Ligation-based detection of genetic variants
a genetic variant and ligation technology, applied in the field of multi-plexed selection, amplification, and detection of targeted regions, can solve the problem of invasive procedures carrying a risk of miscarriage of around 1% mujezinovi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Aspects of the Assay Systems of the Invention
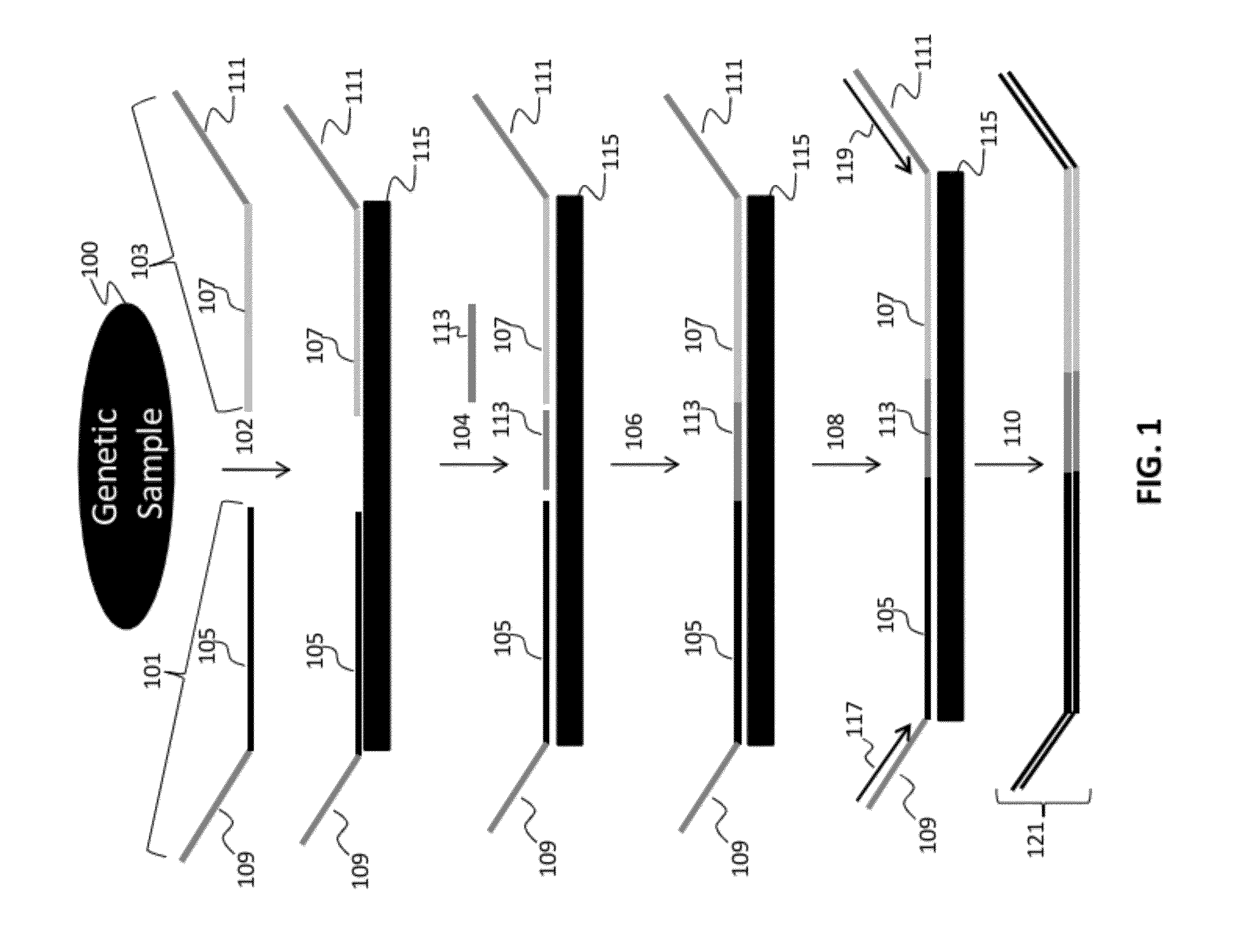
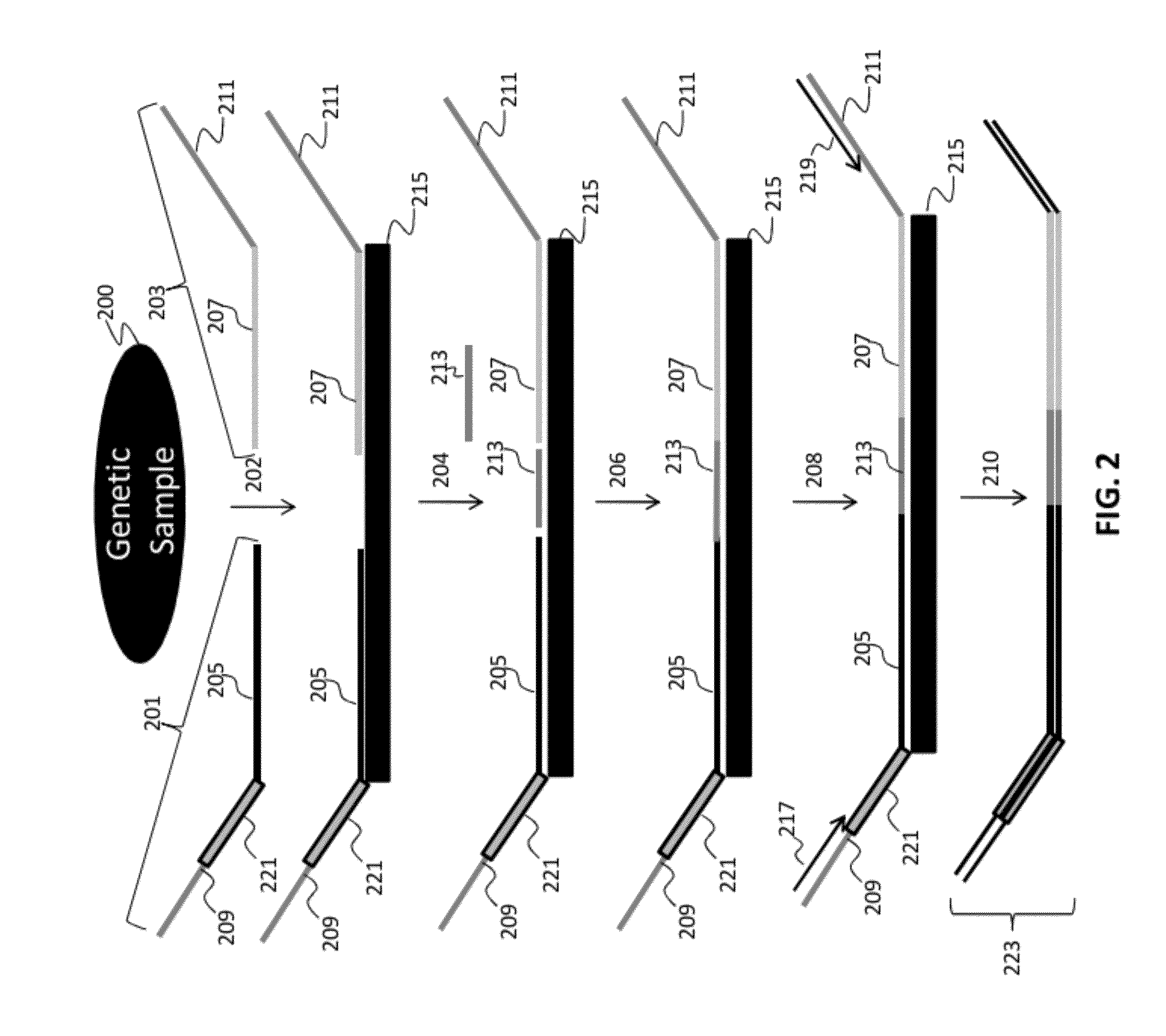
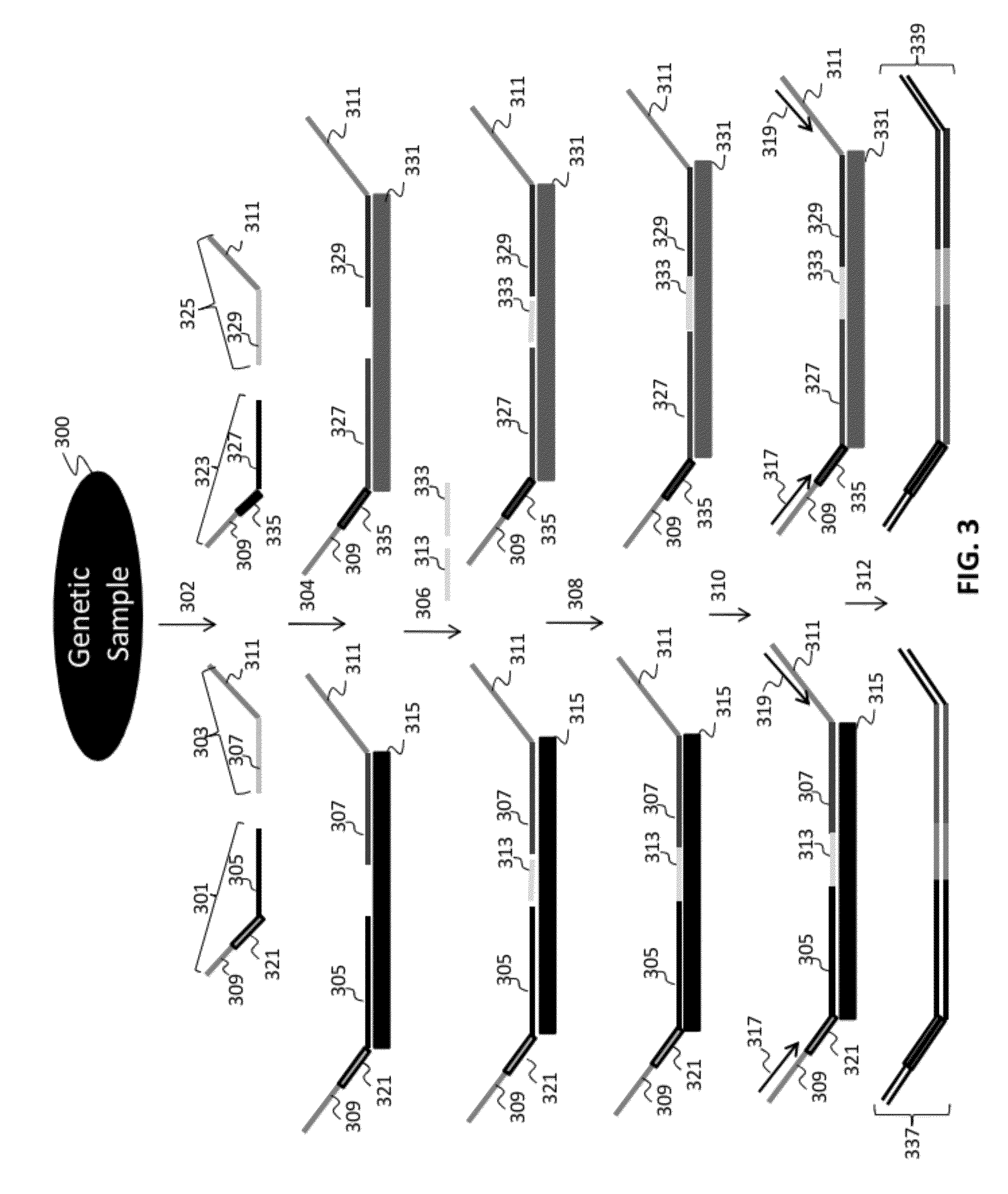
[0175]A number of assay formats were tested to demonstrate the ability to perform selective amplification and detection of independent loci to demonstrate multiplexed, ligation-based detection of a large number (e.g., 96 or more) of nucleic acid regions of interest.
[0176]These assays were designed based on human genomic sequences, and each interrogation consisted of two fixed sequence oligos per selected nucleic acid region interrogated in the assay. The first oligo, complementary to the 3′ region of a genomic region, comprised the following sequential (5′ to 3′) oligo elements: a universal PCR priming sequence common to all assays: TACACCGGCGTTATGCGTCGAGAC (SEQ ID NO:1); a nine nucleotide degenerate identification code where each specific sequence is intended to be specific to a single oligonucleotide molecule and its progeny; a 9 base locus- or locus / allele-specific sequence that acts as a locus code in SNP-independent assay for...
example 2
Preparation of DNA for Use in Tandem Ligation Procedures
[0180]Genomic DNA from a Caucasian male (NA12801) or a Caucasian female (NA11995) was obtained from Coriell Cell Repositories (Camden, N.J.) and fragmented by acoustic shearing (Covaris, Woburn, Mass.) to a mean fragment size of approximately 200 bp.
[0181]The Coriell DNA was biotinylated using standard procedures. Briefly, the Covaris fragmented DNA was end-repaired by mixing the following components in a 1.5 ml microtube: 5 μg DNA, 12 μl 10× T4 ligase buffer, 50 U T4 polynucleotide kinase, and H20 to 120 μl. This reaction was incubated at 37° C. for 30 minutes. The end-repaired DNA was diluted using 10 mM Tris 1 mM EDTA pH 8.5 to a concentration of ˜2 ng / μl.
[0182]5 μl DNA was placed in each well of a 96-well plate. The plate was incubated at 95° C. for 3 minutes, cooled to 25° C., and spun again for 10 seconds at 250×g. 15 uL of biotinylation master mix [1× TdT buffer, 8U TdT, 250 μM CoCl2, 0.01 nmol / μl biotin-16-dUTP (Roche, ...
example 3
Exemplary Assay Formats Using Tandem Ligation
[0184]Numerous tandem ligation assay formats using the biotinylated DNA were tested to illustrate proof of concept for the assay systems of the invention, and demonstrated the ability to perform highly multiplexed, targeted detection of a large number of independent loci using the series of different assay formats. The exemplary assay systems of the invention were designed to comprise 96 or more interrogations per loci in a genetic sample, and in cases where SNPs were detected the assay formats utilized 192 or more separate interrogations, each utilizing the detection of different alleles per 96 loci in genetic samples. The examples described for each assay format utilized two different sets of fixed sequence oligonucleotides and / or bridging oligos (as described in Example 1), comprising a total 96 or 192 interrogation reactions for the selected nucleic acid regions depending upon whether or not SNPs were identified.
[0185]A first exemplar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| v/v | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com