Patents
Literature
313 results about "Prokaryotic cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The word ‘prokaryotic’ means ‘before nucleus’ and eukaryotic cells are thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells. Instead of DNA being enclosed in a nuclear membrane, as it is in eukaryotic cells, the DNA of prokaryotic cells is tightly coiled in a region of the cell called the ‘nucleoid’.
Improving sequence-specific antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair
The invention relates to the improvement of endonuclease-based antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair of double-strand break(s) (DSB(s)) in prokaryotic cells. In this respect, the invention especially concerns a method involving blocking DNA repair after a nucleic acid has been submitted to DSB, in particular by a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) associated programmable double-strand endonuclease. The invention particularly relates to the use of an exogenous molecule that inhibits DNA repair, preferably a protein that binds to the ends of the double-stranded break to block DSB repair. The invention also relates to vectors, particularly phagemids and plasmids, comprising nucleic acids encoding nucleases and Gam proteins, and a pharmaceutical composition and a product containing these vectors and their application.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Methods and compositions for extending the life span and increasing the stress resistance of cells and organisms
ActiveUS20050267023A1Increasing and extending life of cellStress resistantOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderOrganismNicotinamide
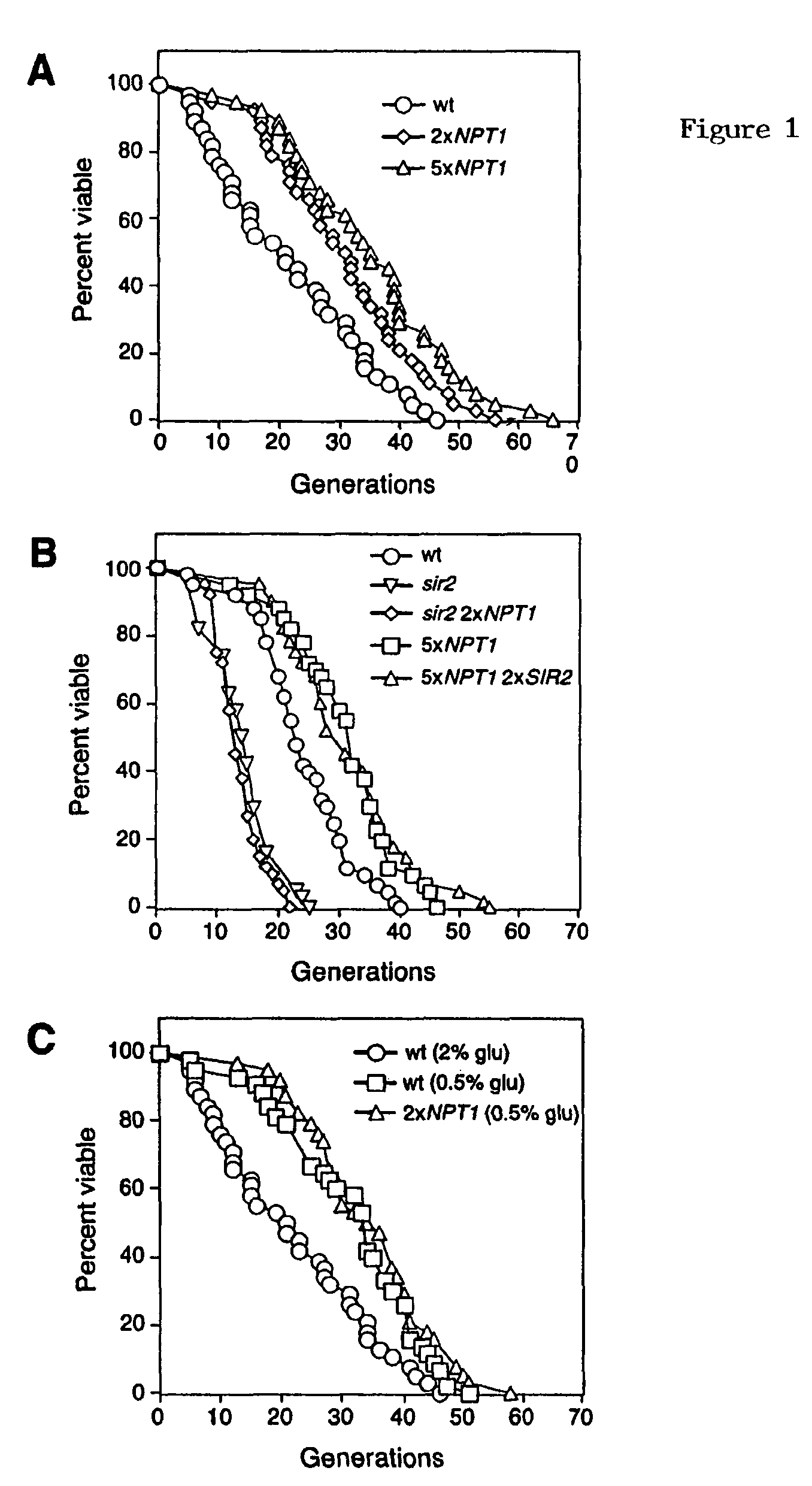
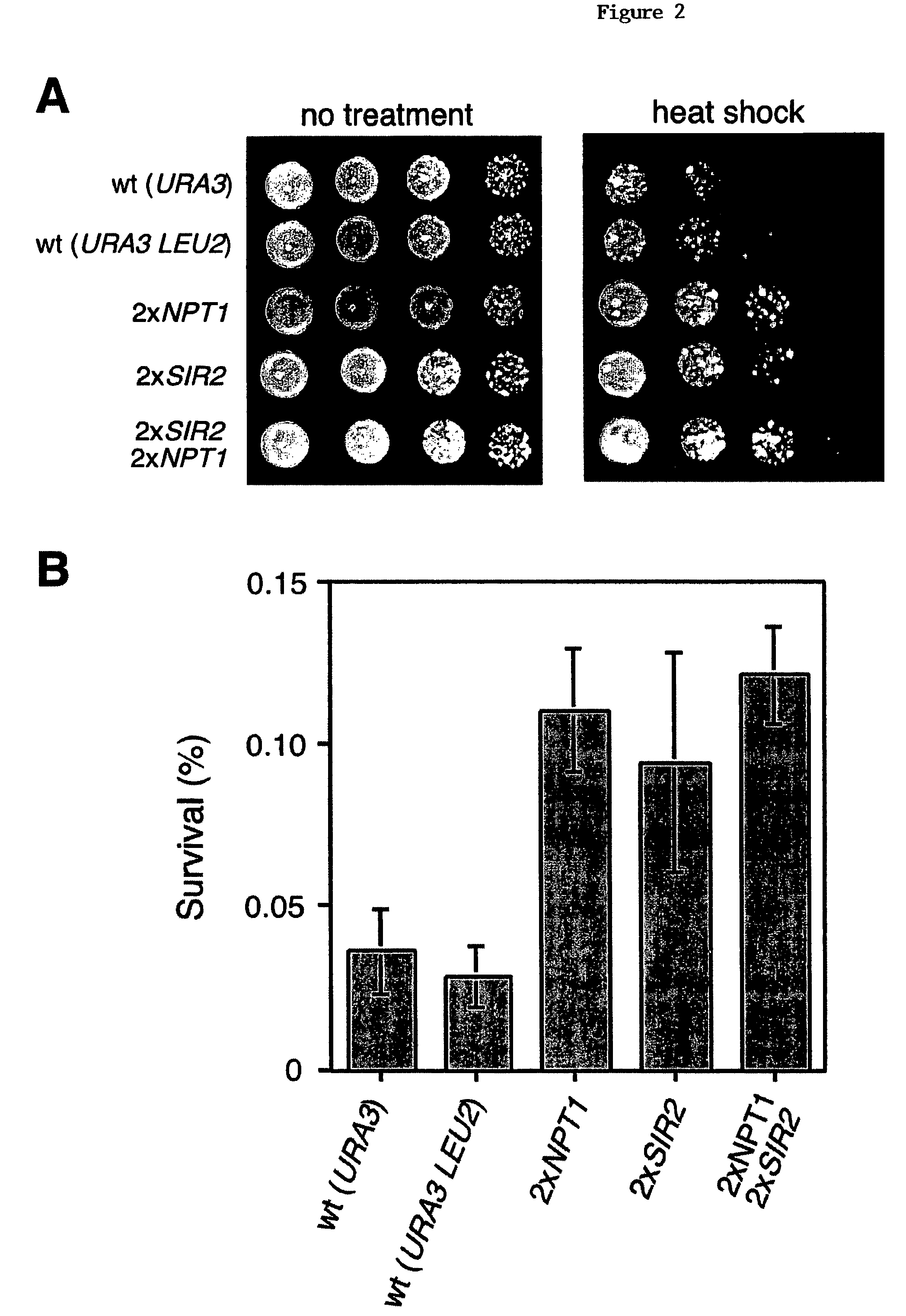
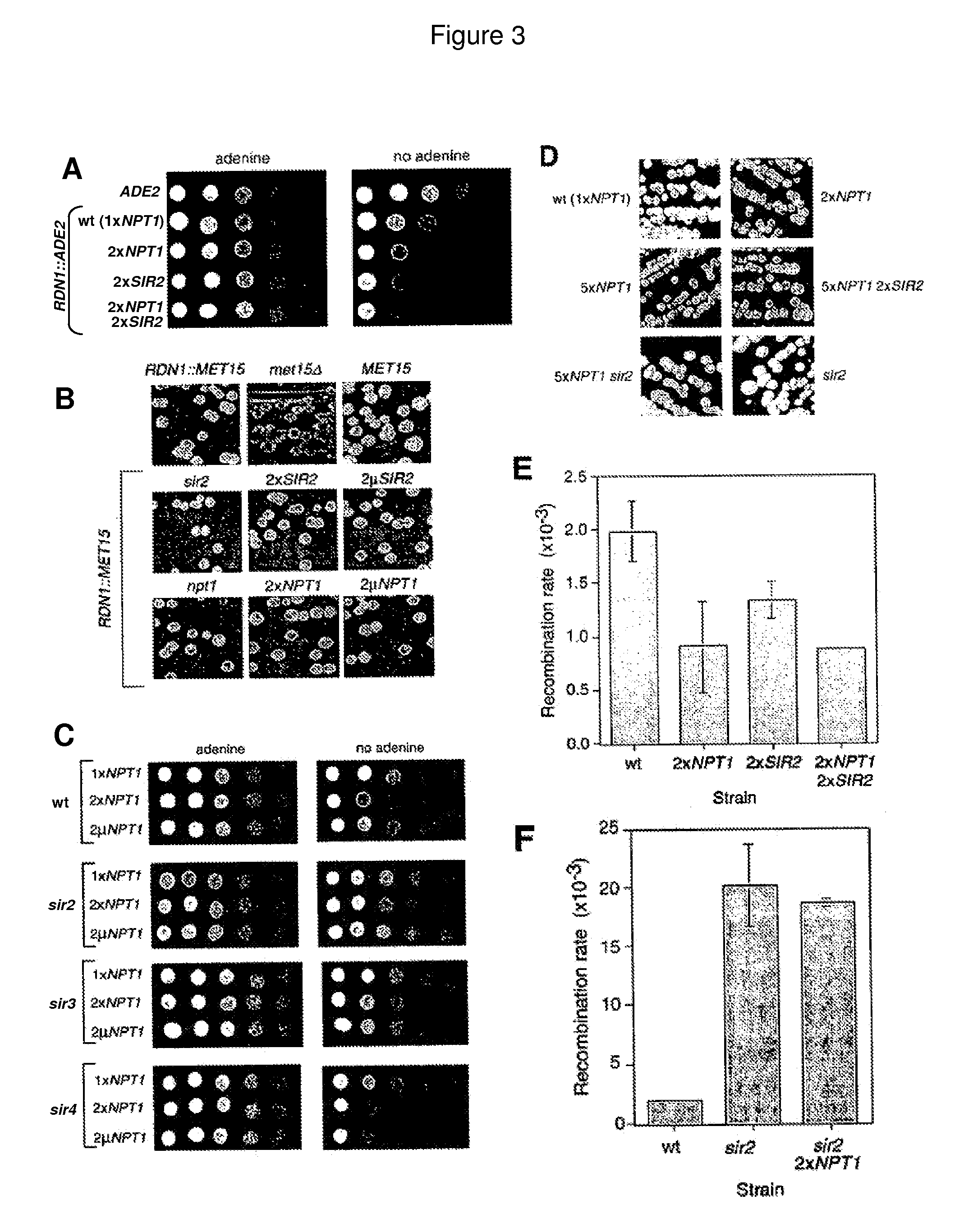
The invention provides methods and compositions for modulating the life span of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and for protecting cells against certain stresses, e.g., heatshock. One method comprises modulating the flux of the NAD+ salvage pathway in the cell, e.g., by modulating the level or activity of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of NPT1, PNC1, NMA1 and NMA2. Another method comprises modulating the level of nicotinamide in the cell.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
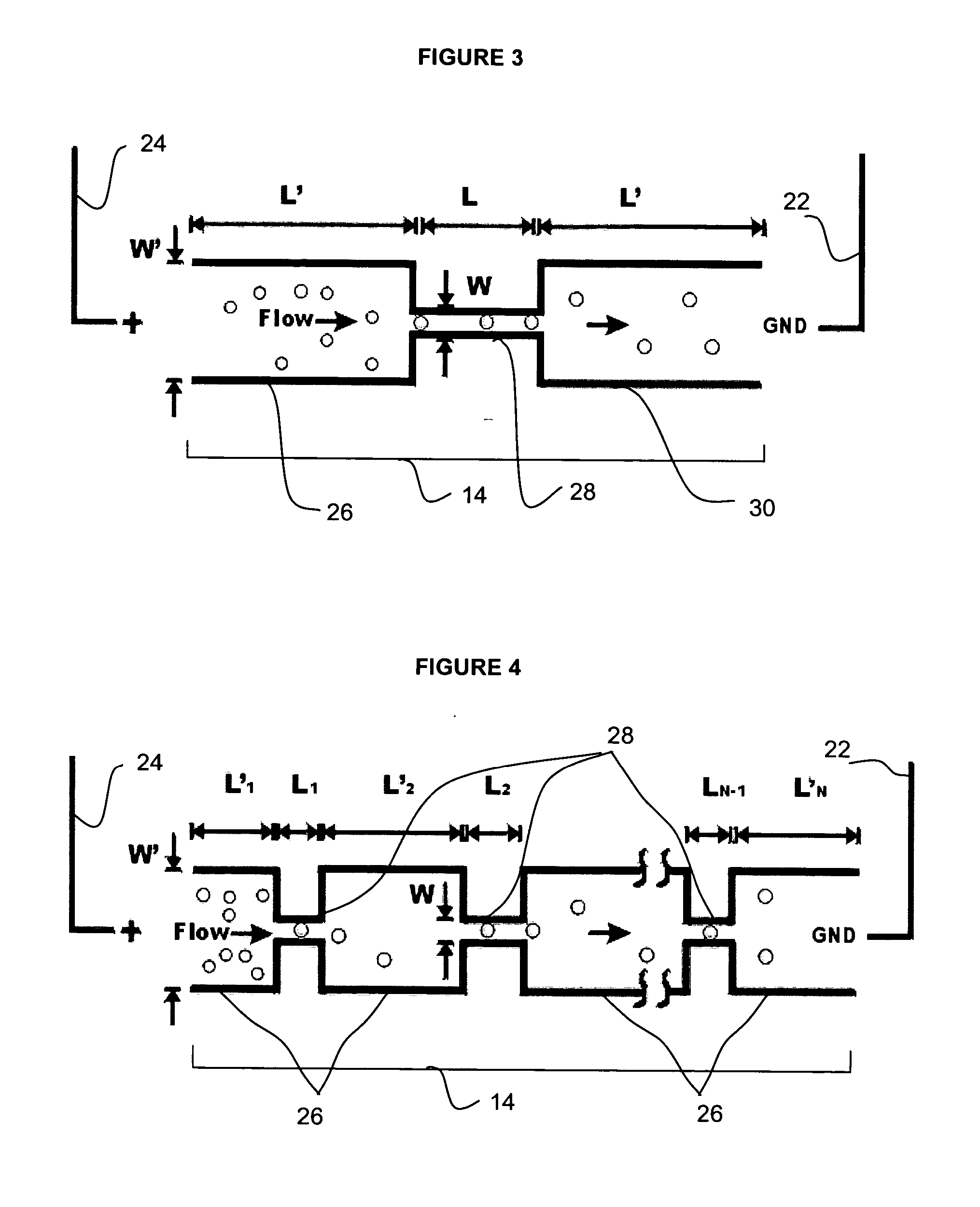
Fluidic device
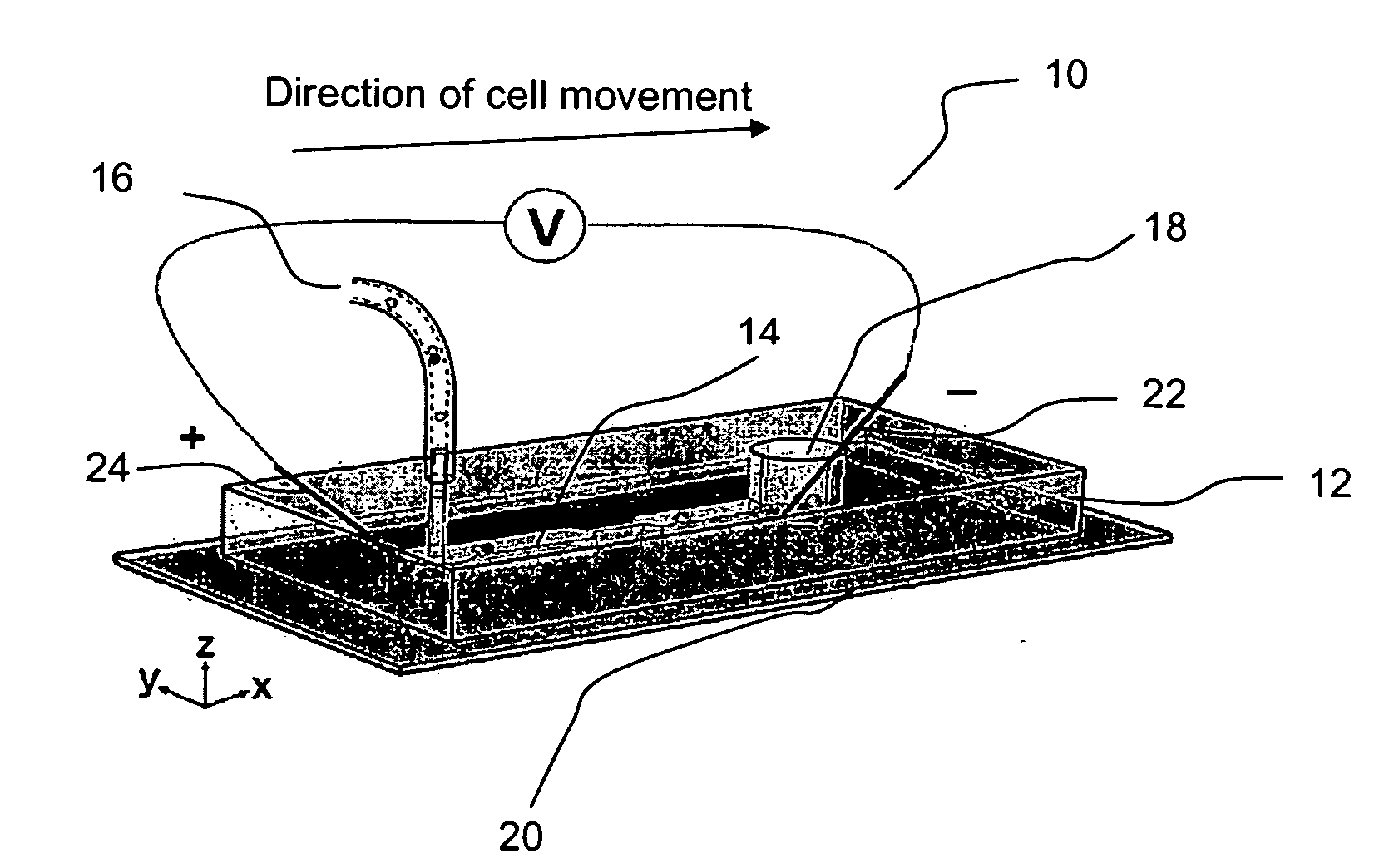
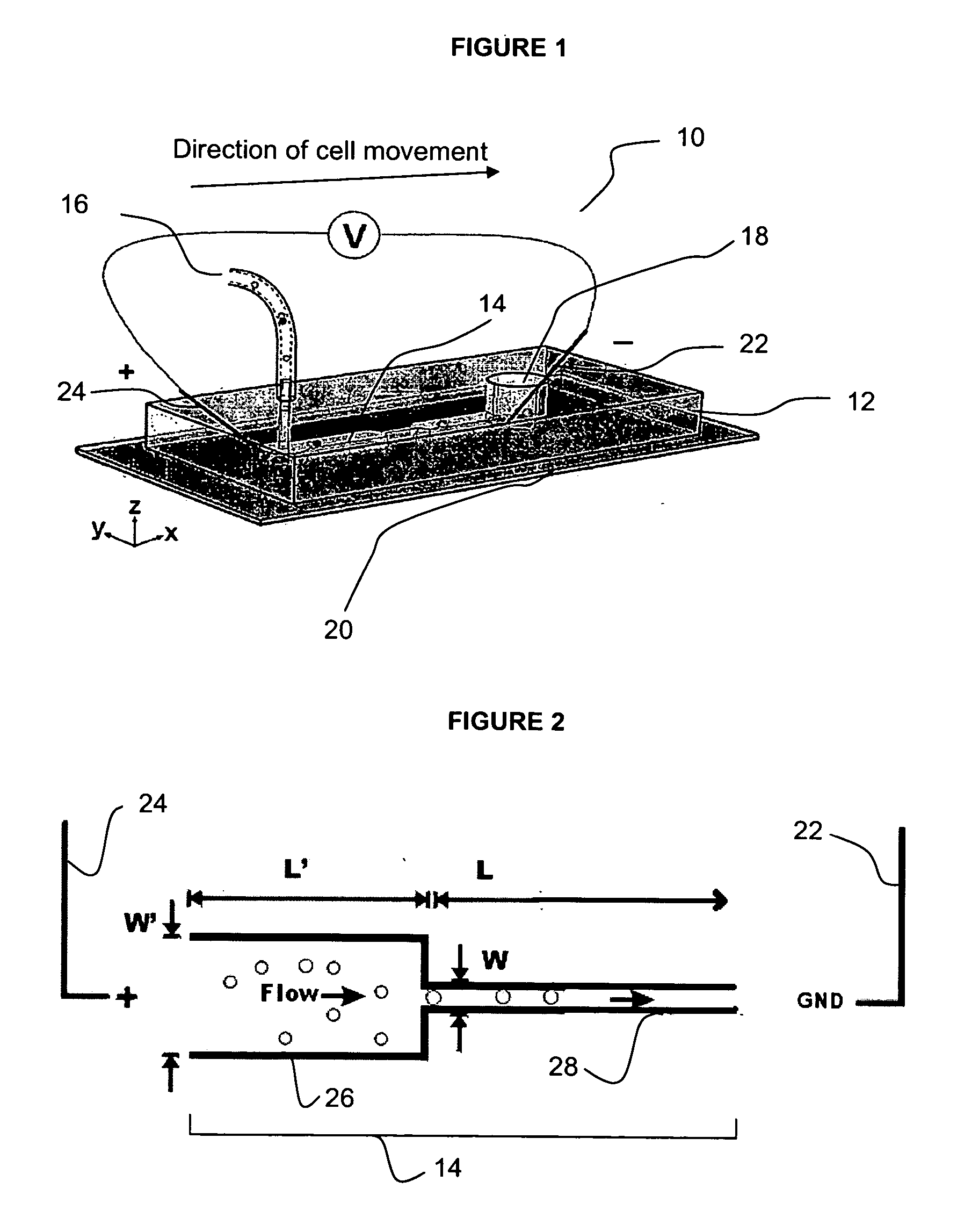
InactiveUS20070105206A1Great electric field intensityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysisElectroporation
A fluidic device for cell electroporation, cell lysis, and cell electrofusion based on constant DC voltage and geometric variation is provided. The fluidic device can be used with prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells. In addition, the device can be used for electroporative delivery of compounds, drugs, and genes into prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells on a microfluidic platform.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
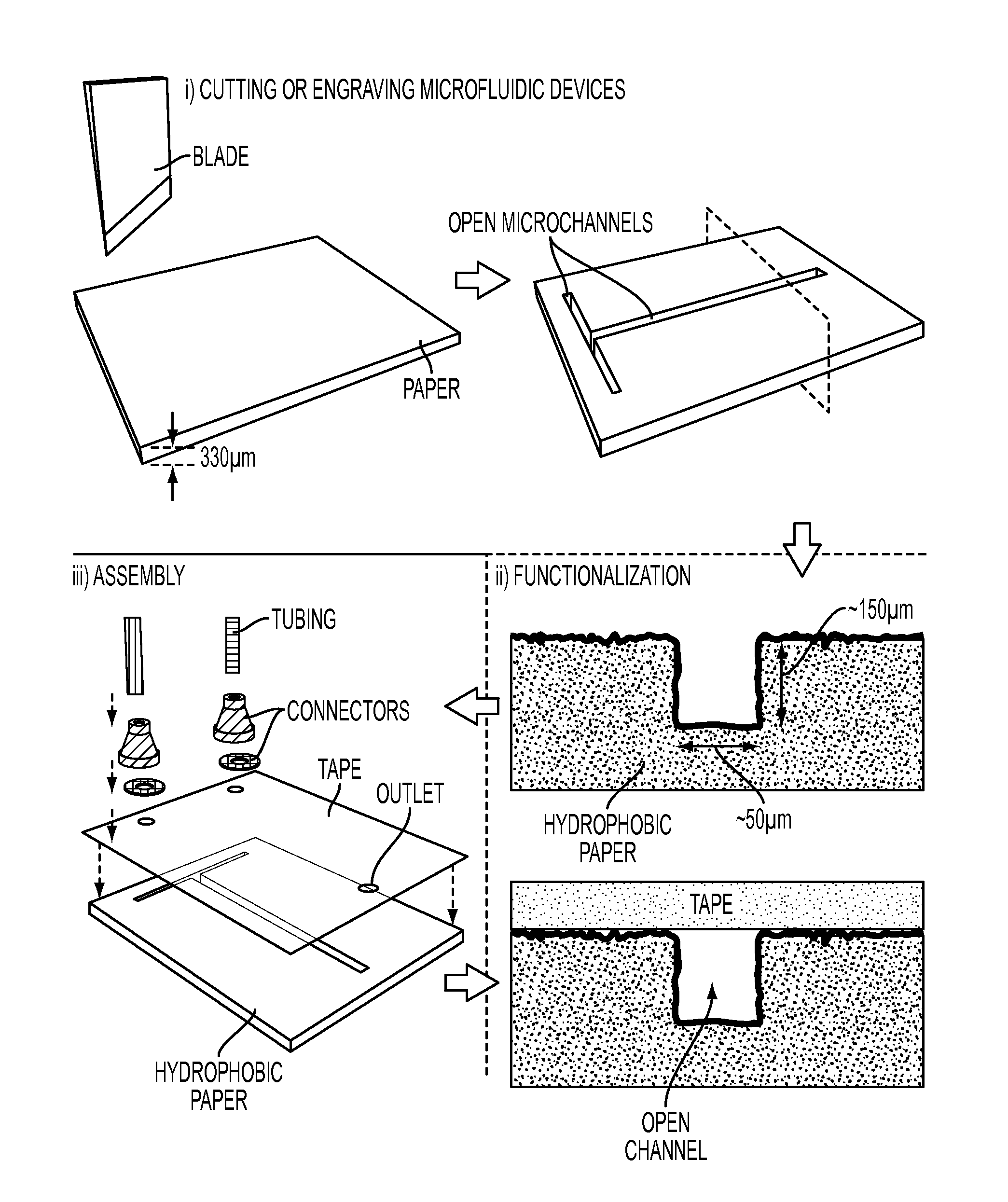
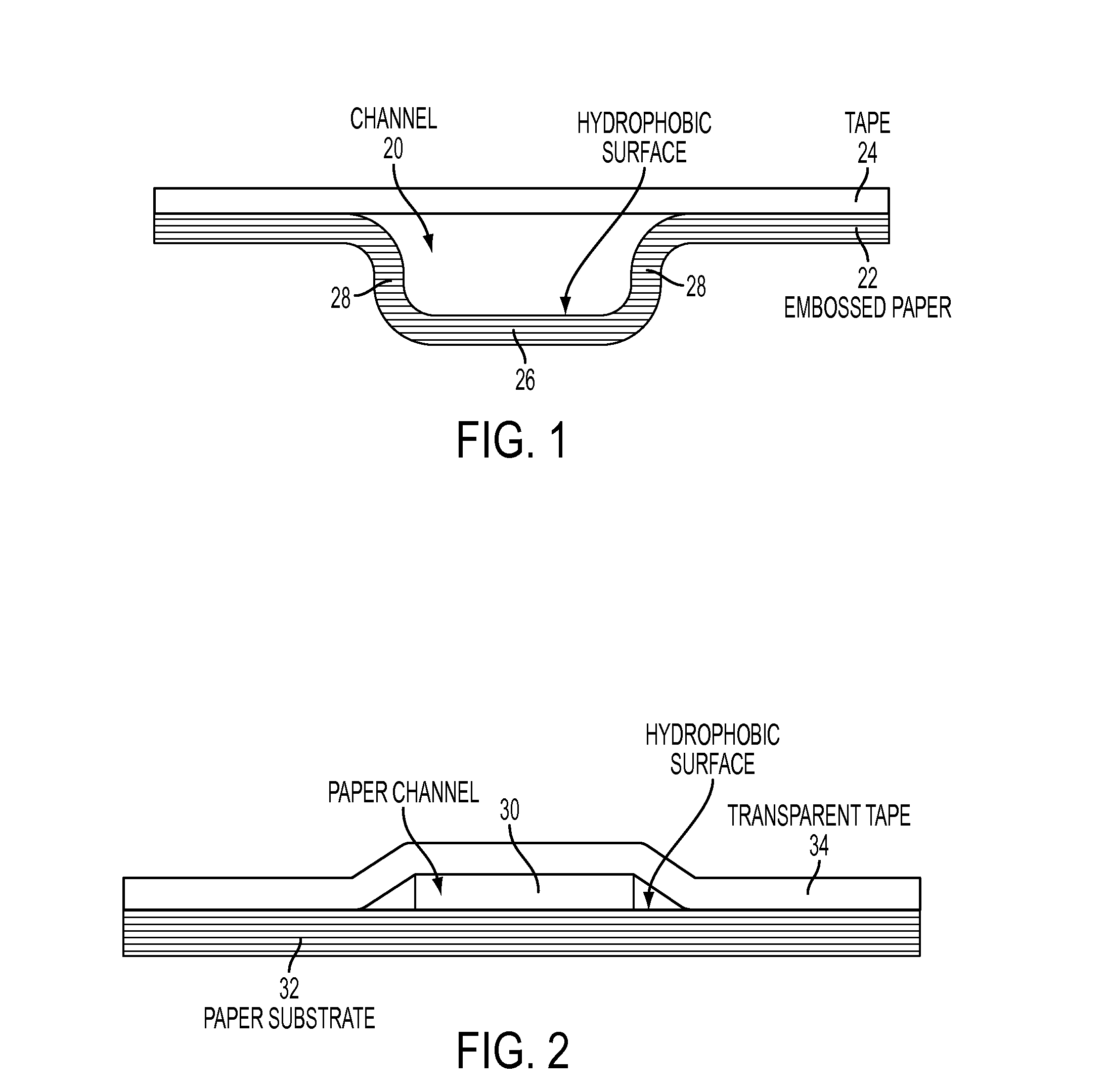
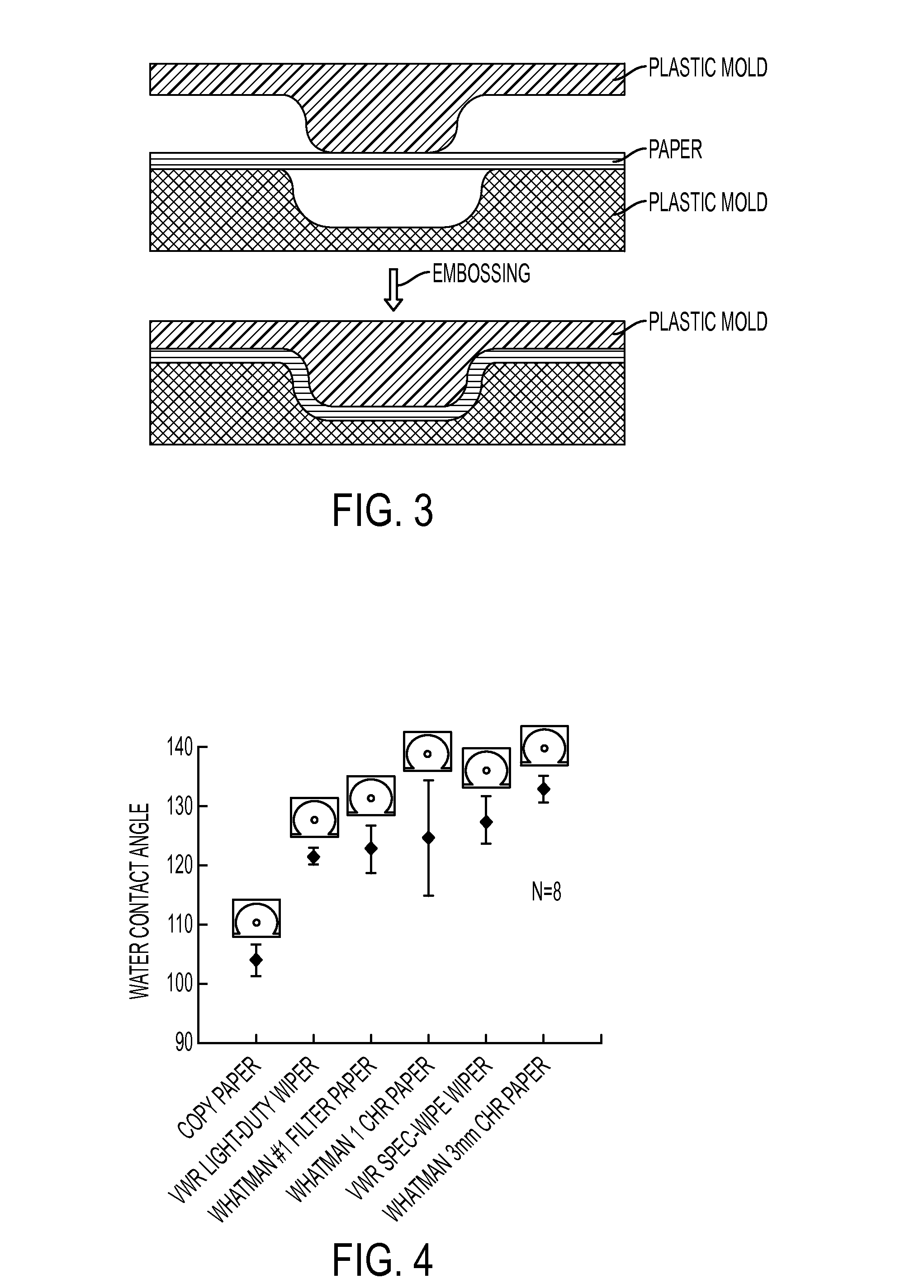
Microfluidic Devices Formed From Hydrophobic Paper
InactiveUS20150132742A1Improve hydrophobicityEasy and inexpensive to fabricateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDevice formEngineering
Microfluidic devices fabricated from paper that has been covalently modified to increase its hydrophobicity, as well as methods of making and using thereof are provided herein. The devices are typically small, portable, flexible, and both easy and inexpensive to fabricate. Microfluidic devices contain a network of microfluidic components, including microfluidic channels, microfluidic chambers, microwells, or combinations thereof, designed to carry, store, mix, react, and / or analyze liquid samples. The microfluidic channels may be open channels, closed channels, or combinations thereof. The microfluidic devices may be used to detect and / or quantify an analyte, such as a small molecules, proteins, lipids polysaccharides, nucleic acids, prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, particles, viruses, metal ions, and combinations thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method of making cell growth surface
InactiveUS20060292690A1Cell density be limitedReduced viabilityCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusCell adhesionCell growth
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional porous growth surface made from polysaccharide material, especially the alginic acid, to enhance cell growth surface, promote cell adherence, immobilization and propagation, maintain surface structure integrity, enable programmable degradation, and thus increase cellular production. The present invention teaches several methods: a method to enhance the integrity of the growth surface by protecting the growth surface in a rigid solid support; a method of use for enhancing the performance of the surface; and a method of modifying a growth surface for eukaryotic and / or prokaryotic cells comprising the steps of increasing surface area by creating porous and 3-D structure, treating a surface to encourage cell attachment, promoting cell growth and proliferation, and disposing the growth surface in any conventional cell cultivating device. The growth surface is able to program degradation and release the cell / tissue mass after the culture is completed.
Owner:CESCO BIOENGINEERING CO LTD
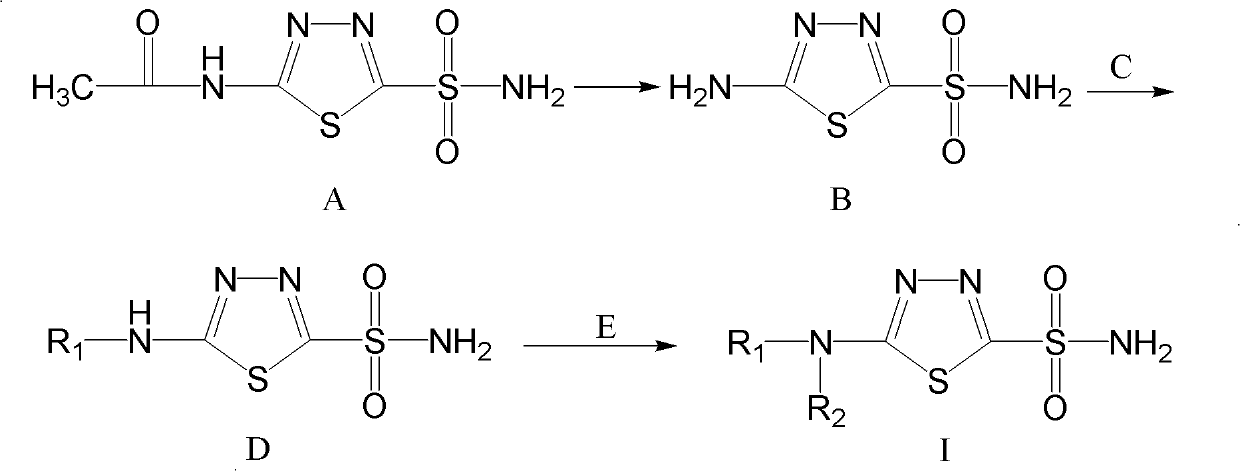
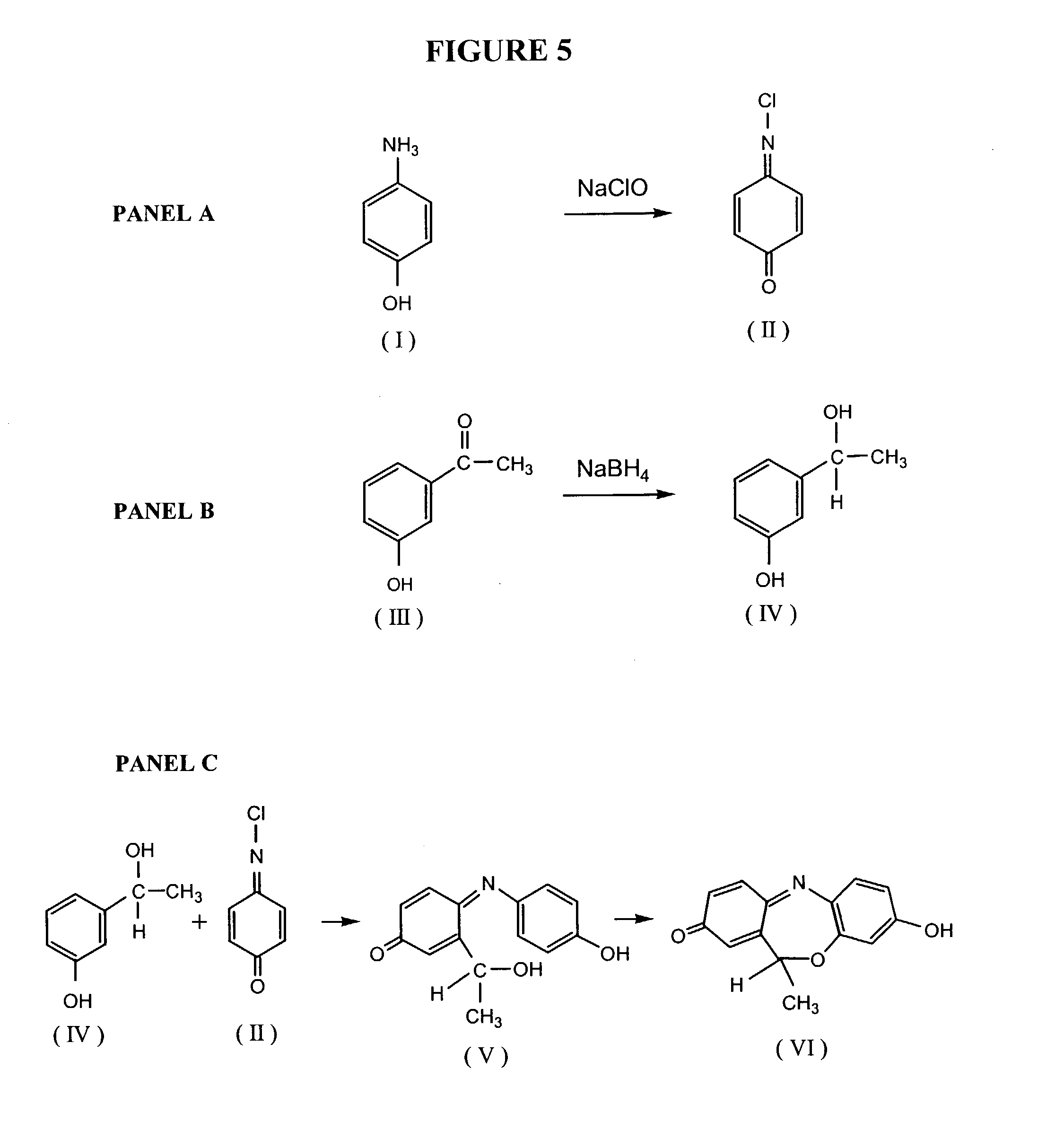
Sulfonamides compound for inhibiting carbonic anhydrase II and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN101921245AHigh resource utilizationThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsCarbonic anhydrase II
The invention relates to a sulfonamides compound for inhibiting carbonic anhydrase II and a synthesis method and an application thereof. The compound has the structure as shown in the specification. The invention features economical and reasonable synthetic route and high utilization of resources. The synthesis method is simple and easy to carry out and is more suitable for large-scale industrialized production. With human carbonic anhydrase II (Human Carbonic Anhydrase II, hCA II) expressed by procaryotic cell as an enzyme source, the invention establishes an in-vitro carbonic anhydrase inhibitor screening model. In addition, the compound of the invention has inhibitive effect on activity of the human carbonic anhydrase II.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL +1
High-activity T-cell promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN104745581AEfficient expressionSequence stabilityGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAdoptive cellular immunotherapyT cell
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a high-activity T-cell promoter and an application thereof. Particularly, the high-activity T-cell promoter comprises an element 1 and an element 2, wherein the element 1 is an EF1 alpha promoter and / or an EF1 alpha promoter containing an intron; and the element 2 is any one or more of an mCMV promoter, an hCMV promoter and a CD3e promoter. The high-activity T-cell promoter provided by the invention can be used for efficiently expressing a foreign gene in a T cell, has a stable sequence and is free from sequence loss during the transfer process of a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. The high-activity T-cell promoter is applicable to driving the high-efficiency expression of the foreign gene, especially a full-length antibody gene, in the T cell during the process of adoptive cellular immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +2
Device for monitoring cells
InactiveUS6900030B2Short timeWithout usingMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationLiquid mediumOxygen
The present invention relates to methods for detection and evaluation of metabolic activity of eukaryotic and / or prokaryotic cells based upon their ability to consume dissolved oxygen. The methods utilize a luminescence detection system which makes use of the sensitivity of the luminescent emission of certain compounds to the presence of oxygen, which quenches (diminishes) the compound's luminescent emission in a concentration dependent manner. Respiring eukaryotic and / or prokaryotic cells will affect the oxygen concentration of a liquid medium in which they are immersed. Thus, this invention provides a convenient system to gather information on the presence, identification, quantification and cytotoxic activity of eukaryotic and / or prokaryotic cells by determining their effect on the oxygen concentration of the media in which they are present.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
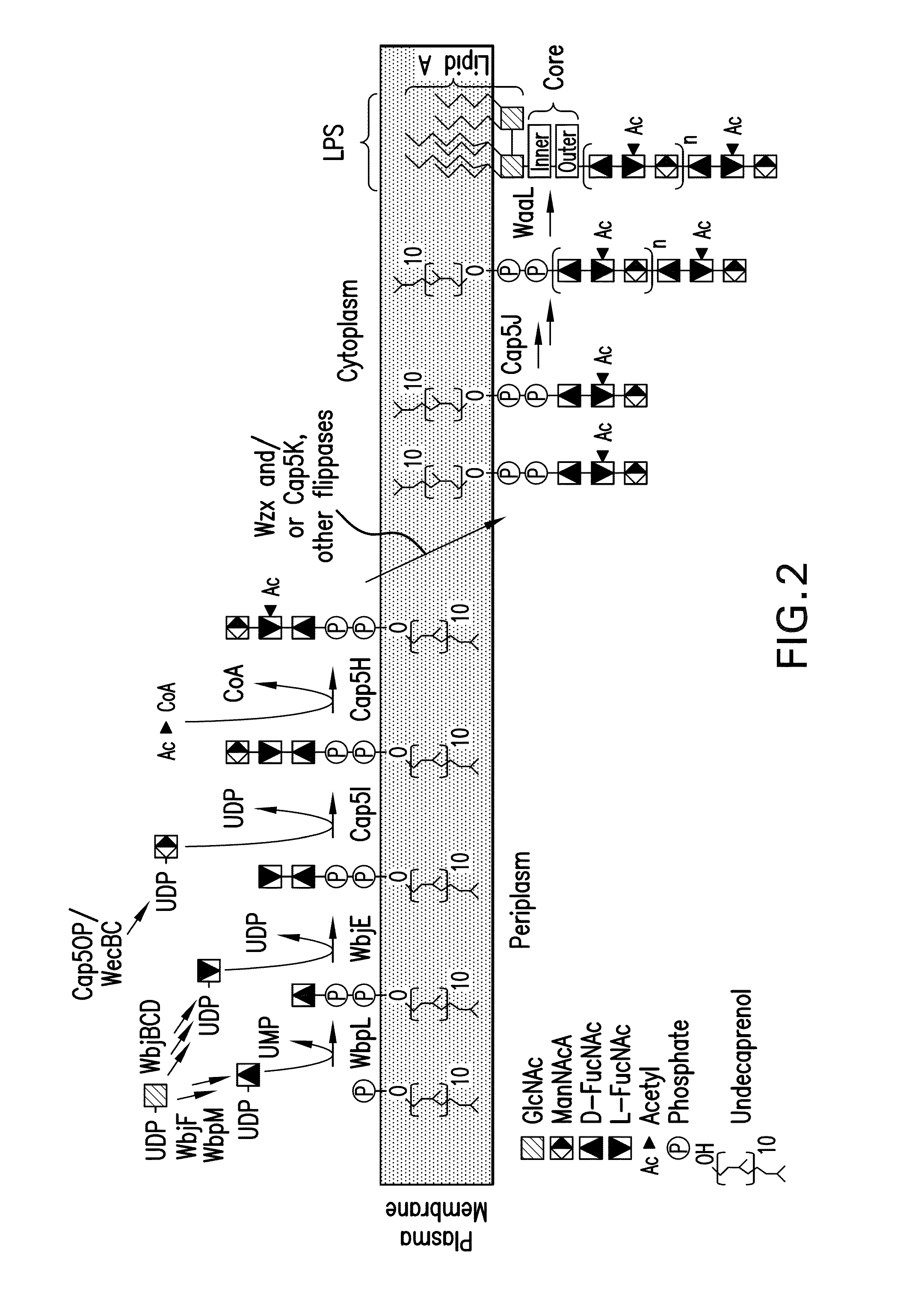
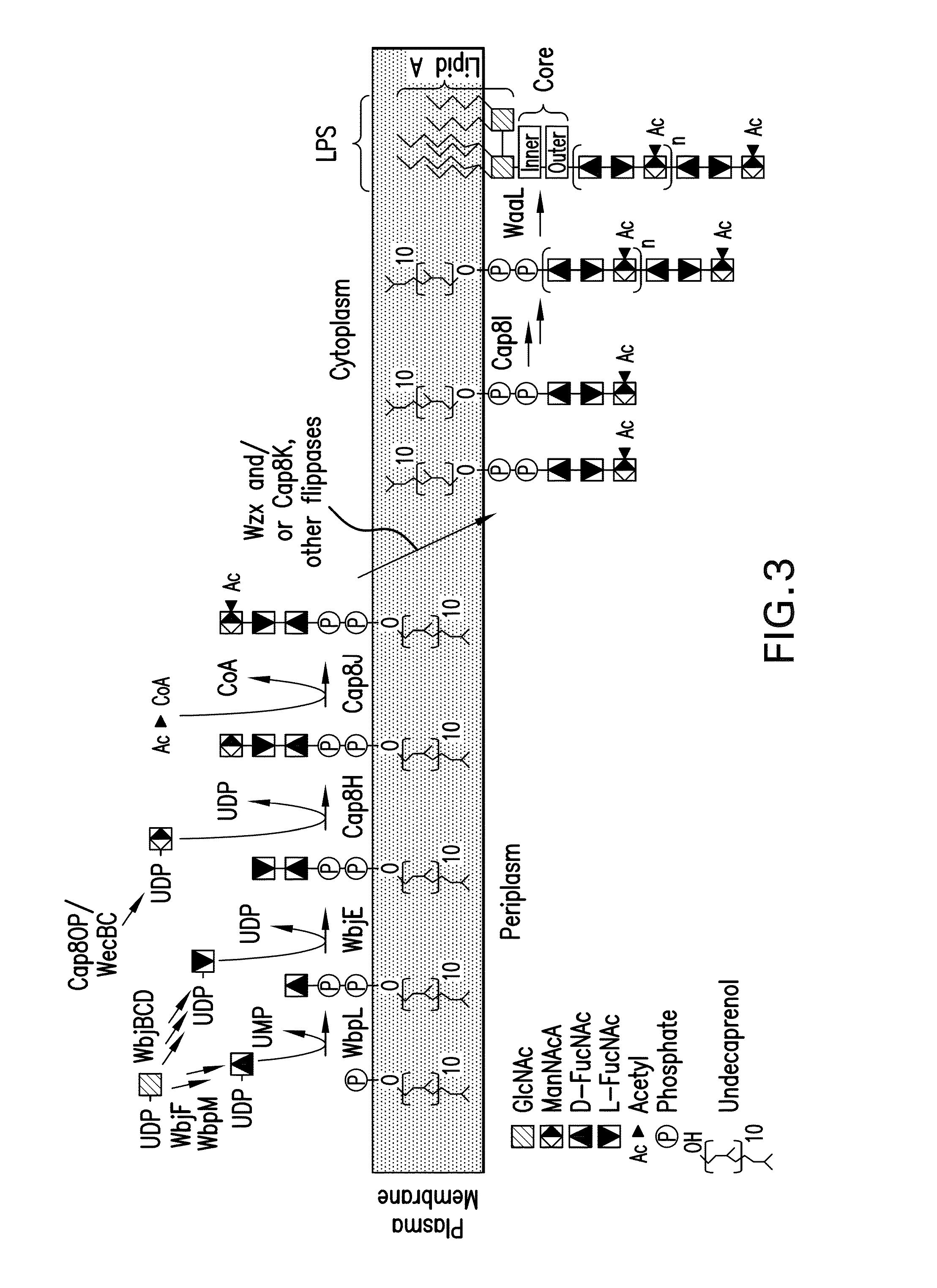
Capsular gram-positive bacteria bioconjugate vaccines
The present invention encompasses a novel S. aureus bioconjugate vaccine. More generally, the invention is directed to Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines containing a protein carrier, at least one polysaccharide such as a capsular Gram-positive polysaccharide, and, optionally, an adjuvant or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The instant invention also includes methods of producing Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines. An N-glycosylated protein is also provided that contains one or more polysaccharides such as Gram-positive polysaccharides. The invention is additionally directed to engineered prokaryotic organisms comprising nucleotide sequences encoding a glycosyltransferase of a first prokaryotic organism and a glycosyltransferase of a second prokaryotic organism. The invention further includes plasmids and prokaryotic cells transformed with plasmids encoding polysaccharides and enzymes which produce an N-glycosylated protein and / or bioconjugate vaccine. Further, the invention is directed to methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal comprising administering said bioconjugate vaccines.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Methods and materials for enhancing functional protein expression in bacteria
ActiveUS20140154743A1Increase productionIncrease volumeBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousBiochemistry
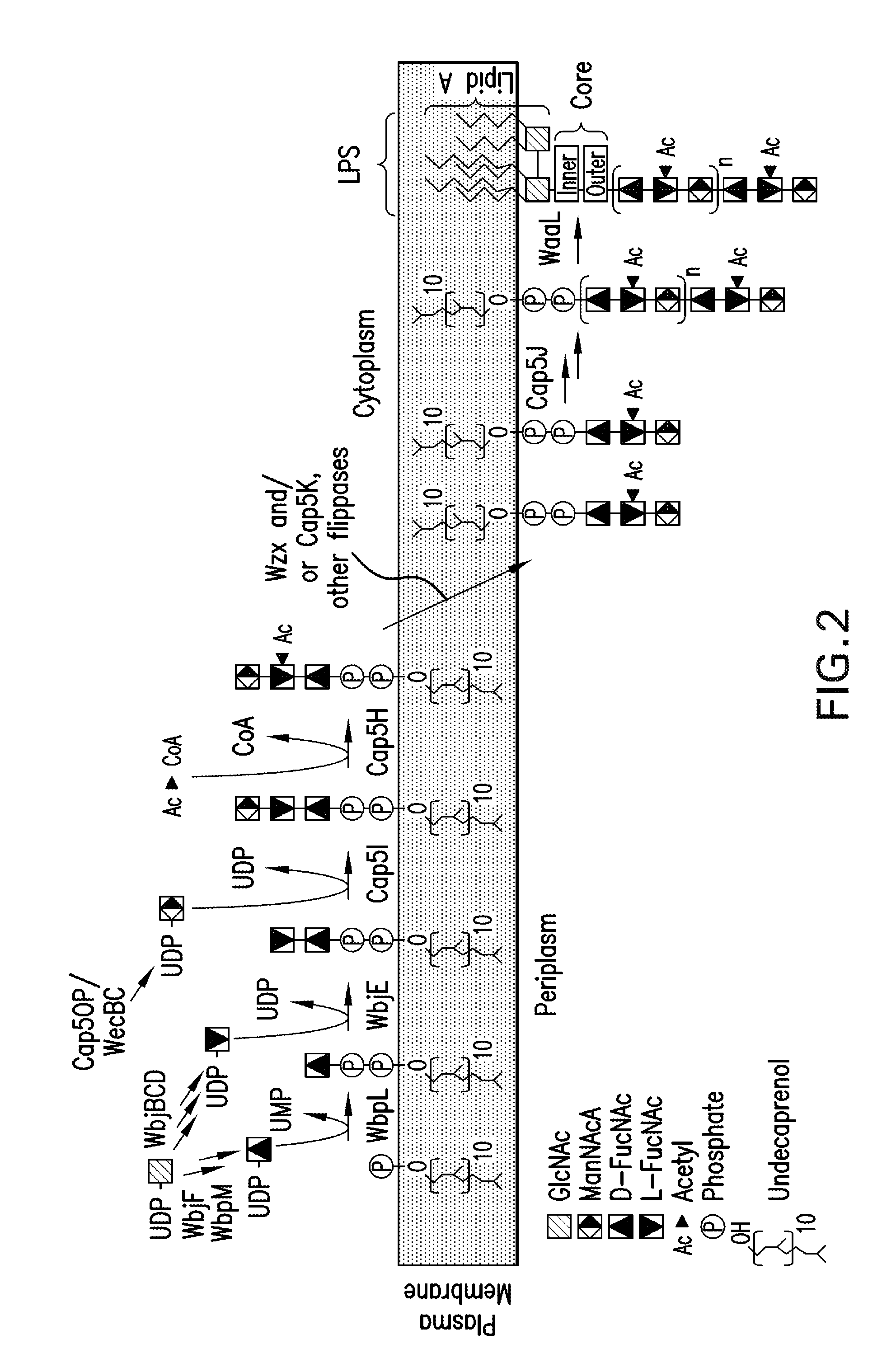
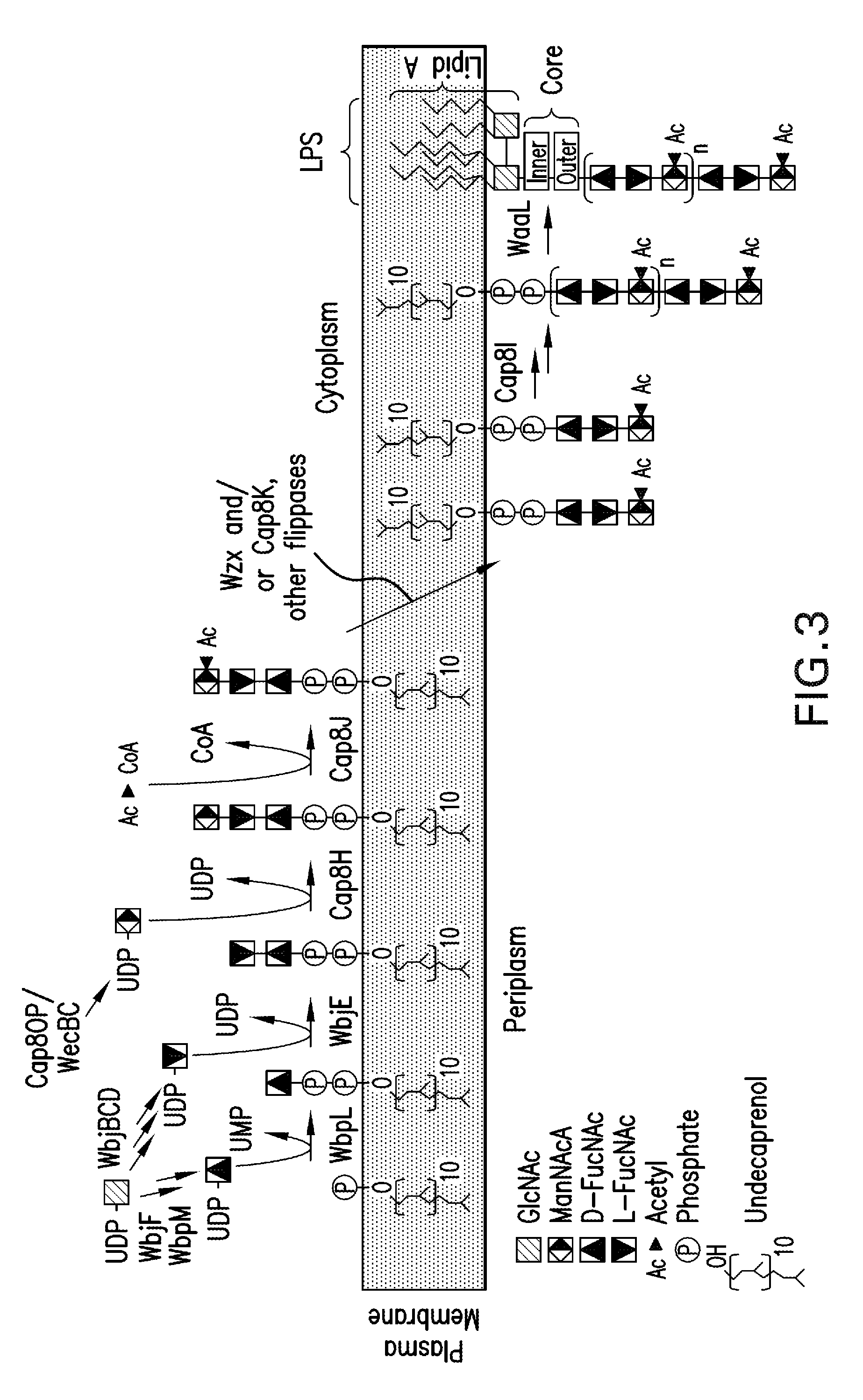
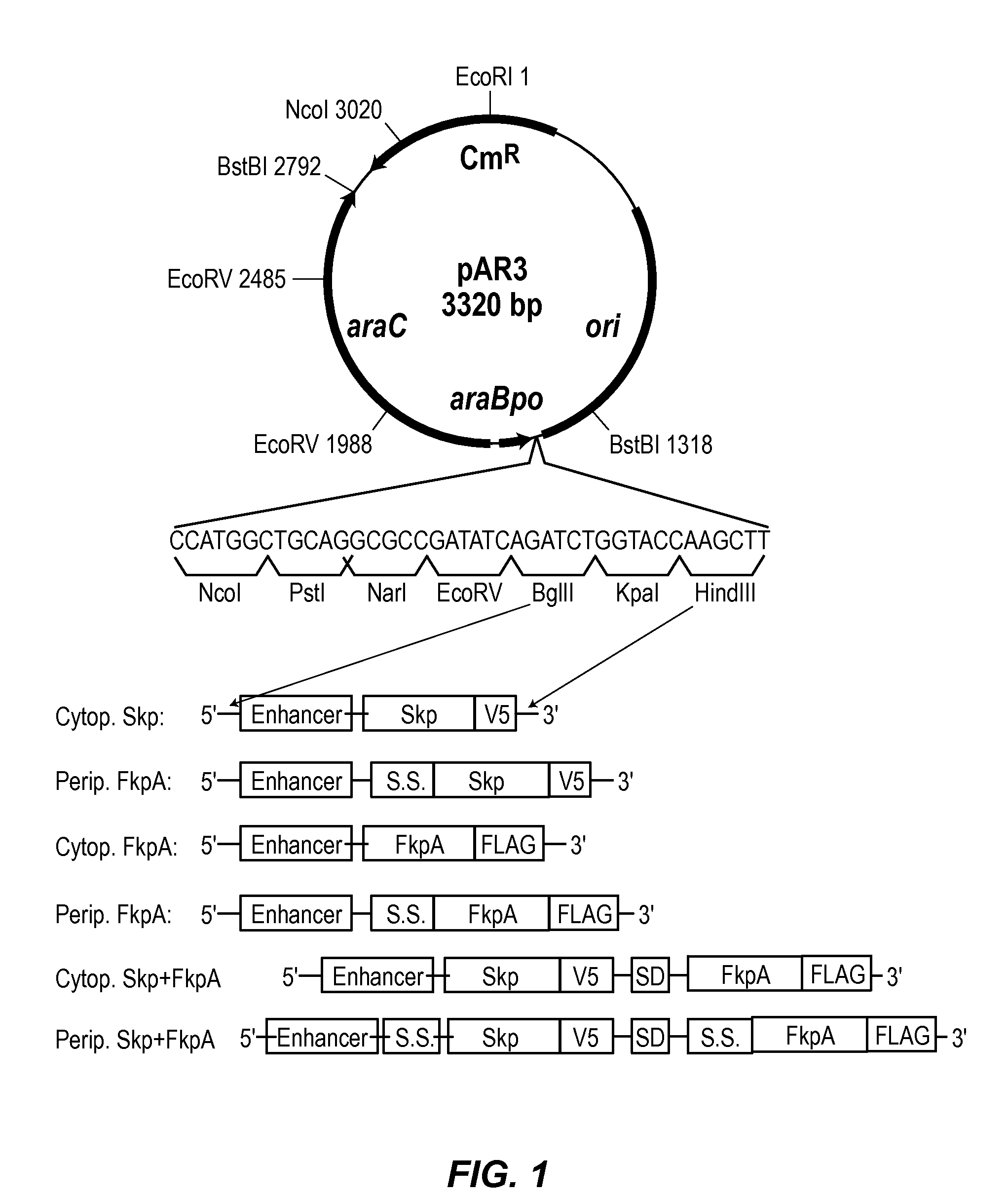
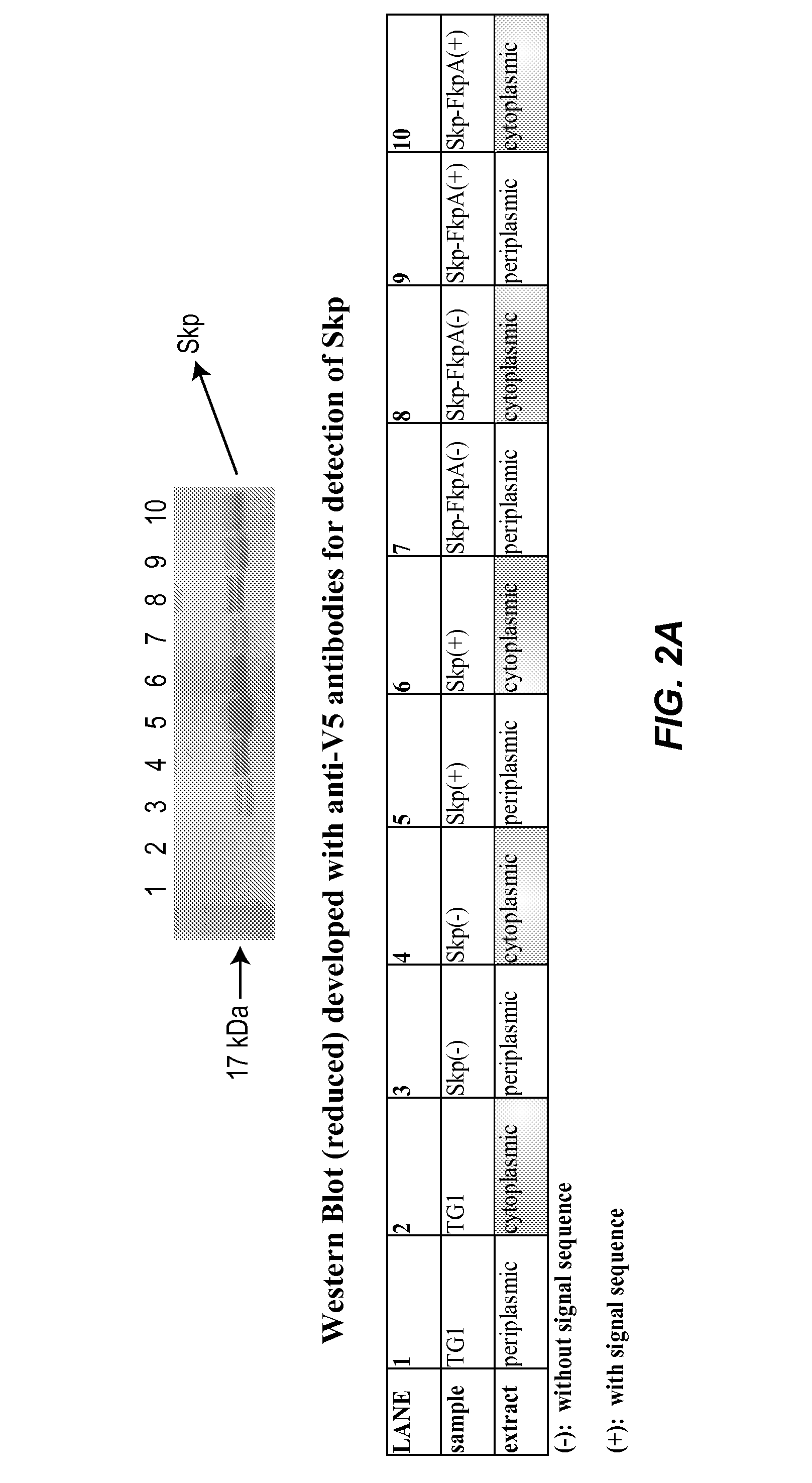
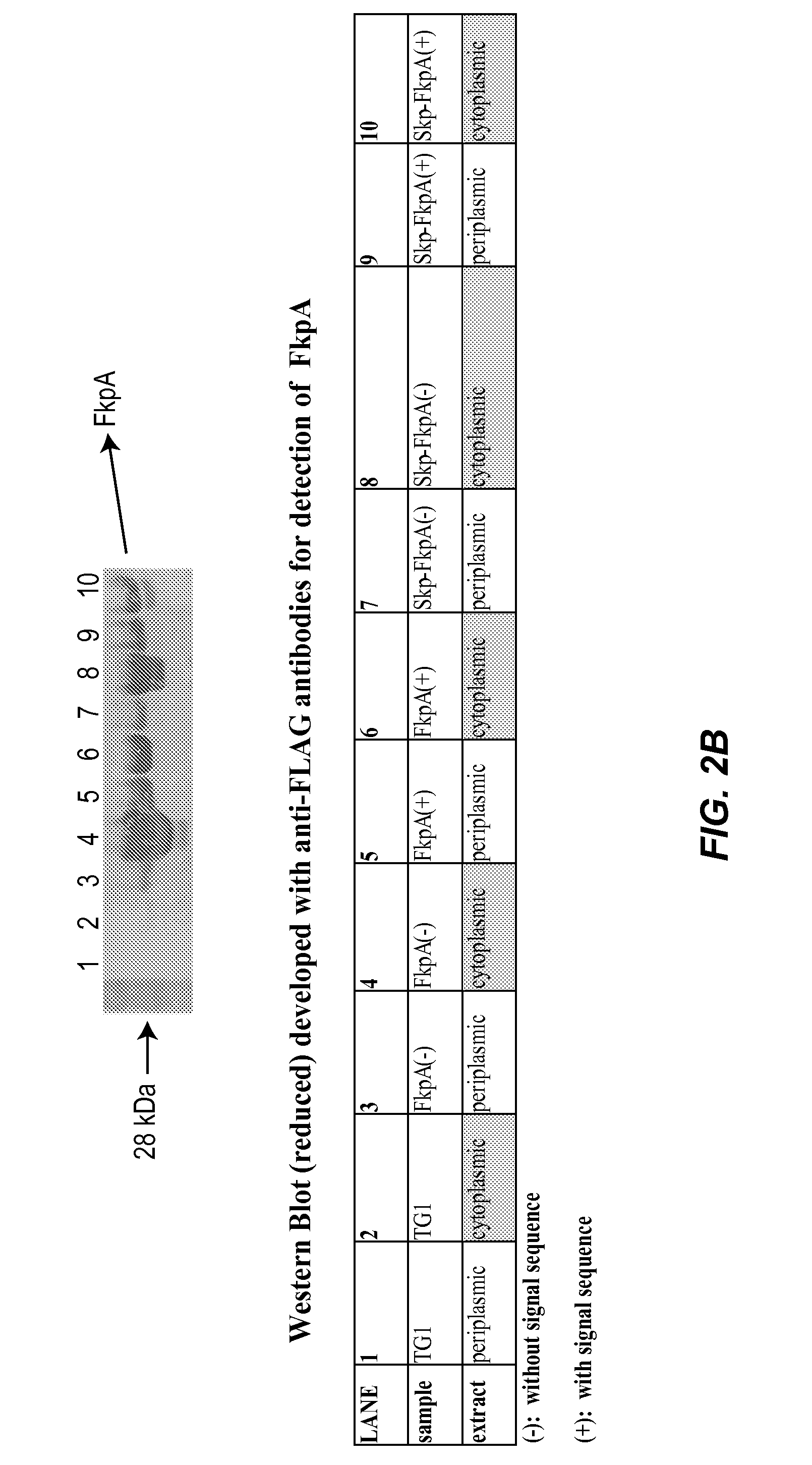
Novel materials and methods useful for expressing heterologous proteins in prokaryotic cells are provided, including prokaryotic cells expressing FkpA and / or Skp.
Owner:XOMA TECH LTD
Methods and compositions for extending the life span and increasing the stress resistance of cells and organisms
The invention provides methods and compositions for modulating the life span of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and for protecting cells against certain stresses, e.g., heatshock. One method comprises modulating the flux of the NAD+ salvage pathway in the cell, e.g., by modulating the level or activity of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of NPT1, PNC1, NMA1 and NMA2. Another method comprises modulating the level of nicotinamide in the cell.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
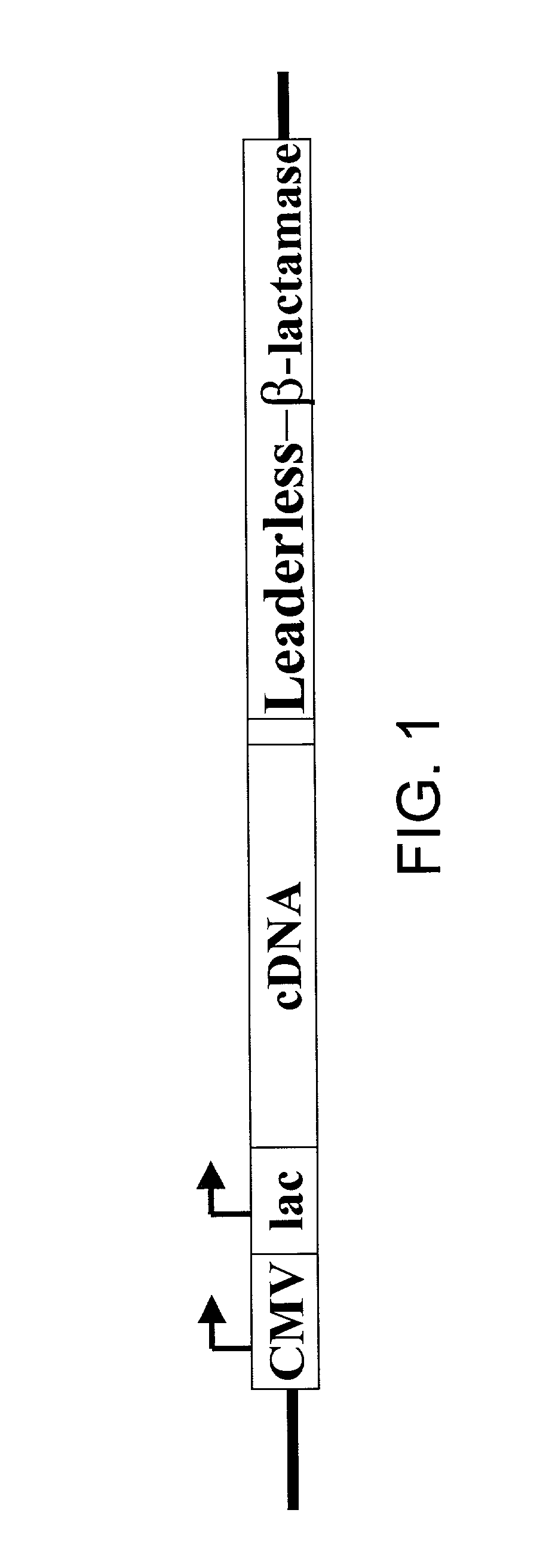
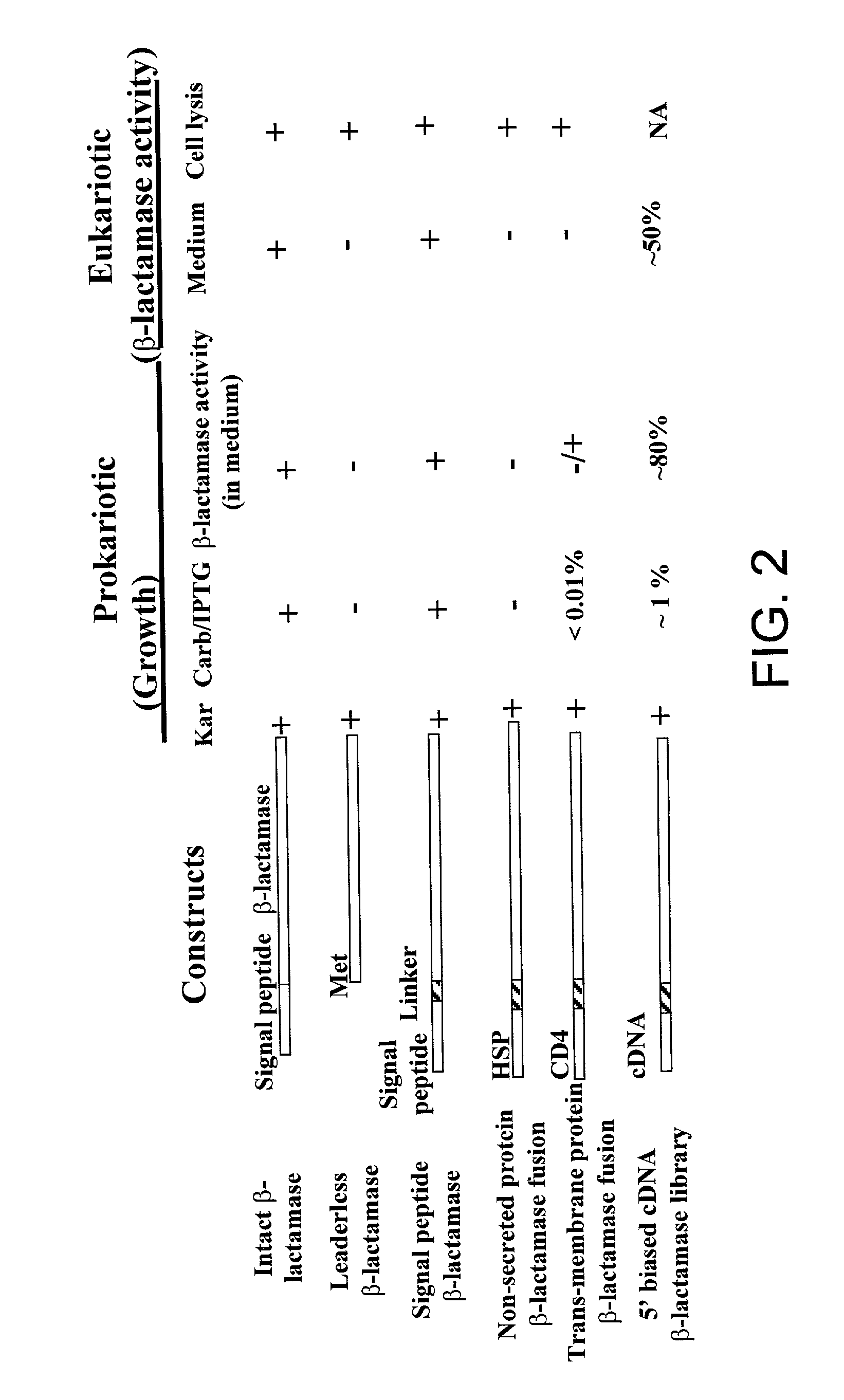
Method for identification of cDNAs encoding signal peptides
InactiveUS20020127557A1Fast wayBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening techniquesPresent method
The present invention provides a method in which cDNAs that encode signal sequences for secreted or membrane-associated proteins are isolated using a fusion protein that directs secretion of a molecule that provides antibiotic resistance, e.g., .beta.-lactamase. The present method allows the isolation of signal peptide-associated proteins that may be difficult to isolate with other techniques. Moreover, the present method is amenable to throughput screening techniques and automation, and especially in validating the presence of the signal sequence via expression of the protein in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This invention provides a powerful and approach to the large scale isolation of novel secreted proteins.
Owner:INCYTE CORP
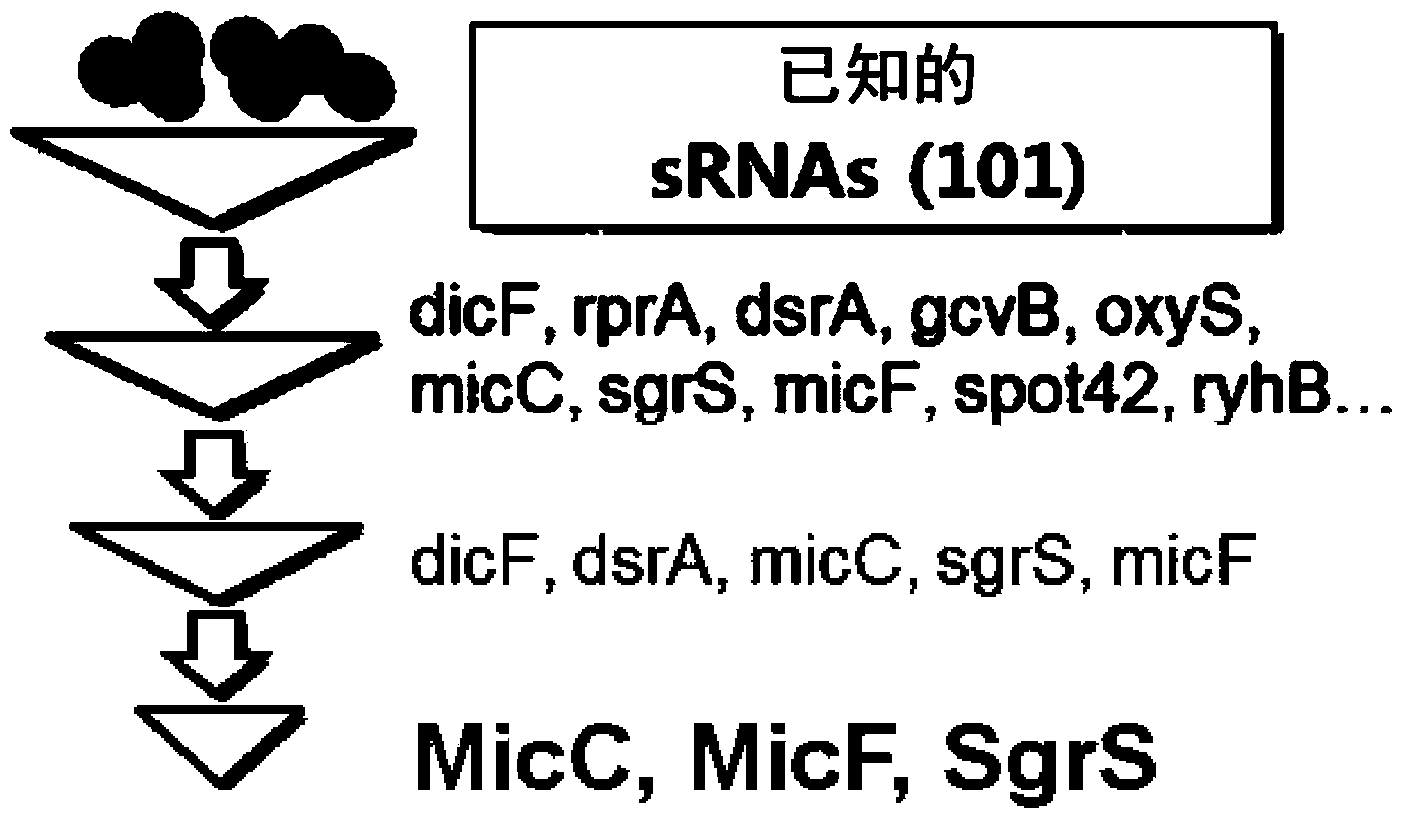
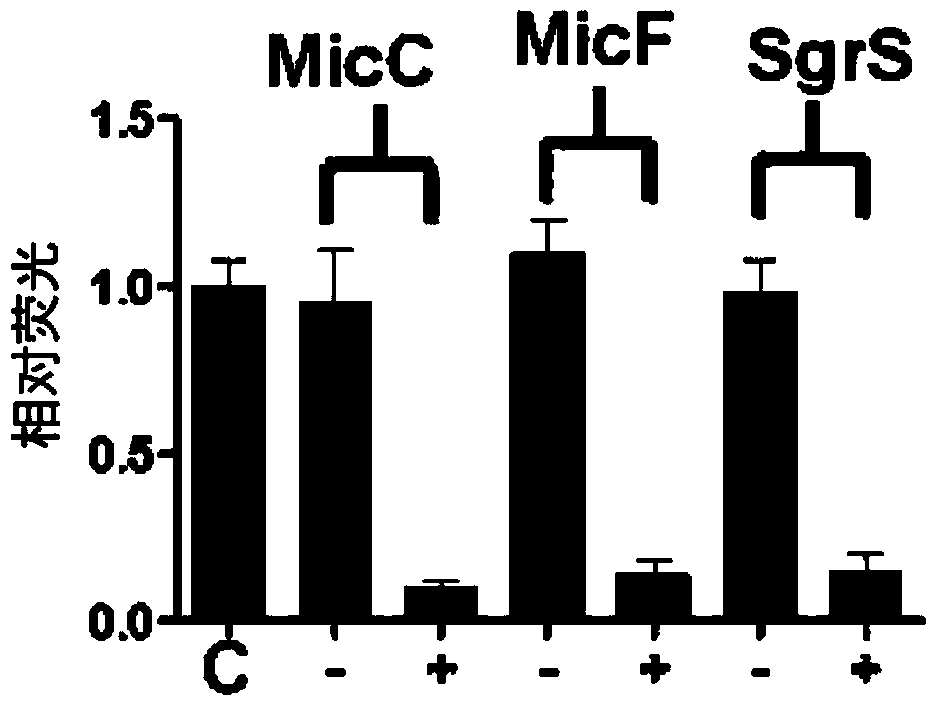
Novel synthesis-regulating srna and method for preparing same
The present invention relates to a customized synthesized sRNA for reducing gene expression in a prokaryotic cell having a new structure, to a method for preparing the synthesized sRNA and to a use of the synthesized sRNA. More particularly, the present invention relates to a synthesized sRNA which contains an Hfg binding site derived from any one sRNA of MicC, SgrS and MicF, and a zone for forming complementary binding with target gene mRNA. The present invention also relates to a method for preparing the synthesized sRNA and to a use of the synthesized sRNA.; The synthesized sRNA according to the present invention has the advantages of regulating the degree of inhibition by regulating the binding force to mRNA of the target gene, and can be effectively produced without deleting an existing gene through synthesized sRNA for regulating gene expression and may reduce an expression of the target gene, thus enabling the synthesized sRNA of the present invention to be valuably used in the production of recombinant microorganisms. The synthesized sRNA of the present invention may be quickly applied to various strains, and therefore, is very suitable for measuring the metabolizability of each strain and selecting an optimum strain.; In addition, recombinant microorganisms for producing tyrosine or cadaverine at a high efficiency according to the present invention, obtained by regulating metabolic flux of microorganisms by means of synthesized sRNA can be valuably used as microorganisms for drugs and industrial solvents. That is, selecting an expression inhibitory target gene for high efficiency production of metabolites can be easily performed using the sRNA of the present invention. Thus, the sRNA of the present invention can be used in producing recombinant strains for the efficient production of various metabolites and in establishing methods for producing efficient production, and thus is very useful.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Comparative phenotype analysis of cells, including testing of biologically active compounds
InactiveUS20030162164A1Easy to atomizeReduce chanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest organismPlant cell
The present invention relates to growing and testing any cell type in a multitest format. The present invention is suited for the characterization of microorganisms, as well as animal and plant cells. The present invention is also particularly suited for analysis of phenotypic differences between strains of organisms, including cultures that have been designated as the same genus and species. The present invention is also suited for the analysis of phenotypic differences between cell lines. In some embodiments, a gel forming matrix is used. The present invention provides methods and compositions for the phenotypic analysis and comparison of eukaryotic, as well as prokaryotic cells. The present invention further provides novel methods and compositions for testing the effect(s) of biologically active chemicals on various cells.
Owner:BIOLOG
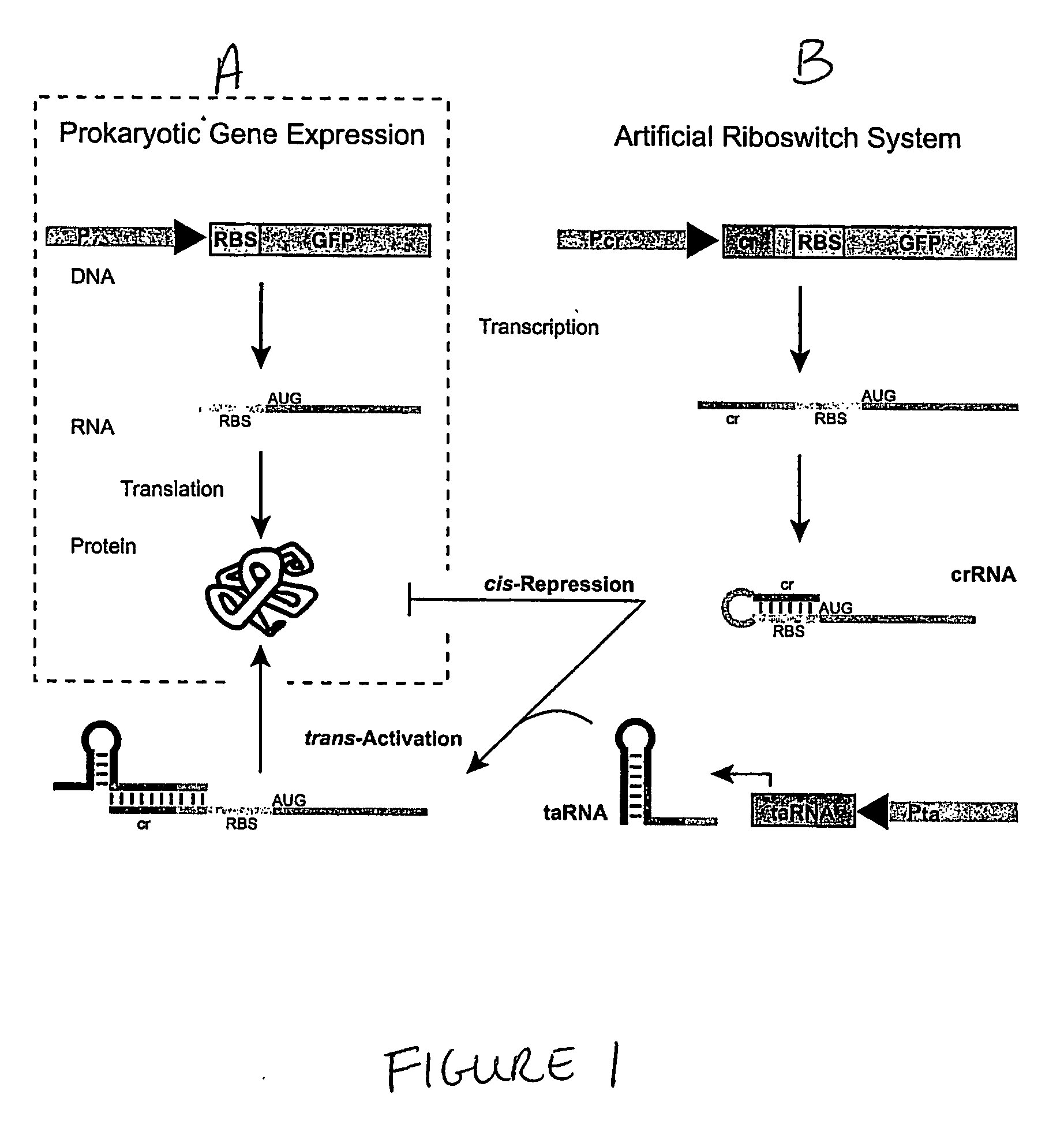
Cis/trans riboregulators
ActiveUS20070136827A1Easy to controlInhibition of translationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameBinding site
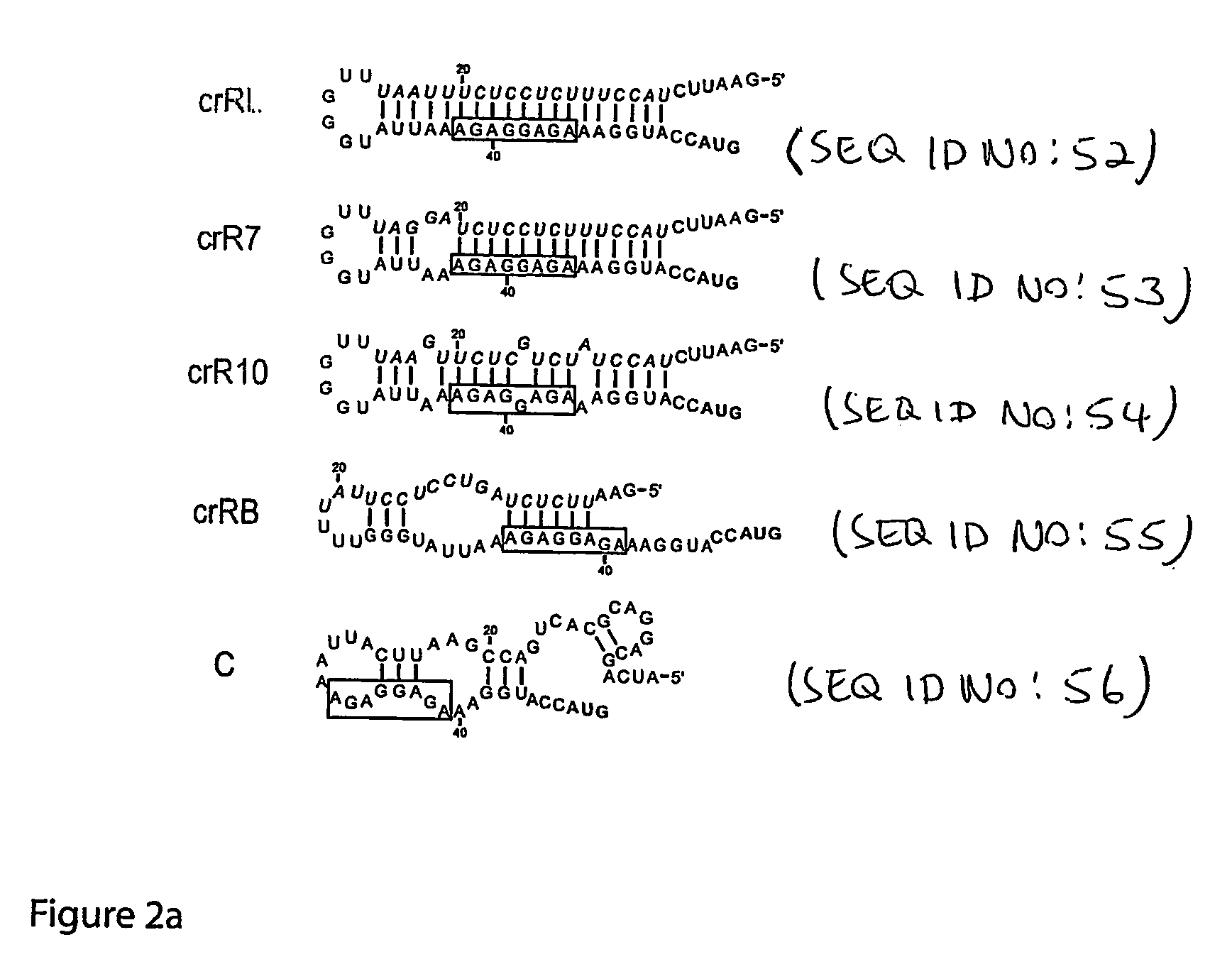
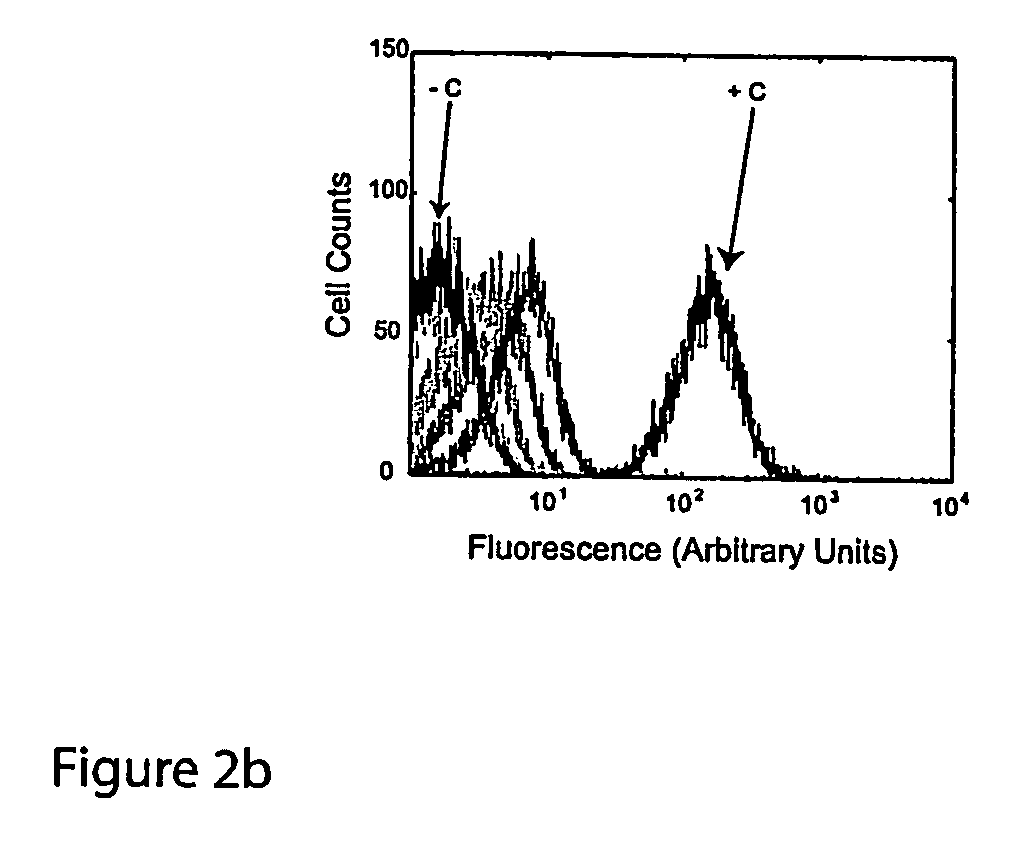
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules, DNA constructs, plasmids, and methods for post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression using RNA molecules to both repress and activate translation of an open reading frame. Repression of gene expression is achieved through the presence of a regulatory nucleic acid element (the cis-repressive RNA or crRNA) within the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) of an mRNA molecule. The nucleic acid element forms a hairpin (stem / loop) structure through complementary base pairing. The hairpin blocks access to the mRNA transcript by the ribosome, thereby preventing translation. In particular, in embodiments of the invention designed to operate in prokaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin secondary structure sequesters the ribosome binding site (RBS). In embodiments of the invention designed to operate in eukaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin is positioned upstream of the start codon, anywhere within the 5′ UTR of an mRNA. A small RNA (trans-activating RNA, or taRNA), expressed in trans, interacts with the crRNA and alters the hairpin structure. This alteration allows the ribosome to gain access to the region of the transcript upstream of the start codon, thereby activating transcription from its previously repressed state.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Recombinant n-glycosylated proteins from procaryotic cells
ActiveUS20100062484A1Efficient productionBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsADAMTS ProteinsAmino acid
The present invention relates to recombinant N-glycosylated proteins, comprising one or more introduced N-glycosylated optimized amino acid sequence(s), nucleic acids encoding these proteins as well as corresponding vectors and host cells. In addition, the present invention is directed to the use of said proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and host cells for preparing medicaments. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods for producing said proteins.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
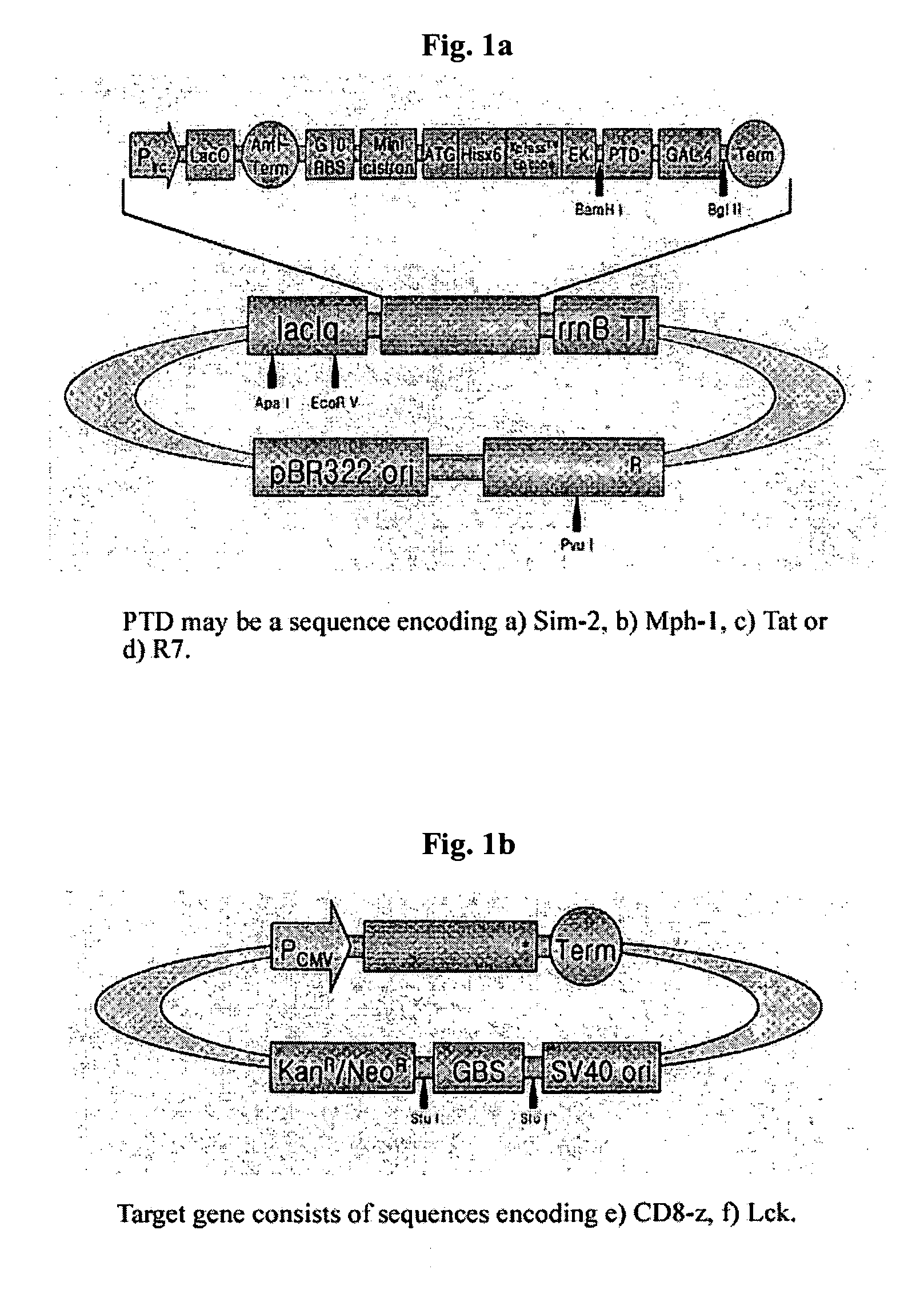
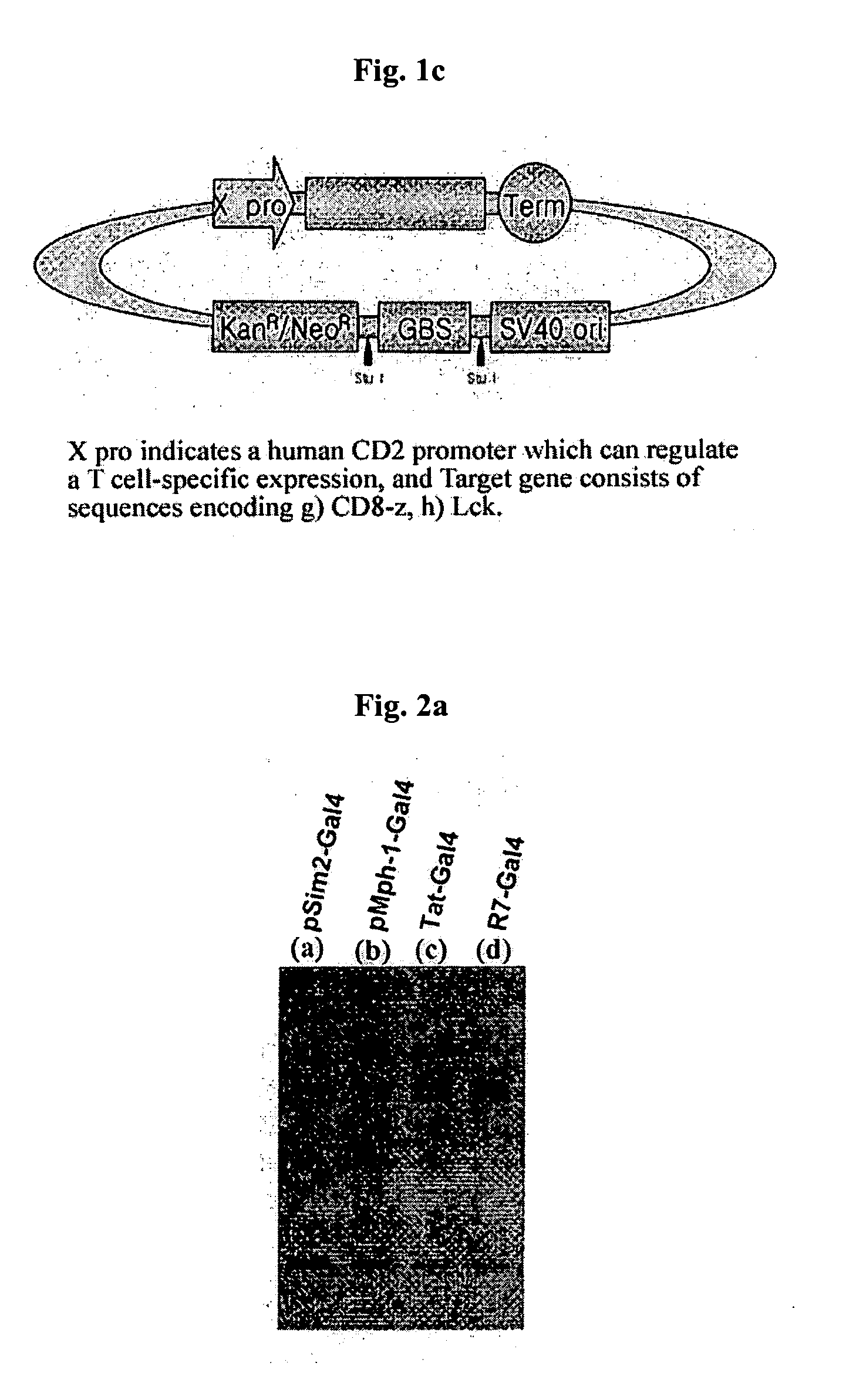
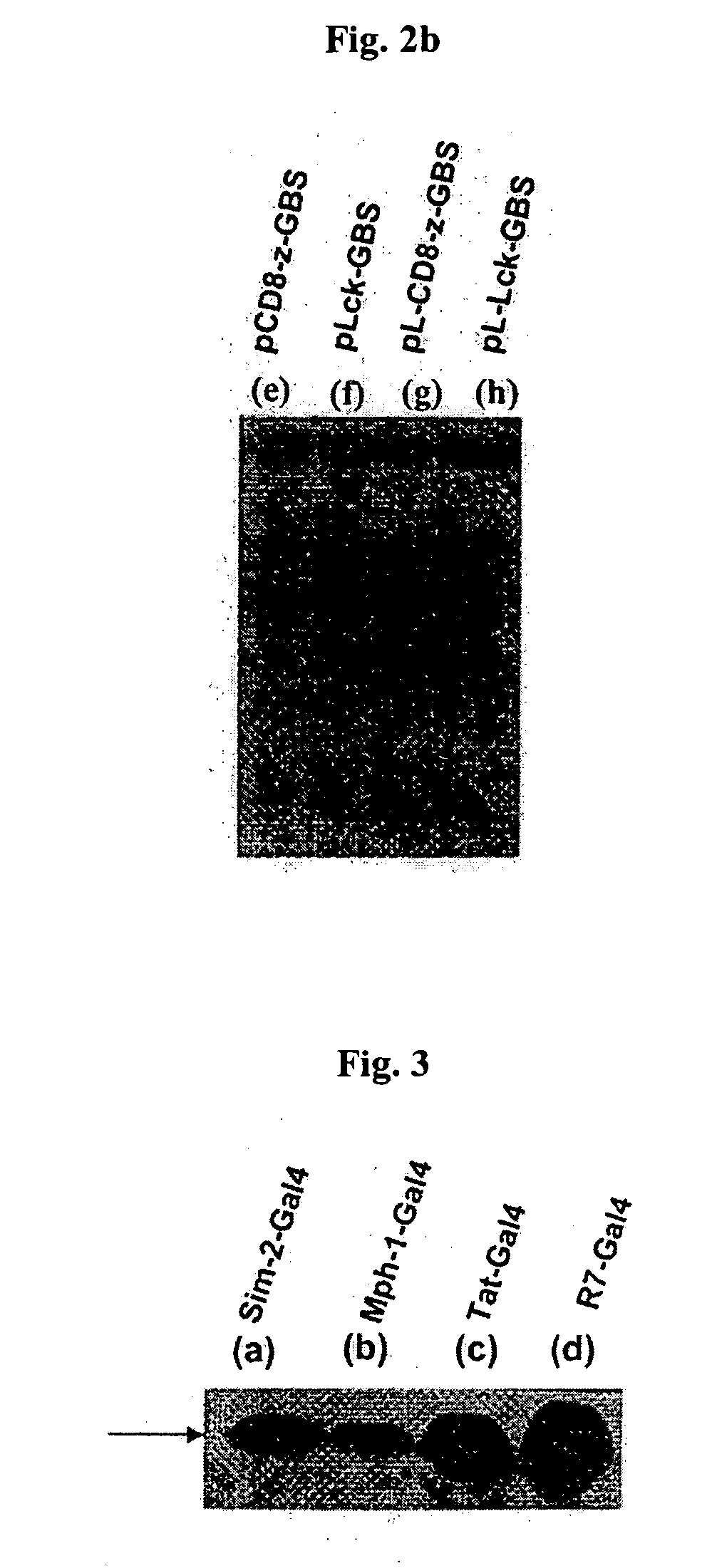
DNA/RNA transduction technology and its clinical and basic applications
InactiveUS20060099677A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainIn vivoCytoplasm
This invention relates to a method for in vivo and in vitro transferring efficiently DNA / RNA coding materials regulating bio-function to cytoplasm or nucleus in eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells using PTD (Protein Transduction Domain) and DNA / RNA binding factor. Particularly, this invention provides a method for in vivo transferring the materials to cells through various routes comprising intramuscular, intraperitoneal, intravein, oral, nasal, subcutaneous, intradermal, mucosal, inhalation. Accordingly, the method of this invention can be used for technology to transfer DNA / RNA to various cell types and express them in the cells transiently or permanently in medicinal applications such as DNA / RNA vaccine and gene therapy, as well as basic applications.
Owner:FORHUMANTECH CO LTD
Preparation of specific tumor killing cell
ActiveCN102526716ABreak immune tolerancePowerful killing functionMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCell immunityT lymphocyte
The invention relates to an antitumor cell immunotherapy technology, in particular to preparation of a specific tumor killing cell. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: 1, sampling a single prokaryotic cell from peripheral blood; 2, separating a DC (Dendritic Cell) from a T cell; 3, maturing the DC and preparing a DC vaccine; 4, preparing a CIK (Cytokine Induced Killer); 5, preparing a CTL (cytotoxic T lymphocyte); and 6, preparing a specific DC-CIK-CTL cell preparation.
Owner:玥特农生物科技河北有限责任公司
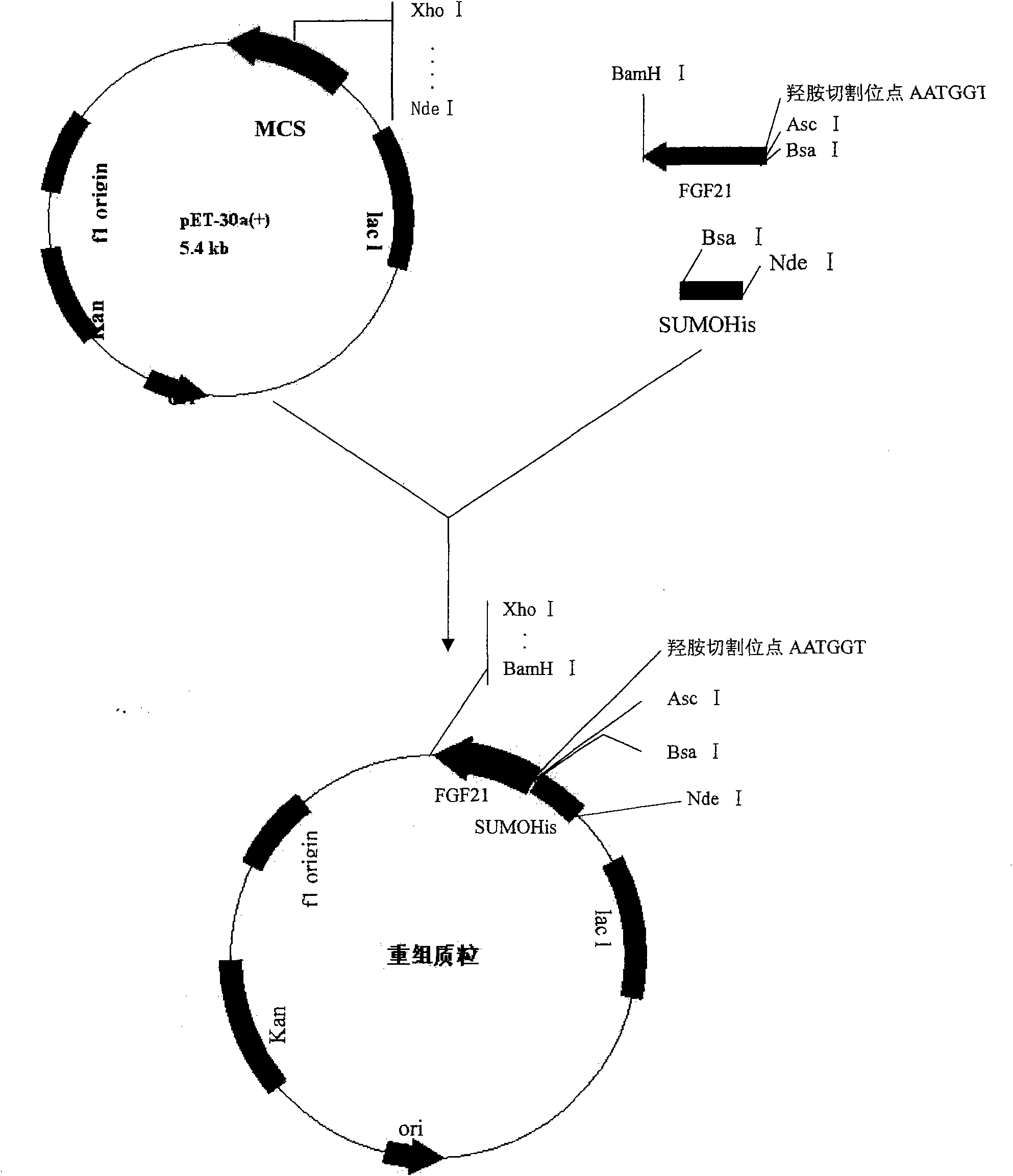
Human FGF21 mutant gene and method for preparing recombinant human FGF21 protein
InactiveCN101967485AStrong specificityImprove stabilityFungiBacteriaHydroxylamineHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
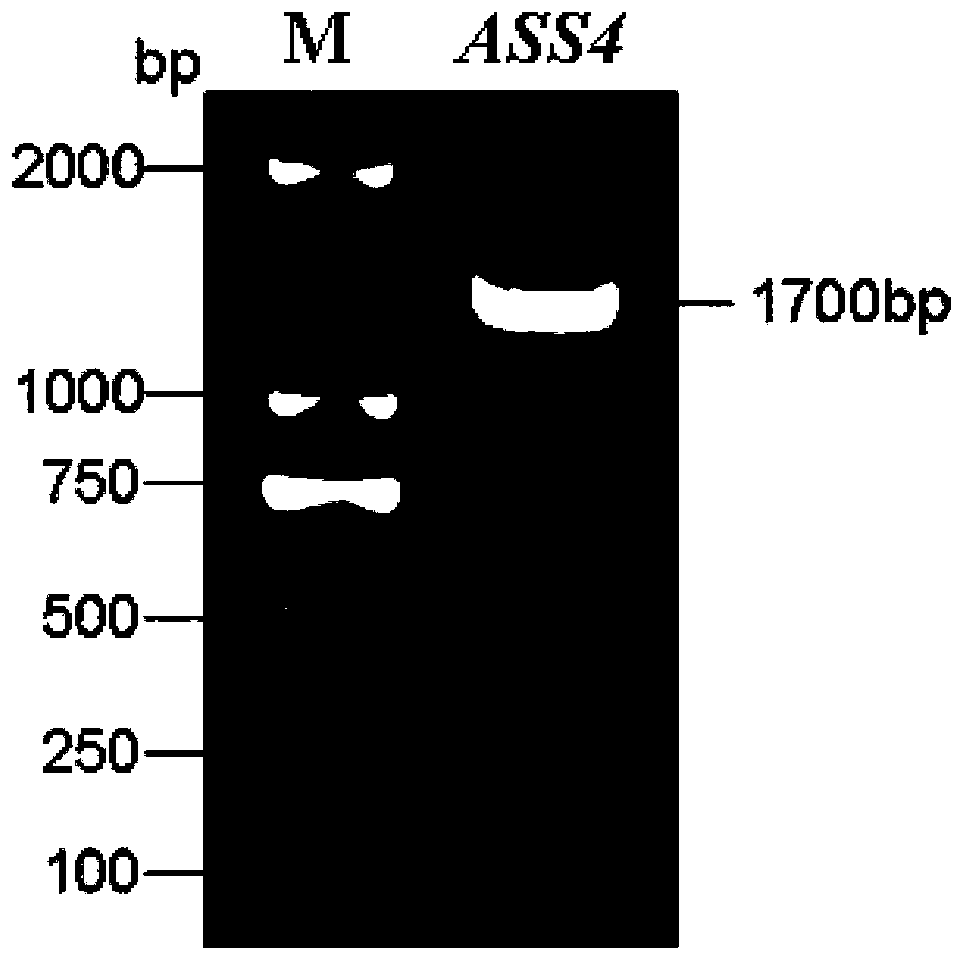
Agilawood sesquiterpenoid synthase protein ASS4 and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention provides agilawood sesquiterpenoid synthase protein ASS4 and an encoding gene ASS4 thereof. The protein comprises the following components: (1), protein formed by amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2; (2), protein derived from the protein in (1), having the same function as the protein in (1), and formed in the way that one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 are replaced and deleted or added. The invention further provides a preparation method and application of the agilawood sesquiterpenoid synthase protein ASS4. The agilawood sesquiterpenoid synthase protein ASS4, provided by the invention, can be used for catalyzing agilawood sesquiterpenoid externally, the gene ASS4 provided by the invention can be converted into prokaryotic cell, yeast or more advanced eukaryocyte, so as to have corresponding agilawood sesquiterpenoid synthase activity, and the mass production of agilawood sesquiterpenoid can be realized, and the damage to the resource of rare and endangered South China medical aquilaria sinensis is reduced, therefore, the agilawood sesquiterpenoid synthase protein ASS4 has significant economic value and application prospect.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
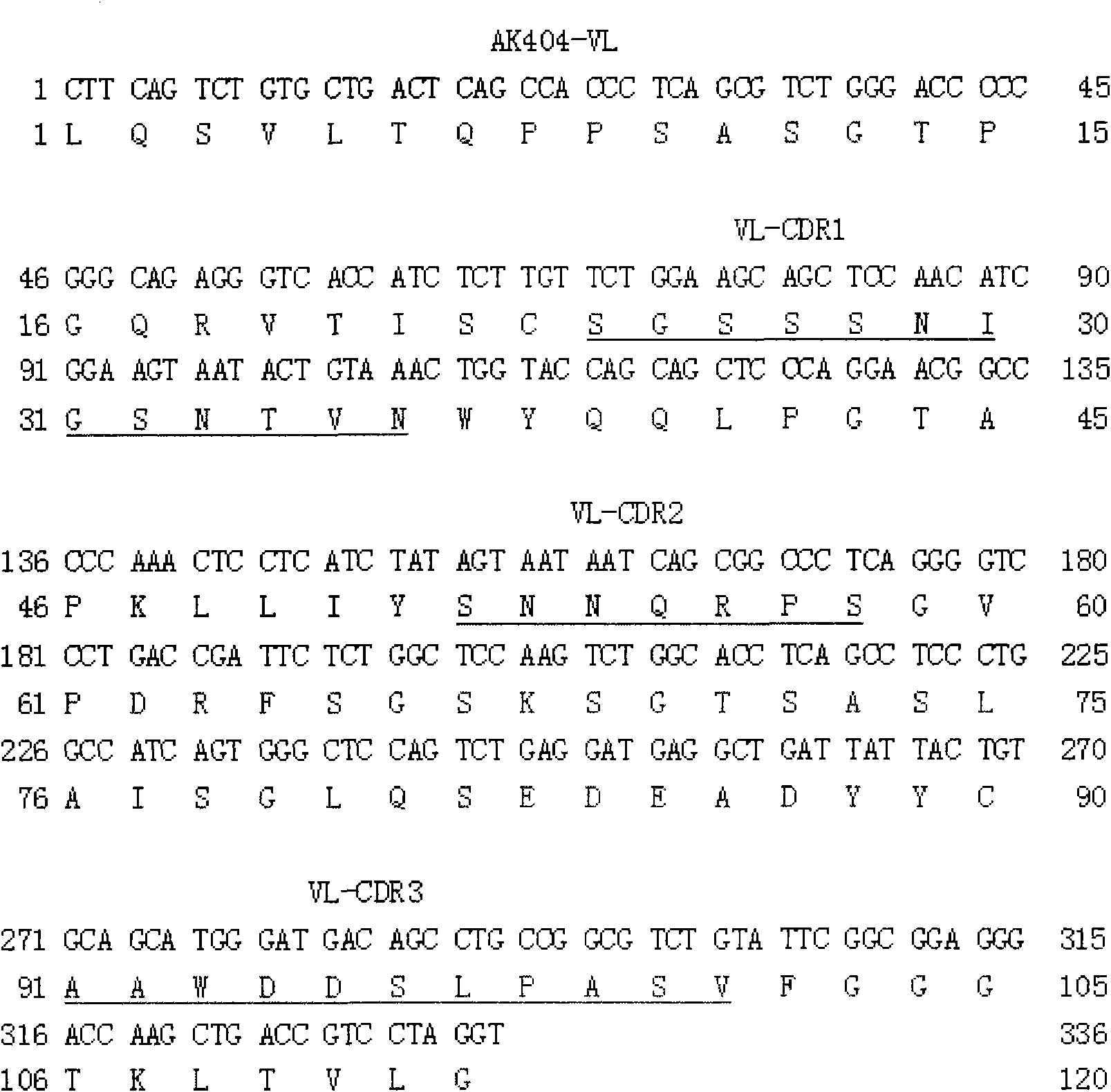
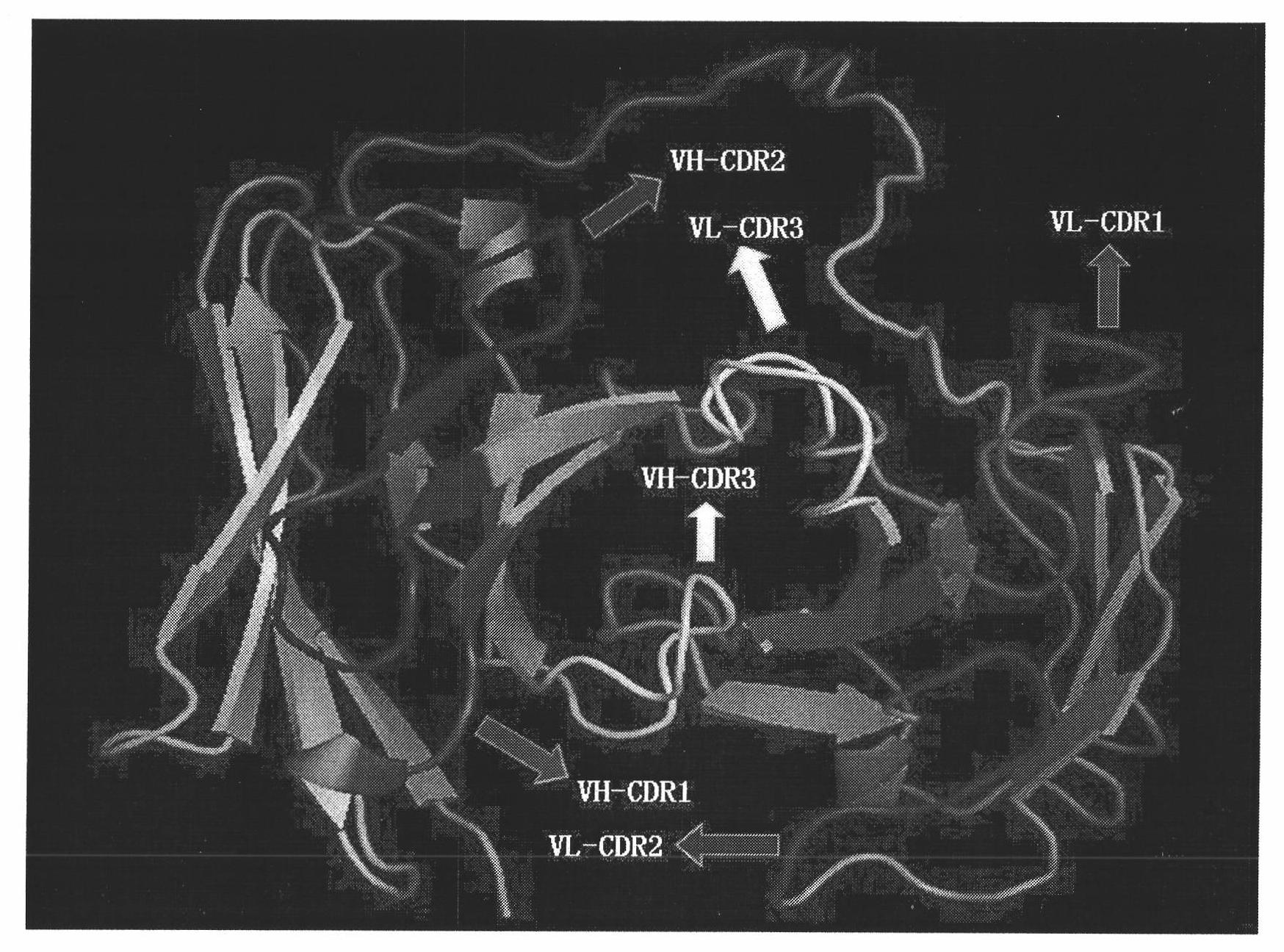
Whole human source anti-vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor 2 single chain antibody
InactiveCN101863980AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMaterial analysisSingle-Chain AntibodiesVascular endothelium
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering antibodies and particularly relates to a whole human source single chain antibody which is designed and expressed by genetic engineering and has specific affinity towards human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2). The invention also provides a nucleotide sequence of heavy chain variable region and light chain variable region immunoglobulin molecules, a nucleotide sequence which comprises the heavy chain variable region and light chain variable region immunoglobulin molecules, an amino acid sequence which comprises variable heavy chain and variable light chain immunoglobulin molecules, and a sequence which corresponds to CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 of a complementary determining region. The invention also provides a method for generating and expressing the anti-VEGFR-2 single chain antibody, by cycling operations of gathering-elution-gathering, an antibody which has specific affinity towards the human vascular endothelial growth factor is screened, and then the single chain antibody is obtained through a prokaryotic cell secretion and expression system and an affinity purification system. The antibody can be coupled with a detectable substance and therapeutic agent.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Hybridoma cell line producing monoclonal antibody against foot-and-mouth disease virus, the monoclonal antibody therefrom, immunoassay reagent and kit, and immunoassay method
ActiveUS20110014639A1Useful for developmentImprove efficacyAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementMonoclonal antibody 14G2AStructural protein
Provided herein are a hybridoma cell line producing monoclonal antibody against foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), the monoclonal antibody therefrom, reagent and kit for ELISA, and immunoassay method. The hybridoma cell line is produced by cell fusion of a parental cell and a myeloma cell line and has the same characteristics as the cell line whose strain designation is CmA40 and deposition number is ATCC (To be Provided). The parental cell is a splenocyte isolated from the spleen of a mouse immunized by an antigen derived from a 3ABC non-structural protein (NSP) of FMDV. The antigen used here is expressed by a prokaryotic cell. The monoclonal antibody produced by the hybridoma cell line can specifically recognize a 3ABC polypeptide and does not cross-react with an antiserum of swine vesicular disease virus.
Owner:NAT INST FOR ANIMAL HEALTH COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Human source Fab antibody for anti recombined alkalescent fibroblast growth factor and application
InactiveCN101092457AHigh affinityImprove featuresImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsSurface displayFibrosis
This invention discloses anti-recombinant alkaline fibroblast growth factor human-derived Fab antibody and its application. The antibody segment genome comprises: heavy chain Fd chain and light chain kappa chain. This invention utilizes phage surface display technique to successfully construct kappa chain and Fd chain genes of human-derived Fab antibody that can neutralize recombinant human bFGF or FGF-2. Functional neutralizing antibody that can specifically bind bFGF or FGF-2 is obtained in prokaryotic cells, yeast cells, insect cells and eukaryotic cells, which can be used to prepare antibody drugs that can diagnose and treat tumors, and inhibit kidney, liver and lung fibrosis. The bFGF or FGF-2 human-derived Fab antibody has high affinity and specificity, and can be directly used to develop antibody drugs.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Modified DNA molecule, recombinant containing the same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6936707B2Good effectImproving immunogenicityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenModified dna
There is provided a DNA molecule derived from a prokaryotic cell in which at least one of the DNA regions encoding NXB (N is asparagine, X is any amino acid other than proline, and B is serine or threonine) has been modified so that no N-glycosylation occurs during the expression in a eukaryotic cell, and since the DNA molecule has been modified at the N-glycosylation site, it produces a non-N-glycosylated protein, which thereby exhibits a high immunogenicity when, for example, it is allowed to produce, in a eukaryotic cell, an antigen protein derived from a prokaryotic cell.
Owner:ZEON CORP
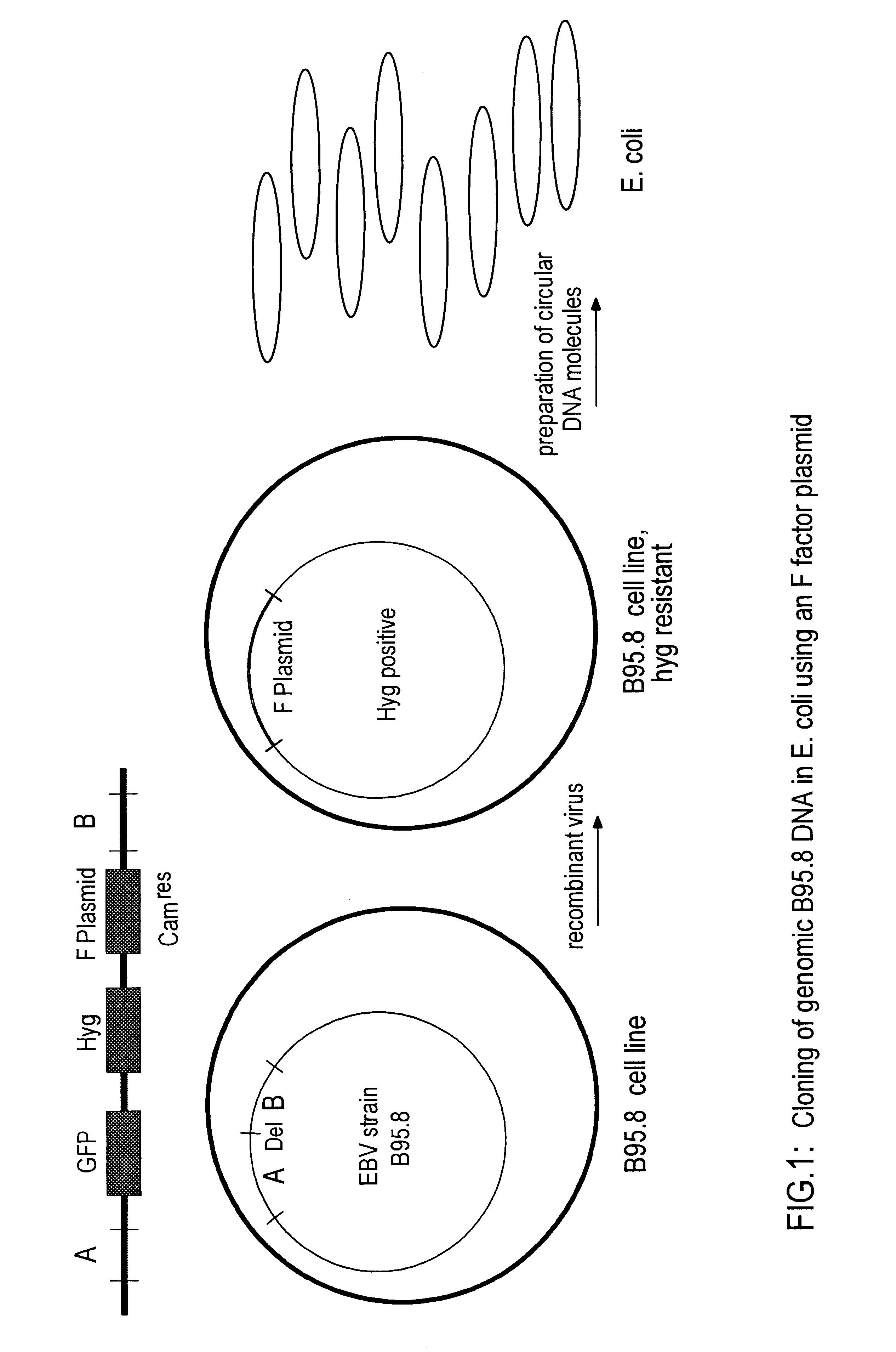
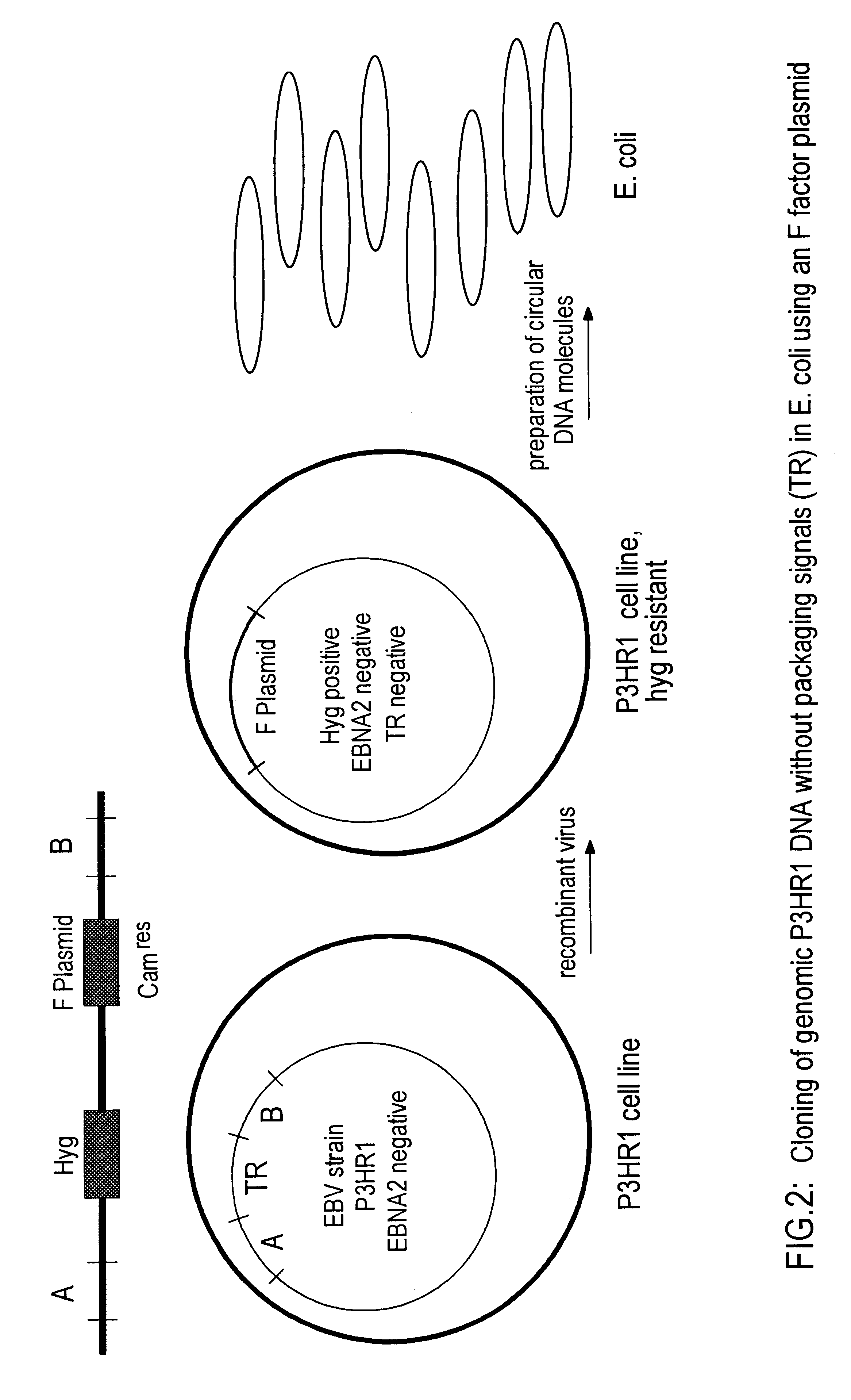
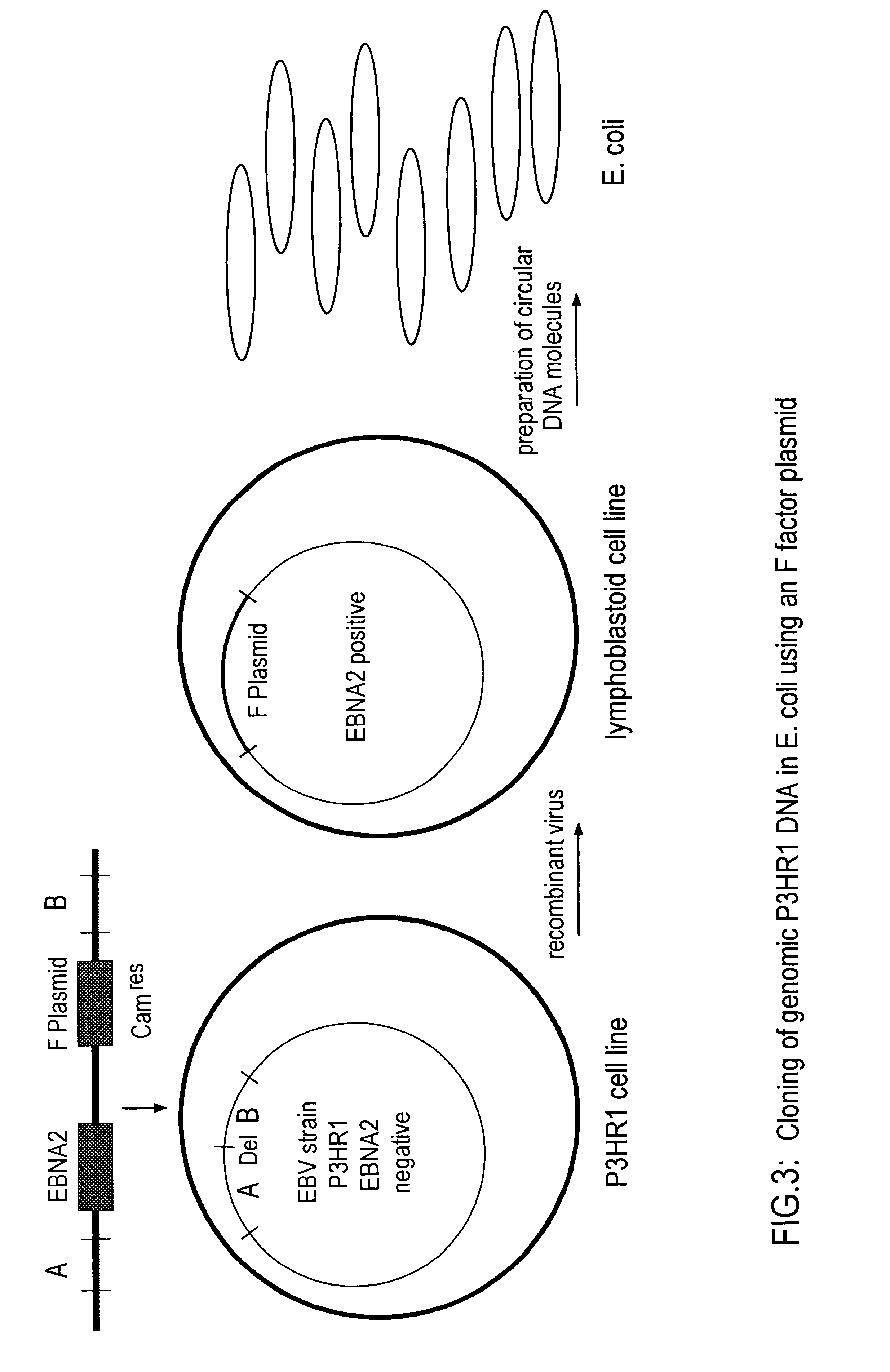
DNA virus vectors and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS6291246B1Improve efficiencyDifficult to controlBacteriaGenetic material ingredientsDna viralVirology
The invention relates to a method for the preparation of DNA virus vectors capable of replication in eukaryotic as well as in prokaryotic cells as well as to DNA virus vectors prepared by this method. Preferably, the method is used to prepare Epstein-Barr virus vectors.
Owner:GSF FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR UMWELT & GESUNDHEIT
Capsular gram-positive bacteria bioconjugate vaccines
The present invention encompasses a novel S. aureus bioconjugate vaccine. More generally, the invention is directed to Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines containing a protein carrier, at least one polysaccharide such as a capsular Gram-positive polysaccharide, and, optionally, an adjuvant or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The instant invention also includes methods of producing Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines. An N-glycosylated protein is also provided that contains one or more polysaccharides such as Gram-positive polysaccharides. The invention is additionally directed to engineered prokaryotic organisms comprising nucleotide sequences encoding a glycosyltransferase of a first prokaryotic organism and a glycosyltransferase of a second prokaryotic organism. The invention further includes plasmids and prokaryotic cells transformed with plasmids encoding polysaccharides and enzymes which produce an N-glycosylated protein and / or bioconjugate vaccine. Further, the invention is directed to methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal comprising administering said bioconjugate vaccines.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
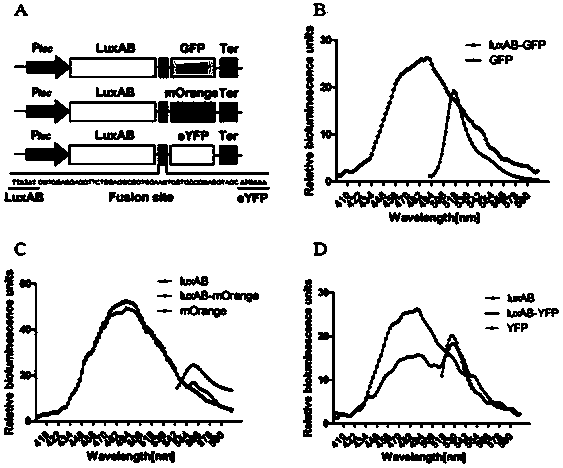
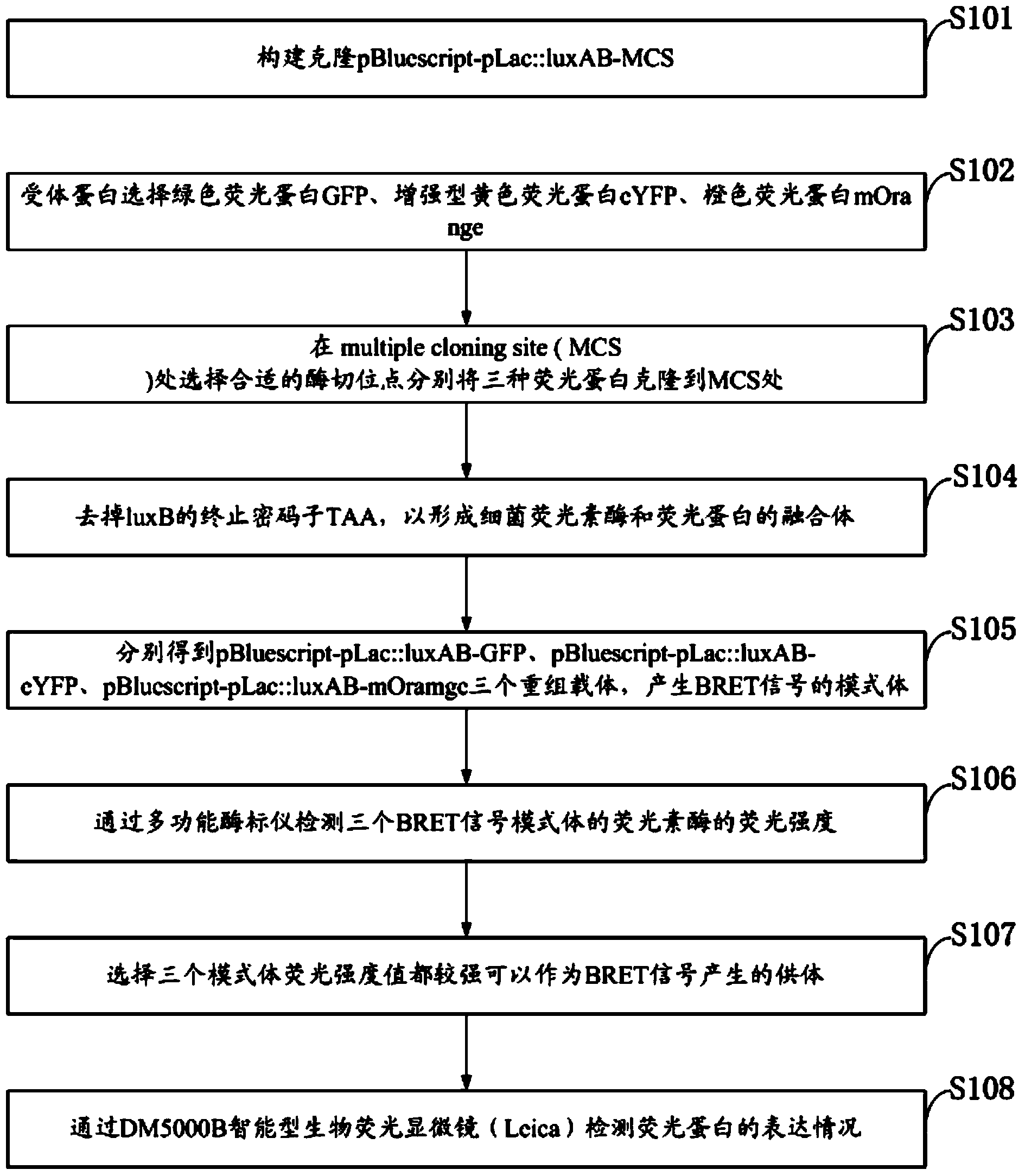
Method for detection of protein-protein interaction through a BRET technology based on bacterial Luciferase
InactiveCN103616502AIncrease reaction rateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBacterial luciferaseFluorescence microscope
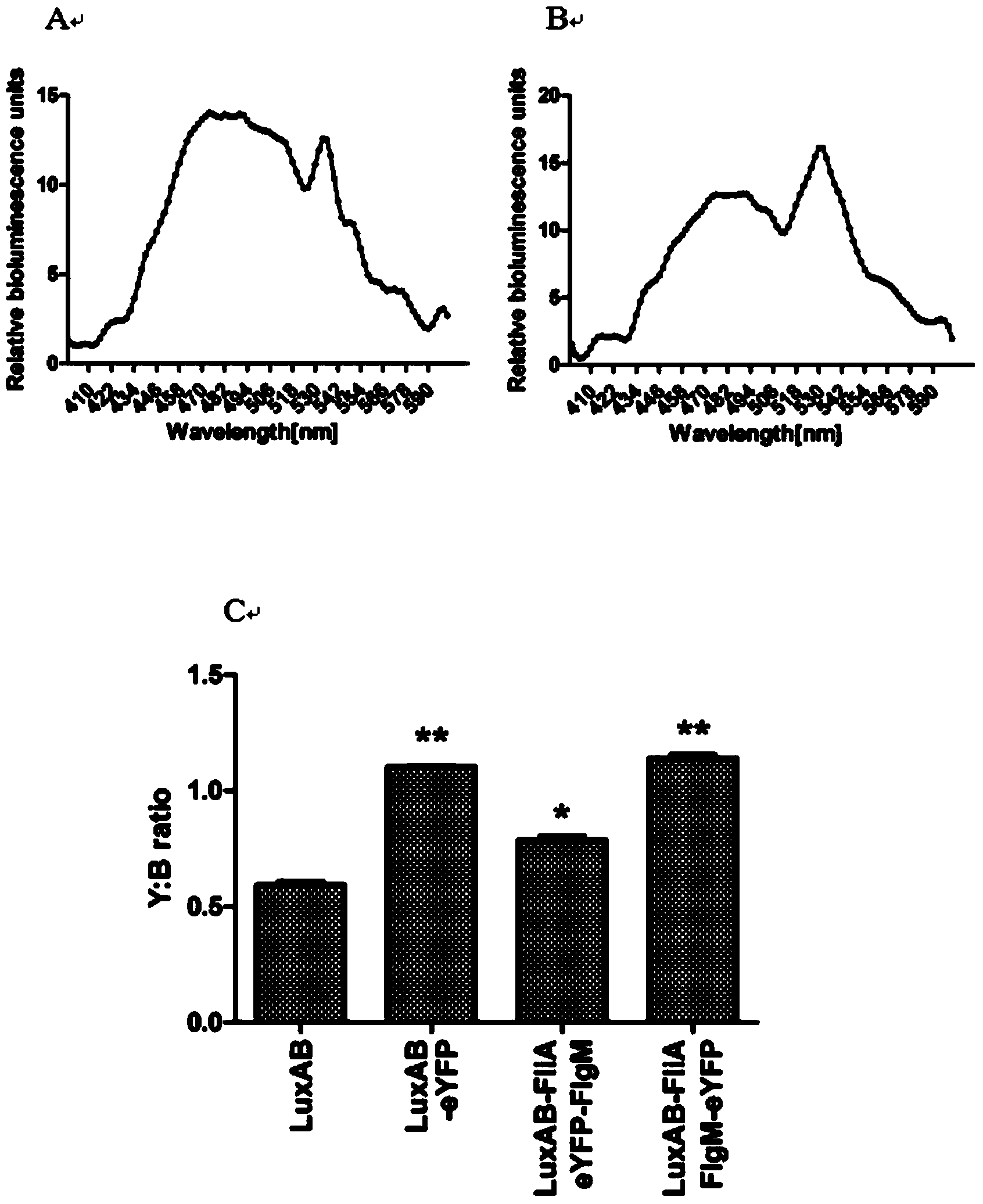
The invention discloses a method for detection of protein-protein interaction through a BRET technology based on bacterial Luciferase. A fluorescent donor clonal pBluescript-pLac::luxAB-MCS is constructed; Green fluorescent protein (GFP) and the like are selected as acceptor proteins; appropriate enzyme cutting sites are chosen in MCS, and three kinds of fluorescent proteins are cloned into the MCS respectively; model bodies of BRET signals are generated; the fluorescence intensity of Luciferase of each of the three BRET model bodies is detected; three model bodies with high fluorescence intensity value are selected as fluorescence donors of BRET signal generation; the expression conditions of the fluorescent proteins are detected through a biological fluorescence microscope (Leica), an appropriate fluorescence acceptor is secleted; The singals of the BRET model bodies are detected through a fluorospectrophotometer. In the method, bacterial Luciferase luxAB as a fluorescence donor for detecting interaction between two proteins and eYFP as a fluorescence acceptor generate BRET signals, and BRET models are constructed. The system can detect dynamic interaction between two proteins in vivo, raise the accuracy of detection of protein-protein interaction, and is an ideal system for detection of protein-protein interaction in prokaryotic cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
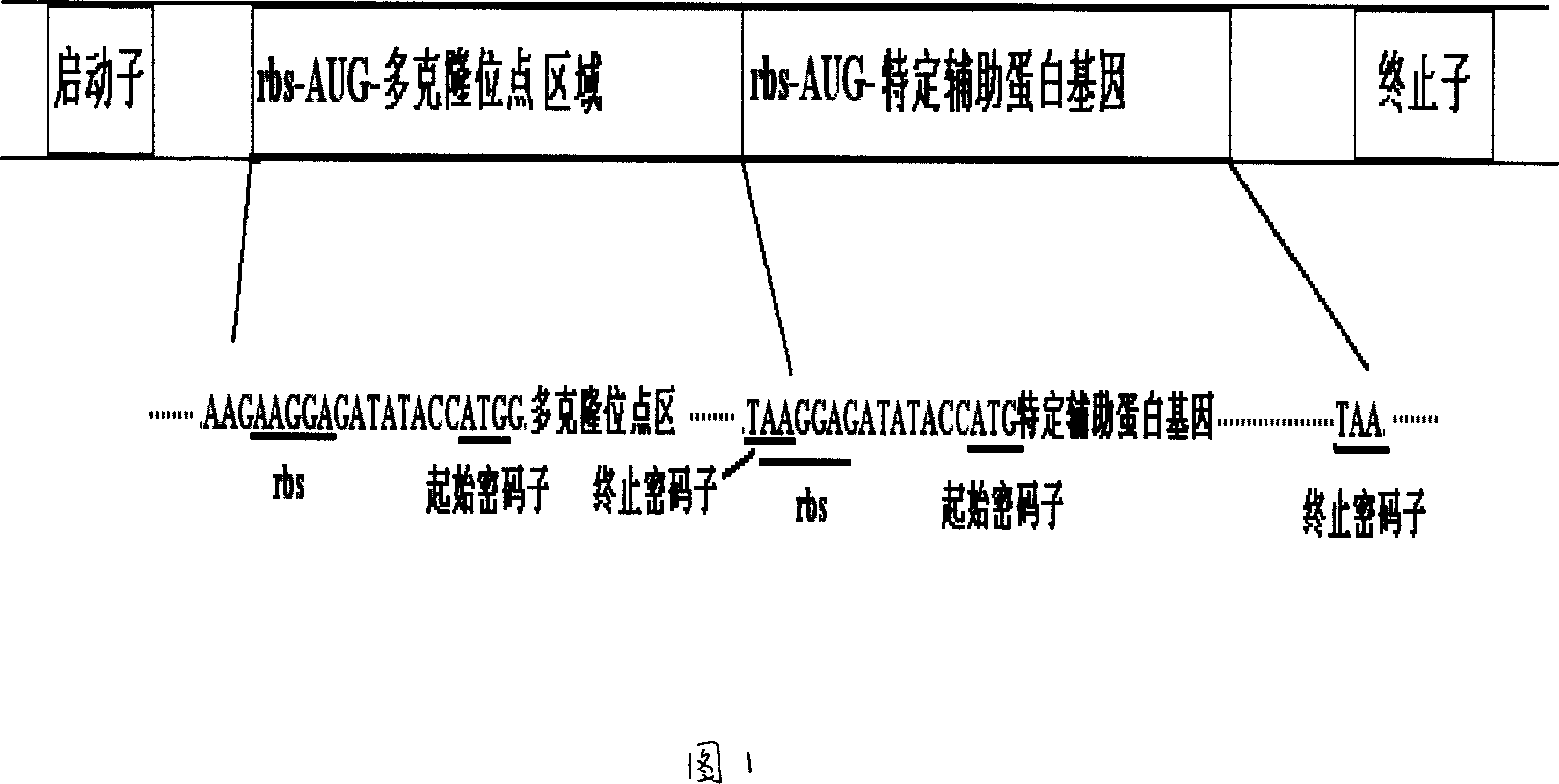
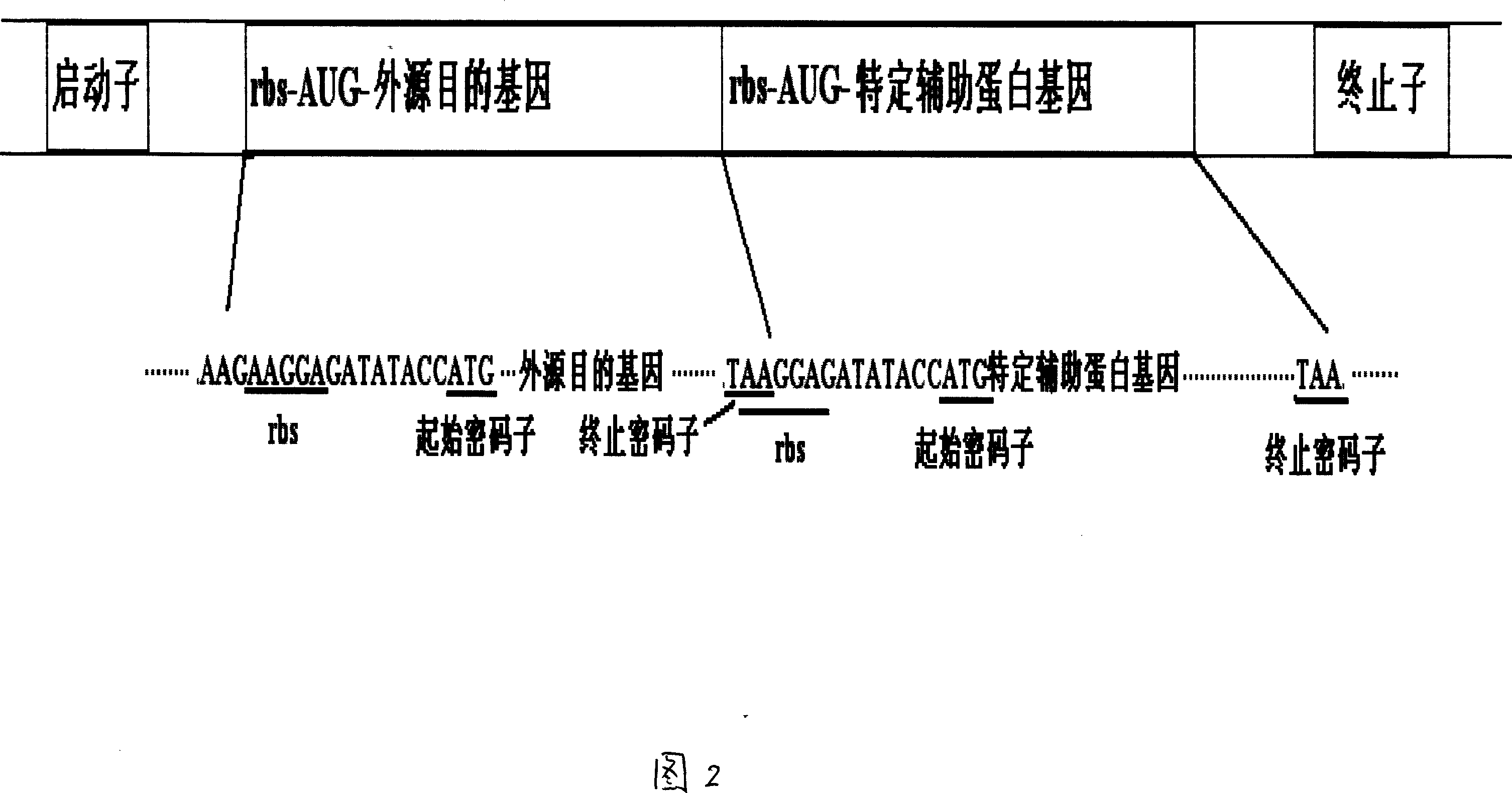
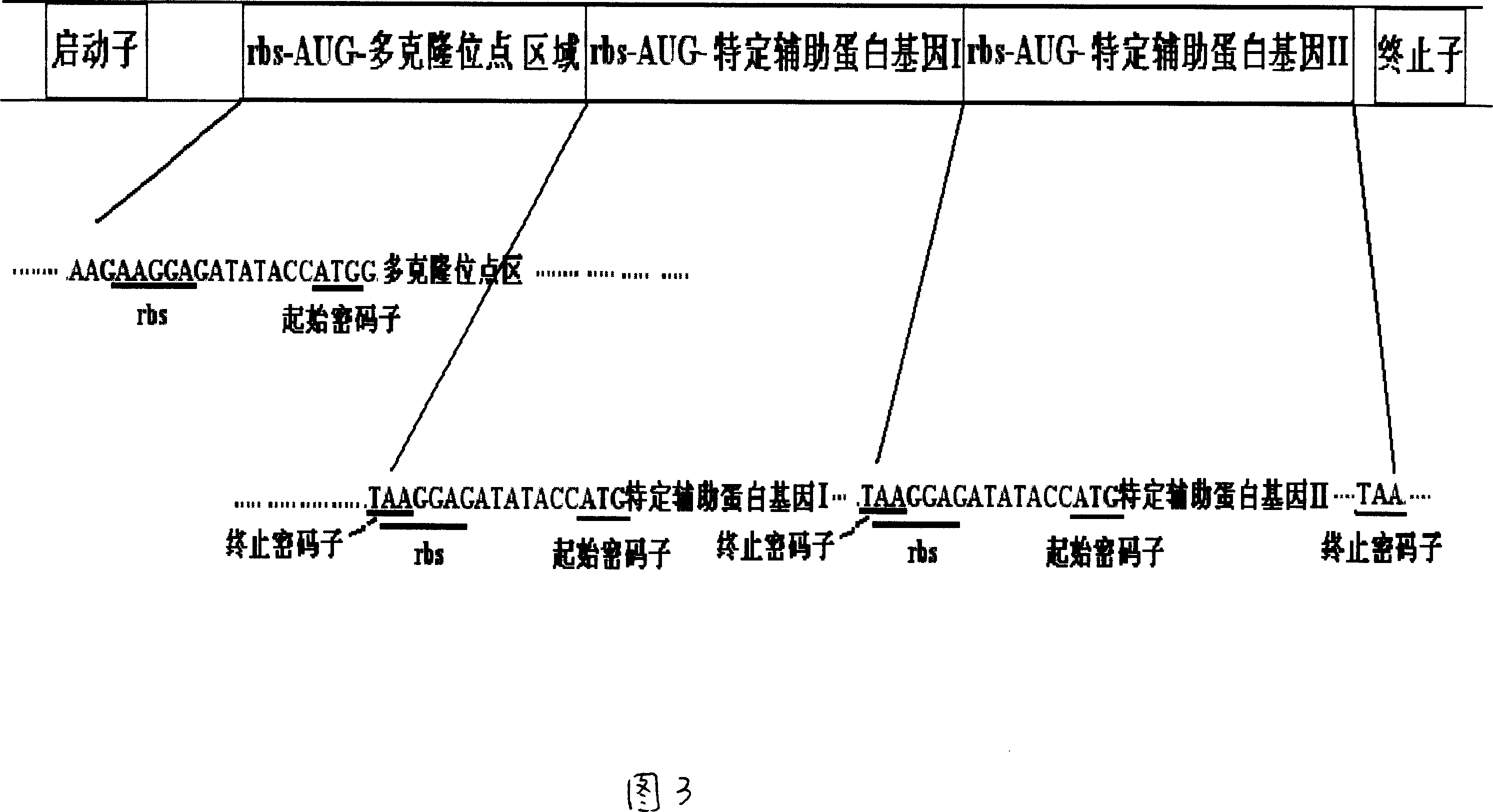
Prokaryotic cell non-fusion soluble expression system
The invention discloses a procaryotic cell non-merge solubility pressing system, which comprises the following steps: building one type auxiliary protein gene or two type auxiliary protein gene and pre-expressing exogenesis goal gene in a transcription unit; proceeding intracellular co-express through each self-contained translational control system of auxiliary protein gene and pre-expressing exogenesis goal gene in the same pronucleus expression host cell; utilizing the auxiliary protein to realize non-merge solubility expression especially to realize non-merge solubility expression with multiple disulfide bond peptide chain. This system can make the expressing quantity of procaryotic cell occupy above 105 of thallus total protein under the normal condition.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Gene for improving plant salt tolerance and drought resistance and use thereof
The invention initially discovers a nucleotide coded sequence which can improve salt resistance and drought resistance of plants, and a nucleotide coded sequence which is artificially synthesized according to codons preferred by plants. The nucleotide coded sequences construct a recombining carrier containing genes and converts the genes into host cells of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells respectively. Experiments prove that after the genes are expressed in the plant, the obtained transgenic plant has enhanced resistance to salt stress, drought stress and the like.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Foot-and-mouth disease hybridoma cell line, monoclonal antibody, detection reagent and kit
ActiveCN102533663AHas the ability to identify specificityNo cross reactionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansVirus peptidesSwine vesicular diseaseStructural protein
The invention provides a hybridoma cell line and a monoclonal antibody thereof, an immune detection reagent containing the monoclonal antibody and a kit thereof, and an immune detection method. The hybridoma cell line is prepared by fusing parental cells and myeloma cells, and has the characteristics represented by the cell line with the preservation number of PTA-11304. The parental cell line is prepared by the following steps that: prokaryotic cells are adopted to express non-structural protein coded by a 3ABC gene fragment of foot-and-mouth disease virus, the non-structural protein is adopted as antigen to immunize mice, and spleen cells of the immunized mice are taken out to prepare the parental cell line. The monoclonal antibody produced from the hybridoma cell line can provide specific recognition for the 3ABC peptide of the foot-and-mouth disease virus, and do not generate the non-specific reaction with the swine vesicular disease antiserum.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com