Patents
Literature
4195 results about "Light scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Light scattering is a form of scattering in which light is the form of propagating energy which is scattered. Light scattering can be thought of as the deflection of a ray from a straight path, for example by irregularities in the propagation medium, particles, or in the interface between two media. Deviations from the law of reflection due to irregularities on a surface are also usually considered to be a form of scattering. When these irregularities are considered to be random and dense enough that their individual effects average out, this kind of scattered reflection is commonly referred to as diffuse reflection. Most objects that one sees are visible due to light scattering from their surfaces. Indeed, this is our primary mechanism of physical observation. Scattering of light depends on the wavelength or frequency of the light being scattered. Since visible light has wavelength on the order of a micrometre, objects much smaller than this cannot be seen, even with the aid of a microscope. Colloidal particles as small as 1 µm have been observed directly in aqueous suspension.
Flow-injection analysis and variable-flow light-scattering methods and apparatus for characterizing polymers
InactiveUS6175409B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
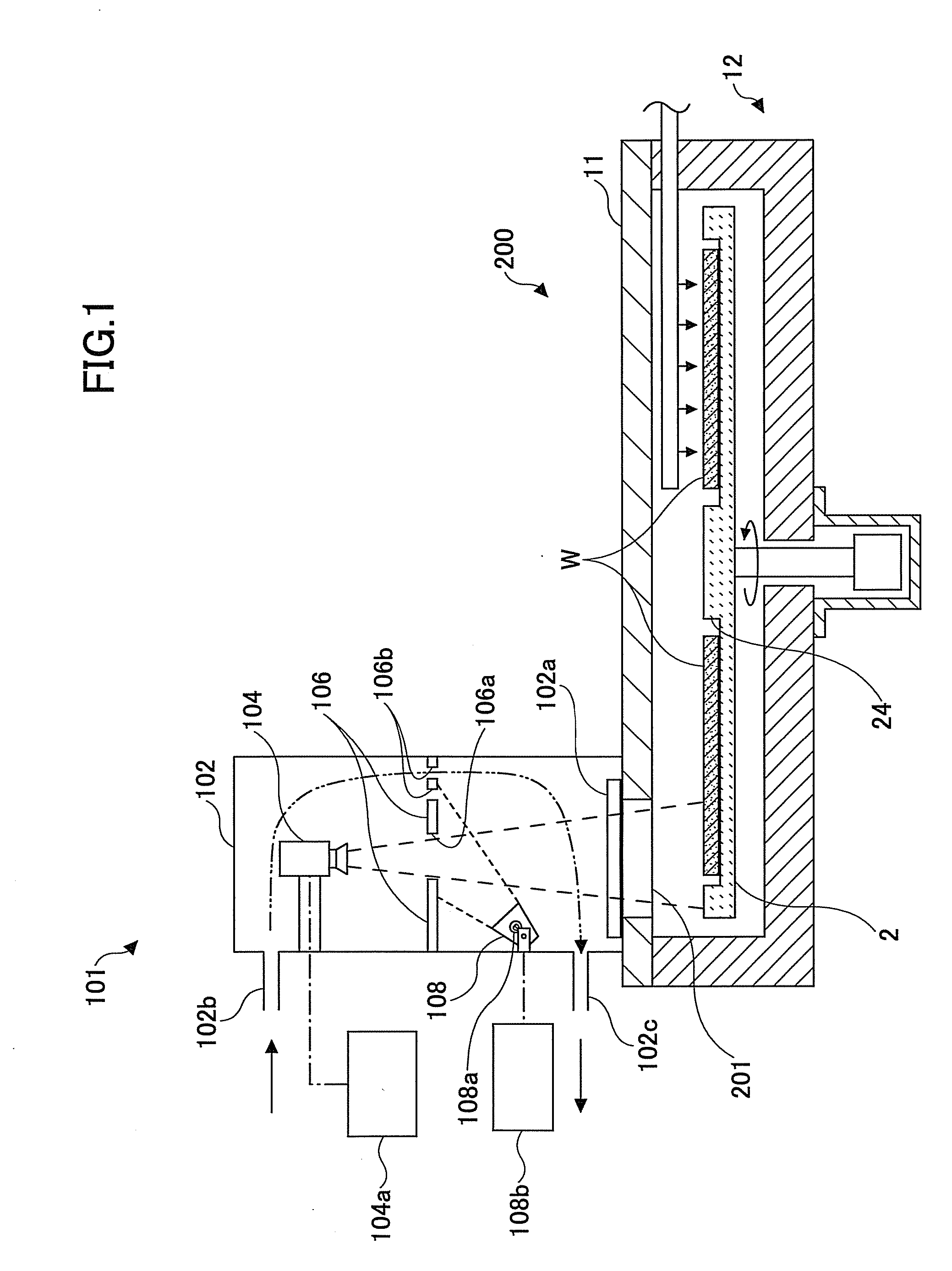
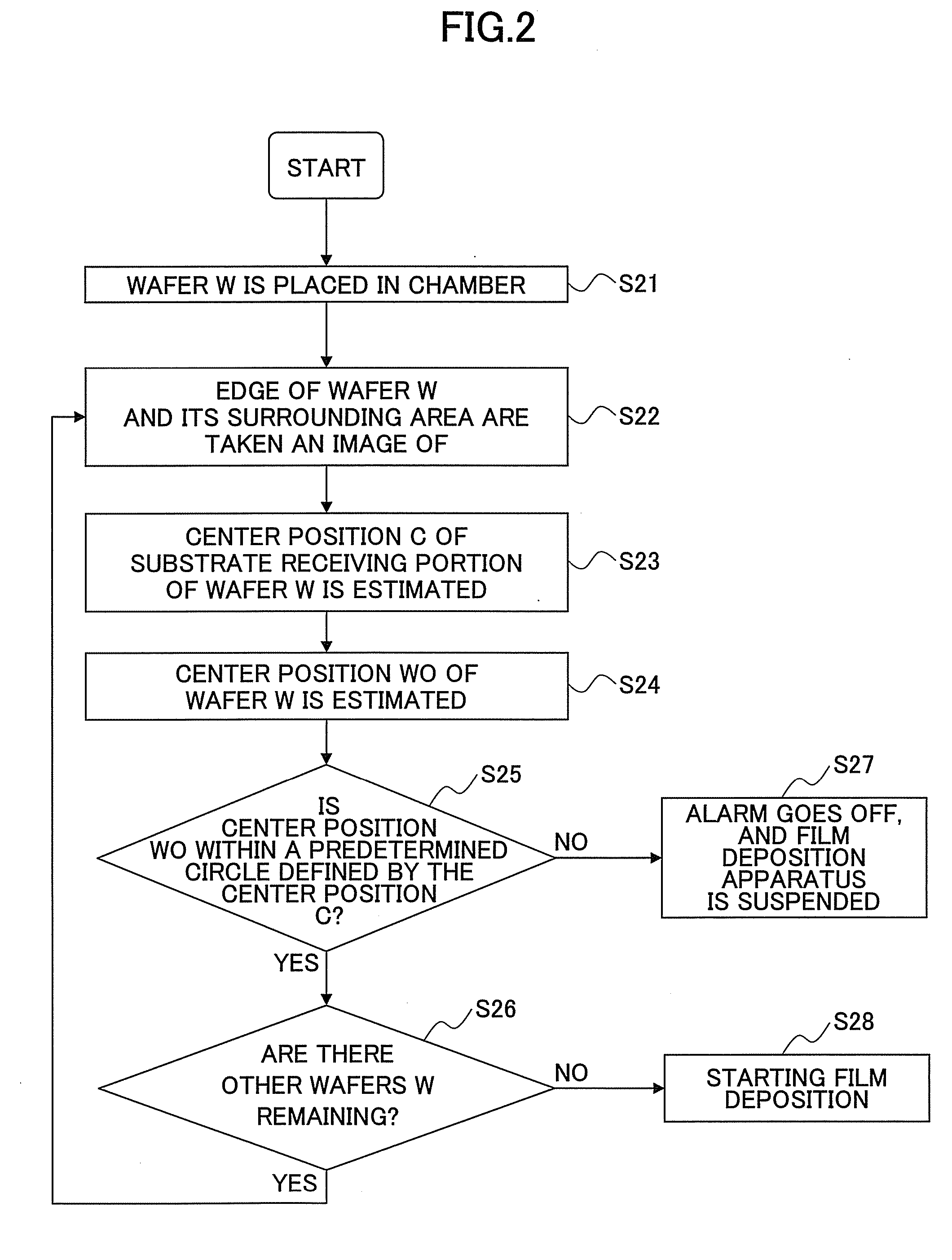
Substrate position detection apparatus, substrate position detection method, film deposition apparatus, film deposition method, and a computer readable storage medium
InactiveUS20100124610A1Reduce detectionLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringField of view
A disclosed substrate position detection apparatus includes an imaging portion configured to take an image of a substrate subject to a position detection; a panel member provided between the imaging portion and the substrate and including a first opening that ensures a field of view for the imaging portion with respect to the substrate, the panel member having a light scattering property; a first illuminating portion configured to illuminate the panel member; and a processing portion capable of determining a position of the substrate in accordance with the image taken through the first opening by the imaging portion.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
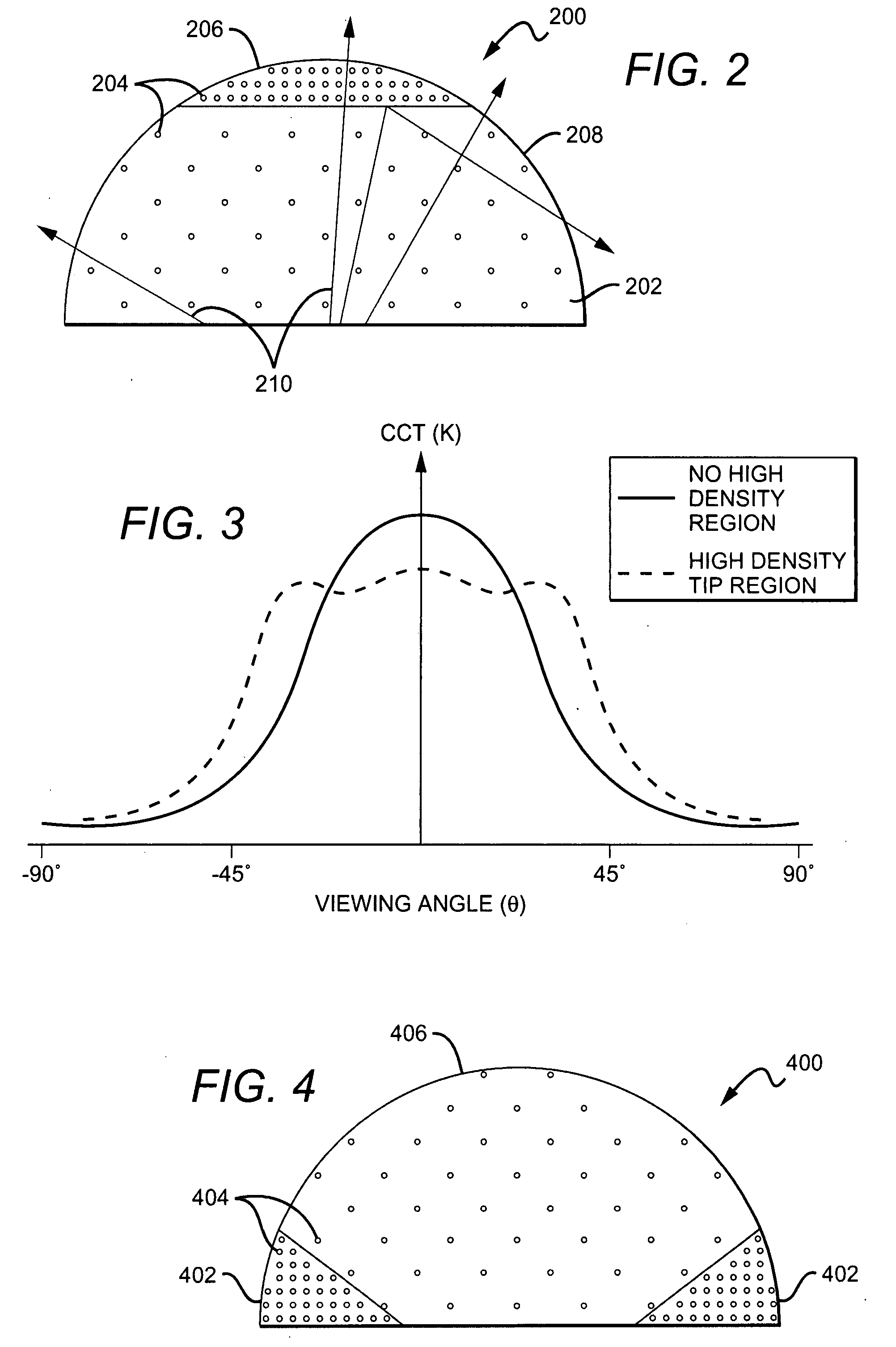
Encapsulant with scatterer to tailor spatial emission pattern and color uniformity in light emitting diodes
ActiveUS20080308825A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityLight beam
A light emitting device having an encapsulant with scattering features to tailor the spatial emission pattern and color temperature uniformity of the output profile. The encapsulant is formed with materials having light scattering properties. The concentration of these light scatterers is varied spatially within the encapsulant and / or on the surface of the encapsulant. The regions having a high density of scatterers are arranged in the encapsulant to interact with light entering the encapsulant over a desired range of source emission angles. By increasing the probability that light from a particular range of emission angles will experience at least one scattering event, both the intensity and color temperature profiles of the output light beam can be tuned.
Owner:CREELED INC
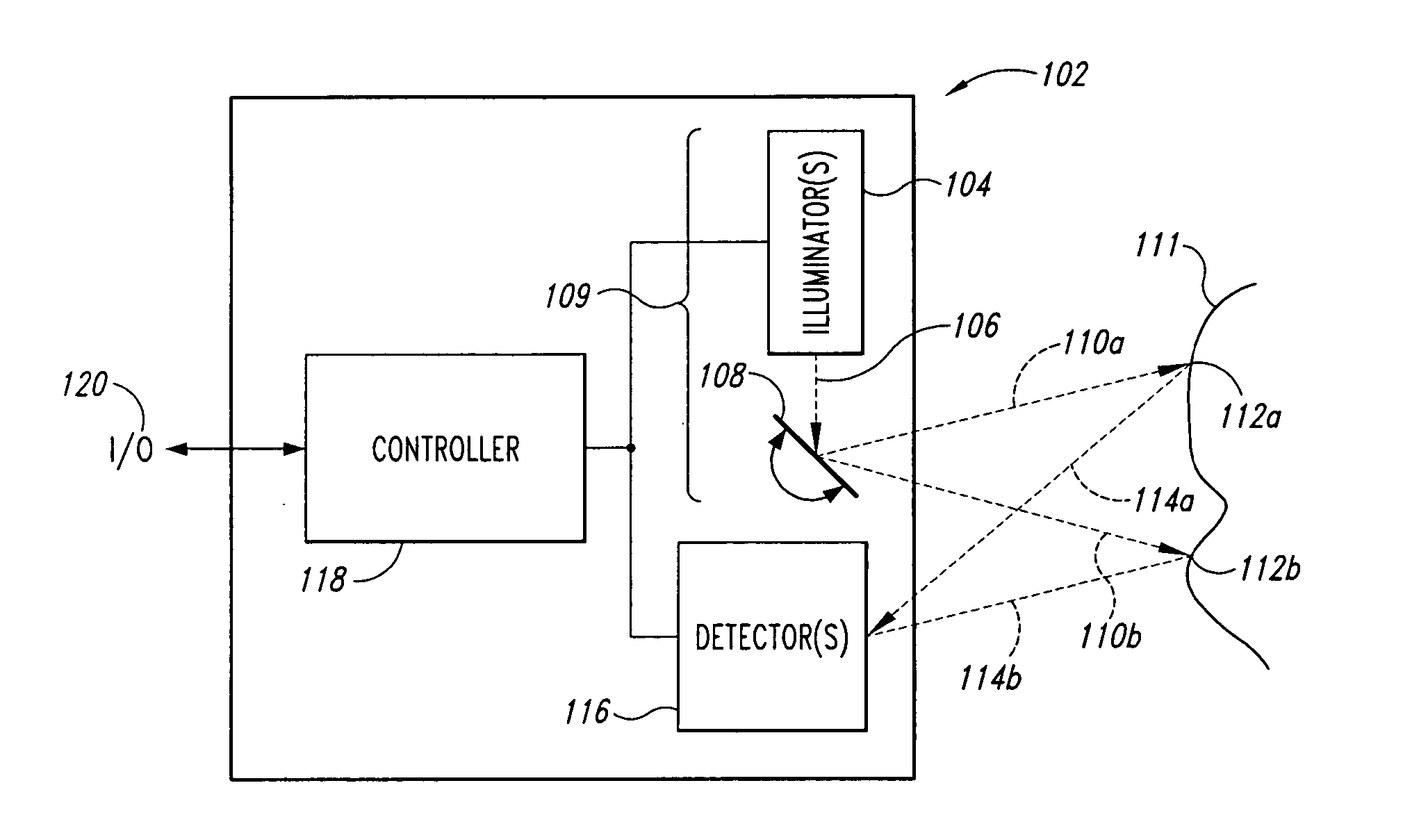
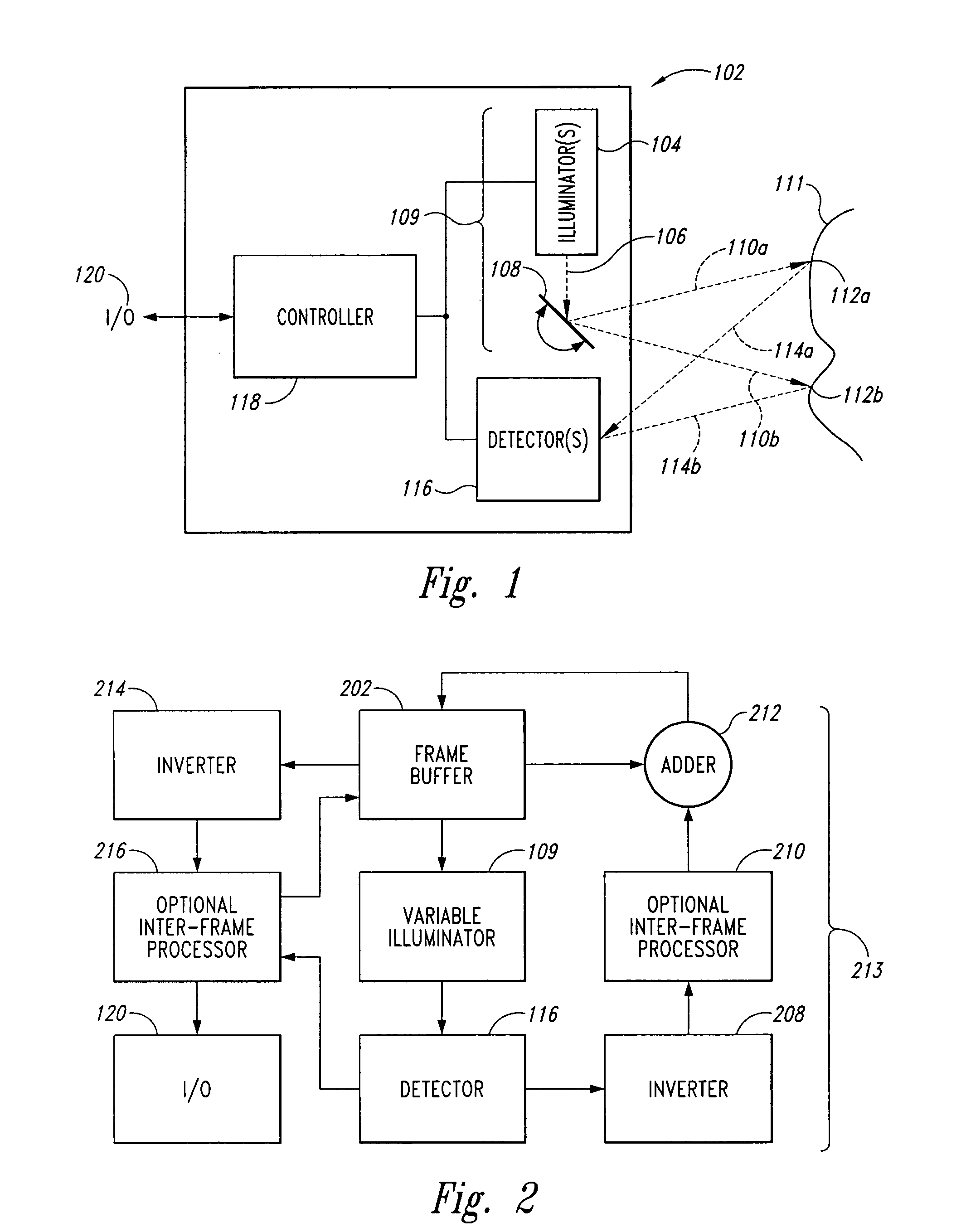
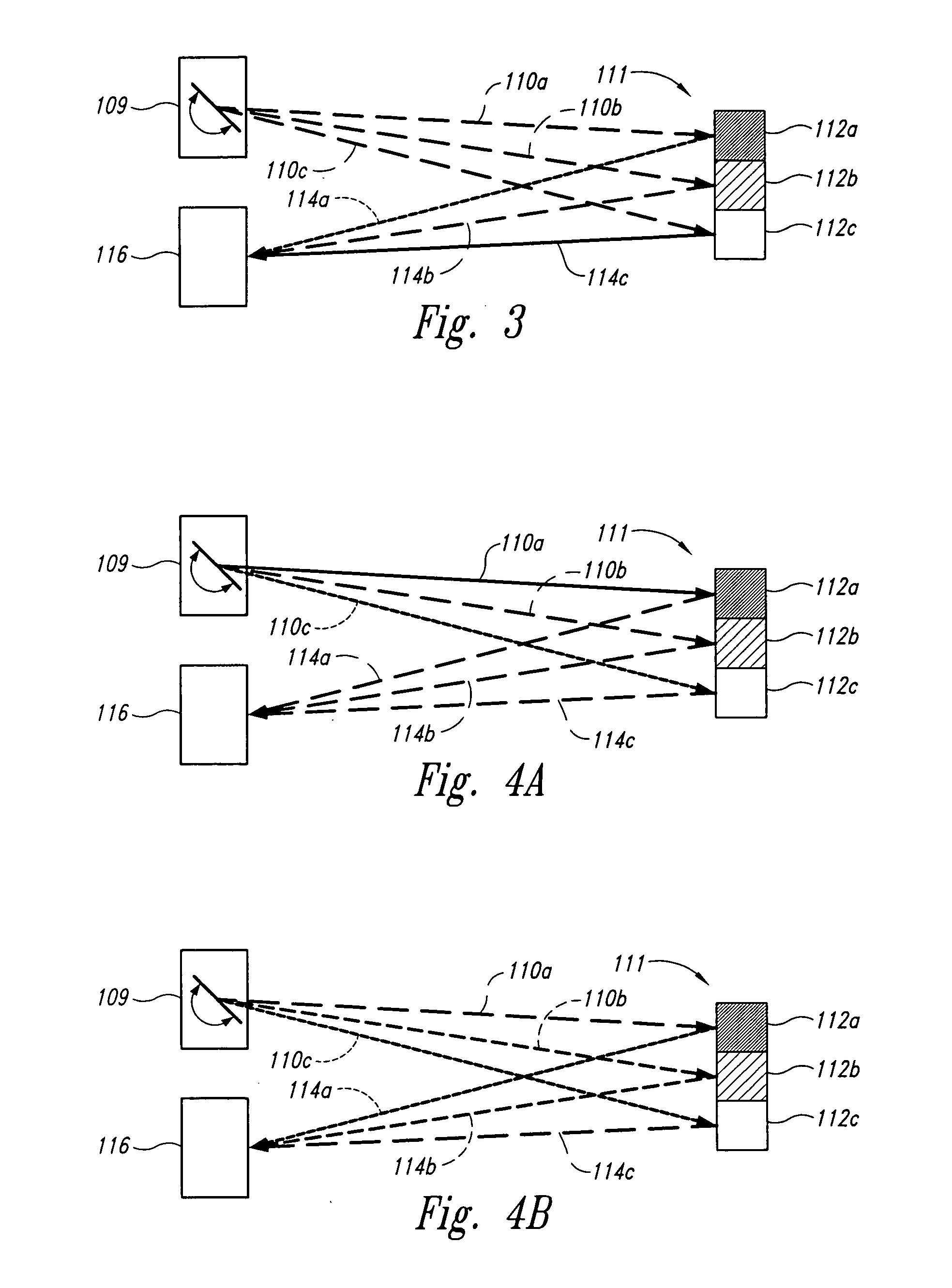
Scanning endoscope
InactiveUS20050020926A1Improve discriminationImprove color gamutTelevision system detailsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityLaser transmitter
A scanning endoscope, amenable to both rigid and flexible forms, scans a beam of light across a field-of-view, collects light scattered from the scanned beam, detects the scattered light, and produces an image. The endoscope may comprise one or more bodies housing a controller, light sources, and detectors; and a separable tip housing the scanning mechanism. The light sources may include laser emitters that combine their outputs into a polychromatic beam. Light may be emitted in ultraviolet or infrared wavelengths to produce a hyperspectral image. The detectors may be housed distally or at a proximal location with gathered light being transmitted thereto via optical fibers. A plurality of scanning elements may be combined to produce a stereoscopic image or other imaging modalities. The endoscope may include a lubricant delivery system to ease passage through body cavities and reduce trauma to the patient. The imaging components are especially compact, being comprised in some embodiments of a MEMS scanner and optical fibers, lending themselves to interstitial placement between other tip features such as working channels, irrigation ports, etc.
Owner:MICROVISION
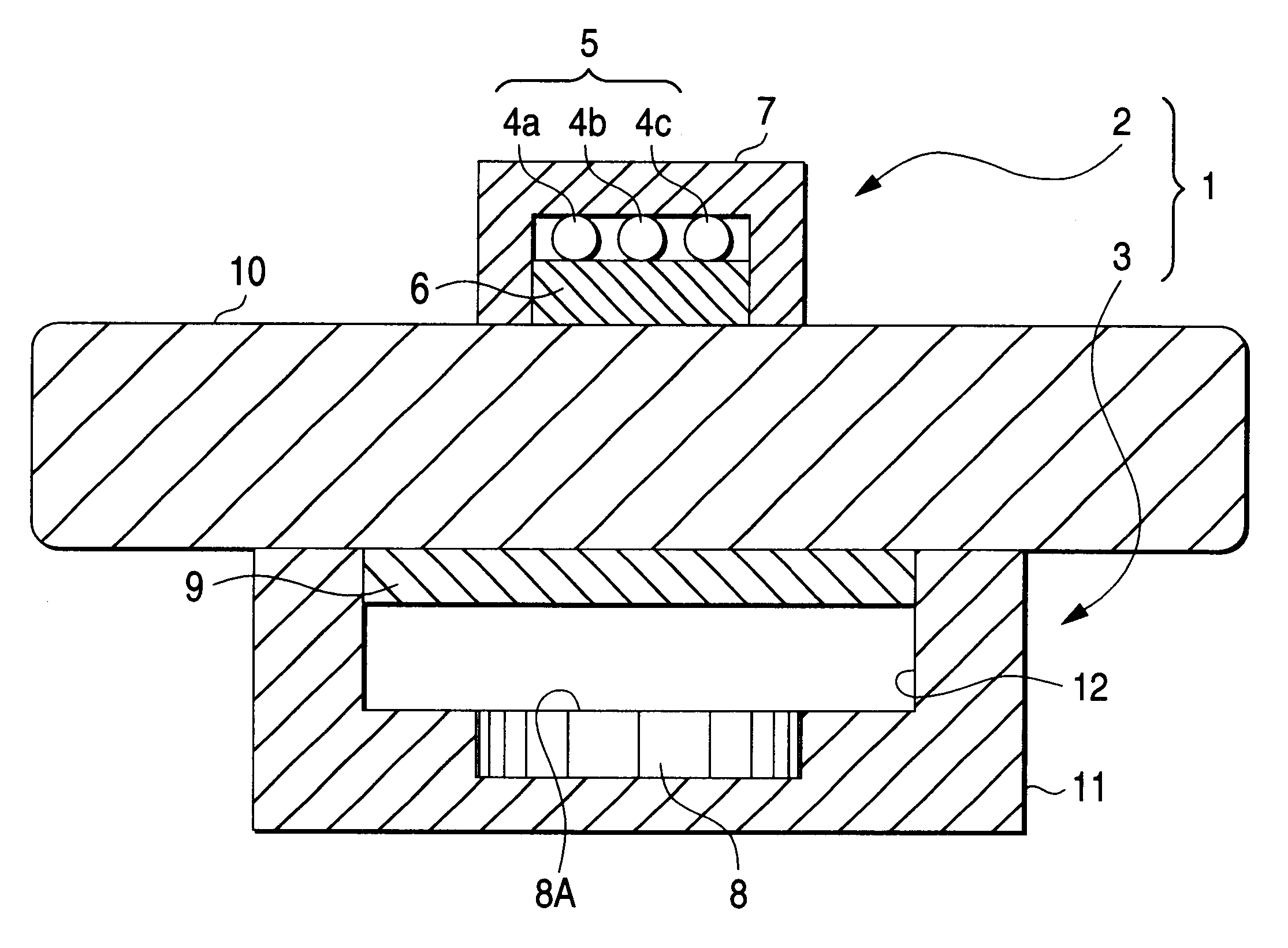
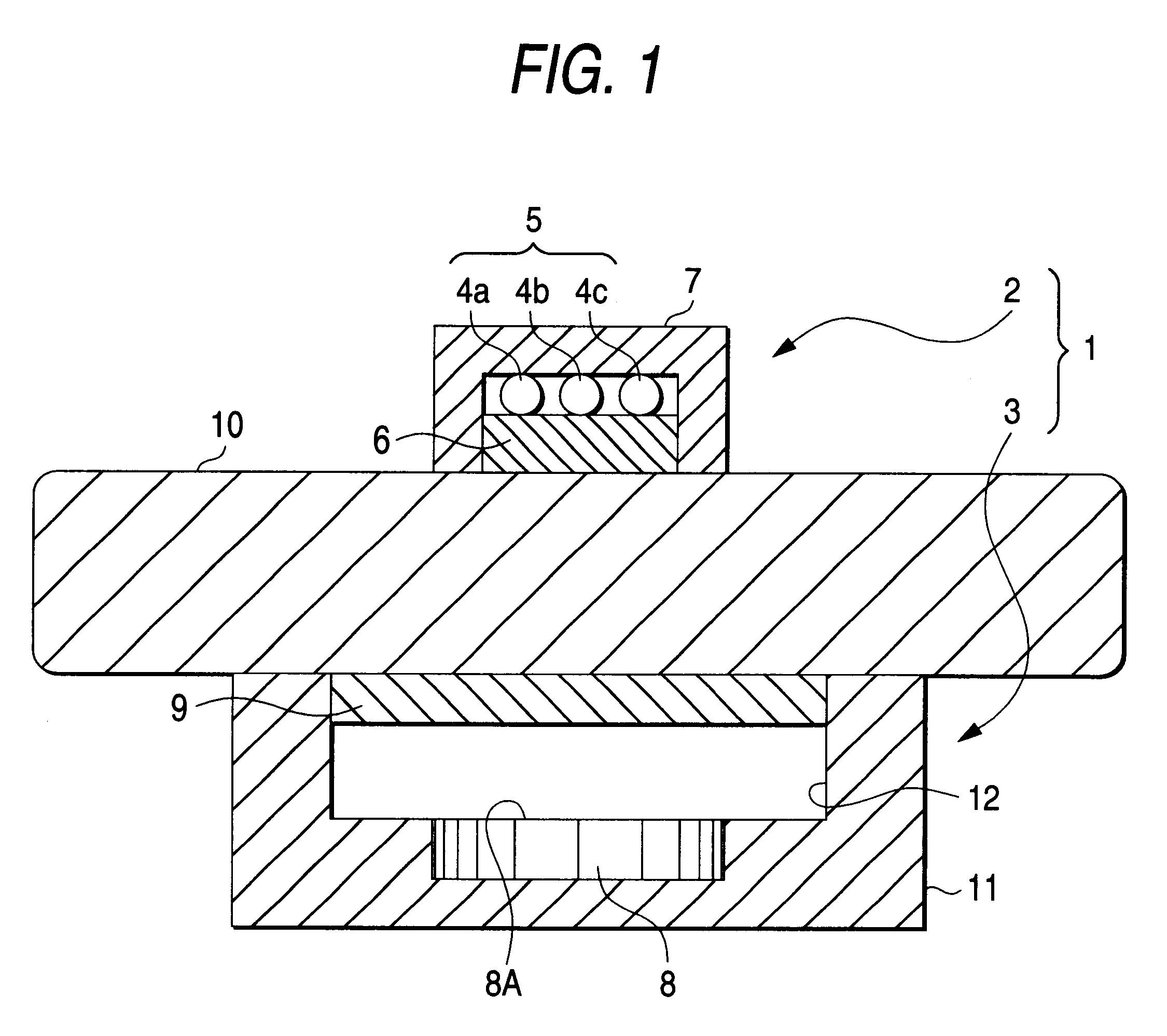
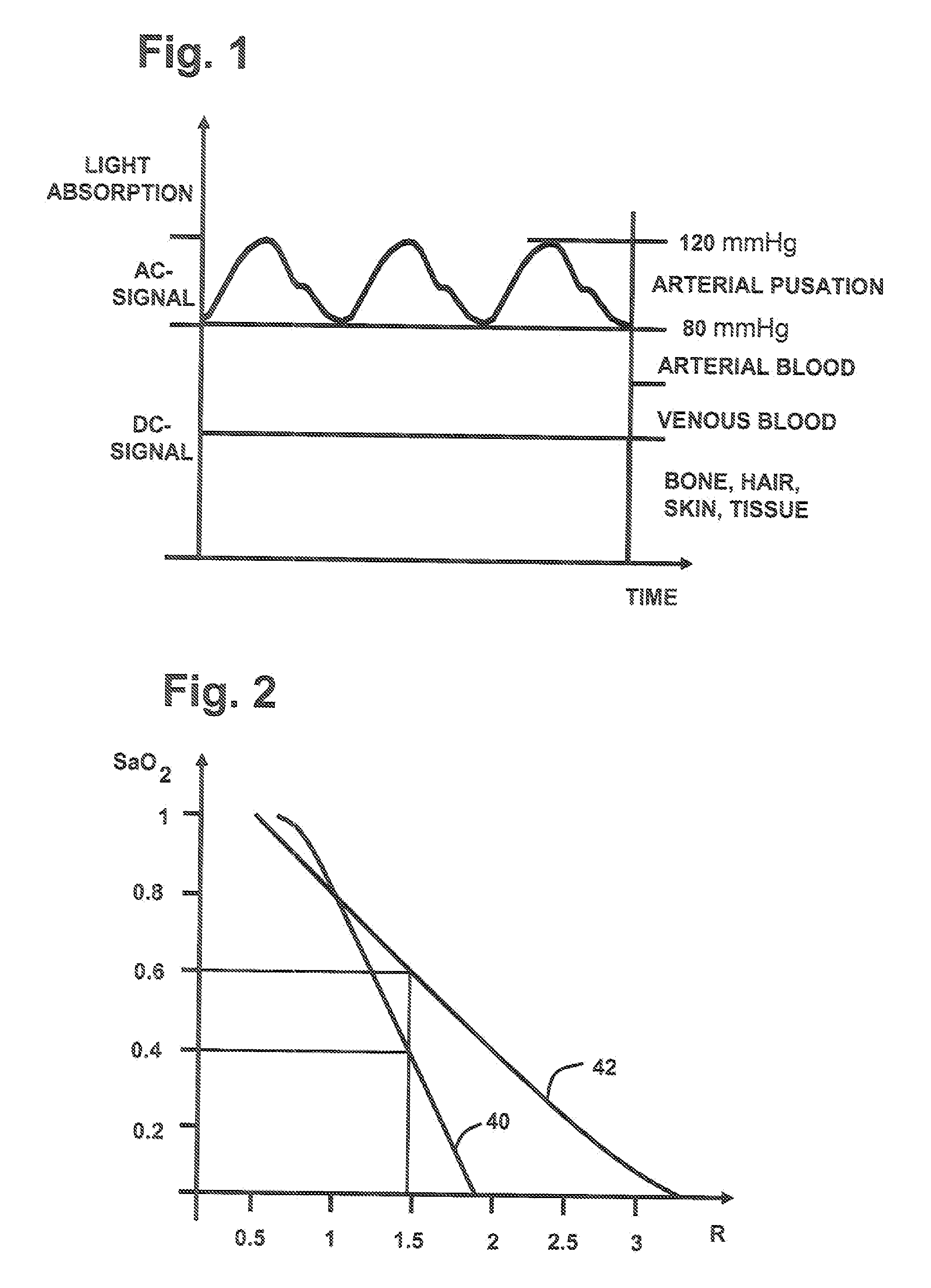
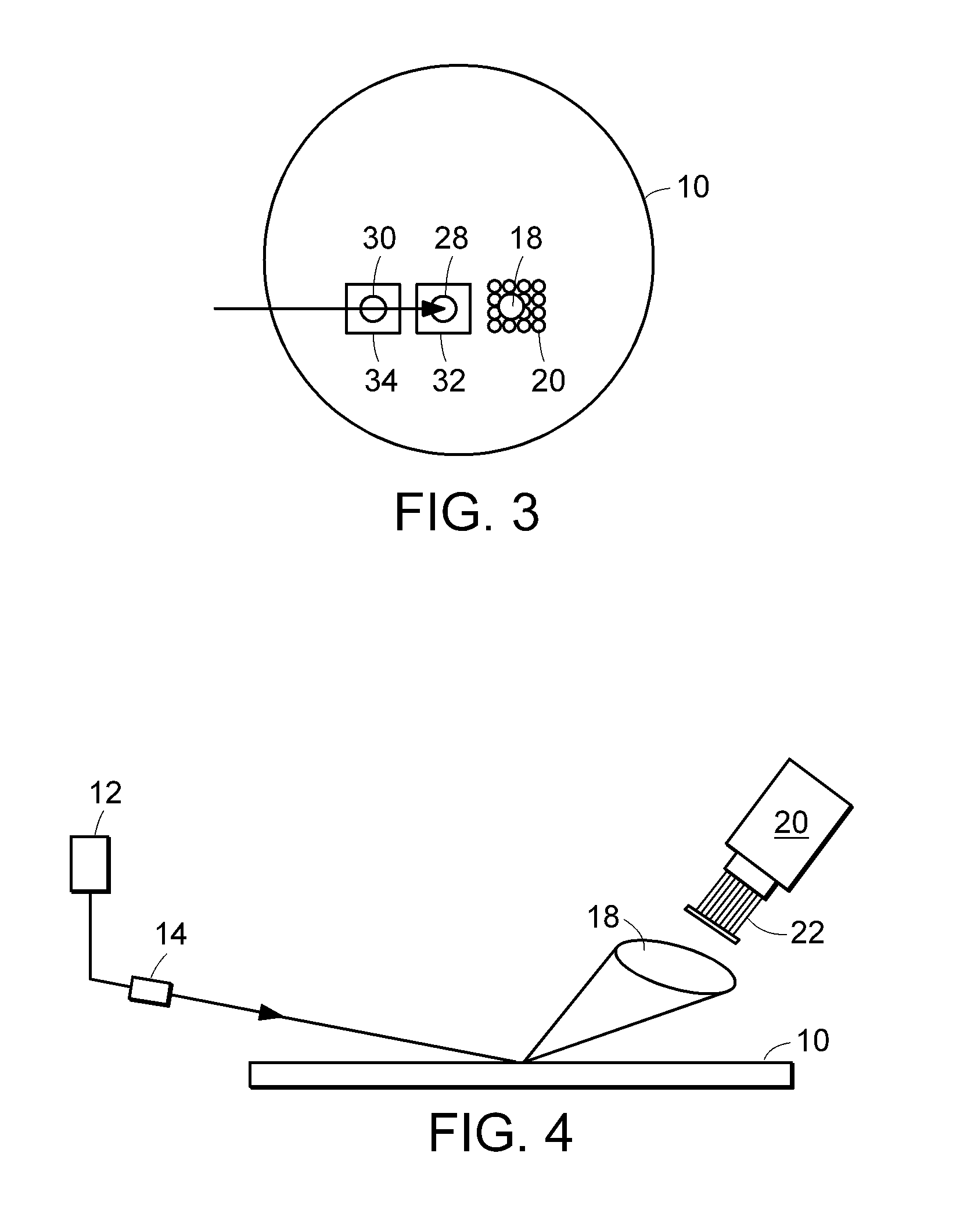
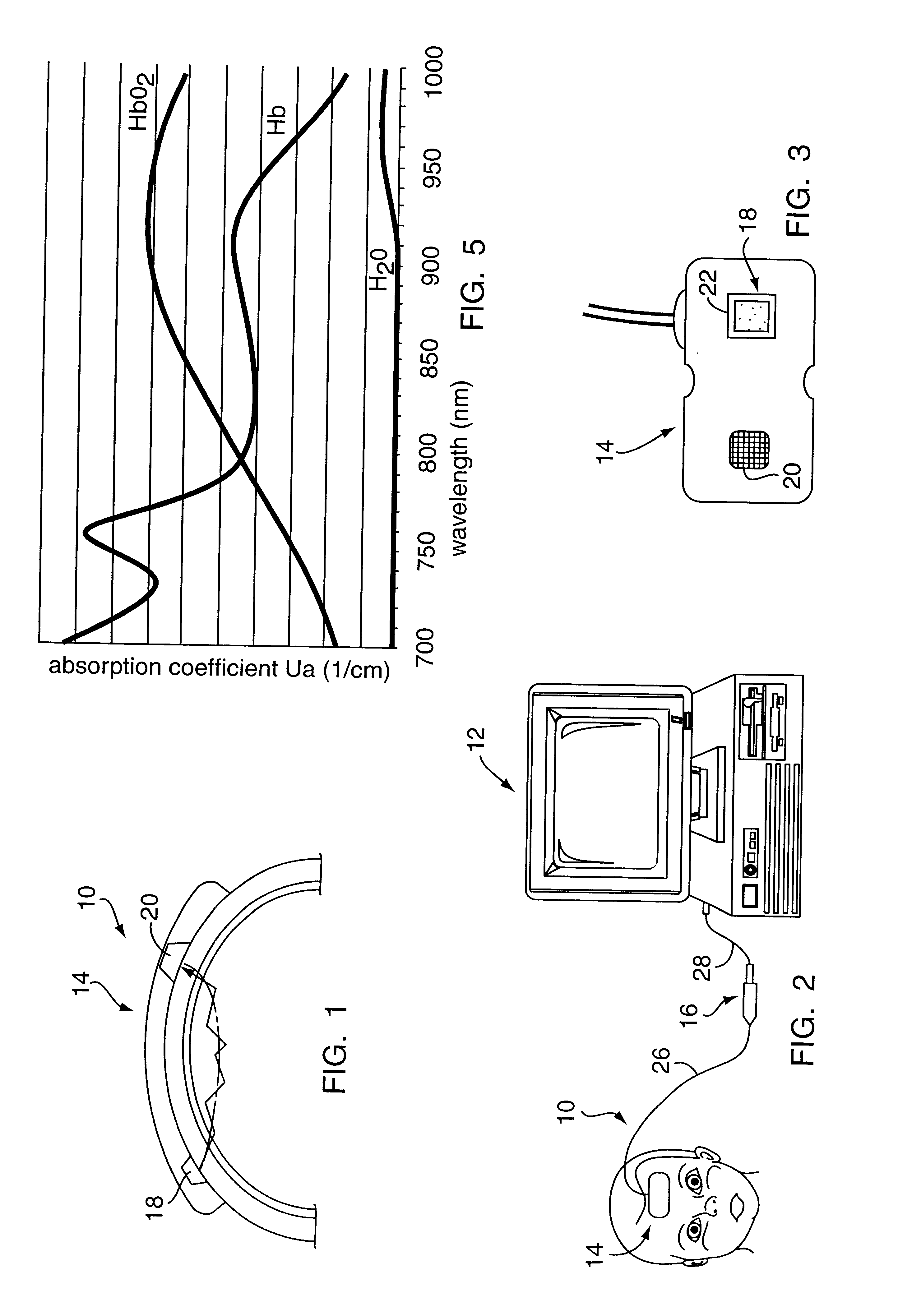
Probe and apparatus for determining concentration of light-absorbing materials in living tissue
InactiveUS6671526B1Minimizing affectionDiagnostics using lightSensorsUltrasound attenuationLength wave
A probe 1 includes a light irradiating device 2 and a light receiving device 3, which are oppositely disposed sandwiching living tissue 10. The light irradiating device 2 includes a light source 5 and a scattering plate 6 located in front of the light source 5. The light receiving device 3 includes a photo diode 8 and a light scattering portion. With such an arrangement, of the attenuation of the living tissue 10, non-absorbing attenuation is free from the wavelength. A ratio of absorbing attenuation and a thickness of a blood layer is not affected by a thickness of living tissue. Further, the absorbing attenuation is not dependent on a depth of the blood layer.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
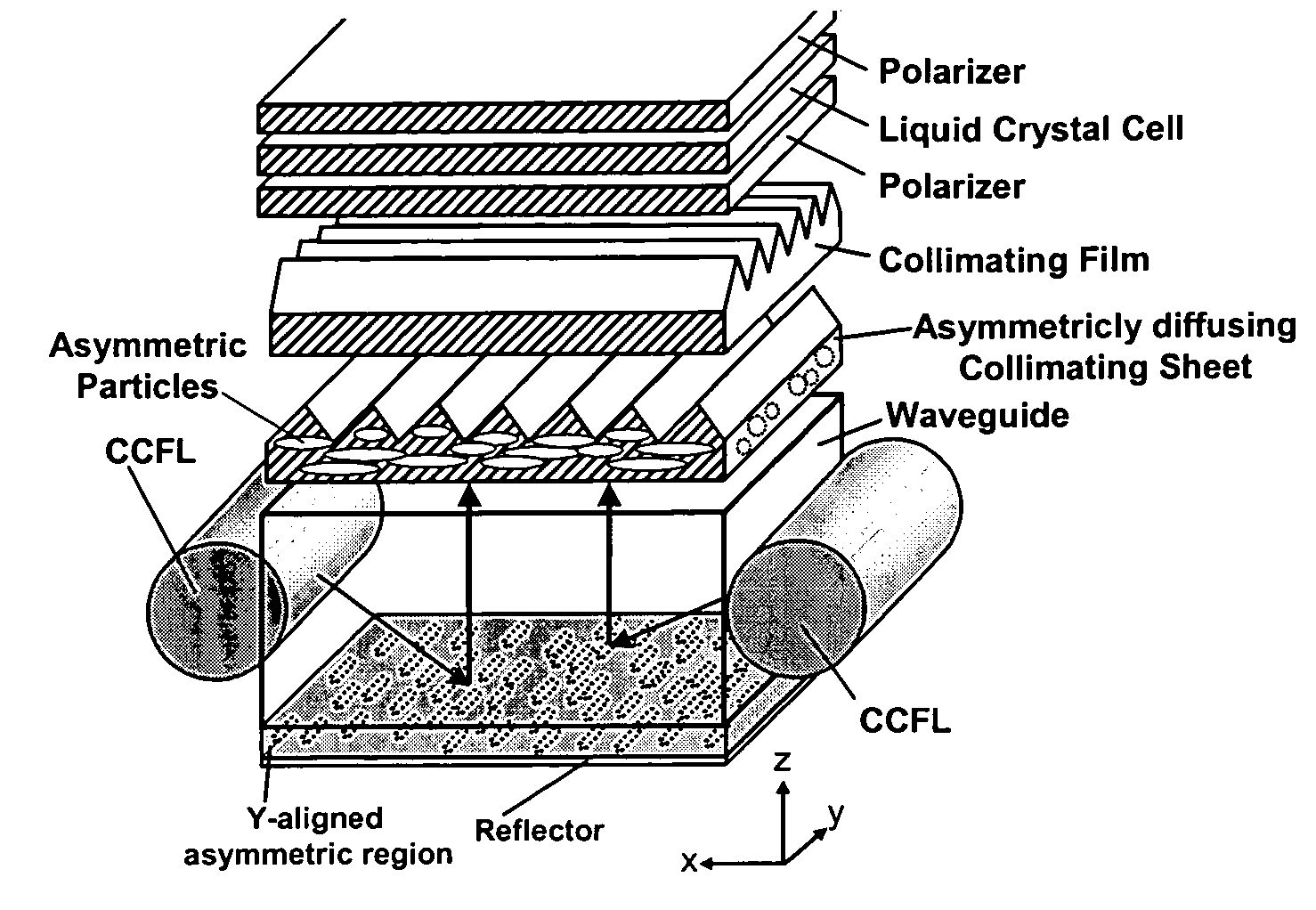
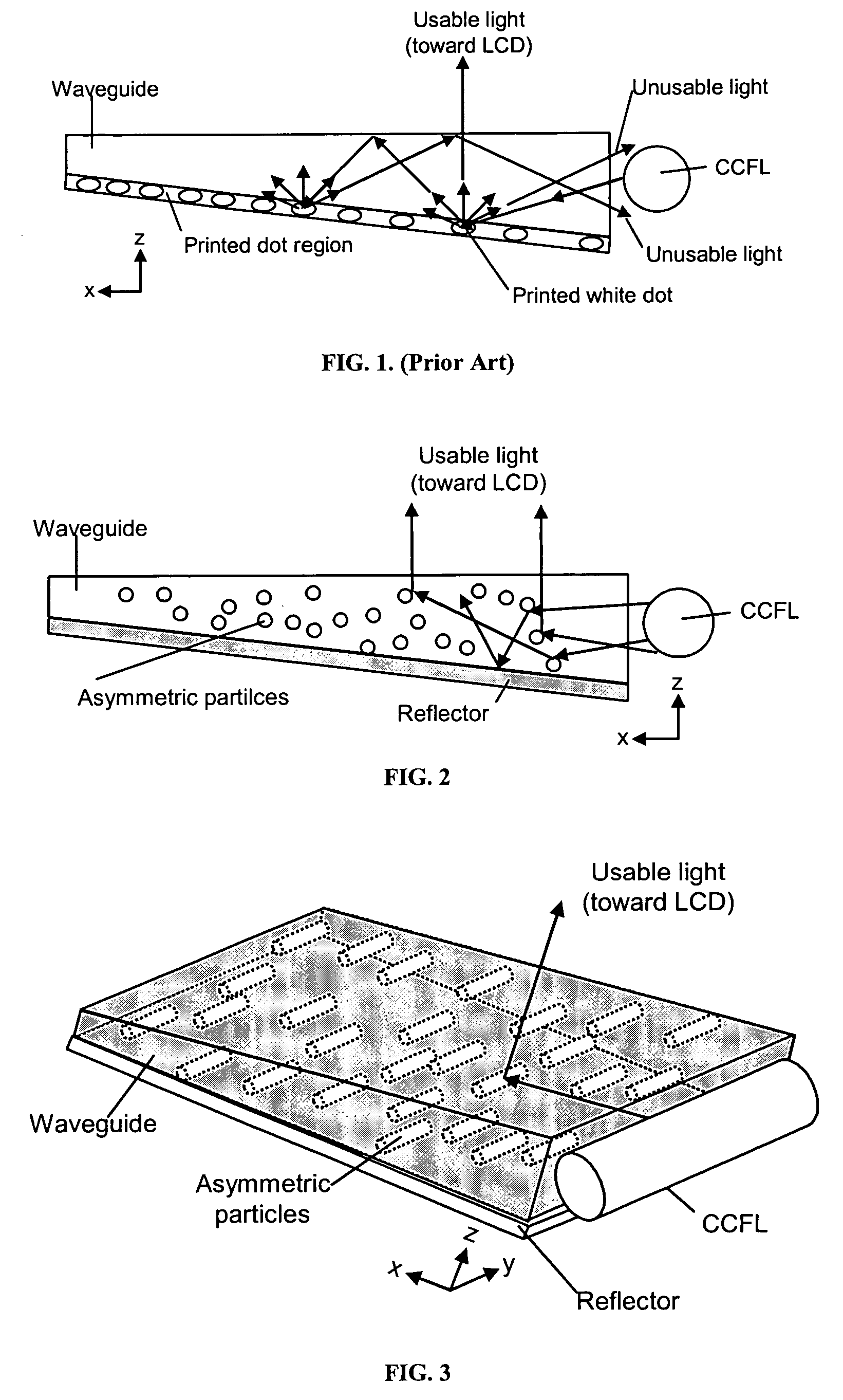
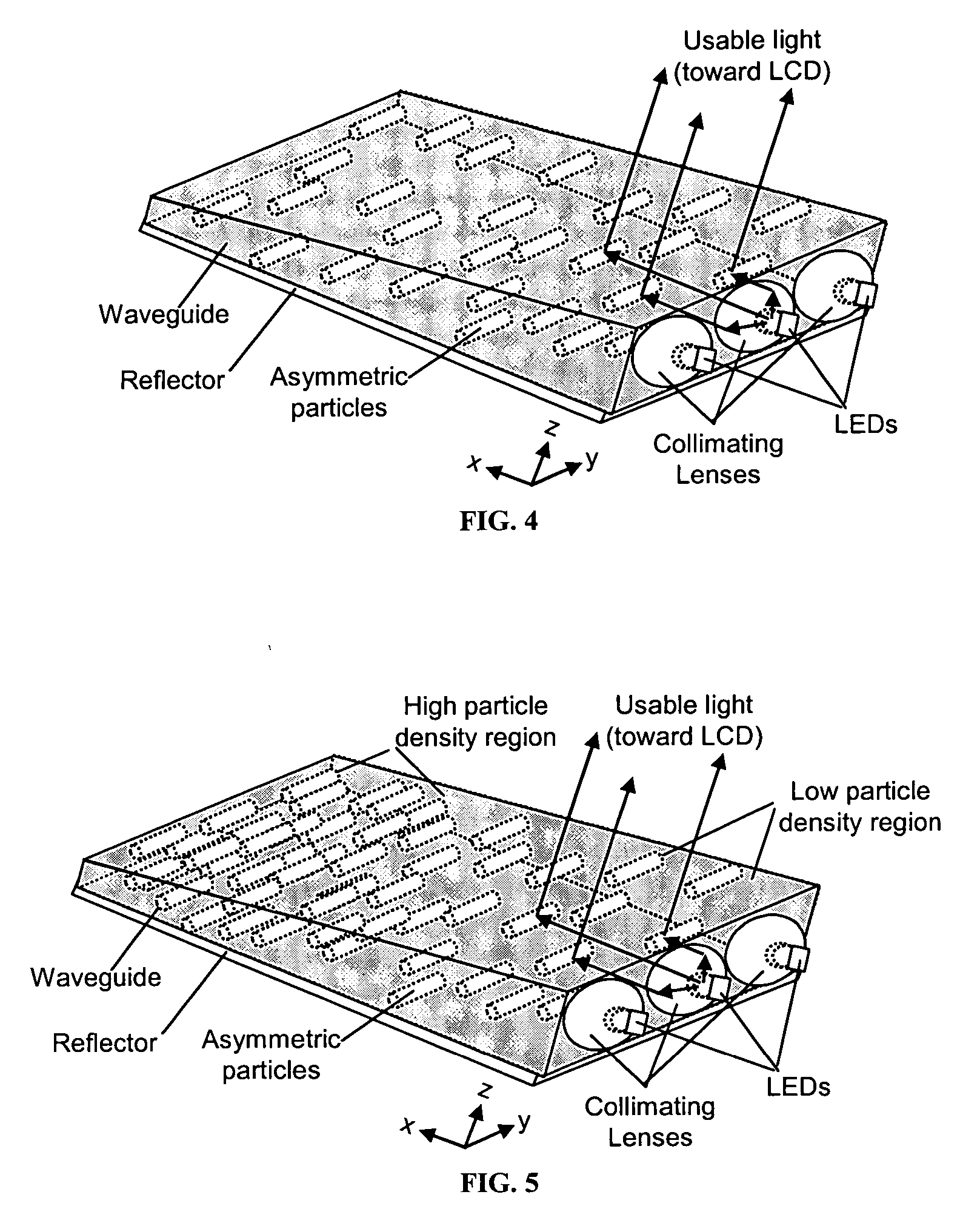
Enhanced LCD backlight
ActiveUS20060056166A1Improved backlight assemblyAvoid less flexibilityElectric discharge tubesDiffusing elementsCompression moldingEllipsoidal particle
The present invention provides an improved light guide with inherently more flexibility for display system designers and higher optical efficiency. By using a light guide containing substantially aligned non-spherical particles, more efficient control of the light scattering can be achieved. One or more regions containing ellipsoidal particles may be used and the particle sizes may vary between 2 and 100 microns in the smaller dimension. The light scattering regions may be substantially orthogonal in their axis of alignment. Alternatively, one or more asymmetrically scattering films can be used in combination with a backlight light guide and a reflector to produce an efficient backlight system. The light guides may be manufactured by embossing, stamping, or compression molding a light guide in a suitable light guide material containing asymmetric particles substantially aligned in one direction. The light scattering light guide or non-scattering light guide may be used with one or more light sources, collimating films or symmetric or asymmetric scattering films to produce an efficient backlight that can be combined with a liquid crystal display or other transmissive display. By maintaining more control over the scattering, the efficiency of the recycling of light by using reflective polarizers can also be increased.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS DEV FINANCE AGENCY
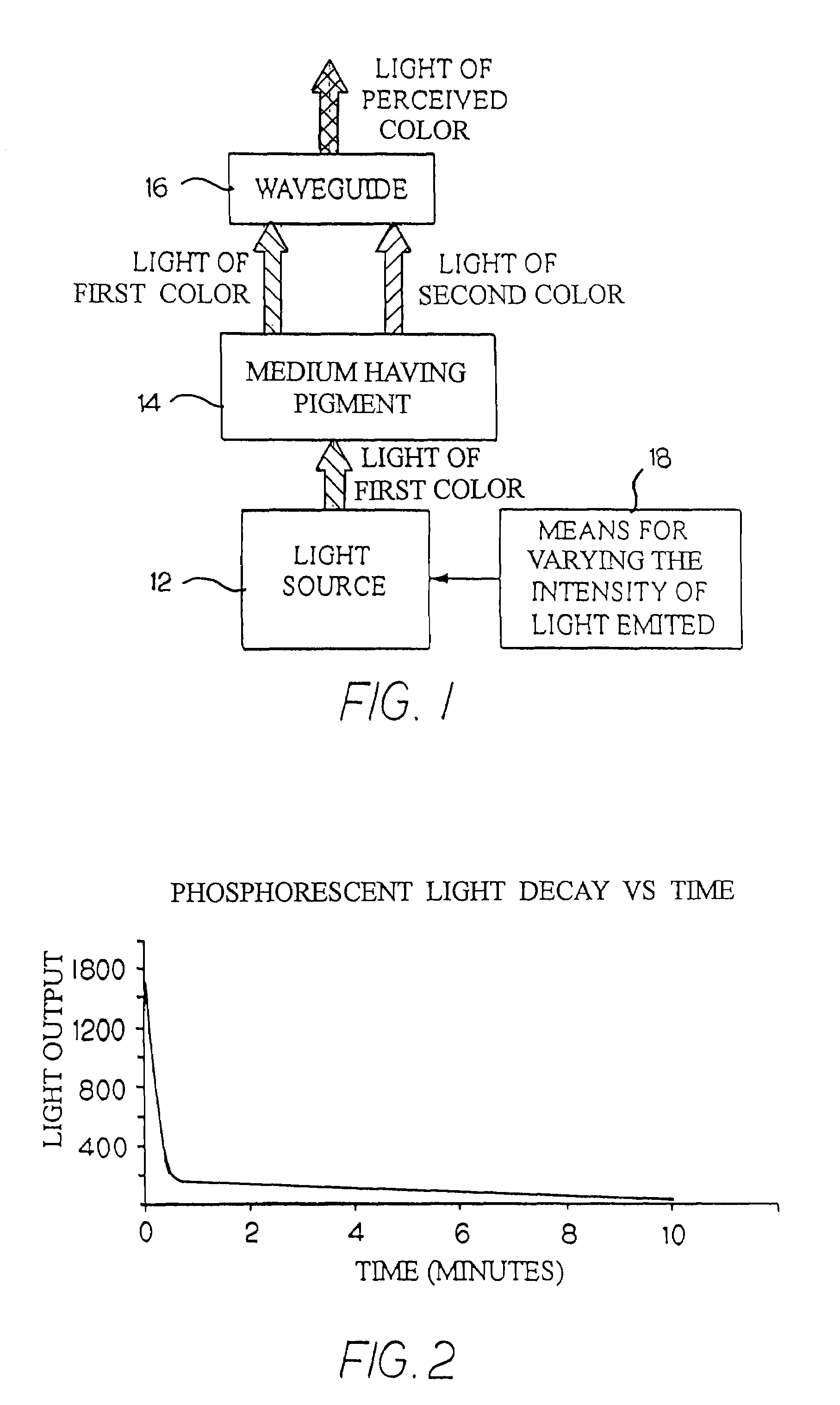
Illumination device for simulating neon or similar lighting in various colors
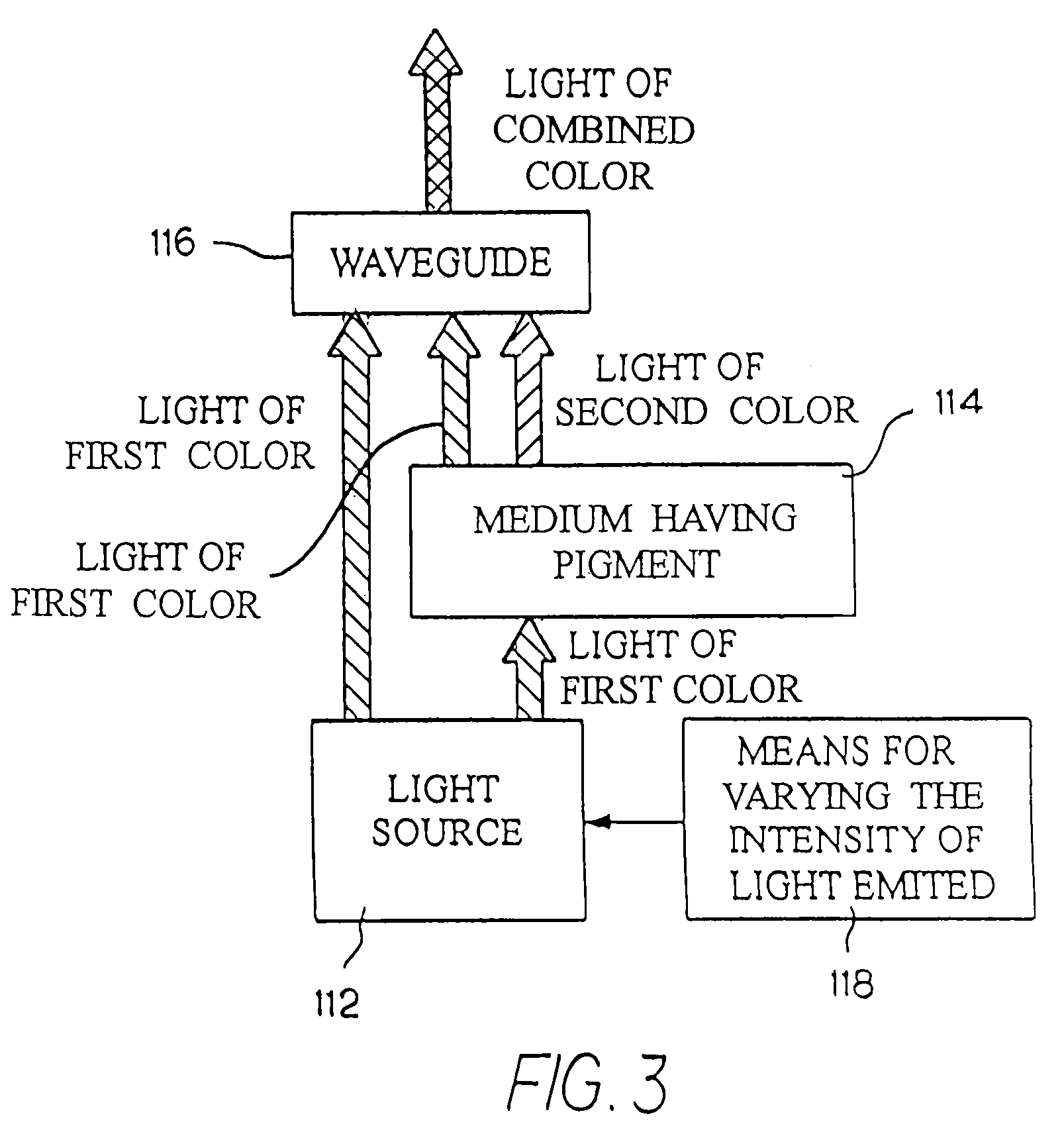
An illumination device has a light source, a waveguide, and a light-transmitting medium. The light source emits light of a first color. The waveguide has both optical waveguide and light scattering properties. The light-transmitting medium is composed of a matrix of substantially translucent material doped with a pigment, and is positioned between the light source and the waveguide such that a portion of the light emitted by the light source passes around the light-transmitting medium and reaches the waveguide directly, and a portion of the emitted light is received by the light-transmitting medium. The pigment changes a portion of the received light to a light of a second color. The waveguide receives and mixes the light of the first color and the light of the second color, and emits light of a combined color.
Owner:ILIGHT TECH INC
Illumination device for simulating neon or similar lighting using phosphorescent dye
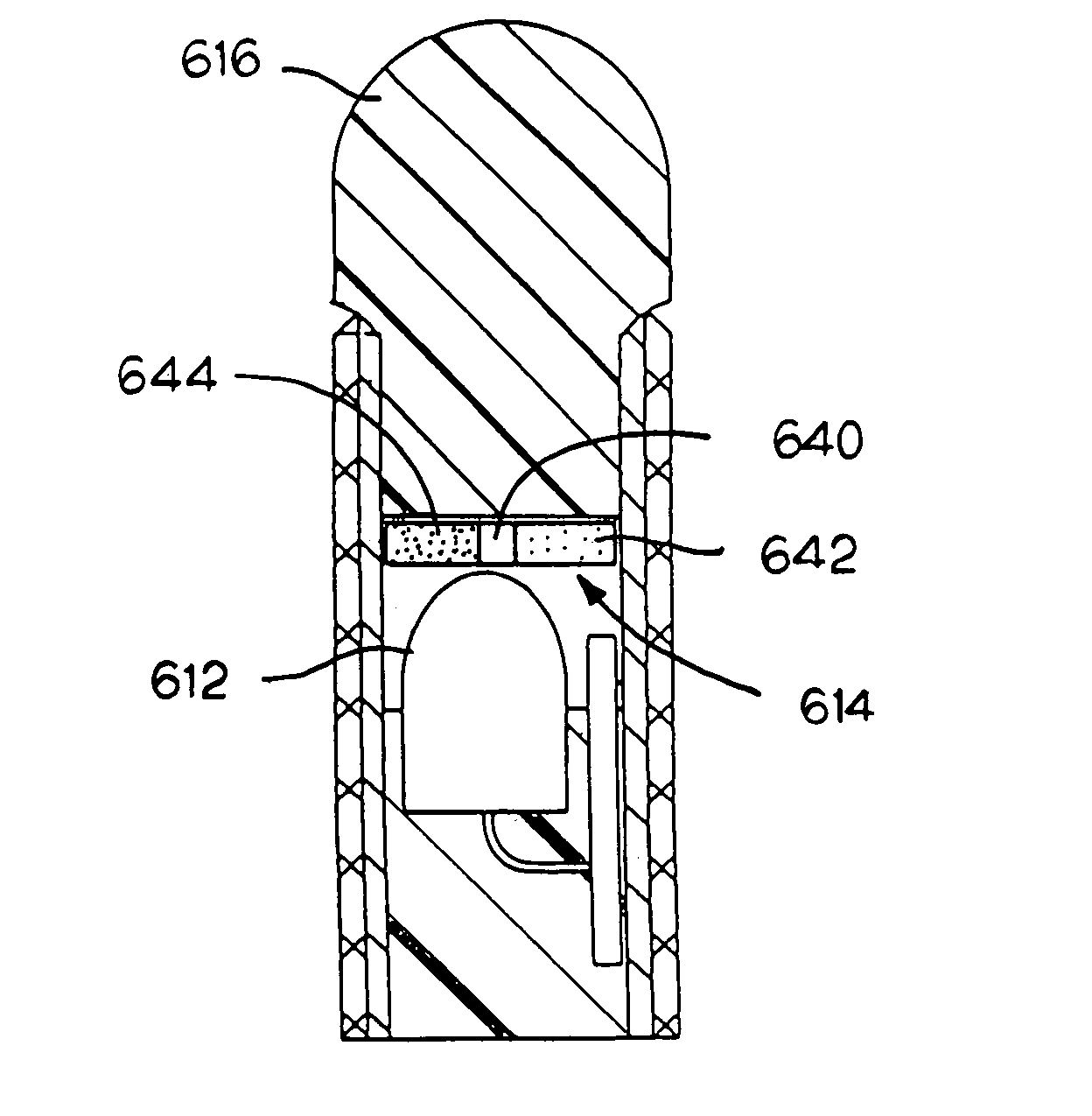
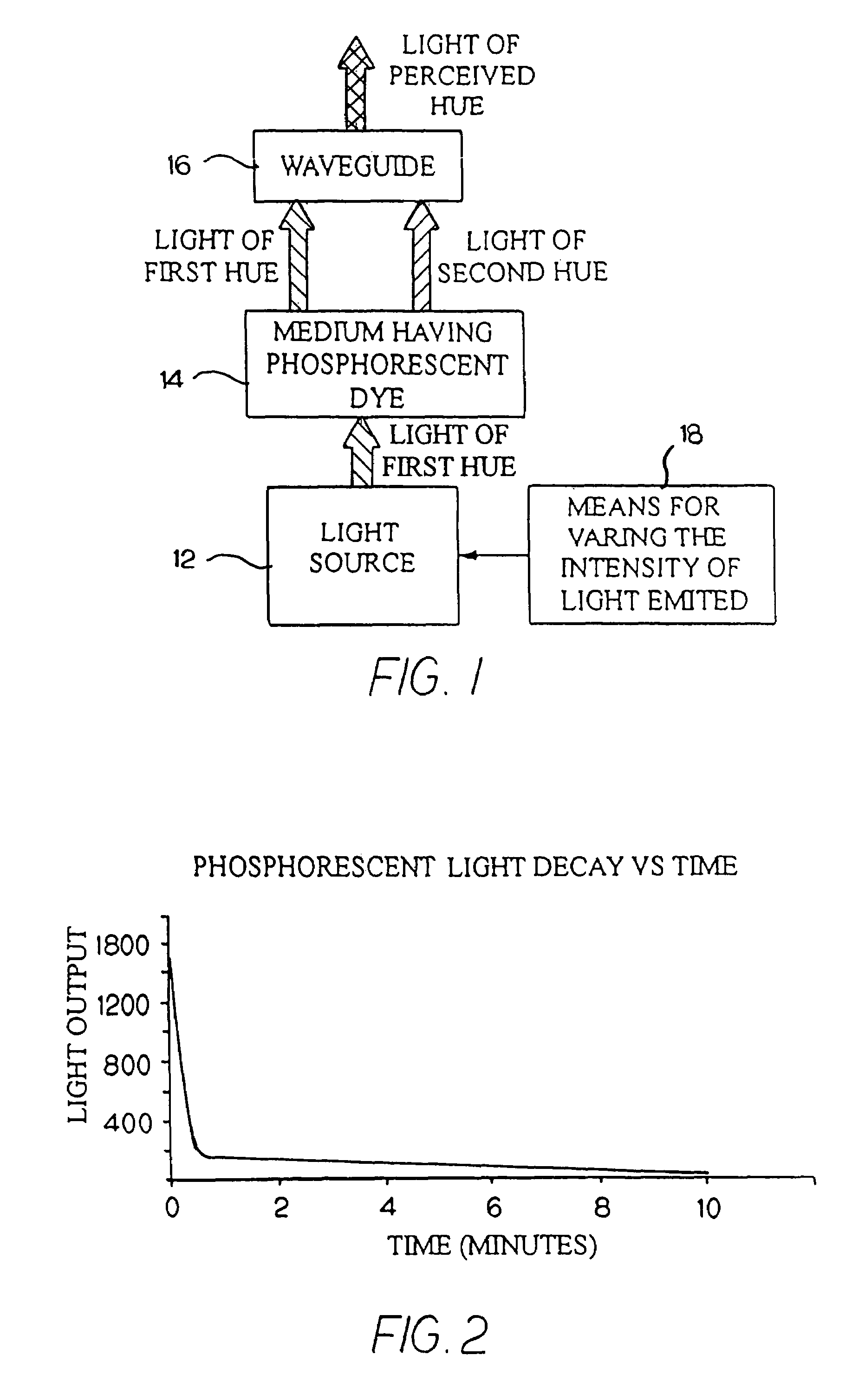
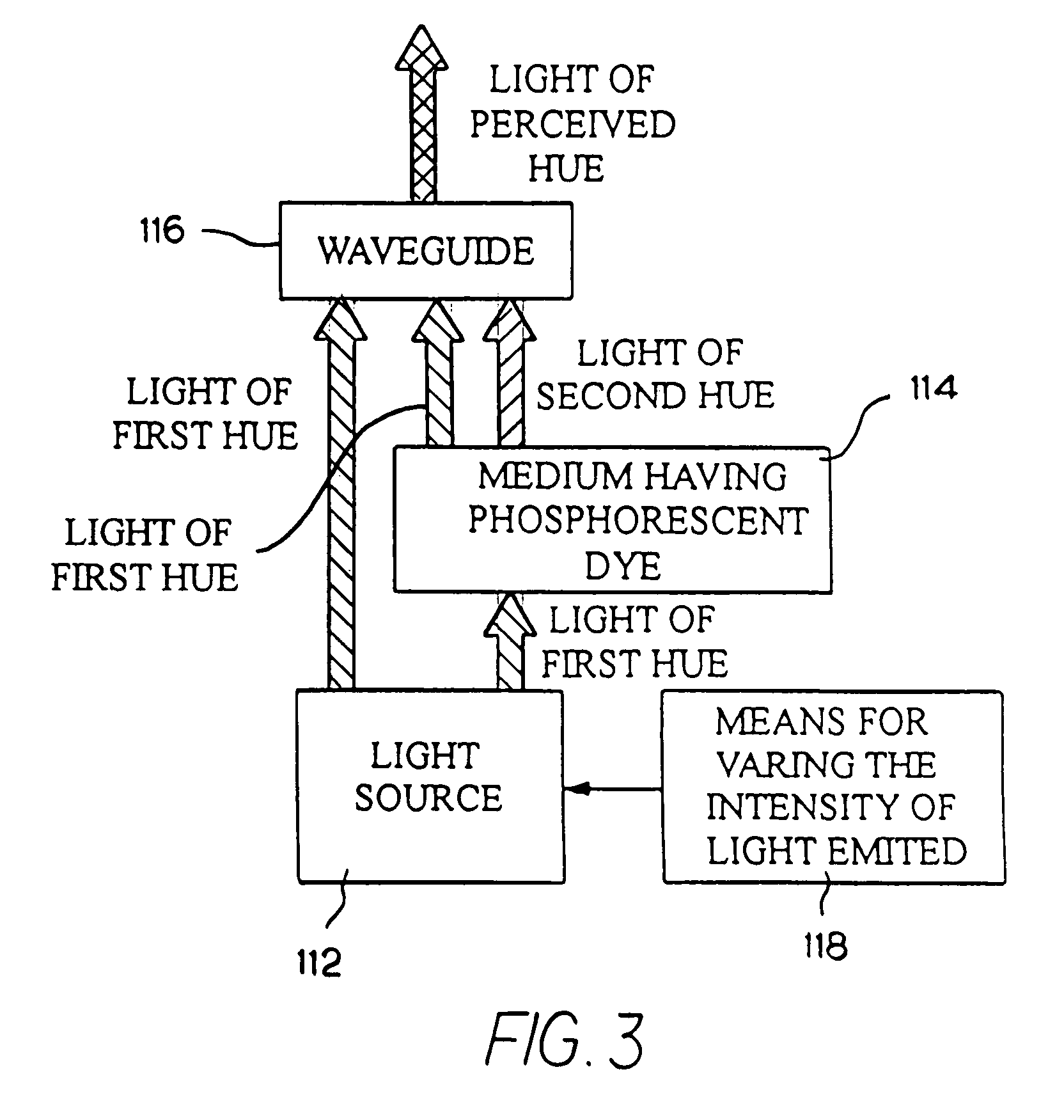
An illumination device simulates neon lighting using a light source for emitting light of a predetermined first hue and a light-transmitting medium having a predetermined density of phosphorescent dye positioned adjacent to the light source. The phosphorescent dye will absorb light emitted by the light source and emit light of a second hue. An observer of the device perceives light that is of a hue that is different from the predetermined first hue. A means for varying the intensity of the light emitted by the light source creates color changing effects in the illumination device. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are a suitable light source. A waveguide having both optical waveguide and light scattering properties is used to diffuse the combined light and simulate the uniform appearance of a neon tube. Alternatively, the waveguide itself can be doped with phosphorescent dye to emit light having the perceived hue.
Owner:ILIGHT TECH INC
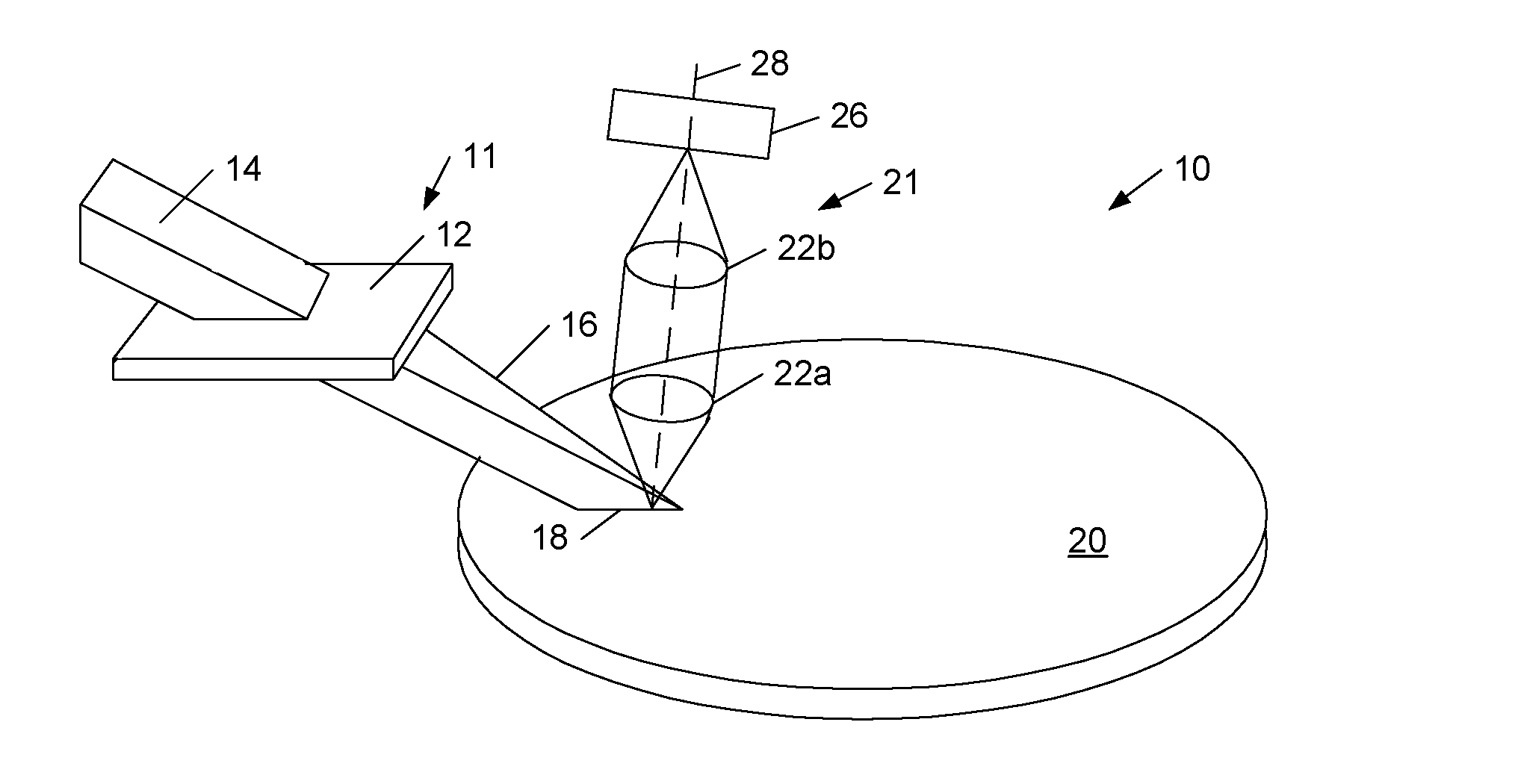
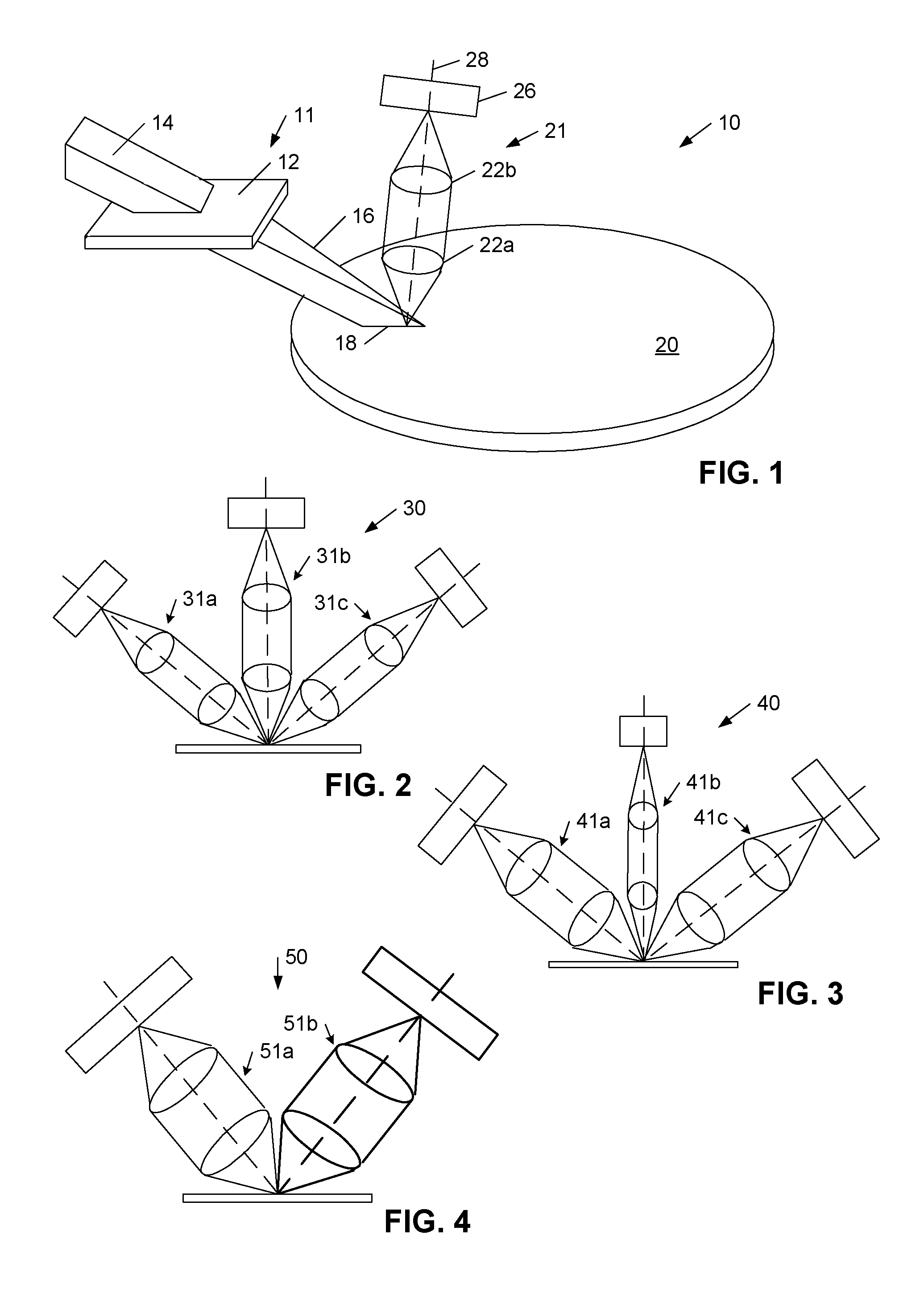
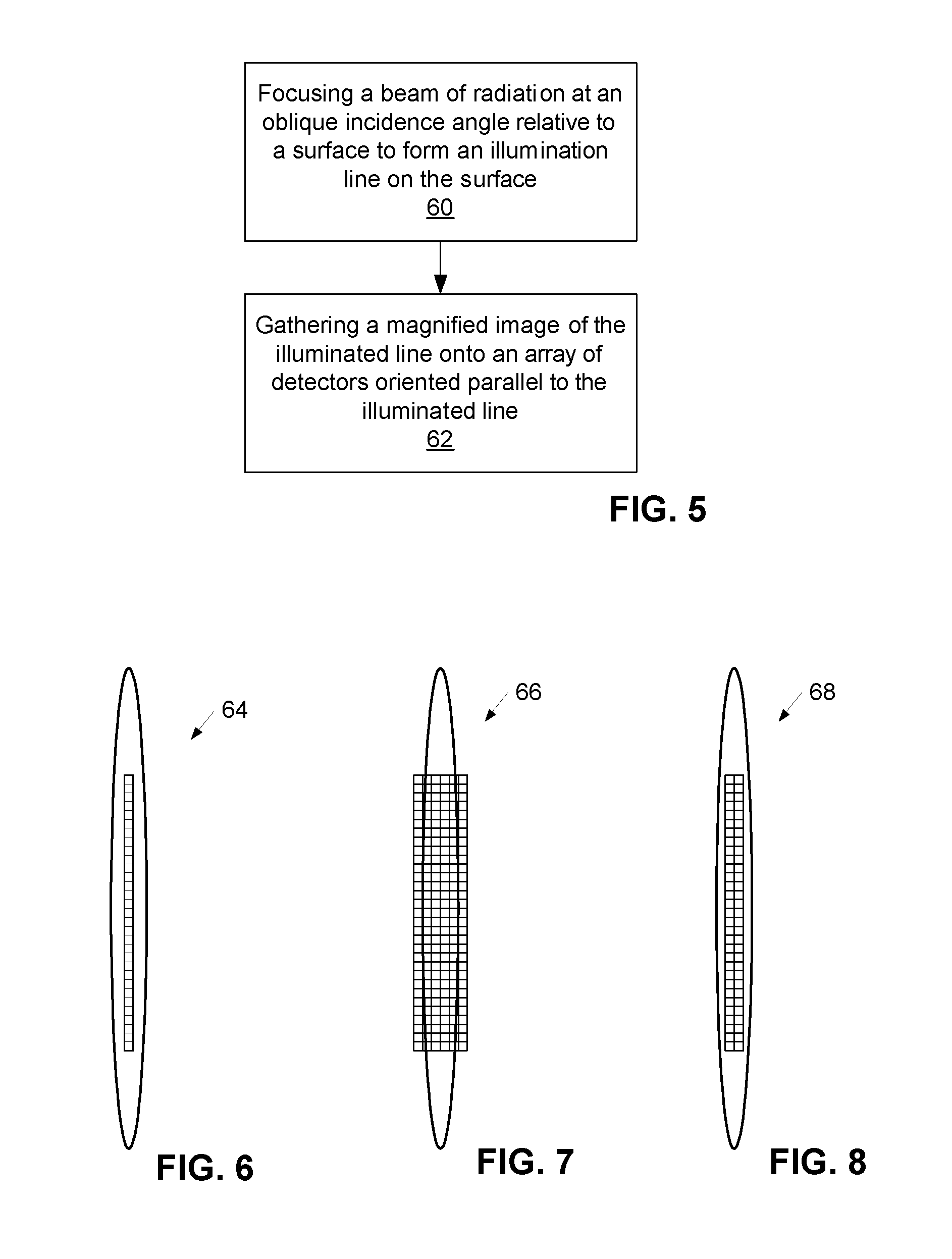
Surface inspection system using laser line illumination with two dimensional imaging
A surface inspection apparatus and a method are provided which include an illumination system configured to focus a beam of radiation at a non-orthogonal incidence angle to form an illumination line on a surface substantially in a plane of incidence of the focused beam. The apparatus and method further include a collection system configured to image the illumination line onto an array of detectors oriented parallel to the illumination line. The collection system includes an imaging lens for collecting light scattered from the illumination line, a focusing lens for focusing the collected light, and the array of detectors, each configured to detect a corresponding portion of the illumination line. The collection system may be configured to image the illumination line such that the width of the imaged illumination line on the array of detectors is larger than the pixel size of the detectors along the same direction.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
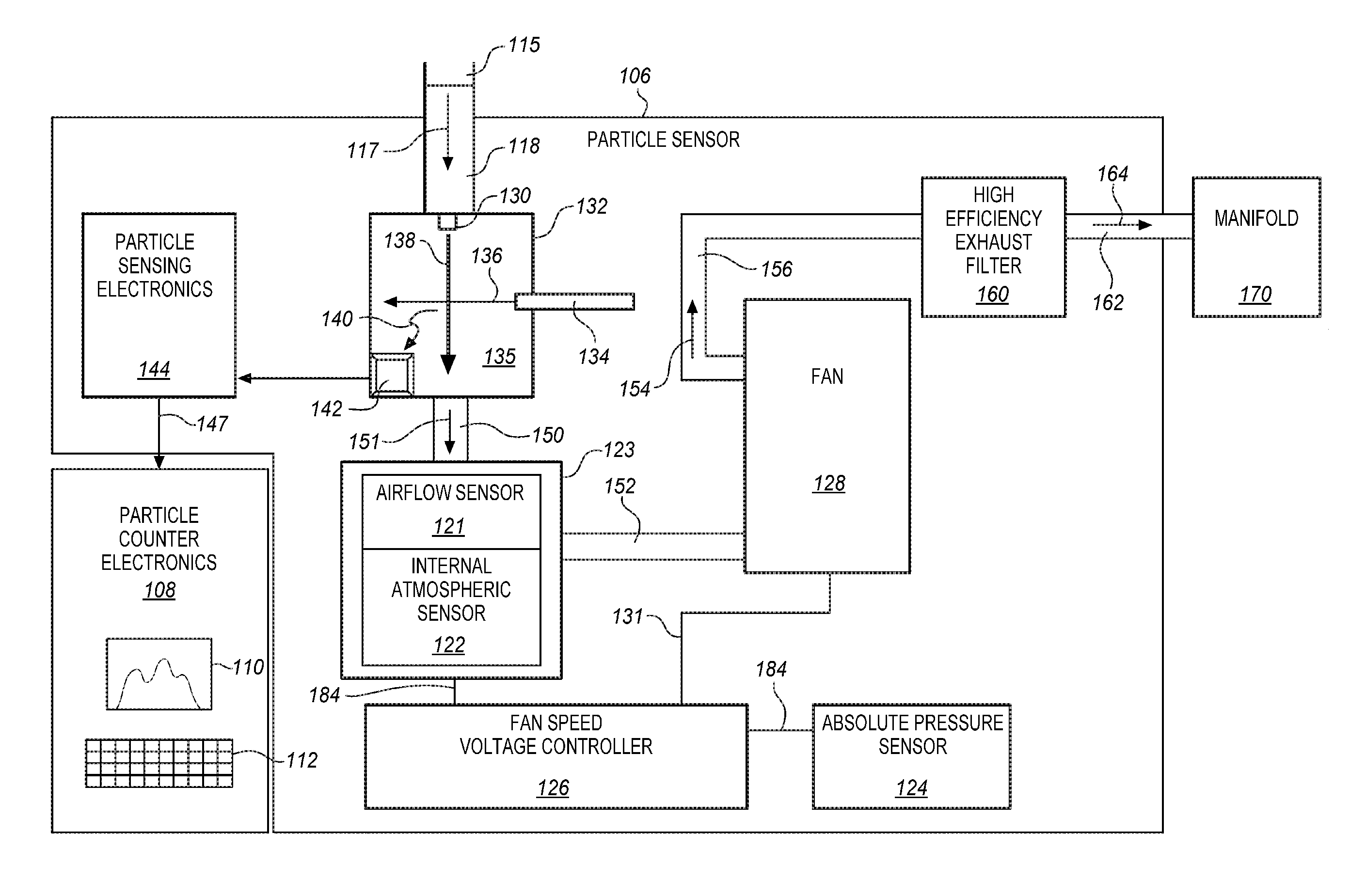
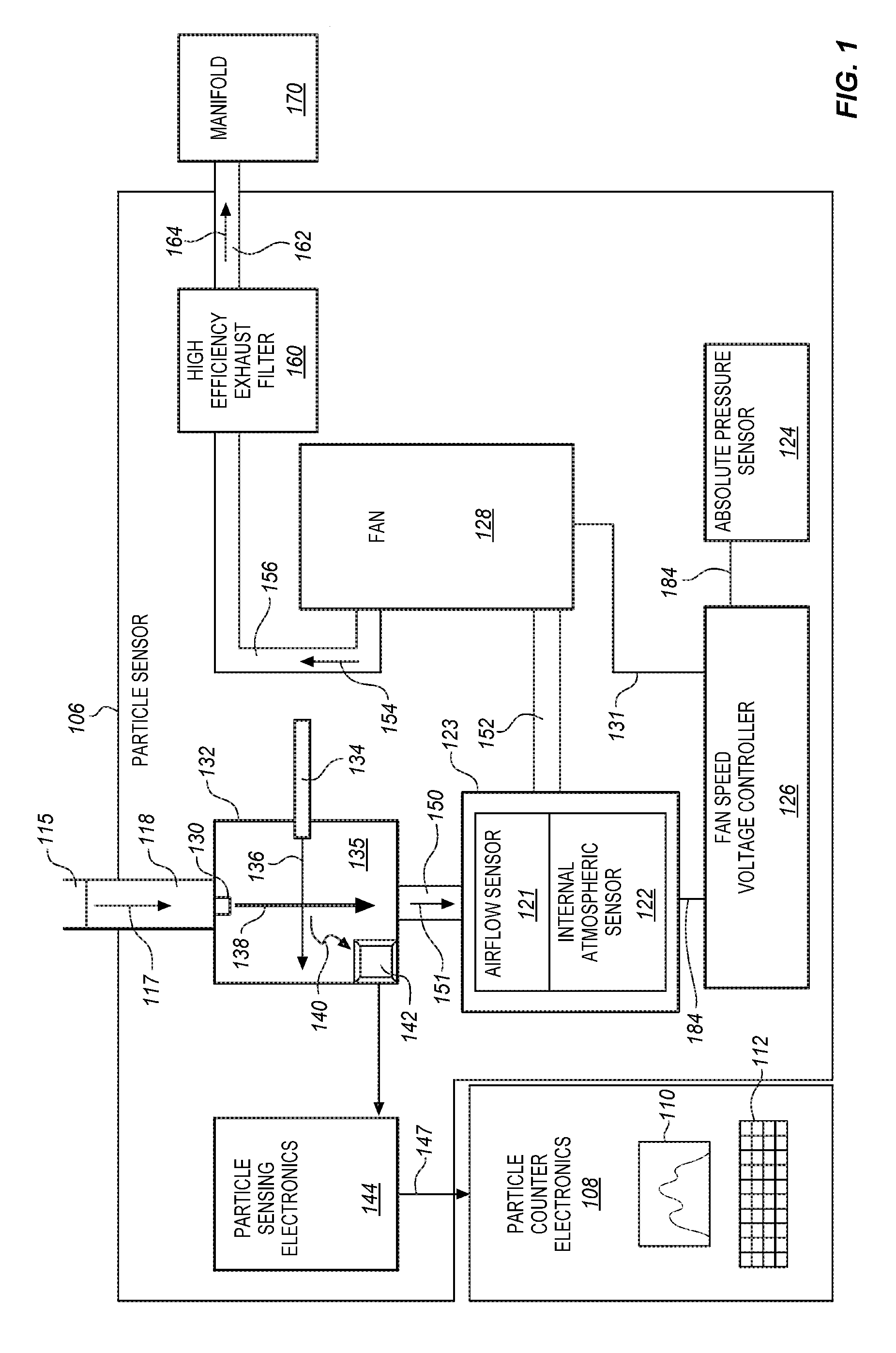
Aerosol particle sensor with axial fan
ActiveUS7667839B2Reduces cost and size and power consumptionWhole plant particle counter systems are greatly simplifiedSamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansSquare MillimeterCollection system
A particle sensor for optically detecting an unconstrained particle suspended in a flowing gas includes a sample chamber having a gas inlet and a gas outlet; a gas flow system for flowing said gas from said gas inlet through said sample chamber to said gas outlet, a source of light; an optical system directing said light through said sample chamber, an optical collection system located to collect light scattered by said particles in the gas, and a detection system located to detect the collected light. The total pressure drop through said gas flow system is 3 inches of water or less. The gas flow system includes an axial fan, which may be a high static pressure fan or a counter-rotating fan. In a 1.0 CFM system, the gas inlet nozzle has an area of 25 square millimeters or more.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Solid state lighting devices comprising quantum dots
Solid state lighting devices containing quantum dots dispersed in polymeric or silicone acrylates and deposited over a light source. Solid state lighting devices with different populations of quantum dots either dispersed in matrix materials or not are also provided. Also provided are solid state lighting devices with non-absorbing light scattering dielectric particles dispersed in a matrix material containing quantum dots and deposited over a light source. Methods of manufacturing solid state lighting devices containing quantum dots are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
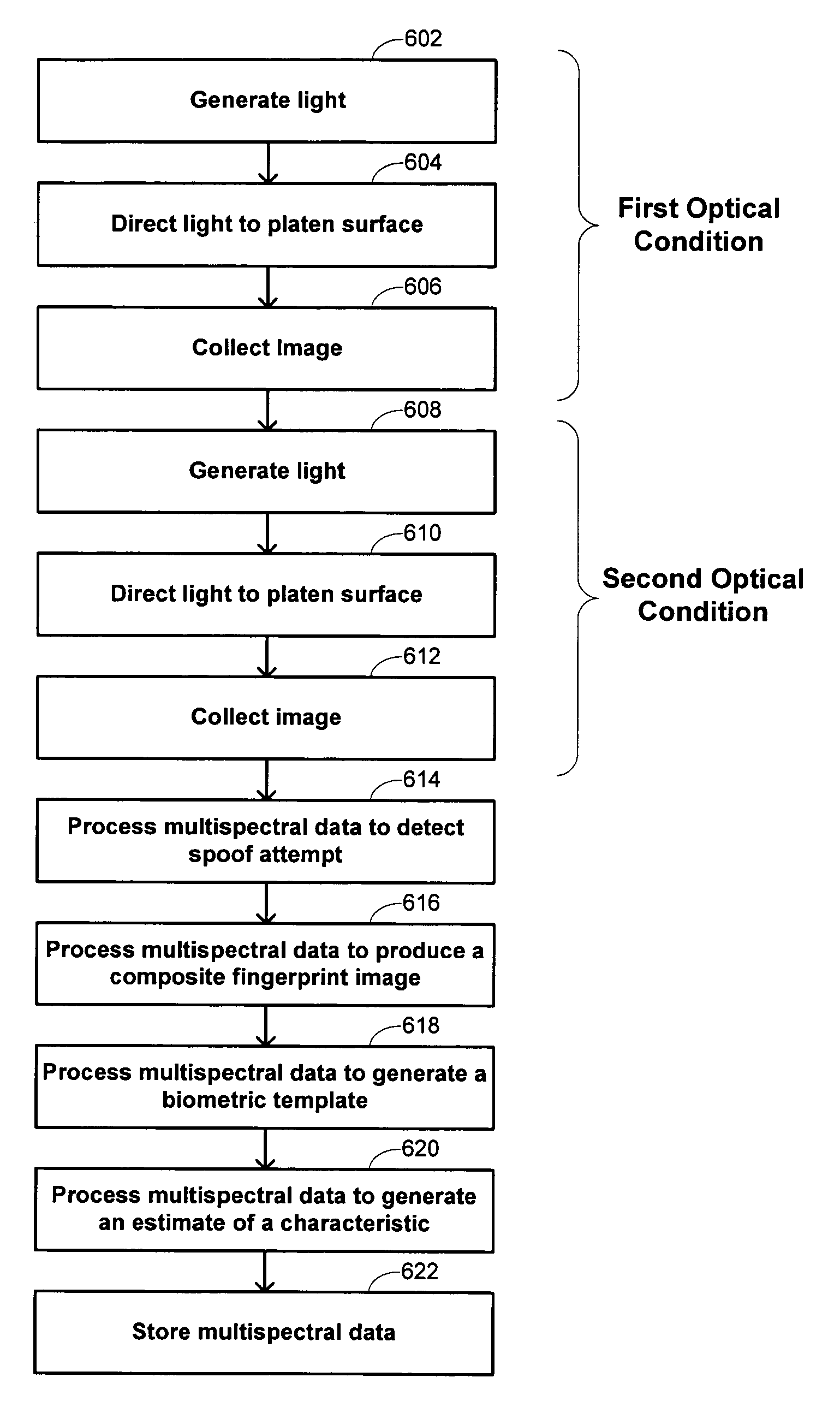
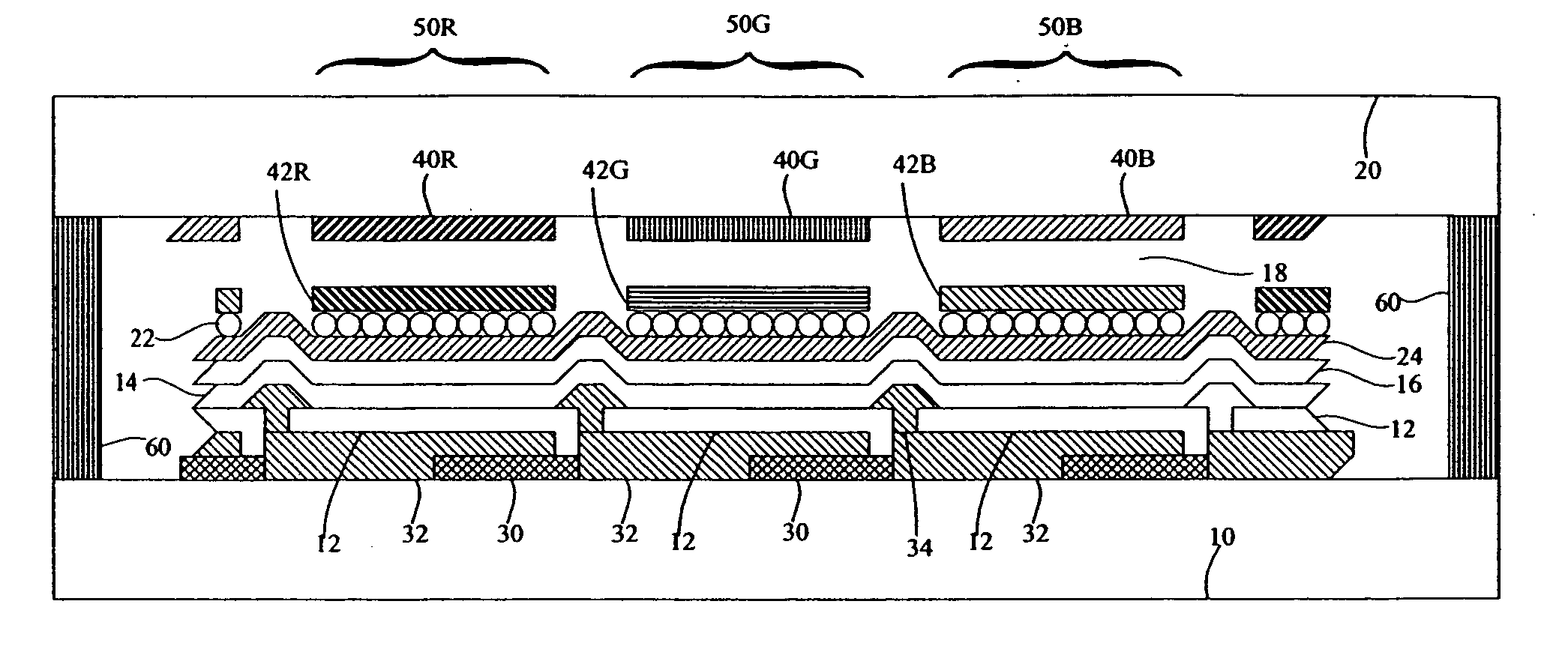
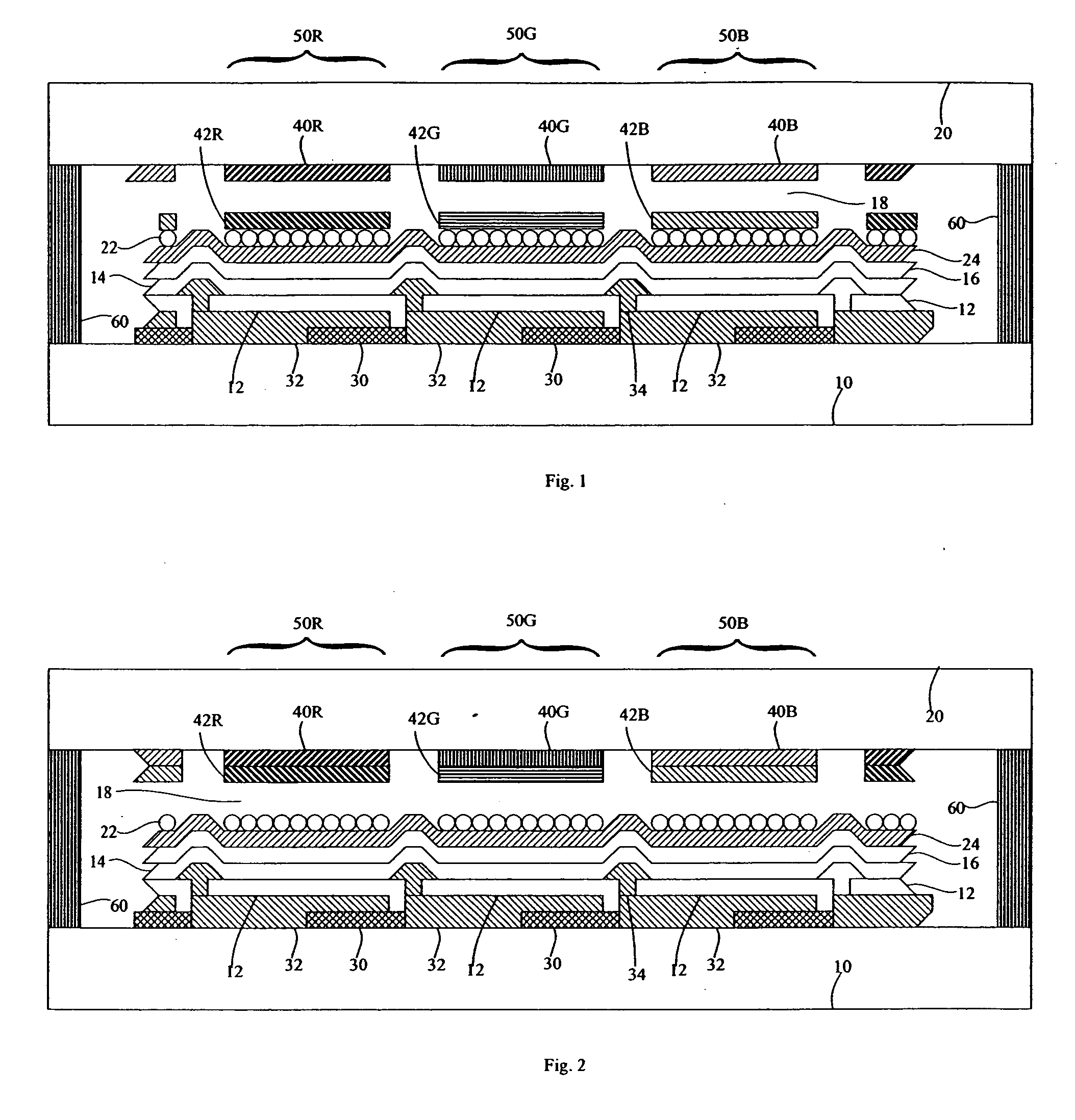
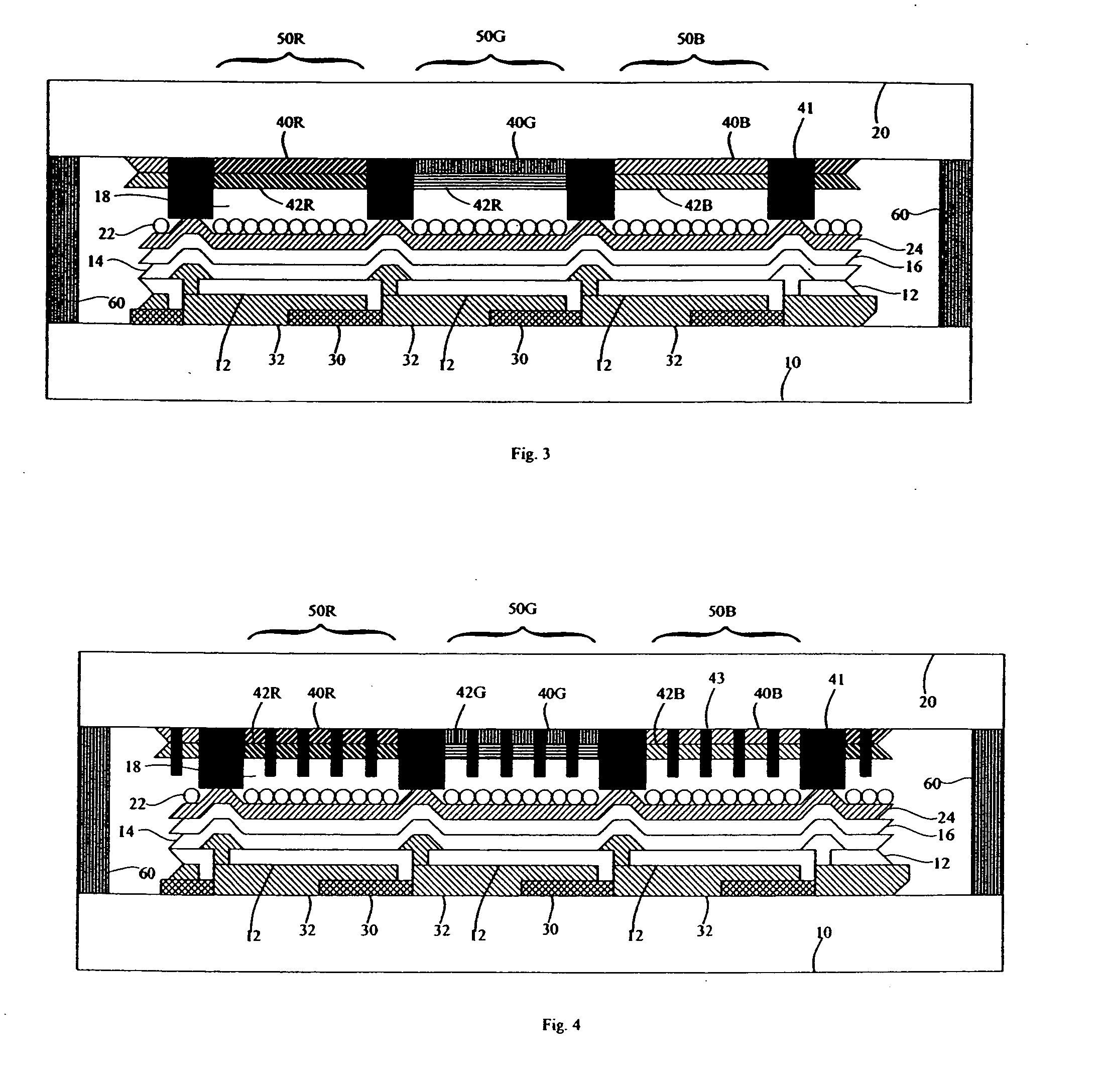
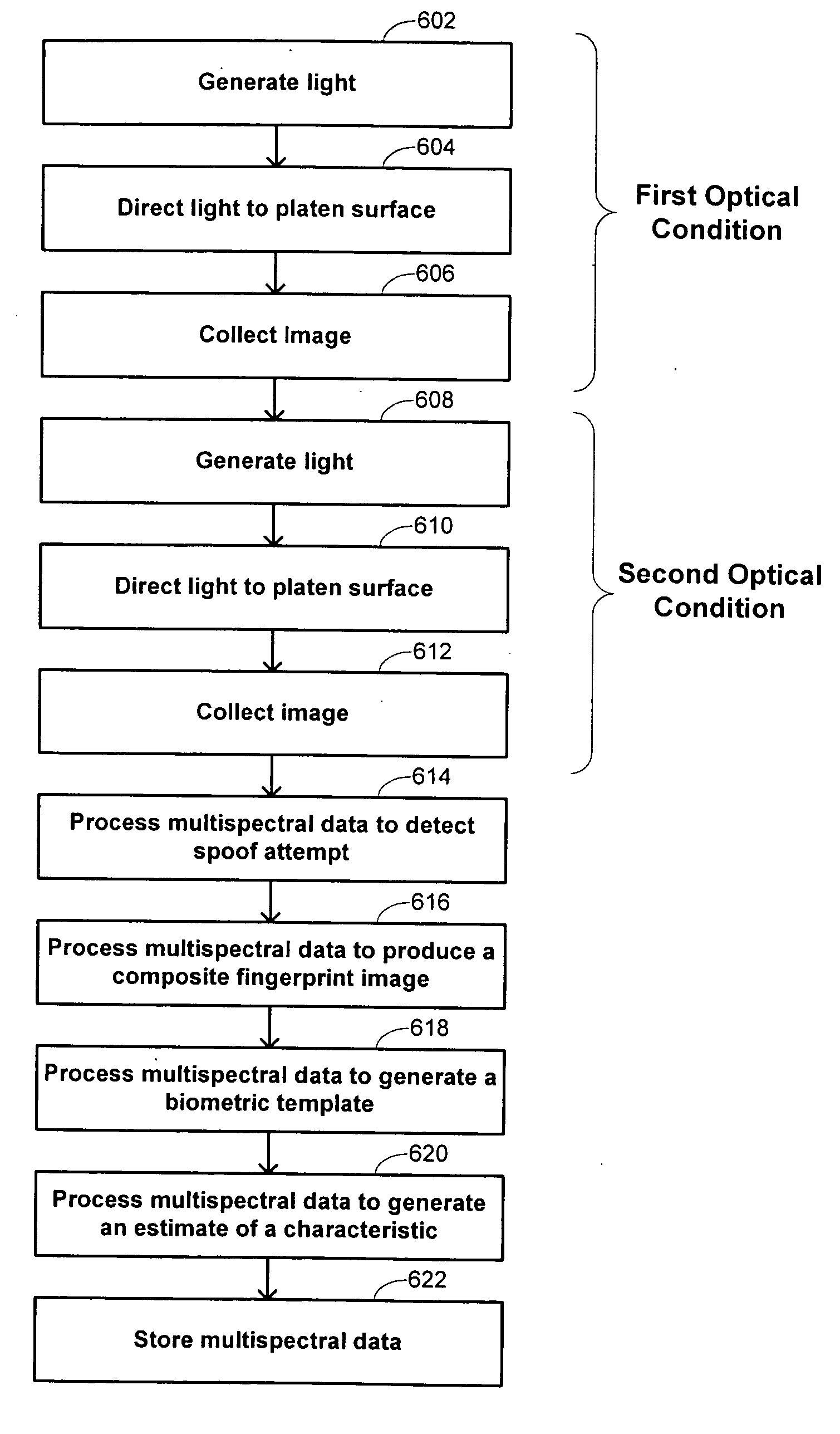
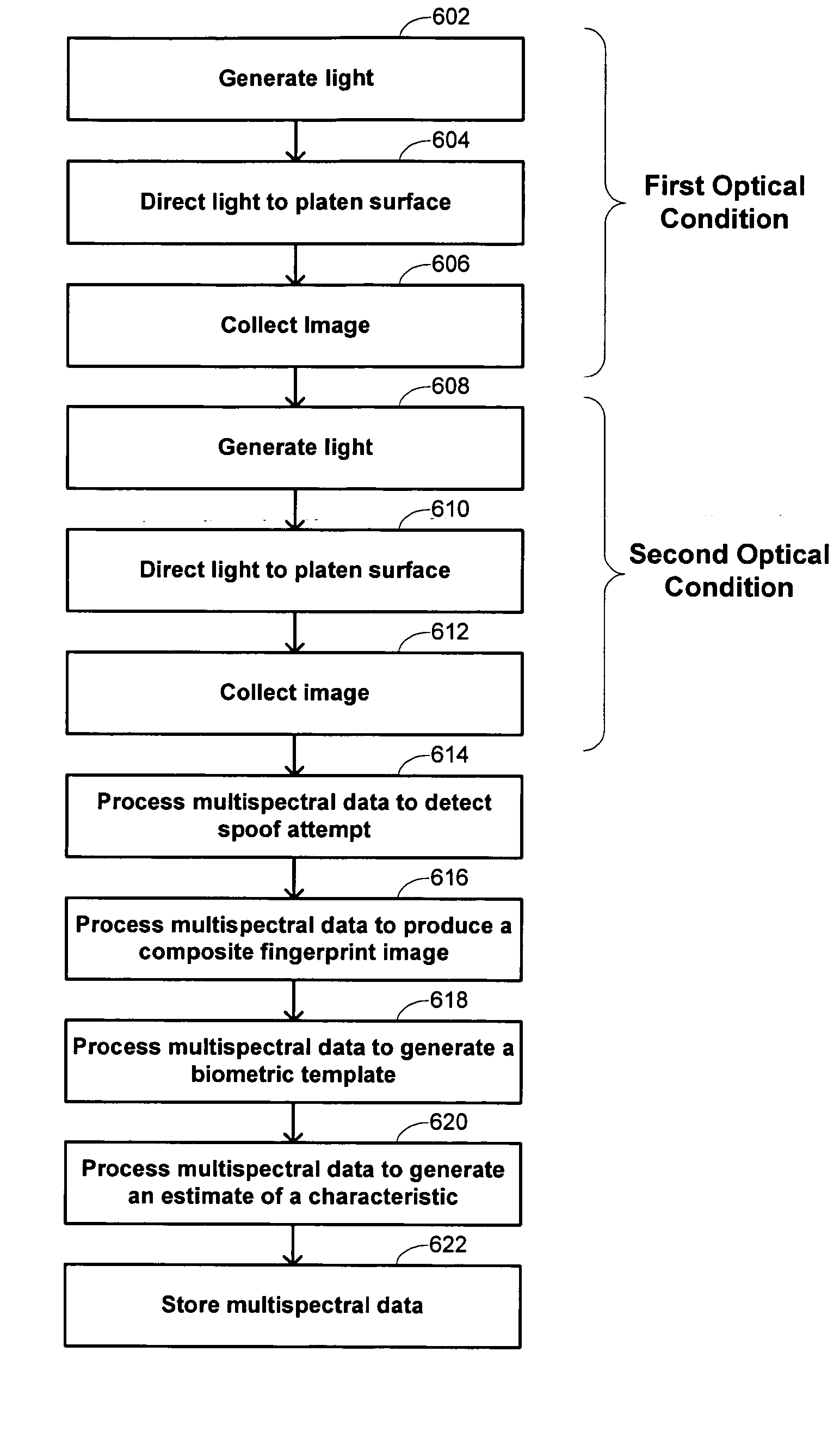
Multispectral imaging biometrics
Methods and systems are provided for performing a biometric measurement on an individual. A purported skin site of the individual is illuminated under a plurality of distinct optical conditions during a single illumination session. Light scattered beneath a surface of the purported skin site is received separately for each of the plurality of distinct optical conditions. A multispectral image of the purported skin site is derived from the received light. A biometric function is performed with the derived multispectral image.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
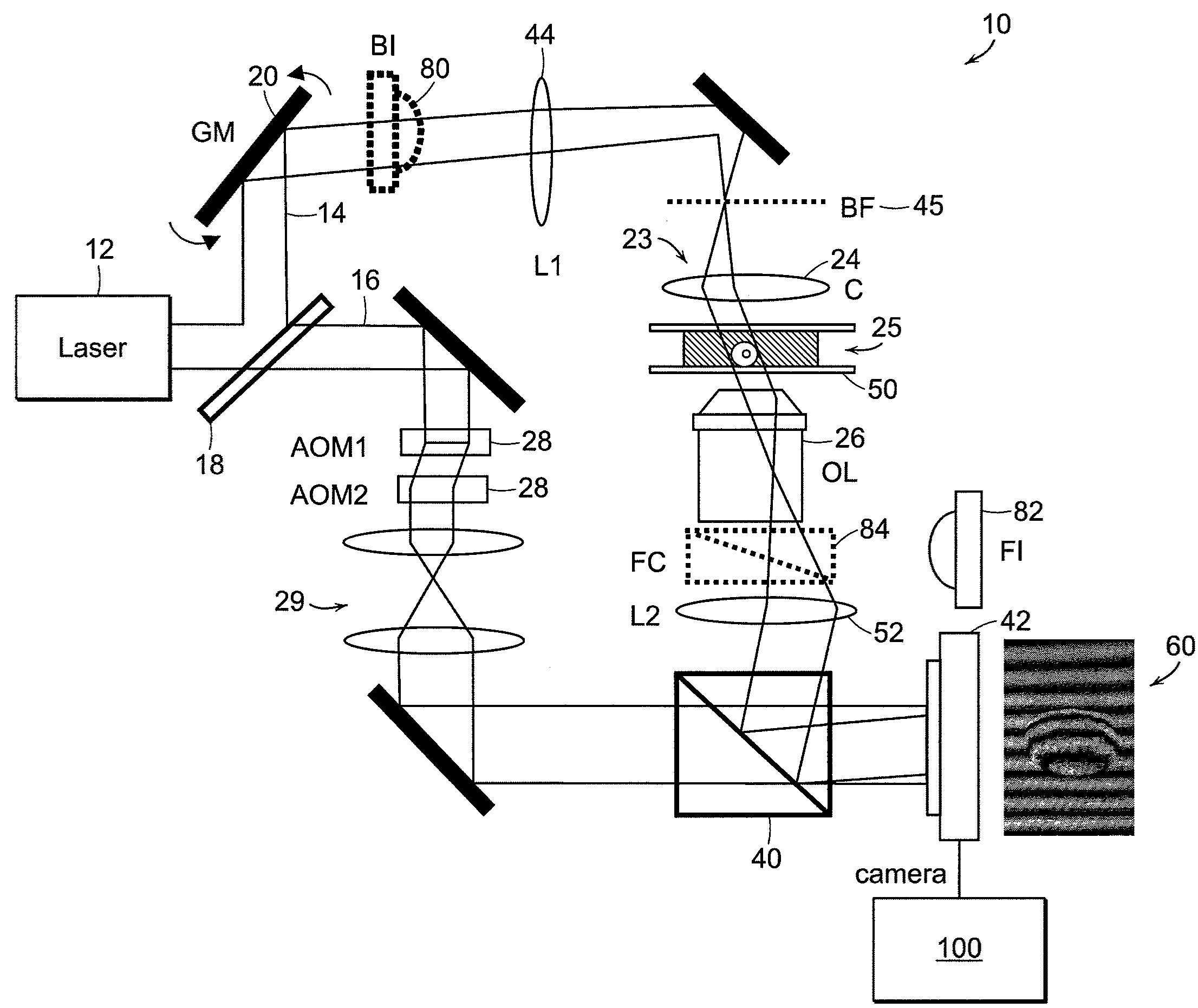
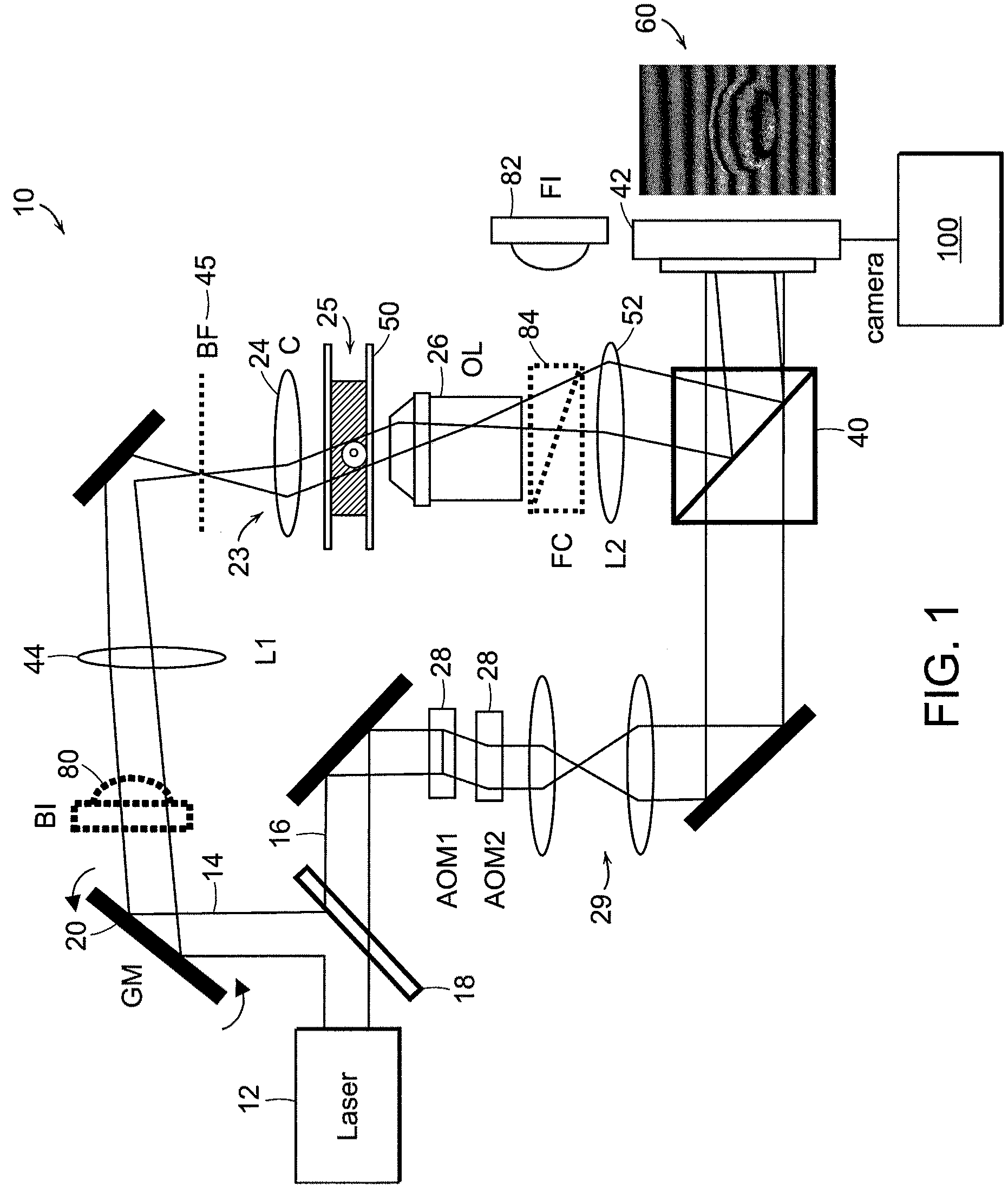
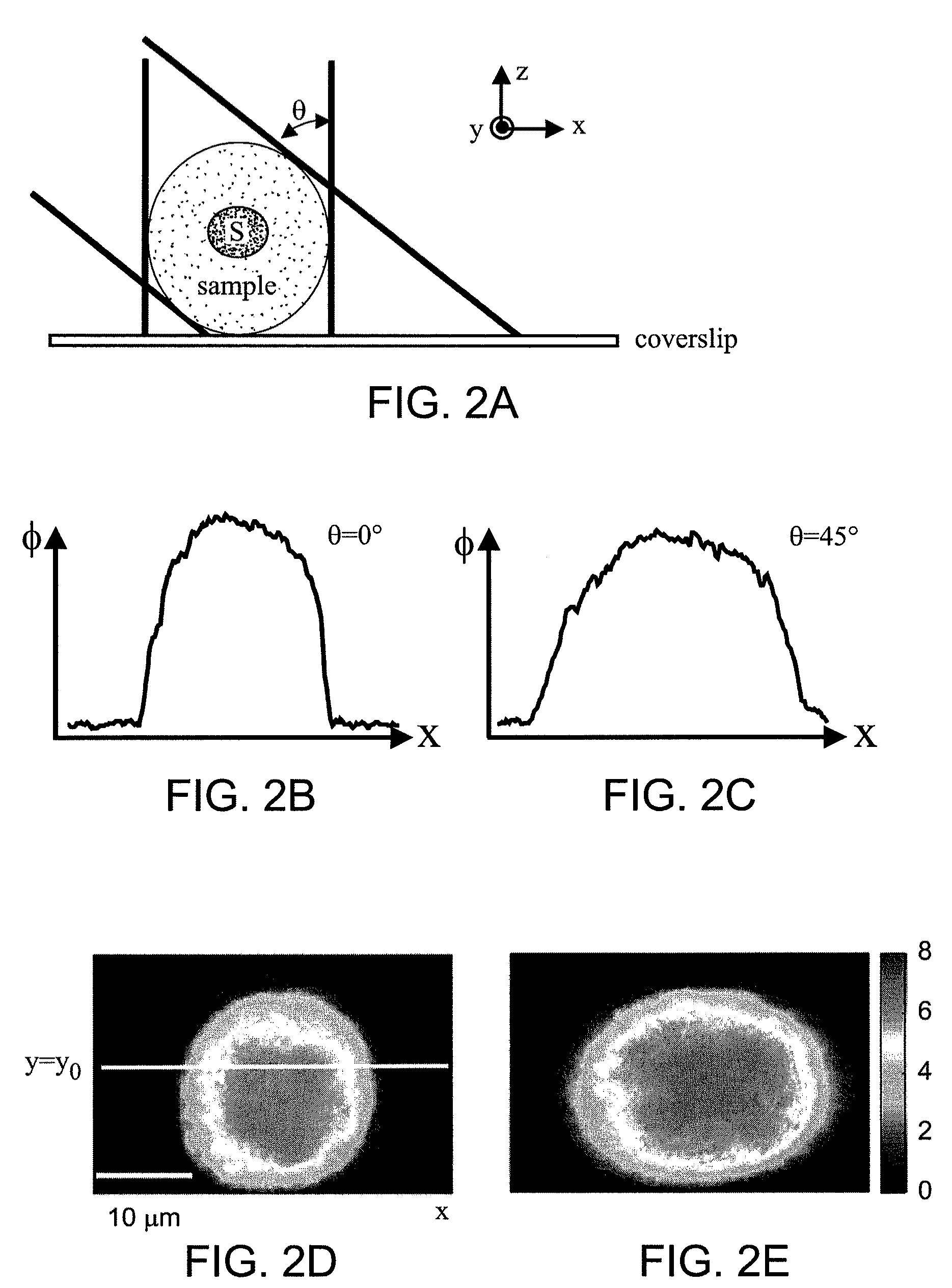
Tomographic phase microscopy
ActiveUS20090125242A1Phase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsRefractive indexOrganism
The present invention relates to systems and methods for quantitative three-dimensional mapping of refractive index in living or non-living cells, tissues, or organisms using a phase-shifting laser interferometric microscope with variable illumination angle. A preferred embodiment provides tomographic imaging of cells and multicellular organisms, and time-dependent changes in cell structure and the quantitative characterization of specimen-induced aberrations in high-resolution microscopy with multiple applications in tissue light scattering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
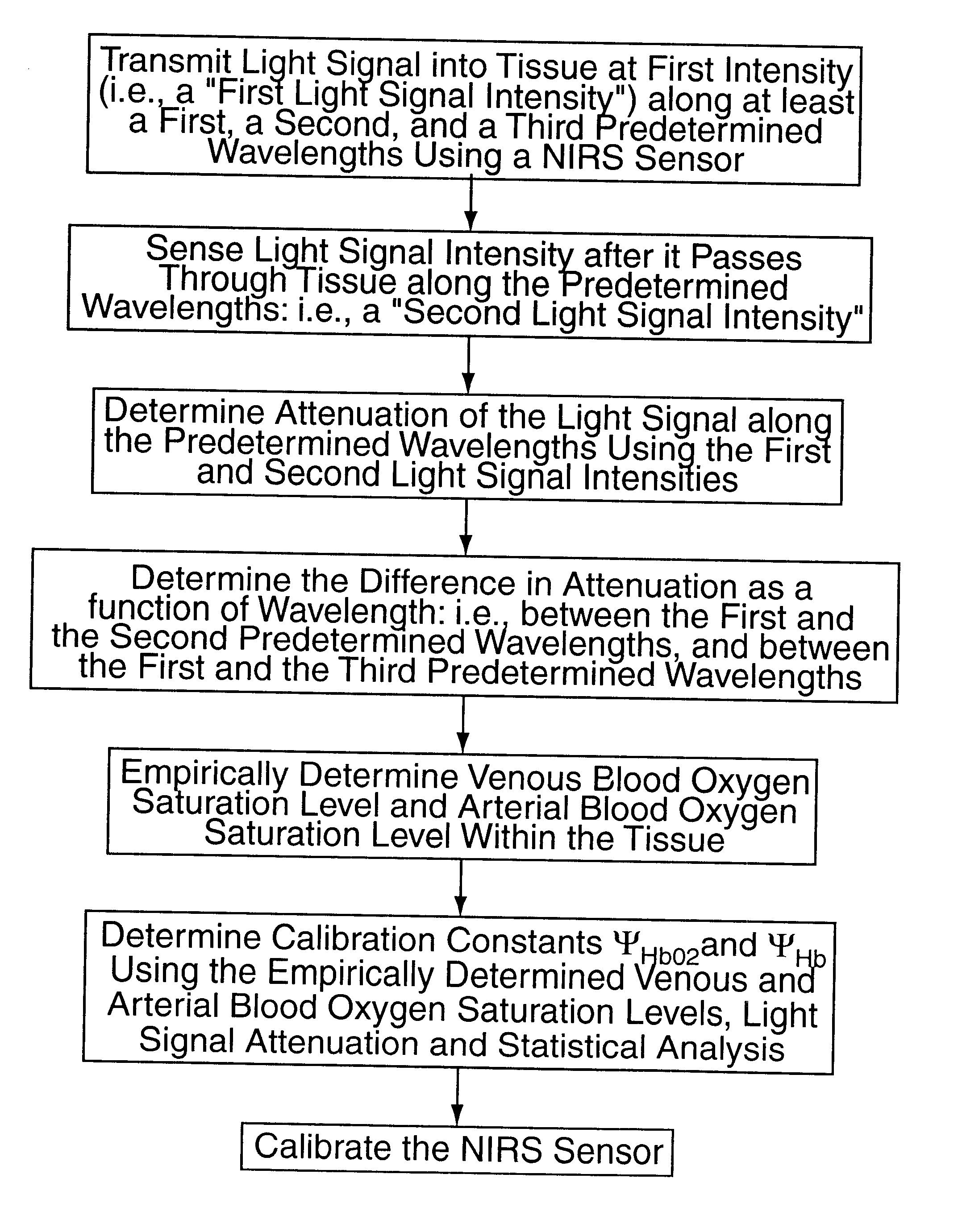
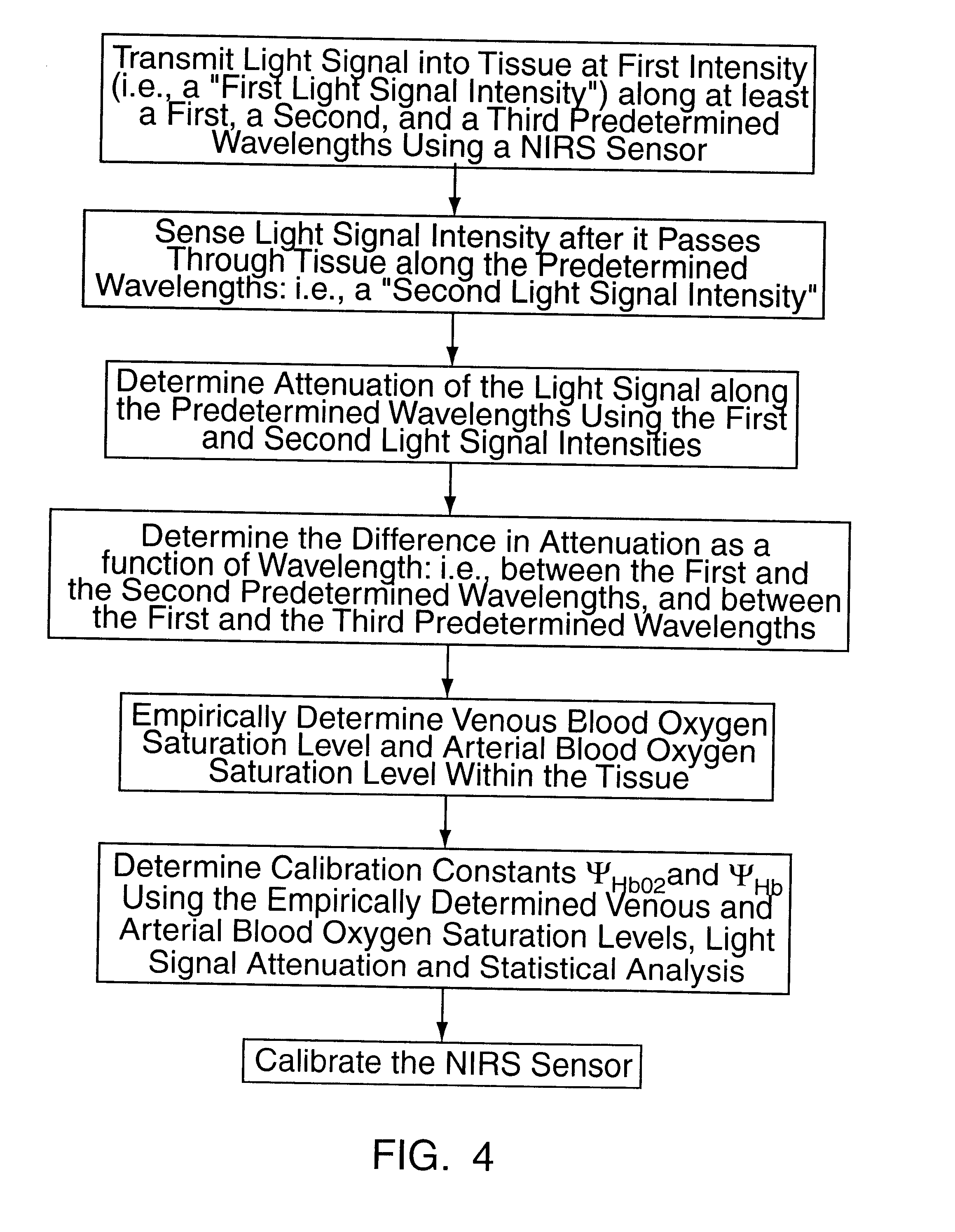
Tissue Oximetry Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20080015424A1Exclude influenceHigh precisionDiagnostic signal processingOptical sensorsVeinOptical property
An apparatus and method for determining tissue oxygenation such as arterial and venous oxygenation and cerebral oxygenation. In one embodiment the optical properties of tissue are determined using measured light attenuations at a set of wavelengths. By choosing distinct wavelengths and using light attenuation information, the influence of variables such as light scattering, absorption and other optical tissue properties can be minimized.
Owner:BERNREUTER PETER
Systems for inspection of patterned or unpatterned wafers and other specimen
ActiveUS7068363B2Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationLighting systemLight scattering
Systems for inspection of patterned and unpatterned wafers are provided. One system includes an illumination system configured to illuminate the specimen. The system also includes a collector configured to collect light scattered from the specimen. In addition, the system includes a segmented detector configured to separately detect different portions of the light such that azimuthal and polar angular information about the different portions of light is preserved. The detector may also be configured to produce signals representative of the different portions of the light. The system may also include a processor configured to detect defects on the specimen from the signals. In another embodiment, the system may include a stage that is configured to rotate and translate the specimen. In one such embodiment, the system may also include an illumination system configured to scan the specimen in a wide scan path during rotation and translation of the specimen.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method for non-invasive spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
InactiveUS6456862B2Non-invasive determinationRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsPresent methodVariable Characteristic
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Top-emitter OLED device structure and method
ActiveUS20070200492A1Improve performanceLow costDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsRefractive indexOLED
A top-emitting OLED device, comprising: one or more OLEDs formed on a substrate; a light-scattering layer formed over the one or more OLEDs; a transparent cover; one or more color filters formed on the transparent cover; a color-conversion material layer formed over the color filters, or formed over or integral with the light-scattering layer; wherein the substrate is aligned and affixed to the transparent cover so that the locations of the color filters and color conversion material correspond to the location of the OLEDs, and the color-conversion material layer, color filters, and the light-scattering layer are between the cover and substrate, and a low-index gap is formed between the light-scattering layer and the color filters, with no light-scattering layer being positioned between the color conversion material layer and the low-index gap.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Multispectral liveness determination
ActiveUS20050265585A1Programme controlElectric signal transmission systemsLivenessMultispectral image
Methods and systems are provided for determining a liveness state of purported tissue. The purported tissue is illuminated under a plurality of distinct optical conditions during a single illumination session. Light scattered from the purported tissue is received separately for each of the plurality of distinct optical conditions. A multispectral image of the purported tissue is derived from the received light. It is verified that the derived multispectral image is consistent with living tissue.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
Line profile asymmetry measurement using scatterometry
InactiveUS6856408B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerLength wave
A method of and apparatus for measuring line profile asymmetries in microelectronic devices comprising directing light at an array of microelectronic features of a microelectronic device, detecting light scattered back from the array comprising either or both of one or more angles of reflection and one or more wavelengths, and comparing one or more characteristics of the back-scattered light by examining data from complementary angles of reflection or performing a model comparison.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
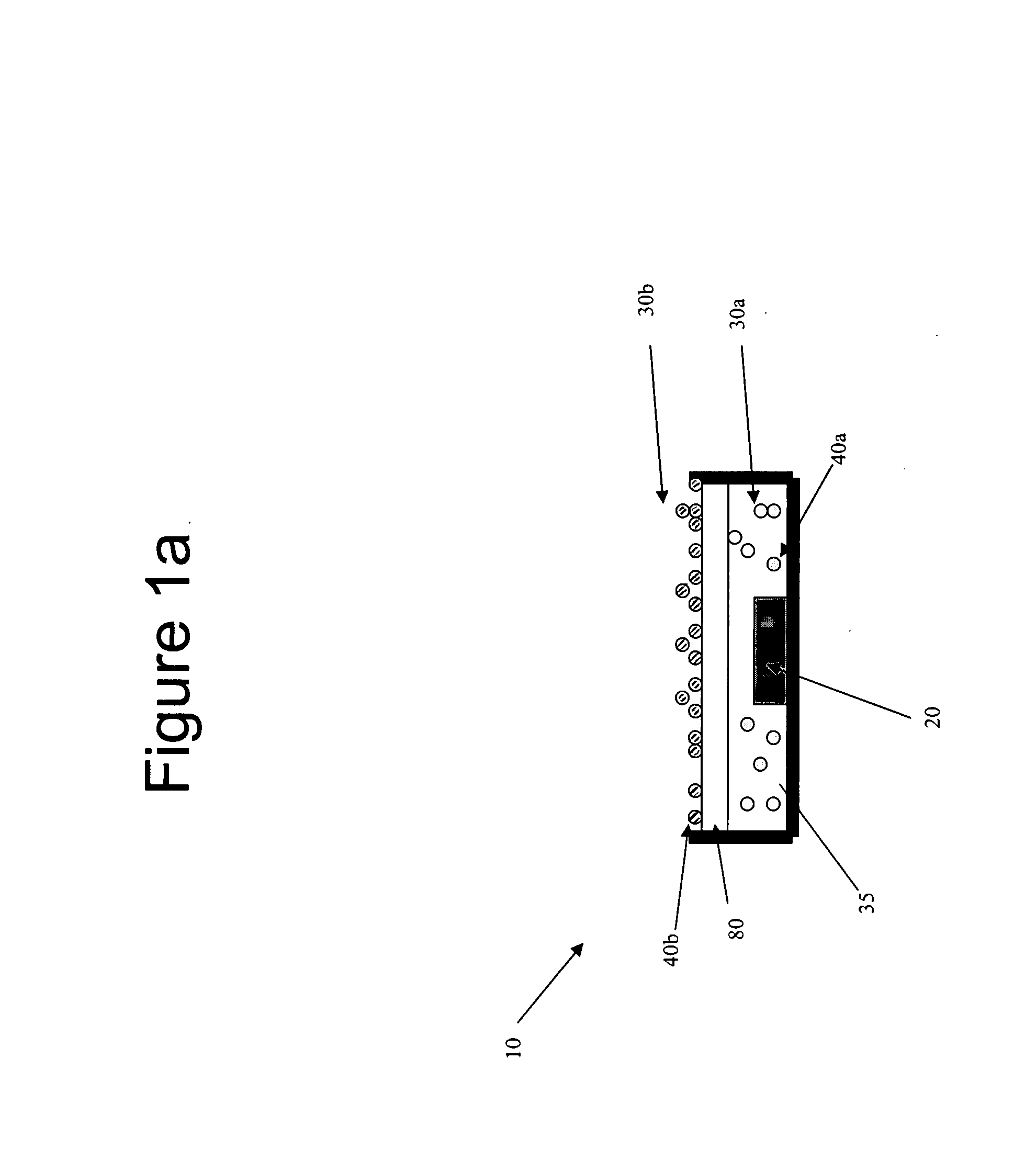
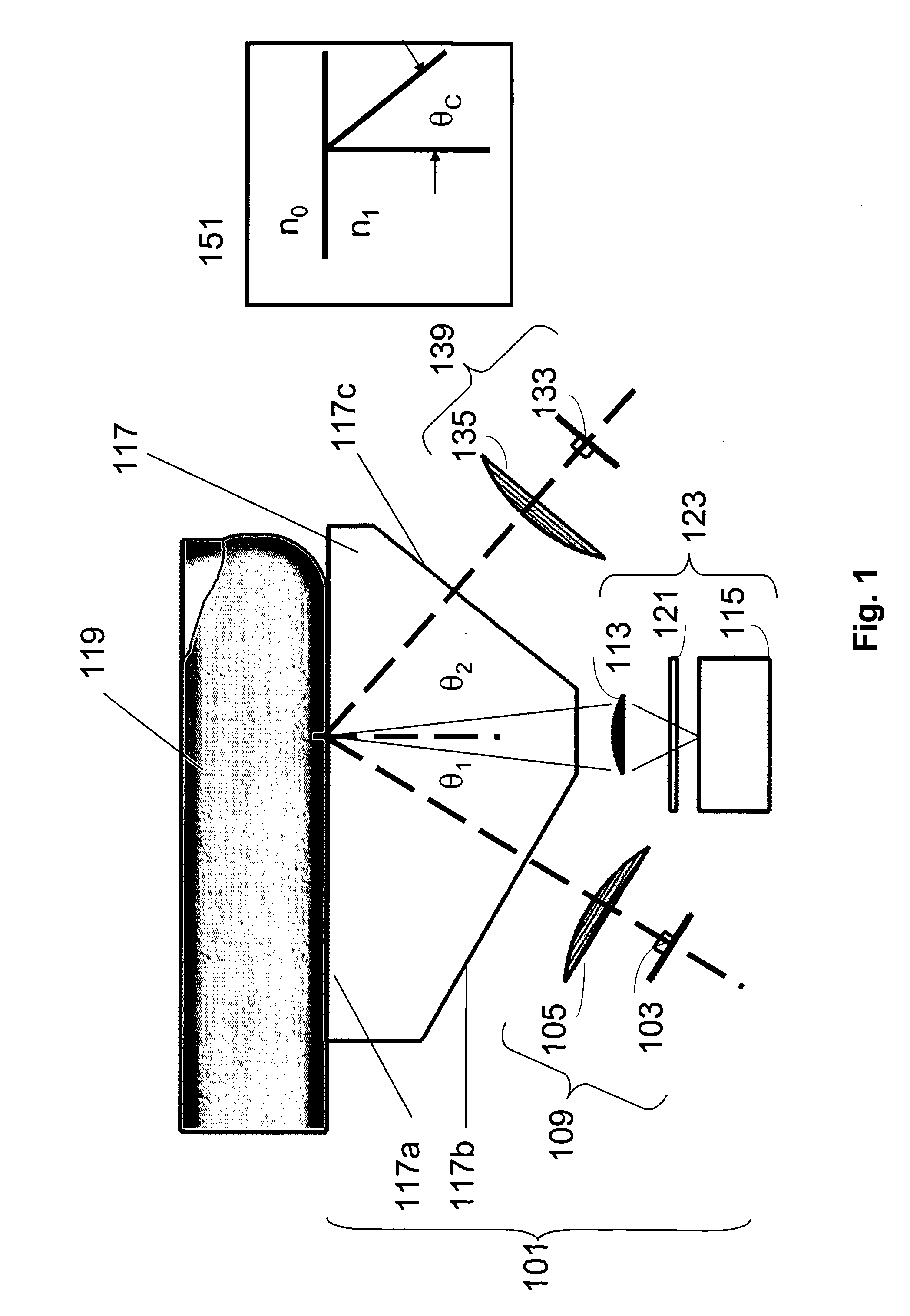
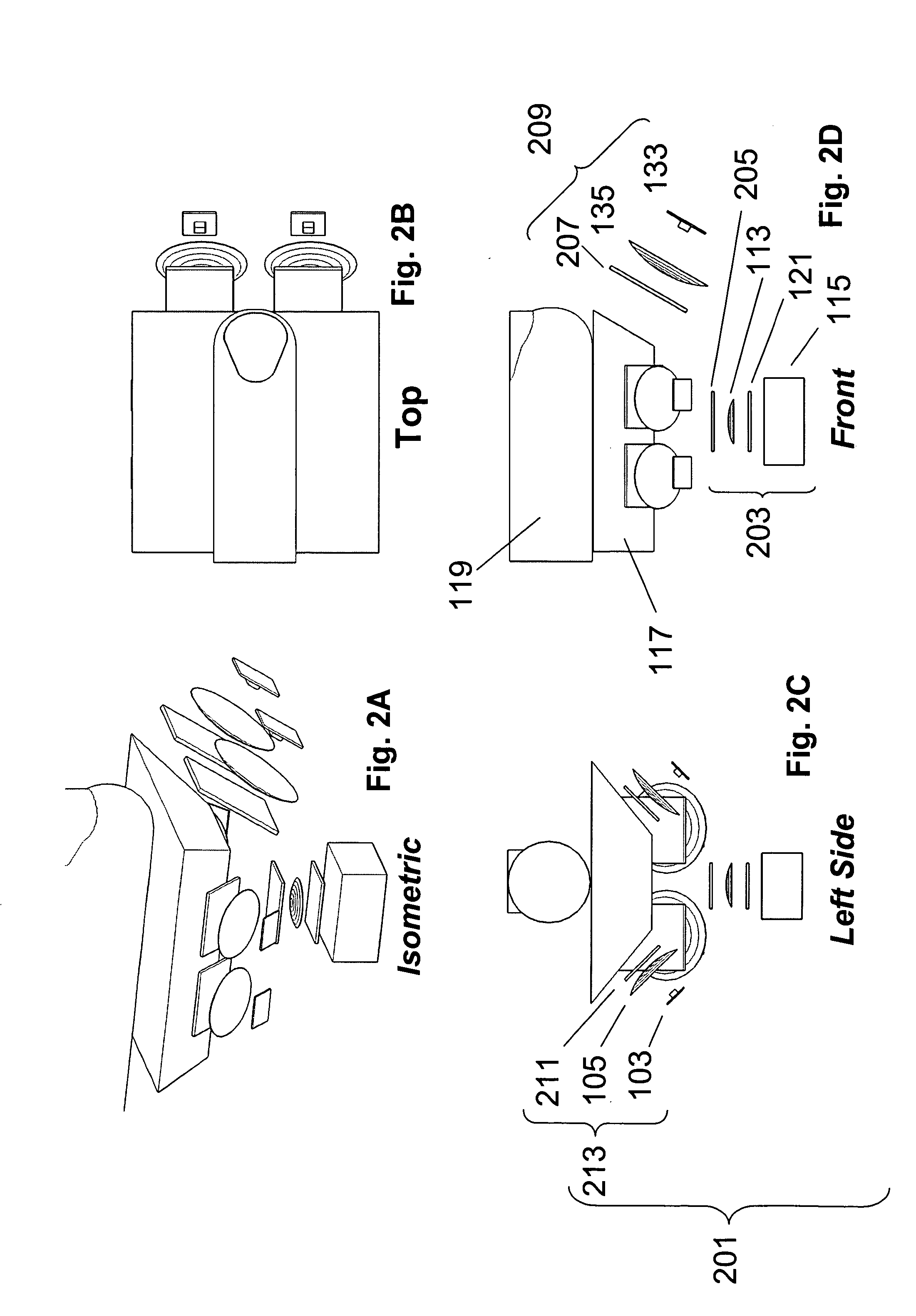
Multispectral biometric imaging
ActiveUS20050265586A1Programme controlElectric signal transmission systemsMultispectral imageBiometrics
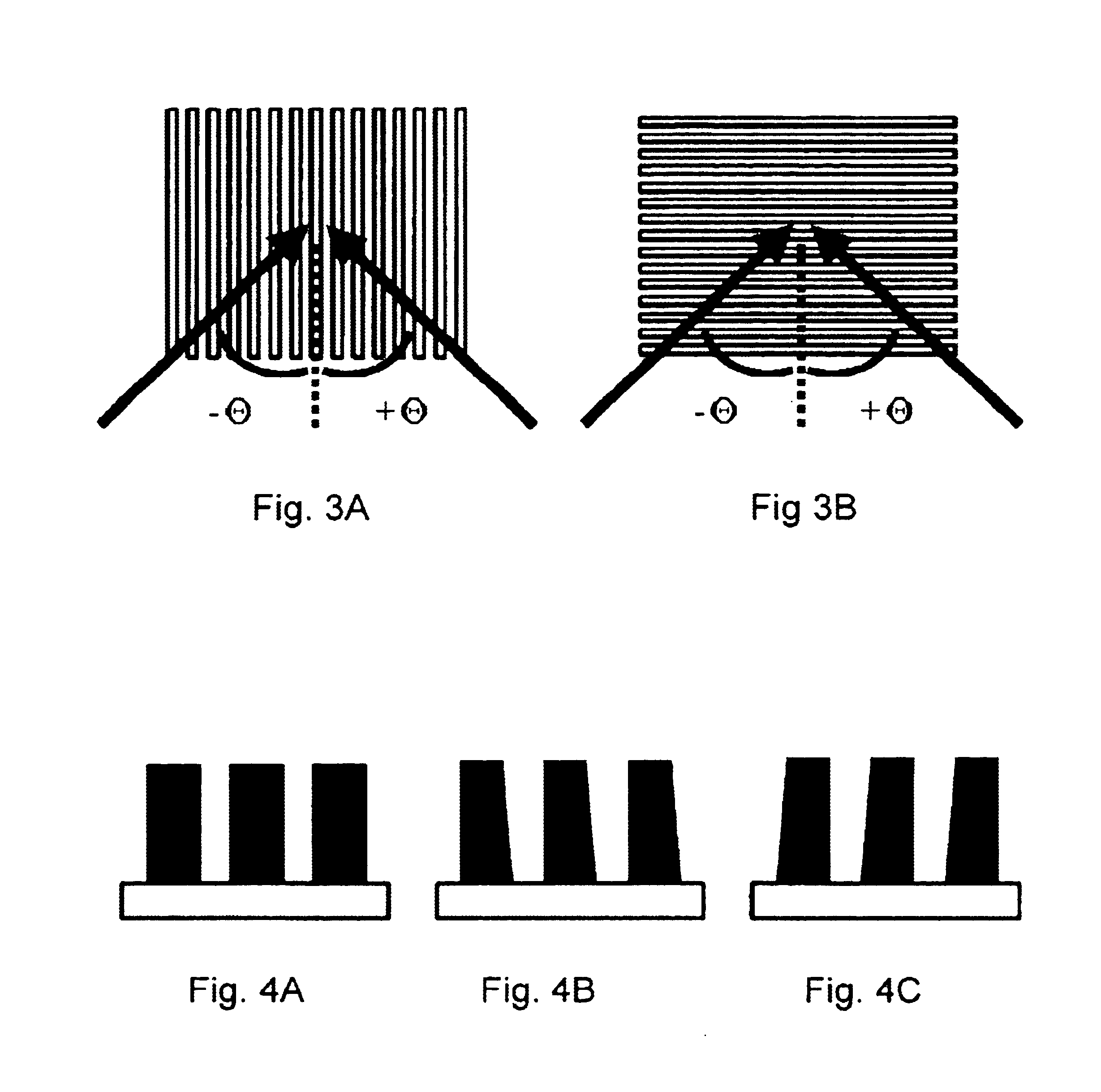
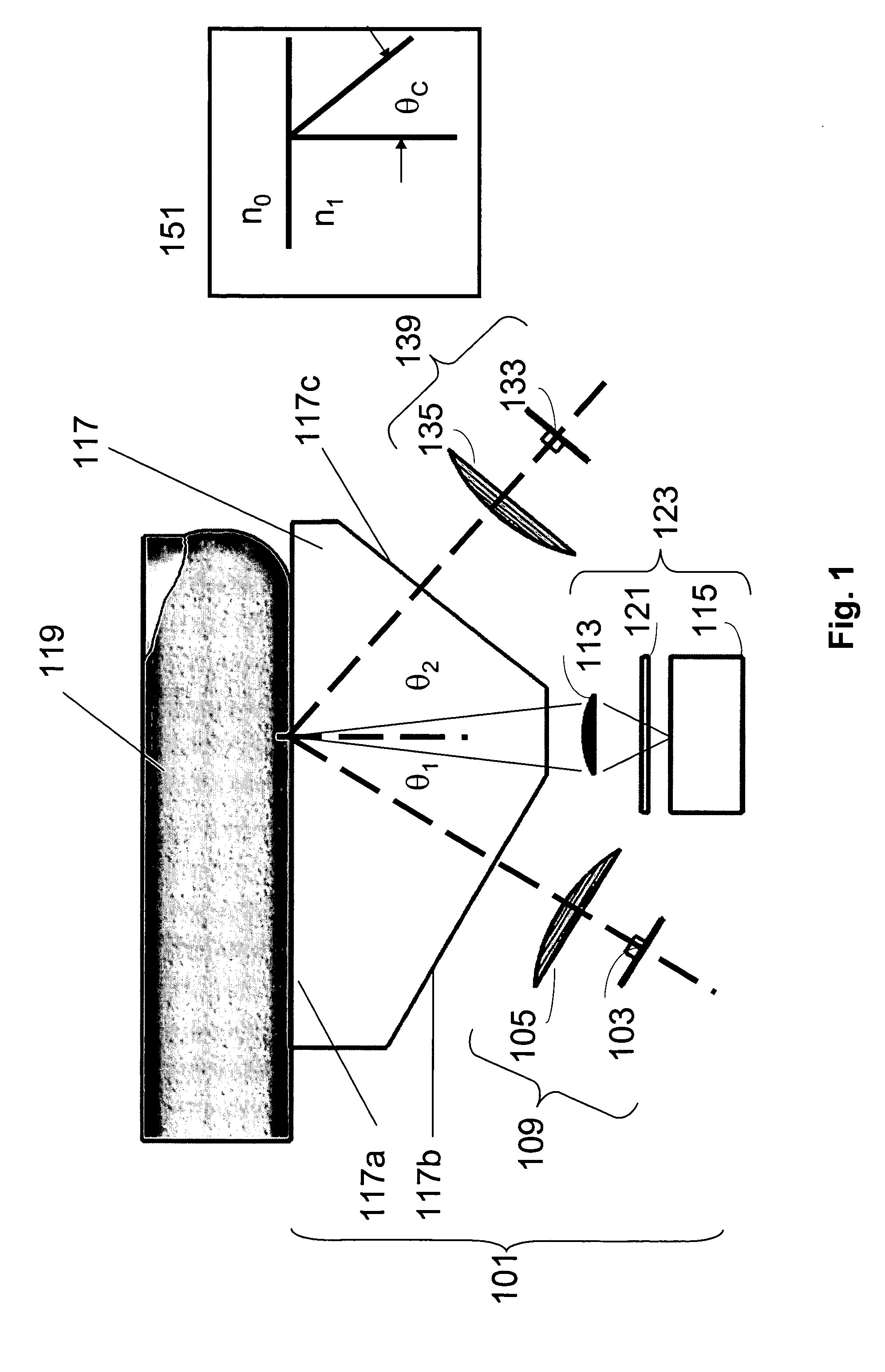
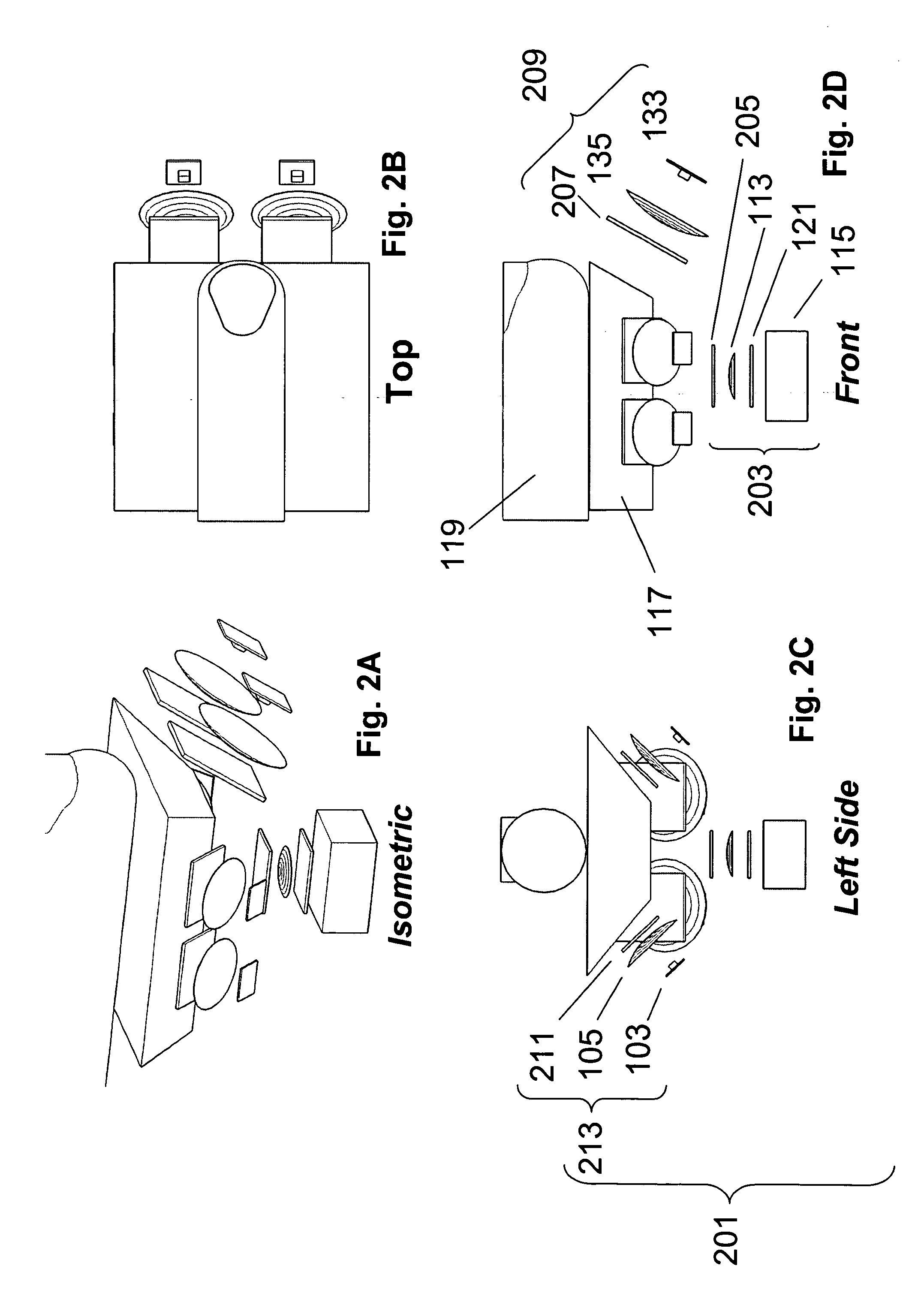
Methods and systems are provided for performing a biometric measurement on an individual. A purported skin site of the individual disposed relative to a platen is illuminated under distinct optical conditions during a single illumination session. At least one of the optical conditions includes illuminating the purported skin site with light at an angle greater than a critical angle defined by an interface of the platen with an external environment. At least another of the distinct optical conditions includes illuminating the purported skin site with light at an angle less than the critical angle. Light scattered from the purported skin site is received separately for each of multiple optical conditions to derive a multispectral image of the purported skin site.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
Organic light-emitting device having enhanced light extraction efficiency
InactiveUS6965197B2Light extraction efficiency can be improvedPlanar light sourcesDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic light emitting deviceOrganic layer
An enhanced light extraction OLED device including a transparent substrate; light scattering layer disposed over a first surface of the transparent substrate; a transparent first electrode layer disposed over the light scattering layer; an organic EL element disposed over the transparent first electrode layer and including one or more organic layers but at least one light emitting layer in which light is produced; and a transparent second electrode layer disposed over the organic EL element.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Speckle-image-based optical position transducer having improved mounting and directional sensitivities
InactiveUS6642506B1Reduce sensitivityAvoid smearingSlide gaugesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage detectionRelative motion
A speckle readhead includes a light source that outputs light towards an optically rough surface. Light scattered from this surface contains speckles. The scattered light is imaged onto an image detector, captured and stored. Subsequently, a second image is captured and stored. The two images are repeatedly compared at different offsets in a displacement direction. The comparison having the highest value indicates the amount of displacement between the readhead and the surface that occurred between taking the two images. An optical system of the readhead includes a lens and an aperture. The aperture can be round, with a diameter chosen so that the average size of the speckles is approximately equal to, or larger than, the dimensions of the elements of the image detector. The dimension of the aperture in a direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement can be reduced. Thus, the imaged speckles in that direction will be greater than the dimension of the image detector elements in that direction. Such a readhead is relatively insensitive to lateral offsets. The lens can be a cylindrical lens that magnifies the relative motion along the direction of displacement but does not magnify relative motions in the direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement. The optical system can also be telecentric. Thus, the readhead is relatively insensitive to both separation and relative motions between the readhead and the surface. The light source can be modulated to prevent smearing the speckles across the image detector. The light source can be strobed to freeze the image.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Electroluminescent device having improved light output
ActiveUS20070257608A1Improve light outputLow costDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesInorganic particleRefractive index
An electroluminescent device including a transparent substrate, a securing layer, a light scattering layer, an electroluminescent unit including a transparent electrode layer, a light emitting element including at least one light emitting layer, and a reflecting electrode layer in that order, wherein the light scattering layer includes one monolayer of inorganic particles having an index of refraction larger than that of the light emitting layer and wherein the securing layer holds the inorganic particles in the light scattering layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Enhanced electroluminescent sign
InactiveUS20060215958A1Signs improvedEfficiently directsCoupling light guidesIlluminated signsElectricityLightness
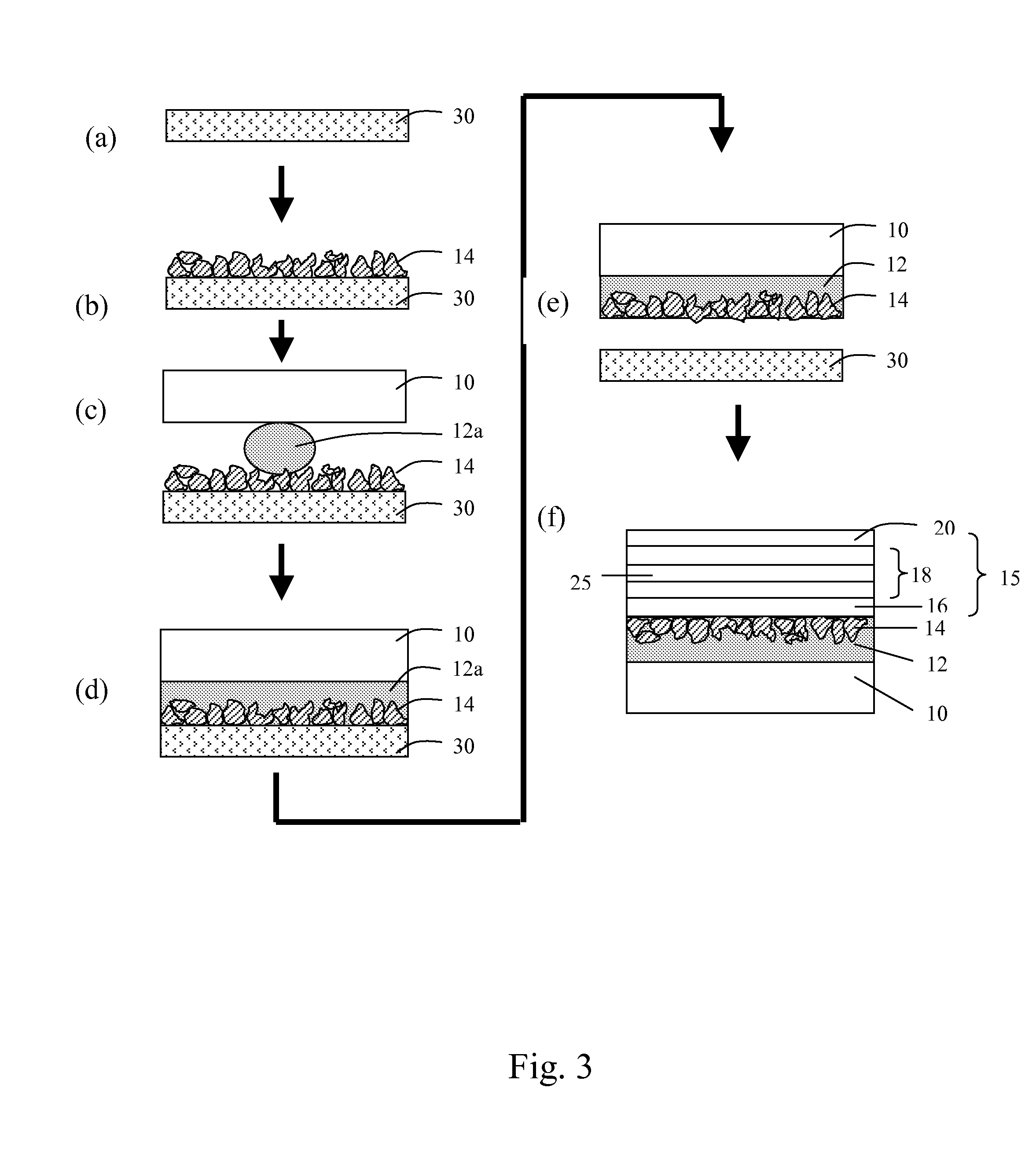
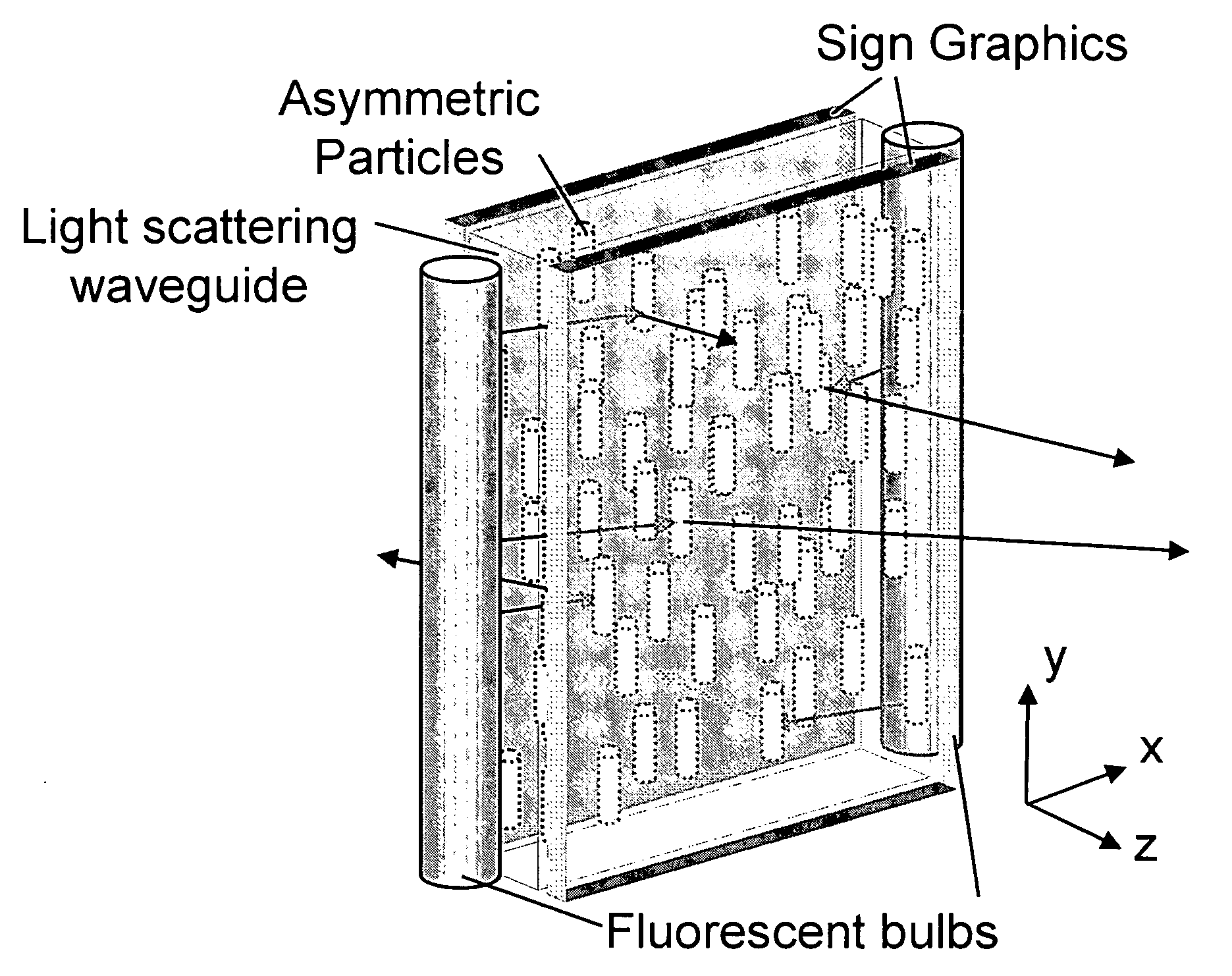
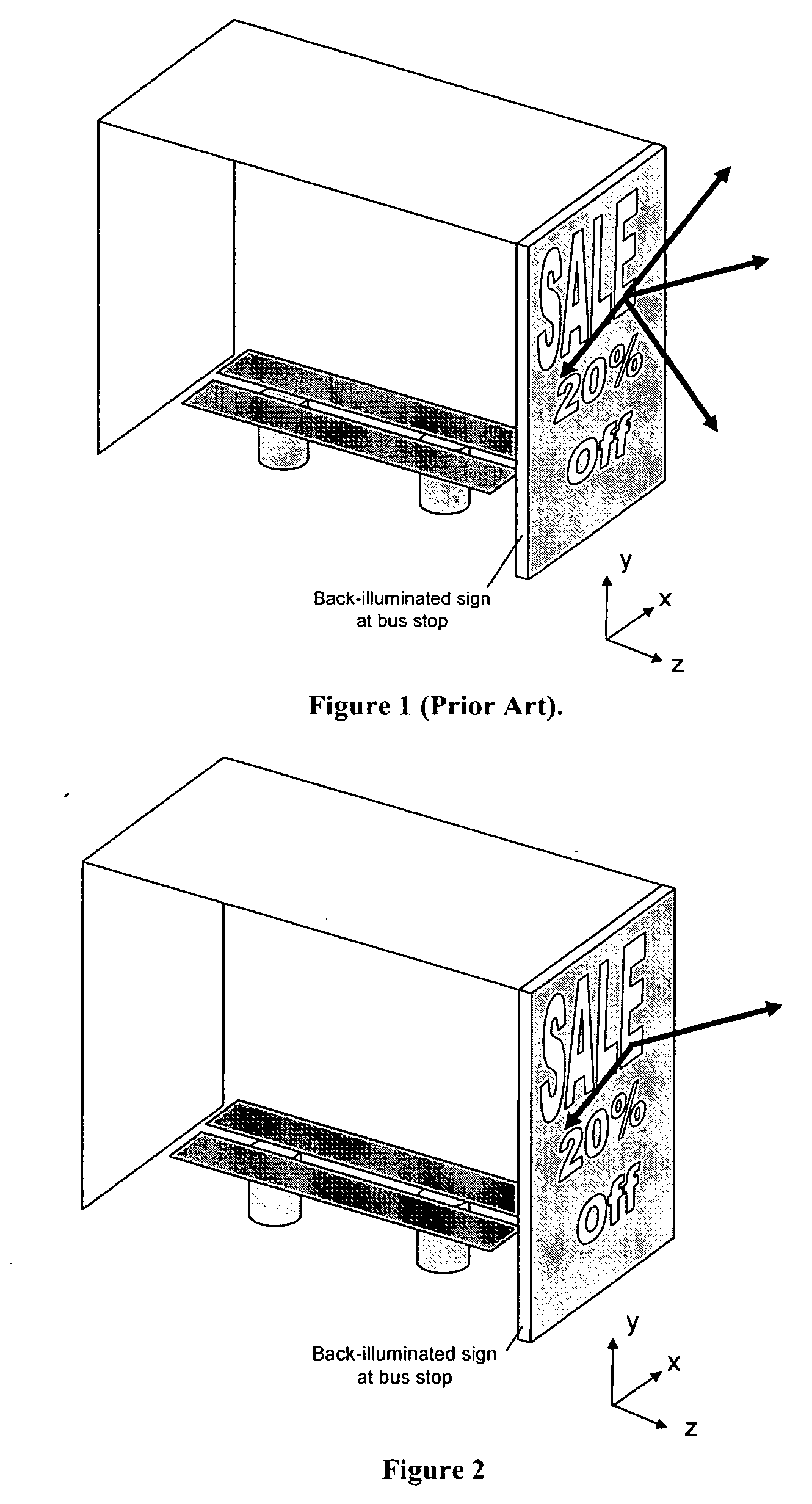
An enhanced electroluminescent sign containing a volumetric, anisotropic scattering element to control the angular spread of light from the sign and the spatial luminance uniformity of the sign. The anisotropic scattering element contains one or more regions of asymmetrically-shaped light scattering particles. The angular spread of light leaving a sign from a light emitting source can be efficiently controlled by using a thin, low cost, volumetric, anisotropic scattering elements to angularly and spatially distribute light, permitting the reduction in number of light sources, a reduction in power requirements, or a more tailored viewing angle.
Owner:FUSION OPTIX
Oled device having improved light output
ActiveUS20060186802A1Improve light outputImprove clarityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesRefractive indexLight-emitting diode
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device, comprising: a substrate; an OLED comprising first and second electrodes and one or more layers of organic light-emitting material formed between the electrodes, wherein at least one electrode comprises a transparent electrode, the transparent electrode and layer(s) of organic light-emitting material having a first refractive index range; and an encapsulating cover; wherein at least one of the substrate or cover comprises a transparent substrate or cover having a second refractive index and through which light from the OLED is emitted; and further comprising a light scattering layer located between the substrate and cover, and a transparent low-index element having a third refractive index lower than each of the first refractive index range and second refractive index and located between the scattering layer and the transparent substrate or cover.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
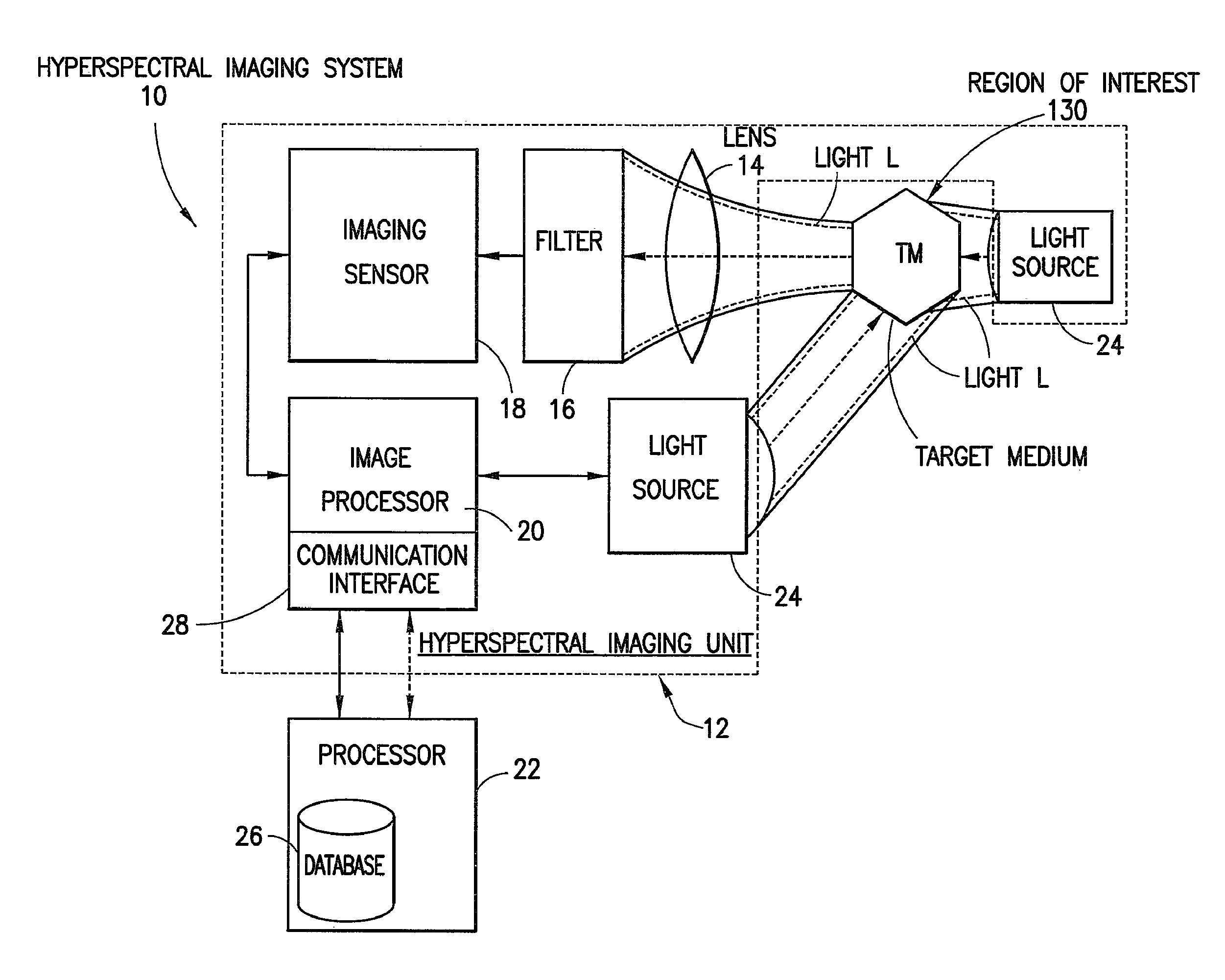
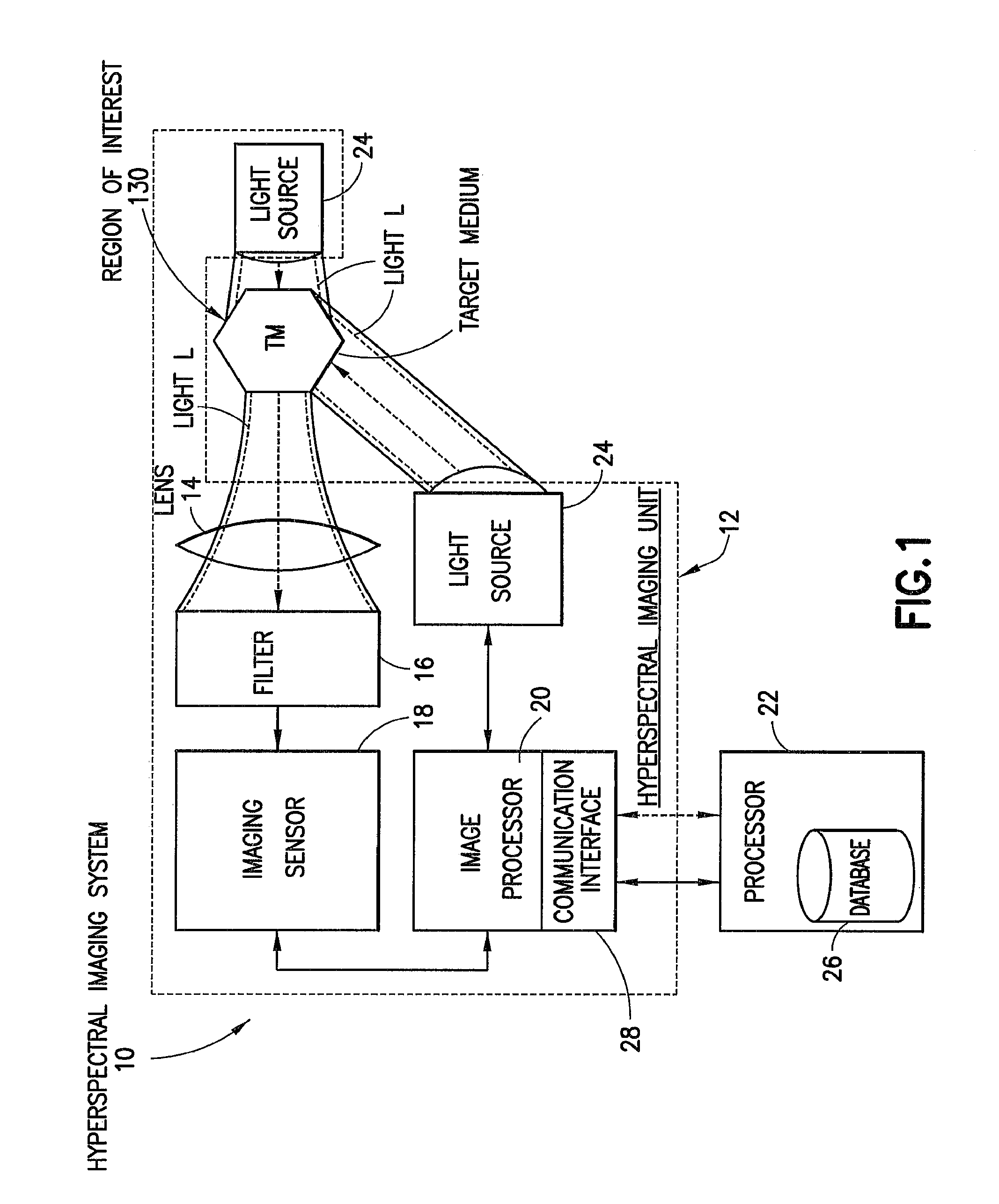
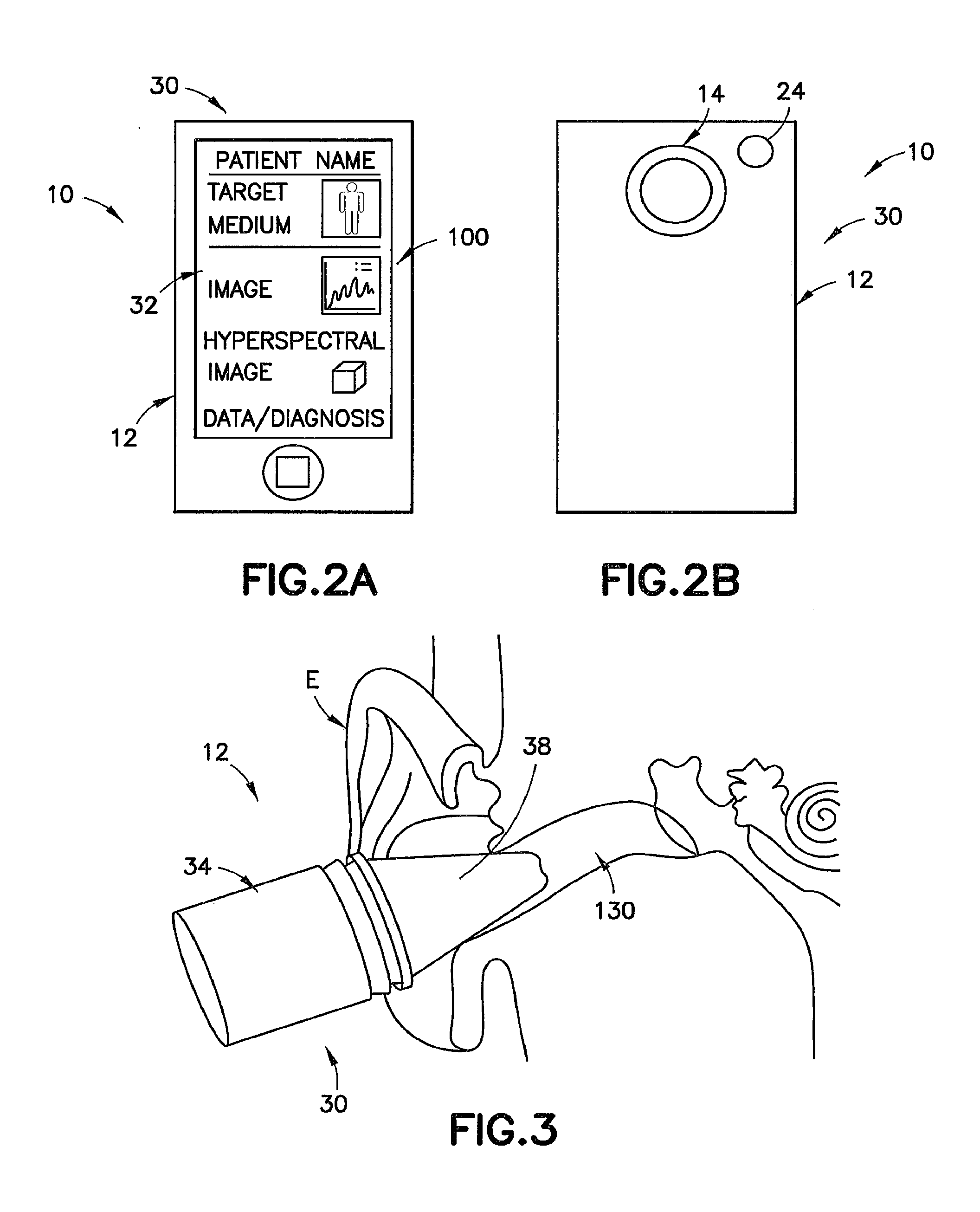
Hyperspectral imaging systems, units, and methods
InactiveUS20150044098A1Superior spectral resolutionImprove data acquisition speedTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometrySpectral bandsImaging data
A hyperspectral imaging system, including: at least one hyperspectral imaging unit, including: at least one lens configured to direct light scattered by, reflected by, or transmitted through a target medium to at least one hyperspectral filter arrangement configured to separate the light into discrete spectral bands; an imaging sensor to: receive the discrete spectral bands from the at least one hyperspectral filter arrangement; detect light by a plurality of pixels for each of the spectral bands; and generate electrical signals based at least in part on at least a portion of the light; and at least one image processor in communication with the at least one imaging sensor and configured to generate hyperspectral image data associated with the target medium; and at least one processor configured to determine biological data based at least partially on at least a portion of the hyperspectral image data.
Owner:SCANADU
Hygienic biometric sensors
Methods and systems for performing a biometric measurement on an individual are disclosed. A containment film is disposed between a skin site of the individual and a platen. Light is directed through the containment film to the skin site to illuminate the skin site under multiple distinct optical conditions. Light scattered from the skin site is received for the multiple optical conditions. A multispectral image of the skin site is derived from the received light. A biometric function is performed with the derived multispectral image.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
Wafer inspection system for distinguishing pits and particles
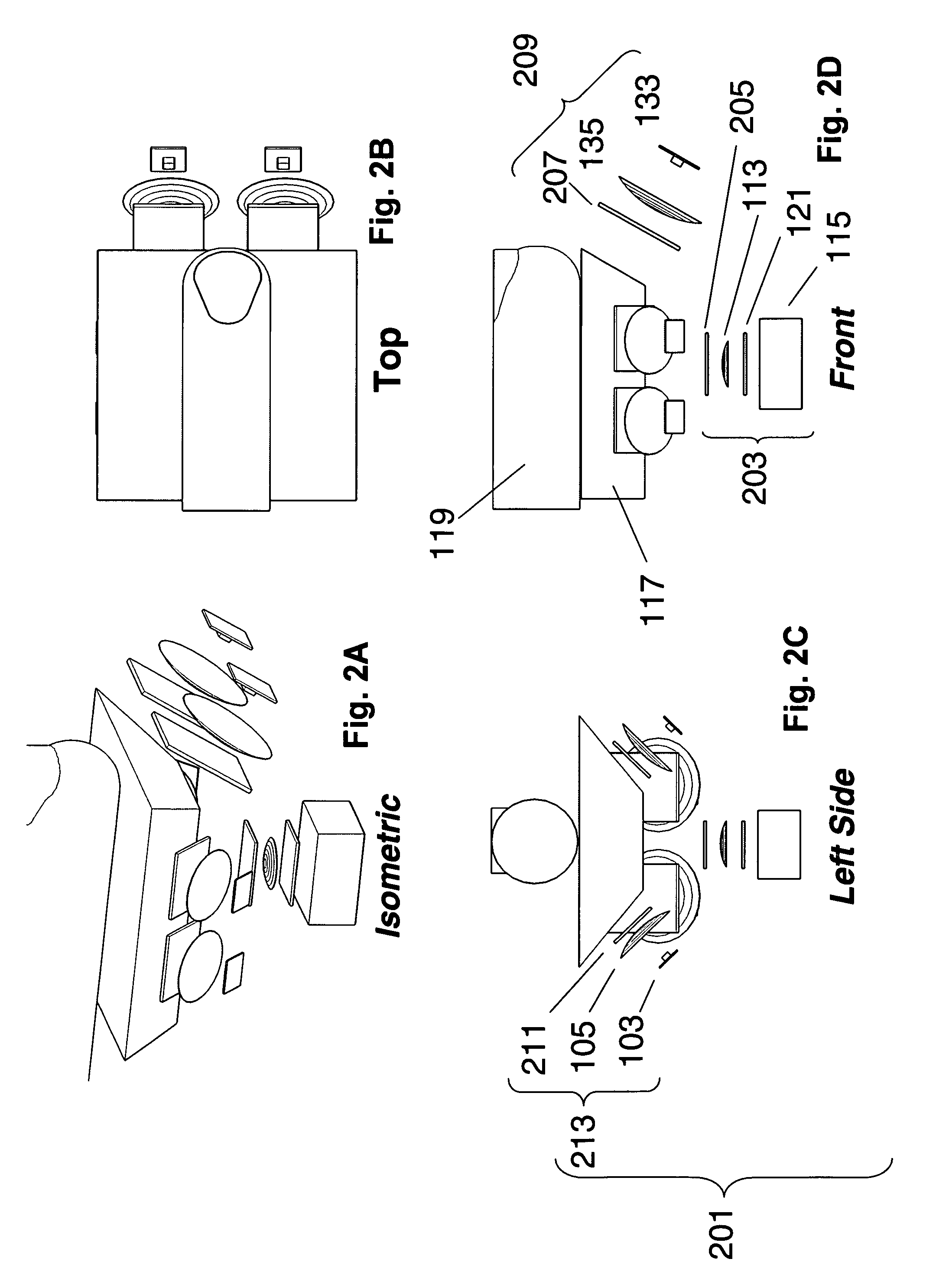
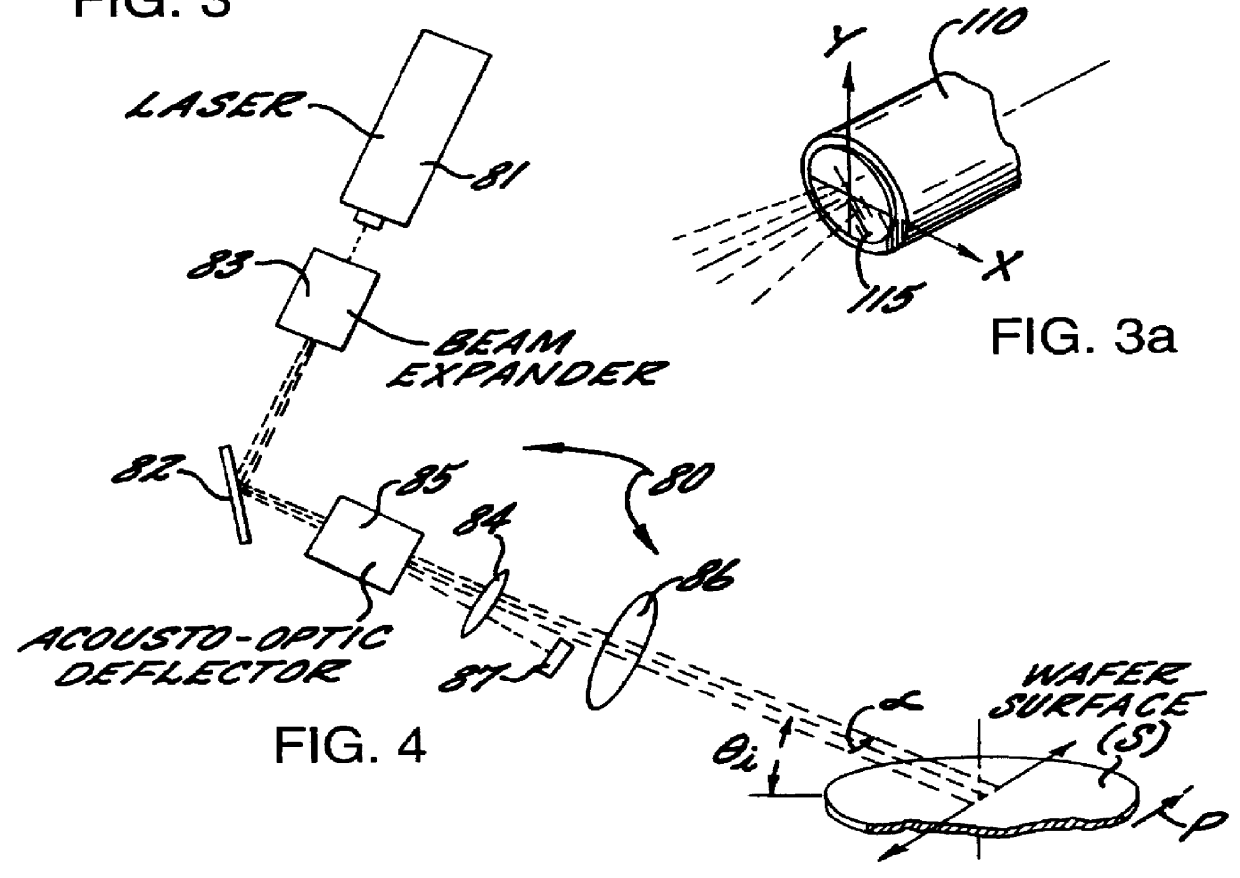
InactiveUS6118525AEasy to classifyEasy to identifySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInvestigating moving sheetsLight beamSilicon
A surface inspection system and method is provided which detects defects such as particles or pits on the surface of a workpiece, such as a silicon wafer, and also distinguishes between pit defects and particle defects. The surface inspection system comprises an inspection station for receiving a workpiece and a scanner positioned and arranged to scan a surface of the workpiece at the inspection station. The scanner includes a light source arranged to project a beam of P-polarized light and a scanner positioned to scan the P-polarized light beam across the surface of the workpiece. The system further provides for detecting differences in the angular distribution of the light scattered from the workpiece and for distinguishing particle defects from pit defects based upon these differences.
Owner:ADE OPTICAL SYST
Image display system
ActiveUS7336271B2Minimizing feelingColor television detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayLight scattering
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
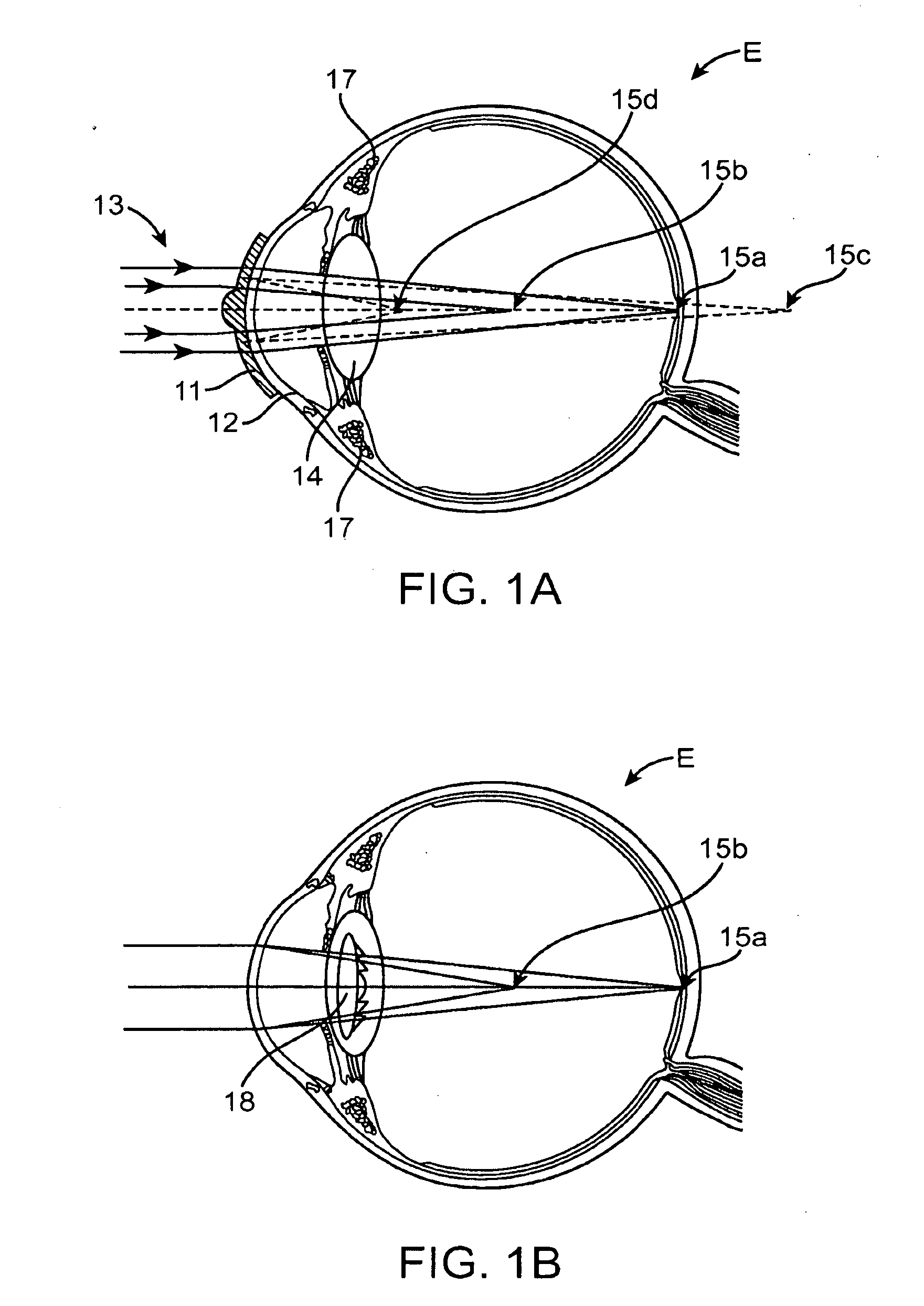
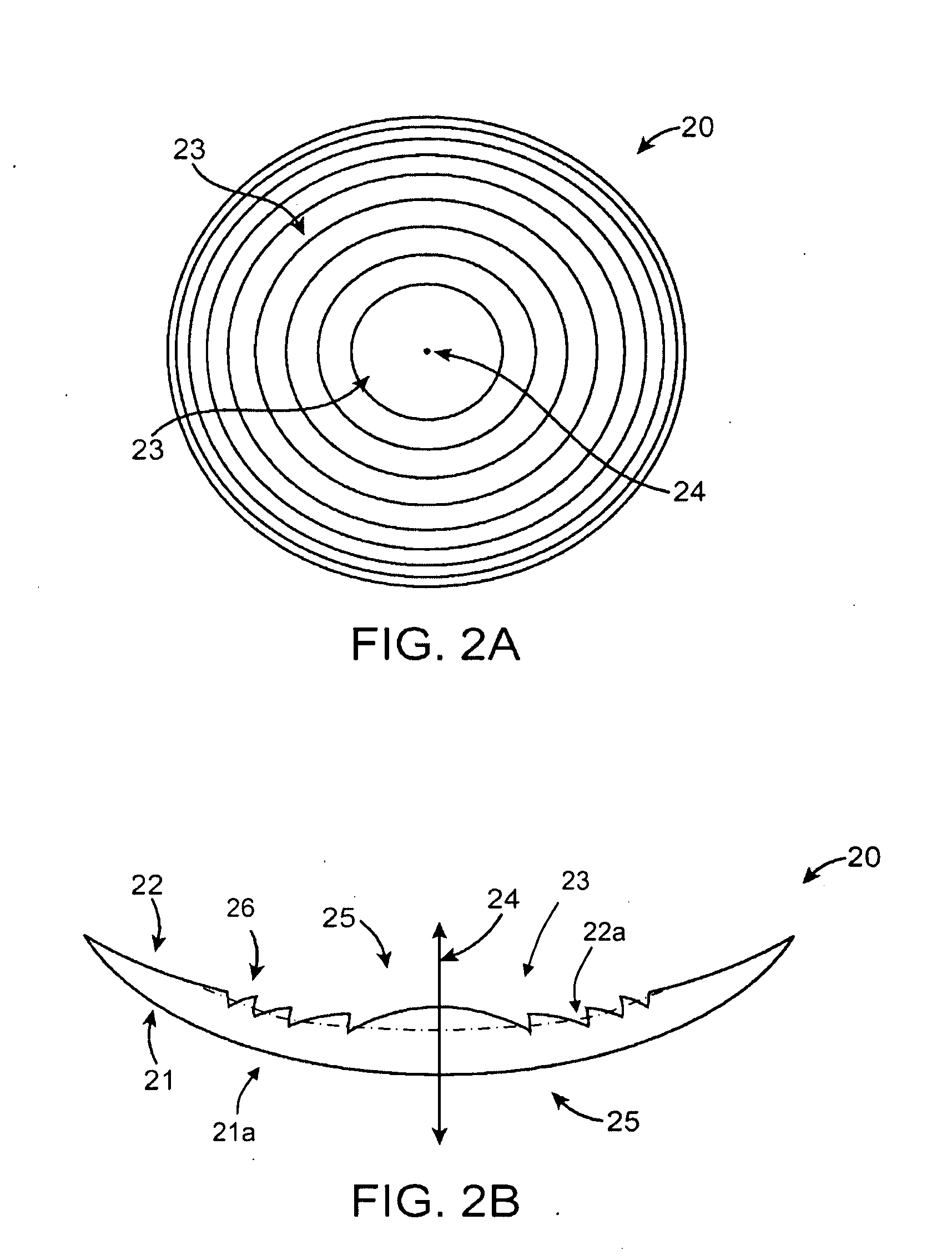
Diffractive lens exhibiting enhanced optical performance
ActiveUS20090268155A1Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsLight energyDiffractive lens
The present invention provides improved ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use. Monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses having reduced light scatter, improved light energy distribution properties, and / or other improvements in optical performance are provided. These properties are provided, at least in part, by the diffractive profiles of the invention, often having subtlety shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Smooth diffractive profiles may be used reduce light scatter. Diffractive profiles may be configured to limit the light energy in certain selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles of may additionally or alternatively vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com