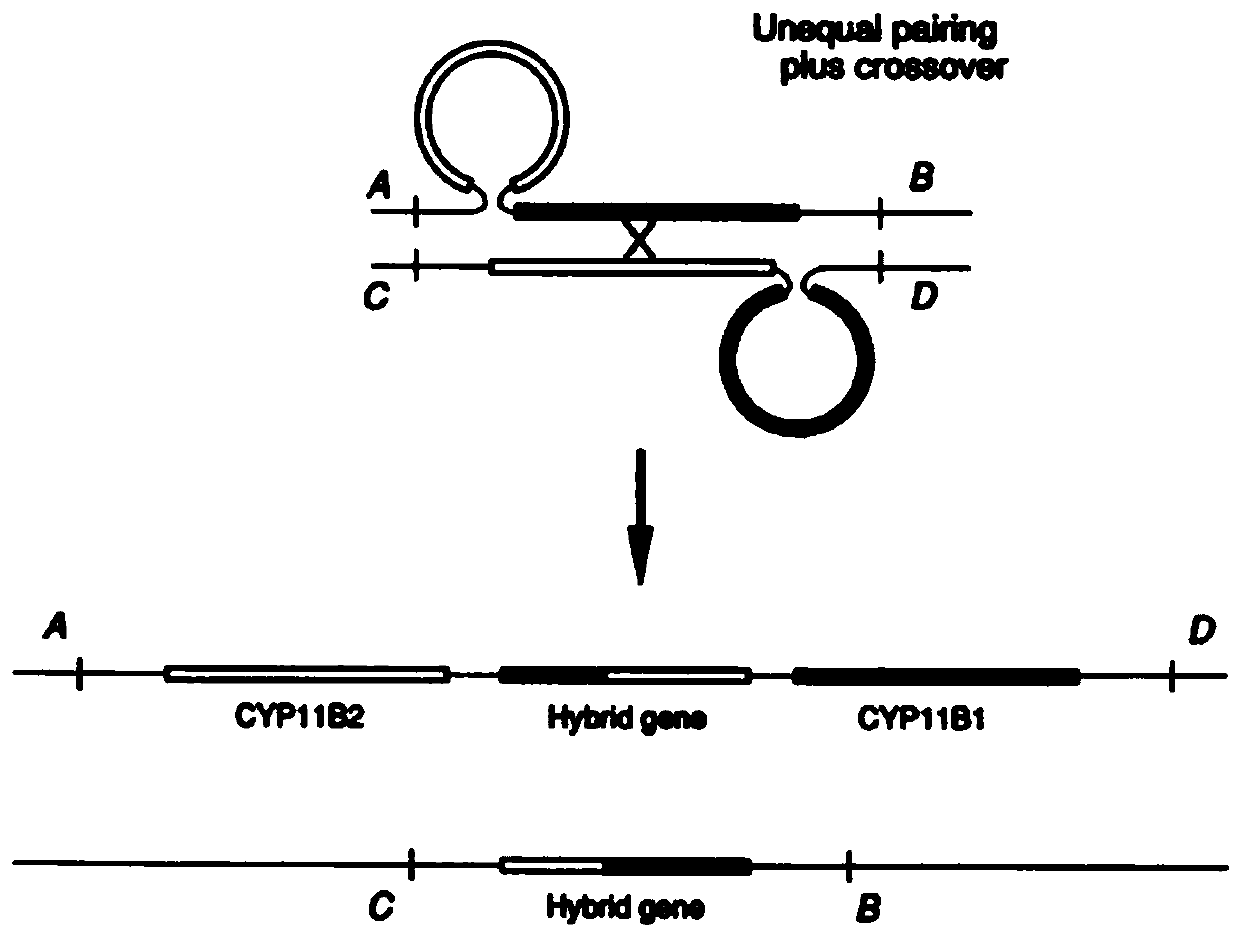
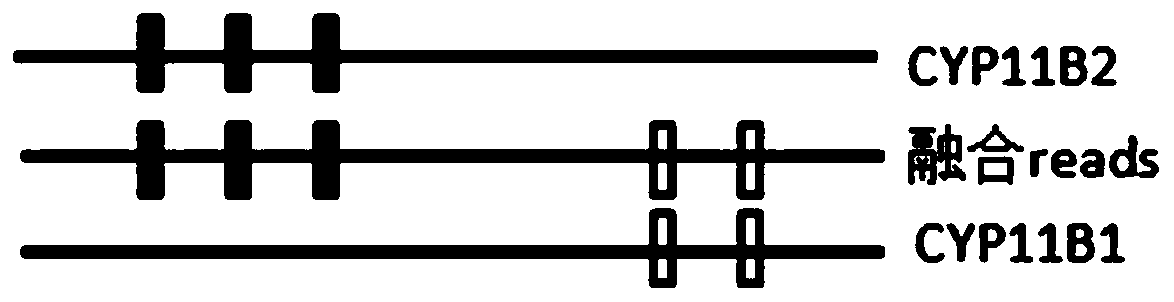
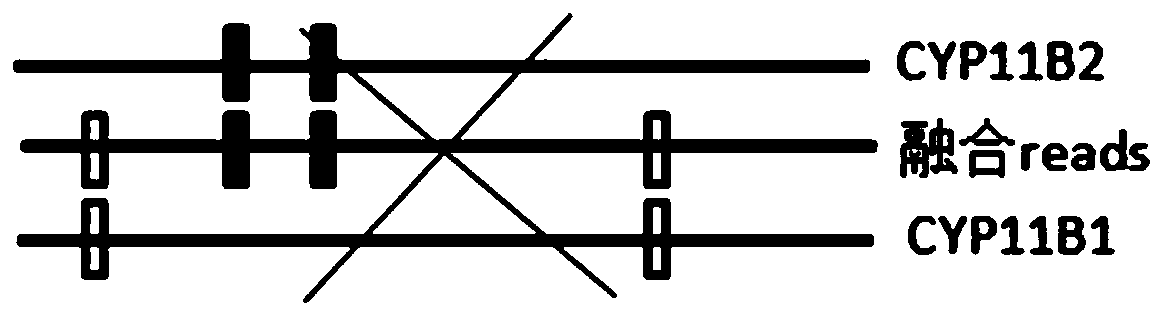
Patents
Literature
147 results about "Structural variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Structural variation (also genomic structural variation) is the variation in structure of an organism's chromosome. It consists of many kinds of variation in the genome of one species, and usually includes microscopic and submicroscopic types, such as deletions, duplications, copy-number variants, insertions, inversions and translocations. Originally, a structure variation affects a sequence length about 1Kb to 3Mb, which is larger than SNPs and smaller than chromosome abnormality (though the definitions have some overlap). However, the operational range of structural variants has widened to include events >50bp. The definition of structural variation does not imply anything about frequency or phenotypical effects. Many structural variants are associated with genetic diseases, however many are not. Recent research about SVs indicates that SVs are more difficult to detect than SNPs. Approximately 13% of the human genome is defined as structurally variant in the normal population, and there are at least 240 genes that exist as homozygous deletion polymorphisms in human populations, suggesting these genes are dispensable in humans. Rapidly accumulating evidence indicates that structural variations can comprise millions of nucleotides of heterogeneity within every genome, and are likely to make an important contribution to human diversity and disease susceptibility.
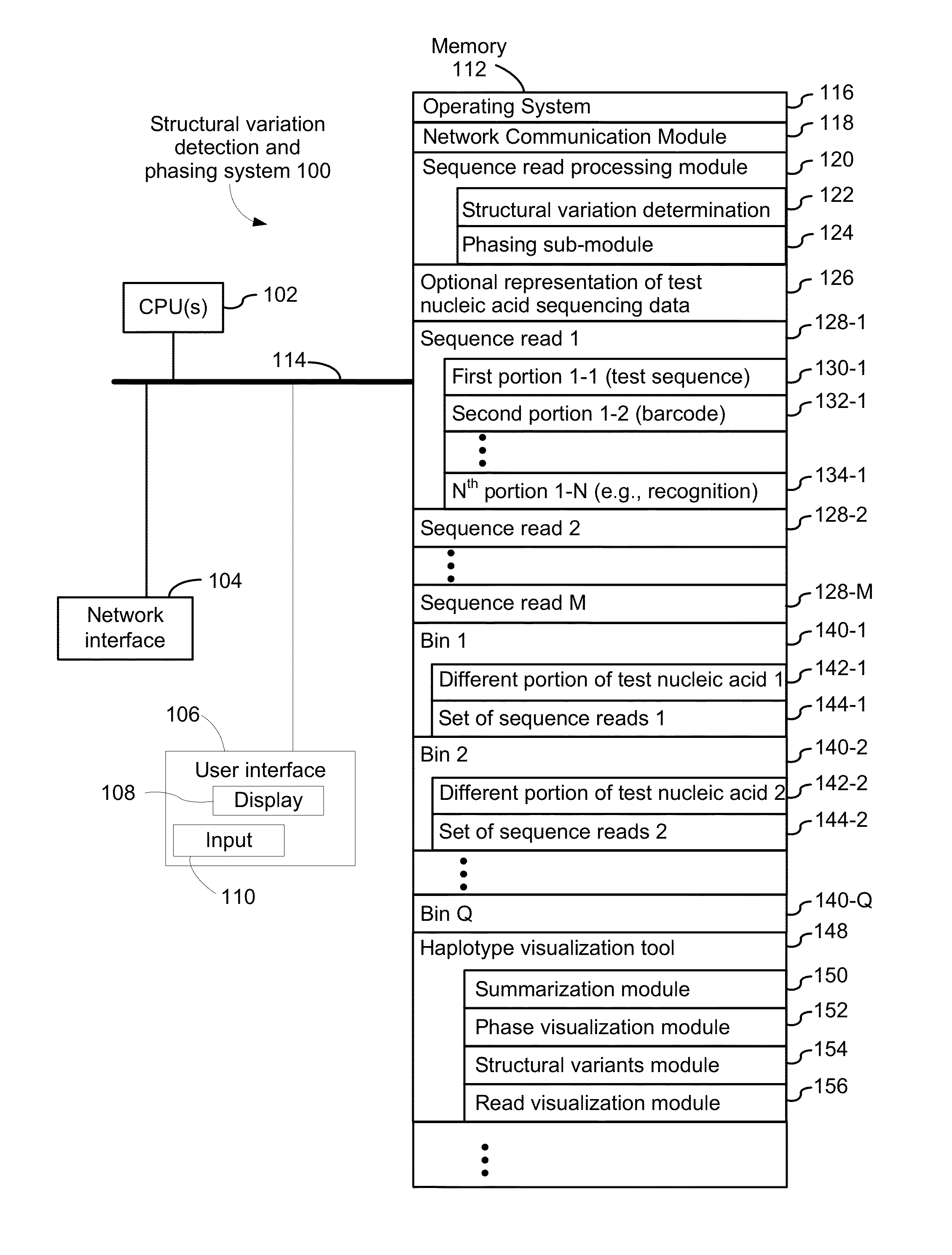
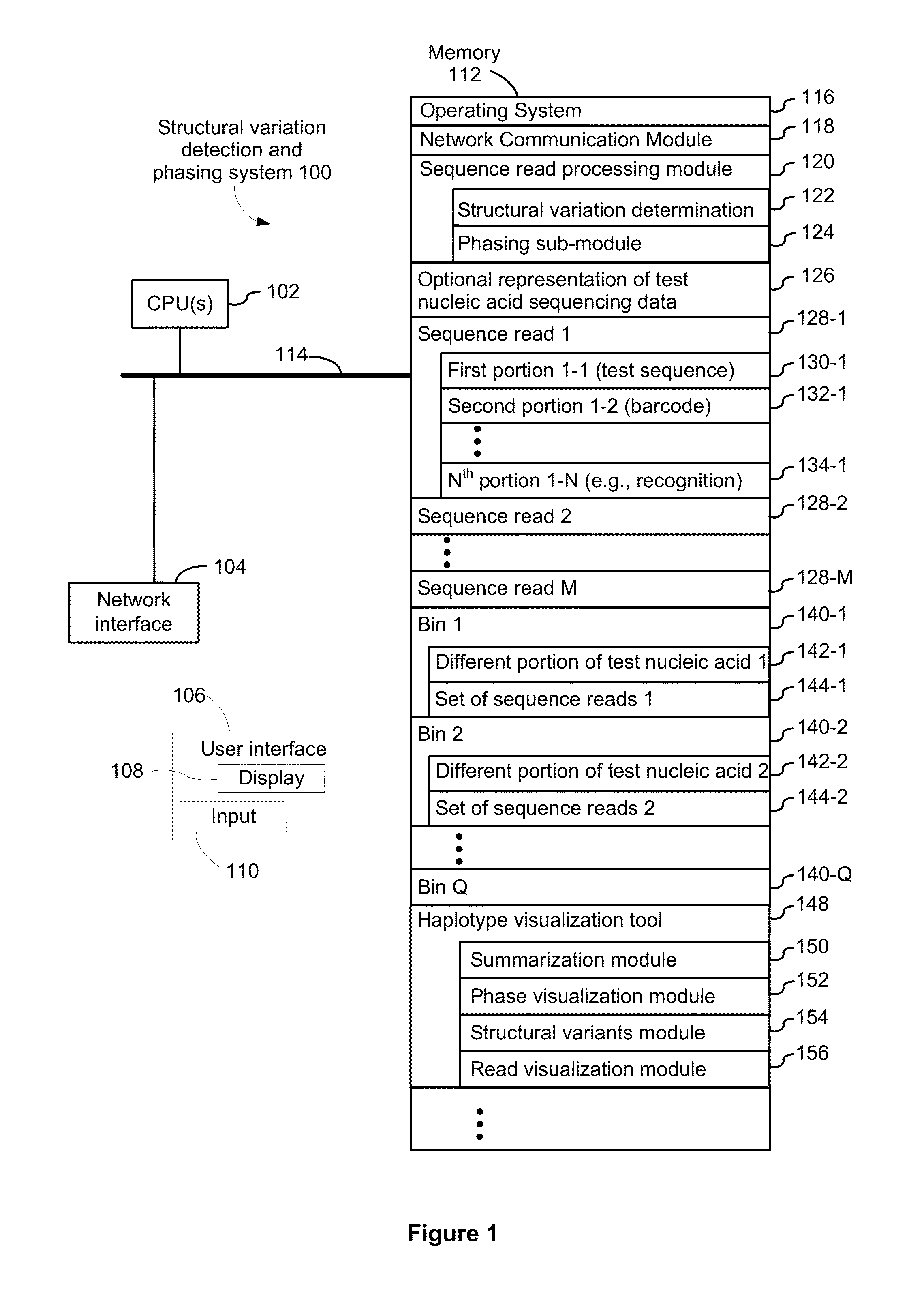
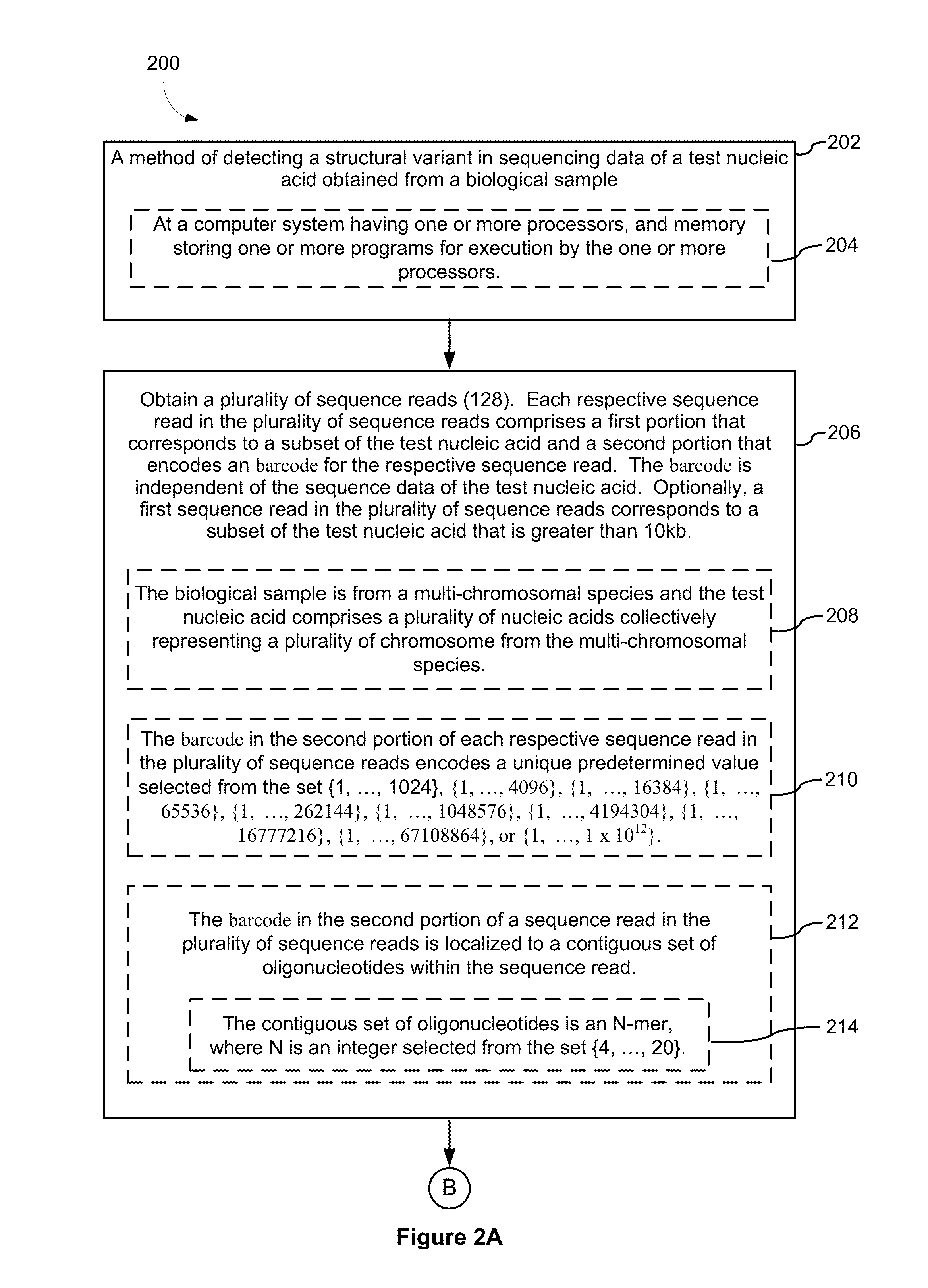
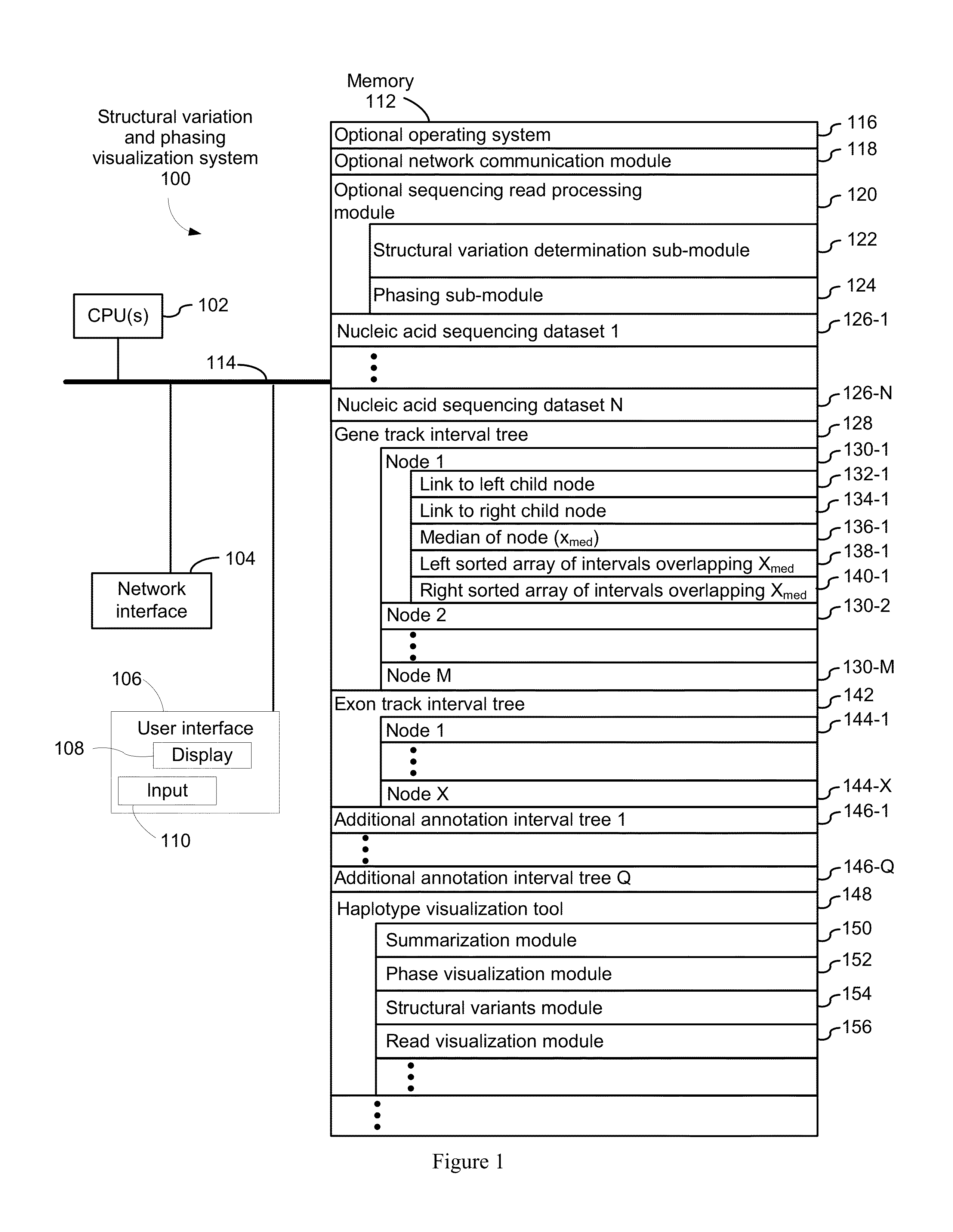
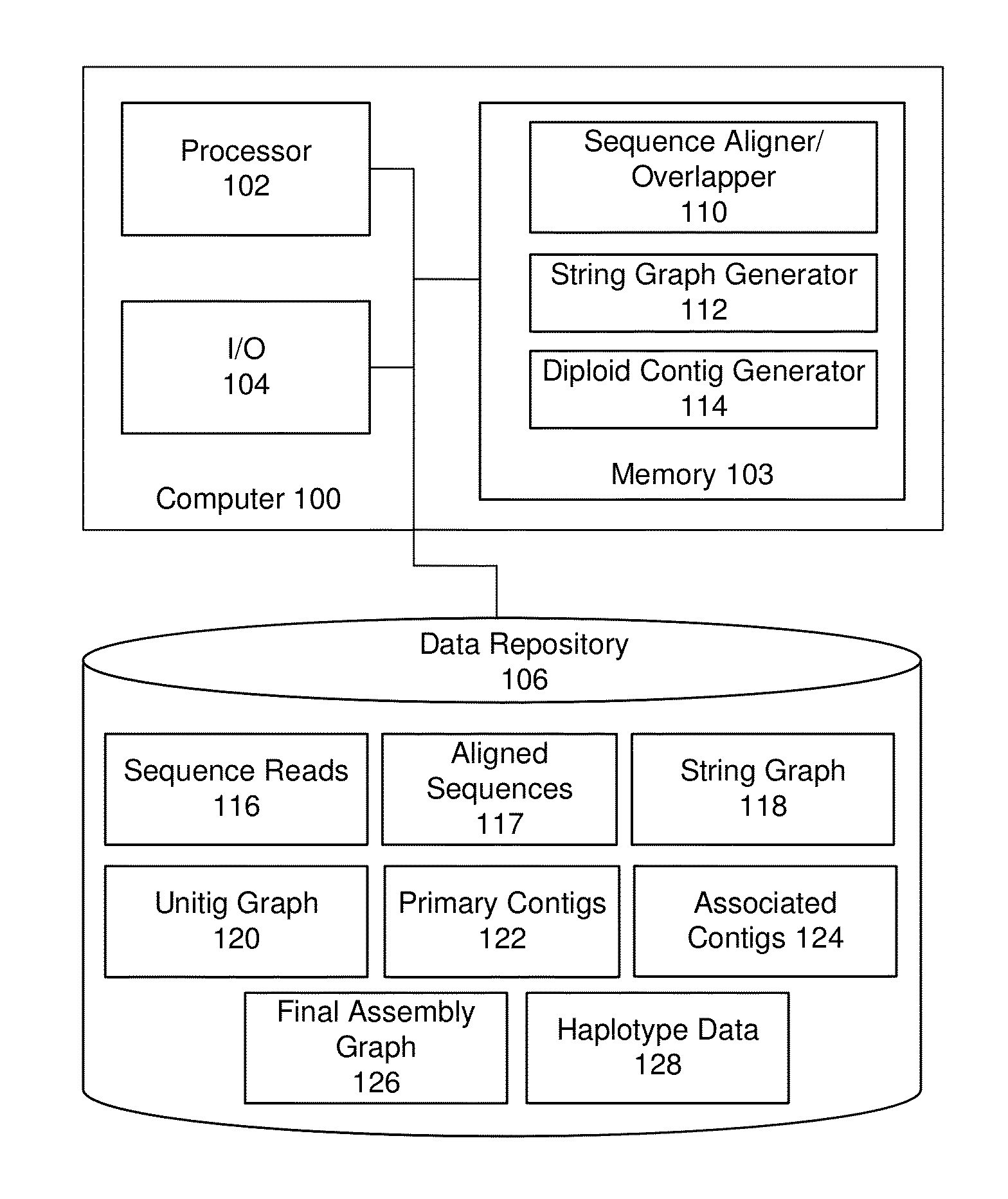
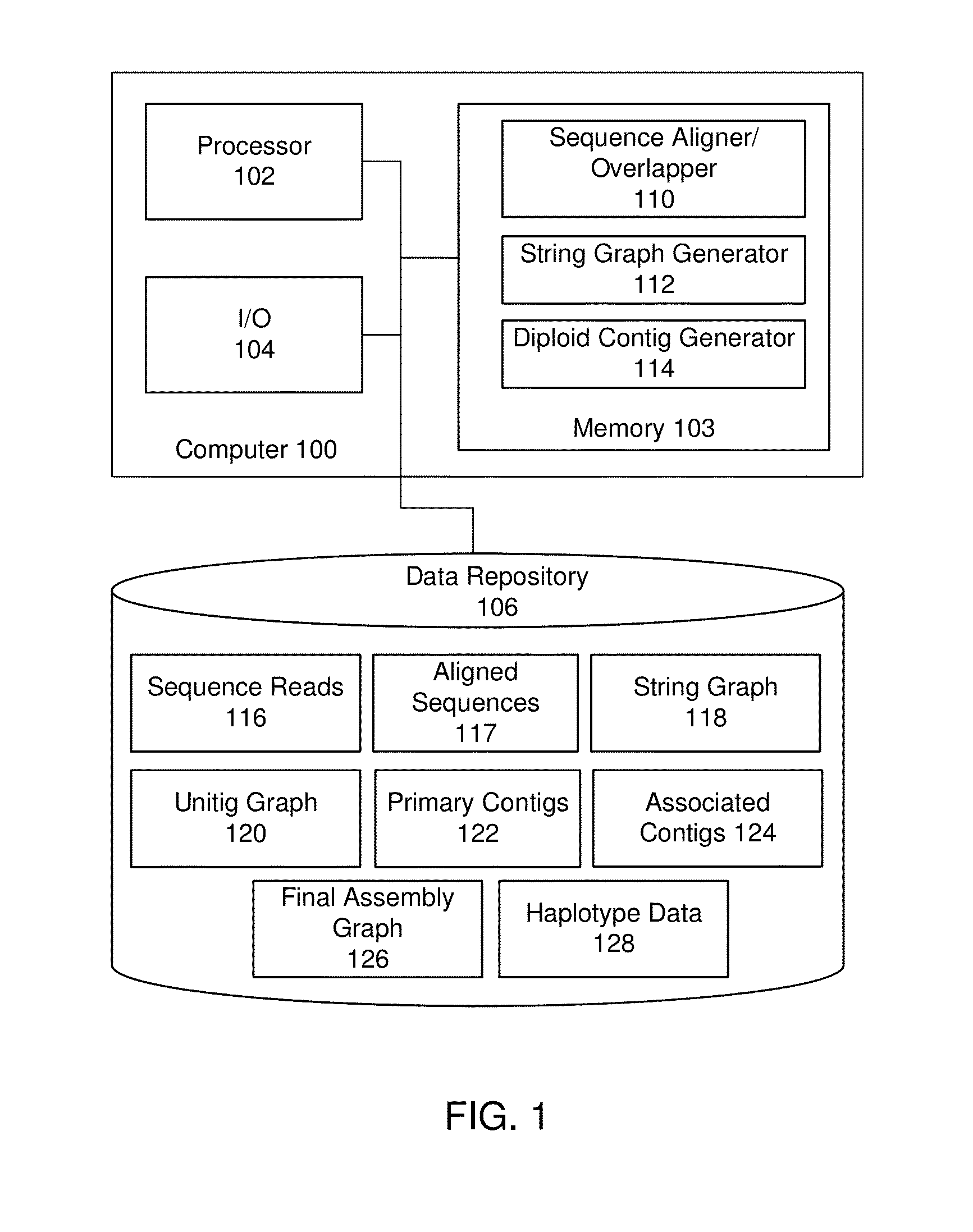
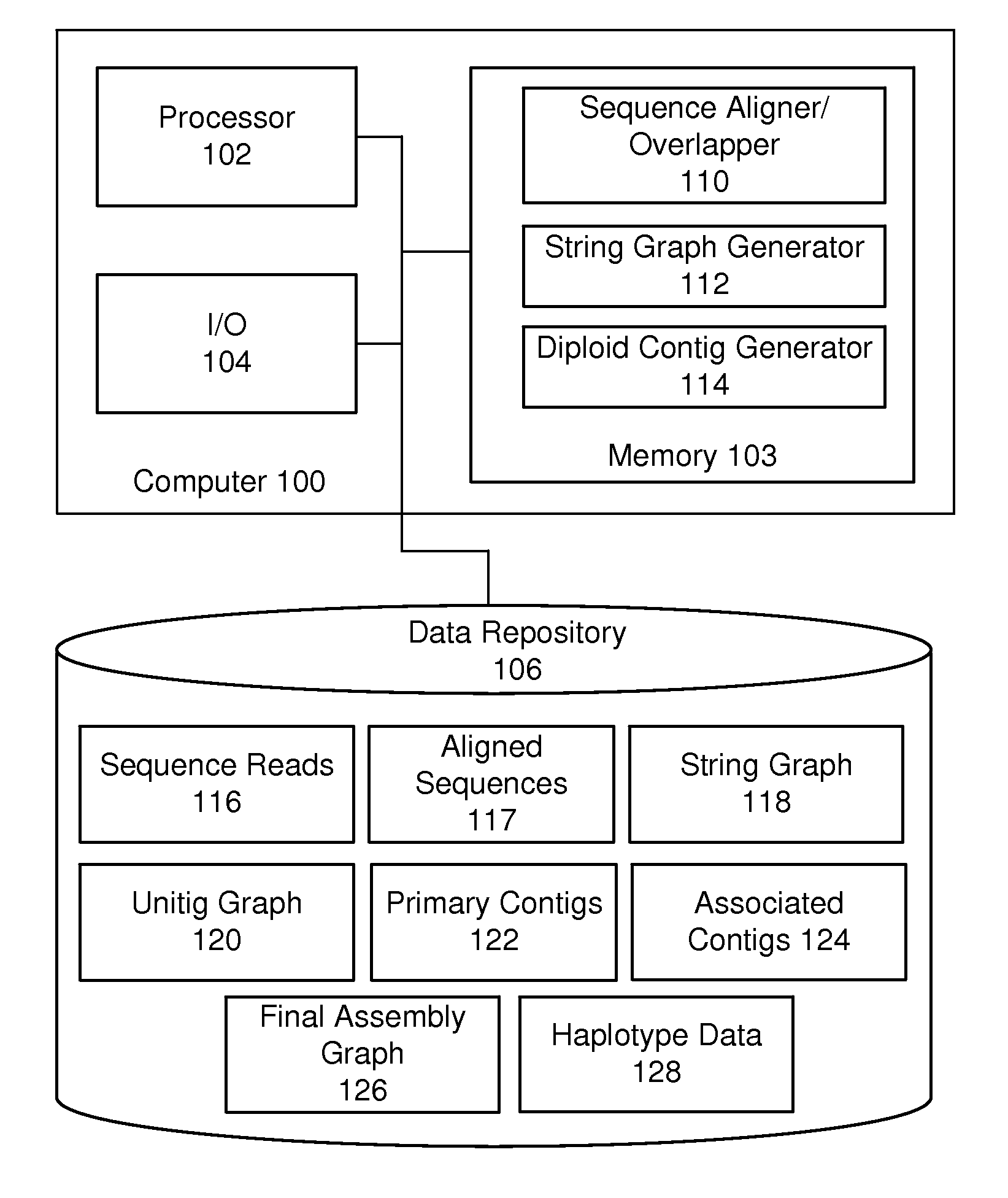
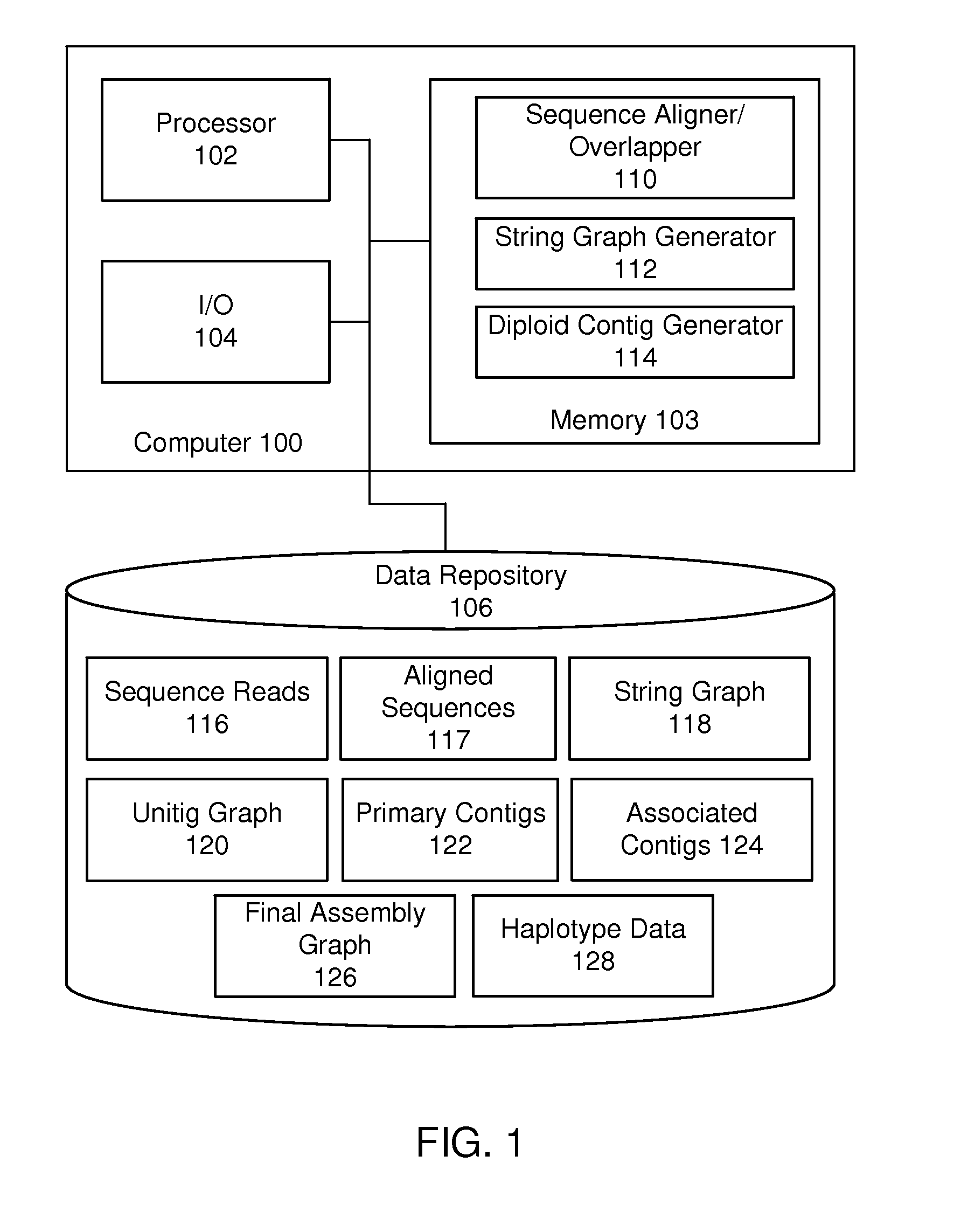
Systems and methods for determining structural variation and phasing using variant call data
ActiveUS20160232291A1Better phasingSimple methodMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementBarcodeData system
Systems and methods for determining structural variation and phasing using variant call data obtained from nucleic acid of a biological sample are provided. Sequence reads are obtained, each comprising a portion corresponding to a subset of the test nucleic acid and a portion encoding a barcode independent of the sequencing data. Bin information is obtained. Each bin represents a different portion of the sample nucleic acid. Each bin corresponds to a set of sequence reads in a plurality of sets of sequence reads formed from the sequence reads such that each sequence read in a respective set of sequence reads corresponds to a subset of the nucleic acid represented by the bin corresponding to the respective set. Binomial tests identify bin pairs having more sequence reads with the same barcode in common than expected by chance. Probabilistic models determine structural variation likelihood from the sequence reads of these bin pairs.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
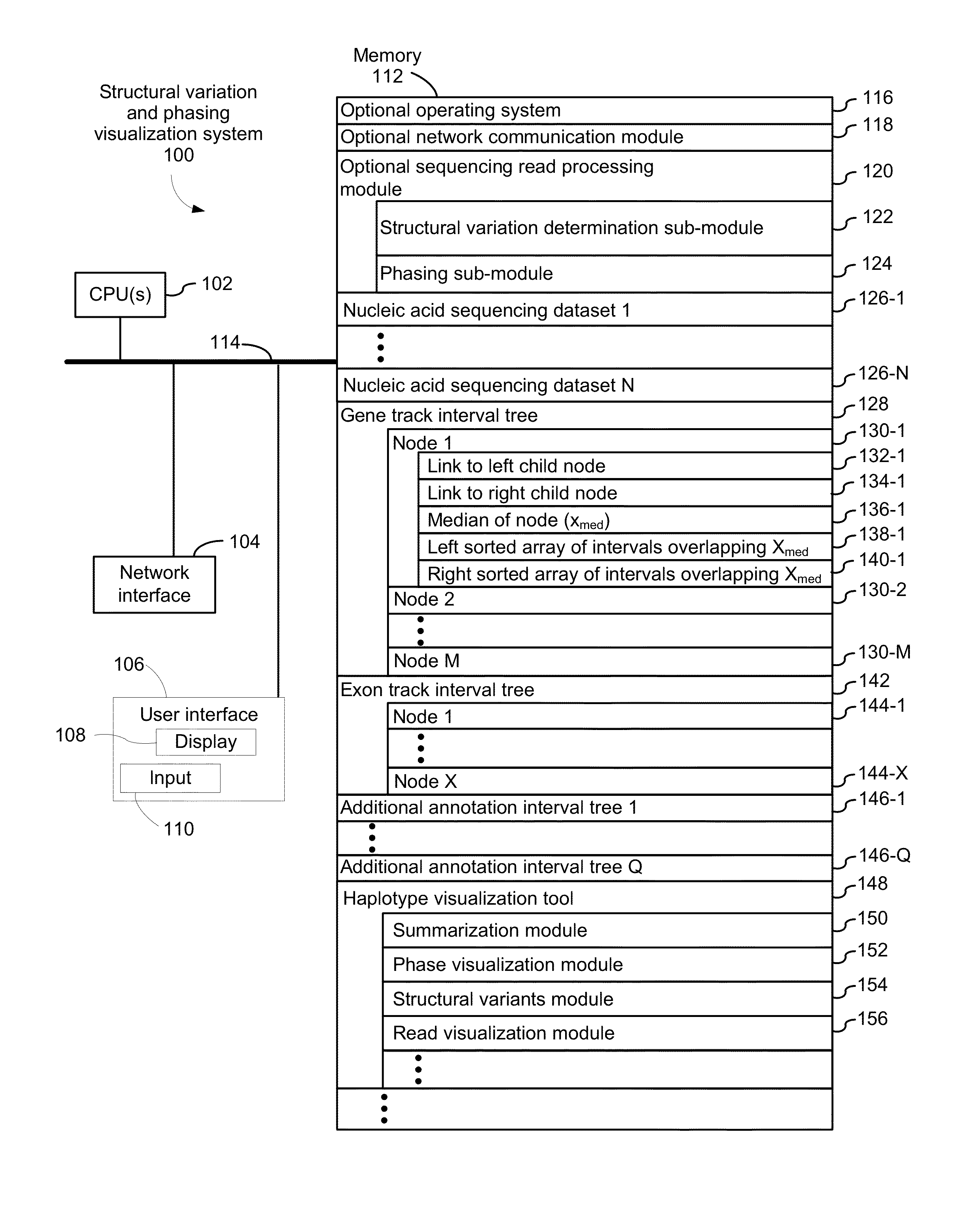
Systems and methods for visualizing structural variation and phasing information
ActiveUS20160203196A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData setNucleic acid sequencing
A system for providing structural variation or phasing information is provided. The system accesses a nucleic acid sequence dataset corresponding to a target nucleic acid in a sample. The dataset comprises a header, synopsis, and data section. The data section comprises a plurality of sequencing reads. Each sequencing read comprises a first portion corresponding to a subset of the target nucleic acid and a second portion that encodes an identifier for the sequencing read from a plurality of identifiers. One or more programs in the memory of the system use a microprocessor of the system to provide a haplotype visualization tool that receives a request for structural variation or phasing information from the dataset. The request is evaluated against the synopsis thereby identifying portions of the data section. Structural variation or phasing information is formatted for display in the haplotype visualization tool using the identified portions of the data section.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
LED optical system with multiple levels of secondary optics
ActiveUS8662704B2Eliminate all waste lightEffective distributionPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusTarget surfaceEffect light
An optical system for lighting fixtures uses light emitting diodes arranged in a 2-D array. In one embodiment, a lighting system comprises a framework carrying a plurality of diodes, where each diode has an associated optic that projects the light with a “high,”“medium” or “low” vertical throw, as provided by prismatic “teeth” that refract and reflect light rays in a predetermined manner so that the combined illumination patterns of each diode can blend to generally uniformly illuminate a target surface without dark spots or regions. Each optic has a common primary portion and a selected secondary portion whose tooth / teeth have a “swept” geometry for better angular (vertical and / or horizontal) control of light rays. Structural variations between different secondary portions reside in various factors, including plurality of teeth, length of the tooth along the longitudinal axis A, curvature(s) in the vertical and / or horizontal directions, and angularity or tightness of curvature of the swept geometry.
Owner:U S POLE
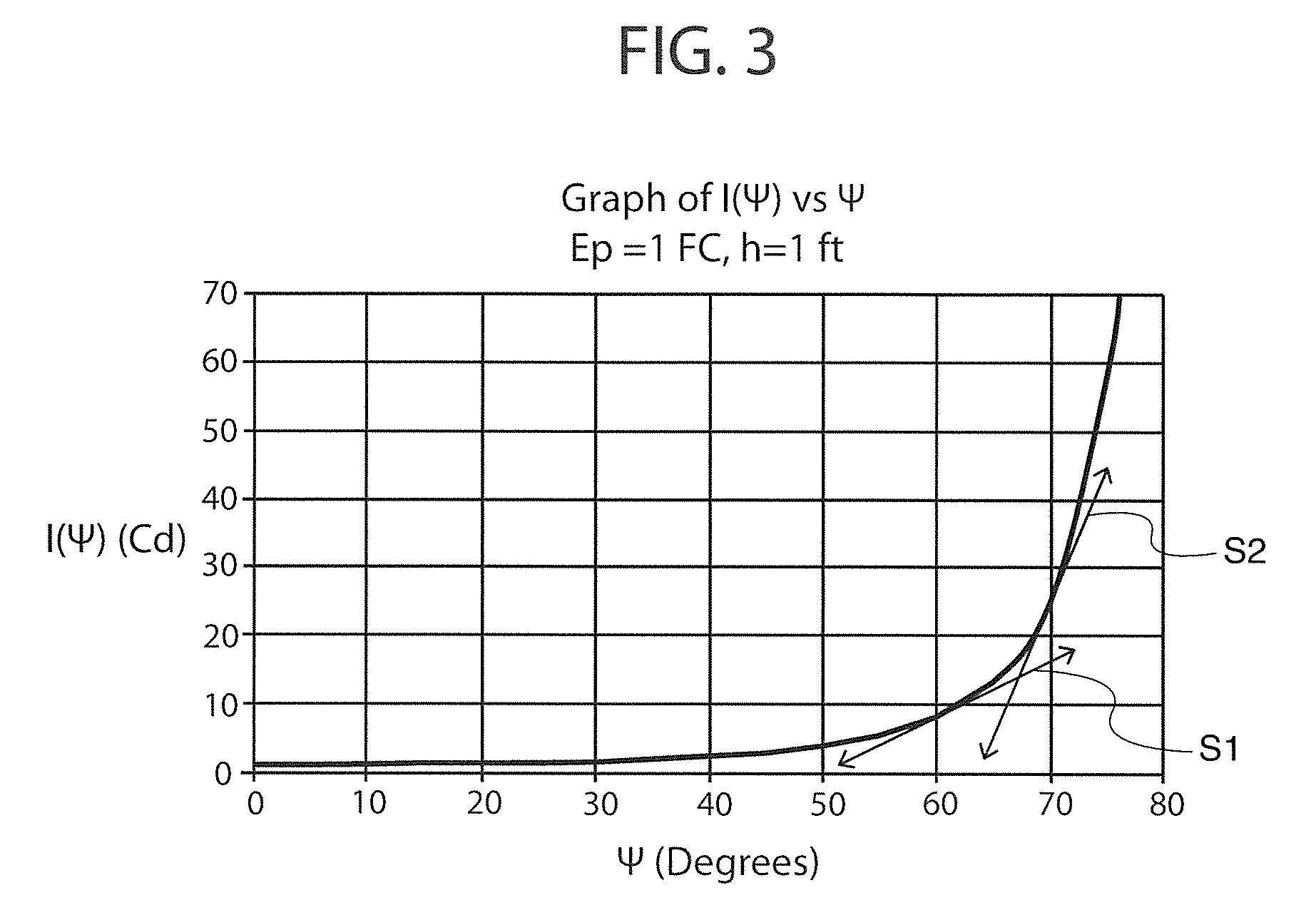
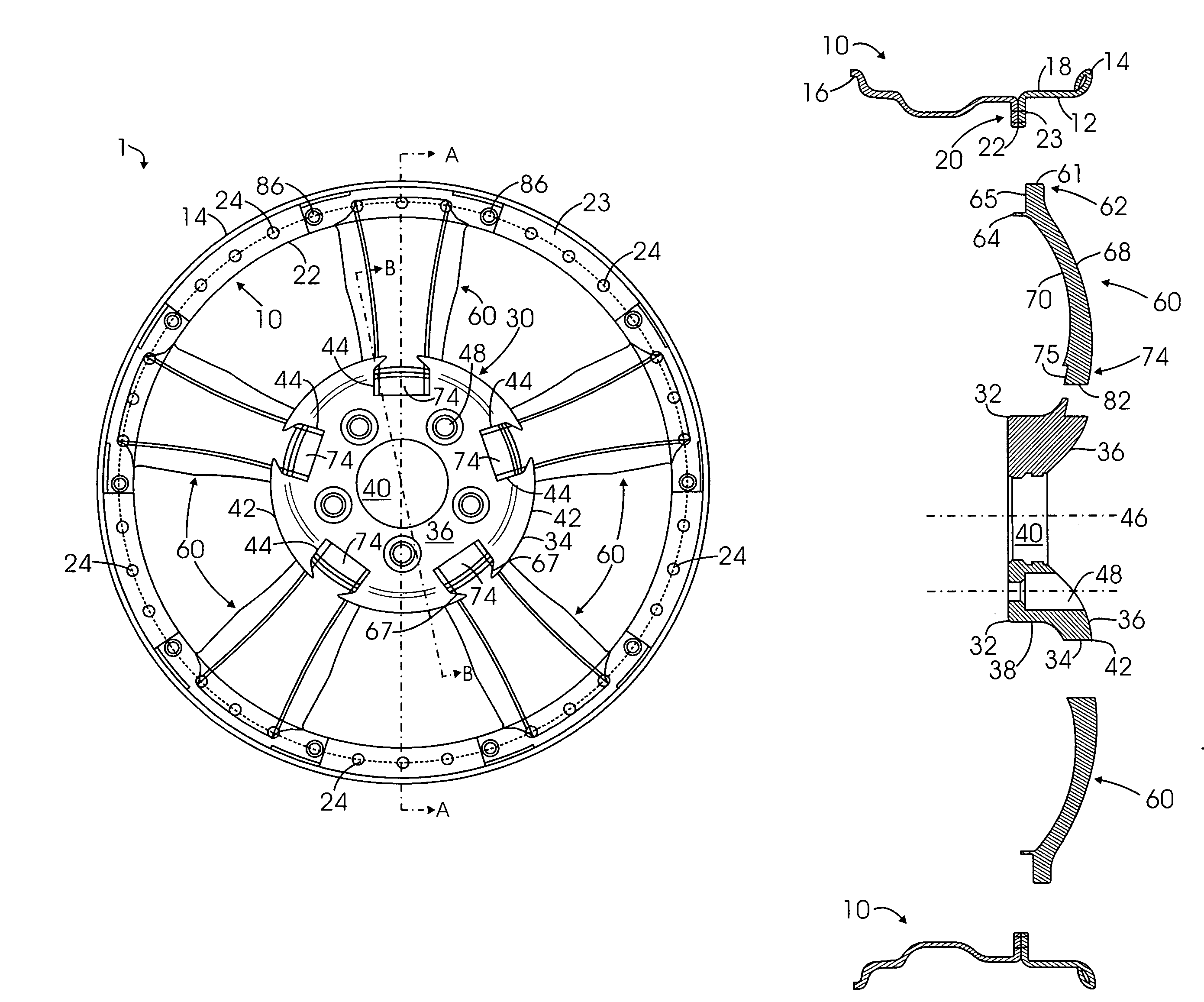
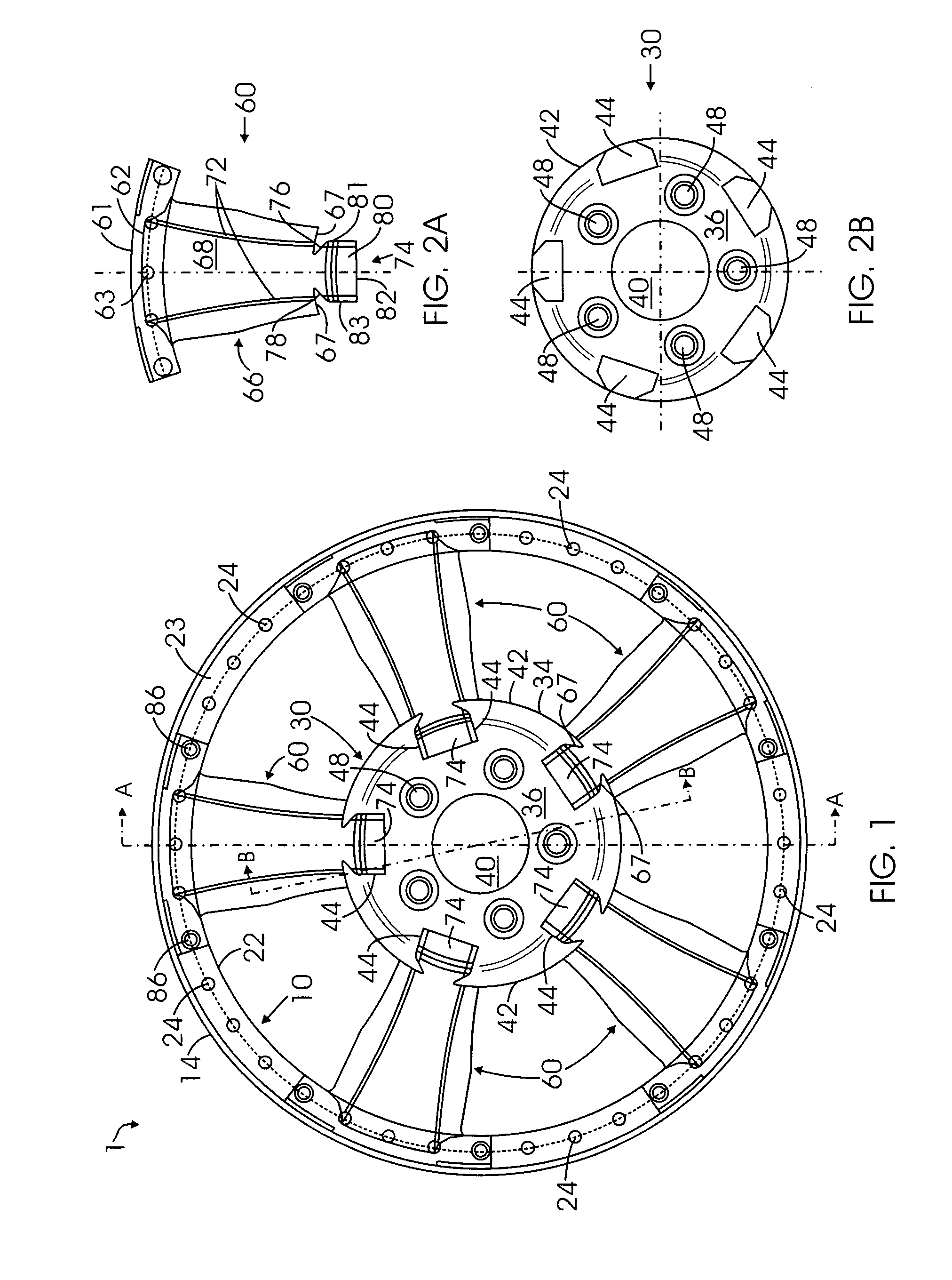
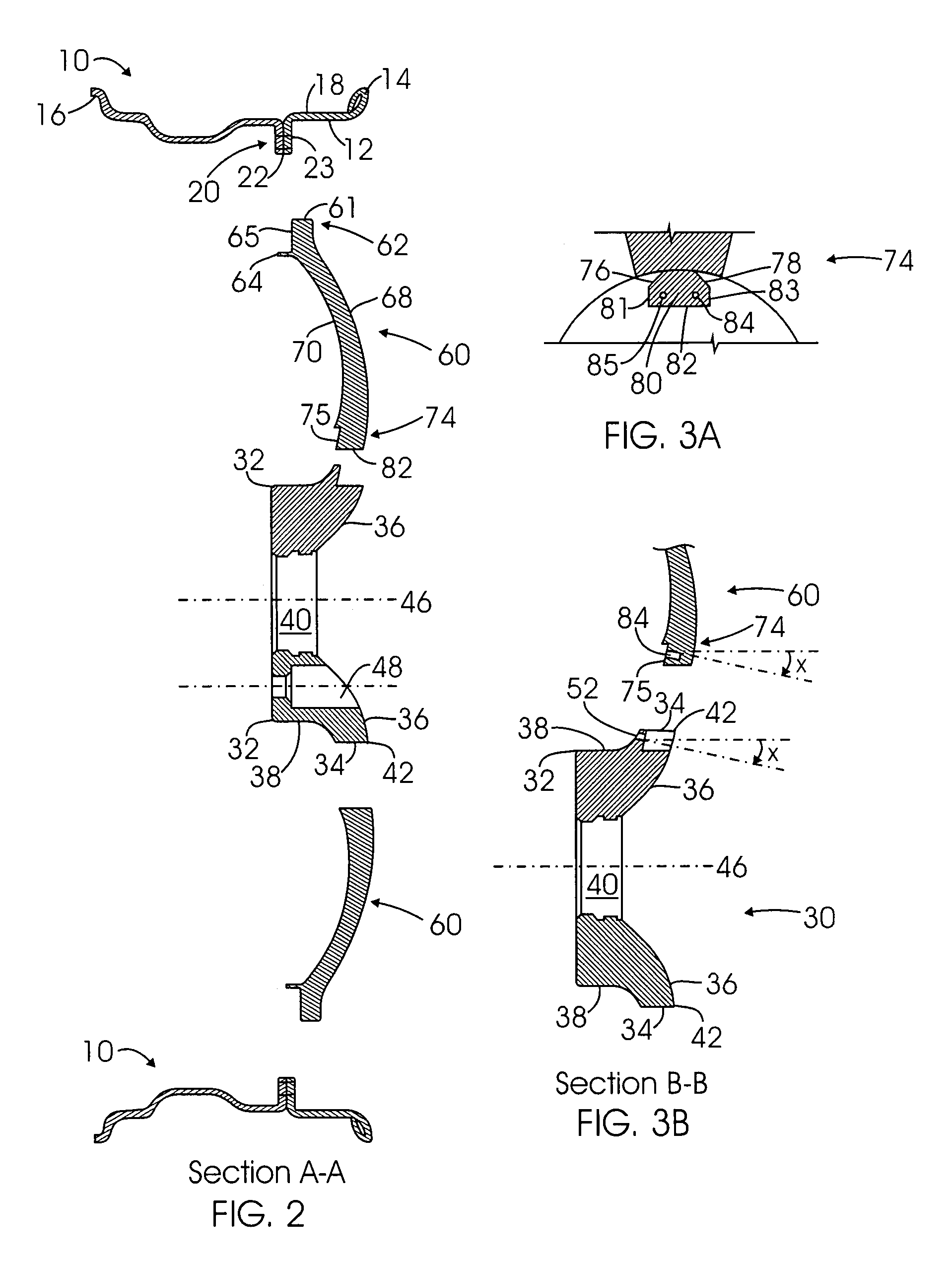
Multi-piece wheel
InactiveUS7681958B1Easy to changeReduce manufacturing costRimsMechanical vibrations separationEngineeringMechanical engineering
A multi-piece wheel, which is assembled with multiple pieces of pre-made structural members, including an outer wheel ring, a central hub and multiple spokes. The outer wheel ring is comprised of a circular wall for affixing a tire on its inner surface and connecting spokes on its outer surface. The spokes are the wheel intermediate members which at their respective first and second end are connected to the respective outer wheel ring and the central hub. The central hub is a circular structure including a central bore and front circular arcuate surface, wherein multiple pockets are placed on the front surface for connecting the spoke second ends to the central hub. Various structural variations of the central hub and spokes regarding their connection are also disclosed, which results in various embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:BAGDASARIAN KEN L
Identification of DNA fragments and structural variations
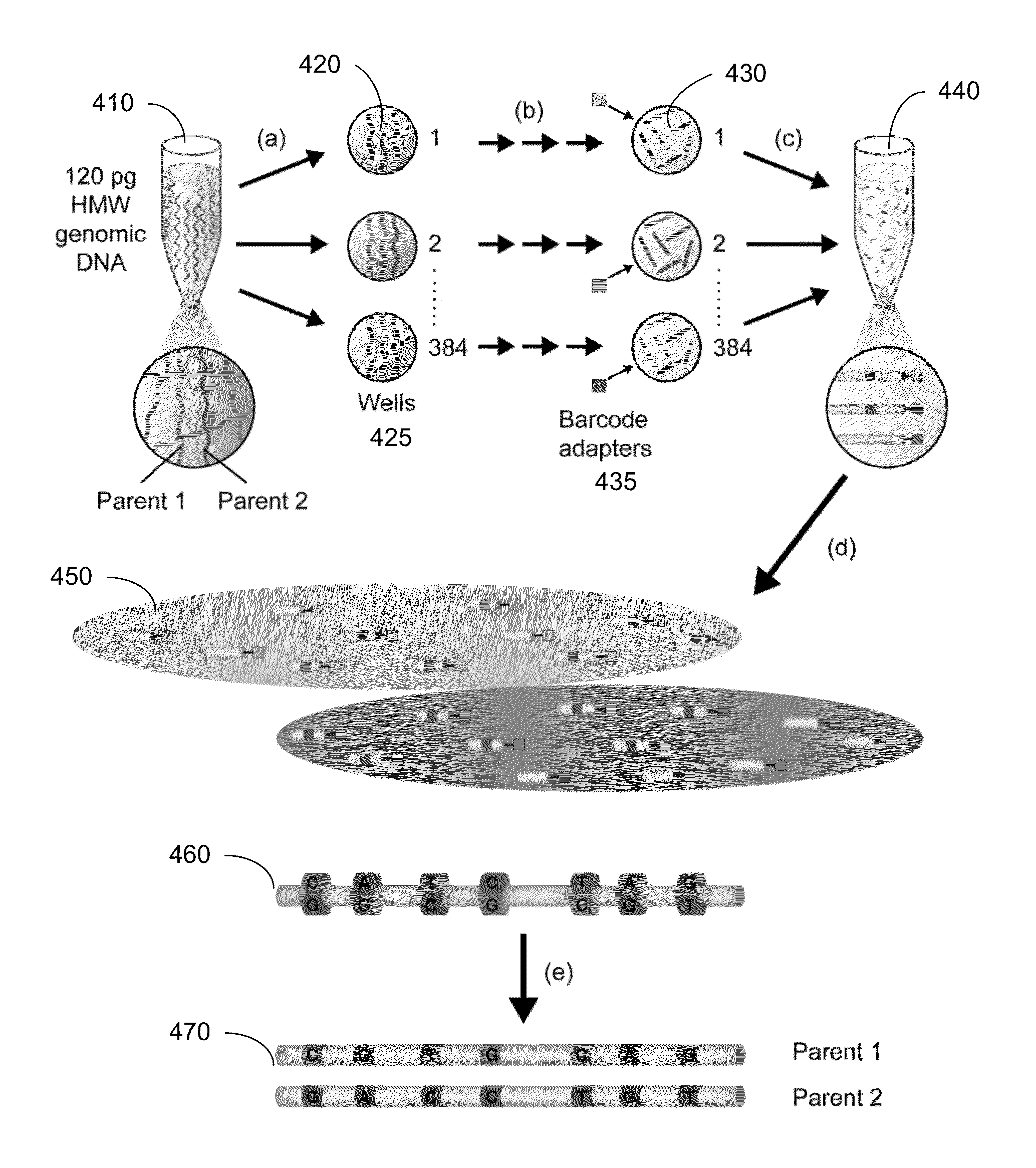
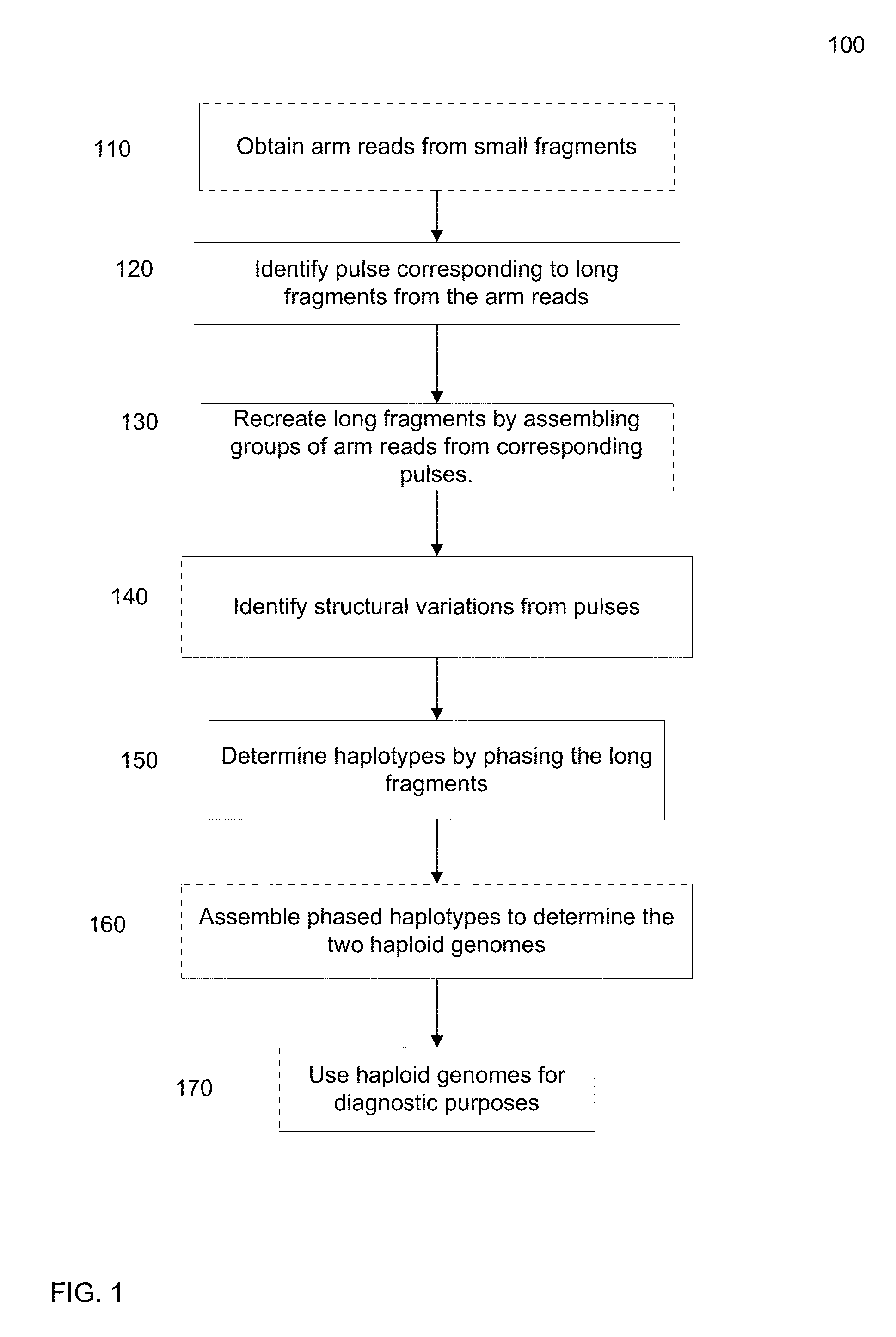
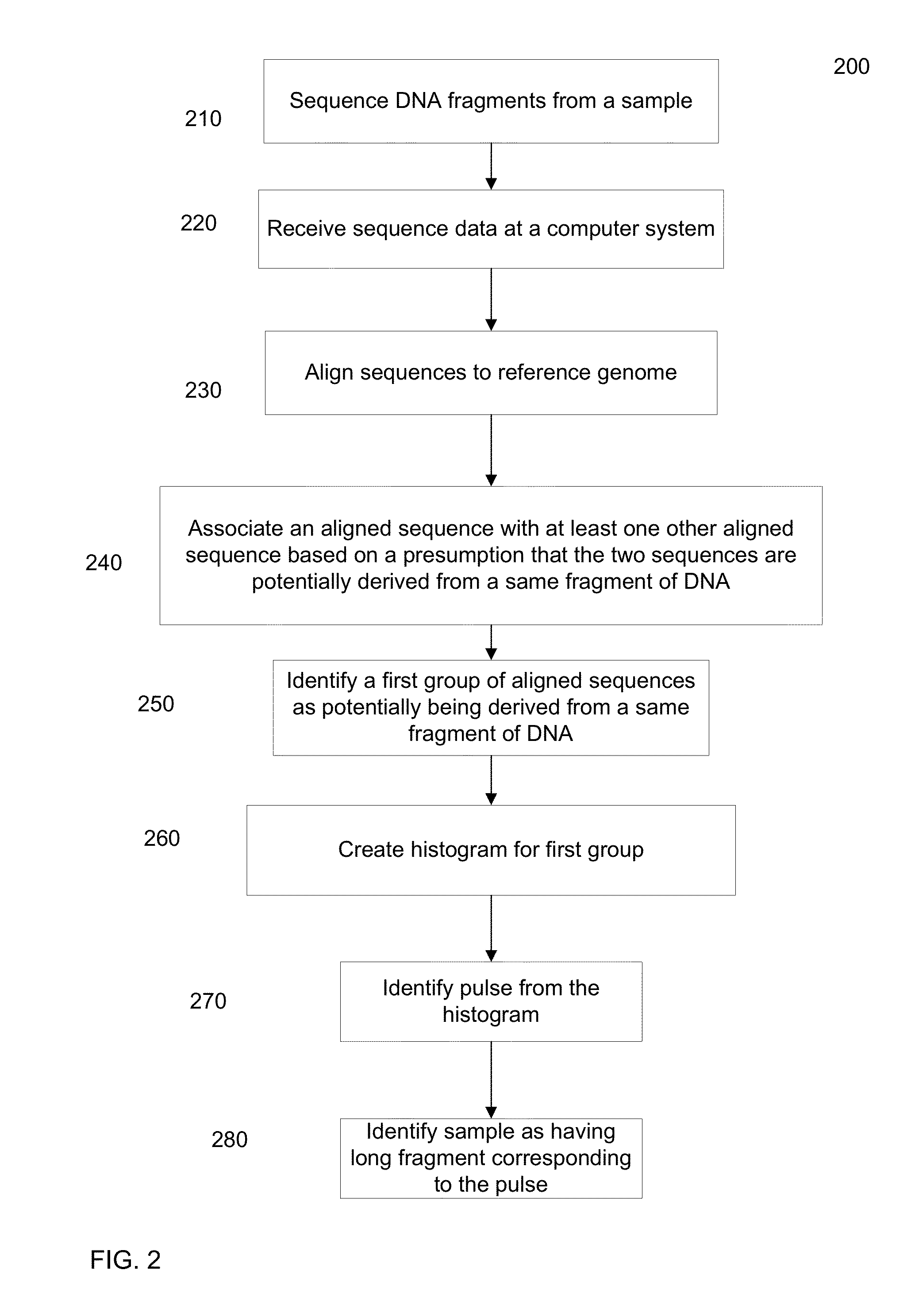
Various short reads can be grouped and identified as coming from a same long DNA fragment (e.g., by using wells with a relatively low-concentration of DNA). A histogram of the genomic coverage of a group of short reads can provide the edges of the corresponding long fragment (pulse). The knowledge of these pulses can provide an ability to determine the haploid genome and to identify structural variations.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS20090325239A1Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid mappingA-DNA
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Building method of library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and kit
PendingCN106497920AImprove recycling efficiencyImprove utilization efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGene targetingGene mutation
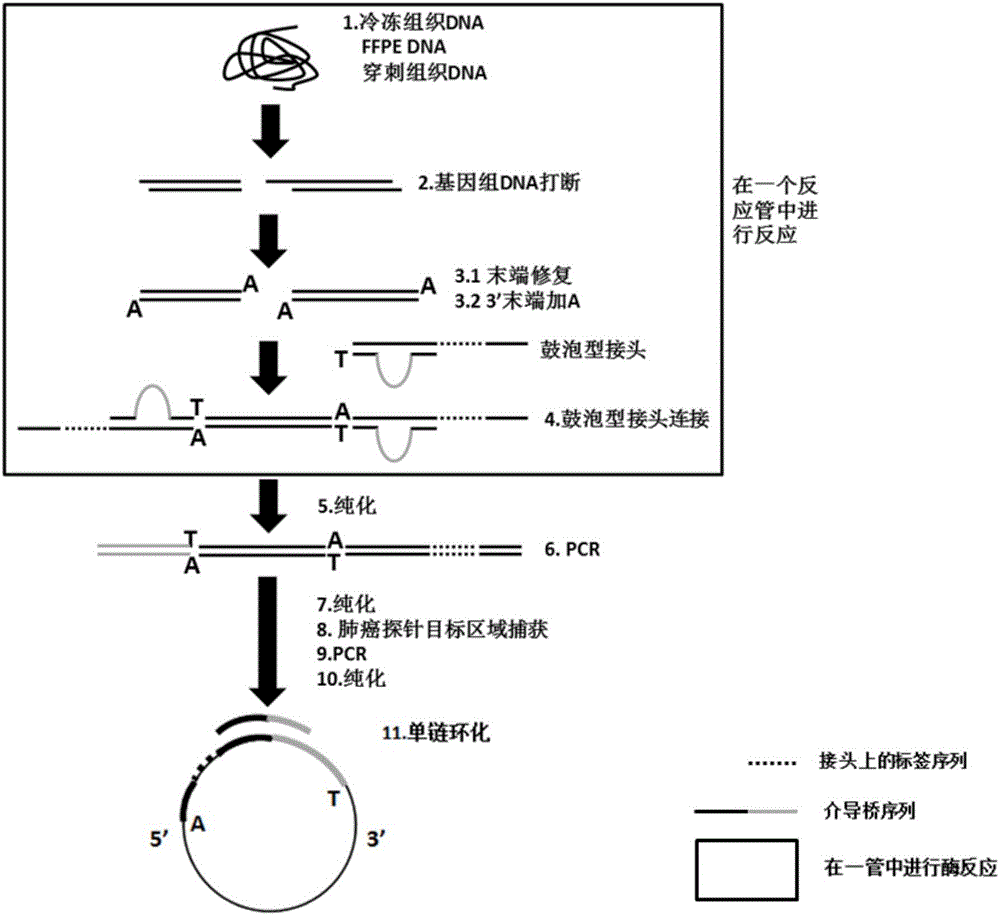
The invention discloses a building method of a library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and a kit. The method includes: using tubular reaction to complete genome DNA breaking and connector connection, performing hybrid capture on connection products after amplification and non-small cell lung cancer related gene target area probes, and performing BGISEQ-500 / 1000 platform sequencing and data analysis to obtain mutation conditions. The method has the advantages that the experiment flow is optimized greatly by the tubular reaction, operation complexity and time are reduced, and the requirements on clinical sample initial amount are lowered; multiple genes and multiple sites can be detected in one step, point mutation, insertion and deletion, structural variation and copy number variation are covered, the detecting result is accurate and overcomes the defect that a PCR capture method cannot detect the structural variation in one step, and the effectiveness of the high-throughput sequencing applied to the detection of the non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation; the method is wide in coverage, high in cost performance, capable of providing a reference basis for the diagnosing, treatment and drug use performed by doctors, and the method is suitable for being popularized and used in a large-scale manner.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
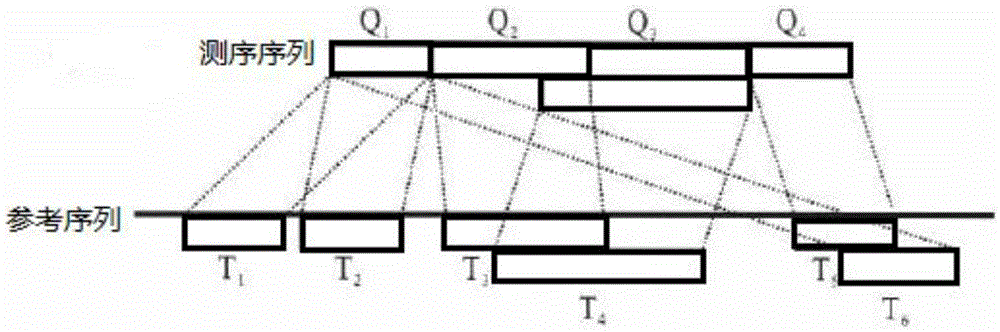
Complex structure variation detecting method based on hybrid strategy
ActiveCN110010193AReduce interference with assembly performanceImprove accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsReference genomeBioinformatics
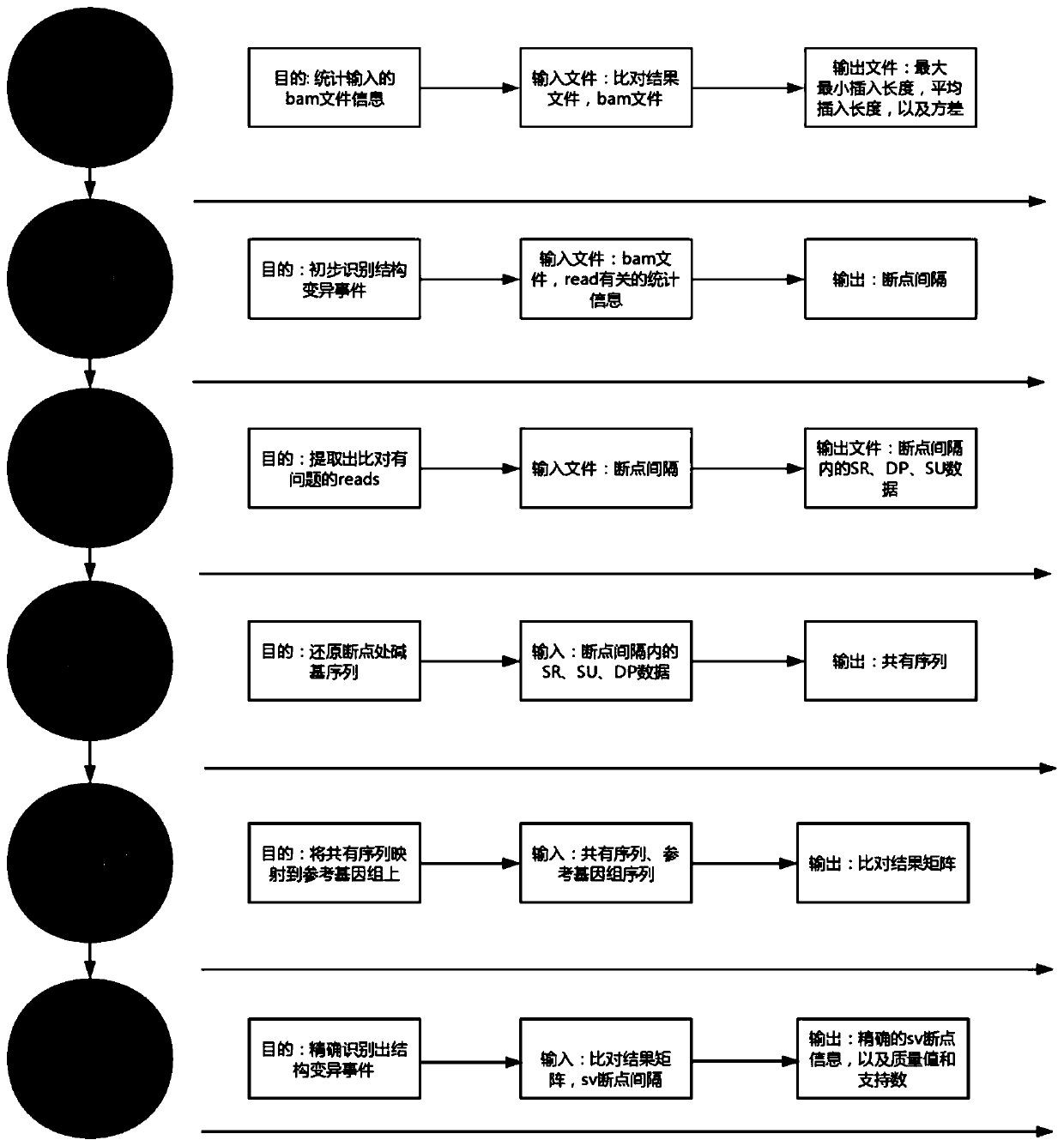
The invention discloses a complex structure variation detecting method based on a hybrid strategy. The method comprises the steps of collecting and performing statistics on inserting fragment length distribution and chain direction information of a read pair in double-end sequencing, determining a read pair contrasting chain direction, an inserting fragment length and the read pair with an abnormal chromosome through two-end read segment contrasting; identifying breakpoints by means of a hybrid strategy of a double-end mapping method, a local assembling method and a split read segment method;wherein the breakpoints are coordinates on a pair of reference genome and are adjacent in a sample and are separated in the reference genome; updating breakpoint position information according to a contrasting result, and changing the breakpoint interval which records the structure variation breakpoint information to an accurate position; wherein the structure variation breakpoint information comprises a structure variation type, a breakpoint starting position and a support read segment number; and recording the contrast quality of the read pair and the read pair number of the support breakpoints, thereby finishing accurate structure variation identification. The complex structure variation detecting method improves variation detecting precision and supplies a checkout method for complex structure variations.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for fabricating openings in a semiconductor topography
InactiveUS6893974B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce variationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTopography
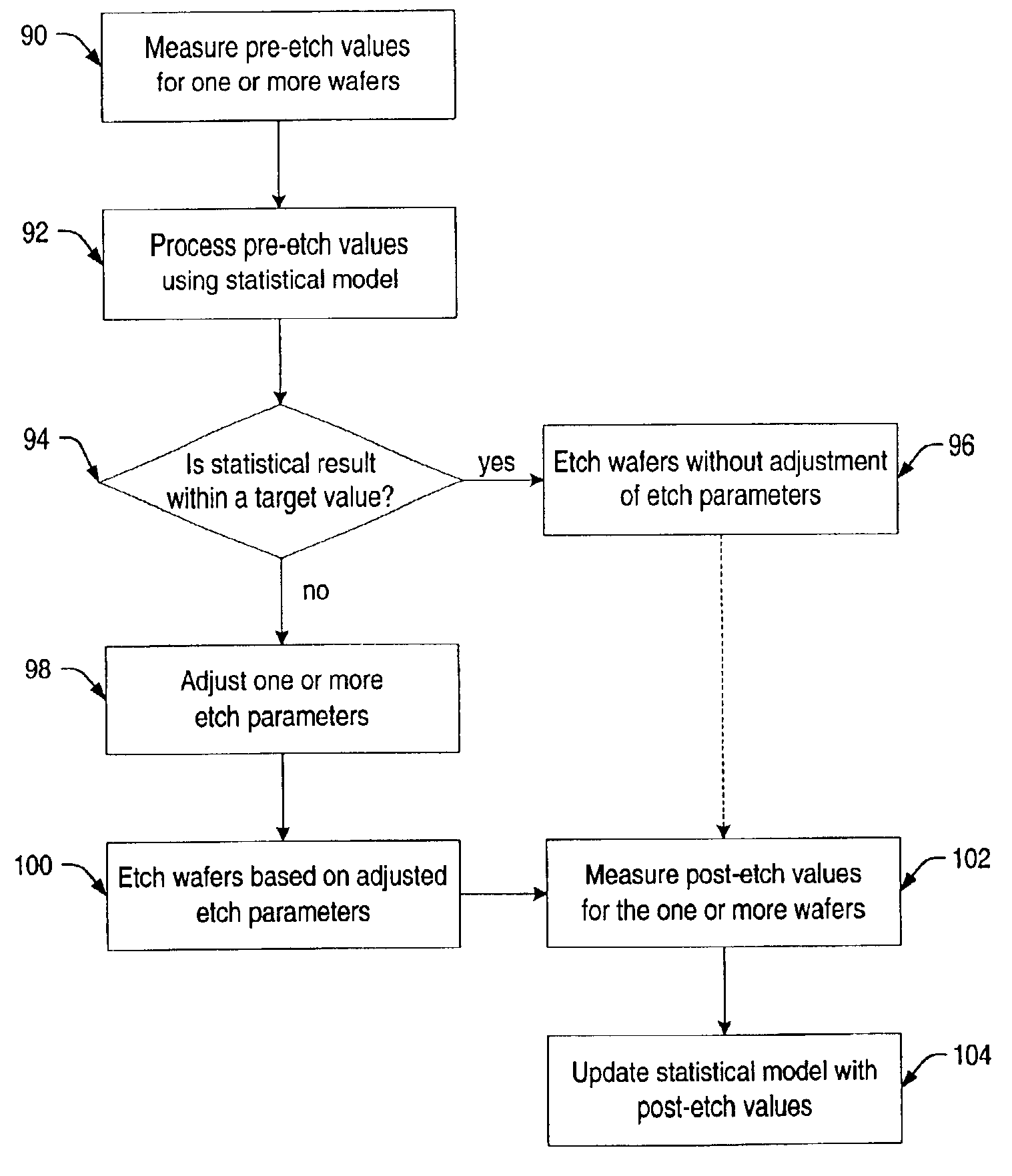
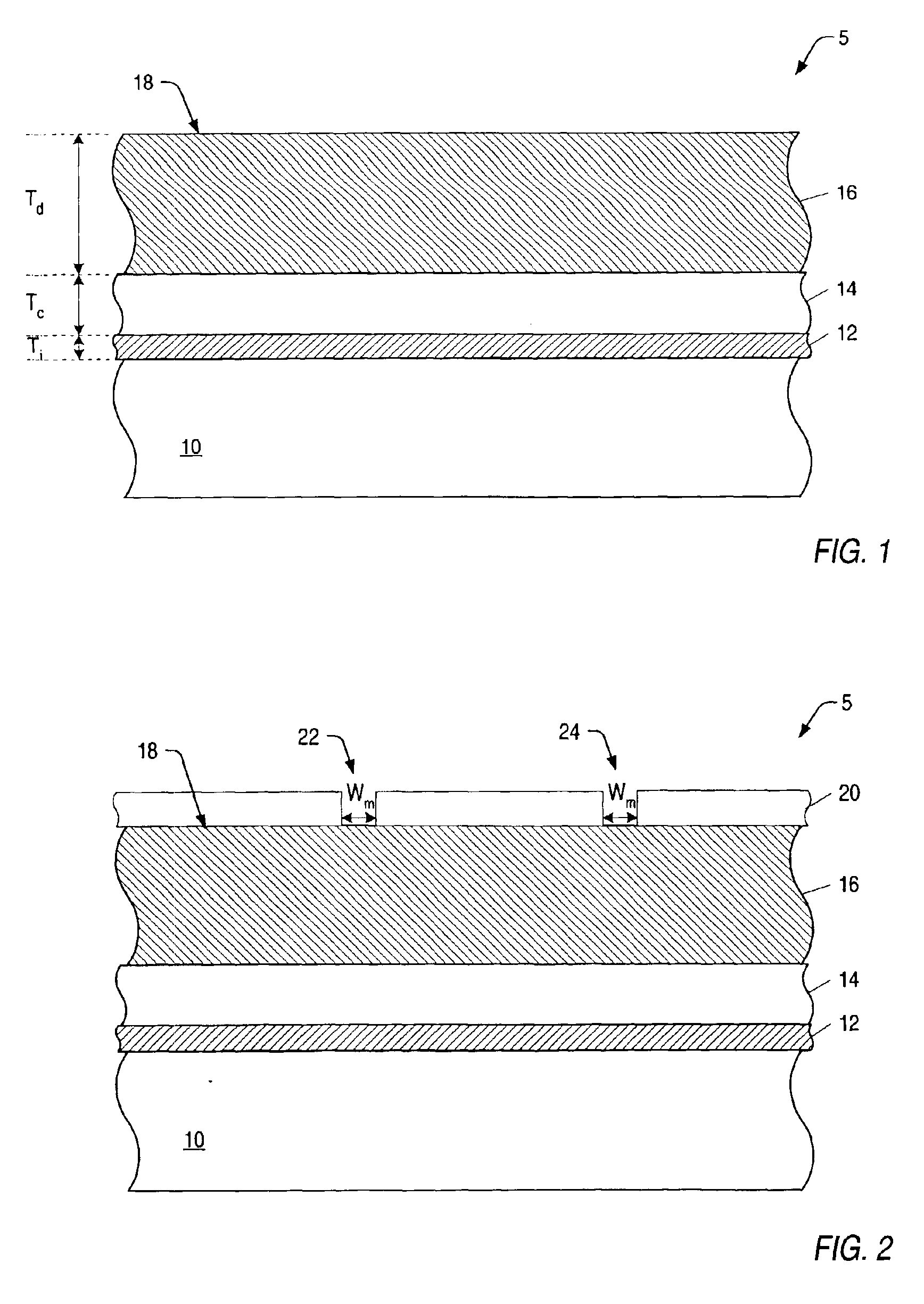
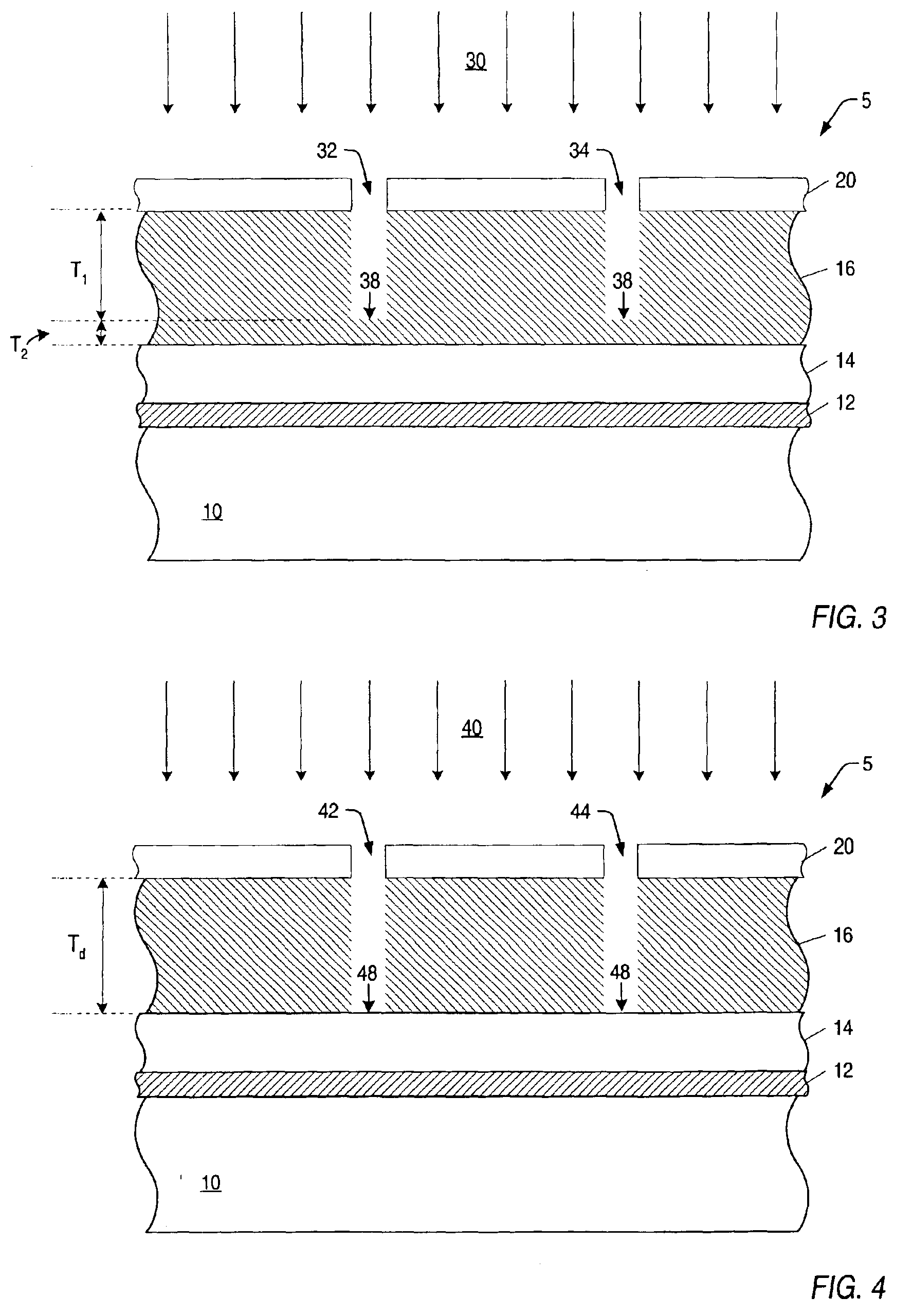
A system and method is provided herein to fabricate openings in a semiconductor topography using feed forward control of etch process parameters. In one embodiment, a method includes measuring one or more dimensional features of a semiconductor topography to obtain pre-etch values. The method also includes determining a statistical result of the pre-etch values and adjusting one or more processing parameters if the statistical result is less than a target value. Subsequently, the method includes etching the semiconductor topography based upon the statistical result to form one or more openings in the semiconductor topography. As such, the system and method described herein fabricates openings using feed forward control of the etch process parameters to compensate for structural variations within semiconductor topographies that may exist between wafer-to-wafer and / or between lot-to-lot. In this manner, the system and method advantageously fabricates openings having profiles and dimensions, which exhibit little to no deviation from a design specification.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids and utilities
ActiveUS7932029B1Rapidly and accurately assembledRapid interrogationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid mappingBioinformatics
Owner:LOK SI
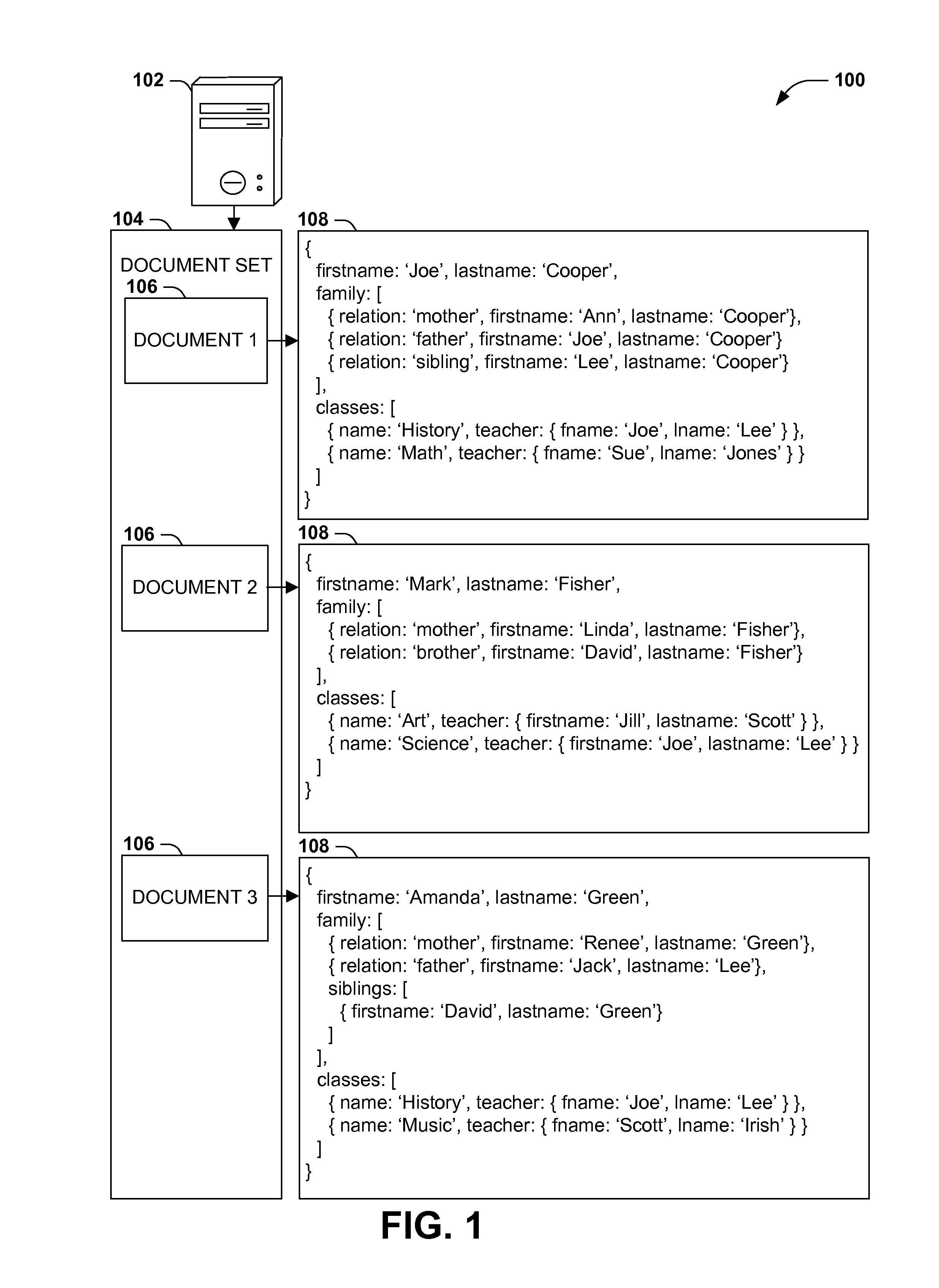
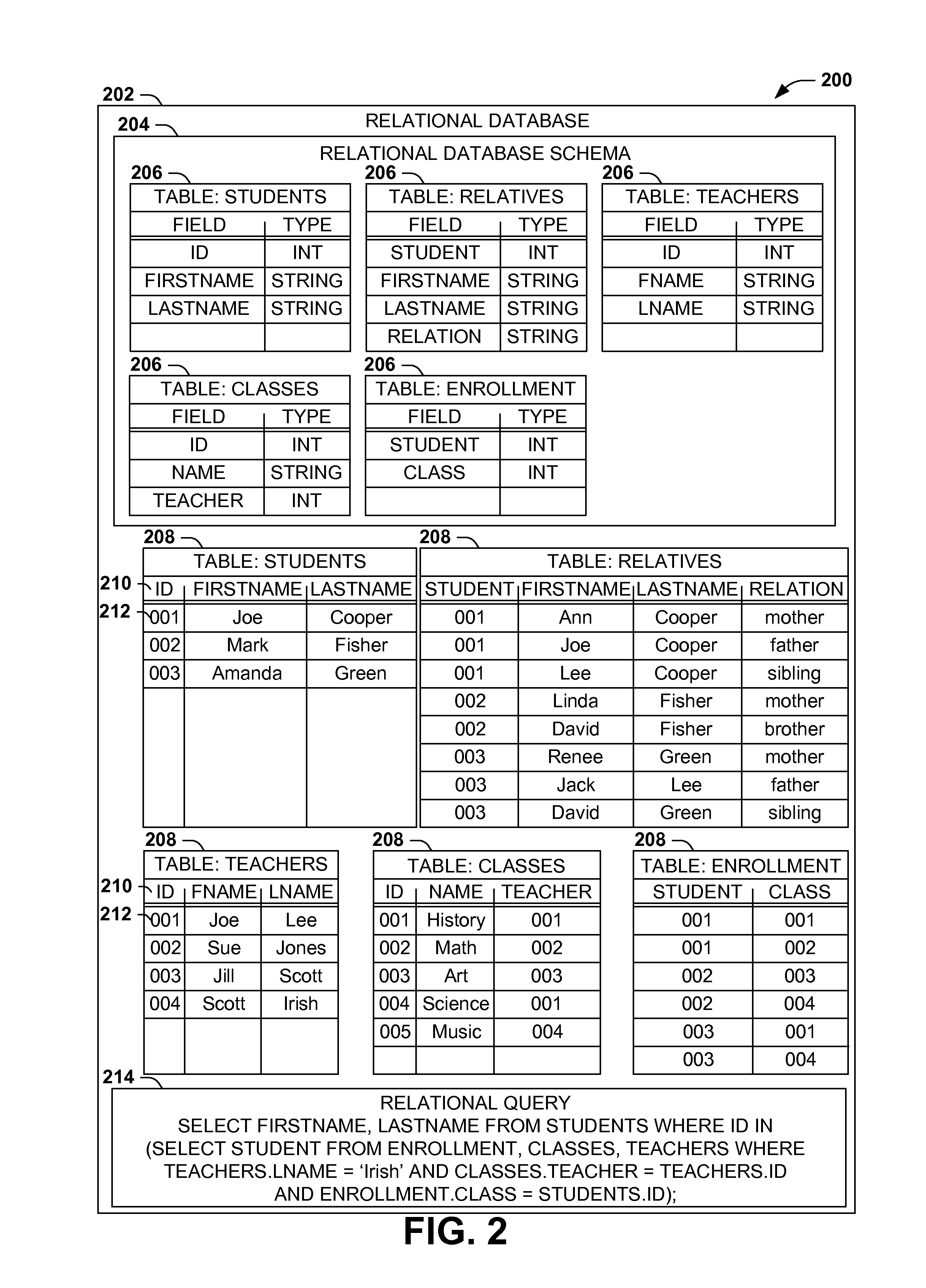
Scalable, schemaless document query model
ActiveUS20140280047A1Digital data processing detailsOther databases queryingRelational databaseDocument preparation
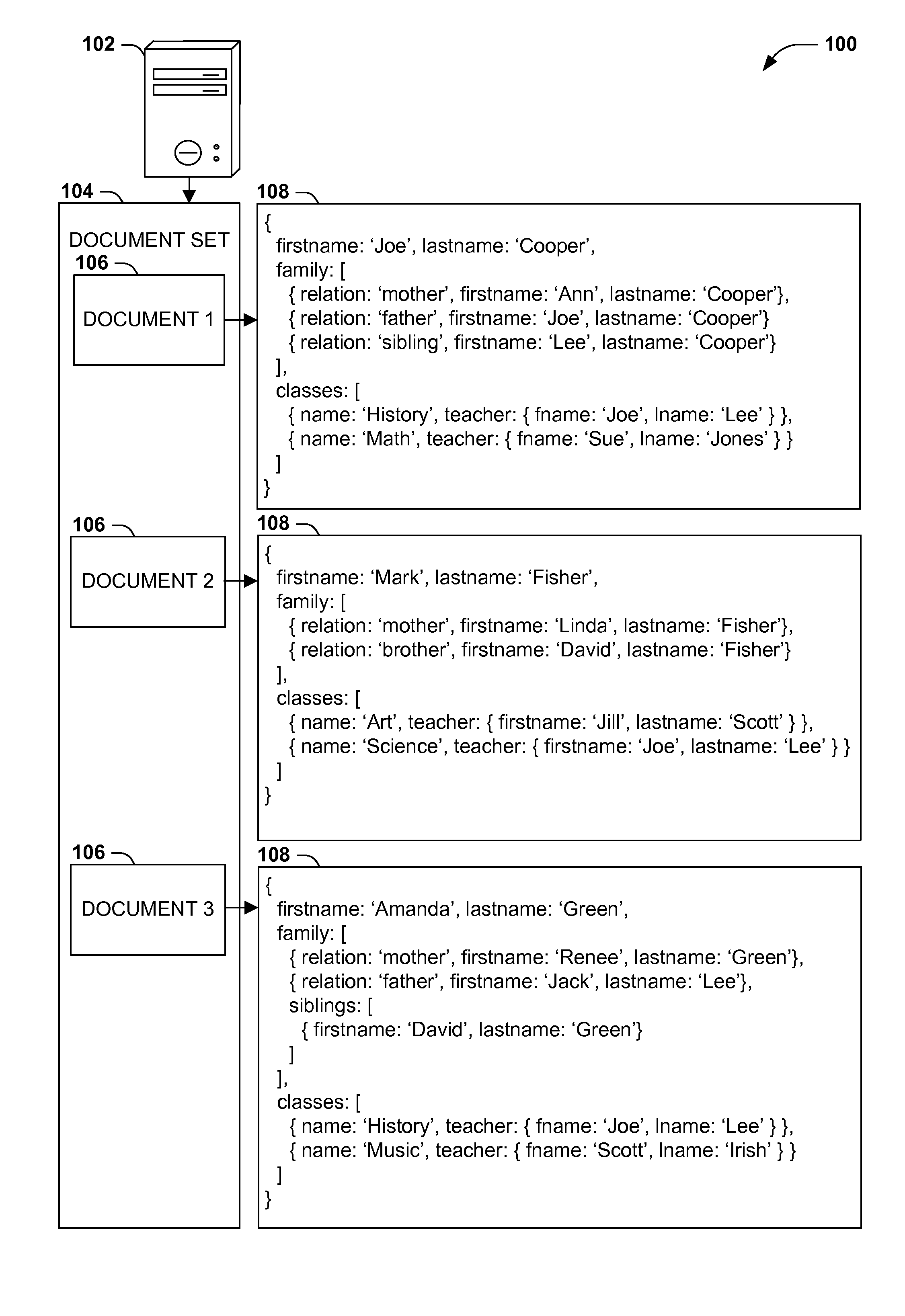
Query models for document sets (such as XML documents or records in a relational database) typically involve a schema defining the structure of the documents. However, rigidly defined schemas often raise difficulties with document validation with even inconsequential structural variations. Additionally, queries developed against schema-constrained documents are often sensitive to structural details and variations that are not inconsequential to the query, resulting in inaccurate results and development complications, and that may break upon schema changes. Instead, query models for hierarchically structured documents that enable “twig” queries specifying only the structural details of document nodes that are relevant to the query (e.g., students in a student database having a sibling named “Lee” and a teacher named “Smith,” irrespective of unrelated structural details of the document). Such “twig” query models may enable a more natural query development, and continued accuracy of queries in the event of unrelated schema variations and changes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Probes, method and chip for detecting alpha and/or beta-thalassemia mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such probes, such method and such chip
ActiveCN106591441AEnables detection of deletions in large regionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBeta thalassemiaNew mutation
The invention provides primers, a method and a chip for detecting alpha and / or beta-thalassemia point mutation and deletion mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such primers, such method and such chip. The primers, the method, the chip and application thereof have the advantages that through designing of capture probes, relevant genes involved in alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia are enriched and all mutation information including SNP and indel in full-length sequences of genes is detected; through addition of autosome, X-chromosome and Y-chromosome regions as well as upstream and downstream regions of coded genes as references, structure variations such as SNV and CNV are detected; compared with existing various hotspot mutation site detection technologies, the method is capable of detecting hotspot mutation information as well as some rare mutations and undiscovered new mutation types to detect and analyze full-length sequence specificity of target genes, fully covers the mutation types and makes up the defect that a conventional detection method easily causes missing detection of low-frequency mutations and rare mutations greatly.
Owner:SHENZHEN E GENE TECH
Super-long genome-based variation detection algorithm and detection system
ActiveCN105483244AHigh sensitivityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmStructural variation
The invention relates to a super-long genome-based variation detection algorithm, a Variation Blast algorithm for short. Under the condition that a long sequence is obtained, large-scale structural variations can be generally detected by comparing a sequence with a reference genome; and because a sequence spanning structural variations can generate part of segments matching a reference sequence, and then by virtue of the comparison between part of the segments of the sequence and corresponding segments of the reference sequence, an accurate point position of the structural variations can be detected, the Variation Blast detects the comparison between every sequence and the reference genome by virtue of a successive comparison method, then all the sequences representing the structural variations are classified and screened, and finally, possible structural variations and respective types thereof are obtained from comparison sites and directions.
Owner:WUHAN FRASERGEN CO LTD
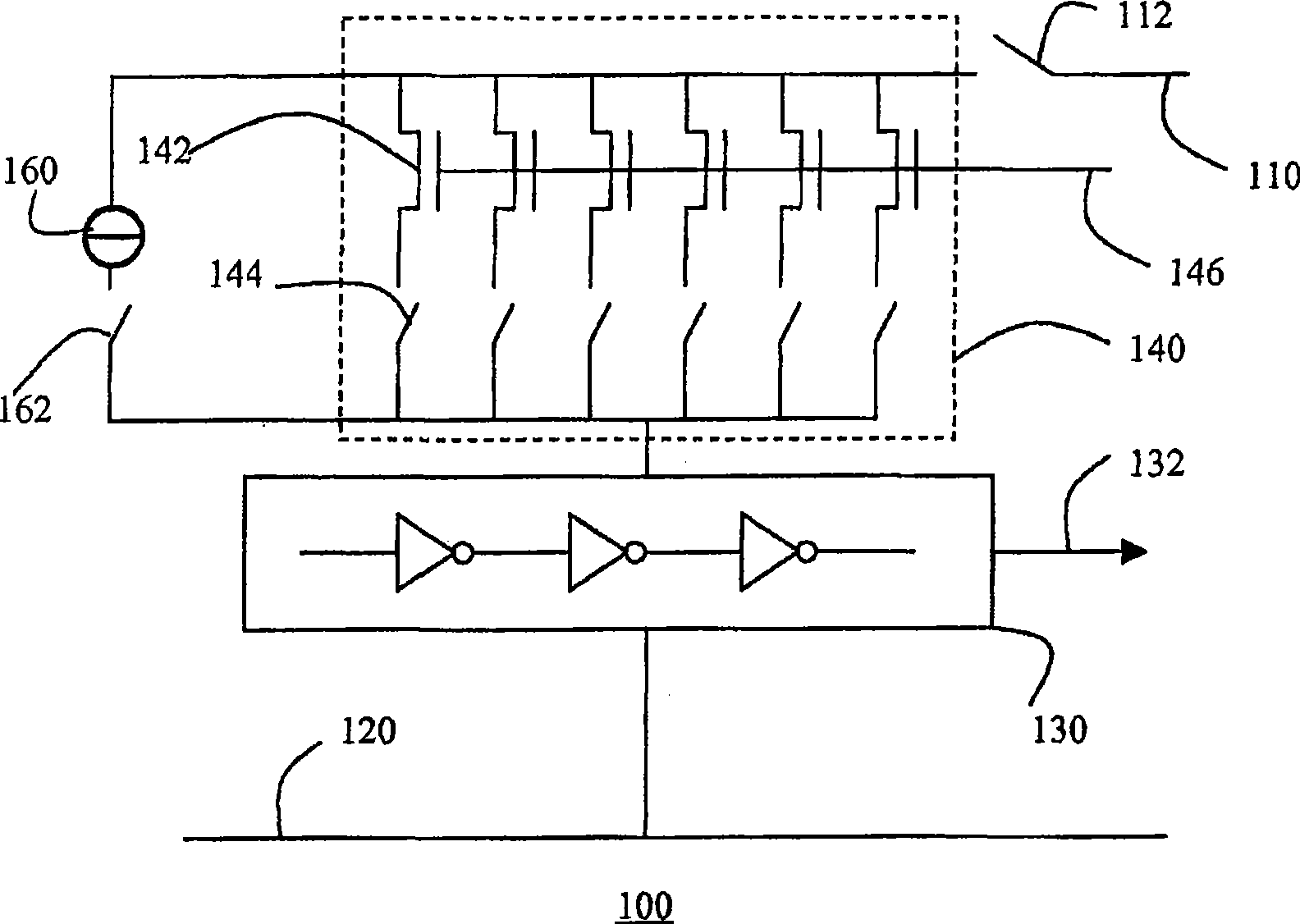
Semiconductor device with test structure and semiconductor device test method
InactiveCN101473237ASure easyIdentify structural changesElectrical testingReference currentEngineering
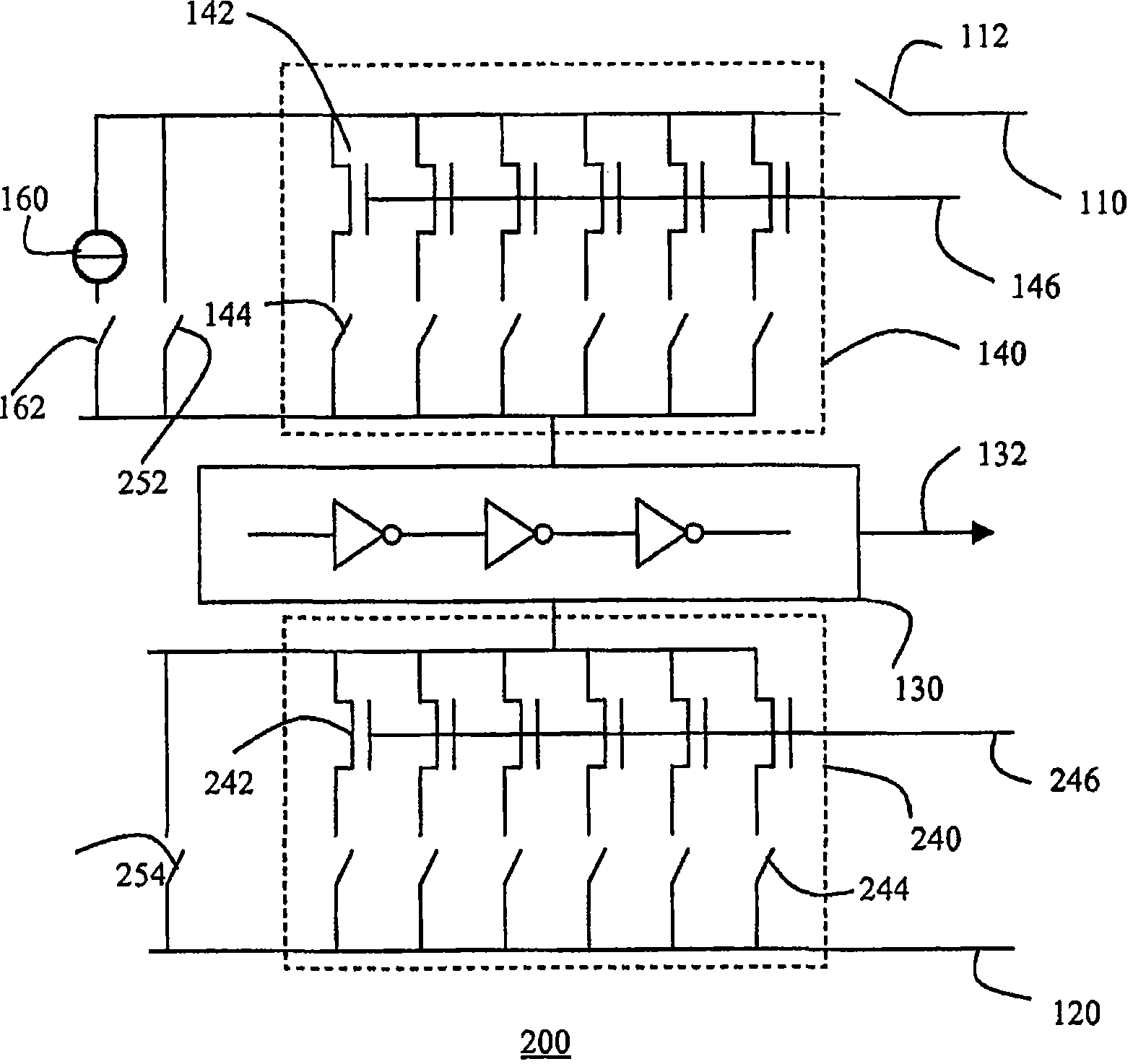
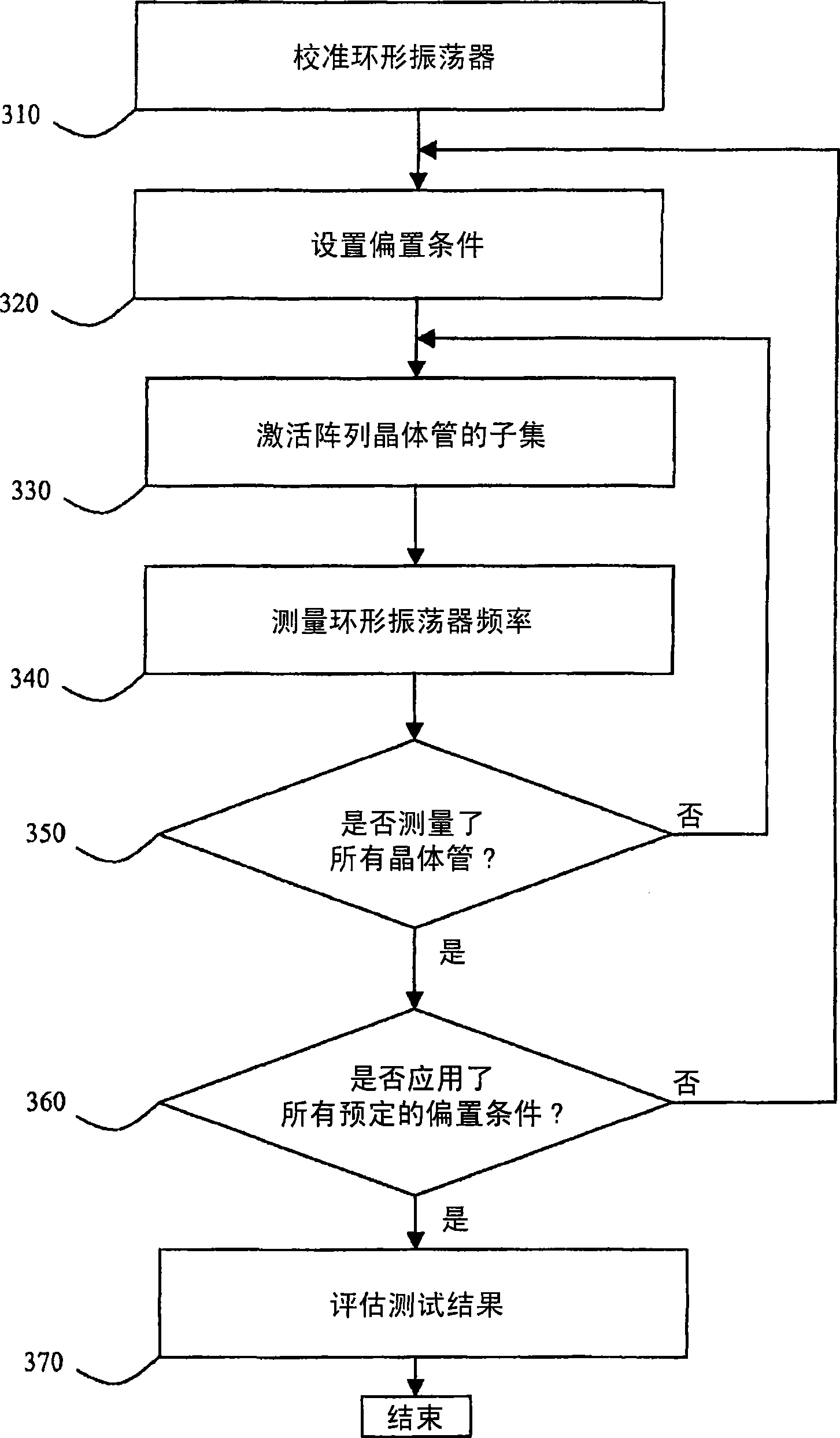
The invention relates to a semiconductor device comprising a test structure (100) for detecting variations in the structure of the semiconductor device, the test structure (100) comprising a first supply rail (110), a second supply rail (120), a ring oscillator (130) coupled between the first supply rail (110) and second supply rail (120), the ring oscillator (130) having an output (132) for providing a test result signal, and an array (140) of individually controllable transistors (142) coupled in parallel between the first supply rail (110) and the ring oscillator (130). Variations in the current output of the respective transistors (142) in the array (140) lead to variations in the respective output frequencies of the ring oscillator (130). This gives a qualitative indication of the aforementioned structural variations. More accurate results can be obtained by inclusion of a reference current source (160) for calibrating the ring oscillator (130) prior to the measurement of the current output of the individual transistors (142).
Owner:NXP BV
Method and system for accurately analyzing DMD gene structural variation breakpoint
ActiveCN107368708AAccurate analysisHigh detection error rateBiostatisticsSequence analysisPositional analysisDmd gene
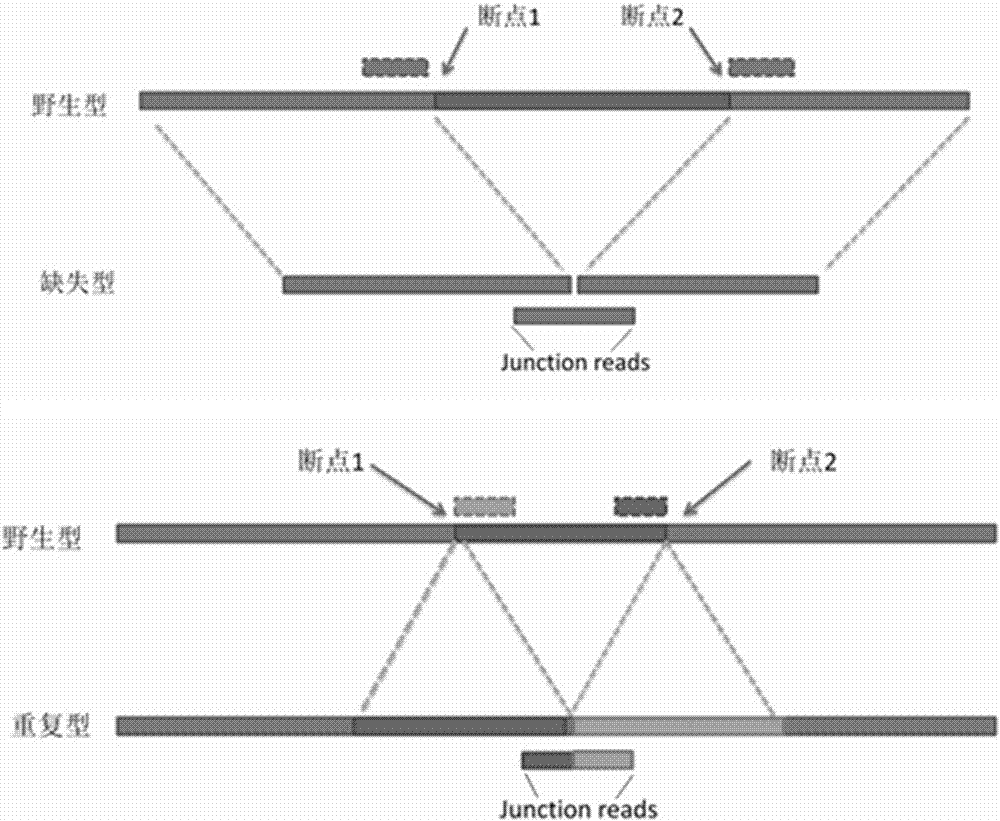
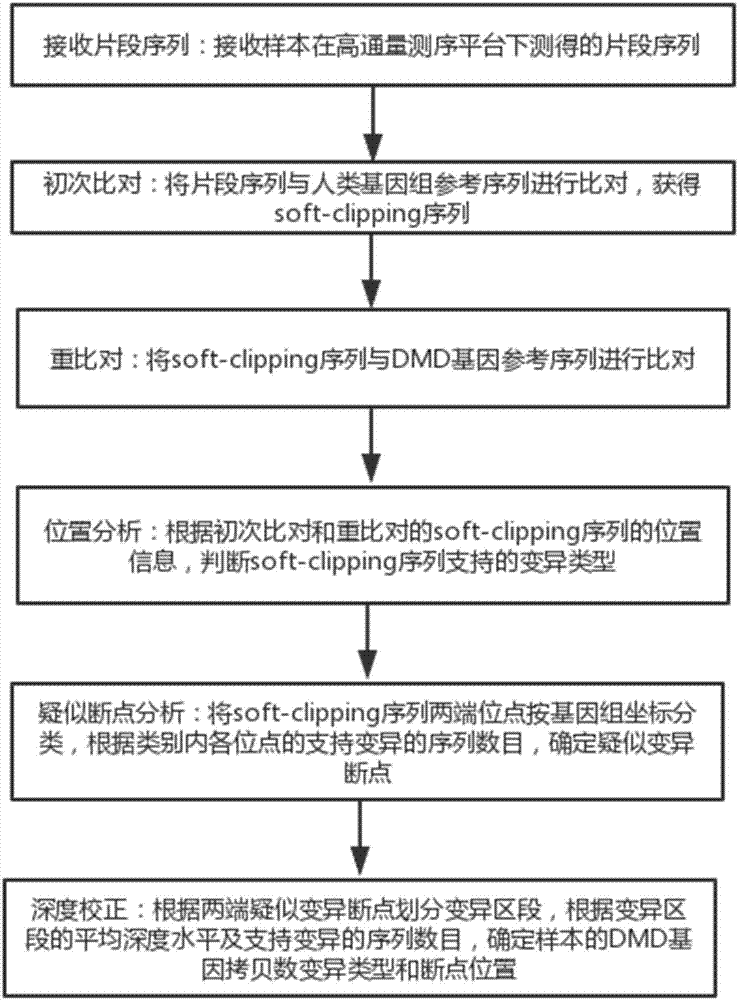
The invention discloses a method and a system for accurately analyzing a DMD gene structural variation breakpoint. The method includes steps of receiving of fragment sequences, initial comparison, repeat comparison, position analysis, analysis of suspected breakpoint, and in-depth correction; through the method, the type and the breakpoint position of DMD gene copy number variation can be accurately analyzed; the mean detection bias rate is less than 4 bp; the accuracy is high, and the stability is good; besides, the method and the system can cover the variation detection of an exon and an introne at the same time, solve the shortcoming that the breakpoint of the gene copy number variation cannot be accurately analyzed in the prior art, and provide technical support for realizing the rapid and parallel DMD breakpoint detection service and the study of the DMD structure gene variation molecular mechanism.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
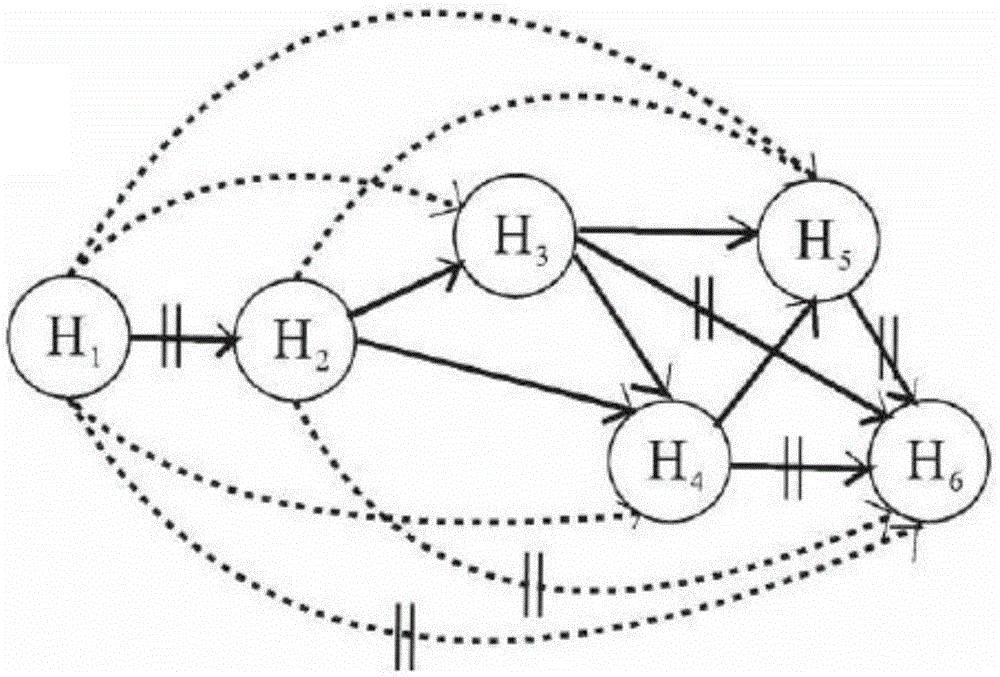
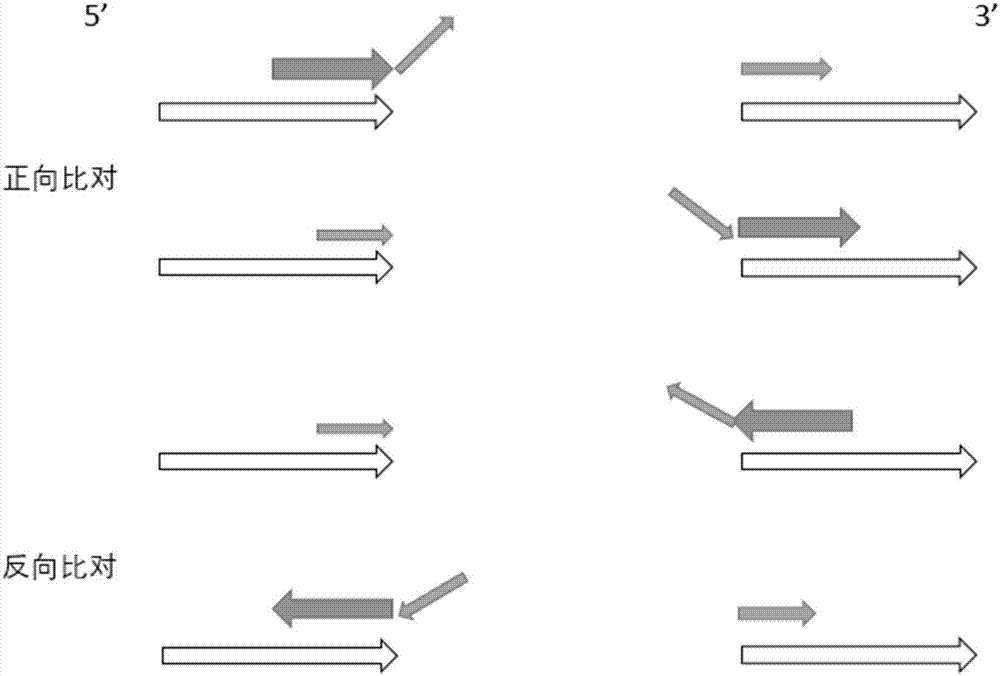
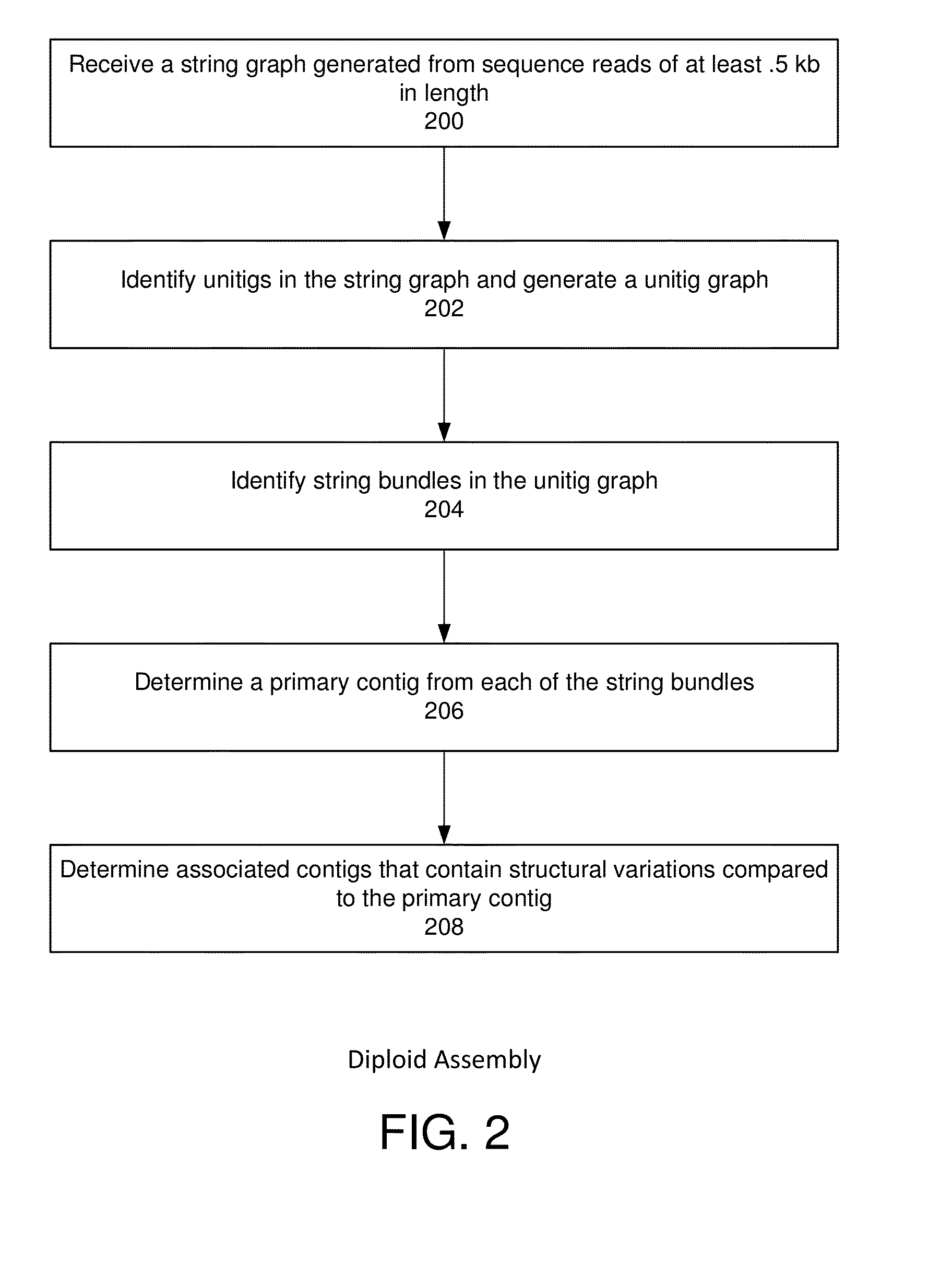
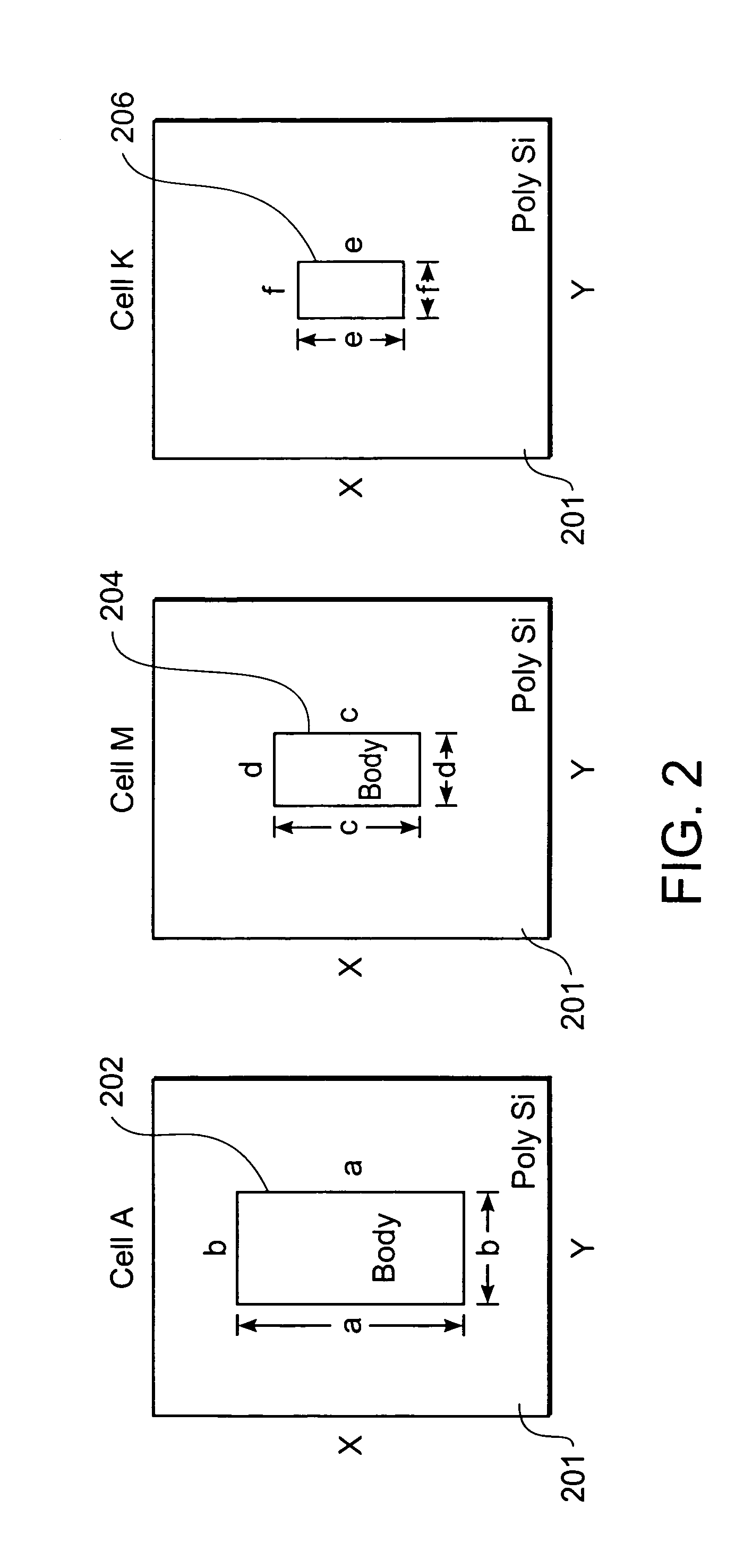
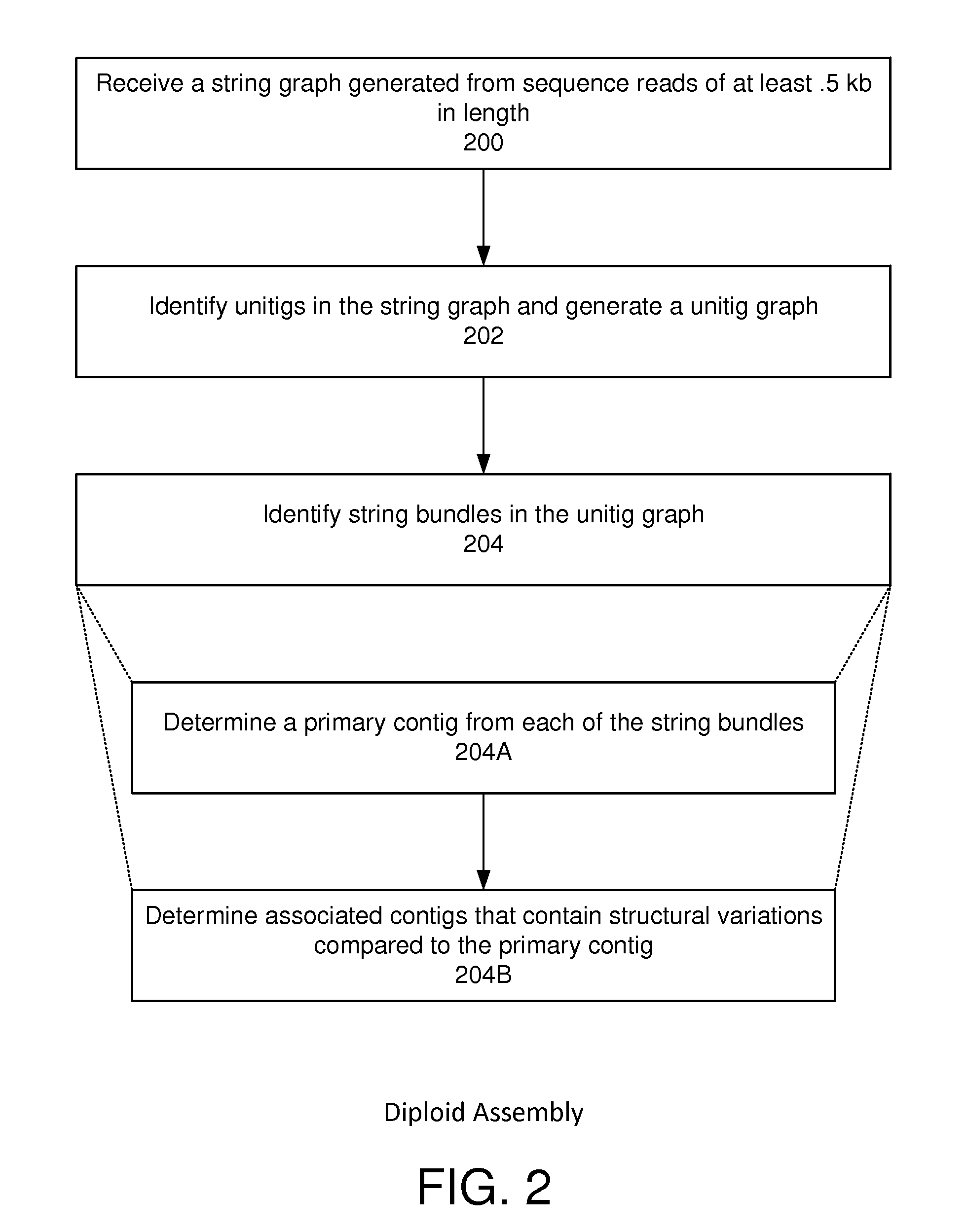
String graph assembly for polyploid genomes
InactiveUS20150169823A1Avoid excessive errorIncrease chanceBiological testingSequence analysisContigTheoretical computer science
Exemplary embodiments provide methods and systems for string graph assembly of polyploid genomes. Aspects of the exemplary embodiment include receiving a string graph generated from sequence reads of at least 0.5 kb in length; identifying unitigs in the string graph and generating a unitig graph; identifying string bundles in the unitig graph; determining a primary contig from each of the string bundles; and determining associated contigs that contain structural variations compared to the primary contig.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Peanut oligonucleotide probes and their design method and use method
ActiveCN106987590AImprove general performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMicrosatellite
The invention discloses peanut oligonucleotide probes and their design method and use method. The peanut oligonucleotide probes comprise eight probes having nucleotide sequences shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1 to NO. 8. The microsatellite and telomere sequences are used for developing the oligonucleotide probes, the novel oligonucleotide probes are combined into a probe set and oligonucleotide types of the peanut cultivar and wild peanut are constructed, an economic, efficient and high universality peanut cytological marker design technique and chromosome recognition technique are built, peanut chromosome markers are enriched, genomes and chromosomes of the peanut cultivar and wild peanut are identified, and chromosomal structural variation of wild peanut species is identified. Through use of a high-throughput small data simplified sequencing (for only measuring the amount of genomic 4Gb data) and bioinformatics analysis, peanut oligonucleotide probe markers are successfully developed. The invention provides a novel effective method for low-cost and high-efficiency development of peanut cytological markers.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
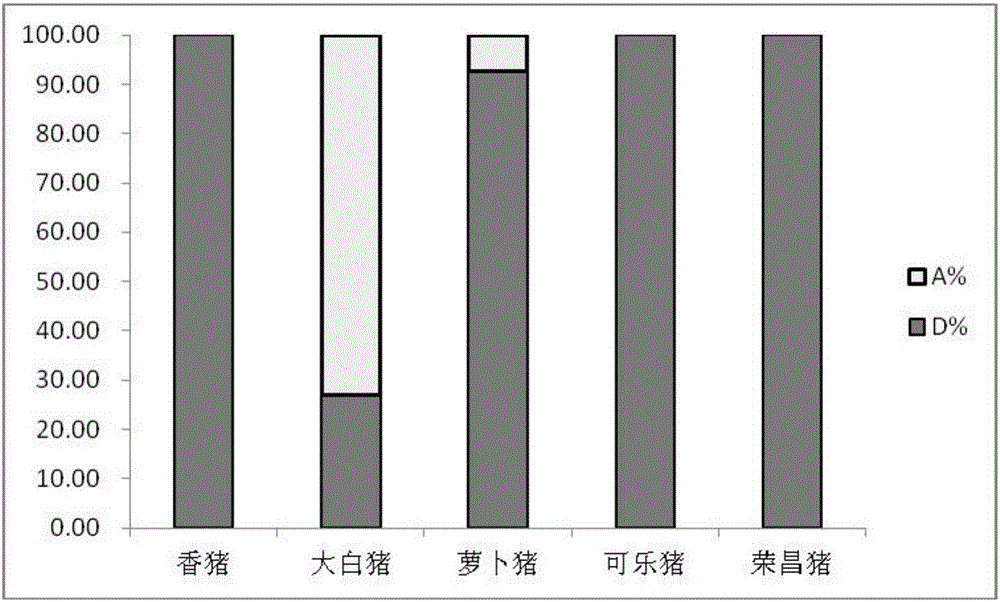
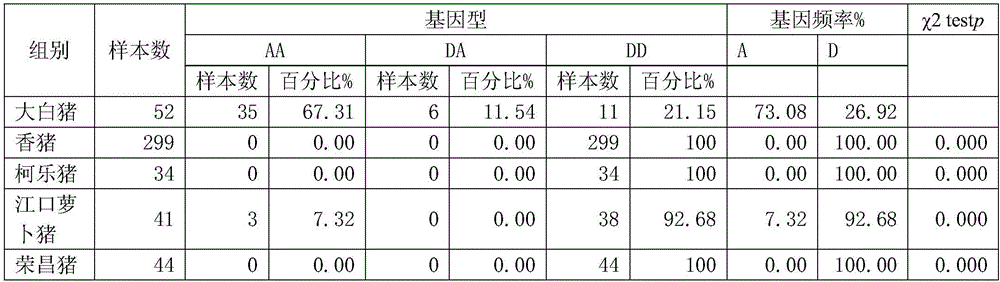
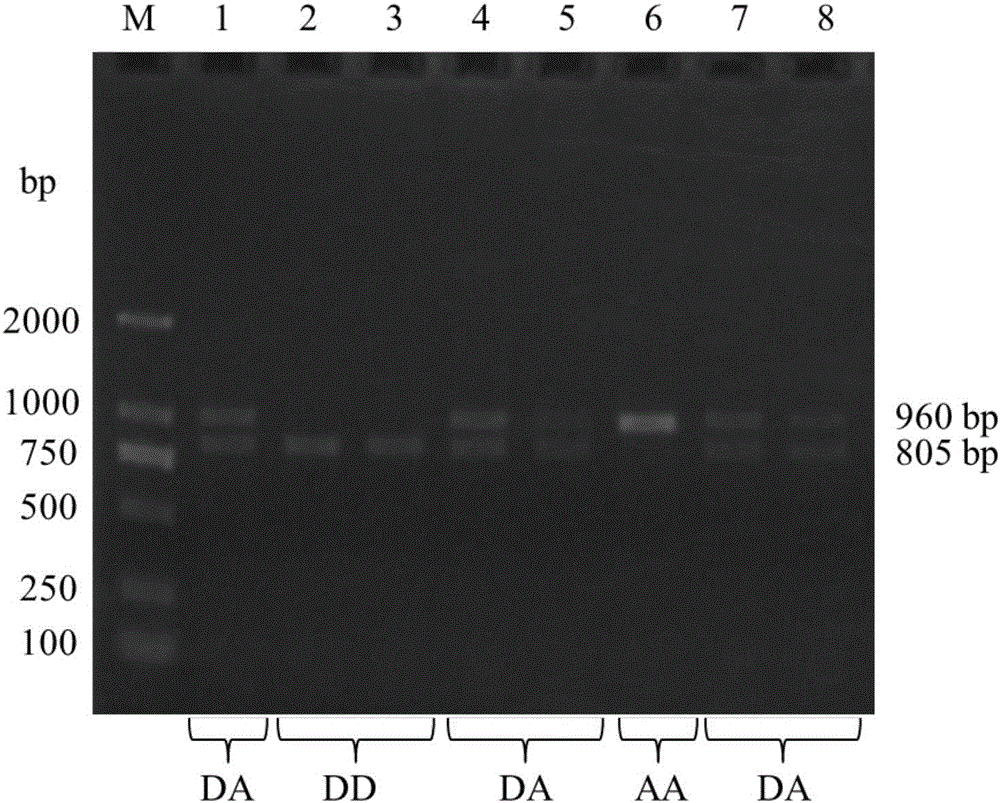
Structural variation 177 (SV177) for distinguishing varieties of large white pigs and Chinese indigenous pigs, and detection technology of SV177
ActiveCN106434931AReliable methodSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterozygous genotypeBiology
The invention discloses a structural variation 177 (SV177) for distinguishing varieties of large white pigs and Chinese indigenous pigs. The SV177 is characterized in that the SV177 is positioned at chrX: 100561156-100562159 of a pig reference genome Sscrofa 10.2, missing genes of the SV177 are determined as D, and normal genes which are not missed are determined as A. When a detection technology provided by the invention is used for detecting the SV177 genotype of a sample, the large white pigs have three genotypes and give priority to the genes A which are not missed, and the Chinese indigenous pigs are free from a heterozygous genotype (DA) and give priority to the missing genes D; therefore, the SV177 can be used for distinguishing the varieties of the large white pigs and the Chinese indigenous pigs as a molecular marker.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS8329400B2Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADigestion
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
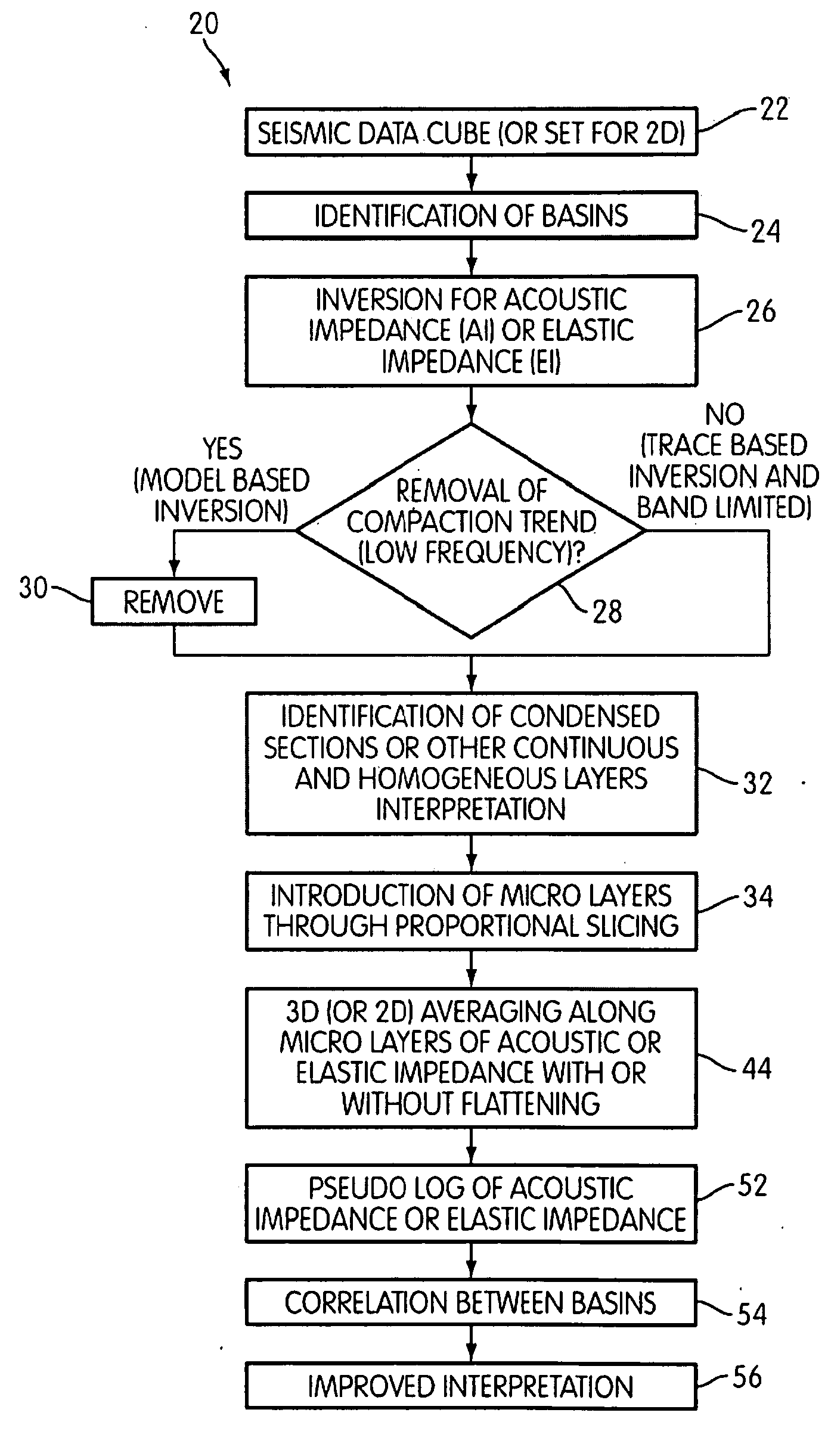
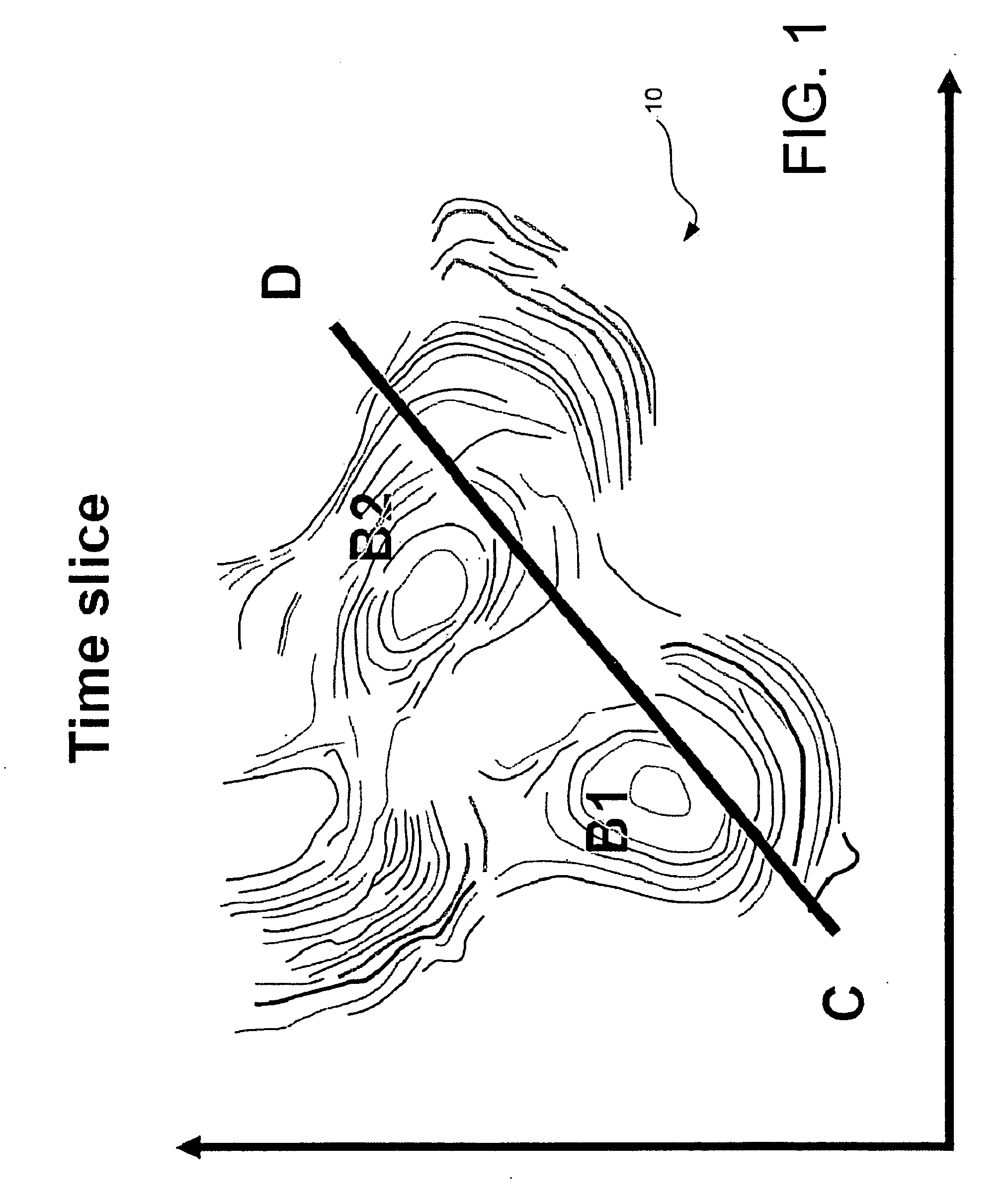
Pseudo logs to improve stratigraphic correlation between sedimentary basins
InactiveUS20100094559A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGeomorphologySedimentary basin
In order to improve the tie between depositionally equivalent beds relative to two or more basins detected within a multi dimensional seismic volume of interest, pseudo logs based on the average of attributes derived from seismic impedance where the compaction trend is not present are created for each basin. The mean is taken over all available azimuths, following the structural variations of introduced micro layers. The correlation between the pseudo log relative to each basin enable a more reliable interpretation between the different basins from which sound exploration decision can be made. Such a process has been successfully applied to seismic data acquired in deep water environment.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Construction method for synthesis of warm corn artificial population Suwan-Lancaster
InactiveCN106665331AExpanding the Germplasm BaseLarge structural variationPlant genotype modificationGenetic gainGermplasm
The invention discloses a construction method for synthesis of warm corn artificial population Suwan-Lancaster. The construction method comprises the following steps: selecting strains respectively from Suwan and Lancaster class groups, carrying out artificial purposeful hybridization for synthesizing the warm corn Suwan-Lancaster population, carrying out open pollination under natural isolation conditions, and continuously carrying out genetic equilibrium for four times to form Suwan-Lancaster original population C0, named Sulan C0. The warm corn artificially synthesized Suwan-Lancaster population has high yield genetic gain and great population structural variation; a half sib recurrent selection method is adopted for improving the Suwan-Lancaster population for three times; and meanwhile, line selection is directly carried out on the improved population, a batch of good inbred lines are bred, and the population has the effect of promoting widening of the existing corn germplasm foundation of China.
Owner:贵州省旱粮研究所
Structural variation SV200 molecular marker for identifying local pig breeds
ActiveCN106434932AAccurate and Reliable Method for Detecting Structural Variation SV200 of Local Pig BreedsSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementIntronReference genome
The invention discloses a structural variation SV200 molecular marker for identifying local pig breeds. The structural variation SV200 molecular marker is characterized in that the structural variation SV200 is positioned at chr 6: 17953135-17953289 of a pig reference genome Sscrofa 10.2; a deletion fragment has the length of 155bp and is positioned in an intron 5 of an MMP-15 gene; the deletion gene of the structural variation SV200 is defined as D, a normal non-deletion gene is defined as A, and the frequency of a D gene in 5 local pig breeds is significantly higher than a corresponding value of a big white pig. The structural variation SV200 molecular marker can be used as the molecular marker for identifying the local pig breeds.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
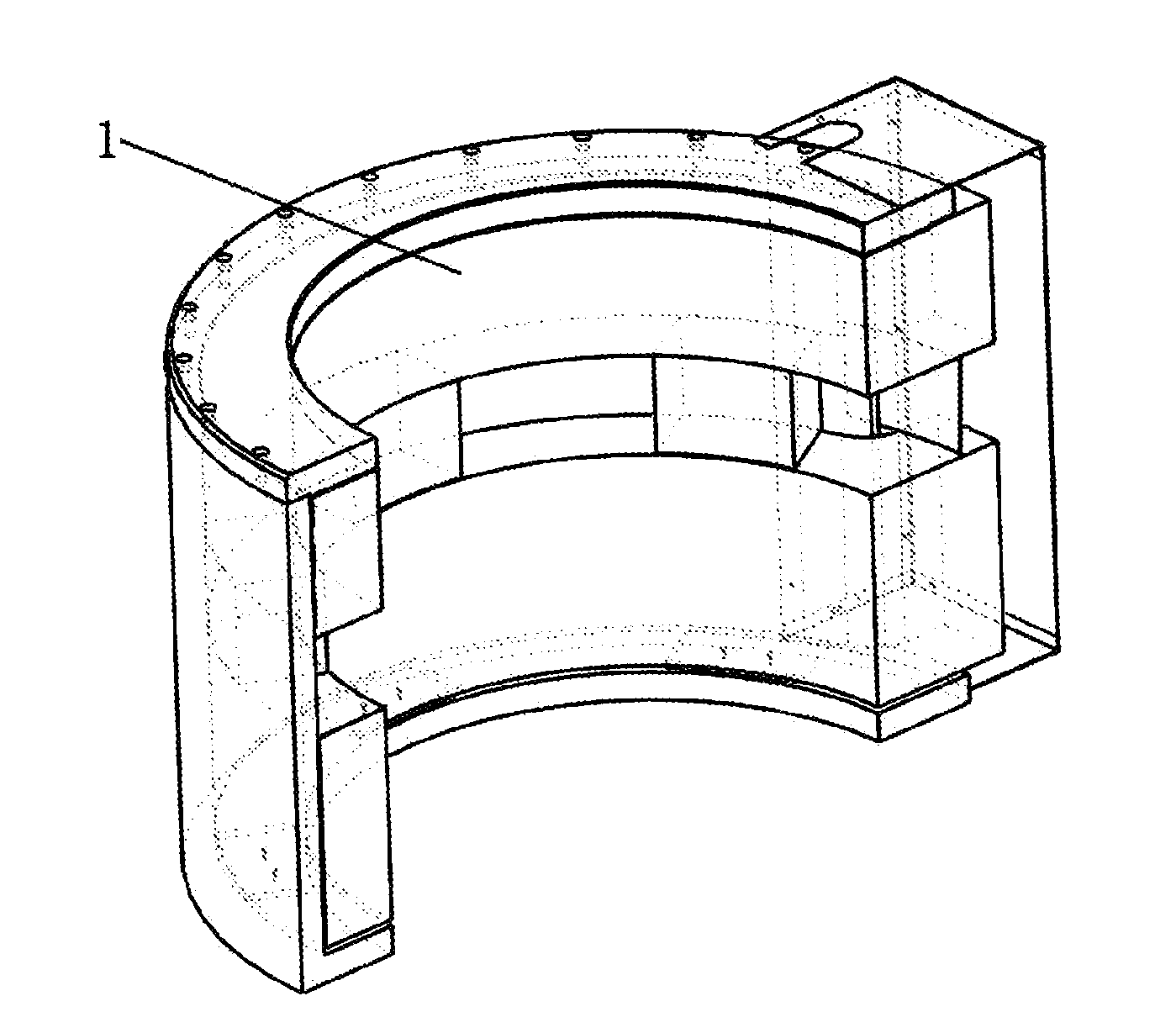
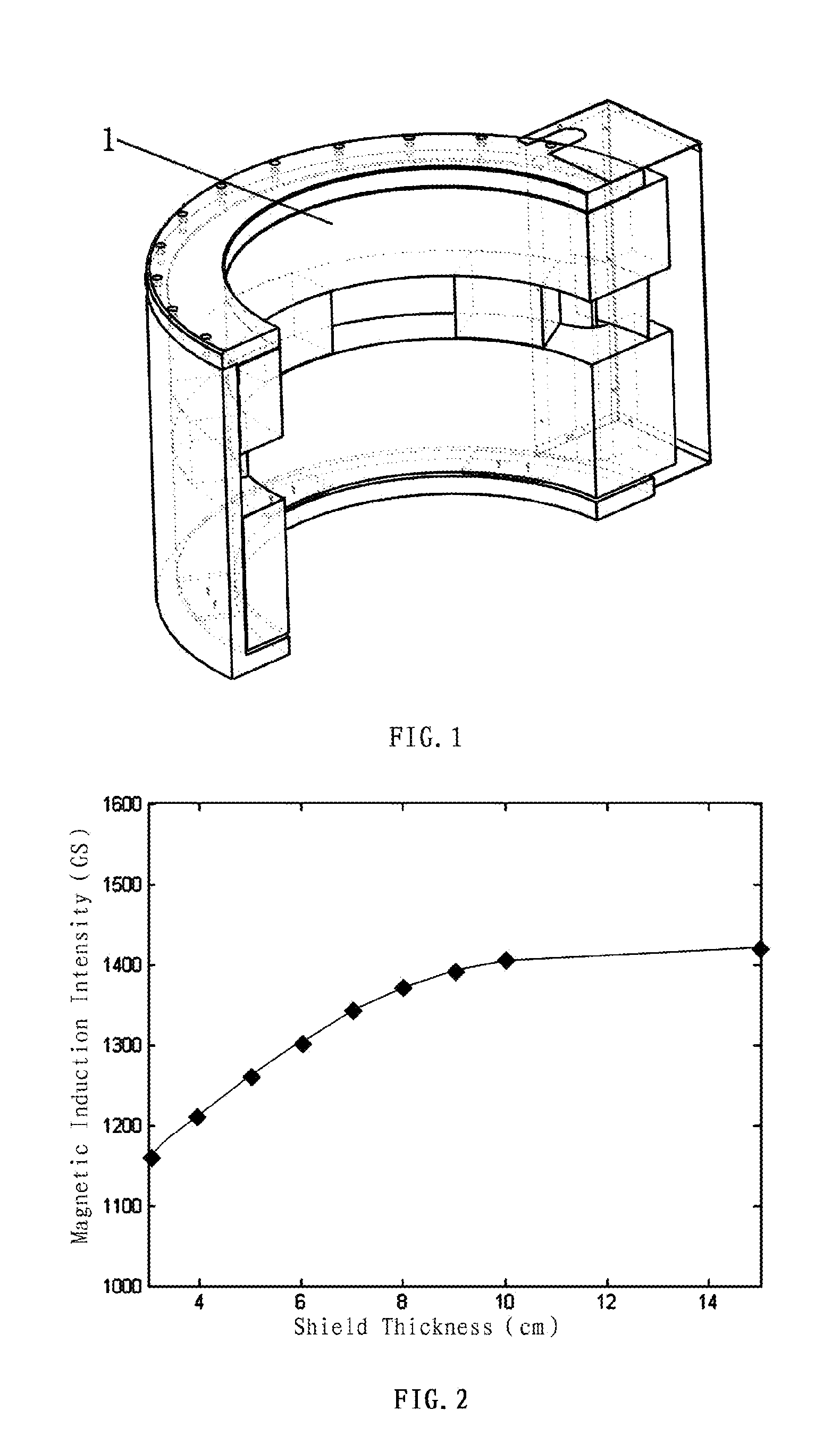
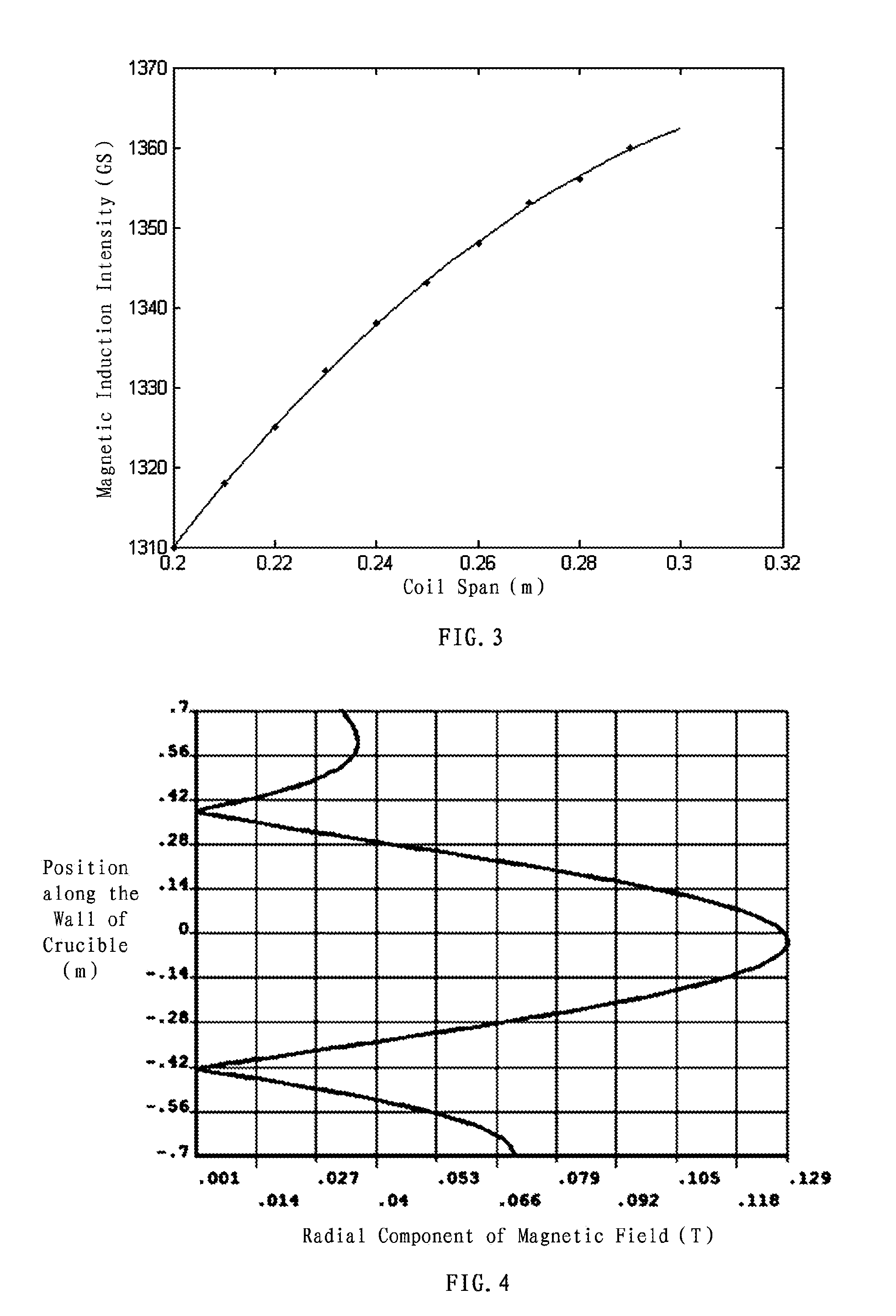
Method of three-dimensional optimization design for asymmetric cusp magnetic field in mcz single crystal furnace
ActiveUS20120035893A1Shorten the development periodReduce experiment costBy pulling from meltComputation using non-denominational number representationSingle crystalField coil
The present invention discloses a method of three-dimensional optimization design for an asymmetric cusp magnetic field in an MCZ single crystal furnace. An optimization design for structural parameters of the magnetic field comprises first establishing a three-dimensional magnetic model by using an Ansys numerical analysis software; and varying parameters of the model, determining the span between the upper and lower parts of coils, the number of transverse turns of coils and the thickness of the shield based on a set magnetic induction intensity of the magnetic field, and determining the numbers of longitudinal layers of coils in the upper and lower parts of the magnetic field. An optimization design for specification parameters of the coils of the magnetic field comprises first determining a relationship between heat and specification parameters of the coils, determining a relationship between heat transfer of the coils at the copper pipe walls and the specification parameters of the coils, analyzing the heat absorbed by cooling water, establishing an optimization model of a system, and optimizing the specification parameters of the coils of the magnetic field by using the Ansys software. According the method of the present invention, the influence of the structural variation of the magnetic field on the variation of distribution and intensity of the magnetic field is intuitively revealed in three-dimension in view of all aspects, thereby reducing develop period and experiment cost on the cusp magnetic field, and increasing the efficiency of generating magnetic induction intensity by the magnetic field.
Owner:XIAN ESWIN MATERIAL TECH CO LTD +1
Fusion detection method based on homologous genes of differential SNP markers
ActiveCN110033829AAvoiding problems encountered in repeat sequence detectionProteomicsGenomicsBioinformaticsSnp markers
The invention relates to a fusion detection method based on homologous genes of differential SNP markers. The fusion detection method utilizes differential SNP signals of two genes to distinguish, bypasses the difference in sequencing depth, and performs consistency comparison on each sequencing reads sequence and the homologous gene sequence by using abnormal inserted fragment length of double-ended reads and the soft clip signal of single-end reads, so as to look for a continuous consistency SNP mark and infer the breakpoint interval. The fusion detection method based on homologous genes ofdifferential SNP markers can obtain the interval where the breakpoint is located, that is, the last site of the first half and the first site of the second half, and the separation distance of the interval depends on the physical distance of the detected two sites, thus avoiding the problem that the conventional structural variation detection method encounters in the detection of repeated sequences.
Owner:北京诺禾心康基因科技有限公司
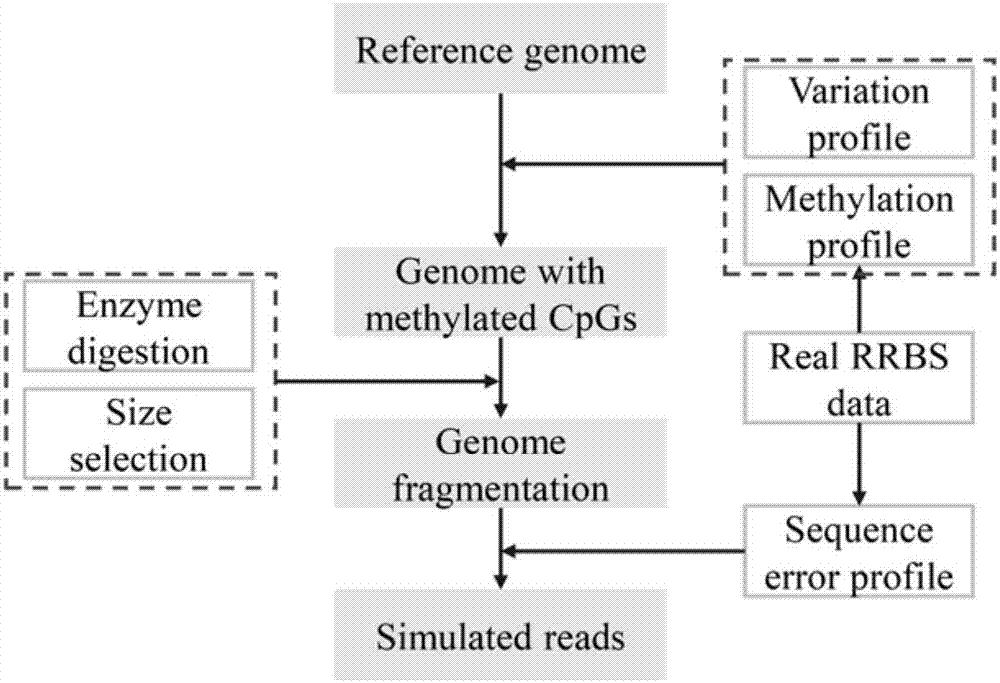
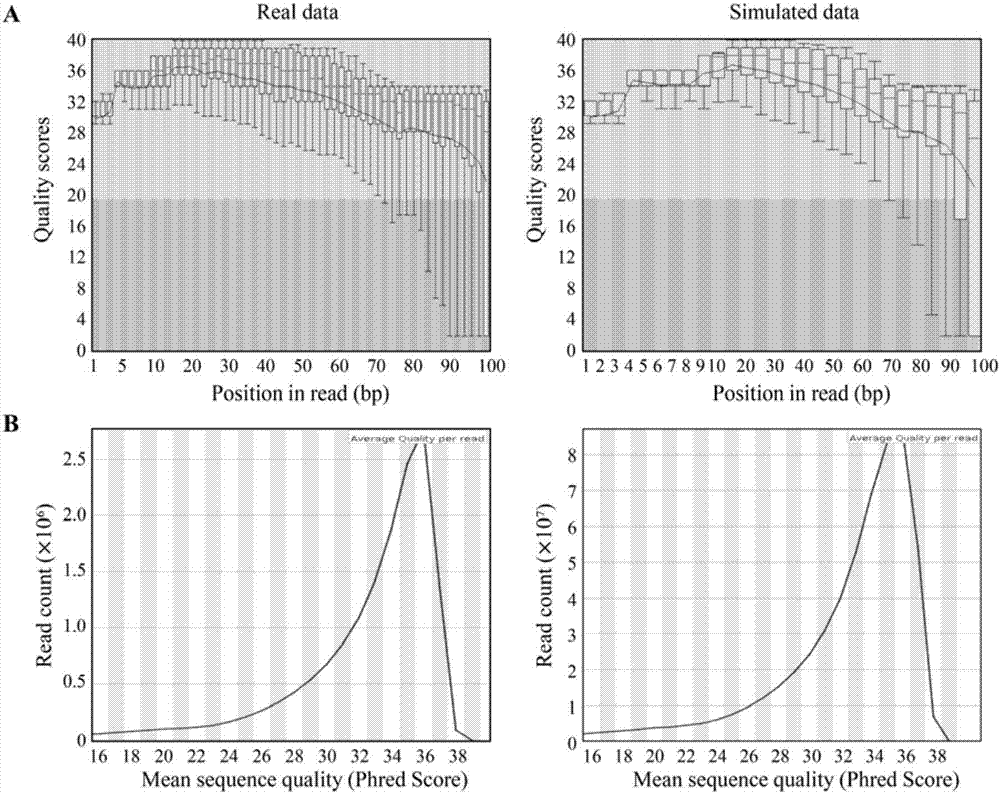
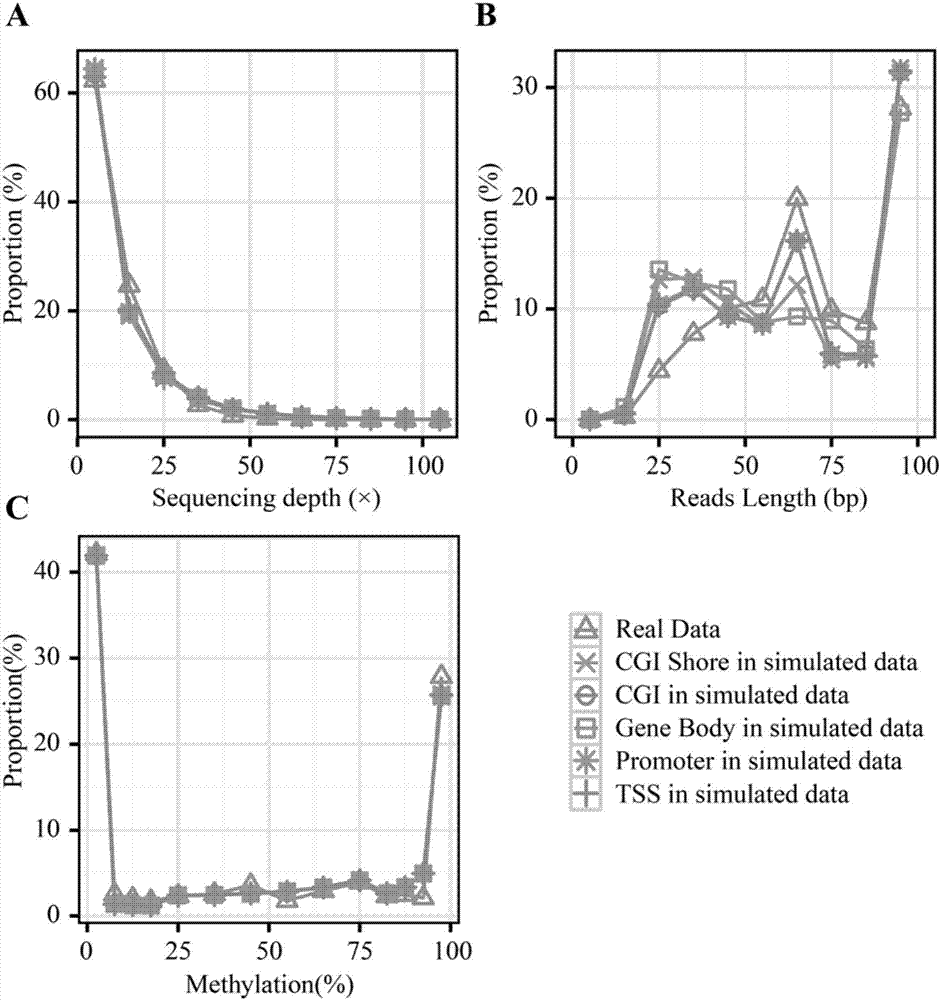
Method for using computer program to simulate and generate simplified DNA methylation sequencing data
The invention discloses a method for using a computer program to simulate and generate simplified DNA methylation sequencing data, which can estimate the efficiency of different simplified genome methylation (RRBS) sequencing data comparison software and the reliability of corresponding data analysis platforms so as to determine the optimal comparison method and a corresponding optimal parameter. The method simulates an RRBS library construction and sequencing process through a computer program, and generates simulation data similar to real RRBS sequencing data according to distribution of a CpGs methylation level. The simulation data simulates other characteristics such as inserting, deletion, mononucleotide variation and structural variation of the real data except for the single base group methylation level so as to enhance the authenticity. During a simulation process of RRBS sequencing, an experience error model is introduced to simulate errors during the sequencing process, and then the authenticity of the simulation data can be further enhanced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hook type frame concealed curtain wall
ActiveCN101016762AHigh precision quality productsIncreased production requirementsWallsBasementMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a wall-hung type stealth-framed partition, comprising a partition frame, a stationary barrier, a basement, a connecting piece, and a plurality of covering material components consisted with each other, wherein the partition frame is arranged on the stationary barrier via the connecting piece, characterized in that the basement is horizontal equipped with a cross bar which is matched with a plurality of hungers with grooves installed on the partition frame, and the hungers are moveable connected with the partition frame whose one side is equipped with an angle adjusting device, and connected and fixed the hungers with the cross bar. The invention not only supplies a flexible angular adjustment and meets the requirement of poly structural variation of partition and construct, but also has a better spreading value.
Owner:广东齐力澳美高新材料股份有限公司
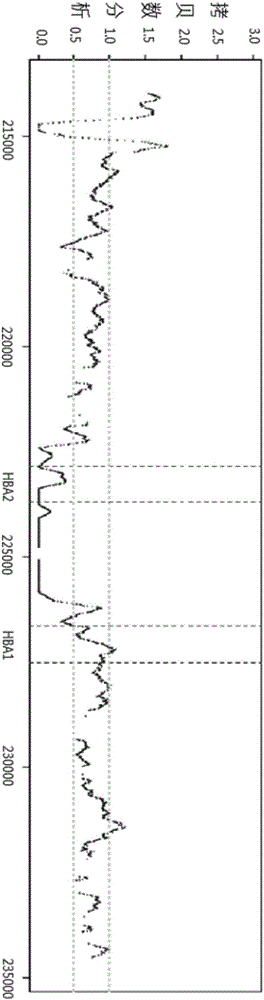
Method for determining chromosome structure variation signal intensity and insert fragment length distribution characteristics of sample, and application thereof
The invention provides a method for determining chromosome structure variation signal intensity and insert fragment length distribution characteristics of a sample, and application thereof. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for determining a sample source. The method comprises the following steps: (1) comparing sequencing read data of chromosomes in a sample with a reference genome,and determining a low-quality comparison rate and a high-quality comparison rate of the sequencing read data of the chromosomes of the sample; (2) determining the structural variation proportion of the chromosomes of the sample, the content of mitochondrial DNA and the proportion of an insert fragment with a predetermined length based on reads corresponding to the high-quality comparison rate; (3)determining the probability of sample sources based on a predetermined tumor prediction model, the structural variation proportion of the chromosomes obtained in the step (2), the content of the mitochondrial DNA and the proportion of the insert fragment with the predetermined length; and (4) determining the source of the sample based on the probability of the sample source.
Owner:深圳思勤医疗科技有限公司
Non-uniform power semiconductor and method for making non-uniform power semiconductor
InactiveUS7157338B2Improve temperature uniformityImprove switching efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringActive cell
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
String graph assembly for polyploid genomes
PendingUS20150286775A1Avoid excessive errorIncrease chanceBiological testingSequence analysisContigTheoretical computer science
Exemplary embodiments provide methods and systems for string graph assembly of polyploid genomes. Aspects of the exemplary embodiment include receiving a string graph generated from sequence reads of at least 0.5 kb in length; identifying unitigs in the string graph and generating a unitig graph; and identifying string bundles in the unitig graph by: determining a primary contig from each of the string bundles; and determining associated contigs that contain structural variations compared to the primary contig.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods and system for detecting sequence variants
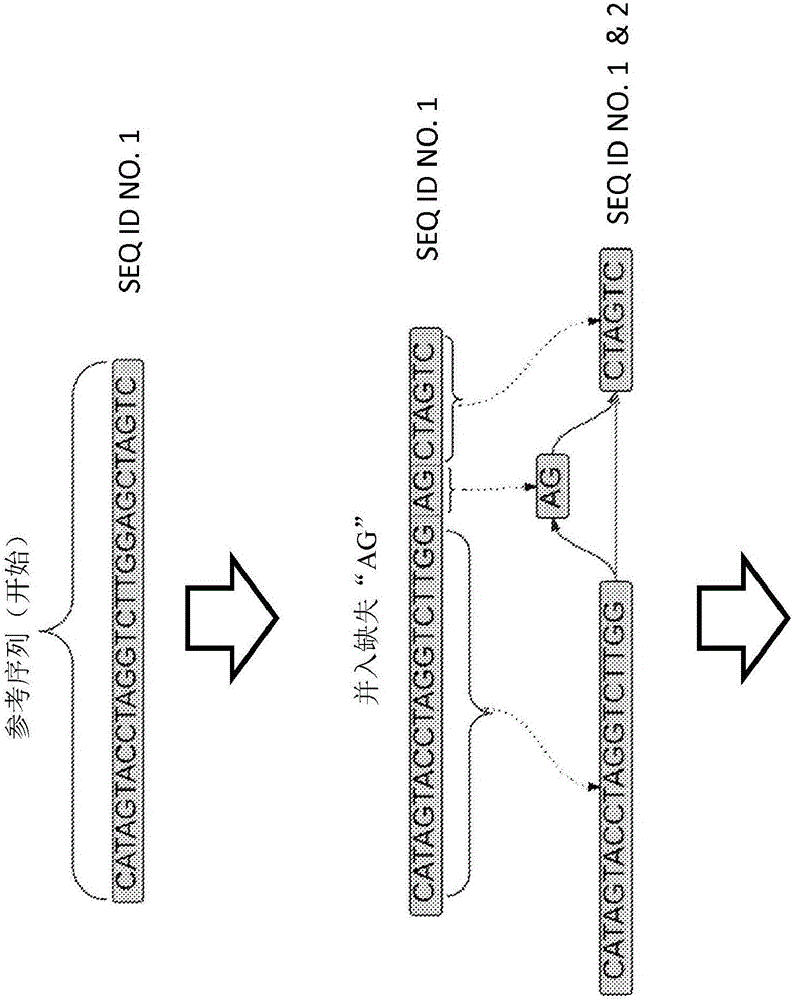
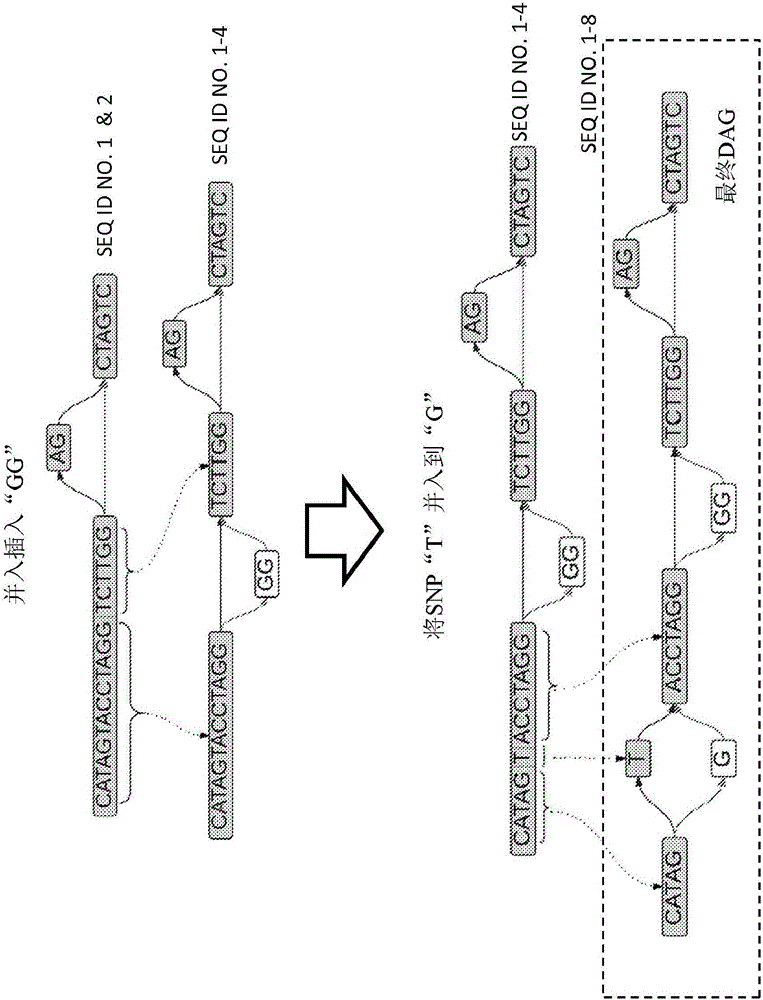
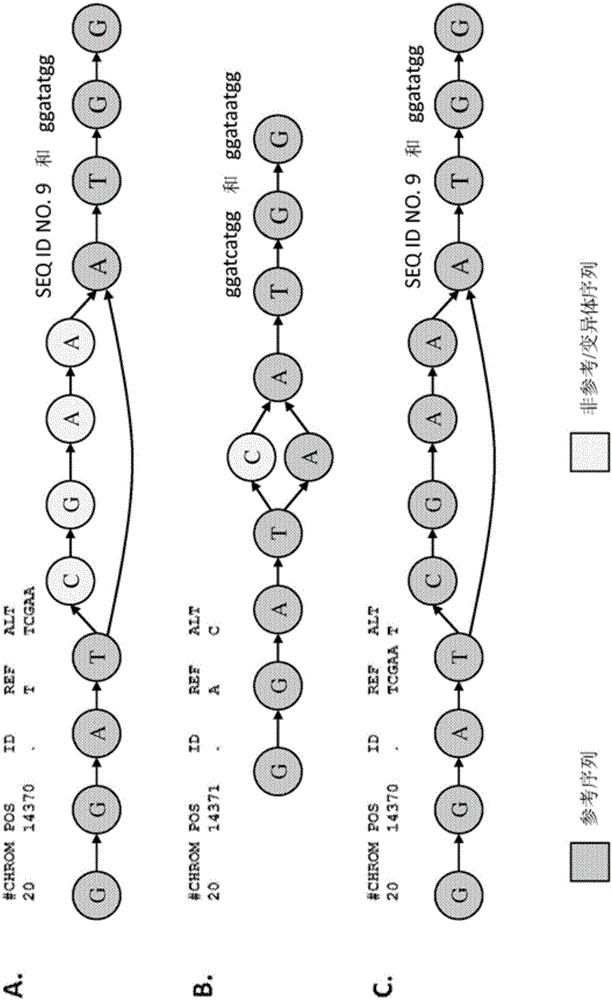
ActiveCN105793859AHigher score thanNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementStructural variationComputational biology
The invention provides methods for identifying rare variants near a structural variation in a genetic sequence, for example, in a nucleic acid sample taken from a subject. The invention additionally includes methods for aligning reads (e.g., nucleic acid reads) to a reference sequence construct accounting for the structural variation, methods for building a reference sequence construct accounting for the structural variation or the structural variation and the rare variant, and systems that use the alignment methods to identify rare variants. The method is scalable, and can be used to align millions of reads to a construct thousands of bases long, or longer.
Owner:SEVEN BRIDGENOMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com