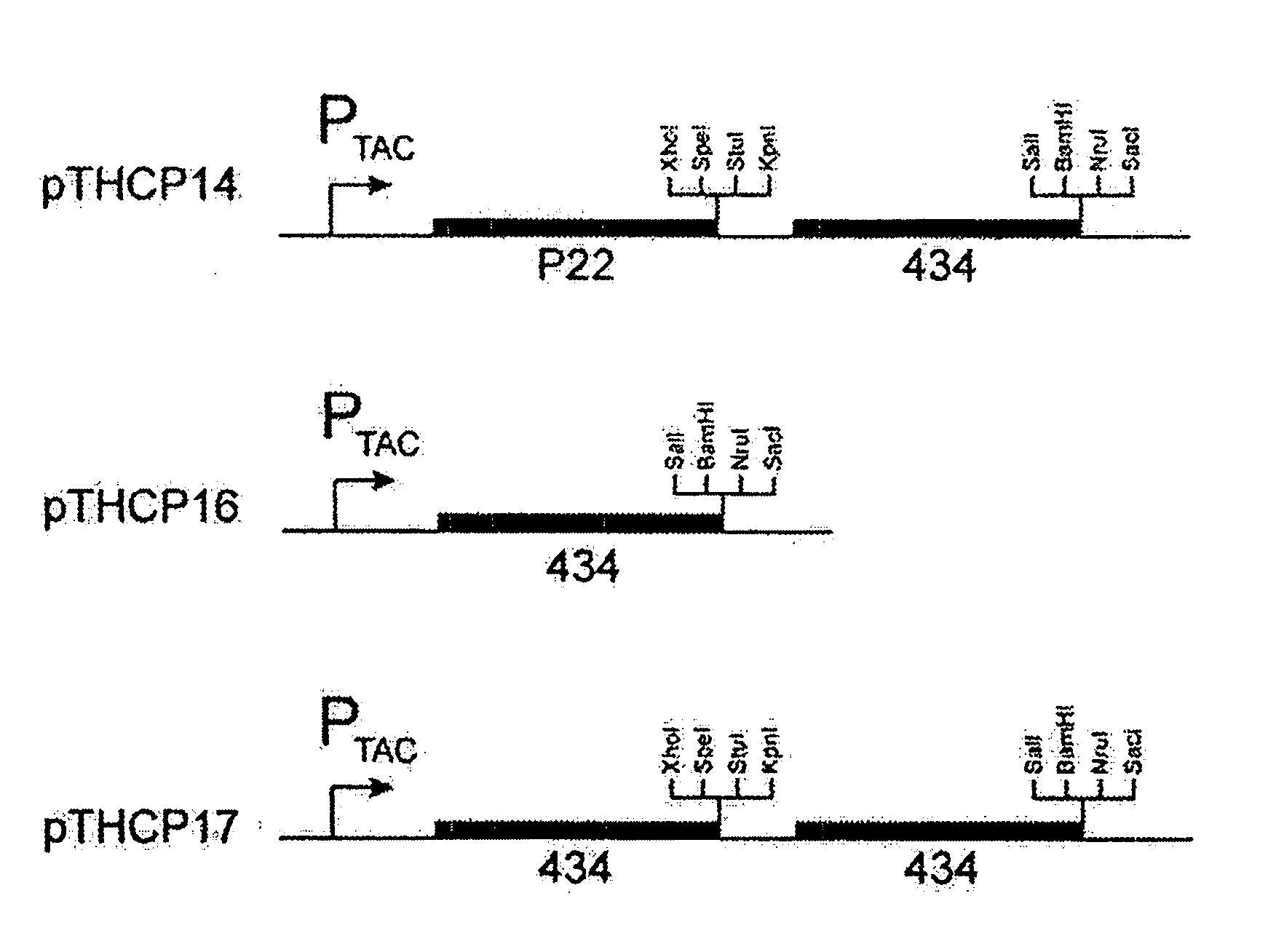
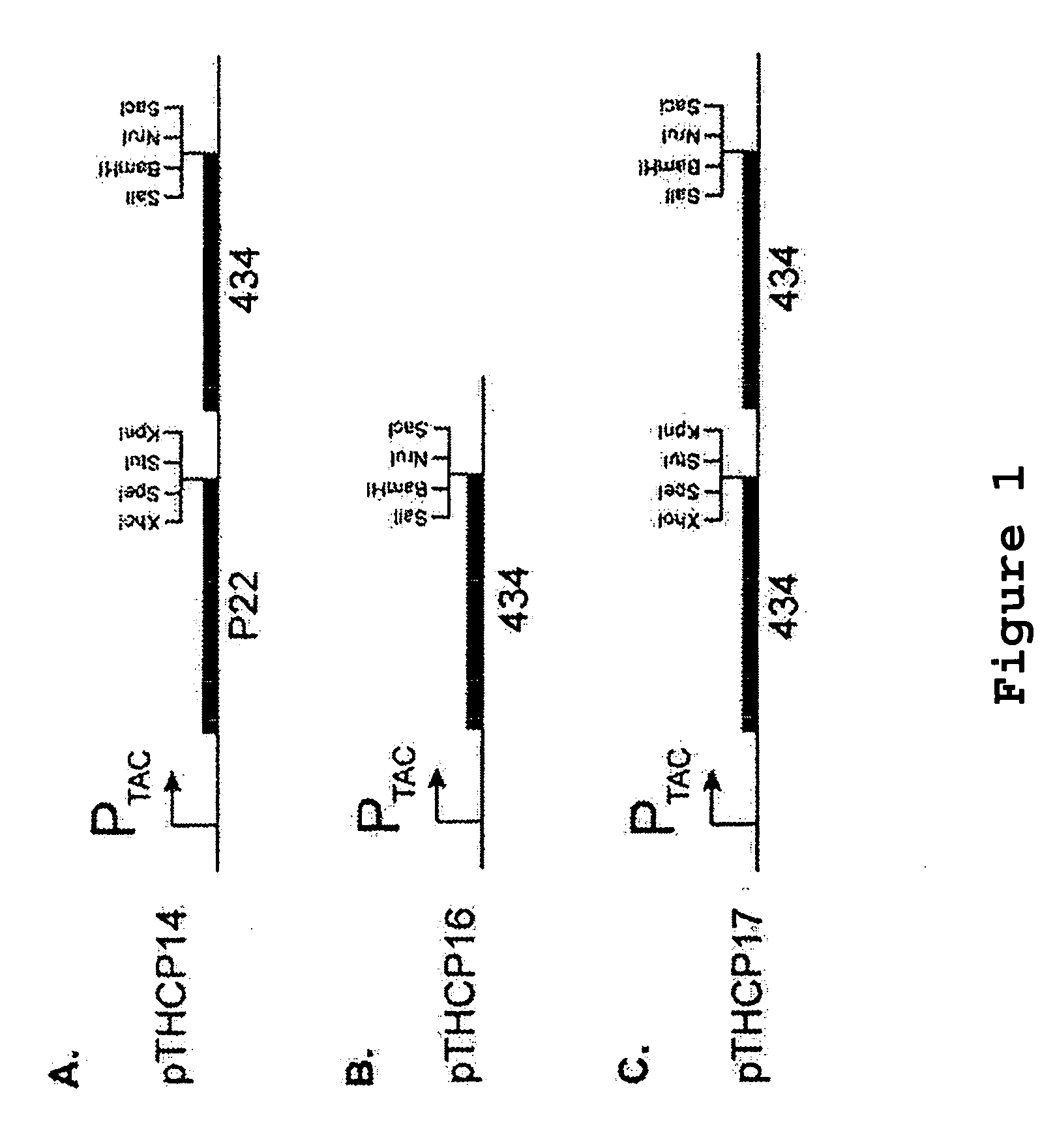
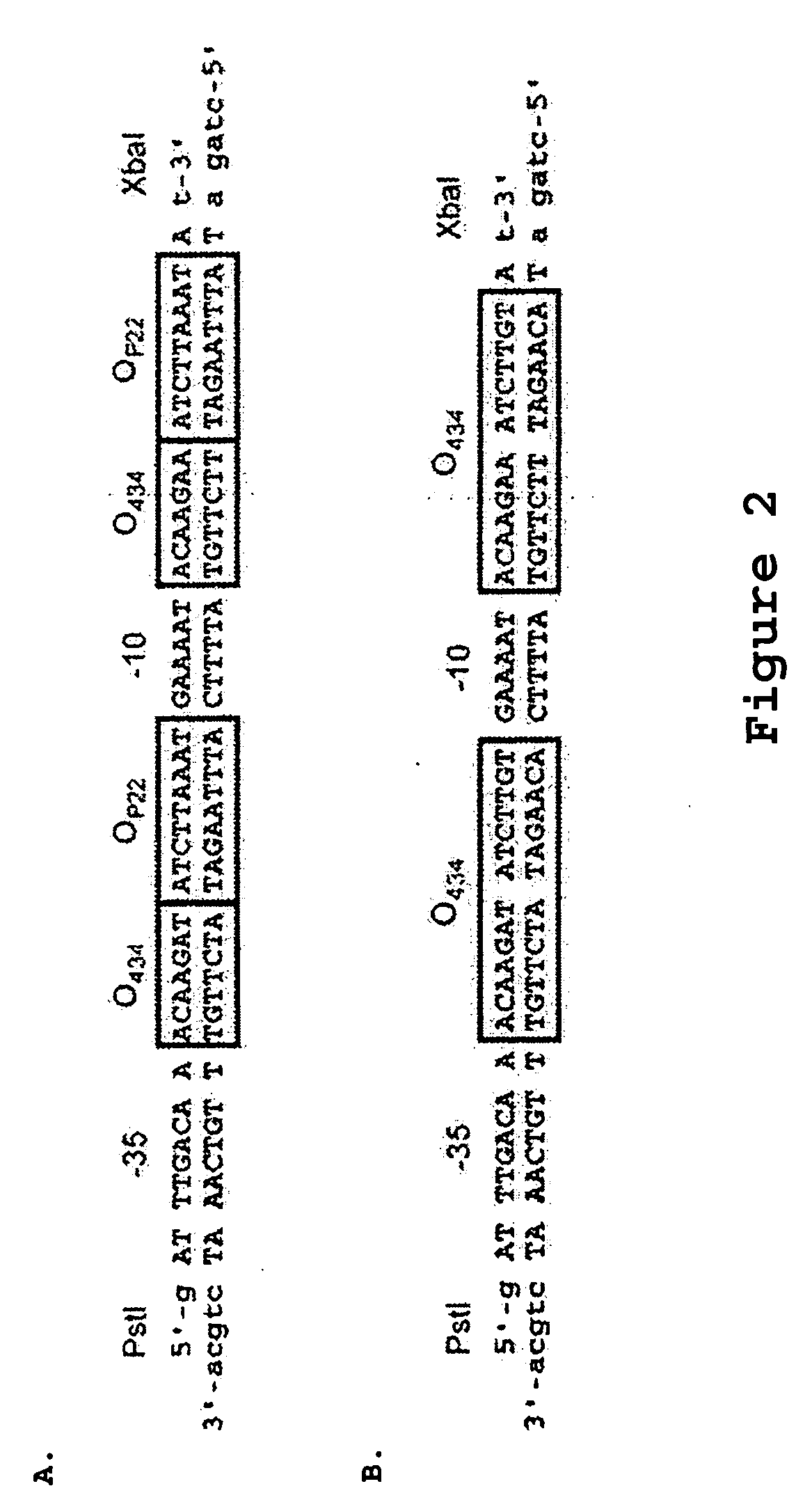
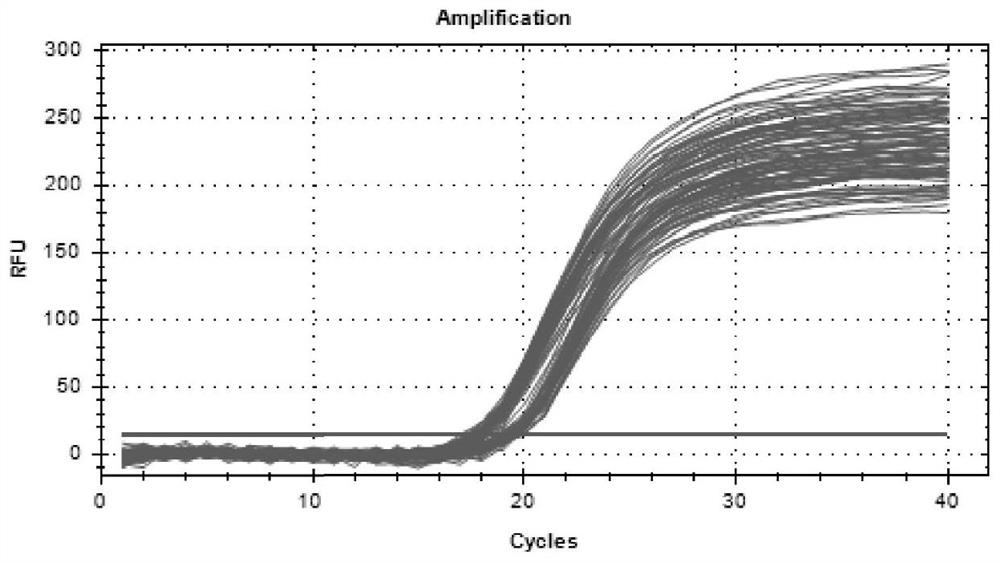
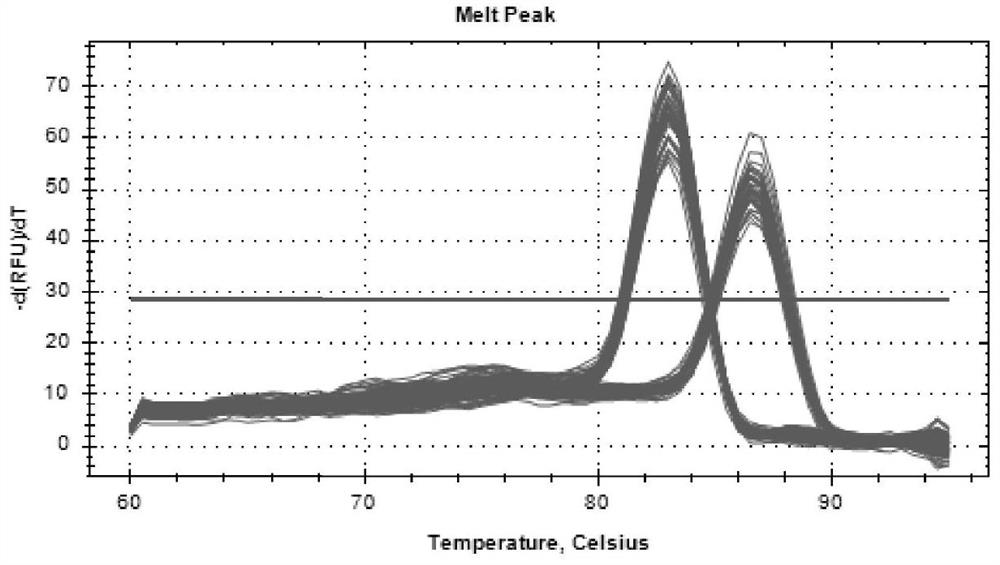
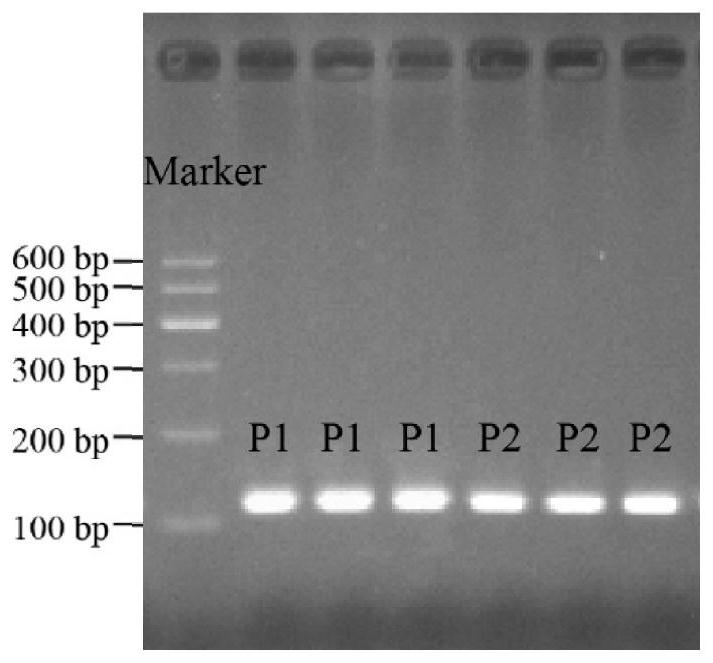
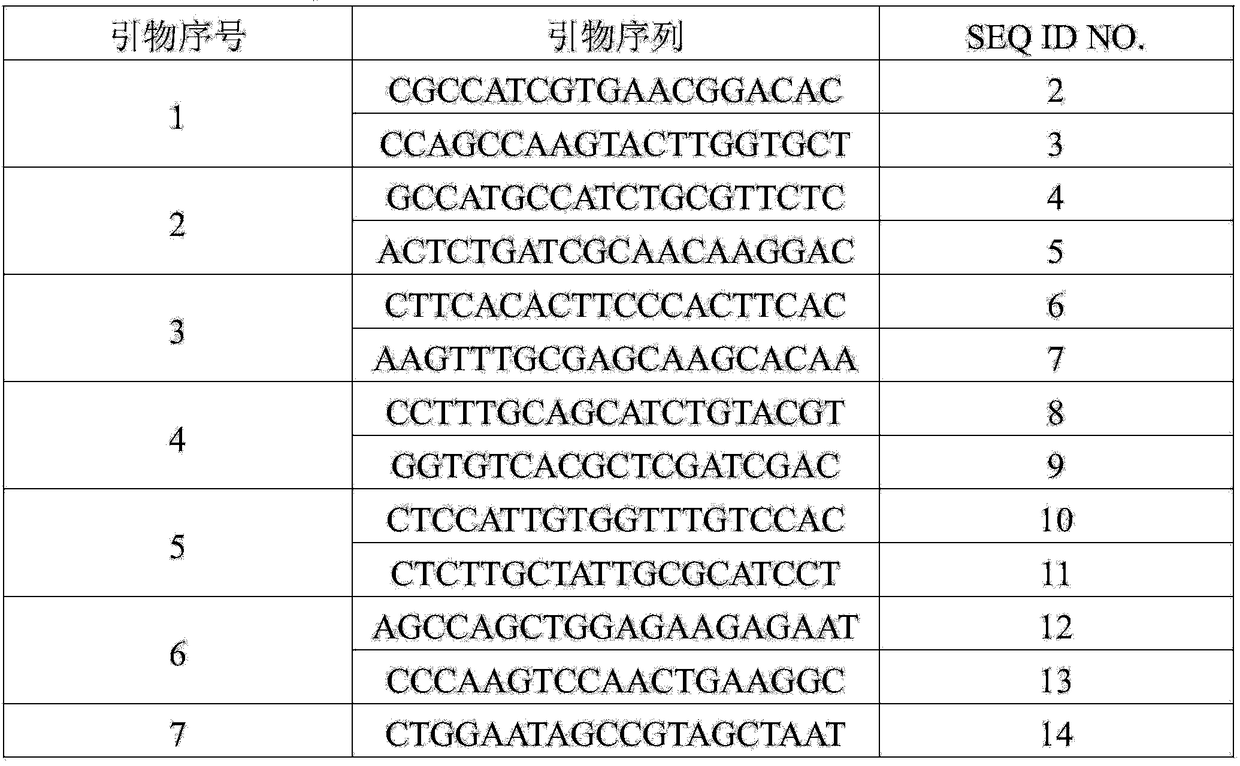
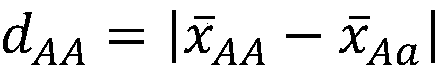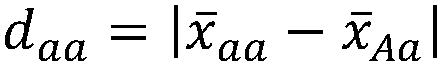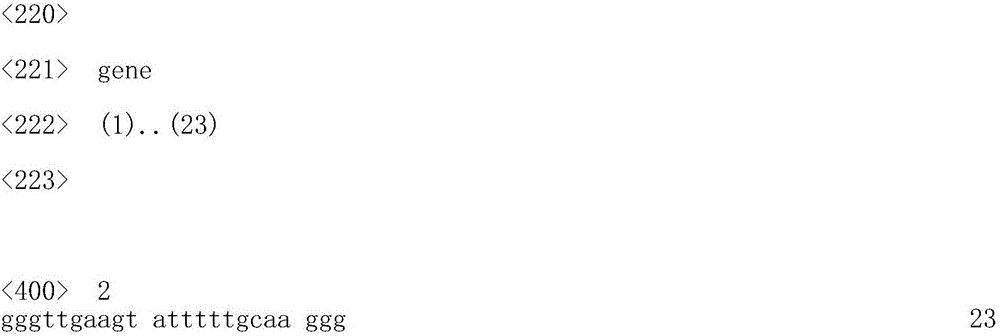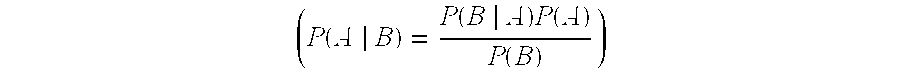Patents
Literature
101 results about "Genetic selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
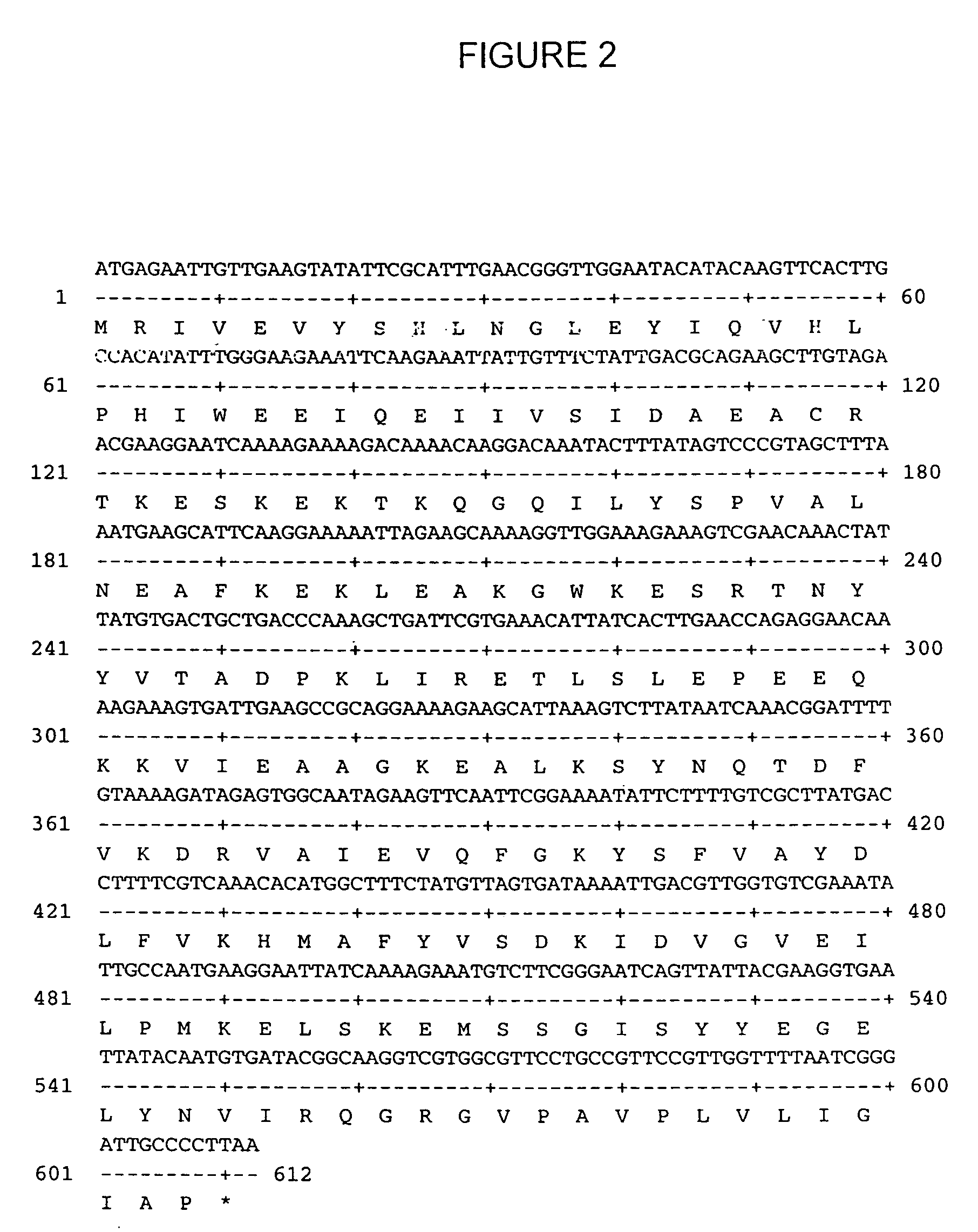
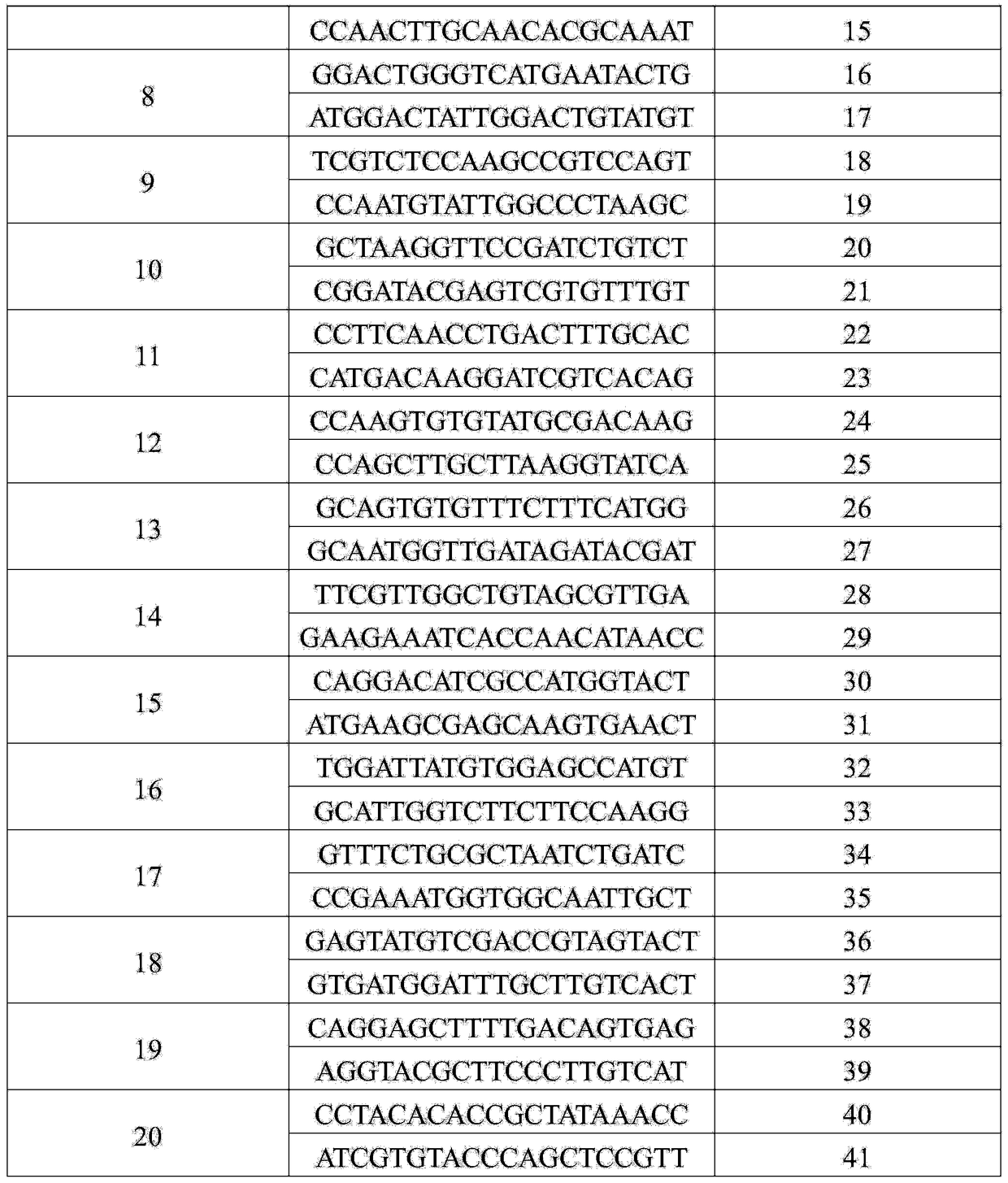
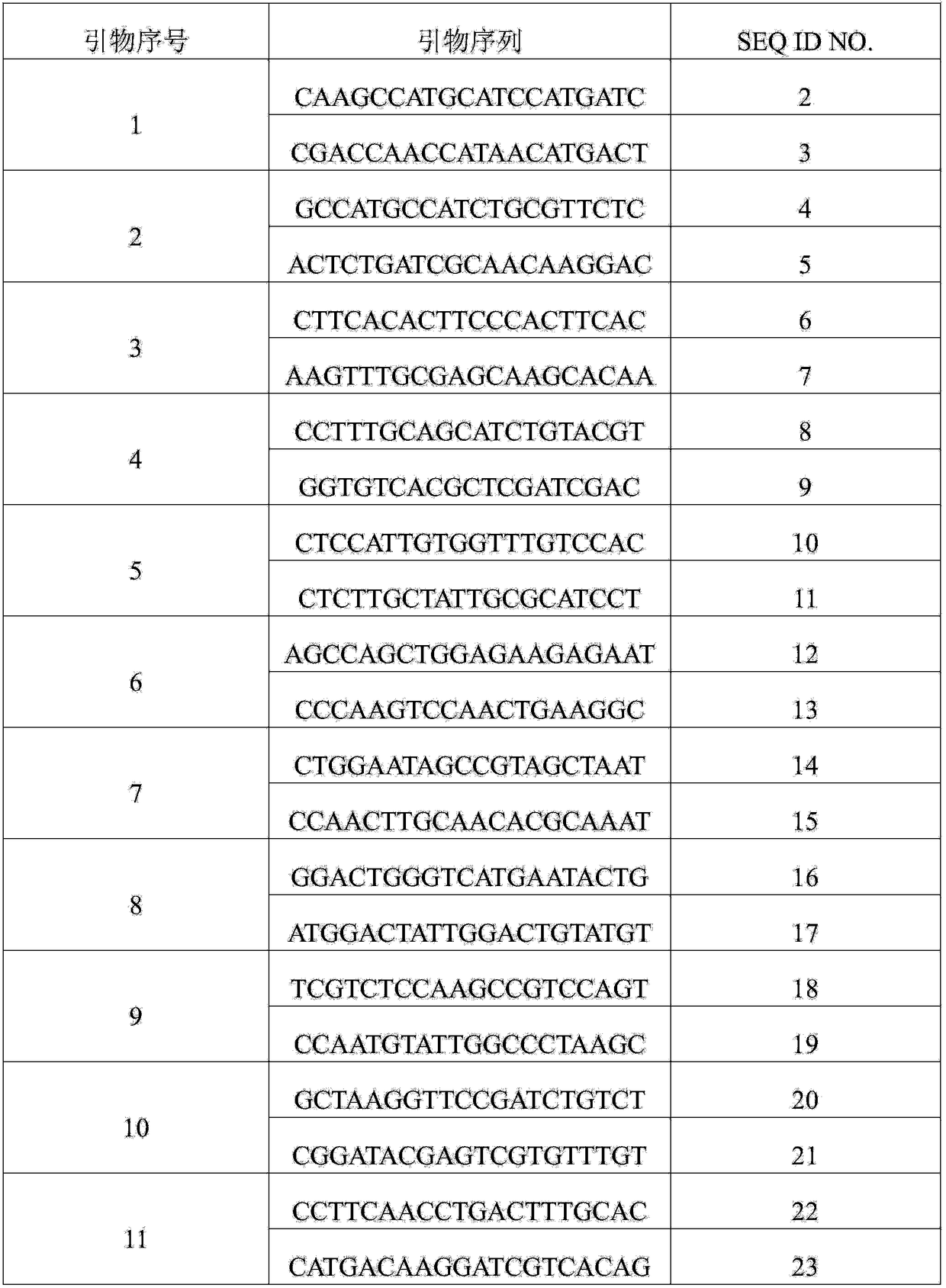
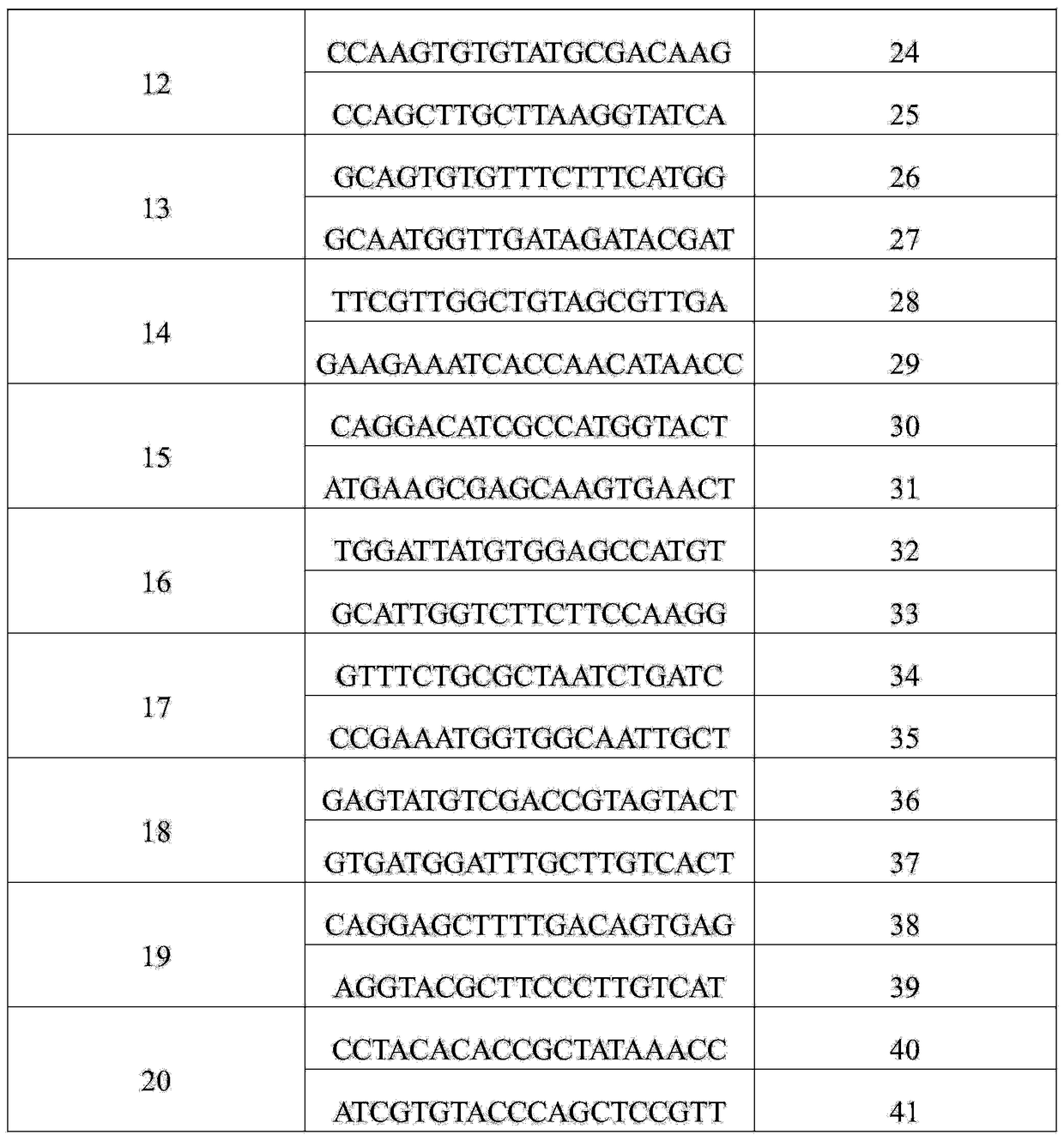
Genetic system and self-cleaving inteins derived therefrom, bioseparations and protein purification employing same, and methods for determining critical, generalizable amino acid residues for varying intein activity
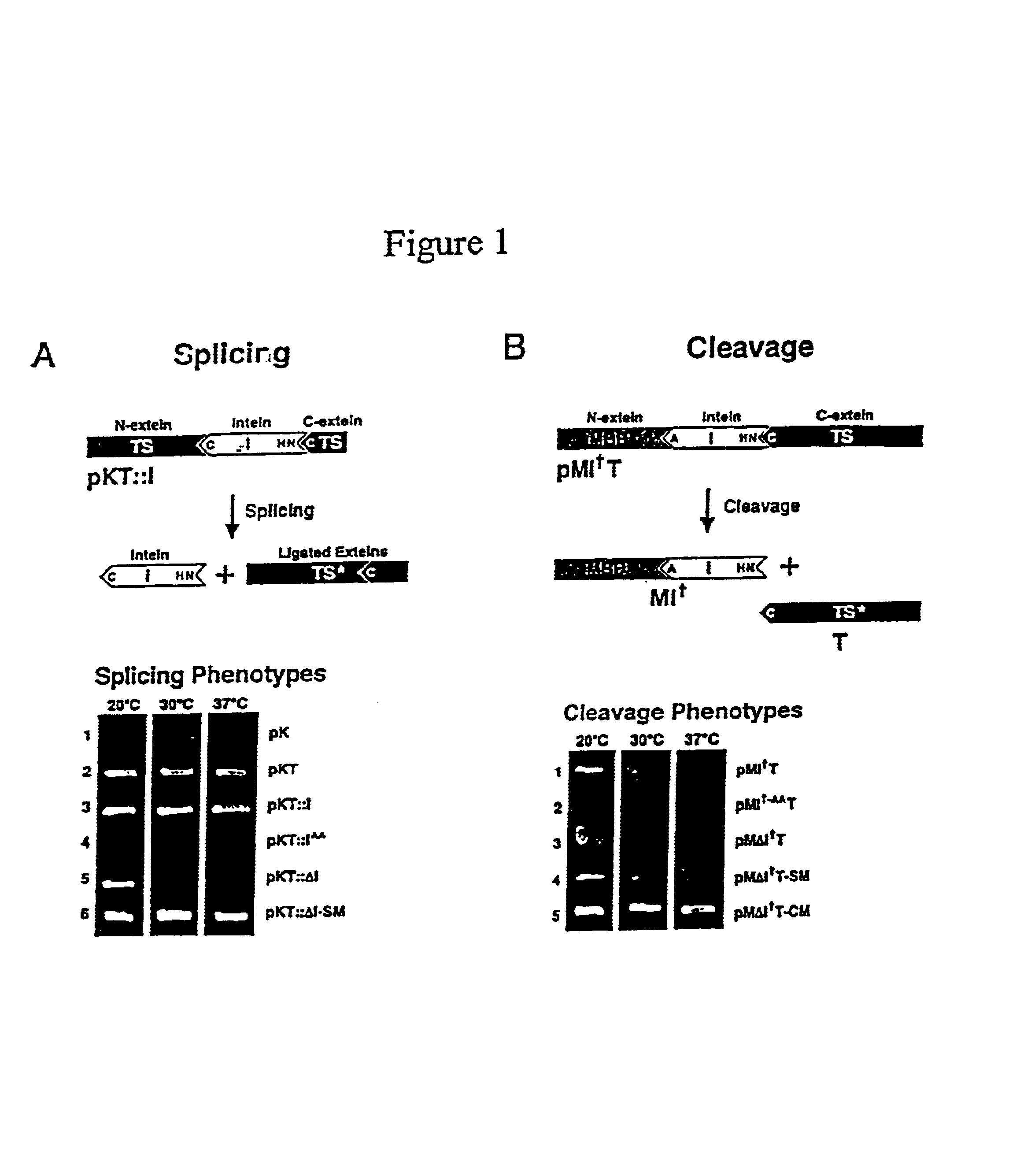
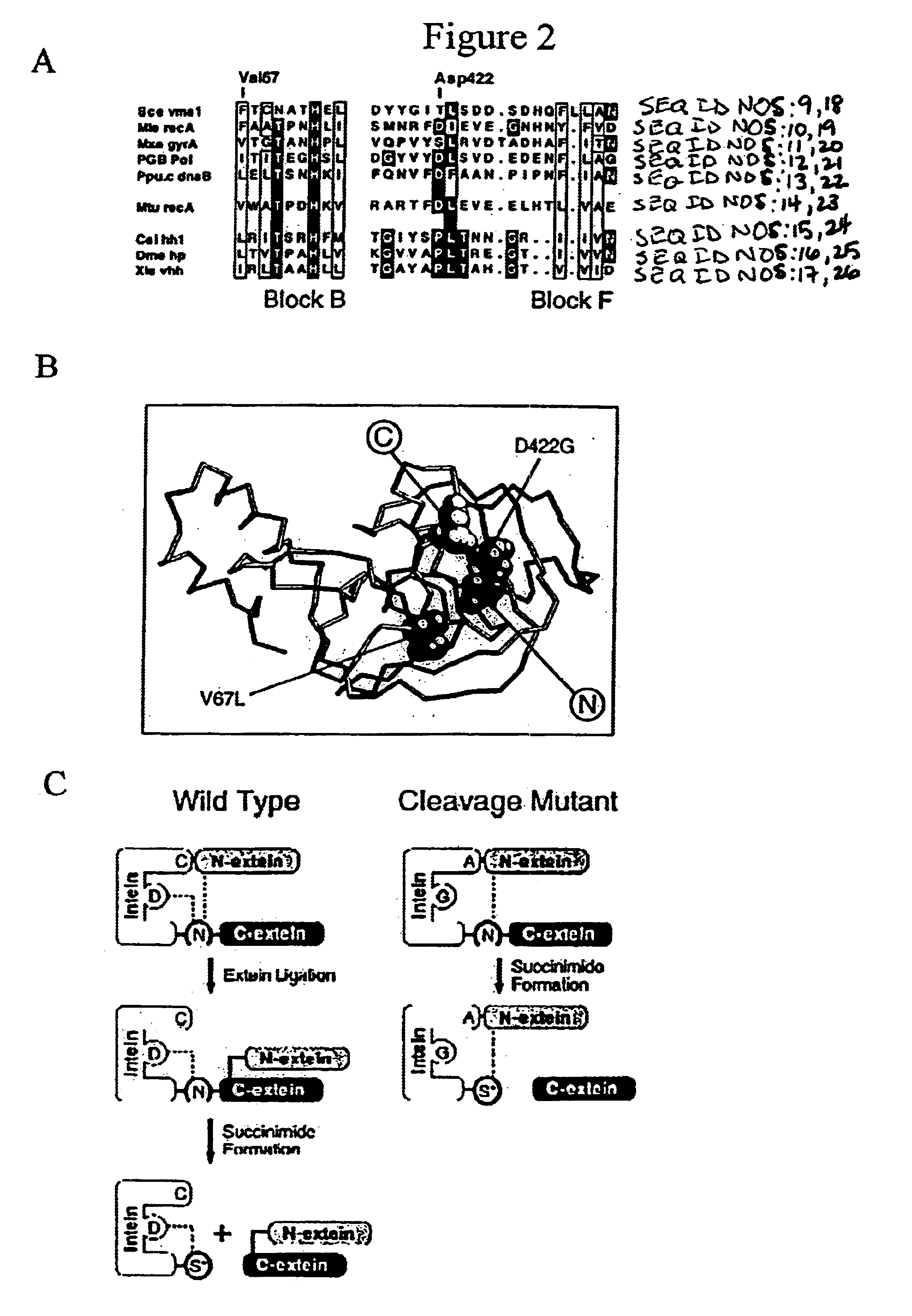
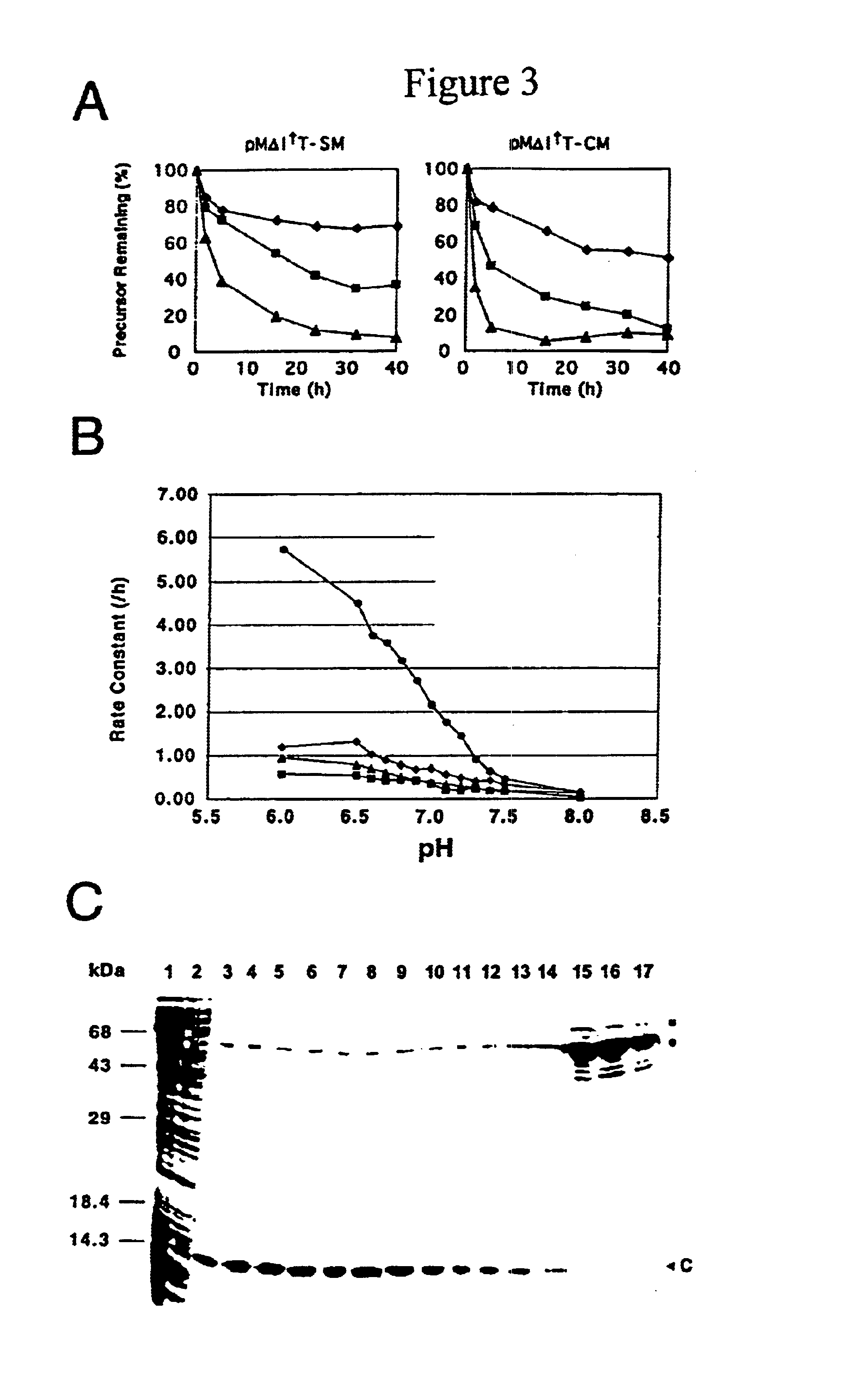
A self-cleaving element for use in bioseparations has been derived from a naturally occurring, 43 kDa protein splicing element (intein) through a combination of protein engineering and random mutagenesis. A mini-intein (18 kDa) previously engineered for reduced size had compromised activity and was therefore subjected to random mutagenesis and genetic selection. In one selection a mini-intein was isolated with restored splicing activity, while in another, a mutant was isolated with enhanced, pH-sensitive C-terminal cleavage activity. The enhanced cleavage mutant has utility in affinity fusion-based protein purification. The enhanced splicing mutant has utility in purification of proteins such as toxic proteins, for example, by inactivation with the intein in a specific region and controllable splicing. These mutants also provide new insights into the structural and functional roles of some conserved residues in protein splicing. Thus, disclosed and claimed are: a genetic system and self-cleaving inteins therefrom; bioseparations employing same; protein purification by inactivation with inteins in specific regions and controllable intein splicing; methods for determining critical, generalizable residues for varying intein activity; and products.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
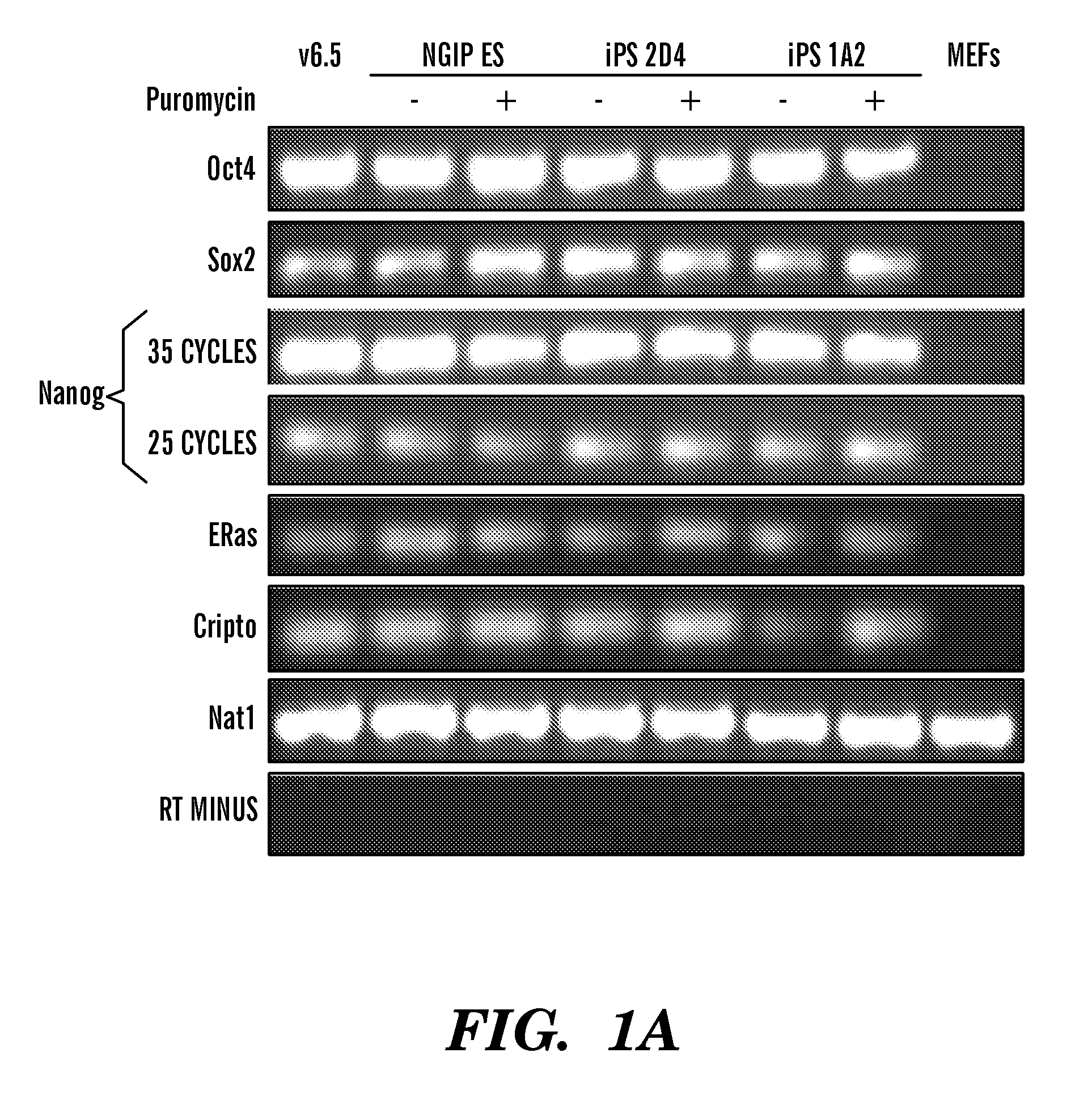
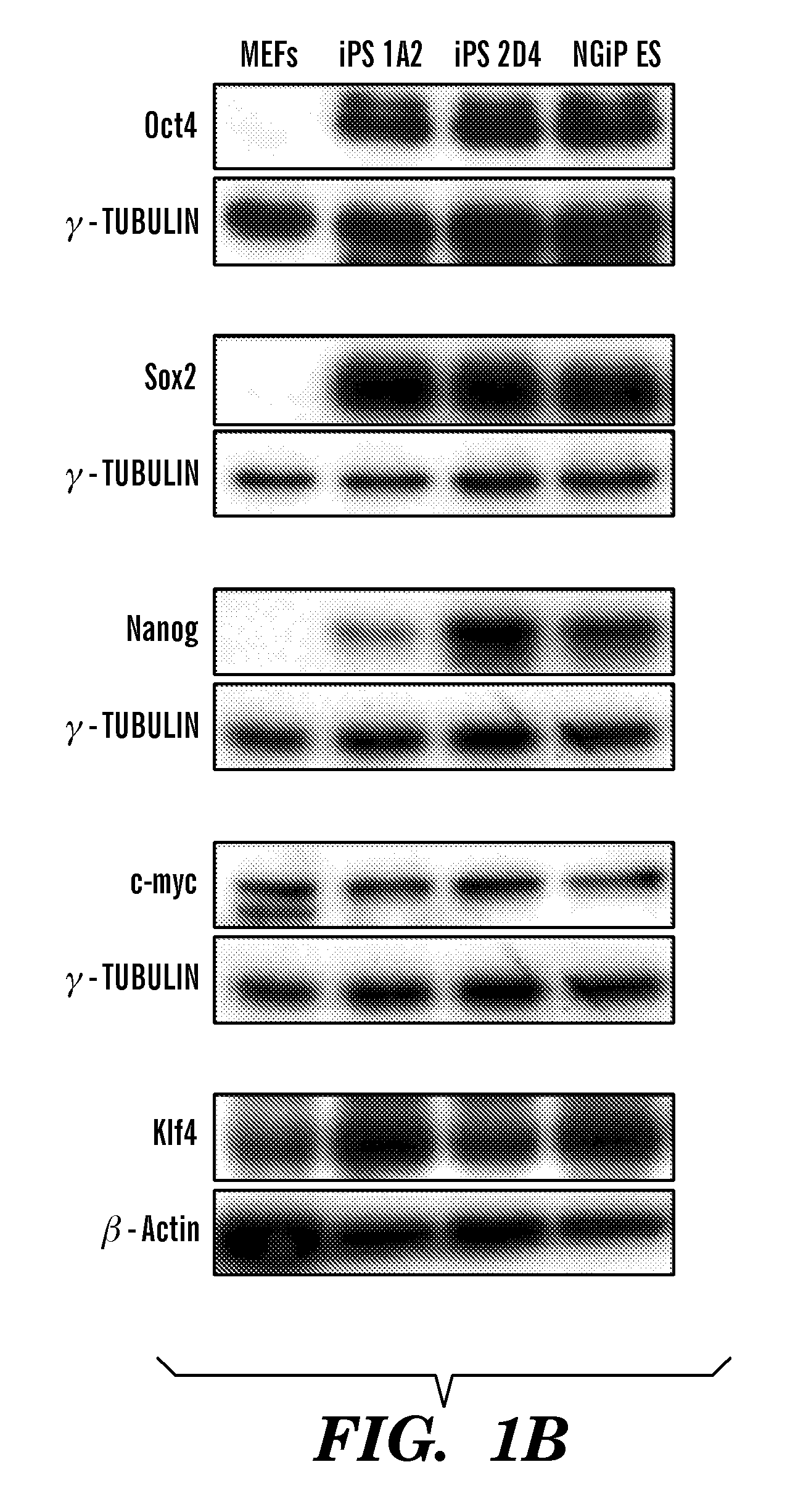
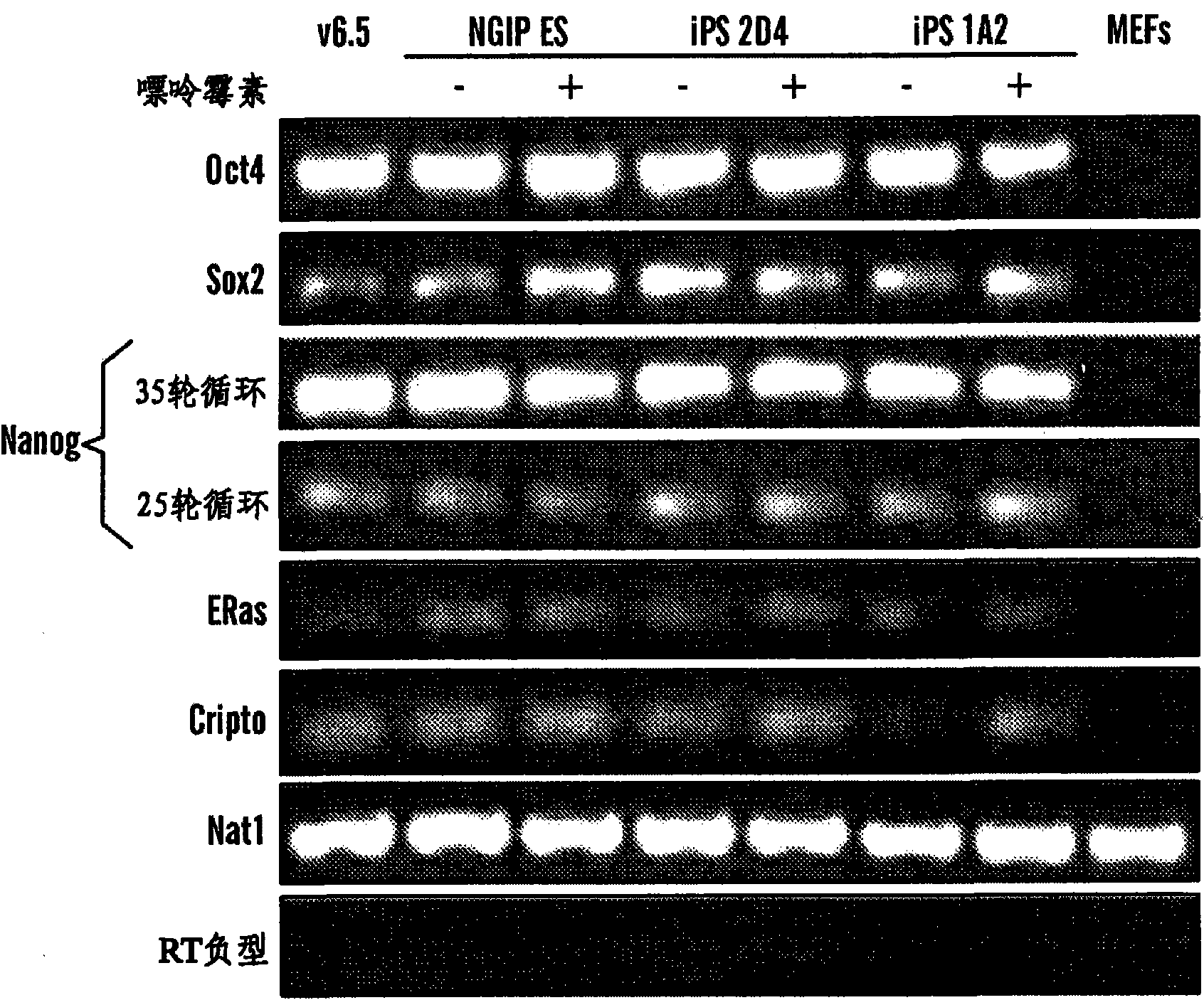
Methods of generating pluripotent cells from somatic cells
InactiveUS20100184051A1Long maintenance periodPromote recoveryGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementColony morphologyX chromosome
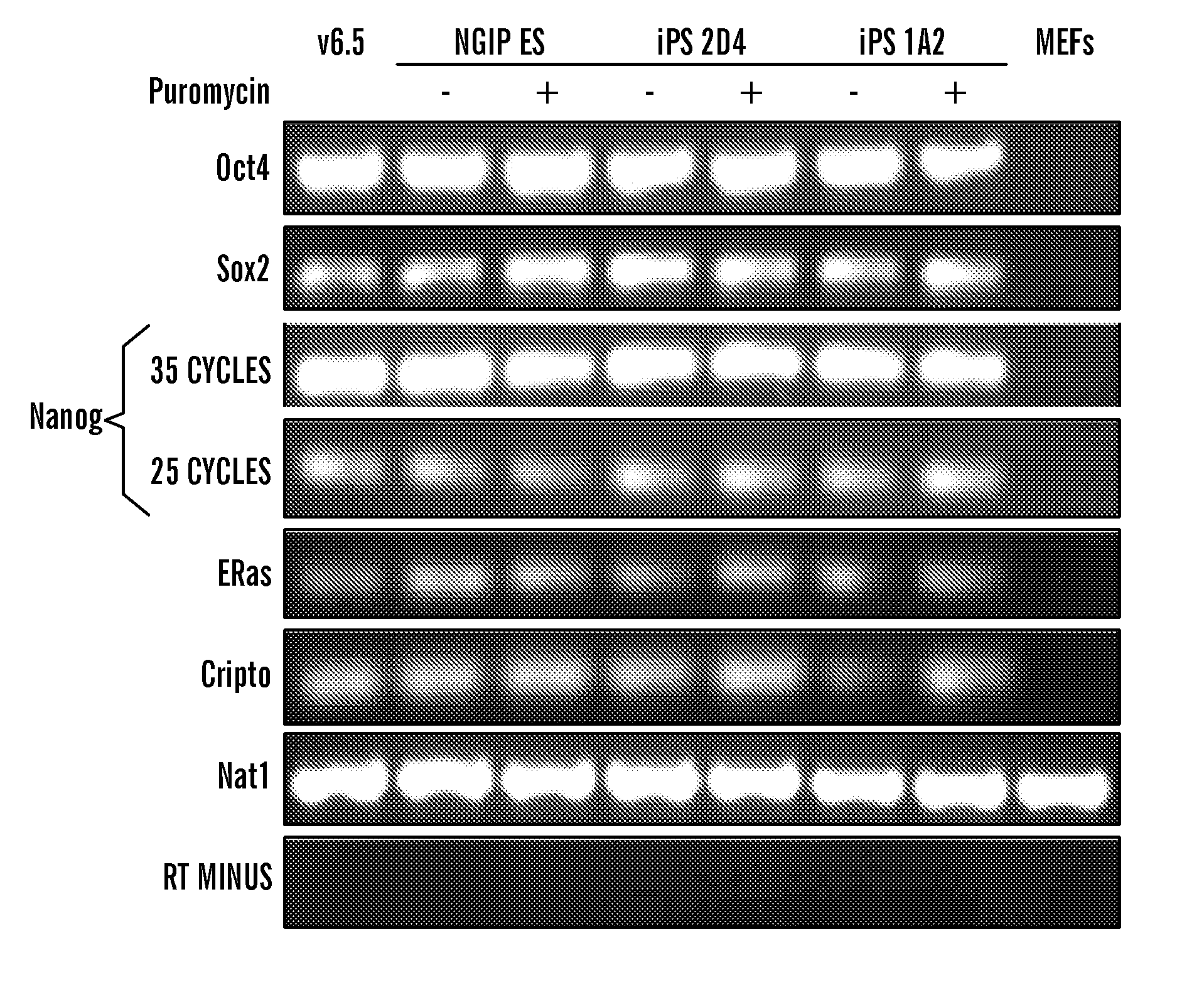
Disclosed herein are methods to select for the generation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cells during developmental reprogramming. The methods described herein relate to the selection of induced pluripotent stem cells, i.e., pluripotent stem cells generated or induced from differentiated cells without a requirement for genetic selection. Described herein are particular embodiments for selection of reprogrammed cells based on 1) colony morphology, or 2) X chromosome reactivation in female cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Hybrid intelligent optimization method
ActiveCN103942419AFast convergenceImprove convergence accuracySpecial data processing applicationsBacteria foragingAlgorithm
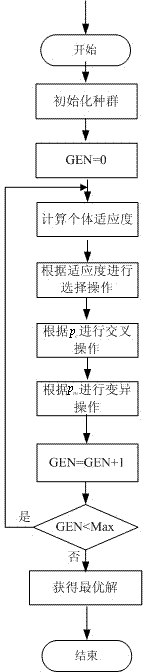
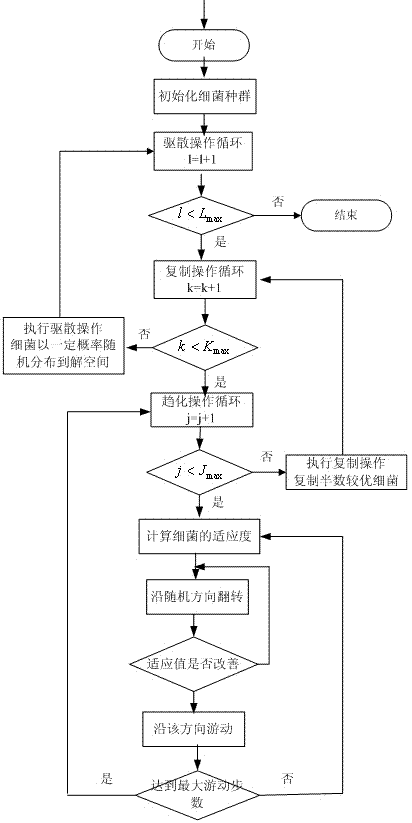
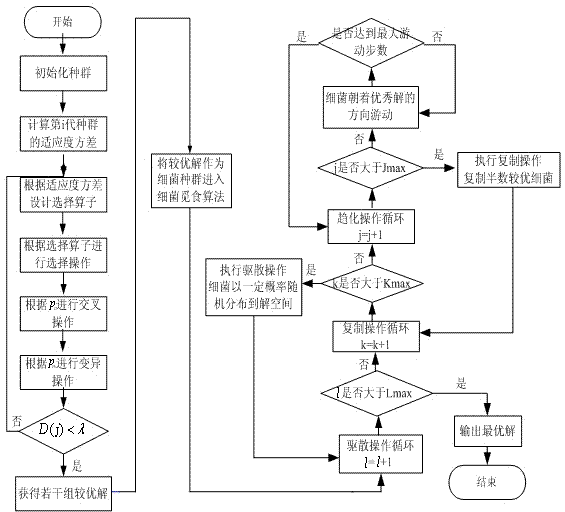
The invention discloses a hybrid intelligent optimization method and belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence and data mining. A genetic optimization algorithm and a bacterial foraging optimization algorithm are organically combined by the hybrid intelligent optimization method. First, a preliminary superior solution is obtained through the breadth searching capacity of the genetic optimization algorithm and serves as an initial bacterial population in the posterior bacterial foraging algorithm, by fully utilizing chemotaxis, duplicating and dispersing operation of the bacterial foraging algorithm, excellent individuals are generated continuously, and finally the solution converges towards the optimal solution. On the basis of the technical scheme, further improvements are made in the four aspects of genetic selection operators, optimal joint pints, bacterial chemotaxis and duplicating operation. Compared with the prior art, the convergence speed and the convergence precision of an optimal solution set can be improved, and the hybrid intelligent optimization method is more extensive in applicability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A method for estimating genomic breeding value integrating dominance effects
ActiveCN109101786AImprove accuracyIntroduce reasonableSpecial data processing applicationsHomozygous genotypeModel complexity
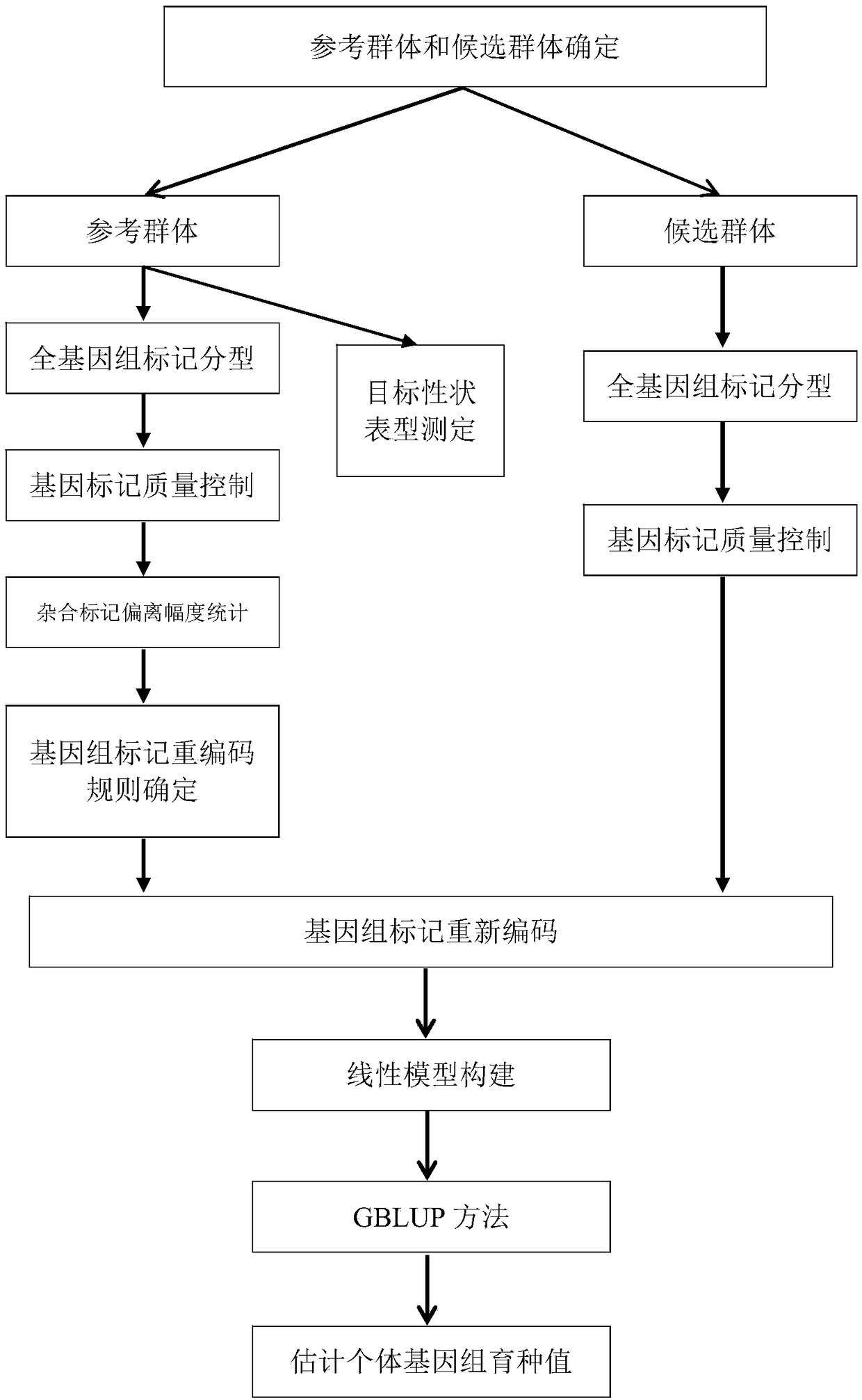
The invention discloses a genome breeding value estimation method for integrating dominant effect, which relates to the technical field of livestock and poultry genetic selection. The method comprisessteps identifying a reference group and a candidate group, the phenotype of the target traits of the reference population was determined, Genome-wide marker typing of reference population, quality control of gene marker of reference population, statistics of heterozygous marker deviation of reference population, formulation of genome marker re-coding rules, genome-wide marker typing of candidatepopulation, quality control of gene marker of candidate population, re-coding of genome marker and estimation of genome breeding value, etc. Based on the deviation degree between the phenotype of theheterozygous genotype and the phenotype of the homozygous genotype, the invention formulates coding rules, starts from the genomic marker end, re-codes the heterozygous genotype, causes the gene marker coding to include dominant effect, and then estimates the genomic breeding value. The invention is adapted to the needs of livestock and poultry genetic breeding, and can greatly improve the accuracy of genome estimation breeding value without increasing the complexity of the model.
Owner:ANIMAL SCI RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Genetic selection of small molecule modulators of protein-protein interactions
InactiveUS20060078875A1Modulate effectSensitivity adjustableFungiBacteriaGene productMethods of production
The present invention provides a method of production and screening of small molecule modulation of inter-macromolecule interaction. The method involves providing a living cell containing a gene that directs expression of a gene product to be assayed for the ability to modulate inter-macromolecule interactions and an inter-macromolecule interaction whose interaction can be monitored. The inter-macromolecule interaction is monitored in the living cell to determine if the inter-macromolecule interaction is modulated in the living cell relative to another, otherwise similar living cell that lacks said gene product.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
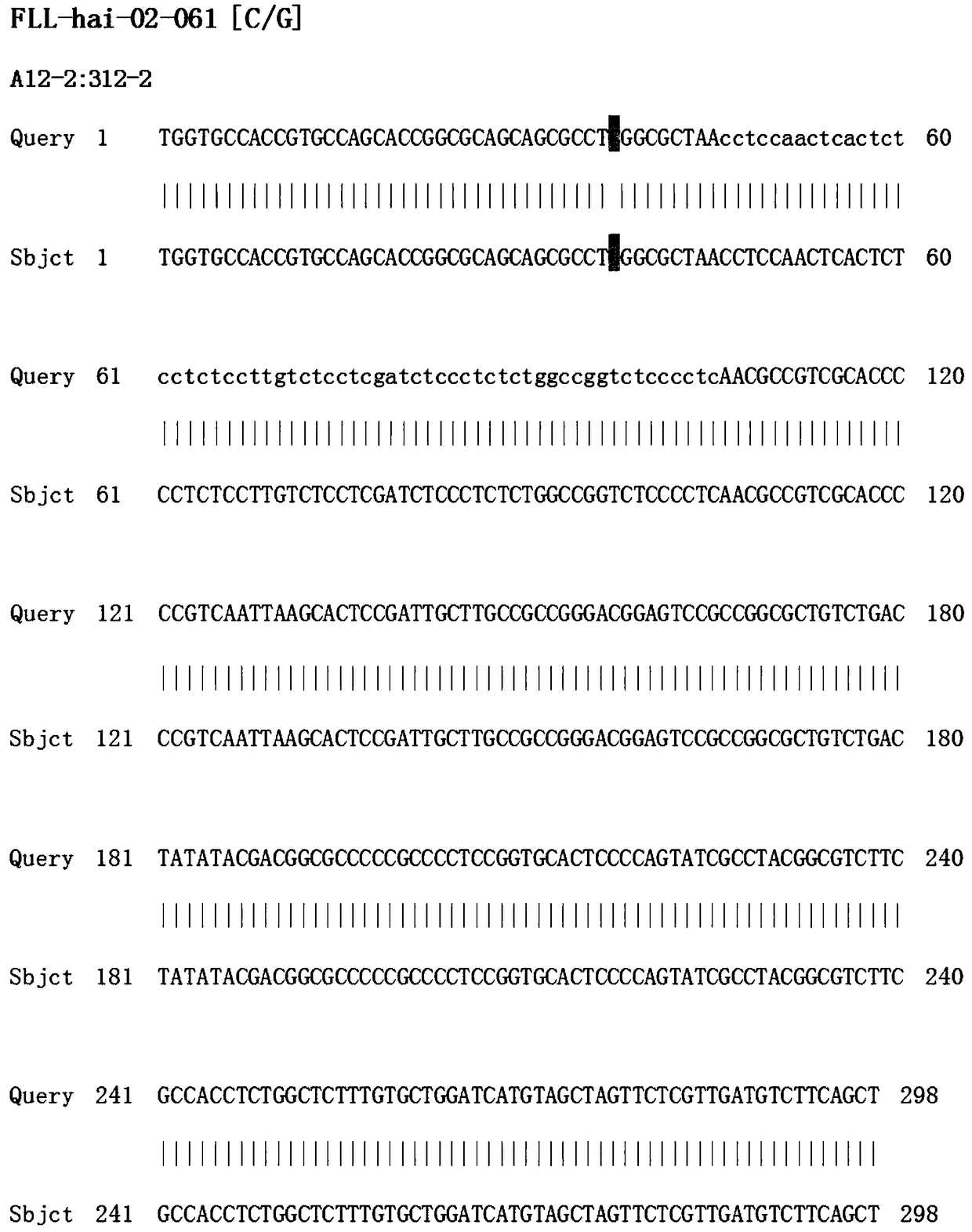
SNP markers linked with color of husked millet, and primers and application thereof
InactiveCN106939342AGood typingSpeed up breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTypingAssistive technology
The invention discloses SNP markers linked with the color of husked millet. The SNP markers comprise a marker HC-06-436 and a marker HC-06-250, wherein the marker HC-06-436 is located at the site 34024436 bp of the sixth chromosome of millet and the marker HC-06-250 is located at the site 34035250 bp of the sixth chromosome of millet. The invention also discloses amplimers for acquiring the SNP markers and application of the SNP markers. The SNP markers linked with the color of husked millet and the amplimers thereof can realize good typing of the color of husked millet and detection of SNP differences, are applicable to molecular marker-aided breeding of the character of the color of husked millet, provide molecular assistive technology support for early identification of the character of the color of husked millet and for screening and breeding, and are of important theoretical and practical guidance significance to acceleration of genetic breeding and improvement of millet varieties.
Owner:山西省农业科学院谷子研究所 +1
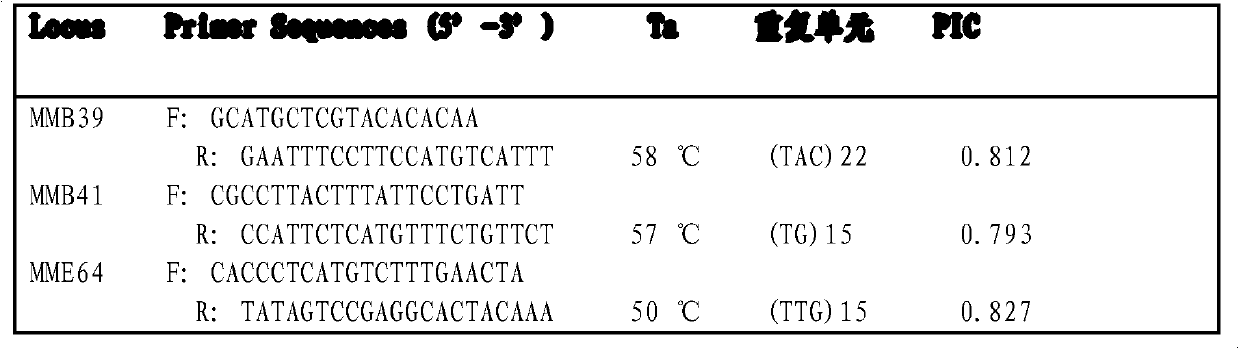
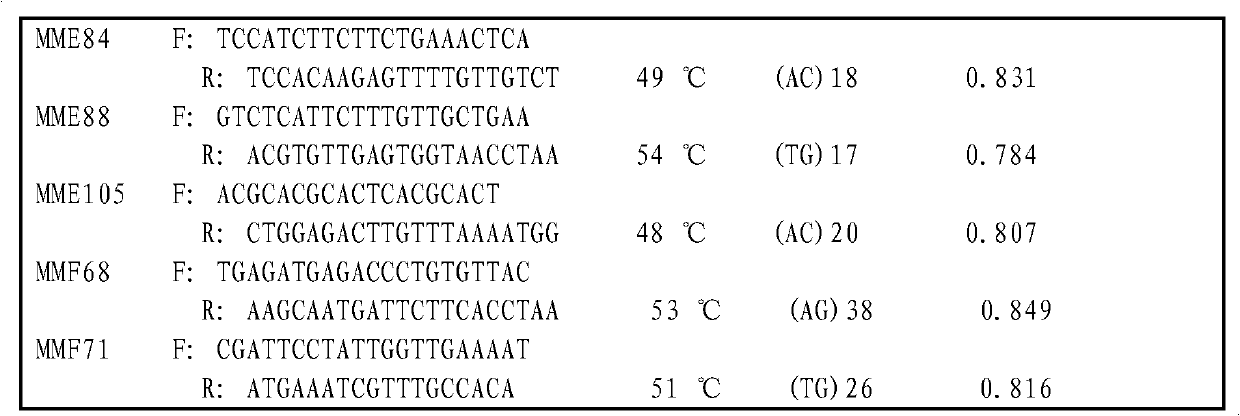
Microsatellite marking method applicable to parentage determination of hard clam
InactiveCN102719527AThe design principle is feasibleEasy to markMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic beadGenetics
The invention relates to a molecular assisted technology for genetic breeding, in particular to a microsatellite marking method applicable to parentage determination of hard clam. The microsatellite marking method comprises four steps of obtaining microsatellite loci source, designing a primer, optimizing the primer and establishing a microsatellite marker parentage determination system, and the specific process is as follows: firstly using a bead enriching library method to screen microsatellite sequences, and using a microsatellite retrieval software to carry out rapid separation of microsatellite fragments; designing a primer on a microsatellite repeated flanking sequence, optimizing the primer and leading the primer to become a microsatellite marker; then carrying out a comprehensive evaluation on repeatability, stability and polymorphism information content value during the amplification process of the microsatellite marker, and determining the microsatellite markers therein as the microsatellite parentage determination system of the hard clam for differentiation among different parentages of the hard clam or identification and determination among individuals. According to the invention, a molecular marking method for genetic breeding of the hard clam is provided.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
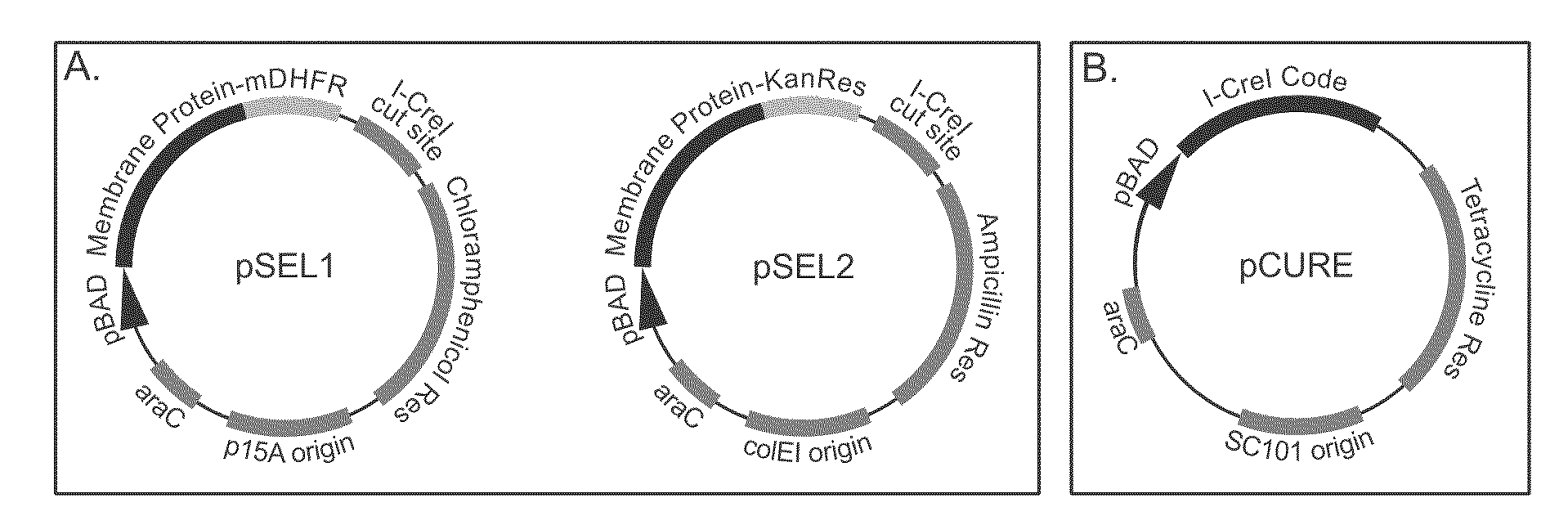
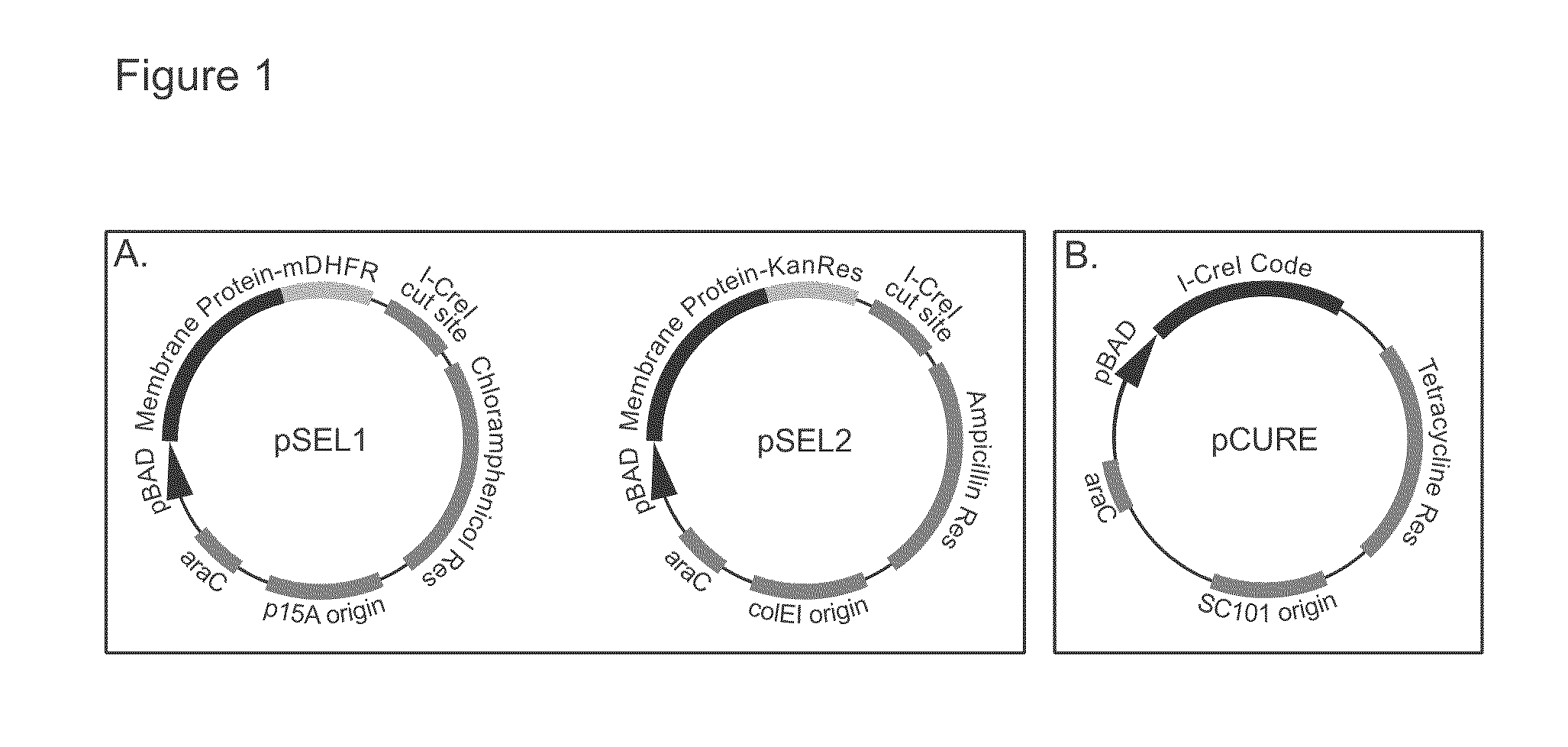
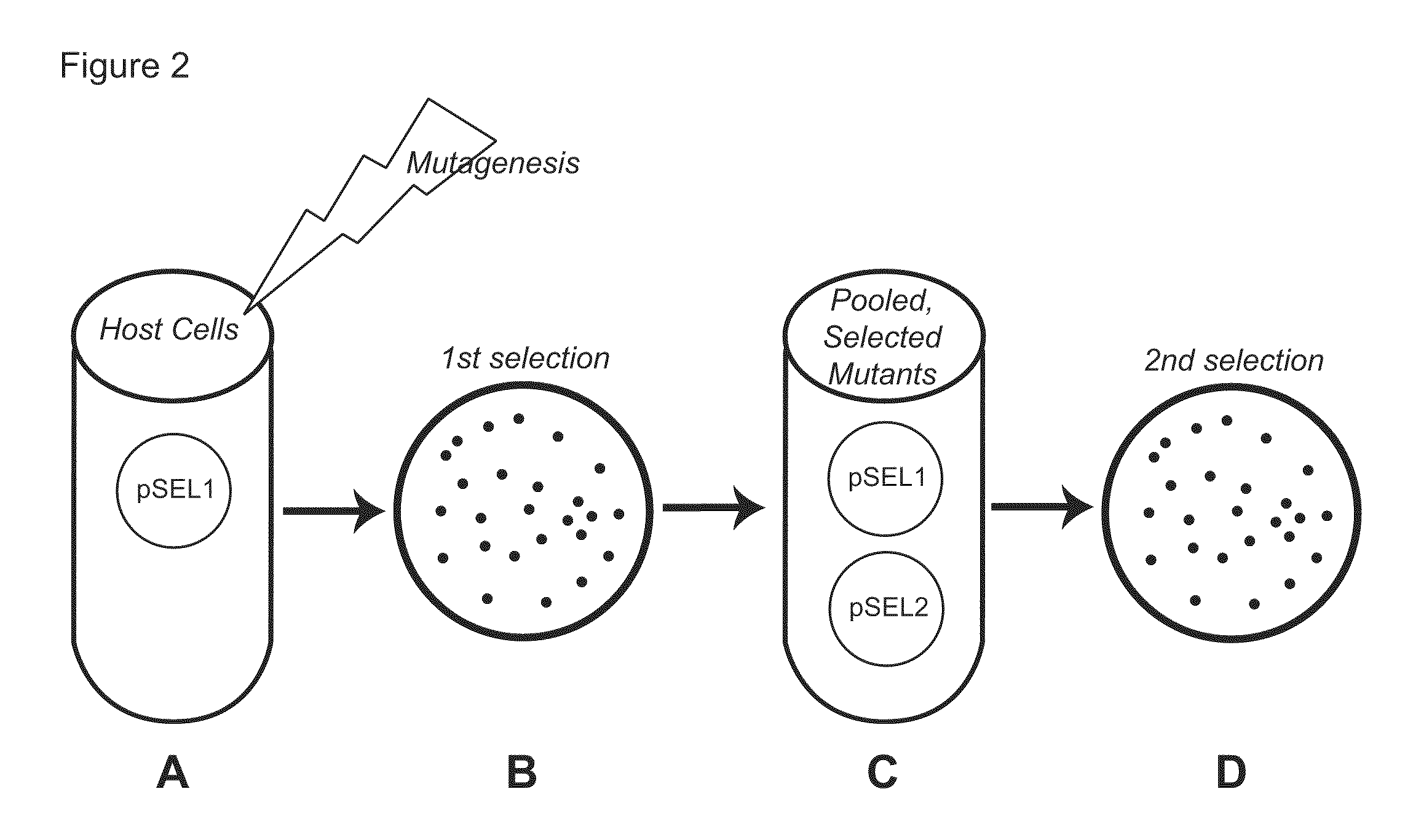
Genetic selection system for improving recombinant protein expression
InactiveUS20100099169A1Improve abilitiesImprove propertiesBacteriaMutant preparationProtein targetHost cell line
A method for selecting host cells with an improved ability to recombinantly overexpress a target protein; the host cells thus generated and their use. The invention also provides a curing method to remove plasmids from host cell lines.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Thermostable polymerases having altered fidelity and methods of identifying and using same
The present invention provides a method for identifying a thermostable polymerase having altered fidelity. The method consists of generating a random population of polymerase mutants by mutating at least one amino acid residue of a thermostable polymerase and screening the population for one or more active polymerase mutants by genetic selection. For example, the invention provides a method for identifying a thermostable polymerase having altered fidelity by mutating at least one amino acid residue in an active site O-helix of a thermostable polymerase. The invention also provides thermostable polymerases and nucleic acids encoding thermostable polymerases having altered fidelity, for example, high fidelity polymerases and low fidelity polymerases. The invention additionally provides a method for identifying one or more mutations in a gene by amplifying the gene with a high fidelity polymerase. The invention further provides a method for accurately copying repetitive nucleotide sequences using a high fidelity polymerase mutant. The invention also provides a method for diagnosing a genetic disease using a high fidelity polymerase mutant. The invention further provides a method for randomly mutagenizing a gene by amplifying the gene using a low fidelity polymerase mutant.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
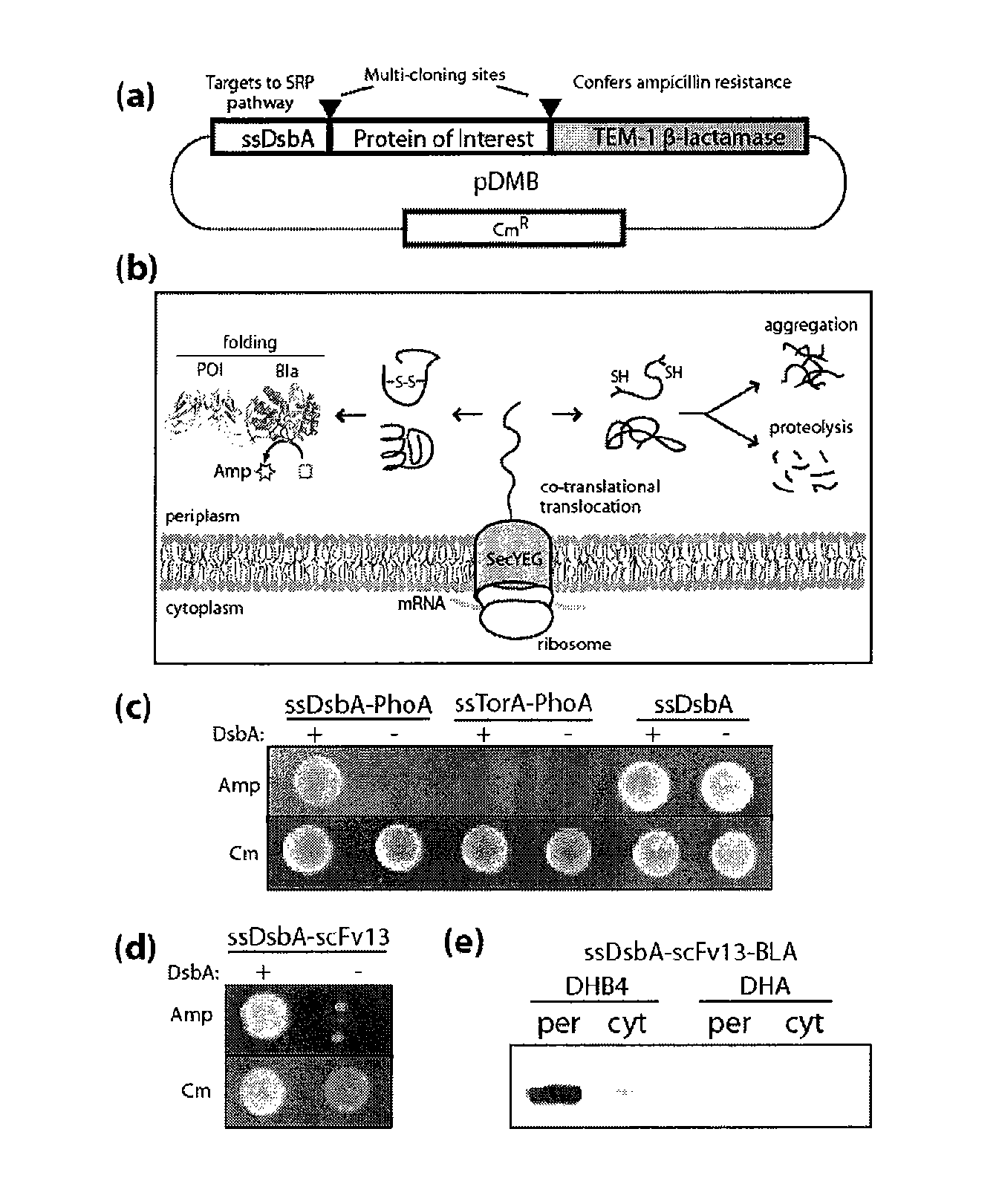
Genetic selection for protein folding and solubility in the bacterial periplasm
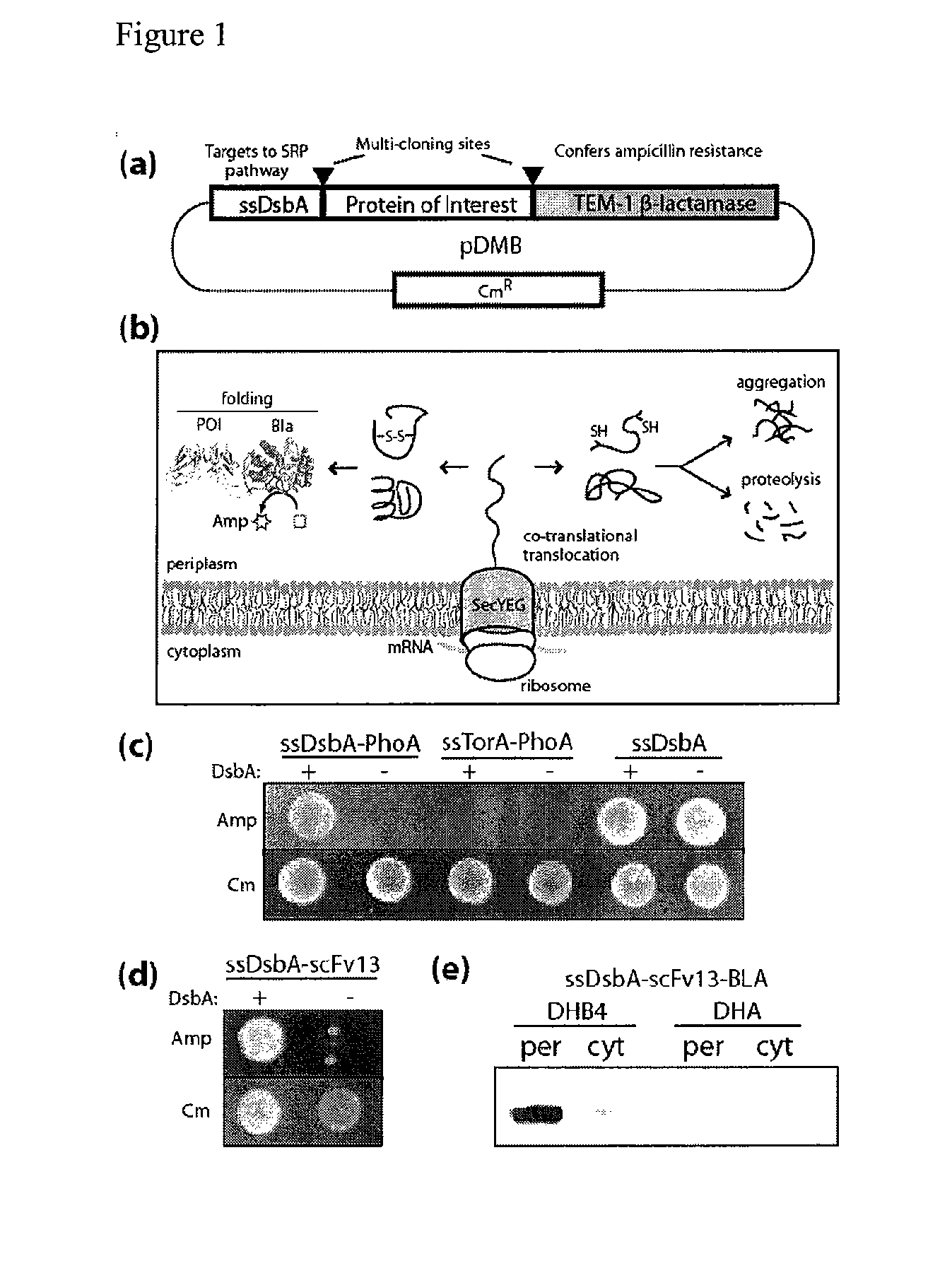
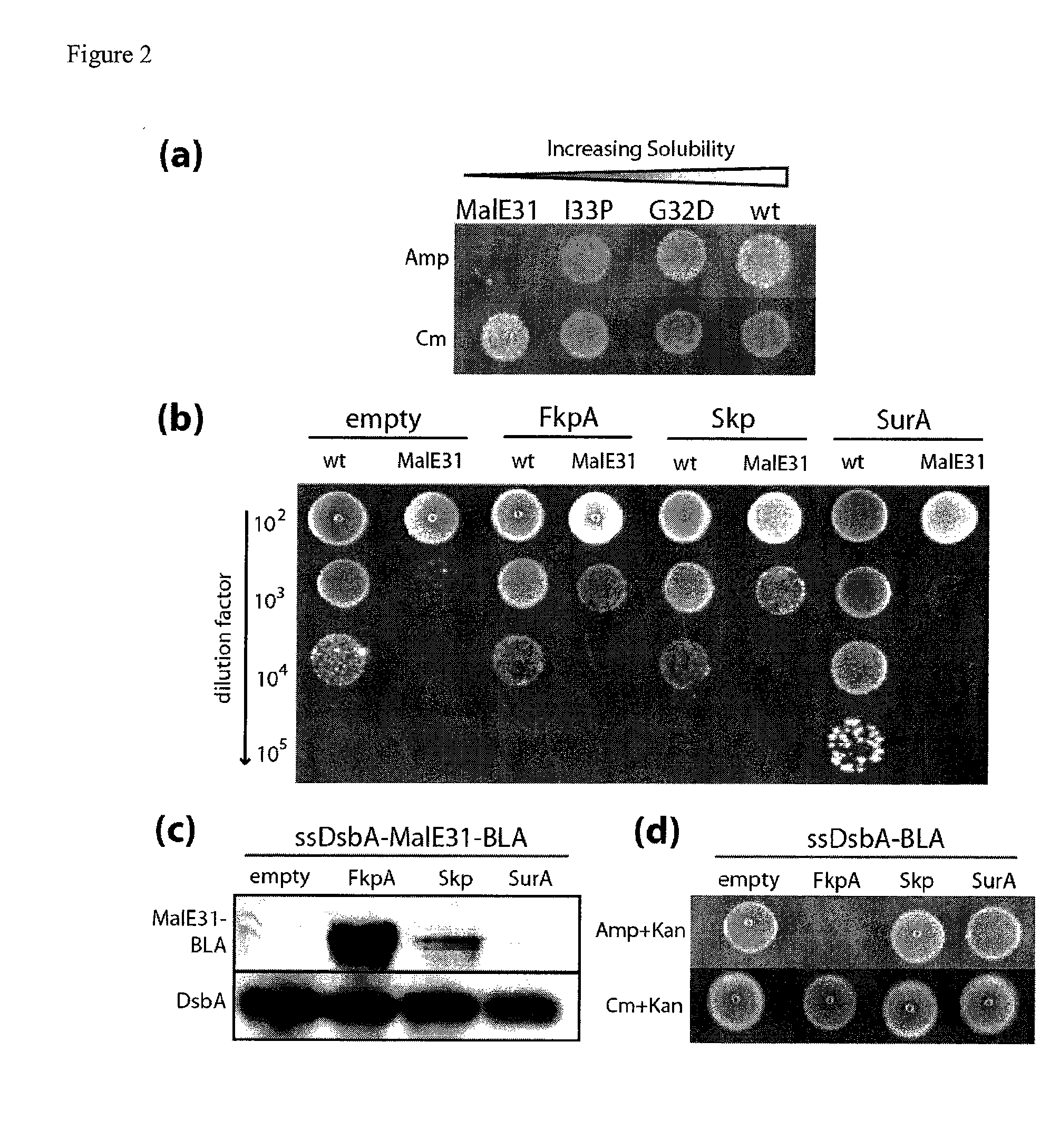
ActiveUS20100144546A1Sugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSignal recognition particleSolubility
The present invention relates to the fields of microbiology, molecular biology and protein biochemistry. More particularly, it relates to compositions and methods for analyzing and altering (e.g., enhancing or inhibiting) protein folding and solubility (e.g., within periplasm). The present invention provides an engineered assay for protein folding and solubility in the E. coli periplasm based on co-translational translocation of a chimera comprising a protein of interest fused to TEM-I β-lactamase that is targeted for export via the signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent pathway. Using an array of native and heterologous proteins, it is demonstrated that periplasmic folding behavior of proteins is intimately coupled to in vivo β-lactamase activity. As a result of this coupling, the reporter is useful for (1) facile discovery of extrinsic periplasmic factors that affect protein folding and solubility; and (2) genetic selection of solubility-enhanced proteins.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method For Genetic Selection Of High-Plasmid Producing E. Coli Clones
InactiveUS20090081681A1Increased IS insertional mutagenesisLow plasmid copy numberMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionProduction rateEscherichia coli
The present invention relates to methods of selecting for highly productive clones of E. coli for the production of plasmid DNA comprising measuring the frequency of IS1 transposon insertional mutagenesis within either the plasmid or genomic DNA of transformed clonal subtypes. An increase in IS1 insertional mutagenesis is correlated with clonal subtypes likely to exhibit a low specific productivity. The PCR-based, genetic selection assays disclosed herein are amenable to high throughput analysis, reducing the time to identify highly productive clones capable of cultivating large quantities of plasmid DNA on an industrial scale.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
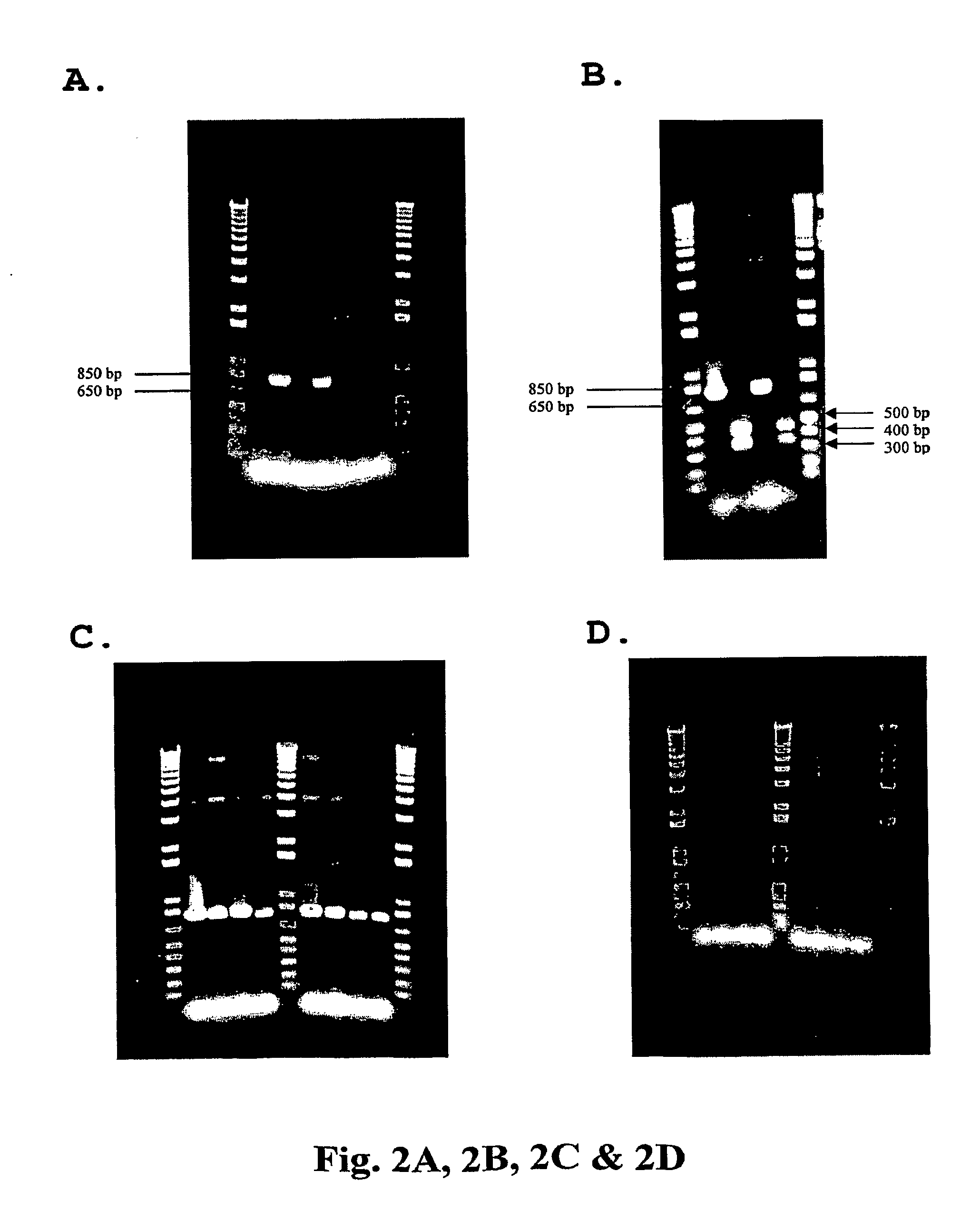
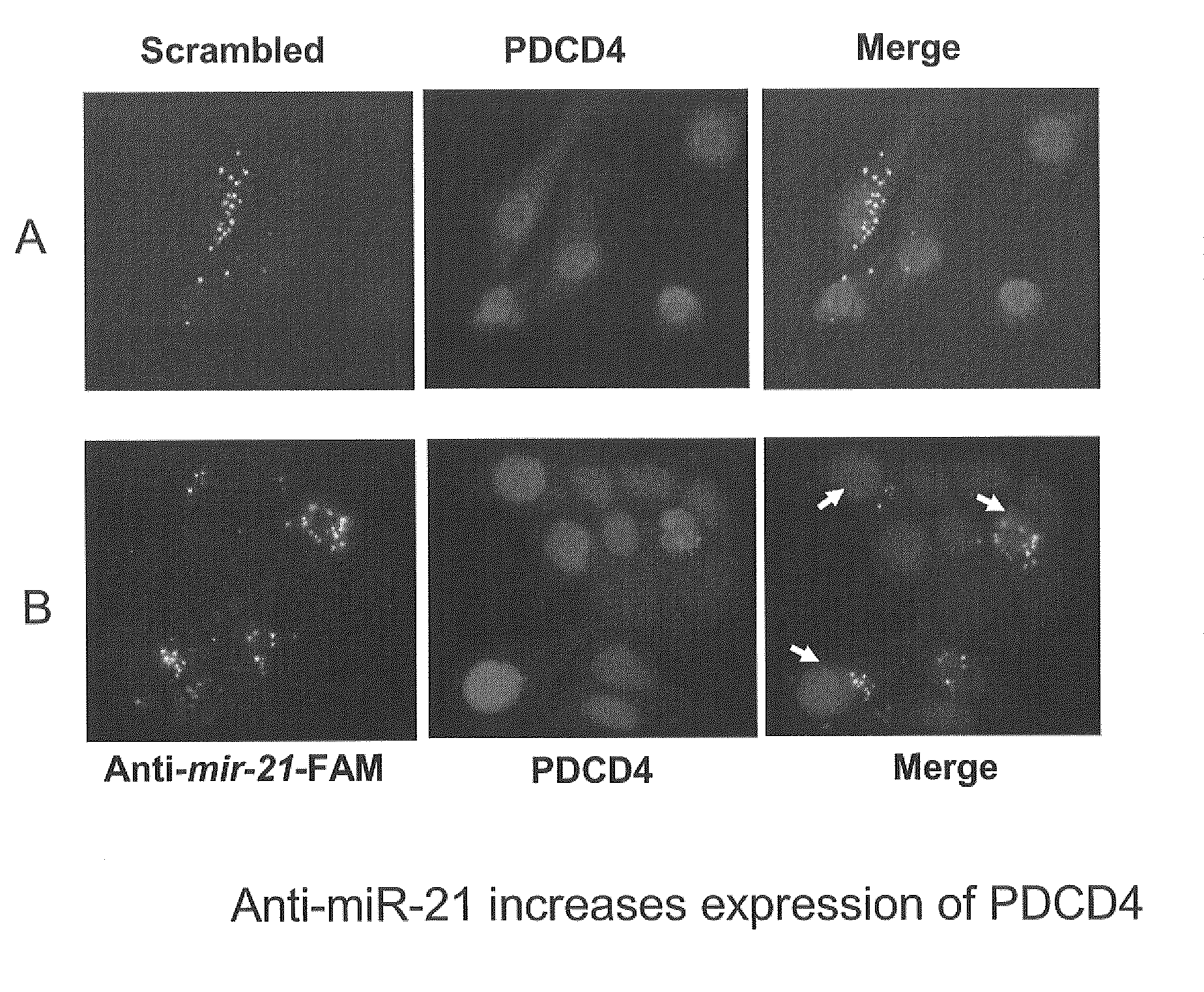
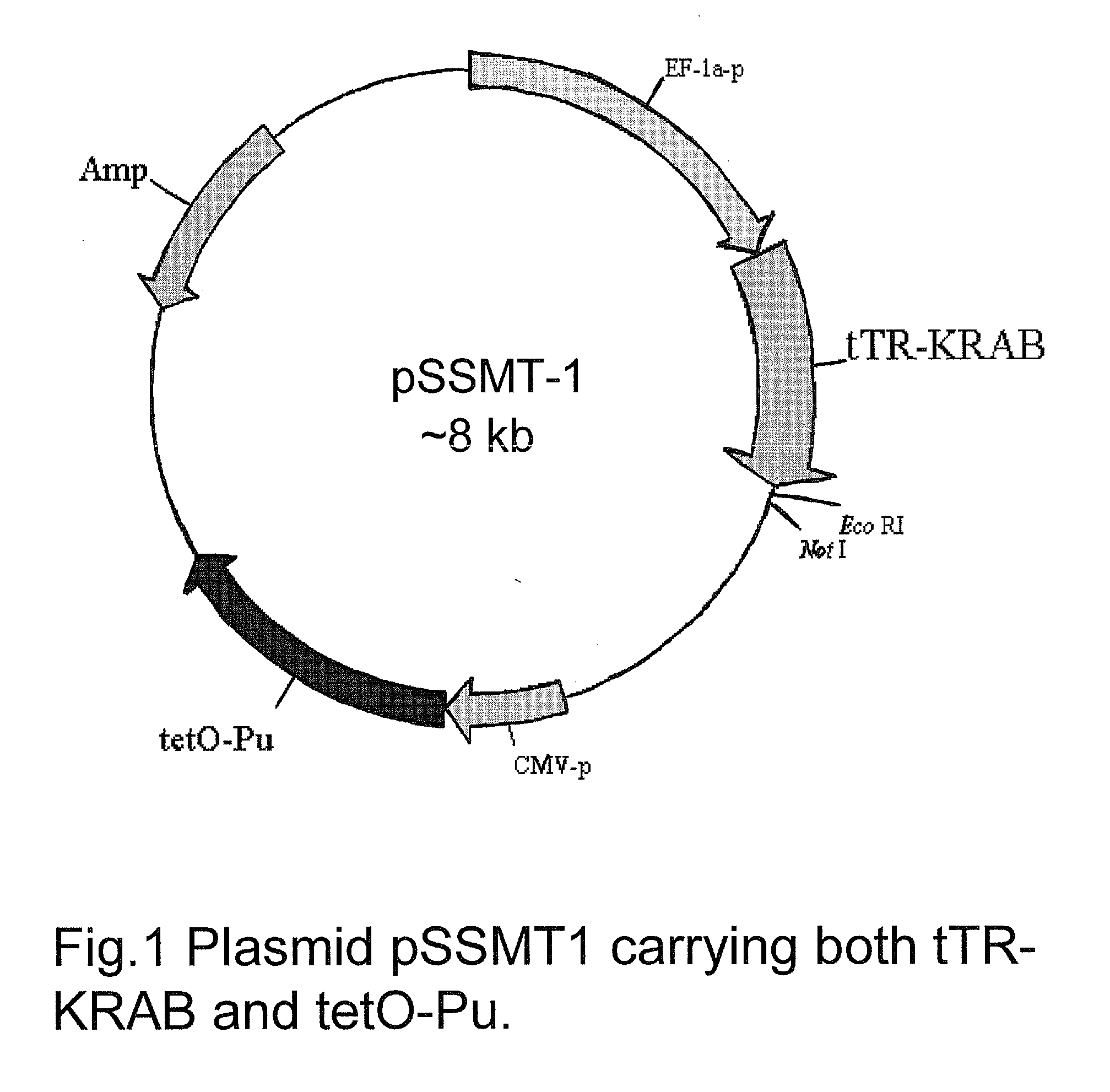
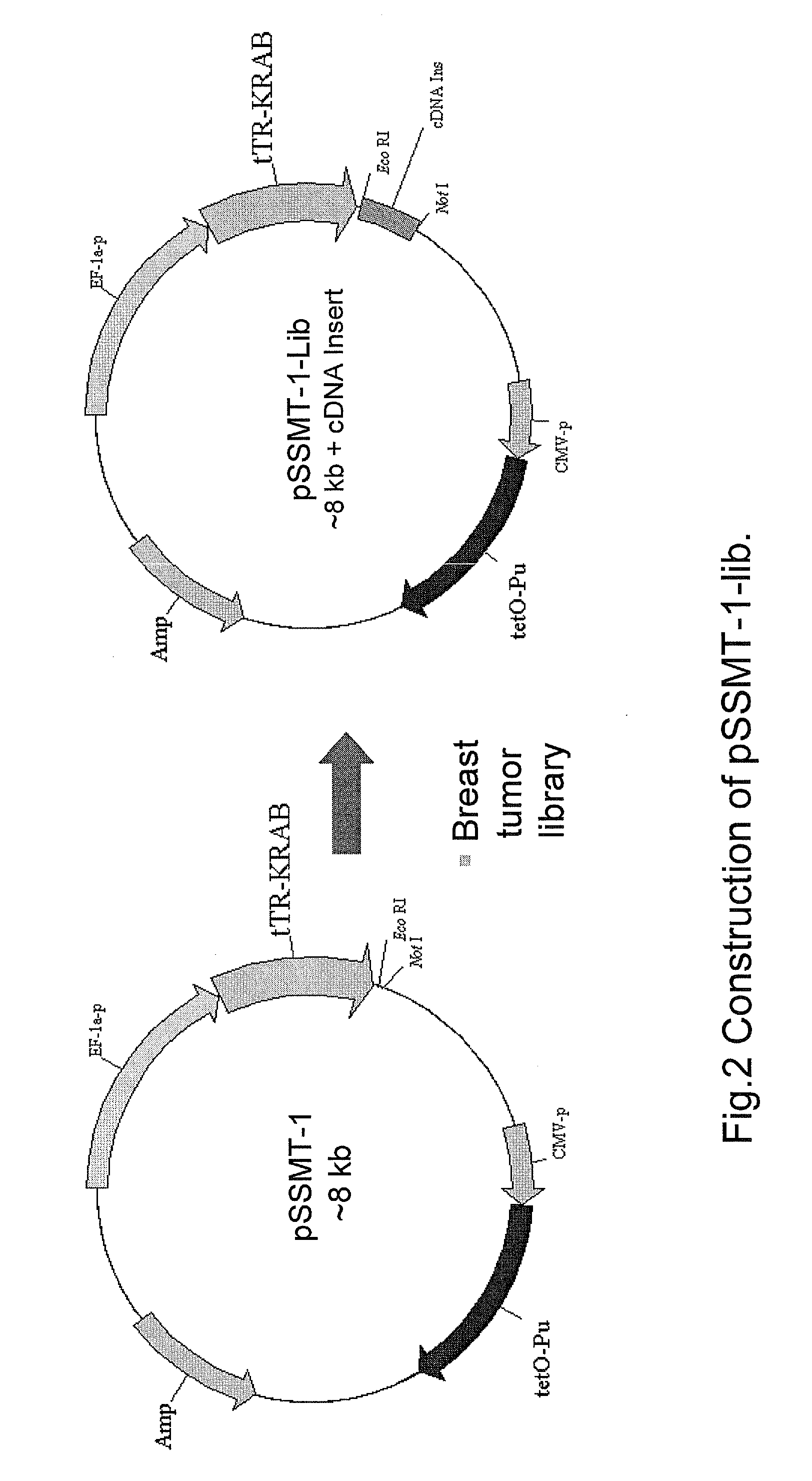
GENETIC SELECTION SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFICATION OF MicroRNA TARGET GENES
There is provided an expression cassette comprising a 3′-UTR cDNA library fragment, mammalian cells transfected with the expression cassette, and kits comprising the same. Furthermore, methods for identifying target genes for microRNAs are provided that utilize the expression cassette hereof.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Growth-related molecular marker in C-type scavenger receptor of Litopenaeusvannamei and application
ActiveCN109055580AImprove selection efficiencyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCandidate Gene Association StudyReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquatic breeding, and particularly relates to a growth-related molecular marker in a C-type scavenger receptor gene (LvSRC) of Litopenaeusvannamei and application thereof to genetic breeding of the Litopenaeusvannamei. A batch of markers related to shrimp growth traits are positioned in the genomic level through genome-wide association analysis, a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker (LvSRC-211-G / T) positioned in a coding region of the LvSRC gene is further screened through gene annotation and by a candidate gene association analysis method, and the genotype of the marker is significantly correlated to the shrimp growth traits (P is smaller than 10<-6>). The marker is positioned at a 211bp position on the LvSRC gene and belongs to G / Ttype mutation, and the GT genotype of the marker is a distinct growth-dominant genotype. The marker provided by the invention can be used as the shrimp breeding molecular marker for assisting in genetic selection of the shrimp growth traits.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
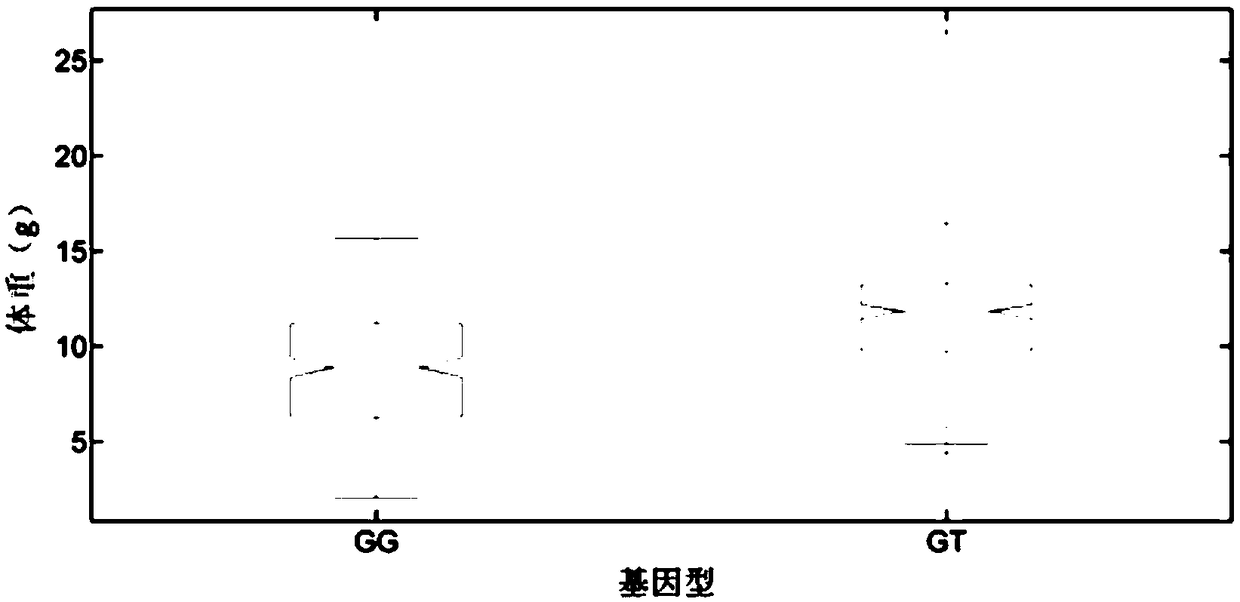
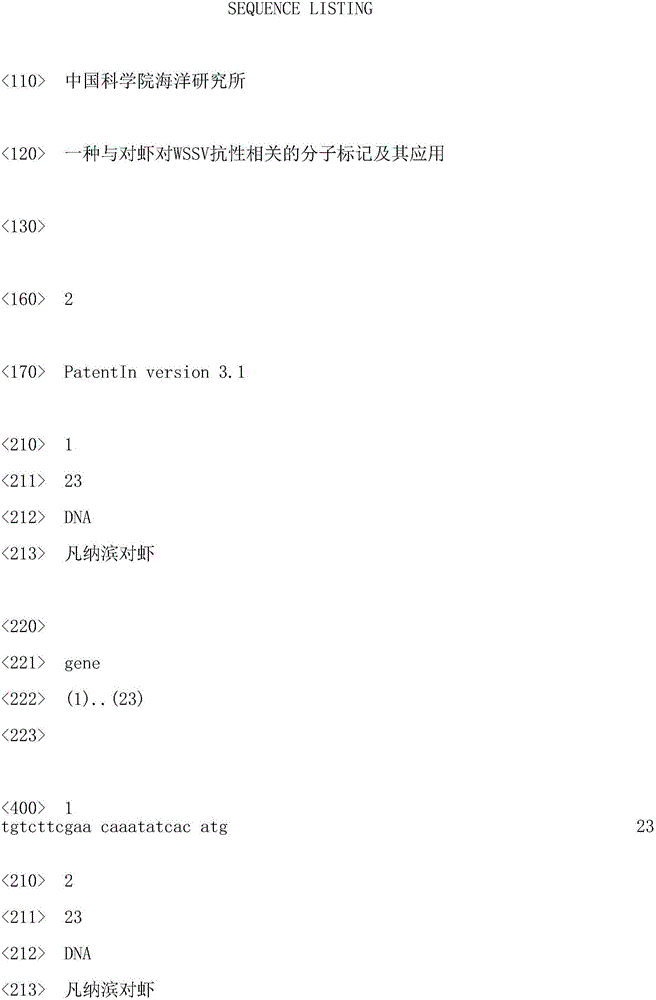
Molecular marker related to prawn WSSV resistance and application thereof
ActiveCN105821155ASolve the difficulty of choosingEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquatic organisms and particularly relates to a molecular marker related to prawn WSSV character resistance and application thereof. The molecular marker remarkably related to prawn WSSV character resistance is located at the 139 bp position of the DNA sequence SEQ ID TRAF 6g of the TRAF 6 gene and is A>G type mutation, a relation analysis method is utilized to identify that the locus is remarkably related to the prawn WSSV resistance character, gene frequency of the AA gene type in the resistance group is higher than that of a vulnerable group (p<0.05), and it is prompted that the AA gene type is a resistance advantage gene type. The marker can serve as the molecular marker for prawn disease resistance breeding and assists in selected genetic breeding of prawns.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
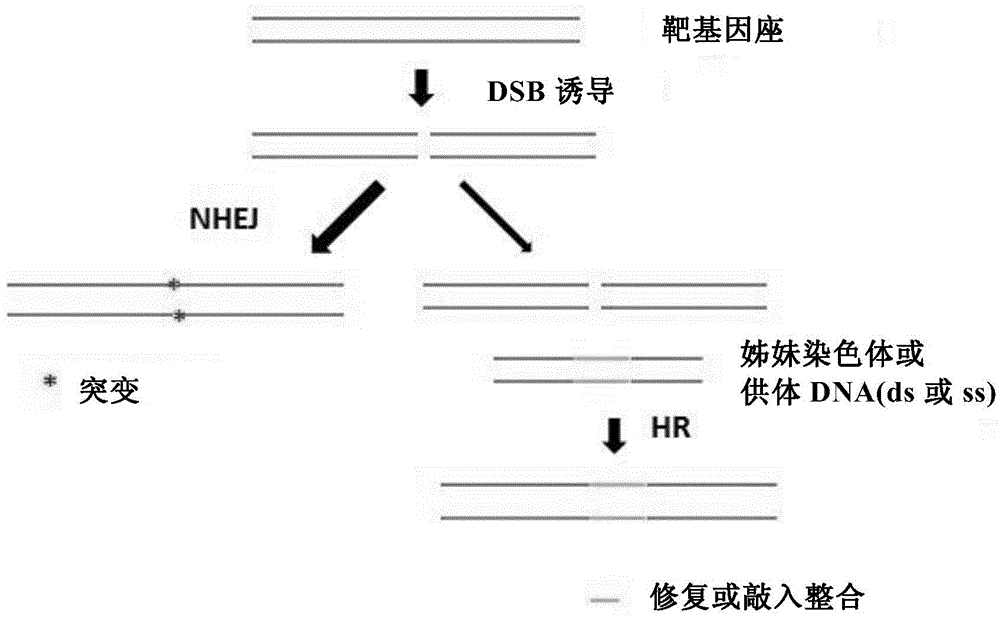
Insect targeted gene knock-in composition, use method and application thereof
ActiveCN105315352AImprove the efficiency of homologous recombinationDepsipeptidesGenetic engineeringNucleotideGenetically modified insect
The invention provides a composition used in insect targeted gene knock-in, which includes a single nickase or an encoding polynucleotide thereof; a recombinant factor or an encoding polynucleotide thereof; and optionally, a donor DNA of an exogenous gene. The invention also provides a corresponding gene knock-in method and a method for preparing transgenic insects. The composition and the method in the invention can achieve high-effective homologous recombination integration in insect cells and meanwhile can avoid the defects in gene knock-in technologies in the prior art. The composition also can stably and high-effectively achieve homologous recombination integration of a fragment being more than 10 kb in length in the insect cells, so that the composition can be used for transferring a genetic selection marker into the insect cells, preferably a visible genetic selection marker, which is convenient to determine strains of transgenic insects.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
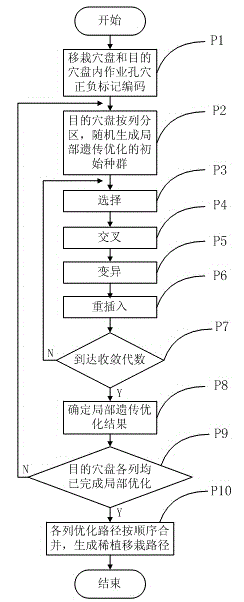
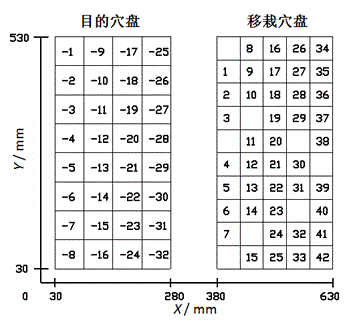
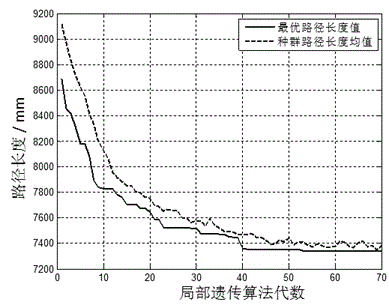
Greedy genetic algorithm-based pot seedling thin planting and transplantation path optimization method
The invention discloses a greedy genetic algorithm-based pot seedling thin planting and transplantation path optimization method. Health information of pot seedlings in a transplantation hole tray of a greenhouse pot seedling thin planting and transplantation machine is obtained through machine vision, and healthy seedling hole positions in the transplantation hole tray and empty hole positions in a target hole tray are subjected to label coding respectively; a greedy genetic selection principle is that the empty holes in the target hole tray are partitioned by column for carrying out current path optimization of a local genetic algorithm; the coding of a column of empty holes in the target hole tray is integrated with the coding of unplanned seedling holes in the transplantation hole tray, random path coding is generated, an initial population of the local genetic algorithm is formed, the selection, crossing, variation and reinsertion operations are circularly carried out until preset convergence generations, and individuals with maximum population fitness serve as local optimal paths; and the successive columns of planned local optimal paths are combined to generate a thin planting and transplantation path of the whole target hole tray. According to the method, an optimal path for greenhouse pot seedling thin planting and transplantation can be generated, the transplantation efficiency can be improved, and the real-time planning requirements of a control system are met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Construction method for Chlymys nobilis satellite mark
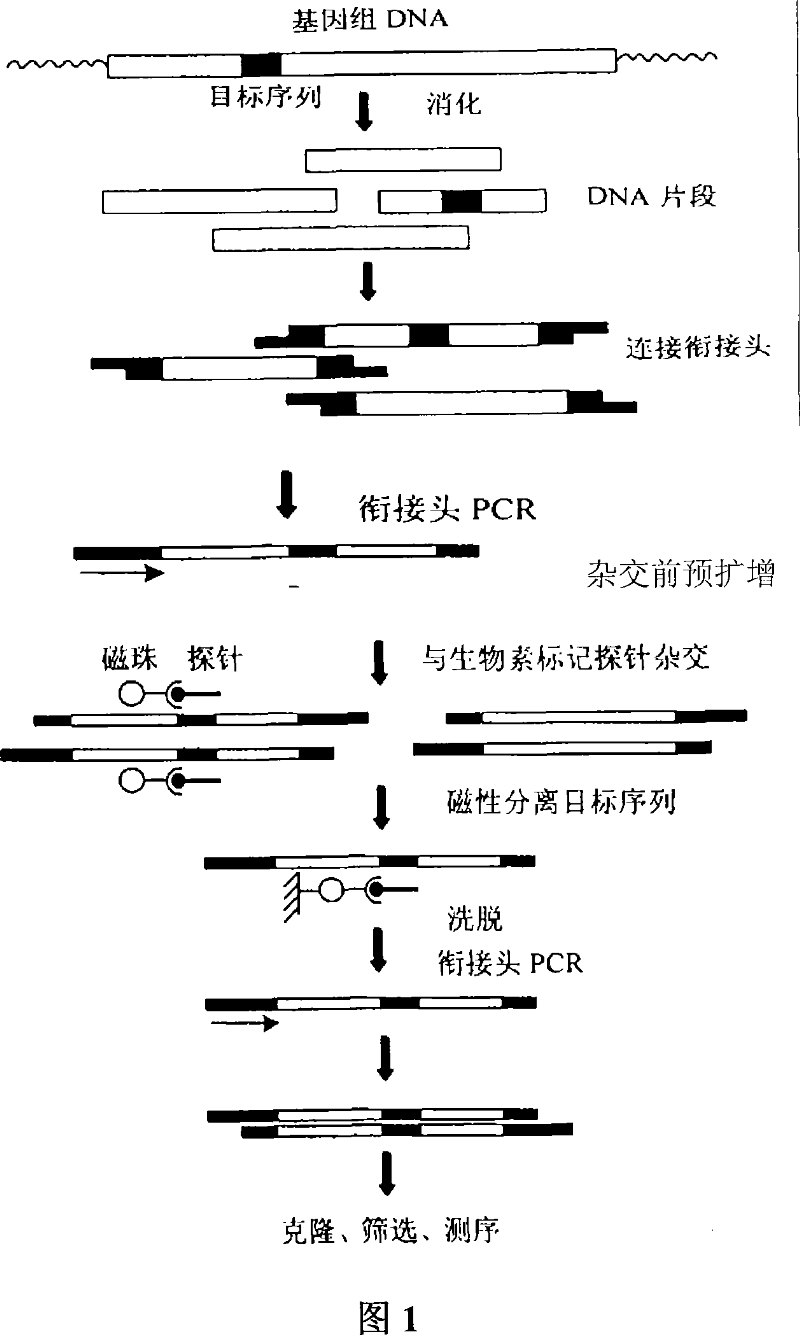
InactiveCN101041856AImprove build efficiencyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMagnetic beadMicrosatellite
The invention discloses a constructing method of micro-satellite marked scallop, which comprises the following steps: extracting DNA; connecting adapter cut by enzyme; preaugumenting before crossing; crossing to enrich micro-satellite sequence through micro-satellite marked by biotin and SAV magnetic bead; obtaining DNA segment with enriched micro-satellite sequence; augumenting the segment; constructing the enriched library with enriched micro-satellite sequence; utilizing PCR to sieve the micro-satellite sequence; obtaining the result of DNA sequence; comparing the quality of segment with enriched micro-satellite sequence; designing the primer of micro-satellite sequence; adopting PAGE to detect and sieve the augumentation, polymorphism and stability of micro-satellite; statisticallizing genetic parameter of corresponding group.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of generating pluripotent cells from somatic cells
InactiveCN101802172AGenetically modified cellsCell culture active agentsColony morphologyPluripotential stem cell
Disclosed herein are methods to select for the generation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cells during developmental reprogramming. The methods described herein relate to the selection of induced pluripotent stem cells, i.e., pluripotent stem cells generated or induced from differentiated cells without a requirement for genetic selection. Described herein are particular embodiments for selection of reprogrammed cells based on 1) colony morphology, or 2) X chromosome reactivation in female cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
SNP marker relevant to plant height character of millet, detection primers for SNP marker, and applications
ActiveCN108642201ASpeed up genetic selectionSpeed up the optimization processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationChromatophoreSnp markers
The invention discloses an SNP marker relevant to the plant height character of millet, detection primers for the SNP marker, and applications. For the SNP marker relevant to the plant height character of millet, the SNP marker is located in the bin markers of the 30703512bp to the 30784296bp of the first chromosome, and the SNP marker is in close linkage with the plant height of millet. The SNP marker relevant to the plant height character of millet can be used for the molecular marker-assisted breeding for the plant height character of millet, through the detection of the SNP marker, the plant height of millet can be predicated, a scientific basis is provided for realizing the early identification or screening breeding for the plant height character of millet, and great theory and practice guiding significance is achieved for accelerating the genetic breeding or improvement process of the varieties of millet. The primer pair for detecting the SNP marker provided by the invention canrealize typing on the plant height of millet and detect the differences of SNP expression.
Owner:ZHANGJIAKOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Genetic selection system to identify proteases, protease substrates and protease inhibitors
The present invention concerns a tester protein for identifying and / or monitoring protease activity in a cellular assay suitable for high throughput screenings by growth selection, wherein the tester polypeptide is a non-regulatory protein carrying a protease cleavage sequence. Upon co-expression of the protease recognizing said cleavage sequence the tester protein is inactivated, which influences the growth and / or survival of the host cells under the chosen conditions. However, in the presence of protease inhibitor the growth phenotype is reversed. The system can be used to identify proteases, protease inhibitors, and protease cleavage sites.
Owner:ONCALIS
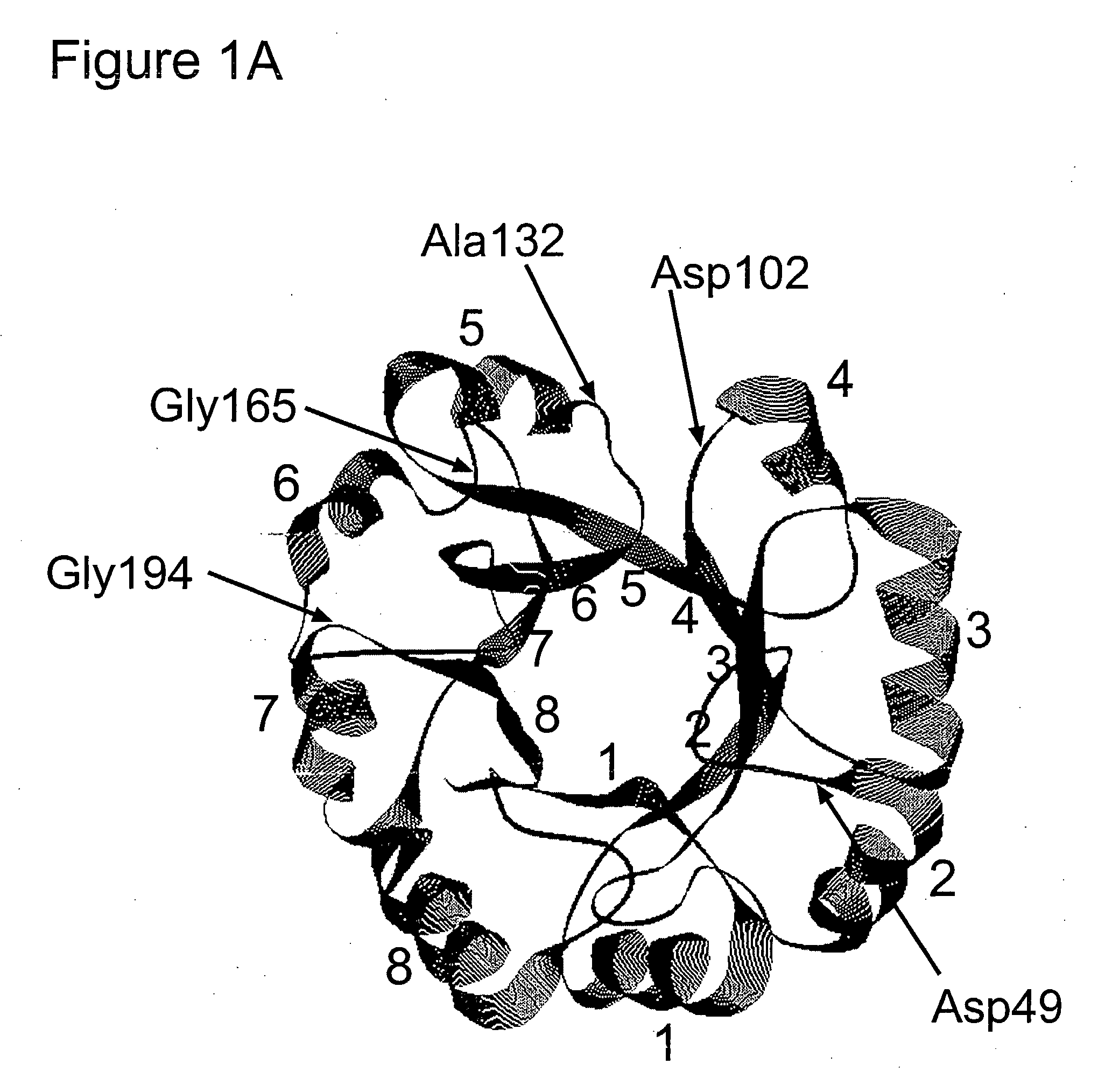
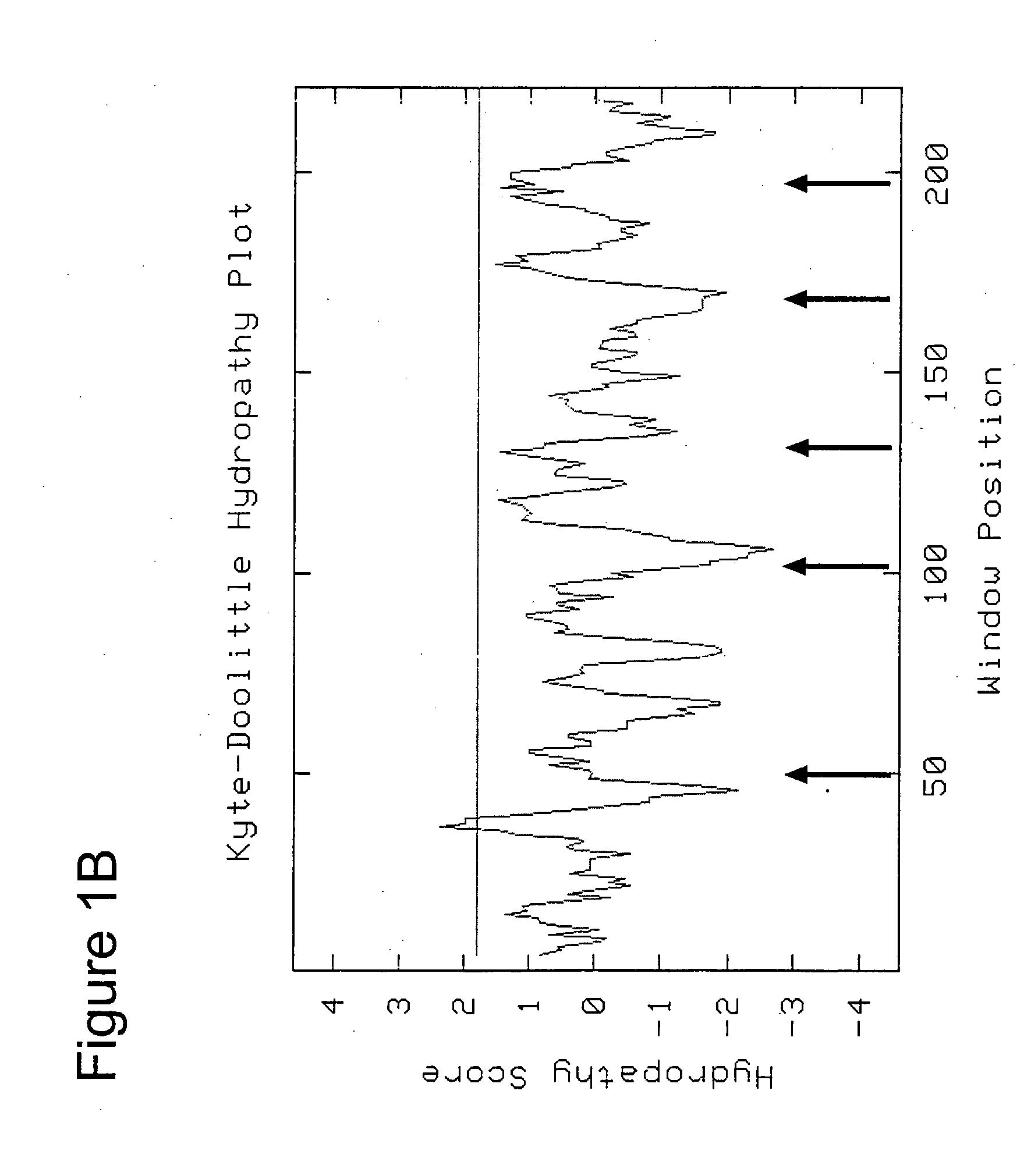
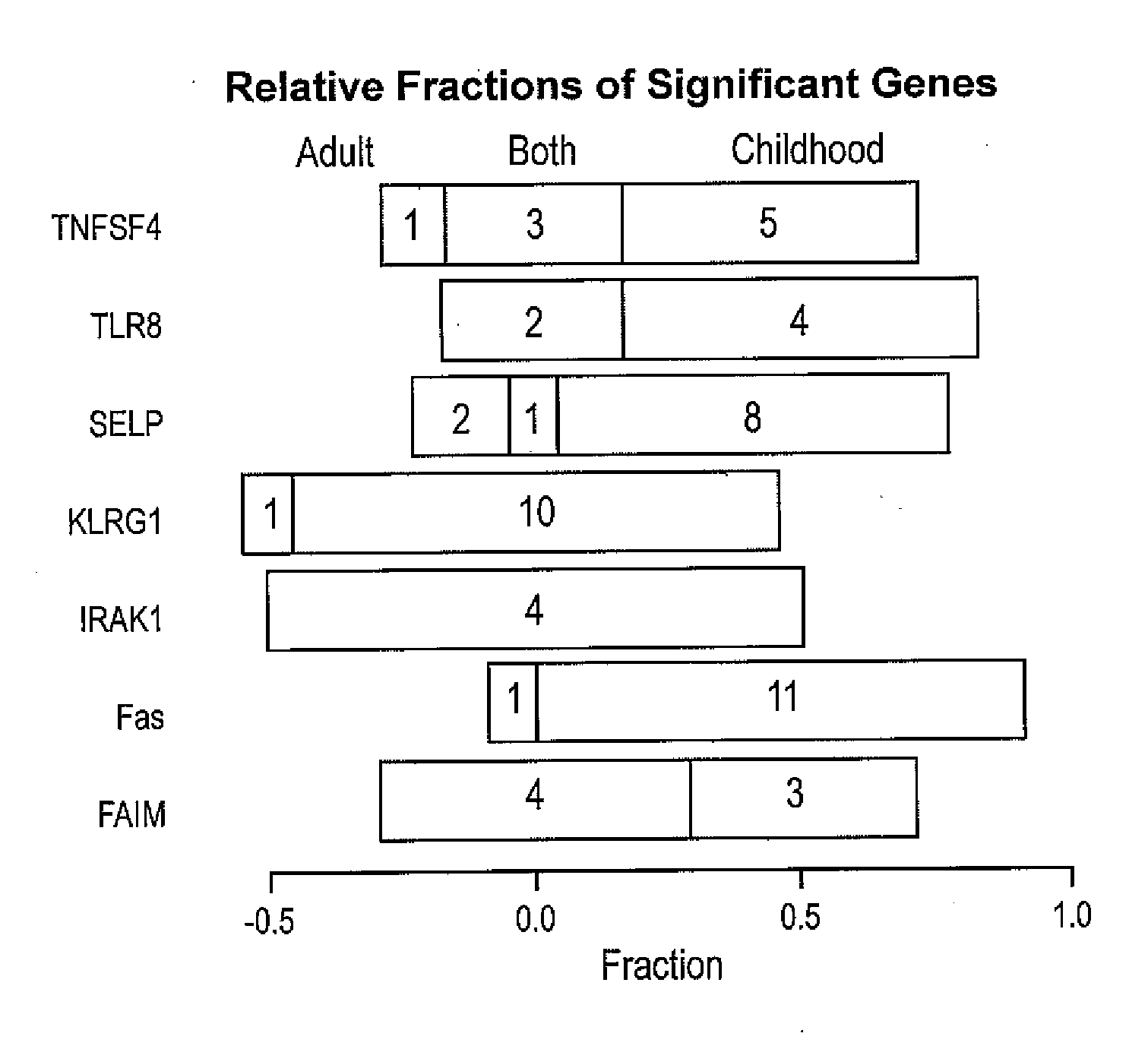
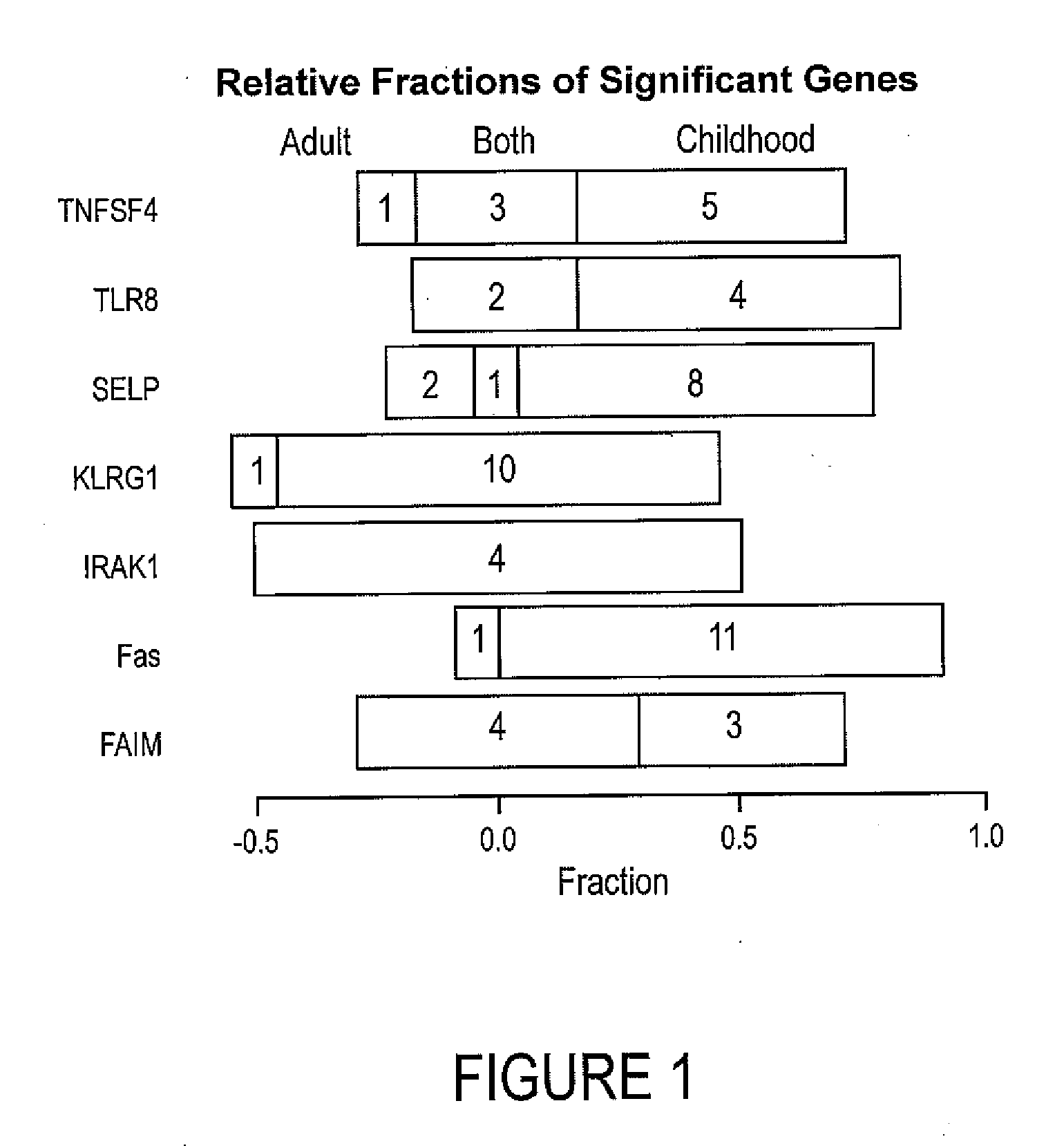
Autoimmune genes identified in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
The present invention relates to a genes and autoimmunity. More specifically, the invention relates to the identification of genes that are associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in children and / or adults. Also disclosed are methods for making and using the genetic selection tool used to identify SLE associated genes, and their uses in diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
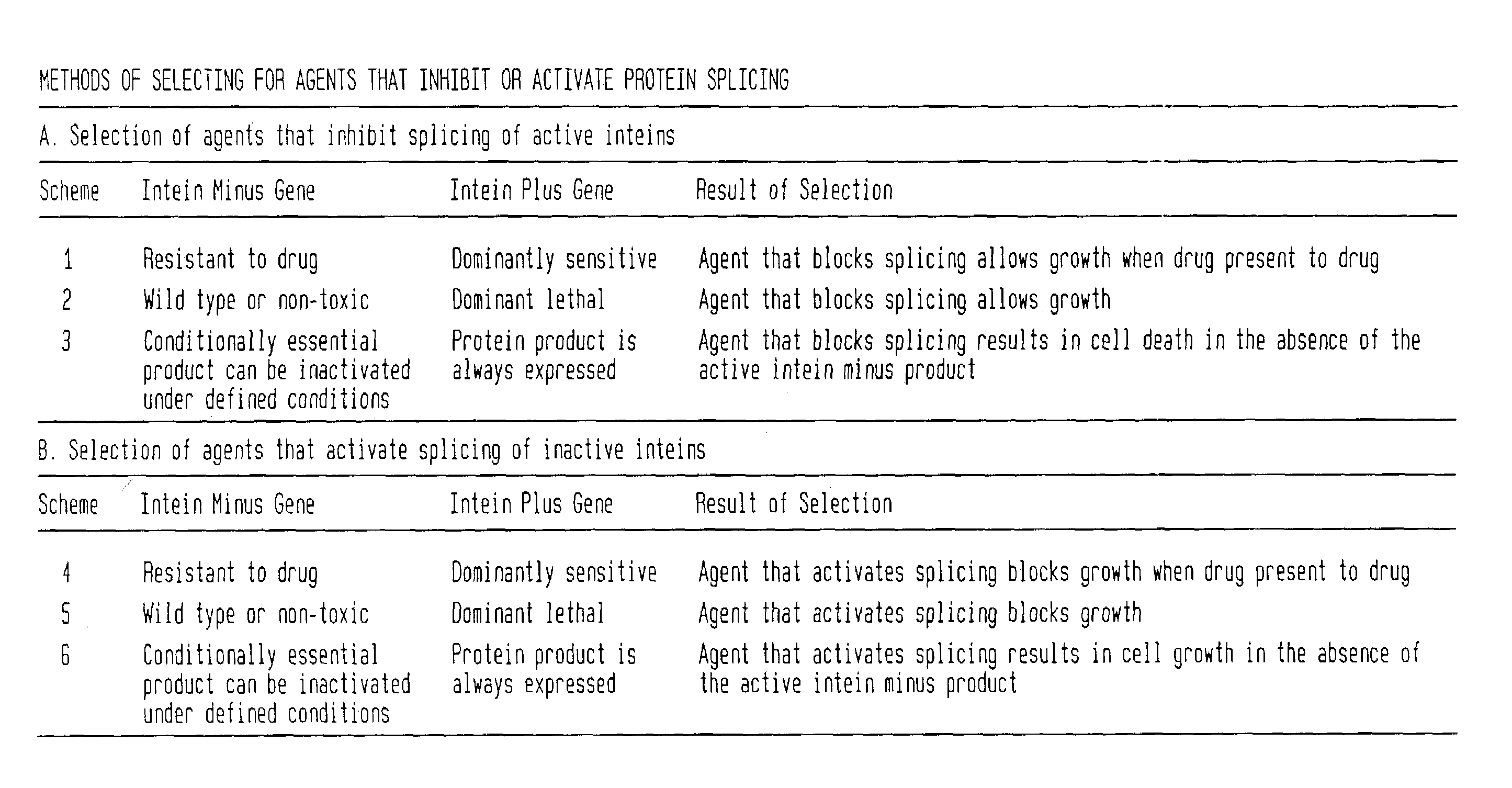
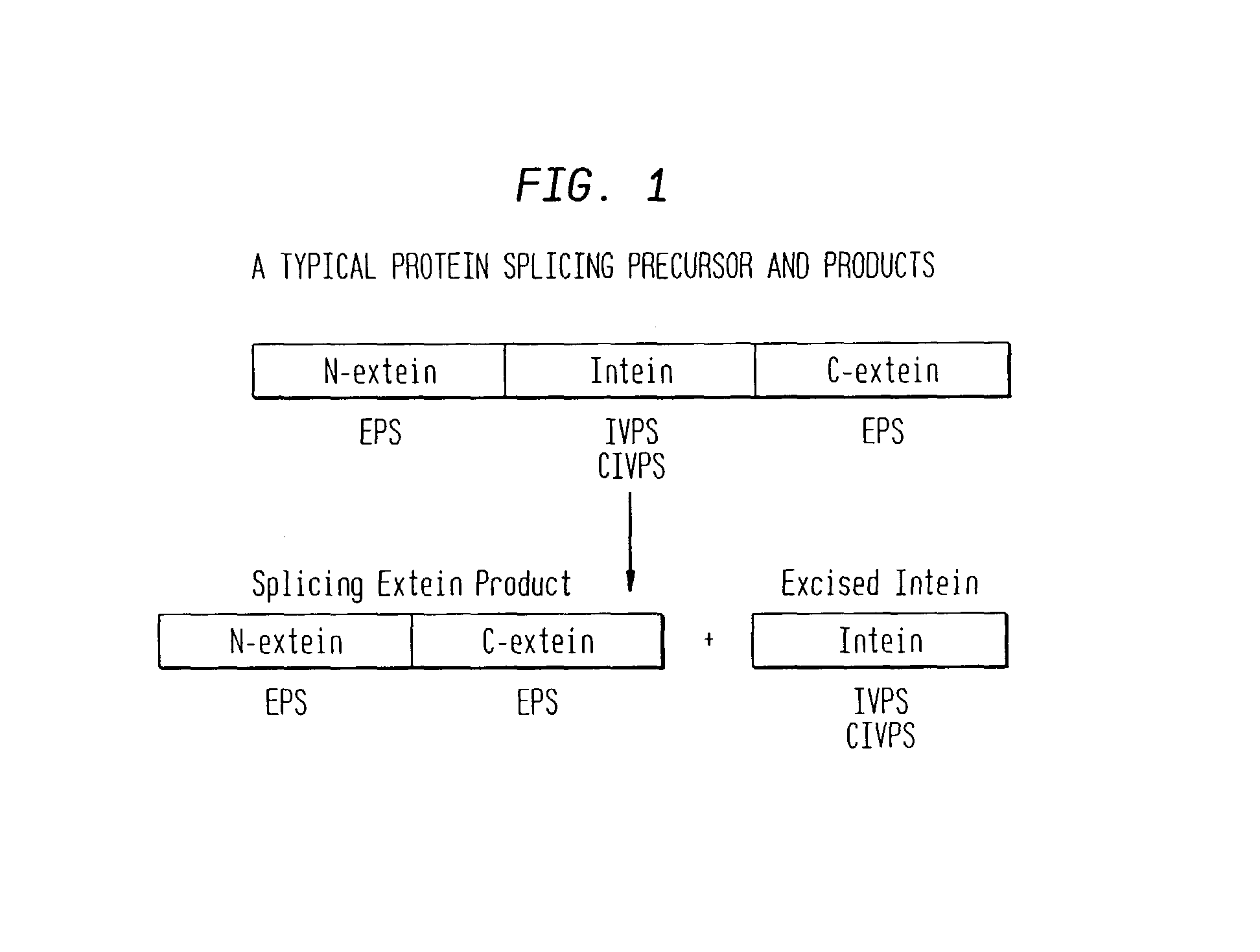
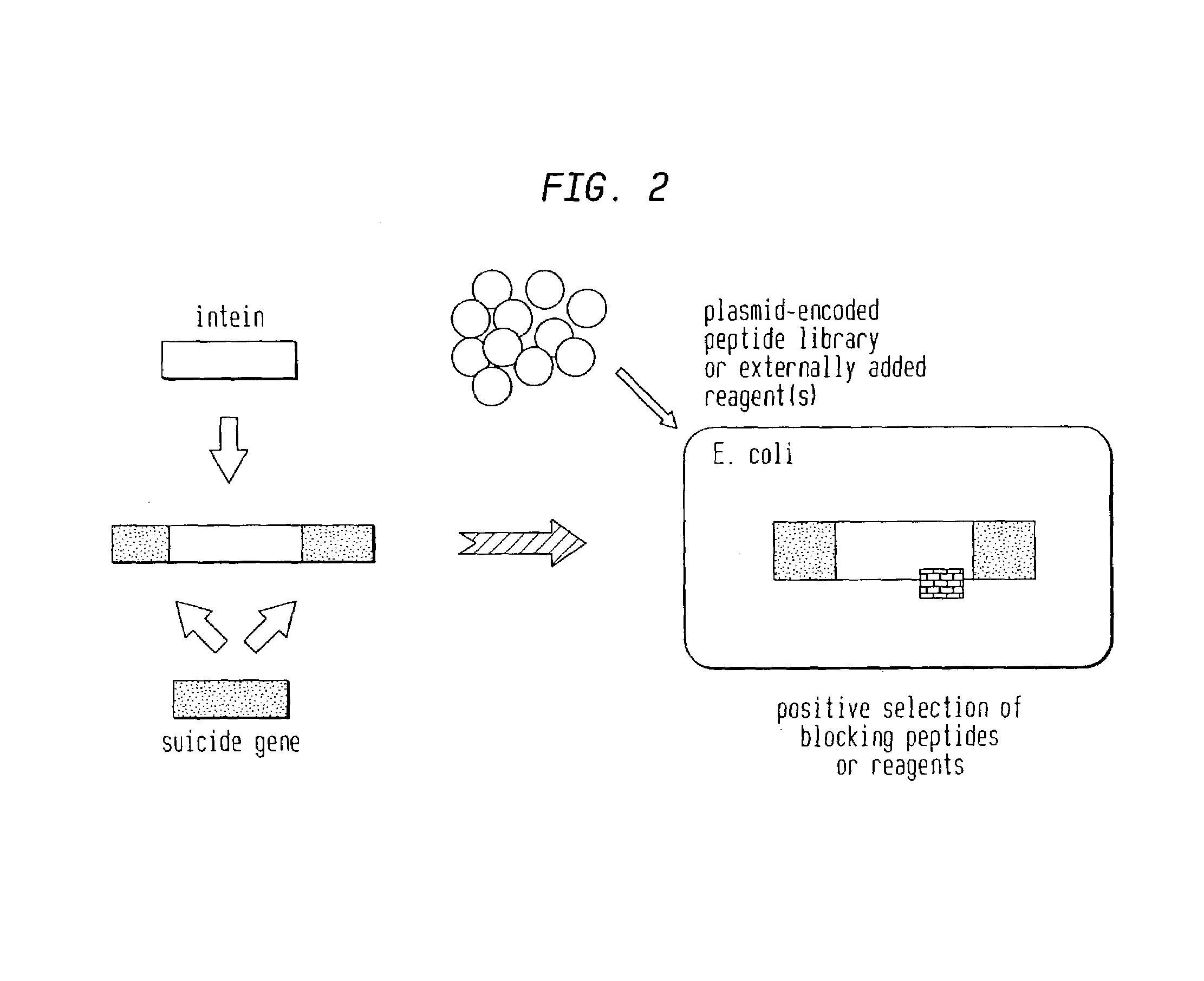
Screening and use of agents which block or activate intein splicing utilizing natural or homologous exteins
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided selection systems and methods for screening for agents that control splicing of inteins in their native host protein (extein) or in homologous exteins. Specifically, there are provided positive genetic selection systems for the screening of agents which inhibit or activate protein splicing which comprise: a host cell containing a chromosomal gene encoding either a drug-resistant form of a target enzyme or a wild-type target enzyme, and a plasmid-borne gene encoding either a drug-sensitive form of the target enzyme, which is dominantly cytotoxic upon interaction with the drug, or a dominantly cytotoxic form of the target enzyme. In these systems the plasmid-borne gene contains an intein, and the inhibition or activation of splicing of the dominant cytotoxic form of the target enzyme by a given reagent results in the survival or death of the host cell. More specifically, positive genetic selection systems which utilize the M. xenopi GyrA intein or M. tuberculosis DnaB helicase intein are provided. Similar reporter systems utilizing native or homologous exteins and systems utilizing controllable inteins are provided, as are methods of controlling in vivo expression of proteins by modulating protein splicing with inhibiting or activating agents, and methods of controlling the delivery of proteinaceous drugs in vivo by modulating protein splicing.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
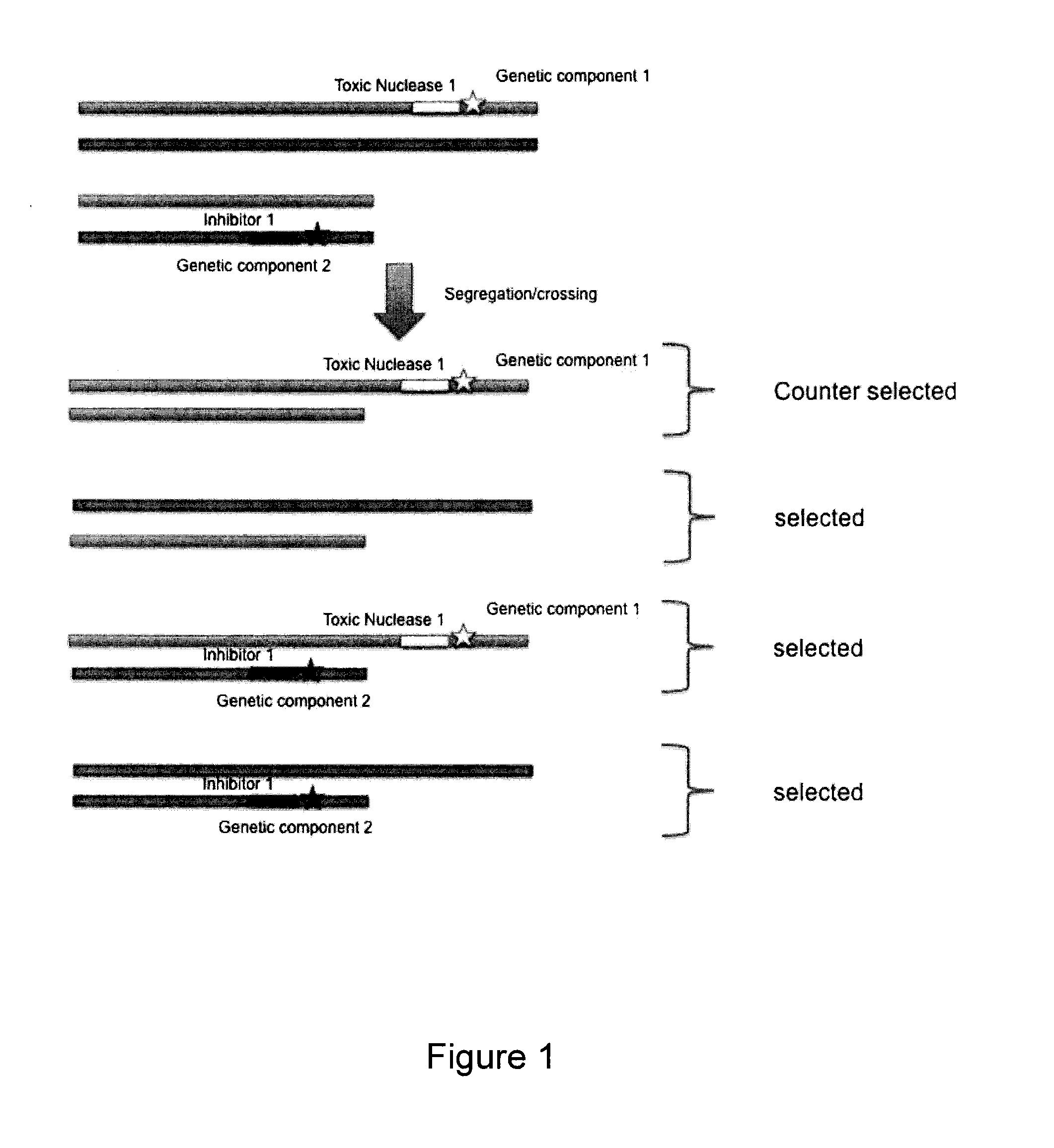
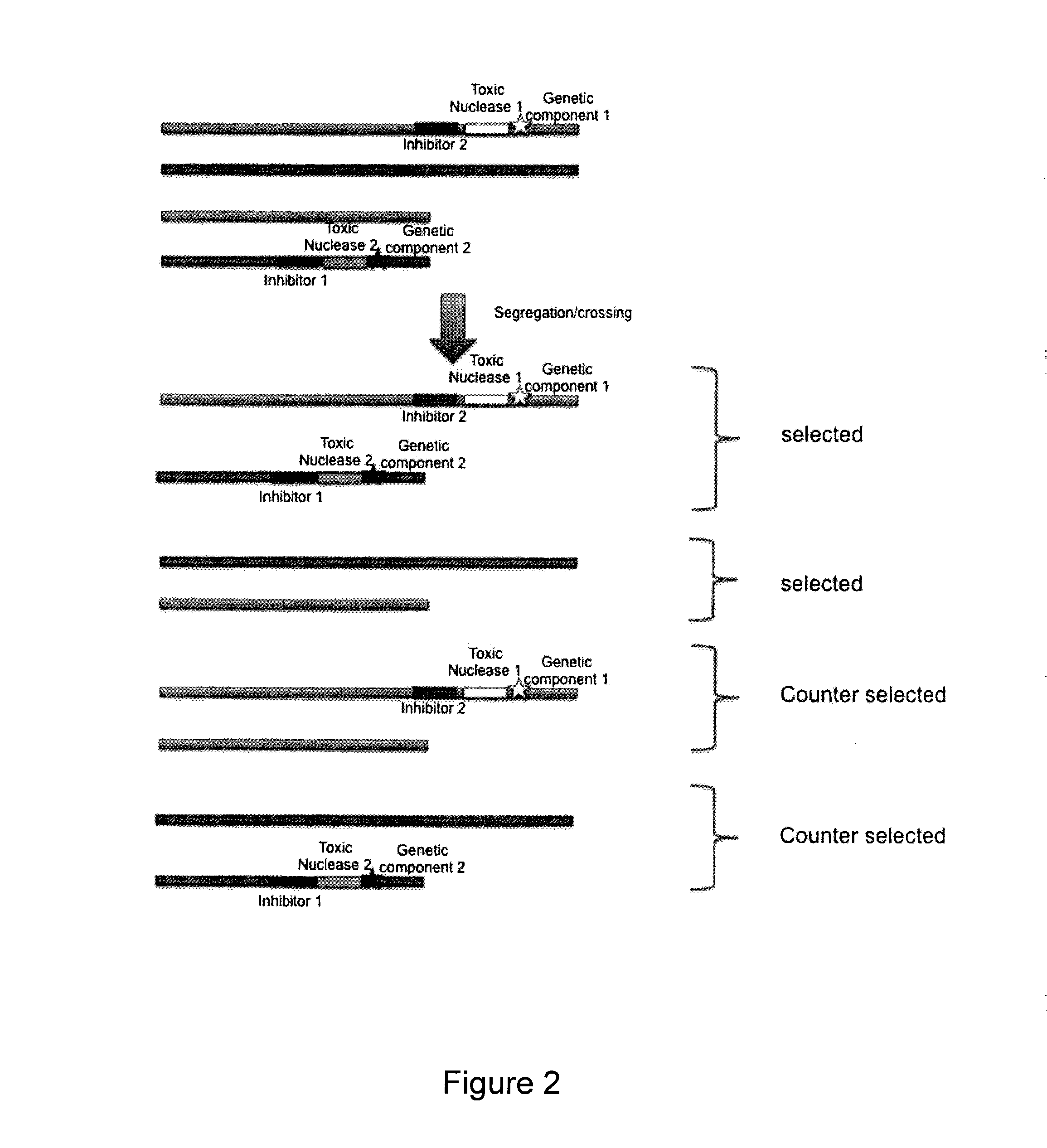
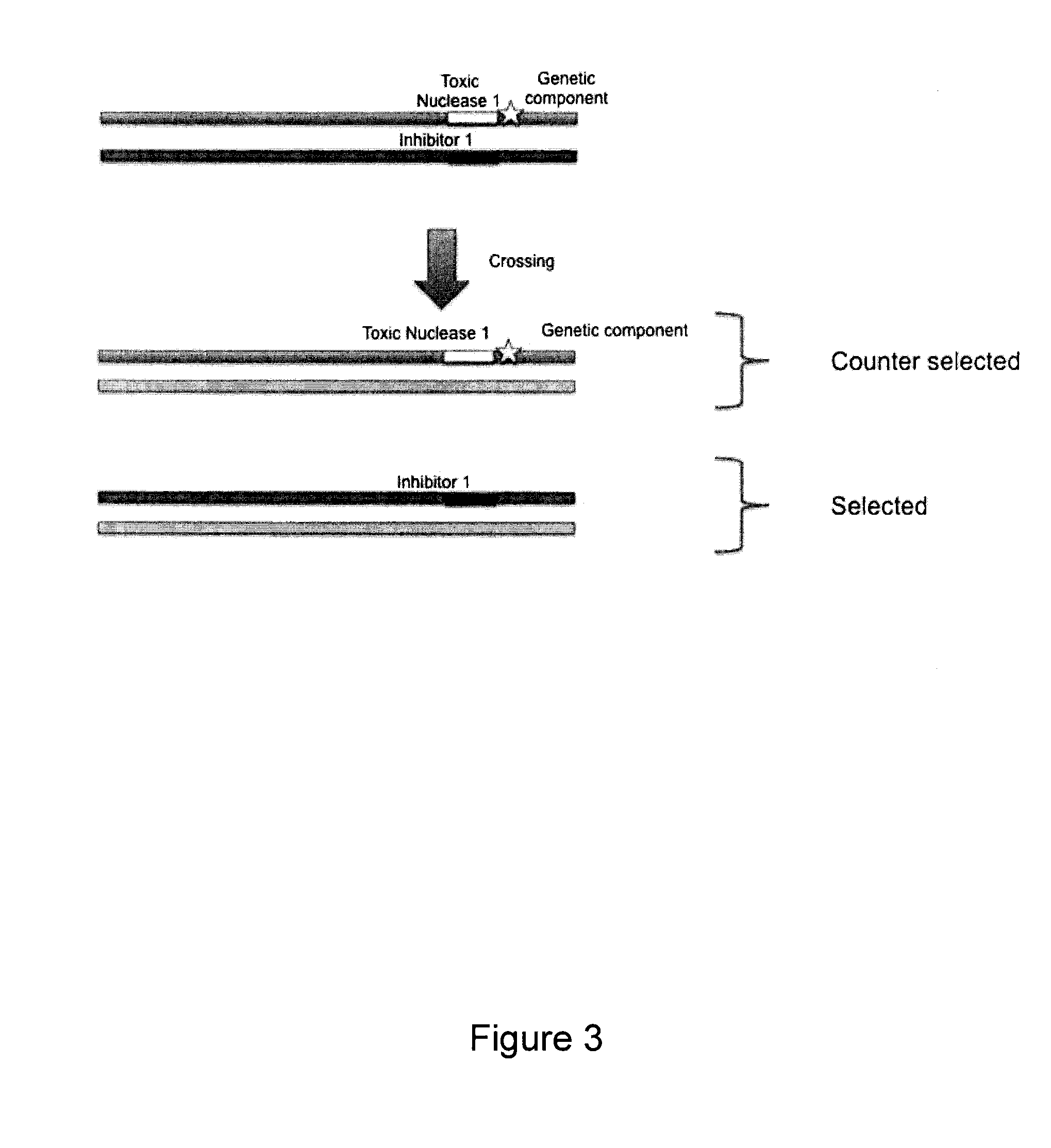
Method to counter-select cells or organisms by linking loci to nuclease components
InactiveUS20150353885A1Genetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsBiological bodyGenetic traits
The present invention relates to the field of genetic selection, where particular genetic traits or loci combinations are sought in a progeny resulting from genetic breeding. The invention provides genetic engineering solutions to select or counter-select the occurrence of genetic events.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
SNP marker related to foxtail millet plant height trait as well as detection primer and application of SNP marker
ActiveCN108715901ASpeed up the optimization processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceSnp markers
The invention discloses an SNP marker related to a foxtail millet plant height trait as well as a detection primer and application of the SNP marker. The SNP marker related to the foxtail millet plantheight trait provided by the invention is located in bin markers of 18022413bp to 21734440bp of a fourth chromosome; and the SNP marker is closely linked to the foxtail millet plant height. The SNP marker related to the foxtail millet plant height trait provided by the invention can be used for molecular marker-assisted breeding of the foxtail millet plant height trait, can predict the foxtail millet plant height by detecting the SNP marker, provides a scientific basis for early identification or screening breeding of the foxtail millet plant height trait, and has important theoretical and practical guiding significance for accelerating genetic breeding or improvement process of foxtail millet varieties; and primer pairs for detecting the SNP marker provided by the invention can classifythe foxtail millet plant height and detect difference in SNP expression.
Owner:ZHANGJIAKOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
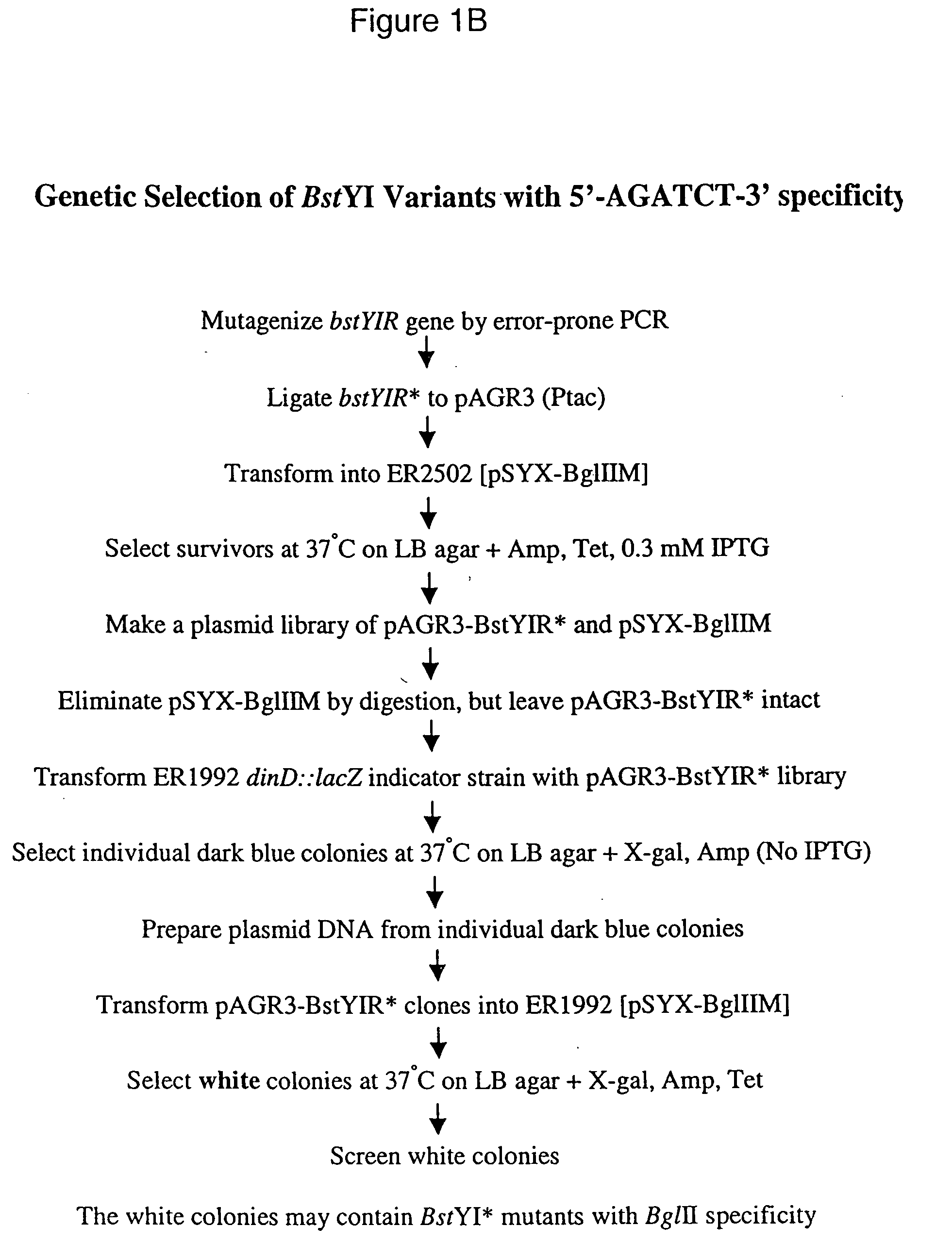
Alteration of restriction endonuclease specificity by genetic selection
InactiveUS20050164186A1Strong specificitySpecificity can be alteredHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDna recognitionSite specificity
Methods and compositions are provided for altering the DNA recognition and cleavage characteristics of an endonuclease without prior knowledge of the endonuclease's three-dimensional structure and / or amino acid residues responsible for activity and / or specificity. Methods include subjecting a mutagenized endonuclease gene library to a genetic selection in prokaryotic cells which tolerate the expression of mutated endonuclease and where the endonuclease is active and determining the altered recognition-site specificity for the endonuclease.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
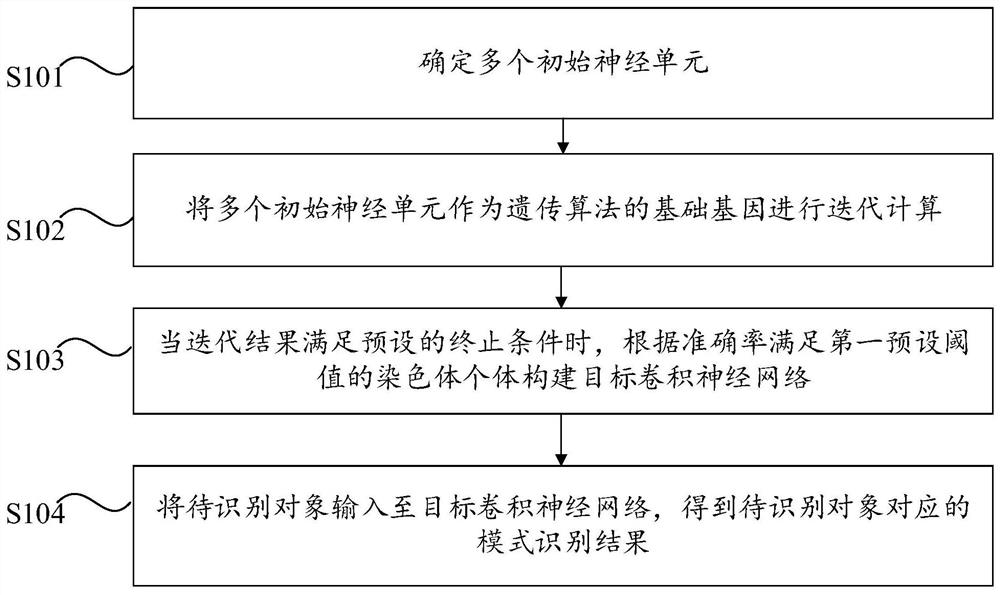
Pattern recognition method and device based on convolutional neural network and computer equipment
PendingCN111666991AImprove accuracyImprove generalization abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesGenetics algorithmsEngineering
The invention provides a pattern recognition method and device based on a convolutional neural network and computer equipment. The pattern recognition method comprises the following steps: determininga plurality of initial neural units; taking the plurality of initial neural units as basic genes of a genetic algorithm to perform iterative computation, wherein genetic selection is performed according to the accuracy of pattern recognition of chromosome individuals in an iterative process, and the higher the accuracy of pattern recognition of the chromosome individuals is, the lower the probability that the chromosome individuals are mutated and crossed; when the iteration result meets a preset termination condition, constructing a target convolutional neural network according to the chromosome individuals of which the accuracy meets a first preset threshold; and inputting the to-be-identified object into the target convolutional neural network to obtain a mode identification result corresponding to the to-be-identified object, wherein the pattern recognition result can be stored in a block chain. According to the pattern recognition method and device, the workload of workers in theprocess of constructing the convolutional neural network model can be reduced, and the efficiency of pattern recognition is improved.
Owner:深圳平安医疗健康科技服务有限公司
Method for detecting Hu sheep NSMF gene CNV marker and application of method
PendingCN112342301AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesPhysiology
The invention provides a method for detecting a Hu sheep NSMF gene CNV marker and an application of the method. The CNV marker refers to copy number variation in a Hu sheep NSMF gene candidate regionchr3: 545787-597706, Hu sheep genome DNA is used as a template, a normal double-copy gene ANKRD1 is used as a reference gene, partial fragments of Hu sheep NSMF genes and partial fragments of reference genes are respectively amplified through fluorescent quantitative PCR, and the Hu sheep individuals are divided into an increasing type, a missing type and a normal type according to the 2 * 2 <-delta Ct> quantitative result. The CNV marker closely related to the body length character of the Hu sheep is detected on the DNA level and applied to molecular marker-assisted selection of the growth character of the Hu sheep, so that the genetic breeding process of the Hu sheep is accelerated.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Molecular marker SIsv0456 closely linked to grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene
InactiveCN108660233AConducive to the establishment of assisted breeding systemEasy to set upMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceChromosome
The invention discloses a molecular marker SIsv0456 closely linked to a grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene. The SIsv0456 marker 500bp is located at 25842647-25843146bp site of the first chromosome of grain. The invention also discloses an amplification primer and an application of the SIsv0456 marker. According to the molecular marker SIsv0456 closely linked to the grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene and the amplification primer disclosed by the invention, the grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene can undergo good typing; the molecular marker is applicable to molecular marker assisted breeding of the grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene; molecular assisted technical support is provided for early identification and screening breeding of grain herbicide resistance traits; and the molecular marker has important theoretical and practical guiding significance for accelerating genetic breeding and improved progress of grain varieties.
Owner:深圳华大小米产业股份有限公司
SNP marker associated with foxtail millet flag leaf length characters and detection primers and application thereof
ActiveCN108707684ASpeed up genetic selectionSpeed up the optimization processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceSnp markers
The invention discloses an SNP marker associated with foxtail millet flag leaf length characters and detection primers and application thereof. According to the SNP marker associated with the foxtailmillet flag leaf length characters, the SNP marker is located between the bin marker of the 39221591th bp and the bin marker of the 39480016th bp of a second chromosome, and the SNP marker is closelylinked with the foxtail millet flag leaf length. The SNP marker associated with the foxtail millet flag leaf length characters can be used for molecular mark assisted breeding of the foxtail millet flag leaf length characters, through detection of the SNP marker, the foxtail millet flag leaf length can be predicted, a scientific basis is provided for achieving early identification or breeding of the foxtail millet flag leaf length characters, and it is of an important theory and practice guiding significance to accelerate genetic breeding or the improvement process of the foxtail millet varieties. By means of the primer pair for detecting the SNP marker, the foxtail millet flag leaf length can be somatotyped, and difference of SNP expressions can be detected.
Owner:ZHANGJIAKOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker SIsv0163 closely linked to grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene
InactiveCN108660230AConducive to the establishment of assisted breeding systemEasy to set upMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceTyping
The invention discloses a molecular marker SIsv0163 closely linked to a grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene. The SIsv0163 marker 609bp is located at 28478302-28478910bp site of the first chromosome of grain. The invention also discloses an amplification primer and an application of the SIsv0163 marker. According to the molecular marker SIsv0163 closely linked to the grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene and the amplification primer disclosed by the invention, the grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene can undergo good typing; the molecular marker is applicable to molecular marker assisted breeding of the grain imazethapyr-resisting herbicide gene; molecular assisted technical support is provided for early identification and screening breeding of grain herbicide resistance traits; and the molecular marker has important theoretical and practical guiding significance for accelerating genetic breeding and improved progress of grain varieties.
Owner:深圳华大小米产业股份有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com