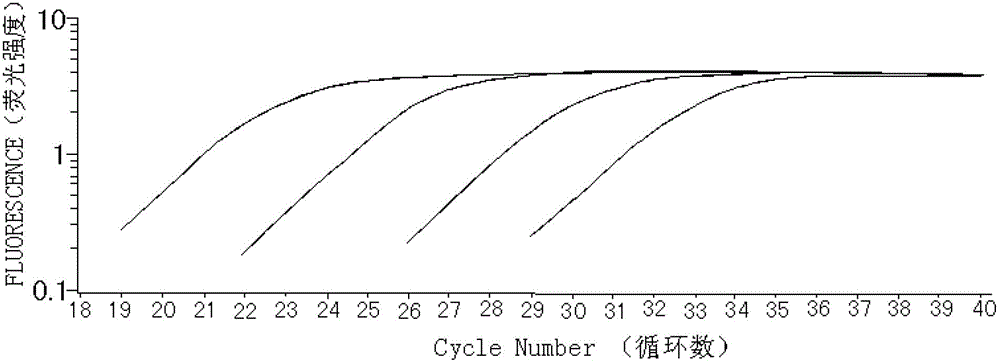
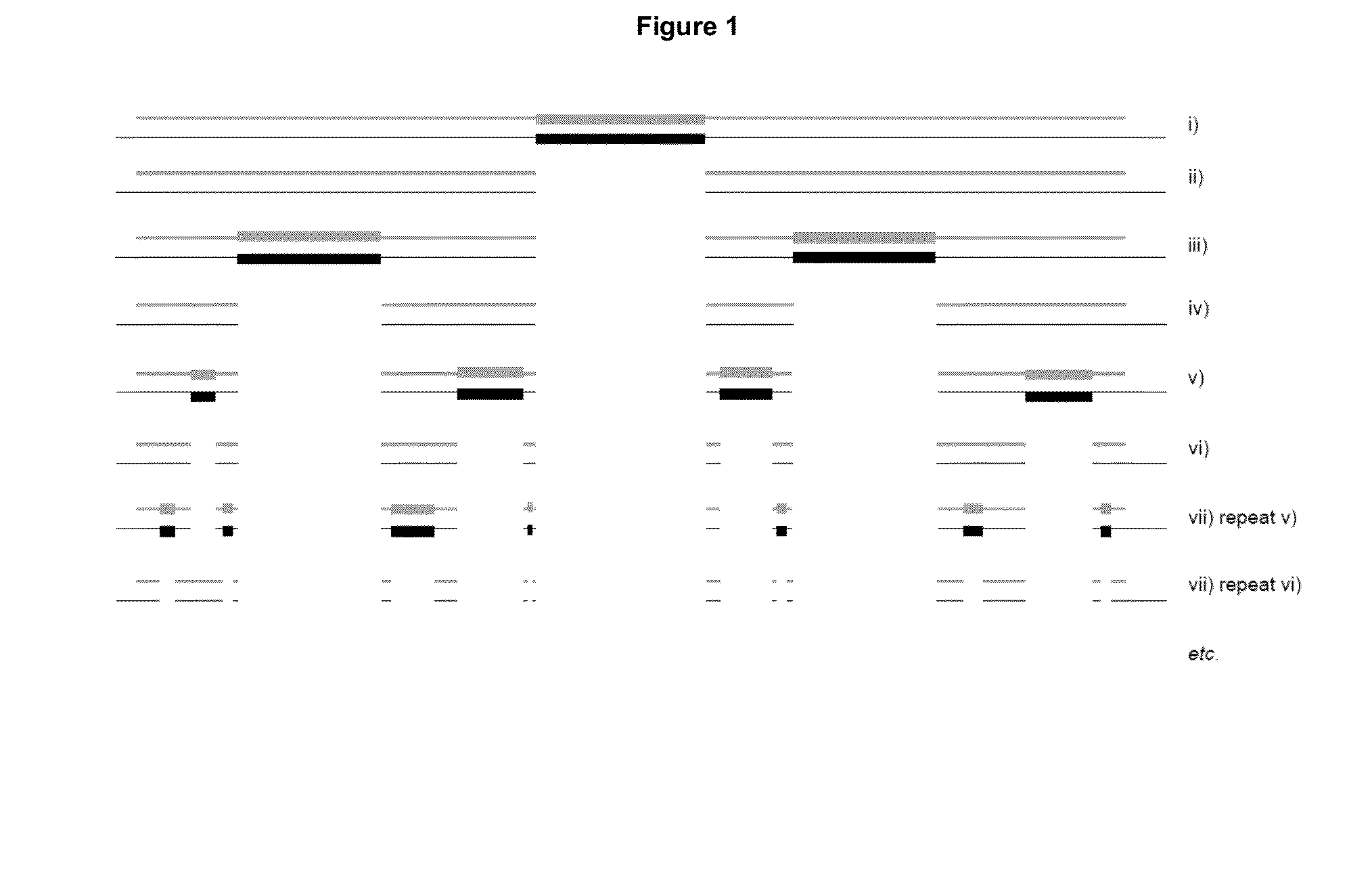
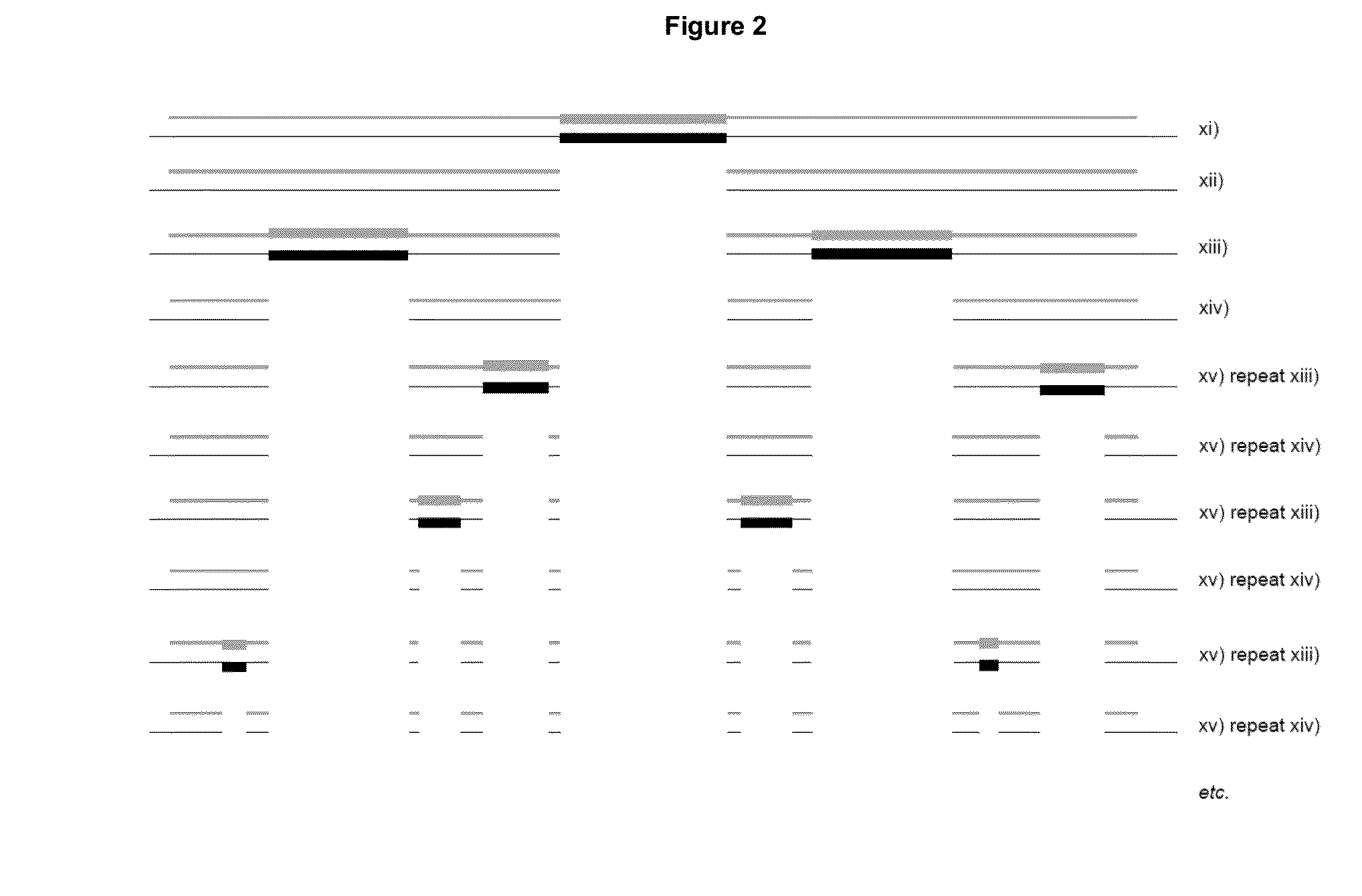
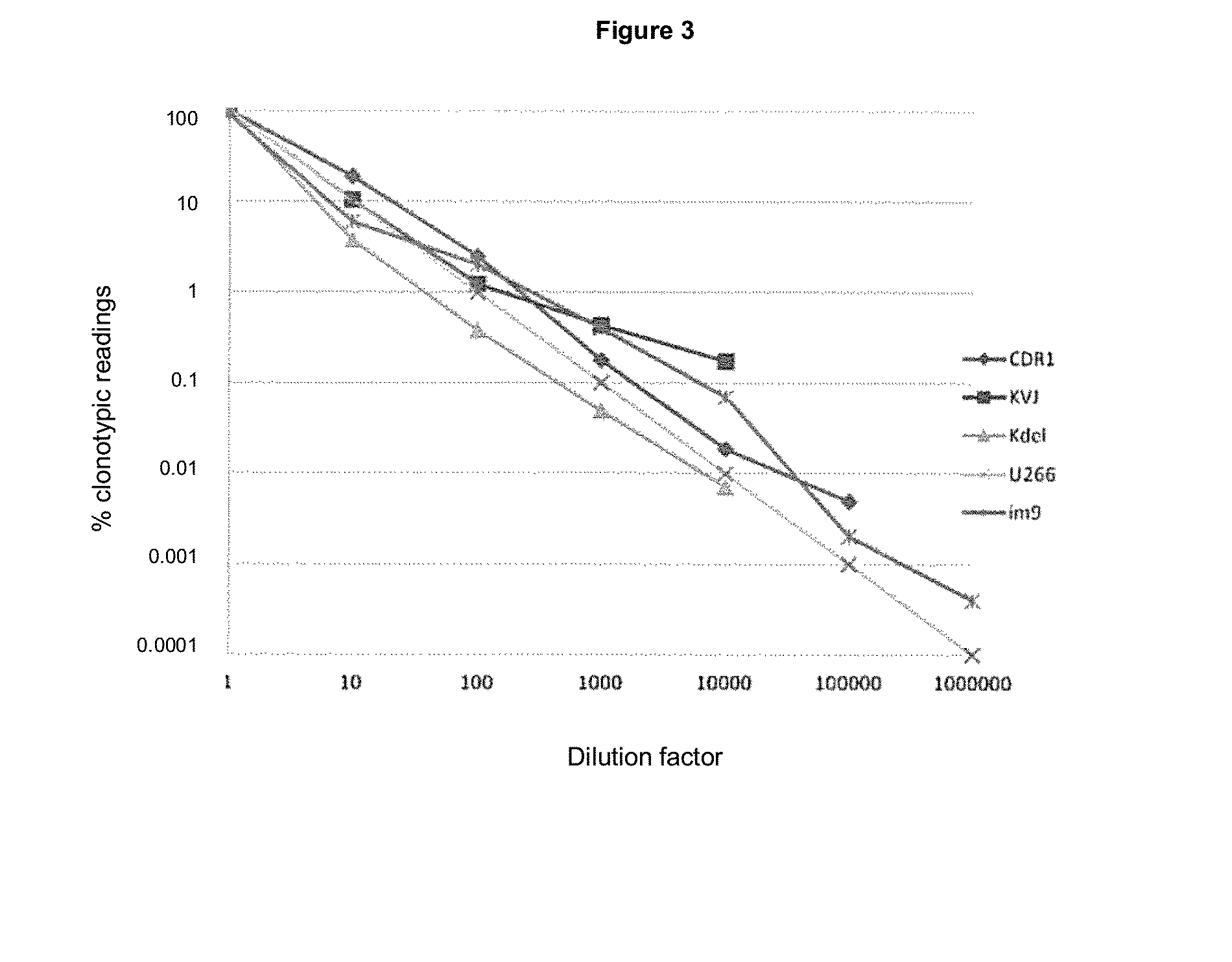
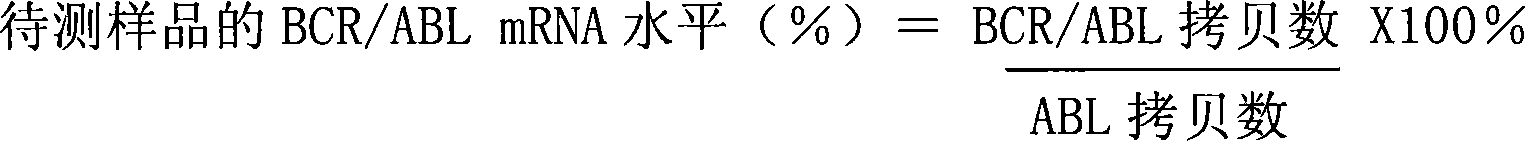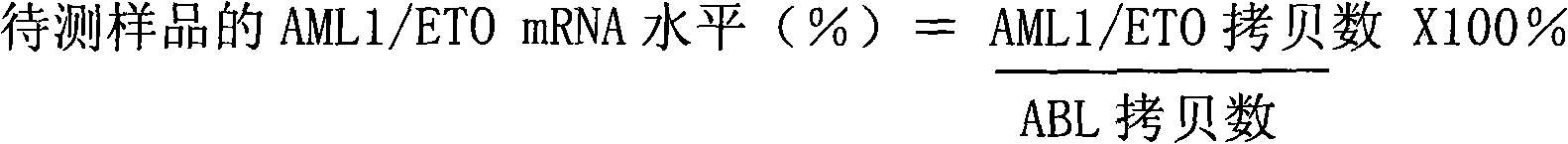Patents
Literature
122 results about "MRD Negative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Minimal residual disease (MRD) is the name given to small numbers of leukaemic cells (cancer cells from the bone marrow) that remain in the person during treatment, or after treatment when the patient is in remission (no symptoms or signs of disease). It is the major cause of relapse in cancer and leukemia.
Prostate cancer biomarkers
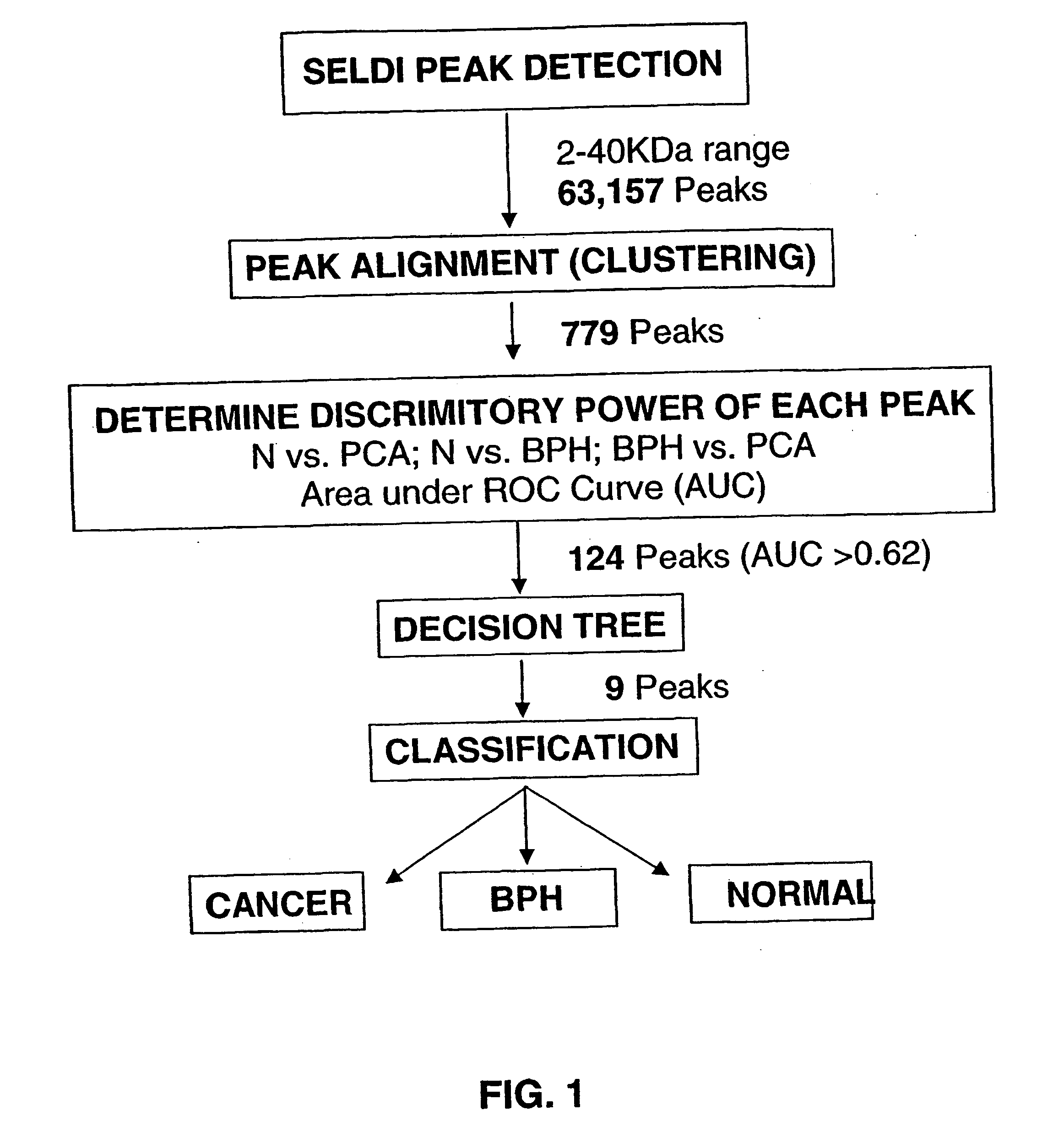
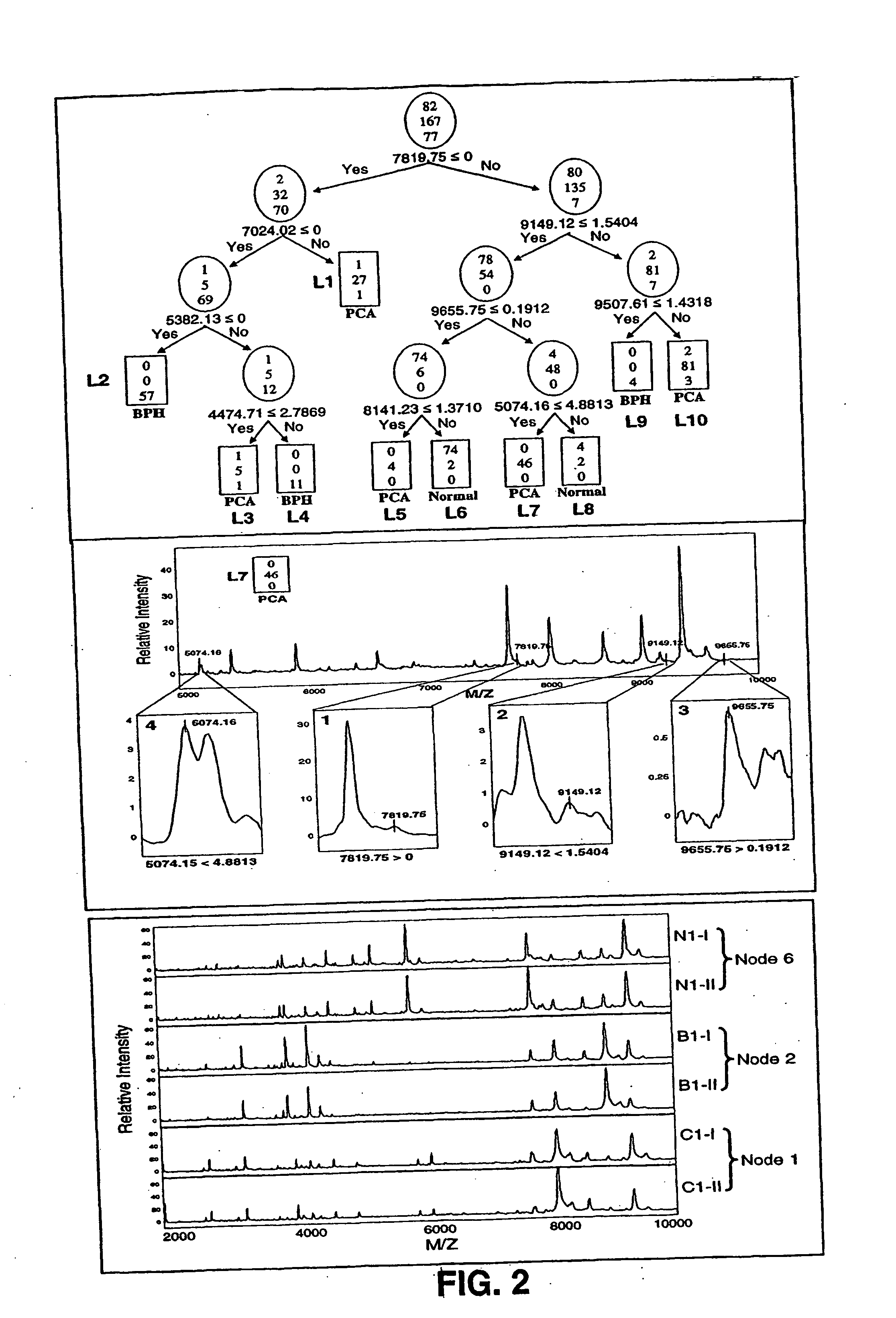
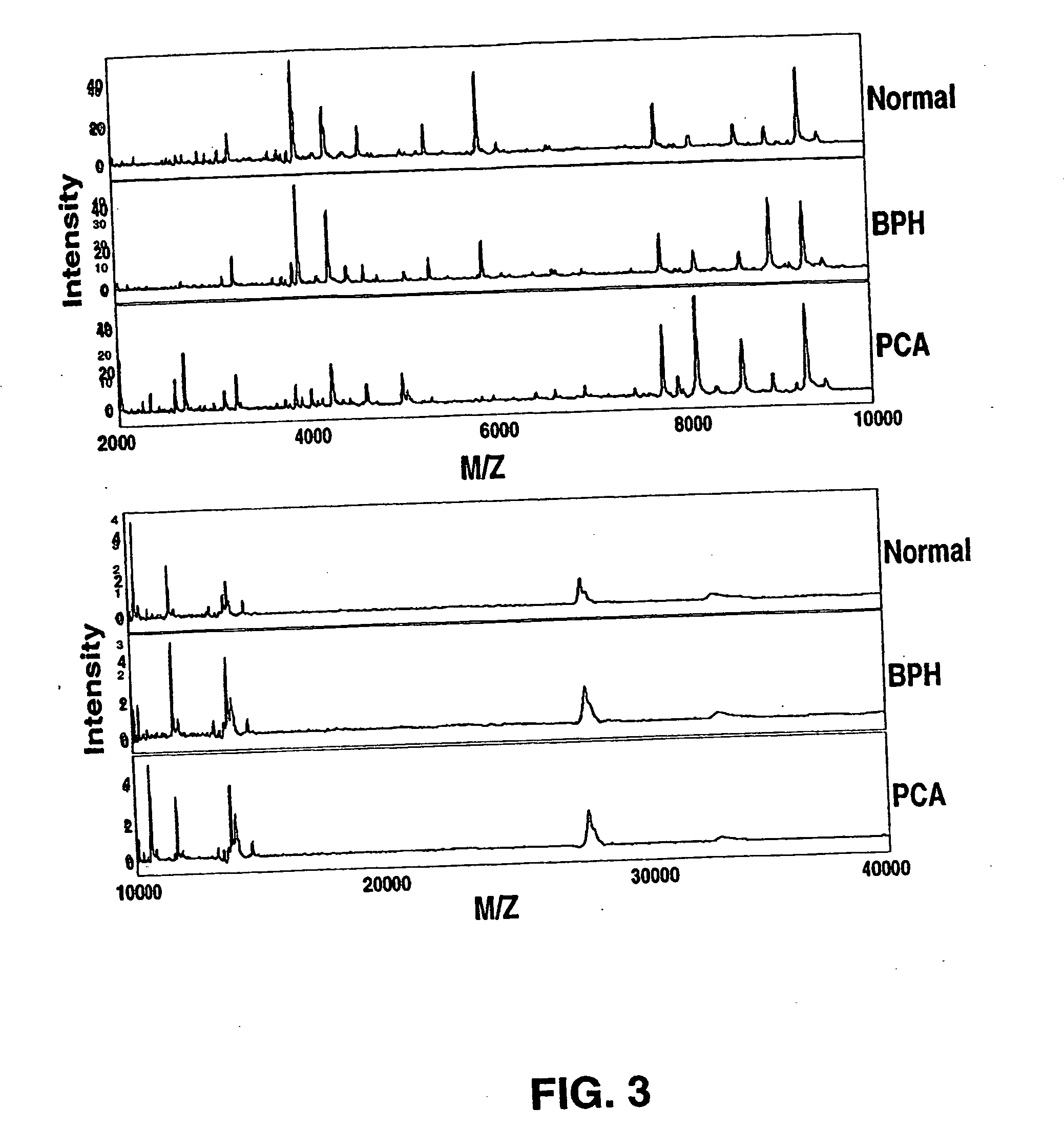
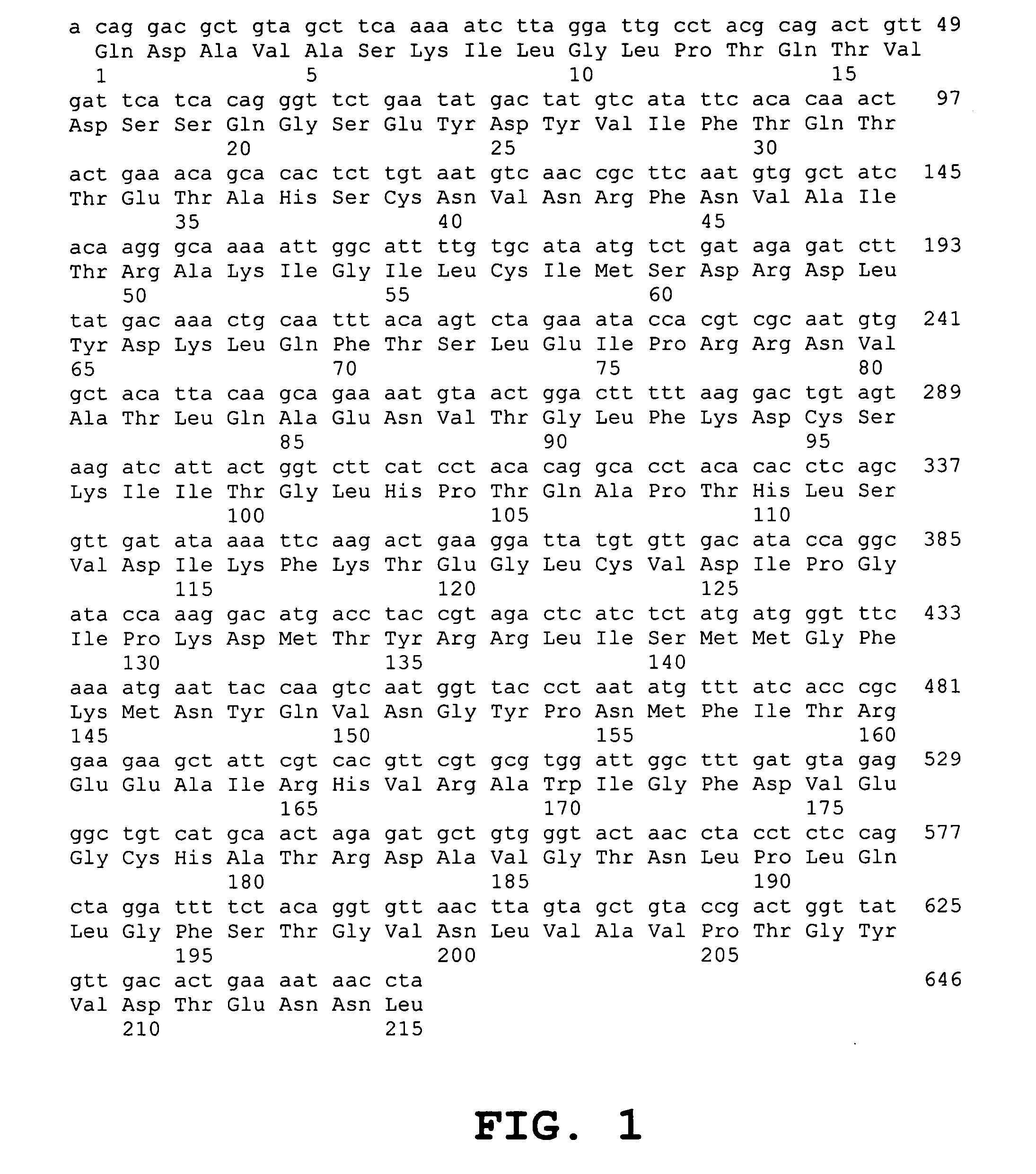
Protein biomarkers that may advantageously be utilized in diagnosing prostate cancer, benign prostate hyperplasia or to make a negative diagnosis are described. Accordingly, in one aspect of the invention, methods for aiding in, or otherwise making, a diagnosis of prostate cancer or benign prostate hyperplasia are provided. In one form of the invention, a method includes detecting various protein biomarkers of defined molecular weight and correlating the detection to a diagnosis of prostate cancer, benign prostate hyperplasia or to a negative diagnosis. In yet another aspect of the invention, kits are provided that may be utilized to detect the biomarkers described herein. In a further of the invention, methods of using a plurality of classifiers to make a probable diagnosis of prostate cancer of benign prostate hyperplasia are provided. In certain forms of the invention, the methods include use of a boosted decision tree analysis. Various computer readable media are also provided.
Owner:EASTERN VIRGINIA MEDICAL SCHOOL
High-throughput diagnostic assay for the human virus causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
InactiveUS20050181357A1Rapid and reliable diagnostic assayHigh detection sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic testPresent method
The present invention relates to a high-throughput diagnostic assay for the virus causing Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans (“hSARS virus”). In particular, the invention relates to a high-throughput reverse transcription-PCR diagnostic test for SARS associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV). The present assay is a rapid, reliable assay which can be used for diagnosis and monitoring the spread of SARS and is based on the nucleotide sequences of the N (nucleocapsid)-gene of the hSARS virus. The present method eliminates false negative results and provides increased sensitivity for the assay. The invention also discloses the S (spike)-gene of the hSARS virus. The invention further relates to the deduced amino acid sequences of the N-gene and S-gene products of the hSARS virus and to the use of the N-gene and S-gene products in diagnostic methods. The invention further encompasses diagnostic assays and kits comprising antibodies generated against the N-gene or S-gene product.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
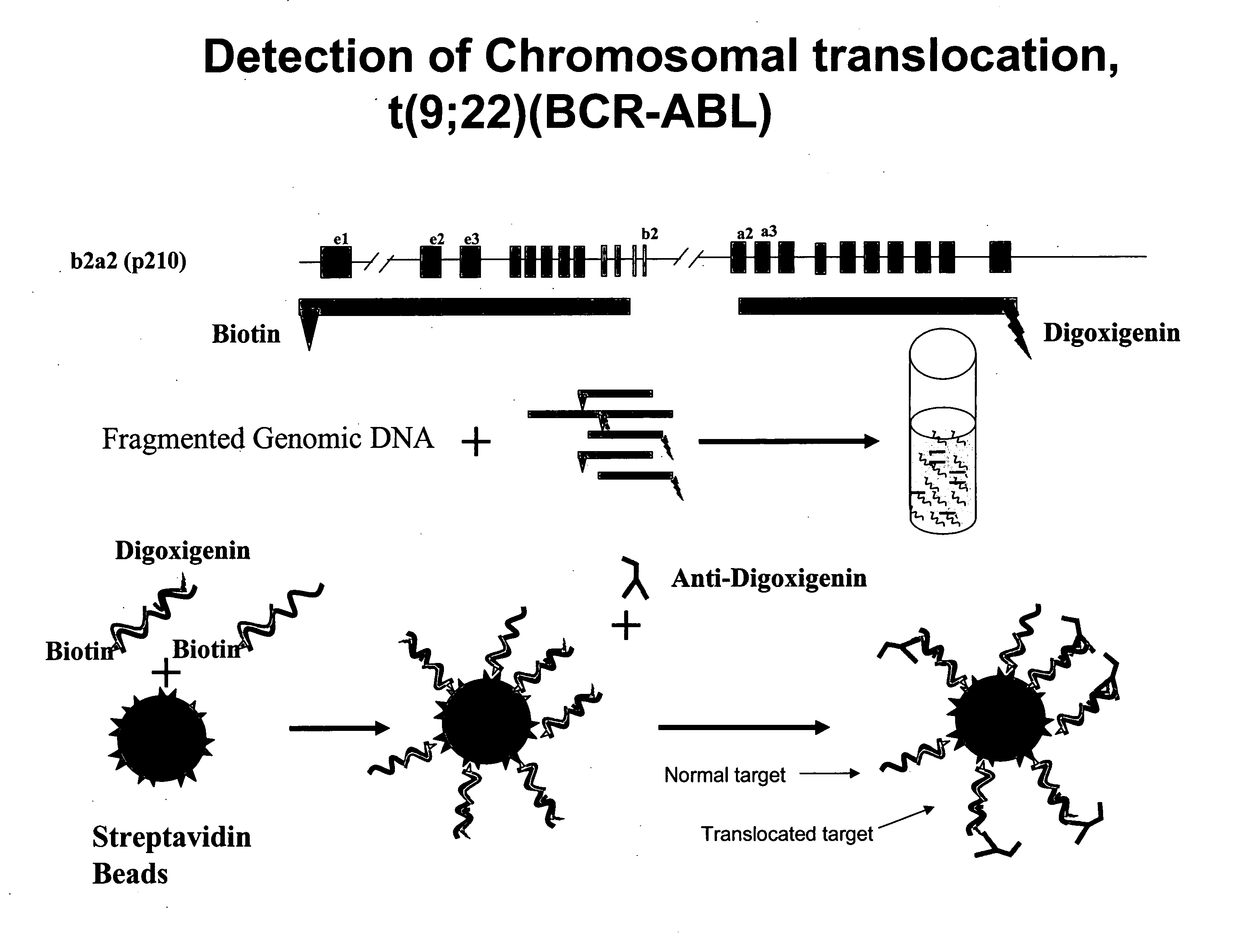
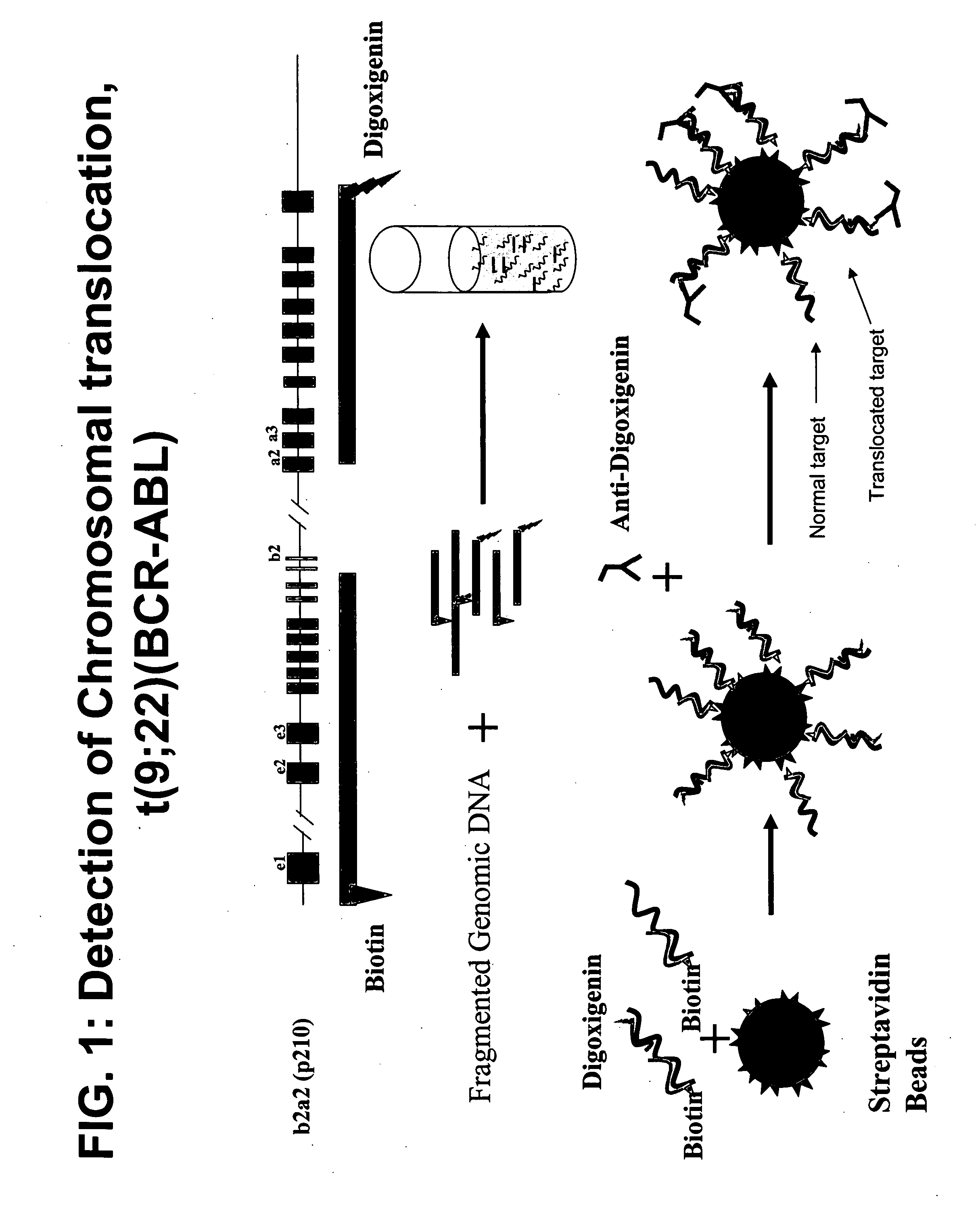
Non-in situ hybridization method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
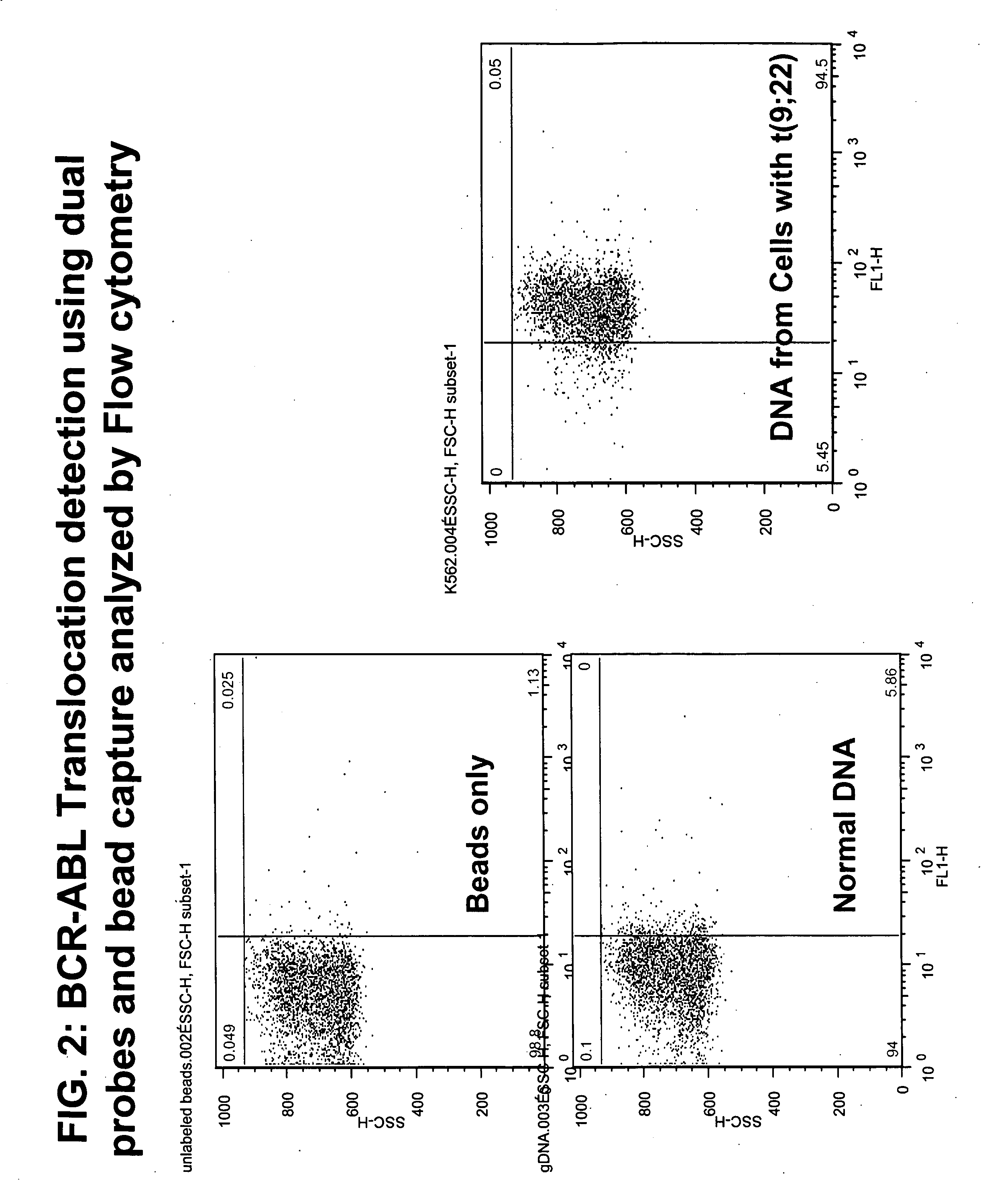
The present invention provides methods of detecting chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases. In particular, the present invention provides advanced methods of performing DNA hybridization, capture, and detection on solid support. Invention methods are useful for the detection, diagnosis, predicting response to therapy, detecting minimal residual disease, prognosis, or monitoring of disease treatment or progression of particular disease conditions such as cell proliferative disorders
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
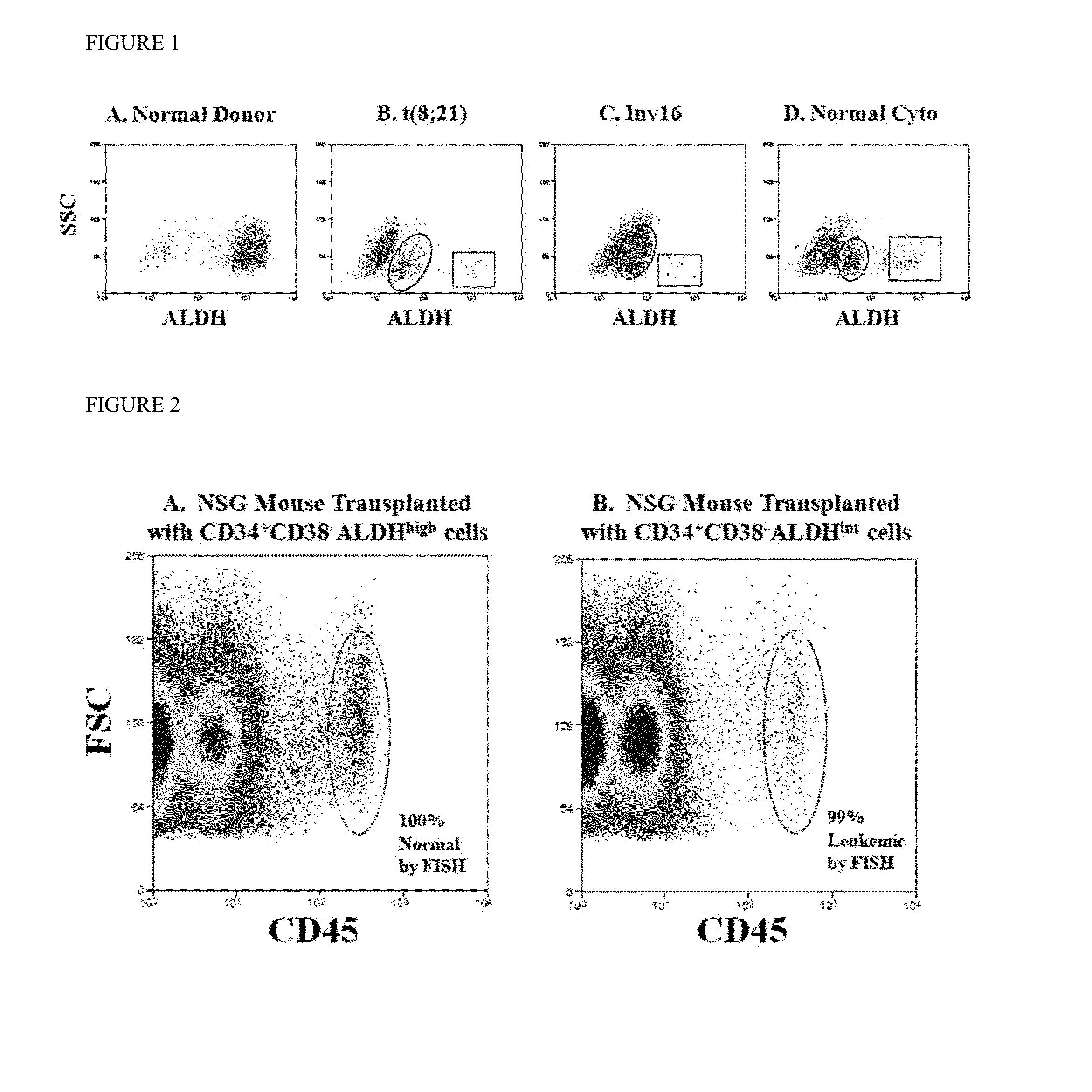
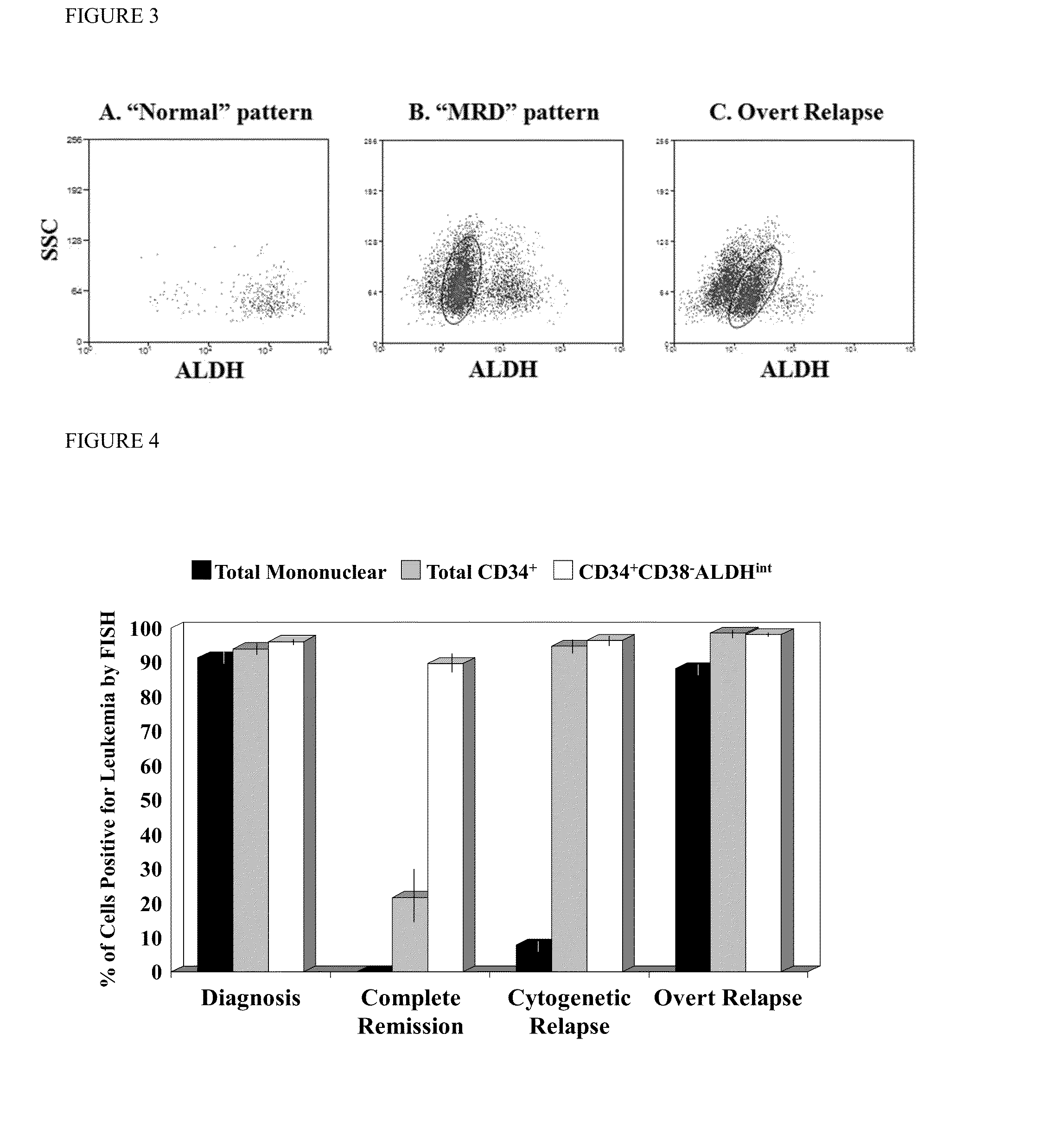
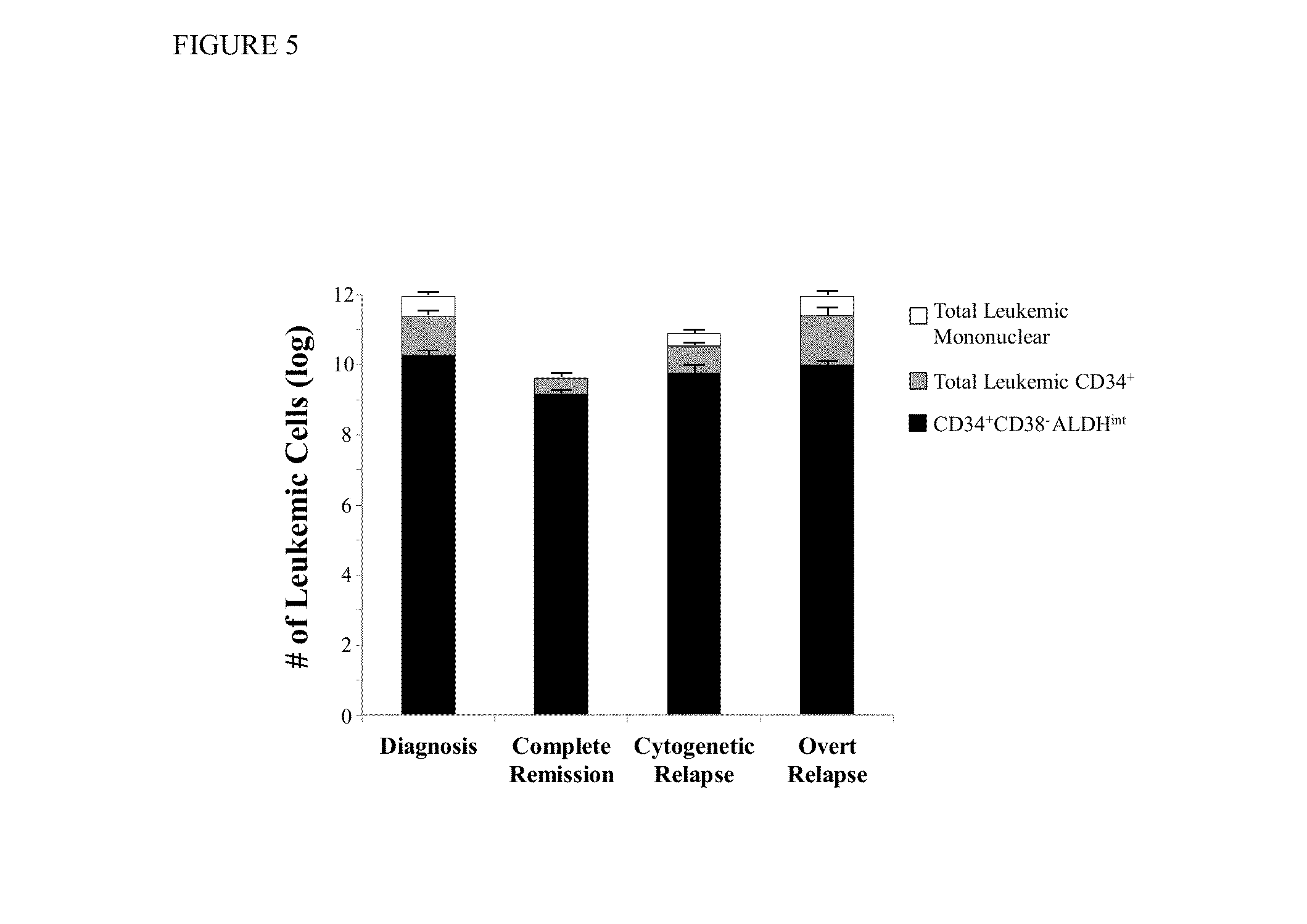
Methods for identifying leukemia stem cells and distinguishing them from normal hematopietic stem cells in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: uses in diagnosis, treatment, and research
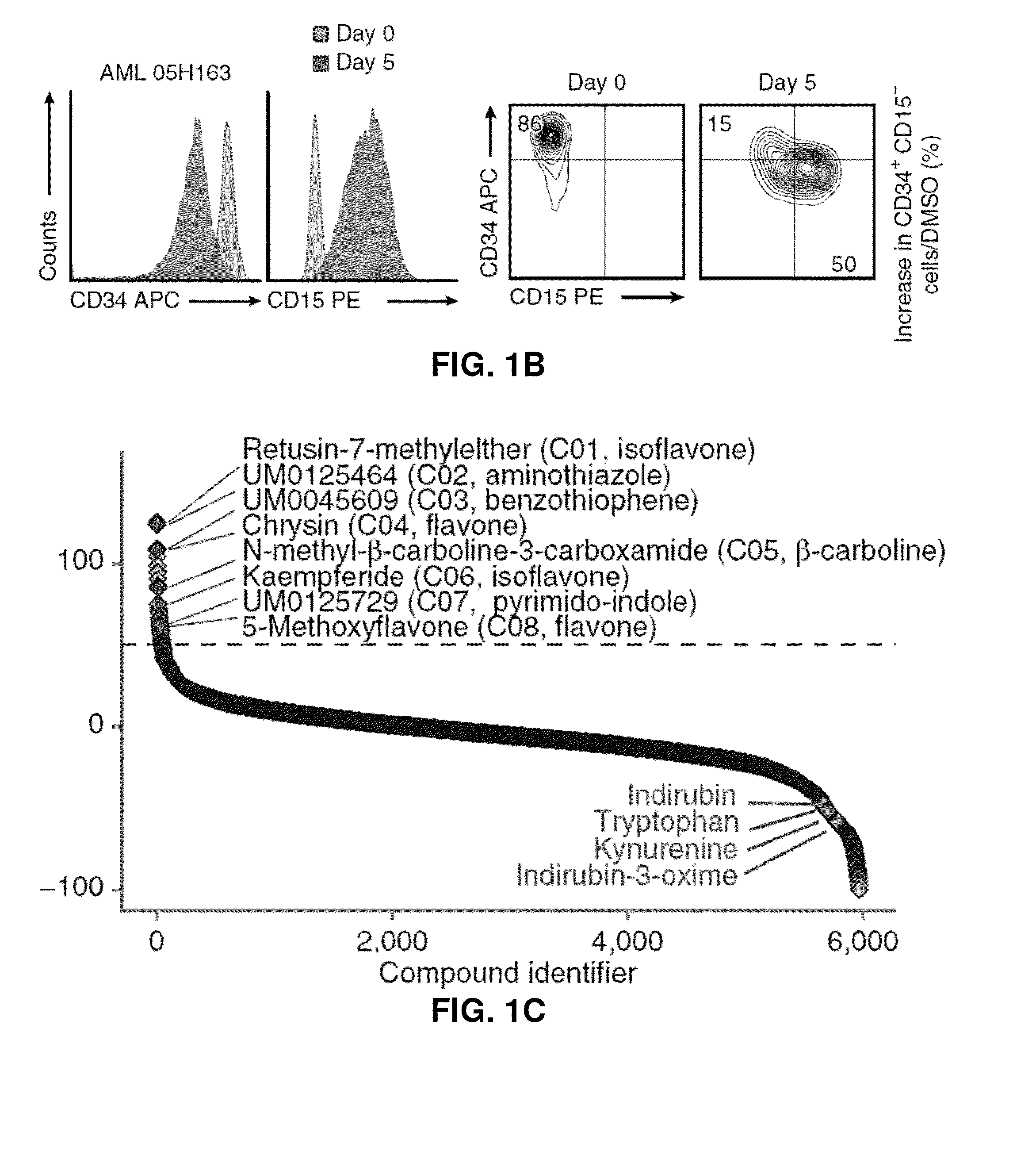
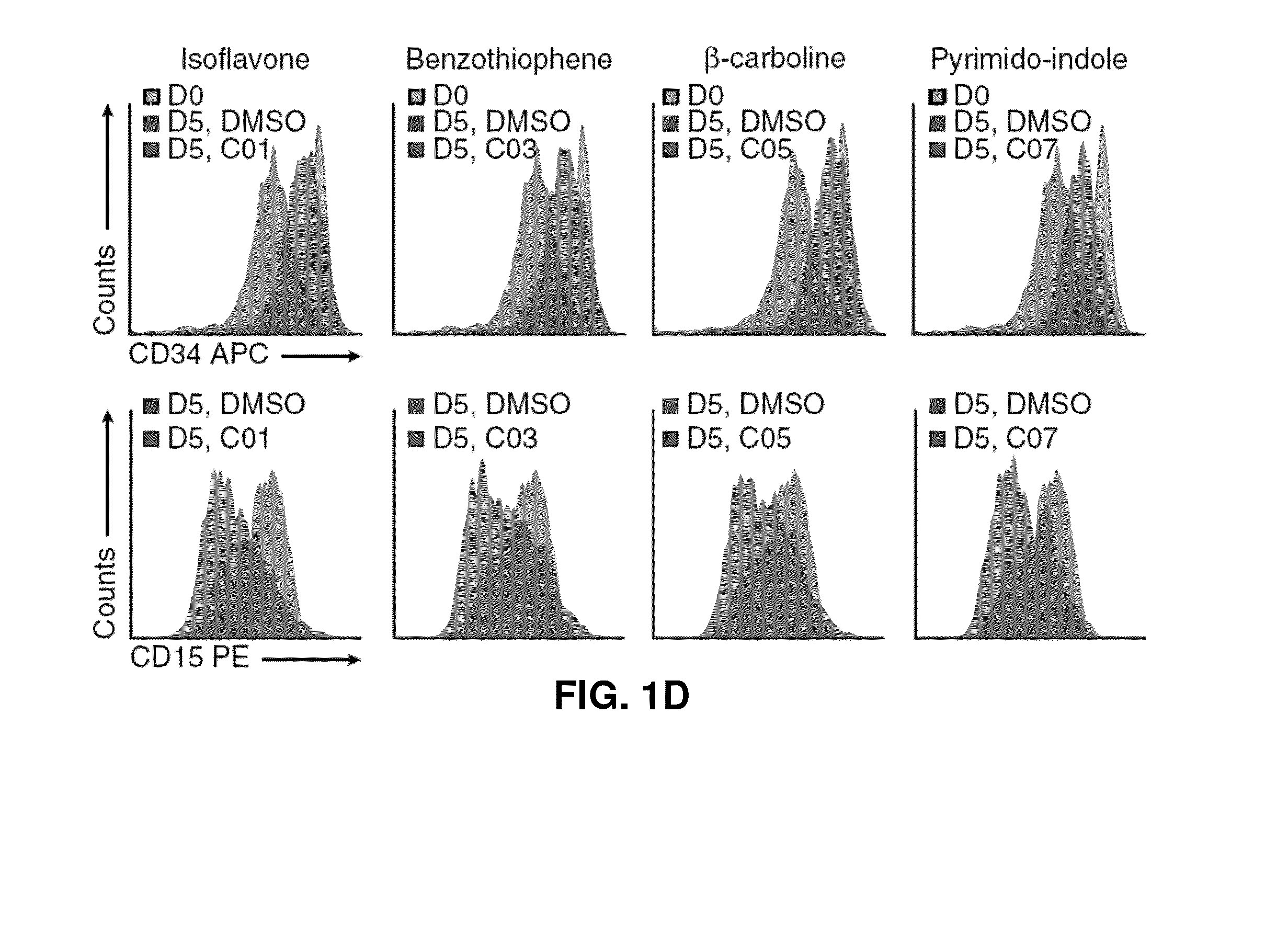
ActiveUS20130079424A1Increase relapse riskIncrease riskBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCD34Minimal residual disease
Using the methods of the present invention, intermediate (int) levels of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity reliably distinguished leukemic CD34+CD38− cells capable of engrafting immunodeficient mice, from residual normal hematopoietic stem cells that exhibited relatively higher ALDH activity. Minimal residual disease (MRD) detected during complete remission was enriched for the CD34+CD38−ALDHint leukemic cells, and the presence of these cells after therapy highly correlated with subsequent clinical relapse. The methods of the present invention can distinguish normal from leukemic CD34+CD38− cells, and identifies those AML cells associated with relapse. Methods of prediction of relapse of AML patients and methods of treatment are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods and compositions for identifying minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
This invention provides methods and kits for diagnosing, ascertaining the clinical course of minimal residual disease associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Specifically the invention provides methods and kits useful in the diagnosis and determination of clinical parameters associated with diseases associated with ALL based on patterns of surface marker expression unique to ALL.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Kit for quantitatively detecting BCR/ABL mRNA level
InactiveCN101624621AWide coverageImprove positive detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementMRD NegativeQuantitative determination
The invention discloses a kit for quantitatively detecting a BCR / ABL mRNA level. The kit comprises a standard product which is used for manufacturing a standard curve, an inner reference gene real-time quantitative PCR system and at least one of the following three real-time quantitative PCR systems: an M-type BCR / ABL real-time quantitative PCR system, m-type BCR / ABL real-time quantitative PCR system and a mu-type BCR / ABL real-time quantitative PCR system. The kit can accurately, quickly and quantitatively detect various BCR / ABL mRNA levels, is used for diagnosing chronic myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia expressed by BCR / ABL and monitoring minimal residual diseases in a treatment process, and provides an important molecular basis for accurate diagnosis of clinical diseases, determination of a treatment proposal, curative effect evaluation and prognosis.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
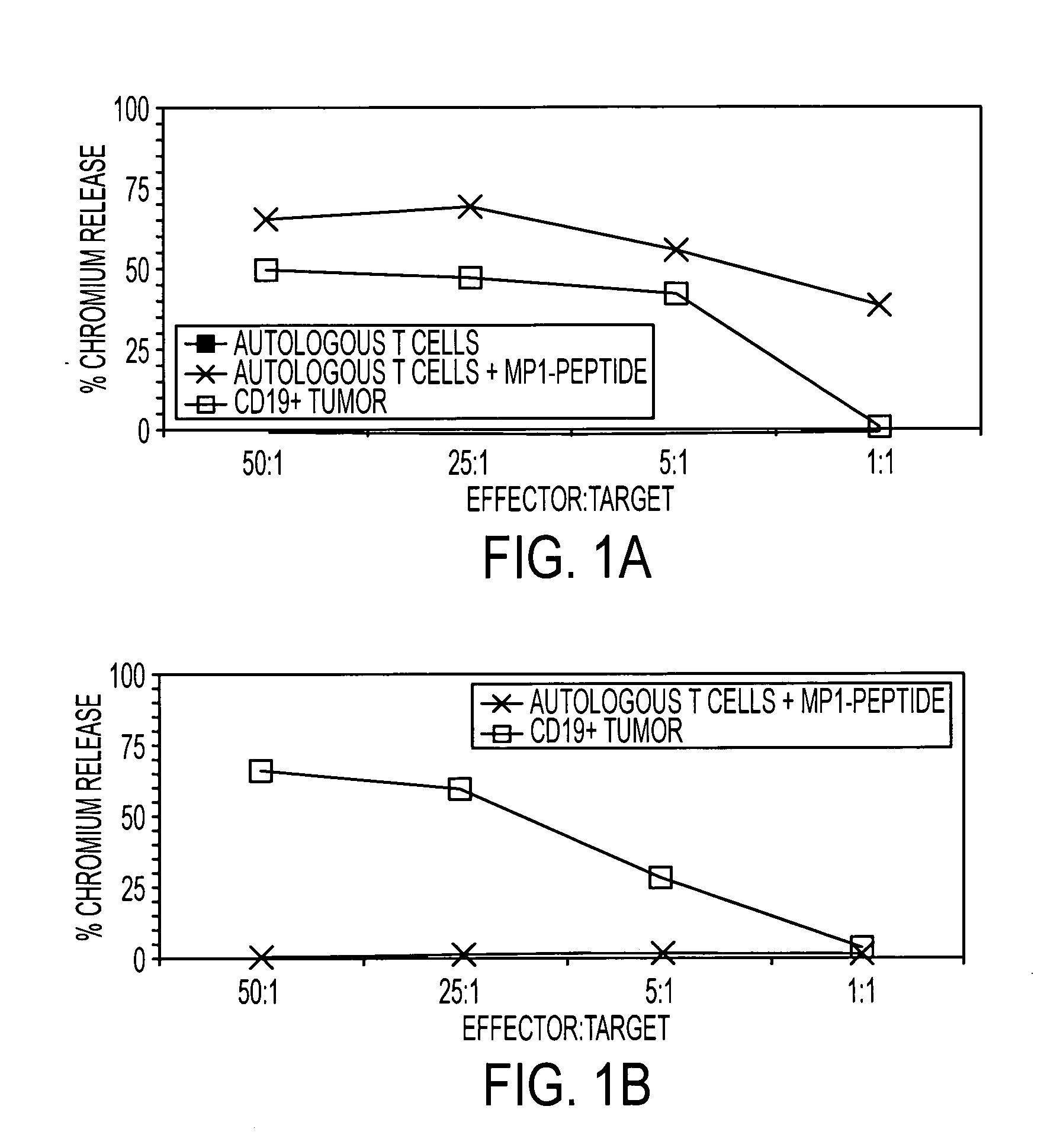
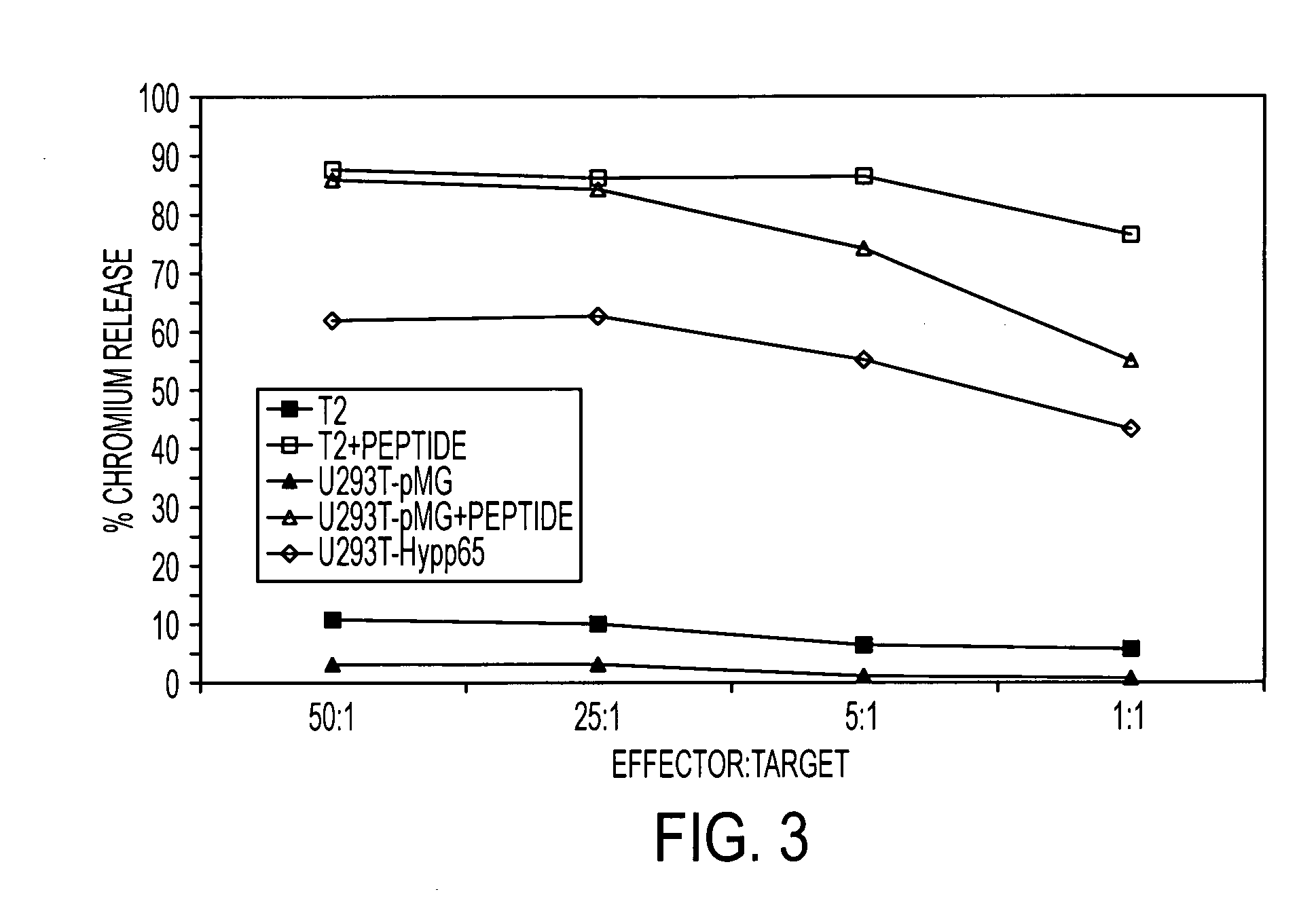
Dual antigen specific T cells with trafficking ability
InactiveUS20060018878A1Maintain in vivo functionEfficient workBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
The present invention is directed to mammalian T cells and methods for using these T cells. More specifically, the invention relates to viral specific T cells that express an endogenous viral antigen receptor, a chimeric anti-tumor receptor and the chemokine receptor CCR7. These T cells are a source of effector cells that persist in vivo in response to stimulation with viral antigen, leading to long-term function after their transfer to patients with cancer and autoimmune diseases and that are able to traffic to lymph nodes and sites of minimal residual disease.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Biomarkers for antibody-drug conjugate monotherapy or combination therapy
PendingUS20210093730A1Predict resistancePredict sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic non-active ingredientsDiseaseAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to biomarkers of use in cancer therapy, wherein the therapy comprises treatment with anti-Trop-2, anti-CEACAM5 or anti-HLA-DR ADCs (antibody-drug conjugates), alone or in combination with and one or more anti-cancer agents, such as a DDR inhibitor, an ABCG2 inhibitor, a microtubule inhibitor, a checkpoint inhibitor, a PI3K inhibitor, an AKT inhibitor, a CDK 4 inhibitor, a CDK 5 inhibior, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor or a platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent. Preferably, the combination therapy has a synergistic effect on inhibiting tumor growth. The biomarkers are of use to predict efficacy and / or toxicity of ADC therapy, determine tumor response to treatment, identify minimal residual disease or relapse, determine prognosis, stratify patients for initial therapy or to optimize treatment for the patient, based on the specific biomarkers detected.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Methods to modulate acute myeloid leukemia stem/progenitor cell expansion and/or differentiation
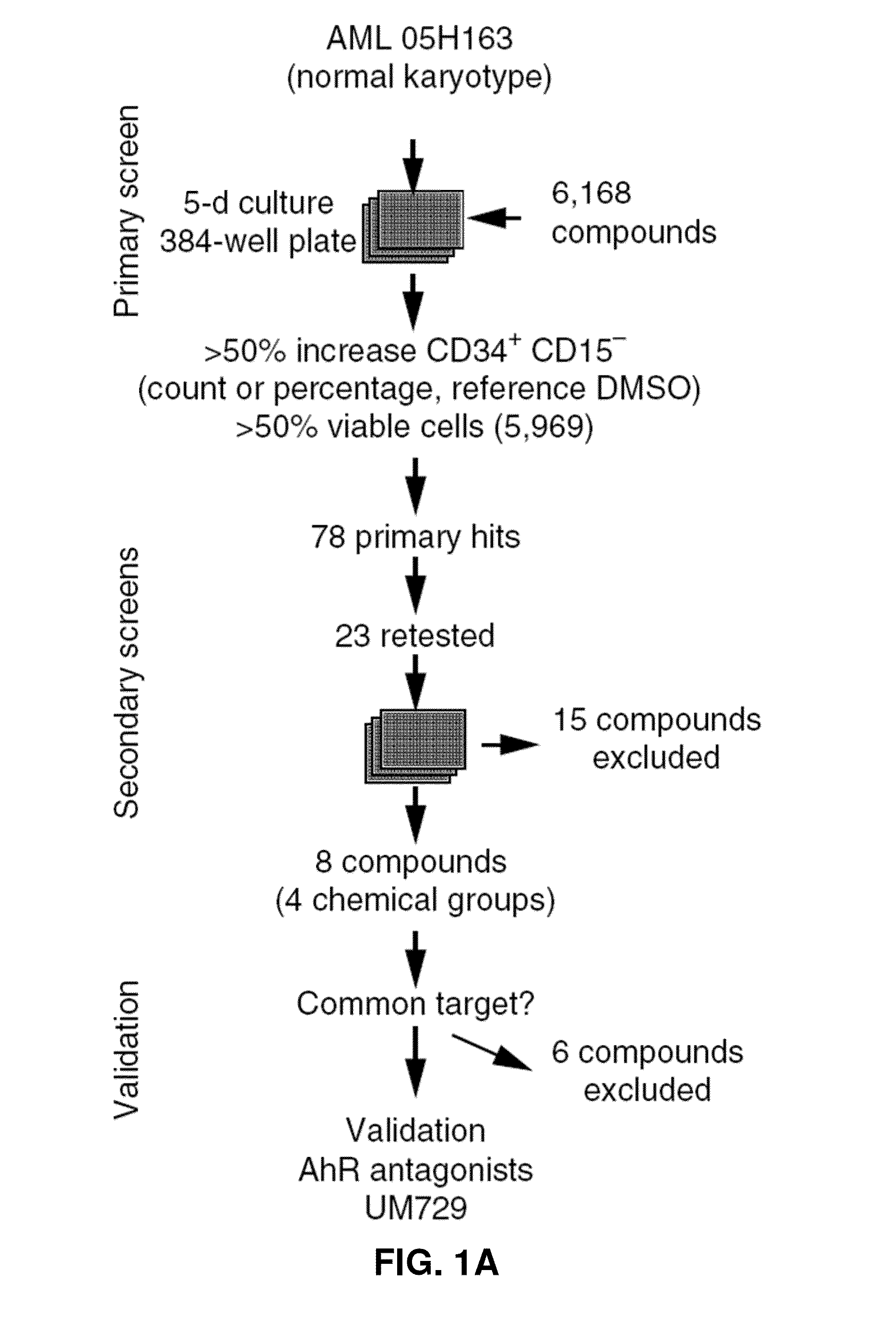
Novel methods for modulating acute myeloid leukemia stem / progenitor cell expansion and / or differentiation are disclosed. These methods are based on the use of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) modulators and / or compounds of formula I or IIScreening assays to identify compounds that may be useful for inhibiting and / or eliminating AML initiating cells using AhR modulators and / or the compounds of formula I or II are also disclosed. The use of pharmaceutically acceptable agonists of the AhR for preventing or inhibiting minimal residual disease (MRD) in an AML patient is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL +1
Multiple PCR primers and method for constructing leukemia minimal residual disease BCR library based on high-flux sequencing
InactiveCN105063032AFull lengthRich quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMRD NegativeNucleotide
The invention provides multiple PCR primers for constructing a leukemia minimal residual disease BCR library based on high-flux sequencing. The multiple PCR primers comprise upstream primers and downstream primers, wherein the upstream primers are an upstream primer group composed of nucleotide sequences which are 0-3 basic groups more or less than the nucleotide sequences shown in the SEQ ID NO: 1-SEQ ID NO: 13, and the downstream primers are composed of nucleotide sequences which are 0-3 basic groups more or less than the nucleotide sequences shown in the SEQ ID NO: 14-SEQ ID NO: 17. The provided multiple PCR primer group can efficiently construct the B lymphocyte receptor high-flux sequencing library of a leukemia patient, so that rich leukemia minimal residual disease BCR rearrangement information can be obtained.
Owner:GENEMIND BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
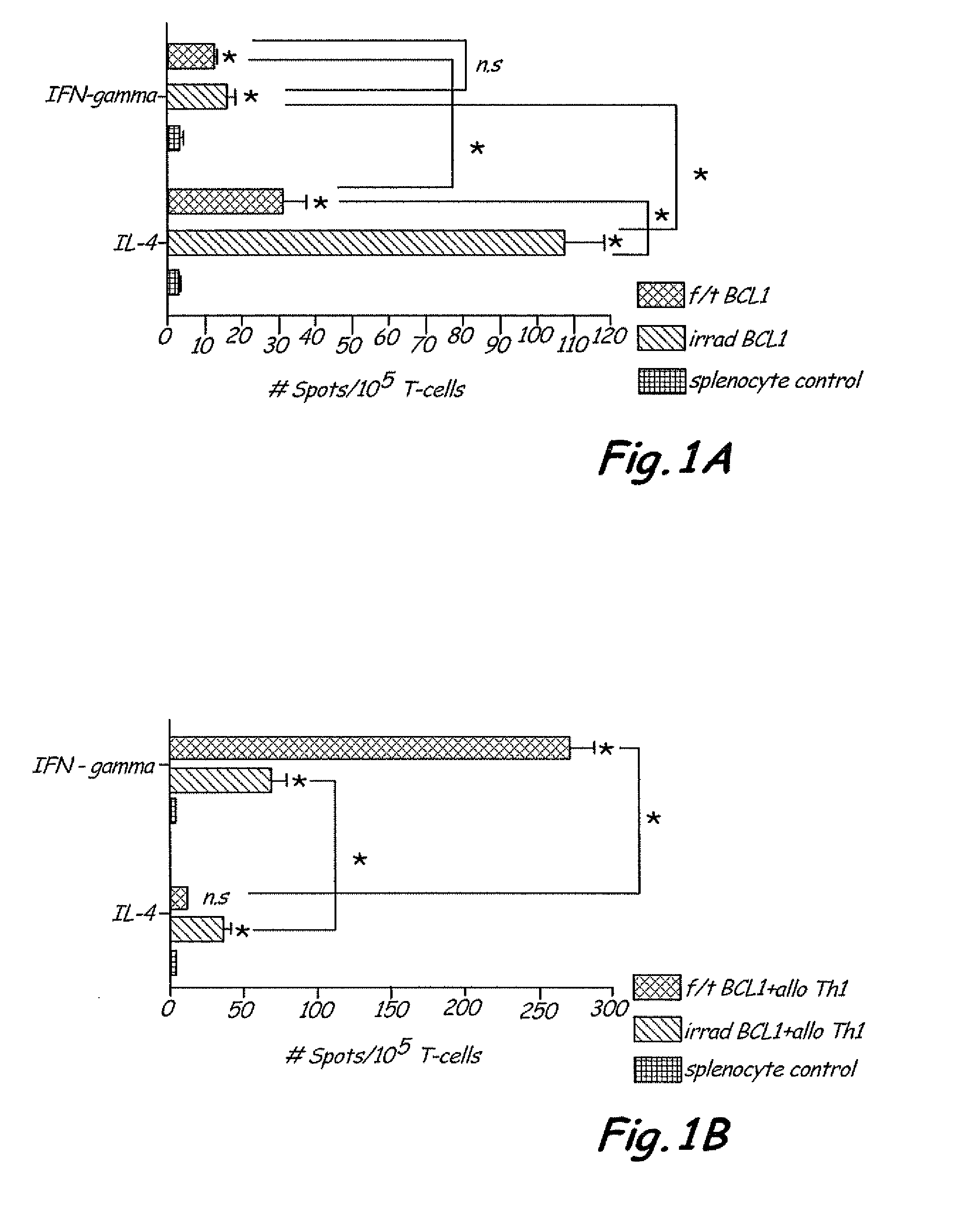
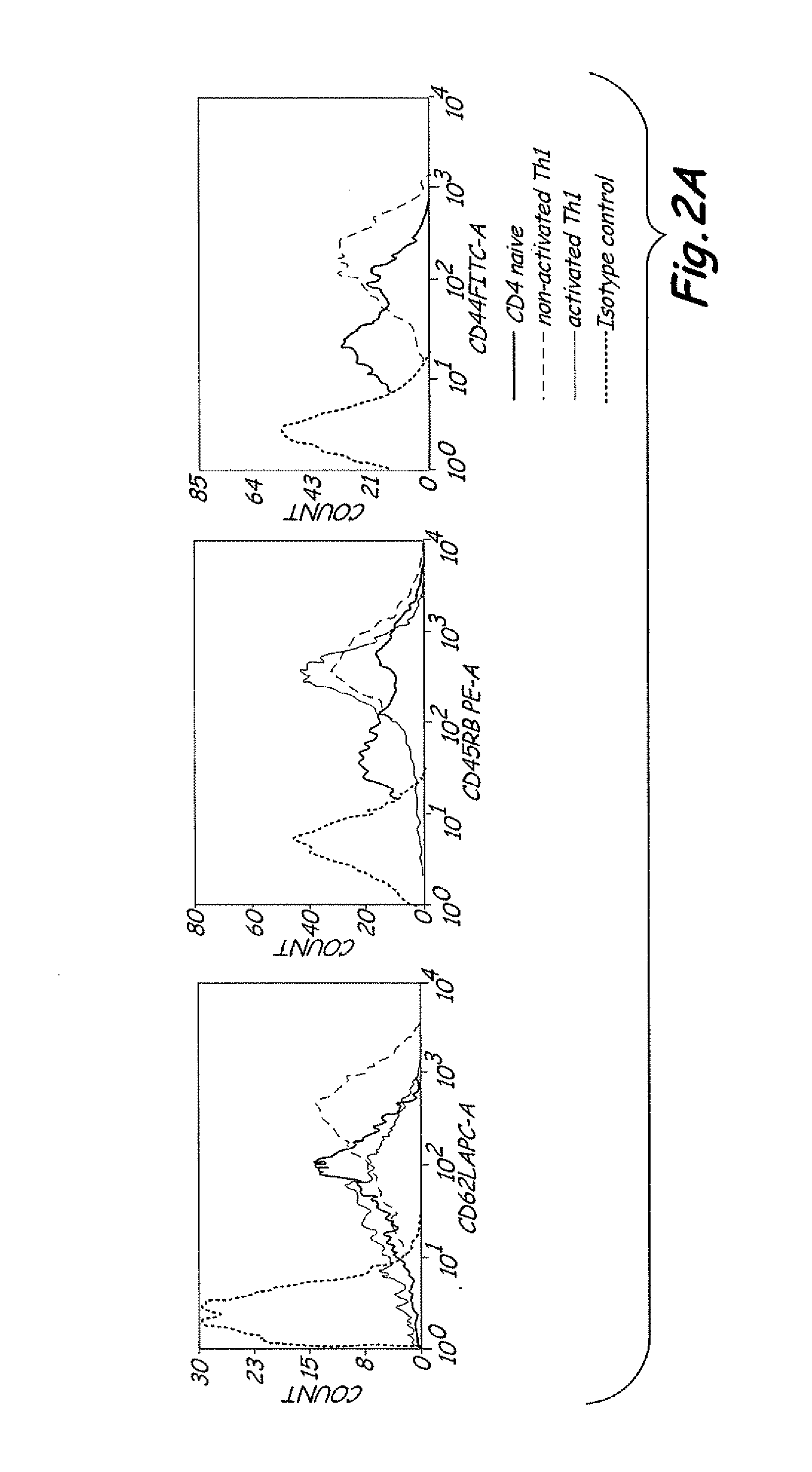
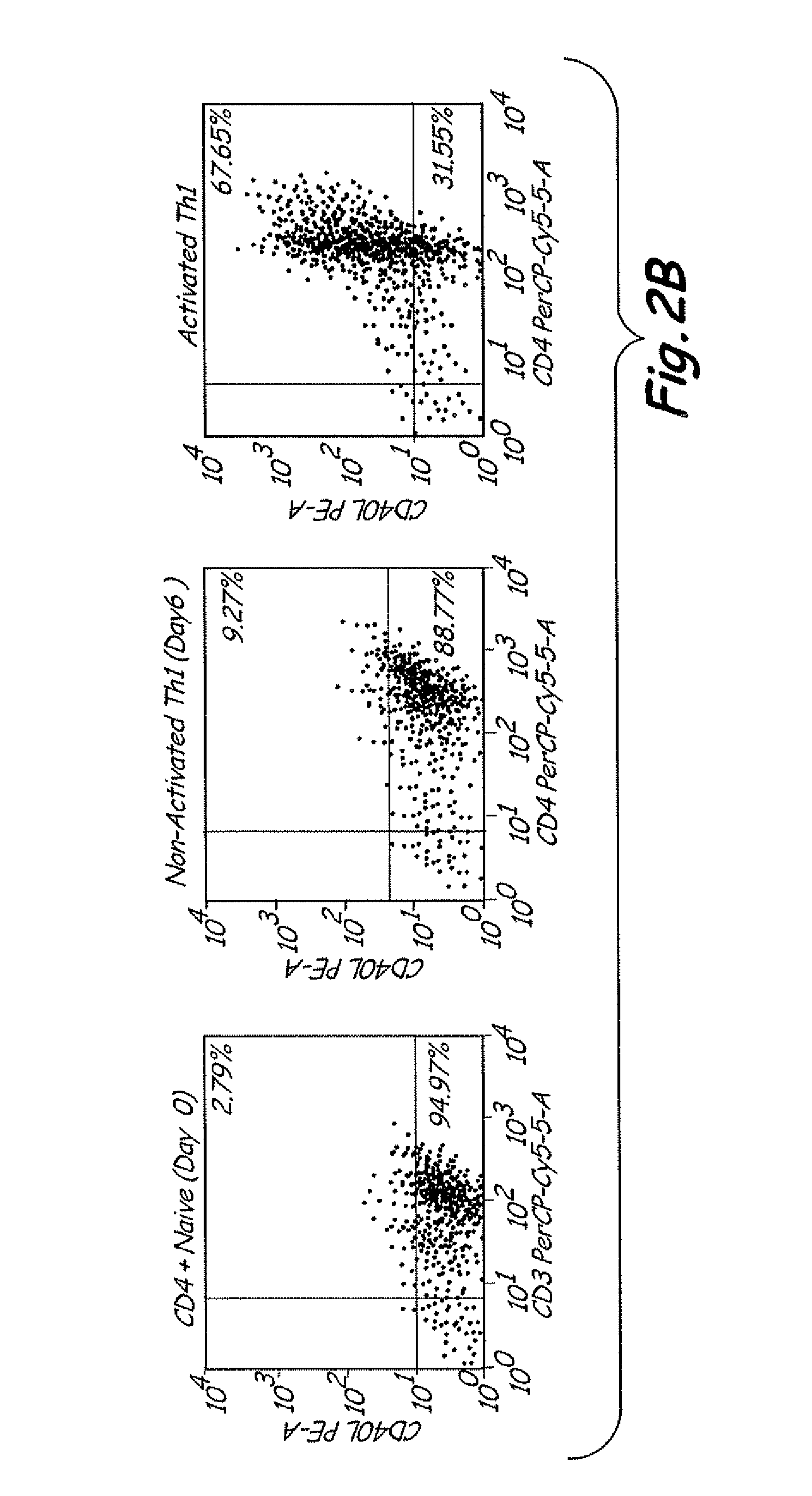
Th1 vaccination priming for active immunotherapy
ActiveUS20100086561A1Good auxiliary effectMaintaining immune healthAntibacterial agentsBiocideMRD NegativeDisease
The present invention includes vaccine compositions and methods for using these vaccine compositions in active immunotherapy. The vaccine compositions include allogeneic activated Th1 memory cells. The compositions can also include one or more disease-related antigens. The methods include administering the vaccine compositions to provide a Th1 footprint in normal individuals or patients susceptible to disease or having minimal residual disease.
Owner:MIRROR BIOLOGICS INC +1
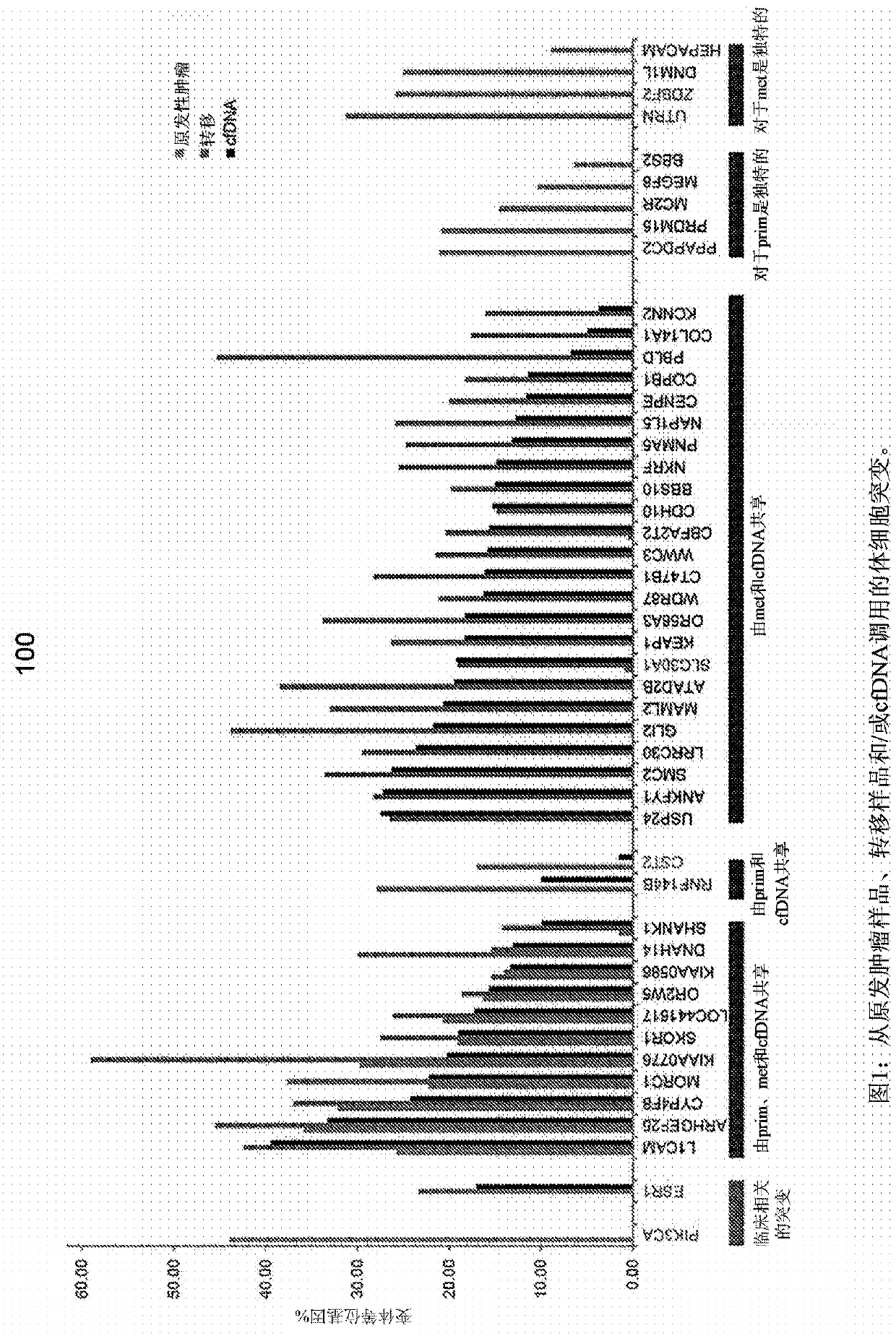
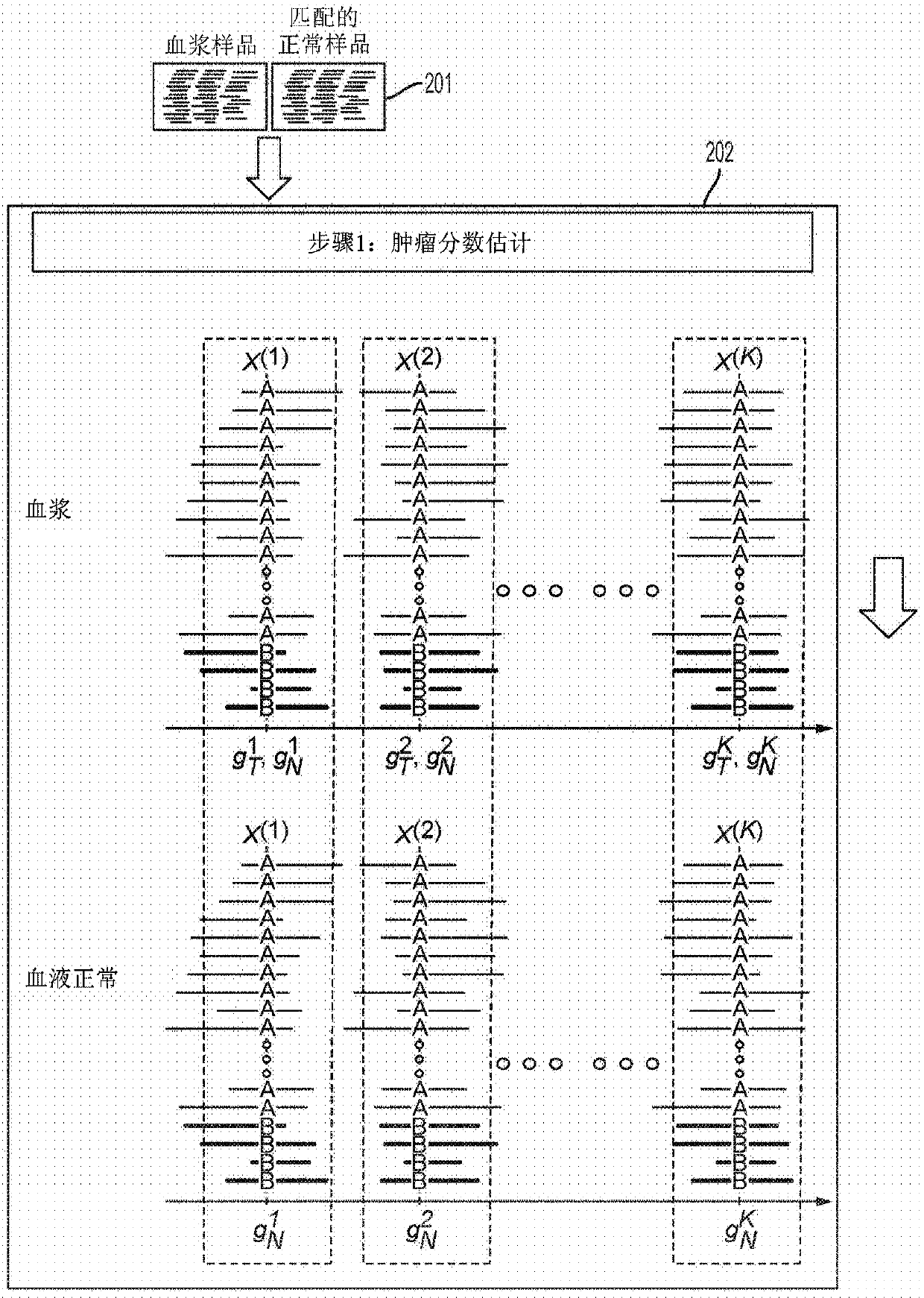
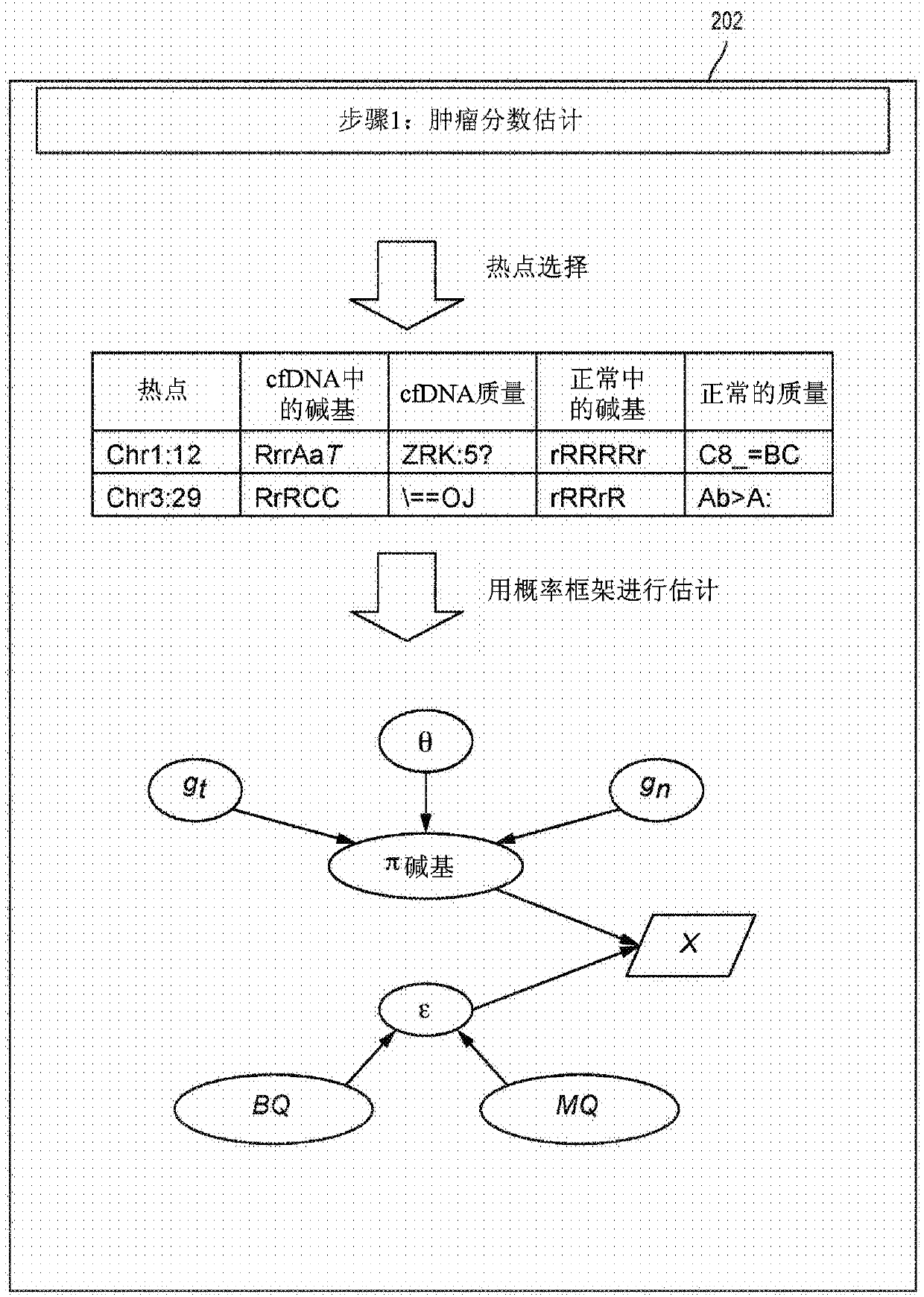
Detecting somatic single nucleotide variants from cell-free nucleic acid with application to minimal residual disease monitoring
The present disclosure provides a probabilistic model for accurate and sensitive somatic single nucleotide variant (SNV) detection in cell-free nucleic acid samples comprising a set of sequence data.A joint genotype may be determined for each locus in the set of sequence data, and germline mutations may be intrinsically removed. A set of filtrations can be applied to eliminate low quality somaticvariant calls. Further, a global tumor cell-free deoxyribonucleic acid (cfDNA) fraction and overlapping read mates can be considered, thereby enabling accurate SNV detection and variant allele frequency estimation from samples with low tumor cfDNA fraction. A sensitive early detection of minimal residual disease (MRD) is designed by using the probabilistic model and the machine learning model fordistinguishing true variants from sequencing errors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-PCR primer and method for constructing leukemia minimal residual disease TCR library based on high-throughput sequencing
ActiveCN105154440AImprove the detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMRD NegativeForward primer
The invention provides a multi-PCR primer for constructing a leukemia minimal residual disease TCR library based on high-throughput sequencing; the primer comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer, wherein the forward primer is a forward primer group consisting of nucleotide sequences which are 0-3 bases more than or less than nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-SEQ ID NO: 25; and the reverse primer consists of nucleotide sequences which are 0-3 bases more than or less than nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 26-SEQ ID NO: 28. The multi-PCR primer group provided by the invention can be used for effectively constructing a T lymphocyte receptor high-throughput sequencing library of patients of leukemia, and abundant leukemia minimal residual disease TCR rearrangement information can be obtained.
Owner:GENEMIND BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
Method, reagents, and kits for detecting minimal residual disease
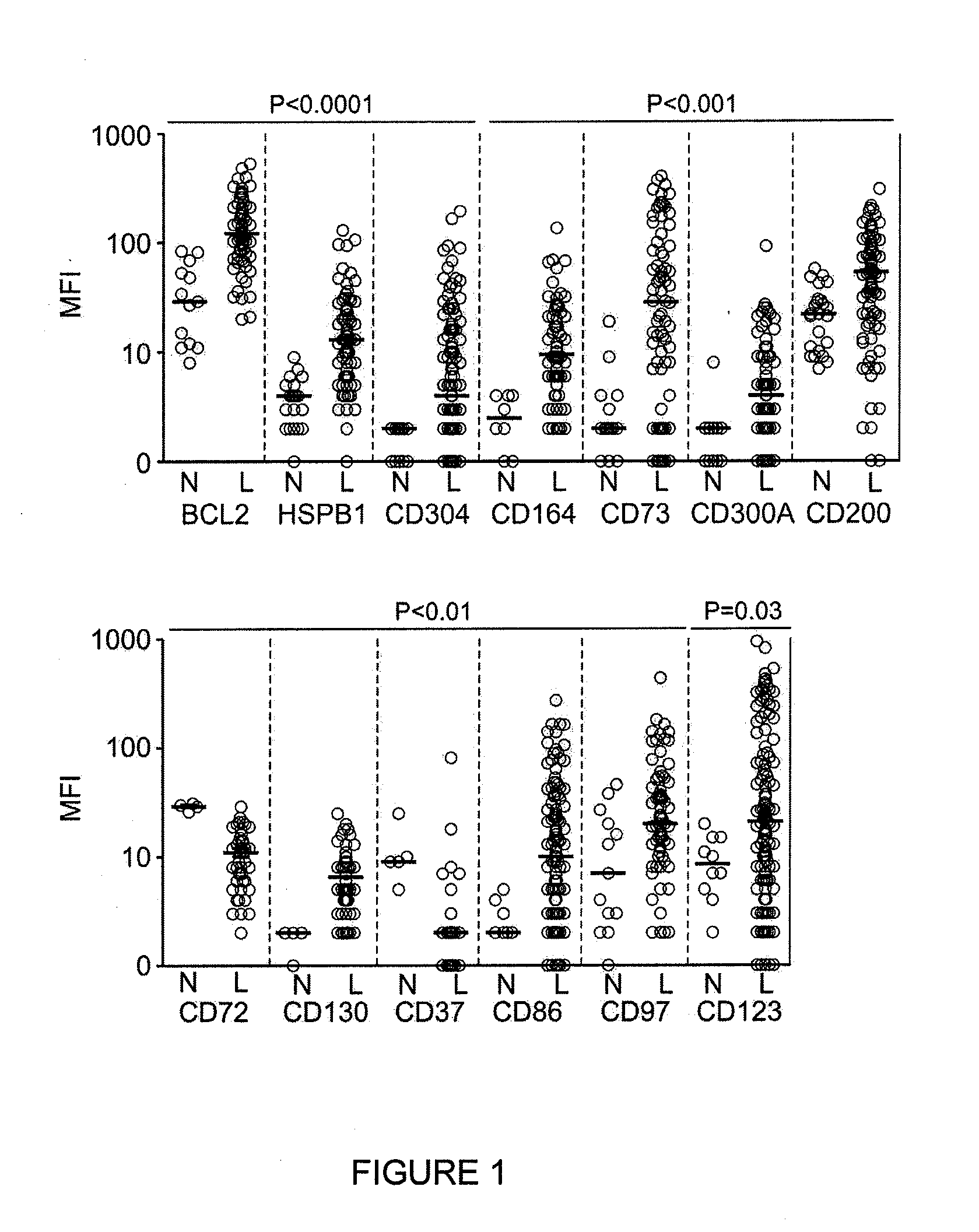
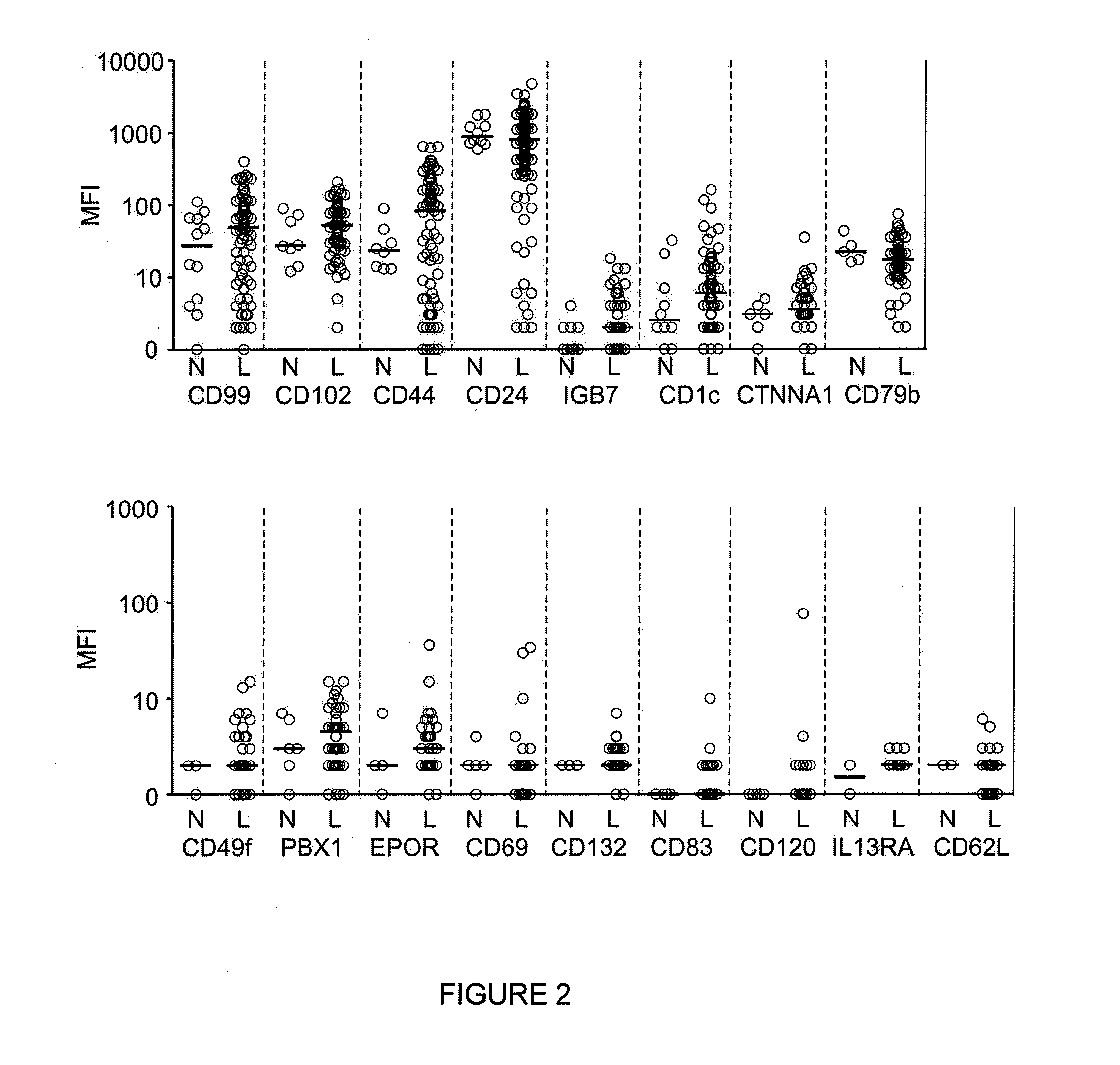
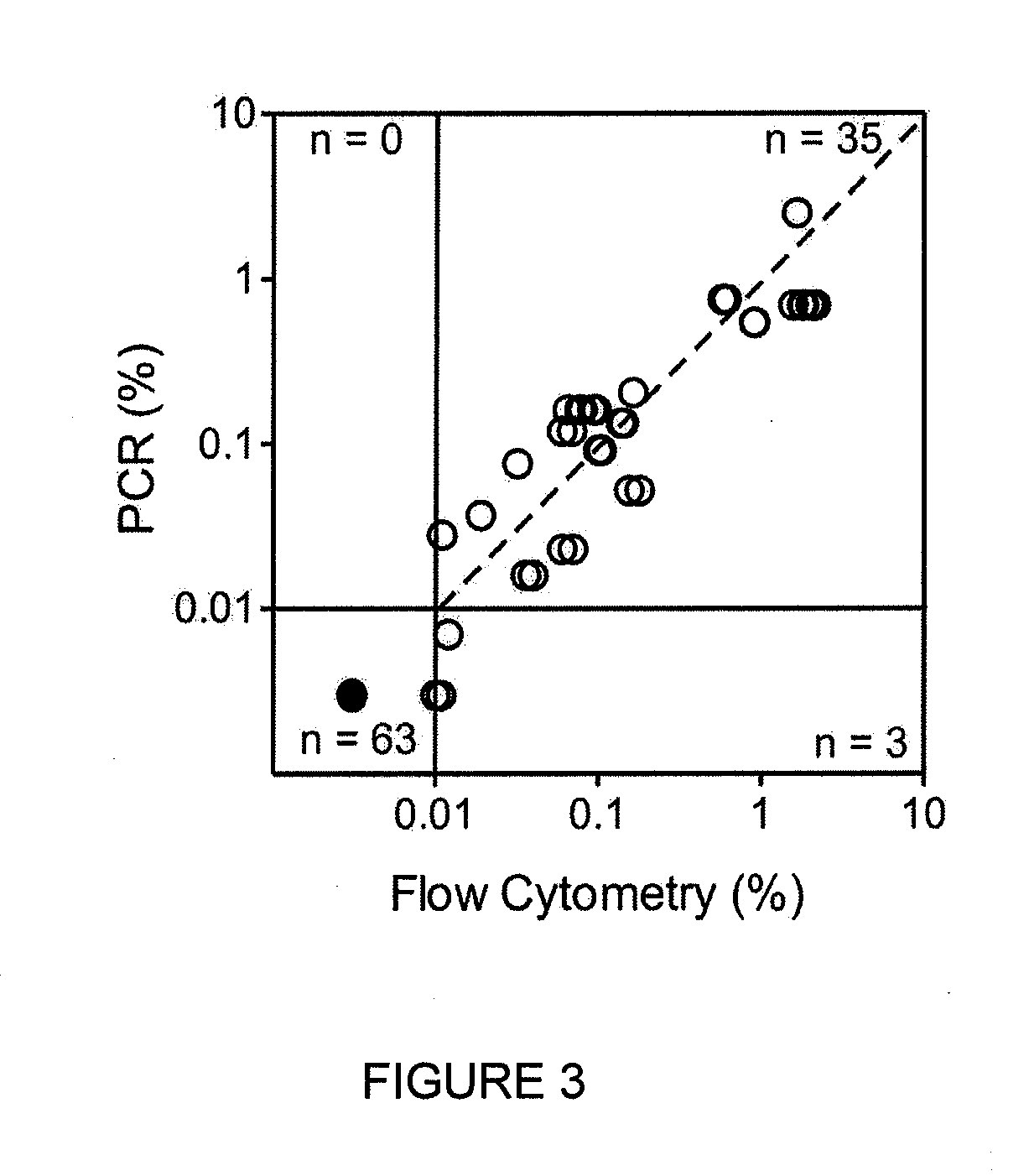
The invention relates to the field of minimal residual disease (MRD) diagnostics, which is progressively more applied for the evaluation of treatment effectiveness in patients with a hematological malignancy, such as B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL), B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL), and multiple myeloma (MM). Provided are unique reagent compositions with carefully selected and thoroughly tested combinations of antibodies, for >=8 color flow cytometric stainings as well as for 10-color and 12-color flow cytometric stainings, which can reach sensitivities of at least 10<-4>, even down to 10<-5>. Also provided are diagnostic kits and methods for detecting MRD.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
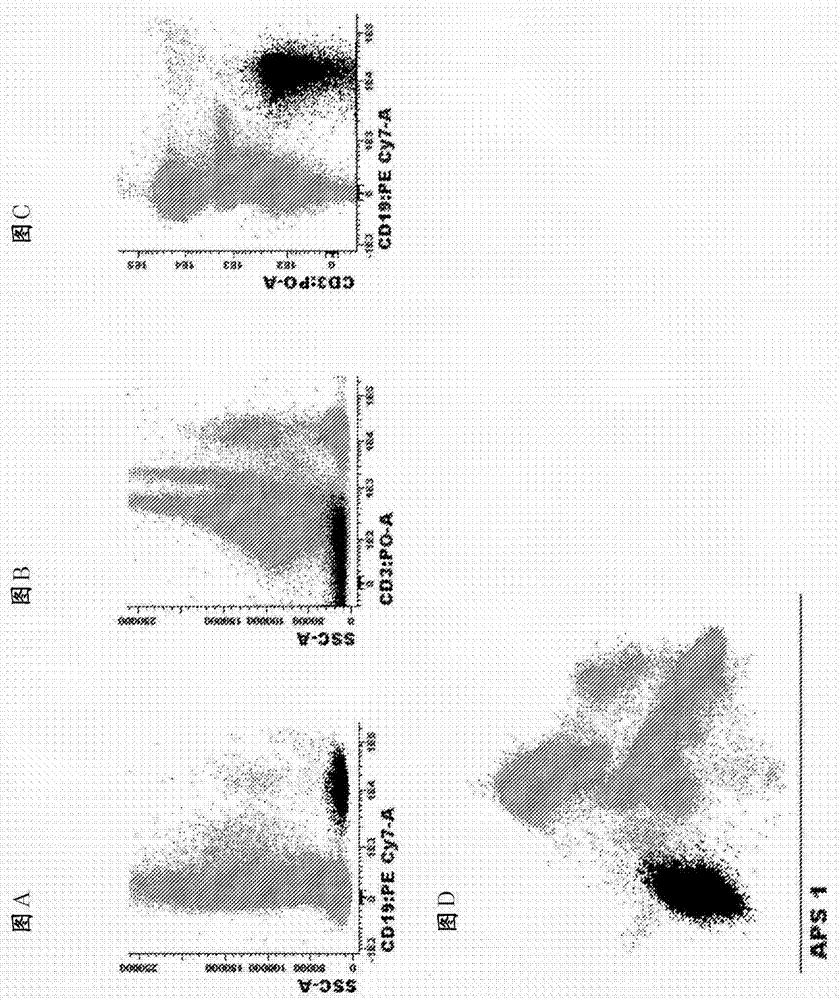
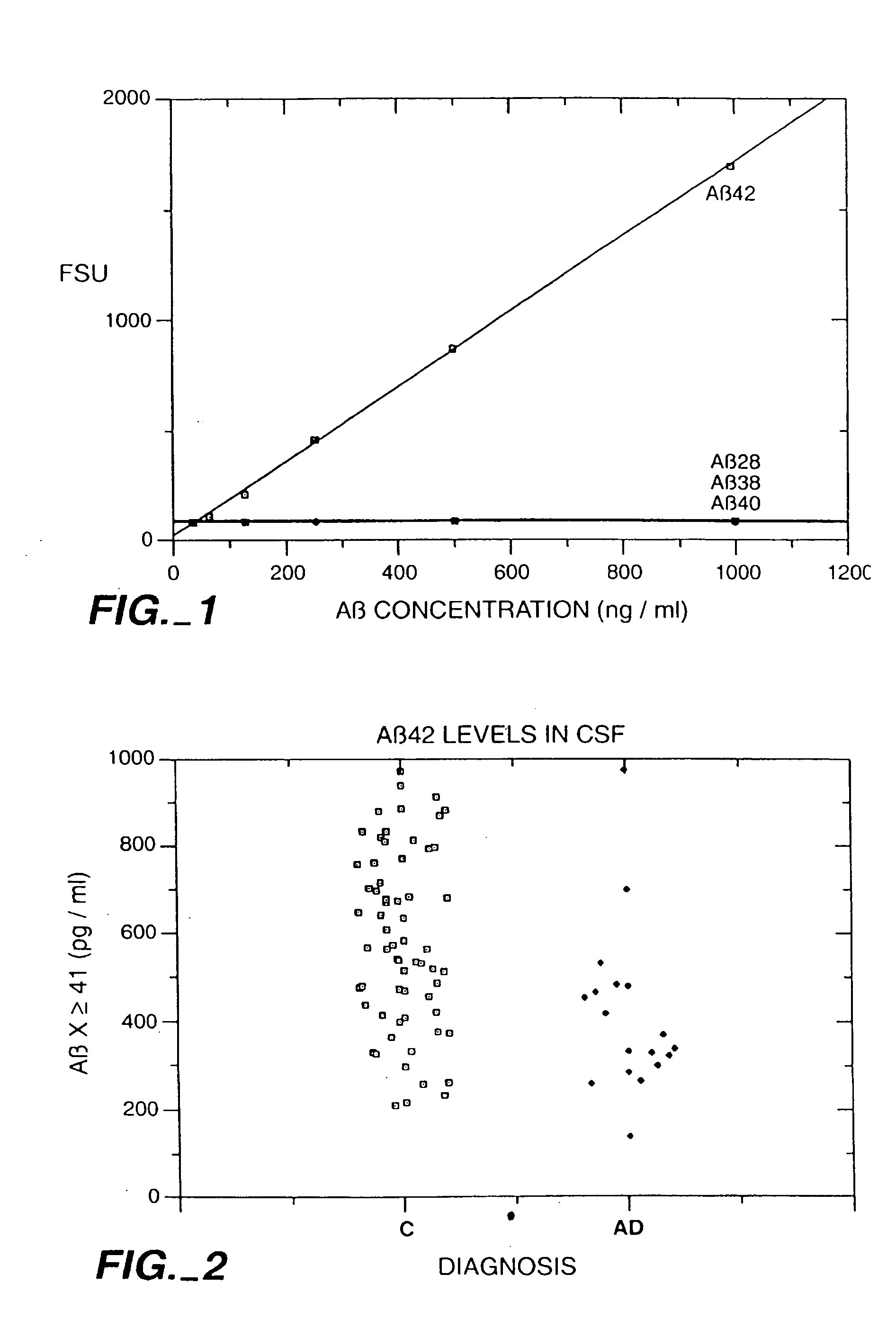
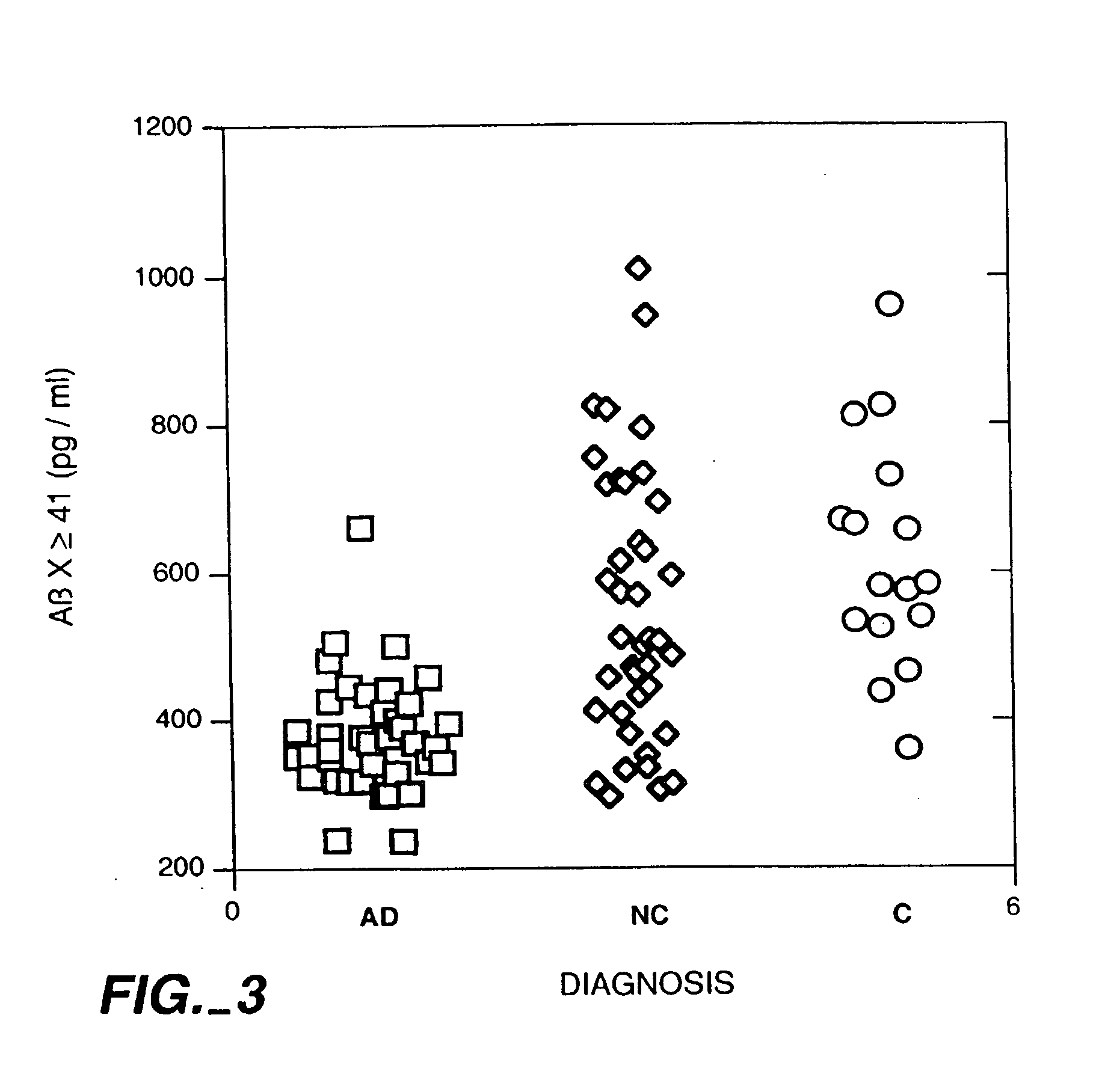
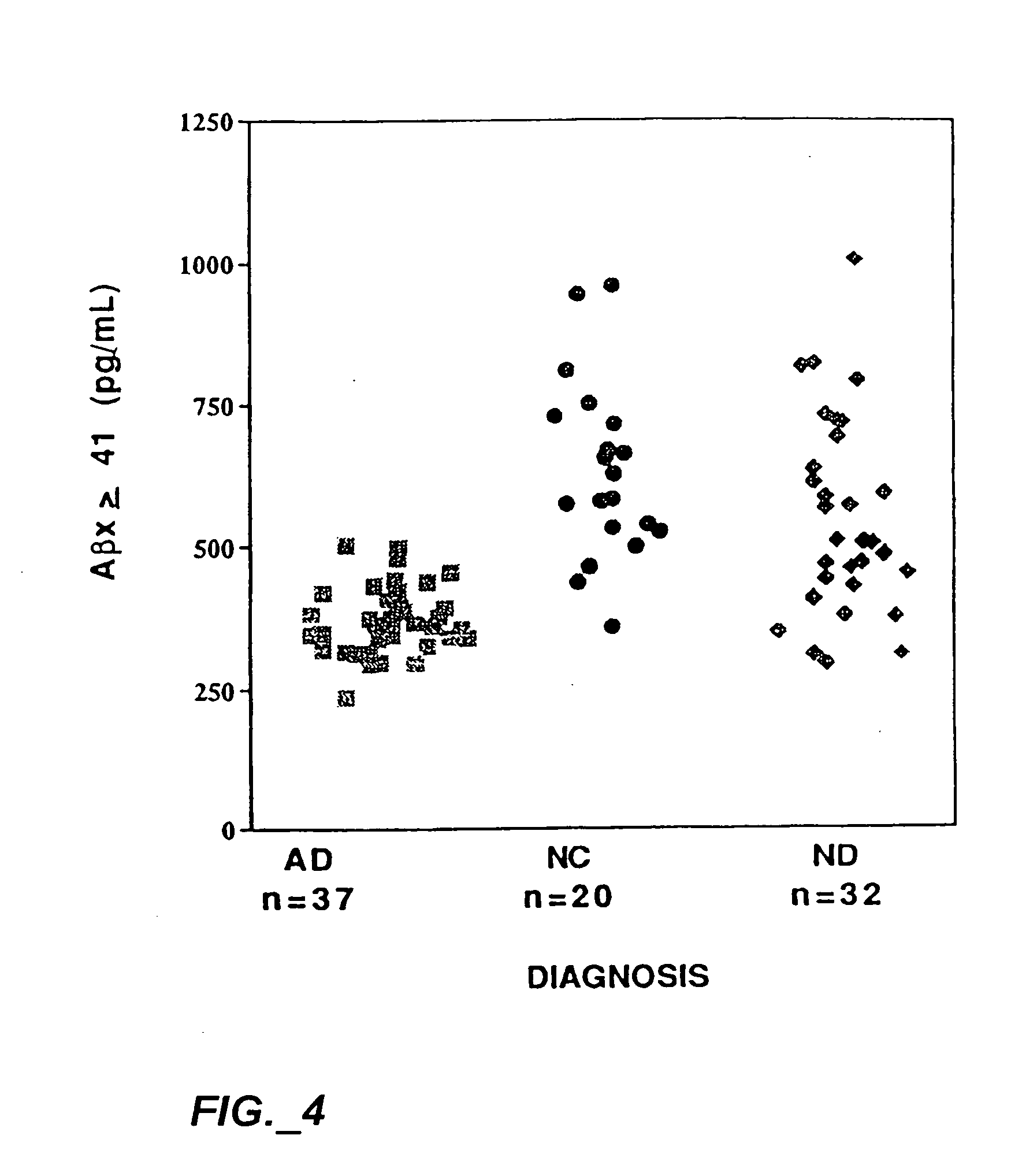
Methods for aiding in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease by measuring amyloid-b peptide (x->41) and tau
InactiveUS20050069968A1High sensitivityStrong specificityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMRD NegativeAmyloid β peptide
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
Method for detecting DNA methylation in cancer cells
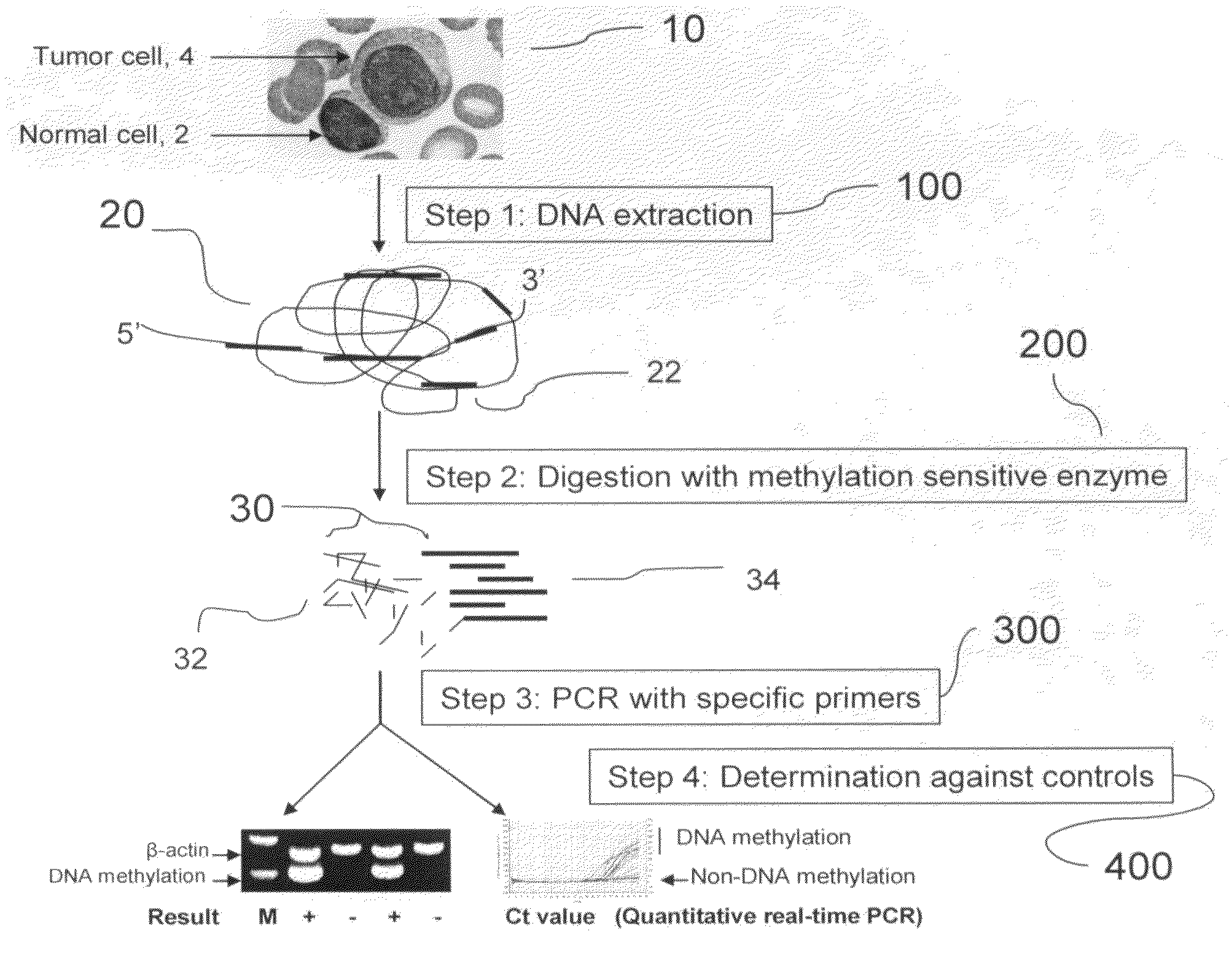
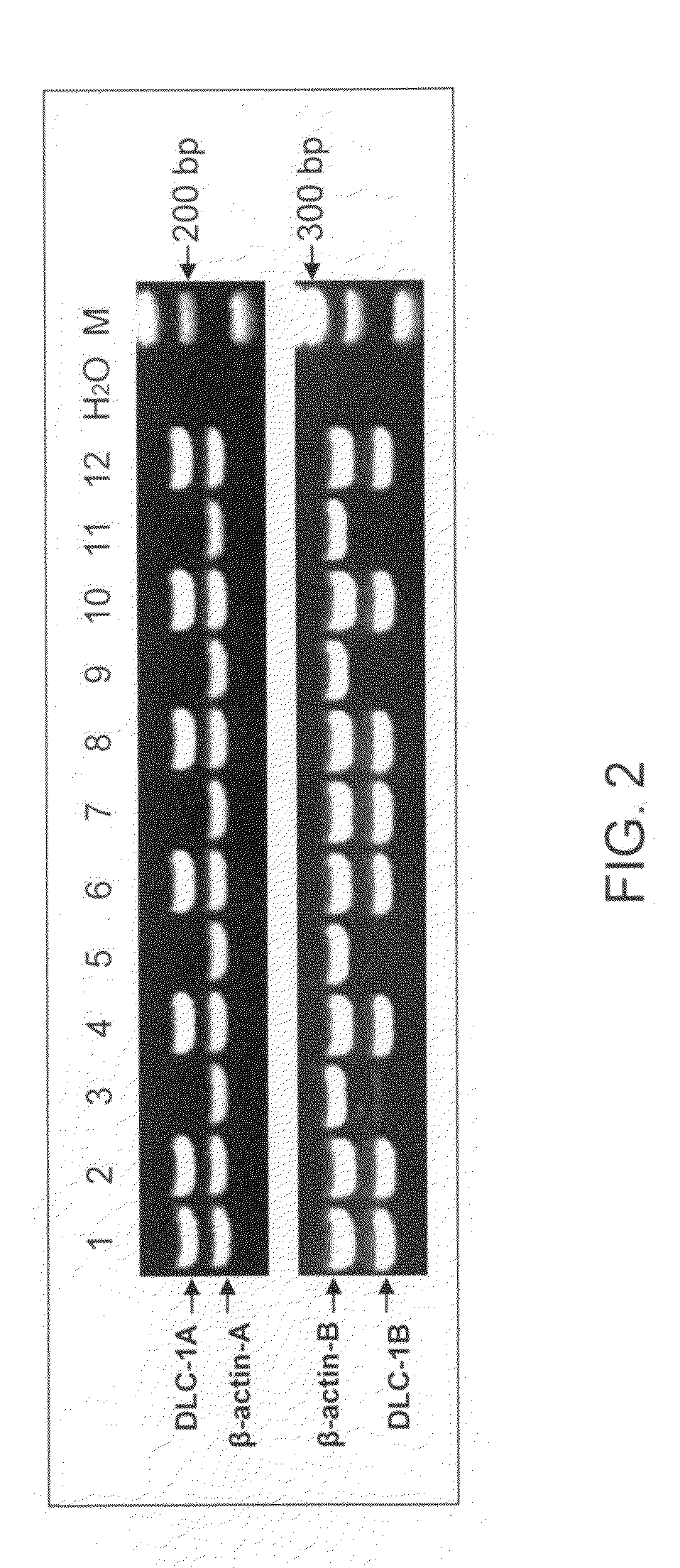
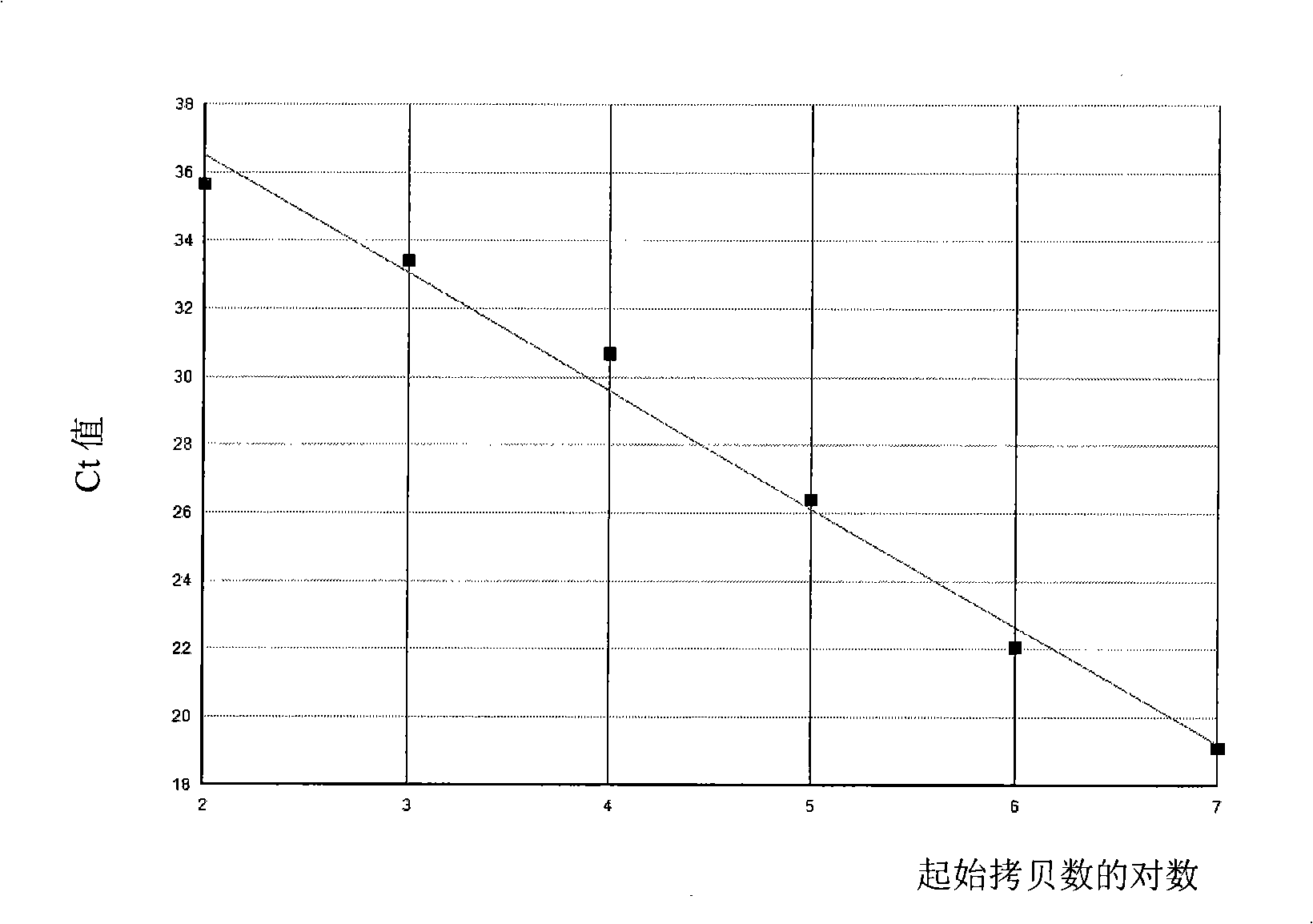
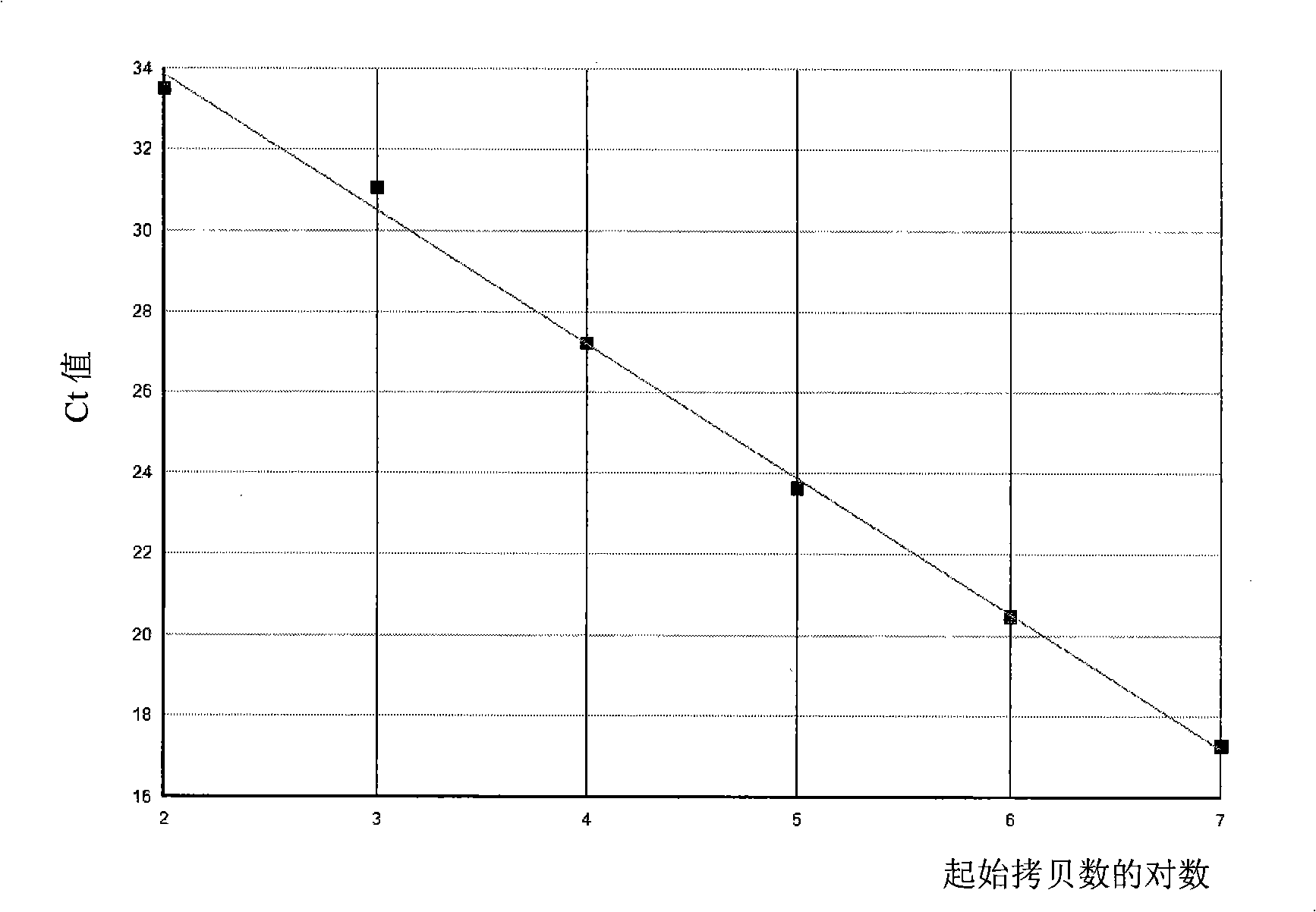
The present invention provides a detecting method of detecting malignant cells in a patient's specimen or a biological sample. Specifically, the inventive method includes the steps of extracting a genomic DNA, digesting said genomic DNA with one or multiple methylation sensitive restriction enzymes, and amplifying by PCR with one or multiple selected primers. The PCR can be performed in a conventional or a real-time platform. The inventive method can detect leukemia cells in 90% ALL patients at a sensitivity of up to 10−6. The inventive method also provides broad clinical applications in cancer (including hematopoietic and solid tumors) screening and risk assessment, early detection and diagnosis confirmation, and therapeutic monitoring, minimal residual disease detection and prognostic prediction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
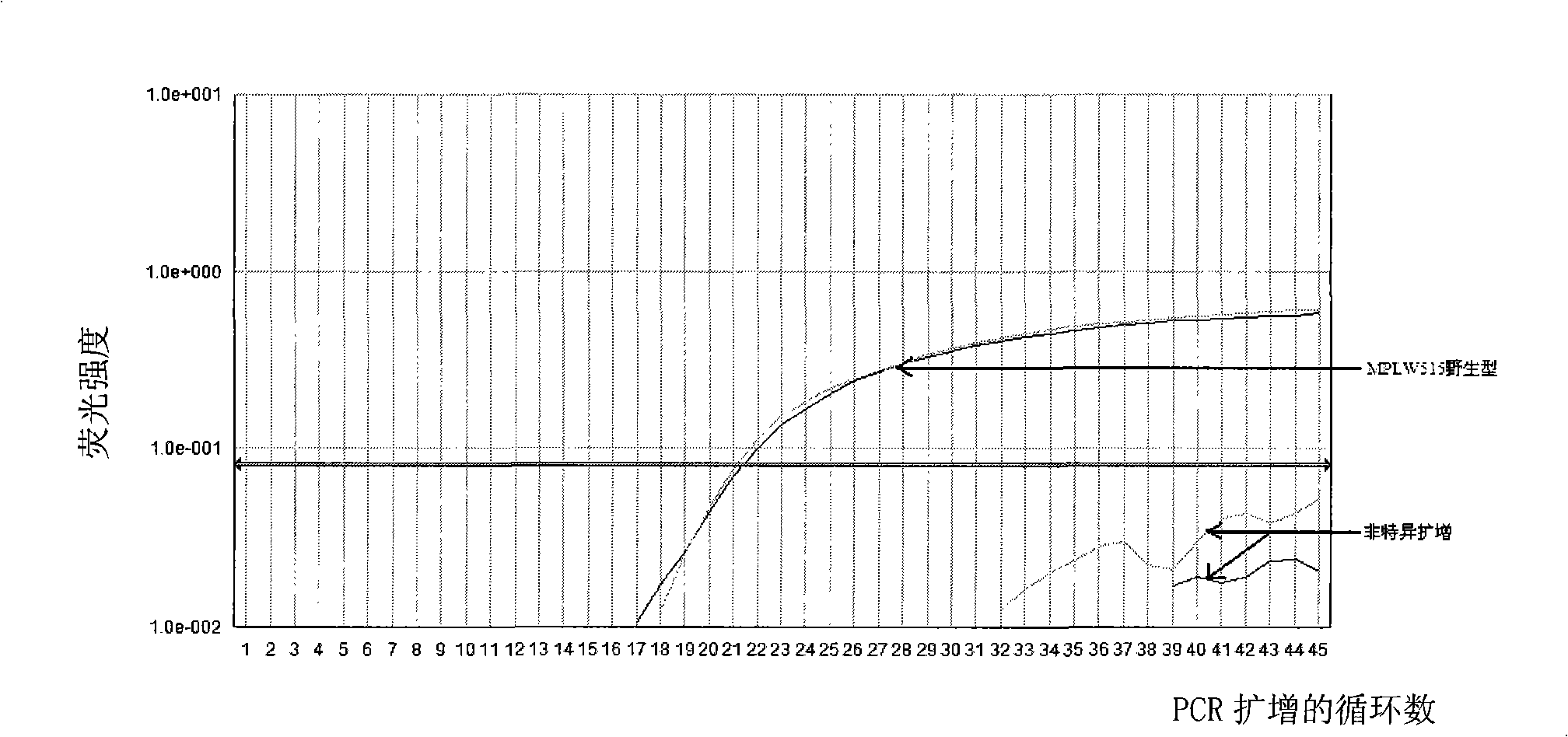
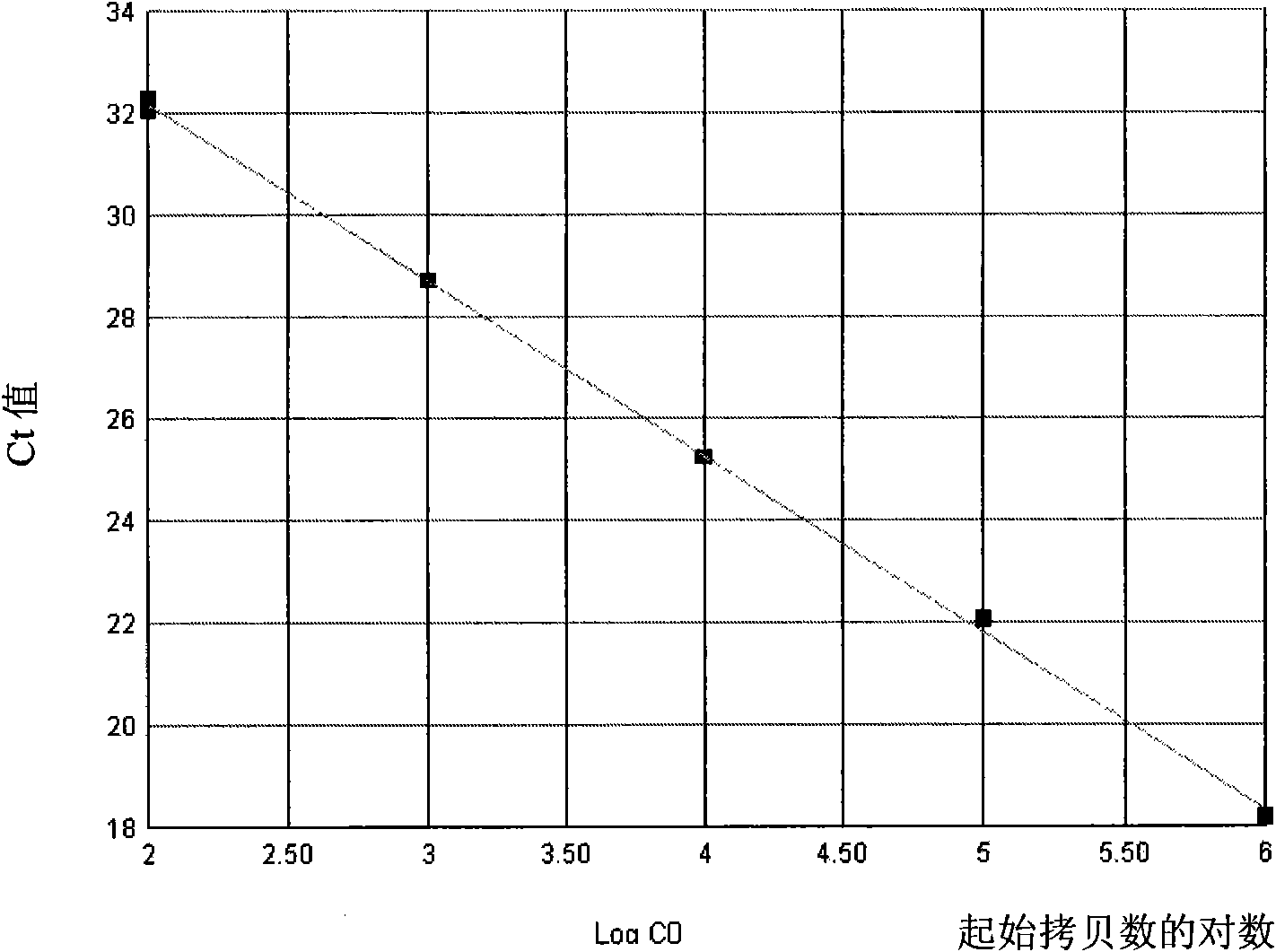
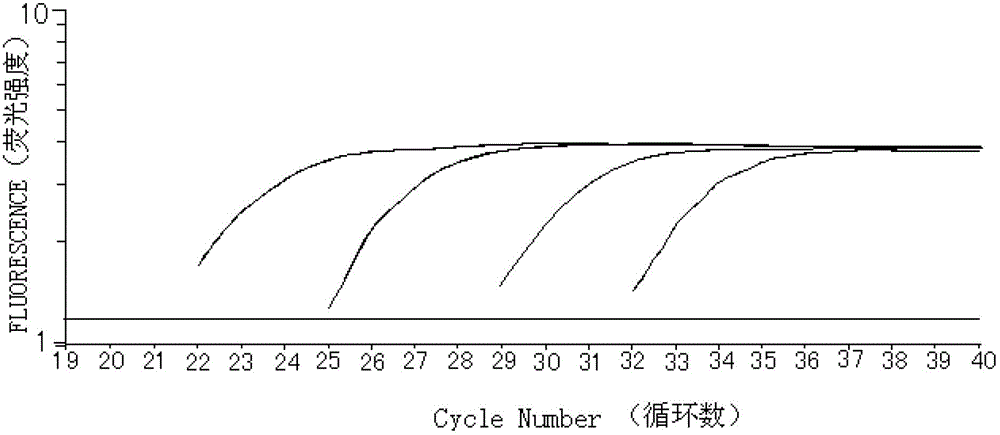
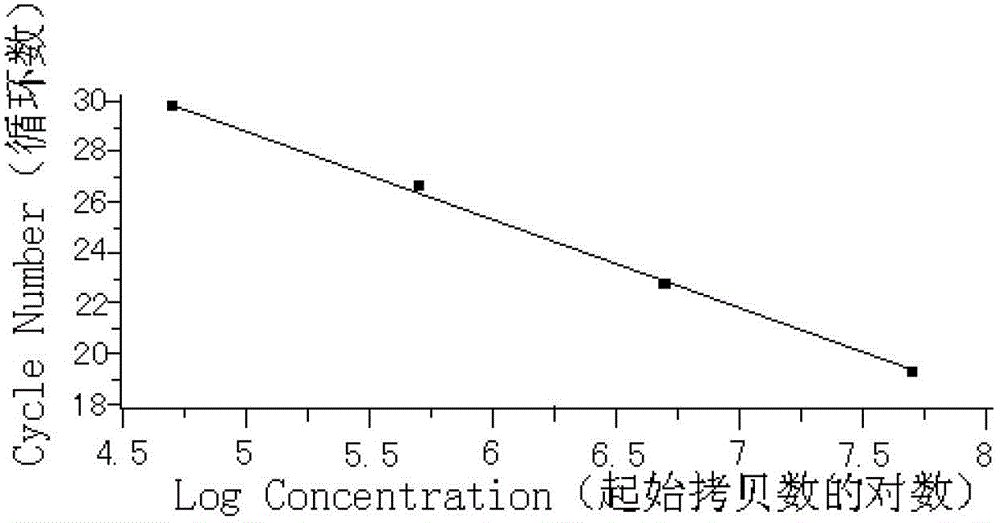
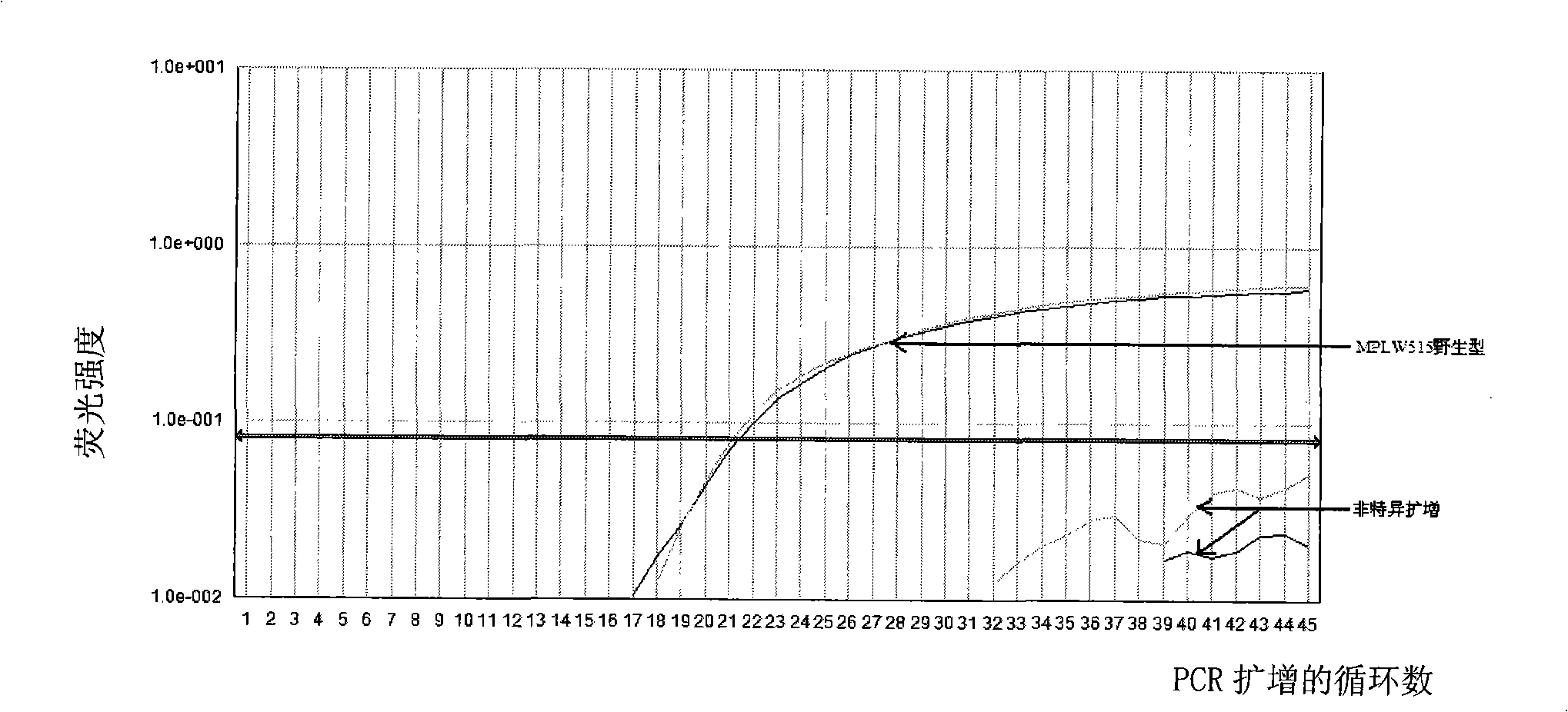
Reagent kit for detecting bone marrow proliferative diseases MPLW515L mutation, special-purpose primer and probe thereof
InactiveCN101403009AFast new wayReliable new wayMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionMpl geneMyeloid proliferation
The invention discloses a kit and a special primer and probe thereof which are used for detecting the MPLW515L mutation of myeloid proliferation diseases. The kit provided by the invention comprises a primer and a TaqMan-MGB probe; wherein, the nucleotide sequence of the primer is shown by SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 in a sequence table; the nucleotide sequence of the TaqMan-MGB probe is shown by SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO:4 in the sequence table. The kit provided by the invention is used for detecting the MPLW515L mutation in clinic and scientific research, which not only provides a fast, reliable and accurate new way for diagnosing MPDs, but also can furthermore provide the exact ratio of the mutation genes of MPLW515L and the genes of wild MPL, thus providing proof for curative effect observation and the dynamic observation of minimal residual diseases.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
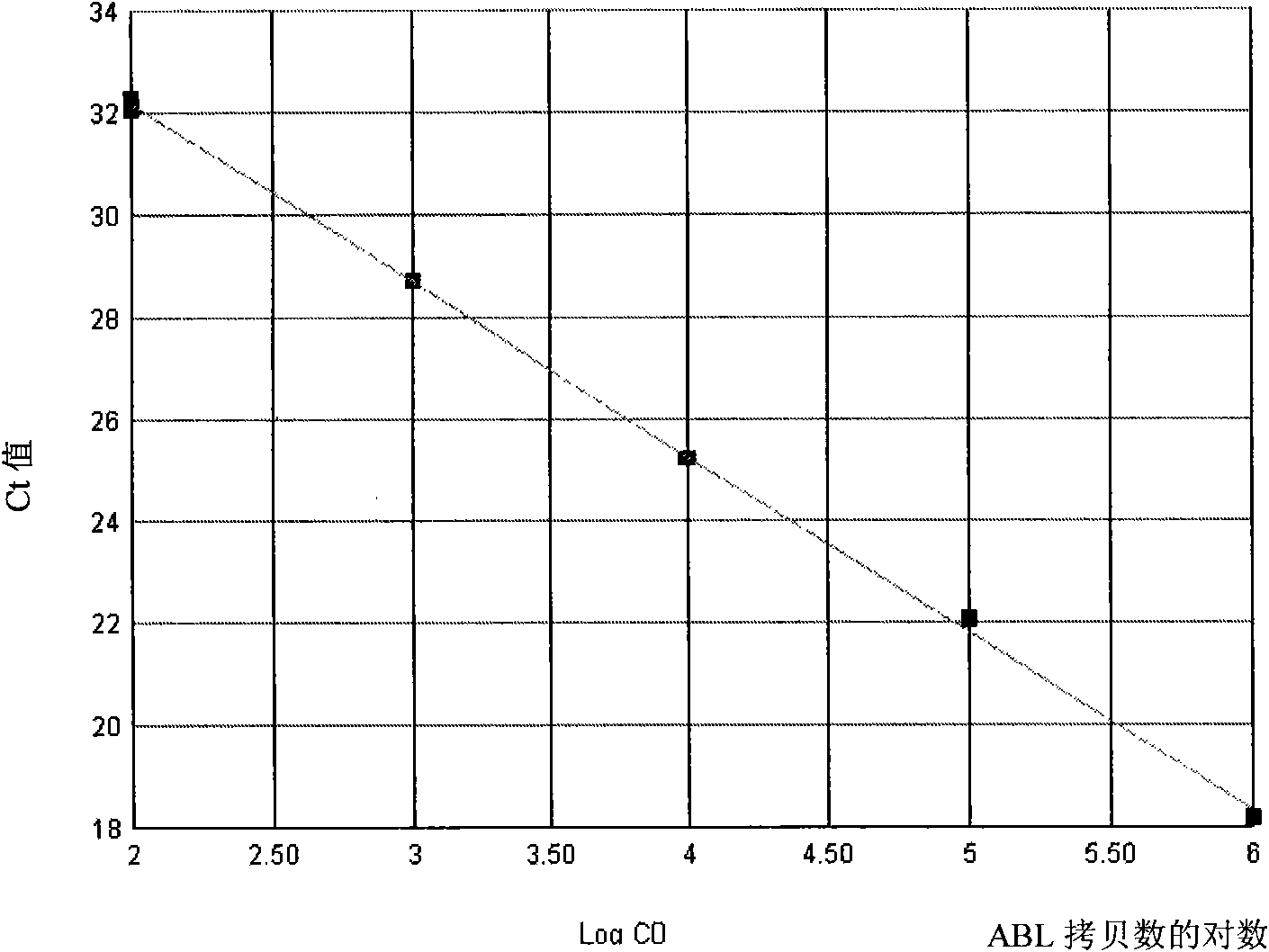
Kit for quantitatively detecting ABL mRNA level
InactiveCN101624623AWide coverageIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular diagnosticsBiology
The invention discloses a kit for quantitatively detecting ABL mRNA level. The kit comprises a standard product for manufacturing a standard curve and an internal reference gene real-time quantitative PCR system. The kit can accurately, rapidly and quantitatively detect the ABL mRNA level. In various leukaemia fusion gene detections, ABL is taken as the internal reference gene, the kit is used for performing quantitation of the internal reference gene to realize accurate, rapid and quantitative detection of various leukaemia fusion gene, further accurately and rapidly performs molecular diagnosis of leukaemia and monitoring of minimal residual diseases during treatment, and provides important molecular basis for confirmed diagnosis of clinic diseases, determination of treatment proposals, curative effect evaluation and prognosis.
Owner:秦亚溱 +2
Kit for detecting expression index of mRNA (messager Ribose Nucleic Acid) of WT1 (Wilms Tumor 1) gene
ActiveCN102912018AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNewly diagnosedDisease monitoring
The invention relates to a kit for detecting an expression index of mRNA (messager Ribose Nucleic Acid) of a WT1 (Wilms Tumor 1) gene, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The kit comprises detection primers, a fluorescent probe, a cDNA (complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) first strand synthesis reagent, a fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) mixed solution, negative reference and positive reference, wherein the detection primers and the fluorescent probe comprise a WT1 gene primer, an internal reference gene ABL primer and a Taqman fluorescent probe. The WT1 gene is related with hematopoietic tumor incidence, is of over-expression in about 80% of patients with newly diagnosed acute myelocytic leukemia and acute lymphocytic leukemia, is recognized as a leukemia marker gene, and can serve as an independent minimal residue disease monitoring and prognosis prompting index. The level of the mRNA of the WT1 gene is detected by adopting a fluorescent quantitative PCR technology with higher sensitivity and specificity, and both the specificity and the sensitivity of a detection result are remarkably improved. The kit provides a brand-new quick, simple and convenient gene diagnosis technology for prognosing the acute myelocytic leukemia and the acute lymphocytic leukemia and confirming chemotherapy regimens.
Owner:童永清 +1
Method for quantifying the level of minimal residual disease in a subject
The present invention belongs to the field of diagnosis of disease. Thus the present invention is focused on a method and kit for quantifying the level of minimal residual disease (MRD) in a subject who has been treated for said disease, which comprises:(a) identifying, amplifying and sequencing a nucleotide sequence in a biological sample obtained from said subject after treatment for said disease, wherein the gDNA of said biological sample has an average weight, k, per cell, and wherein said nucleotide sequence is identified using primers and is amplified using an amount, D, to afford a first list of characters;(b) identifying, amplifying and sequencing a nucleotide sequence in a biological sample obtained from a subject with said disease using the same primers as in step (a) to afford a second list of characters;(c) determining, for each first list of characters obtained in step (a), the degree of similarity, DS, with each second list of characters obtained in step (b);(d) selecting, for each first list of characters obtained in step (a), the DS of highest value, DSHV;(e) adding up the number of first lists of characters obtained in step (a) which have a DSHV that is greater than a threshold value, T, to obtain Lc;(f) adding up the total number of lists of characters, Lt, in the first list of characters; and(g) calculating the level of minimal residual disease (MRD) according to either of the following formulae:MRD=(Lc×k) / (Lt×D)orMRD=Lc×(D / k) / Lt2.
Owner:FUNDACION DE INVESTIGACION HOSPITAL 12 DE OCTUBRE
Method of detecting JAK2V617F mutation and its special primer and TaqMan MGB probe
InactiveCN1932038AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMRD NegativeAgricultural science
The present invention discloses method of detecting JAK2V617F mutation and its special primer and TaqMan-MGB probe. The primer for detecting the genome DNA JAK2V617F mutation of myeloproliferative diseases is the primer pair shown in the SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2 in the sequence list. The primer for detecting cDNA JAK2V617F mutation of myeloproliferative diseases is the primer pair shown in the SEQ ID No. 3 and SEQ ID No. 4 in the sequence list. The TaqMan-MGB probe has the DNA sequence shown in the SEQ ID No. 5 and SEQ ID No. 6 in the sequence list; and the DNA sequence has reporter fluorophore of different colors in the 5' end, and quenching group marked in the 3' end and connected dihydro clyclic indol porphyrin-tripeptide. The present invention provides one fast, reliable and accurate way for the diagnosis of MPDs, and can further provide the determined ratio between JAK2 mutation gene and wild JAK2 gene, so as to provide basis for treating observation.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Establishment method and application of tumor classification and identification model
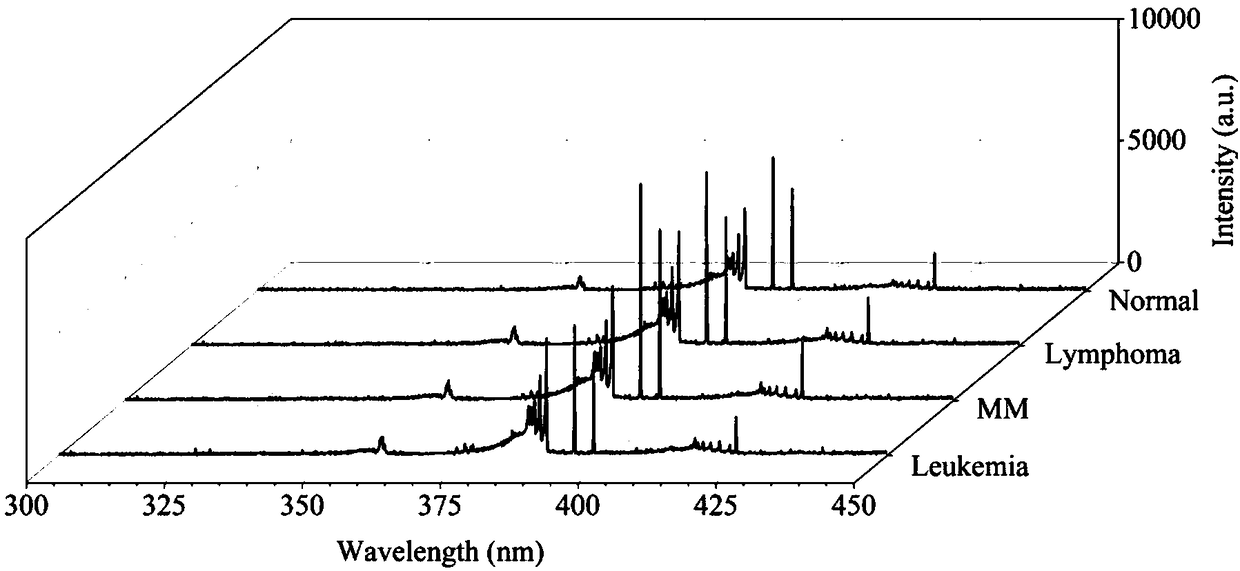
ActiveCN108169184AThe detection process is fastRealize instant inspectionMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseTime-Consuming
The invention discloses an establishment method and application of a tumor classification and identification model, belongs to the field of medical disease diagnosis, aims at the problems that samplepreprocessing is complex and time-consuming due to need of location and collection of tumor focus specimens in current pathological diagnosis, small tumor tissues such as early tumor, small residual diseases and circulating tumor cannot be screened diagnosed in the prior art, and provides the establishment method of the tumor classification and identification model. The method is established basedon a plasma emission spectrum of a biological liquid sample, and is combined with chemometrics and a machine learning classification algorithm. The model established through the method can be integrated into a tumor diagnosis and screening instrument, and a rapid and accurate method for large-scale tumor screening and diagnosis of the early tumor and precancerous lesion stage diseases is provided.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Primer combination and kit for detecting minimal residual diseases of T-cell leukemia by high-throughput sequencing
ActiveCN106957906AAmplified whole sequenceBuild Efficiency and EfficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMRD NegativeGenetics
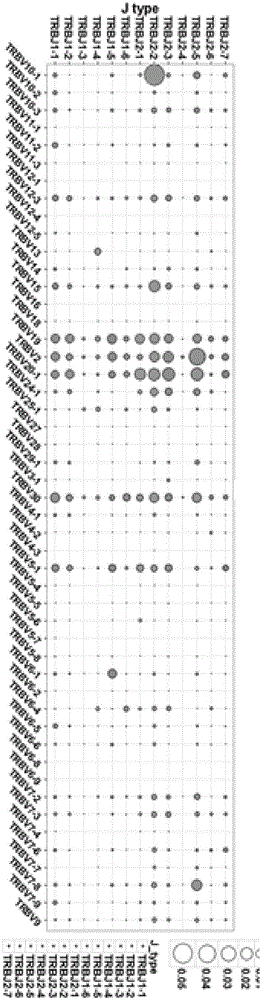
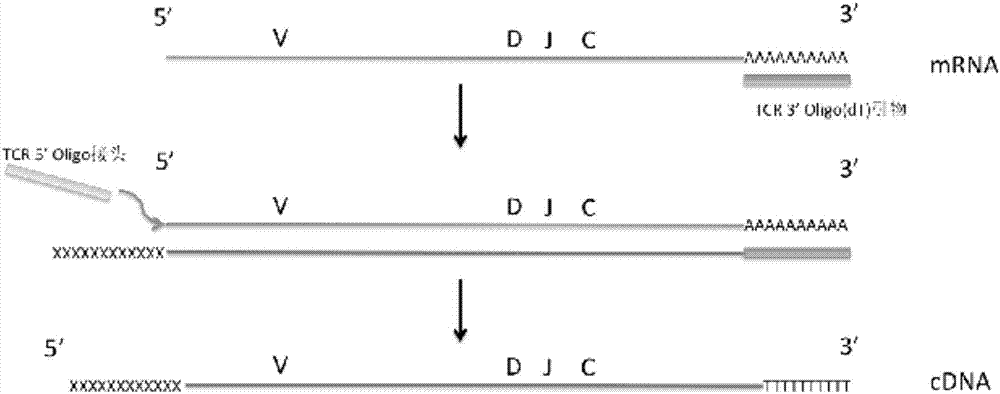
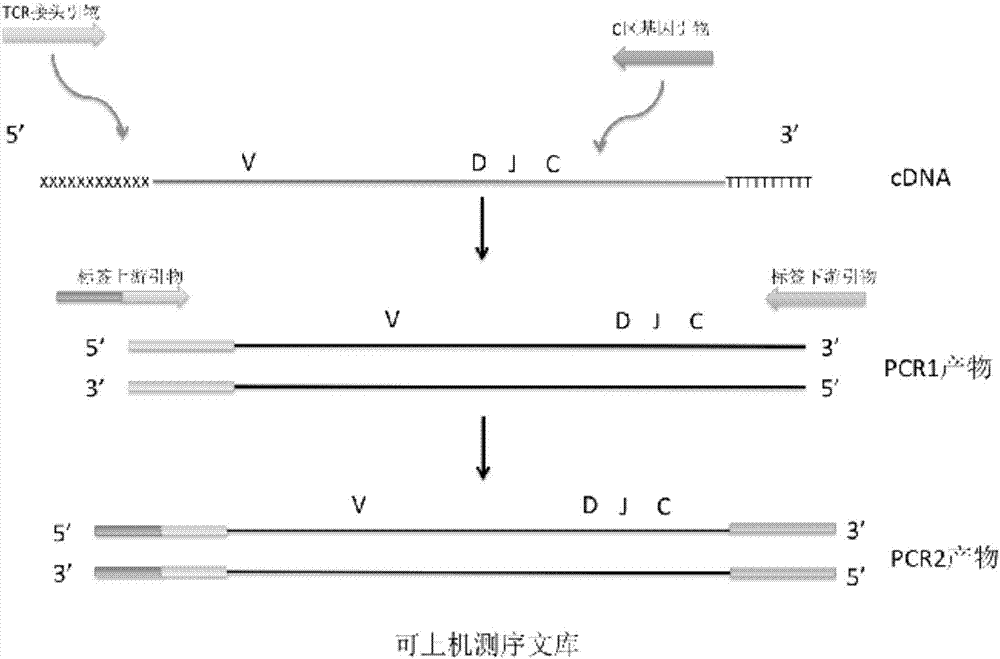
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and in particular relates to a primer combination and kit for detecting minimal residual diseases of T-cell leukemia by high-throughput sequencing. The primer combination is characterized by comprising a TCR (T Cell Receptor) 5'Oligo connector, a TCR 3'Oligo (dT) primer, a TCR C-region primer and upstream and downstream primers of a label; and the kit comprises the primer combination in claim 1 or 2. Full-length information of a TCR gene sequence is obtained from the upstream primer of the connector to a downstream primer of a C region.
Owner:杭州艾沐蒽生物科技有限公司
Diagnostic tests for inflammatory bowel diseases
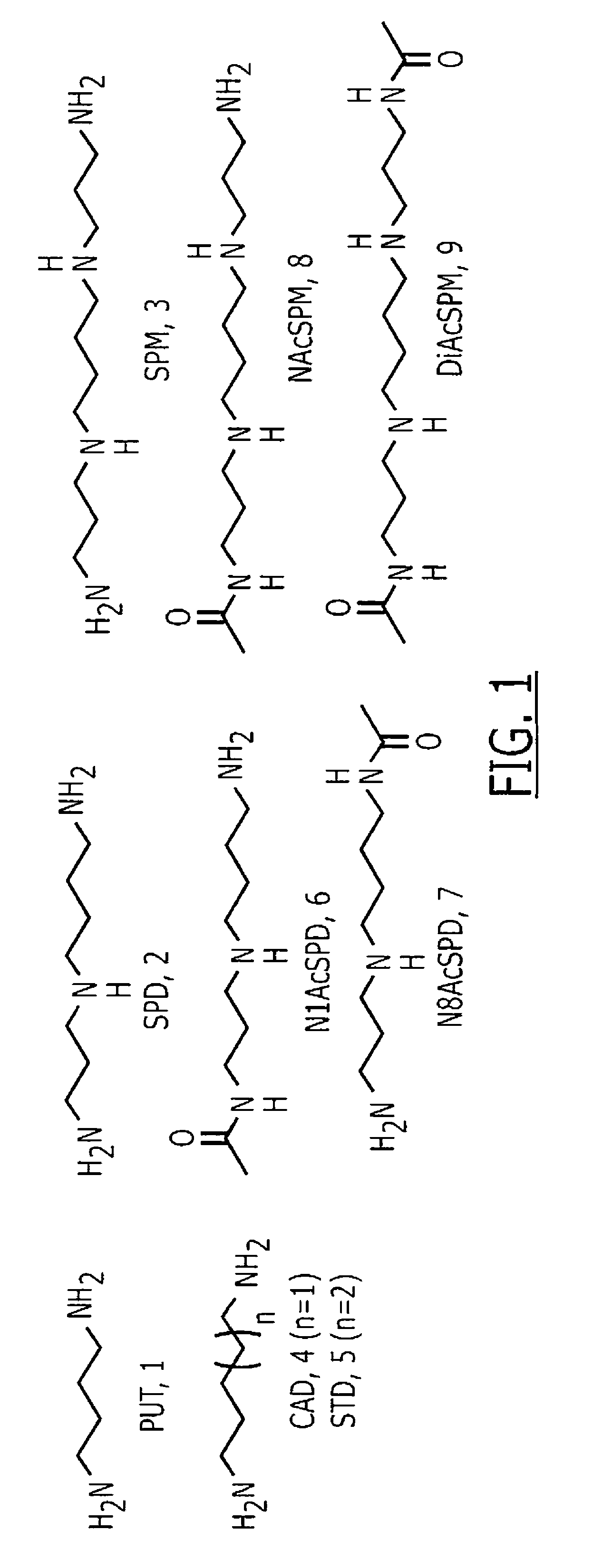
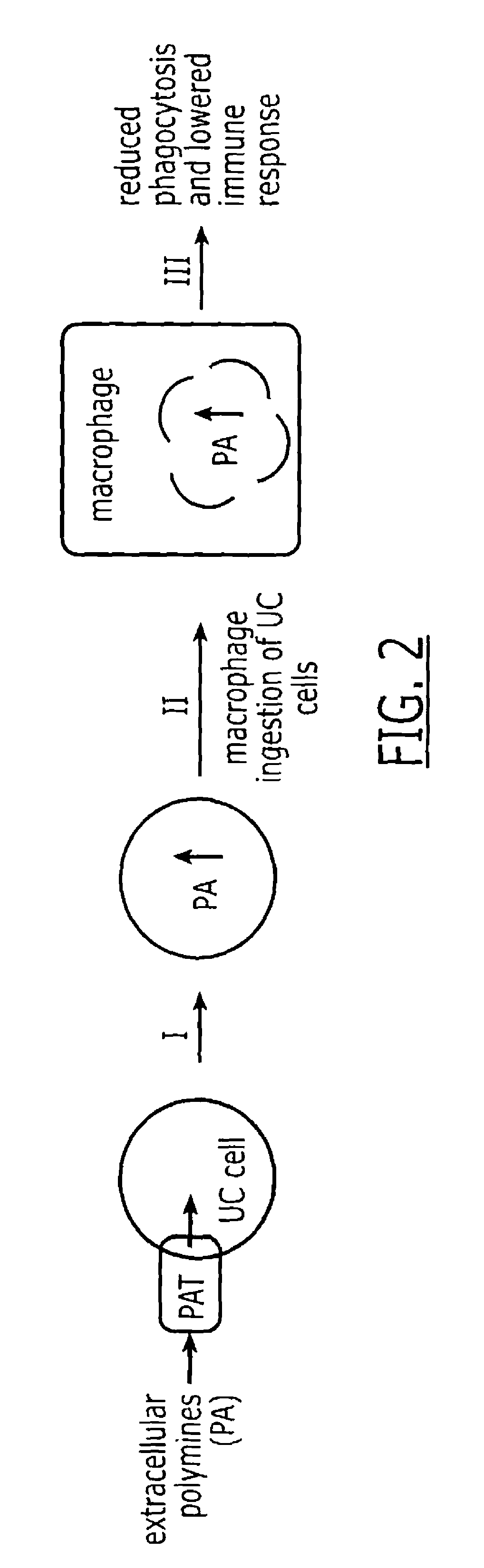
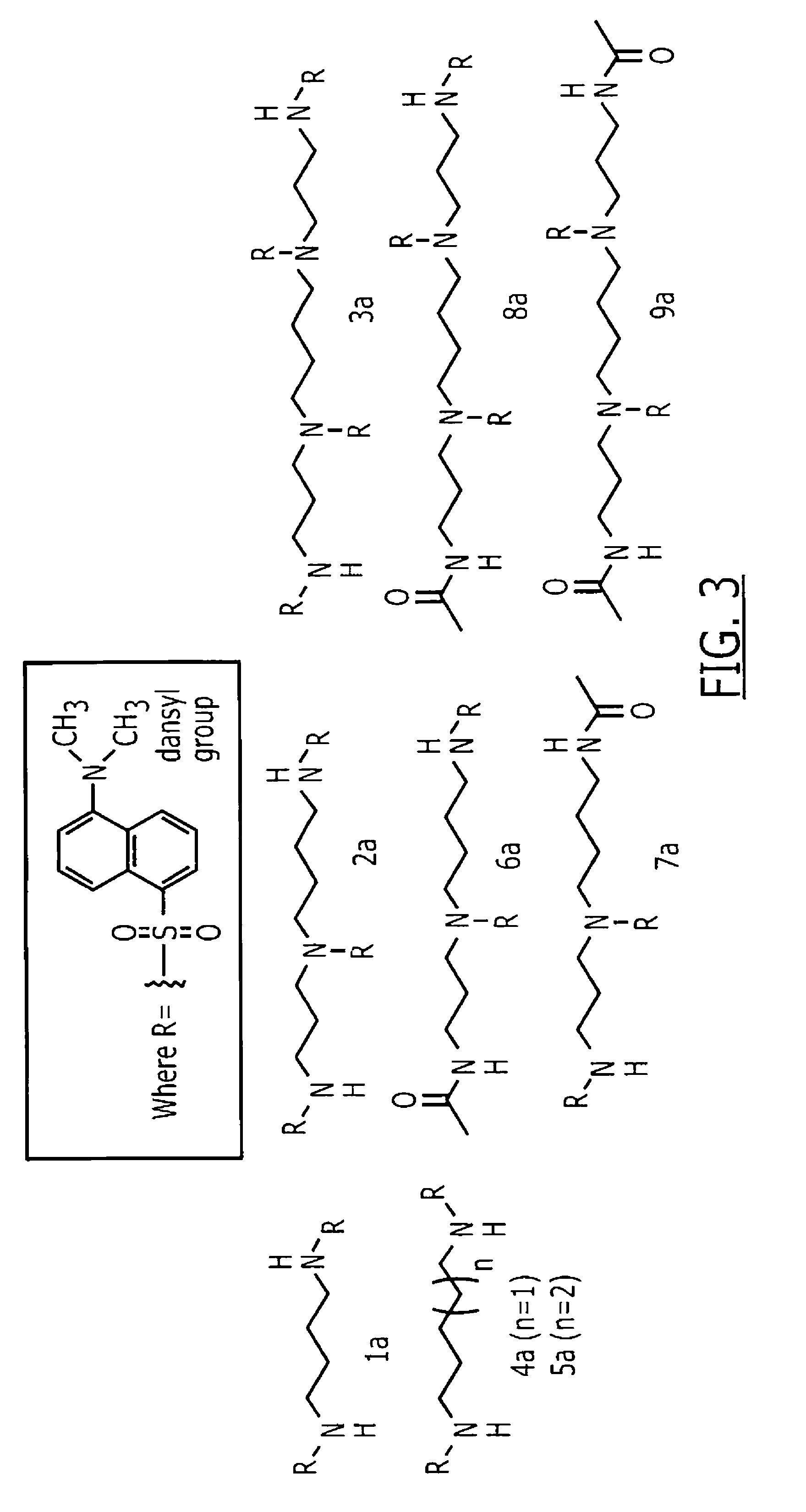
InactiveUS7972807B1Improved diagnostic testingMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisWhite blood cellCadaverine
Disclosed are diagnostic tests helpful in indicating presence of an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in a human patient. In one embodiment, the test comprises obtaining a sample of mucosal tissue from the ileum or sigmoid colon of the patient; evaluating sample quality by testing for cadaverine and continuing the diagnostic test if the sample has no detectable cadaverine; testing the cadaverine negative sample for N-acetylated spermine; and correlating a detectable level of N-acetylated spermine in the sample with presence of IBD in the patient. Another, less invasive, method disclosed includes a diagnostic test comprising isolating mononuclear leukocytes from the patient's blood; testing the isolated mononuclear leukocytes for level of spermidine; and correlating a level of spermidine higher than that in mononuclear leukocytes of normal subjects as indicative of an inflammatory bowel disease in the patient.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
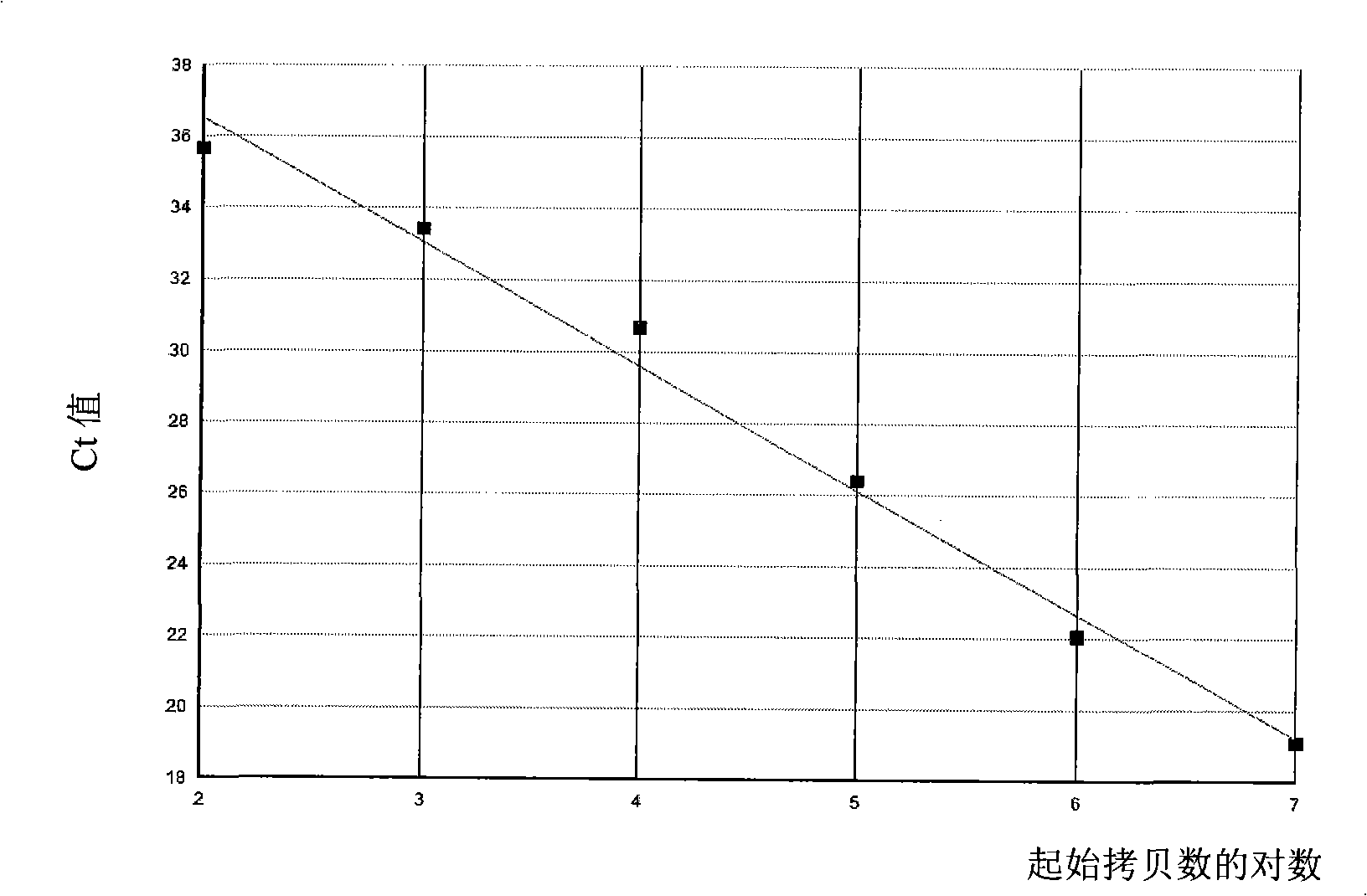
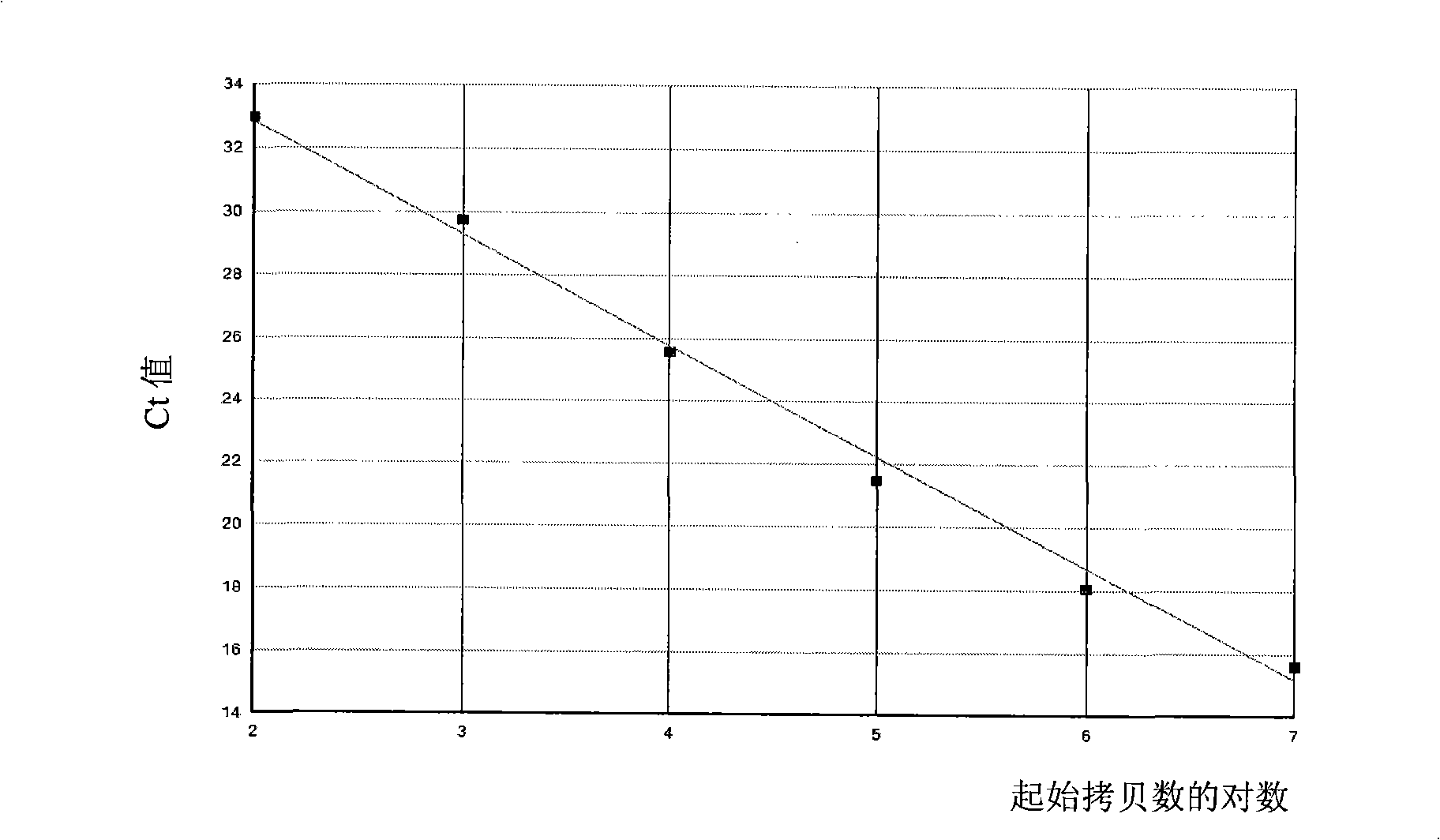
Kit for quantitatively detecting AML1/ETO mRNA level
InactiveCN101624620AIncreased sensitivityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMRD NegativeCurative effect
The invention discloses a kit for quantitatively detecting an AML1 / ETO mRNA level. The kit comprises a standard product which is used for manufacturing a standard curve, an inner reference gene real-time quantitative PCR system and an AML1 / ETO real-time quantitative PCR system. The kit can accurately, quickly and quantitatively detect the AML1 / ETO mRNA level, is used for diagnosing acute myelogenous leukemia and monitoring minimal residual diseases in a treatment process, and provides an important molecular basis for accurate diagnosis of clinical diseases, determination of a treatment proposal, curative effect evaluation and prognosis.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Reagent kit for detecting bone marrow proliferative diseases MPLW515K mutation, special-purpose primer and probe thereof
InactiveCN101403010AFast new wayReliable new wayMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMRD NegativeMpl gene
The invention discloses a kit and a special primer and probe thereof which are used for detecting the MPLW515K mutation of myeloid proliferation diseases. The kit provided by the invention comprises a primer and a TaqMan-MGB probe; wherein, the nucleotide sequence of the primer is shown by SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 in a sequence table; the nucleotide sequence of the TaqMan-MGB probe is shown by SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO:4 in the sequence table. The kit provided by the invention can be used for detecting the MPLW515K mutation in clinic and scientific research, which not only provides a fast, reliable and accurate new way for diagnosing MPDs, but also can furthermore provide the exact ratio of the mutation genes of MPLW515K and the genes of wild MPL, thus providing proof for curative effect observation and the dynamic observation of minimal residual diseases.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
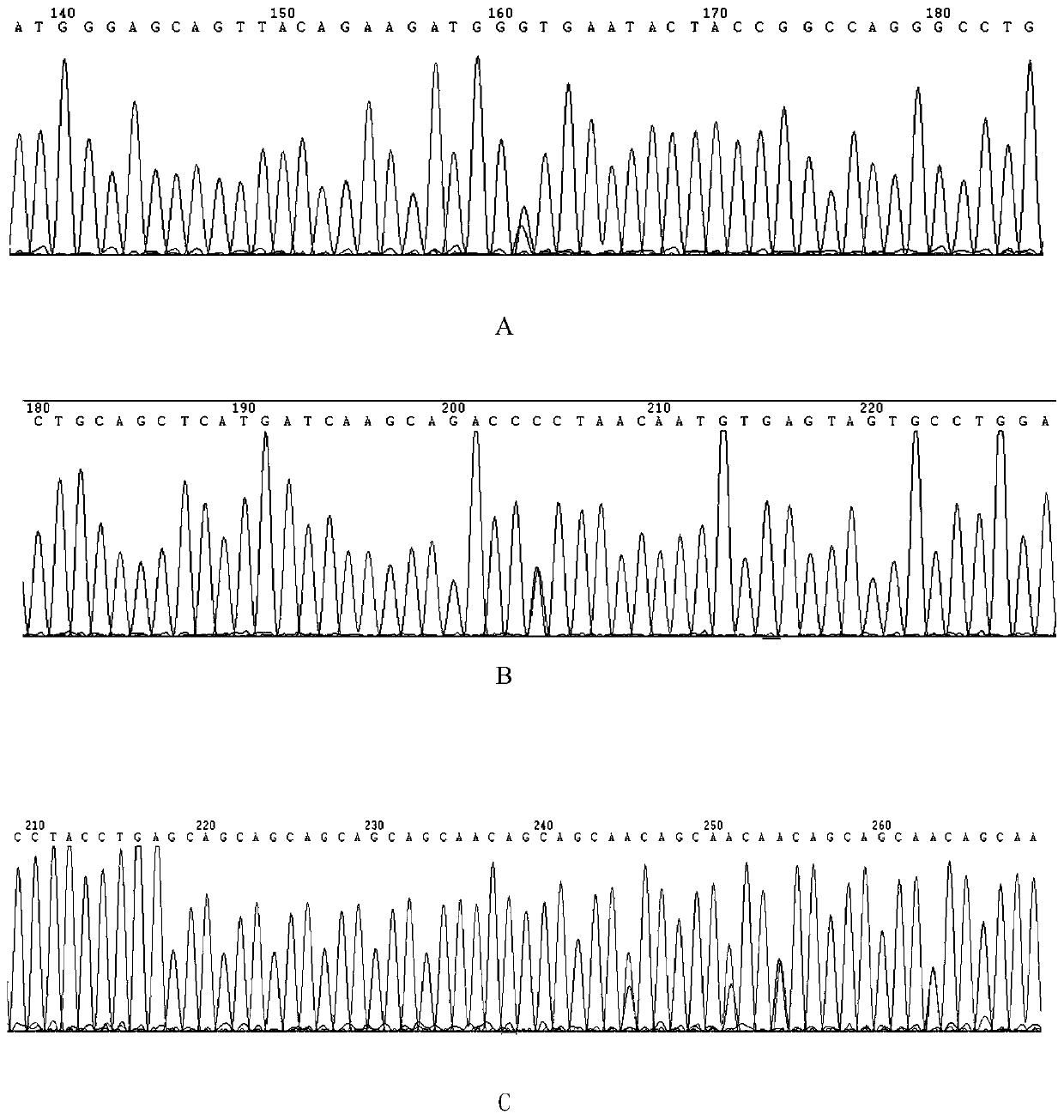
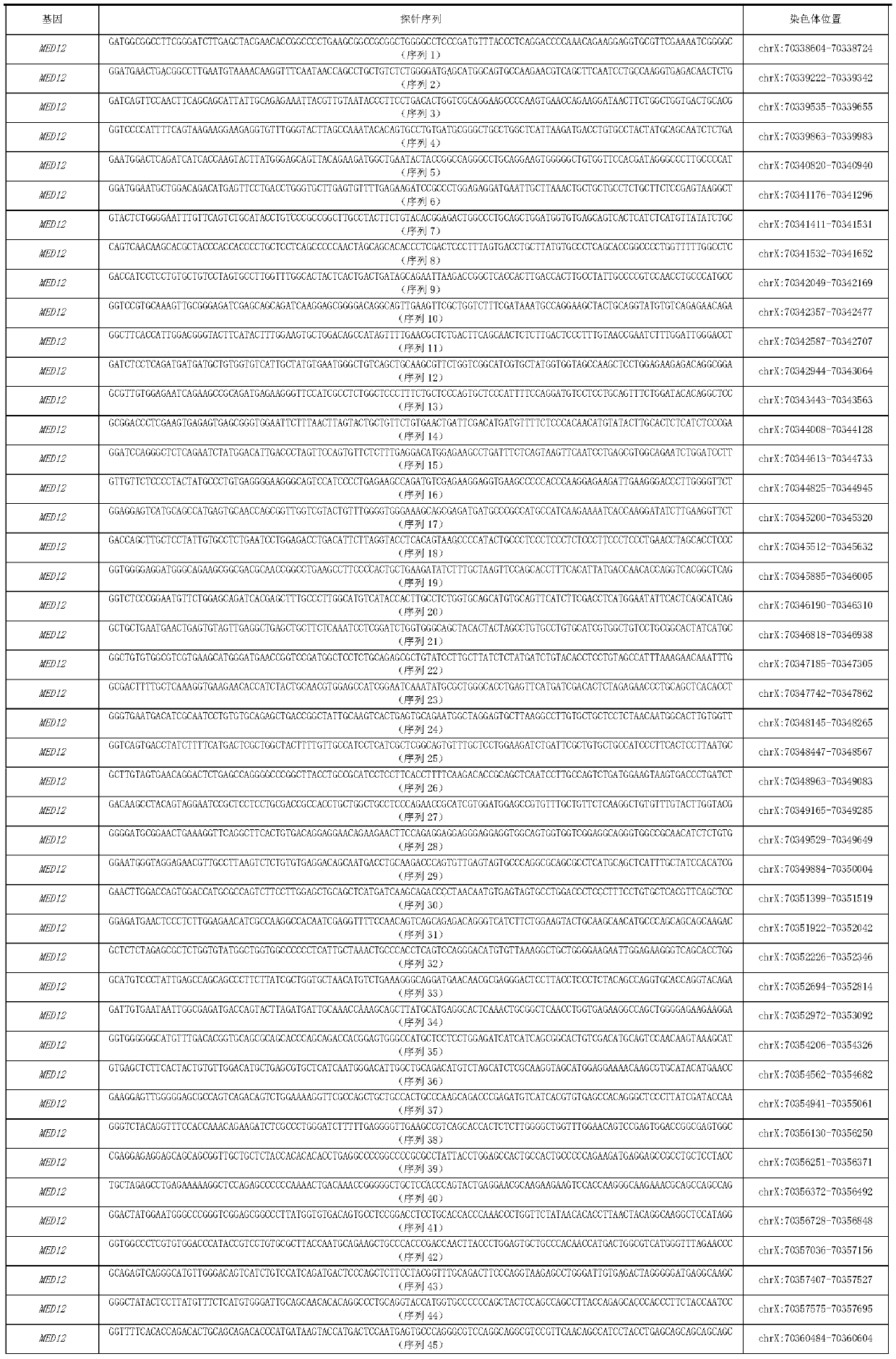
MED12 gene mutation detecting kit and application thereof
ActiveCN110229897AThe detection method is simpleSensitive detection methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMRD NegativeHematological Tumor
The present invention discloses a MED12 gene mutation detecting kit and an application thereof. The kit comprises probe sets for detecting MED12 gene mutations and the probe sets consist of a probe 1to a probe 48. The kit can be used for detecting MED12 somatic mutations and germline mutations at a tumor genome level, can also be used for assistant diagnosis and minimal residual disease monitoring and prognosis evaluation, etc. of patients with hematological tumors, especially patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Besides, the kit is simple, sensitive and accurate in detection method and plays an important role in the field of medical detection
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
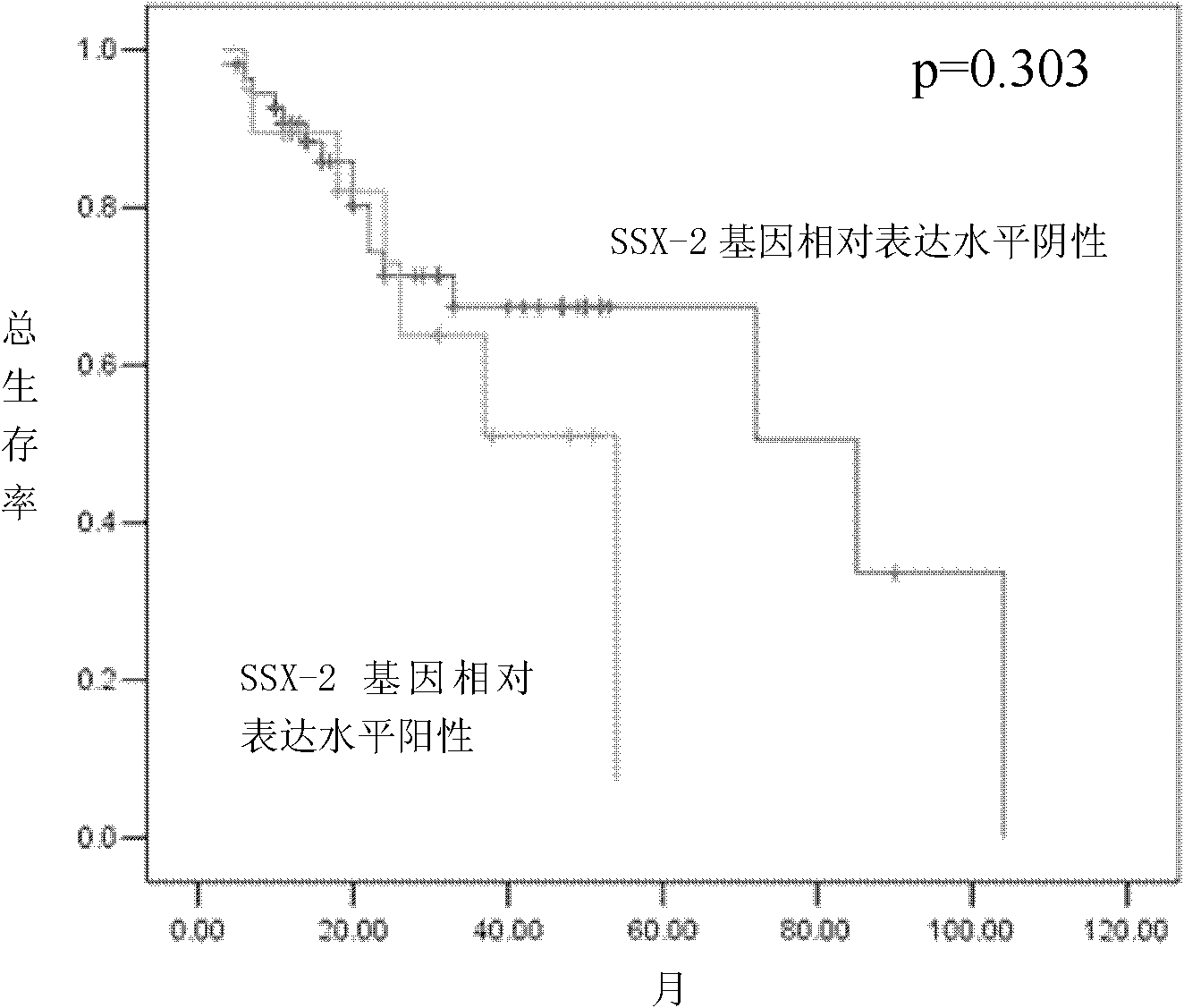
Quantitative detection kit for SSX-2 gene-based assisted diagnosis of multiple myeloma patients
InactiveCN102251035AUnderstanding Pathological MechanismsFast new wayMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesMRD Negative
The invention discloses a quantitative detection kit for SSX-2 gene-based assisted diagnosis of multiple myeloma patients, which comprises a specific primer pair A and a probe A, wherein the specific primer pair A is a primer pair composed of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) disclosed as Sequence 1 and DNA disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table; and the nucleotide sequence of the probe A is disclosed as Sequence 3 in the sequence table. The kit disclosed by the invention not only can be used for qualitative diagnosis of multiple myeloma, but also can be used for detecting the expression level of the SSX-2 gene of the patient through the reference gene. The invention provides a quick, reliable and accurate new way for diagnosis of multiple myeloma, and provides references for observing curative effects and dynamically observing minimal residual disease. The invention can perform vital functions in the field of medical detection.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Nucleophosmin protein (npm) mutants, corresponding gene sequences and uses thereof
InactiveCN101160320AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMRD NegativeOncology
Owner:B·法利尼 +1
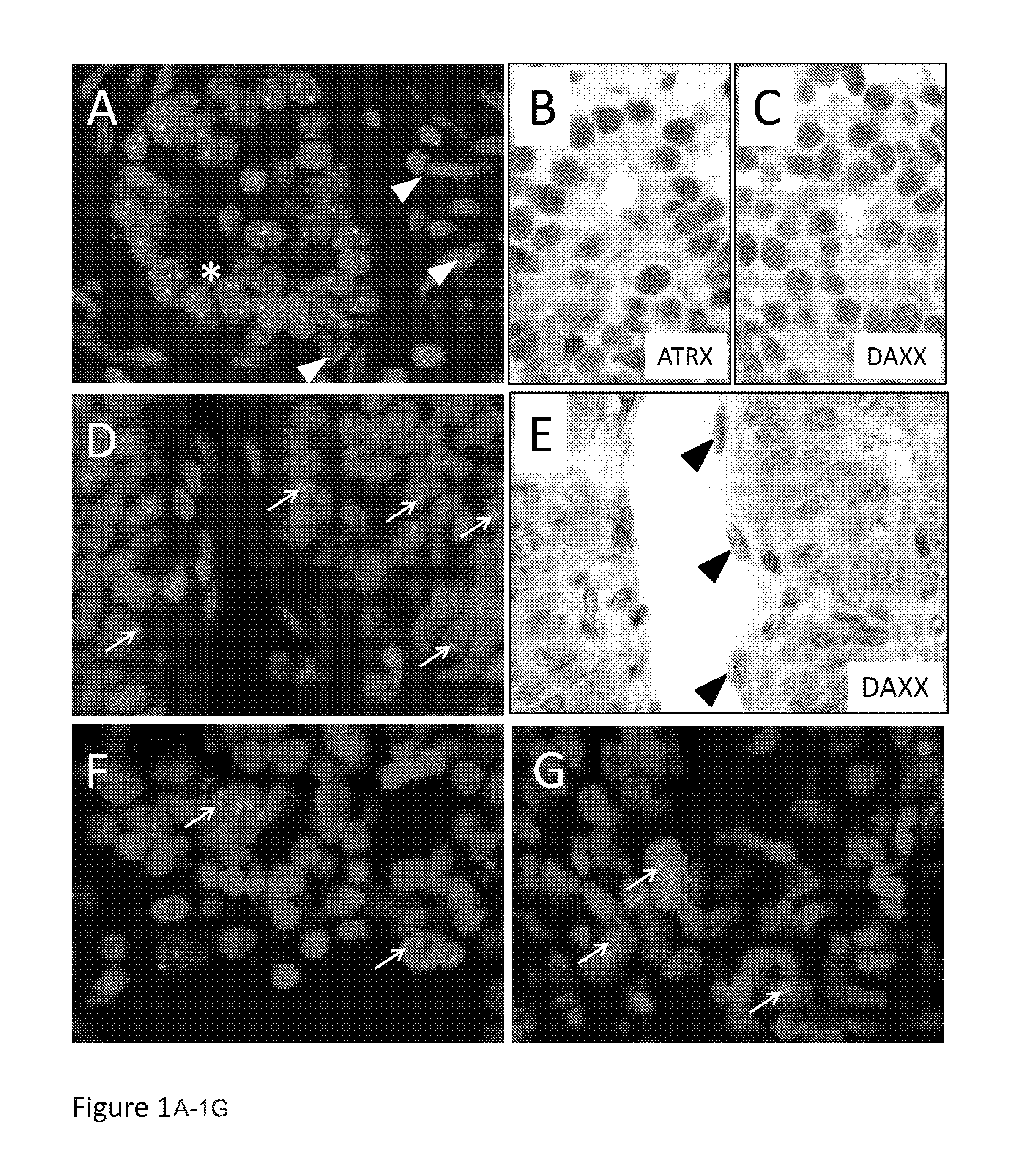
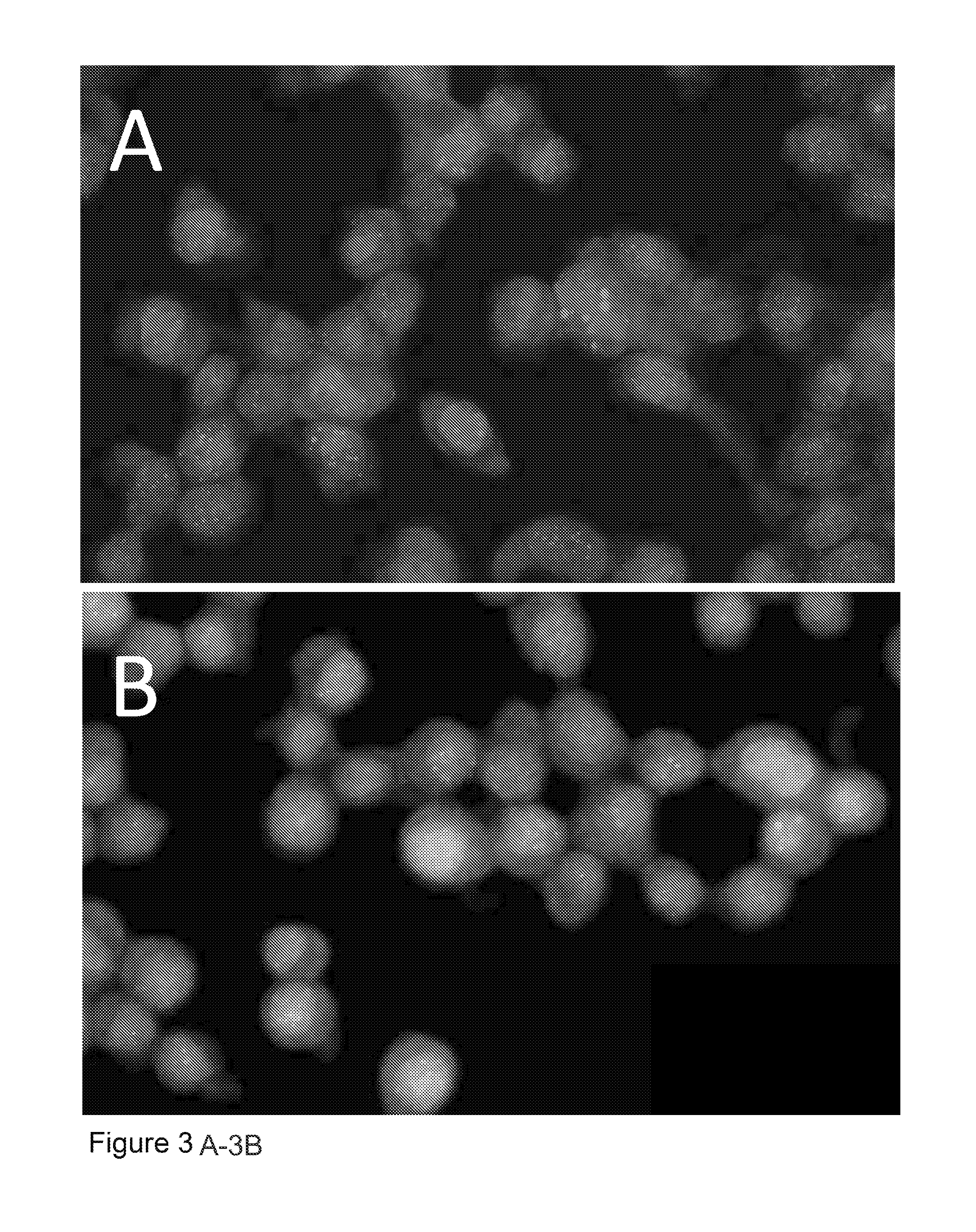
Somatic mutations in atrx in brain cancer
We determined the sequence of ATRX and DAXX in 447 cancers from various sites. We found mutations most commonly in pediatric glioblastoma multiformae (GBM) (11.1%), adult GBM (6.5%), oligodendrogliomas (7.7%) and medulloblastomas (1.5%); and showed that Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres (ALT), a telomerase-independent telomere maintenance mechanism found in cancers that have not activated telomerase, perfectly correlated with somatic mutations of either gene. In contrast, neuroblastomas, and adenocarcinomas of the ovary, breast, and pancreas were negative for mutations in ATRX and DAXX. Alterations in ATRX or DAXX define a specific molecular pathway that is closely associated with an alternative telomere maintenance function in human cancers.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com