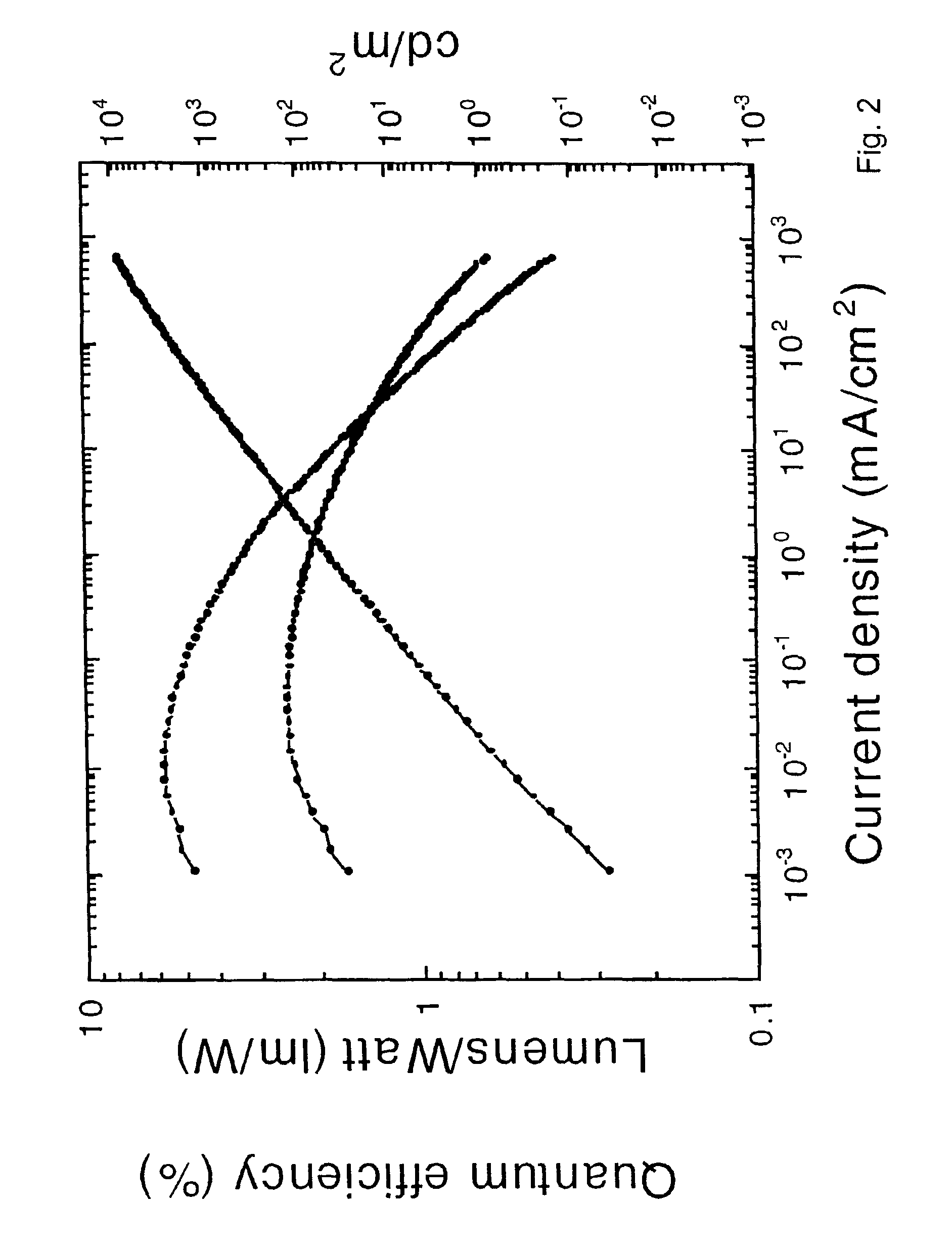
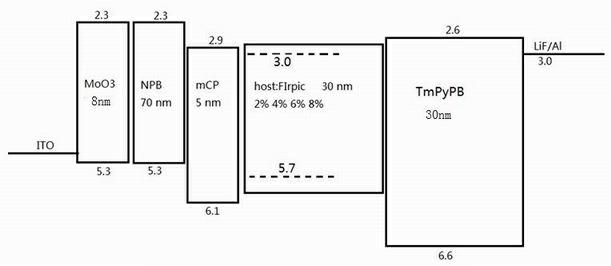
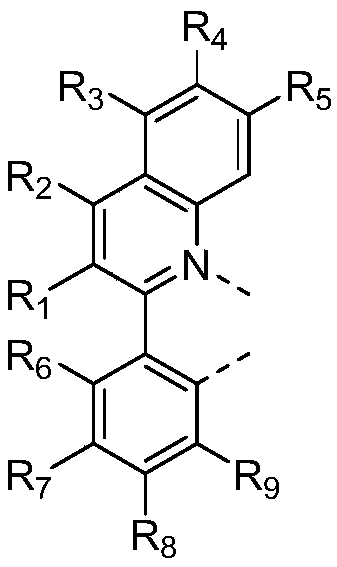
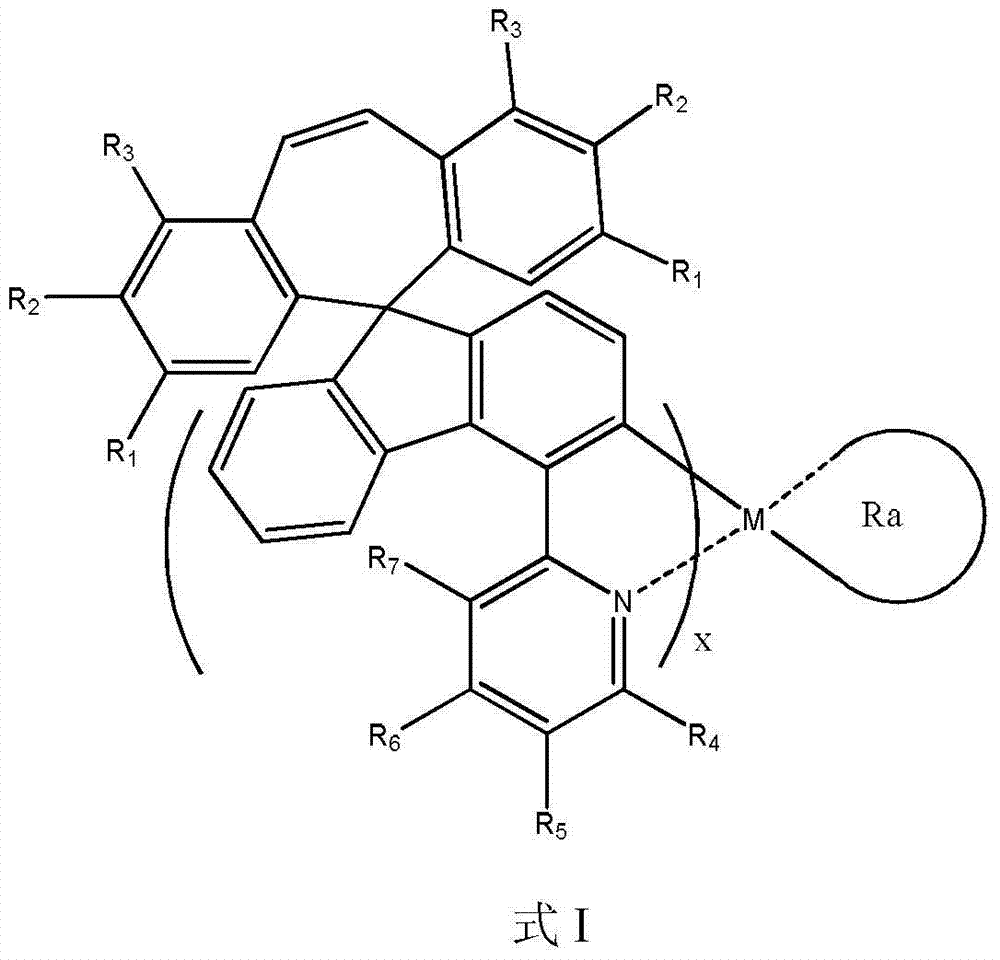
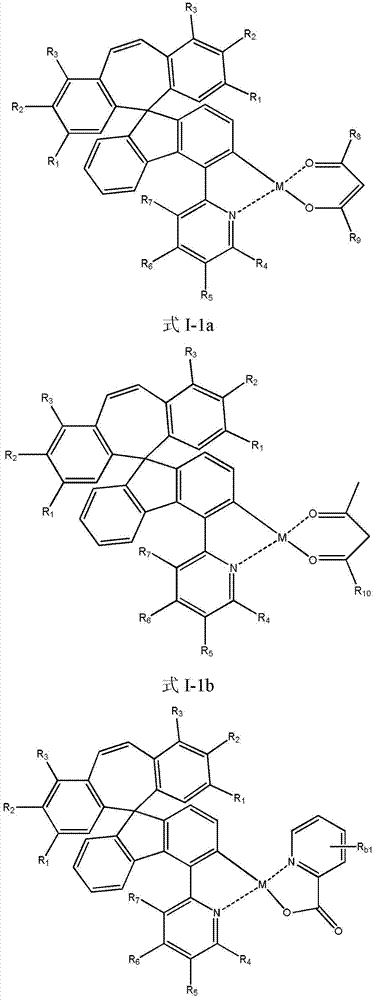
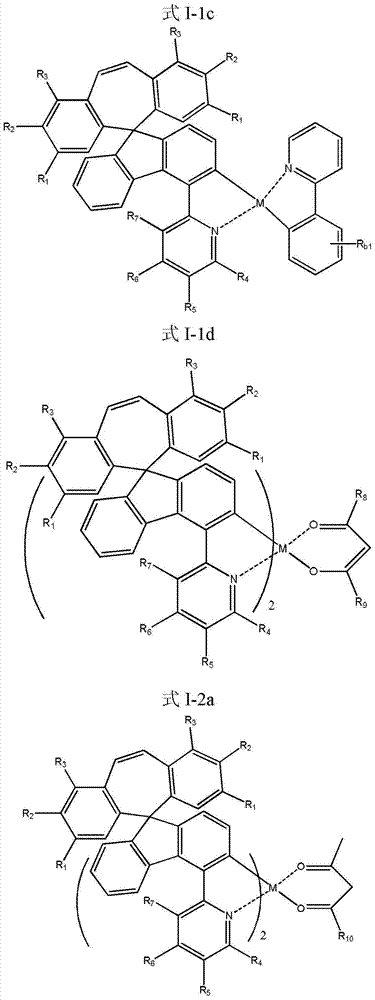
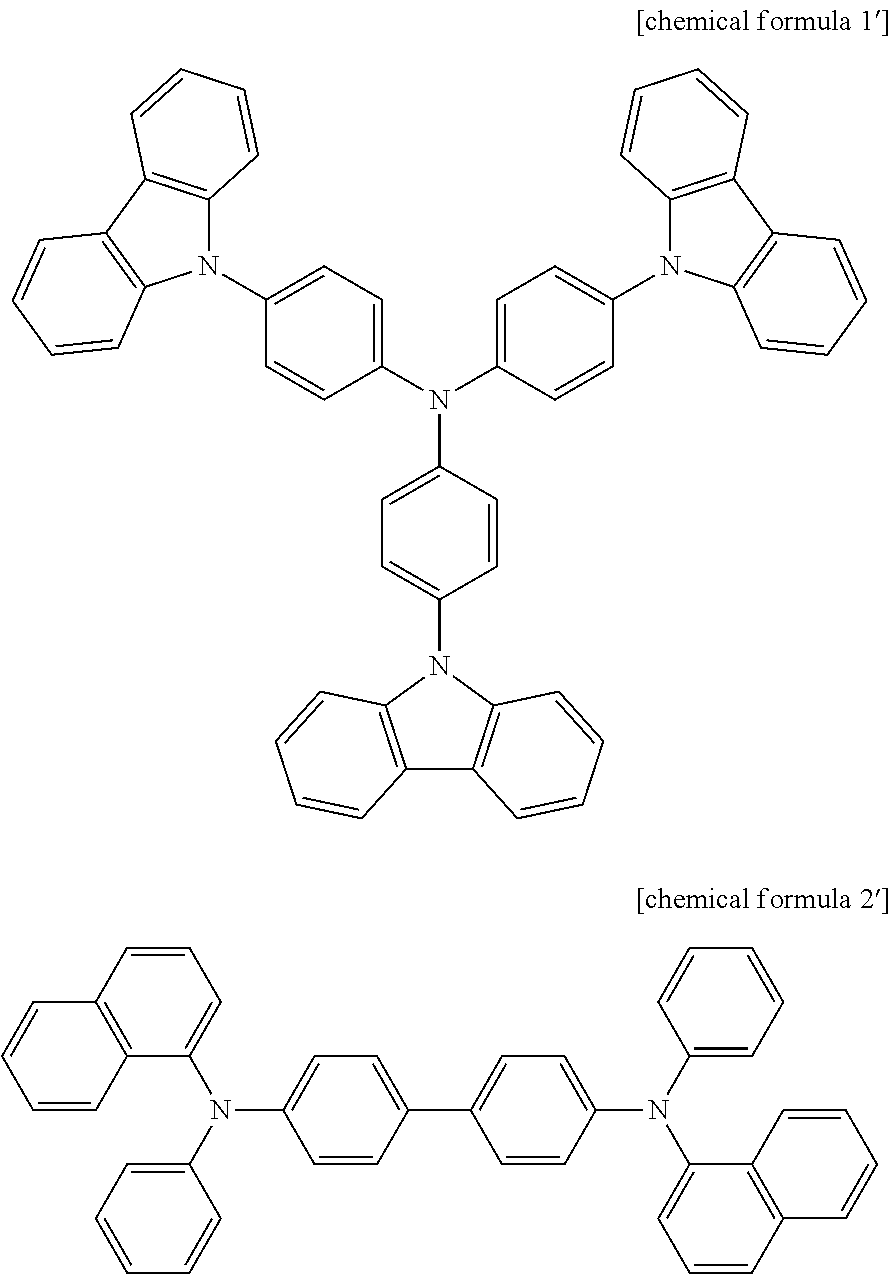
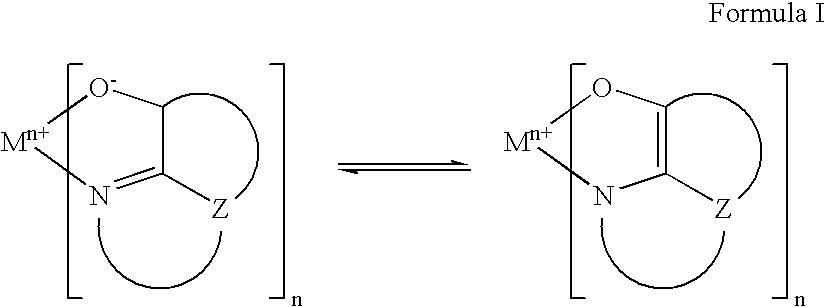Patents
Literature
65 results about "Phosphorescent oleds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
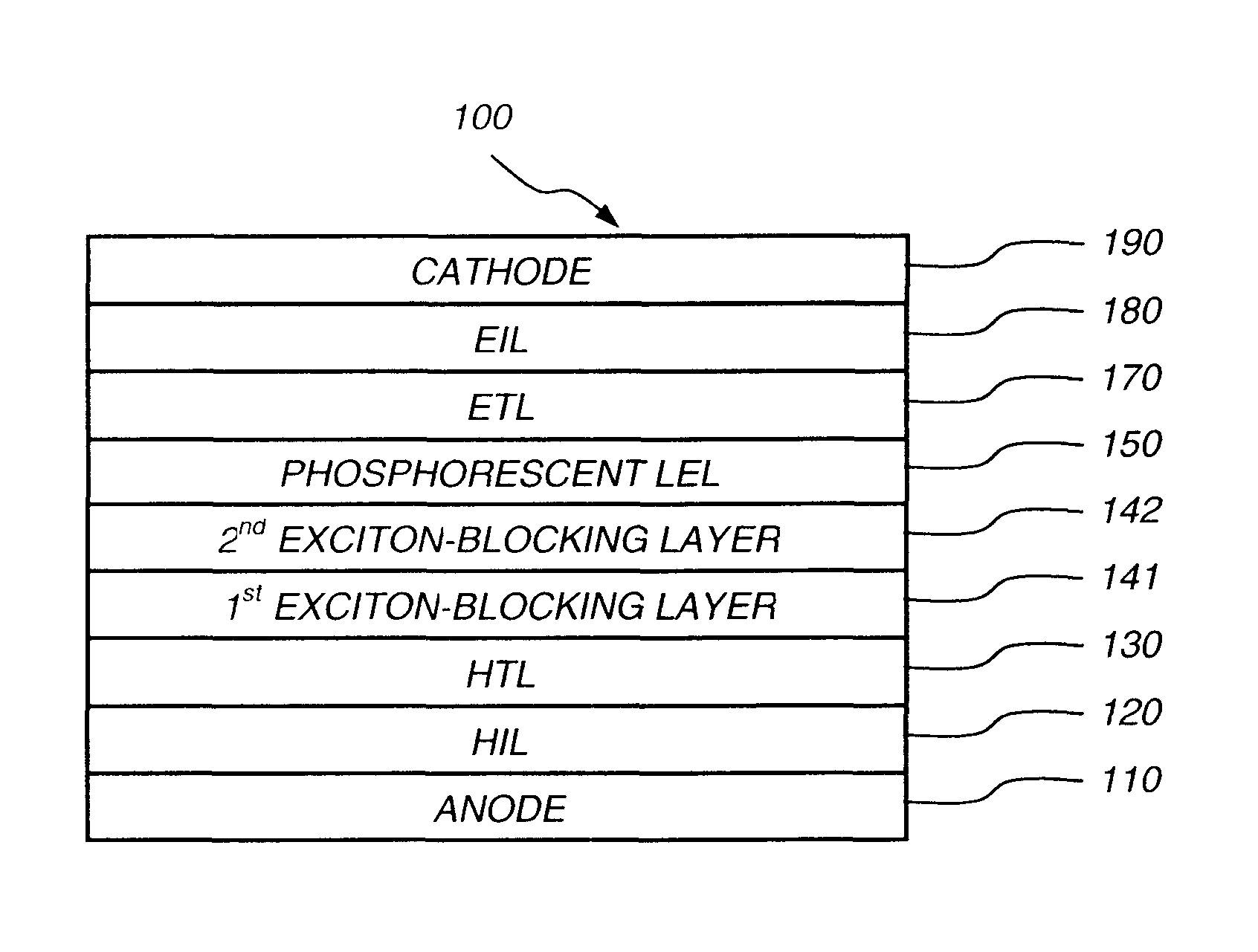
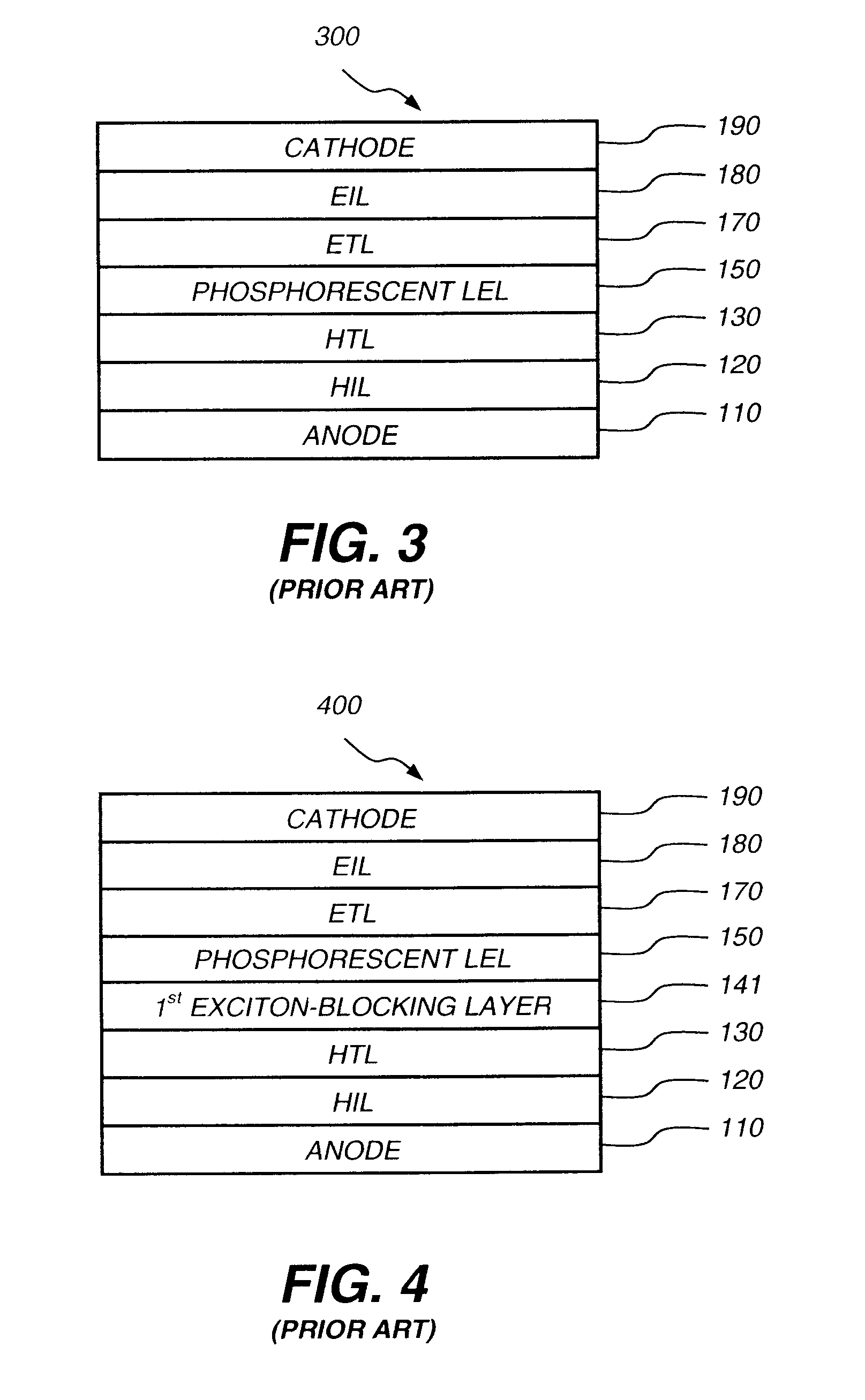
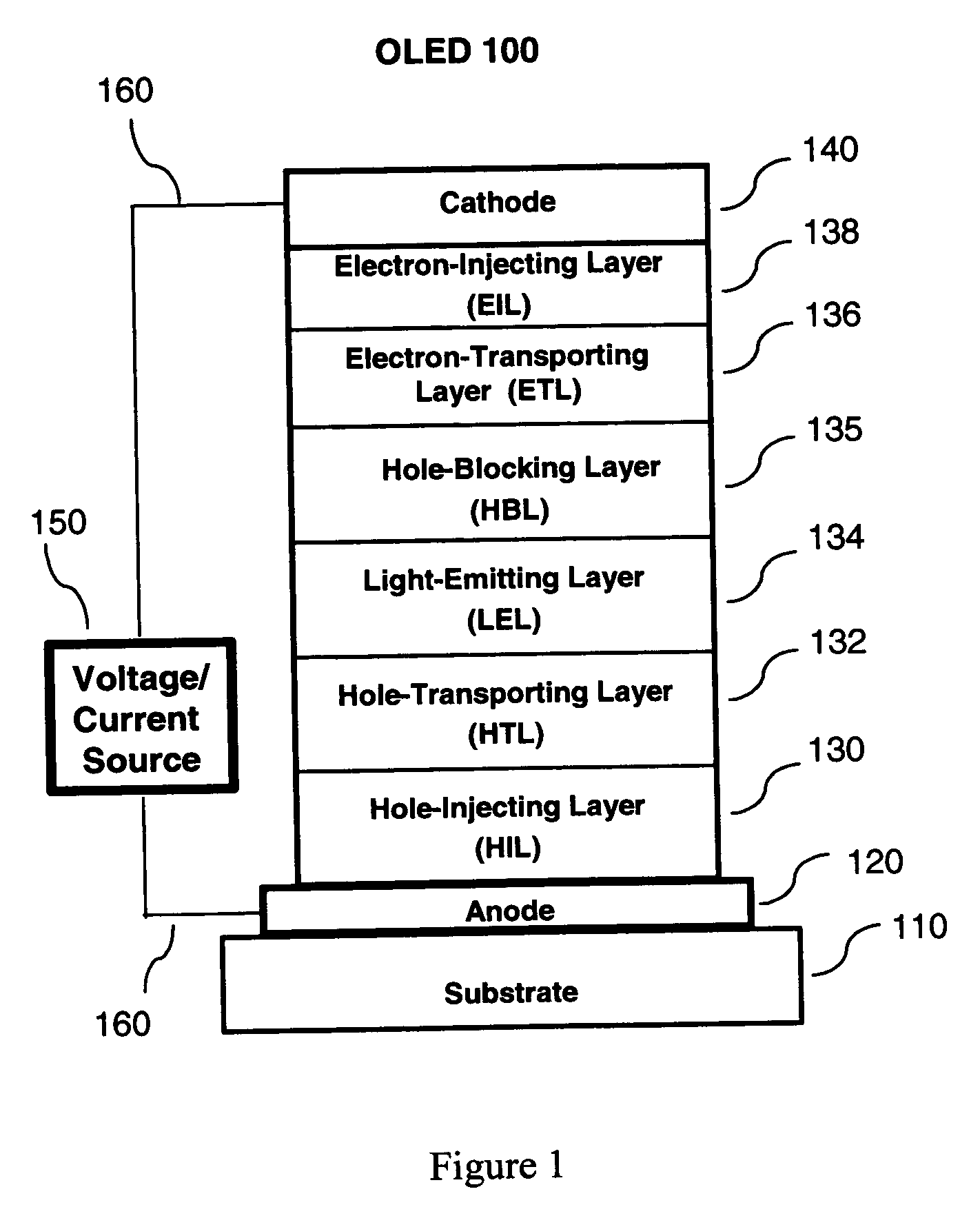
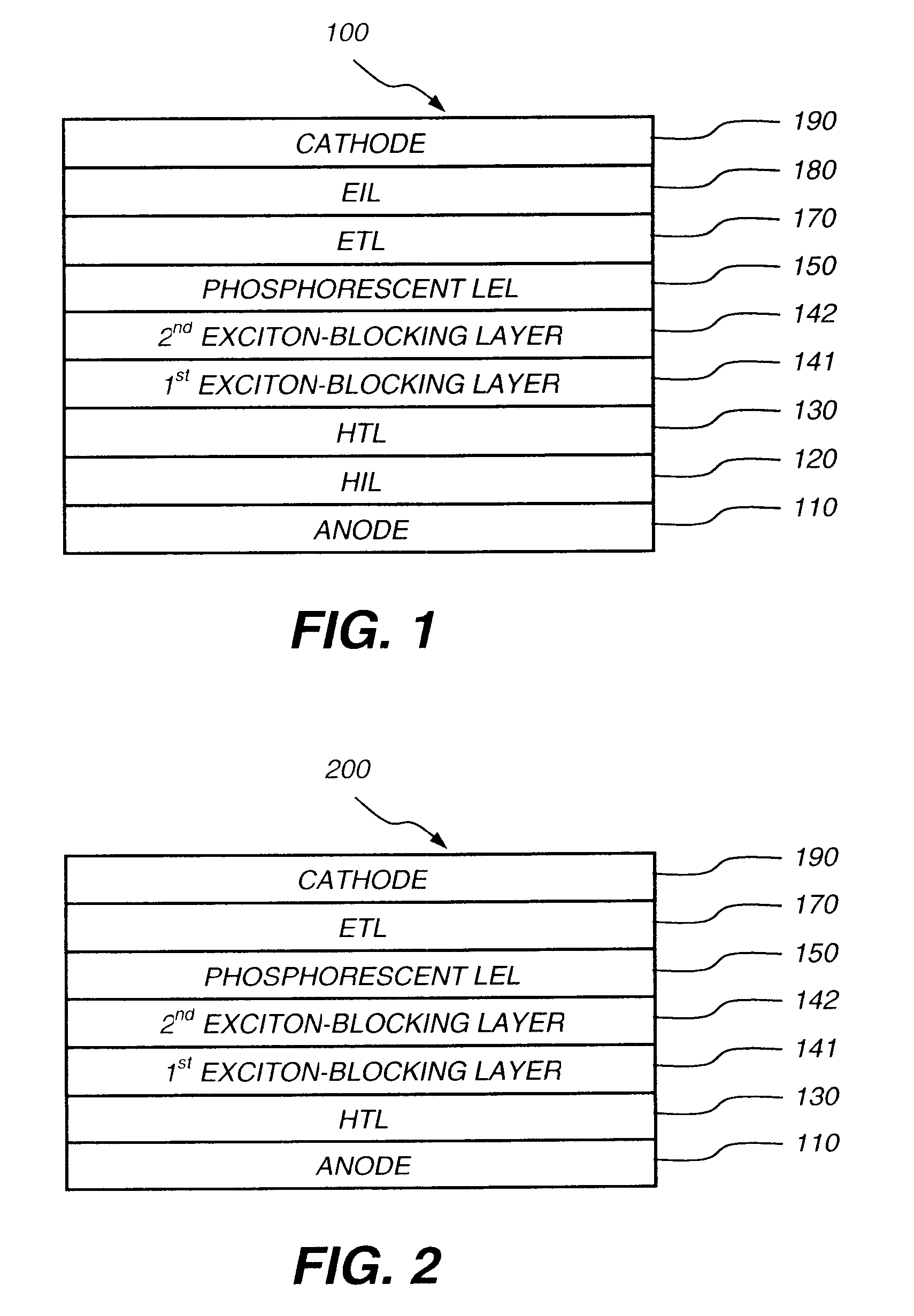
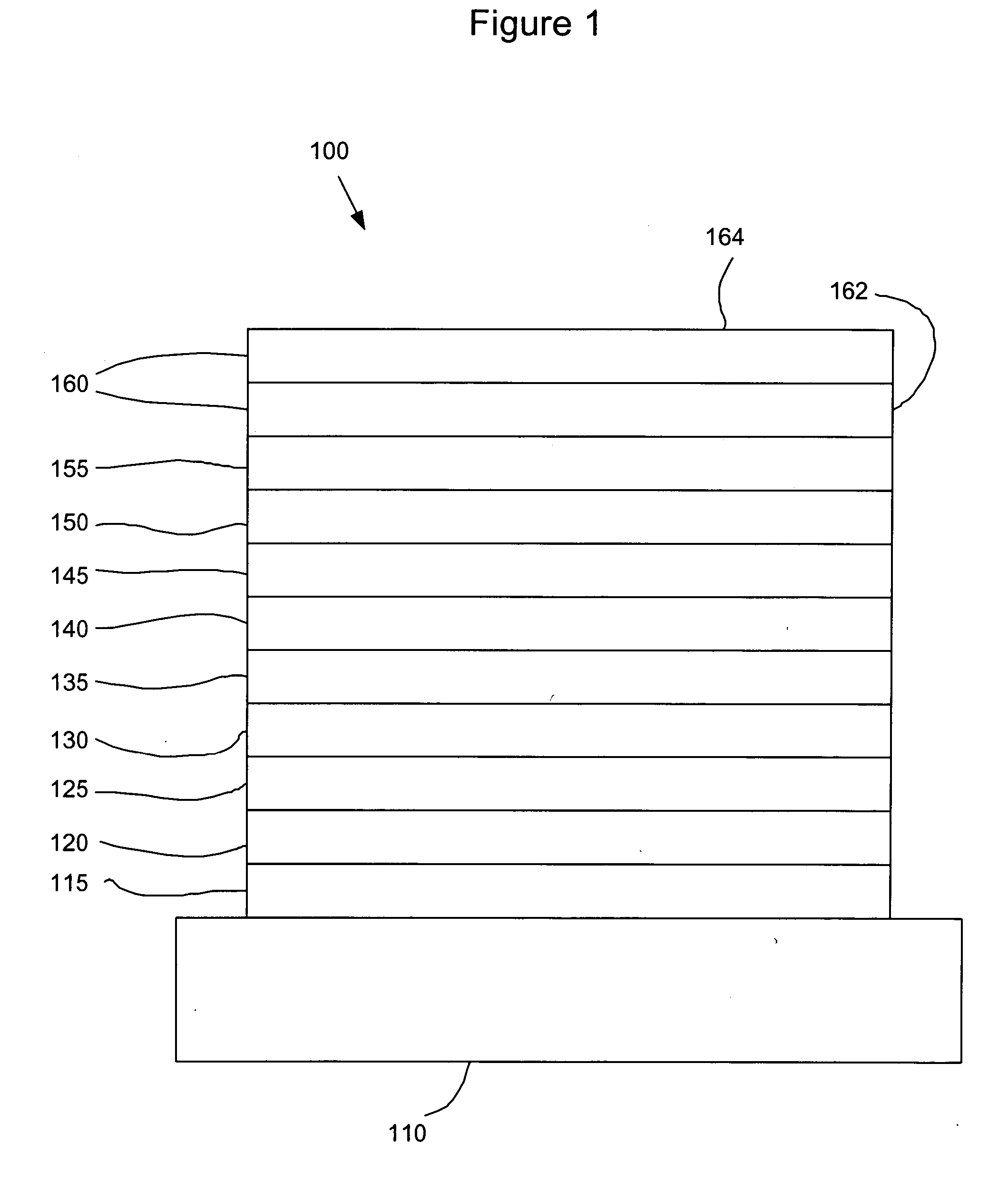
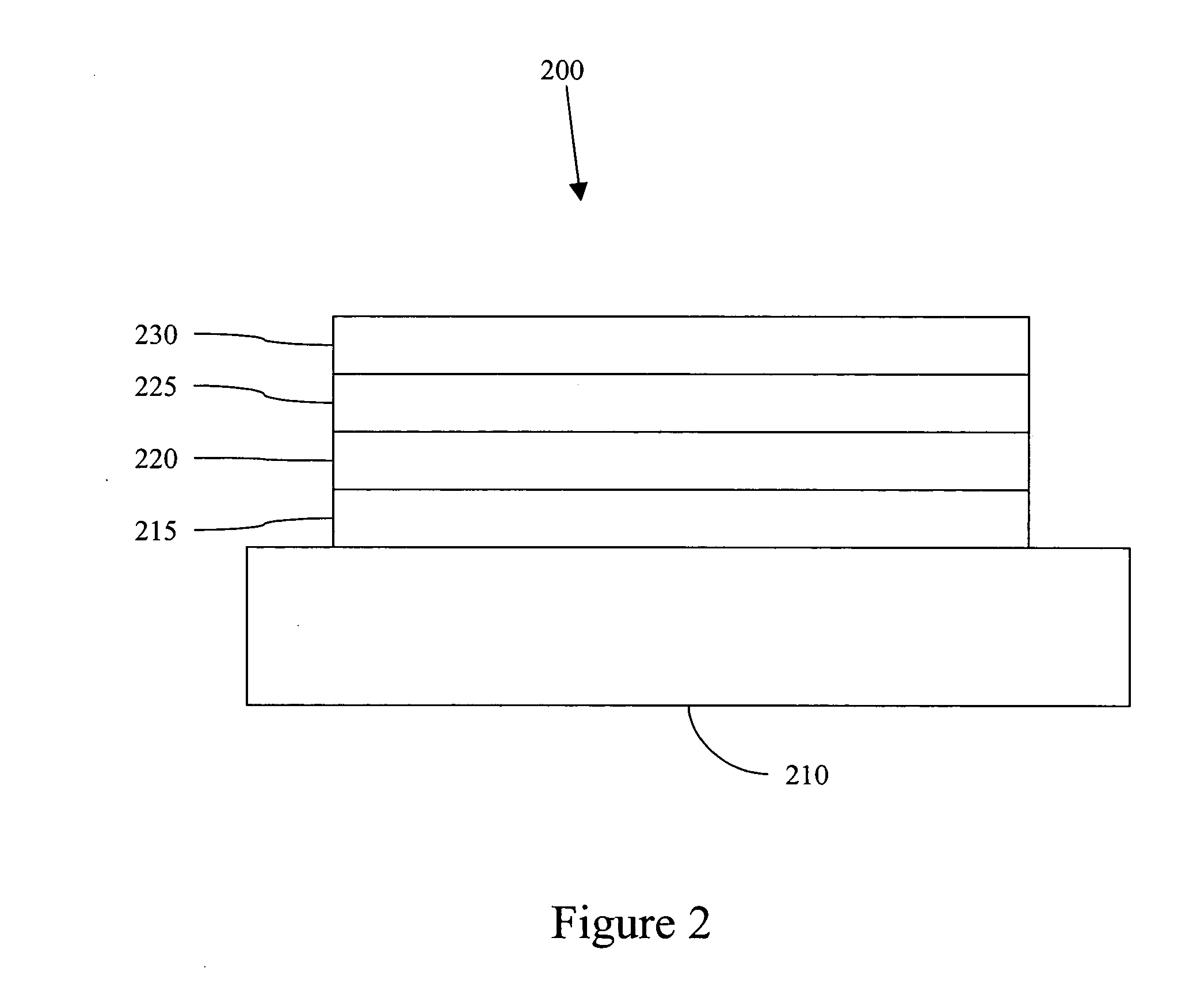
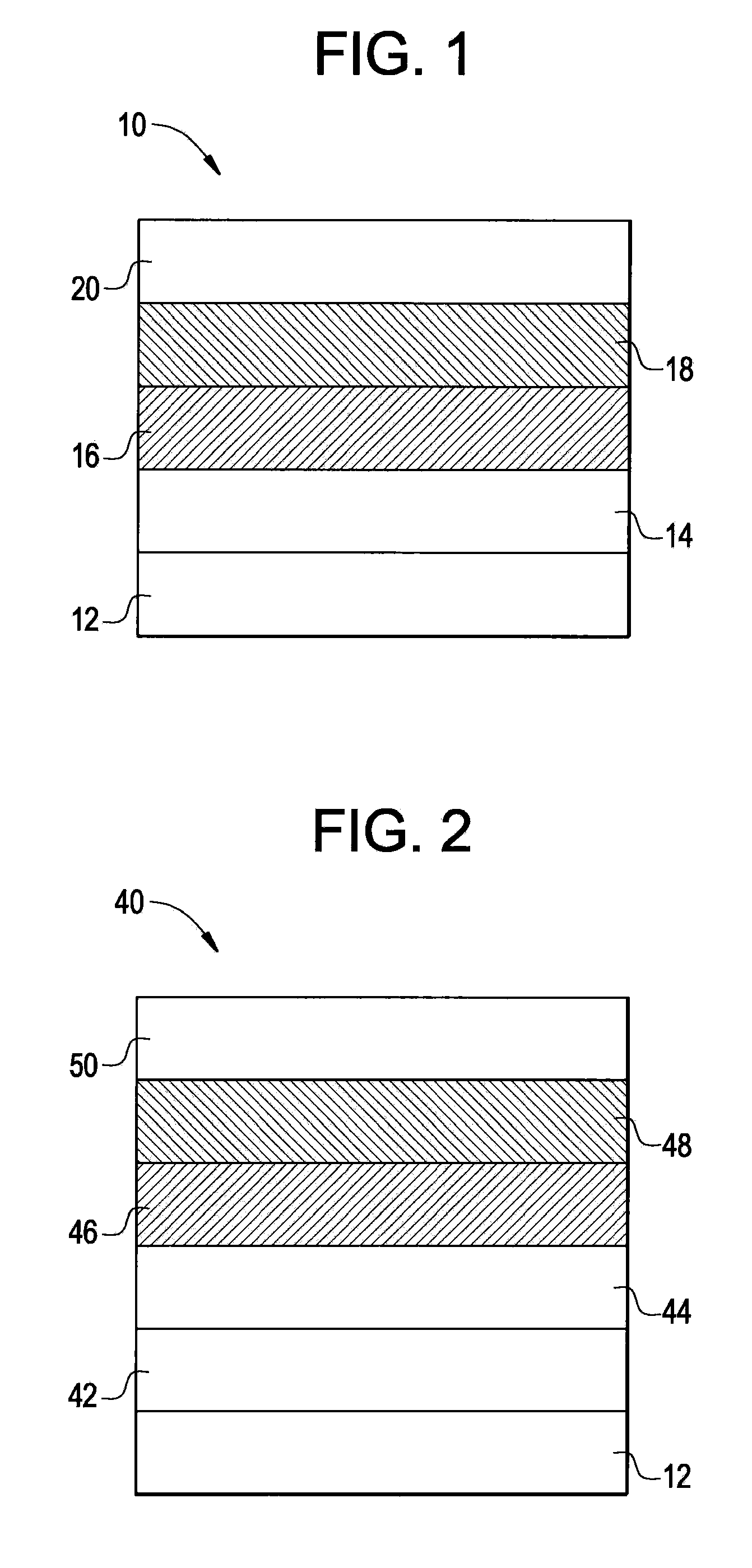
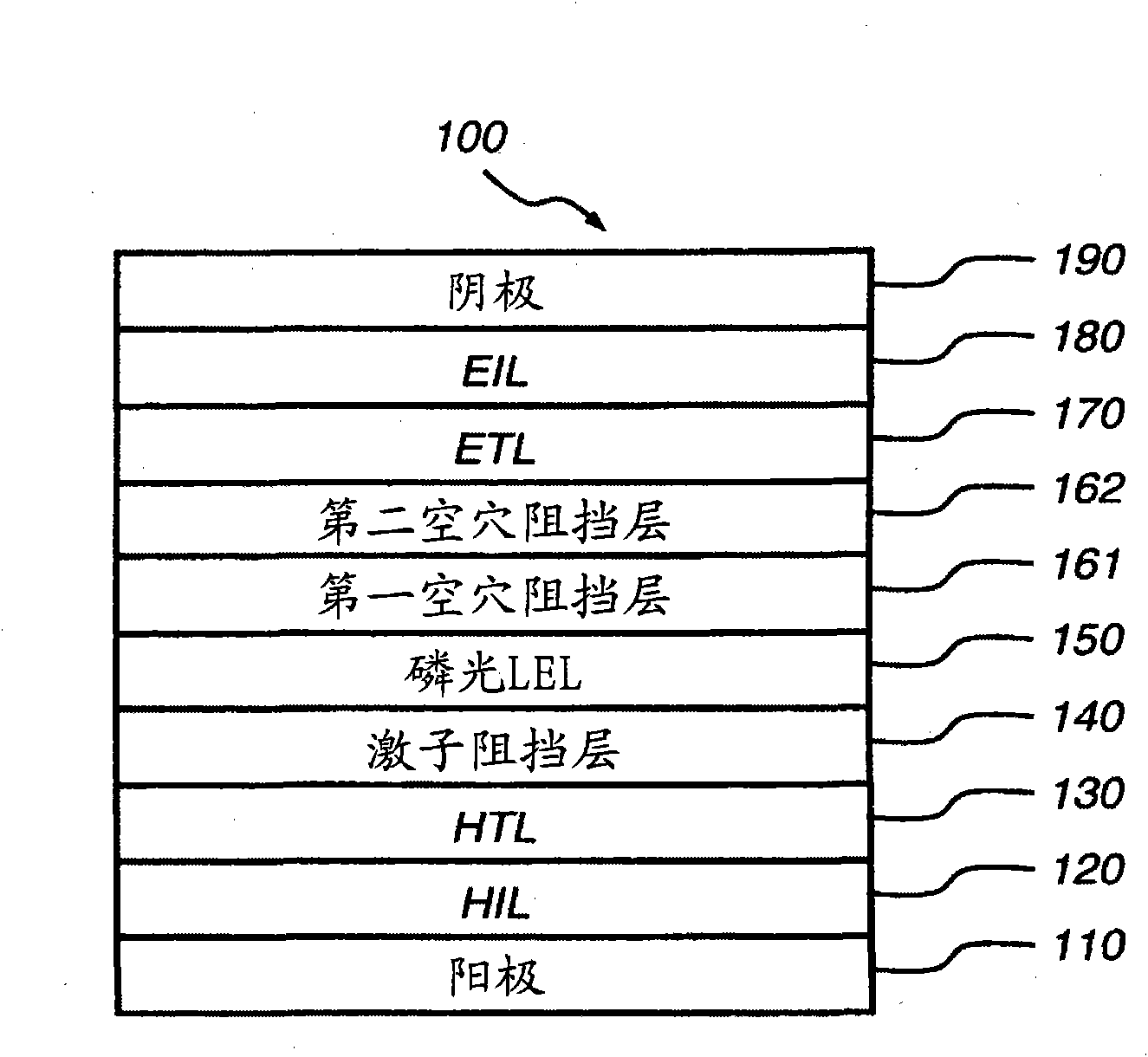
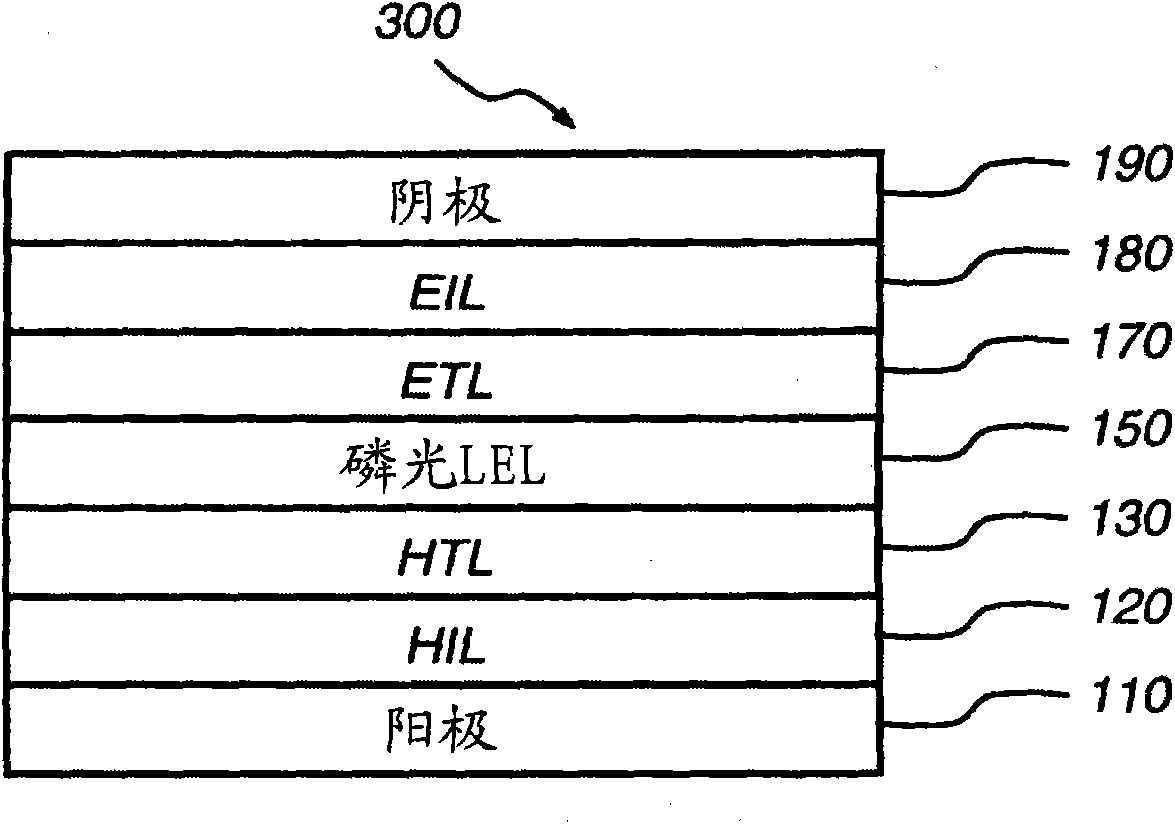
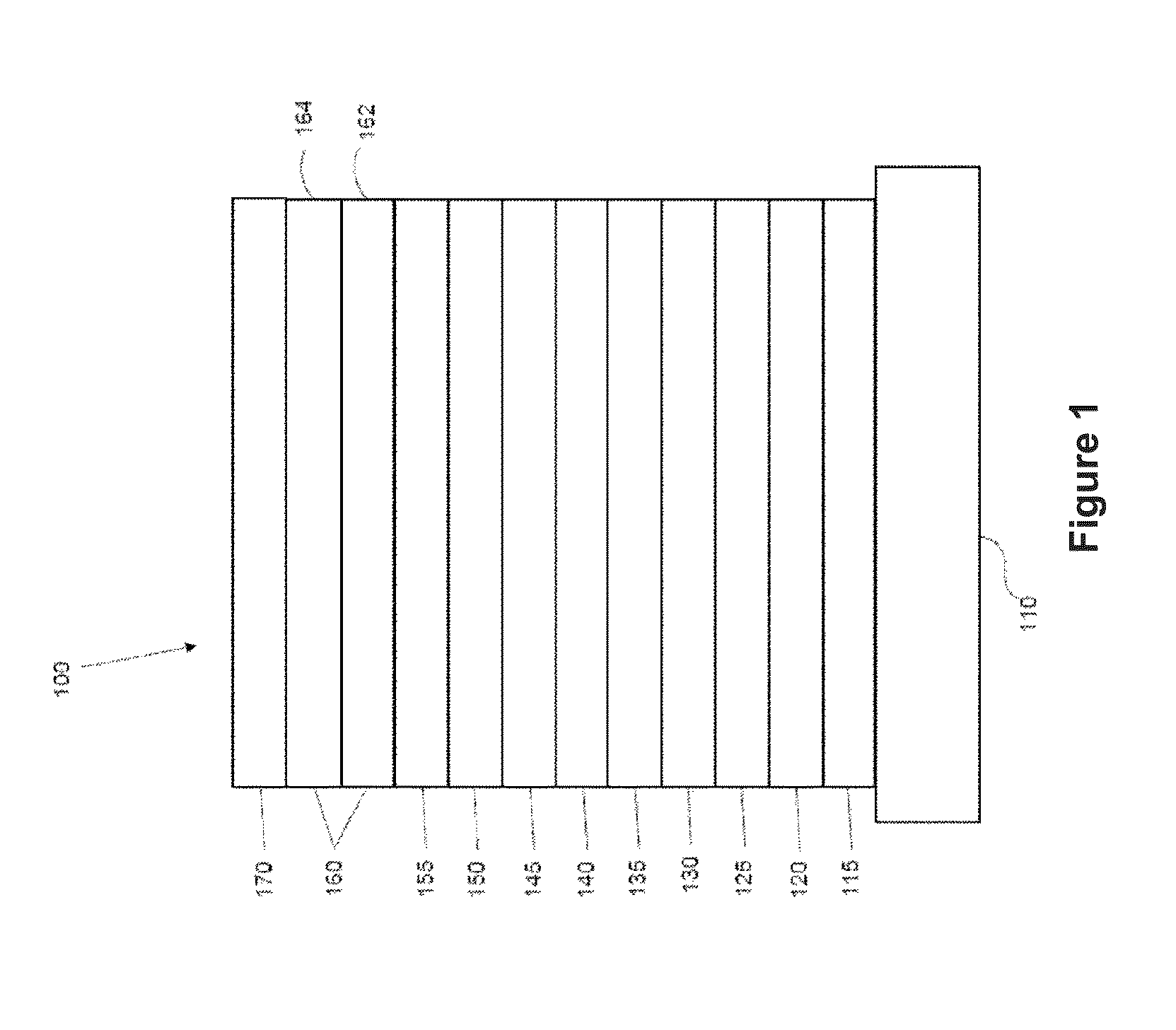
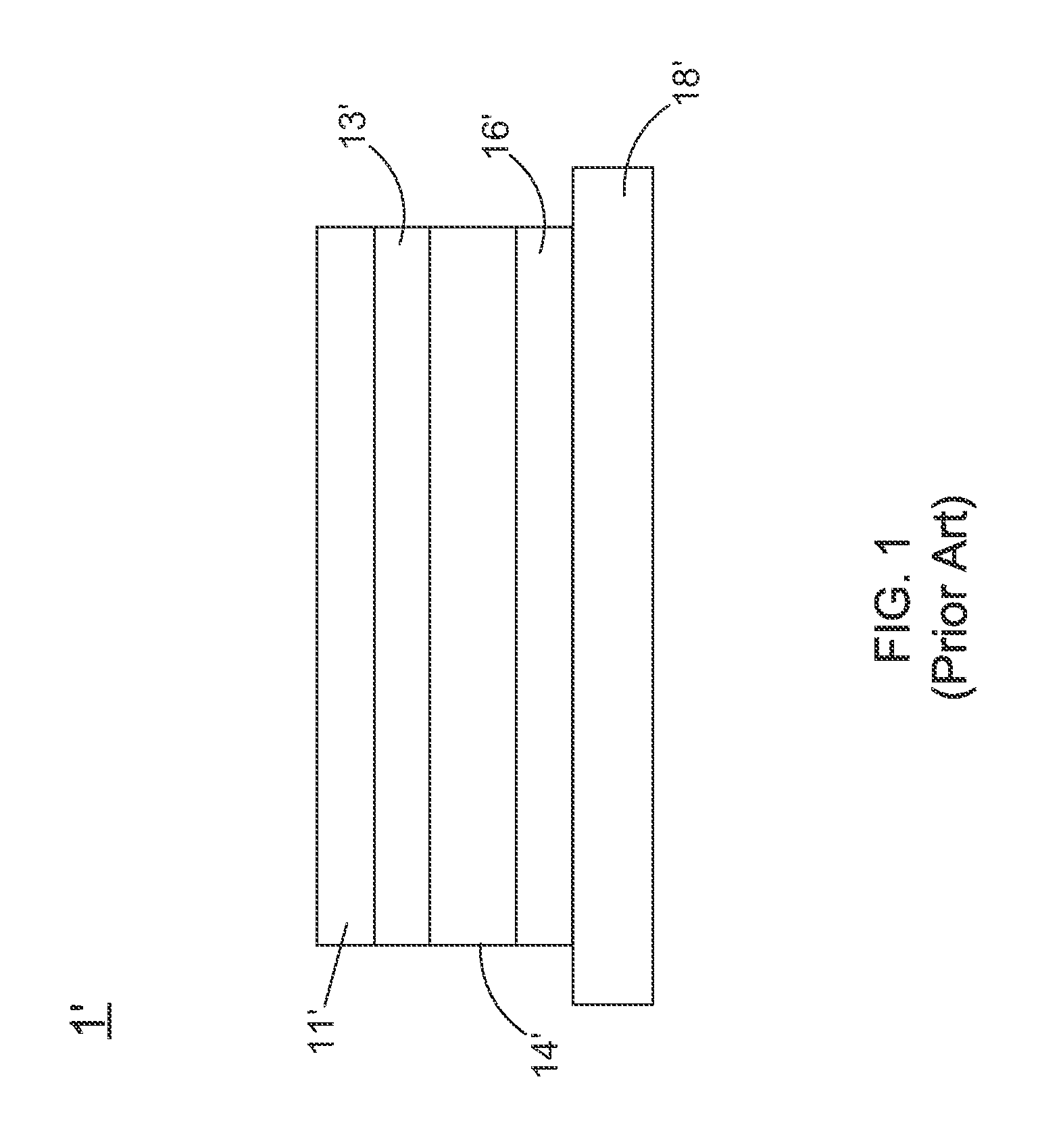
Phosphorescent oleds with exciton blocking layer
ActiveUS20060134460A1Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron holePhosphorescent oleds
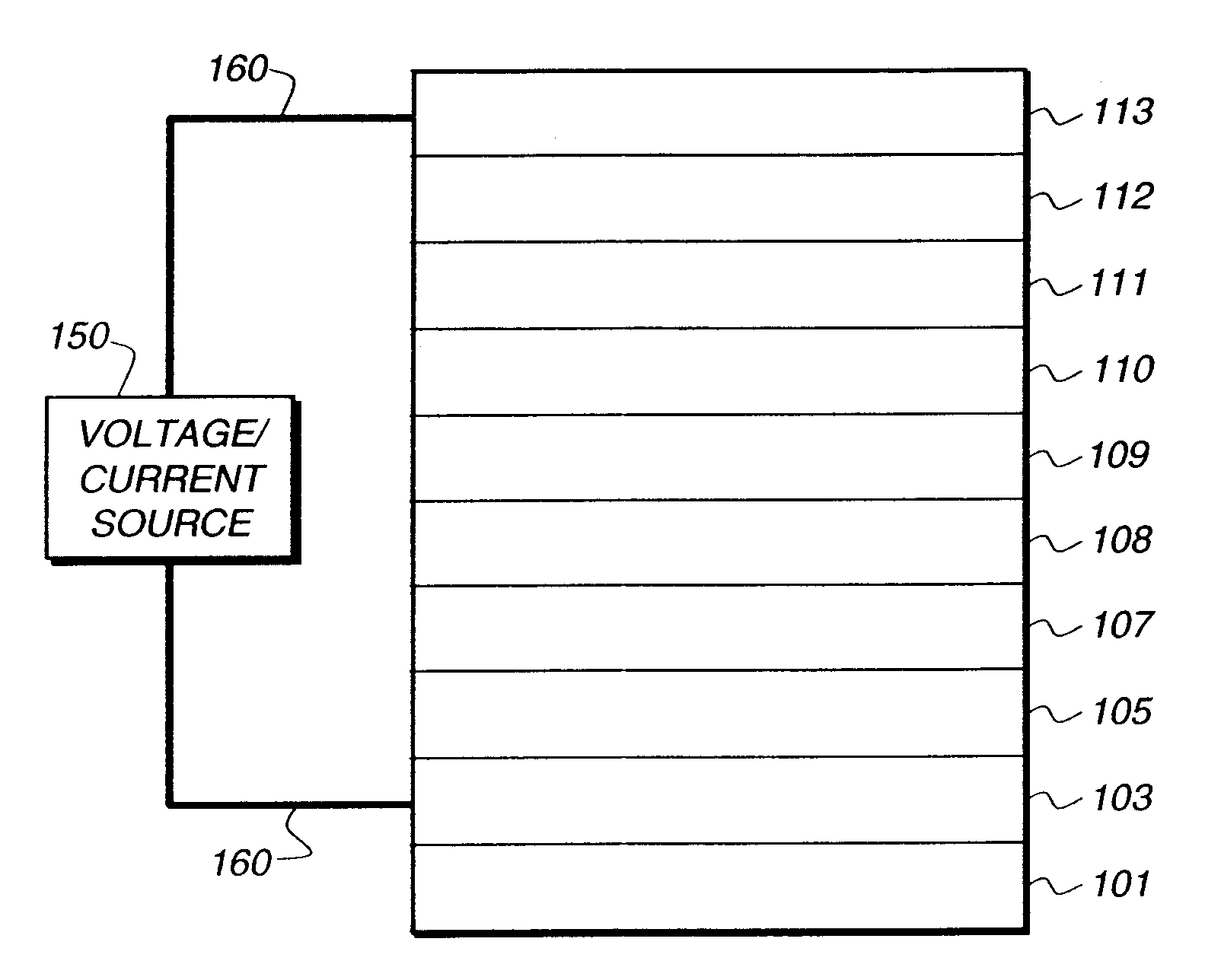
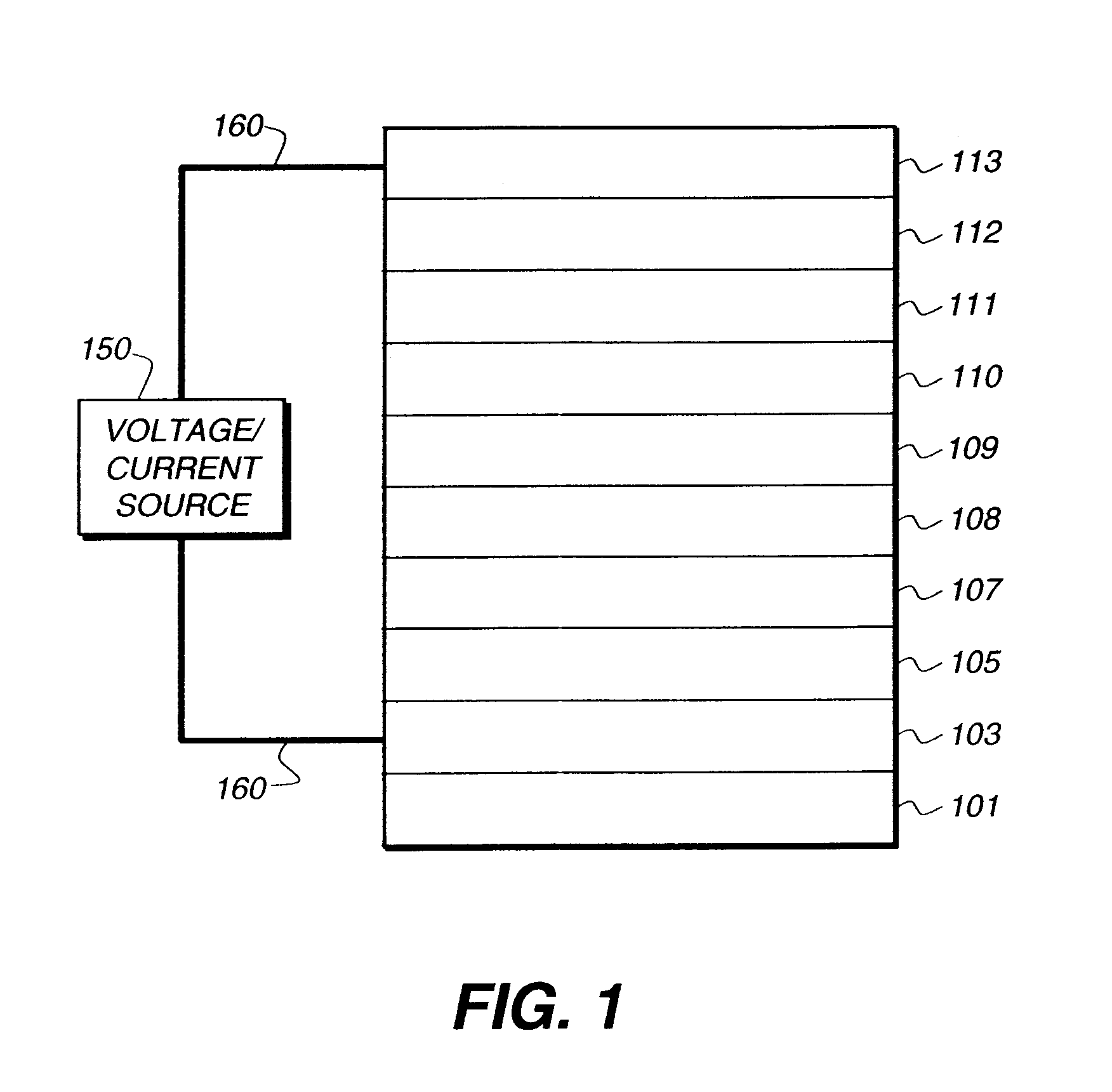
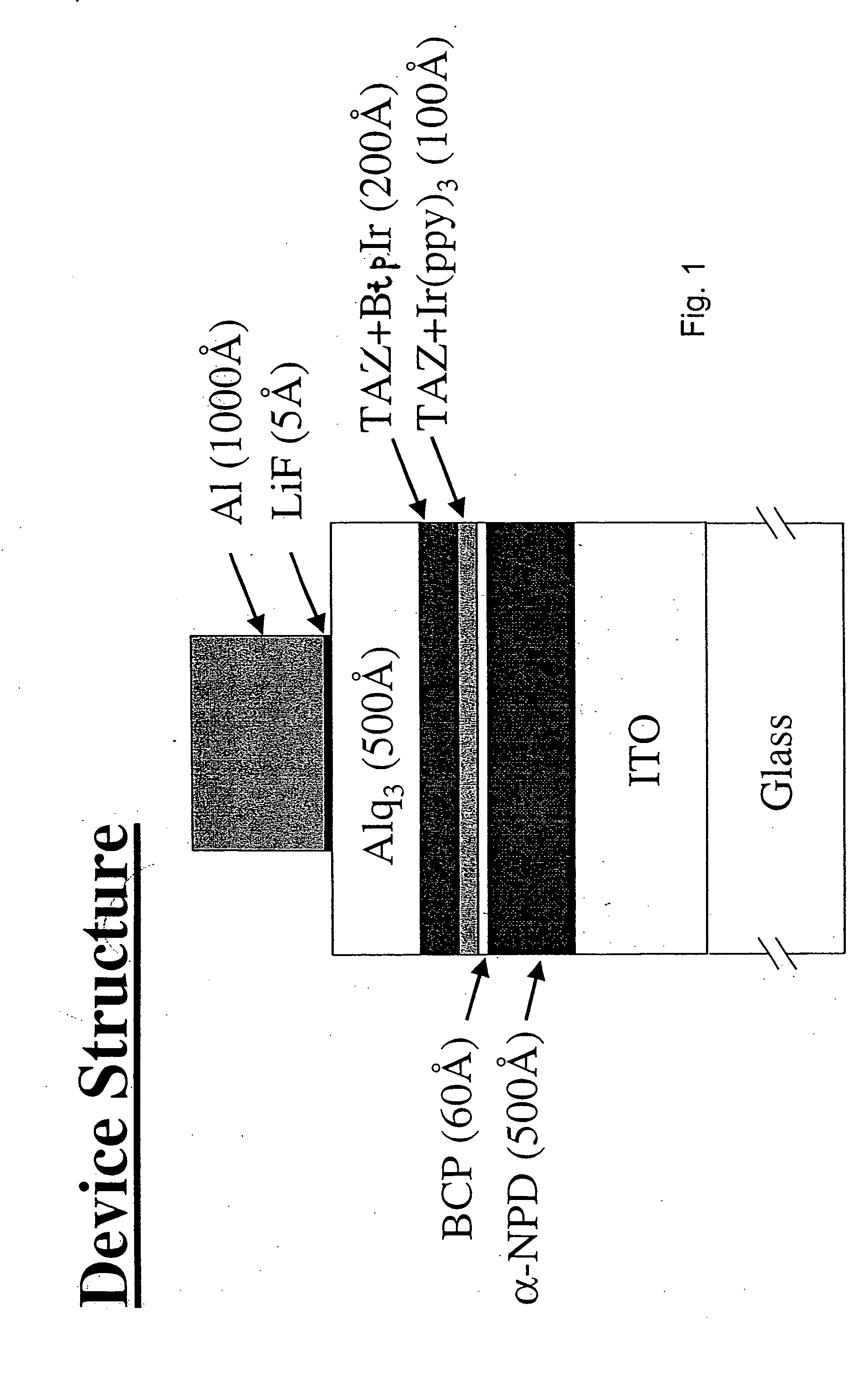
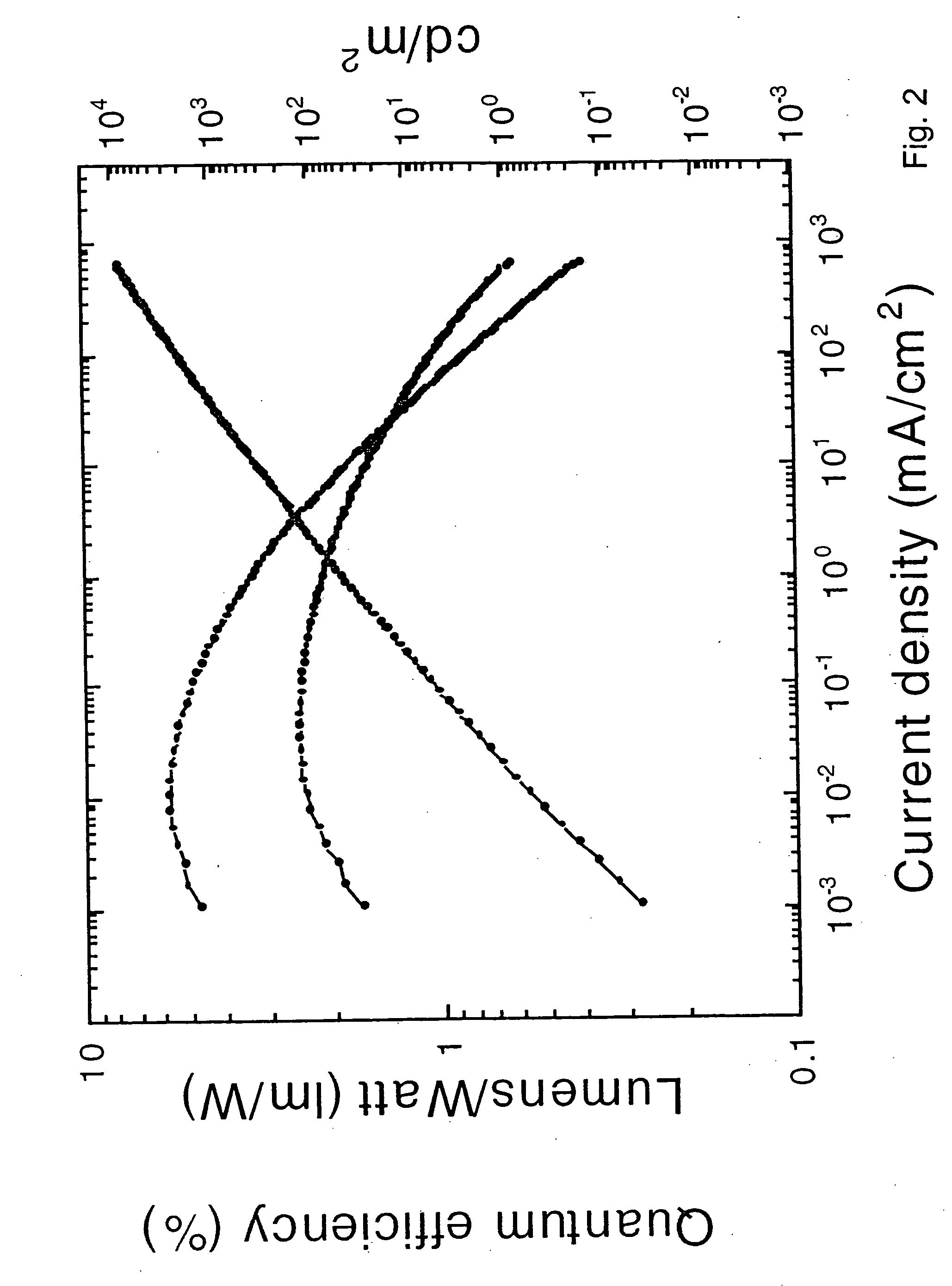
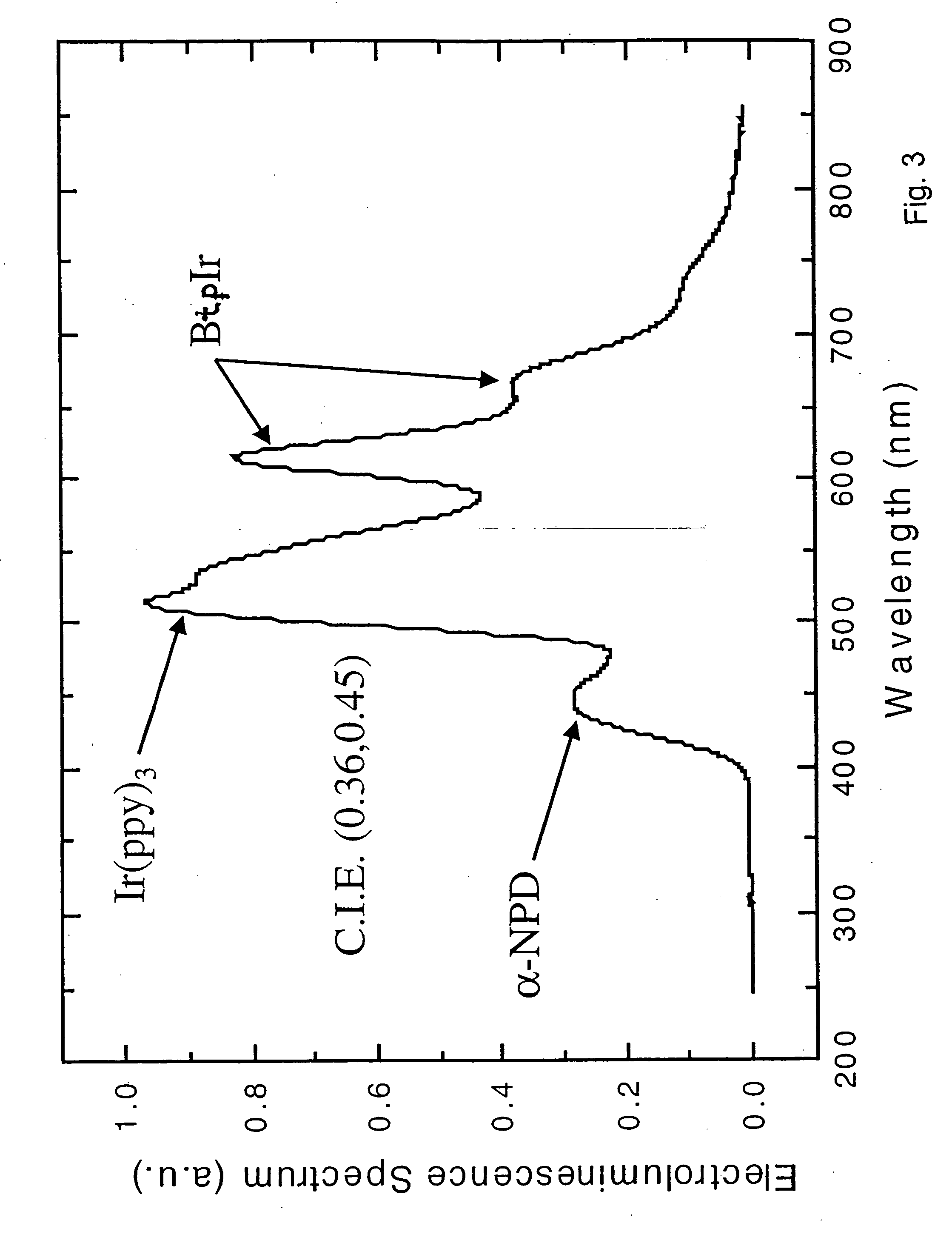
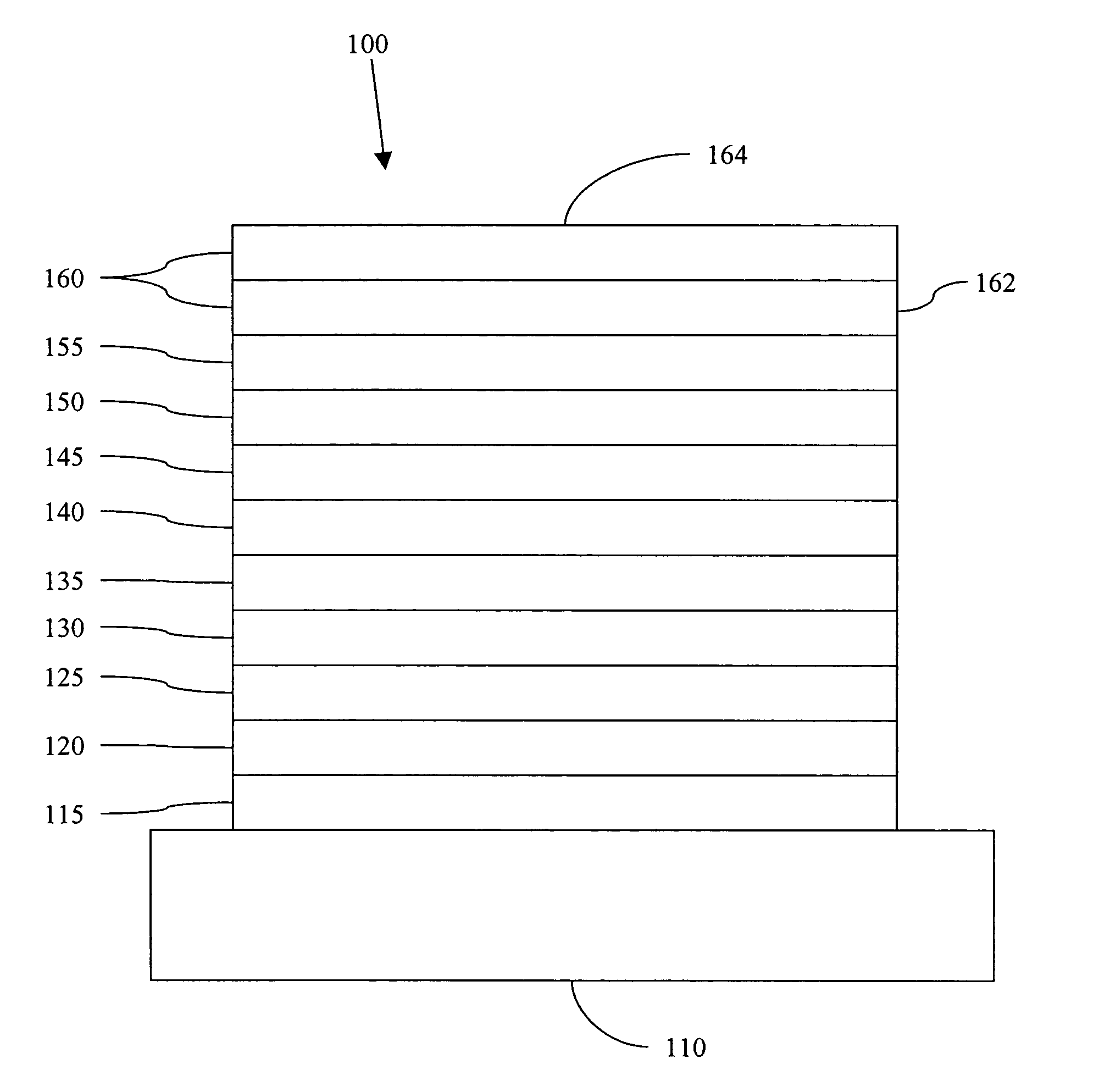
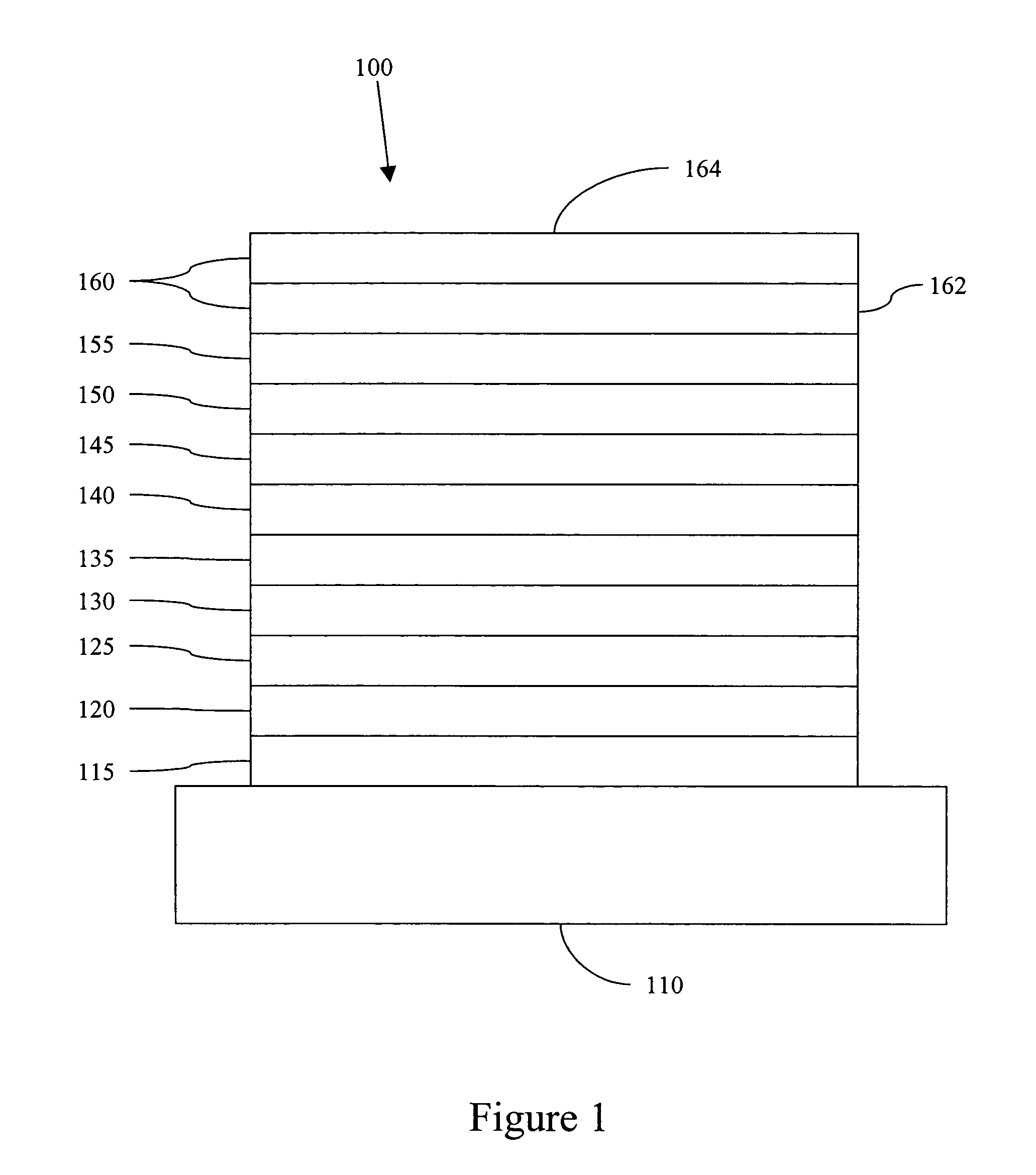
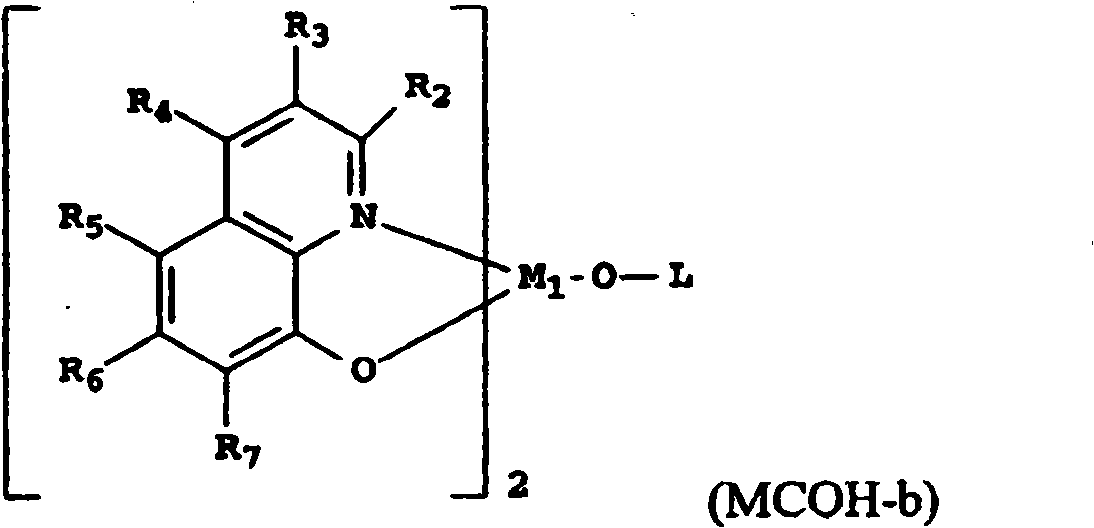
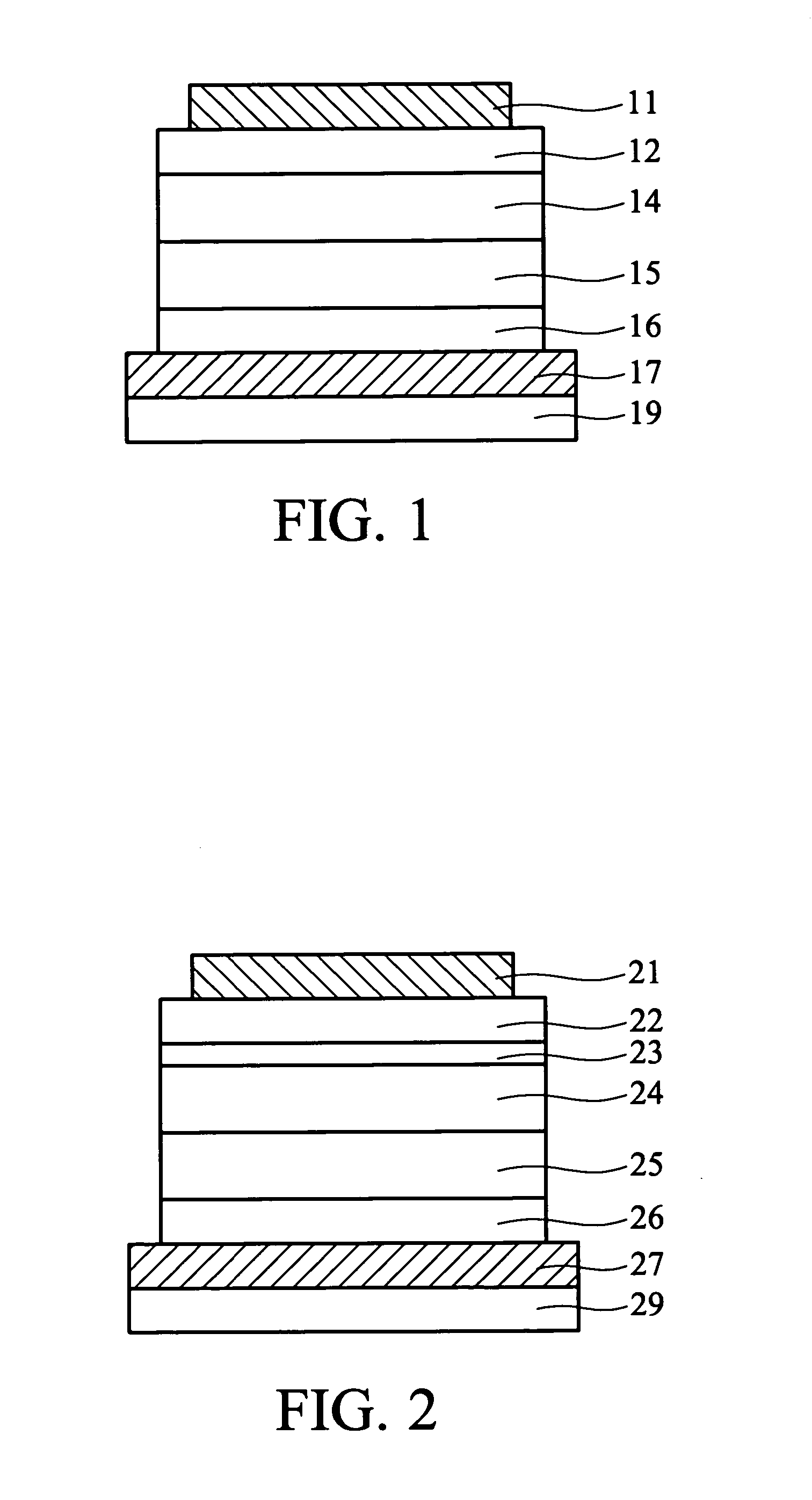
An electroluminescent device comprises a cathode and an anode; and, located therebetween, a light-emitting layer (LEL) comprising at least one hole transporting co-host and at least one electron transporting co-host, together with at least one phosphorescent emitter, and wherein the triplet energy of each of the co-host materials is greater than the triplet energy of the phosphorescent emitter, and further containing an exciton blocking layer comprising a hole transporting material with triplet energy greater or equal to 2.5 eV adjacent the emitting layer on the anode side. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency at low voltage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
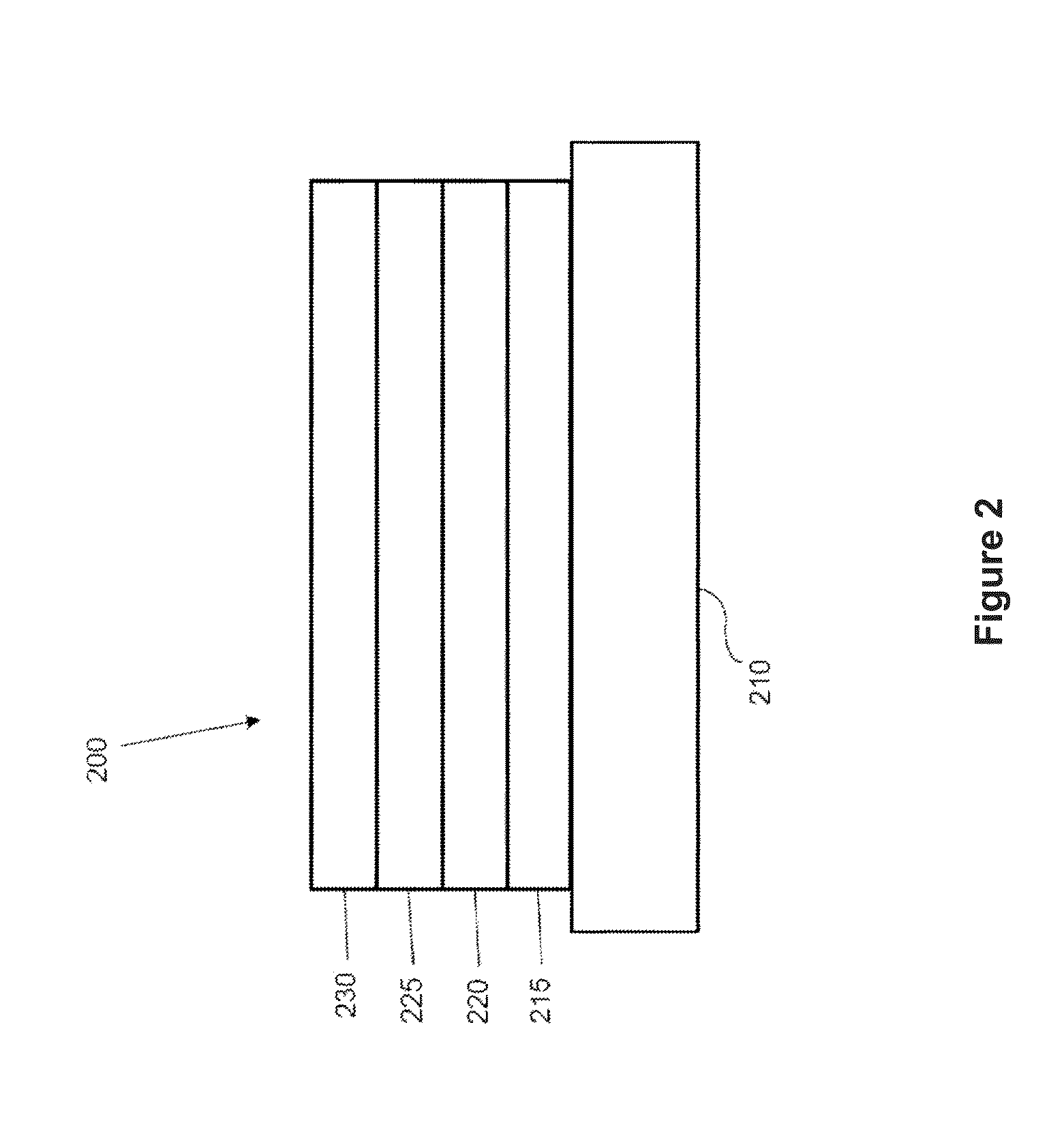
Phosphorescent OLEDs with exciton blocking layer
ActiveUS7597967B2Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorescent oledsLow voltage
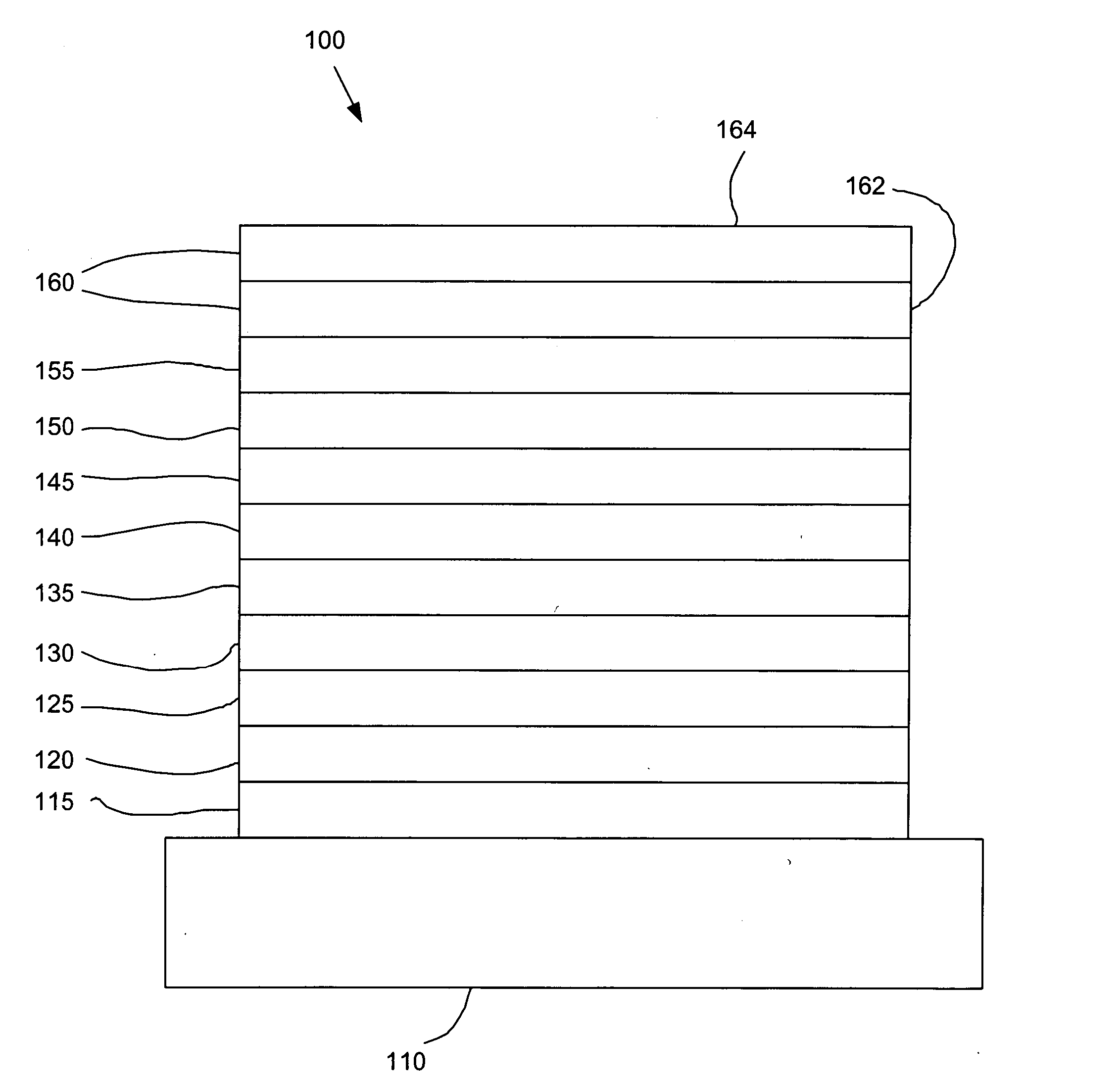
An electroluminescent device comprises a cathode and an anode; and, located therebetween, a light-emitting layer (LEL) comprising at least one hole transporting co-host and at least one electron transporting co-host, together with at least one phosphorescent emitter, and wherein the triplet energy of each of the co-host materials is greater than the triplet energy of the phosphorescent emitter, and further containing an exciton blocking layer comprising a hole transporting material with triplet energy greater or equal to 2.5 eV adjacent the emitting layer on the anode side. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency at low voltage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
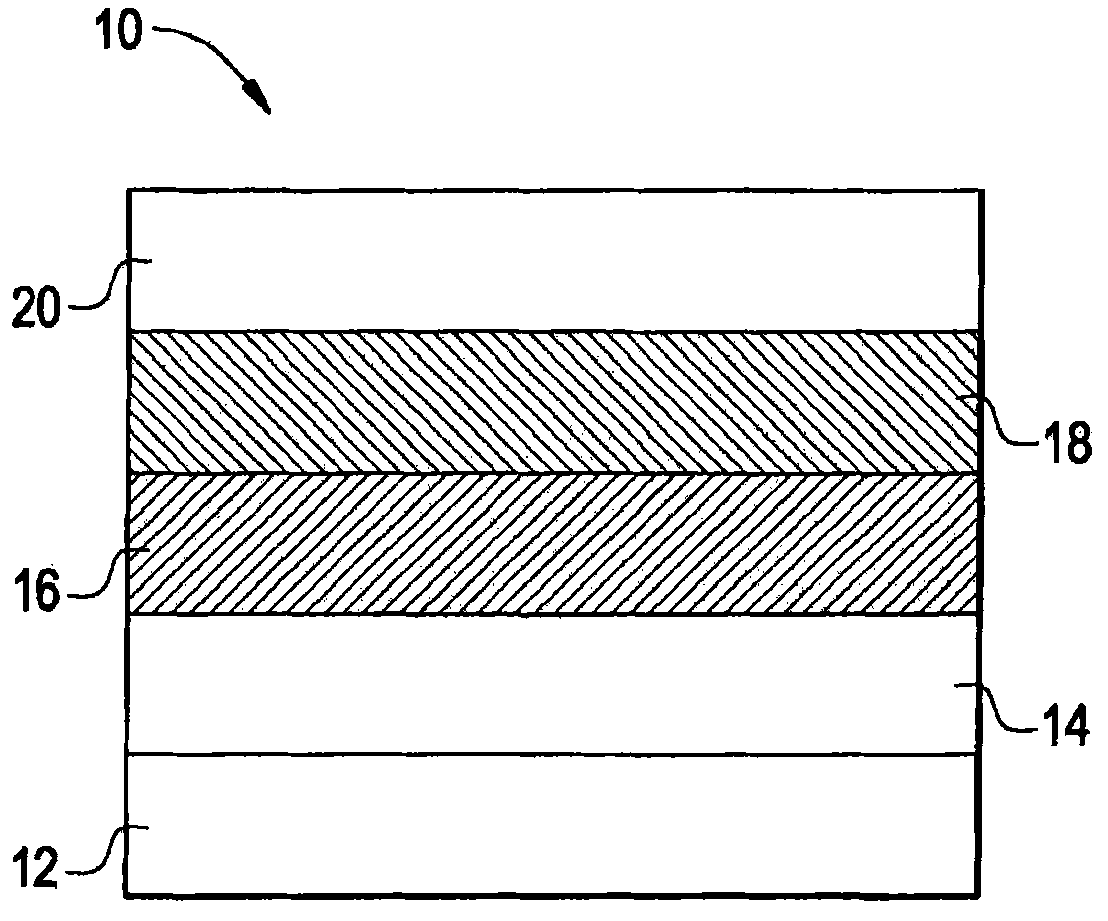
High efficiency multi-color electro-phosphorescent OLEDs
InactiveUS7009338B2High power and quantum efficiencyBright whiteDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesDopantPhosphorescent oleds
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
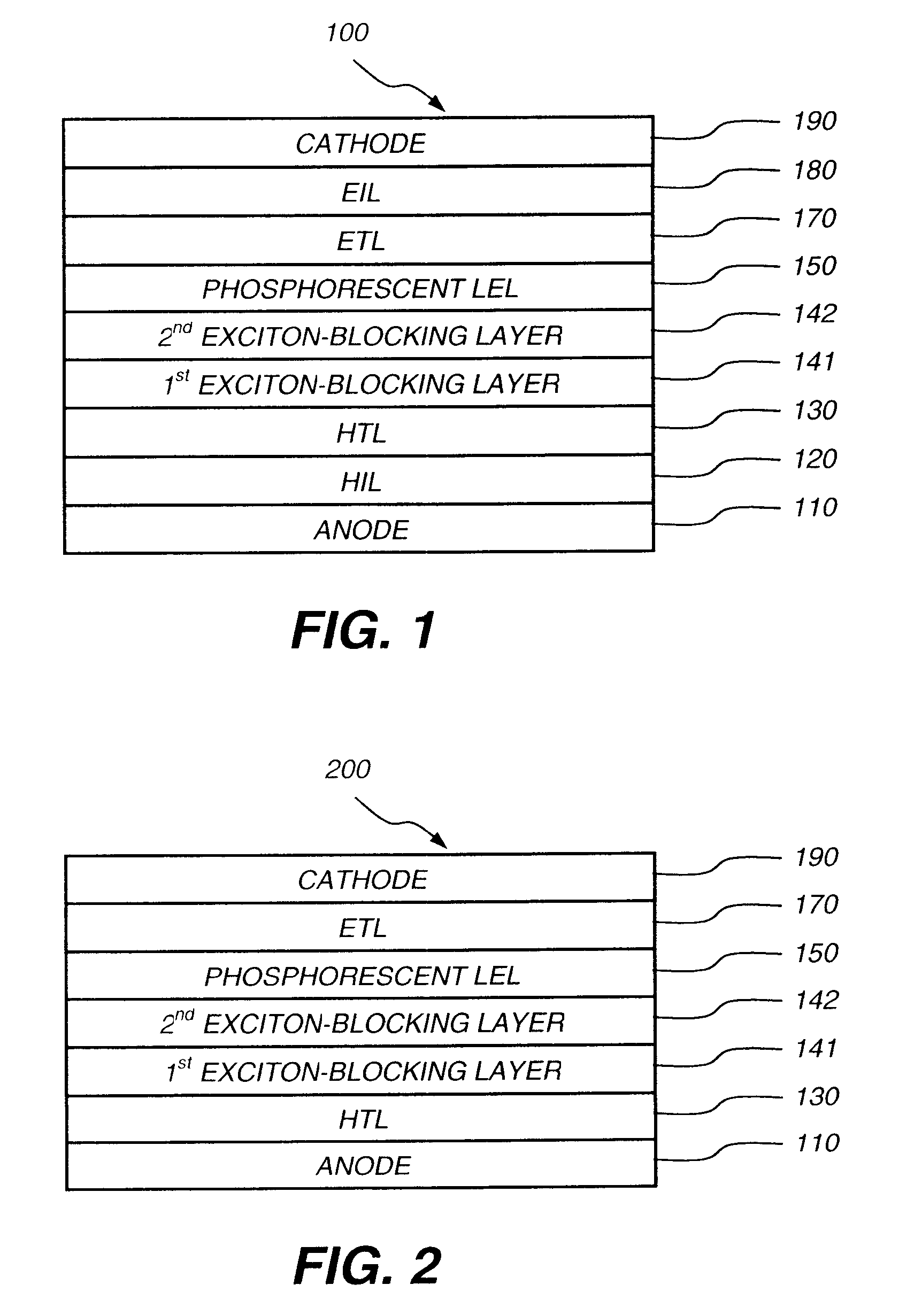
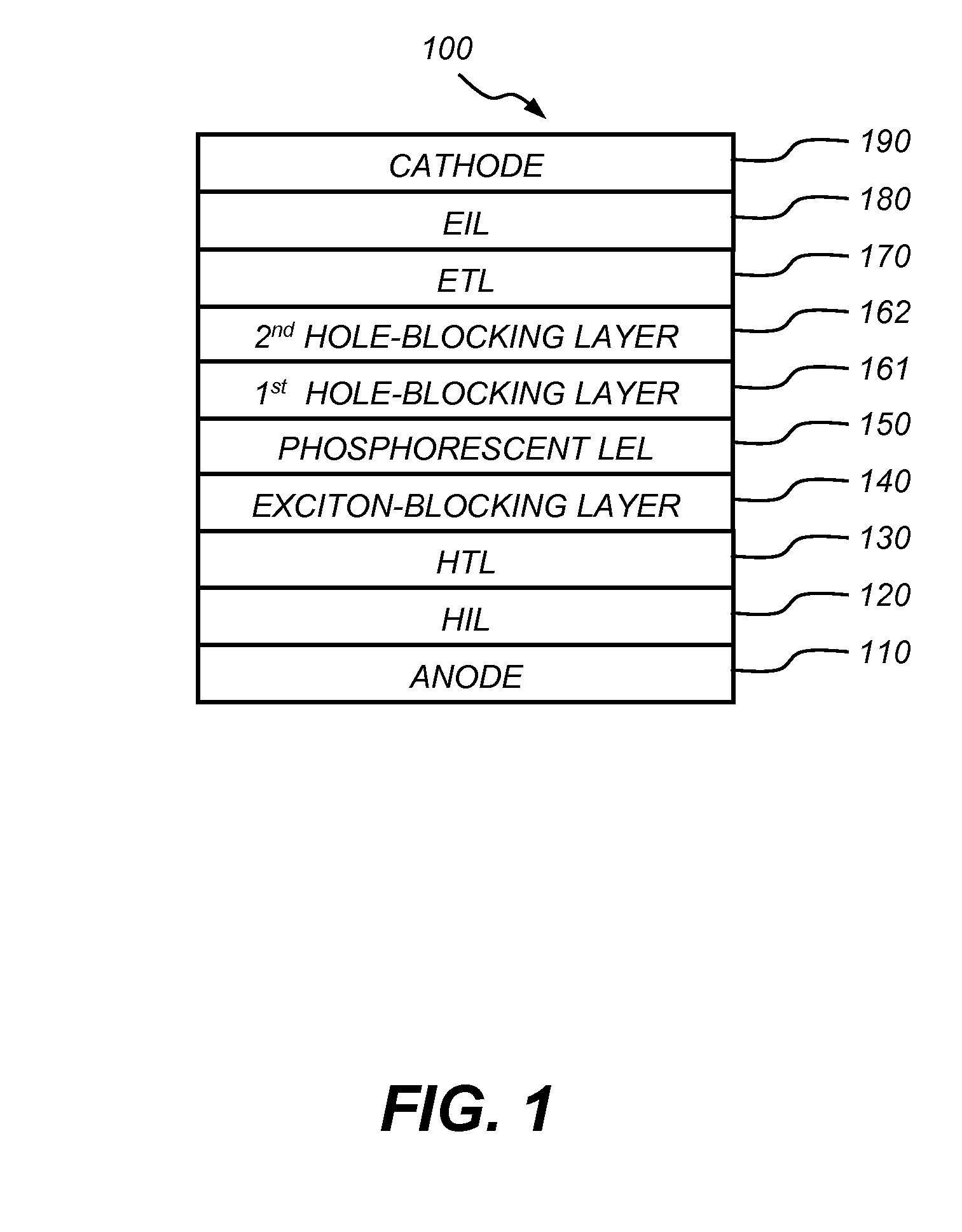
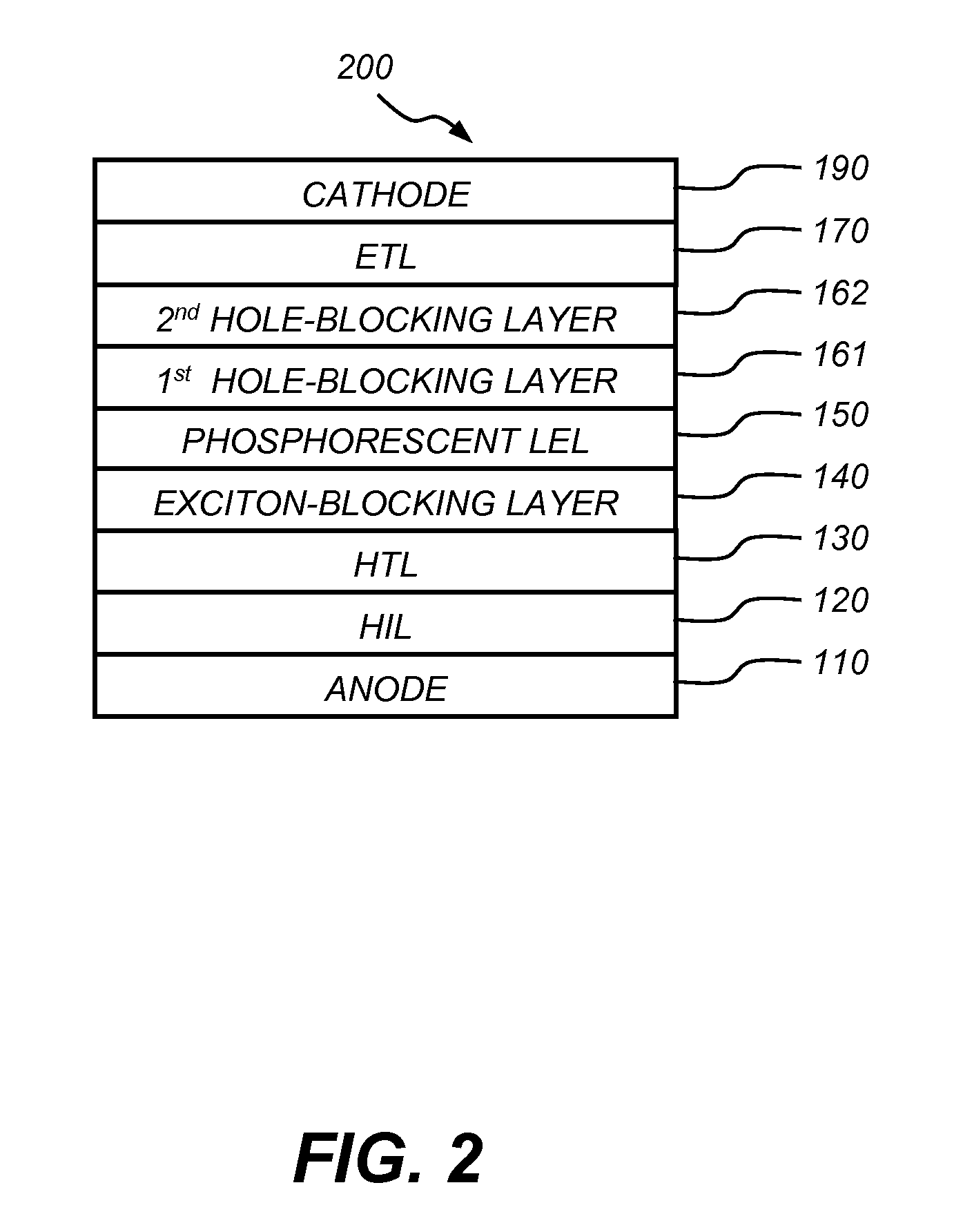
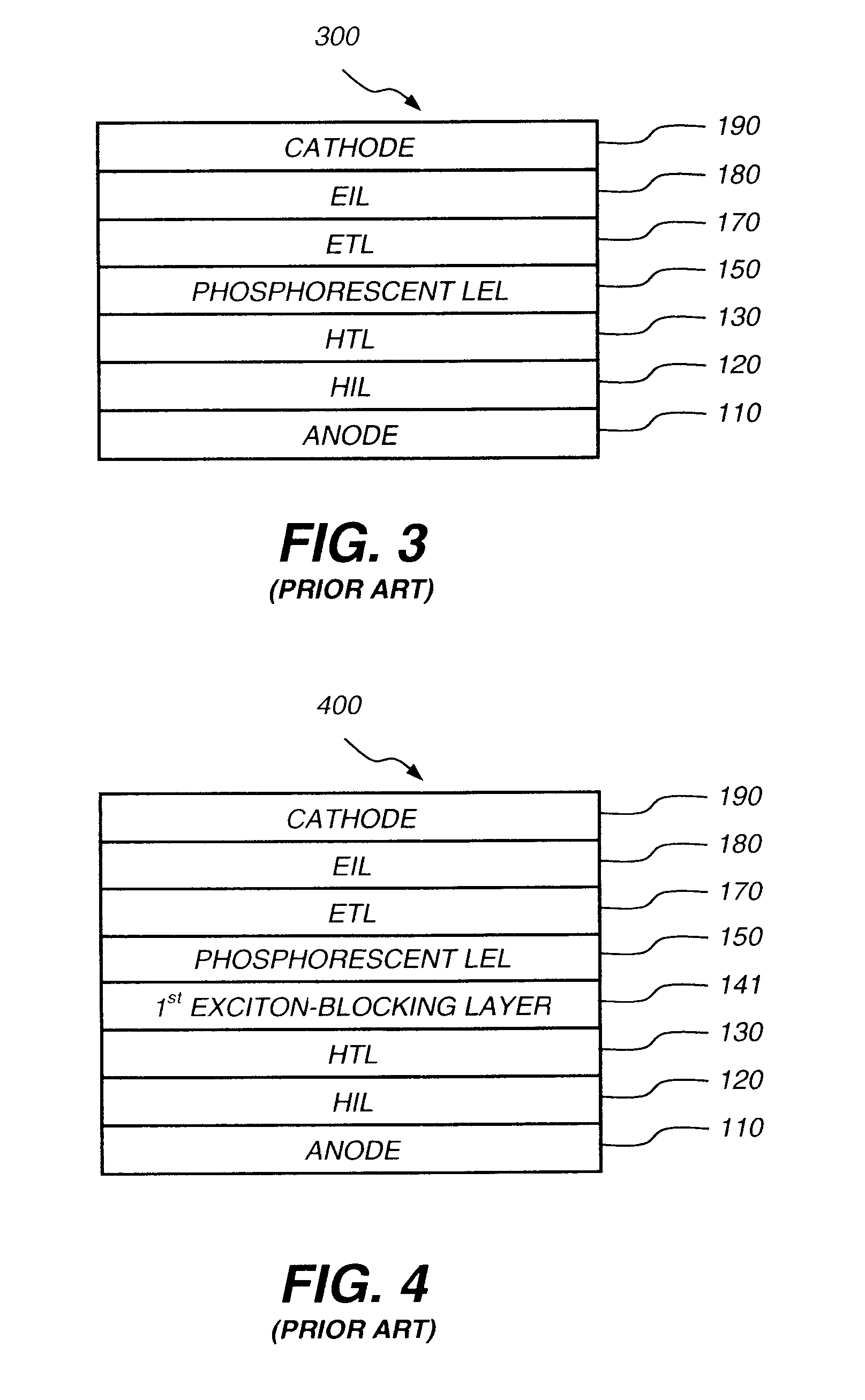
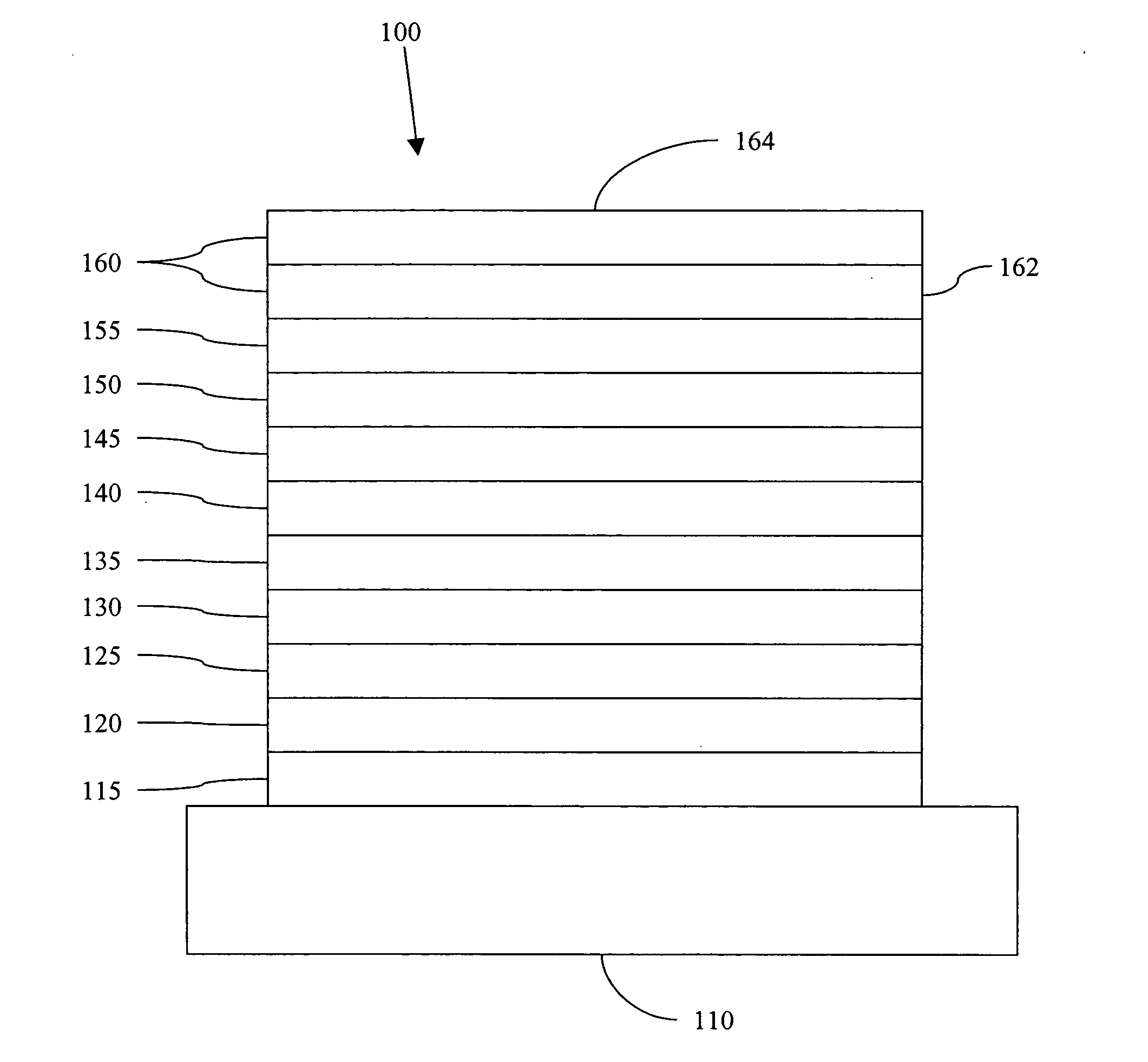
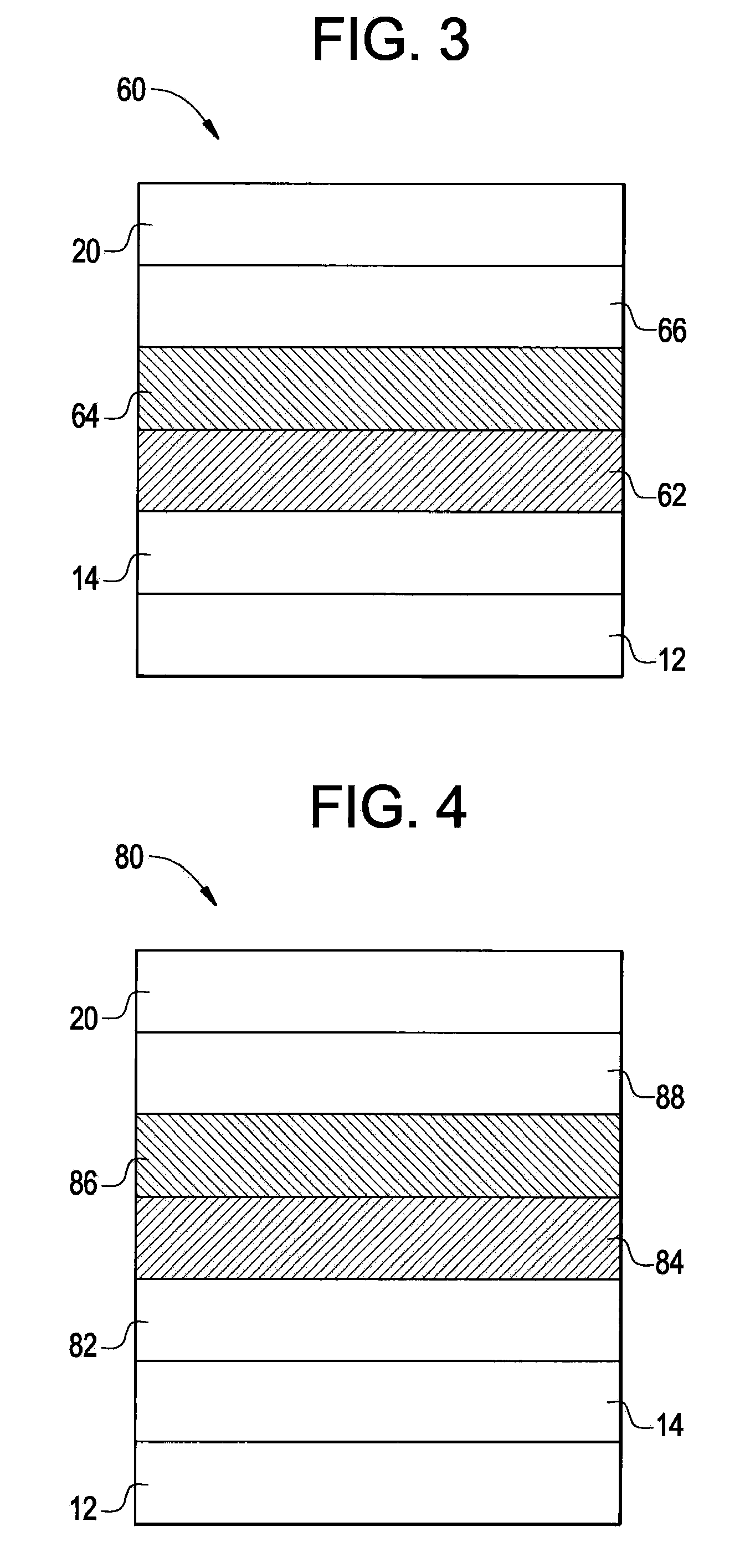
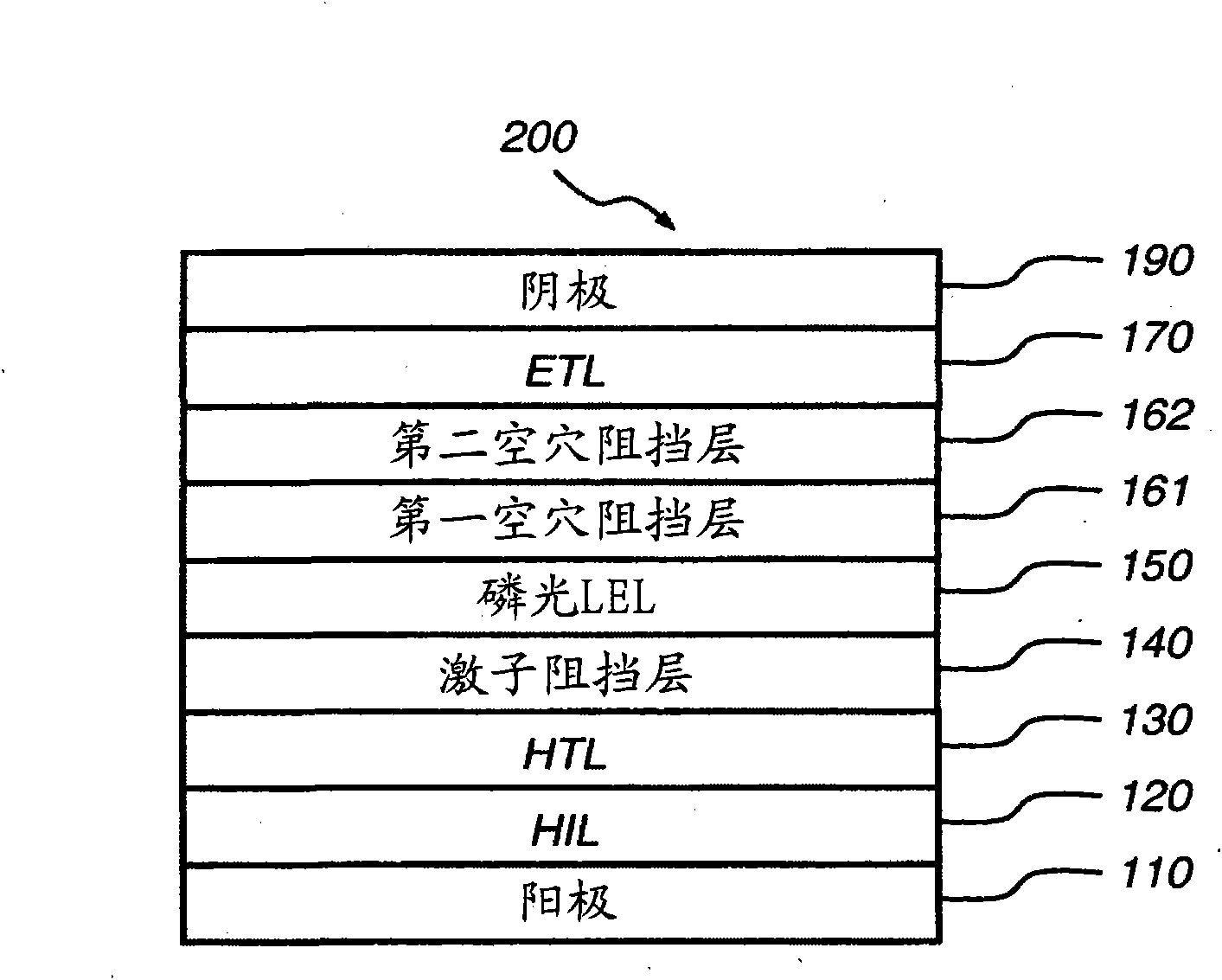
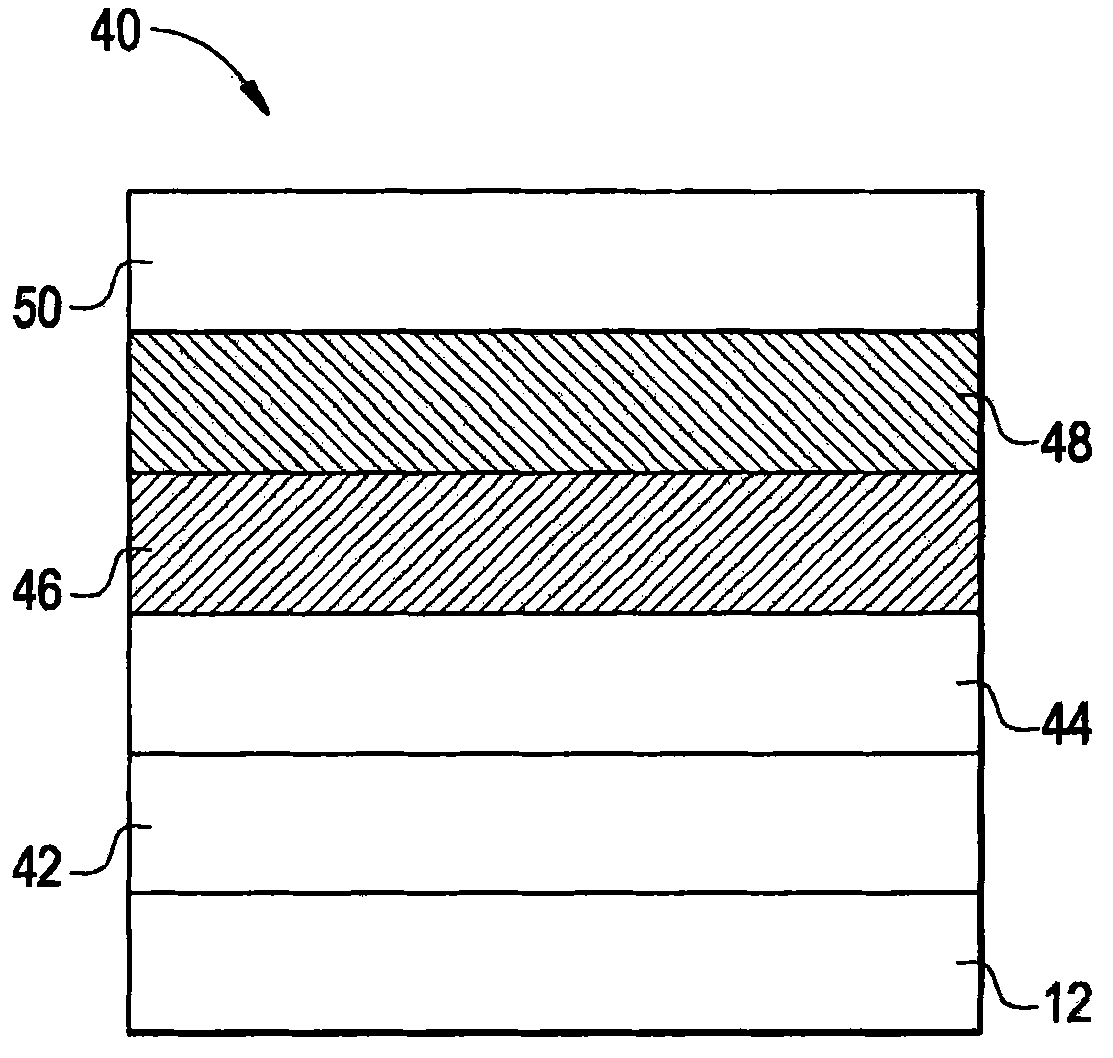
Phosphorescent oled having double exciton-blocking layers
ActiveUS8034465B2Good effectImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantElectron hole
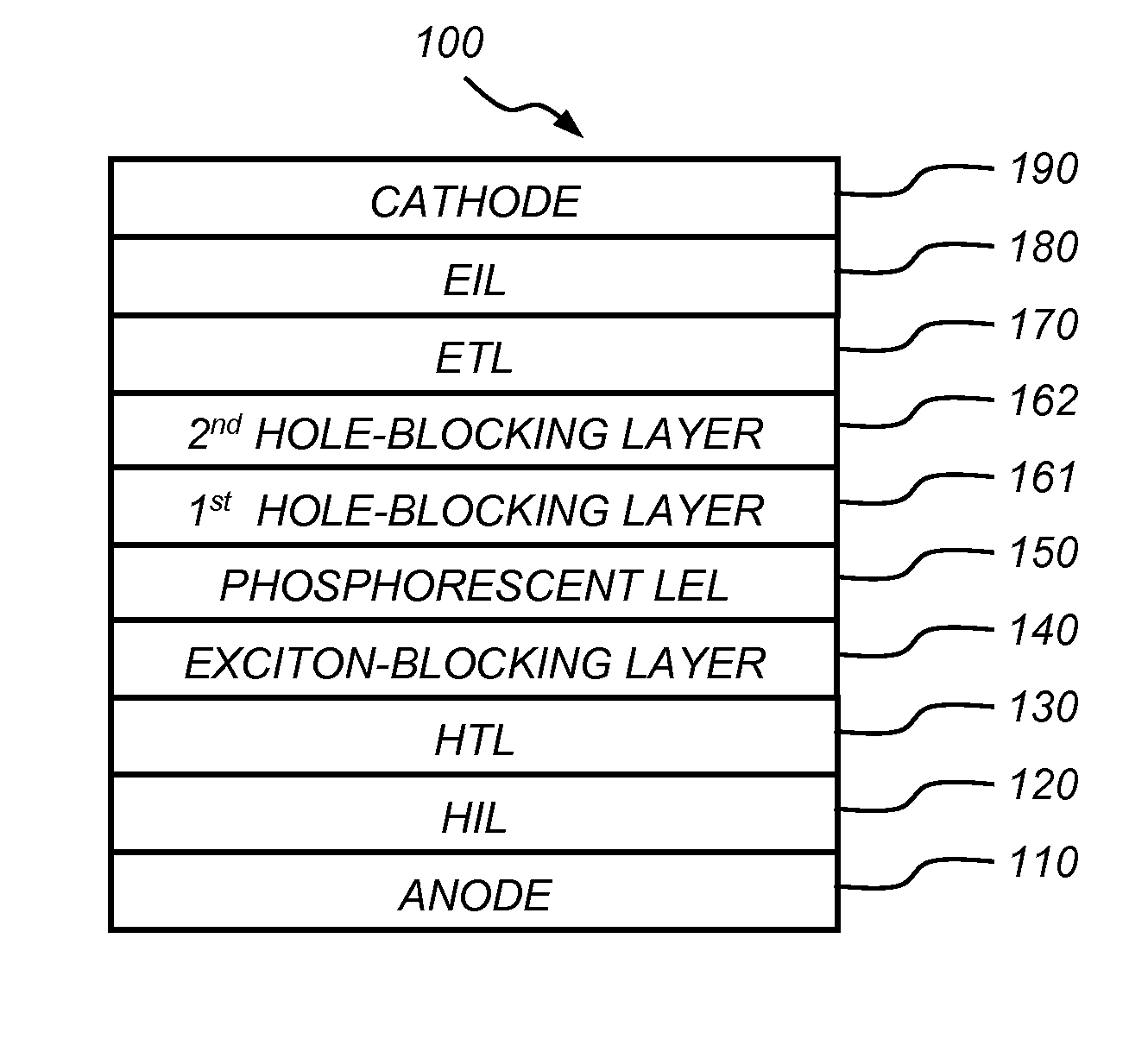
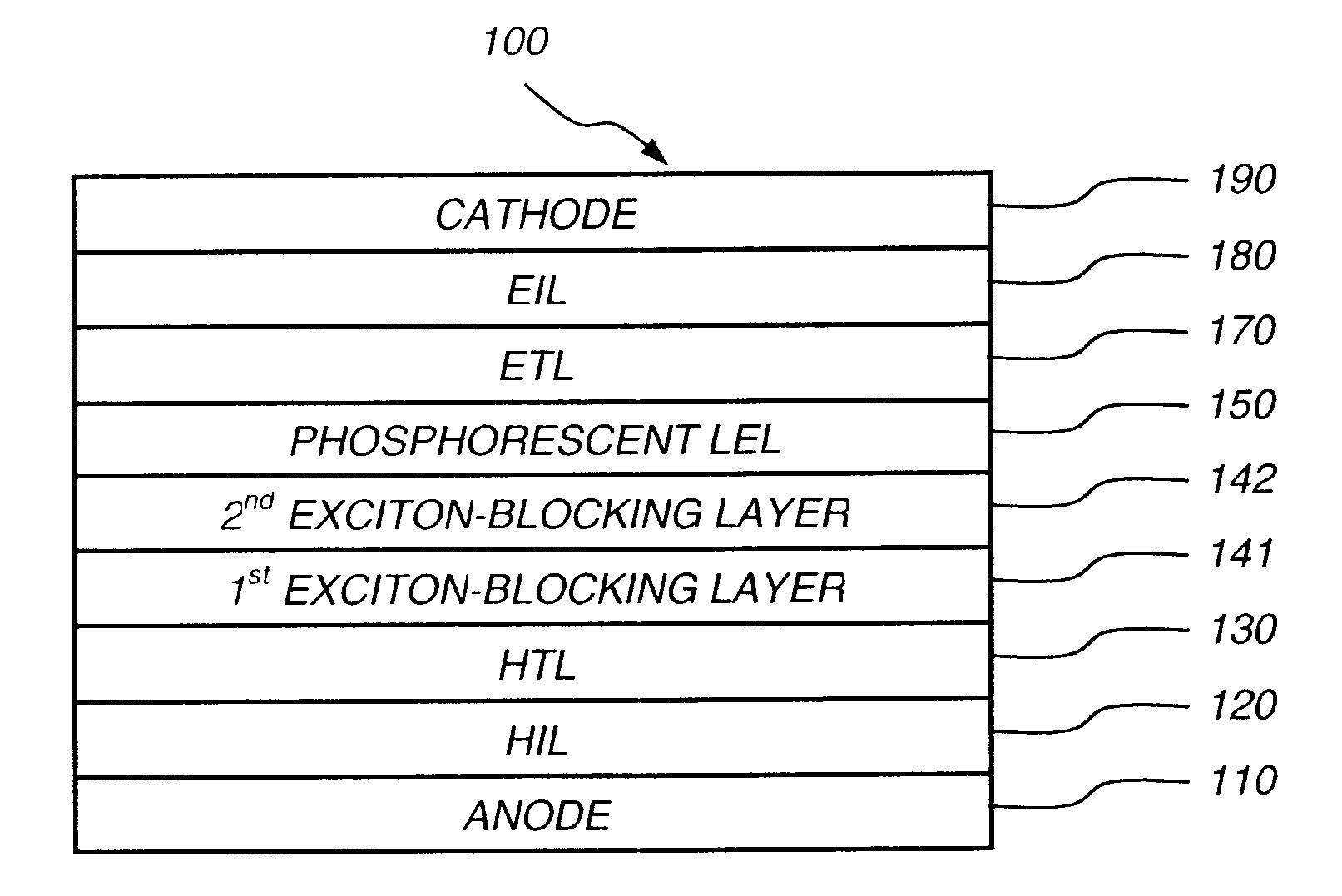
An organic light-emitting device comprising an anode; a cathode; a hole-transporting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode; a phosphorescent light-emitting layer disposed between the hole-transporting layer and the cathode, wherein the phosphorescent light-emitting layer includes at least one host and at least one phosphorescent dopant; a first exciton-blocking layer disposed between the hole-transporting layer and the phosphorescent light-emitting layer; wherein the first exciton-blocking layer has a triplet energy greater than the triplet energy of the host in the phosphorescent light-emitting layer; and a second exciton-blocking layer disposed between the first exciton-blocking layer and the phosphorescent light-emitting layer, wherein the second exciton-blocking layer is in contact with the phosphorescent light-emitting layer, and wherein the second exciton-blocking layer has a triplet energy less than the triplet energy of the first exciton-blocking layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Hybrid fluorescent/phosphorescent oleds
InactiveUS20080284318A1Improve efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorescent oledsHost material
An electroluminescent device comprisesa) a fluorescent light emitting layer comprising a fluorescent emitter and a fluorescent host material wherein the HOMO energy level of the fluorescent host material is not more than 0.1 eV more negative than that of the fluorescent emitter;b) a phosphorescent light emitting layer comprising a phosphorescent emitter and a phosphorescent host material; andc) a spacer layer interposed between the fluorescent light emitting layer and the phosphorescent light emitting layer;wherein the triplet energy of the fluorescent host material is not more than 0.2 eV less than the triplet energy of both the spacer layer material and of the phosphorescent host material. The materials within these layers are selected so that the HOMO and triplet energy levels satisfy certain interrelationships. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
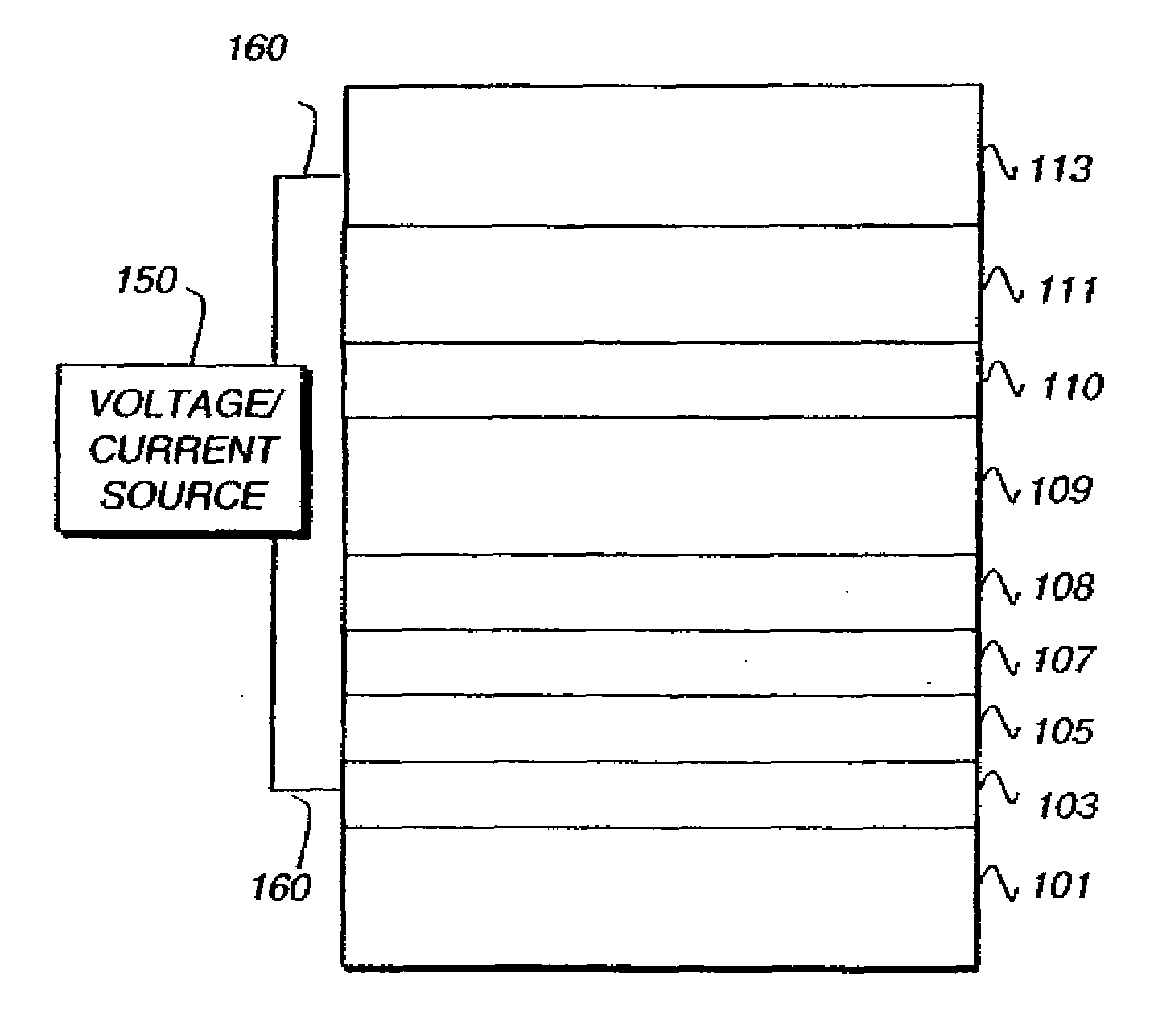
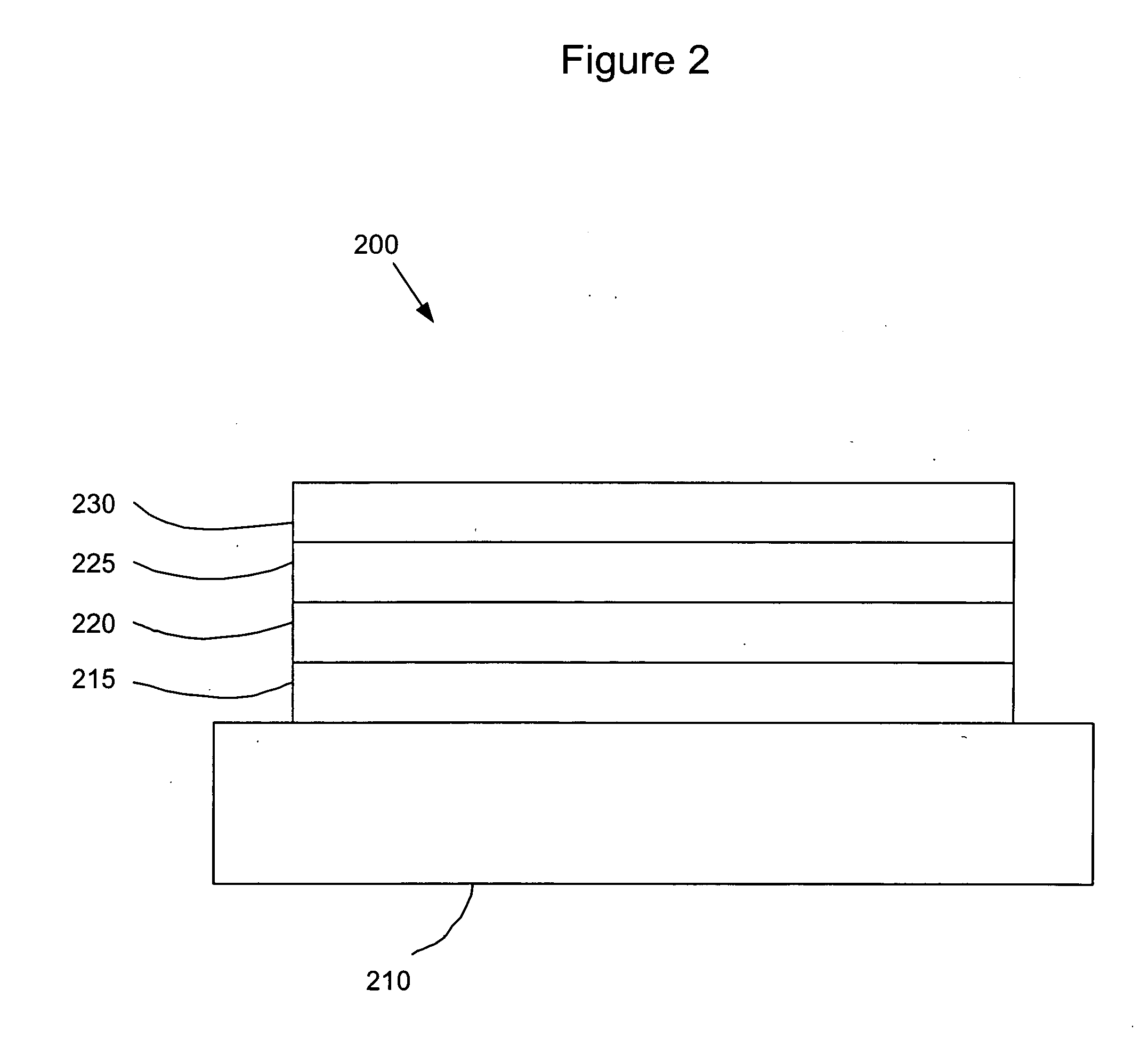
Phosphorescent OLED having double hole-blocking layers
InactiveUS20090191427A1Good effectFacilitates electron injectionSolid-state devicesNatural mineral layered productsDopantPhosphorescent oleds
An organic light-emitting device has a first hole-blocking layer in contact with a phosphorescent light-emitting layer and a second hole-blocking layer in contact with the first. The material in the first hole-blocking layer has a triplet energy greater than the host of the phosphorescent layer and the material in the second hole-blocking layer has a triplet energy higher than the dopant in the phosphorescent layer. Both hole-blocking materials have lower HOMO energies than the host of the phosphorescent light-emitting layer
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Phosphorescent oled with mixed electron transport materials
InactiveUS20060246315A1Reduce the driving voltageImprove luminanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorescent oledsLow voltage
An OLED device comprises, in sequence, an anode, a light-emitting layer that comprises a phosphorescent light-emitting organometallic compound, a hole-blocking layer, and a cathode, and between the hole-blocking layer and the cathode, a further layer containing: a) a first compound that has the lowest LUMO value of the compounds in the layer, the amount being greater than or equal to 10% by volume and less than 100% by volume of the layer; b) at least one second compound that is a low voltage electron transport material, exhibiting a higher LUMO value than the first compound, the total amount of said compound(s) being less than or equal to 90% by volume and more than 0% by volume of the layer. Such a device provides improved drive voltage.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Double doped-layer, phosphorescent organic light emitting devices
InactiveUS6867538B2Improve efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorescent oledsOrganic light emitting device
Phosphorescent OLEDs having a double doped-layer structure wherein the OLEDs include a hole transporting layer (HTL) having a phosphorescent material doped therein, and an electron transporting layer (ETL) having the same phosphorescent material doped therein. Typically, these phosphorescent OLEDs have an anode, a first HTL over the anode, a second HTL that is doped with a phosphorescent material over the first HTL, a first ETL that is doped with a phosphorescent material over the second HTL, a second ETL over the first ETL, and a cathode over the second ETL. These phosphorescent OLEDs preferably include blue phosphorescent OLEDs with high efficiency levels.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
High efficiency multi-color electro-phosphorescent OLEDs
InactiveUS20050282036A1Solve low luminous efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesDopantPhosphorescent oleds
The present invention relates to efficient organic light emitting devices (OLEDs) doped with multiple light-emitting dopants, at least one dopant comprising a phosphorescent emitter, in a thin film emissive layer or layers. The present invention is directed to an efficient phosphorescent organic light emitting device utilizing a plurality of emissive dopants in an emissive region, wherein at least one of the dopants is a phosphorescent material. Thus, the present invention provides an organic light emitting device comprising an emissive region, wherein the emissive region comprises a host material, and a plurality of emissive dopants, wherein the emissive region is comprised of a plurality of bands and each emissive dopant is doped into a separate band within the emissive region, and wherein at least one of the emissive dopants emits light by phosphorescence.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
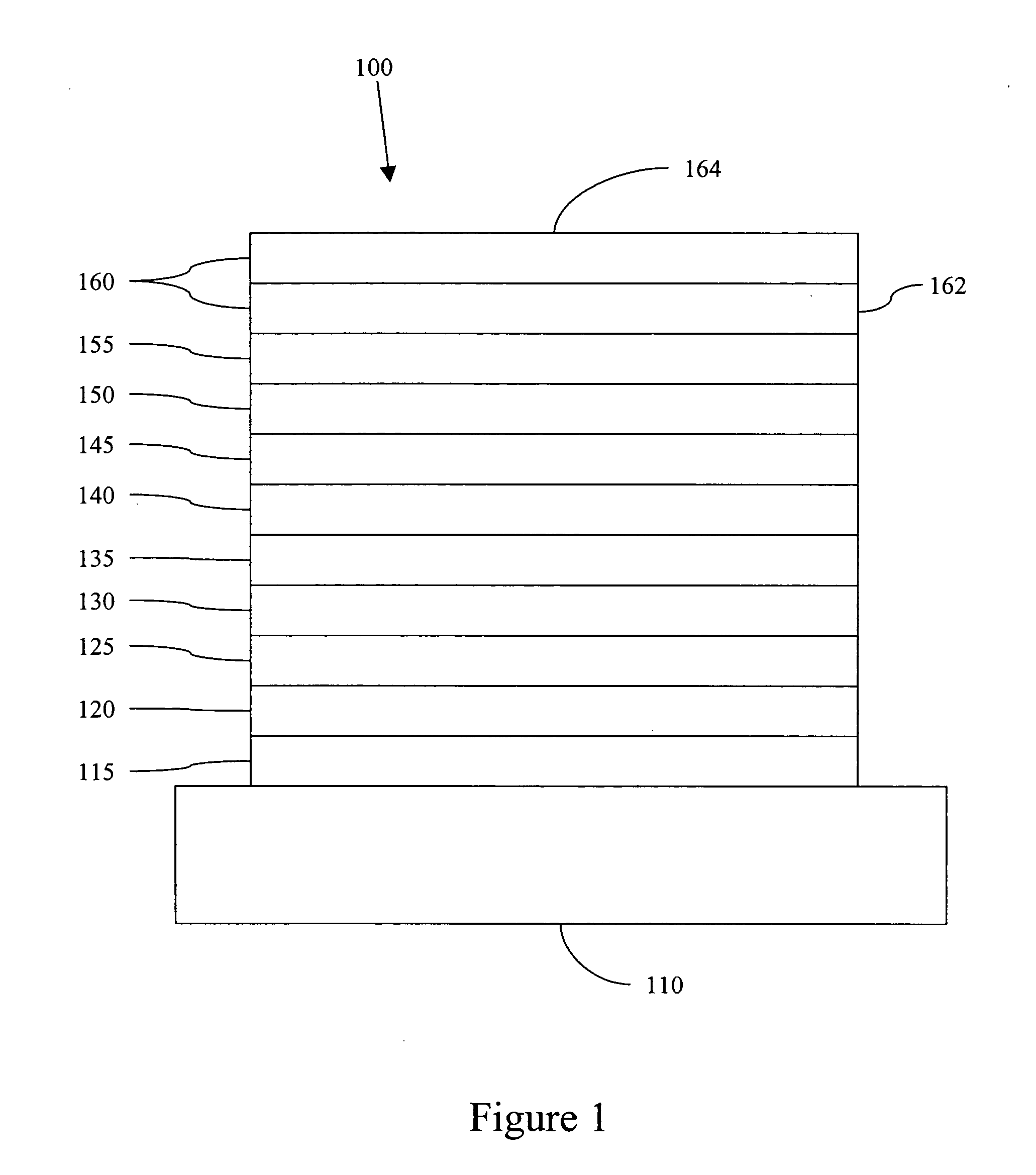
Phosphorescent OLED having double exciton-blocking layers
ActiveUS20080315753A1Good effectImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantElectron hole
An organic light-emitting device comprising an anode; a cathode; a hole-transporting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode; a phosphorescent light-emitting layer disposed between the hole-transporting layer and the cathode, wherein the phosphorescent light-emitting layer includes at least one host and at least one phosphorescent dopant; a first exciton-blocking layer disposed between the hole-transporting layer and the phosphorescent light-emitting layer; wherein the first exciton-blocking layer has a triplet energy greater than the triplet energy of the host in the phosphorescent light-emitting layer; and a second exciton-blocking layer disposed between the first exciton-blocking layer and the phosphorescent light-emitting layer, wherein the second exciton-blocking layer is in contact with the phosphorescent light-emitting layer, and wherein the second exciton-blocking layer has a triplet energy less than the triplet energy of the first exciton-blocking layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Phosphorescent OLED device with mixed hosts
ActiveUS20090309487A1Improve luminanceImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorescent oledsHost material
An OLED device comprises a cathode, an anode, and has therebetween a light-emitting layer containing a phosphorescent emitter that emits yellow, orange or red light; a tertiary arylamine compound as a first host material, and a gallium complex with only nitrogen bidentate ligands as a second host material. Desirably, the phosphorescent emitter is an iridium complex.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
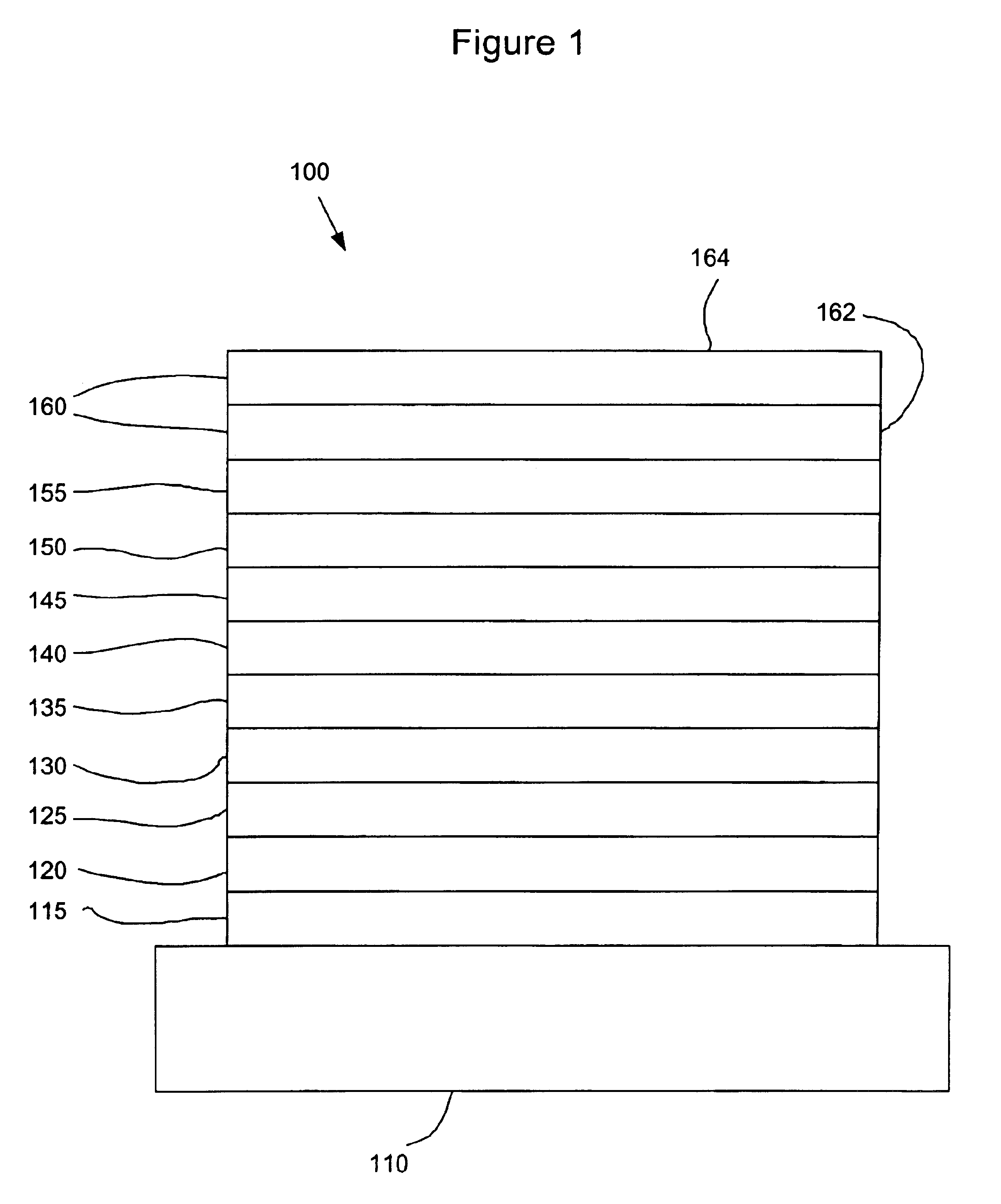
Organic light emitting device structure for obtaining chromaticity stability
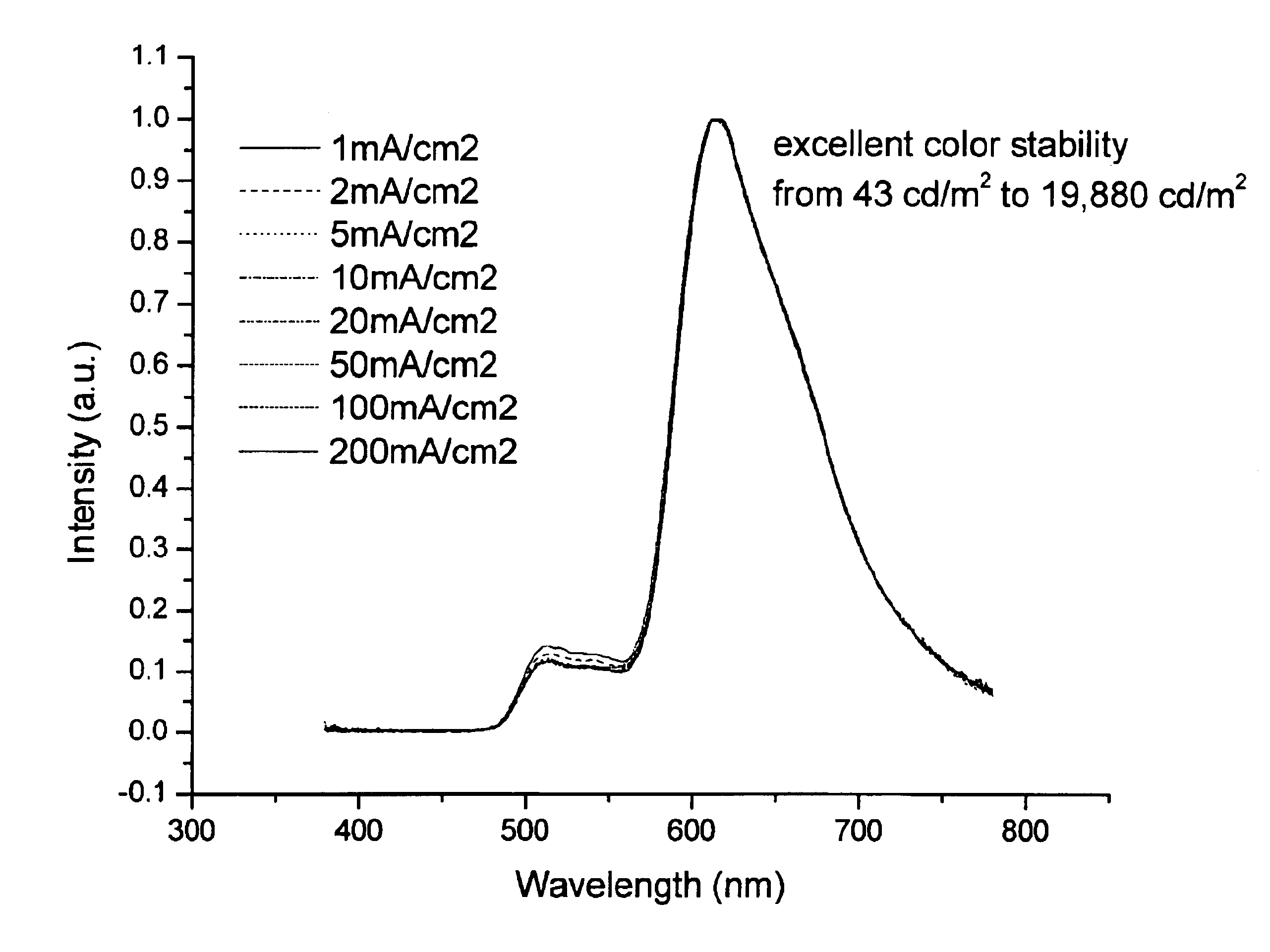
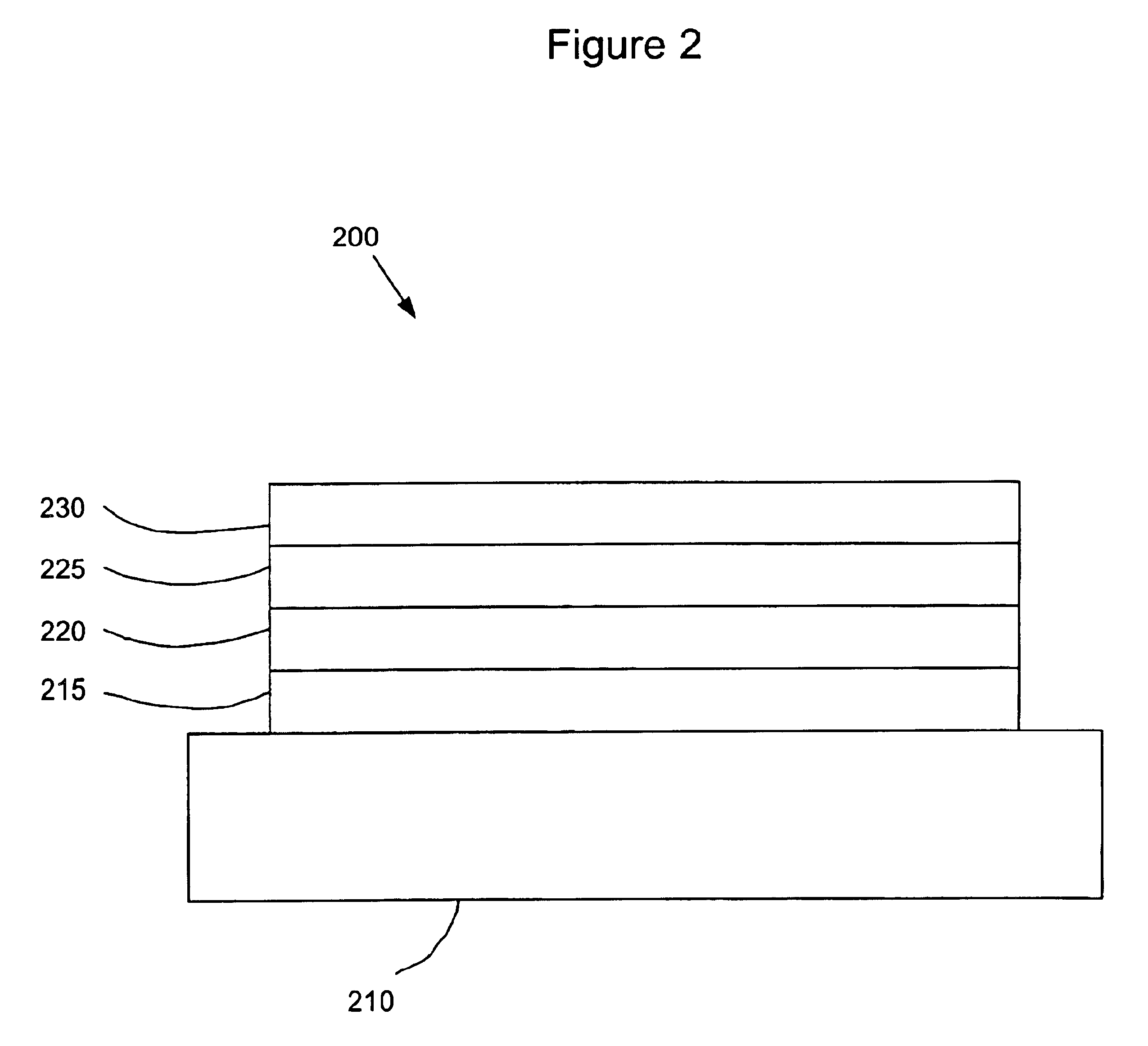
InactiveUS7211823B2High color stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDopantPhosphorescent oleds
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Organic light emitting device structures for obtaining chromaticity stability
ActiveUS20050006641A1High color stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantPhosphorescent oleds
The present invention relates to organic light emitting devices (OLEDs). The devices of the present invention are efficient white or multicolored phosphorescent OLEDs which have a high color stability over a wide range of luminances. The devices of the present invention comprise an emissive region having at least two emissive layers, with each emissive layer comprising a different host and emissive dopant, wherein at least one of the emissive dopants emits by phosphorescence.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Organic light emitting device structure for obtaining chromaticity stability
InactiveUS20050006642A1High color stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantPhosphorescent oleds
The present invention relates to organic light emitting devices (OLEDs). The devices of the present invention are efficient white or multicolored phosphorescent OLEDs which have a high color stability over a wide range of luminances. The devices of the present invention comprise an emissive region having at least two emissive layers, with each emissive layer comprising a different host and emissive dopant, wherein at least one of the emissive dopants emits by phosphorescence.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Organic light emitting device structures for obtaining chromaticity stability
InactiveUS6885025B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDopantPhosphorescent oleds
The present invention relates to organic light emitting devices (OLEDs). The devices of the present invention are efficient white or multicolored phosphorescent OLEDs which have a high color stability over a wide range of luminances. The devices of the present invention comprise an emissive region having at least two emissive layers, with each emissive layer comprising a different host and emissive dopant, wherein at least one of the emissive dopants emits by phosphorescence.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Fluorene-based bridged blue phosphorescent host material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102276514AIncrease the effective molecular weightImprove luminous brightnessGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesTriplet stateUnit structure
The invention relates to an organic blue phosphorescent main body material with fluorene as a center unit structure, and a preparation method and application thereof in a blue organic light-emitting diode (OLED). In the material, fluorene is used as a main body structure, and different electron properties of groups are bonded to 3-, 6- and 9- positions of fluorene, thereby the conjugated system of the main body material is effectively reduced, the effective molecular weight of the compound is increased, and the triplet energy and glass transition temperature of the material are improved to some extent. In addition, the polarity of the compound can be adjusted by drawing / withdrawing electron groups; compared with the commonly used blue phosphorescent main body materials including 4,4'-(9-carbazole)-biphenyl (CBP) and N,N'-dicarbazoyl-1,3-benzene (m-CP), the efficiency roll-off problem under a high luminescence condition of the blue phosphorescent OLED devices is effectively solved under a condition of appropriate polarization rate; and the main body material can be widely used in the organic light-emitting field.
Owner:武汉承胜创业投资有限公司
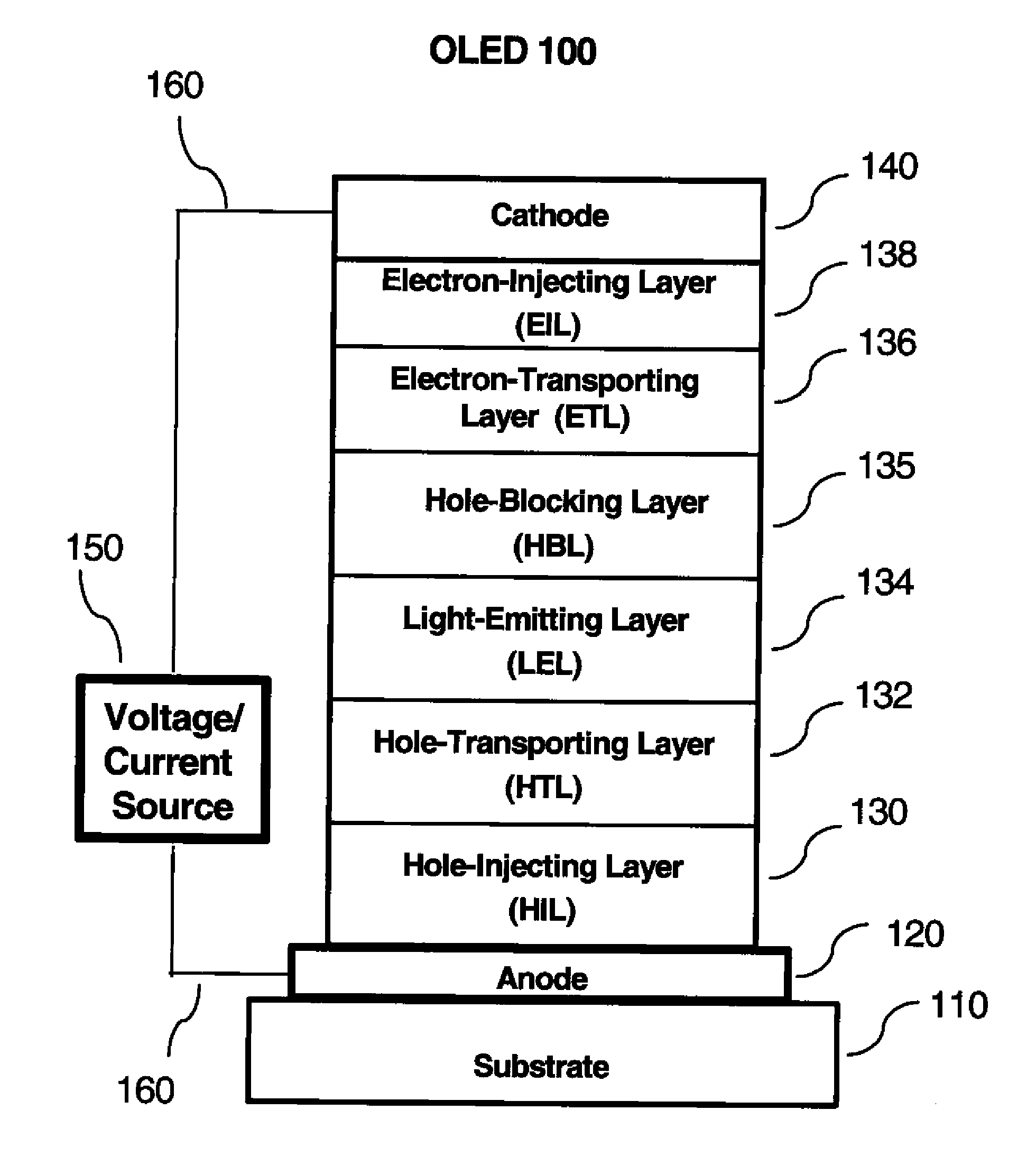
Method of Manufacture of a Multi-Layer Phosphorescent Organic Light Emitting Device, and Articles Thereof
A method for forming multi-emissive phosphorescent layers for a phosphorescent OLED comprises coating a first phosphorescent material from a first solvent onto a first electrode and removing the first solvent to form a first emissive layer; and coating a second phosphorescent material from a second solvent onto the first emissive layer and removing the second solvent to form a second emissive layer, wherein the first and second emissive layers are not cured after coating, and wherein the first emissive layer has negligible solubility in the second solvent.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Phosphorescent OLED device with certain fluoranthene host
ActiveUS20090108736A1Improve efficiencyHigh operational stabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsDopantPhosphorescent oleds
An OLED device comprising a cathode, an anode, and having there between a red light emitting layer containing a non-light-emitting fluoranthene compound with a 7,10-diaryl substituted fluoranthene nucleus having no aromatic rings annulated to the fluoranthene nucleus, and a red light-emitting phosphorescent dopant.OLED devices of the invention provide reduced drive voltage and improved color, and provide embodiments with other improved features such as operational stability and high luminance.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Phosphorescent OLED with mixed electron transport materials
ActiveUS20080258615A1Reduce the driving voltageLuminous stabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorescent oledsLow voltage
An OLED device comprising, in sequence, an anode, a light-emitting layer that comprises a phosphorescent light-emitting organometallic compound, a hole-blocking layer, and a cathode, and between the hole-blocking layer and the cathode, a further layer containing a mixture of a first compound that is a tetracene compound that has the lowest LUMO value of the compounds in the layer, in an amount greater than or equal to 10% and less than 90% and a second compound that is a low voltage electron transport material, exhibiting a higher LUMO value than the first compound in an amount less than or equal to 90% and more than 10%.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Phosphorescent OLED having double hole-blocking layers
ActiveCN101978528AImprove the blocking effectImprove electron injection performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantPhosphorescent oleds
An organic light-emitting device has a first hole-blocking layer in contact with a phosphorescent light-emitting layer and a second hole-blocking layer in contact with the first. The material in the first hole-blocking layer has a triplet energy greater than the host of the phosphorescent layer and the material in the second hole-blocking layer has a triplet energy higher than the dopant in the phosphorescent layer. Both hole-blocking materials have lower HOMO energies than the host of the phosphorescent light-emitting layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Hybrid fluorescent/phosphorescent oleds
ActiveCN101682002AImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorescent oledsHost material
An electroluminescent device comprises a) a fluorescent light emitting layer comprising a fluorescent emitter and a fluorescent host material wherein the HOMO energy level of the fluorescent host material is not more than 0.1 eV more negative than that of the fluorescent emitter; b) a phosphorescent light emitting layer comprising a phosphorescent emitter and a phosphorescent host material; and c)a spacer layer interposed between the fluorescent light emitting layer and the phosphorescent light emitting layer; wherein the triplet energy of the fluorescent host material is not more than 0.2 eVless than the triplet energy of both the spacer layer material and of the phosphorescent host material. The materials within these layers are selected so that the HOMO and triplet energy levels satisfy certain interrelationships. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency.
Owner:乐金显示光电科技(中国)有限公司
Metal complexes containing heterocycle substituted ligands, and electroluminescent devices and formulations containing the complexes
PendingCN109956977AIndium organic compoundsSolid-state devicesPhosphorescent oledsOrganic electroluminescence
Metal complexes having heterocycle substituted ligands are disclosed, which can be used as emitters in the emissive layer of an organic electroluminescent device. The application of these novel compounds as emitters in phosphorescent OLED devices enables to obtain deep red and near infrared colors. Also disclosed are an electroluminescent device and a formulation containing the complexes.
Owner:BEIJING SUMMER SPROUT TECH CO LTD
Organic phosphorescent OLED materials
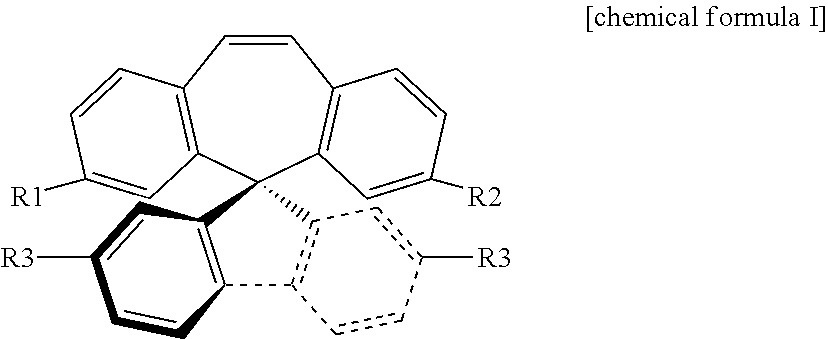
ActiveCN103833790AImprove capture abilityImprove luminous efficiencyGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesPhosphorescent oledsDouble bond
The invention discloses a series of organic phosphorescent OLED materials. A structural general formula of the organic phosphorescent OLED materials is shown as a formula I. The materials are obtained by using 10,11-dihydrogen spirofluorene as a main body and modifying with 2-pyridyl. Due to the influence of double bonds of electron deficient groups at 10 and 11 sites, hole transportation between molecules is facilitated; and capturing capacity for excitons is greatly increased. Due to distortion of spirofluorene molecules, [pai]-[pai] overlapping space of the molecules is greatly enlarged; phosphorescence lifetime is effectively shortened; luminescence efficiency is increased; and the performance of luminescent devices is improved. A compound related by the invention has the advantages of excellent film-forming property and high luminescent efficiency. The formula I is shown as the description.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG CHENGZHI YONGHUA DISPLAY MATERIALS CO LTD
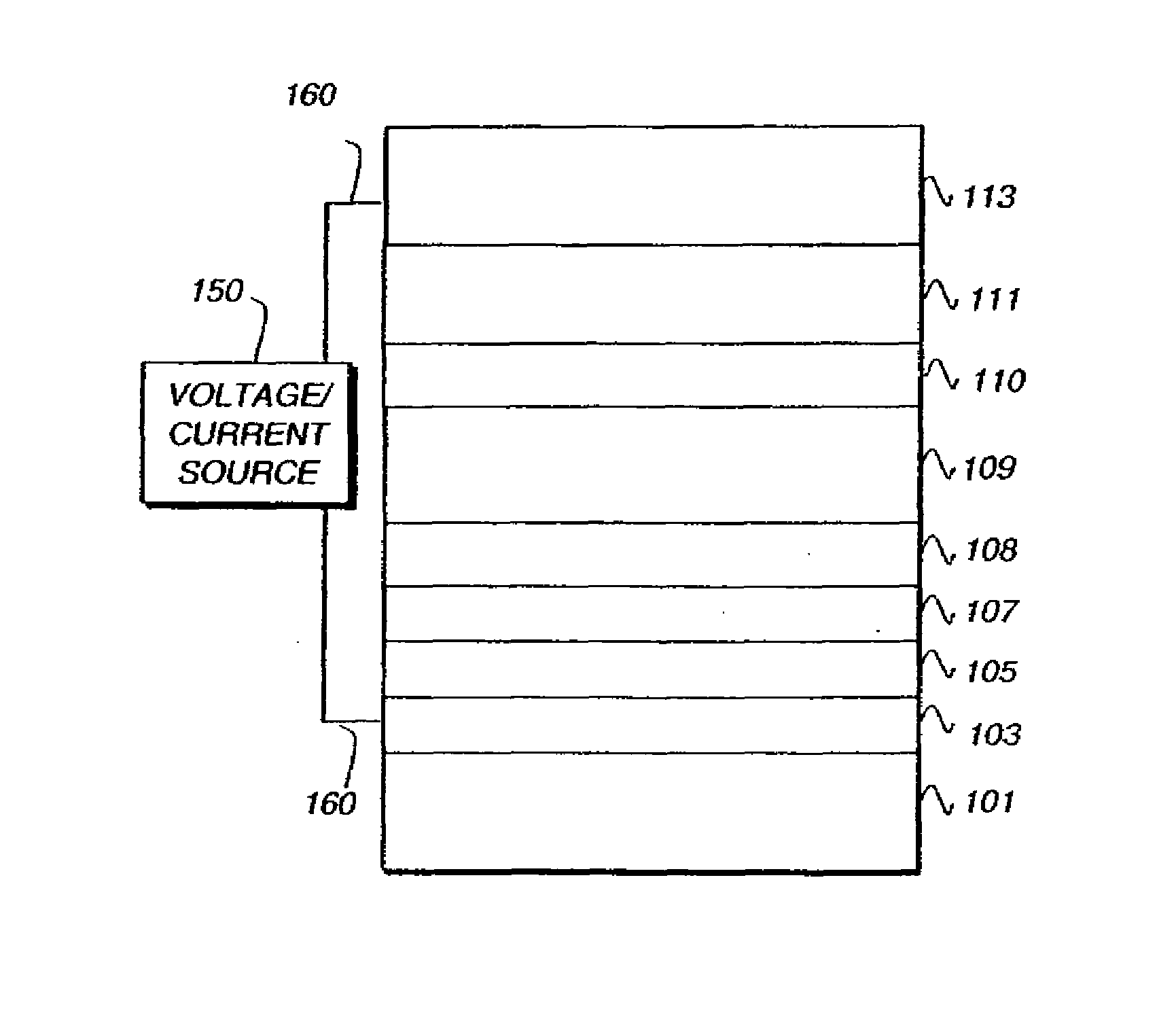
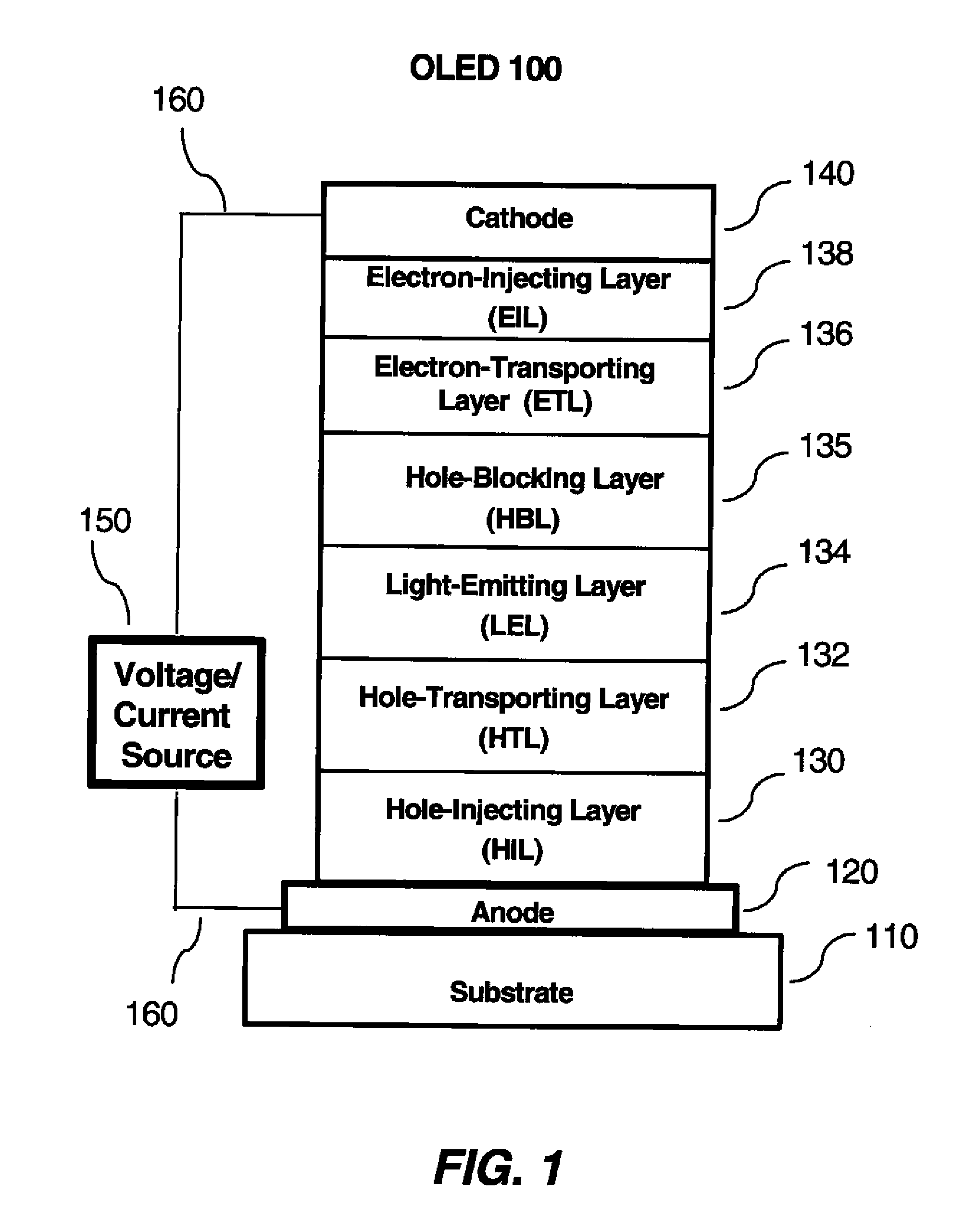
Phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes
A phosphorescent OLED has a light emitting layer which includes a phosphorescent host material, an exiton blocking material, and a phosphorescent dopant. The invention obviates the use of a hole blocking layer while substantially preventing hole diffusion to the electron transport layer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Phosphorescent OLED device with mixed hosts
ActiveUS8324800B2Improve efficiencyImprove luminanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorescent oledsHost material
An OLED device comprises a cathode, an anode, and has therebetween a light-emitting layer containing a phosphorescent emitter that emits yellow, orange or red light; a tertiary arylamine compound as a first host material, and a gallium complex with only nitrogen bidentate ligands as a second host material. Desirably, the phosphorescent emitter is an iridium complex.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Red and green phosphorescent OLED device and manufacturing method thereof
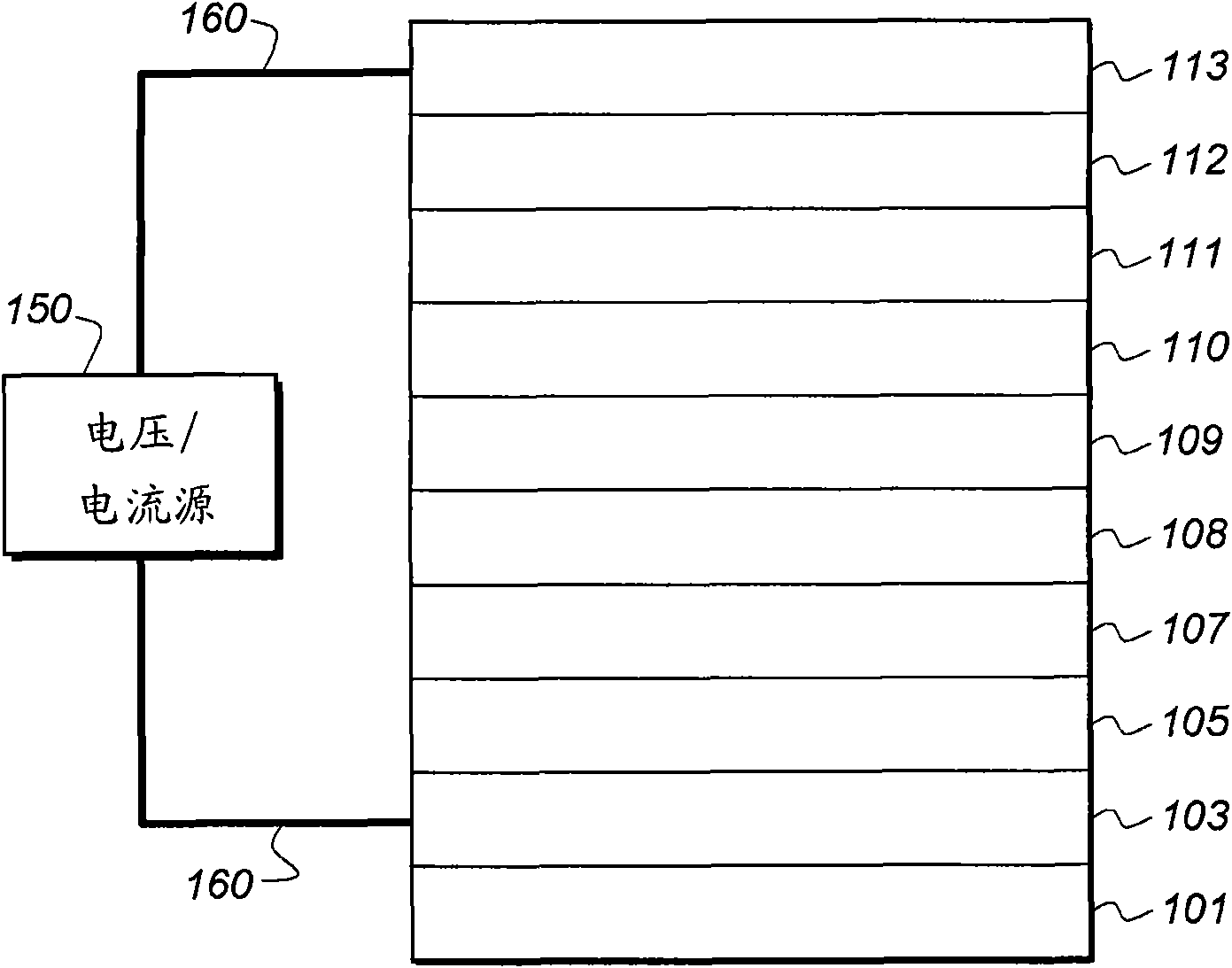
ActiveCN103227294AImprove lighting effectsIncrease brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorescent oledsTransport layer
The invention provides a red and green phosphorescent OLED (organic light emitting diode) device and a manufacturing method thereof. The red and green phosphorescent OLED device comprises a glass substrate, and an ITO (indium tin oxide) anode, a hole injection layer, a hole transport layer, an electronic barrier layer, a luminous layer, a hole barrier layer, an electronic transport layer, an electronic injection layer and an aluminum cathode which are arranged on the glass substrate sequentially, wherein a wire is led out of each of the ITO anode and the aluminum cathode, and connected with an external direct-current power supply. According to the red and green phosphorescent OLED device and the manufacturing method, excitons and carriers are adjusted to be in different areas of the luminous layer, so that the luminous efficiency and the luminance of the device are improved, and the service life of the device is prolonged indirectly.
Owner:陕西诺菲尔光电科技有限公司
Tunable OLED Lighting Source
ActiveUS20160172330A1Consistent outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorescent oledsEffect light
Described herein are devices and methods related to lighting systems that are color tunable and have a long lifetime. In certain embodiments, the device comprises two independently controlled phosphorescent OLED lighting panels coupled together in one package to emit light in one direction. In certain embodiment, aspects of the device are tunable, such as RGB color, color temperature, and luminance.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Method of manufacture of a multi-layer phosphorescent organic light emitting device, and articles thereof
InactiveCN102171850ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorescent oledsOrganic light emitting device
A method for forming multi-emissive phosphorescent layers for a phosphorescent OLED comprises coating a first phosphorescent material from a first solvent onto a first electrode and removing the first solvent to form a first emissive layer; and coating a second phosphorescent material from a second solvent onto the first emissive layer and removing the second solvent to form a second emissive layer, wherein the first and second emissive layers are not cured after coating, and wherein the first emissive layer has negligible solubility in the second solvent.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Metal complexes containing heterocycle substituted ligands, and electroluminescent devices and formulations containing the complexes
Metal complexes having heterocycle substituted ligands are disclosed, which can be used as emitters in the emissive layer of an organic electroluminescent device. The application of these novel compounds as emitters in phosphorescent OLED devices enables to obtain deep red and near infrared colors. Also disclosed are an electroluminescent device and a formulation containing the complexes.
Owner:BEIJING SUMMER SPROUT TECH CO LTD
Spirally Configured Cis-Stilbene/Fluorene Hybrid Materials for Organic Light-Emitting Diode
ActiveUS20160111648A1Improve efficiencyExcellent lifetimeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorescent oledsPower flow
The present invention provides a series of spirally configured cis-stilbene / fluorene hybrid materials, which are spirally-configured cis-stilbene / fluorene derivatives having glass transition temperatures ranged from 105° C. to 130° C., decomposition temperatures ranged from 385° C. to 415° C., reversible electron transport property, and balanced charges motilities. Moreover, a variety of experimental data have proved that the yellow fluorescent, the green phosphorescent, the yellow phosphorescent, and the red phosphorescent OLEDs using this spirally configured cis-stilbene / fluorene derivatives as the electron transport layers having hole blocking functions can indeed show excellent EQE, current efficiency, power efficiency, maximum luminance, and device lifetime performances much better than the conventional or commercial yellow fluorescent, green phosphorescent, yellow phosphorescent, and red phosphorescent OLEDs.
Owner:NICHEM FINE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com