Patents
Literature
2247results about "Cathode ray tubes/electron beam tubes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
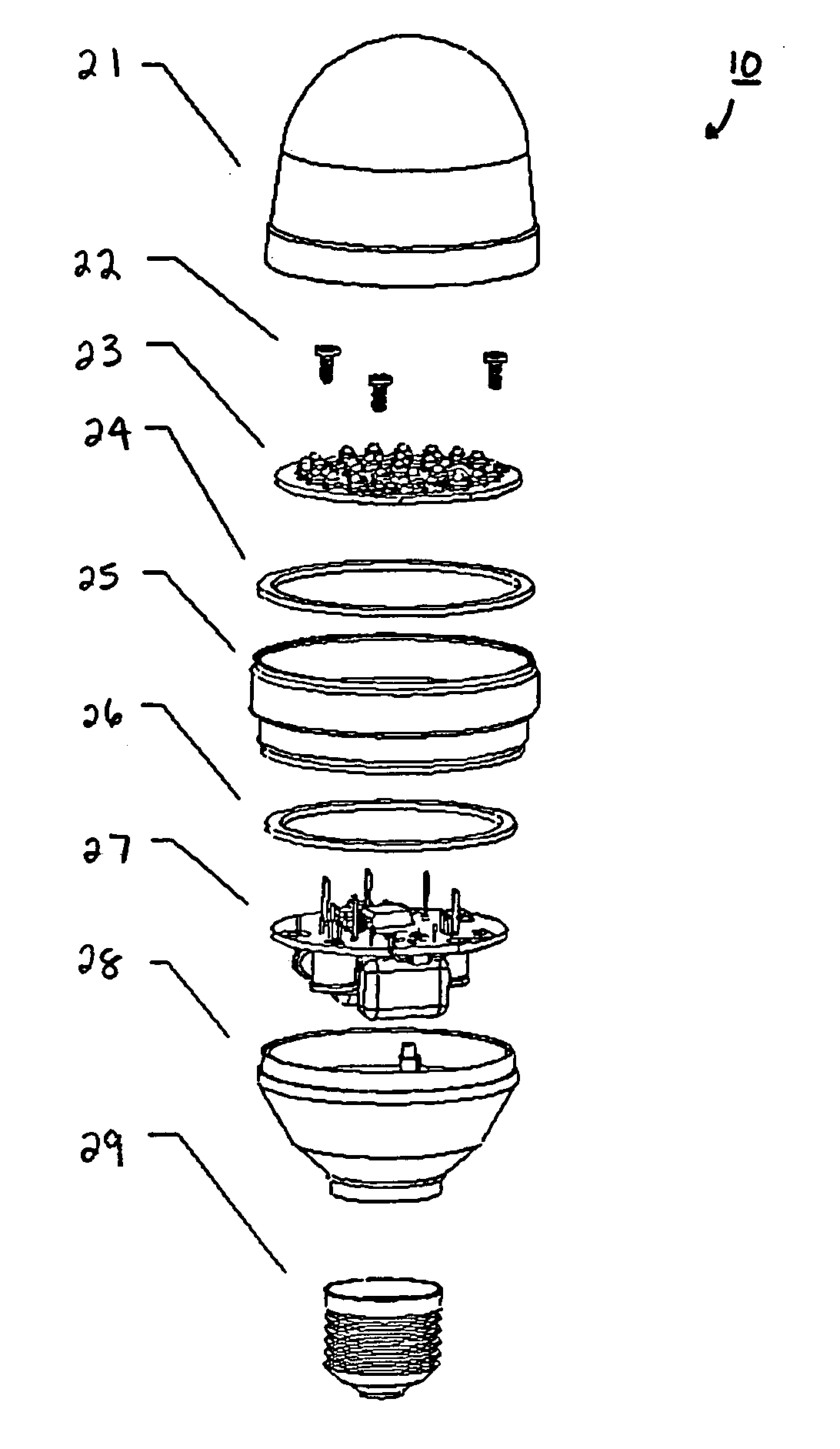
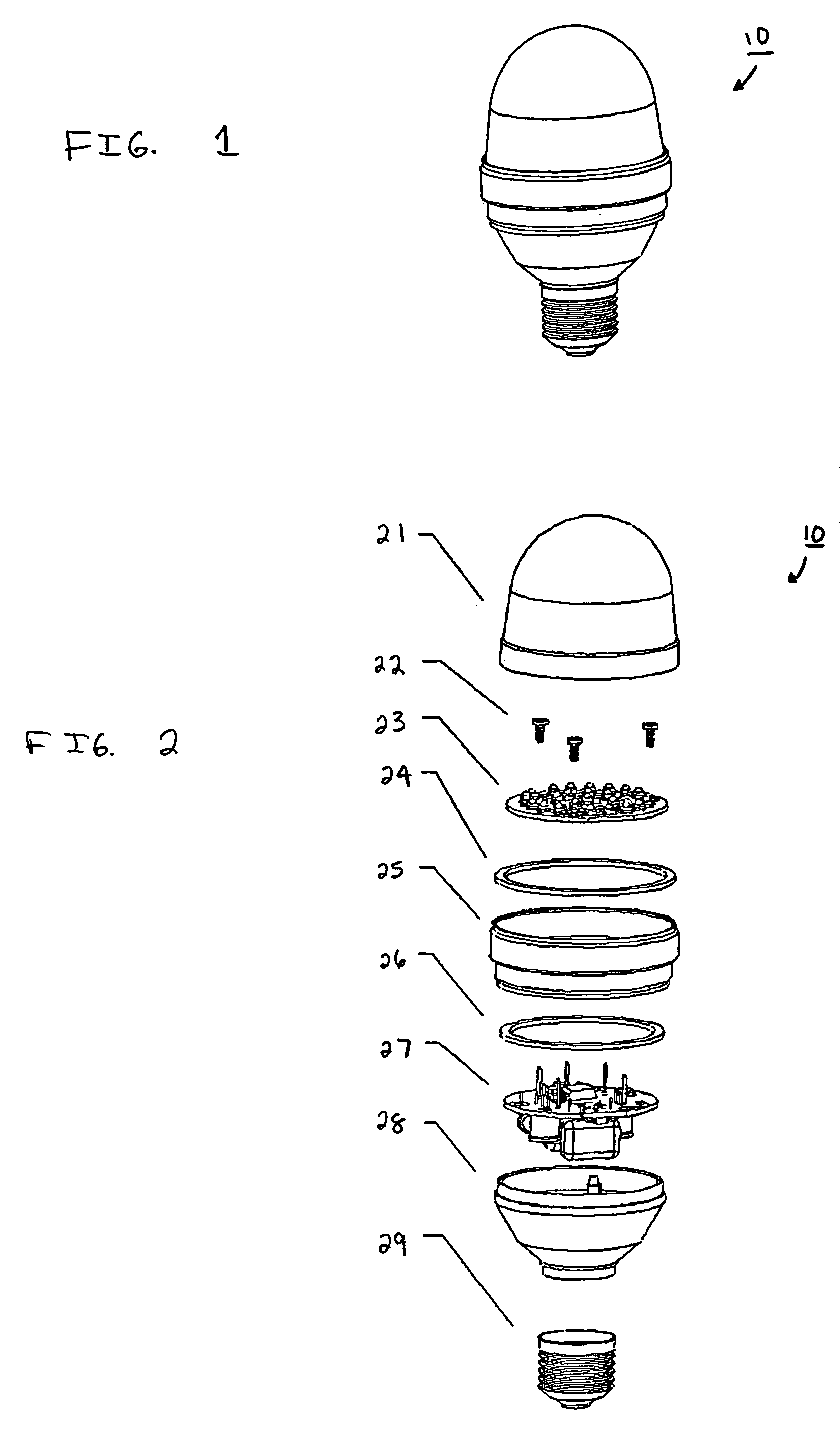
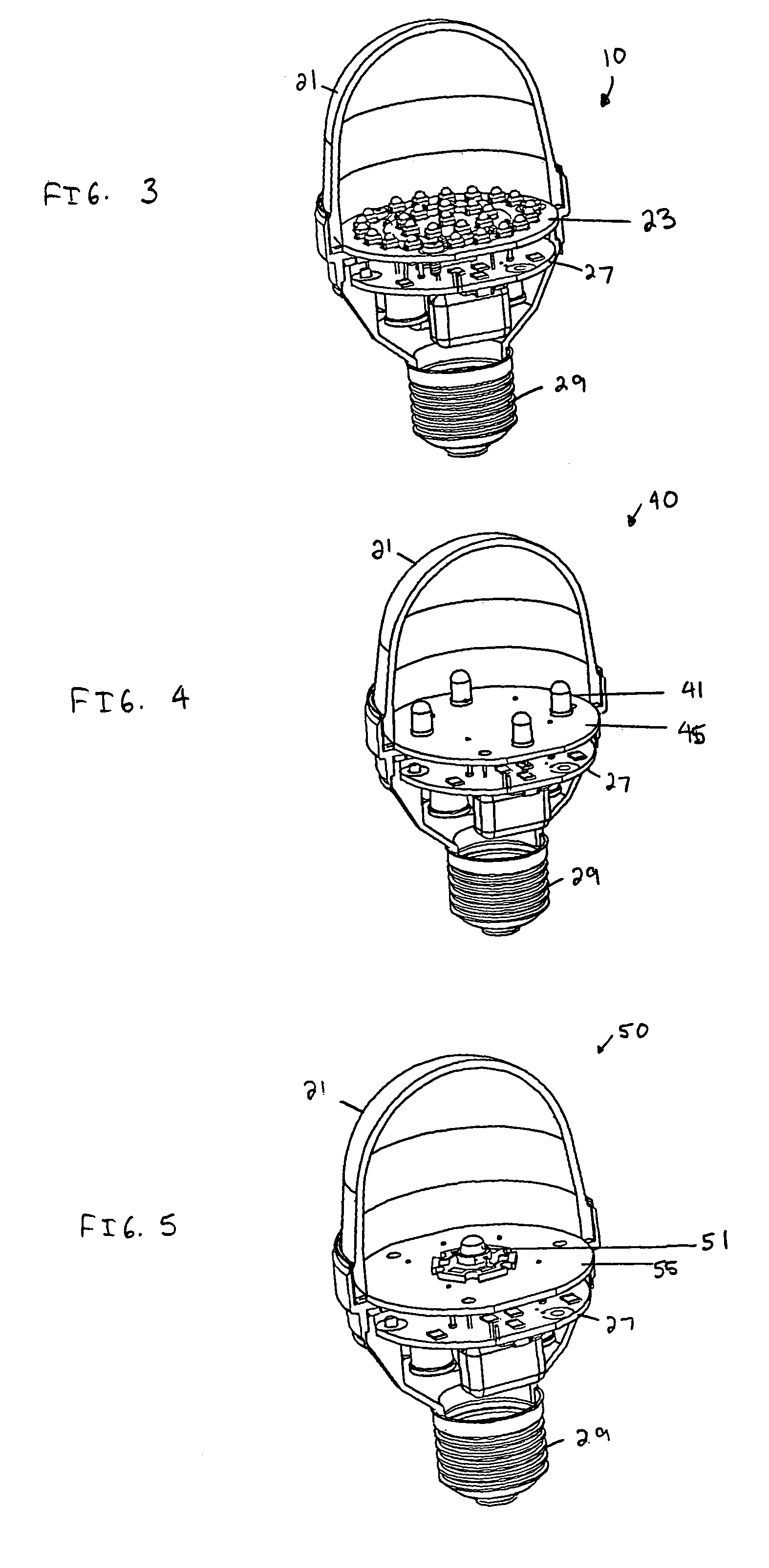
Light emitting diode (LED) light bulbs
ActiveUS6948829B2Improve performanceEasy to manufactureFurnace componentsPoint-like light sourceEngineeringPrinted circuit board
A light emitting diode (LED) light bulb that includes plural individual elements as sub-assembly elements of the overall light bulb. Different sub-assembly elements of a lens, a LED printed circuit board, a housing also functioning as a heat sink, a lower housing, and other individual sub-assembly components are utilized. The LED printed circuit board sub-assembly containing the LEDs can also be provided relatively close to a base.
Owner:DIALIGHT CORP
Free-standing and aligned carbon nanotubes and synthesis thereof
One or more highly-oriented, multi-walled carbon nanotubes are grown on an outer surface of a substrate initially disposed with a catalyst film or catalyst nano-dot by plasma enhanced hot filament chemical vapor deposition of a carbon source gas and a catalyst gas at temperatures between 300° C. and 3000° C. The carbon nanotubes range from 4 to 500 nm in diameter and 0.1 to 50 μm in length depending on growth conditions. Carbon nanotube density can exceed 104 nanotubes / mm2. Acetylene is used as the carbon source gas, and ammonia is used as the catalyst gas. Plasma intensity, carbon source gas to catalyst gas ratio and their flow rates, catalyst film thickness, and temperature of chemical vapor deposition affect the lengths, diameters, density, and uniformity of the carbon nanotubes. The carbon nanotubes of the present invention are useful in electrochemical applications as well as in electron emission, structural composite, material storage, and microelectrode applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Photoluminescent objects
InactiveUS9057021B2Improve stabilityGeneration of luminanceX-ray/infra-red processesCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesPhotoluminescenceComputer science
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
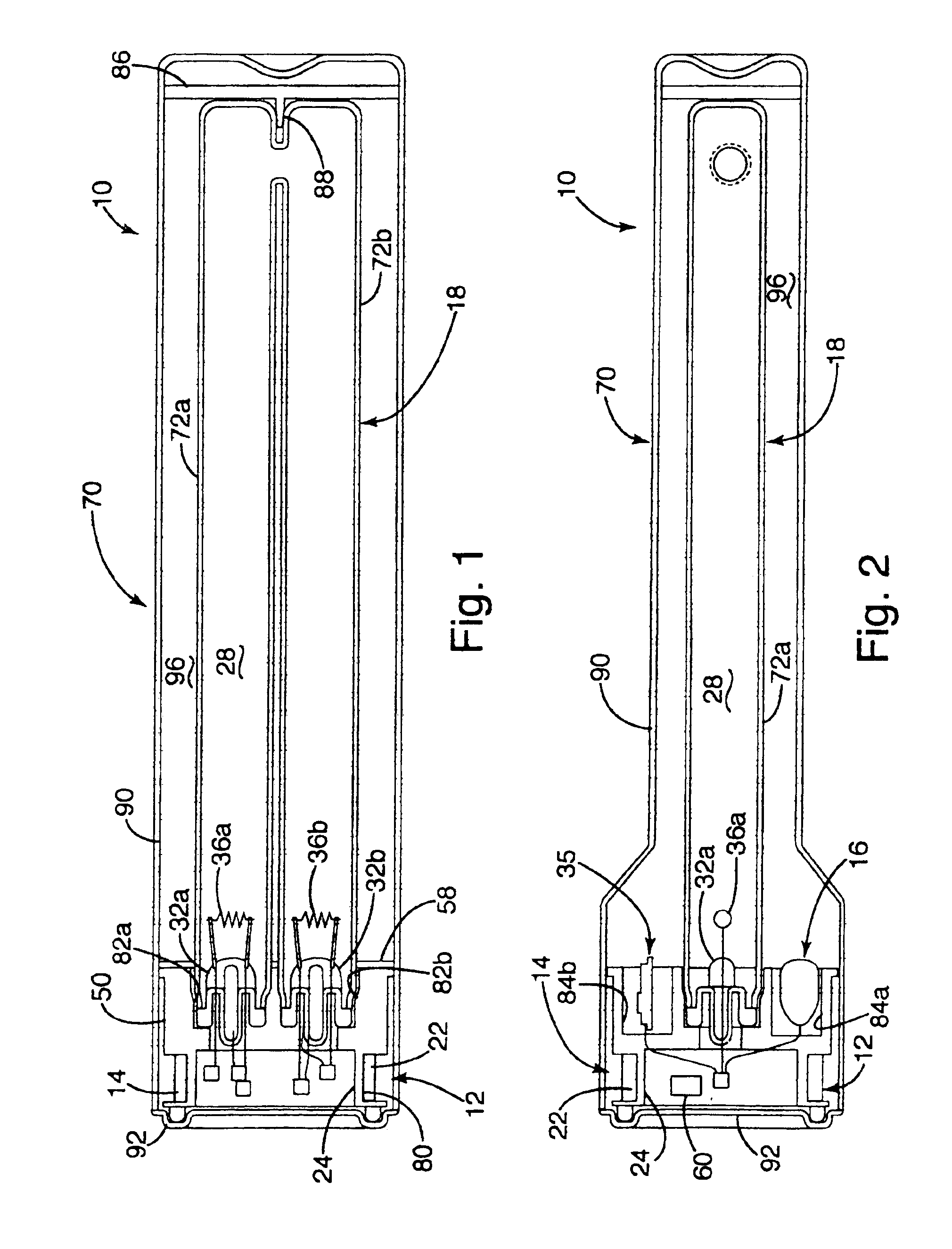
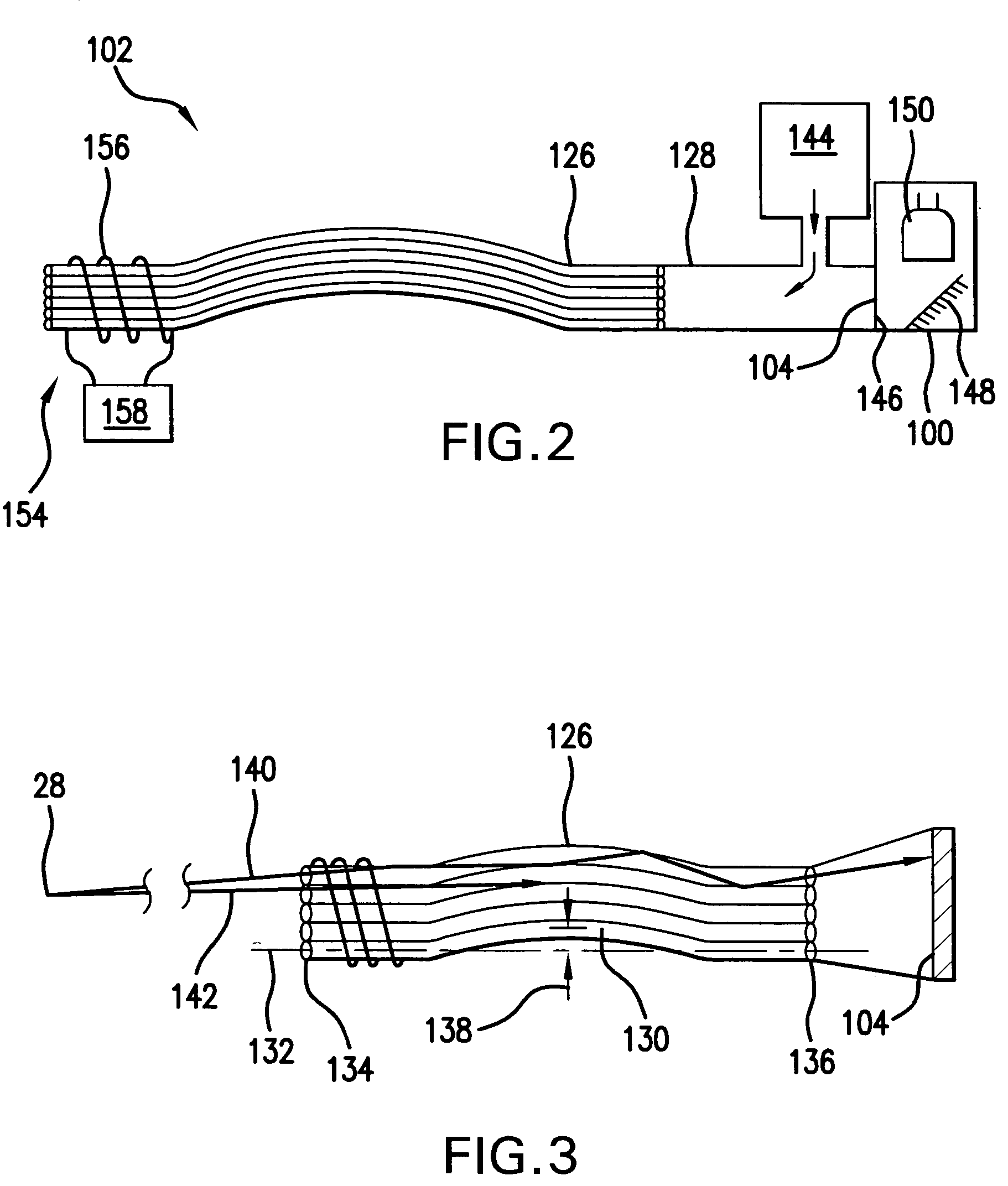
Inductively powered lamp assembly
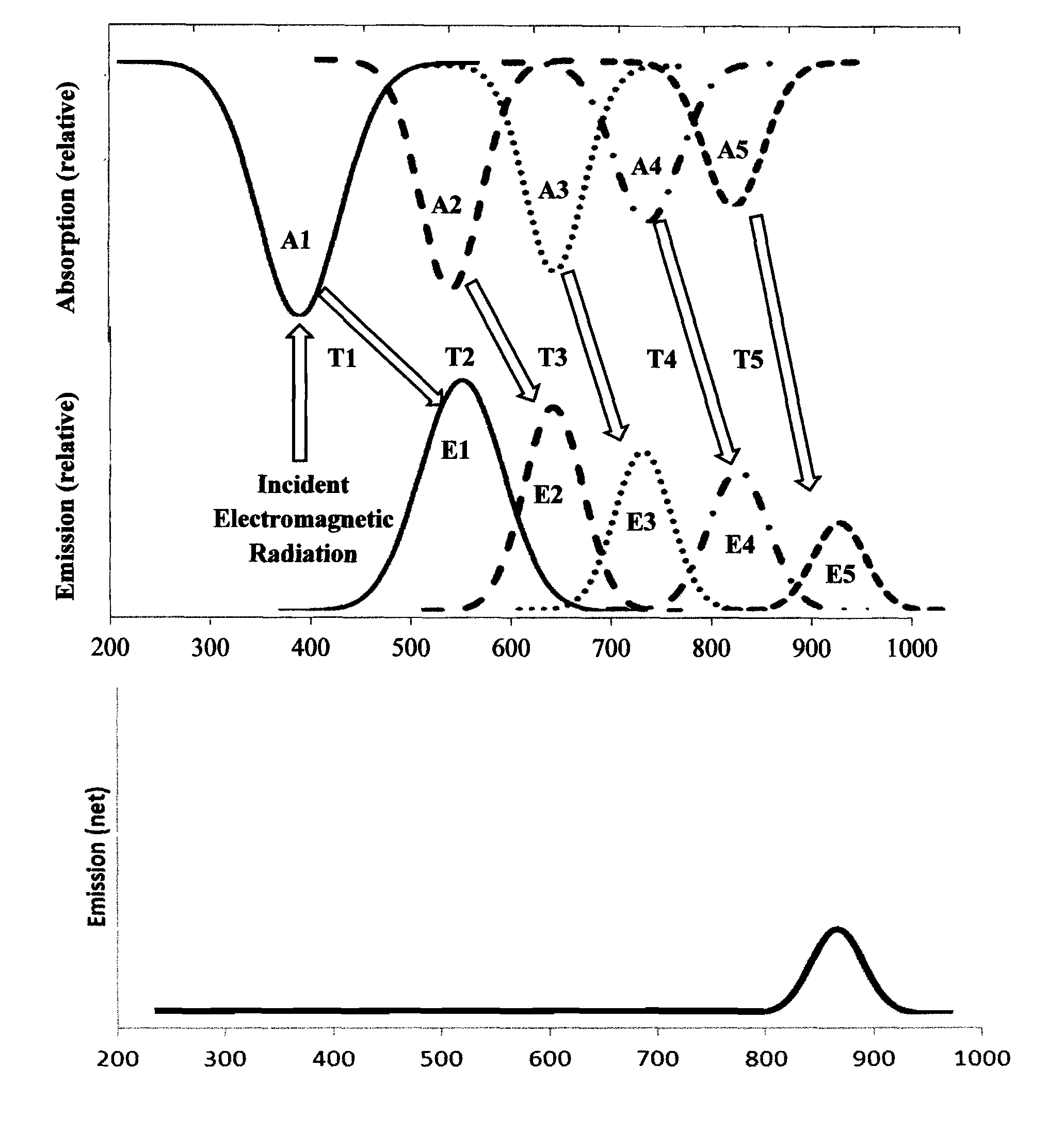
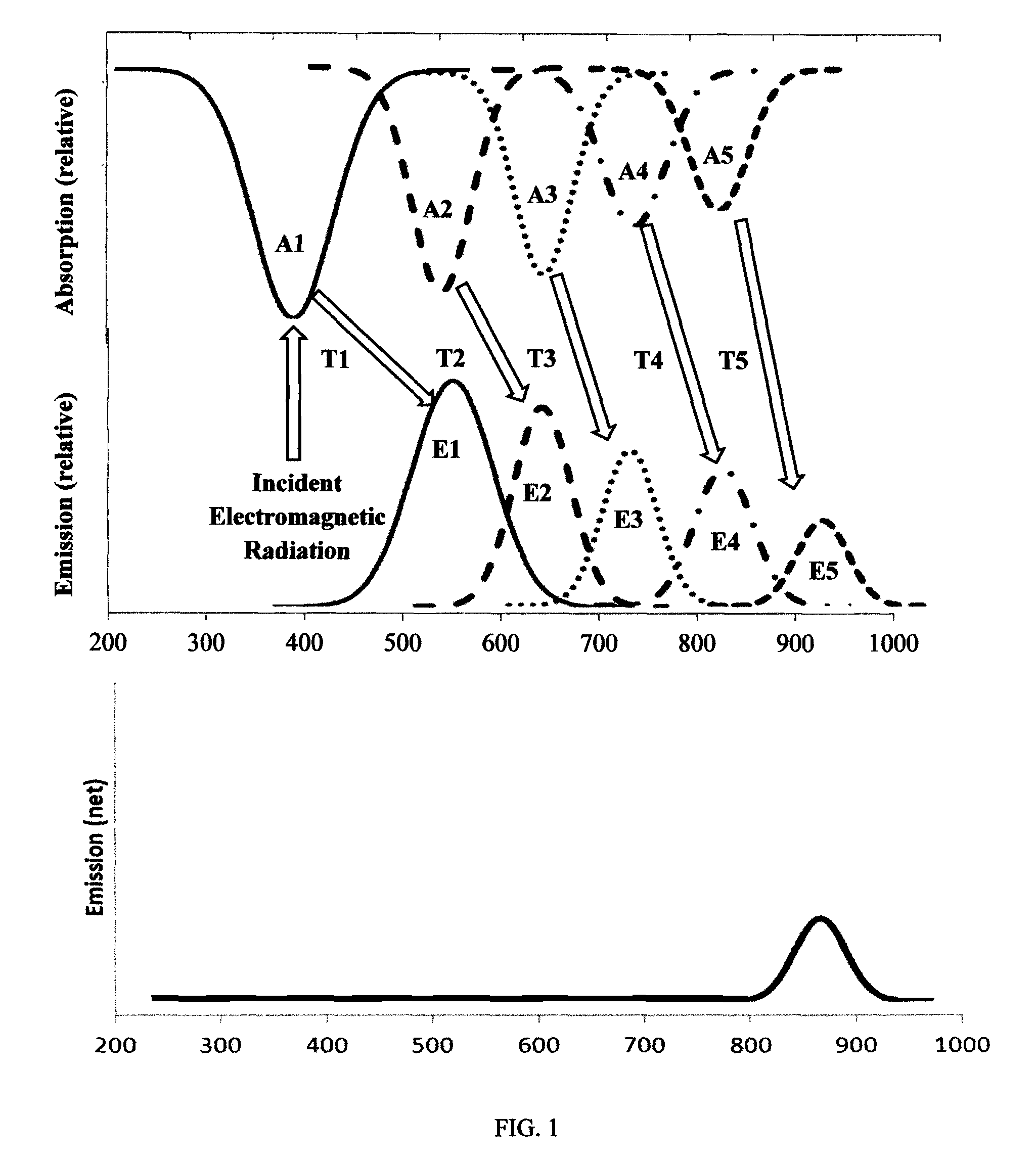
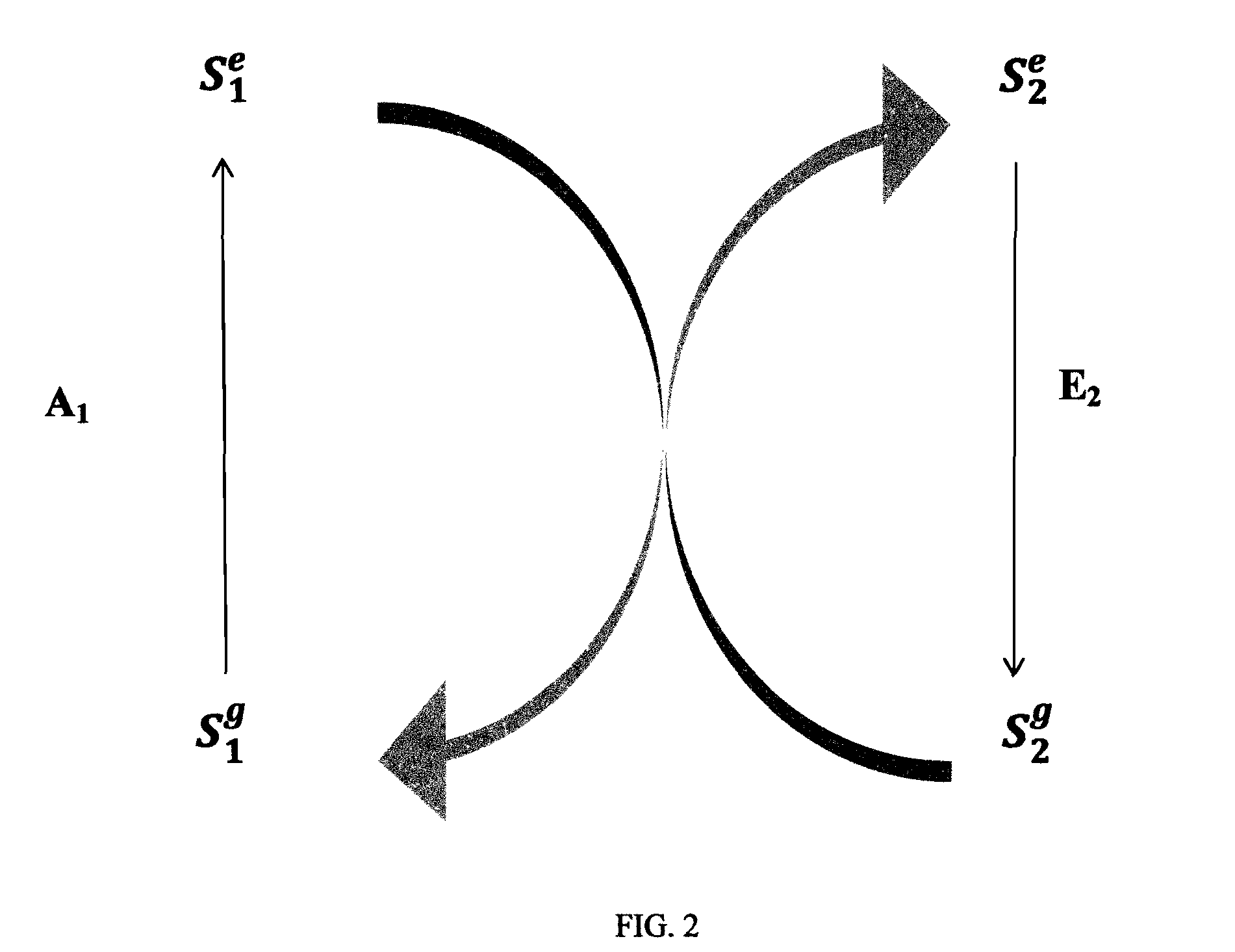
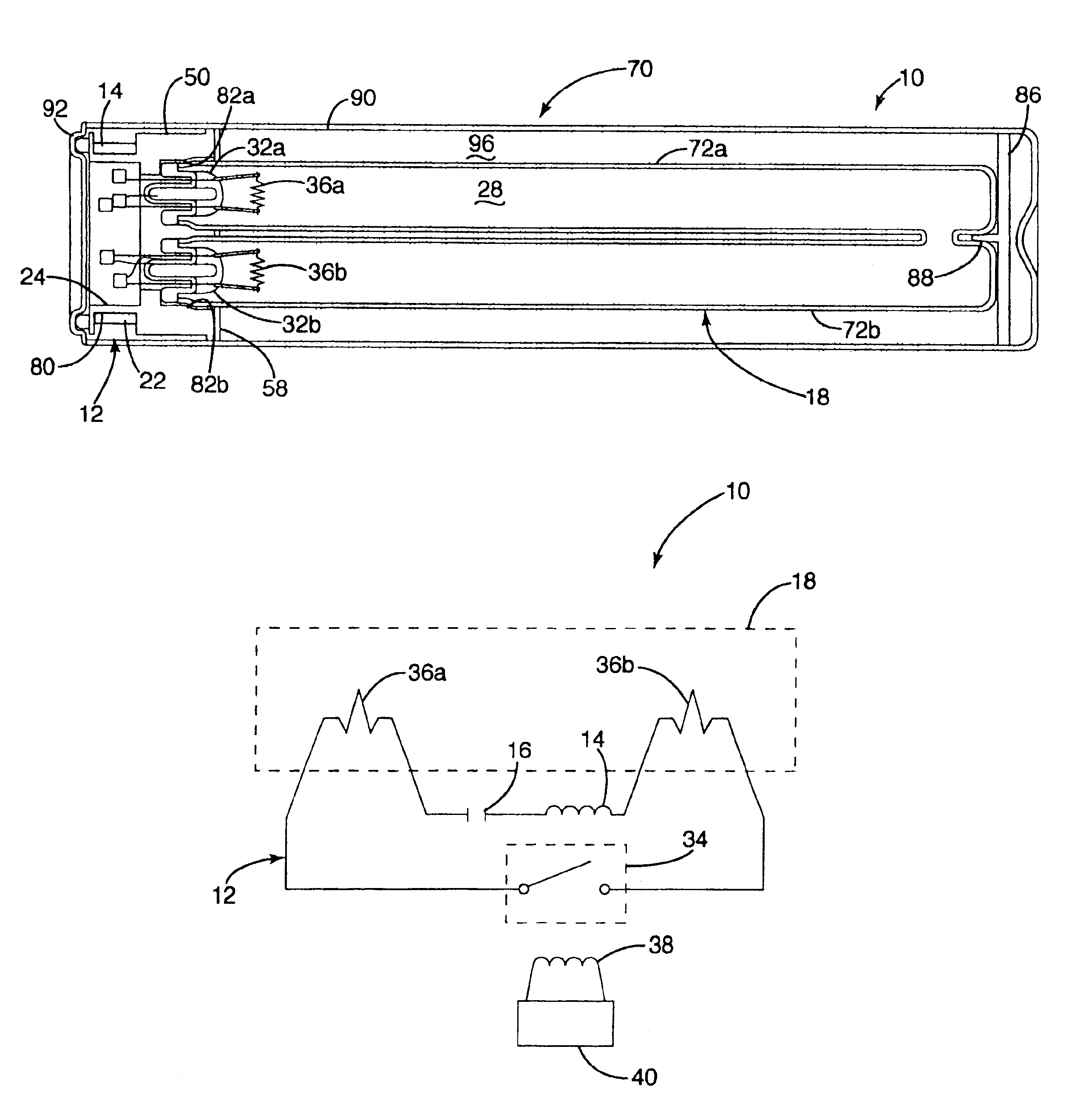
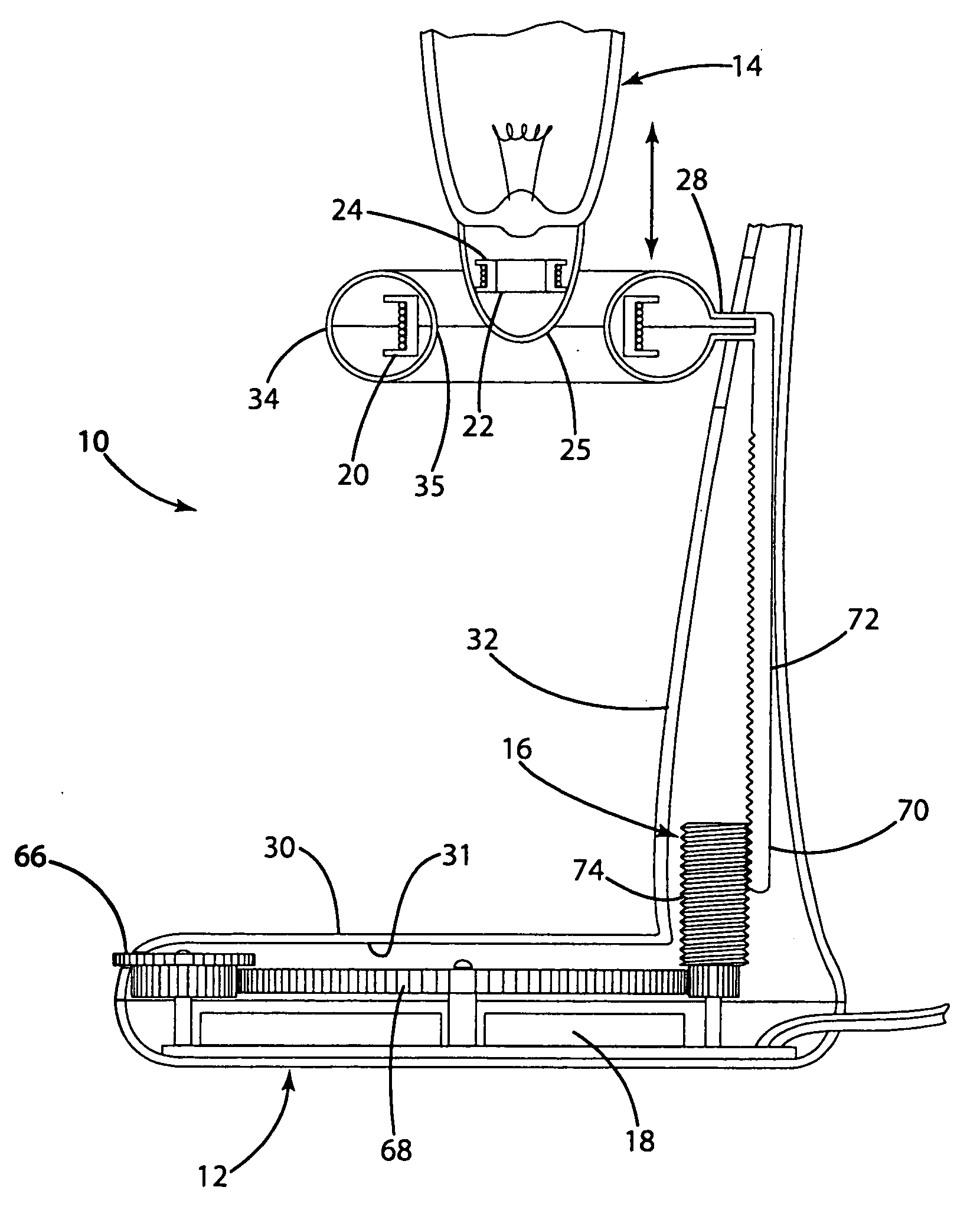
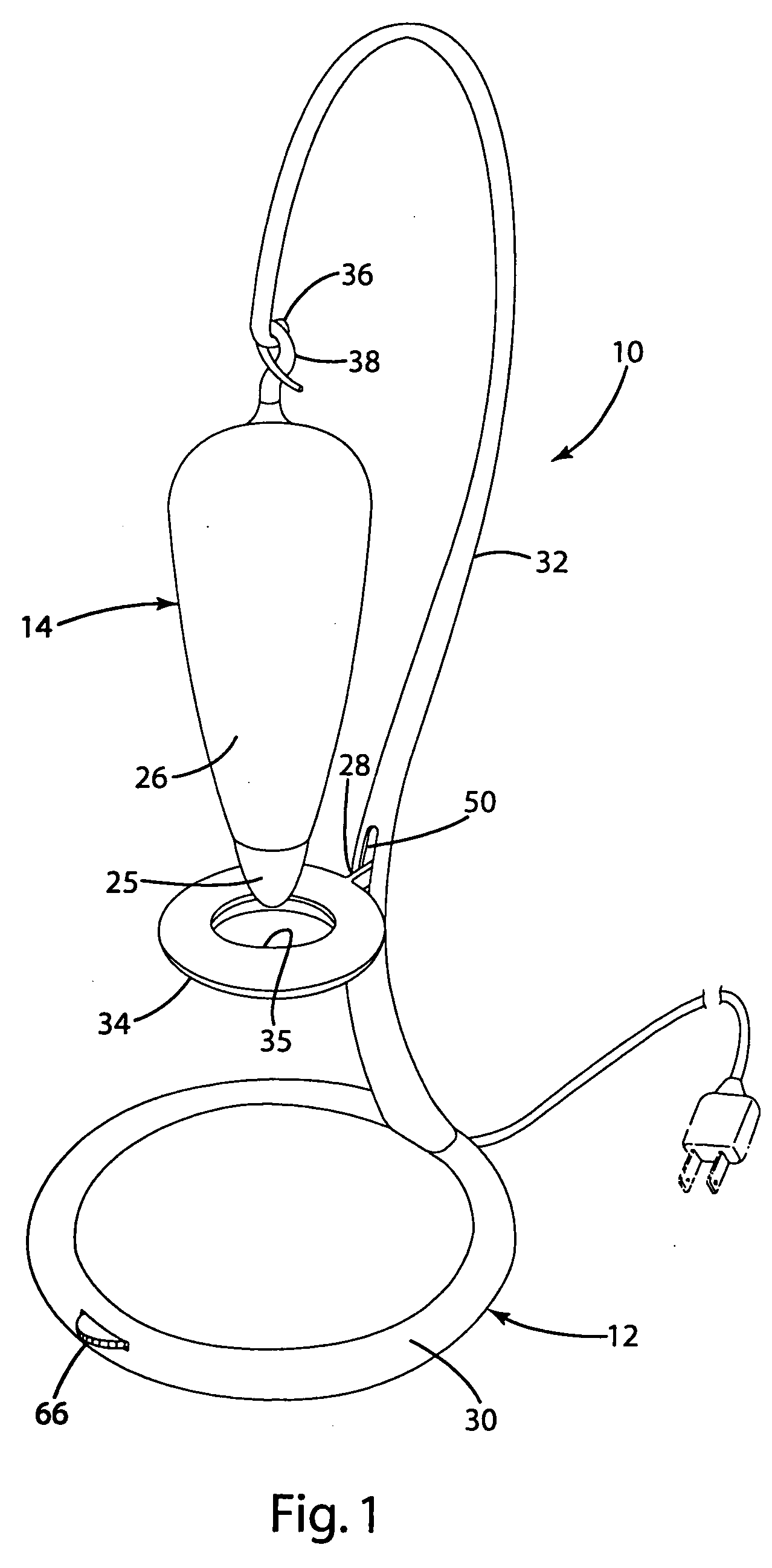
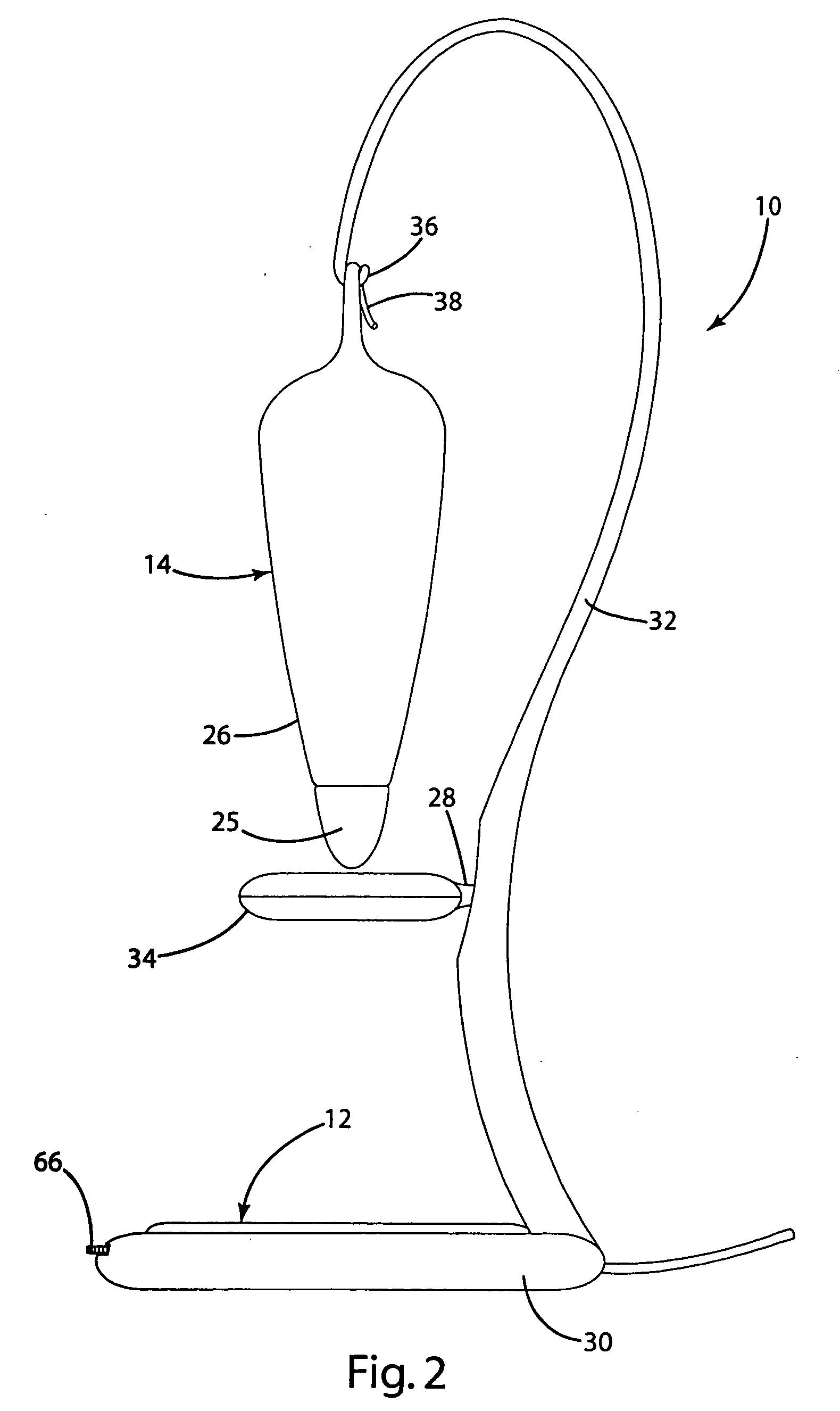
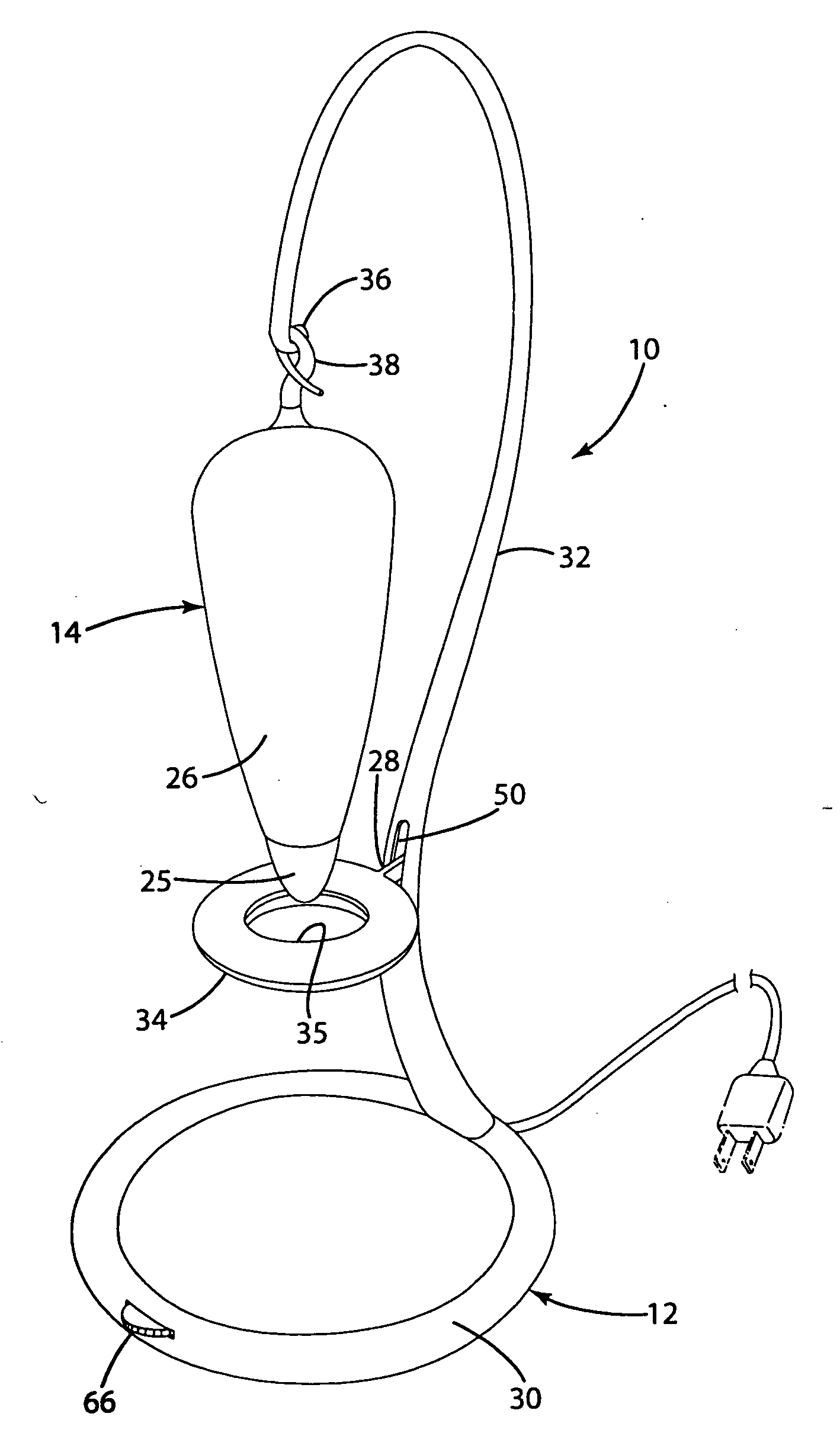
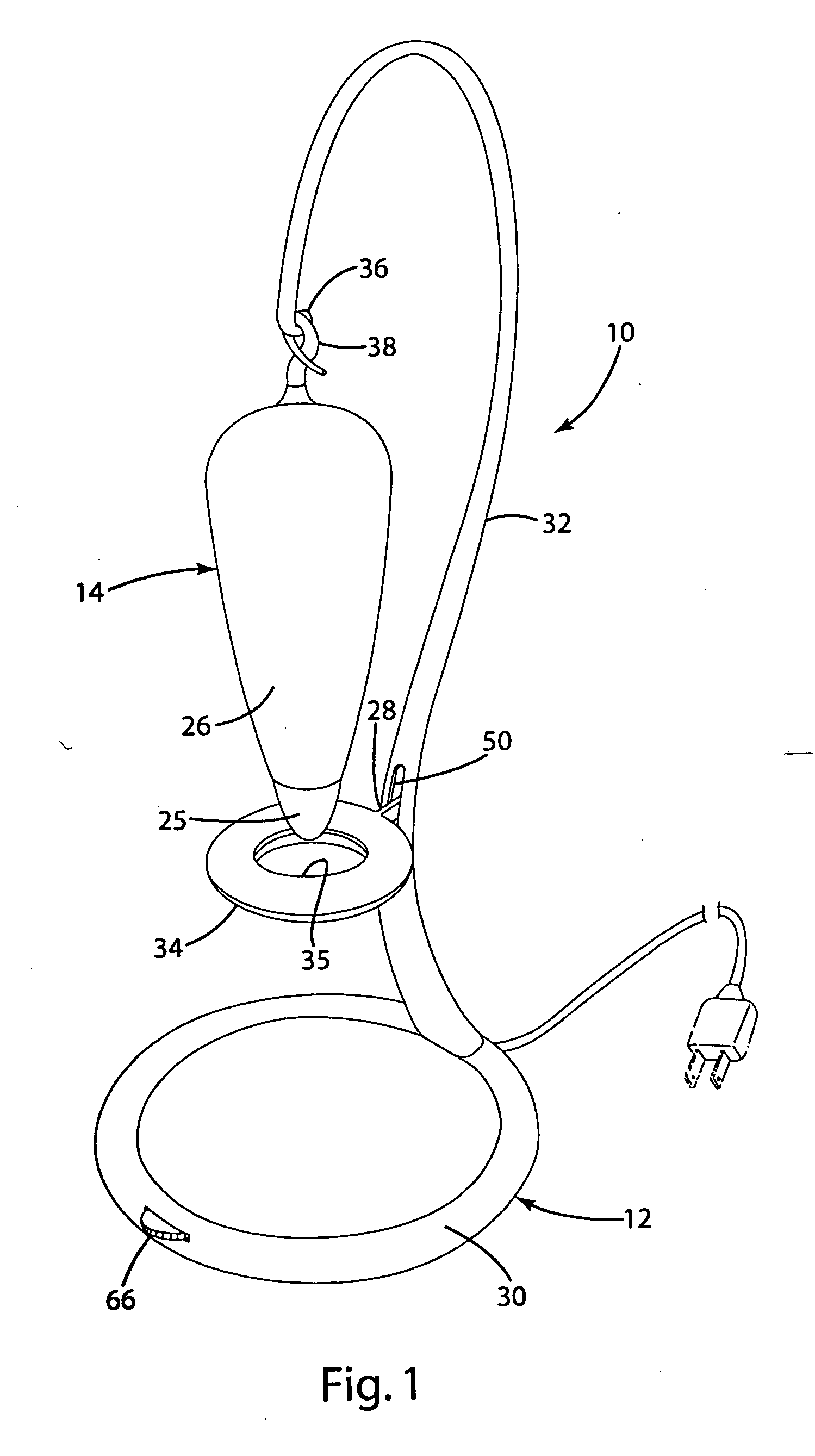
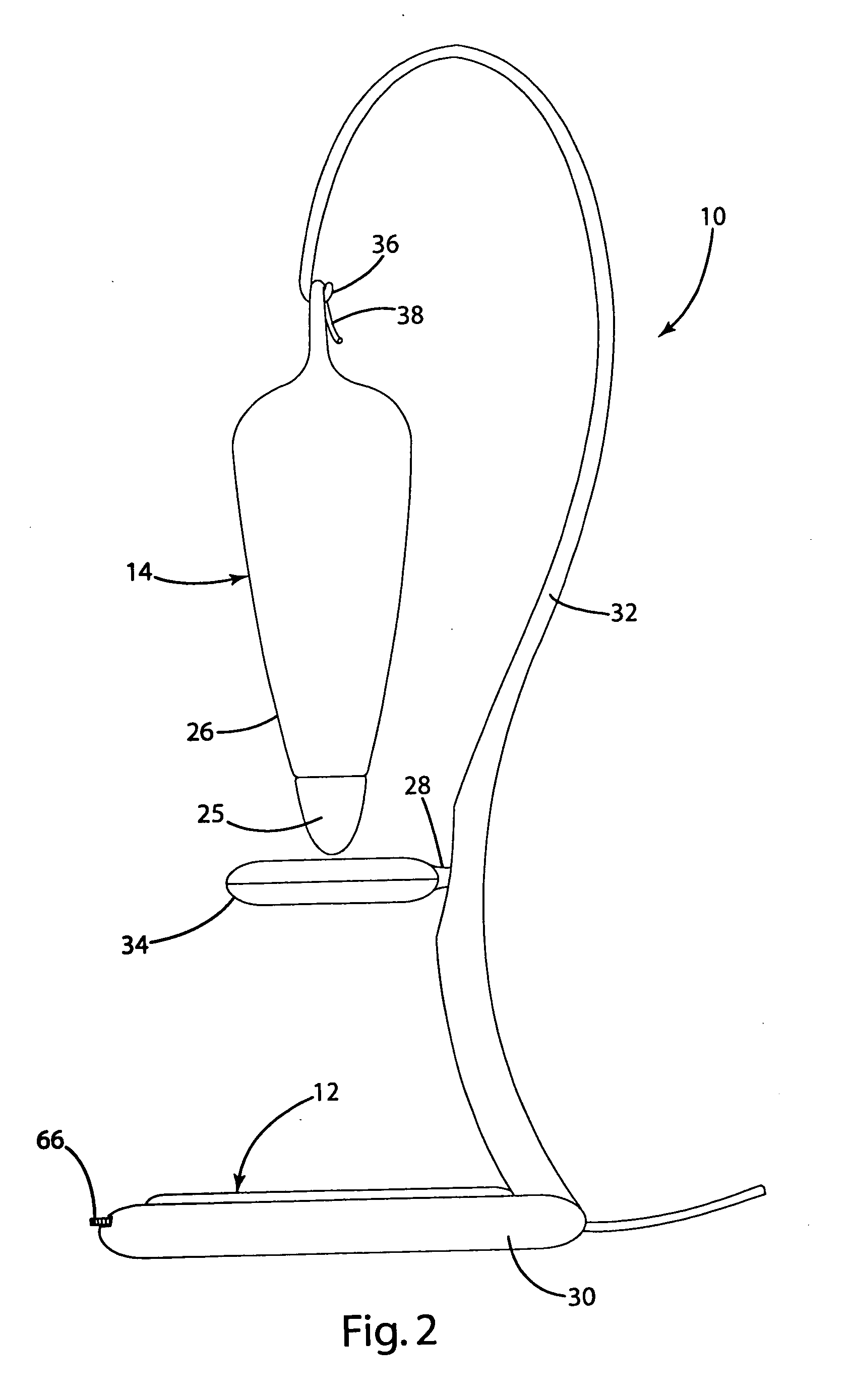
InactiveUS6917163B2Quiet operationLess-precise alignmentPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesResonanceCapacitor
A lamp assembly configured to inductively receive power from a primary coil. The inductively powered lamp assembly includes a lamp circuit including a secondary and a lamp connected in series. In a first aspect, the lamp circuit includes a capacitor connected in series with the lamp and the secondary to tune the circuit to resonance. The capacitor is preferably selected to have a reactance that is substantially equal to or slightly less than the reactance of the secondary and the impedance of the lamp. In a second aspect, the inductively powered lamp assembly includes a sealed transparent sleeve that entirely encloses the lamp circuit so that the transparent sleeve is fully closed and unpenetrated. The transparent sleeve is preferably the lamp sleeve itself, with the secondary, capacitor and any desired starter mechanism disposed within its interior.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Photoluminescent objects
InactiveUS20140065442A1Improve stabilityGeneration of luminanceCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesSynthetic resin layered productsPhotoluminescenceComputer science
An object comprising a low rare earth mineral photoluminescent structure incorporated onto or into one or more portions of the object, the object being a photoluminescent object is disclosed. Further disclosed is a method for fabricating the object. An object comprising a low rare earth mineral photoluminescent composition incorporated onto or into one or more portions of the object, the object being a photoluminescent object is also disclosed, as well as, a method for fabricating the object.
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
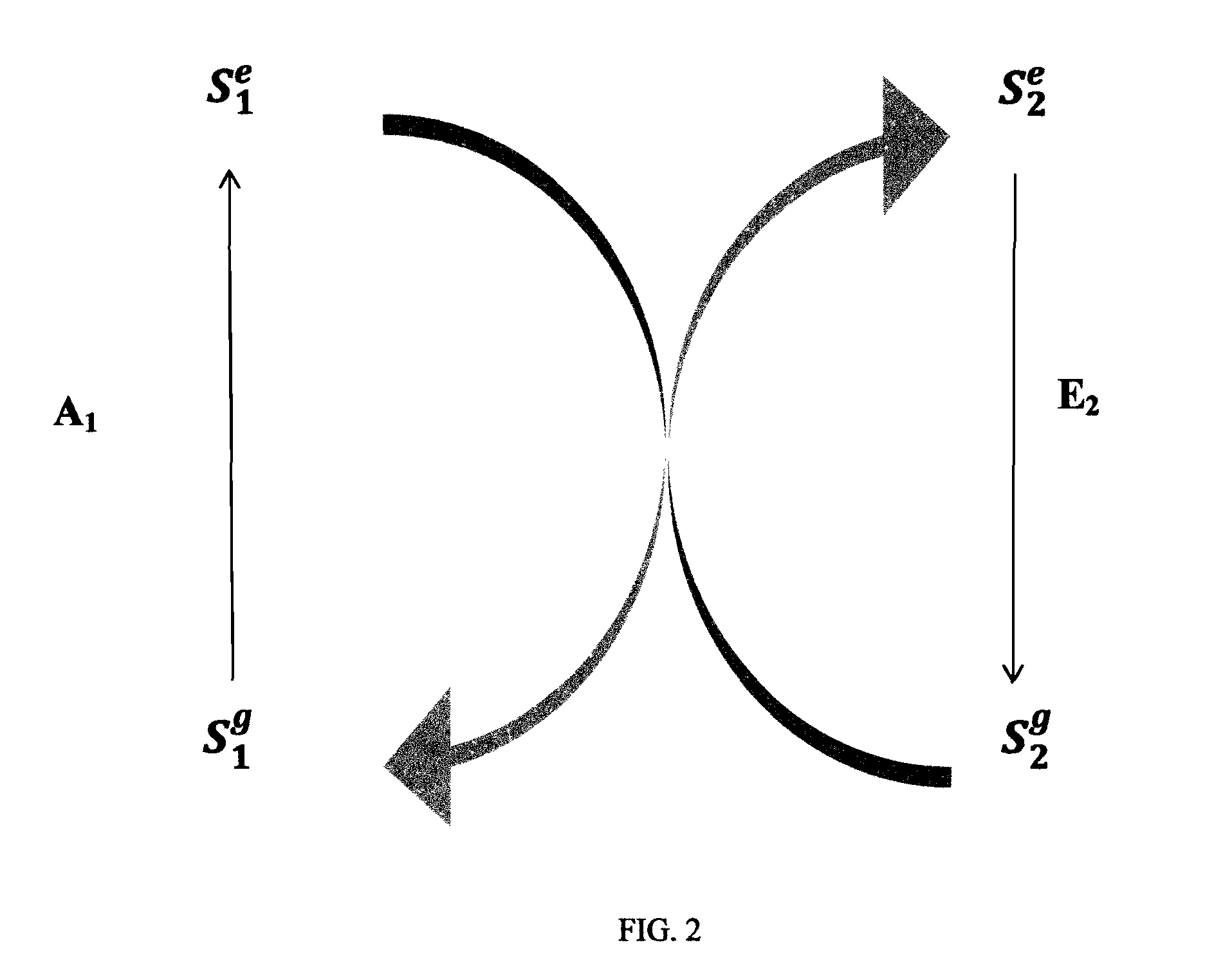
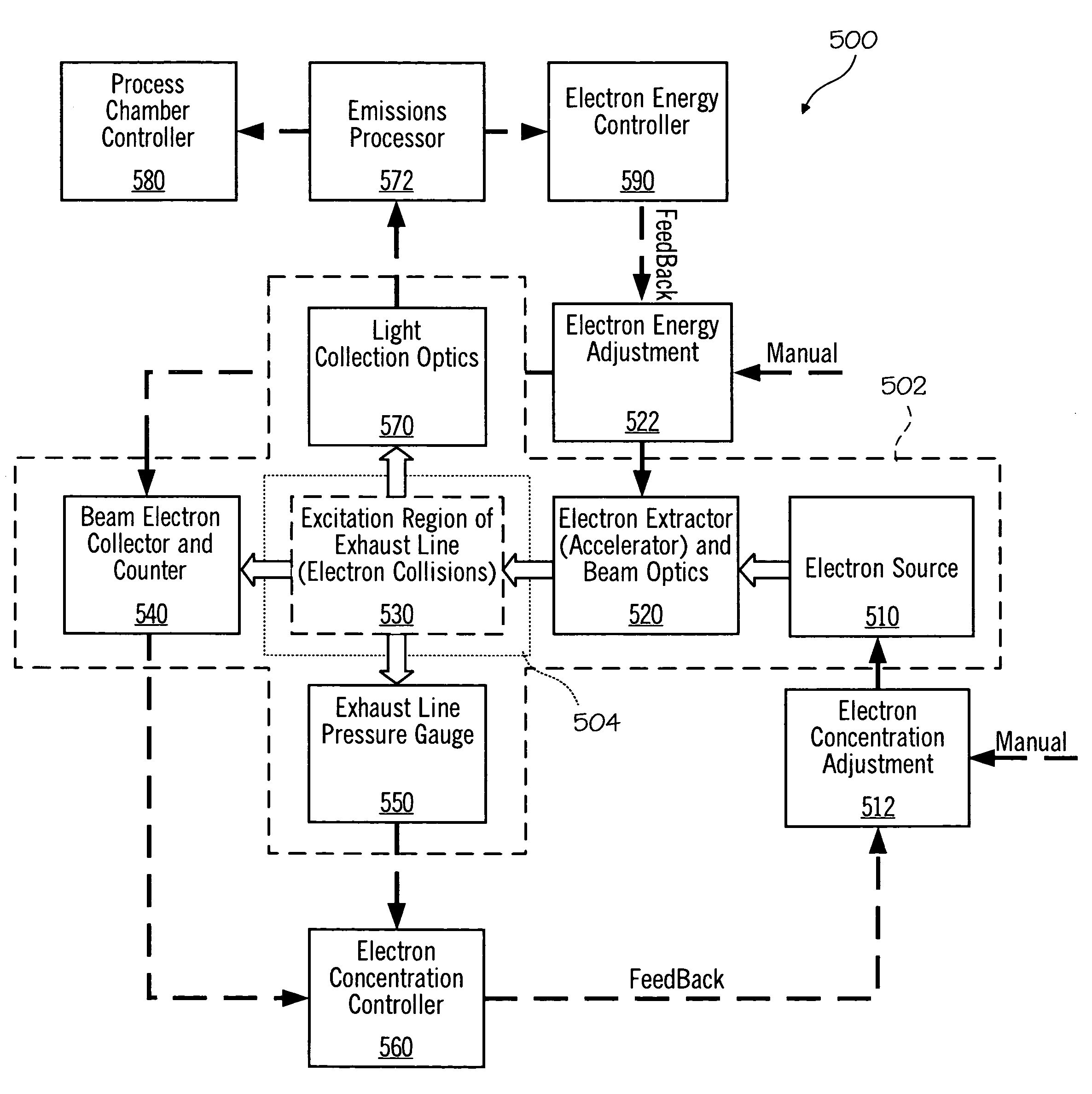
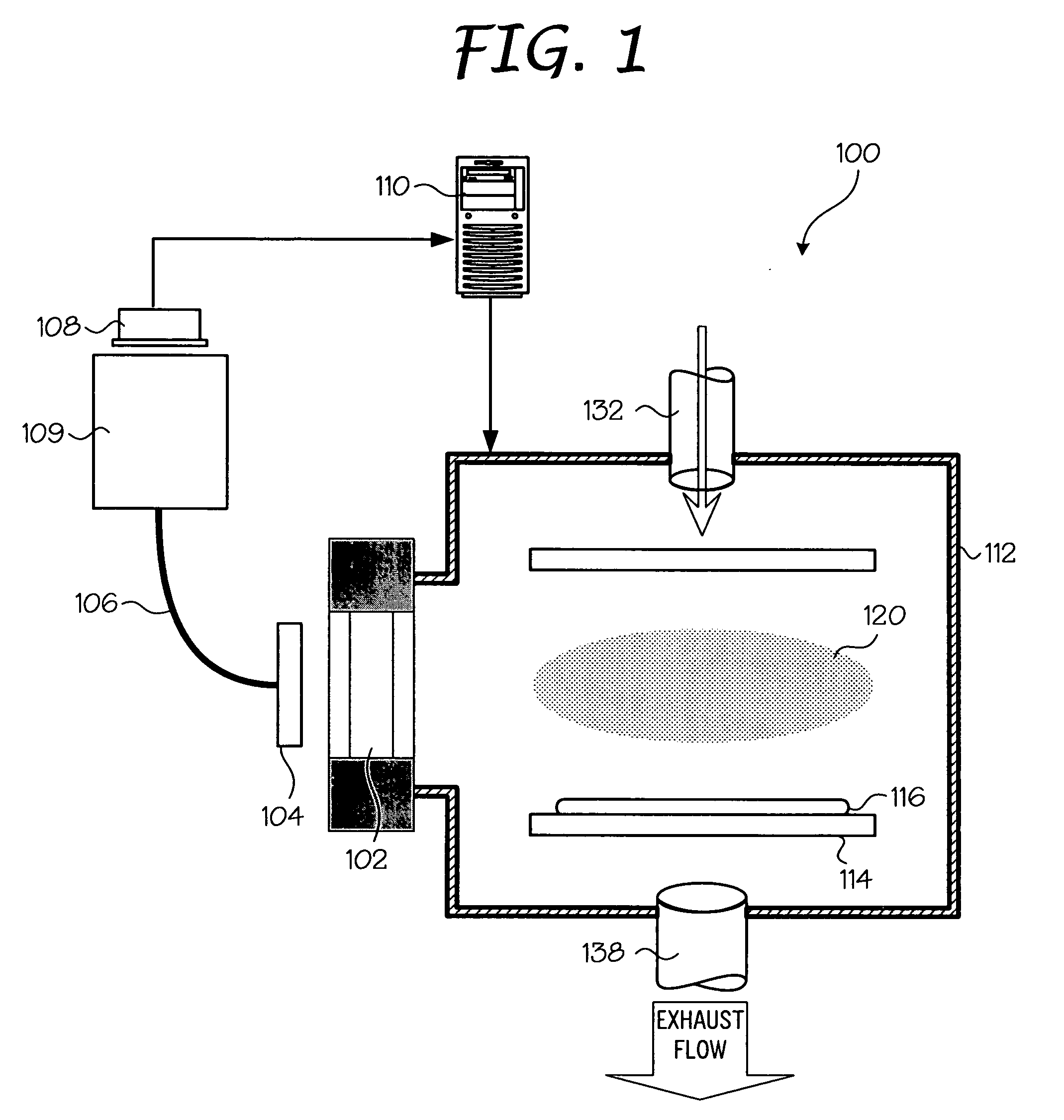
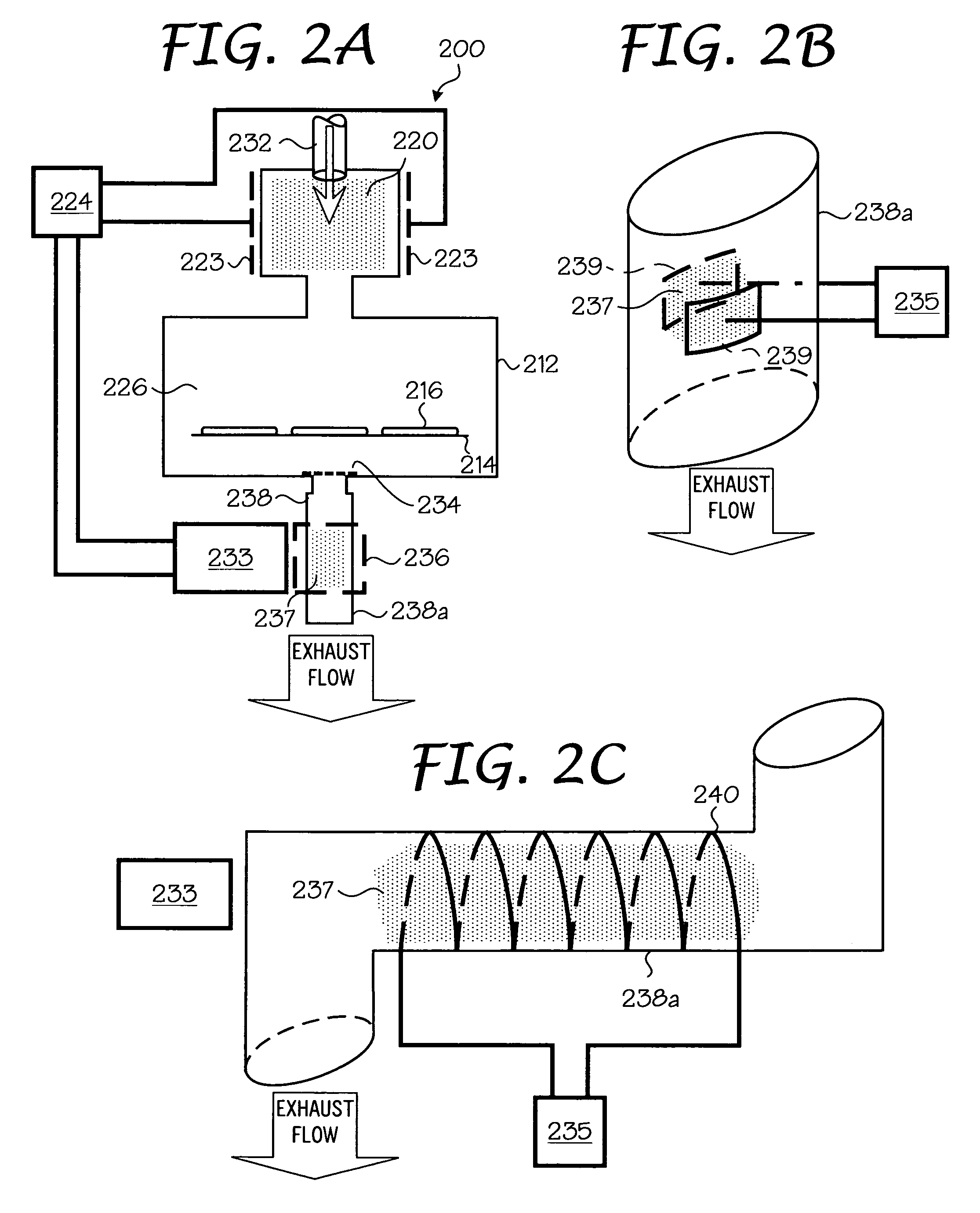
Electron beam exciter for use in chemical analysis in processing systems
ActiveUS20100032587A1Disparity will become so greatHigh electron energyCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesRadiation therapyElectron sourceFluorescence
The present invention is directed to a gas line electron beam exciter, gas line electron beam excitation system and method for exciting a gas using an electron beam exciter. The electron beam exciter generally comprises a variable density electron source for generating a cloud of electrons in an electron chamber and a variable energy electron extractor for accelerating electrons from the electron chamber as an electron beam and into an effluent stream for fluorescing species in the effluent. The electron density of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting the excitation power applied to the variable density electron source. The electrons in the electron chamber reside at a reference electrical potential of the chamber, typically near ground electrical potential. The electron energy of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting an electrical potential across the variable energy electron extractor, which energizes the electrons through an extraction hole of the chamber and toward the extractor. The greater the difference in the electrical potential between the electron extractor and the electron source, the higher the energy imparted to the electrons in the electron beam. The excitation power applied to the electron source can be adjusted independently from the electron energy of the electron beam, thereby altering the electron density of the electron beam without changing the energy level of the electrons of the electron beam.
Owner:VERITY INSTR +1
Inductively powered apparatus
InactiveUS20050122058A1Brightness of light can be controlledEfficiently receive powerLiquid separation auxillary apparatusPoint-like light sourcePower apparatusElectric power
An inductive power supply system for providing power to one or more inductively powered devices. The system includes a mechanism for varying the physical distance or the respective orientation between the primary coil and secondary coil to control the amount of power supplied to the inductively powered device. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to an inductive power supply system having a primary coil and a receptacle disposed within the magnetic field generated by the primary coil. One or more inductively powered devices are placed randomly within the receptacle to receive power inductively from the primary coil. The power supply circuit includes circuitry for adjusting the power supplied to the primary coil to optimize operation based on the position and cumulative characteristics of the inductively powered device(s) disposed within the receptacle.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Inductively powered apparatus
InactiveUS20050127849A1Brightness variesEfficient powerLiquid separation auxillary apparatusPoint-like light sourceEngineeringPower apparatus
An inductive power supply system for providing power to one or more inductively powered devices. The system includes a mechanism for varying the physical distance or the respective orientation between the primary coil and secondary coil to control the amount of power supplied to the inductively powered device. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to an inductive power supply system having a primary coil and a receptacle disposed within the magnetic field generated by the primary coil. One or more inductively powered devices are placed randomly within the receptacle to receive power inductively from the primary coil. The power supply circuit includes circuitry for adjusting the power supplied to the primary coil to optimize operation based on the position and cumulative characteristics of the inductively powered device(s) disposed within the receptacle.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Systems and methods for reducing the influence of plasma-generated debris on the internal components of an EUV light source
ActiveUS7196342B2Prevented from reachingRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsSputteringHydrogen
Systems and methods are disclosed for reducing the influence of plasma generated debris on internal components of an EUV light source. In one aspect, an EUV meteorology monitor is provided which may have a heater to heat an internal multi-layer filtering mirror to a temperature sufficient to remove deposited debris from the mirror. In another aspect, a device is disclosed for removing plasma generated debris from an EUV light source collector mirror having a different debris deposition rate at different zones on the collector mirror. In a particular aspect, an EUV collector mirror system may comprise a source of hydrogen to combine with Li debris to create LiH on a collector surface; and a sputtering system to sputter LiH from the collector surface. In another aspect, an apparatus for etching debris from a surface of a EUV light source collector mirror with a controlled plasma etch rate is disclosed.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
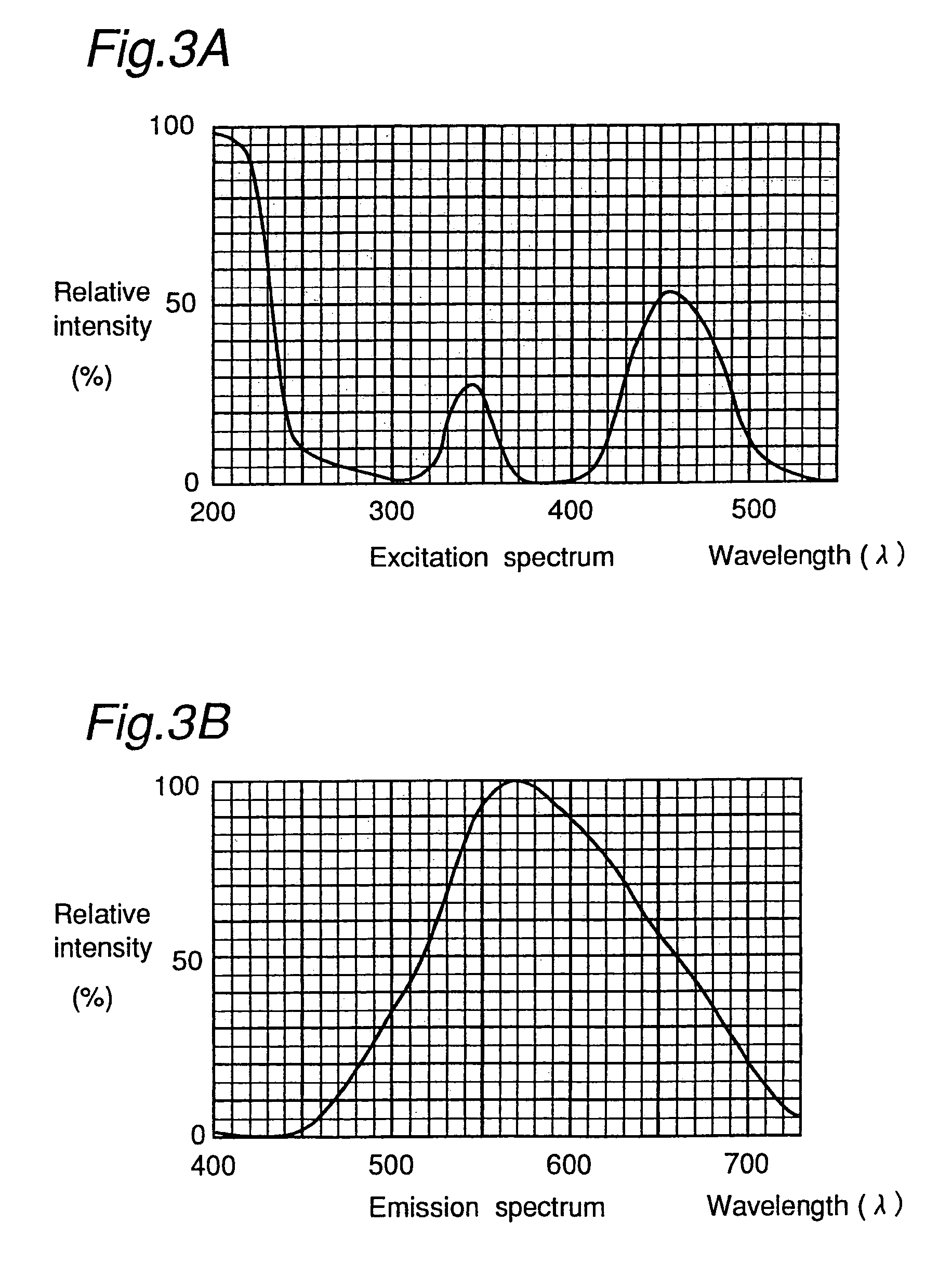
Light emitting device with blue light LED and phosphor components
InactiveUS7026756B2Low degree of deterioration in emission light intensityIncrease brightnessMechanical apparatusDischarge tube luminescnet screensIndiumPhosphor
A light emitting device includes a light emitting component having an active layer of a semiconductor and a phosphor capable of absorbing a part of light emitted from the light emitting component and emitting light of wavelength different from that of the absorbed light, wherein the light emitting component is a LED which has an active layer constituting a gallium nitride based semiconductor containing Indium and is capable of emitting a blue color light with a peak wavelength within the range from 420 to 490 nm. The phosphor is a garnet fluorescent material activated with cerium which is capable of absorbing a part of the blue color light and thereby emitting light having a broad emission spectrum with a peak wavelength existing around the range from 510 to 600 nm and a tail continuing into the region from 700 to 750 nm.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
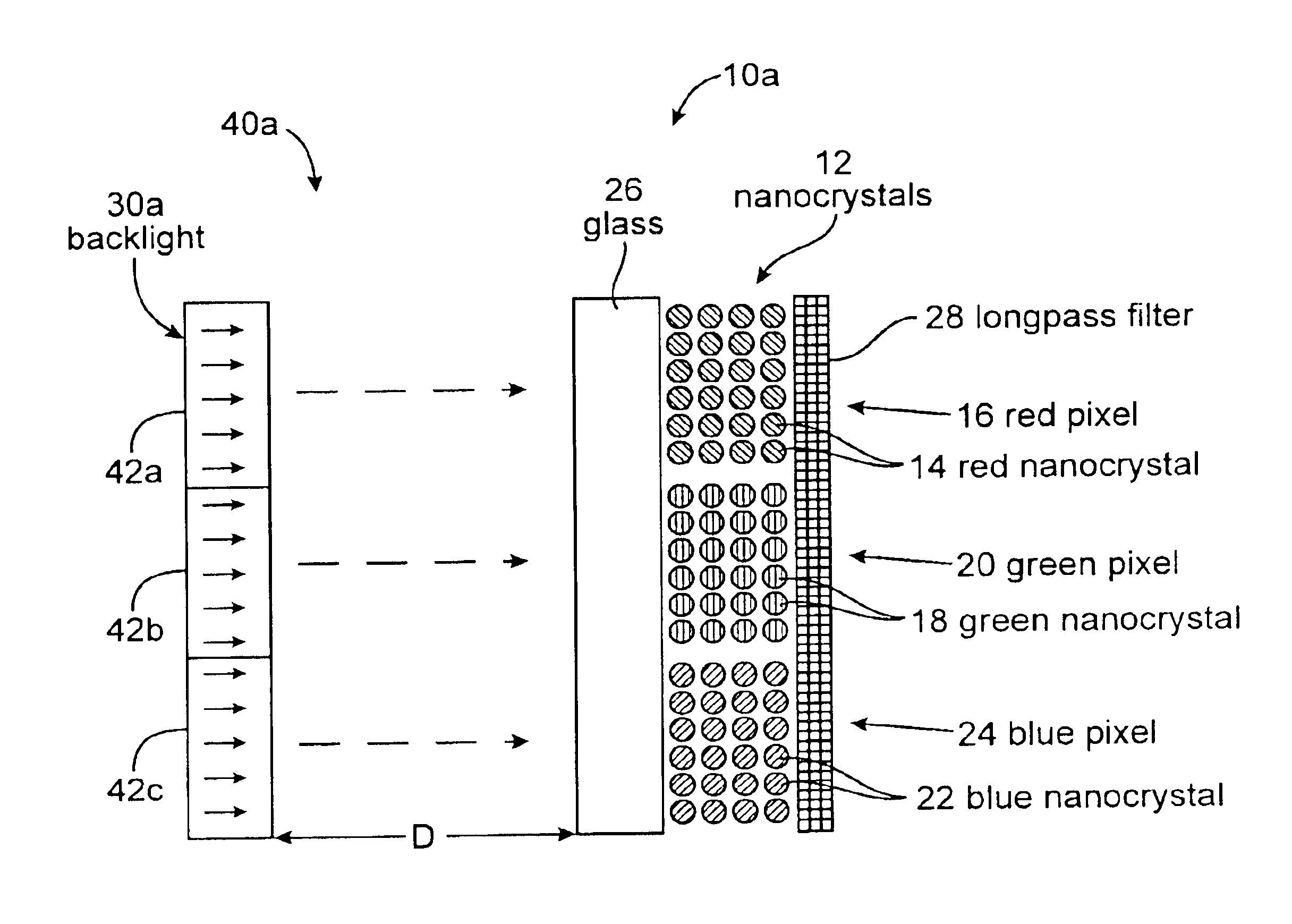
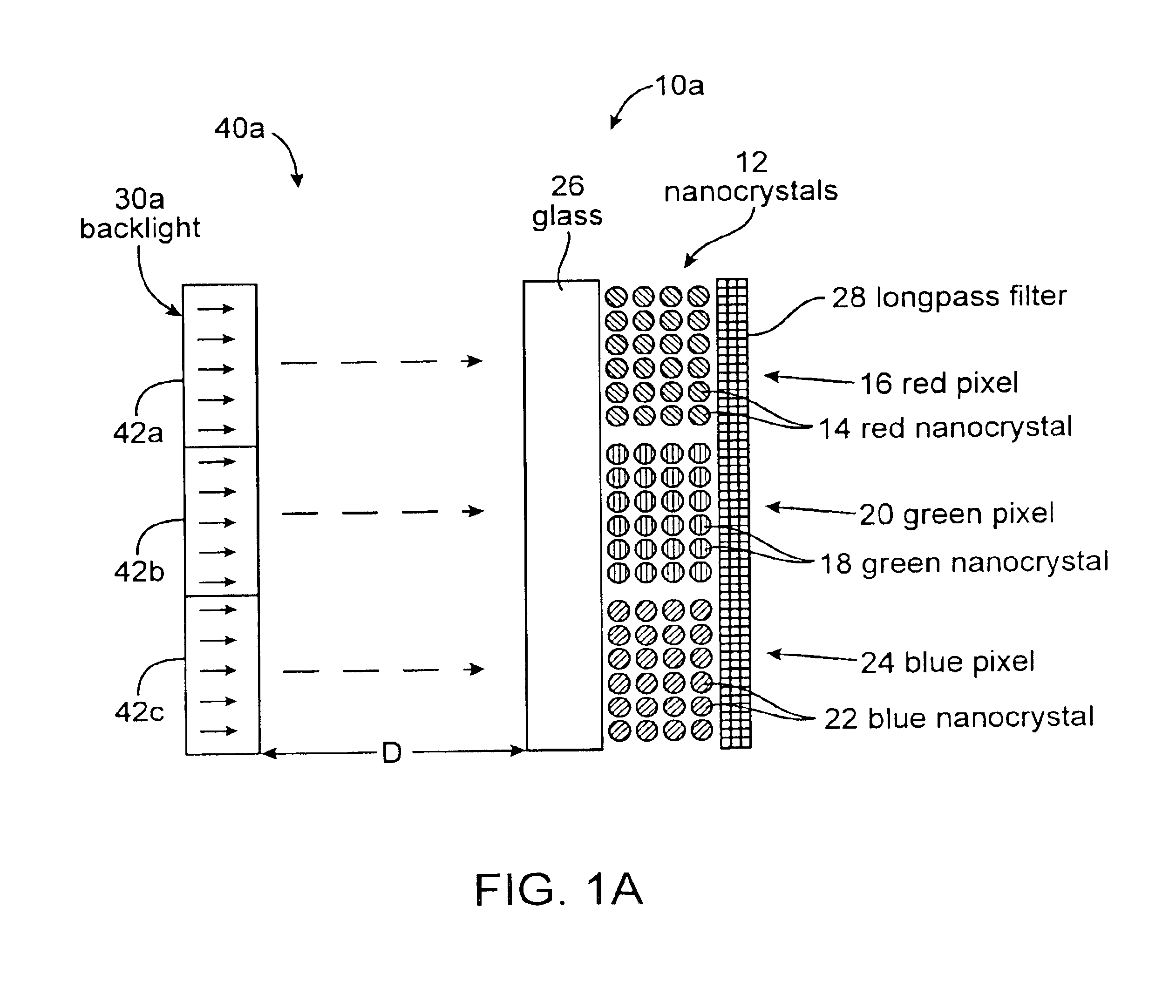
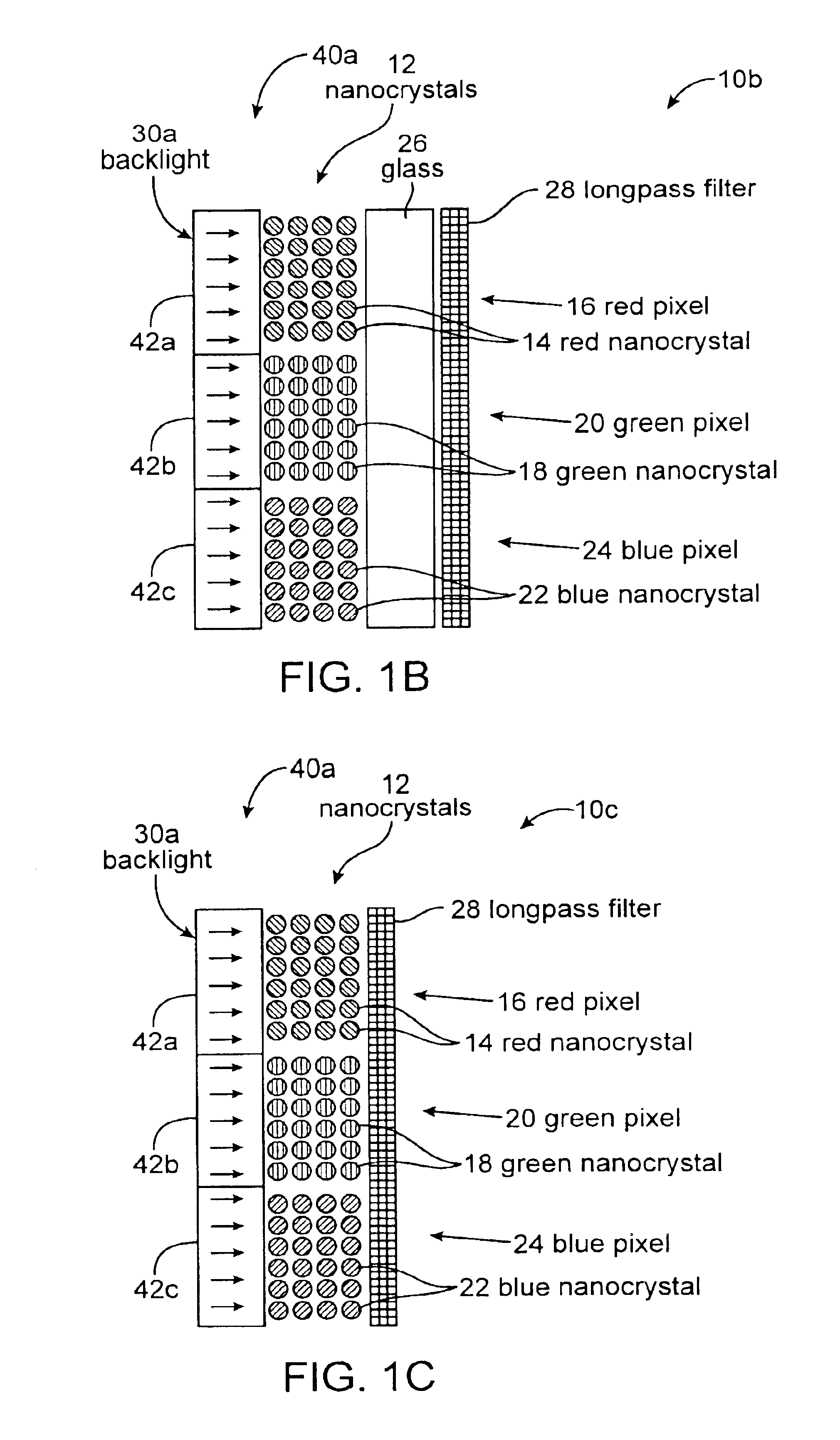
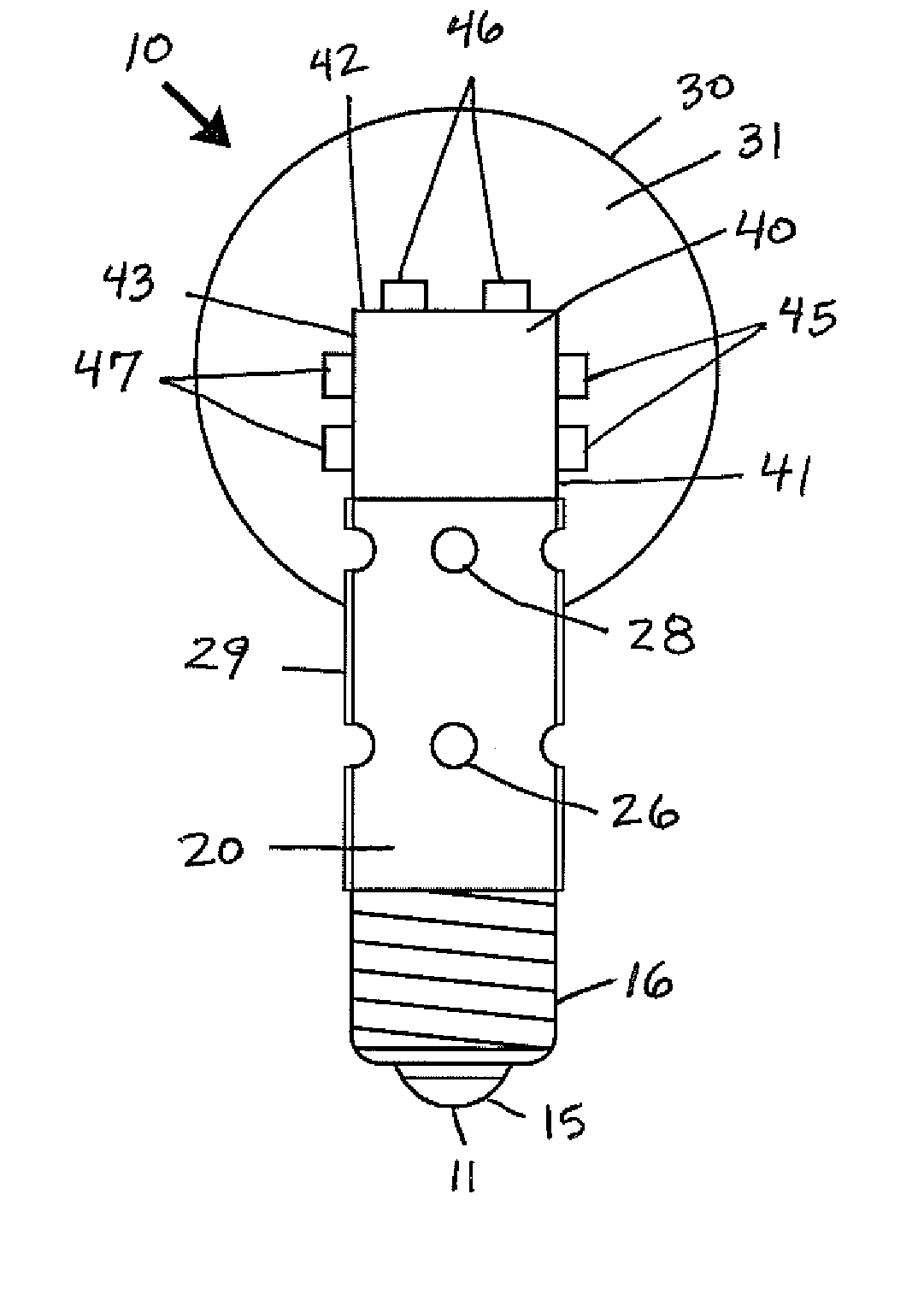
Electronic displays using optically pumped luminescent semiconductor nanocrystals
InactiveUS6864626B1Good flexibilityLiquid crystal compositionsMaterial nanotechnologyDisplay deviceSemiconductor nanocrystals
A multicolor electronic display is based on an array of luminescent semiconductor nanocrystals. Nanocrystals which emit light of different colors are grouped into pixels. The nanocrystals are optically pumped to produce a multicolor display. Different sized nanocrystals are used to produce the different colors. A variety of pixel addressing systems can be used.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
LED light bulbs
ActiveUS20110298371A1Address limitationsPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLED lamp
LED light bulbs include openings in base or cover portions, and optional forced flow elements, for convective cooling. Thermally conductive optically transmissive material may be used for cooling, optionally including fins. A LED light engine may be fabricated from a substrate via planar fabrication techiques and shaped to form a substantially rigid upright support structure. Mechanical, electrical, and thermal connections may be made between a LED light engine and a LED light bulb.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
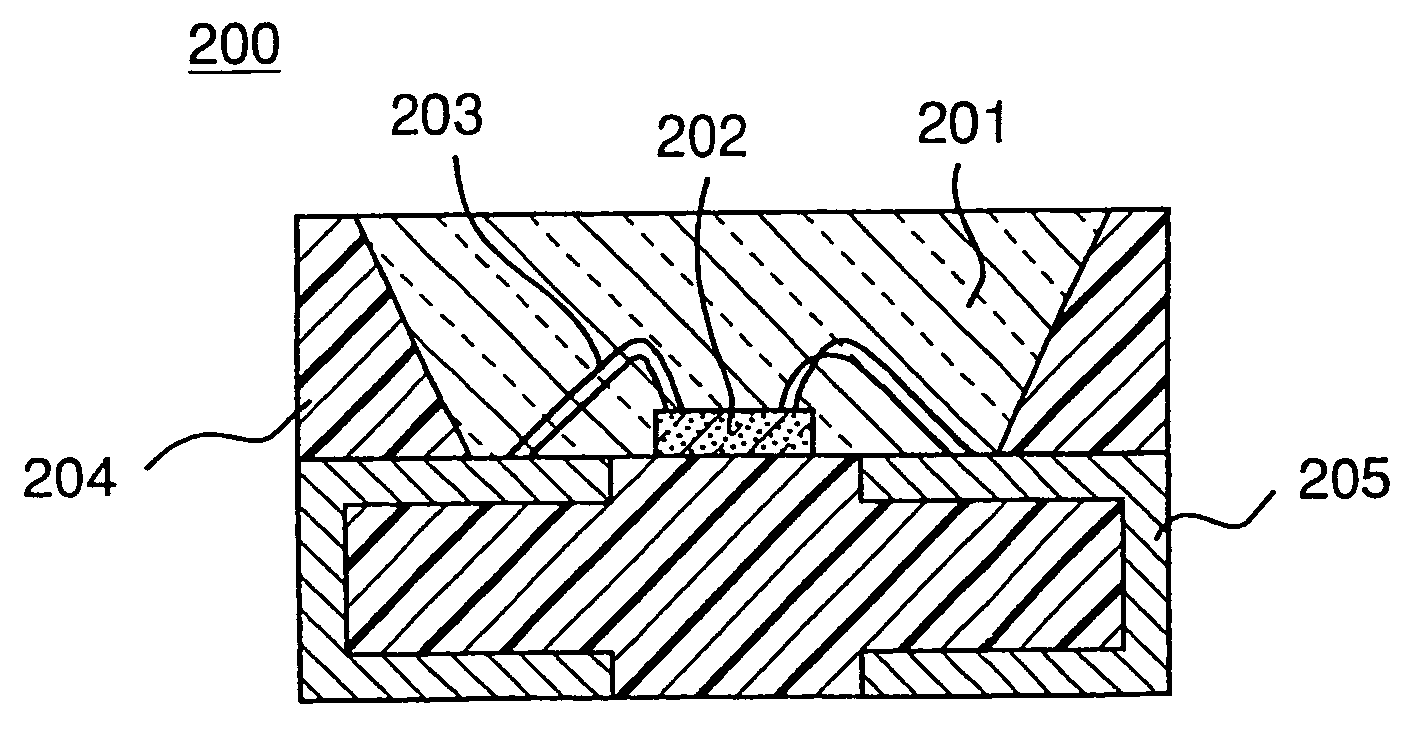
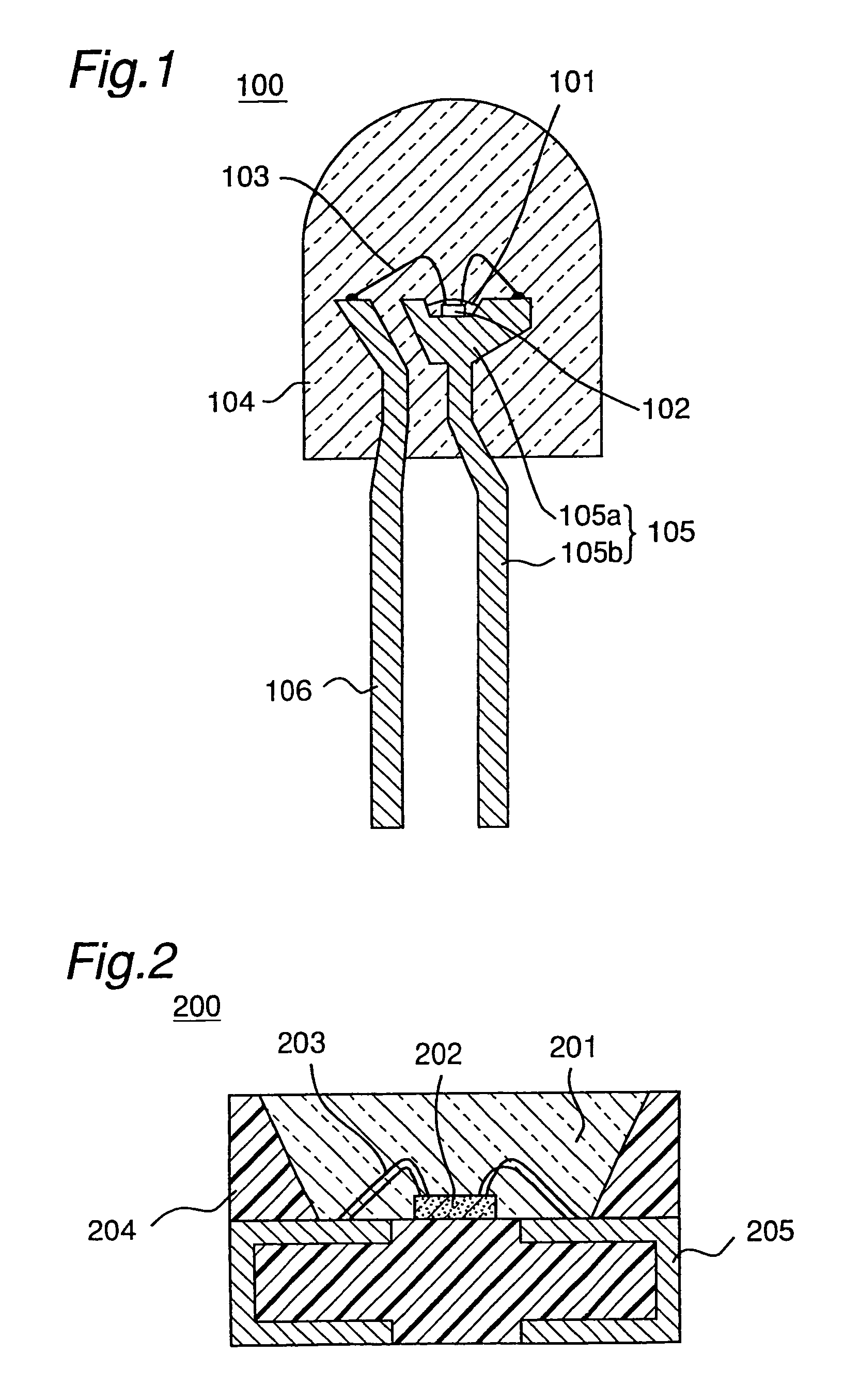
Luminescent device
InactiveUS7572522B2High carrier mobilityEasy to useDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesDopantLight emitting device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electroluminescent device with anthracene derivative host
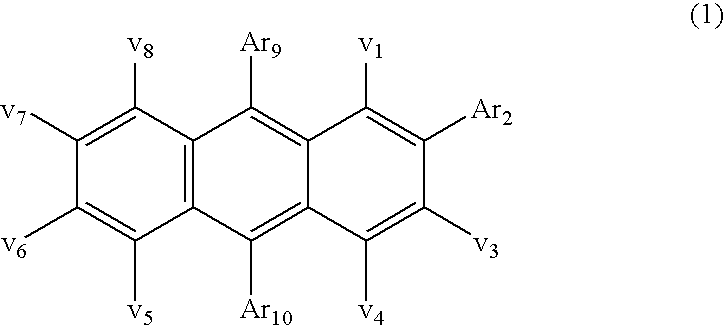
InactiveUS7326371B2Desirable hueEasy to manufactureCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesElectroluminescent light sourcesArylAnthracene
An electroluminescent device comprises a light emitting layer including an anthracene material bearing at least one aryl ring in the 2-position and having a hydrogen or an alkyl group in the 6-position and having up to 12 aromatic carbocyclic rings including at least one naphthalene group in the 9-position of the anthracene group and an aryl group in the 10-position, the anthracene material including among the rings only carbocyclic rings.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Vortex transducer
InactiveUS7273459B2Reliably aimCheap and cost-effective manufacturing processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesChiropractic devicesElectricityTransducer
A mechanically formed vortex transducer is described. The transducer has a plurality of piezoelectric elements suspended in an epoxy and heat molded into a desired shape. An irregularity in the transducer shape provides for a mechanically induced vortex focal field without the need for electronic steering or lens focusing. A system and methods of making the same are also described.
Owner:LIPOSONIX
Sheet-shaped heat and light source, method for making the same and method for heating object adopting the same
InactiveUS20090096348A1Efficient use ofNanotechDischarge tube luminescnet screensCarbon nanotubeOptoelectronics
The present invention relates to a sheet-shaped heat and light source. The sheet-shaped heat and light source includes a carbon nanotube film and at least two electrodes. The at least two electrodes are separately disposed on the carbon nanotube film and electrically connected thereto. Moreover, a method for making the sheet-shaped heat and light source and a method for heating an object adopting the same are also included.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
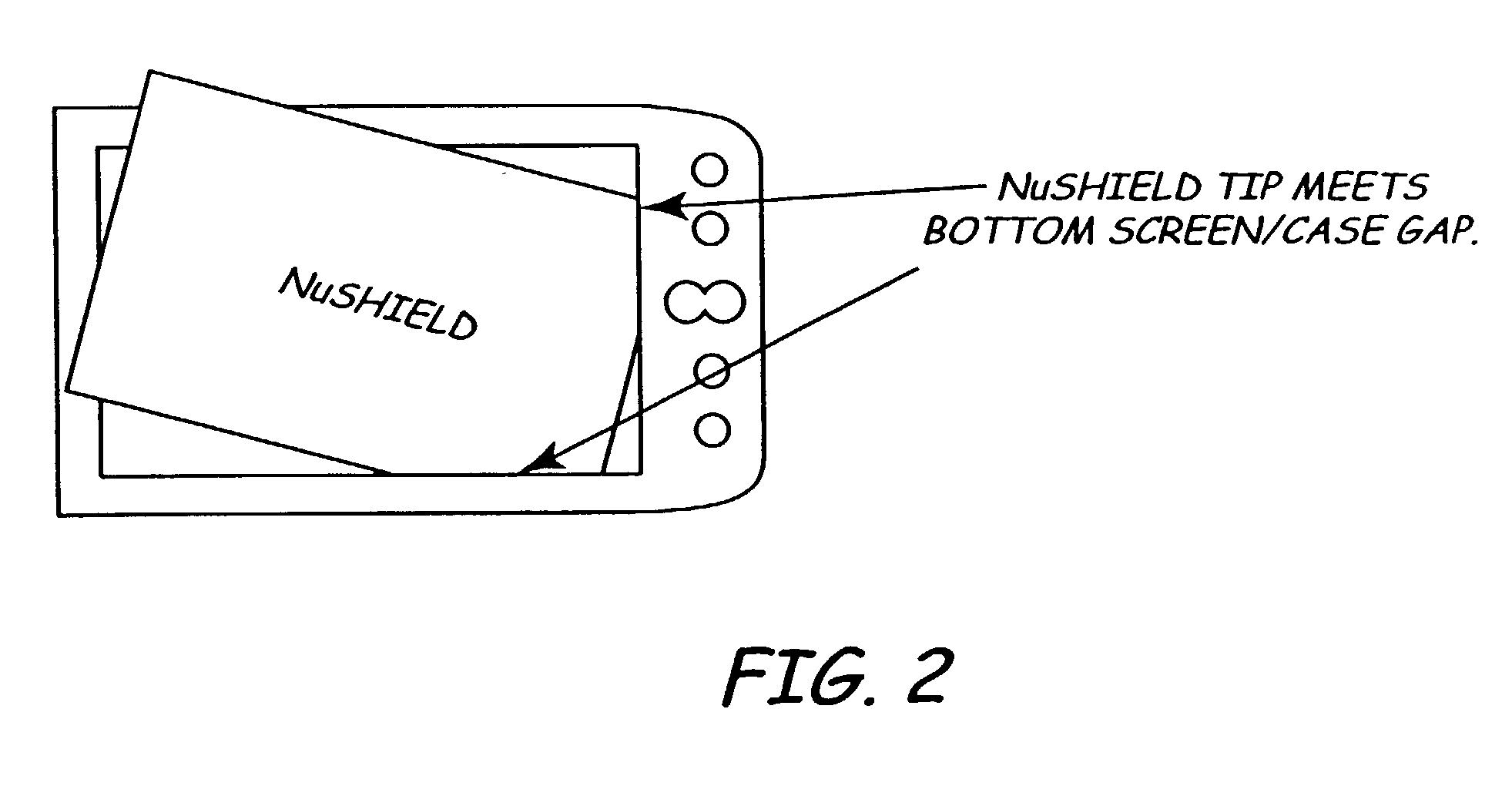
Screen protector
InactiveUS7070837B2Prevents orMinimize formationLiquid crystal compositionsAdhesive processesRefractive indexEngineering
A plastic film screen protector that prevents interference patterns from arising when the film touches the screen is described. The advantages are accomplished by the film having a slightly roughened surface so that the majority of the film facing an electronic device screen does not substantially touch the screen. These physical aberrations prevent Newton ring interference patterns and spots caused by refractive index differences between air and the film material.
Owner:ROSS MARK
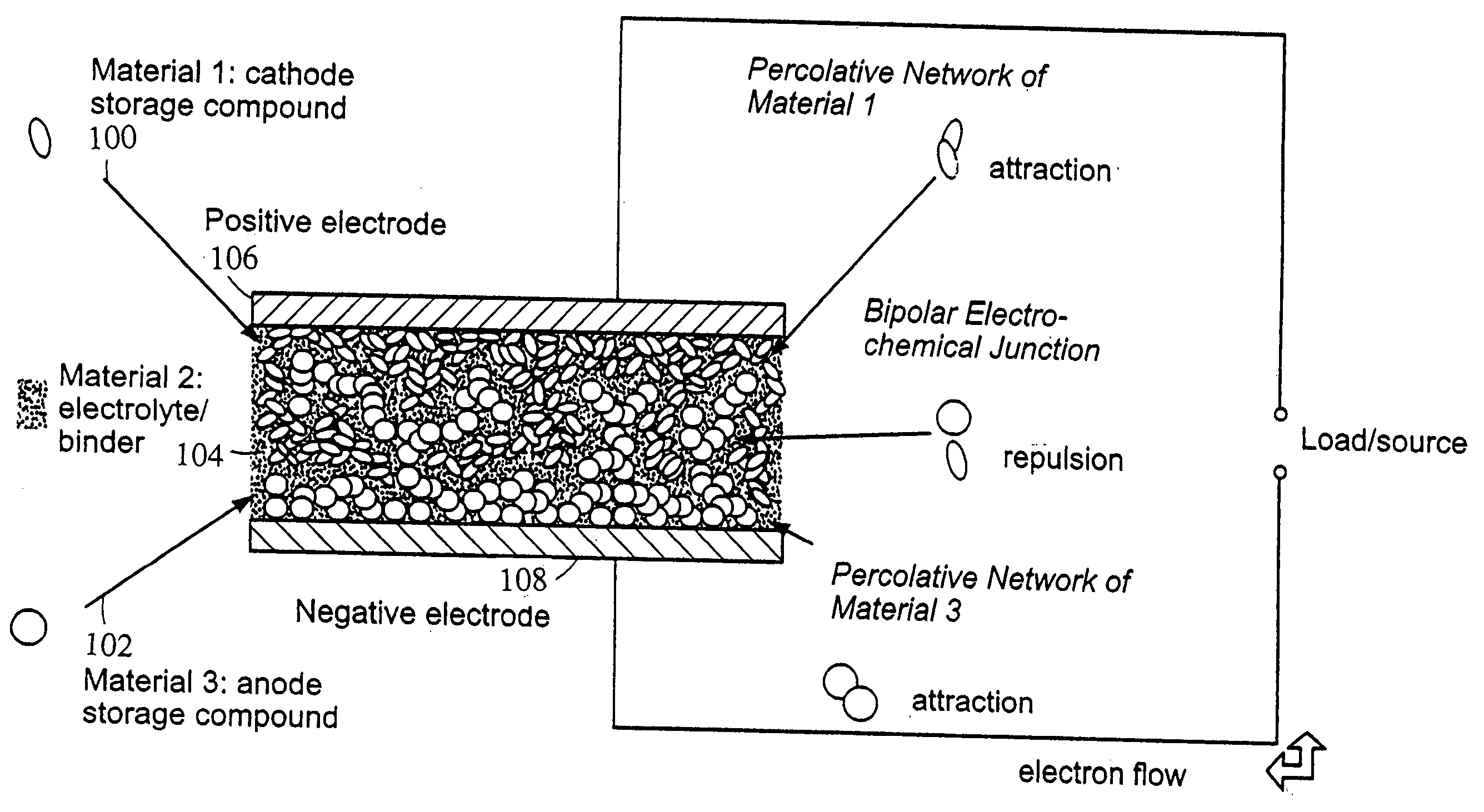
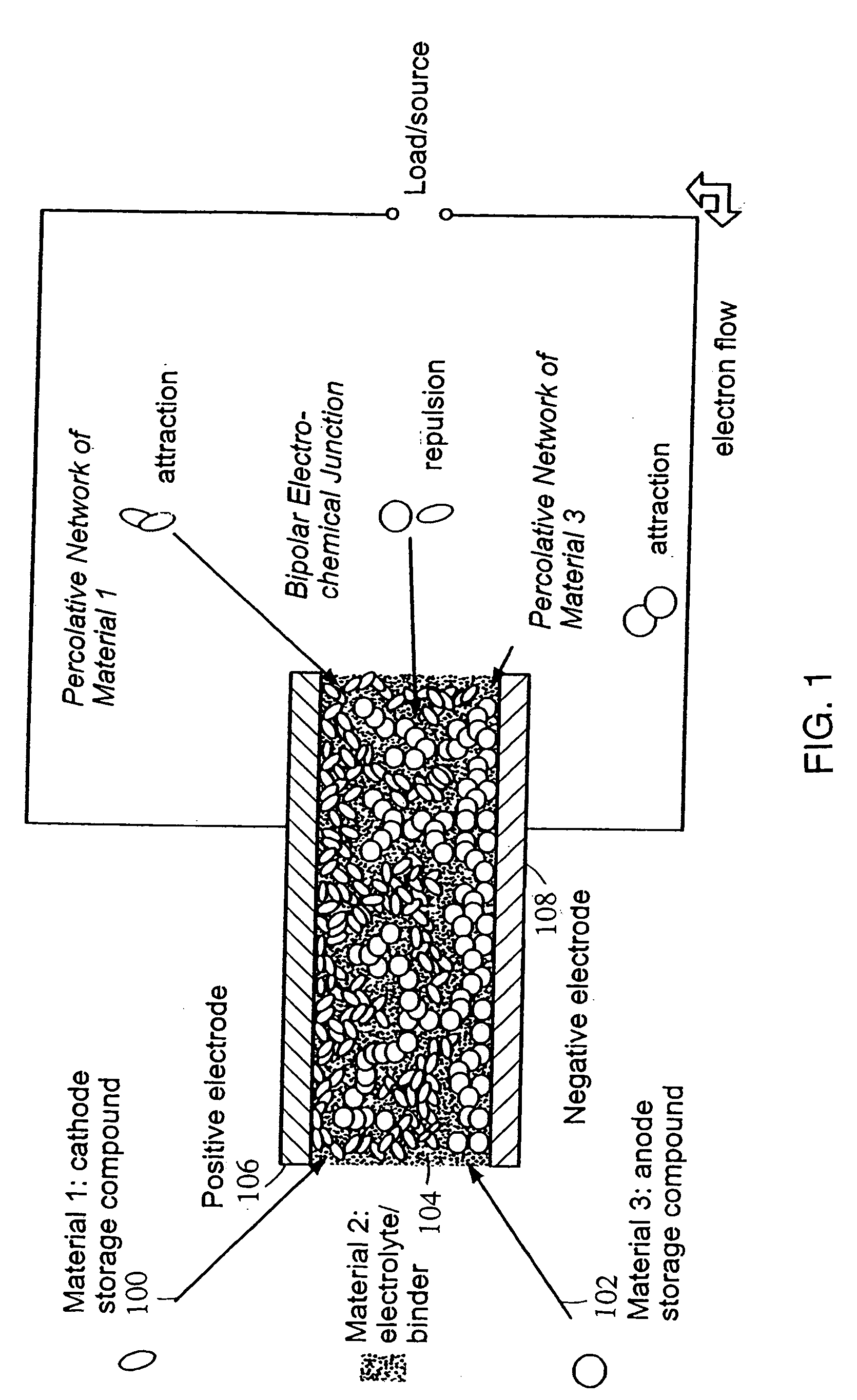
Polymer composition for encapsulation of electrode particles
InactiveUS20050034993A1Pigmenting treatmentElectrode carriers/collectorsRefractive indexParticle composition
Compositions and methods are provided for coating electroactive particles. Coating materials include a conductive component and a low refractive index component. Coatings are provided in which the conductive and low refractive index components are linked and / or do not form phases having lengthscales greater than about 0.25 μm. Coatings are provided in which the components are contained in sequential layers.
Owner:A123 SYSTEMS LLC
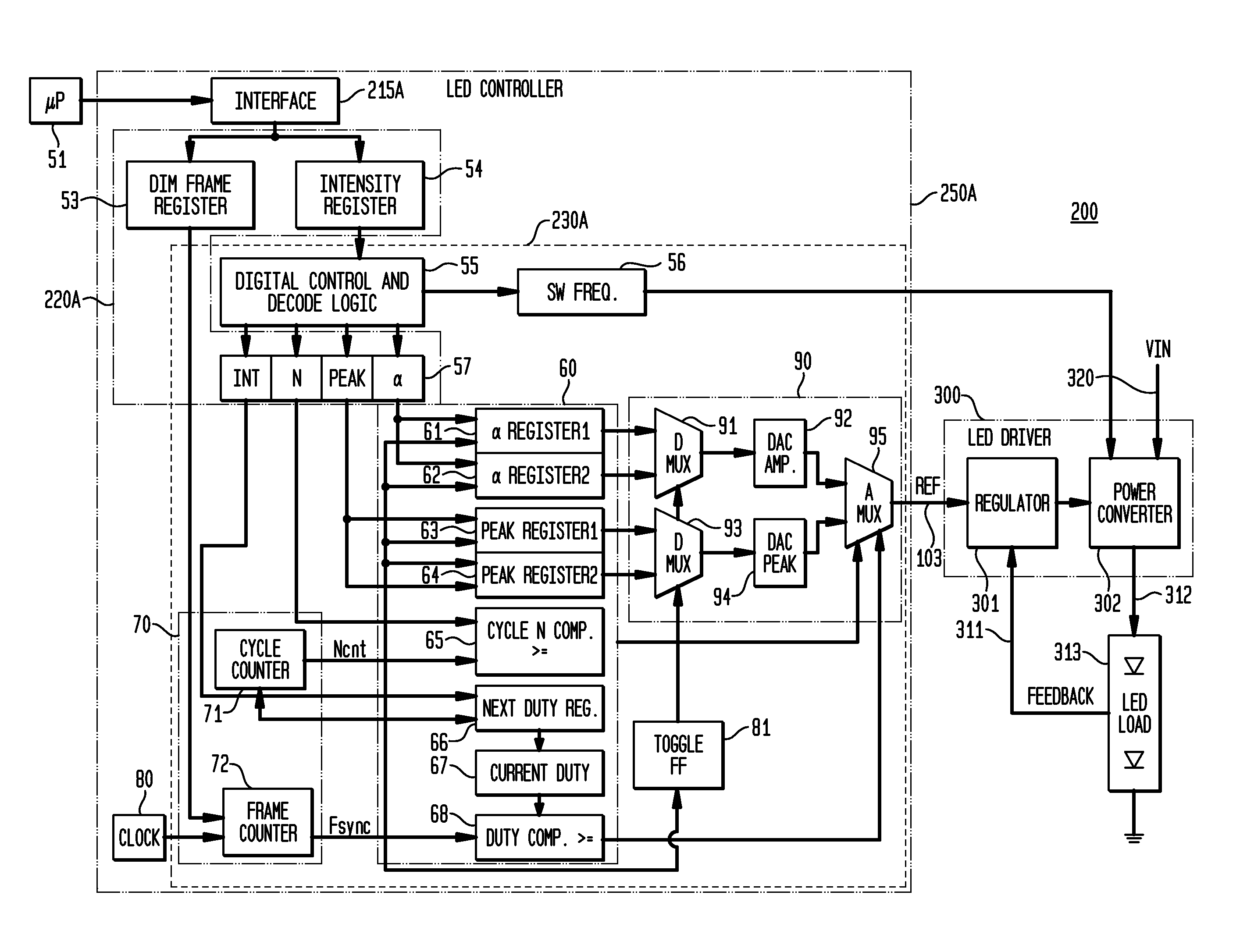
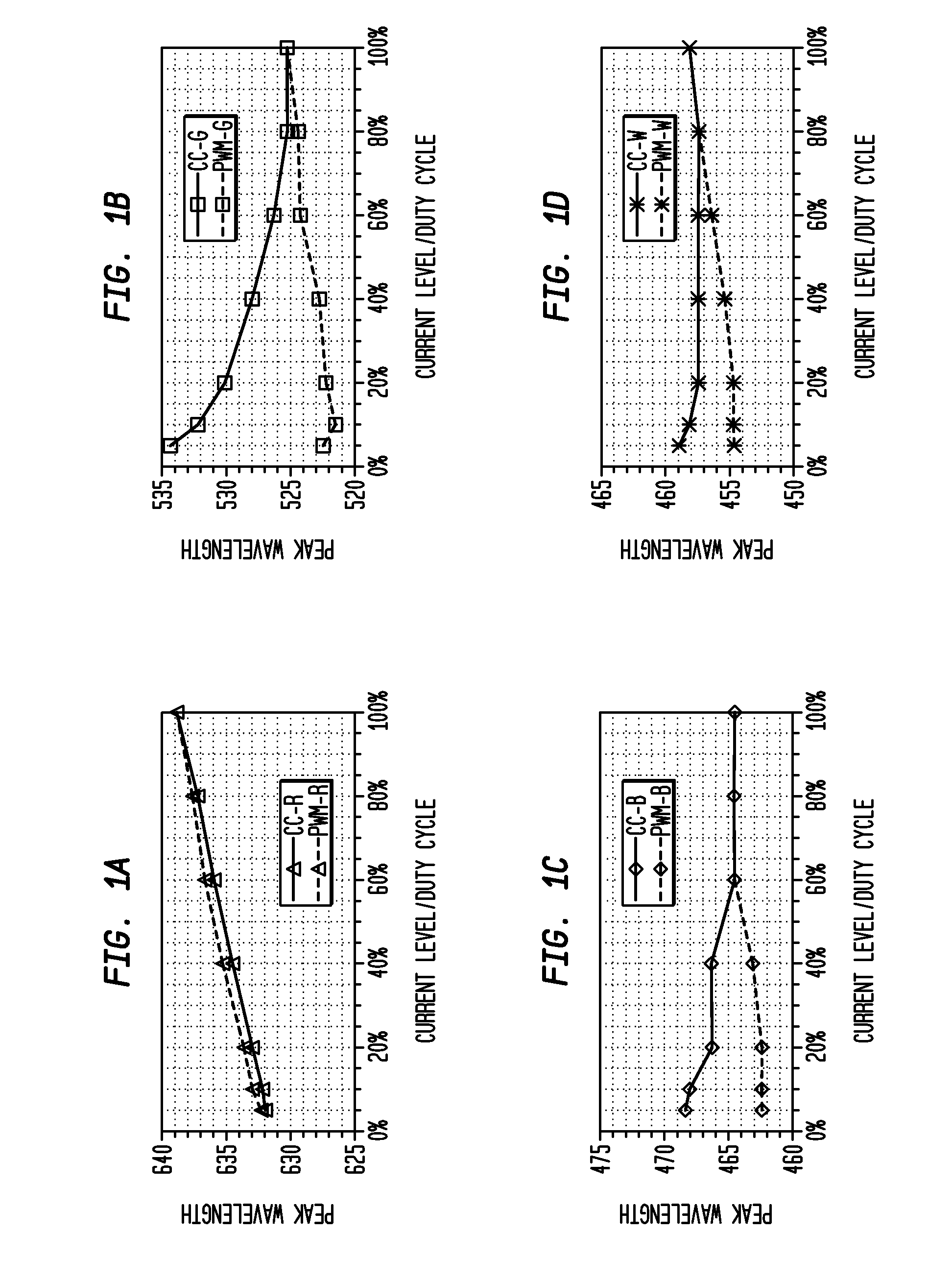
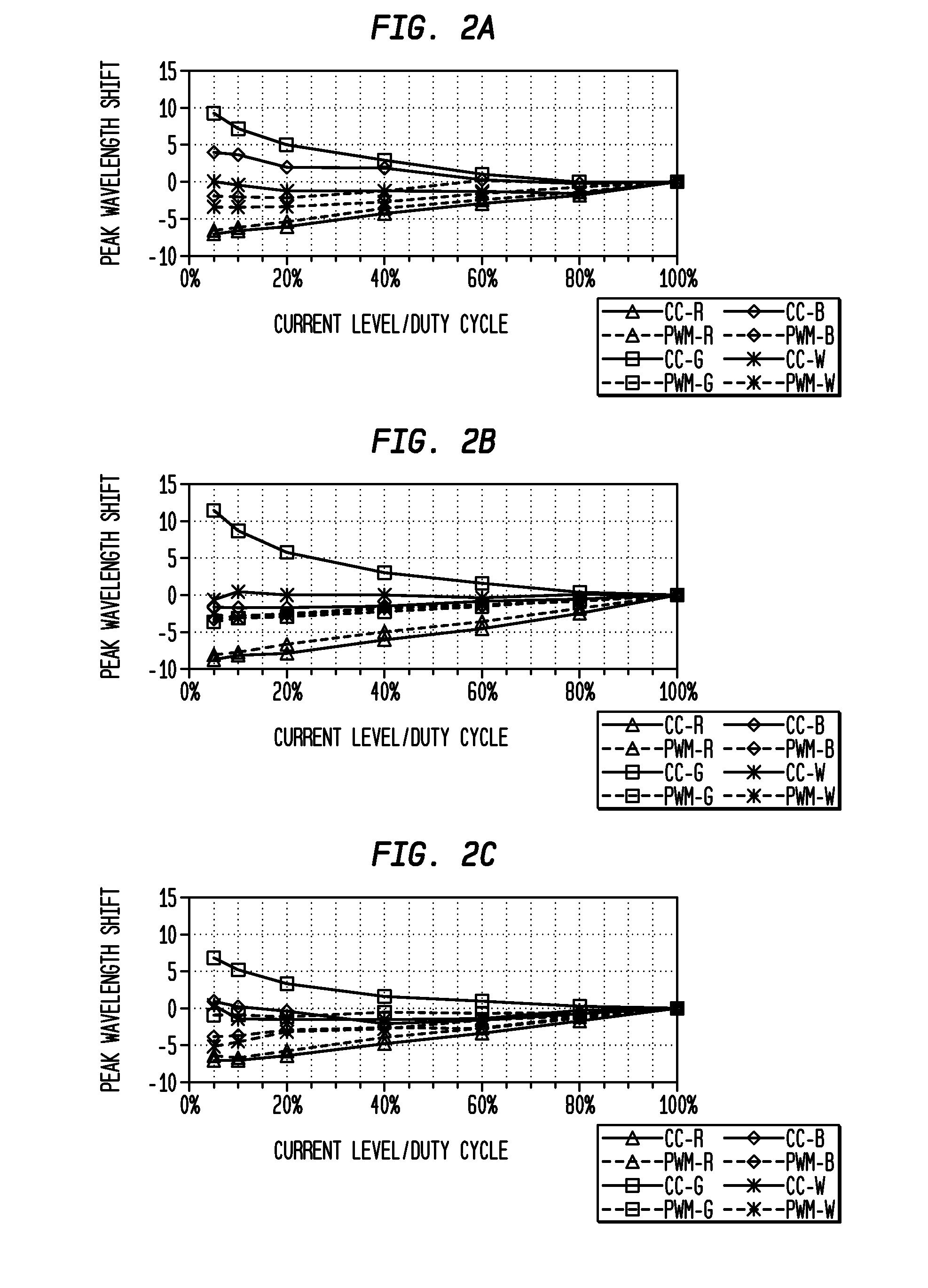
Regulation of Wavelength Shift and Perceived Color of Solid State Lighting with Intensity and Temperature Variation
ActiveUS20090079362A1Improve efficiencyLow costDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesEngineeringWavelength
Exemplary embodiments of the invention provide a system, apparatus, and method of controlling an intensity and spectrum of light emitted from a solid state lighting system. The solid state lighting has a first emitted spectrum at full intensity and at a selected temperature, with a first electrical biasing for the solid state lighting producing a first wavelength shift, and a second electrical biasing for the solid state lighting producing a second, opposing wavelength shift. Exemplary embodiments provide for receiving information designating a selected intensity level or a selected temperature; and providing a combined first electrical biasing and second electrical biasing to the solid state lighting to generate emitted light having the selected intensity level and having a second emitted spectrum within a predetermined variance of the first emitted spectrum over a predetermined range of temperatures.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
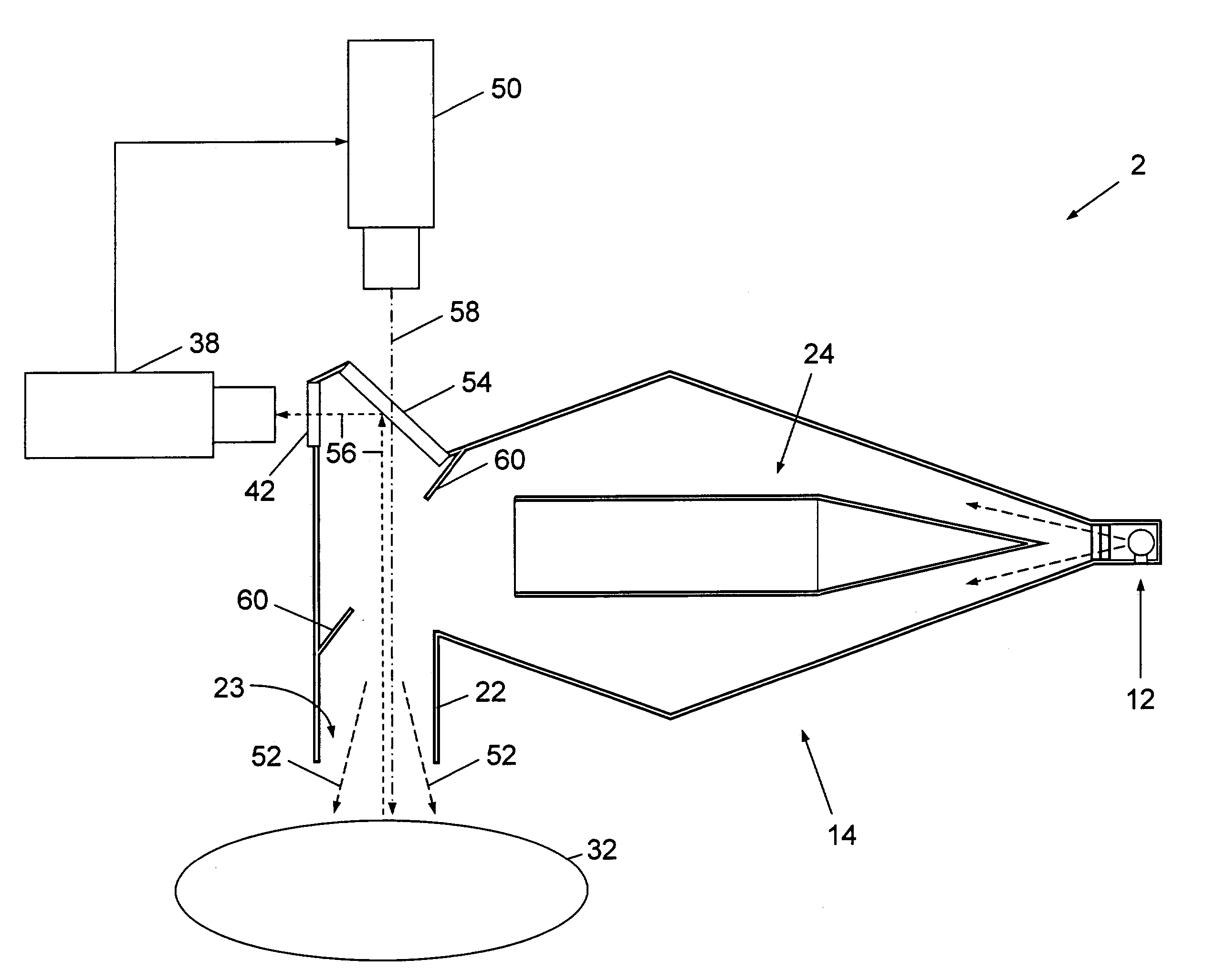
Imaging system using diffuse infrared light
An imaging system illuminates body tissue with infrared light to enhance visibility of subcutaneous blood vessels, and generates a video image of the body tissue and the subcutaneous blood vessels based on reflected infrared light. The system includes an infrared light source for generating the infrared light and a structure for diffusing the infrared light. The diffusing structure includes one or more layers of diffusing material for diffusing the light. The system further includes a video imaging device for receiving the infrared light reflected from the body tissue and for generating a video image of the body tissue based on the reflected infrared light.
Owner:CHRISTIE MEDICAL HLDG
Modular Networked Light Bulb
ActiveUS20110095687A1Point-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsElectricityNetworking protocol
Various methods of manufacturing a lighting apparatus and embodiments of a modular networked lighting apparatus are disclosed. One method defines a mechanical form factor with a minimum set of electrical connections for a networking module, builds a subassembly of the networked lighting apparatus, the subassembly comprising attachment points compatible with the mechanical form factor for the networking module and contacts for the minimum set of electrical connections for the networking module, installs a networking module into the subassembly of the networked lighting apparatus, the networking module compatible with a selected networking protocol for the networked lighting apparatus, completes the final assembly of the networked lighting module, and marks the networked lighting apparatus to indicate the selected networking protocol for the networked lighting apparatus. In some embodiments, the lighting apparatus may function without the networking module installed. One embodiment of the modular, networked light bulb has means for supporting and holding an electronics module conforming with a predetermined form factor in place, and means for allowing the electronics module to control at least a brightness level of the at least one LED. The modular networked light bulb may have a networked controller conforming with the predetermined form factor used as the electronics module. The networked controller is able to connect to a network and may be positioned and held by the means for supporting and holding an electronics module.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
High efficiency multi-color electro-phosphorescent OLEDs
InactiveUS7009338B2High power and quantum efficiencyBright whiteDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesDopantPhosphorescent oleds
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Phosphors containing oxides of alkaline-earth and group-IIIB metals and white-light sources incorporating same
InactiveUS7077978B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesAlkaline earth metalManganese
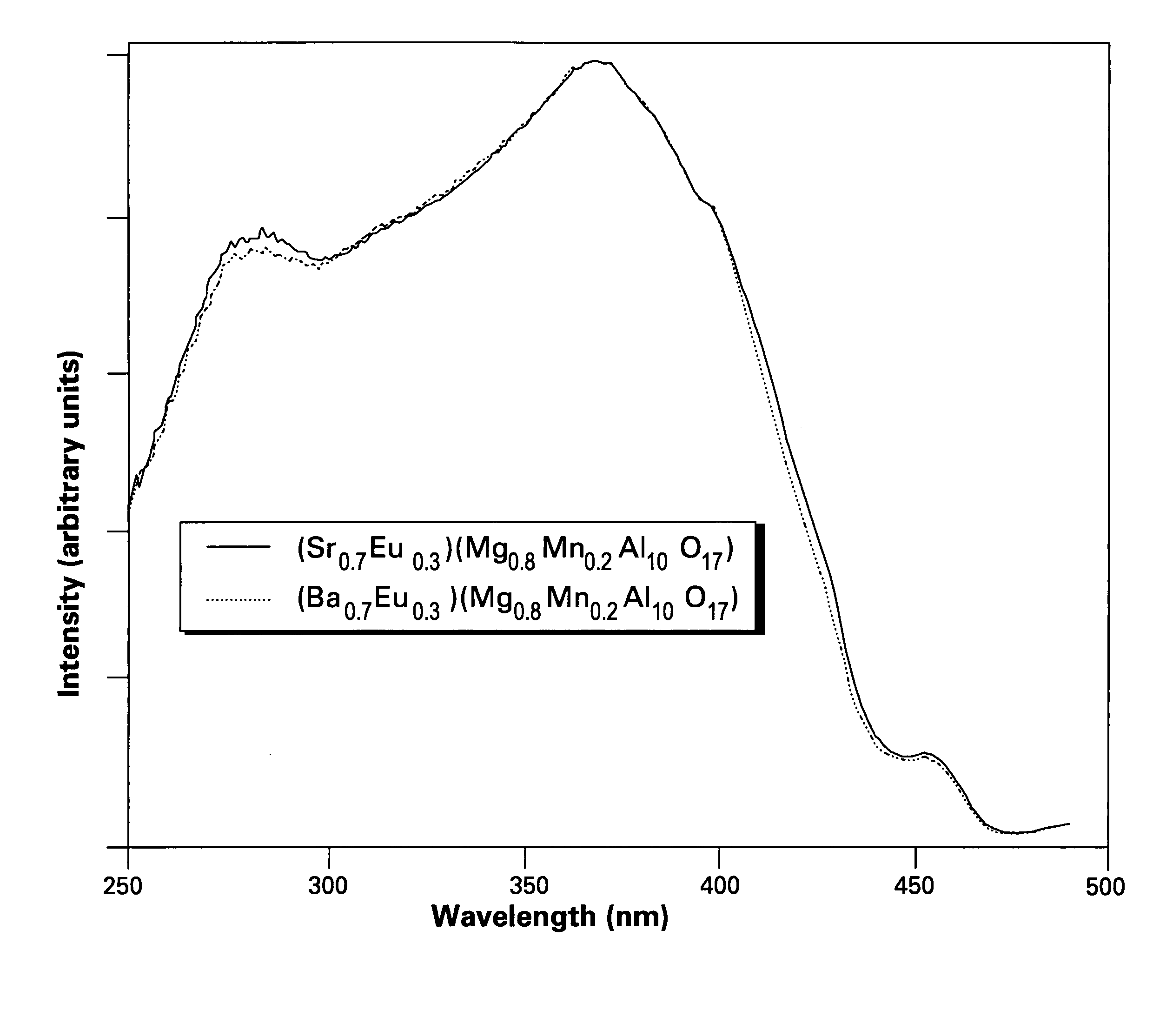
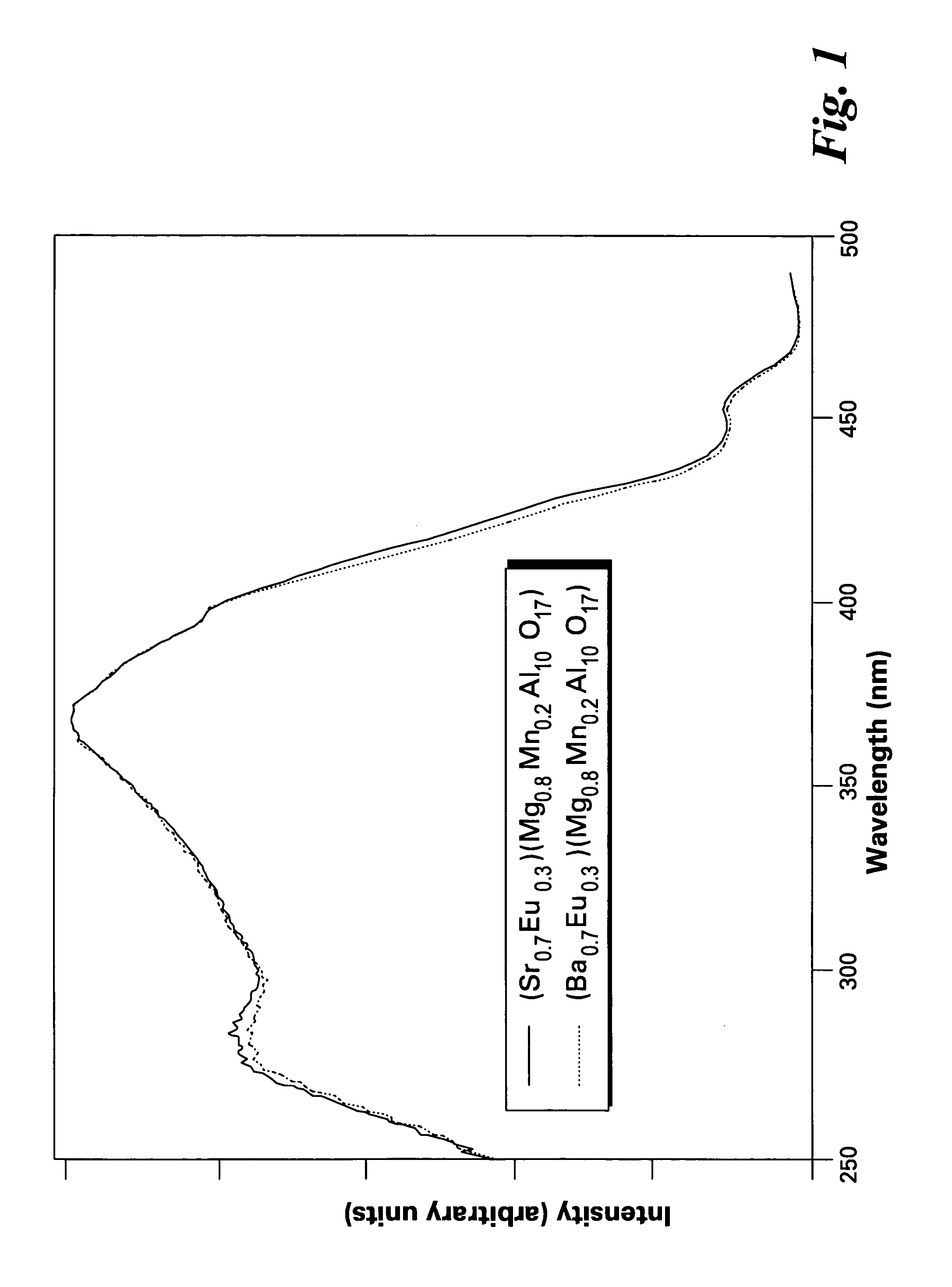
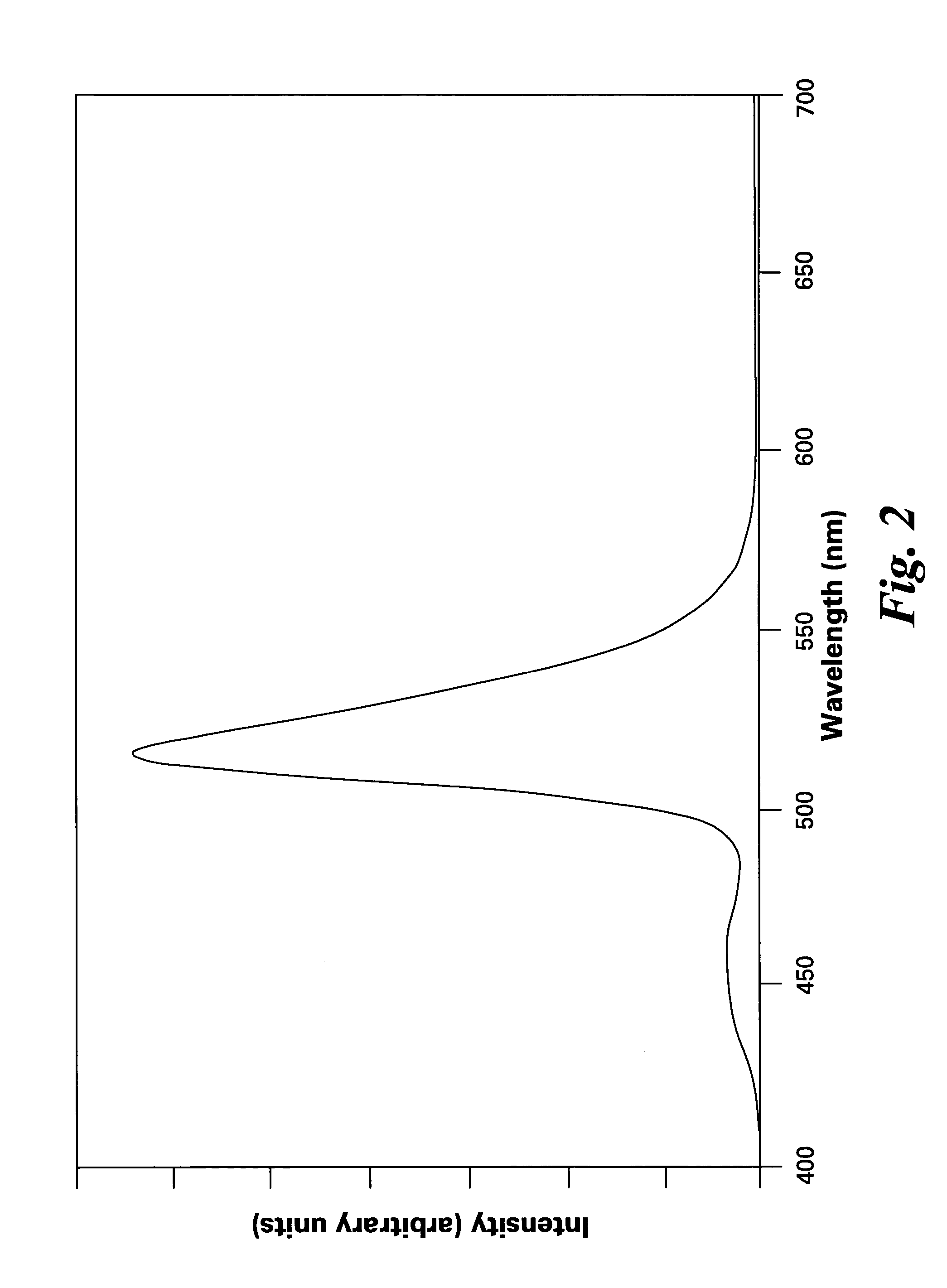
A phosphor comprises a material having a formula of AMgD10O17:Eu2+,Mn2+, wherein A is at least an alkaline-earth metal selected from the group consisting of Ba, Sr, Ca, and combinations thereof; and D is at least a metal selected from the group consisting of Al, Ga, In, and combinations thereof; wherein Eu2+ ions are present in an amount from about 10 to about 50 atom percent of a combined quantity of A ions and europium ions, and Mn2+ ions are present in an amount from about 5 to about 30 atom percent of a combined quantity of magnesium ions and manganese ions. The phosphor is used alone or in conjunction with other phosphors to convert UV / blue radiation emitted by a source, such as an LED or a gas discharge device, to visible light.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High data rate smart sensor technology
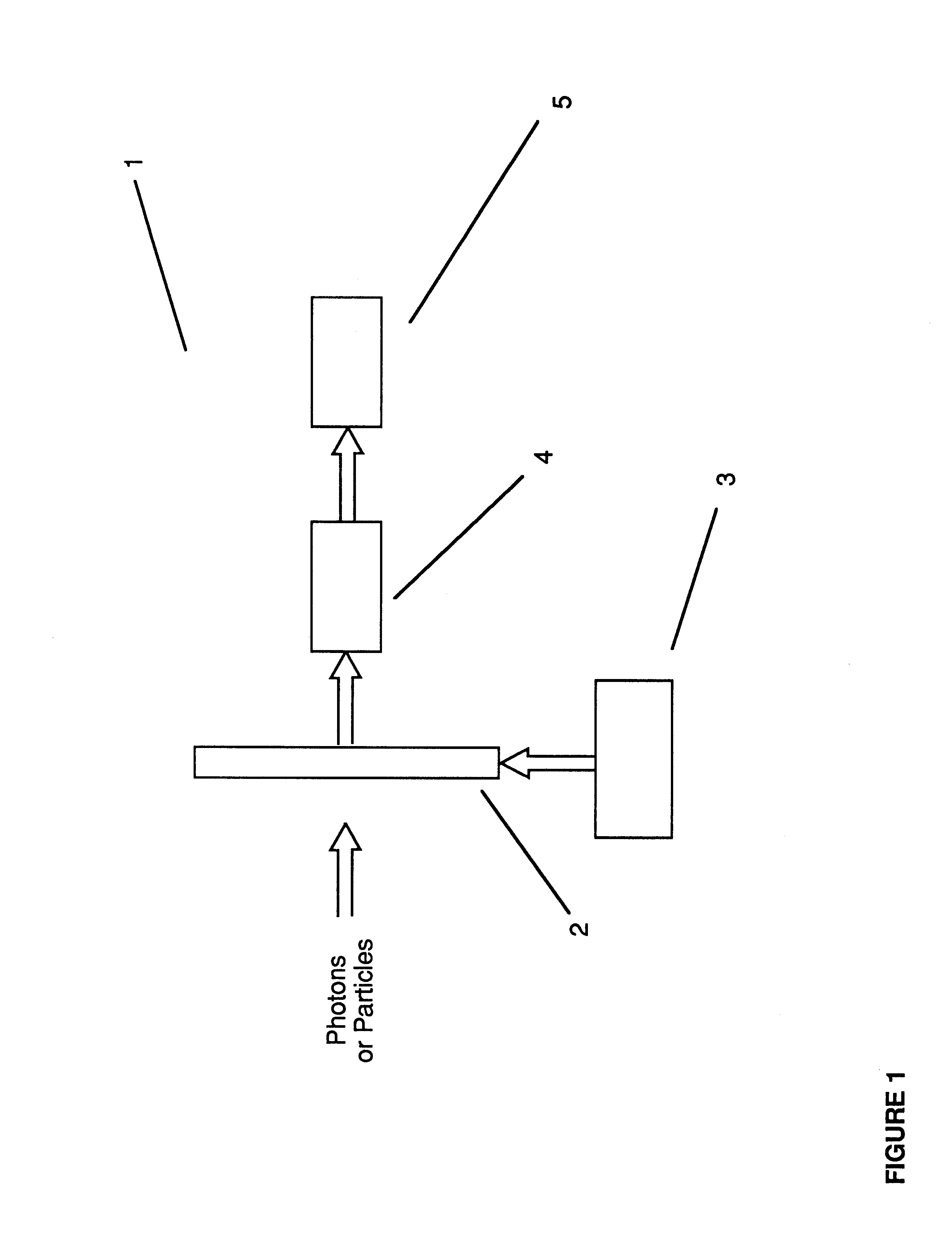
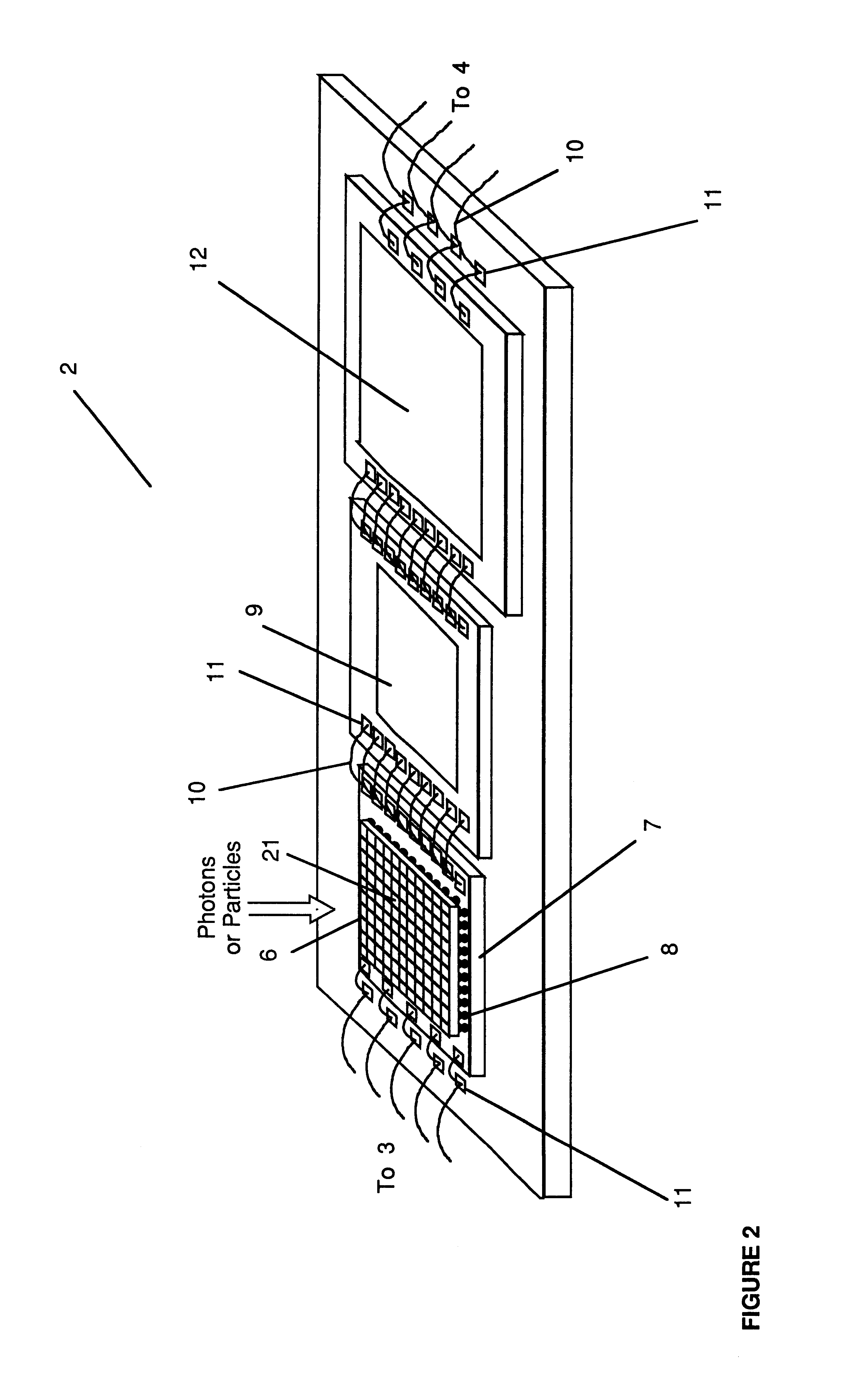
InactiveUS6362482B1Overcome problemsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesSolid-state devicesAnalog image processingSignal on
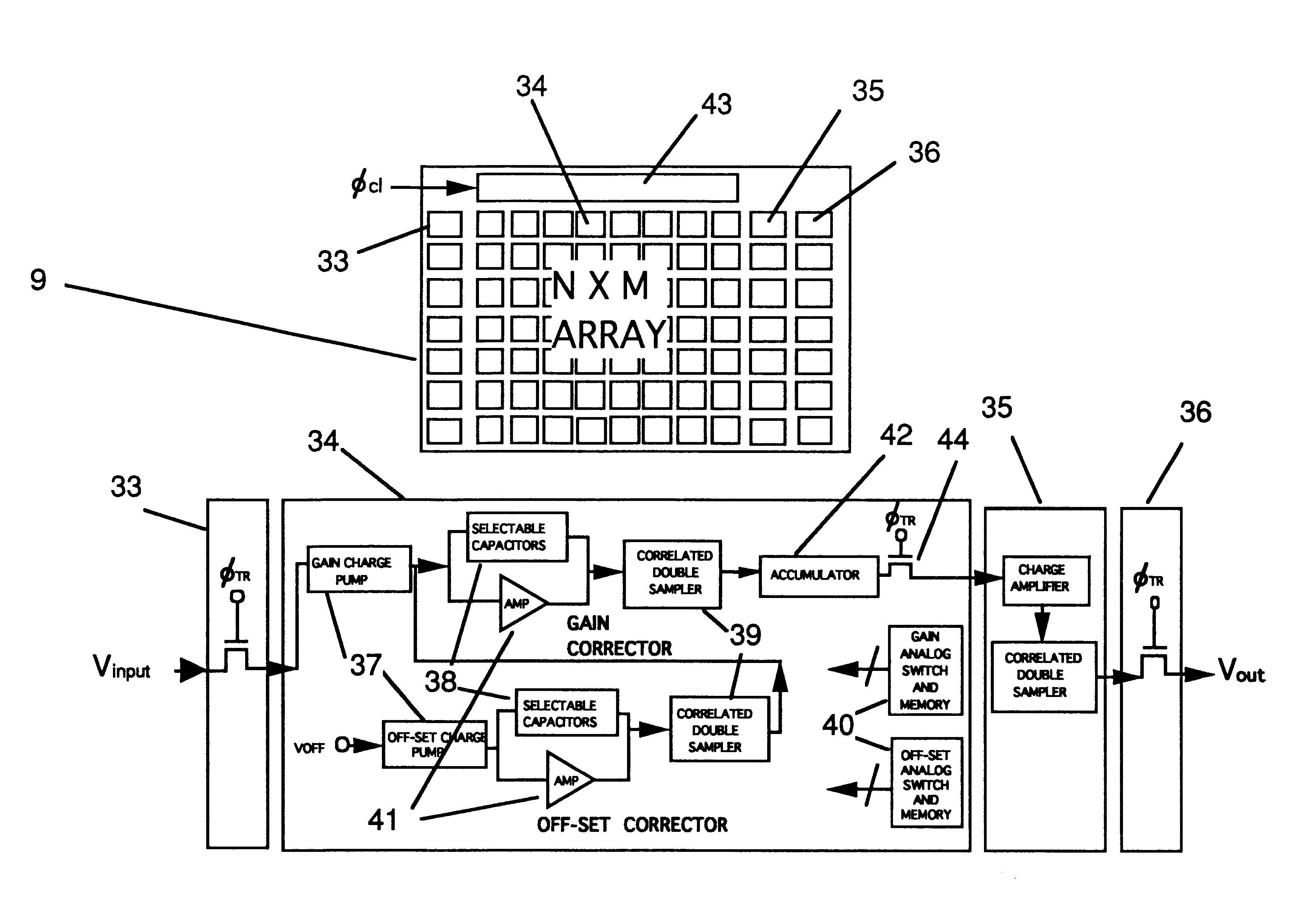
A device for the high-speed analysis of photon- or particle-generated image data or for the high-speed energy-discrimination analysis of photon- or particle-counting data. The device uses a sensor that collects the photons or particles on an array of solid state detectors, as electrical analog signals, and stores the analog-signal information on capacitors of readout arrays associated with the detector arrays. Integration of the photon or particle flux signals on the readout arrays proceeds for a given time frame and then image-related signals are transferred to an analog correction processor. The analog correction processor is comprised of one or more integrated circuit chips where each chip contains an array of correction processor unit cells. In these unit cells signals are corrected, in parallel, for gain and offset nonuniformities in the detection and processing chain. Corrections to all the signals are made in a time frame or less and the information is then transferred to an analog image processor. Particle-counting data is transferred directly from the readout array chips to the analog image processor. The analog image processor is comprised of one or more integrated circuit chips where each chip is made up of an array of image processor unit cells. Each unit cell contains circuitry for implementing an image processing or energy discrimination algorithm, and circuitry for outputting the signals and / or the position of only those unit cells for which the algorithm is satisfied. The analog image processor chip may also contain circuitry that counts the number of cells for which the algorithms have been satisfied. The analog image processor implements the algorithm and outputs the data in a time frame or less.
Owner:CONTINENTAL ADVANCED LIDAR SOLUTIONS US LLC
Nanocomposite photonic structures for solid state lighting
InactiveUS7259400B1Quality improvementHigh color rendering indexDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesPhosphorNanoparticle
A photonic structure for “white” light generation by phosphors under the excitation of a LED. The photonic structure mounts the LED and an optically transparent nanocomposite matrix having dispersed therein phosphors which will emit light under the excitation of the radiation of the LED. The phosphors dispersed in the matrix may be nanocrystalline, or larger sized with the addition of non light emitting, non light scattering nanoparticles dispersed within the matrix material so as to match the index of refraction of the matrix material to that of the phosphors. The nanocomposite matrix material may be readily formed by molding and formed into a variety of shapes including lenses for focusing the emitted light. A large number of the photonic structures may be arranged on a substrate to provide even illumination or other purposes.
Owner:NANOCRYSTAL LIGHTING
Patient positioning device
ActiveUS7741623B2Assure freedomKeep postureRadioactive sourcesChemical conversion by chemical reactionCouplingComputer module
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST PARTICLE THERAPY GMBH & CO KG
Light-emitting diode (LED) with amorphous fluoropolymer encapsulant and lens
InactiveUS6921929B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesUltravioletFluoropolymer
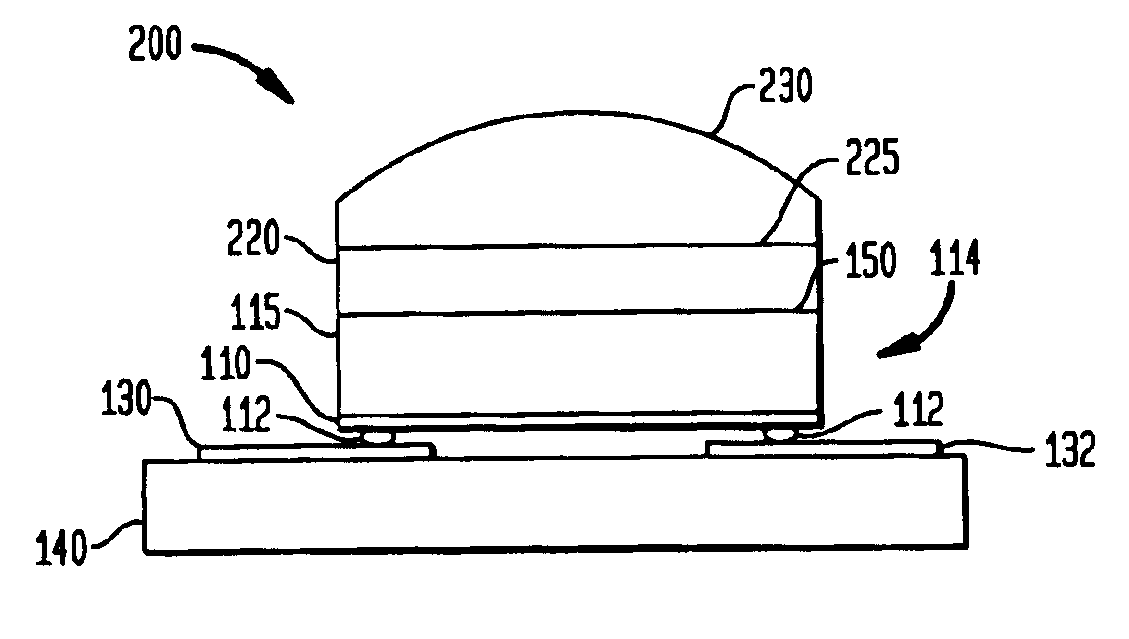
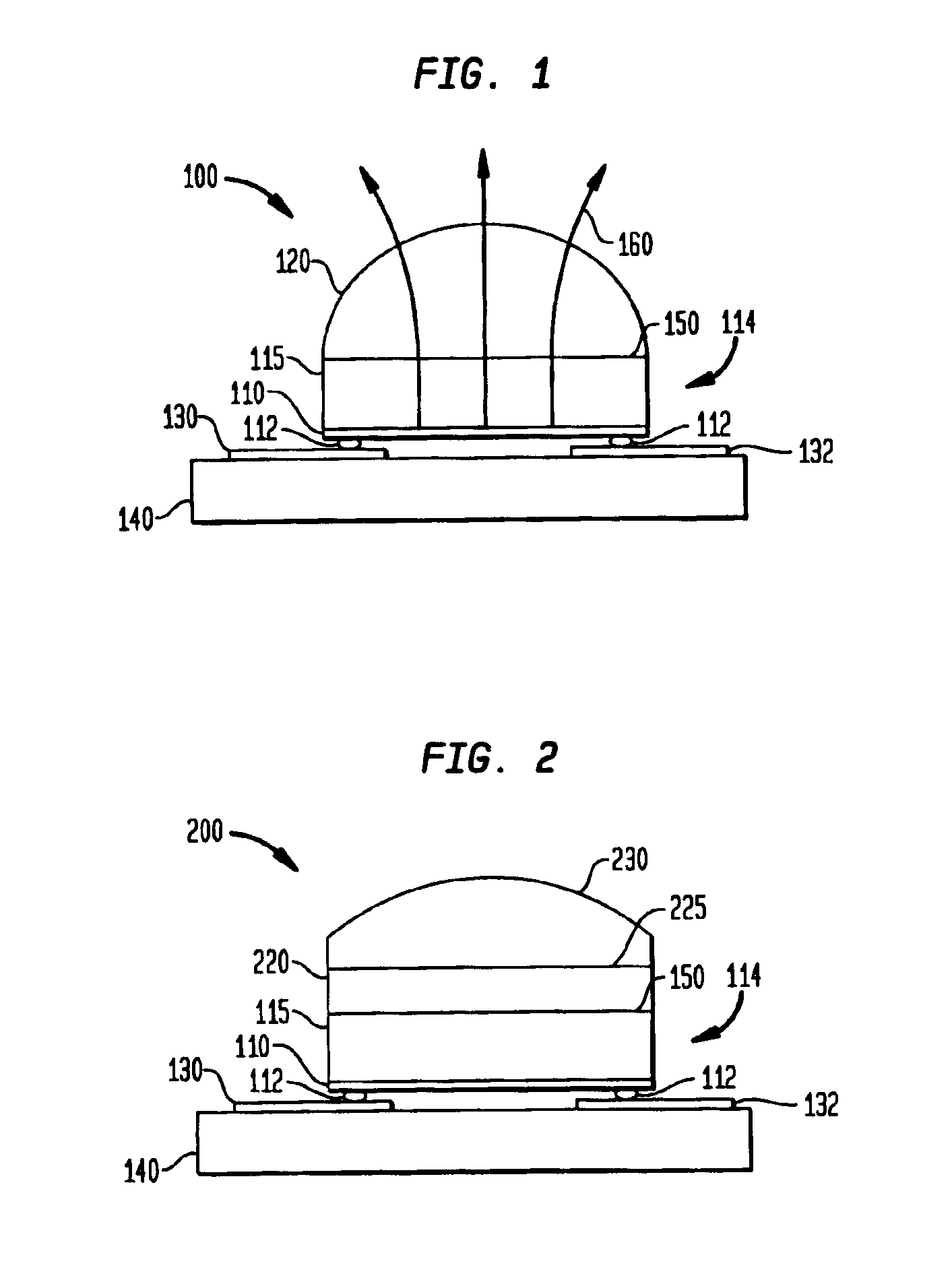
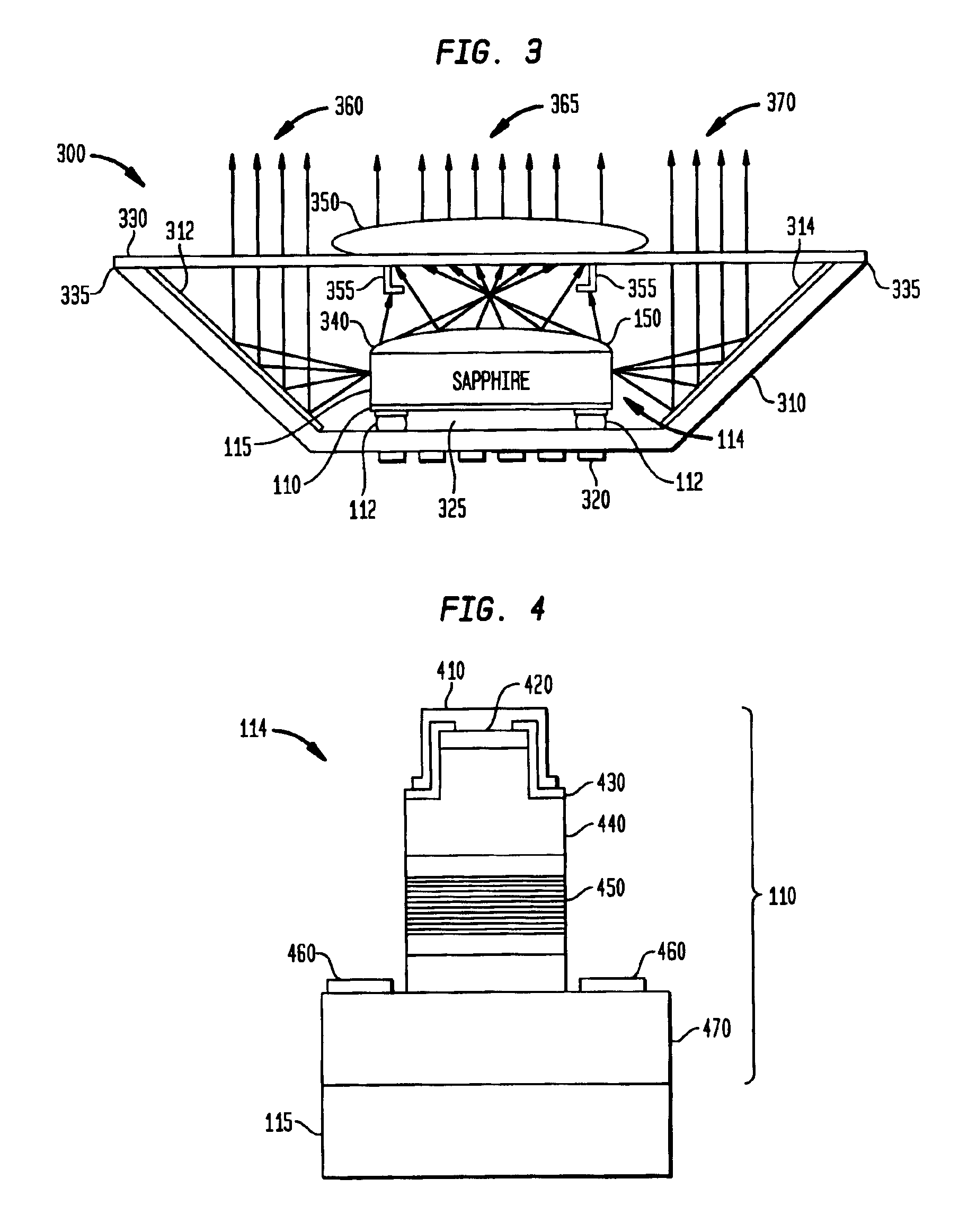
A lens and encapsulant made of an amorphous fluoropolymer for a light-emitting diode (LED) or diode laser, such as an ultraviolet (UV) LED (UVLED). A semiconductor diode die (114) is formed by growing a diode (110) on a substrate layer (115) such as sapphire. The diode die (114) is flipped so that it emits light (160, 365) through the face (150) of the layer (115). An amorphous fluoropolymer encapsulant encapsulates the emitting face of the diode die (114), and may be shaped as a lens to form an integral encapsulant / lens. Or, a lens (230, 340) of amorphous fluoropolymer may be joined to the encapsulant (220). Additional joined or separate lenses (350) may also be used. The encapsulant / lens is transmissive to UV light as well as infrared light. Encapsulating methods are also provided.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
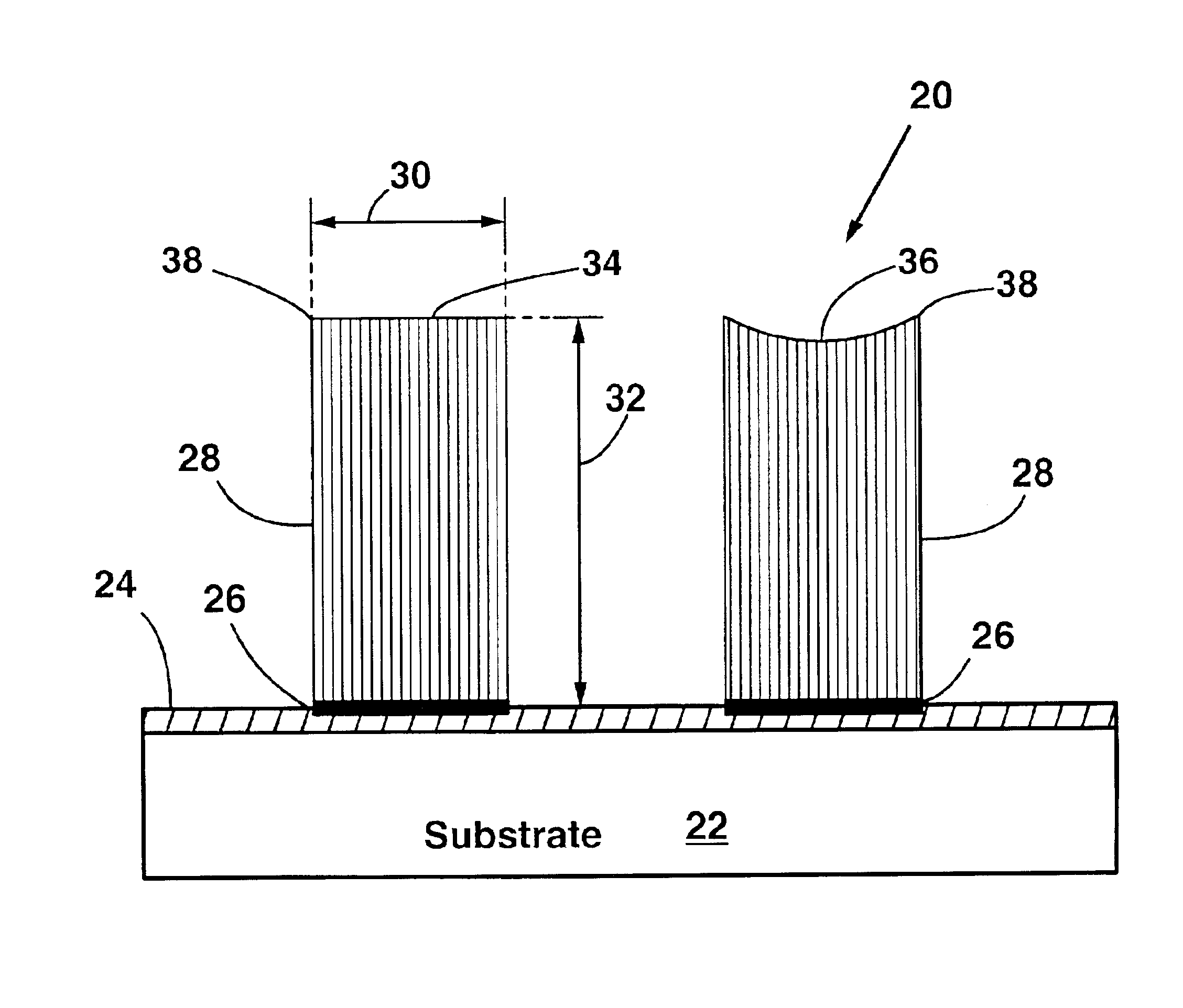
Self-oriented bundles of carbon nanotubes and method of making same
A field emission device having bundles of aligned parallel carbon nanotubes on a substrate. The carbon nanotubes are oriented perpendicular to the substrate. The carbon nanotube bundles may be up to 300 microns tall, for example. The bundles of carbon nanotubes extend only from regions of the substrate patterned with a catalyst material. Preferably, the catalyst material is iron oxide. The substrate is preferably porous silicon, as this produces the highest quality, most well-aligned nanotubes. Smooth, nonporous silicon or quartz can also be used as the substrate. The method of the invention starts with forming a porous layer on a silicon substrate by electrochemical etching. Then, a thin layer of iron is deposited on the porous layer in patterned regions. The iron is then oxidized into iron oxide, and then the substrate is exposed to ethylene gas at elevated temperature. The iron oxide catalyzes the formation of bundles of aligned parallel carbon nanotubes which grow perpendicular to the substrate surface. The height of the nanotube bundles above the substrate is determined by the duration of the catalysis step. The nanotube bundles only grow from the patterned regions.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Filter for displaying, display unit and production method therefor
InactiveUS20030156080A1High color purityGood colorMagnetic/electric field screeningStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceCopper foil
The display filter is constituted by laminating a transparent adhesive layer (C) 31 containing dye, a polymer film (B) 20, a transparent electrically conductive layer (D) 10, a transparent adhesive layer (E) 40, and a functional transparent layer (A) 60 having an anti-reflection property, a hard coat property, a gas barrier property, an antistatic property and an anti-fouling property sequentially in this order, adhered on a display area 00; on this occasion, the transparent electrically conductive layer (D) 10 is grounded to a ground terminal of the display via an electrode 50 and an electrically conductive copper foil adhesive tape 80.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Solid-state light bulb
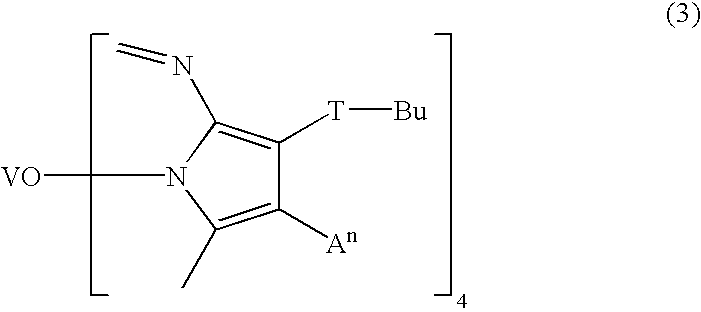
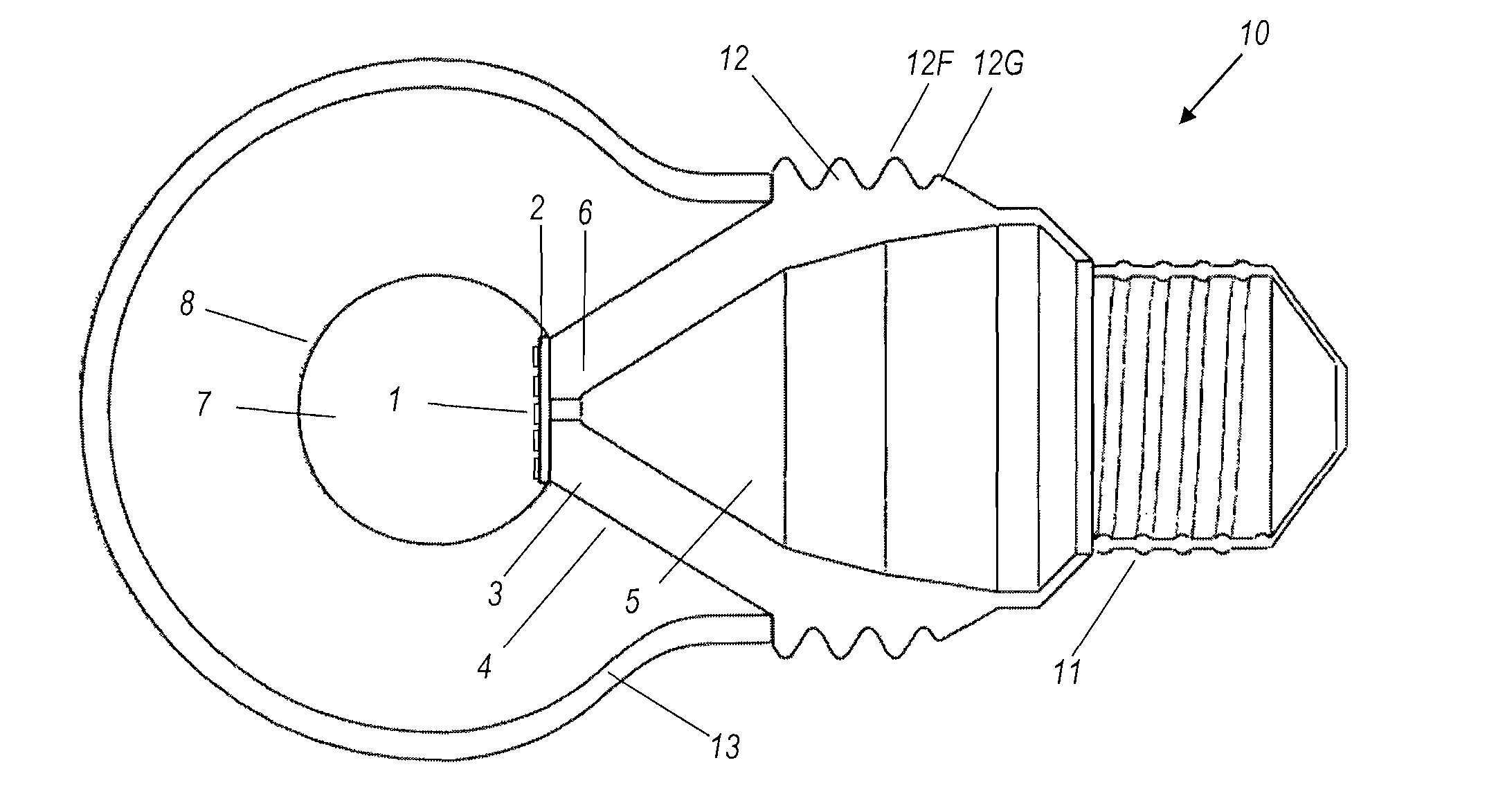
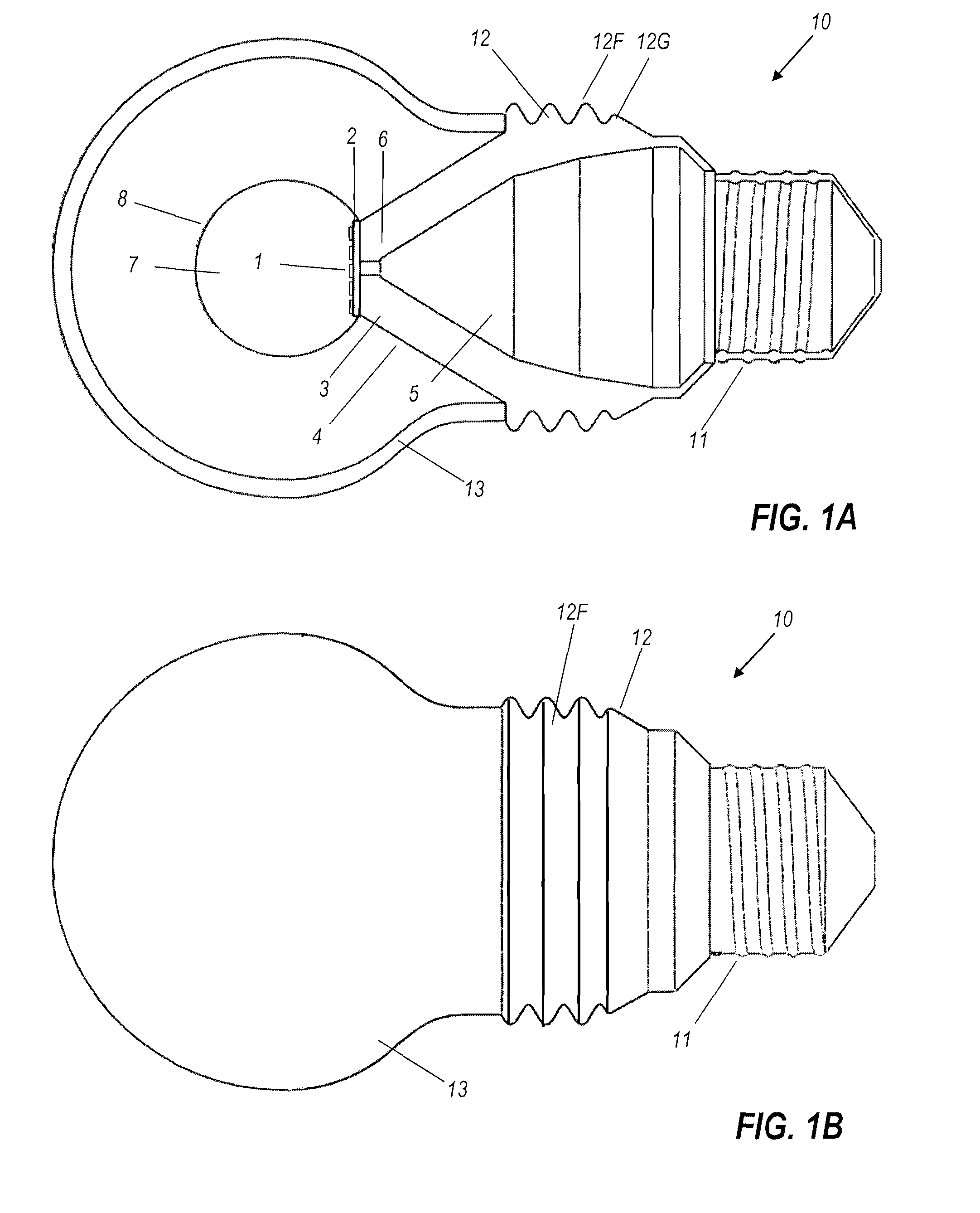
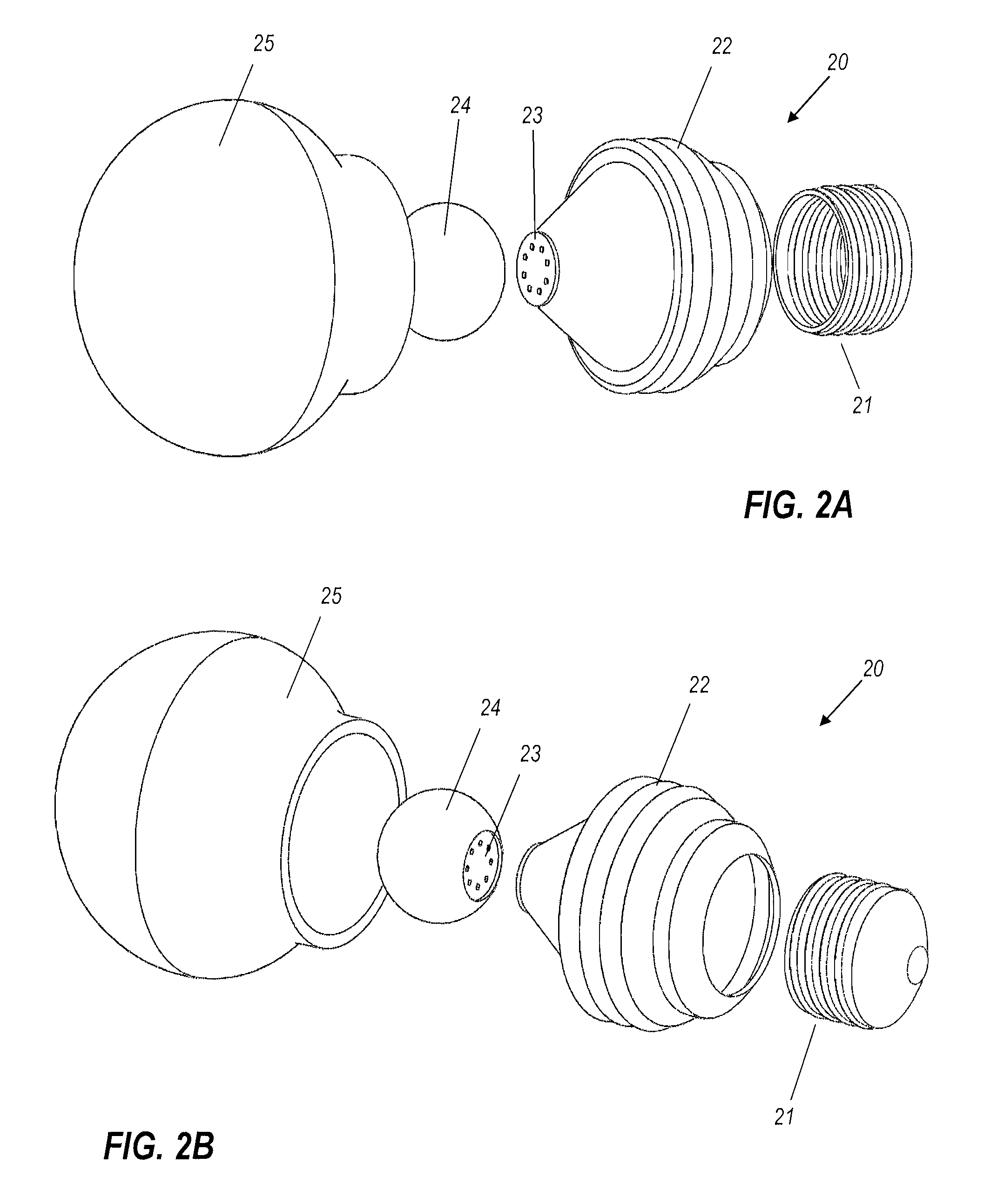
InactiveUS8322896B2Reduce heat loadAccelerated dissipationLight source combinationsLighting support devicesPhosphorLed array
An example of this light bulb has a light emitting element (which may be an LED array) mounted on a circuit board. The circuit board is mounted on one end of a heat-conducting frame. An Edison screw or other suitable connector, for attaching the light bulb electrically and mechanically to a receptacle, is mounted on the other end of the frame. A transparent phosphor-coated ball has a flat chord face optically bonded to said array. A light-permeable globular enclosure is mounted on the frame, surrounding the ball and both homogenizing the white light output of the bulb but also concealing the yellowing unlit appearance of the remote phosphor ball centrally located within it.
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com