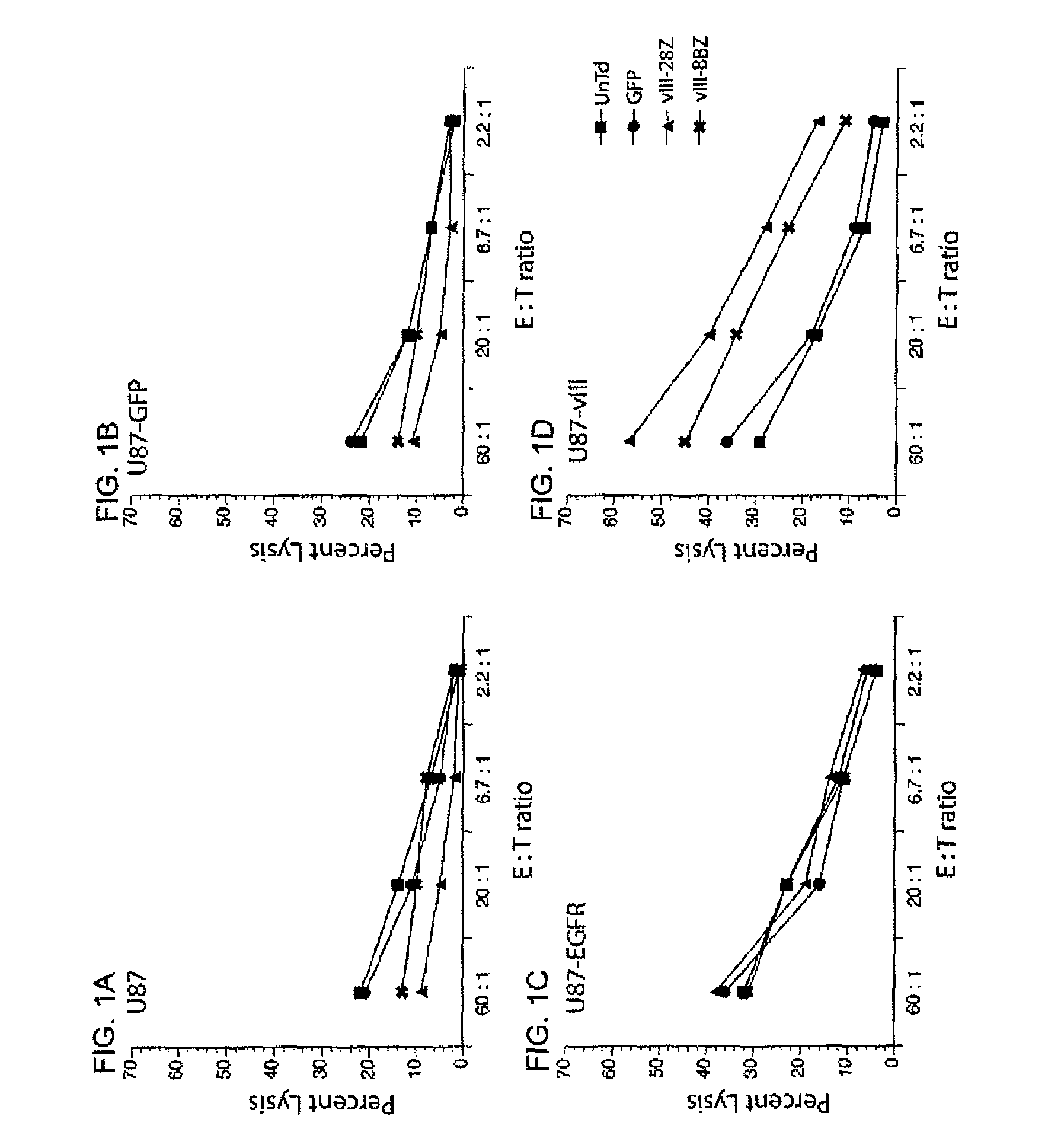
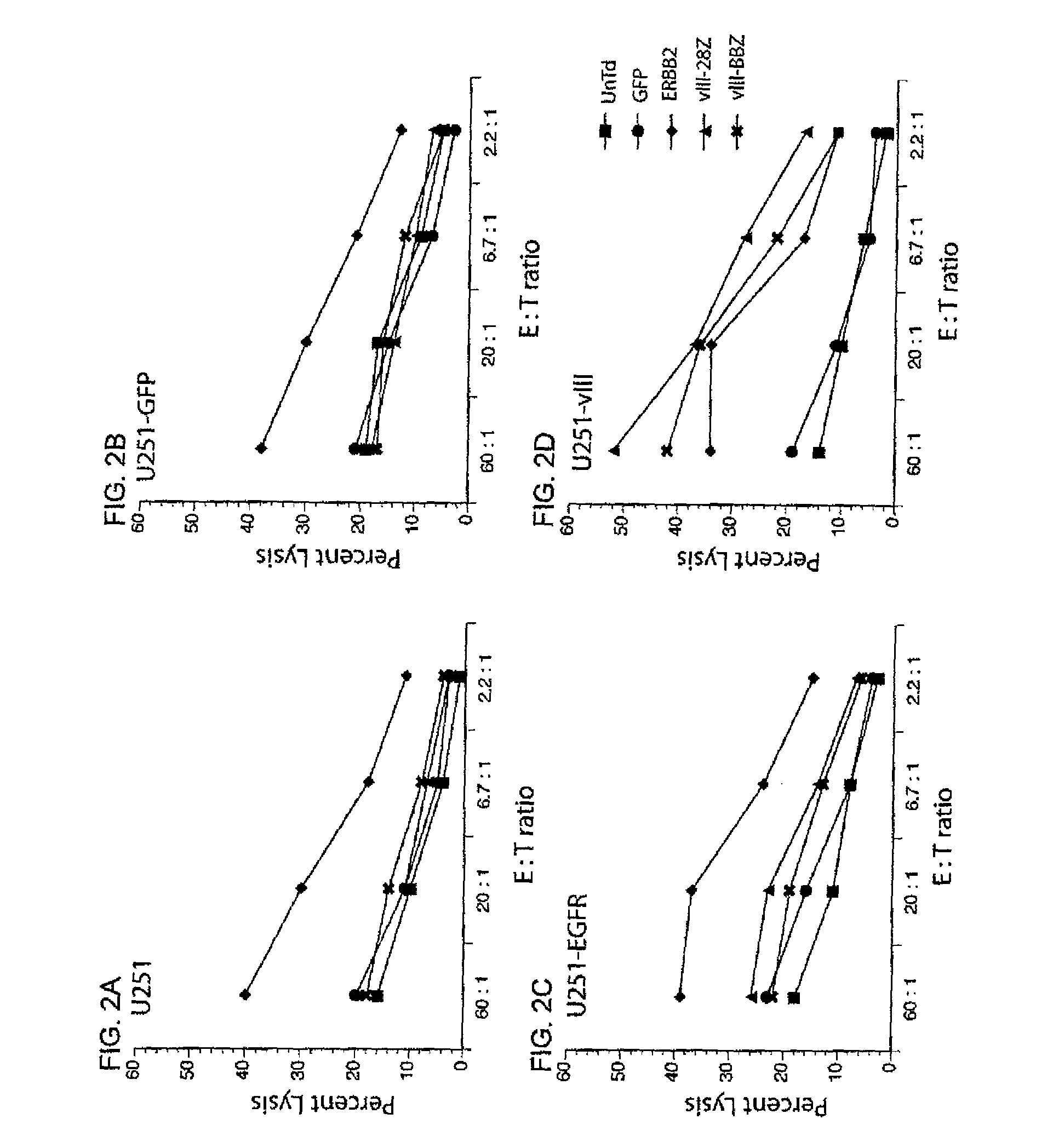
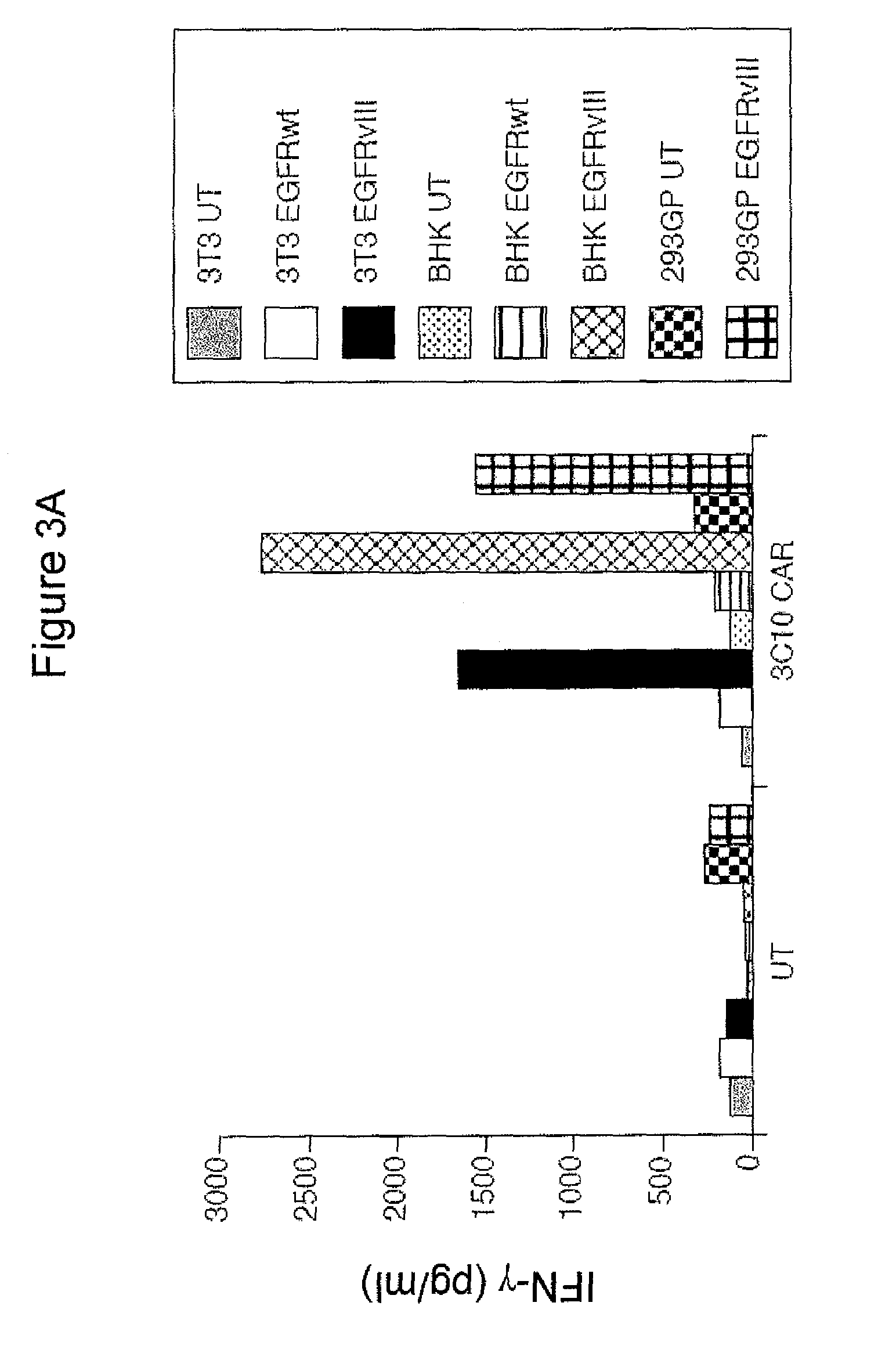
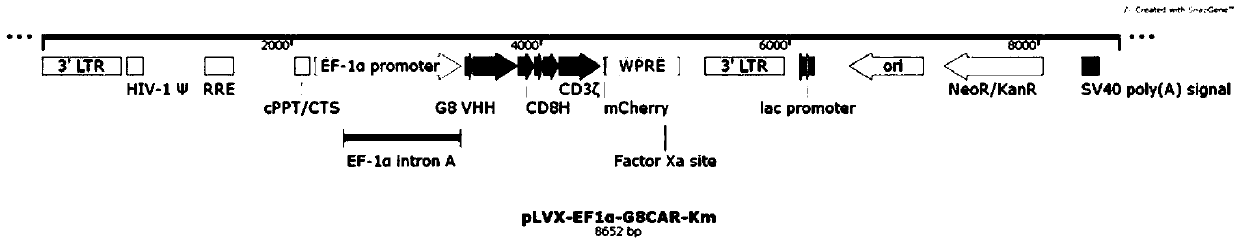
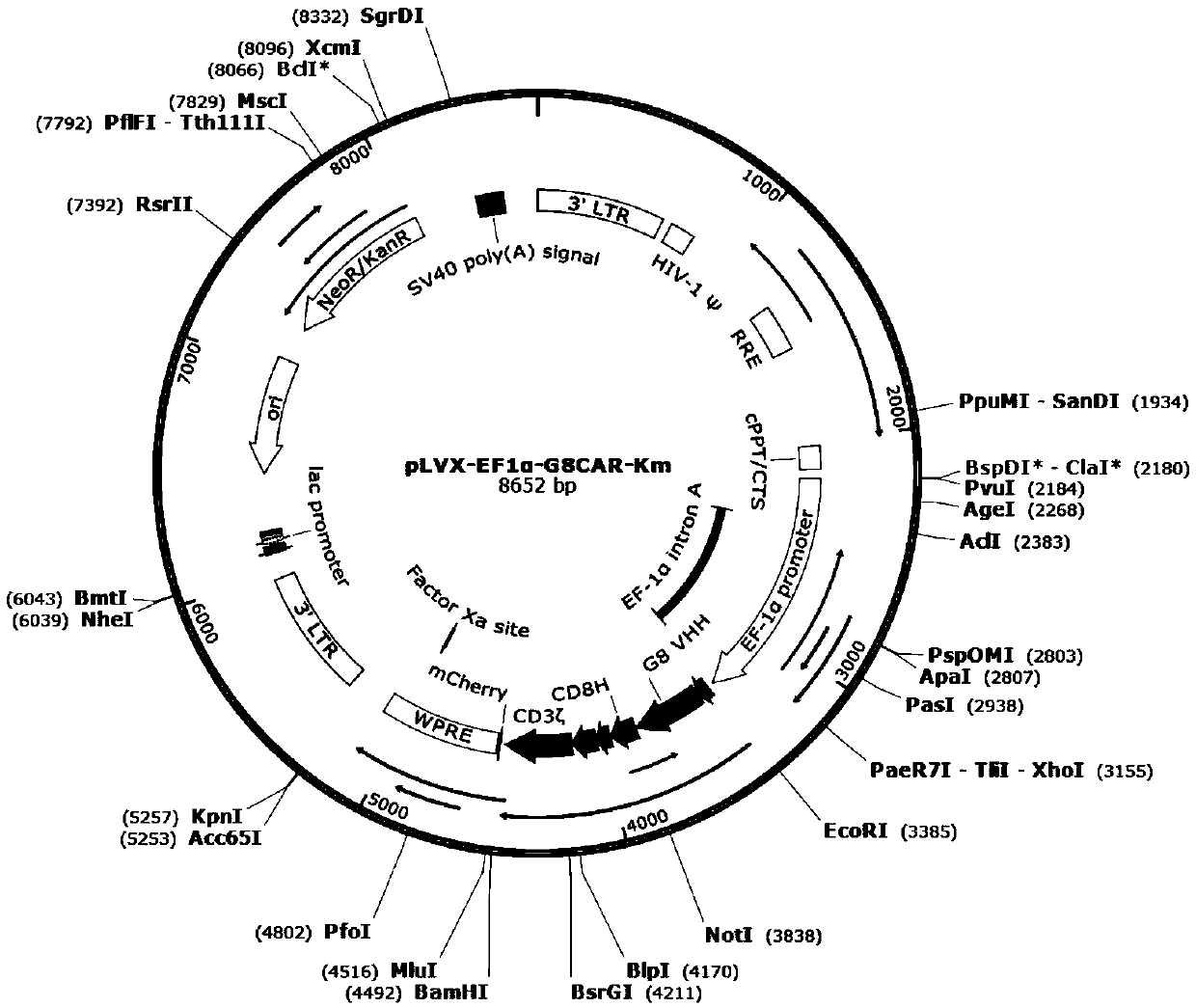
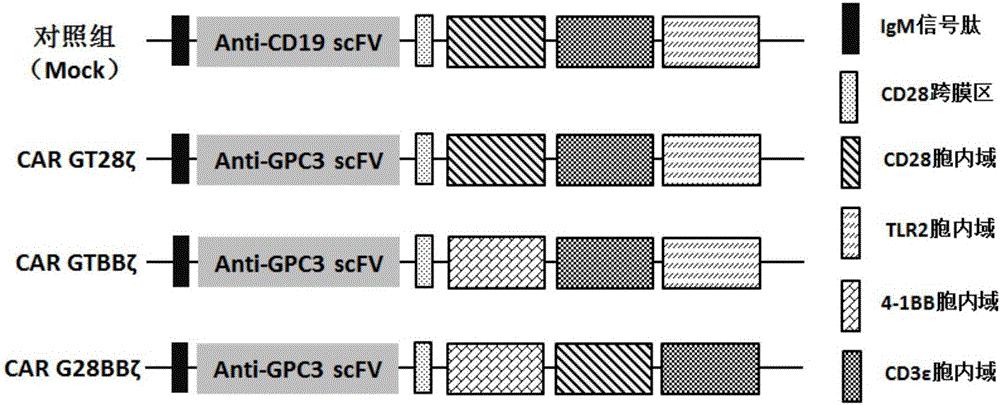
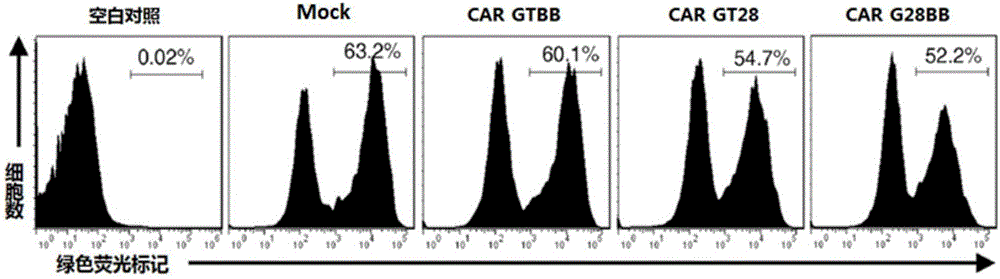
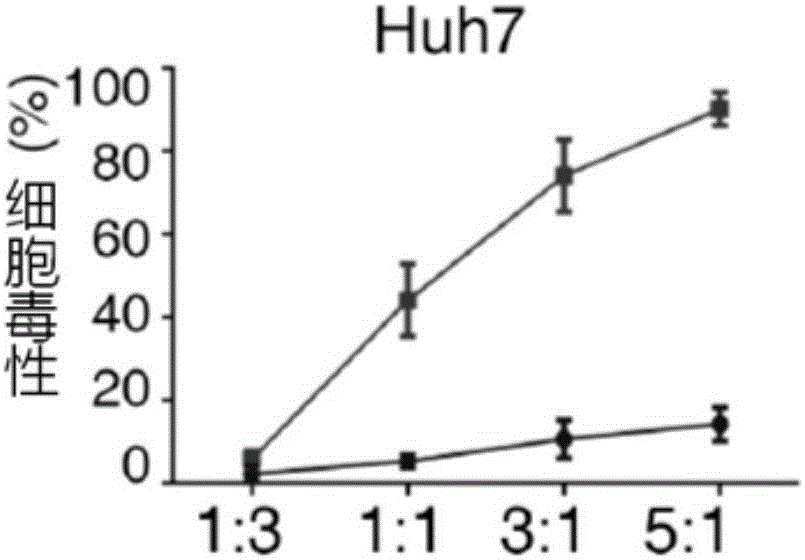
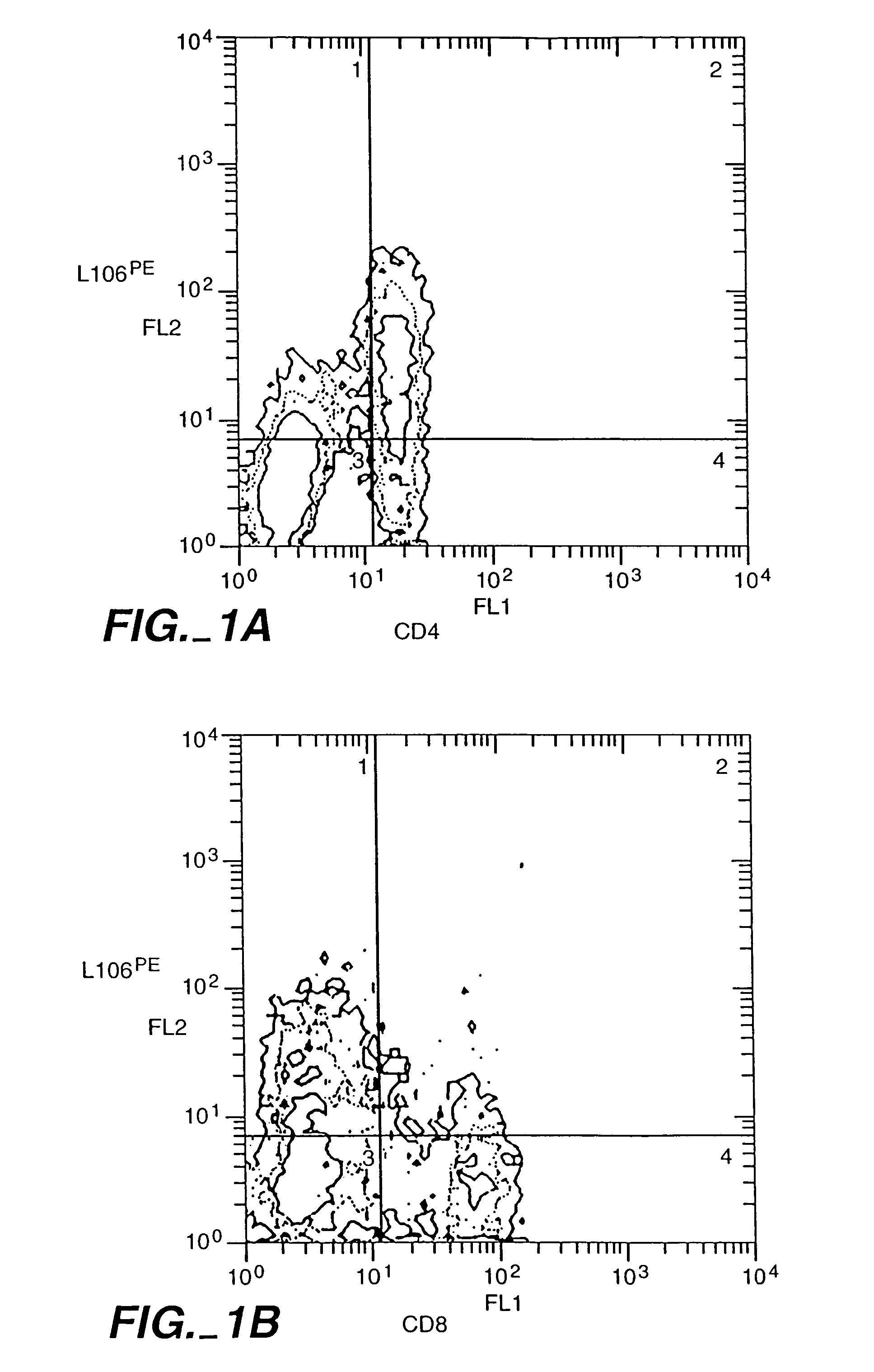
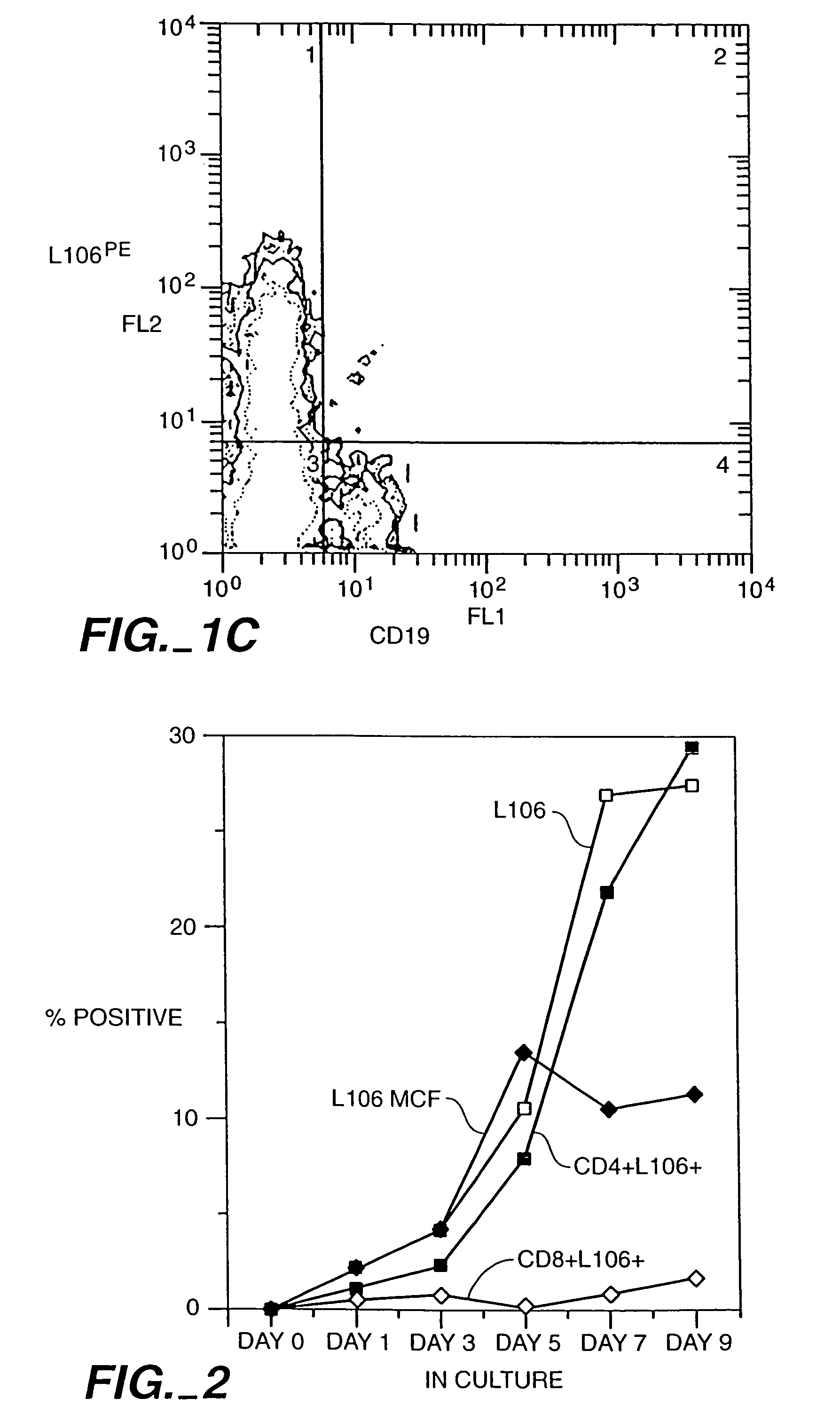
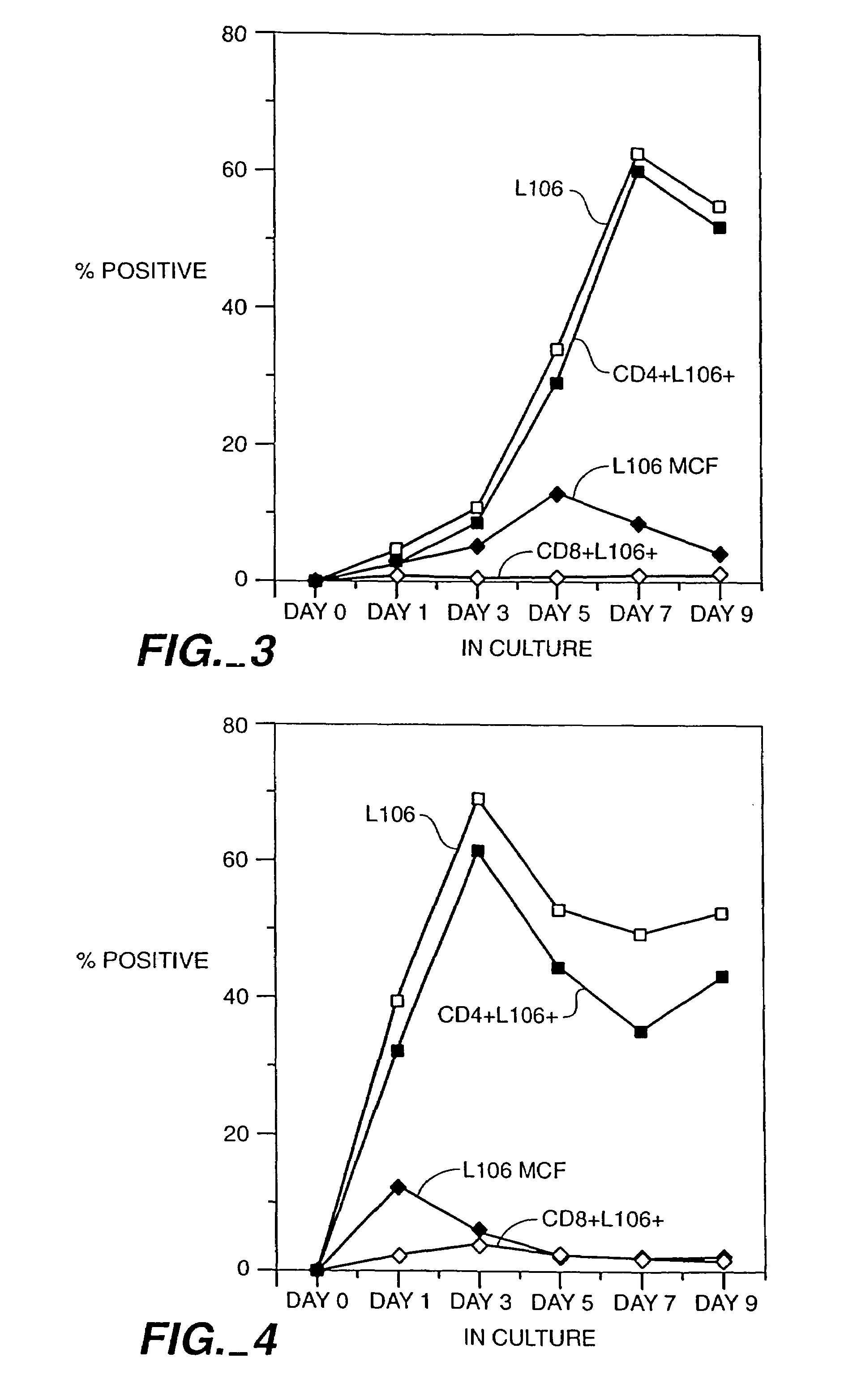
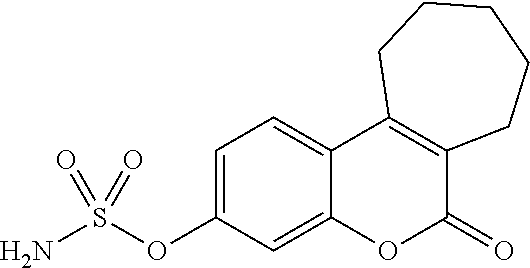
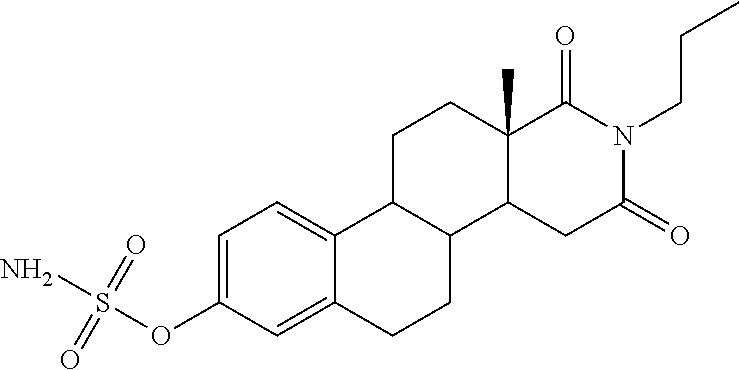
Patents
Literature
216 results about "Intracellular domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intracellular domain Domain (or cytoplasm) cells of the receptor interacts with the interior of the laying organelle or cell, of the signal.
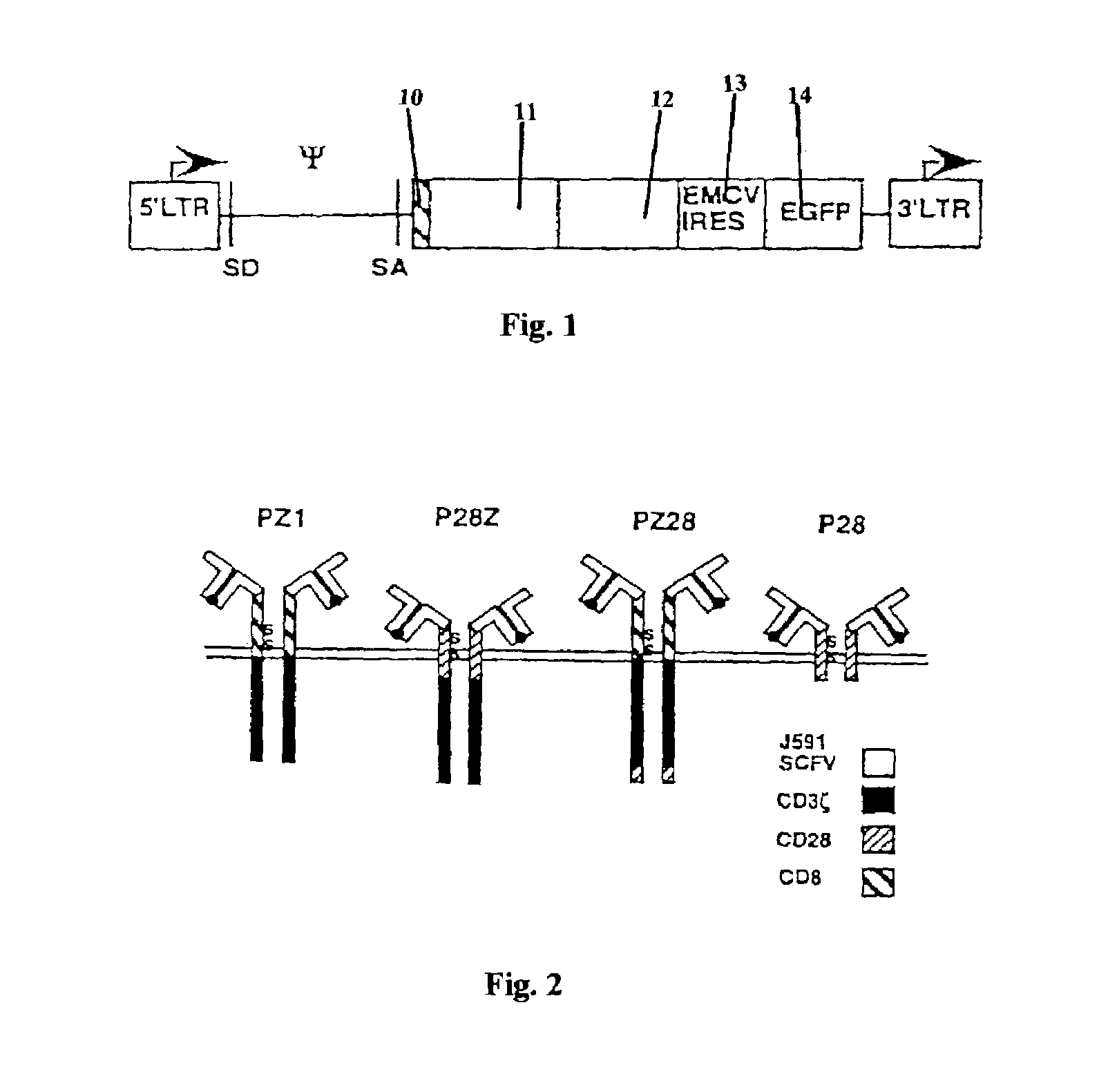
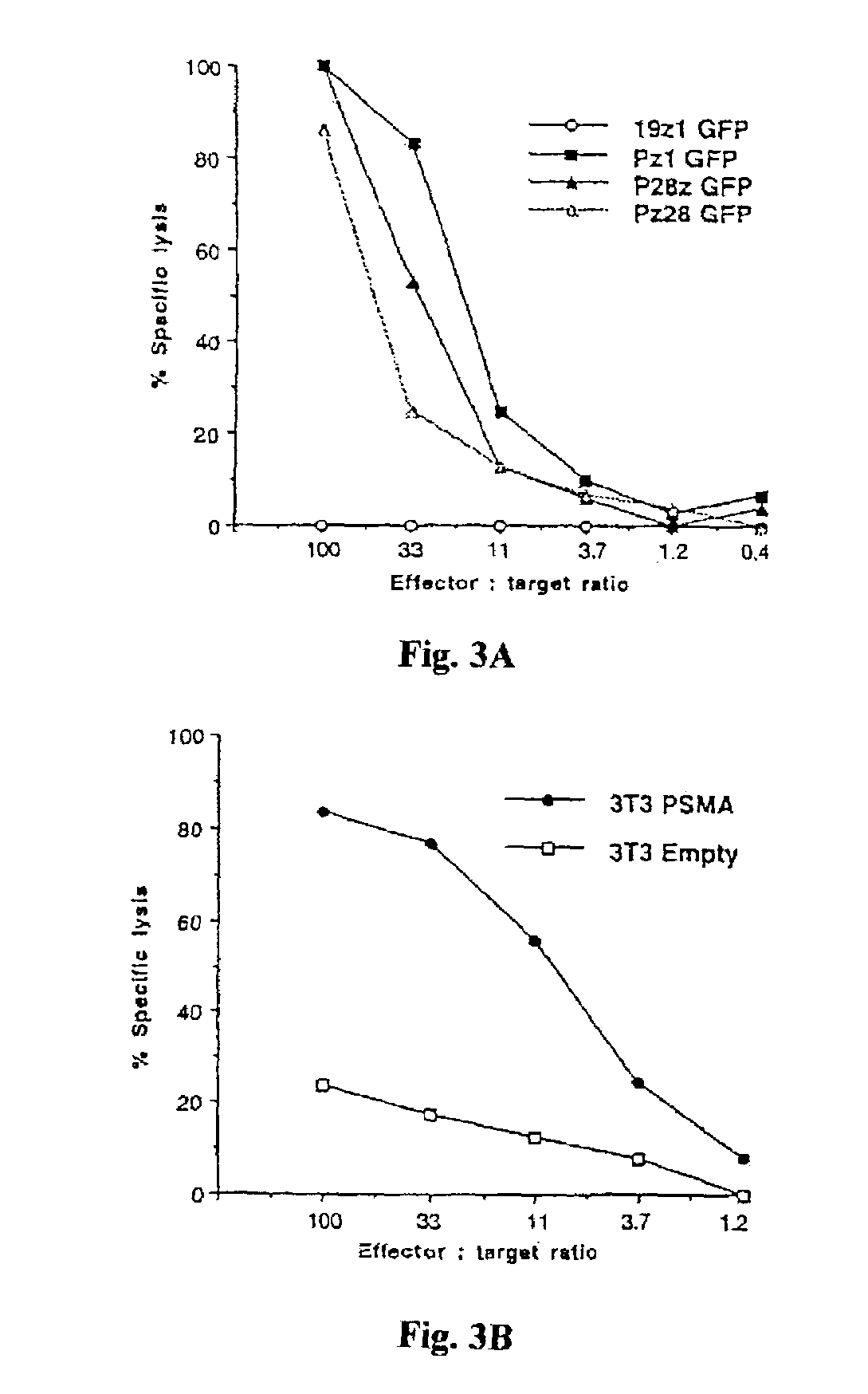
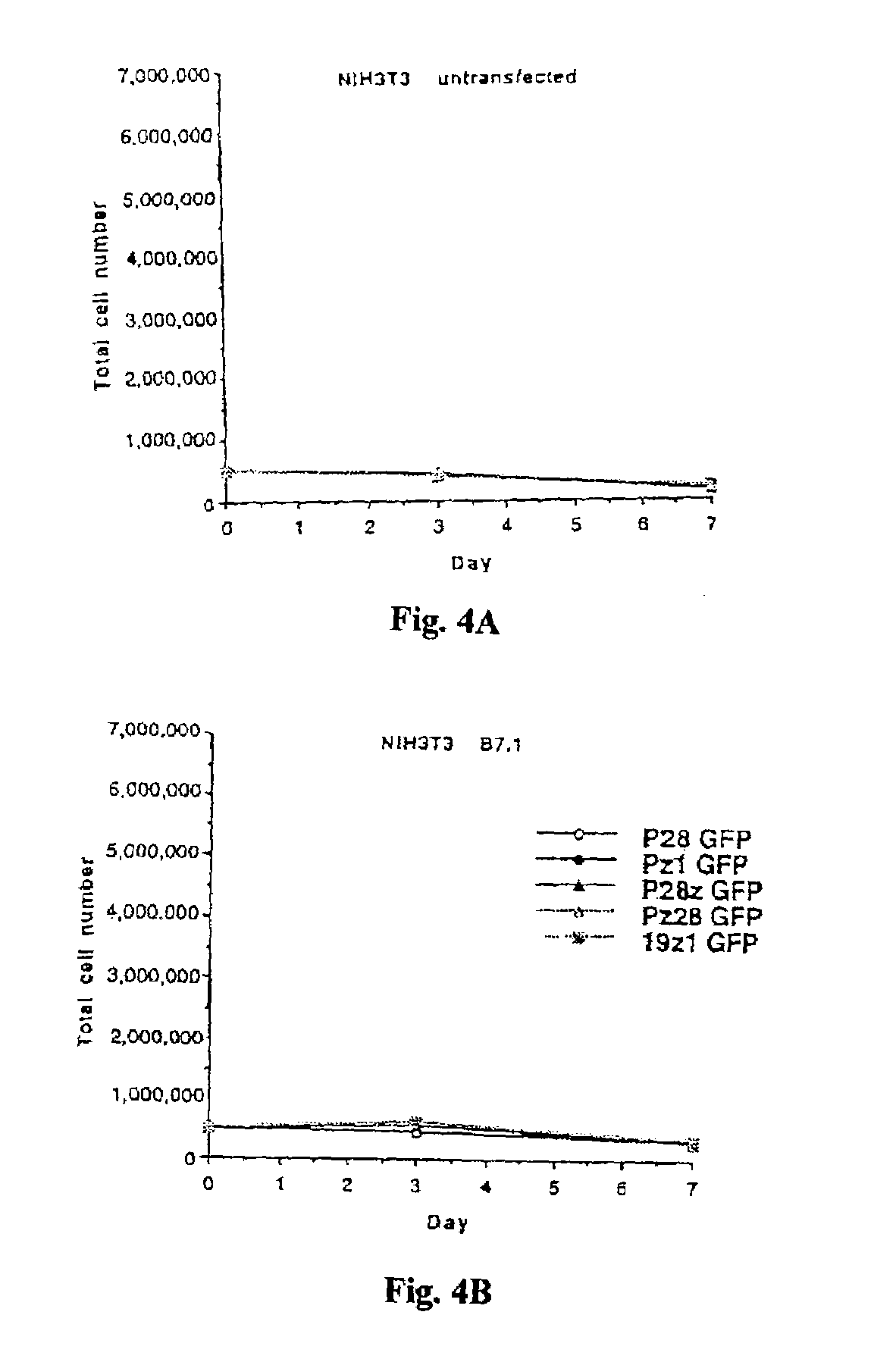
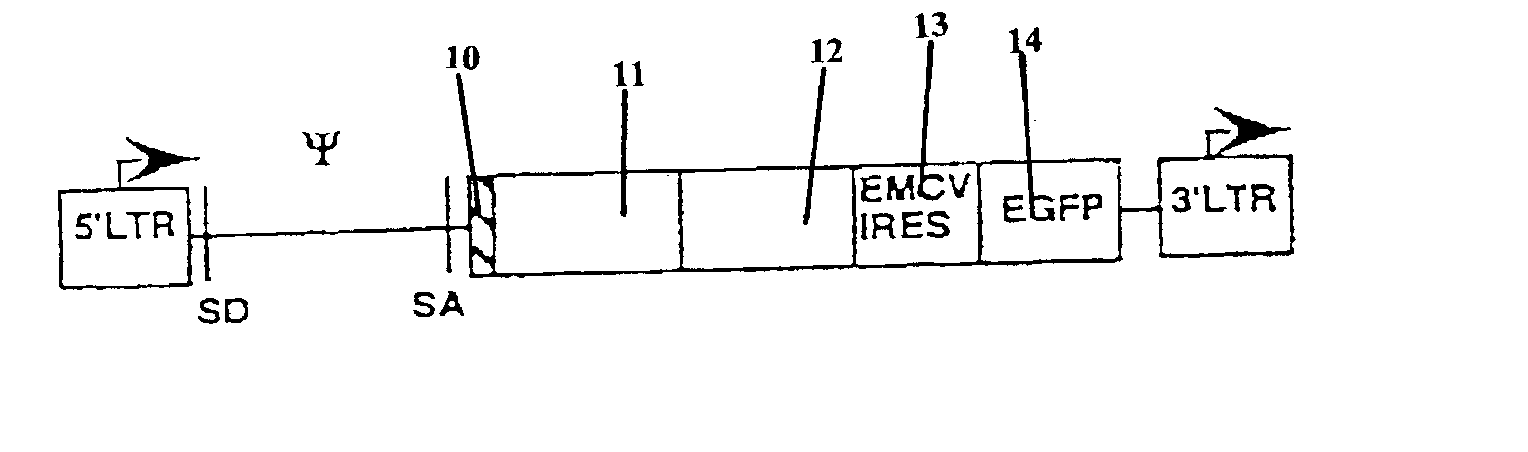
Nucleic acids encoding chimeric T cell receptors
ActiveUS7446190B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCytotoxicityBiological activation
Chimeric T cell receptors (TCR) are provided that combine, in a single chimeric species, the intracellular domain of CD3 ζ-chain, a signaling region from a costimulatory protein such as CD28, and a binding element that specifically interacts with a selected target. When expressed, for example in T-lymphocytes from the individual to be treated for a condition associated with the selected target, a T cell immune response is stimulated in the individual to the target cells. The chimeric TCR's are able to provide both the activation and the co-stimulation signals from a single molecule to more effectively direct T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity against the selected target and T-lymphocyte proliferation.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor
InactiveUS7446179B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingTransmembrane domain
The present invention relates to a genetically engineered, CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor and to immune cells expressing the chimeric receptor The present invention also relates to the use of such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CD9+ malignancies and for abrogating any untoward B cell function. The chimeric receptor is a single chain scFvFc:ζ receptor where scFvFc designates the extracellular domain, scFv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CD19, Fc represents at least part of a constant region of an IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. The extracellular domain scFvFc and the intracellular domain ζ are linked by a transmembrane domain such as the transmembrane domain of CD4. In one aspect, the chimeric receptor comprises amino acids 23-634 of SEQ I DNO:2. The present invention further relates to a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Chimeric T cell receotors
ActiveUS20040043401A1Minimize the numberSmall doseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLymphocyte proliferationCytotoxicity
Chimeric T cell receptors (TCR) are provided that combine, in a single chimeric species, the intracellular domain of CD3 zeta-chain, a signaling region from a costimulatory protein such as CD28, and a binding element that specifically interacts with a selected target. When expressed, for example in T-lymphocytes from the individual to be treated for a condition associated with the selected target, a T cell immune response is stimulated in the individual to the target cells. The chimeric TCR's are able to provide both the activation and the co-stimulation signals from a single molecule to more effectively direct T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity against the selected target and T-lymphocyte proliferation.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveUS20140242701A1High expressionHigh cytotoxic activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAntigen receptor
Provided are a chimeric antigen receptor comprising an extracellular domain capable of binding to an antigen, a transmembrane domain and at least one intracellular domain, the chimeric antigen receptor being characterized in that an intracellular domain of a glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) is contained as the intracellular domain; a nucleic acid encoding the chimeric antigen receptor; a cell expressing the chimeric antigen receptor; and a method for producing the cell.
Owner:MIE UNIVERSITY
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveUS20080085870A1Reduce in quantityDecreased immunological responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based cytomegalovirus vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding HCMV antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the HCMV antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. HCMV antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to pp65, glycoprotein B (gB), IE1, and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. In certain embodiments, sequences have been deleted, e.g., the Arg435-Lys438 putative kinase in pp65 and the membrane anchor and endocellular domains in gB. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to HCMV in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
Novel interleukin-1 receptor intracellular ligand proteins and inhibitors of ligand binding
Novel IL-1-R intracellular ligand proteins are disclosed. Polynucleotides encoding the IL-1-R intracellular ligand protein are also disclosed, along with vectors, host cells, and methods of making the IL-1-R intracellular ligand protein. Pharmaceutical compositions containing the IL-1-R intracellular ligand protein, methods of treating inflammatory conditions, and methods of inhibiting IL-1-R intracellular domain binding are also disclosed. Methods of identifying inhibitors of IL-1-R intracellular domain binding and inhibitors identified by such methods are also disclosed.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
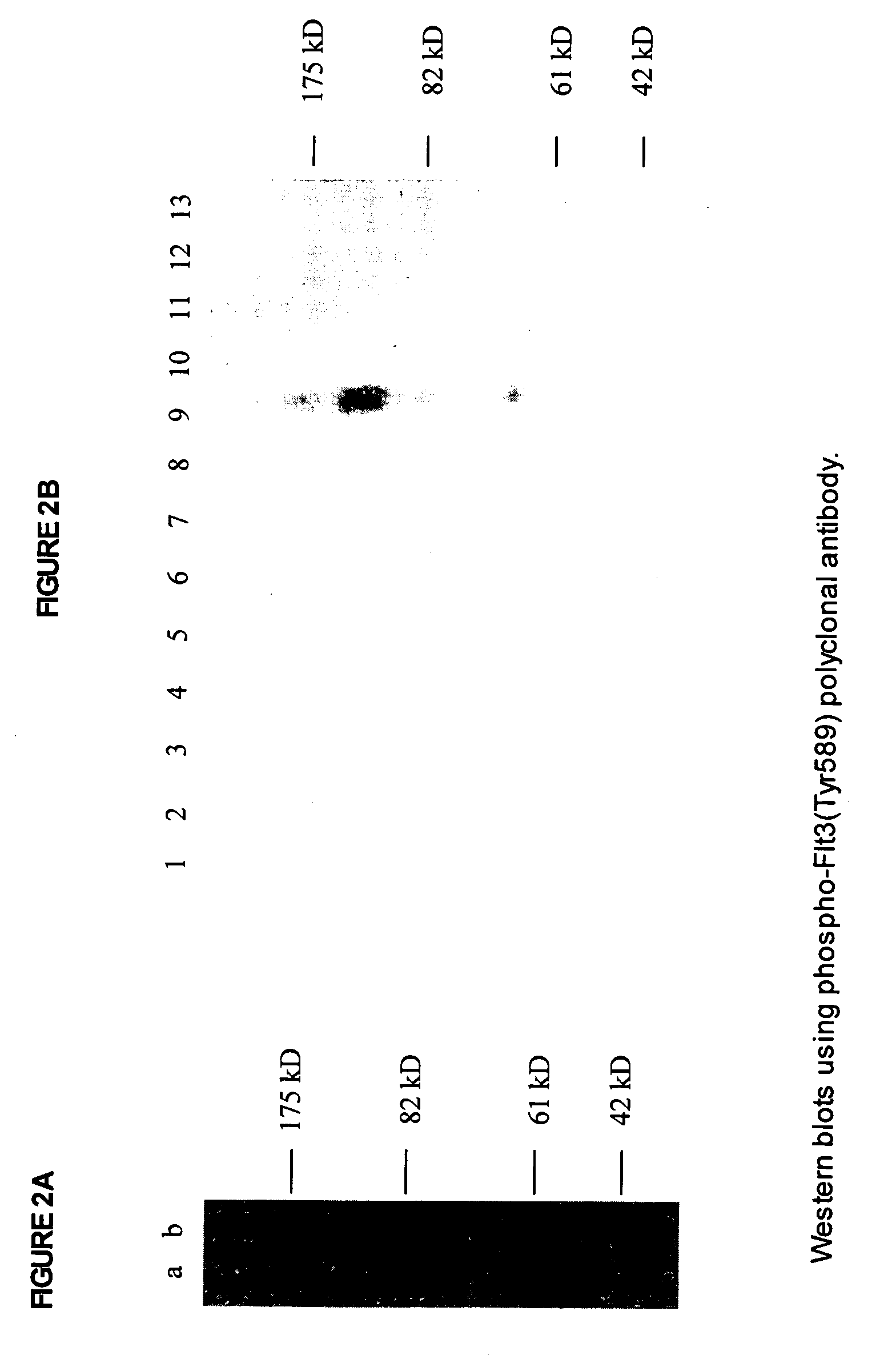
Phospho-specific antibodies to Flt3 and uses thereof
ActiveUS7183385B2Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTyrosinePhospho-Specific Antibodies
The invention discloses two newly-discovered Flt3 phosphorylation sites, tyrosine 589 (Tyr589) and tyrosine 591 (Tyr591) in the intracellular domain, and provides antibodies, both polyclonal and monoclonal, that selectively bind to Flt3 when phosphorylated at these novel sites. Also provided are assays utilizing these reagents, including methods for determining the phosphorylation of Flt3 in a biological sample, selecting a patient suitable for Flt3 inhibitor therapy, profiling Flt3 activation in a test tissue, and identifying a compound that modulates phosphorylation of Flt3 in a test tissue, by using a detectable reagent, such as the disclosed antibodies, that binds to Flt3 when phosphorylated at Tyr589 or Tyr591. The sample or test tissue may be taken from a subject suspected of having cancer, such as acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Spinal cord stimulation guidance system and method of use
ActiveUS20160157769A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationEvoked compound action potentialGuidance system
A system and method for modeling patient-specific spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is disclosed. The system and method acquire impedance and evoked compound action potential (ECAP) signals from a lead positioned proximate to a spinal cord (SC). The lead includes at least one electrode. The system and method determine a patient-specific anatomical model based on the impedance and ECAP signals, and transform a dorsal column (DC) map template based on a DC boundary of the patient-specific anatomical model. Further, the system and method map the transformed DC map template to the patient-specific anatomical model. The system and method may also include the algorithms to solve extracellular and intracellular domain electrical fields and propagation along neurons. The system and method may also include the user interfaces to collect patient responses and compare with the patient-specific anatomical model as well as using the patient-specific anatomical model for guiding SCS programming.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor variant III chimeric antigen receptors and use of same for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS9266960B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorsAntigen binding
The disclosure provides chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) comprising an antigen binding domain of human antibody 139, an extracellular hinge domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain T cell receptor signaling domain. Nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding portions thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the CARs are disclosed. Methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a host and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a host are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Chimeric antigen receptor dendritic cell (car-dc) for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20170151281A1High proliferation rateIncrease productionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsIntracellular signallingDendritic cell
The current invention provides monocytic cells transfected with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) to selectively home to tumors and upon homing differentiate into dendritic cells capable of activating immunity which is inhibitory to said tumor. In one embodiment of the invention, monocytic cells are transfected with a construct encoding an antigen binding domain, a transcellular or structural domain, and an intracellular signaling domain. In one specific aspect of the invention, the antigen binding domain interacts with sufficient affinity to a tumor antigen, capable of triggering said intracellular domain to induce an activation signal to induce monocyte differentiation into DC.
Owner:MYELOID THERAPEUTICS INC
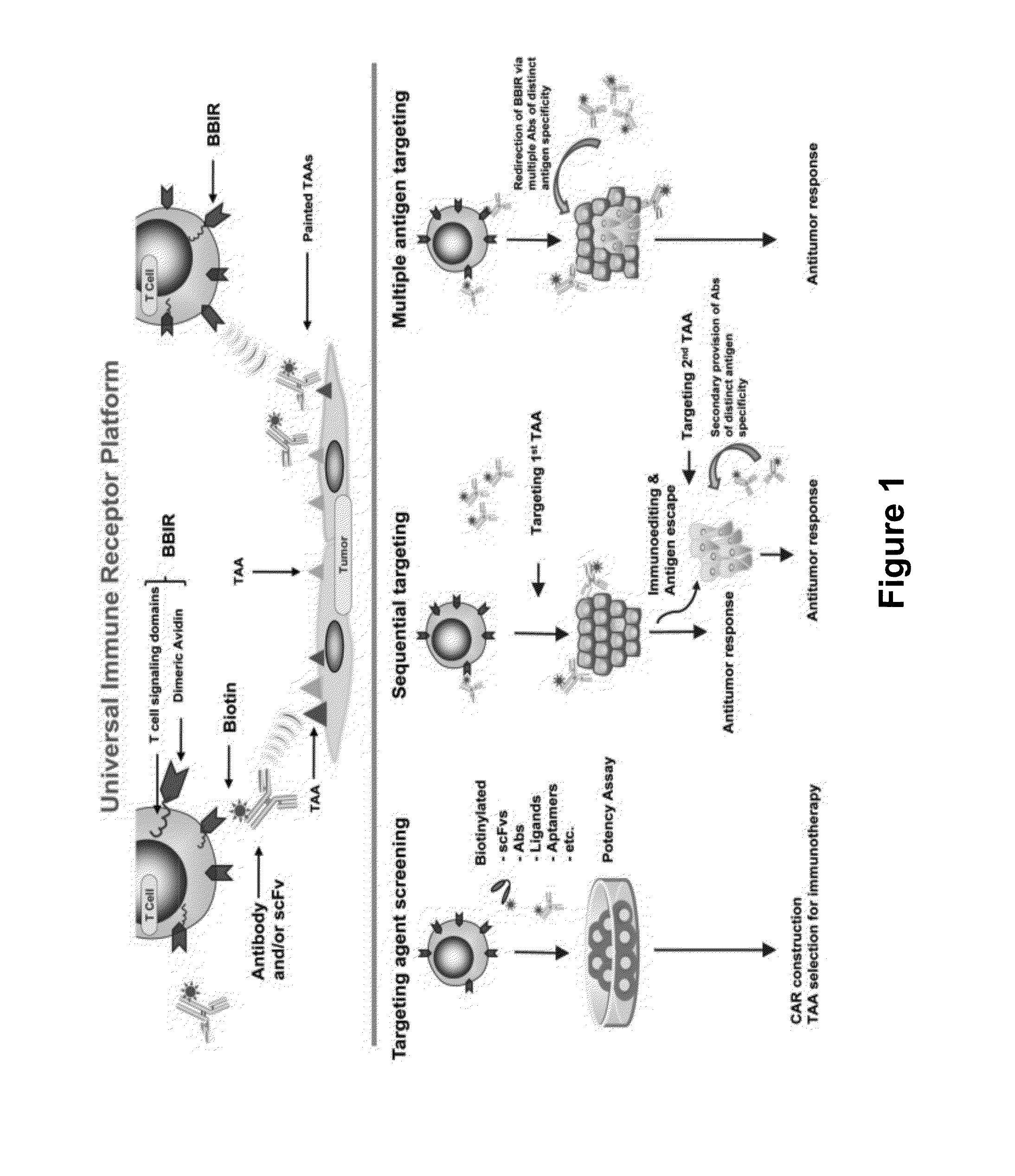
Universal Immune Receptor Expressed by T Cells for the Targeting of Diverse and Multiple Antigens
ActiveUS20140234348A1Stimulate immune responseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureAntigenAutoimmune responses
The invention provides compositions and methods for adoptive T cell therapy in treating a variety of disorders including cancer, infections, and autoimmune disorders. In one embodiment, the invention provides a universal immune receptor (UnivIR) that comprises an extracellular label binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain or otherwise an intracellular domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveUS9175308B2High expressionHigh cytotoxic activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenTumor necrosis factor receptor
Provided are a chimeric antigen receptor comprising an extracellular domain capable of binding to an antigen, a transmembrane domain and at least one intracellular domain, the chimeric antigen receptor being characterized in that an intracellular domain of a glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) is contained as the intracellular domain; a nucleic acid encoding the chimeric antigen receptor; a cell expressing the chimeric antigen receptor; and a method for producing the cell.
Owner:MIE UNIVERSITY
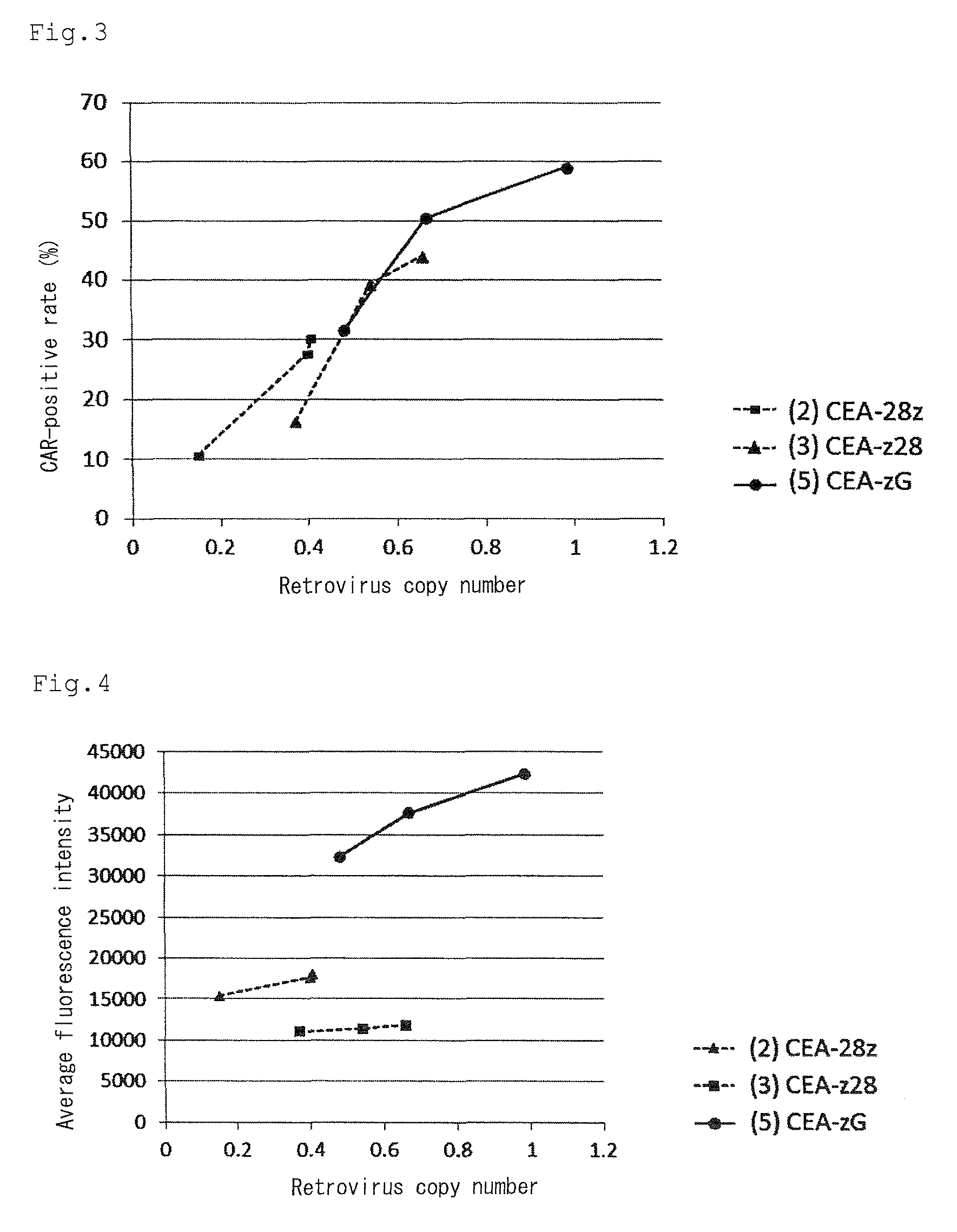
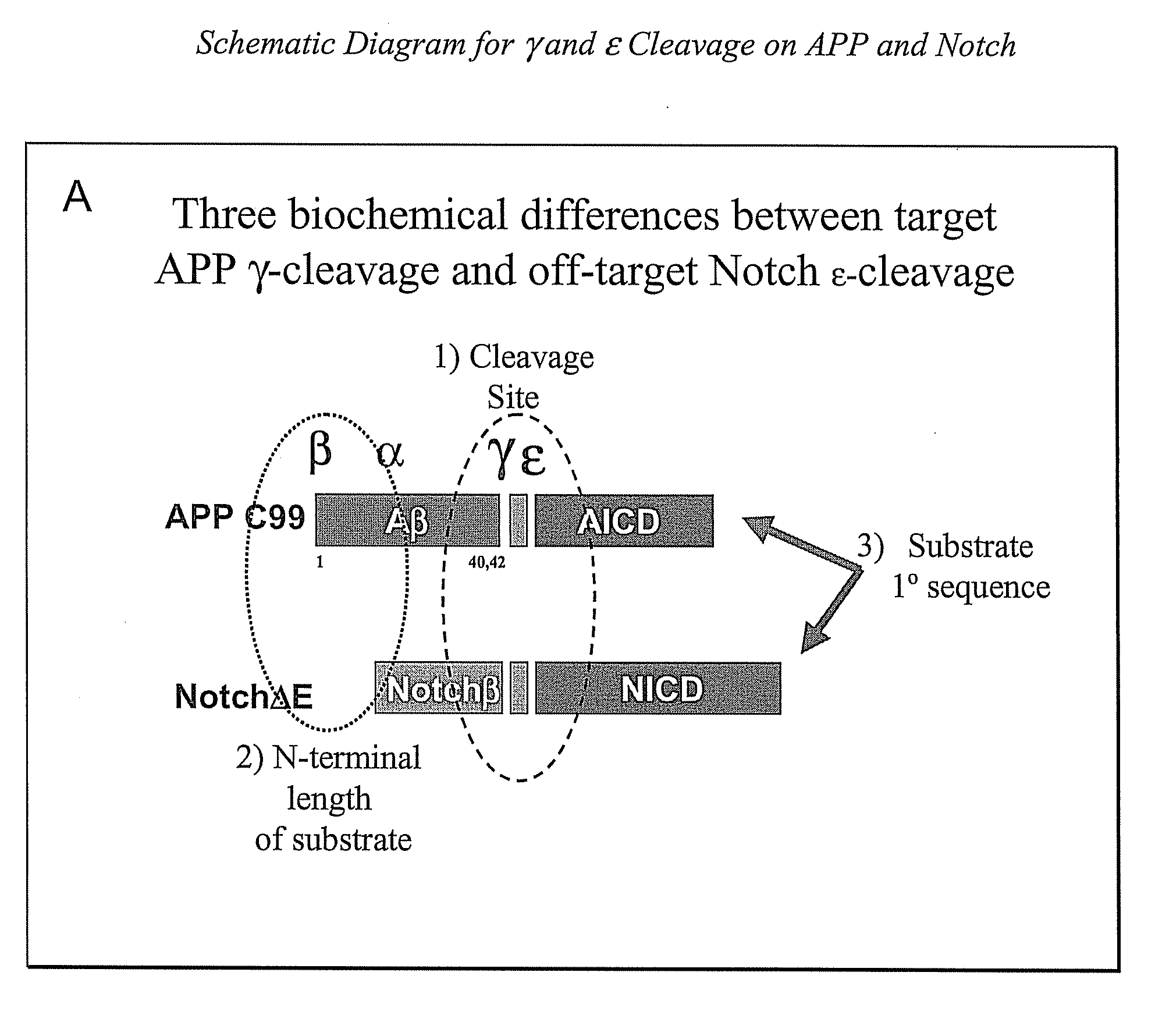
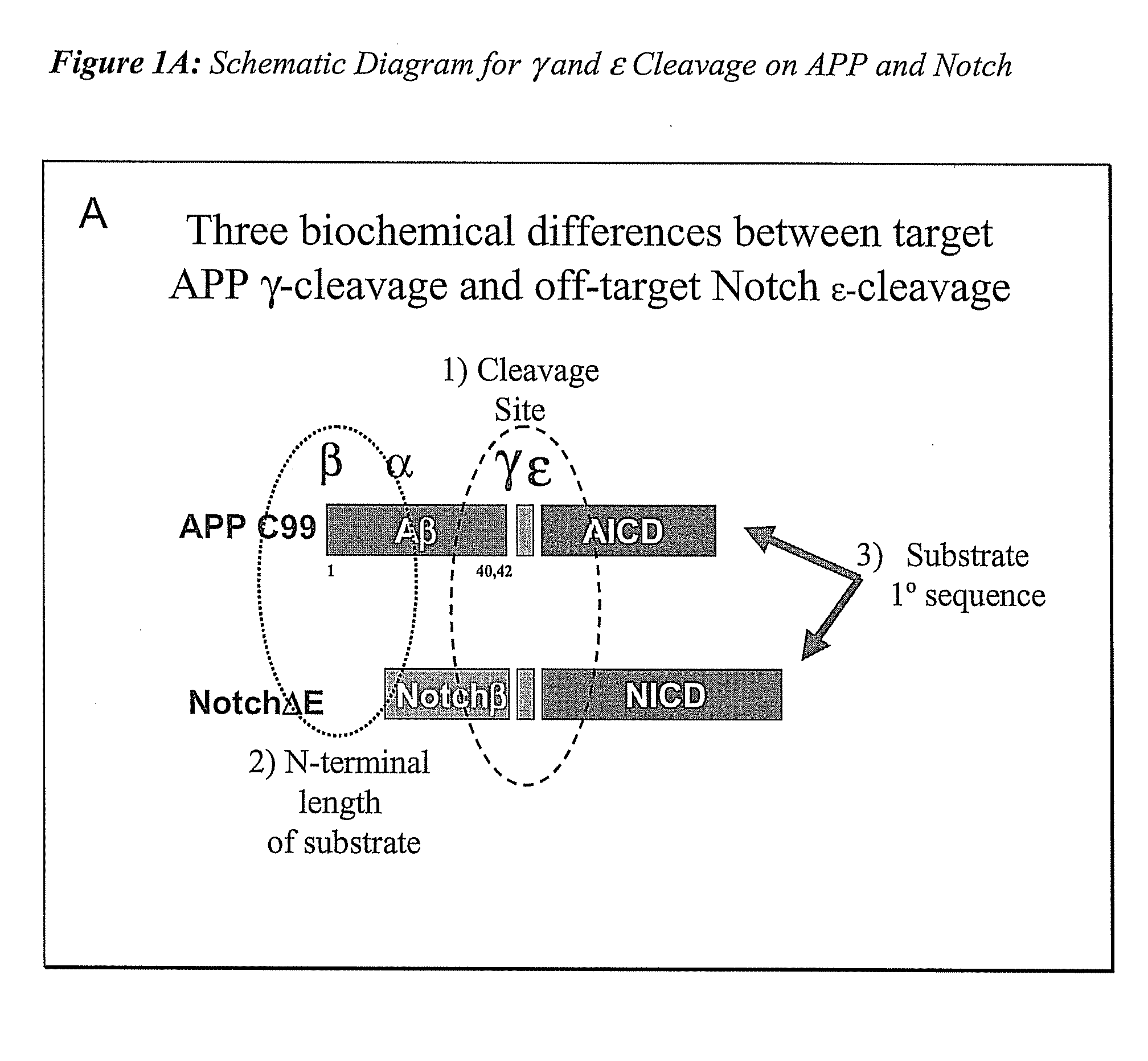
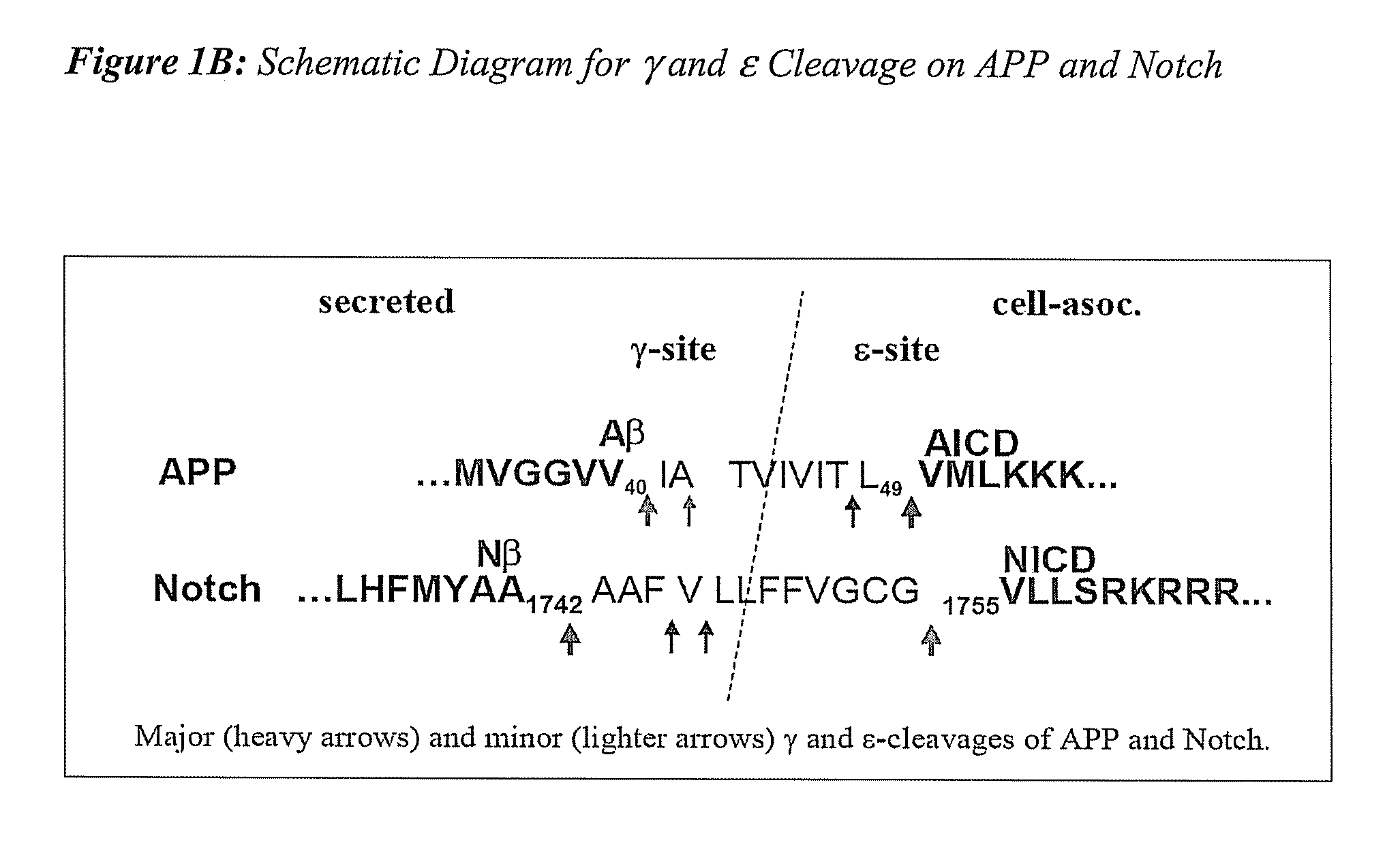
Triple Assay System for Identifying Substrate Selectivity of Gamma Secretase Inhibitors
The invention provides assays and methods for determining whether a compound inhibits gamma secretase in a substrate specific manner. The invention provides an isolated cell wherein the cell stably expresses APP and at least one gamma secretase substrate other than APP. The invention provides assays and methods comprising contacting a cell with gamma secretase and detecting production of Abeta, detecting production of intracellular domain (ICD), and detecting a signal from a reporter gene under transcriptional control of the ICD. The invention also provides compounds that inhibit gamma secretase, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and methods of treating Alzheimer's disease using such compounds.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
Method for recombinant expression of varicella-zoster virus truncation type glycoprotein E and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for the recombinant expression of a varicella-zoster virus truncation type glycoprotein E and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: guiding a gene of a varicella-zoster virus (VZV) truncation type glycoprotein E (gpE) in which a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain are removed and an His label is added into a host cell so as to obtain the recombinant varicella-zoster virus truncation type glycoprotein E by expression. The expression method is beneficial to enhancing the expression quantity of a target protein, the downstream purifying operation is simplified, and the large-scale production of the protein can be realized in an easier way; and moreover, the quality between batches is stable. The recombinant protein disclosed by the invention is used as a capturing antigen and can be used for the indirect ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) detection of specific immunoglobulin for resisting a varicella-zoster virus in a plasma specimen, the accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of VZV infection can be enhanced, and the recombinant protein is also used for other fields needing VZV specific immunoglobulin to carry out high-throughput detection.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Universal donor chimeric antigen receptor cells
InactiveUS20160237407A1Good curative effectImprove localizationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyProgenitorCord blood stem cell
Disclosed are allogeneic cells useful for the treatment of cancer in a universal donor, off the shelf, manner. In one embodiment of the invention cord blood derived T cell progenitors are matured with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28, interleukin-7 and transfected with a construct encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting a tumor antigen or a tumor endothelial associated antigen on the antigen binding domain. The intracellular domain containing CD3 zeta chain and at least one shRNA domain encoding a transcript which generates at least one siRNA capable of inhibiting expression of HLA I and / or HLA II. In another embodiment mesenchymal stem cells are transfected with CAR to enhance migration into tumors and induce tumor death, reduction of inflammation, or immune sensitization. In another embodiment universal donor CAR-MSC are disclosed.
Owner:BATU BIOLOGICS
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 5
InactiveUS20010021516A1Reduce capacityIncreased apoptosisBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTRAIL ReceptorsAgonist
The present invention relates to a novel human gene encoding a polypeptide which is a member of the TNF receptor family, and has now been found to bind TRAIL. More specifically, an isolated nucleic acid molecule is provided encoding a human polypeptide named tumor necrosis factor receptor-5, sometimes referred to as "TNFR-5" or "TR5," and now referred to hereinafter as "TRAIL receptor without intracellular domain" or "TRID." TRID polypeptides are also provided, as are vectors, host cells, and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists or antagonists of TRAIL polypeptide activity. Also provided are diagnostic and therapeutic methods utilizing such compositions.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
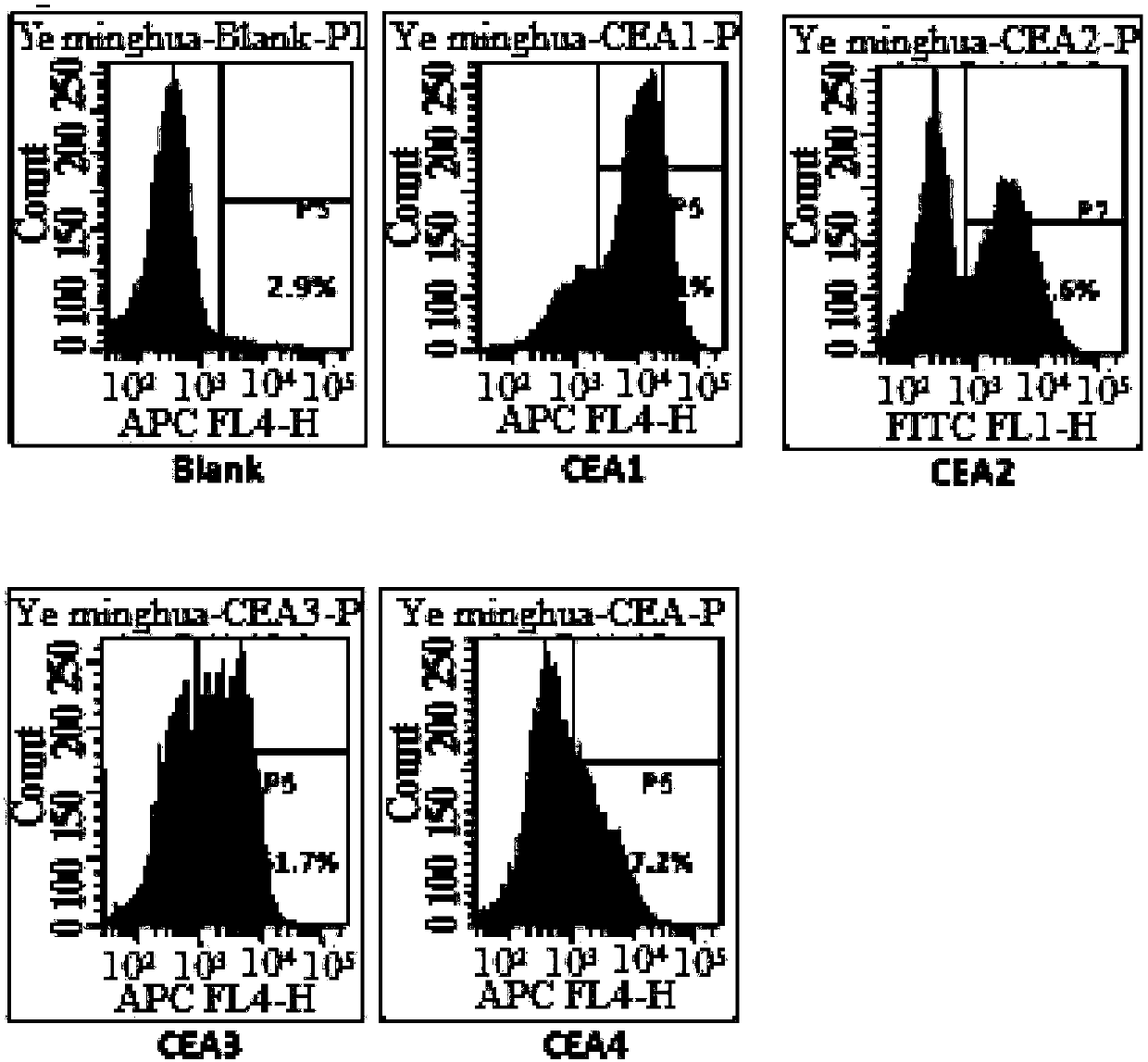
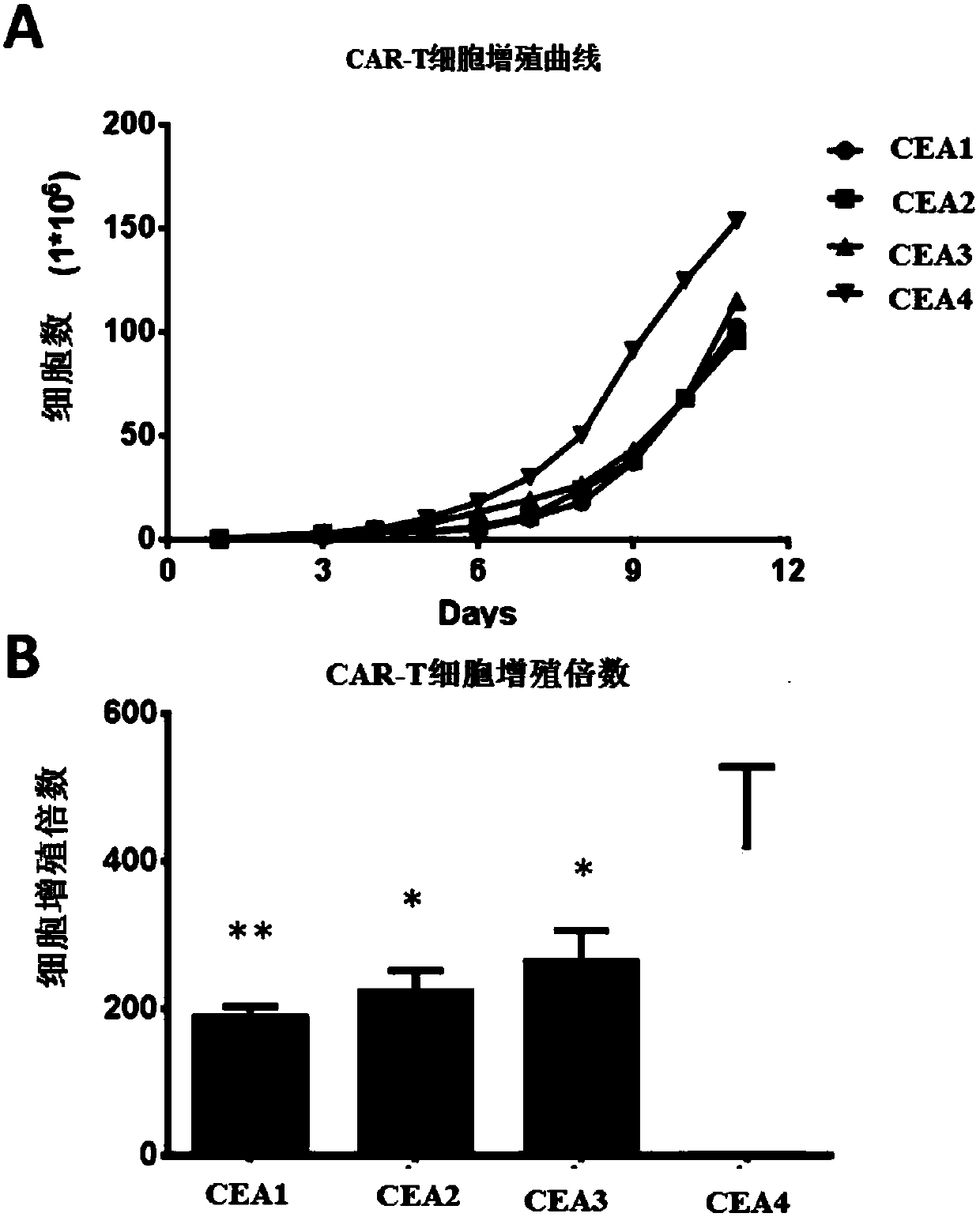
Chimeric antigen receptor containing CD27 intracellular domain, lentiviral vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105949325AHave the ability to bind antigenEfficient killingMammal material medical ingredientsNucleic acid vectorAntigenSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a chimeric antigen receptor containing a CD27 intracellular domain, a lentiviral vector and application thereof. The immune receptor tyrosine activation sequence motif of the chimeric antigen receptor containing CD27 intracellular domain contains CD27molecule intracellular signal domain and T cell costimulatory signal molecules. The CD27molecule intracellular signal domain is connected with costimulatory signals related to T cell activation, so that the in-vitro proliferation and apoptosis effect of T cells can be obviously enhanced, and the ratio of young sample Tscm cells (CD45RA+CD62L+) with in vivo therapeutic action and central memory cells (CD45RO+CD62L+) in CAR-T cells is increased; expression of IL-10 factors capable of restraining immunization is reduced, an obvious effect of improving the CAR-T (T cell chimeric antigen receptor) cellular therapy effect is achieved, and a new idea and a new selection are provided for the field of CAR-T cellular therapy.
Owner:CHONGQING PRECISION BIOTECH CO LTD
Chimeric Fc-gamma Receptor and Method for Determination of ADCC Activity by Using the Receptor
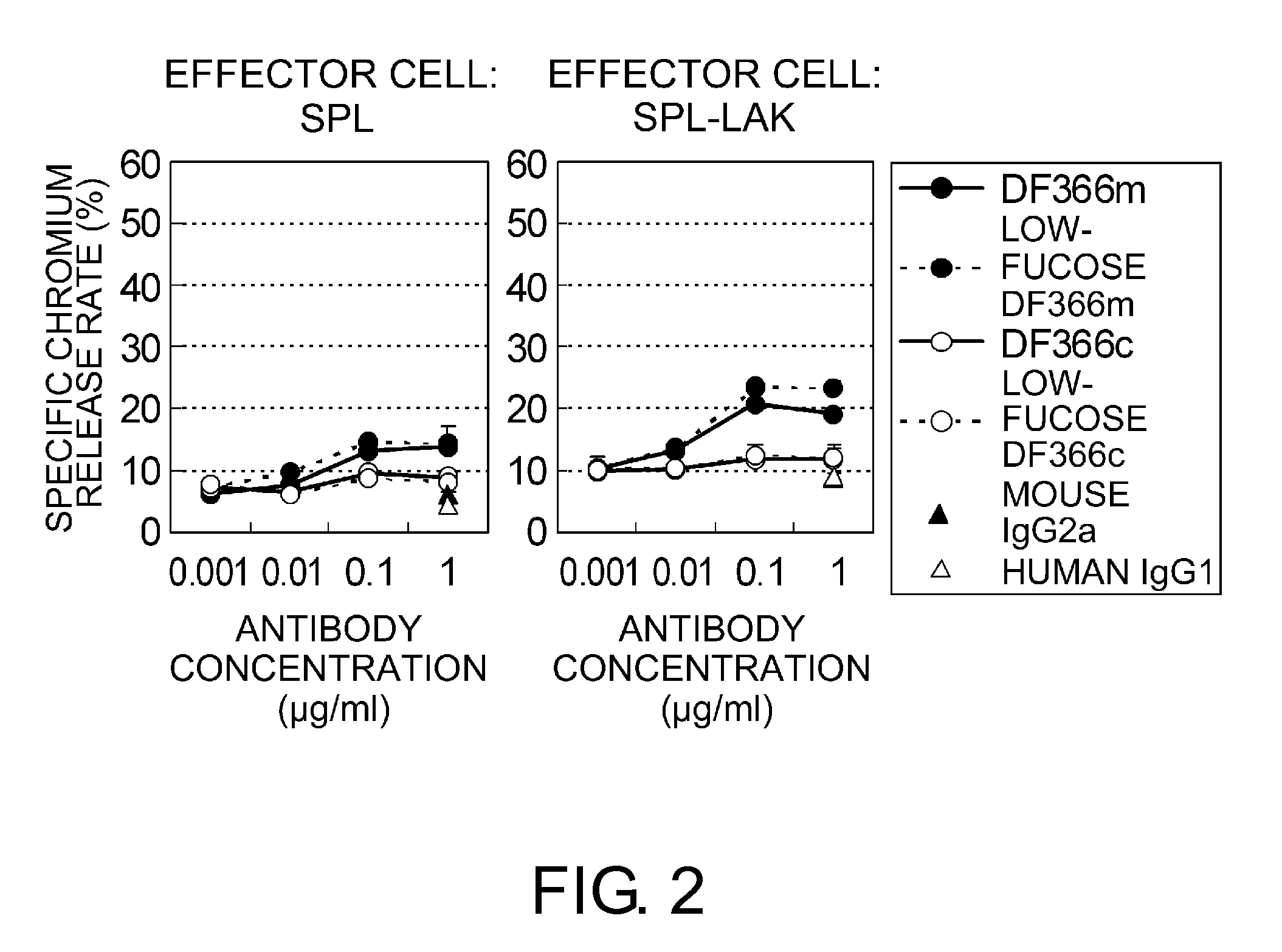
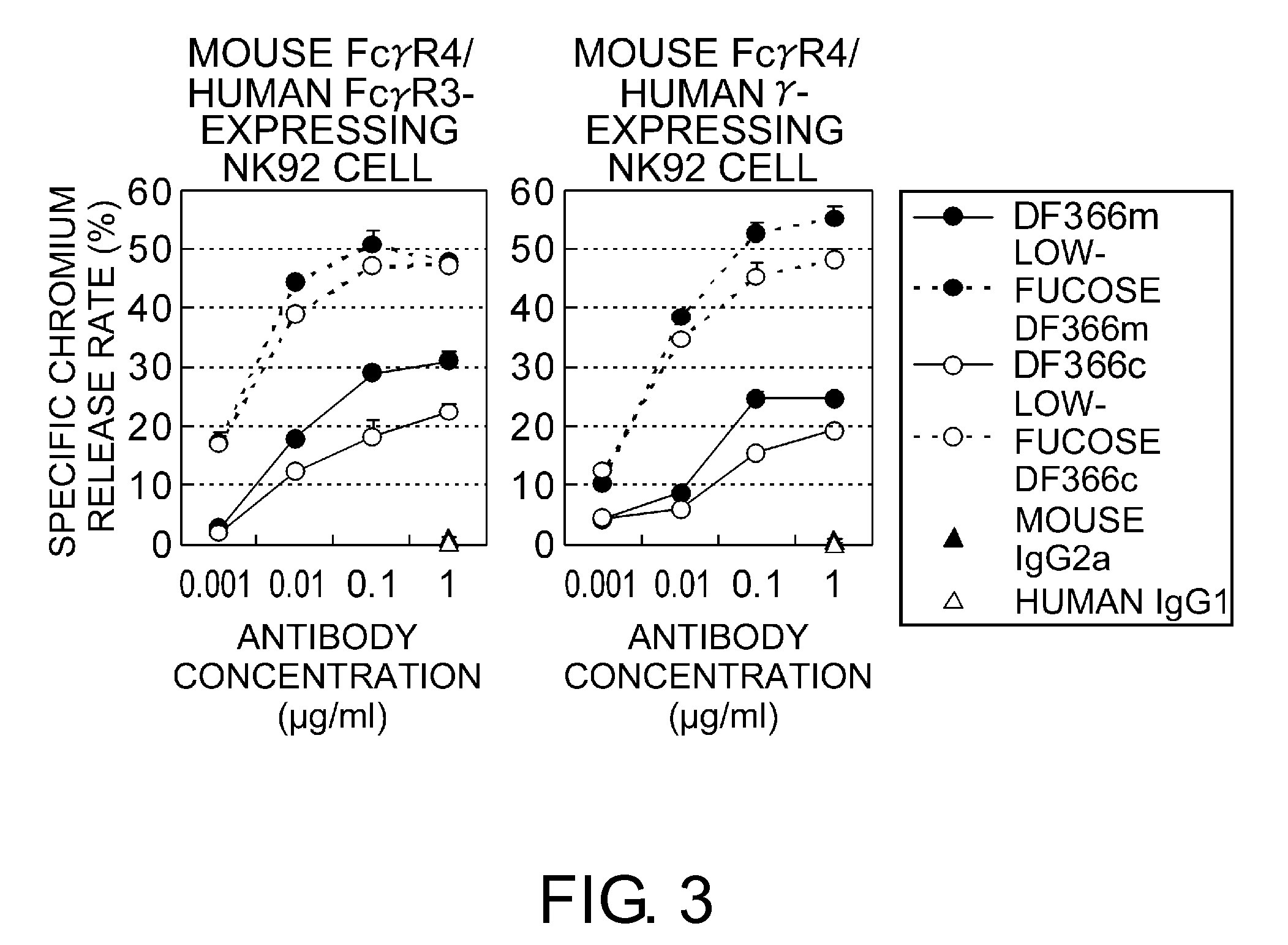
An objective of the present invention is to provide chimeric receptors containing a mouse Fcγ receptor extracellular domain and a human Fcγ receptor transmembrane domain, or chimeric receptors containing a mouse Fcγ receptor extracellular domain and a human γ chain transmembrane domain. Another objective of the present invention is to provide methods for measuring the ADCC activity of mouse antibodies and methods of screening for mouse antibodies having ADCC activity, using the chimeric receptors.To accomplish the above-mentioned objectives, the present inventors produced chimeric molecules by fusing the extracellular domain of mouse FcγR3 or mouse FcγR4 with the transmembrane domain / intracellular domain of human γ chain or human FcγR3, and expressed the chimeric molecules in human NK92 cells. It was revealed that the ADCC activity can be induced by the chimeric receptors produced by any combination of the domains, and that the ADCC activity of mouse antibodies can be measured using the chimeric receptors of the present invention.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Compositions and methods for dendritic cell-based immunotherapy
Disclosed are immunostimulatory fusion proteins and methods for generating protective DC-induced, T cell-mediated immune responses in vitro and in vivo. The immunostimulatory fusion proteins comprise a polypeptide antigen component and an immunostimulatory component derived from the intracellular domain of the HER-2 protein. Also disclosed are immunostimulatory compositions comprising dendritic cells pulsed with such an immunostimulatory fusion protein and methods for immunotherapy using the compositions.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA LLC
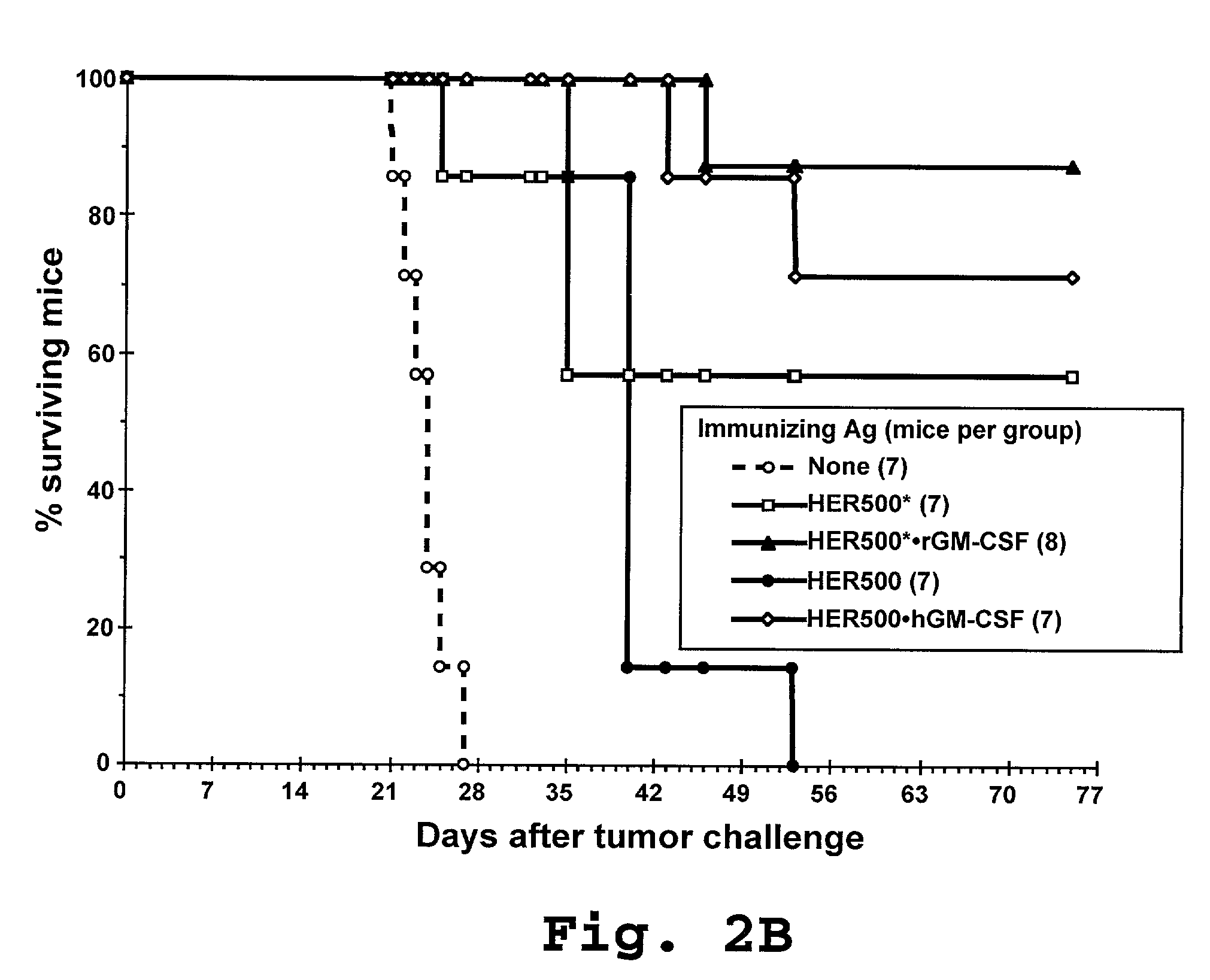
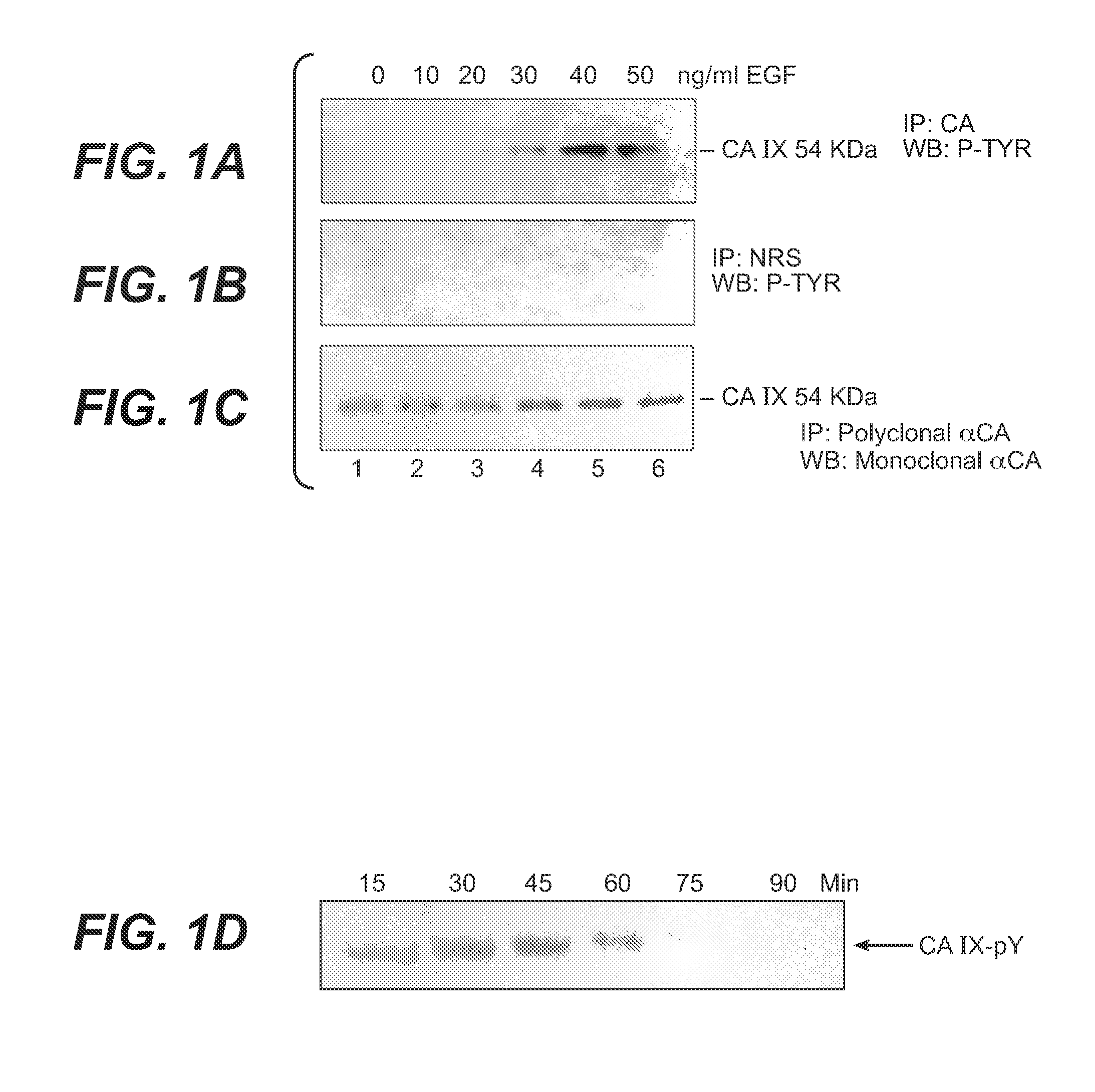
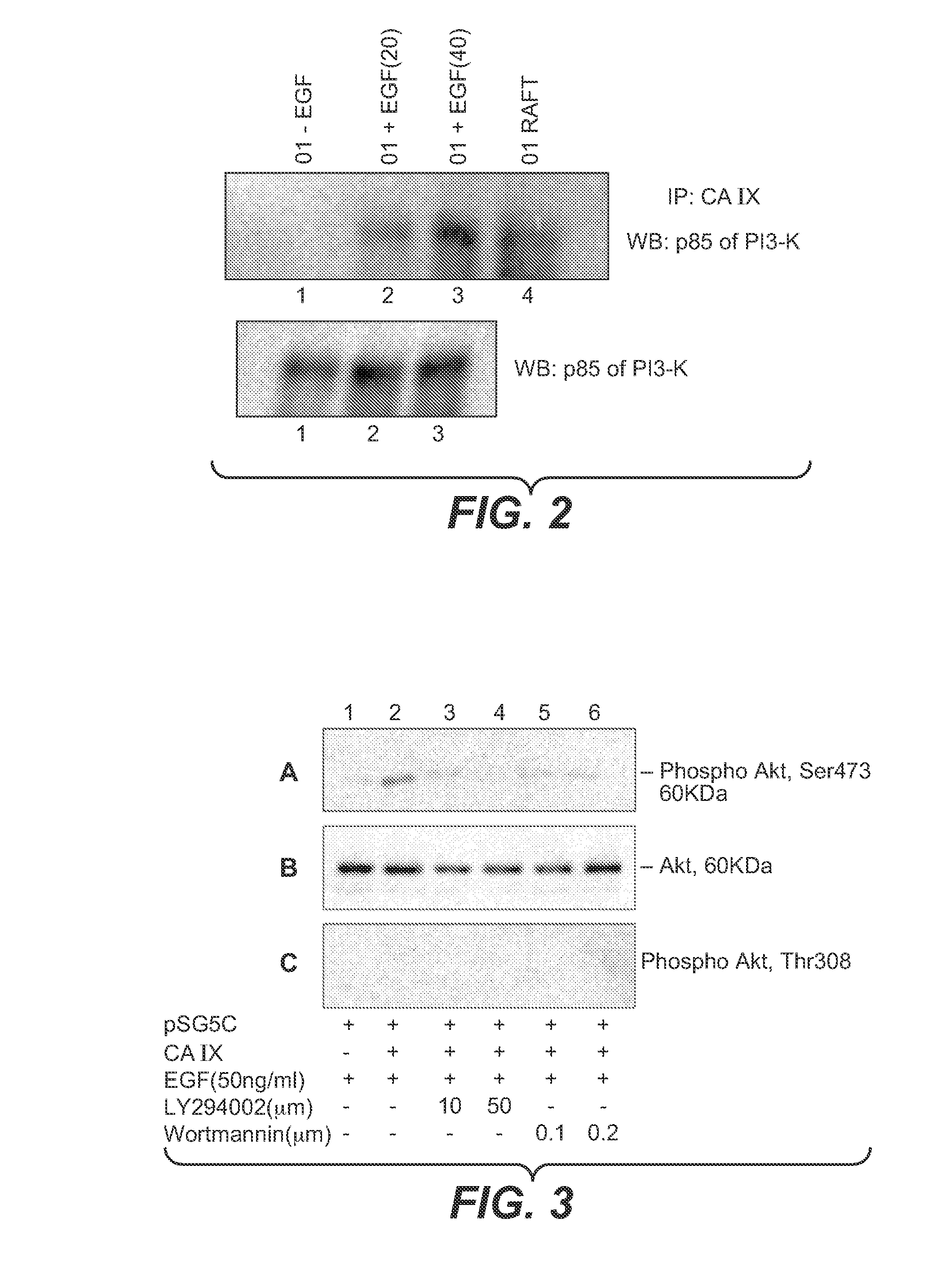
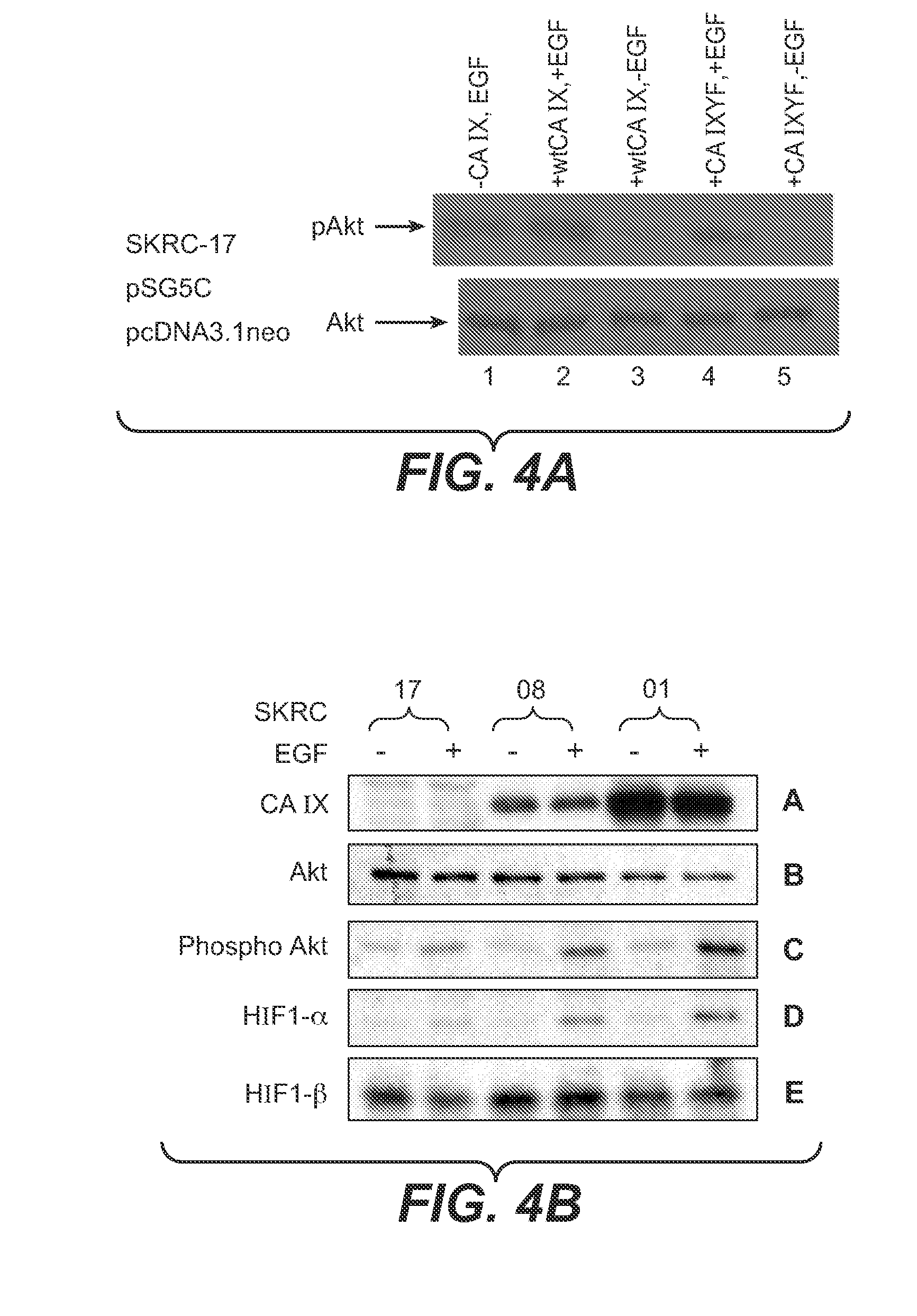
MN/CA IX and EGFR Pathway Inhibition
InactiveUS20080112960A1Inhibit phosphorylationBiocideBiological material analysisDiseaseEgfr pathway
The invention is based upon the discovery that the EGFR pathway can stimulate a previously unknown tumorigenic function of CA IX, via phosphorylation of the sole tyrosine residue present in CA IX's intracellular domain. EGFR-phosphorylated CA IX then interacts with the p85 subunit of PI3K to activate Akt, which in turn is associated with anti-apototic function and increased cell survival. The latter finding indicates that there is a positive feedback loop for CA9 expression mediated by the PI3K pathway in preneoplastic / neoplastic diseases. Disclosed herein are novel therapeutic methods for treating preneoplastic / neoplastic diseases associated with abnormal MN / CA IX expression, using EGFR pathway inhibitors. Preferably, the EGFR pathway inhibitors are tyrosine kinase inhibitors or EGFR-specific antibodies. Further disclosed are methods for patient therapy selection for EGFR pathway inhibitors, preferably in combination with other cancer therapies, based on detection of abnormal MN / CA9 gene expression in preneoplastic / neoplastic tissues.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
Fully human anti-BCMA (B Cell Maturation Antigen) chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
ActiveCN109485733ALow immunogenicityReduce rejectionMammal material medical ingredientsImmunoglobulinsHeavy chainAntigen receptors
The invention relates to a fully human anti-BCMA (B Cell Maturation Antigen) chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular domain, a membrane spanning domain and at least one intracellular domain capable of binding antigens, wherein the extracellular domain is an anti-BCMA single domain antibody; and the fully human anti-BCMA antibody comprises a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region having specific sequences. The chimeric antigen receptor disclosed by the invention has low immunogenicity, small rejection reaction and high safety, the solid tumor foci can be effectively reduced, and the tumor treatment effect is effectively improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO GENE TECH CO LTD
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting BCMA and application thereof
ActiveCN109651511AEffective treatment optionsGood treatment effectAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenSide effect
The invention relates to a chimeric antigen receptor targeting BCMA, which comprises an extracellular domain capable of binding to an antigen, a transmembrane domain and at least one intracellular domain, wherein the extracellular domain is an anti-BCMA single domain antibody; wherein the amino acid sequence of the anti-BCMA single domain antibody is selected from: (a) an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; or (b) a variant which is formed by substitution, addition or deletion of one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and which is capable of specifically binding to the chimeric antigen receptor and has a function of binding to BCMA and inducing T cell signaling conduction. The chimeric antigen receptor has smaller clinical side effects and highersafety, can effectively reduce solid tumor focus and effectively improve the treatment effect of tumors.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO GENE TECH CO LTD
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting of tumor endothelium
InactiveUS20160228547A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCell membraneAntigen binding
Disclosed are methods, protocols, and compositions of matter related to utilization of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) expressing cells for the targeting of tumor endothelium utilizing chimeric antigen receptor expressing stem cells. In one embodiment tumor endothelium specific antigens are utilized as targets of the antigen binding domain of a CAR, which is attached to an extracellular hinge domain, a domain that transverses the T cell membrane and an intracellular domain associated with T cell signaling. Suitable antigens for the practice of the invention include TEM-1, ROBO-4, surviving, and FasL. In other aspects of the invention antigens are identified through serological analysis of recombinant cDNA expression libraries (SEREX) using plasma from a patient immunized with placental endothelial cells.
Owner:BATU BIOLOGICS
Use of chimeric receptors in a screening assay for identifying agonists and antagonists of cell receptors
InactiveUS20070072202A1Increased level of calcium mobilizationOptimal cell surface expression optimalLibrary screeningTissue cultureScreening methodAgonist
The present invention provides novel materials and screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of cell receptors. Methods are disclosed for identifying agonists and antagonists using chimeric receptors comprising the extracellular ligand-binding domain of a first receptor fused with the transmembrane and intracellular domains of a second receptor containing an intracellular immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM).
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Recombinant lentivirus and application thereof
ActiveCN106749675ASignificant in vivo and in vitro amplificationSignificant tumor killing effectMammal material medical ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAbnormal tissue growthMicro environment
The invention relates to the field of tumor cellular immunotherapy, and in particular relates to a recombinant lentivirus and application thereof. The recombinant lentivirus comprises a chimeric antigen receptor, wherein the chimeric antigen receptor mainly comprises signal peptide, an antigen recognition domain, a transmembrane domain, an intracellular co-stimulation signal transduction domain and a CD3 zeta signal transduction domain which are serially connected; the intracellular co-stimulation signal transduction domain mainly comprises a human TLR2 (Toll Like Receptor 2) intracellular domain. A GPC3 CAT T (Glypican 3 CAT T) cell prepared from the recombinant lentivirus has an intense cell killing effect on liver cancer cells, a Th1 cell factor can be highly expressed, a tumor killing effect caused by non-CAR T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T) cell can be stimulated to the maximum extent, escape and potential reoccurrence risk of GPC 3-tumor cells can be effectively prevented, the tumor cells can be killed by T cells expressing the chimeric antigen receptor, normal tissue can be slightly damaged, a tumor immunosuppression micro environment can be broken through, and thus a relatively good treatment effect on solid tumor can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN IN VIVO BIOMEDICINE TECH LTD
Antibody to receptor on the surface of activated T-cells: ACT-4
InactiveUS7364733B2Antibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsExtracellular StructureTransmembrane domain
The invention provides purified ACT-4 receptor polypeptides, antibodies against these polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding ACT-4 receptor polypeptides. Also provided are methods of diagnosis and treatment using the same. ACT-4 receptors are preferentially expressed on the surface of activated CD4+ T-cells. ACT-4 receptors are usually expressed at low levels on the surface of activated CD8+ cells, and are usually substantially absent on resting T-cells, and on monocytes and B-cells (resting or activated). An exemplary ACT-4 receptor, termed ACT-4-h-1, has a signal sequence, an extracellular domain comprising three disulfide-bonded intrachain loops, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method of treatment of EGFR inhibitor toxicity
InactiveUS20110190244A1Reduce severityGood curative effectBiocideSenses disorderErlotinibTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The invention provides a method of treating and / or preventing a toxicity associated with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor therapy in a subject, the method comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of a steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitor. The toxicity may be ocular toxicity; or dermatologic toxicity, such as papulopustular rash. The EGFR inhibitor may be selected from the group consisting of: a small molecule; an antibody or derivative or fragment thereof; another agent that targets the extracellular or intracellular domain of the EGFR, such as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor selected from the group consisting of: erlotinib; gefitinib; lapatinib; and any combination thereof. The EGFR inhibitor may also be antibody selected from the group consisting of: cetuximab; panitumumab; and any combination thereof.Preferably the STS inhibitor is selected from the group consisting of: alternative STS substrates; reversible STS inhibitors; and irreversible STS inhibitors; and any combination thereof. A preferred STS inhibitor is the irreversible nonsteroidal STS inhibitor STX64.In some embodiments, the subject receiving EGFRI therapy has a cancer comprising cells that express wildtype k-ras and / or wildtype b-raf. In other embodiments, the cancer may be hormone-dependent. Cancers that may be treated with EGFRI therapy include colorectal cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:PETER MACCALLUM CANCER INST
Intrabodies
InactiveUS20100143371A1Inhibit enzyme activityInhibit transformationHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsIntracellular pH
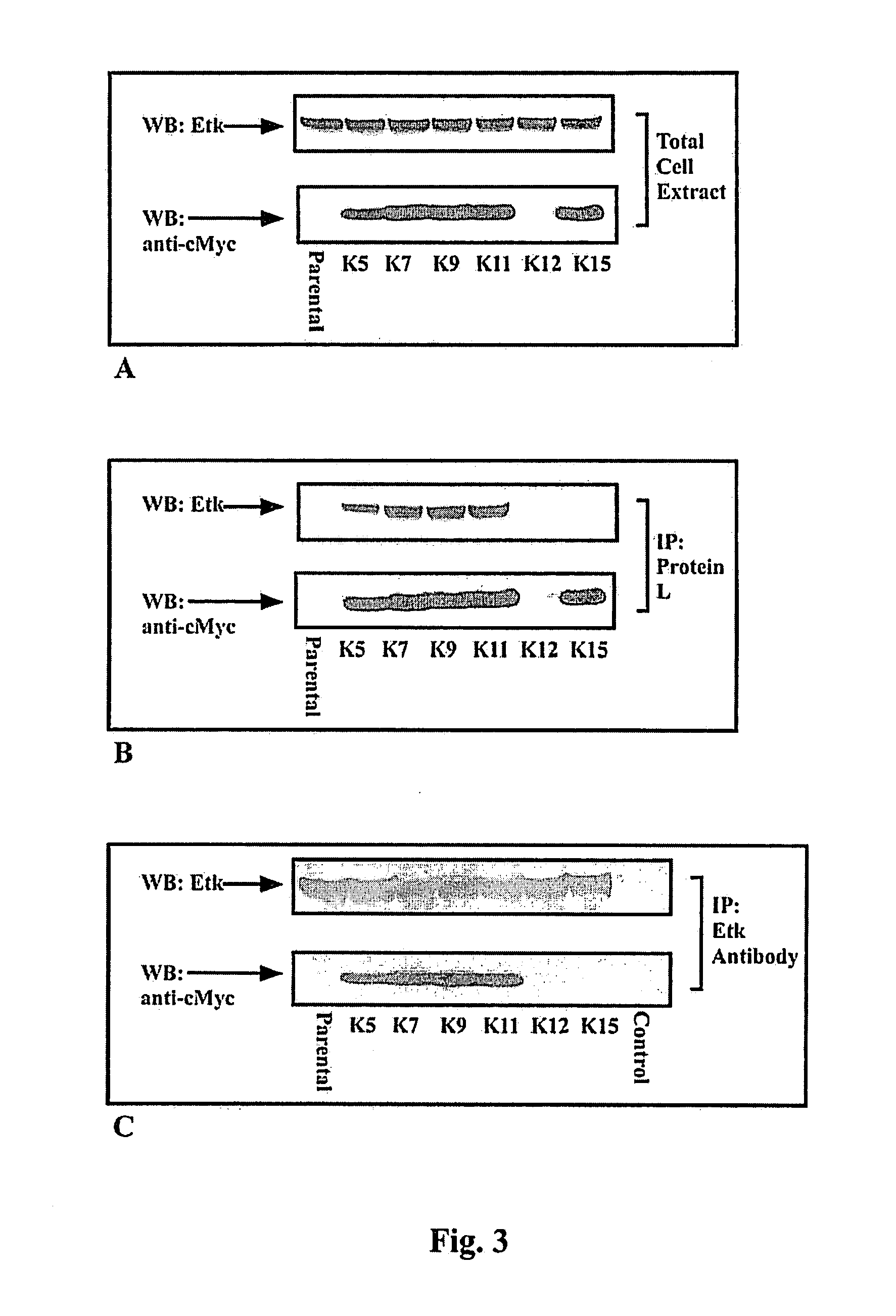
A single domain intrabody that binds to an intracellular protein or to an intracellular domain of an intracellular protein, such as Etk. Also provided is a method of inhibiting an intracellular enzyme, and treating a tumor in a patient by administering the intrabody or a nucleic acid expressing the inventive intrabody.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Inhibitors of PDE4 and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20100216703A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionPhosphodiesteraseNeurotrophin Receptor p75
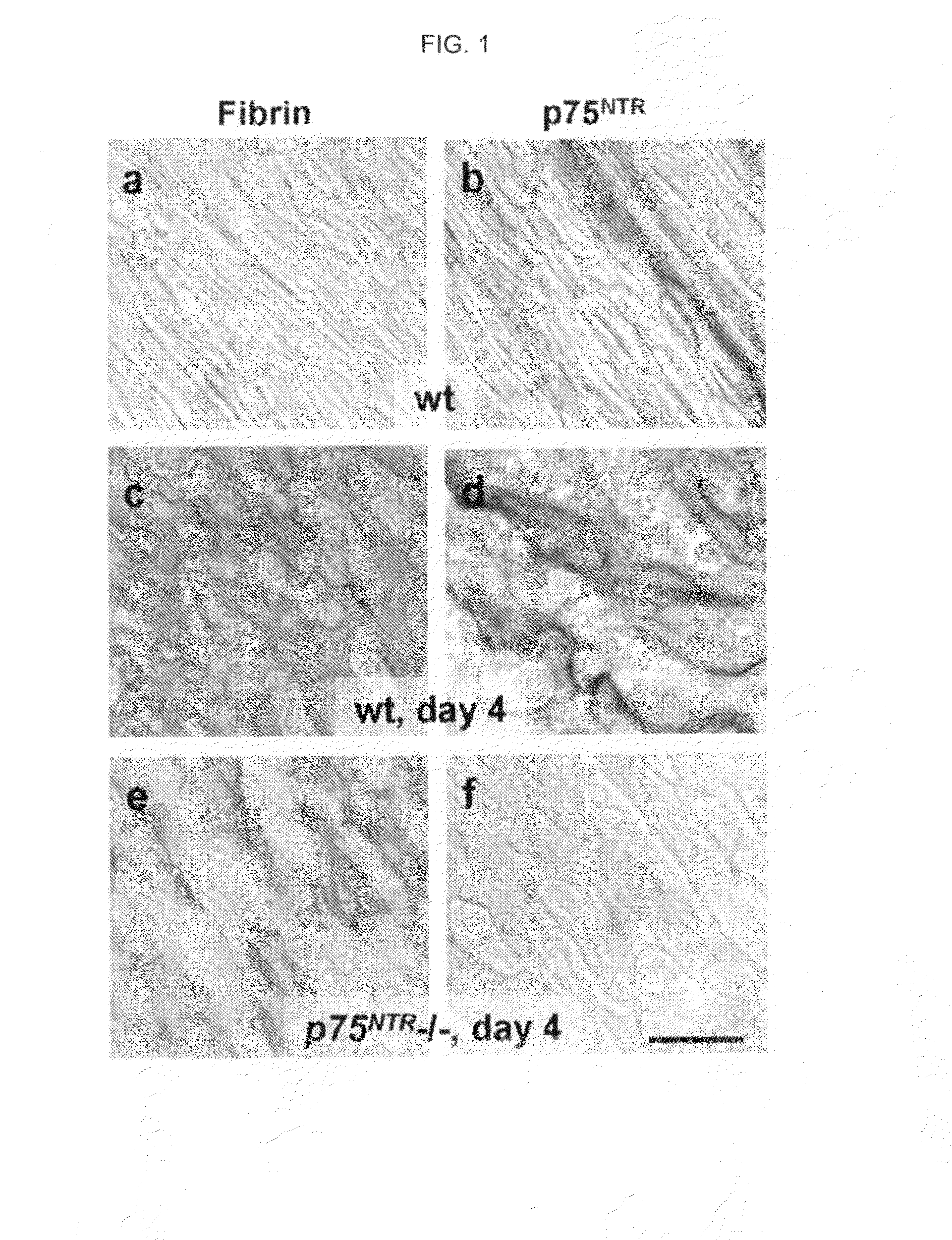
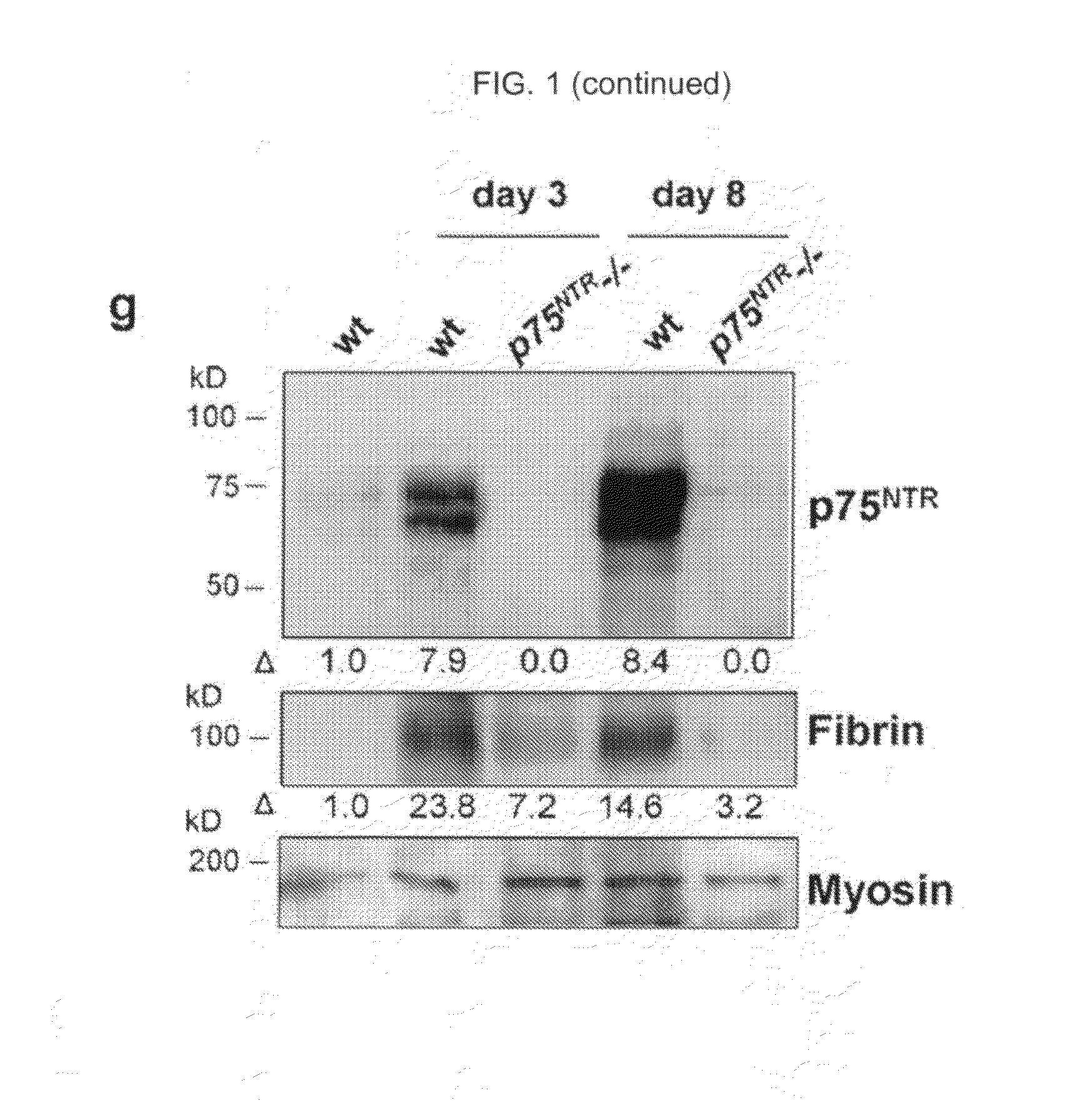
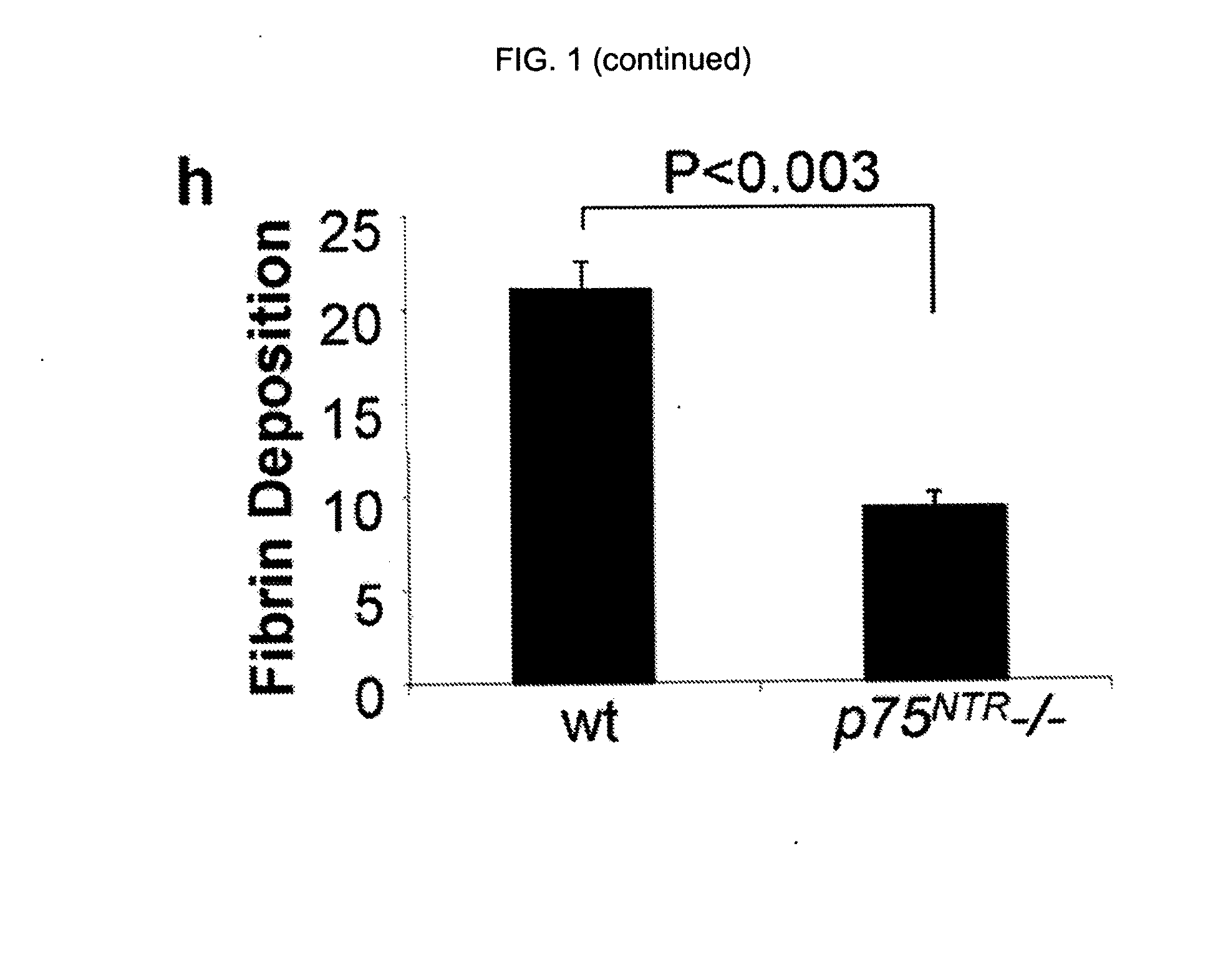
The inventors have succeeded in discovering that the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) is directly involved in the degradation of cAMP via interaction of its intracellular domain with phosphodiesterase 4A4 / 5 (PDE4A4 / 5). Provided herein are methods and compositions for the treatment of conditions of PDE4A4 / 5 and p75NTR expression (such as pulmonary disease and nerve regeneration) by blocking the interaction of PDE4A4 / 5 and p75NTR, as well as methods for the screening of agents useful in such applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GLASGOW +2
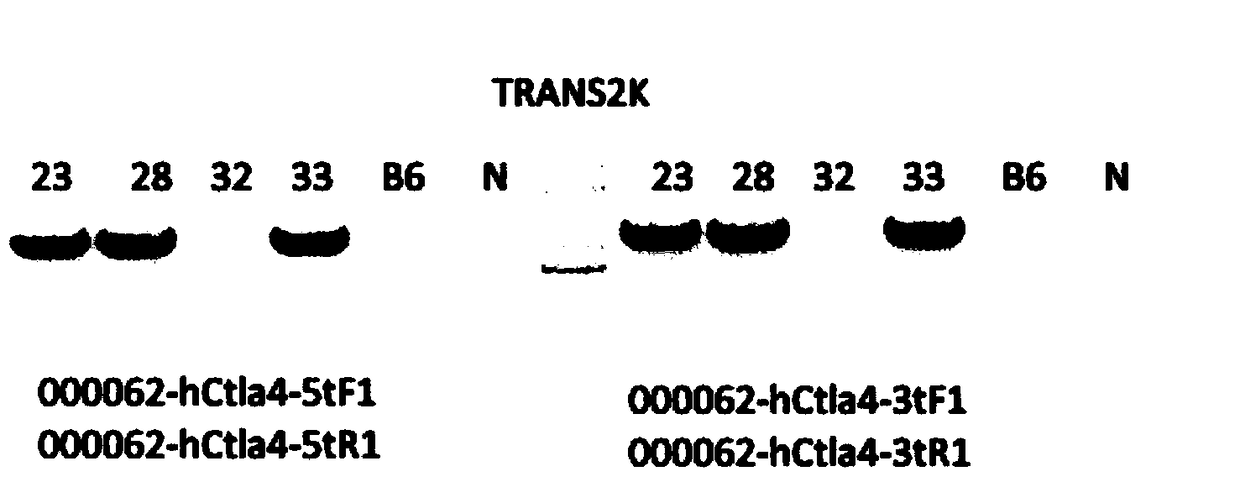
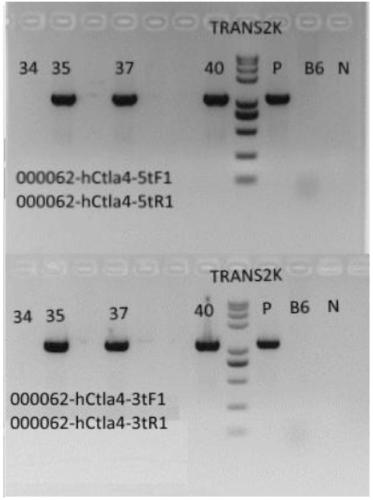
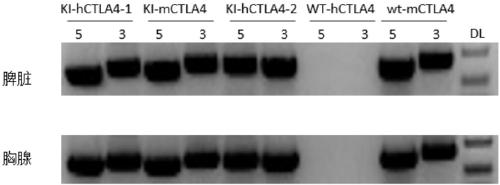
Establishment method of CTLA4 gene humanized animal model and application thereof
ActiveCN109022443AIncreased odds of homologous recombination repairIntracellular signaling is not affectedStable introduction of DNAPeptidesDrug developmentIn vivo
The invention belongs to the fields of animal gene engineering and genetic modification and particularly relates to an establishment method of a CTLA4 gene humanized animal model and an application thereof. In the invention, the extracellular domain of mouse CTLA4 gene is replaced by a human-source sequence while the intracellular domain holds a complete mouse-source sequence. The CTLA4 gene humanized animal model not only can be used for evaluating the efficacy on tumors of antibodies and has important guiding significance on clinical effect of medicine development, but also is an excellent model for security evaluation on anti-human CTLA4 antibody medicines. The establishment method also includes pre-clinical in-vivo evaluation on the toxicology of the CTLA4 antibody medicine, thus filling market gap.
Owner:GEMPHARMATECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com