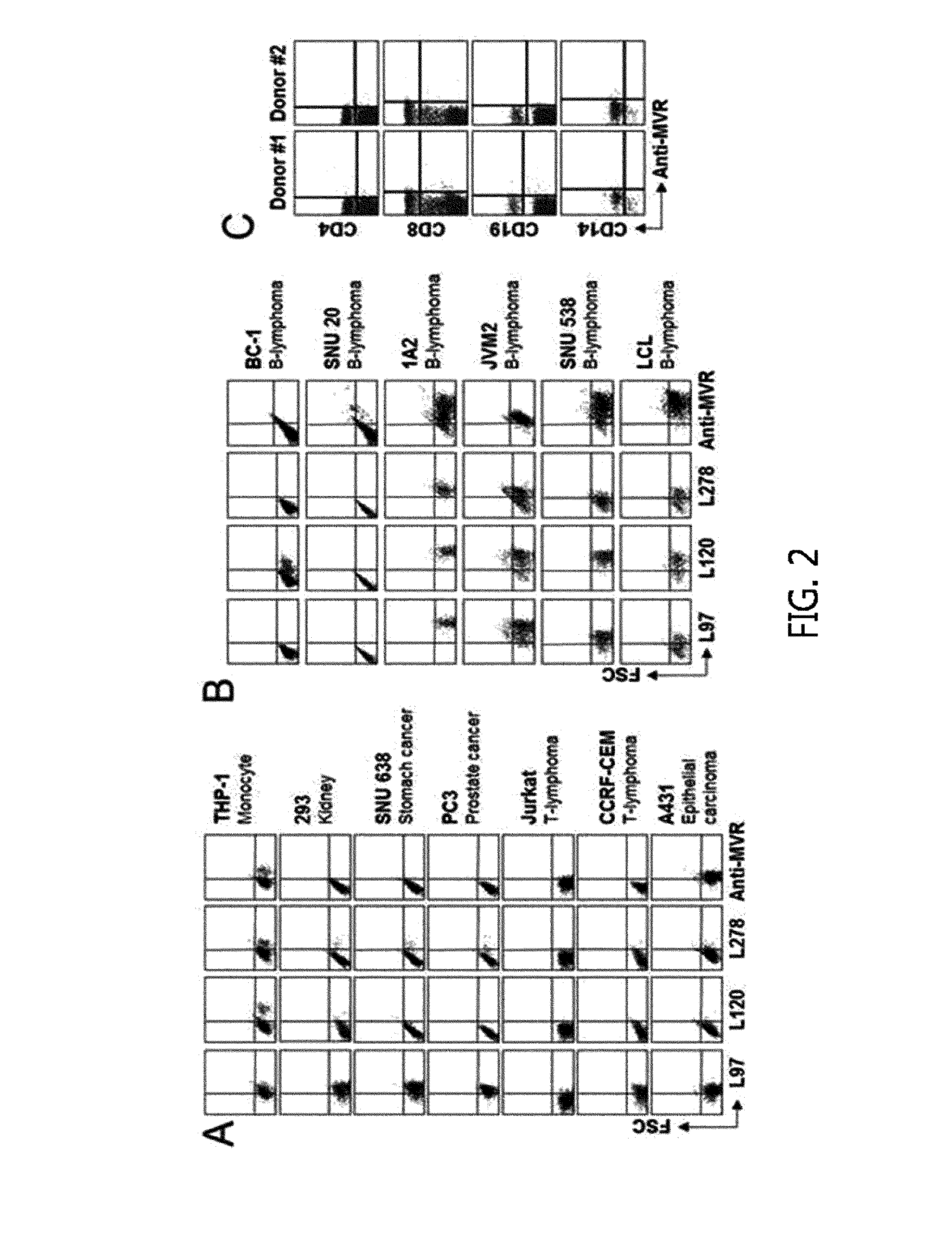
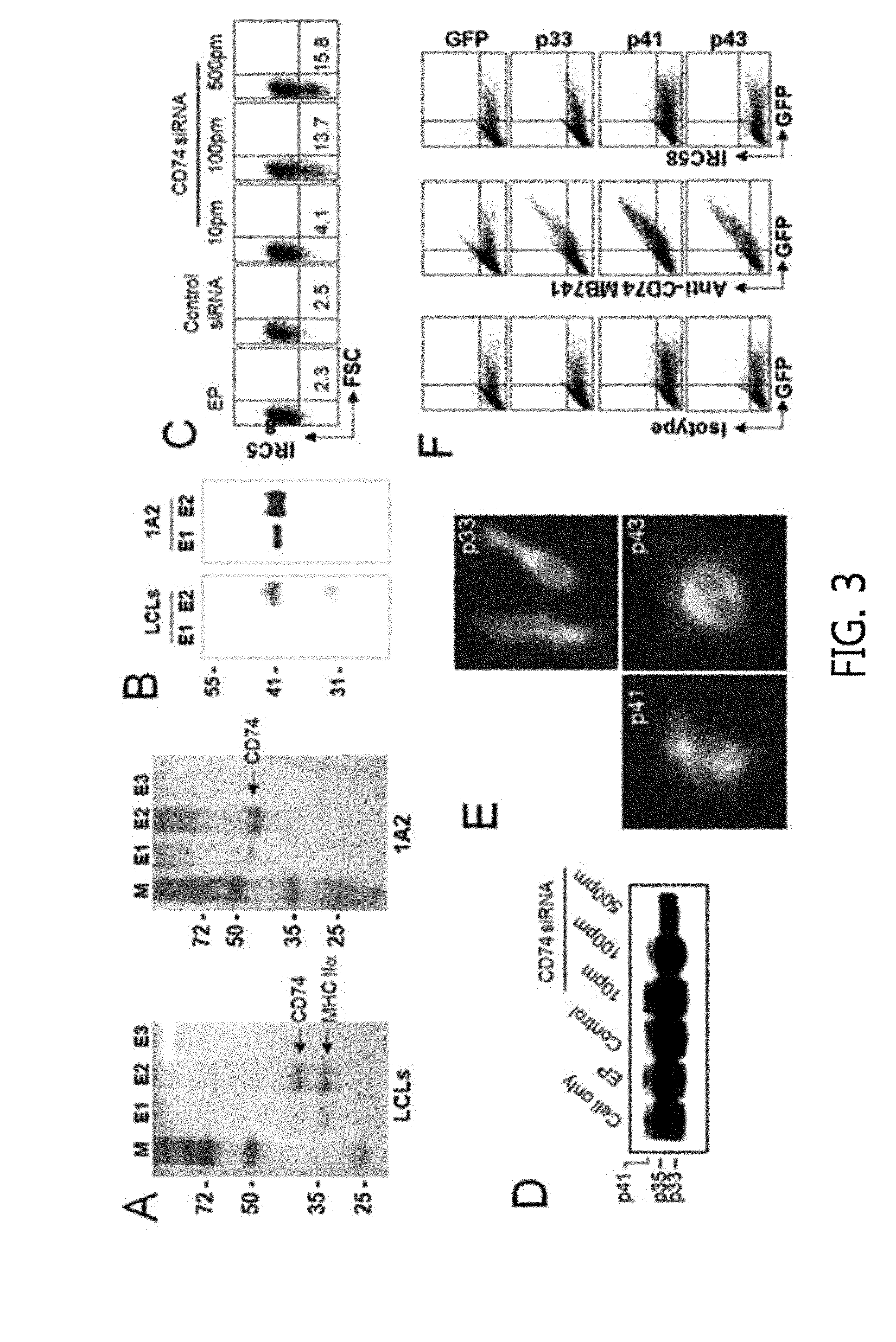
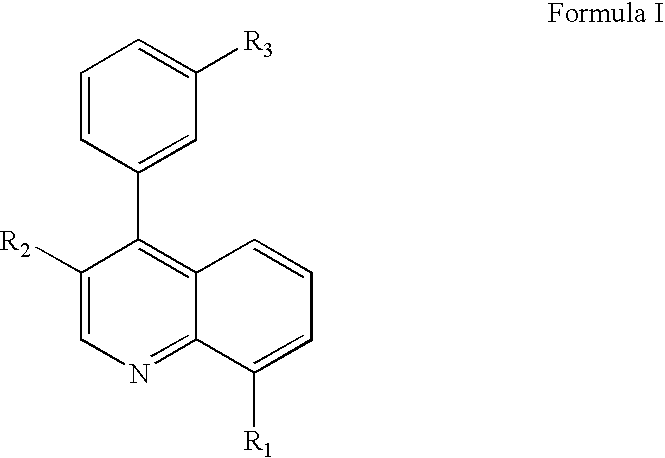
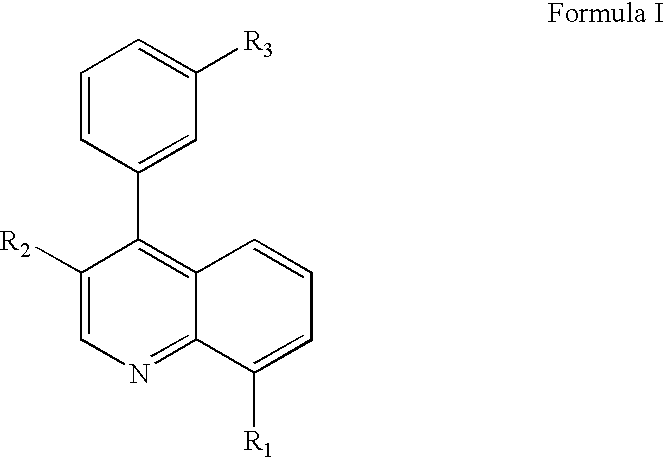
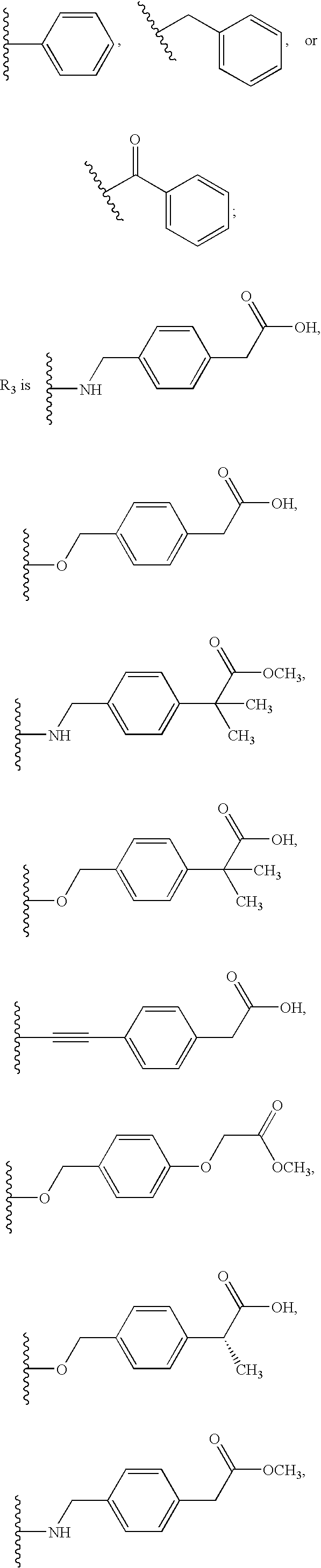
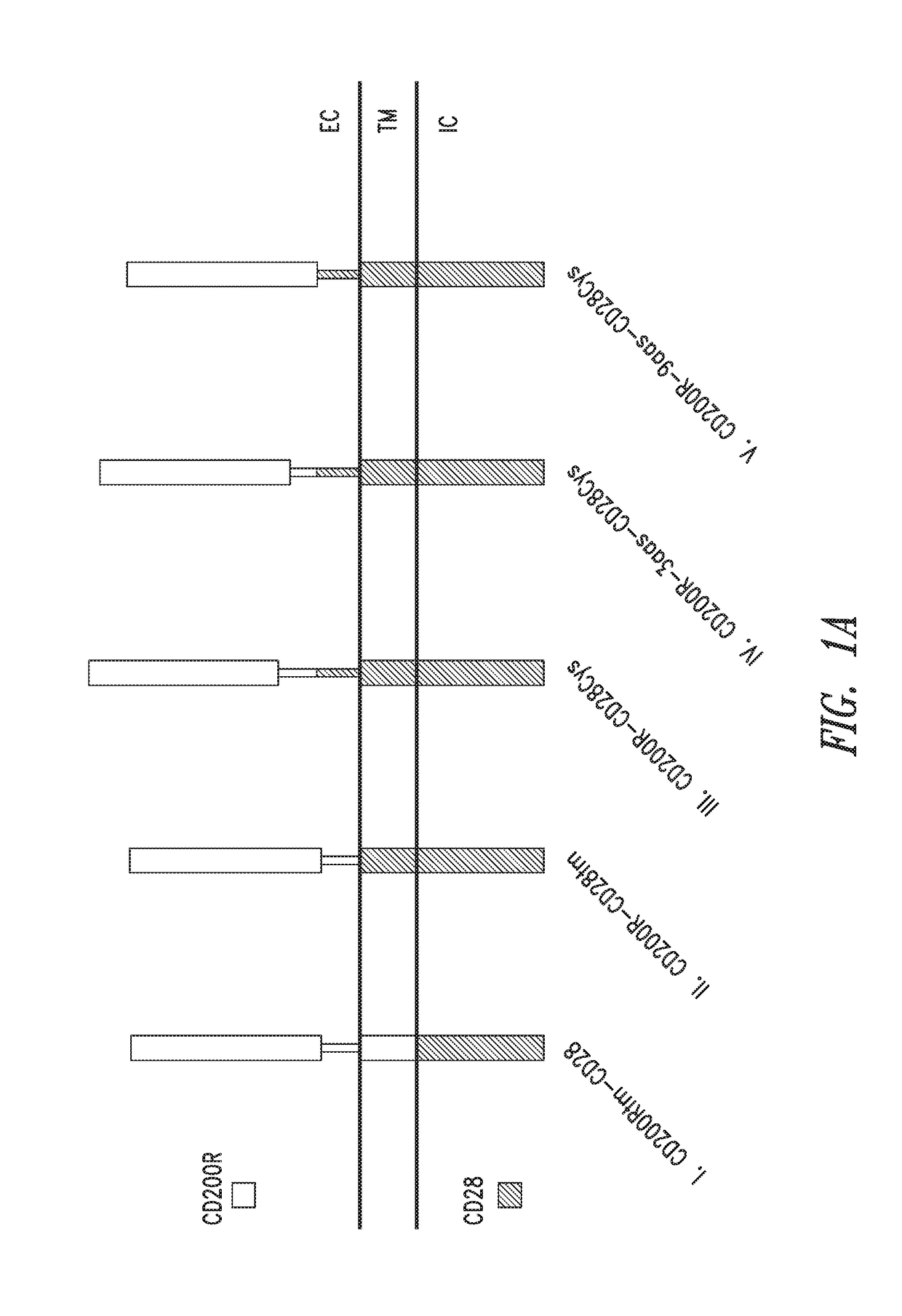
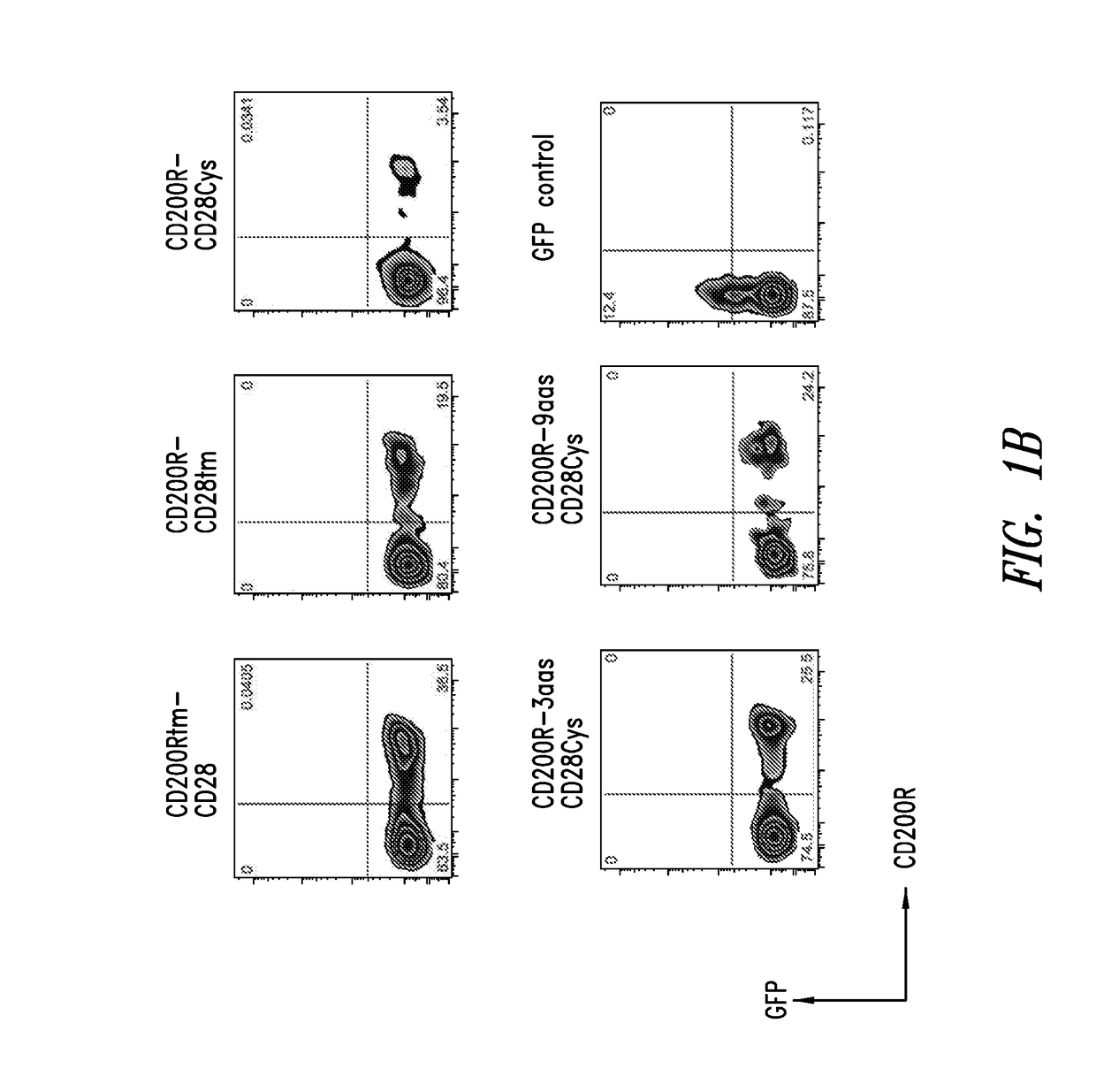
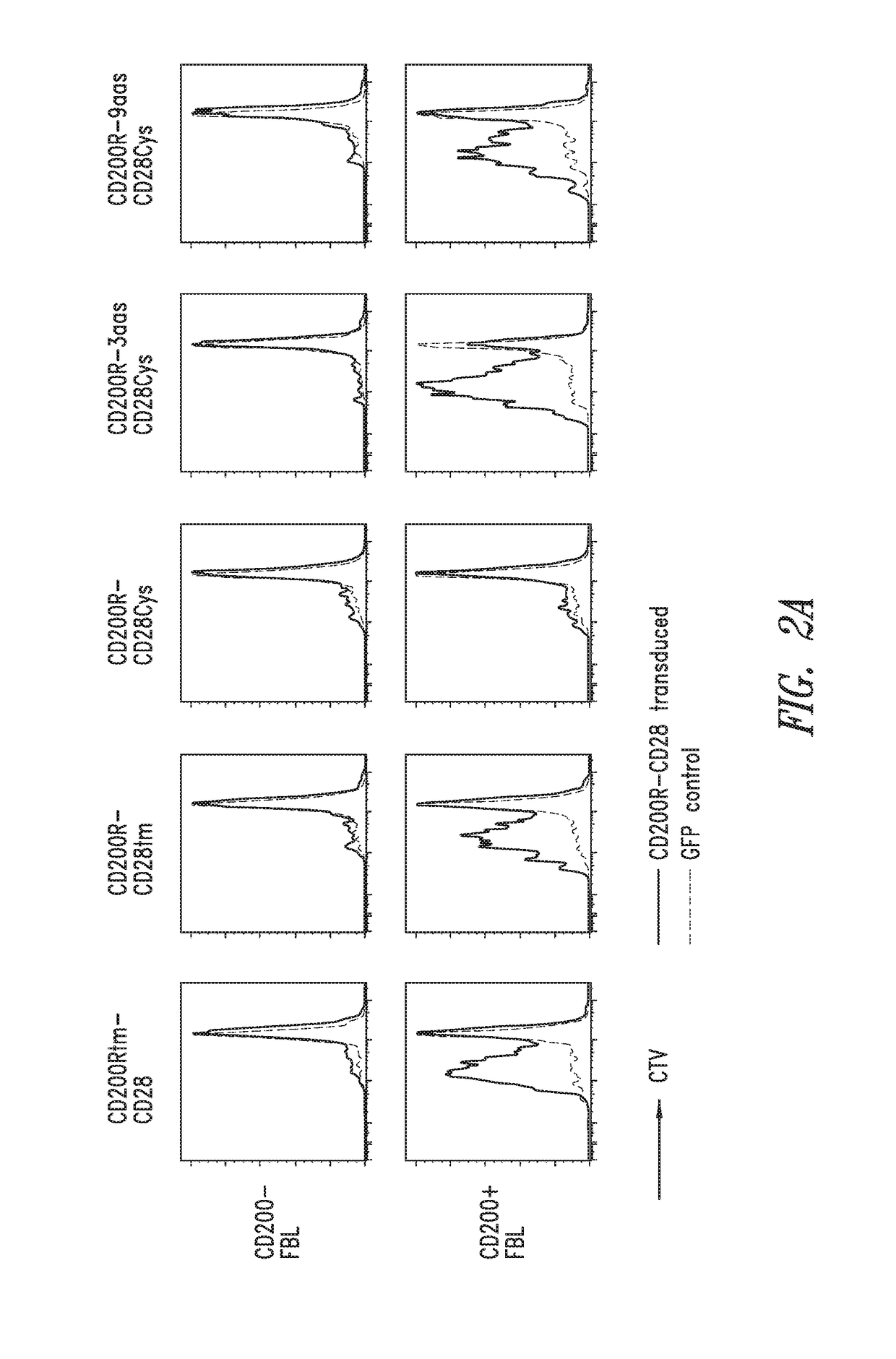
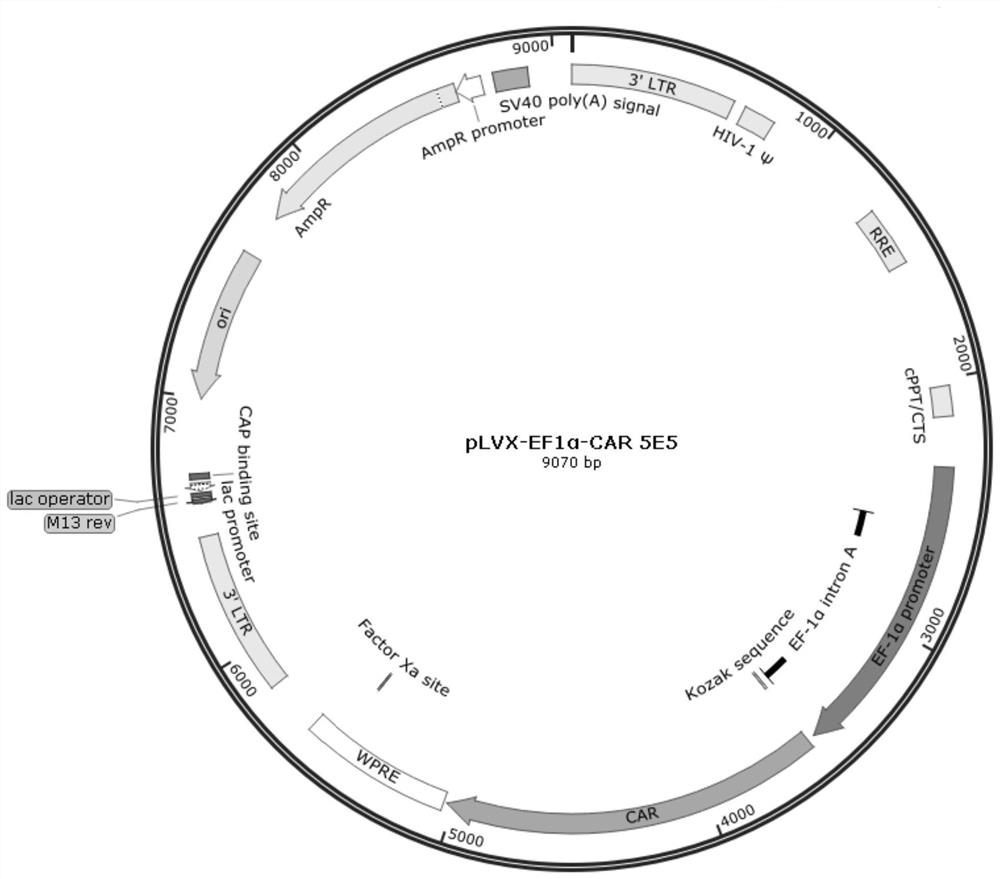
Patents
Literature
109 results about "Intracellular signalling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
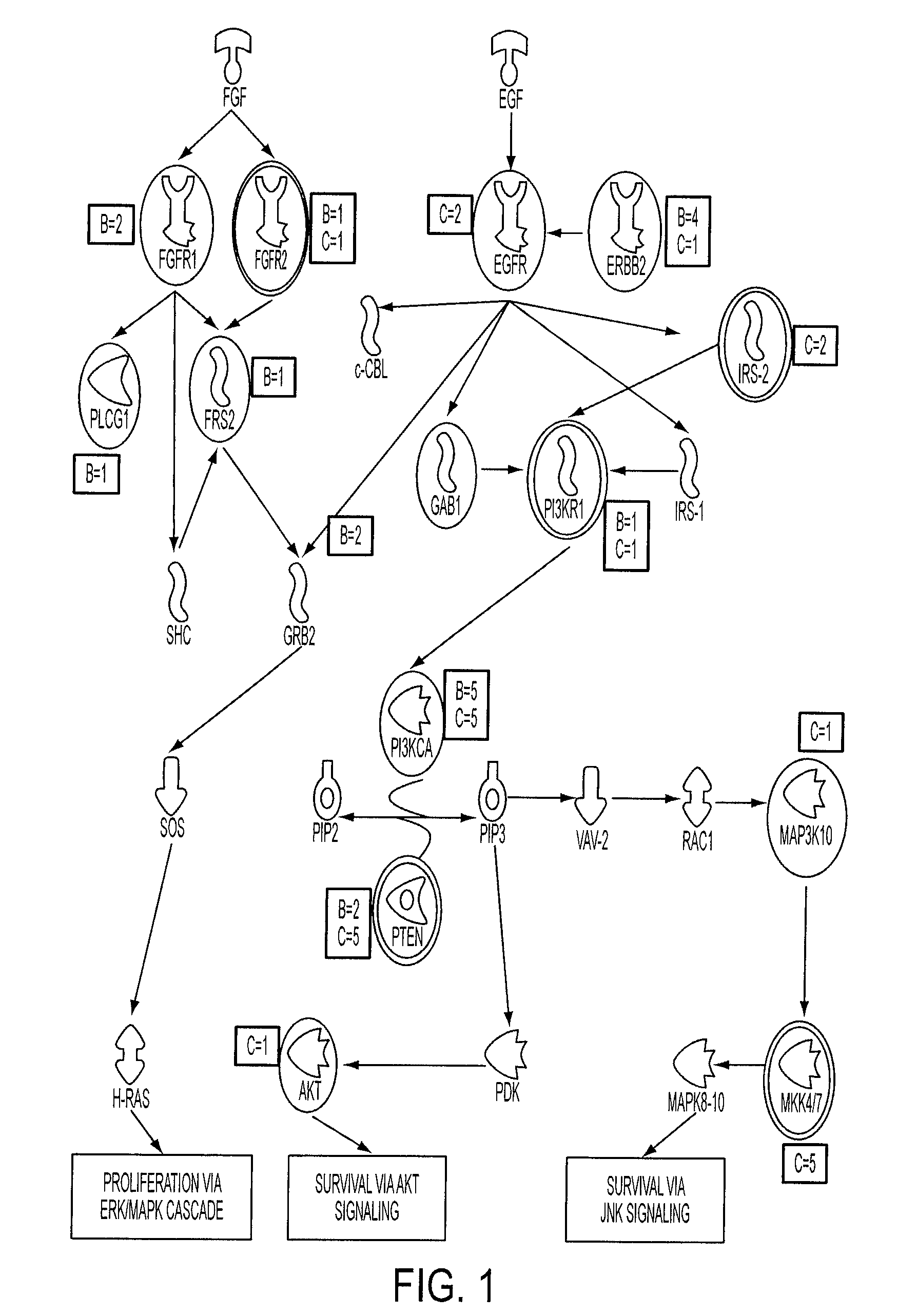
Intracellular signaling is one of the most widely studied areas in biology. Extracellular information perceived at the surface of a cell must be translated into an intracellular response that involves a complex network of interwoven signaling cascades. These signaling events regulate cellular responses like proliferation,...
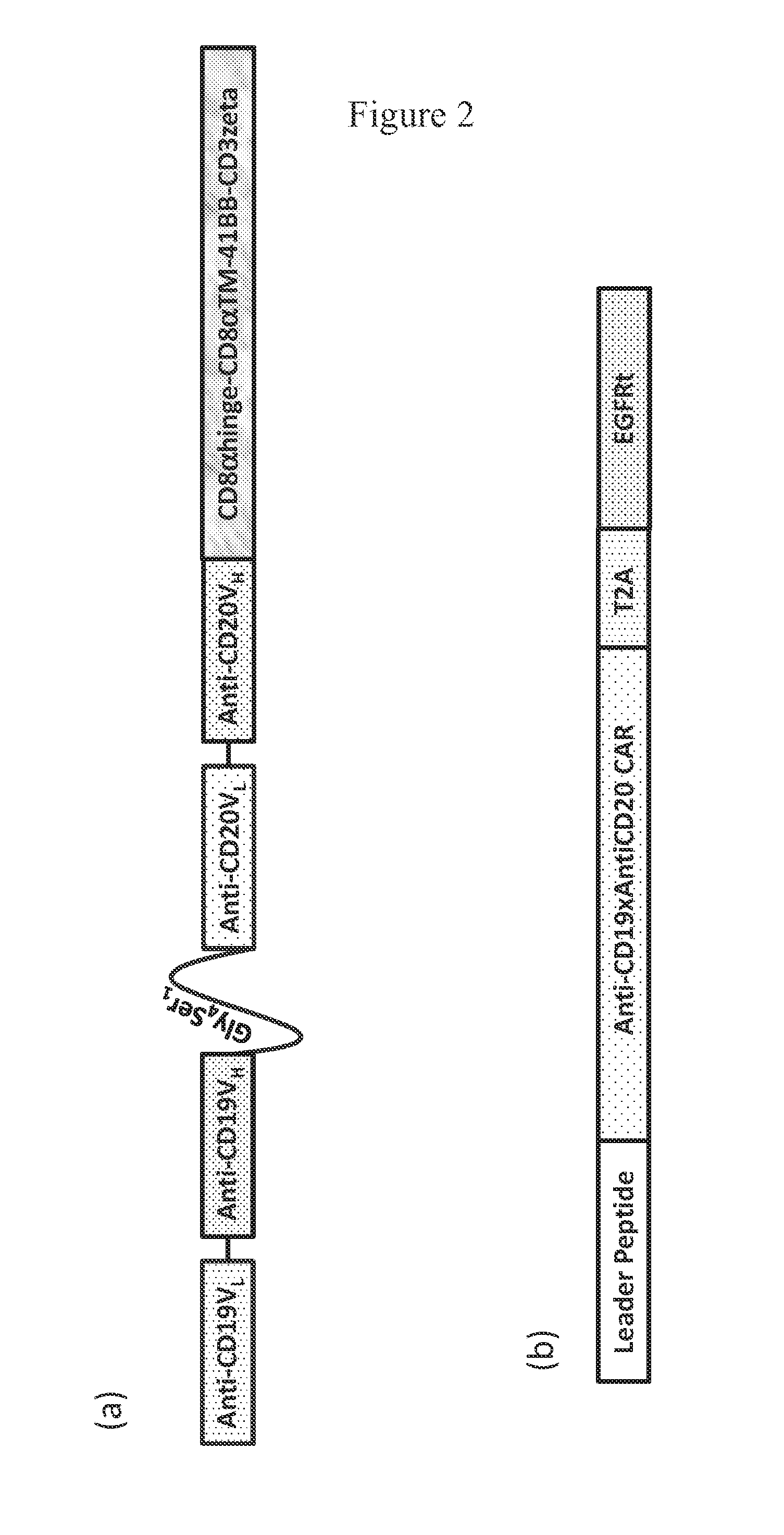
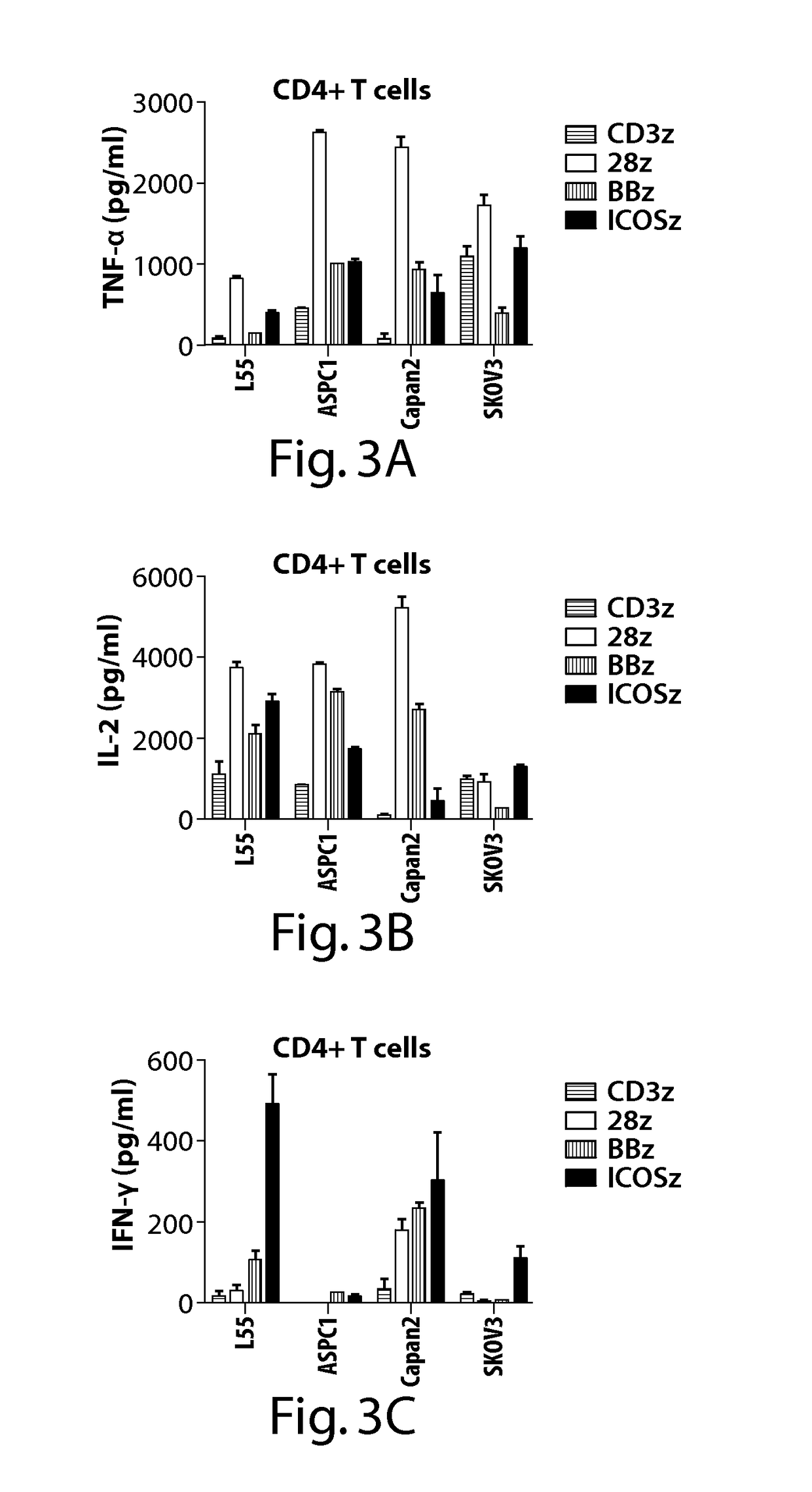
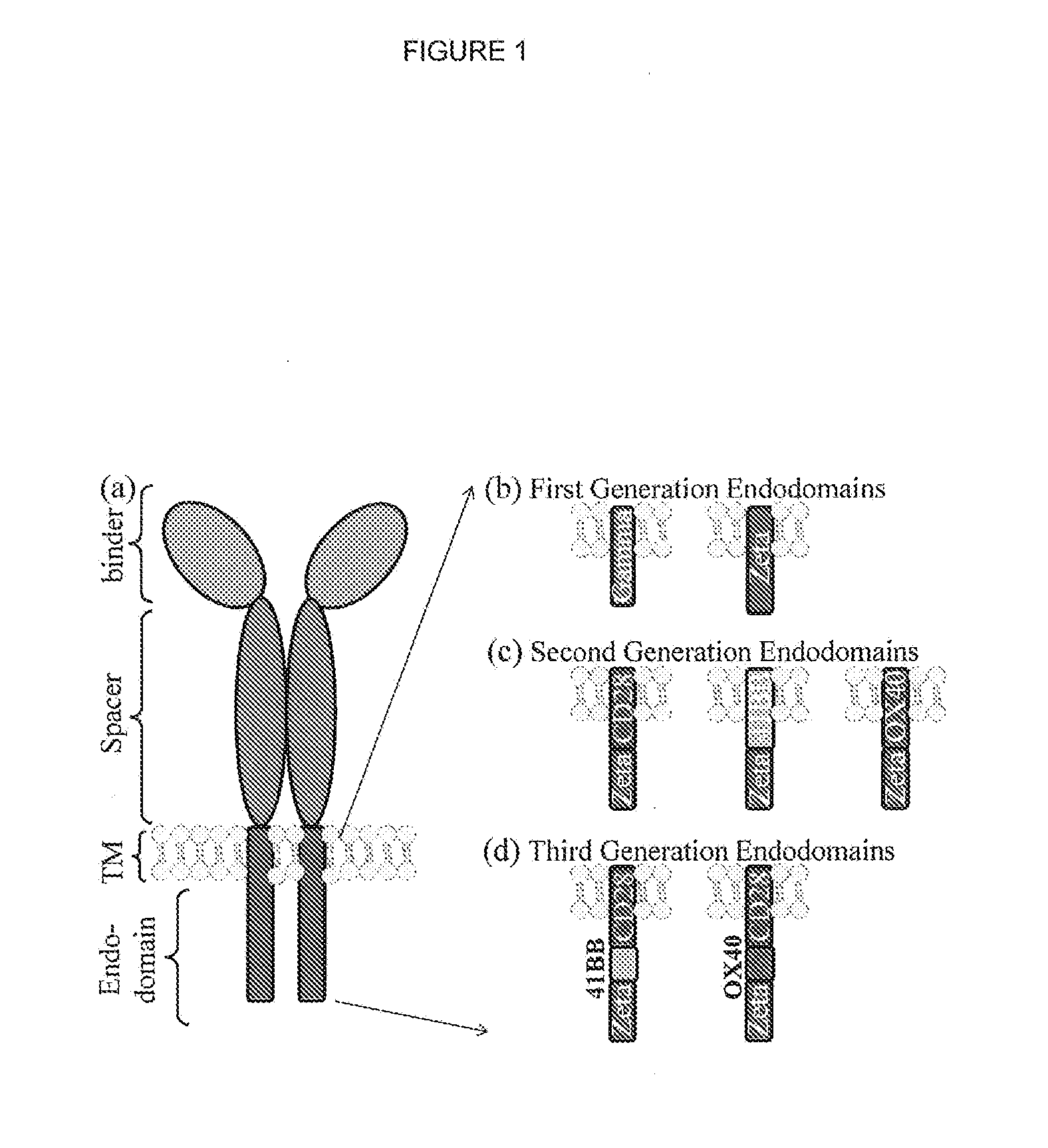
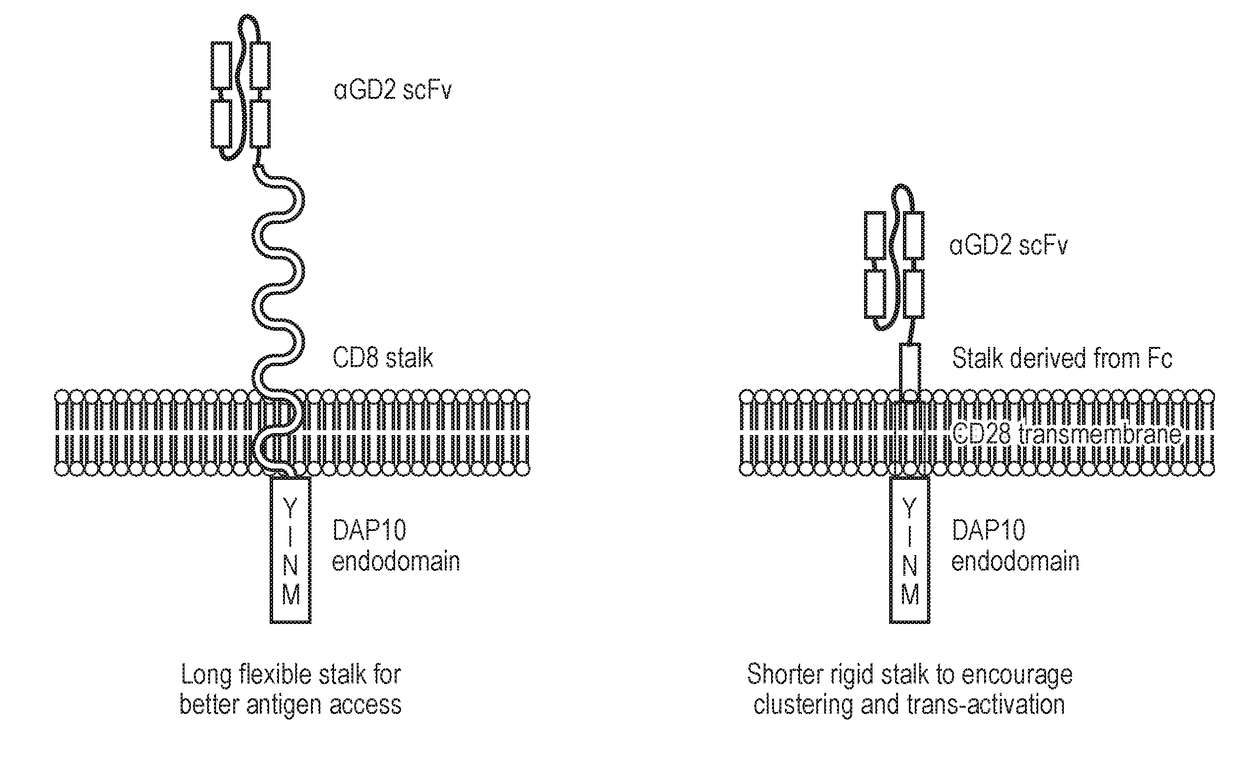
CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor
InactiveUS7446179B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingTransmembrane domain
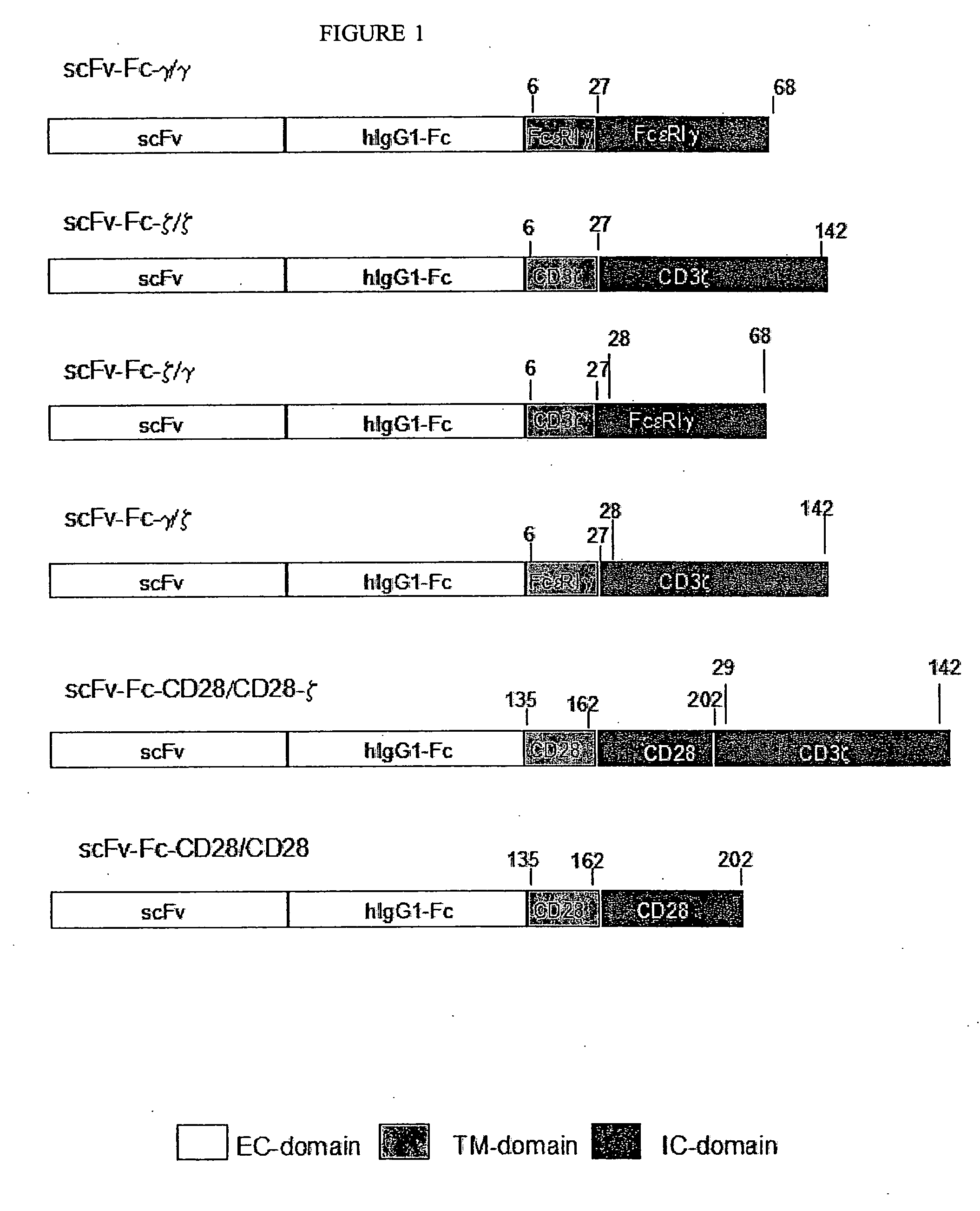
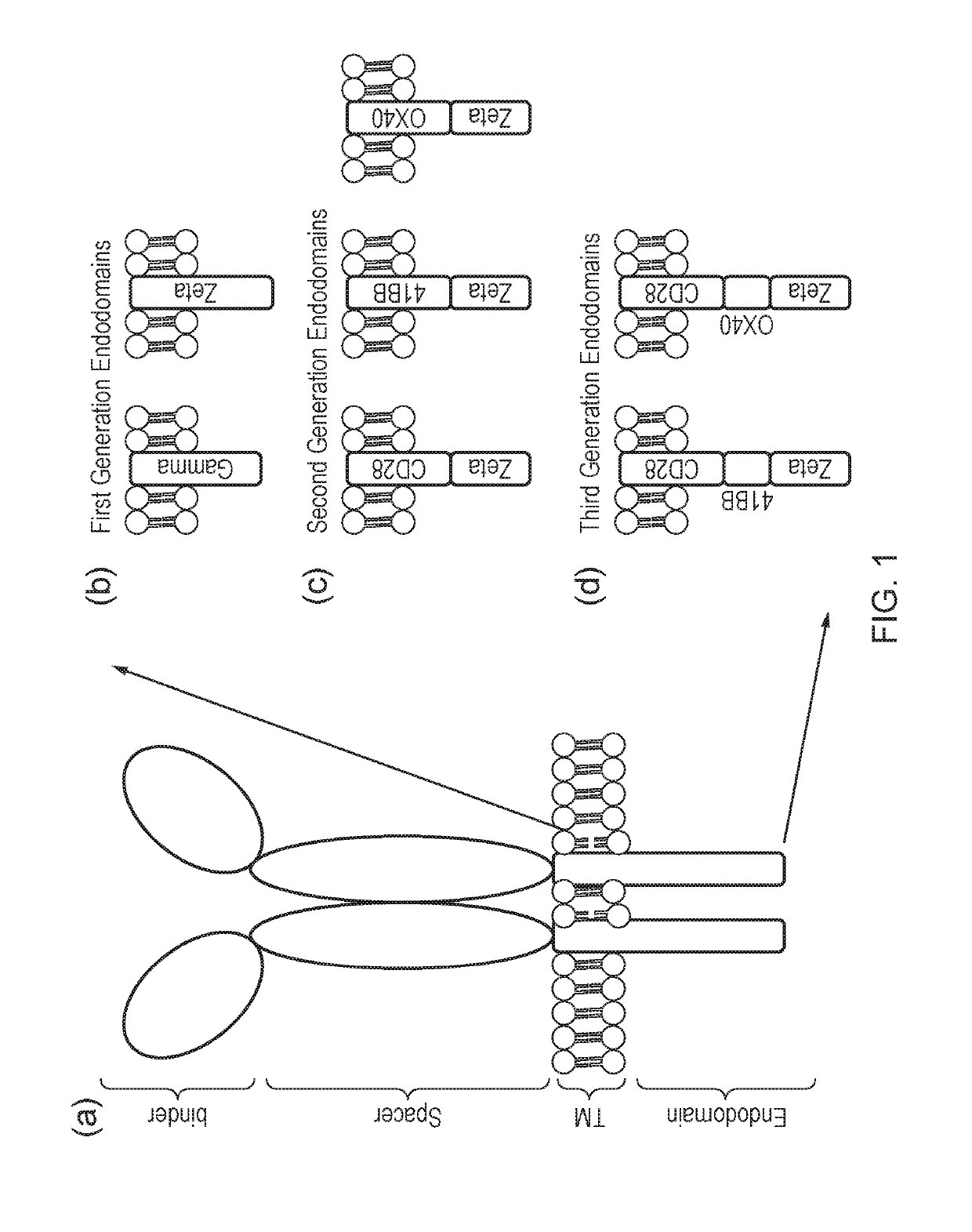
The present invention relates to a genetically engineered, CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor and to immune cells expressing the chimeric receptor The present invention also relates to the use of such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CD9+ malignancies and for abrogating any untoward B cell function. The chimeric receptor is a single chain scFvFc:ζ receptor where scFvFc designates the extracellular domain, scFv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CD19, Fc represents at least part of a constant region of an IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. The extracellular domain scFvFc and the intracellular domain ζ are linked by a transmembrane domain such as the transmembrane domain of CD4. In one aspect, the chimeric receptor comprises amino acids 23-634 of SEQ I DNO:2. The present invention further relates to a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
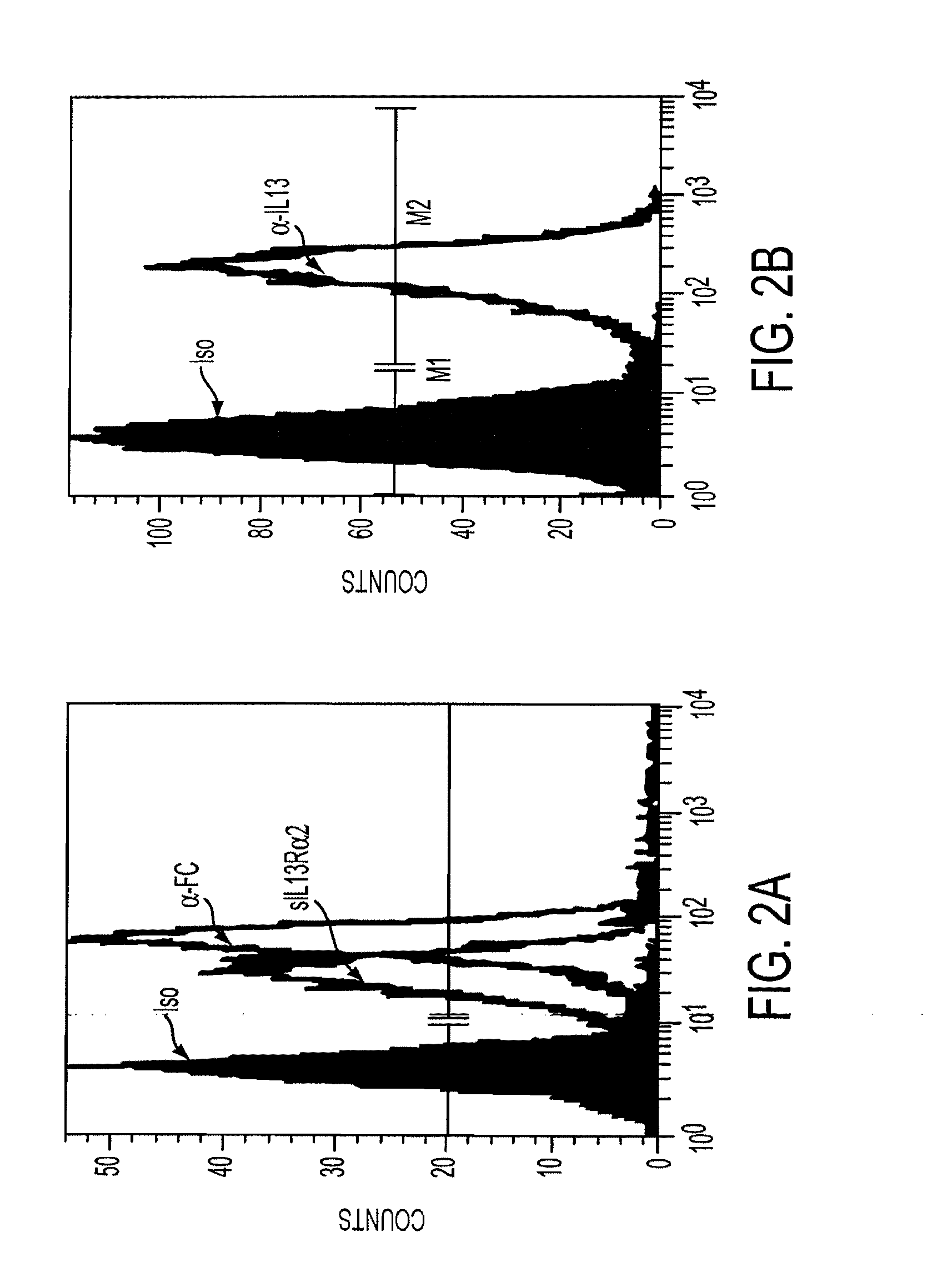
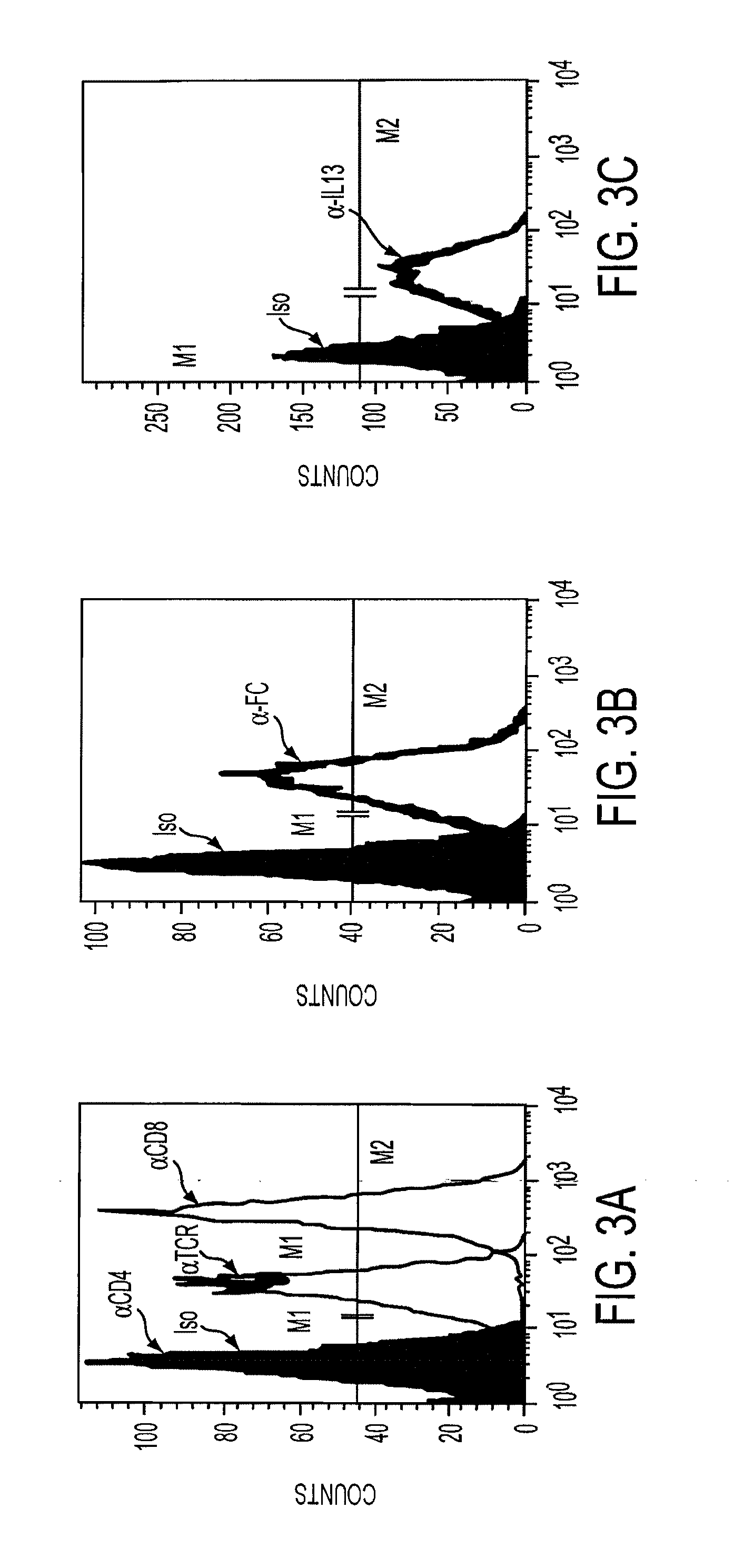
Chimeric immunoreceptor useful in treating human gliomas
InactiveUS7514537B2Negligible toxicityPotent and selectiveBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingHuman glioma
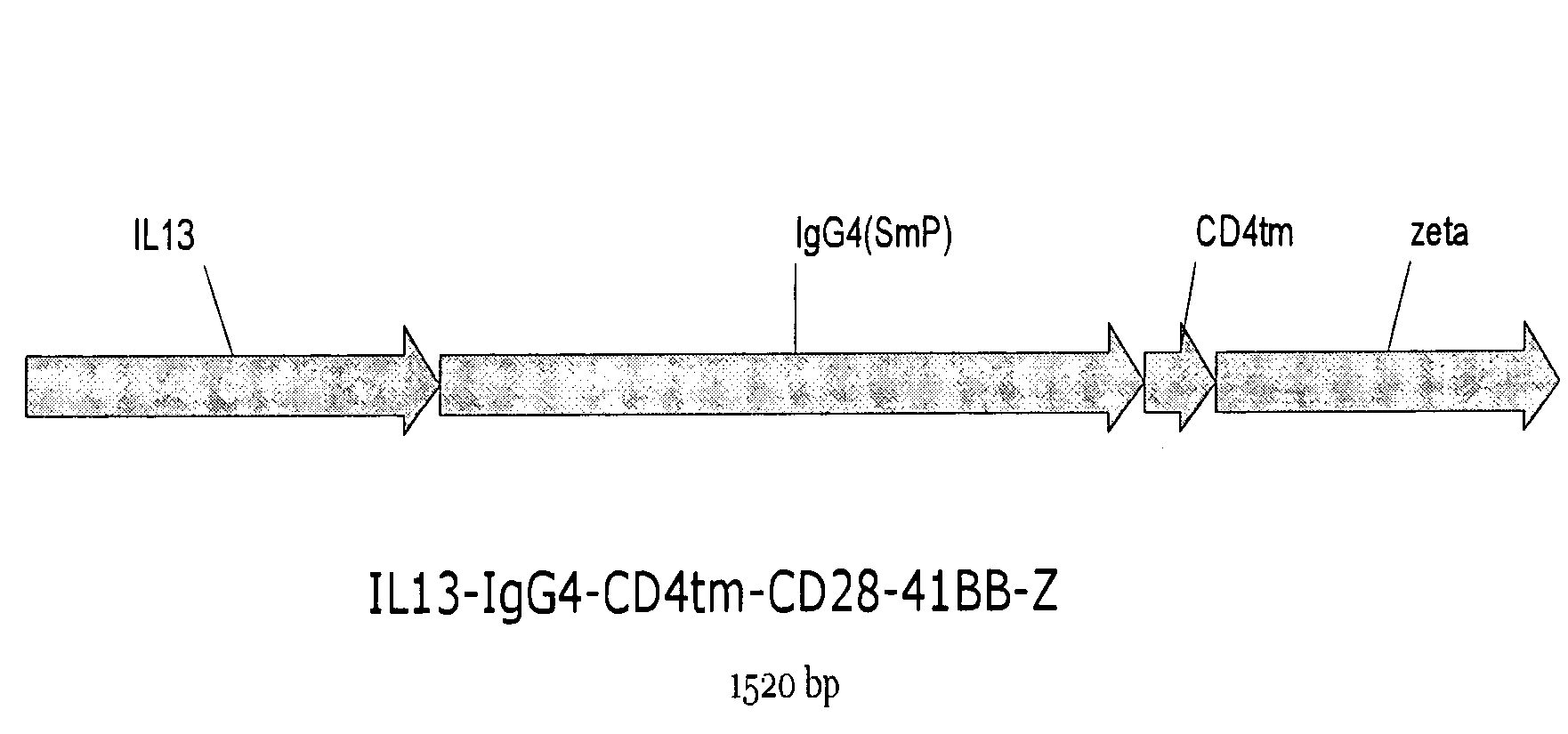
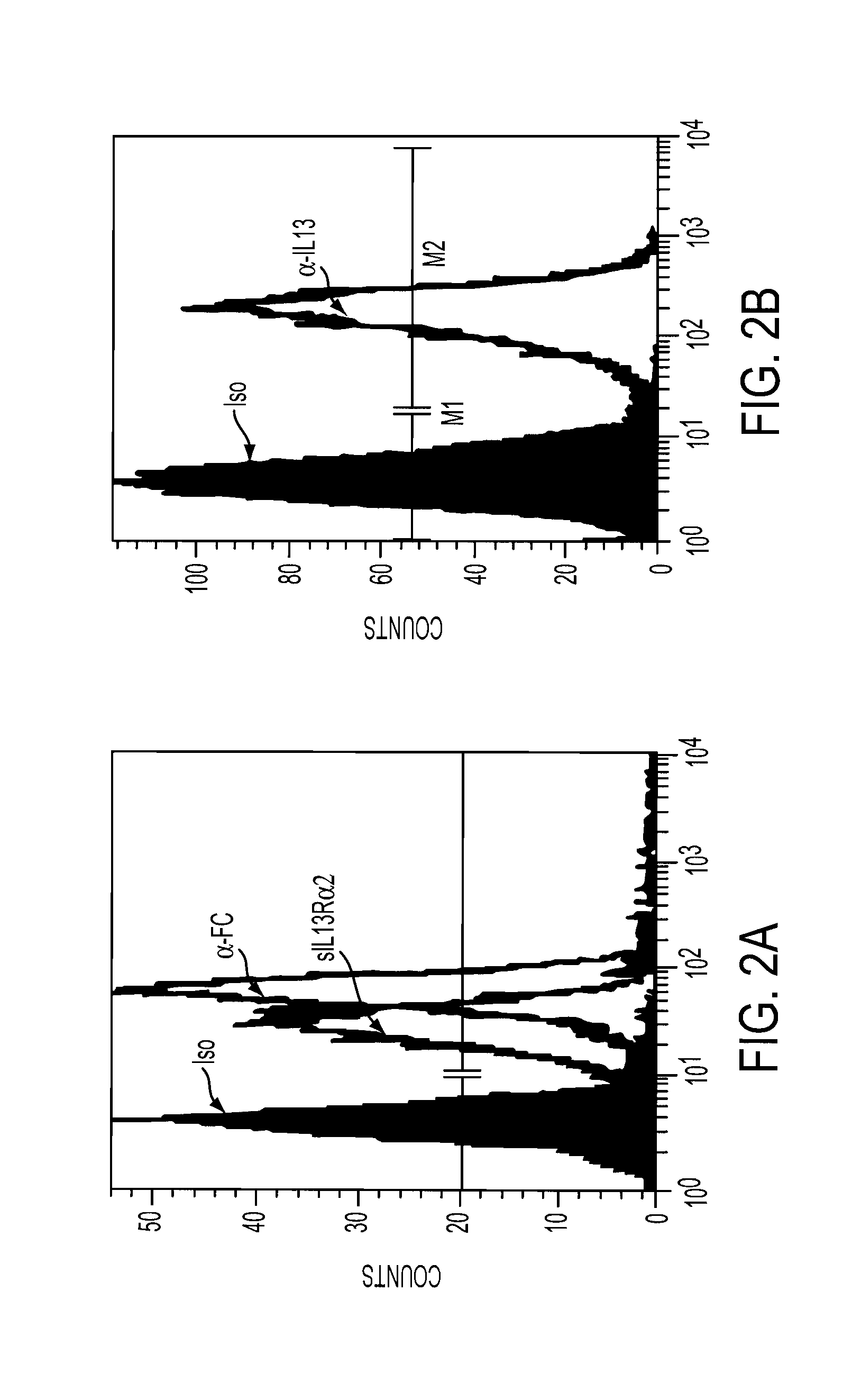
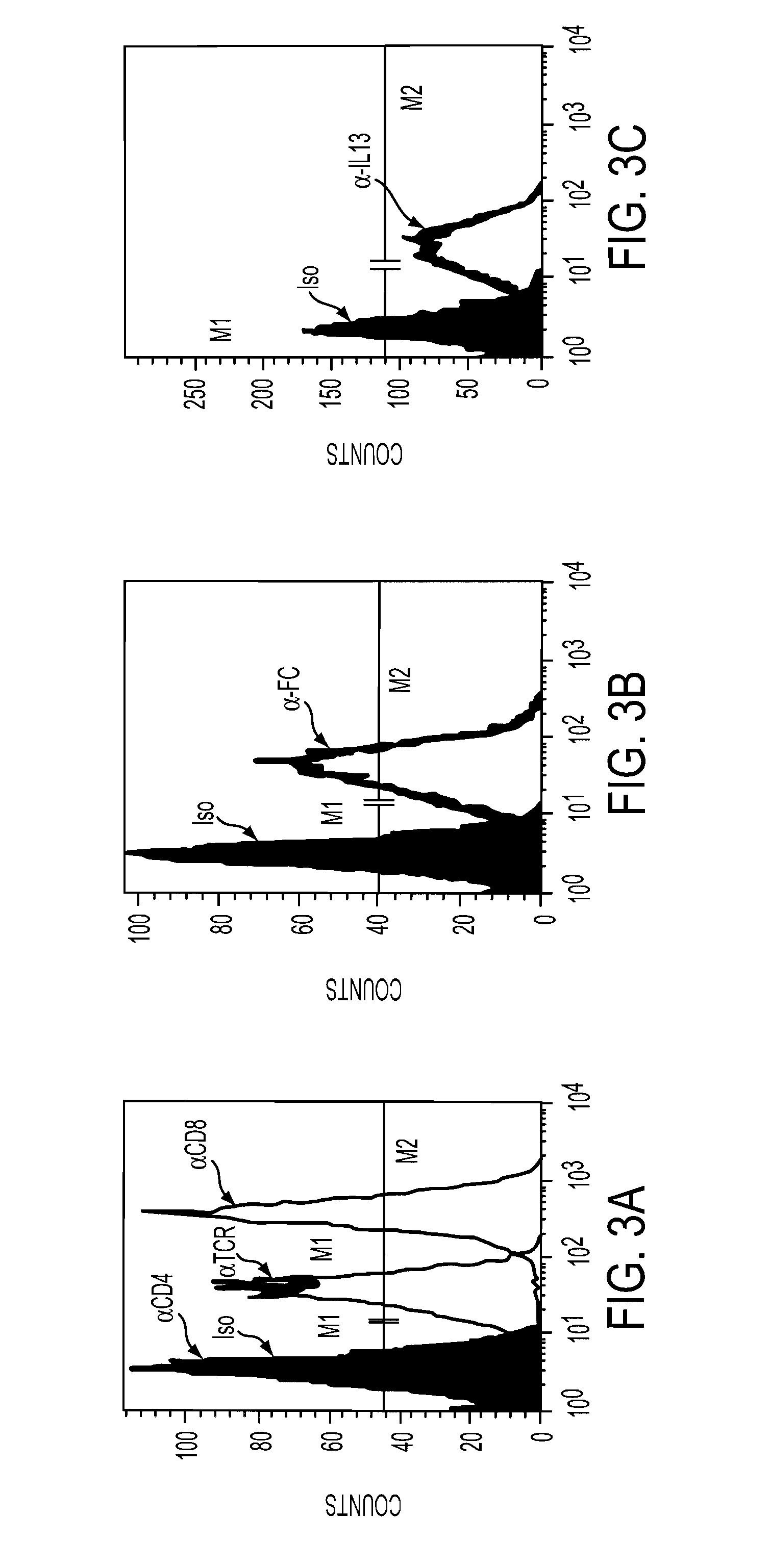
The present invention relates to chimeric transmembrane immunoreceptors, named “zetakines,” comprised of an extracellular domain comprising a soluble receptor ligand linked to a support region capable of tethering the extracellular domain to a cell surface, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signaling domain. Zetakines, when expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes, direct T cell activity to those specific cells expressing a receptor for which the soluble receptor ligand is specific. Zetakine chimeric immunoreceptors represent a novel extension of antibody-based immunoreceptors for redirecting the antigen specificity of T cells, with application to treatment of a variety of cancers, particularly via the autocrin / paracrine cytokine systems utilized by human maligancy. In a preferred embodiment is a glioma-specific immunoreceptor comprising the extracellular targeting domain of the IL-13Rα2-specific IL-13 mutant IL-13(E13Y) linked to the Fc region of IgG, the transmembrane domain of human CD4, and the human CD3 zeta chain.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
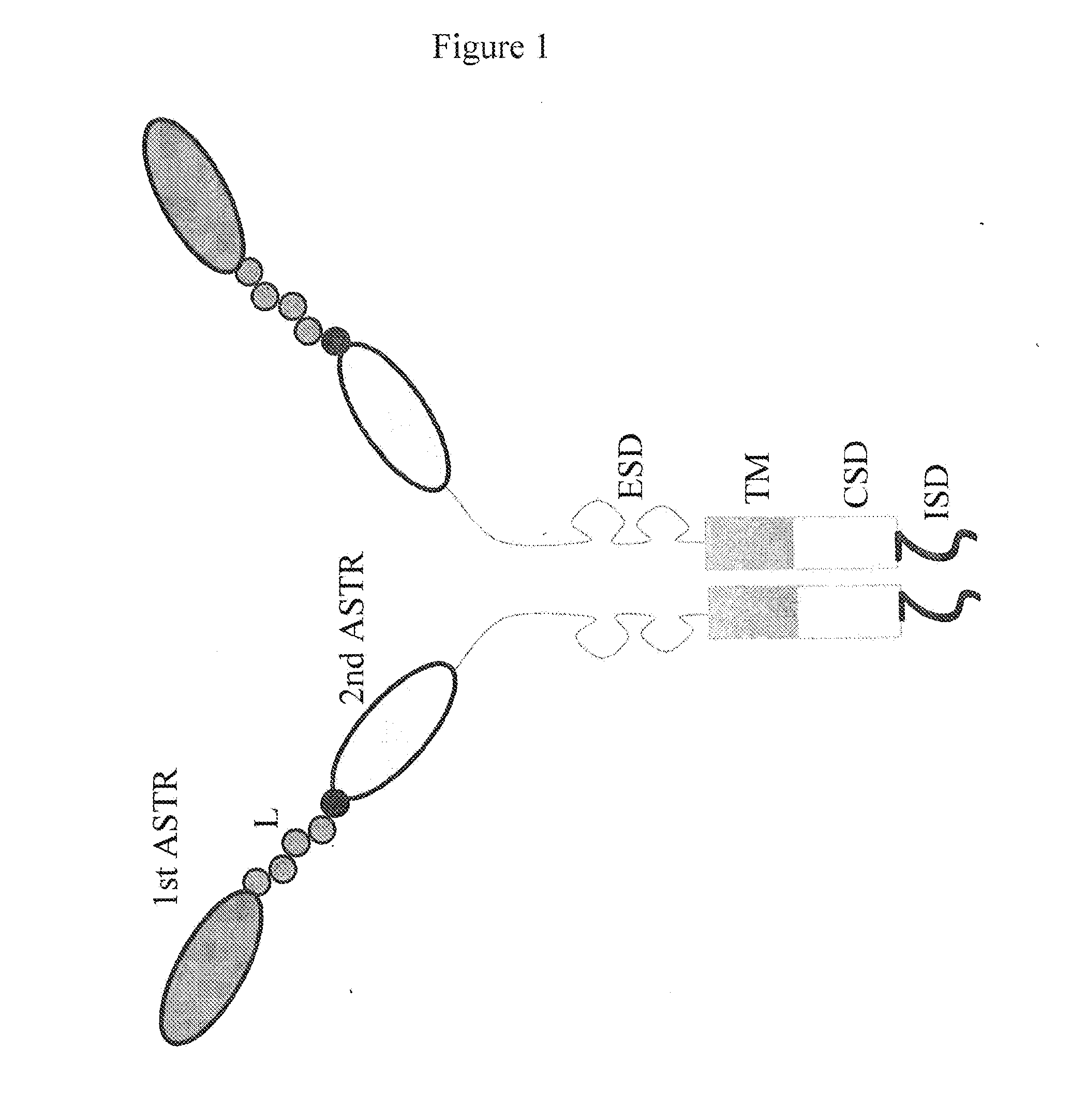
Bispecific chimeric antigen receptors and therapeutic uses thereof
ActiveUS20150038684A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingAntigen receptors
The invention is directed to a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor, comprising: (a) at least two antigen-specific targeting regions; (b) an extracellular spacer domain; (c) a transmembrane domain; (d) at least one co-stimulatory domain; and (e) an intracellular signaling domain, wherein each antigen-specific targeting region comprises an antigen-specific single chain Fv (scFv) fragment, and binds a different antigen, and wherein the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor is co-expressed with a therapeutic control. The invention also provides methods and uses of the bispecific chimeric antigen receptors.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Chimeric immunoreceptor useful in treating human cancers
InactiveUS20090257994A1Negligible toxicityPotent and selectiveBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsIntracellular signallingMalignancy
The present invention relates to chimeric transmembrane immunoreceptors, named “zetakines,” comprised of an extracellular domain comprising a soluble receptor ligand linked to a support region capable of tethering the extracellular domain to a cell surface, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signalling domain. Zetakines, when expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes, direct T cell activity to those specific cells expressing a receptor for which the soluble receptor ligand is specific. Zetakine chimeric immunoreceptors represent a novel extension of antibody-based immunoreceptors for redirecting the antigen specificity of T cells, with application to treatment of a variety of cancers, particularly via the autocrin / paracrine cytokine systems utilized by human malignancy. In a preferred embodiment is a glioma-specific immunoreceptor comprising the extracellular targetting domain of the IL-13Rα2-specific IL-13 mutant IL-13(E13Y) linked to the Fc region of IgG, the transmembrane domain of human CD4, and the human CD3 zeta chain.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Redirected, genetically-engineered t regulatory cells and their use in suppression of autoimmune and inflammatory disease
InactiveUS20100135974A1Effective quantityOvercome scarcityBiocideAntipyreticIntracellular signallingInflammatory Bowel Diseases
A redirected Treg cell is endowed with specificity toward a selected target antigen or ligand. The cell contains a chimeric receptor polypeptide that is expressed in a single, continuous chain, with an extracellular recognition region displayed on the surface of the cell, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signaling region. The extracellular recognition region is specific for the selected target antigen or ligand. The intracellular signaling region includes a combination of T-cell signaling polypeptide moieties, which combination, upon binding of the extracellular recognition region to the selected target antigen or ligand, triggers activation of the redirected Treg cells to cause suppression of T-cell mediated immunity. Such redirected Treg cells may be used to suppress undesired activity of T effector cells thereby mediating an immune or inflammatory response. They are particularly useful in treating T effector cell-mediated diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, transplant rejection and GVH disease.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Subset-optimized chimeric antigen receptor-containing t-cells
PendingUS20170209492A1Improve anti-tumor activityIncreased persistenceOrganic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseIntracellular signalling
This disclosure provides, for instance subset-optimized CART cells and related methods. For instance, the disclosure describes methods and compositions of CD4′ and CD8′ T cells that express CARs containing specific combinations of intracellular signaling domains can be used to increase persistence and anti-tumor activity of the infused CAR-expressing T cells for treating a subject having a disease, e.g., a cancer.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
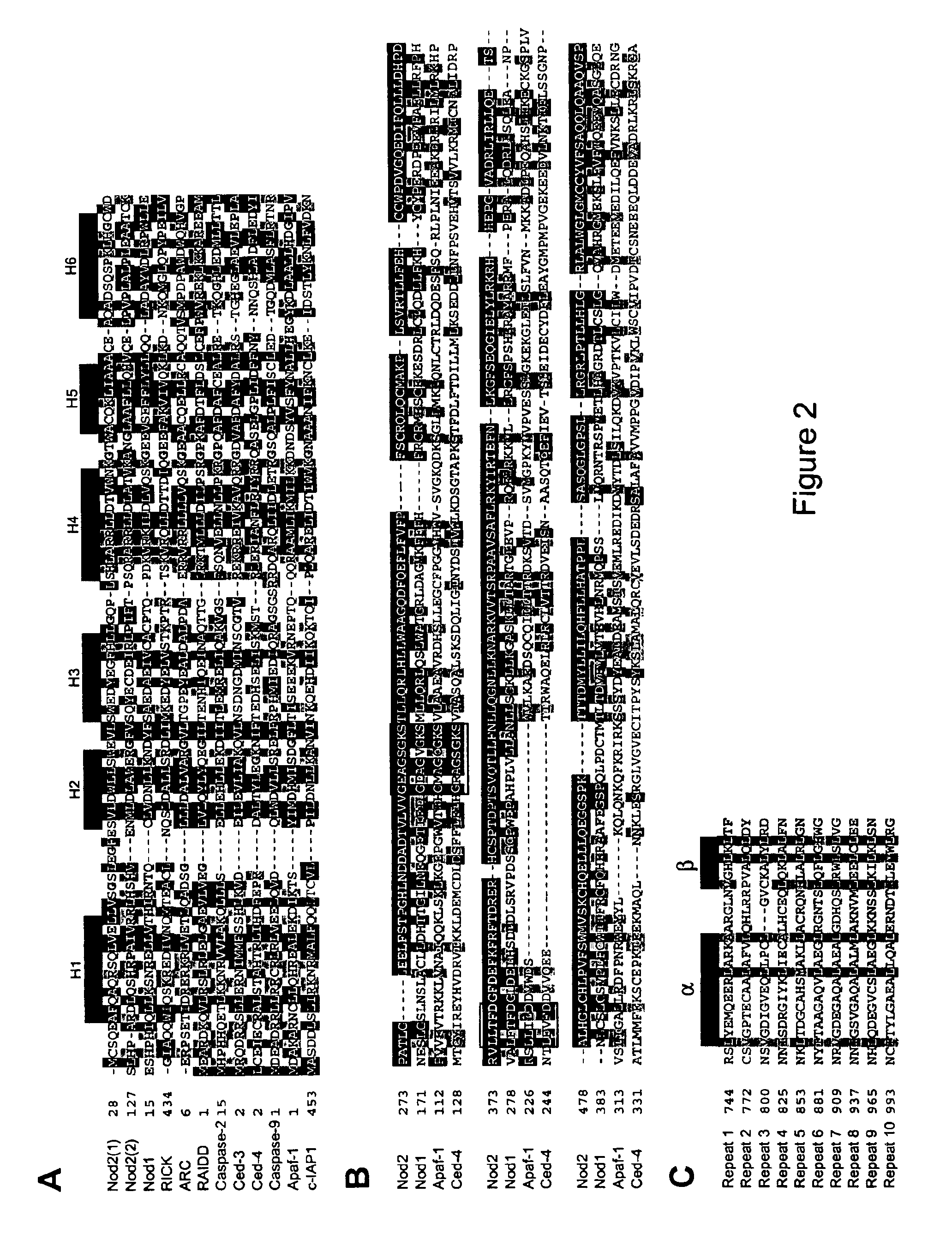
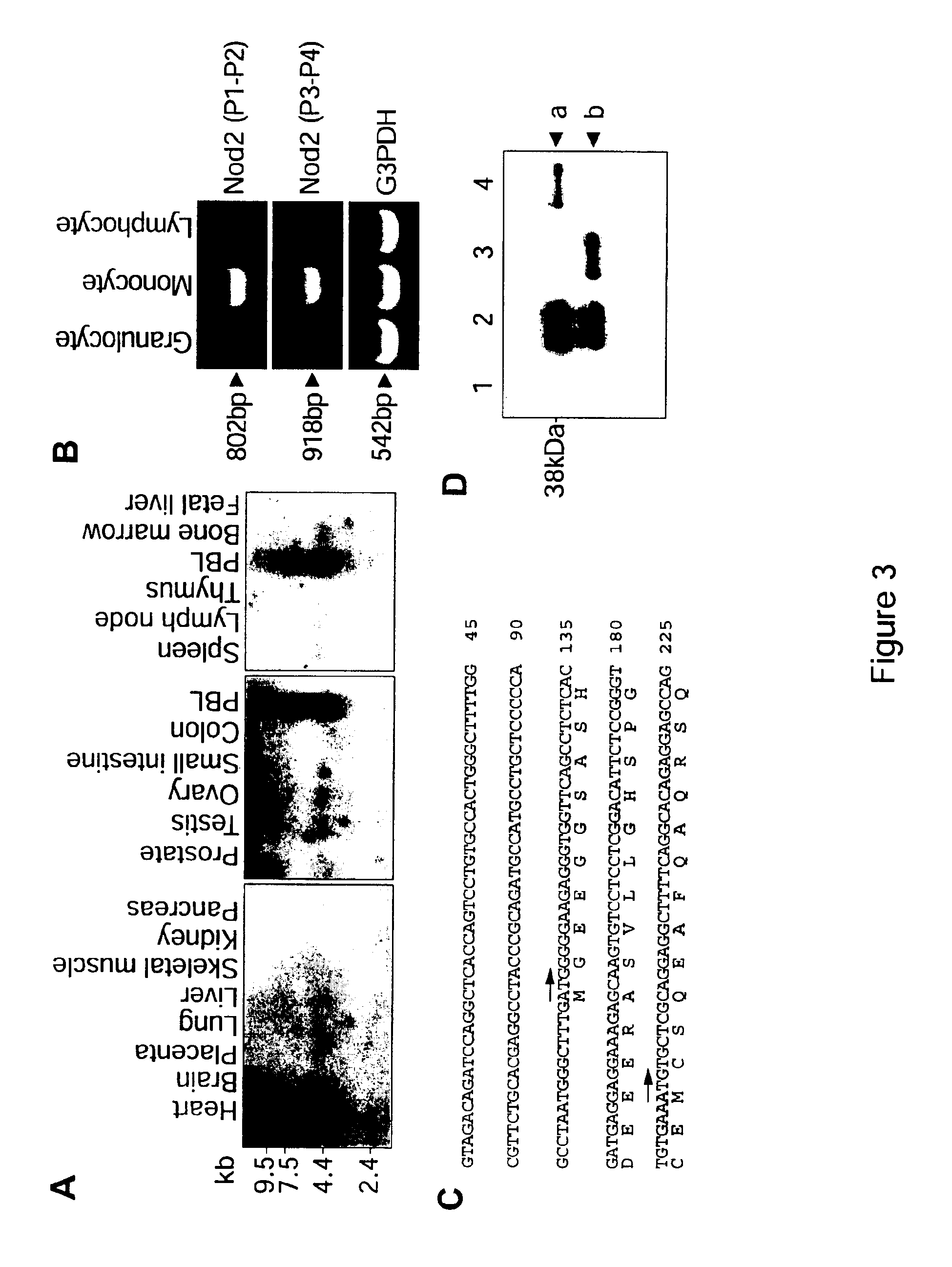
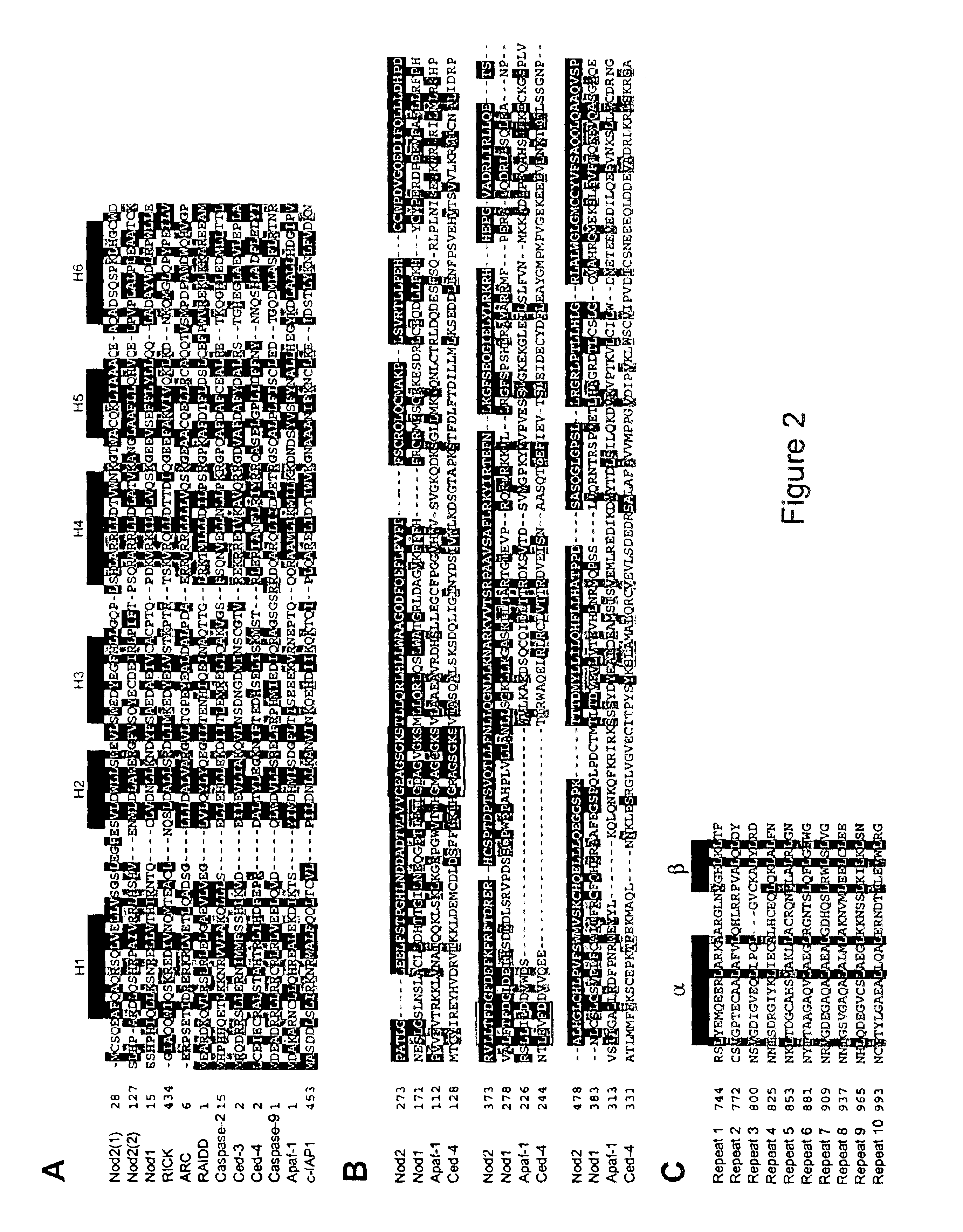
Nod2 nucleic acids and proteins
InactiveUS6858391B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIntracellular signallingNucleotide
The present invention relates to intracellular signalling molecules, in particular the Nod2 protein and nucleic acids encoding the Nod2 protein. The present invention provides isolated nucleotide sequence encoding Nod2, isolated Nod2 peptides, antibodies that specifically bind Nod2, methods for the detection of Nod2, and methods for screening compounds for the ability to alter Nod2 associated signal transduction. The present invention also provides Nod2 variant alleles. The present invention further provides methods of identifying individuals at increased risk of developing Crohn's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
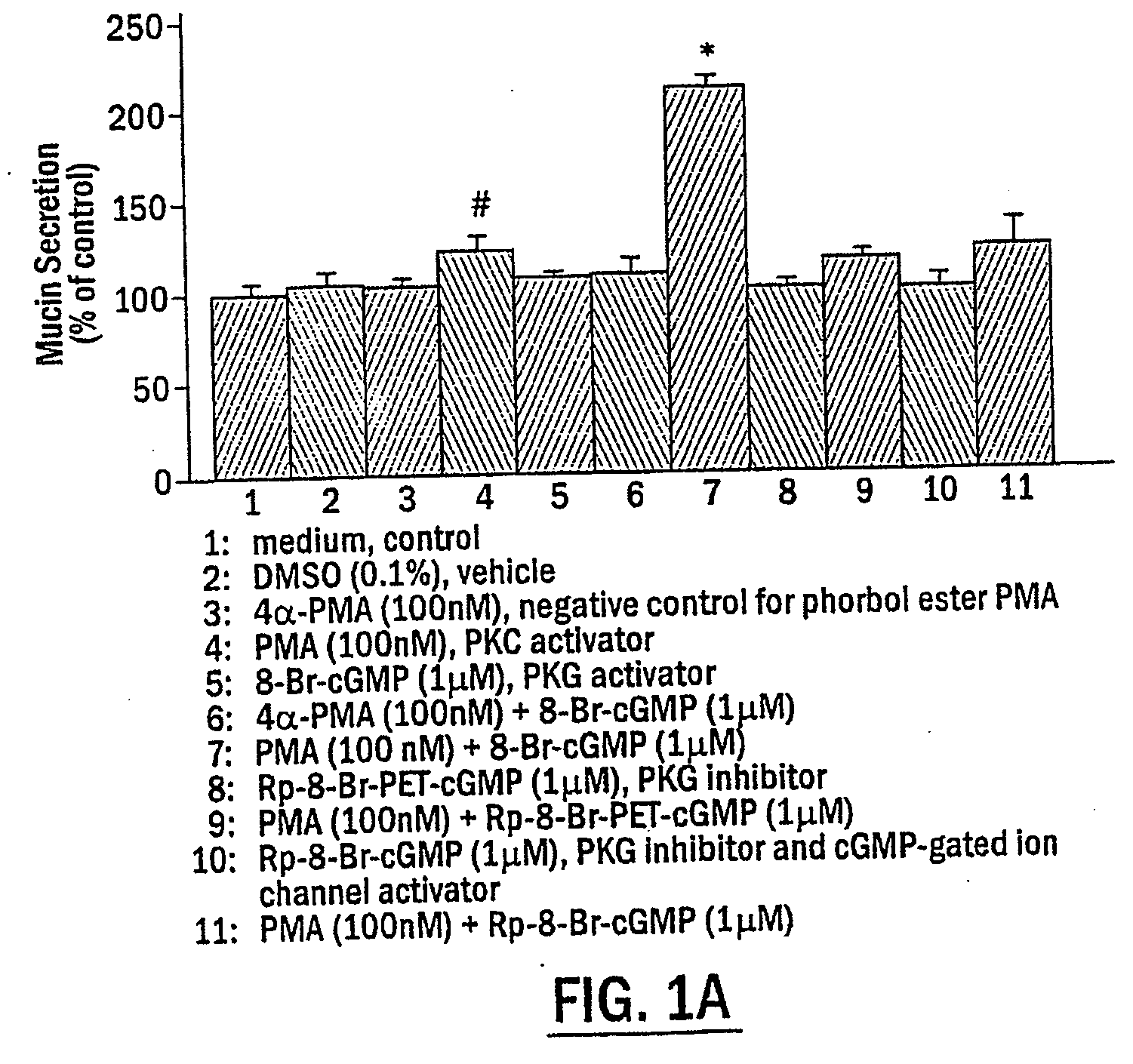
Methods for regulating inflammatory mediators and peptides useful therein
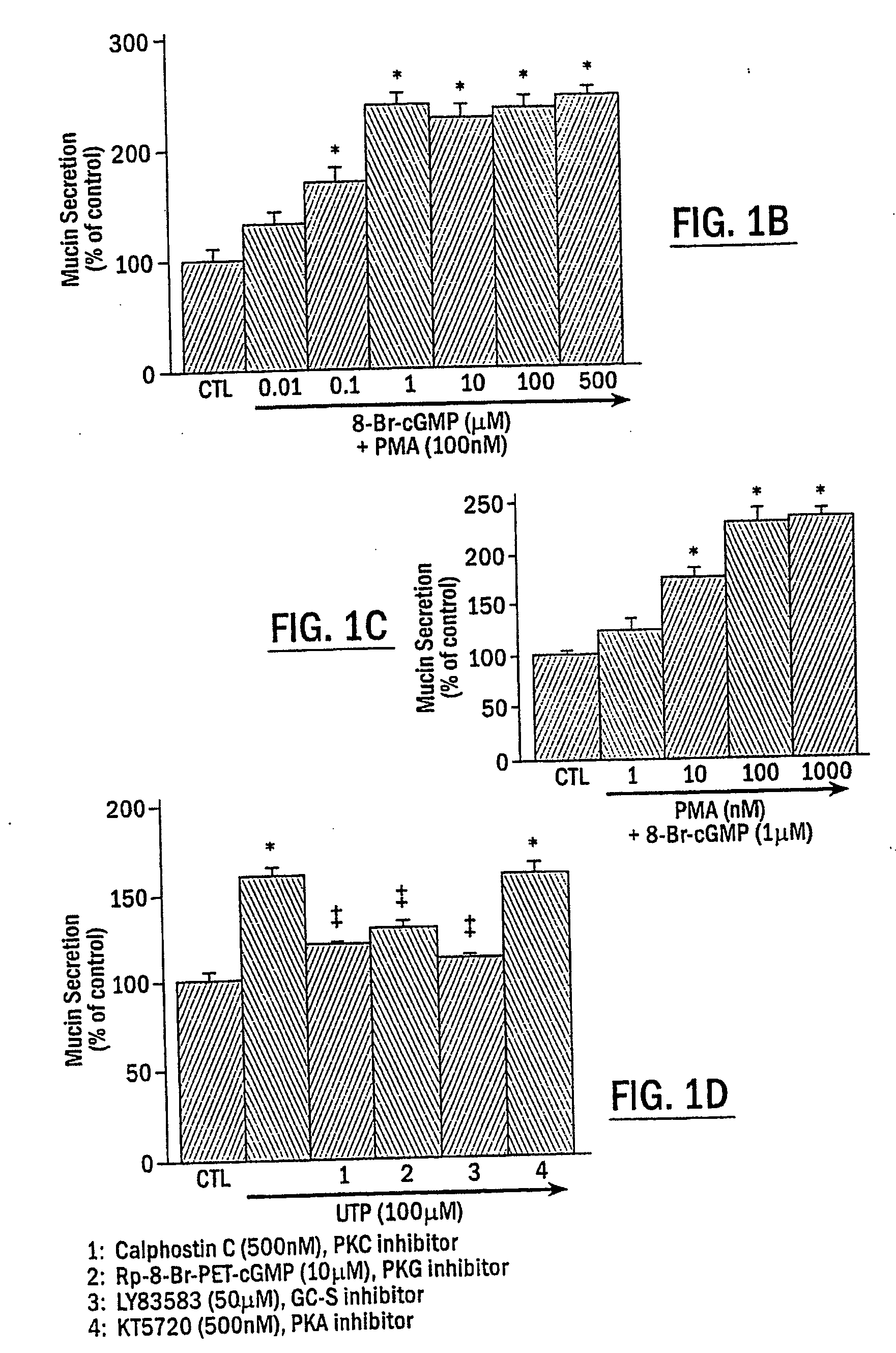
The present invention includes methods of modulating cellular secretory processes. More specifically the present invention relates to modulating or reducing the release of inflammatory mediators from inflammatory cells by inhibiting the mechanism associated with the release of inflammatory mediators from the vesicles or granules in the inflammatory cells. In this regard, the present invention discloses an intracellular signaling mechanism that illustrates several novel intracellular targets for pharmacological intervention in disorders involving secretion of inflammatory mediators from vesicles in inflammatory cells. MANS peptide and active fragments thereof are useful in such methods.
Owner:BIOMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LTD +1
Chimeric immunoreceptor useful in treating human cancers
InactiveUS20060067920A1Negligible toxicityPotent and selectiveBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingAutocrine paracrine
The present invention relates to chimeric transmembrane immunoreceptors, named “zetakines,” comprised of an extracellular domain comprising a soluble receptor ligand linked to a support region capable of tethering the extracellular domain to a cell surface, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signalling domain. Zetakines, when expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes, direct T cell activity to those specific cells expressing a receptor for which the soluble receptor ligand is specific. Zetakine chimeric immunoreceptors represent a novel extension of antibody-based immunoreceptors for redirecting the antigen specificity of T cells, with application to treatment of a variety of cancers, particularly via the autocrin / paracrine cytokine systems utilized by human maligancy. In a preferred embodiment is a glioma-specific immunoreceptor comprising the extracellular targetting domain of the IL-13Rα2-specific IL-13 mutant IL-13(E13Y) linked to the Fc region of IgG, the transmembrane domain of human CD4, and the human CD3 zeta chain.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Chimeric antigen receptor dendritic cell (car-dc) for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20170151281A1High proliferation rateIncrease productionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsIntracellular signallingDendritic cell
The current invention provides monocytic cells transfected with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) to selectively home to tumors and upon homing differentiate into dendritic cells capable of activating immunity which is inhibitory to said tumor. In one embodiment of the invention, monocytic cells are transfected with a construct encoding an antigen binding domain, a transcellular or structural domain, and an intracellular signaling domain. In one specific aspect of the invention, the antigen binding domain interacts with sufficient affinity to a tumor antigen, capable of triggering said intracellular domain to induce an activation signal to induce monocyte differentiation into DC.
Owner:MYELOID THERAPEUTICS INC
Masking chimeric antigen receptor t cells for tumor-specific activation
ActiveUS20180148508A1Further flexibilityFurther stabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingBiological activation
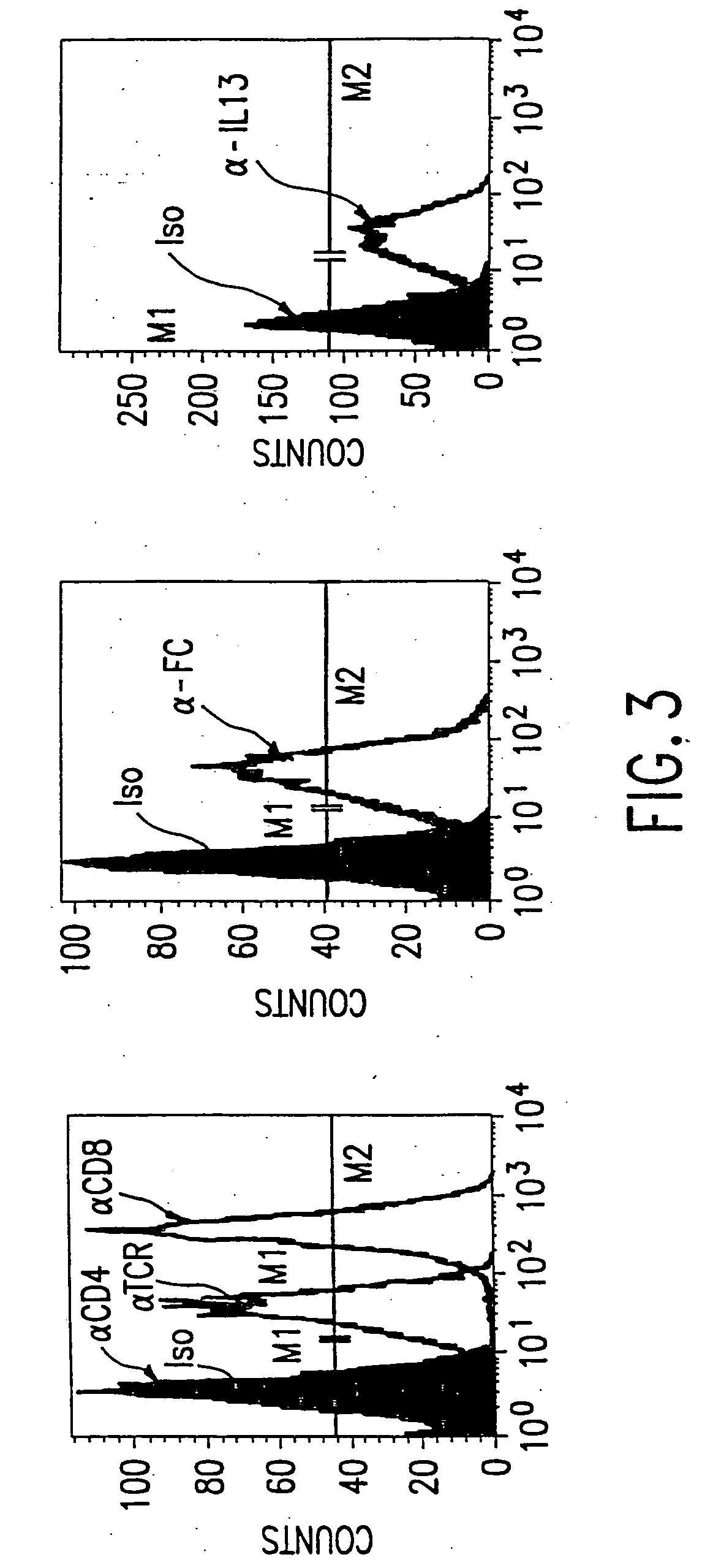
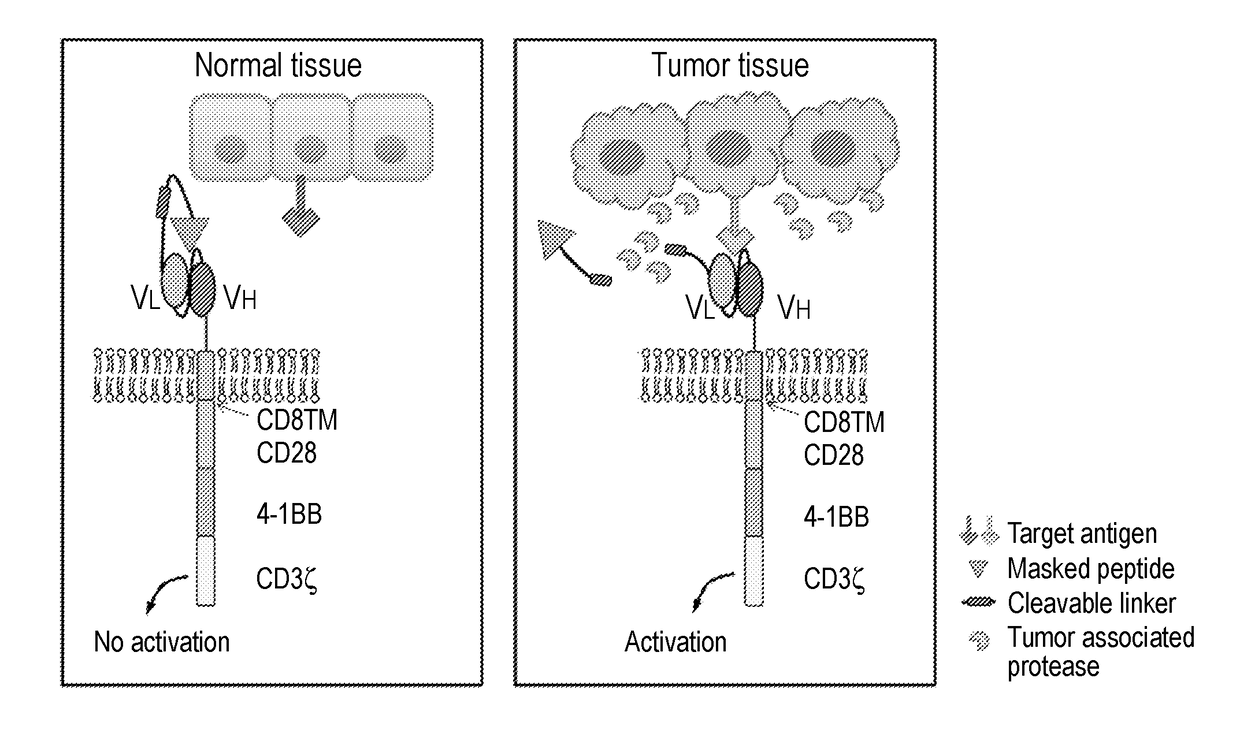
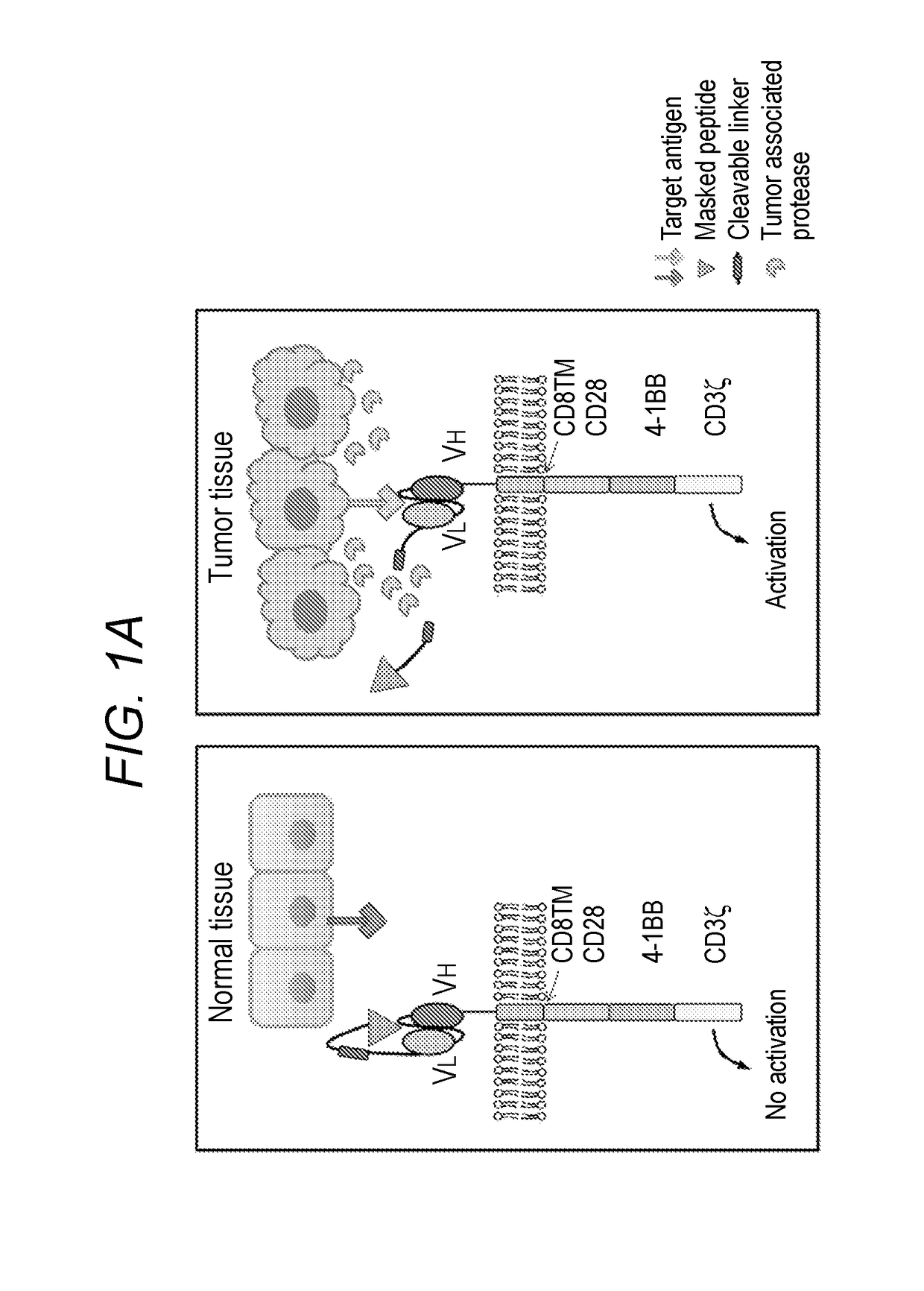
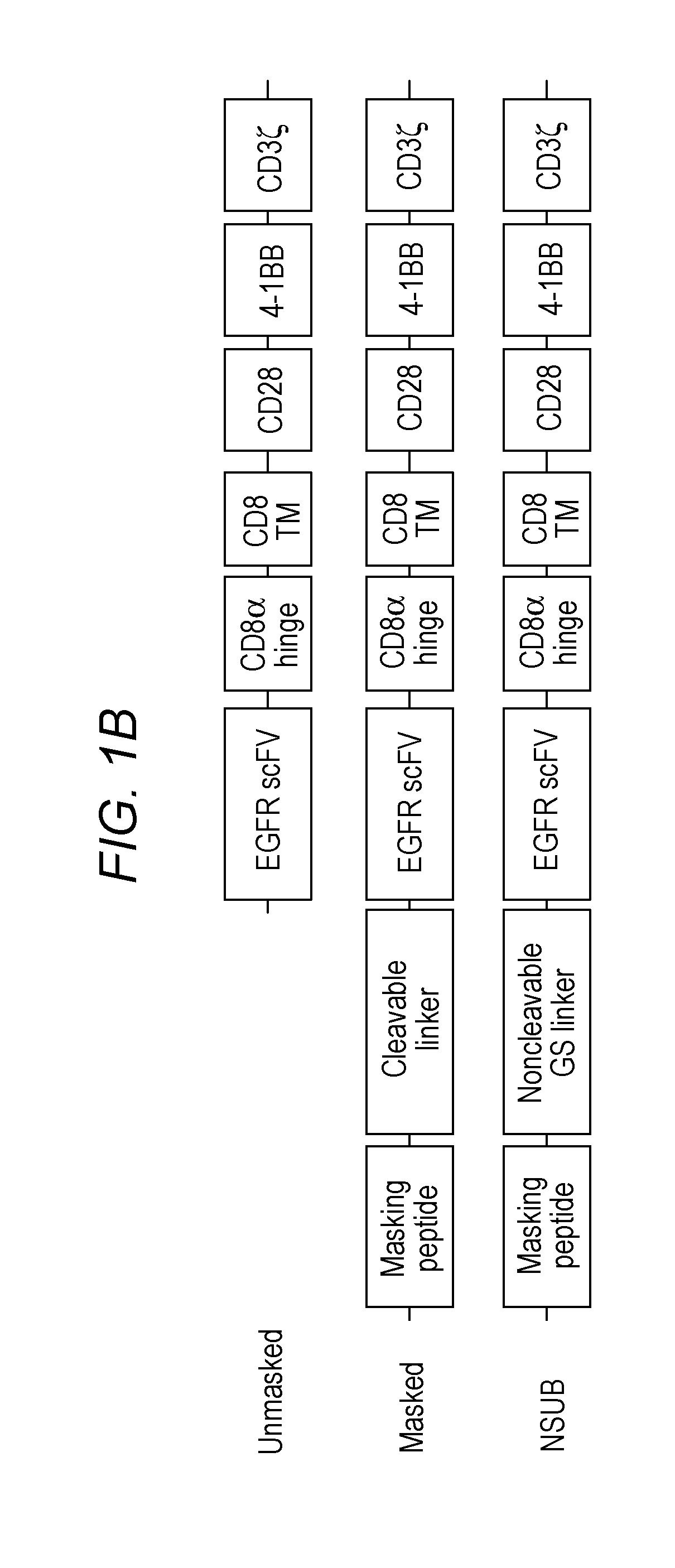
The invention is directed to a masked chimeric antigen receptor, comprising: (a) a masking peptide; (b) one or more antigen-specific targeting domains; (c) an extracellular spacer domain; (d) a transmembrane domain; (e) at least one co-stimulatory domain; and (f) an intracellular signaling domain. The mCARs are activated upon cleavage of the masking peptide.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
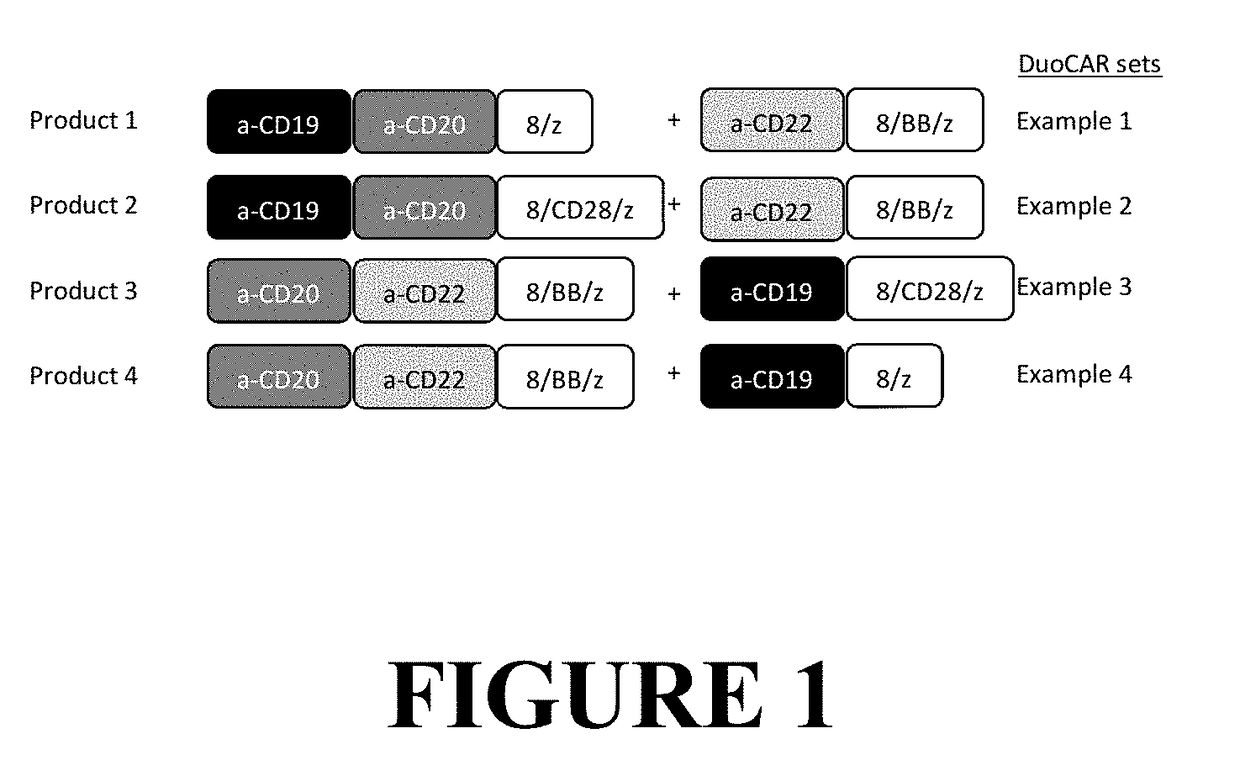
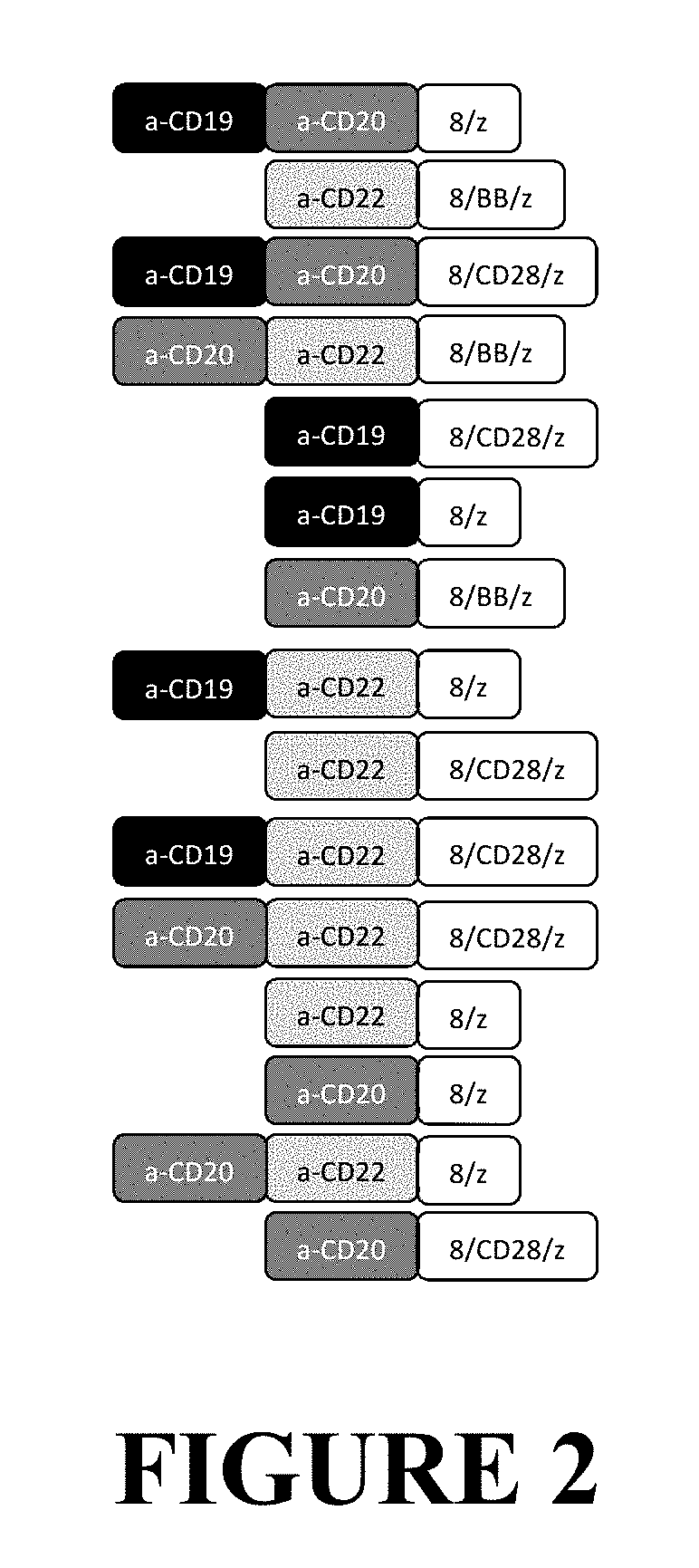
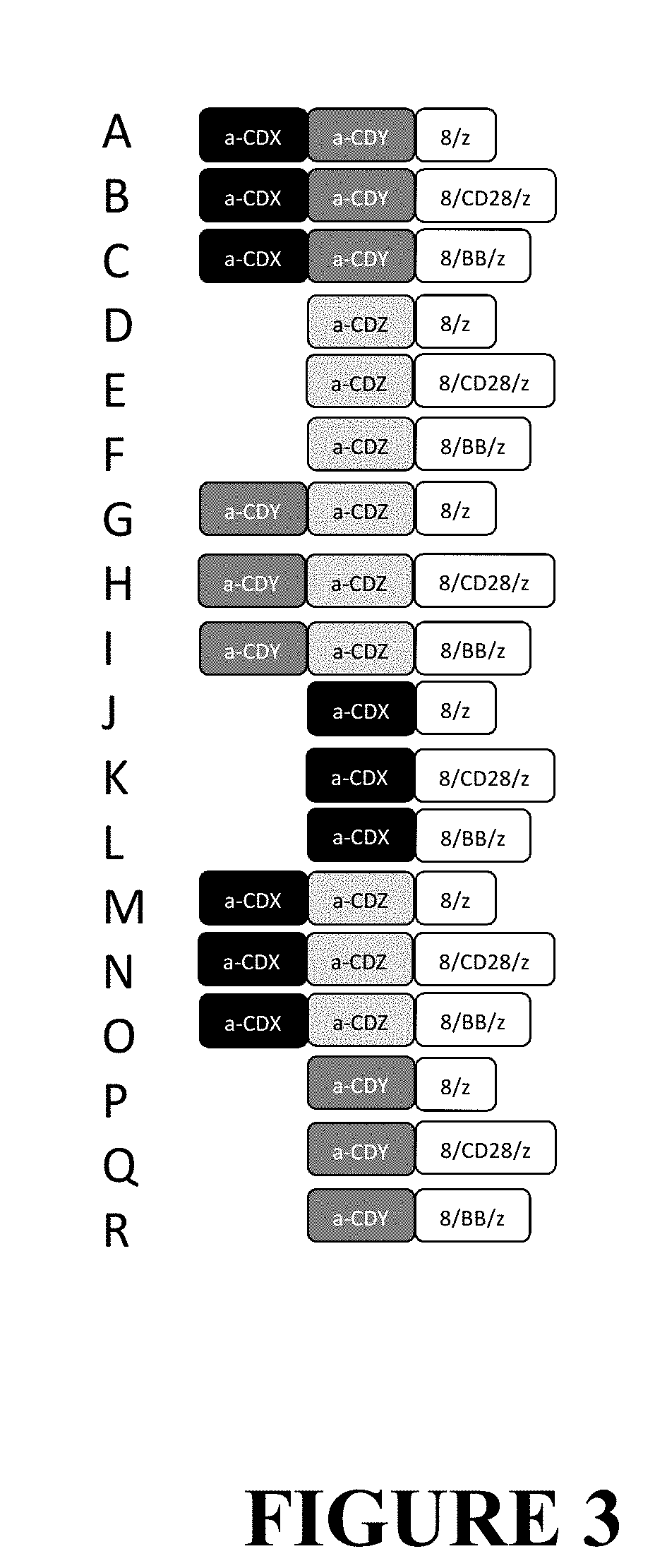
Compositions and Methods for Treating Cancer with DuoCARs
ActiveUS20190083596A1Prevent and ameliorate relapseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsIntracellular signallingDisease
Novel therapeutic immunotherapy compositions comprising at least two vectors, each vector encoding a functional CAR, whereby the combination of vectors results in the expression of two or more non-identical binding domains, wherein each vector encoded binding domain(s) are covalently linked to a transmembrane domain and one or more non-identical intracellular signaling motifs are provided herein as well as are methods of use of same in a patient-specific immunotherapy that can be used to treat cancers and other diseases and conditions.
Owner:LENTIGEN TECH INC
Nod2 nucleic acids and proteins
The present invention relates to intracellular signalling molecules, in particular the Nod2 protein and nucleic acids encoding the Nod2 protein. The present invention provides isolated nucleotide sequence encoding Nod2, isolated Nod2 peptides, antibodies that specifically bind Nod2, methods for the detection of Nod2, and methods for screening compounds for the ability to alter Nod2 associated signal transduction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Chimeric immunoreceptor useful in treating human cancers
InactiveUS20110223129A1Negligible toxicityPotent and selectivePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingImmune receptor
The present invention relates to chimeric transmembrane immunoreceptors, named “zetakines,” comprised of an extracellular domain comprising a soluble receptor ligand linked to a support region capable of tethering the extracellular domain to a cell surface, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signalling domain. Zetakines, when expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes, direct T cell activity to those specific cells expressing a receptor for which the soluble receptor ligand is specific. Zetakine chimeric immunoreceptors represent a novel extension of antibody-based immunoreceptors for redirecting the antigen specificity of T cells, with application to treatment of a variety of cancers, particularly via the autocrin / paracrine cytokine systems utilized by human maligancy. In a preferred embodiment is a glioma-specific immunoreceptor comprising the extracellular targeting domain of the IL-13Rα2-specific IL-13 mutant IL-13(E13Y) linked to the Fc region of IgG, the transmembrane domain of human CD4, and the human CD3 zeta chain.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
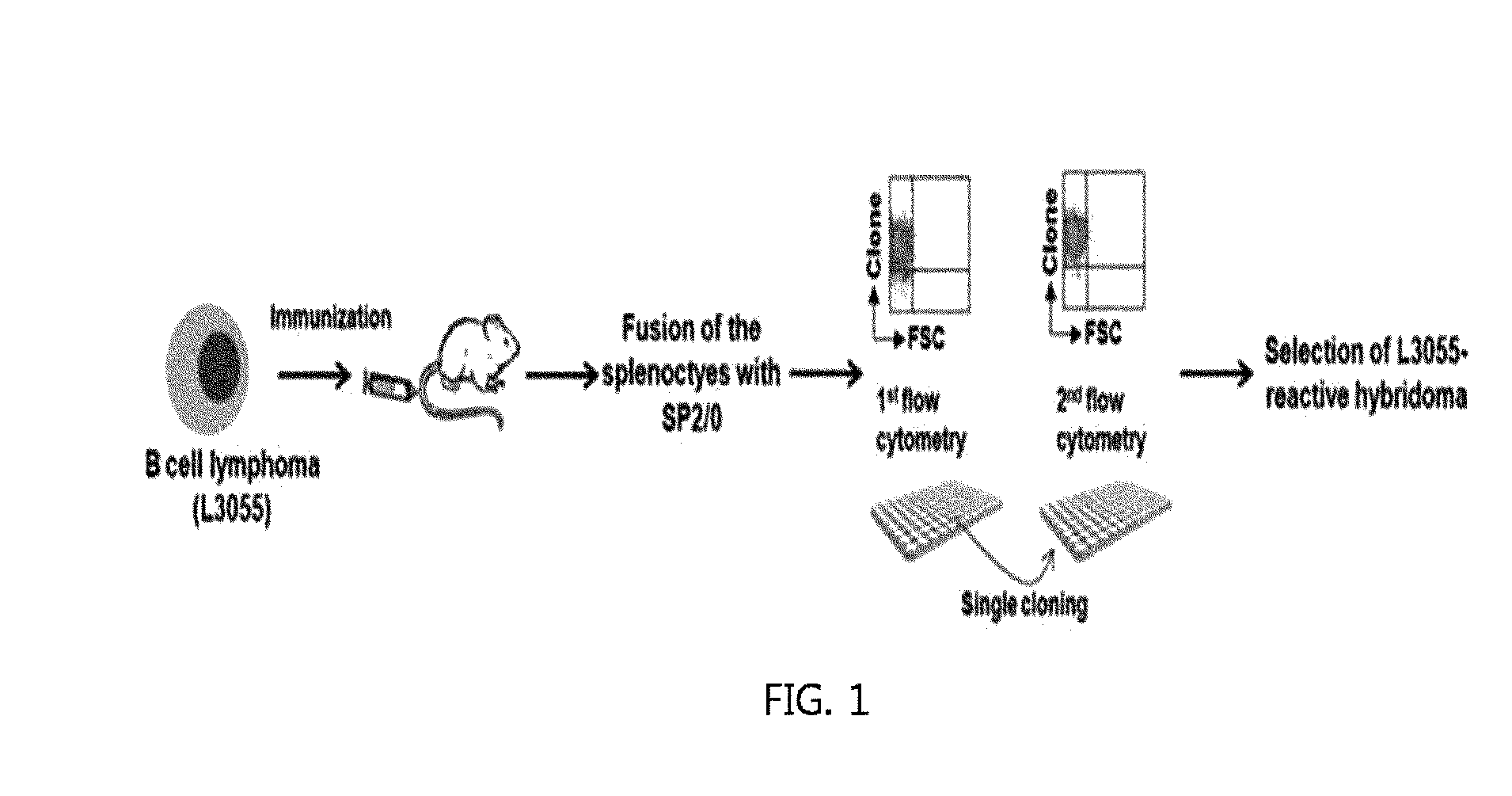
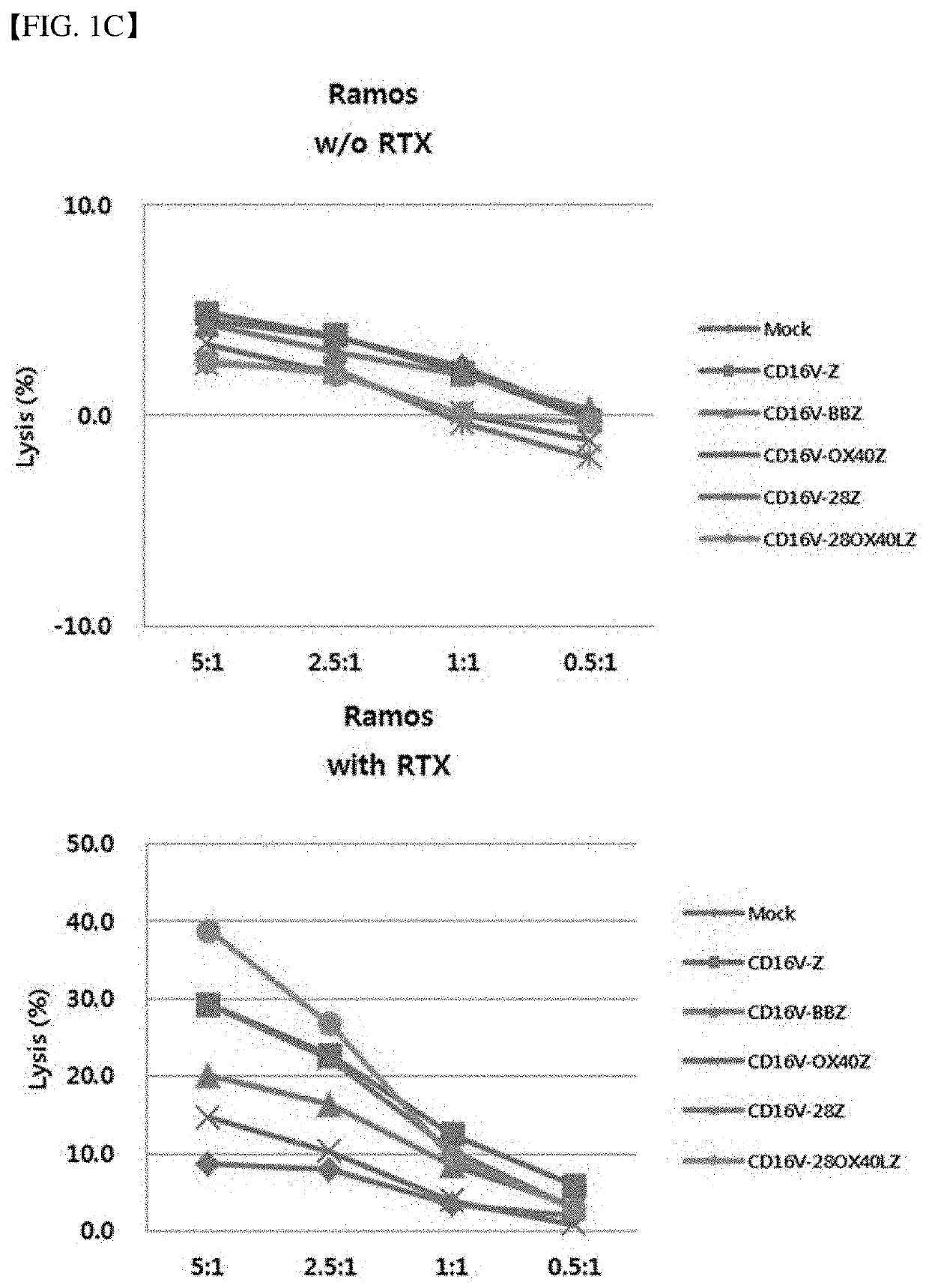
Monoclonal Antibody Which Specifically Recognizes B Cell Lymphoma and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20160257762A1Reduce expressionGood anticancer effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsIntracellular signallingCAR PROTEIN
Provided is a monoclonal antibody which specifically recognizes B cell lymphoma cells and a use thereof. More specifically, provided are the monoclonal antibody; a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating B cell lymphoma including the monoclonal antibody; a composition for diagnosing B cell lymphoma including the monoclonal antibody; a method for providing information for diagnosing B cell lymphoma using the monoclonal antibody; a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) protein including i) the antibody, ii) a transmembrane domain, and iii) an intracellular signaling domain; a recombinant vector which expresses the CAR protein; a CAR-modified T cell transformed with the recombinant vector; a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating B cell lymphoma including the CAR-modified T cell; and an antibody-drug conjugate wherein the monoclonal antibody and a drug are conjugated.
Owner:EUTILEX CO LTD
5-Lipoxygenase modulators
The present invention provides the use of Liver X Receptor (LXR) modulators that have been identified to downregulate 5-lipoxygenase gene expression in order to treat various diseases and disorders that involve the function of the 5-LO protein in intracellular signaling (or other cellular processes) or the function of protein products downstream of 5-LO in intracellular signaling (i.e., leukotrienes).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Recombinant immunoreceptors
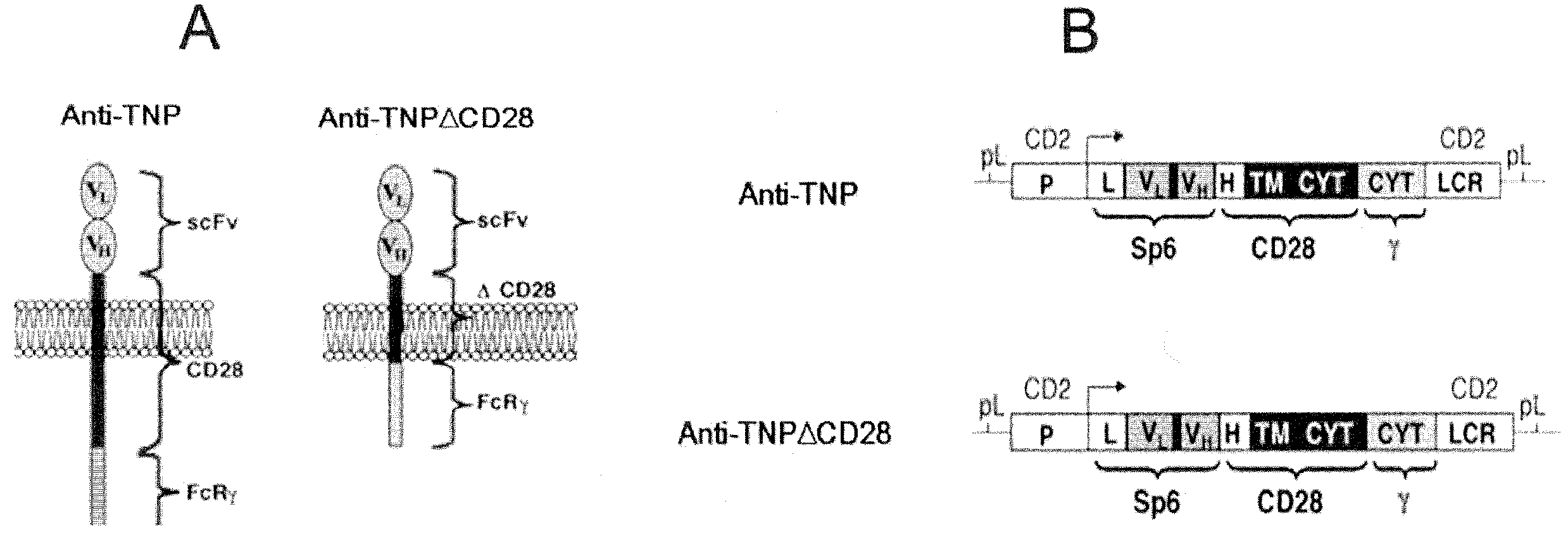
InactiveUS20050118185A1Restored cell surface expressionImpaired stabilitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingCell activation
Described are recombinant immunoreceptors composed of an extracellular antigen binding domain (scFv) and a transmembrane region derived from the CD3ζ-chain and / or the FcεRIγ-chain linked to an intracellular signaling domain with cell activation properties. Moreover, nucleic acid sequences encoding said immunoreceptor, immune cells expressing said immunoreceptor as well as therapeutic uses of said immunoreceptor, e.g. adoptive immunotherapy, are described.
Owner:CELL CENT COLOGNE
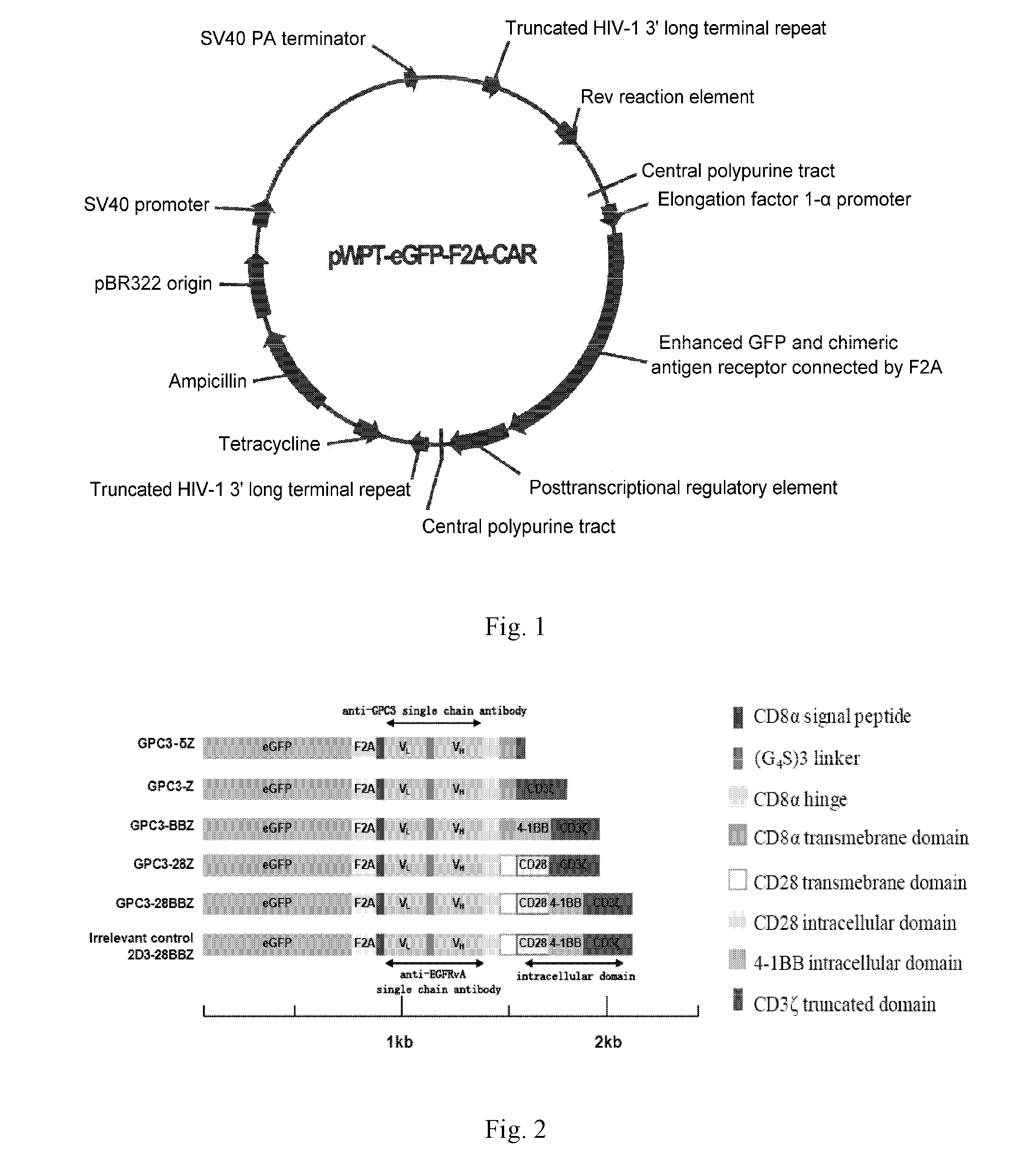
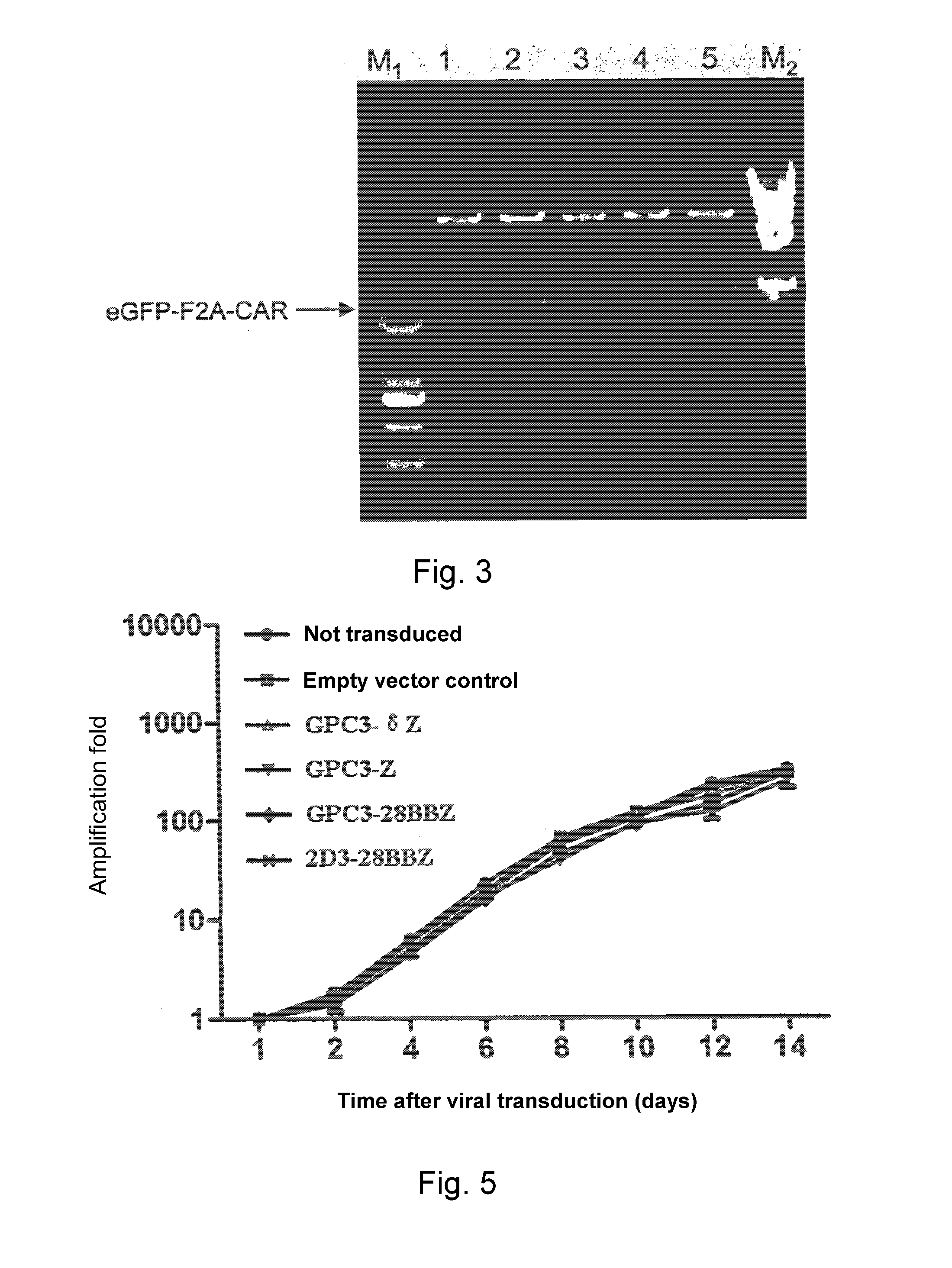
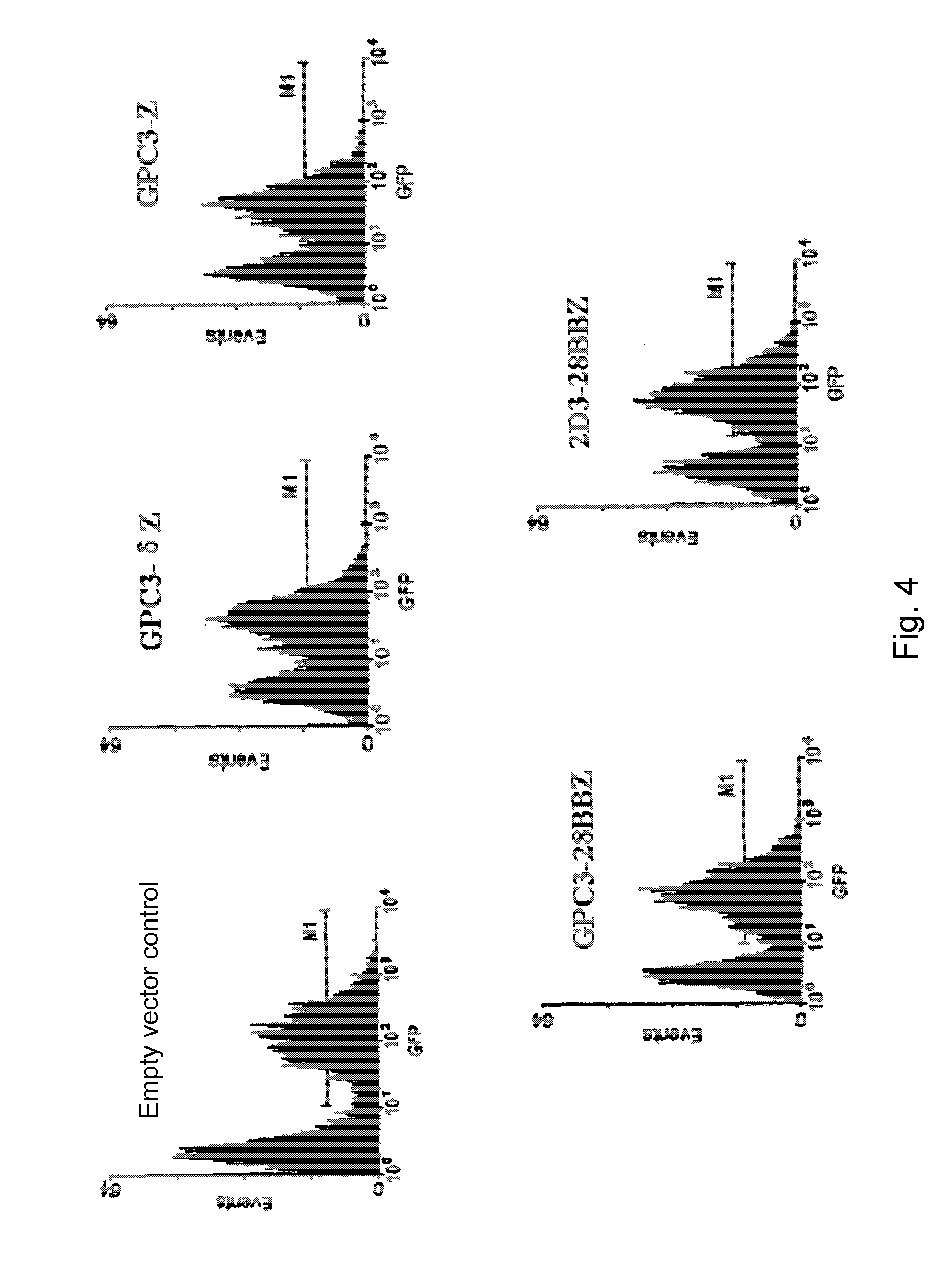
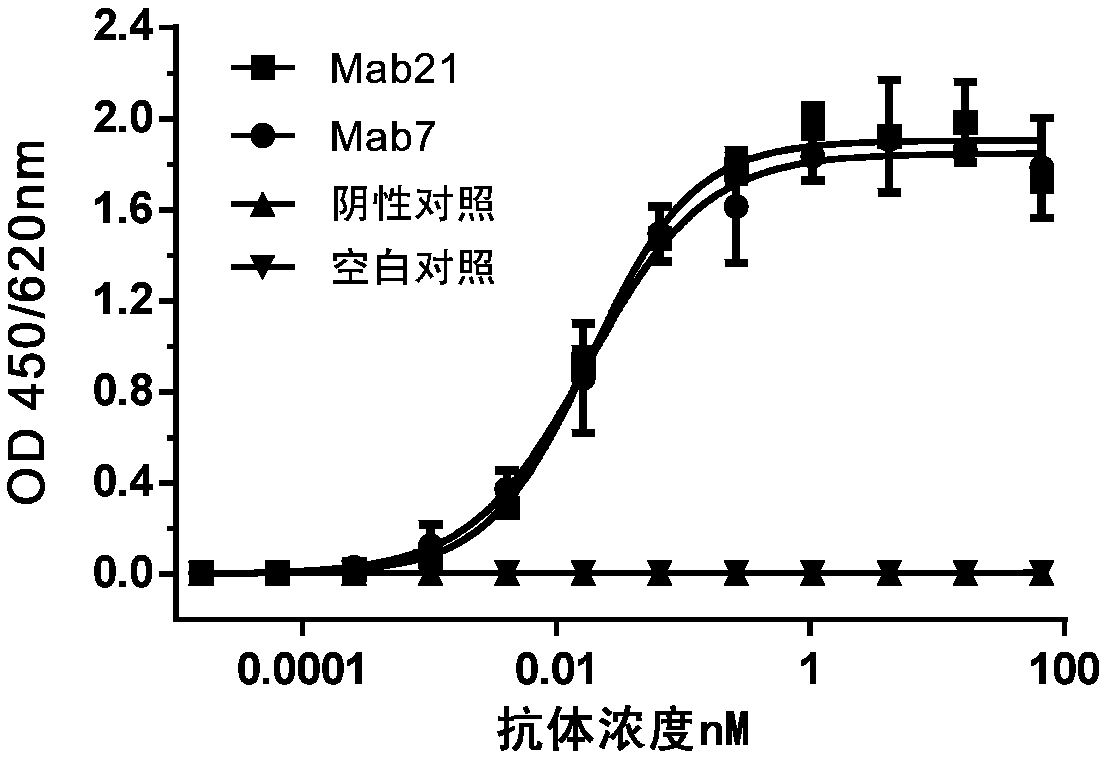
Nucleic Acid Of Coded GPC3 Chimeric Antigen Receptor Protein And T Lymphocyte Expressing GPC3 Chimeric Antigen Receptor Protein
ActiveUS20160215261A1Improve the level ofGood effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingSingle-Chain Antibodies
A nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor expressed at surface of a T lymphocyte, said chimeric antigen receptor comprises, connected in the order of, an extracellular binding domain, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular signaling domain, wherein the extracellular binding domain comprises a single chain antibody, scFv(GPC3), which specifically recognizes the C-terminal epitope of GPC3. A genetically modified T lymphocyte having a chimeric antigen receptor expressed at surface thereof, and the chimeric antigen receptor is expressed by the nucleic acid described above.
Owner:CRAGE MEDICAL CO LTD
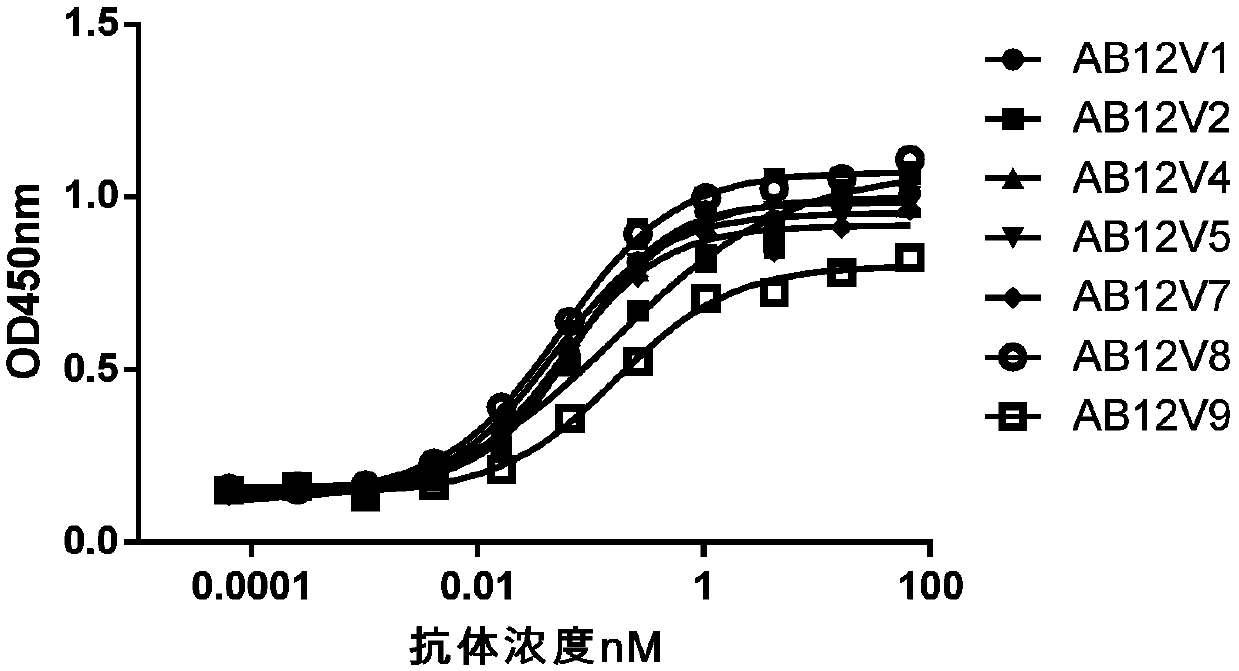
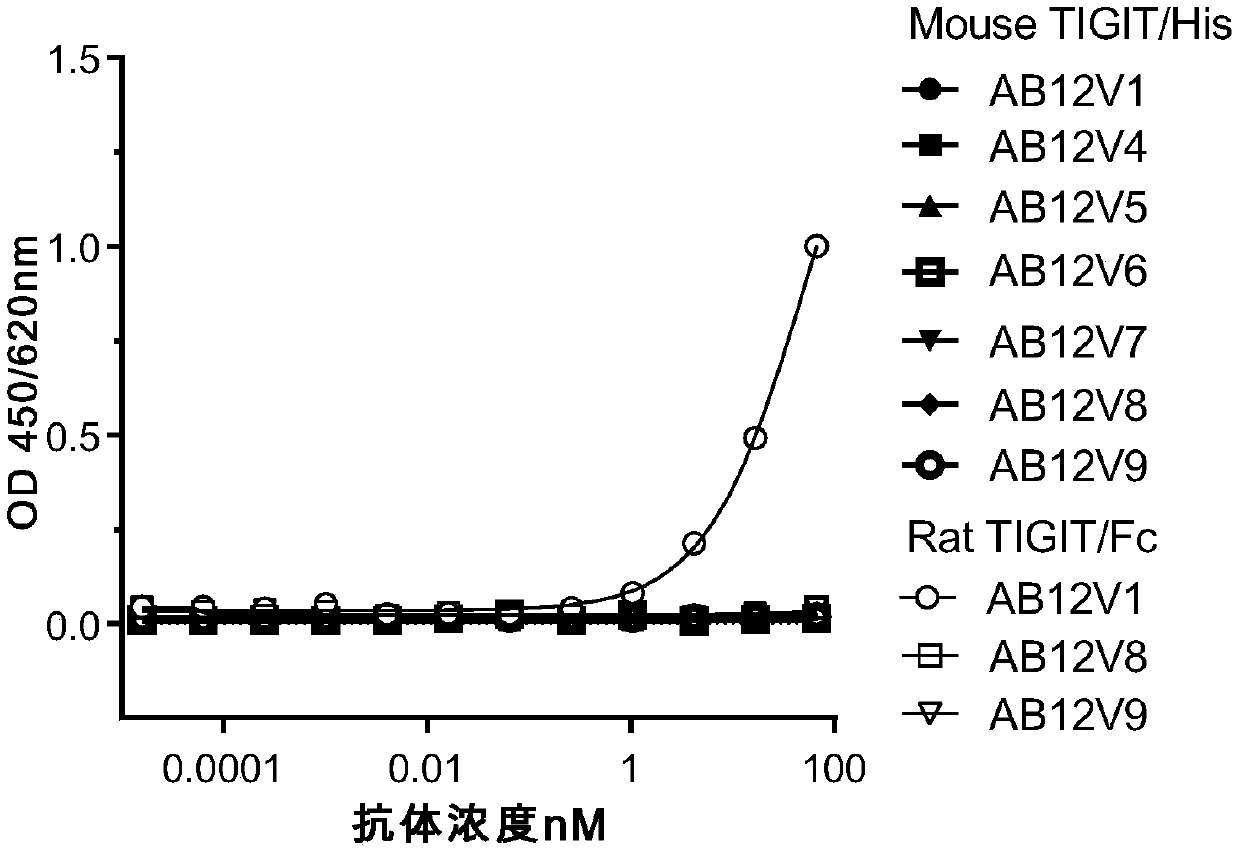
Anti-TIGIT antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveCN111196852AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsIntracellular signallingAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention relates to the field of disease treatment and immunology, and in particular, to anti-TIGIT antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof, nucleic acid molecules encoding the anti-TIGIT antibody and the antigen-binding fragment, and a preparation method thereof. The anti-TIGIT antibody or the antigen binding fragment thereof provided by the invention has high specificity andhigh affinity to TIGIT, can effectively block the binding of TIGIT and a ligand thereof, and inhibits and / or blocks intracellular signal transduction mediated by the binding of TIGIT and the ligand thereof. Therefore, the invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising said antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof, and to the use thereof in the preparation of a medicine for enhancing immune cell activity, enhancing immune response, or for preventing and / or treating tumors, infections or infectious diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN KELUN BIOTECH BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
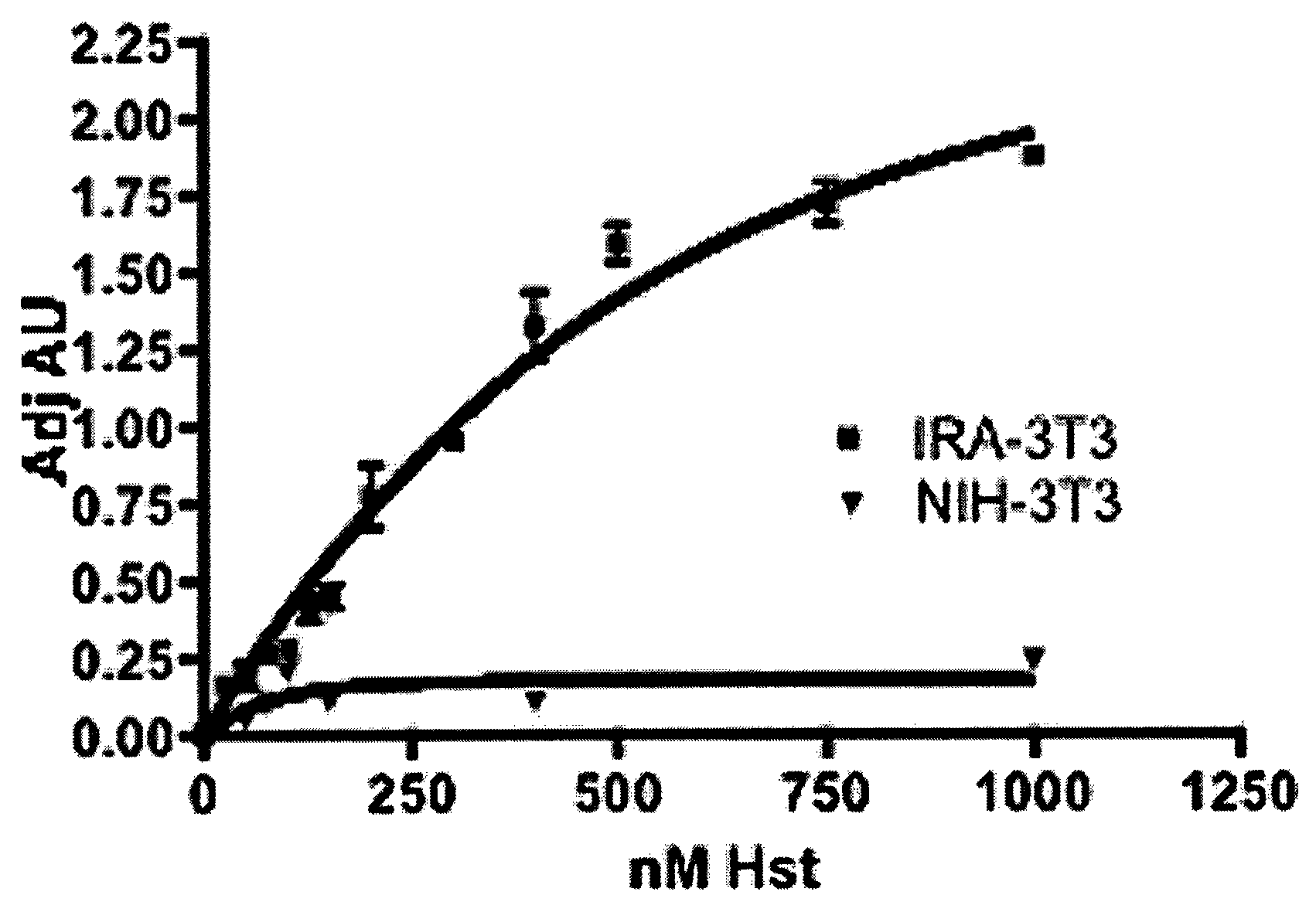
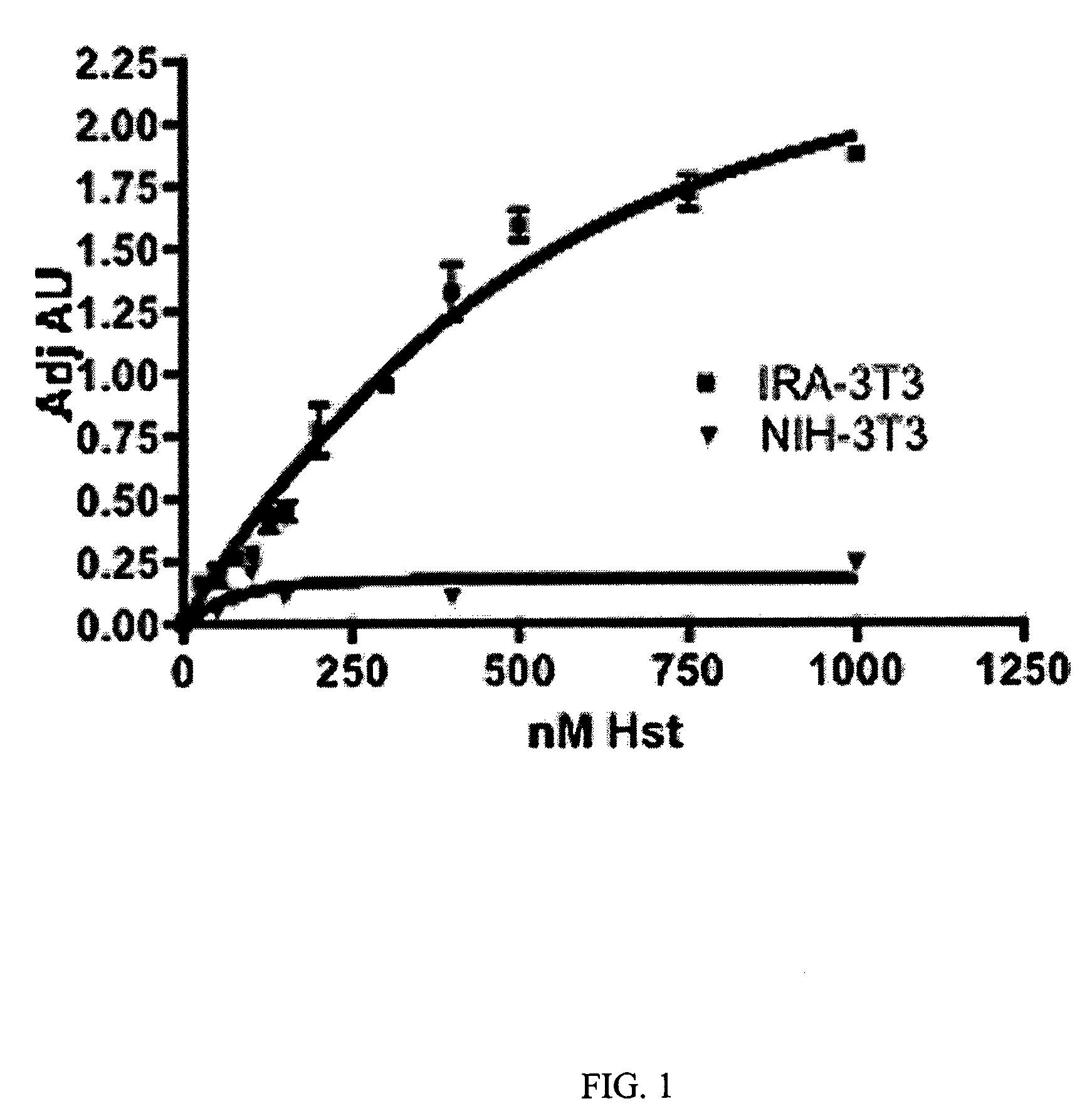
Compositions and Methods for Treating Disease
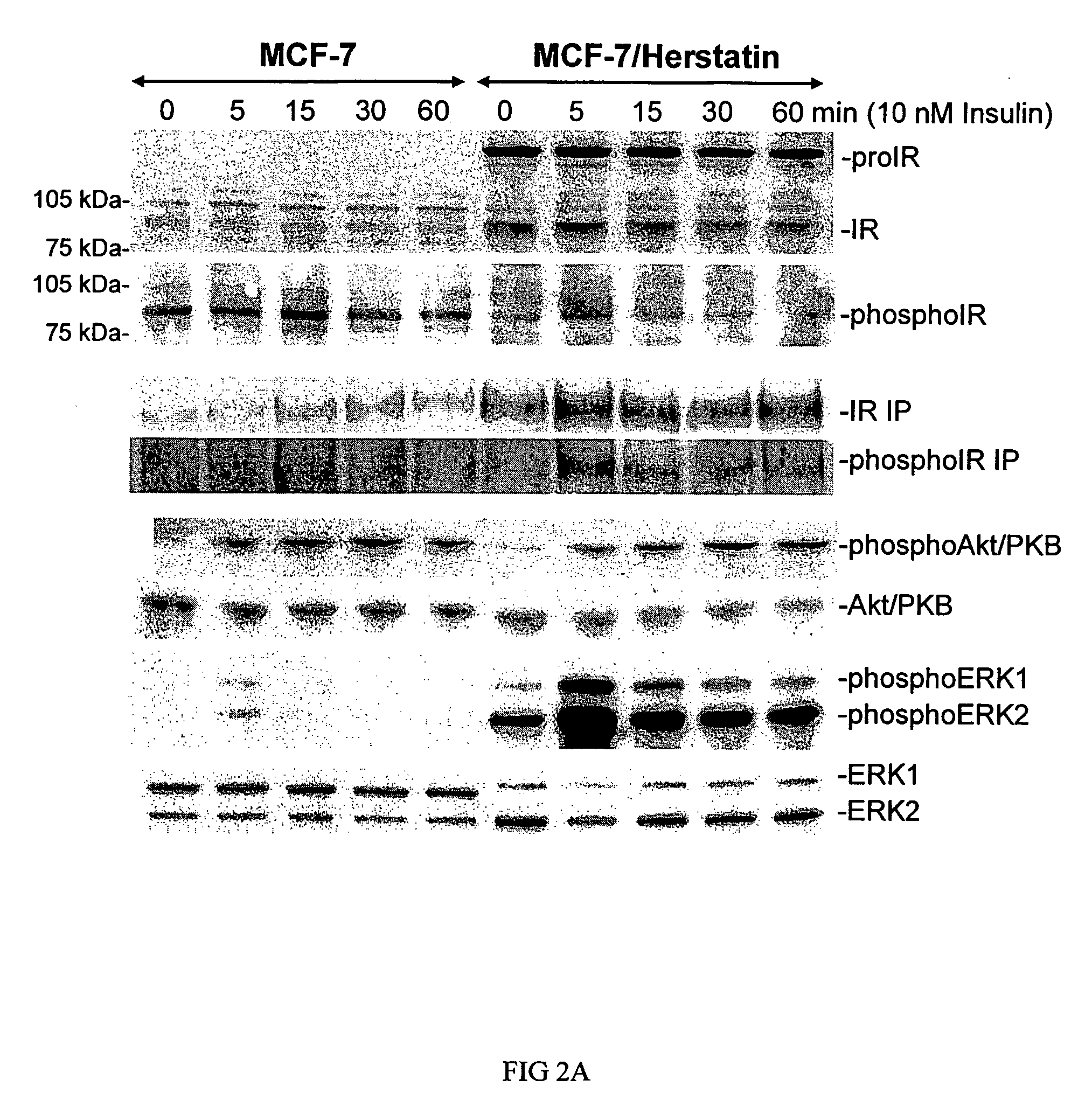
InactiveUS20080206231A1Significant positive effectIncreasing IR-mediated ERK pathway activationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiabetic heartDyslipidemia
The present invention discloses for the first time that the insulin receptor (IR) is a target of Herstatin, which modulates IR and IR-mediated intracellular signaling. In preferred aspects, Herstatin binds at nM concentrations to cell-surface IR, up-regulates basal IR expression by several-fold, induces the accumulation of pro-IR, and stimulates insulin activation of the ERK pathway. Moreover, these changes in insulin signaling are accompanied by alterations in IGF-IR expression, IRS-2 levels, and the serine phosphorylation state of both IRS-1 and IRS-2. Preferred aspects provide novel therapeutic methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of conditions associated with altered IR expression or IR-mediated signaling, including but not limited to insulin resistance syndrome, pre-diabetic conditions, metabolic syndrome, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, cardiac disease, diabetes-associated vascular disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes-associated lipid metabolism disorders (dyslipidemia), obesity, critical illness, neurodegenerative disorders, and combinations thereof, and cancer.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Integrated Analyses of Breast and Colorectal Cancers
InactiveUS20100136560A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCellular pathwaysIntracellular signalling
Genome-wide analysis of copy number changes in breast and colorectal tumors used approaches that can reliably detect homozygous deletions and amplifications. The number of genes altered by major copy number changes—deletion of all copies or amplification of at least twelve copies per cell—averaged thirteen per tumor. These data were integrated with previous mutation analyses of the Reference Sequence genes in these same tumor types to identify genes and cellular pathways affected by both copy number changes and point alterations. Pathways enriched for genetic alterations include those controlling cell adhesion, intracellular signaling, DNA topological change, and cell cycle control. These analyses provide an integrated view of copy number and sequencing alterations on a genome-wide scale and identify genes and pathways that are useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods of treating neurodegenerative disorders and diseases
InactiveUS20120010196A1Inhibiting growth cone collapseBiocideNervous disorderIntracellular signallingScreening method
This invention is directed to a novel method of treating neurodegenerative disorders and diseases. Another, related aspect of this invention is directed to a screening method of identifying compounds that can be used to treat neurodegenerative disorders and diseases. The foregoing aspects of the invention particularly relate to neurodegenerative disorders and diseases have degeneration of neuronal axons as part of their pathologies. The method of treatment involves administering a pharmaceutical formulation that comprises a compound or mixture of compounds that inhibits one or more intracellular signaling mechanism that regulate axon degeneration or growth cone collapse. The screening method aspect of the invention identifies test compounds that can be used for the treatment or prevention of neurodegenerative disorders based on the test compound's ability to inhibit axon degeneration or growth cone collapse.
Owner:WESTERN UNIV OF HEALTH SCI
Methods for regulating inflammatory mediators and peptides useful therein
InactiveUS7544772B2Reduce releaseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsIntracellular signallingMANS peptide
Owner:BIOMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LTD +1
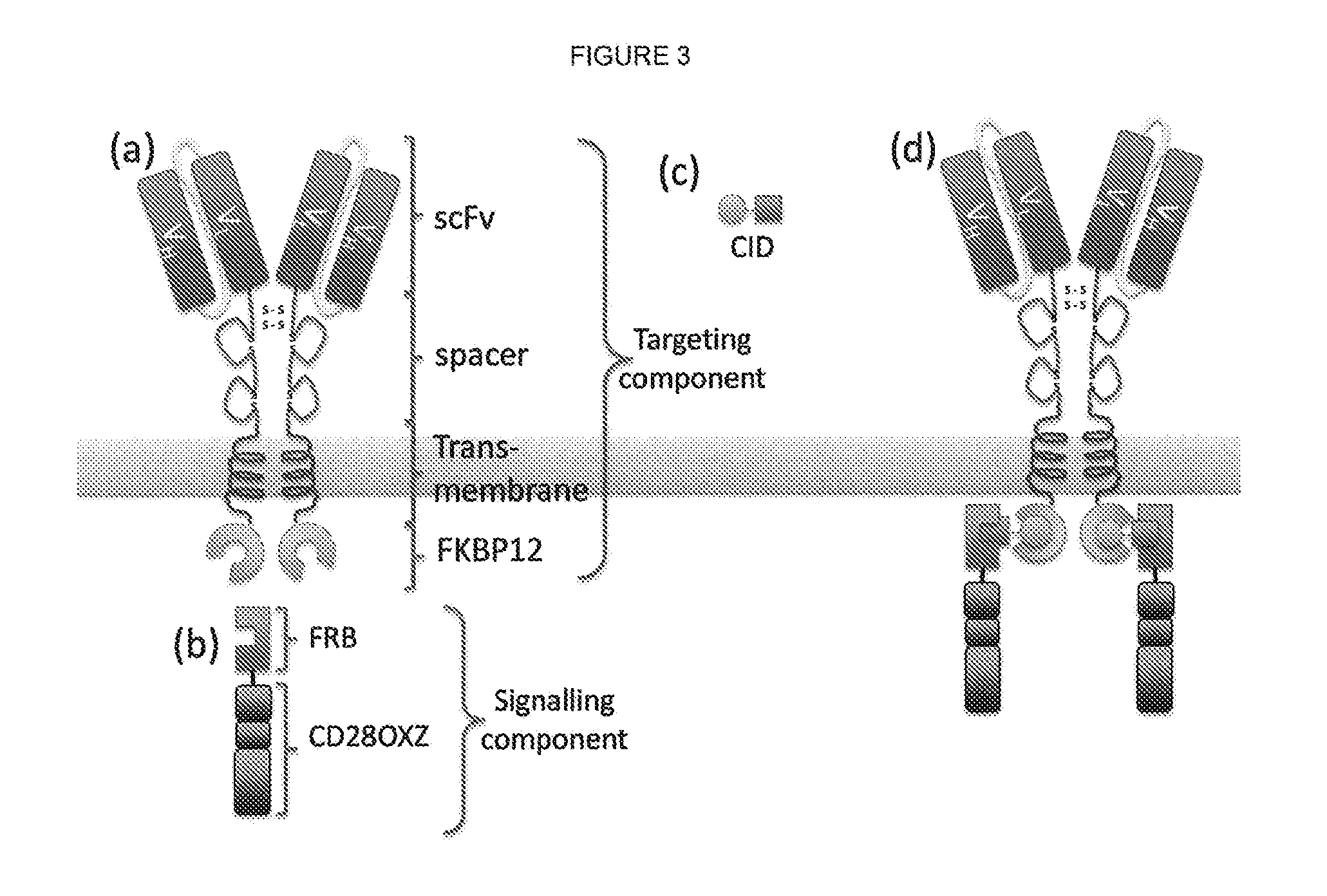
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) signalling system
ActiveUS20170014508A1Possible to separateAvoid toxicityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousIntracellular signalling
The present invention relates to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) signalling system comprising; (i) a receptor component comprising an extracellular antigen-binding domain, a transmembrane domain and a intracellular first chemical inducer of dimerization binding domain 1 (CBD1); and (ii) an intracellular signalling component comprising a signalling domain and a second chemical inducer of dimerization binding domain 2 (CBD2); wherein CBD1 and CBD2 are capable of simultaneously binding to a chemical inducer of dimerization (CID); wherein, in the absence of the CID, binding of the antigen-binding component to antigen does not result in signalling through the signalling component; whilst, in the presence of the CID, the receptor component and the signalling component heterodimerize and binding of the antigen-binding domain to antigen results in signalling through the signalling domain.
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
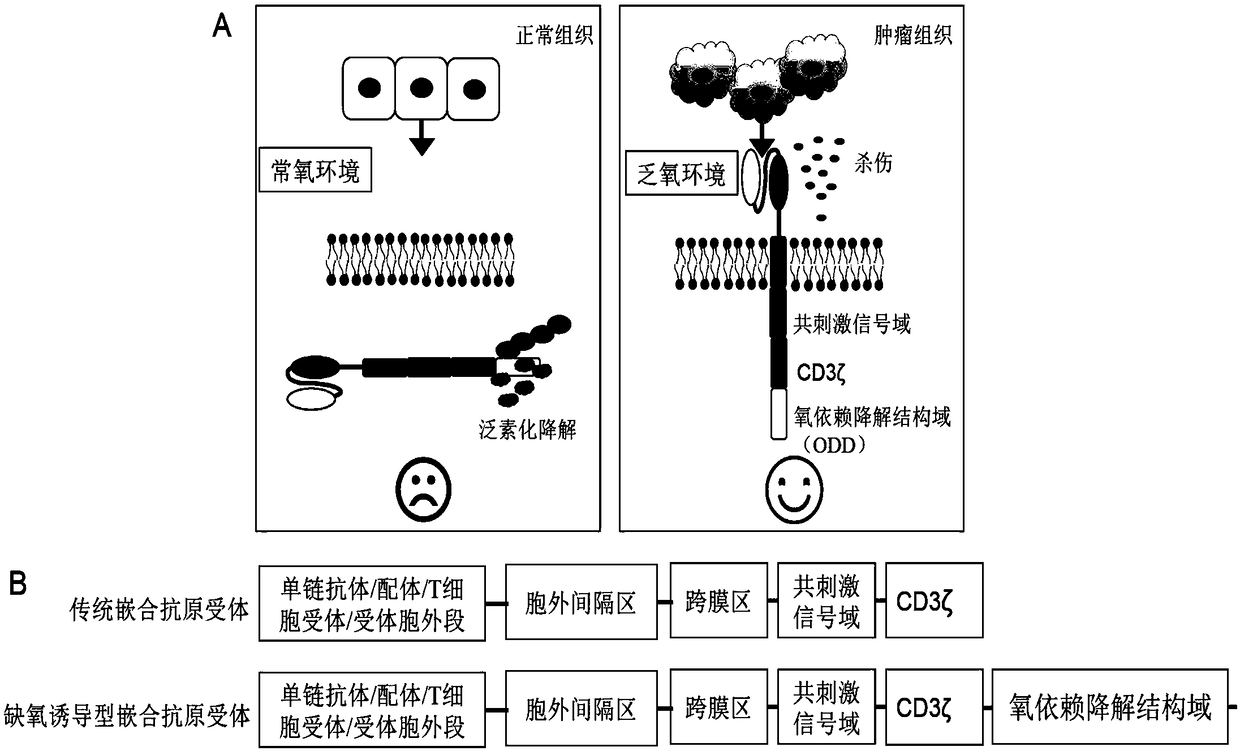
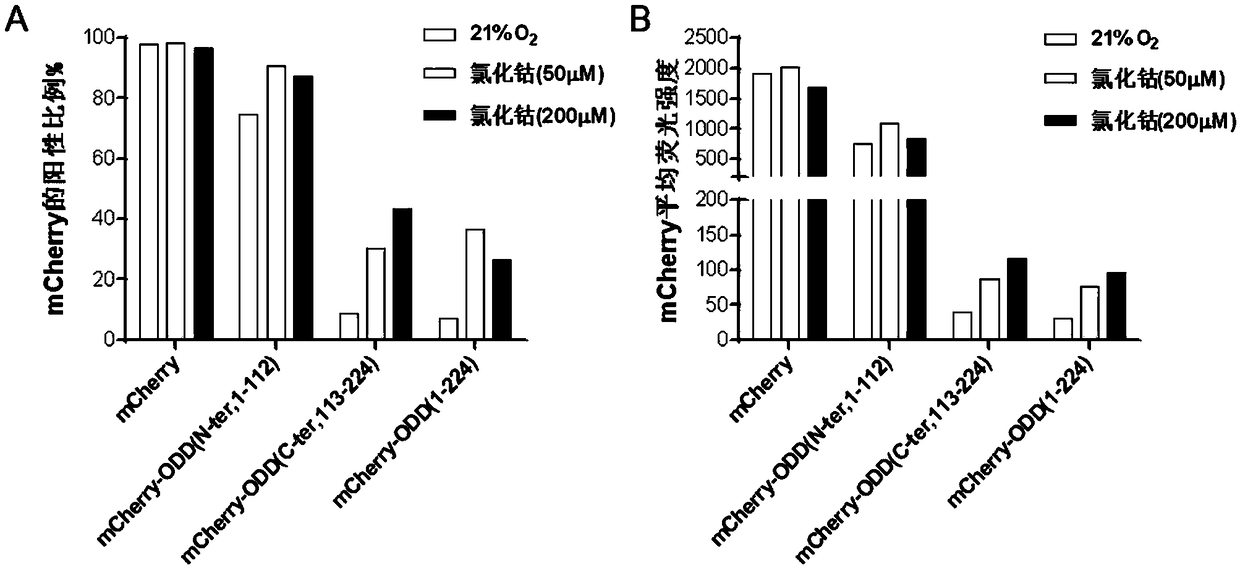
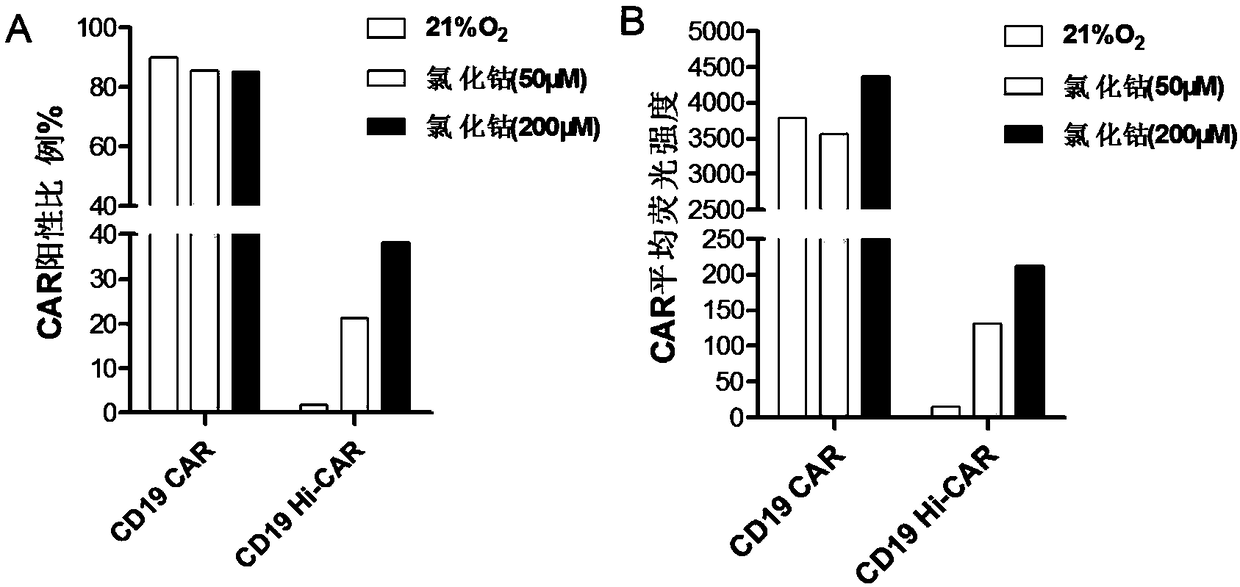
Hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor capable of achieving specific activation of tumor microenvironment
ActiveCN109280086AStay targetedStay lethalPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingCell membrane
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical science, and relates to a hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor capable of achieving specific activation of a tumor microenvironment. The structural domain of the hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor comprises: (1) one or more structural domains with specific combination of target antigens; (2) a structural domain in an extracellular spacer region; (3) a transmembrane structural domain; (4) one or more costimulatory signal structural domain and a cytokine receptor signal-transduction structural domain; (5) an intracellularsignal-transduction structural domain; and (6) an oxygen-dependent degradation structural domain. Once the hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor is exposed to an anoxic environment, efficient expression of the Hi-CAR on effect cell membranes is achieved, and specific recognition of target antigens is achieved, so that the specific activation property of the anoxic microenvironment is achieved; and since the anoxic situation of the tumor microenvironment is more significant than that of normal tissue, damage to the normal tissue can be reduced significantly, and meanwhile the activity ofspecific killing of tumors is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
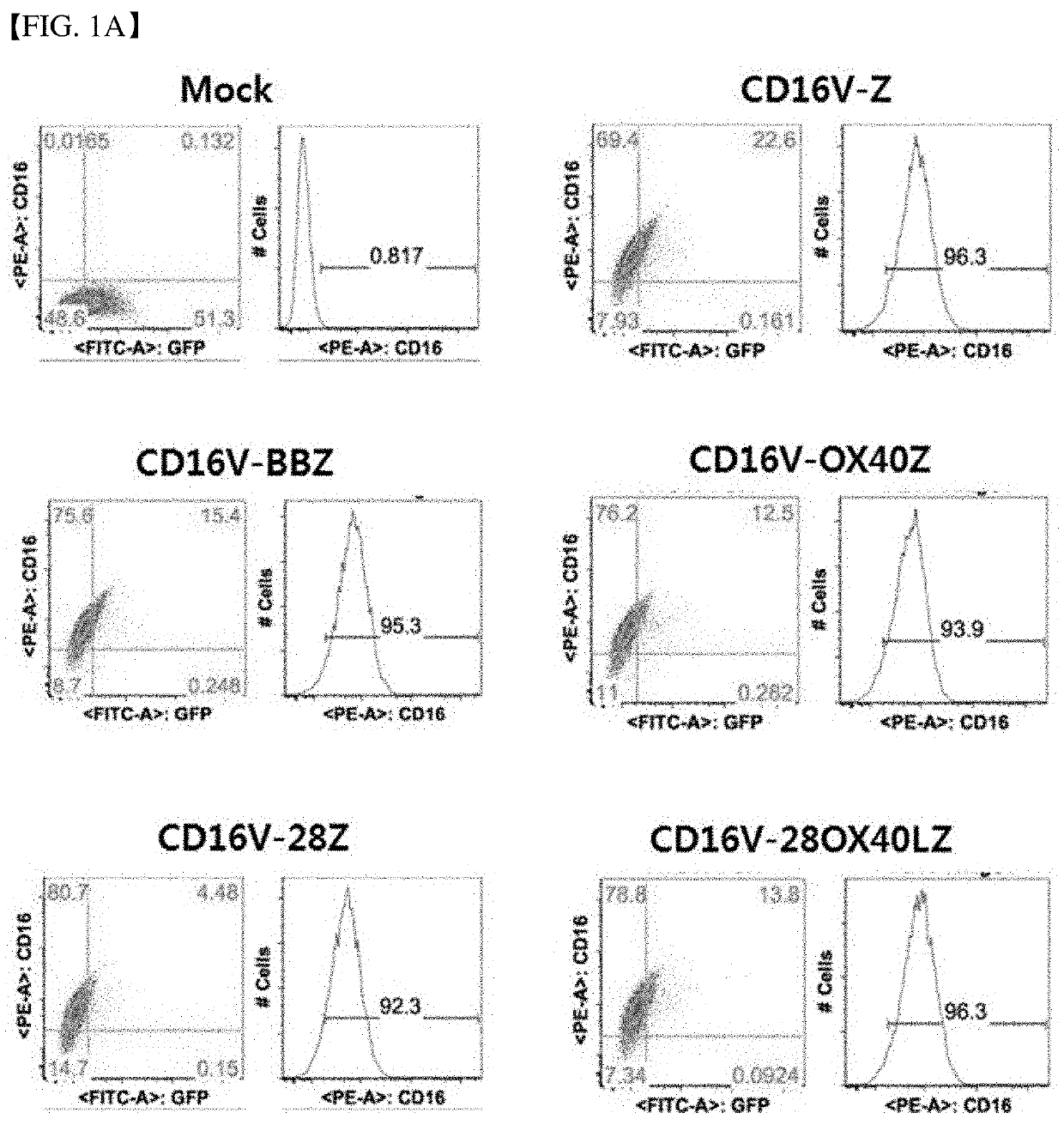
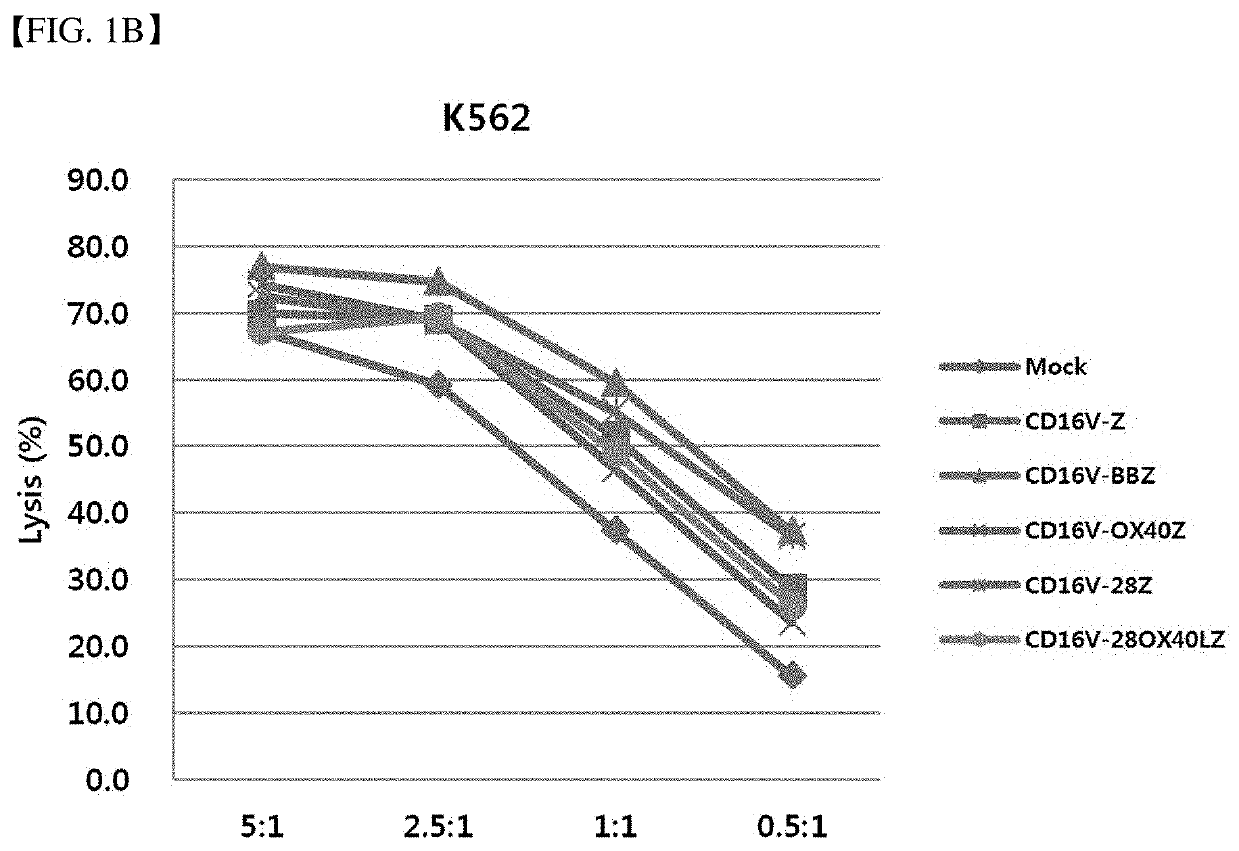
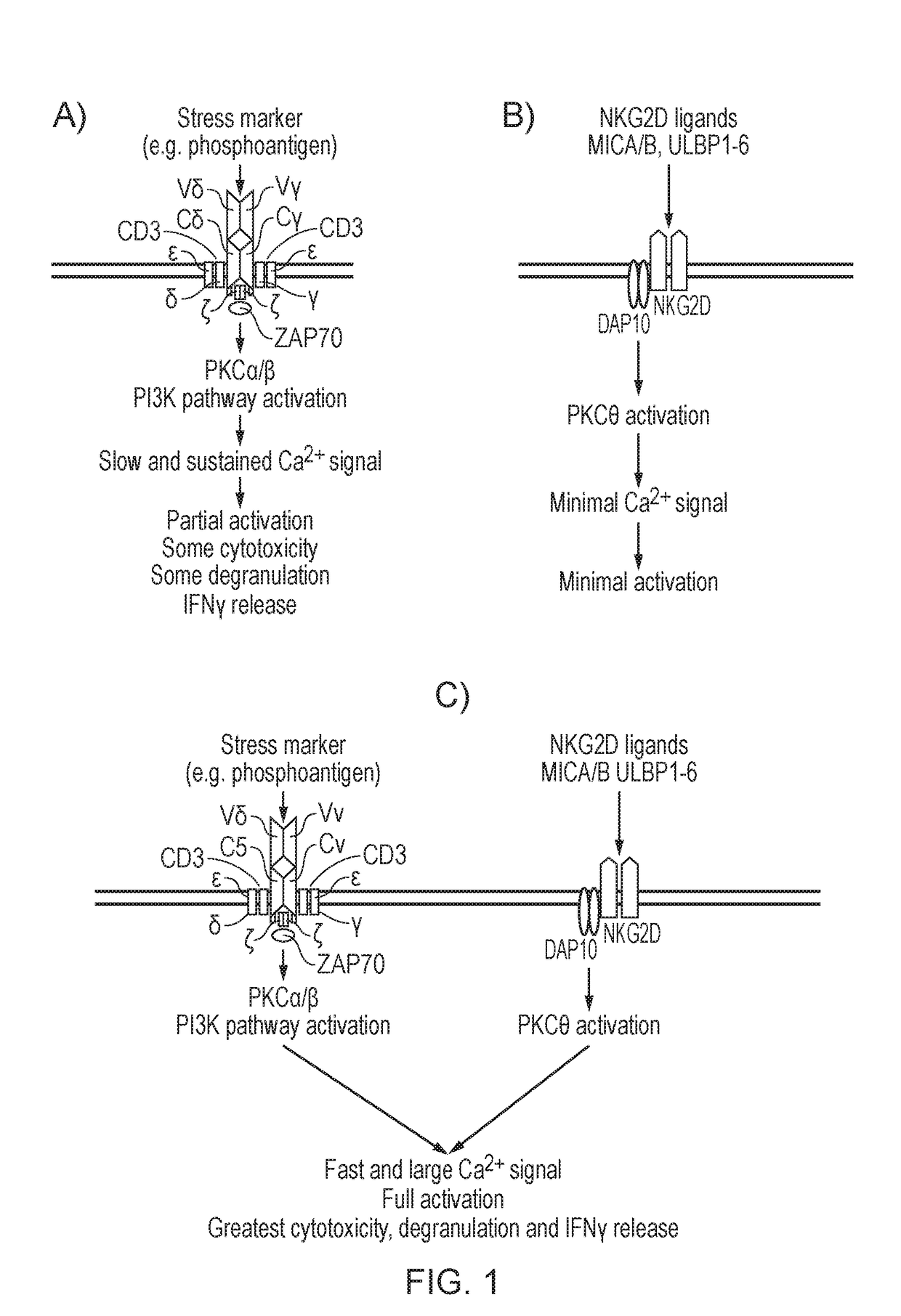
Chimeric antigen receptor and natural killer cells expressing same
InactiveUS20190336533A1Excellent in NK cell activation efficiencyStrong cytotoxicityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingAntigen receptor
The present invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor and natural killer cells expressing the same, and particularly, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) which includes an intracellular signaling domain including the whole or a portion of an OX40 ligand (CD252), thereby having excellent effects of increasing anticancer activity of immune cells, and immune cells expressing the same.
Owner:GC CELL CORP
Tunable Chimeric Antigen Receptors
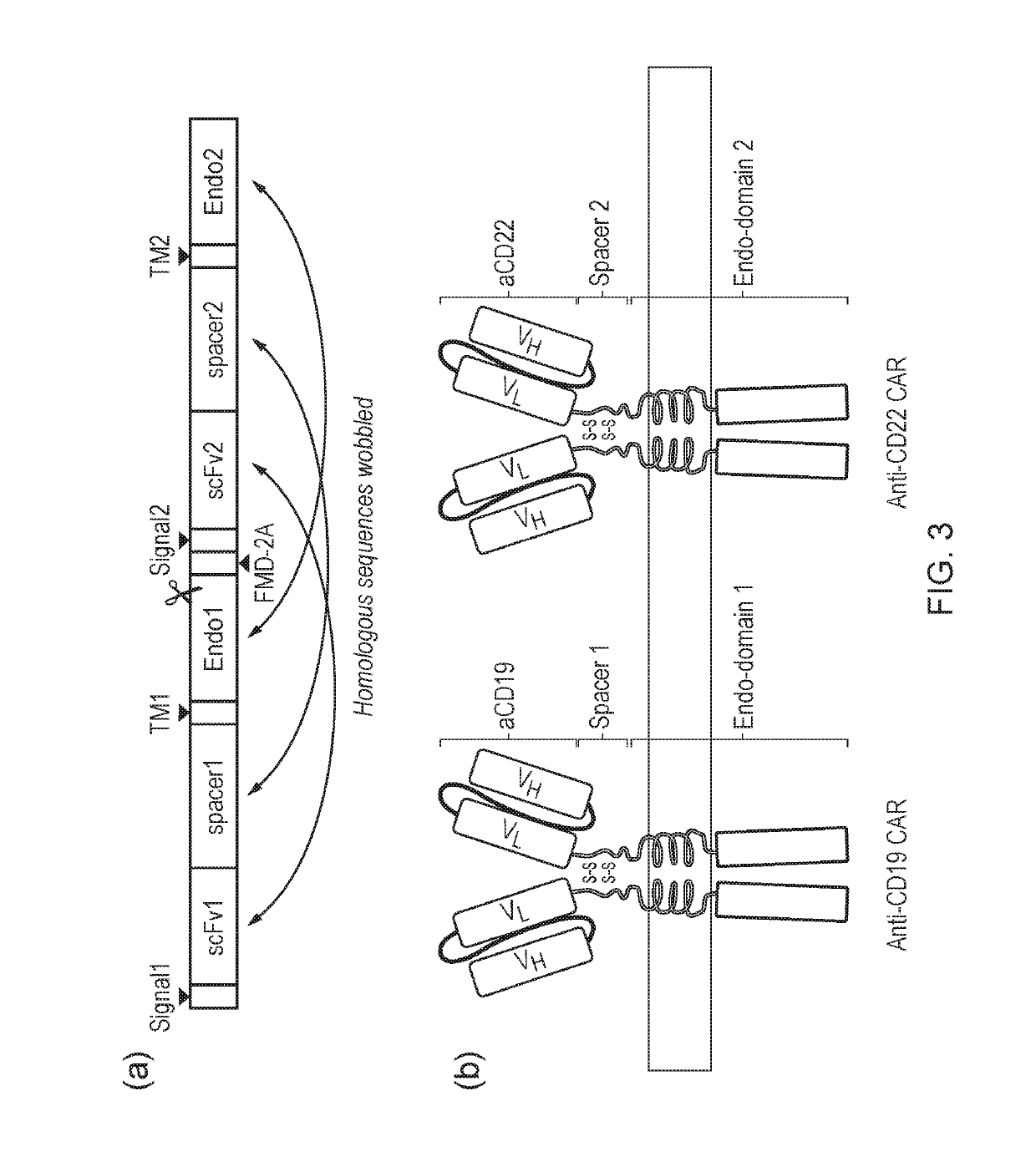
InactiveUS20190330337A1Reduce decreaseSimple procedurePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingAntigen receptors
The present invention provides a cell which co-expresses a first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) and second CAR at the cell surface, each CAR comprising an antigen-binding domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain wherein the antigen-binding domain of the first CAR binds to CD19 and the antigen-binding domain of the second CAR binds to CD22; and wherein the first and / or second CAR is a tunable CAR having an intracellular domain comprising a heterodimenzation domain, which intracellular domain is capable of binding a separate intracellular signalling molecule which comprises a reciprocal heterodimenzation domain and a signalling domain.
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
Immunomodulatory fusion proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20180044404A1Improve cell activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsIntracellular signallingExtracellular
The present disclosure relates to immunomodulatory fusion proteins containing an extracellular binding domain and an intracellular signaling domain, wherein binding of a target can generate a modulatory signal in a host cell, such as a T cell. The present disclosure also relates to uses of immune cells expressing such immunomodulatory fusion proteins to treat certain diseases, such as cancer or infectious disease.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
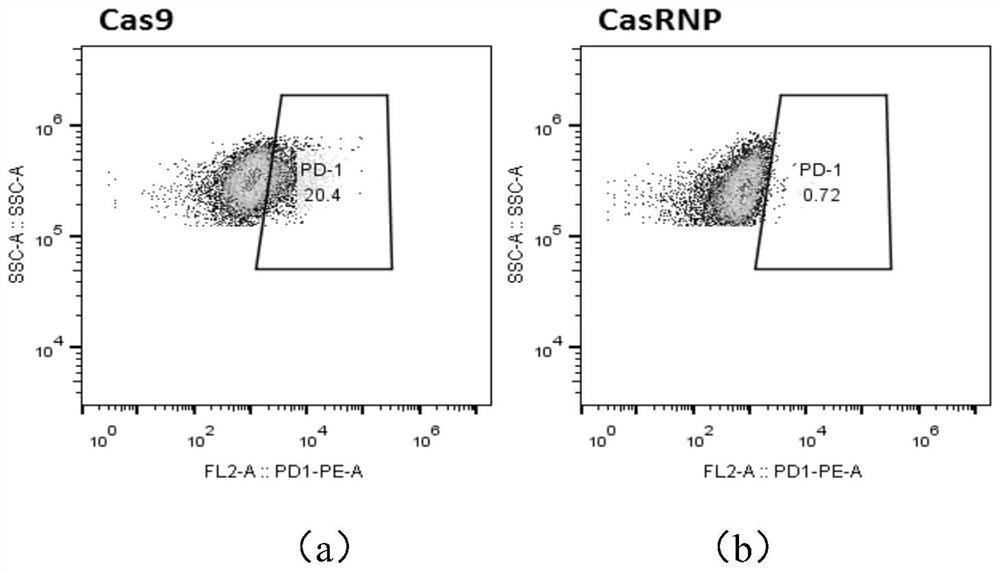
PD-1 gene knockout MUC1-targeting CAR-T cell as well as preparation method and application of PD-1 gene knockout MUC1-targeting CAR-T cell
PendingCN112940137AStrong specificityImprove securityNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsIntracellular signallingAntigen binding
The invention belongs to the technical field of cellular immunotherapy, and particularly relates to a PD-1 gene knockout MUC1-targeting CAR-T cell as well as a preparation method and application thereof. An MUC1-targeting chimeric antigen receptor is prepared firstly, wherein the MUC1-targeting chimeric antigen receptor comprises an antigen binding structural domain, a transmembrane structural domain, a co-stimulation structural domain and an intracellular signal transduction structural domain. Tn glycosylation MUC1 is used as a target spot, the target spot specificity is high, off-target is not likely to occur, and the safety of the CAR-T cells is improved. On the basis, the PD-1 gene knockout MUC1-targeting CAR-T cell is obtained, and after the PD-1 gene is knocked out and the CAR-T cell is transfused back into a body, the CAR-T cell failure and inactivation caused by PD-L1 expressed by tumors cannot occur, so that the efficient specific cell killing effect on tumor cells is achieved, and the curative effect of the CAR-T cell is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ANJIE BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
T cell which expresses a gamma-delta t cell receptor (TCR) and a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)
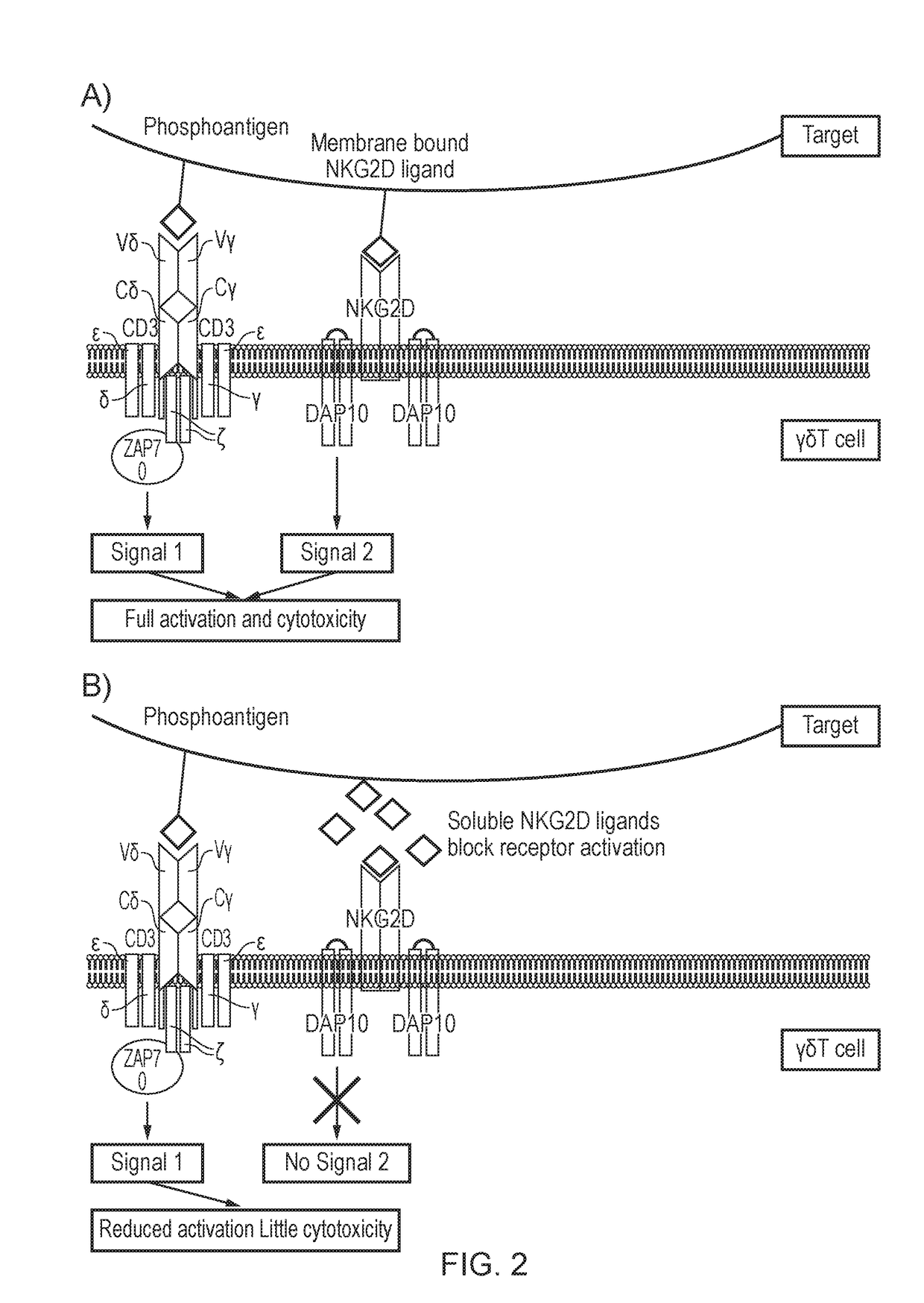
InactiveUS20180125890A1Reducing unwanted ‘ on target-off tumour ’ effectUnwanted effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibacterial agentsIntracellular signallingGamma-delta T-Cell Receptor
The present invention provides a T cell which expresses a gamma-delta T cell receptor (TCR) and a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), wherein the CAR comprises: an antigen binding domain; a transmembrane domain; and a co-stimulatory intracellular signalling domain; wherein the intracellular signalling domain provides a co-stimulatory signal to the T cell following binding of antigen to the antigen binding domain.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com