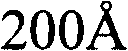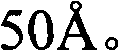Patents
Literature
7033 results about "Blocking layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
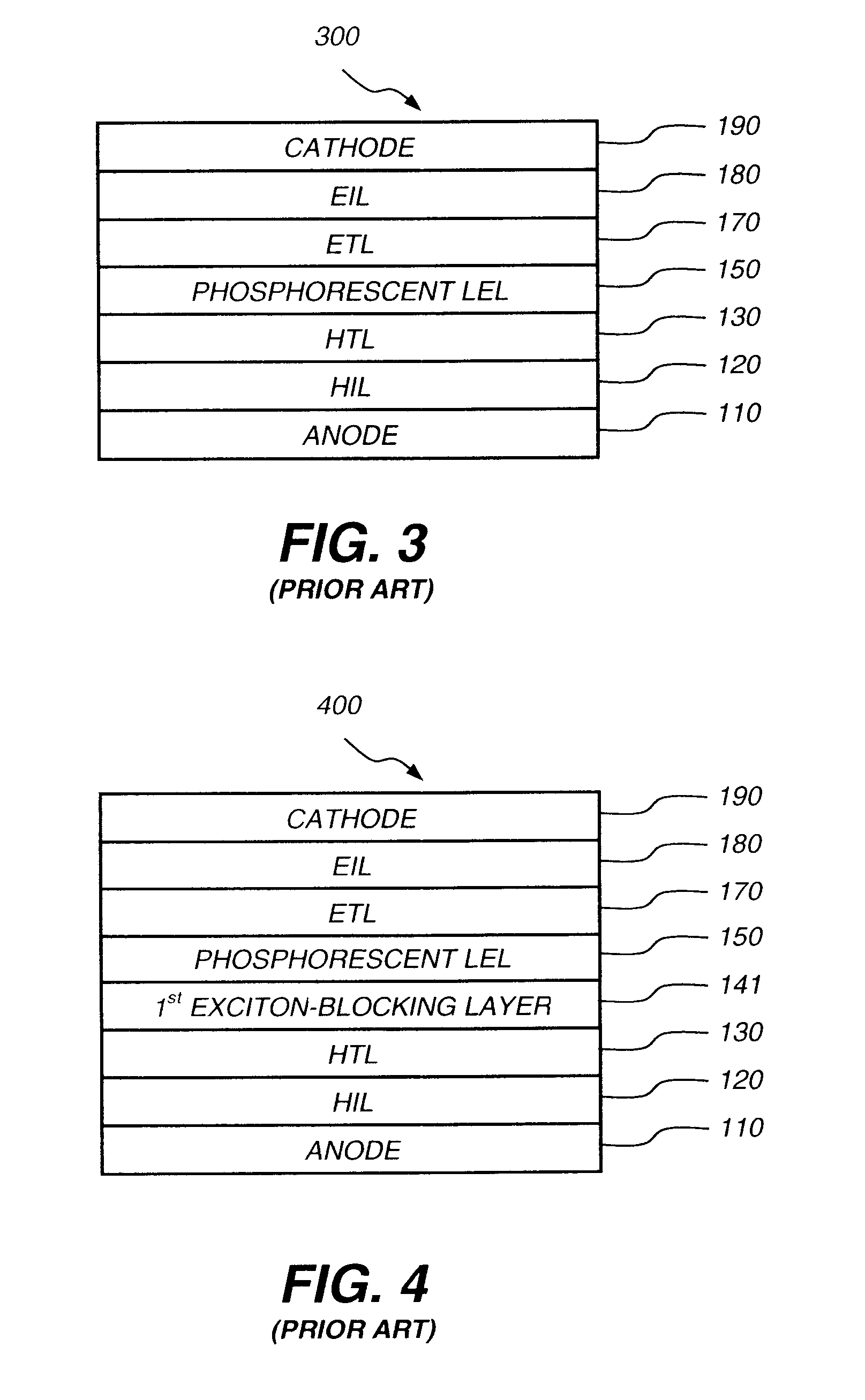
Organic electroluminescent element, illuminator, display and compound
InactiveUS20050069729A1Improve emission efficiencySolution to short lifeMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceBoron
An organic electroluminescent element comprising a light emission layer and a hole blocking layer adjacent to the light emission layer, wherein, (i) the light emission layer contains a compound having a specified partial structure and having a molecular weight of not more than 1700; and (ii) the hole blocking layer contains a derivative selected from the group consisting of a styryl derivative, a boron derivative and a carboline derivative.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
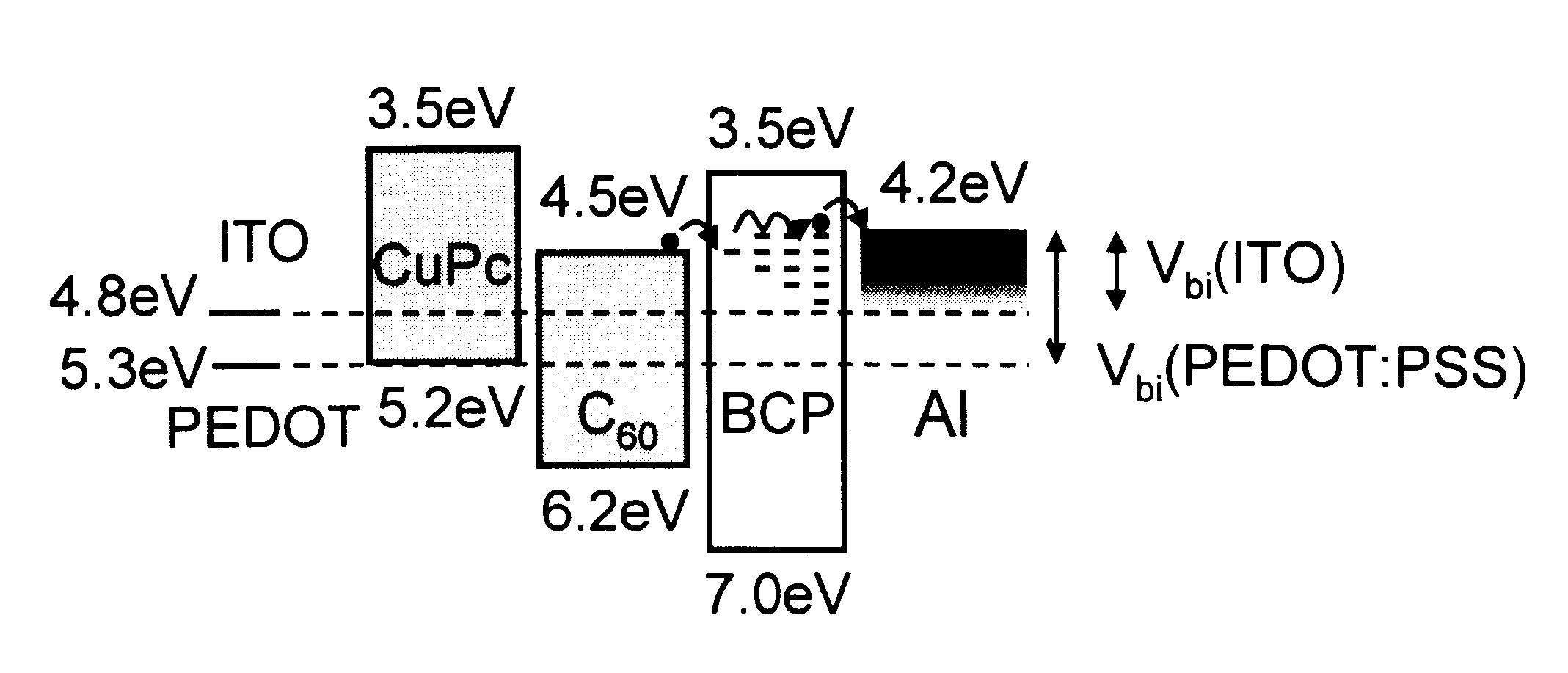
Solar cells using fullerenes
InactiveUS6580027B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the electric field strengthPV power plantsNanoinformaticsSolar cellFullerene
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices are disclosed. The devises comprise photoconductive organic thin films in a heterostructure, which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. The use of fullerenes in the electron conducting layer has lead to devices with high efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Devices having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Electron transporting compounds and organic electroluminescent devices using the same
InactiveUS20140284580A1Prolonged lifetime stabilityLow working voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Disclosed is a novel compound of Formula 1 and an organic electroluminescent device using the same. In Formula 1, X and Y independently represents a hydrogen, an aromatic or a hetero aromatic hydrocarbon having C5 to C10 carbons; X and Y may be the same or different; Ar1 to Ar2 each represent a hydrogen, an unsubstituted or substituted aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons, or an unsubstituted or substituted condensed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons; Ar1 to Ar2 can form a fused aromatic ring system with the adjacent aromatic hydrocarbons. The compound of Formula 1 is present in the electron injection or a transport material, or an exciton blocking layer in the organic light emitting device, and thereby improving the device stability, lowering the operational voltage.
Owner:E RAY OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
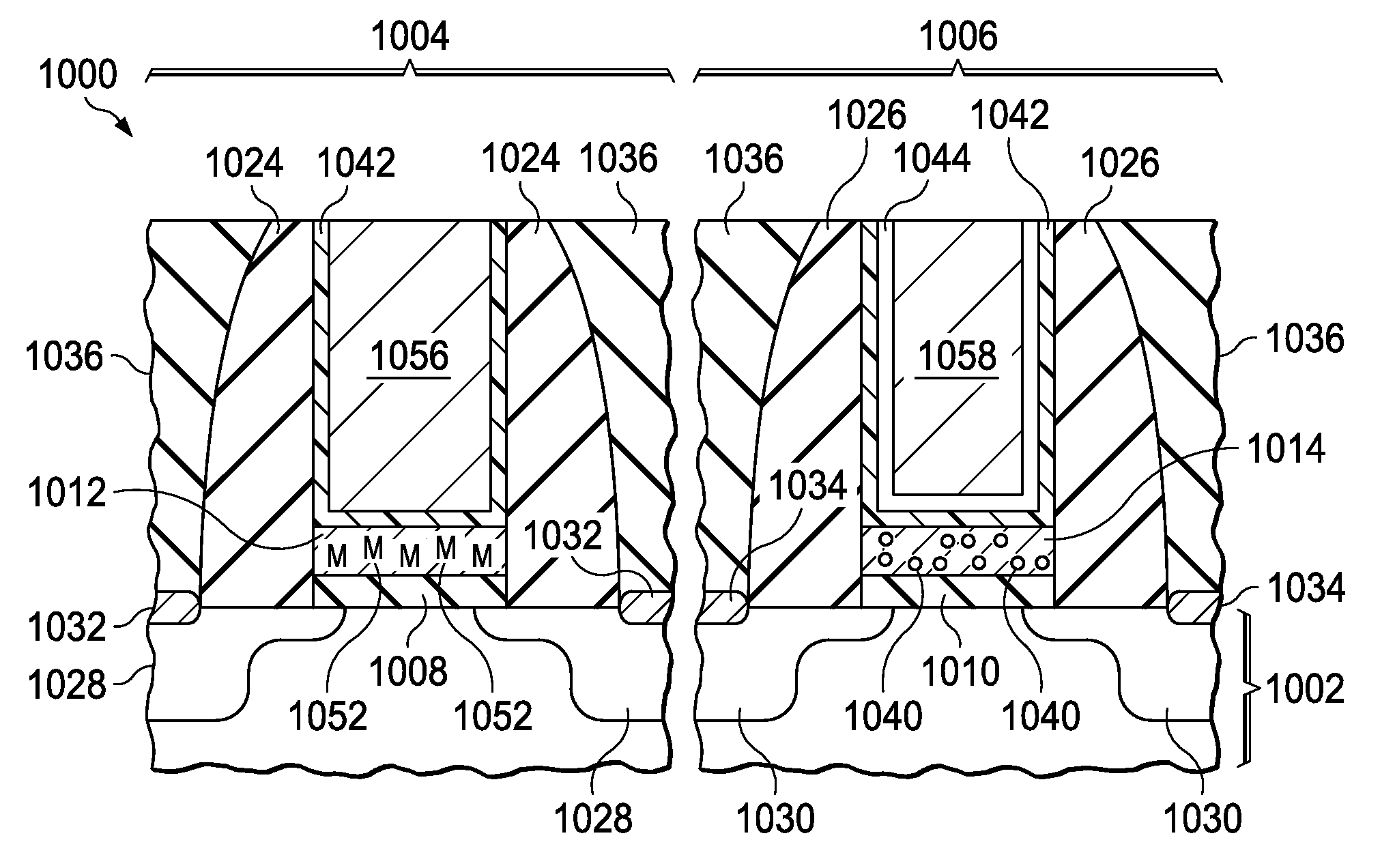
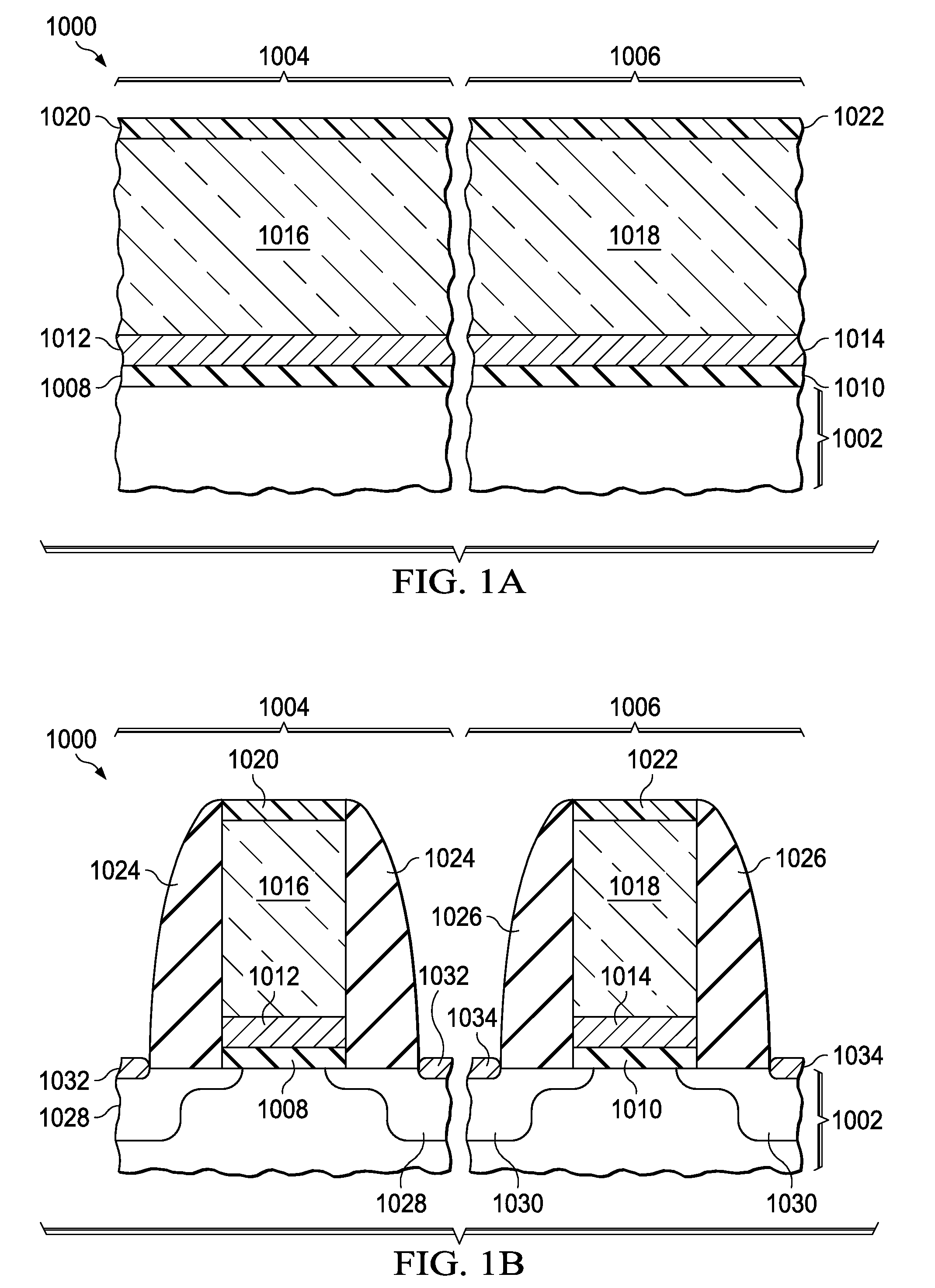
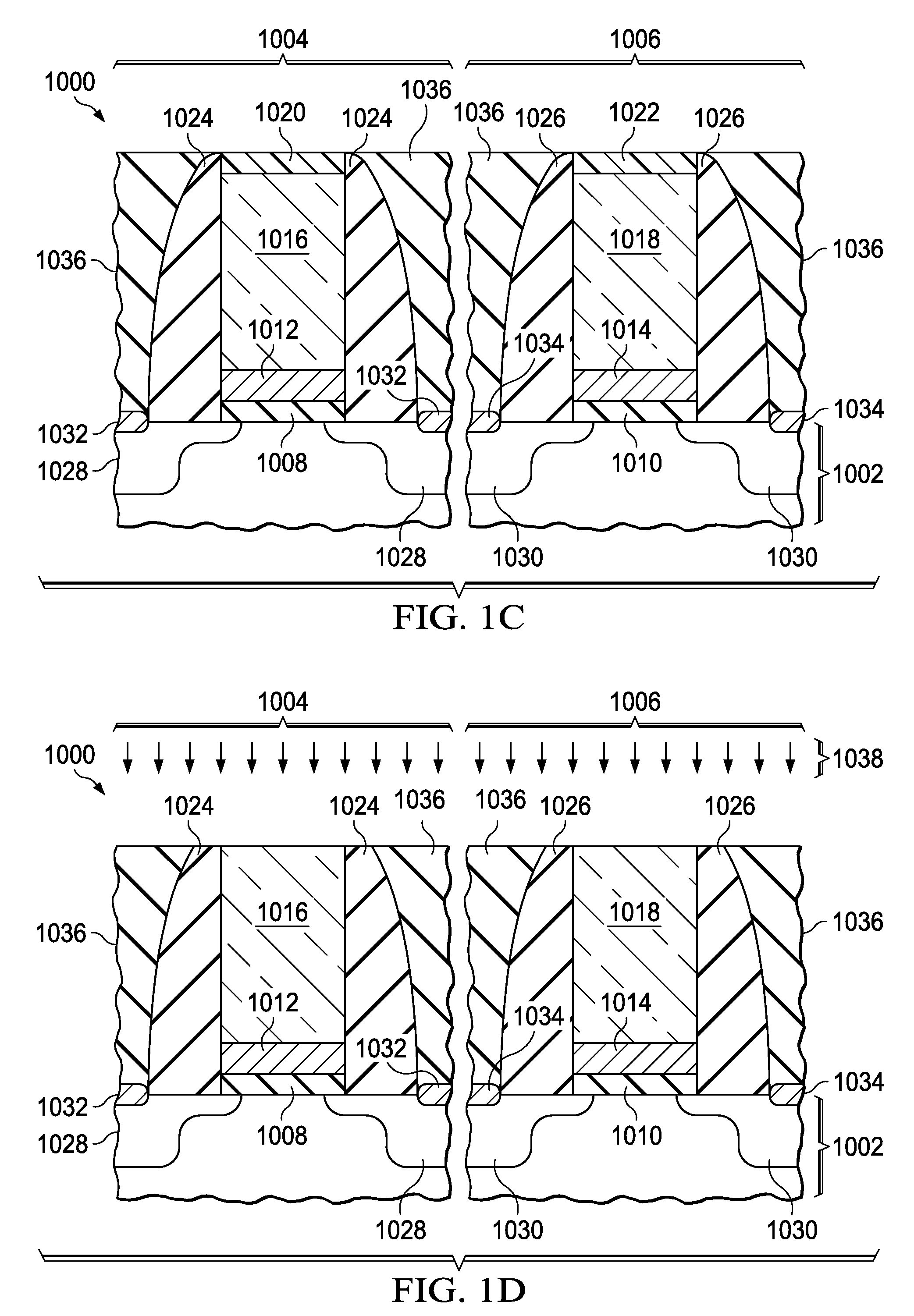
Vertical channel type nonvolatile memory device and method for fabricating the same
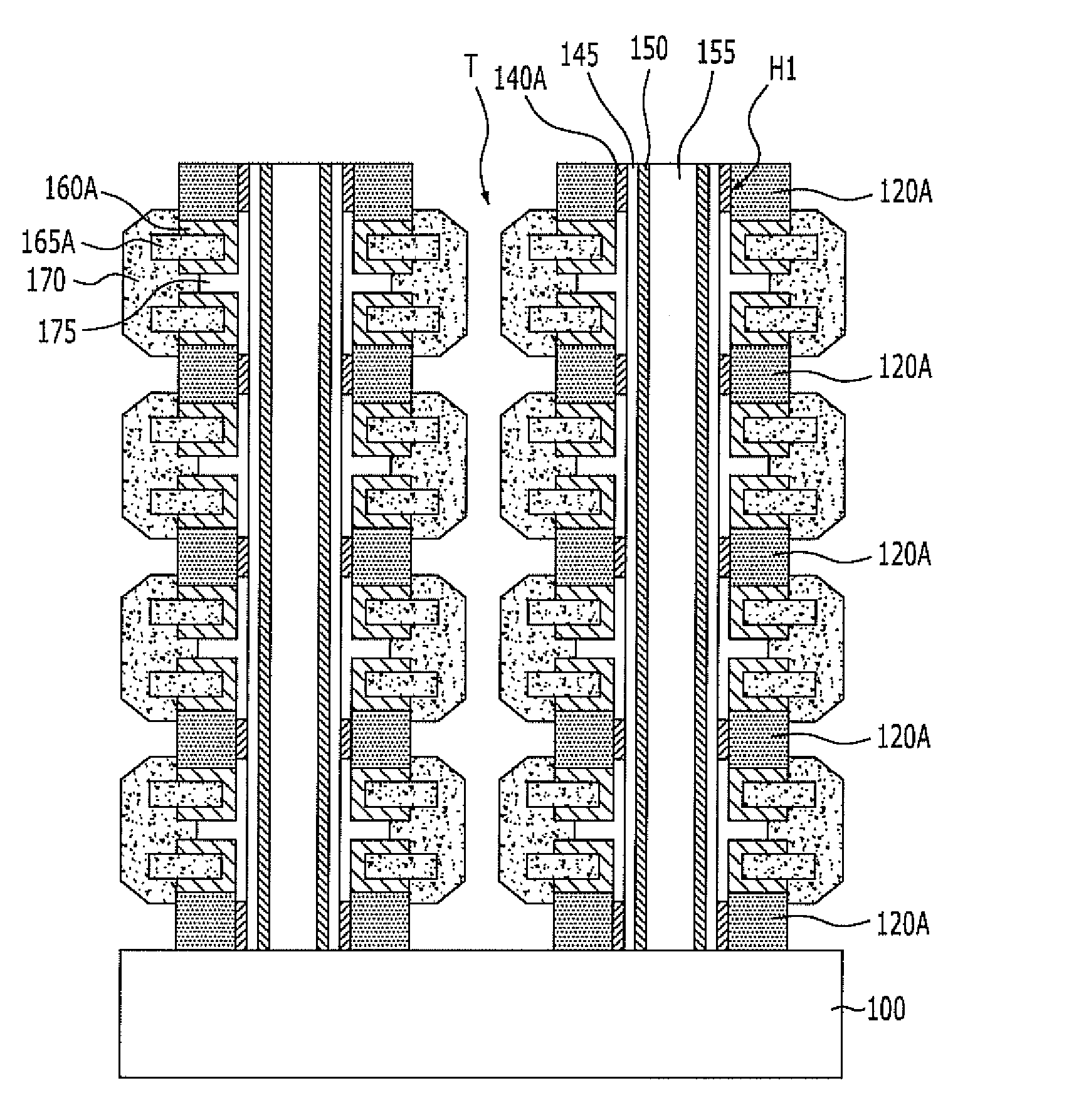
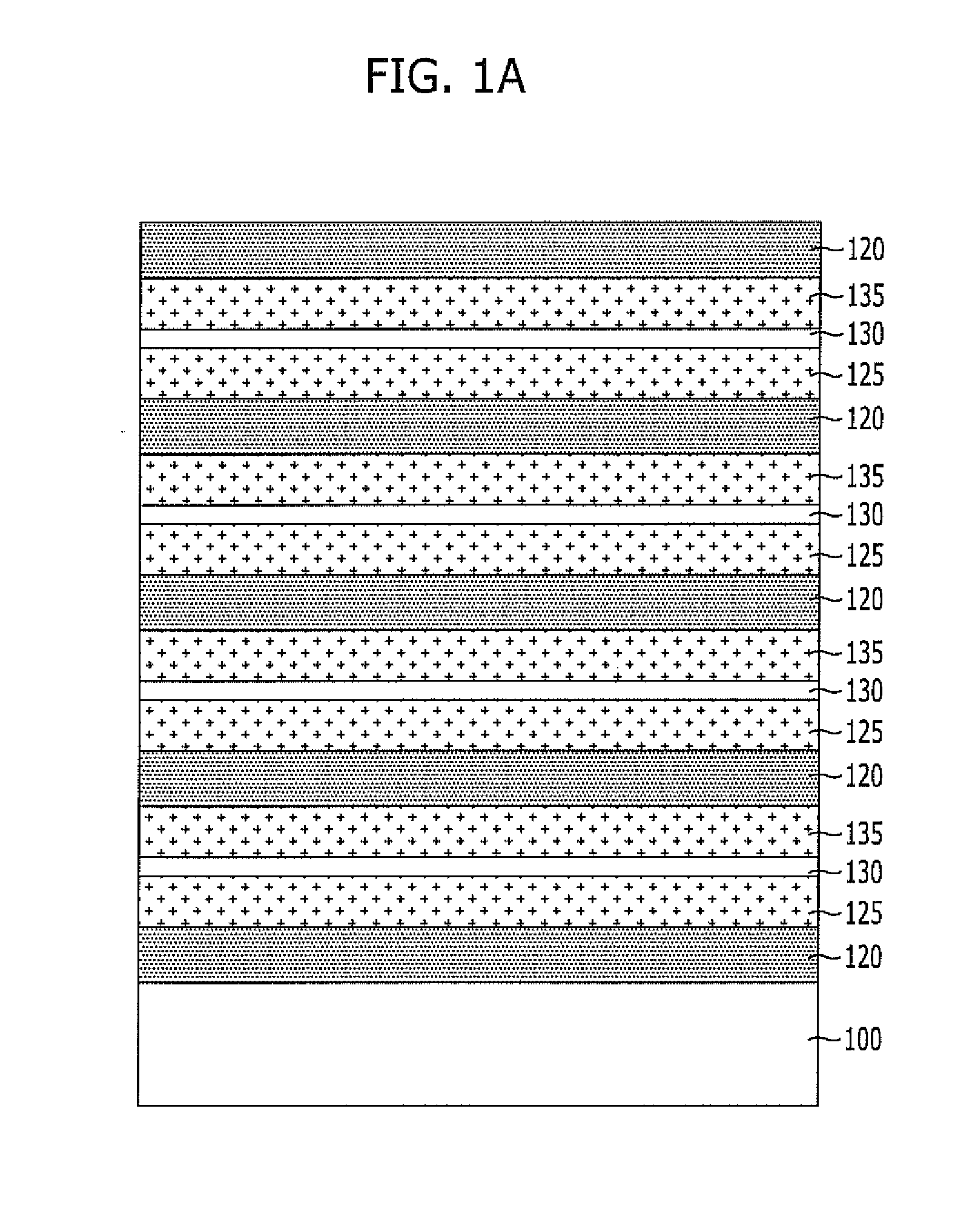
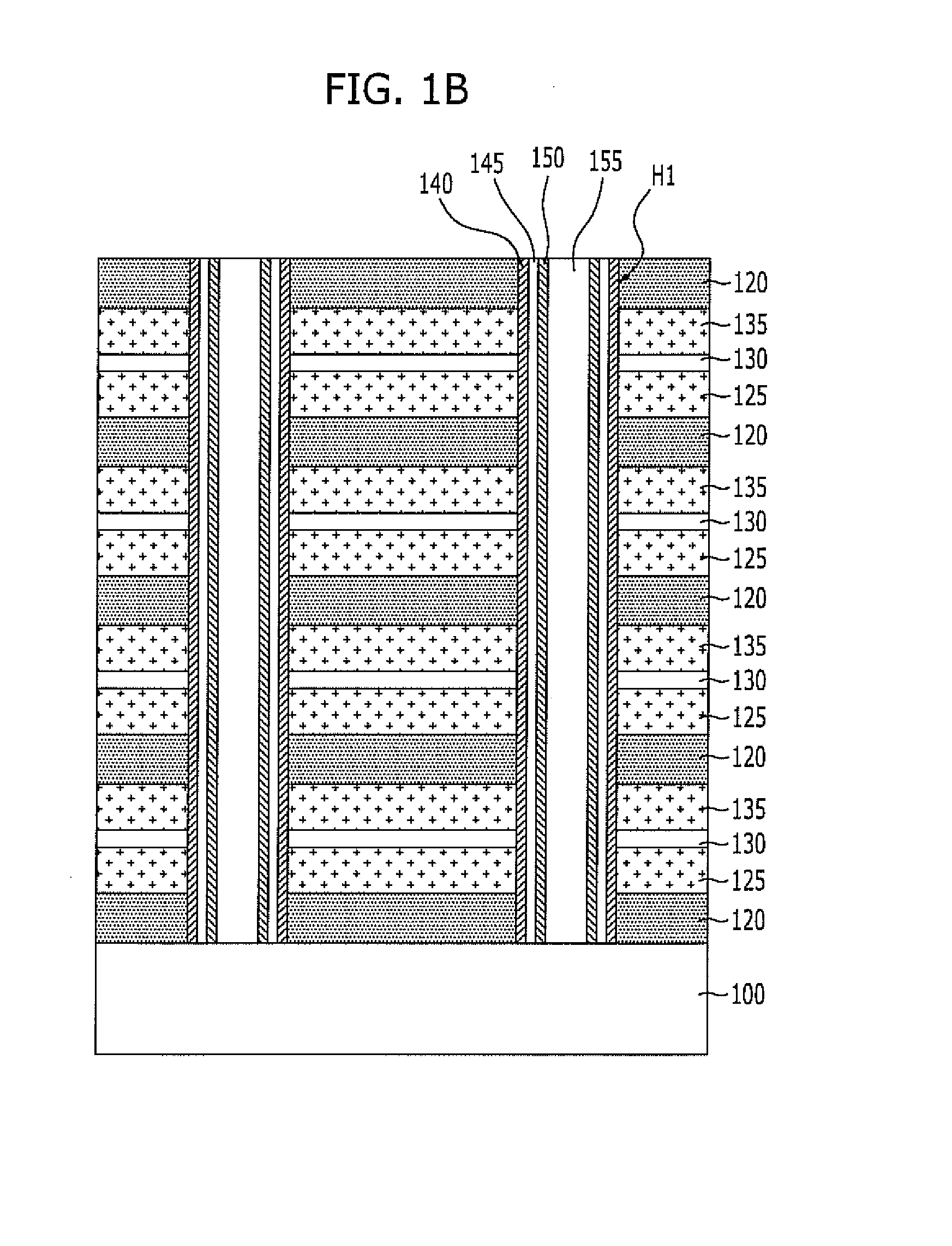
A method for fabricating, a vertical channel type nonvolatile memory device includes: alternately forming a plurality of sacrificial layers and a plurality of interlayer dielectric layers over a semiconductor substrate; etching the sacrificial layers and the interlayer dielectric layers to form a plurality of first openings for channel each of which exposes the substrate; filling the first openings to form a plurality of channels protruding from the semiconductor substrate; etching the sacrificial layers and the interlayer dielectric layers to form second openings for removal of the sacrificial layers between the channels; exposing sidewalls of the channels by removing the sacrificial layers exposed by the second openings; and forming a tunnel insulation layer, a charge trap layer, a charge blocking layer, and a conductive layer for gate electrode on the exposed sidewalls of the channels.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
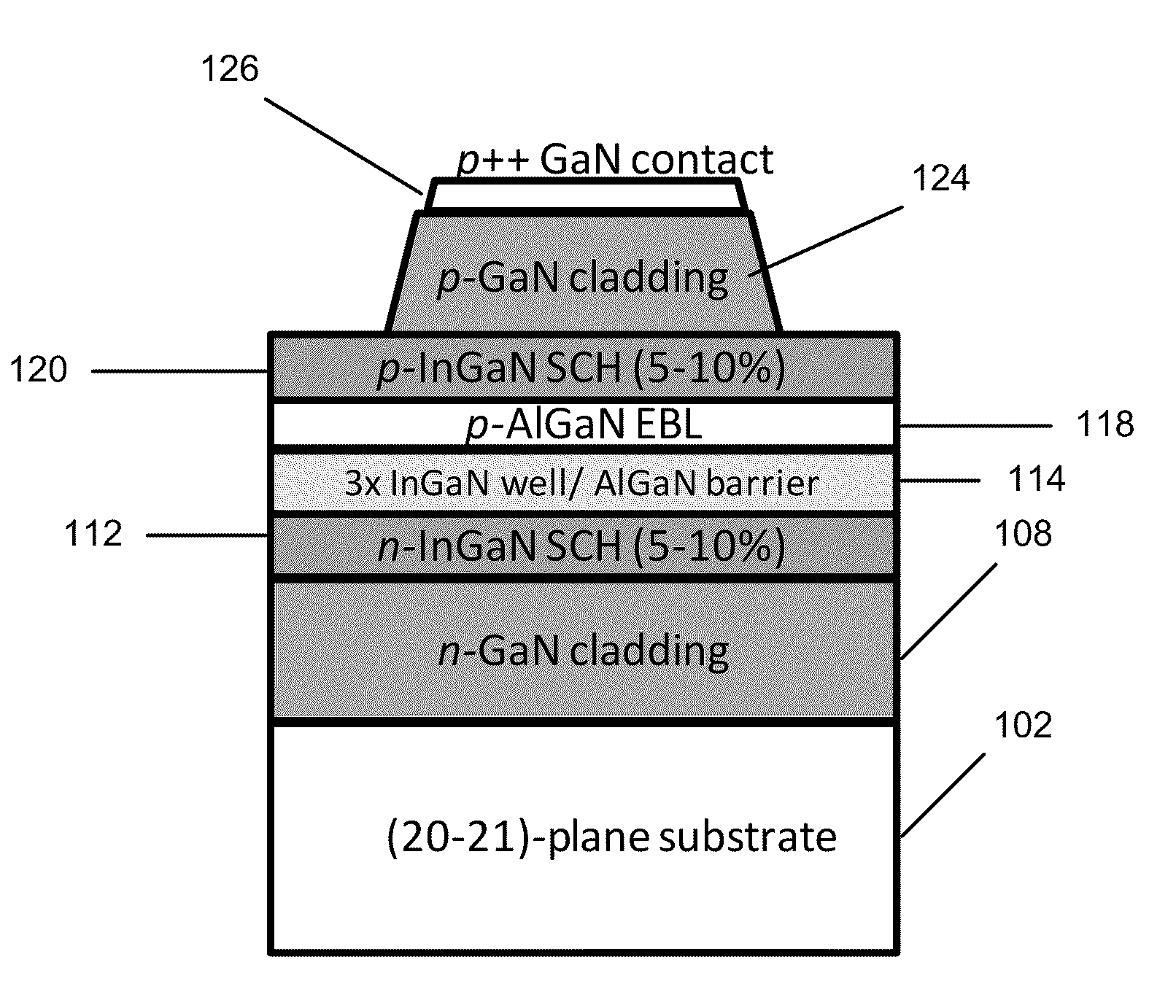
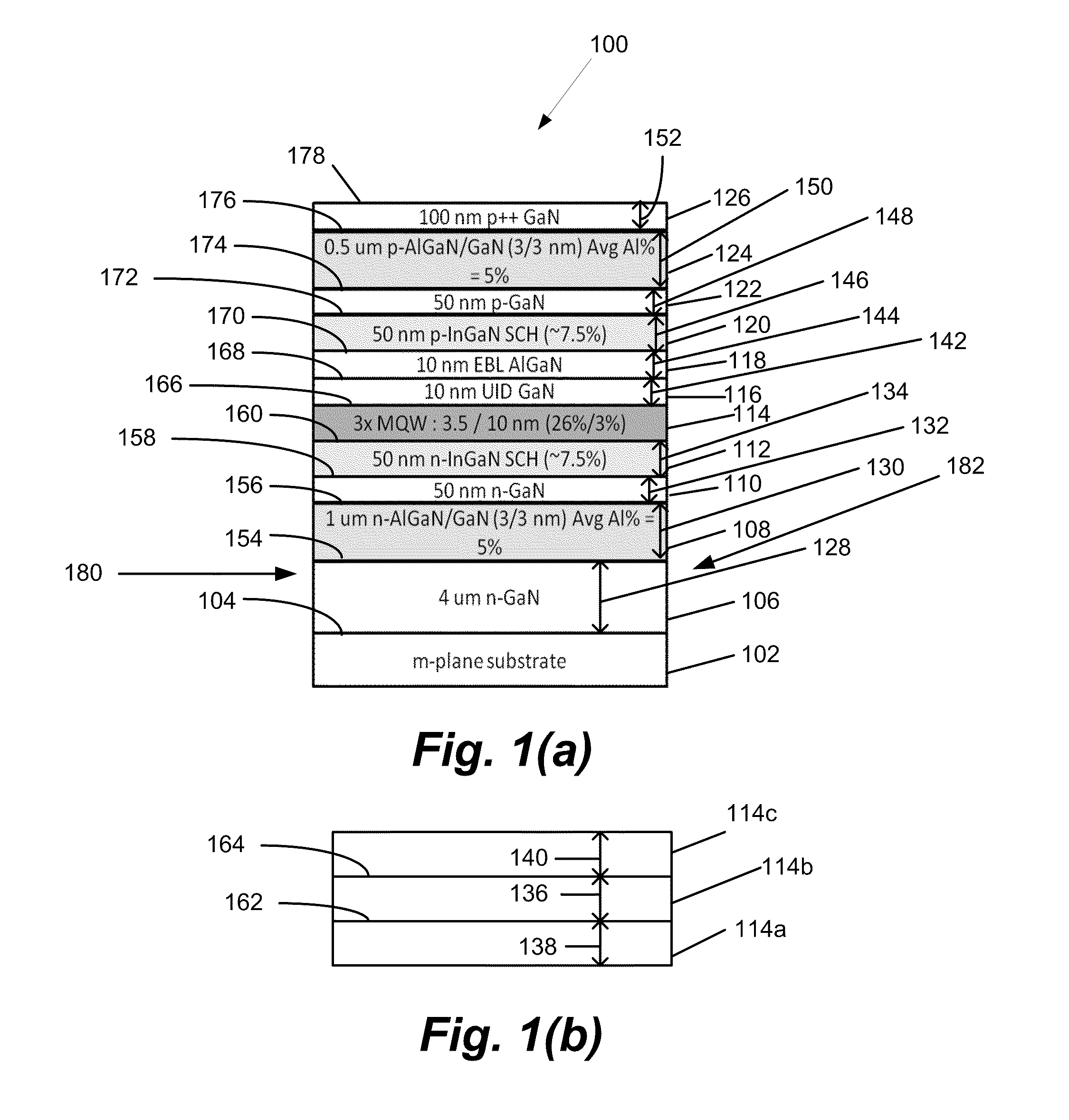
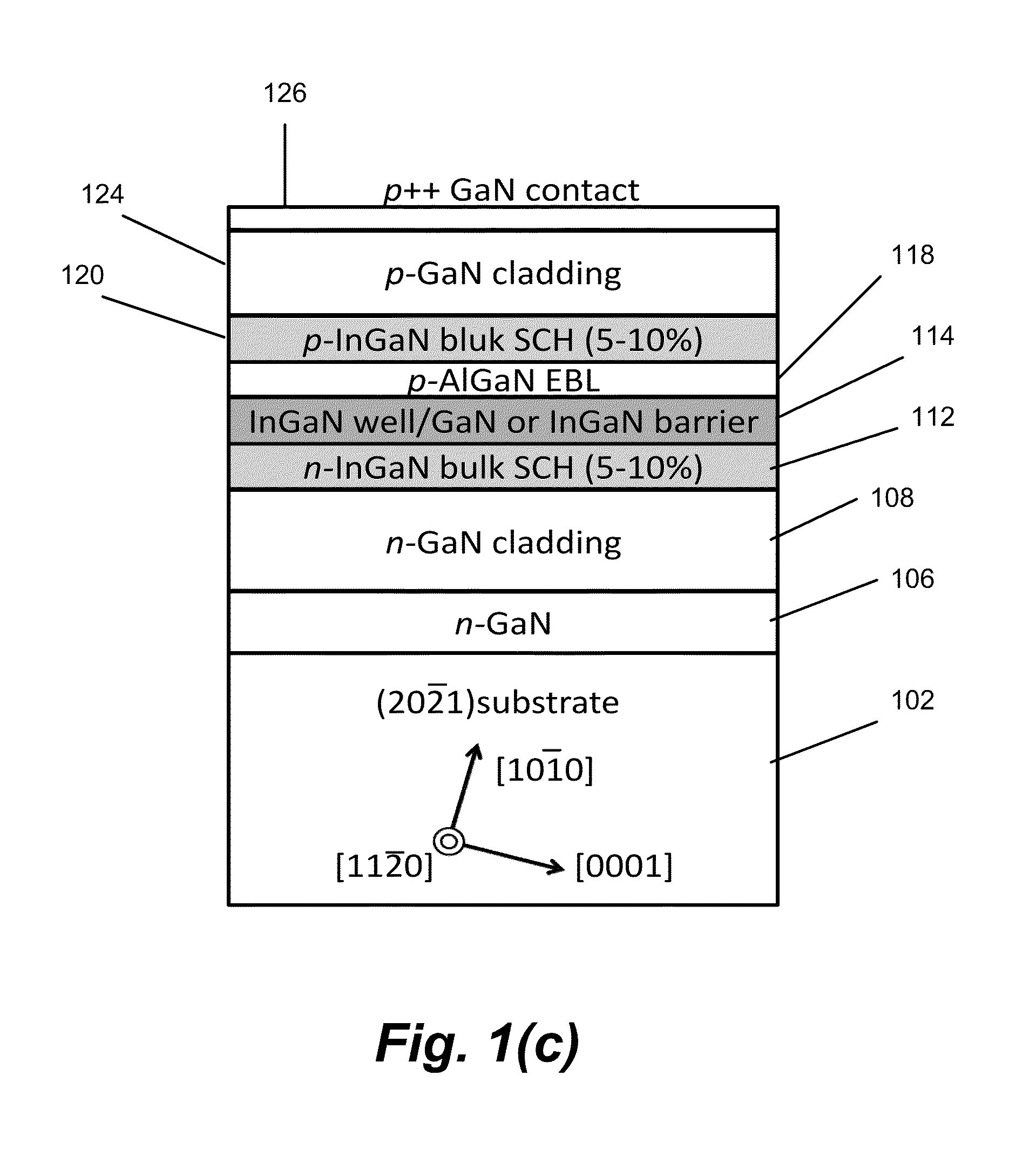
LONG WAVELENGTH NONPOLAR AND SEMIPOLAR (Al,Ga,In)N BASED LASER DIODES
InactiveUS20100309943A1Simple structureImprove electricityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsContact layerStimulated emission
A laser diode, grown on a miscut nonpolar or semipolar substrate, with lower threshold current density and longer stimulated emission wavelength, compared to conventional laser diode structures, wherein the laser diode's (1) n-type layers are grown in a nitrogen carrier gas, (2) quantum well layers and barrier layers are grown at a slower growth rate as compared to other device layers (enabling growth of the p-type layers at higher temperature), (3) high Al content electron blocking layer enables growth of layers above the active region at a higher temperature, and (4) asymmetric AlGaN SPSLS allowed growth of high Al containing p-AlGaN layers. Various other techniques were used to improve the conductivity of the p-type layers and minimize the contact resistance of the contact layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Light emitting component comprising organic layers
InactiveUS7074500B2Inhibit injectionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesTransport layerCharge carrier
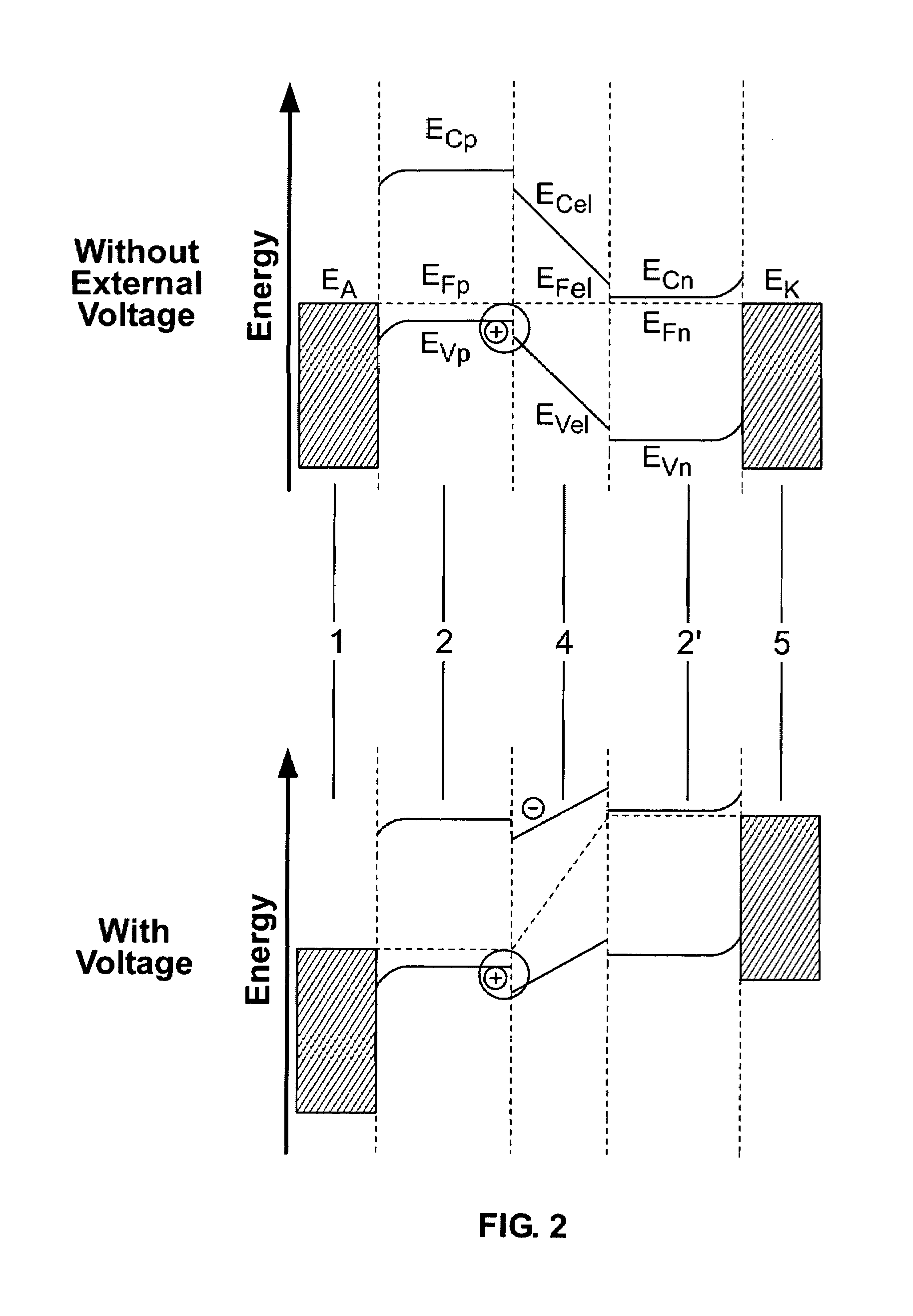
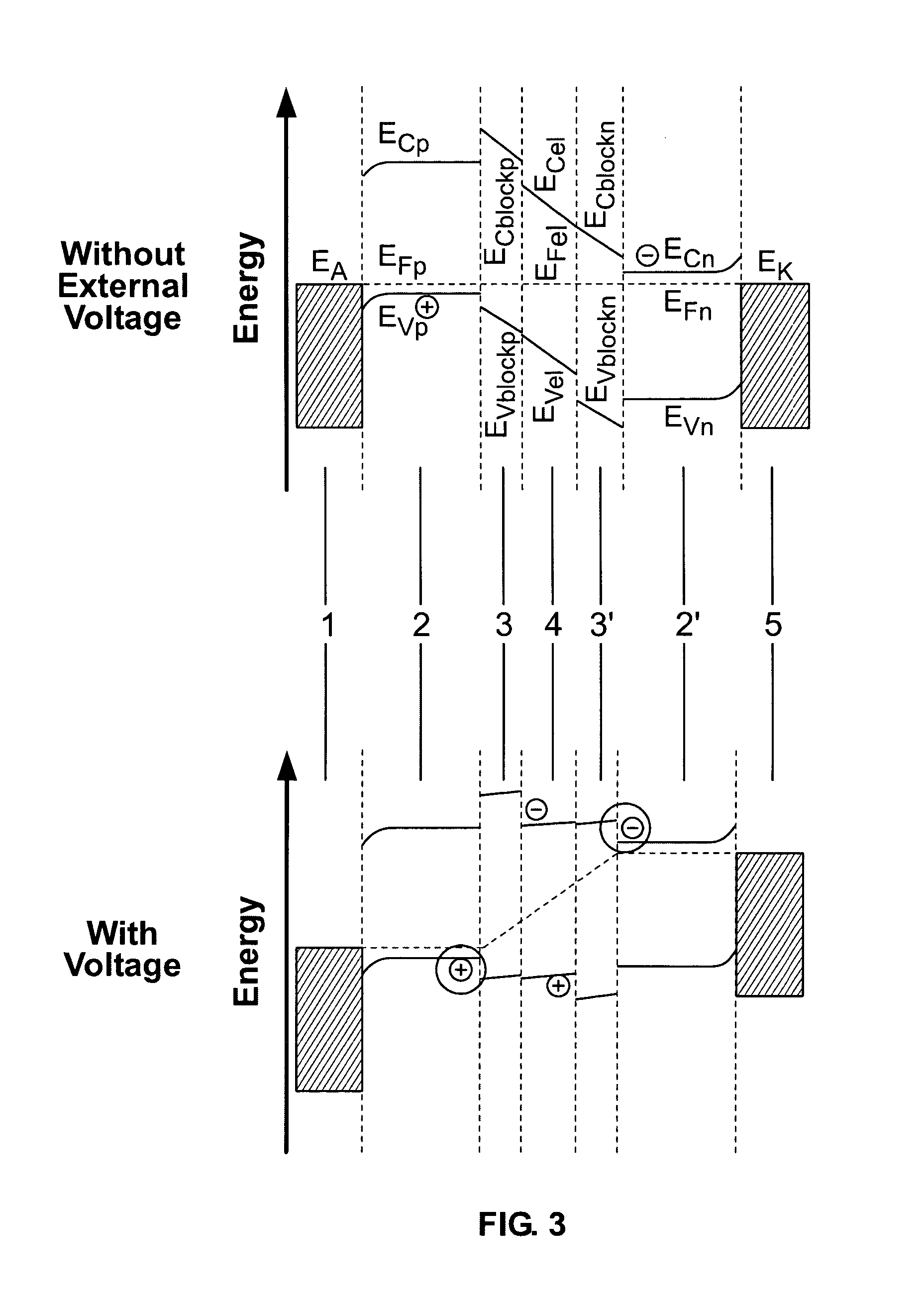
The invention relates to a light-emmiting component having organic layers, in particular to an organic light-emmiting diode. The component has at least one doped charge carrier transport layer (2), a light-emmiting layer (4) and contact layers (1, 5) and also has a blocking layer (3; 3′) wherein an organic material is provided between the charge carrier transport layer (2, 2′) and the light-emmiting layer (4). The energy levels of the charge carried transport layer are chosen in such a way that efficient doping is possible and the blocking layer nevertheless ensures that non-radiating recombination processes on the interface with the emitting layer are prevented.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
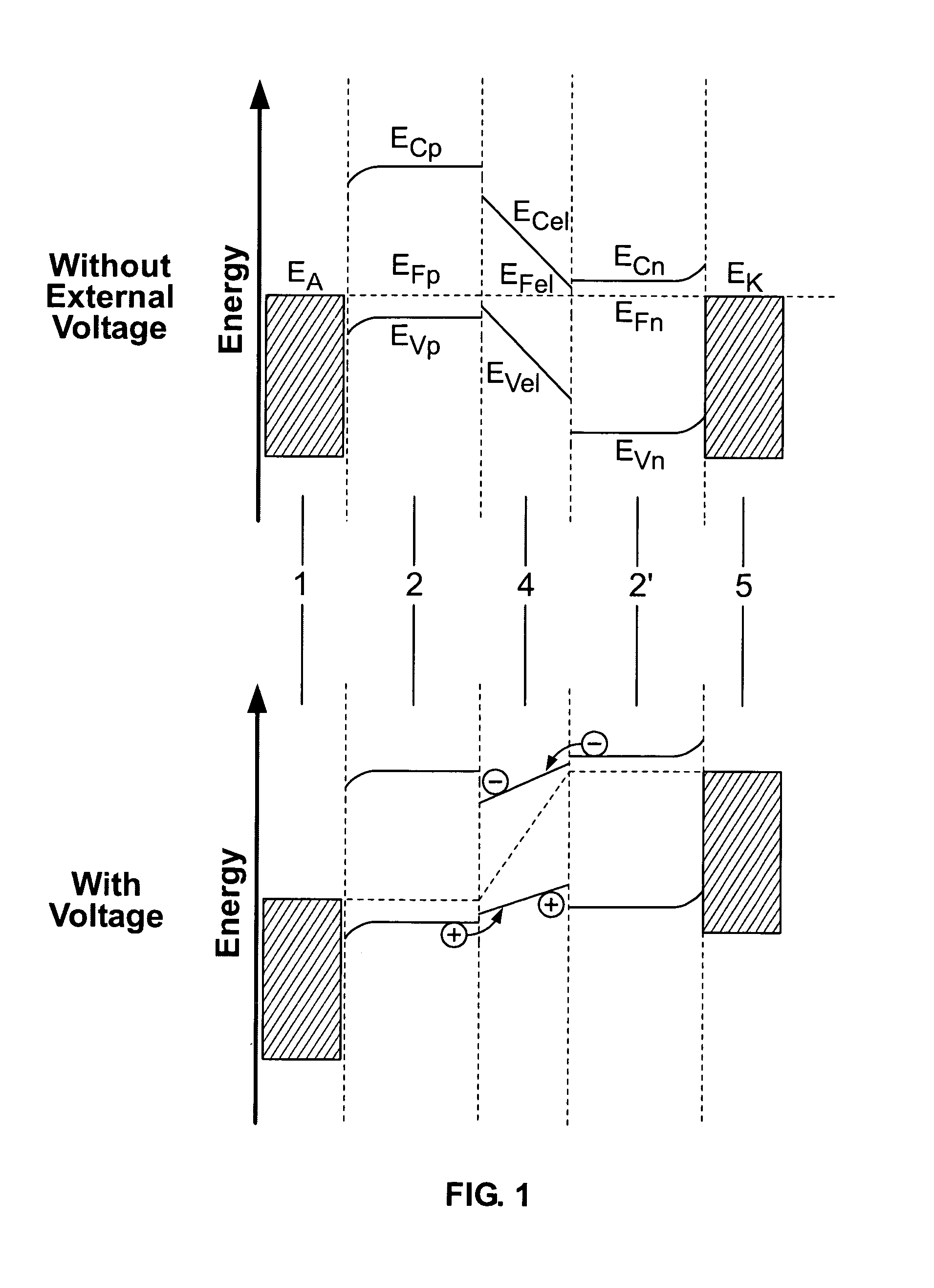
Group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS20070110112A1Increase fixed chargeEasy to overflowOptical wave guidanceSolid-state devicesElectron blocking layerActive layer
A group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device according to the present invention includes an immediate layer formed of AlxGa1-x-yInyN (0<x<1, 0<y<1, x+y<1) between an active layer and a cladding layer and an electron blocking layer formed of p-type group III nitride semiconductor having a smaller electron affinity than that of the intermediate layer so as to be in contact with the intermediate layer. The semiconductor light emitting layer may be a laser diode or a LED.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
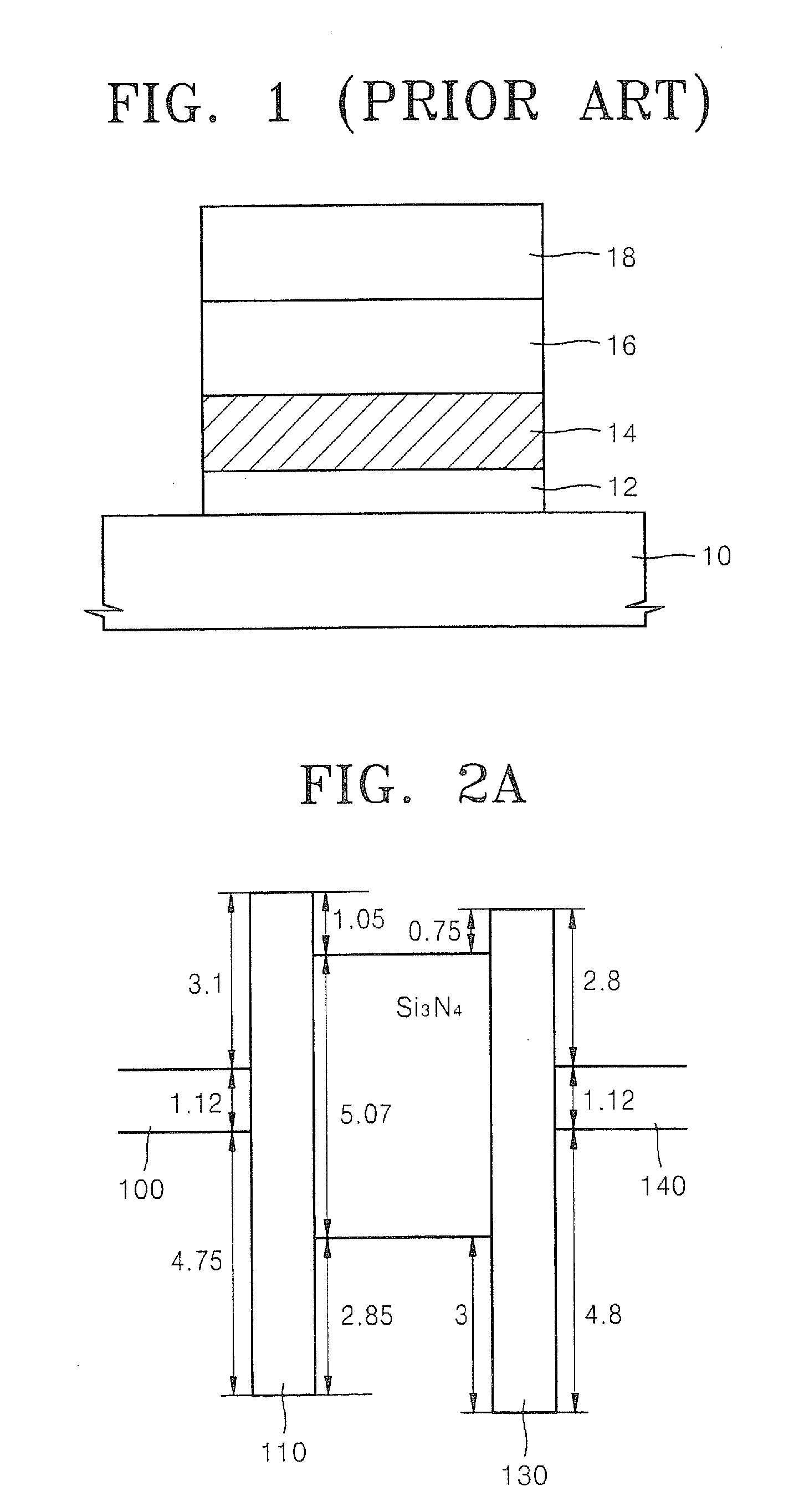
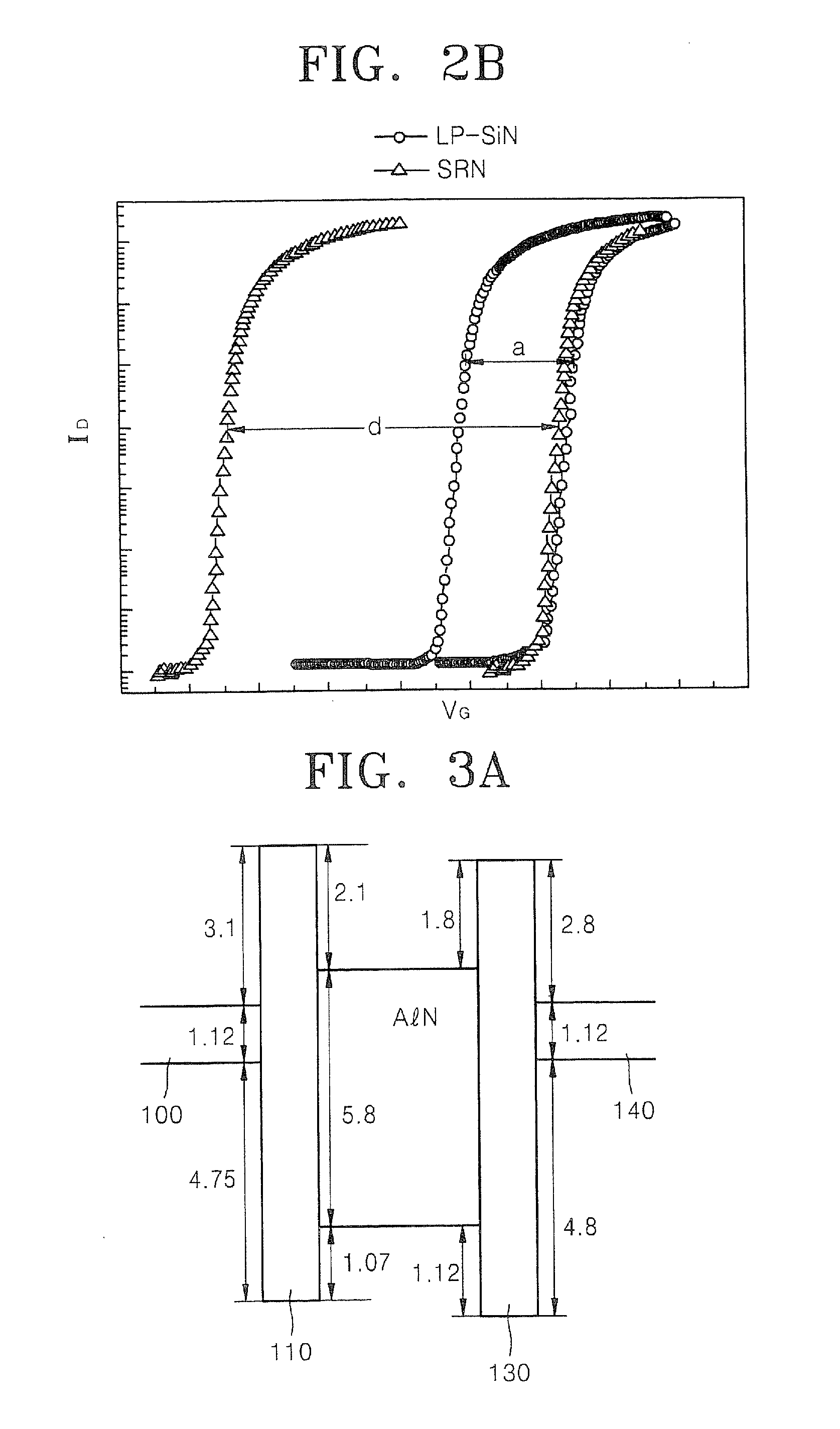
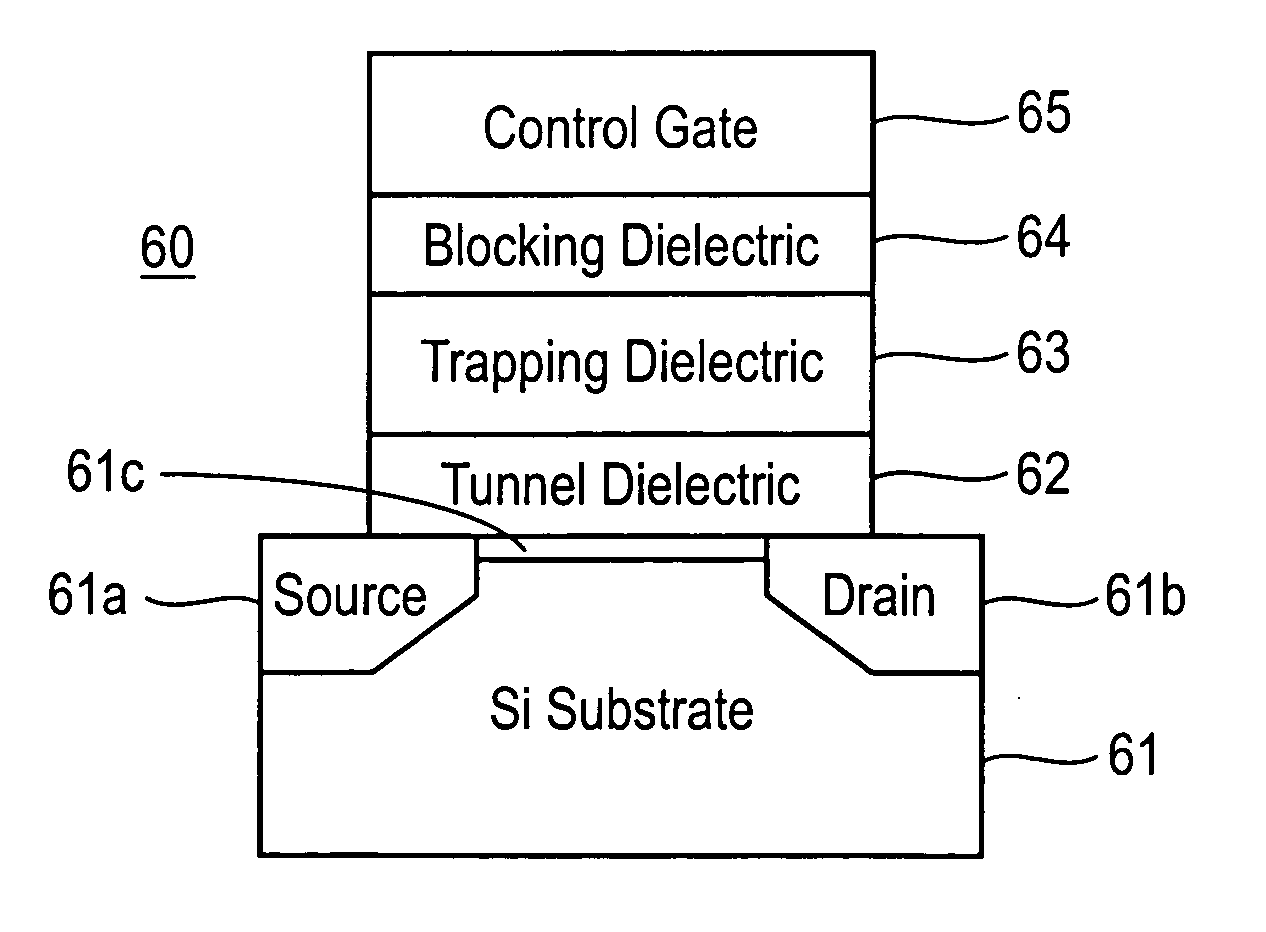
Semiconductor memory device including charge trap layer with stacked nitride layers
A semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor substrate, a tunnel insulating layer, charge trap layer, and a blocking layer. The tunnel insulating layer is on the semiconductor substrate. The charge trap layer is on the tunnel insulating layer and includes at least one pair of a first nitride layer with a higher trap density of holes than electrons and a second nitride layer with a higher trap density of electrons than holes. The blocking layer is on the charge trap layer opposite to the tunnel insulating layer. The first nitride layer may include silicon rich nitride, which may have a ratio of silicon to nitride of greater than 1 and less than or equal to 2. The second nitride layer may include aluminum nitride which may have a hexagonal crystalline structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
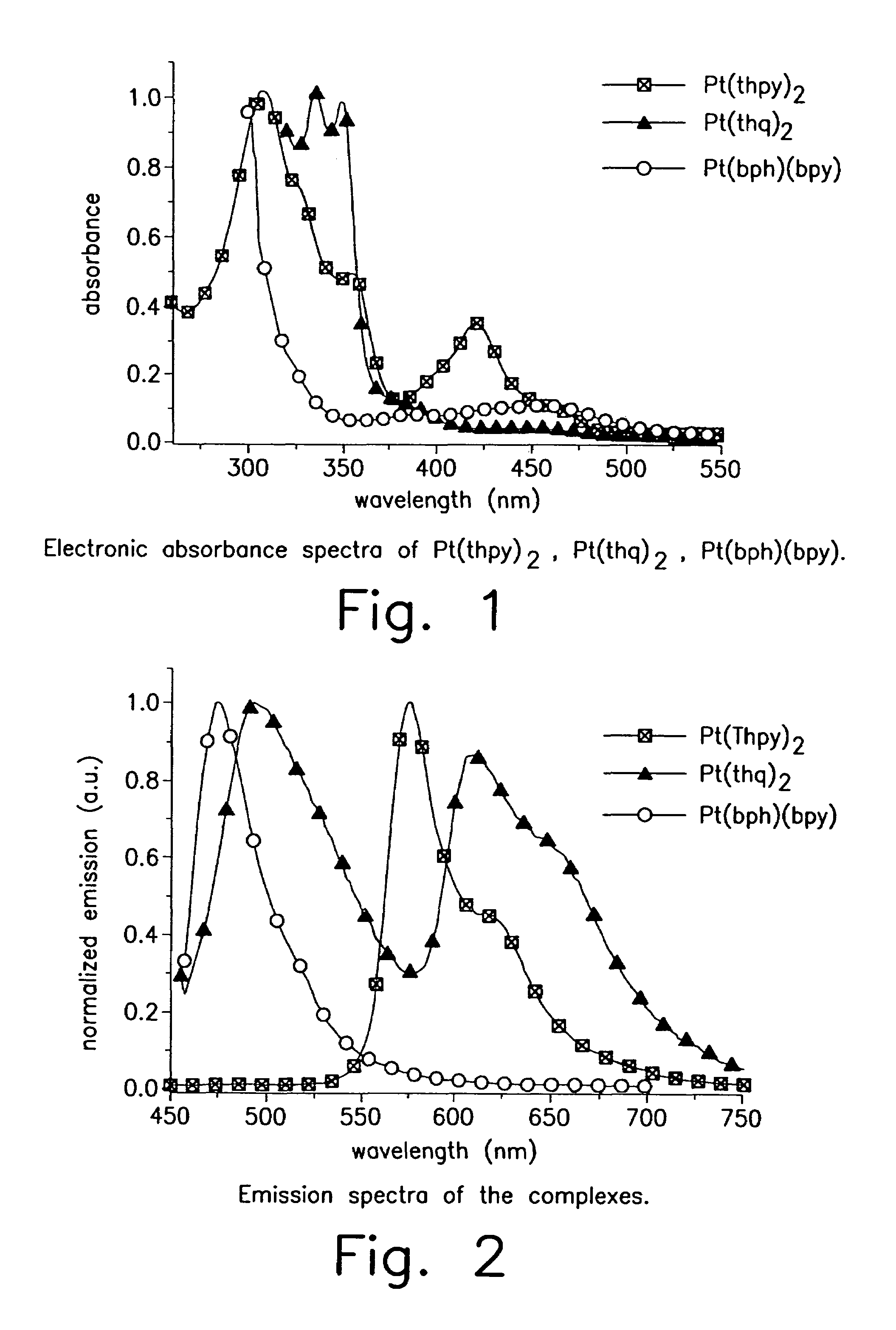
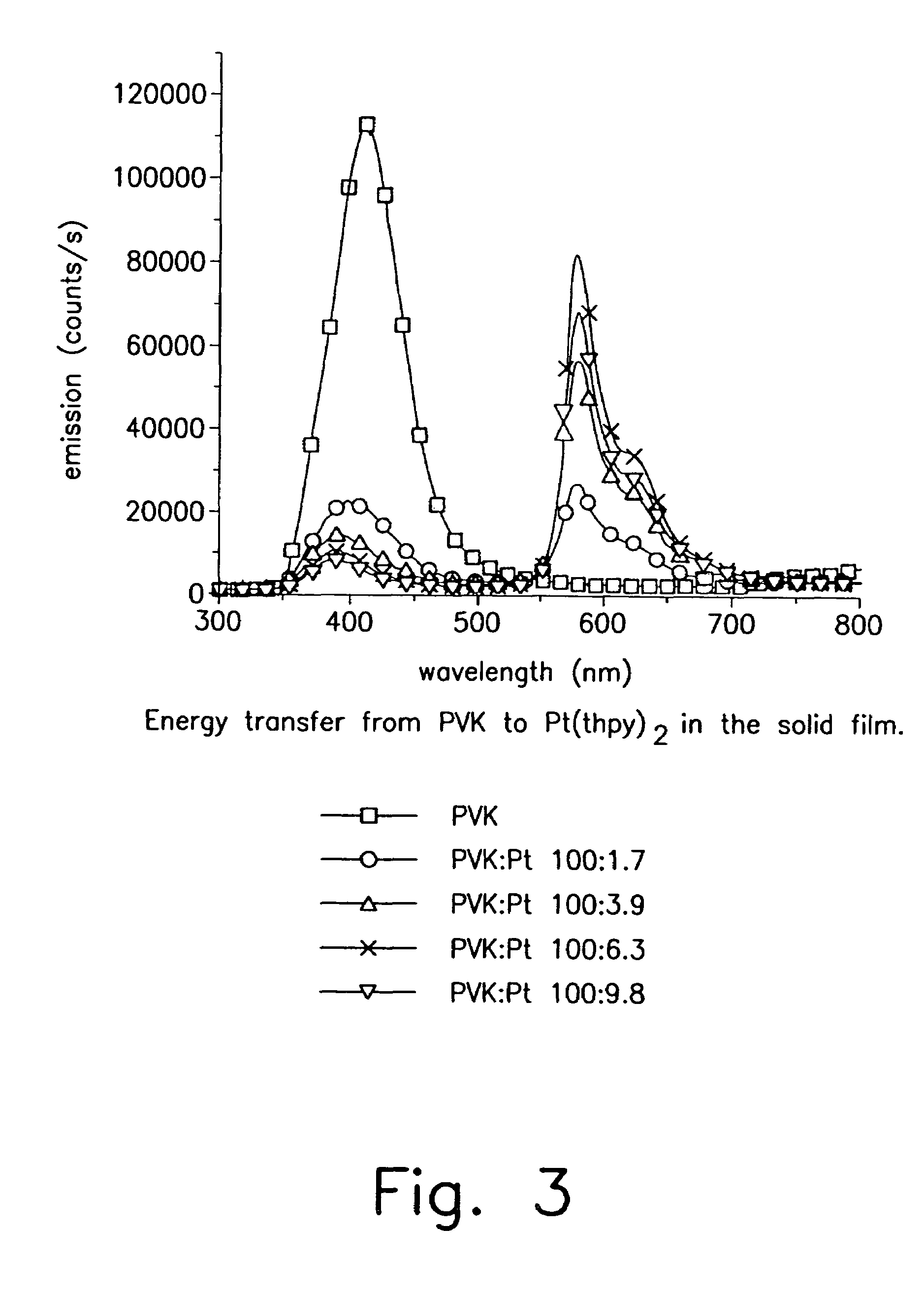
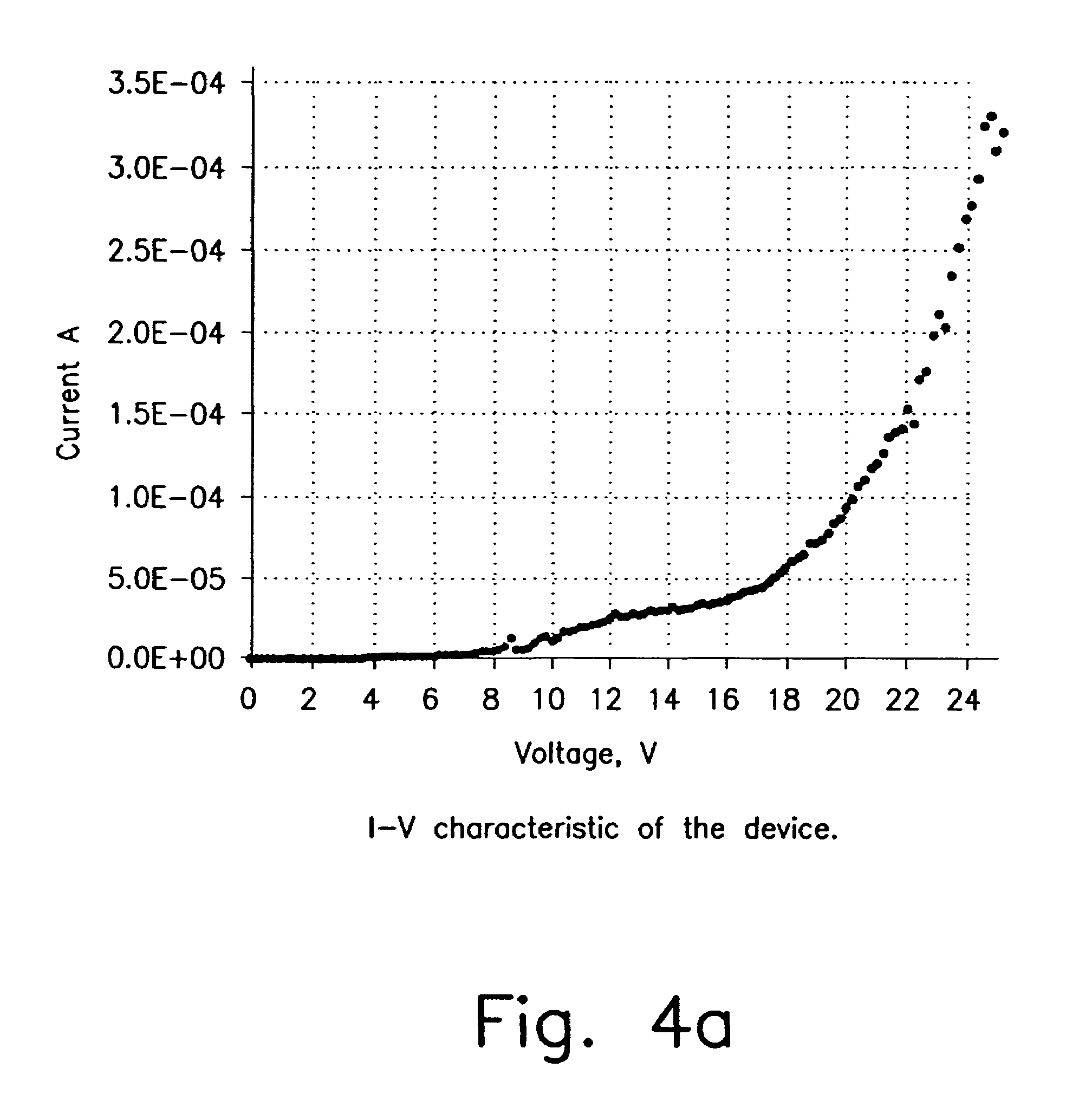
Organometallic complexes as phosphorescent emitters in organic LEDs
InactiveUS7001536B2Easy to combineDeterioration in emission qualityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesIridiumPt element
Organic light emitting devices are described wherein the emissive layer comprises a host material containing an emissive molecule, which molecule is adapted to luminesce when a voltage is applied across the heterostructure, and the emissive molecule is selected from the group of phosphorescent organometallic complexes, including cyclometallated platinum, iridium and osmium complexes. The organic light emitting devices optionally contain an exciton blocking layer. Furthermore, improved electroluminescent efficiency in organic light emitting devices is obtained with an emitter layer comprising organometallic complexes of transition metals of formula L2MX, wherein L and X are distinct bidentate ligands. Compounds of this formula can be synthesized more facilely than in previous approaches and synthetic options allow insertion of fluorescent molecules into a phosphorescent complex, ligands to fine tune the color of emission, and ligands to trap carriers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
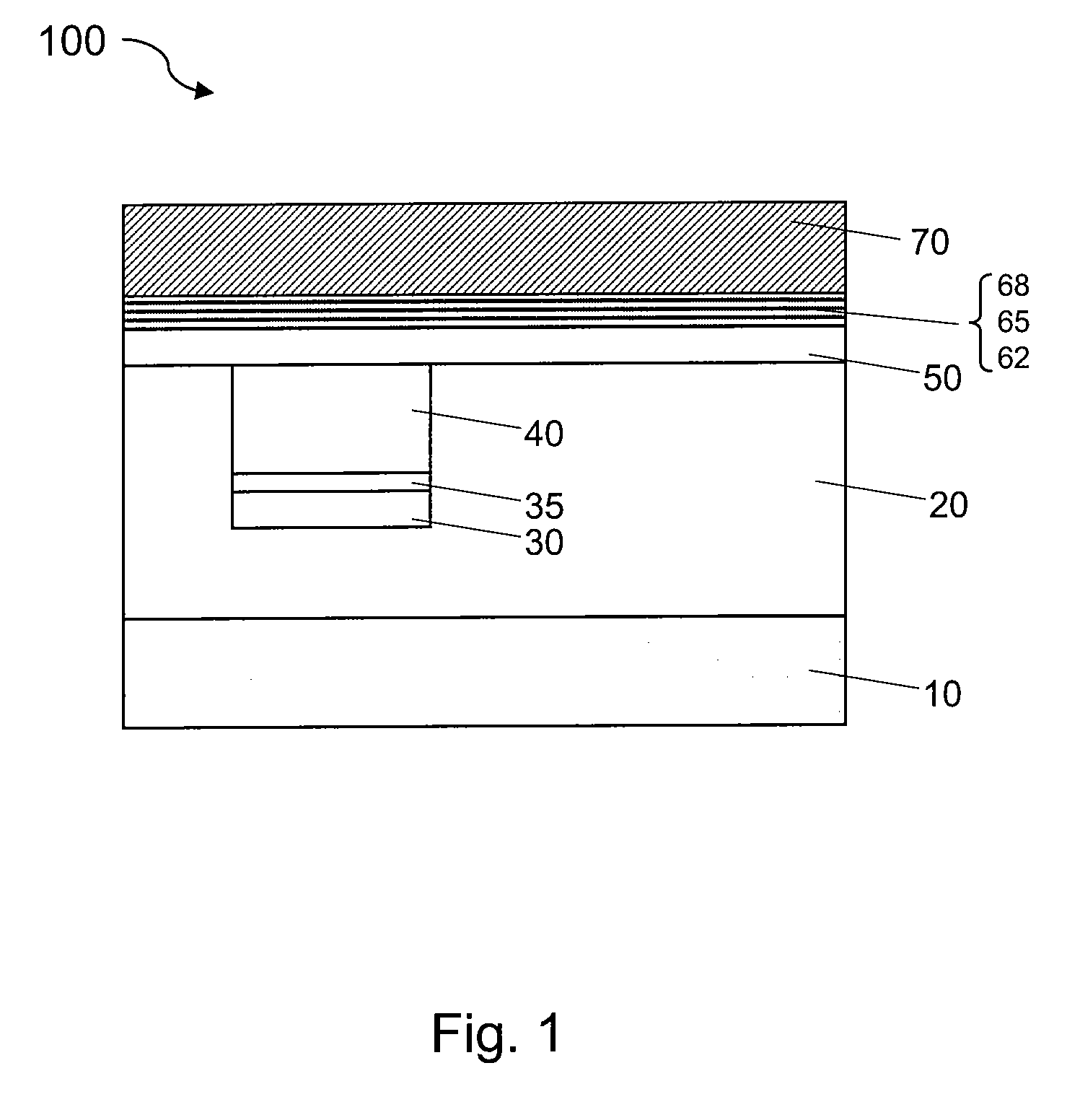
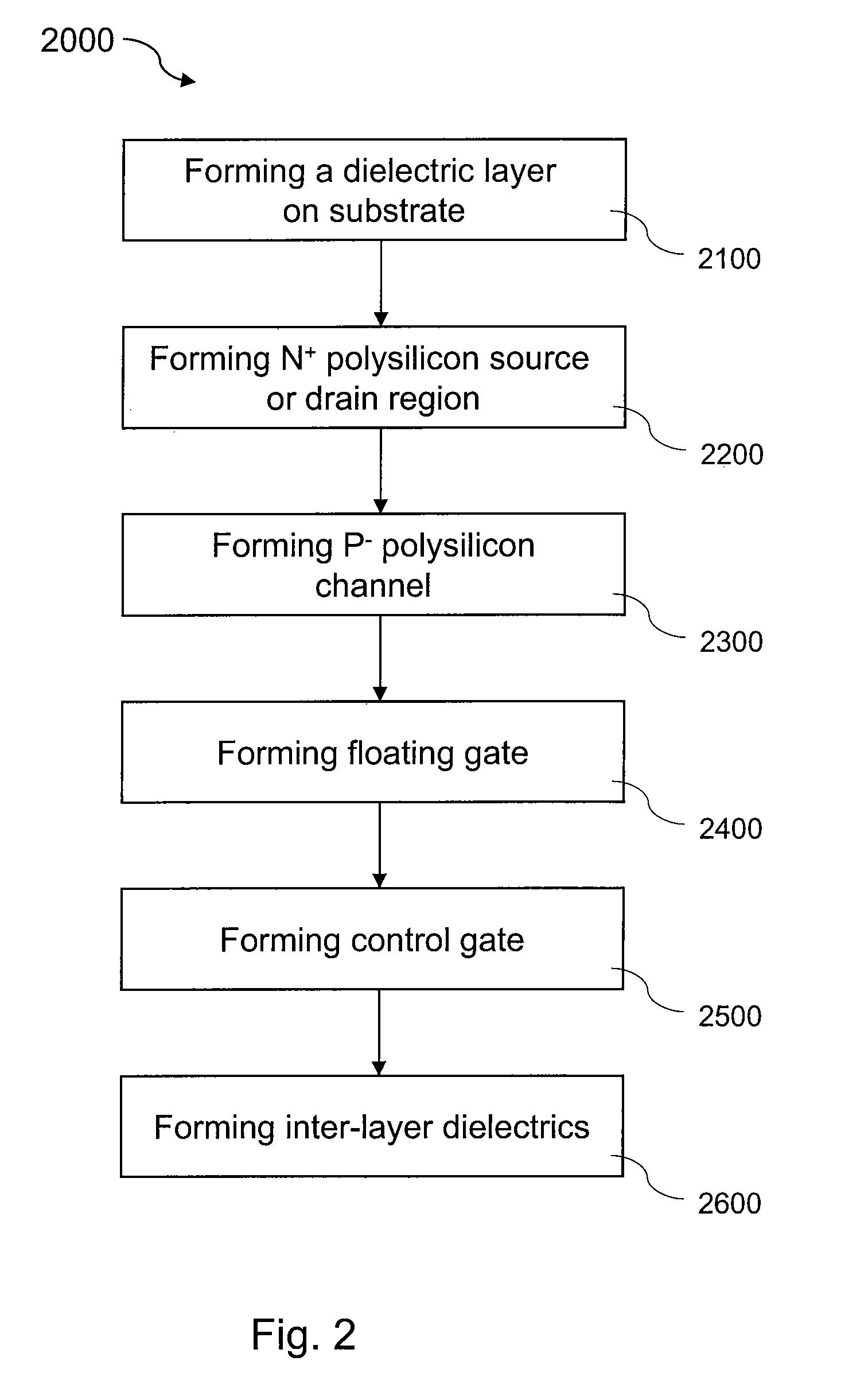
TFT floating gate memory cell structures
ActiveUS20100001282A1Improve reliabilitySmall geometric cell sizeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffusion barrierDielectric layer
A device having thin-film transistor (TFT) floating gate memory cell structures is provided. The device includes a substrate, a dielectric layer on the substrate, and one or more source or drain regions being embedded in the dielectric layer. the dielectric layer being associated with a first surface. Each of the one or more source or drain regions includes an N+ polysilicon layer on a diffusion barrier layer which is on a first conductive layer. The N+ polysilicon layer has a second surface substantially co-planar with the first surface. Additionally, the device includes a P− polysilicon layer overlying the co-planar surface and a floating gate on the P− polysilicon layer. The floating gate is a low-pressure CVD-deposited silicon layer sandwiched by a bottom oxide tunnel layer and an upper oxide block layer. Moreover, the device includes at least one control gate made of a P+ polysilicon layer overlying the upper oxide block layer. A method of making the same memory cell structure is provided and can be repeated to integrate the structure three-dimensionally.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
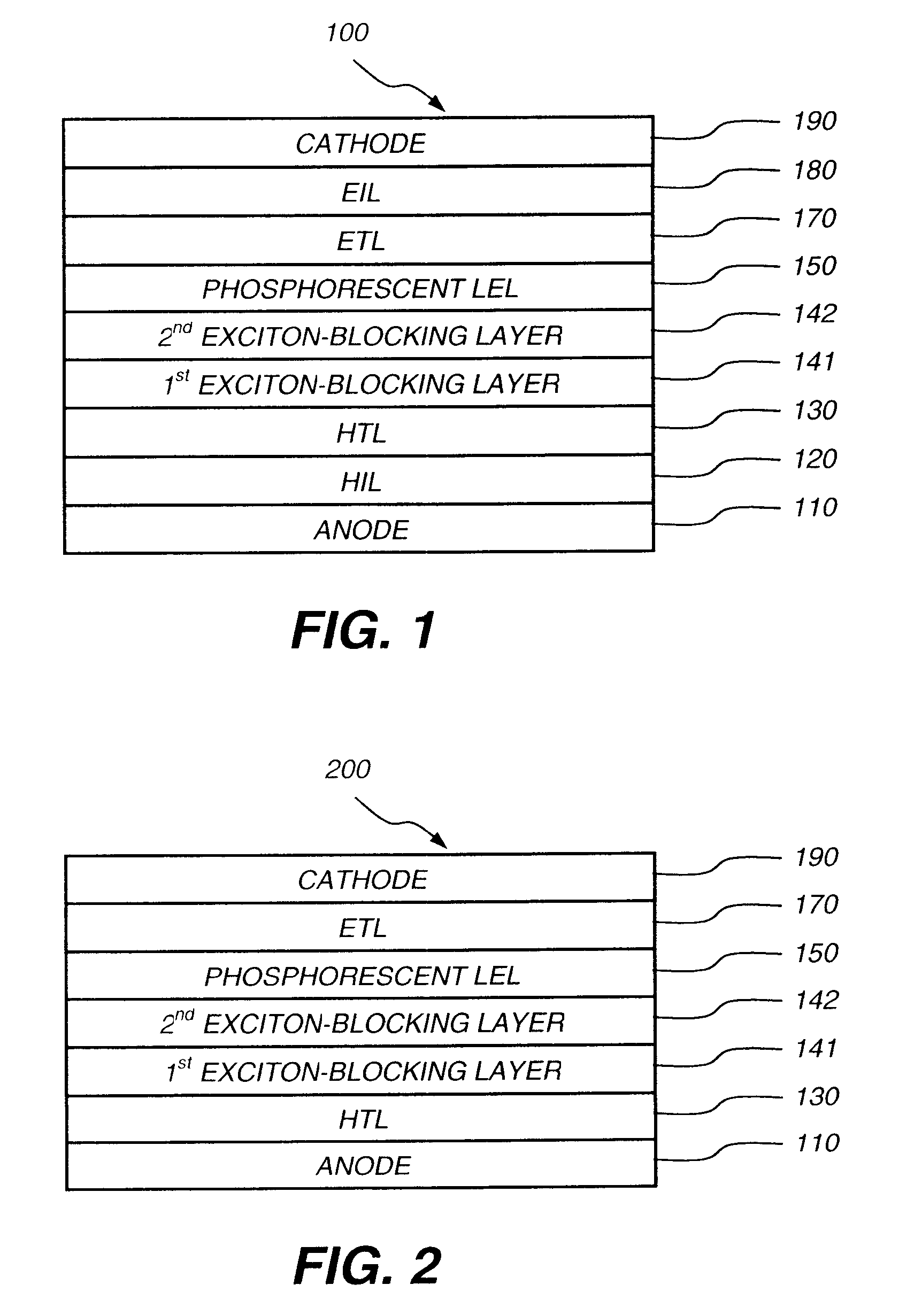
Phosphorescent oleds with exciton blocking layer
ActiveUS20060134460A1Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron holePhosphorescent oleds
An electroluminescent device comprises a cathode and an anode; and, located therebetween, a light-emitting layer (LEL) comprising at least one hole transporting co-host and at least one electron transporting co-host, together with at least one phosphorescent emitter, and wherein the triplet energy of each of the co-host materials is greater than the triplet energy of the phosphorescent emitter, and further containing an exciton blocking layer comprising a hole transporting material with triplet energy greater or equal to 2.5 eV adjacent the emitting layer on the anode side. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency at low voltage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7115966B2Small sizeAvoid influenceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon oxideCopper
On a semiconductor substrate a silicon oxide film is formed and provided with a recess. In the recess a reflector layer of copper is disposed as a blocking layer with a barrier metal posed therebetween. The reflector layer of copper is covered with a silicon oxide film and thereon a fuse region provided with a plurality of fuses is provided. The reflector layer of copper has a plane of reflection recessed downward to reflect a laser beam. The reflector layer of copper is arranged to overlap substantially the entirety of the fuse region, as seen in a plane. A laser beam radiated to blow the fuse can have a reduced effect on a vicinity of the fuse region. A semiconductor device reduced in size can be obtained.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Nonvolatile memory device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20110266611A1Excellent characteristicsIncrease speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerDielectric layer
A nonvolatile memory device includes a plurality of interlayer dielectric layers and conductive layers for gate electrodes alternately stacked over a substrate, a channel trench passing through the interlayer dielectric layers and the conductive layers and exposing the substrate, a charge blocking layer and a charge trap or charge storage layer formed on sidewalls of the trench, a coupling prevention layer formed at the surface of the charge trap or charge storage layer, and a tunnel insulation layer formed over the coupling prevention layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
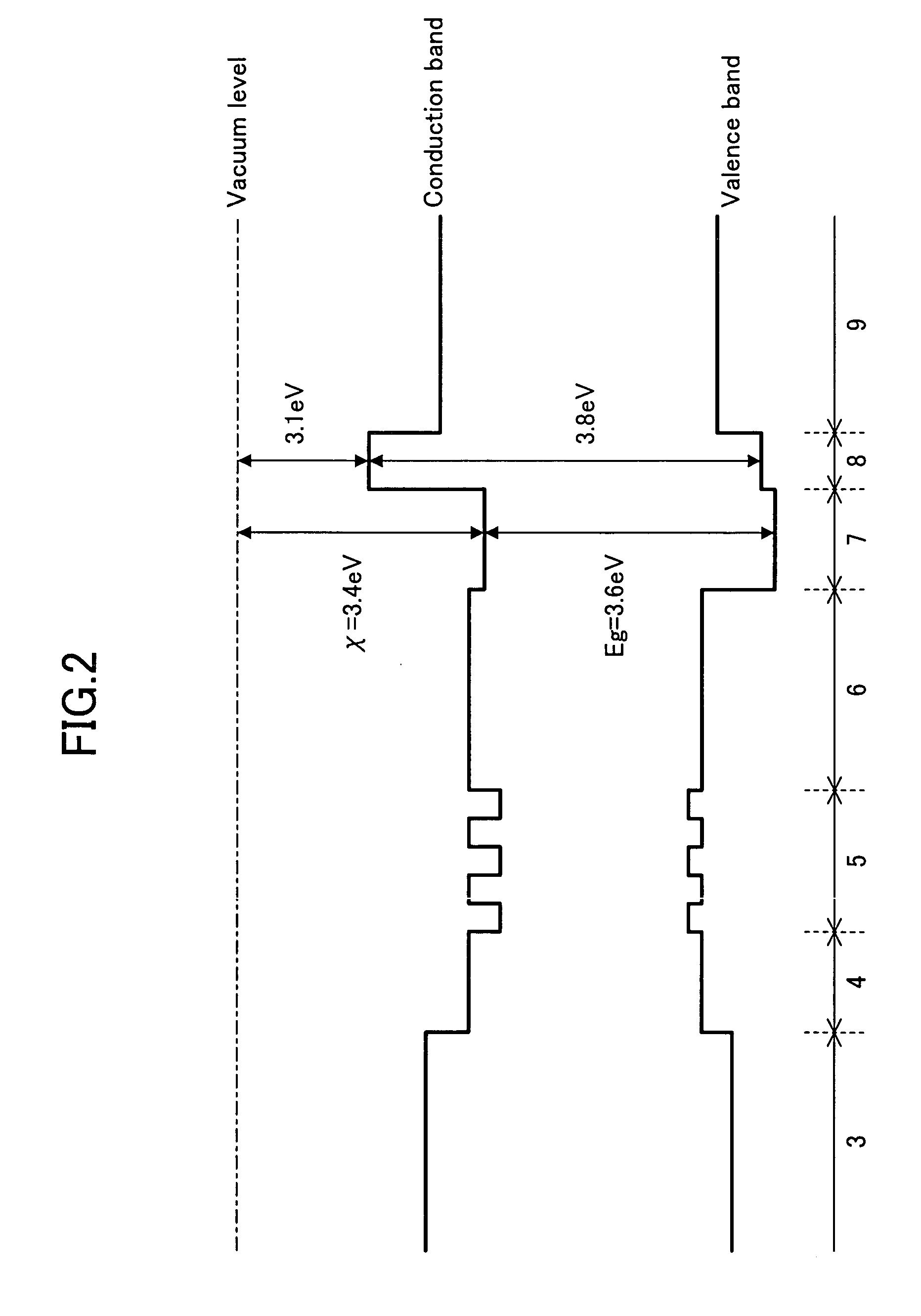
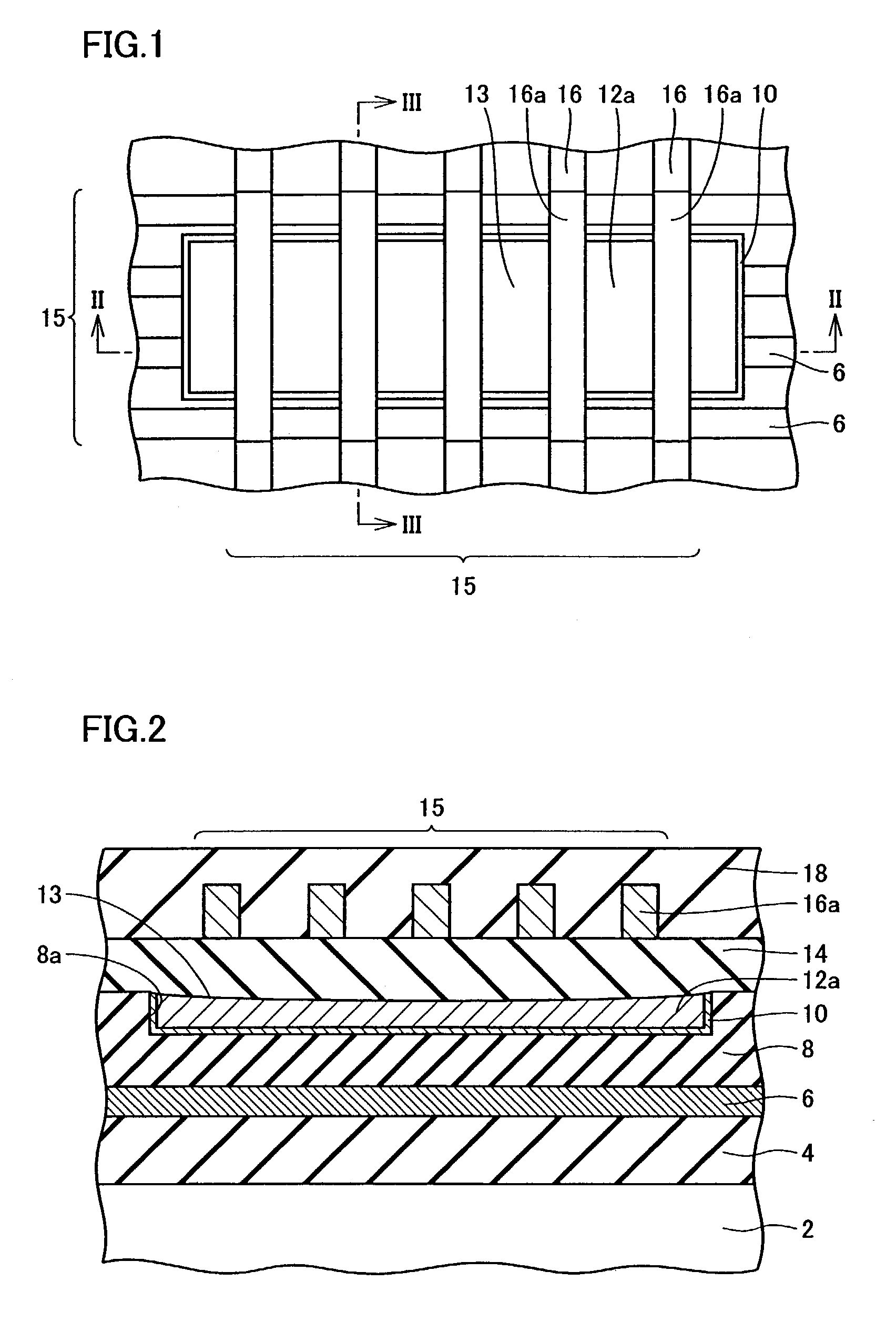
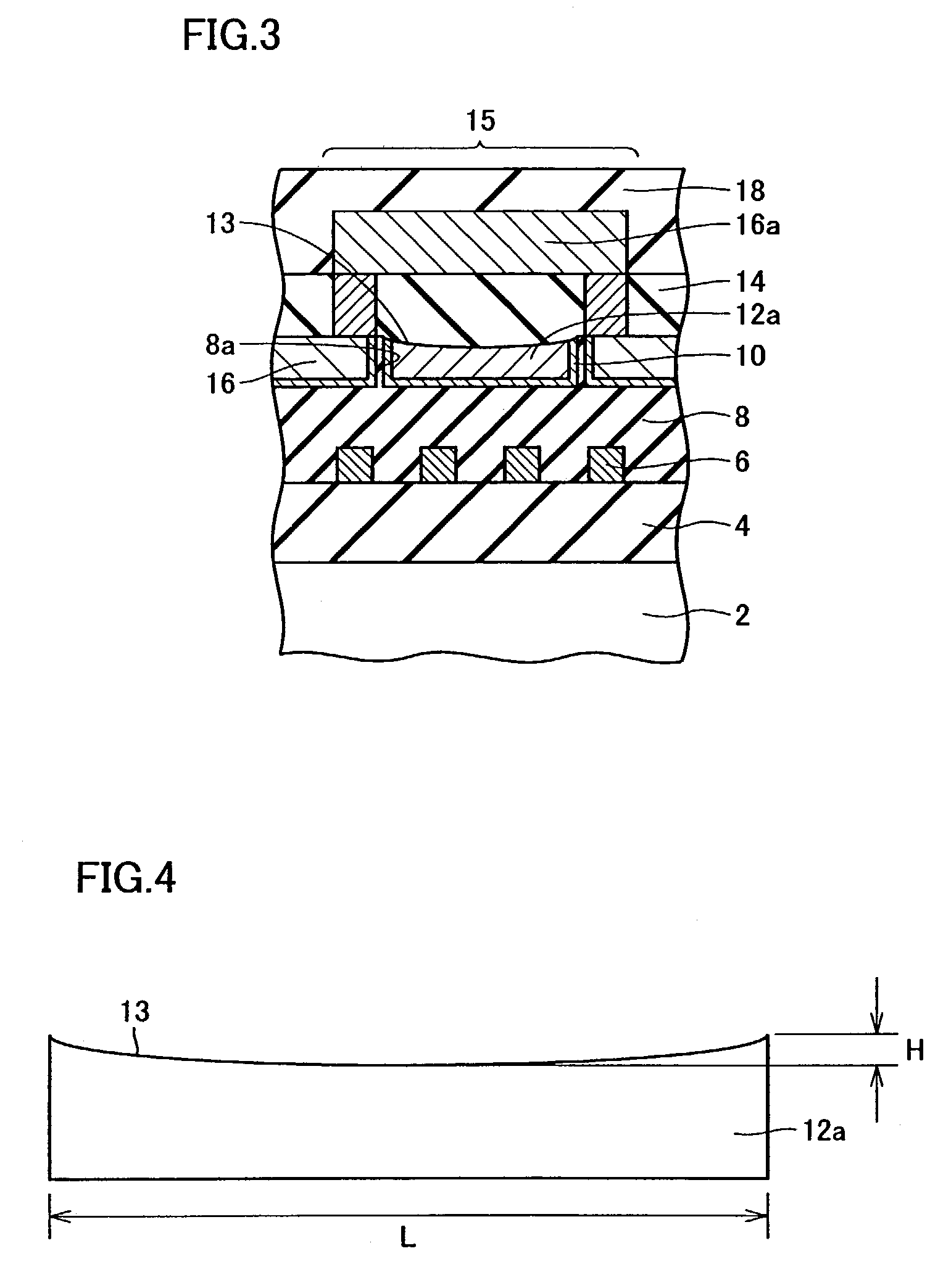
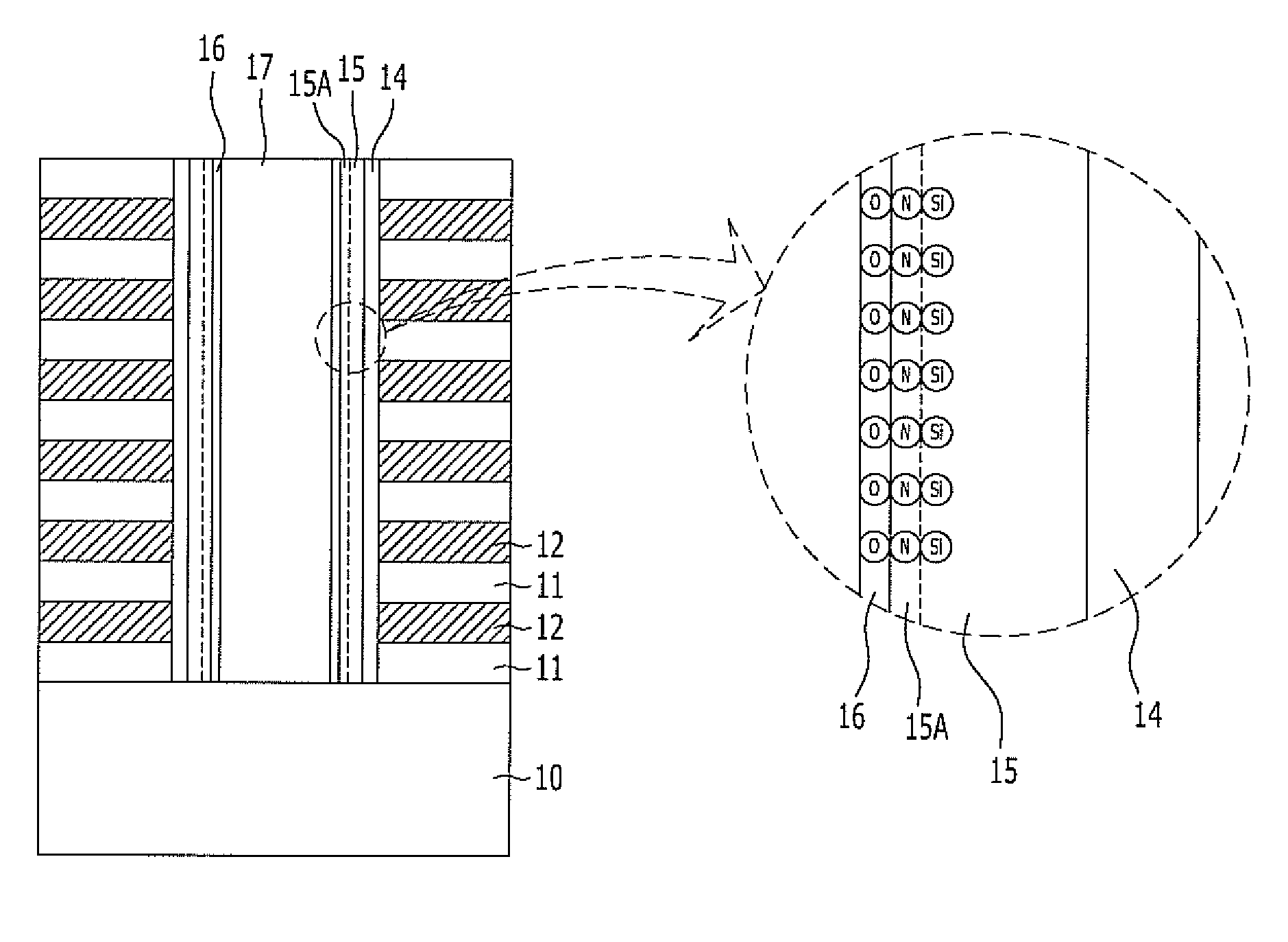
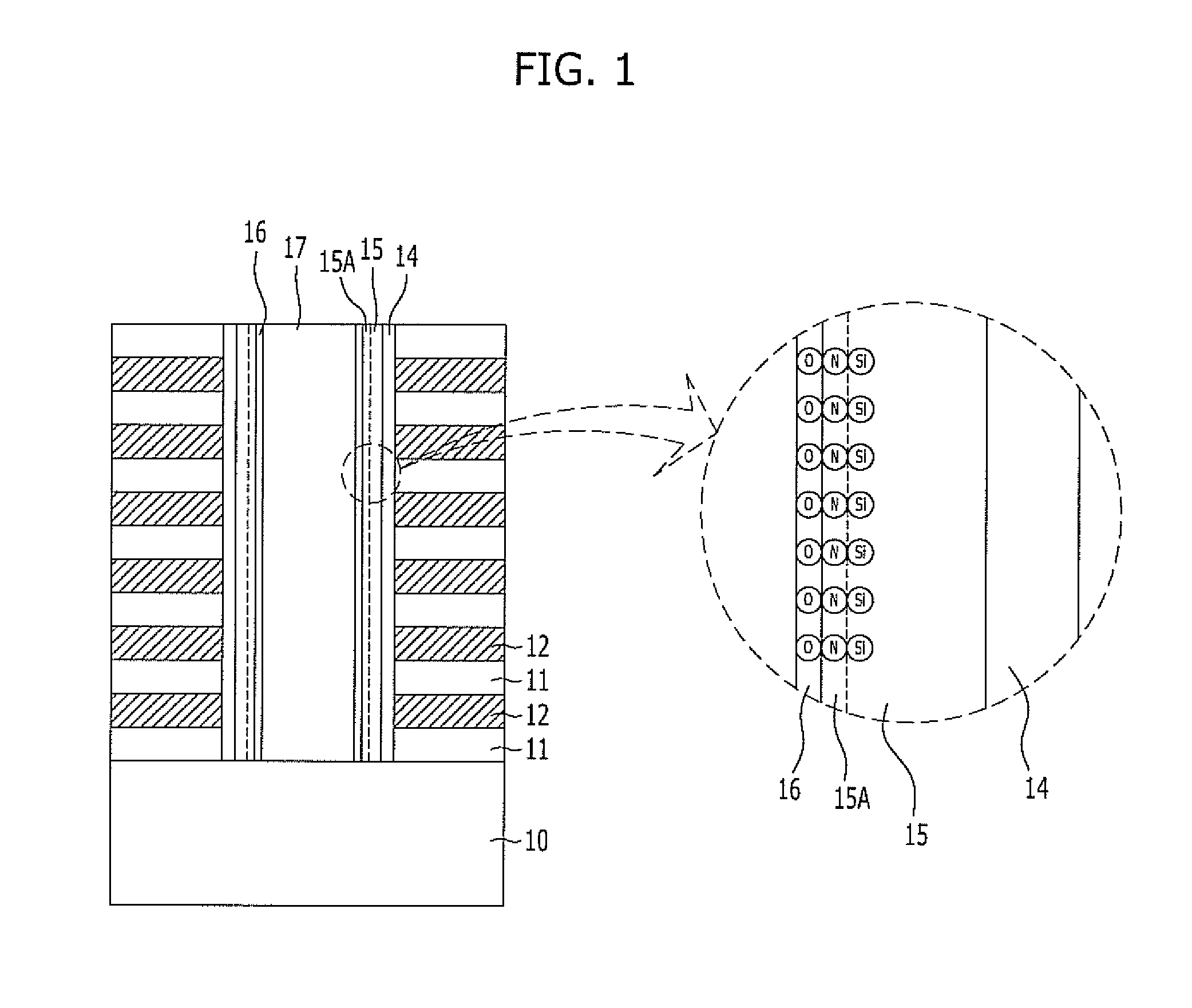
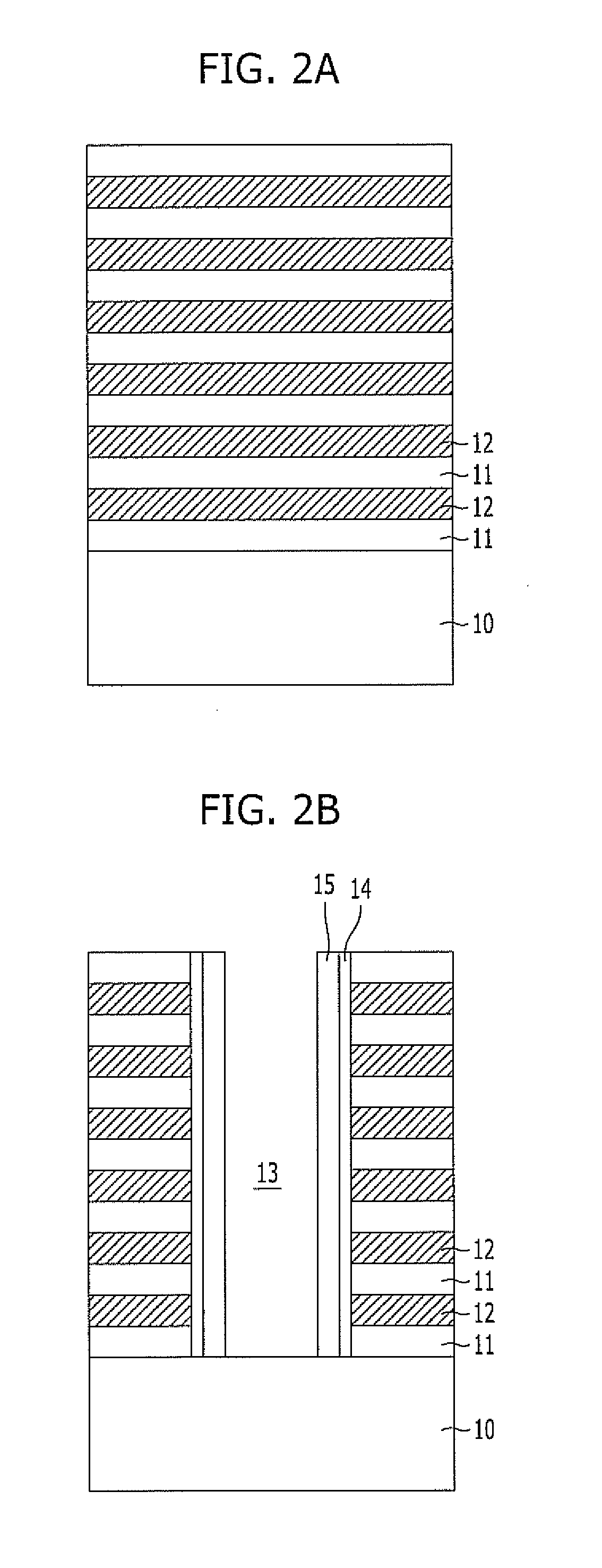
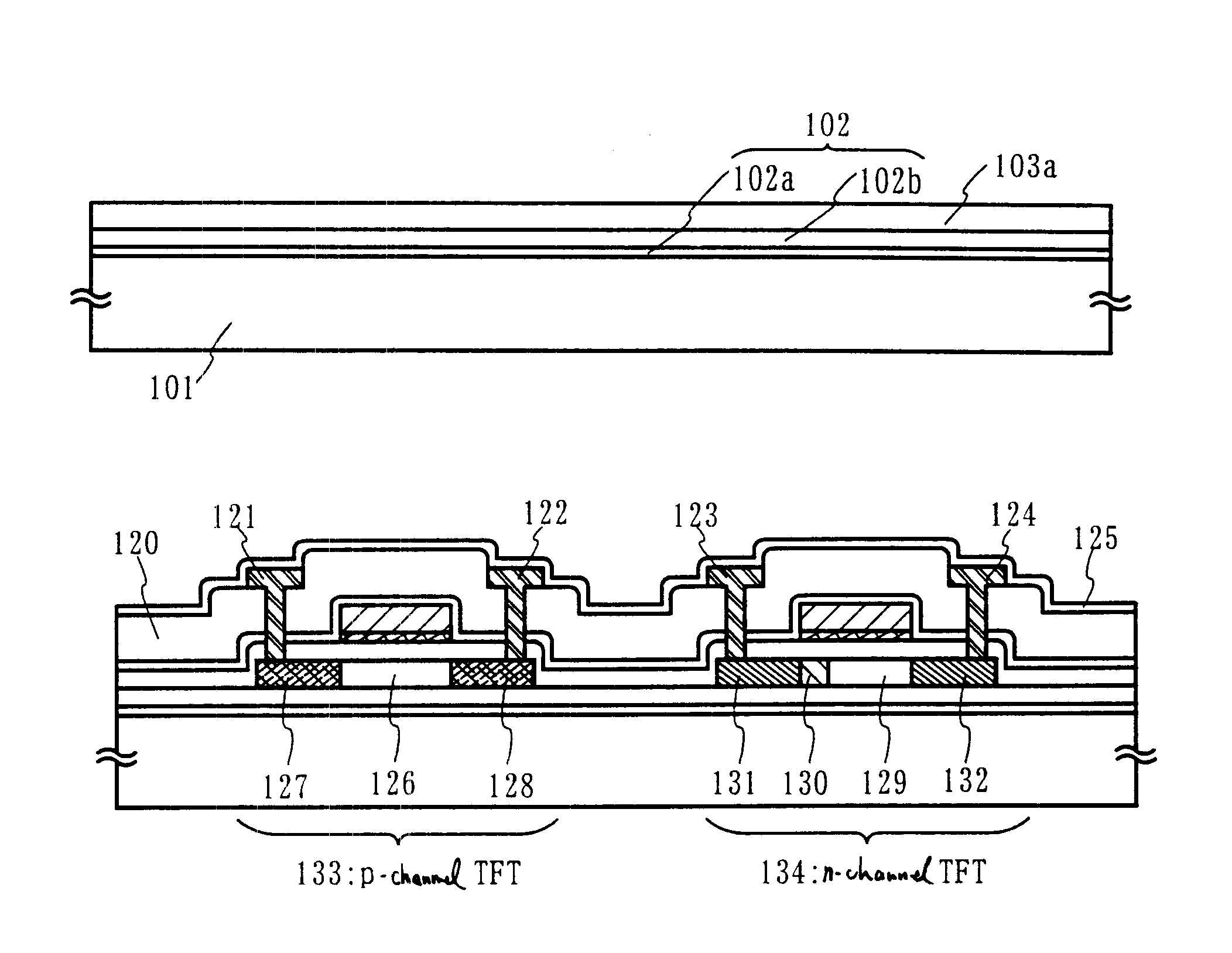
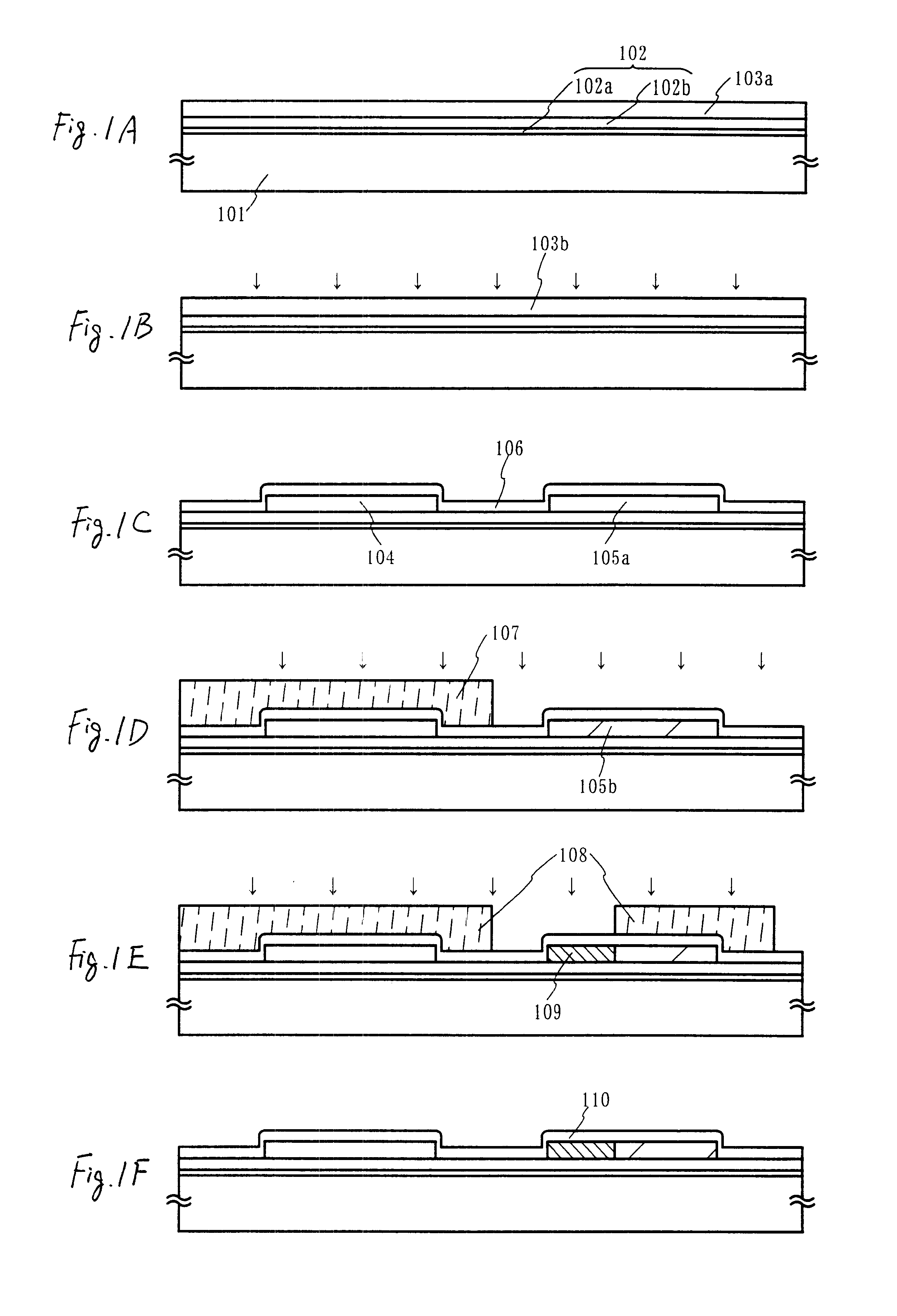
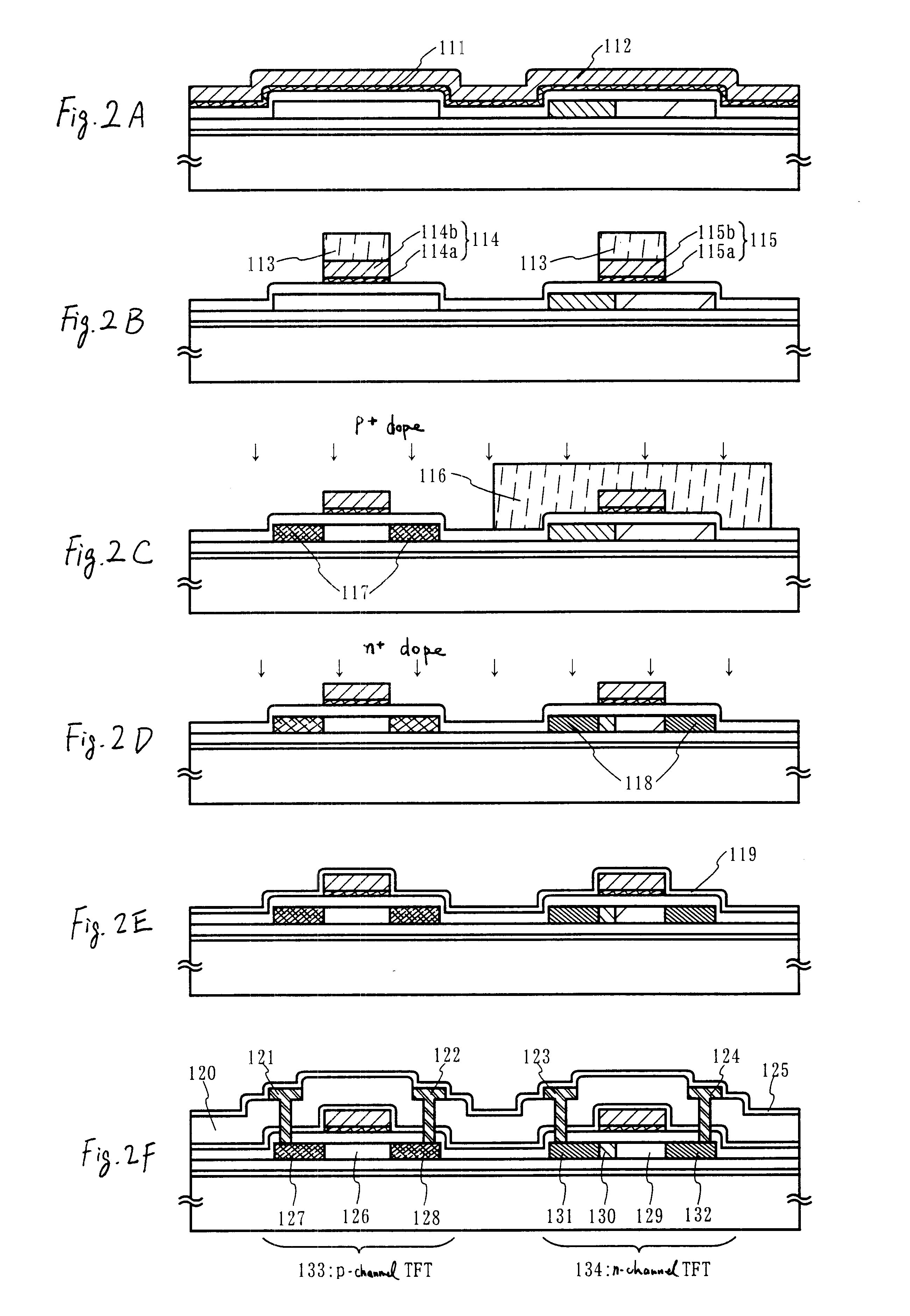
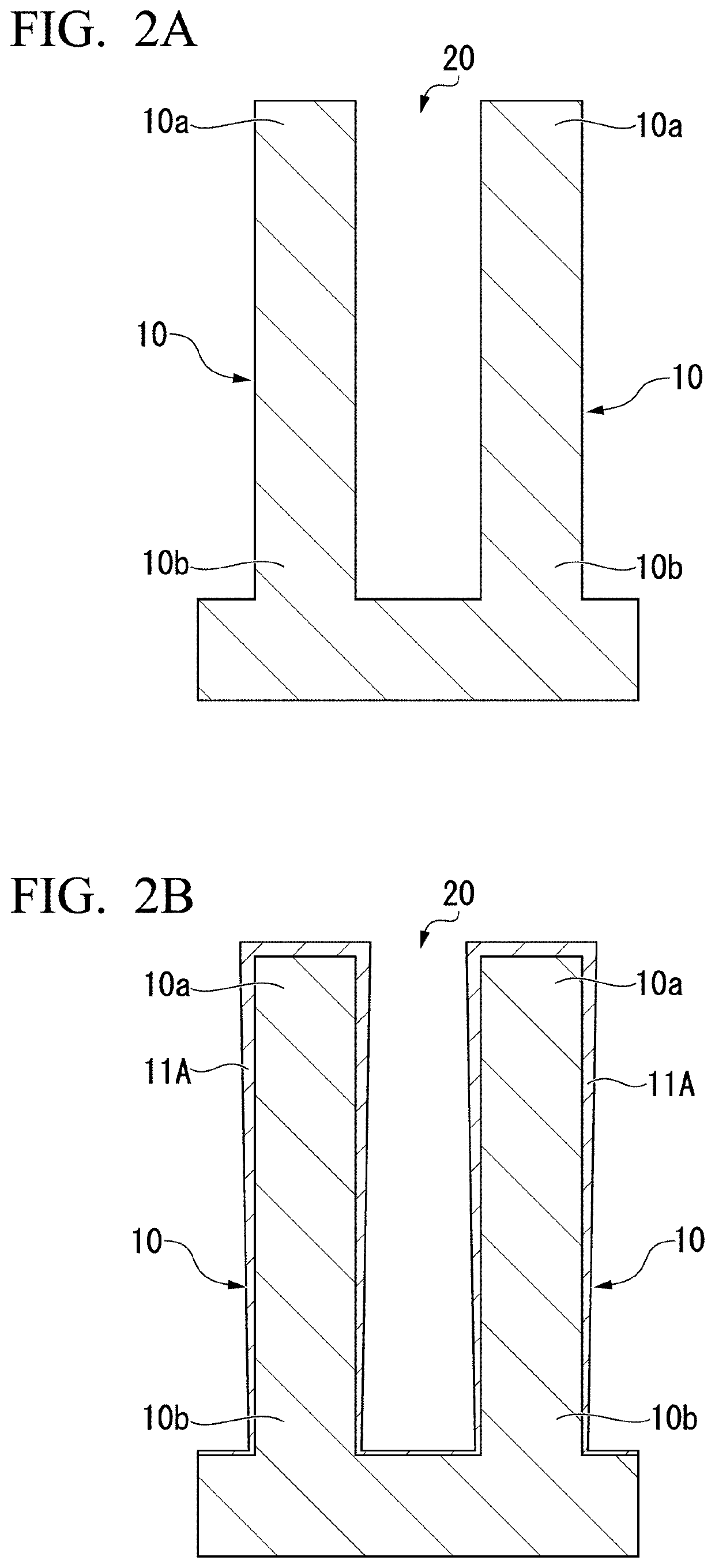
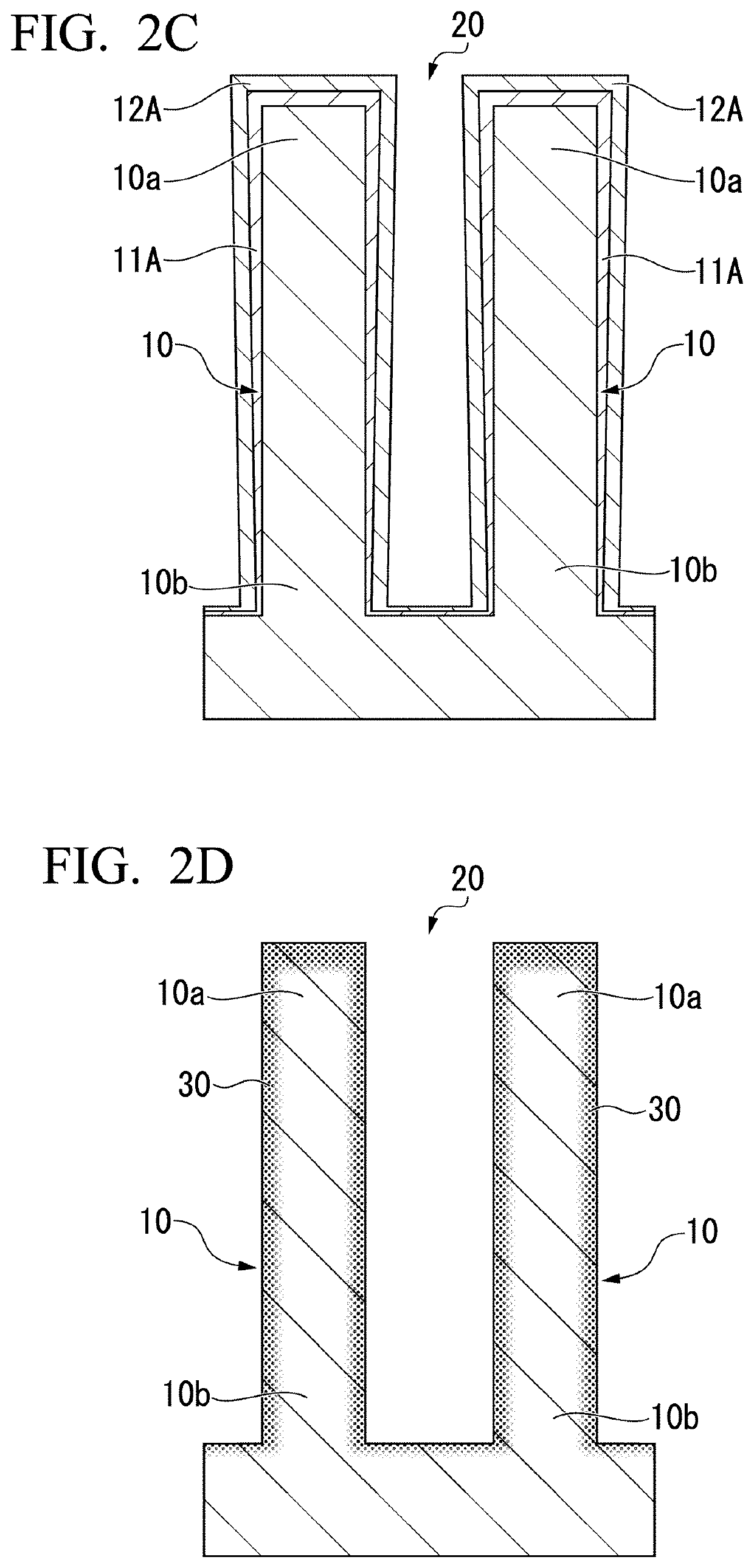
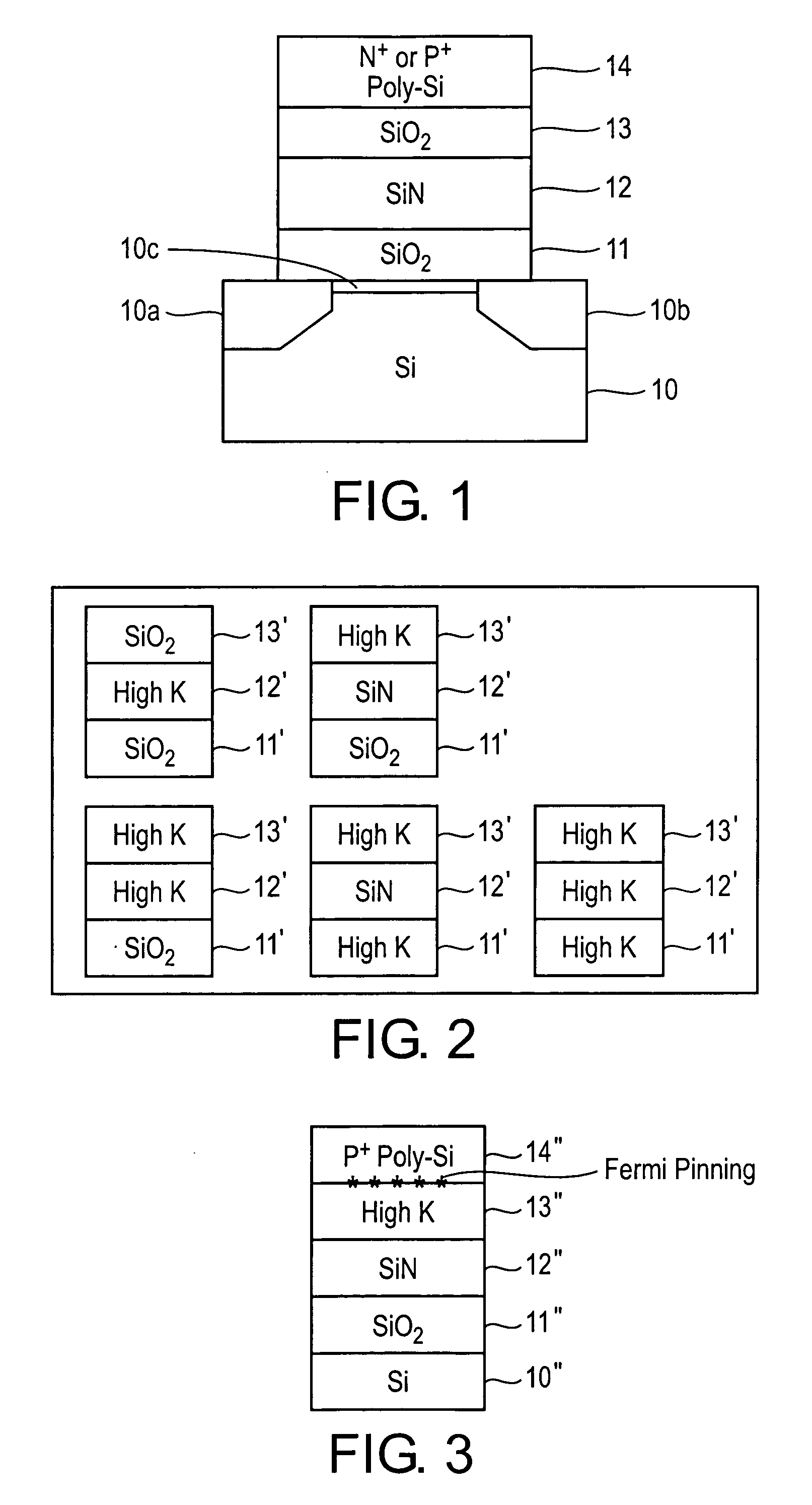
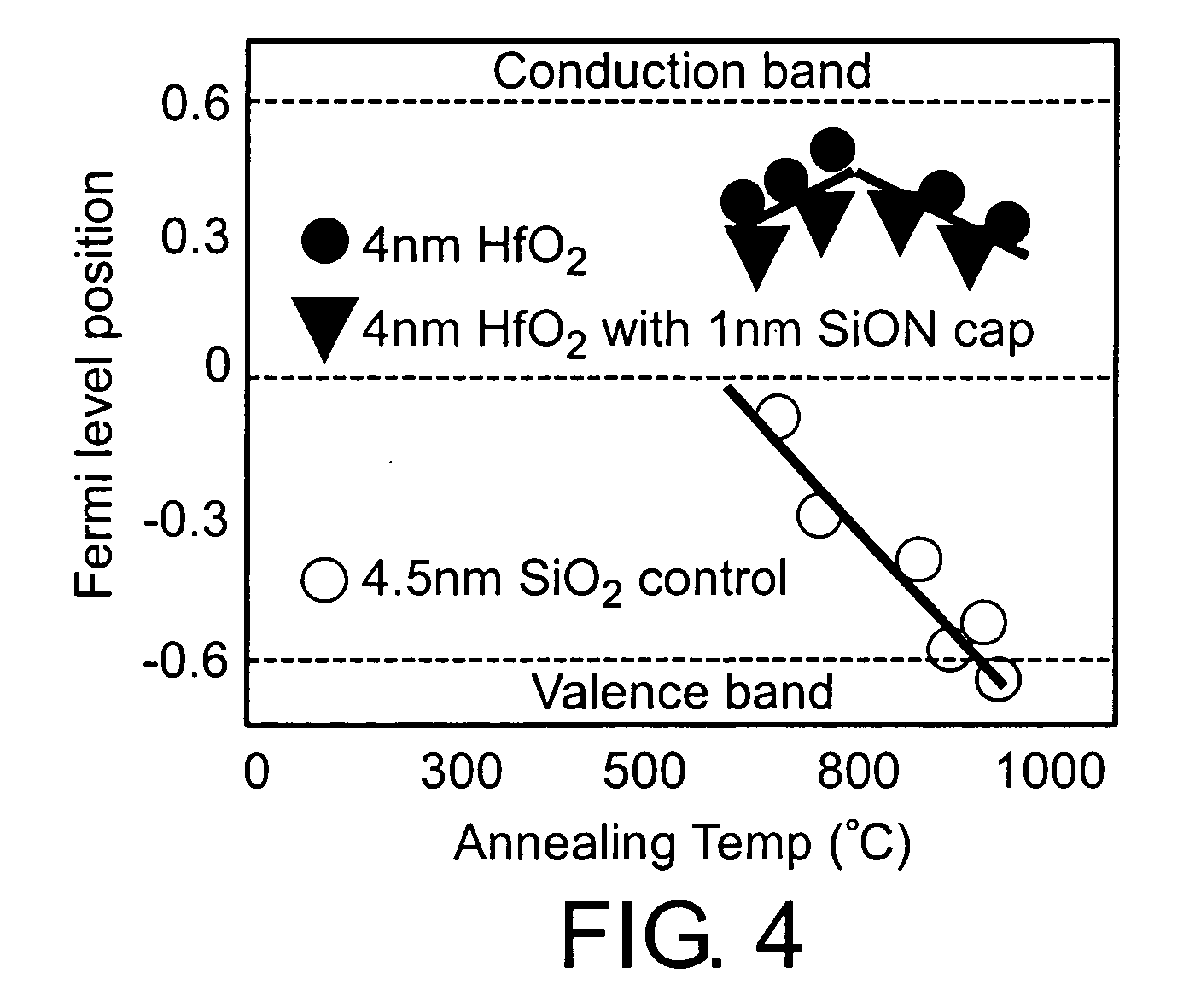
Oxynitride laminate "blocking layer" for thin film semiconductor devices
Channel doping is an effective method for controlling Vth, but if Vth shifts to the order of -4 to -3 V when forming circuits such as a CMOS circuit formed from both an n-channel TFT and a P-channel TFT on the same substrate, then it is difficult to control the Vth of both TFTs with one channel dope. In order to solve the above problem, the present invention forms a blocking layer on the back channel side, which is a laminate of a silicon oxynitride film (A) manufactured from SiH4, NH3, and N2O, and a silicon oxynitride film (B)manufactured from SiH4and N2O. By making this silicon oxynitride film laminate structure, contamination by alkaline metallic elements from the substrate can be prevented, and influence by stresses, caused by internal stress, imparted to the TFT can be relieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Non-volatile memory device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20130161726A1Improve erase operation characteristicImprove operating characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInter layerDielectric layer
A non-volatile memory device includes a channel layer vertically extending from a substrate, a plurality of inter-layer dielectric layers and a plurality of gate electrodes that are alternately stacked along the channel layer, and an air gap interposed between the channel layer and each of the plurality of gate electrodes. The non-volatile memory device may improve erase operation characteristics by suppressing back tunneling of electrons by substituting a charge blocking layer interposed between a gate electrode and a charge storage layer with an air gap, and a method for fabricating the non-volatile memory device.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Atomic layer deposition of tungsten material
InactiveCN101308794ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseNucleation
An implementing mode of the invention provides an improved technology for depositing materials containing tungsten. The technology utilizes an infusion technology and a gaseous phase deposition technology, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD), to provide tungsten-containing materials with obviously improved surface evenness and yield. In one implementing mode, a method for forming tungsten-containing materials on a substrate is provided. The method comprises deposing a substrate, which contains a bottom coating deposited thereon, in a technological chamber; exposing the substrate orderly in a precursor of tungsten and reducing gases so as to deposit a tungsten nucleation layer on the bottom coating, during the ALD technology; and depositing a tungsten block layer on the tungsten nucleation layer. The invention is characterized in that the reducing gases comprise a hydrogen gas / hydride flow ratio of 40:1, 100:1, 500:1, 800: 1, 1000:1 or more, and comprise hydride such as diborane, silicane or silicoethane.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
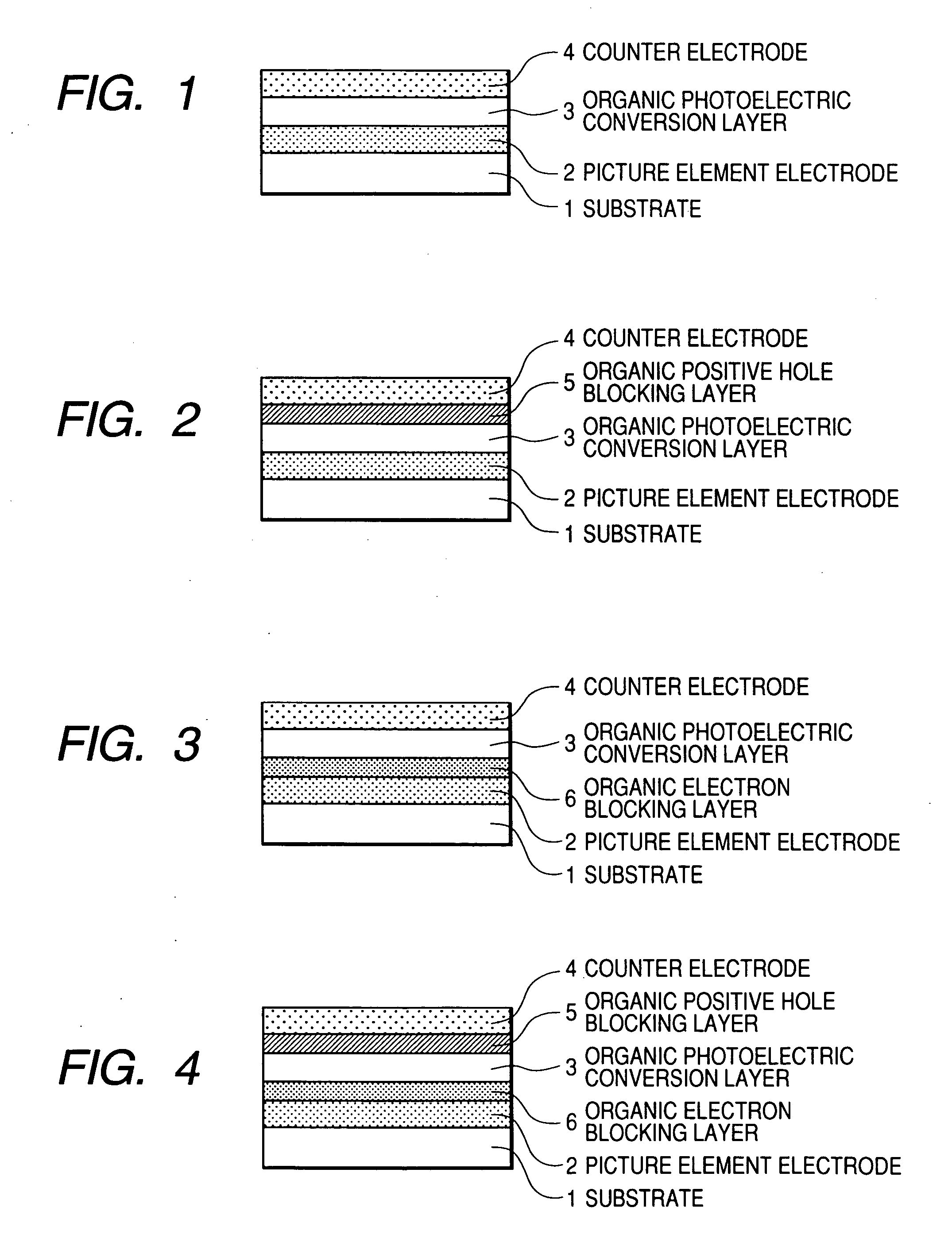
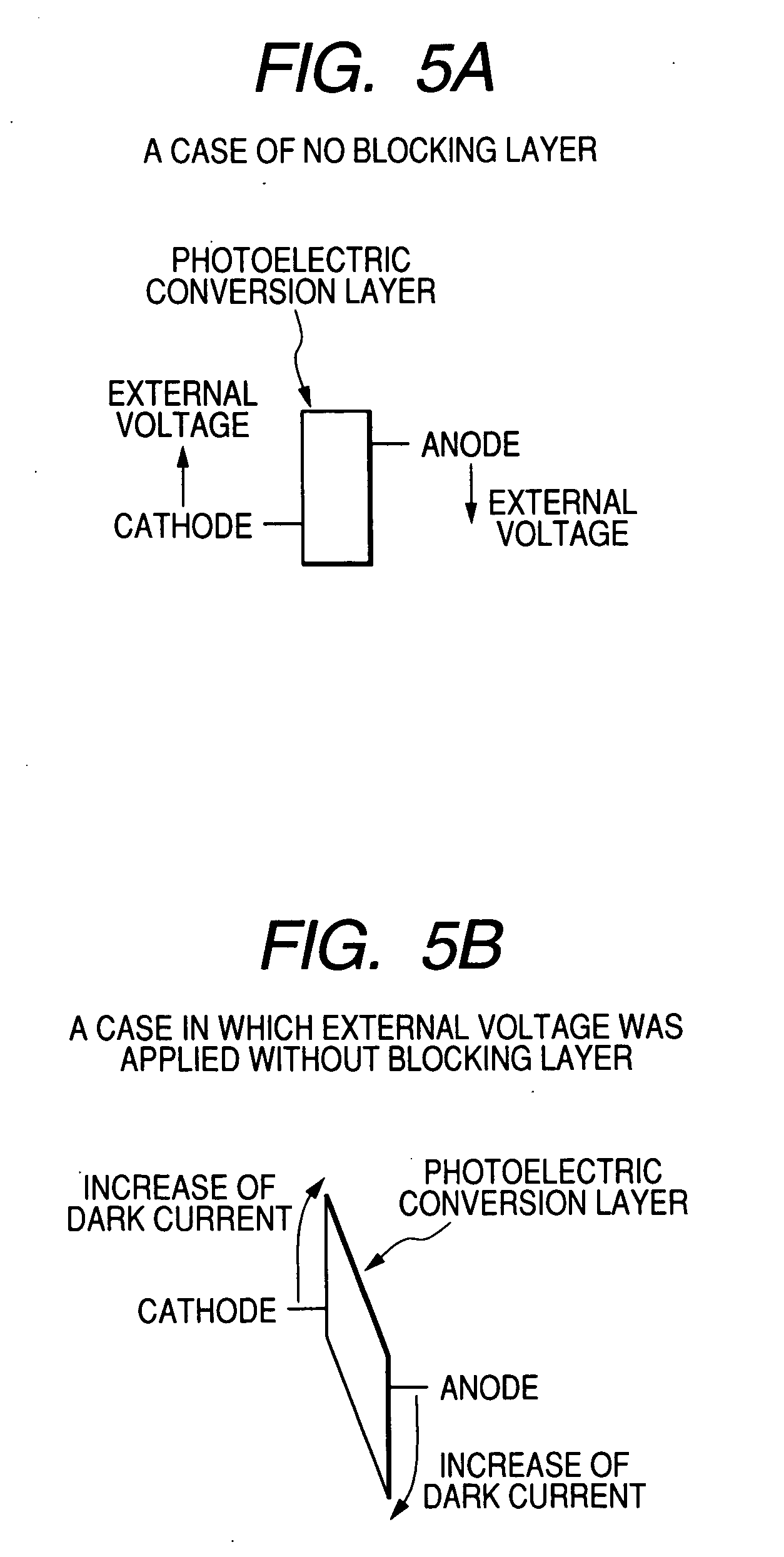
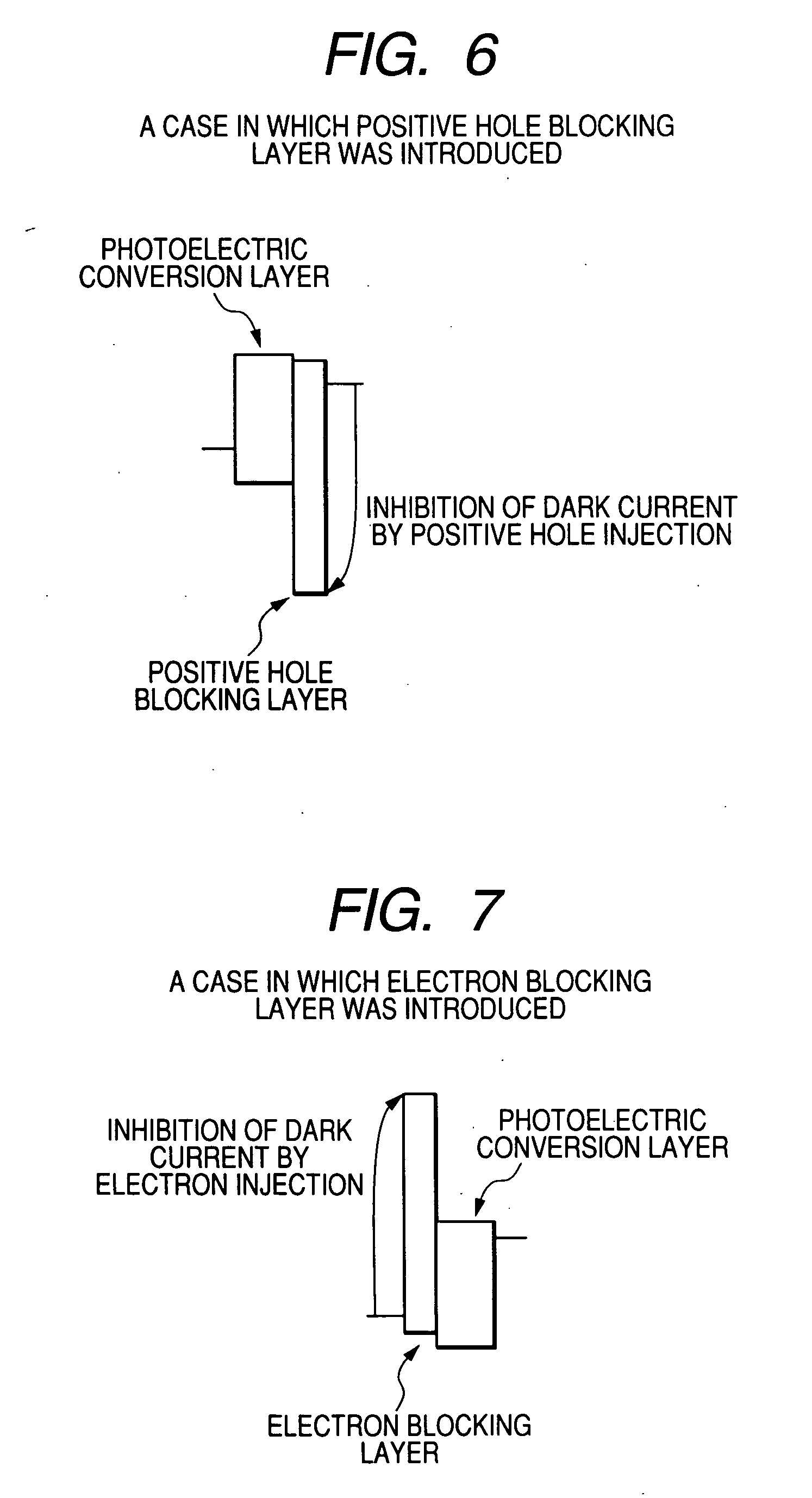
Photoelectric conversion element and solid-state image pickup device
InactiveUS20080035965A1Effective reduction in dark currentTotal current dropTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
A photoelectric conversion element comprises a photoelectric conversion section that includes: a pair of electrodes; and a photoelectric conversion layer disposed between the pair of electrodes, wherein the photoelectric conversion section further comprises between one of the pair of electrodes and the photoelectric conversion layer a first charge-blocking layer that restrains injection of charges from the one of the electrodes into the photoelectric conversion layer when a voltage is applied to the pair of electrodes, and the first charge-blocking layer comprises a plurality of layers.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Solar cells using fullerenes
InactiveUS20020189666A1Improve efficiencyImprove photovoltaic performanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSolar cellFullerene
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices are disclosed. The devises comprise photoconductive organic thin films in a heterostructure, which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. The use of fullerenes in the electron conducting layer has lead to devices with high efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Devices having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Band engineered nano-crystal non-volatile memory device utilizing enhanced gate injection
ActiveUS20070045718A1Increased device feature scalingEfficient erasureTransistorNanoinformaticsCharge retentionNon symmetric
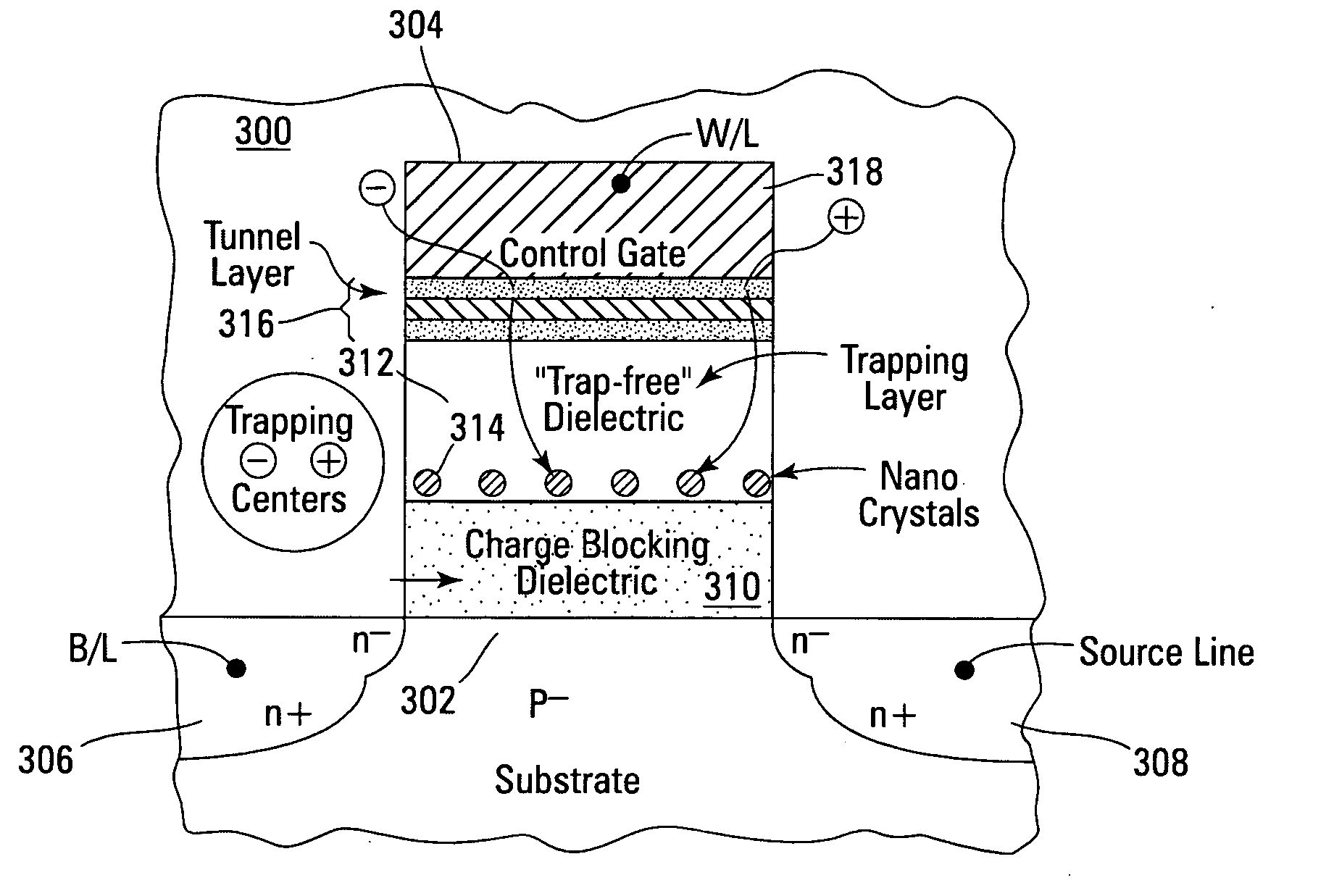
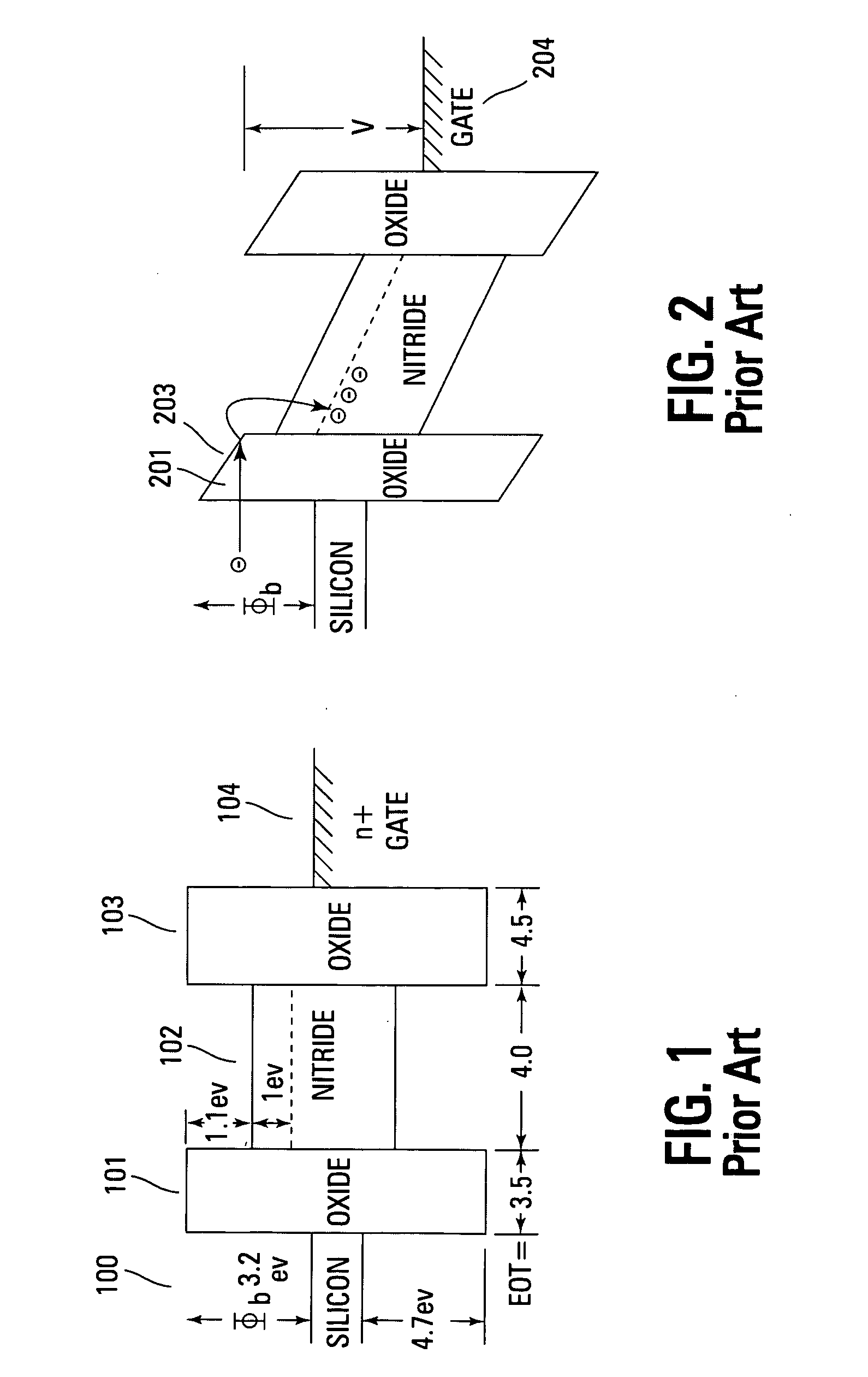
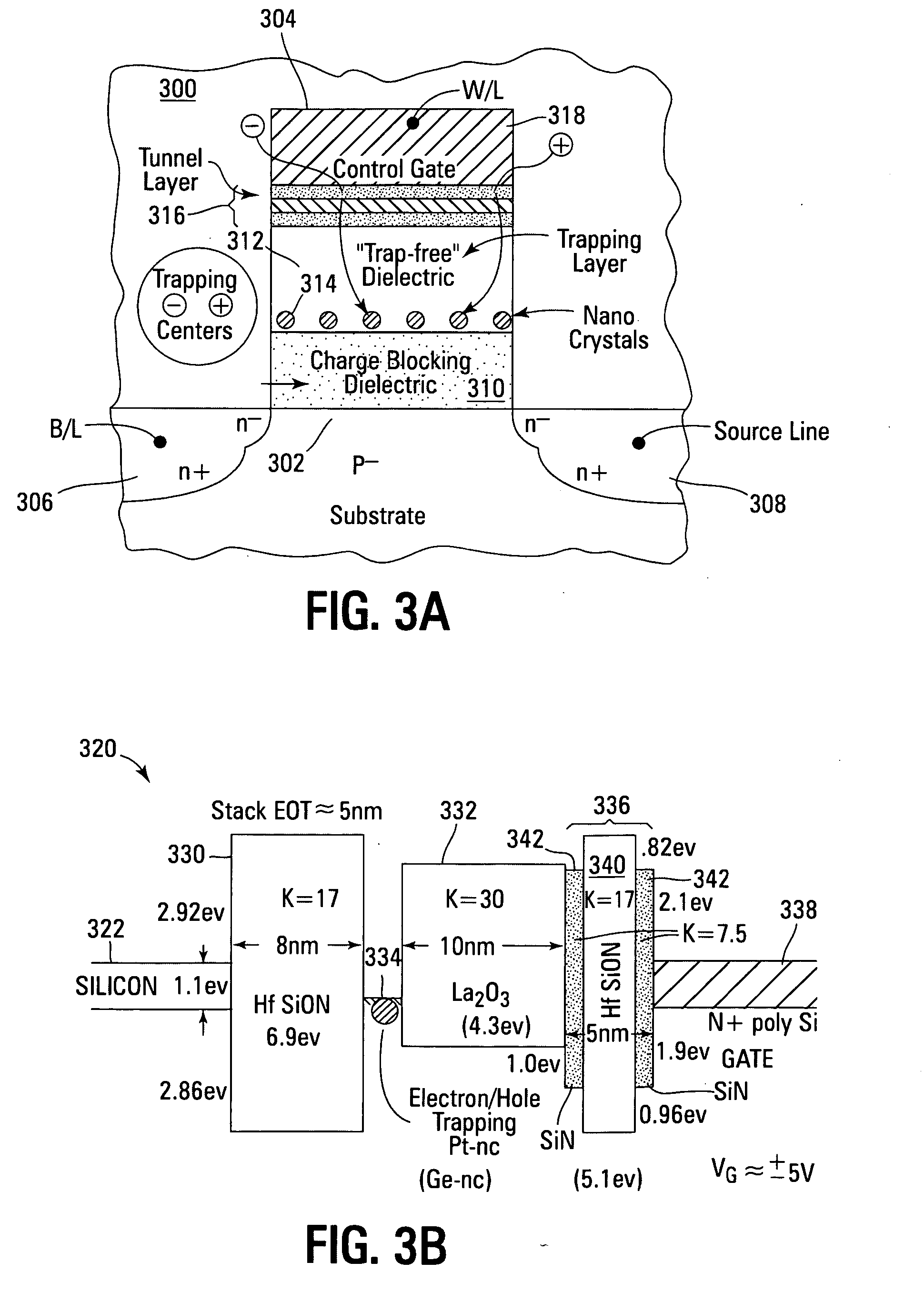
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize reverse mode non-volatile memory cells that have band engineered gate-stacks and nano-crystal charge trapping in EEPROM and block erasable memory devices, such as Flash memory devices. Embodiments of the present invention allow a reverse mode gate-insulator stack memory cell that utilizes the control gate for programming and erasure through a band engineered crested tunnel barrier. Charge retention is enhanced by utilization of high work function nano-crystals in a non-conductive trapping layer and a high K dielectric charge blocking layer. The band-gap engineered gate-stack with symmetric or asymmetric crested barrier tunnel layers of the non-volatile memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
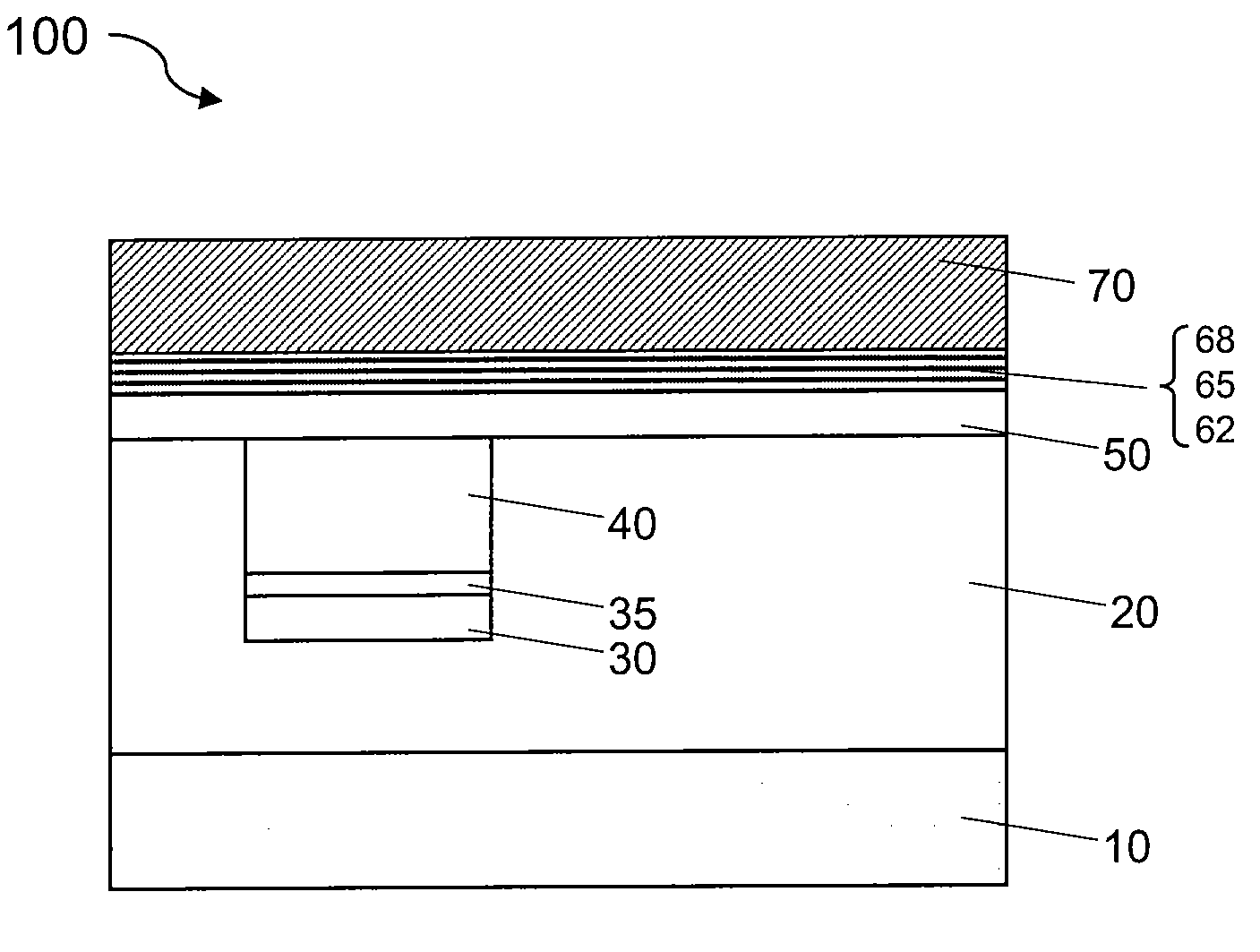
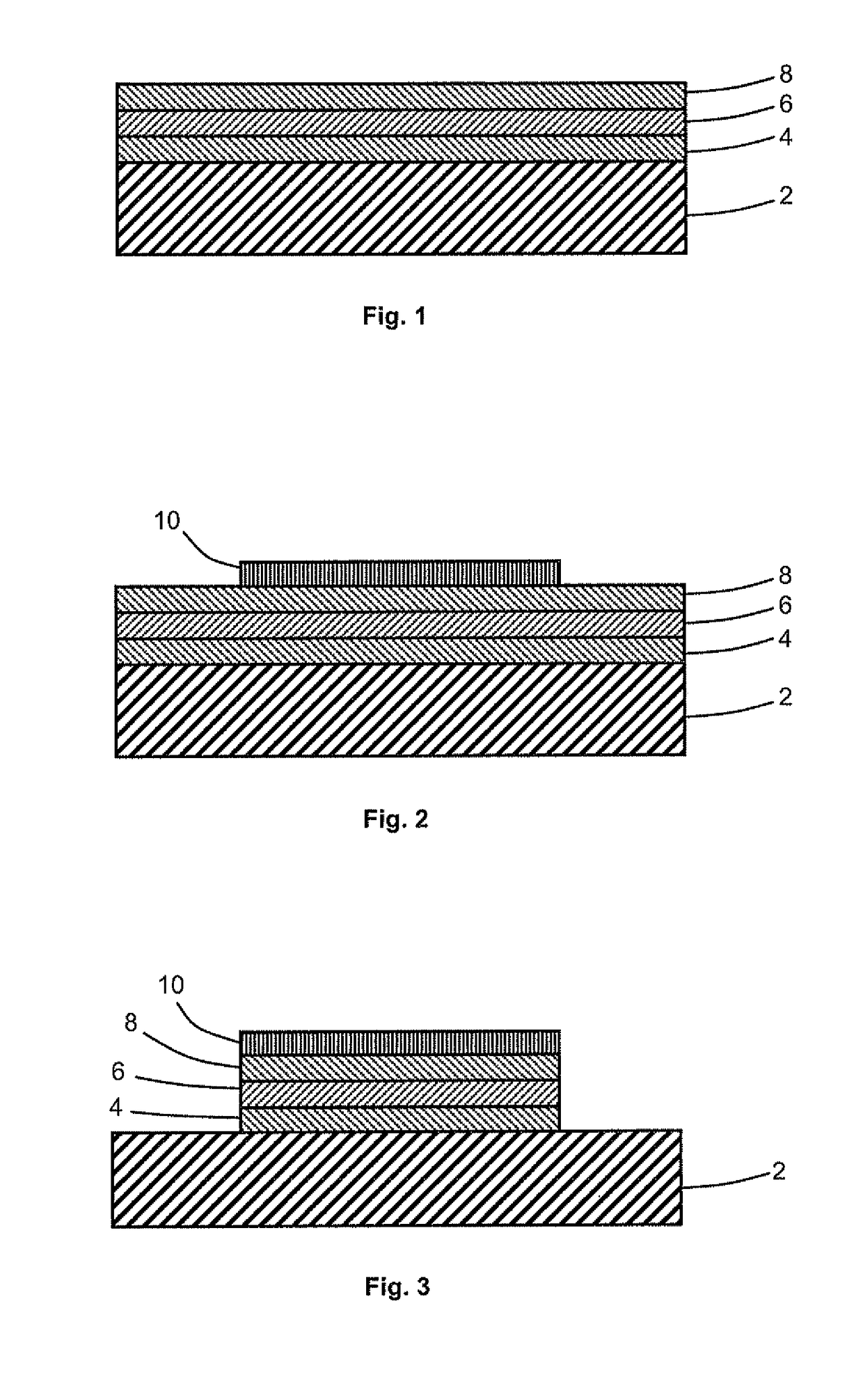
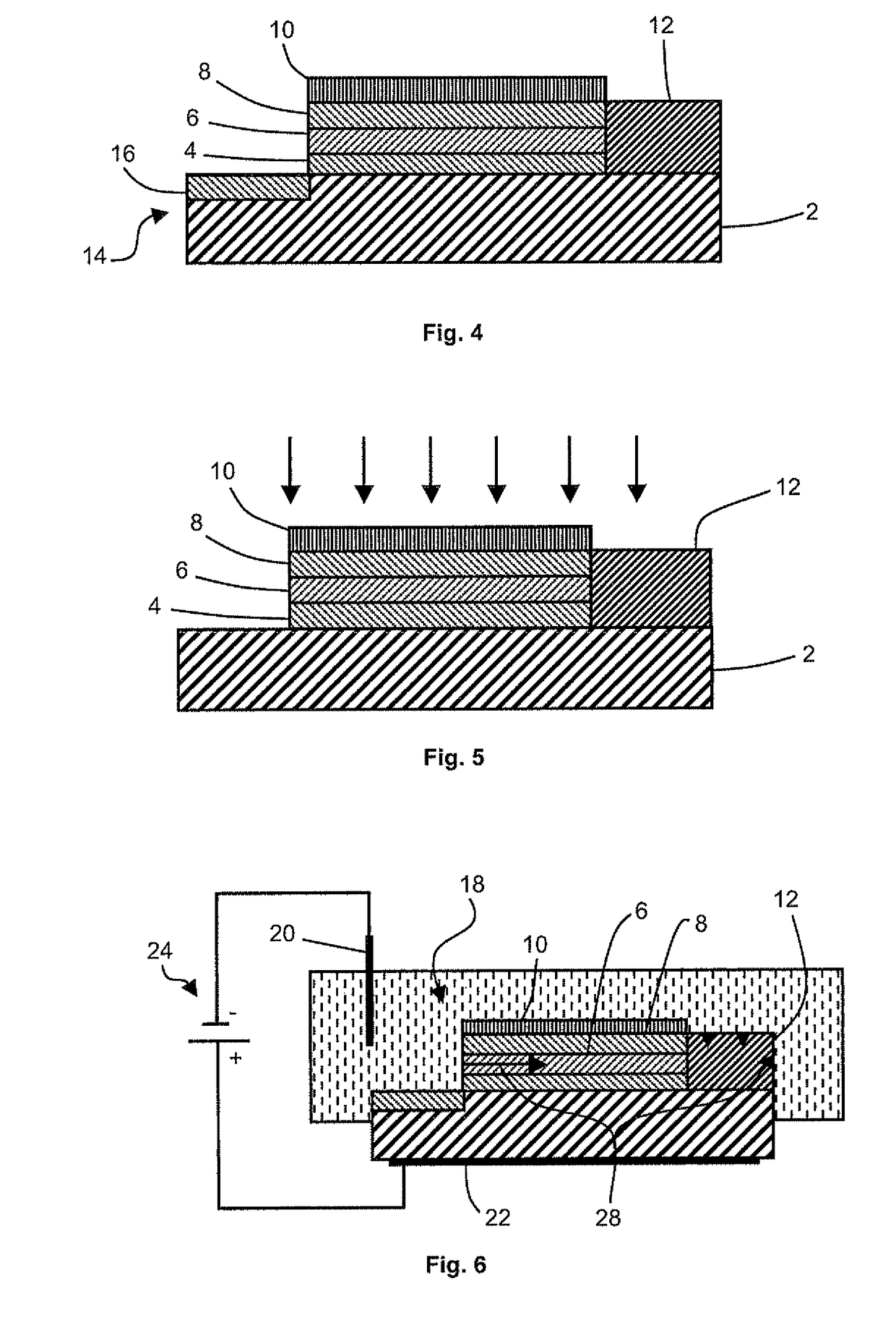
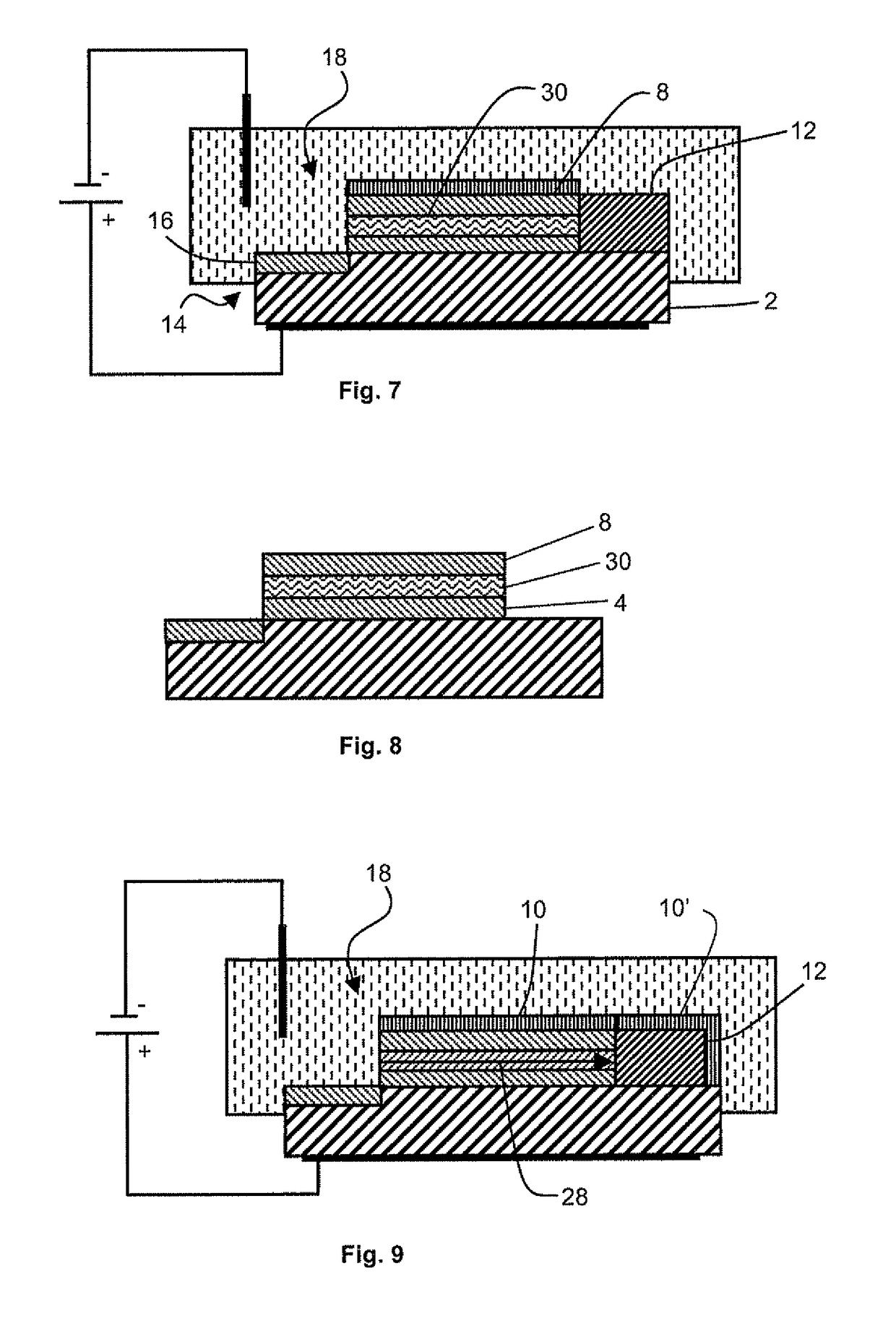
Method for forming a multilayer structure
ActiveUS8470689B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrostructural device manufactureElectron holeDopant
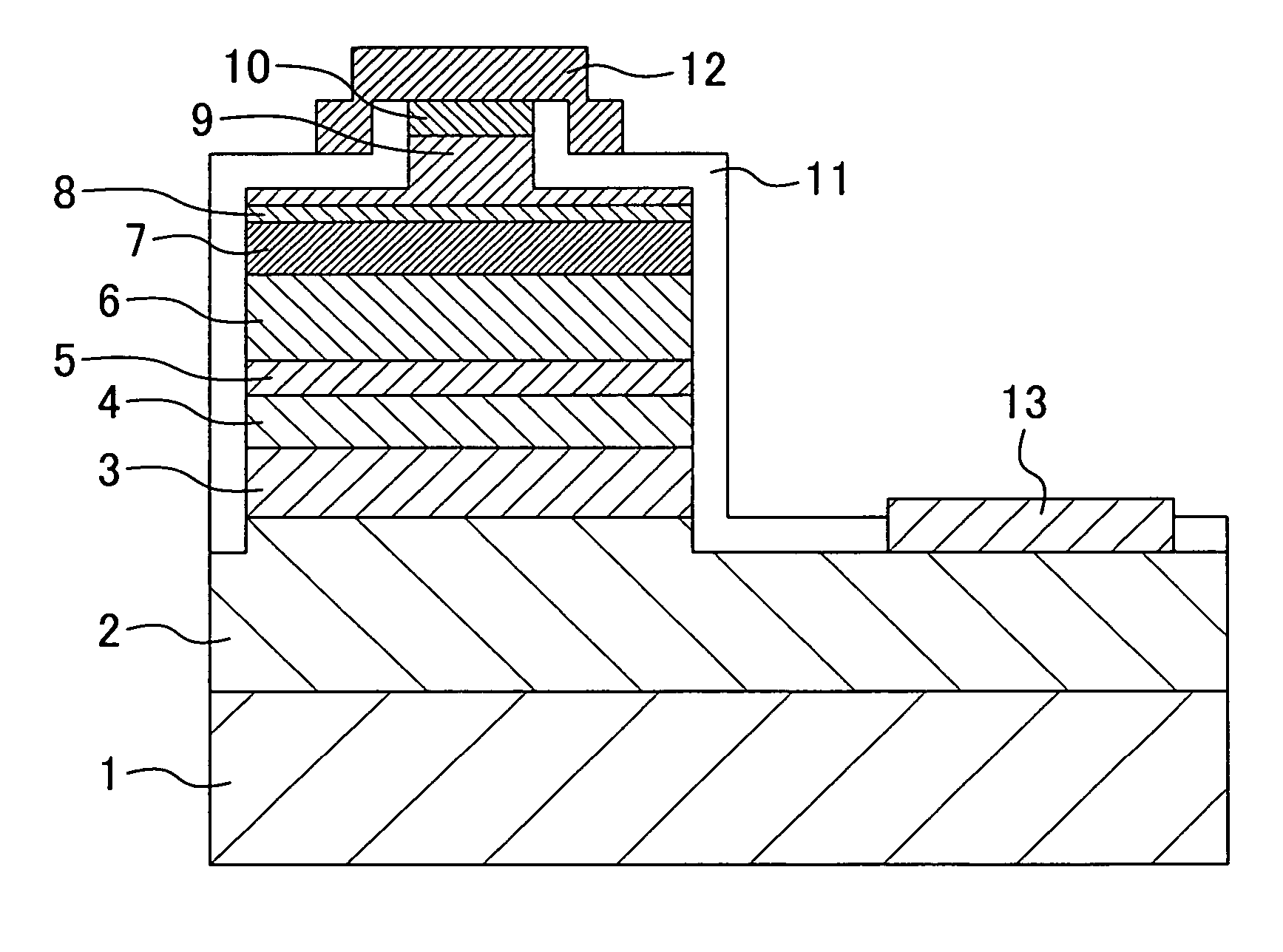
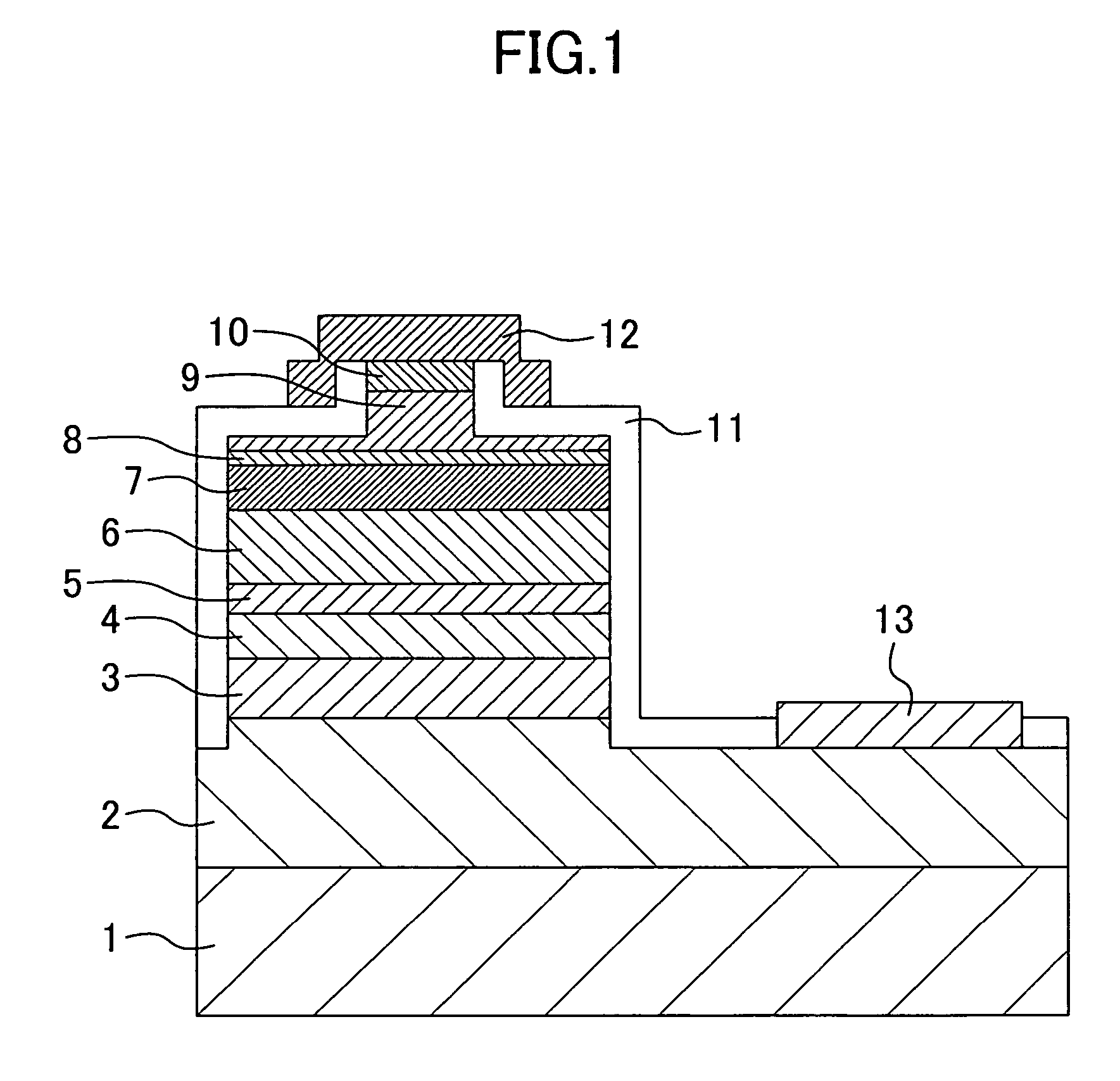
The method for forming a multilayer structure on a substrate comprises providing a stack successively comprising an electron hole blocking layer, a first layer made from N-doped semiconductor material having a dopant concentration greater than or equal to 1018 atoms / cm3 or P-doped semiconductor material, and a second layer made from semiconductor material of different nature. A lateral electric contact pad is made between the first layer and the substrate, and the material of the first layer is subjected to anodic treatment in an electrolyte.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Phosphorescent OLEDs with exciton blocking layer
ActiveUS7597967B2Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorescent oledsLow voltage
An electroluminescent device comprises a cathode and an anode; and, located therebetween, a light-emitting layer (LEL) comprising at least one hole transporting co-host and at least one electron transporting co-host, together with at least one phosphorescent emitter, and wherein the triplet energy of each of the co-host materials is greater than the triplet energy of the phosphorescent emitter, and further containing an exciton blocking layer comprising a hole transporting material with triplet energy greater or equal to 2.5 eV adjacent the emitting layer on the anode side. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency at low voltage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
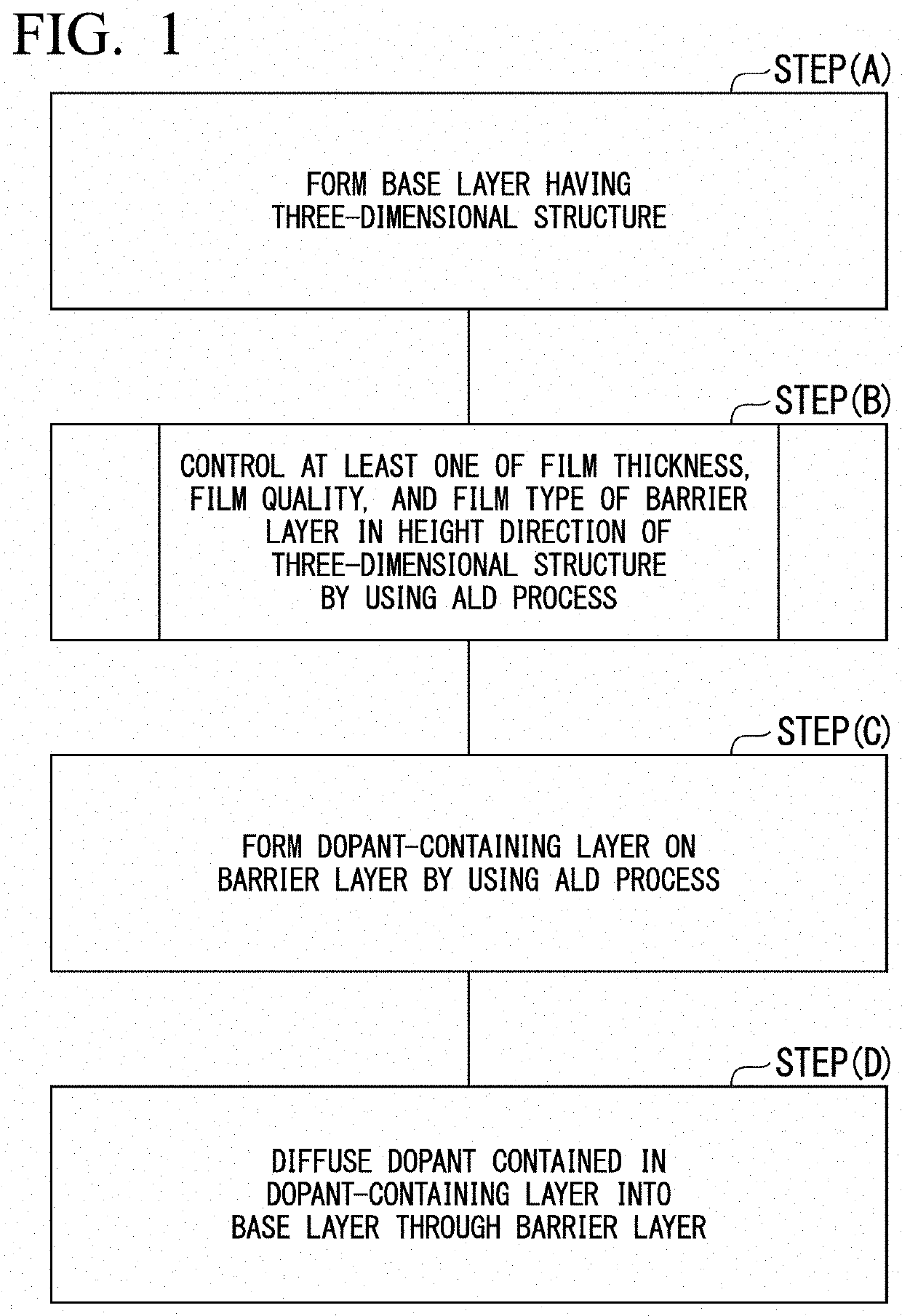
Method for forming barrier layer and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
PendingUS20210313178A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDopantDevice material
In a method for forming a barrier layer, the barrier layer is formed on a base layer having a three-dimensional structure before a dopant-containing layer is formed on the base layer. At this time, at least one of a film thickness, a film quality, and a film type of the barrier layer is controlled in a height direction of the three-dimensional structure by using an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
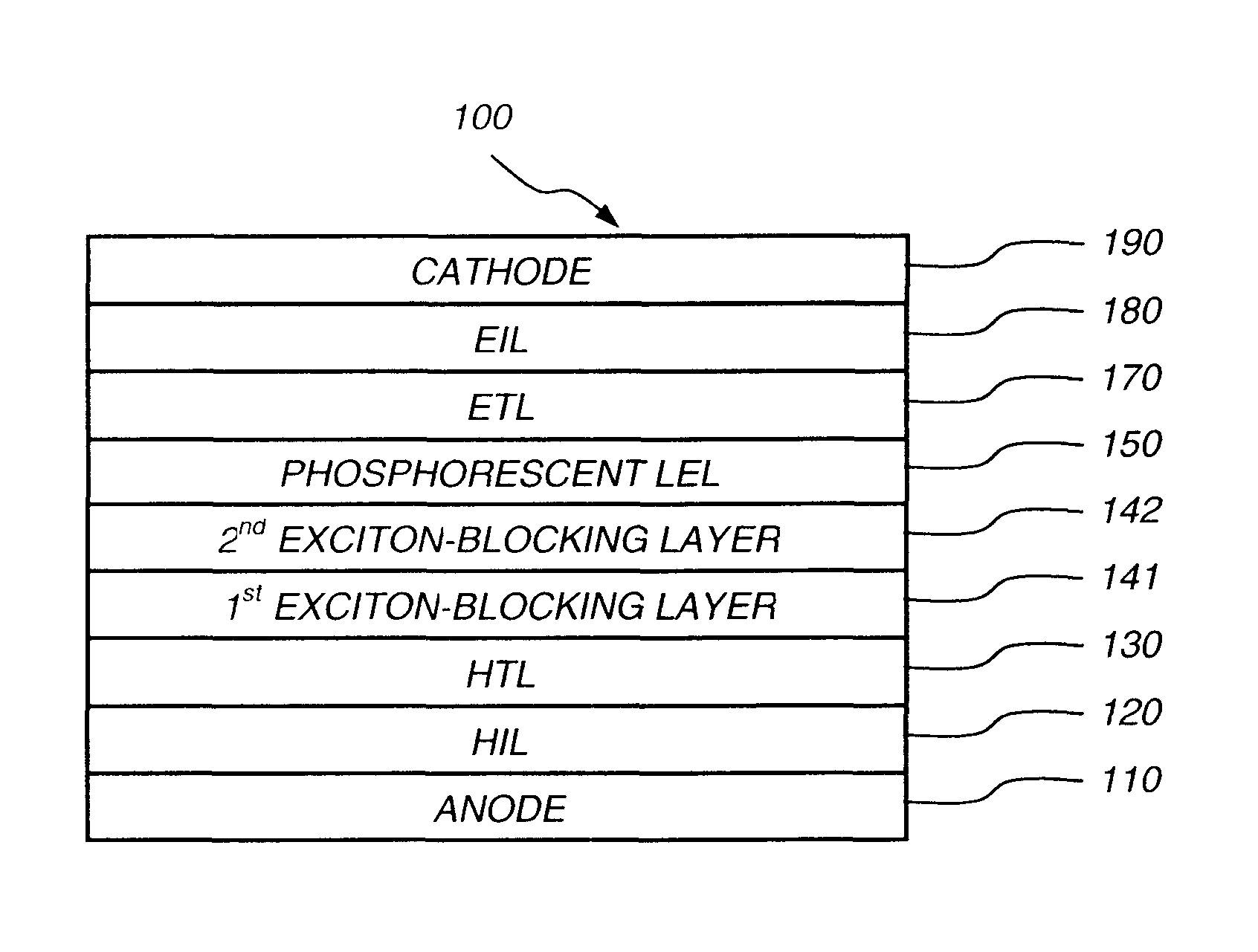
Phosphorescent oled having double exciton-blocking layers
ActiveUS8034465B2Good effectImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantElectron hole
An organic light-emitting device comprising an anode; a cathode; a hole-transporting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode; a phosphorescent light-emitting layer disposed between the hole-transporting layer and the cathode, wherein the phosphorescent light-emitting layer includes at least one host and at least one phosphorescent dopant; a first exciton-blocking layer disposed between the hole-transporting layer and the phosphorescent light-emitting layer; wherein the first exciton-blocking layer has a triplet energy greater than the triplet energy of the host in the phosphorescent light-emitting layer; and a second exciton-blocking layer disposed between the first exciton-blocking layer and the phosphorescent light-emitting layer, wherein the second exciton-blocking layer is in contact with the phosphorescent light-emitting layer, and wherein the second exciton-blocking layer has a triplet energy less than the triplet energy of the first exciton-blocking layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
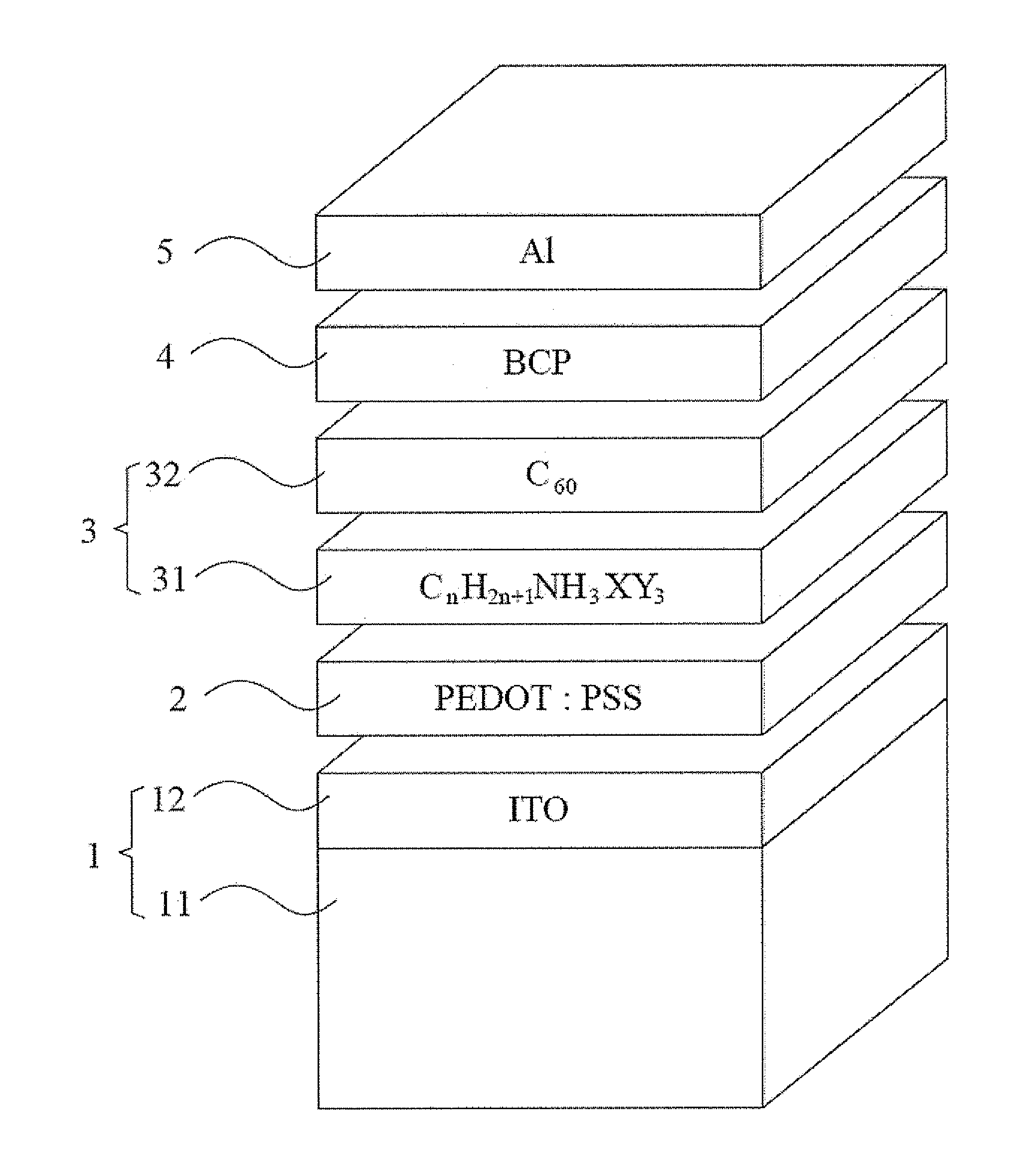
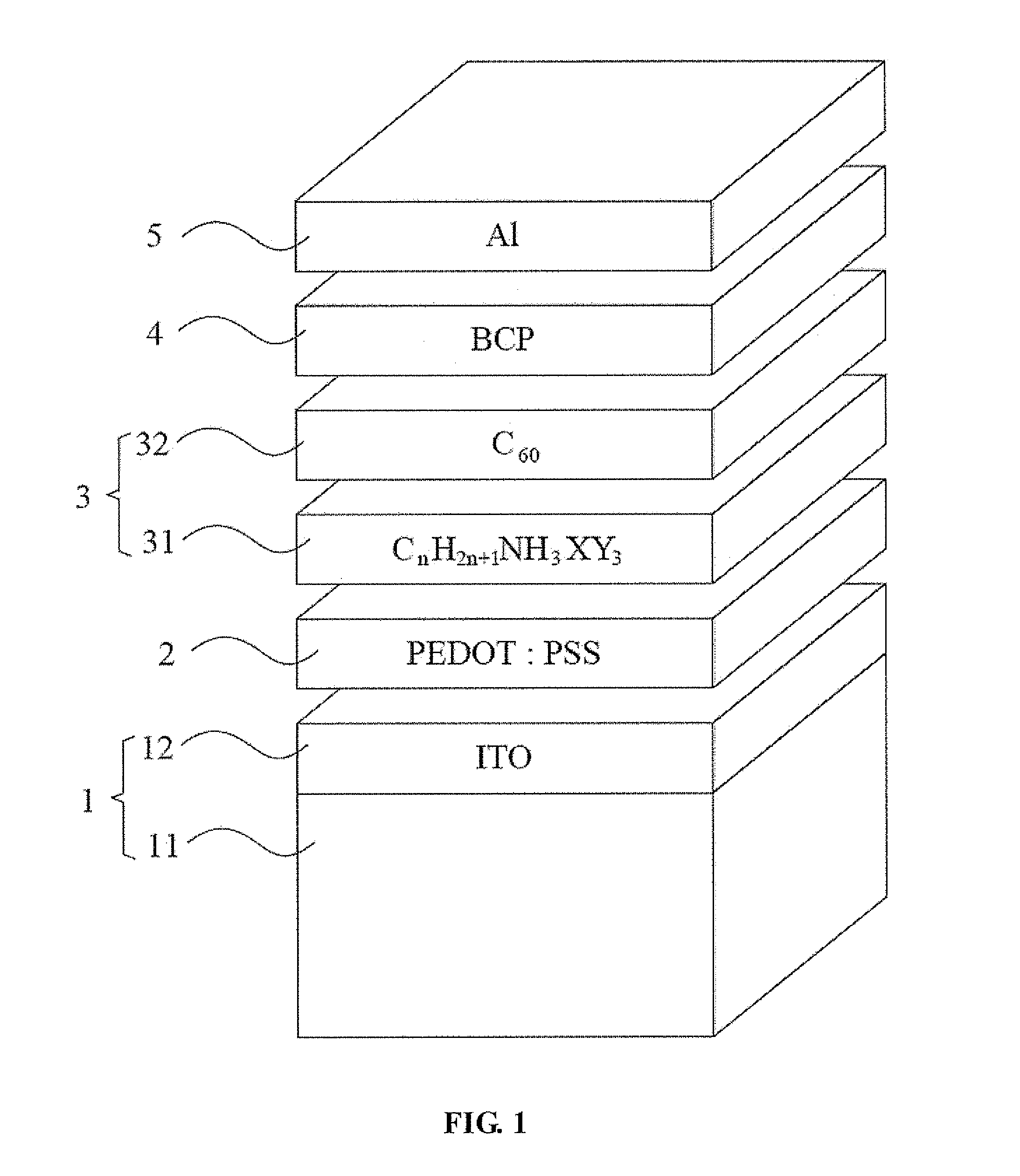
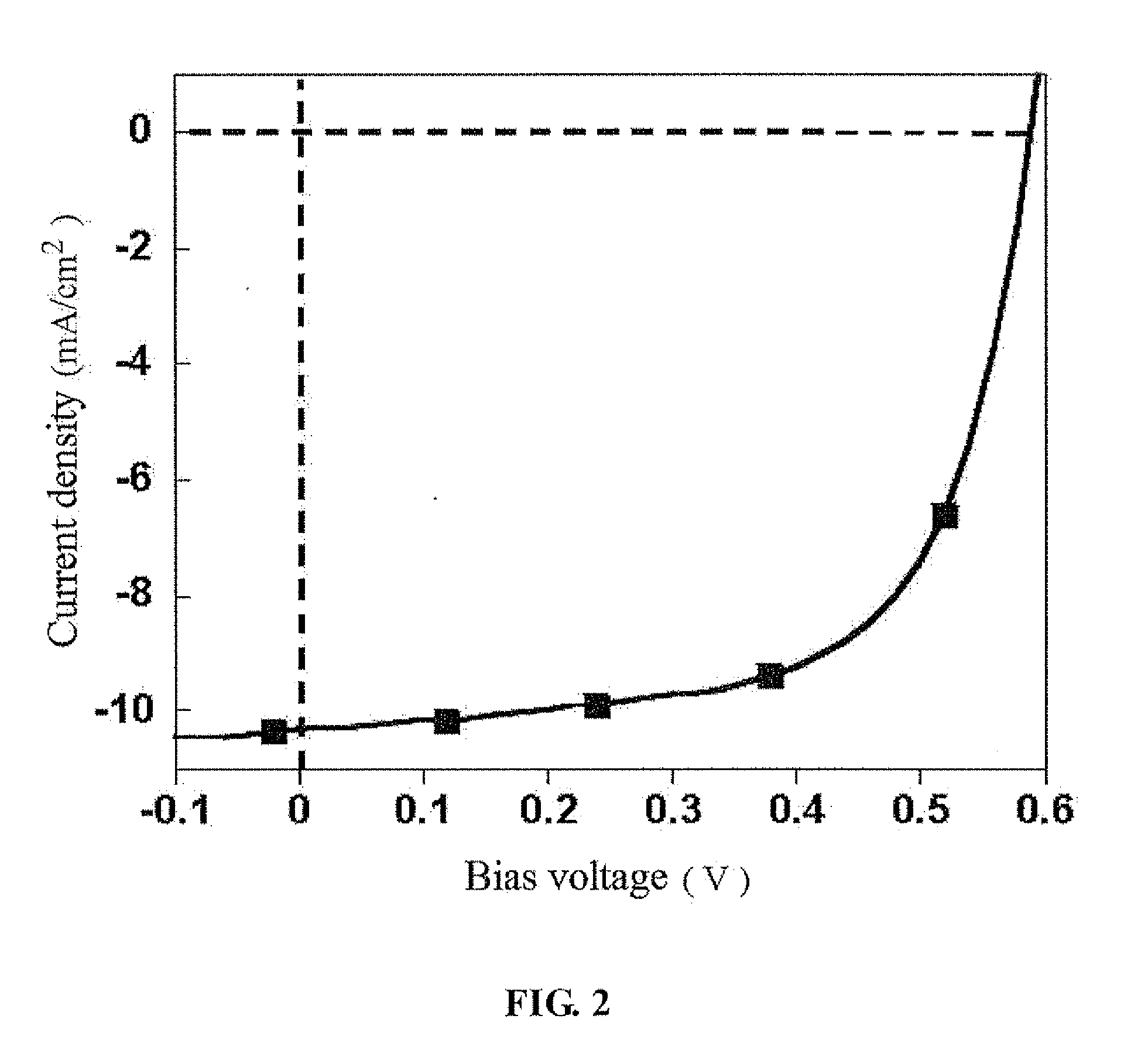
Hybrid organic solar cell with perovskite structure as absorption material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140332078A1Low costSimple processFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionOrganic solar cell
A hybrid organic solar cell (HOSC) with perovskite structure as absorption material and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The HOSC includes a conductive substrate, a hole transport layer, an active layer, a hole blocking layer and a negative electrode. The active layer has a light absorption layer (LAL) and an electron acceptor layer (EAL). The LAL is made of perovskite material represented by the following equation: CnH2n+1NH3XY3, n is positive integer form 1 to 9; X is Pb, Sn or Ge; and Y is at least one of I, Br or Cl. The EAL is made of at least one type of fullerene or derivatives thereof. A planar heterojunction (PHJ) is formed between the LAL and the EAL. The LAL has simple structure and fabricating process with relatively low cost, so that it is advantageous to carry out the mass production of HOSCs of flexible solid-state form.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Structure and method for metal gate stack oxygen concentration control using an oxygen diffusion barrier layer and a sacrificial oxygen gettering layer
ActiveUS20100127336A1Increase their effective work functionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWork functionDiffusion barrier
A process is disclosed of forming metal replacement gates for NMOS and PMOS transistors with oxygen in the PMOS metal gates and metal atom enrichment in the NMOS gates such that the PMOS gates have effective work functions above 4.85 eV and the NMOS gates have effective work functions below 4.25 eV. Metal work function layers in both the NMOS and PMOS gates are oxidized to increase their effective work functions to the desired PMOS range. An oxygen diffusion blocking layer is formed over the PMOS gate and an oxygen getter is formed over the NMOS gates. A getter anneal extracts the oxygen from the NMOS work function layers and adds metal atom enrichment to the NMOS work function layers, reducing their effective work functions to the desired NMOS range. Processes and materials for the metal work function layers, the oxidation process and oxygen gettering are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Photoconductive imaging members
A photoconductive imaging member comprised of a supporting substrate, a hole blocking layer, an optional adhesive layer, a photogenerator layer, and a charge transport layer, and wherein said blocking layer is comprised of a polyhaloalkylstyrene.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device with alternative metal gate material
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device comprises a substrate including a source region, a drain region and a channel region provided between the source region and the drain region with a gate stack located above the channel region with a metal gate located above the gate stack. The metal gate is comprised of a metal having a specific metal work function relative to a composition of a layer of the gate stack that causes electrons to travel through the entire thickness of the blocking layer via direct tunneling. The gate stack preferably comprises a multiple layer stack selected from a group of multiple layer stacks consisting of: ONO, ONH, OHH, OHO, HHH, or HNH, where O is an oxide material, N is SiN, and H is a high κ material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic photoelectric conversion element and image element
InactiveUS20070063156A1Photoelectric conversion efficiency is not reducedImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesInvestigating moving sheetsElectron holeWork function
An organic photoelectric conversion element comprises: a pair of electrodes; an organic photoelectric conversion layer arranged between the pair of electrodes; and an positive hole blocking layer arranged between one of the pair of electrodes and the organic photoelectric conversion layer, wherein an ionization potential of the positive hole blocking layer is larger than a work function of the adjoining electrode by 1.3 eV or more, and wherein an electron affinity of the positive hole blocking layer is equal to or larger than that of the adjoining organic photoelectric conversion layer. An electron blocking layer may be arranged between the other one of the pair of electrodes and the organic photoelectric conversion layer, wherein its electron affinity is smaller than a work function of the adjoining electrode by 1.3 eV or more, and its ionization potential is equal to or smaller than that of the adjoining organic photoelectric conversion layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Confined Defect Profiling within Resistive Random Memory Access Cells
ActiveUS20150034898A1Improvement of resistive switching characteristicDigital storageBulk negative resistance effect devicesTitanium nitrideResistive switching
Provided are resistive random access memory (ReRAM) cells and methods of fabricating thereof. A stack including a defect source layer, a defect blocking layer, and a defect acceptor layer disposed between the defect source layer and the defect blocking layer may be subjected to annealing. During the annealing, defects are transferred in a controllable manner from the defect source layer to the defect acceptor layer. At the same time, the defects are not transferred into the defect blocking layer thereby creating a lowest concentration zone within the defect acceptor layer. This zone is responsible for resistive switching. The precise control over the size of the zone and the defect concentration within the zone allows substantially improvement of resistive switching characteristics of the ReRAM cell. In some embodiments, the defect source layer includes aluminum oxynitride, the defect blocking layer includes titanium nitride, and the defect acceptor layer includes aluminum oxide.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Touch panel
InactiveUS20150346866A1High detection sensitivityImprove reliabilityDigital computer detailsDetails for portable computersEngineeringBlocking layer
To increase the detection sensitivity of a touch panel, provide a thin touch panel, provide a foldable touch panel, or provide a lightweight touch panel. A display element and a capacitor forming a touch sensor are provided between a pair of substrates. Preferably, a pair of conductive layers forming the capacitor each have an opening. The opening and the display element are provided to overlap each other. A light-blocking layer is provided between a substrate on the display surface side and the pair of conductive layers forming the capacitor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com