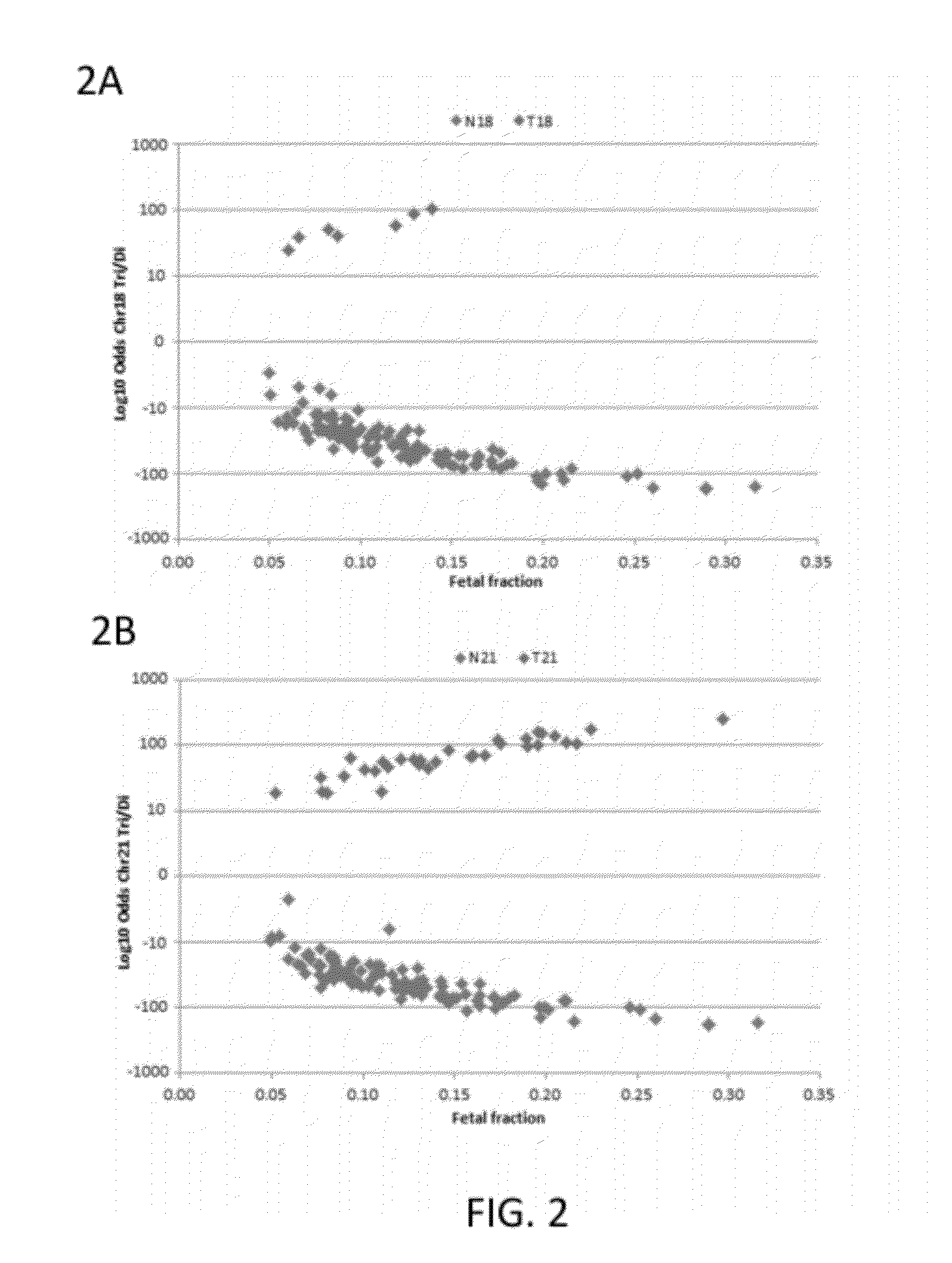
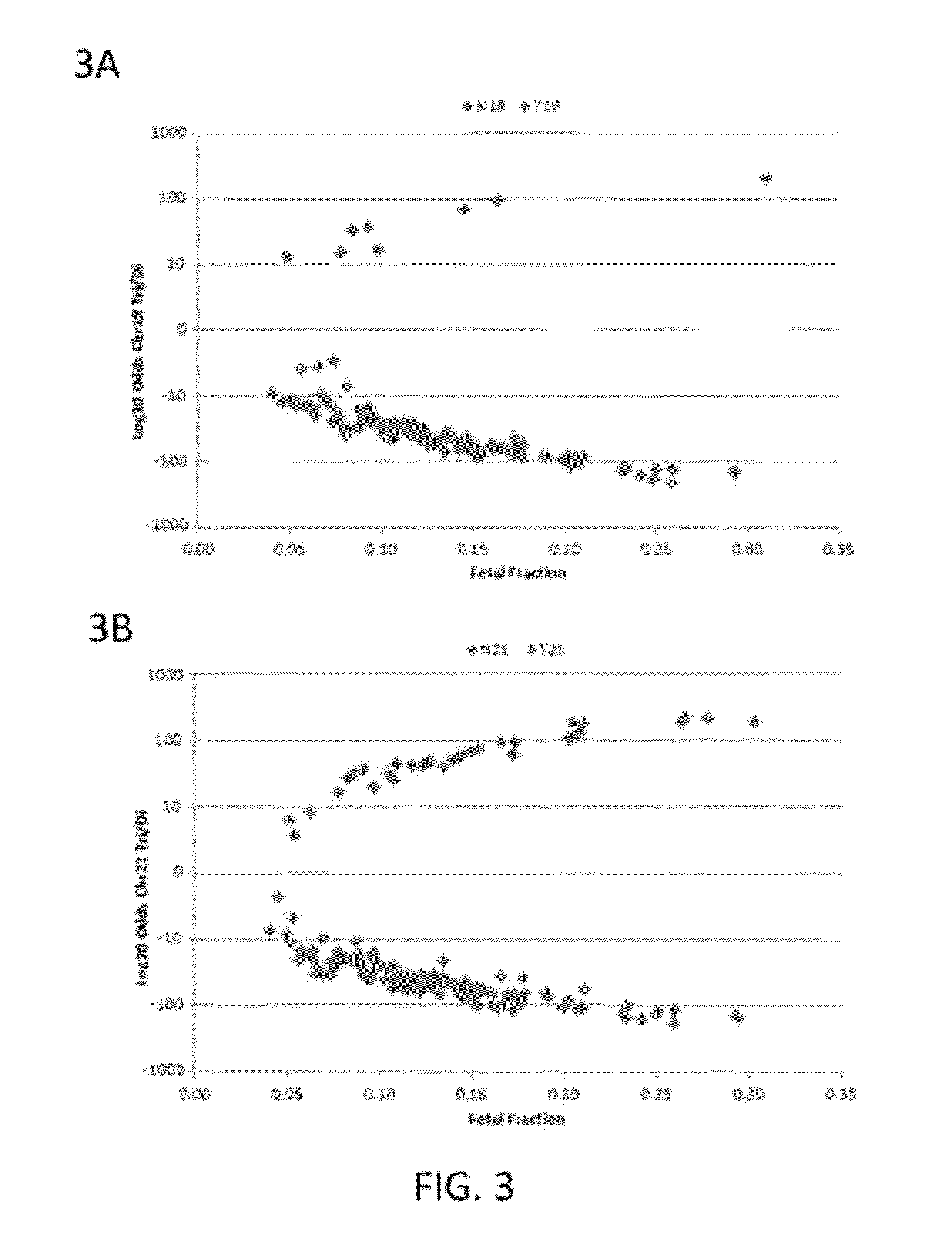
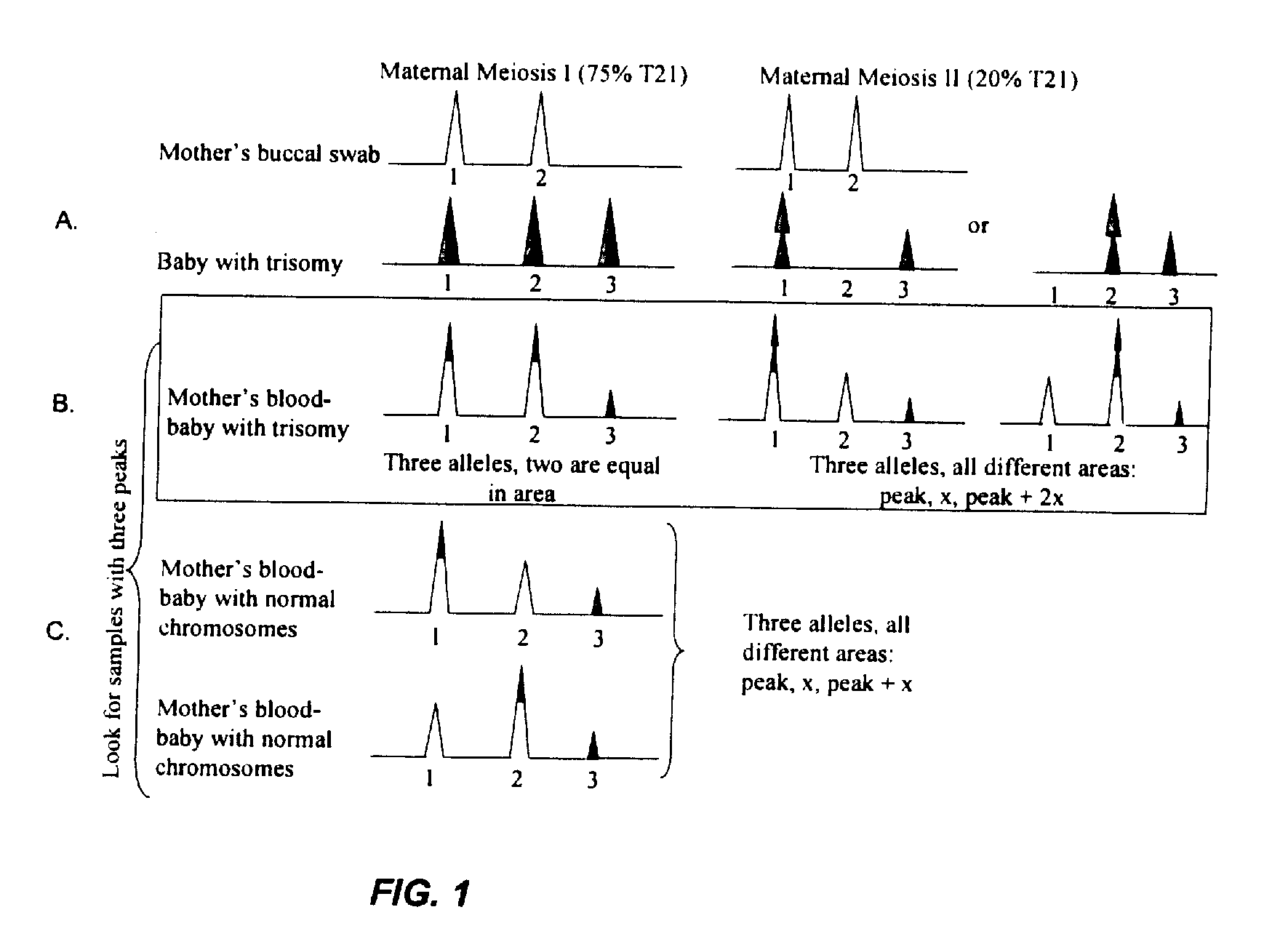
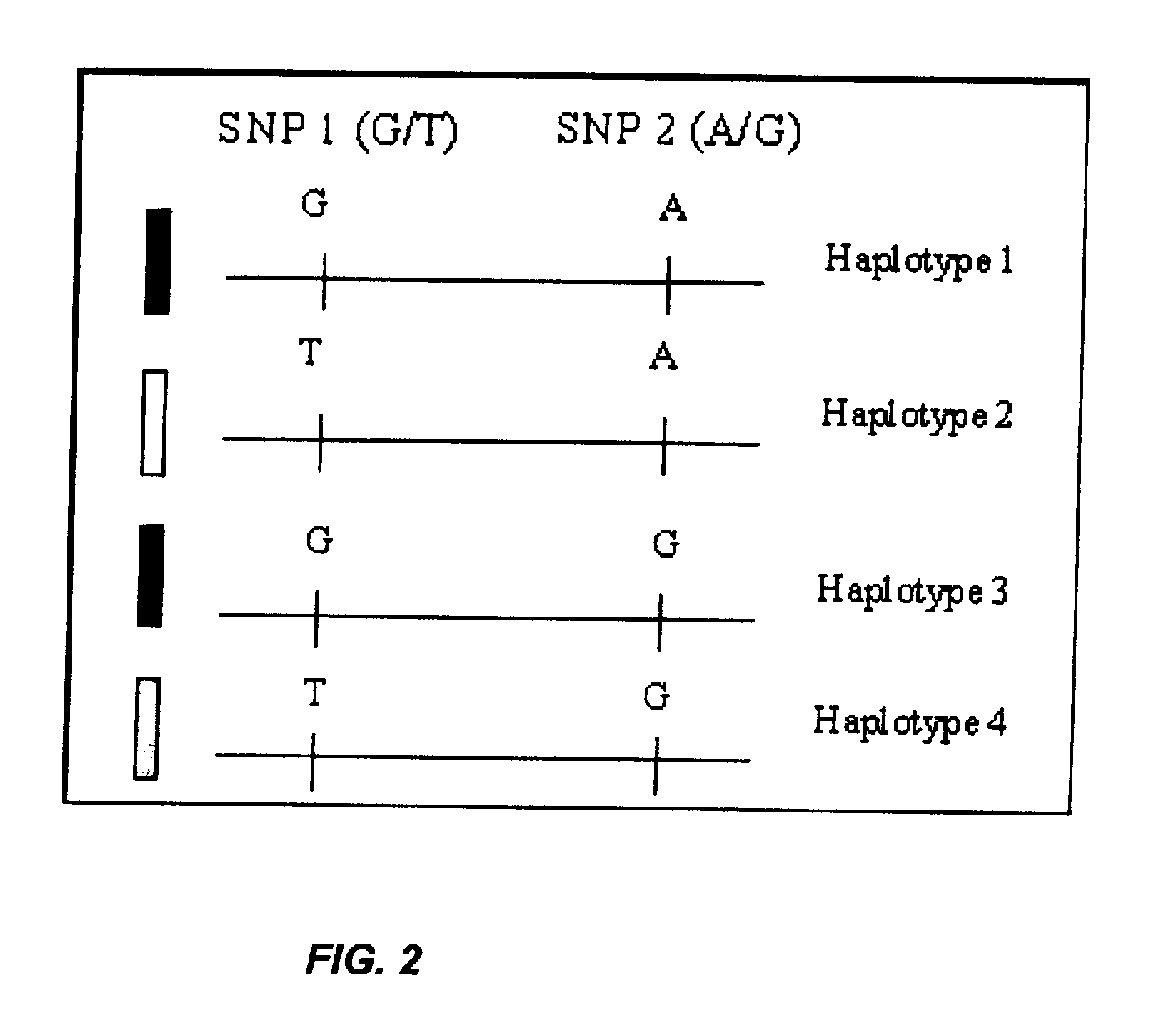
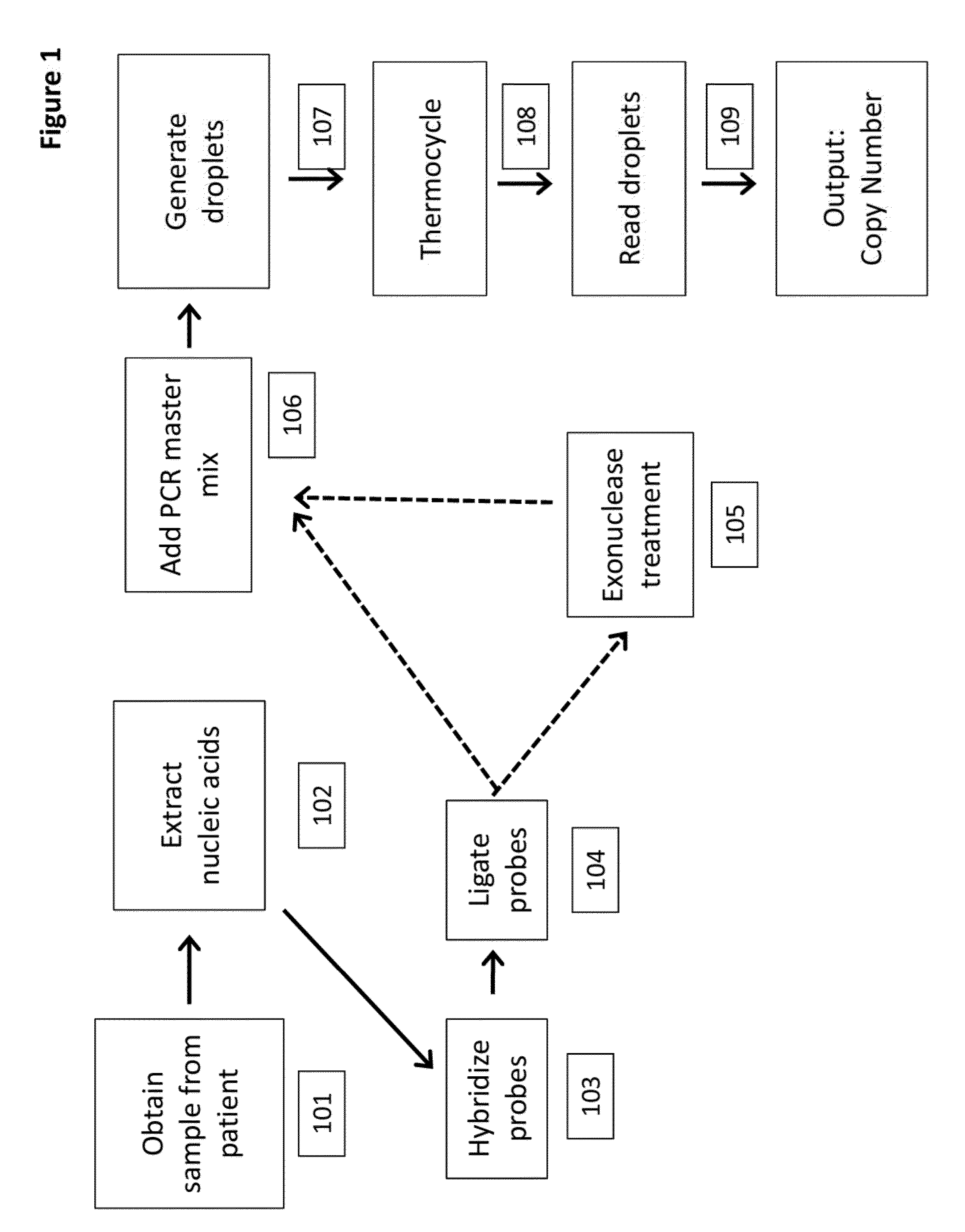
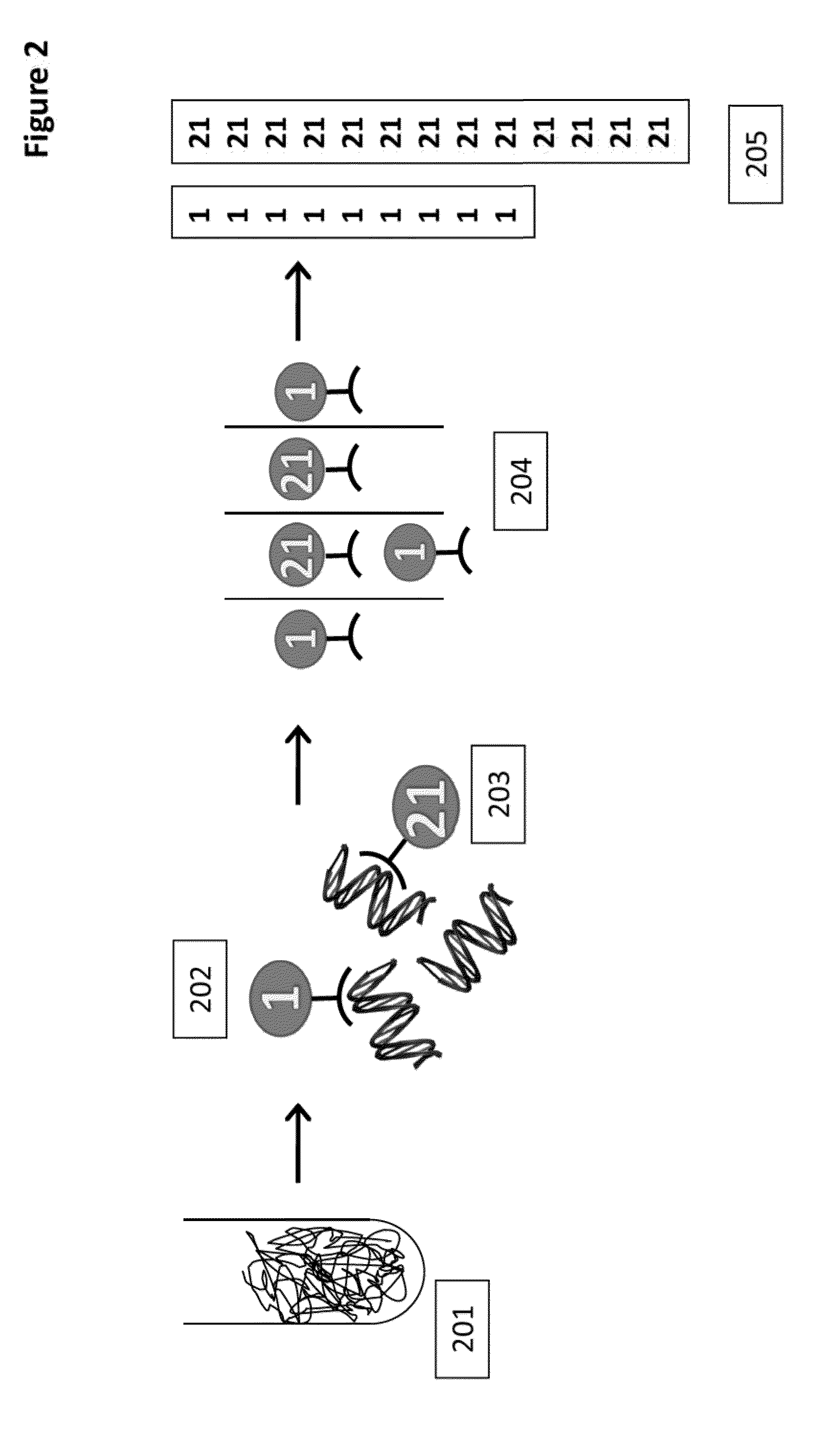
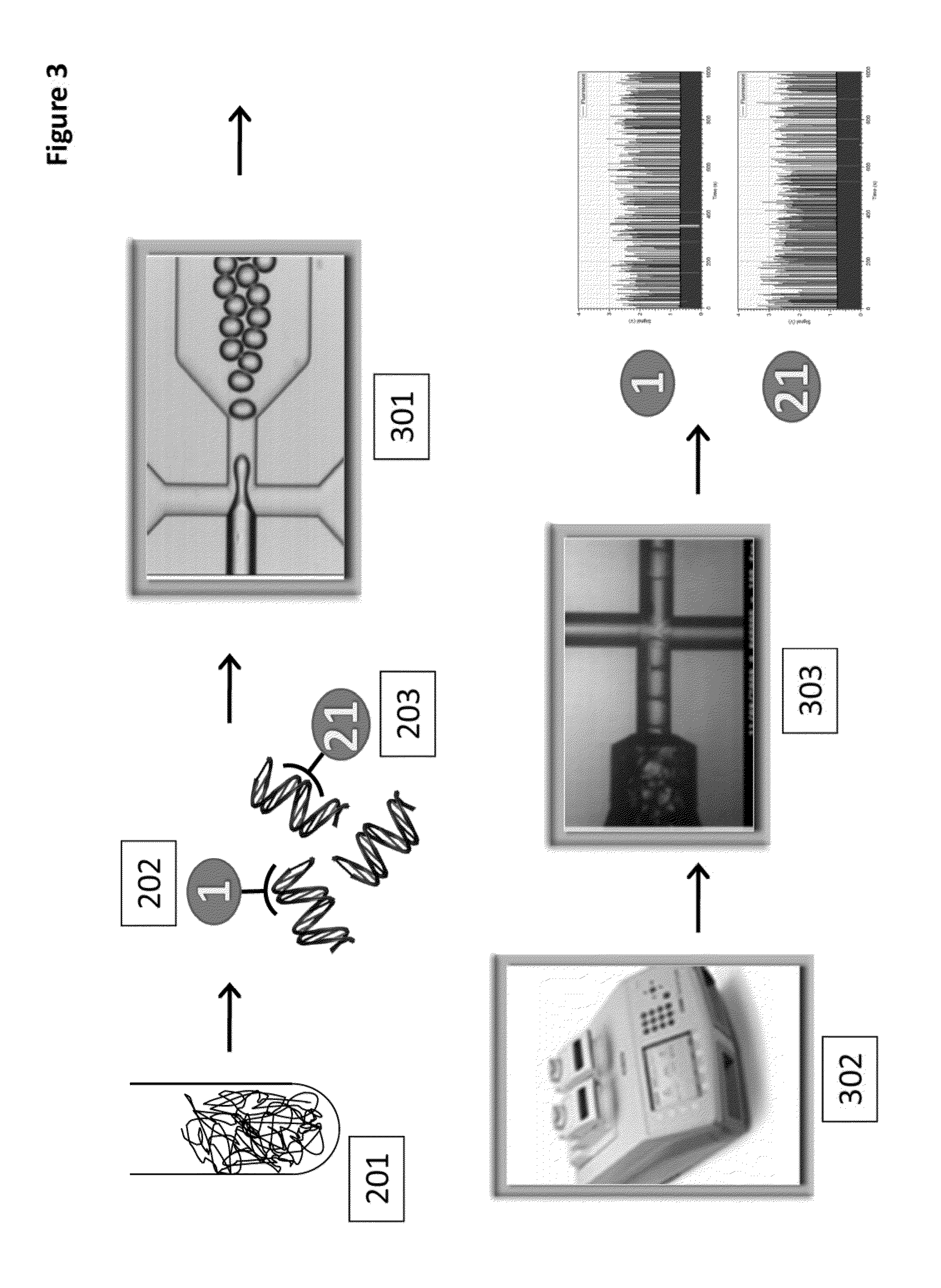
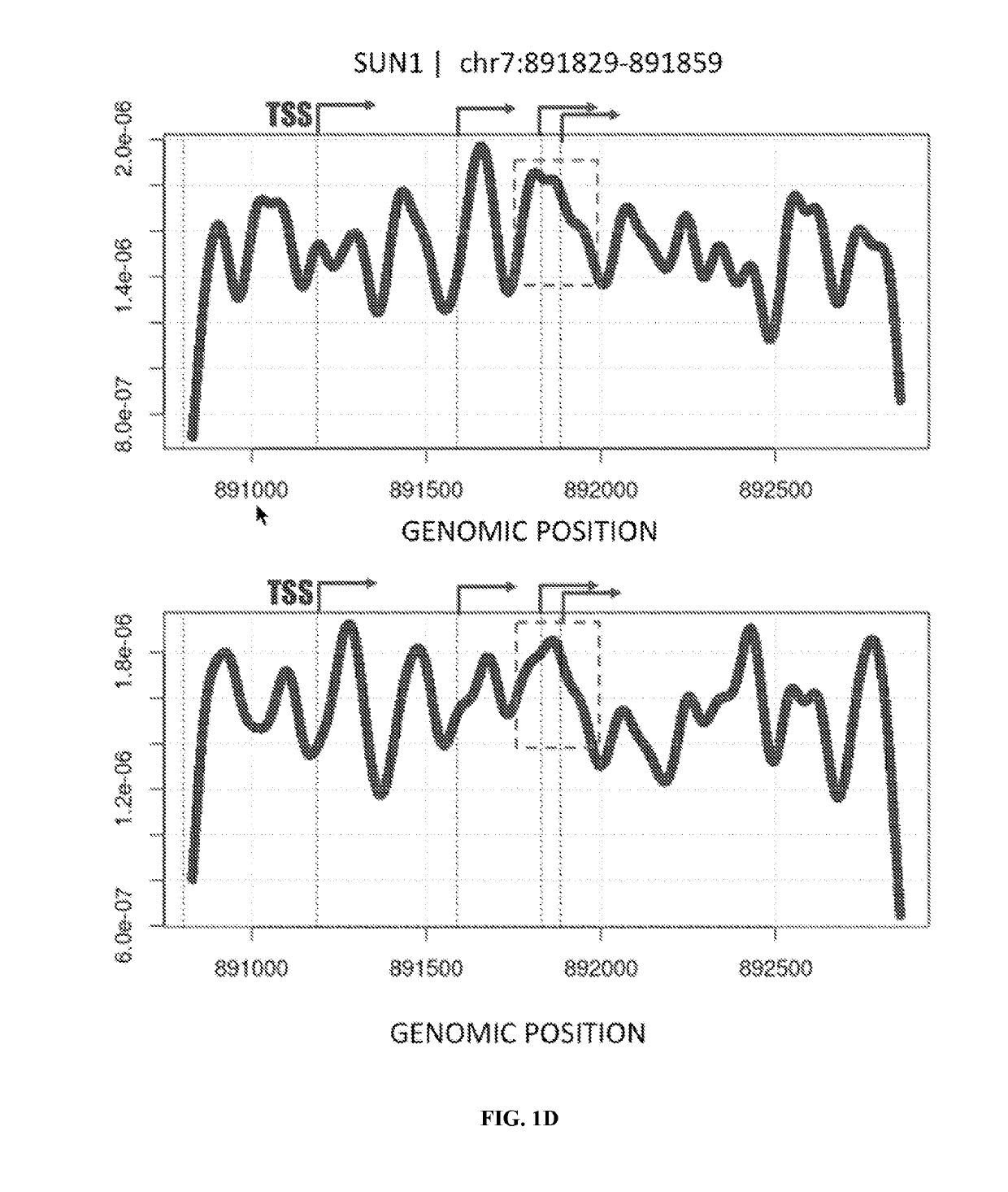
Patents
Literature
80 results about "GENETIC ABNORMALITY" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic abnormality - a disease or disorder that is inherited genetically. congenital disease, genetic defect, genetic disease, genetic disorder, hereditary condition, hereditary disease, inherited disease, inherited disorder. disease - an impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning.
Non-invasive methods for detecting non-host DNA in a host using epigenetic differences between the host and non-host DNA
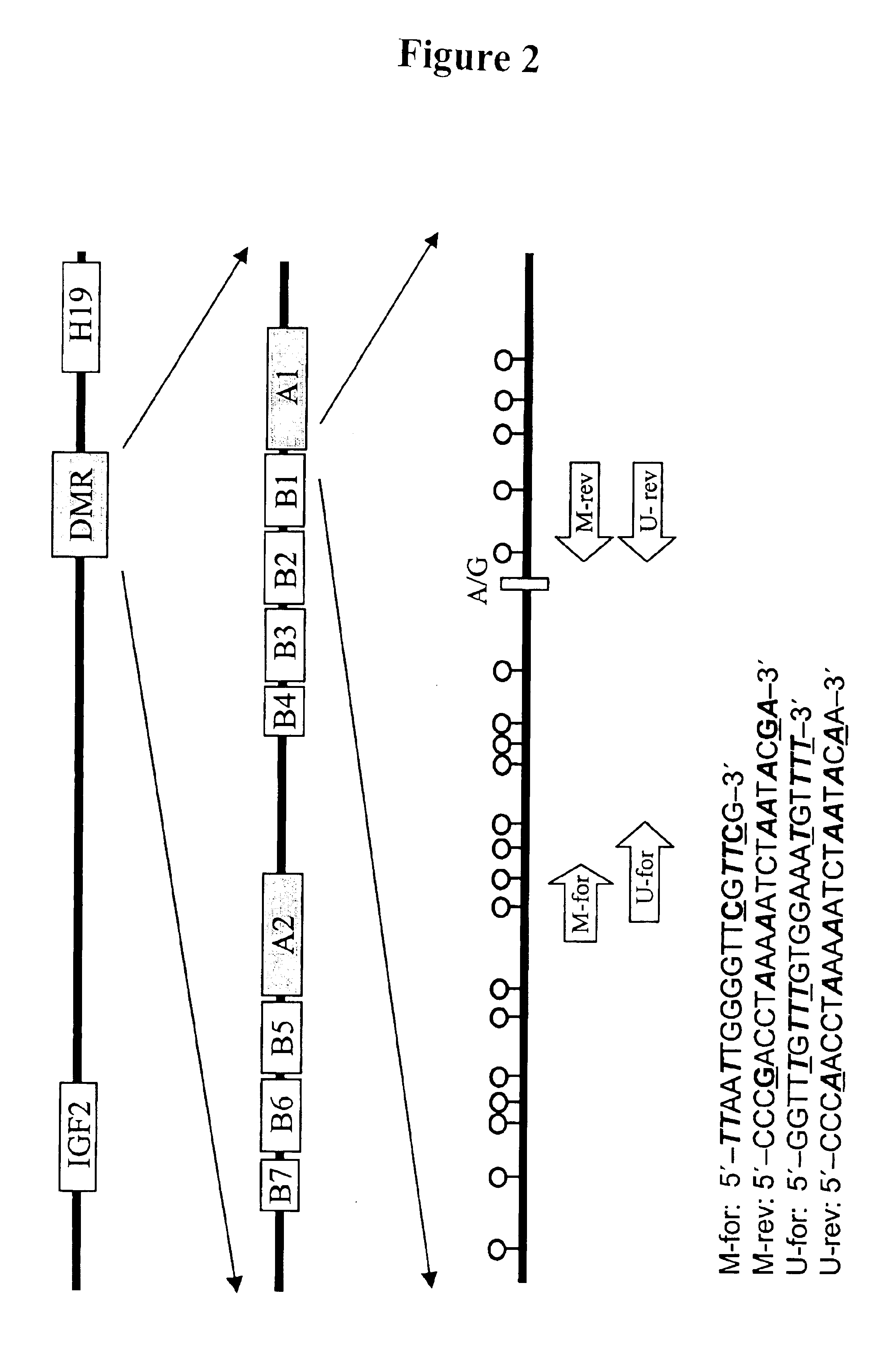
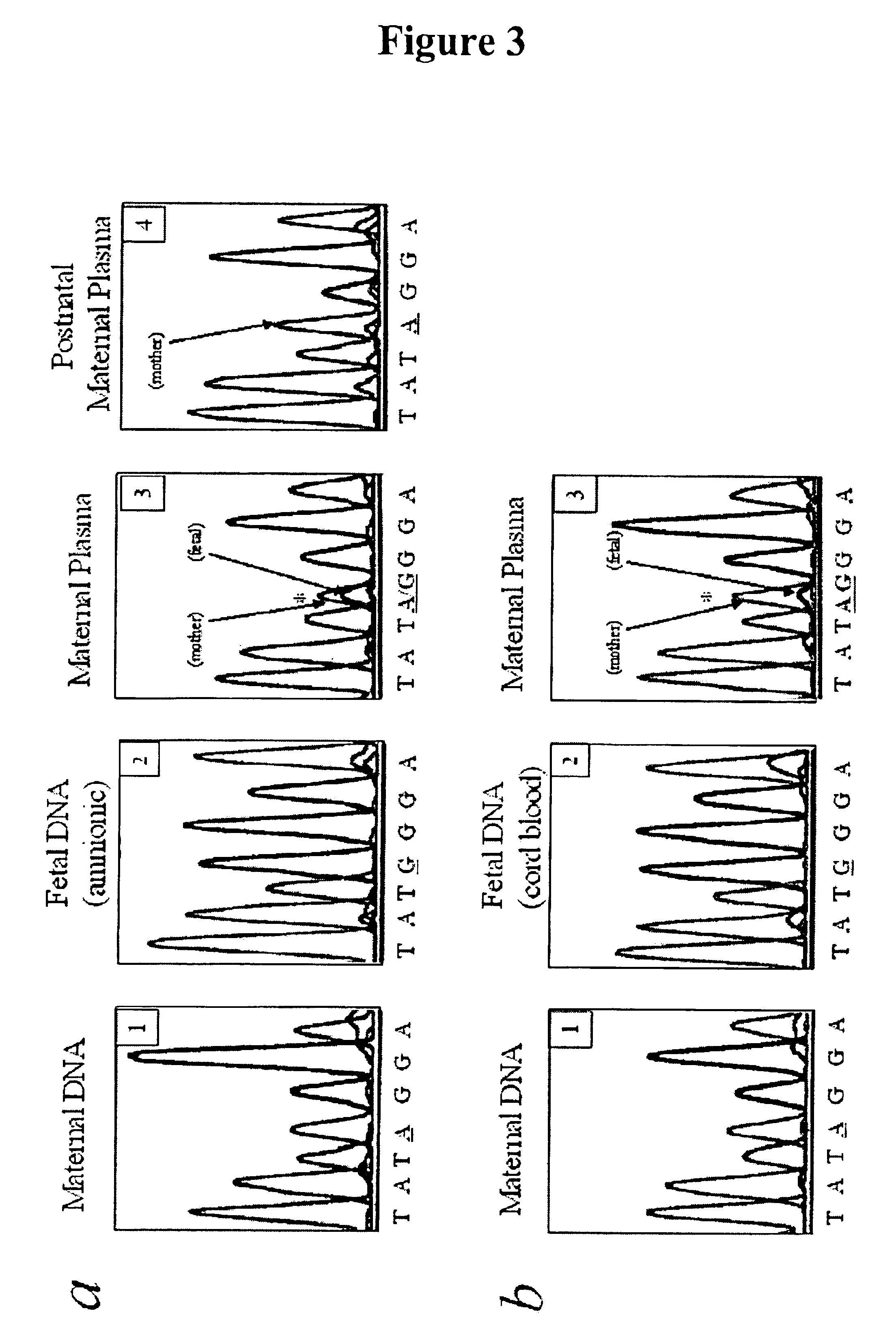
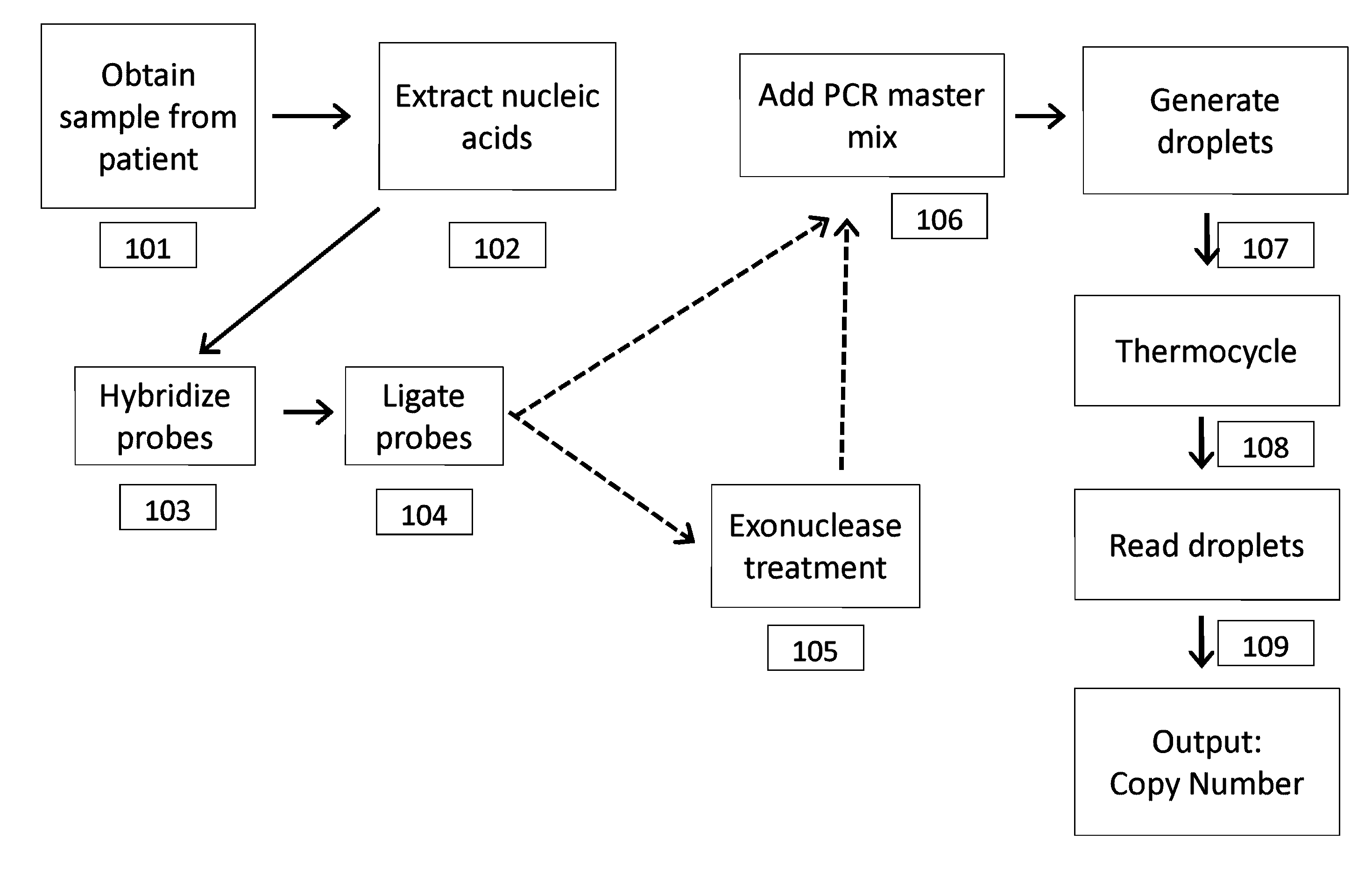
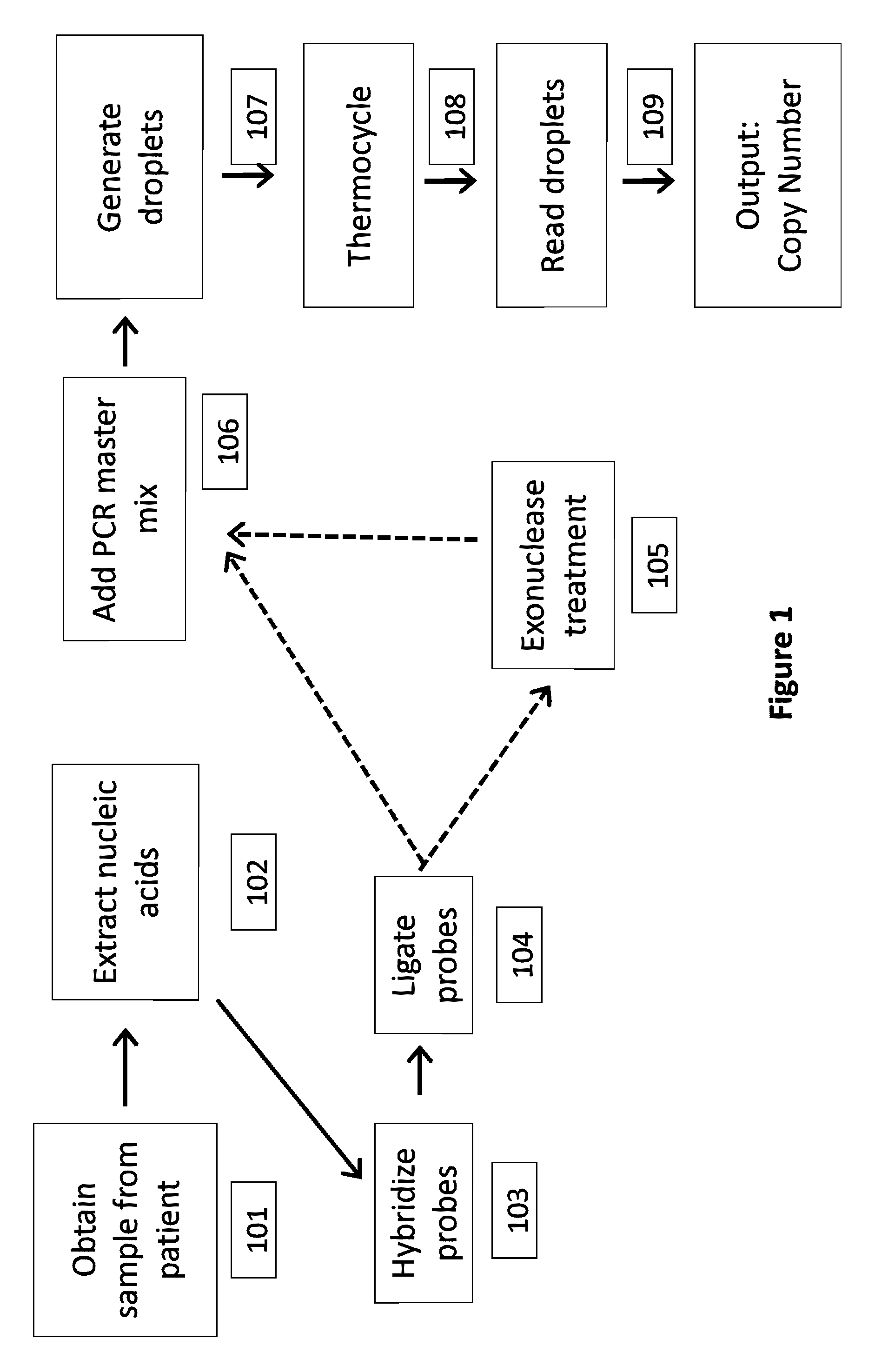
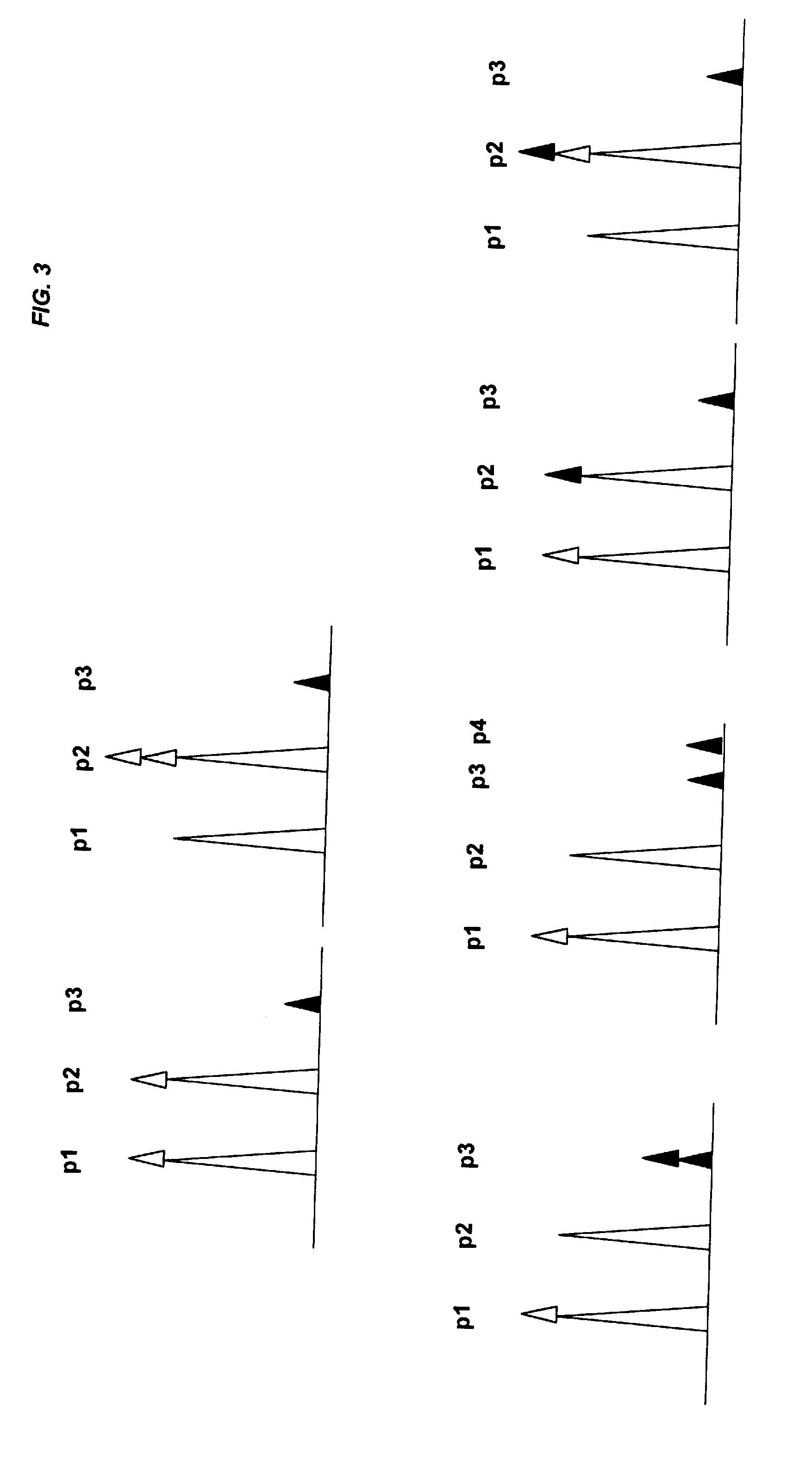
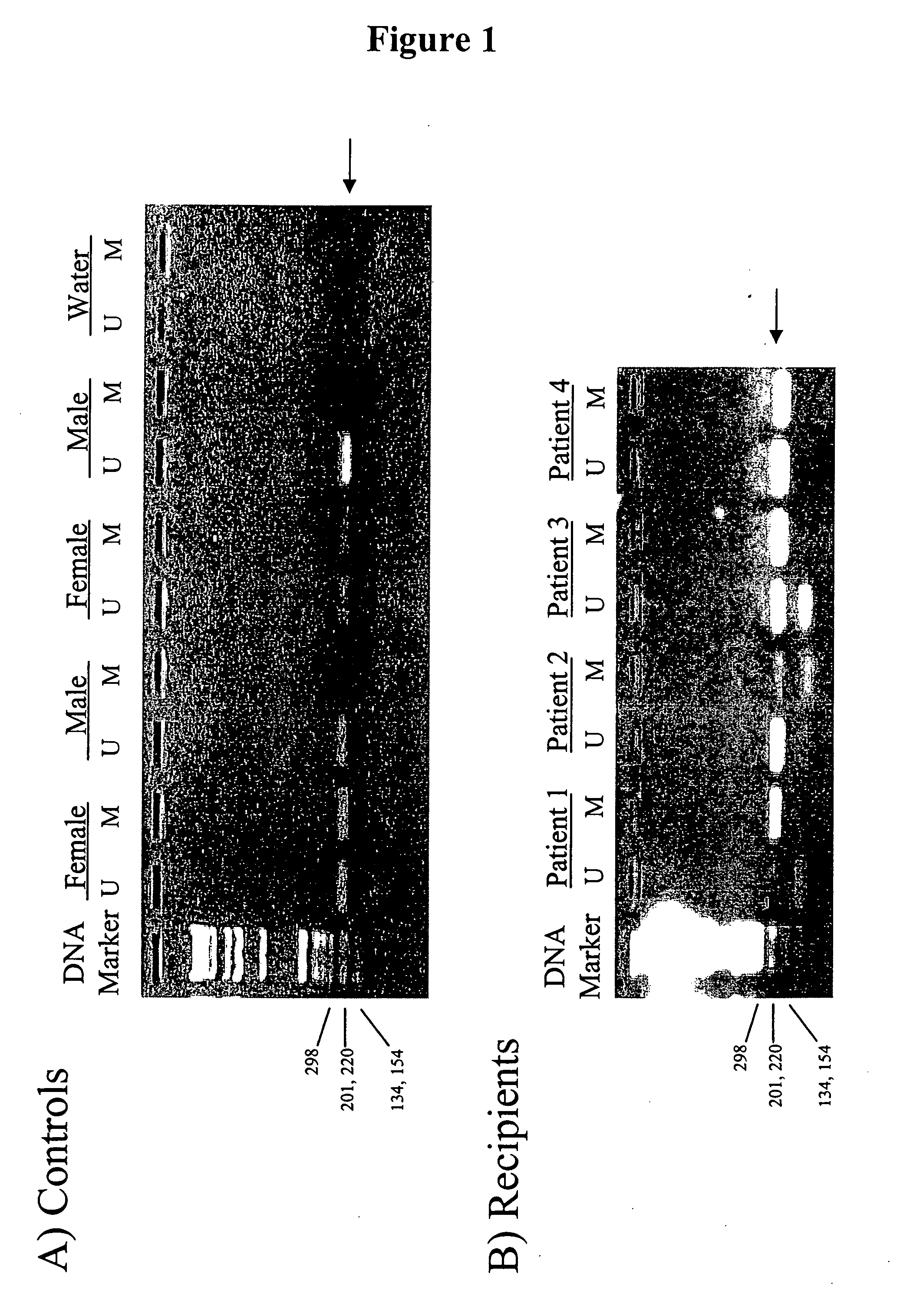
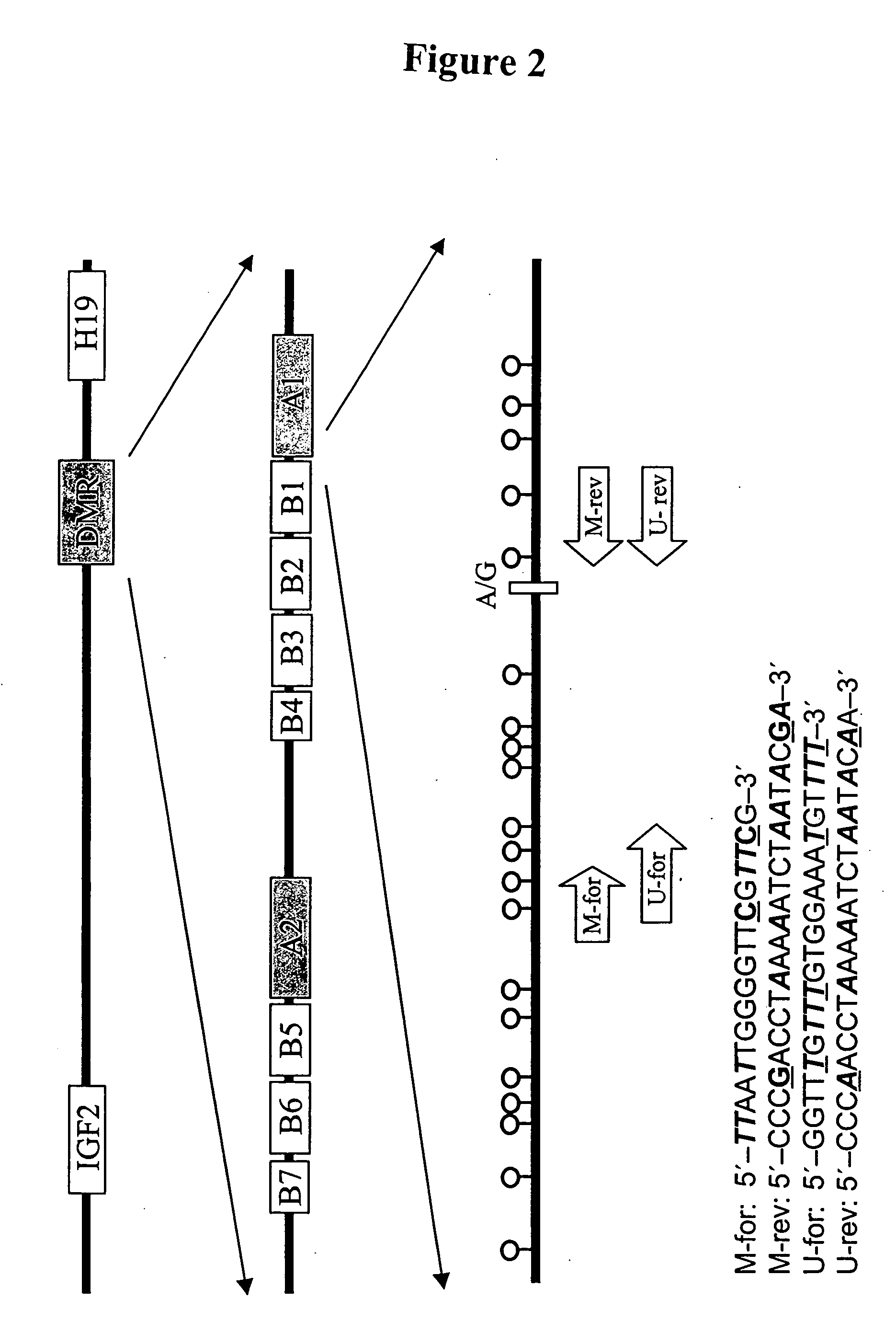
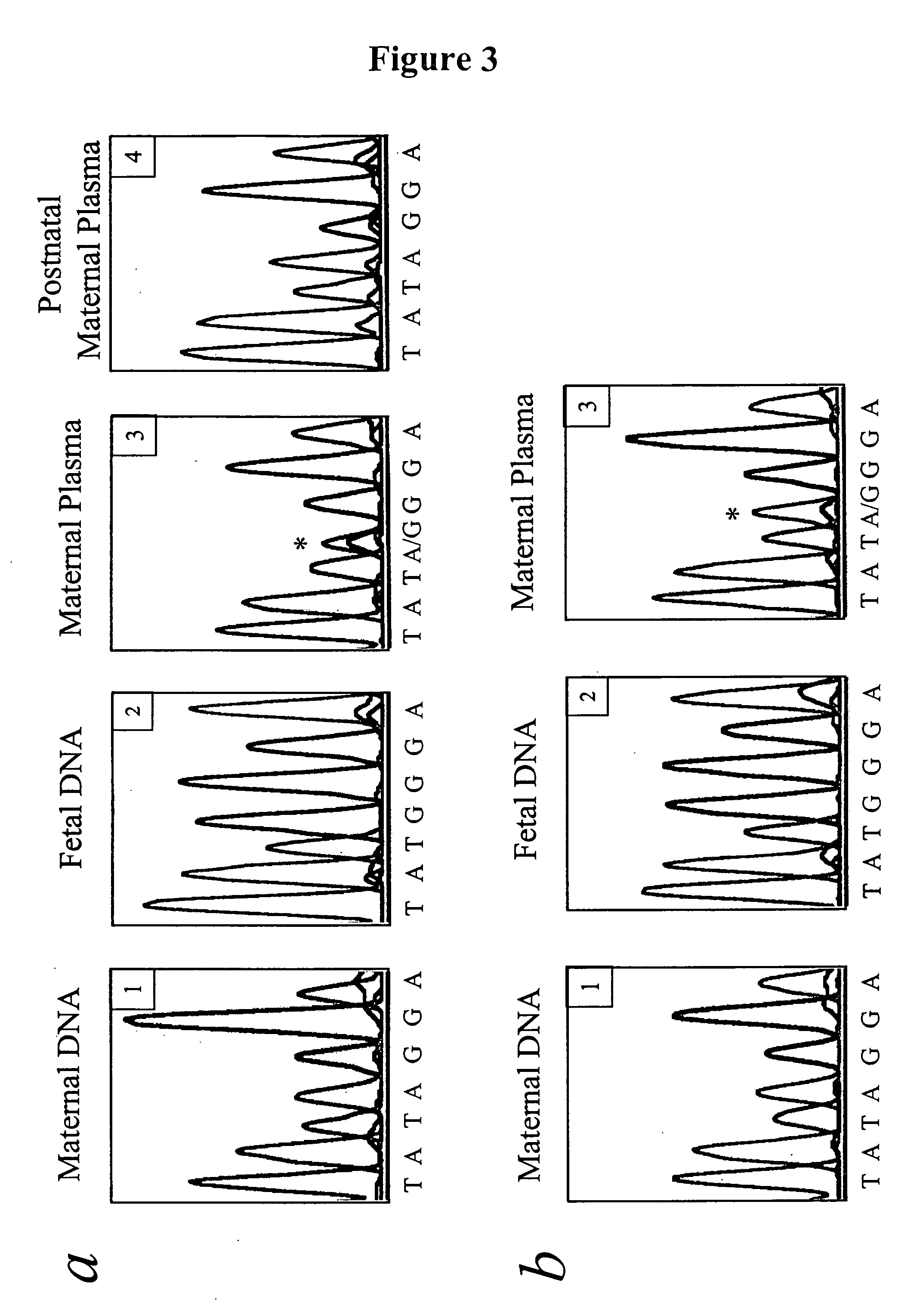
In a first aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample. These methods may be used to differentiate or detect fetal DNA in a maternal sample or to differentiate DNA of an organ donor from DNA of an organ recipient. In preferred embodiments, the DNA species are differentiated by observing epigenetic differences in the DNA species such as differences in DNA methylation. In a second aspect, the present invention features methods of detecting genetic abnormalities in a fetus by detecting fetal DNA in a biological sample obtained from a mother. In a third aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from an organ donor from those of an organ recipient. In a fourth aspect, the present invention features kits for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Detection of genetic abnormalities
InactiveUS20120190020A1Quick sortingEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
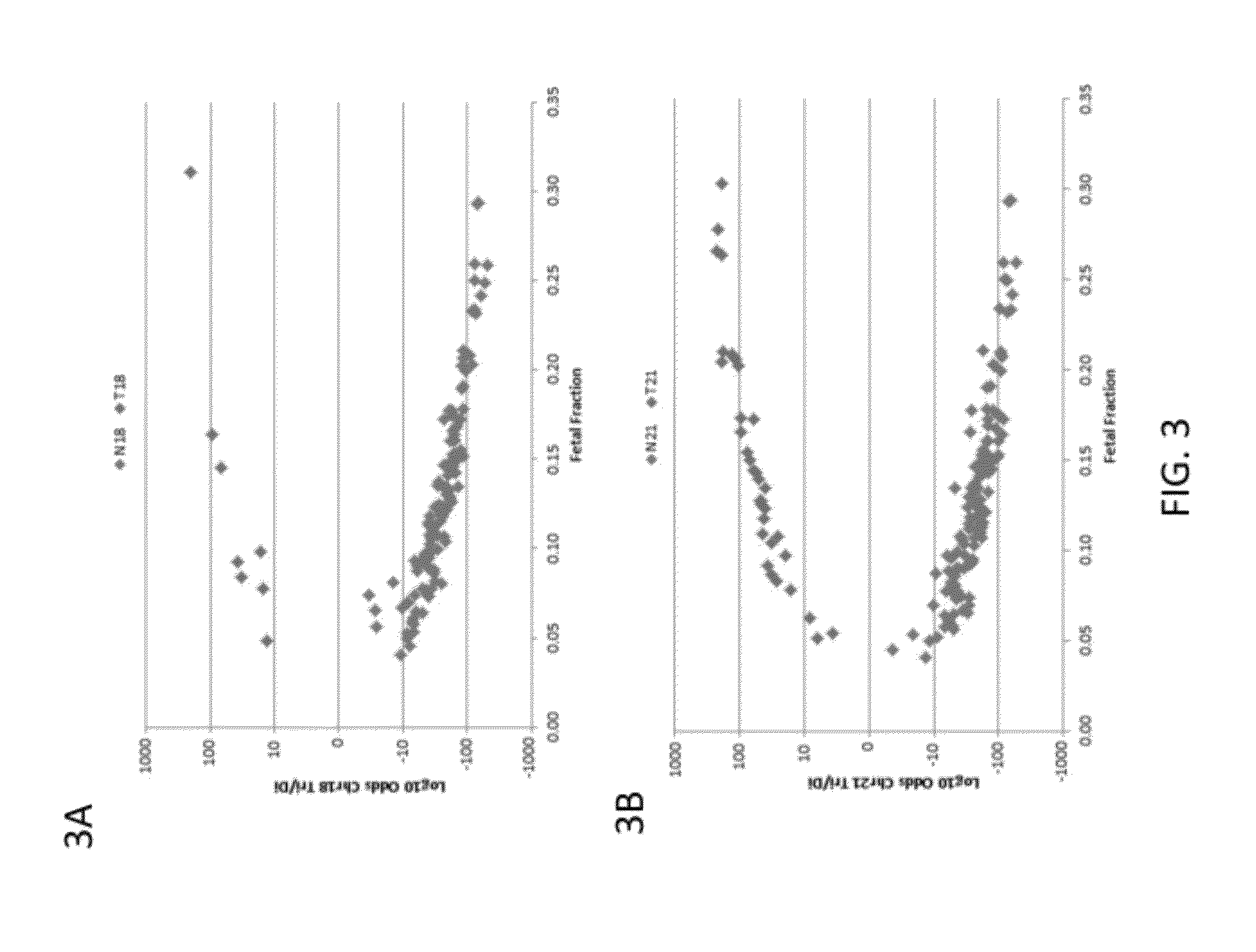
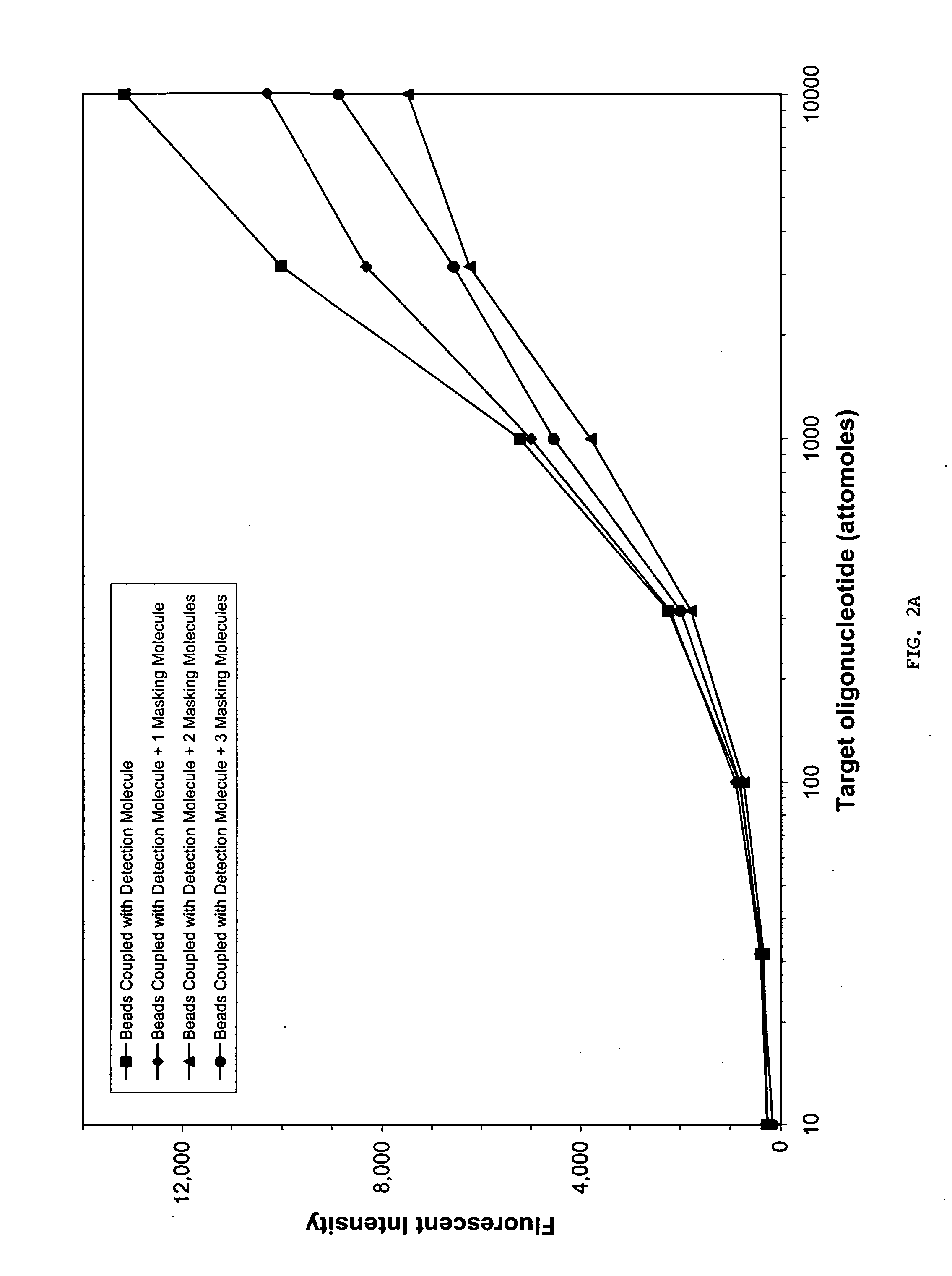
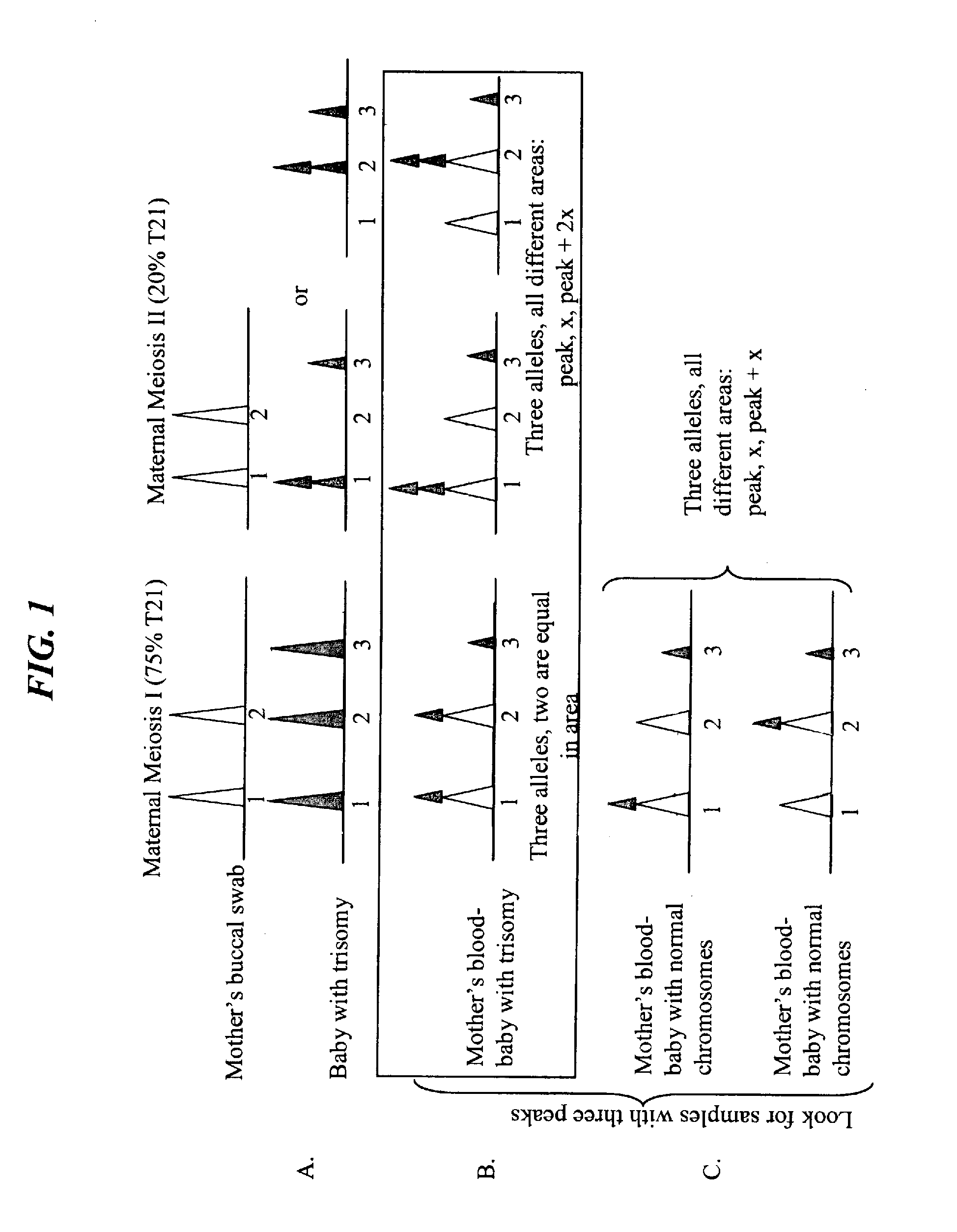
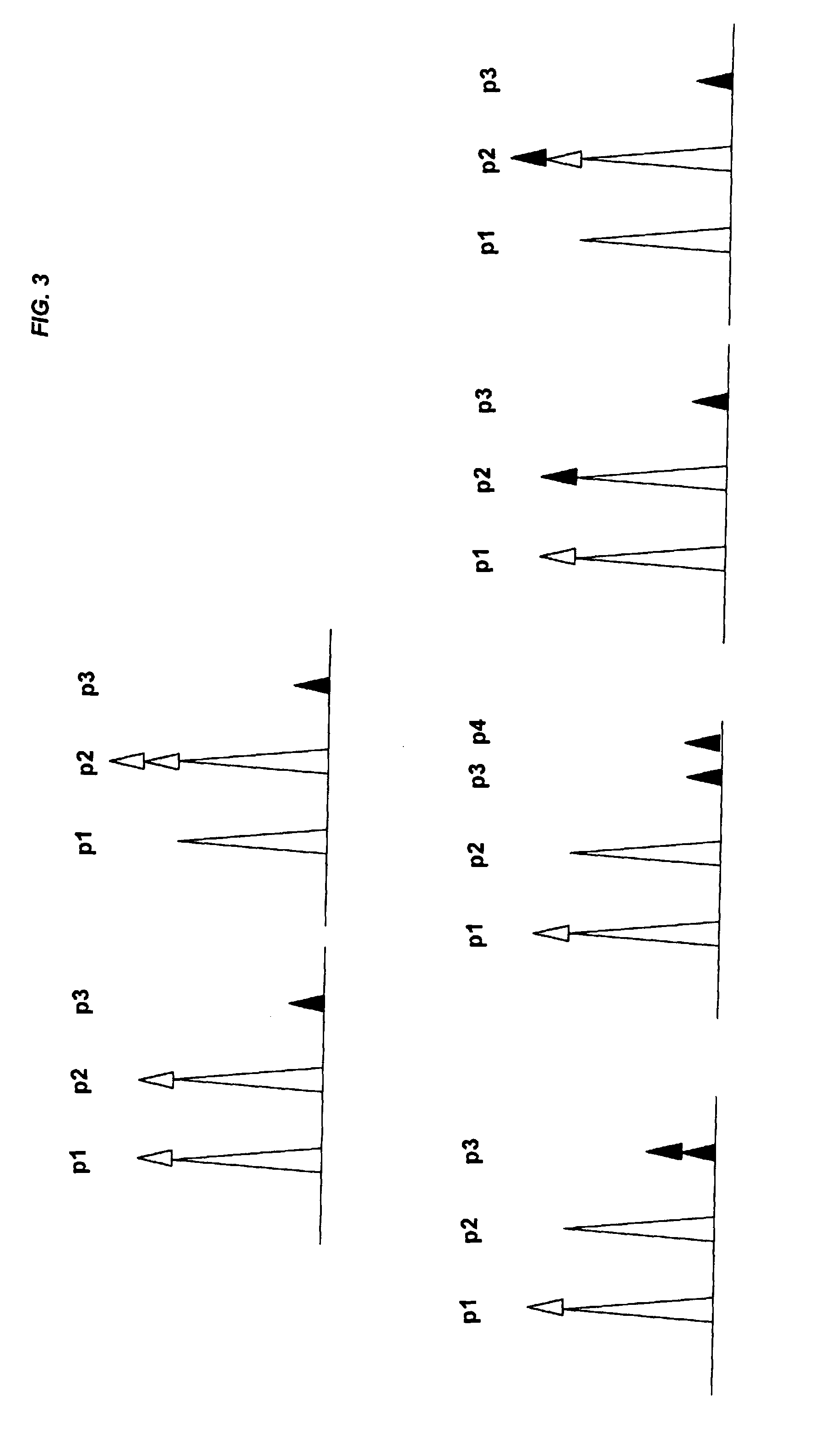
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods and compositions for detecting genetic material
InactiveUS20110159499A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsPolynucleotide
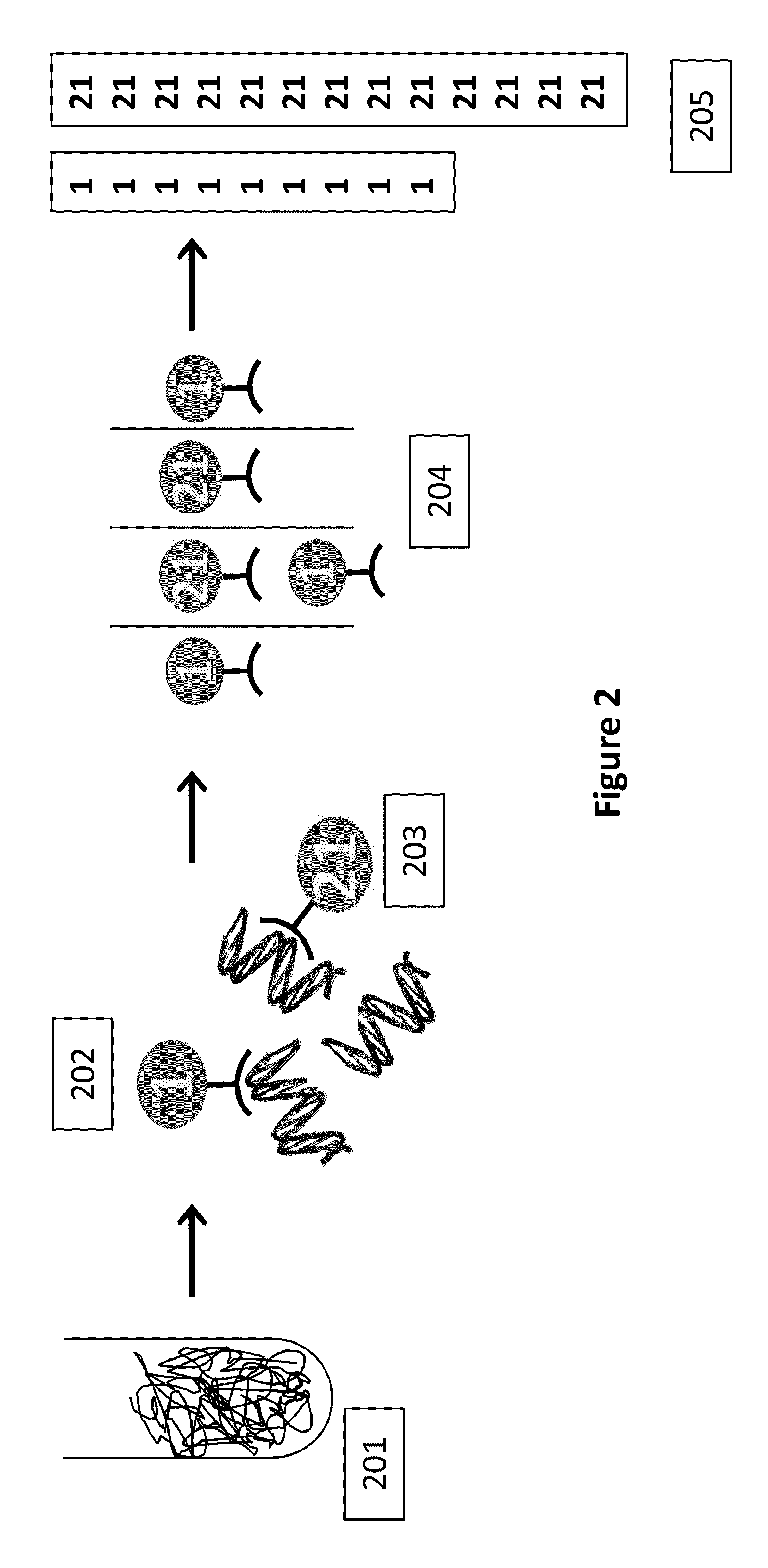
This invention provides compositions and methods for detecting differences in copy number of a target polynucleotide. In some cases, the methods and compositions provided herein are useful for diagnosis of fetal genetic abnormalities, when the starting sample is maternal tissue (e.g., blood, plasma). The methods and materials described apply techniques for allowing detection of small, but statistically significant, differences in polynucleotide copy number.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Enrichment of circulating fetal DNA
InactiveUS20070243549A1High accuracy of resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansNon invasiveMolecular diagnostics
A non-invasive screening or diagnostic method for determining the likelihood of a fetus with a genetic abnormality or a potential pregnancy complication, which utilizes a liquid blood sample from a pregnant woman. Antibodies specific to a section of histone 3.1 which is exposed to a far greater extent in chromatin of fetal origin than in chromatin of maternal origin are used to sequester and isolate such fetal nucleosomes including the associated fetal DNA. Following isolation / enrichment of such fetal DNA, genetic analysis is carried out using known molecular diagnostics.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
System and method for inhibiting the decryption of a nucleic acid probe sequence used for the detection of a specific nucleic acid
InactiveUS20060073487A1Reduce or impede a person's ability to designAvoid identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic AnomalyNucleic Acid Probes
Sequence-specific nucleic acid hybridization assays are used for the detection of specific genetic sequences as indicators of genetic anomalies, mutations, and disease propensity. In addition, they are used for the detection of various biological agents and infectious pathogens. Because a complementary probe or nucleic acid sequence is required to detect a sequence of interest in a hybridization-based assay, nucleic acid sequencing techniques can rapidly determine the specific probe sequence being used for detection. This allows reverse engineered assays to be produced rapidly. In addition, it enables the circumvention of hybridization-based assays for biological agent or infectious pathogen detection by providing the information necessary to create or alter nucleic acid sequences to produce false positives or false negatives. The present invention provides methods and compositions for inhibiting the identification of specific detection sequences. More specifically, the invention provides masking sequences that mask the identity of specific detection sequences.
Owner:RADIX BIOSOLUTIONS
Detection of genetic abnormalities
InactiveUS20120190021A1Quick sortingEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Detecting Genetic Abnormalities
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Method For Monitoring Disease Progression or Recurrence
ActiveUS20080161420A1BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease progressionGENETIC ABNORMALITY
Owner:ESOTERIX GENETIC LAB
Methods for detecting DNA originating from different individuals
InactiveUS20050282185A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDNA methylationOrganism
In a first aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample. These methods may be used to differentiate or detect fetal DNA in a maternal sample or to differentiate DNA of an organ donor from DNA of an organ recipient. In preferred embodiments, the DNA species are differentiated by observing epigenetic differences in the DNA species such as differences in DNA methylation. In a second aspect, the present invention features methods of detecting genetic abnormalities in a fetus by detecting fetal DNA in a biological sample obtained from a mother. In a third aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from an organ donor from those of an organ recipient. In a fourth aspect, the present invention features kits for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for Monitoring Disease Progression or Recurrence
InactiveUS20150329917A1BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease progressionGENETIC ABNORMALITY
Owner:ESOTERIX GENETIC LAB
Detecting Genetic Abnormalities
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
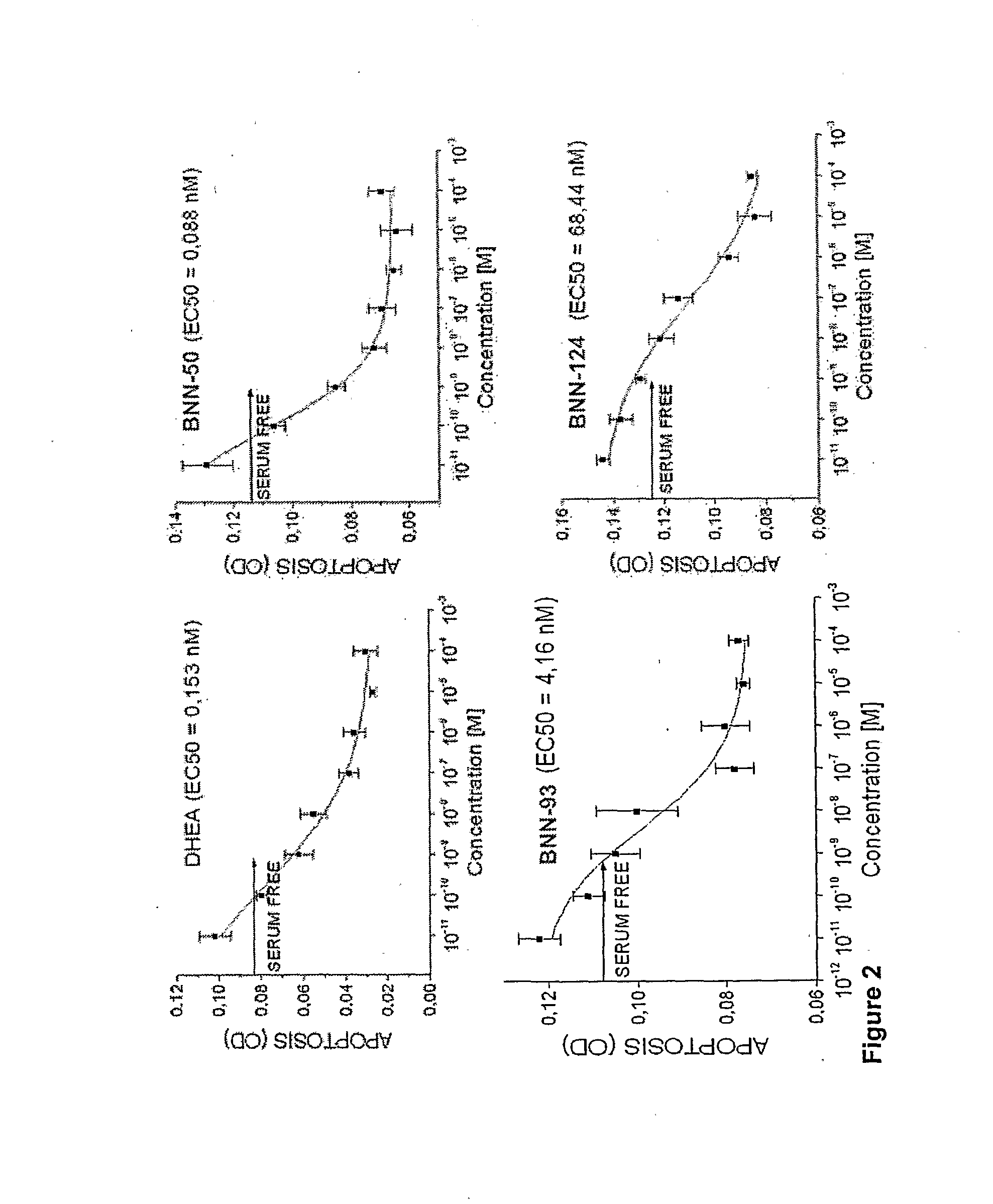
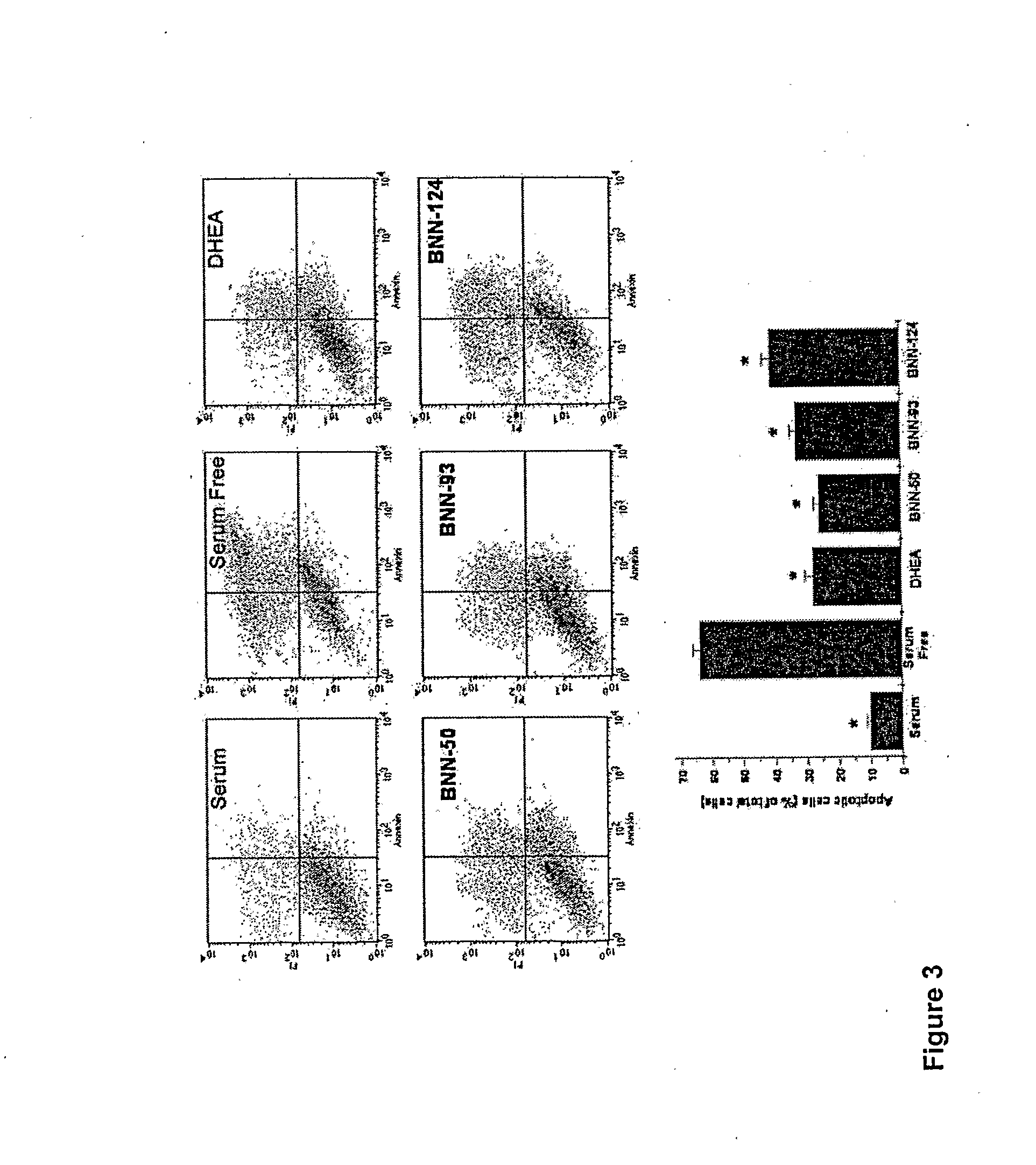
Neurosteroid compounds
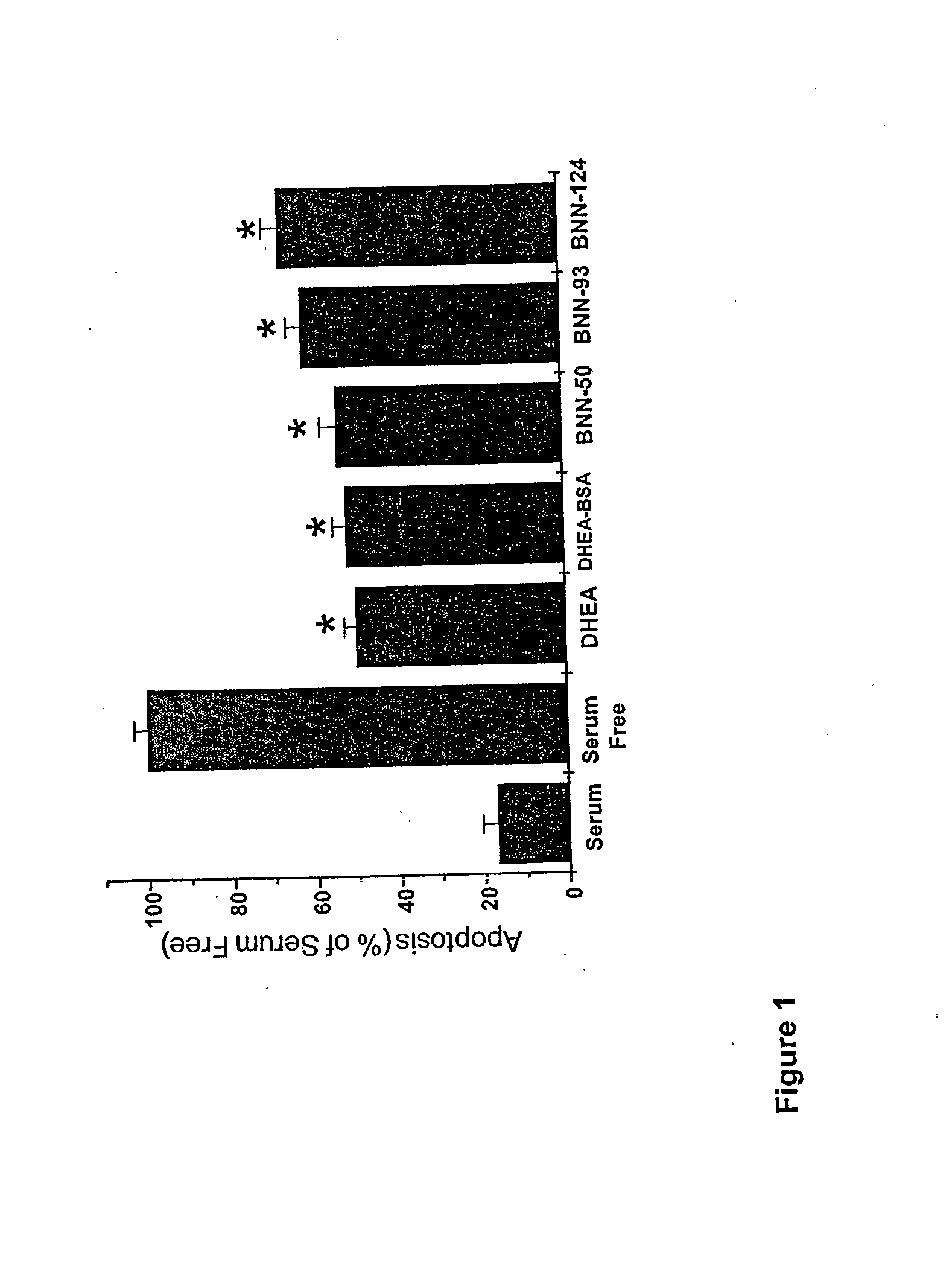
The present invention relates to novel neurosteroid derivatives with anti-apoptotic, neuroprotective and neurogenic properties that act on the nervous system as well as methods for making the same and their applications in the treatment and / or prevention or amelioration of neurodegenerative diseases related to neuronal apoptosis or neuronal injury, or conditions related to or resulting from apoptosis, including but not limited to Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), retinal degeneration and detachment, peripheral neuropathy caused by genetic abnormalities, diabetes, polio, herpes, AIDS and chemotherapy, brain trauma, or ischemia and stroke. The active compounds are represented by Formula (I): wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A, B, X, Y and Z are defined in the description of the invention. The present invention also includes compositions which comprise one or more of the compounds of Formula (I).
Owner:BIONATURE E A LTD
Identification and isolation of fetal cells and nucleic acid
The present invention provides methods, antibodies and kits useful for detecting the presence of a fetal cell and / or fetal nucleic acids in a biological sample obtained from a maternal host. It also provides methods and kits for isolating fetal nucleic acid from maternal cervical mucus samples, and for testing or screening the isolated fetal nucleic acid for genetic abnormalities in fetuses.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
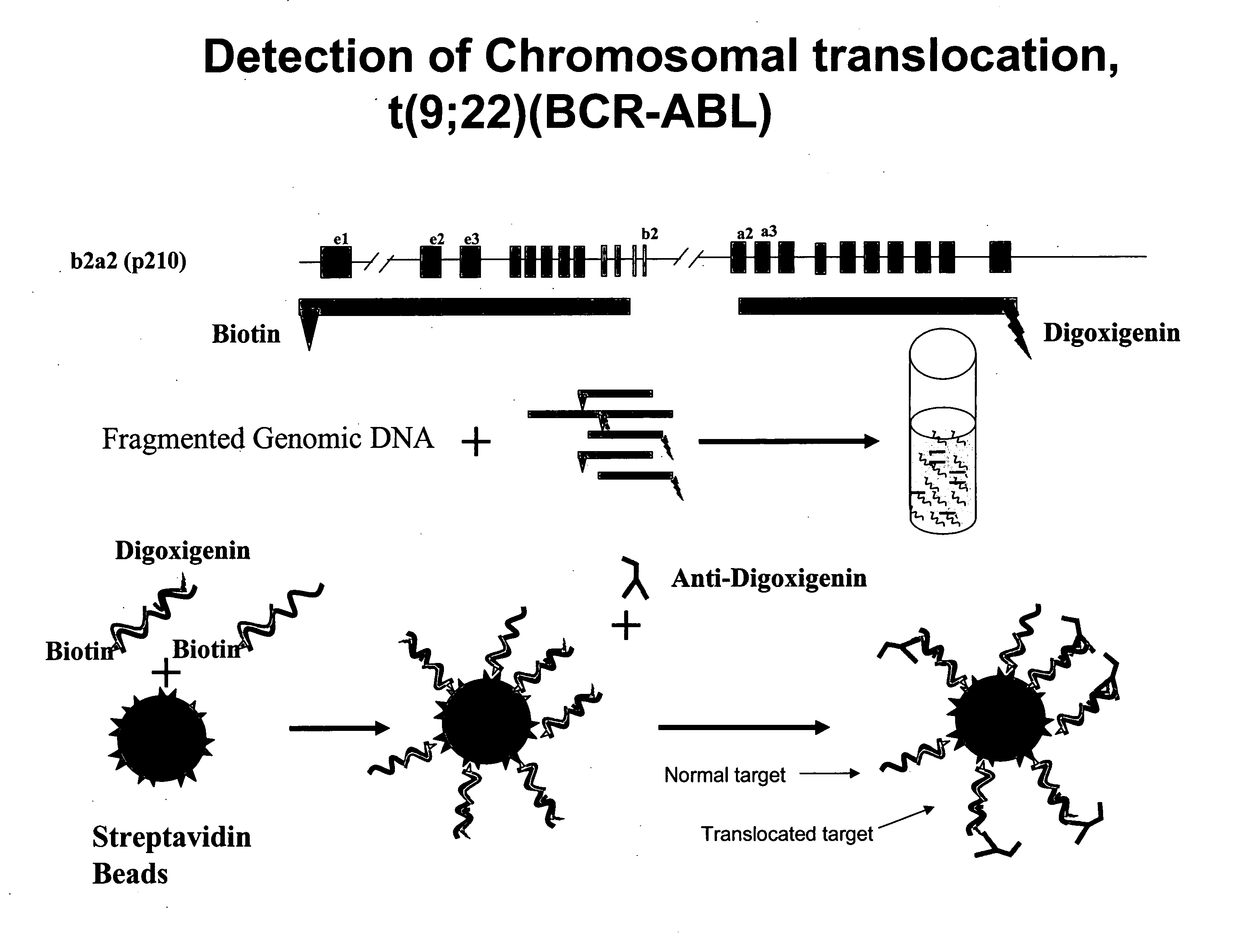
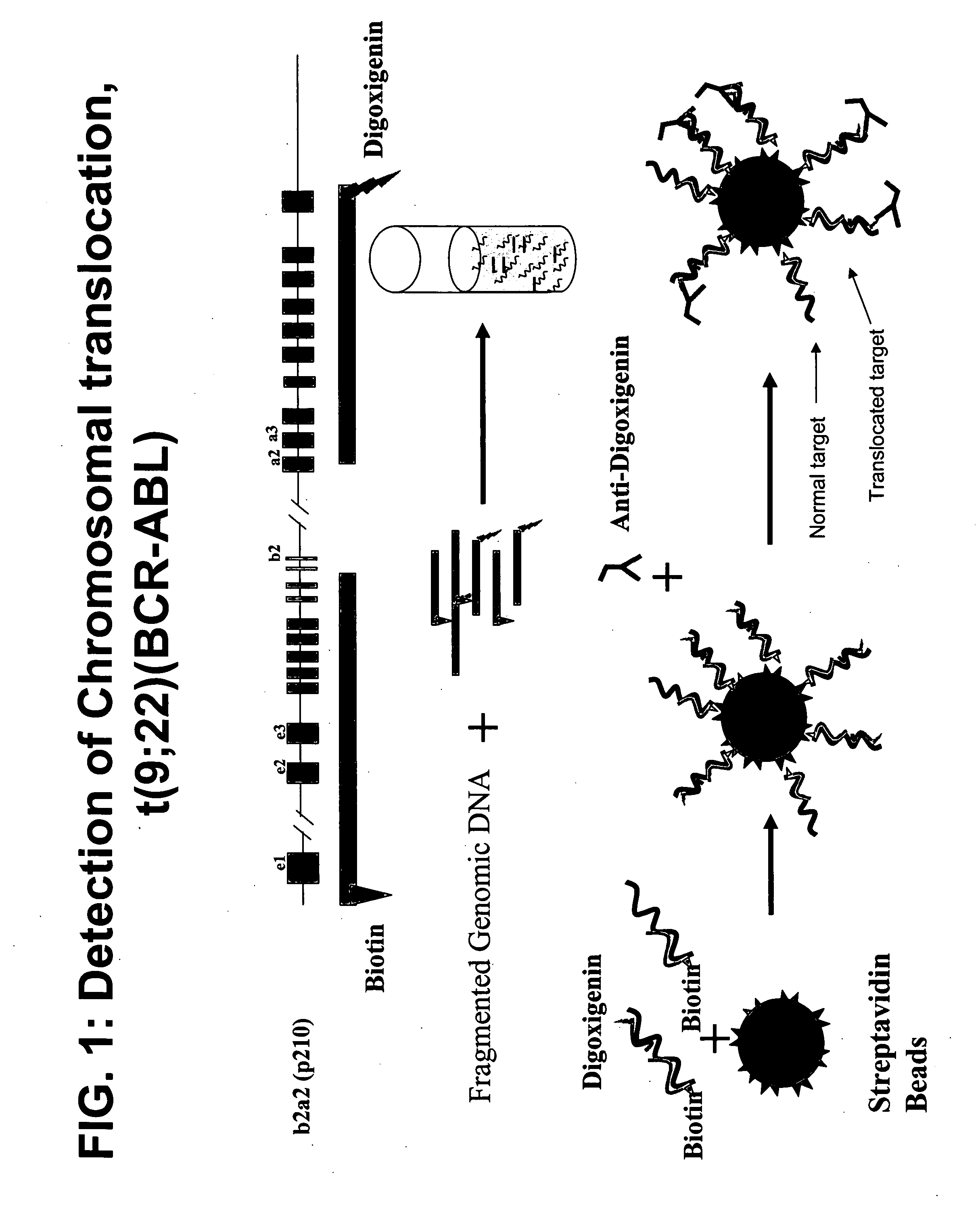
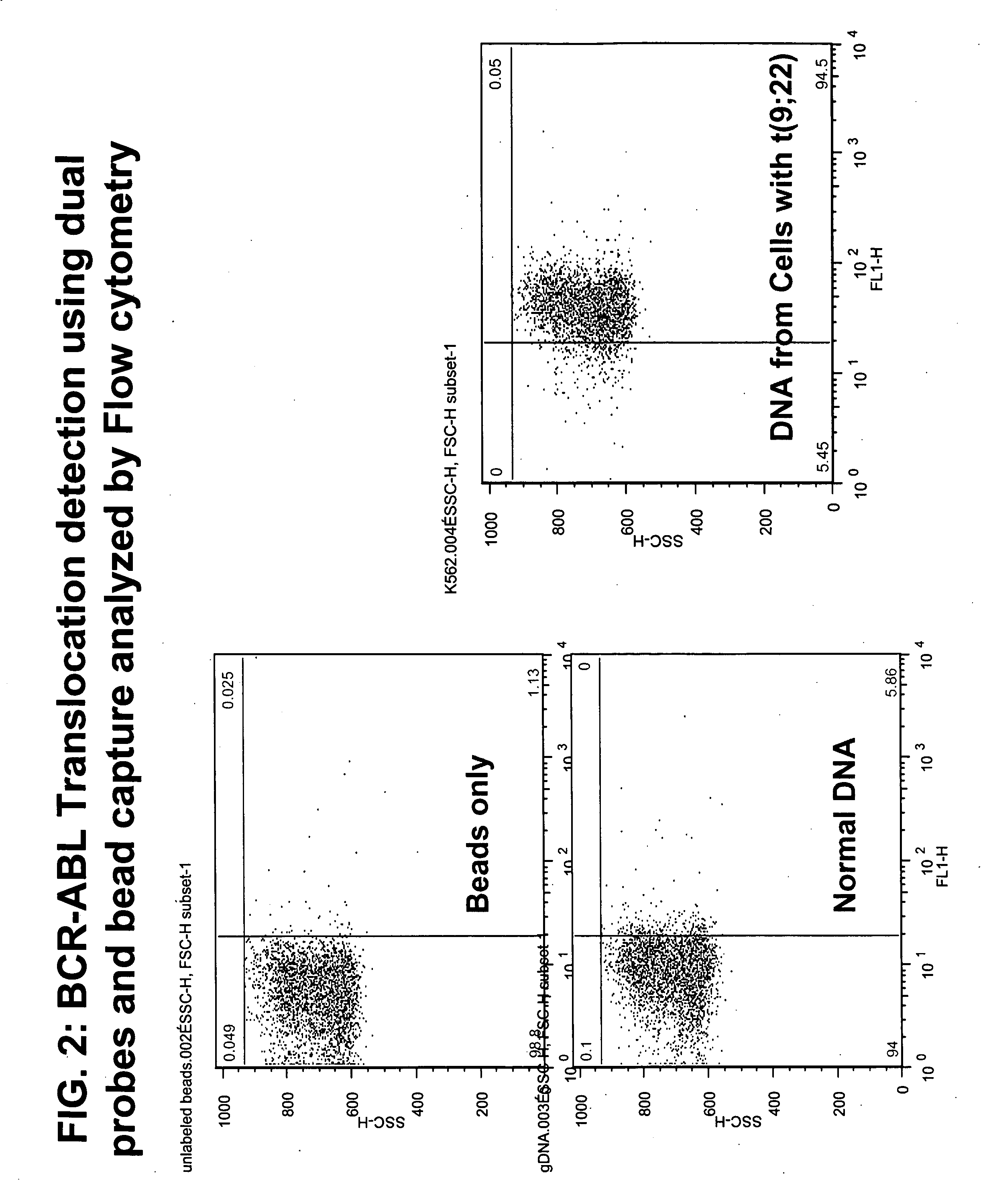
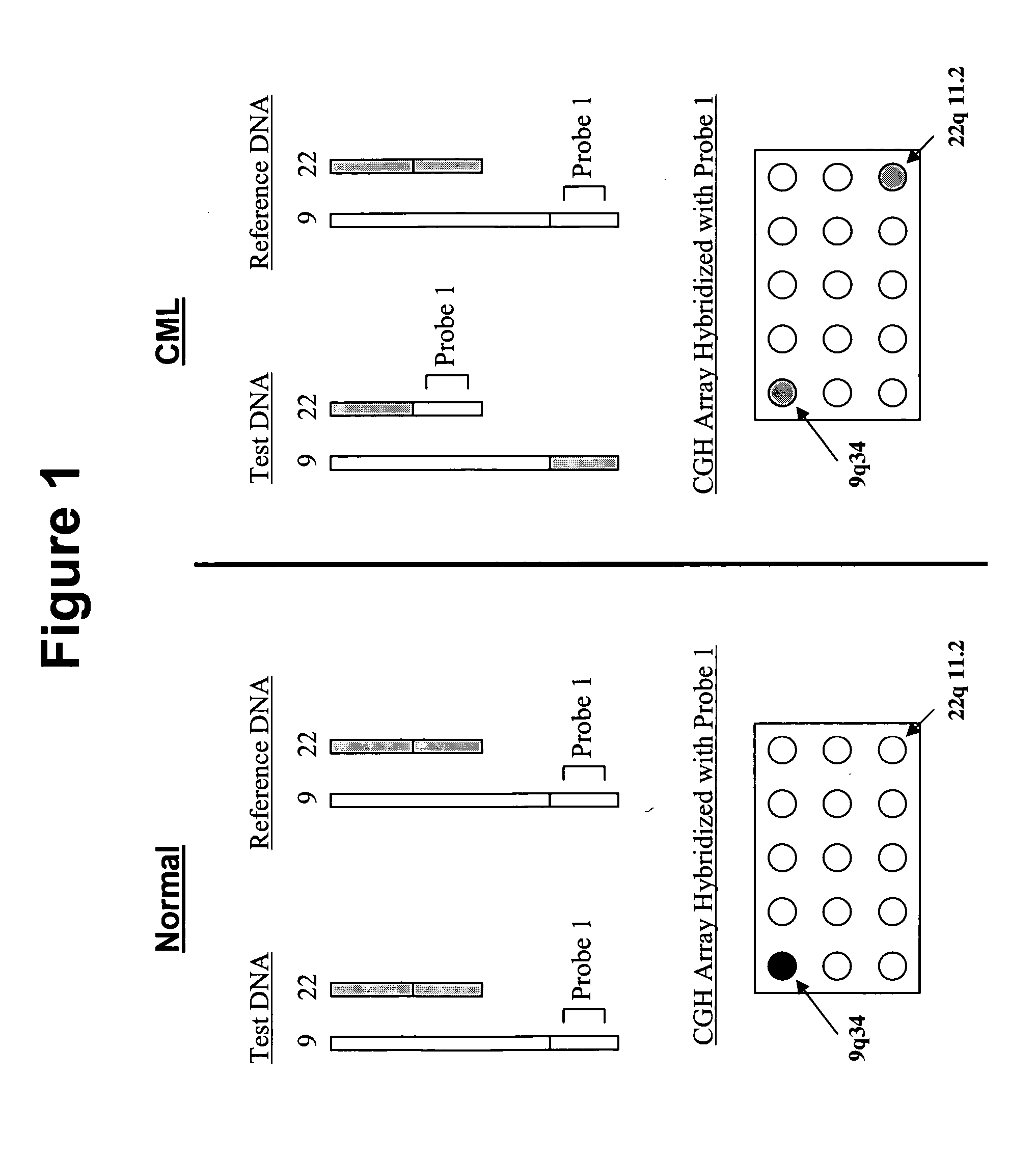
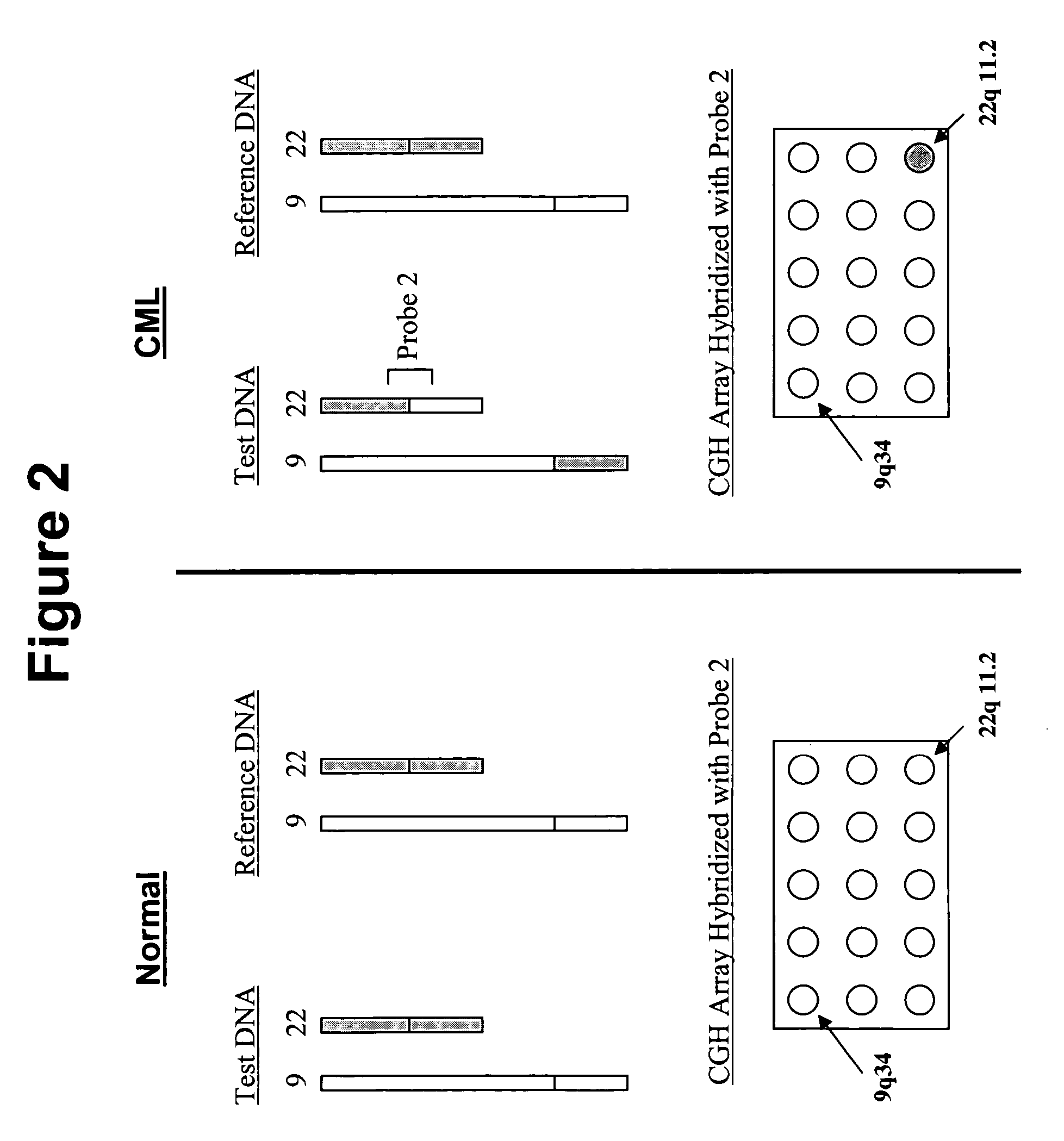
Non-in situ hybridization method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
The present invention provides methods of detecting chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases. In particular, the present invention provides advanced methods of performing DNA hybridization, capture, and detection on solid support. Invention methods are useful for the detection, diagnosis, predicting response to therapy, detecting minimal residual disease, prognosis, or monitoring of disease treatment or progression of particular disease conditions such as cell proliferative disorders
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
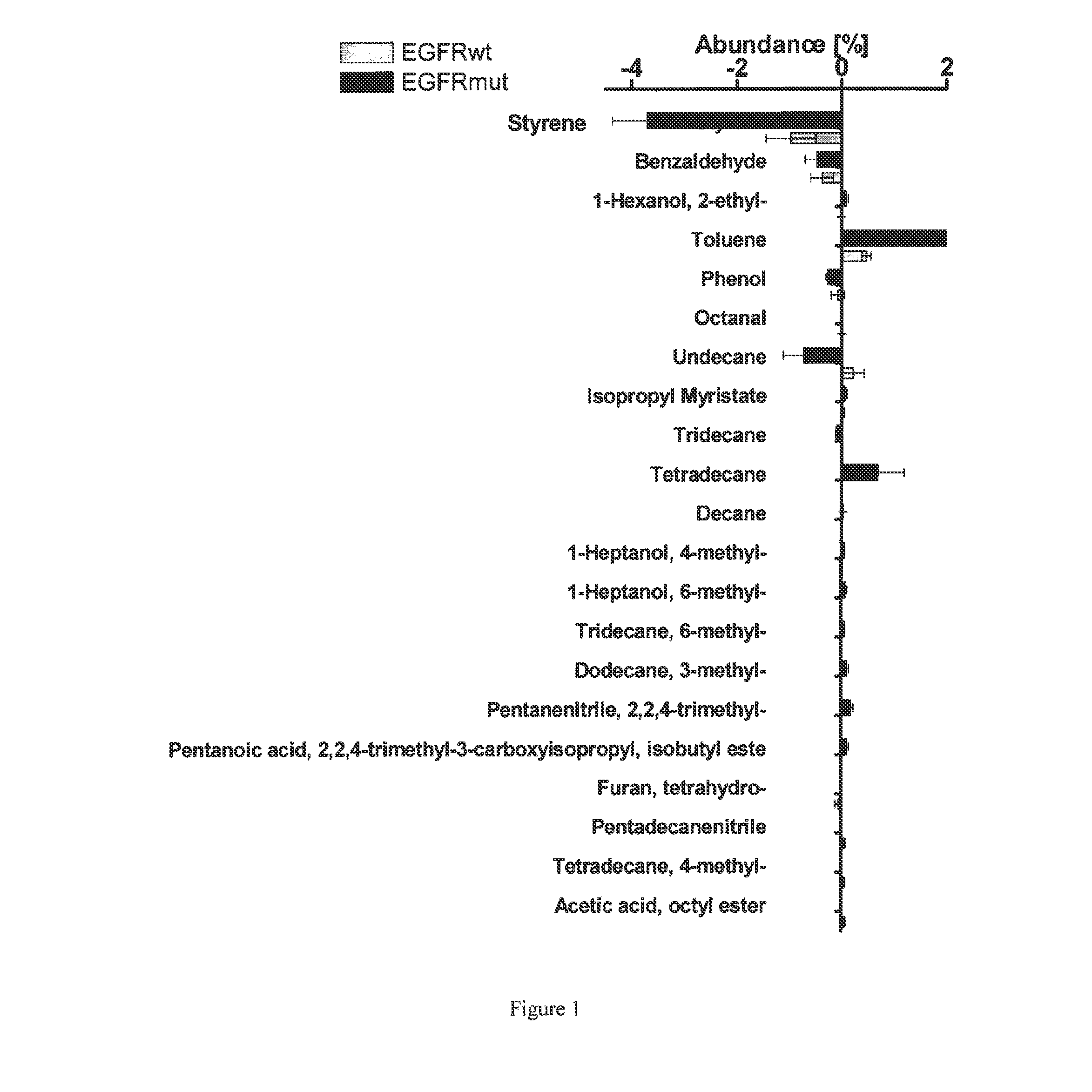
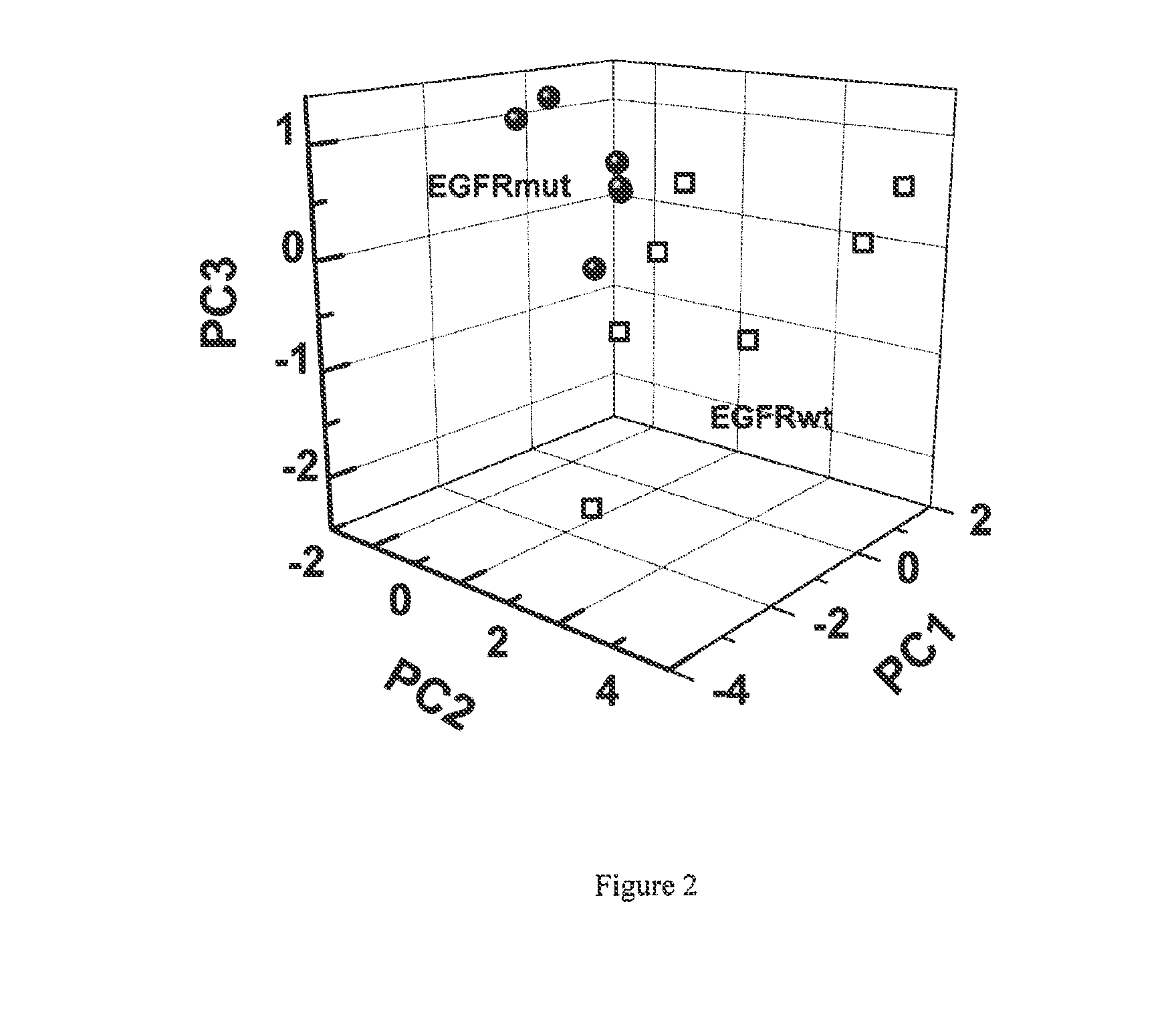
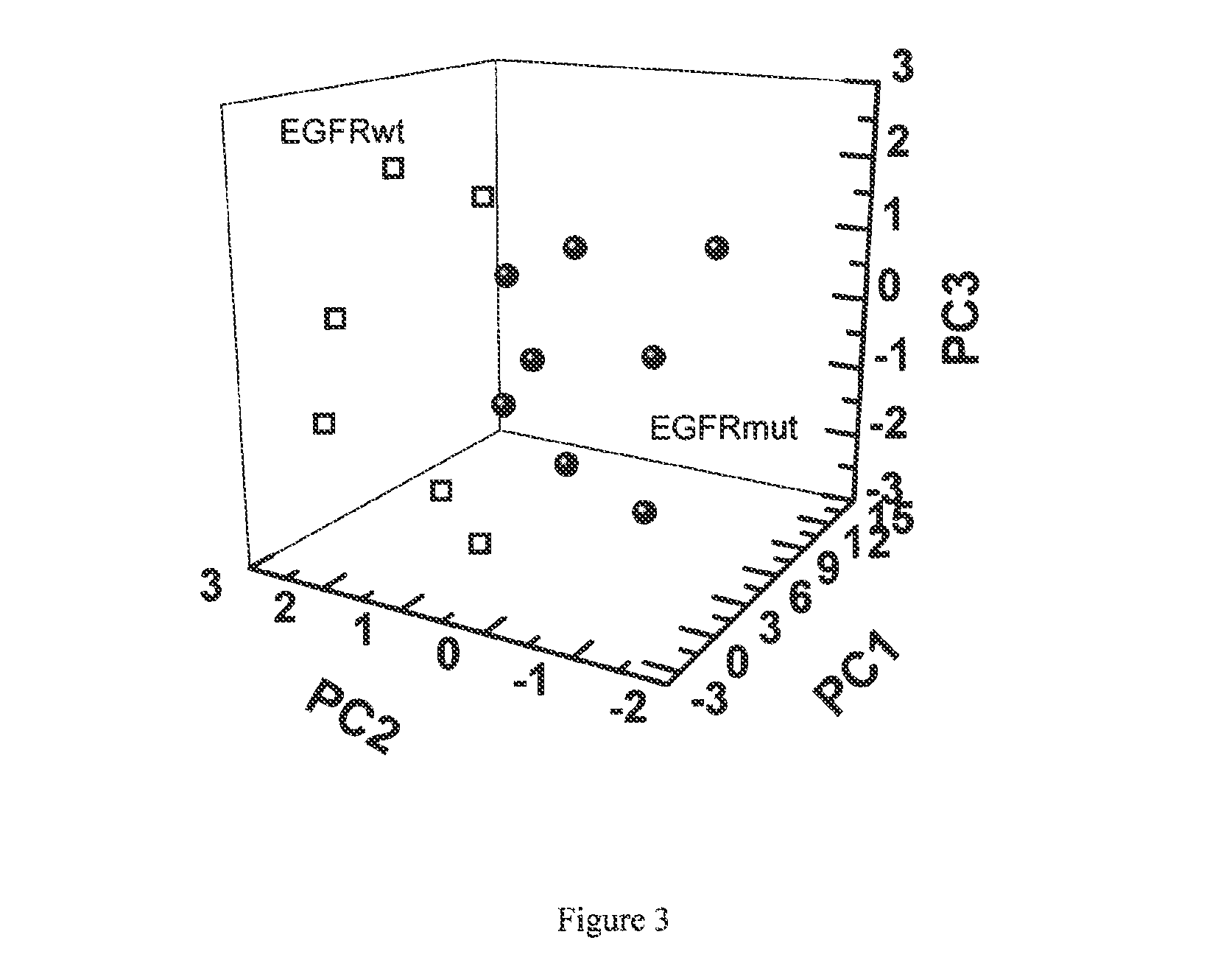
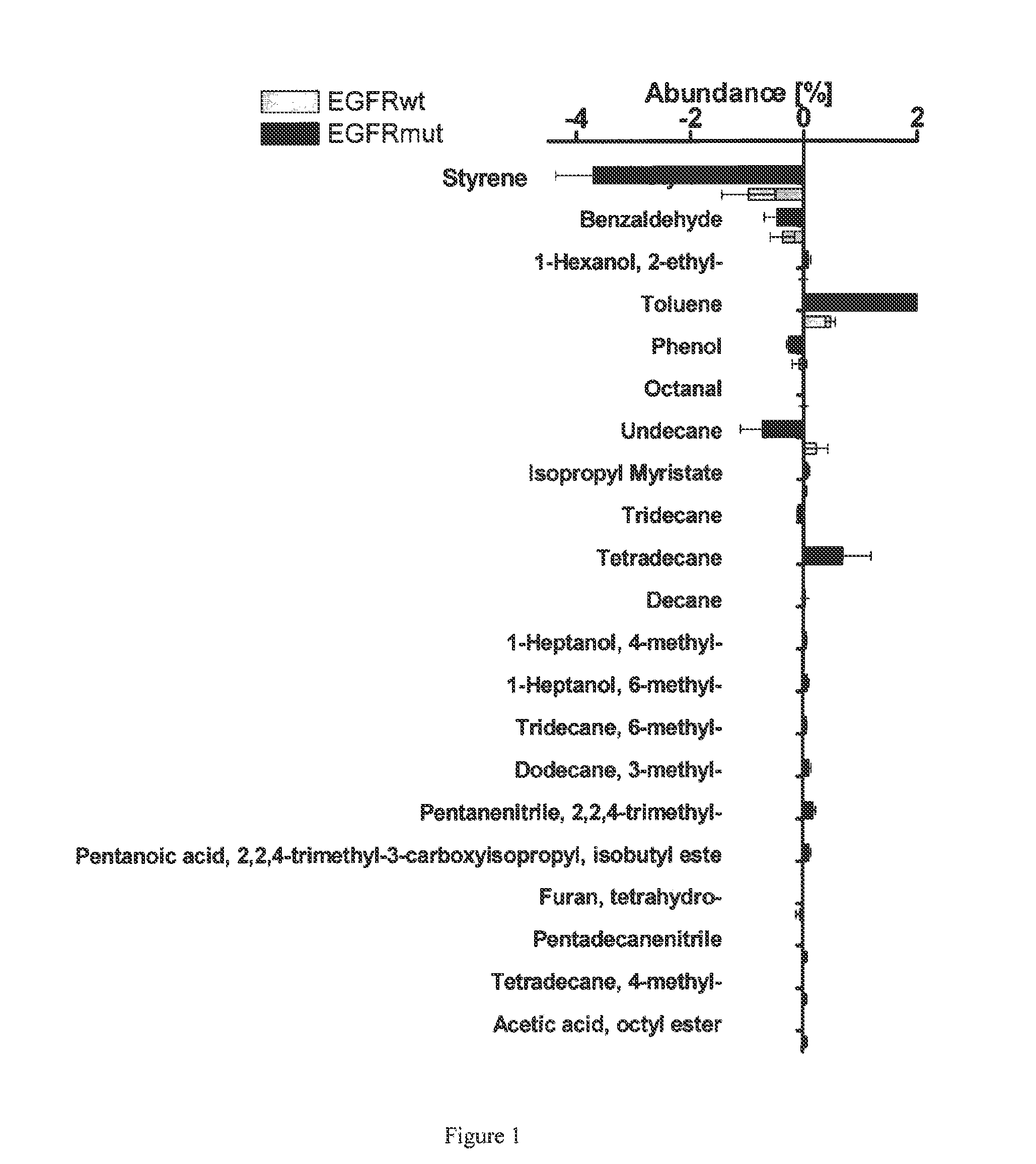
Volatile organic compounds for detecting cell dysplasia and genetic alterations associated with lung cancer
ActiveUS20130143247A1Increased riskComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBronchial epitheliumOncology
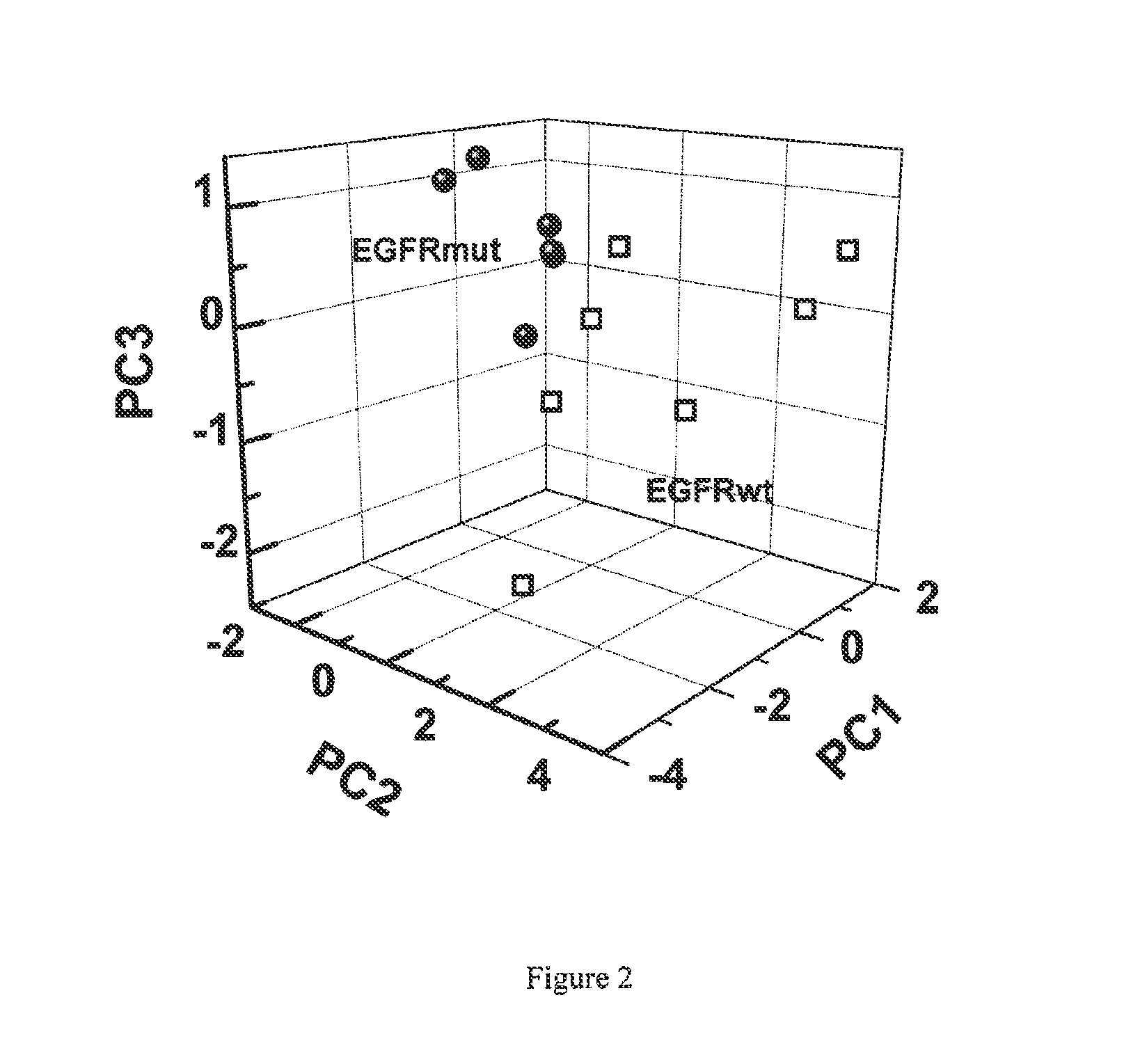
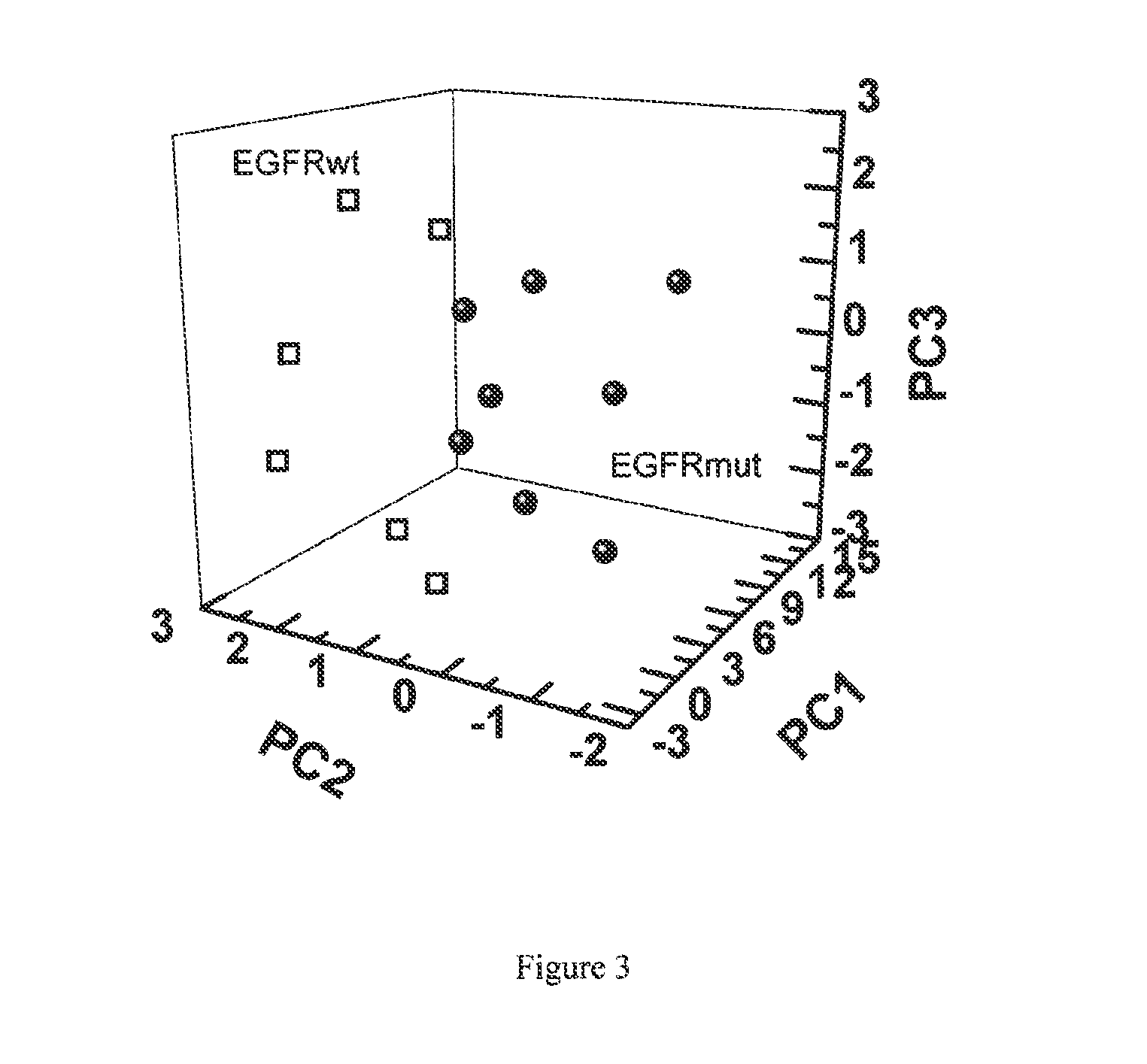
The present invention provides methods of identifying a genetic abnormality such as mutation in EGFR or KRAS or ALK which is associated with the management of lung cancer or diagnosing, prognosing or monitoring the treatment of pre-cancerous conditions of the lung, such as bronchial dysplasia or atypical alveolar hyperplasia (AAH), through the detection of at least one volatile organic compound indicative of these states.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
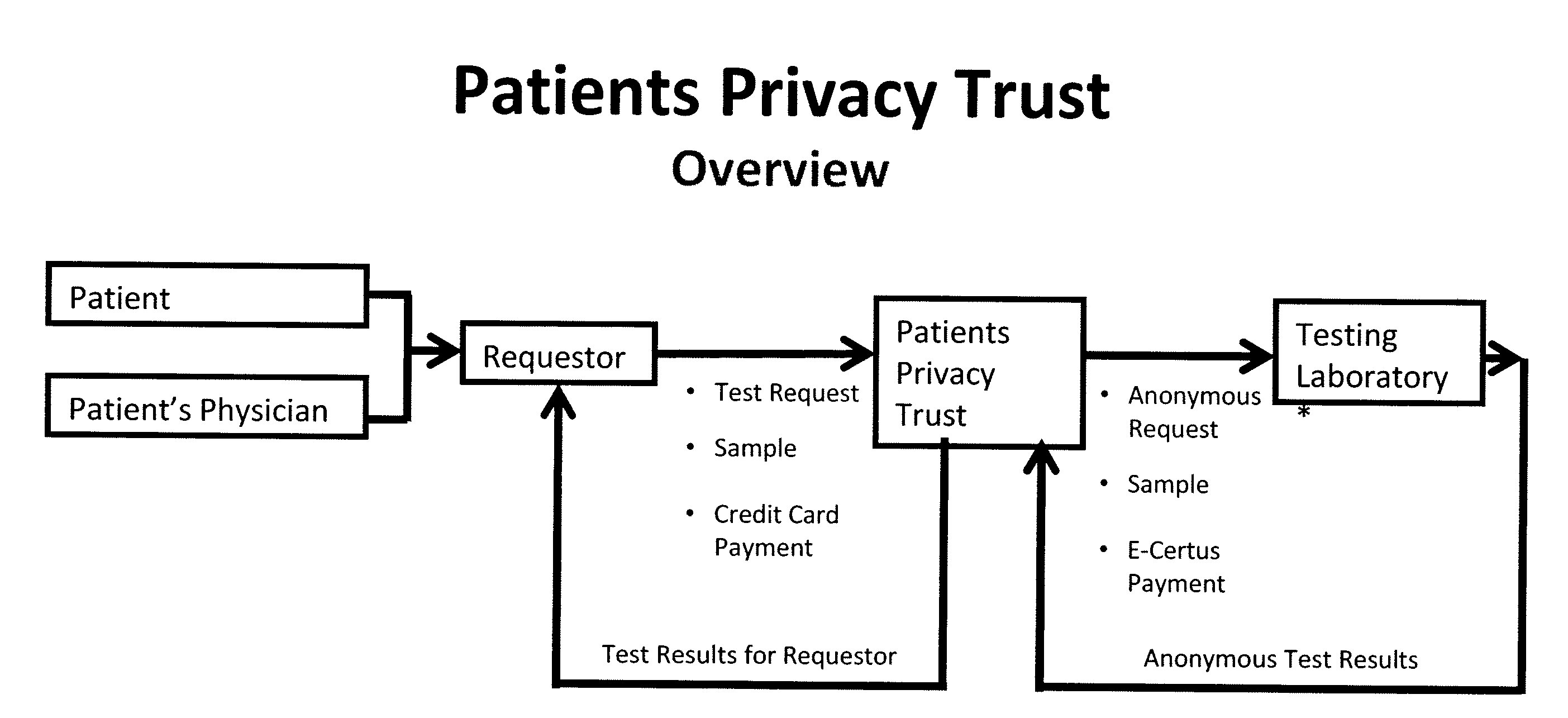
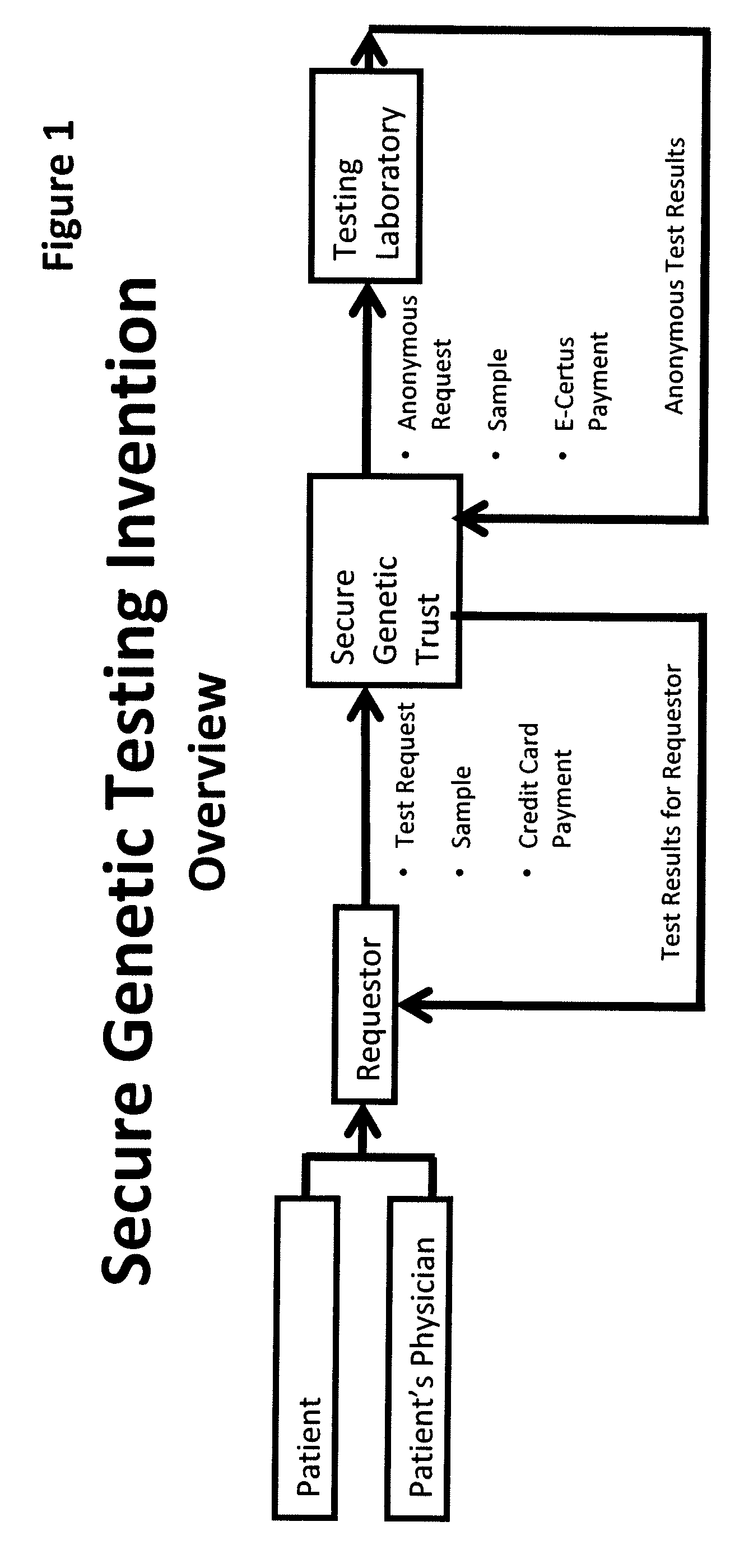
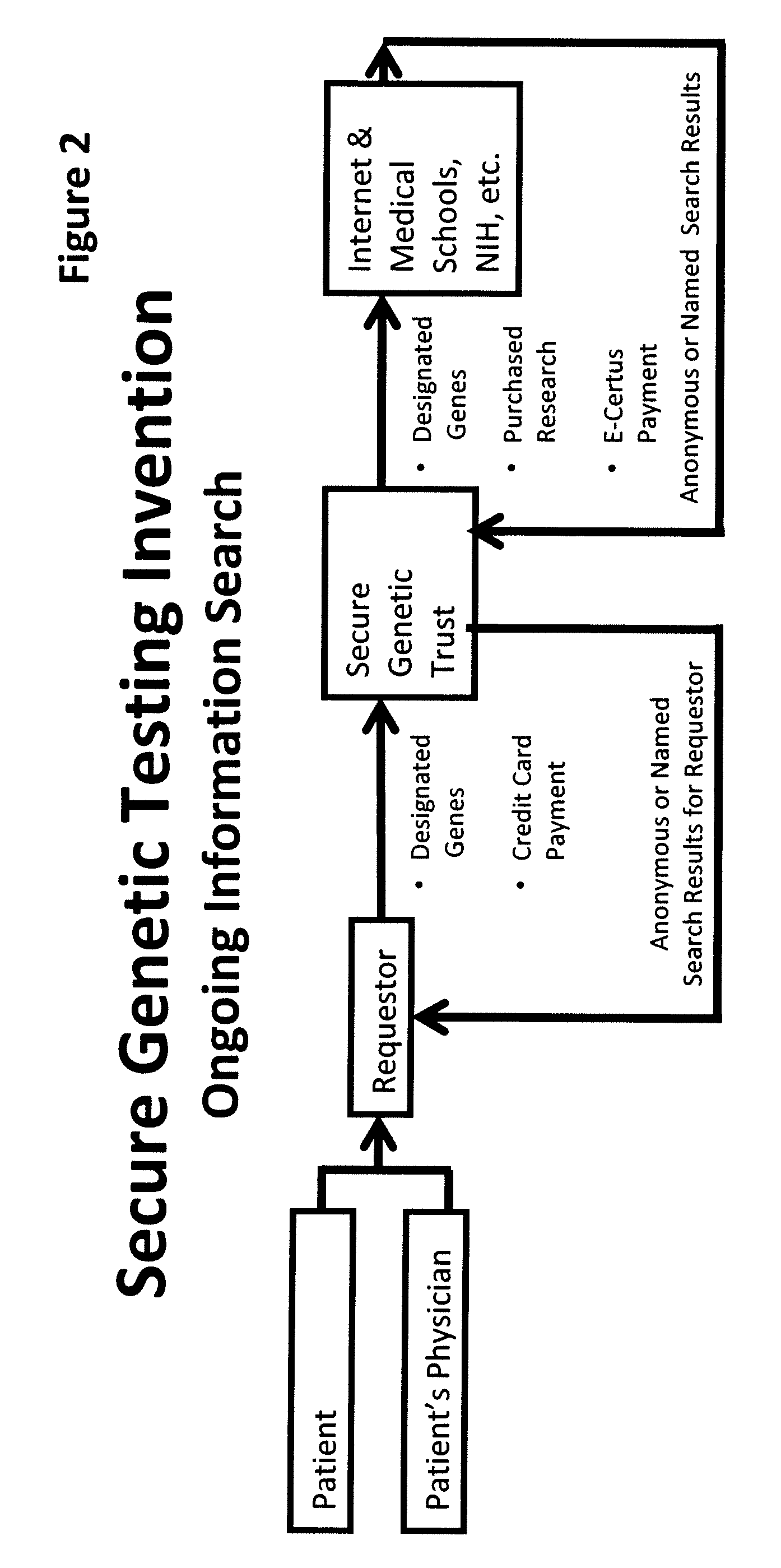
System for gene testing and gene research while ensuring privacy
InactiveUS20090198519A1Data processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic databaseGENETIC ABNORMALITY
A system, method and program product, the method comprising, in one embodiment, providing a secure testing service for patient's identification and payment data encrypted at the data level, non-identifiable method for a patient to have a genetic tests to identify variants or mutations of their genes or combinations of genes that predispose the patient to develop or have an identified disease, comprising: obtaining electronically genomic information for a patient comprising at least one of, (a) DNA information, (b) RNA information, (c) complementary DNA or RNA information, (d) transfer RNA (tRNA) information (e) messenger RNA (mRNA) information, and (f) Expressed Sequence Tags (EST) to identify an abnormal gene; searching by one or more computers electronic databases using the identified abnormal gene to obtain genetic sequencing and basic research, patient predispositions, and pharmacognetics that predict the response and reaction of patients with identified genetic abnormalities related to the identified abnormal gene and individual medications that may be prescribed relating to the identified abnormal gene or a relationship with said identified abnormal gene; performing an update search on at least a periodic basis to learn about subsequent genomic research developments and treatments for the identified abnormal gene, specific genes with variants or mutated genes identified in the genetic test; sending electronically via an Internet communication link data comprising or derived from the searching step and the update search to the patient or a third party; and with the sending step performed using a privacy component that prevents transmission to any third party unless predetermined permission clearance data is in the system.
Owner:MCNAMAR RICHARD TIMOTHY
Detection of genetic abnormalities and infectious disease
InactiveUS20120077185A1Determine the prognosis of a diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementInfectious agentBlood plasma
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for detecting genetic abnormalities and infectious agents in maternal samples. Exemplary maternal samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include maternal blood, plasma or serum.
Owner:TANDEM DIAGNOSTICS
Detection of genetic abnormalities
ActiveUS20120164646A1Determine the prognosis of a diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods and compositions for detecting genetic material
This invention provides compositions and methods for detecting differences in copy number of a target polynucleotide. In some cases, the methods and compositions provided herein are useful for diagnosis of fetal genetic abnormalities, when the starting sample is maternal tissue (e.g., blood, plasma). The methods and materials described apply techniques for allowing detection of small, but statistically significant, differences in polynucleotide copy number.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for monitoring disease progression or recurrence
Owner:ESOTERIX GENETIC LAB
Volatile organic compounds for detecting cell dysplasia and genetic alterations associated with lung cancer
The present invention provides methods of identifying a genetic abnormality such as mutation in EGFR or KRAS or ALK which is associated with the management of lung cancer or diagnosing, prognosing or monitoring the treatment of pre-cancerous conditions of the lung, such as bronchial dysplasia or atypical alveolar hyperplasia (AAH), through the detection of at least one volatile organic compound indicative of these states.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Balanced translocation in comparative hybridization
InactiveUS20070122820A1Quicker and more methodIncrease profitSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention provides comparative genomic hybridization methods for detecting and mapping chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases, or to detecting the phenomena of large scale copy number variants. The method includes hybridization with one or more probes for detecting balanced translocations. Such probes may be complementary to the moving genomic segment which is translocated or may be complementary to the translocation break point.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Detection of gene duplications
InactiveUS20050255485A1Easy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsFluorescenceGenetic Anomaly
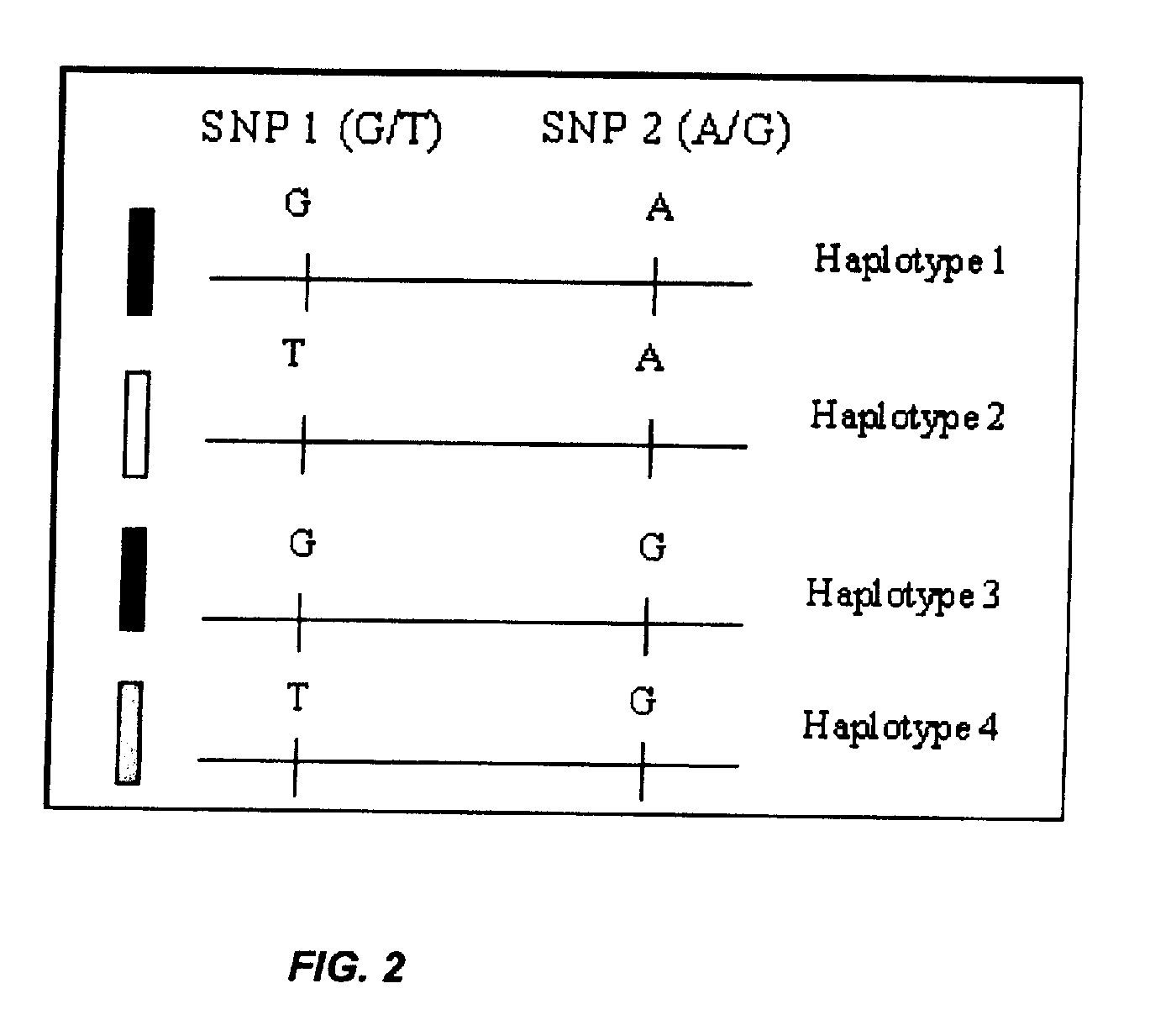
Methods of detecting a candidate genetic anomaly such as a candidate duplication in a genome are disclosed. The methods comprise quantifying fluorogenic assays for alleles of a genetic locus from a plurality of individual genomes, identifying ranges of fluorescent intensities indicative of individual genomes homozygous for a first allele, homozygous for a second allele, or heterozygous for both alleles, and identifying individual genomes in which the fluorescence intensities are outside the range of intensities indicative of homozygosity or heterozygosity for the genetic locus.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Multiplexed parallel analysis of targeted genomic regions for non-invasive prenatal testing
ActiveUS20160340733A1Highly accurate countingHighly accurate assessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisTarget captureStatistical analysis
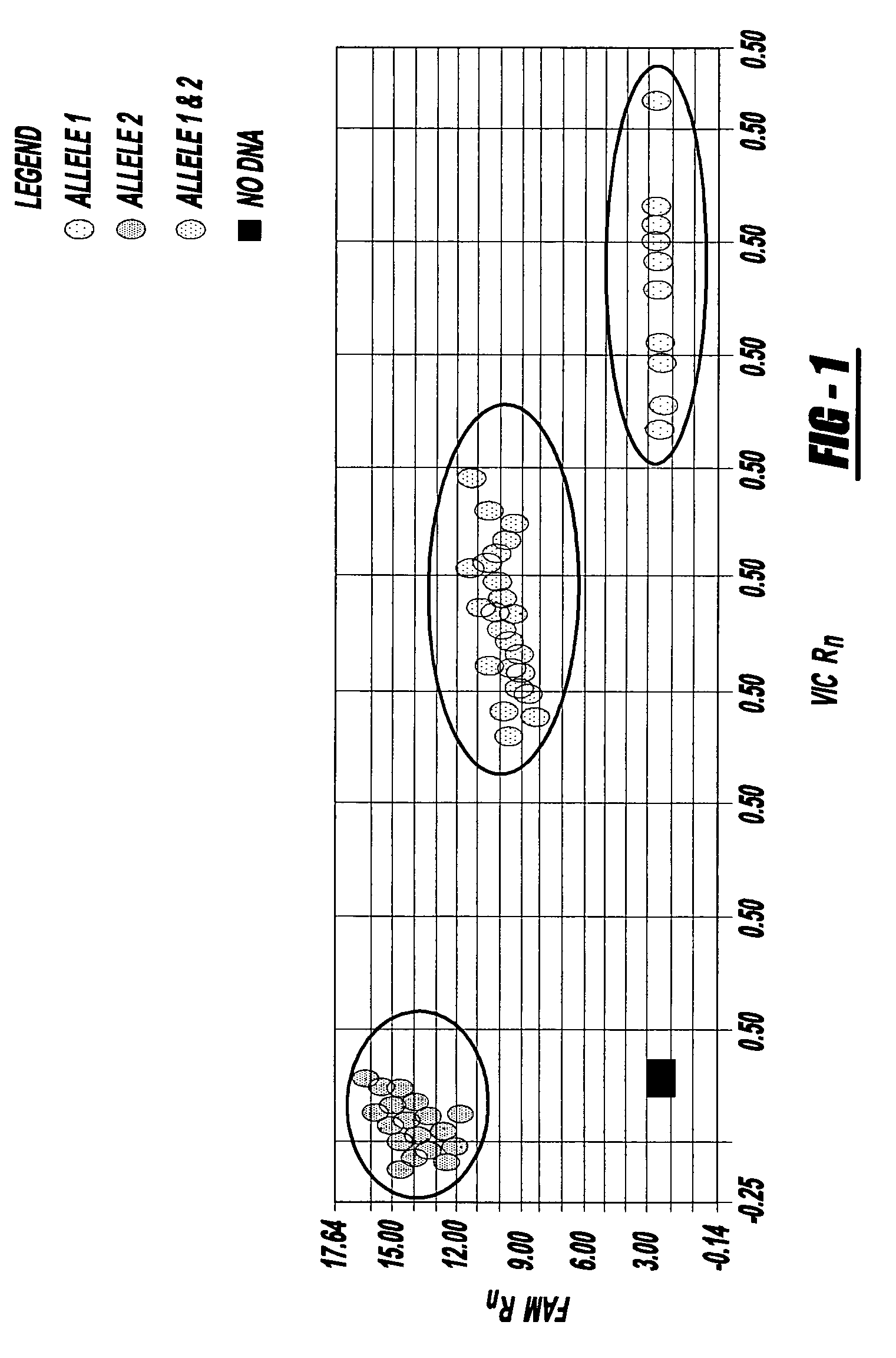
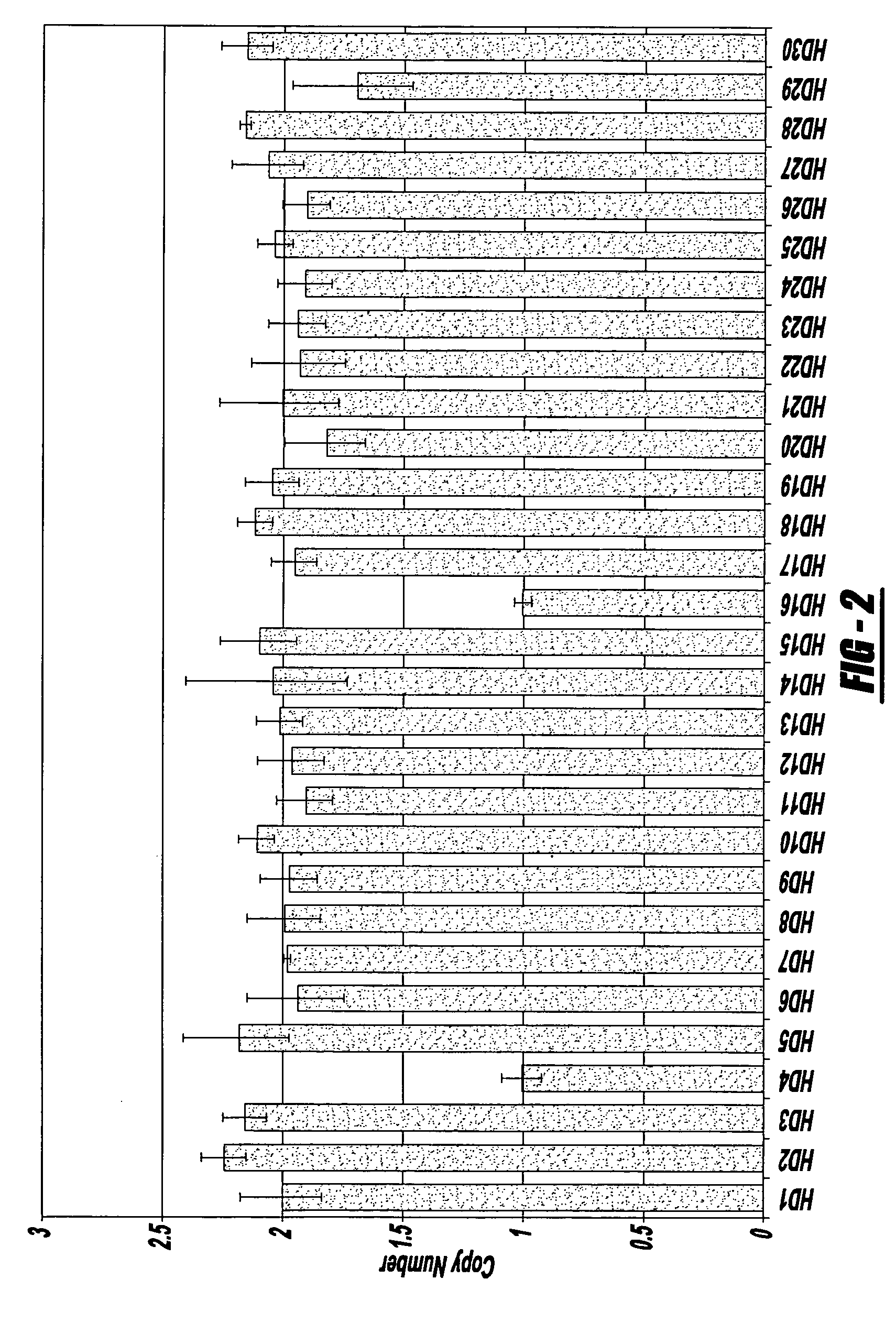
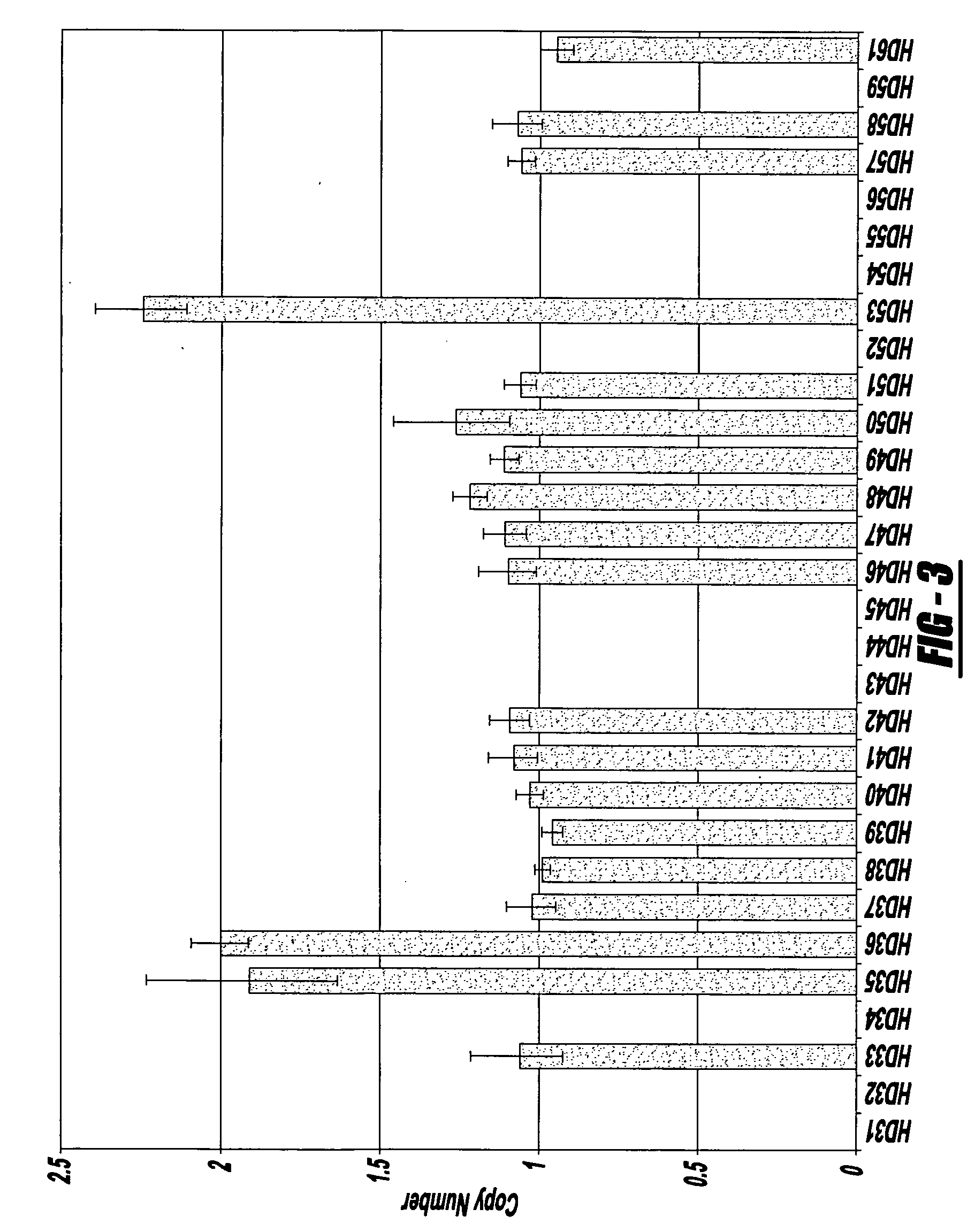
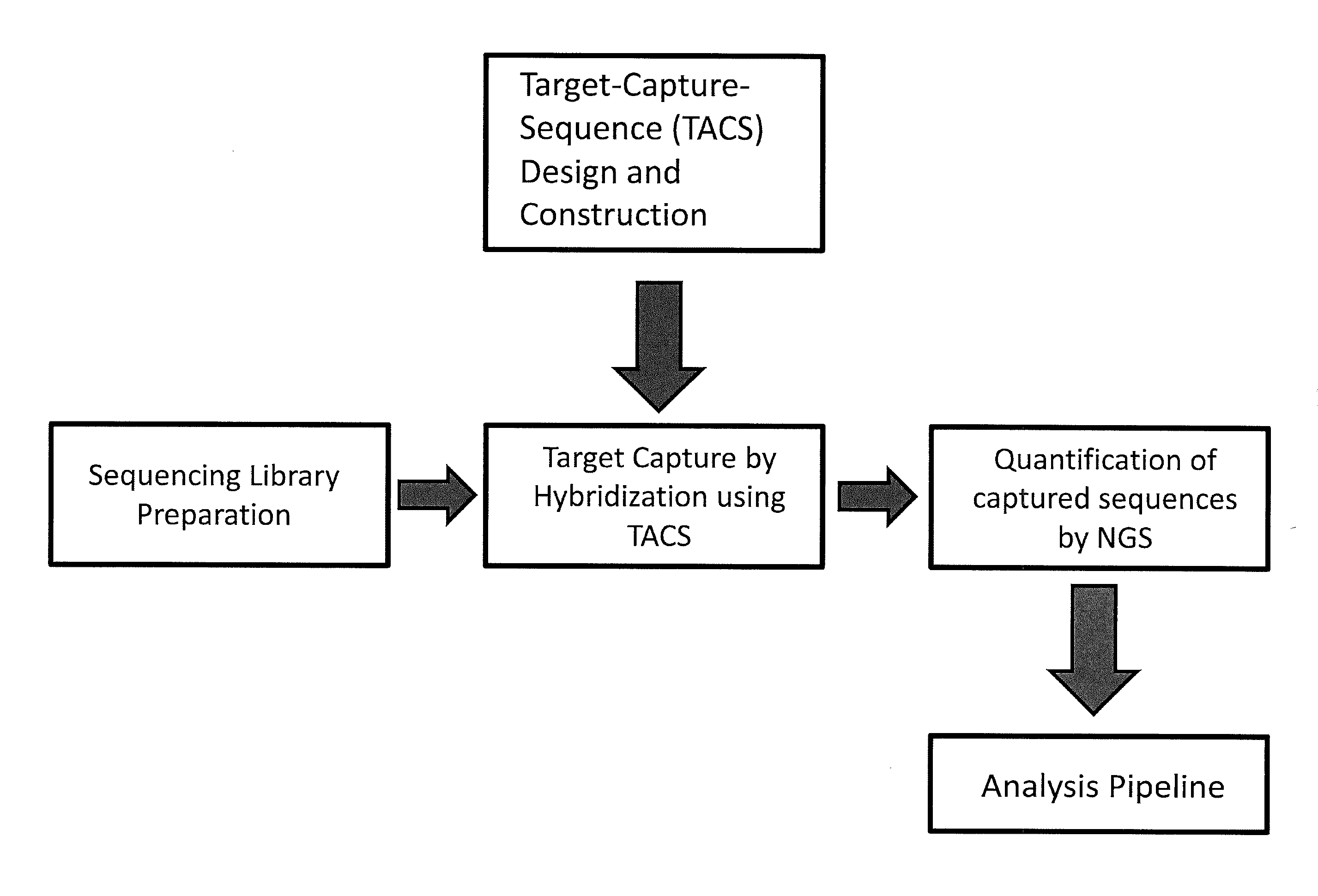
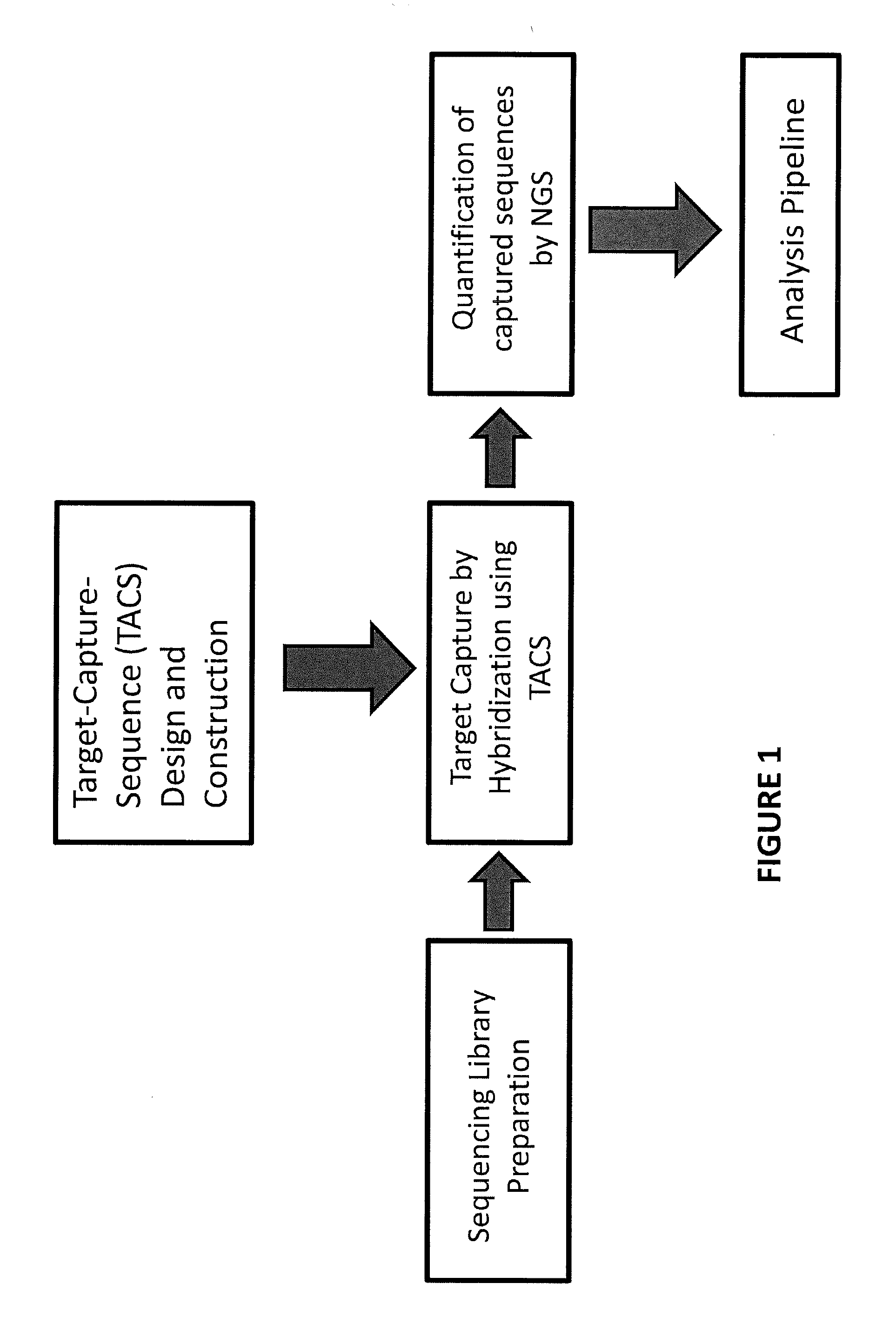
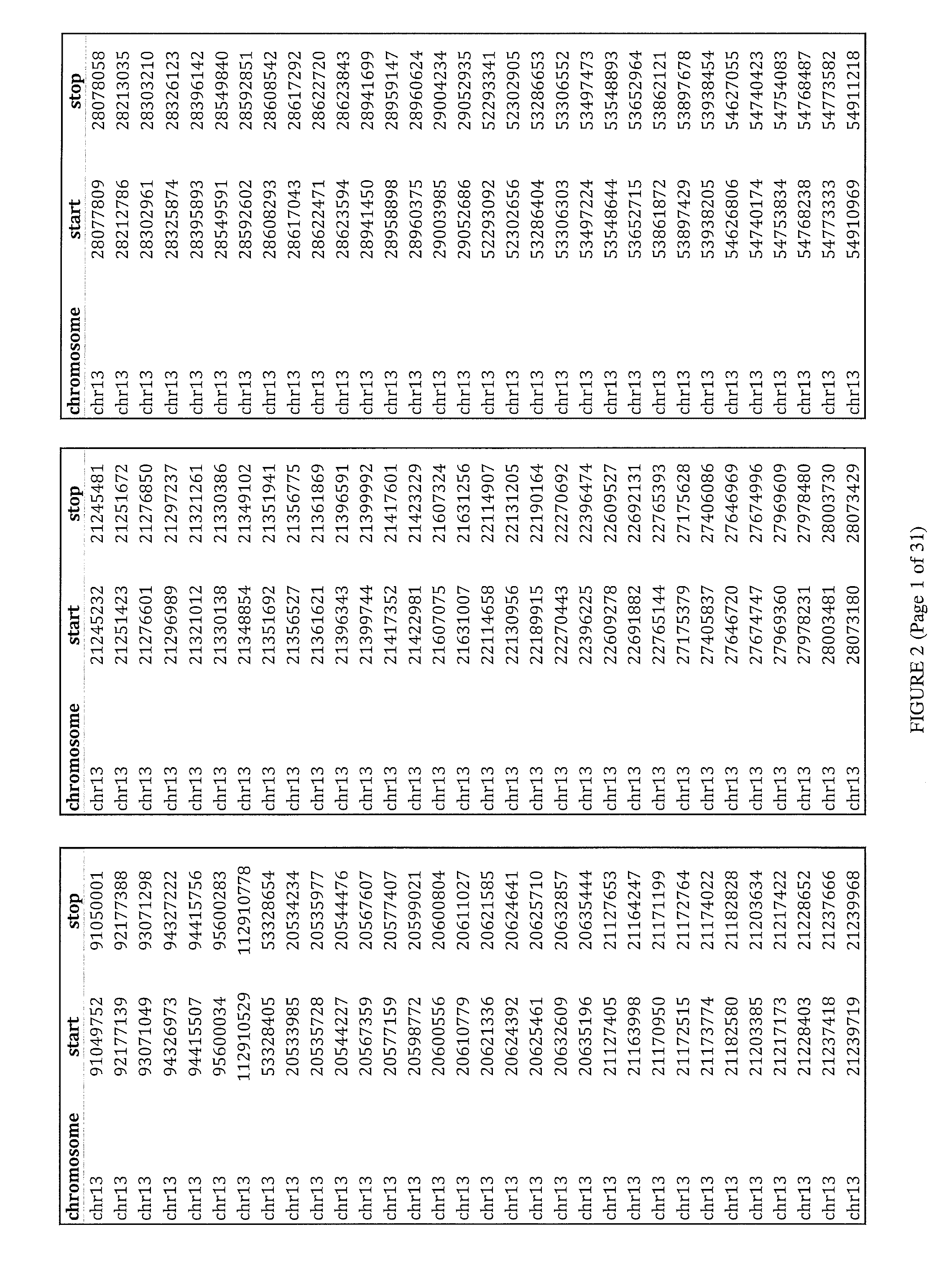
The invention provides methods for non-invasive prenatal testing that allow for detecting risk of chromosomal and subchromosomal abnormalities, including but not limited to aneuploidies, microdeletions and microduplications, insertions, translocations, inversions and small-size mutations including point mutations and mutational signatures. The methods of the invention utilize a pool of TArget Capture Sequences (TACS) to enrich for sequences of interest in a mixed sample containing both maternal and fetal DNA, followed by massive parallel sequencing and statistical analysis of the enriched population to thereby detect the risk of a genetic abnormality in the fetal DNA. Kits for carrying out the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:NIPD GENETICS PUBLIC CO LTD
Method for removing GC preferences in euchromosomes and between chromosomes as well as detection system
InactiveCN105825076AAvoid distortionIncreased sensitivitySpecial data processing applicationsAnomaly detectionHigh throughput sequence
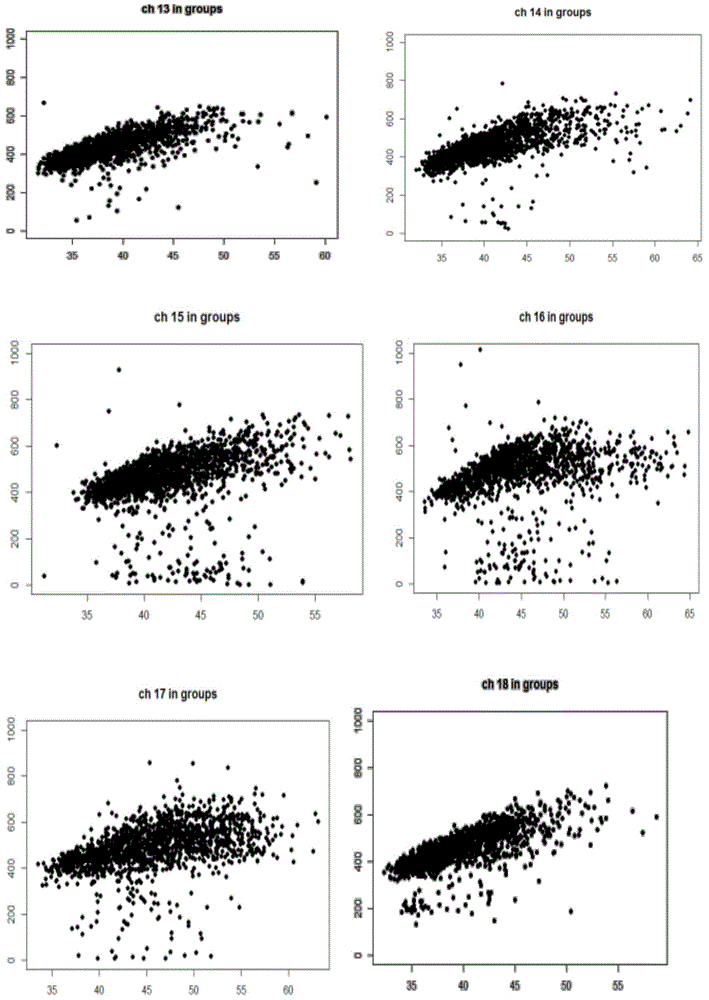
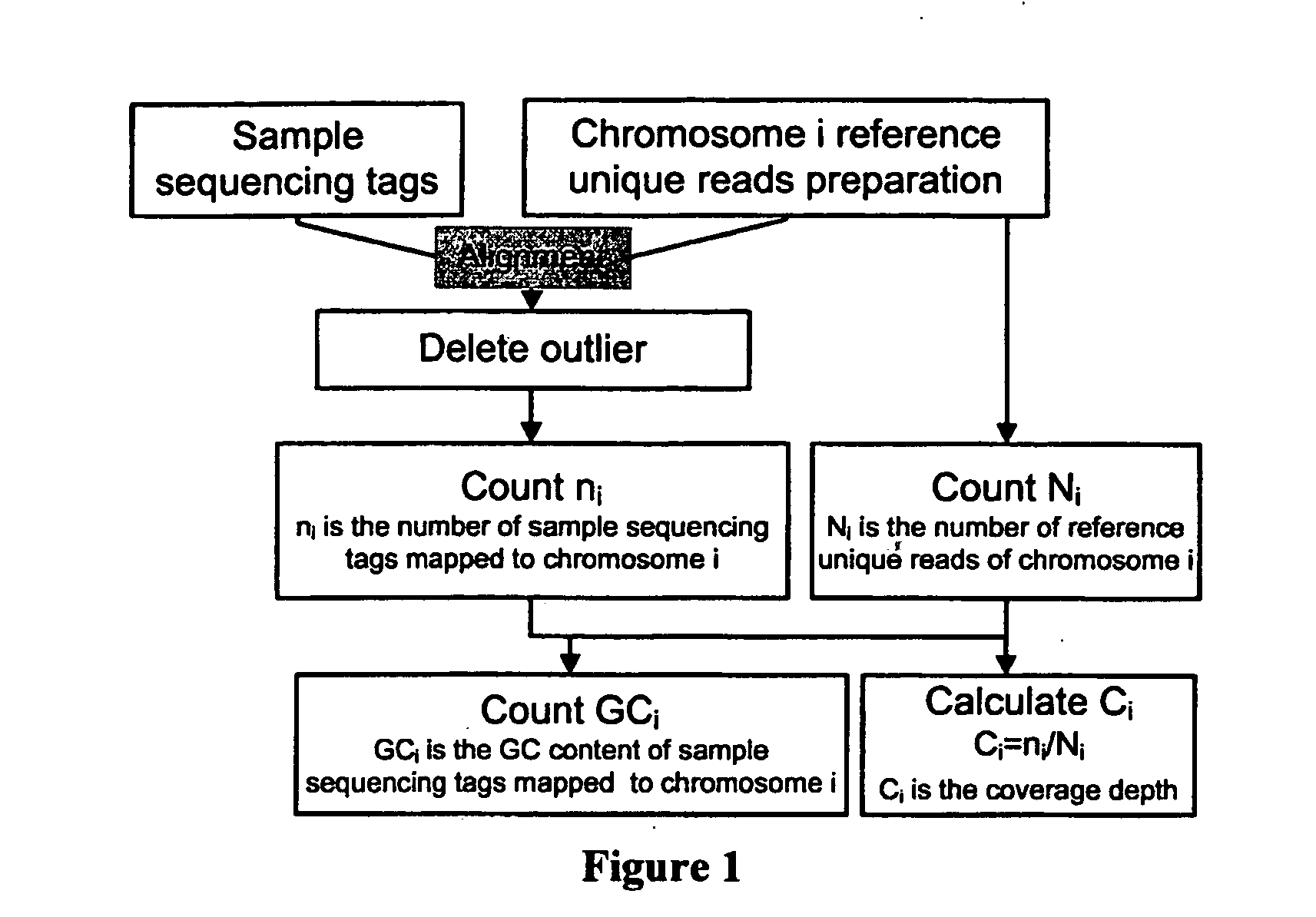
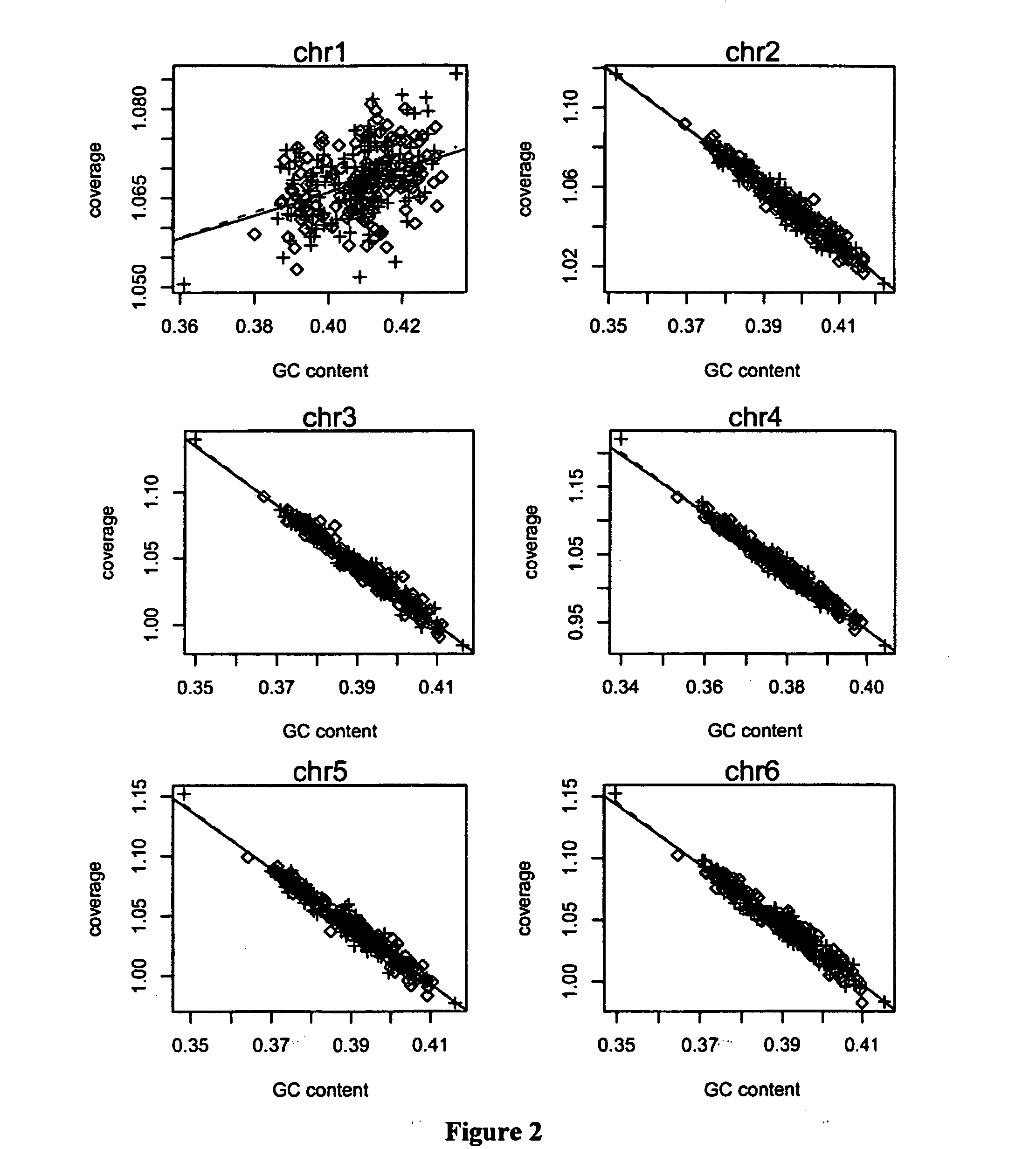
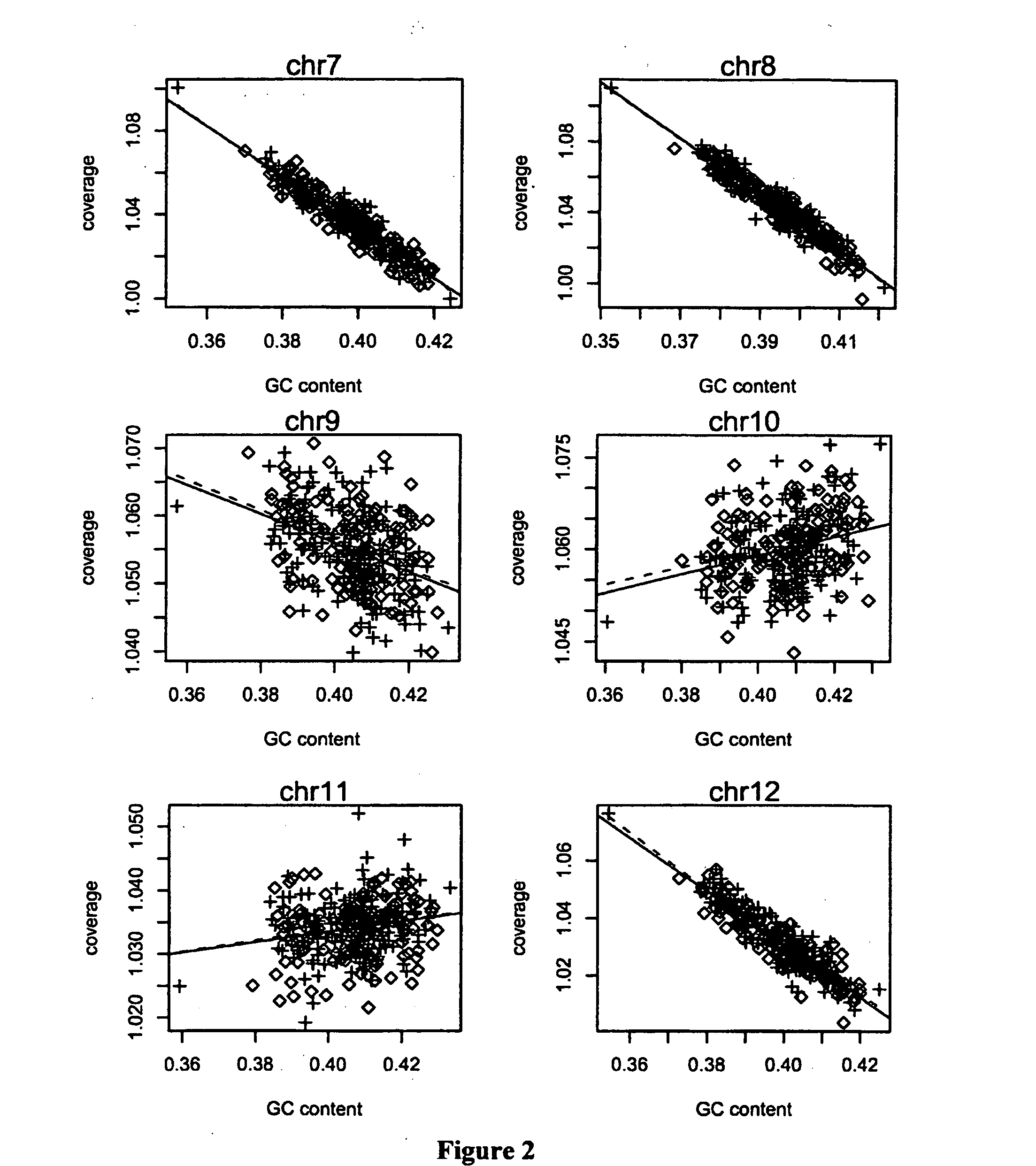
The invention discloses a method for removing GC preferences in euchromosomes and between chromosomes as well as a detection system. The detection system comprises (1) a high-throughput sequencing instrument used for obtaining a whole genome sequence of a sample through high-throughput sequencing, and (2) a computer readable medium used for executing a plurality of instructions in the following steps: a, constructing a system for removing GC deviations, b, constructing another system for removing the GC deviations, and c, constructing a detection system for detecting non euploids and normal samples in samples: judging whether the samples are the non euploids or not finally according to Z values obtained by two different corrections. With the adoption of the detection system, the GC deviations are removed, so that the fetal genetic abnormality detection with higher sensitivity can be carried out while the data distortion is avoided. The detection system is used for defining parameters used for a statistic test according to the GC content. In addition, parameters in statistical sense are obtained according to a large batch of data through a Z value statistics method, so that higher accuracy can be achieved.
Owner:杭州天译基因科技有限公司
Noninvasive detection of fetal genetic abnormality
ActiveUS20140099642A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLarge-Scale SequencingFetal aneuploidy
The current invention is directed to methods for noninvasive detection of fetal genetic abnormalities by large-scale sequencing of nucleotides from maternal biological sample. Further provided are methods to remove GC bias from the sequencing results according to the difference in GC content of a chromosome. The current invention not only makes the detection much more accurate but also represents a comprehensive method for fetal aneuploidy detection including sex chromosome disorders such as XO, XXX, XXY, and XYY, etc.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Crenolanib for Treating FLT3 Mutated Proliferative Disorders Associated Mutations
ActiveUS20180117031A1Increase chances of survivalPoor prognosisOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseTumor Sample
Owner:AROG PHARMA
Methods for fragmentome profiling of cell-free nucleic acids
The present disclosure contemplates various uses of cell-free DNA. Methods provided herein may use sequence information in a macroscale and global manner, with or without somatic variant information, to assess a fragmentome profile that can be representative of a tissue of origin, disease, progression, etc. In an aspect, disclosed herein is a method for determining a presence or absence of a genetic aberration in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragments from cell-free DNA obtained from a subject, the method comprising: (a) constructing a multi-parametric distribution of the DNA fragments over a plurality of base positions in a genome; and (b) without taking into account a base identity of each base position in a first locus, using the multi-parametric distribution to determine the presence or absence of the genetic aberration in the first locus in the subject.
Owner:GUARDANT HEALTH
Highly aggressive human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain with add(11)(q23) chromosome abnormality
The invention belongs to the field of microbial animal cell lines, and relates to a new human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain CHH-1. The in vitro isolate of the mononuclear cell of the marrow of a patient with firstly-diagnosed acute B lymphocytic leukemia undergoes cell primary culture to obtain the highly aggressive human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain with add(11)(q23) chromosome abnormality, the preservation number of the cell strain is CGMCC No.11797, and the highly aggressive human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain with add(11)(q23) chromosome abnormality is named as human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain CHH-1, has a same clone source with patient's leukemia cells, can be infinitely and stably passed in vitro, and has the characteristics of clonality add(11)(q23) genetic abnormality, high tumorigenicity and high aggressiveness. The new human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain CHH-1 provides a new good cell model for researches of human acute lymphocytic leukemia with No.11 chromosome long arm structure abnormality and development of biomedicines, and has wide prospect and great practical values in revelation of the pathogenesis of the human acute lymphocytic leukemia and development of medicines.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Detection of genetic abnormalities
InactiveUS20130143213A1Quick sortingEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com