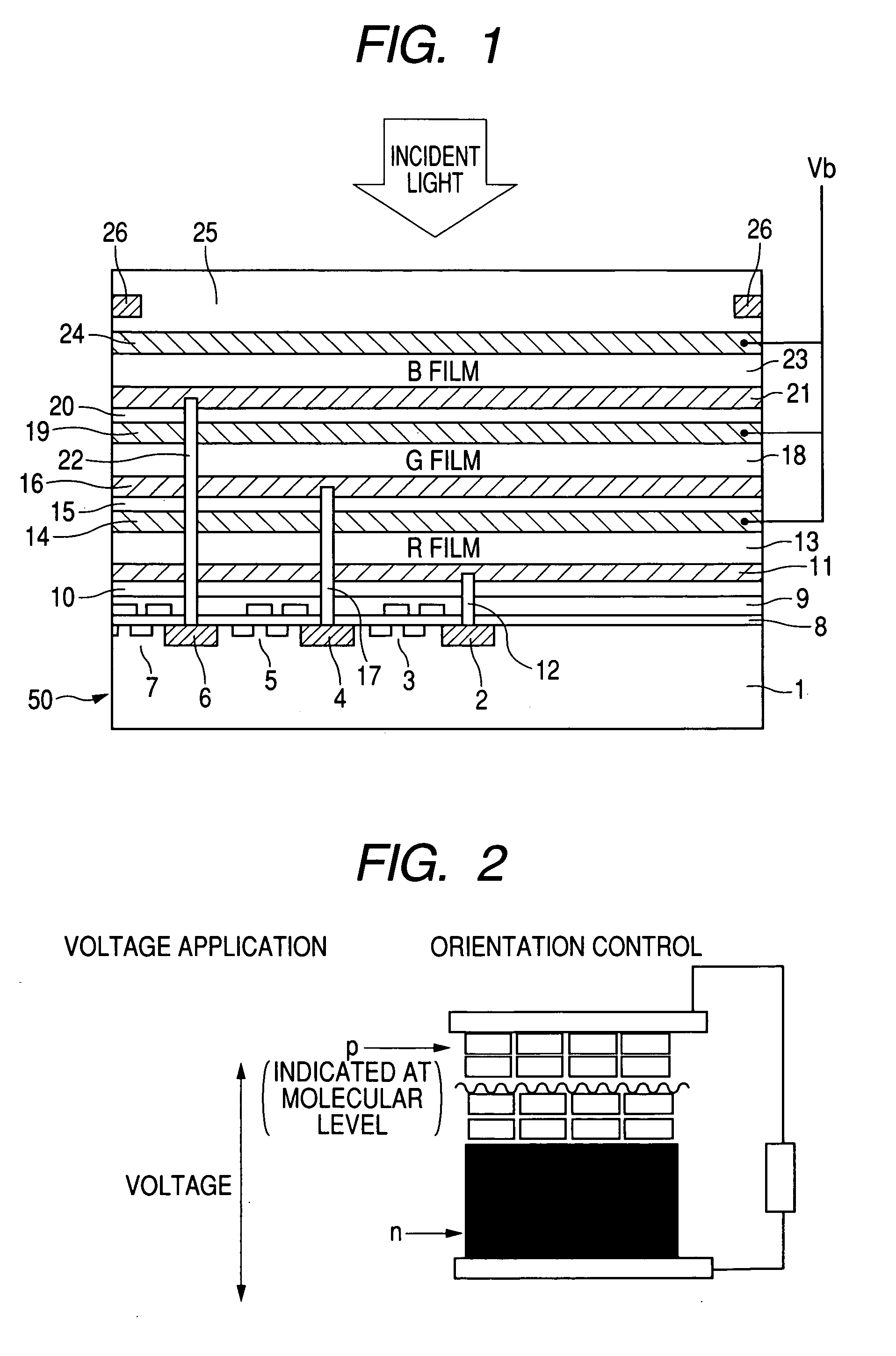
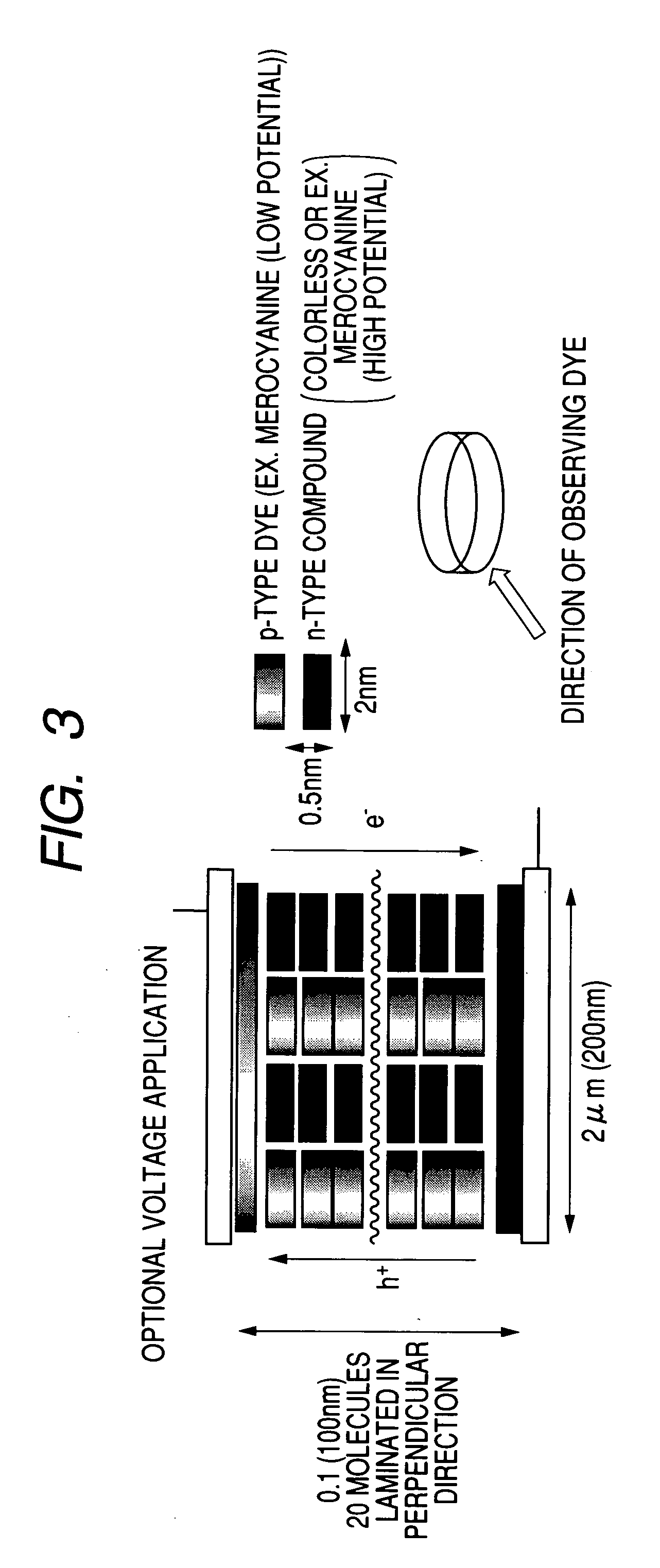
A photoelectric conversion device includes, in the following order: a first electrode; an electron blocking layer; a photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye; a hole blocking layer; and a transparent electrode as a second electrode, and an absorption maximum wavelength in a thin film absorption spectrum of the photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye is within a range of from 400 to 520 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Solar cell using carbon nanotubes and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060186502A1Easy to produceImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureCarbon nanotubeEngineering
A solar cell includes a p-type semiconductor substance, and an n-type semiconductor substance. The p-type semiconductor substance and the n-type semiconductor substance form a pn junction or a pin junction, and the p-type semiconductor substance or the n-type semiconductor substance includes a structure film having a plurality of carbon nanotubes electrically connected to each other.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Tandem thin-film photoelectric transducer and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050145972A1Improve conversion efficiencyGood effectChemical vapor deposition coatingPhotovoltaic energy generationTransducerPhotoelectric conversion
A tandem thin film photoelectric converter includes a transparent electrode, a plurality of photoelectric conversion units and back electrode deposited in sequence on a transparent insulating substrate. An intermediate layer for partially reflecting and transmitting light is inserted along at least one interface between the plurality of photoelectric conversion units. The intermediate layer has an average thickness in the range of 10 to 90 nanometers. The upper surface of the intermediate layer includes an uneven surface geometry having an average peak-to-peak pitch in the range of 10 to 50 nanometers.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
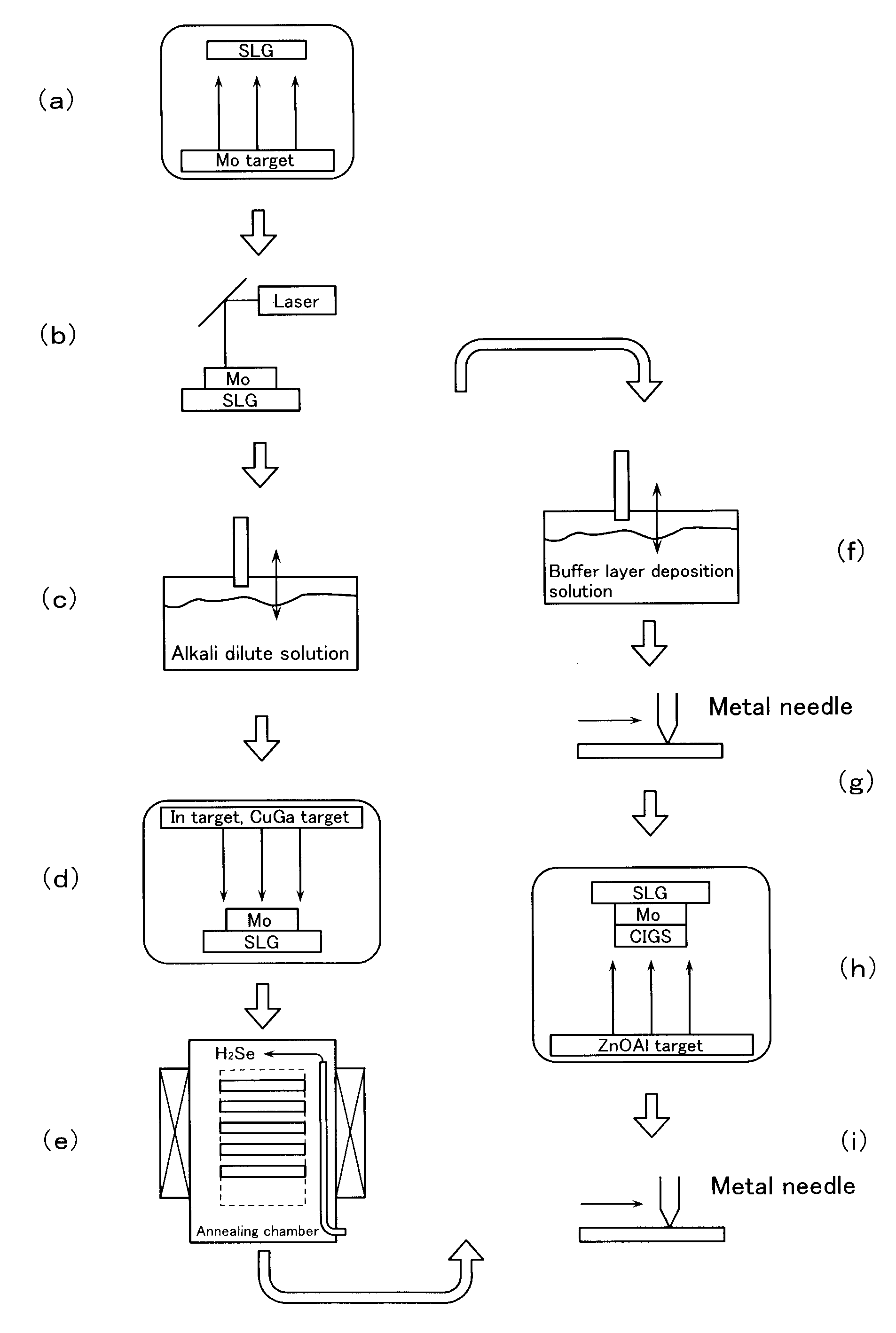
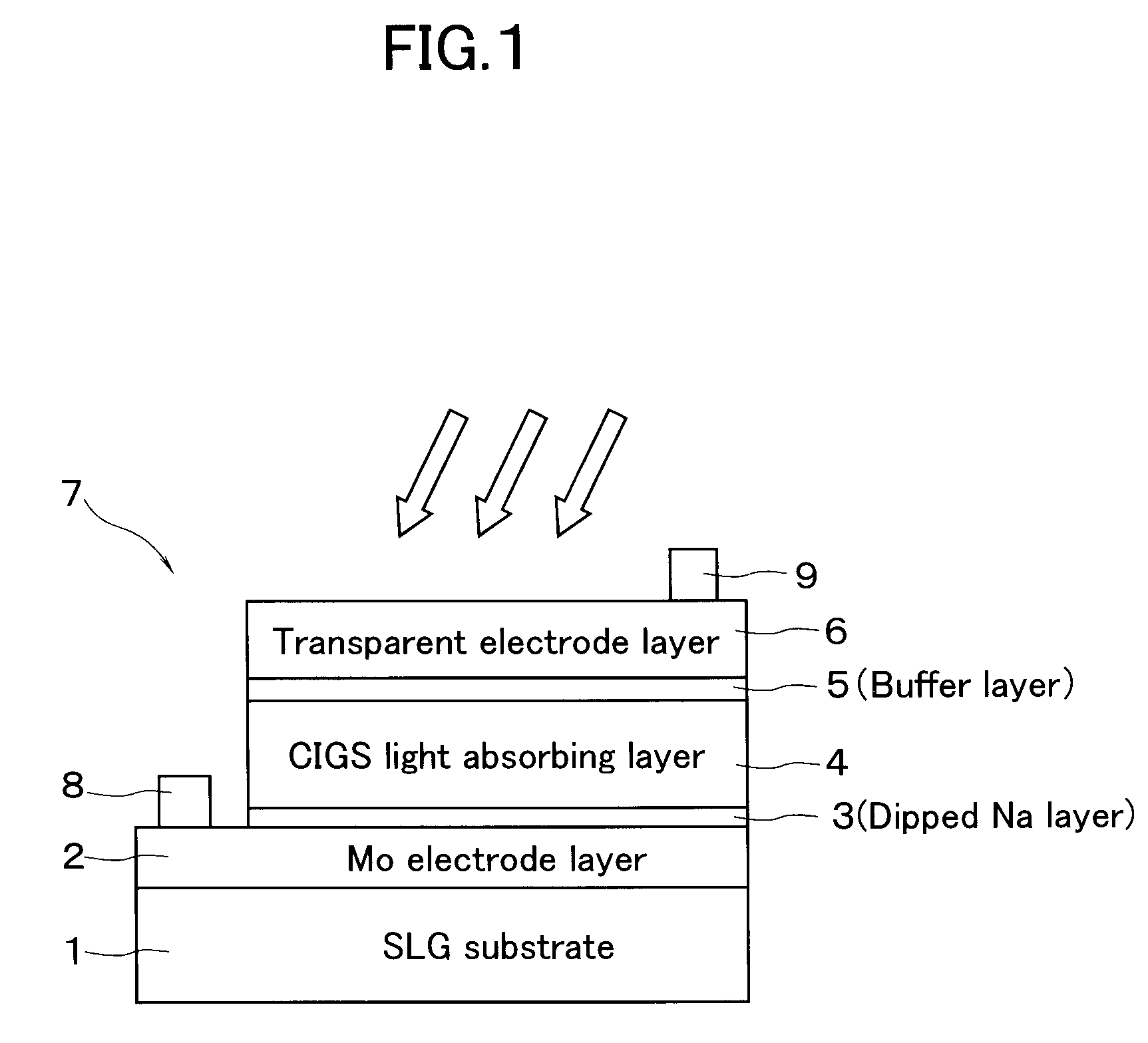
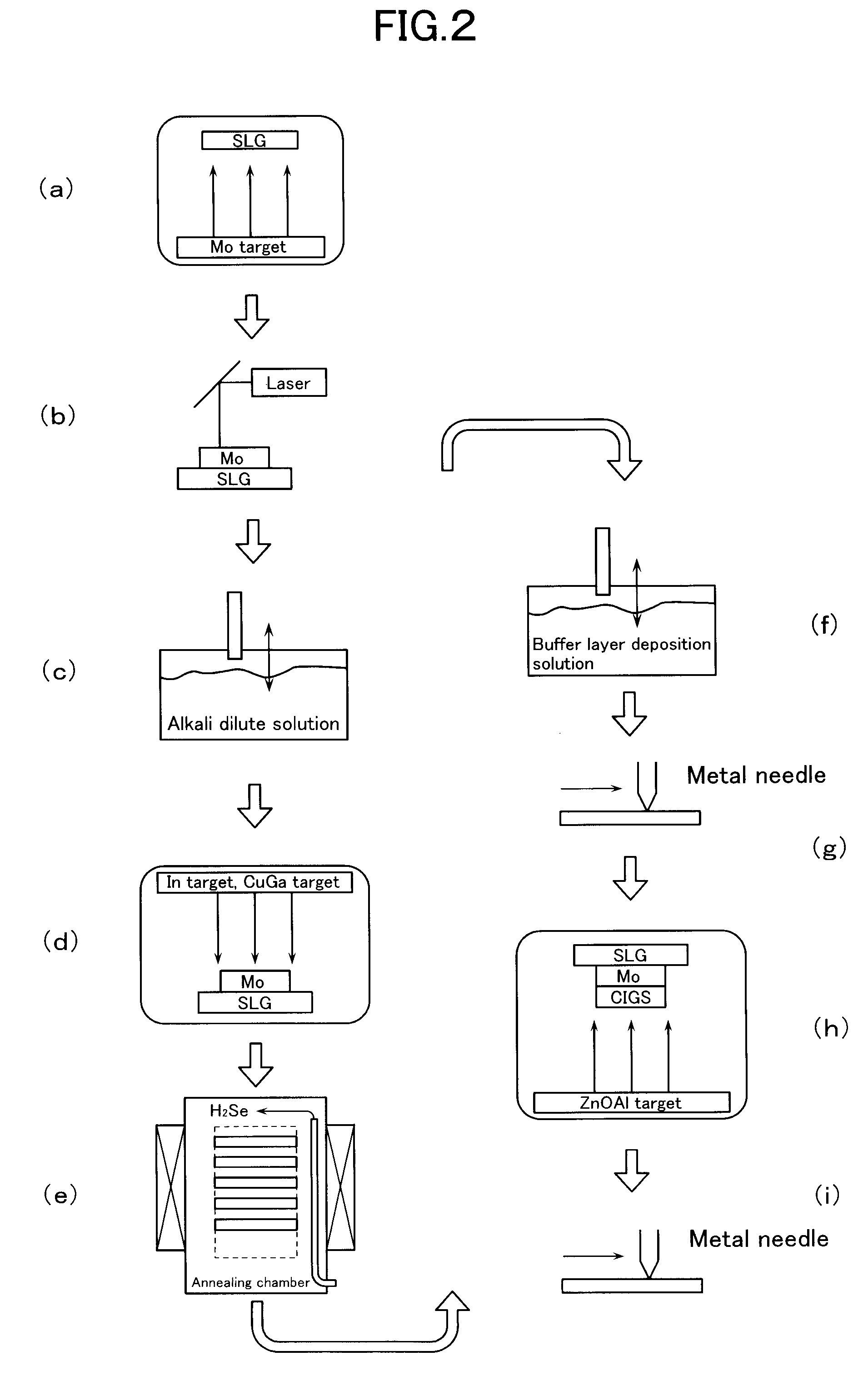
Method for Manufacturing Chalcopyrite Thin-Film Solar Cell
InactiveUS20080283389A1External appearance defectImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePV power plantsSputteringAlloy
A method for fabricating a chalcopyrite-type thin film solar cell includes a first step of forming onto a Mo electrode layer 2 a precursor including an In metal layer and a Cu—Ga alloy layer by sputtering, a second step of attaching an alkali-metal solution onto the precursor, a selenization step of subjecting the substrate 1 which has undergone both the first and the second steps to a selenization treatment, and a transparent electrode forming step of depositing an optically transparent conductive layer. As the alkali-metal solution, an aqueous solution of an alkali metal compound, such as sodium tetraborate, sodium sulfide, and sodium aluminum sulfate, can be used.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Photoelectric conversion layer, photoelectric conversion device and imaging device, and method for applying electric field thereto
InactiveUS20070052051A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyIncreased durabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen atomPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion layer comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1): wherein R1 to R10 each independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent; L represents a monovalent group or a divalent or polyvalent connecting group; m is 0 or 1; and n represents an integer of from 1 to 4.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Lead-free silver conductive paste used for positive electrode of solar battery and preparation technique thereof
InactiveCN101609850AStrong adhesionLower resistanceFinal product manufactureConductive materialConductive pasteSilver electrode
The invention provides a lead-free silver conductive paste used for positive electrode of solar battery and a preparation technique thereof. The paste comprises the following materials by weight percentage: 65 to 85 percent of silver powder, 2 to 8 percent of lead-free glass powder, 10 to 25 percent of organic carrier and 0.1 to 3 percent of additive. The paste adopts the lead-free glass powder of Si-B-Bi-Al-Ti-Zn-O series to replace the traditional lead-bearing glass powder; and the series glass powder has lower softening point, can lead the silver electrode to have good adhesive force after sintering, and ensures the silver electrode to be well contacted with a silicon substrate. In addition, zinc resinate is used as the additive in the invention, not only can well improve the printing performance of the paste, but also can improve the electrical property of the electrode.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
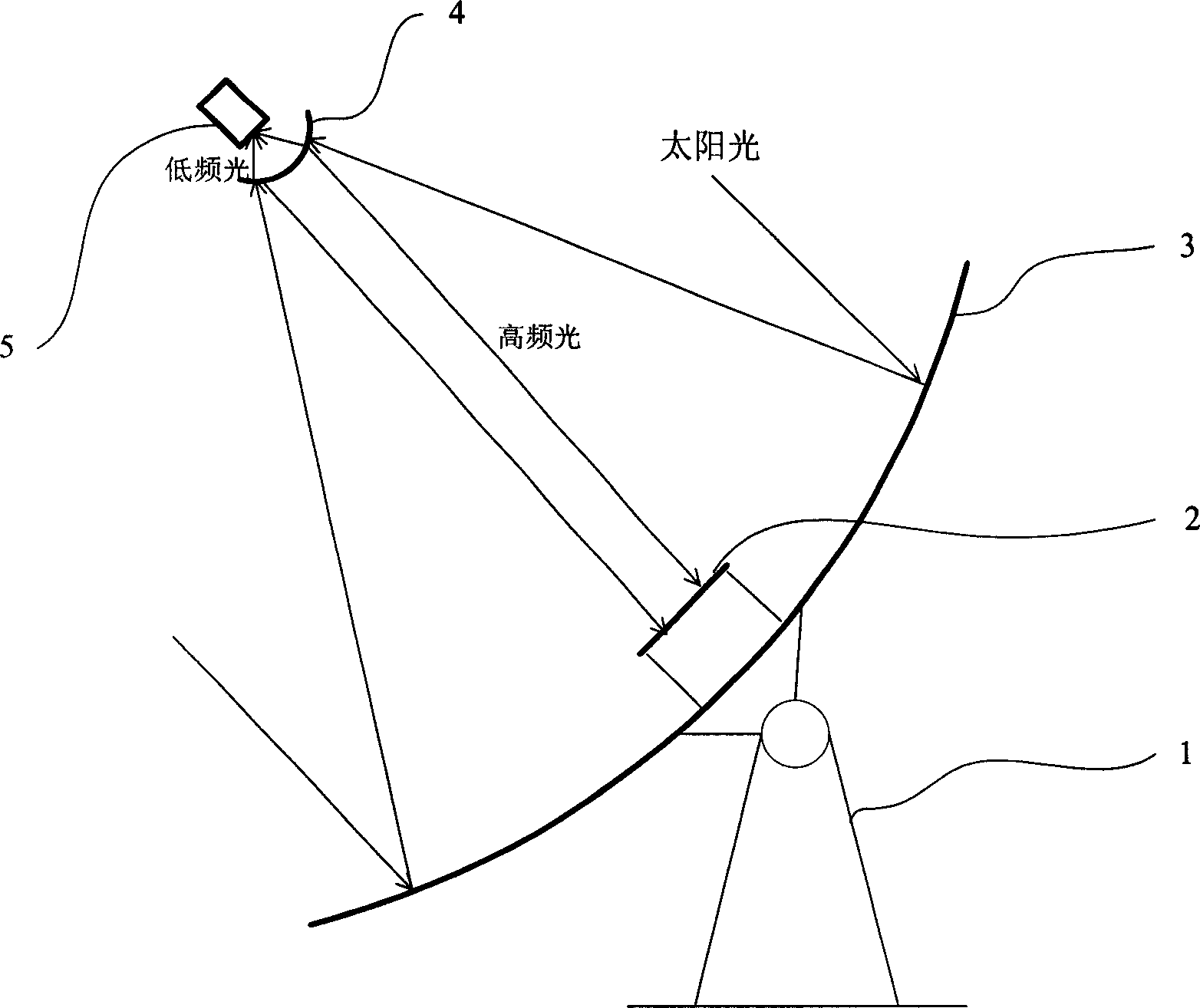
Solar energy thermoelectric co-supply system
InactiveCN1773190AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersControl systemEngineering
The present invention relates to a solar heating and power generation combined supply system. Said system includes the following several components: rotating parabolic saucer condenser, rotating hyperbolic spectral control system, light-gathering photovoltaic group battery and hot-pipe type water heater. Said invention also provides the concrete structure of the above-mentioned every portion and the working principle of said system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
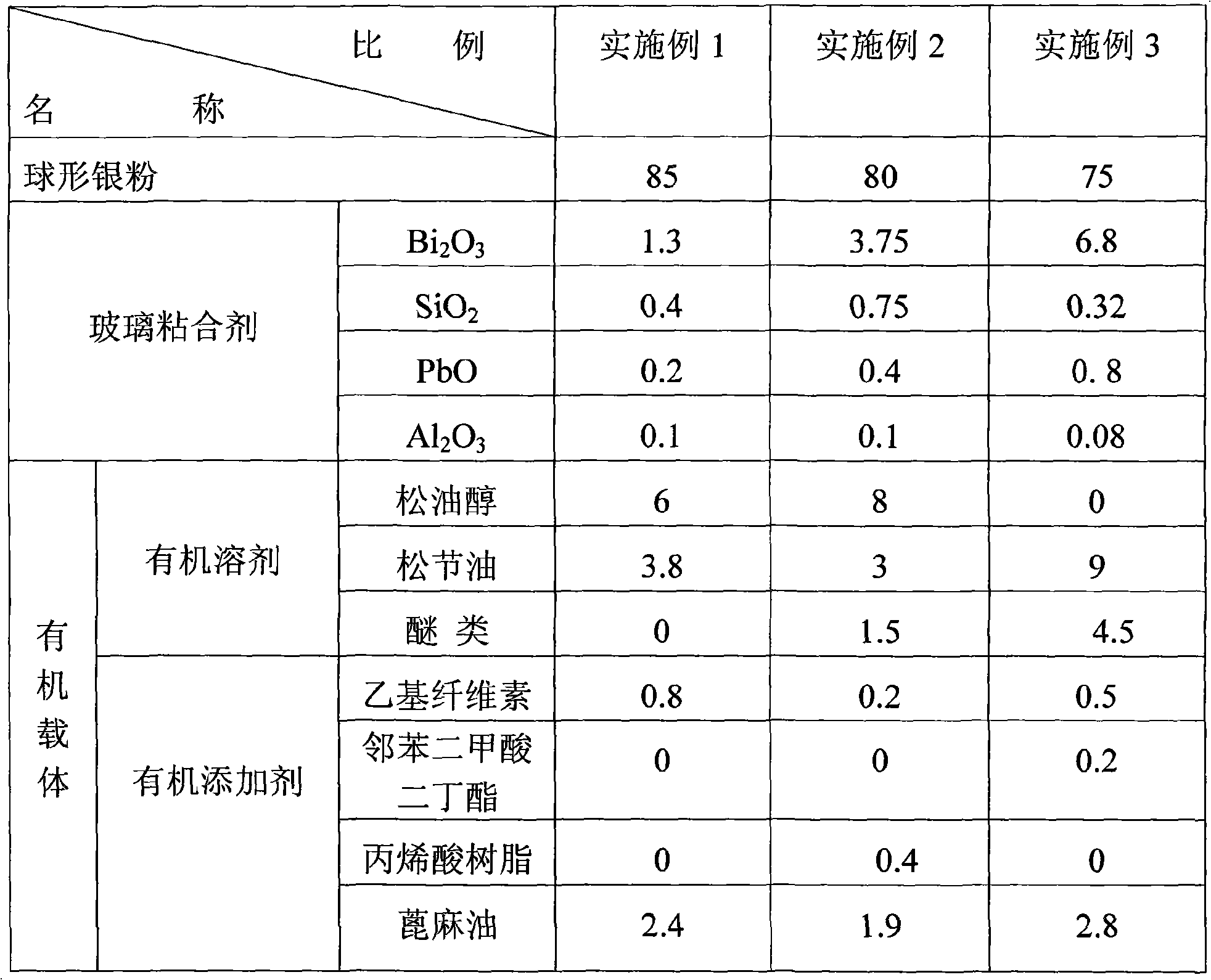
High-viscosity solar cell front side silver paste and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101271928AIncrease aspect ratioImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialScreen printingSilver paste
The invention relates to a high viscosity solar cell front silver serum and a preparation method thereof. The composition and the weight ratio of the high viscosity solar cell front silver serum are that conductive silver powder accounts for 75-85 percent, glass glue accounts for 2-10 percent, organic carrier accounts for 5.5-20 percent, the particle size of the conductive silver powder is 0.2-2mum; the composition and the weight ratio of the glass glue are that Bi2O3 accounts for 65-85 percent, SiO2 accounts for 5-20 percent, PbO accounts for 1-15 percent and Al2O3 accounts for 1-5 percent. After such processes are carried out by the serum as screen printing, low temperature drying and high temperature sintering, the aspect ratio of a conducting electrode formed on the surface of solar cell is high, the solar cell produced by using the method has small front shading area and high photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:EGING PHOTOVOLTAIC TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Thin Film Solar Cell Having Photo-Luminescent Medium Coated Therein And Method For Fabricating The Same
InactiveUS20100012183A1Improving spectrum sensibilityImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyCoatingsSpecial surfacesLong wavelengthElectrical battery
A thin film solar cell having a photo-luminescent medium coated therein and a method for fabricating the same are provided. The thin film solar cell at least includes a transparent layer, a front electrode layer, a photoconductive layer, and a back electrode layer, which are sequentially stacked in that order from a light incident surface of the thin film solar cell. The transparent layer is a cover glass or a transparent substrate. The thin film solar cell further includes a photo-luminescent medium disposed on outer surface or inner surface of the transparent layer for absorbing the rest short wavelength light contained in the incident light and is then excited to emit a long wavelength light which can be effectively absorbed by the photoconductive layer. In such a way, the spectrum of the incident light is shifted, and thus an improved energy conversion efficiency is achieved.
Owner:NEXPOWER TECH
Method for manufacturing solar cell and solar cell, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
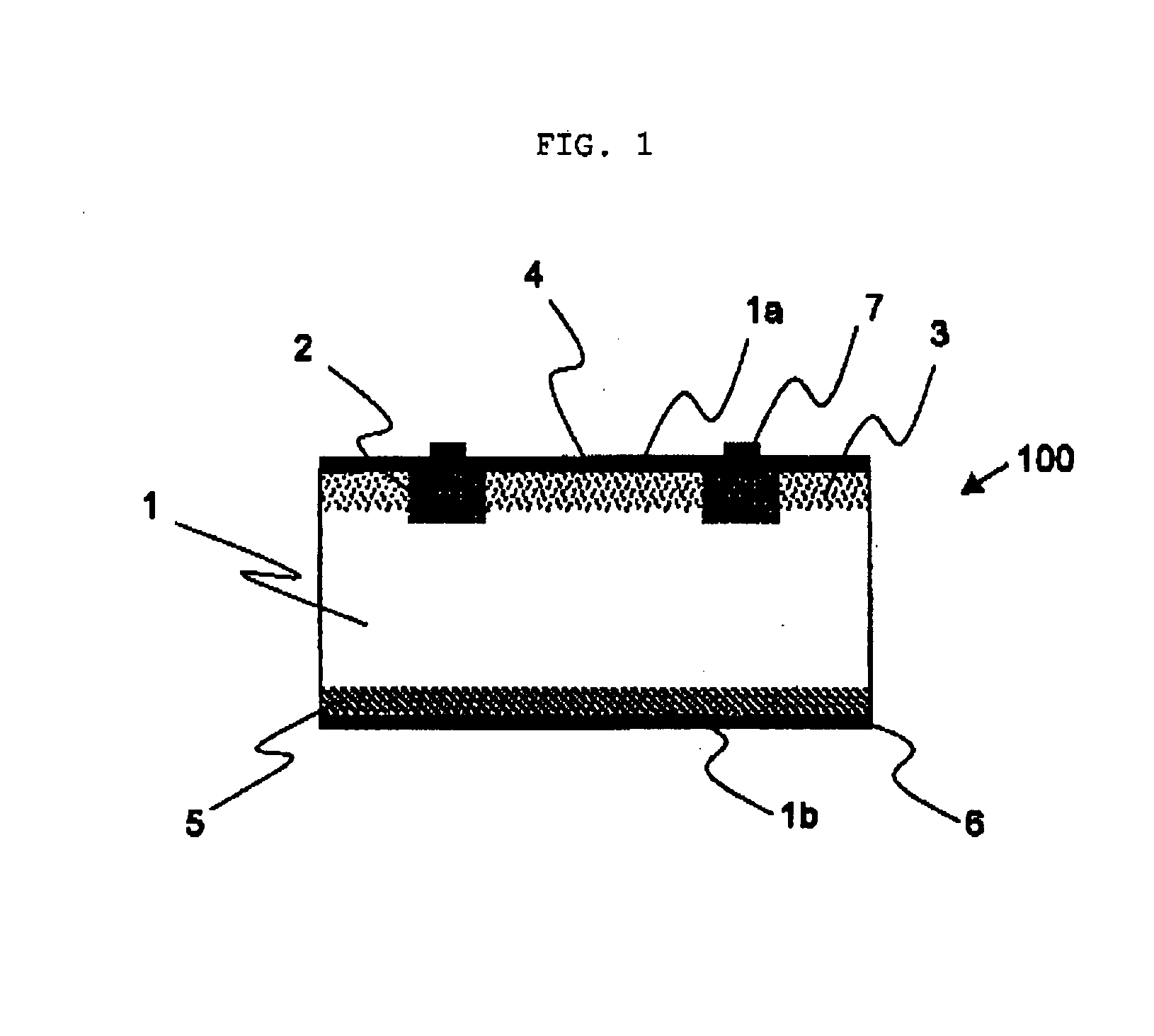
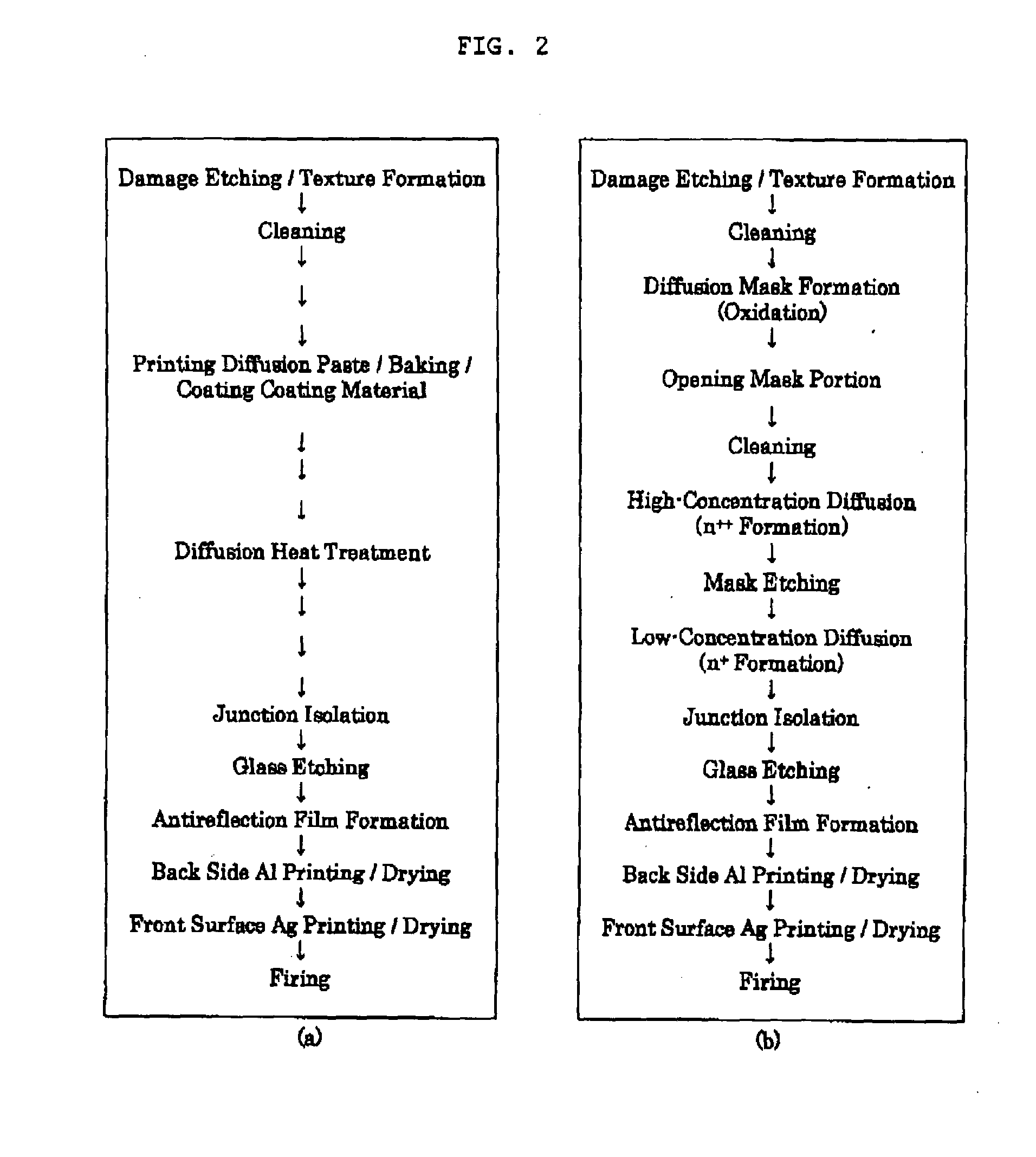
InactiveUS20090020158A1Convenient coatingEasy to implementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWater-setting substance layered productDiffusionDopant
The present invention is a method for manufacturing a solar cell by forming a p-n junction in a semiconductor substrate having a first conductivity type, wherein, at least: a first coating material containing a dopant and an agent for preventing a dopant from scattering, and a second coating material containing a dopant, are coated on the semiconductor substrate having the first conductivity type so that the second coating material may be brought into contact with at least the first coating material; and, a first diffusion layer formed by coating the first coating material, and a second diffusion layer formed by coating the second coating material the second diffusion layer having a conductivity is lower than that of the first diffusion layer are simultaneously formed by a diffusion heat treatment; a solar cell manufactured by the method; and a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device. It is therefore possible to provide the method for manufacturing the solar cell, which can manufacture the solar cell whose photoelectric conversion efficiency is improved at low cost and with a simple and easy method by suppressing surface recombination in a portion other than an electrode of a light-receiving surface and recombination within an emitter while obtaining ohmic contact; the solar cell manufactured by the method; and the method for manufacturing the semiconductor device.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD +2
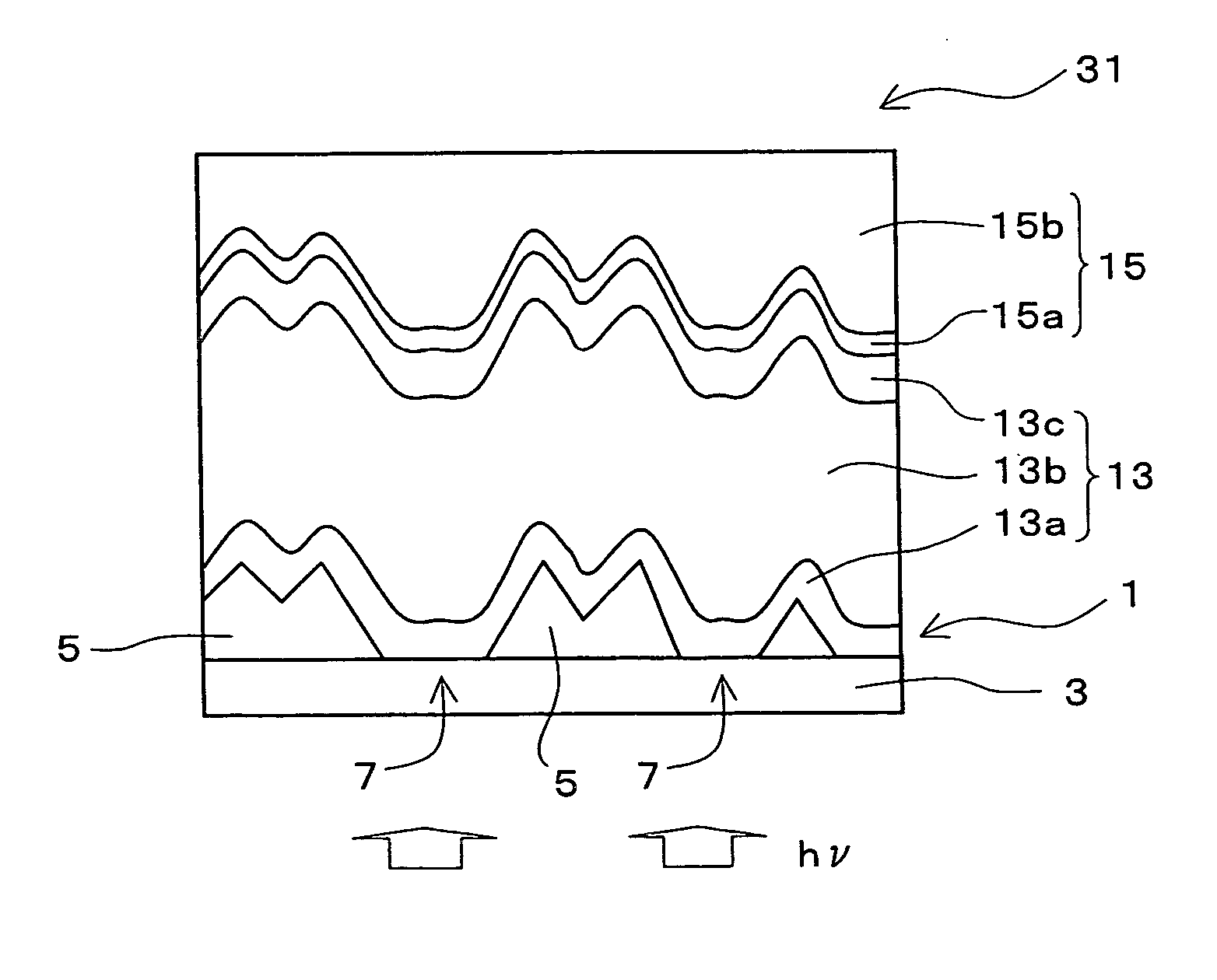
Stacked solar cell device
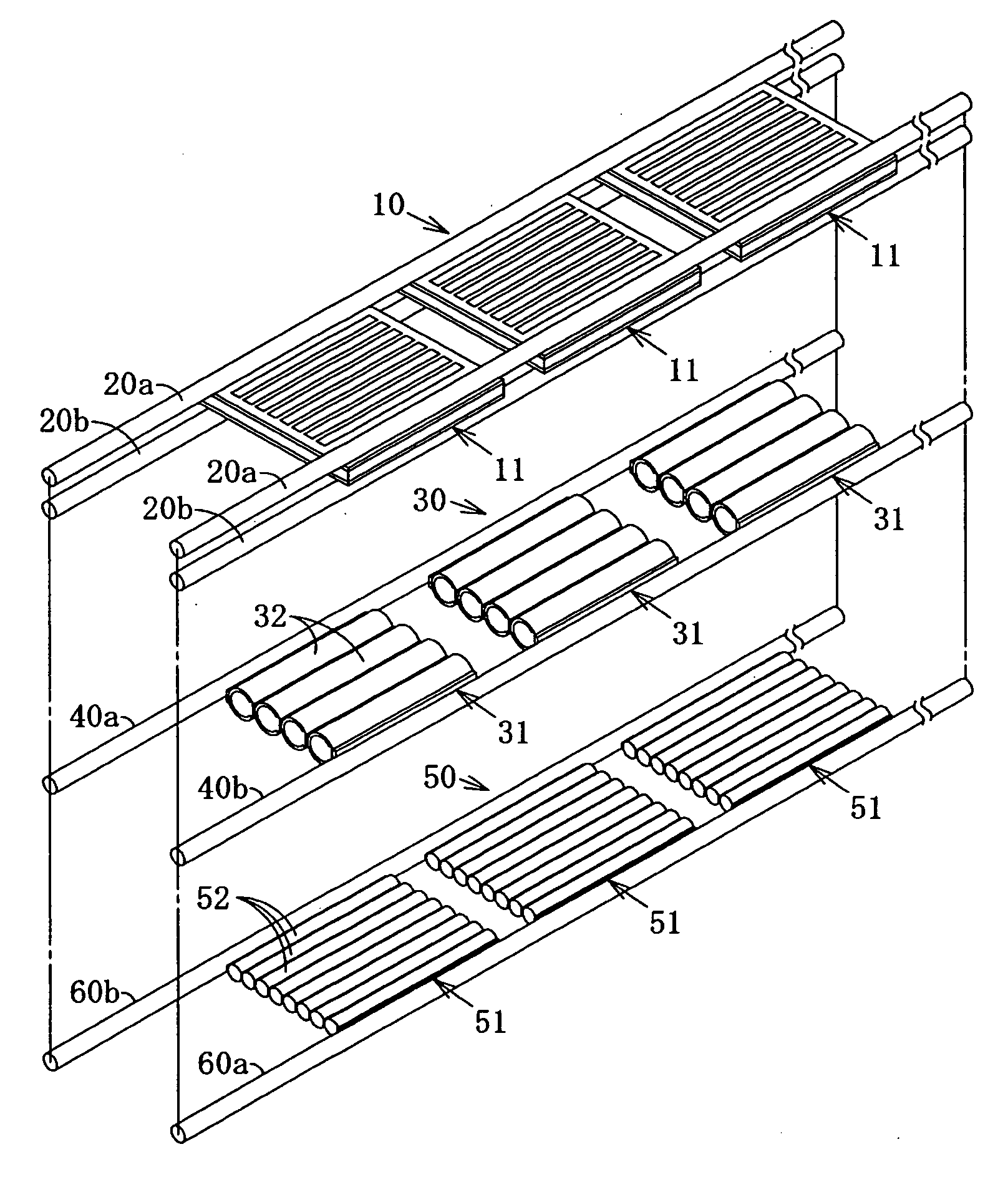
InactiveUS20100018568A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyGenerate uniformPhotovoltaic supportsPV power plantsEngineeringSolar cell
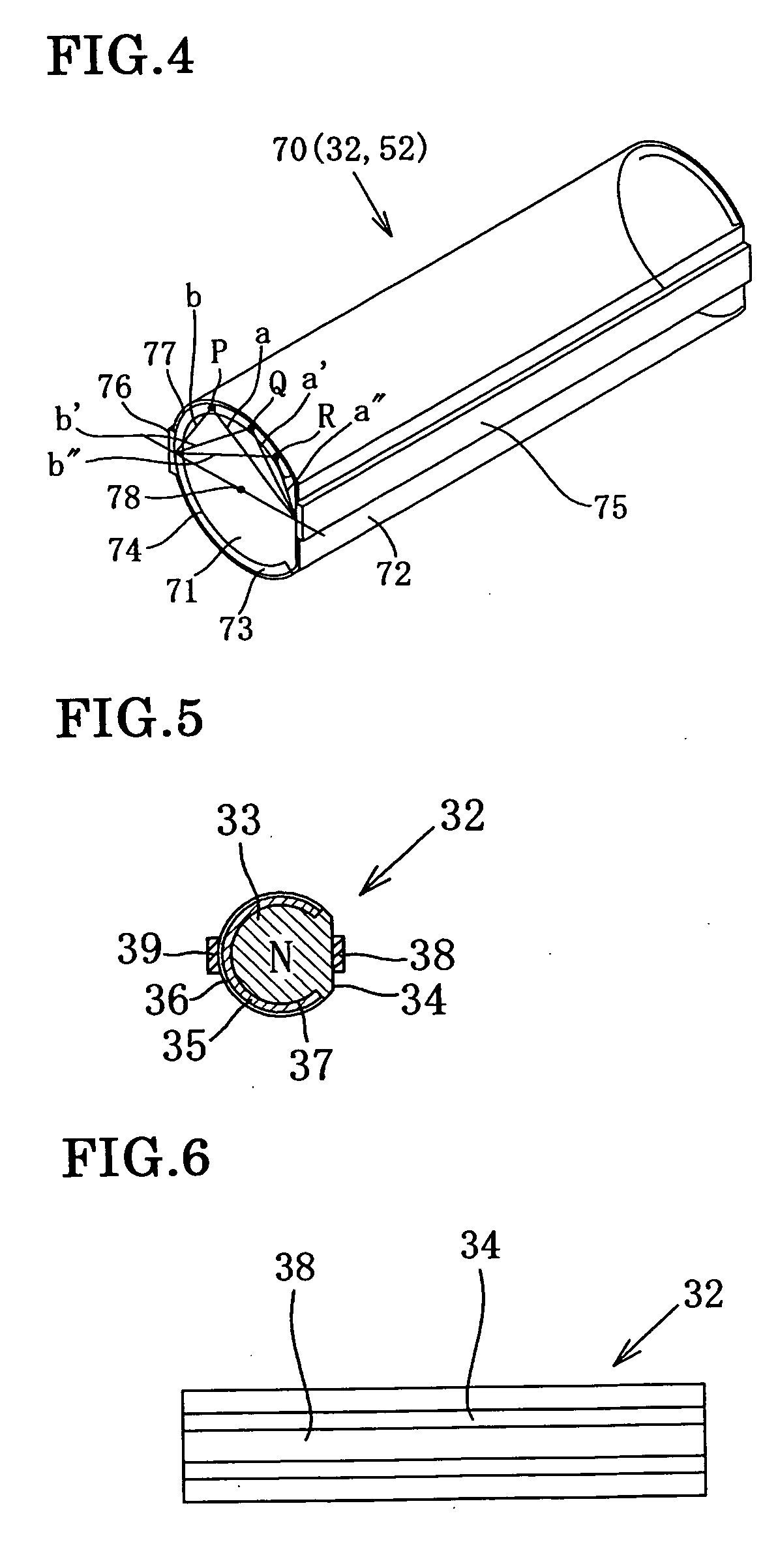
This stacked solar battery device includes a plurality of solar battery units 4, an enclosure case made of a metal plate to house these solar battery units 4 therein, a cover glass having a partial cylindrical lens formed. The plurality of solar battery units 4 are housed in a plurality of recesses of the enclosure case, and are sealed with a sealing material of synthetic resin. The solar battery unit 4 has a planar light receiving solar battery module 10, and rod light receiving solar battery modules 30 and 50 stacked so that the module having a shorter center wavelength of the sensitivity wavelength band is positioned closer to the incident side of the sunlight. The solar battery module 10 is configured so that five planar light receiving solar-battery cells 11 are connected in parallel with four connection rods 20a and 20b, and the sunlight modules 30 and 50 are configured so that five sub modules 31 and 51 are connected in parallel respectively with the connection rods 40a, 40b, 60a and 60b. The sub modules 31 and 51 are configured so that a plurality of rod-shaped solar battery cells 32 and 52 respectively are connected in series.
Owner:SPHELAR POWER
Photoelectric conversion element and solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20090188547A1Sufficient dark current-suppressing effectHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyPV power plantsNanoinformaticsElectrically conductiveBlock layer
A photoelectric conversion element is provided and includes: a pair of electrodes; a photoelectric conversion layer between the pair of electrodes; and a charge-blocking layer between one of the pair of the electrodes and the photoelectric conversion layer. The charge-blocking layer is capable of suppressing injection of a charge from the one of the pair of electrodes into the photoelectric conversion layer upon application of a voltage across the pair of electrodes, and the charge-blocking layer contains an insulating material and an electrically conductive material.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
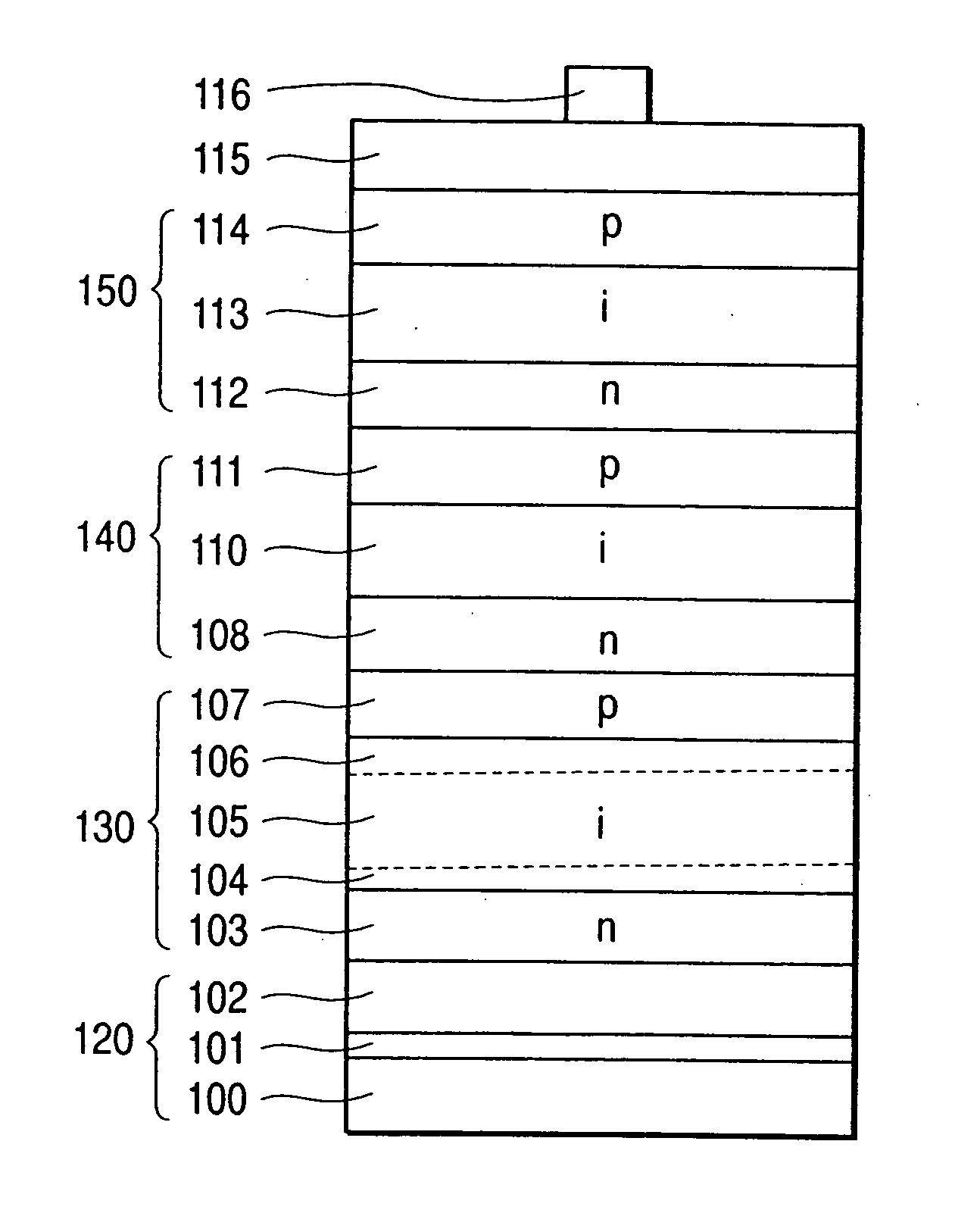
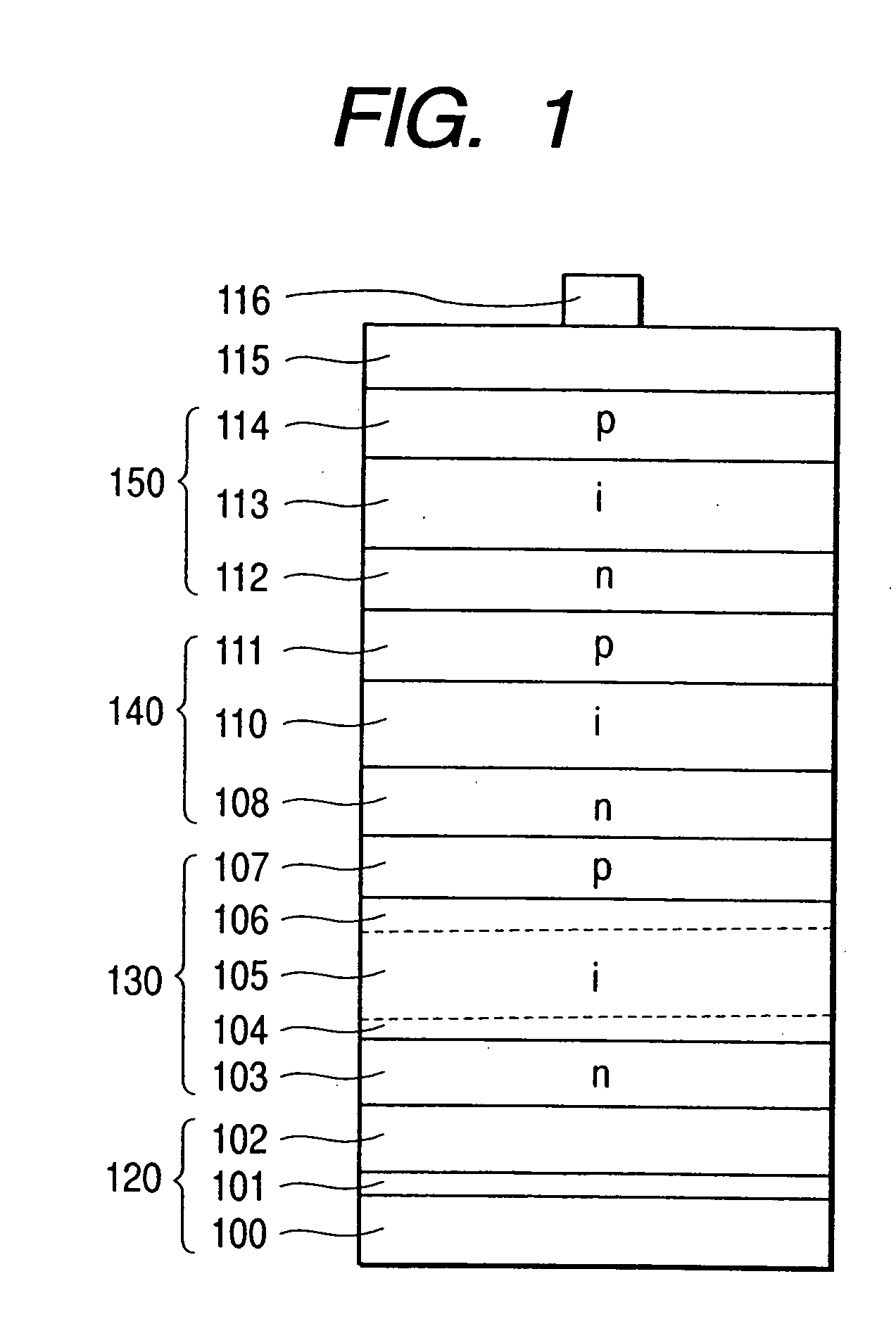
Stacked photovoltaic device
InactiveUS7064263B2Improve reliabilityImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePV power plantsSingle crystalMicrocrystalline silicon
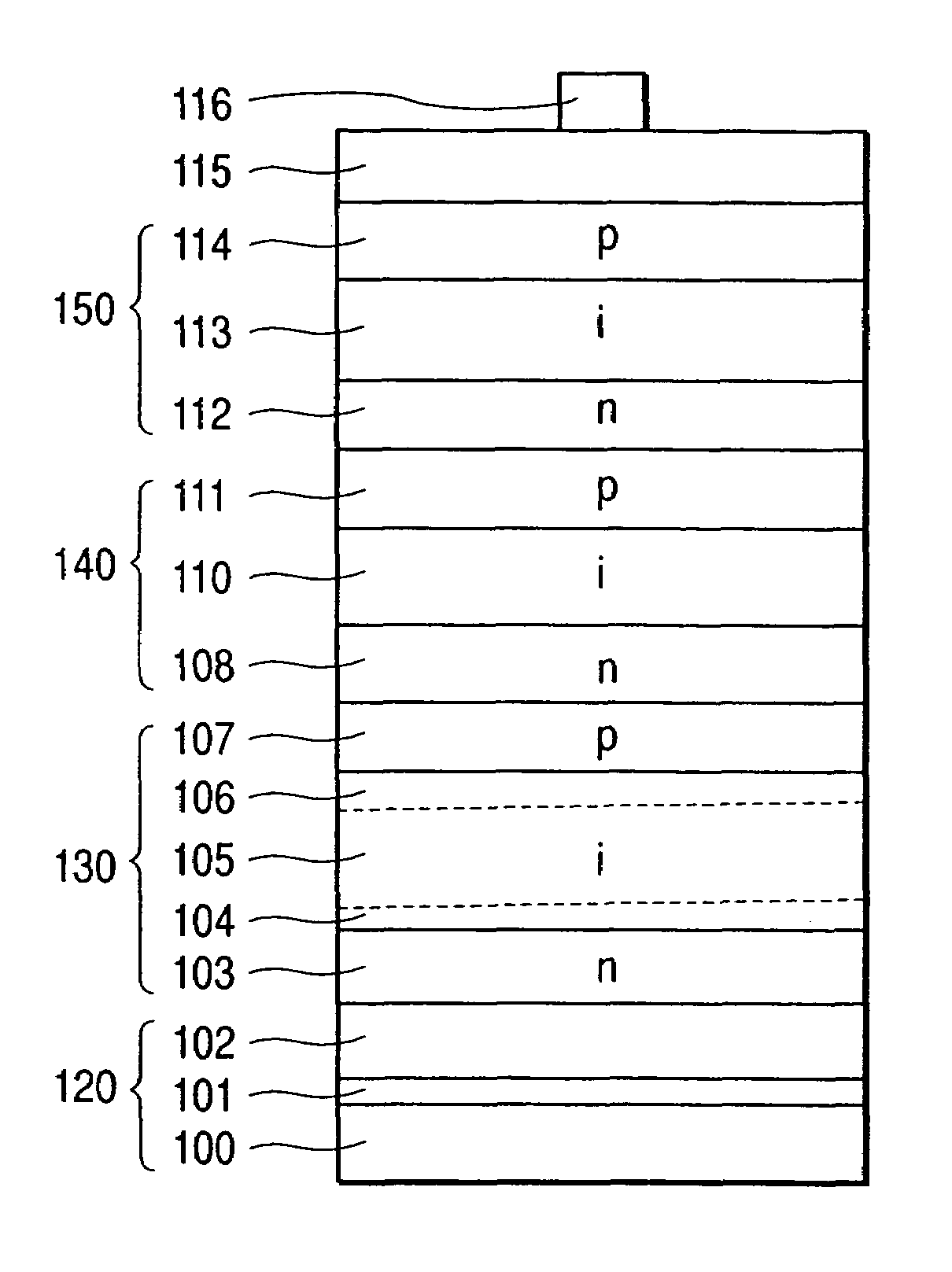
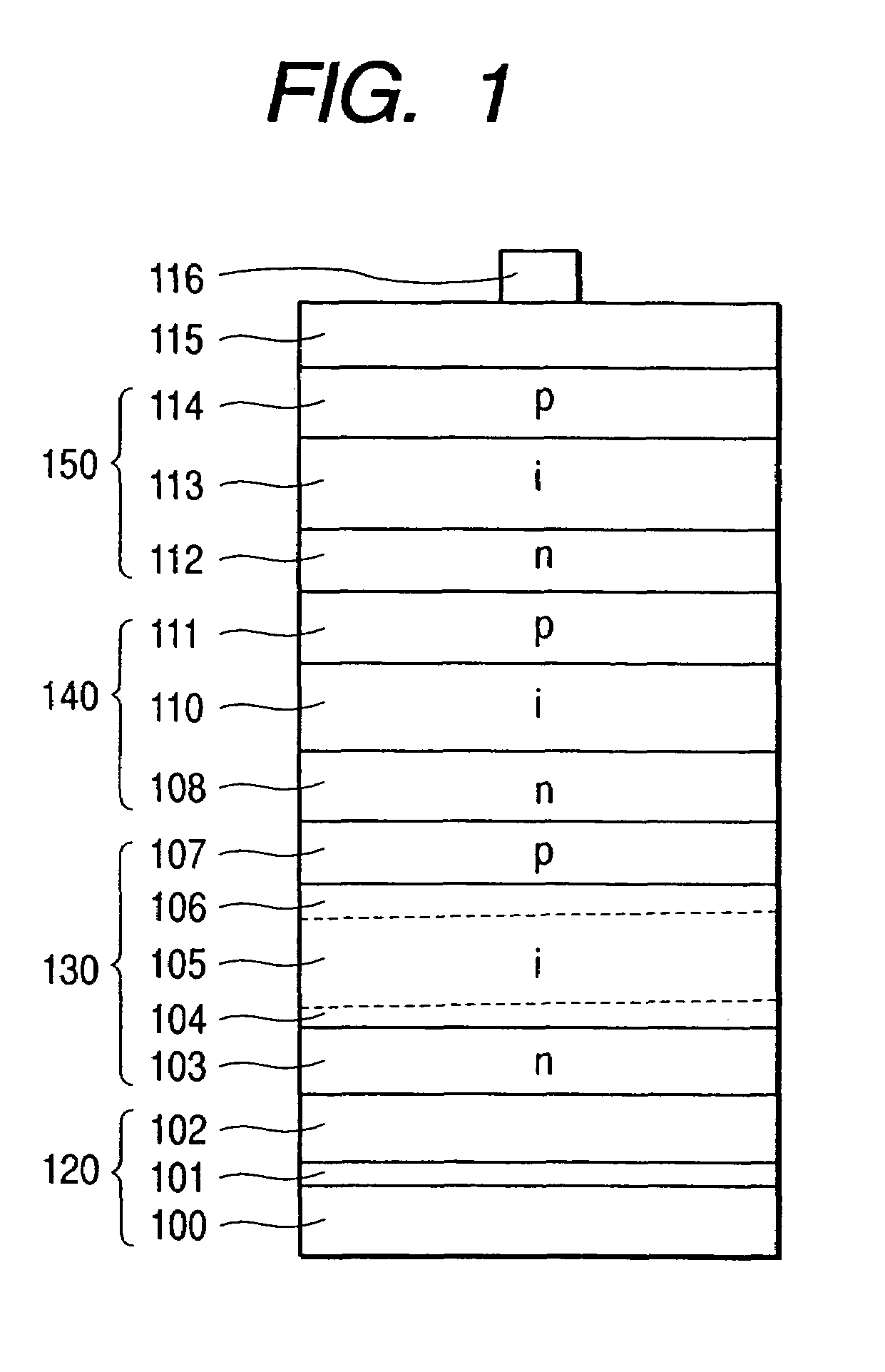
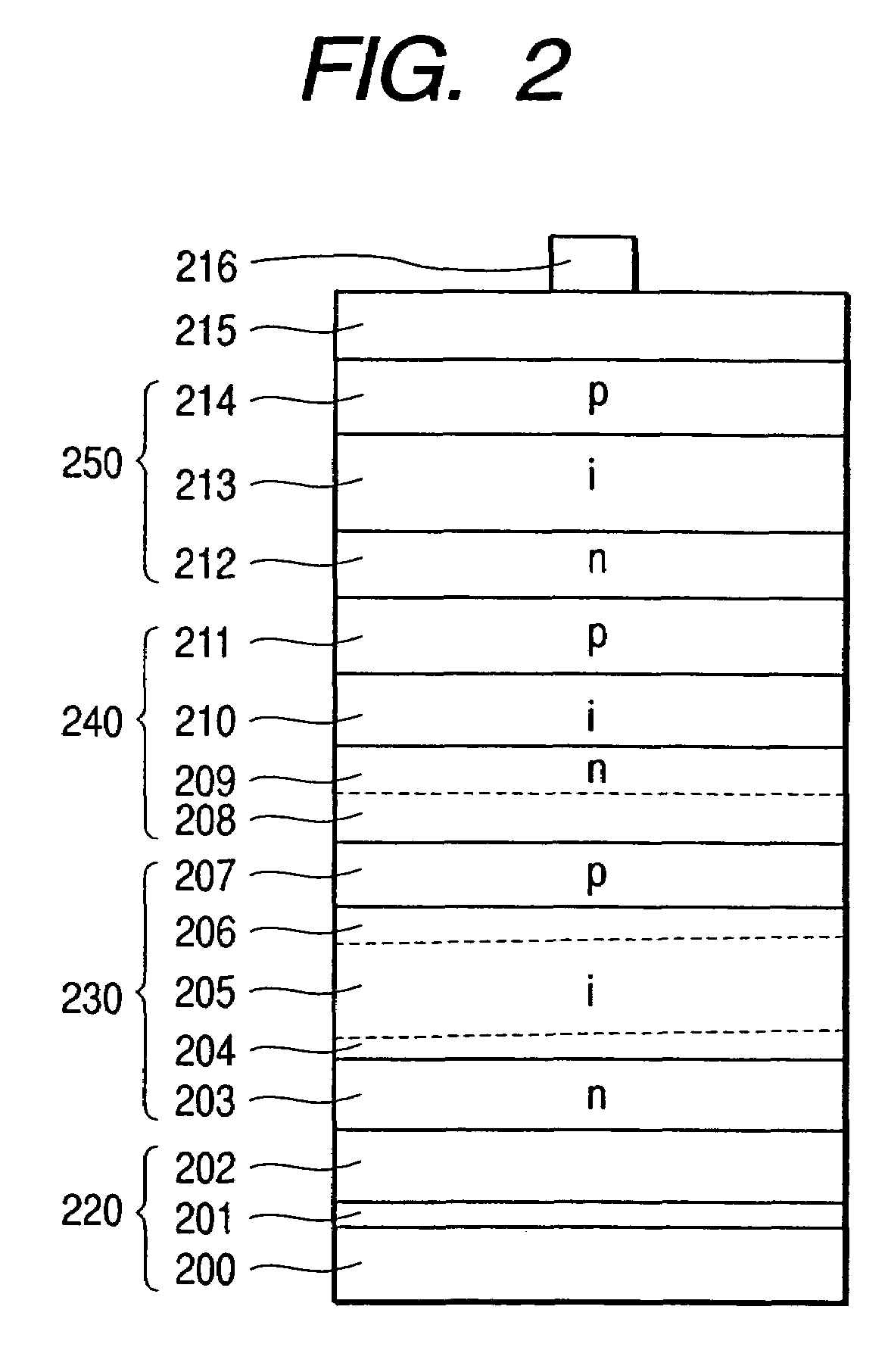
A stacked photovoltaic device comprises at least three p-i-n junction constituent devices superposed in layers, each having a p-type layer, an i-type layer and an n-type layer which are formed of silicon non-single crystal semiconductors. An amorphous silicon layer is used as the i-type layer of a first p-i-n junction, a microcrystalline silicon layer is used as the i-type layer of a second p-i-n junction and a microcrystalline silicon layer is used as the i-type layer of a third p-i-n junction, the first to third layers being in order from the light incident side. In this way, a stacked photovoltaic device can be provided which is practical and low-cost and yet has high reliability and high photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of manufacturing photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20090142879A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencySuppressing consumption of resourceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid phasesPhysics
A fragile layer is formed in a region at a depth of less than 1000 nm from one surface of a single crystal semiconductor substrate, and a first impurity semiconductor layer and a first electrode are formed at the one surface side. After bonding the first electrode and a supporting substrate, the single crystal semiconductor substrate is separated using the fragile layer or the vicinity as a separation plane, thereby forming a first single crystal semiconductor layer over the supporting substrate. An amorphous semiconductor layer is formed on the first single crystal semiconductor layer, and a second single crystal semiconductor layer is formed by heat treatment for solid phase growth of the amorphous semiconductor layer. A second impurity semiconductor layer having a conductivity type opposite to that of the first impurity semiconductor layer and a second electrode are formed over the second single crystal semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Photoelectric conversion element, method for producing photoelectric conversion element, and solid-state imaging device
ActiveUS20090050881A1Suppress generationImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyTelevision system detailsFinal product manufactureEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion element is provided and includes a photoelectric conversion portion. The photoelectric conversion portion includes: a pair of electrodes; and a photoelectric conversion layer between the pair of electrodes, and at least part of the photoelectric conversion layer includes a mixed layer of a p-type organic semiconductor and a fullerene, and a mixing ratio of the fullerene to the p-type organic semiconductor in terms of thickness ratio is less than 1:1.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
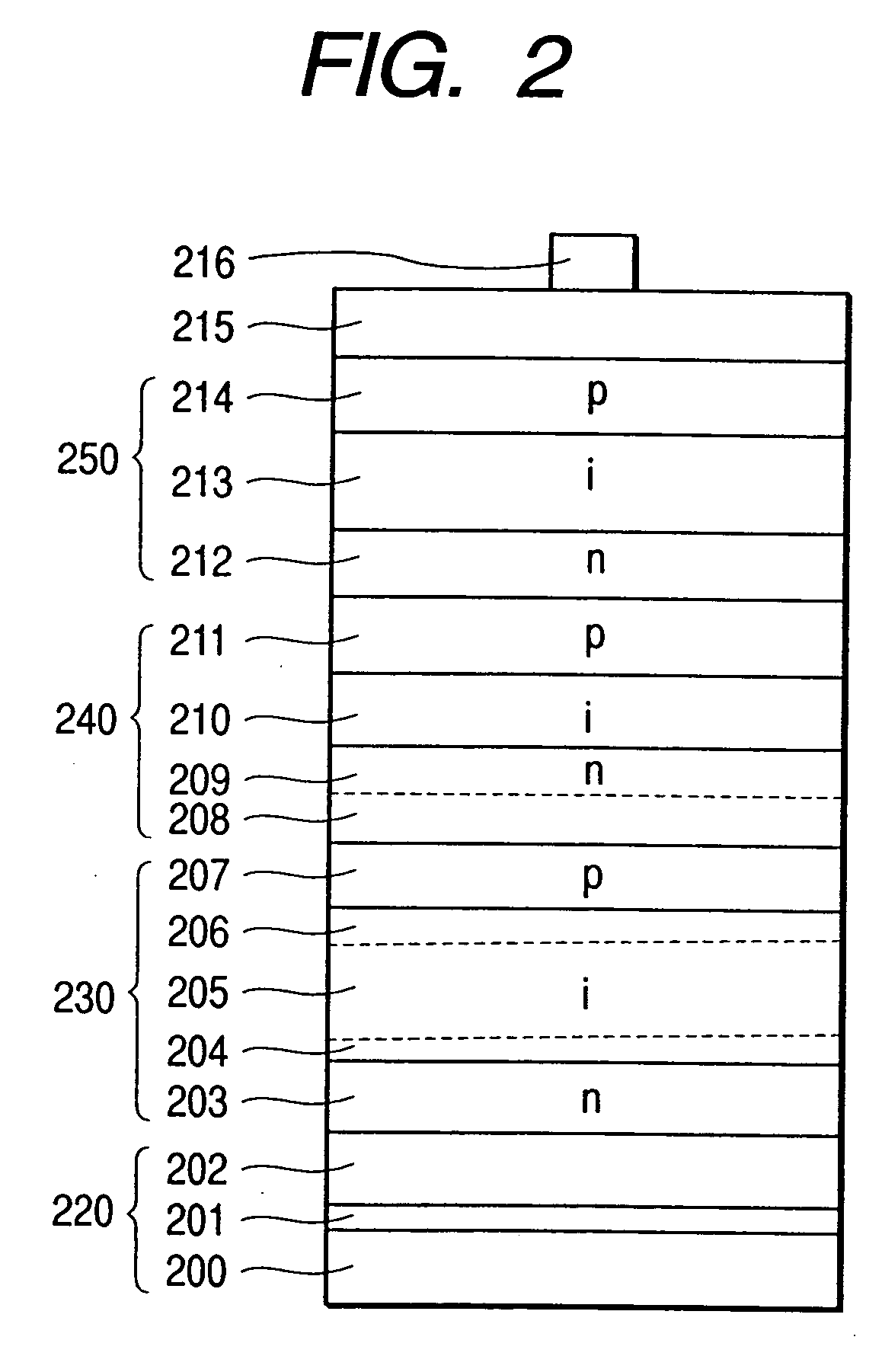
Stacked photovoltaic device
InactiveUS20050028860A1Inhibit deteriorationHigh currentFinal product manufacturePV power plantsSingle crystalMicrocrystalline silicon
[Problem(s)] A stacked photovoltaic device can be provided which is practicable and low-cost and yet has a high reliability, and also has a high photoelectric conversion efficiency. [Means for Solving the Problem] A stacked photovoltaic device comprises at least three p-i-n junction constituent devices superposed in layers, each having a p-type layer, an i-type layer and an n-type layer which are formed of silicon type non-single-crystal semiconductors. An amorphous silicon is used as the i-type layer of a first p-i-n junction, a microcrystalline silicon is used as the i-type layer of a second p-i-n junction and a microcrystalline silicon is used as the i-type layer of a third p-i-n junction, the first to third layers being in the order from the light-incident side.
Owner:CANON KK
Photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20030196692A1Smooth movementImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsPhotosensitizerDecomposition
Disclosed is a photovoltaic cell comprising a substrate having an electrode layer (1) on the surface and having a porous metal oxide semiconductor film (2) which is formed on the electrode layer (1) and on which a photosensitizer is adsorbed, a substrate having an electrode layer (3) on the surface, both of said substrates being arranged in such a manner that the electrode layer (1) and the electrode layer (3) face each other, and an electrolyte layer provided between the semiconductor film (2) and the electrode layer (3), wherein the semiconductor film (2) contains an inhibitor of back current, and at least one pair of substrate and electrode layer thereon have transparency. The photovoltaic cell is capable of inhibiting back current and decomposition of a spectrosensitizing dye caused by the ultraviolet rays, has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and is capable of generating high electromotive force.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com