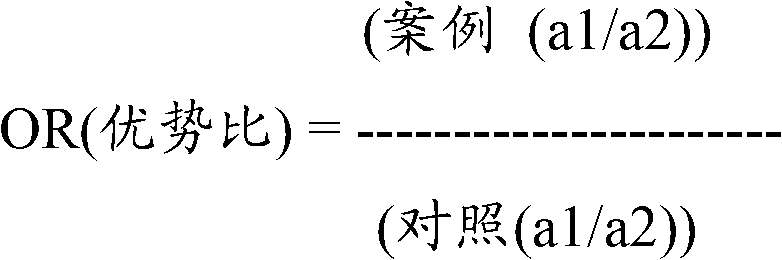
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Genetic samples" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic analysis and authentication
InactiveUS7157228B2Reduce morbidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyGenetic Screening (procedure)
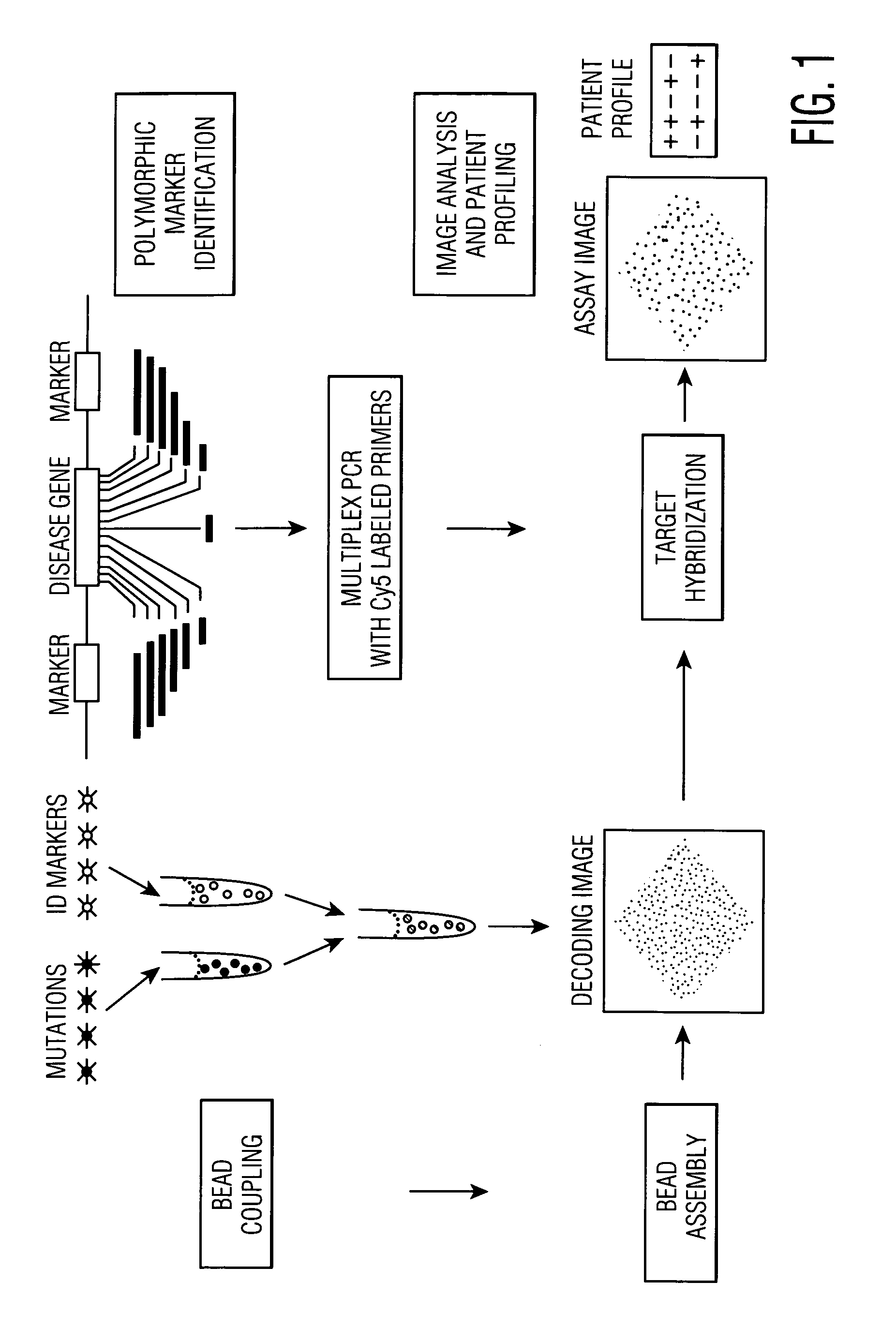
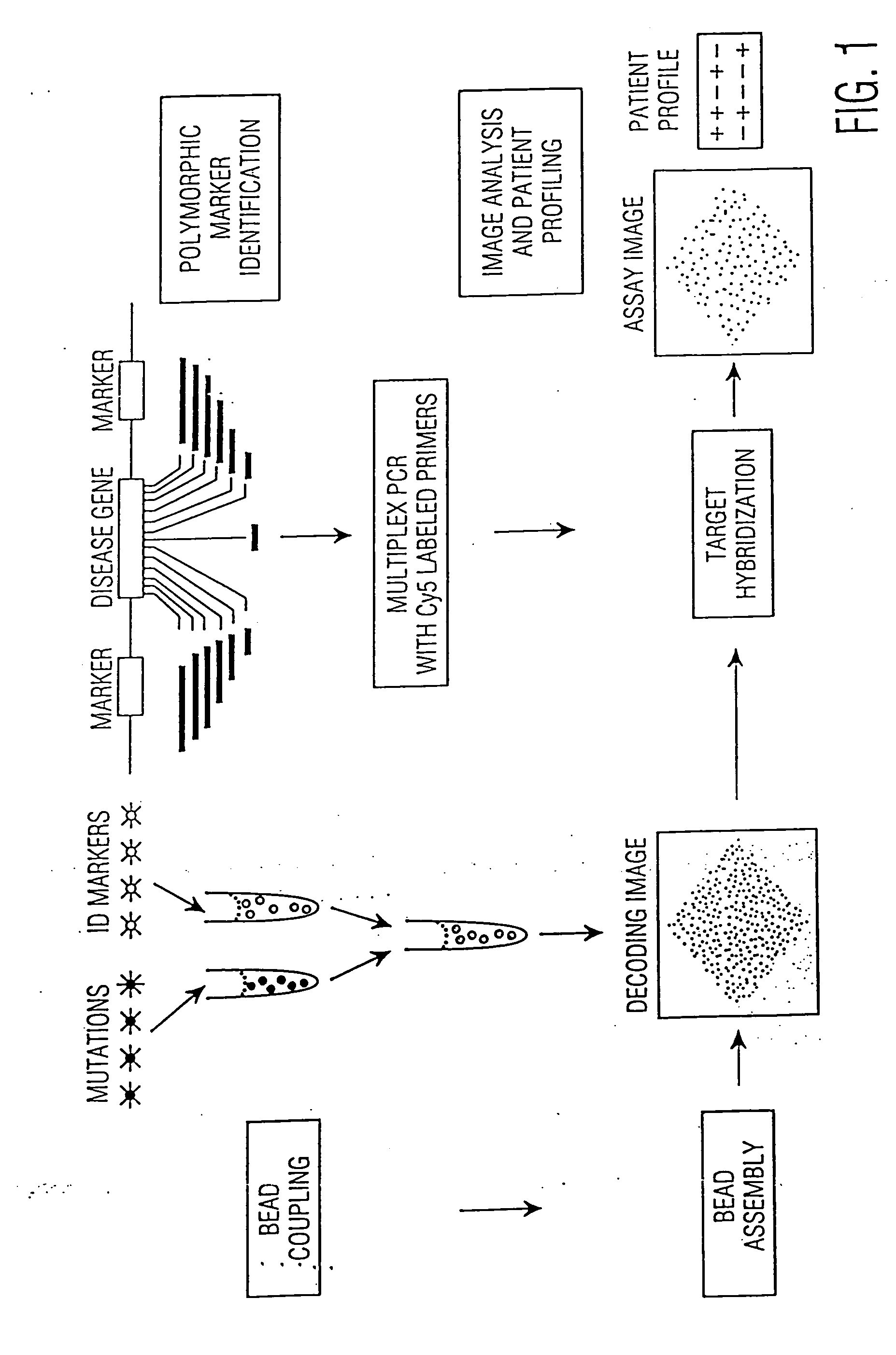
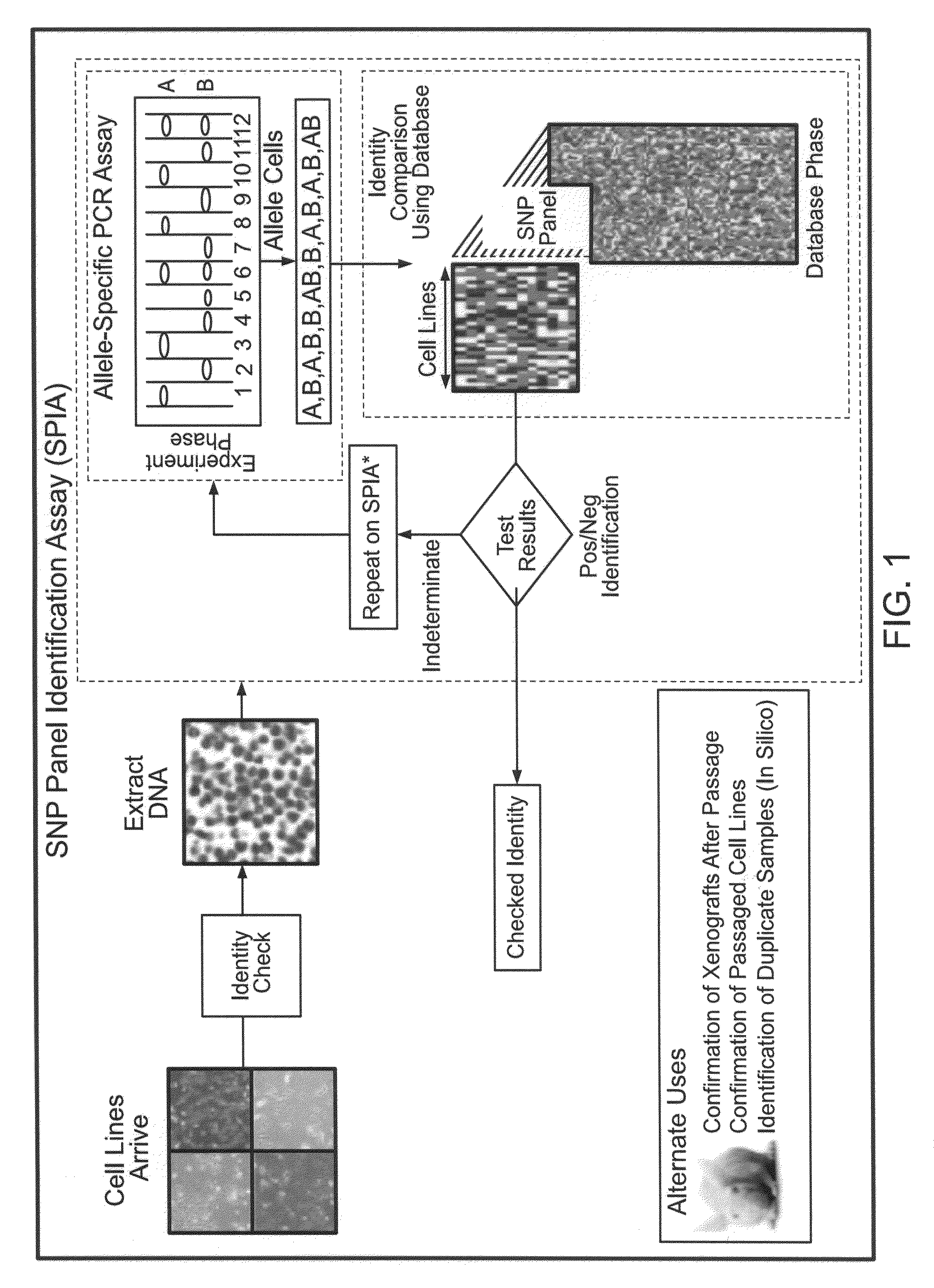
This invention provides compositions and methods for genetic testing of an organism and for correlating the results of the genetic testing with a unique marker that unambiguously identifies the organism. The markers may be internal markers, such as for example single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), short tandem repeats (STRs), or other sites within a genomic locus. Alternatively, the markers may be external, such that they are separately added to the genetic sample before testing.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Methods for identifying and using SNP panels
ActiveUS7981609B2Accurately identifying and distinguishingCost effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGeneticsBiology
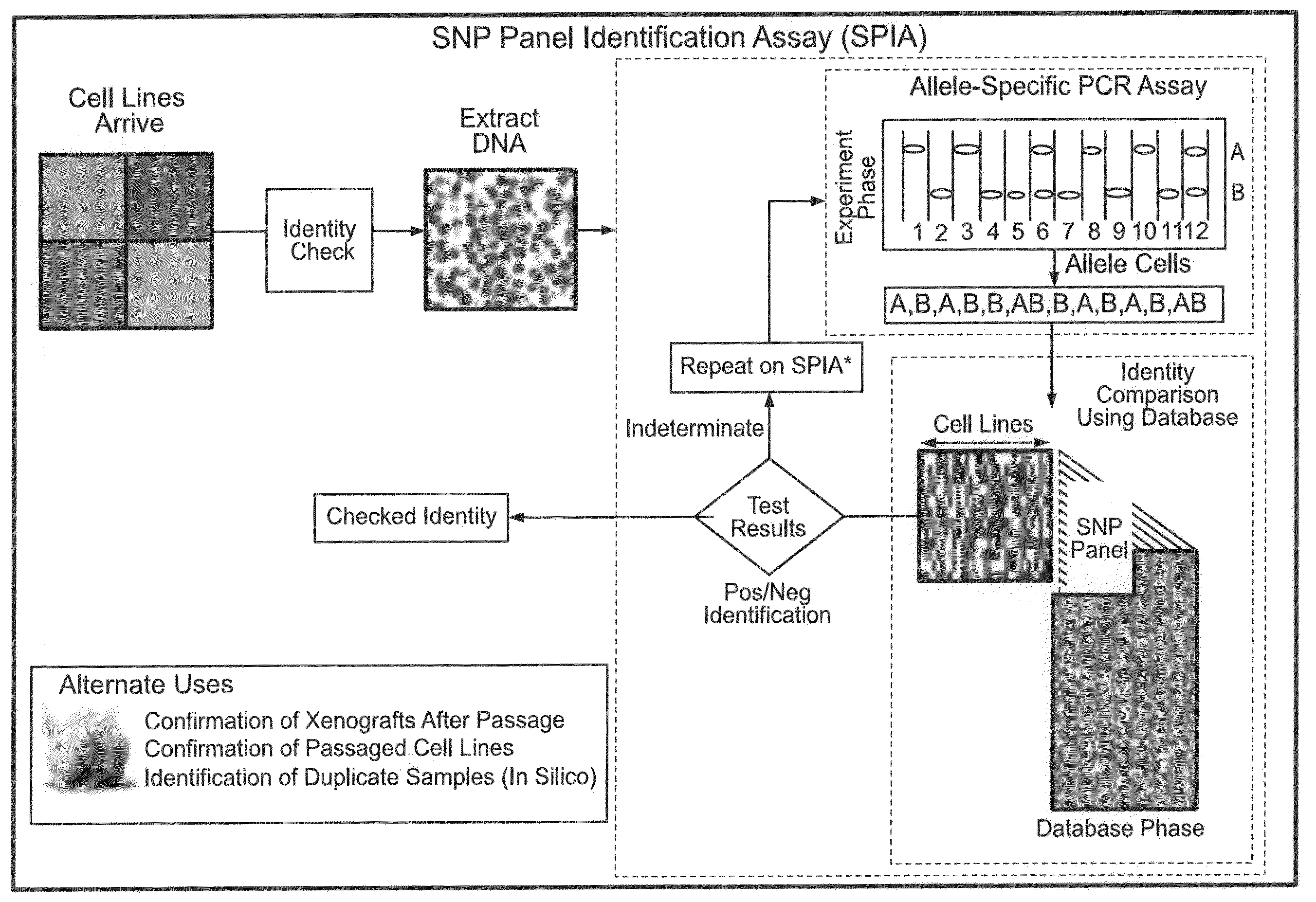
Described are methods for identifying single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) that are useful for analyzing genetic samples, and for using said SNPs to determine genetic identity of samples.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Systems and methods for improving efficiencies in livestock production
InactiveUS20050065736A1Improve efficiencyAccurate predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringBiotechnologyGenotype
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for improving the efficiency of livestock production using genetic information obtained from the animal. The methods of the invention comprise obtaining a genetic sample from an animal or embryo, determining the genotype of the animal or embryo with respect to specific quality traits, grouping animals with like genotypes, and optionally, further sub-grouping animals based on like phenotypes. Based on the genotype, an animal is treated in a particular way. For example, uniform feeding regimens are designed for a particular group so as to maximize feed efficiencies and accurately predict slaughter times among like animals possessing a desired quality trait. Such methods include obtaining and maintaining the genetic data obtained from each animal, and optionally other data relating to the animal's health, condition or parentage, or to its herd, and providing this data to others through systems that are web-based, contained in a database, or attached to the animal itself such as by an implanted microchip.
Owner:MERIAL LTD
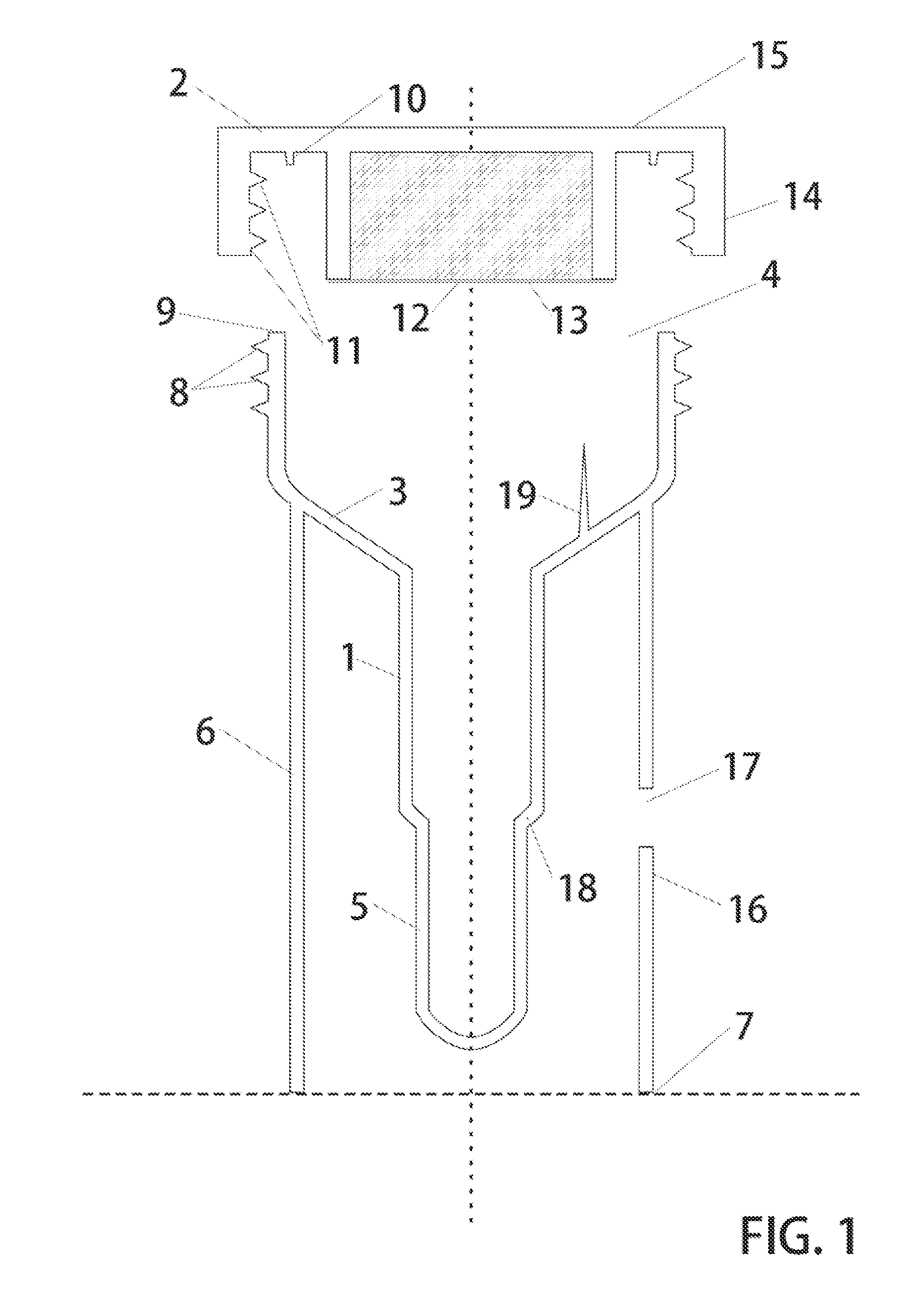
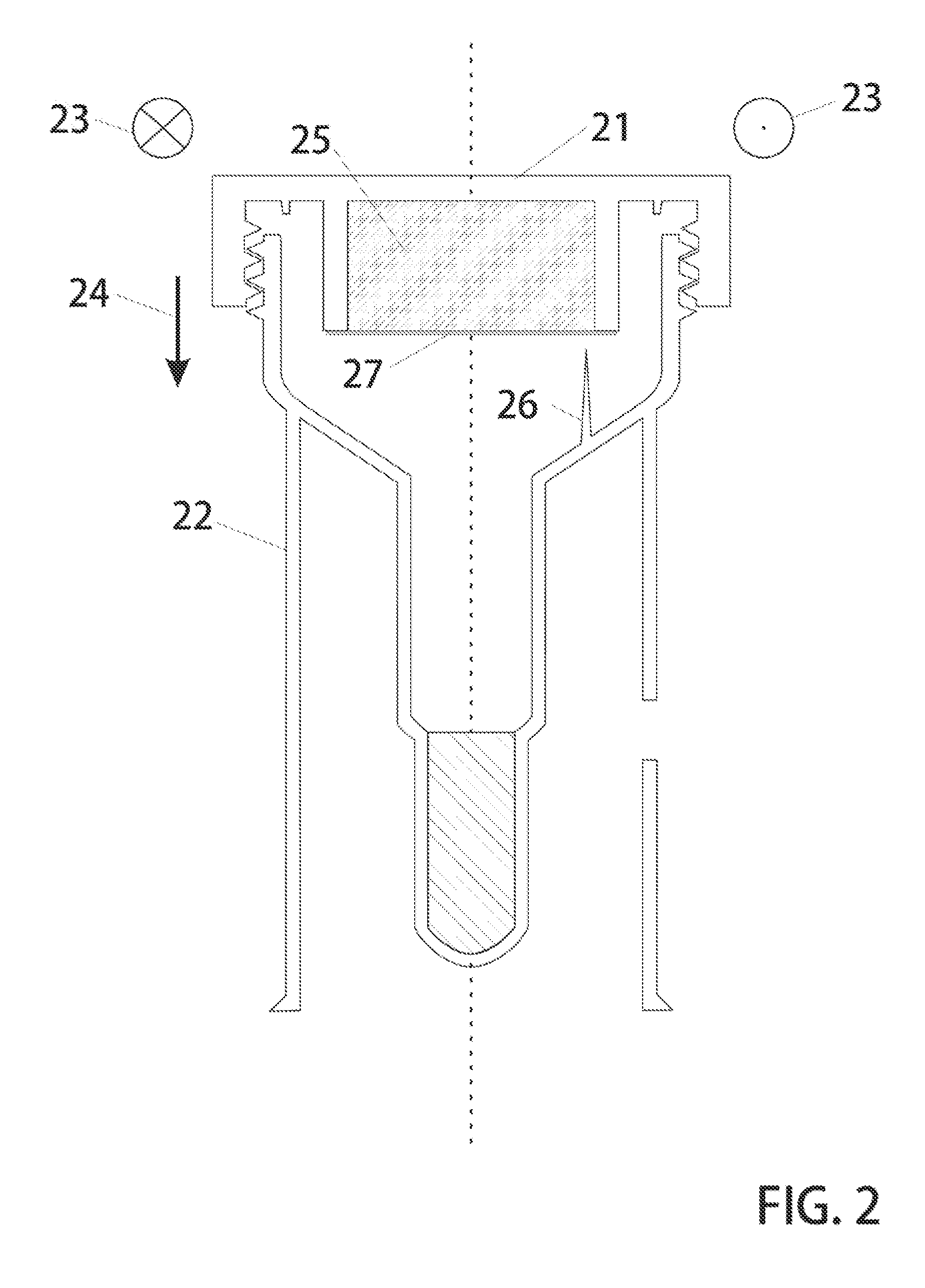
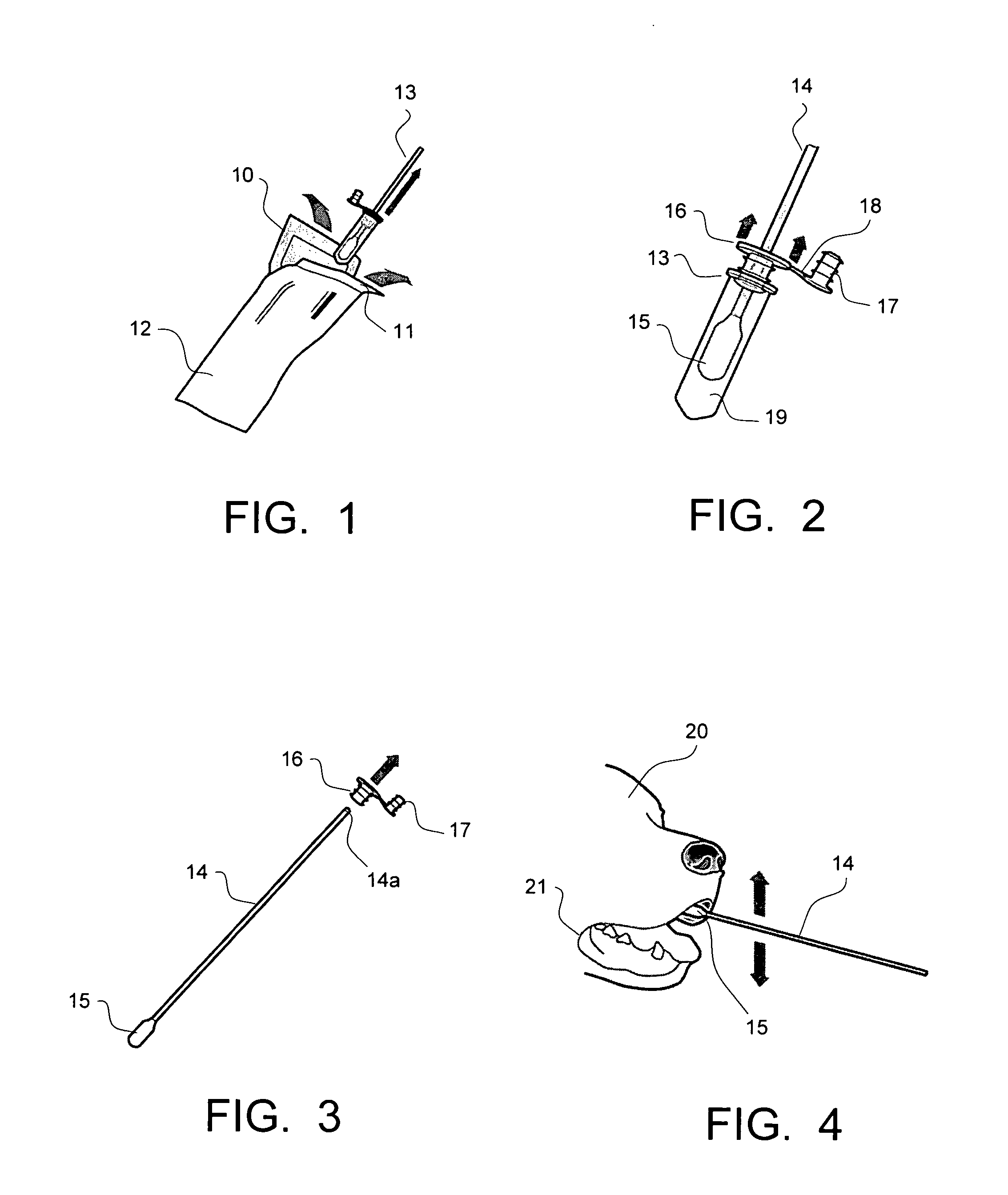
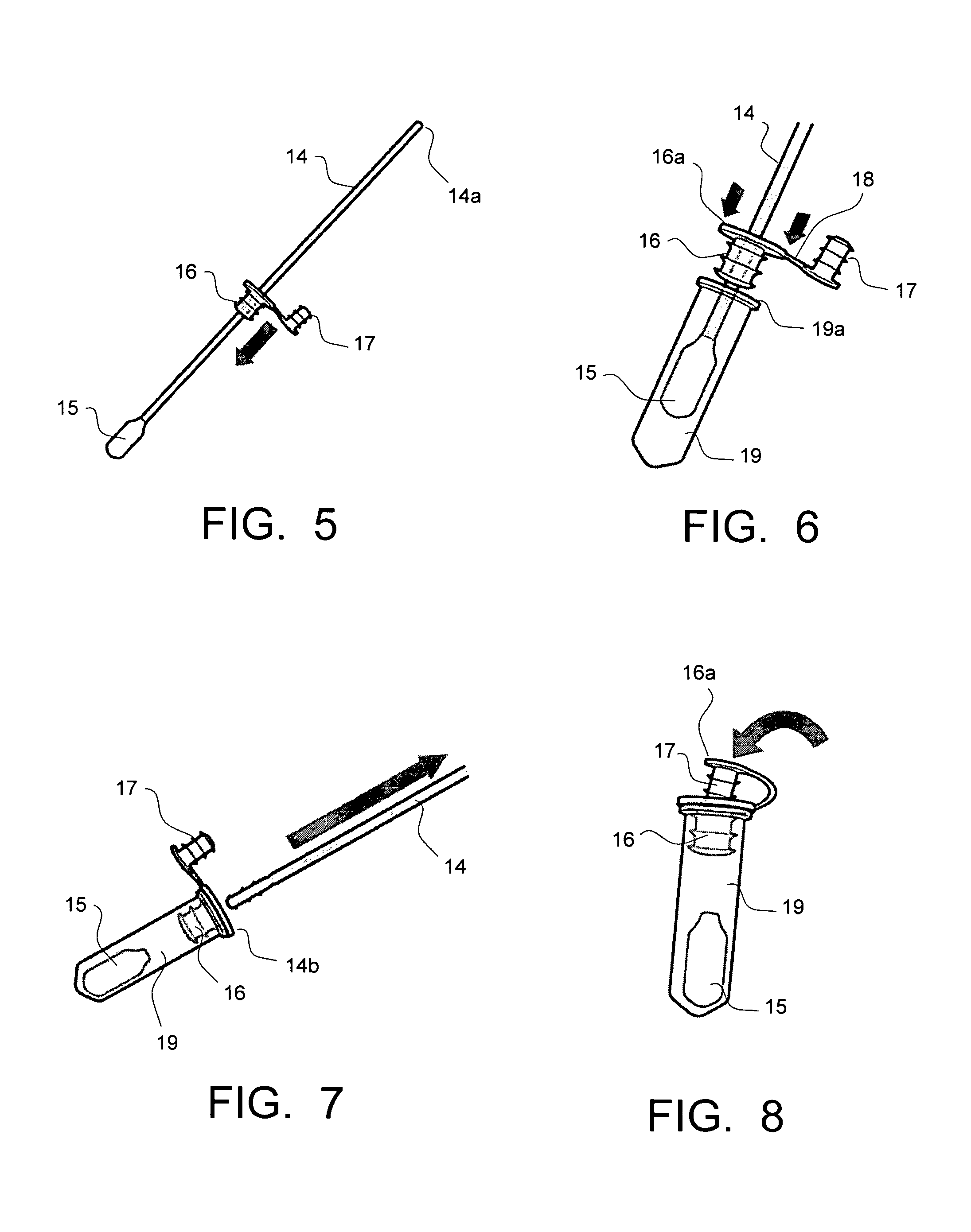
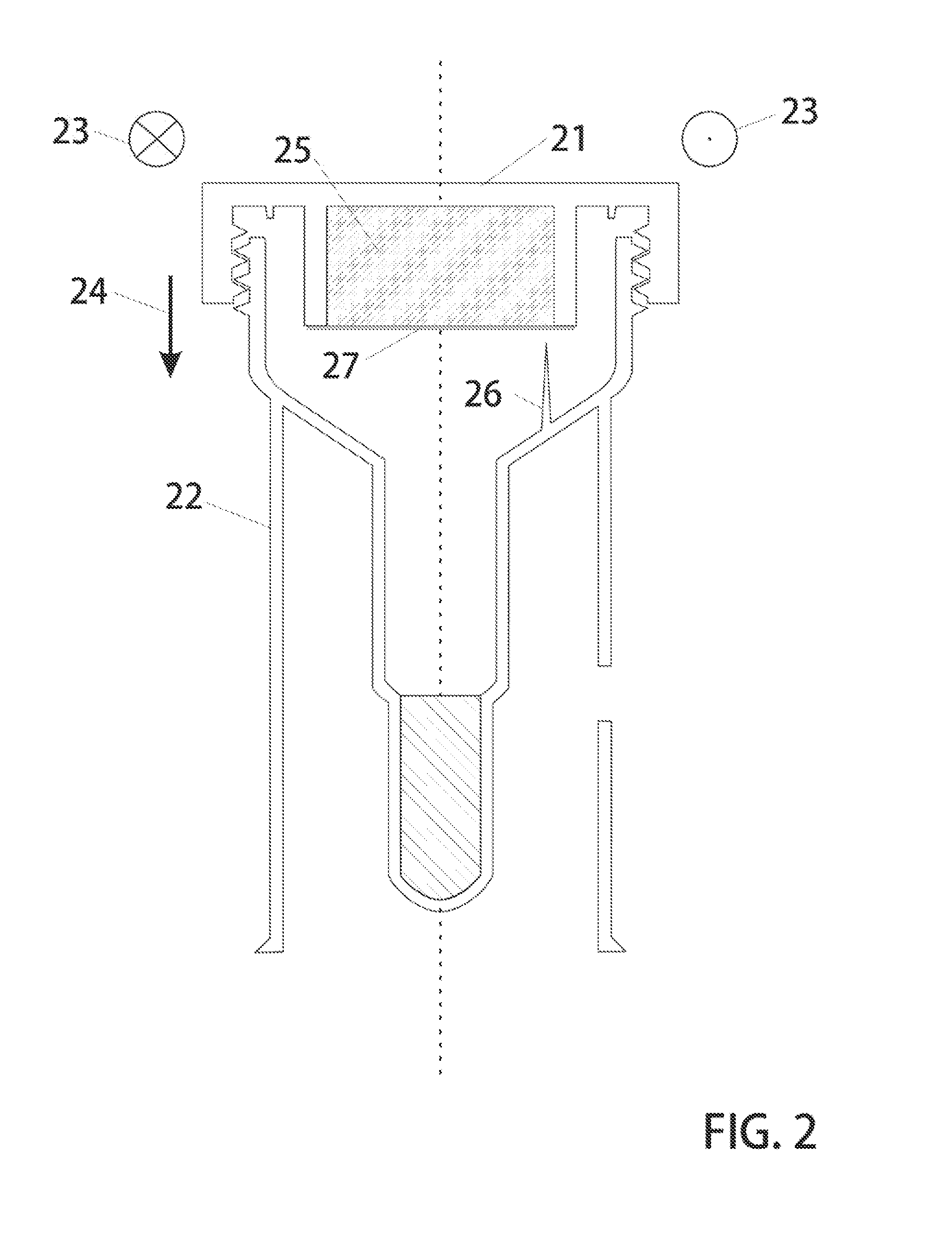
Genetic Sample Collection Systems
InactiveUS20130164738A1Easy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCollection systemBiology
Biological sample collection kits are devised with physical features to enable a high performance collection system which delivers preprocessed biological matter via conventional shipping means to a testing laboratories. In particular, untrained and unskilled users deposit biological matter such as saliva or blood into a receiving vessel. By sealing the container, the user causes release of a premixed solution containing preservatives and optionally lysis reagents. In addition, a purification agent is arranged to bind to target molecules and facilitate their removal from solution. These time consuming processes occur while the sample is in transit to the testing facility such that when it arrives, it is in a preconditioned state immediately ready for execution of washing steps. Thus, the high performance containers taught herein are useful for collection biological samples and performing initial process steps on received matter—steps which are largely effected during the shipping stage of the transfer process.
Owner:PATHWAY GENOMICS
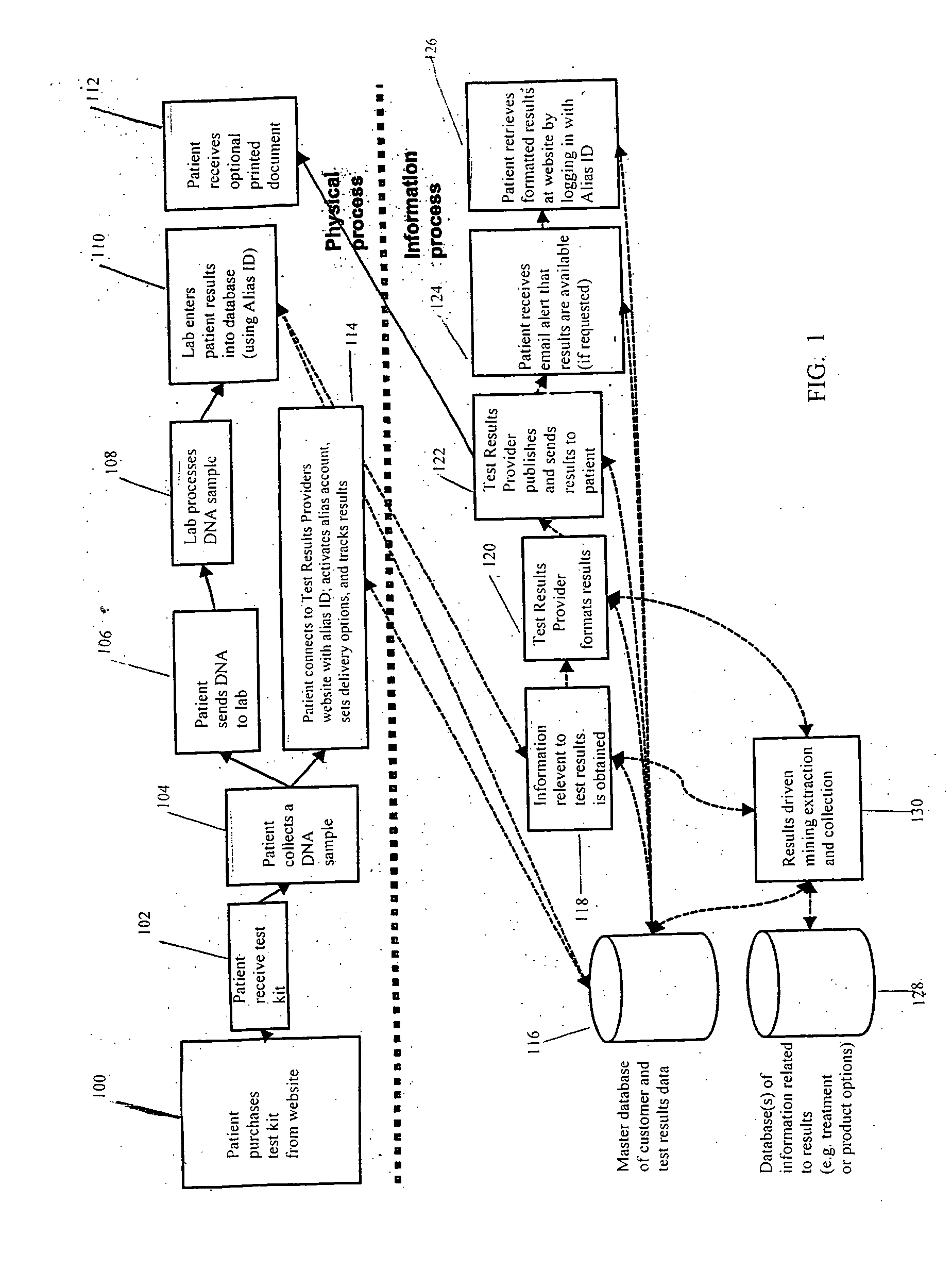
Anonymous testing system and kit
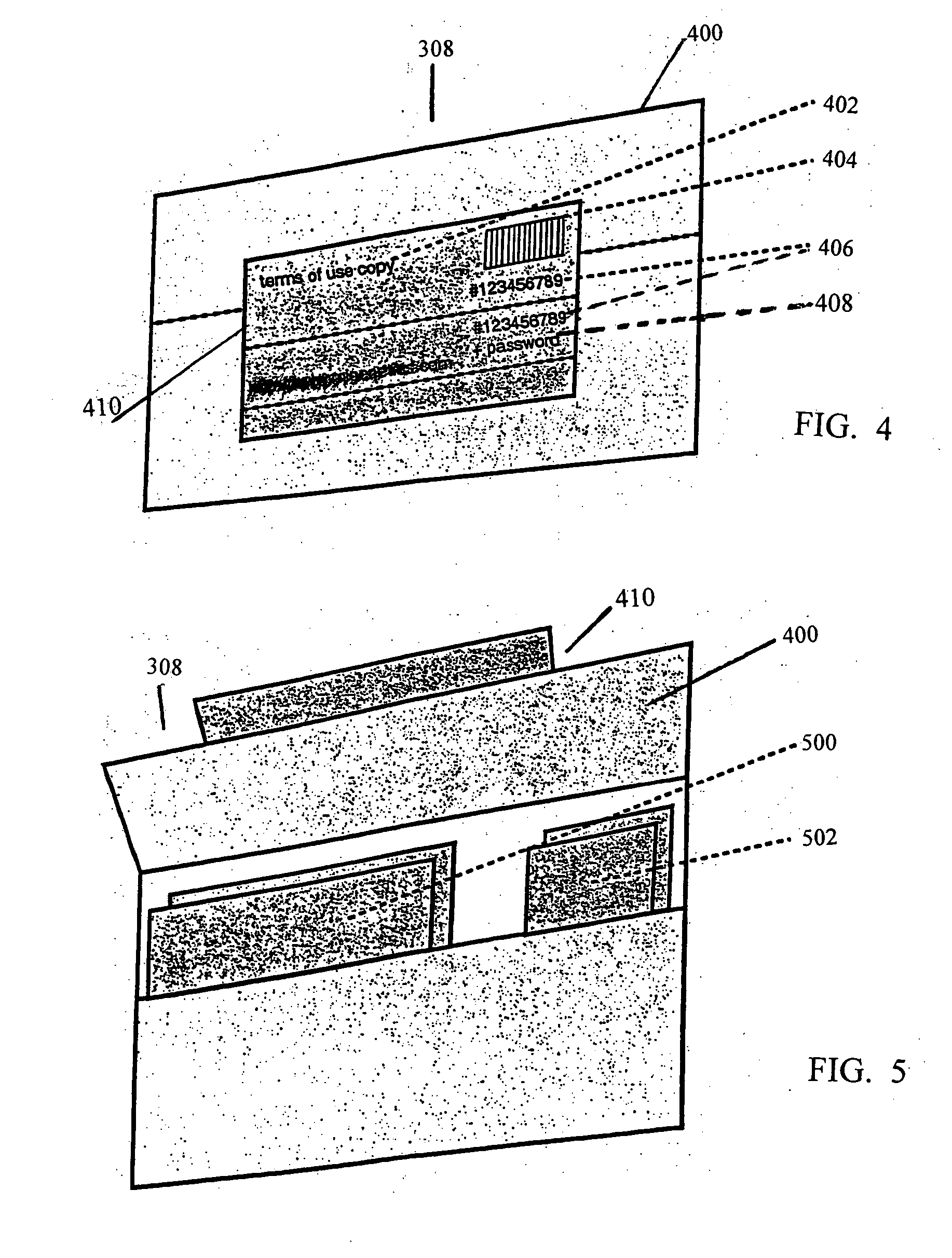
Disclosed are methods and kits for conducting anonymous genetic testing. The methods and kits include provide a patient with an Alias ID and Password. The Alias ID is used to track a genetic sample from the patient. Both the Alias ID and Password are then used by the patient to obtain the results of the genetic test. The methods and kits allow a patient to have a genetic test performed while remaining anonymous.
Owner:TYLER TROY S +1
Bovine CASTgene SNP and meat tenderness
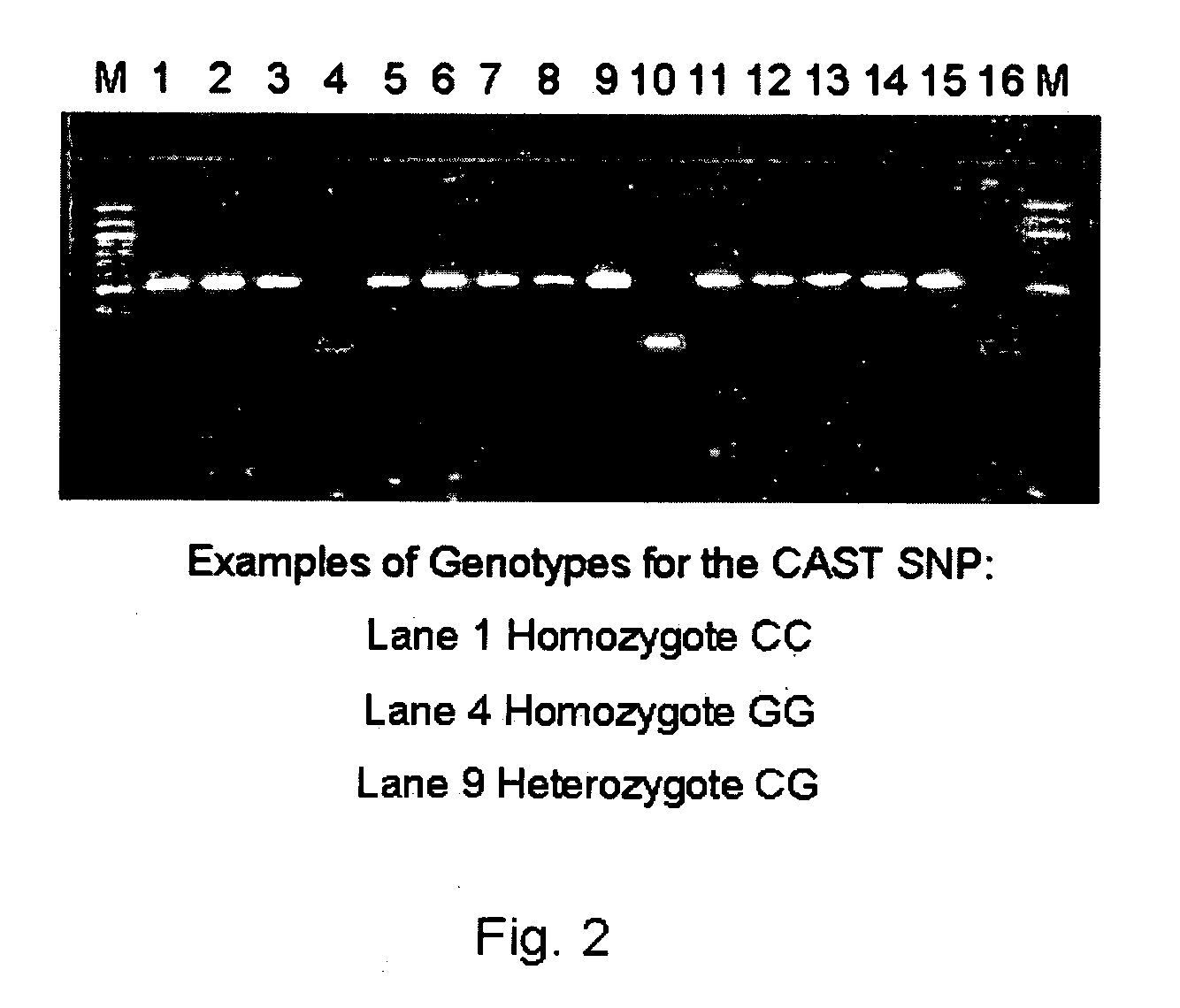
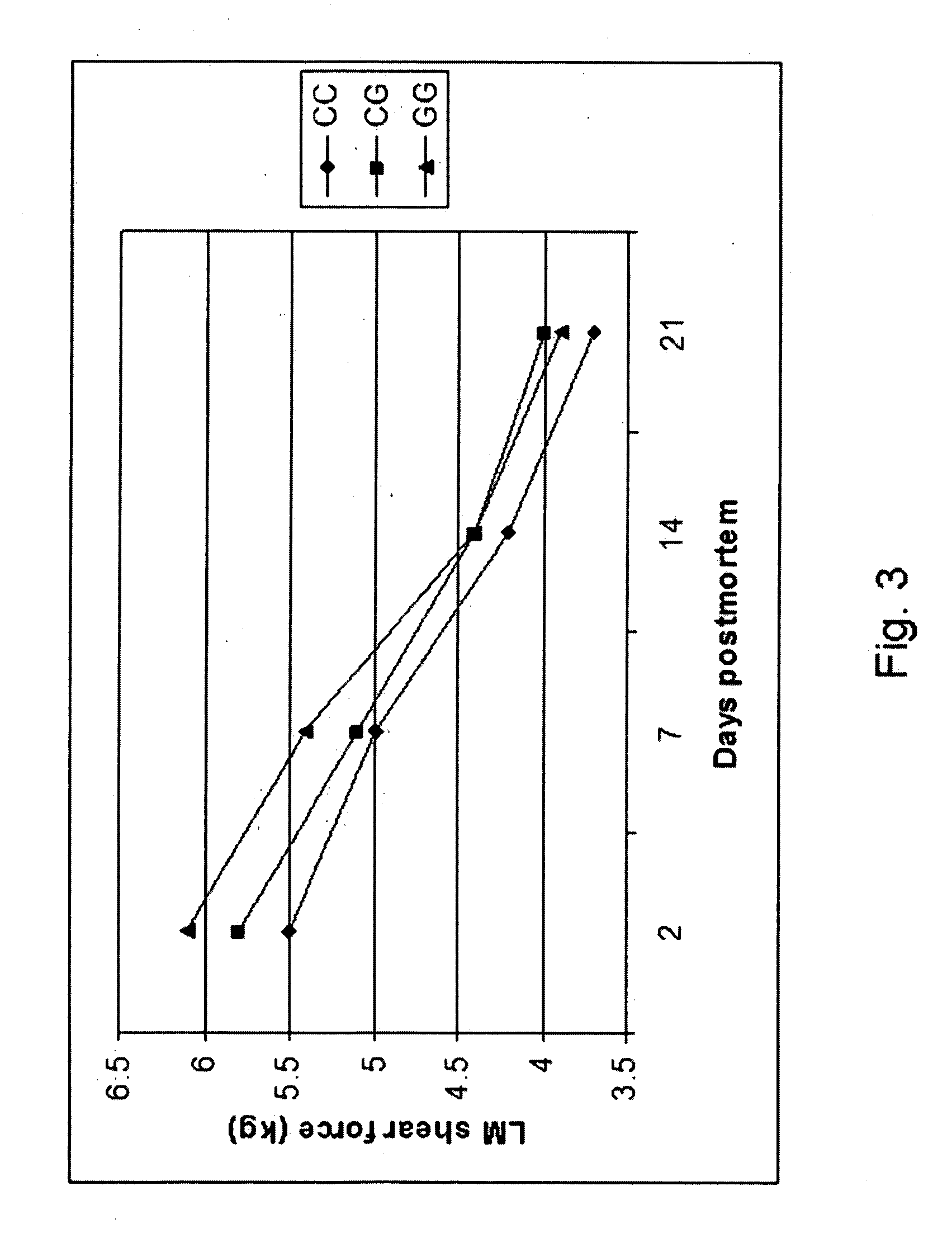
ActiveUS20060211006A1Increase productivityHigh frequencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideComputer-aided
The present invention relates to the identification of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) within the bovine CAST locus encoding the calpastatin protein, wherein the allelic variation of the SNP is a G / C transversion associated with post-mortem muscle tenderness. The invention further relates to oligonucleotides useful in identifying the genotype of bovines as it relates to the CAST locus polymorphic site. The invention also encompasses computer-assisted methods and systems for improving the production efficiency for livestock having marketably tender meat using multiple data, and in particular the genotype of the animals as it relates to the CAST SNP. These methods of the invention encompass obtaining a genetic sample from each animal in a herd of livestock, determining the genotype of each animal with respect to specific quality traits as defined by a panel of at least two single polynucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), one SNP corresponding to a site between exons 5 and 6 of the bovine CAST locus, grouping animals with like genotypes, and optionally, further sub-grouping animals based on like phenotypes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Pet DNA specimen sampling for transport and long term storage
A kit and method for collecting, storing and transporting genetic samples from an animal to a storage facility. The kit comprises at least a collection swab, a protective tube, a follicle sample collection card, and an extraction device. The collection swab is housed within a sterile protective package. The collection swab has a shaft connected at one end by a collection head. The collection swab includes a cap and plug, wherein the cap is encircled around the shaft of the collection swab. The protective tube is adapted to receive the collection head of the collection swab. The follicle sample collection card has a protective backing covering an adhesive strip disposed on the follicle sample collection card. The extraction device is provided to pull at least one hair with follicle from the animal. The kit may also include a specimen storage enrollment card to record pertinent information, and an envelope may be provided for storage and delivery of the protective tube and the follicle sample collection card including the respective genetic samples to a storage facility for processing and storage of the genetic samples at a controlled temperature above freezing.
Owner:STIVERS JOHN ELLIOT RANDAL
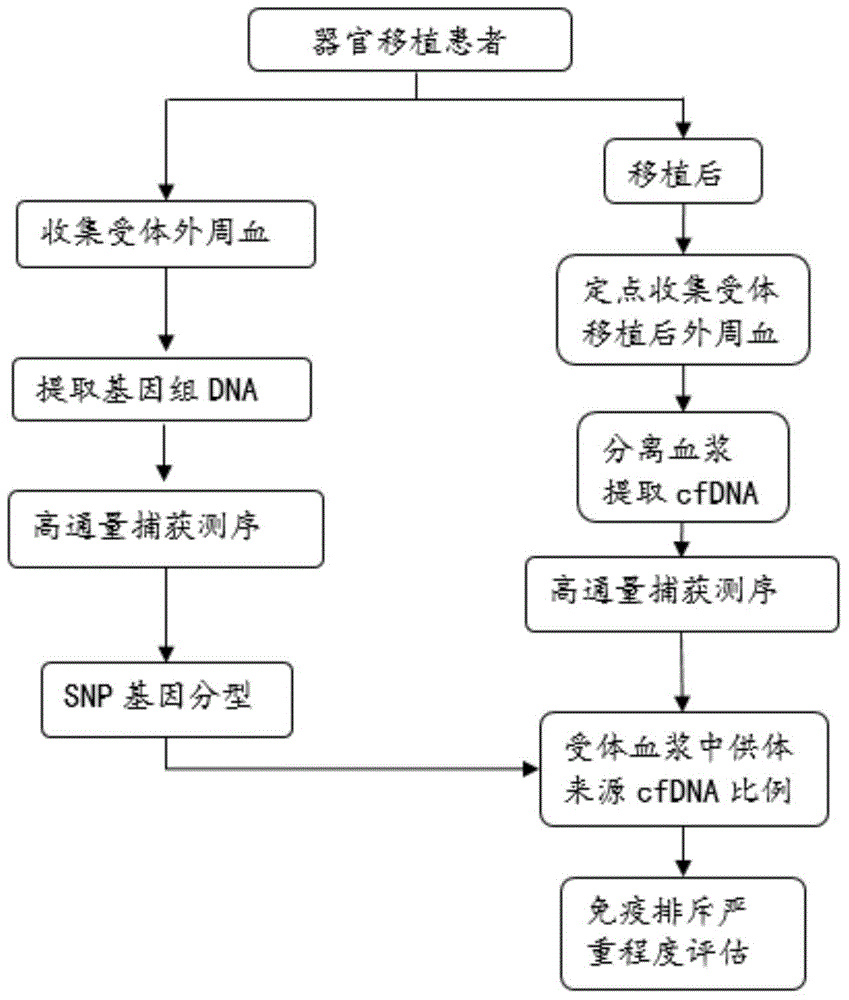
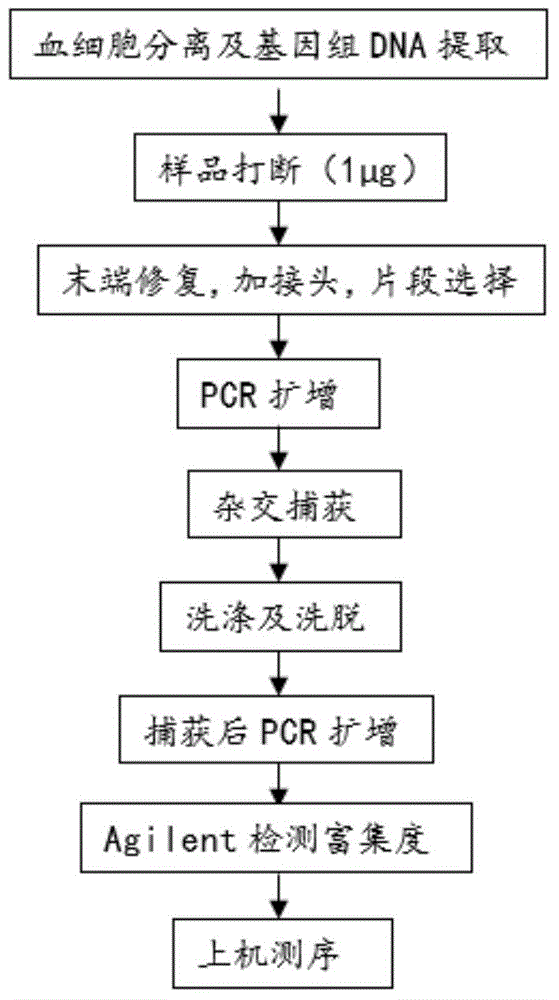
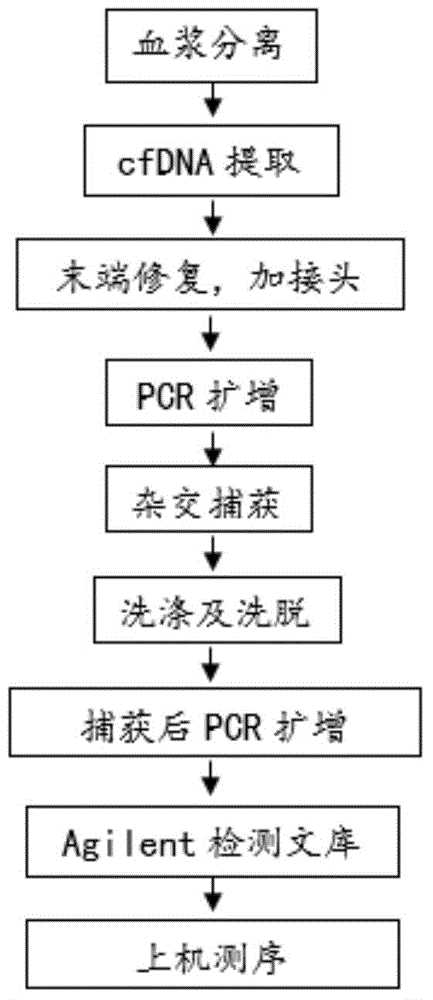
Method of determining cfDNA ratio of donor source in receptor cfDNA sample
ActiveCN106544407AGet rid of dependenceThe test result is accurateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlleleBioinformatics
The invention discloses a method of determining a cfDNA ratio of a donor source in a receptor cfDNA sample. The method comprises acquiring first and second sequencing data comprising at least one part of sequencing results of the receptor gDNA and the receptor cfDNA, respectively comparing the first and second sequencing data and a reference sequence to obtain first and second comparison results, carrying out SNP detection based on the first comparison result to obtain a first classification result comprising a number of primary homozygous SNPs expressed as AA, and determining a proportion of cfDNA of the donor source based on the amount of a second reading section matching with secondary homozygous SNP in the second comparison result, wherein the secondary homozygous SNP is least one part of the allele A-nonsupport primary homozygous SNP of the second reading section matching with the site. The method can accurately determine the content of the donor source cfDNA in a receptor cfDNA without a donor genetic sample.
Owner:BGI GUANGZHOU MEDICAL LAB CO LTD +1
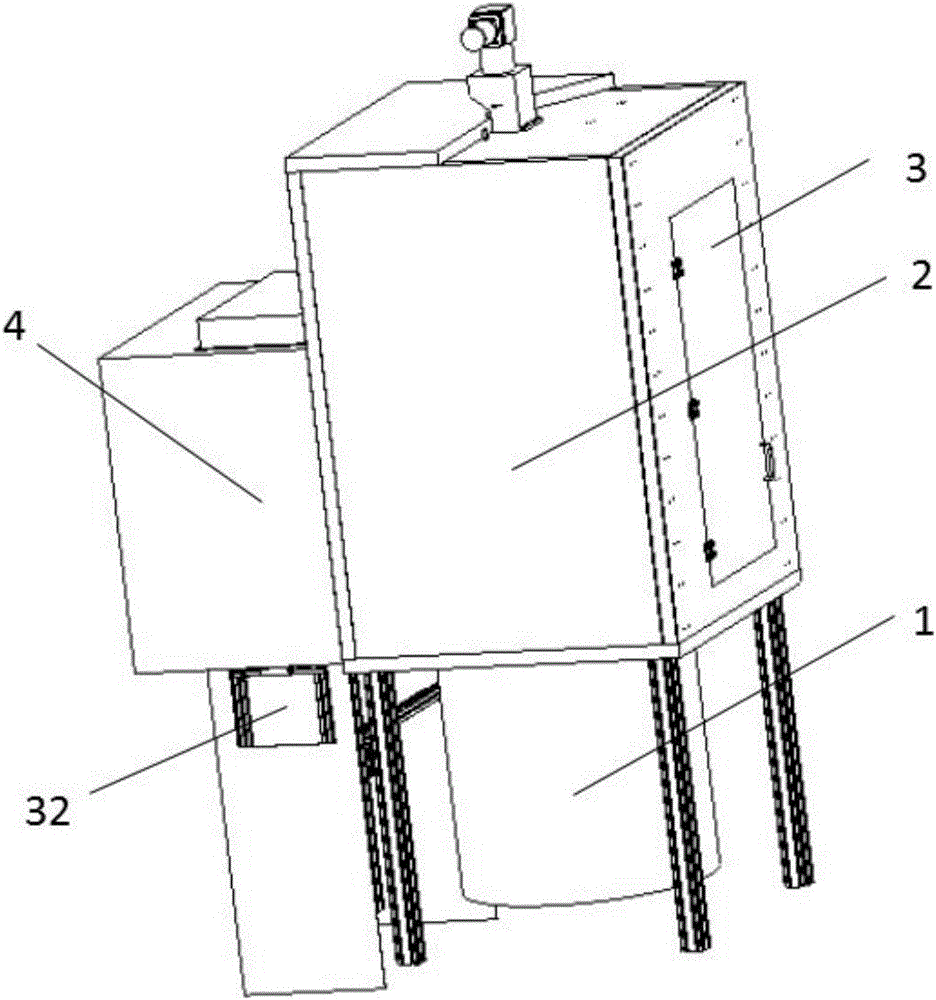
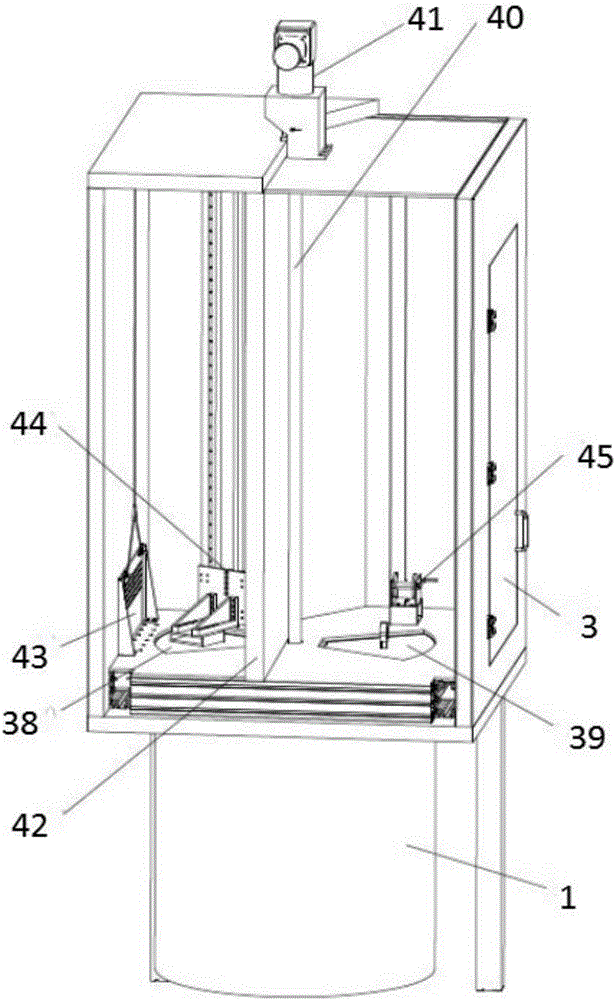
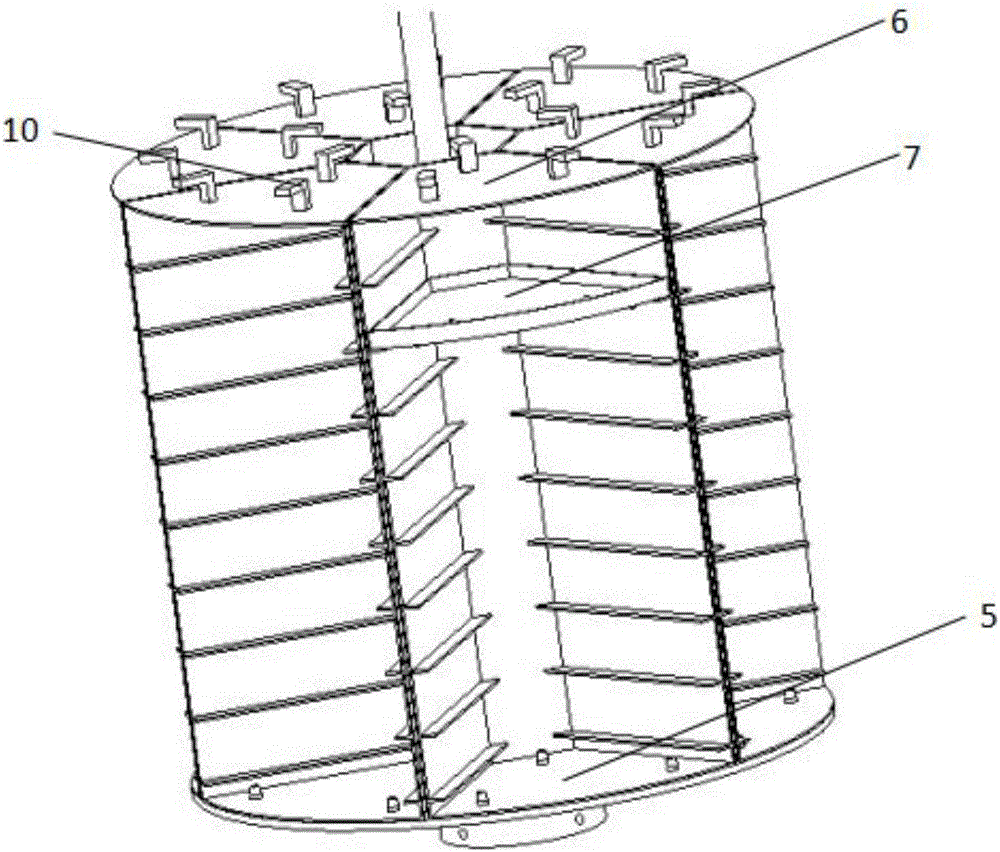
Automatic storage and taking device for biological samples
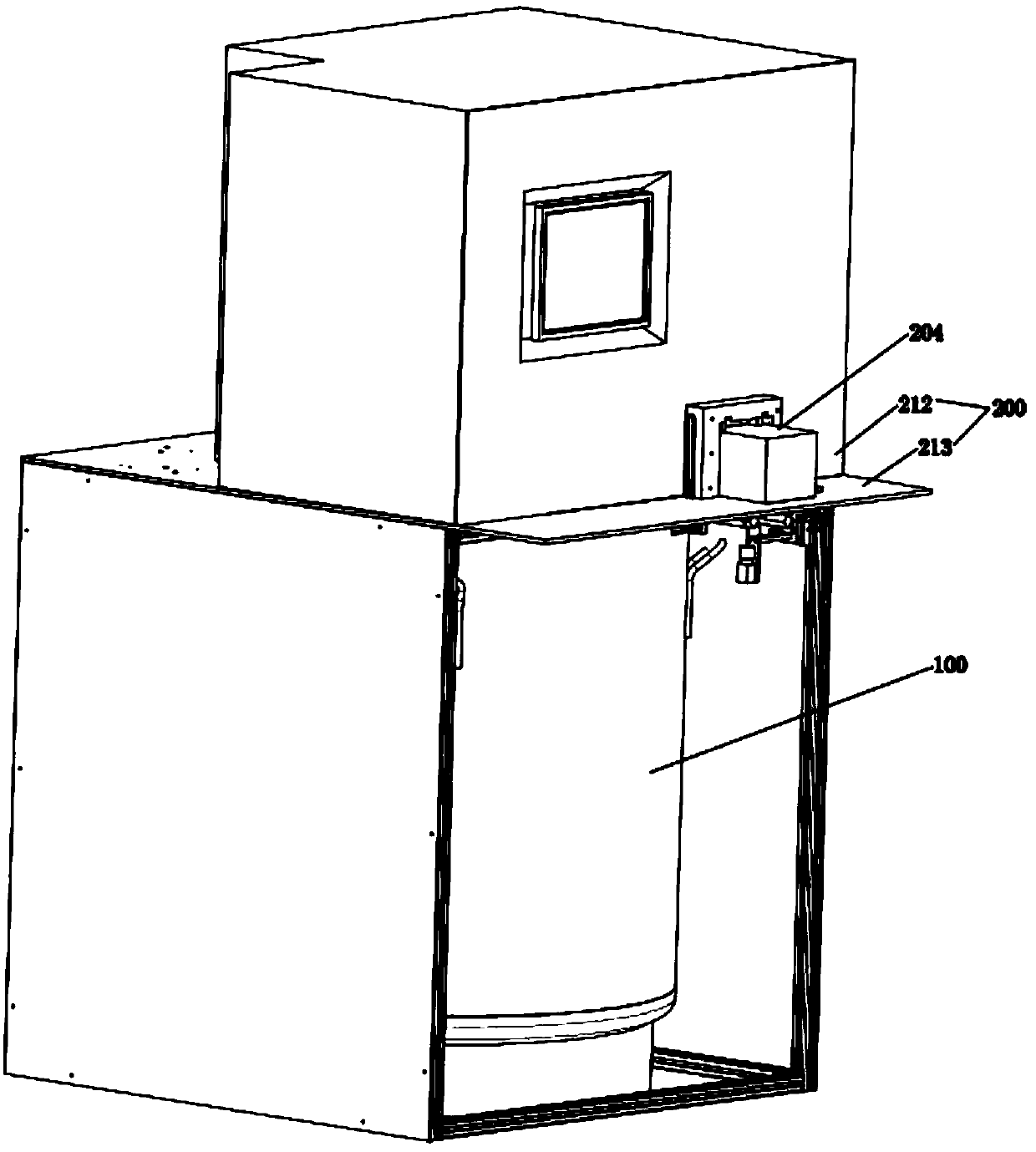
ActiveCN106395223AAvoid removal processAvoid temperature changesStorage devicesEngineeringRecognition system
The invention discloses an automatic storage and taking device for biological samples, and belongs to freezing storage devices of biological samples. The automatic storage and taking device comprises a freezing storage tank, a taking chamber positioned on the freezing storage tank, a sample storage rack positioned inside the freezing storage tank, a storage and taking bin which communicates with the taking chamber, and a sample recognition system positioned inside the storage and taking bin, wherein the sample storage rack comprises a chassis rotatably arranged inside the freezing storage tank and a plurality of lifting racks on the chassis; a plurality of layers of storage boxes are placed on the lifting racks; the lifting racks are equipped with lifting devices; a bracket which slides towards the taking chamber and supports the storage boxes is arranged inside the storage and taking bin; a clamping device positioned above the bracket is arranged inside the storage and taking bin; the clamping device is equipped with a driving mechanism used for driving the clamping device to move; a sample taking hole is formed in the bottom of the storage and taking bin; a sealing cover is equipped with an opening-closing device; and a sample transfer device is arranged below the sealing cover. According to the automatic storage and taking device, the problems that in the prior art, the storage and taking are inconvenient, the activity of other biological samples is affected, and the taking and placing accuracy and efficiency of the storage and taking bin for genetic samples are relatively low are solved.
Owner:基点生物科技(上海)有限公司
Determination of the number of tandem repeat nucleotides using encoded probe-displaying beads
InactiveUS20060257916A1Reduce morbidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyGenetic Screening (procedure)
This invention provides compositions and methods for genetic testing of an organism and for correlating the results of the genetic testing with a unique marker that unambiguously identifies the organism. The markers may be internal markers, such as for example single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), short tandem repeats (STRs), or other sites within a genomic locus. Alternatively, the markers may be external, such that they are separately added to the genetic sample before testing.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Methods for identifying and using SNP panels
ActiveUS20090004652A1Accurately identifying and distinguishingCost effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenetic samplesSingle-nucleotide polymorphism
Described are methods for identifying single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) that are useful for analyzing genetic samples, and for using said SNPs to determine genetic identity of samples.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Traceability process and security elements used in said process
InactiveUS20100049661A1Big and varied productionMeat/sausages markingCarcasses classification/gradingData centerHeifer calf
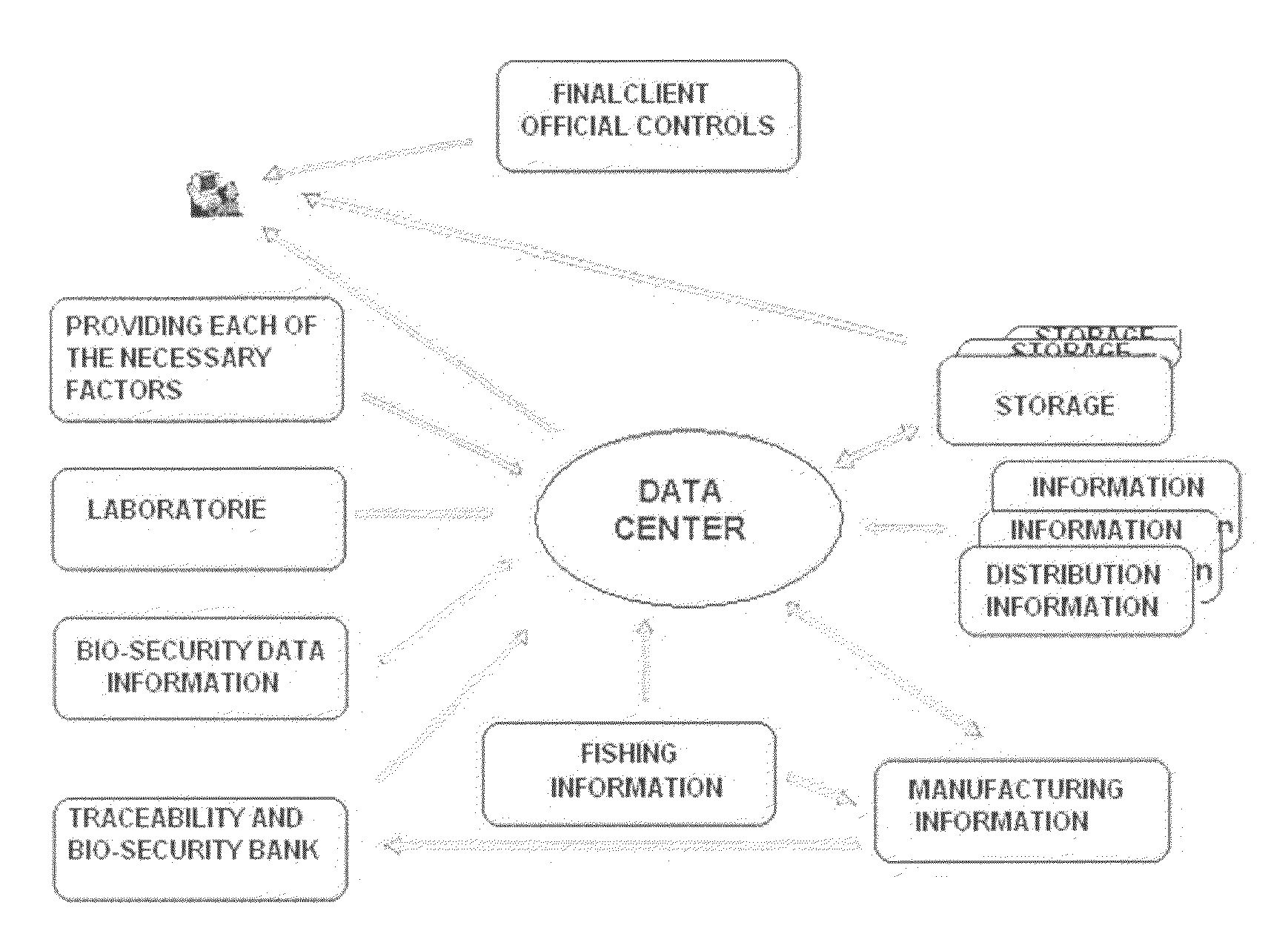
Bi-directional cattle traceability process comprising five basic stages: a first document traceability and sanitary certification chain stage, wherein the animals are identified by birth certificates, animal identification attached to the animal's ear and registered in a data centre. A second stage for transfer of animals to another establishment, wherein genetic material is extracted from the offspring not yet weaned, filed and registered and registered in the data centre. A third stage for slaughtering of animals, wherein the slaughtered animal's ear is cut off where the animal identification is attached and the animal identification is read on line, the half carcases have sealed strips applied to them, DNA samples are extracted from the animal, then deposited in the official genetic bank and on each cut a locket sampler is attached encrypting a genetic and biochemical sample. A fourth stage for transfer or exporting of cuts, wherein the barcode that originated the cut is identified and applied to each portion of this cut or piece into which it is divided and then the locket sampler is removed from each sliced or minced cut, to deposit it in the cold storage chamber. A fifth and last stage of traceability auditing, wherein three samples of the identified portion of a cut to de audited are taken and adulteration of the cut or non-adulteration is determined by comparing the genetic sample taken in the third stage with the encrypted genetic sample in the locket sampler that held the original cutting extracted in the fourth stage.Alternative traceability processes addressed to fishing and canning and a set of elements used in the different stages of the three processes are also disclosed.
Owner:LIMA SPA
Automatic storing and taking equipment for biological sample
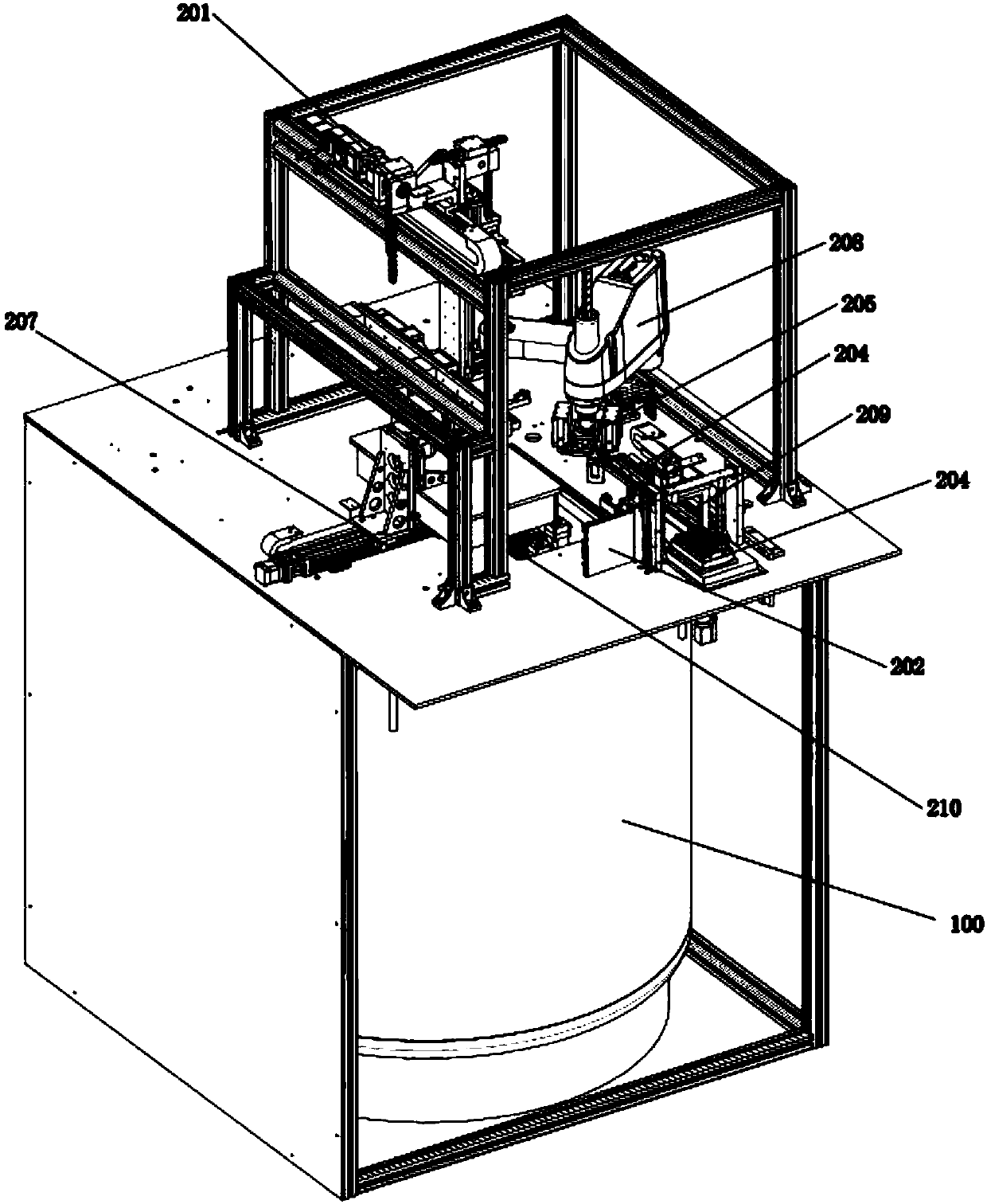
The invention discloses automatic storing and taking equipment for a biological sample and relates to the technical field of storing and taking equipment for biological gene samples. The automatic storing and taking equipment comprises a low-temperature storing tank, a conveying bin arranged above the low-temperature storing tank and an extracting opening for enabling the conveying bin to be communicated with the low-temperature storing tank; a sample storing rack, a sample box temporary placing area and a second manipulator for storing and taking a sample box in the low-temperature storing tank, wherein multiple lines of unit racks are arranged on the sample storing rack; a first manipulator is arranged in the conveying bin; in addition, a sealing cover matched with the extracting openingand an uncovering mechanism for opening and closing the sealing cover are also arranged in the conveying bin. According to the automatic storing and taking equipment disclosed by the invention, the condition that the quality of the sample is affected because the sample is taken out of the low-temperature storing tank, and enters a noncryogenic environment for transferring and extraction is avoided; meanwhile, the consumption of low-temperature nitrogen is reduced.
Owner:GENEPOINT BIOLOGICAL TECH (CHENGDU) CO LTD
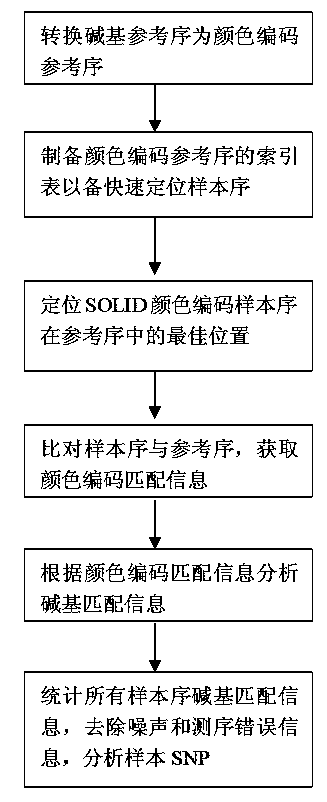
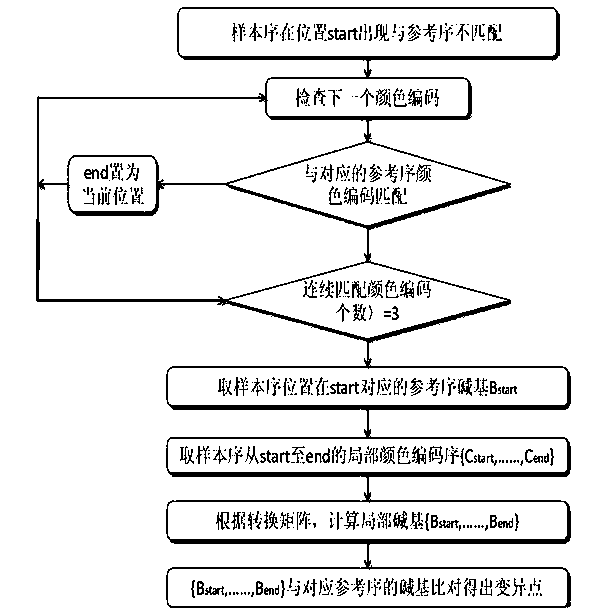
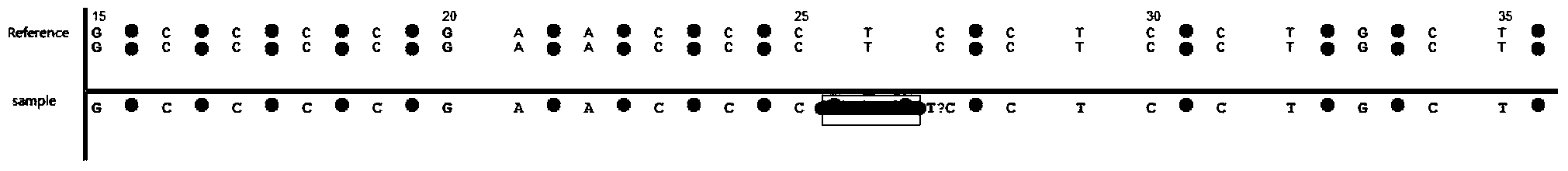
Gene SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site detection method based on SOLID (supported oligo ligation detection) sequencing technique
InactiveCN103451279AImprove accuracyImprove noise immunityMicrobiological testing/measurementOptimal matchingGene
The invention belongs to field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site detection method based on an SOLID (supported oligo ligation detection) sequencing technique. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a color sequence of a gene sample to be detected in an SOLID sequencing manner; (2) preparing the color sequence of a reference order; (3) preparing an index table of a color coding reference order to rapidly position a sample order; (4) comparing an SOLID sequencing sample order with the color coding reference order so as to find out the optimal matching position of the sample order in the reference order, comparing the sample order with the reference order so as to obtain color encoding matching information; (5) analyzing base matching information of the SOLID sample order and the color encoding reference order according to the color encoding matching information, and determining uncertain change points; (6) counting the obtained uncertain change points, and removing noise and the uncertain change points caused by a sequencing error, so as to obtain a sample SNP site. By adopting the SNP detection method disclosed by the invention, the characteristic of high positioning accuracy of an SOLID data in a comparison process is kept; the accuracy of the SNP analysis method is also improved.
Owner:JIANGSU TODAYSOFT TECH
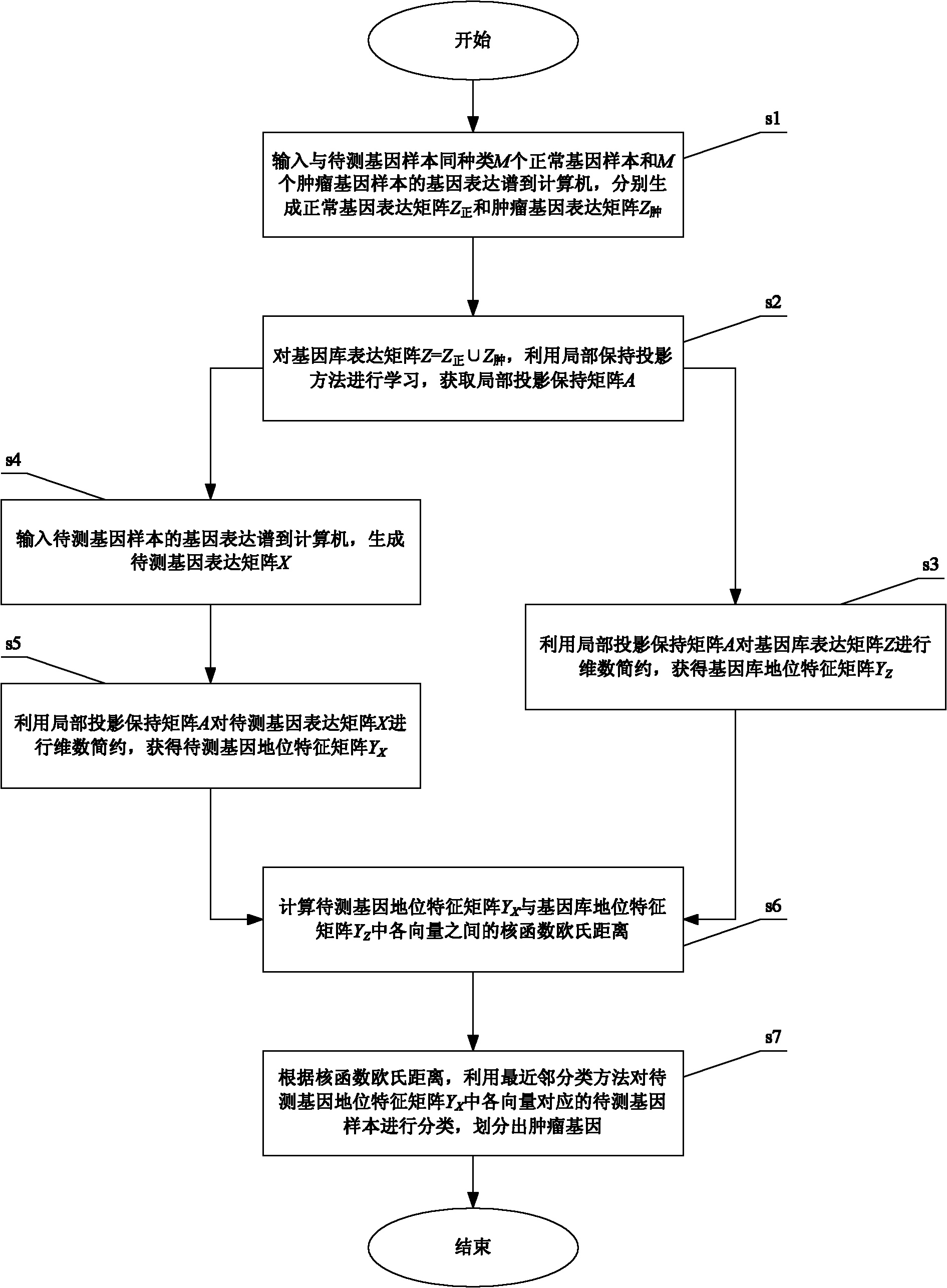
Tumor gene identification method based on gene expression profile
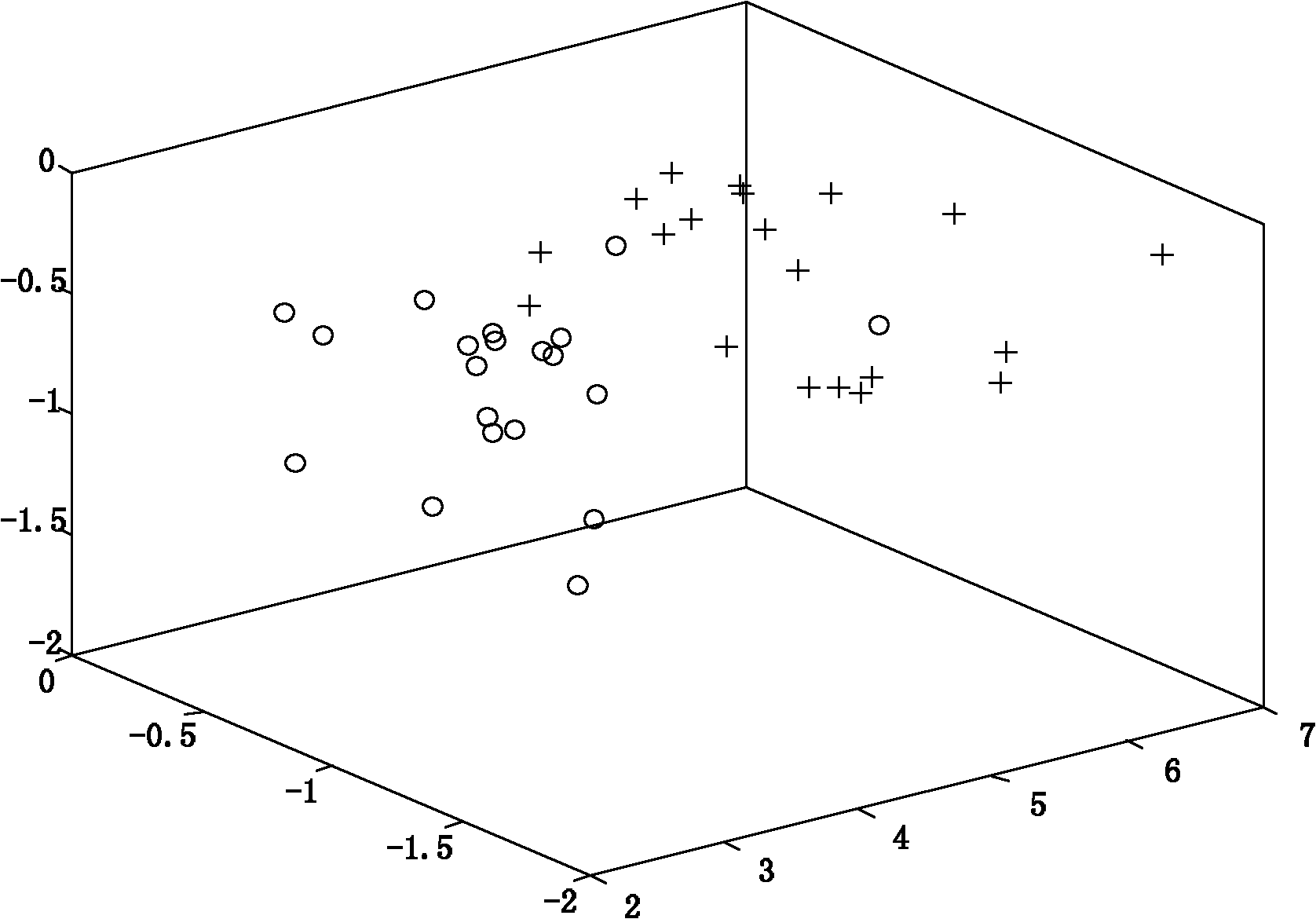
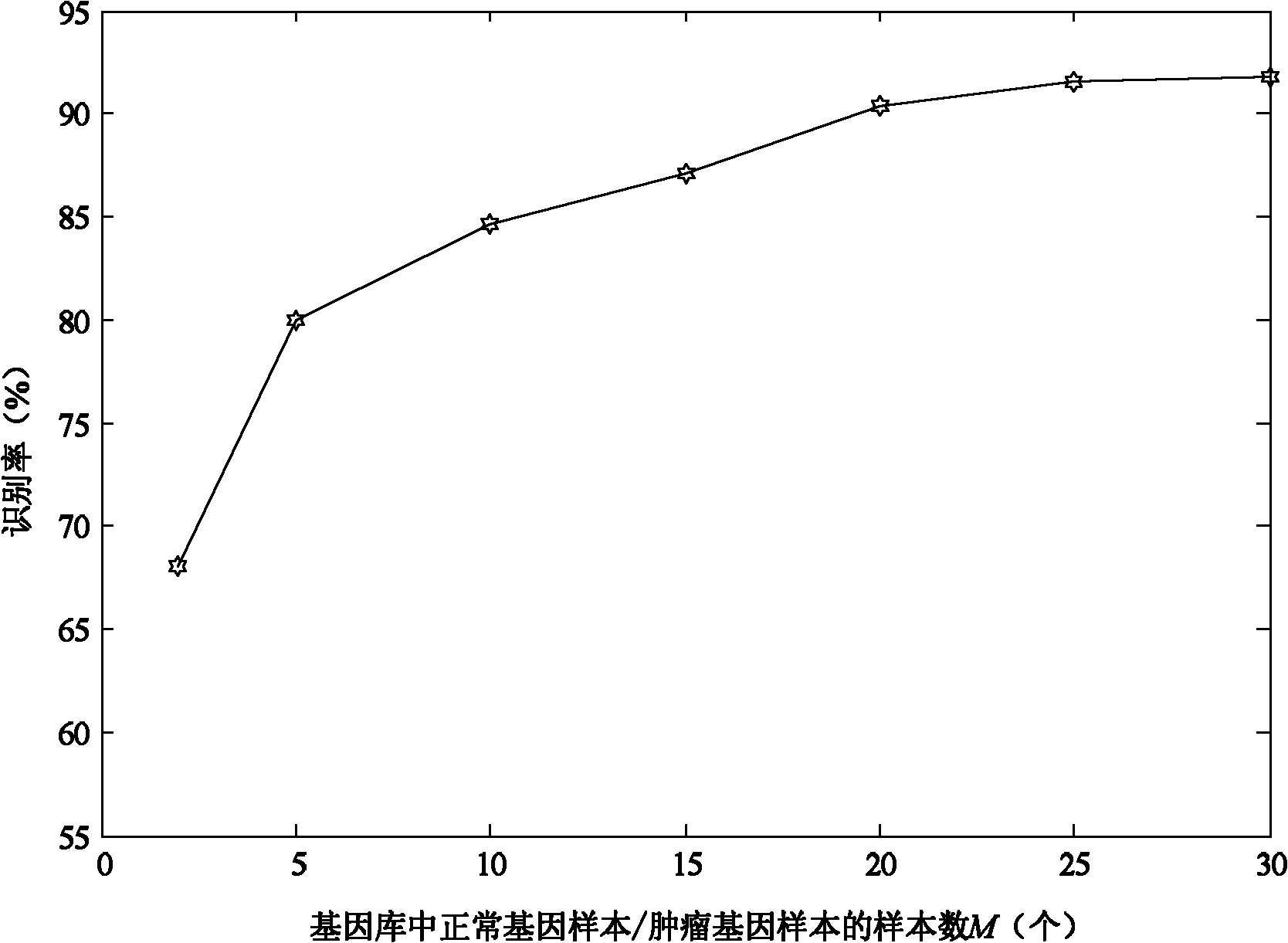
InactiveCN102073799ARealize identificationReduce redundancySpecial data processing applicationsGene expression matrixClassification methods
The invention provides a tumor gene identification method based on a gene expression profile, which is characterized in that gene expression matrixes of gene samples are studied by adopting a locality preserving projection method and a kernel-function nearest neighbor classification method under the assistance of a computer, the gene expression matrixes of the gene samples are projected into a low-dimensional embedding space so as to reveal a low-dimensional manifold structure hidden in high-dimensional gene expression profile data, and low-dimensional characteristic matrixes are classified by adopting the kernel-function nearest neighbor classification method so that the unrevealed characteristics in the low-dimensional characteristic matrixes are revealed, further the tumor genes in the gene samples are distinguished, and the tumor genes are identified. The method provided by the invention has high rate of identification and good reference value to the clinical diagnosis of the tumor genes and can be applied to establishing a tumor gene identification system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Tools and Methods for the Quantification of Dna Repeats
The invention relates to an assay method allowing the quantification of the copy number of a repeated nucleic acid sequence in a genetic sample. Typically such sample comprises the genome of a microbial, plan, animal or human subject. Furthermore, the invention provides a particular example wherein the assay is used to determine the susceptibility to disease of a subject. Such information can be used in selecting the optimal treatment for a particular diseased subject.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
Evolutionary models of multiple sequence alignments to predict offspring fitness prior to conception
A system, device and method for receiving multiple aligned genetic sequences obtained from genetic samples of multiple organisms of one or more different species. A measure of evolutionary variation may be computed for one or more alleles at each of one or more aligned genetic loci. The aligned genetic loci in the multiple organisms may be derived from one or more common ancestral genetic loci or may be otherwise related. The measure of evolutionary variation may be a function of variation in alleles at corresponding aligned genetic loci in the multiple aligned genetic sequences. One or more likelihoods may be computed that an allele mutation at each of the one or more genetic loci in a simulated virtual progeny will be deleterious based on the measure of evolutionary variation of alleles at the corresponding aligned genetic loci for the multiple organisms.
Owner:ANCESTRY COM DNA
Reliable and Secure Detection Techniques for Processing Genome Data in Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Genetic samples are obtained from separate people, and at least a portion of each are purposefully combined before testing to form a pooled genetic sample. The pooled genetic sample is tested for the presence of a signature for a given known ailment. DNA identification uses discovered InDels in a region of InDel variation in a genetic sample. A pair-wise comparison is performed to reference InDels, and a distance is measured between the first InDel and the reference Indel. Reference kmers are identified in a reference genome, and in a test sample. The plurality of sample kmers are filtered to those which have a 1 edit distance from a corresponding one of the plurality of reference kmers. Reads that have kmers that do not have a 1 edit distance from the corresponding one of the plurality of reference kmers are identified, and multiple single-mutations are eliminated from candidate InDel reads.
Owner:CRYSTAL GENETICS INC
Macronutrient sensitivity
The present invention relates to a method and a kit for identifying a subjects macronutrient sensitivity. The method involves assaying a genetic sample from the subject to determine a polymorphism profile, analysing the polymorphism profile to identify risk alleles and determining the macronutrient sensitivity based on the number of risk alleles present. This information can be used for determining an appropriate diet to induce satiety, formulating a diet for inducing satiety, or for treating a range of medical complaints associated with metabolism.
Owner:GENETICS INVESTMENTS
Gene Detecting Method
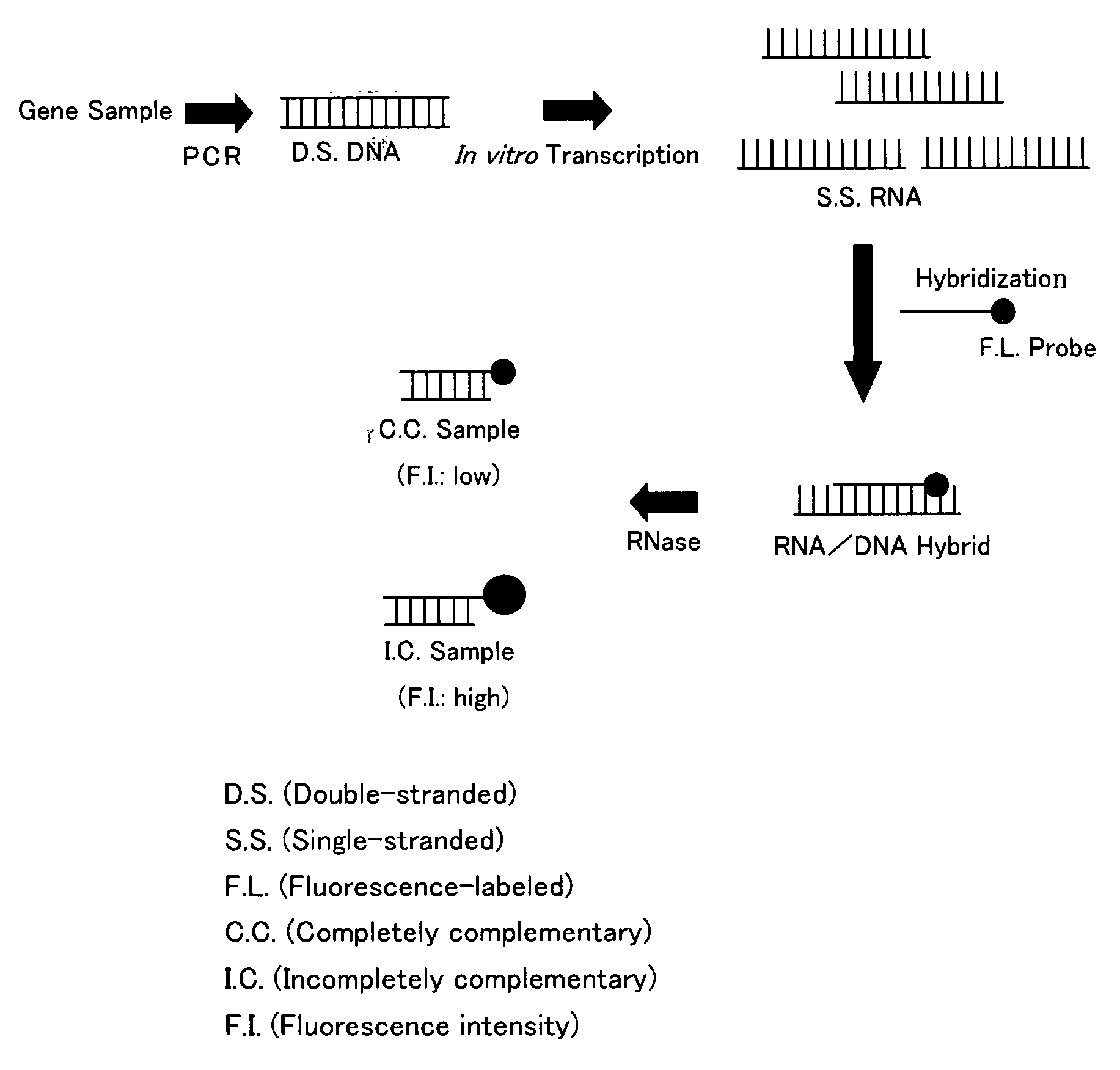
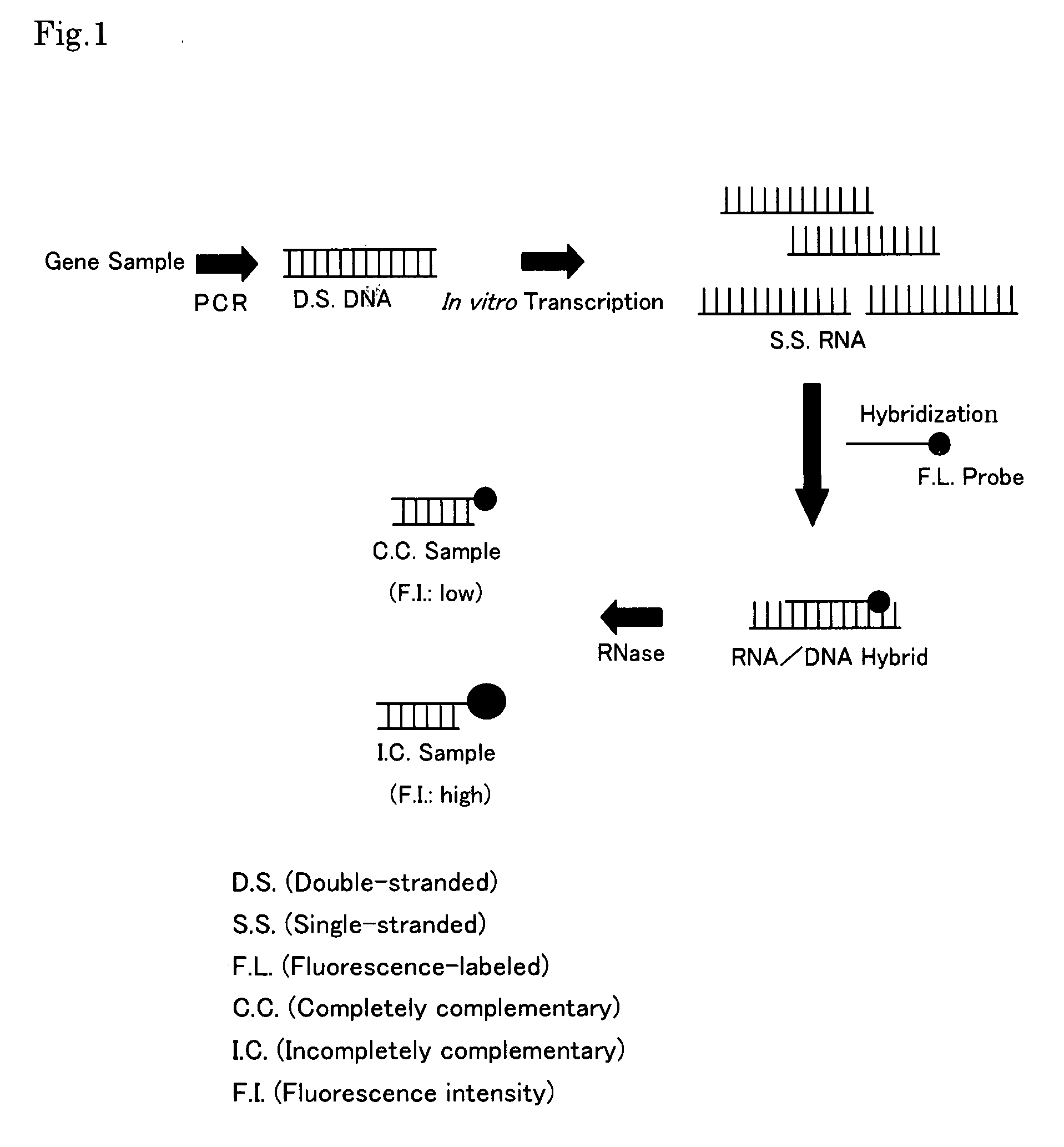
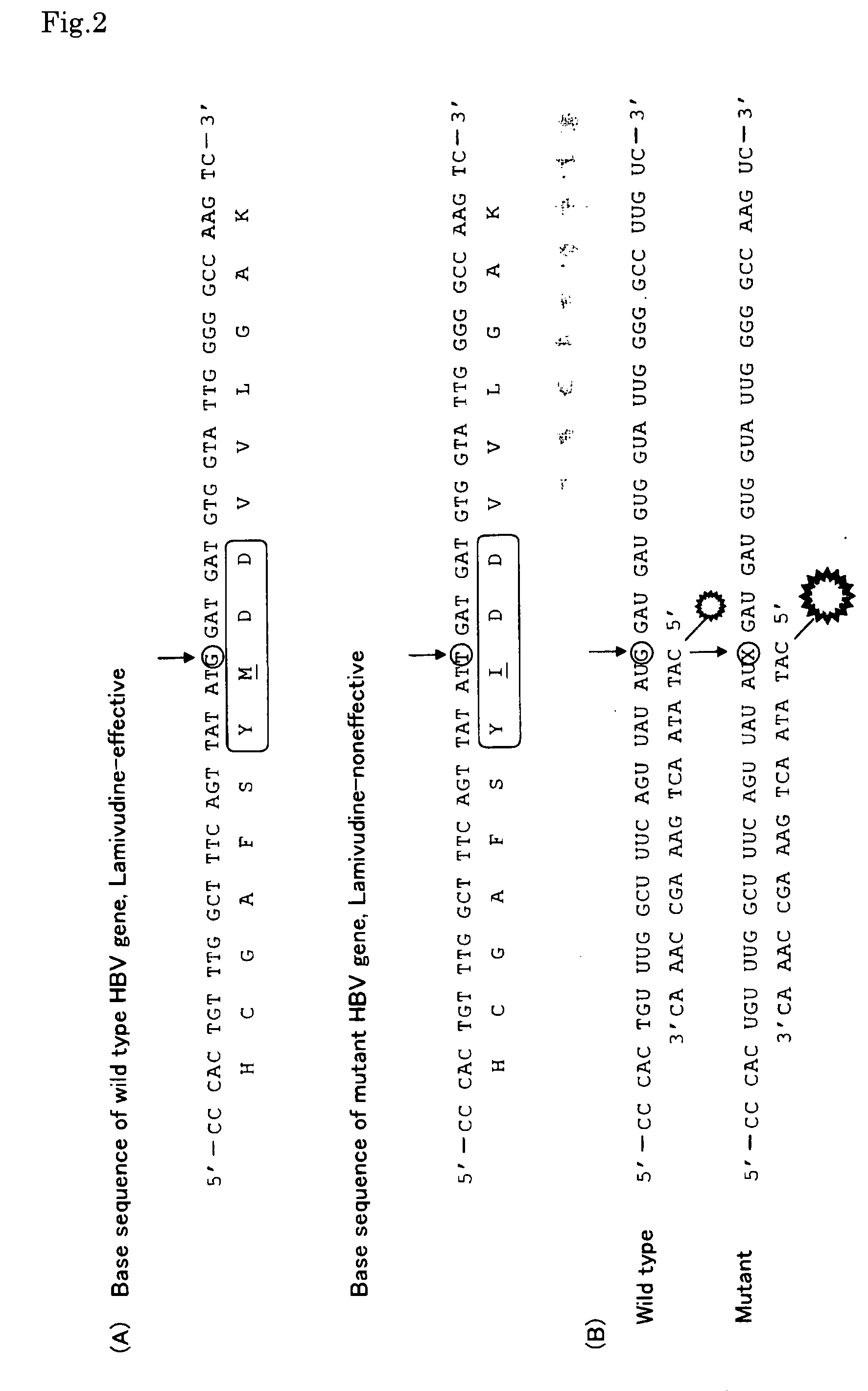
InactiveUS20080274464A1Low reliabilityShorten timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDouble strandedMutation
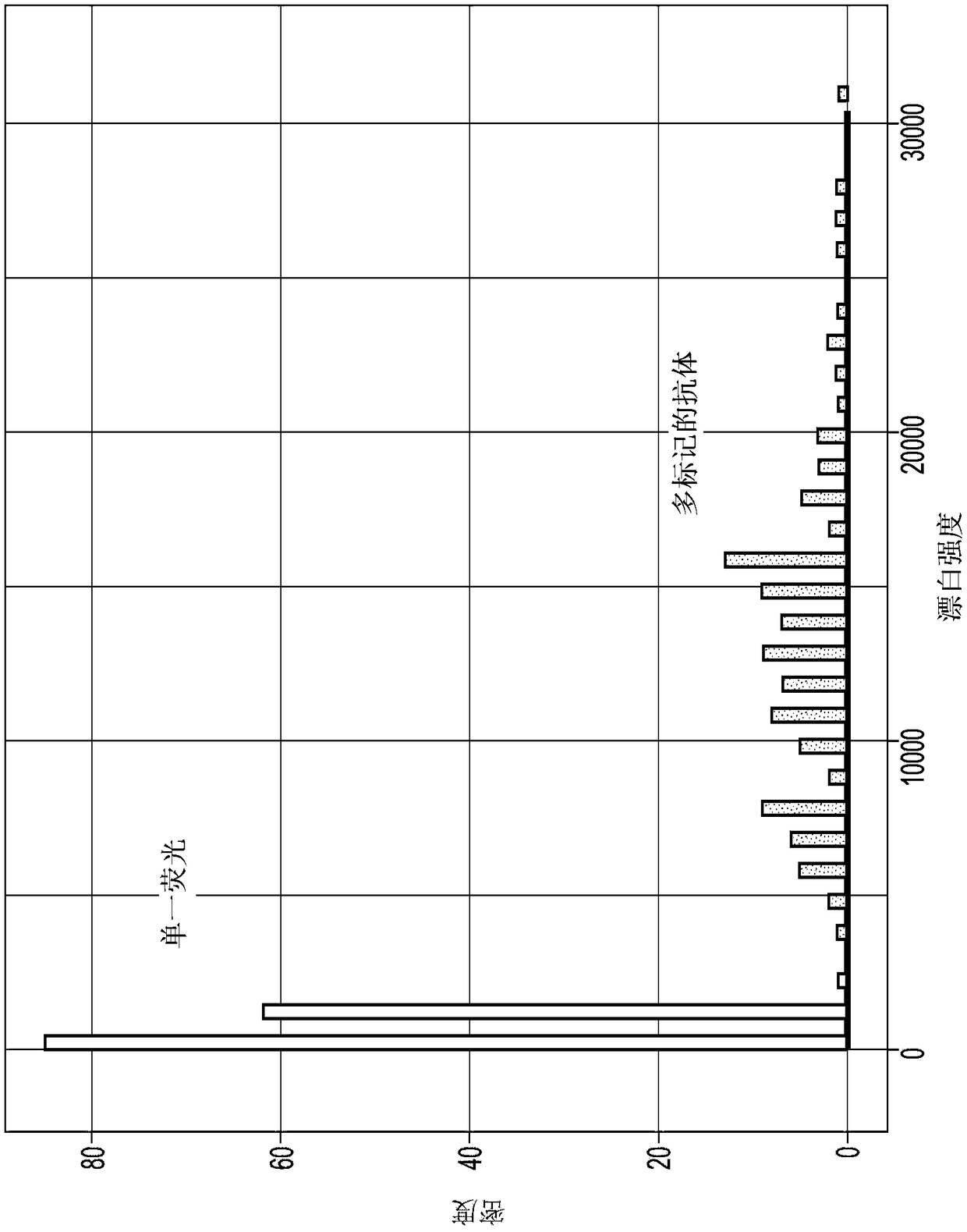
Disclosed is a gene detecting method for determining mutation of a specific base or presence / absence of a specific base in a target gene. There are provided a the target gene sample and a control gene sample having a base sequence which is wild-type or standard-type with respect to the target gene. The method comprises steps of (i) independently subjecting the target gene sample and the control gene sample to a PCR reaction for amplification, using primers having an RNA polymerase promoter sequence at the 5′-end thereof, (ii) independently subjecting the double-stranded DNAs produced by said PCR reaction from the target gene sample and from the control gene sample, to an in vitro transcription reaction to form a single-stranded RNA, (iii) independently hybridizing the single-stranded RNAs with a fluorescence-labeled probe composed of a single-stranded DNA having a base sequence complementary to at least part of the base sequence of the control gene and being combined with a fluorescent dye, to form an RNA / DNA hybrid, and then (iv) comparing the fluorescence intensity of the RNA / DNA hybrid derived from the target gene sample with that of the RNA / DNA hybrid derived from the control gene sample.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Arrays for single molecule detection and uses thereof
InactiveCN109477095ASequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAnalysis method
The invention relates to methods of detecting a genetic variation in a genetic sample from a subject using labeled probes and counting the number of labels in the probes. The invention also relates tomanufacturing and using arrays and analytical approaches based on single molecule detection techniques.
Owner:SINGULAR BIO
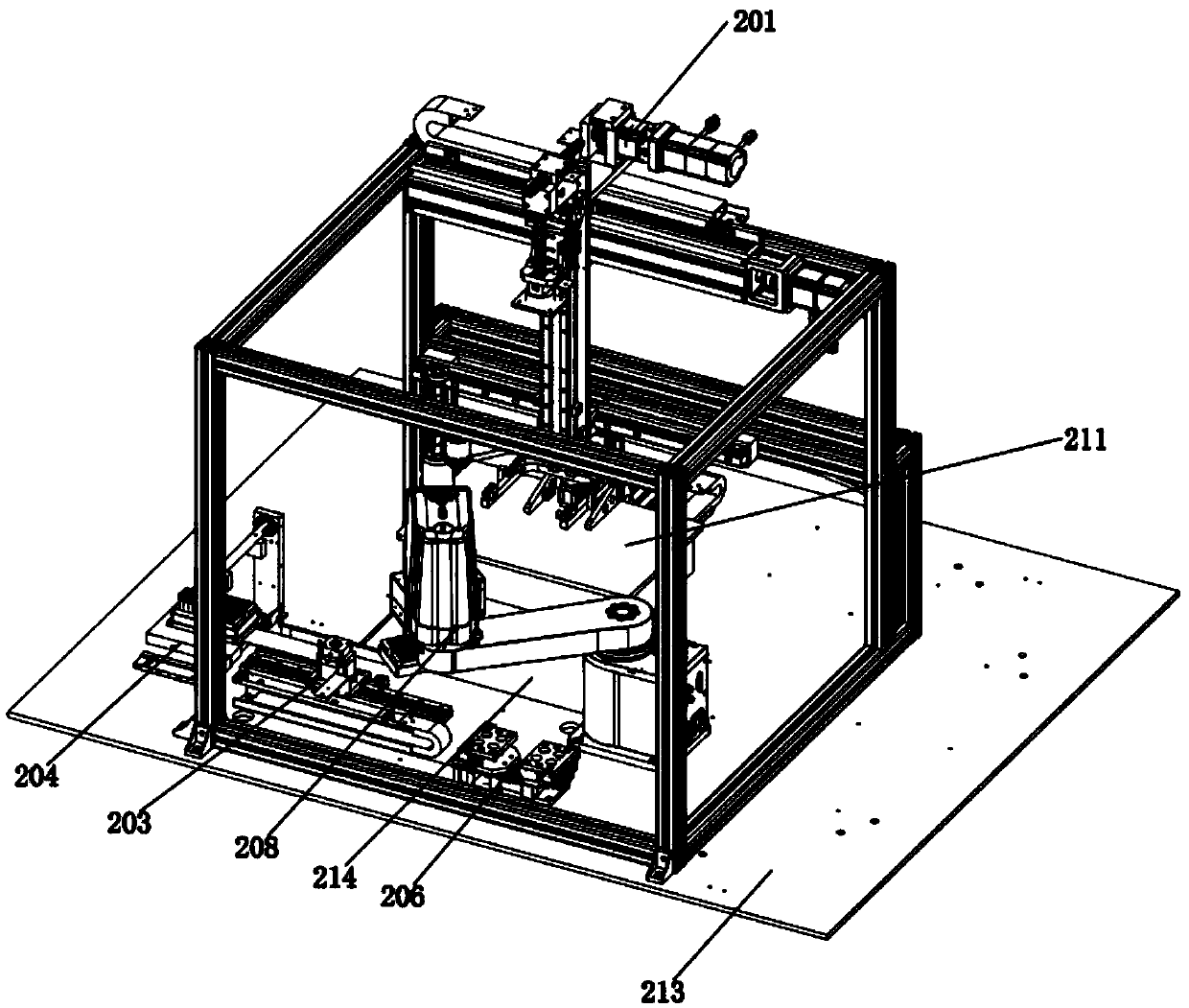
Gene sample transfer bin
The invention discloses a gene sample transfer bin and relates to the technical field of biological gene sample storing and taking equipment. The gene sample transfer bin comprises a bin body, a feedmechanism, a mechanical arm, a unit frame extraction mechanism and a fixture supporting mechanism, wherein the feed mechanism, the mechanical arm, the unit frame extraction mechanism and the fixture supporting mechanism are mounted in the bin body. The bin body comprises a table board and a shell cover. The shell cover is provided with a feed port corresponding to the feed mechanism. The shell cover is provided with a door opening and closing mechanism used for opening and closing the feed port. The table board is provided with a sampling port and a sealing cover matched with the sampling port. The sealing cover is equipped with a cover opening mechanism. The gene sample transfer bin can effectively protect low-temperature nitrogen in the bin body against leakage and reduce loss of liquidnitrogen and meanwhile can guarantee good activity of biological tissues in test tubes in the process of transferring the test tubes.
Owner:GENEPOINT BIOLOGICAL TECH (CHENGDU) CO LTD
Methods and systems for genotyping genetic samples
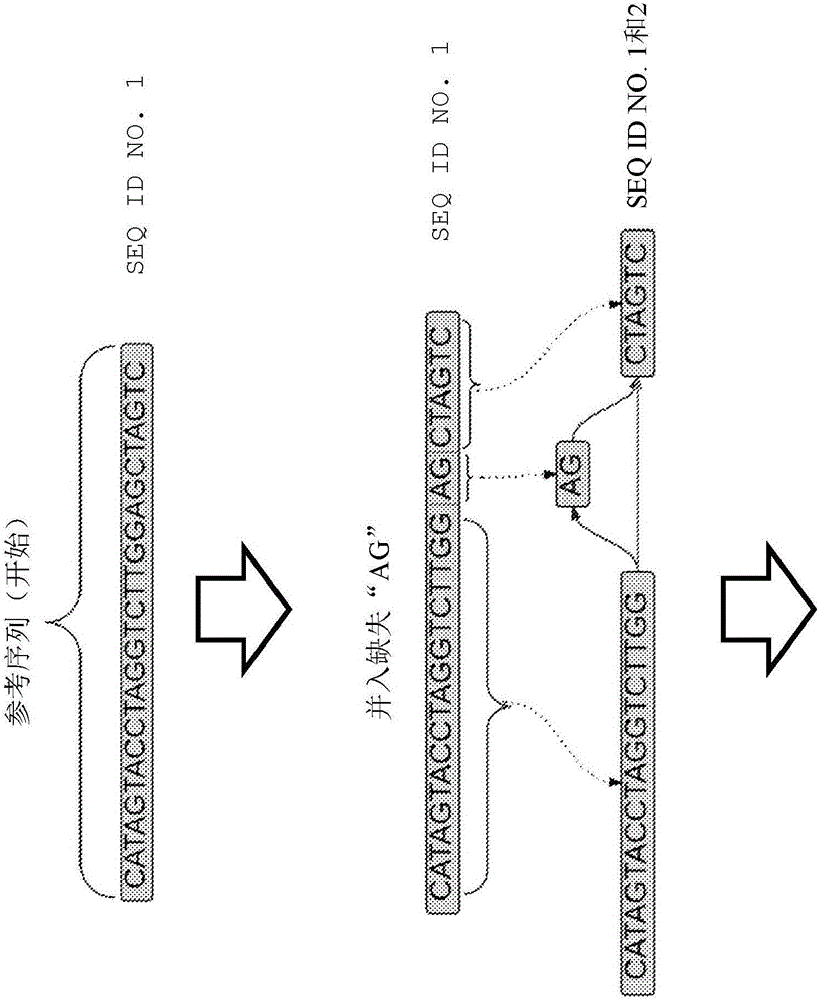
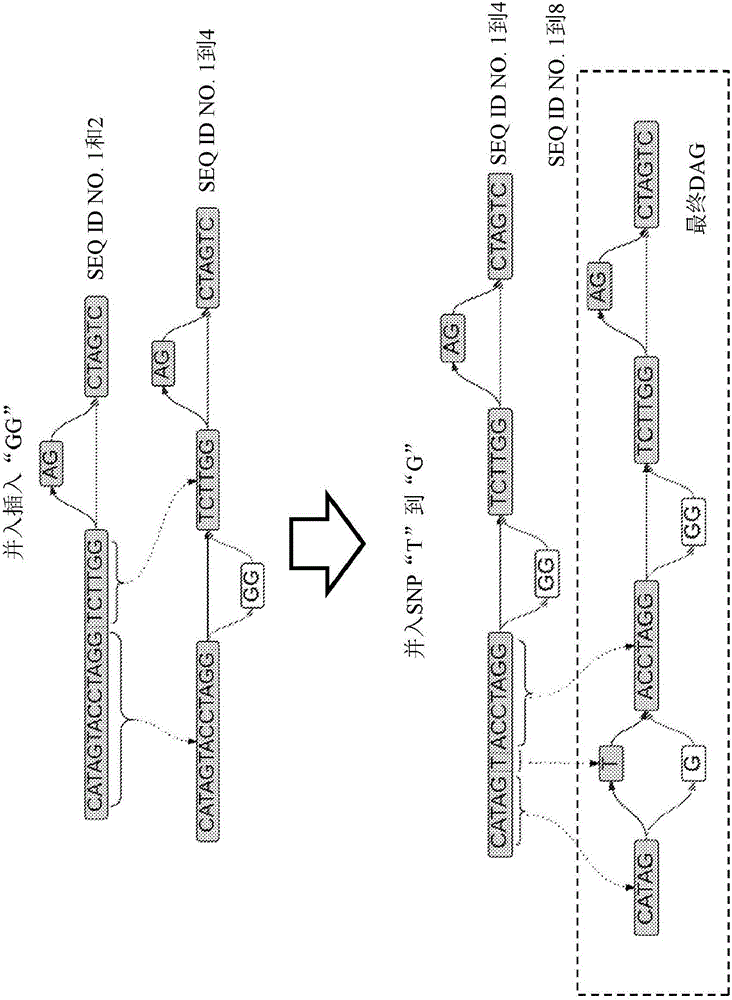
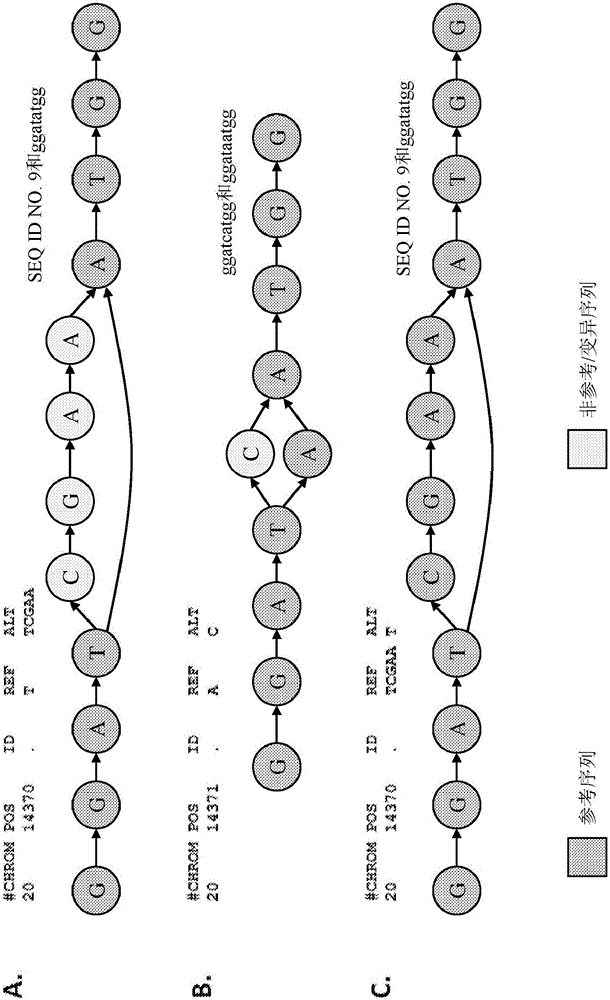
The invention provides methods and system for making specific base calls at specific loci using a reference sequence construct, e.g., a directed acyclic graph (DAG) that represents known variants at each locus of the genome. Because the sequence reads are aligned to the DAG during alignment, the subsequent step of comparing a mutation, vis-a-vis the reference genome, to a table of known mutations can be eliminated. The disclosed methods and systems are notably efficient in dealing with structural variations within a genome or mutations that are within a structural variation.
Owner:SEVEN BRIDGENOMICS
Genetic marker group and individual gene identification card and application thereof
InactiveCN109321660AImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIndividual geneHaplotype block
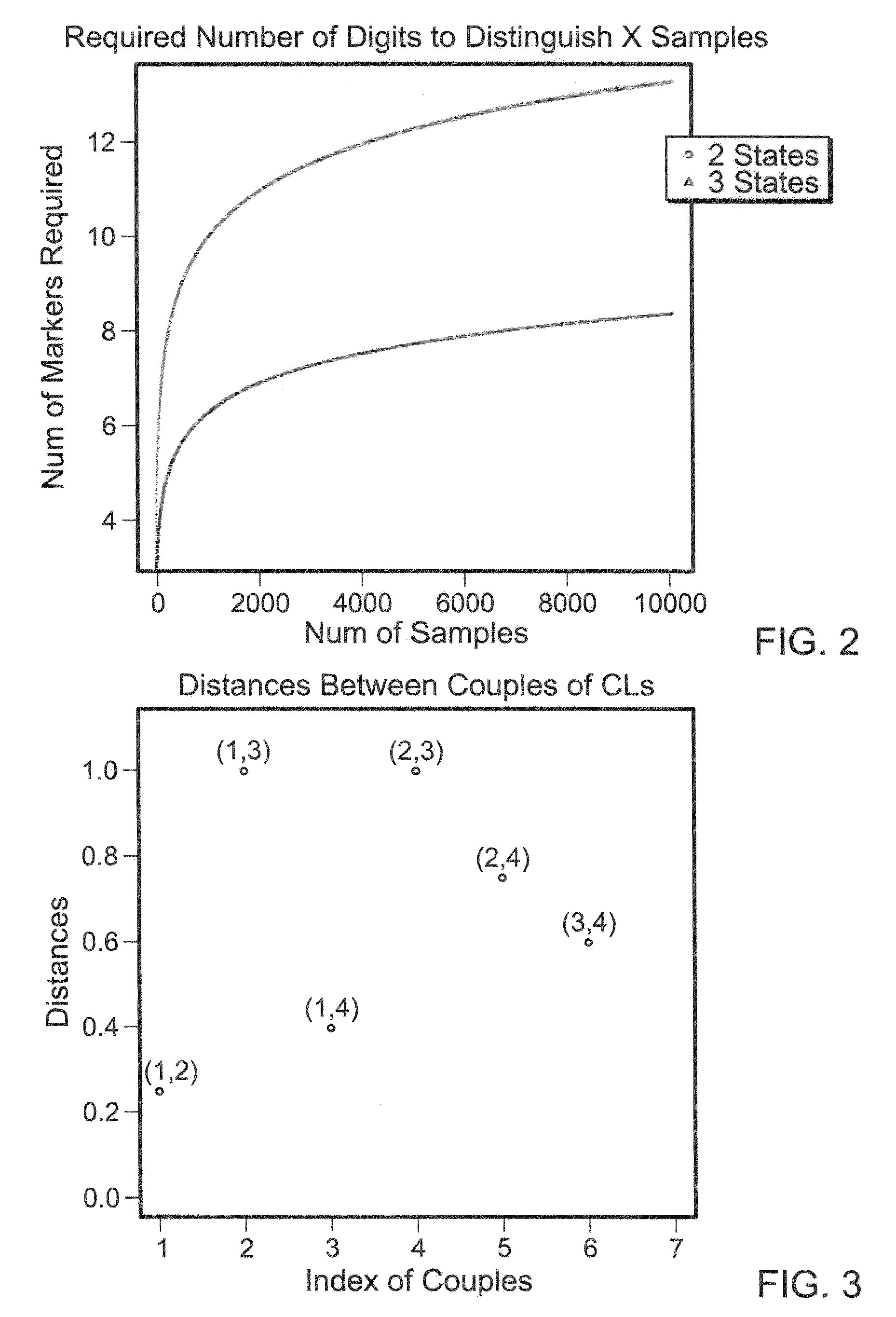
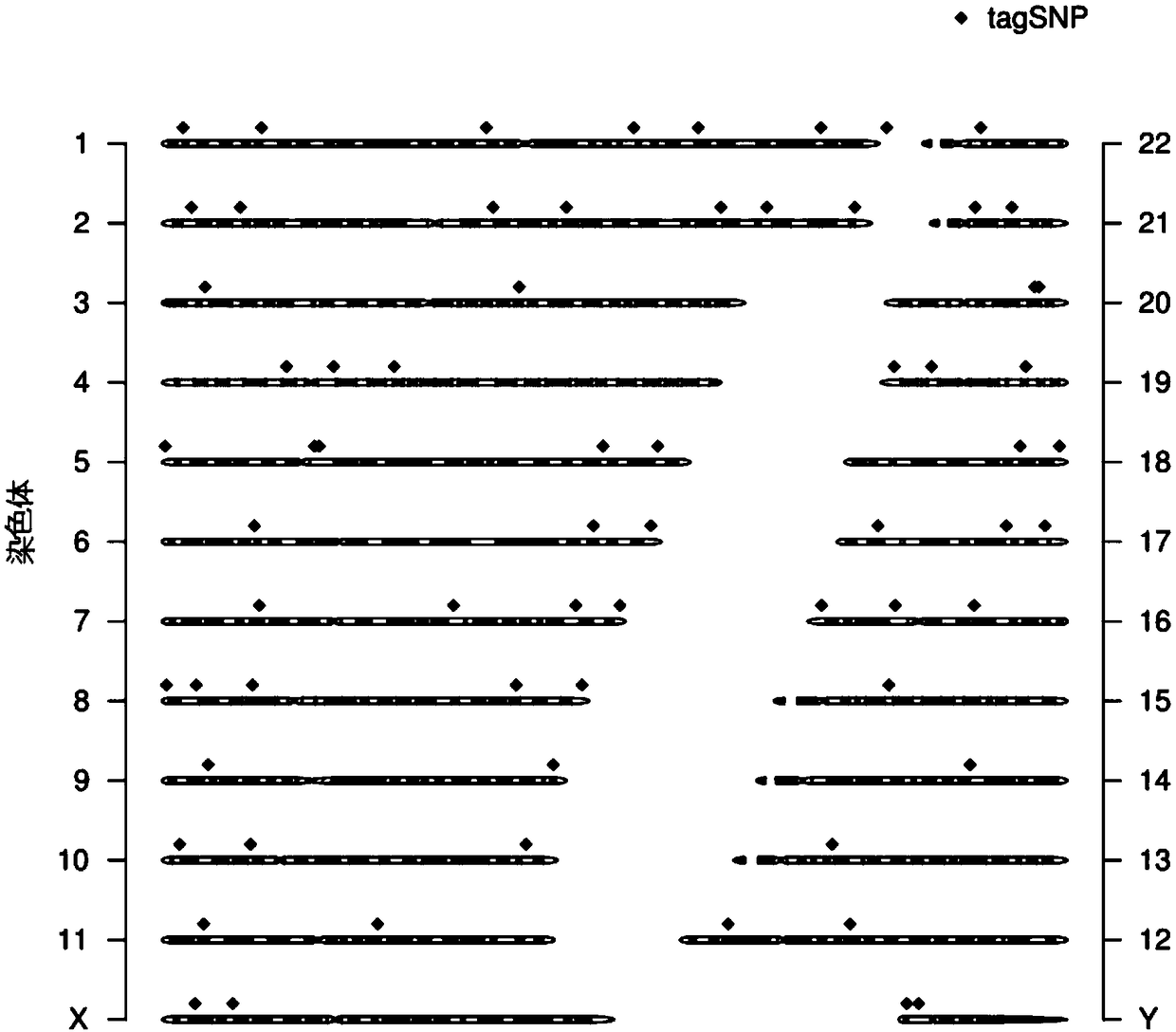
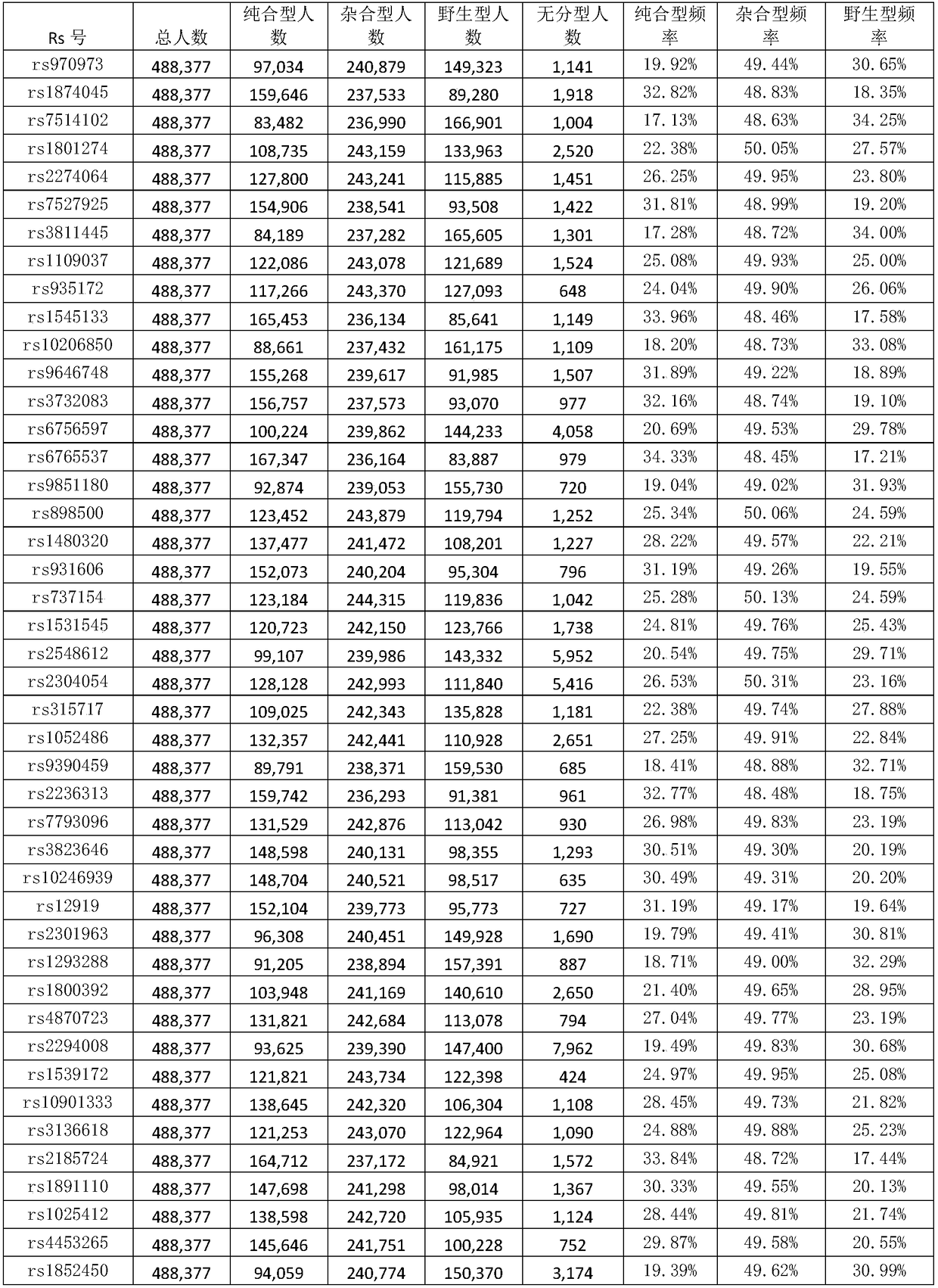
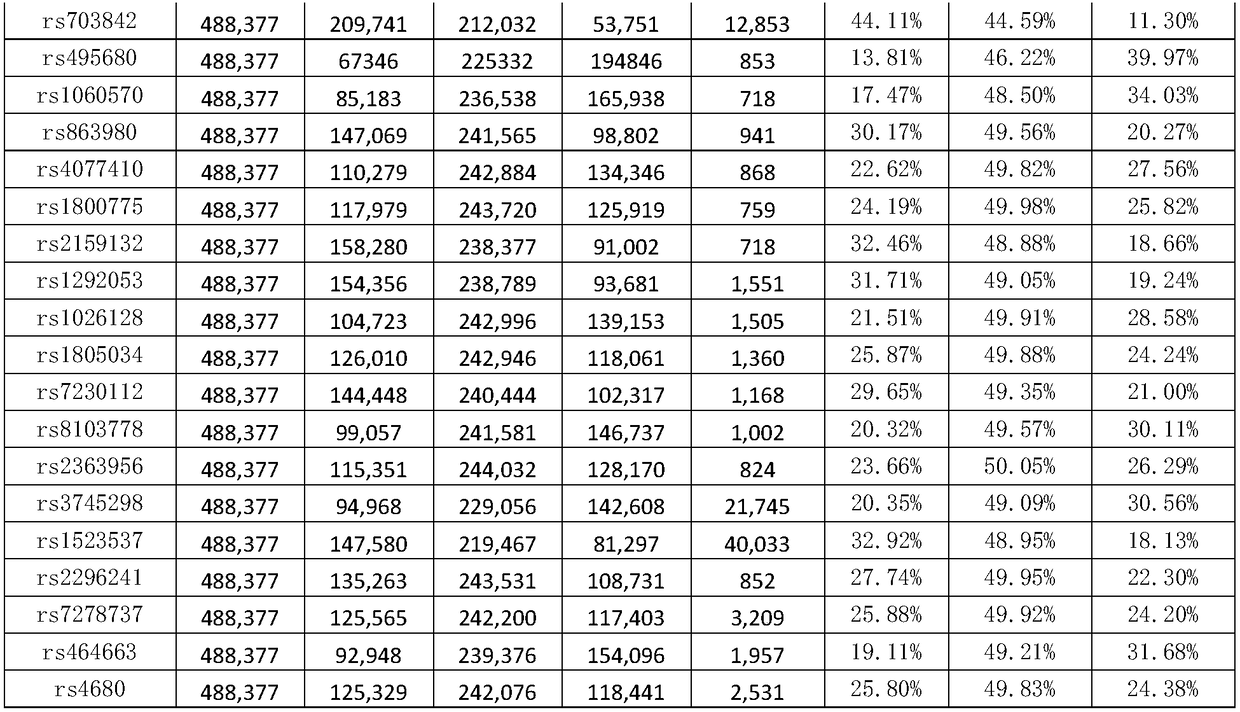
The invention discloses a genetic marker group and an individual gene identification card and application thereof. The genetic marker group comprises multiple SNP sites, wherein the multiple SNP sitesare tagSNPs located in different haplotype areas, the MAF is between 0.48 to 0.505, the adjacent SNP sites are not in linkage relationships, the distance among the adjacent SNP sites is larger than 1M, and variation information non A / T or C / G and the SNPs are evenly distributed in all chromosomes. By applying the technical scheme, through effective combination of the SNP sites, the set of genetic marker group which is simple in technology, economical and practical is formed, and can be used as the individual DNA identification card, and when the SNP sites are selected, linkage relationships,the MAF, distance, variation situations and the evenness of distribution on the chromosomes of the sites are taken into account, so that the accuracy of judging a certain gene sample is improved.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
Gene detection unmanned sale experience system and device
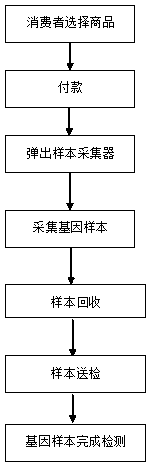
InactiveCN109273049AShorten the timeImprove experienceDigital data protectionProteomicsData informationTerminal equipment
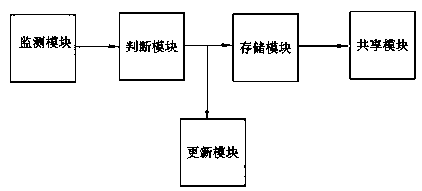
The invention belongs to the medical field and relates to a biological (gene) information detection and auxiliary diagnosis service device, in particular, a gene detection unmanned sale experience system. The implementation process of the system includes the following steps that: 1, consumer gene detection project products are introduced and sold, samples are acquired and collected, and the gene samples are stored in an acquisition device; 2, professionals transport the genetic samples from the acquisition device to a detection center, and the detection center detects the gene samples; and 3,gene sample detection results are sent to consumers. The gene detection experience device comprises a monitoring module used for detecting whether a first terminal device acquires data information, astorage module used for storing the data information, and an update module used for updating the data information. With the system and device provided by the embodiments of the present invention adopted, the consumers can be facilitated to perform gene detection, and the information security of the consumers can be ensured.
Owner:范祎丹
Targeted Therapies for Cancer
Methods of selecting a chemotherapy regimen for treatment of cancer in a patient are disclosed. A patient genetic sample from a bilary cancer such as cholangiocarcinoma is analyzed for a mutation in ERRFI1 and a chemotherapeutic agent is selected as a result of the analysis. If a mutation in ERRFI1 is present, treatment with an inhibitor of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) is shown to have inhibitory effects on tumor growth. In this manner, the chemotherapy regimen is targeted to a given mutation in a patient's cancer.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
Systems and methods for predicting a livestock marketing method
InactiveUS20090055243A1Improve efficiencyImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementResourcesEmbryoGenotype
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for improving the efficiency of livestock production using genetic information obtained from the animal. The methods of the invention comprise obtaining a genetic sample from an animal or embryo, determining the genotype of the animal or embryo with respect to specific quality traits, grouping animals with like genotypes, and optionally, further sub-grouping animals based on like phenotypes. The invention is further directed to a method of predicting the carcass quality of an animal by correlating the rate of change in carcass traits with the genotype of the animal.
Owner:MERIAL LTD
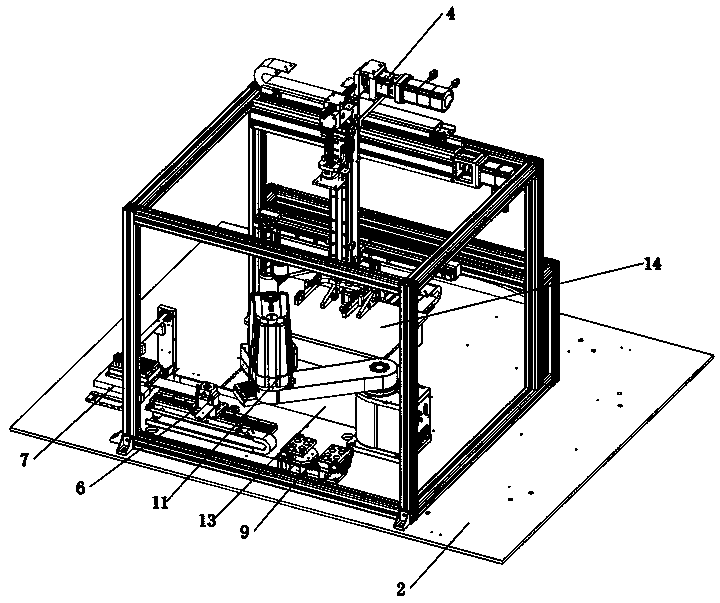
Gene detection equipment
PendingCN114276924AContamination-free transferAvoid cross contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLogistics managementSample purification
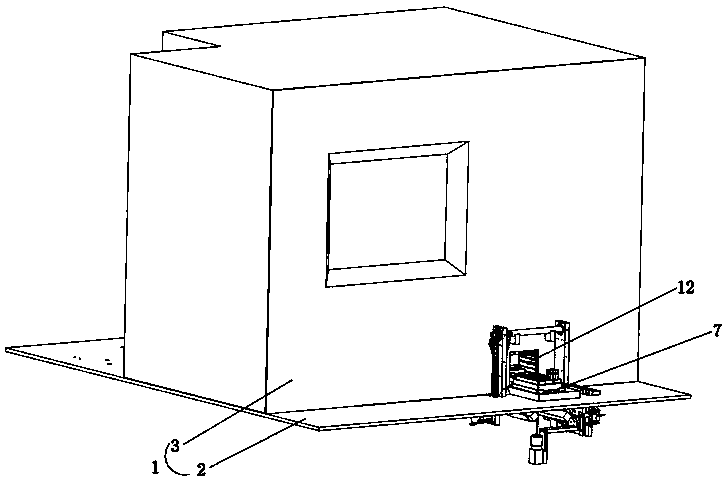
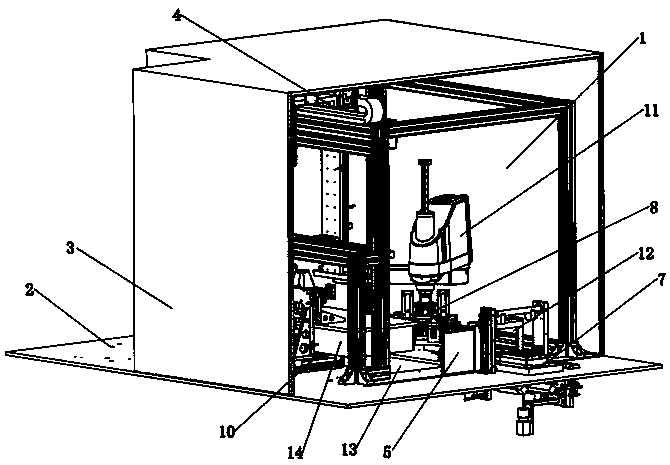
The invention discloses gene detection equipment, and relates to the field of gene detection, the gene detection equipment comprises a safety cabinet, the safety cabinet comprises an upper layer cabinet body and a lower layer cabinet body; three mutually independent mounting chambers are arranged in the upper-layer cabinet body and are respectively used for placing and adding an amplification reagent, placing and purifying a gene sample and amplifying and detecting a gene; three mounting chambers which can be communicated with one another are arranged in the lower-layer cabinet body, and a logistics transportation module is arranged in each mounting chamber and is used for transporting PCR plates; a second processing module is arranged in a mounting chamber for placing and purifying a gene sample and comprises a plurality of sets of placing racks for placing a purification reagent and the gene sample, a fixing device, an air inducing assembly, a vibrating part A, a heating module and a cooling module B, and the placing racks can be placed in the mounting chamber in a drawer manner. According to the present invention, the automatic, pollution-free and high-efficiency gene sample purification treatment process can be achieved, only a small part of the operation involves manual operation during the working process, and the operation intensity is low.
Owner:HC BIOENG (CHENGDU) CO LTD
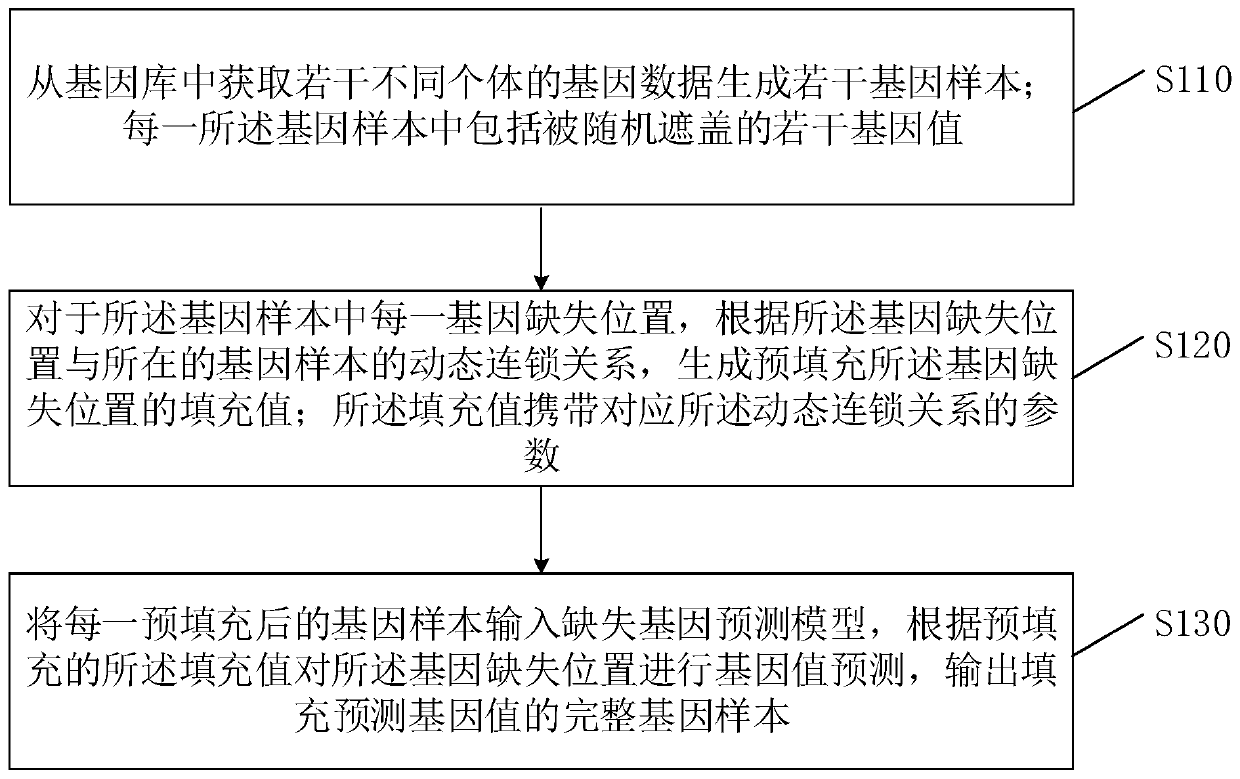
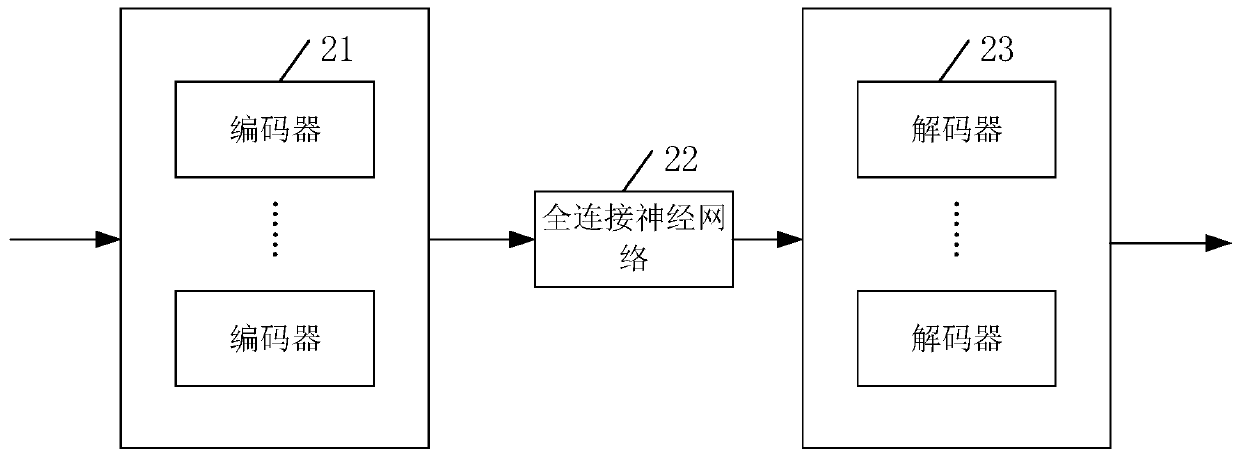
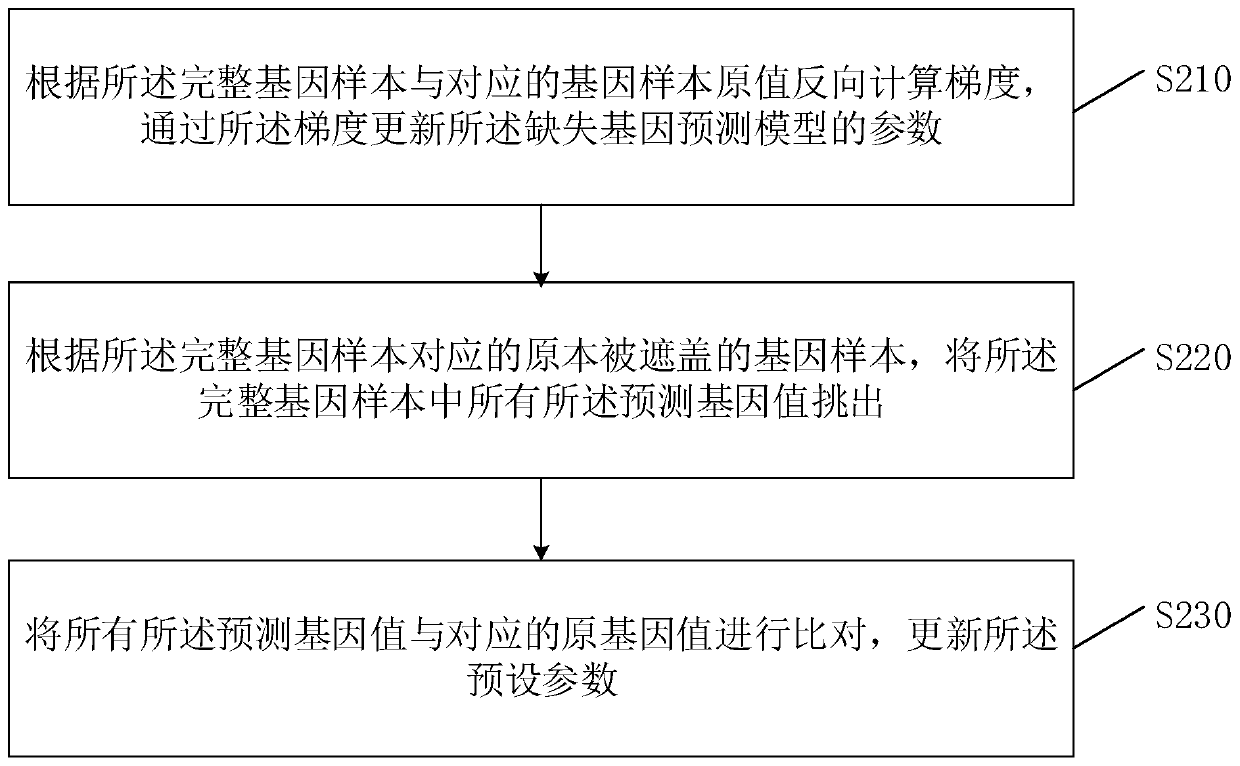
Filling method and device for genotype data missing and server
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene prediction, and provides a filling method and device for genotype data missing and a serve. The method comprises the steps: obtaining gene data ofa plurality of different individuals from a gene pool, and generating a plurality of gene samples; for each gene deletion position in the gene sample, generating a filling value for pre-filling the gene deletion position according to a dynamic linkage relationship between the gene deletion position and the gene sample where the gene deletion position is located;; and inputting each pre-filled genesample into a missing gene prediction model, carrying out gene value prediction on the gene missing position according to the pre-filled filling value, and outputting a complete gene sample filled with the predicted gene value. Each gene sample comprising a plurality of gene values which are randomly covered; and the filling value carries a parameter corresponding to the dynamic linkage relationship. According to the embodiment of the invention, the problems of low filling efficiency and high error rate of the predicted gene filling value are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genetic sample collection systems
InactiveUS20150251176A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCollection systemBiology
Biological sample collection kits are devised with physical features to enable a high performance collection system which delivers preprocessed biological matter via conventional shipping means to a testing laboratories. In particular, untrained and unskilled users deposit biological matter such as saliva or blood into a receiving vessel. By sealing the container, the user causes release of a premixed solution containing preservatives and optionally lysis reagents. In addition, a purification agent is arranged to bind to target molecules and facilitate their removal from solution. These time consuming processes occur while the sample is in transit to the testing facility such that when it arrives, it is in a preconditioned state immediately ready for execution of washing steps. Thus, the high performance containers taught herein are useful for collection biological samples and performing initial process steps on received matter—steps which are largely effected during the shipping stage of the transfer process.
Owner:PATHWAY GENOMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com