Patents
Literature
377 results about "Variome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The variome is the whole set of genetic variations found in populations of species that have gone through a relatively short evolution change. For example, among humans, about 1 in every 1,200 nucleotide bases differ. However, as the human species diverged only 10,000 years ago, this variation rate is comparatively small. In practice, the variome can be the sum of the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the population. The Human Variome Project seeks to compile this genetic variation data worldwide. Variomics is the study of variome and a branch of bioinformatics.
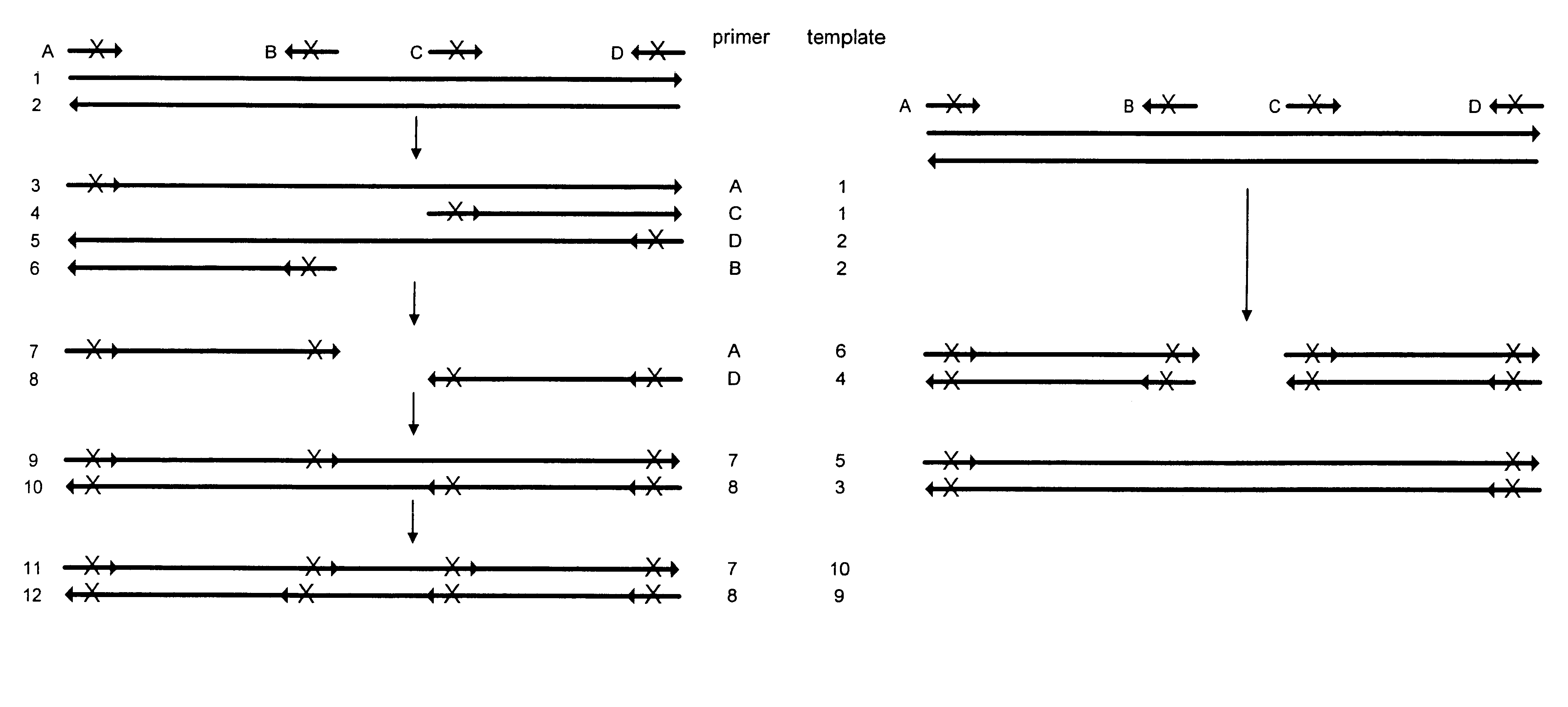
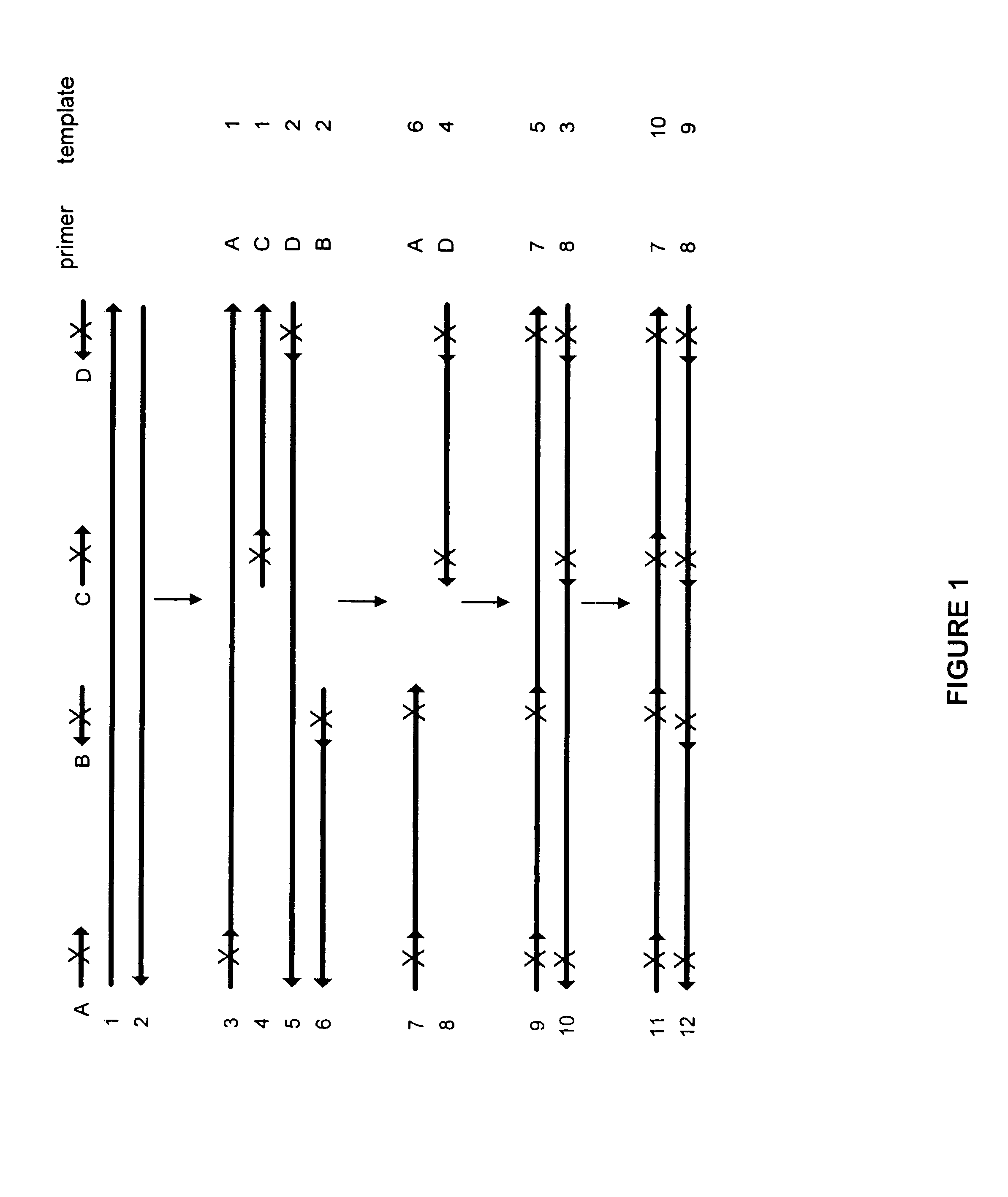
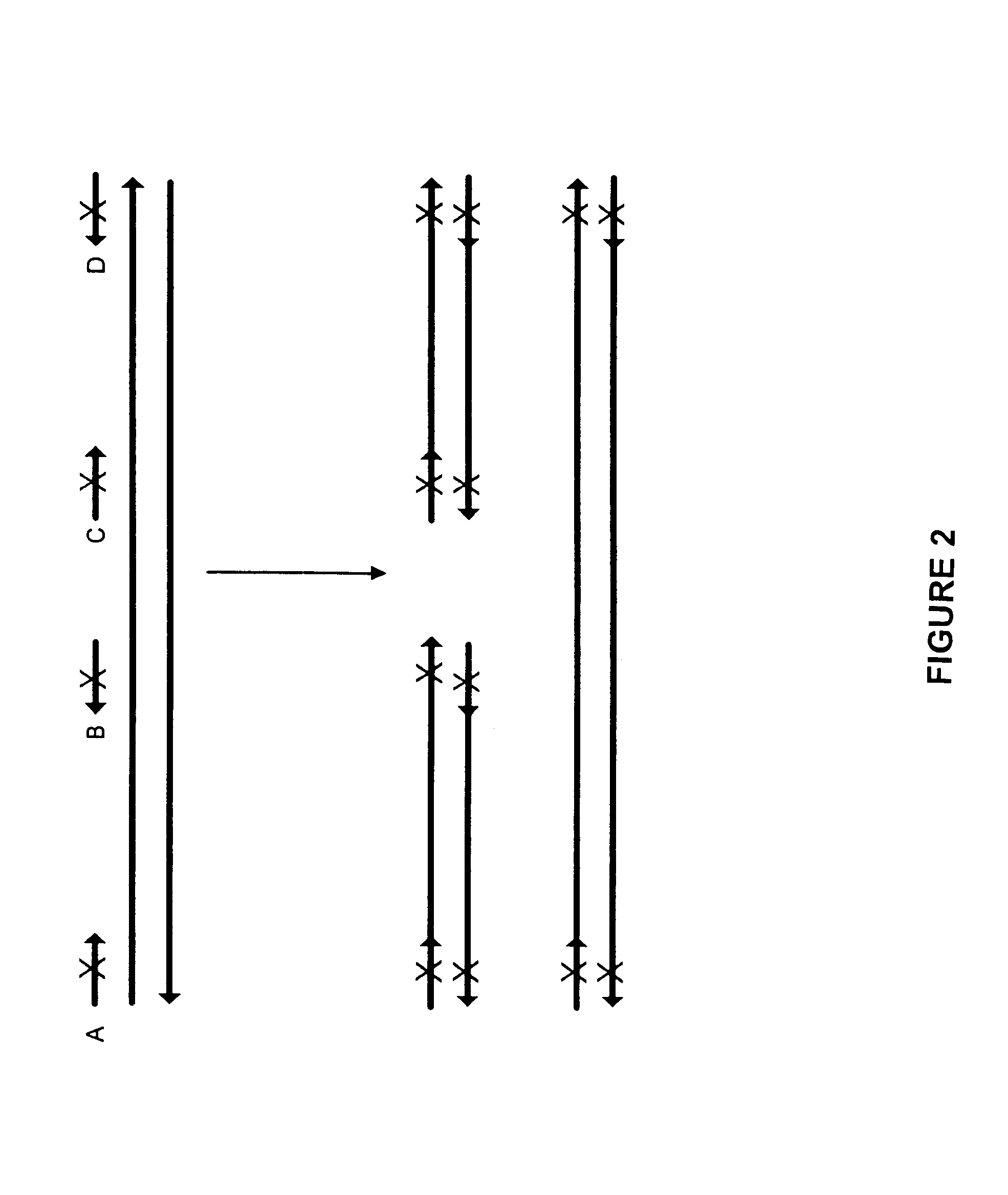
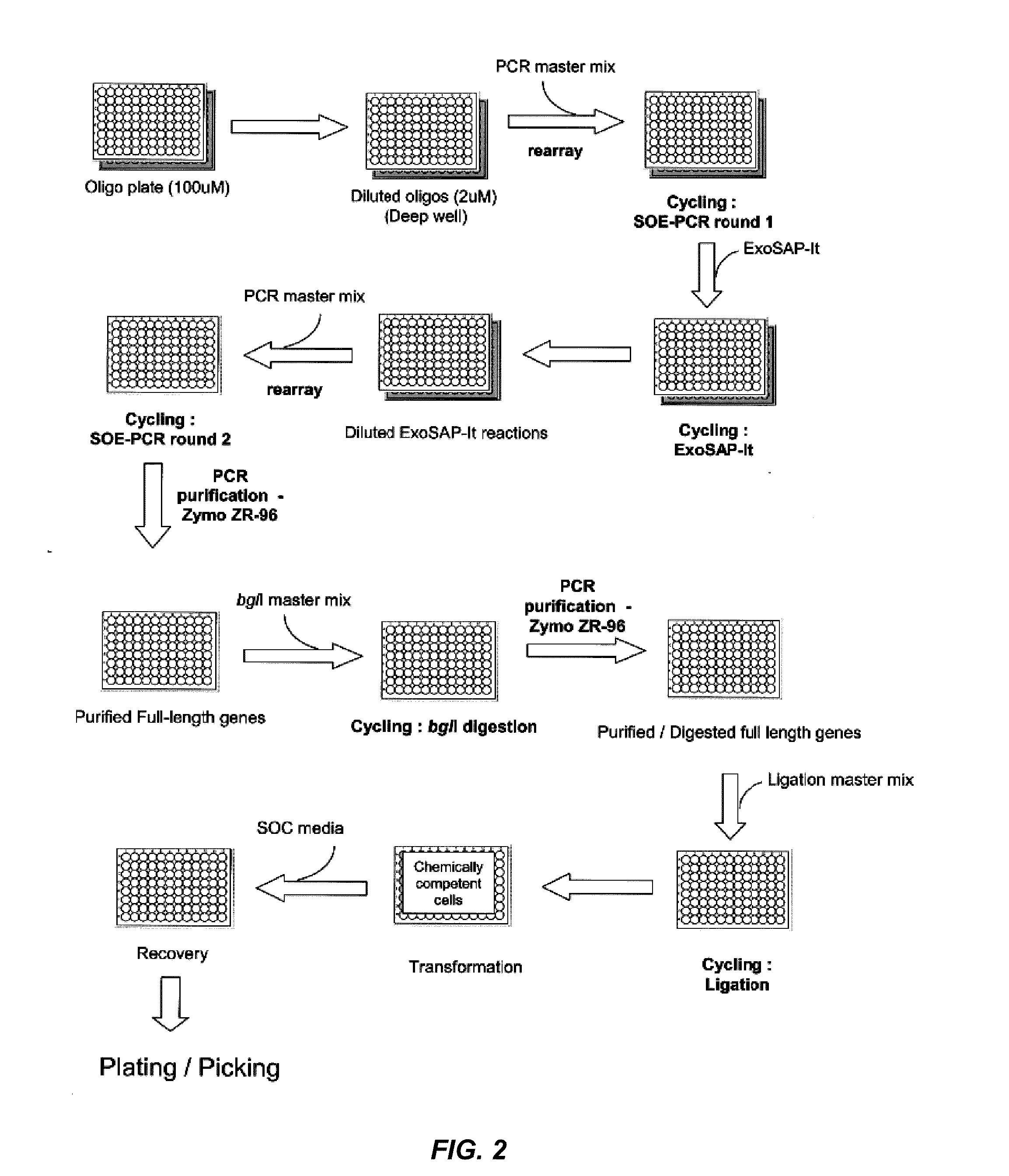
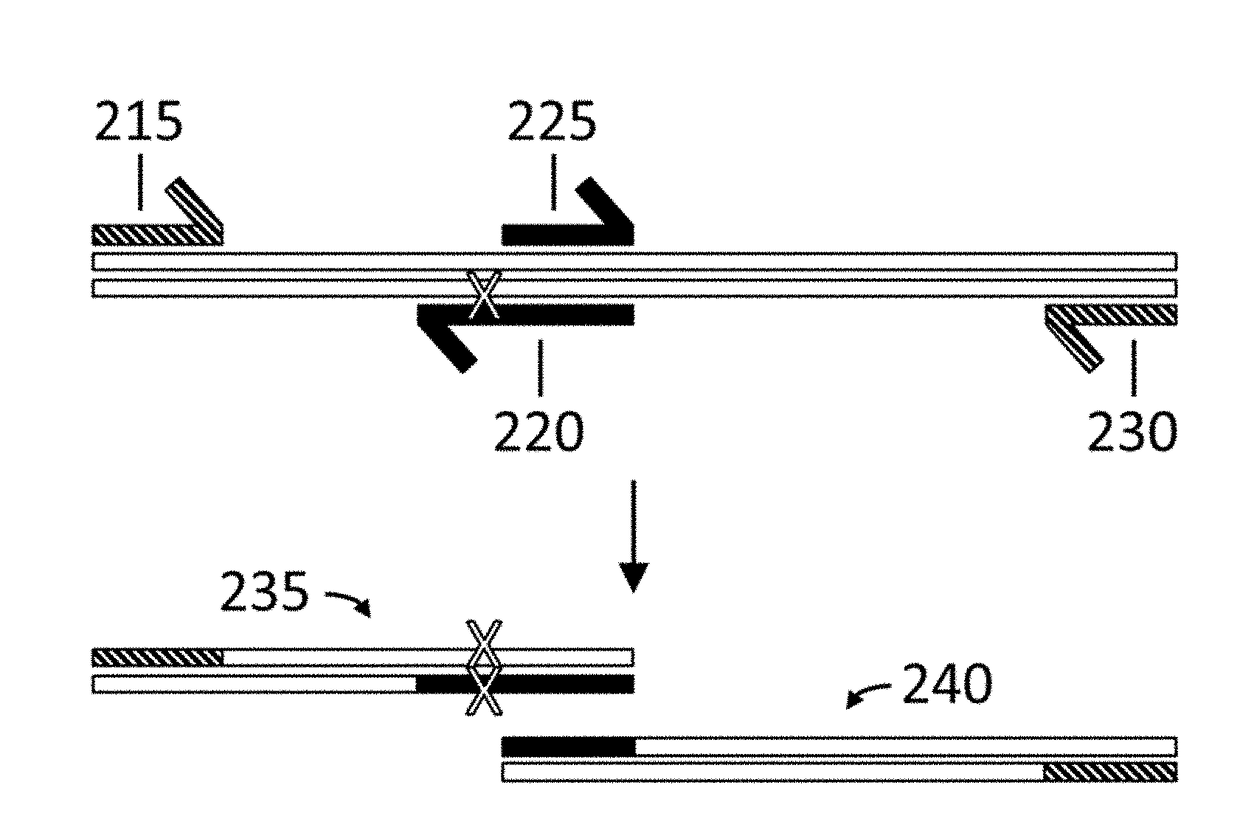
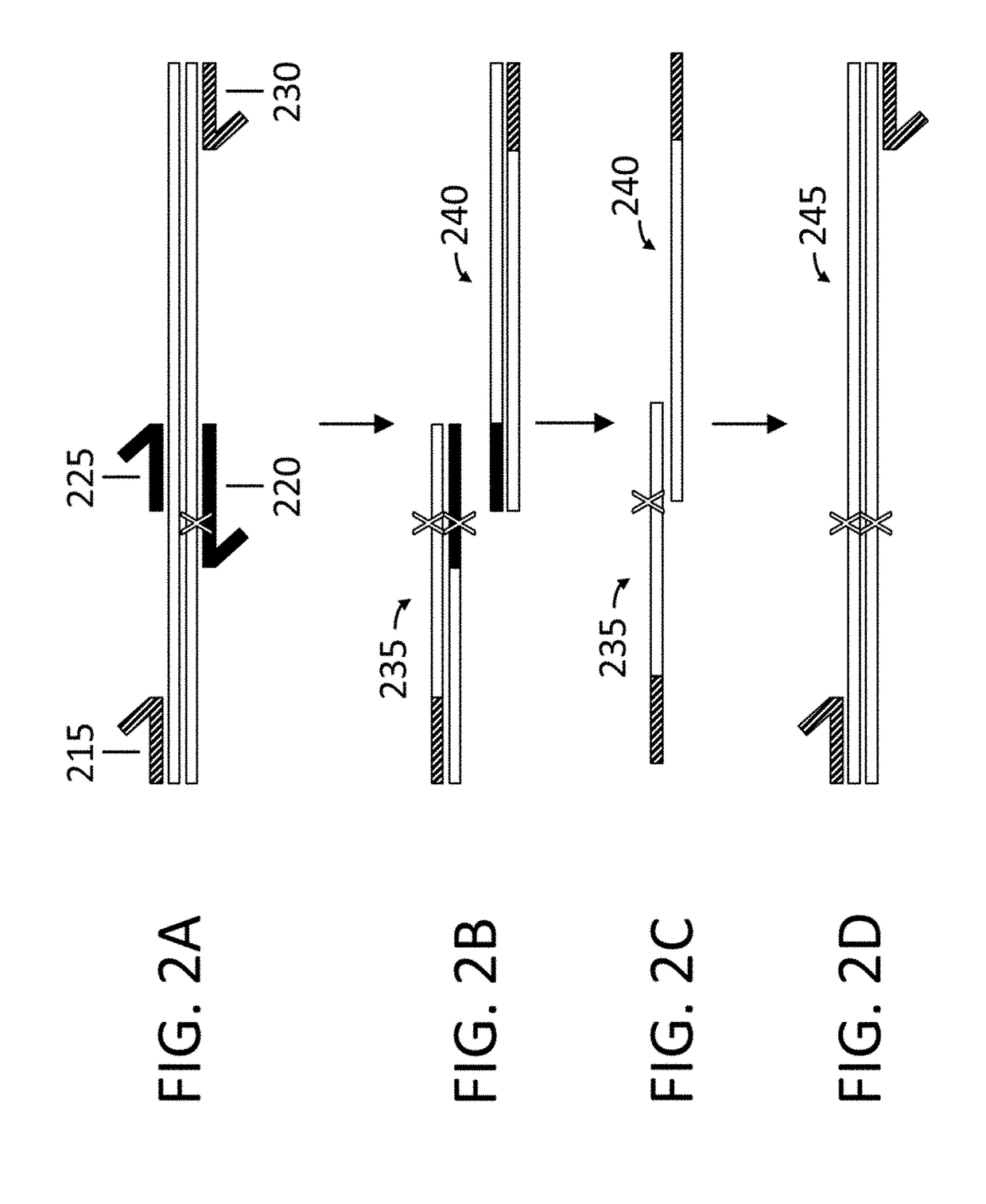
Method for generating a library of oligonucleotides comprising a controlled distribution of mutations
InactiveUS6582914B1Microbiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsOligonucleotideComputational biology
Methods are disclosed for producing libraries of nucleic acid molecules which libraries are derived from a nucleic acid template. The libraries comprise variant nucleic acids which are produced from a mutagenesis strategy using, e.g., a plurality of defined mutagenic and / or non-mutagenic primers and specific reaction conditions which favor the production of varied combinatorial mutants.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Polymorphisms in known genes associated with human disease, methods of detection and uses thereof
The present invention is based on the discovery of novel polymorphisms (SNPs) in the genes known in the art to contribute to human disease. Such polymorphisms can lead to a variety of disorders that are mediated / modulated by a variant human disease associated protein. The present invention provides reagents used for detecting and expressing the variant nucleic acid / protein sequence as well as methods of identifying and using these variants.
Owner:APPLERA
Methods and uses for molecular tags
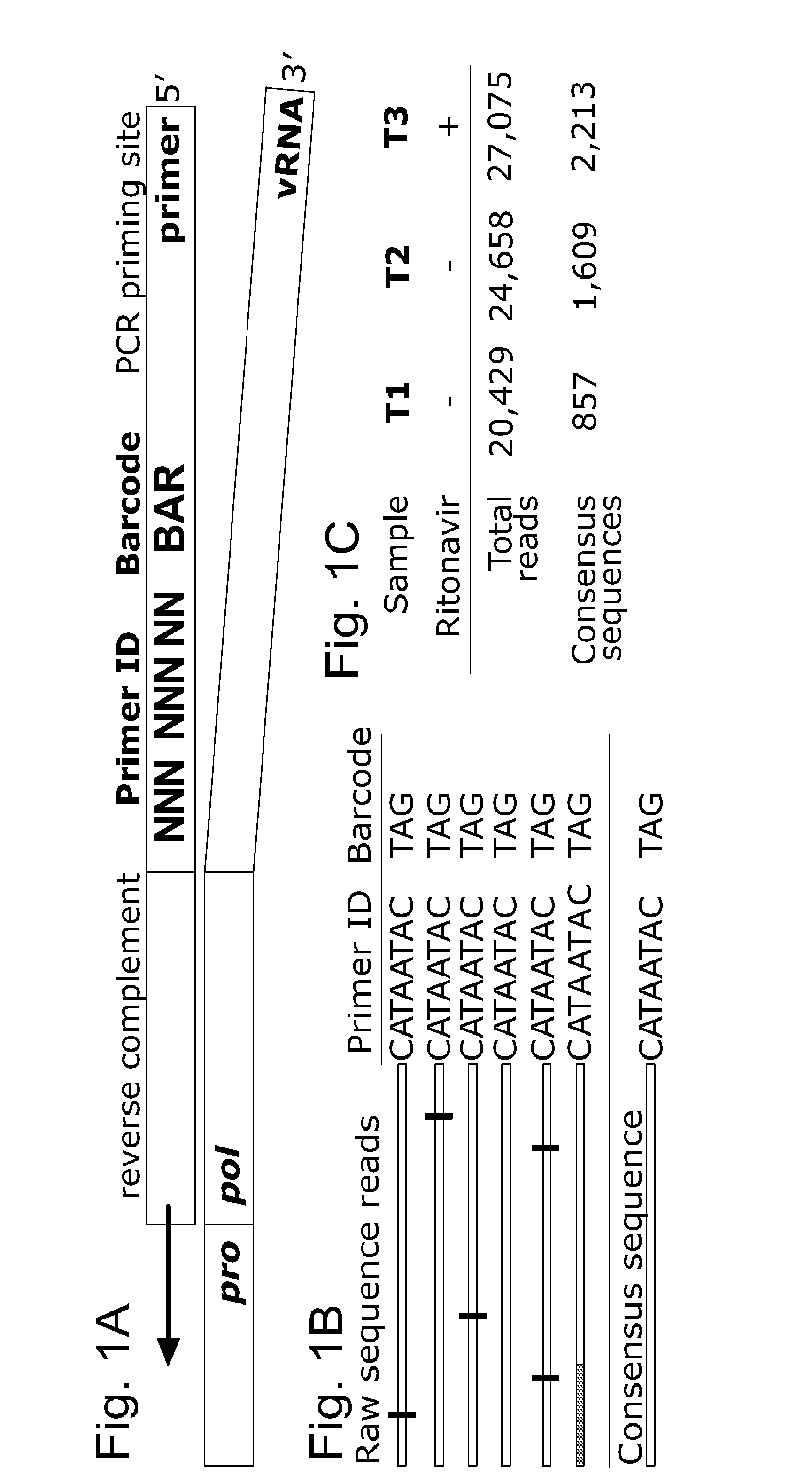
ActiveUS20160026758A1Overcome limitationsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenetic analysisComputational biology
Methods and uses for molecular tags are disclosed. Molecular tags may be attached to nucleic acid molecules. The attachment of the nucleic acid molecules prior to PCR amplification and sequencing improves the accuracy of genetic analysis and detection of genetic variations and diversity. Molecular tags may also be used for detection of drug-resistant variants. Methods for using molecular tags for determining and correcting PCR errors and / or sequencing error are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
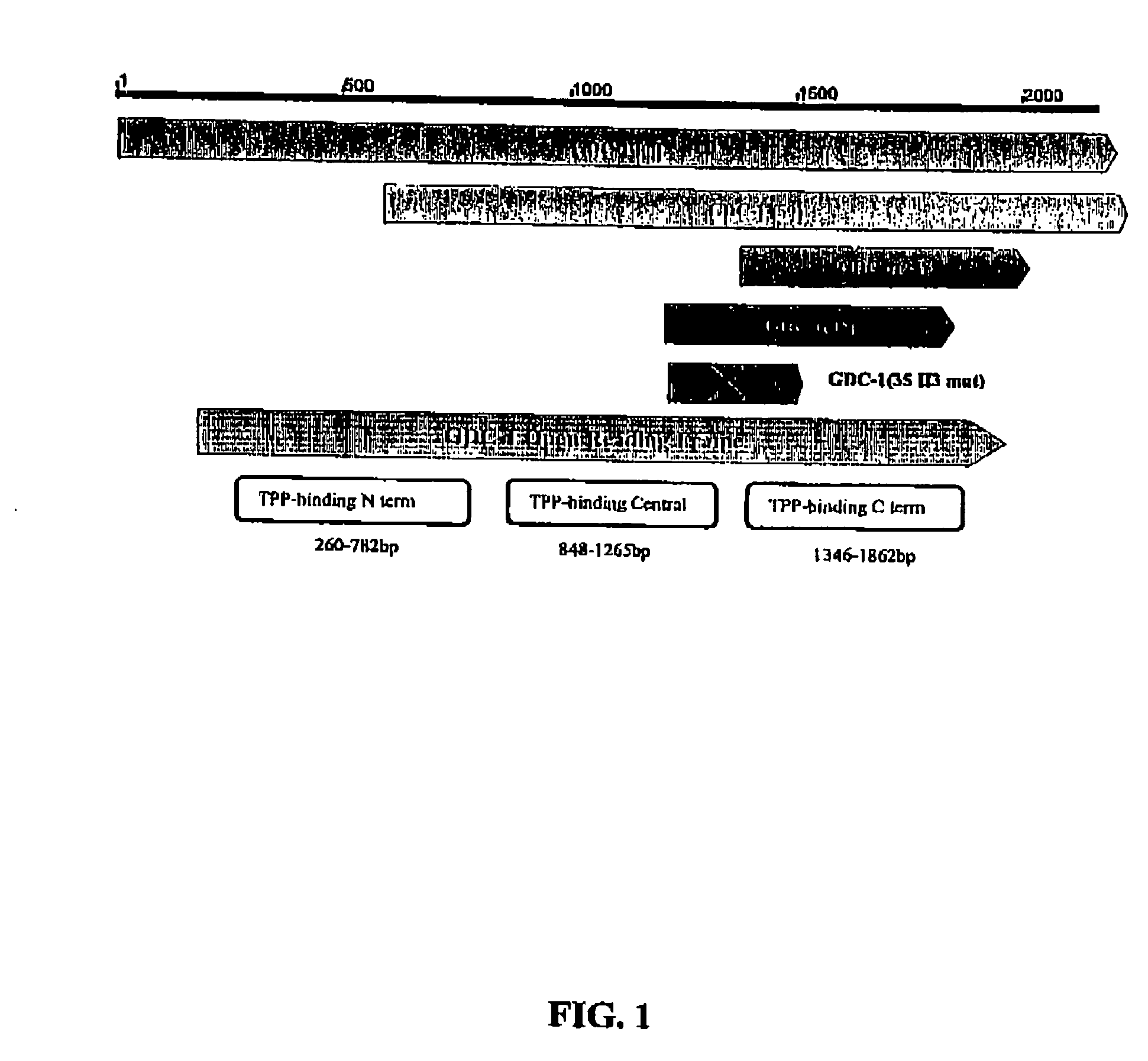
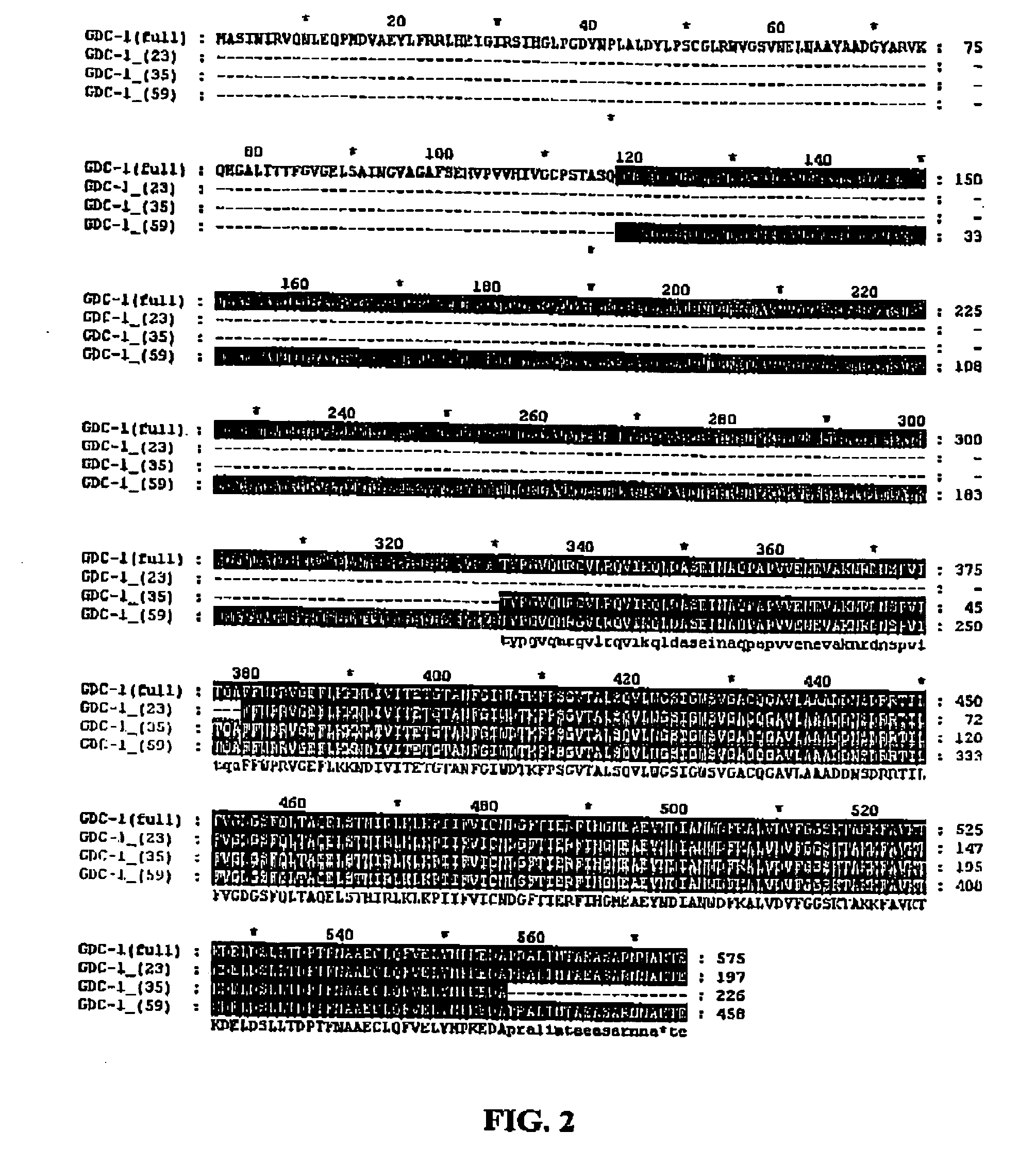
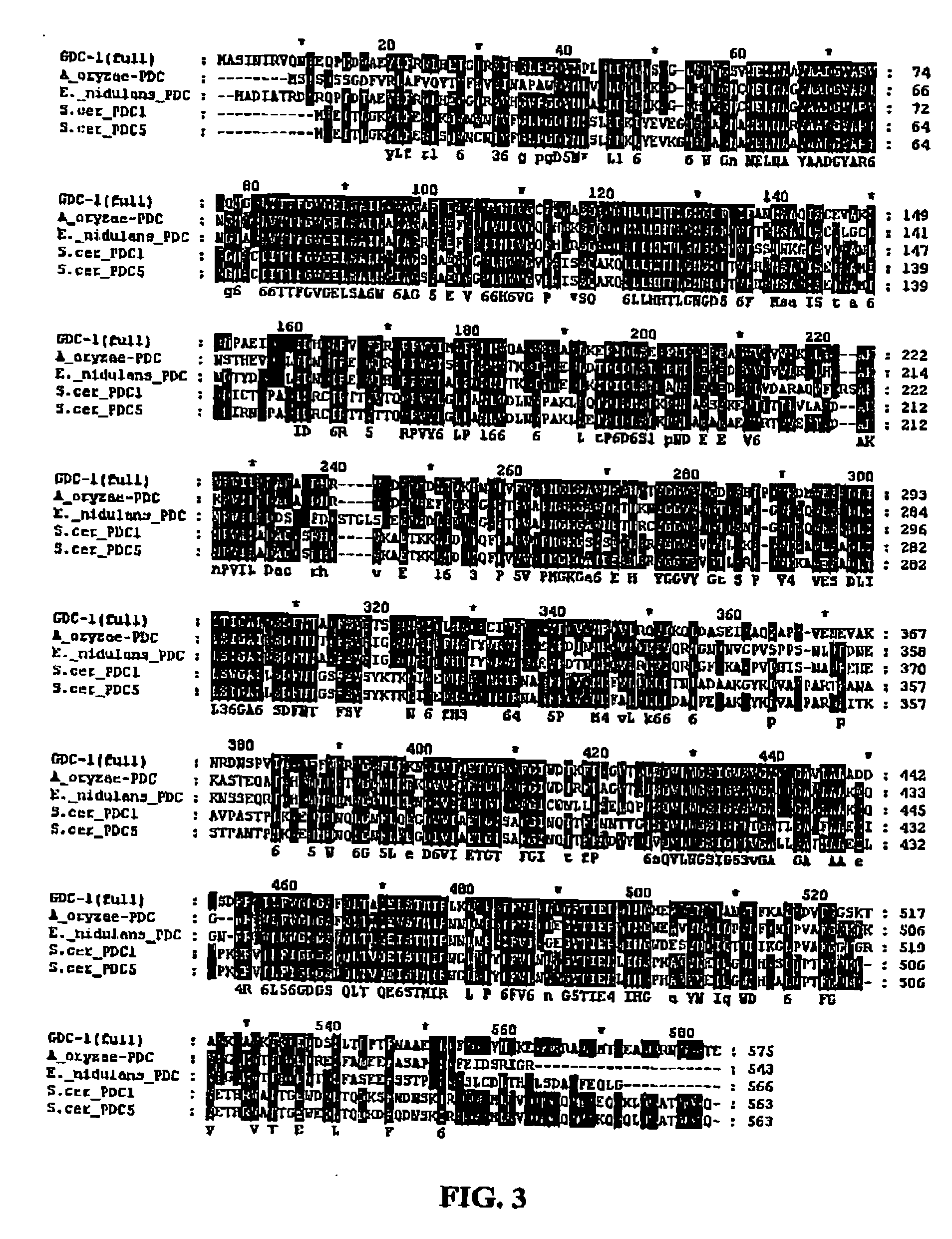
GDC-1 genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a polypeptide that confers resistance or tolerance to glyphosate herbicides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants. Compositions also comprise transformed plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules corresponding to glyphosate resistant nucleic acid sequences are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:3, 6, 8, 11, 19, or 21, or a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 18, or 20, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
Methods and compositions for isolating nucleic acid sequence variants
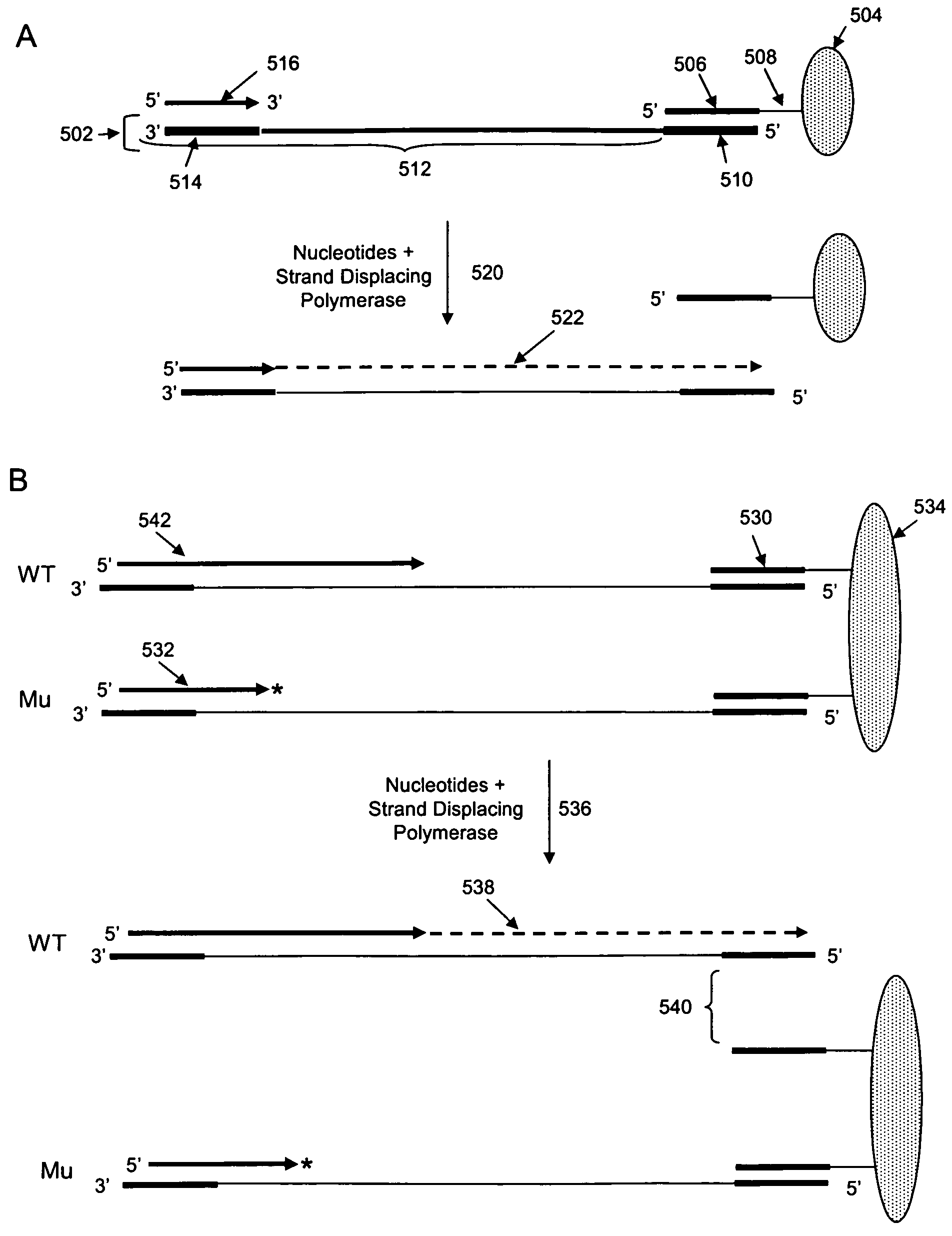
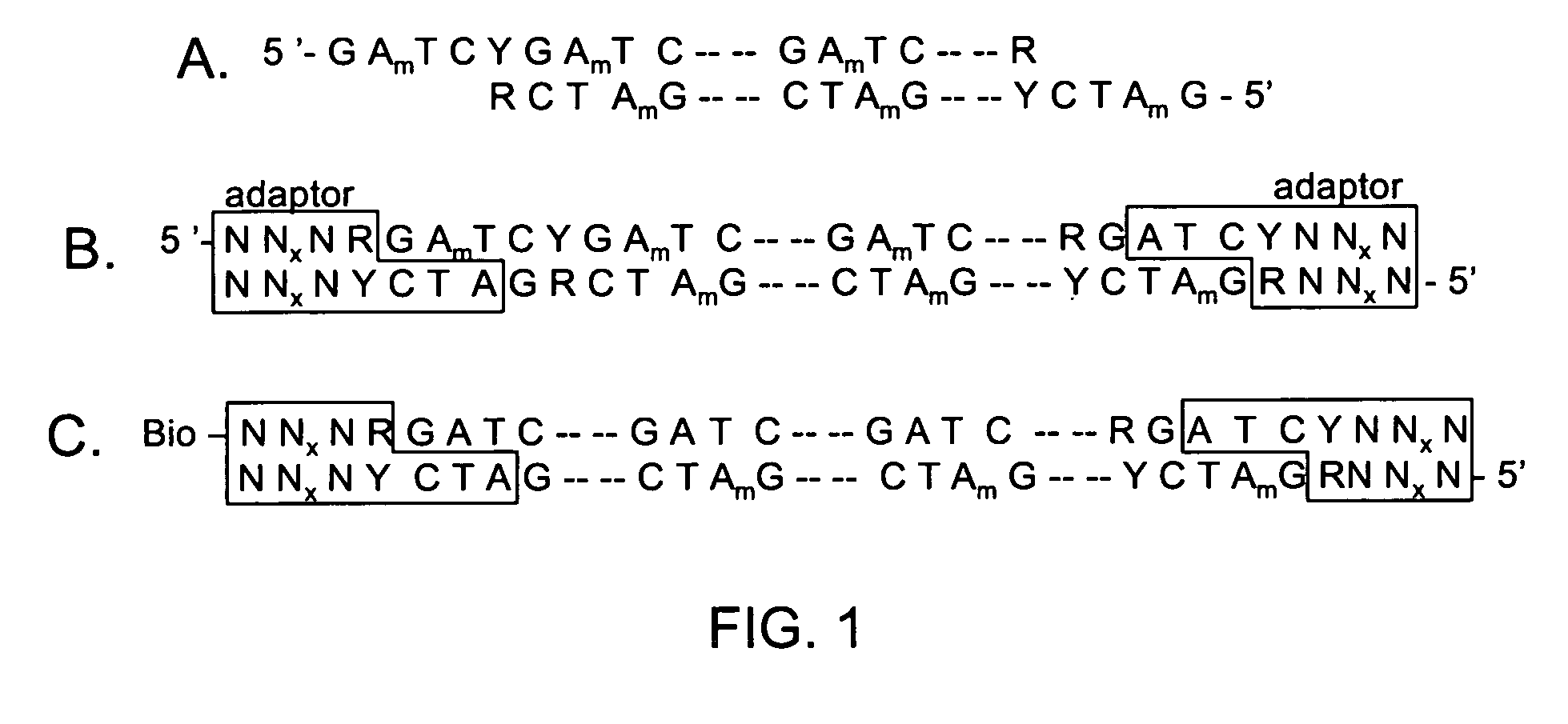
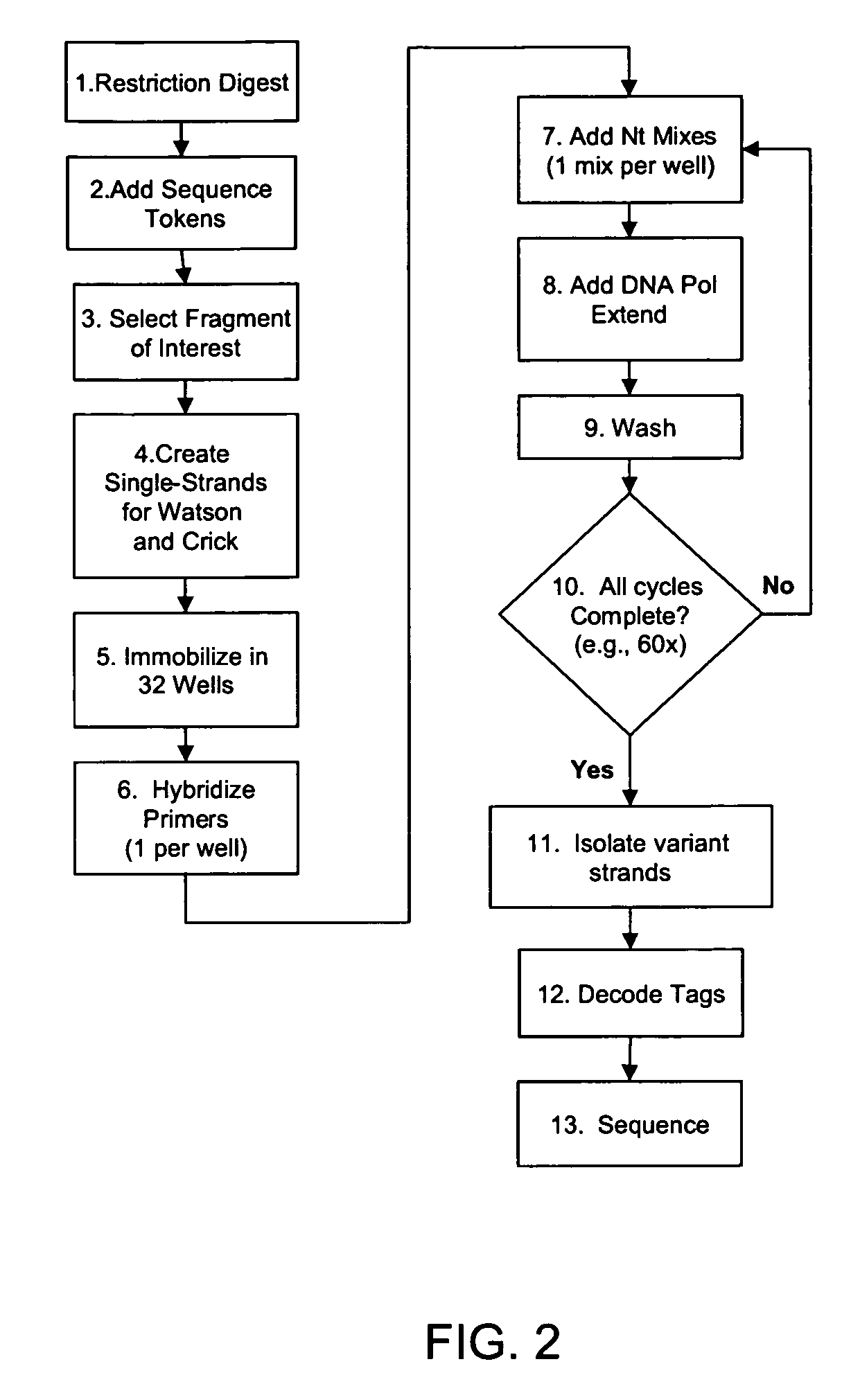
The invention is drawn to isolating sequence variants of a genetic locus of interest using a modified iterative primer extension method. The nucleic acids analyzed are generally single stranded and have a reference sequence which is used as a basis for performing iterative single nucleotide extension reactions from a hybridized polymerization primer. The iterative polymerization reactions are configured such that polymerization of the strand will continue if the sequence of the nucleic acid being analyzed matches the reference sequence, whereas polymerization will be terminated if the nucleic acid being analyzed does not match the reference sequence. Nucleic acid strands that have mutations can be isolated using a variety of methods and sequenced to determine the precise identity of the mutation / polymorphism. By performing the method on both strands of the nucleic acid being analyzed, virtually all possible mutations can be identified.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
AXMI-008, a delta-endotoxin gene and methods for its use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a delta-endotoxin and delta-endotoxin-associated polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated delta-endotoxin and delta-endotoxin-associated nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NOS:3, 5, and 7, and the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 2, 4, and 6, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Plant breeding method
InactiveUS20050144664A1Other foreign material introduction processesAgricultureNumeral systemPlant variety
Methods for using genetic marker genotype (e.g., gene sequence diversity information) to improve the process of developing plant varieties (e.g., single cross hybrids) with improved phenotypic performance are provided. Methods for predicting the value of a phenotypic trait in a plant are provided. The methods use genotypic, phenotypic, and optionally family relationship information for a first plant population to identify an association between at least one genetic marker and the phenotypic trait, and then use the association to predict the value of the phenotypic trait in one or more members of a second, target population of known marker genotype. Methods for identifying new allelic variants affecting the trait are also provided. Plants selected, provided, or produced by any of the methods herein, transgenic plants created by any of the methods herein, and digital systems for performing the methods herein are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
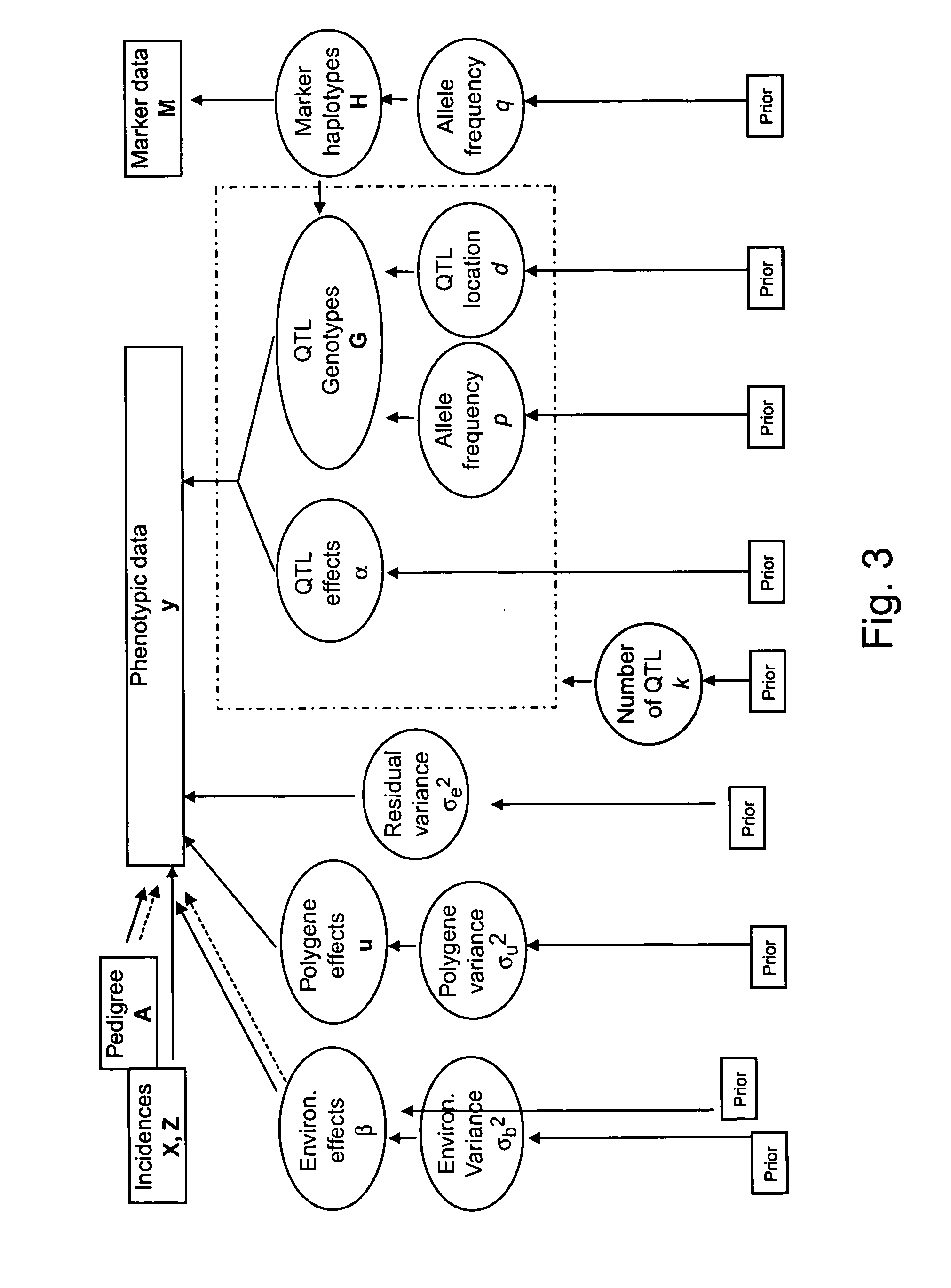
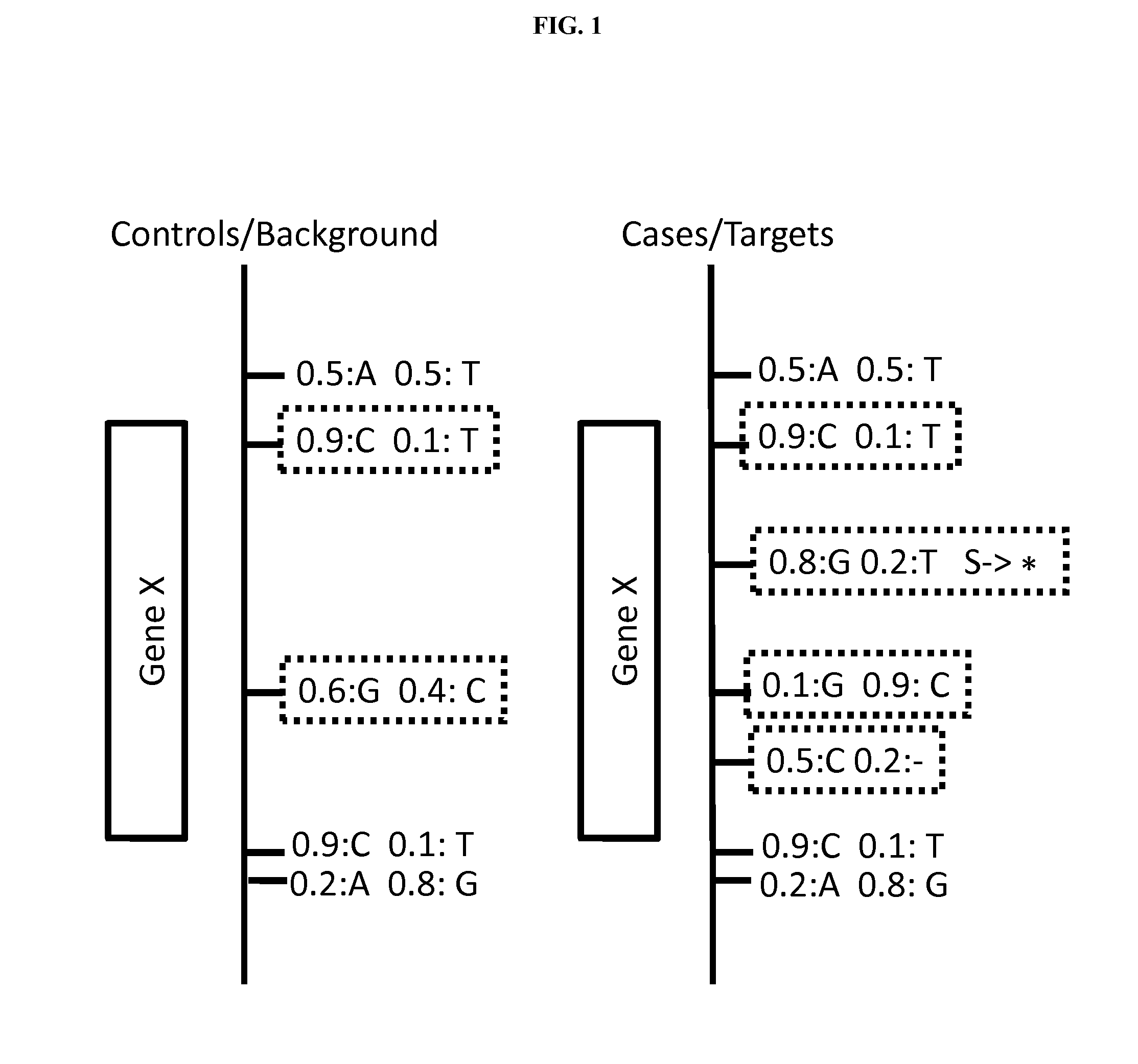
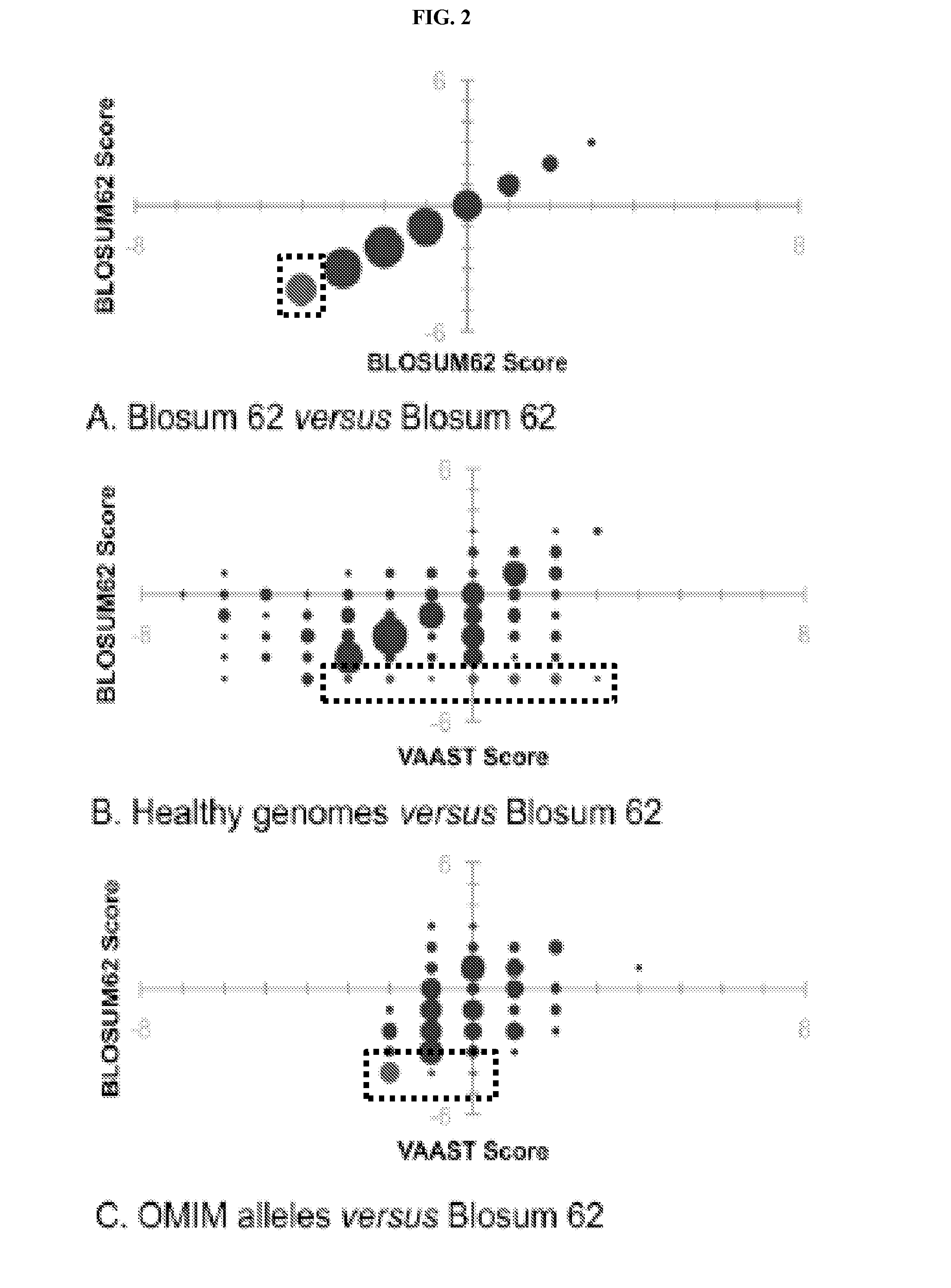
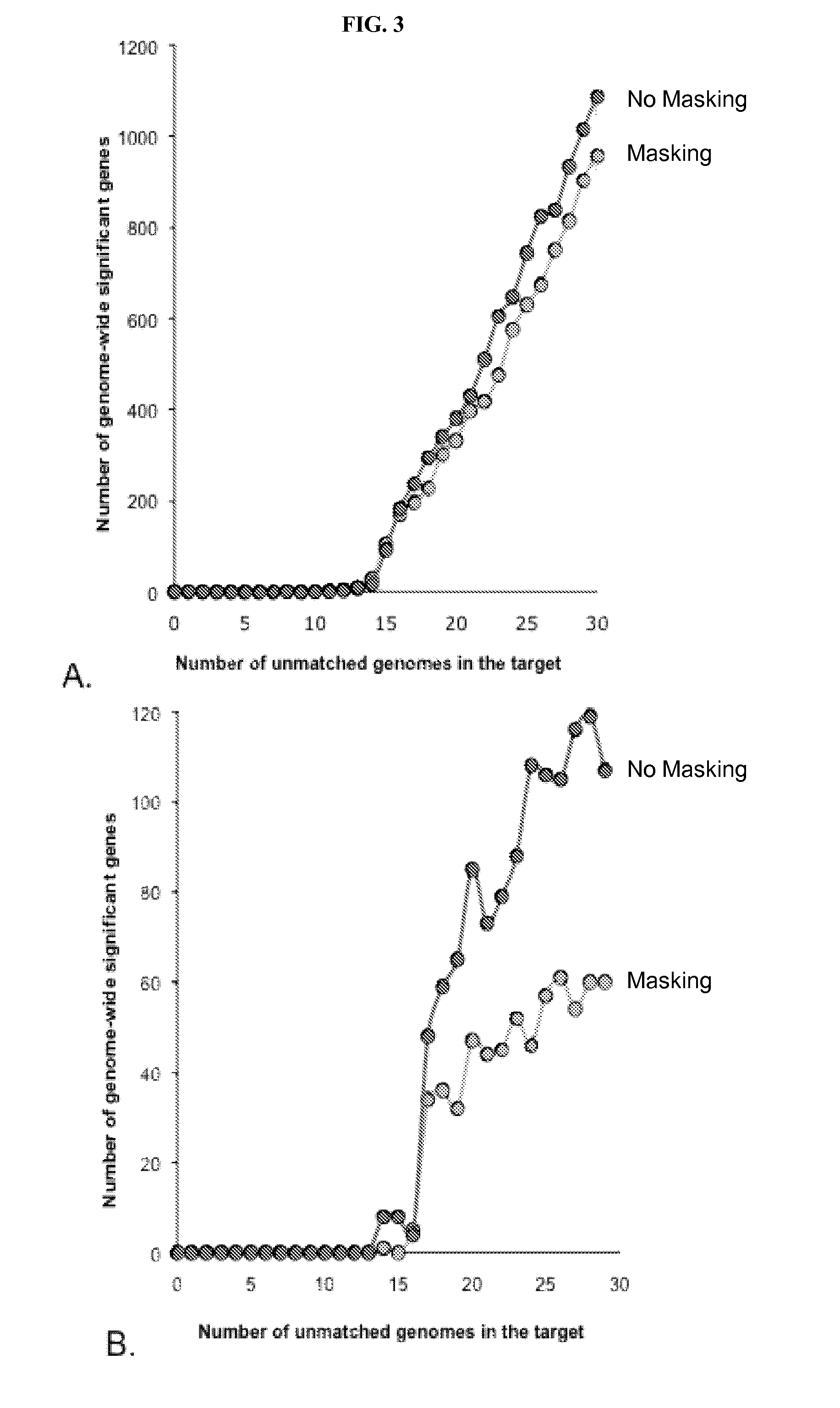
Variant annotation, analysis and selection tool
Disclosed are methods for detecting and / or prioritizing phenotype-causing genomic variants and related software tools. The methods include genomic feature based analysis and can combine variant frequency information with sequence characteristics such as amino acid substation. The methods disclosed are useful in any genomics study; for example, rare and common disease gene discovery, tumor growth mutation detection, personalized medicine, agricultural analysis, and centennial analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
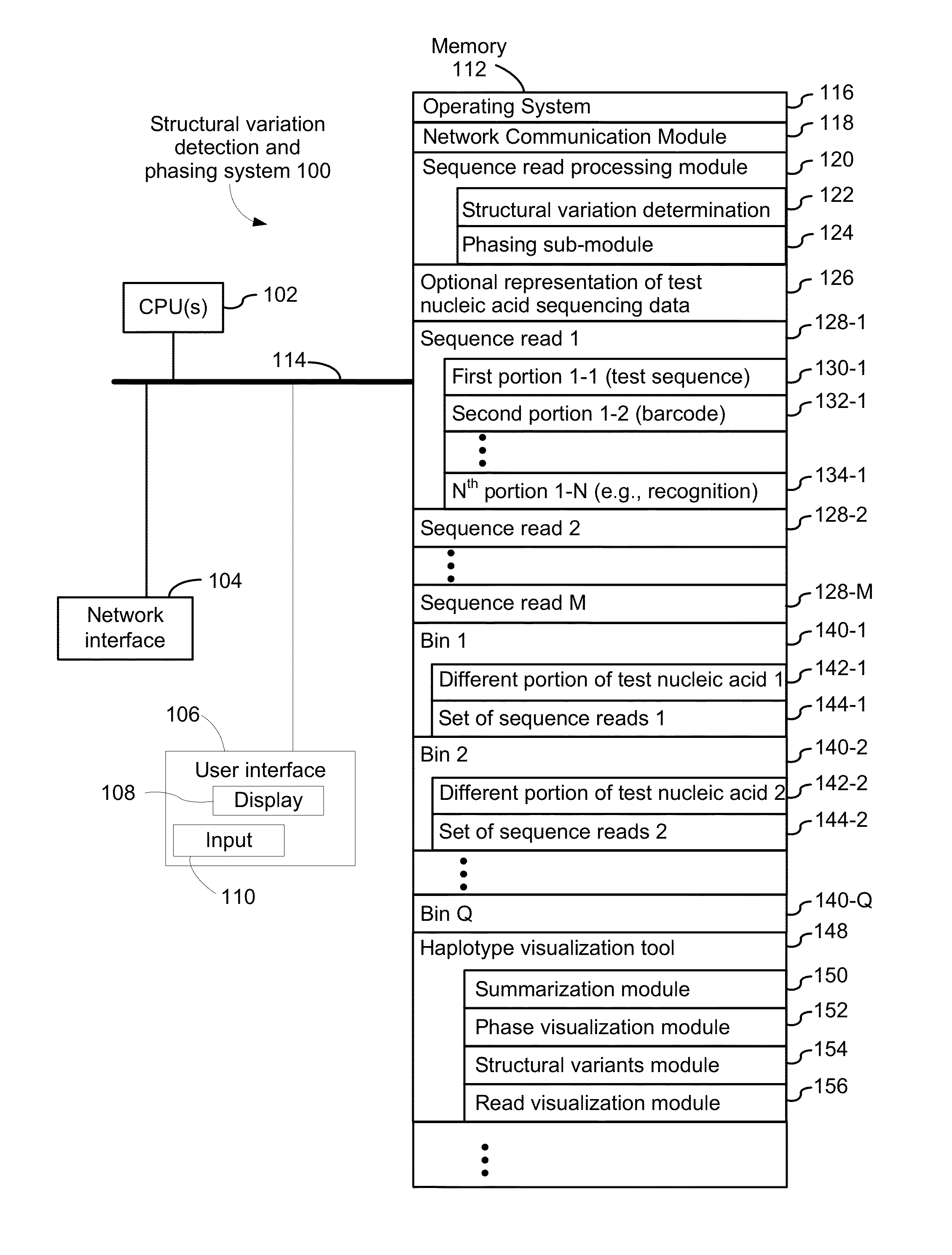
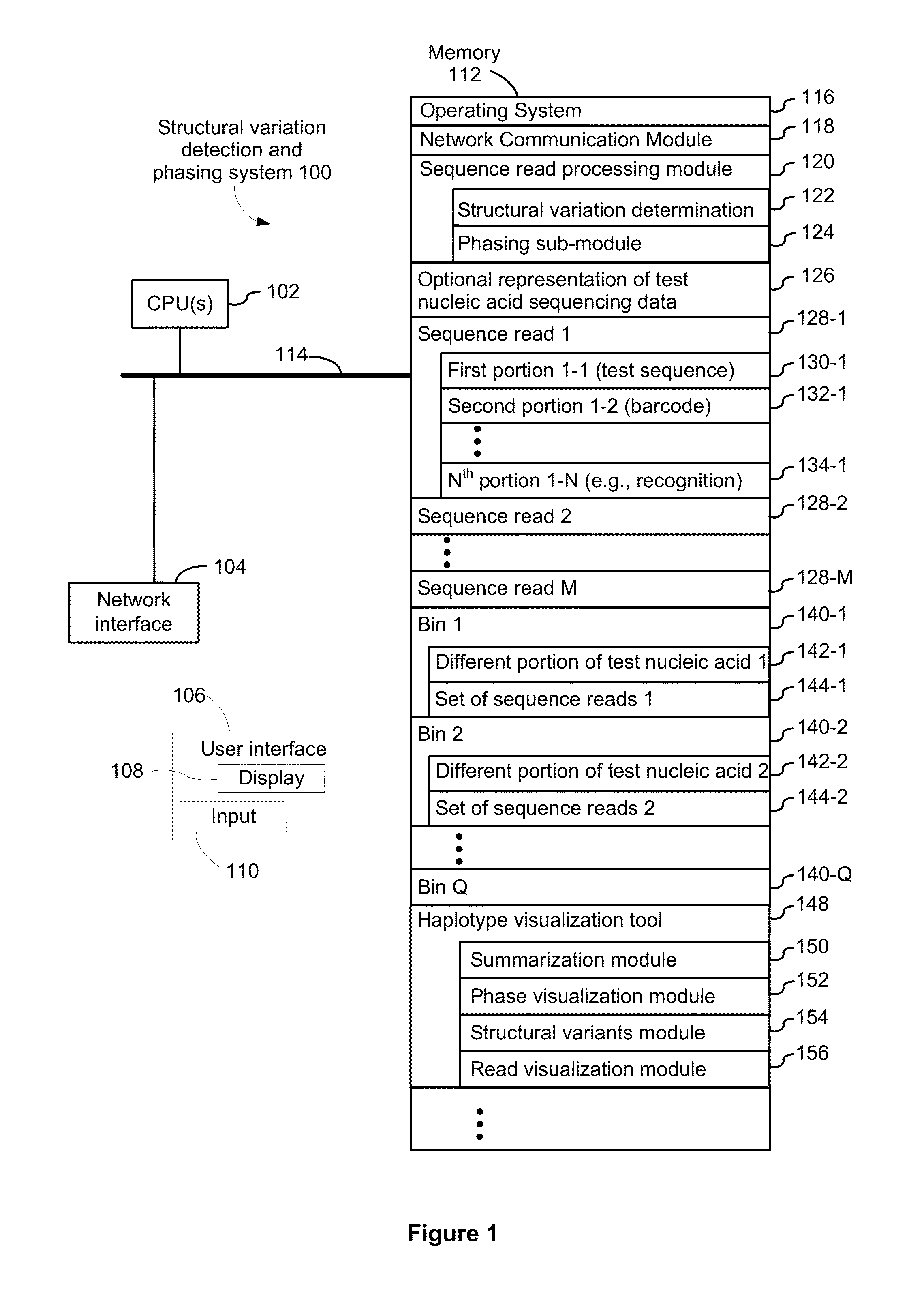
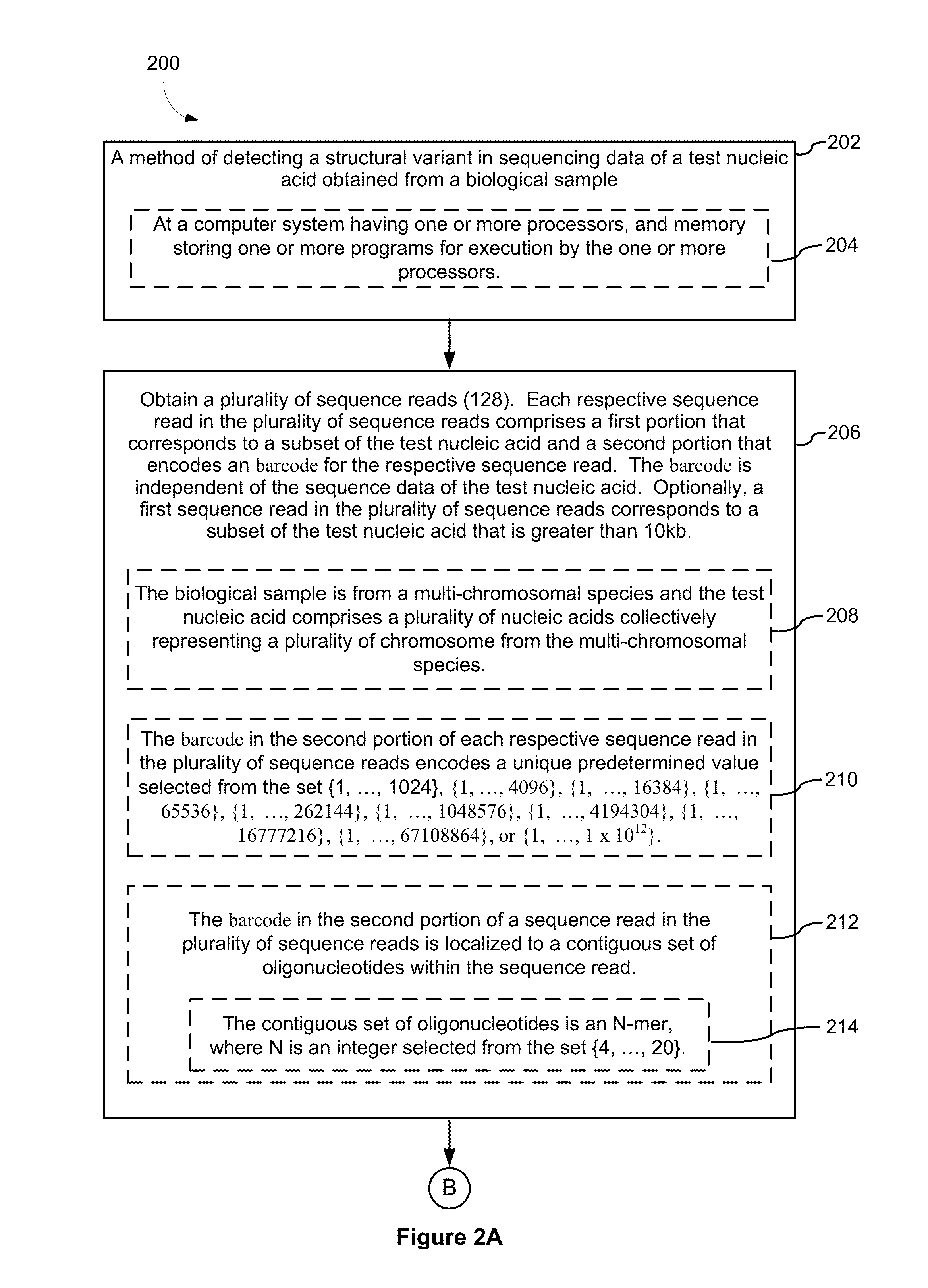
Systems and methods for determining structural variation and phasing using variant call data
ActiveUS20160232291A1Better phasingSimple methodMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementBarcodeData system
Systems and methods for determining structural variation and phasing using variant call data obtained from nucleic acid of a biological sample are provided. Sequence reads are obtained, each comprising a portion corresponding to a subset of the test nucleic acid and a portion encoding a barcode independent of the sequencing data. Bin information is obtained. Each bin represents a different portion of the sample nucleic acid. Each bin corresponds to a set of sequence reads in a plurality of sets of sequence reads formed from the sequence reads such that each sequence read in a respective set of sequence reads corresponds to a subset of the nucleic acid represented by the bin corresponding to the respective set. Binomial tests identify bin pairs having more sequence reads with the same barcode in common than expected by chance. Probabilistic models determine structural variation likelihood from the sequence reads of these bin pairs.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
System and Methods for Detecting Genetic Variation
The invention provides methods, apparatuses, and compositions for high-throughput amplification sequencing of specific target sequences in one or more samples. In some aspects, barcode-tagged polynucleotides are sequenced simultaneously and sample sources are identified on the basis of barcode sequences. In some aspects, sequencing data are used to determine one or more genotypes at one or more loci comprising a causal genetic variant. In some aspects, systems and methods of detecting genetic variation are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD WOMENS HEALTH INC
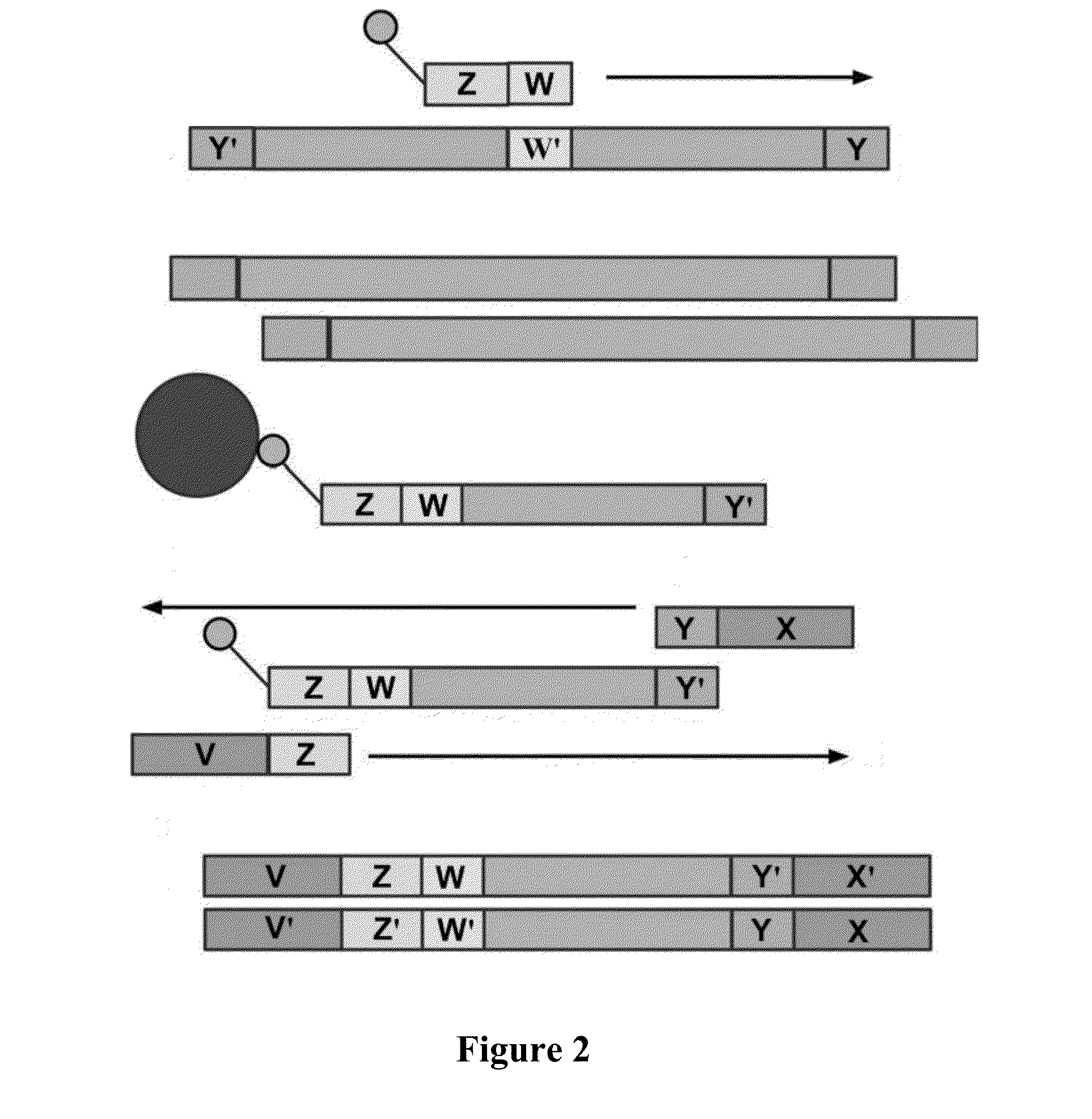
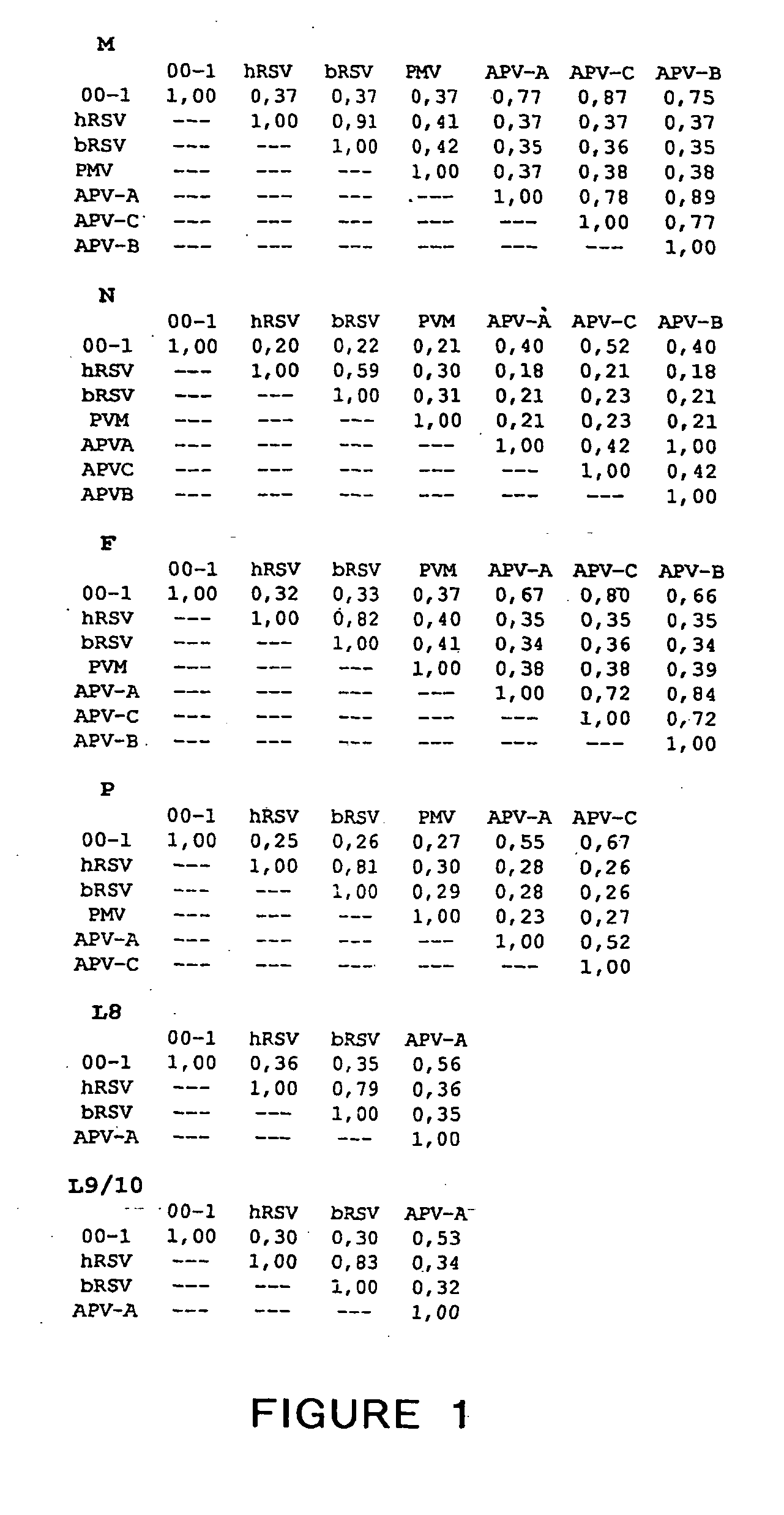
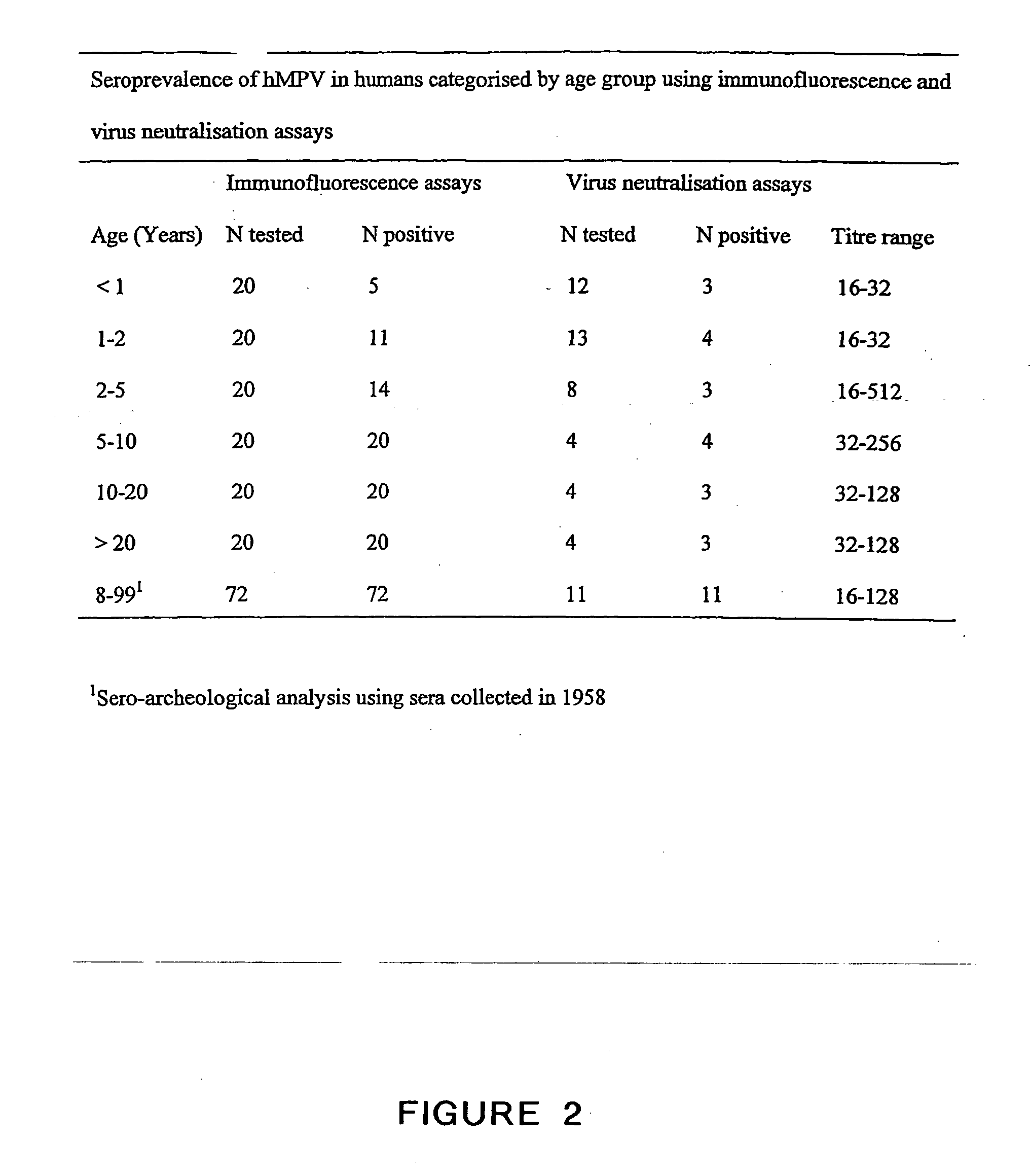
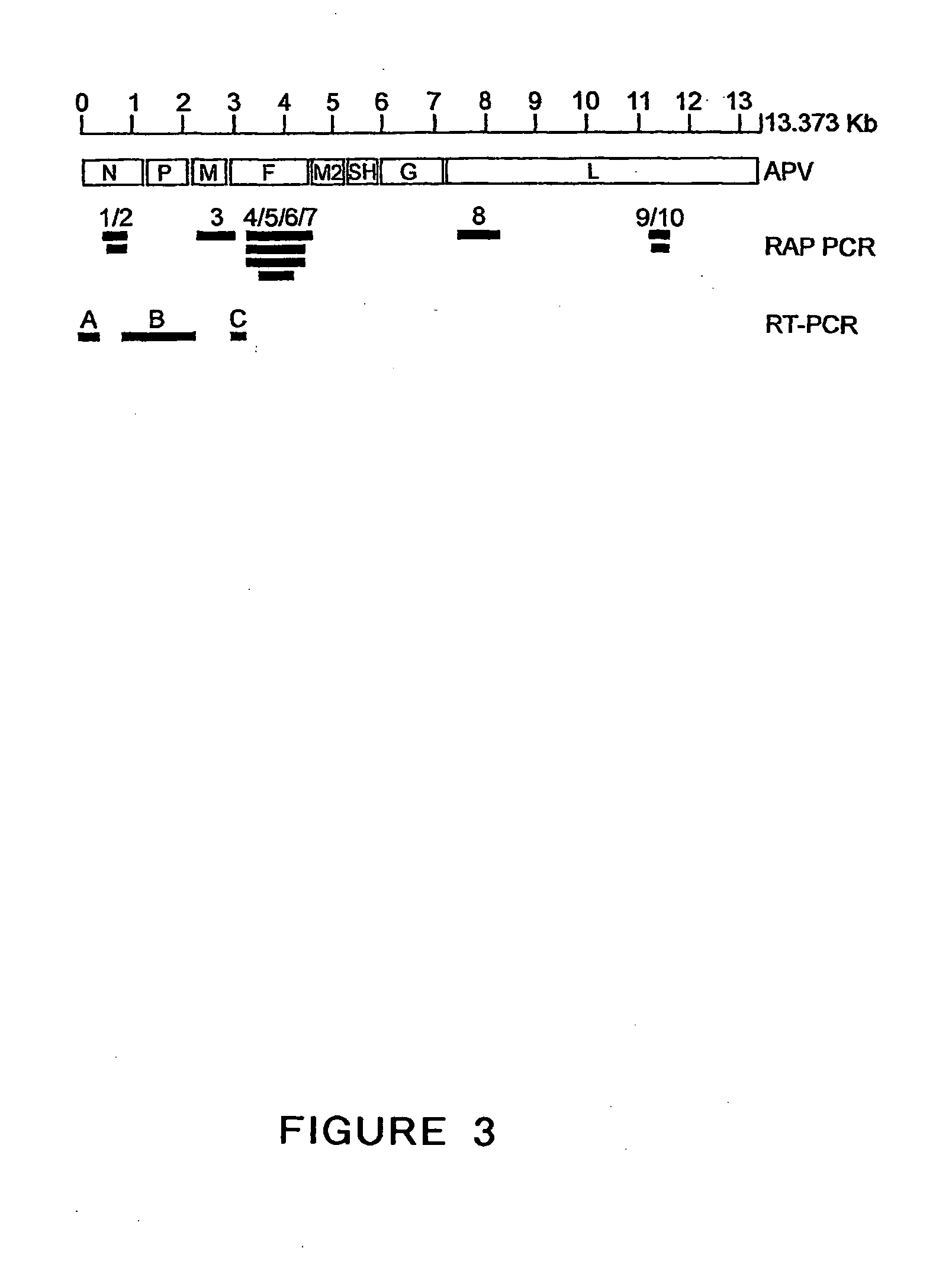
Metapneumovirus strains and their use in vaccine formulations and as vectors for expression of antigenic sequences and methods for propagating virus
ActiveUS20050019891A1Narrow downSymptoms improvedSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesNegative strandHeterologous
The present invention provides an isolated mammalian negative strand RNA virus, metapneumovirus (MPV), within the sub-family Pneumoviridae, of the family Paramyxoviridae. The invention also provides isolated mammalian negative strand RNA viruses identifiable as phylogenetically corresponding or relating to the genus Metapneumovirus and components thereof. In particular the invention provides a mammalian MPV, subgroups and variants thereof. The invention relates to genomic nucleotide sequences of different isolates of mammalian metapneumoviruses, in particular human metapneumoviruses. The invention relates to the use of the sequence information of different isolates of mammalian metapneumoviruses for diagnostic and therapeutic methods. The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences encoding the genome of a metapneumovirus or a portion thereof, including both mammalian and avian metapneumovirus. The invention further encompasses chimeric or recombinant viruses encoded by said nucleotide sequences. The invention also relates to chimeric and recombinant mammalian MPV that comprise one or more non-native or heterologous sequences. The invention further relates to vaccine formulations comprising mammalian or avian metapneumovirus, including recombinant and chimeric forms of said viruses. The vaccine preparations of the invention encompass multivalent vaccines, including bivalent and trivalent vaccine preparations. The invention also provide methods for propagating virus.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
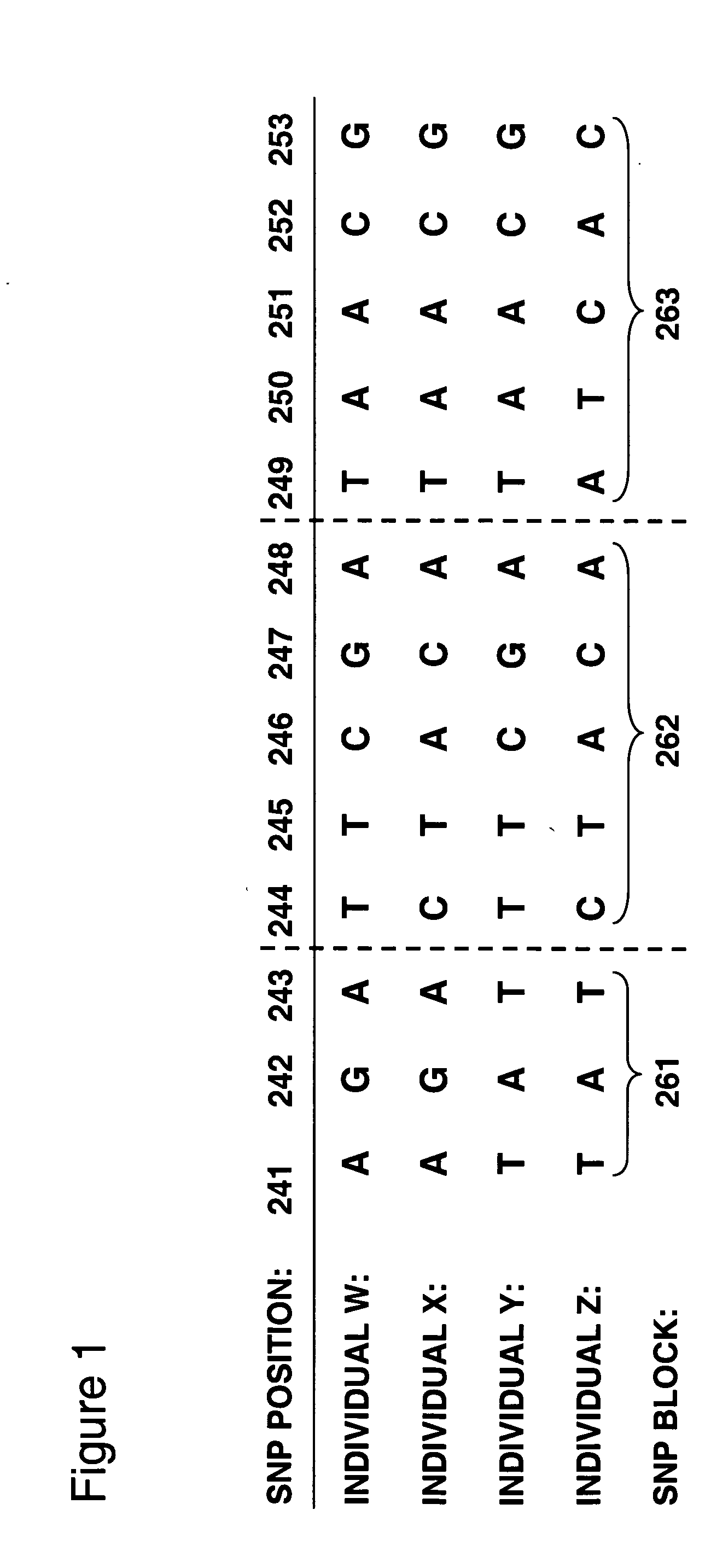
Allele-specific expression patterns
The invention provides methods of analyzing genes for differential relative allelic expression patterns. Haplotype blocks throughout the genomes of individuals are analyzed to identify haplotype patterns that are associated with specific differential relative allelic expression patterns. Haplotype blocks that contain associated haplotype patterns may be further investigated to identify genes or variants of genes involved in differential relative allelic expression patterns.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Dideoxynucleotide-triphosphate utilization by the hyper-thermophilic DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus
InactiveUS6333183B1High sensitivityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesBinding site
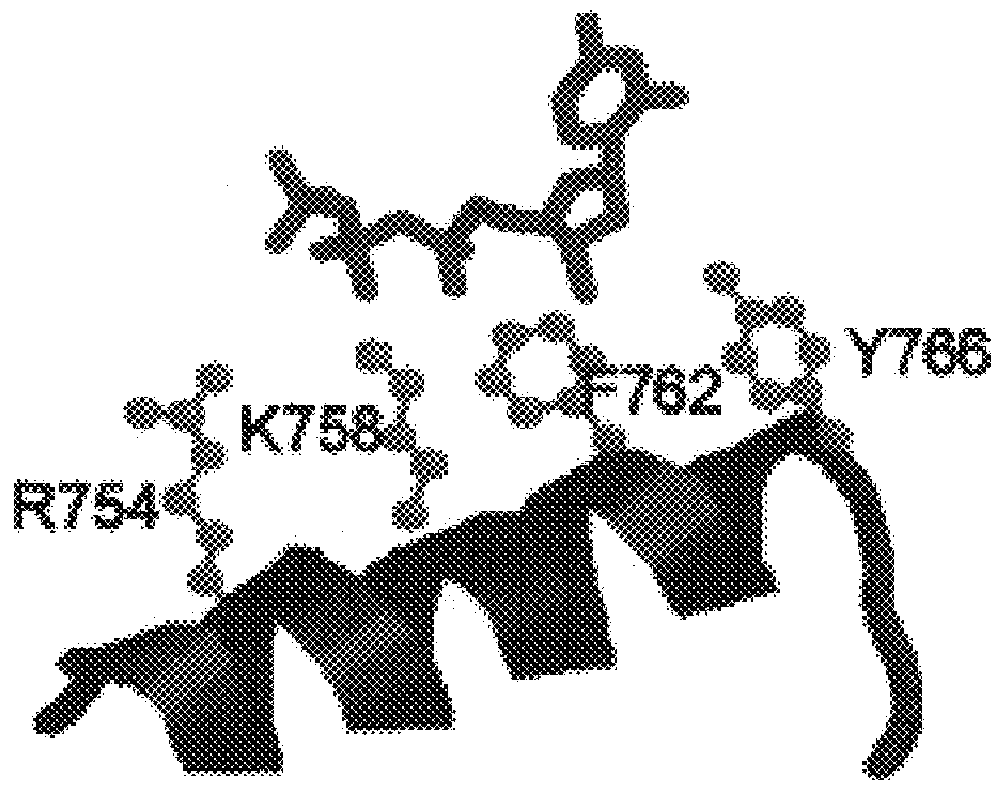
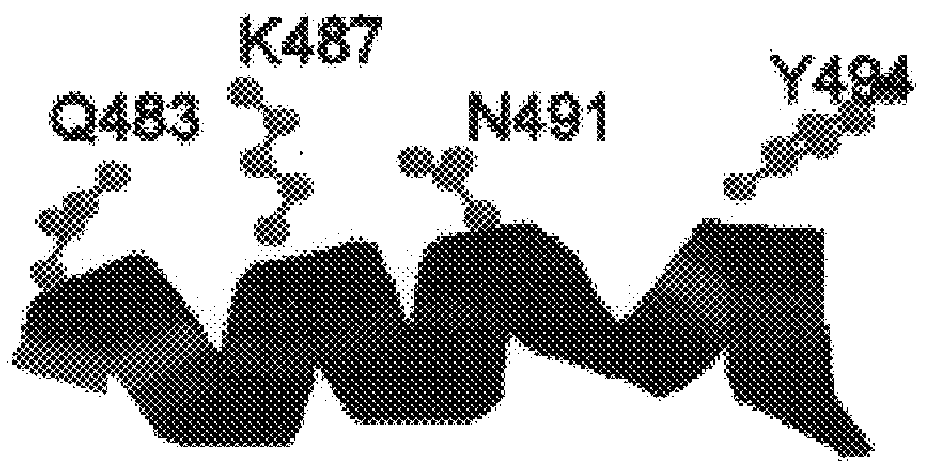
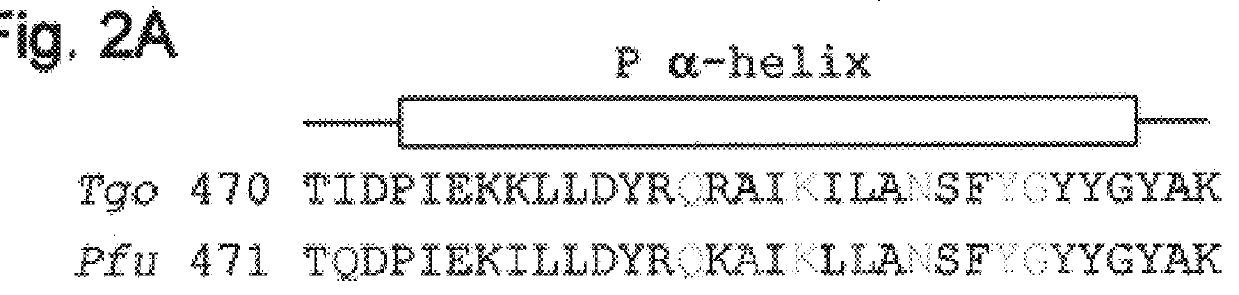
Polymerases from the Pol I family which are able to efficiently use ddNTPs have demonstrated a much improved performance when used to sequence DNA. A number of mutations have been made to the gene coding for the Pol II family DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus with the aim of improving ddNTP utilisation. "Rational" alterations to amino acids likely to be near the dNTP binding site (based on sequence homologies and structural information) did not yield the desired level of selectivity for ddNTPs. However, alteration at four positions (Q472, A486, L490 and Y497) gave rise to variants which incorporated ddNTPs better than the wild type, allowing sequencing reactions to be carried out at lowered ddNTP:dNTP ratios. Wild type Pfu-Pol required a ddNTP:dNTP ratio of 30:1; values of 5:1 (Q472H), 1:3 (L490Y), 1:5 (A486Y) and 5:1 (Y497A) were found with the four mutants; A486Y representing a 150-fold improvement over the wild type. A486, L490 and Y407 are on an alpha-helix that lines the dNTP binding groove, but the side chains of the three amino acids point away from this groove; Q472 is in a loop that connects this alpha-helix to a second long helix. None of the four amino acids can contact the dNTP directly. Therefore, the increased selectivity for ddNTPs is likely to arise from two factors: 1) Small overall changes in conformation that subtly alter the nucleotide triphosphate binding site such that ddNTPs become favoured; 2) interference with a conformational change that may be critical both for the polymerisation step and discrimination between different nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Methods and Systems for Identification of Causal Genomic Variants
PendingUS20140359422A1Chemical property predictionDigital data information retrievalData setGenomic information
Methods and systems for filtering variants in data sets comprising genomic information are provided herein.
Owner:QIAGEN REDWOOD CITY
Method of detecting tumour recurrence
PendingUS20200248266A1High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsMultiplexCell free
The invention relates to subject-specific methods for detecting recurrence of tumours based on an understanding of the clonal / subclonal mutation profile of the subject's tumour and detection of the mutations in their cell-free DNA (cfDNA), typically by multiplex PCR of tumour mutations such as single nucleotide variants (SNVs).
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
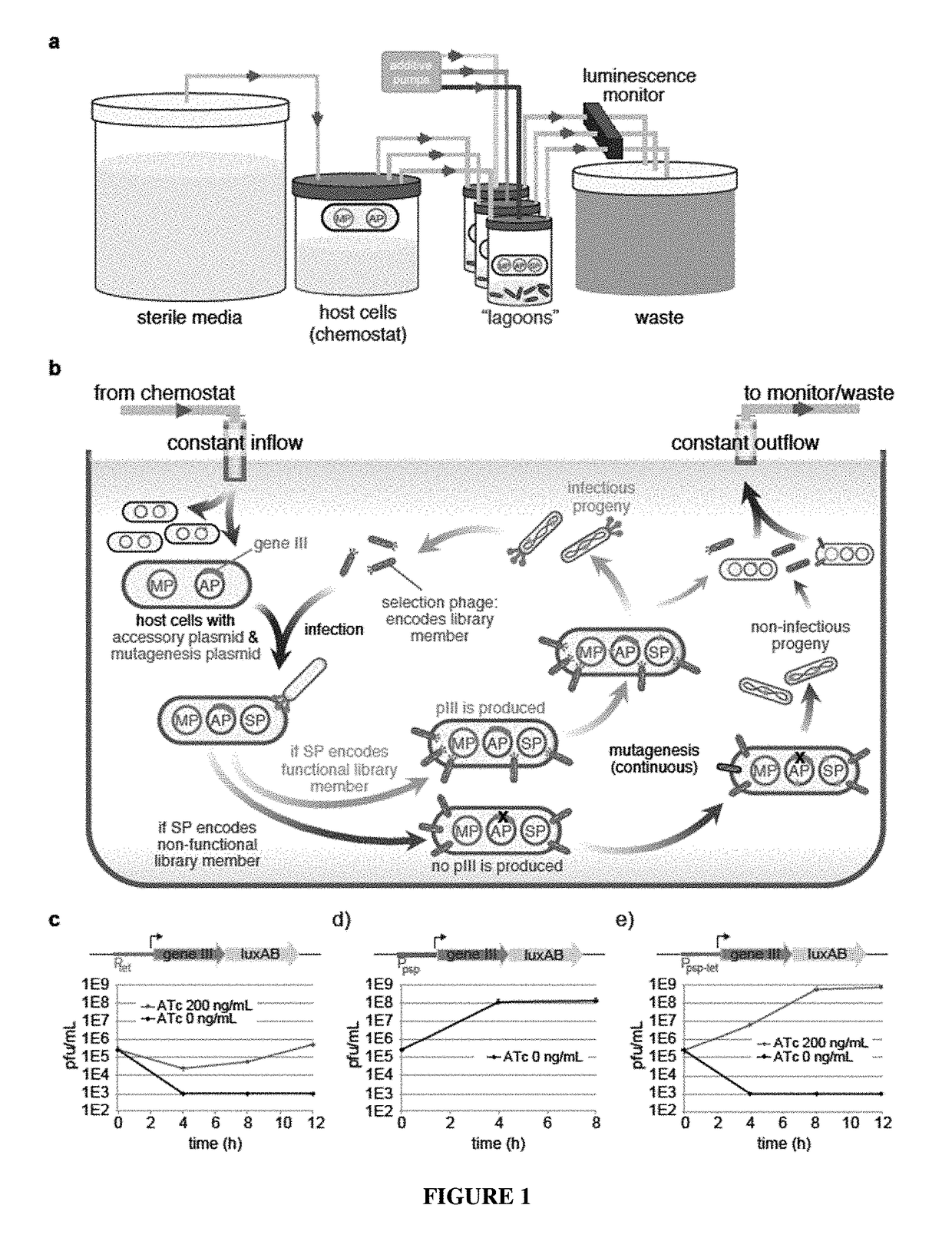
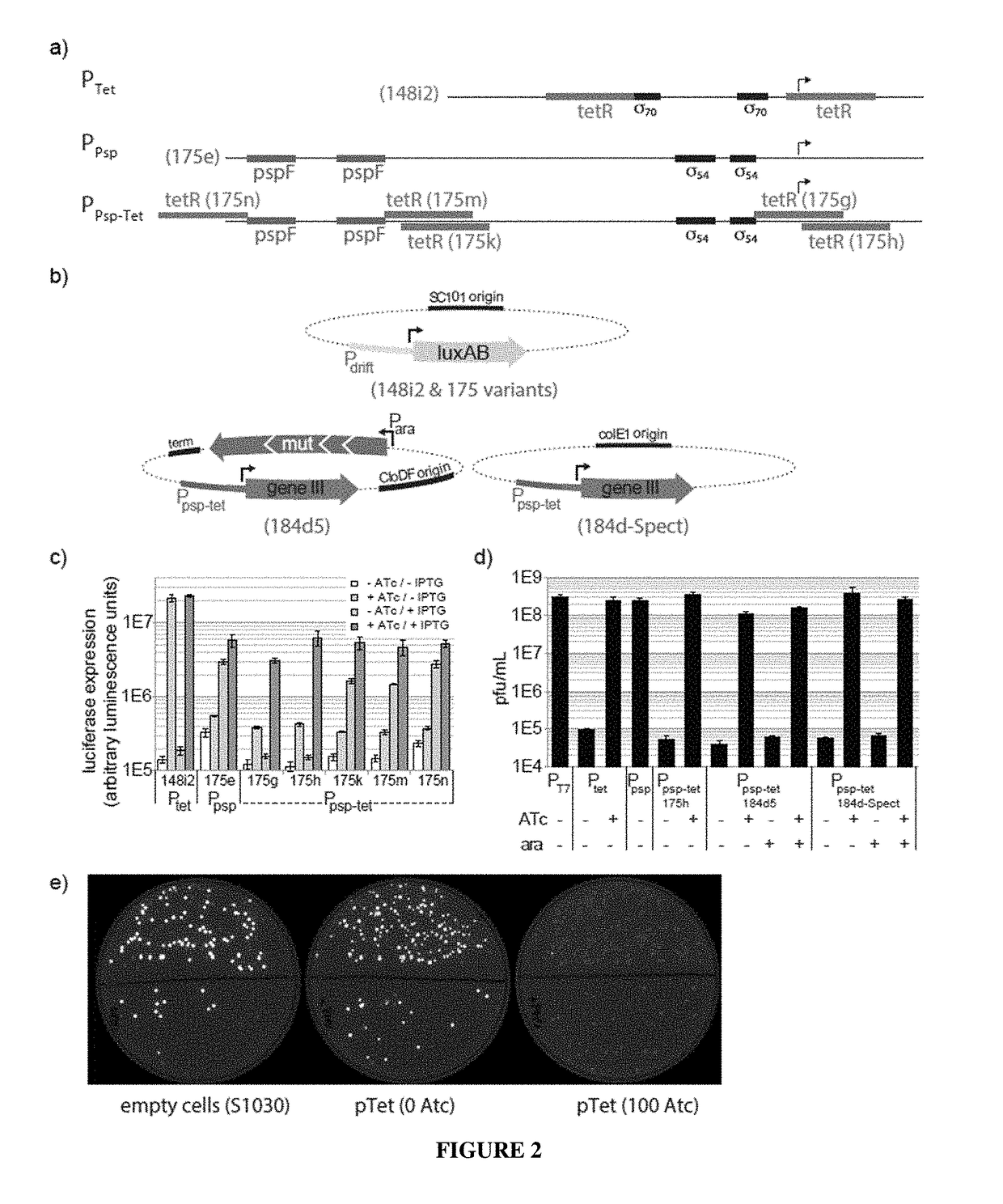
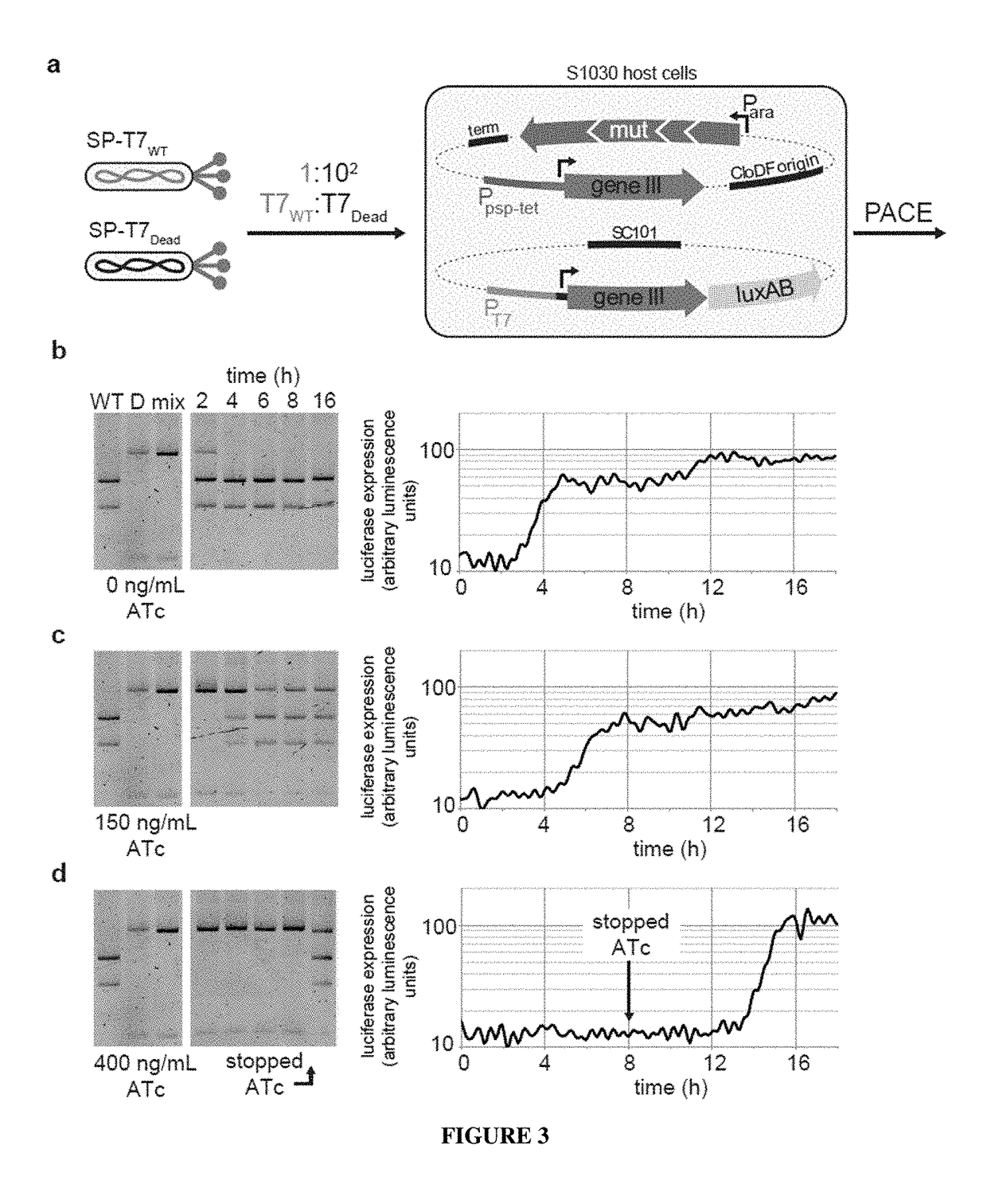
Negative selection and stringency modulation in continuous evolution systems
ActiveUS10179911B2High selectivityStrong specificityFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPositive selectionBiology
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for phage-assisted continuous evolution are provided herein. These include strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits allowing for stringency modulation to evolve weakly active or inactive biomolecule variants, negative selection of undesired properties, and / or positive selection of desired properties.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
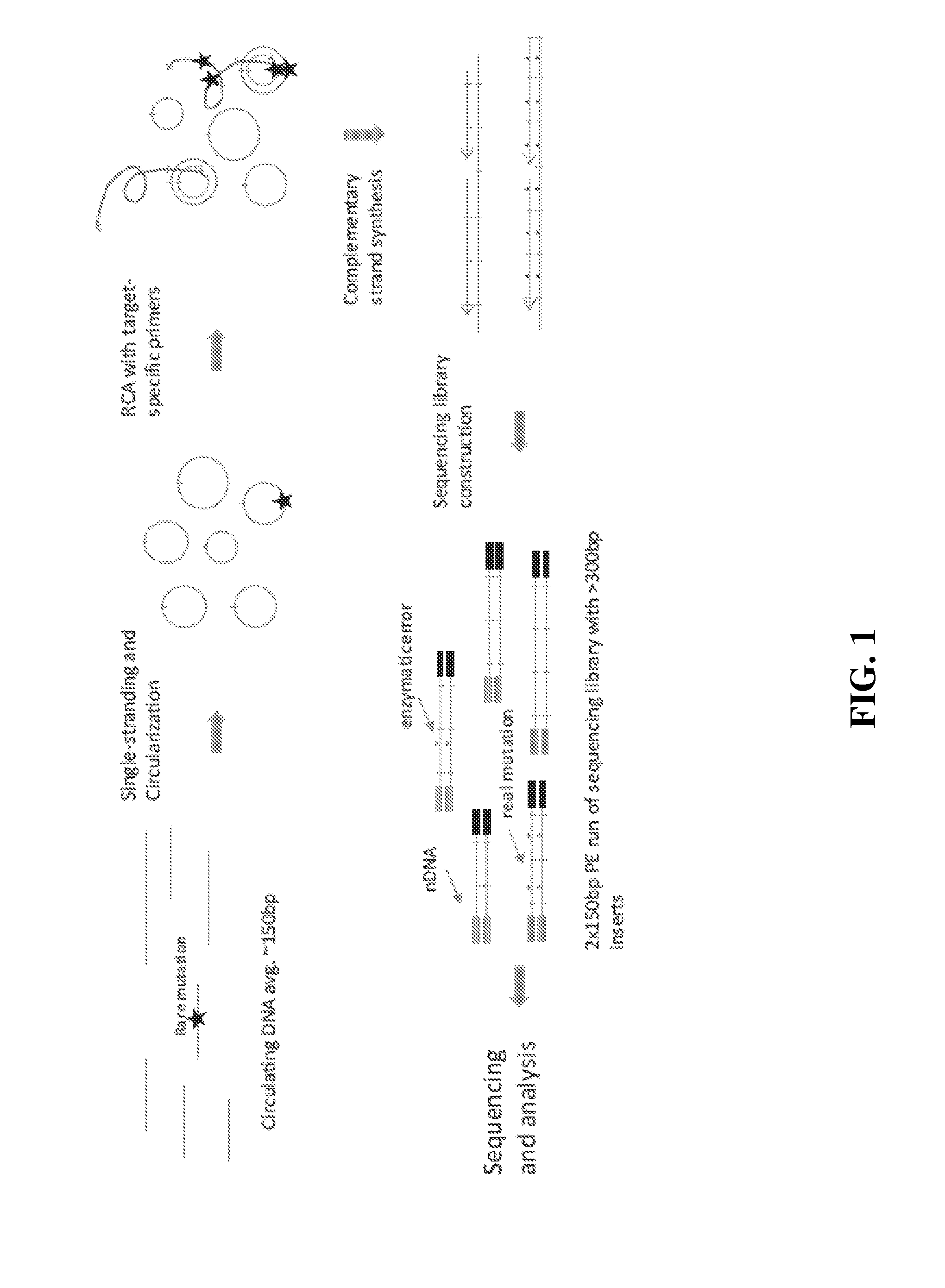
Compositions and methods for detecting rare sequence variants
ActiveUS20160304954A1Simple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotidePolynucleotide
In some aspects, the present disclosure provides methods for identifying sequence variants in a nucleic acid sample. In some embodiments, a method comprises identifying sequence differences between sequencing reads and a reference sequence, and calling a sequence difference that occurs in at least two different circular polynucleotides, such as two circular polynucleotides having different junctions, as the sequence variant. In some aspects, the present disclosure provides compositions and systems useful in the described methods.
Owner:ACCURAGEN HLDG LTD
Oligonucleic acid variant libraries and synthesis thereof
ActiveUS20170081660A1Enhance or reduce enzymatic activityModulate activityAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementPopulationNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are methods for the generation of highly accurate oligonucleic acid libraries encoding for predetermined variants of a nucleic acid sequence. The degree of variation may be complete, resulting in a saturated variant library, or less than complete, resulting in a selective library of variants. The variant oligonucleic acid libraries described herein may designed for further processing by transcription or translation. The variant oligonucleic acid libraries described herein may be designed to generate variant RNA, DNA and / or protein populations. Further provided herein are method for identifying variant species with increased or decreased activities, with applications in regulating biological functions and the design of therapeutics for treatment or reduction of disease.
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
Method for amplification and assay of RNA fusion gene variants, method of distinguishing same and related primers, probes, and kits
Method for amplification, alone or in further combination with detection or detection and quantitation, of RNA from fusion gene variants, method of distinguishing same, and oligonucleotide primers and probes and kits for use in the methods.
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC A CORP ORGANISED & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF DELAWARE
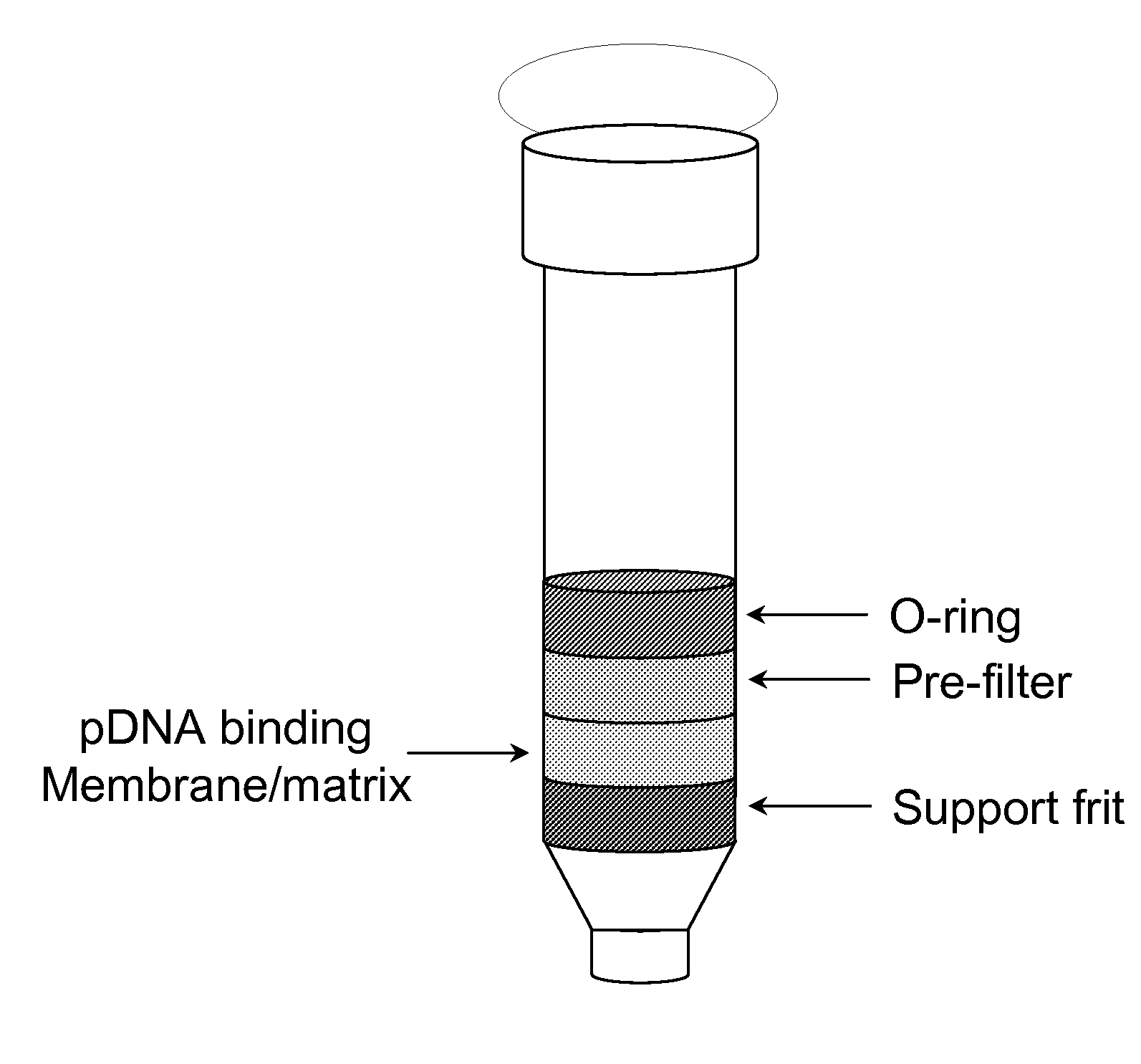
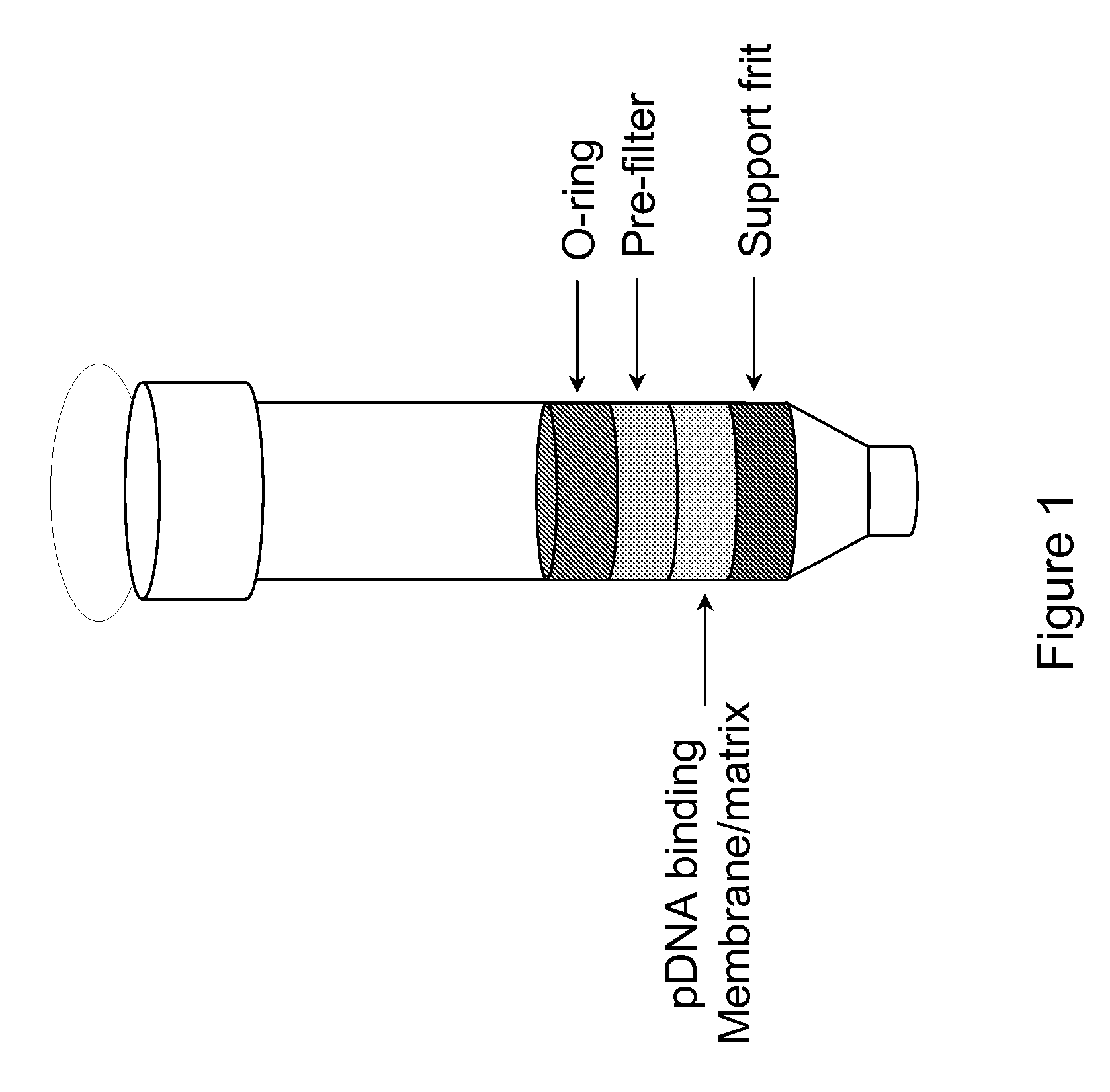
Modified spin column for simple and rapid plasmid DNA extraction
InactiveUS20080300397A1Rapid isolationImprove system performanceSamplingSugar derivativesCellular DebrisSpins
The invention relates to a modified spin column for the isolation and purification of plasmid DNA. A pre-filtration disc is included in a traditional spin column. During plasmid DNA isolation, the lysate can be loaded directly to the modified spin column, eliminates the need to first remove the flocculants containing cellular debris. This results in a much shortened process. Variation of the invention includes a depth filter in between the pre-filtration disc and the main separation matrix. Also provided are kits for isolation of plasmid DNA including the modified spin columns.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Genetic analysis systems and methods
InactiveUS6897025B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNAGenetics
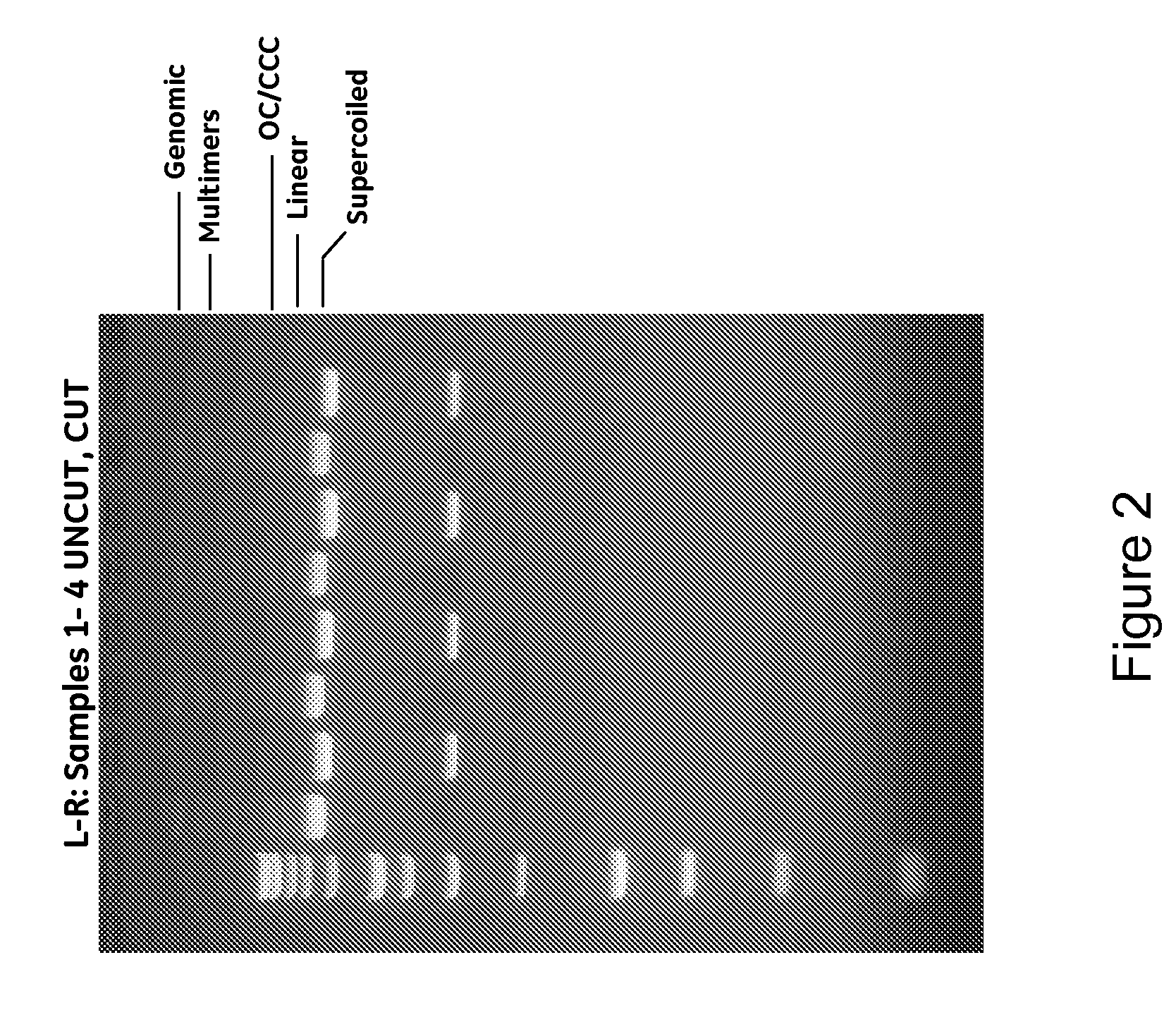
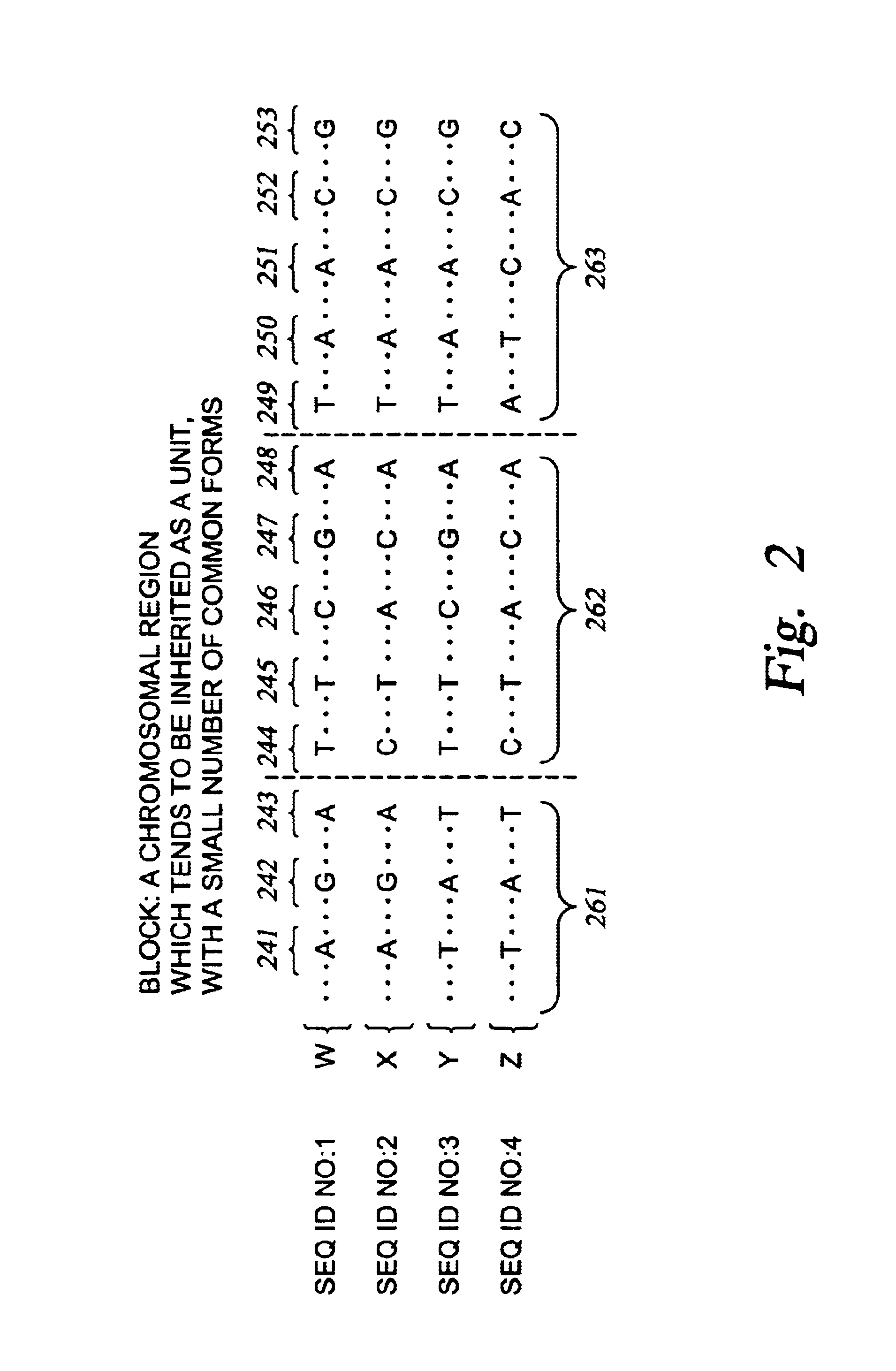
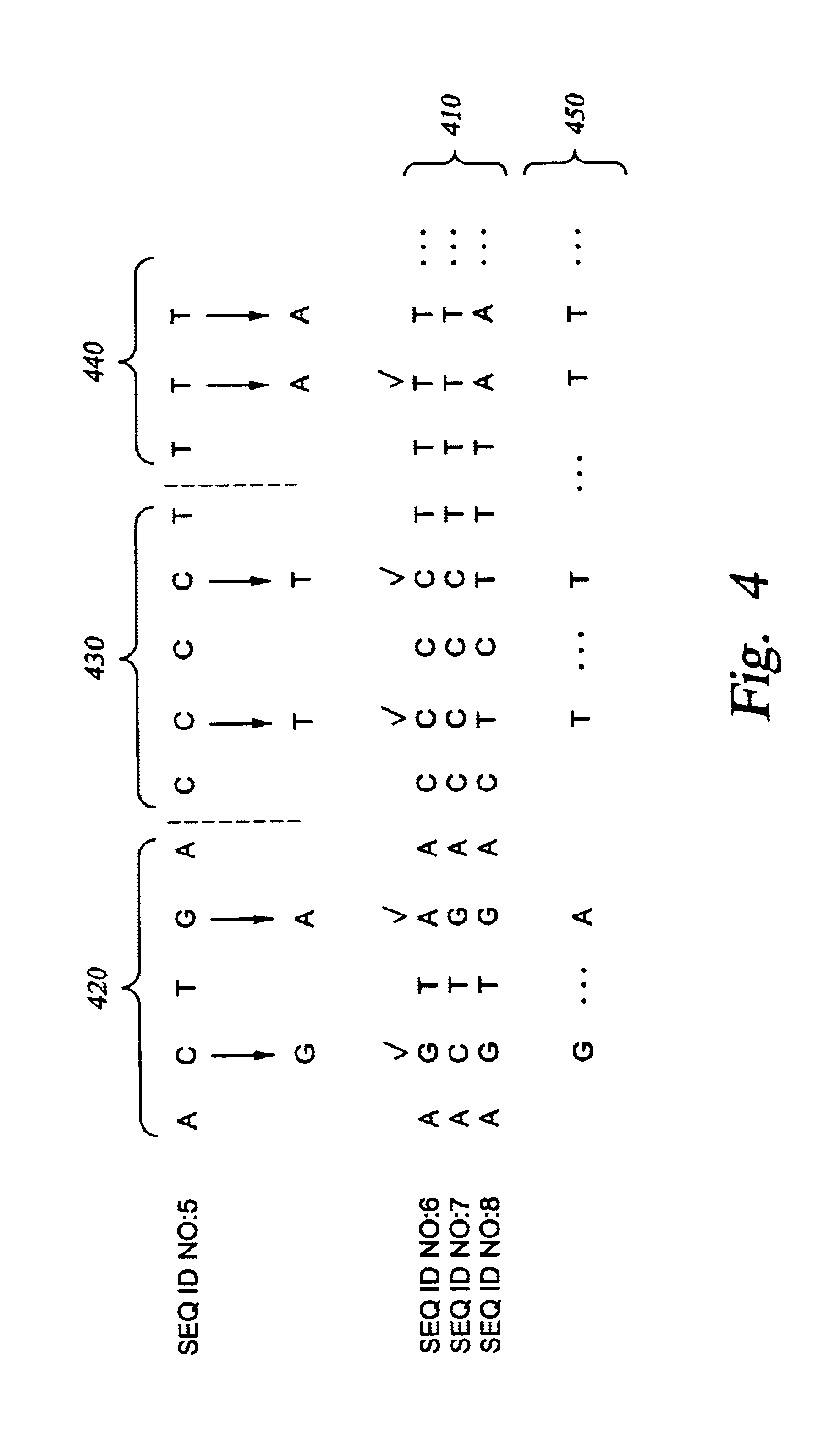
Improved systems and methods for performing genetic analyses. Full genomic DNA scans are performed on the genetic DNA from a plurality of individuals to identify genetic variants. For those variants, but not based on a full genetic DNA scan, the variants alone are scanned in additional individuals to identify blocks of the variants that tend to be inherited together.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Nucleic acid detection
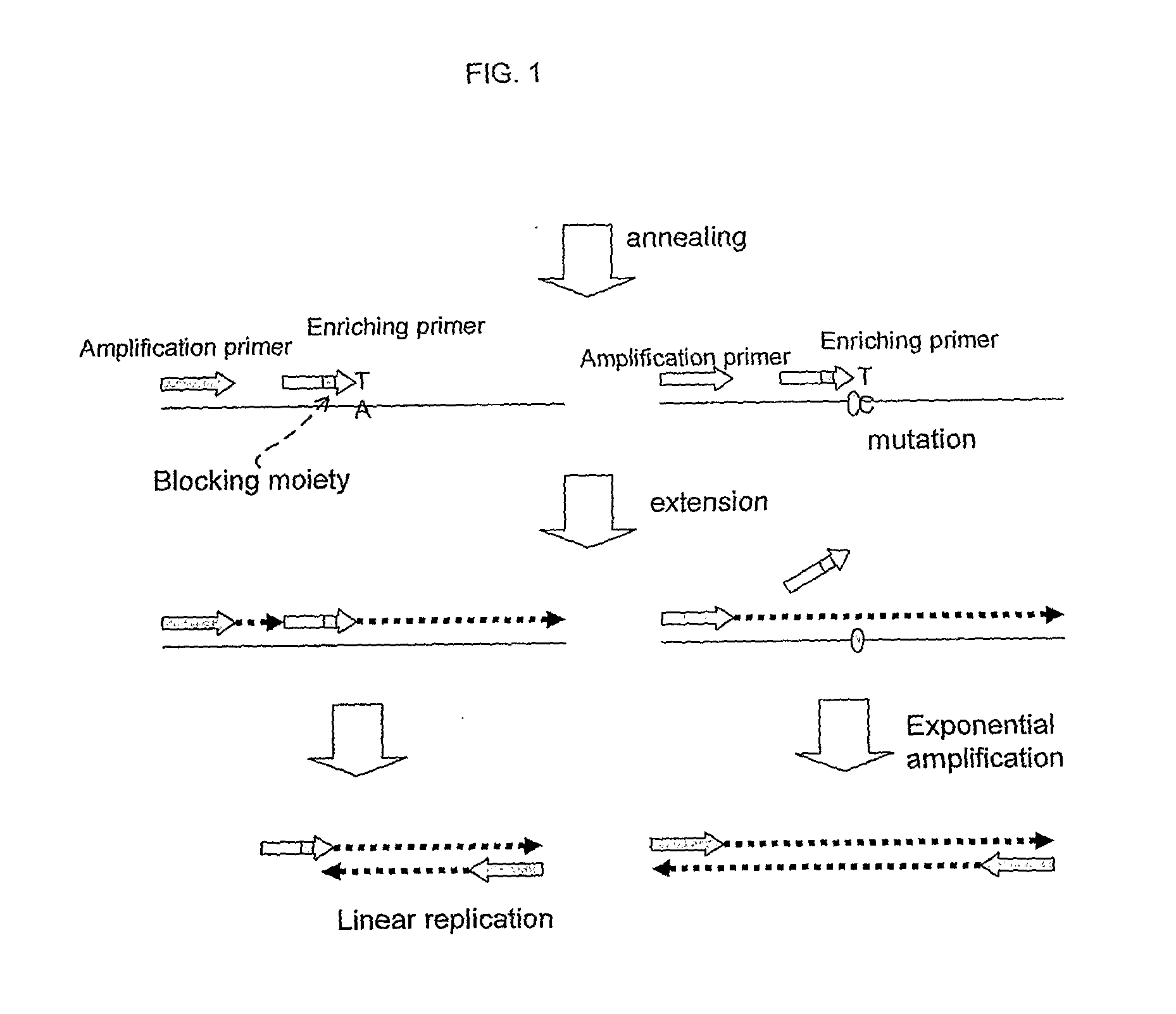
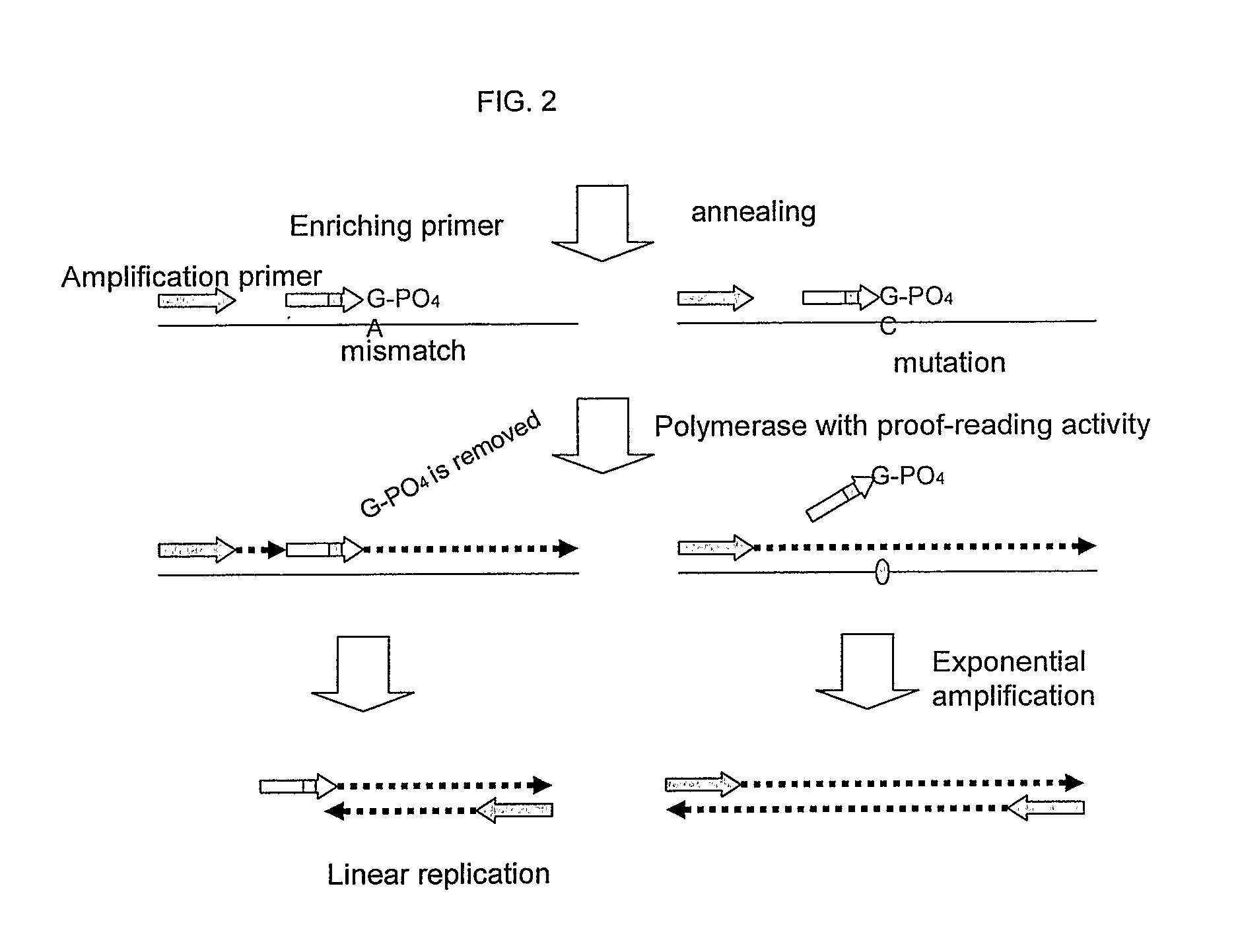
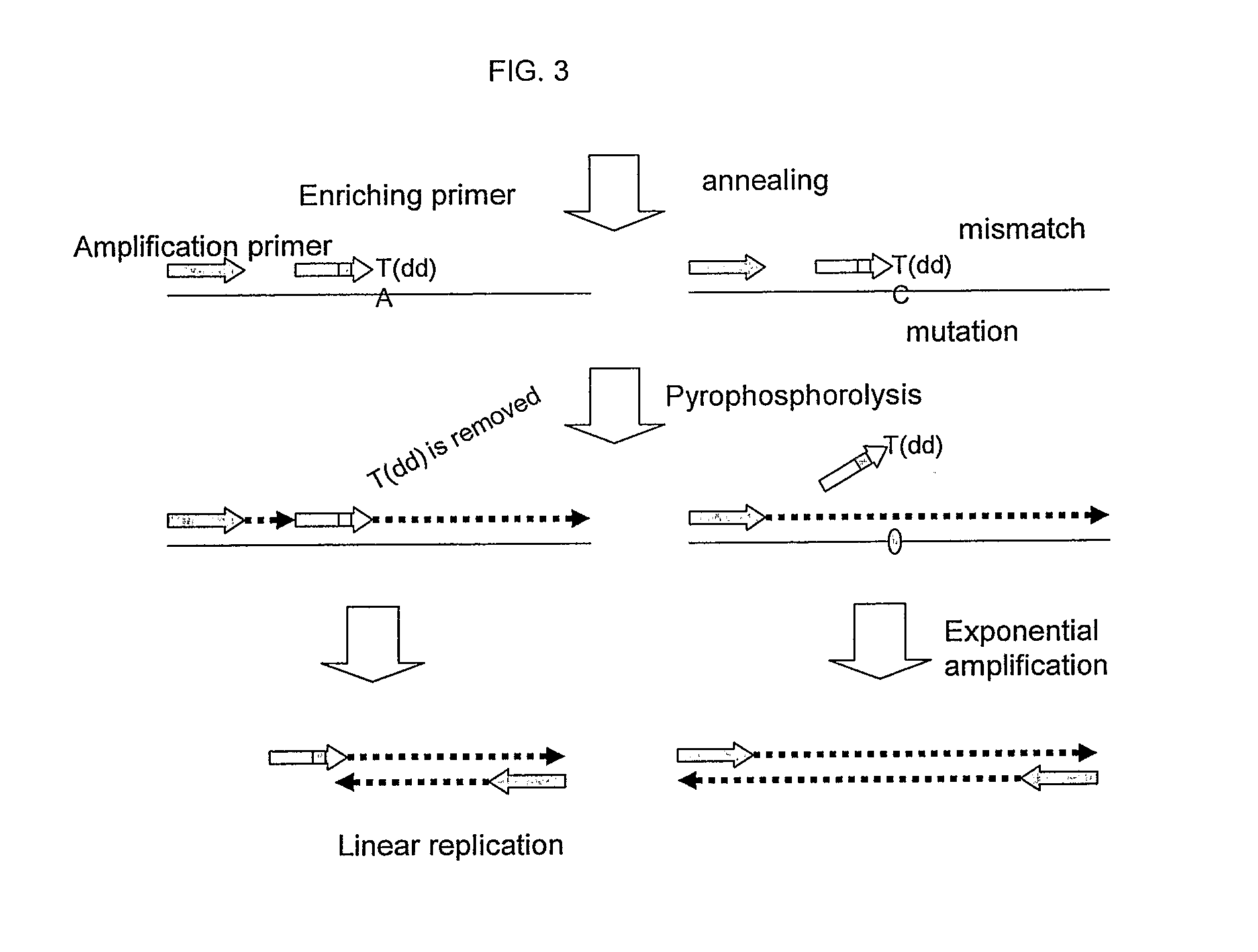
ActiveUS20100227320A1Rapid and sensitive detectionRapid and sensitive and improved enrichment and detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid detectionNucleotide
This invention provides methods and kits for enriching and / or detecting a nucleic acid with at least one variant nucleotide from a nucleic acid population in a sample. Methods employ the use of enriching primers and bridge-probes for enriching and detecting target nucleic acids. Extension of the enriching primer permits amplification of the target nucleic acid having the variant nucleotide.
Owner:360 GENOMICS
Combined automated parallel synthesis of polynucleotide variants
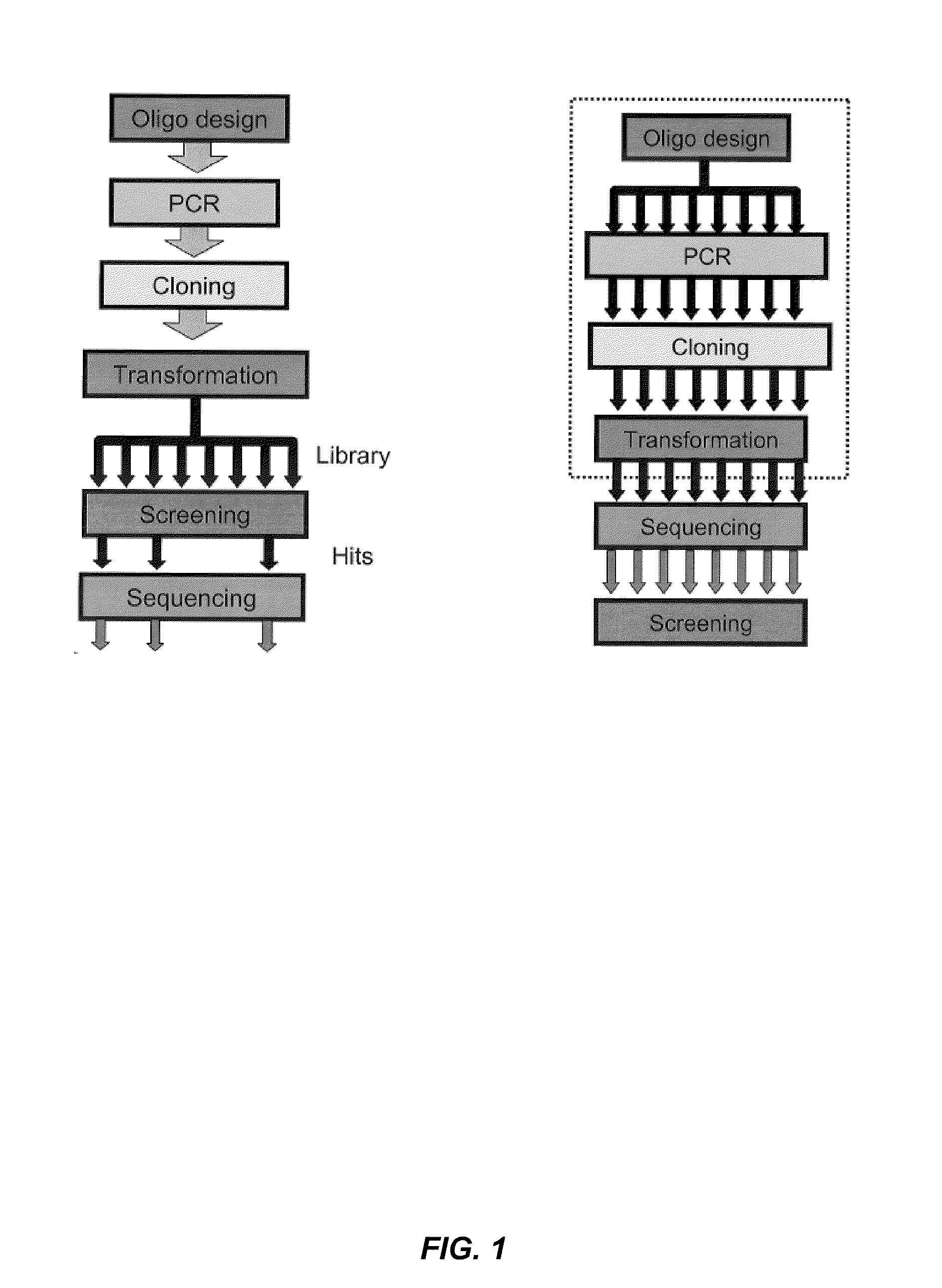
ActiveUS20100093560A1Generate efficientlyEasy to filterPeptide librariesSugar derivativesPolynucleotideComputational biology
The present disclosure relates to methods for efficient synthesis, cloning, transformation and screening of large diverse libraries of polynucleotide variants comprising well-defined nucleotide differences relative to a reference polynucleotide.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Variant libraries of the immunological synapse and synthesis thereof
ActiveUS20180171509A1Strong specificityIncreased avidityImmunoglobulin superfamilyLibrary screeningDiseaseAntigen
Disclosed herein are methods for the generation of highly accurate nucleic acid libraries encoding for predetermined variants of a nucleic acid sequence. The nucleic acid sequence may encode for all or part of a TCR or a TCR-binding antigen. The degree of variation may be complete, resulting in a saturated variant library, or less than complete, resulting in a non-saturating library of variants. The variant nucleic acid libraries described herein may designed for further processing by transcription or translation. The variant nucleic acid libraries described herein may be designed to generate variant RNA, DNA and / or protein populations. Further provided herein are method for identifying variant species with increased or decreased activities, with applications in regulating biological functions and the design of therapeutics for treatment or reduction of a disease, such as cancer.
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
DNA containing variant FRT sequences
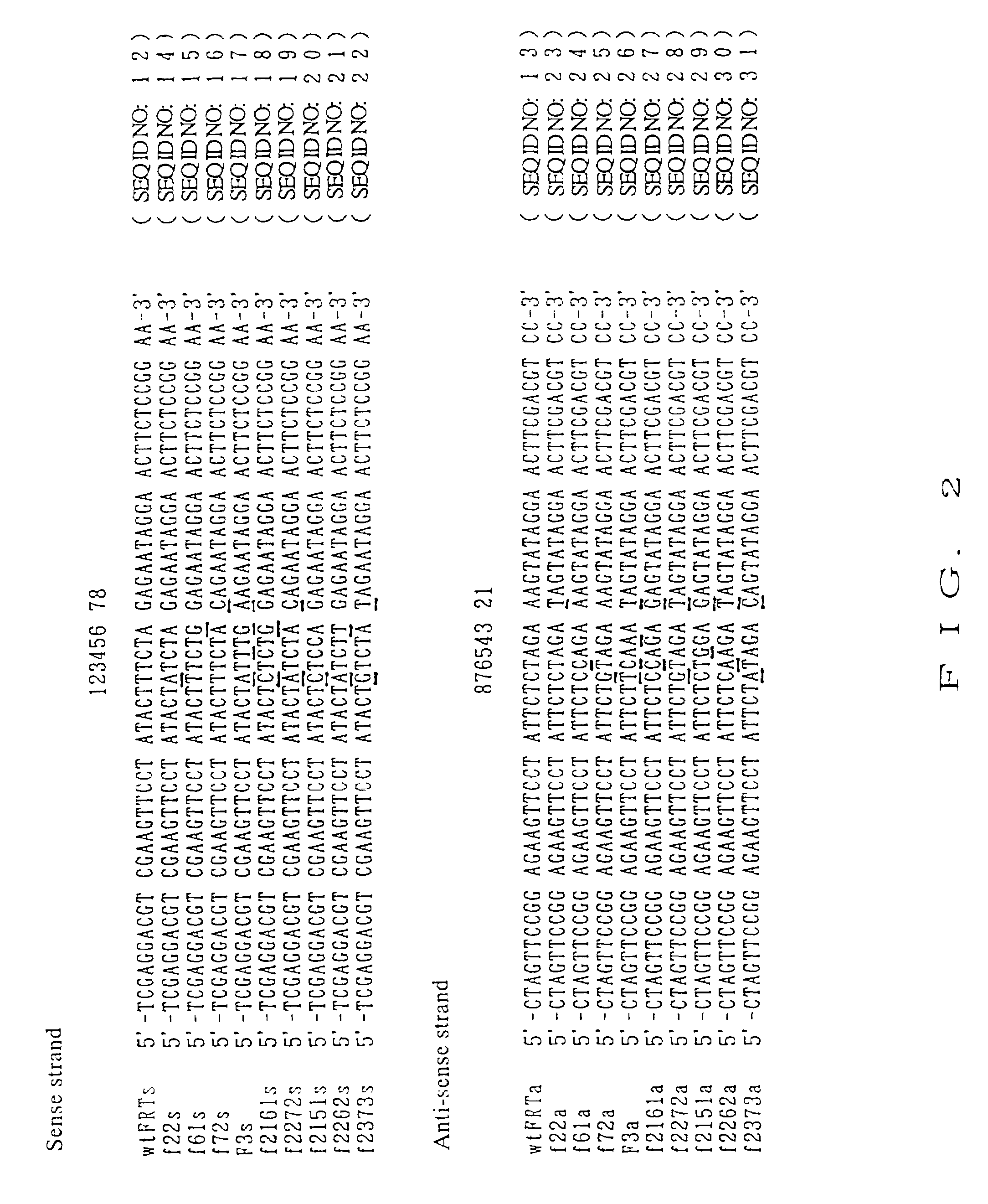
To provide DNA comprising mutant FRT sequence which causes recombination reaction between two mutant FRT sequences having an identical sequence to each other but does not cause recombination reaction with a wild-type FRT sequence, in the presence of FLP recombinase; and a method for performing high-efficiency, gene insertion or gene replacement. A DNA comprising a mutant FRT sequence. A DNA comprising a mutant FRT sequence possessing (A) causing no specific DNA recombination reaction with wild type FRT, even if FLP recombinase is present, and (B) causing specific DNA recombination reaction with another mutant FRT sequence having an identical sequence thereto in the presence of recombinase FLP; gene replacement method using the DNA in the presence of recombinase FLP; and a specific DNA recombination method, characterized in that a specific DNA recombination reaction is carried out by using two mutant FRT sequences in the presence of recombinase FLP.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD +1
Nucleic acid sequences that can be used as primers and probes in the amplification and detection of all subtypes of HIV-1
InactiveUS6881537B1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeSpecific detection
The present invention is related to nucleic acid sequences that can be used in the field of virus diagnostics, more specifically the diagnosis of infections with the AIDS causing Human Immuno-deficiency Virus (HIV).With the present invention nucleotide sequences are provided that can be used as primers and probes in the amplification and detection of HIV-1 nucleic acid. The oligonucleotide sequences provided with the present invention are located in the LTR part of the HIV viral genome. It has been found that, by using the sequences of the present invention in methods for the amplification and detection of nucleic acid a sensitive and specific detection of HIV-1 can be obtained. The benefit of the sequences of the present invention primarily resides in the fact that, with the aid of primers and probes comprising the sequences according to the invention the nucleic acid of all presently known subtypes of HIV-1 can be detected with high accuracy and sensitivity. So far no primer pairs or hybridization probes have been developed that would allow the detection of such a broad range of HIV-1 variants.The oligonucleotide sequences according to the present invention are especially useful in methods for the amplification of nucleic acid.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
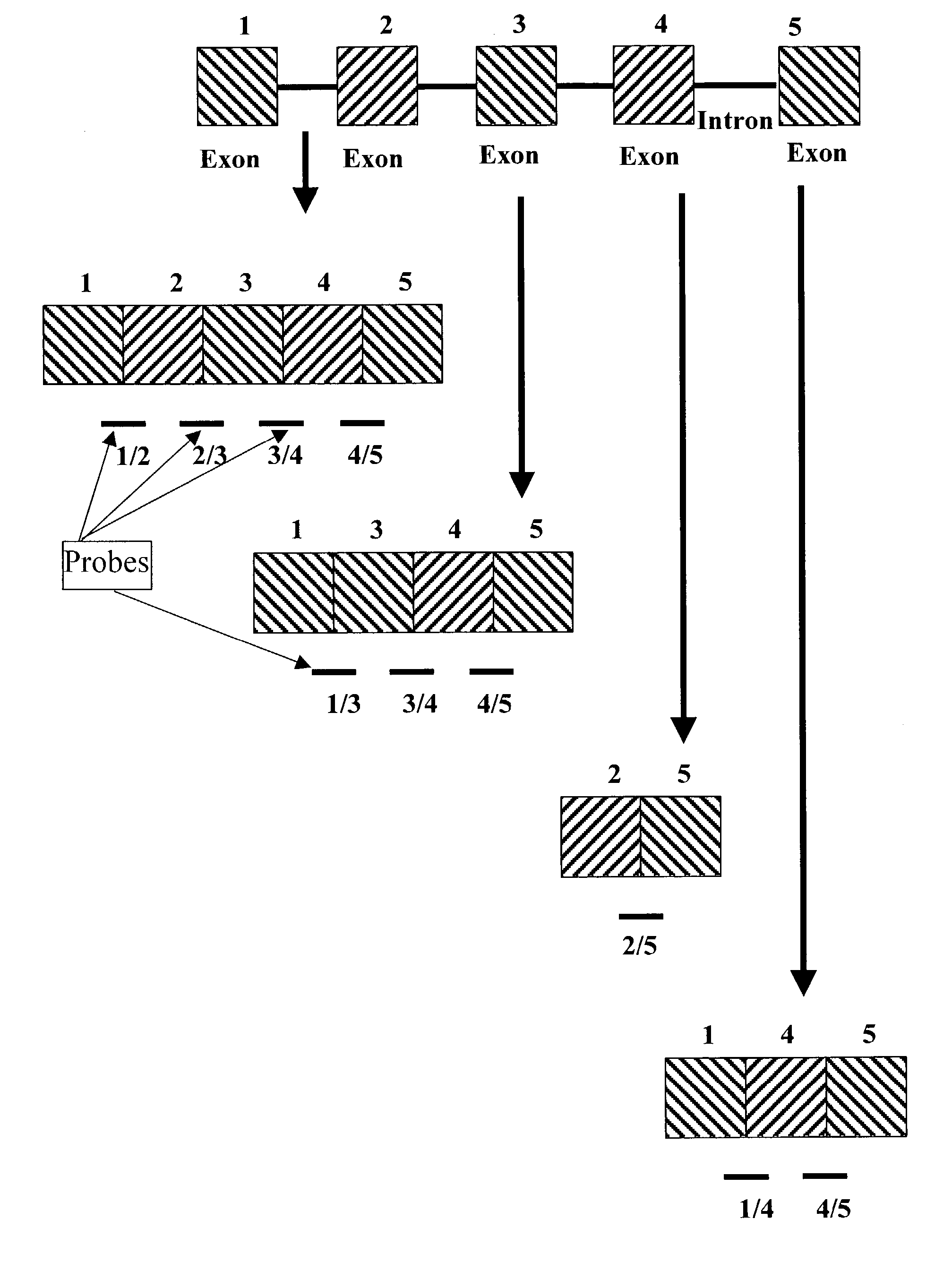
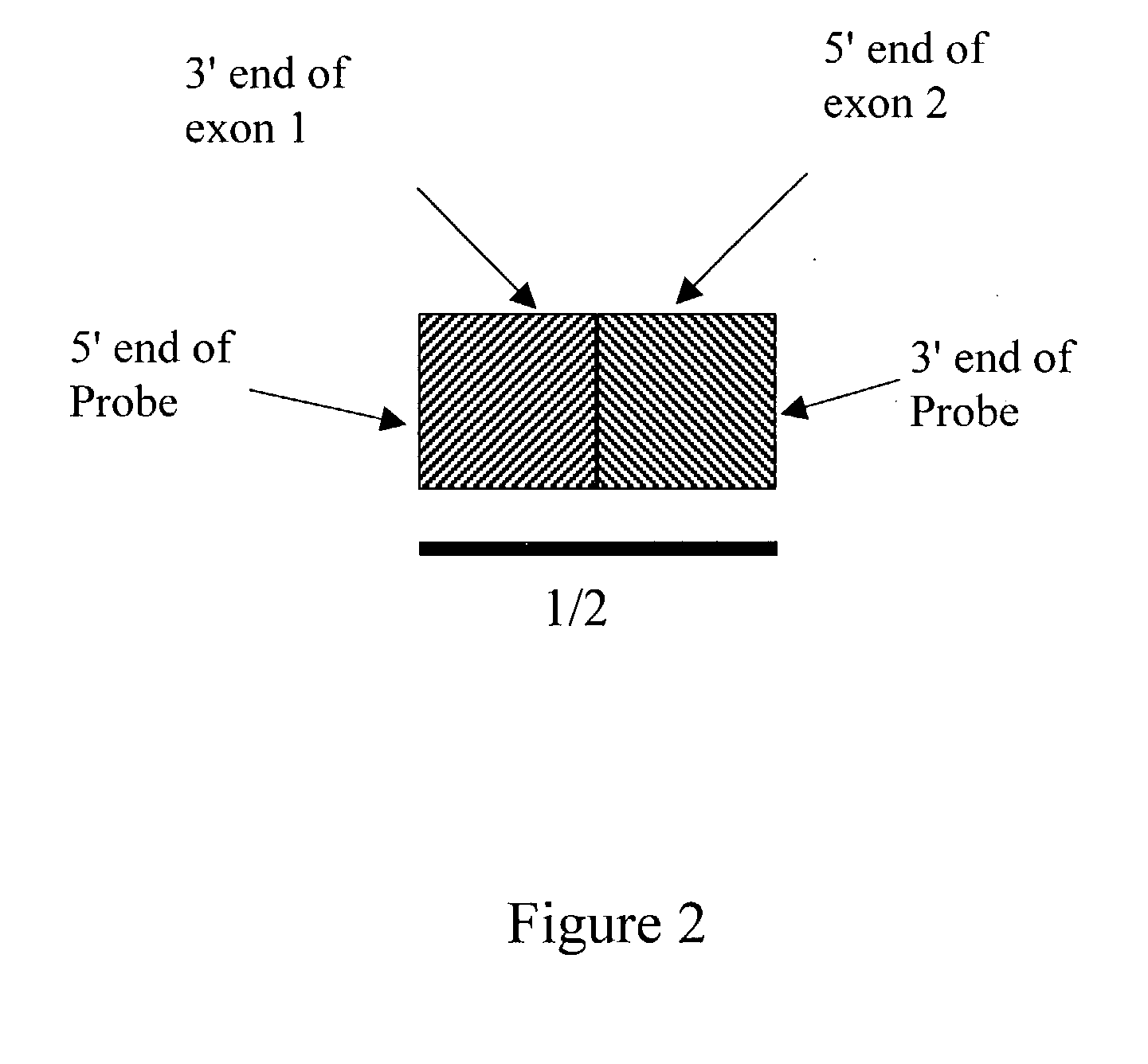
Detection of alternative and aberrant mRNA splicing
Disclosed is a method of determining alternatively spliced mRNAs by hybridization of mRNAs to exon / intron junction specific polynucleotide probes. Such polynucleotide probes allow the identification of alternative and aberrant splicing of known exons of a gene. These polynucleotide probes may by contained in DNA arrays to allow the screening of a large number of alternative and aberrant splicing variants.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
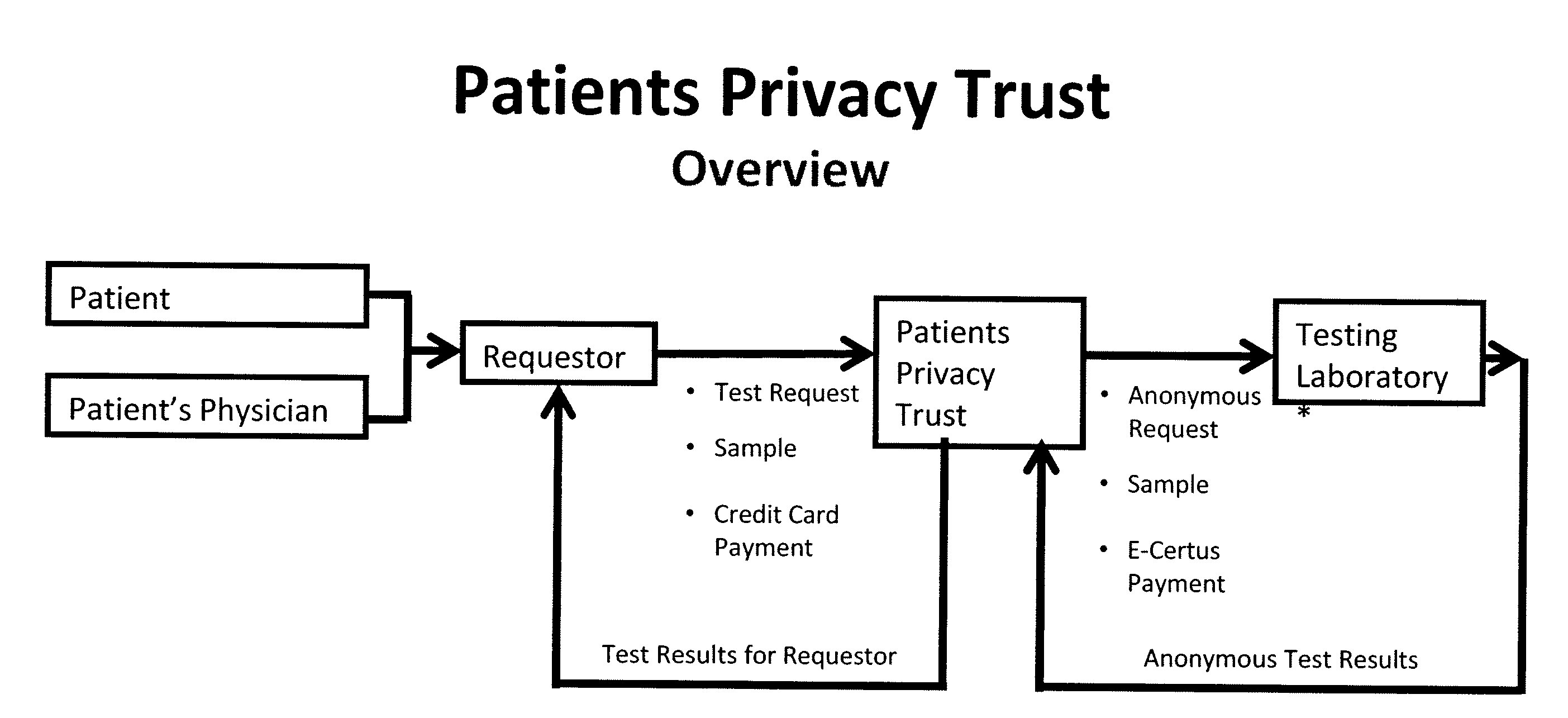
System for gene testing and gene research while ensuring privacy
InactiveUS20090198519A1Data processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic databaseGENETIC ABNORMALITY
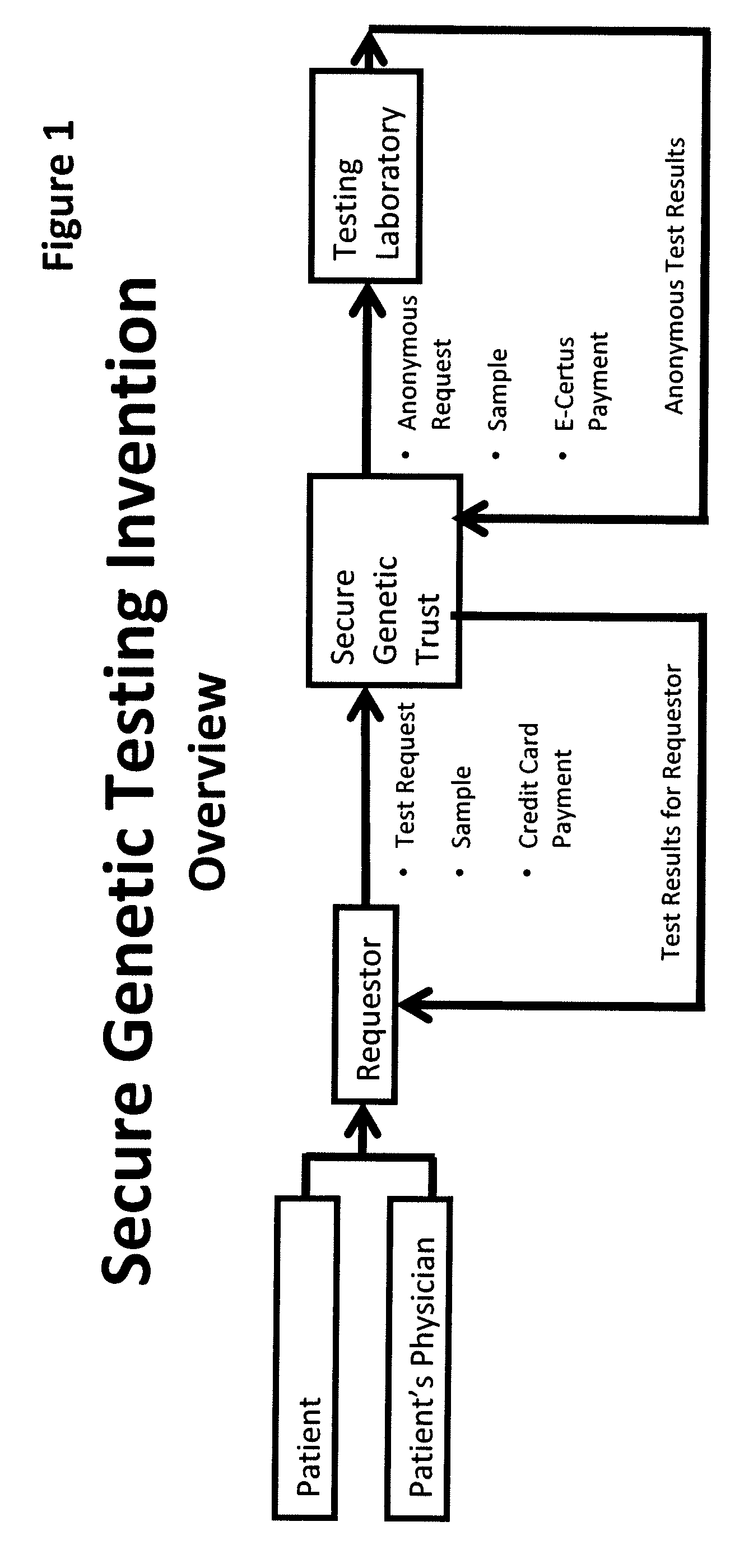
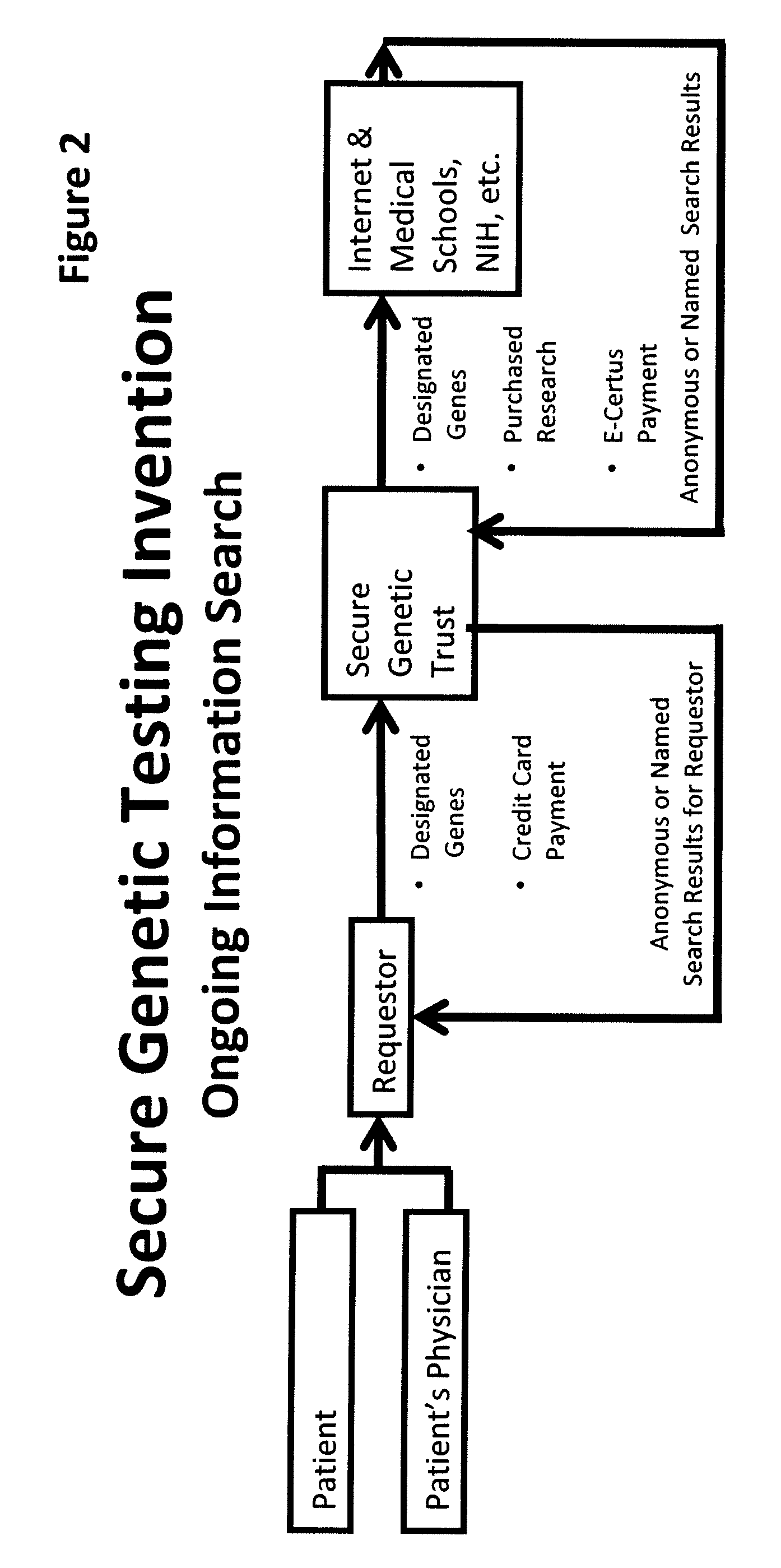
A system, method and program product, the method comprising, in one embodiment, providing a secure testing service for patient's identification and payment data encrypted at the data level, non-identifiable method for a patient to have a genetic tests to identify variants or mutations of their genes or combinations of genes that predispose the patient to develop or have an identified disease, comprising: obtaining electronically genomic information for a patient comprising at least one of, (a) DNA information, (b) RNA information, (c) complementary DNA or RNA information, (d) transfer RNA (tRNA) information (e) messenger RNA (mRNA) information, and (f) Expressed Sequence Tags (EST) to identify an abnormal gene; searching by one or more computers electronic databases using the identified abnormal gene to obtain genetic sequencing and basic research, patient predispositions, and pharmacognetics that predict the response and reaction of patients with identified genetic abnormalities related to the identified abnormal gene and individual medications that may be prescribed relating to the identified abnormal gene or a relationship with said identified abnormal gene; performing an update search on at least a periodic basis to learn about subsequent genomic research developments and treatments for the identified abnormal gene, specific genes with variants or mutated genes identified in the genetic test; sending electronically via an Internet communication link data comprising or derived from the searching step and the update search to the patient or a third party; and with the sending step performed using a privacy component that prevents transmission to any third party unless predetermined permission clearance data is in the system.
Owner:MCNAMAR RICHARD TIMOTHY
Methods for the detection of nucleic acid differences
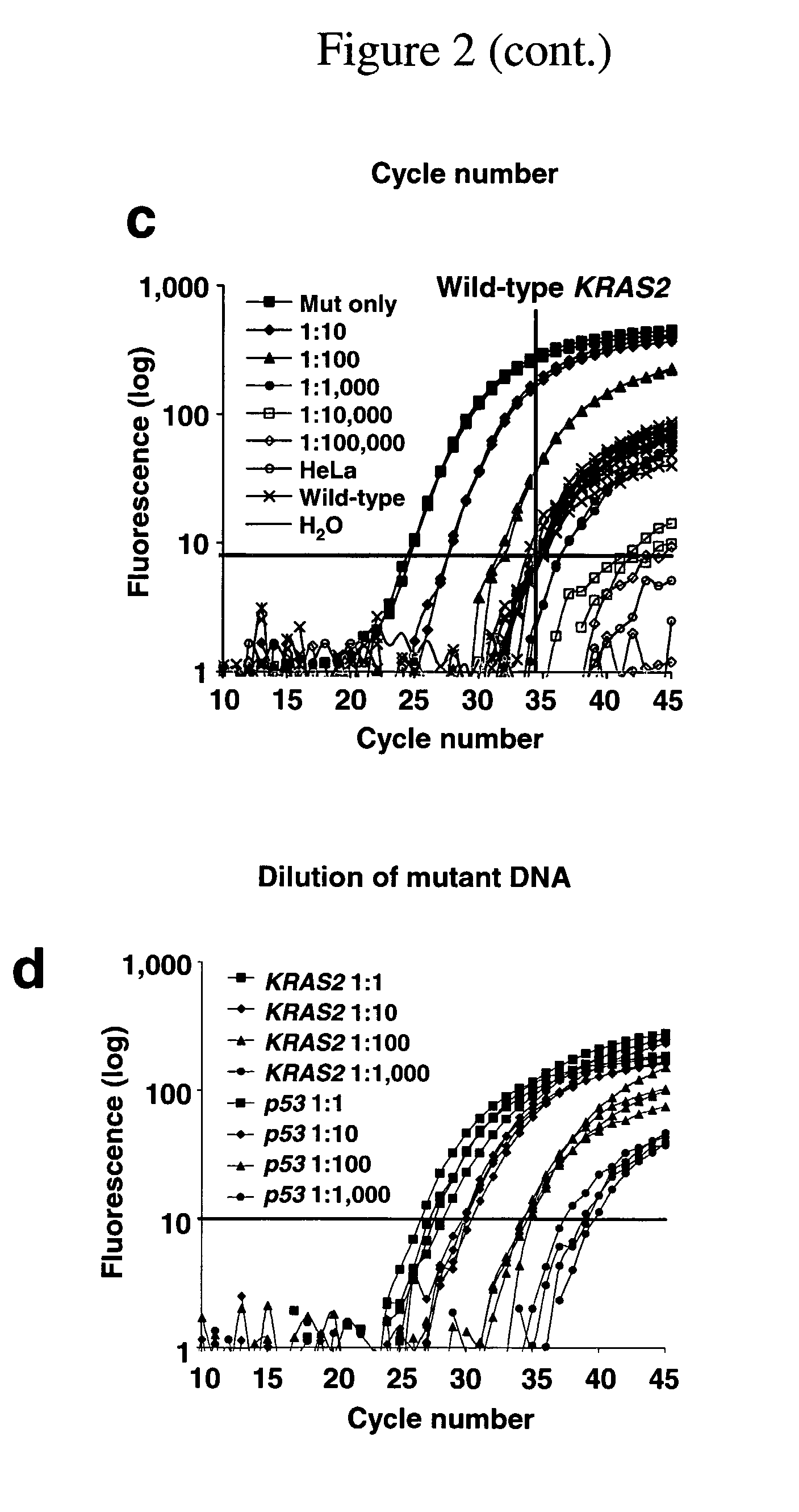
The invention provides methods permitting the detection of small amounts of different nucleic acids in the presence of an excess amount of wild-type nucleic acids. Also provided herein are method so detecting infectious disease minority variants, methods of forensic identification, methods of diagnosing cancer and monitoring disease progress.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com