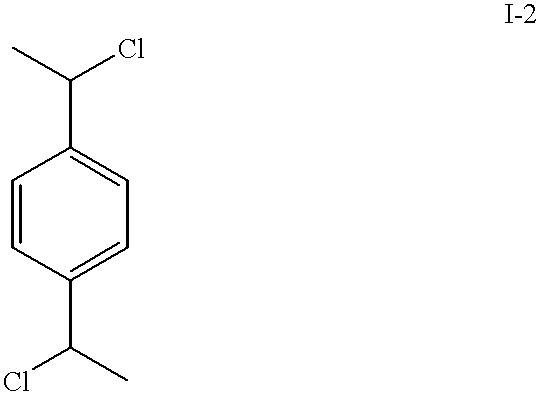
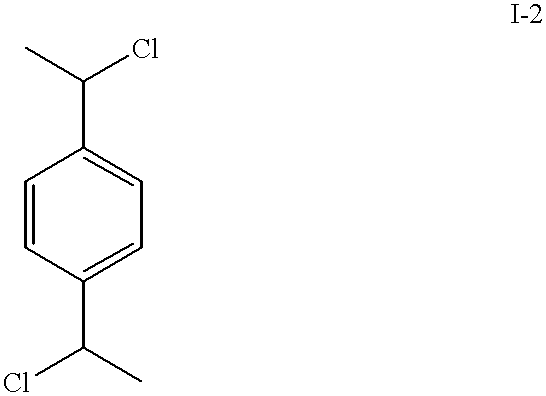
Patents
Literature
3854 results about "Weight distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
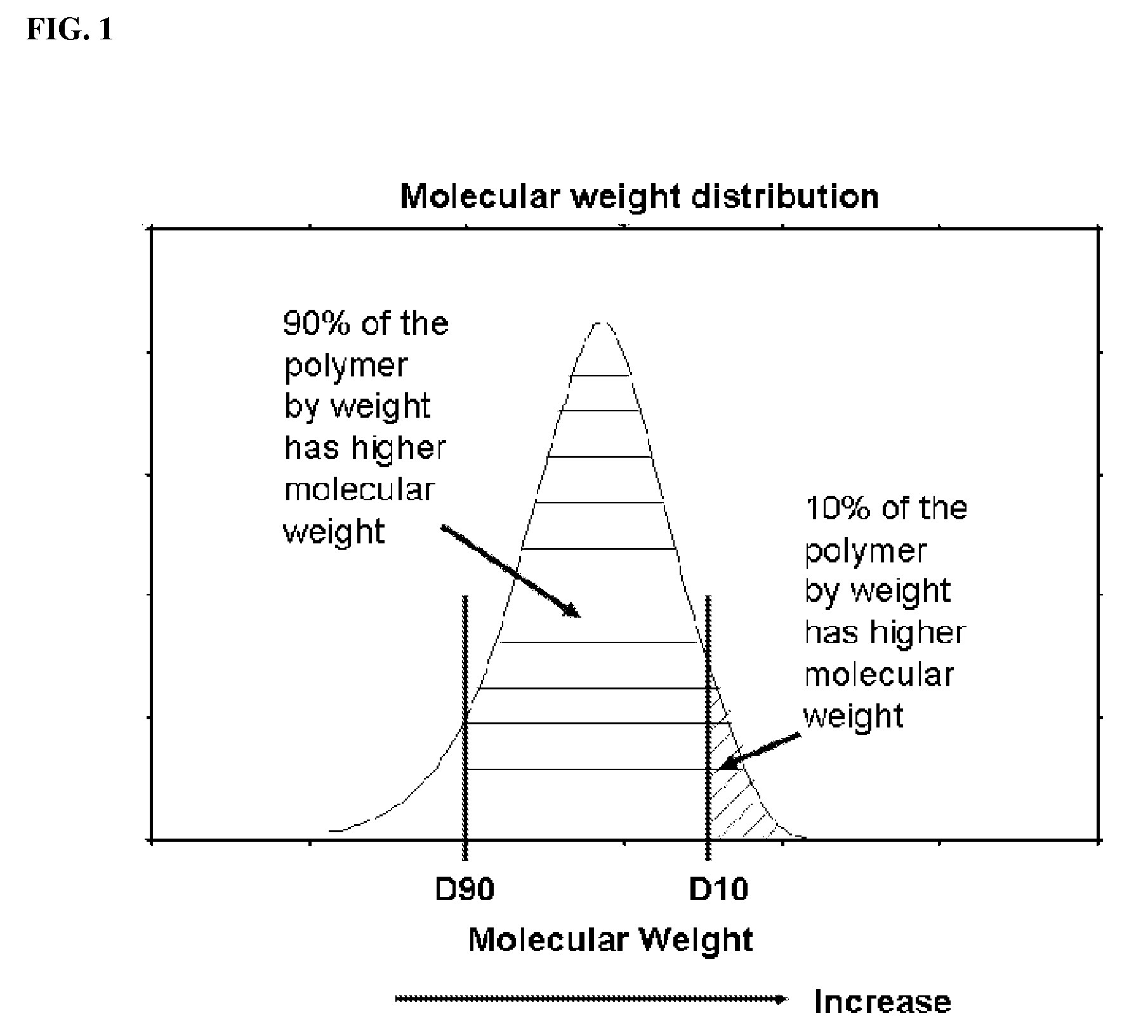
Weight distribution is the apportioning of weight within a vehicle, especially cars, airplanes, and trains. Typically, it is written in the form x/y, where x is the percentage of weight in the front, and y is the percentage in the back.
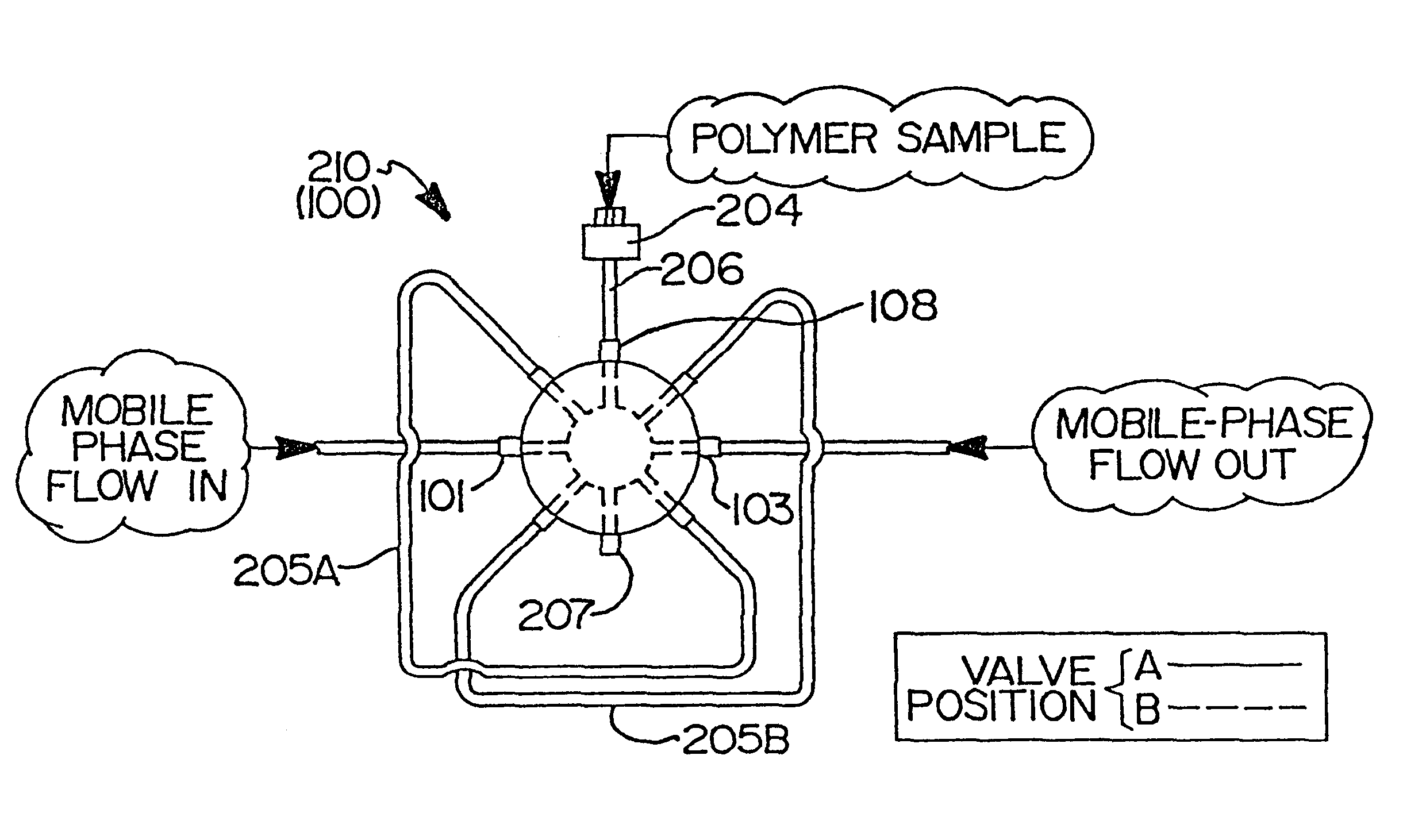
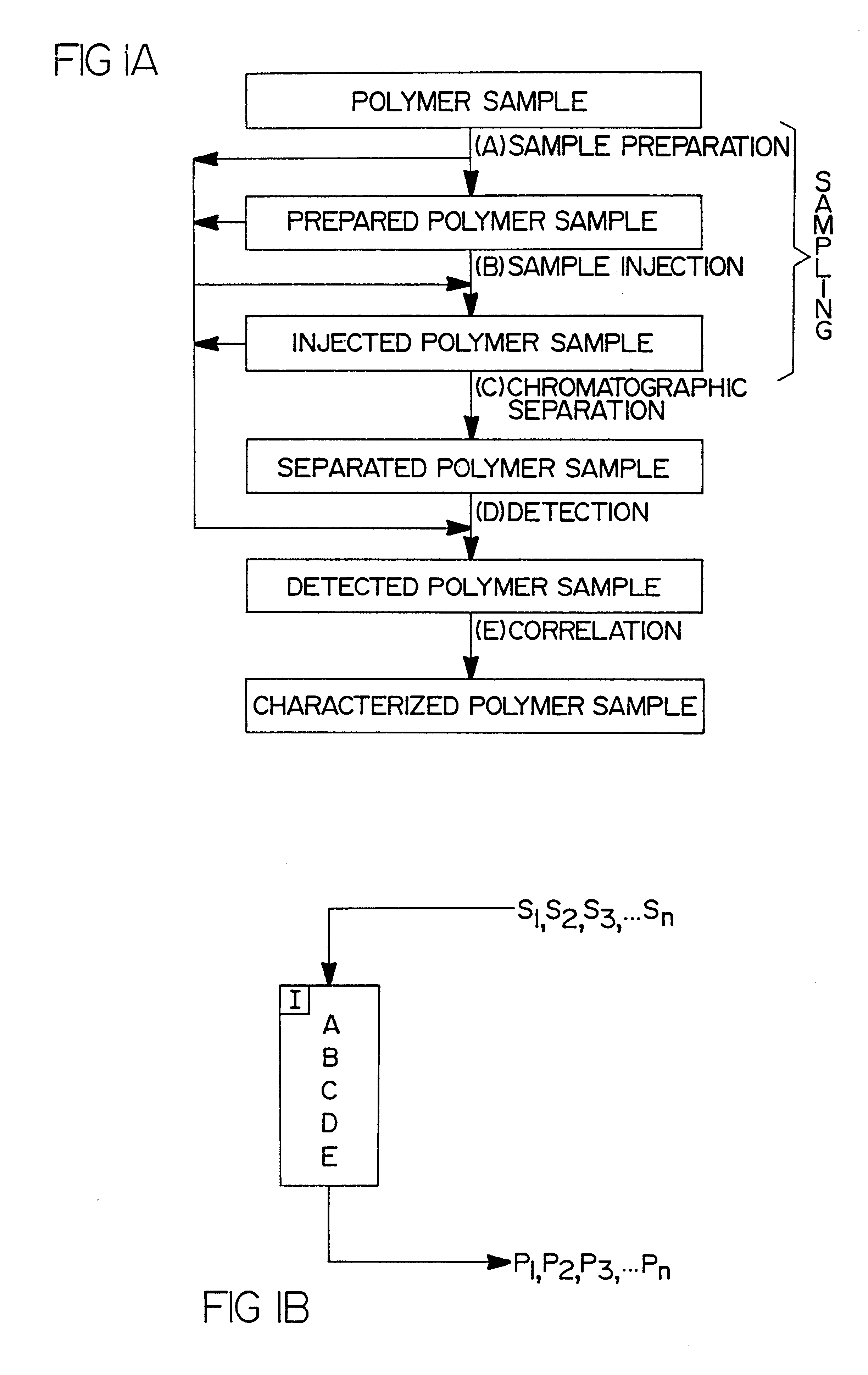
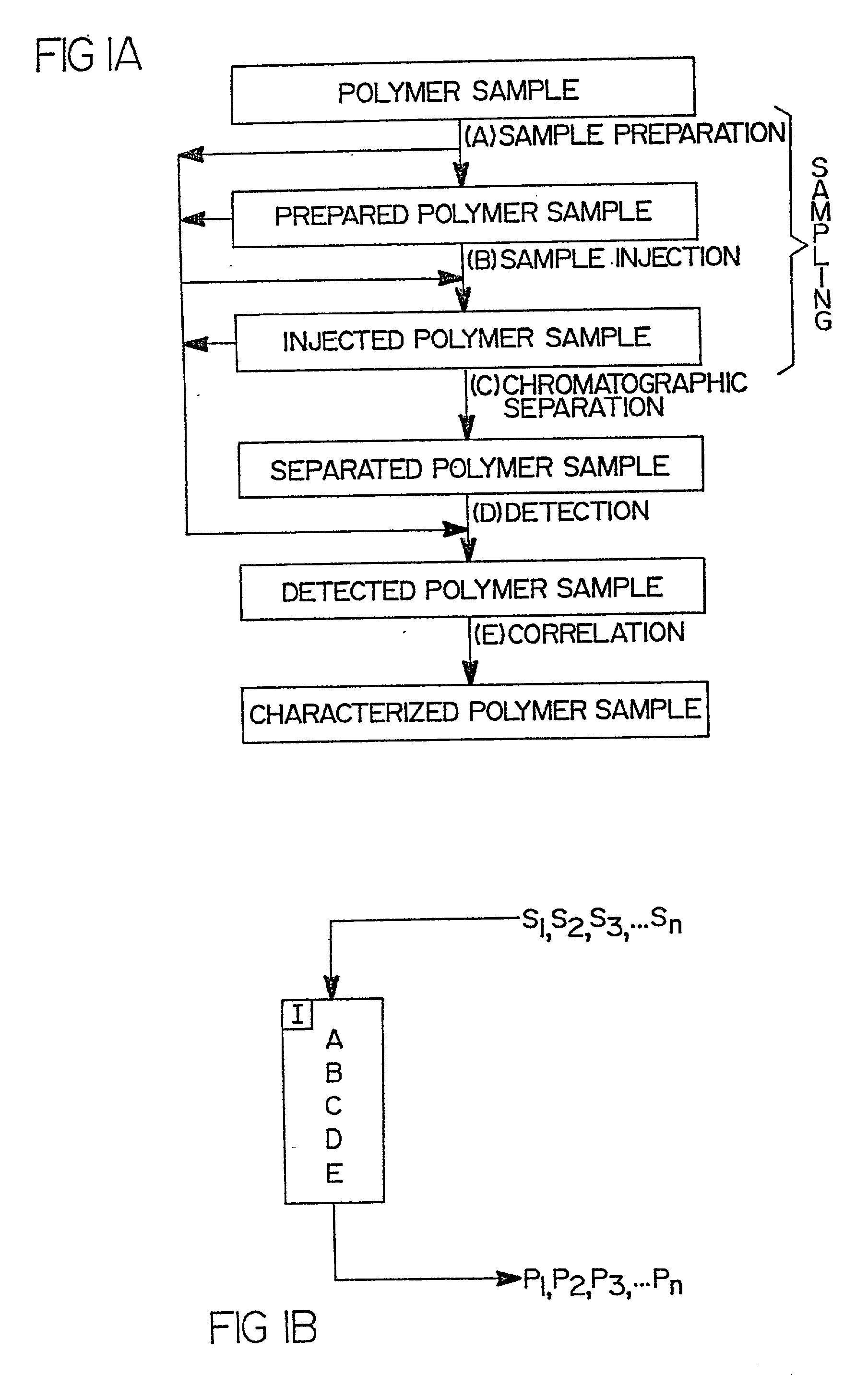
Flow-injection analysis and variable-flow light-scattering methods and apparatus for characterizing polymers
InactiveUS6175409B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High-temperature characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6260407B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationElutionChromatography column
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. In preferred high-temperature embodiments, the polymer sample is maintained at a temperature of not less than about 75° C. during sample preparation, loading into a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, injection into a mobile phase of a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, and / or elution from chromatographic column. The described methods, systems, and device have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Indirect calibration of polymer characterization systems
InactiveUS6294388B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputIon-exchange process apparatusSamplingPolymer characterizationFlow injection analysis
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
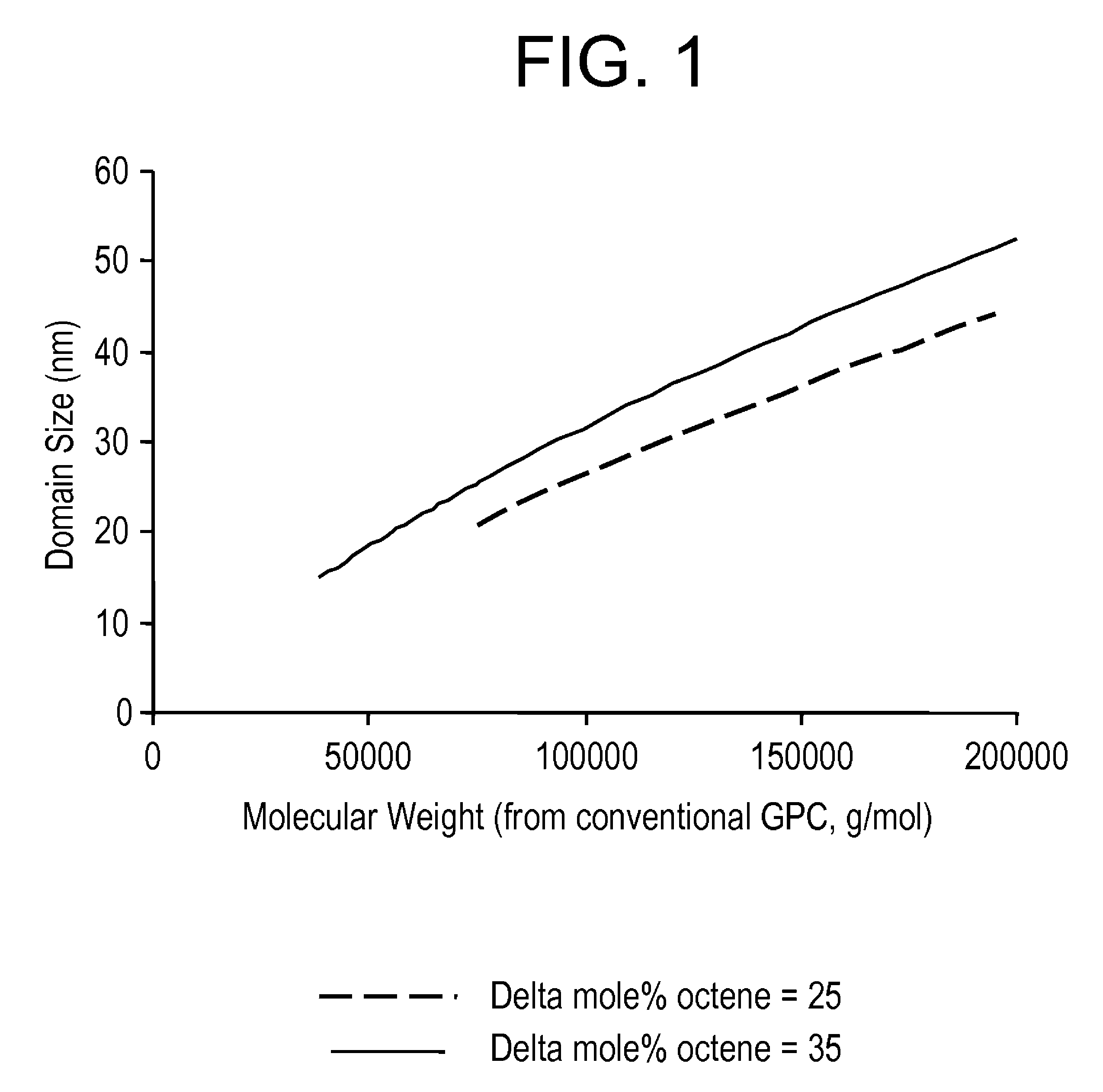
Ethylene/α-olefin block copolymers
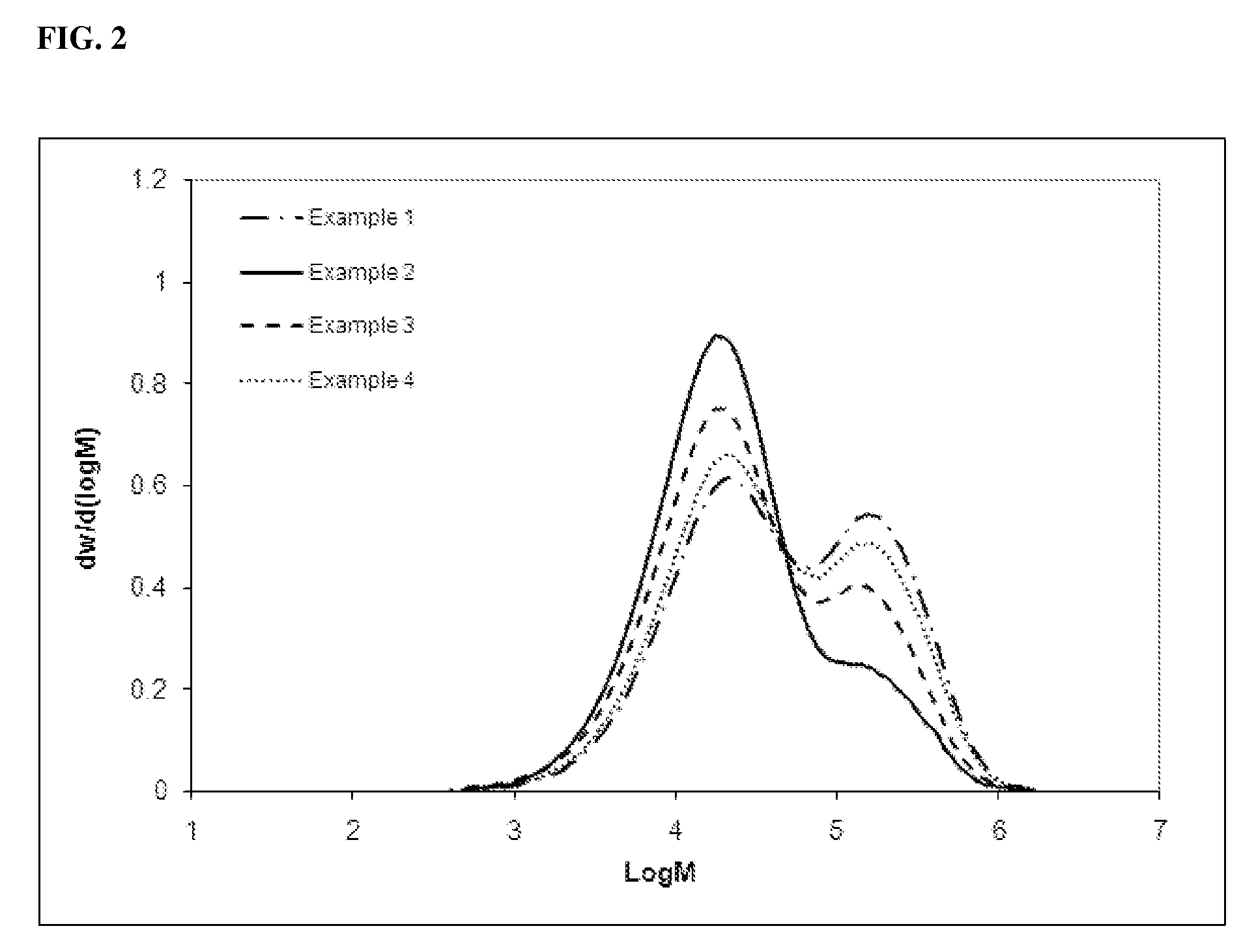
Embodiments of the invention provide a class of ethylene / α-olefin block interpolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are characterized by an average block index, ABI, which is greater than zero and up to about 1.0 and a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3. Preferably, the block index is from about 0.2 to about 1. In addition or alternatively, the block ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is characterized by having at least one fraction obtained by Temperature Rising Elution Fractionation (‘TREF’), wherein the fraction has a block index greater than about 0.3 and up to about 1.0 and the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer has a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.4.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
High-melting polyolefin copolymer elastomers, catalysts and methods of synthesis
InactiveUS6169151B1Property is limitedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElastomerPolymer science
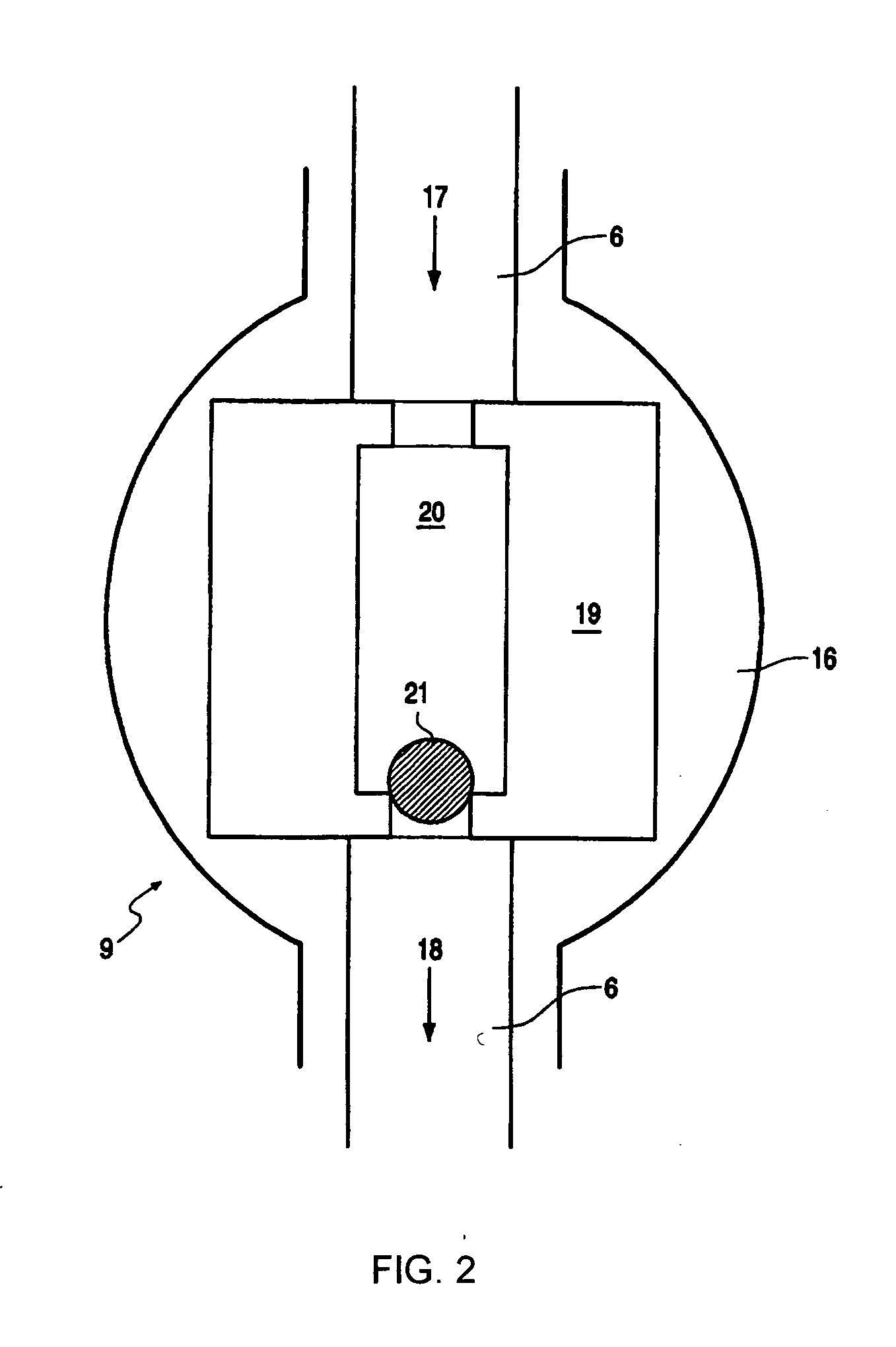
This invention relates to high melting polyolefin copolymers suitable as thermoplastic elastomers and catalysts and methods for their synthesis. These elastomeric olefin copolymers are characterized by a mole fraction of crystallizable component Xc from about 30 to about 99%; low glass transition temperatures, below -20° C., and typically below -50° C.; melting points above about 90° C.; high molecular weights; a molecular weight distribution MW / Mn< / =10; and a narrow composition distribution between chains of < / =15%. The novel copolymers of the invention range from reactor blends to multiblock copolymers that can be sequentially fractionated into fractions of differing crystallinities, which fractions nevertheless show compositions of comonomers which differ by less than 15% from the parent polymer (reactor product). The invention also relates to a process for producing such copolymers by utilizing an unbridged, substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl metallocene catalyst that is capable of interconverting between states with different copolymerization characteristics, which interconversion is controlled by selecting the substituents of the cyclopentadienyl ligands so that the rate of interconversion of the two states is within several orders of magnitude of the rate of formation of a single polymer chain. Where ri>rf the polymer can be characterized as multiblock; where ri<rf, the result is a polymer blend and where ri / rf is close to 1, the resulting polymer is a mixture of blend and multiblock. The metallocene catalysts of the invention are able to interconvert between more than two states, with embodiments of four states being shown in FIG. 2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
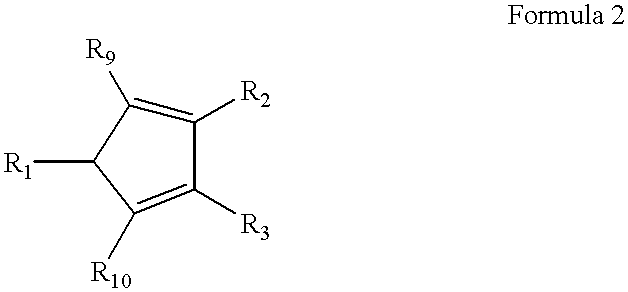
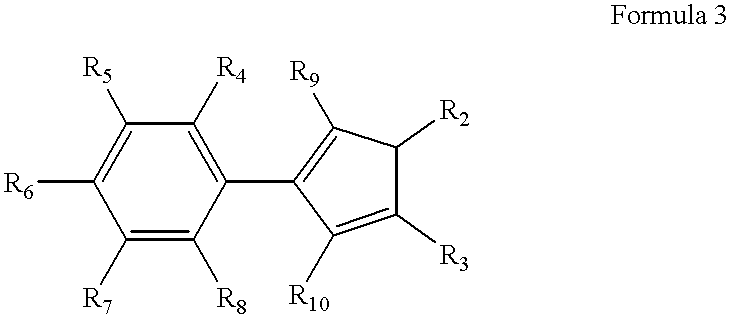
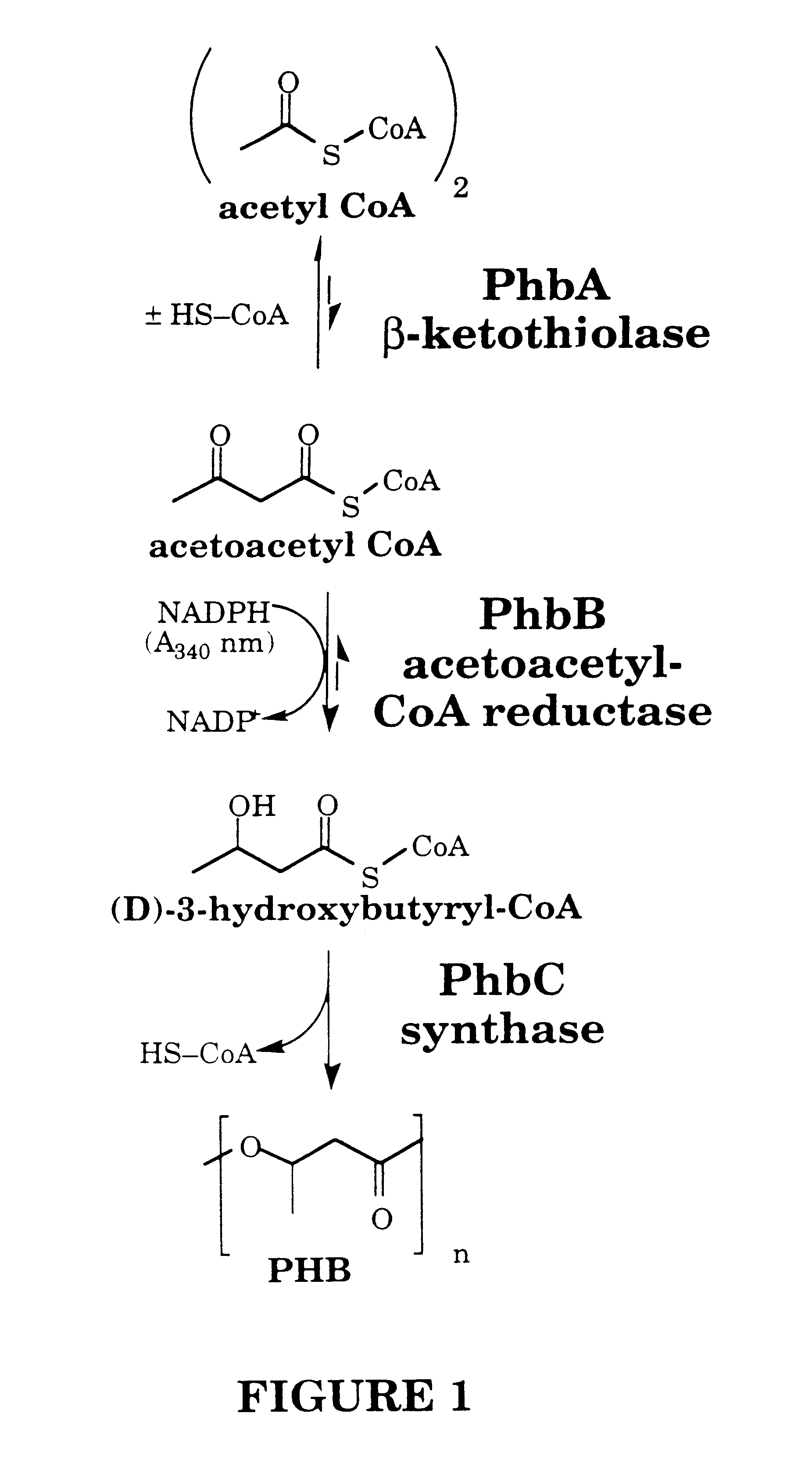
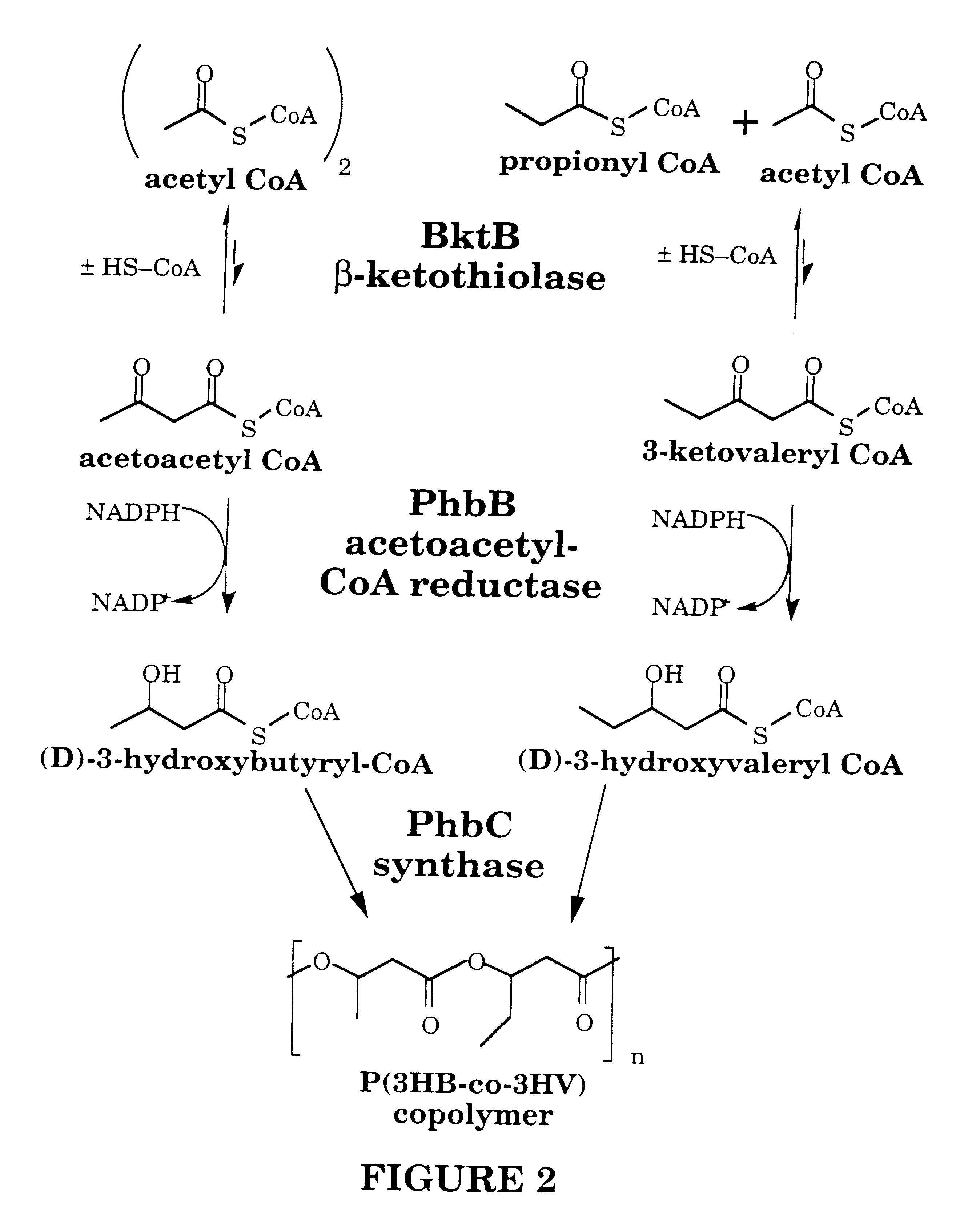
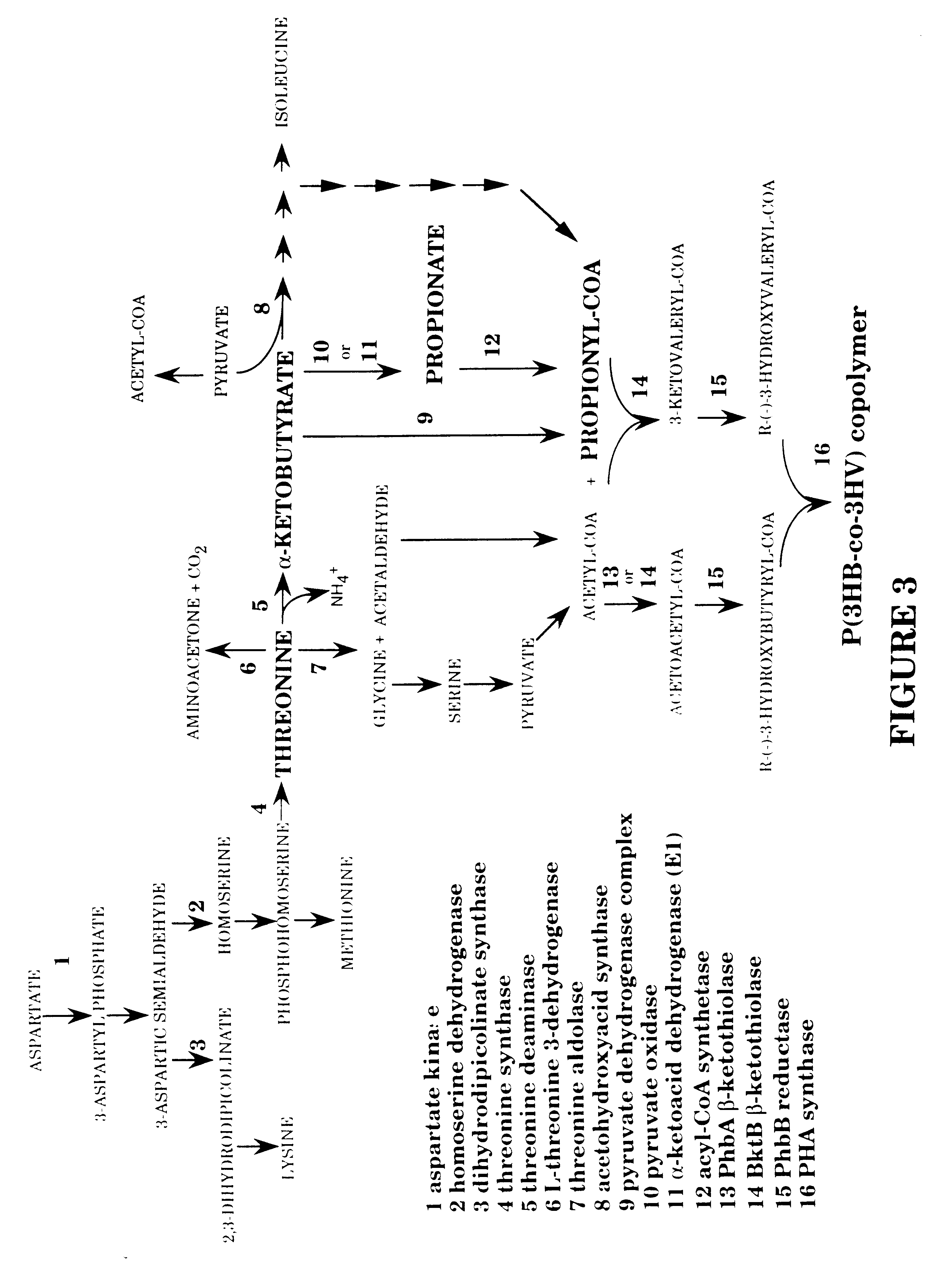
Polyhydroxyalkanoates of narrow molecular weight distribution prepared in transgenic plants
Methods for the biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate homopolymers and copolymers are described. In a preferred embodiment, the polymers have a single mode molecular weight distribution, and more preferably have a distribution of between about 2 and about 4, and most preferably about 2.1 or 2.5.
Owner:METABOLIX
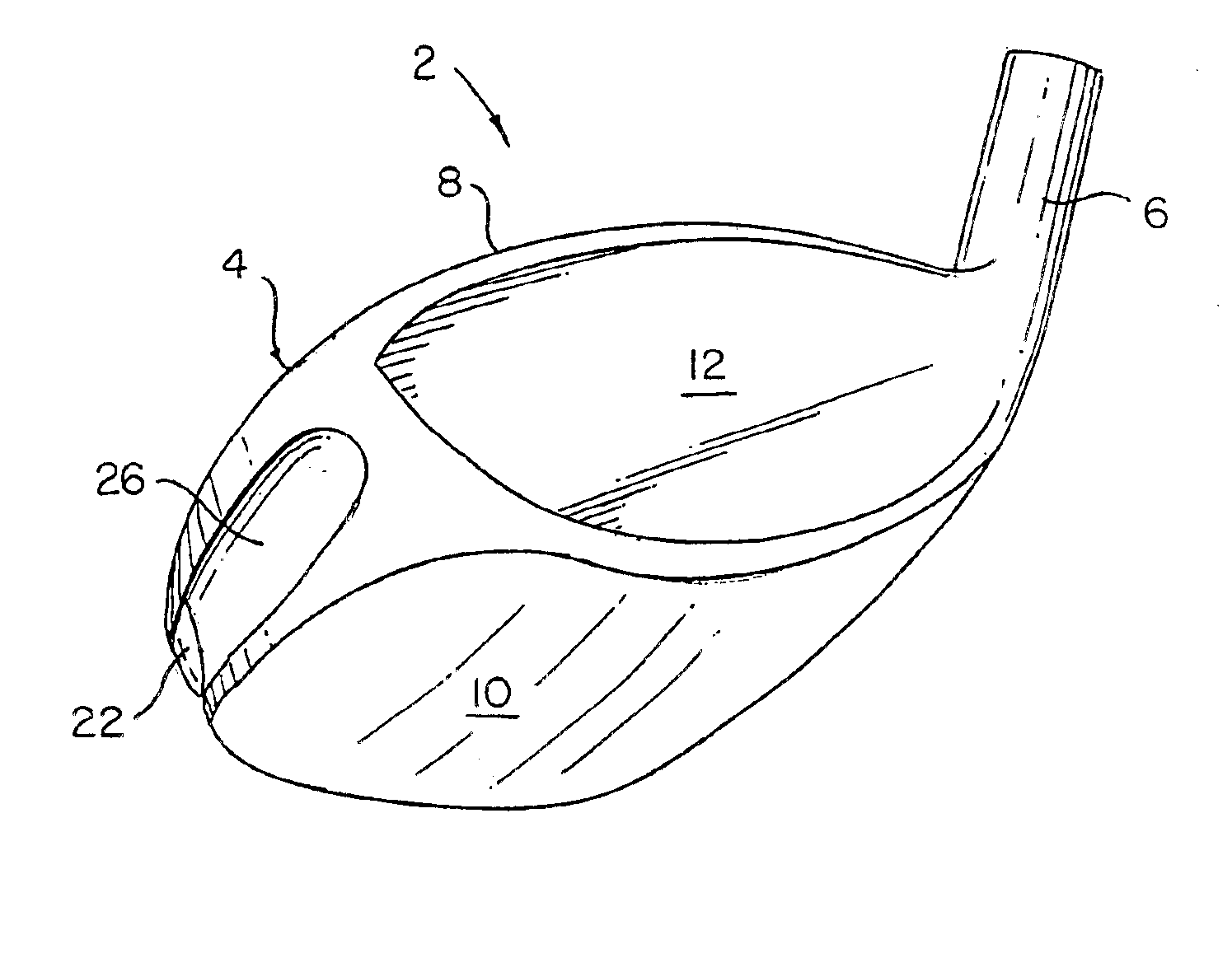
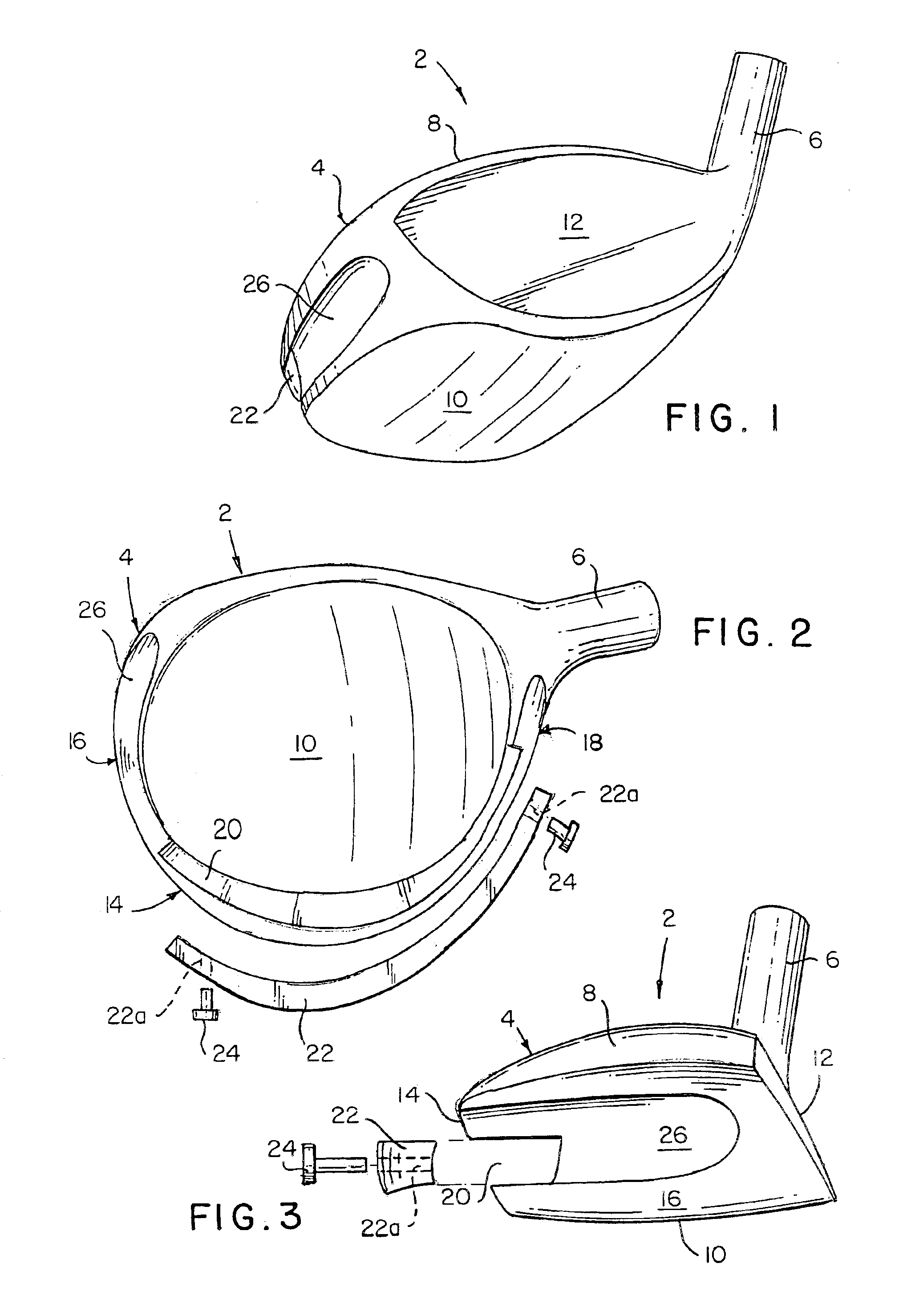
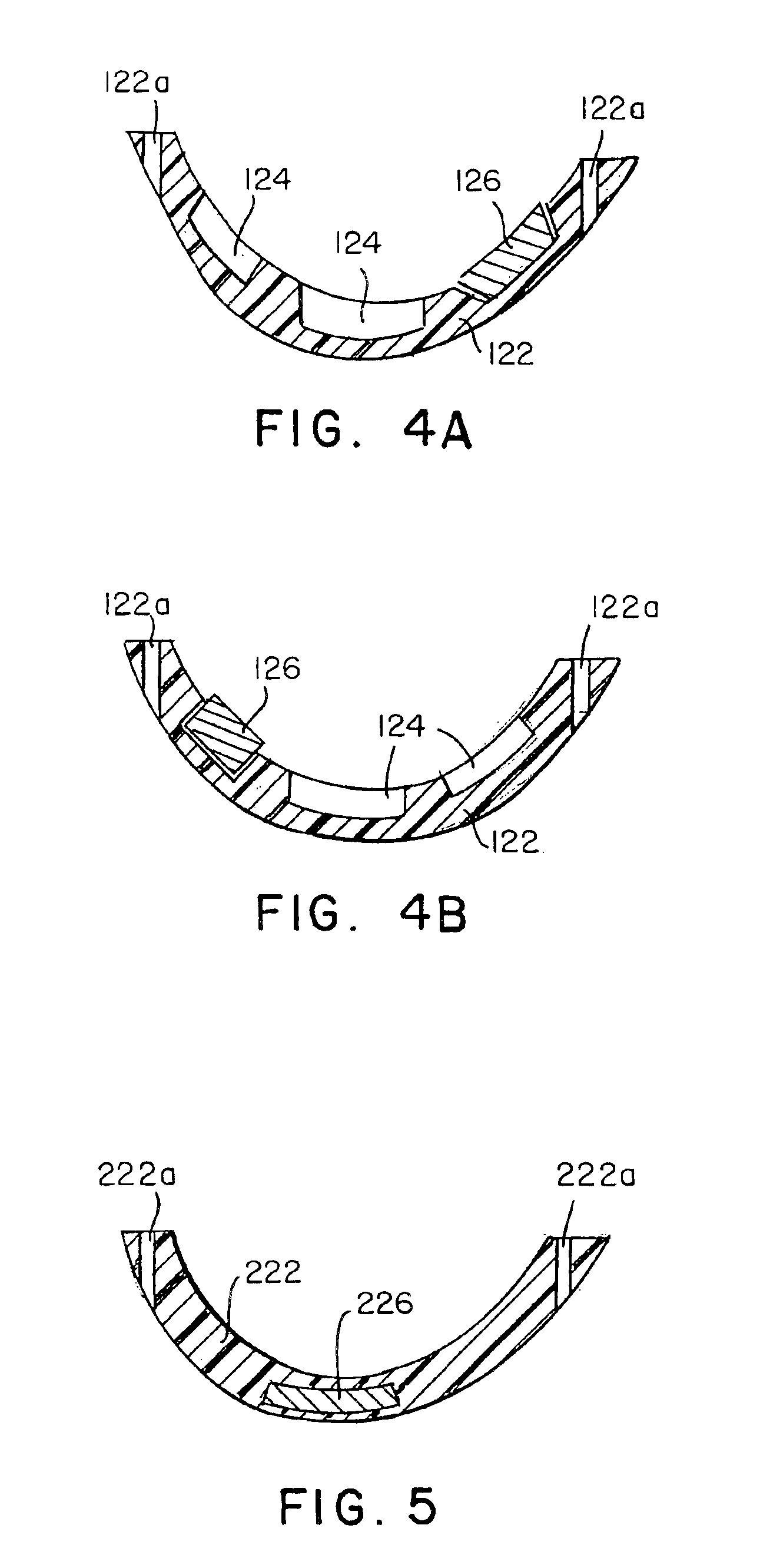
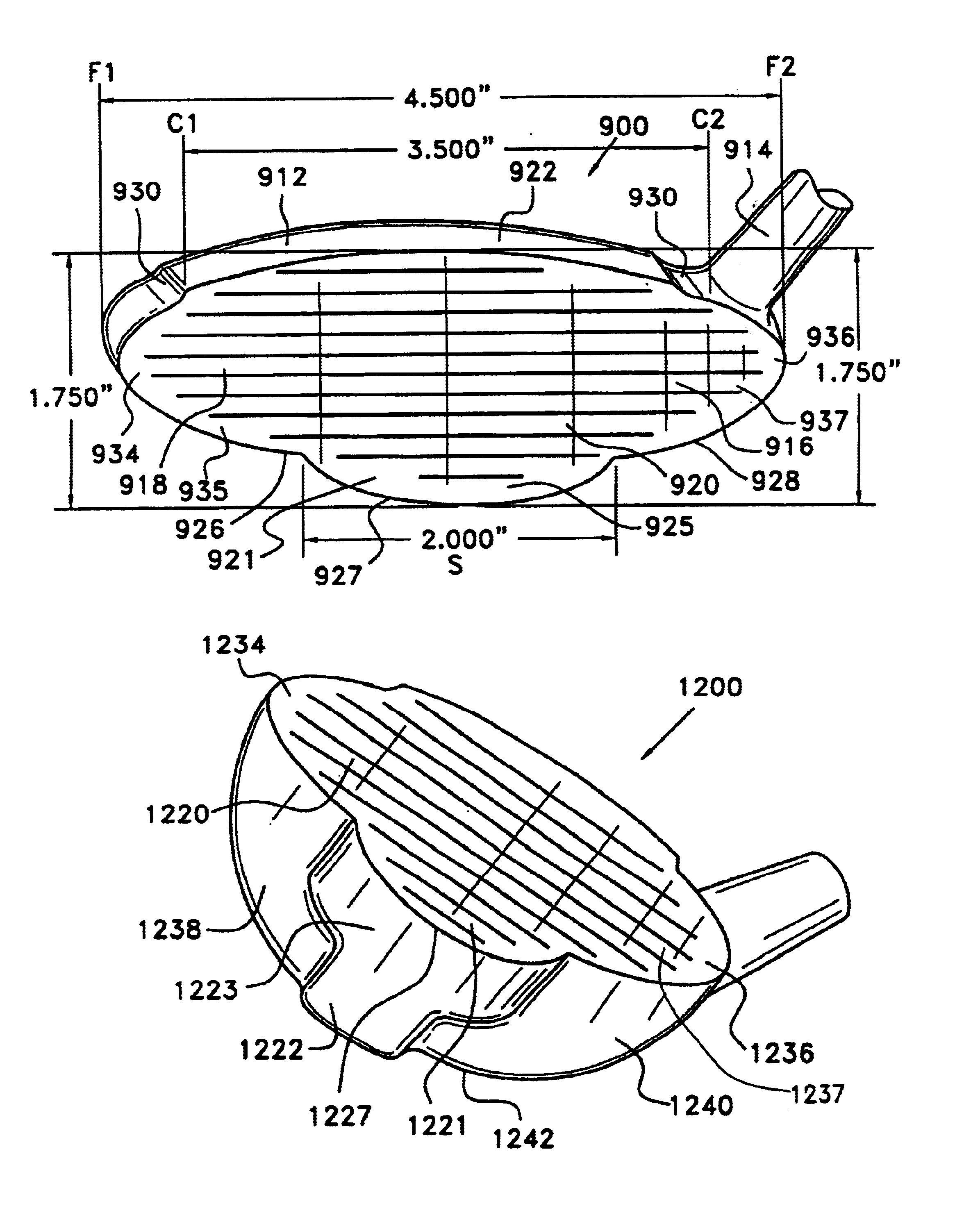
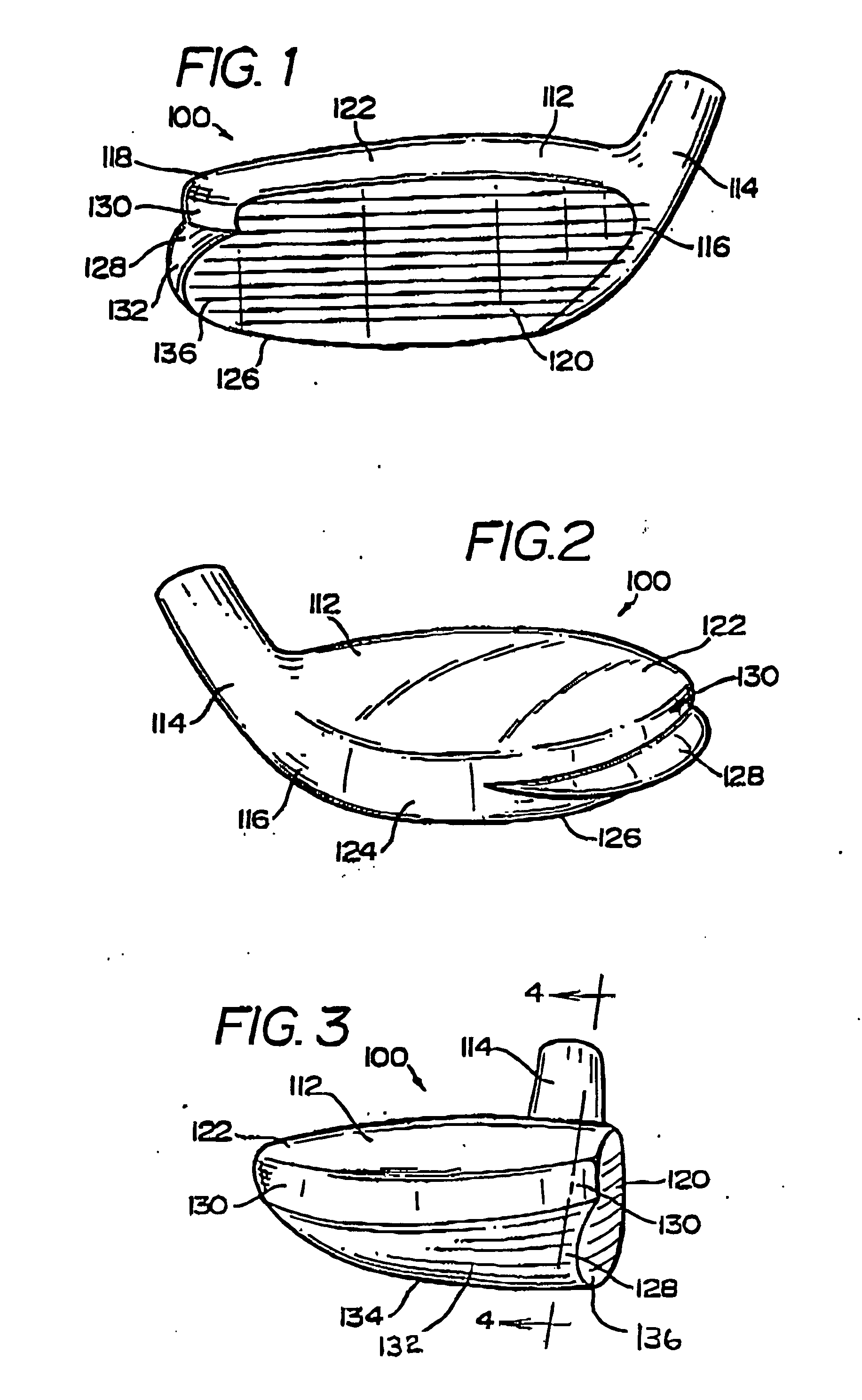
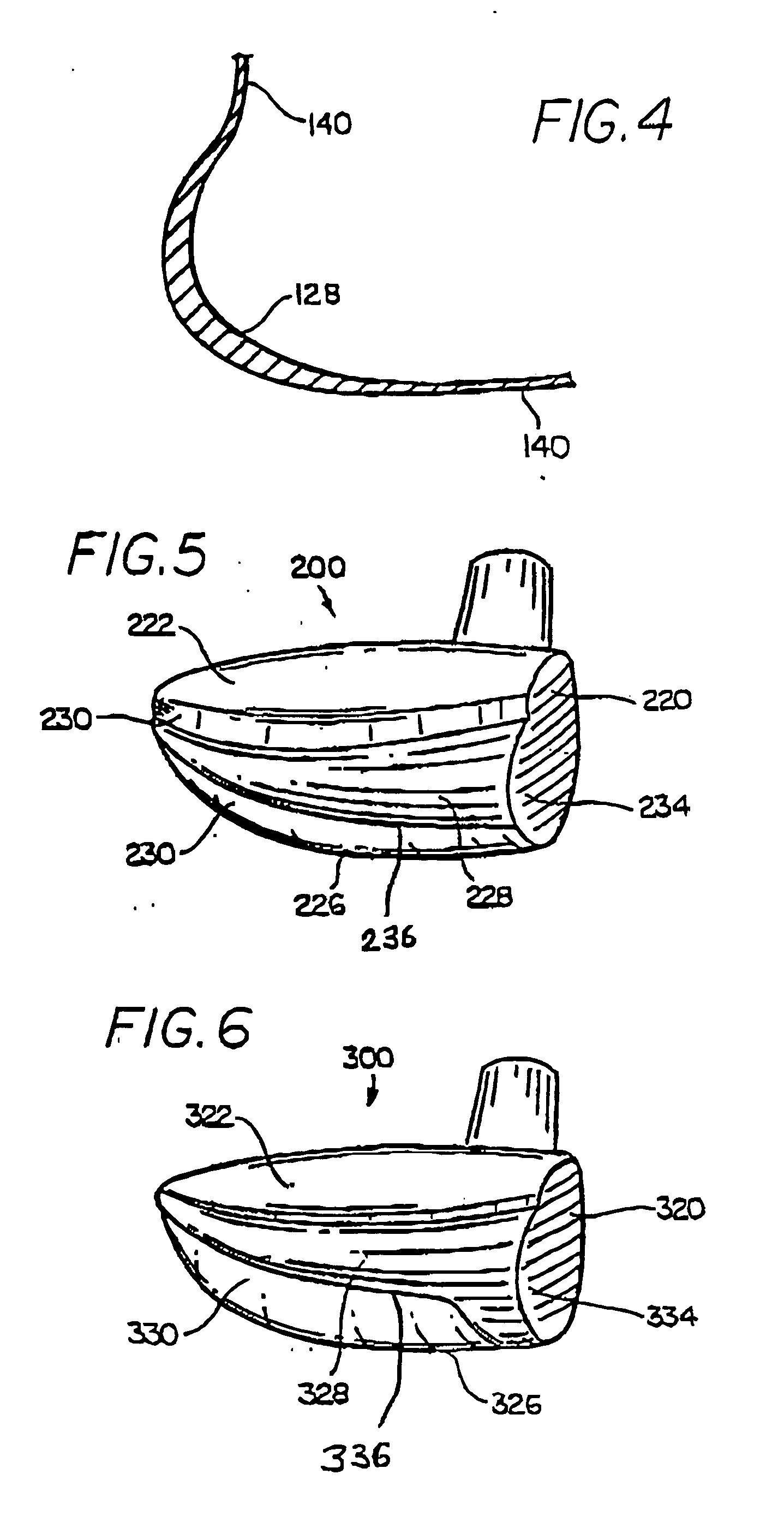
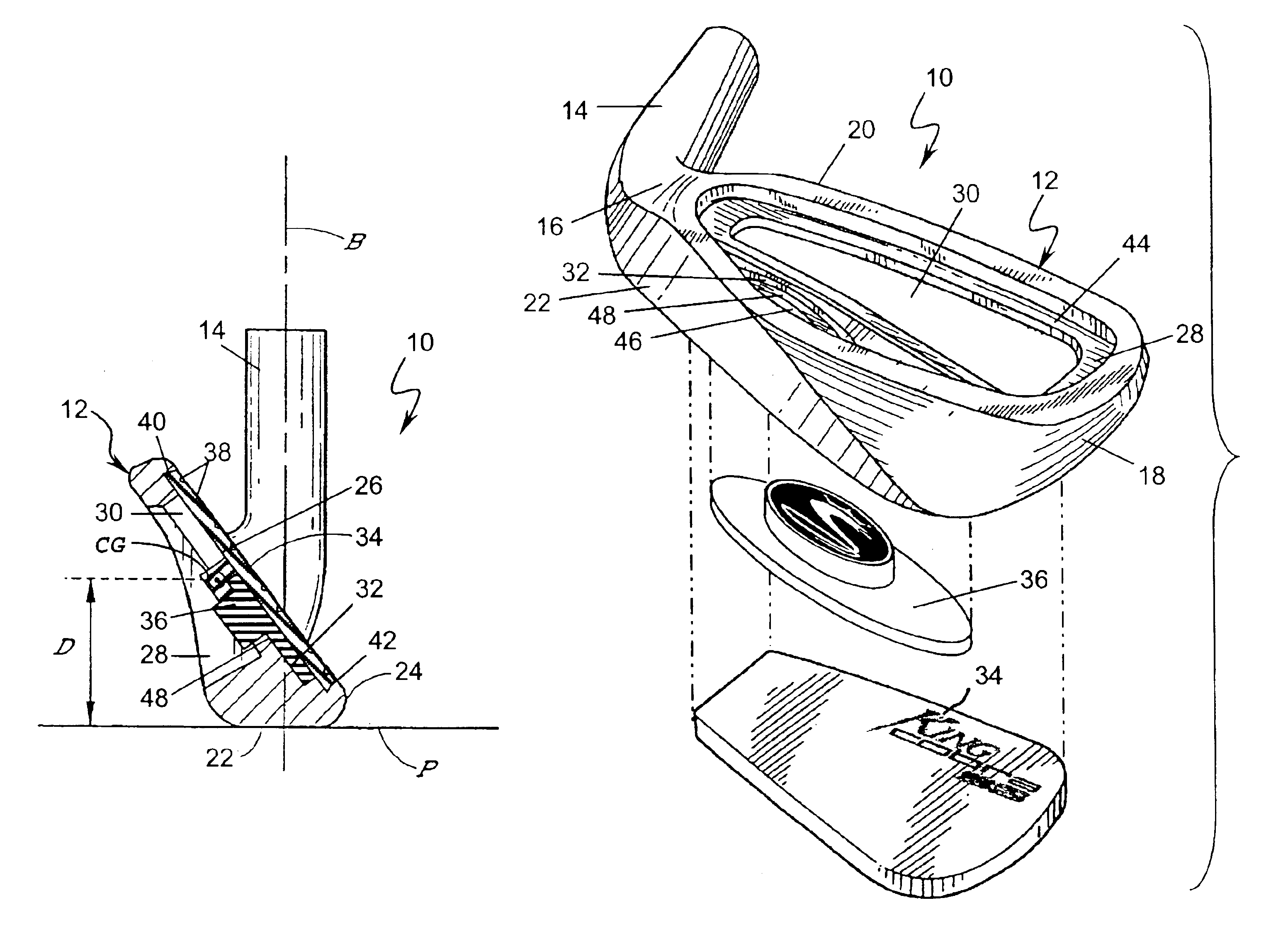
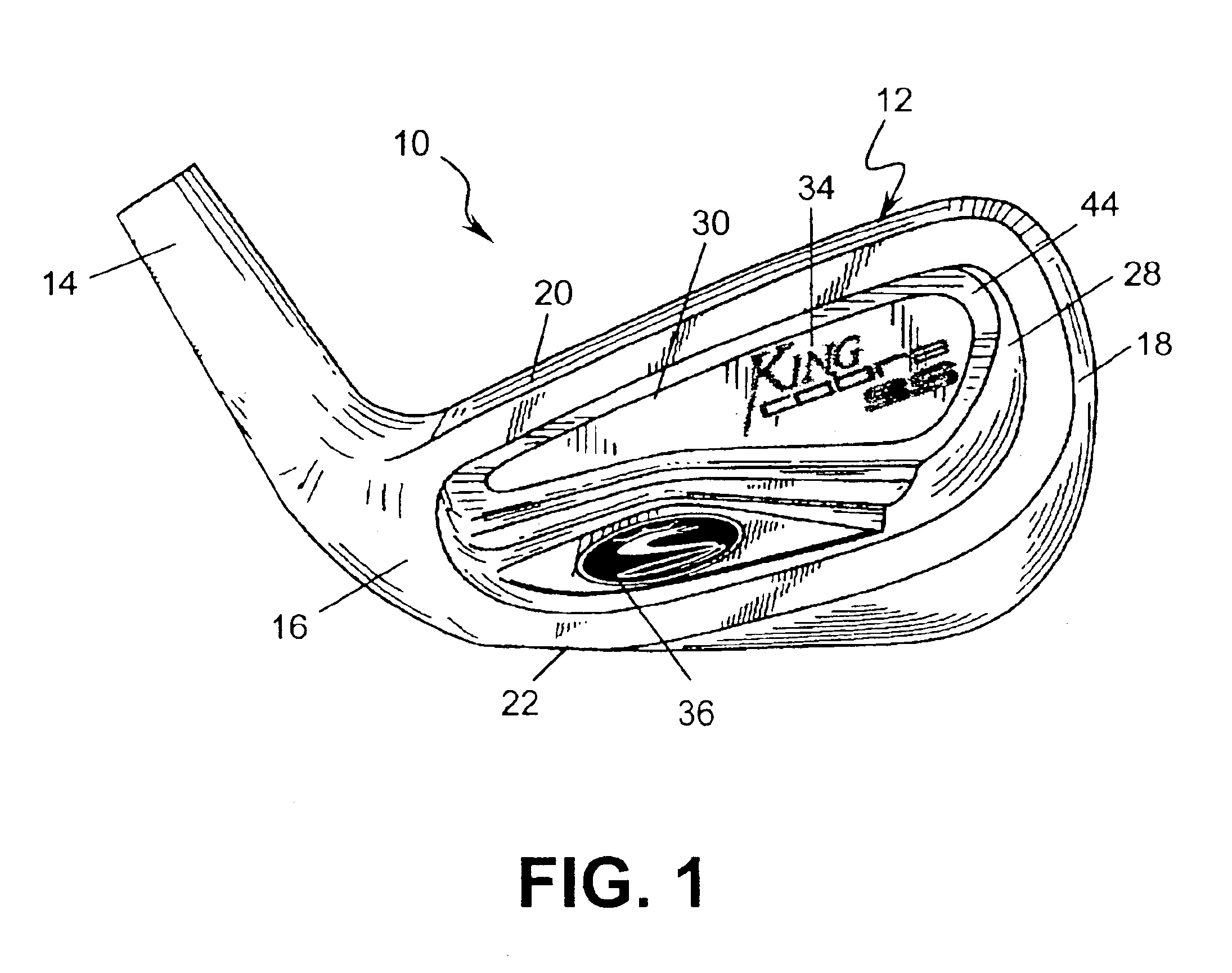
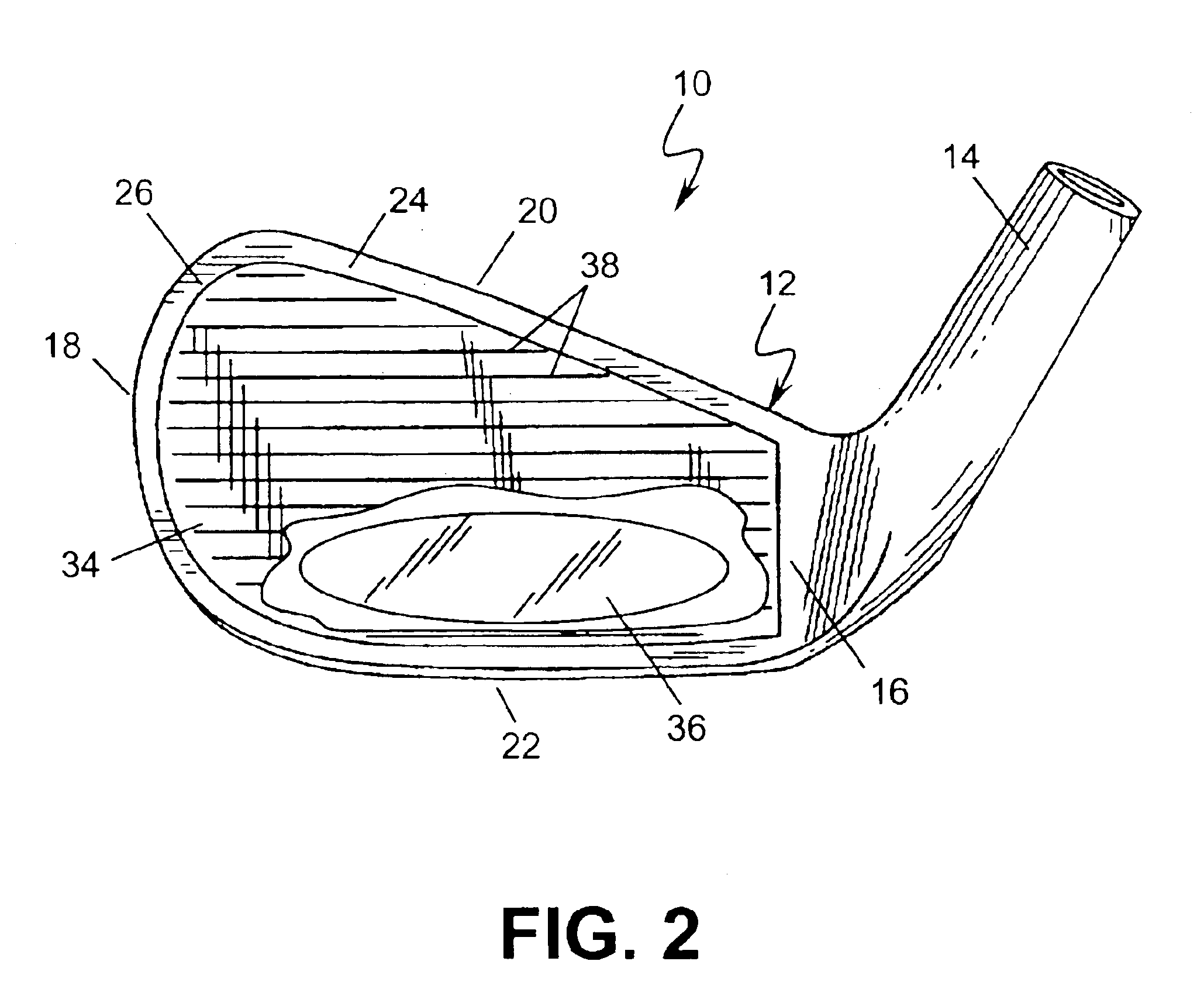
Golf club head with peripheral weighting
InactiveUS6890267B2Increase moment of inertiaVariable distributionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWound drainsMoment of inertiaGolf Ball
A golf club head with low peripheral and rearward weighting includes C-shaped and annular weights connected with at least one of the rear and bottom surfaces, respectively, of the head. The weighting within the peripheral weights is adjustable between the heel, rear, and toe portions of the head to customize the weight distribution of the head in accordance with a golfer's swing. The added weight and its orientation increases the moment of inertia of the head and reduces the rotation thereof.
Owner:THE TOP FLITE GOLF
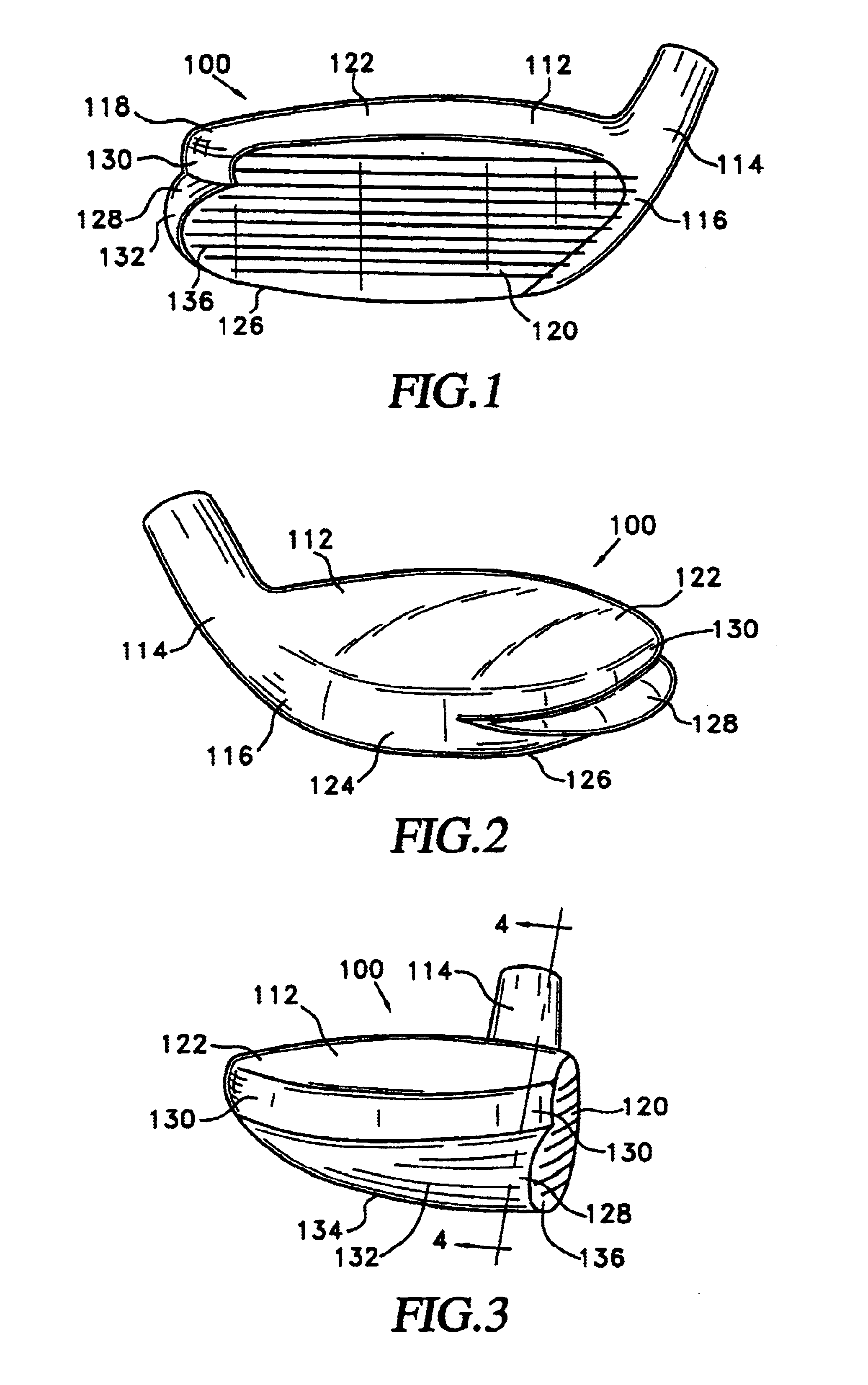
Metalwood type golf clubhead having expanded sections extending the ball-striking clubface
InactiveUS6855068B2Increases critical MomentReduces and minimizes negative effectGolf clubsStringed racketsEngineeringGolf Ball
A metalwood type golf clubhead including a clubhead body having a toe, heel, upper crown surface, bottom sole surface, side surfaces, rear surface and ball-striking clubface having at least one raised, elongated, aerodynamically shaped reinforcing and stabilizing member extending outwardly from the clubhead body and having at least one frontal ball-striking surface coincident with the ball-striking clubface. The structure provides improved weight distribution for better balance, additional strength and stability to clubhead and provides more effective aerodynamic surfaces to increase clubhead speed.
Owner:ANTONIOUS ANTHONY J
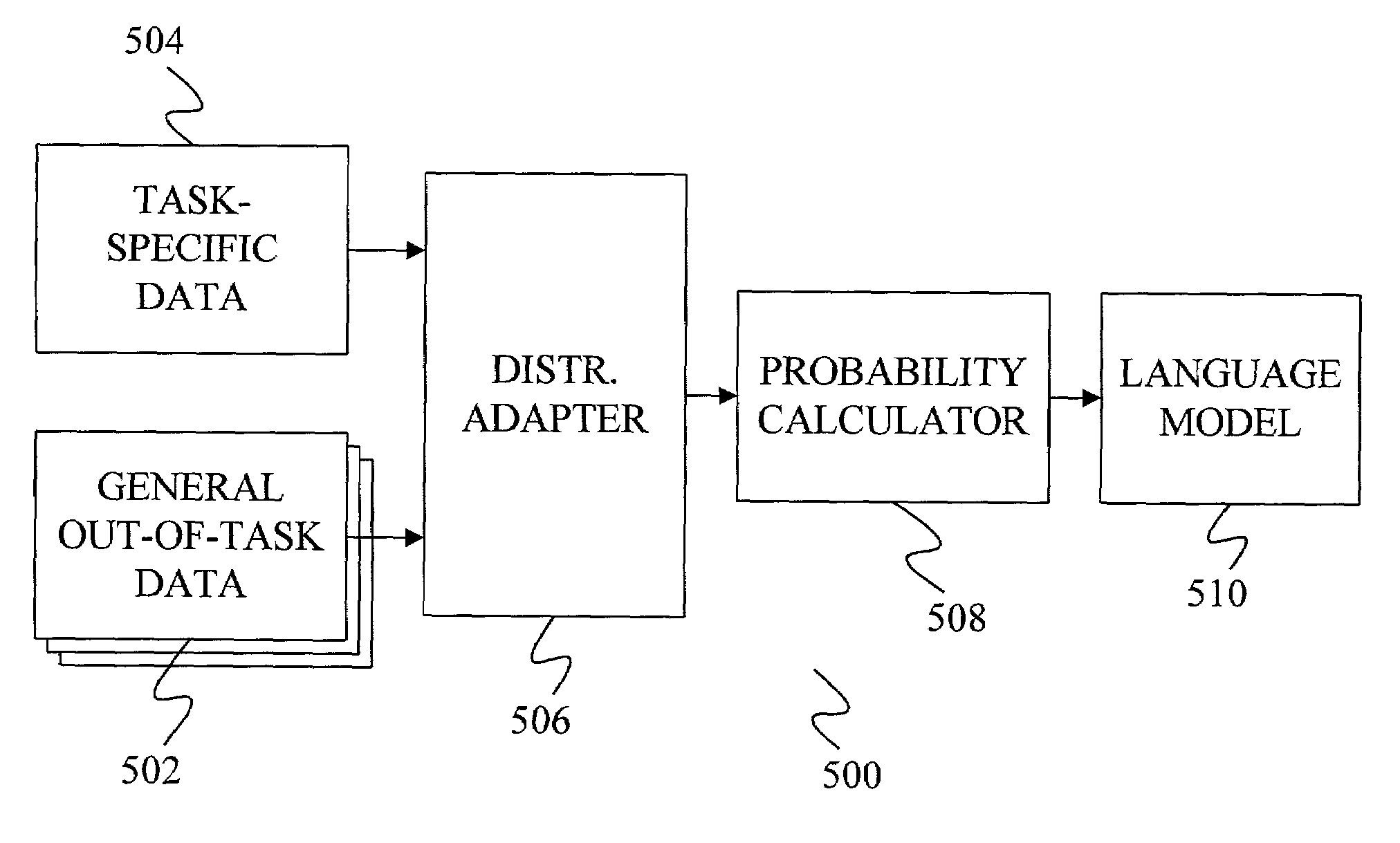
Method and apparatus for distribution-based language model adaptation
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Double loop technology
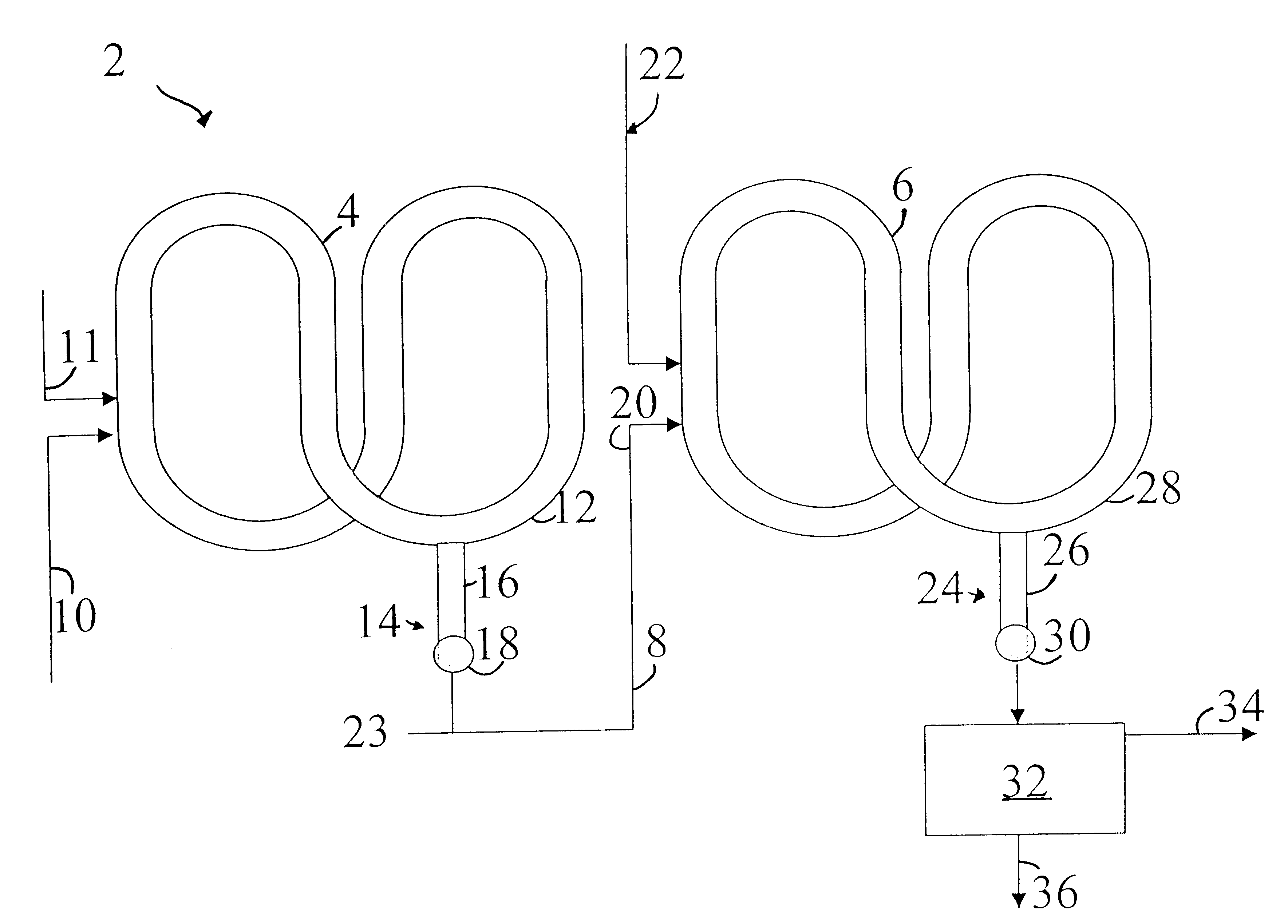
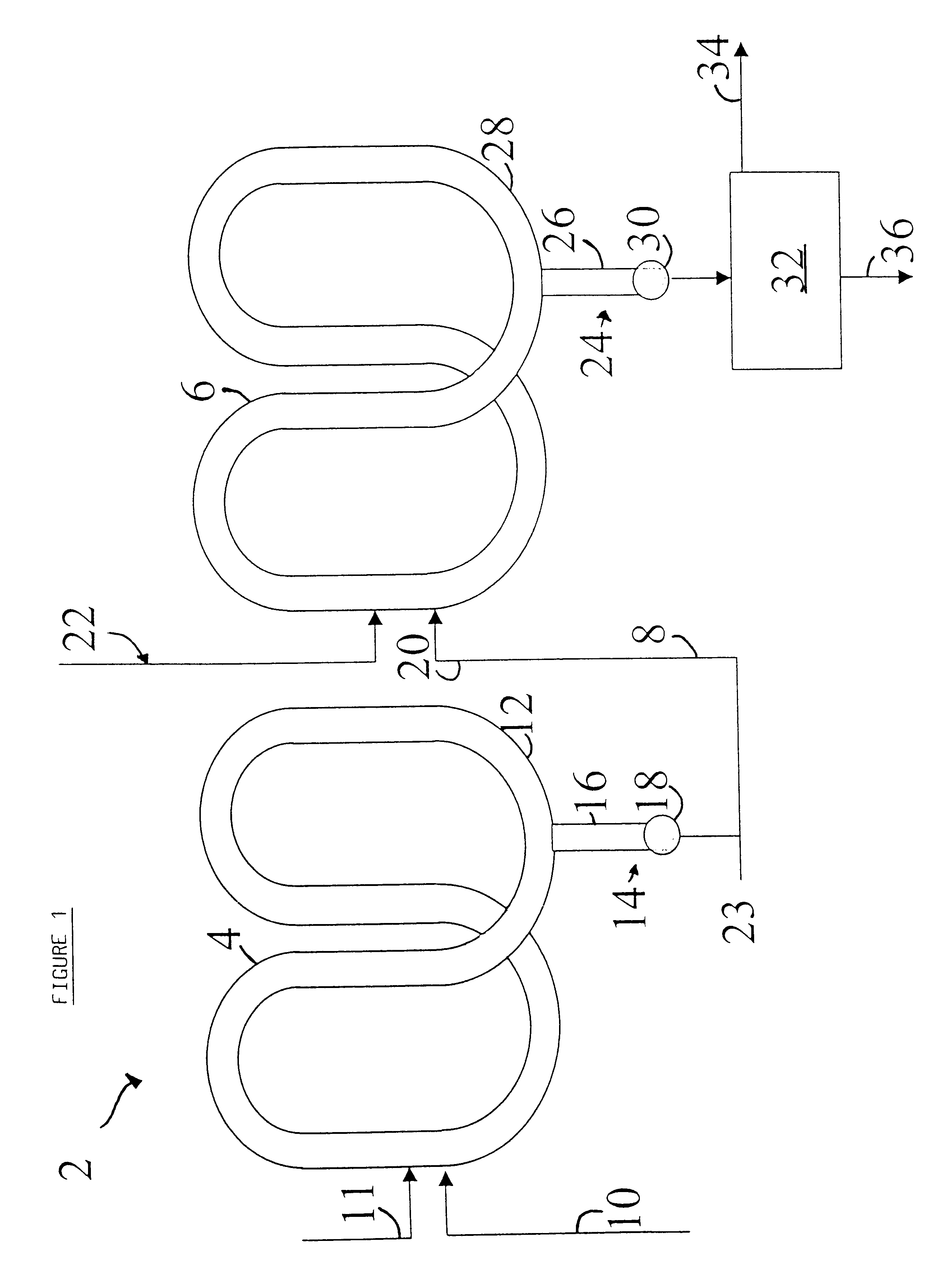
InactiveUS20050272891A1Constant levelLimited wayControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsExhaust apparatusPolymer sciencePolyolefin
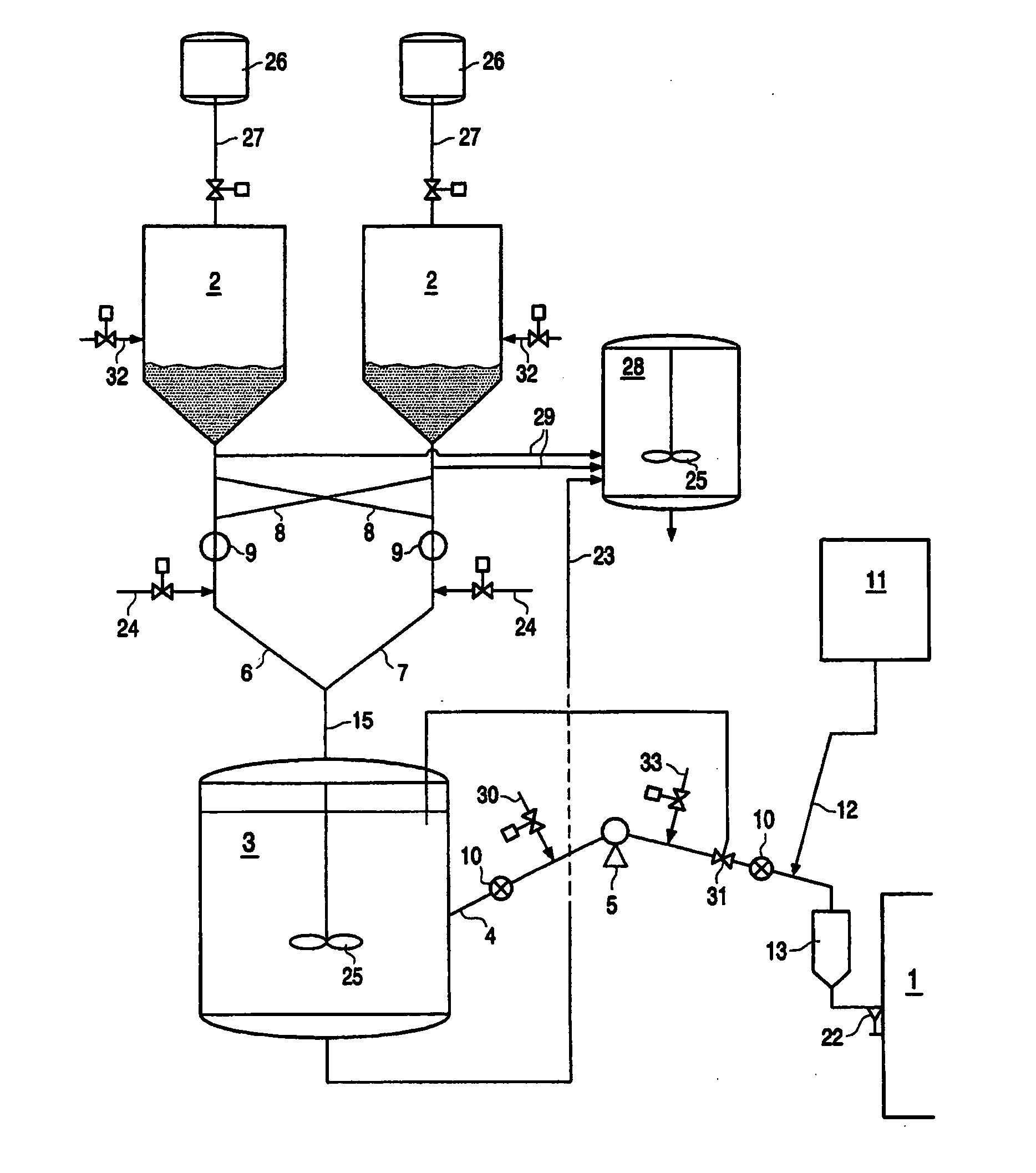
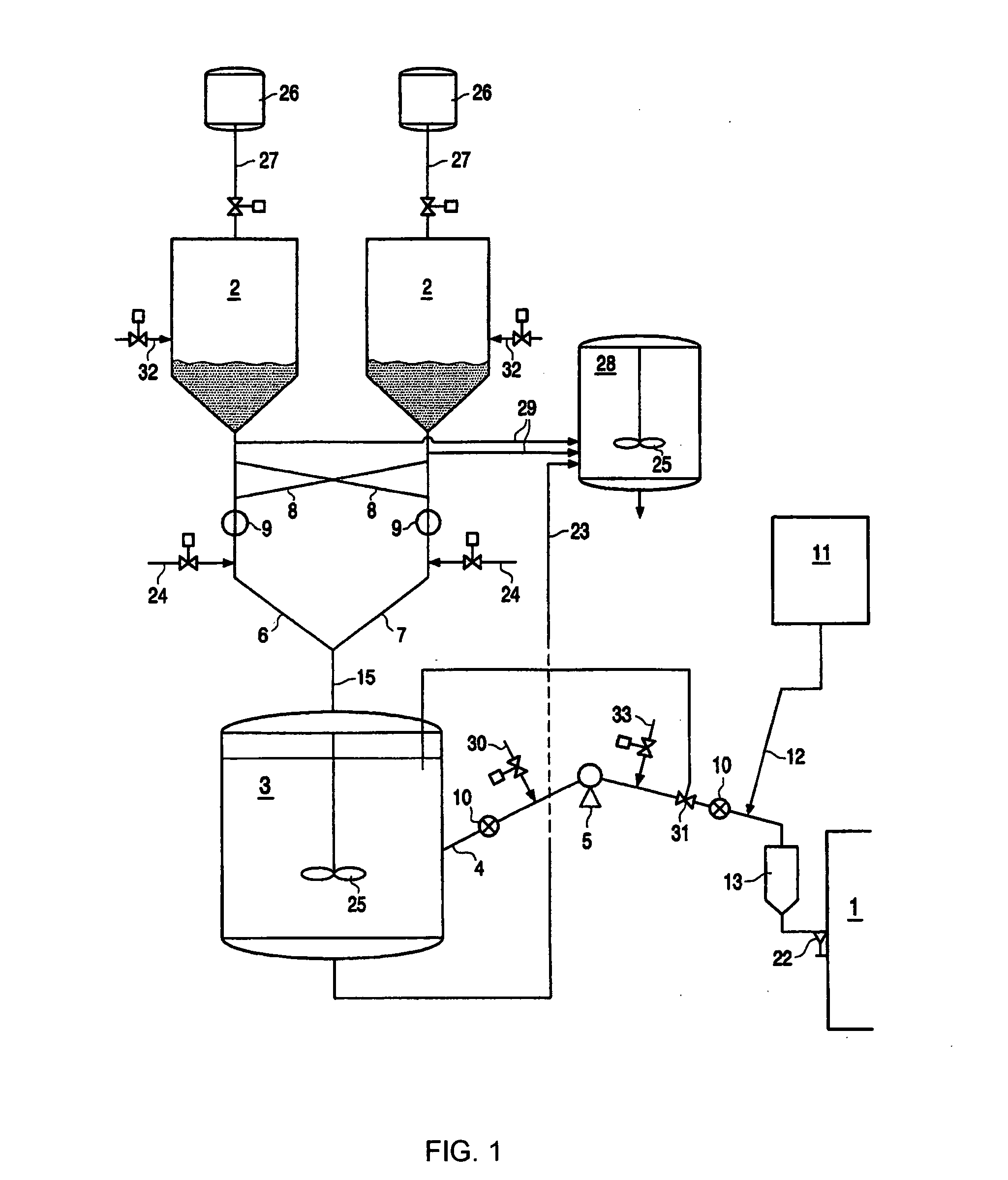
The present invention relates to an apparatus and process for polymerizing olefins. One embodiment comprises polymerizing at least one monomer in a first loop reactor in the presence of a catalyst to produce a first polyolefin fraction. A portion of the first polyolefin fraction is transferred to a second loop reactor, connected in series with the first loop reactor. The process further comprises polymerizing in the second loop reactor at least one monomer in the presence of a catalyst to produce a second polyolefin fraction in addition to the first polyolefin fraction. The combination of the first and second polyolefin fractions can produce a polymer resin fluff having bimodal molecular weight distribution.
Owner:TOTAL RES & TECH FELUY
Automated sampling methods for rapid characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6265226B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High-melting polyolefin copolymer elastomers, catalysts and methods of synthesis
InactiveUS6518378B2Property is limitedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationElastomerPolyolefin
This invention relates to high melting polyolefin copolymers suitable as thermoplastic elastomers and catalysts and methods for their synthesis. These elastomeric olefin copolymers are characterized by a mole fraction of crystallizable component Xc from about 30 to about 99%; low glass transition temperatures, below -20° C., and typically below -50° C.; melting points above about 90° C.; high molecular weights; a molecular weight distribution MW / Mn< / =10; and a narrow composition distribution between chains of < / =15%. The novel copolymers of the invention range from reactor blends to multiblock copolymers that can be sequentially fractionated into fractions of differing crystallinities, which fractions nevertheless show compositions of comonomers which differ by less than 15% from the parent polymer (reactor product). The invention also relates to a process for producing such copolymers by utilizing an unbridged, substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl metallocene catalyst that is capable of interconverting between states with different copolymerization characteristics, which interconversion is controlled by selecting the substituents of the cyclopentadienyl ligands so that the rate of interconversion of the two states is within several orders of magnitude of the rate of formation of a single polymer chain. Where ri>rf the polymer can be characterized as multiblock; where ri<rf, the result is a polymer blend and where ri / rf is close to 1, the resulting polymer is a mixture of blend and multiblock. The metallocene catalysts of the invention are able to interconvert between more than two states, with embodiments of four states being shown in FIG. 2.
Owner:BP AMOCO CORP +1
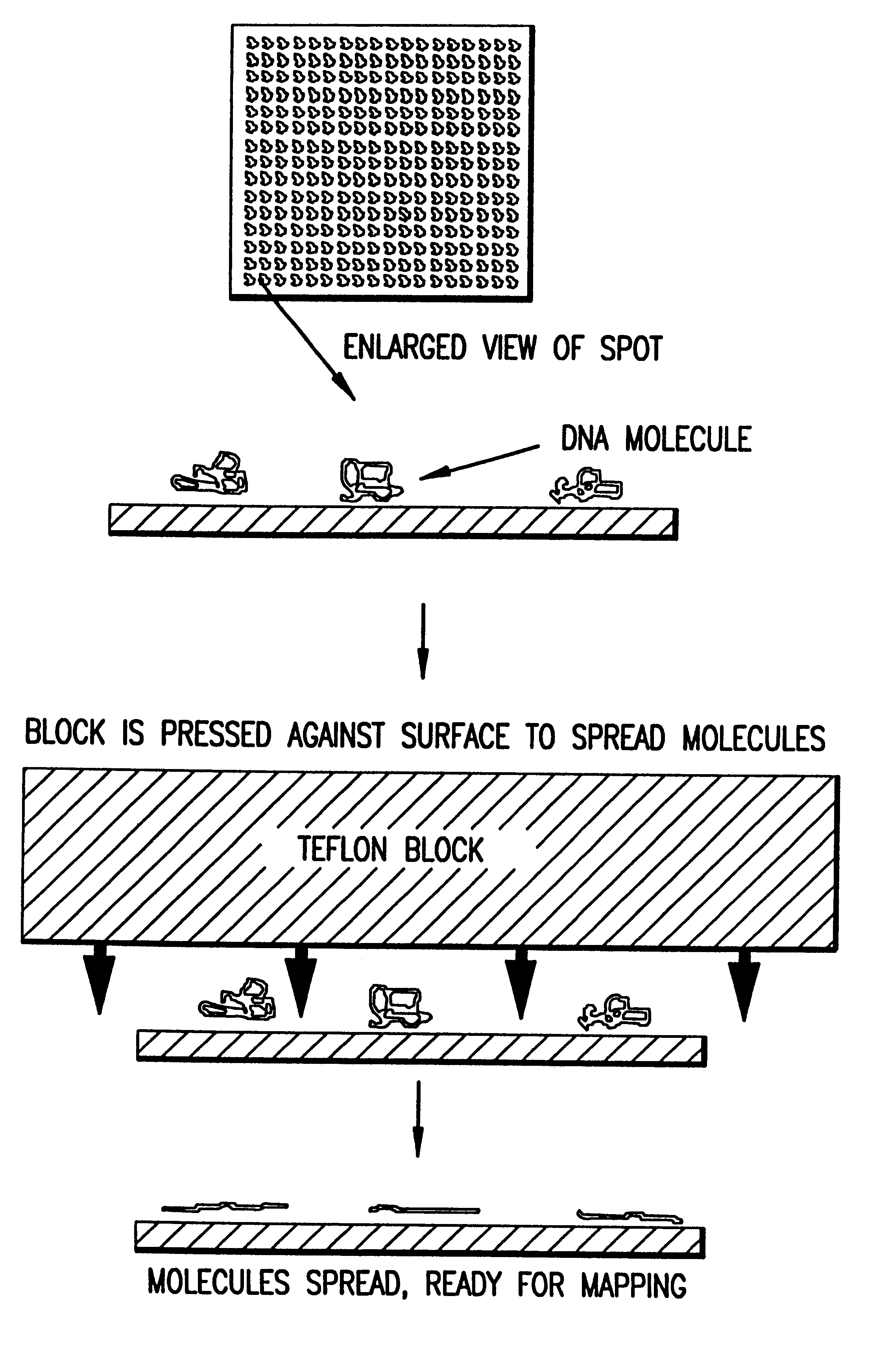
Methods and compositions for the manipulation and characterization of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6147198AQuick analysisQuick buildSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroscope slideMap Location
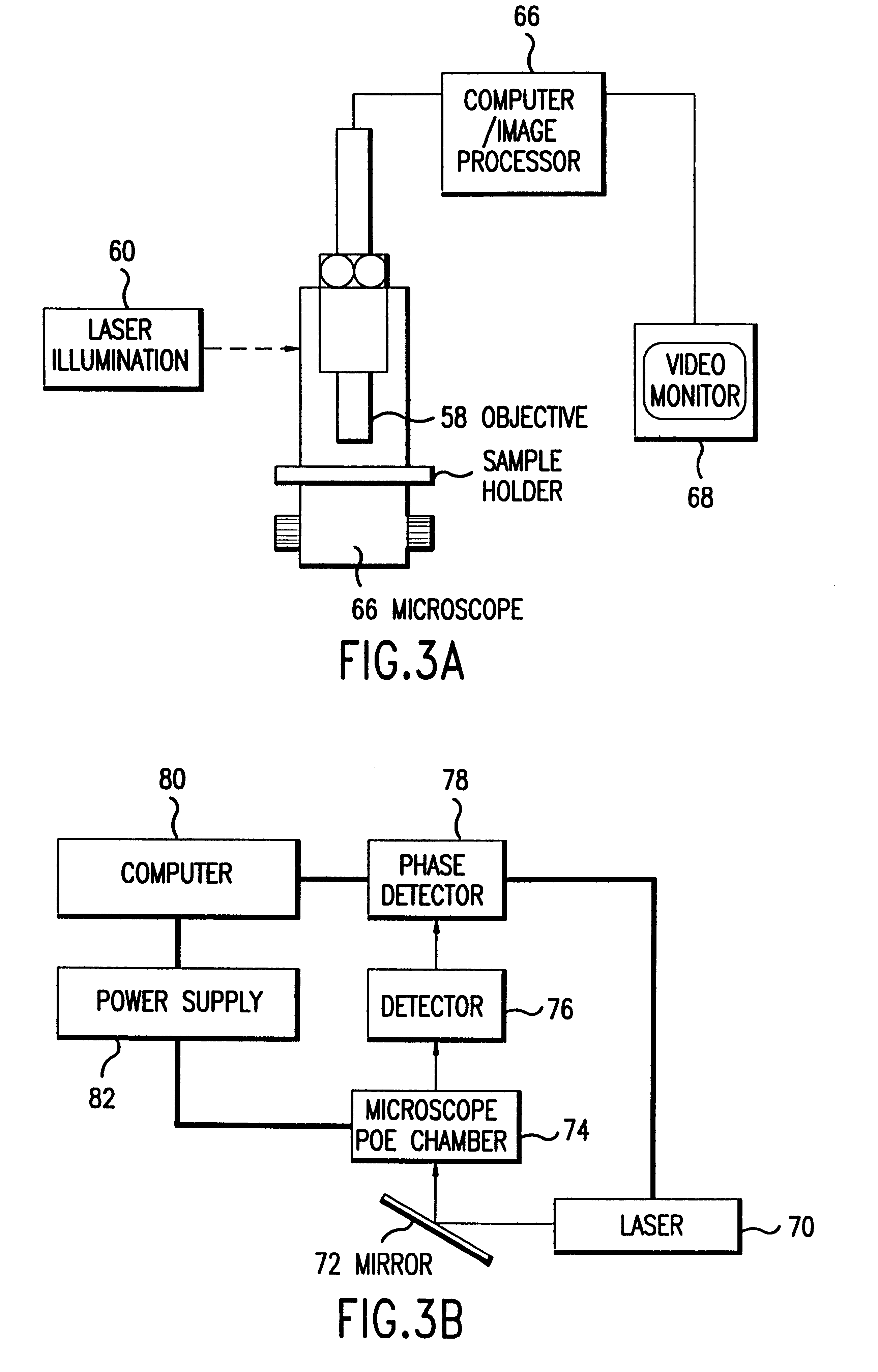
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
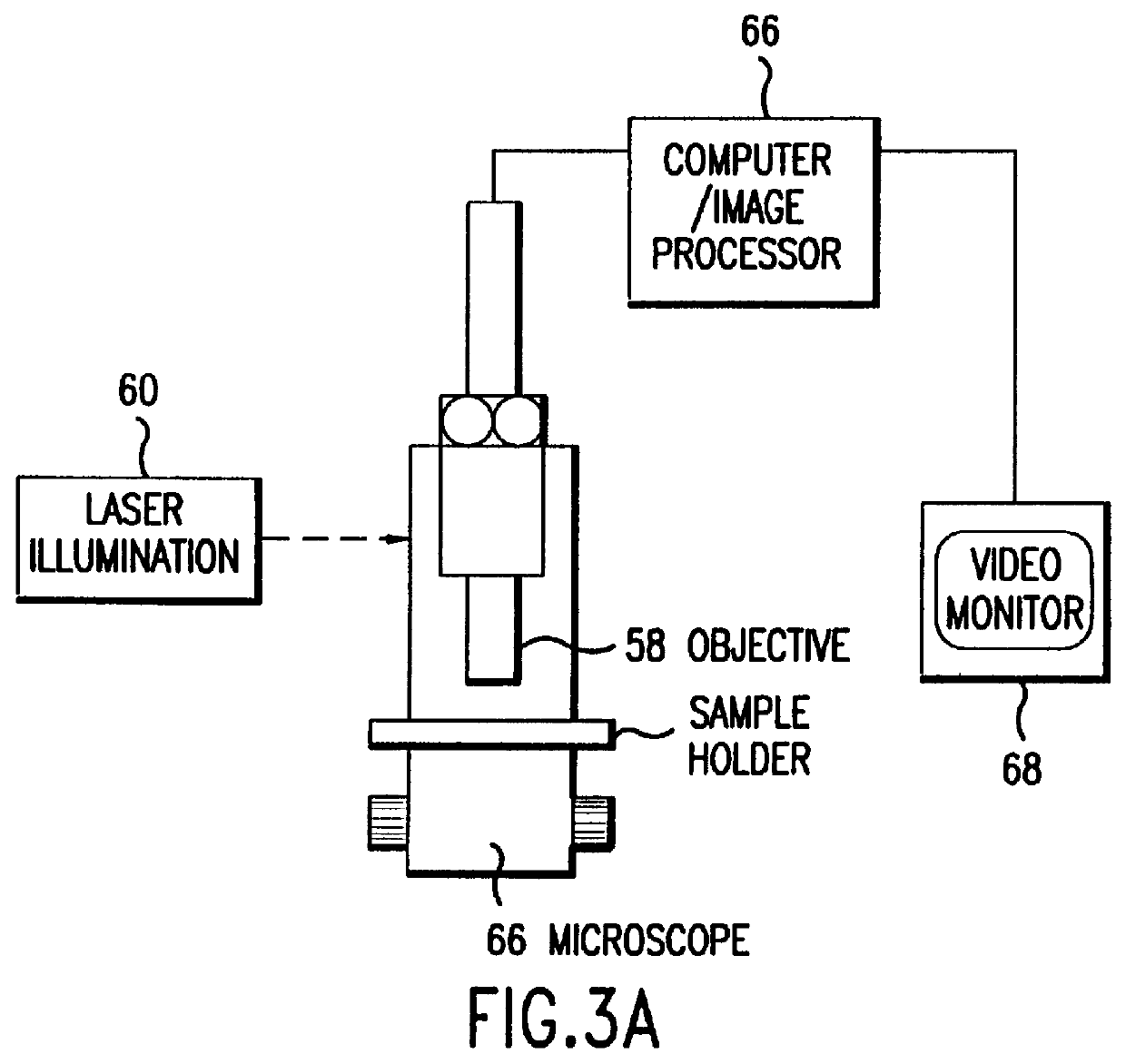
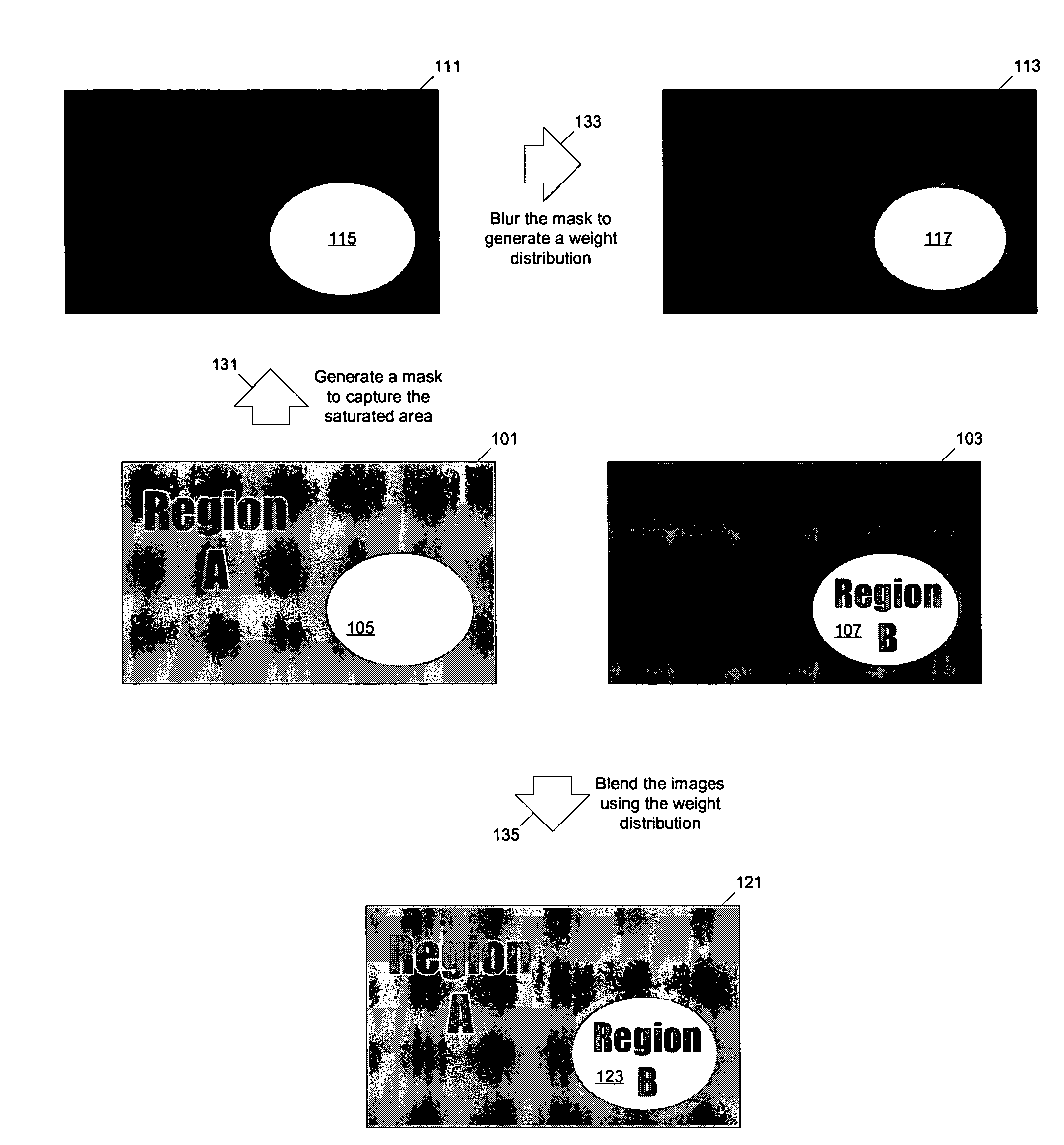
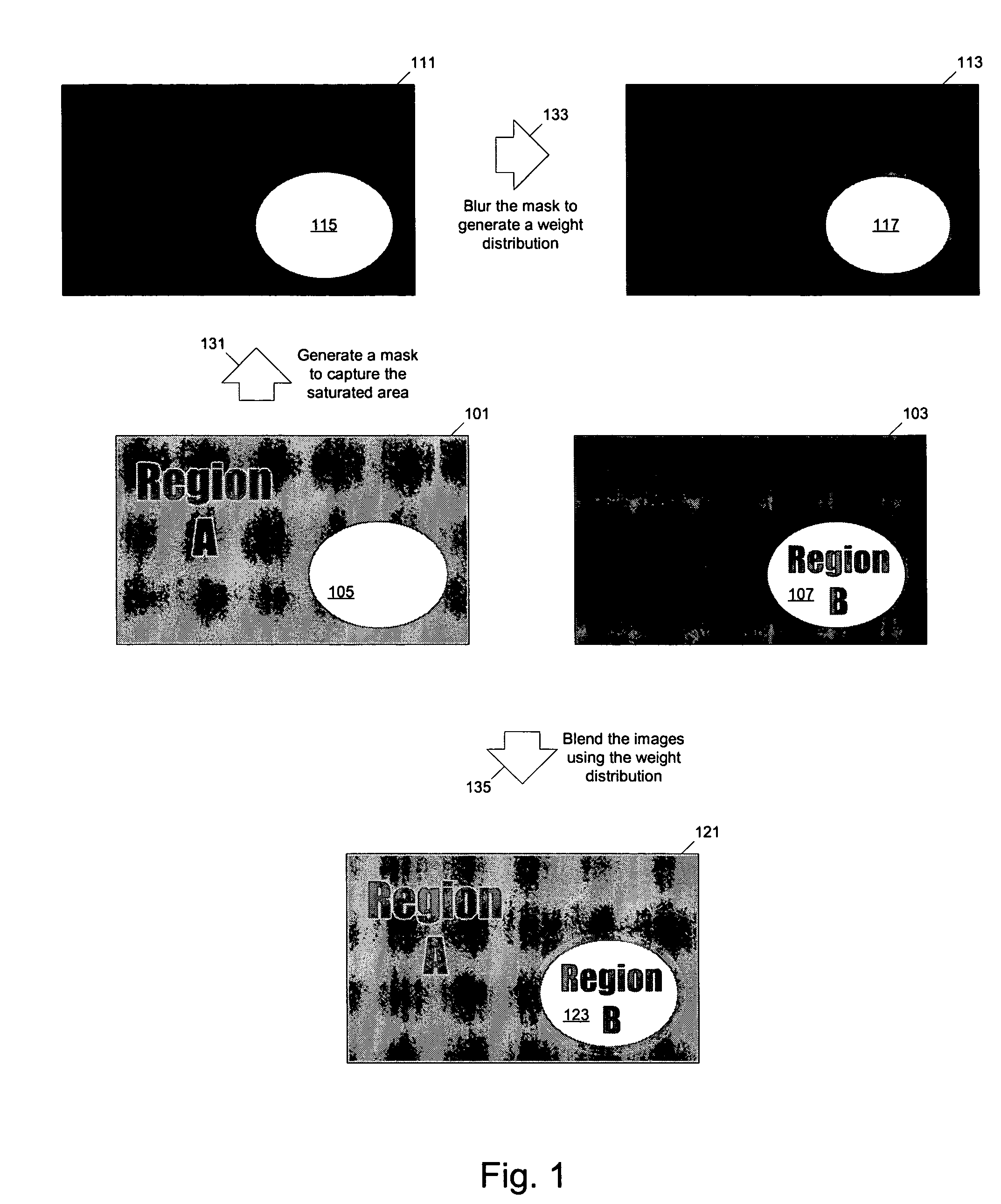
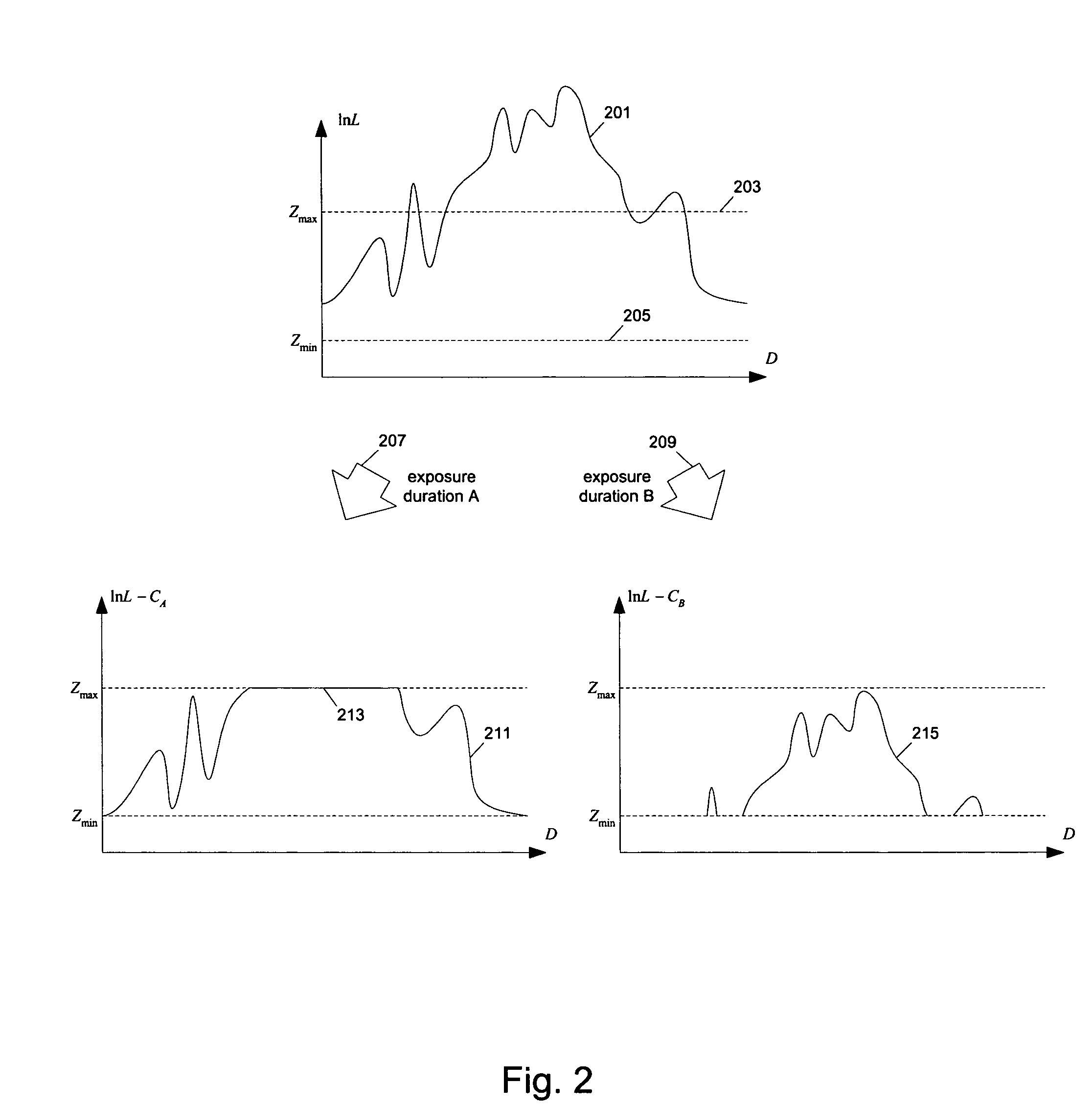
Methods and apparatuses for image processing
ActiveUS7612804B1Reduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingMethod of images
Methods and apparatuses for generating a low dynamic range image for a high dynamic range scene. In one aspect, a method to generate a low dynamic range image from a high dynamic range image, includes: determining one or more regions of the high dynamic range image containing pixels having values that are outside a first range and inside a second range; computing a weight distribution from the one or more regions; and generating the low dynamic range image from the high dynamic range image using the weight distribution. In another aspect, a method of image processing, includes: detecting one or more regions in a first image of a high dynamic range scene according to a threshold to generate a mask; and blending the first image and a second image of the scene to generate a third image using the mask.
Owner:APPLE INC
Polypropylene block-copolymer resin and process for producing it
Polypropylene block-copolymer resin exhibiting high melt tension and improved moldability with balanced stiffness and impact resistance may be molded at high speed into large-sized articles, including, stretched films, with good appearance and resistance to deformation. The block copolymer includes a higher molecular weight polypropylene segment, a lower molecular weight polypropylene segment and an ethylene alpha-olefin copolymer segment. When subjected to dissolution fractionation m paraxylene, a large proportion is insoluble at 23° C. but soluble at 135° C., and a smaller portion is soluble at 23° C. The block copolymer has a melt flow rate of 0.01 to 5 g / 10 min at 230 C. (2.16 kg) and a molecular weight distribution Mw / Mn of 6-20 and Mz / Mw of at least 3.5. A continuous multistage polymerization may be used to form the block copolymer.
Owner:PRIME POLYMER CO LTD
Process for producing polyolefins
InactiveUS6355741B1Reduce amountReduce the amount requiredChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsChemical recyclingPolyolefinDiluent
A process for producing polyolefins having a bimodal molecular weight distribution, the process comprising producing a first polyolefin fraction in the presence of a catalyst in a first loop reactor, and producing a second polyolefin fraction in the presence of the catalyst in a second loop reactor which is serially connected to and downstream of the first loop reactor, the first and second polyolefin fractions being blended in the second loop reactor to form a polyolefin having a bimodal molecular weight distribution, at least the first loop reactor containing a diluent under supercritical conditions which is circulated around the loop of the reactor, and wherein at least the first loop reactor is provided with a fluff concentrating device communicating with the loop and in which polyolefin fluff of the first fraction is concentrated in the supercritical diluent, and polyolefin fluff of the first polyolefin fraction is transferred together with an amount of supercritical diluent from the fluff concentrating device of the first loop reactor into the second loop reactor.
Owner:FINA RES SA
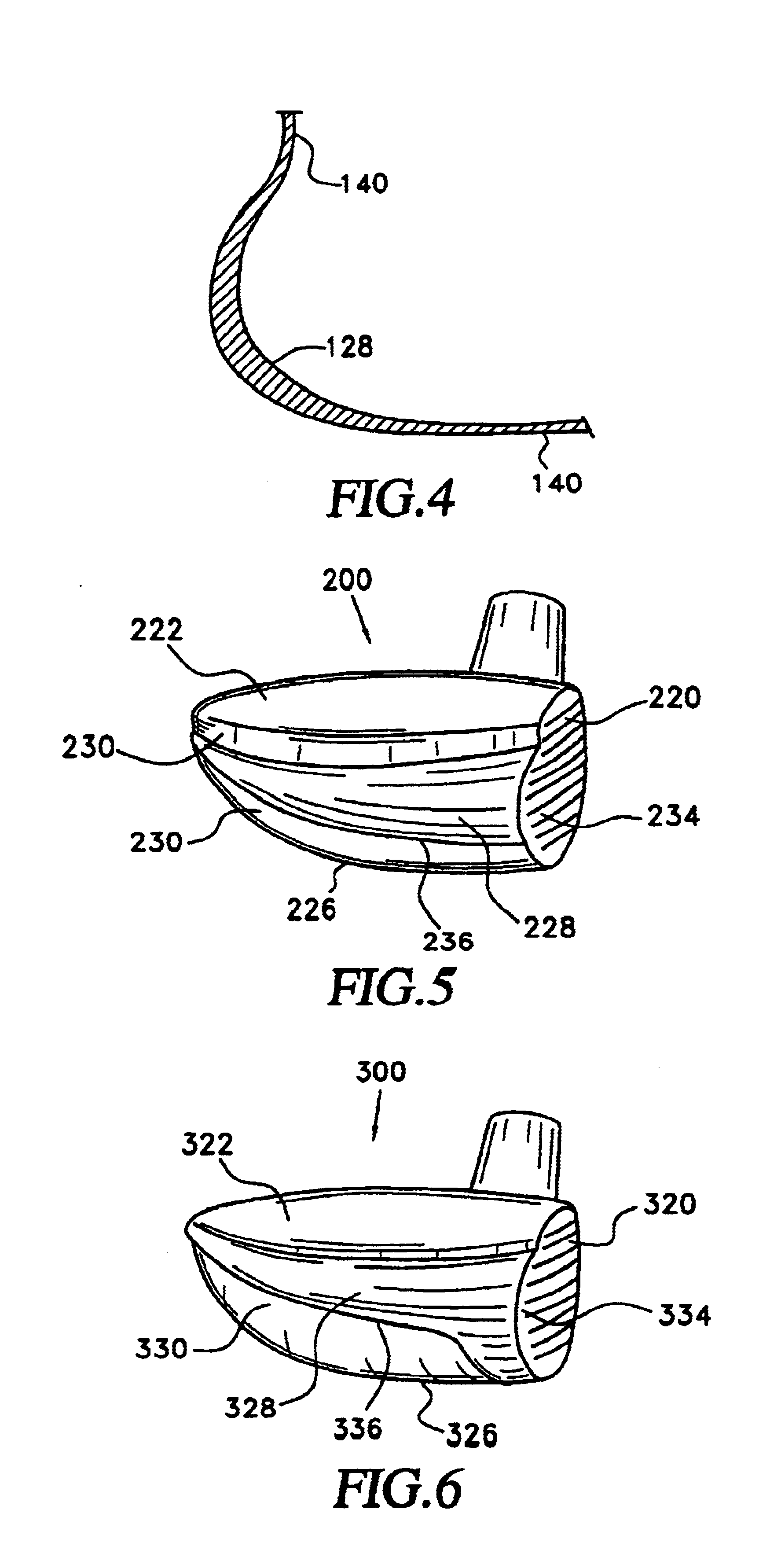
Metalwood type golf clubhead having an improved structural system for reduction of the cubic centimeter displacement and the elimination of adverse aerodynamic drag effect
InactiveUS20050009622A1Reduces cubic-centimeter displacementReduce the effect of dragGolf clubsRacket sportsAerodynamic dragEngineering
A metalwood type golf clubhead, including a clubhead body having a toe, heel, top crown surface, bottom sole surface, side surfaces, rear surface and ball-striking clubface, having an inwardly disposed lower surface located between the bottom sole surface and the top crown surface. The inwardly disposed lower structure provides improved weight distribution for better balance, additional strength and stability to clubhead and considerably decreases the overall cc displacement and overall weight / mass at the bottom of the clubhead without decreasing the size of the ball striking face and / or the upper top crown surface.
Owner:ANTONIOUS ANTHONY J
Catalysts for producing broad molecular weight distribution polyolefins in the absence of added hydrogen
ActiveUS8288487B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogenPolyolefin
The present invention provides a polymerization process utilizing a dual metallocene catalyst system for the production of broad or bimodal molecular weight distribution polymers, generally, in the absence of added hydrogen. Polymers produced from the polymerization process are also provided, and these polymers can have a Mn in a range from about 9,000 to about 30,000 g / mol, and a short chain branch content that decreases as molecular weight increases.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6294136B1Improve throughputQuick buildMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresMicroscope slideMap Location
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
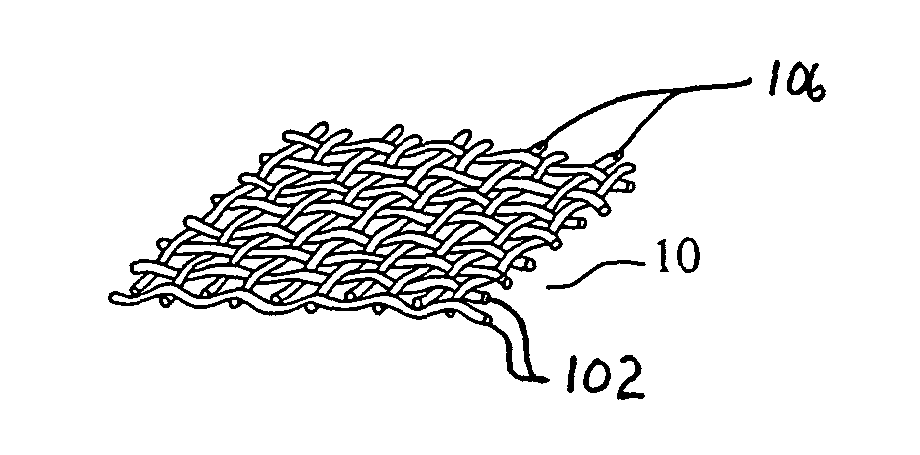
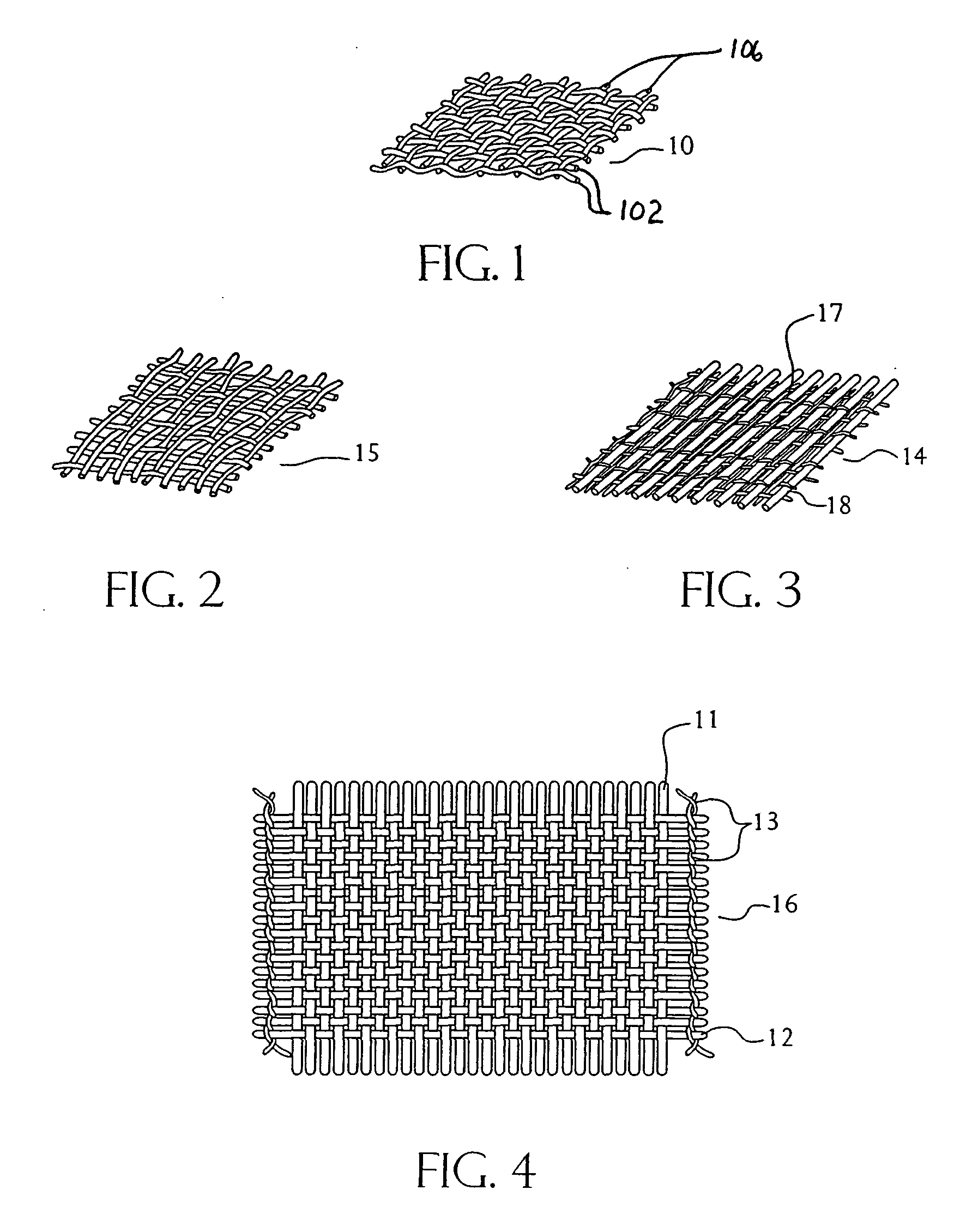
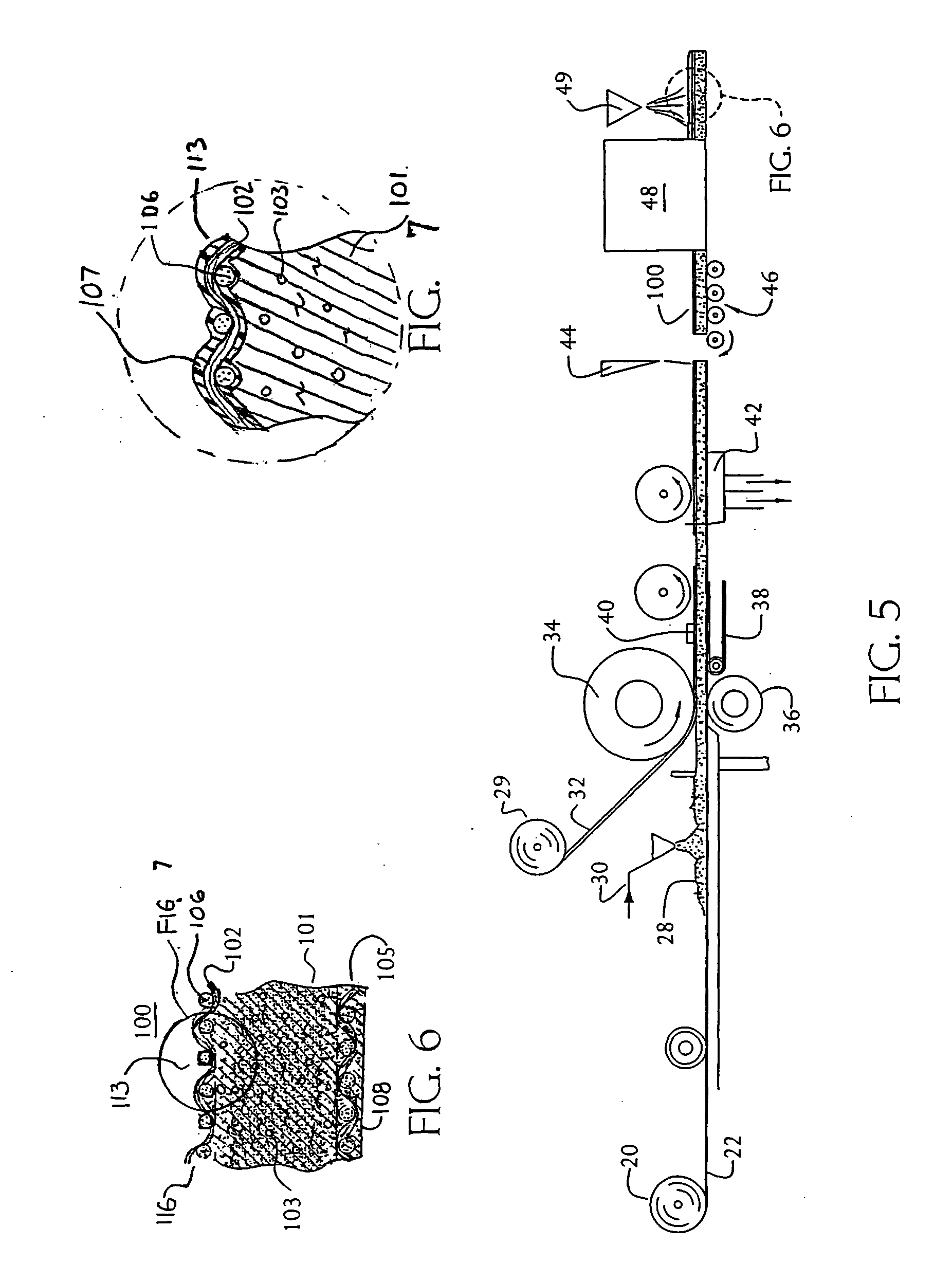
Fabric reinforcement and cementitious boards faced with same
ActiveUS20050009428A1Improve coating uniformityConvenient coatingDecorative surface effectsPretreated surfacesCement boardEngineering
Fabric and reinforcements are provided by this invention which, in a first embodiment, include a plurality of warp yarns having a first twist (turns / inch) and a plurality of weft yarns having a second twist which is greater than the first twist. A coating is applied over a substantial portion of the warp and weft yarns after they are assembled or laid together, so as to produce a weight distribution ratio of less than about 2.0:1, based upon the weight of the resinous coating of the weft yarns over the weight of the resinous coating on the warp yarns. This can be achieved, in substantial part, due to the difference in the twist ratios of the warp and weft yarns, which difference permits a more uniform coating to be applied. Further embodiments of this invention include a cementitious board and methods of making a coated fabric and cementitious board.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ADFORS CANADA LTD
Set of golf club irons
A set of golf club irons with improved vibration damping and weight distribution, each golf club comprising a shaft and a head comprising a body portion having a front portion and a back portion, wherein the body portion defines an upper aperture and a lower aperture extending through the body portion communicating with the front portion and the back portion.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6509158B1Quick analysisQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMicroscope slideMap Location
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Production of polyethylene having a broad molecular weight distribution
InactiveUS6221982B1High densityImprove mechanical propertiesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolymer scienceZiegler–Natta catalyst
A process for producing high density polyethylene in the presence of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst system in two liquid full loop reactors in series, wherein in a first reactor a first polyethylene product is polymerized substantially by homopolymerization of ethylene and hydrogen, optionally with a minor degree of copolymerization of ethylene with an alpha-olefinic comonomer comprising from 3 to 8 carbon atoms, and in a second reactor serially connected to the first reactor downstream thereof a second polyethylene product is copolymerized from ethylene and an alpha-olefinic comonomer comprising from 3 to 8 carbon atoms, and a hydrogenation catalyst is introduced into the reactants downstream of the first reactor.
Owner:FINA RES SA
Golf club
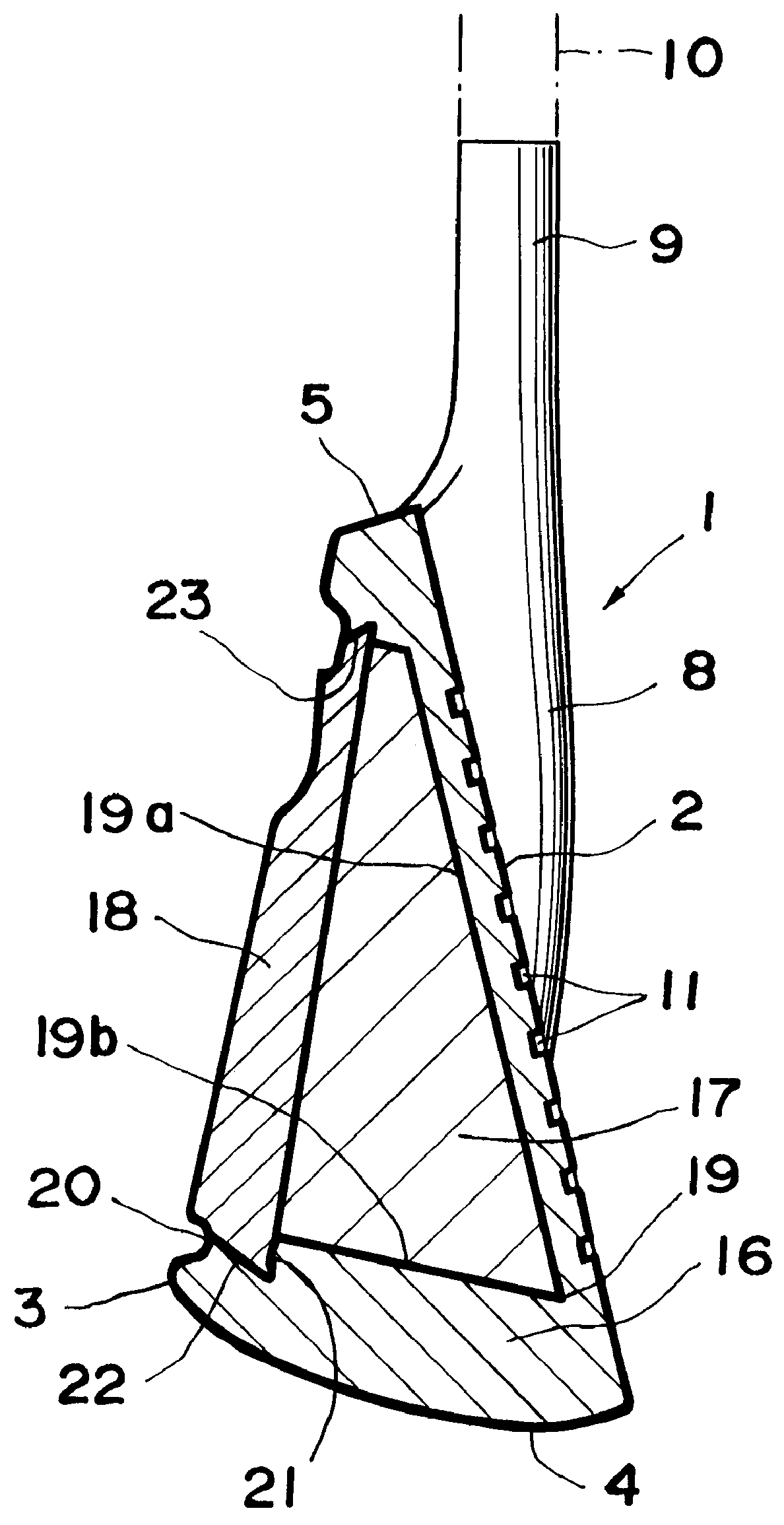
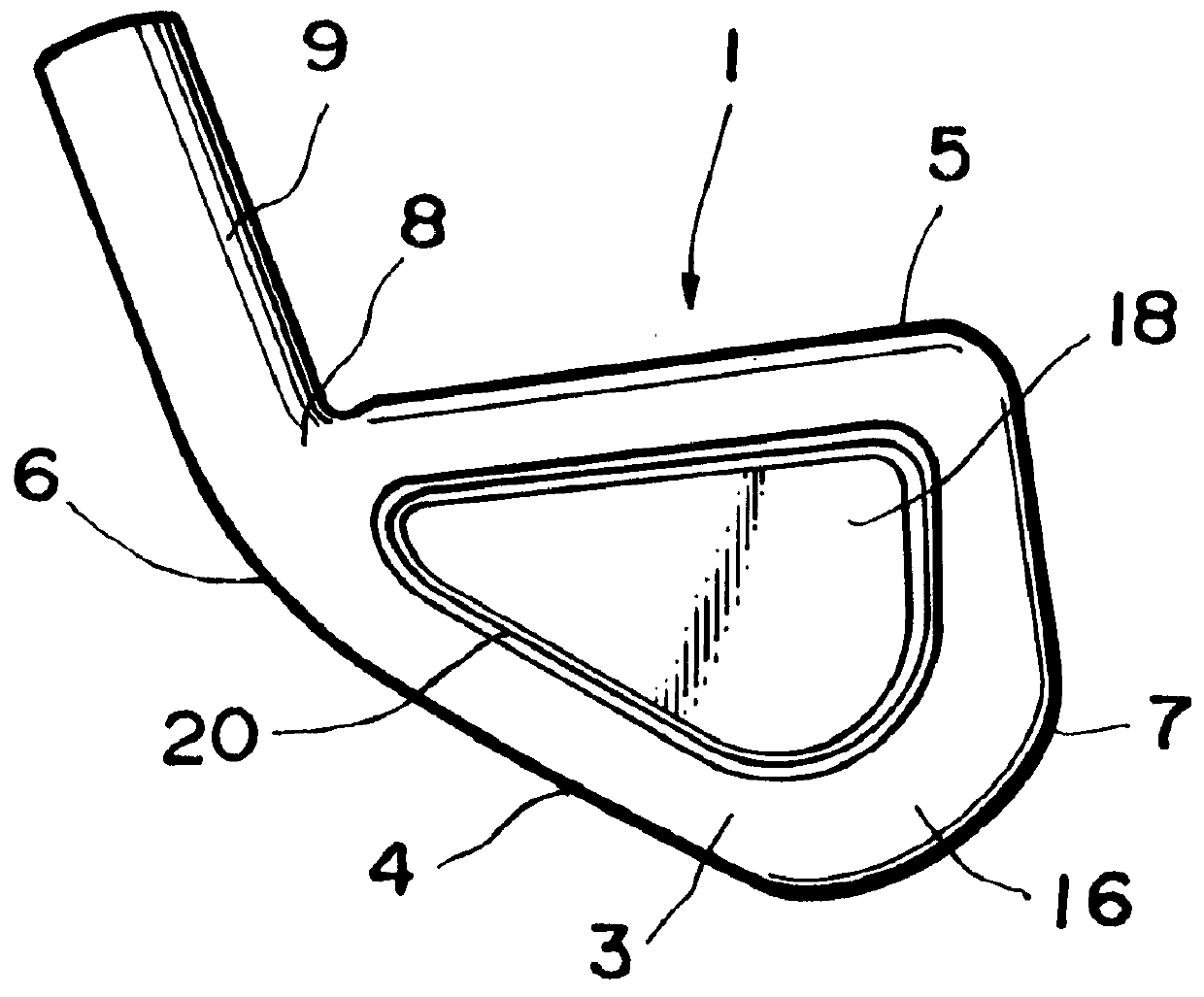
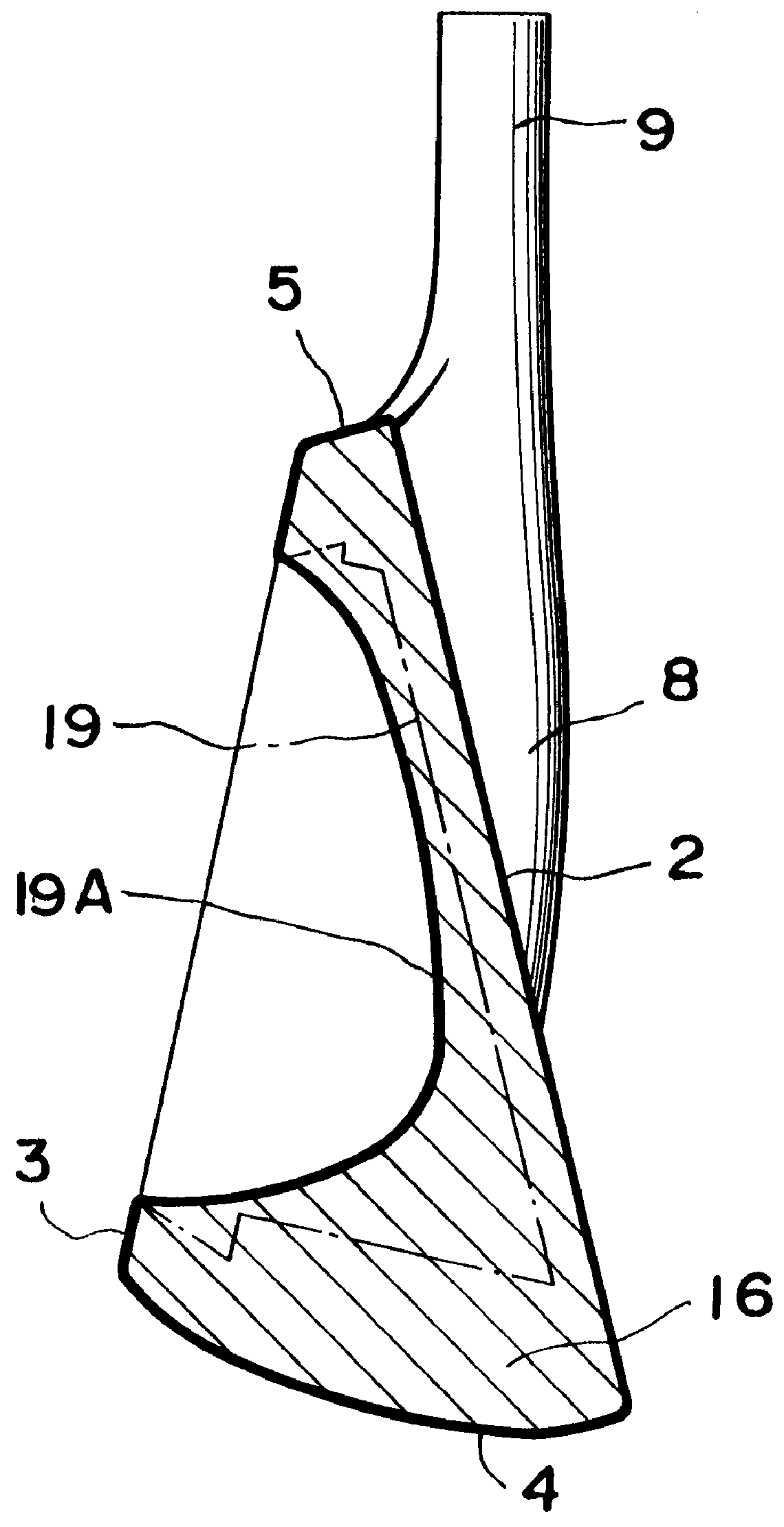
A golf club with which you can strike a strong ball with a sharp feeling in striking as well as an enlarged sweet area. A concave portion 19 is formed at a rear side of a head body 16. A metallic balance weight 17 is fitted into the concave portion 19. A cover 18 for covering the balance weight 17 is fixed to the rear side of the head body 16. The specific gravity of a material for the balance weight 17 is smaller than that of the head body 16. Accordingly, a more sharp feeling in striking can be obtained as compared to a conventional head whose concave portion is hollow. Additionally, a sweet area can be enlarged owing to the weight distribution biased toward the periphery. The specific gravity of a material for the cover 18 is at least equal to that of the material for the head body 16. As a result, the depth of the center of gravity is made greater, thereby further widening a sweet area.
Owner:ENDO MFG COMPANY
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6610256B2Quick analysisQuick buildBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideImaging processing
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
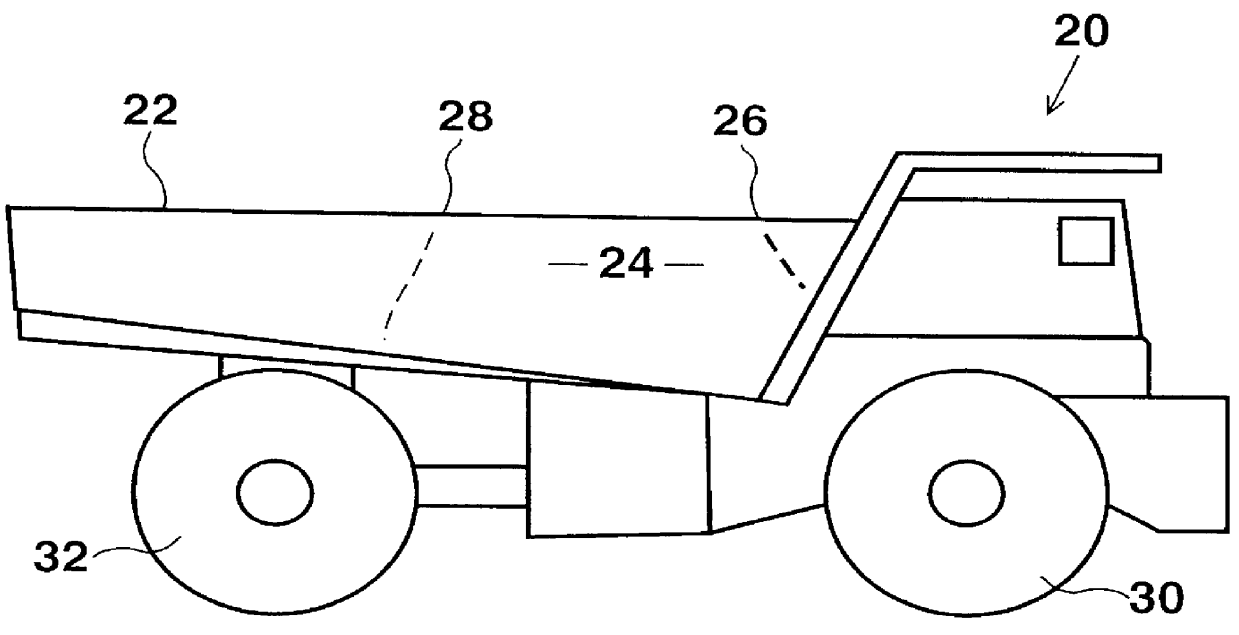
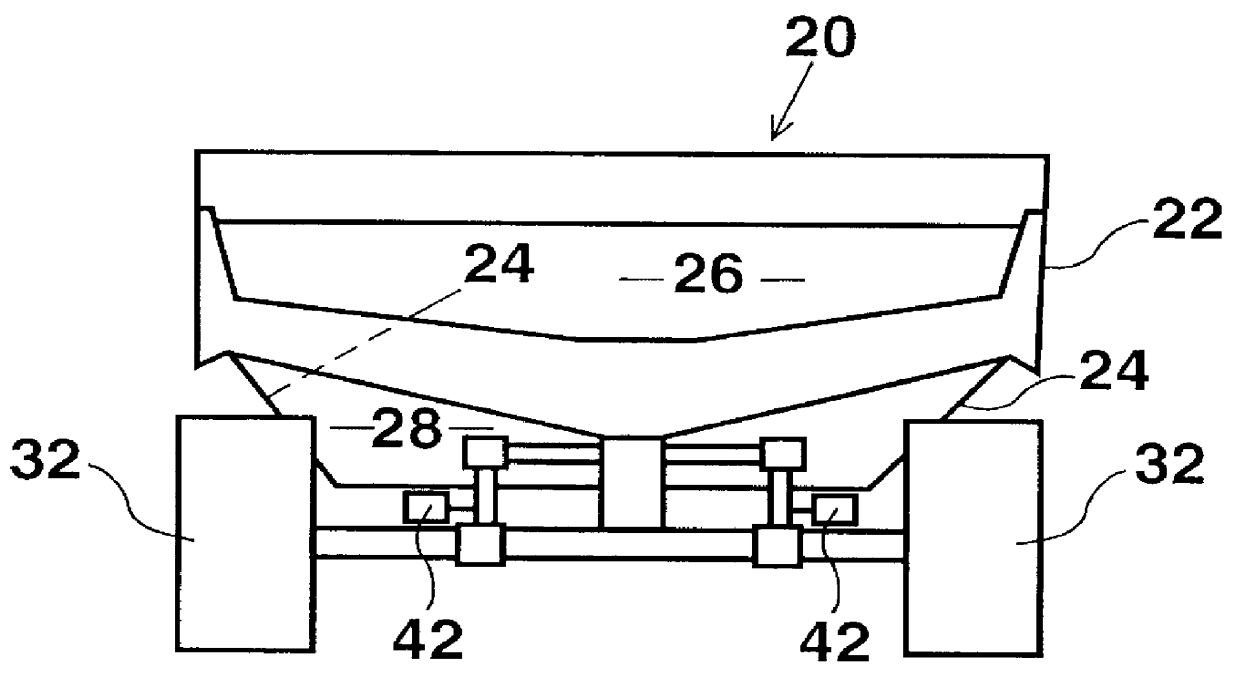
Load distribution system for haulage trucks
InactiveUS6157889AMechanical machines/dredgersMeasurement arrangements for variableAutomated algorithmEngineering
Weight sensors coupled to the bed of a conventional haulage truck measure the weight applied to each tire strut as the truck is being loaded. Based on the weight applied to each strut, the exact position of the center of gravity of the load in the truck's bed is calculated and displayed on a monitor relative to a target position deemed optimal for uniform weight distribution. Based on this information, the operator of the loading machine can complete the loading operation in such a way as to shift the center of gravity toward the chosen target position. In another embodiment of the invention, an automated algorithm calculates and displays where the next bucket load should be dropped, based on its approximate weight, in order to shift the center of gravity toward the target location.
Owner:MODULAR MINING SYSTEMS
Rapid characterization of polymers for combinatorial, analytical and process control applications
InactiveUS20010027949A1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Gel with wide distribution of Mw in mid-block
A gelatinous elastomer comprising an A-B-A triblock copolymer and a plasticizer useful, for example, in casting fine-detail molds at a low processing temperature. The gelatinous elastomer comprises copolymer molecules having a molecular weights generally evenly distributed across a range of molecular weights rather than having a relatively narrow molecular weight distribution centered about a single molecular weight. The A-B-A triblock copolymer may include SEBS, SEEPS, or other triblock copolymers. The plasticizer may include mineral oil or other plasticizing fluids.
Owner:PURPLE INNOVATION LLC
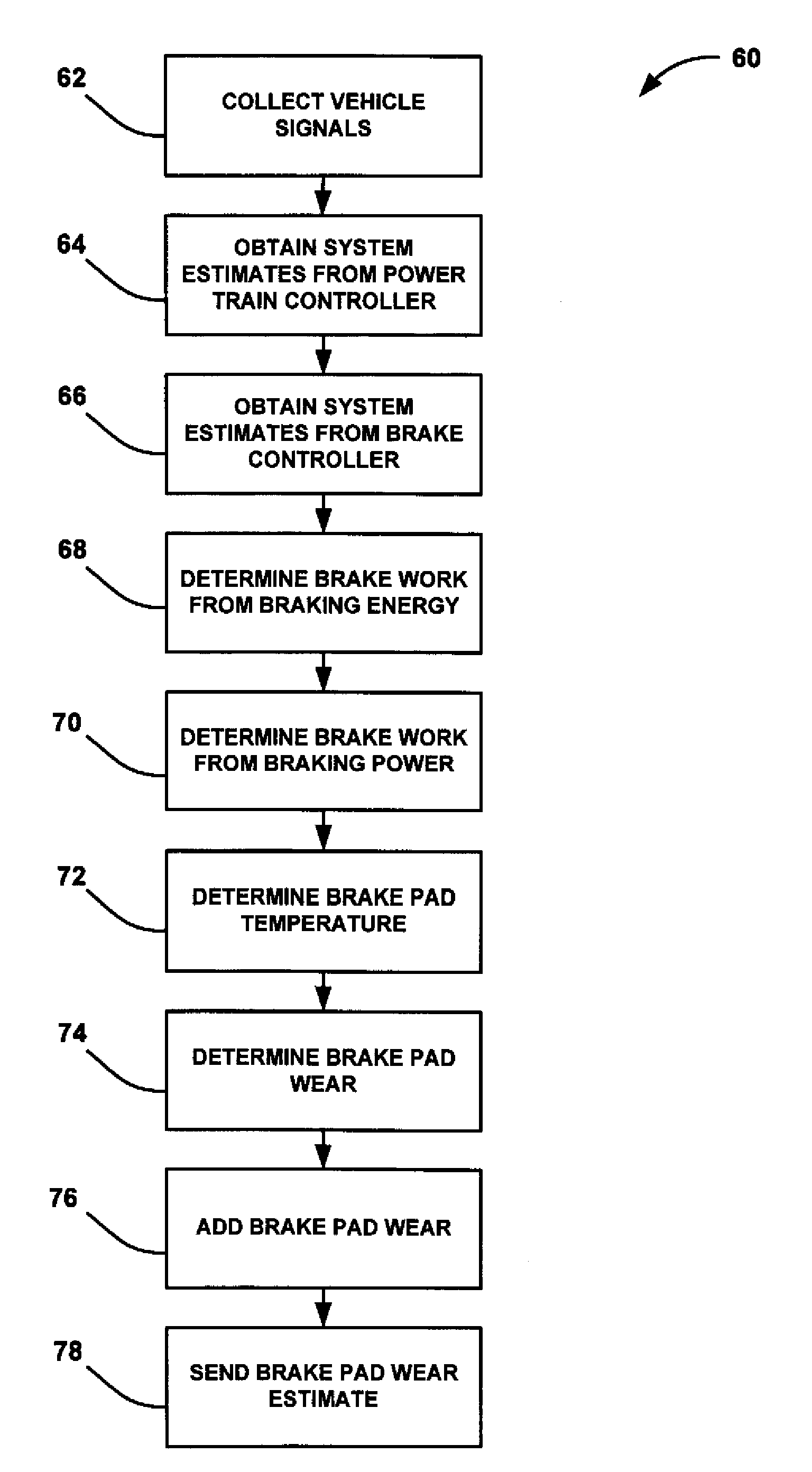
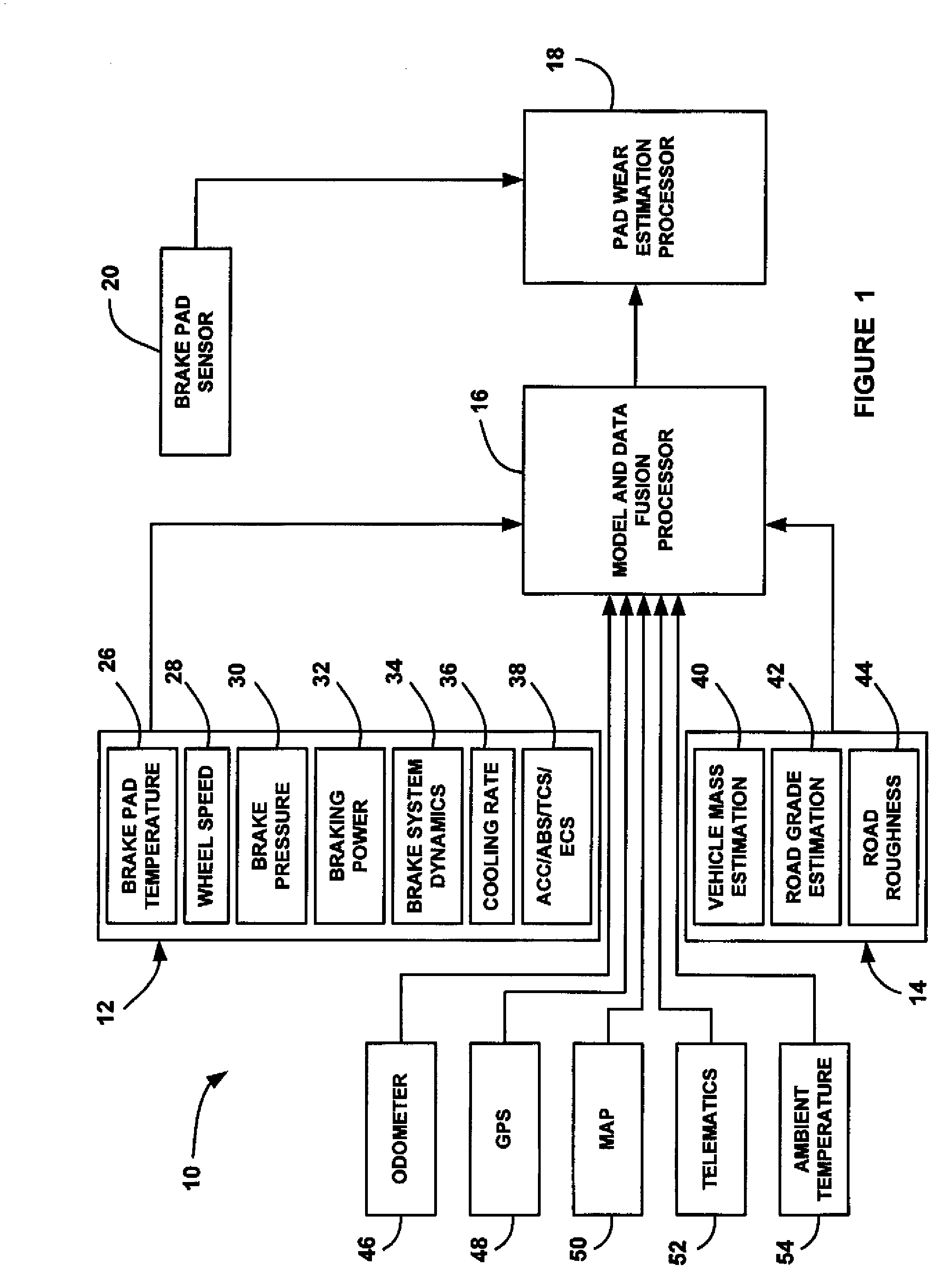
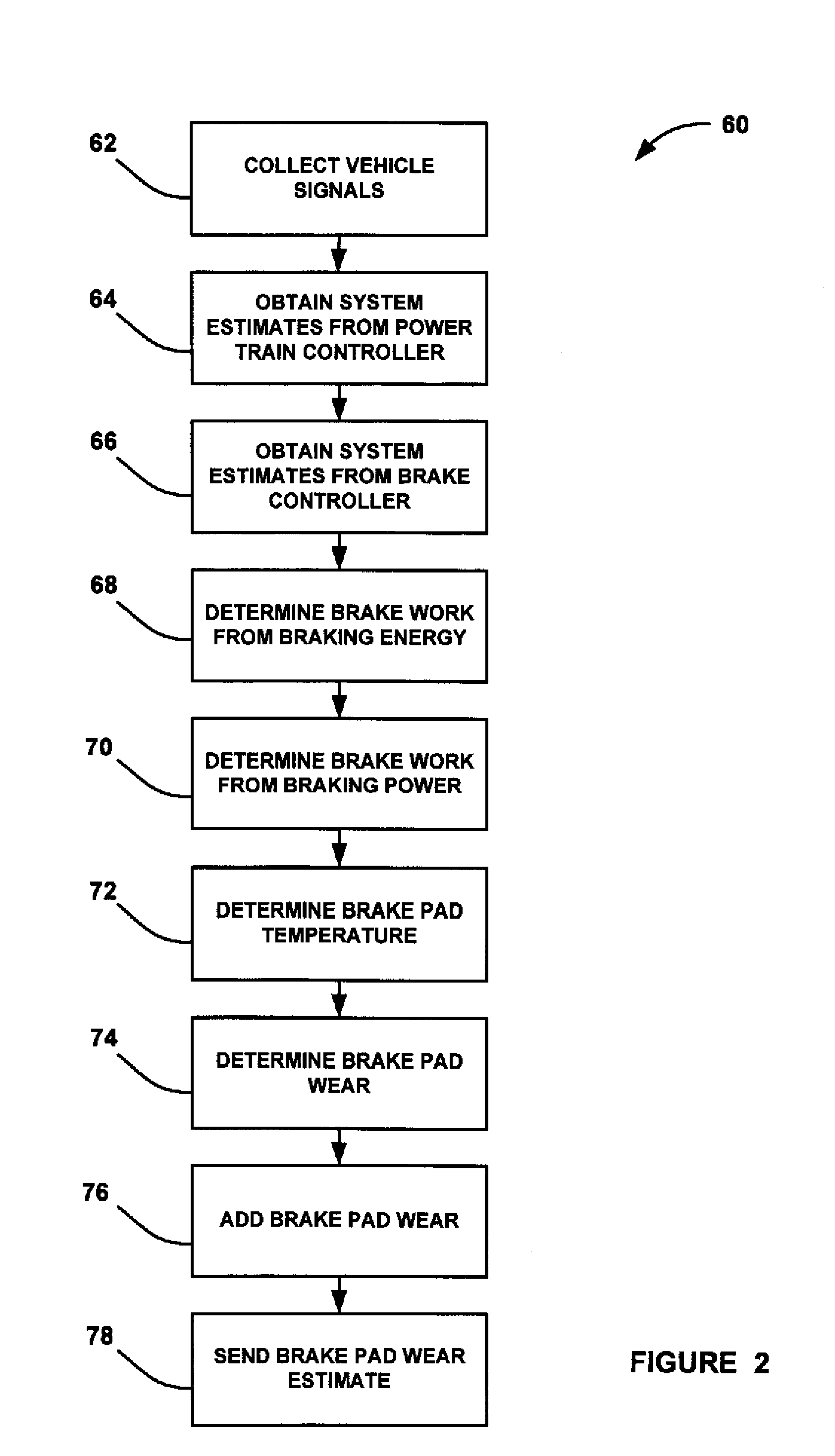
Brake pad prognosis system
A method for providing an estimate of brake pad thickness. The method employs fusion of sensors, if used, and driver brake modeling to predict the vehicle brake pad life. An algorithm is employed that uses various inputs, such as brake pad friction material properties, brake pad cooling rate, brake temperature, vehicle mass, road grade, weight distribution, brake pressure, brake energy, braking power, etc. to provide the estimation. The method calculates brake work using total work minus losses, such as aerodynamic drag resistance, engine braking and / or braking power as braking torque times velocity divided by rolling resistance to determine the brake rotor and lining temperature. The method then uses the brake temperature to determine the brake pad wear, where the wear is accumulated for each braking event. A brake pad sensor can be included to provide one or more indications of brake pad thickness from which the estimation can be revised.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
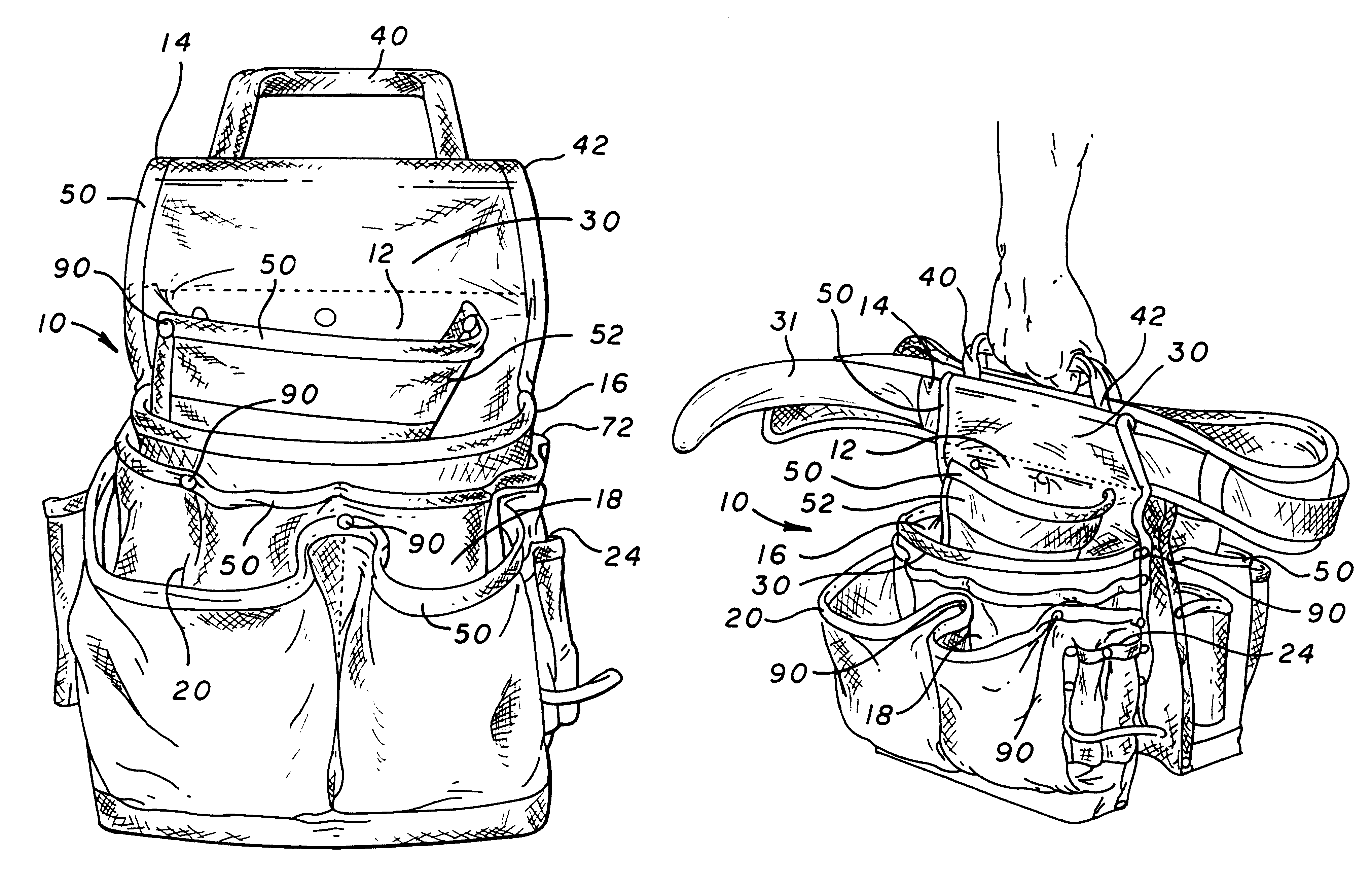
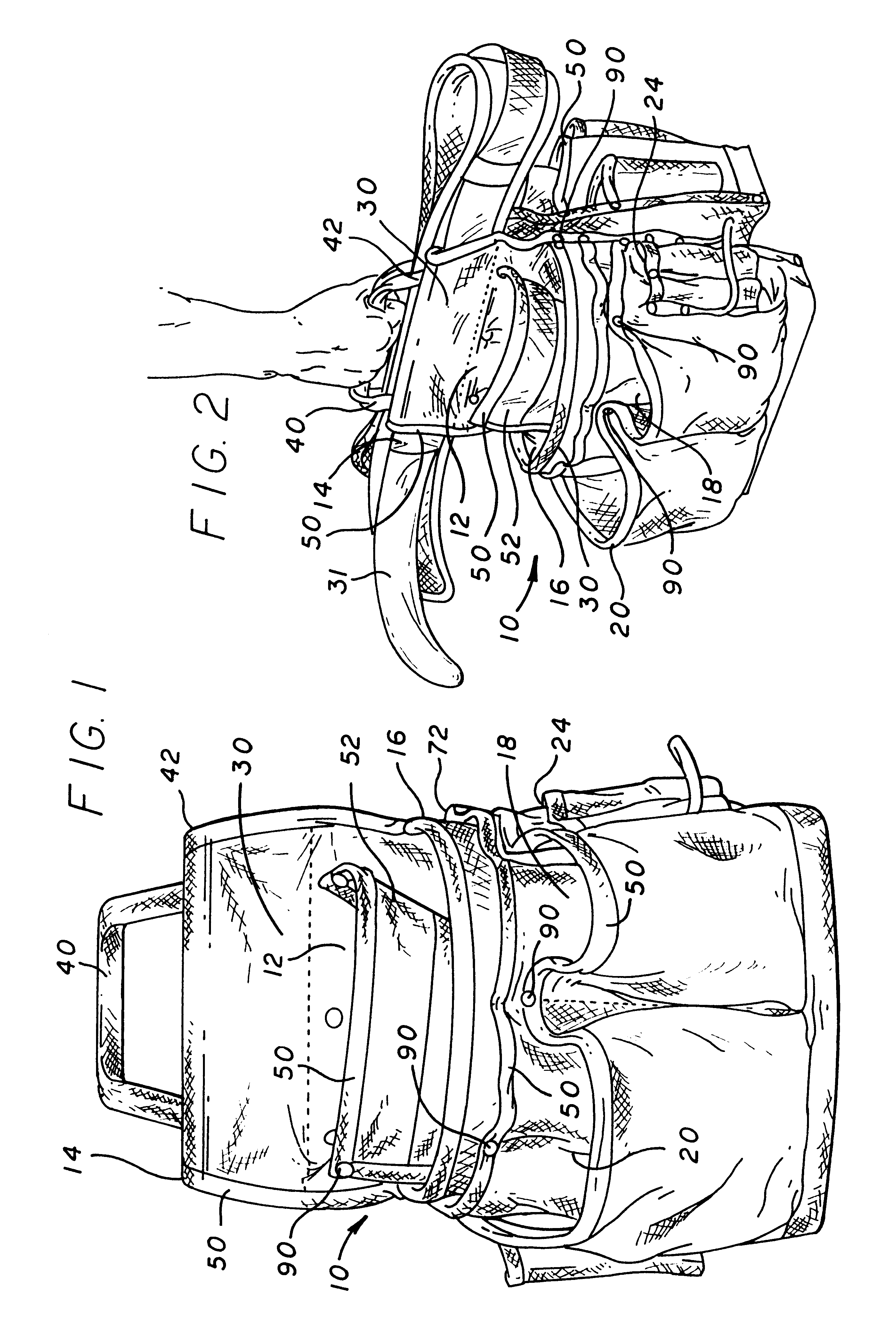
Specially configured tool carrier
The present invention relates to tool carriers usually used on work belts, aprons, bucket carriers and the like. The present invention comprises a tool carrier or bag that has at least one handle on the top thereof so that it can be carried from place to place in an upright position, either while it is still on a work belt that is not currently being worn or being carried by itself. In the preferred embodiment, a structurally strong handle is attached to the back of the tool carrier proximate the area in which a belt may be inserted through the tool carrier by heavy duty attachment means. It is preferable to use two tool carriers each having a handle through which the user's hand is inserted in order to provide even weight distribution when the belt is being carried from place to place.
Owner:CUSTOM LEATHERCRAFT MFG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com