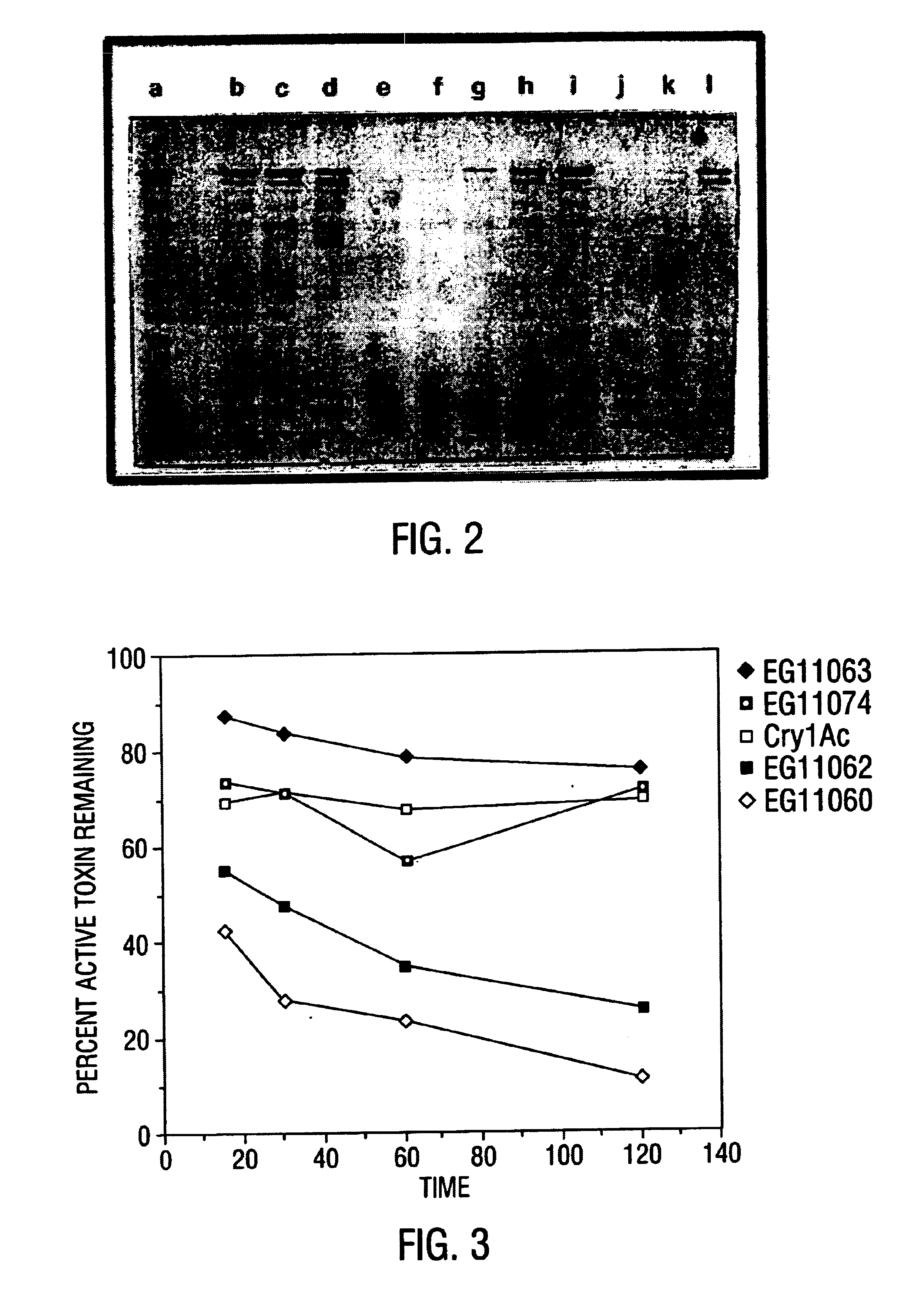
Patents
Literature
4820 results about "GMO Plants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
FACT:There are 10 genetically modified crops commercially available today: alfalfa, apples, canola, corn (field and sweet), cotton, papaya, potatoes, soybeans, squash and sugar beets. This chartexplains why each of the 10 GMO crops are genetically modified.
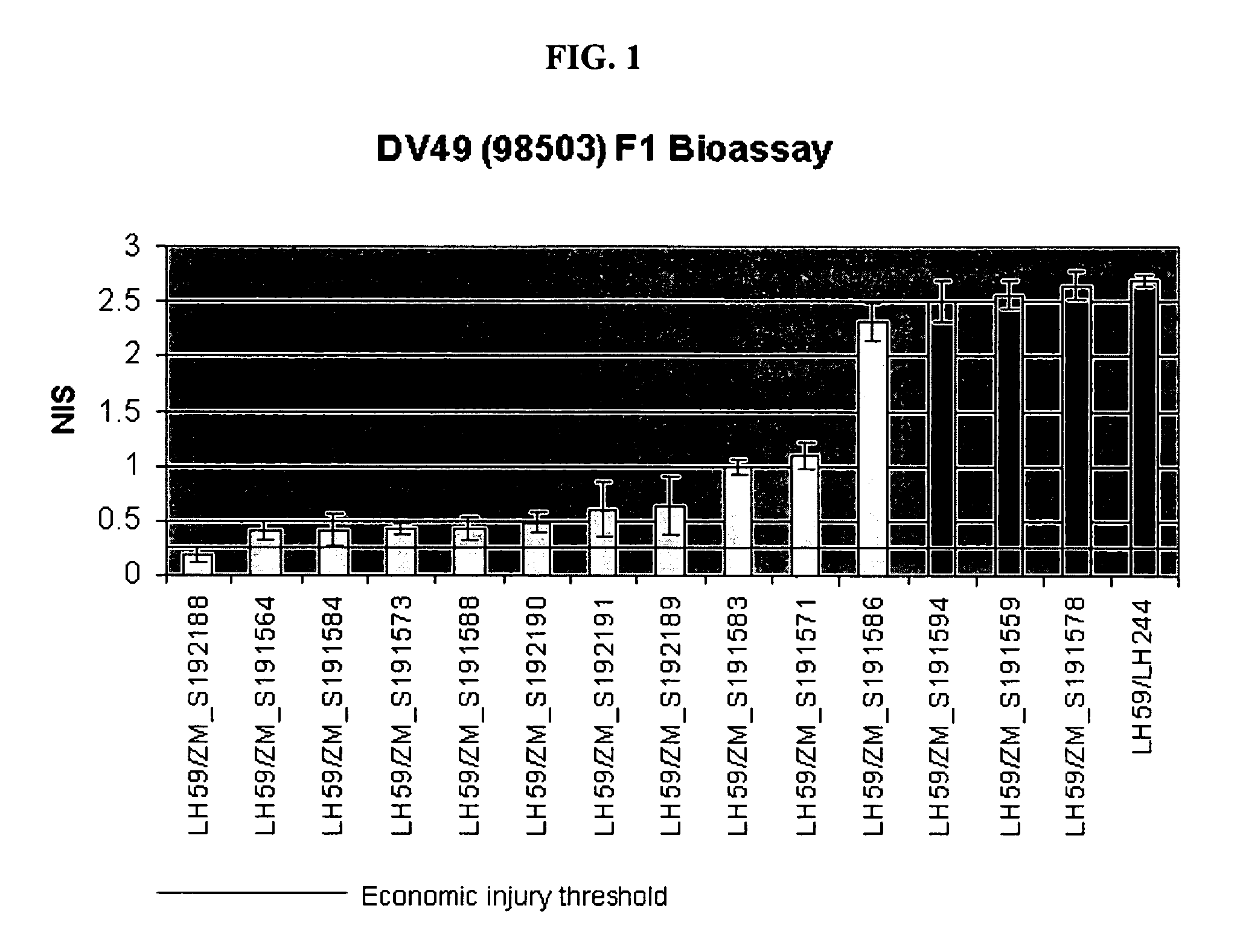
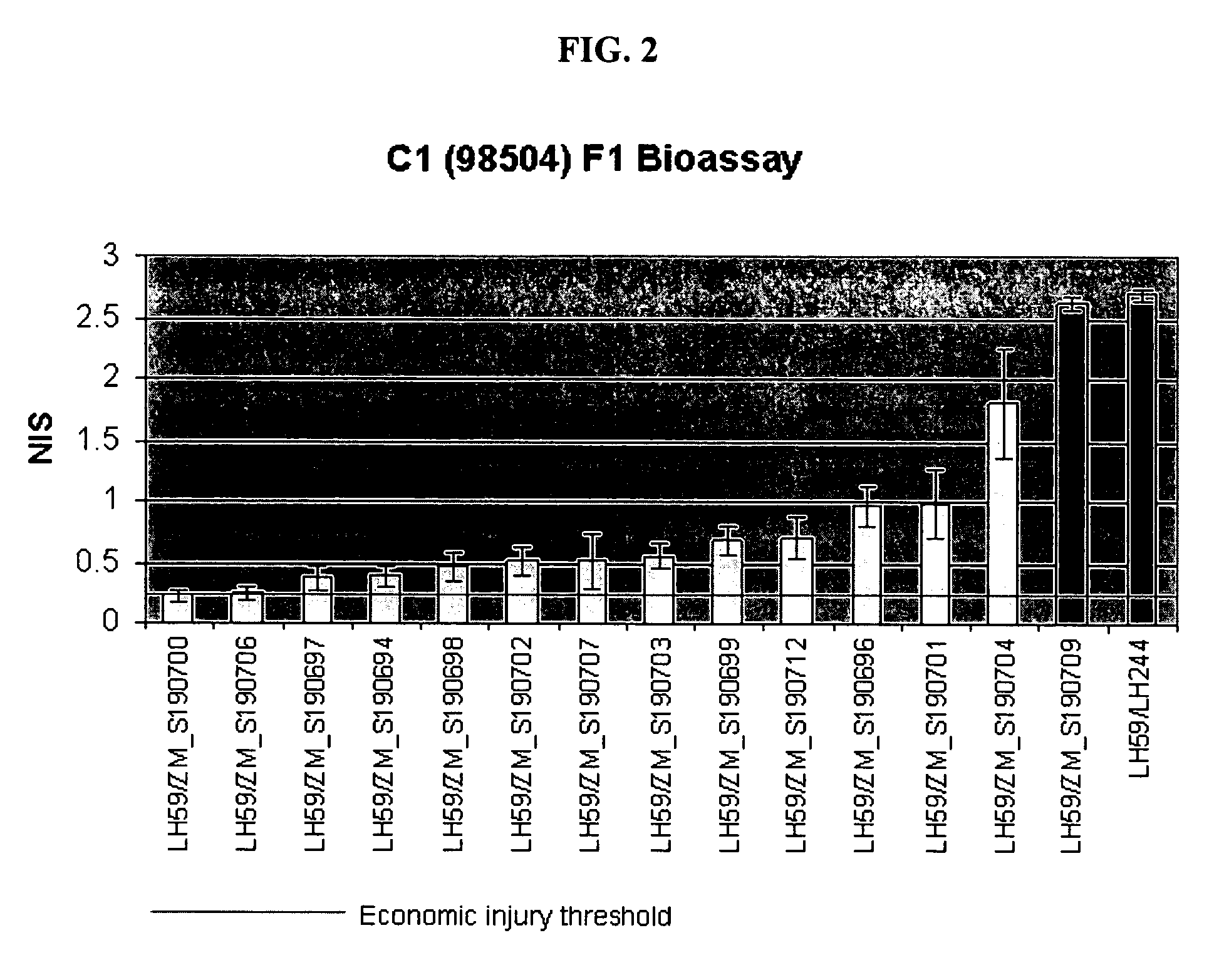
Inbred corn line LH283BtMON810
InactiveUS6852915B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetic Materials
An inbred corn line, designated LH283BtMON810, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of inbred corn line LH283BtMON810, to the plants of inbred corn line LH283BtMON810 and to methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing the inbred line LH283BtMON810 with itself or another corn line. The invention further relates to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from the inbred LH283BtMON810.
Owner:HOLDENS FOUND SEEDS
Cropping systems for managing weeds
The invention provides cropping systems for managing weeds in crop environments. The cropping systems comprise, in one embodiment, transgenic plants that display tolerance to an auxin-like herbicide such as dicamba. Method for minimizing the development of herbicide resistant weeds are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
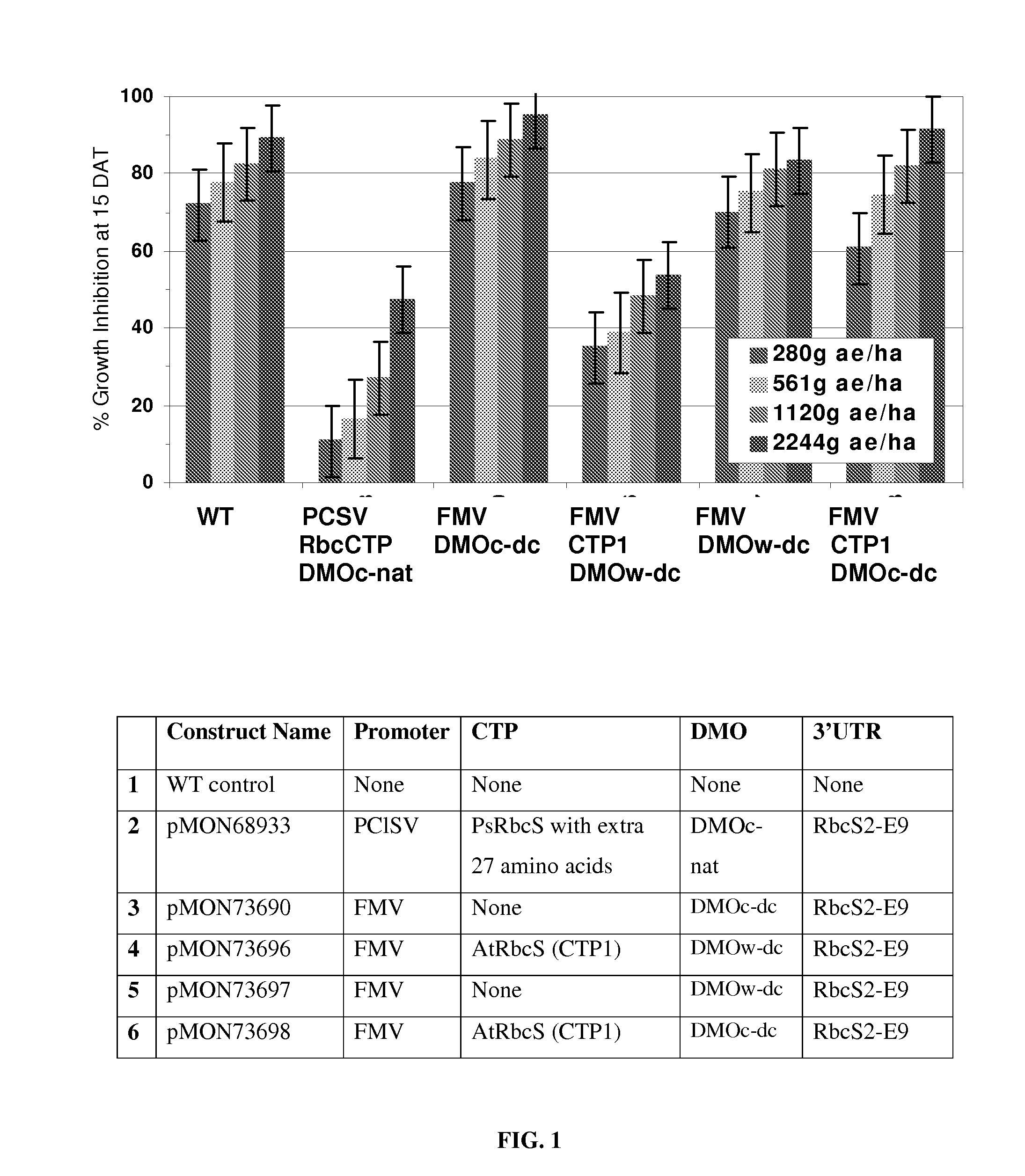
Chloroplast transit peptides for efficient targeting of DMO and uses thereof
ActiveUS7838729B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesMonooxygenaseGMO Plants
The invention provides for identification and use of certain chloroplast transit peptides for efficient processing and localization of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO) enzyme in transgenic plants. Methods for producing dicamba tolerant plants, methods for controlling weed growth, and methods for producing food, feed, and other products are also provided, as well as seed that confers tolerance to dicamba when it is applied pre- or post-emergence.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Full-length plant cDNA and uses thereof
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
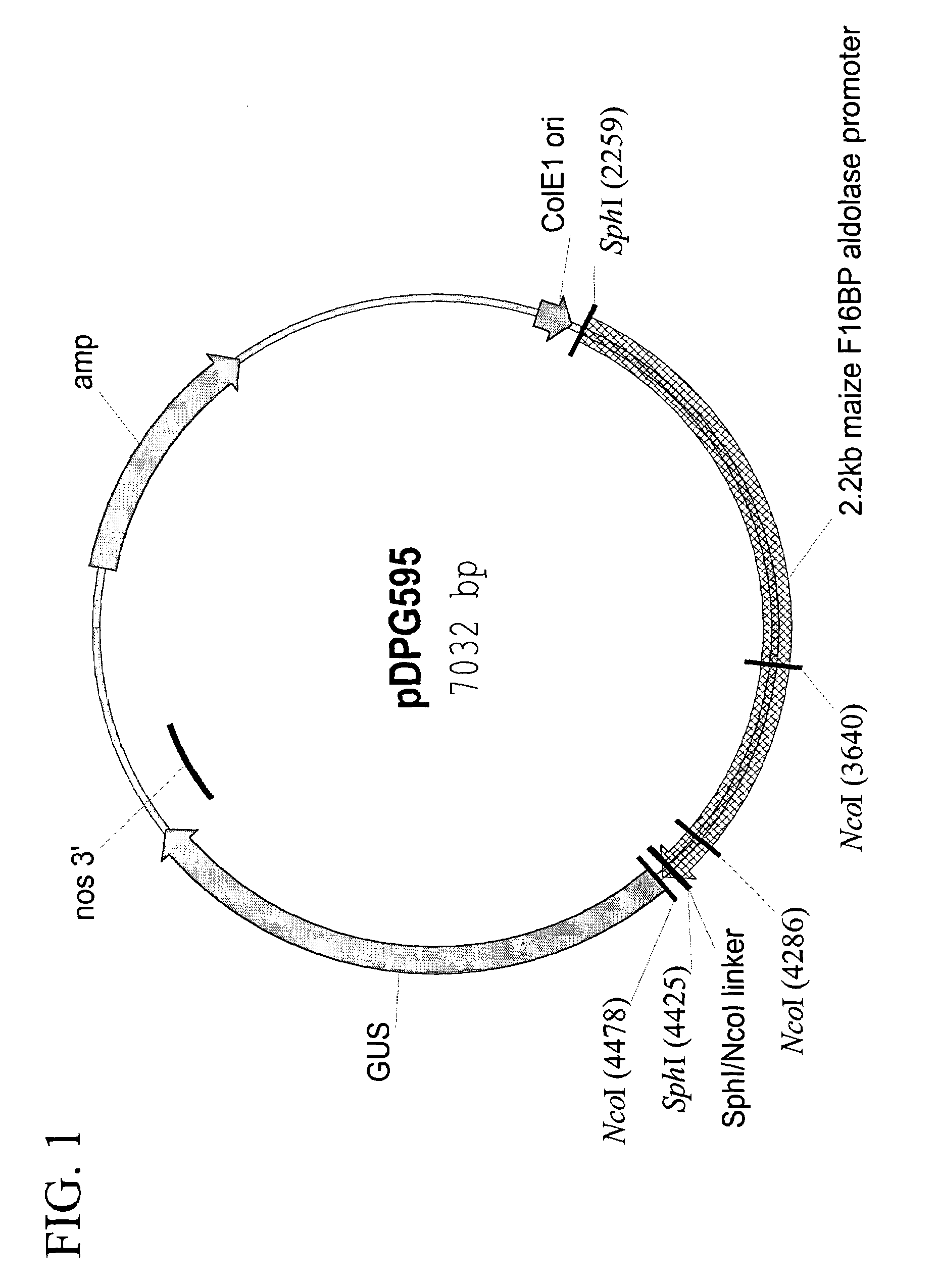
Maize chloroplast aldolase promoter compositions and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS7151204B2Simple compositionQuality improvementSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFructoseTransgene
The current invention provides the promoter of the Zea mays nuclear gene encoding chloroplast-localized fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F16BP) aldolase. Compositions comprising this sequence are described, as are plants transformed with such compositions. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the chloroplastic F16BP aldolase promoter by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Polypeptide compositions toxic to diabrotic insects, and methods of use
InactiveUS6468523B1Easy to storeInhibit microbial growthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDelta endotoxinPolynucleotide
Disclosed is a novel Lepidopteran- and Coleopteran-active delta-endotoxin polypeptide, and compositions comprising the polypeptide, peptide fragments thereof, and antibodies specific therefor. Also disclosed are vectors, transformed host cells, and transgenic plants that comprise nucleic acid segments encoding the polypeptide. Also disclosed are methods of identifying related polypeptides and polynucleotides, methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel sequences of the invention, as well as methods for controlling an insect population, such as the Western Corn Rootworm and Colorado potato beetle, and for conferring to a plant population resistance to the target insect species.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Recombinant DNA constructs and methods for controlling gene expression
InactiveUS20060200878A1Reduce accumulationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The present invention provides molecular constructs and methods for use thereof, including constructs including heterologous miRNA recognition sites, constructs for gene suppression including a gene suppression element embedded within an intron flanked on one or on both sides by non-protein-coding sequence, constructs containing engineered miRNA or miRNA precursors, and constructs for suppression of production of mature microRNA in a cell. Also provided are transgenic plant cells, plants, and seeds containing such constructs, and methods for their use. The invention further provides transgenic plant cells, plants, and seeds containing recombinant DNA for the ligand-controlled expression of a target sequence, which may be endogenous or exogenous. Also disclosed are novel miRNAs and miRNA precursors from crop plants including maize and soy.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
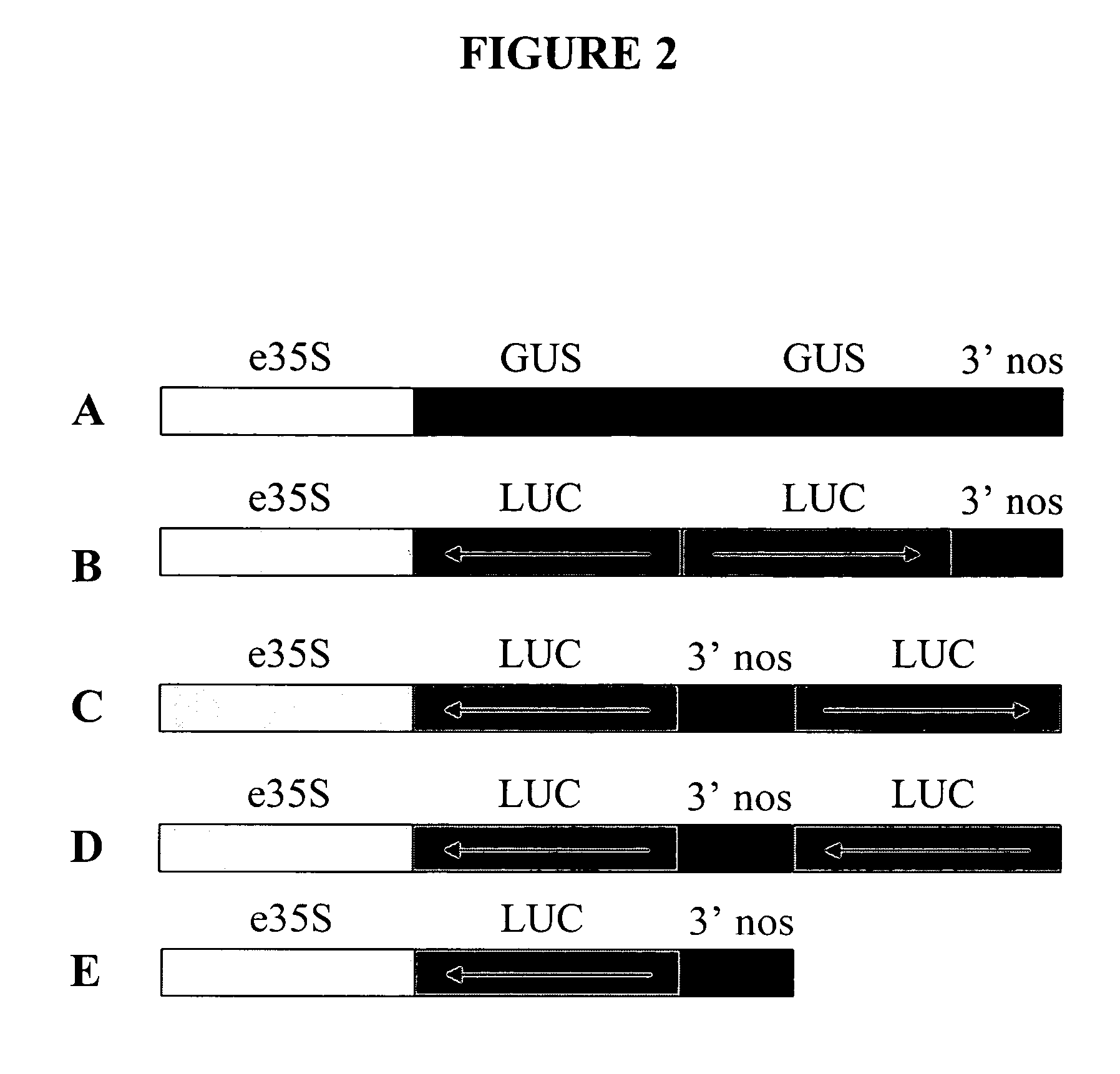
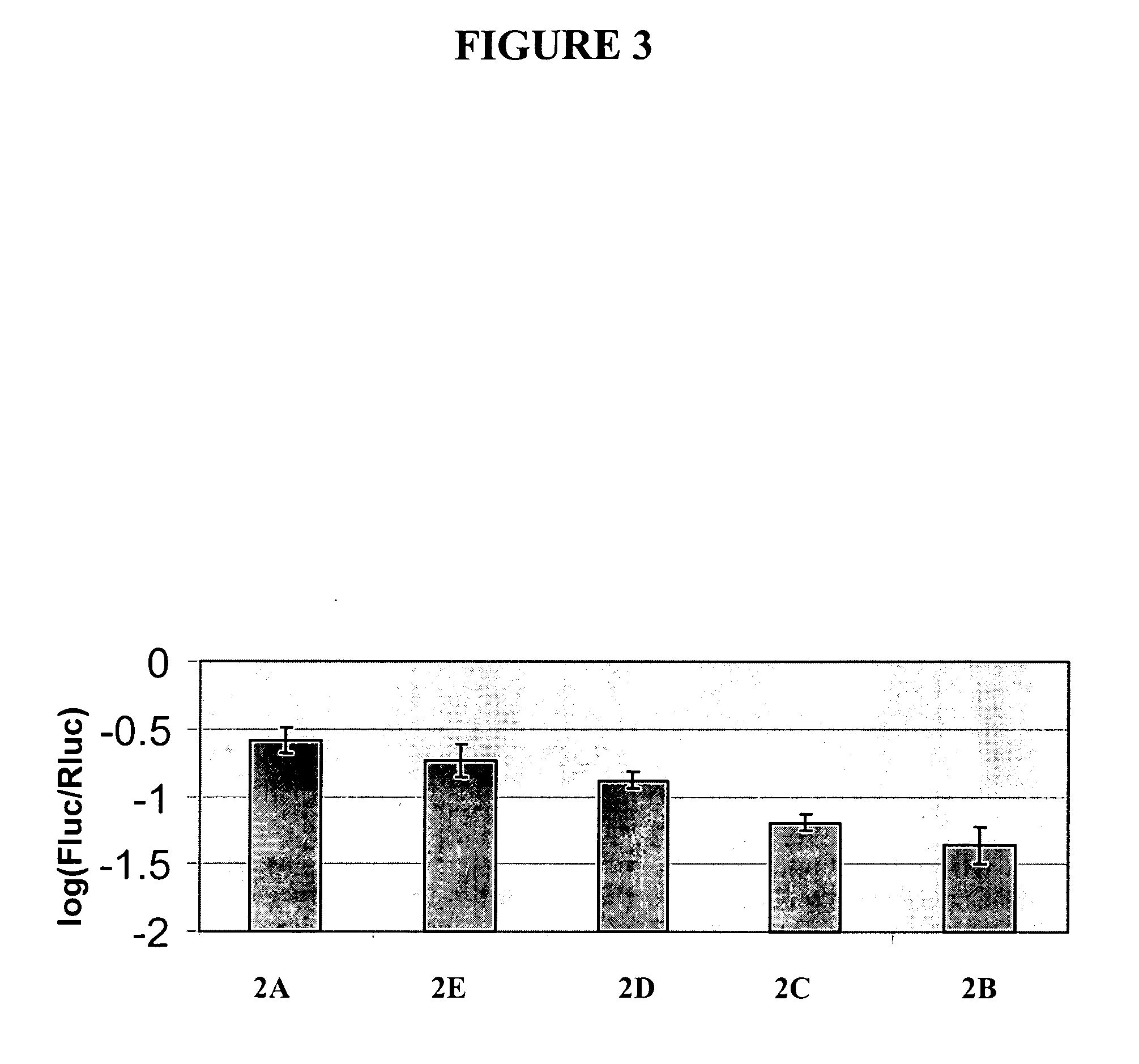
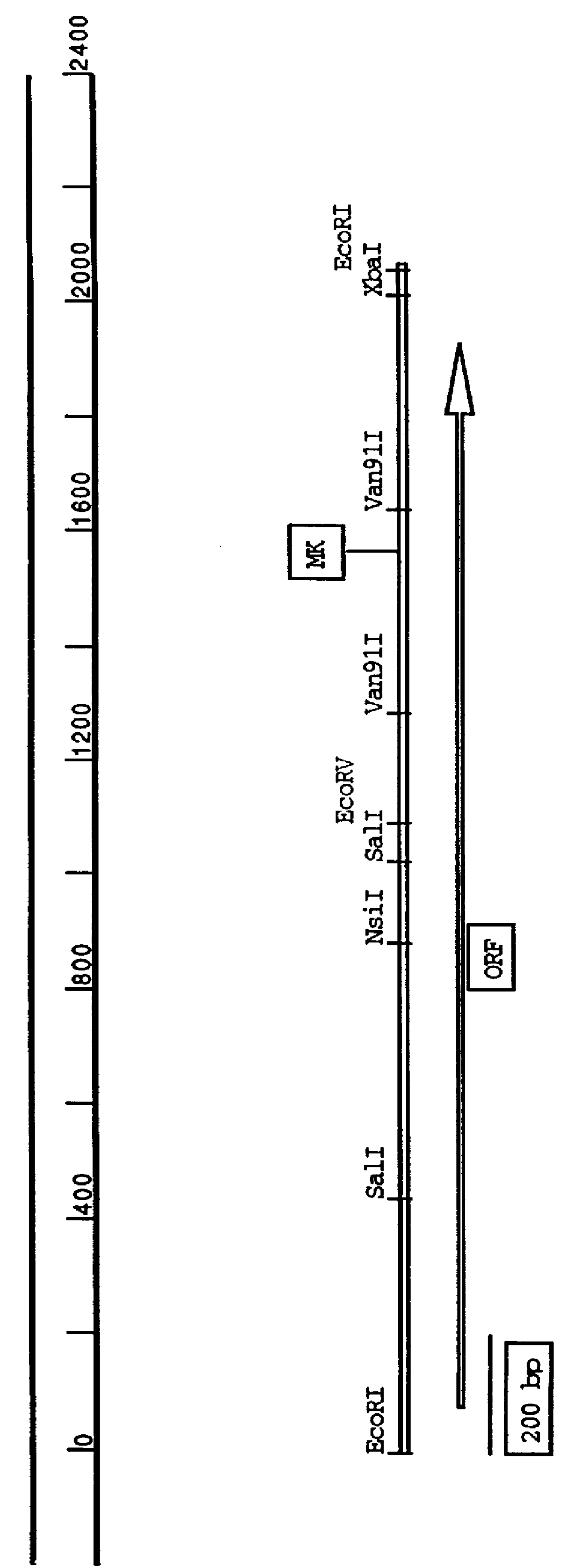
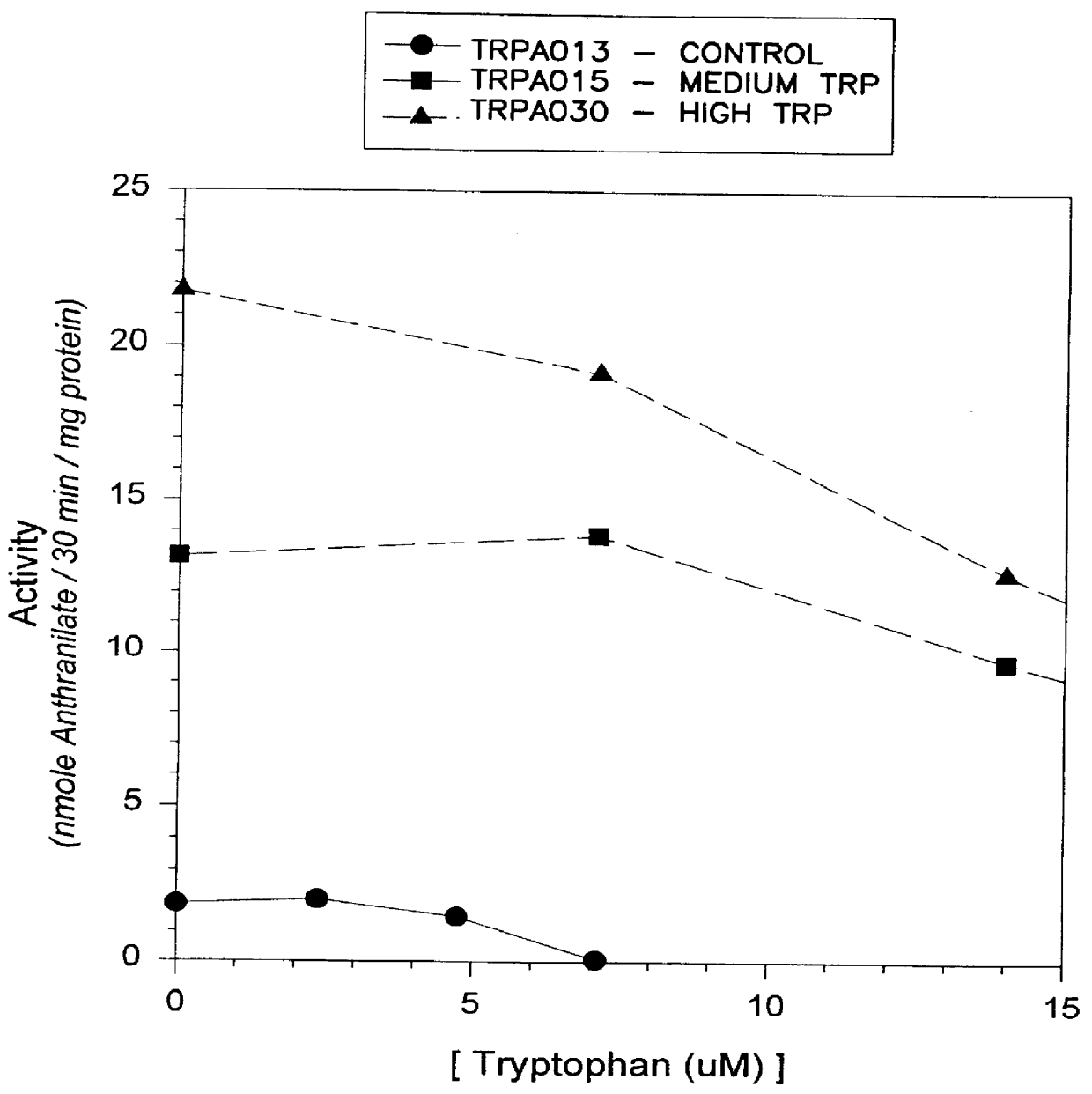
Anthranilate synthase gene and method of use thereof for conferring tryptophan overproduction
InactiveUS6118047AGrowth inhibitionNot susceptibleSugar derivativesBacteriaDNA fragmentationGMO Plants
The present invention provides a method for conferring tolerance to an amino acid analog of tryptophan to a plant and / or altering the tryptophan content of a plant by introducing and expressing an isolated DNA segment encoding an anthranilate synthase in the cells of the plant. Transgenic plants transformed with an isolated DNA segment encoding an anthranilate synthase, as well as seeds and progeny derived from these plants, are also provided. The present invention also provides a cDNA sequence of an alpha and a beta subunit of a maize anthranilate synthase.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Polypeptide compositions toxic to coleopteran insects
InactiveUS6063597AHigh expressionStably occupyBiocideSugar derivativesBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed are Coleopteran-toxic B. thuringiensis delta -endotoxins, nucleic acid sequences, and transgenic plants expressing these genes. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bollworm insect resistance management in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20090313717A1Prevent and delay resistance developmentPreventing and delaying insect resistance developmentClimate change adaptationGenetic engineeringHelicoverpaHelicoverpa zea
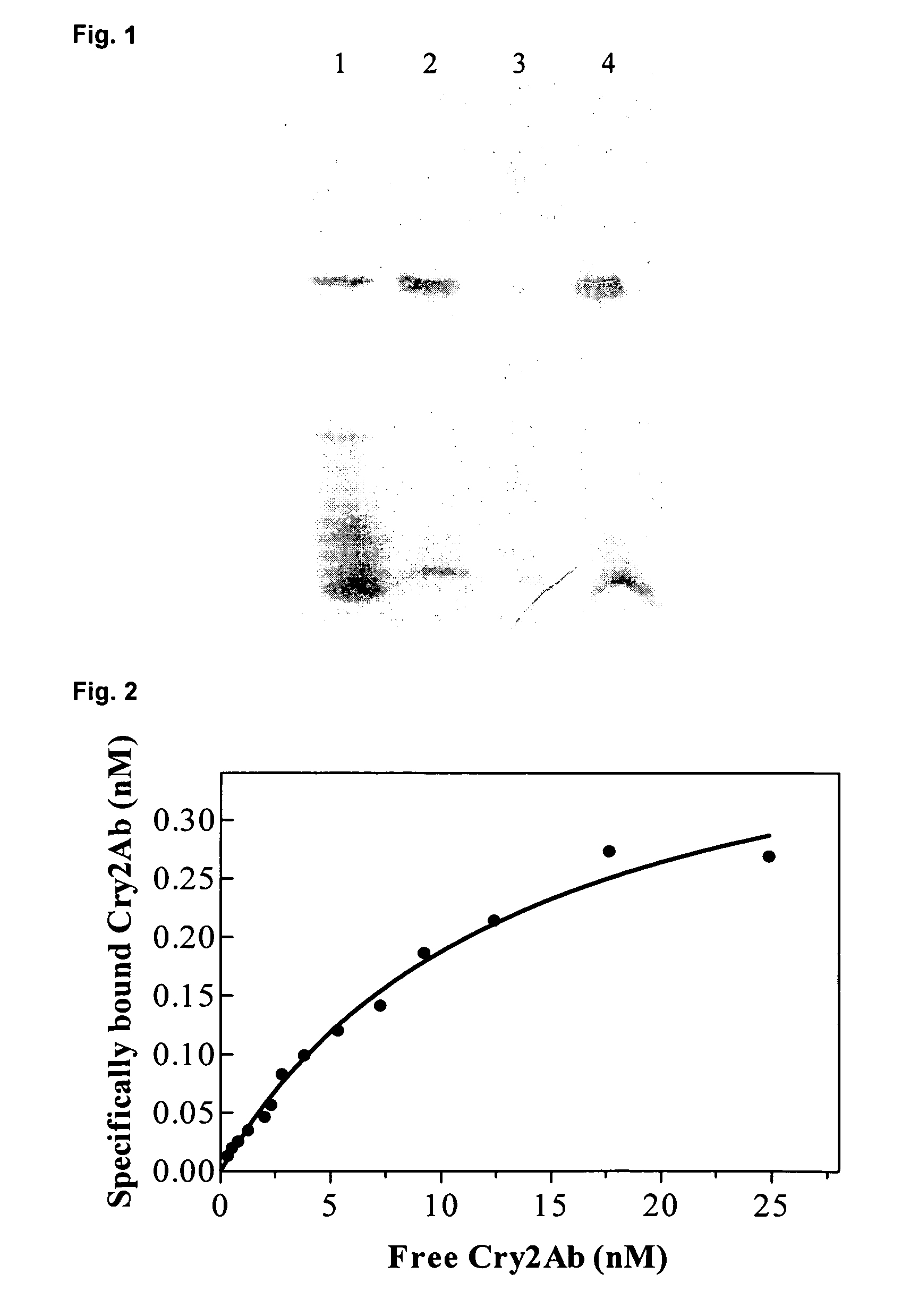
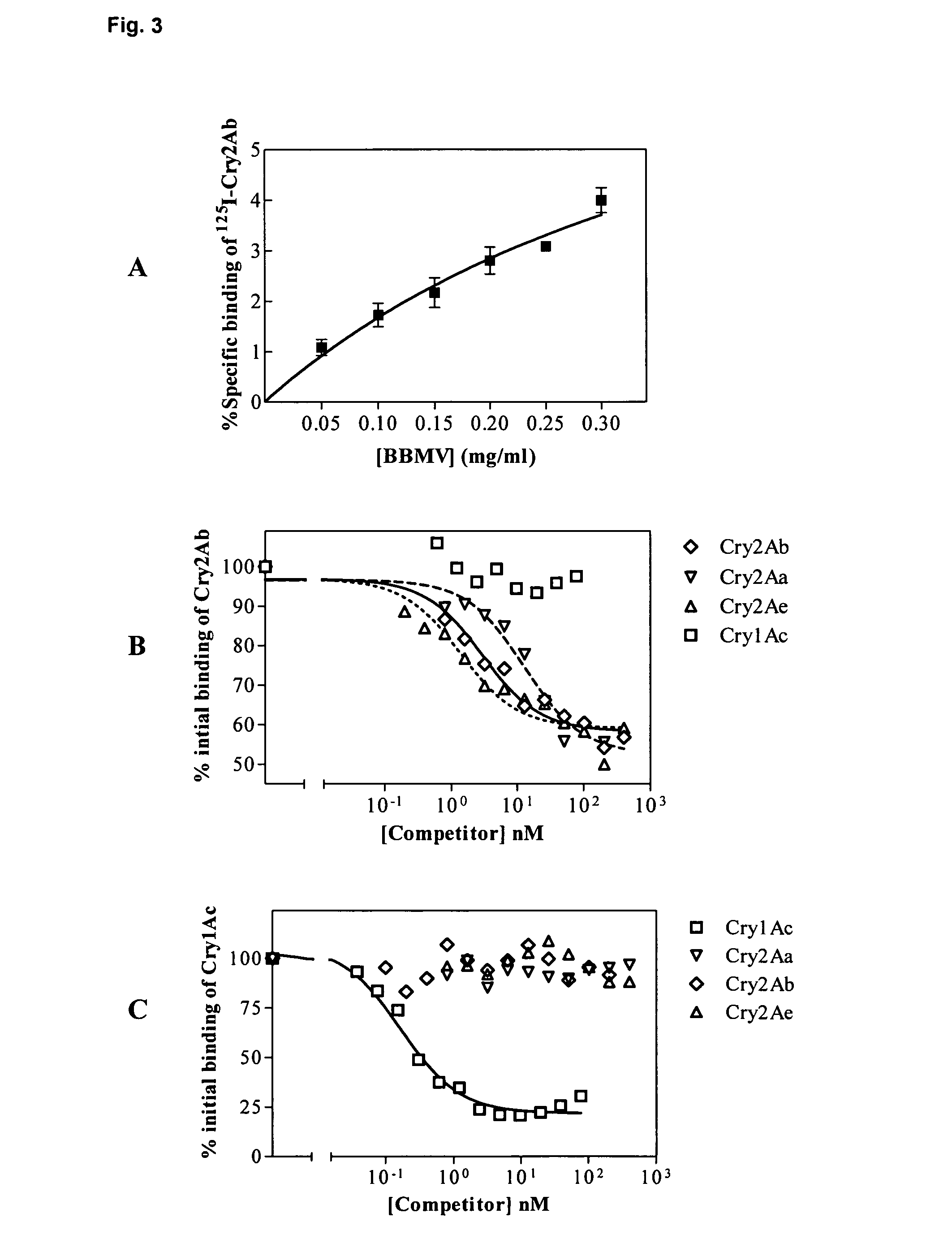
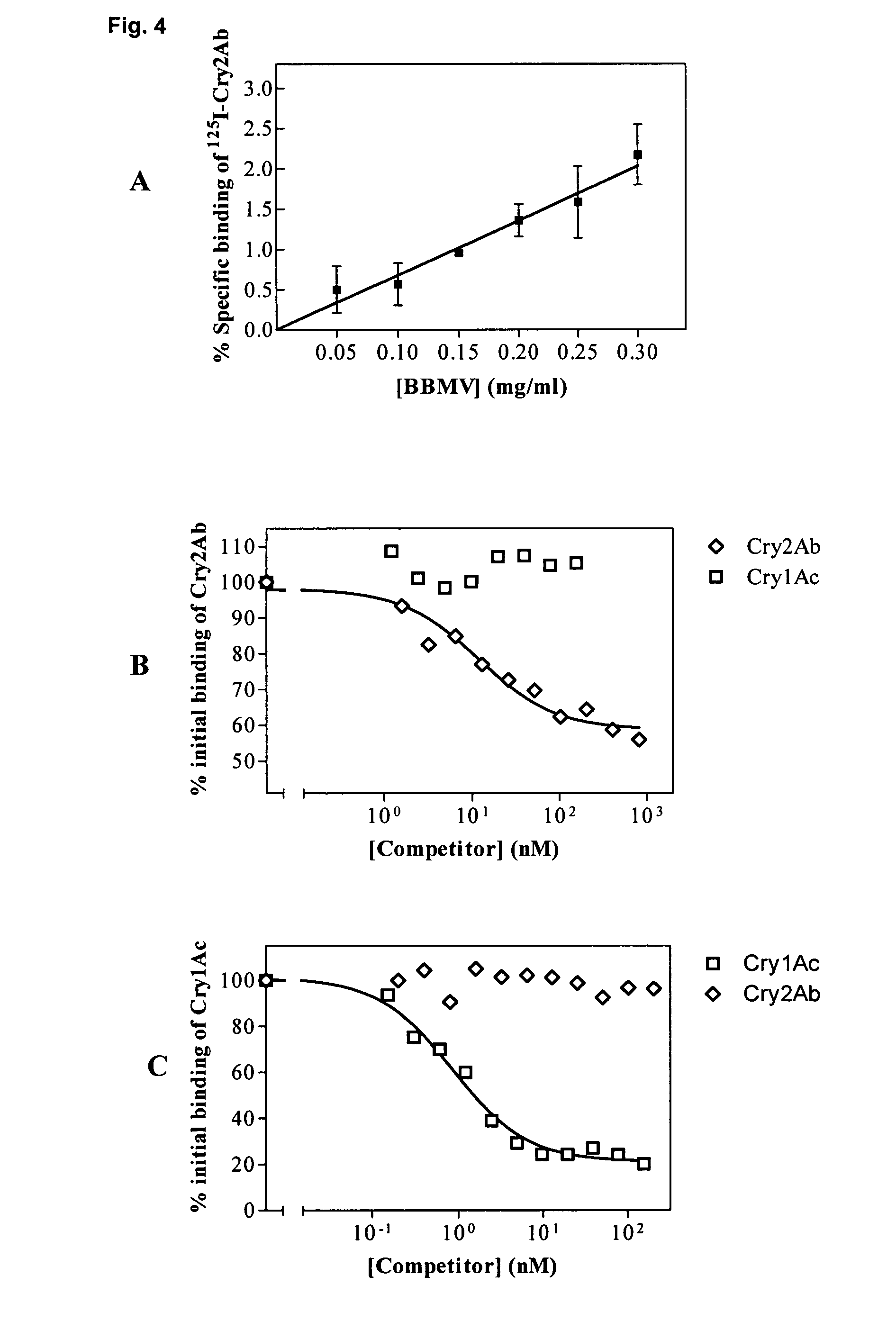
This invention relates to the use of a combination of different proteins insecticidal to Helicoverpa zea or Helicoverpa armigerain an insect resistance management process, wherein such proteins are: a) a Cry2A protein such as Cry2Aa, Cry2Ab, or Cry2Ae and b) a Cry1A, Cry1F or VIP3A protein, particularly wherein such proteins binds saturably to the insect midgut membrane of Helicoverpa zea or Helicoverpa armigera, as well as plants and seeds expressing such combination of proteins, which are used to delay or prevent the development of resistance in populations of such insect species.
Owner:BAYER BIOSCIENCE N V
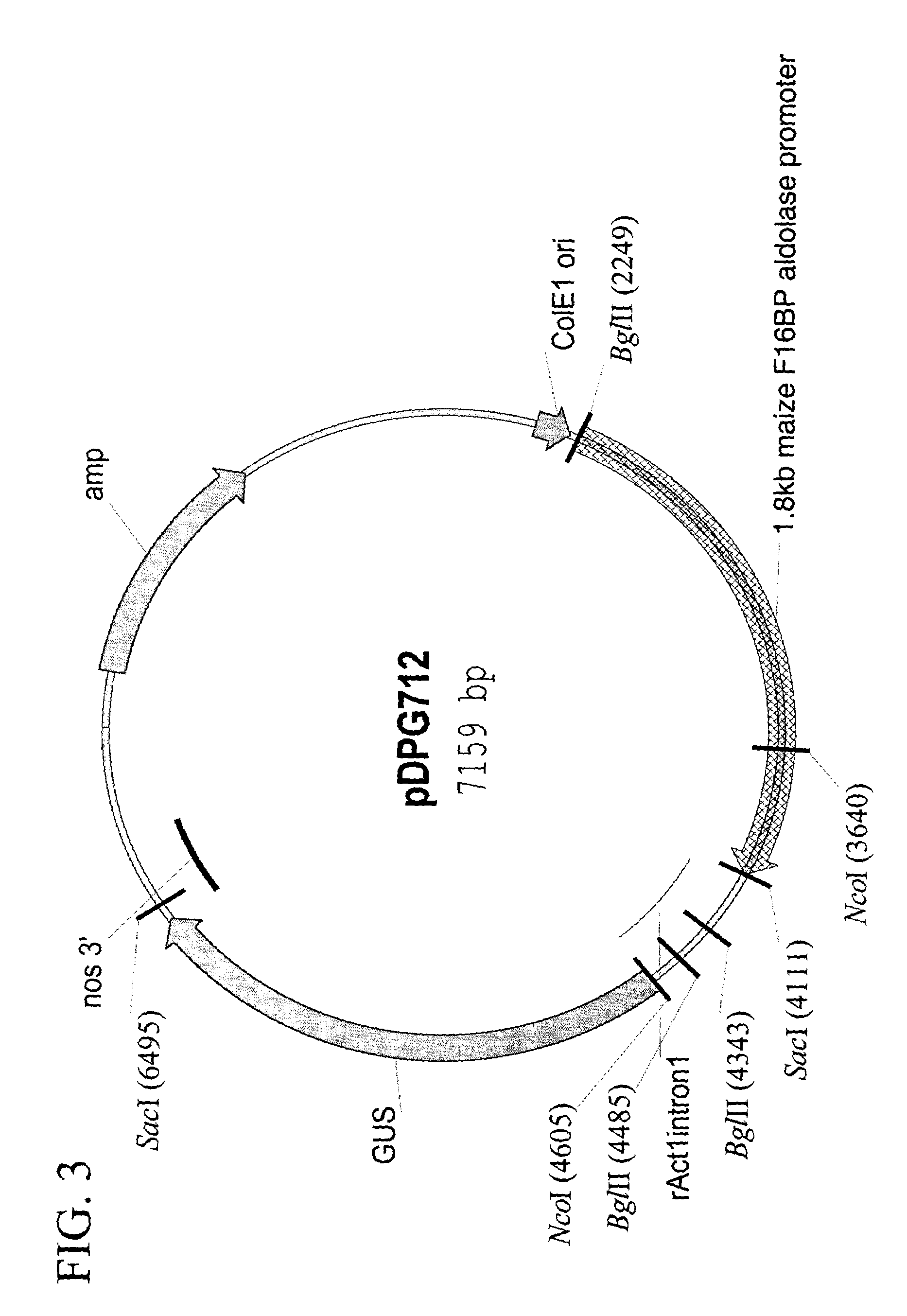
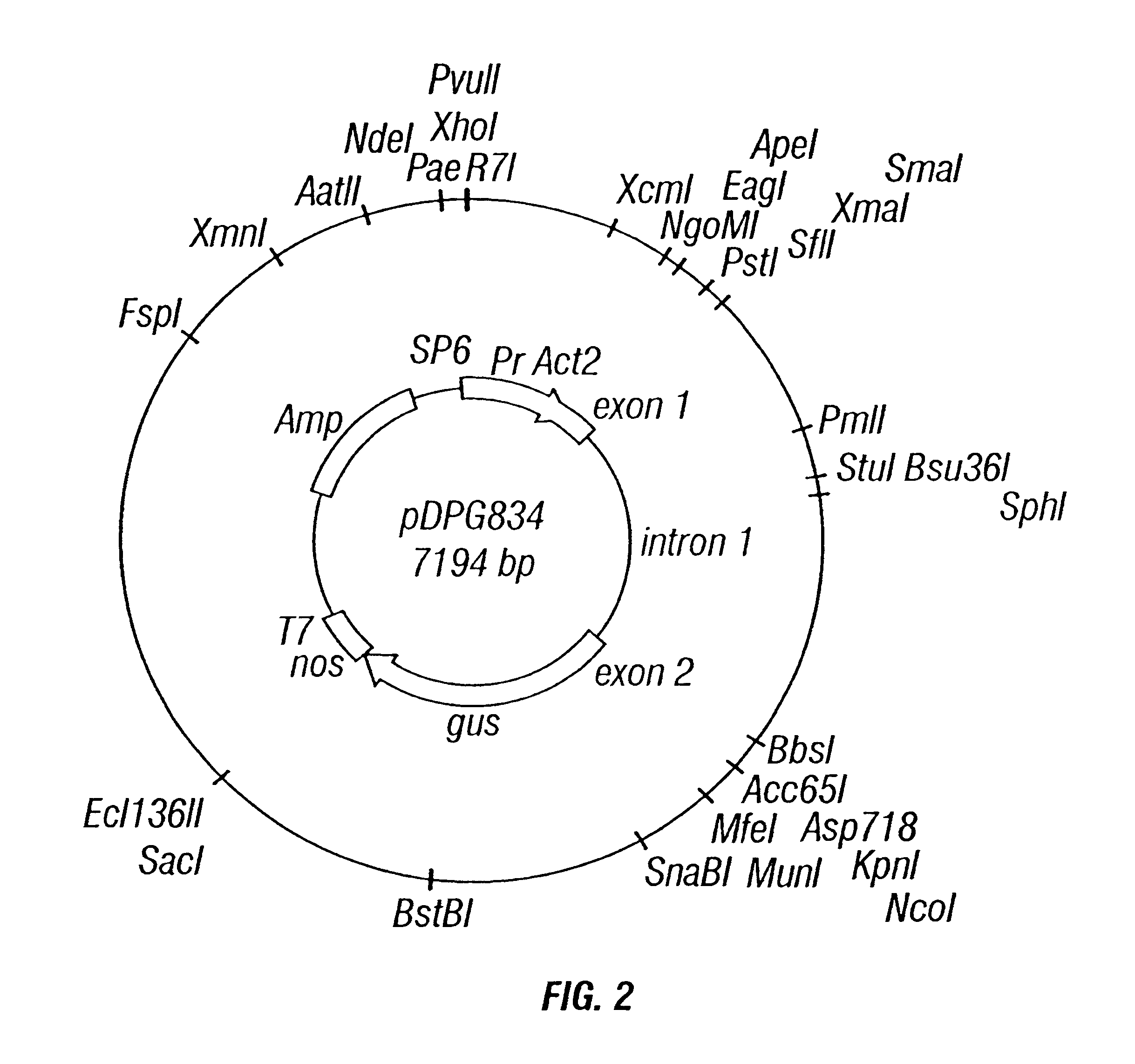
Rice actin 2 promoter and intron and methods for use thereof
The current invention provides regulatory regions from the rice actin 2 gene. In particular, the current invention provides the rice actin 2 promoter and actin 2 intron. Compositions comprising these sequences are described, as well as transformation constructs derived therefrom. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the rice actin 2 intron and / or promoter directly by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The actin 2 sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Broad-spectrum delta-endotoxins
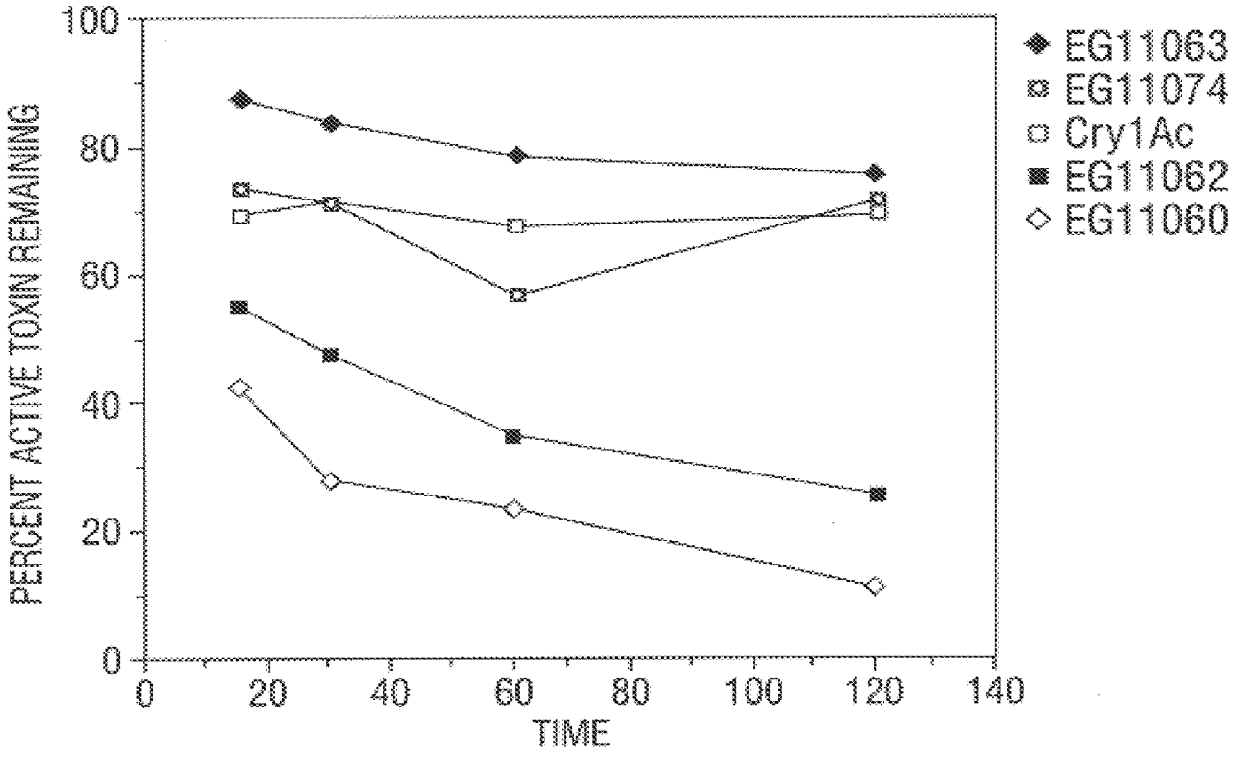
InactiveUS6713063B1Improved insecticidal activity and broader host-range activityImproving immunogenicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity and broader insect host range against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Insect-resistant transgenic plants
The invention provides transgenic plants and transformed host cells which express modified cry 3B genes with enhanced toxicity to Coleopteran insects. Also disclosed are methods of making and using these transgenic plants, methods of making recombinant host cells expressing these delta -endotoxins, and methods of killing insects such as Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata howardi Barber) and western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
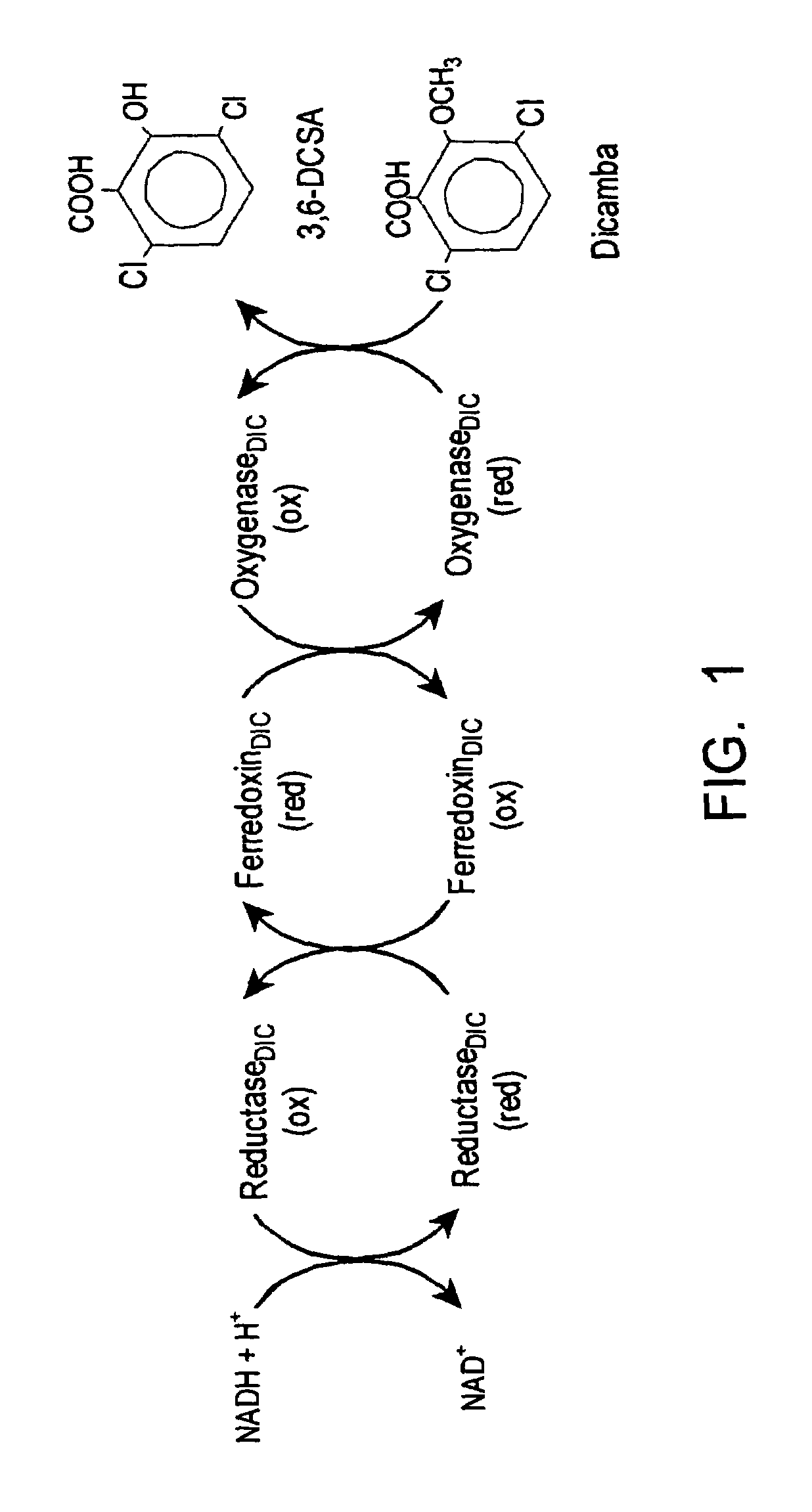
Methods and materials for making and using transgenic dicamba-degrading organisms
The invention provides isolated and at least partially-purified dicamba-degrading enzymes, isolated DNA molecules coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, DNA constructs coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, transgenic host cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, and transgenic plants and plant parts comprising one or more cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes. Expression of the dicamba-degrading enzymes results in the production of dicamba-degrading organisms, including dicamba-tolerant plants. The invention further provides a method of controlling weeds in a field containing the transgenic dicamba-tolerant plants of the invention and a method of decontaminating a material containing dicamba comprising applying an effective amount of a transgenic microorganism or dicamba-degrading enzyme of the invention to the material. Finally, the invention provides a method of selecting transformed plants and plant cells based on dicamba tolerance and a method of selecting or screening transformed host cells, intact organisms and parts of organisms based on the fluorescence of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid produced as a result of dicamba degradation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Coleopteran-resistant transgenic plants and methods of their production using modified Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Bb nucleic acids
Disclosed are nucleic acid segments comprising synthetically-modified genes encoding modified Coleopteran-toxic B. thuringiensis Cry 3Bb* delta-endotoxins. Also disclosed are methods of using these genes for preparing a Coleopteran-resistant transgenic plant and reducing insect in restations, and plants thereby produced.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
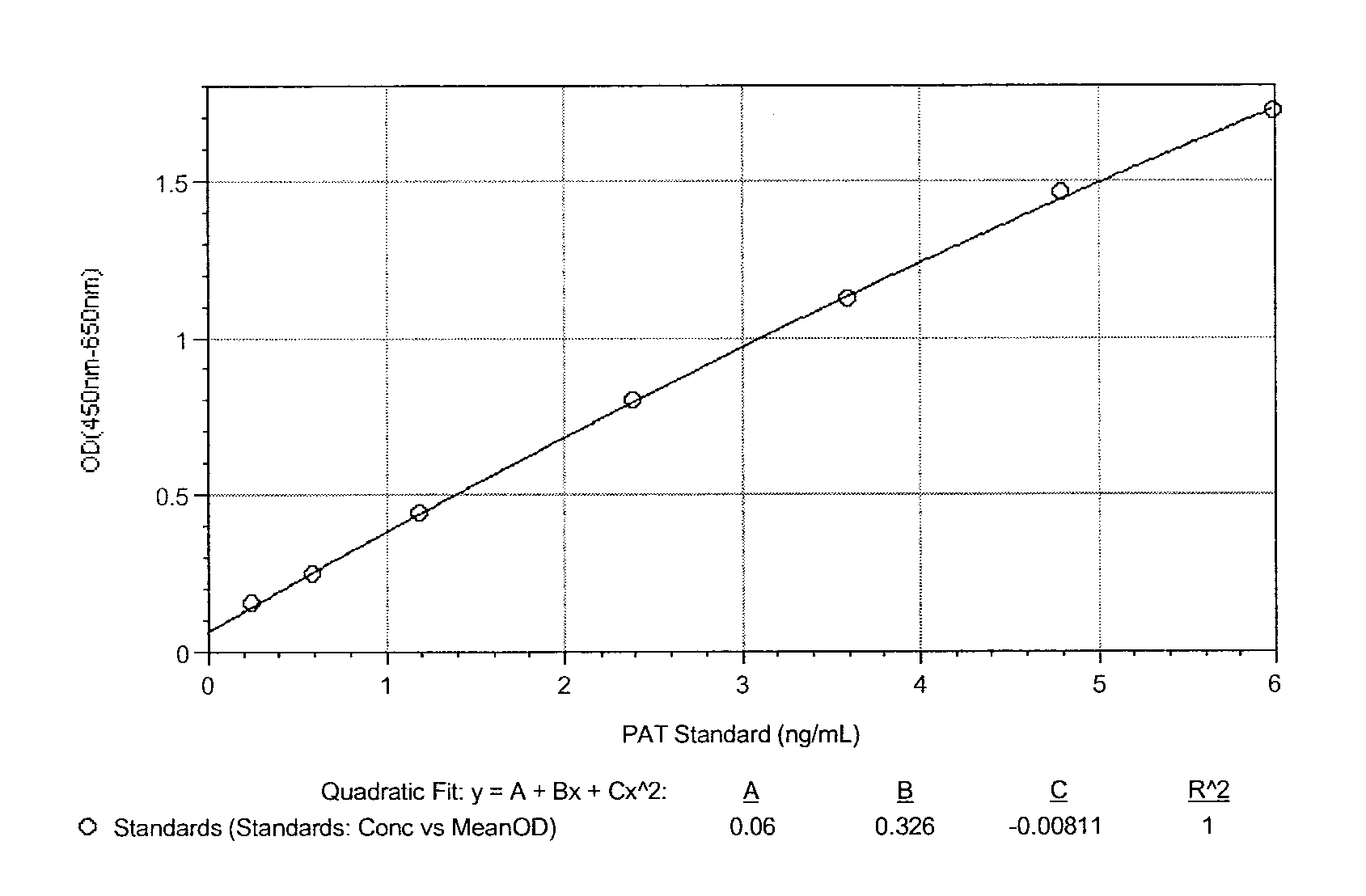
Monoclonal antibodies and detection methods for phosphinothricin-N-acetyl-transferase enzyme
ActiveUS9371394B2Immunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological material analysisN-acetyltransferaseAcetyltransferase
Described herein are monoclonal antibodies and methods useful for determining and quantitating the presence of a phosphinothricin-N-acetyl-transferase enzyme. The claimed antibodies and methods are particularly useful for identifying and quantitating the presence of phosphinothricin-N-acetyl-transferase expressed in trangenic plants.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Transgenic plant event detection
ActiveUS8700336B2Reduce in quantityExtension of timeMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGenetic MaterialsTransgene
The present invention relates to detection of materials derived from transgenic plant events. In particular, the invention provides methods, reagents, kits and reference materials for detecting the presence or absence in a sample of genetic material derived from and attributable to select transgenic plant events.
Owner:SCIENSANO
Compositions and methods for control of insect infestations in plants
InactiveUS20060021087A1Limiting and eliminating invertebrateInhibit expressionBiocideSugar derivativesInvertebrateOrganism
The present invention is directed to controlling pest infestation by inhibiting one or more biological functions in an invertebrate pest. The invention discloses methods and compositions for use in controlling pest infestation by feeding one or more different recombinant double stranded RNA molecules to the pest in order to achieve a reduction in pest infestation through suppression of gene expression. The invention is also directed to methods for making transgenic plants that express the double stranded RNA molecules, and to particular combinations of transgenic pesticidal agents for use in protecting plants from pest infestation.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Polynucleotide compositions encoding broad spectrum delta-endotoxins
InactiveUS7070982B2Improved insecticidal activity and broader host-range activityHigh insecticidal activitySugar derivativesBacteriaNucleotidePolynucleotide
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
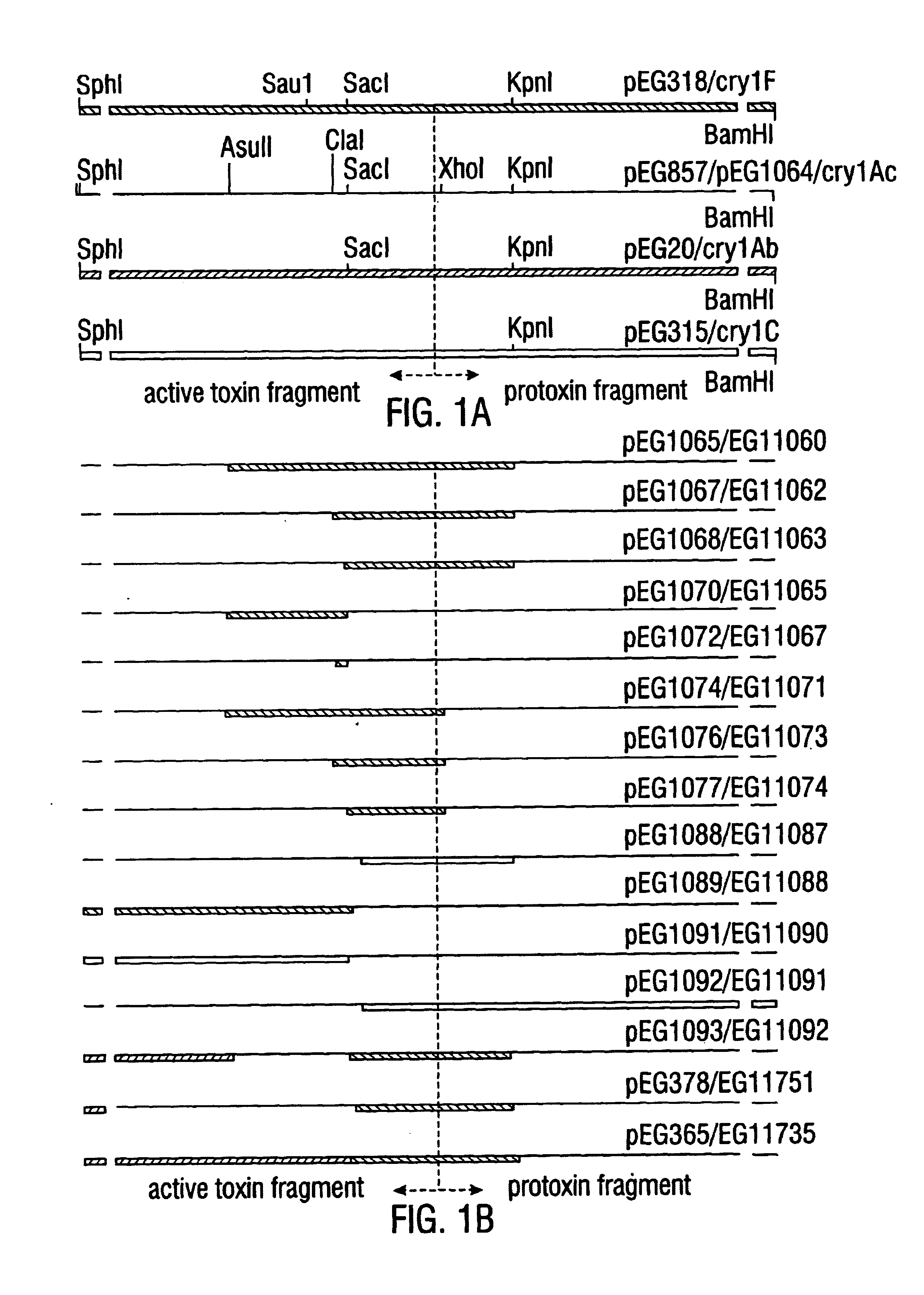
CRY1C polypeptides having improved toxicity to lepidopteran insects
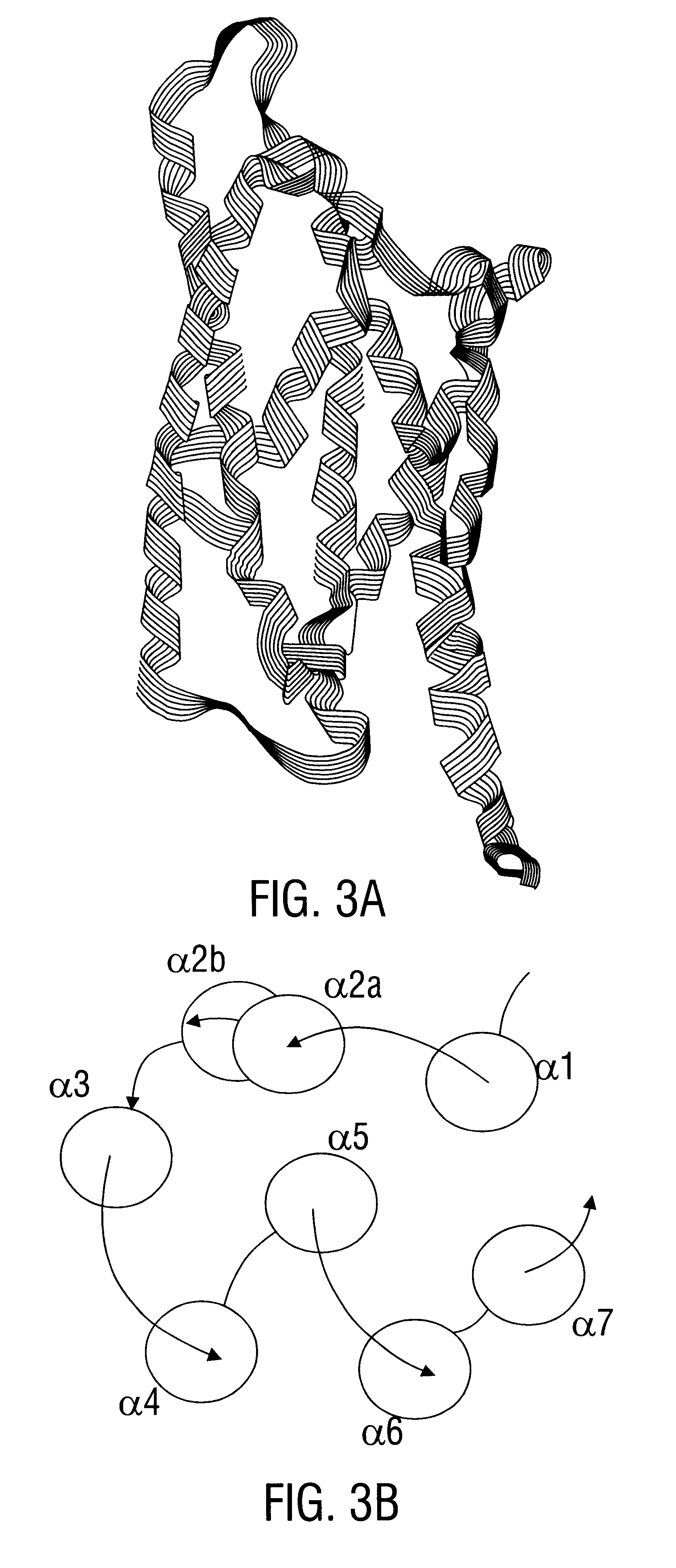
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis nucleic acid segments encoding delta -endotoxins having insecticidal activity against lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are synthetic crystal proteins encoded by these novel nucleic acid sequences. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention. Also disclosed are methods for modifying, altering, and mutagenizing specific loop regions between the alpha helices in domain 1 of these crystal proteins, including Cry1C, to produce genetically-engineered recombinant cry* genes, and the proteins they encode which have improved insecticidal activity. In preferred embodiments, novel Cry1C* amino acid segments and the modified cry1C* nucleic acid sequences which encode them are disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Broad-spectrum insect resistant transgenic plants
InactiveUS6281016B1Improve insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityBiocideNanotechAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and tansgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
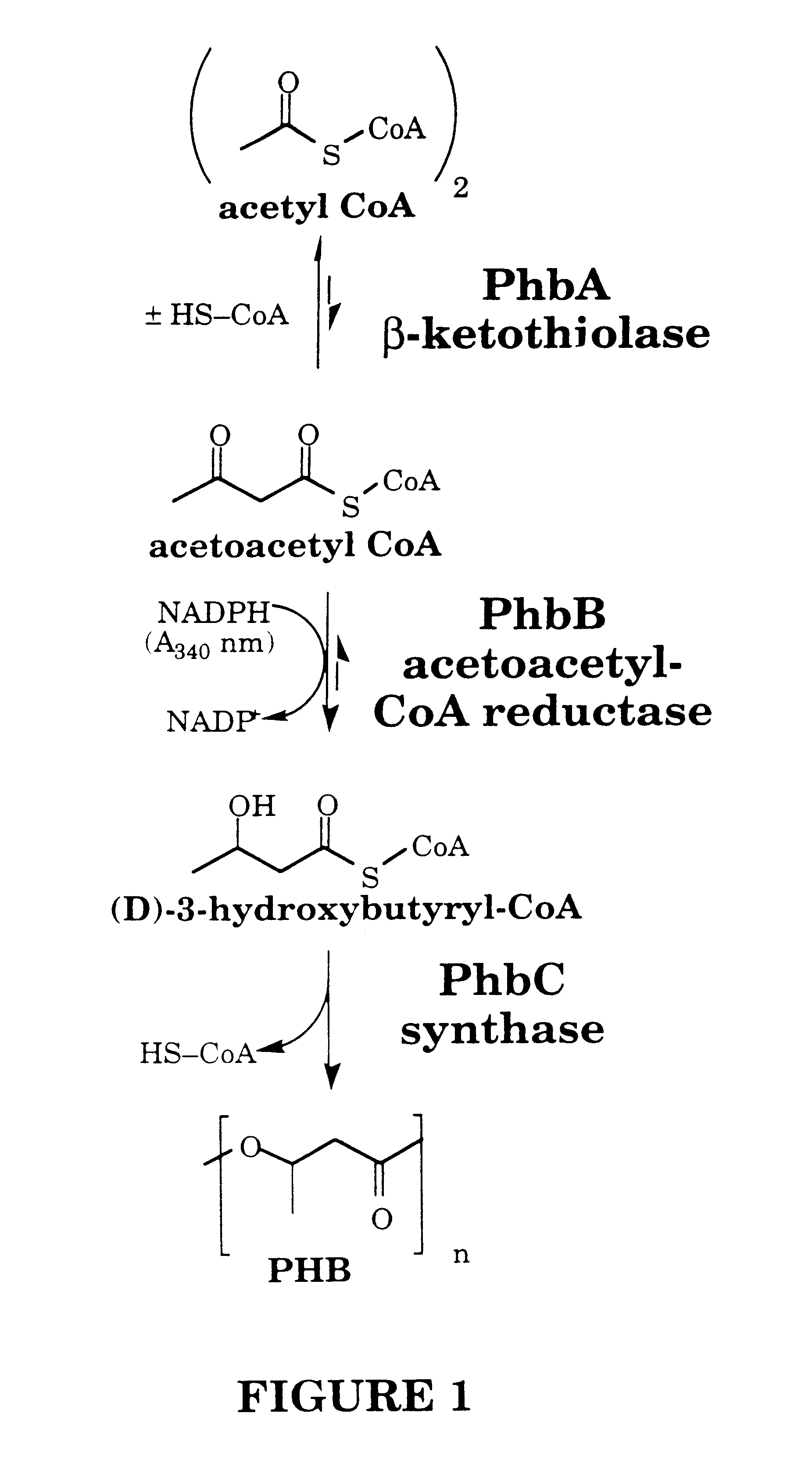
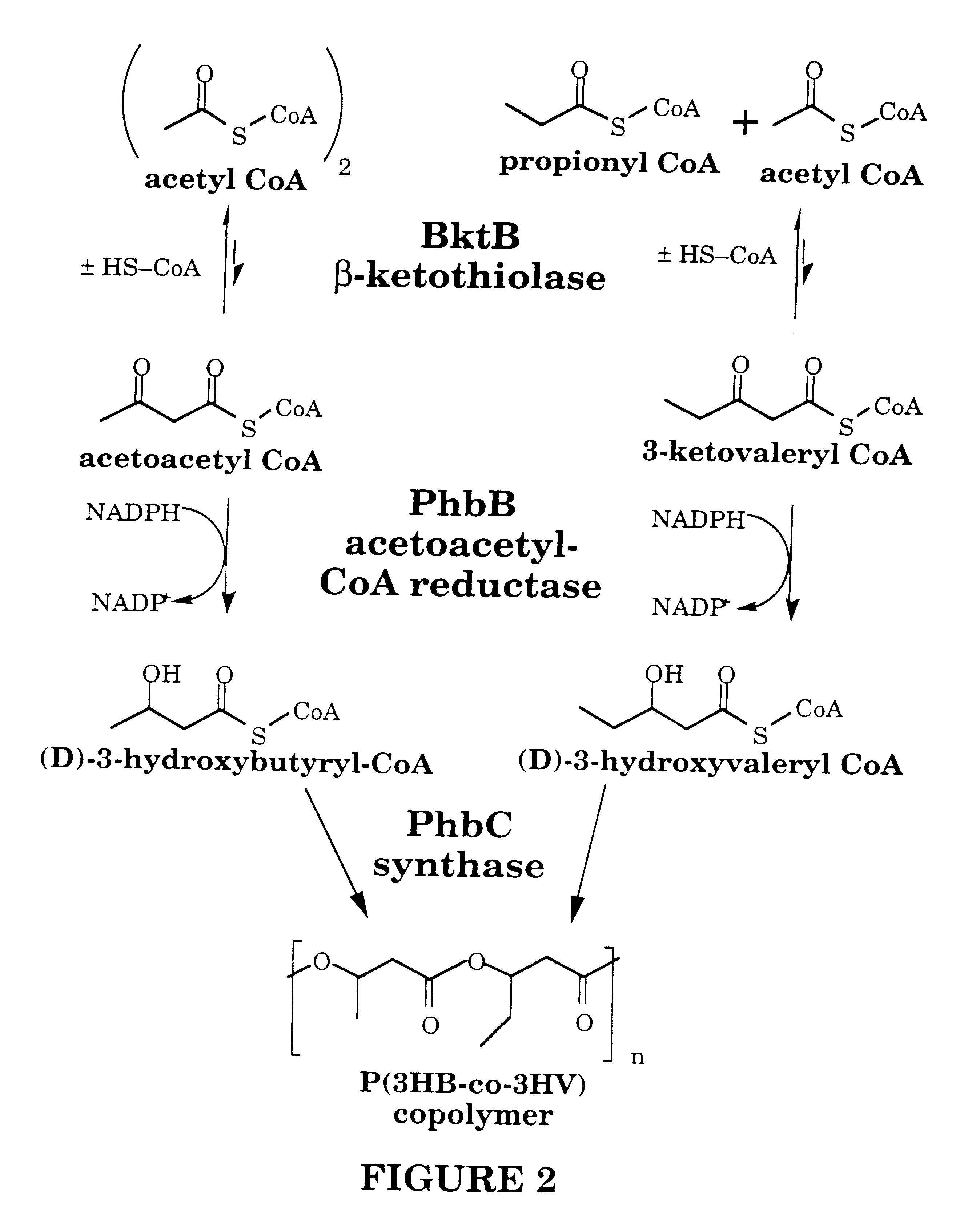
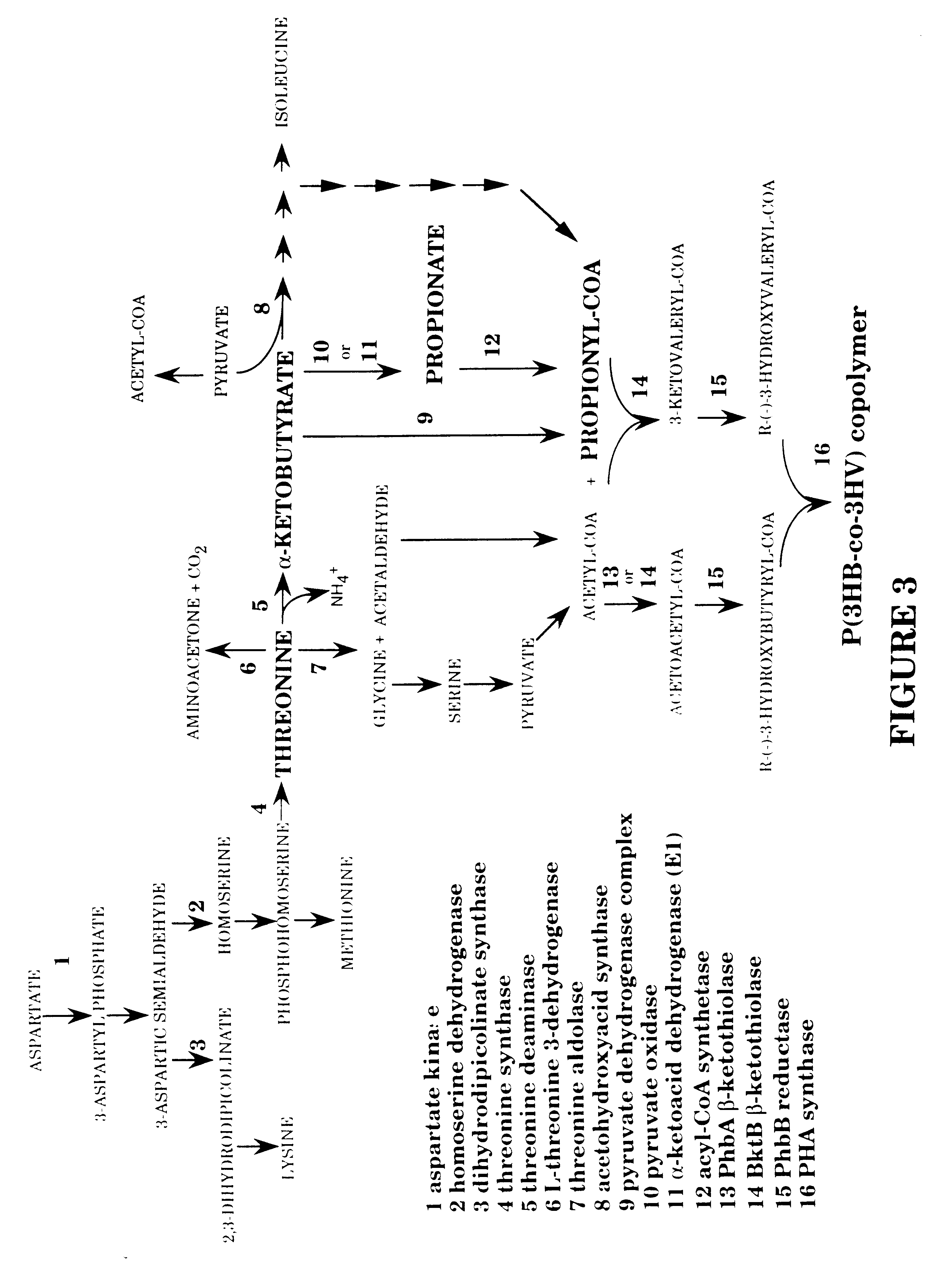
Polyhydroxyalkanoates of narrow molecular weight distribution prepared in transgenic plants
Methods for the biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate homopolymers and copolymers are described. In a preferred embodiment, the polymers have a single mode molecular weight distribution, and more preferably have a distribution of between about 2 and about 4, and most preferably about 2.1 or 2.5.
Owner:METABOLIX
Broad-spectrum delta -endotoxins
InactiveUS6110464AImprove insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityNanotechBacteriaAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6093695ARemarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaBacillus thuringiensisCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta -endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against colcopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneur). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for genetic control of insect infestations in plants and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20070124836A1Inhibit expressionReduced expression levelSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyDouble strand
The present invention relates to control of pest infestation by inhibiting one or more biological functions. The invention provides methods and compositions for such control. By feeding one or more recombinant double stranded RNA molecules provided by the invention to the pest, a reduction in pest infestation is obtained through suppression of gene expression. The invention is also directed to methods for making transgenic plants that express the double stranded RNA molecules, and to particular combinations of transgenic pesticidal agents for use in protecting plants from pest infestation.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS7868149B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsPlant biochemistry
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
DIG-3 insecticidal Cry toxins
DIG-3 Cry toxins, polynucleotides encoding such toxins, and transgenic plants that produce such toxins are useful to control insect pests.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Regulated expression of genes in plant seeds
InactiveUS6992237B1Improve the level ofIncrease in sizeSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationPlanting seedTransgene
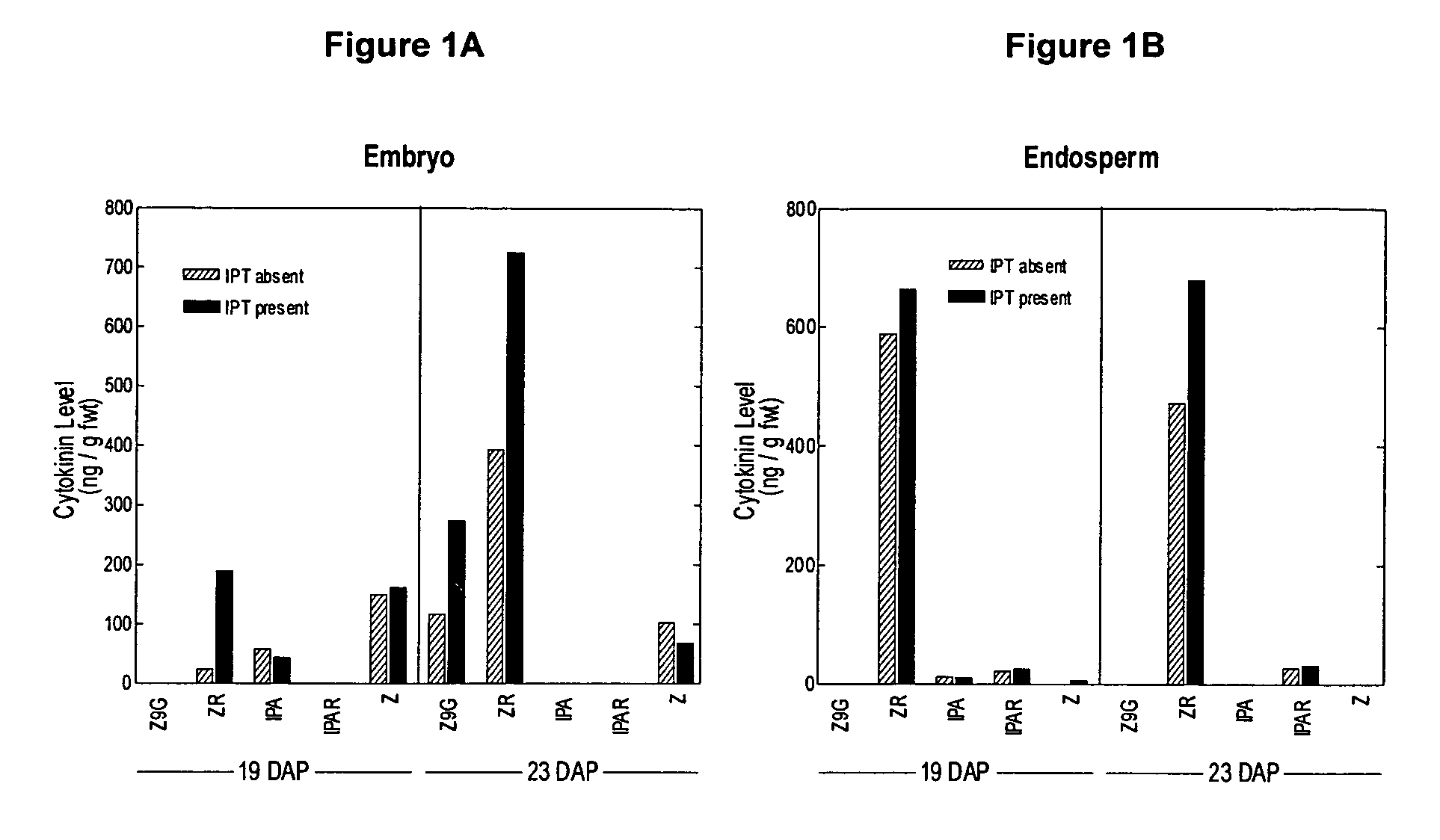
This invention relates generally to the field of plant molecular biology. More specifically, this invention relates to methods and reagents for the temporal and / or spatial expression of genes that affect metabolically effective levels of cytokinins in plant seeds and related maternal tissue. This invention further relates to transgenic plants having enhanced levels of cytokinin expression wherein the transgenic plant exhibits useful characteristics, including: improved seed size, decreased tip kernel abortion, increased seed set during unfavorable environmental conditions, and stability of yield.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Nucleotide sequences and polypeptides encoded thereby useful for modifying plant characteristics
ActiveUS20070039067A1Increased biomass productionIncrease productionImmunoglobulinsFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide sequencing
Owner:CERES INC
Transgenic plants that exhibit enhanced nitrogen assimilation
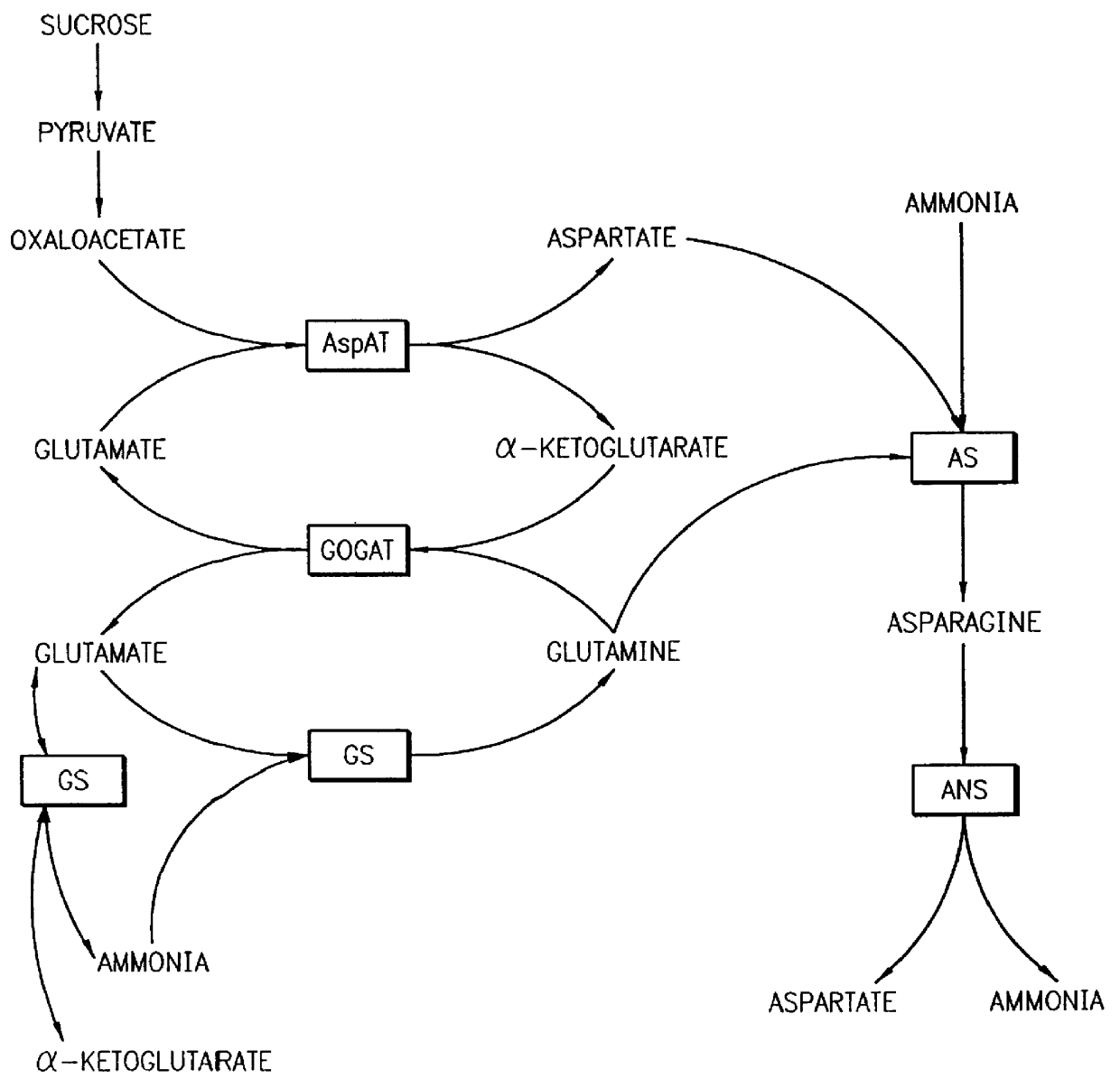
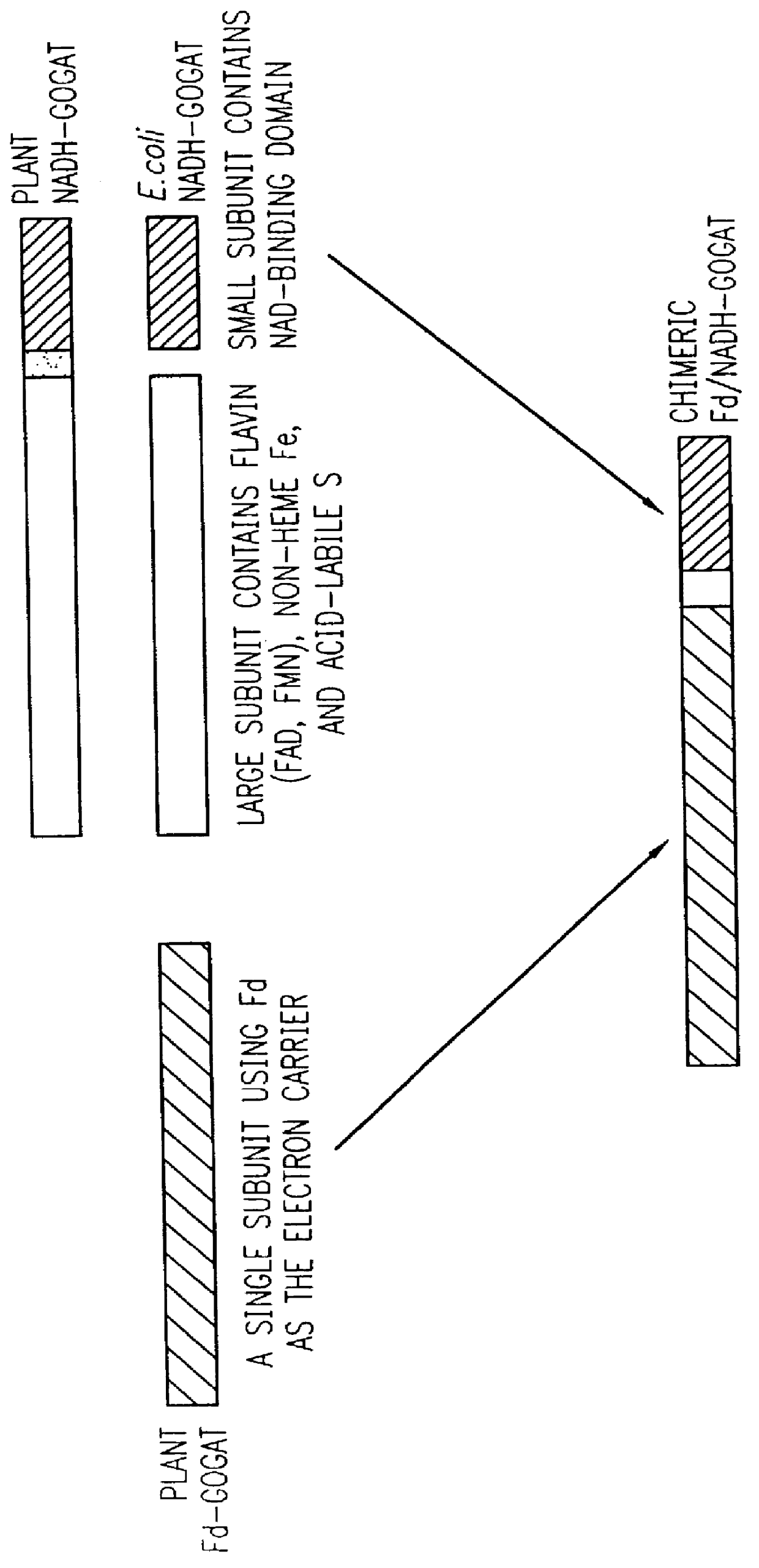
InactiveUS6107547AImprove featuresReduce investmentSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyNitrogen assimilation
The present invention relates to a method for producing plants with improved agronomic and nutritional traits. Such traits include enhanced nitrogen assimilatory and utilization capacities, faster and more vigorous growth, greater vegetative and reproductive yields, and enriched or altered nitrogen content in vegetative and reproductive parts. More particularly, the invention relates to the engineering of plants modified to have altered expression of key enzymes in the nitrogen assimilation and utilization pathways. In one embodiment of the present invention, the desired altered expression is accomplished by engineering the plant for ectopic overexpression of one of more the native or modified nitrogen assimilatory enzymes. The invention also has a number of other embodiments, all of which are disclosed herein.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com