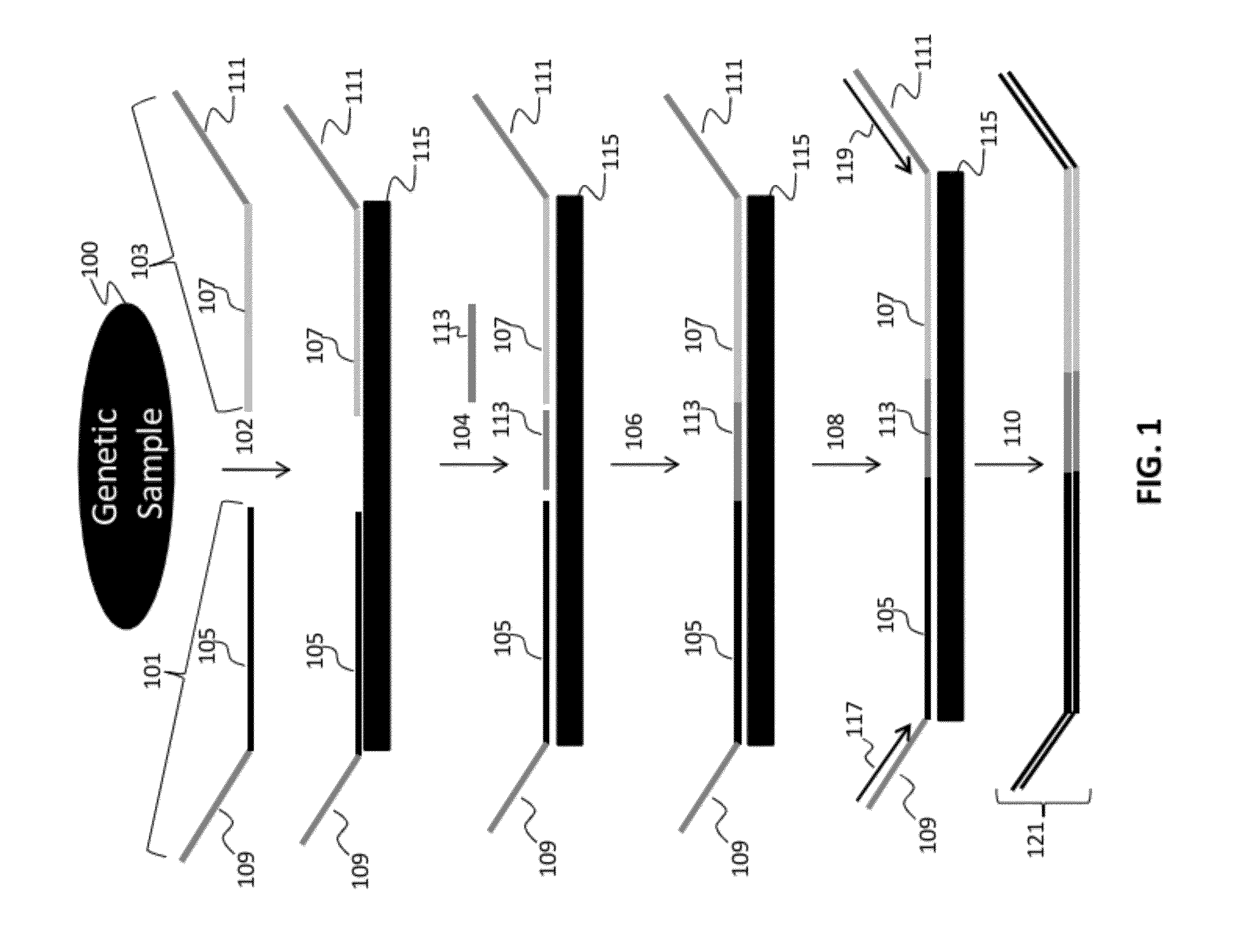
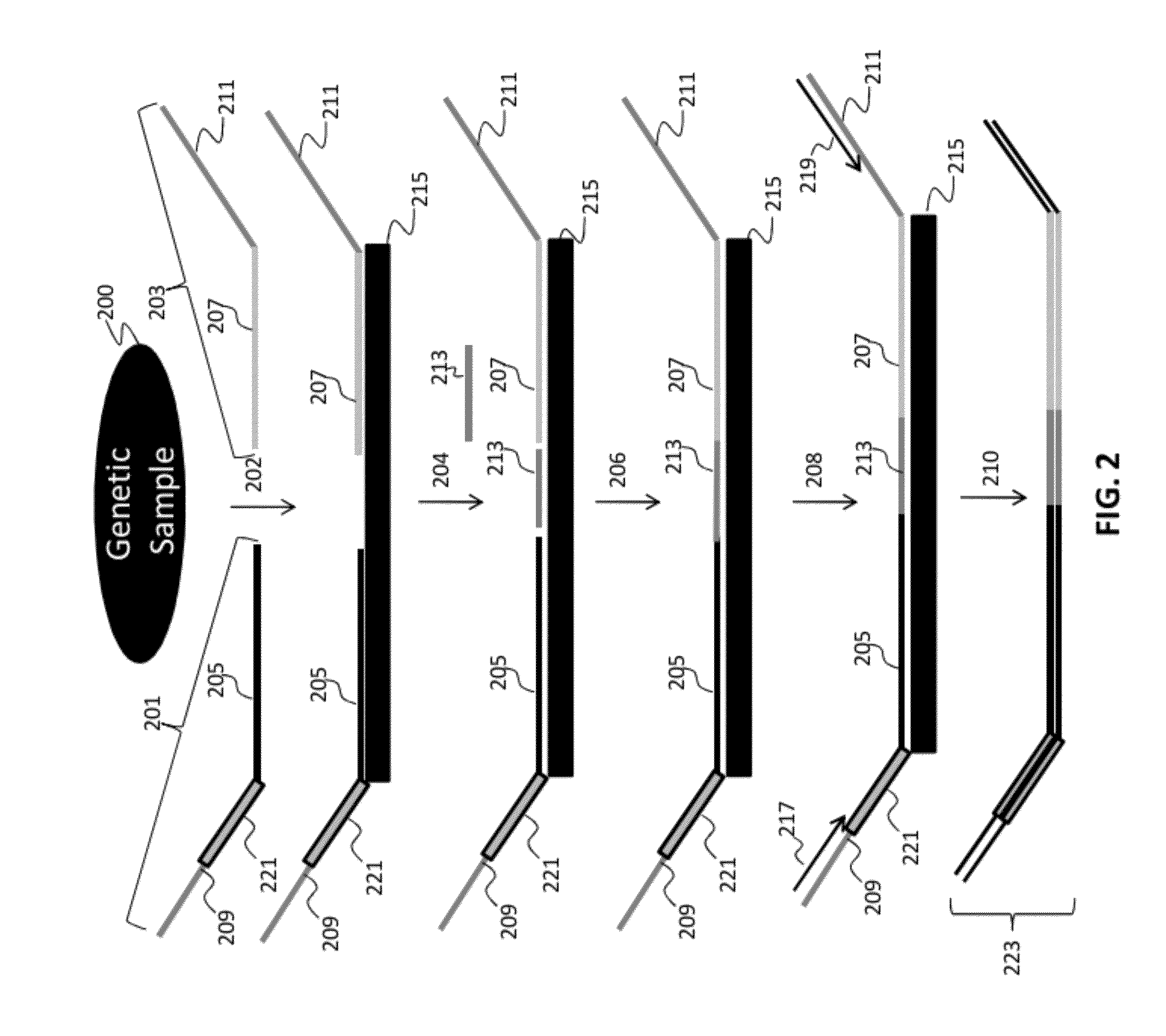
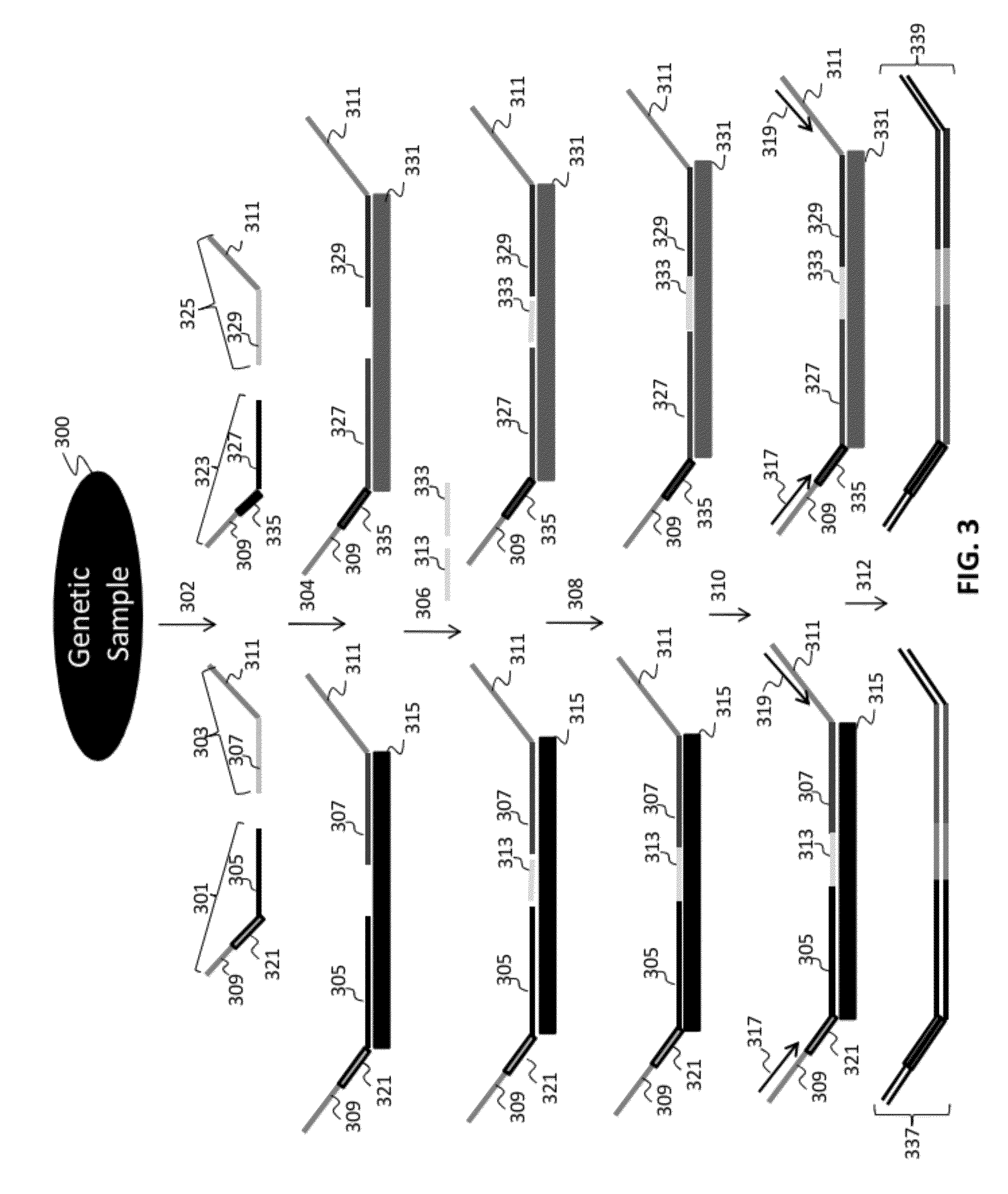
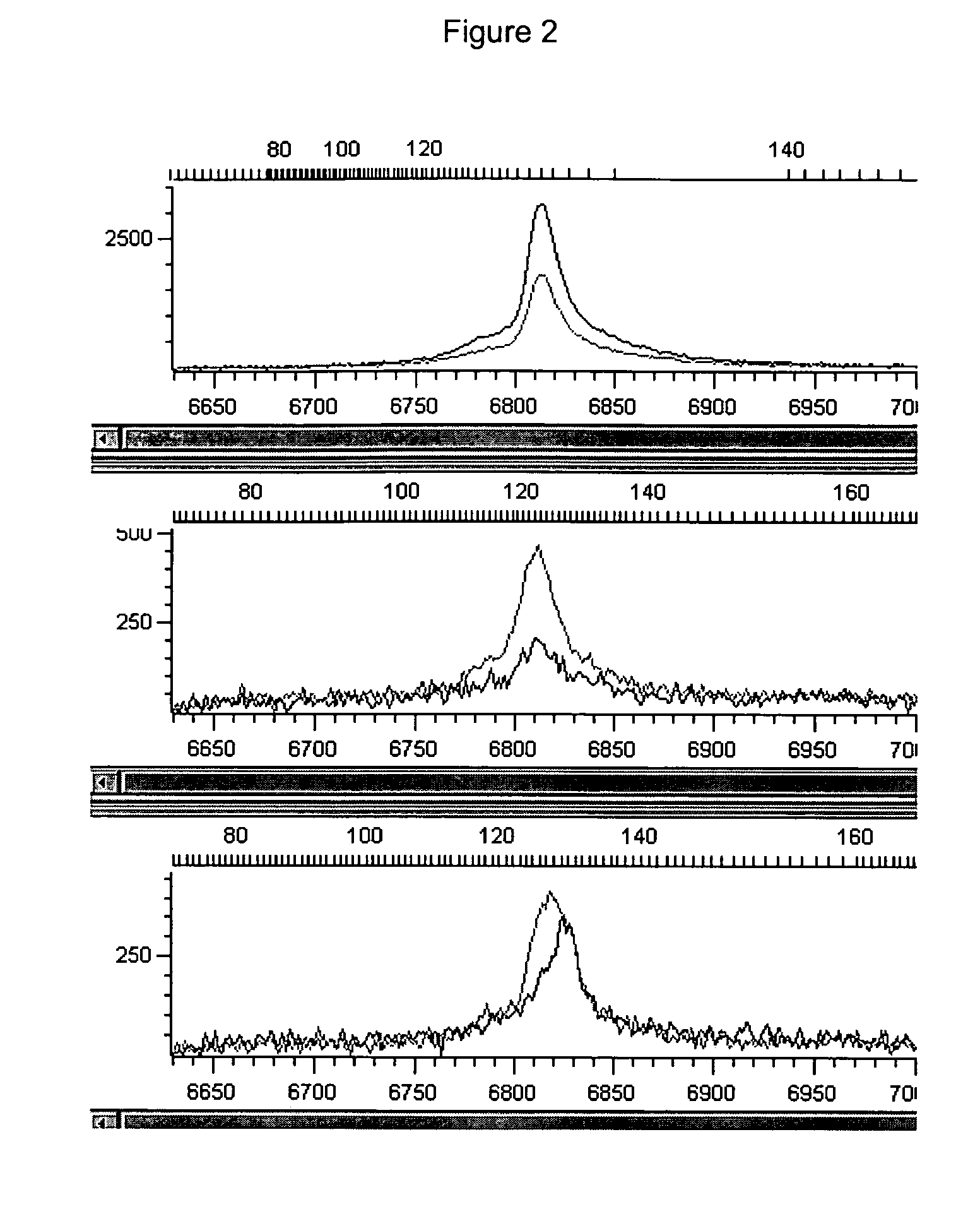
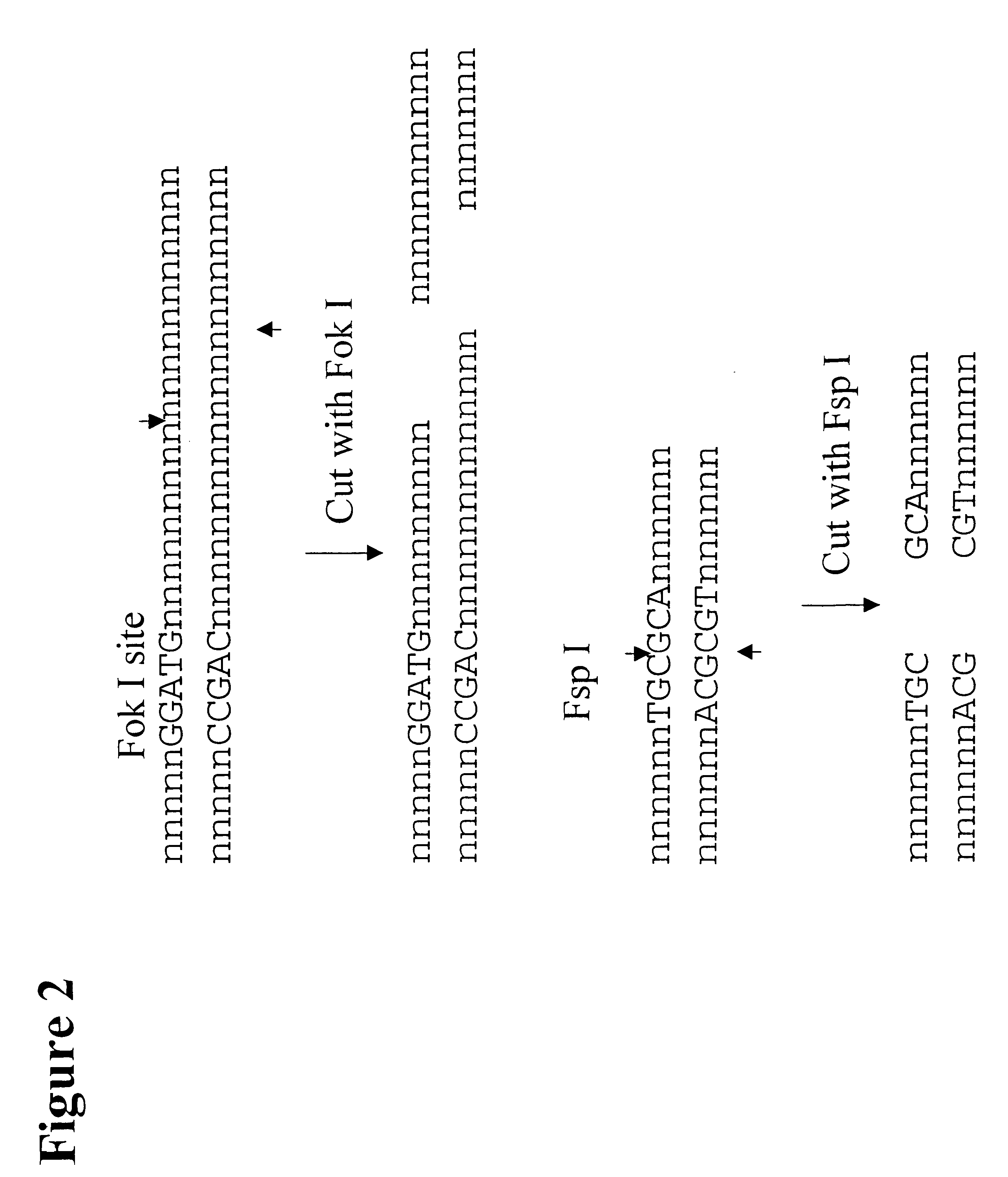
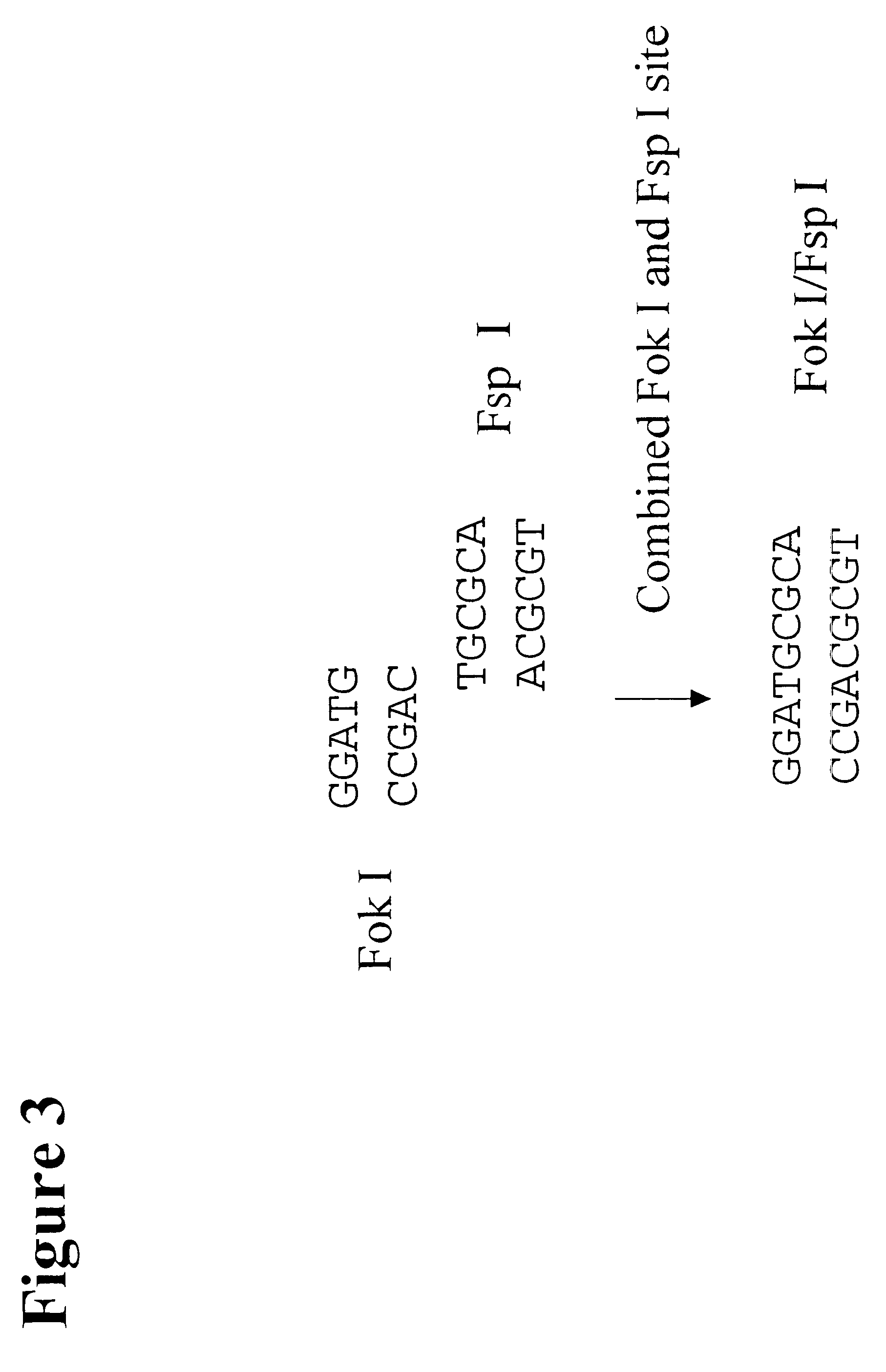
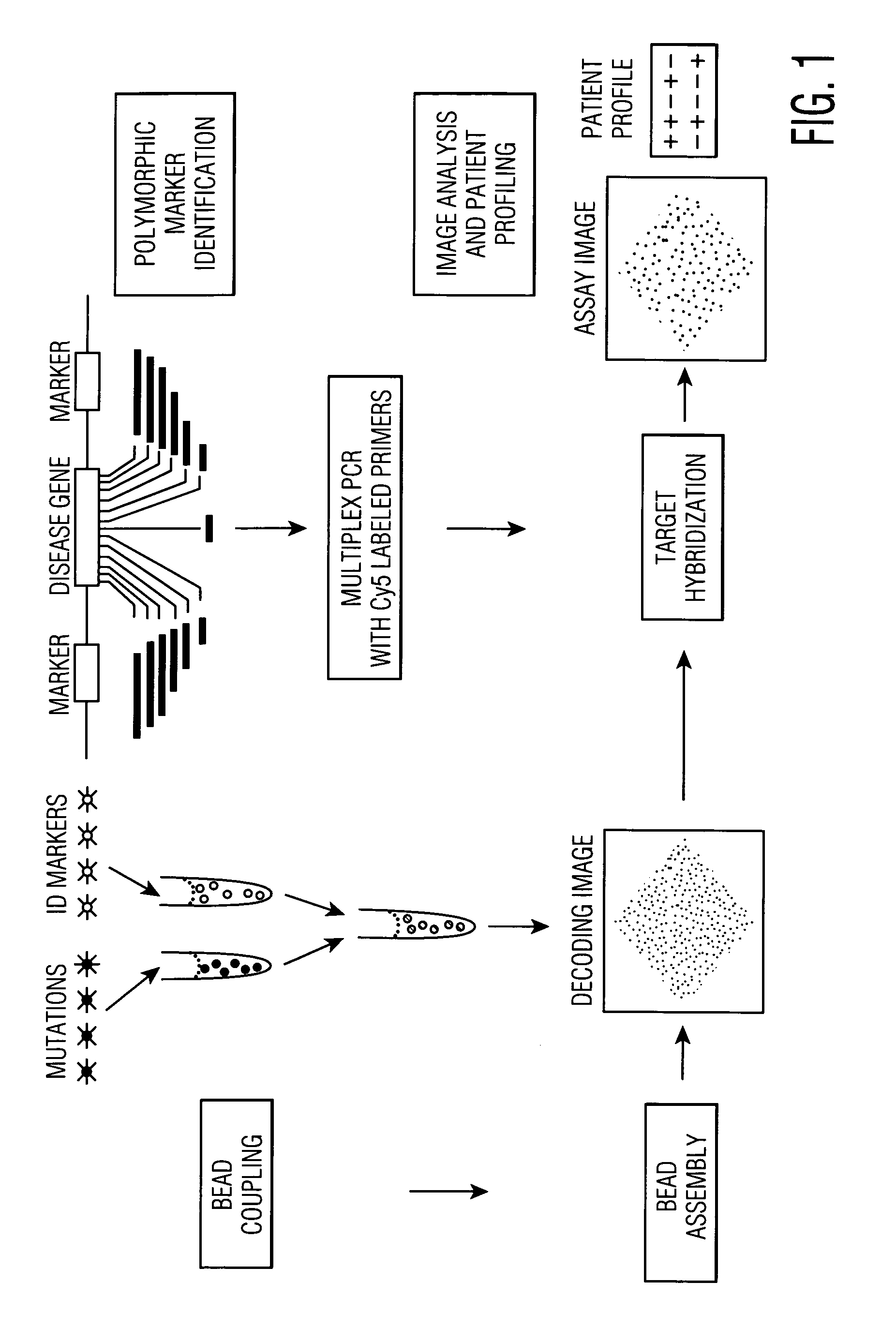
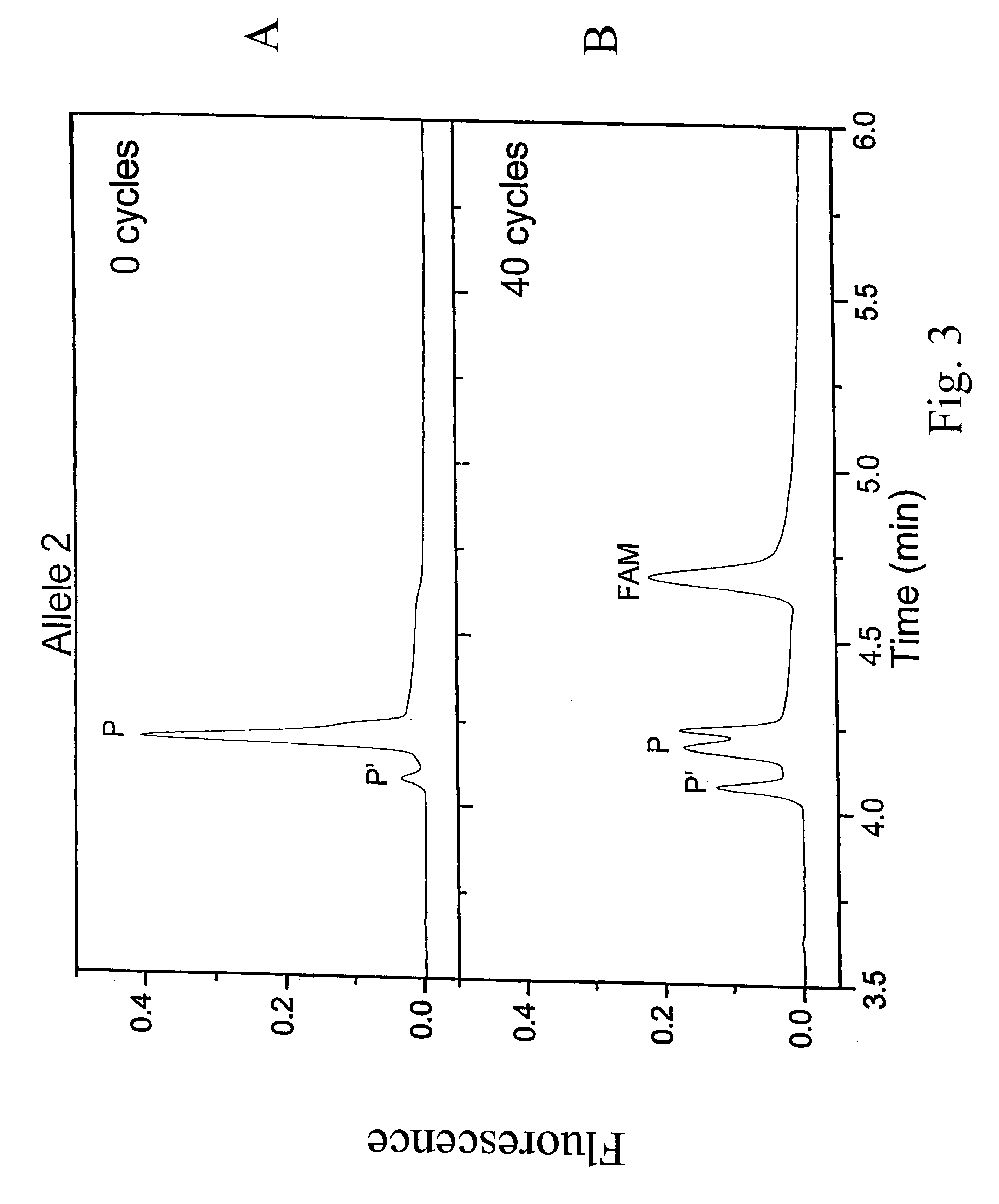
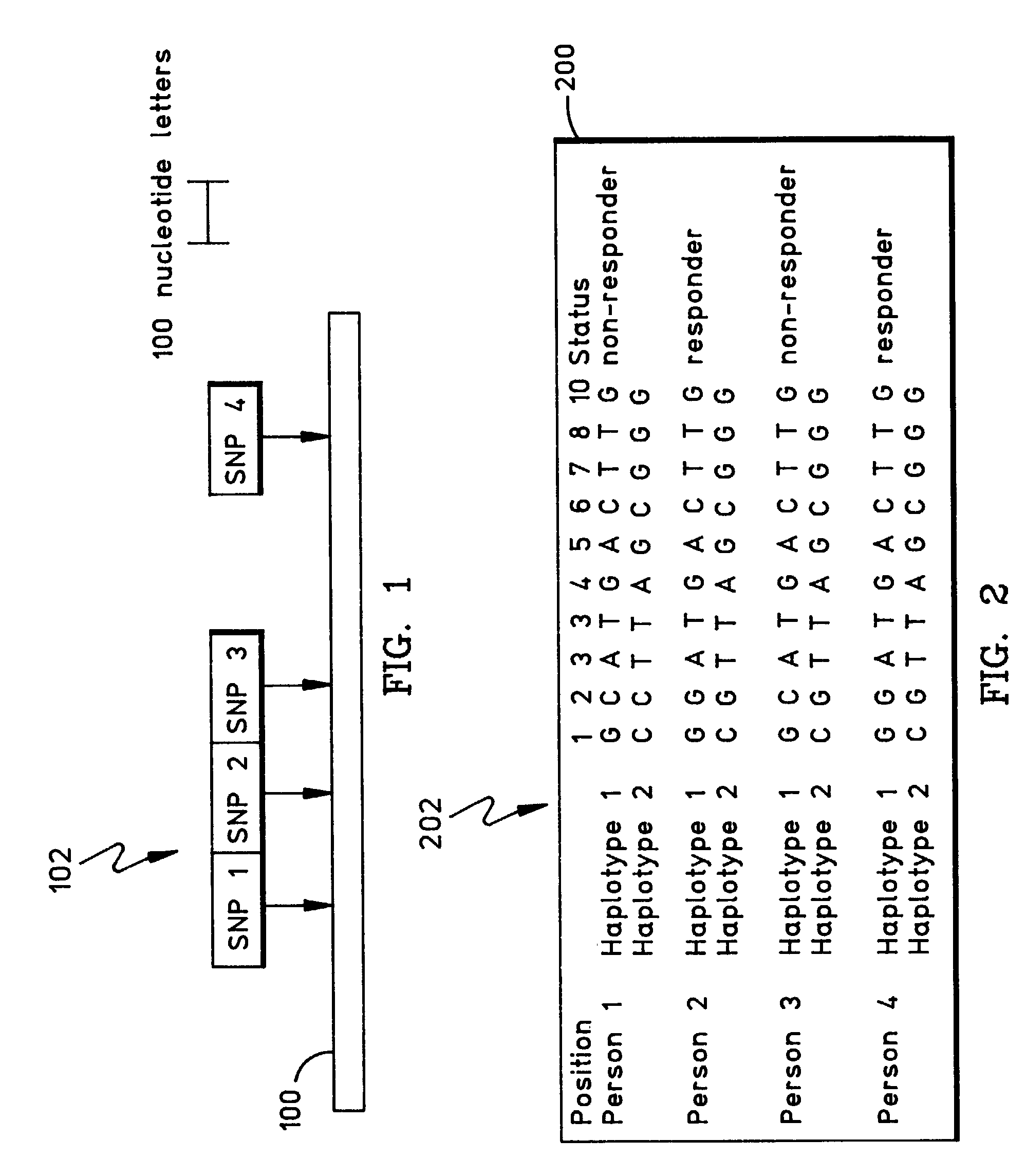
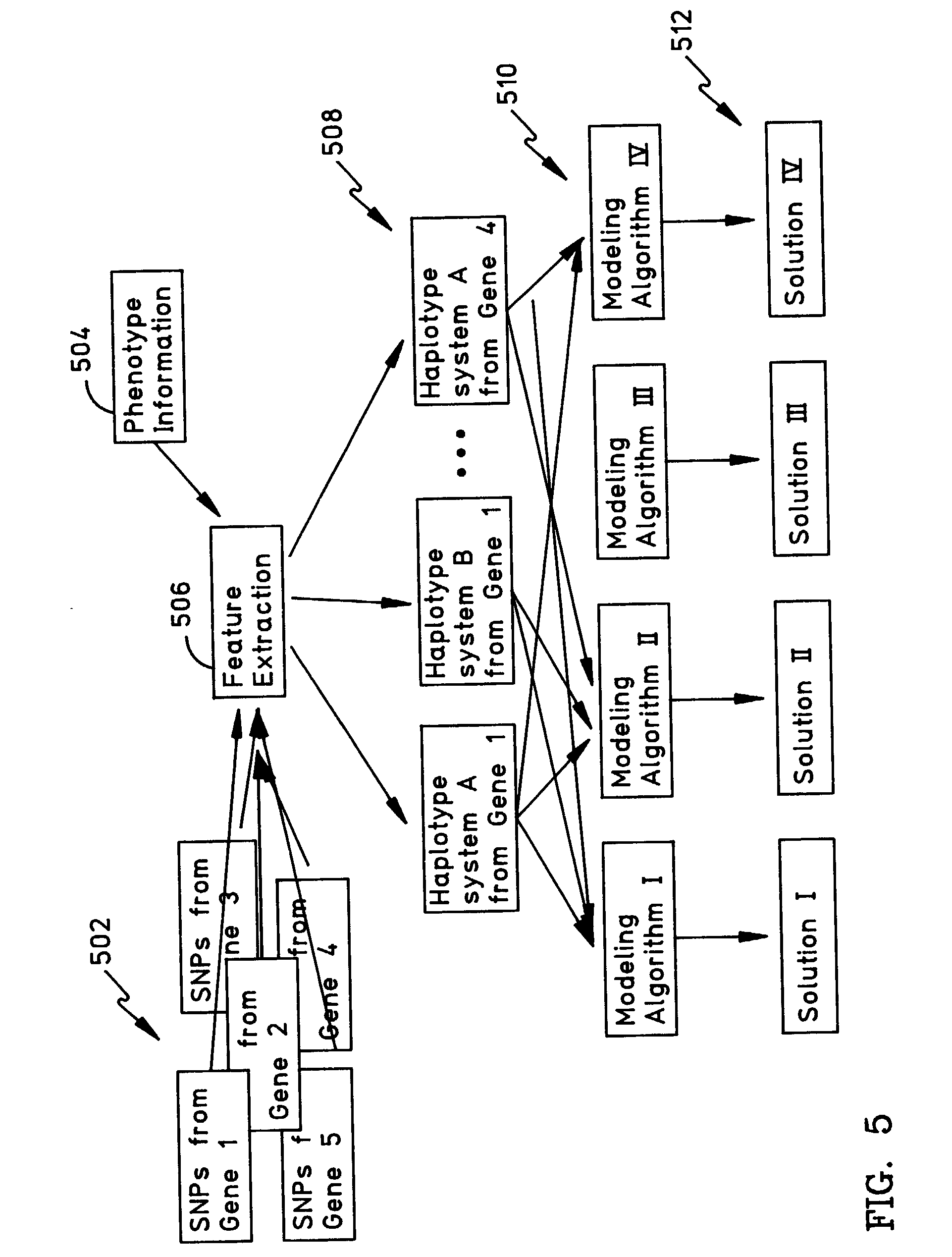
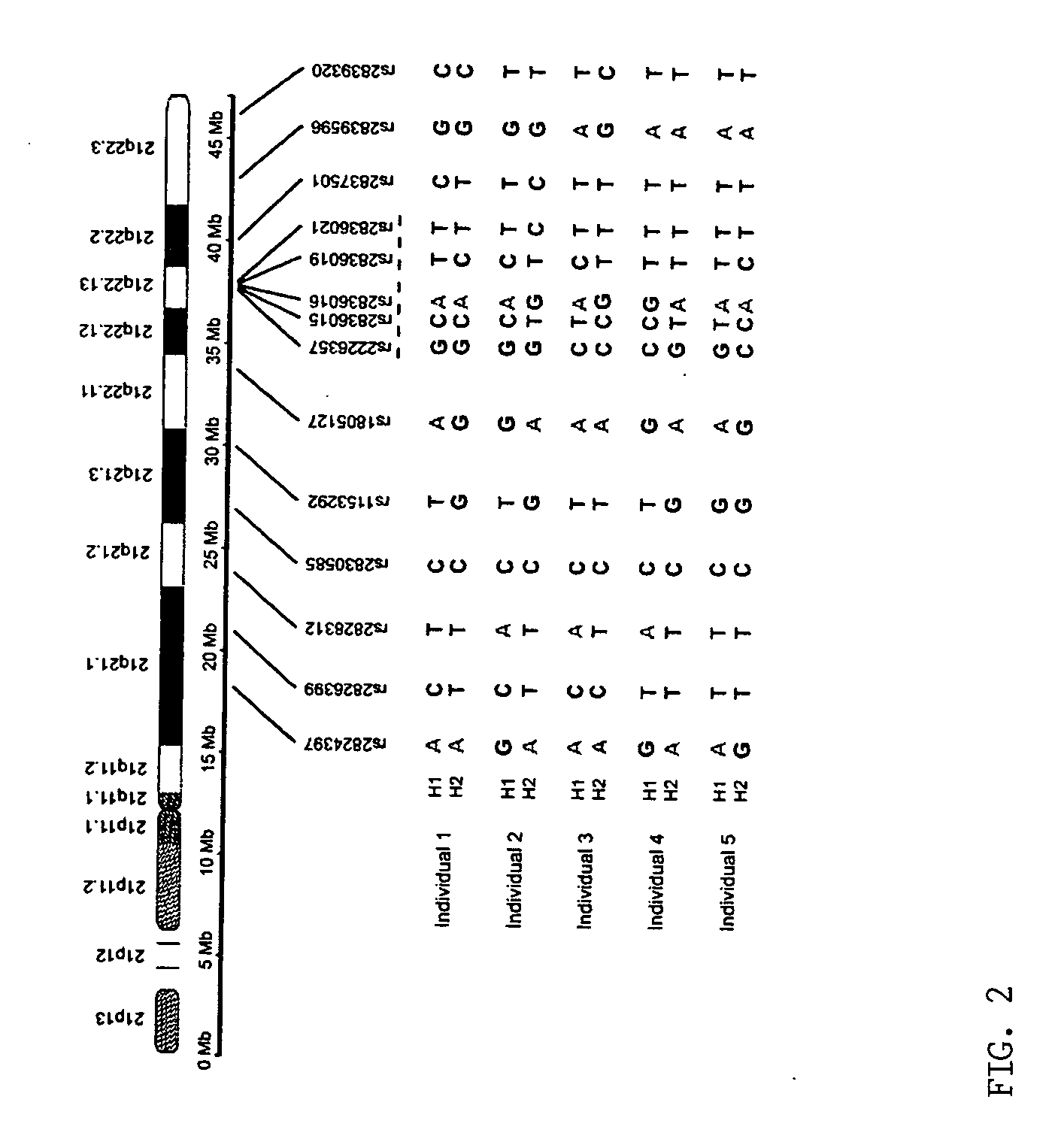
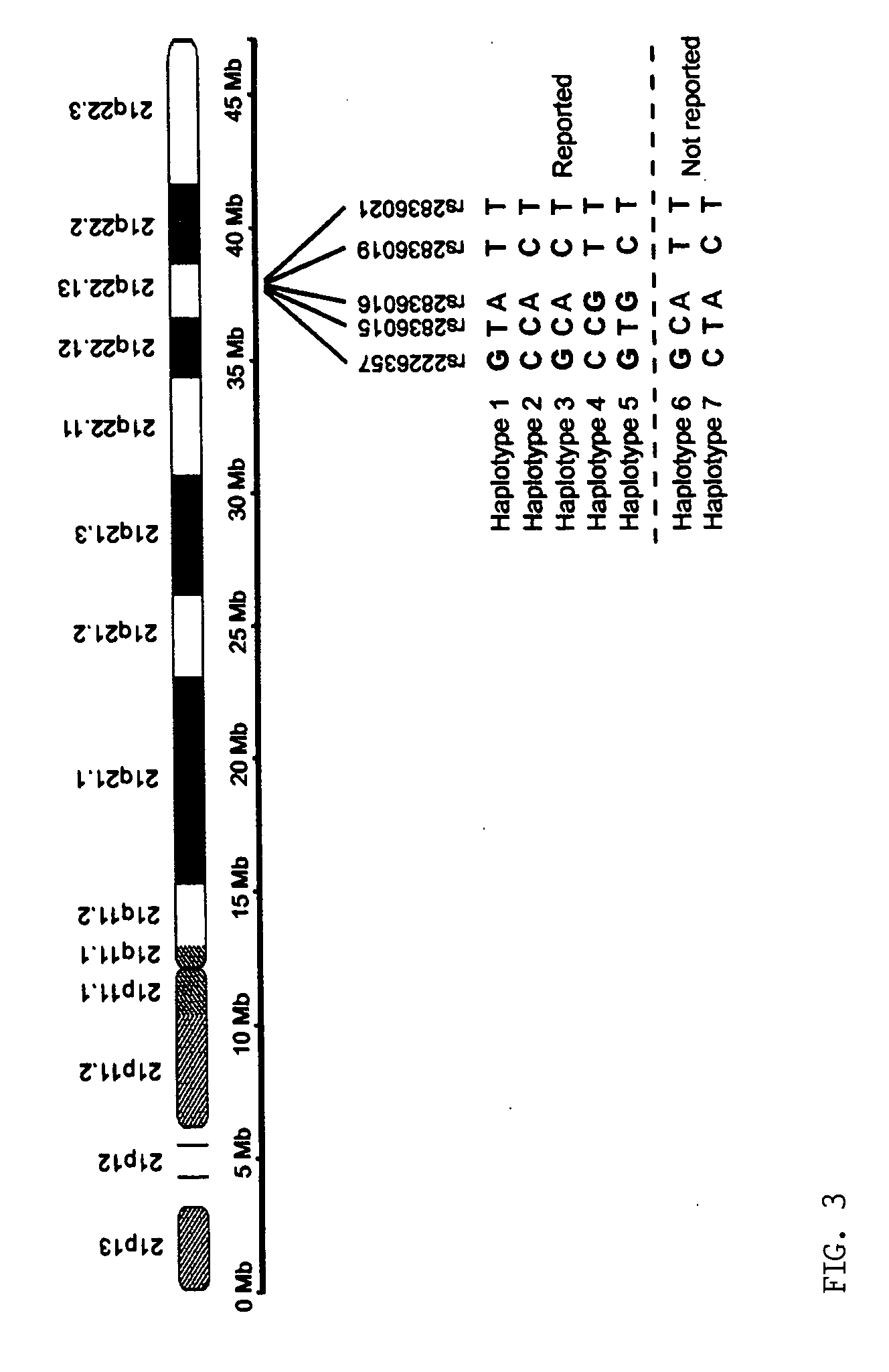
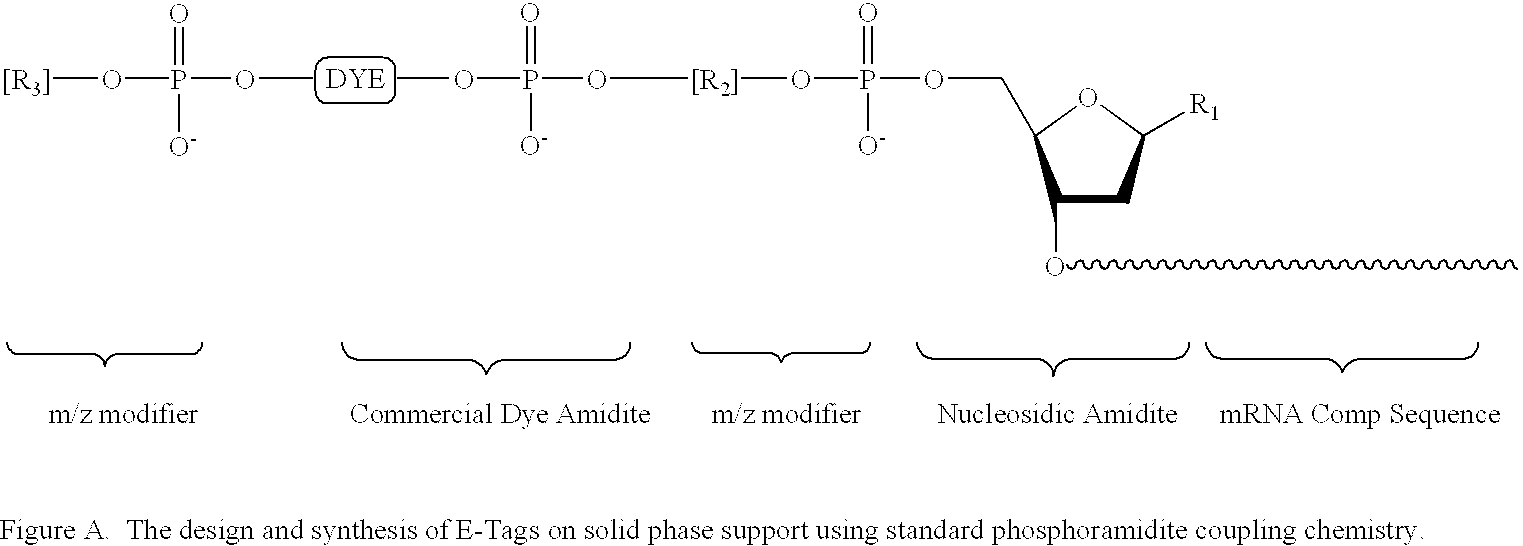
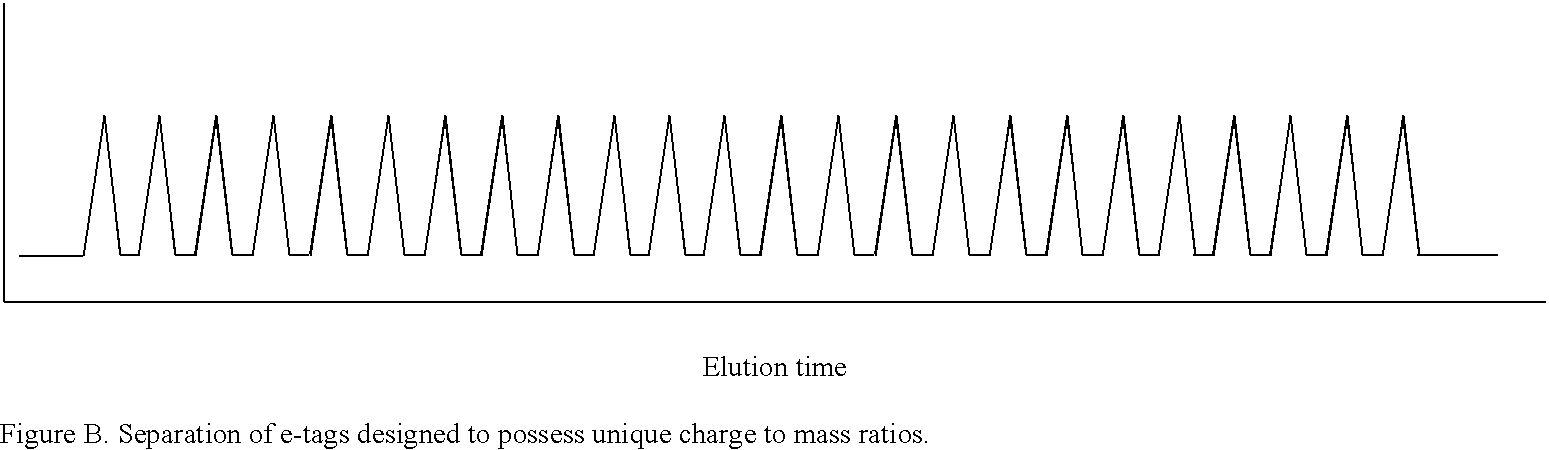
Patents
Literature
2577 results about "Single-nucleotide polymorphism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP; /snɪp/; plural /snɪps/) is a substitution of a single nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome, where each variation is present at a level of <1% in the population.
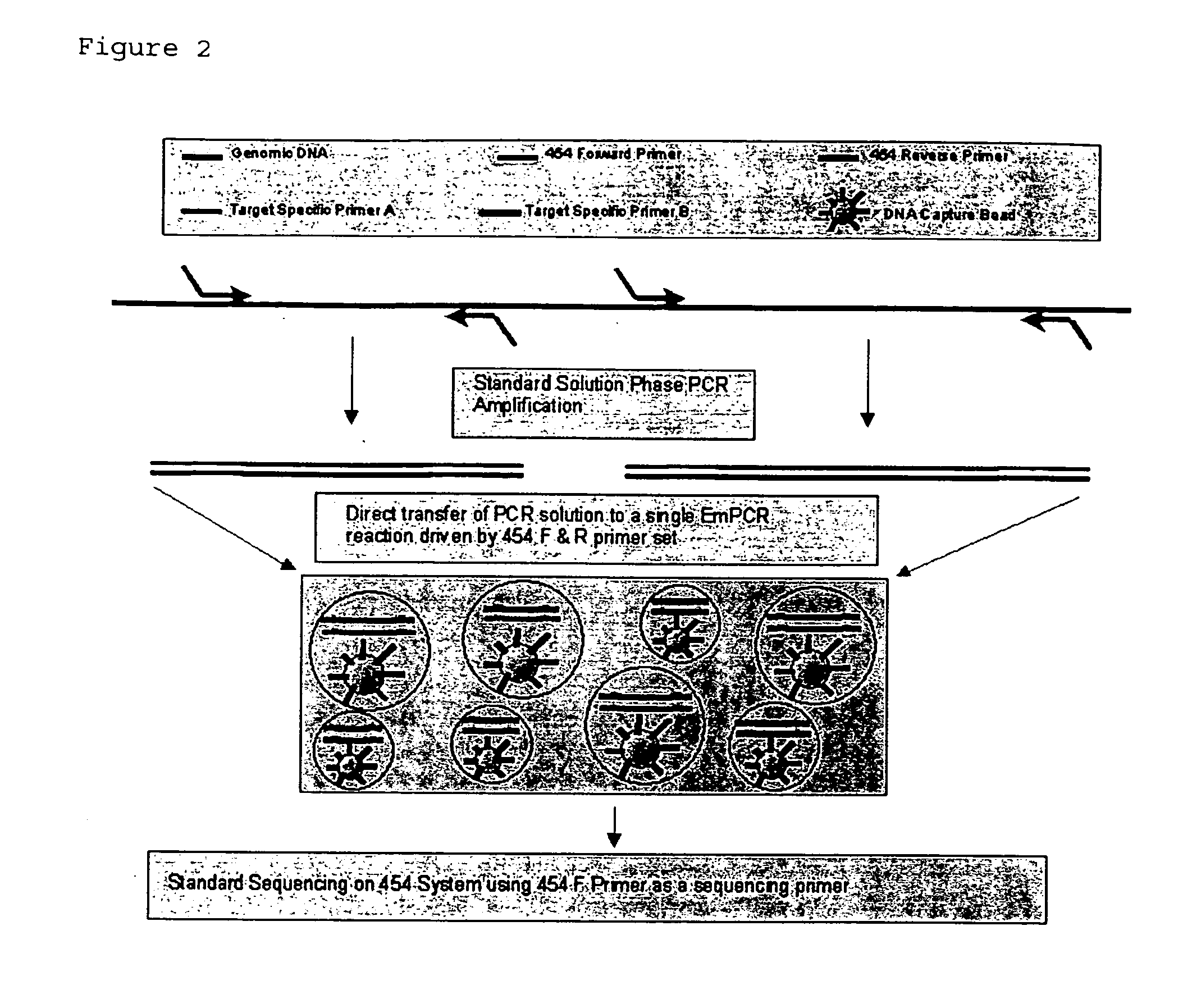
Methods for determining sequence variants using ultra-deep sequencing
InactiveUS20060228721A1Reduce effortShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationUltra deep sequencingDirect sequencing
The claimed invention provides for new sample preparation methods enabling direct sequencing of PCR products using pyrophosphate sequencing techniques. The PCR products may be specific regions of a genome. The techniques provided in this disclosure allows for SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) detection, classification, and assessment of individual allelic polymorphisms in one individual or a population of individuals. The results may be used for diagnostic and treatment of patients as well as assessment of viral and bacterial population identification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Nucleic acid analysis by random mixtures of non-overlapping fragments
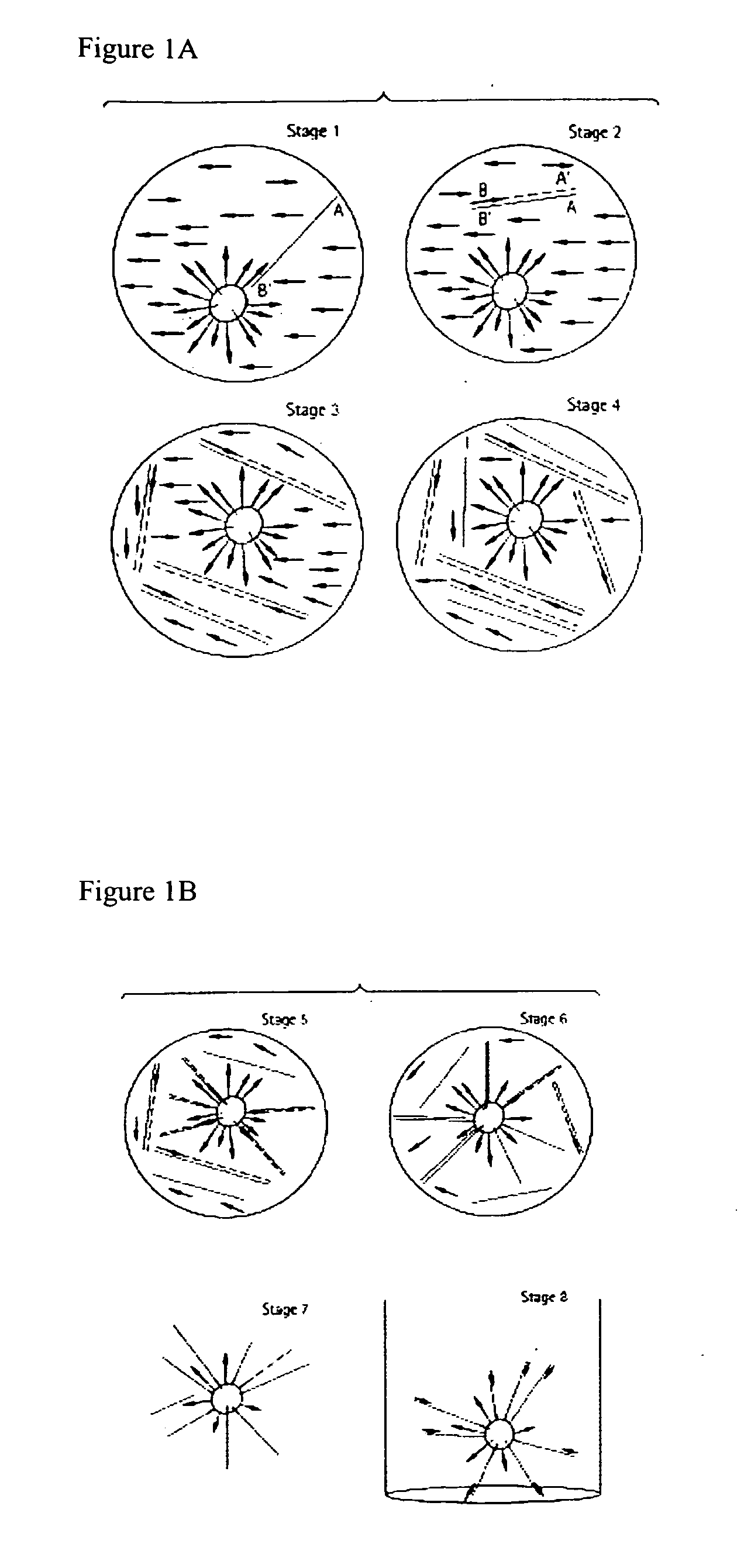
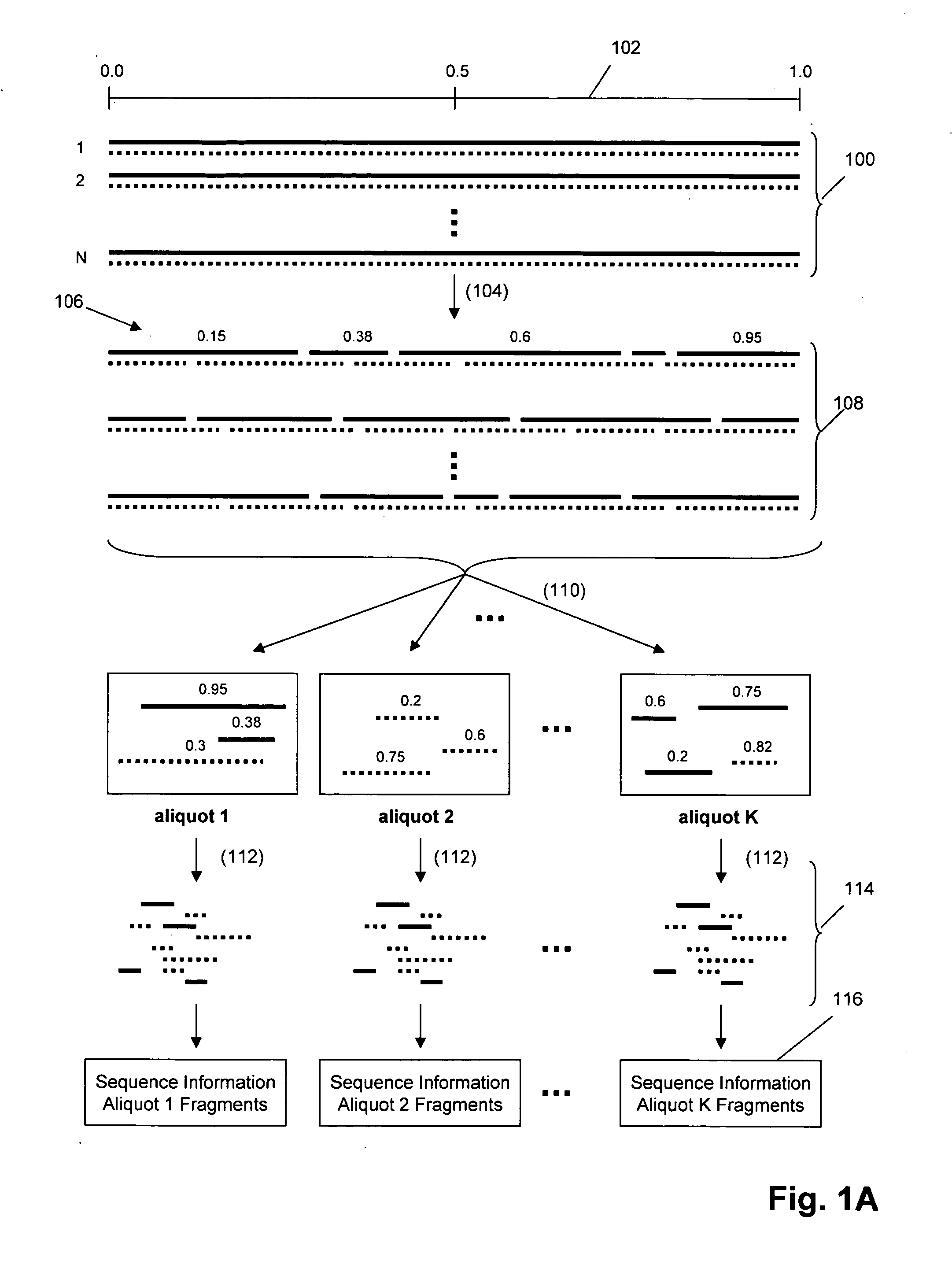
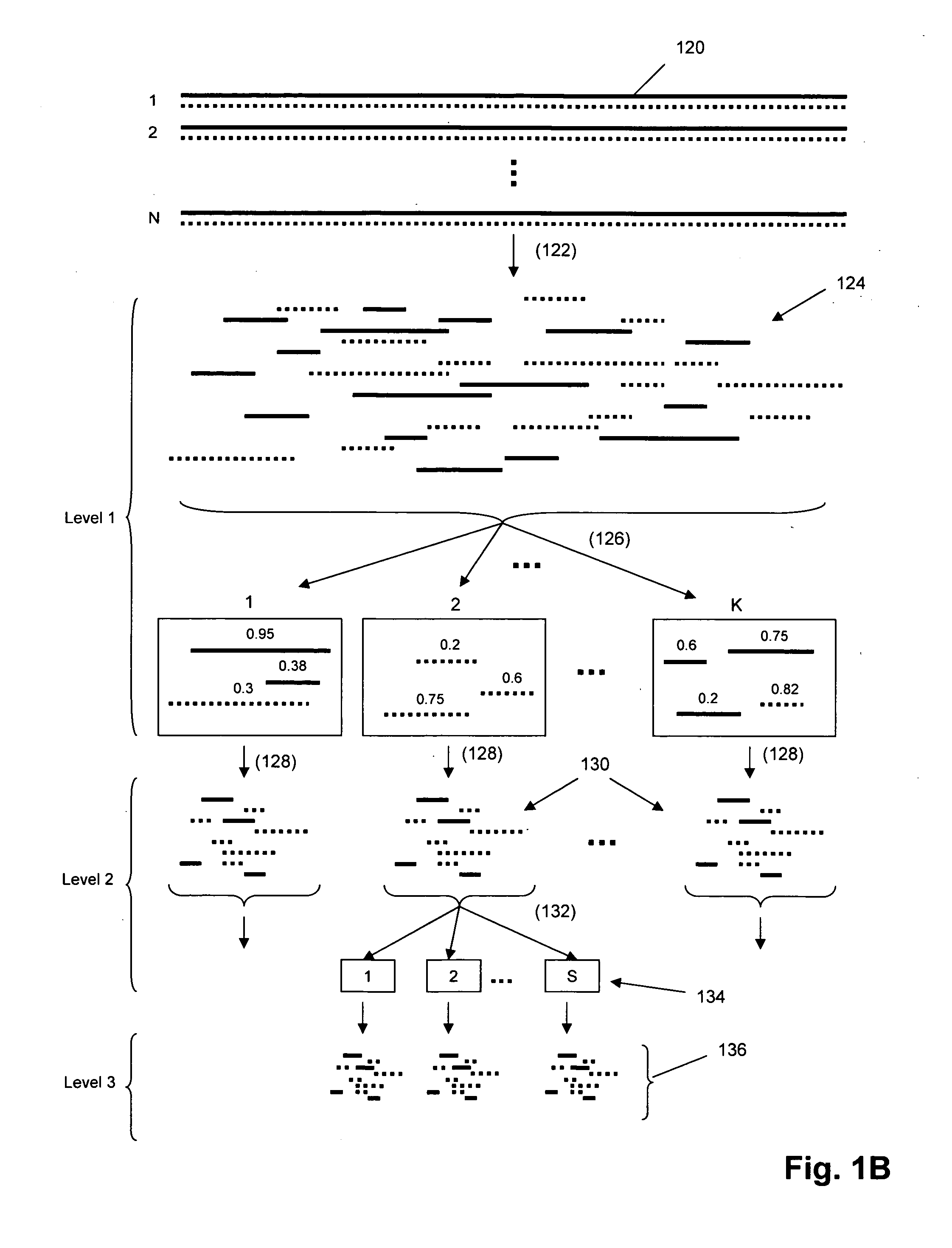
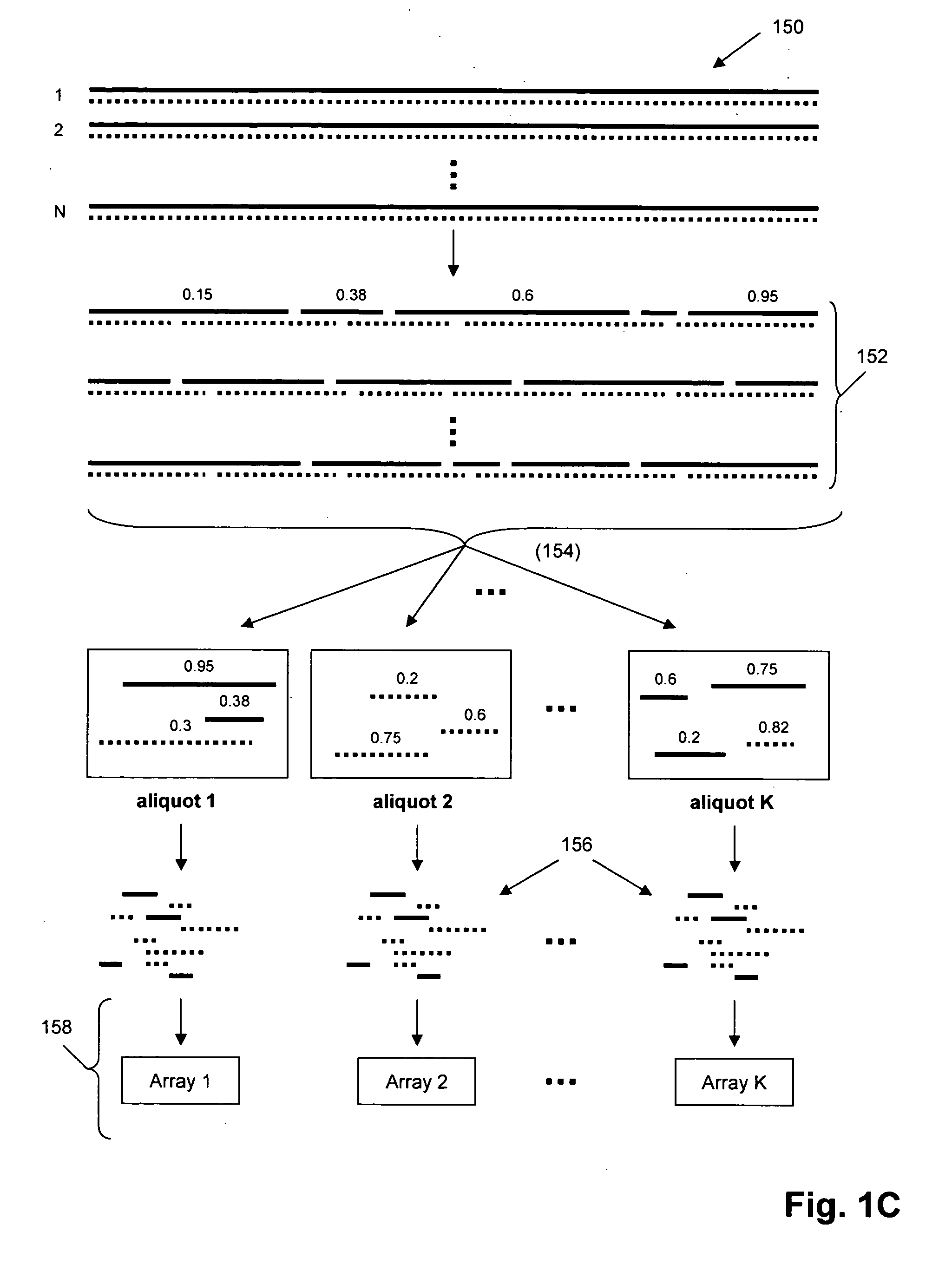
The invention provides methods and kits for ordering sequence information derived from one or more target polynucleotides. In one aspect, one or more tiers or levels of fragmentation and aliquoting are generated, after which sequence information is obtained from fragments in a final level or tier. Each fragment in such final tier is from a particular aliquot, which, in turn, is from a particular aliquot of a prior tier, and so on. For every fragment of an aliquot in the final tier, the aliquots from which it was derived at every prior tier is known, or can be discerned. Thus, identical sequences from overlapping fragments from different aliquots can be distinguished and grouped as being derived from the same or different fragments from prior tiers. When the fragments in the final tier are sequenced, overlapping sequence regions of fragments in different aliquots are used to register the fragments so that non-overlapping regions are ordered. In one aspect, this process is carried out in a hierarchical fashion until the one or more target polynucleotides are characterized, e.g. by their nucleic acid sequences, or by an ordering of sequence segments, or by an ordering of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), or the like.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
InactiveUS20090186349A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideMicrosphere
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS7868149B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsPlant biochemistry
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
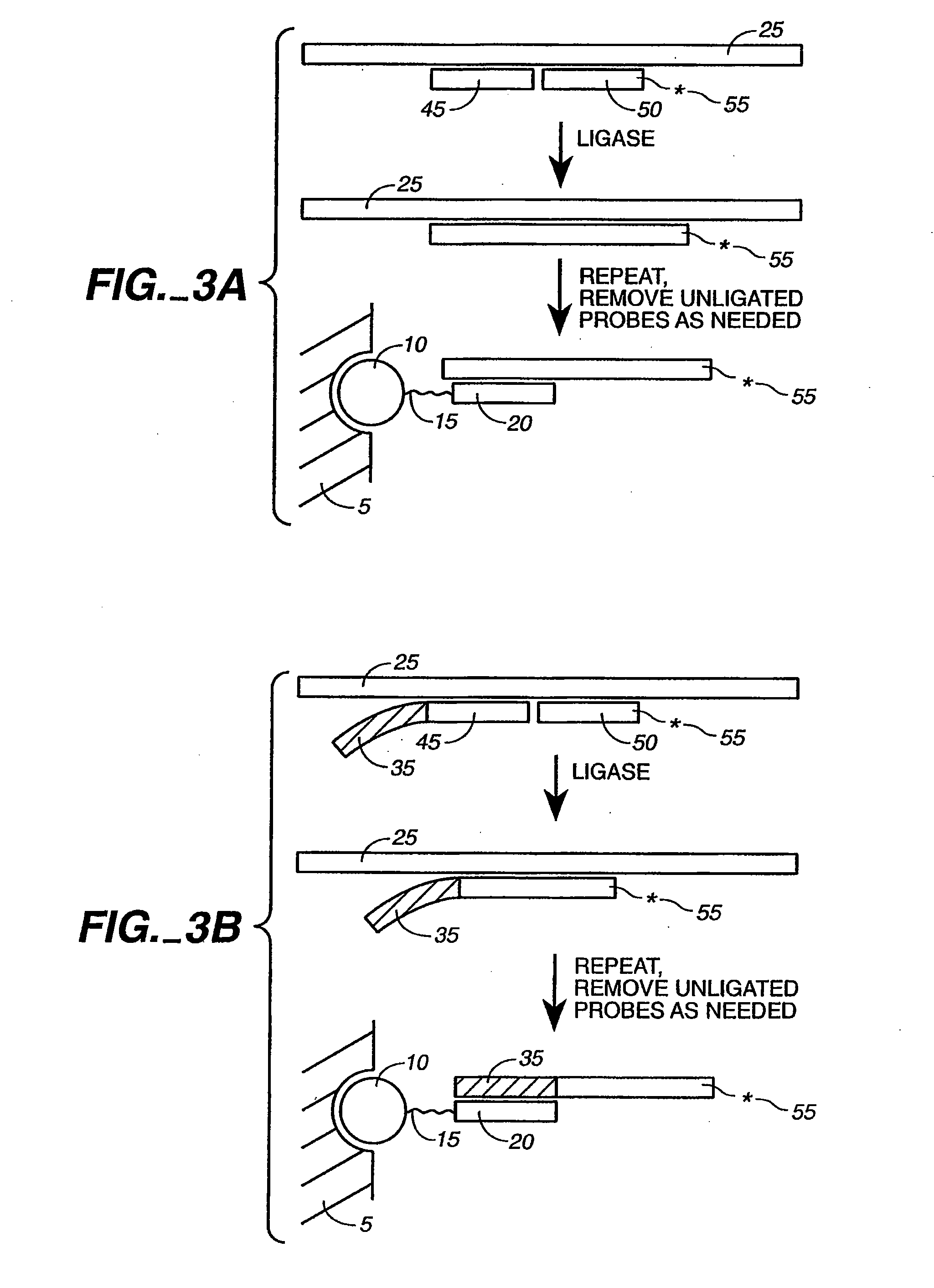
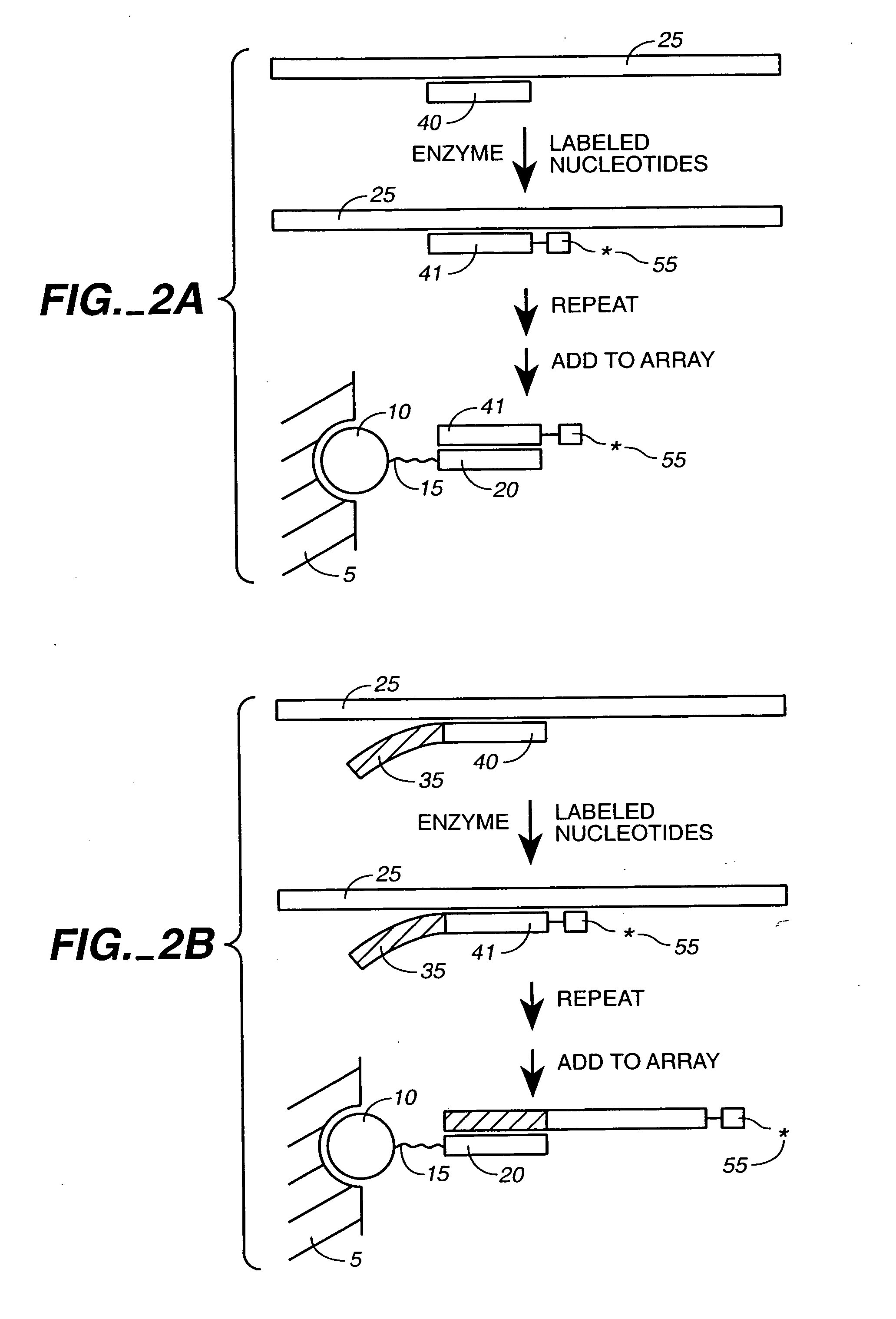
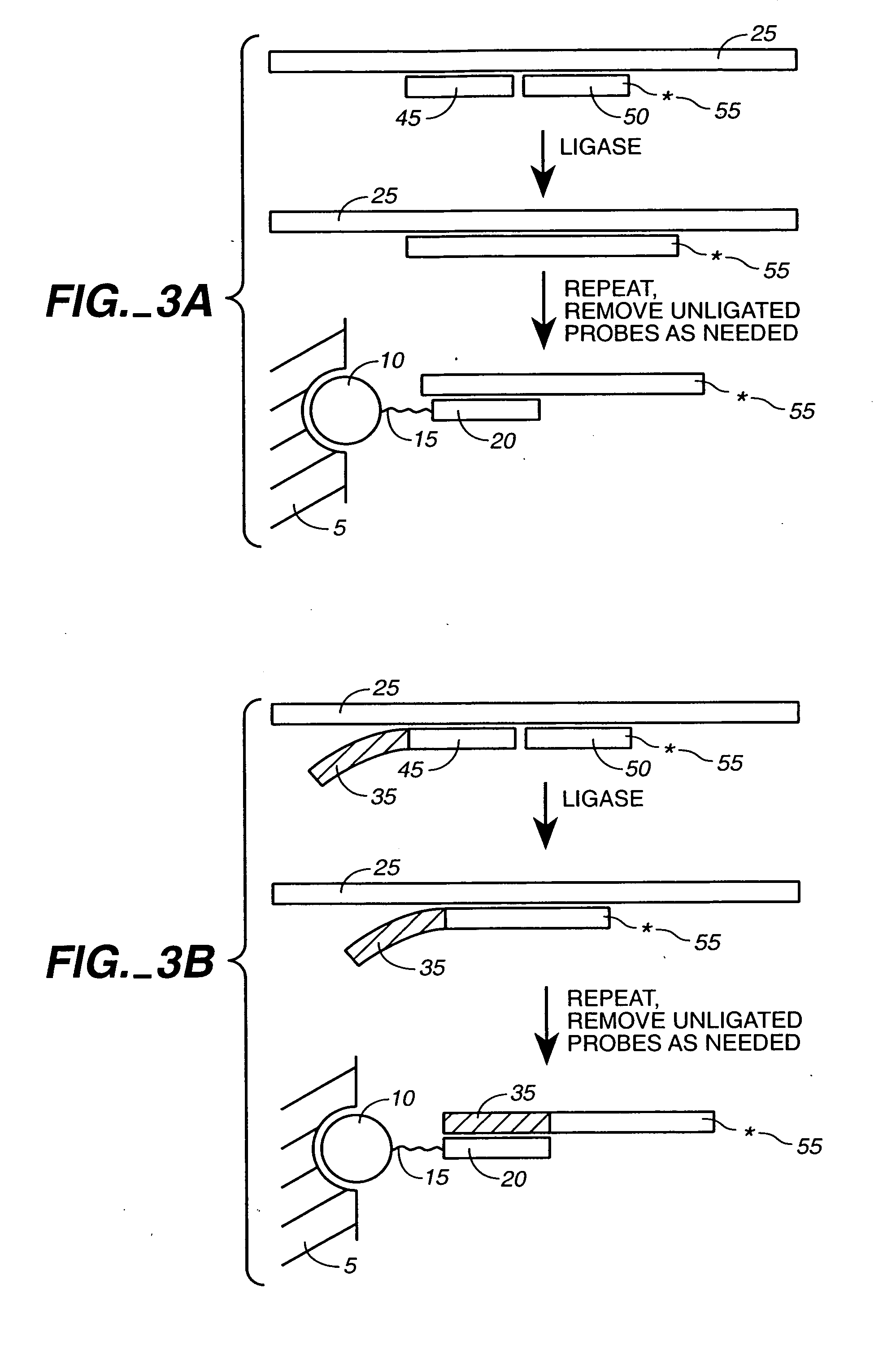
Ligation-based detection of genetic variants
InactiveUS20120034603A1Eliminate needElimination contentMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsOligonucleotide
The present invention provides assays systems and methods for detection of genetic variants in a sample, including copy number variation and single nucleotide polymorphisms. The invention preferably employs the technique of tandem ligation, i.e. the ligation of two or more fixed sequence oligonucleotides and one or more bridging oligonucleotides complementary to a region between the fixed sequence oligonucleotides.
Owner:TANDEM DIAGNOSTICS
Parallel polymorphism scoring by amplification and error correction
InactiveUS20070009954A1Easy to processFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesPolymerase LBinding domain
This invention provides a method of detecting polymorphisms, e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), by amplification and error correction. The invention encompasses methods of performing amplification and error correction using an improved generation of nucleic acid polymerases, and methods of multiplexing the assay. The improvement to the polymerases is the joining of a sequence-non-specific nucleic-acid-binding domain to the enzyme in a manner that enhances the ability of the enzyme to bind and catalytically modify the nucleic acid.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Methods for genetic analysis of DNA using biased amplification of polymorphic sites
InactiveUS6475736B1Efficient amplificationEasily and robustly analyzedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHaplotypeDNA
Methods for determining genotypes and haplotypes of genes are described. Also described are single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes in the ApoE gene and methods of using that information.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Methods for single nucleotide polymorphism detection
InactiveUS6632606B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNABioinformatics
Methods and compositions are provided for determining large numbers of single nucleotide polymorphisms in target DNA employing particles having (1) primers complementary to sequences in the target DNA where the next succeeding 3'-nucleotide is a potential single nucleotide polymorphism and coding composition members, where the members are unique for each primer, and (2) differentially labeled terminating nucleotides, where the label permits separation of the terminating nucleotides. Desirably the particles are separated into groups having a common prevalent next succeeding nucleotide. The particles and target DNA are combined under nucleotide extending conditions, the particles separated into groups in accordance with the terminating nucleotide and the coding members identified, so that one knows the sequence and the single nucleotide polymorphism. Various protocols are provided for the determination.< / PTEXT>
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Genetic analysis and authentication
InactiveUS7157228B2Reduce morbidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyGenetic Screening (procedure)
This invention provides compositions and methods for genetic testing of an organism and for correlating the results of the genetic testing with a unique marker that unambiguously identifies the organism. The markers may be internal markers, such as for example single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), short tandem repeats (STRs), or other sites within a genomic locus. Alternatively, the markers may be external, such that they are separately added to the genetic sample before testing.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
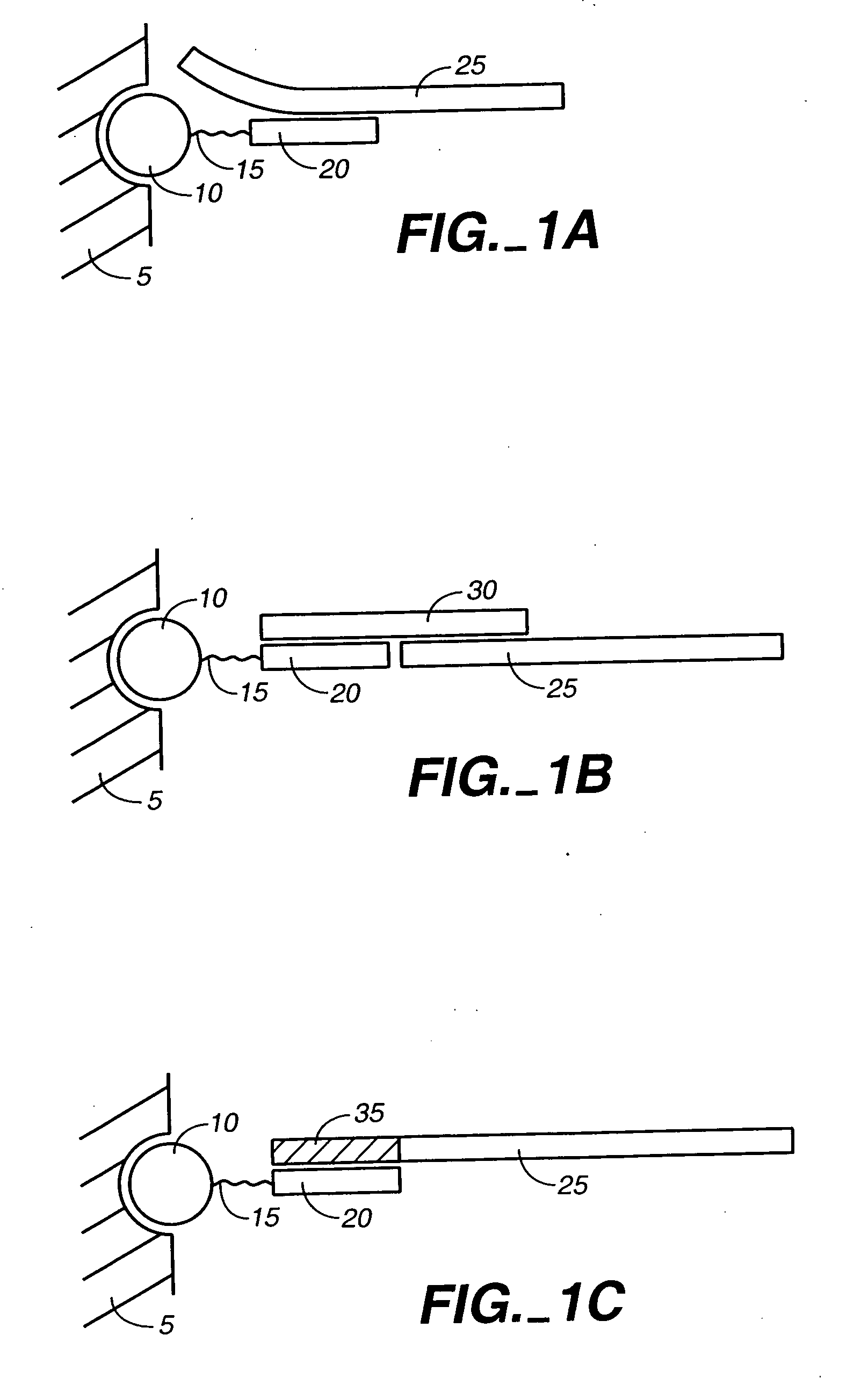
Pyrophosphorolysis and incorporation of nucleotide method for nucleic acid detection
InactiveUS7090975B2Useful in detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDepolymerizationNucleic acid detection
Processes are disclosed using the depolymerization of a nucleic acid hybrid and incorporation of a suitable nucleotide to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze for the presence of predetermined nucleic acid target sequences. Applications of those processes include the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms, identification of single base changes, genotyping, medical marker diagnostics, mirosequencing, and.
Owner:PROMEGA
Single nucleotide detection using degradation of a fluorescent sequence
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms using a pair of oligonucleotides, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence hybridizes to the target DNA downstream from the primer and in the direction of primer extension. The snp detection sequence is characterized by having a nucleotide complementary to the snp and adjacent nucleotide complementary to adjacent nucleotides in the target and an electophoretic tag bonded to the 5'-nucleotide. The pair of oligonucleotides is combined with the target DNA under primer extension conditions, where the polymerase has 5'-3' exonuclease activity. When the snp is present, the electophoretic tag is released from the snp detection sequence, and can be detected by electrophoresis as indicative of the presence of the snp in the target DNA.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070039076A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsGenomic DNA
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for the identification of genetic features for complex genetics classifiers
InactiveUS7107155B2Easy to measureReduce in quantityComputer controlMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic traitsStatistical analysis
A candidate single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) combination is selected from a plurality of candidate SNP combinations for a gene associated with a genetic trait. Haplotype data associated with this candidate SNP combination are read for a plurality of individuals and grouped into a positive-responding group and a negative-responding group based on whether a predetermined trait criteria for an individual is met. A statistical analysis on the grouped haplotype data is performed to obtain a statistical measurement. The acts of selecting, reading, grouping, and performing are repeated as necessary to identity the candidate SNP combination having the optimal statistical measurement. In one approach, a directed search based on results of previous statistical analysis of SNP combinations is performed until the optimal statistical measurement is obtained. In addition, the number of SNP combinations selected and analyzed may be reduced based on a simultaneous testing procedure.
Owner:DNAPRINT GENOMICS +1
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
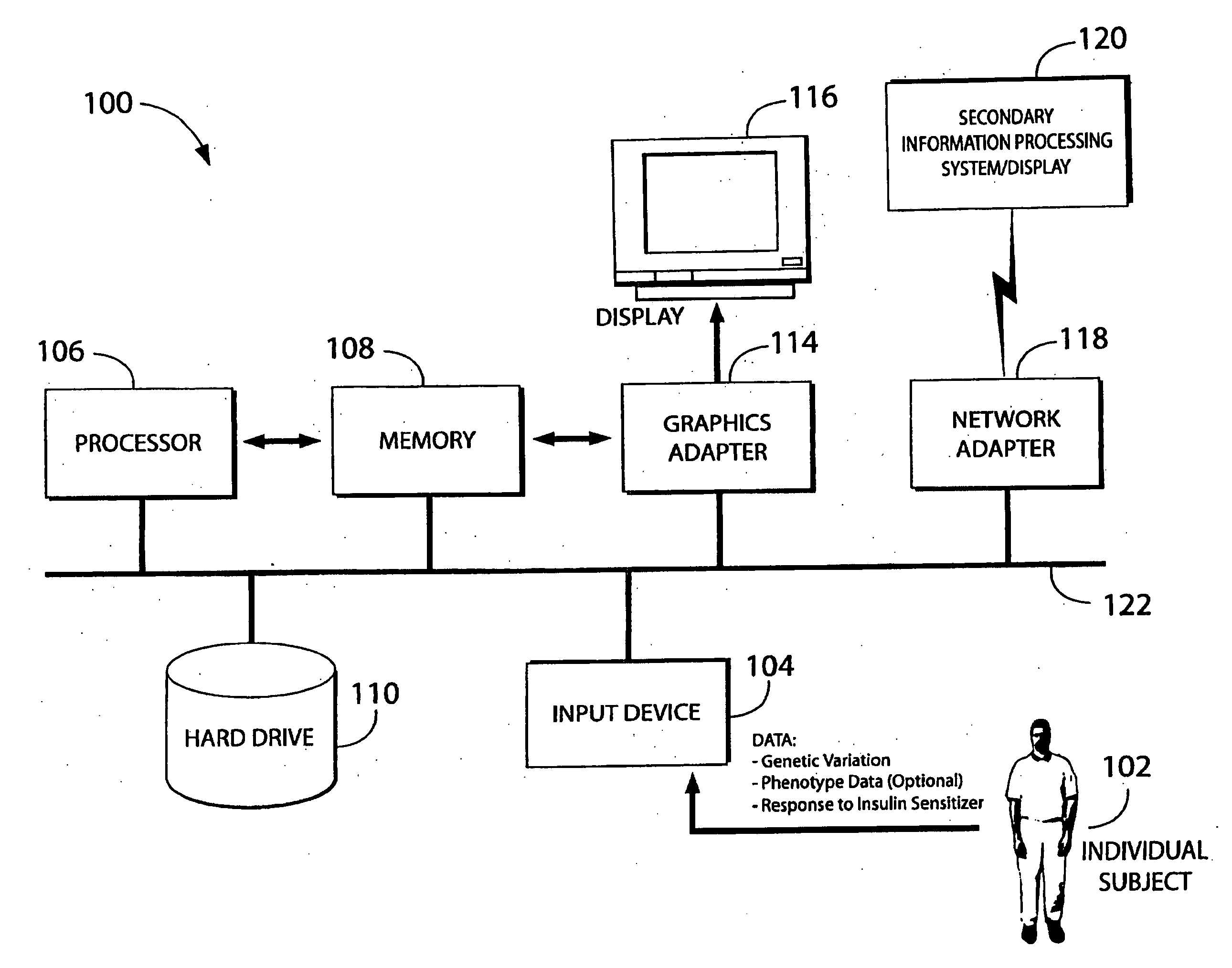
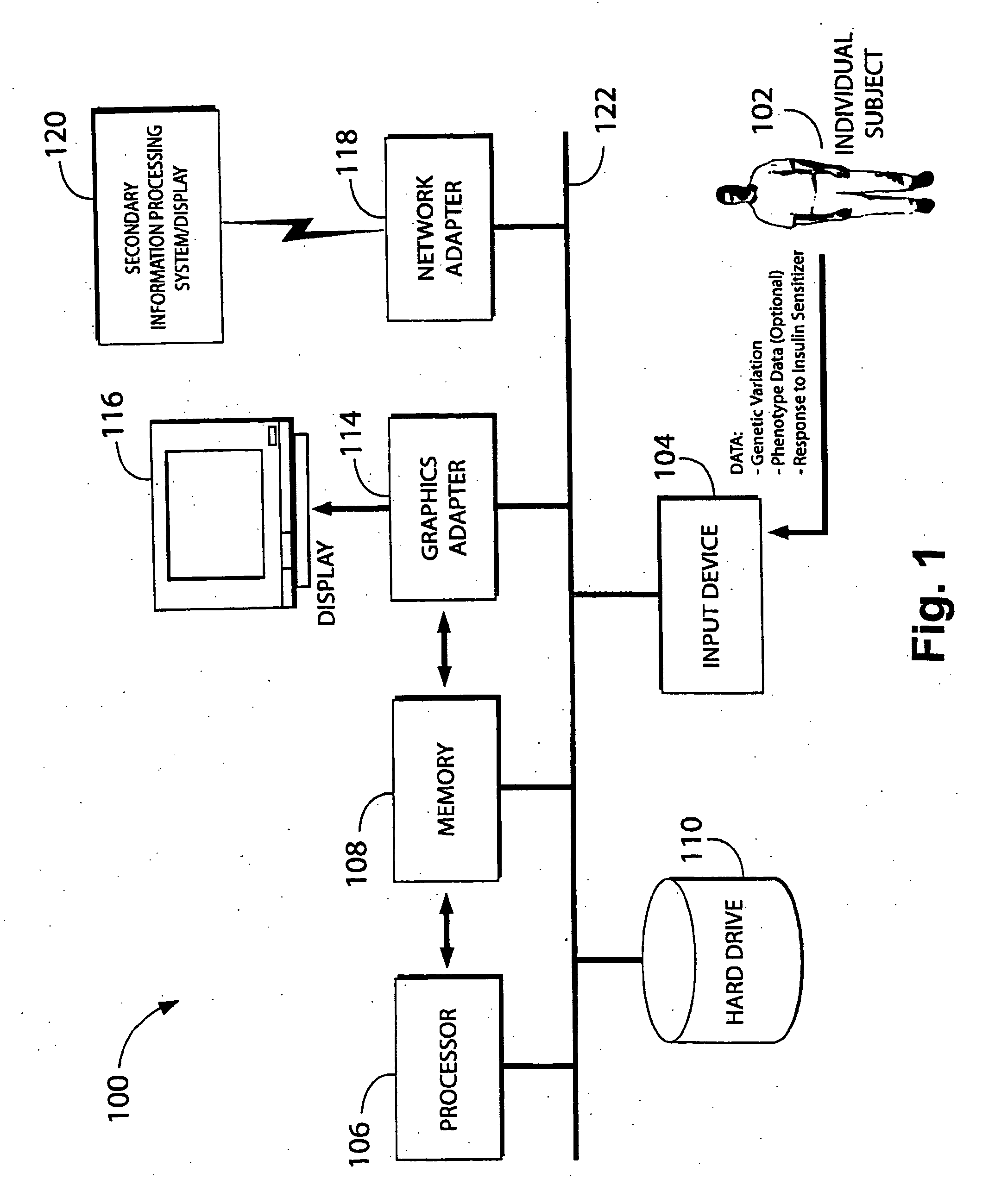
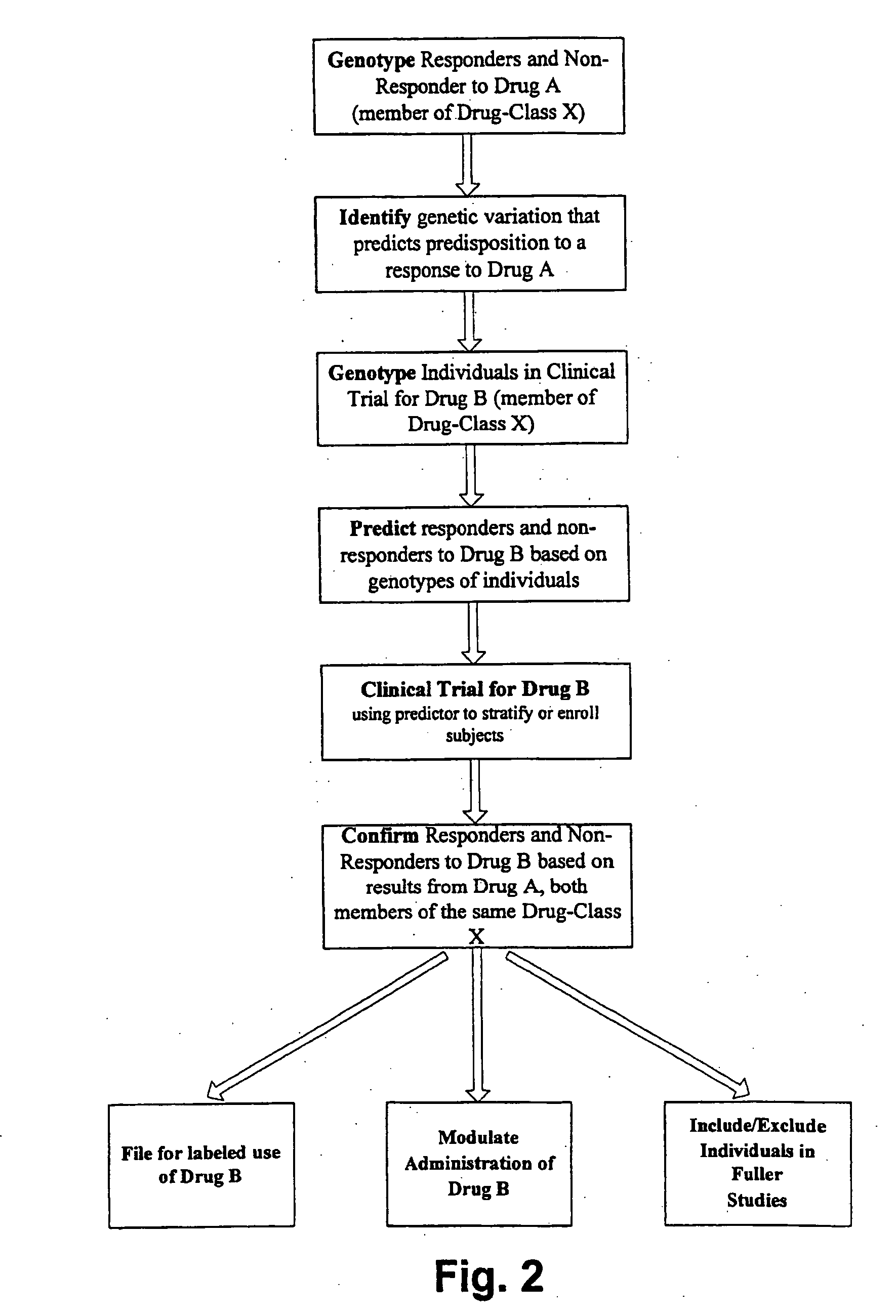
Methods and compositions for screening and treatment of disorders of blood glucose regulation
InactiveUS20080280955A1High frequencyIncrease appetiteBiocideSenses disorderInsulin resistanceScreening Result
In one aspect, the invention provides a method of screening and, optionally, treatment of an individual suffering from an insulin resistance disorder by screening an individual in need of treatment for an insulin resistance disorder for one or more genetic variations indicating a predisposition to a response to an insulin sensitizer; and, optionally, administering or not administering an insulin sensitizer to the individual based on the results of the screening. The insulin sensitizer for which the individual is screened and the insulin sensitizer that is administered or not administered may be the same or different. In another aspect, the invention provides methods comprising identifying one or more genetic variations, e.g., one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms, that at least partly differentiate between a subset of a plurality of individuals who experience a response when administered an insulin sensitizer, and a subset of said plurality of individuals who do not experience a response when administered the insulin sensitizer. The invention also provides nucleic acids, polypeptides, antibodies, kits, and business methods associated with these screening and association methods.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Microdissection-based methods for determining genomic features of single chromosomes
InactiveUS20060211001A1Quick fixPromote associationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAChromosome regions
The present provides a microdissection-based method for identifying a genomic feature present within a visible chromosome region. The method includes steps of: (a) micro-dissecting a single copy of a chromosome to obtain a visible chromosome region; (b) amplifying the visible chromosome region to obtain amplified single chromosome DNA; and (c) subjecting the amplified single chromosome DNA to micro-array analysis whereby such analysis identifies at least one genomic feature present within the visible chromosome region. The method is applicable to determining genomic features including, but not limited to, genomic DNA size, gene content, DNA breakpoint, or DNA polymorphism (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Nucleic acid detection using degradation of a tagged sequence
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting target molecules, e.g. DNA sequences, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms, using a pair of nucleotide sequences, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence binds downstream from the primer to the target DNA in the direction of primer extension, or ligands and receptors. The methods employ e-tags comprising a mobility-identifying region joined to a detectable label and a target-binding region. The result of the binding of the target-binding region to the target is to have a bond cleaved in the starting material with the production of a detectable product with a different mobility from the starting material, where the different e-tags can be separated and detected.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
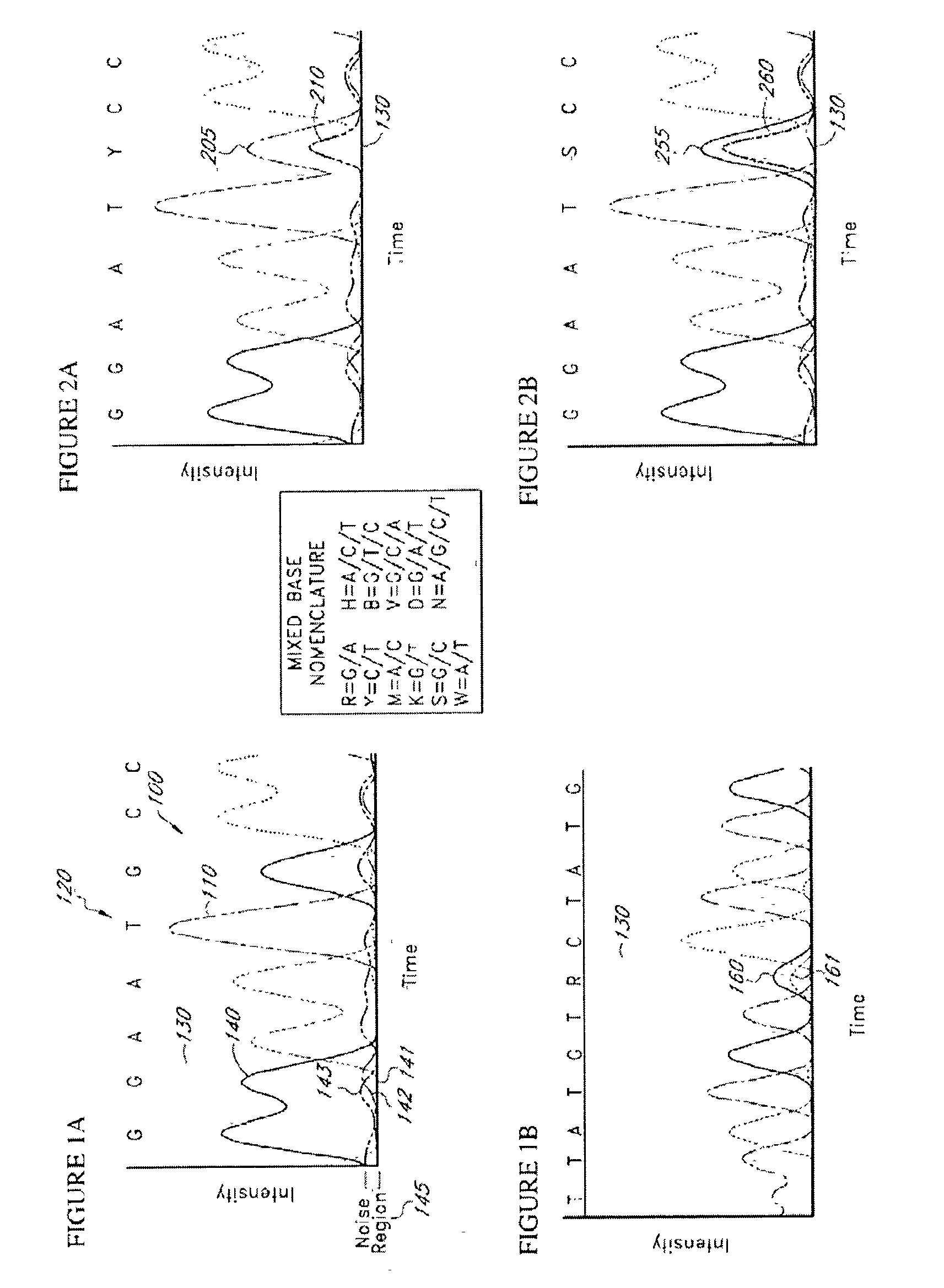
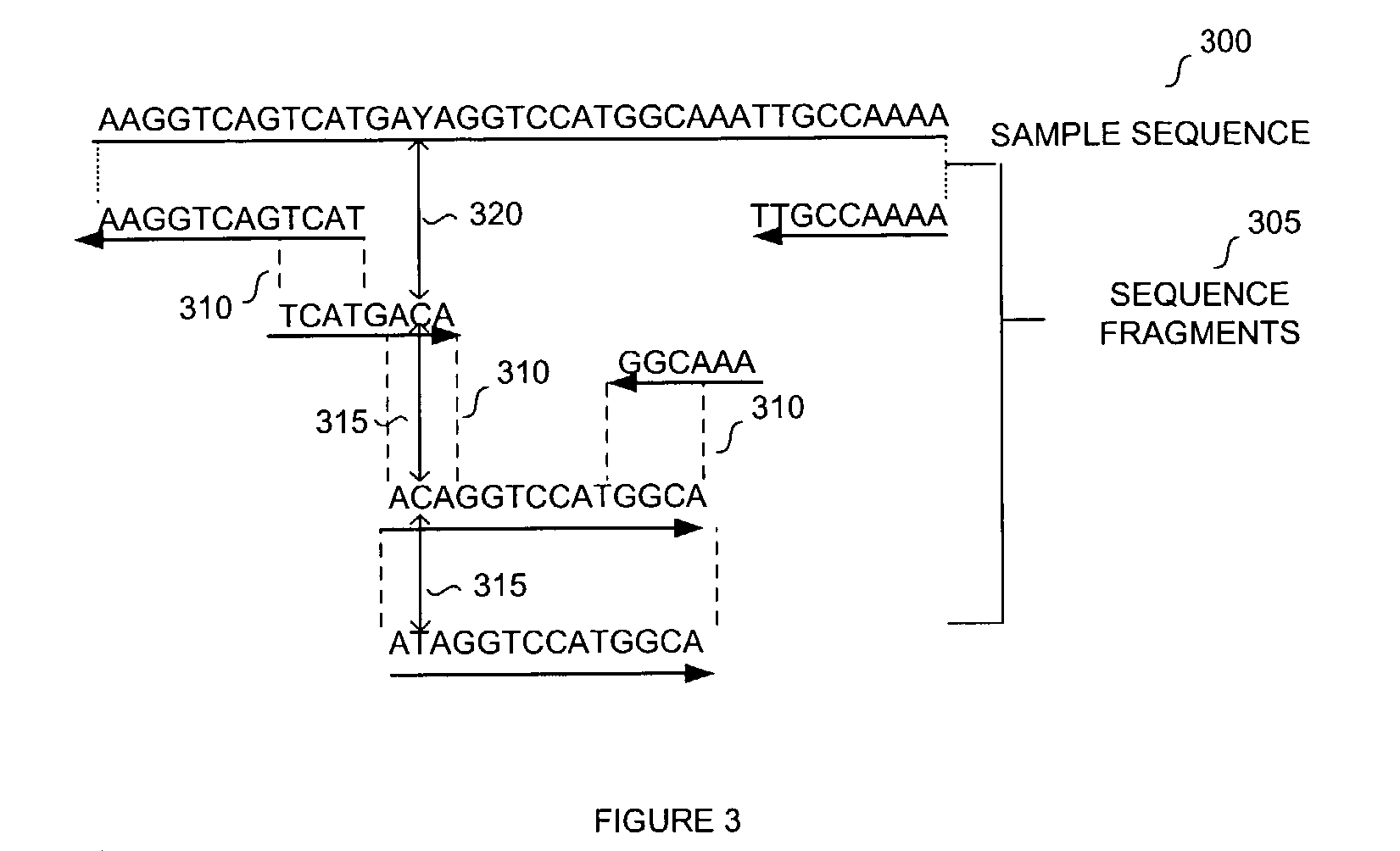
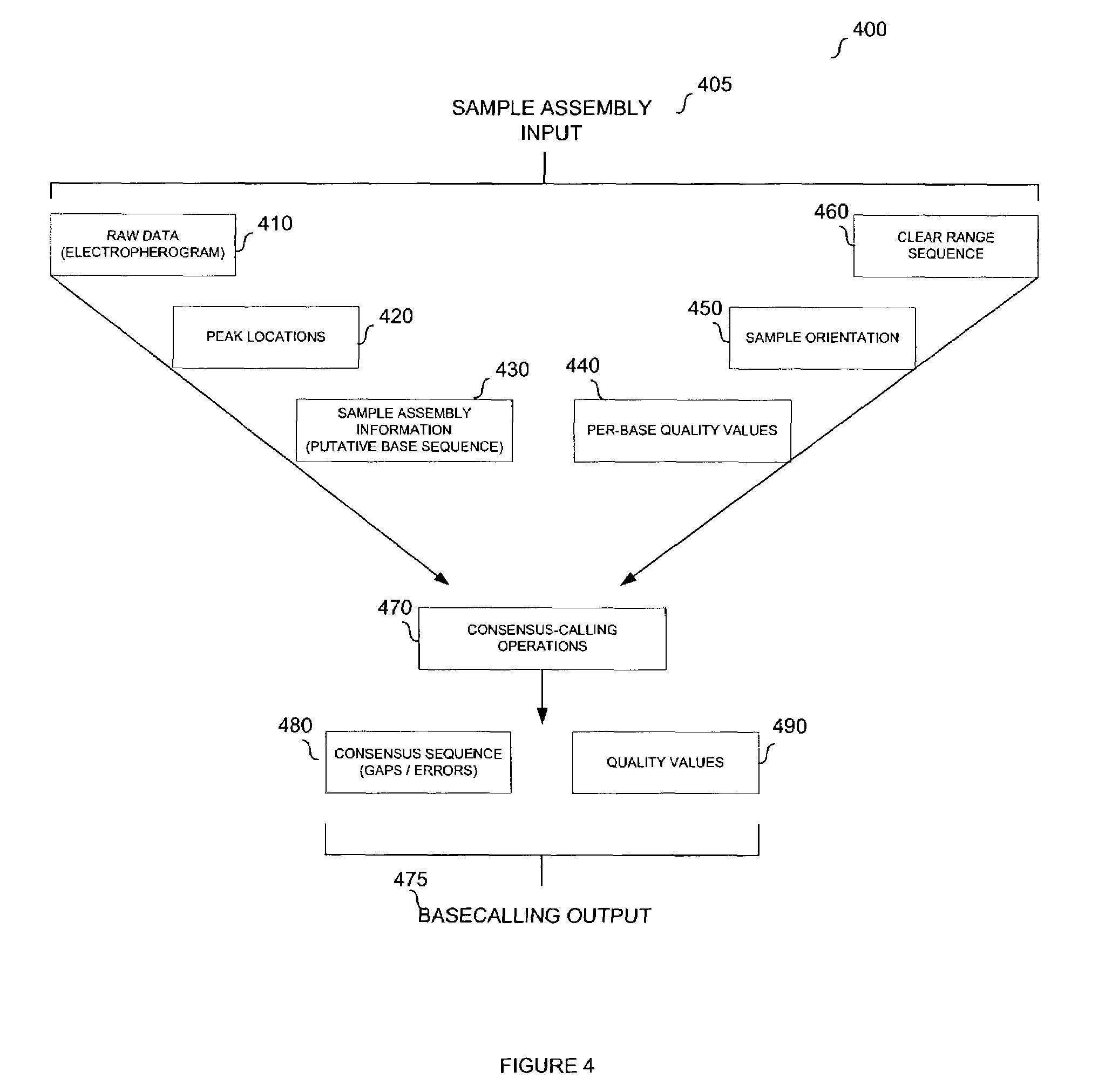
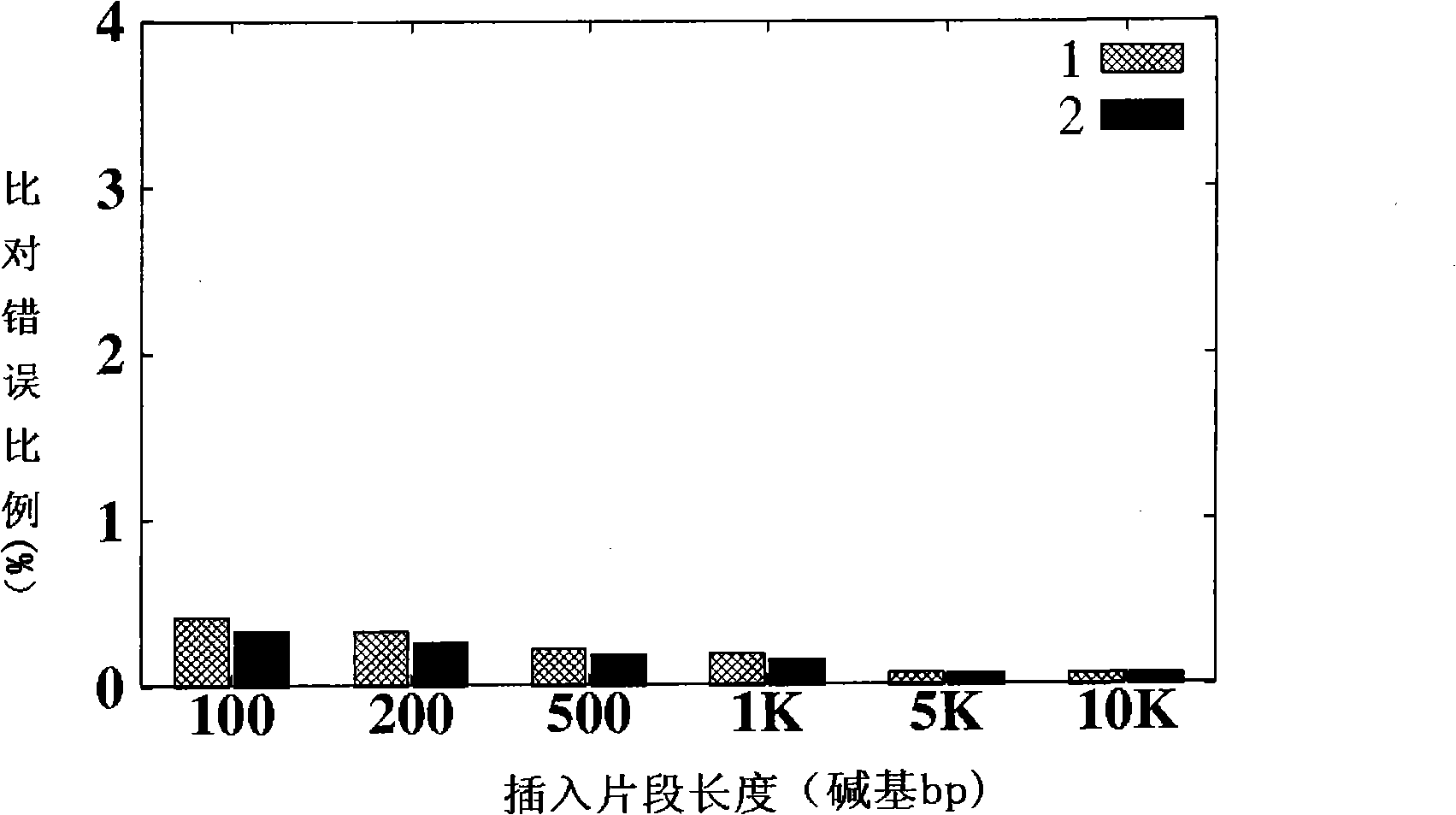
System and method for consensus-calling with per-base quality values for sample assemblies
InactiveUS7406385B2Quality improvementRemove uncertaintyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence analysisNucleotide
The present teachings disclose a method for evaluation of a polynucleotide sequence using a consensus-based analysis approach. The sequence analysis method utilizes quality values for a plurality of aligned sequence fragments to identify consensus basecalls and calculate associated consensus quality values. The disclosed method is applicable to resolution of single nucleotide polymorphisms, mixed-based sequences, heterozygous allelic variants, and heterogeneous polynucleotide samples.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Mutation analysis using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6503710B2Rapid and economic sample preparationAccurate massSamplingSugar derivativesChemical treatmentFree form
The invention presents a method for examining genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) to detect the presence of pre-known mutations, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), using mass spectrometry with ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). The invention uses nucleoside triphosphates with modified sites for the method of primer extension in a duplicating, enzymatic reaction and at least partially removal of primers from the extension product, in combination with product neutralization by chemical treatment of the modified sites, so that the resulting DNA products can be, by using special matrix materials, preferredly ionized in an adduct-free form over other constituents in the reaction solution without any further cleaning. The method is particularly suitable for simultaneous identification of several mutations by multiplexing.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
Compositions of microbiota and methods related thereto
Methods and compositions are generally provided for treating metabolic disorders, e.g., obesity. One aspect discloses methods and compositions for obtaining a biological sample from the subject, evaluating the sample for the presence or absence of a genetic indicator, wherein the genetic indicator is selected from a single nucleotide polymorphism and a level of gene expression, and performing a first metabolic procedure if the genetic indicator is present, or performing an alternative second metabolic procedure if the genetic indicator is absent. One aspect discloses methods and compositions for obtaining a sample including deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) from the subject, evaluating the DNA for an absence or presence of one or more genetic indicators and performing a first metabolic procedure or an alternative second metabolic procedure based on the absence or presence of the genetic indicator(s). Other aspects are also disclosed.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Techniques for Determining Haplotype by Population Genotype and Sequence Data
ActiveUS20140045705A1Better phasingImprove accuracyLibrary member identificationProteomicsHaplotypeSequencing data
A novel phasing algorithm harnesses sequencing read information from next generation sequencing technologies to guide and improve local haplotype reconstruction from genotypes. Techniques include determining correlated occurrences of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes of a population of individuals. A plurality of sequences of nucleotide bases in one or more individuals from the populations of individuals is determined based on ultra-high throughput sequencing of a sample from the one or more individuals. Haplotypes included in the population of individuals are determined based on both the correlated occurrences and the plurality of sequences. The inclusion of paired end read data is especially advantageous for the phasing of rare variants, including singletons.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:GUNDERSON KEVIN +2
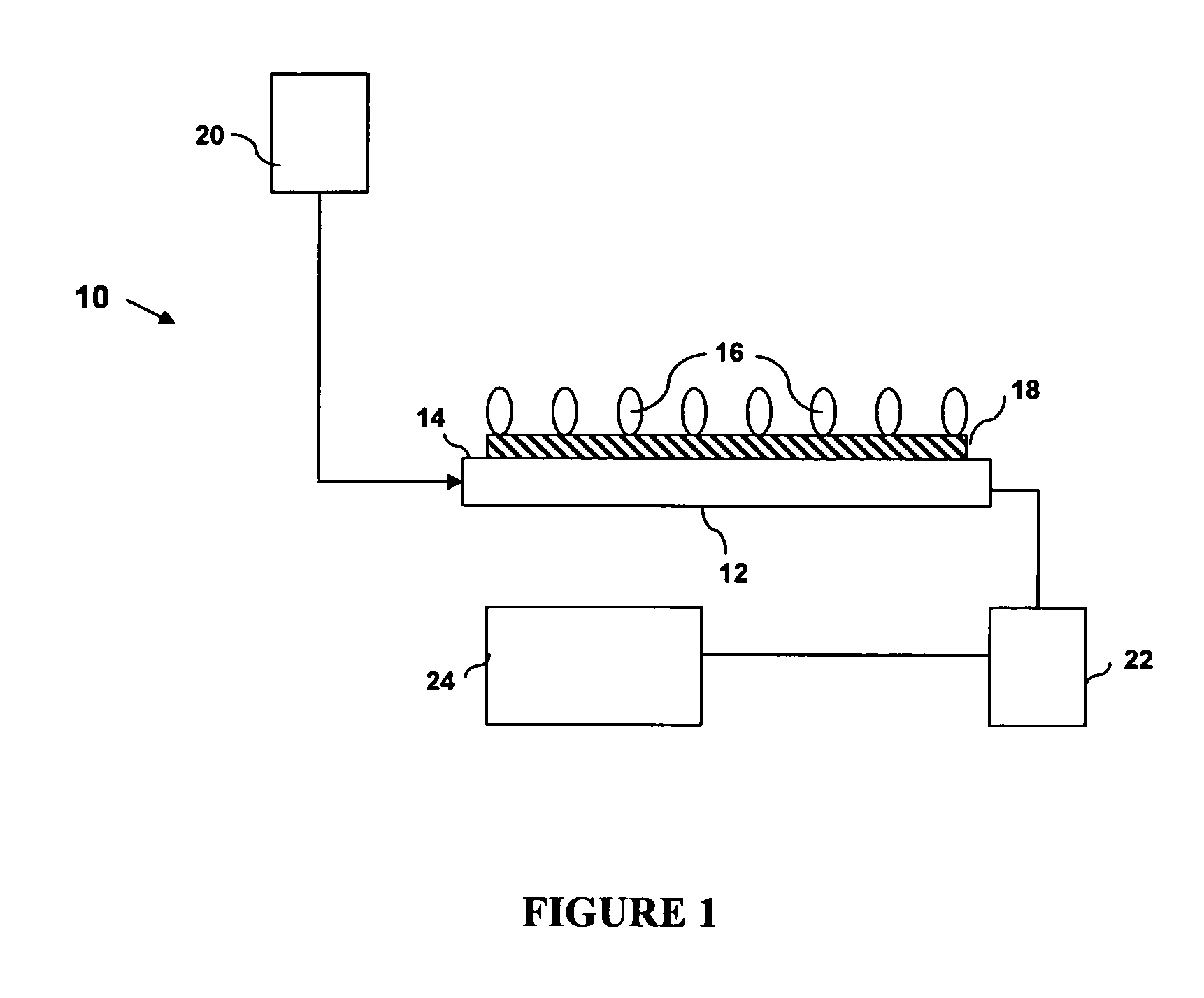
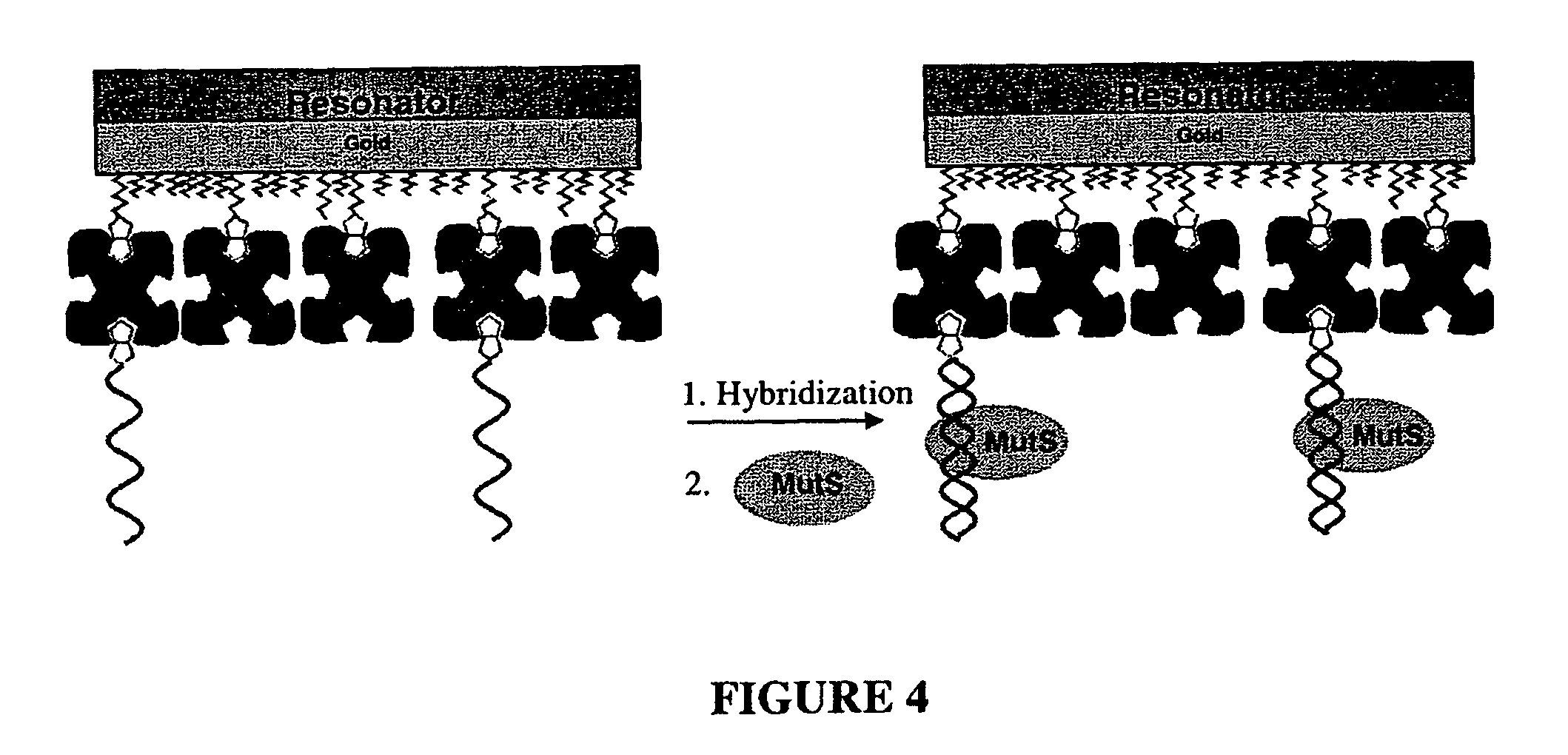
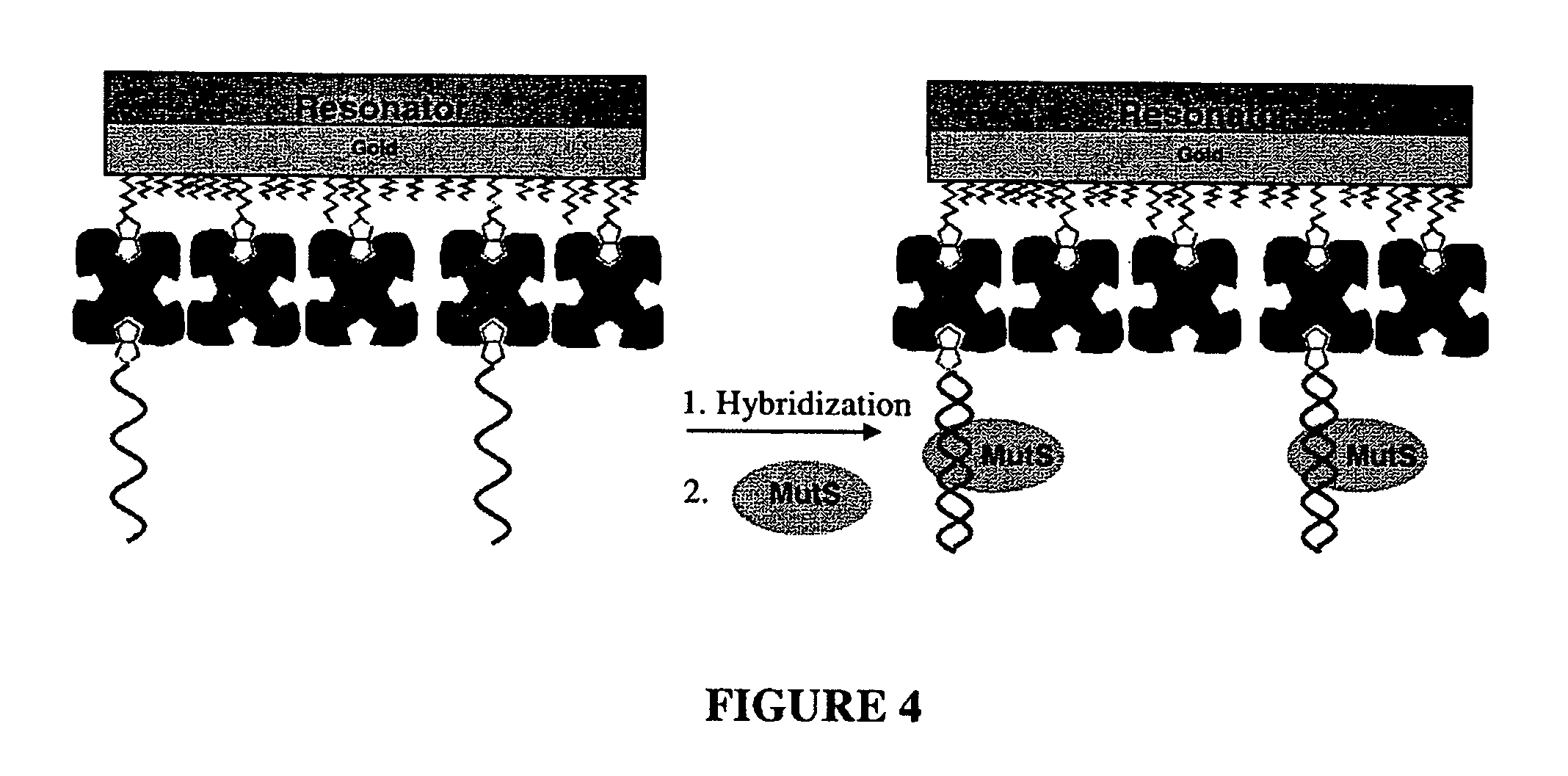
Device and method of detecting mutations and polymorphisms in DNA
InactiveUS8105780B2The instrumentation is simpleMiniaturizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideBiology
There is provided a resonator sensor useful for detecting polymorphisms and mutations in DNA. The resonator sensor has a capture molecule immobilised on its surface, the capture molecule being either a probe DNA containing a reference sequence, or a mismatch binding molecule, and being capable of forming a probe DNA / target DNA / mismatch binding molecule complex on the surface of the resonator. A method for detecting mutations in a target DNA, including single nucleotide polymorphisms, is also provided.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
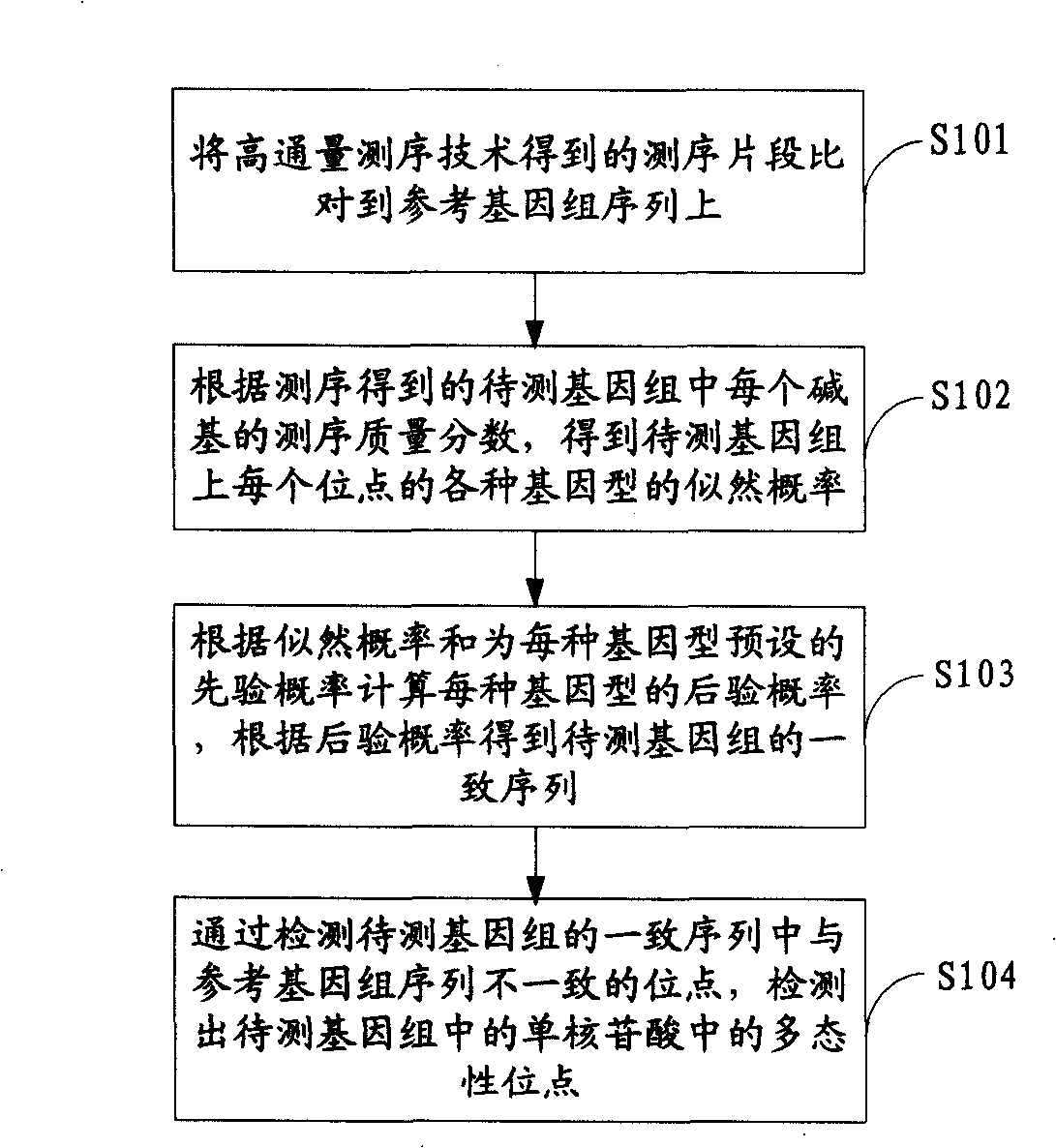
Method for detecting mononucleotide polymorphism
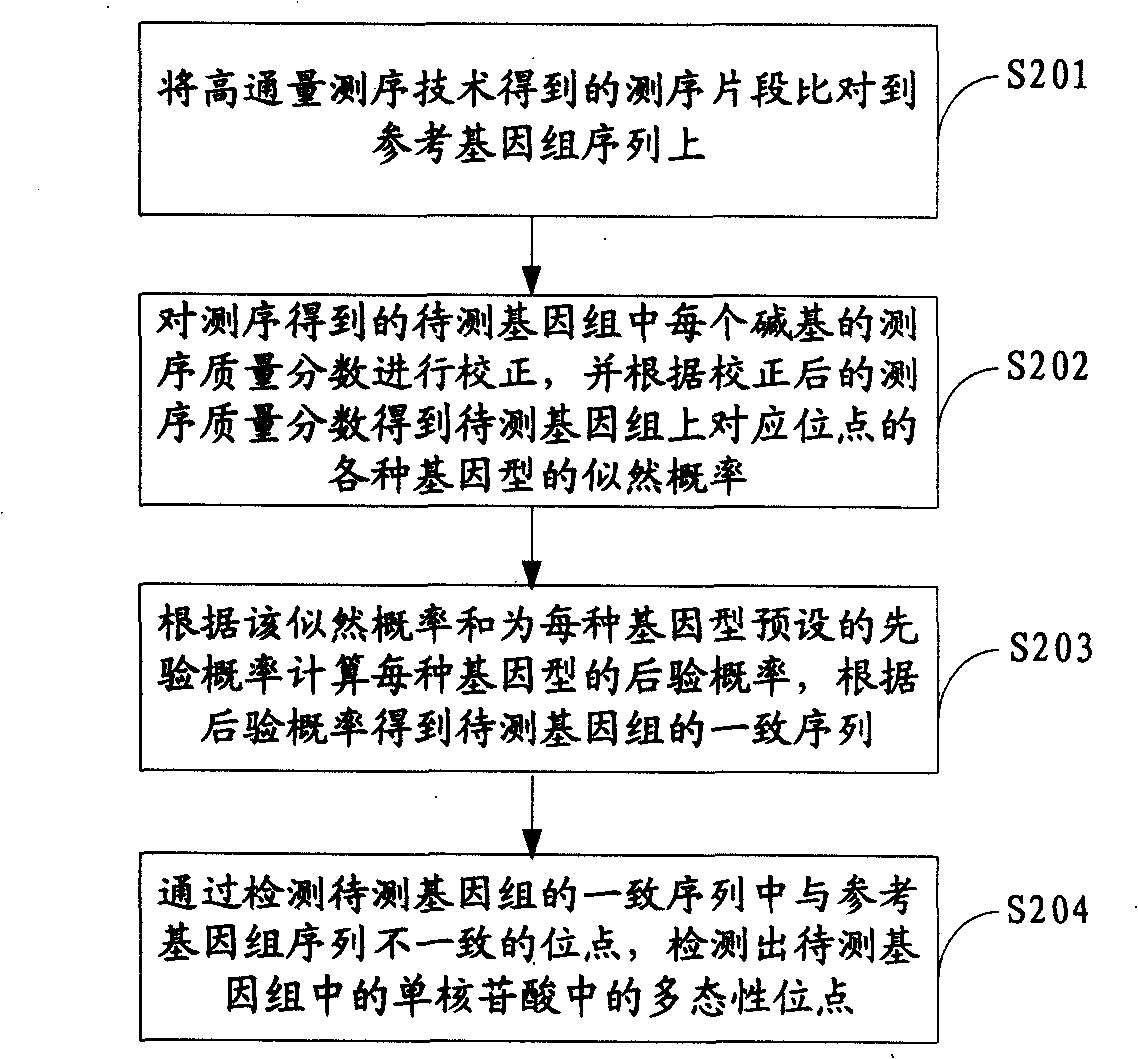
ActiveCN101539967AMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceGenotype determination
The invention is applicable to the field of biological engineering and provides a method for detecting mononucleotide polymorphism. The method comprises the following steps: sequencing fragments obtained by high throughput sequencing technology are compared on a referenced genome sequence; the likelihood ratio of various genotypes of the corresponding sites on the genome to be tested is obtained according to the sequencing mass fraction of each basic group in the genome to be tested and obtained by sequencing; the posterior probability of each genotype of each site on the referenced genome is calculated according to the likelihood ratio and the prior probability preset for each genotype, and the genotype which has the highest posterior probability is determined as the most likely right genotype of the corresponding sites on the genome to be tested to obtain the consistent sequence of the genome to be tested; and the sites of the genome to be tested, which are inconsistent with the sequence of the referenced genome in the consistent sequence are detected to obtain the polymorphism sites of the genome to be tested. The embodiment of the invention can achieve a more accurate test result as the influence of the prior probability on mononucleotide polymorphism test result is considered in advance.
Owner:WUHAN BGI CLINICAL LAB CO LTD
Device and method of detecting mutations and polymorphisms in DNA
InactiveUS20050164236A1The instrumentation is simpleMiniaturizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyDNA
There is provided a resonator sensor useful for detecting polymorphisms and mutations in DNA. The resonator sensor has a capture molecule immobilised on its surface, the capture molecule being either a probe DNA containing a reference sequence, or a mismatch binding molecule, and being capable of forming a probe DNA / target DNA / mismatch binding molecule complex on the surface of the resonator. A method for detecting mutations in a target DNA, including single nucleotide polymorphisms, is also provided.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Identification and mapping of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human genome
InactiveUS20060057564A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
The invention relates to the role of genes in human diseases. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions and methods for identifying genes that are involved in human disease conditions. The invention provides identification and mapping of a very large number of SNPs throughout the entire human genome. This contribution allows scientists to isolate and identify genes that are relevant to the prevention, causation, or treatment of human disease conditions.
Owner:SNP CONSORTIUM
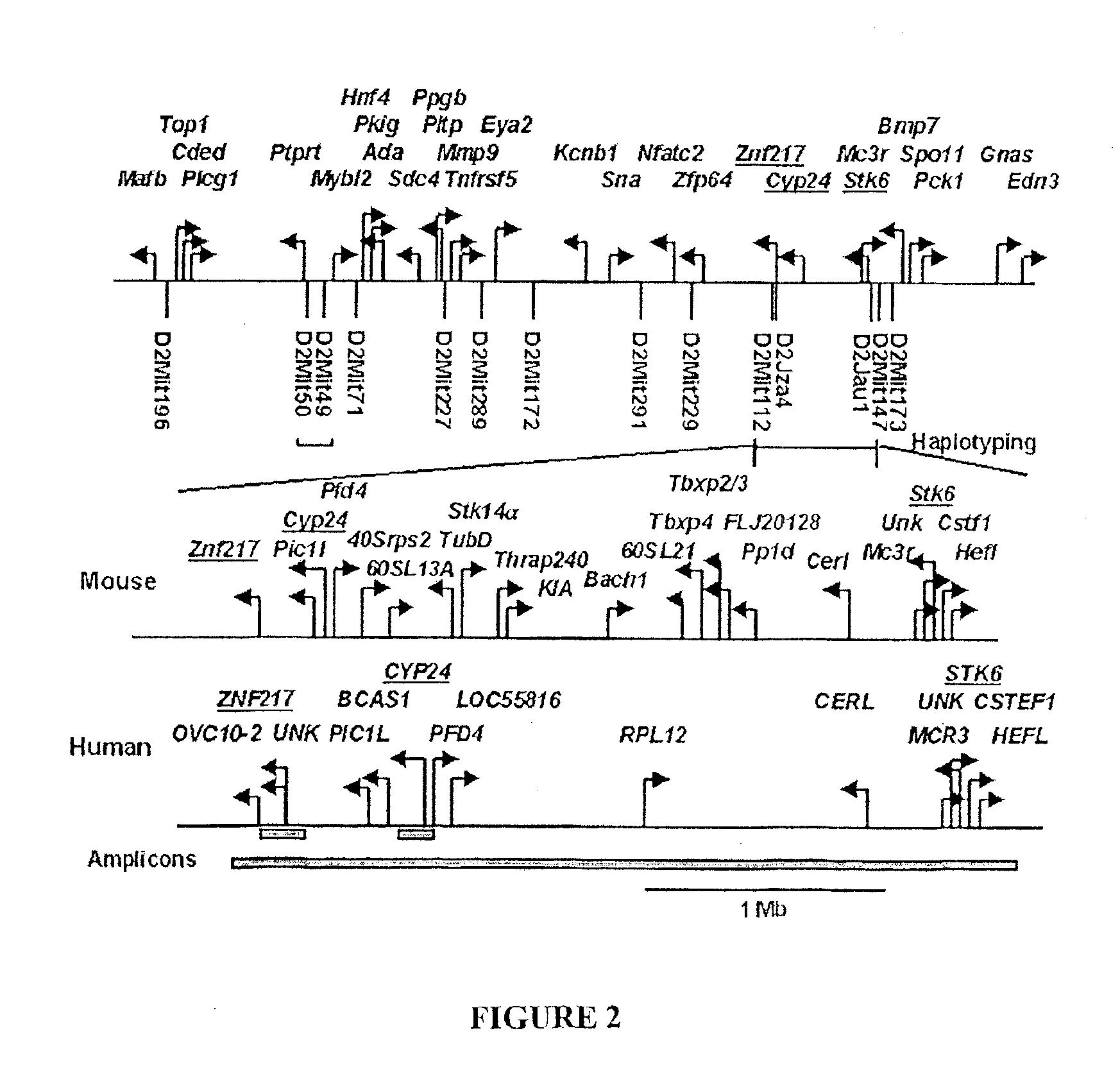
STK15 (STK6) gene polymorphism and methods of determining cancer risk
The present invention provides methods for determining cancer susceptibility in a human subject by identifying in a nucleic acid sample from the subject, a nucleotide occurrence of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of the STK15 gene, including the STK15 Ile31 polymorphism. The invention provides isolated polynucleotides, polypeptides, specific binding pair members, and cells useful for identifying agents that affect tumor susceptibility. Furthermore, the invention provides methods for detecting low penetrance tumor susceptibility genes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
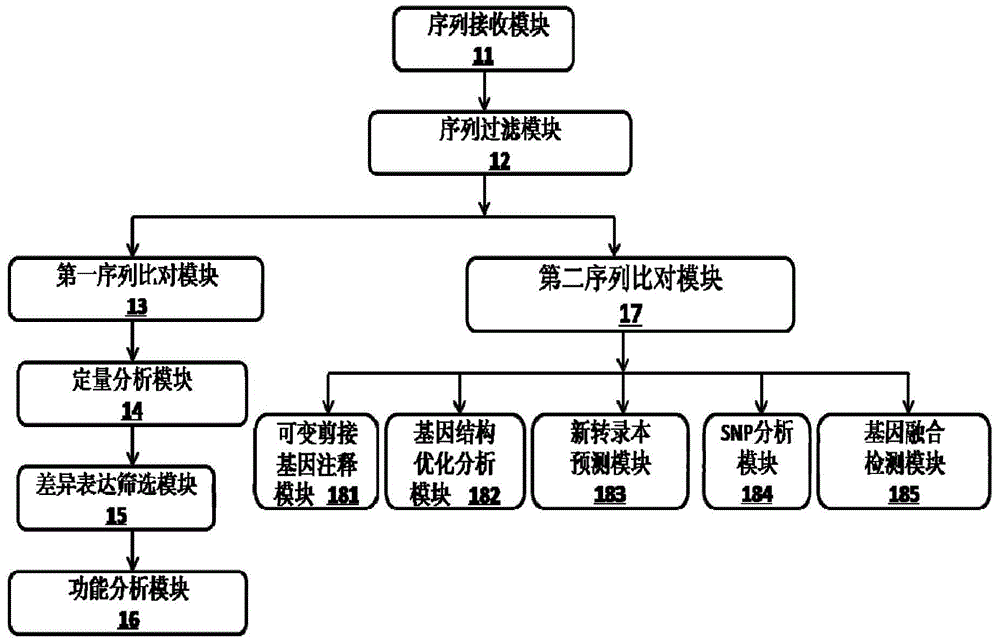
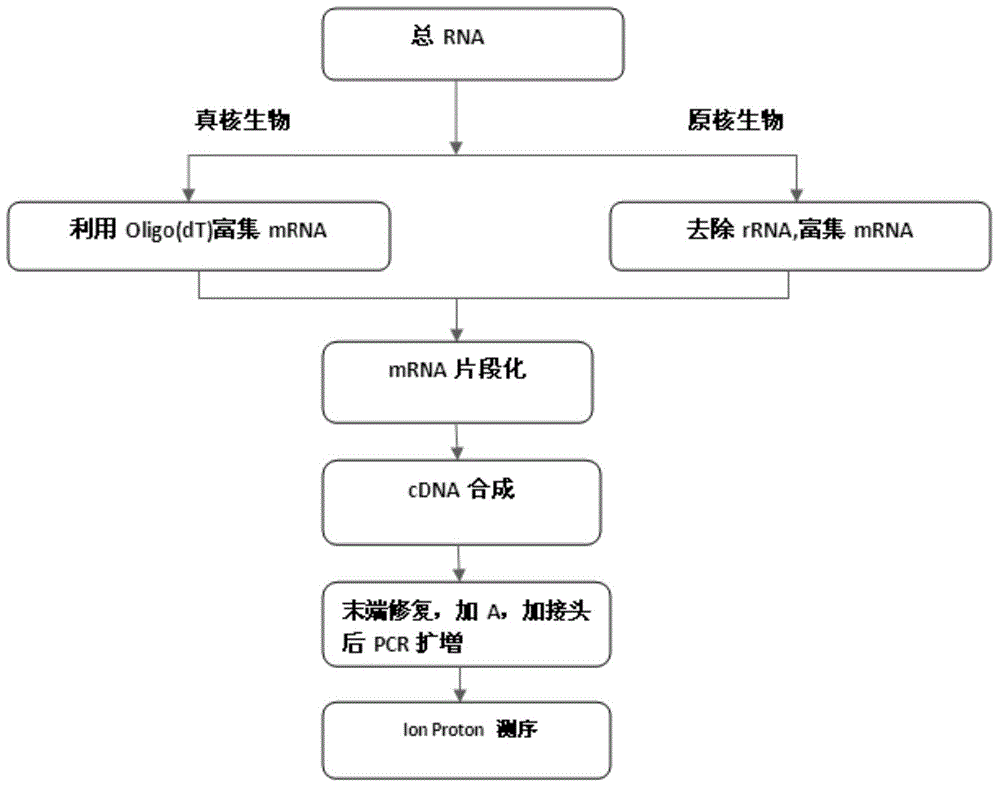
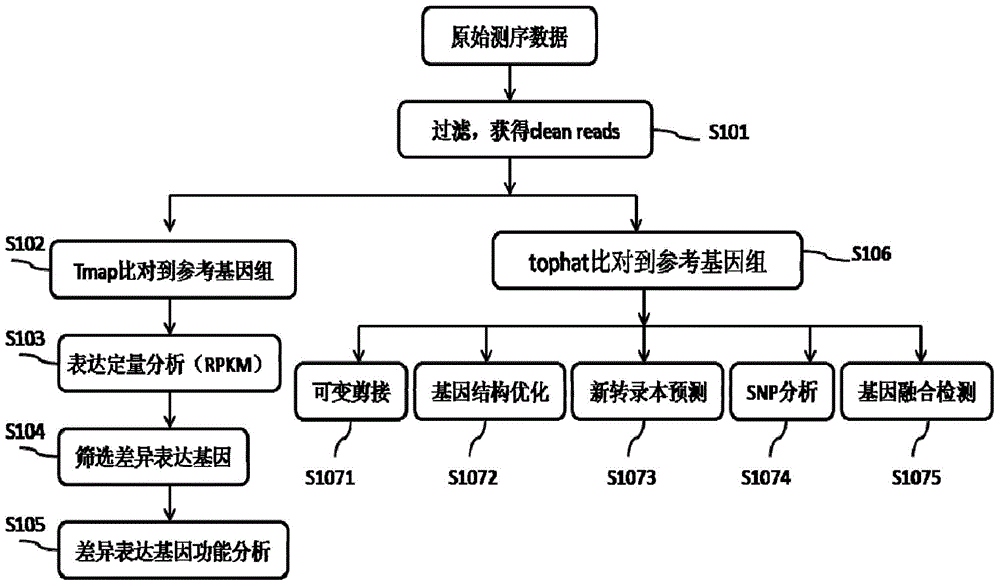
Proton-based transcriptome sequencing data comparison and analysis method and system
InactiveCN104657628AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsDifferentially expressed genesSingle-nucleotide polymorphism
The invention provides a Proton-based transcriptome sequencing data comparison and analysis method and system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring original sequencing data of at least two transcriptomes of a certain species by virtue of a Proton sequencing platform; filtering unqualified data to obtain clean reads; performing first-step analysis and second-step analysis, wherein the first-step analysis comprises the steps of comparing the clean reads with a reference genome of the species respectively, performing transcript quantitative analysis, screening significantly differently expressed genes and performing significantly differently expressed gene function analysis; the second-step analysis comprises the steps of comparing the clean reads to the reference genome of the species respectively, performing alternative splicing analysis, performing gene structure optimization analysis, performing new transcript prediction, performing SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) analysis and performing gene fusion detection. According to the method and the system, the transcriptome sequencing data comparison and analysis accuracy and reliability can be improved.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Methods and sequences to preferentially suppress expression of mutated huntingtin
InactiveUS20070161590A1Suppress expression and formationInhibit expressionSpecial deliverySugar derivativesHuntingtons choreaNucleotide sequencing
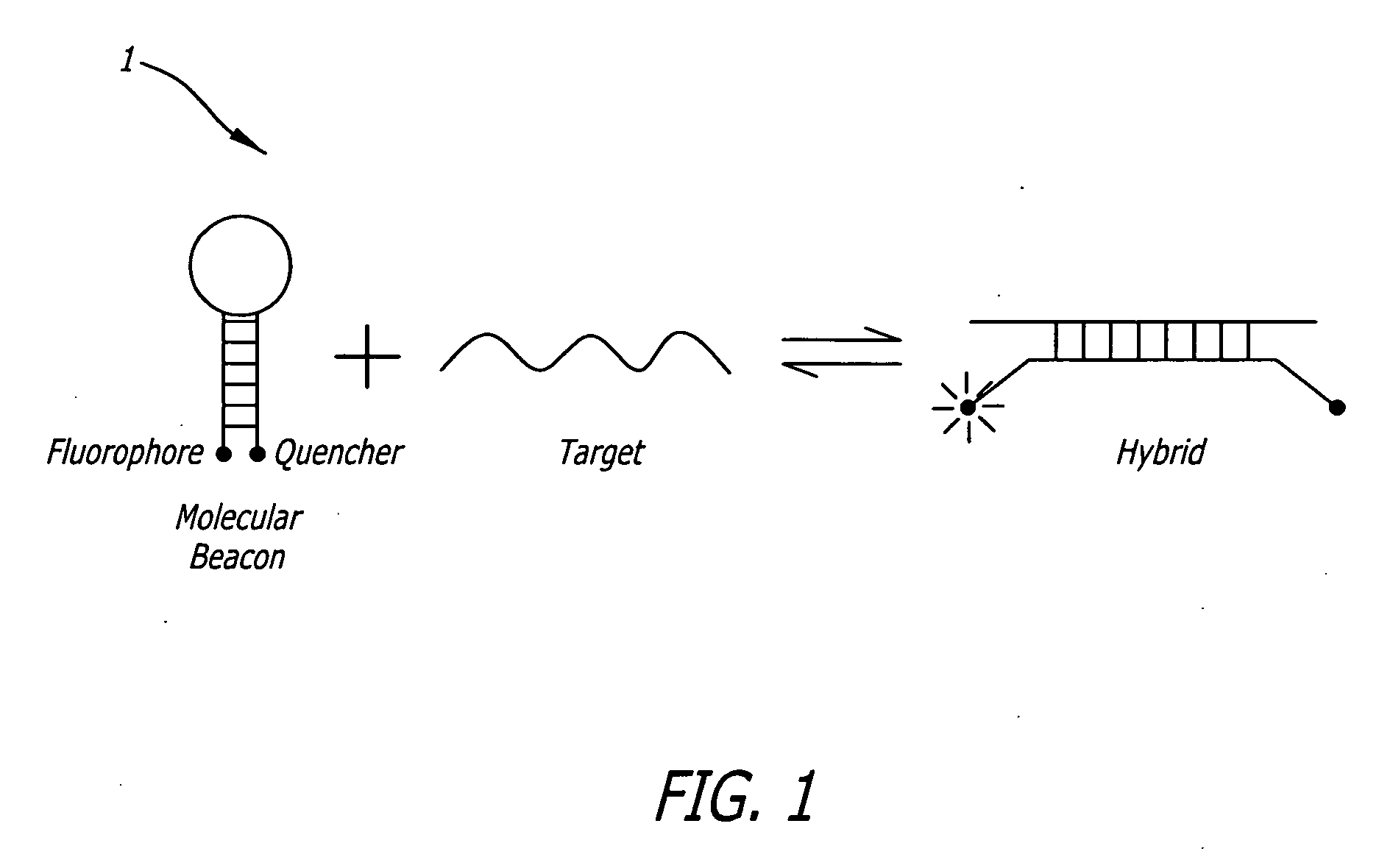
Disclosed herein are methods and sequences to preferentially suppress the expression of the mutated huntingtin (“htt”) protein over expression of the normal htt protein. Also disclosed are methods comprising screening an individual for the heterozygous presence of one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms within the individual's Huntington's genes; administering nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences that preferentially suppress the expression of amino acid sequences encoding for mutated huntingtin (“htt”) over suppressing the expression of amino acid sequences encoding for normal htt by targeting an area of a Huntington's disease gene that is heterozygous for the presence of one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com