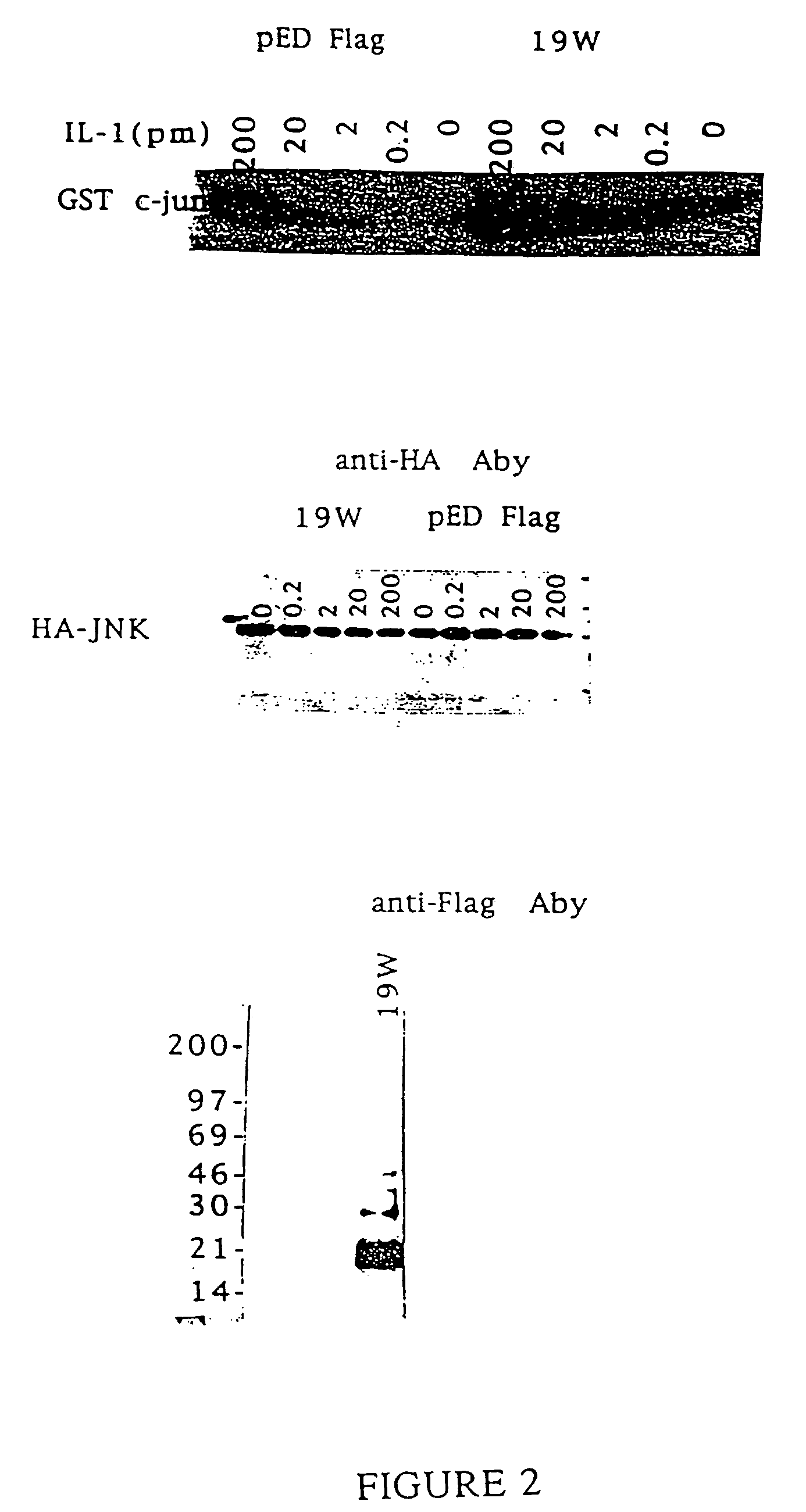
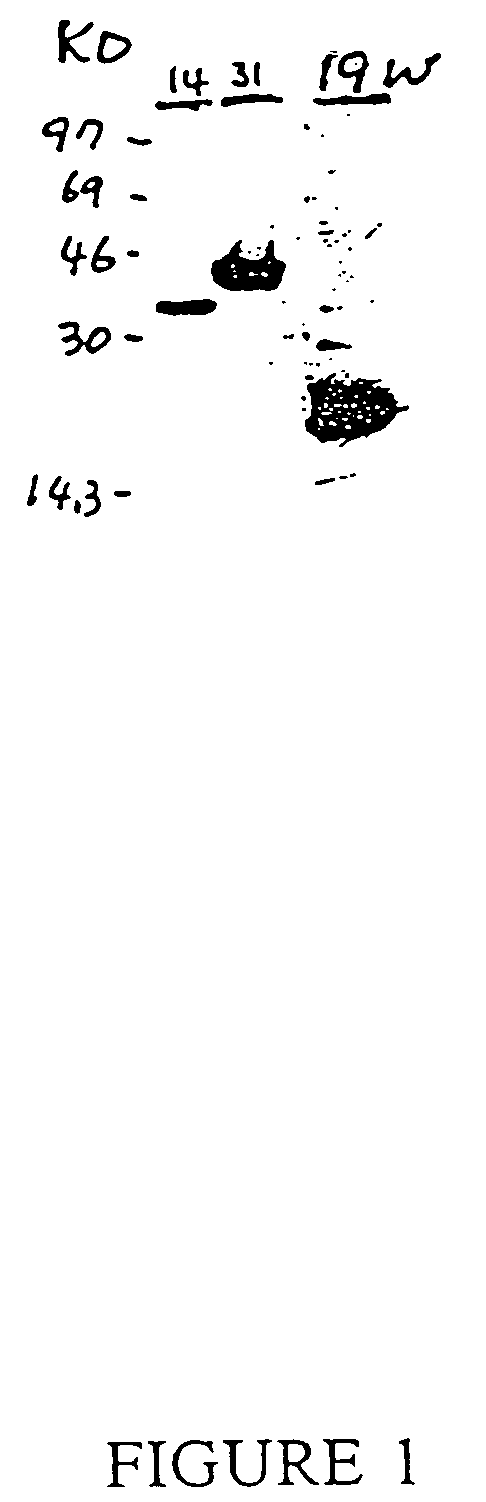Novel interleukin-1 receptor intracellular ligand proteins and inhibitors of ligand binding
a technology of interleukin-1 receptor and intracellular ligand, which is applied in the field of antiinflammatory substances, can solve the problems of ligands which bind to the il-1-r intracellular domain that have yet to be identified, and achieve the effect of preventing or ameliorating an inflammatory condition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cloning of IL-1-R Intracellular Ligand Protein Encoding Polynucleotide
[0110] A yeast genetic selection method, the “interaction trap” [Gyuris et al, Cell 75:791-803, 1993, which is incorporated herein by reference], was used to screen W138 and HeLa cell cDNA libraries (preparation see below) for proteins that interact with IL-1-R-1c, the cytoplasmic portion (intracellular domain) of the interleukin-1 receptor p80, or type I. The IL-1-R-1c DNA, encoding amino acids 340 to 552 of the type I IL-1 receptor, was obtained via the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of a human W138 cell cDNA library. This IL-1-R-1c DNA was then cloned into pEG202 by an EcoRI site, generating the bait plasmid, pEG202-IL-1-R-1c. This plasmid contains the HIS3 selectable marker, and expression of the bait, the LexA-IL-1-R-1c fusion protein, is from the strong constitutive ADH1 promoter. To create the reporter strain carrying the bait protein, yeast strain EGY48, containing the reporter sequence LexAop-Leu2 in pl...
example 2
Expression of the IL-1-R Intracellular Ligand Protein
[0120] cDNAs encoding IL-1-R intracellular ligand proteins were released from the pJG4-5 vector with the appropriate restriction enzymes. For example. EcoRI and XhoI were used to release cDNA from the relevant clone. Where the restriction sites were also present in the internal sequence of the cDNA. PCR was performed to obtain the cDNA. These cDNAs were then cloned into various expression vectors. These included pGEX (Pharmacia) or pMAL (New England Biolabs) for expression as a GST (Glutathione-S-transferase) or MBP (maltose binding protein) fusion protein in E. coli, a pED-based vector for mammalian expression, and pVL or pBlueBacHis (Invitrogen) for baculovirus / insect expression. For the immunodetection of IL-1-R intracellular ligand expression in mammalian cells. an epitope sequence, “Flag,” was inserted into the translational start site of the pED vector, generating the pED-Flag vector. cDNAs were then inserted into the pED-F...
example 3
Assays of IL-1-R Intracellular Domain Binding
[0122] Two different methods were used to assay for IL-1-R intracellular ligand protein activity. The first assay measures binding in the yeast strain in “interaction trap,” the system used here to screen for IL-1-R-1c interacting proteins. In this system, the expression of reporter genes from both LexAop-Leu2 and LexAop-LacZ relies on the interaction between the bait protein, in this case IL-1-R-1c, and the prey, the IL-1-R intracellular ligand. Thus, one can measure the strength of the interaction by the level of Leu2 or LacZ expression. The most simple method is to measure the activity of the LacZ encoded protein, β-galactosidase. This activity can be judged by the degree of blueness on the X-Gal containing medium or filter. For the quantitative measurement of β-galactosidase activity, standard assays can be found in “Methods in Yeast Genetics” Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1990 (by Rose, M. D., Winston, F., and Hieter, P.).
[0123] Th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com