Patents
Literature
43 results about "Transfer DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The transfer DNA (abbreviated T-DNA) is the transferred DNA of the tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid of some species of bacteria such as Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes(actually an Ri plasmid). The T-DNA is transferred from bacterium into the host plant's nuclear DNA genome. The capability of this specialized tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid is attributed to two essential regions required for DNA transfer to the host cell. As the T-DNA is bordered by 25-base-pair repeats on each end. Transfer is initiated at the right border and terminated at the left border and requires the vir genes of the Ti plasmid.
Chemical processing cartridge and method of using same
InactiveUS20070082331A1Easy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentBiopolymer
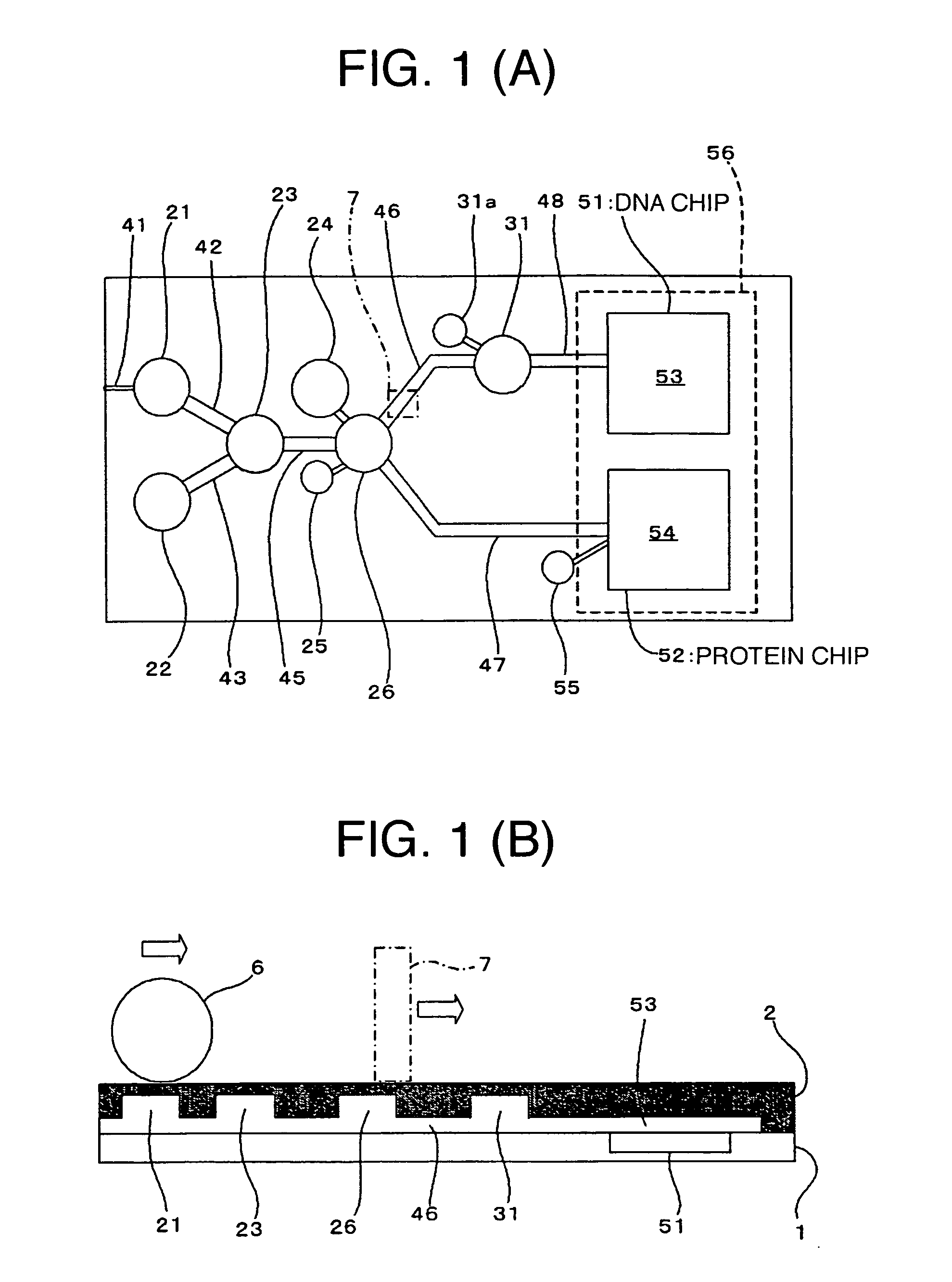
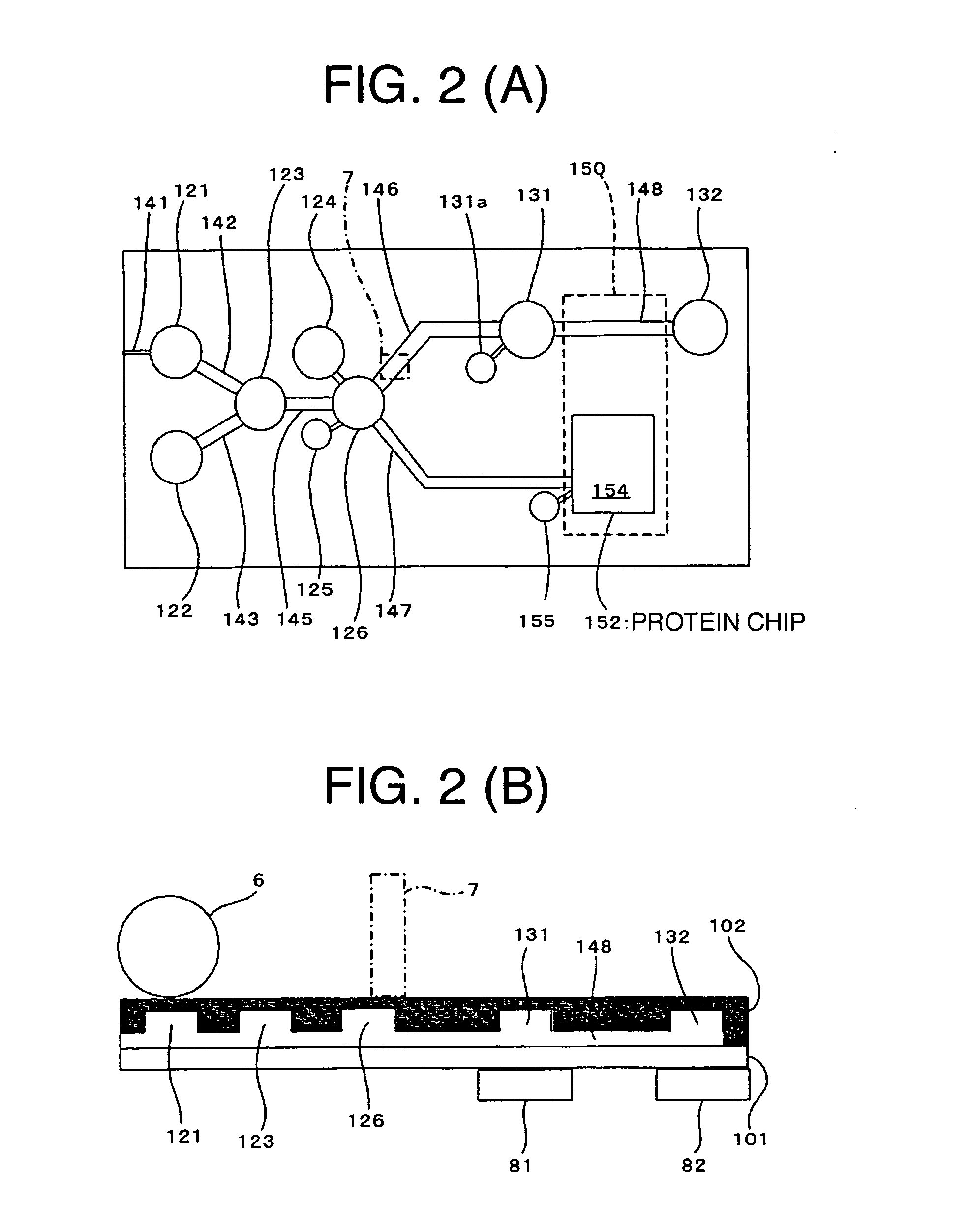
A cartridge capable of making effective use of a sample is provided. A blood sample is injected into a well via an injection path by use of a syringe, and so forth. A roller, in a state as kept pressed into contact with the cartridge, is rotated rightward, whereupon an elastic member undergoes elastic deformation to cause the blood sample held in the well, and a liquid solvent held in a well to reach a well, and the blood sample is thereby mixed with the liquid solvent. Since the liquid solvent contains surfactant, blood cells are destroyed in the well. The liquid solvent reaches a well via a flow path. At this point in time, magnetic particles held in the well, and a cleaning liquid held in the well are merged with the mixed liquid in the well. A magnet is shifted from a position corresponding to the well to a position corresponding to the well along the flow path, thereby separating and transferring DNA caught by the magnetic particles to the well. Residue inside the well after removal of DNA is transferred to a well by the roller. The separated biopolymers are analyzed in the cartridge.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Method for production of polypeptide
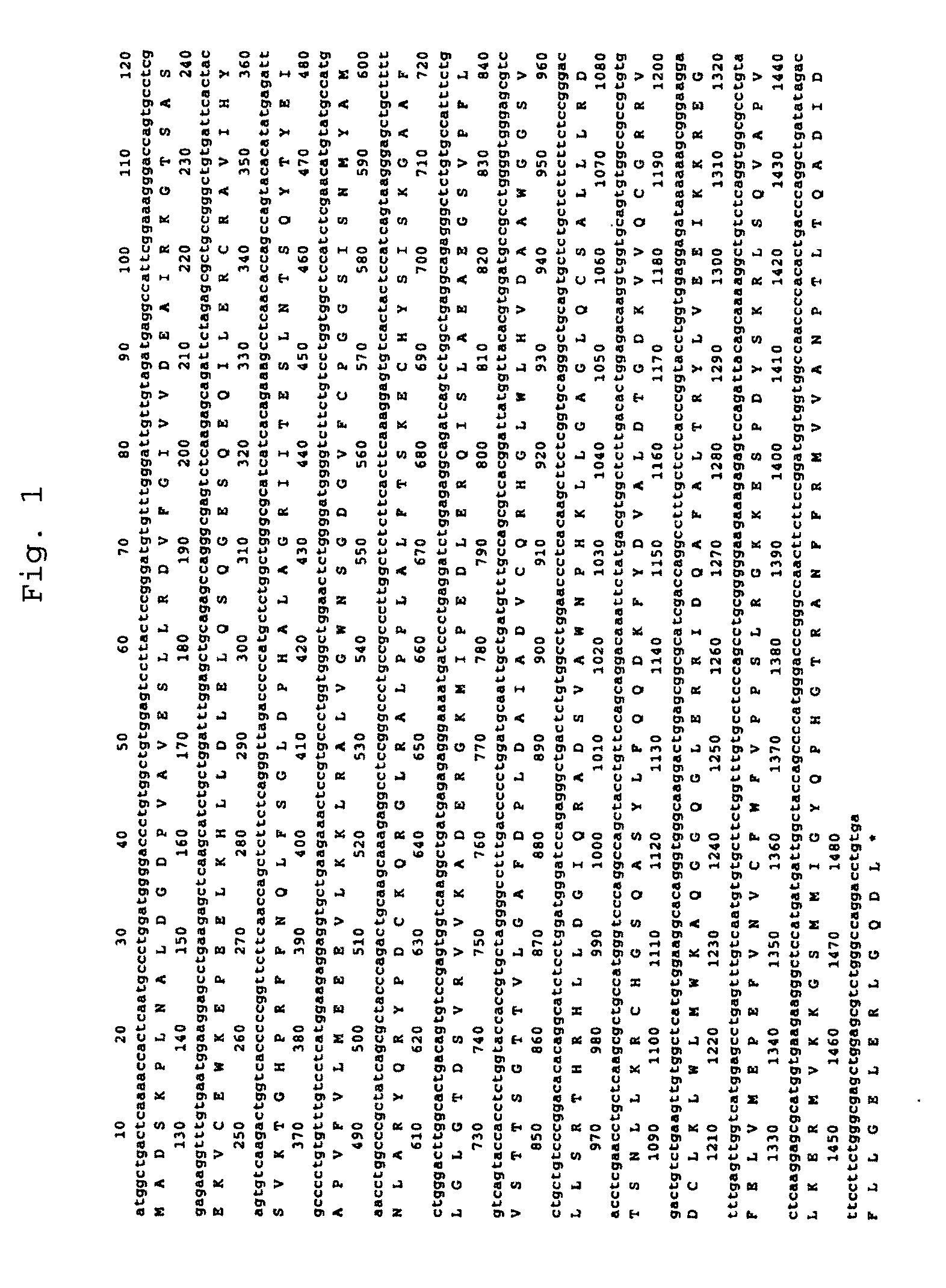
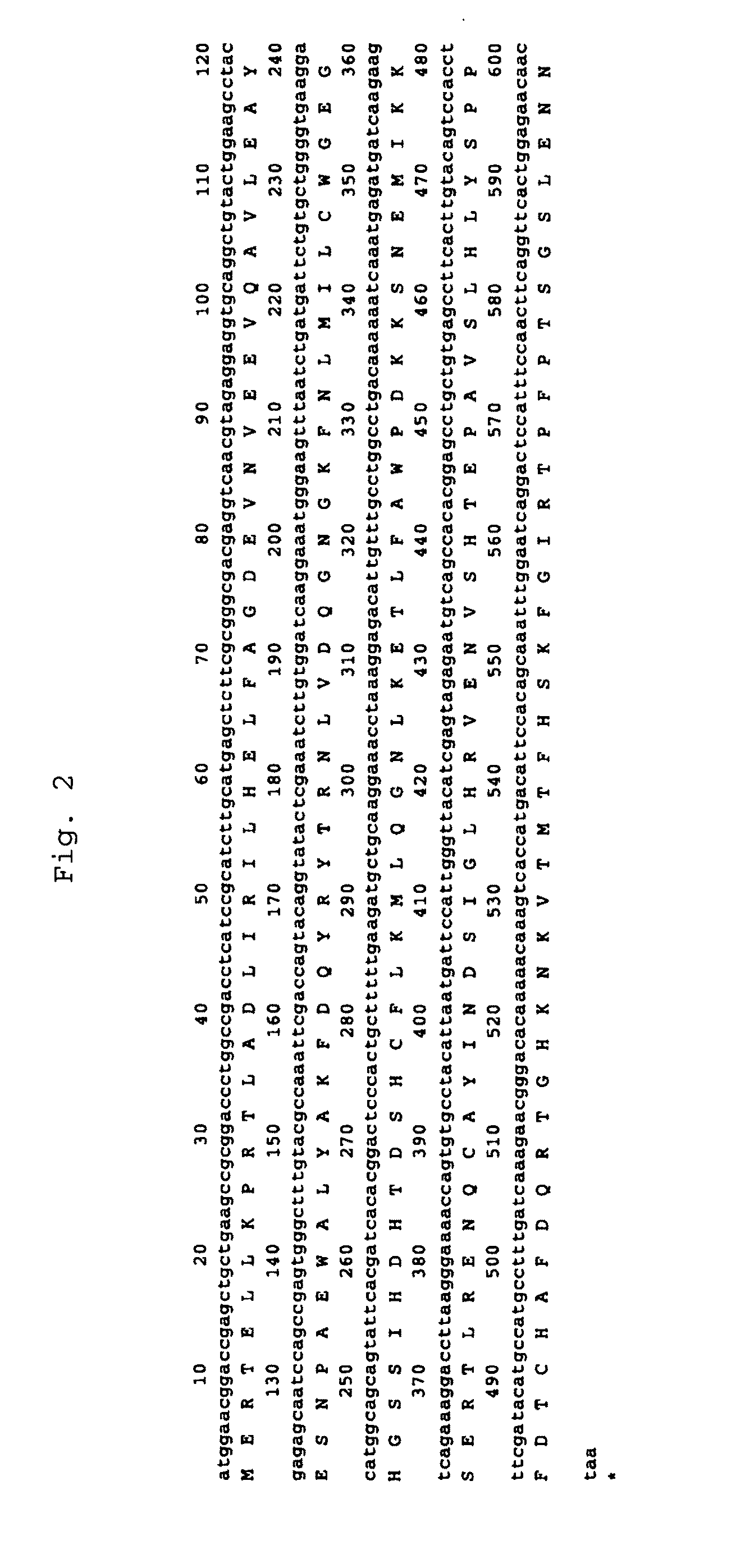
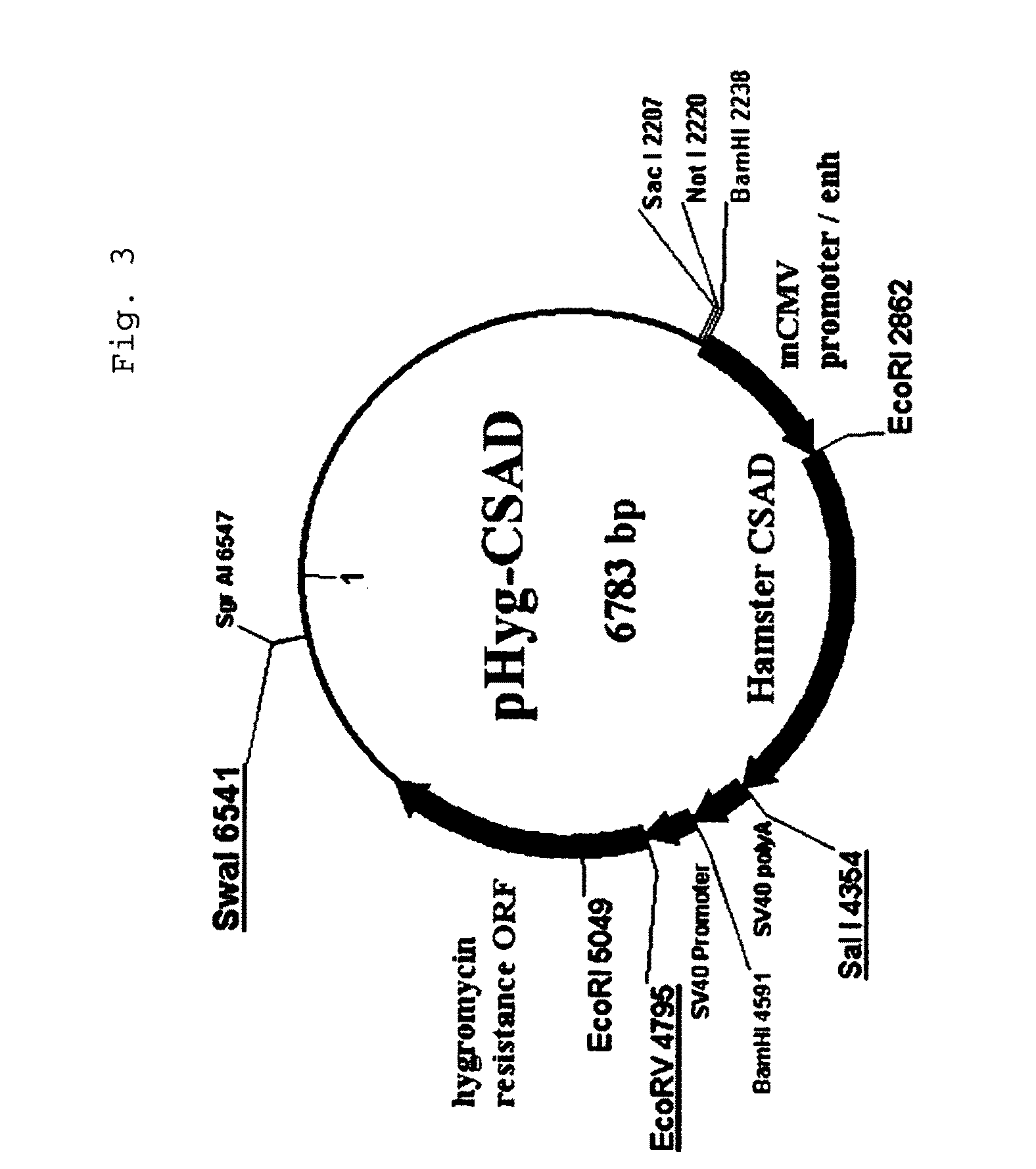
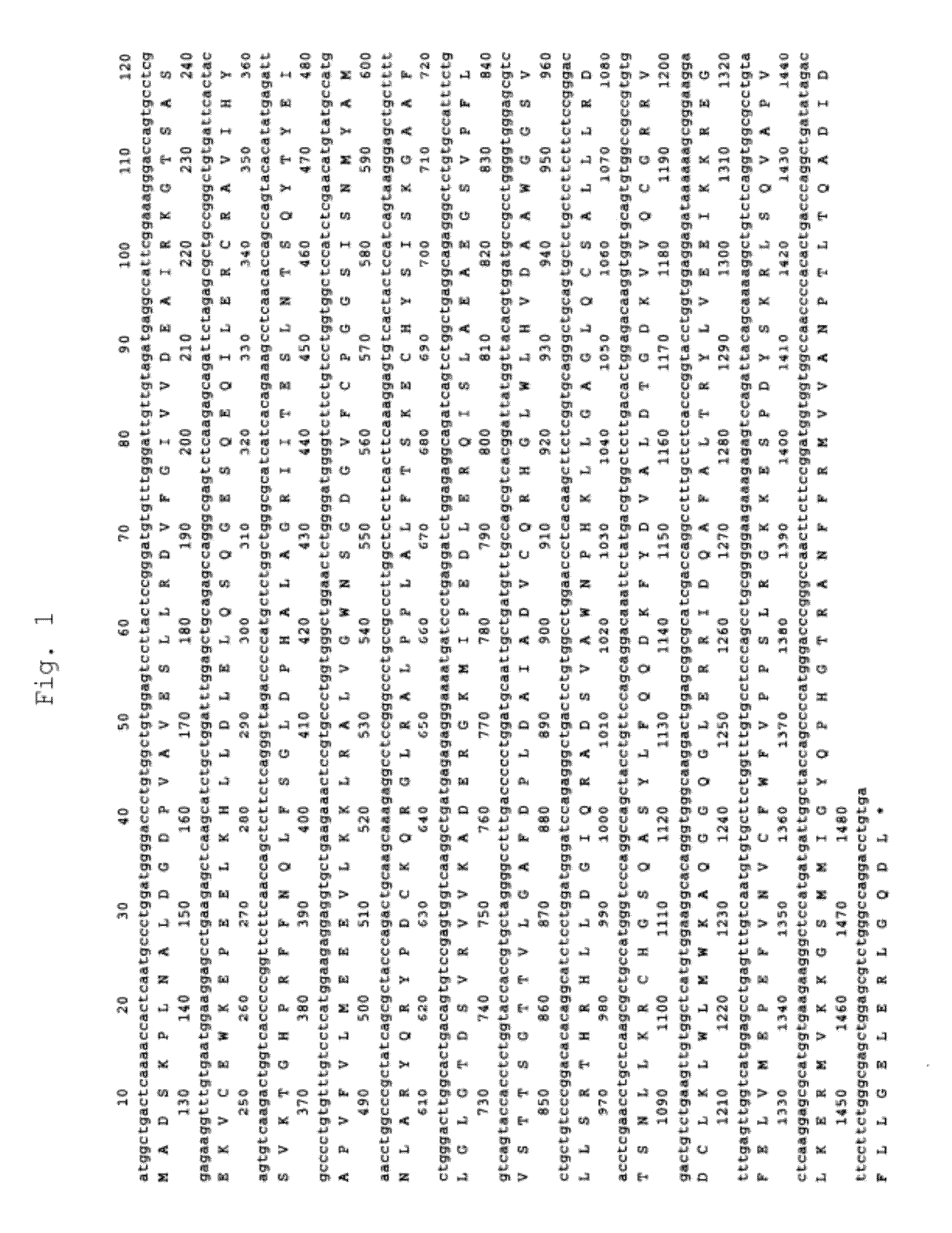
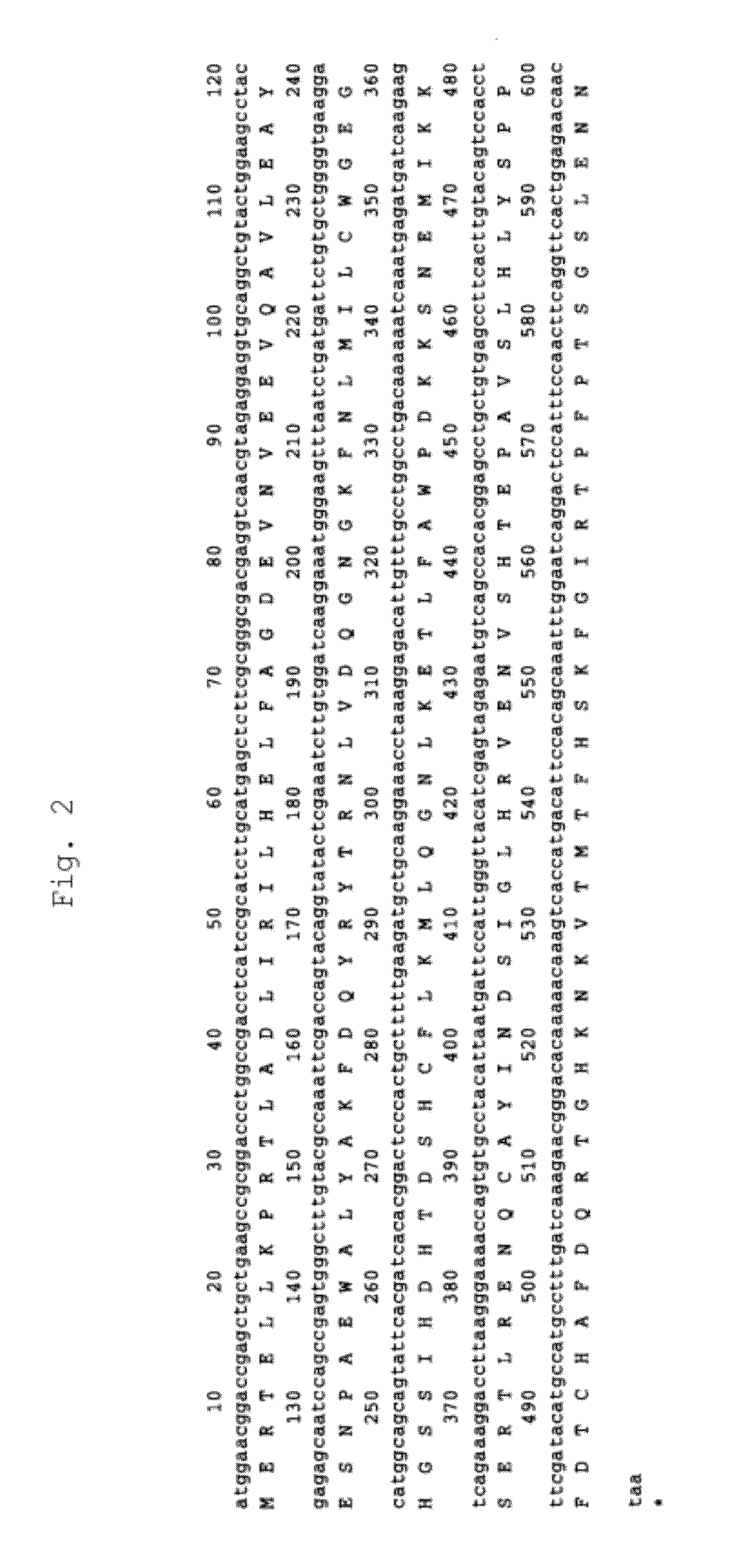
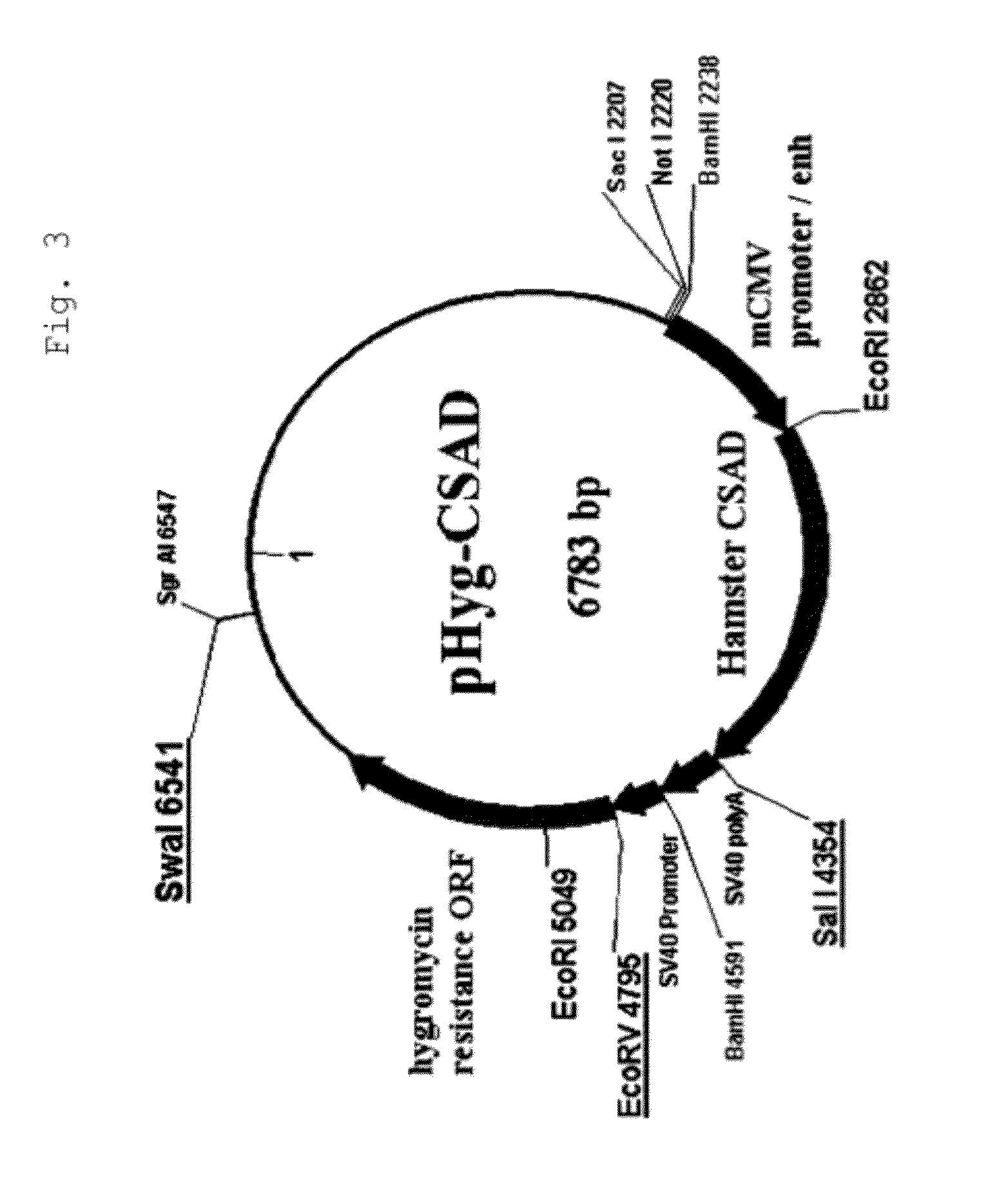
The present invention provides a method capable of producing a natural or recombinant protein in high yield.The present invention relates to a method of producing a polypeptide, comprising culturing a cell which strongly expresses cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase and has a transferred DNA encoding a desired polypeptide and thereby allowing the cell to produce the polypeptide. Hamster cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase, a DNA encoding the same, a recombinant vector and a transformed cell are also provided.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
DNA/RNA transduction technology and its clinical and basic applications
InactiveUS20060099677A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainIn vivoCytoplasm
This invention relates to a method for in vivo and in vitro transferring efficiently DNA / RNA coding materials regulating bio-function to cytoplasm or nucleus in eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells using PTD (Protein Transduction Domain) and DNA / RNA binding factor. Particularly, this invention provides a method for in vivo transferring the materials to cells through various routes comprising intramuscular, intraperitoneal, intravein, oral, nasal, subcutaneous, intradermal, mucosal, inhalation. Accordingly, the method of this invention can be used for technology to transfer DNA / RNA to various cell types and express them in the cells transiently or permanently in medicinal applications such as DNA / RNA vaccine and gene therapy, as well as basic applications.
Owner:FORHUMANTECH CO LTD
Method of producing heterogeneous protein
The present invention provides a method capable of producing a natural or recombinant protein in high yield.The present invention relates to a method of producing a polypeptide, comprising culturing a cell which strongly expresses alanine aminotransferase and has a transferred DNA encoding a desired polypeptide and thereby allowing the cell to produce the polypeptide.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
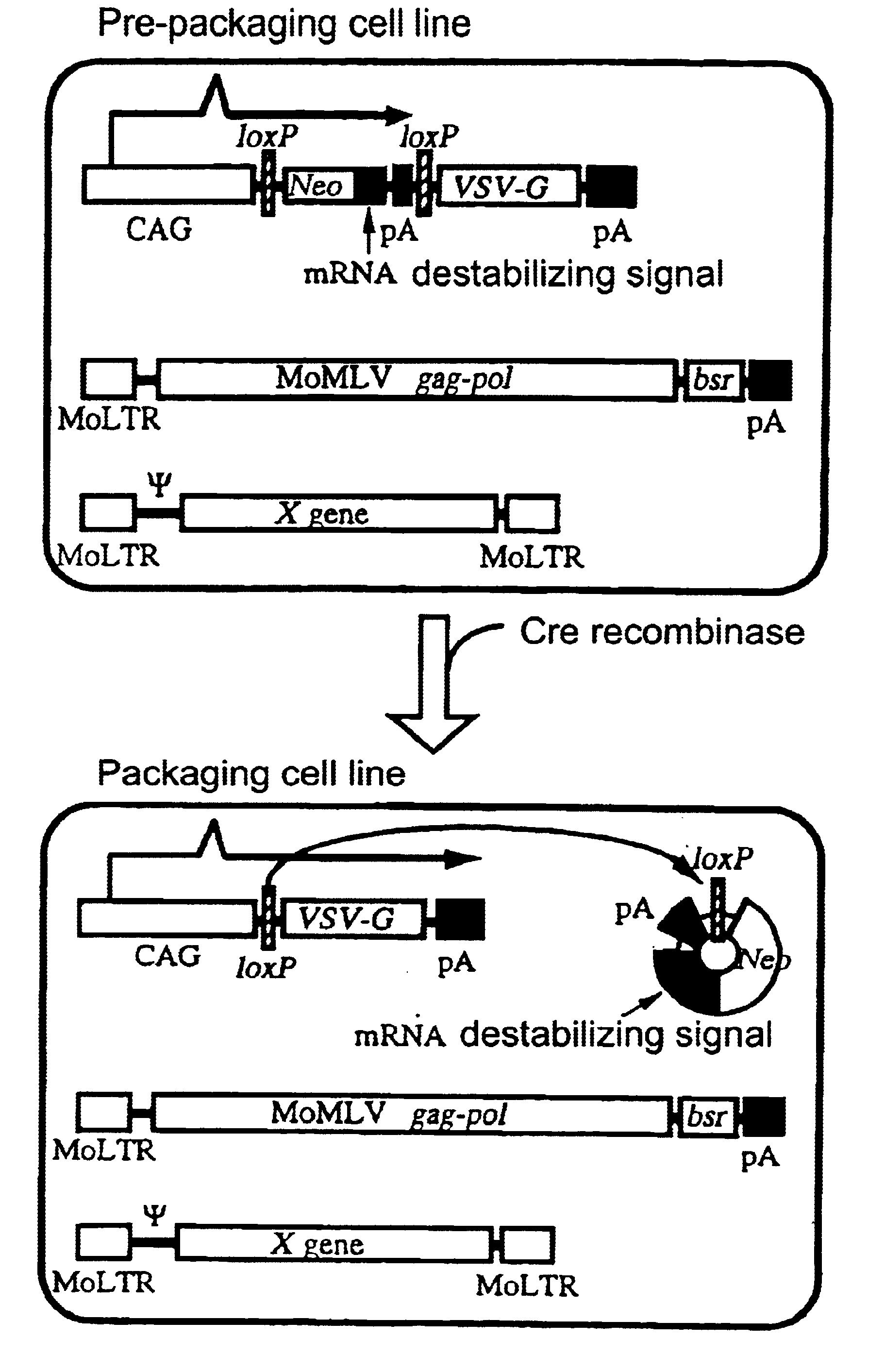
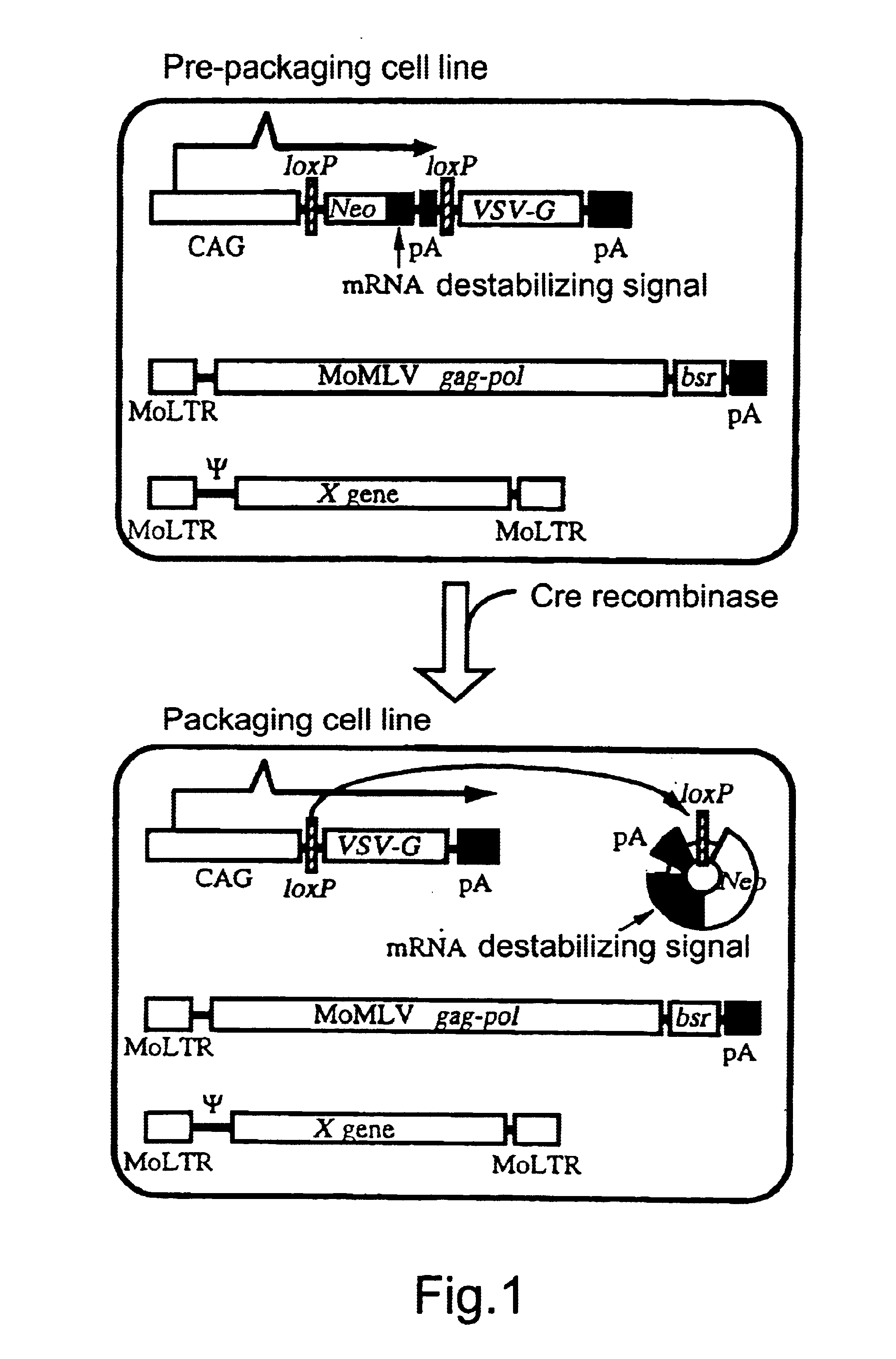
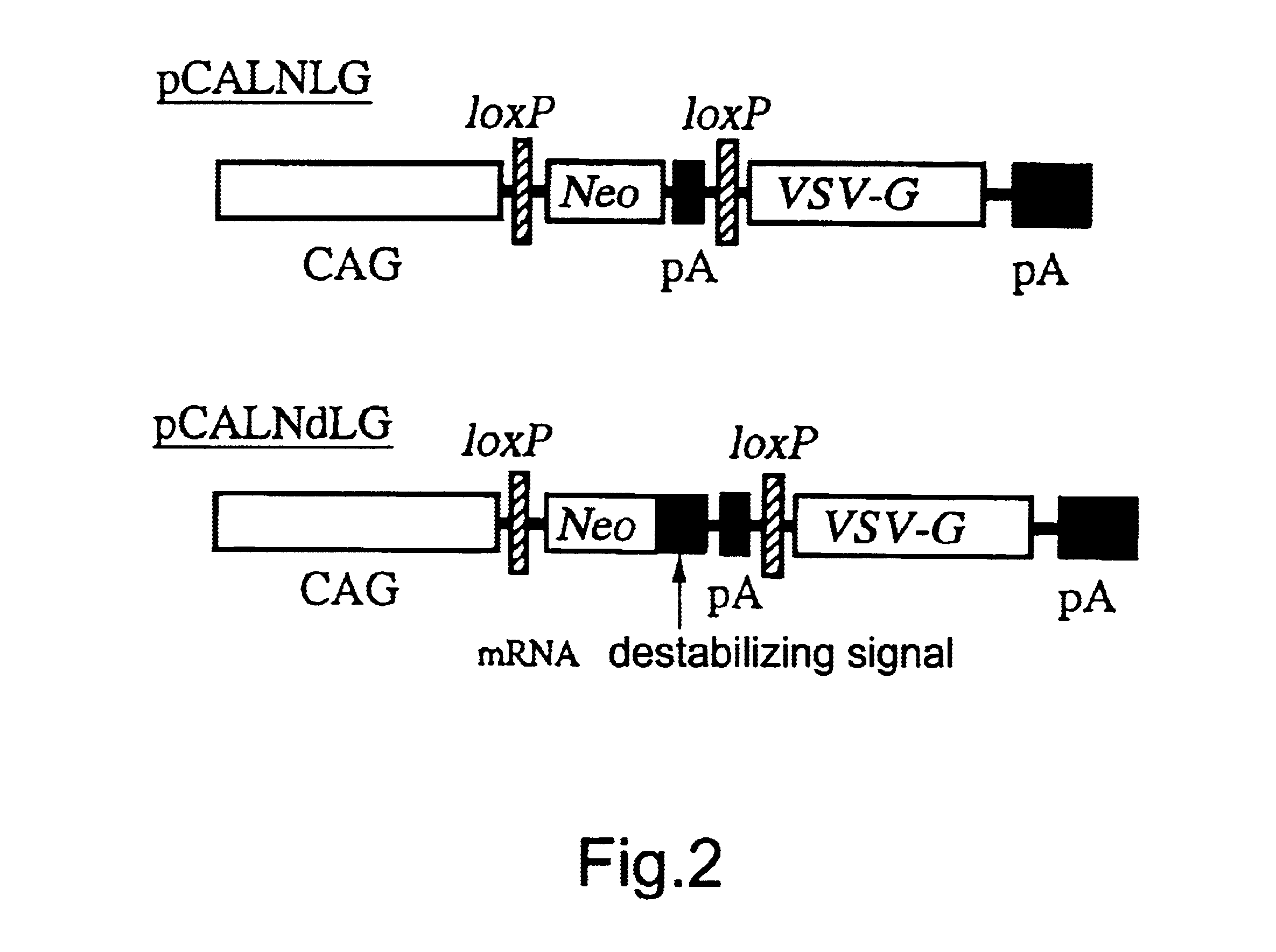
Method for preparing retrovirus vector for gene therapy
InactiveUS6743620B1High recovery rateStably produced at a high titerVectorsSugar derivativesPol genesA-DNA
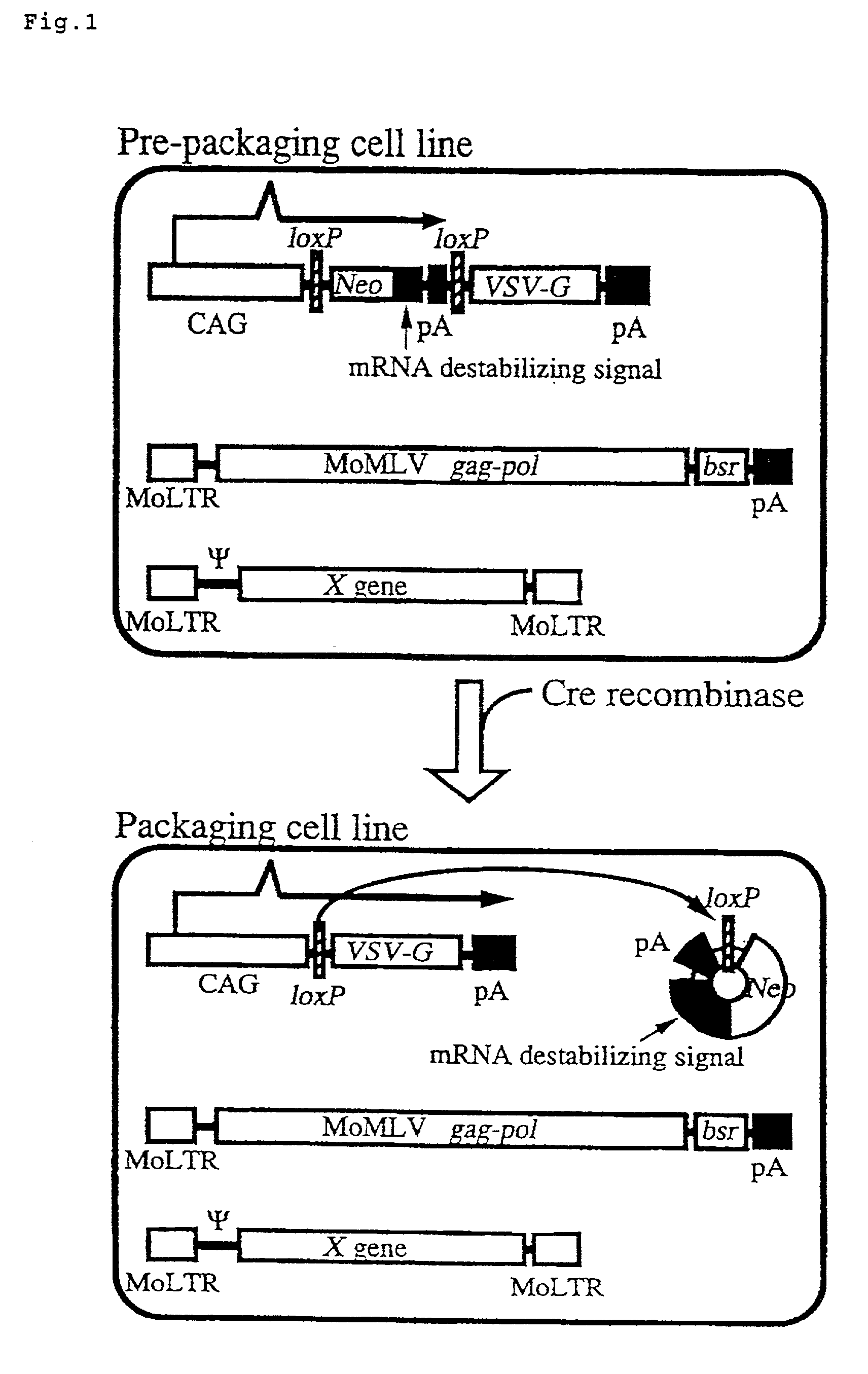
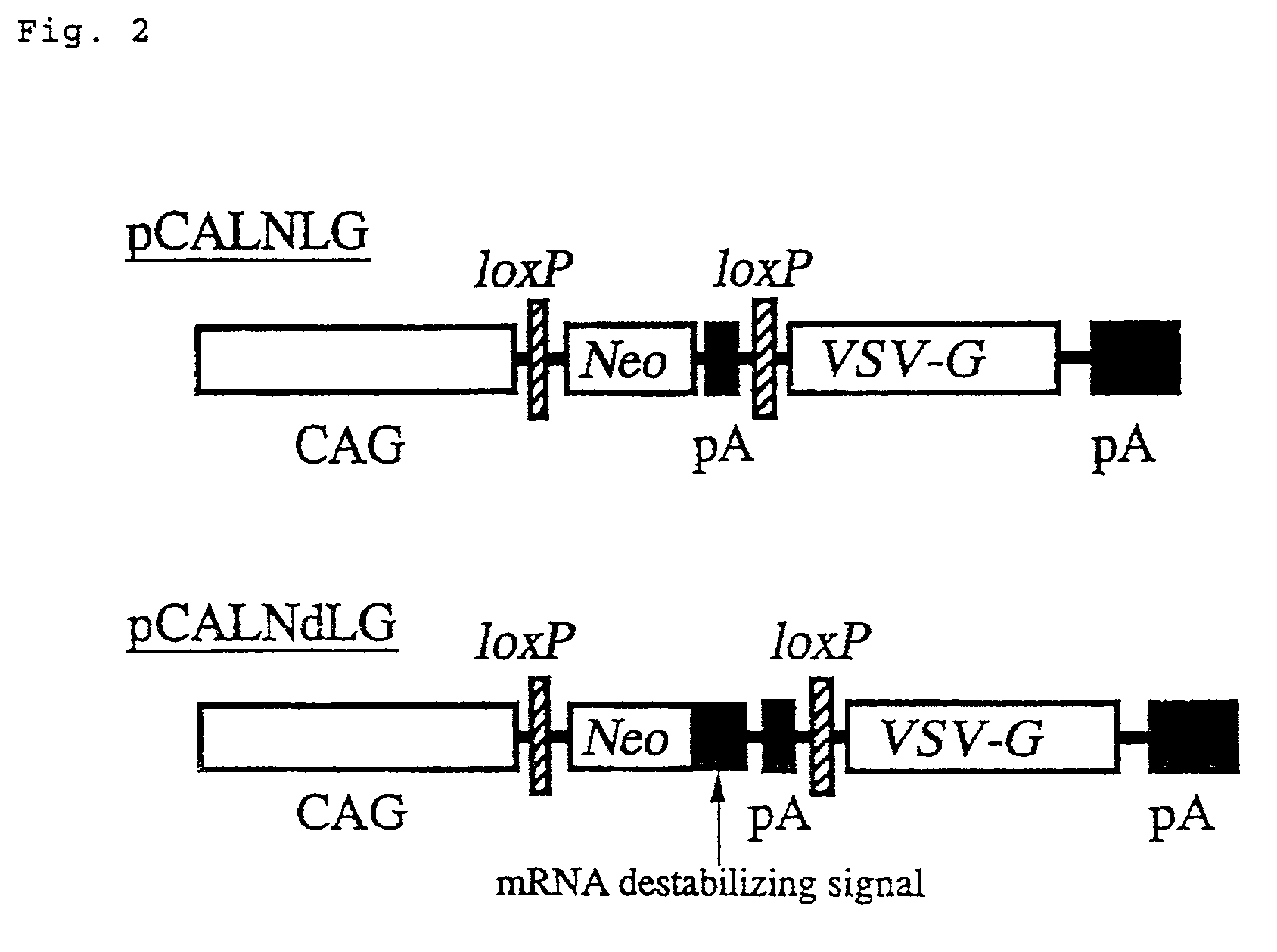
The present invention provides a process for preparing a retrovirus to be expressed at a high titer by specifically transferring a desired foreign gene into target cells. A pseudotyped retrovirus vector having a high titer can be prepared by transferring a DNA construction wherein a promoter, an loxP sequence, a VSV-G gene and a polyA addition signal are arranged in this order is transferred into cells carrying the retrovirus gag and pol gene expression systems, and then transferring a retrovirus vector containing the desired foreign gene thereinto, followed by treatment with a recombinase.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
In vivo gene transfer methods for wound healing
InactiveUS20020193338A1Promote wound healingVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic proteinDna encoding
The present invention relates to an in vivo method for specific targeting and transfer of DNA into mammalian repair cells. The transferred DNA may include any DNA encoding a therapeutic protein of interest. The invention is based on the discovery that mammalian repair cells proliferate and migrate into a wound site where they actively take up and express DNA. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions that may be used in the practice of the invention to transfer the DNA of interest. Such compositions include any suitable matrix in combination with the DNA of interest.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN STEVEN A +1
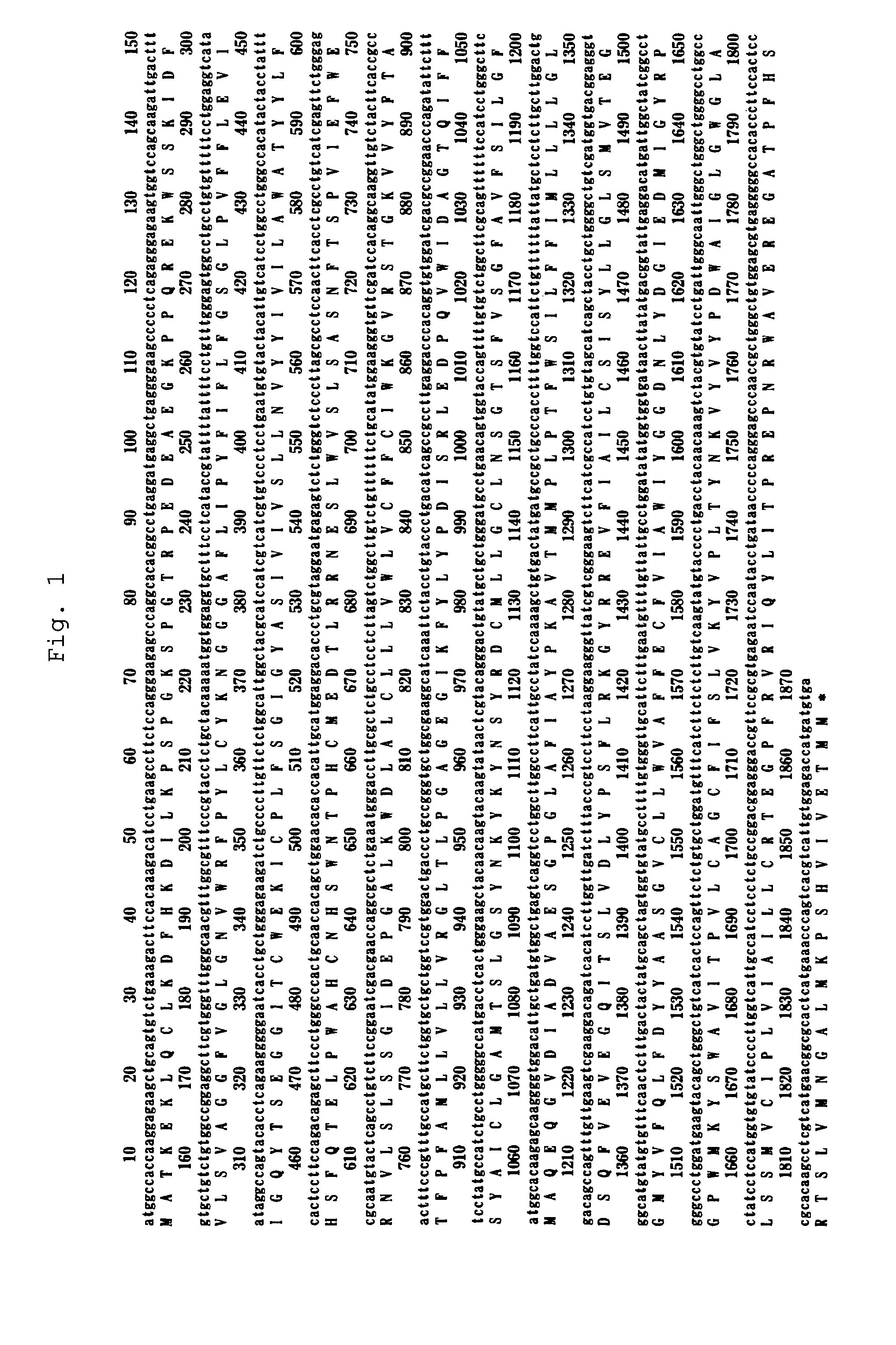
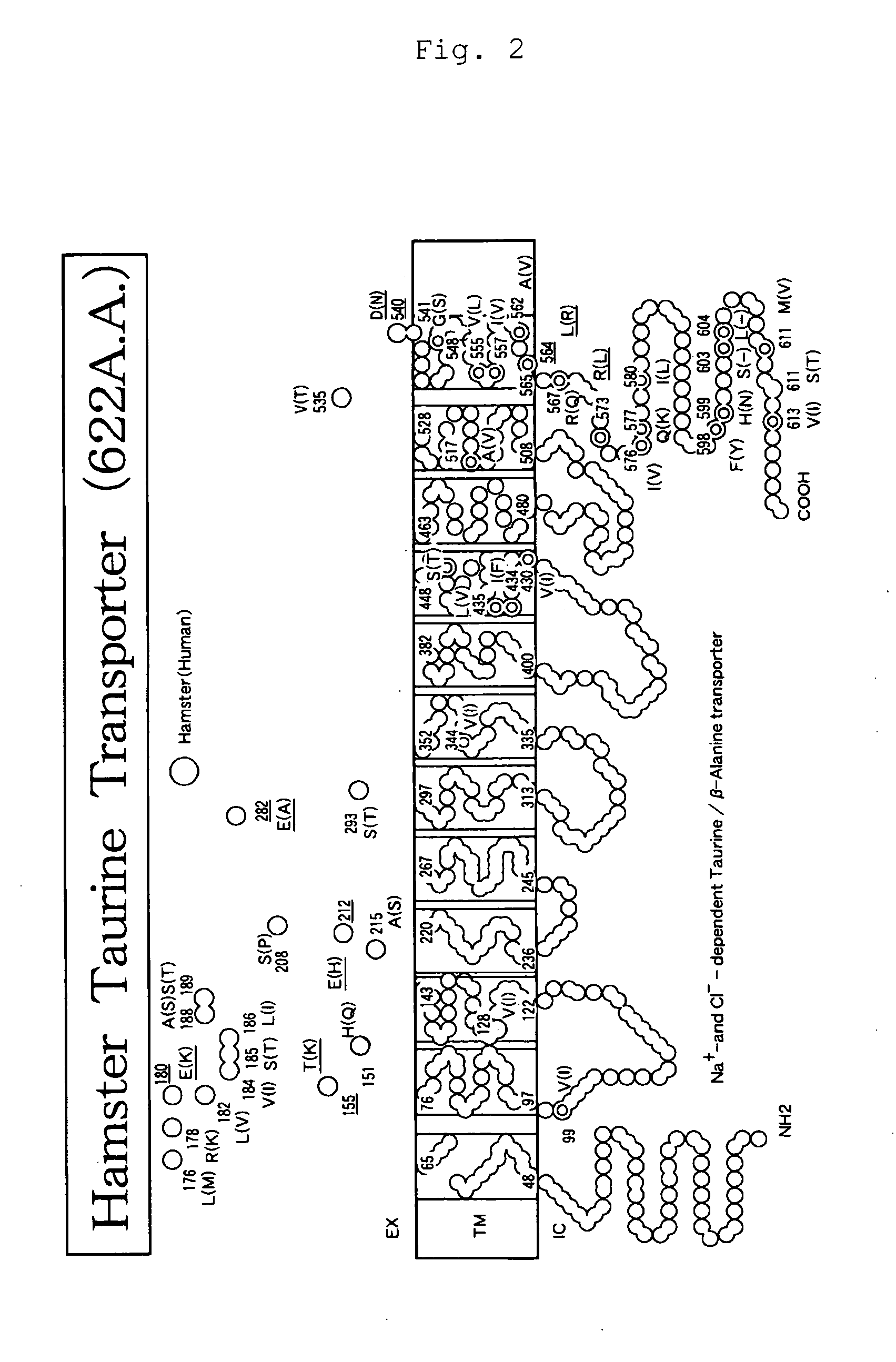
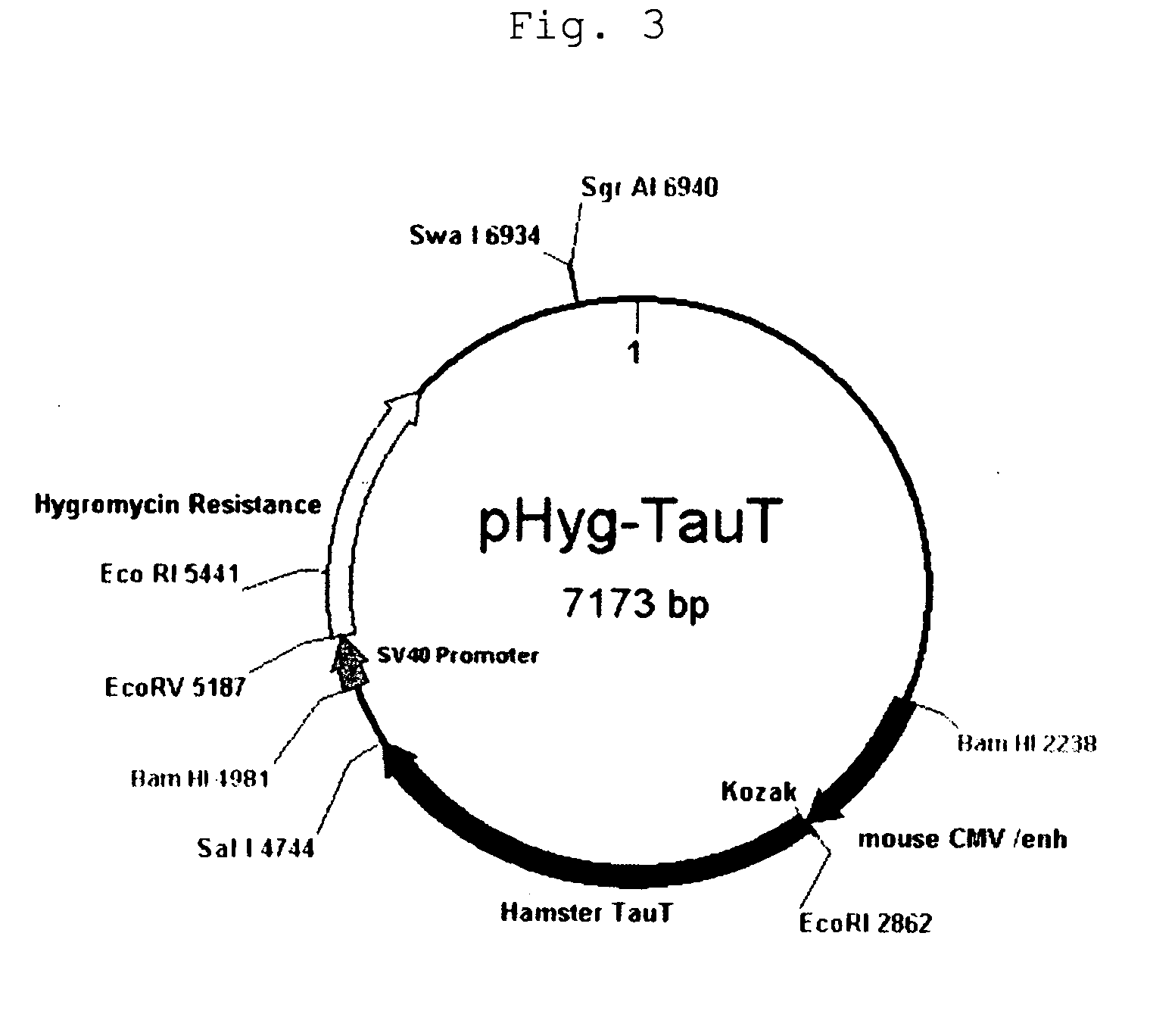
Taurine Transporter Gene
The present invention provides a method capable of producing a natural or recombinant protein at low cost.The present invention relates to a method of producing a polypeptide, comprising culturing a cell which strongly expresses a taurine transporter and has a transferred DNA encoding a desired polypeptide and thereby allowing the cell to produce the polypeptide. Hamster taurine transporter, a DNA encoding the same, a recombinant vector and a transformed cell are also provided.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Process for preparing retrovirus vector for gene therapy
InactiveUS20010018203A1High recovery rateStably produced at a high titerVectorsGenetic material ingredientsPol genesA-DNA
The present invention provides a process for preparing a retrovirus to be expressed at a high titer by specifically transferring a desired foreign gene into target cells. A pseudotyped retrovirus vector having a high titer can be prepared by transferring a DNA construction wherein a promoter, an loxP sequence, a VSV-G gene and a polyA addition signal are arranged in this order is transferred into cells carrying the retrovirus gag and pol gene expression systems, and then transferring a retrovirus vector containing the desired foreign gene thereinto, followed by the treatment with a recombinase.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Cloning using rapidly matured oocytes
InactiveUS20030217378A1Improve efficiencyImprove usabilityMicroinjection basedFermentationProphase IMammal
A method of producing a cloned or genetically modified non-human mammalian embryo comprising: (a) providing a cell culture comprising a plurality of in vitro matured oocytes; (b) preferentially selecting from the cell culture a rapidly matured oocyte or developmentally competent oocyte; (c) transferring DNA from a donor cell derived from non-human mammalian tissue to the matured oocyte to form a nuclear transfer unit; and (d) culturing said nuclear transfer unit to form an embryo. At the initiation of maturation, oocytes are preferably beyond the GV-II stage of prophase I. Porcine oocytes most preferably mature in about 20-28 hours.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Method of producing heterogeneous protein
The present invention provides a method capable of producing a natural or recombinant protein in high yield.The present invention relates to a method of producing a polypeptide, comprising culturing a cell which strongly expresses alanine aminotransferase and has a transferred DNA encoding a desired polypeptide and thereby allowing the cell to produce the polypeptide.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
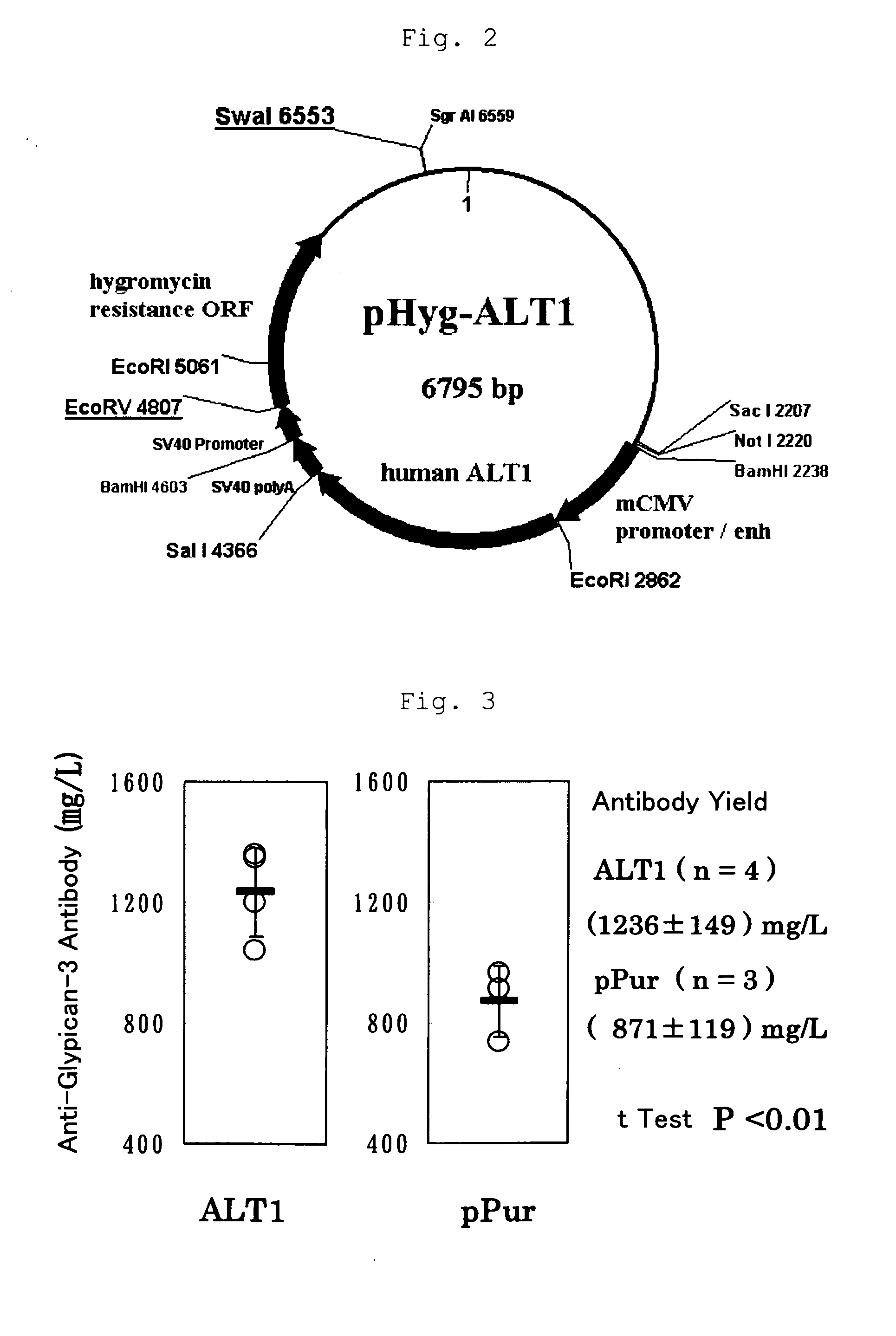
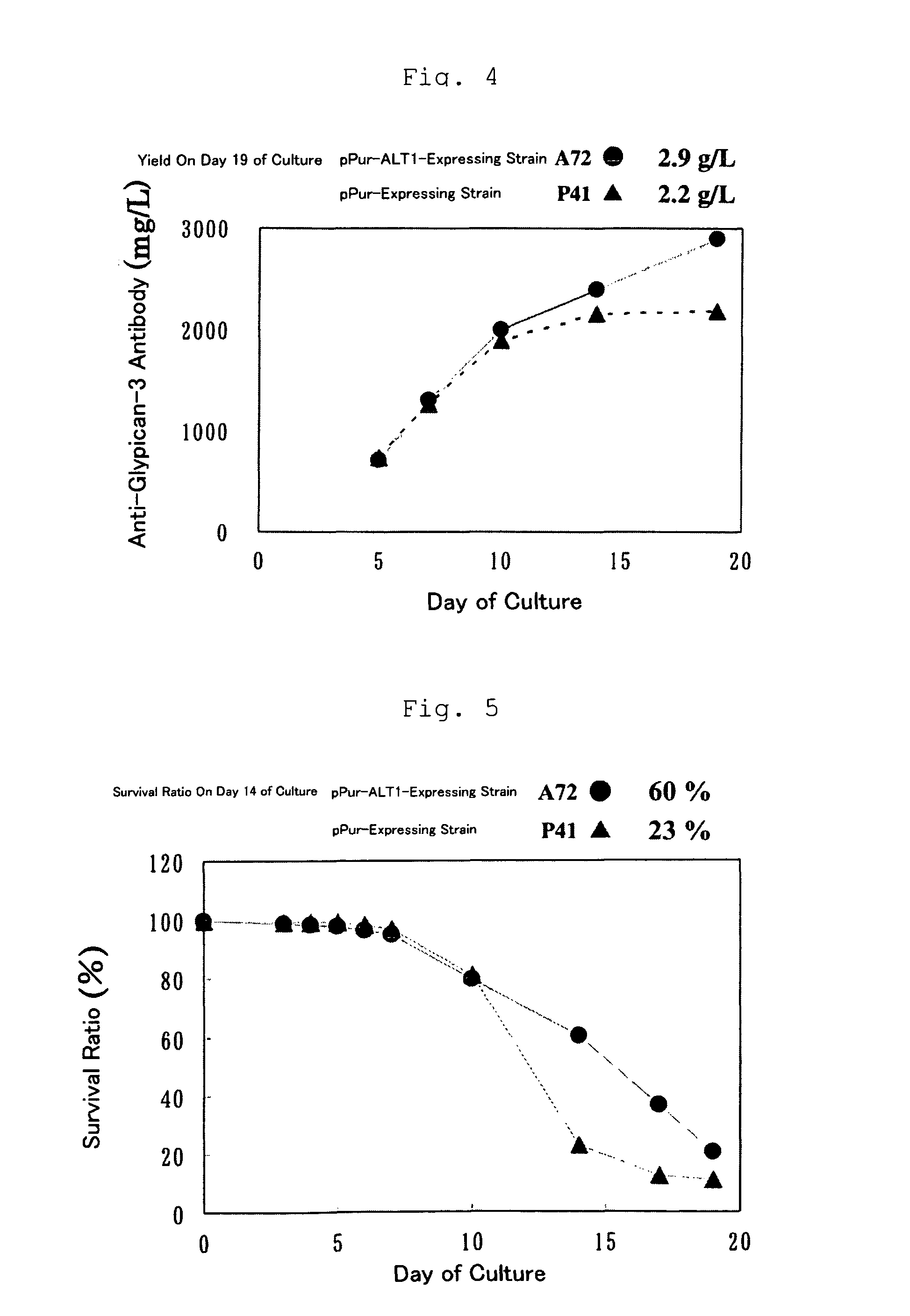
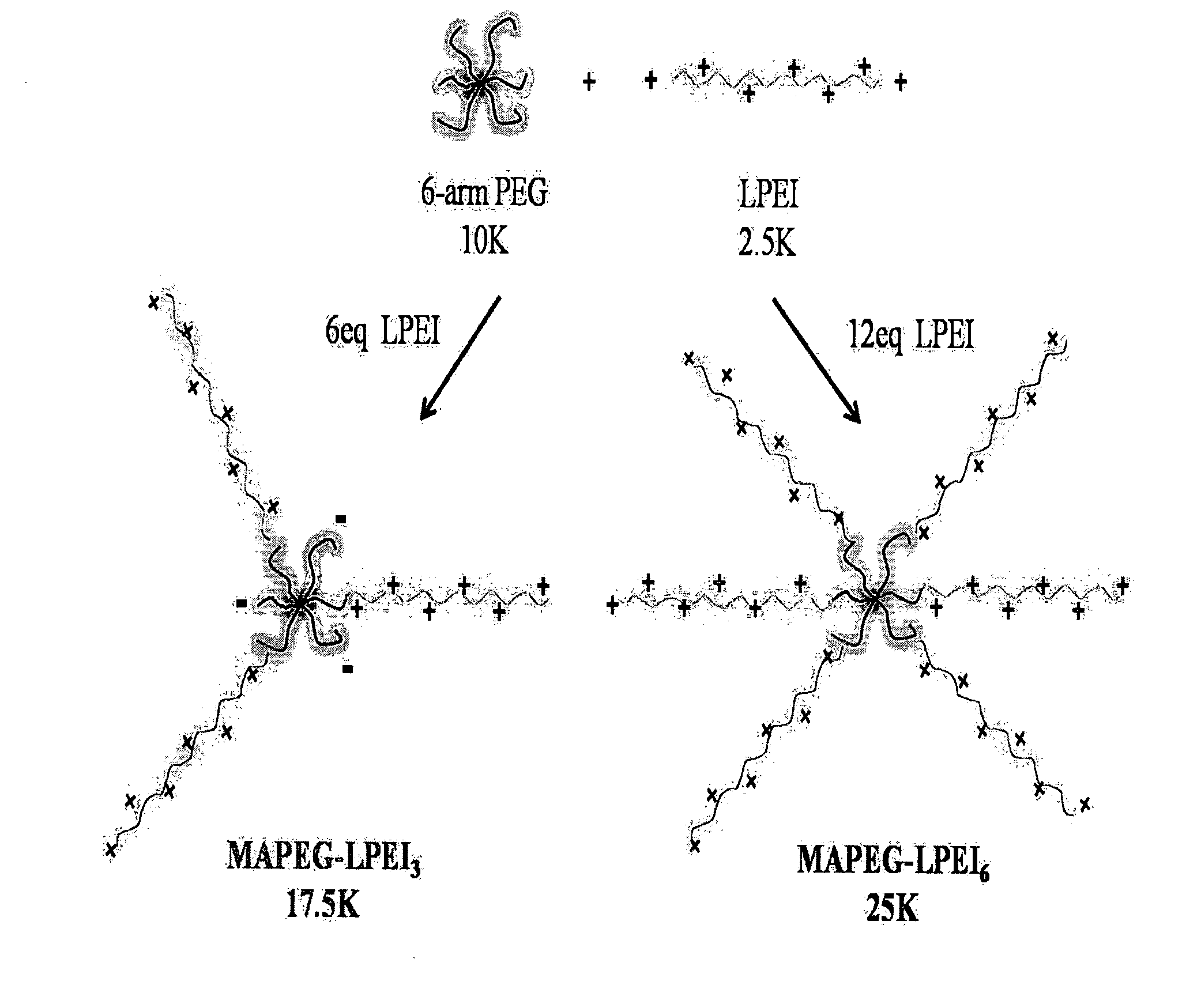
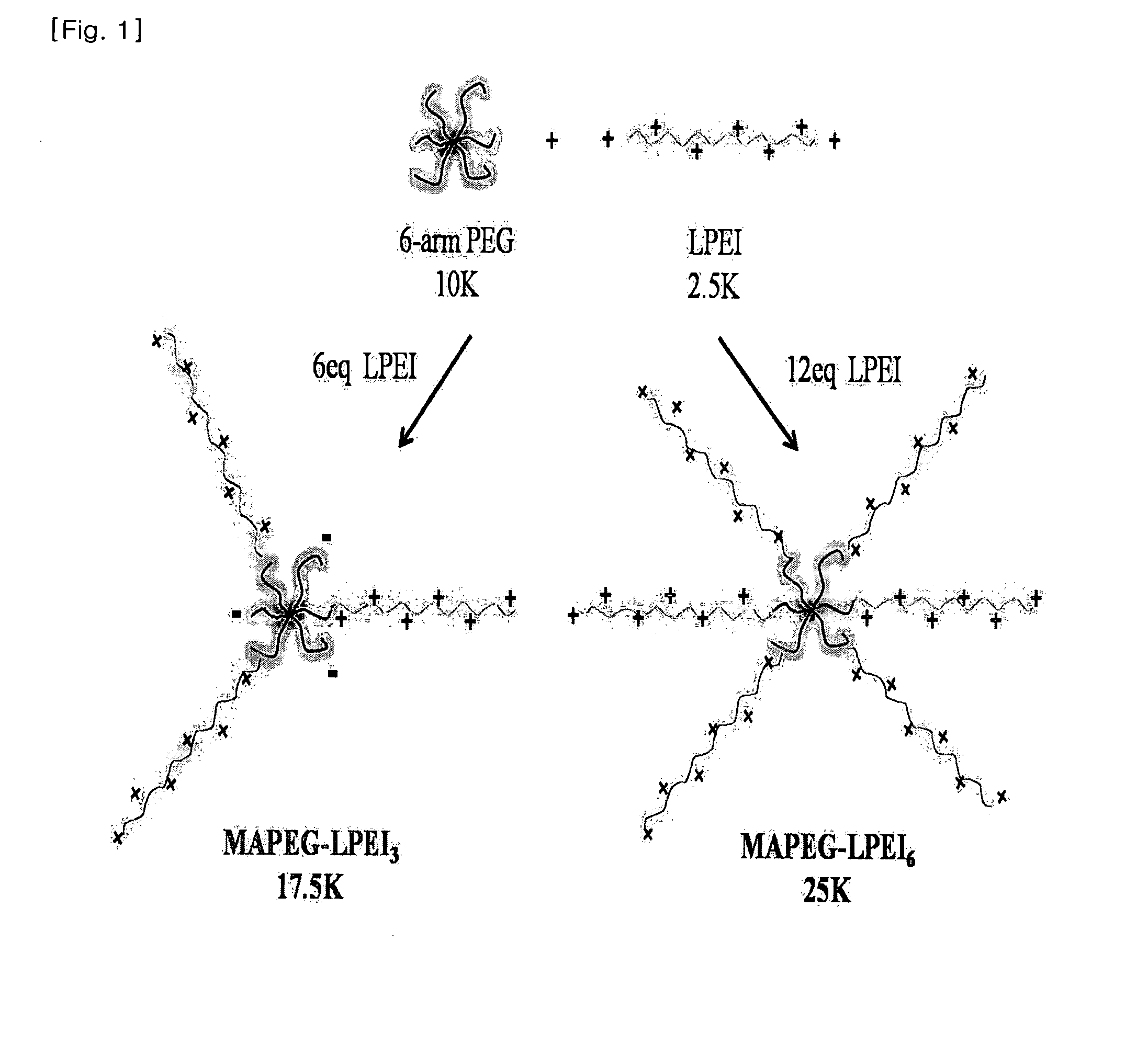
Conjugate of arm-type polyethyleneglycol with linear polyethyleneimine as gene carrier and synthesis thereof
ActiveUS20110311817A1Efficient transferImprove securityOrganic chemistrySynthetic resin layered productsPolyethylene glycolDNA
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Method for extracting residual DNA in edible vegetable oil
InactiveCN101100479ASuccessfully removedSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationWater bathsVegetable oil
A method for extracting residual DNA in edible vegetable oil is carried out by transferring DNA in oil and fat and enriching into aseptic water by water-emulsifying method, adding extracted buffer liquor with CTAB, Tris, NaCl and EDTA into water bath between 63-67 deg. C, keeping temperature for 30-60 mins to obtain aqueous extract, adding purifying agent with phenol, trichloromethane and isopropyl alcohol into aqueous extract, purifying, removing organic phase and aqueous phase to obtain purified liquor, adding precipitant into pre-cooled purified liquor, agitating, laying aside at -25--18 deg. C, precipitating while eluting DNA, separating, washing, and drying to obtain final product. It can be used to extract DNA from soya bean oil, corn oil, rapeseed oil and cottonseed coil. It has high-purity template DNA and need to purify.
Owner:上海新云数据技术有限公司
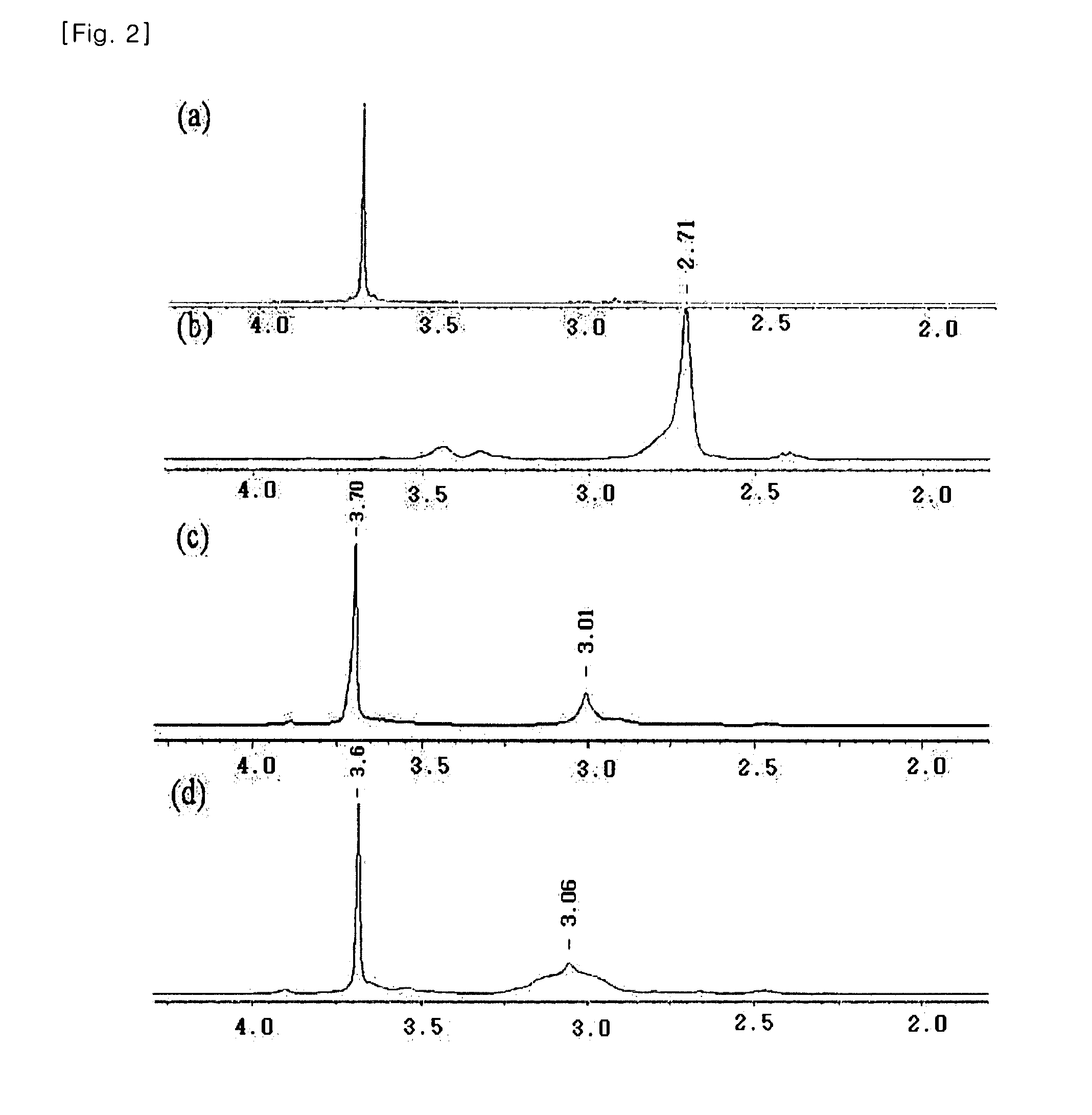
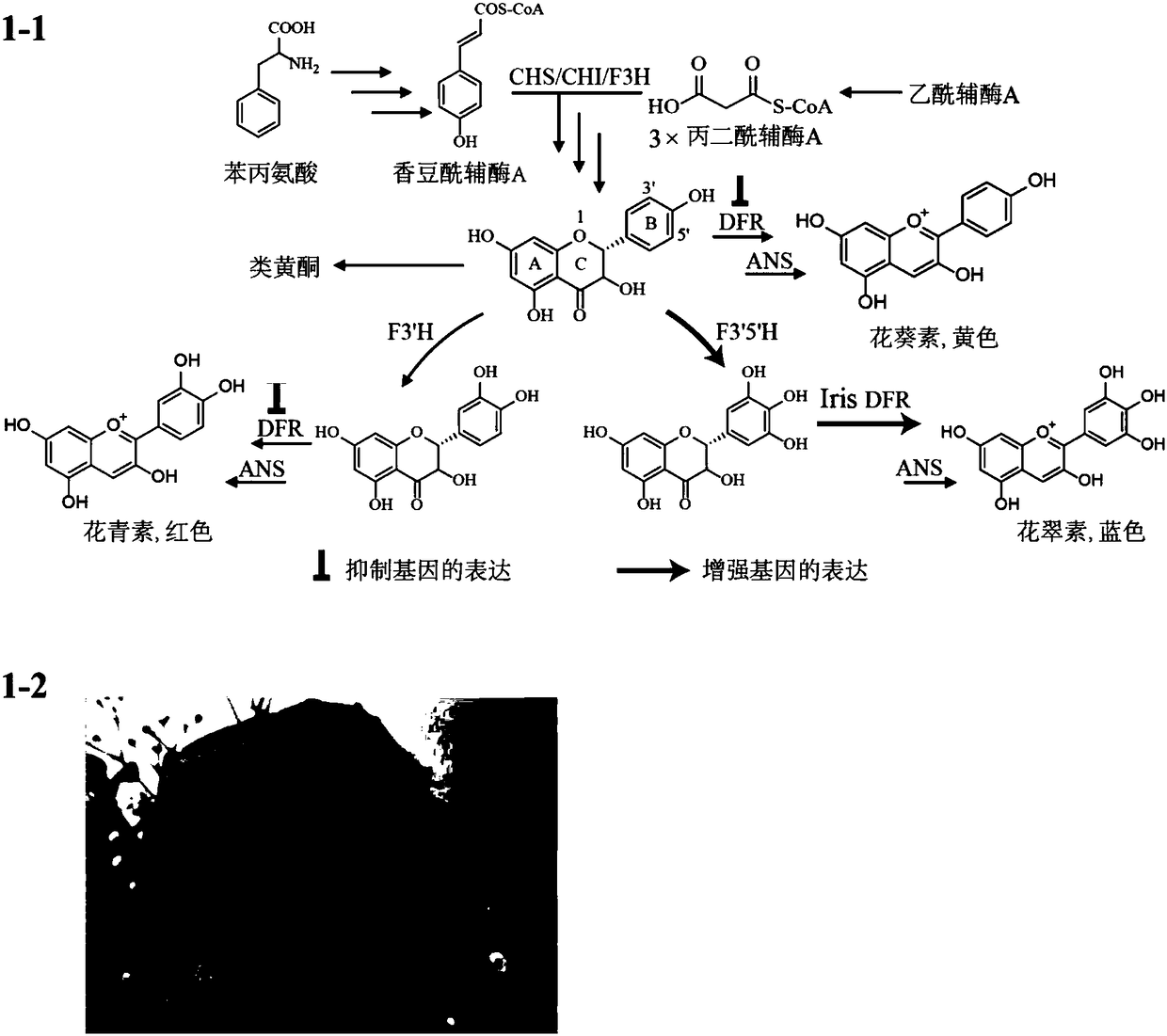
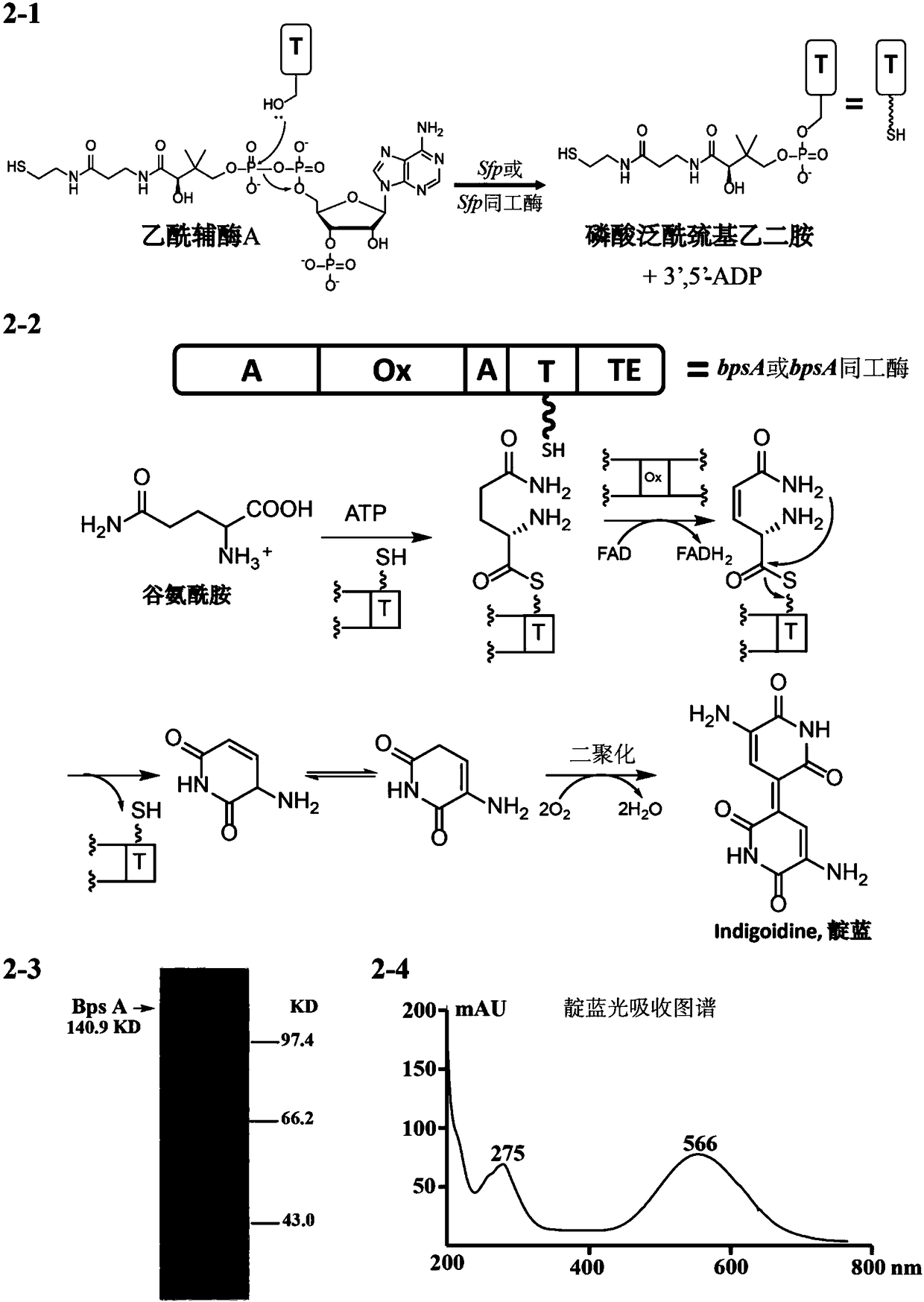
Transgene method for obtaining blue flowers through indigo blue synthesis via glutamine catalysis
ActiveCN108330146AObvious artifactsGood decolorizationTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliTransgenesis
The invention discloses a transgene method for obtaining blue flowers through indigo blue synthesis via glutamine catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting a gene Sfp for coding phosphopantetheine transferase and a gene bpsA for coding indigo blue synthetase; respectively cloning the genes into a plant promoter downstream of plasmids containing plant promoters; (2) amplifying the obtained plasmids in escherichia coli; transferring the plasmids into soil agrobacterium; (3) transferring DNA containing Sfp and bpsA into plants. The produced blue flowers have various characteristics of natural flowers, are fresh, have flower fragrance, realize color fastness and is nontoxic. The transgenic enzymes and generated indigo blue are not in vacuoles, are not influenced by low pH of the plant vacuole, and can form the pure blue color. The precursor materials of blue substances are generated; the enzyme substances are glutamine richly contained in the plant bodies; the related enzymatic reaction only has one step; the transgenic transformation can be performed from white flowers existing in the nature.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
Hydrogel and preparation method thereof
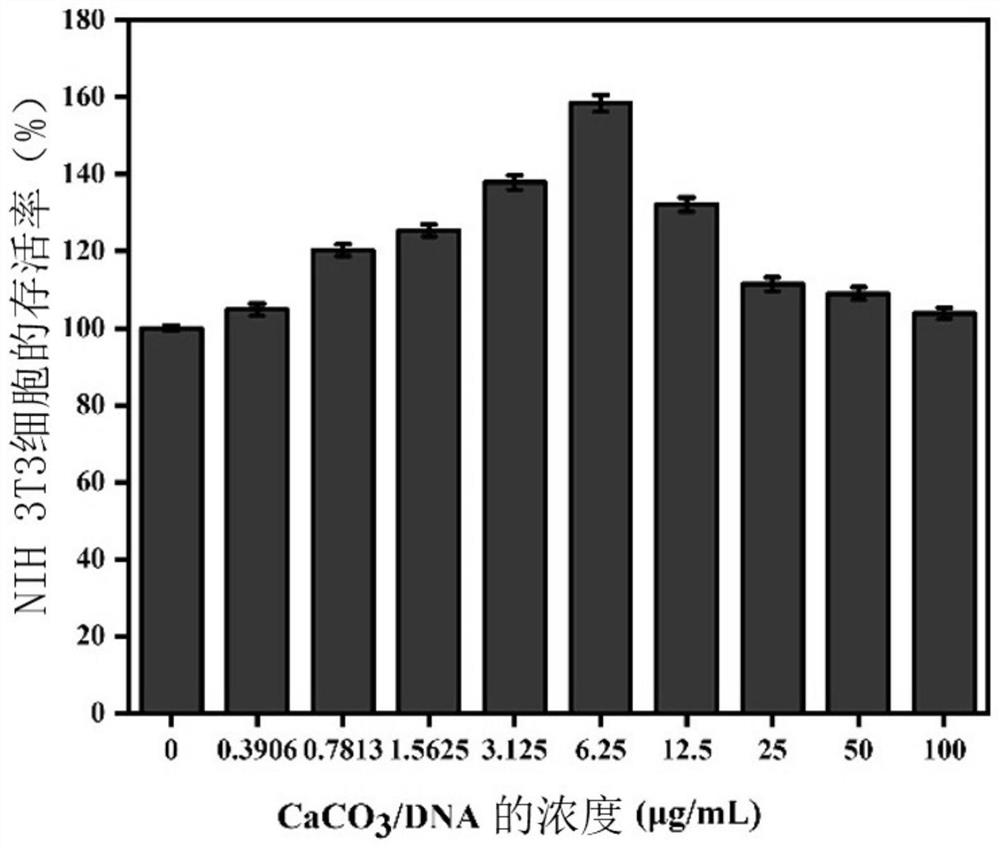
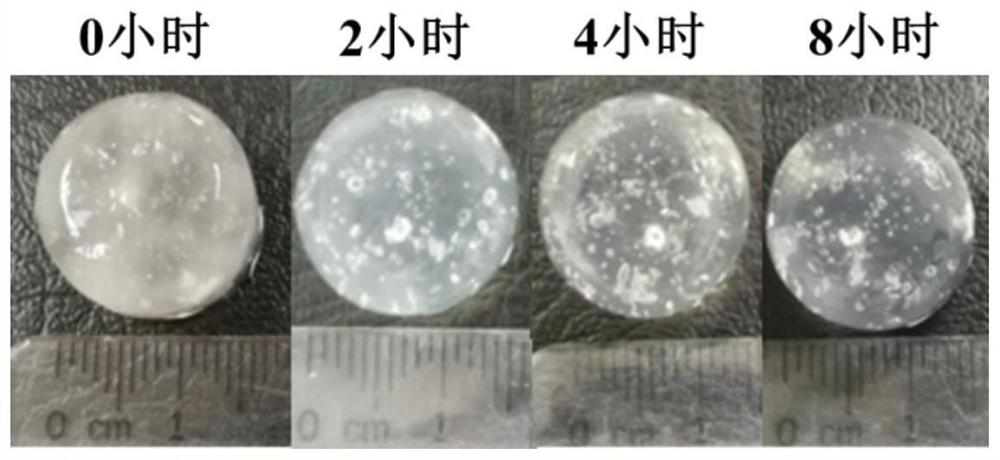
The invention relates to a hydrogel and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of medical materials. According to the main technical scheme, the preparation method of the hydrogel comprises the following steps: step 1), preparing calcium carbonate nanoparticle CaCO3 at DNA loaded with DNA; 2) preparing a first reaction solution from sodium alginate, chitosan and CaCO3 atDNA; adding gluconolactone into the first reaction solution and stirring, and obtaining a mixed solution; and standing the mixed solution to obtain the hydrogel. The preparation method is mainly usedfor preparing the hydrogel which can slowly release DNA and is good in structural uniformity; when the hydrogel is applied to a wound sore surface, seepage can be adsorbed, bacteria can be blocked, and a wet environment can be maintained; meanwhile, salt in the body fluid and Ca < 2 + > in the hydrogel are subjected to ion exchange, so that the alginic acid network is slowly degraded, and the calcium carbonate nanoparticles loaded with DNA are released. Compared with free DNA molecules, the calcium carbonate nanoparticles can transfer DNA into cells more efficiently, and proliferation of the cells is promoted.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Method for production of polypeptide
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
In vivo gene transfer
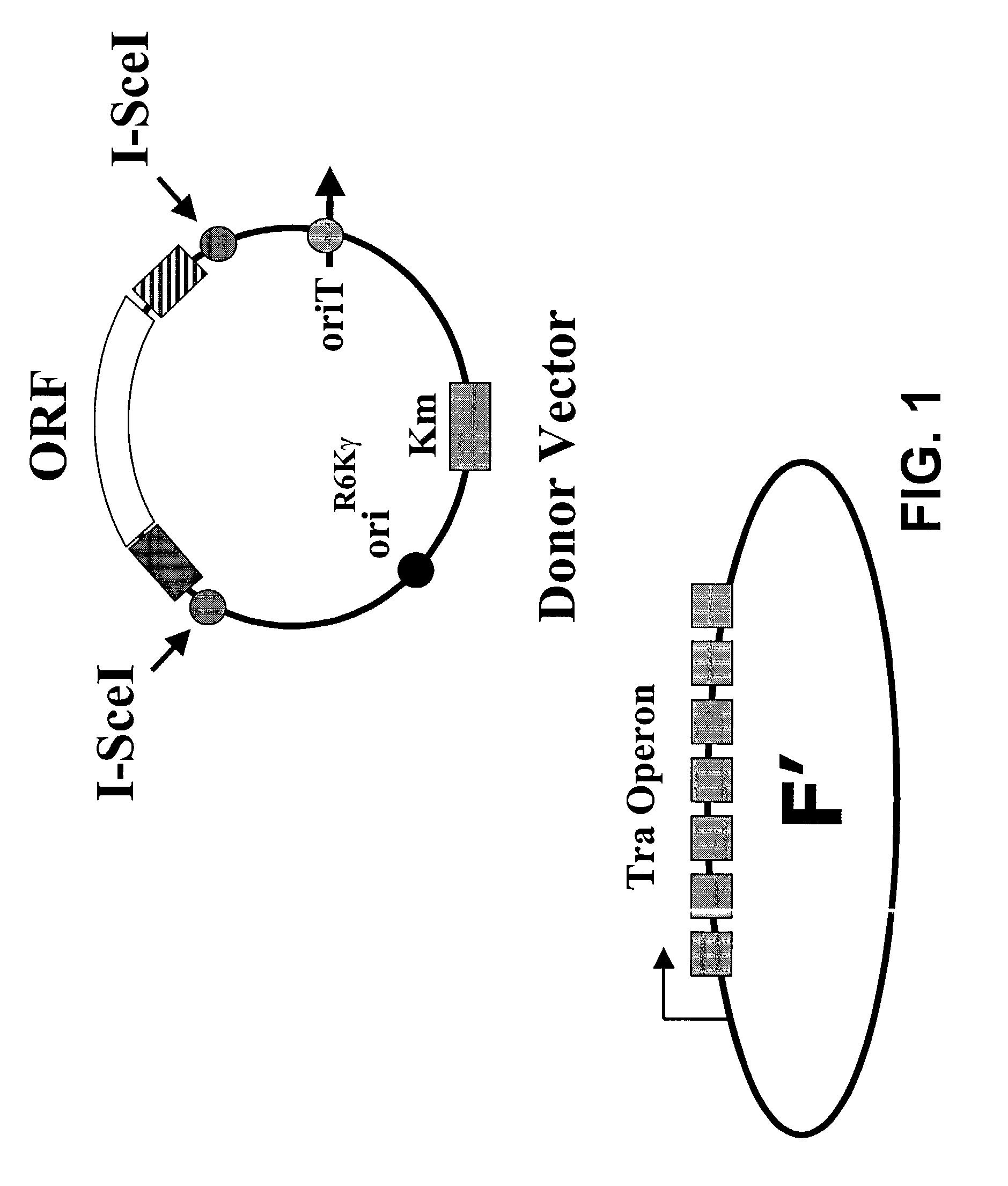
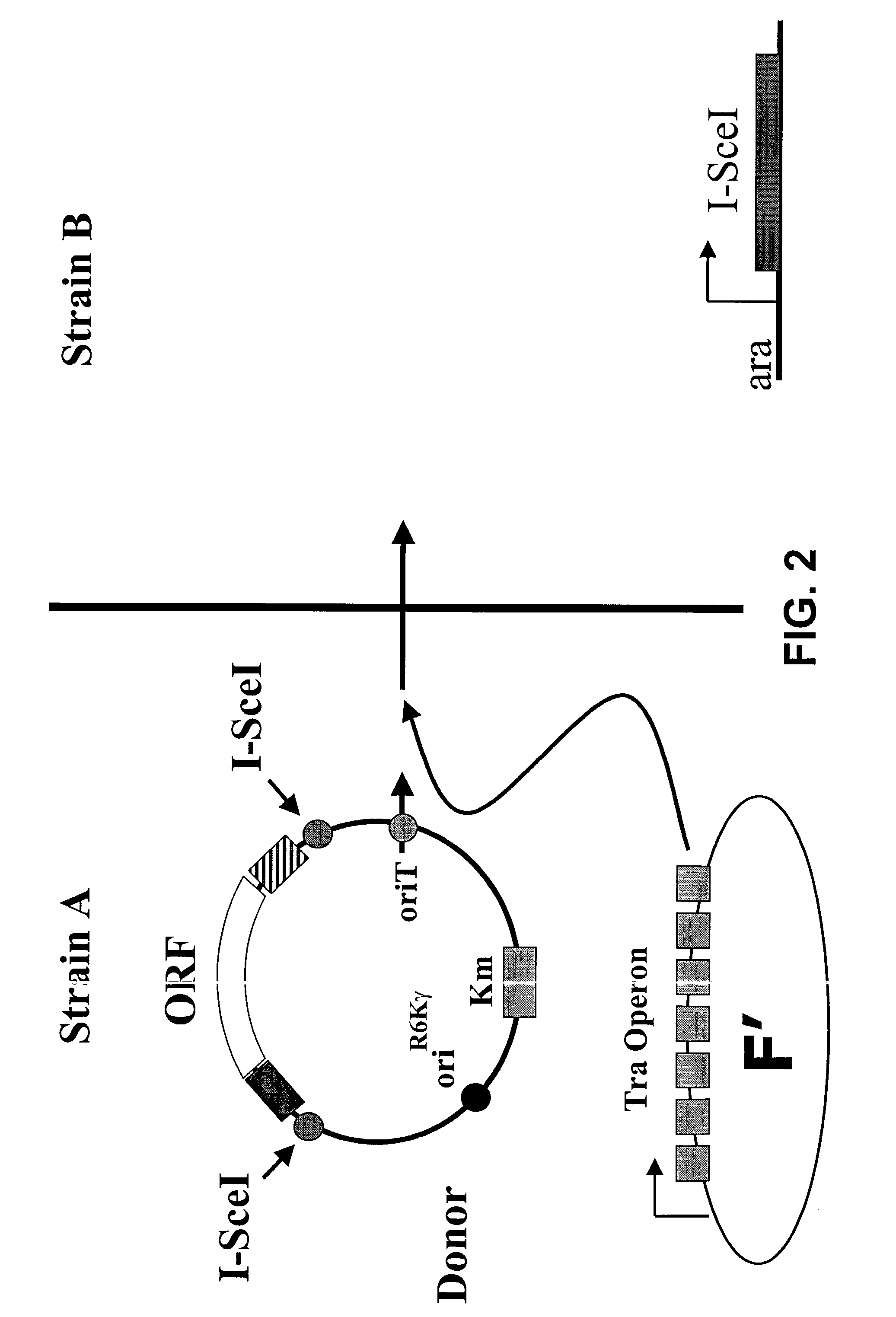
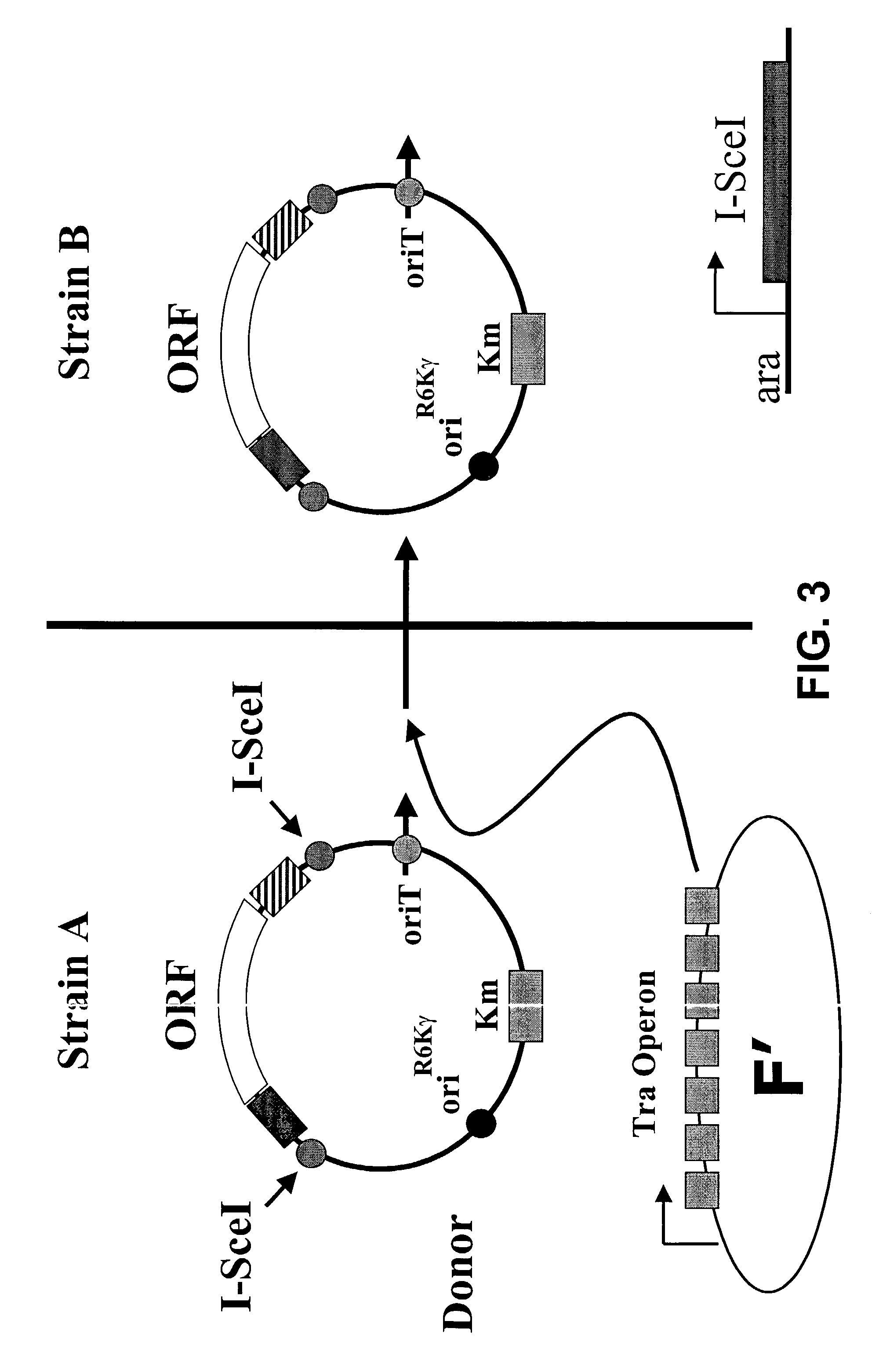
The present invention is directed to an in vivo method of transferring DNA from a donor cell to a recipient cell. In a specific embodiment, the method comprises a highly efficient process of bacterial mating. In a preferred embodiment, selection for a recombinant plasmid against a parent host plasmid and donor plasmid is based on recircularization of the host plasmid by its recombination with a gene of interest such that it is now no longer cleaved by a restriction enzyme expressed in the recipient cell.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
In vivo transfer methods for wound healing
InactiveUS20120100107A1Promote wound healingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTherapeutic proteinDna encoding
The present invention relates to an in vivo method for specific targeting and transfer of DNA into mammalian repair cells. The transferred DNA may include any DNA encoding a therapeutic protein of interest. The invention is based on the discovery that mammalian repair cells proliferate and migrate into a wound site where they actively take up and express DNA. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions that may be used in the practice of the invention to transfer the DNA of interest. Such compositions include any suitable matrix in combination with the DNA of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
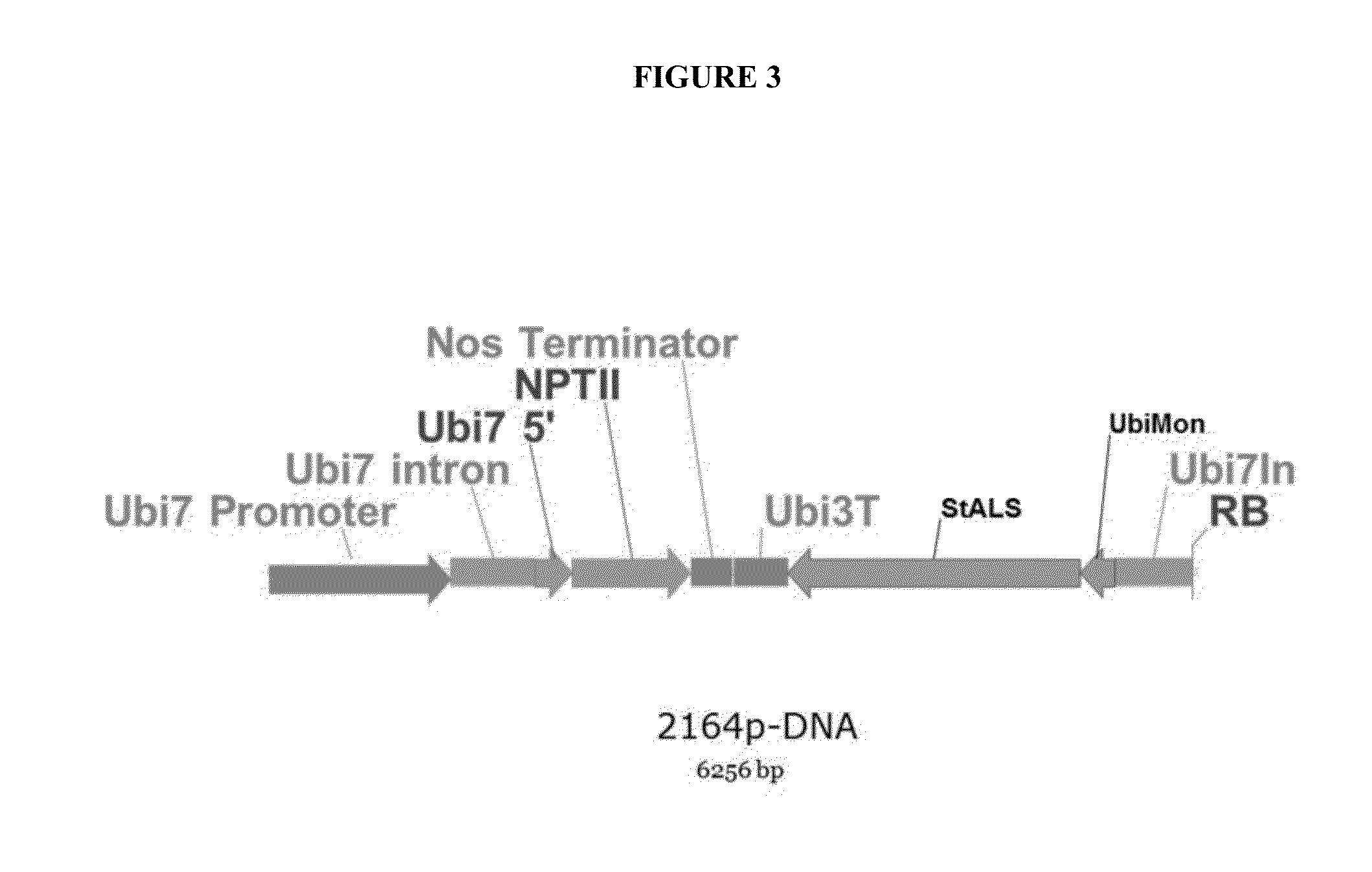
Tal-mediated transfer DNA insertion
InactiveUS20140363561A1Confer resistancePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainPolynucleotideCell biology
The invention relates to methods for stably integrating a desired polynucleotide into a plant genome.
Owner:J R SIMPLOT
In vivo gene transfer methods for wound healing
InactiveUS20100189792A1Promote wound healingPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinDna encoding
The present invention relates to an in vivo method for specific targeting and transfer of DNA into mammalian repair cells. The transferred DNA may include any DNA encoding a therapeutic protein of interest. The invention is based on the discovery that mammalian repair cells proliferate and migrate into a wound site where they actively take up and express DNA. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions that may be used in the practice of the invention to transfer the DNA of interest. Such compositions include any suitable matrix in combination with the DNA of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
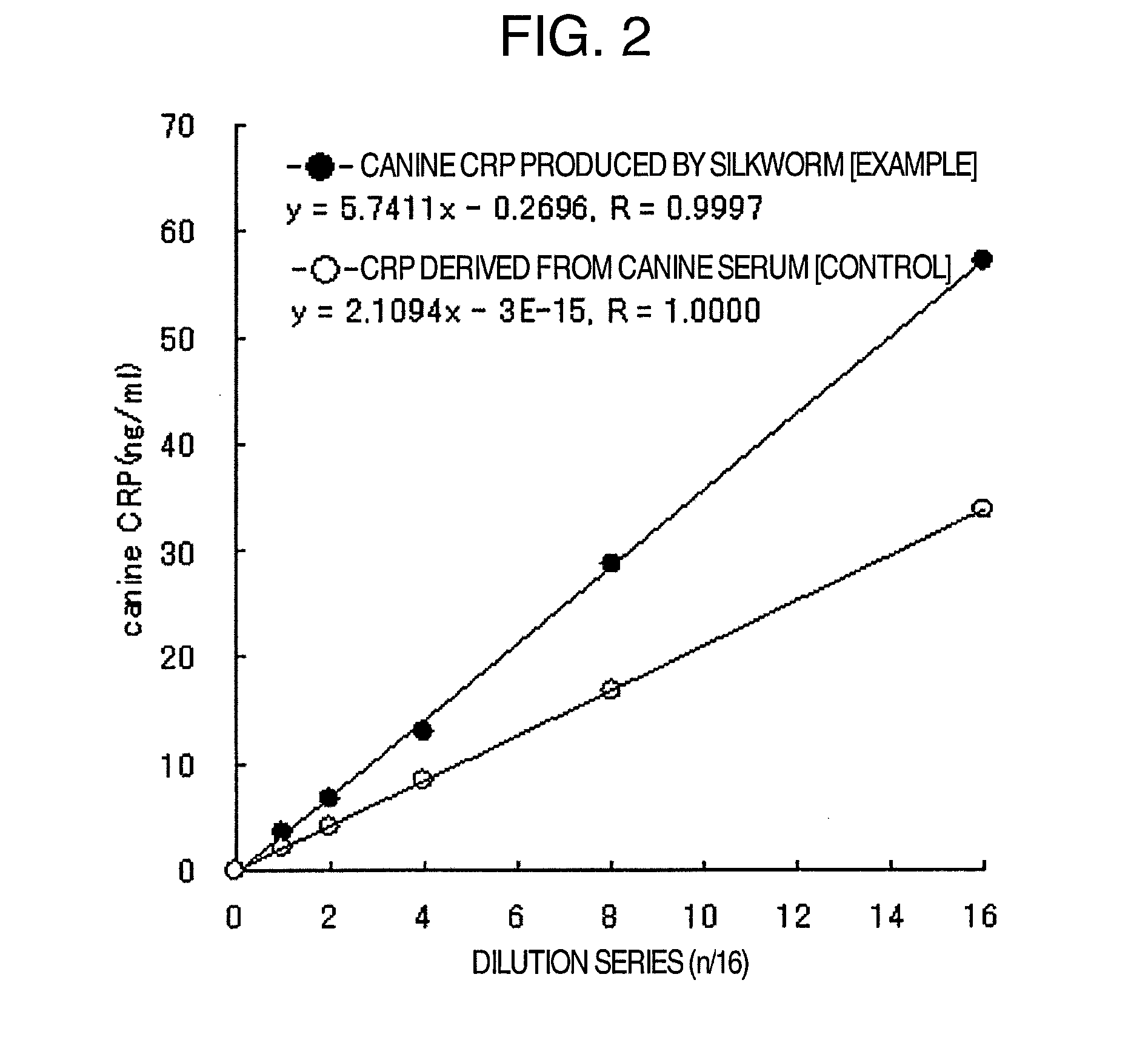
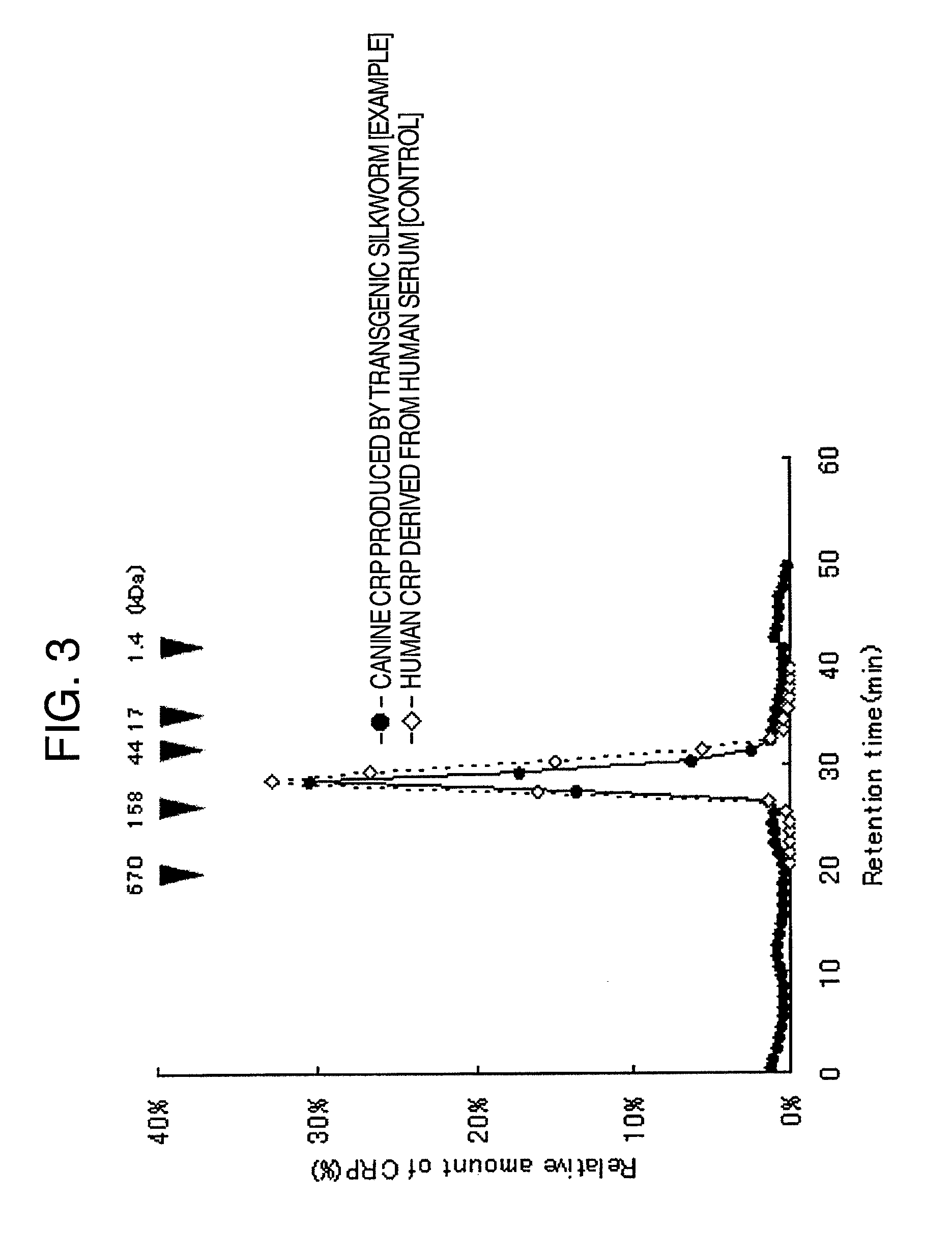
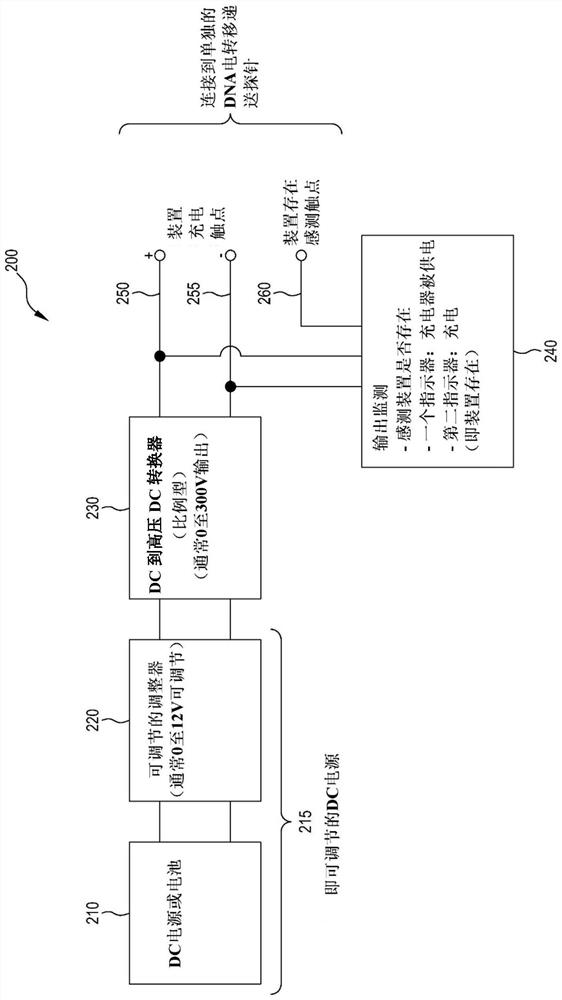
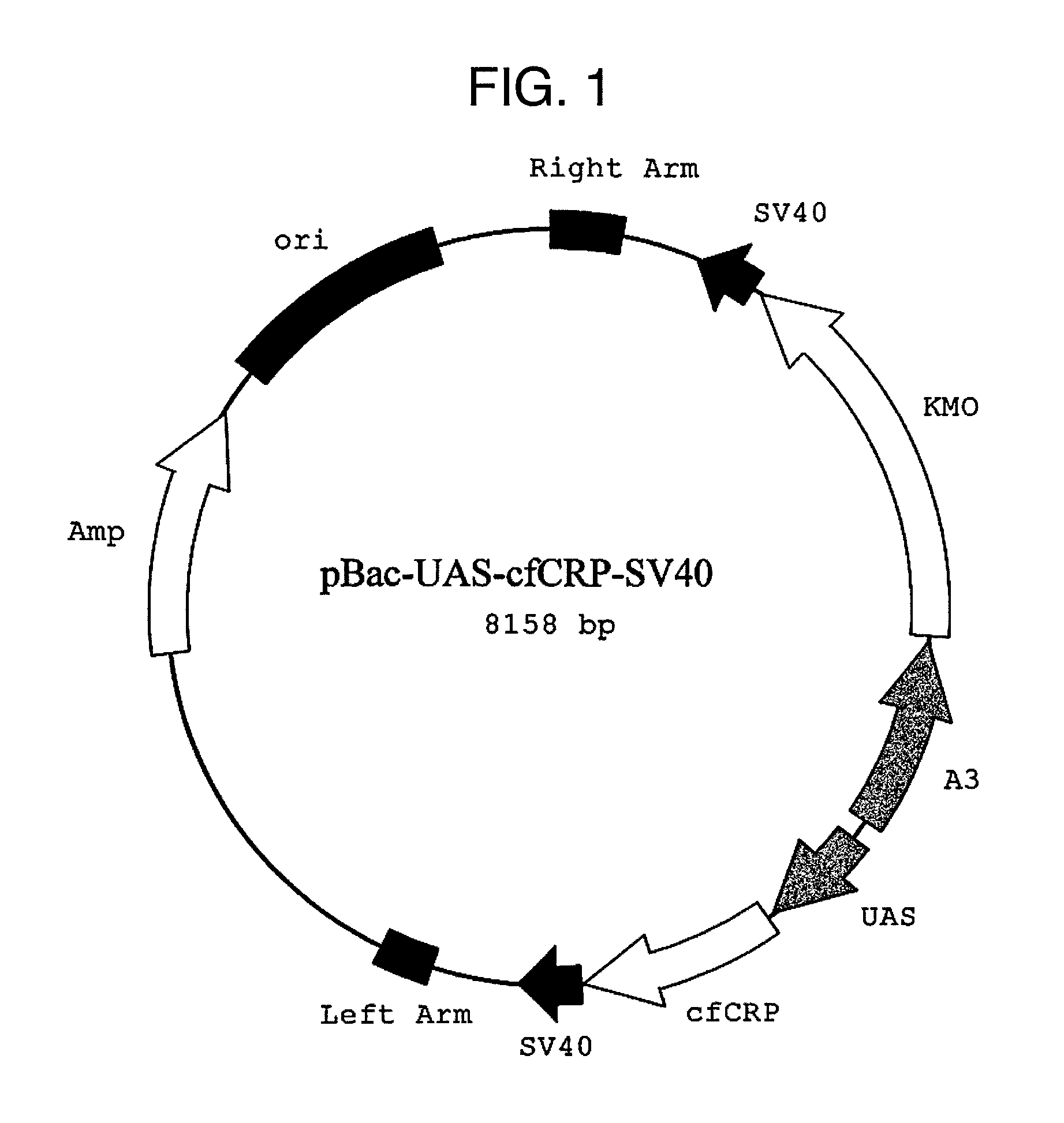
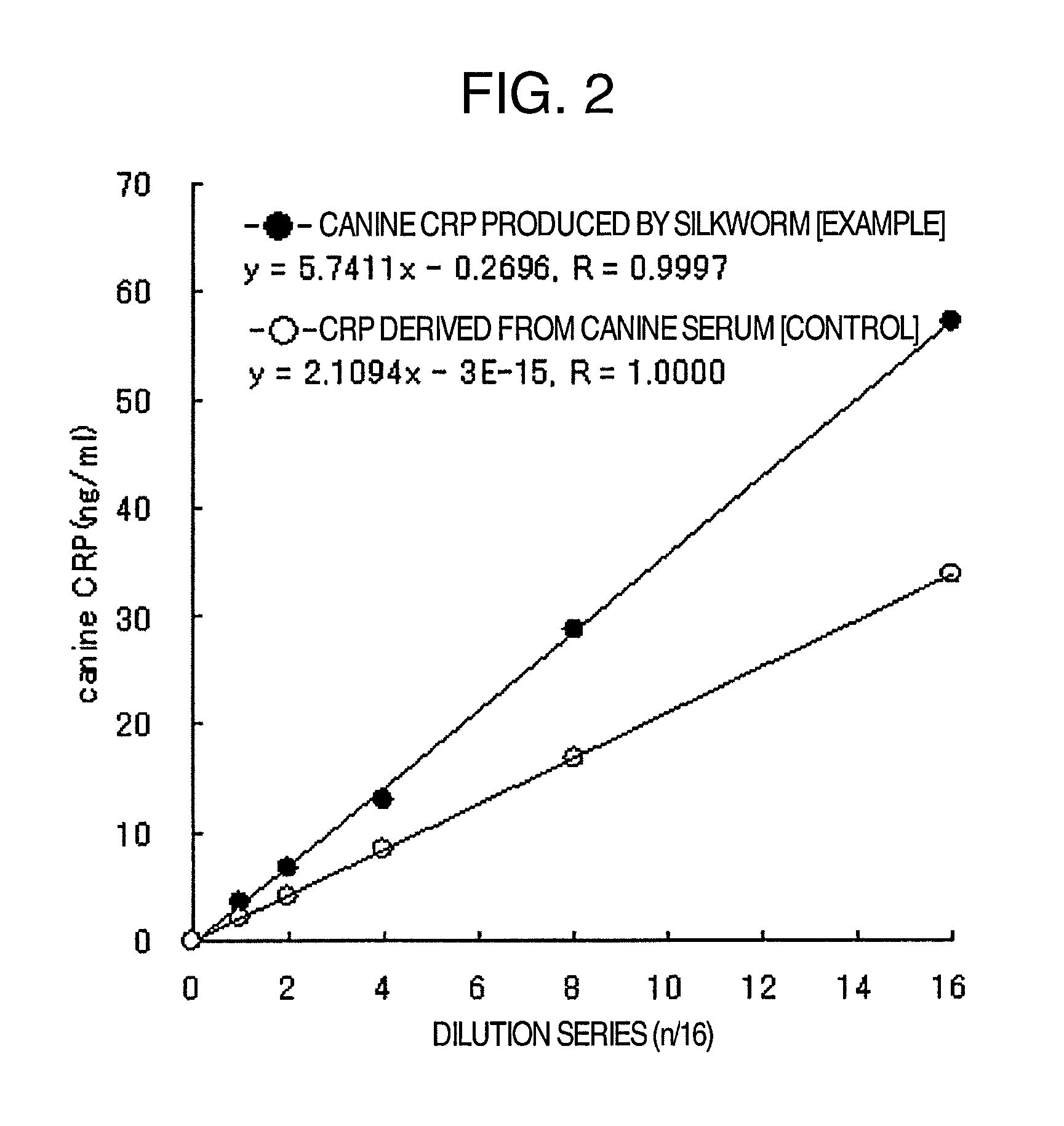
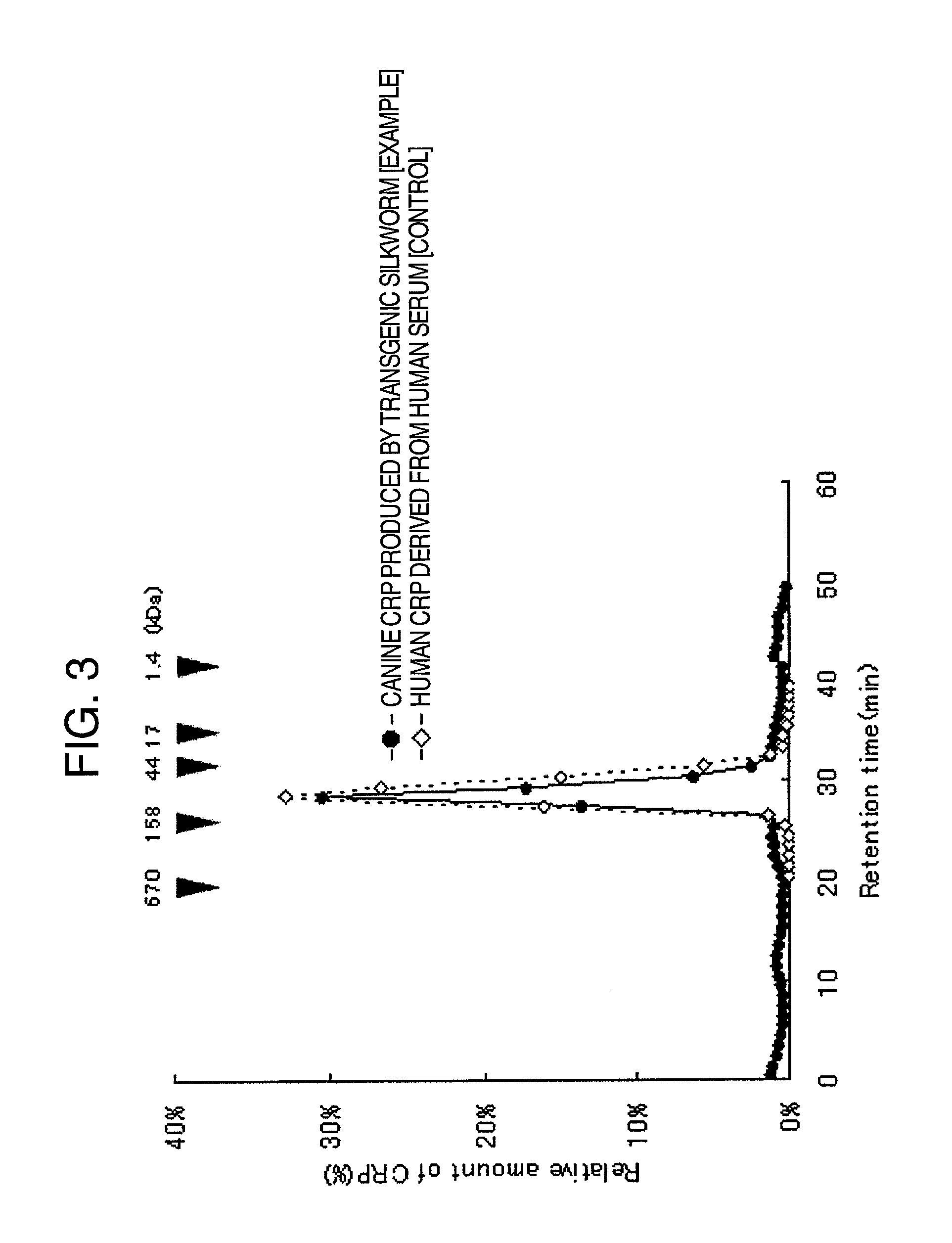
Method for producing pentameric crp, pentameric crp-producing transgenic silkworm and method for constructing same, DNA encoding canine monomeric crp and expression vector containing the DNA
ActiveUS20130212717A1Improve efficiencyEasy to collectSugar derivativesFermentationBiotechnologyPentamer
Pentameric CRP is produced at a high efficiency by transferring DNA, which encodes monomeric CRP, into a silkworm to thereby construct a transgenic silkworm and then collecting and purifying pentameric CRP that is produced by the transgenic silkworm constructed above.
Owner:NITTO BOSEIKI CO LTD +1
TAL-mediated transfer DNA insertion
InactiveUS20140154397A1Lower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to methods for stably integrating a desired polynucleotide into a plant genome, comprising transforming plant material with a first vector comprising nucleotide sequences encoding TAL proteins designed to recognize a target sequence; transforming the plant material with a second vector comprising (i) a marker gene that is not operably linked to a promoter (“promoter-free marker cassette”) and which comprises a sequence homologous to the target sequence; and (ii) a desired polynucleotide; and identifying transformed plant material in which the desired polynucleotide is stably integrated.
Owner:J R SIMPLOT
Refined plant transformation
InactiveUS7928292B2Improve drought toleranceReduce the overall heightTissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellGenome
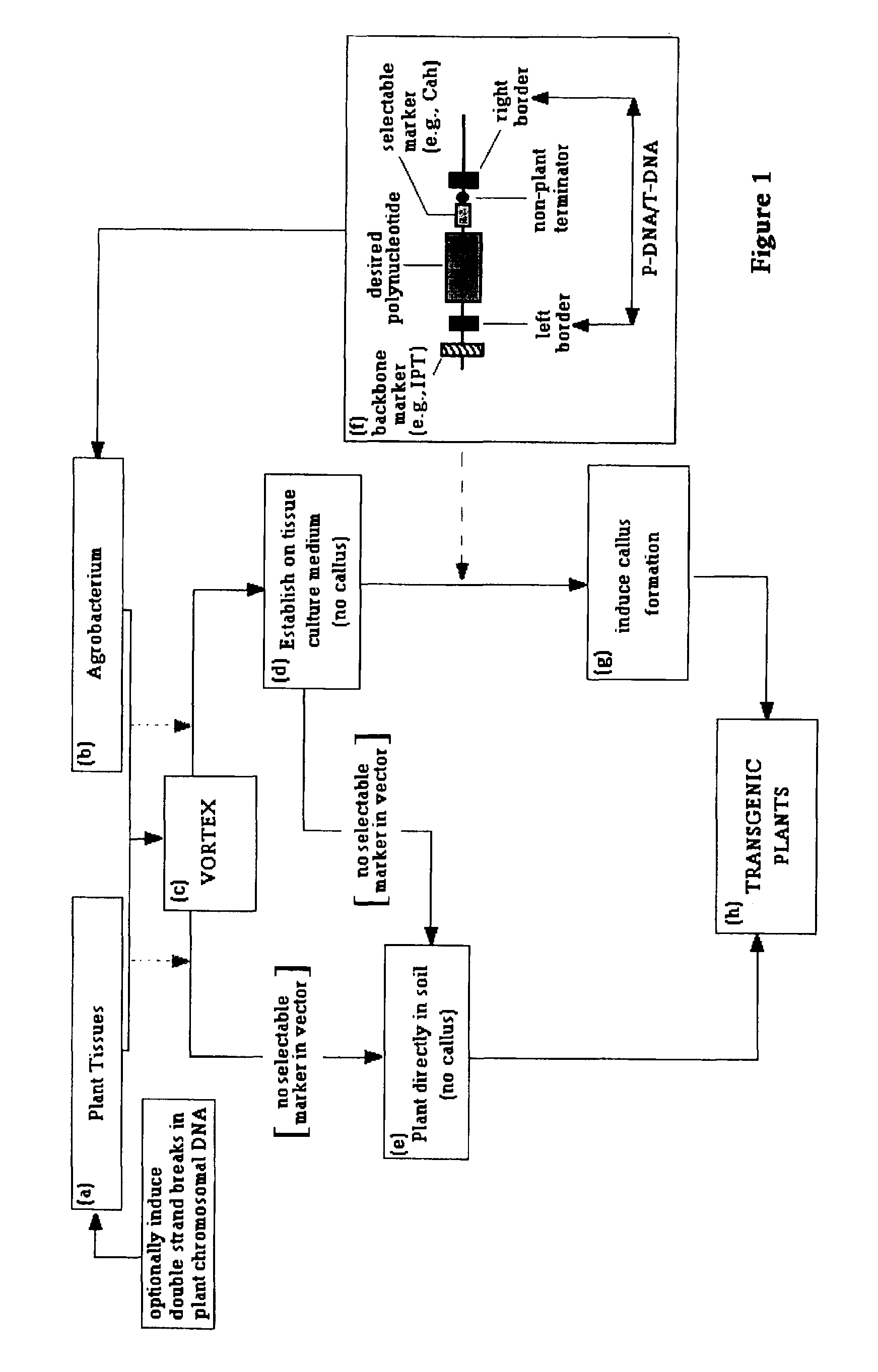
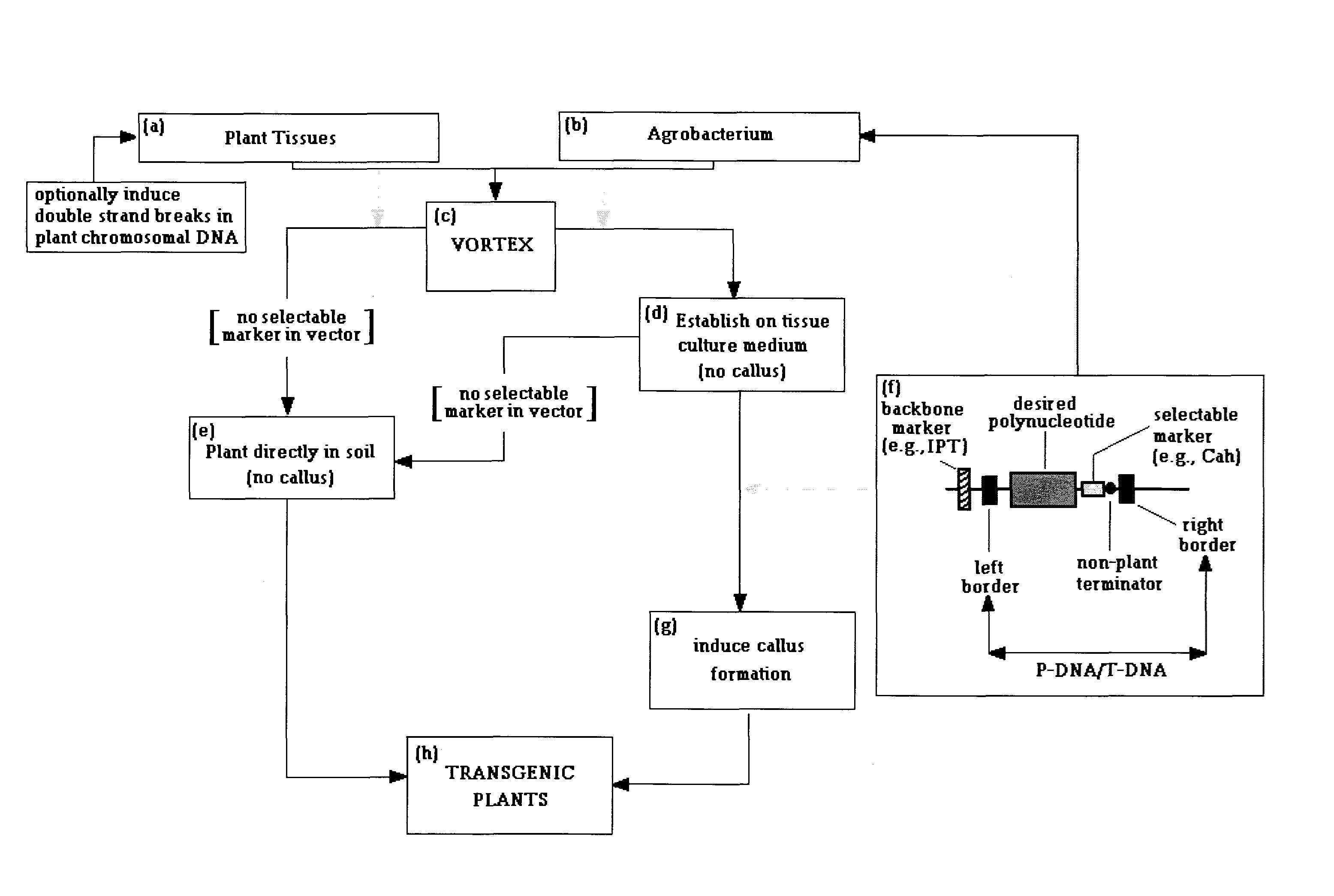
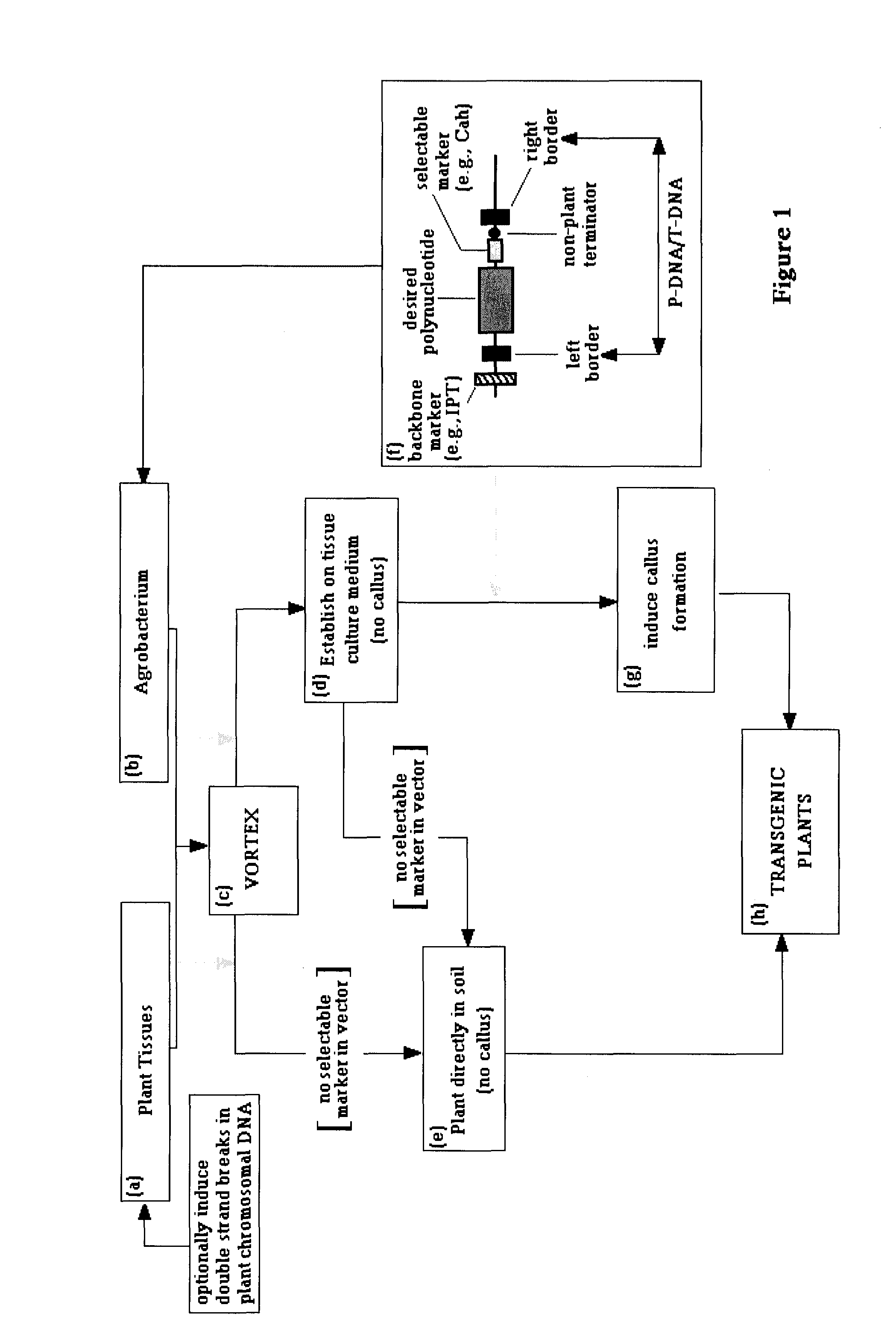
The present invention provides methods for producing transgenic plants based on an optimized transfer of DNA from Agrobacterium to plant cells, and / or on an optimized integration of the transferred DNAs into plant cell genomes. It also provides Agrobacterium-transformation vectors that can be used to limit or eliminate the transfer of undesirable DNA. The present invention can be applied to essentially any species of plants, including many recalcitrant plant species.
Owner:J R SIMPLOT
Ochrobactrum-mediated transformation of plants
InactiveCN108513584ABacteria peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionOrigin of replicationVirulent characteristics
Methods and compositions for Ochrobactrum-mediated transformation of plants are provided. Methods include but are not limited to using an Ochrobactrum strain to transfer a polynucleotide of interest to a plant cell. These include VirD2-dependent methods. Compositions include an Ochrobactrum strain, transfer DNAs, constructs and / or plasmids. These include Ochrobactrum strains having a plasmid comprising one or more virulence gene(s), border region, and / or origin of replication. Plant cells, tissues, plants, and seeds comprising a polynucleotide of interest produced by the methods are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Refined Plant Transformation
InactiveUS20100199375A1Improve drought toleranceReduce the overall heightOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellGenome
The present invention provides methods for producing transgenic plants based on an optimized transfer of DNA from Agrobacterium to plant cells, and / or on an optimized integration of the transferred DNAs into plant cell genomes. It also provides Agrobacterium-transformation vectors that can be used to limit or eliminate the transfer of undesirable DNA. The present invention can be applied to essentially any species of plants, including many recalcitrant plant species.
Owner:J R SIMPLOT
TAL-mediated transfer DNA insertion
InactiveUS9756871B2Vector-based foreign material introductionFood scienceNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to methods for stably integrating a desired polynucleotide into a plant genome, comprising transforming plant material with a first vector comprising nucleotide sequences encoding TAL proteins designed to recognize a target sequence; transforming the plant material with a second vector comprising (i) a marker gene that is not operably linked to a promoter (“promoter-free marker cassette”) and which comprises a sequence homologous to the target sequence; and (ii) a desired polynucleotide; and identifying transformed plant material in which the desired polynucleotide is stably integrated.
Owner:J R SIMPLOT
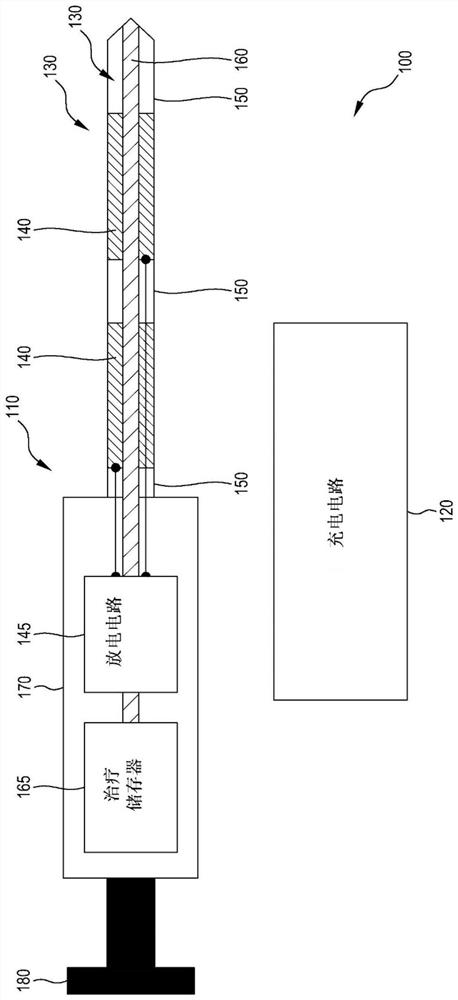
Electrotransfer therapy delivery devices, systems, and methods
Disclosed is a device capable of efficiently electrotransferring DNA into cells by means of single-capacitance discharge. The principles of the system involve storing charge quanta on a capacitor and then discharging it through an array of electrodes configured to generate an electric field having an electric field potential gradient focused to a region through an array configuration and having an intensity sufficient to efficiently electrically transfer DNA into cells. The DNA or associated ribonucleic acid molecules or even other charged molecules, once entering the cell, affect the change in biological function.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Pentameric CRP-producing transgenic silkworm
Owner:NITTO BOSEIKI CO LTD +1
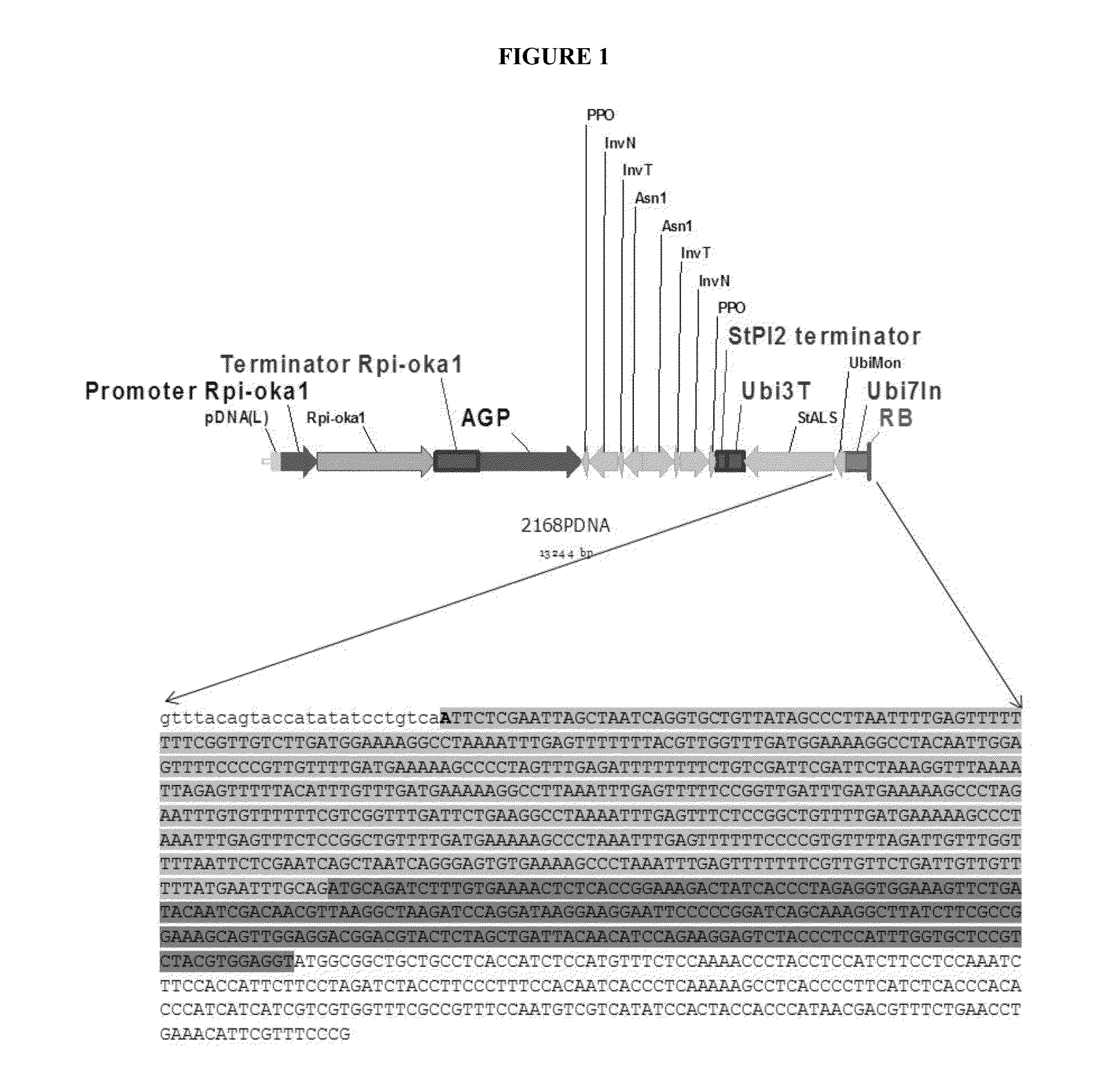
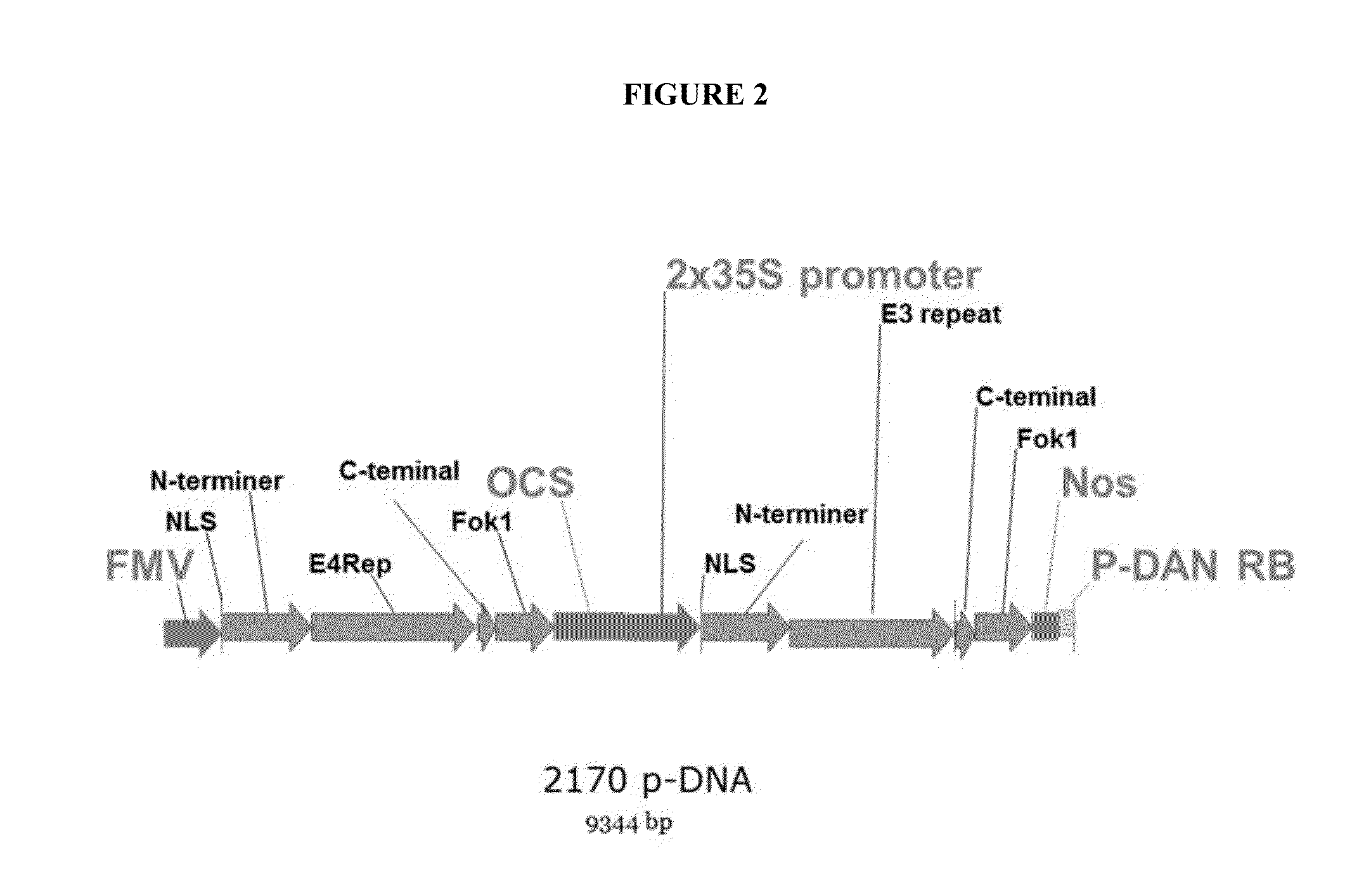
Binary vectors with minimized biosafety concerns and high transformation rates by engineered plant-derived transfer-DNA
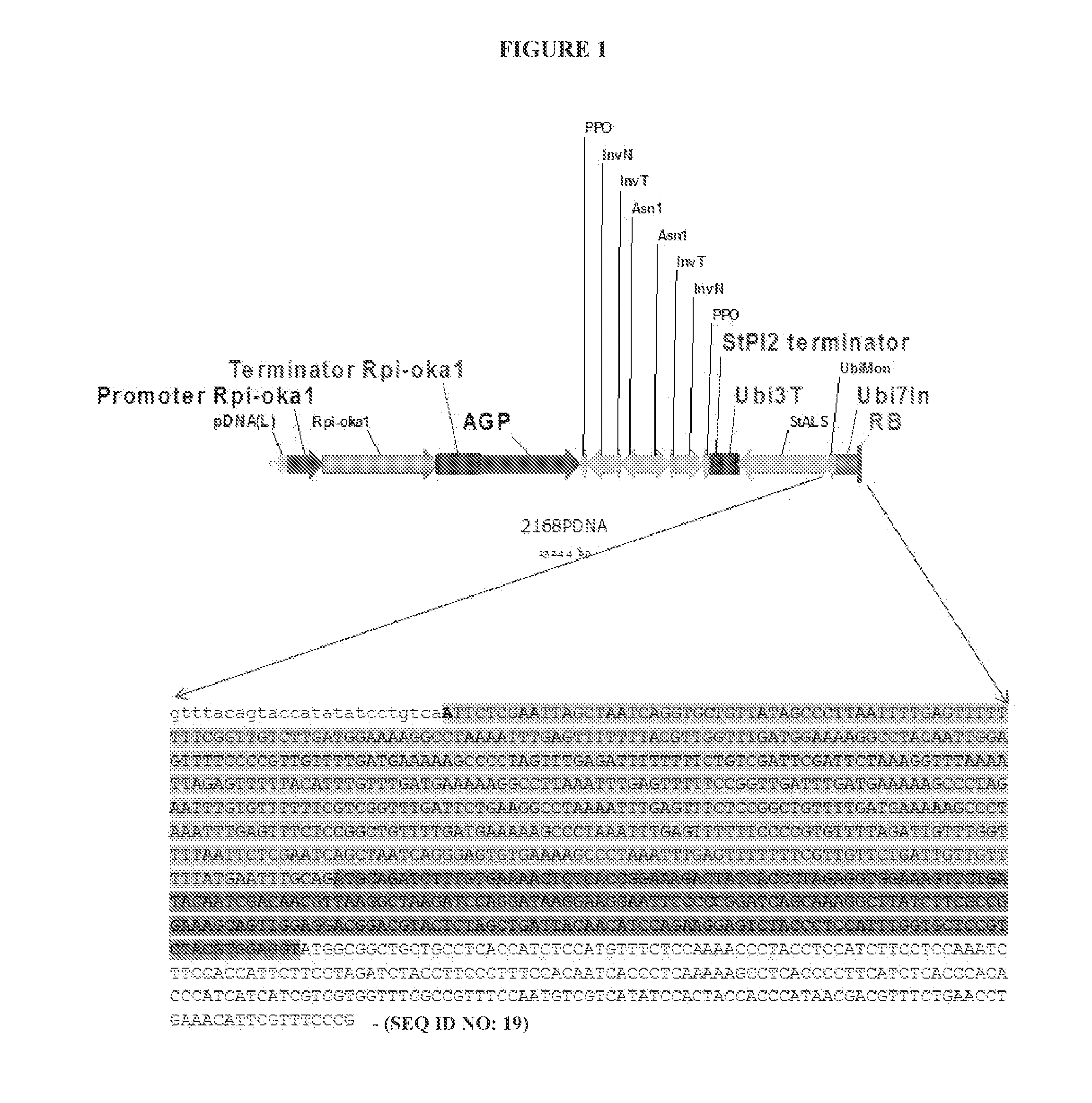
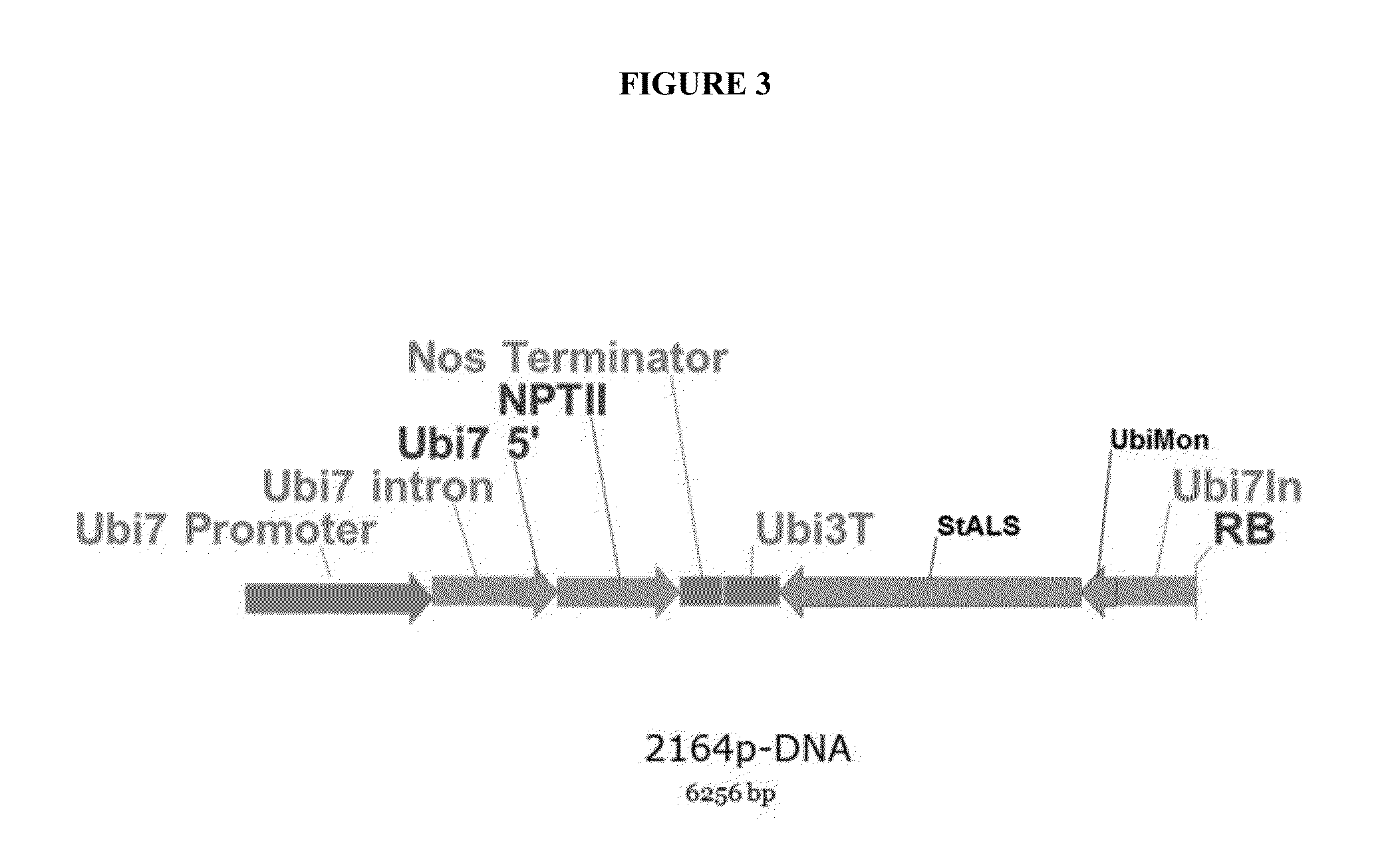
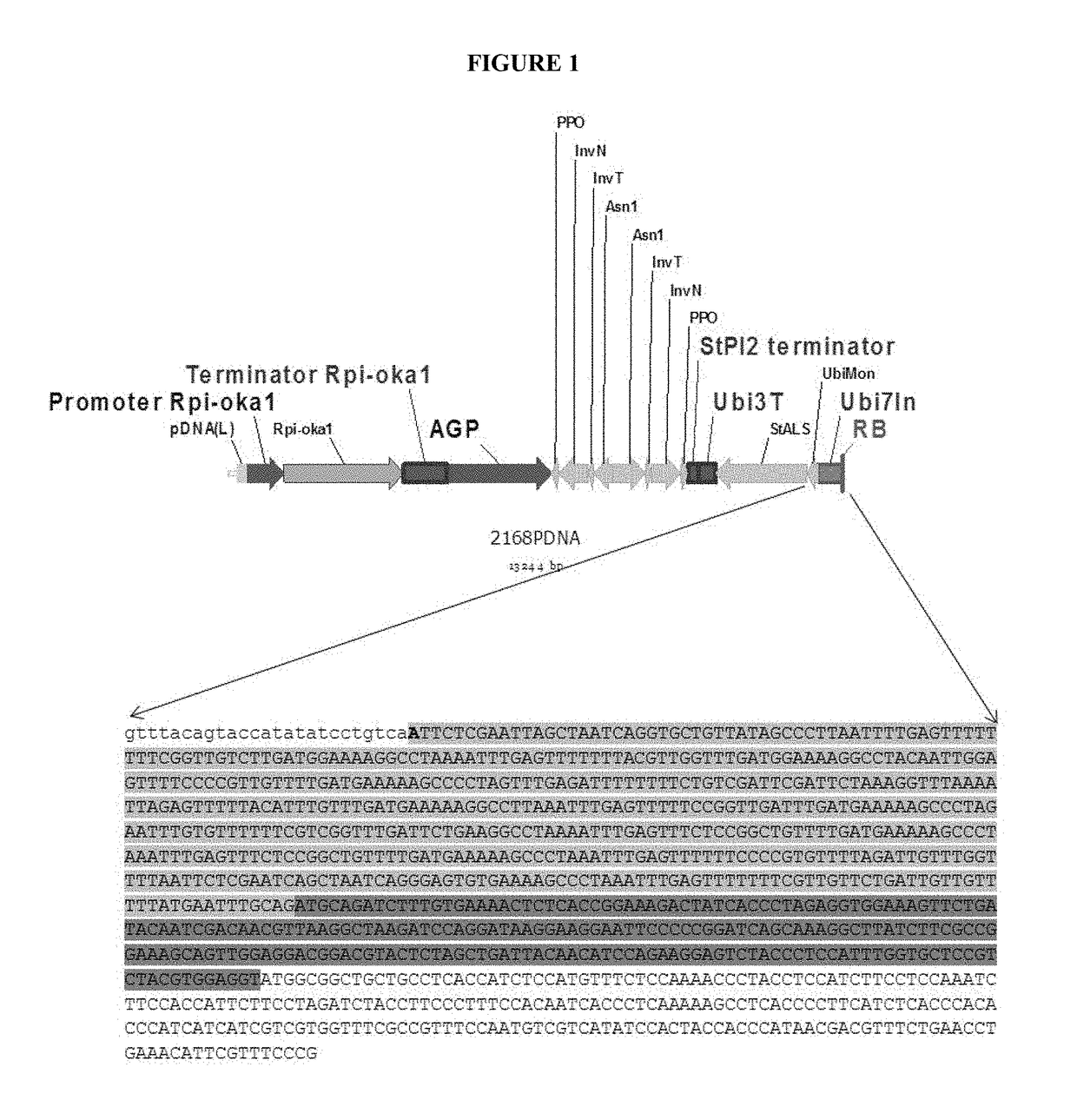
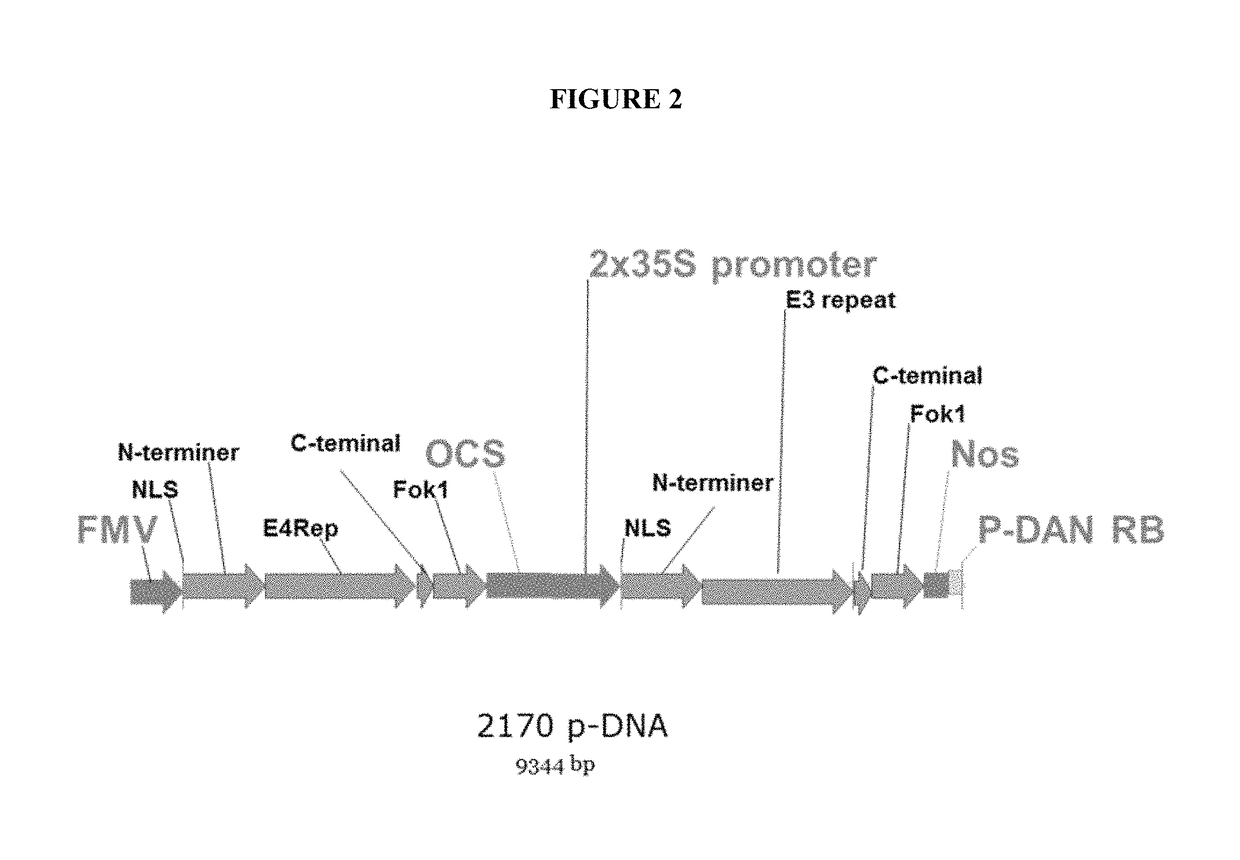
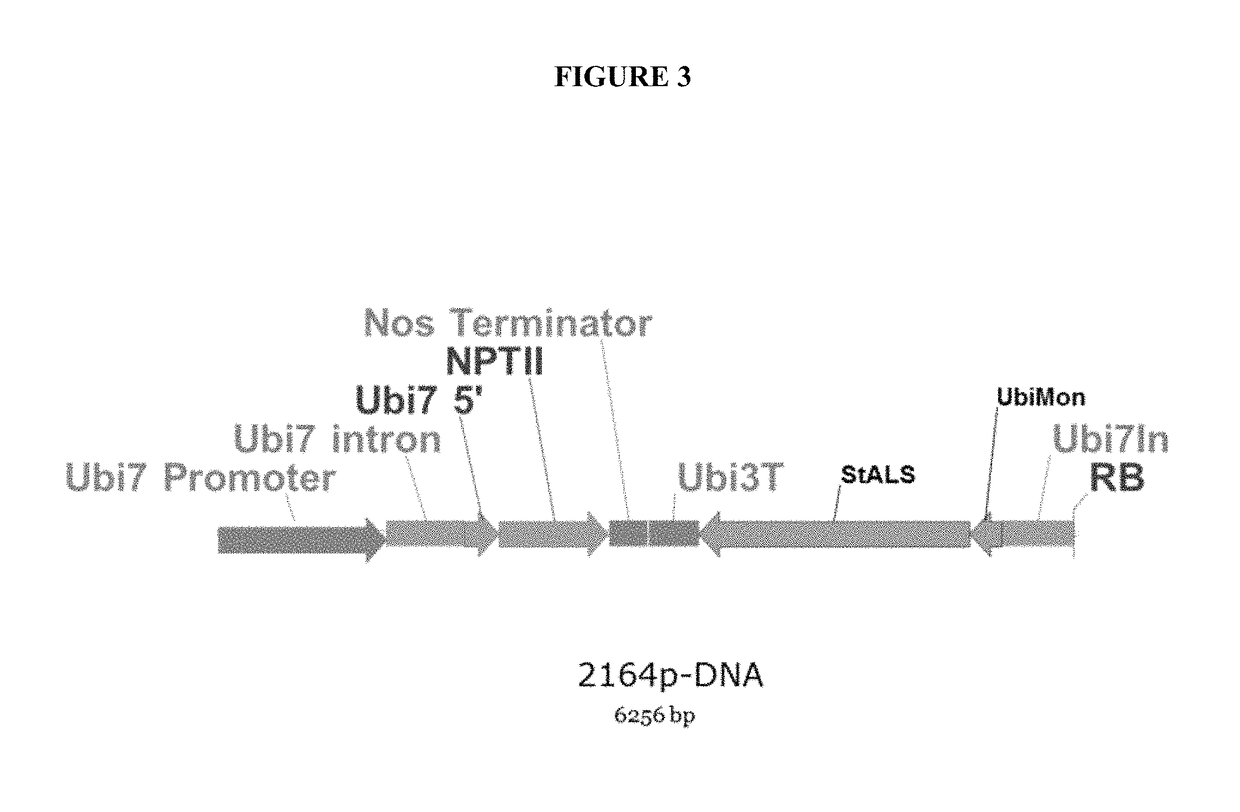
An engineered plant-derived transfer (P-)DNA was designed and constructed based on a couple of T-DNA homologous sequences in sugar beet genome. Plant transformation efficacy of the engineered P-DNA was analyzed compared to conventional T-DNA in two independent systems, stable transformation of tobacco plant and sugar beet hairy roots. The outcomes demonstrated that plant transformation is directed well by vectors carrying the engineered P-DNA with higher efficiency than the conventional binary vector in both experimental systems. This vector was further improved by adding two matrix attachment regions within P-DNA. This new vector was even more efficient in gene transfer, higher than conventional binary vector.
Owner:ZARE BAHAR +3
In vivo gene transfer for wound healing
InactiveCN102274522AMeet short-term dosing requirementsSuture equipmentsVirusesTherapeutic proteinMammal
The present invention relates to an in vivo method for specific targeting and transfer of DNA into mammalian repair cells. The transferred DNA may include any DNA encoding a therapeutic protein of interest. The invention is based on the discovery that mammalian repair cells proliferate and migrate into a wound site where they actively take up and express DNA. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions that may be used in the practice of the invention to transfer the DNA of interest. Such compositions include any suitable matrix in combination with the DNA of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
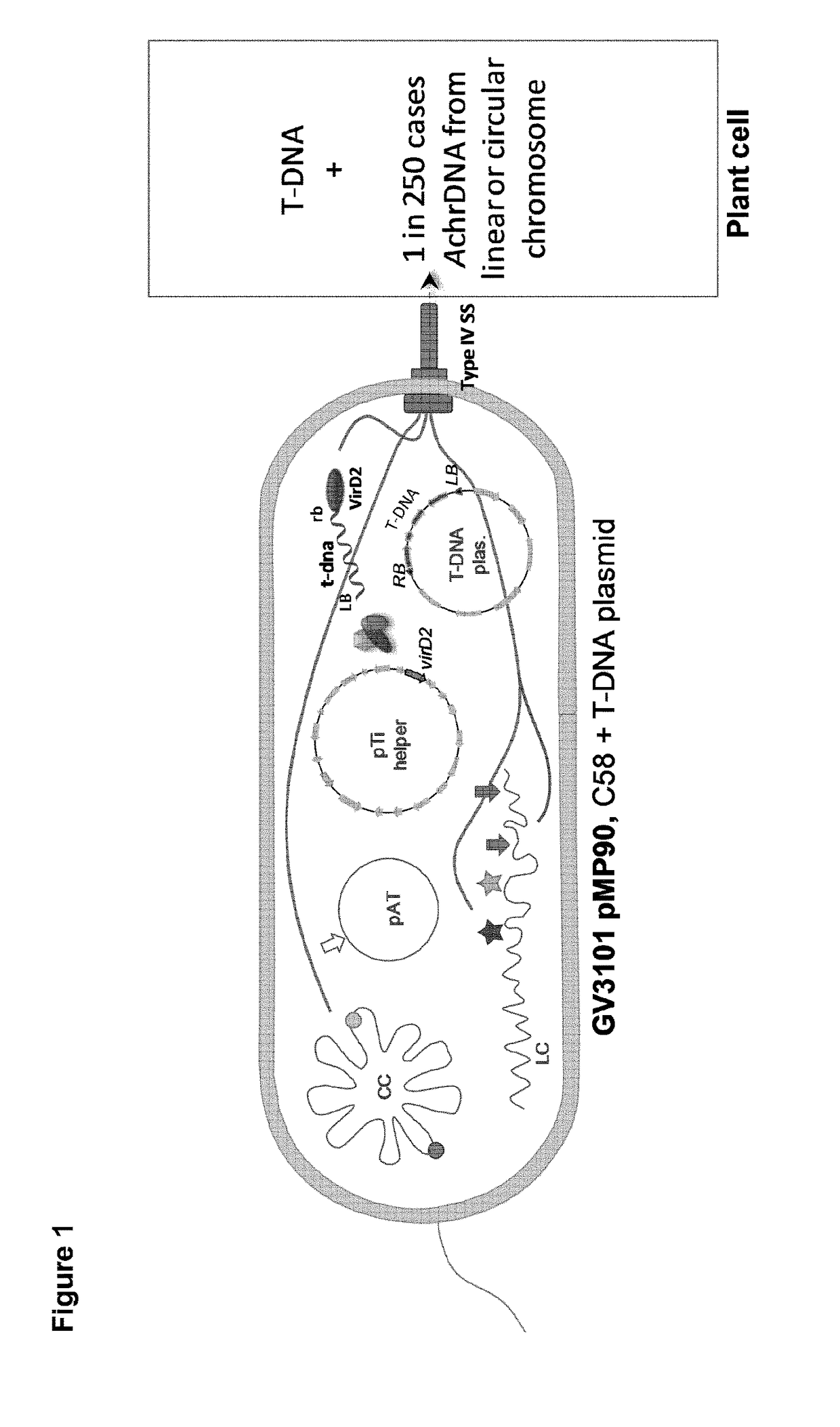
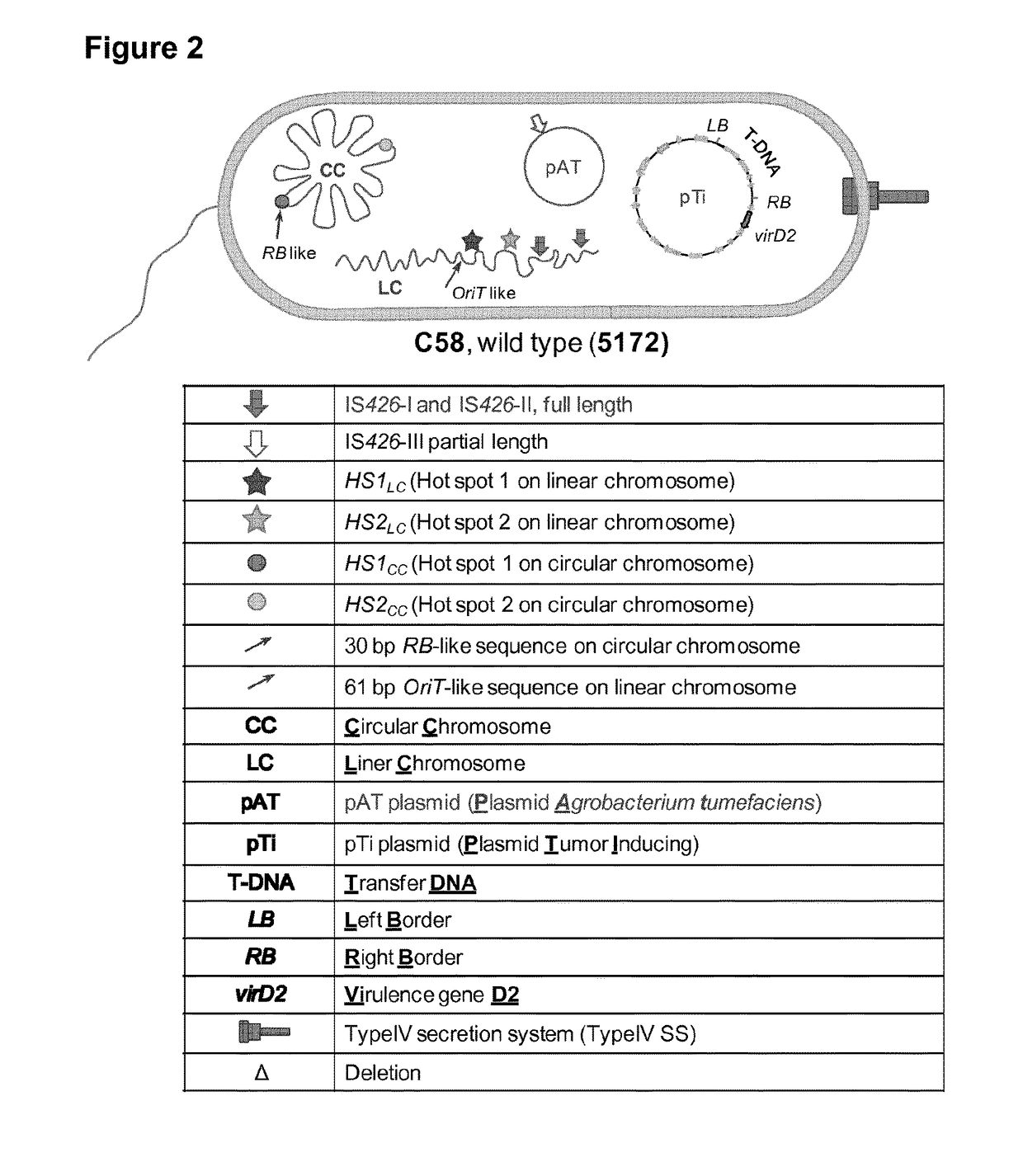
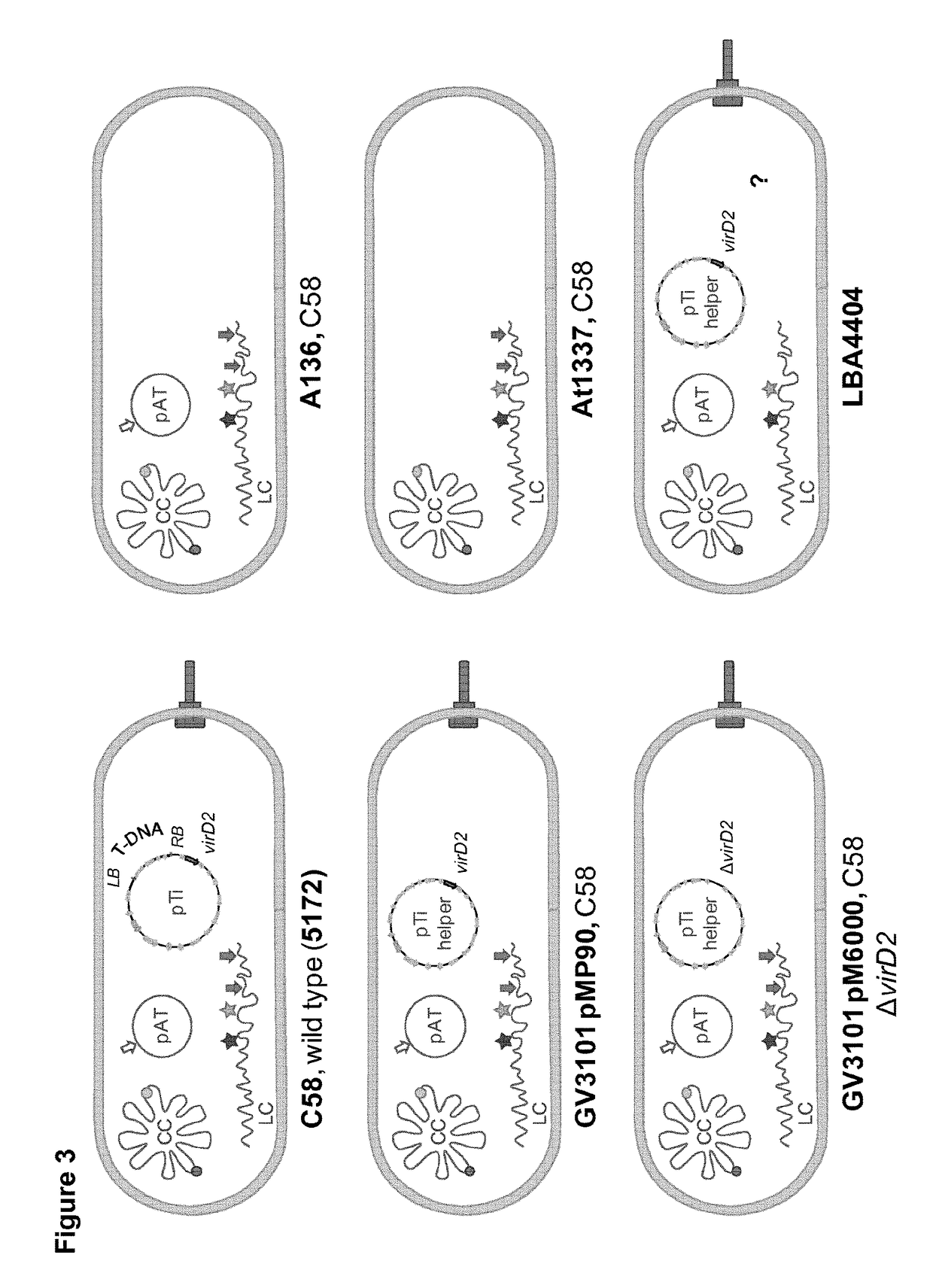
Improved strains of agrobacterium tumefaciens for transferring DNA into plants
The present invention relates to Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains that comprise at least one deletion / mutation in a sequence selected from the group of IS426 copy I, IS426 copy II, the OriT-like sequence, and the border-like sequences, and their uses in safer and improved transformation procedures for cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BONN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com