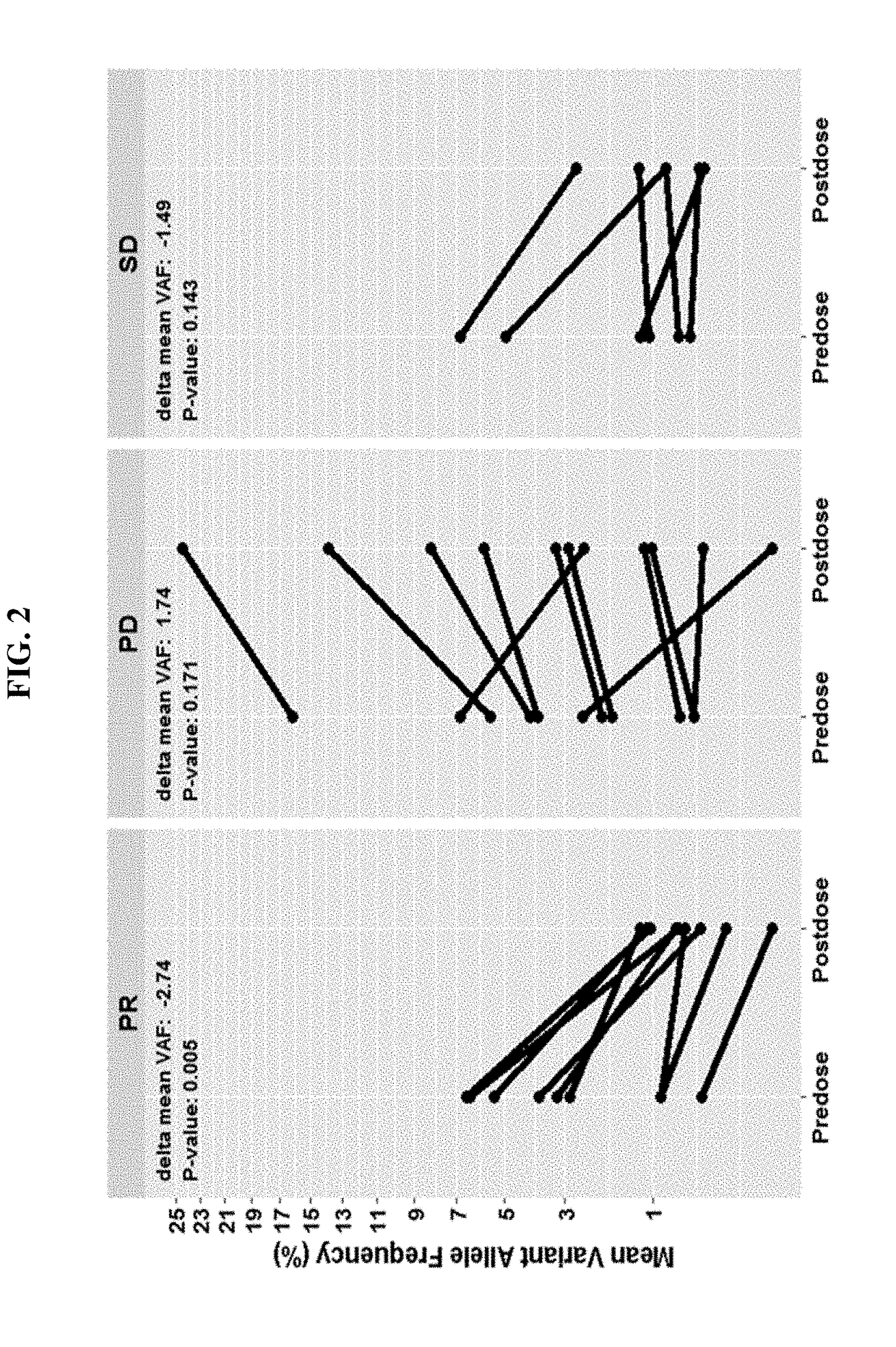
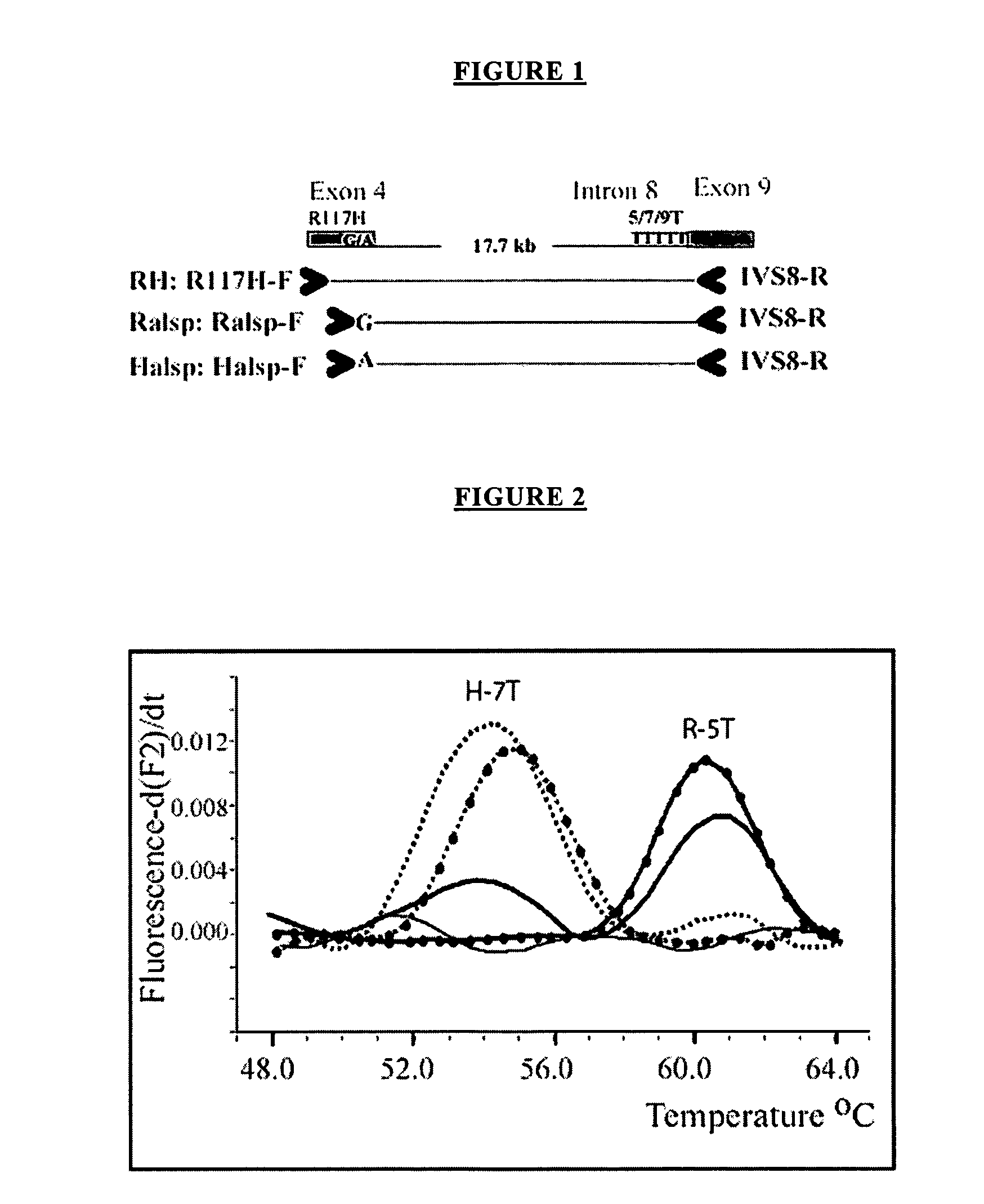
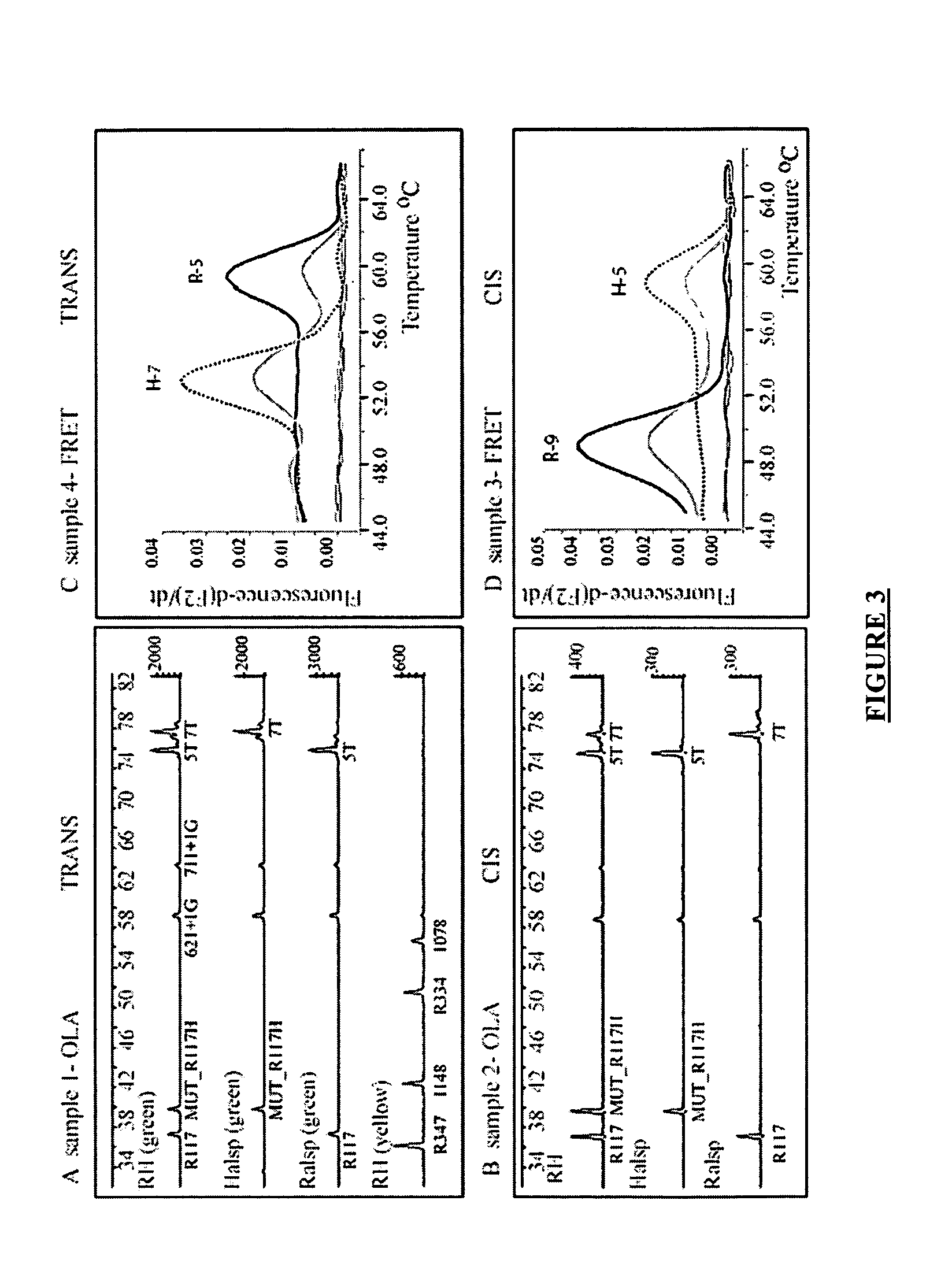
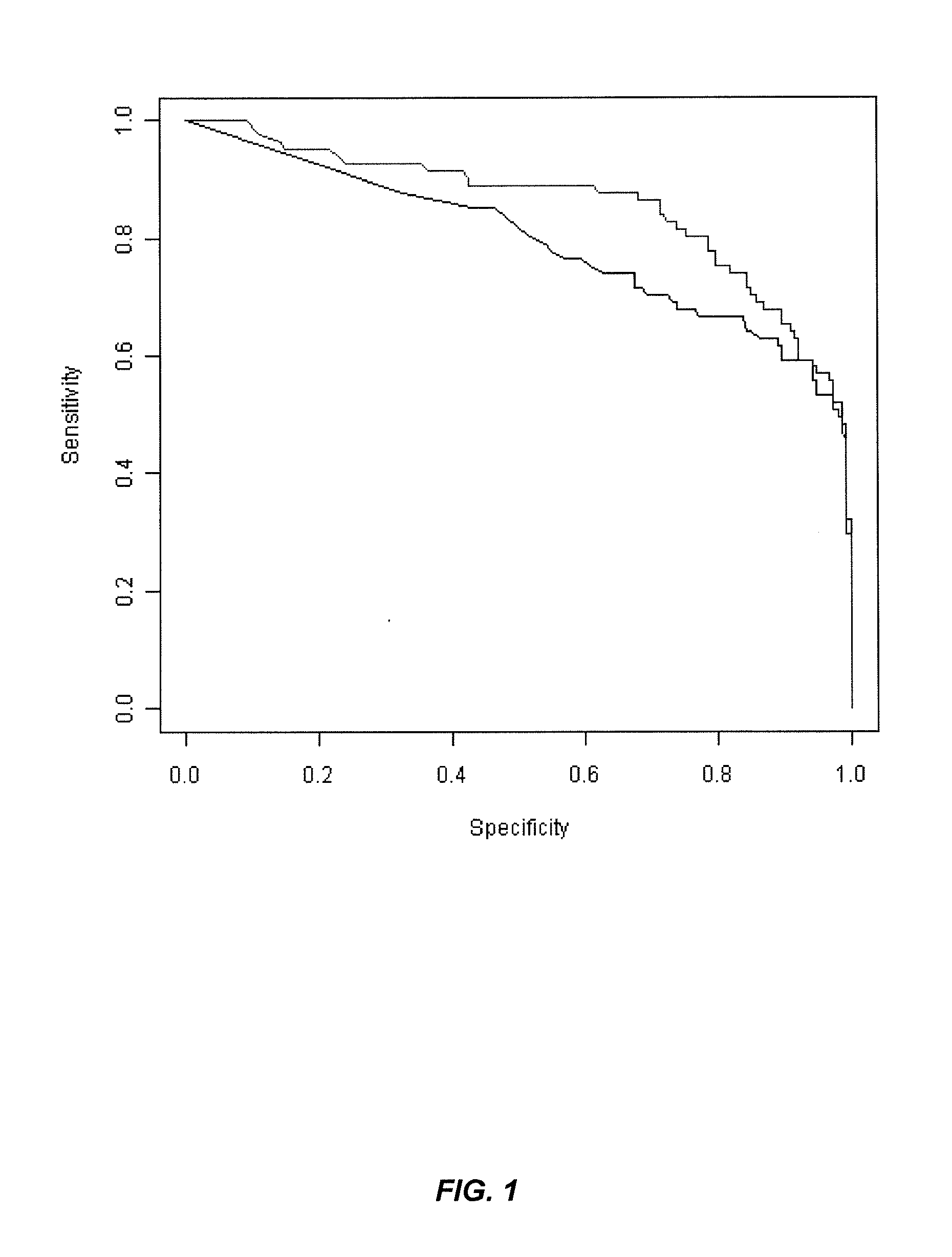
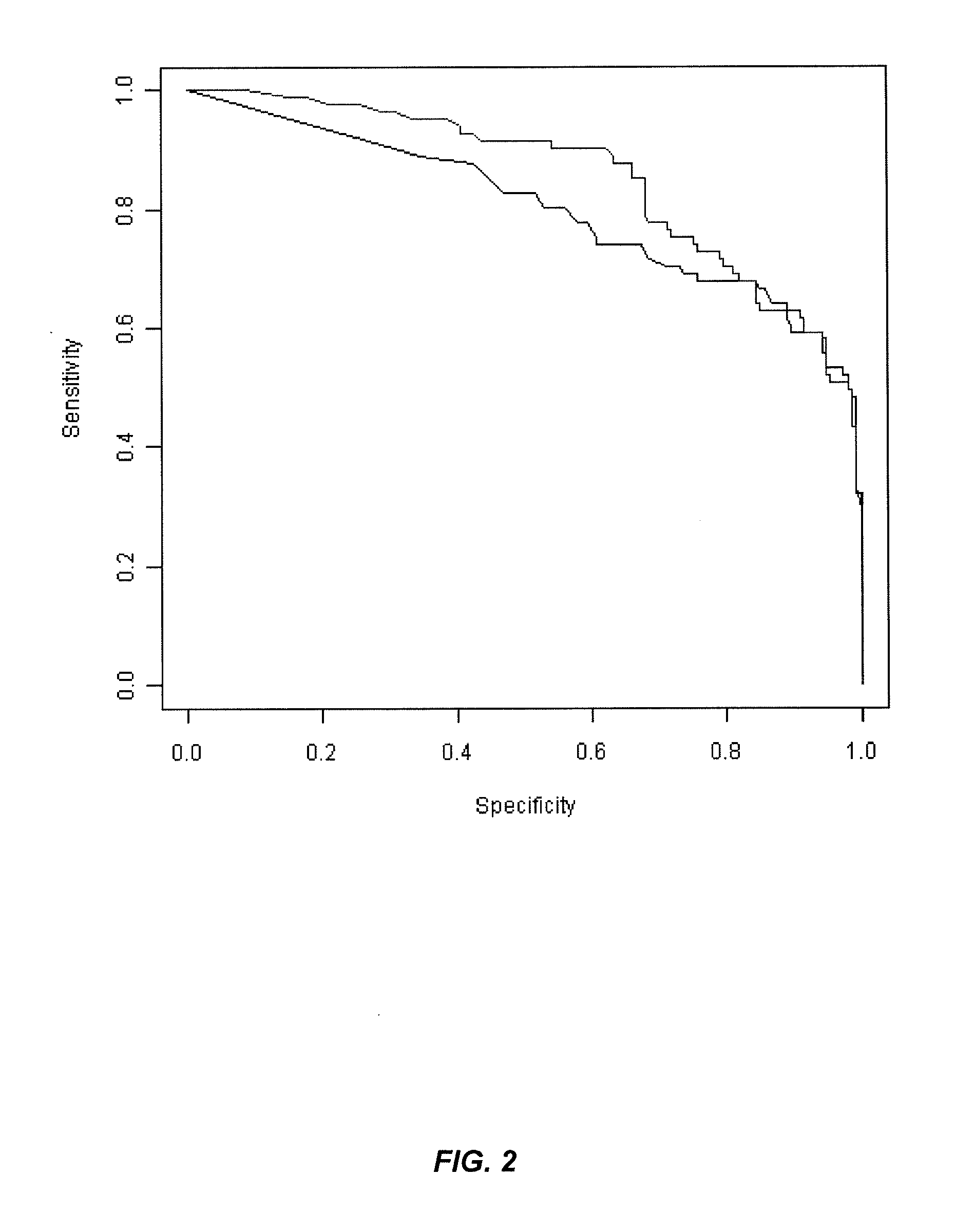
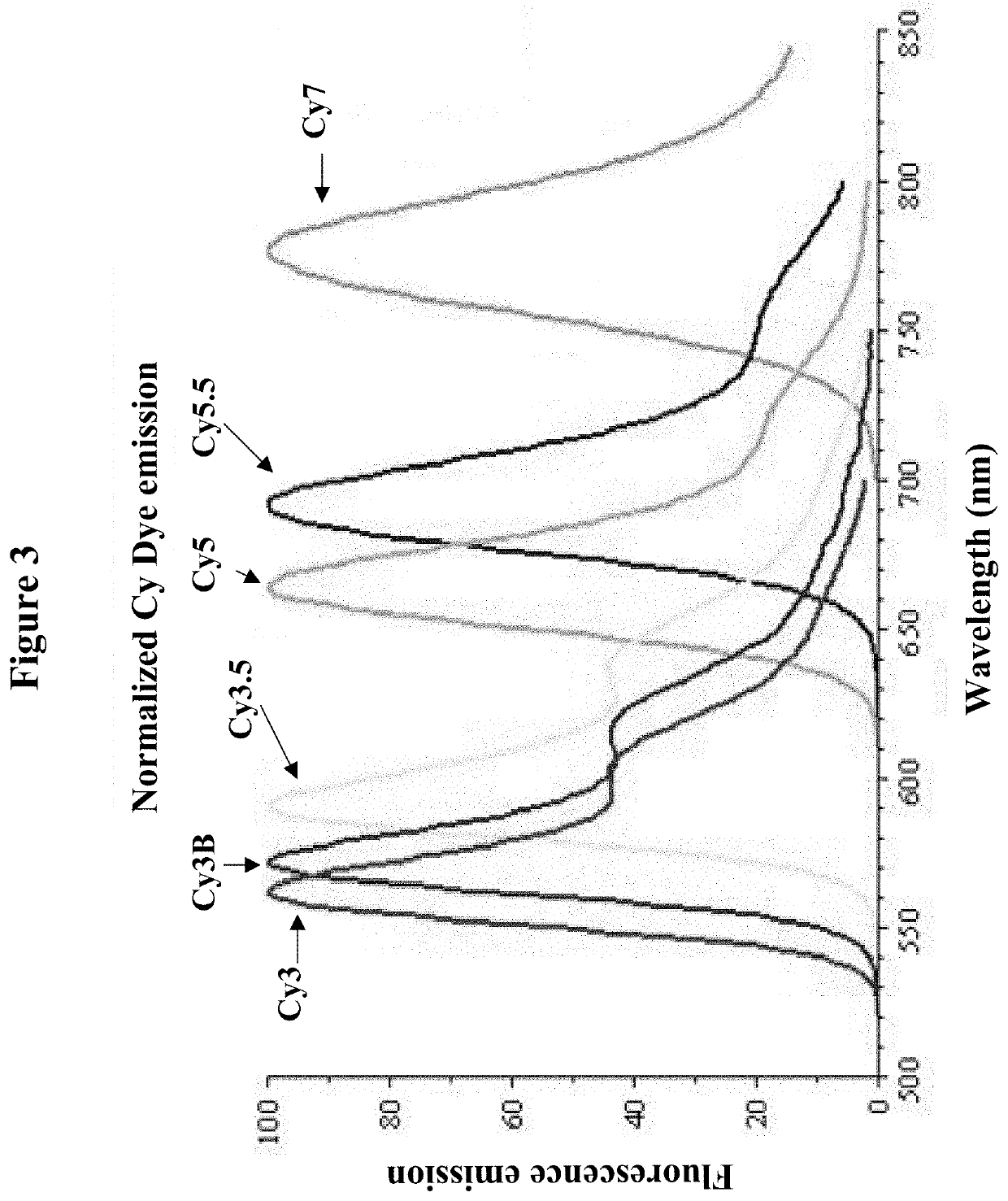
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Variant allele" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An allele (short for allelomorph) is a variant of a gene were the DNA sequence differs between two or more variants. Allelic variation describes the presence or number of different allele forms at a particular locus (locus or loci = place) on a chromosome (allelic variation is sometimes used more loosely to describe the overall diversity present).
Probe-based analysis of heterozygous mutations using two-color labelling
InactiveUS6013449ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementVariant alleleHeterozygous mutation
The invention provides methods of analyzing a nucleic acid in a target sample for variant alleles. In such methods, a first-labelled control sample and a second-labelled target sample are hybridized to at least one set of probes. The control sample comprises a homozygous reference allele. The target sample comprises the homozygous reference allele, or variant alleles differing from the reference allele at a locus, or one variant allele differing from the reference allele at the locus and one reference allele. The probes in the probe set span the locus and are complementary to the reference allele. After hybridization the intensity of first and second label bound to each probe in the set is measured. This information is then used to indicate the presence of one variant allele and one reference allele, or the presence of two variant alleles in the target sample.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES UNITED STATES OF AMERICA REPRESENTED BY THE +1
Probe-based analysis of heterozygous mutations using two-color labelling
InactiveUS6342355B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVariant alleleGenomic clone
The invention provides methods of analyzing a nucleic acid in a target sample for variant alleles. In such methods, a first-labelled control sample and a second-labelled target sample are hybridized to at least one set of probes. The control sample comprises a homozygous reference allele. The target sample comprises the homozygous reference allele, or variant alleles differing from the reference allele at a locus, or one variant allele differing from the reference allele at the locus and one reference allele. The probes in the probe set span the locus and are complementary to the reference allele. After hybridization the intensity of first and second label bound to each probe in the set is measured. This information is then used to indicate the presence of one variant allele and one reference allele, or the presence of two variant alleles in the target sample.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
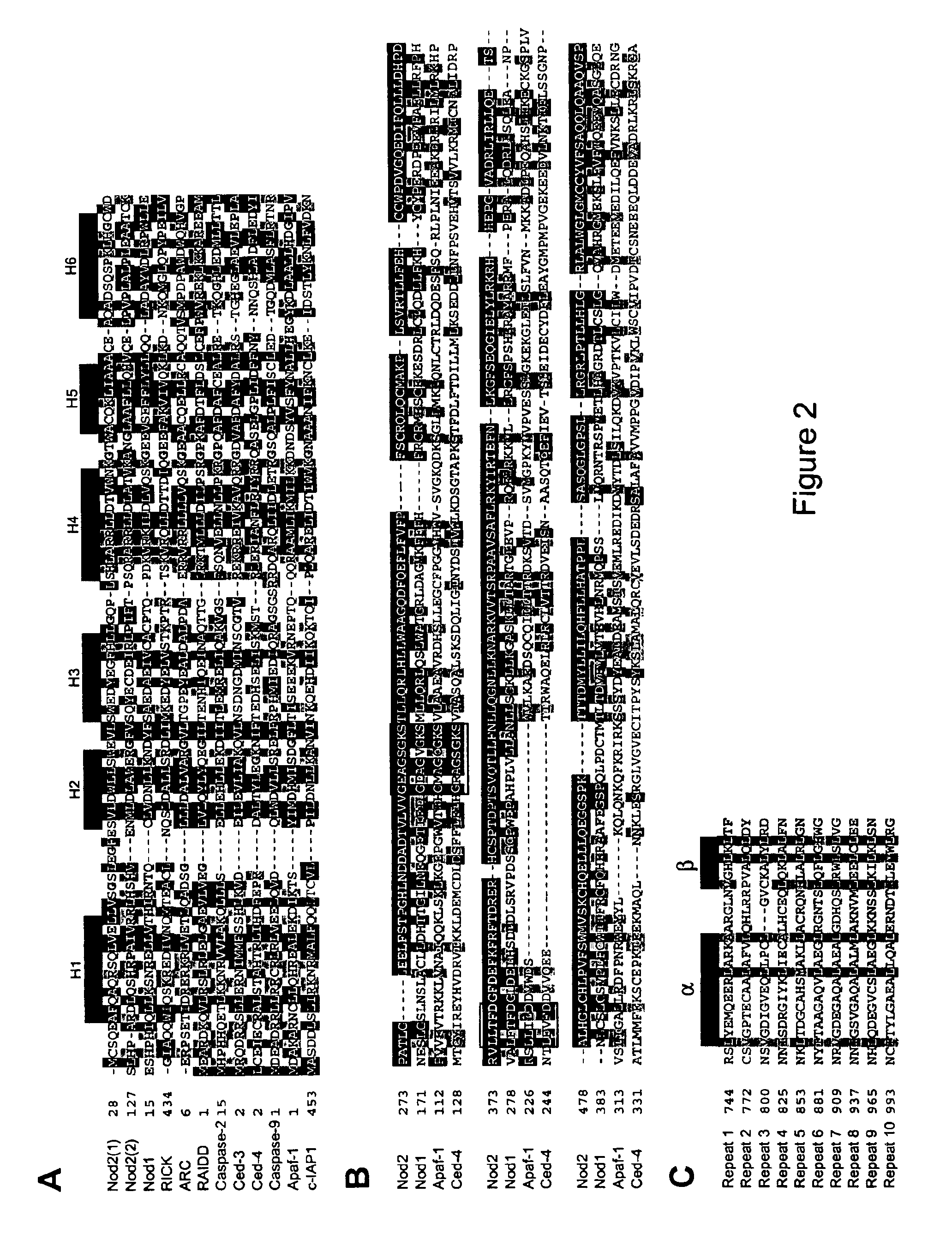
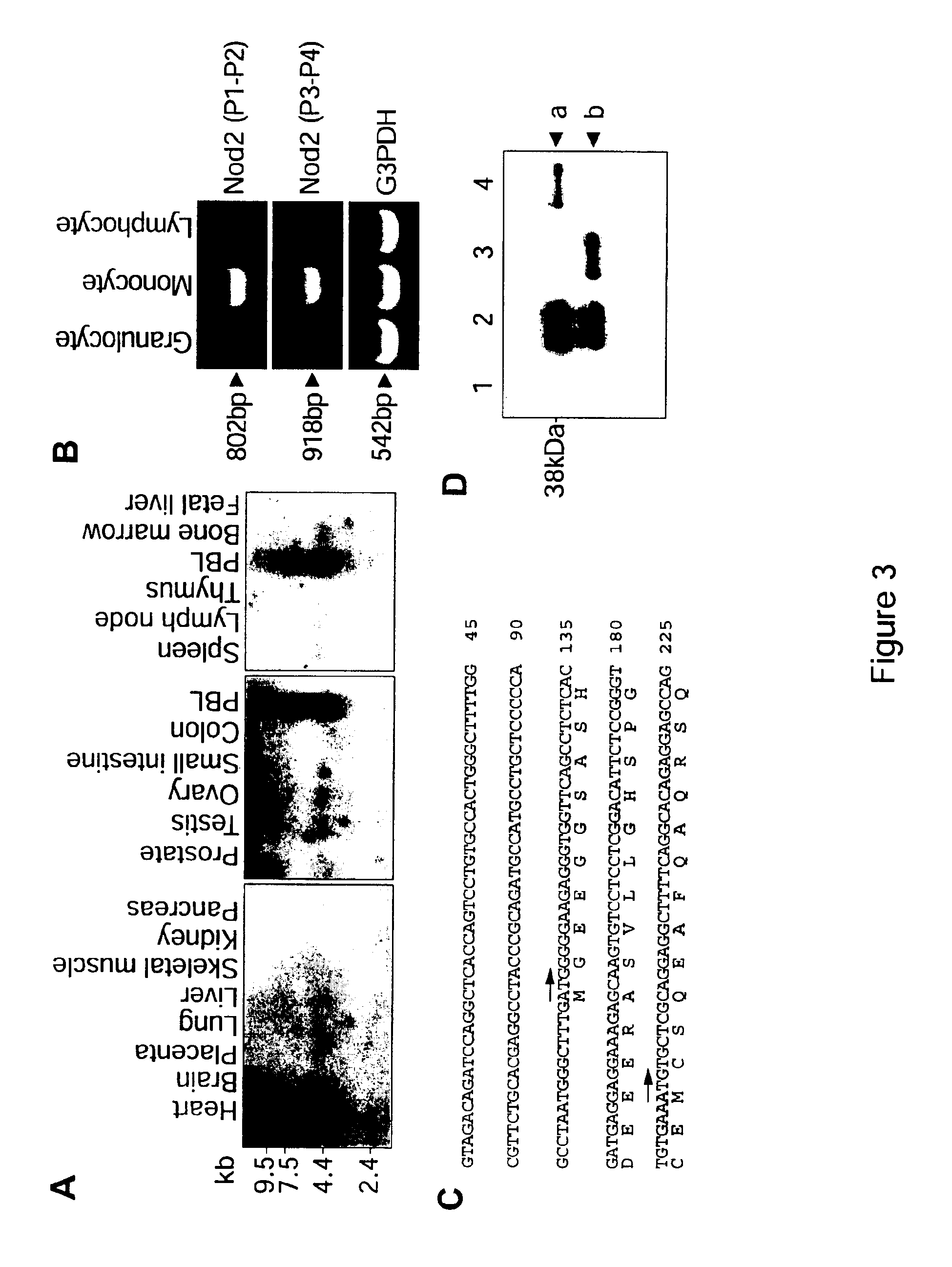
Nod2 nucleic acids and proteins
InactiveUS6858391B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIntracellular signallingNucleotide
The present invention relates to intracellular signalling molecules, in particular the Nod2 protein and nucleic acids encoding the Nod2 protein. The present invention provides isolated nucleotide sequence encoding Nod2, isolated Nod2 peptides, antibodies that specifically bind Nod2, methods for the detection of Nod2, and methods for screening compounds for the ability to alter Nod2 associated signal transduction. The present invention also provides Nod2 variant alleles. The present invention further provides methods of identifying individuals at increased risk of developing Crohn's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Method for long range allele-specific PCR
InactiveUS20070184457A1Enhanced hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LA-DNA
The present invention is directed to a method and kit for determining the molecular haplotype of a gene in a diploid DNA sample. The method discriminates between two haplotypes on the basis of a difference of one or more nucleotides using allele-specific PCR amplification in combination with long range PCR, using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, using annealing temperature conditions sufficiently greater than the predicted annealing temperature (Tm) to effect selective hybridization and extension of an allele-specific extension primer to the target allele relative to the variant allele. The present invention is particularly useful, for example, to determine the haplotype of a gene having multi-allelic genetic loci separated by a distance in which accurate PCR amplification of a single fragment containing the multiple genetic loci cannot be performed without using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, generally about 5 kilobases or more.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Resequencing methods for identification of sequence variants
InactiveUS20090233809A1Improve accuracyHelp studyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTarget captureEnrichment methods
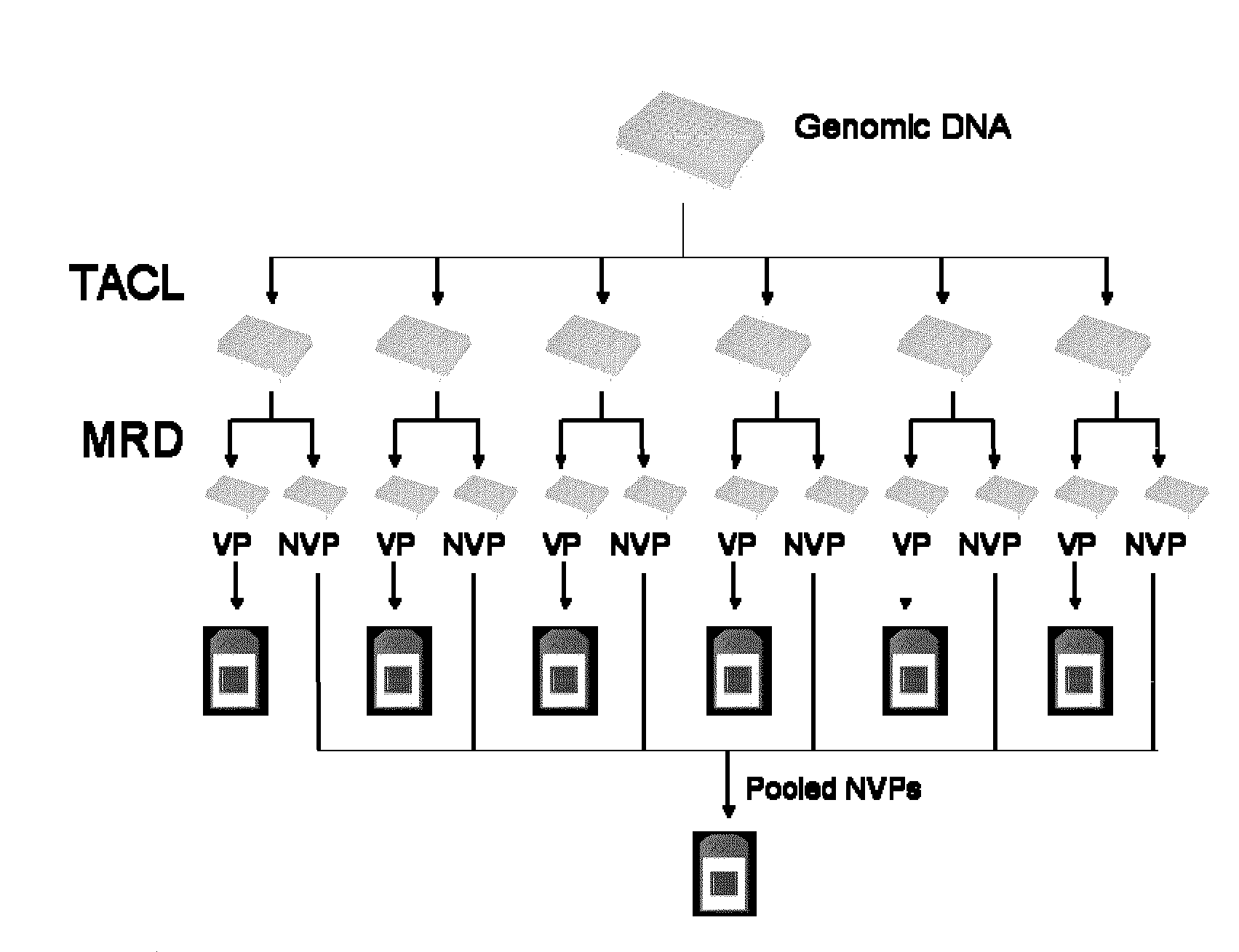
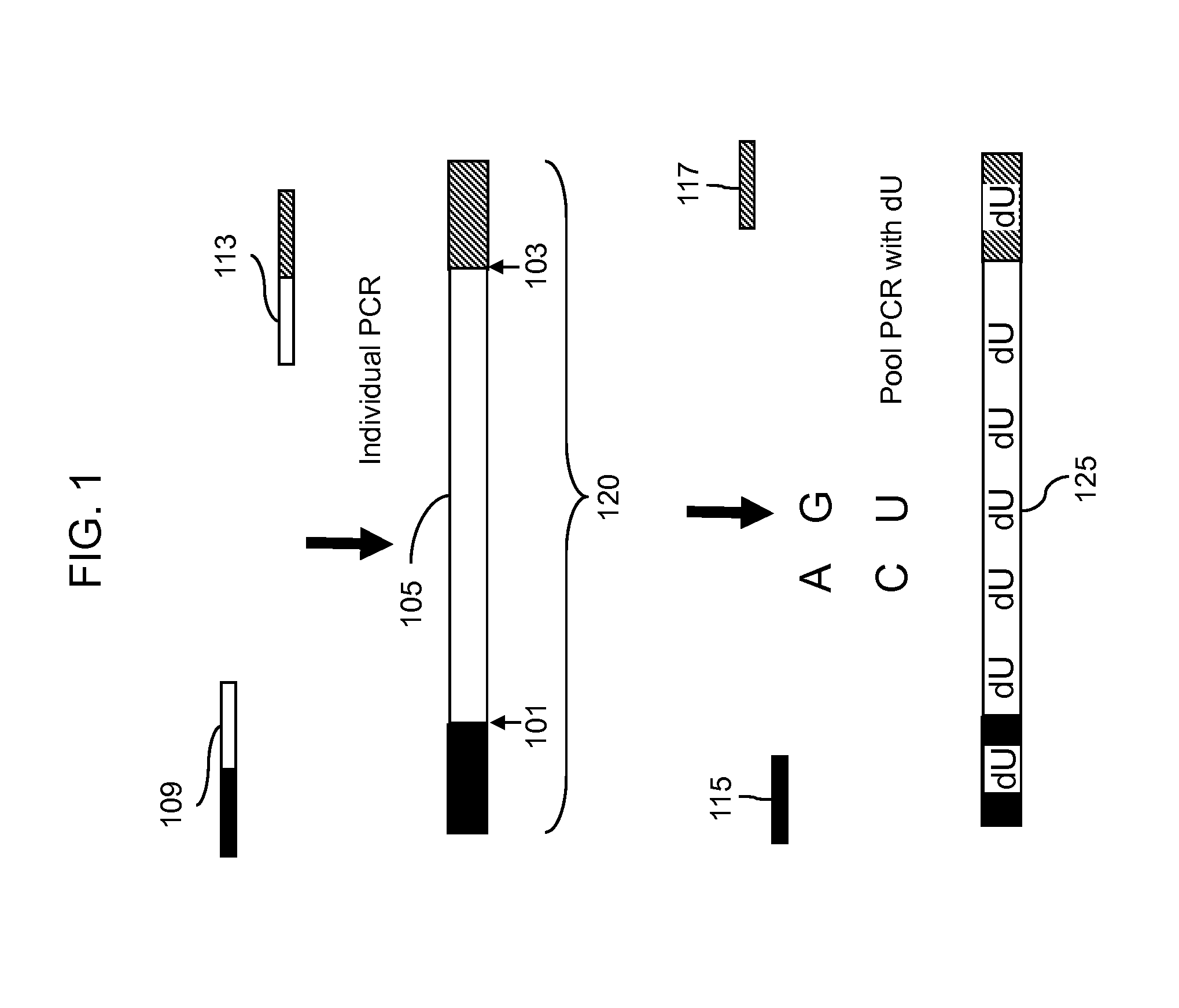
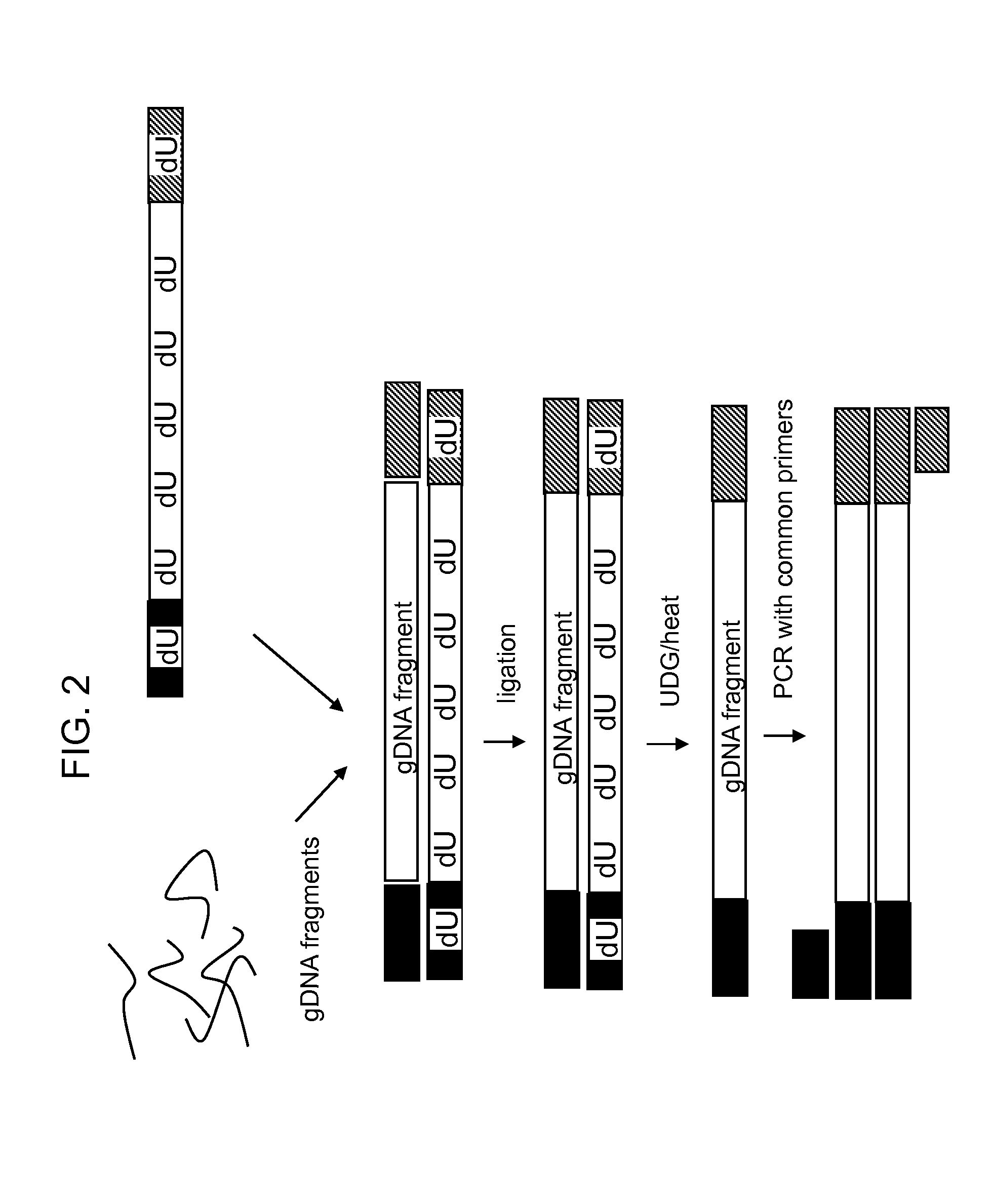
Methods for detection of variant alleles are disclosed. In preferred aspects variants are detected by hybridization patterns to arrays of probes that are contain a single mismatch to a reference sequence, thus reducing the number of probes needed for resequencing by hybridization. The target capture method used is Target Amplification by Capture and Ligation (TACL), and is capable of amplifying many thousands of loci together. Mismatch Repair Detection (MRD) is used as an allele enrichment method to efficiently sort variant and non-variant alleles in thousands of loci simultaneously.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
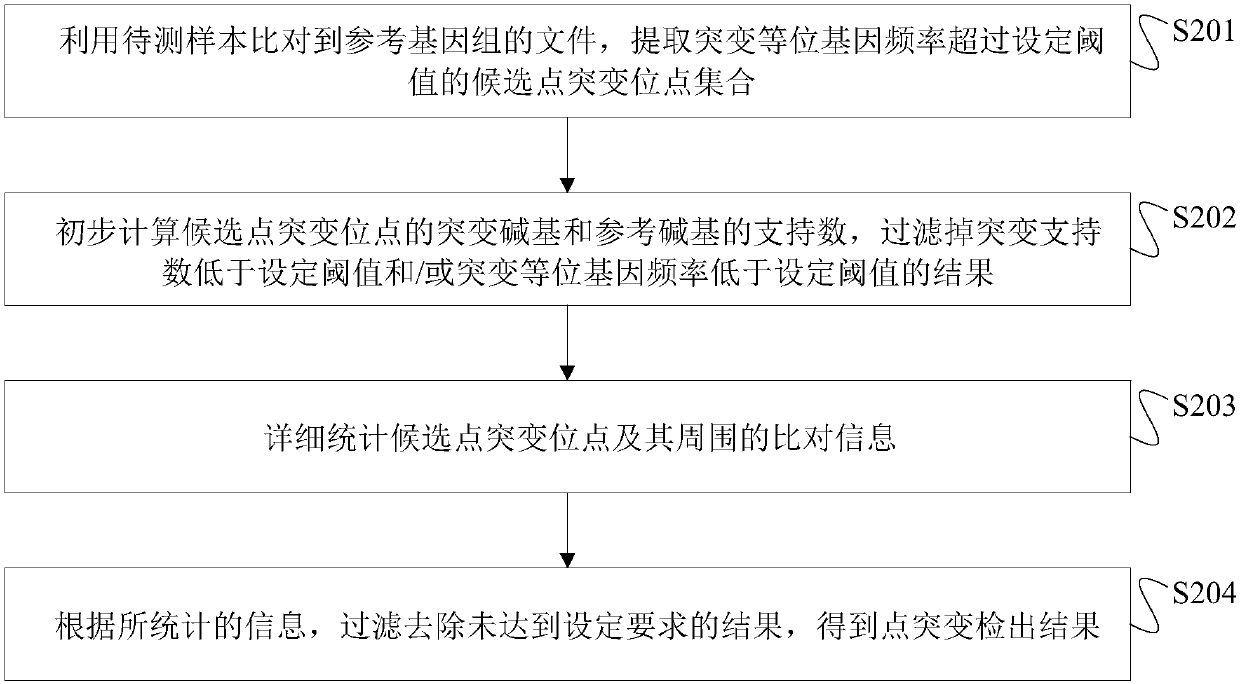
Next generation sequencing-based point mutation detection filtering method and apparatus, and storage medium
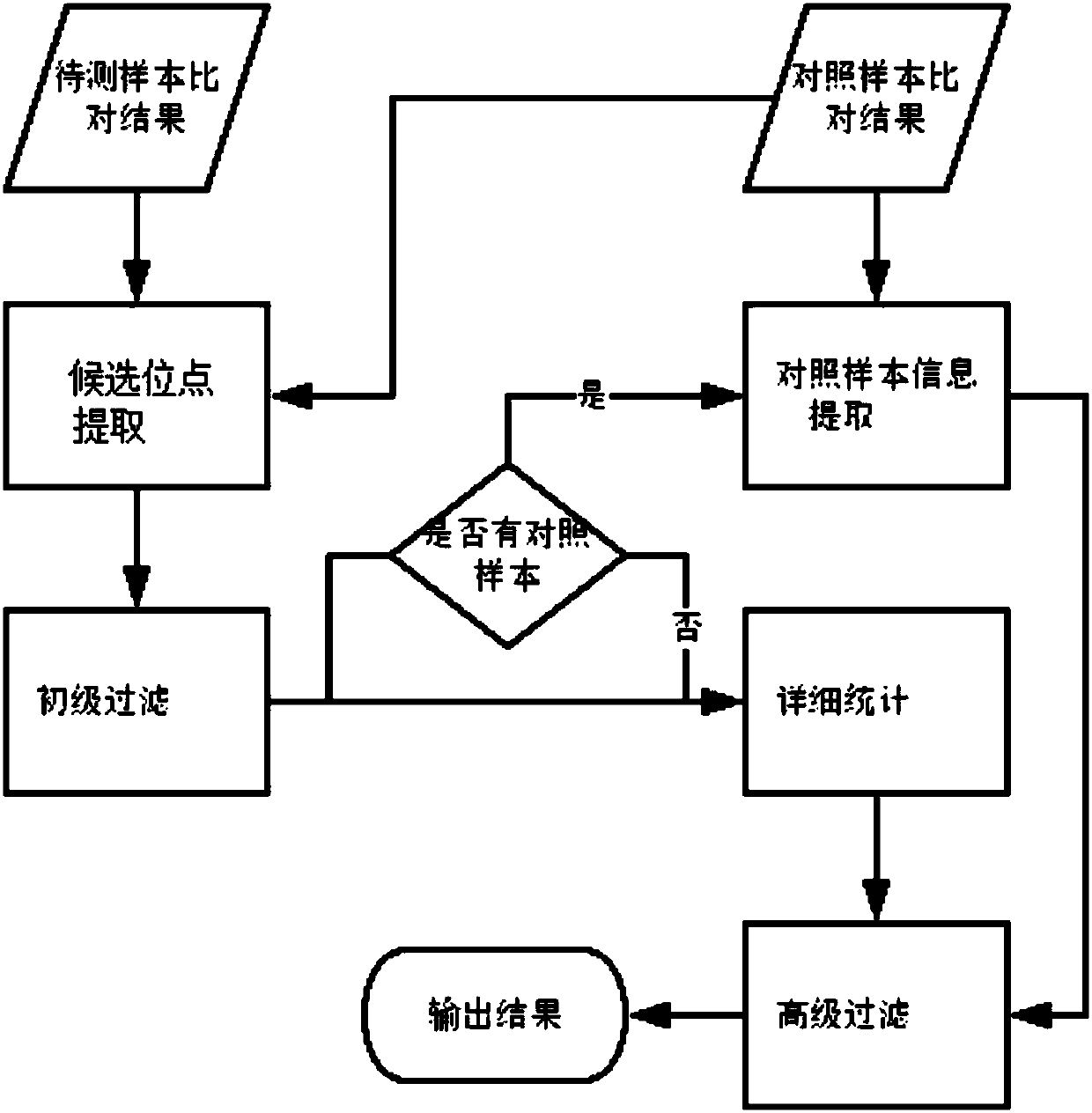
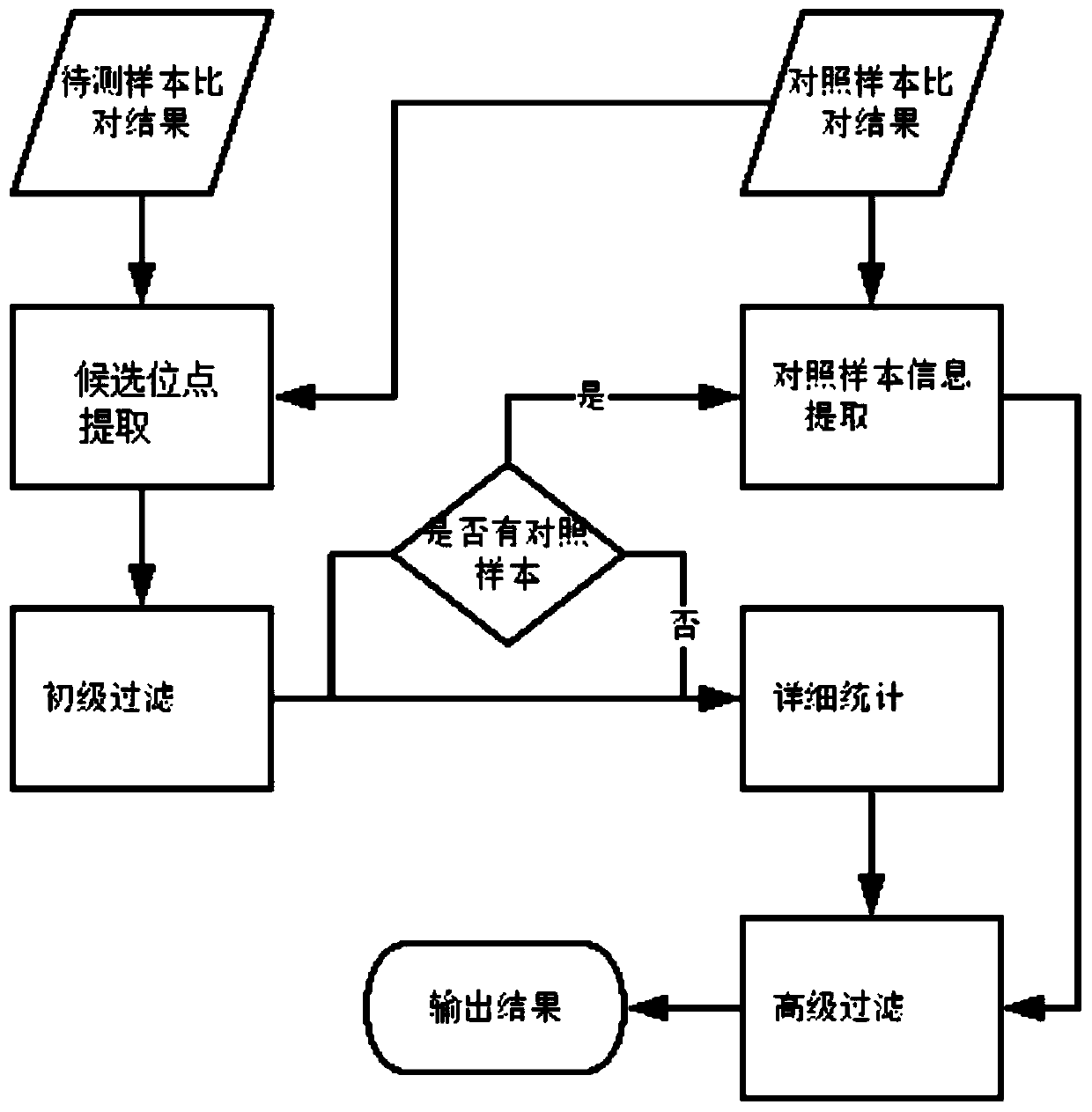
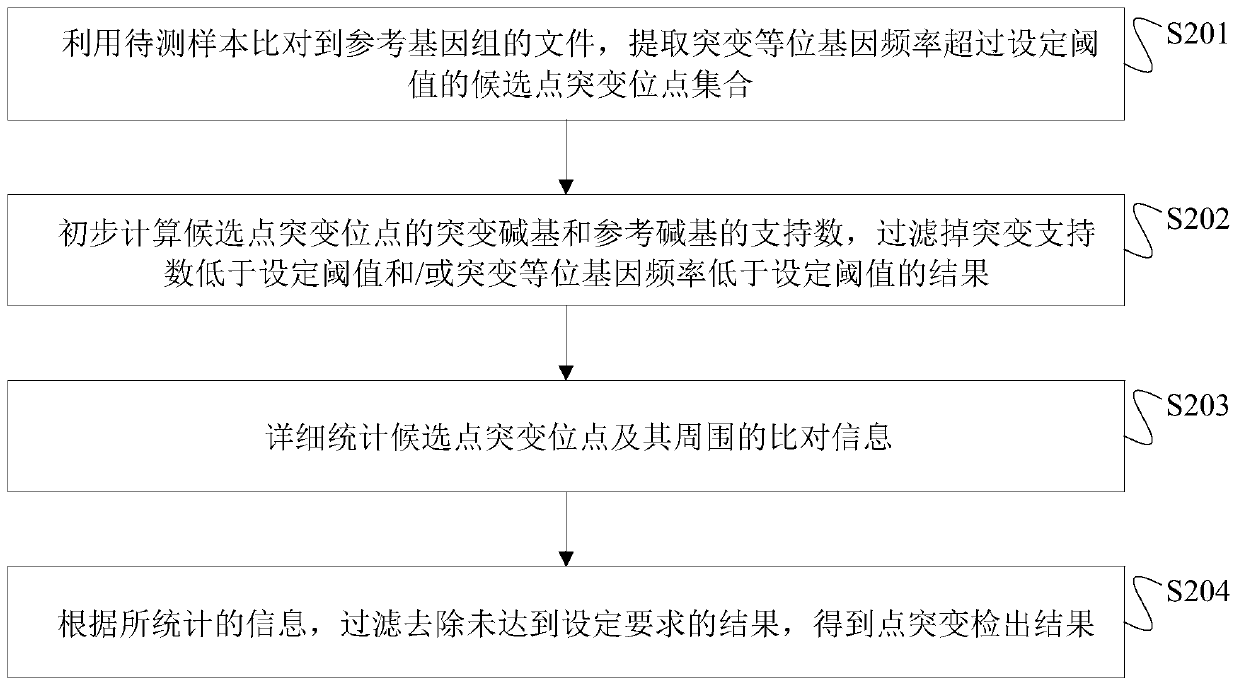
The invention discloses a next generation sequencing-based point mutation detection filtering method and apparatus, and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of performing comparison with files of a reference genome by utilizing a to-be-detected sample, and extracting candidate point mutation site sets with variant allele frequencies exceeding a set threshold; preliminarily calculatingsupport numbers of mutant bases and reference bases of candidate point mutation sites, and filtering results with the mutant support numbers lower than the set threshold and / or the variant allele frequencies lower than the set threshold; performing detailed statistics on the candidate point mutation sites and surrounding comparison information, wherein the information comprises at least one of thefollowing information: the support numbers of the mutant bases and the reference bases of the candidate point mutation sites, base and comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non reference base and insertion / deletion statuses, and surrounding read quality; and according to the statistical information, filtering the results which do not meet set requirements to obtain a point mutation detection result. While the resource demands and the detection speed are optimized, the sensitivity and specificity of point mutation detection are improved.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
Method of Inducing Melanogenesis in Humans With Mc1R Variant Alleles
A method for inducing melanogenesis in a human subject having a melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) variant allele associated with loss of or diminished receptor function comprises administering to said subject an amount of an α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) analogue effective to induce melanogenesis by the melanocytes in the skin or other epidermal tissue of the subject.
Owner:CLINUVEL PHARMA
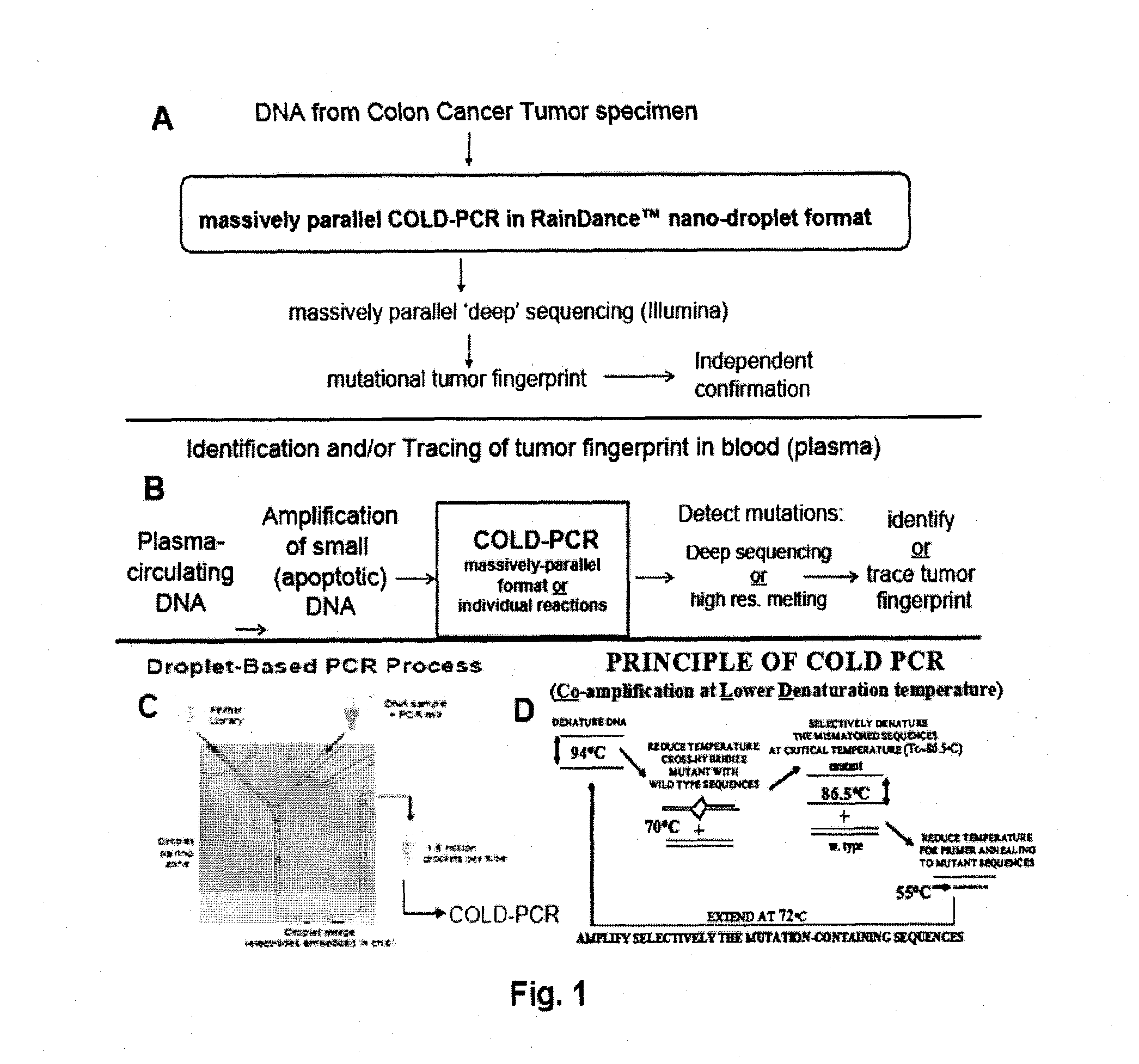
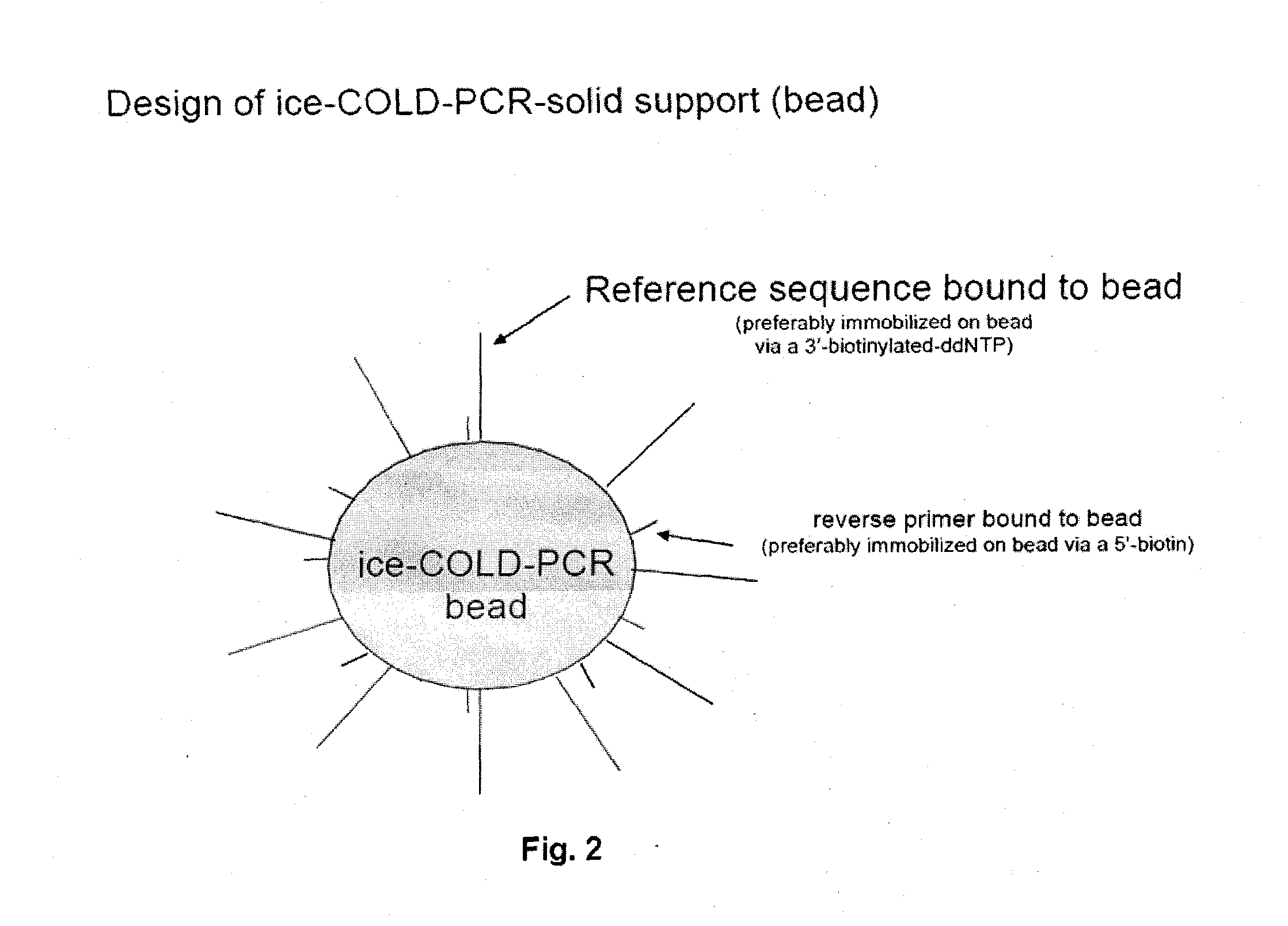
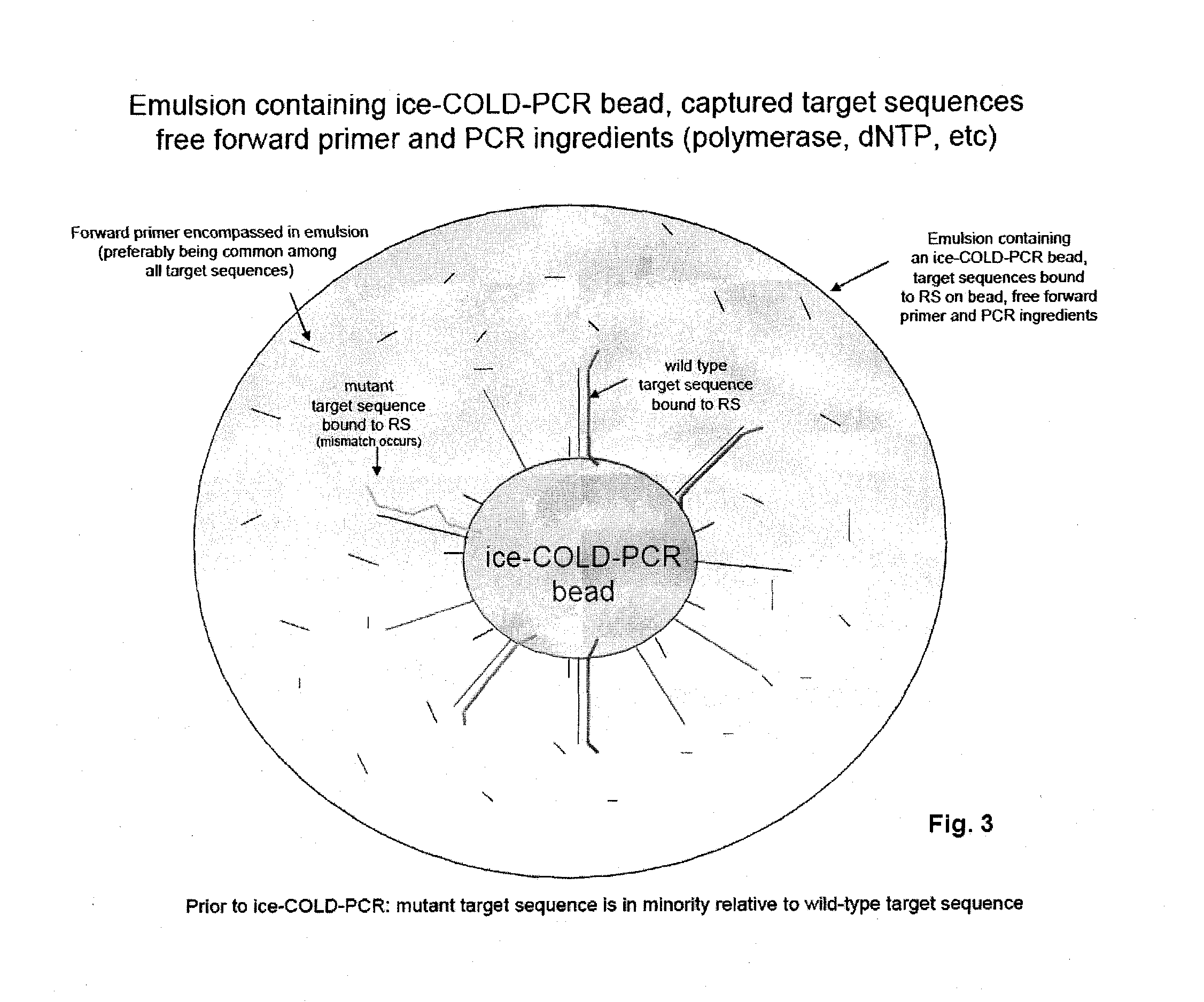
Methods and compositions to enable multiplex cold-pcr
ActiveUS20140051087A1Many sequenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LDNA fragmentation
The present invention is directed to methods, compositions and reaction mixtures for multiplexing COLD-PCR / ice-COLD-PCR to enrich simultaneously several low abundance alleles (mutant target sequences) from a sample. The invention also involves COLD-PCR / ice-COLD-PCR amplification performed on DNA fragments that have different melting temperatures, and therefore different critical denaturation temperatures, in a graded temperature approach such that mutation enrichment is achieved on all diverse DNA fragments simultaneously (temperature-independent COLD-PCR or TI-COLD-PCR). The invention also involves methods for enabling identification of variant-sequence alleles in the presence of a large excess of non-variant alleles in nucleic acids without the complication of polymerase-introduced errors or other primer-introduced artifacts.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Detecting Cross-Contamination in Sequencing Data Using Regression Techniques
PendingUS20180237838A1Easy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsTest sampleVariant allele
Cross-contamination of a test sample used to determine cancer is identified using gene sequencing data. Each test sample includes a number of test sequences that may include a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) that can be indicative of cancer. The test sequences are be filtered to remove or negate at least some of the SNPs from the test sequences. Negating the test sequences allows more test sequences to be simultaneously analyzed to determine cross-contamination. Cross-contamination is determined by modeling the variant allele frequency for the test sequences as a function of minor allele frequency, contamination level, and background noise. In some cases, the variant allele frequency is based on a probability function including the minor allele frequency. Cross-contamination of the test sample is determined if the determined contamination level is above a threshold and statistically significant.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
Detecting somatic single nucleotide variants from cell-free nucleic acid with application to minimal residual disease monitoring
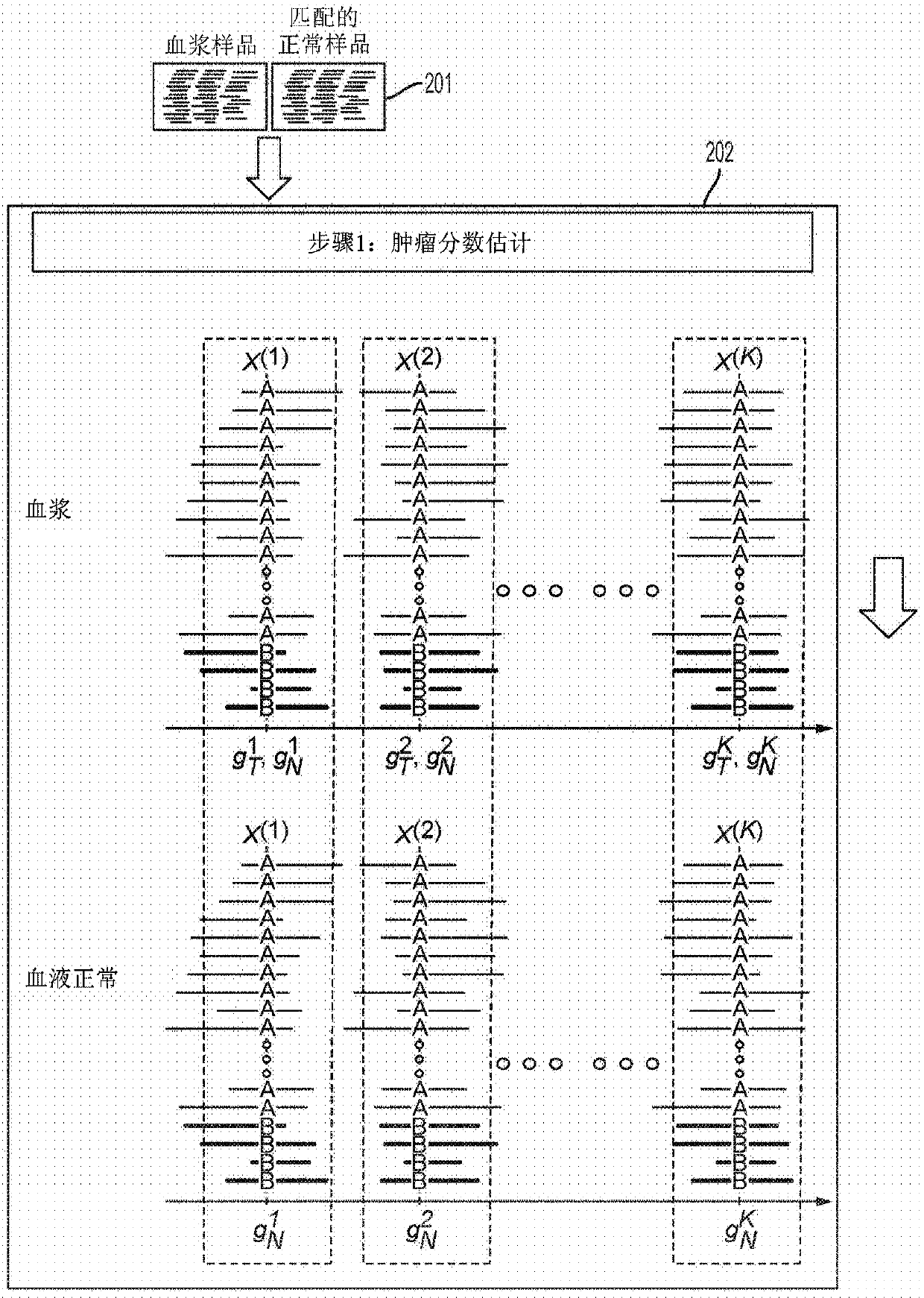
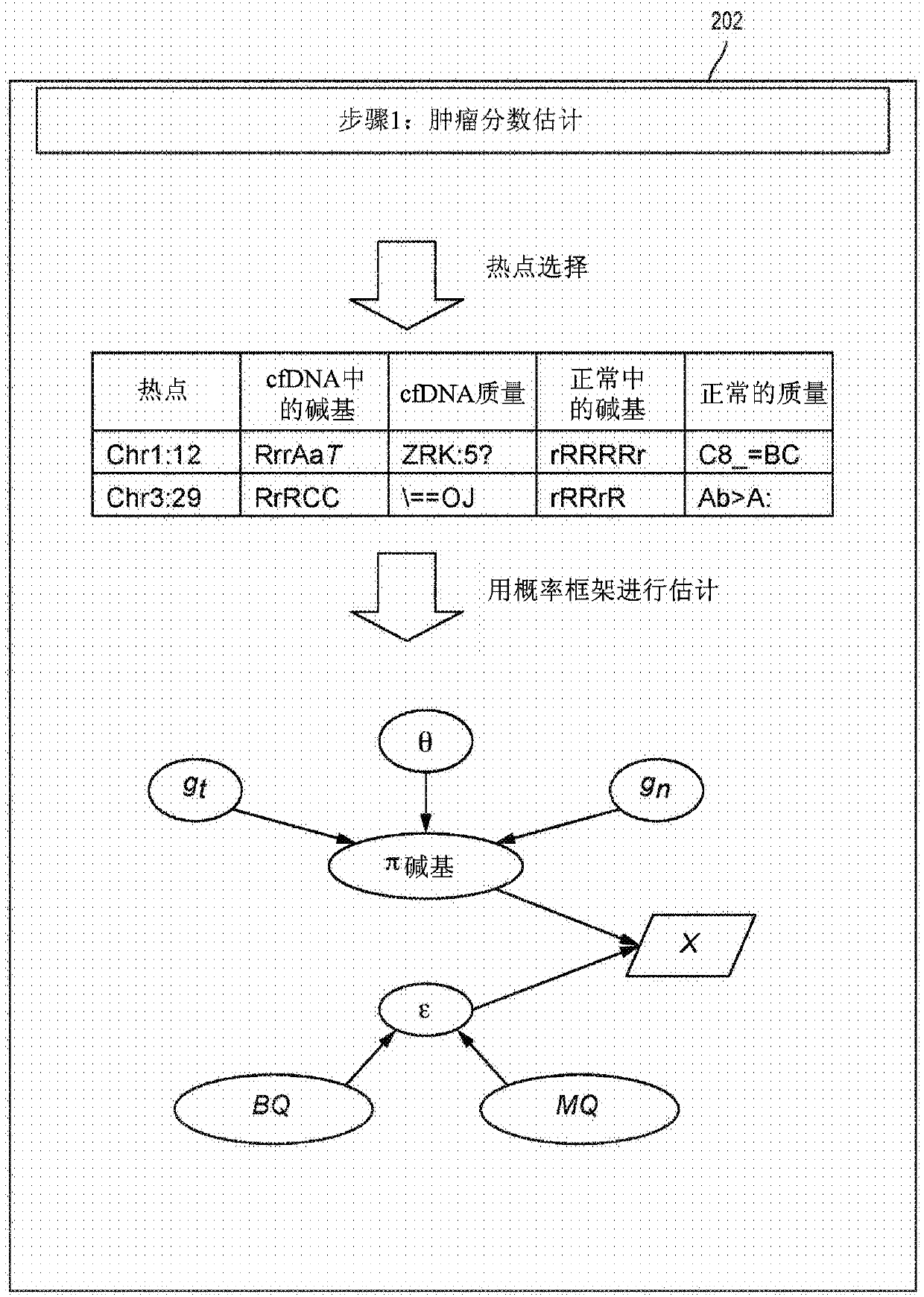
The present disclosure provides a probabilistic model for accurate and sensitive somatic single nucleotide variant (SNV) detection in cell-free nucleic acid samples comprising a set of sequence data.A joint genotype may be determined for each locus in the set of sequence data, and germline mutations may be intrinsically removed. A set of filtrations can be applied to eliminate low quality somaticvariant calls. Further, a global tumor cell-free deoxyribonucleic acid (cfDNA) fraction and overlapping read mates can be considered, thereby enabling accurate SNV detection and variant allele frequency estimation from samples with low tumor cfDNA fraction. A sensitive early detection of minimal residual disease (MRD) is designed by using the probabilistic model and the machine learning model fordistinguishing true variants from sequencing errors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tumor burden as measured by cell free DNA
InactiveUS20180282417A1Good chanceLong survivalMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCell freeAllele frequency
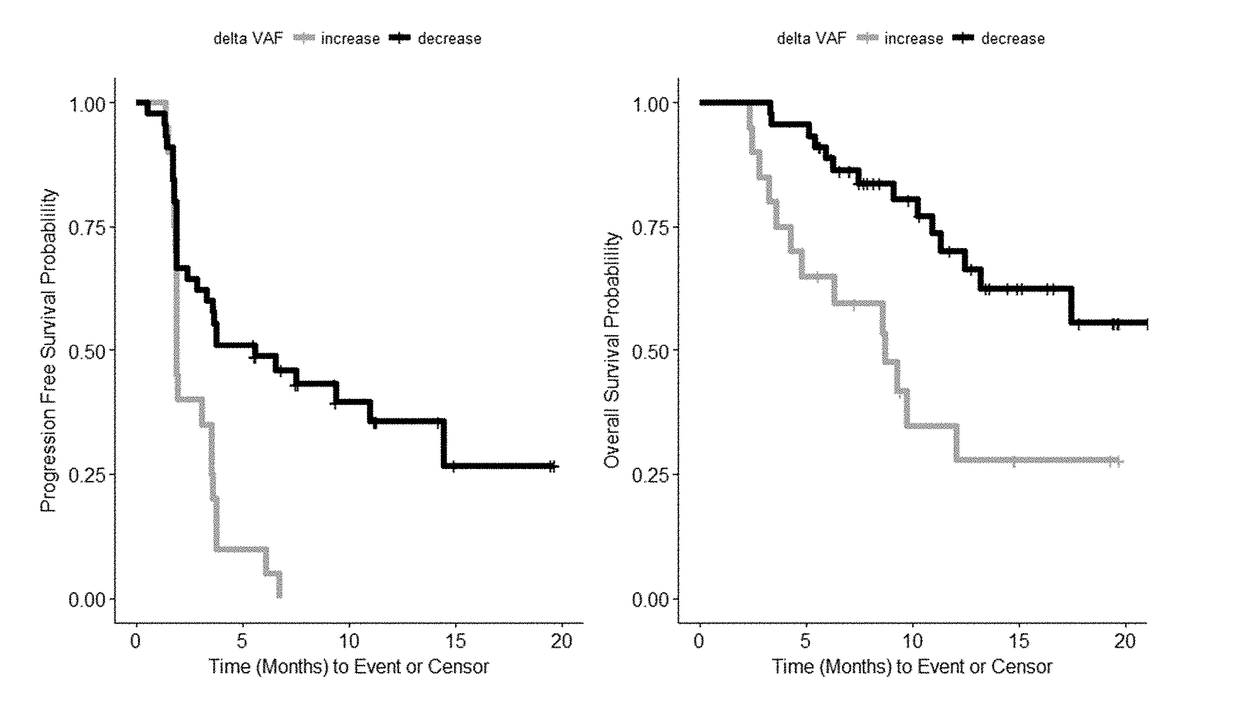
Disclosed are methods for treating cancer (e.g., solid tumor cancers, lung cancer, bladder head and neck cancer) with an anti-PD-L1 antibody in a patient identified as being responsive to anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy by detecting a mutation in one or more disclosed circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) markers. Also disclosed are methods for determining the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapeutic antibody treatment in a patient having lung cancer or bladder cancer comprising detecting variant allele frequency in ctDNA in plasma samples and determining the difference of the variant allele frequency in ctDNA between the first and at least second plasma samples, wherein a decrease in the variant allele frequency in the at least second plasma sample relative to the first plasma sample identifies the anti-PD-L1 antibody treatment as effective. The disclosure also provides methods of identifying a subject having a cancer responsive to a therapy comprising an anti-PD-L1 antibody by detecting the expression of a mutation in one or more circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) markers.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Single nucleotide polymorphisms and the identification of lactose intolerance
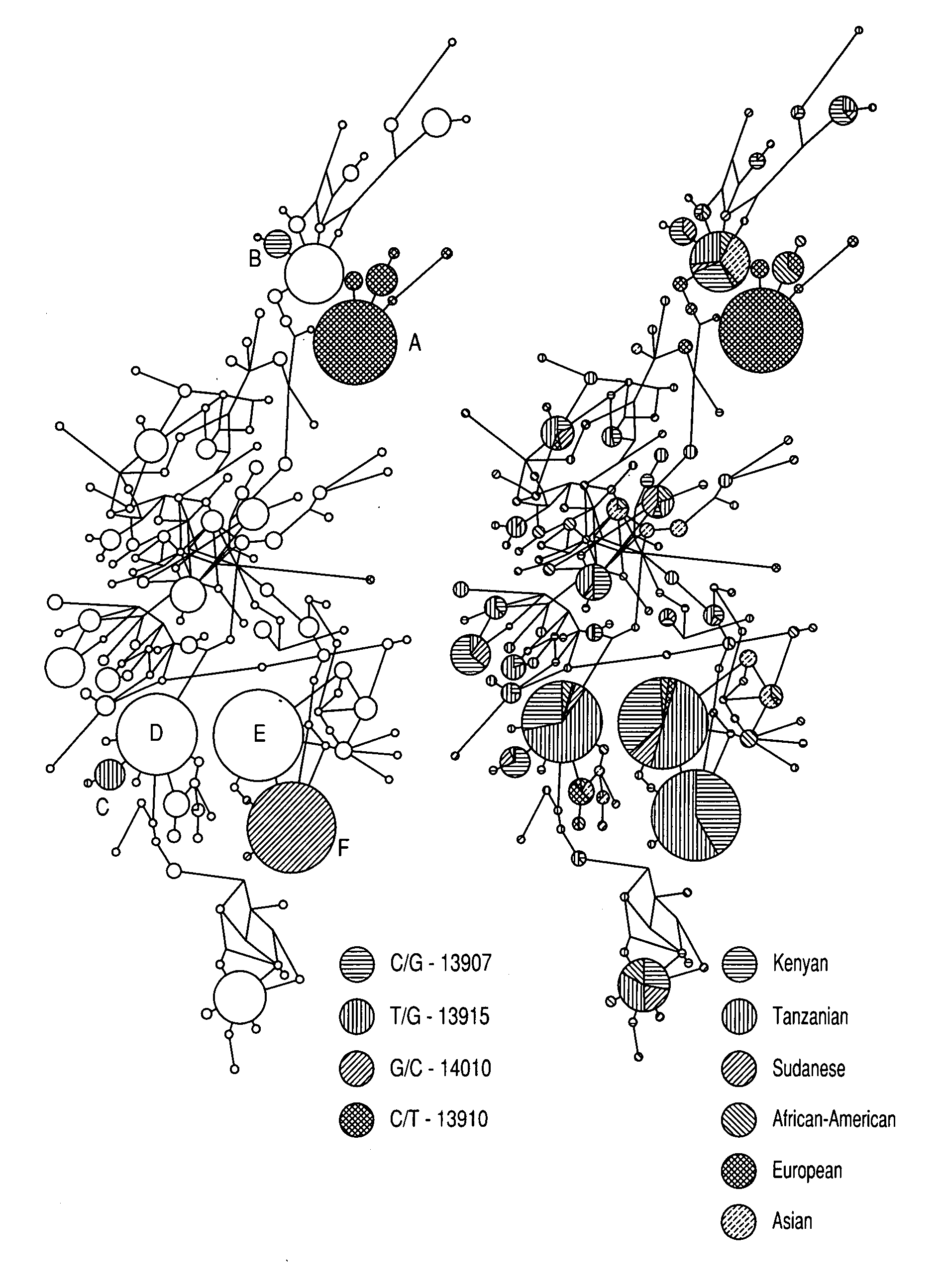
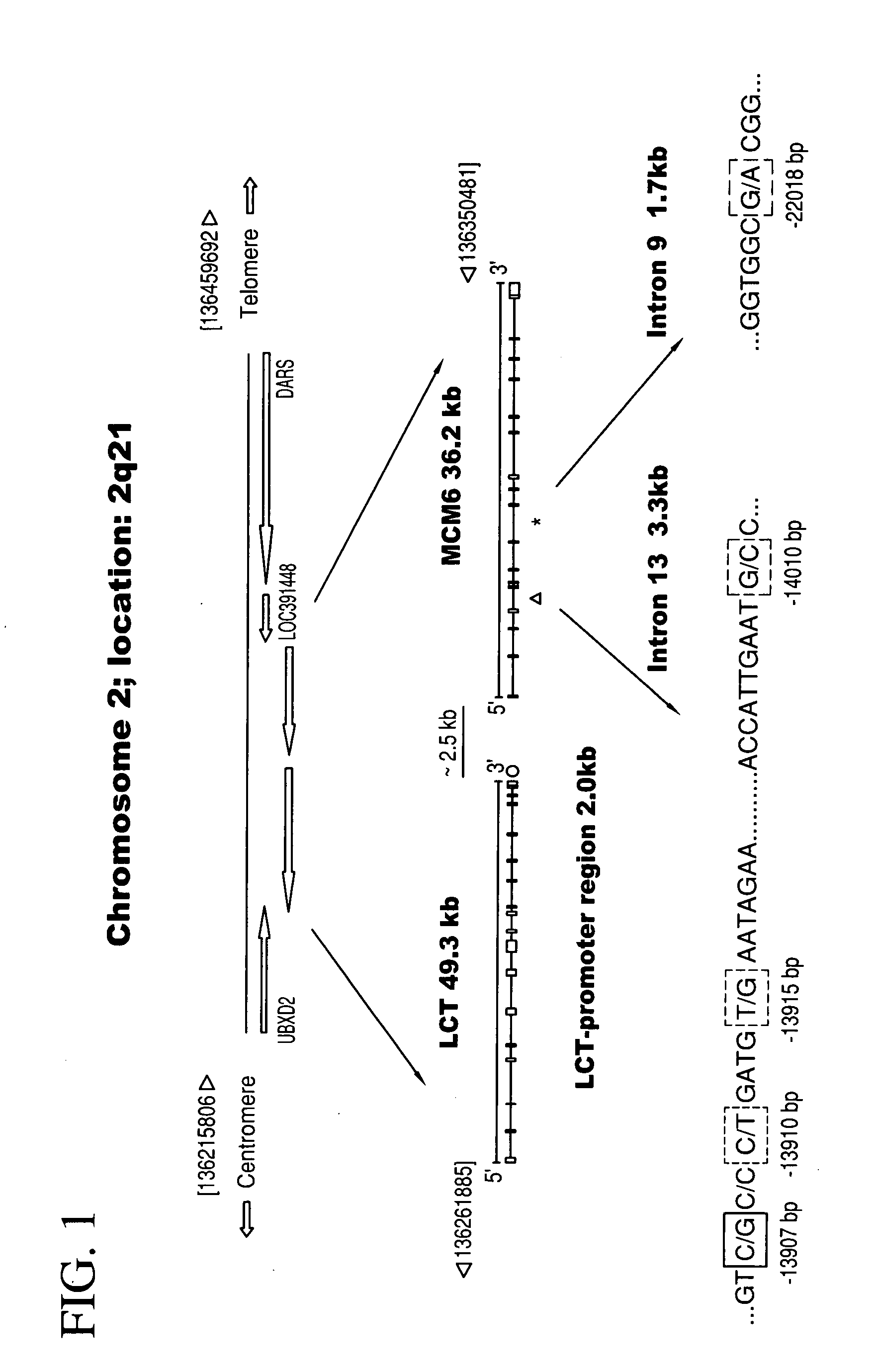
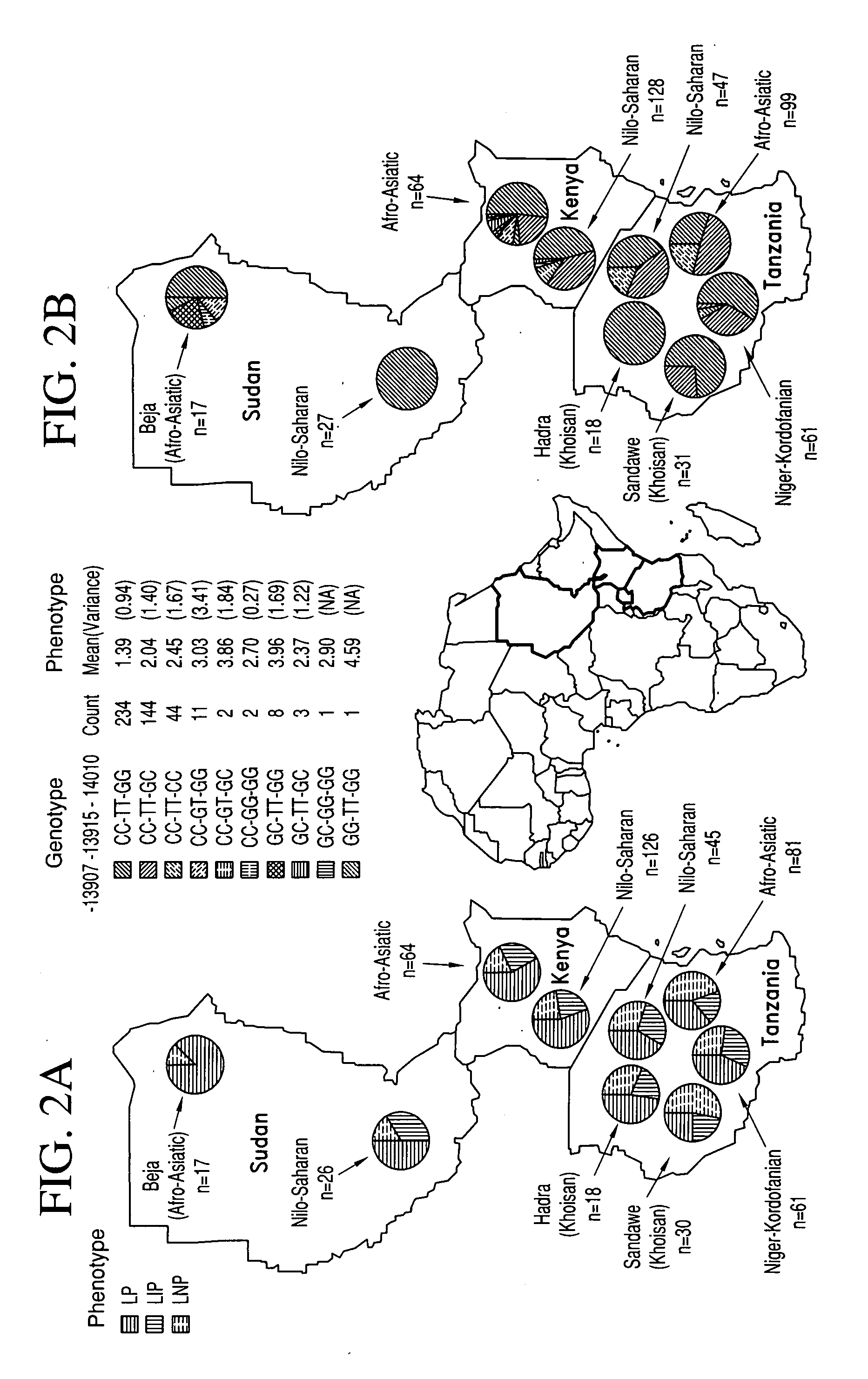
The present invention relates generally to methods, kits, genotyping and / or nucleic acid molecules associated with the identification of a predisposition for lactase persistence, lactase non-persistence, lactose tolerance and / or lactose intolerance. The methods of the present invention comprise in general determining the presence or absence of at least one variant allele having one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms within a gene associated with the expression of lactase-phlorizin hydrolase. The single nucleotide polymorphism is selected from the group consisting essentially of C-14010, G-13915 and G-13907, as measured from the start of the LCT gene.
Owner:TISHKOFF SARAH A +1
Method for long range allele-specific PCR
The present invention is directed to a method and kit for determining the molecular haplotype of a gene in a diploid DNA sample. The method discriminates between two haplotypes on the basis of a difference of one or more nucleotides using allele-specific PCR amplification in combination with long range PCR, using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, using annealing temperature conditions sufficiently greater than the predicted annealing temperature (Tm) to effect selective hybridization and extension of an allele-specific extension primer to the target allele relative to the variant allele. The present invention is particularly useful, for example, to determine the haplotype of a gene having multi-allelic genetic loci separated by a distance in which accurate PCR amplification of a single fragment containing the multiple genetic loci cannot be performed without using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, generally about 5 kilobases or more.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Methods for improving inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis
InactiveUS20130203053A1Improved clinical parameterPromote differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementUlcerative colitisMedicine
The present invention provides methods and systems to diagnose the ulcerative colitis (UC) subtype of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) by detecting the presence or absence of one or more variant alleles in the GLI1, MDR1, and / or ATG16L1 genes. Advantageously, with the present invention, it is possible to provide a diagnosis of UC and to differentiate between UC and Crohn's disease (CD) with increased accuracy.
Owner:NESTEC SA
sPLA2 IIA Polymorphism Analysis for the Diagnosis/Prognosis of a Cardiovascular Disease/Event
InactiveUS20120225427A1Reduce riskReduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideIncreased risk
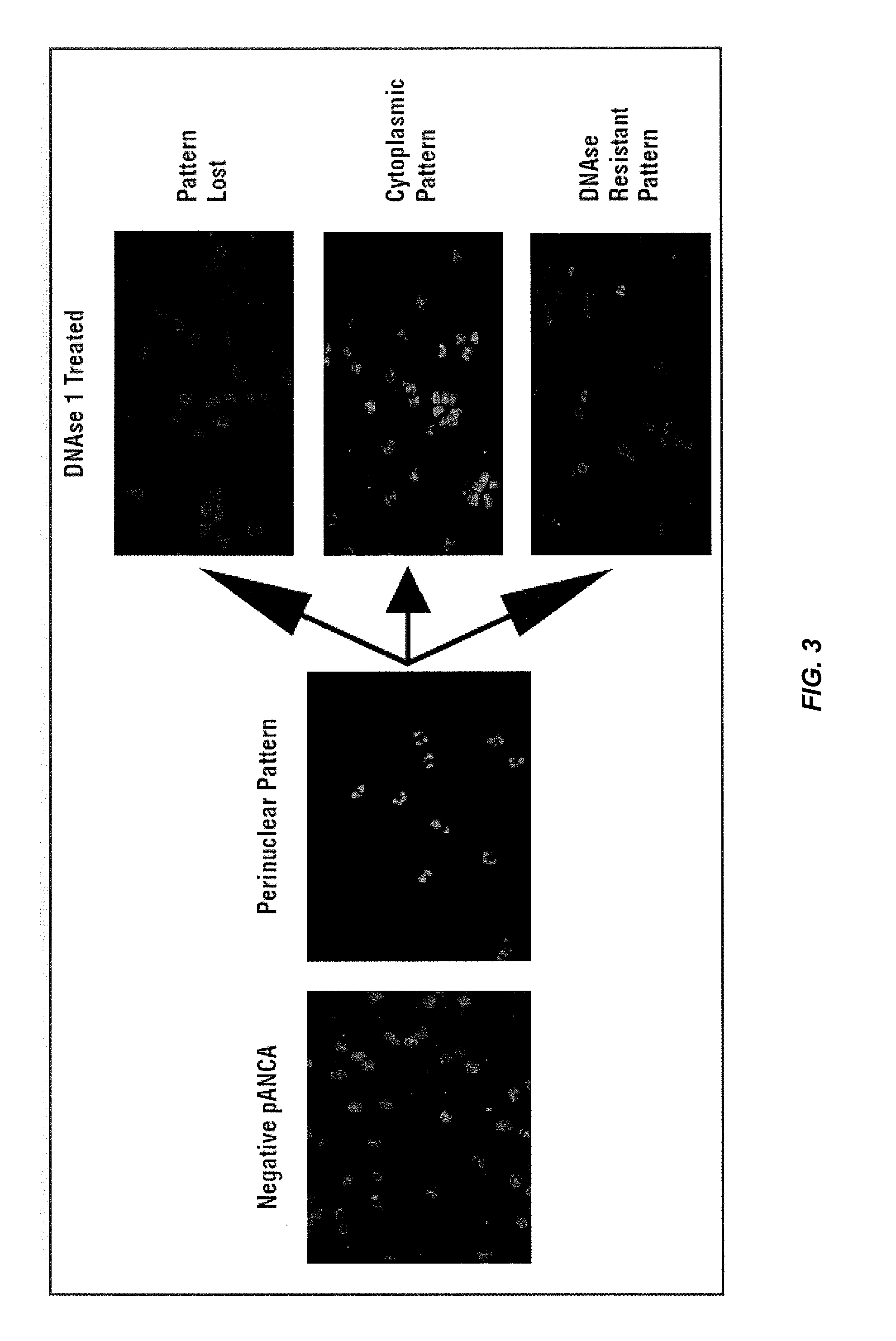
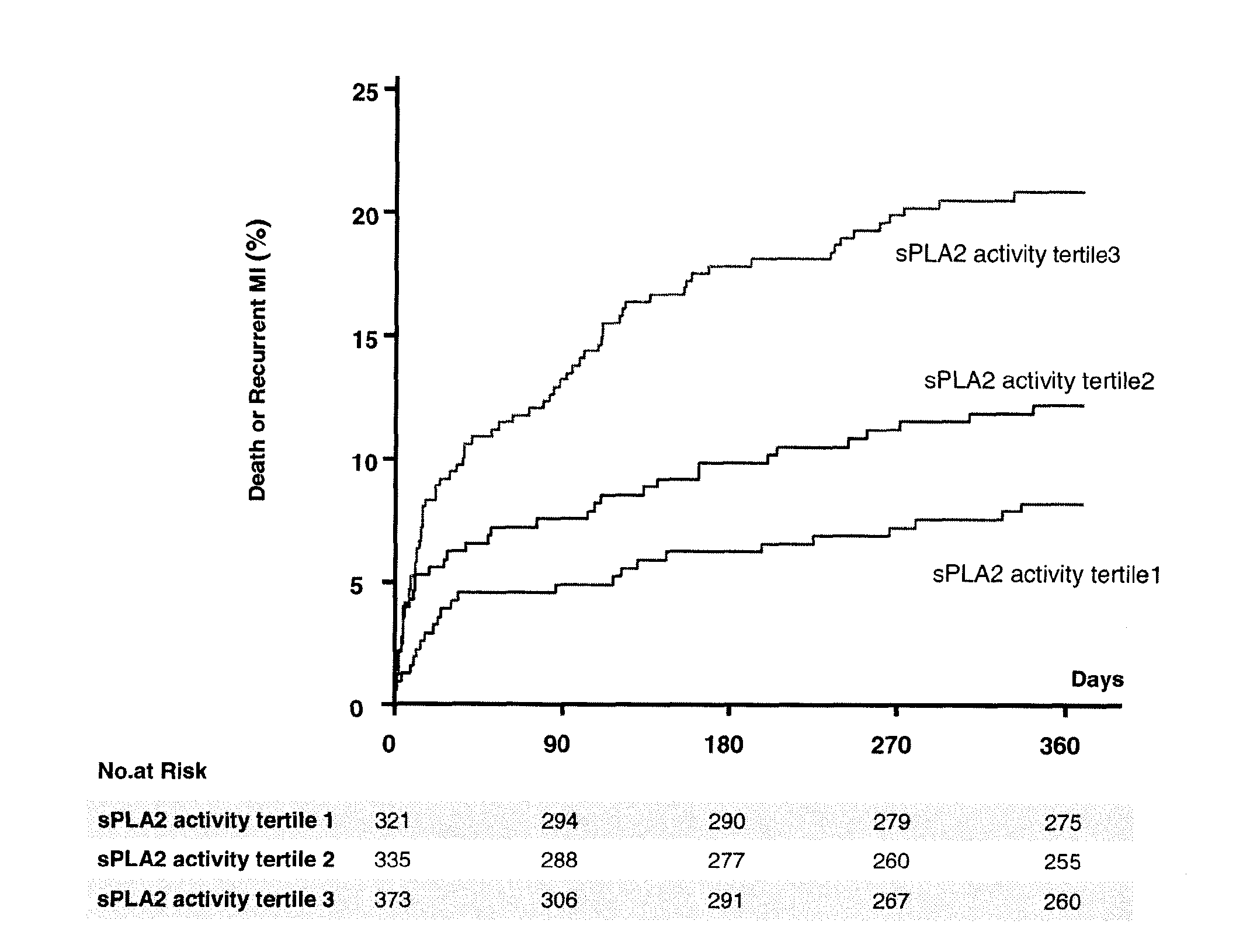
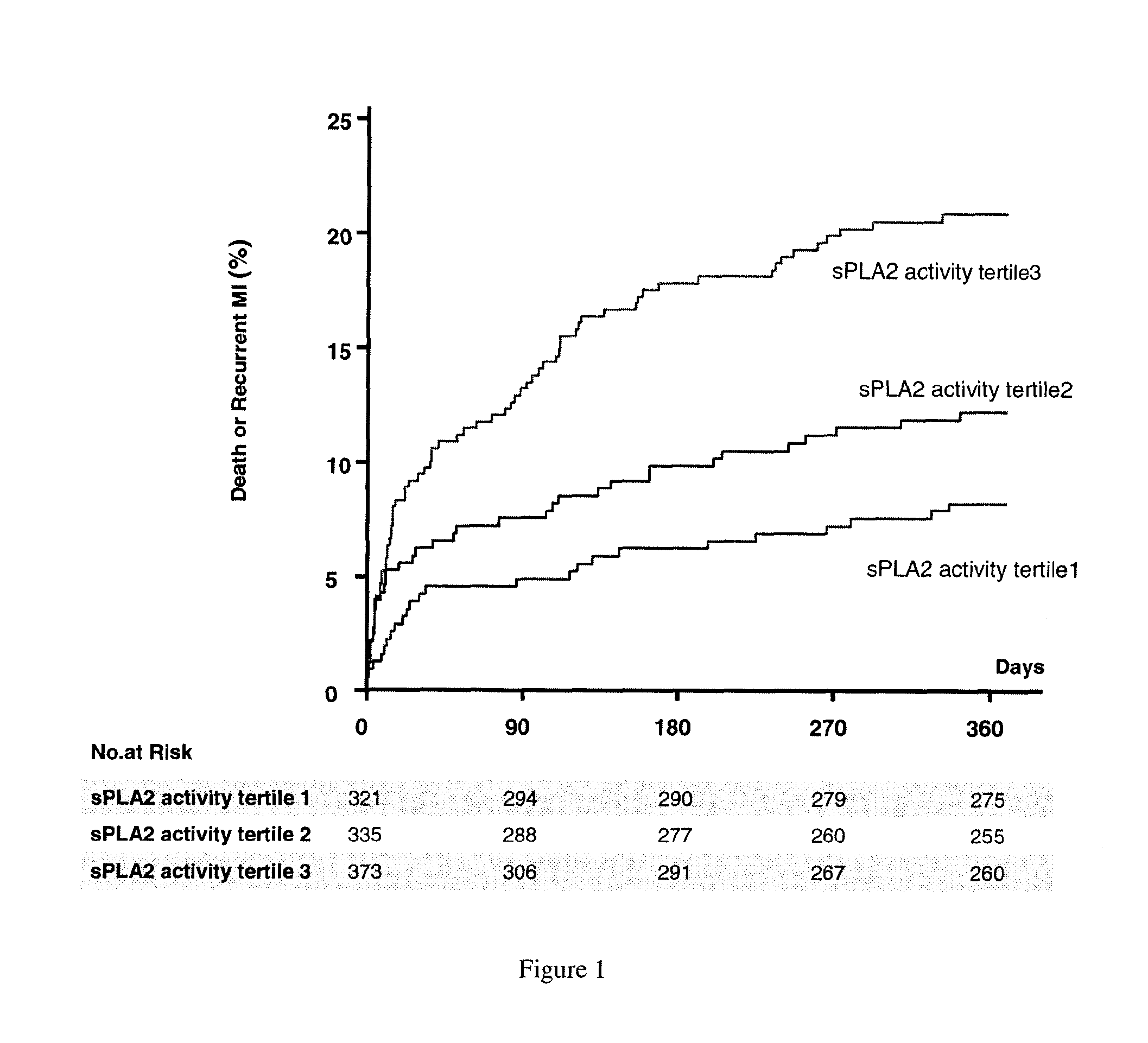
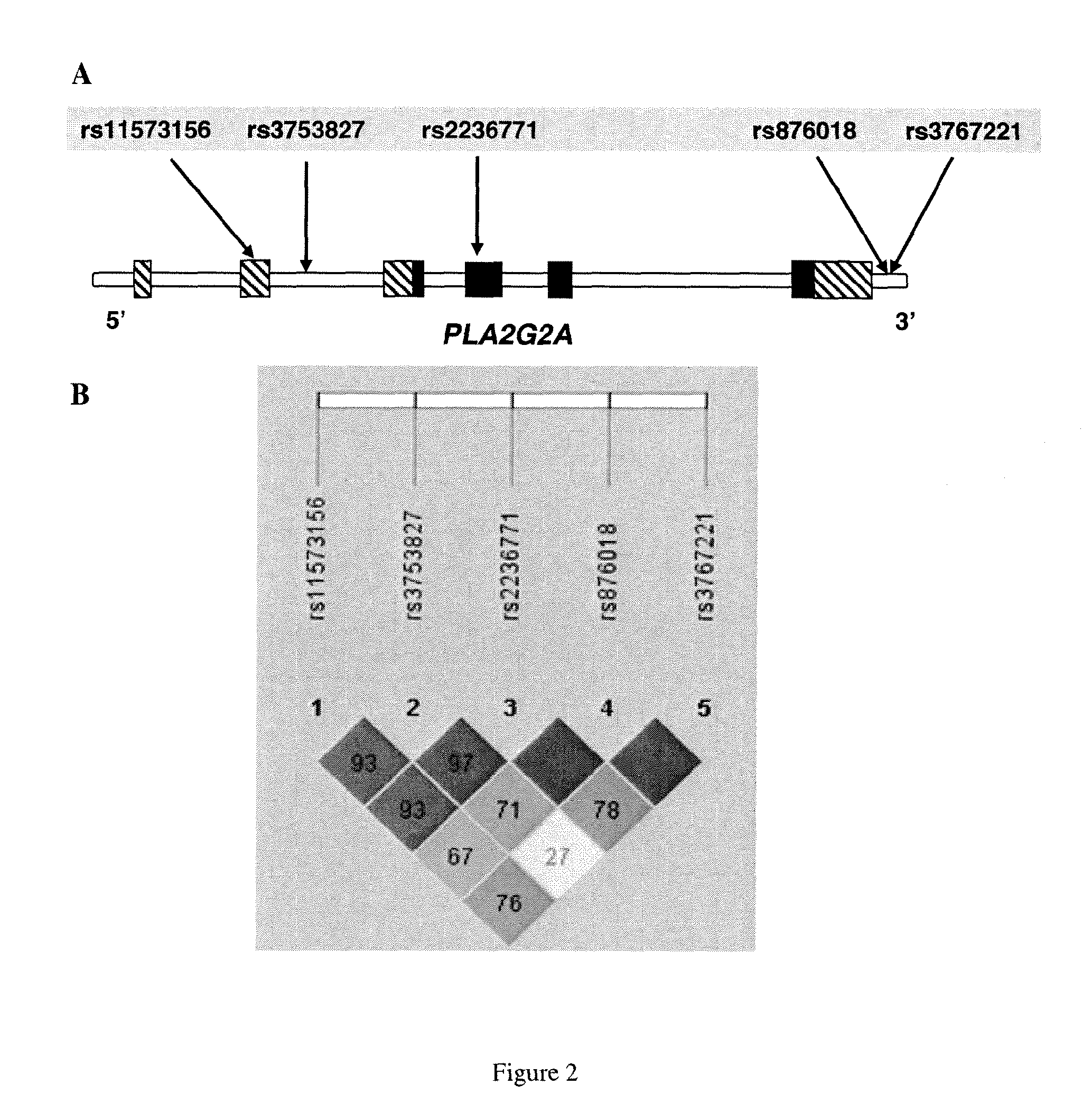
The invention relates to a method of identifying a subject having or at risk of having or developing a cardiovascular disease and / or a cardiovascular event, comprising determining, in a sample obtained from said subject, the presence or absence of a variant allele of nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of the sPLA2 type IIA nucleic acid, wherein the SNP is selected from the group consisting of rs11573156 and rs2236771, wherein the presence of the minor allele (G) of SNP rs11573156 indicates an increased risk of having or being at risk of having or developing a cardiovascular disease and / or cardiovascular event, and the presence of the minor allele (C) of SNP rs2236771 indicates a decreased risk of having or being at risk of having or developing a cardiovascular disease and / or cardiovascular event.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
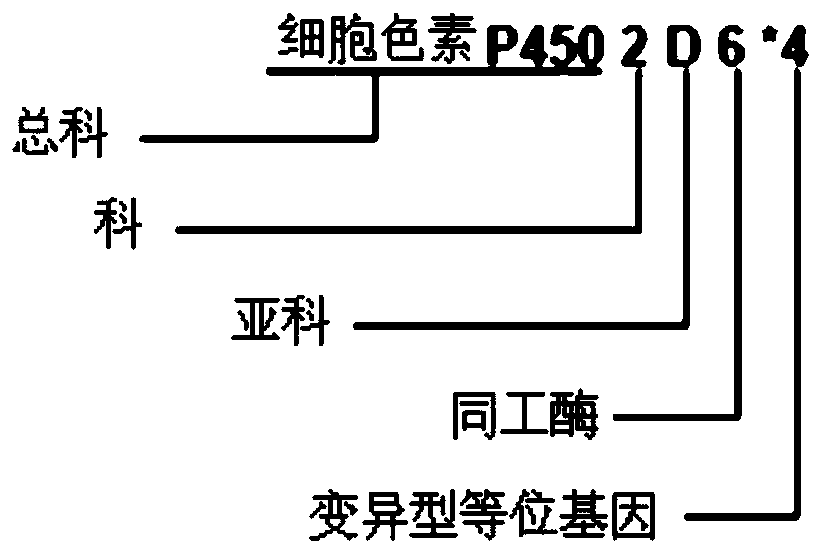
Drug metabolic enzyme metabolism type evaluation method
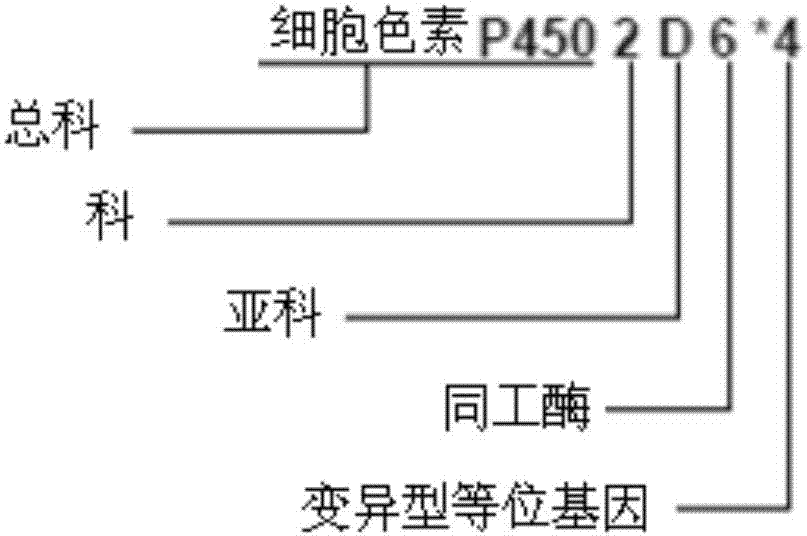
ActiveCN107885970AImprove detection accuracyImprove detection efficiencyBioinformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsMetabolic enzymesHaplotype
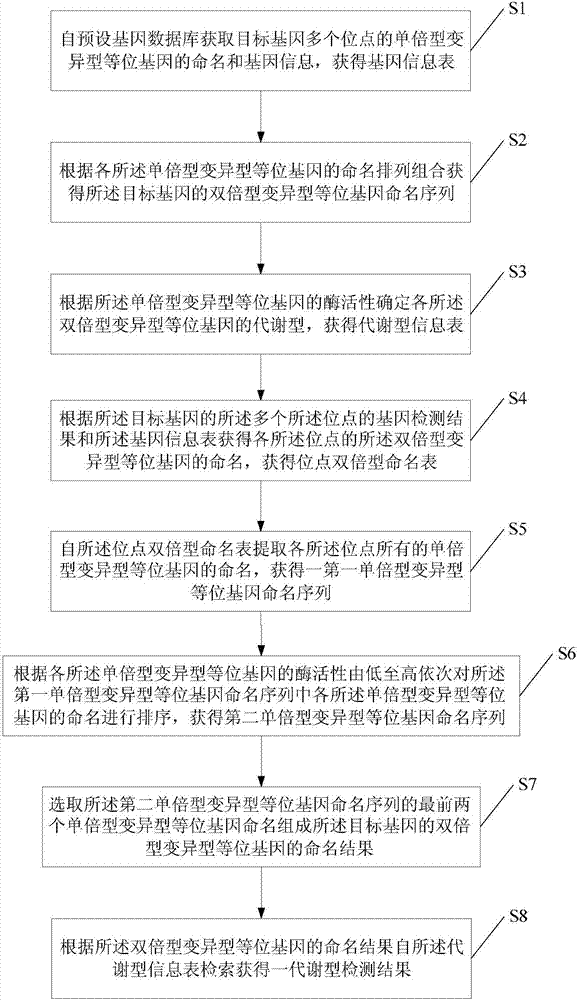
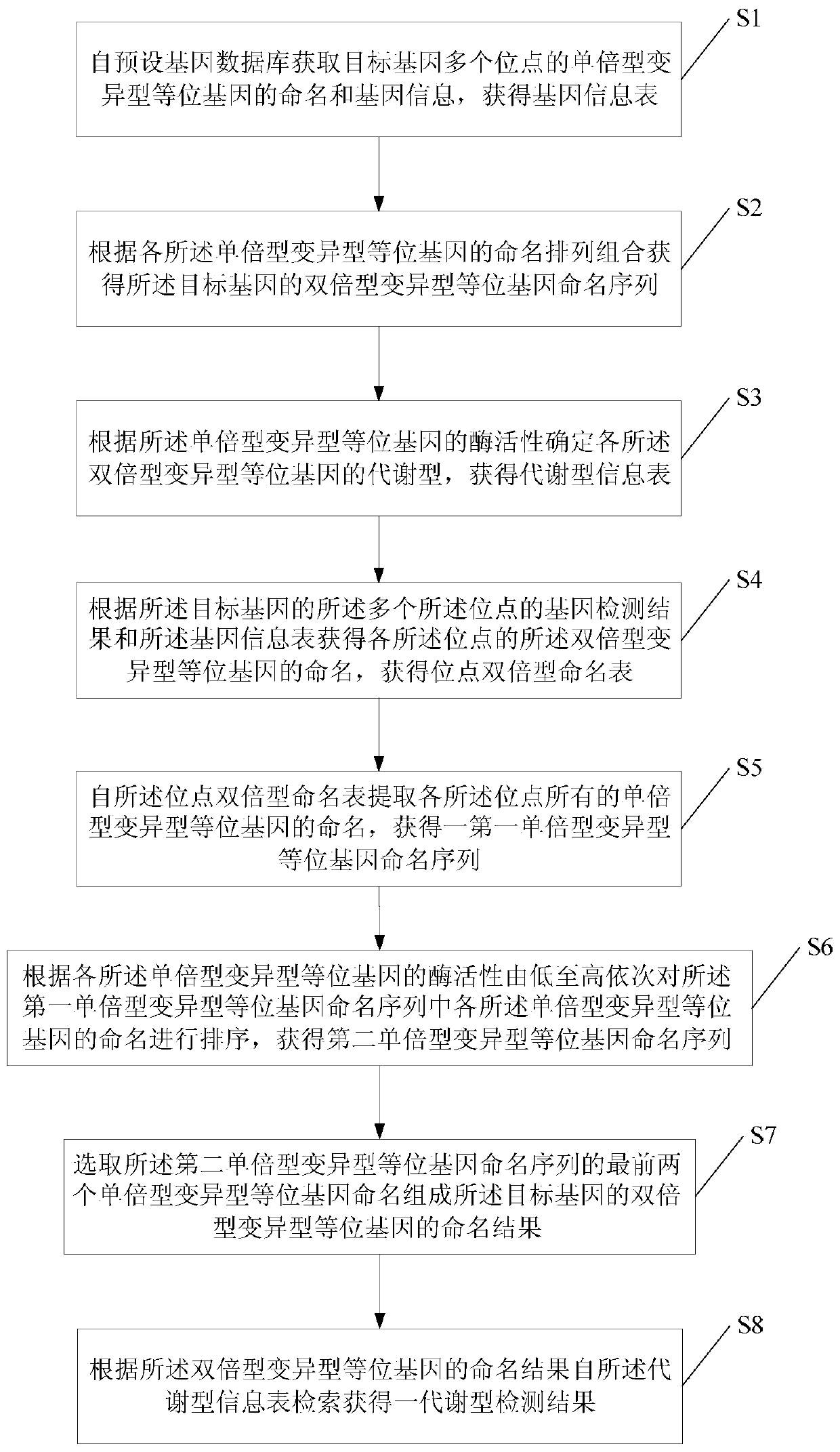
The invention provides a drug metabolic enzyme metabolism type evaluation method, comprising steps: S1, acquiring haploid variant allele names of genes from a preset gene data bank, to form a gene information table; S2, according to the gene information table, obtaining a diploid variant allele name sequence; S3, forming metabolism types, to obtain a metabolism type information table; S4, according to gene detection results, obtaining a locus diploid name table; S5, obtaining a first haploid variant allele name sequence; S6, according to enzymatic activity of each haploid variant allele, obtaining a second haploid variant allele name sequence; S7, from the second haploid variant allele name sequence, obtaining a diploid variant allele name result; S8, retrieving from the metabolism type information table, to obtain a metabolism type detection result. The drug metabolic enzyme metabolism type evaluation method can accurately determine a gene metabolism type, and has important meaning on drug metabolic enzyme gene detection and personalized medication aspects.
Owner:慧算基因科技上海有限公司
Haplotyping and copy number typing using polymorphic variant allelic frequencies
PendingUS20160210402A1Alleviates erroneous discrete PV-callsSimple methodData visualisationProteomicsGenetic AnomalyTyping
The present invention provides a method for the analysis of genetic material of a subject, said method comprising: —obtaining continuous polymorphic variant allele frequency (PVAF) values of genetic material of a subject; —obtaining genotype information of a first and second parent; —categorizing the continuous PVAF values in a category corresponding to the first parent based on the genotype information of the first parent and second parent; —segmenting said categorized PVAF values; and —providing the segmented PVAF values to indicate a genetic anomaly in the genetic material of the subject and / or inheritance of the genetic material of the subject.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
DNA mutation detection employing enrichment of mutant polynucleotide sequences and minimally invasive sampling
ActiveUS20190330692A1Growth inhibitionEasy to detectNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele frequencyNucleotide
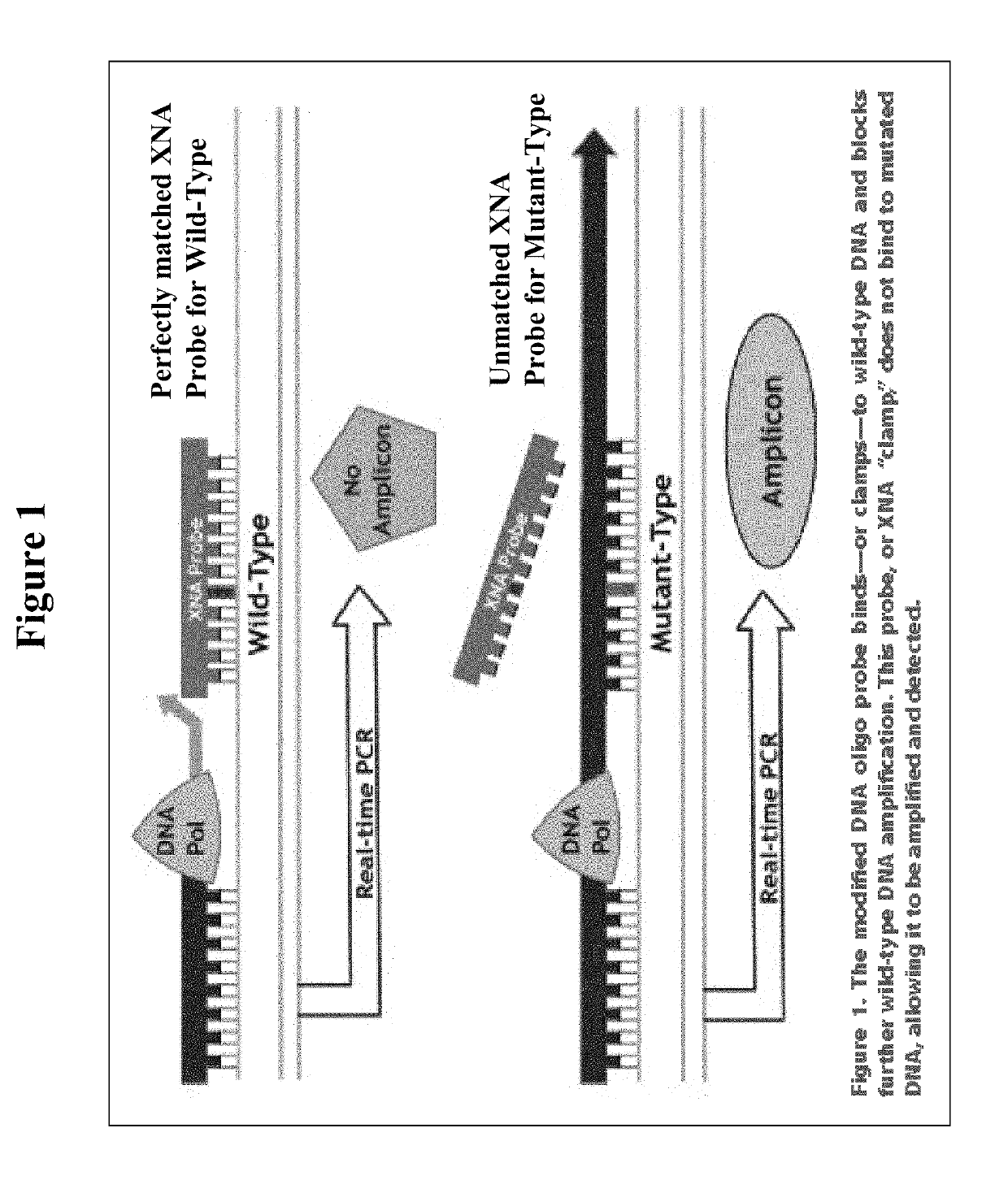
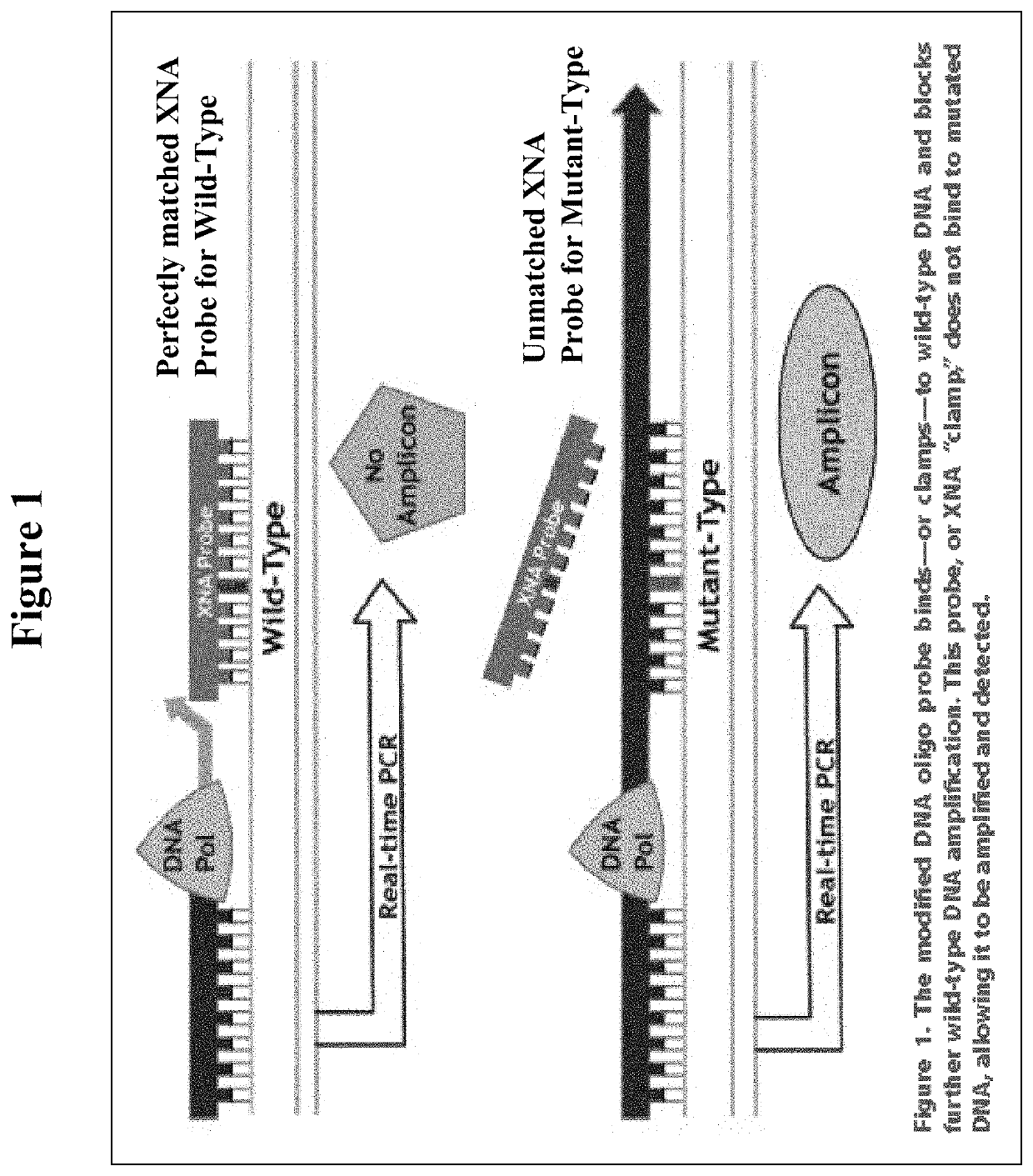
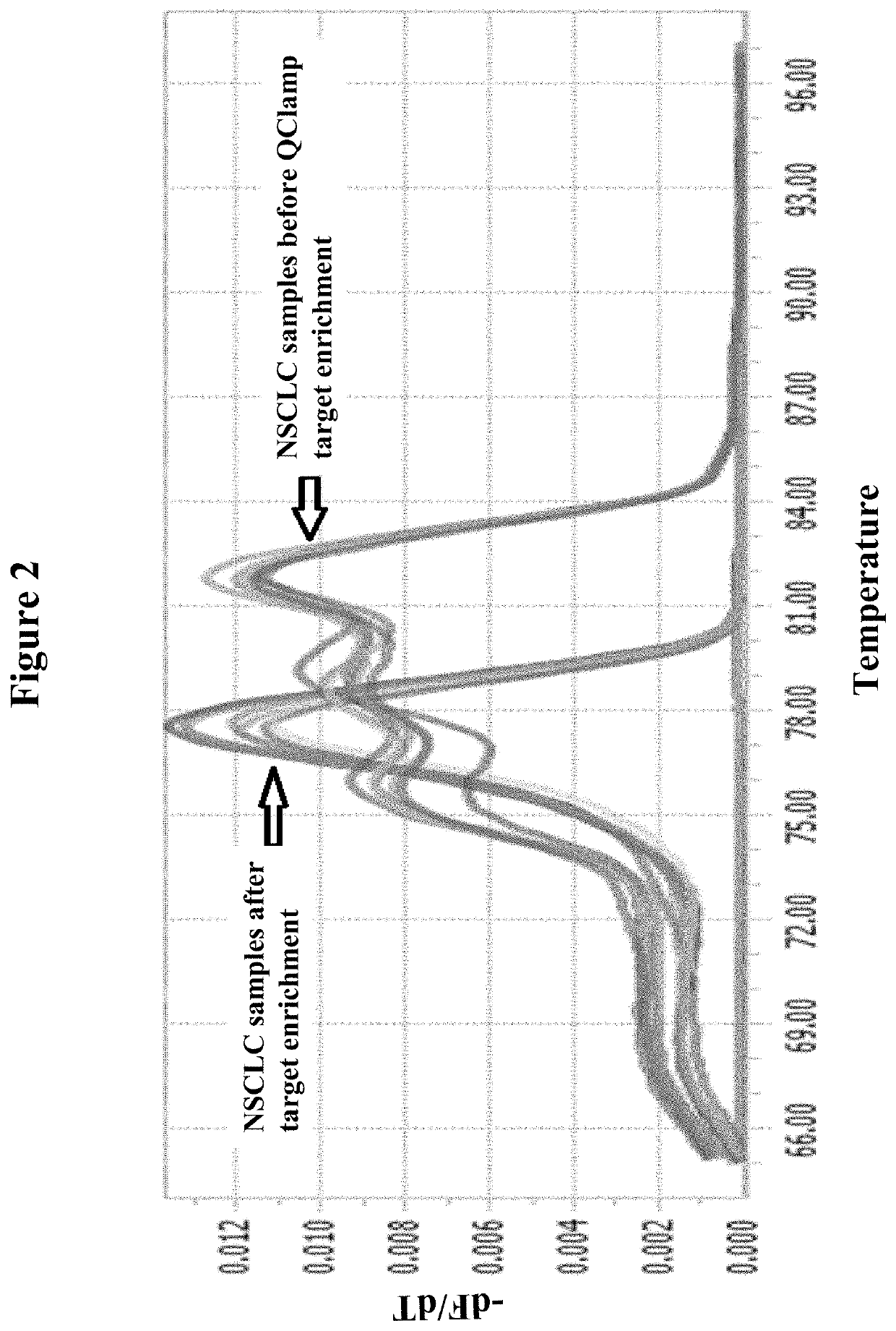
The invention relates to a method for enriching a target polynucleotide sequence containing a genetic variation said method comprising: (a) providing two primers targeted to said target polynucleotide sequence; (b) providing a target specific xenonucleic acid clamp oligomer specific for a wildtype polynucleotide sequence; (c) generating multiple amplicons using PCR under specific temperature cycling conditions; and (d) detecting said amplicons. We introduce a novel molecule, Xenonucleic Acid (XNA) for the NGS library preparation. XNA is able to selectively suppress amplification of DNA with wild type alleles and amplify DNA containing mutant alleles. Mutants with low allelic frequency will be easily detectable without deep sequencing after enrichment by adding XNA in multiplex PCR. The 17 actionable mutants related to lung or colorectal cancer diseases at different variant allelic frequency (VAF)% were investigated. Clinical sensitivity is significantly improved with XNA in various types of samples.
Owner:DIACARTA LTD
Method of inducing melanogenesis in humans with MC1R variant alleles
Owner:CLINUVEL PHARMA
DNA mutation detection employing enrichment of mutant polynucleotide sequences and minimally invasive sampling
ActiveUS11208689B2Improved and efficientGrowth inhibitionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMultiplex
The invention relates to a method for enriching a target polynucleotide sequence containing a genetic variation said method comprising: (a) providing two primers targeted to said target polynucleotide sequence; (b) providing a target specific xenonucleic acid clamp oligomer specific for a wildtype polynucleotide sequence; (c) generating multiple amplicons using PCR under specific temperature cycling conditions; and (d) detecting said amplicons. We introduce a novel molecule, Xenonucleic Acid (XNA) for the NGS library preparation. XNA is able to selectively suppress amplification of DNA with wild type alleles and amplify DNA containing mutant alleles. Mutants with low allelic frequency will be easily detectable without deep sequencing after enrichment by adding XNA in multiplex PCR. The 17 actionable mutants related to lung or colorectal cancer diseases at different variant allelic frequency (VAF) % were investigated. Clinical sensitivity is significantly improved with XNA in various types of samples.
Owner:DIACARTA LTD
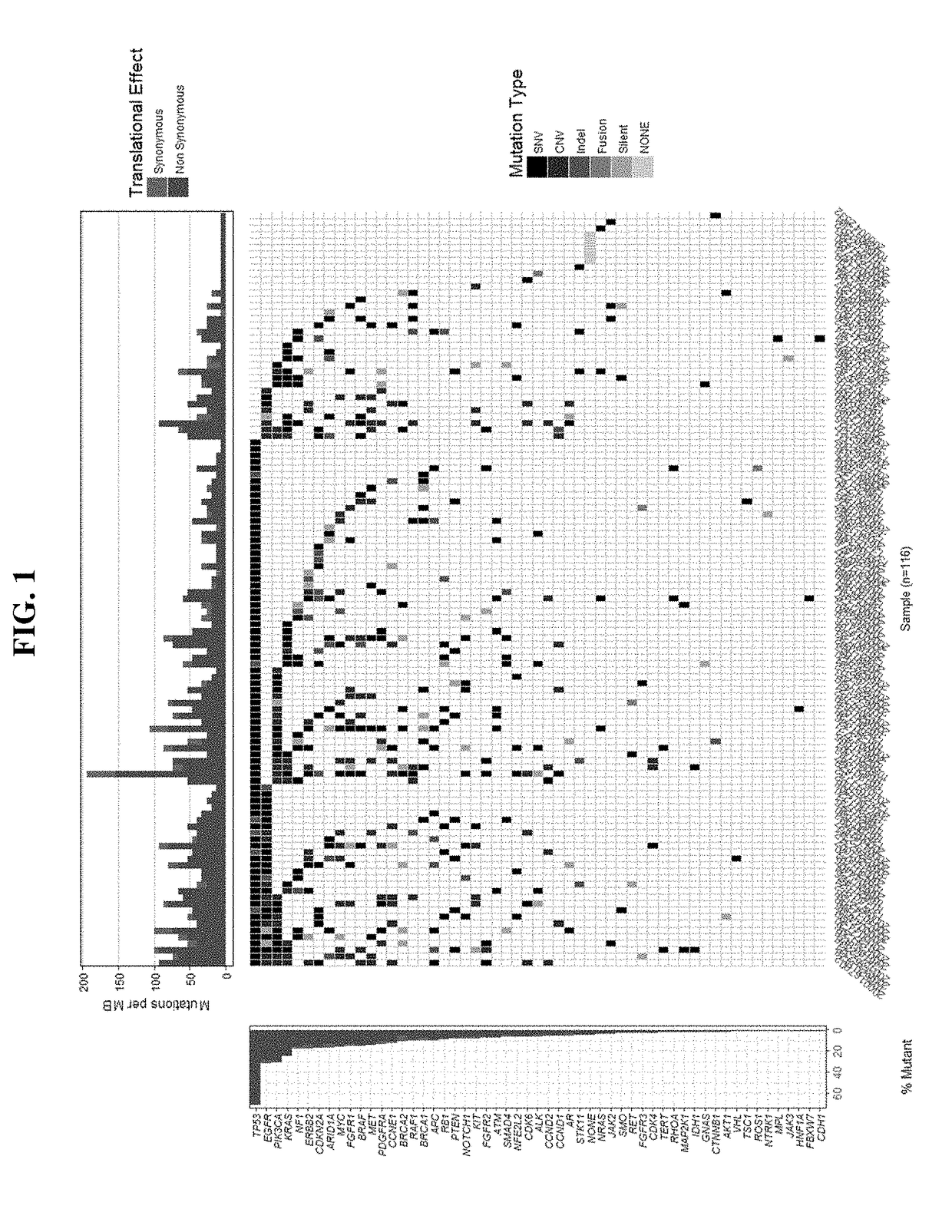
Tumor functional mutation and epitope loads as improved predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy response
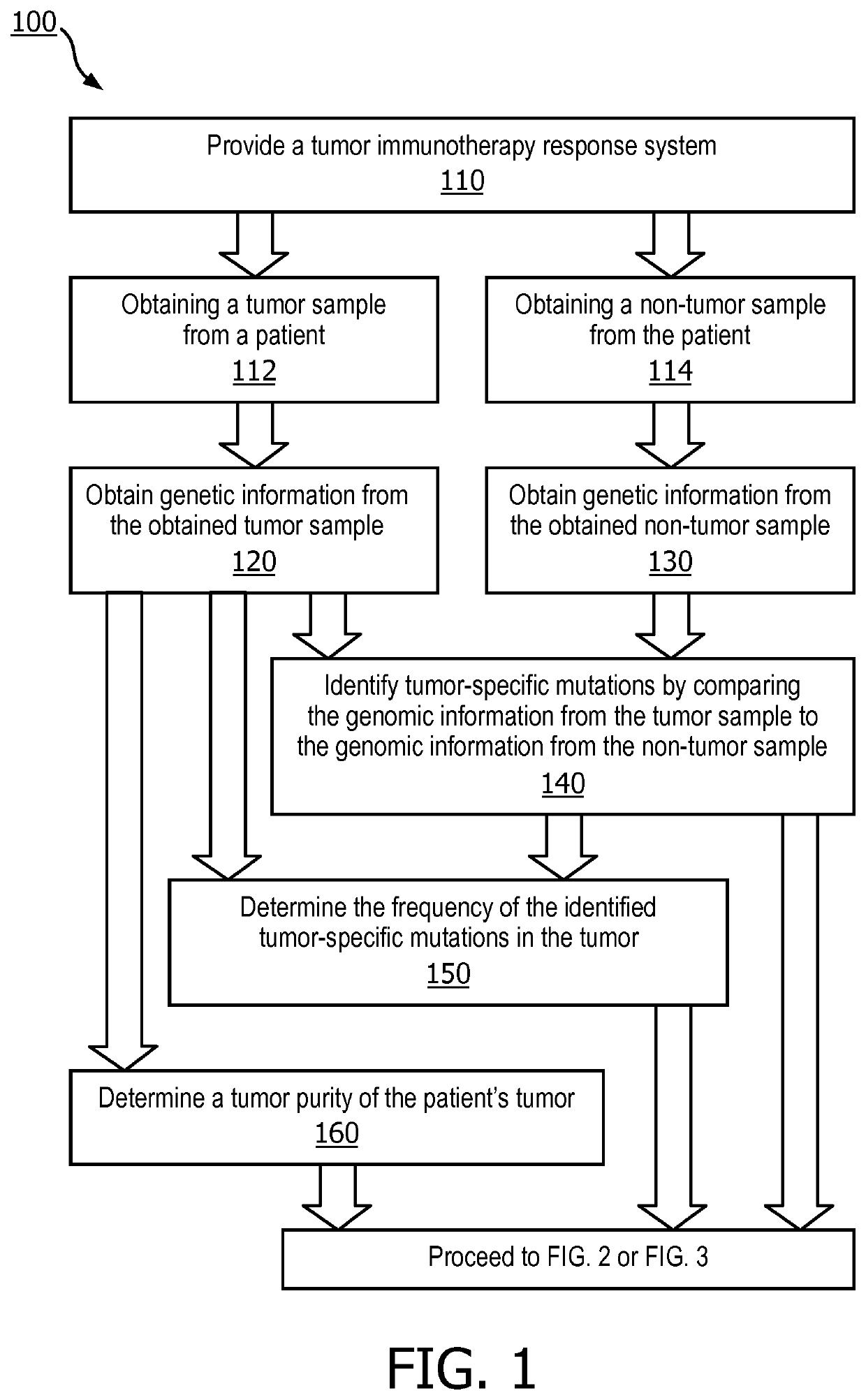
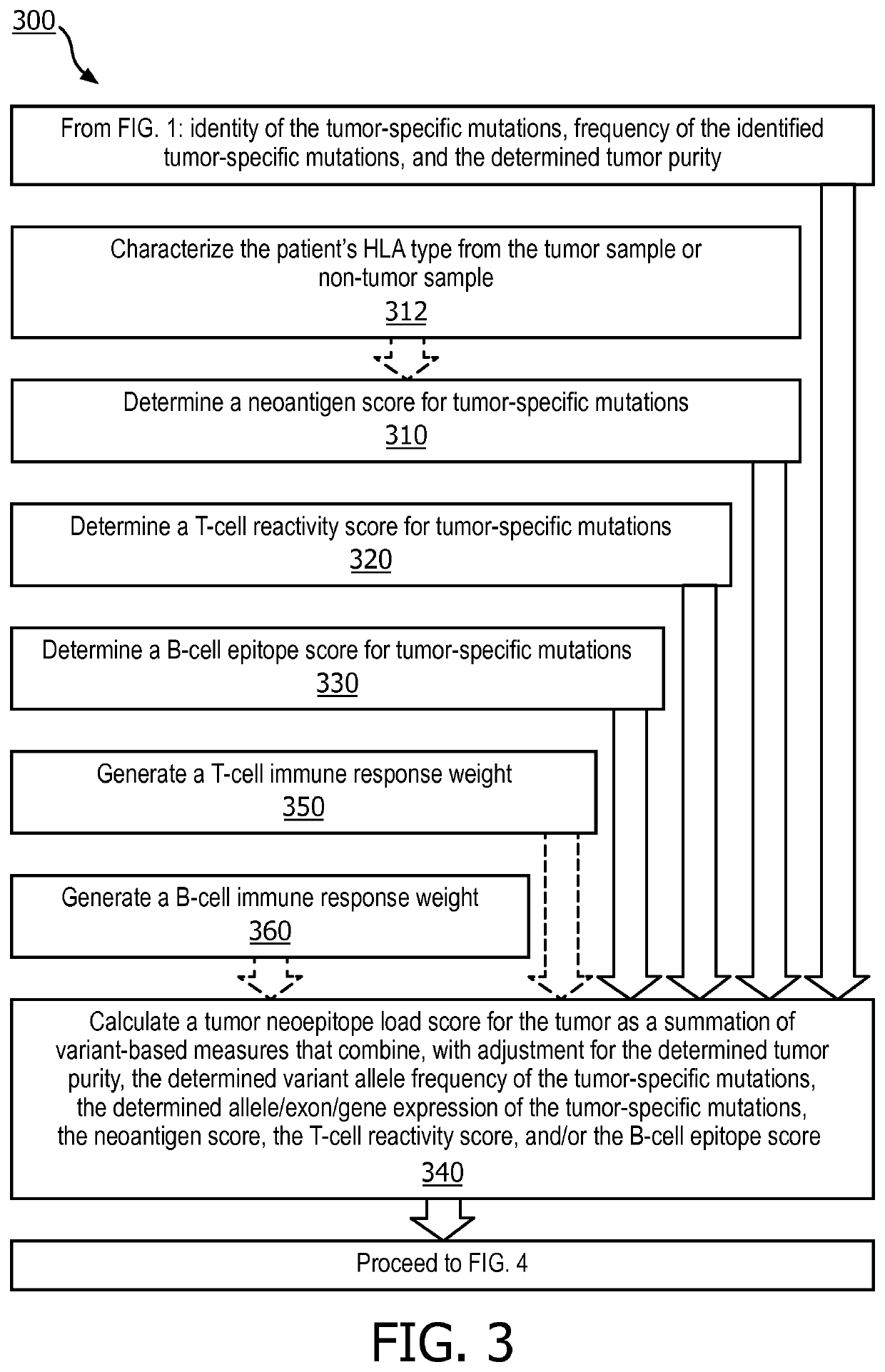
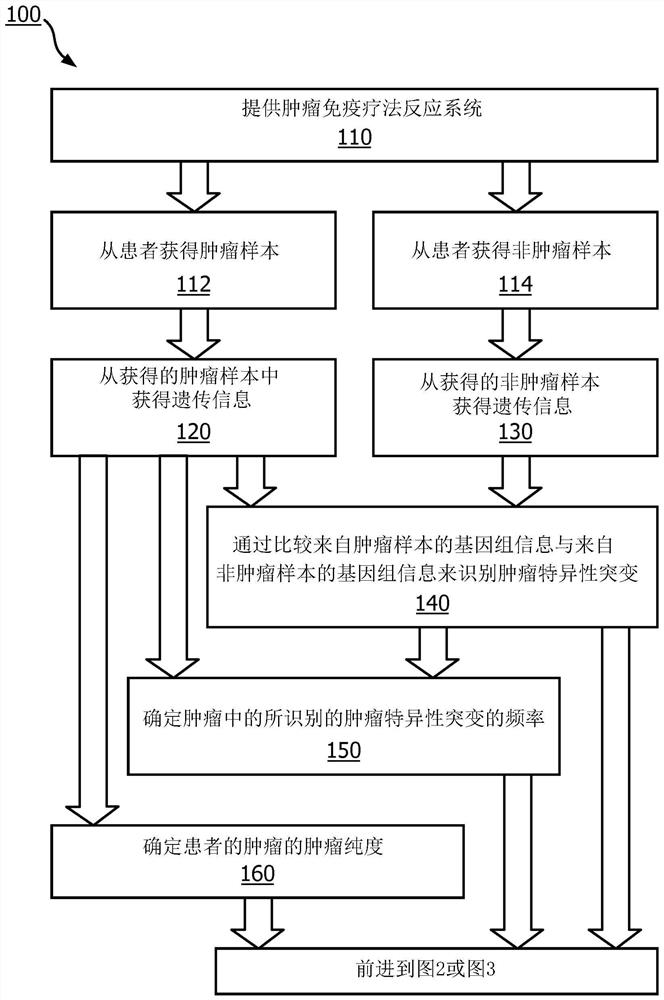
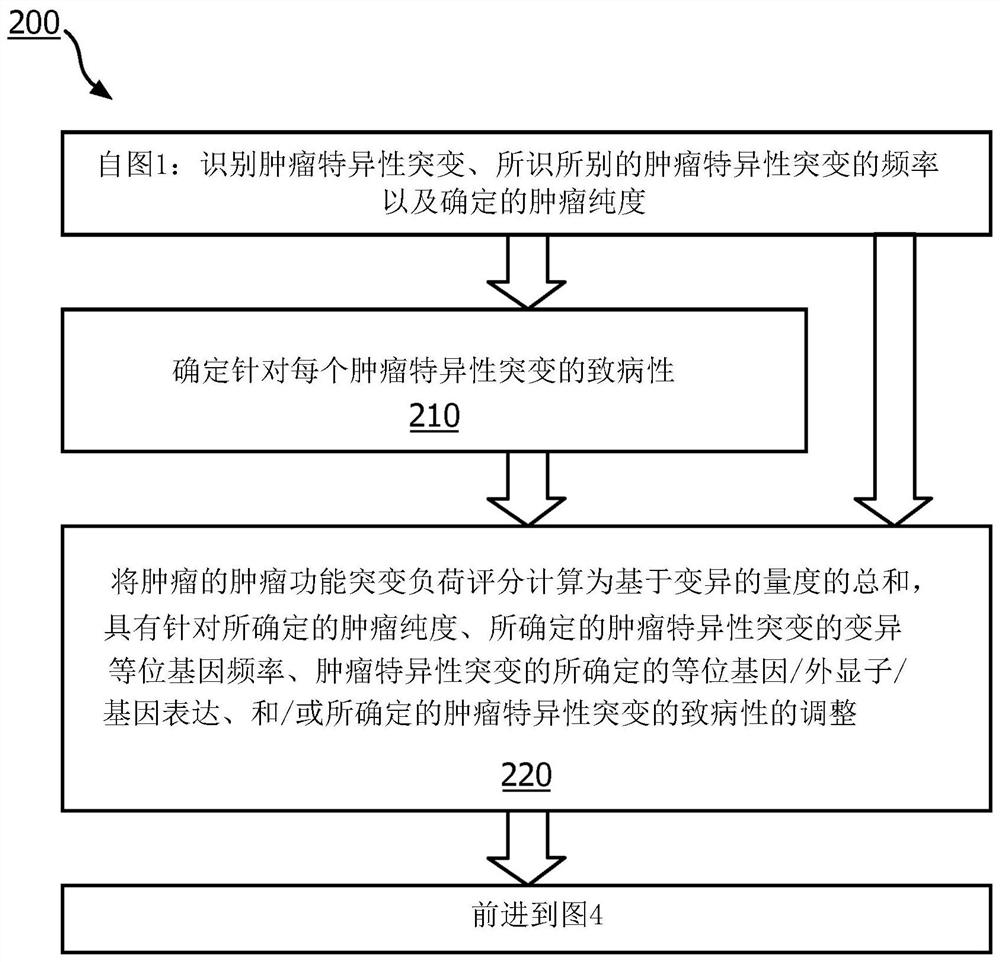
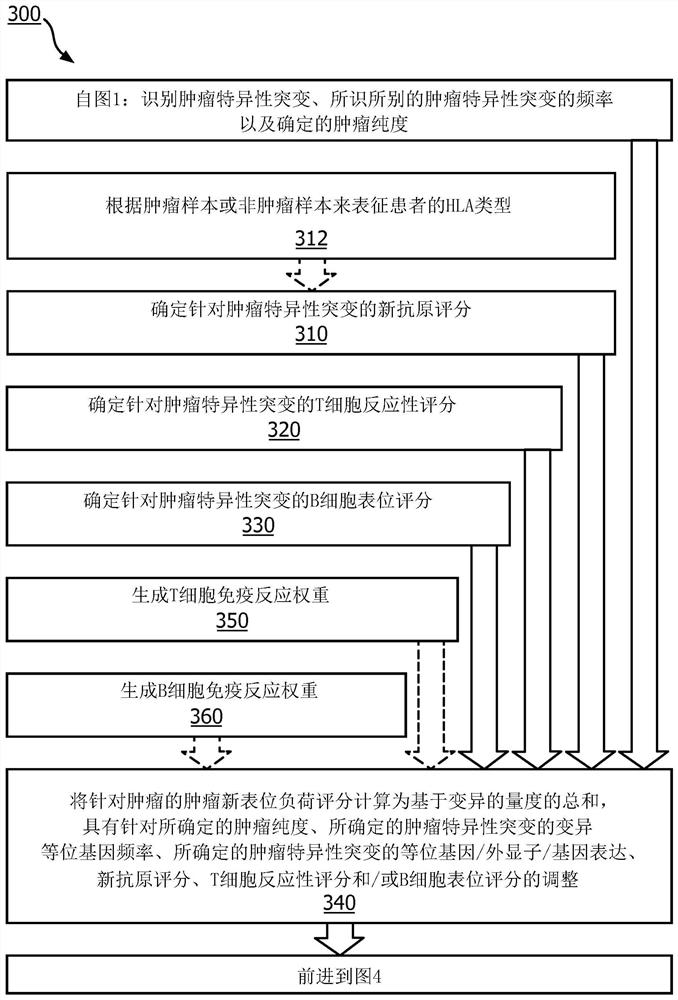
A method (100, 200, 400) for predicting a response of a tumor to immunotherapy, comprising: analyzing (120) a tumor sample; analyzing (130) a non-tumor sample obtained from the patient; identifying (140) one or more tumor-specific mutations; analyzing (150) the genetic information from the tumor sample to determine a variant allele frequency for the identified tumor-specific mutations; analyzing (160) genetic information to determine a tumor purity of the patients tumor; determining (210) a pathogenicity for the identified tumor-specific mutations; calculating (220), from: (i) the determined variant allele frequency and / or a determined allele-specific expression, exon expression, or gene expression of the one or more tumor-specific mutations; (ii) the determined tumor purity; and (iii) the determined pathogenicity, a tumor functional mutation load score; predicting (410), based on the score, a response of the patients tumor to an immunotherapy treatment; and determining (420), based on said prediction, a treatment for the patient.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
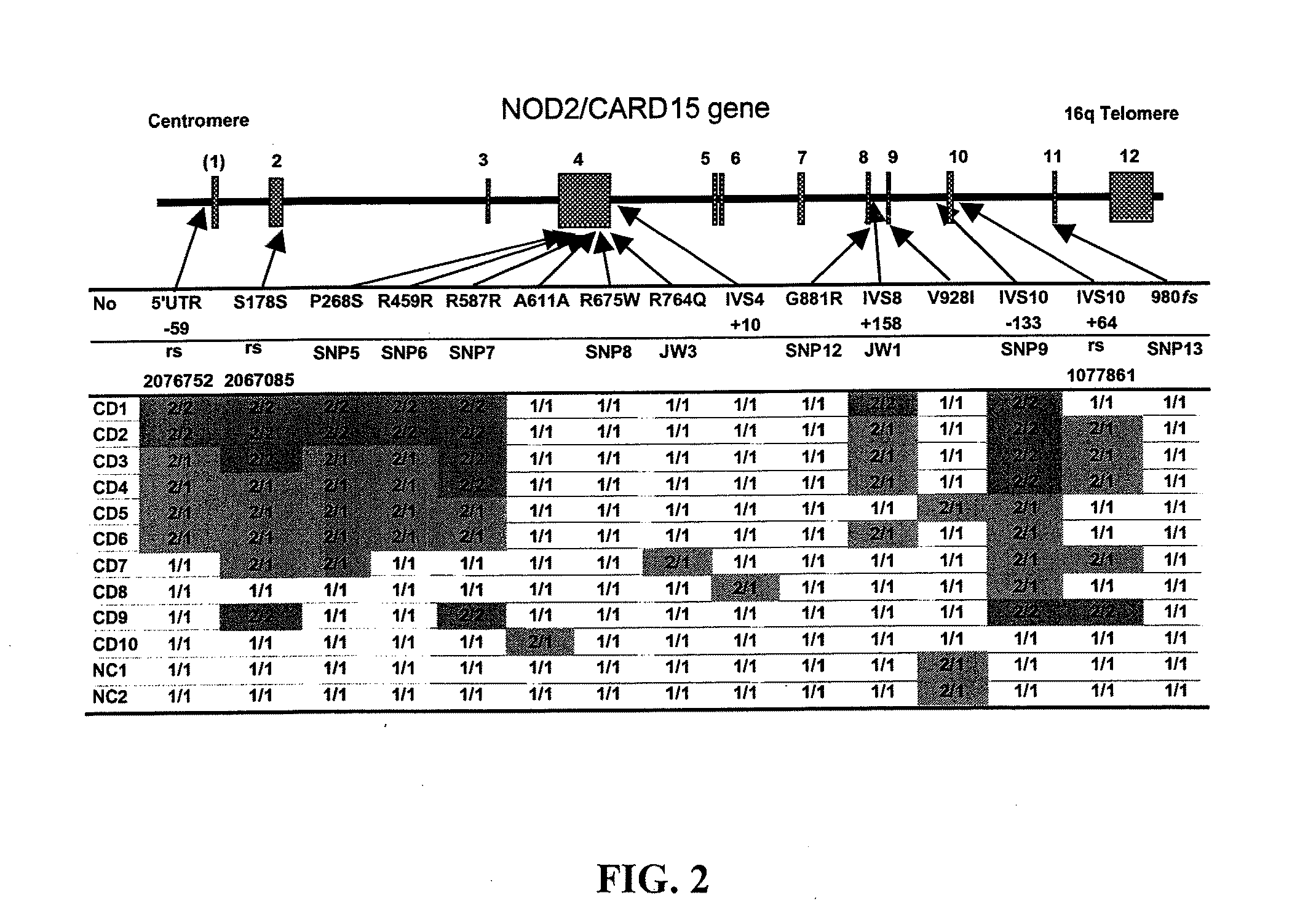
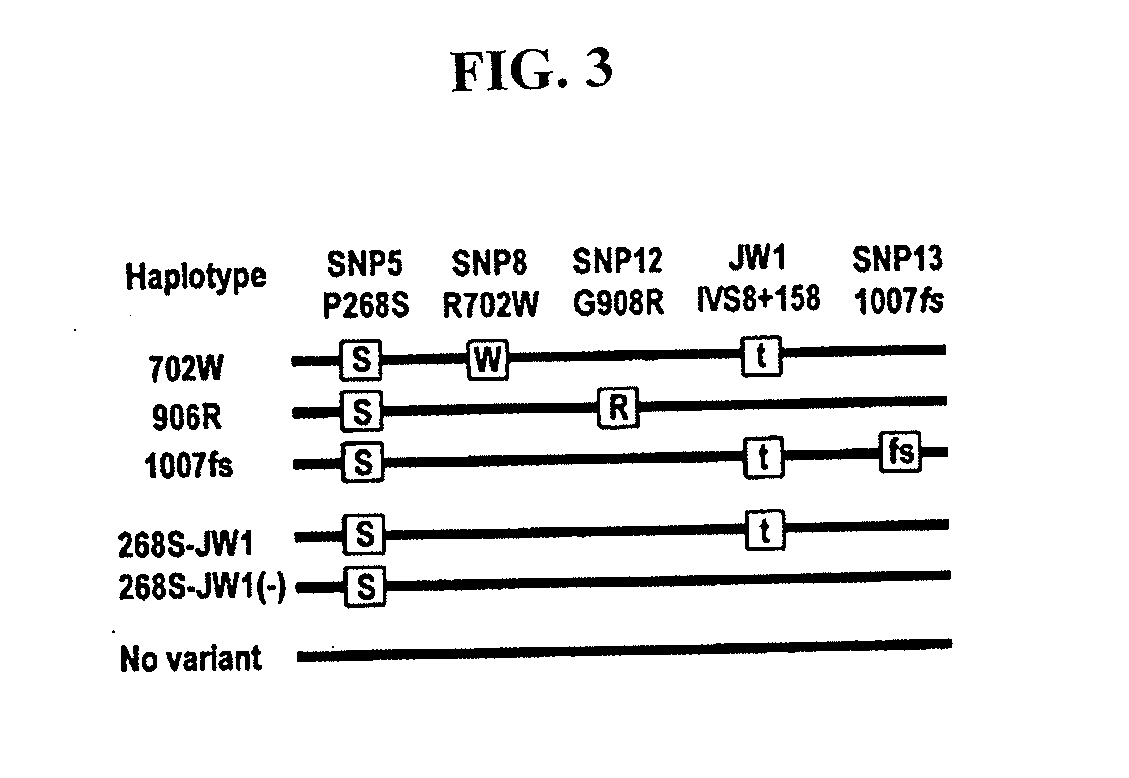
Methods of using a nod2/card15 haplotype to diagnose crohn's disease
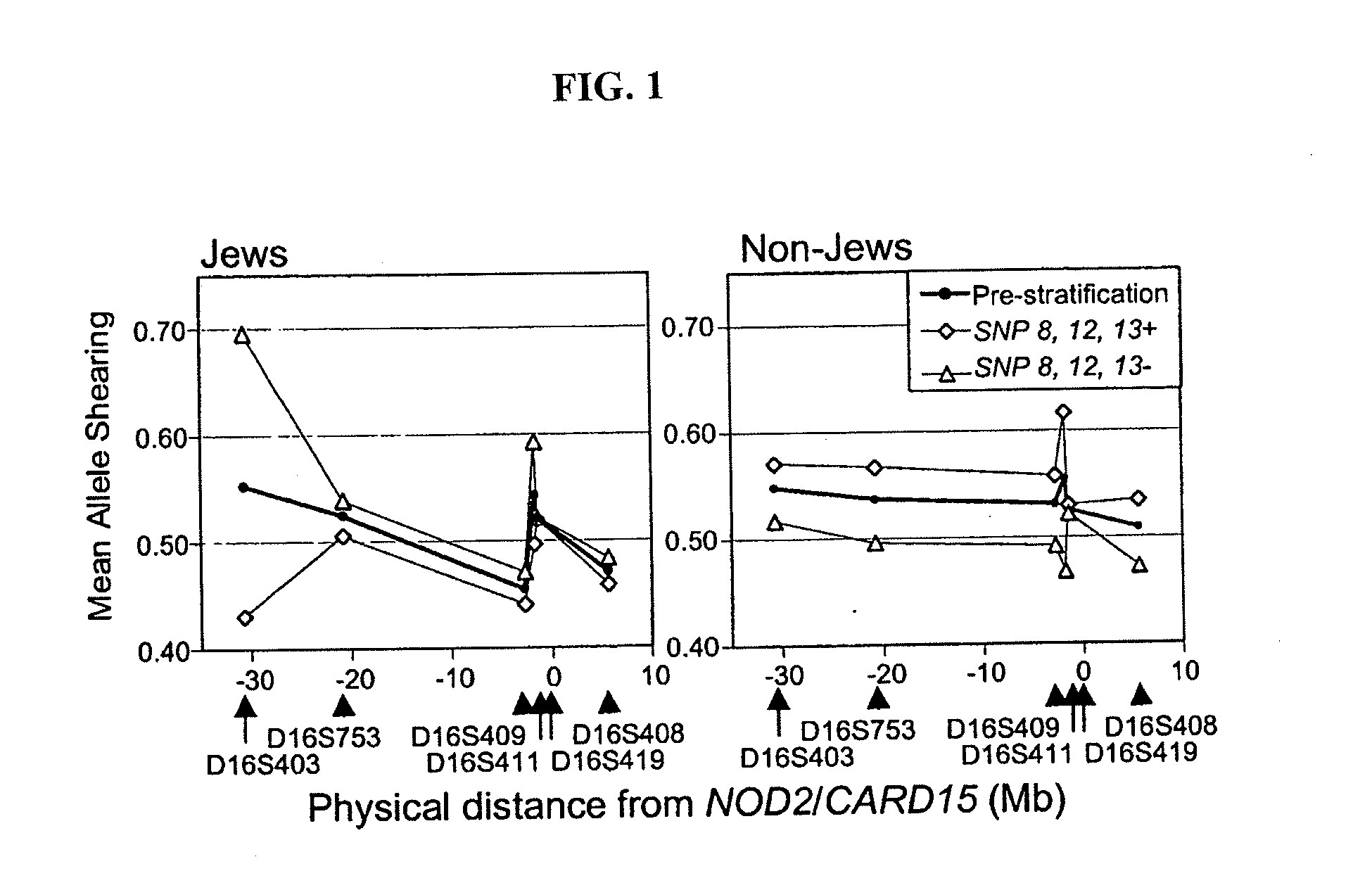
The present invention provides a method of diagnosing or predicting susceptibility to Crohn's disease in an individual by determining the presence or absence in the individual of a disease-predisposing haplotype containing a JW1 variant allele at the NOD2 / CARD15 locus, where the presence of the disease-predisposing haplotype is diagnostic of or predictive of susceptibility to Crohn's disease.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
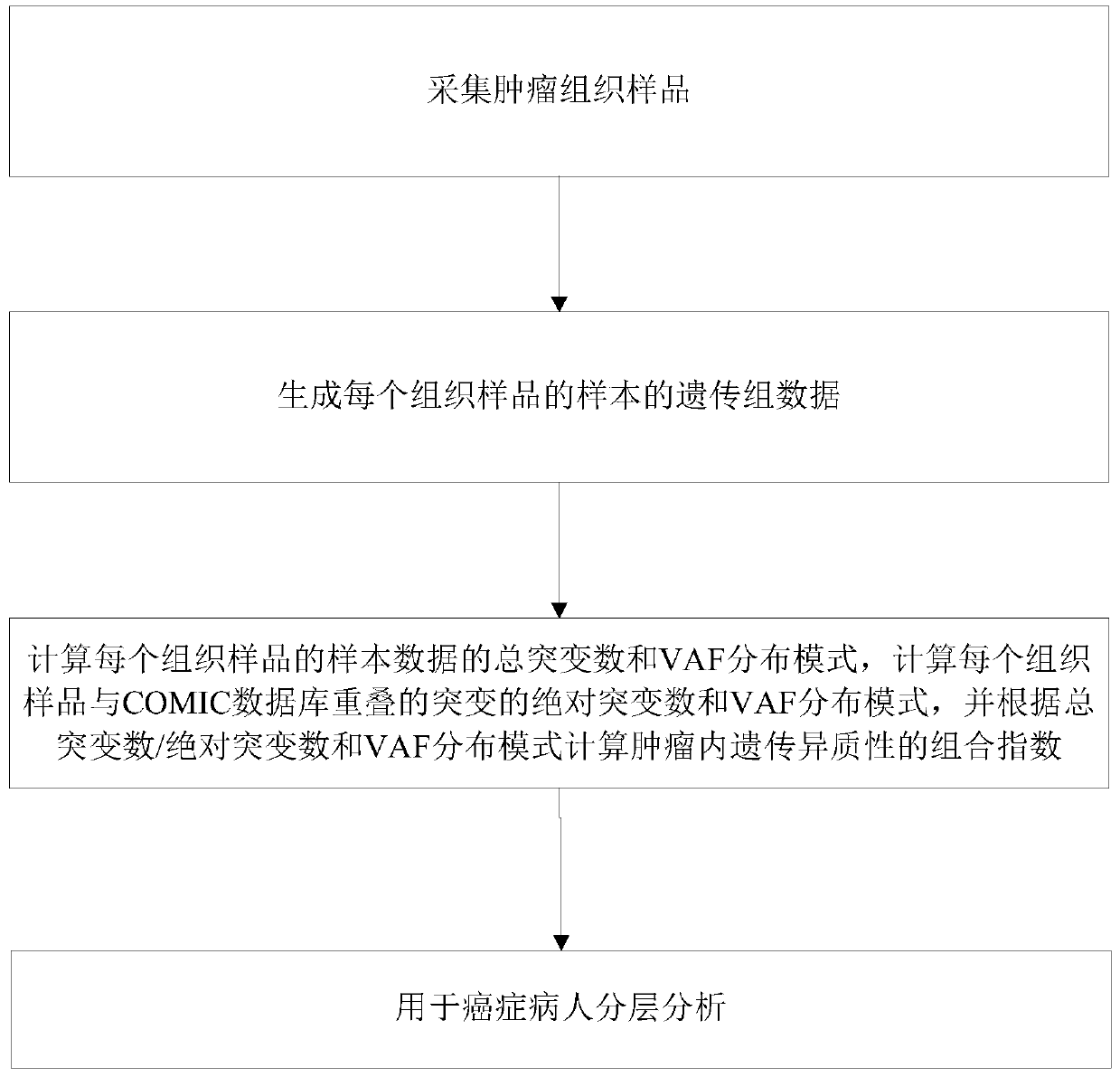
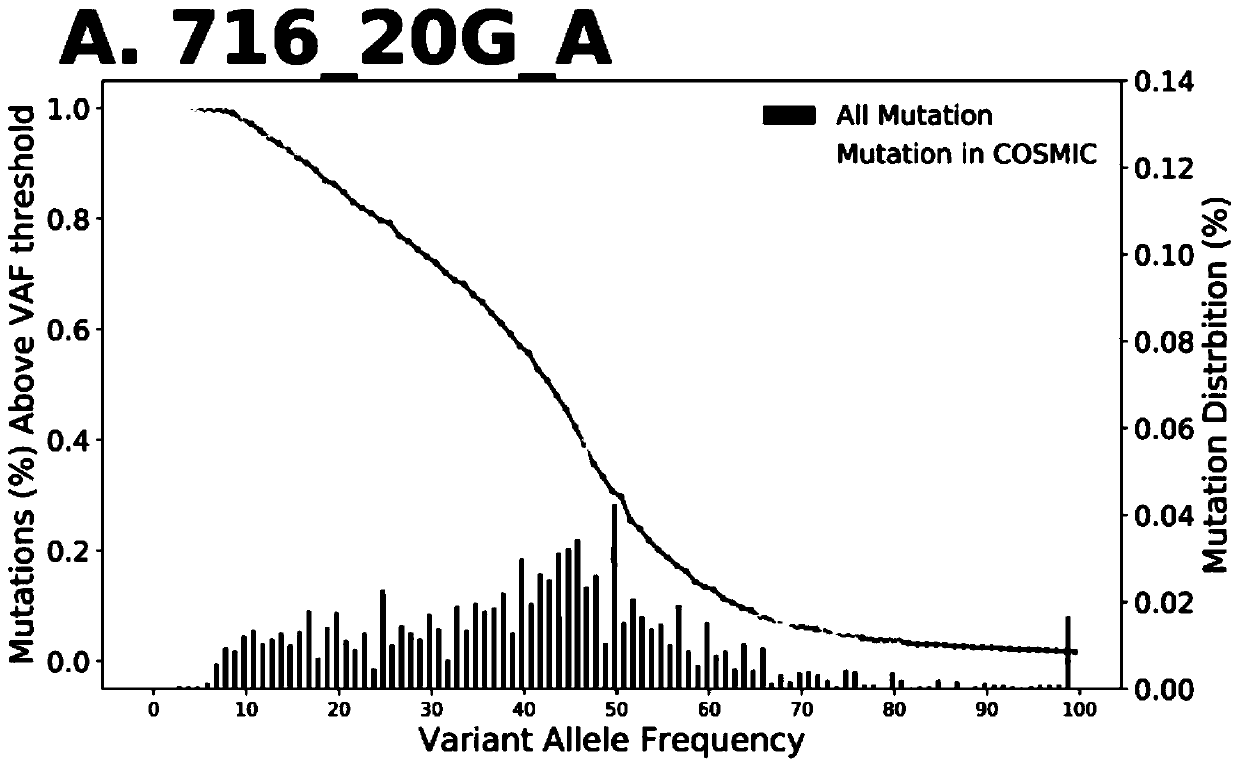
Method for calculating intratumor heterogeneity
The invention discloses a method for calculating intratumor heterogeneity and belongs to the field of cancers. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring tumor tissue samples, and generatingmutation group data of each tissue sample; and calculating mix indexes of intratumor heterogeneity according to the mutation group data. By adopting the method, the mix indexes are calculated on the basis of mutation of sample data of each tissue sample and variation allele frequency corresponding to the mutation, the mix indexes function as indexes of intratumor heterogeneity, and a quantizationtool is provided for stratification analysis on tumor patients.
Owner:信华生物药业(广州)有限公司
Tumor burden as measured by cell free DNA
InactiveCN110913901AMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsTherapy resistantAntiendomysial antibodies
Disclosed are methods for treating cancer (e.g., solid tumor cancers, lung cancer, bladder head and neck cancer) with an anti-PD-Ll antibody in a patient identified as being responsive to anti- PD-Llantibody therapy by detecting a mutation in one or more disclosed circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) markers. Also disclosed are methods for determining the efficacy of anti-PD-Ll therapeutic antibody treatment in a patient having lung cancer or bladder cancer comprising detecting variant allele frequency in ctDNA in plasma samples and determining the difference of the variant allele frequency in ctDNAbetween the first and at least second plasma samples, wherein a decrease in the variant allele frequency in the at least second plasma sample relative to the first plasma sample identifies the anti-PD-Ll antibody treatment as effective. The disclosure also provides methods of identifying a subject having a cancer responsive to a therapy comprising an anti-PD-Ll antibody by detecting the expression of a mutation in one or more circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) markers.
Owner:免疫医疗有限责任公司
Tumor functional mutation and epitope loads as improved predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy response
PendingCN112292464AMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsAllele frequencyPredictive biomarker
A method (100, 200, 400) for predicting a response of a tumor to immunotherapy, comprising: analyzing (120) a tumor sample; analyzing (130) a non-tumor sample obtained from the patient; identifying (140) one or more tumor-specific mutations; analyzing (150) the genetic information from the tumor sample to determine a variant allele frequency for the identified tumor- specific mutations; analyzing(160) genetic information to determine a tumor purity of the patient's tumor; determining (210) a pathogenicity for the identified tumor-specific mutations; calculating (220), from: (i) the determinedvariant allele frequency and / or a determined allele-specific expression, exon expression, or gene expression of the one or more tumor-specific mutations; (ii) the determined tumor purity; and (iii) the determined pathogenicity, a tumor functional mutation load score; predicting (410), based on the score, a response of the patient's tumor to an immunotherapy treatment; and determining (420), basedon said prediction, a treatment for the patient.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Drug-metabolizing enzyme metabotype assessment method
ActiveCN107885970BImprove detection accuracyImprove detection efficiencyProteomicsGenomicsMetabolic enzymesPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a drug metabolic enzyme metabolism type evaluation method, comprising steps: S1, acquiring haploid variant allele names of genes from a preset gene data bank, to form a gene information table; S2, according to the gene information table, obtaining a diploid variant allele name sequence; S3, forming metabolism types, to obtain a metabolism type information table; S4, according to gene detection results, obtaining a locus diploid name table; S5, obtaining a first haploid variant allele name sequence; S6, according to enzymatic activity of each haploid variant allele, obtaining a second haploid variant allele name sequence; S7, from the second haploid variant allele name sequence, obtaining a diploid variant allele name result; S8, retrieving from the metabolism type information table, to obtain a metabolism type detection result. The drug metabolic enzyme metabolism type evaluation method can accurately determine a gene metabolism type, and has important meaning on drug metabolic enzyme gene detection and personalized medication aspects.
Owner:慧算基因科技上海有限公司
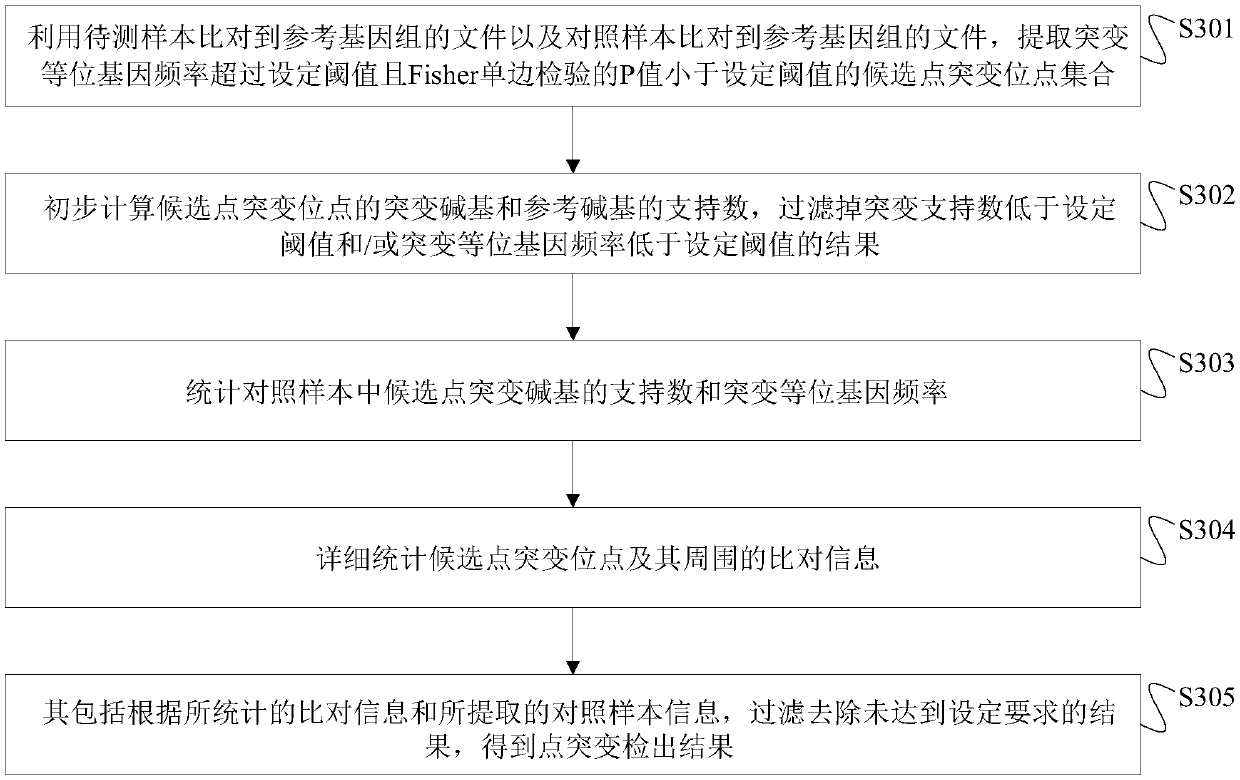
Method, device and storage medium for point mutation detection and filtering based on next-generation sequencing
ActiveCN107944223BIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityProteomicsGenomicsTrue positive rateMutant allele
The invention discloses a next generation sequencing-based point mutation detection filtering method and apparatus, and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of performing comparison with files of a reference genome by utilizing a to-be-detected sample, and extracting candidate point mutation site sets with variant allele frequencies exceeding a set threshold; preliminarily calculatingsupport numbers of mutant bases and reference bases of candidate point mutation sites, and filtering results with the mutant support numbers lower than the set threshold and / or the variant allele frequencies lower than the set threshold; performing detailed statistics on the candidate point mutation sites and surrounding comparison information, wherein the information comprises at least one of thefollowing information: the support numbers of the mutant bases and the reference bases of the candidate point mutation sites, base and comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non reference base and insertion / deletion statuses, and surrounding read quality; and according to the statistical information, filtering the results which do not meet set requirements to obtain a point mutation detection result. While the resource demands and the detection speed are optimized, the sensitivity and specificity of point mutation detection are improved.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
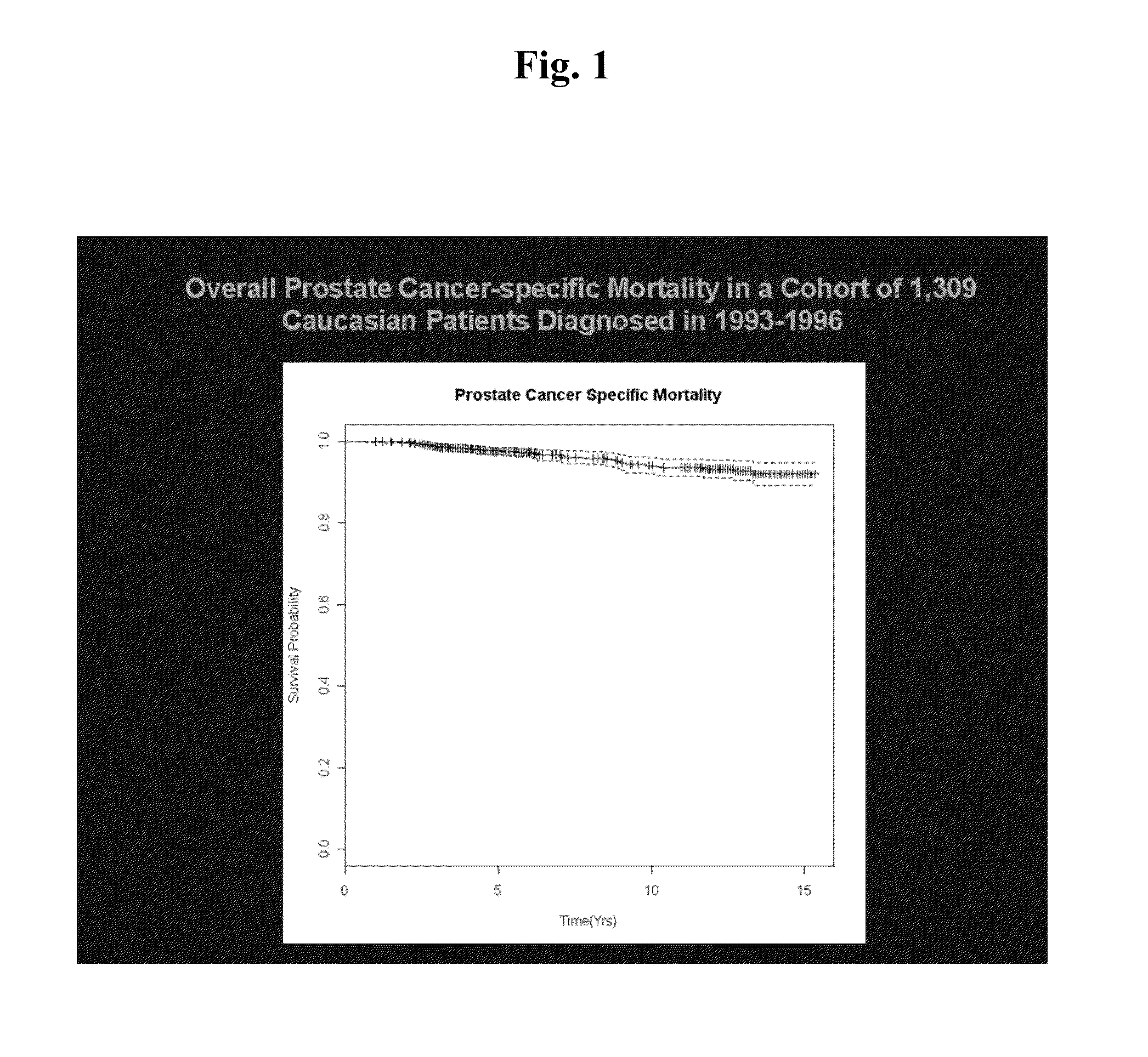
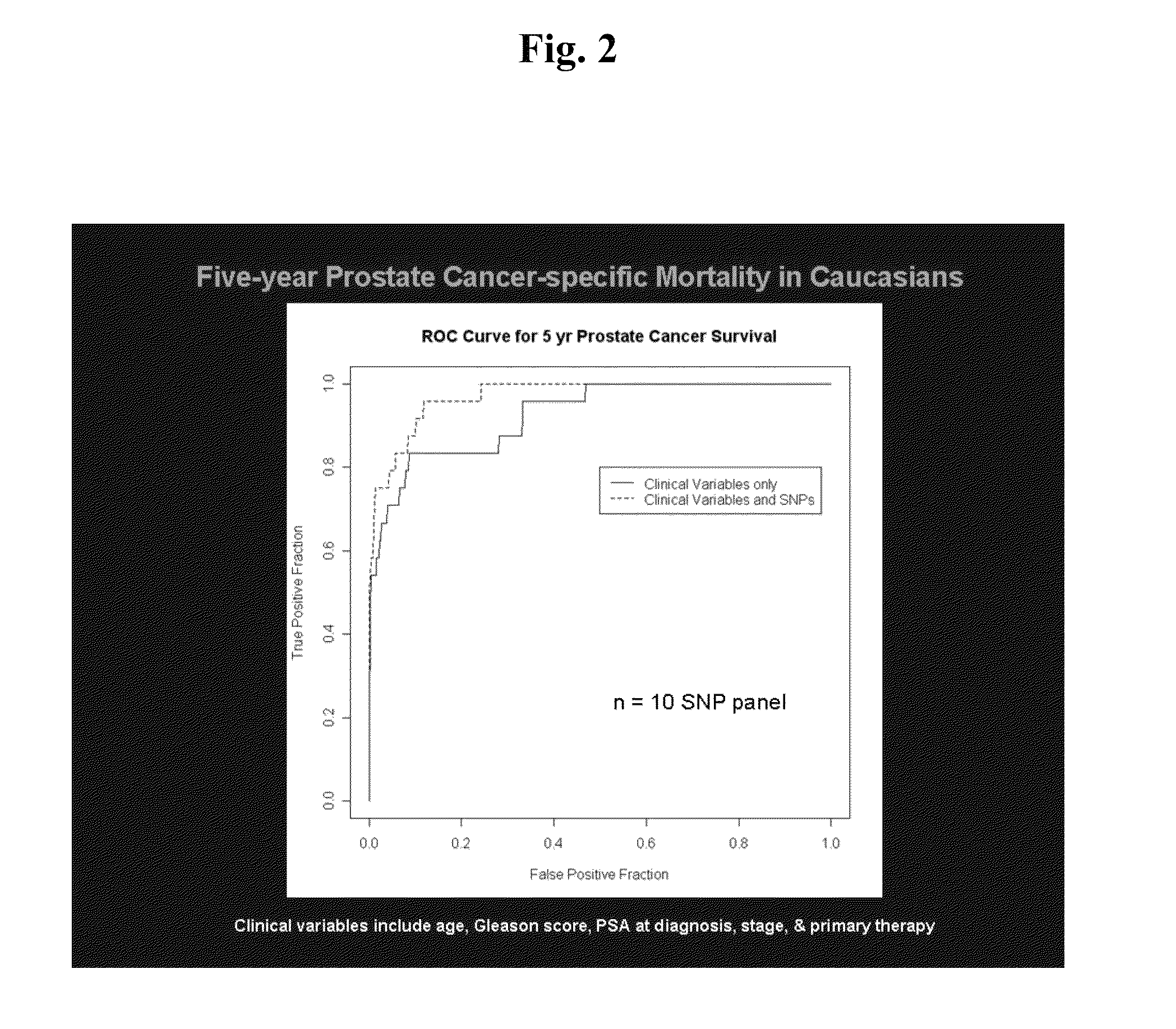
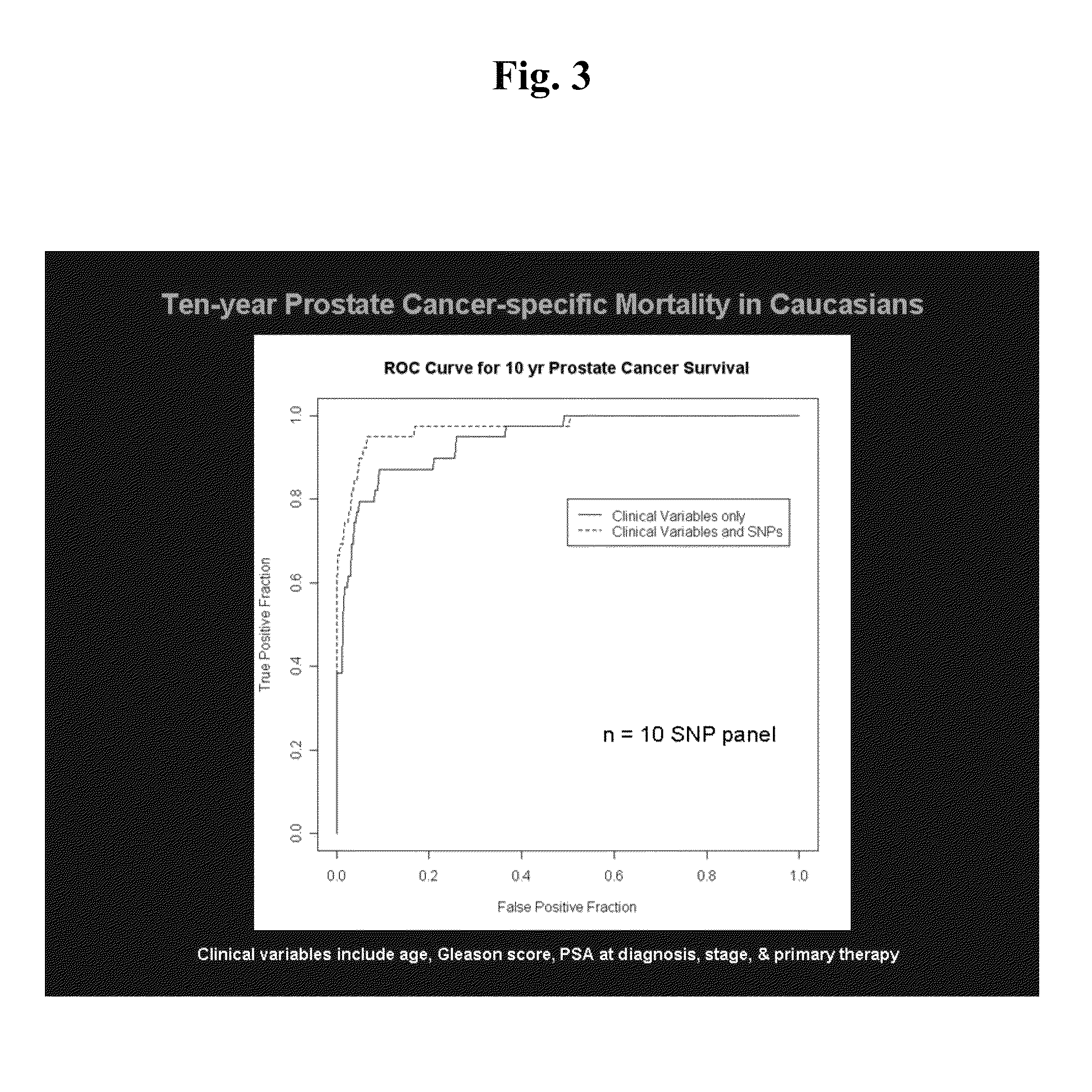
SNP panels for predicting prostate cancer-specific mortality
Provided are SNP panels and methods that employ SNP panels for predicting prostate cancer-specific mortality in a human patient. Exemplary SNP panels presented herein comprise one or more of the SNPs designated rs1137100, rs228697, rs2839685, rs1799814, rs627839, rs5993891, rs635261, rs11710277, rs11205, rs2494750, rs4608577, rs4645959, rs1799964, rs25487, rs2308327, rs915927, rs2070874, rs1029153, rs12467911, rs10778534, rs523349, and rs4583514 and are exemplified by SNP panels comprising variant alleles in one or more of the SNPs designated rs1137100, rs2070874, rs10778534, rs627839, and rs5993891.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
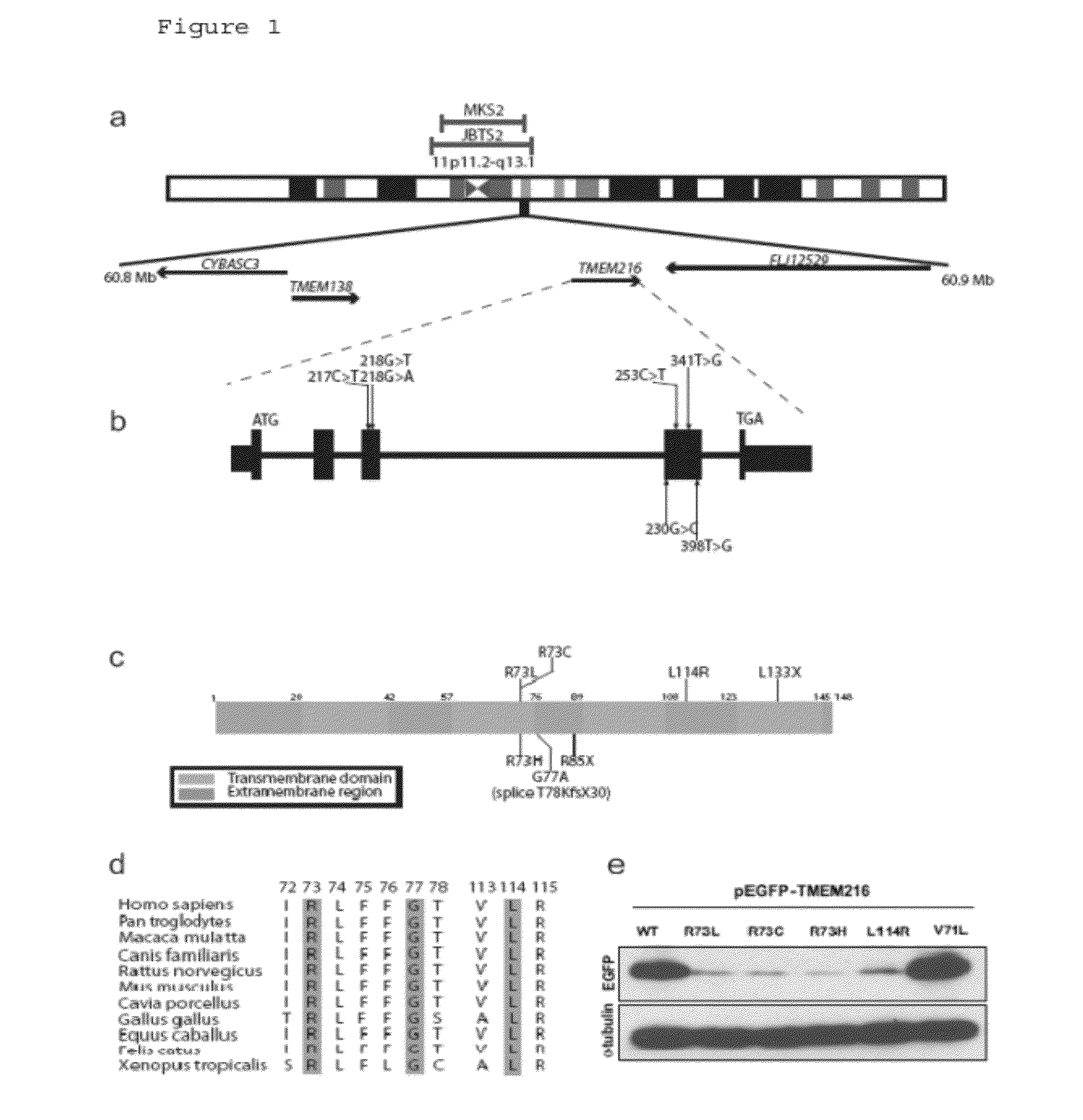
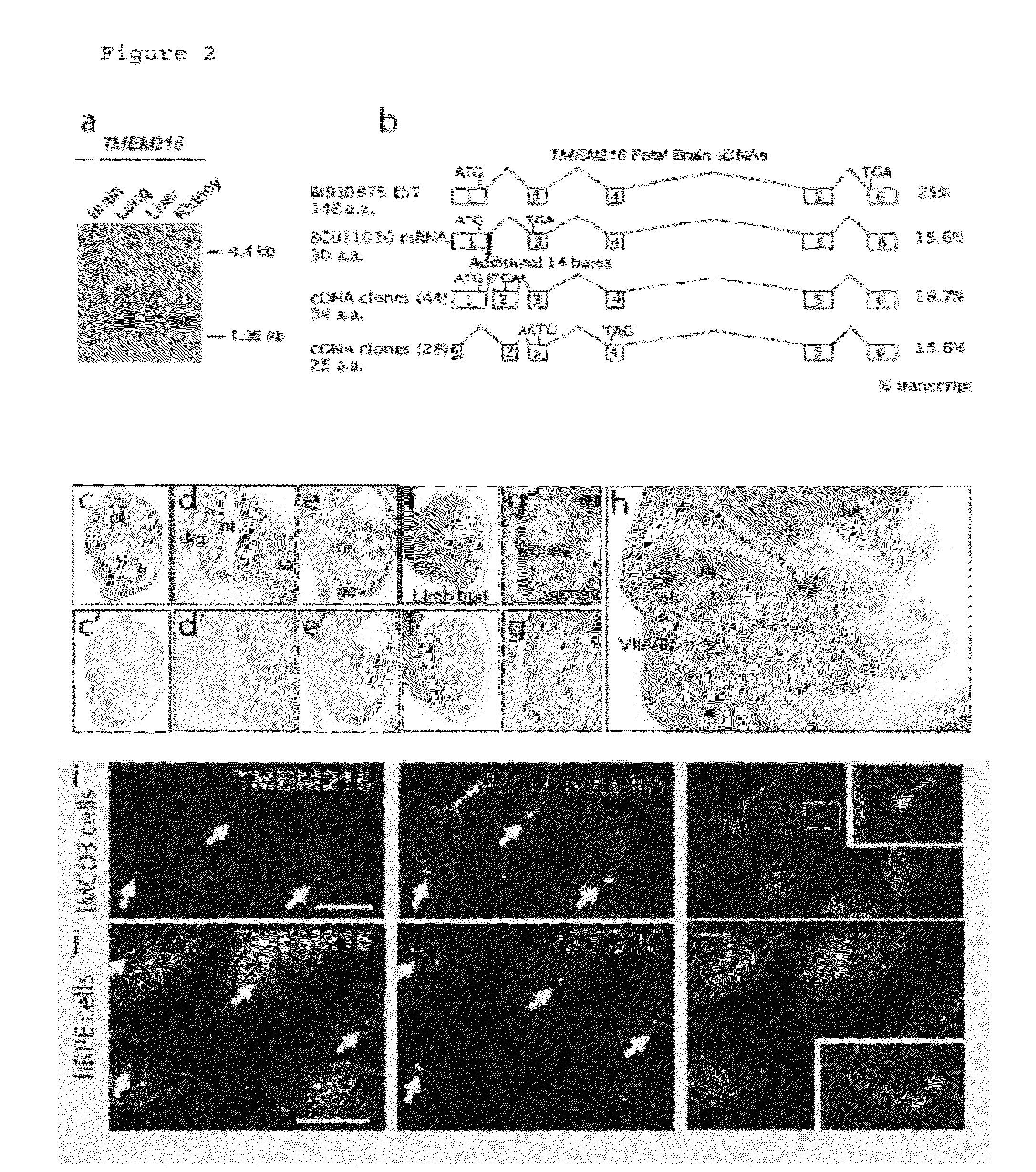
Compositions and methods for determining genetic polymorphisms in the tmem216 gene
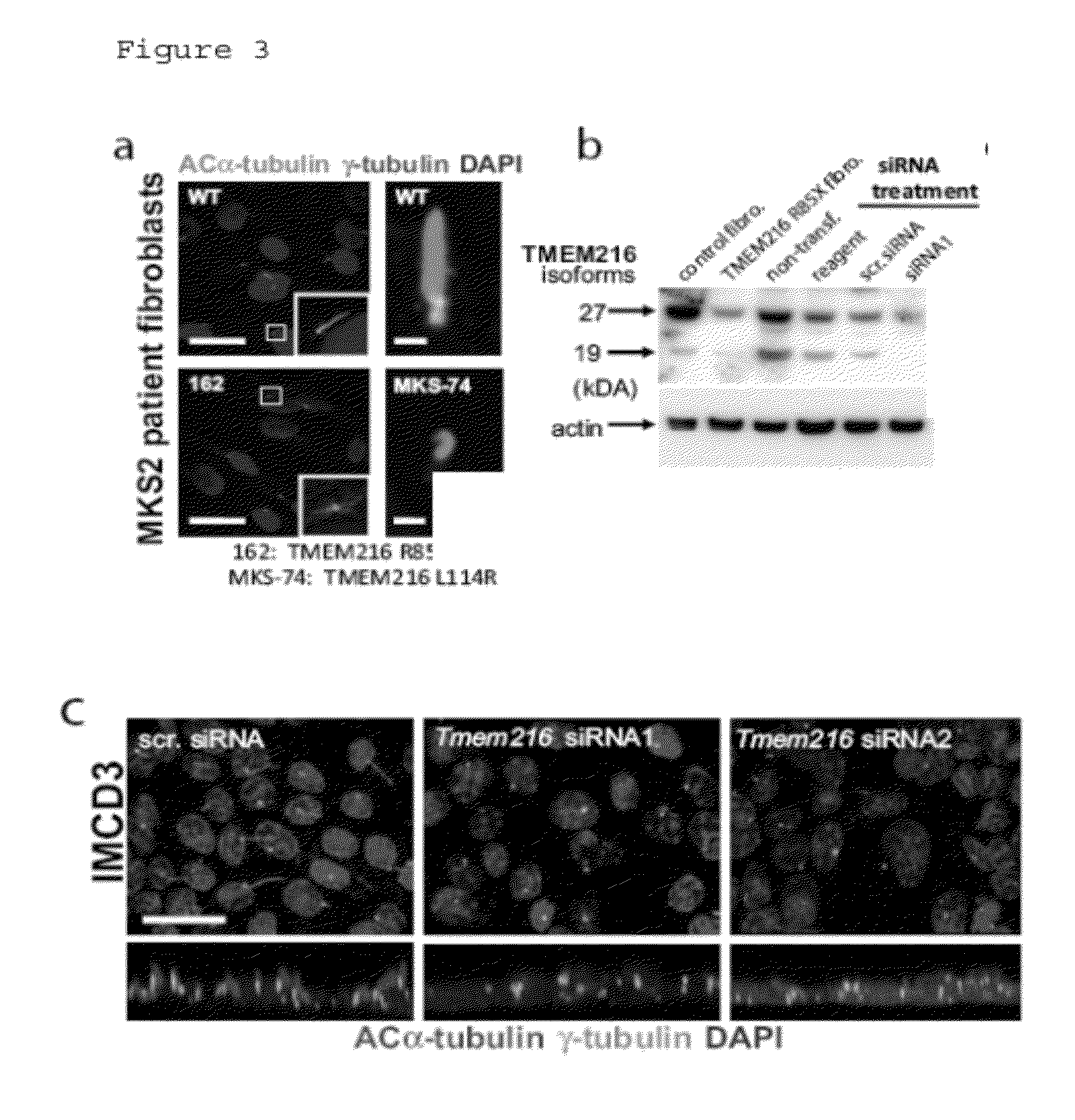
In alternative embodiments, the invention provides nucleic acid sequences that are genetic polymorphic variations of the human TMEM216 gene, and TMEM216 polypeptide encoded by these variant alleles. In alternative embodiments, the invention provides methods of determining or predicting a predisposition to, or the presence of, a ciliopathy (or any genetic disorder of a cellular cilia or cilia anchoring structure, basal body or ciliary function) in an individual, such as a Joubert Syndrome (JS), a Joubert Syndrome Related Disorder (JSRD) or a Meckel Syndrome (MKS). In alternative embodiments, the invention provides compositions and methods for the identification of genetic polymorphic variations in the human TMEM216 gene, and methods of using the identified genetic polymorphisms and the proteins they encode, e.g., to screen for compounds that can modulate the human TMEM216 gene product, and possibly treat JS, JSRD or MKS. In alternative embodiments, the invention provides cells, cell lines and / or non-human transgenic animals that can be used as screening or model systems for studying ciliopathies and testing various therapeutic approaches in treating ciliopathies, e.g., JS, JSRD or MKS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Quantitative amplicon sequencing for multiplexed copy number variation detection and allele ratio quantitation
Provided herein are methods of quantitative amplicon sequencing, for labeling each strand of targeted genomic loci in a DNA sample with an oligonucleotide barcode sequence by polymerase chain reaction, and amplifying the genomic region(s) for high-throughput sequencing. The methods can be used for the simultaneous detection of copy number variation (CNV) in a set of genes of interest, by quantifying the frequency of extra copies of each gene. In addition, these methods provide for the quantitation of the allele ratio of different genetic identities for targeted genomic loci using multiplexed PCR. In addition, these methods provide for the detection of mutations and quantitation of the variant allele frequency.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com