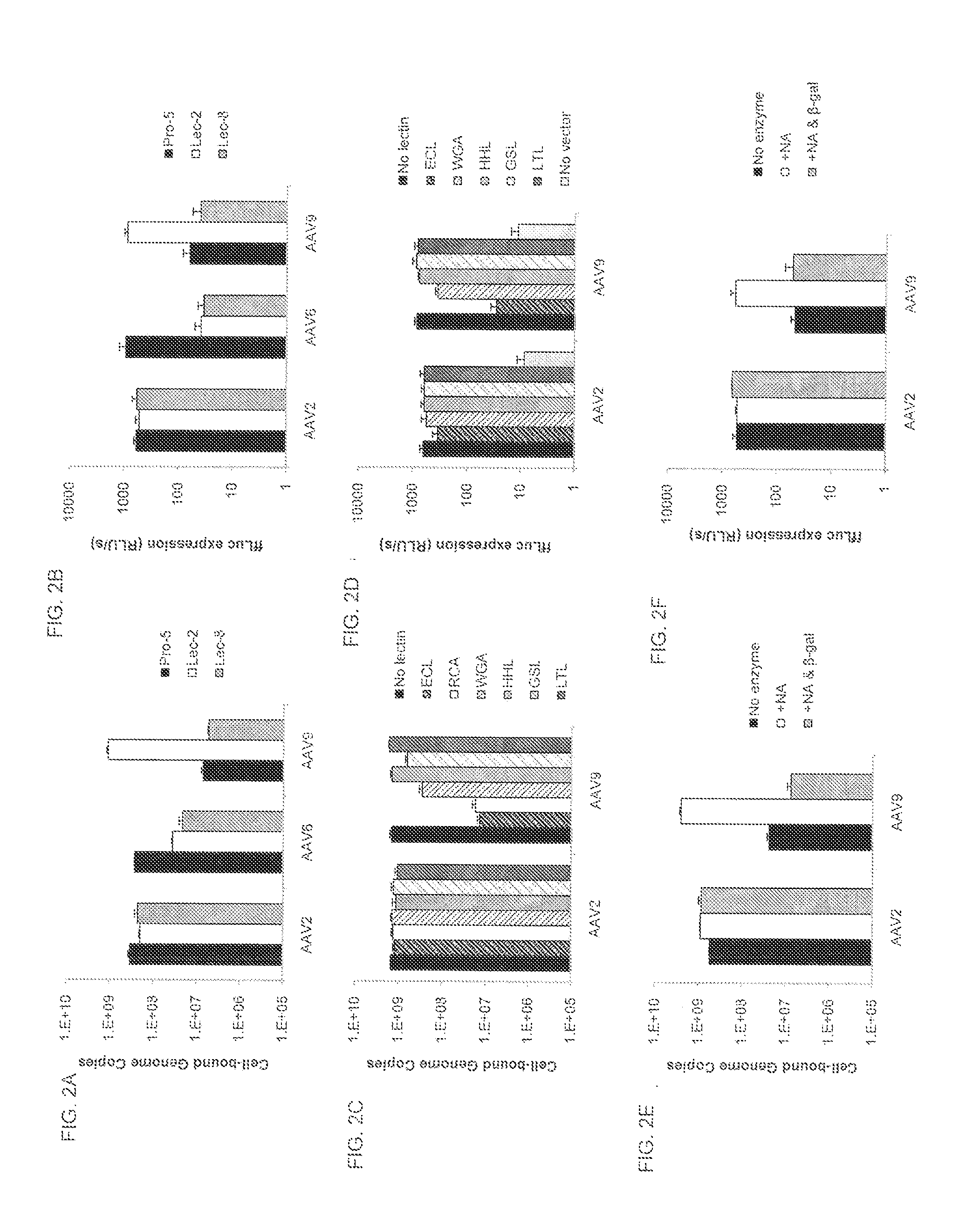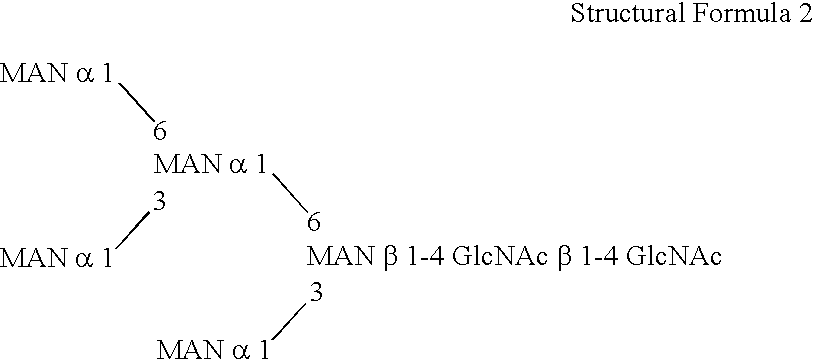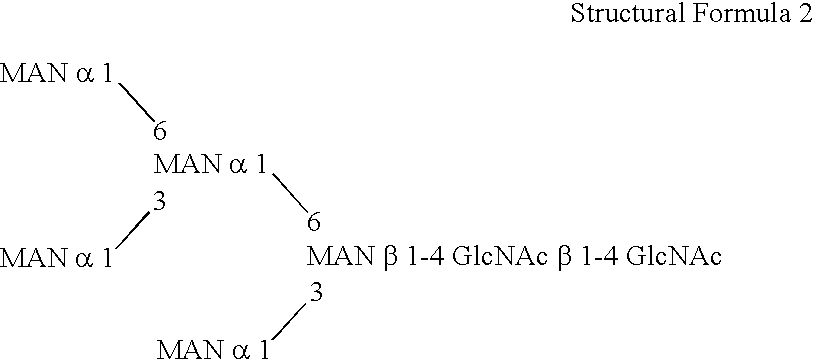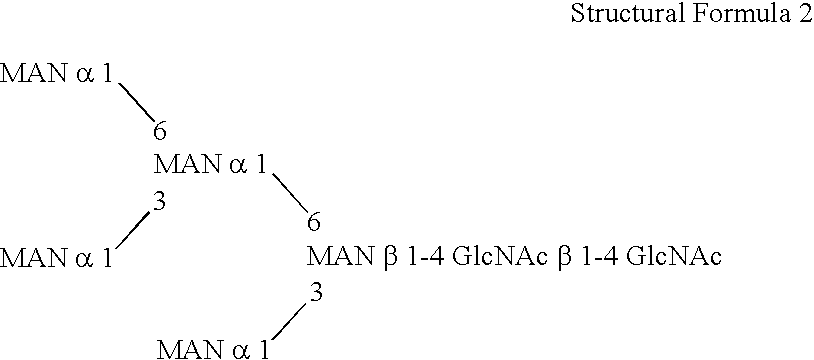Patents
Literature
639 results about "Gene transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Gene transfer format (GTF) is a file format used to hold information about gene structure. It is a tab-delimited text format based on the general feature format (GFF), but contains some additional conventions specific to gene information. A significant feature of the GTF that can be validated: given a sequence and a GTF file, one can check that the format is correct. This significantly reduces problems with the interchange of data between groups.
Medical device
InactiveUS20050002981A1Reduce connective tissue hyperplasiaReduce restenosisStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological propertyConnective tissue fiber
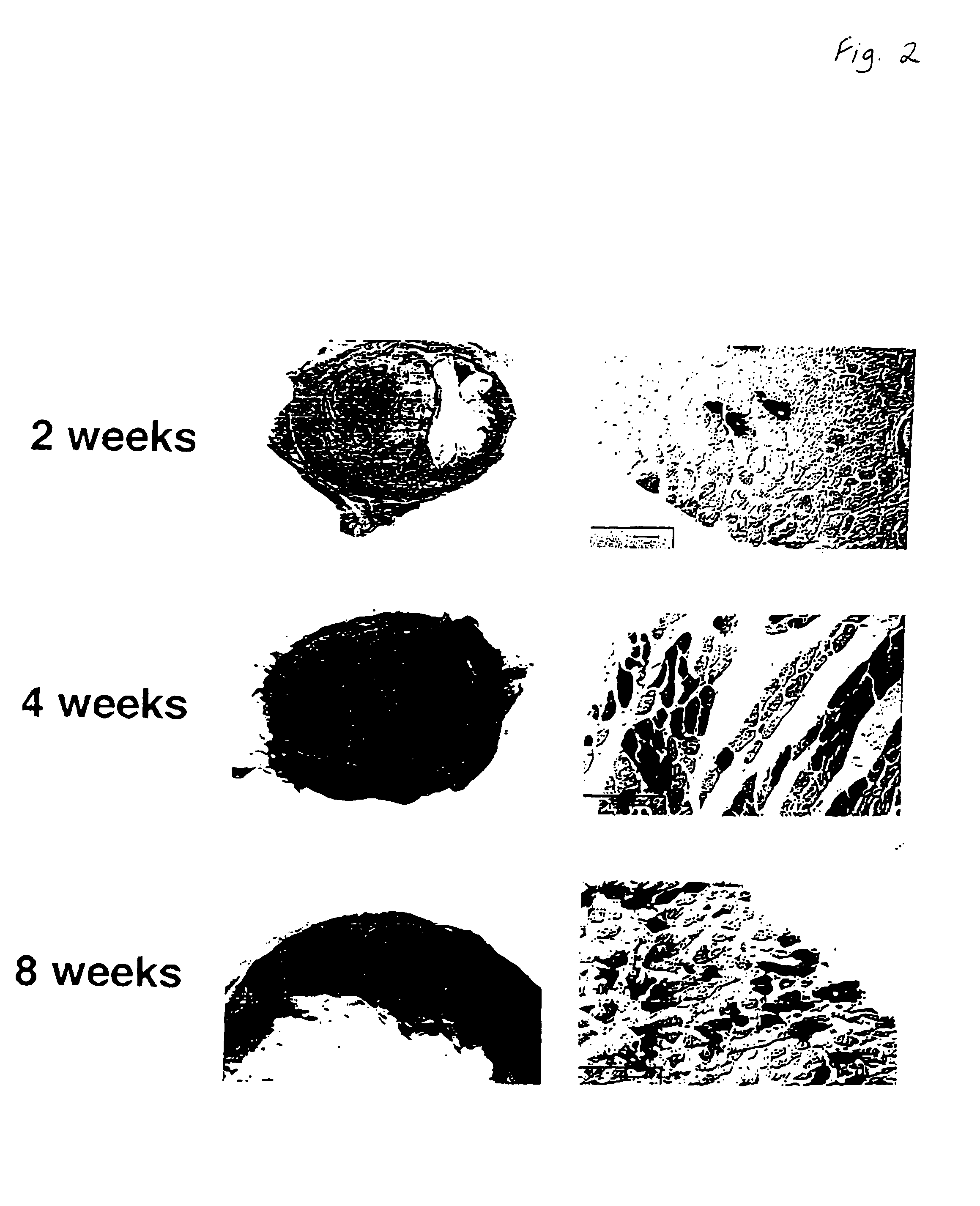
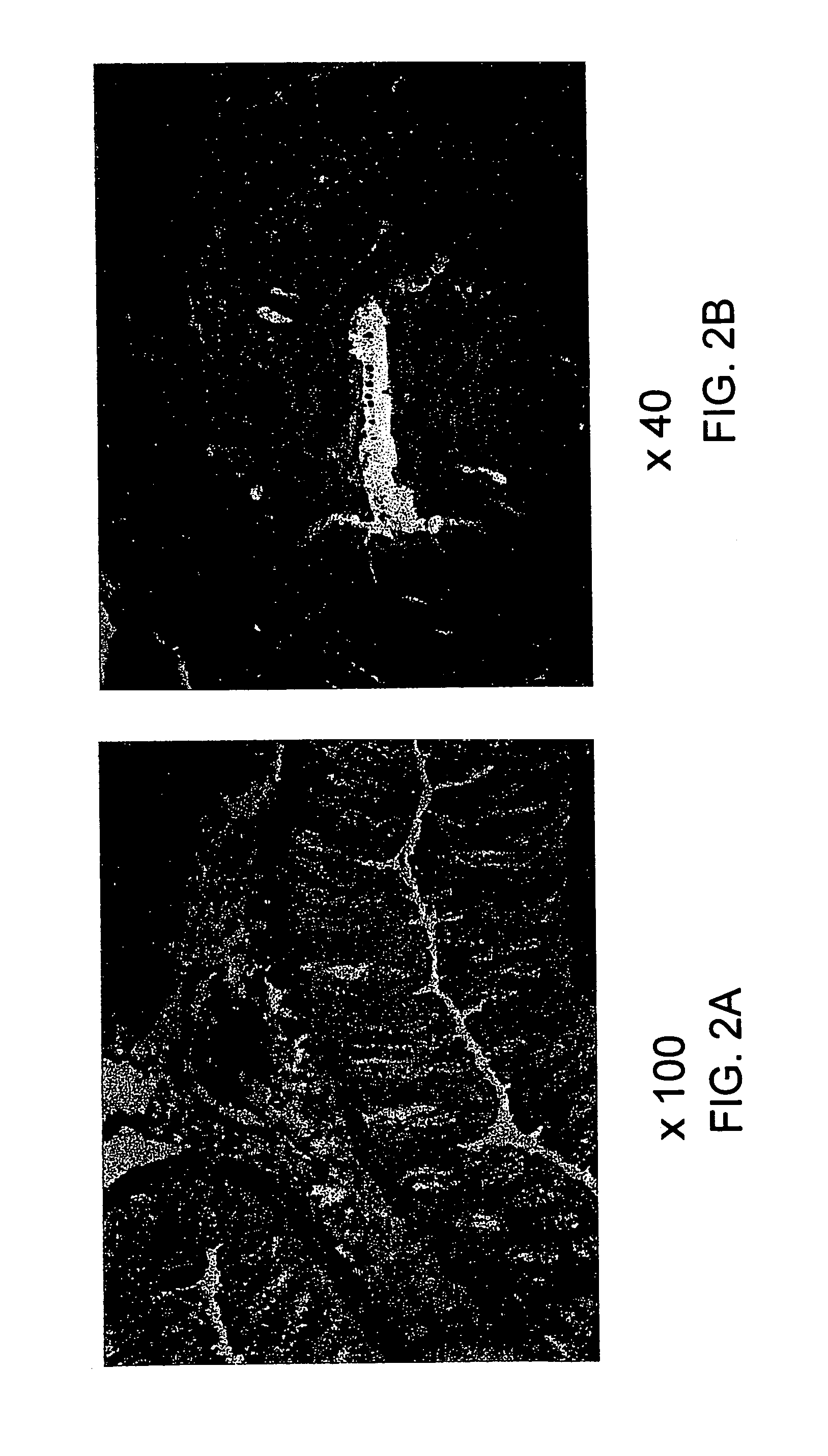
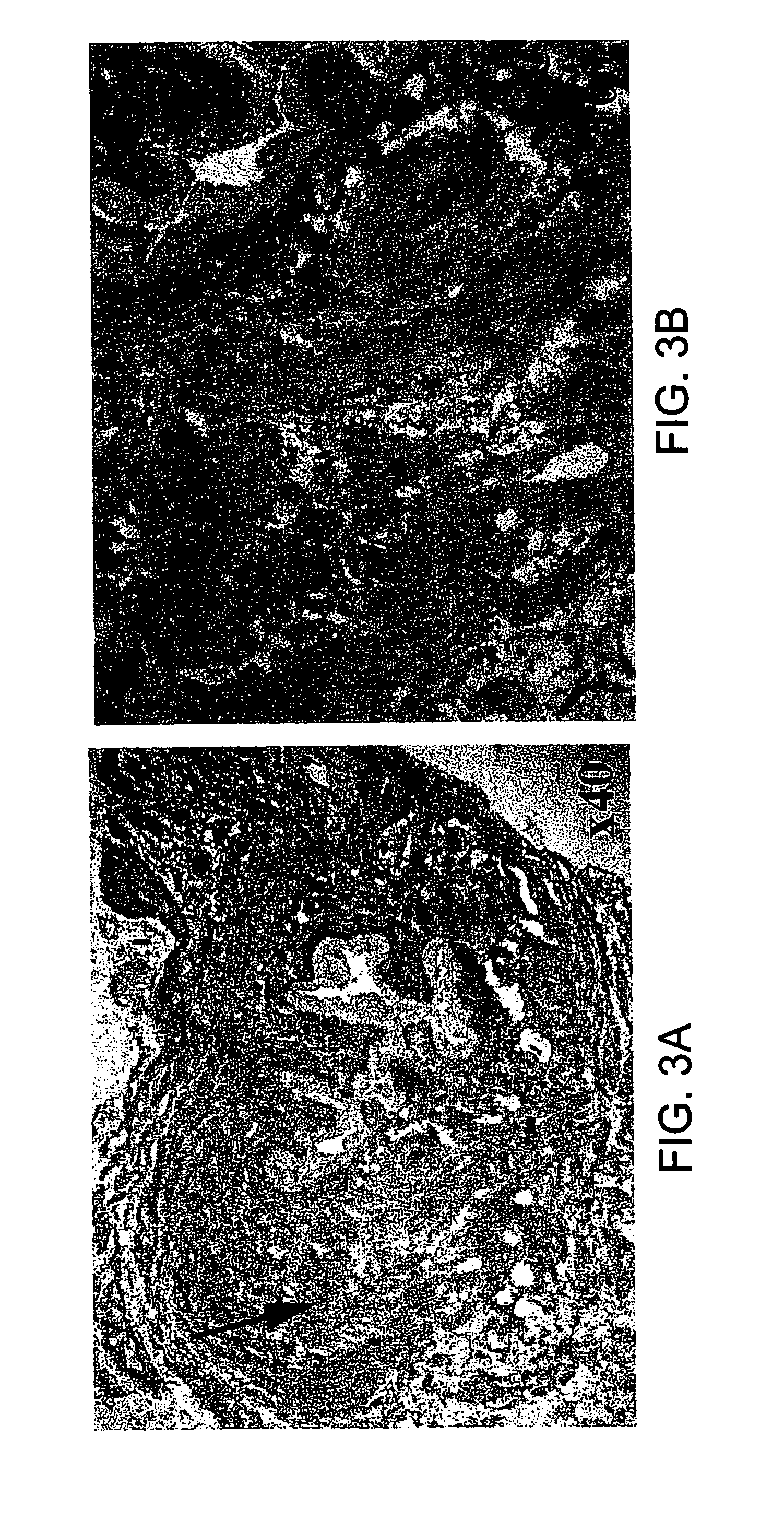
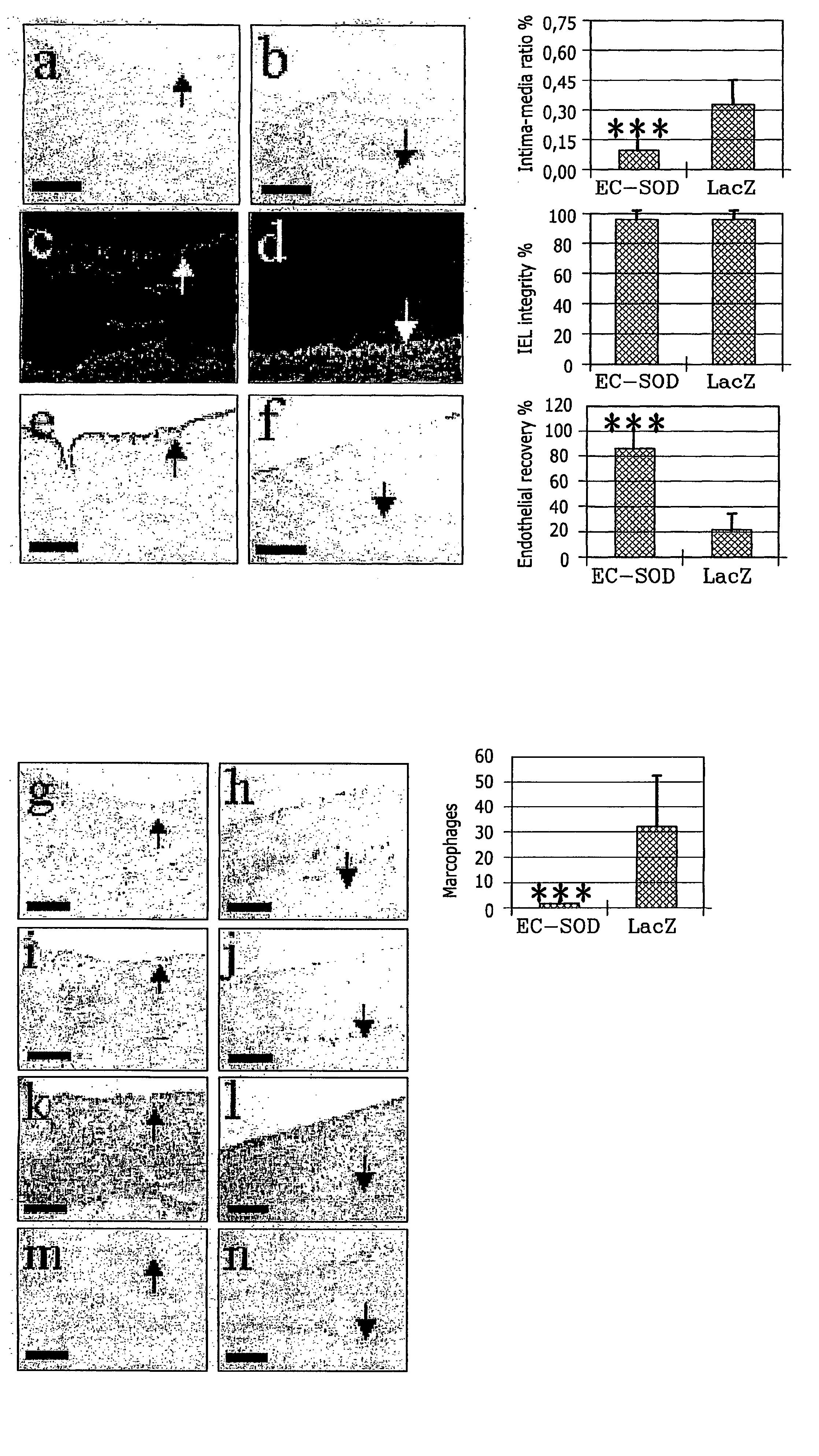
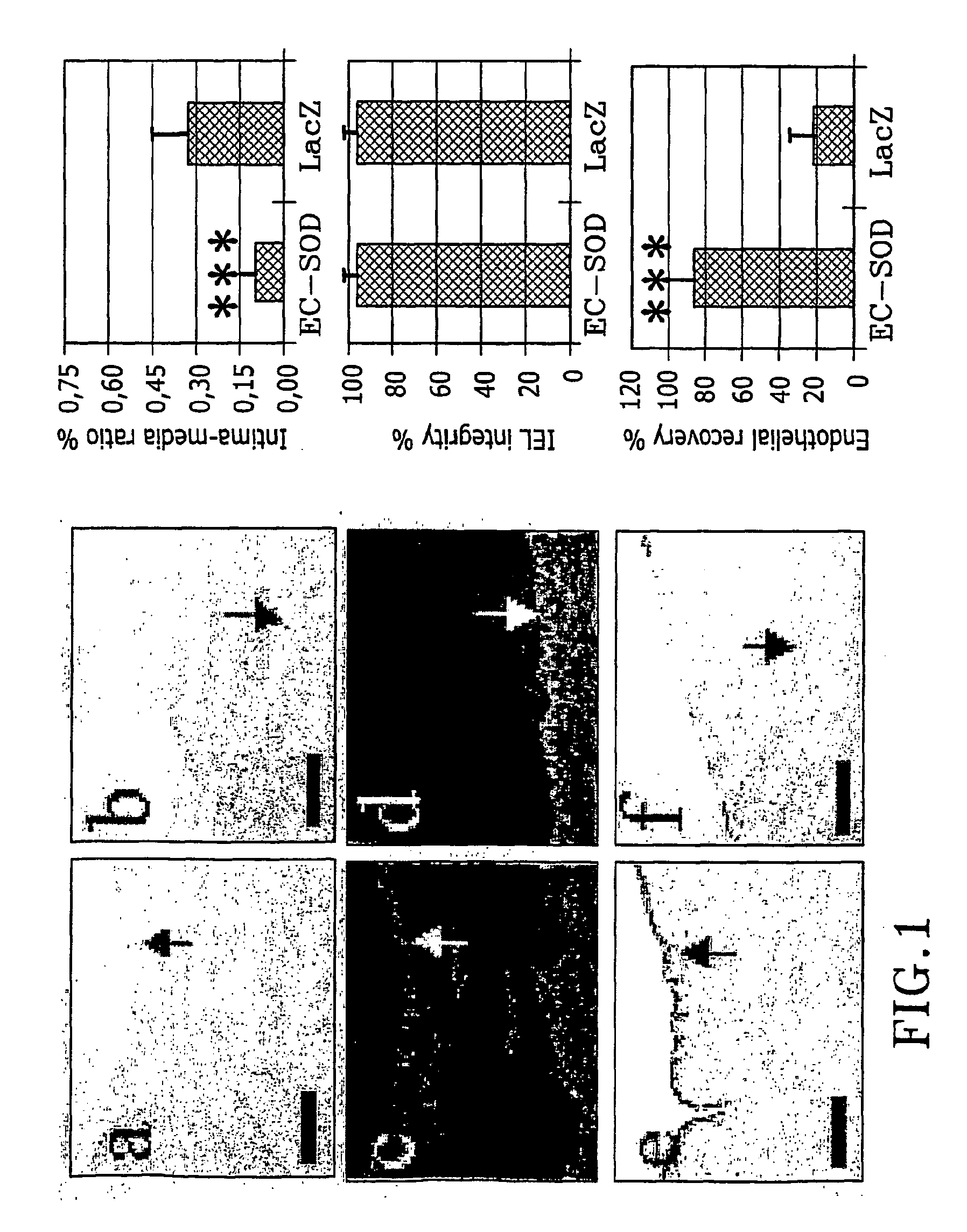
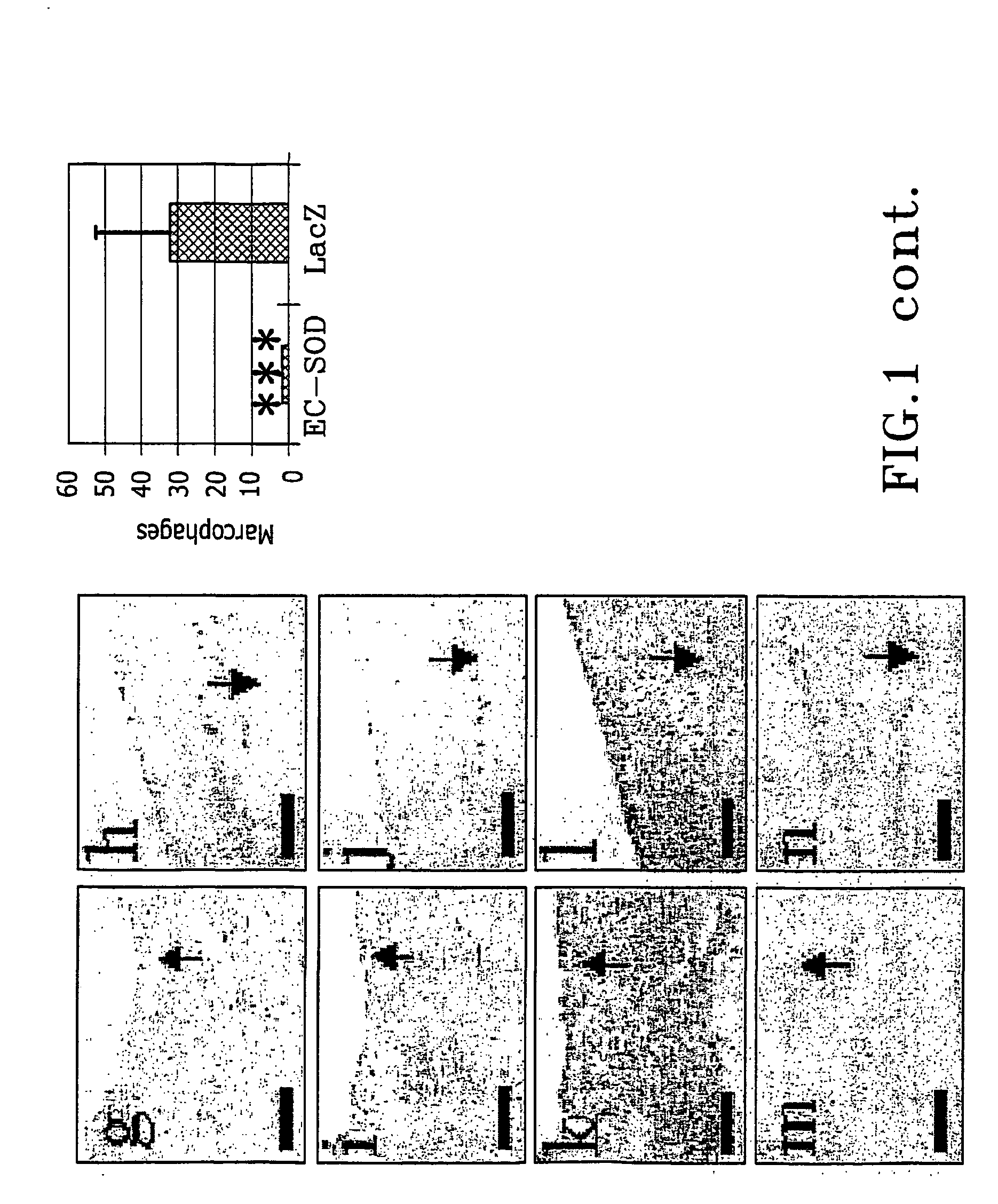
The present invention relates to the use of a gene transfer product to reduce hyperplastic connective tissue growth after tissue trauma or implantation of a medical device. The present invention also relates to a medical device with improved biological properties for an at least partial contact with blood, bodily fluids and / or tissues when introduced in a mammalian body, which device comprises a core and a nucleic acid, encoding a product capable of leading to production of extracellular superoxide dismutase present in a biologically compatible medium. Said nucleic acid encodes a translation or transcription product, which is capable of inhibiting hyperplastic connective tissue growth and promoting endothelialisation in vivo at least partially on a synthetic surface of said core. The present invention also relates to a method of producing a medical device according to the invention.
Owner:FIT BIOTECH OY PLC
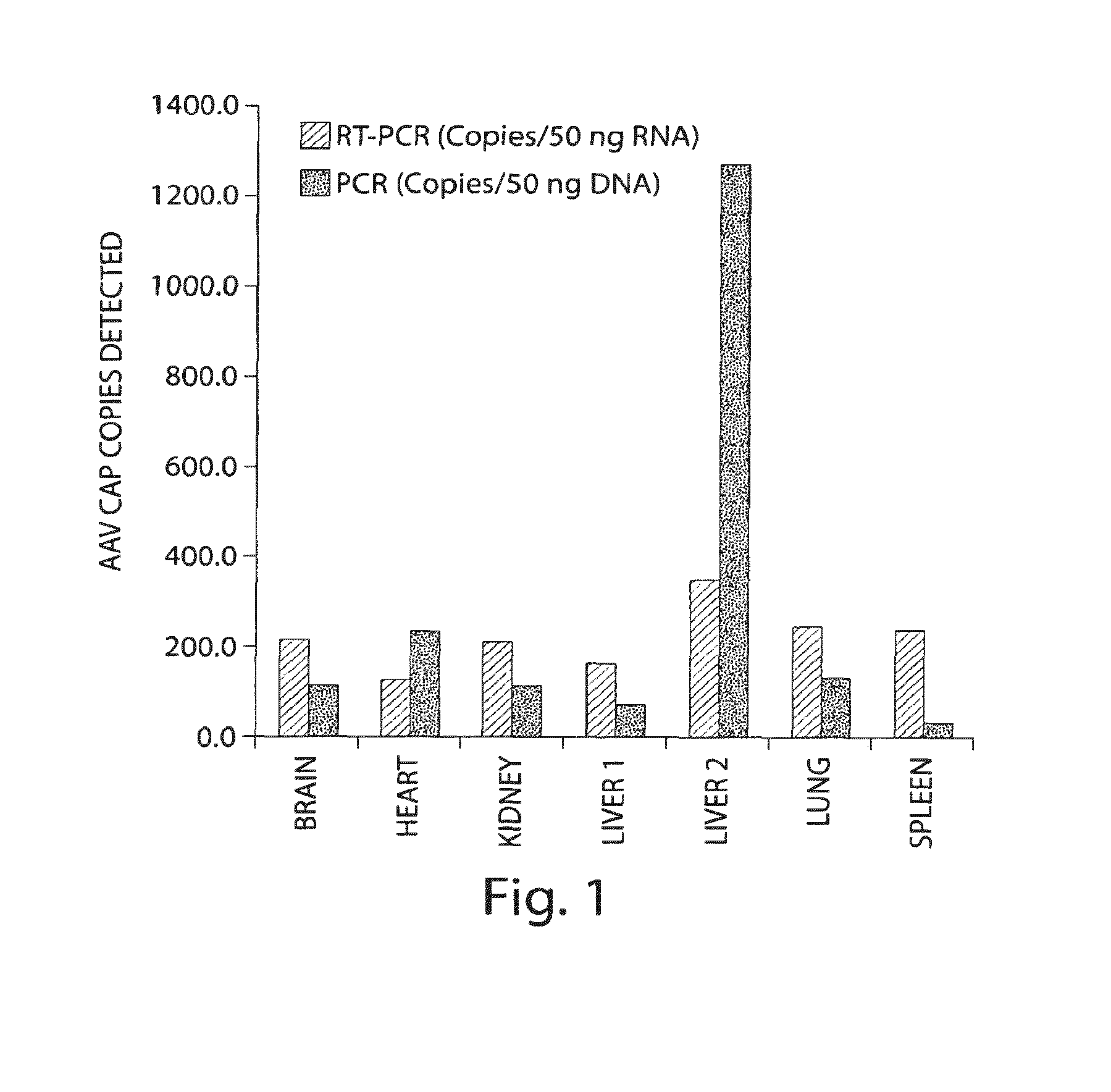
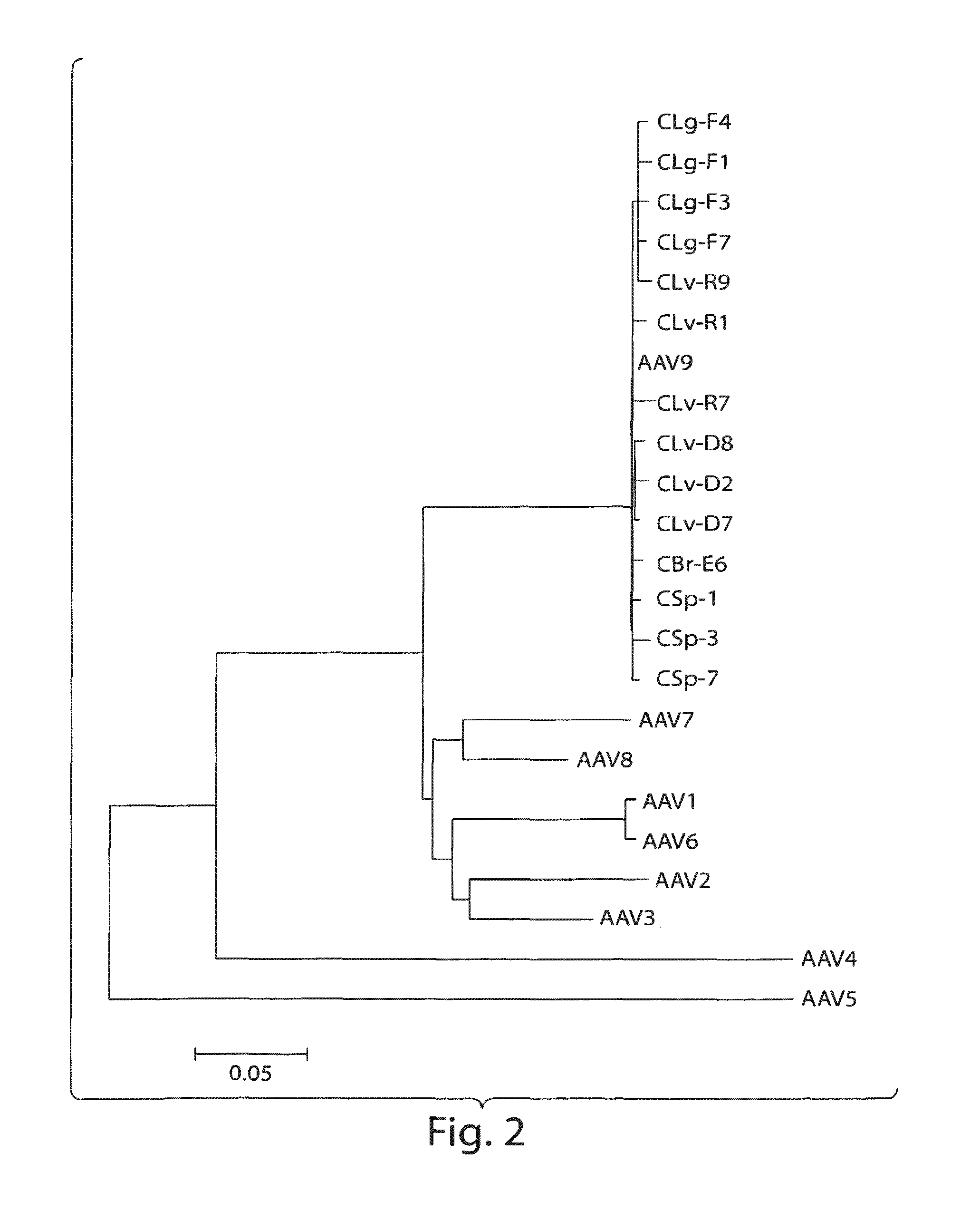
AAV's and uses thereof
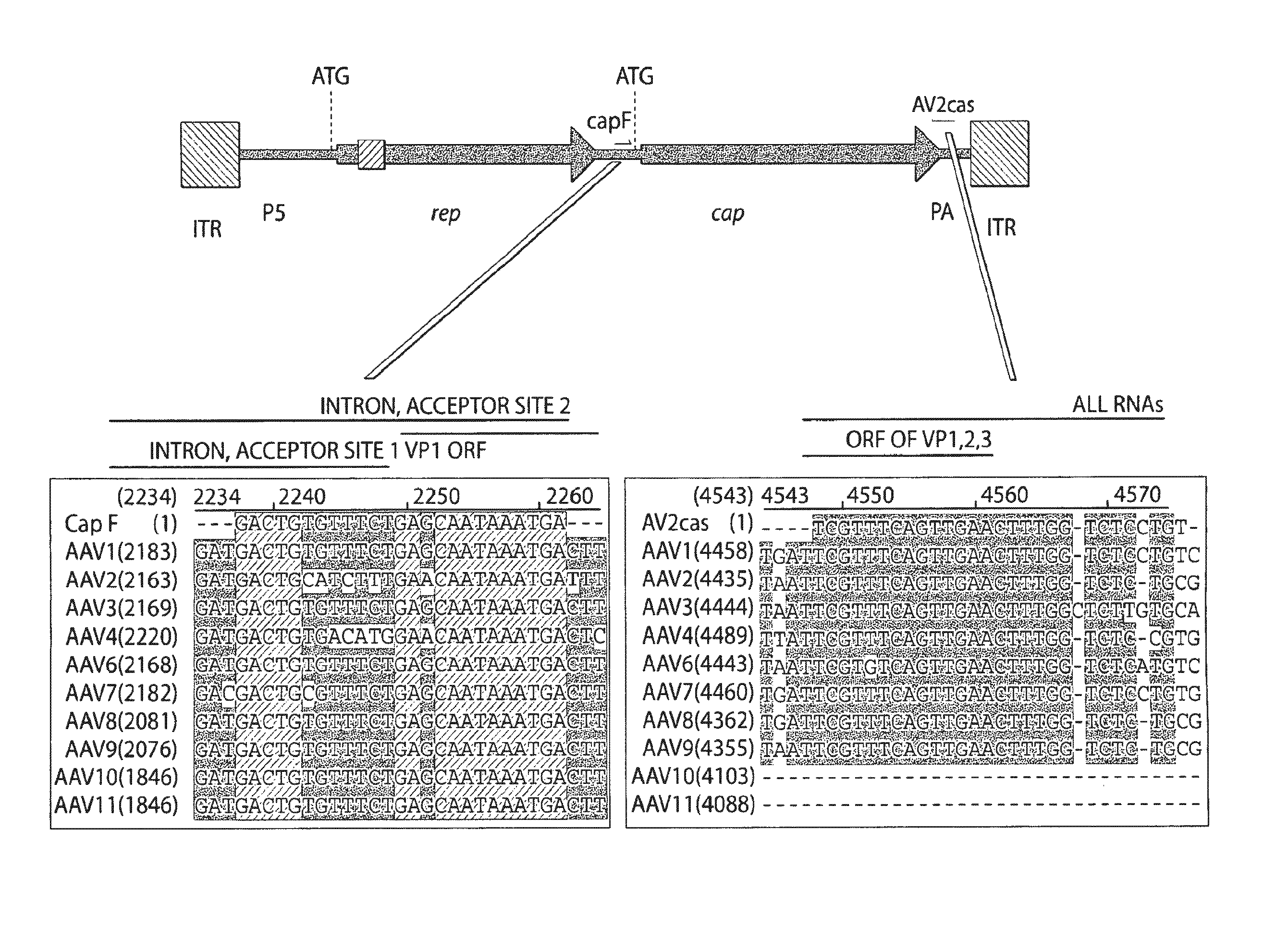
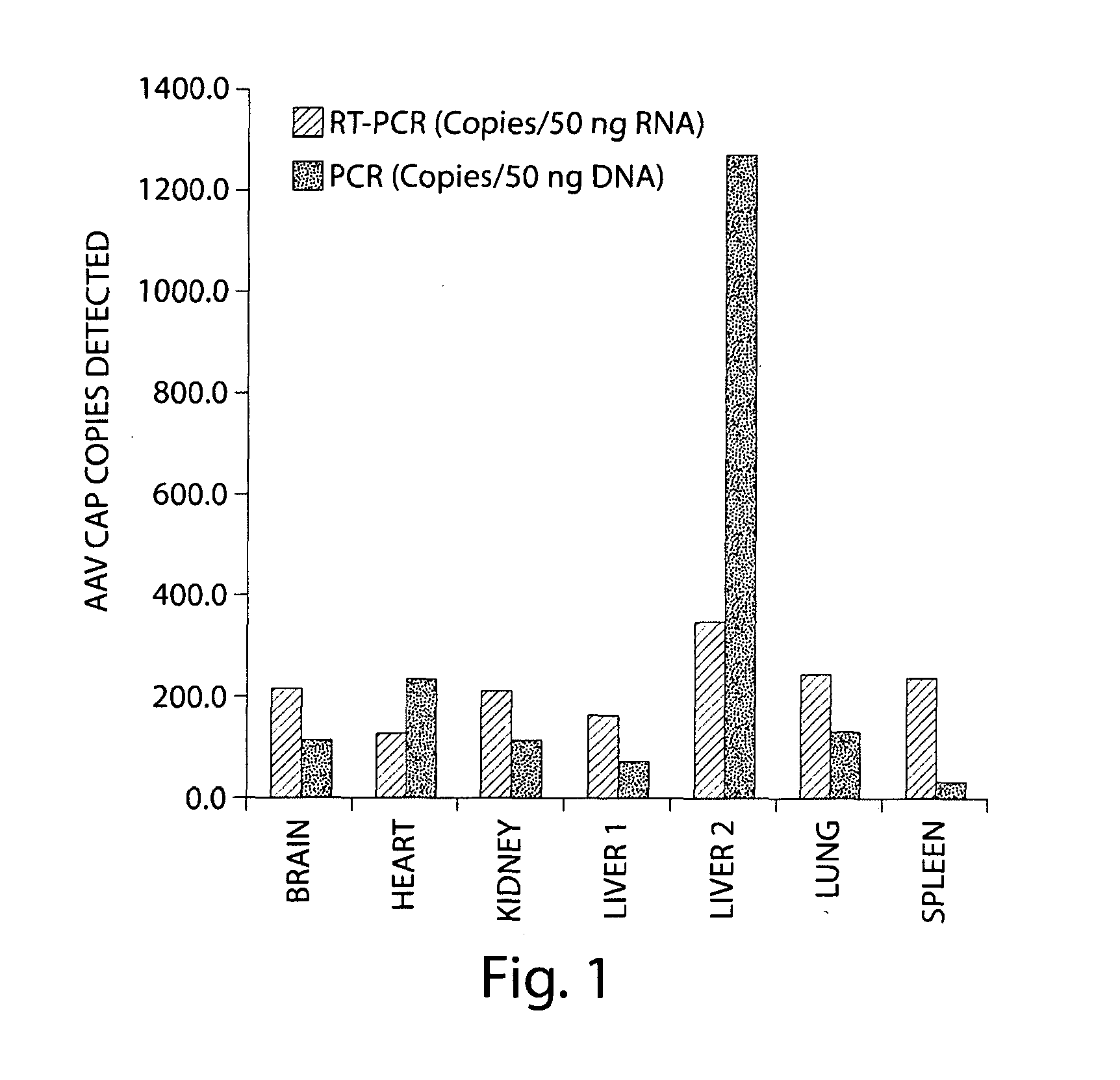
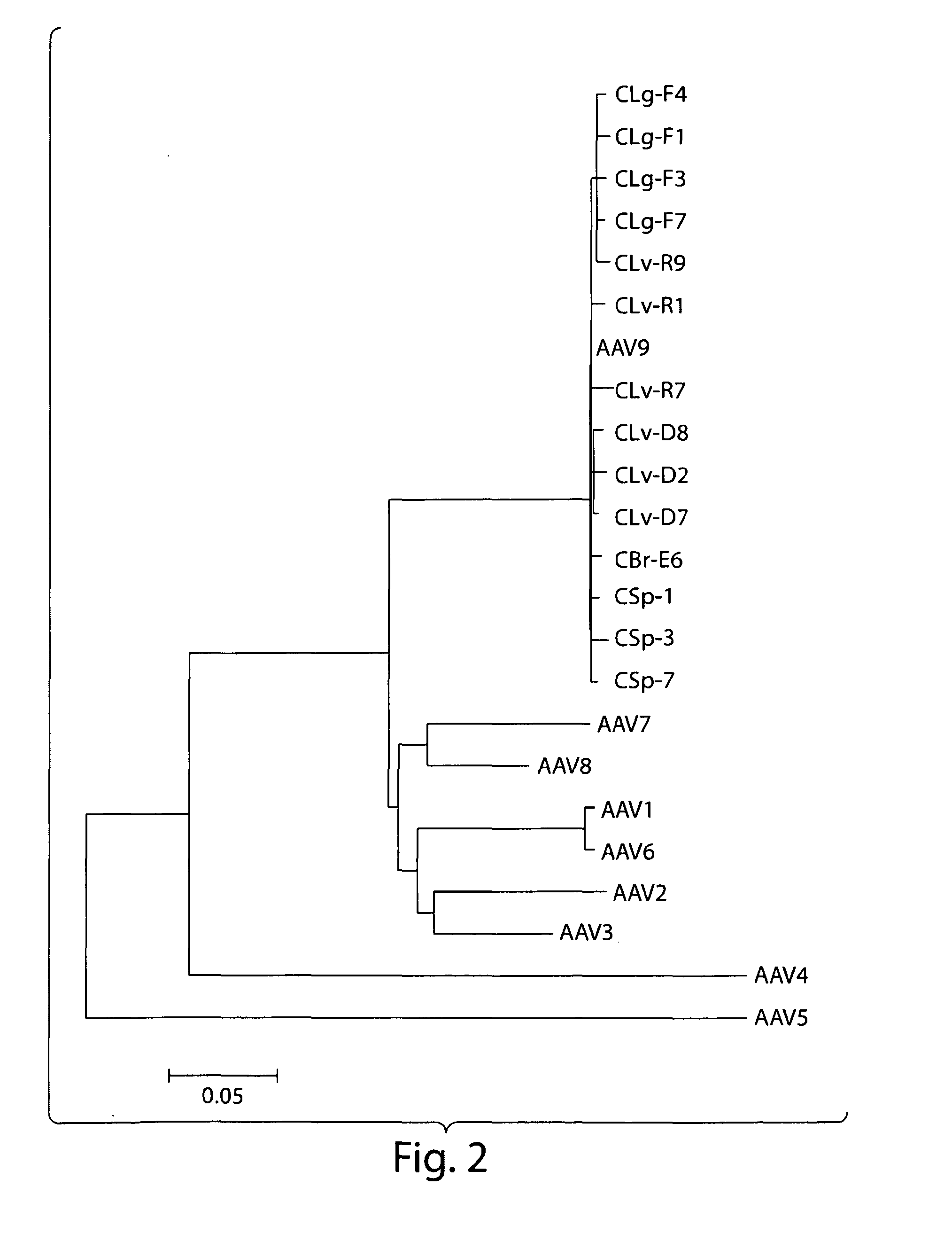
The invention in some aspects relates to recombinant adeno-associated viruses having distinct tissue targeting capabilities. In some aspects, the invention relates to gene transfer methods using the recombinant adeno-associate viruses. In some aspects, the invention relates to isolated AAV capsid proteins and isolated nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
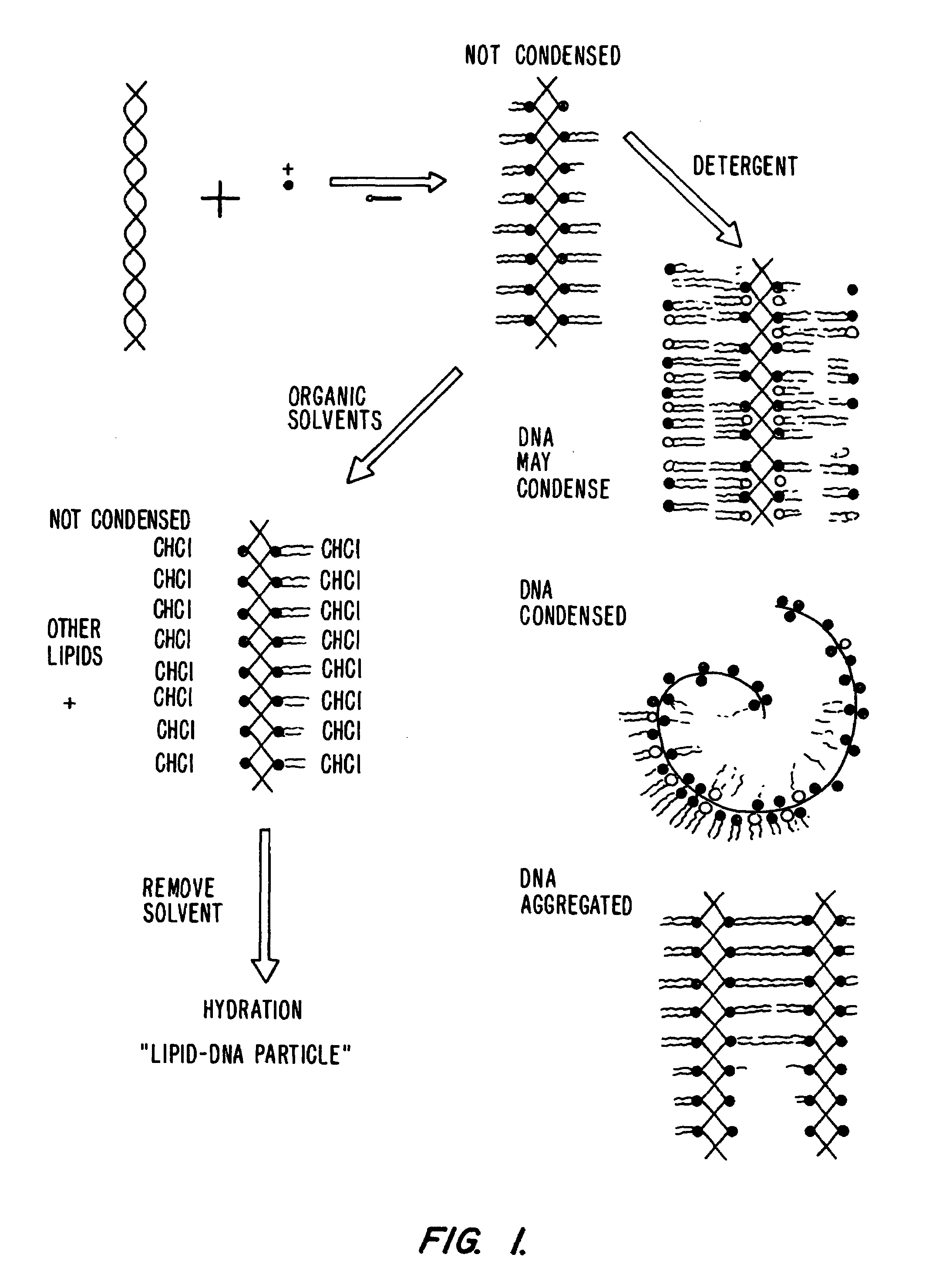
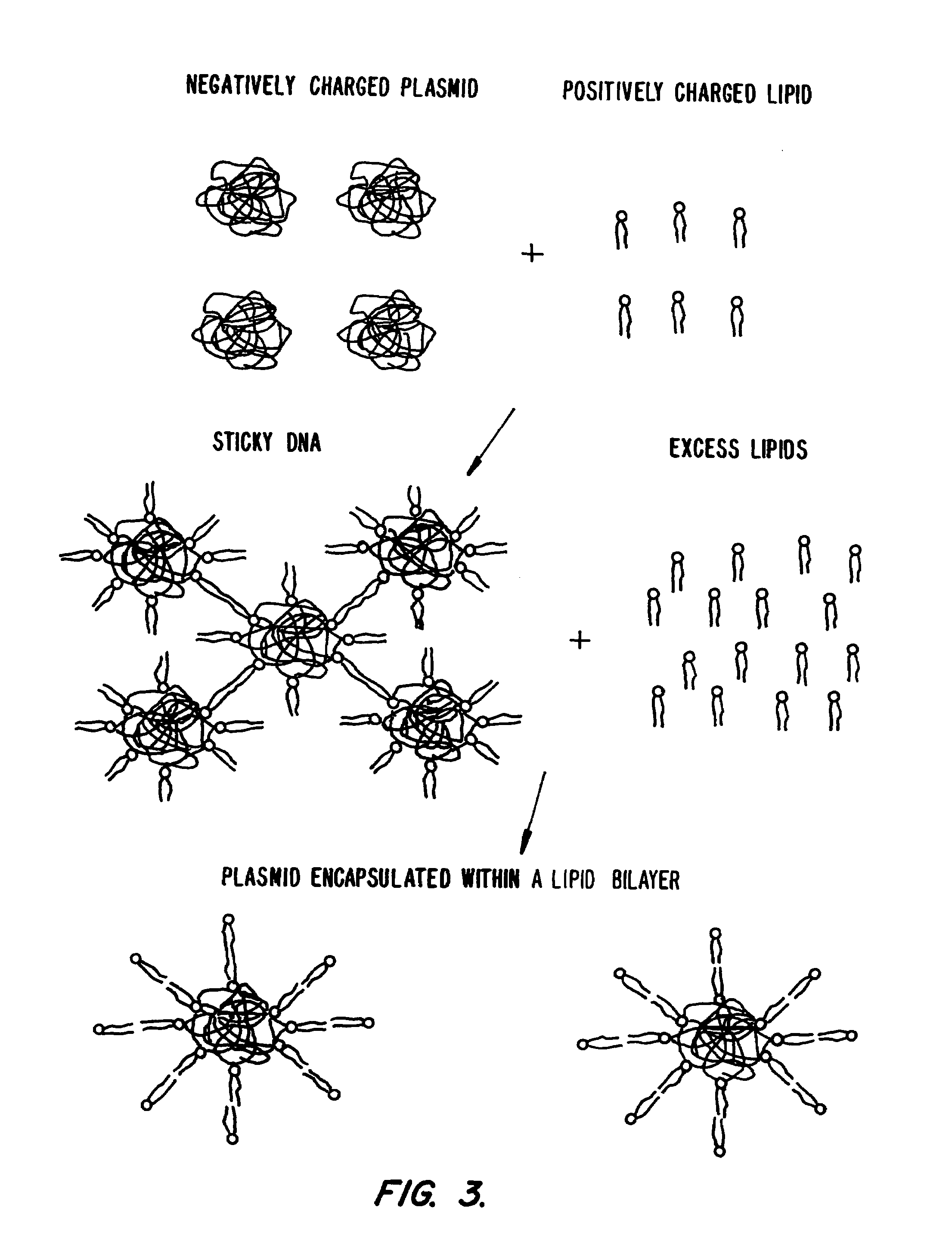
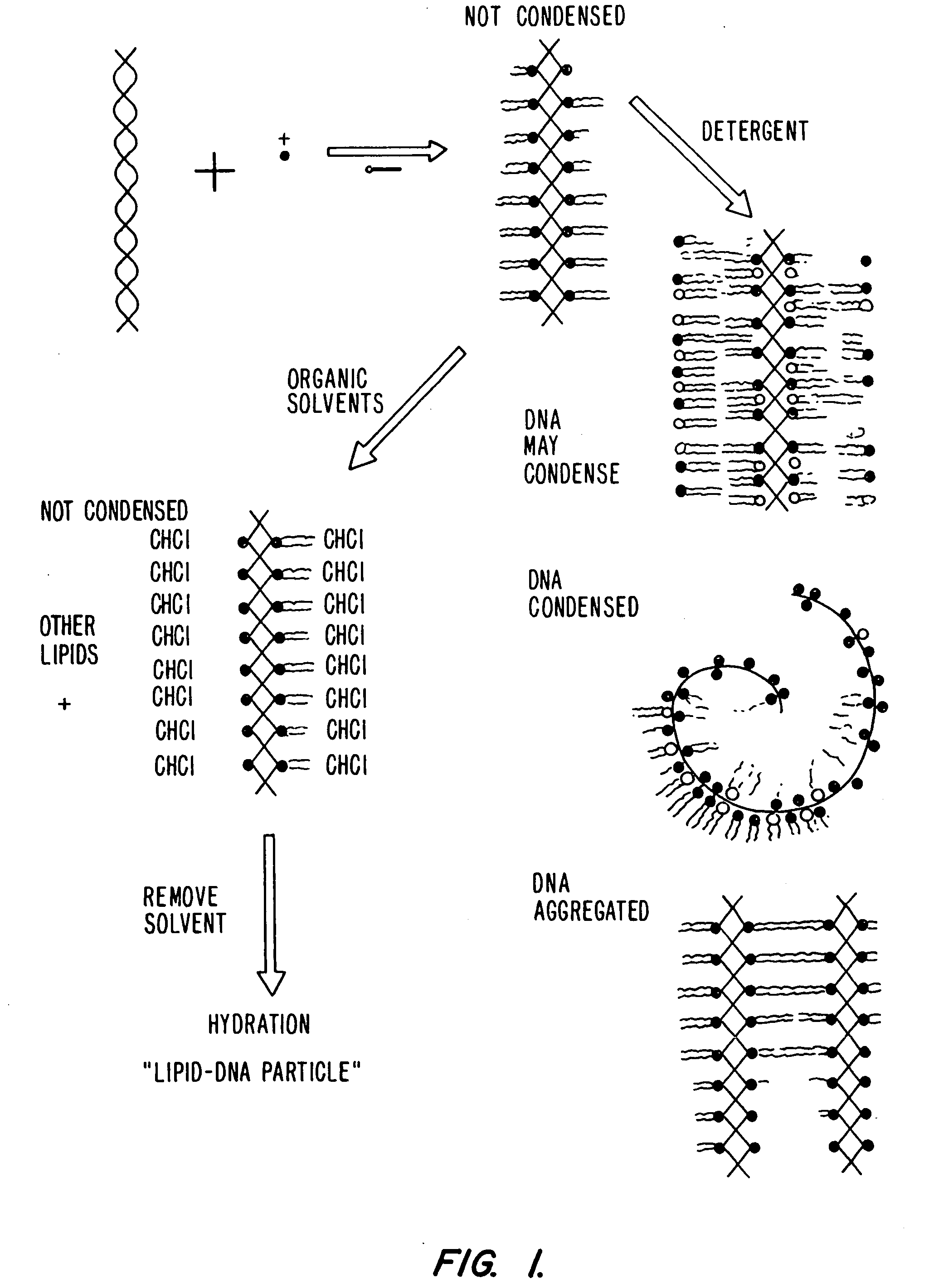
Lipid-nucleic acid particles prepared via a hydrophobic lipid-nucleic acid complex intermediate and use for gene transfer
Novel lipid-nucleic acid particulate complexes which are useful for in vitro or in vivo gene transfer are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. Upon removal of a solubilizing component (i.e., detergent or an organic solvent) the lipid-nucleic acid complexes form particles wherein the nucleic acid is serum-stable and is protected from degradation. The particles thus formed have access to extravascular sites and target cell populations and are suitable for the therapeutic delivery of nucleic acids.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
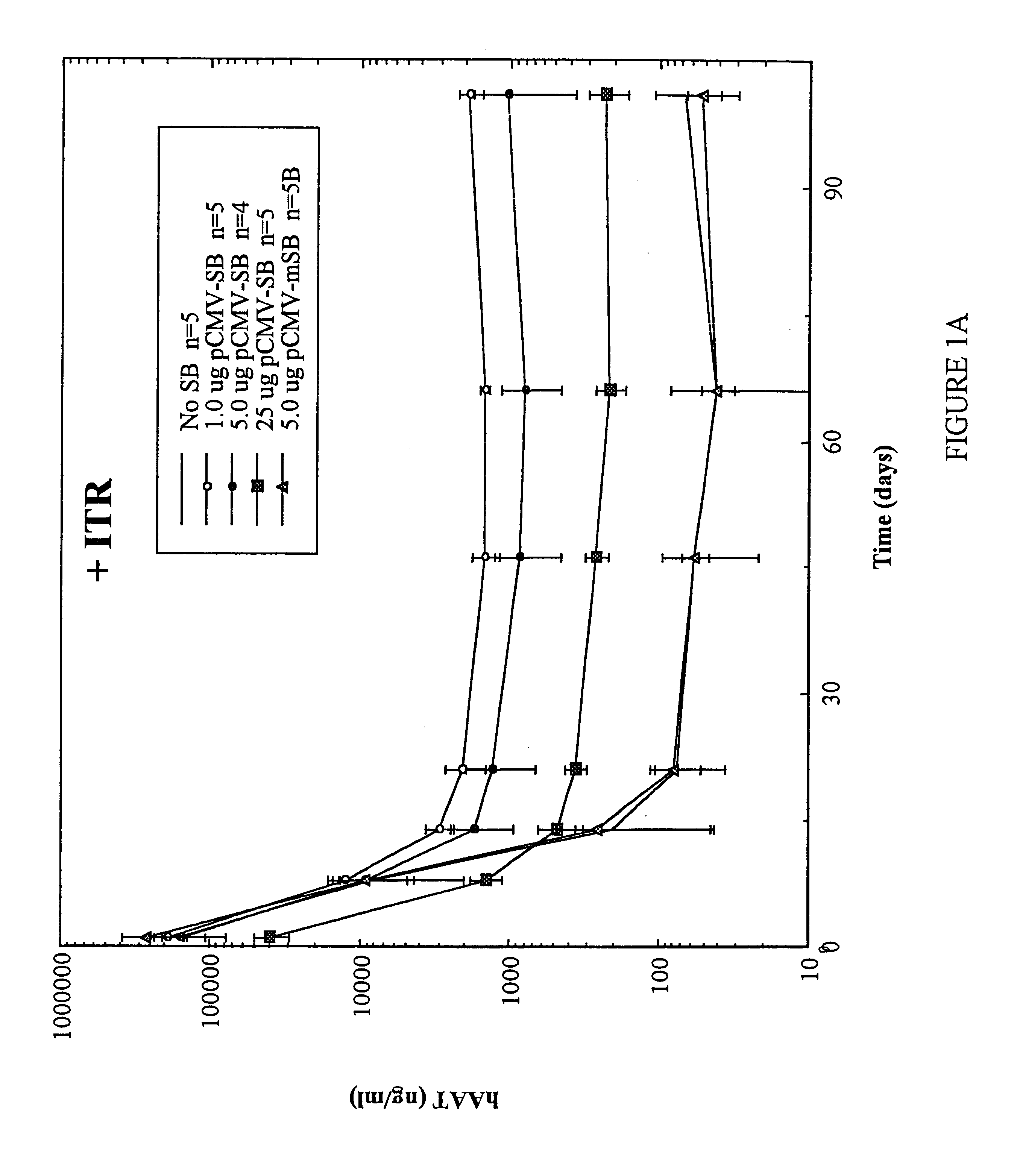
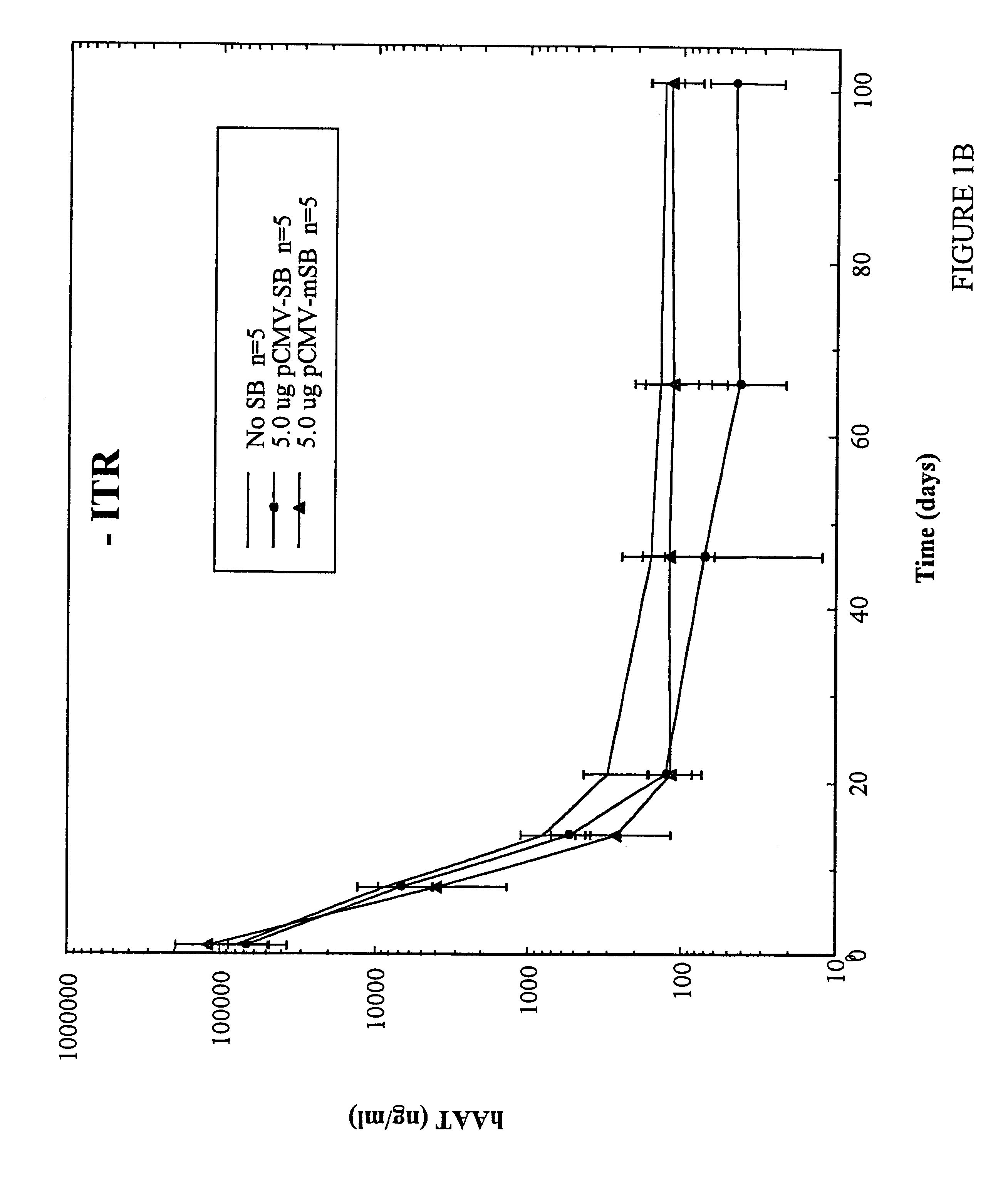
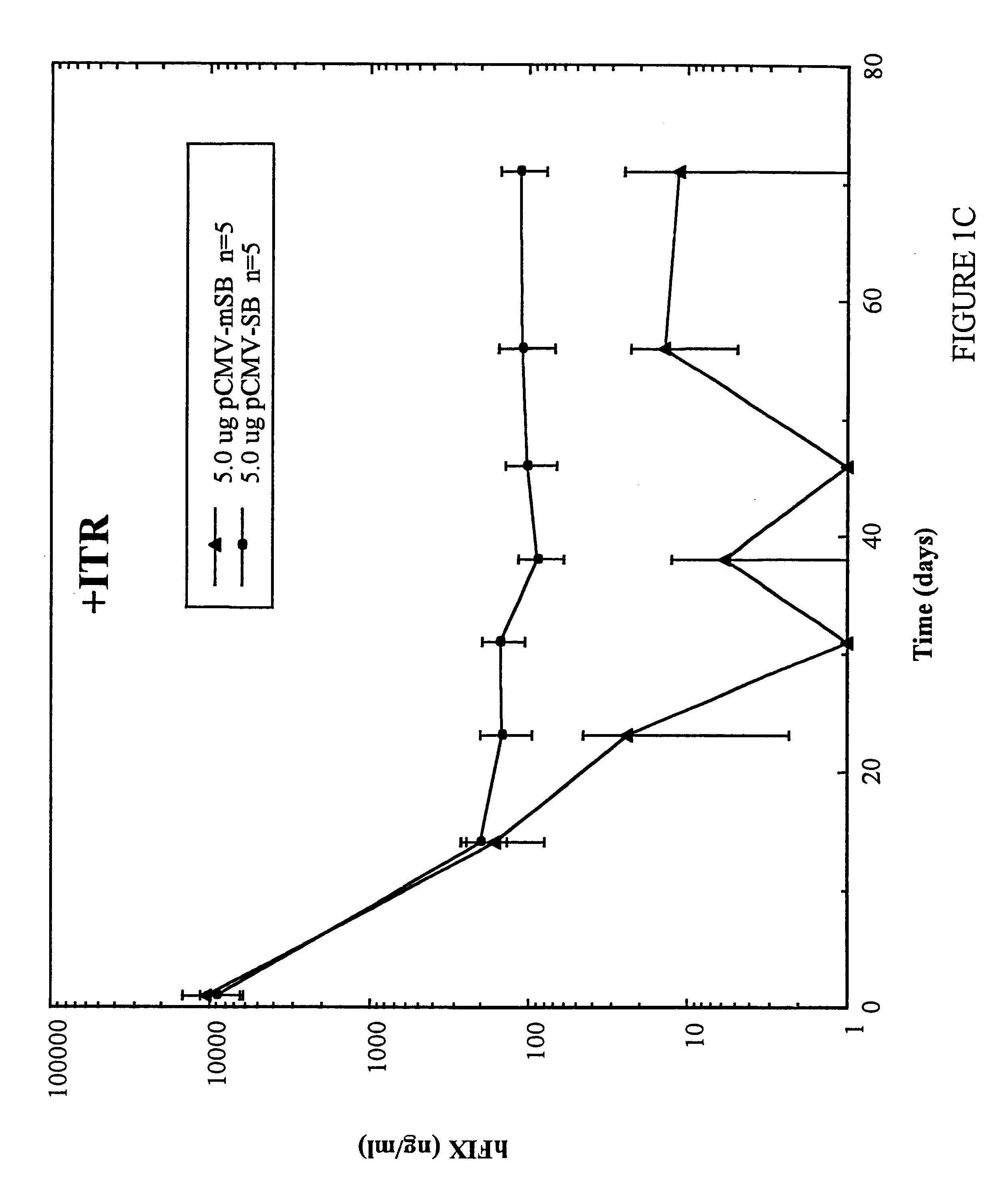
Methods of in vivo gene transfer using a sleeping beauty transposon system
InactiveUS6613752B2Observed effectPromote cloningBiocideHydrolasesSleeping Beauty transposon systemMulticellular organism
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of at least one cell of a multicellular organism are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is administered to the multicellular organism along with a source of a Sleeping Beauty transposase activity. Administration of the transposon and transposase results in integration of the transposon, as well as the nucleic acid present therein, into the genome of at least one cell of the multicellular organism The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications, including the in vivo transfer of genes for use in, among other applications, gene therapy applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
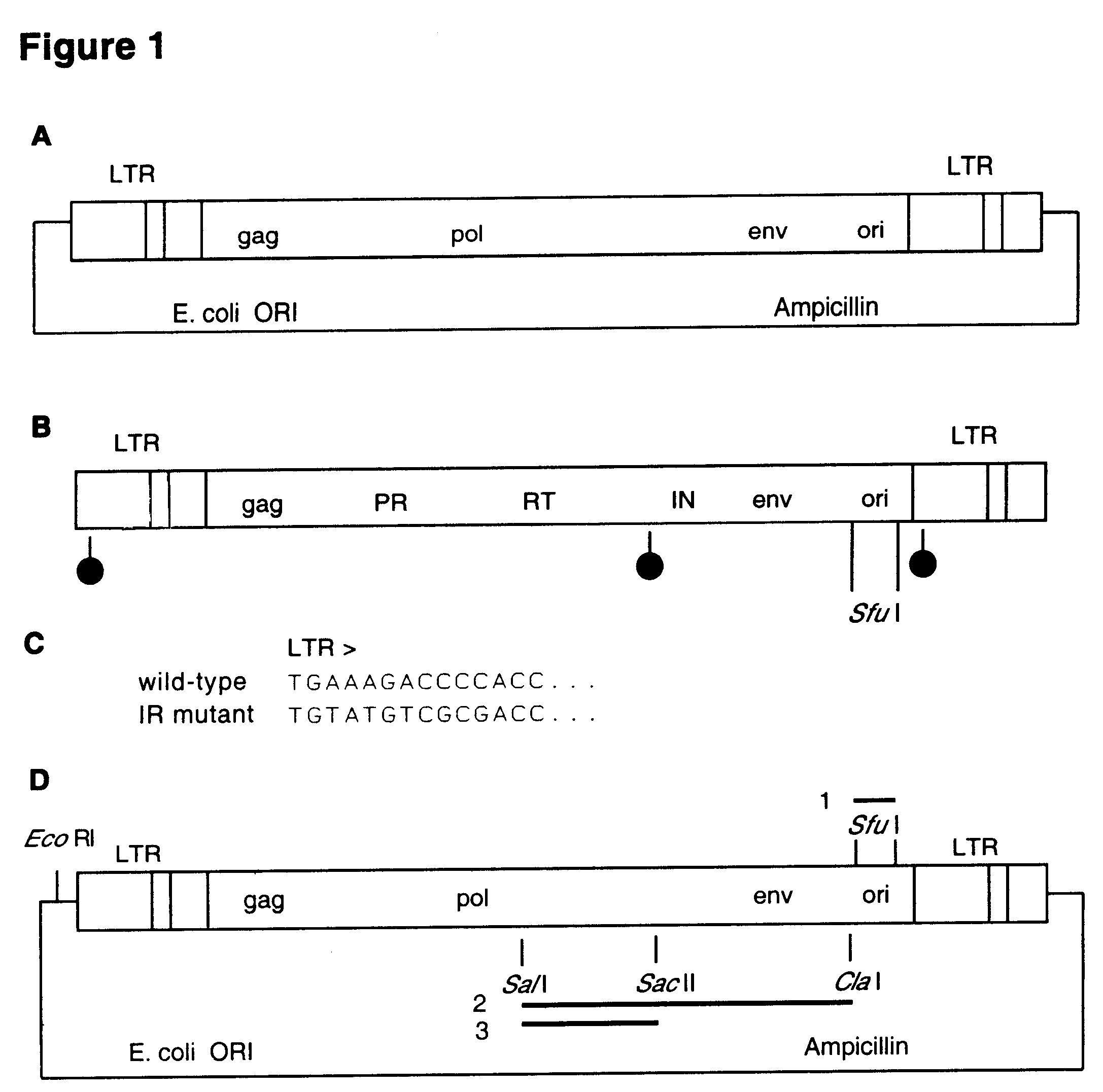
Retrovirus and viral vectors
InactiveUS6635472B1Prevent and attenuate diseaseEnhance immune responseGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesVirus-RetrovirusDna viral
This invention relates to the fields of genetic engineering, virus replication and gene transfer. More specifically, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors, wherein an ori derived from a DNA virus capable of replicating in vertebrate cells is inserted into the retrovirus, allowing the retrovirus following the reverse transcription to efficiently replicate as extrachromosomal or episomal DNA without the necessity of integration into the host cell chromosome. Additionally, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors replicating episomally without aid of an ori and related elements. Also, this invention encompasses preventive, therapeutic, and diagnostic applications employing said constructs, viruses and vectors.
Owner:RUBICON LABS
Efficient and stable in vivo gene transfer to cardiomyocytes using recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors
InactiveUS7078387B1The process is stable and efficientBiocideSugar derivativesCoronary sinusAdeno associate virus
This invention relates to the use of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors to transduce cardiomyocytes in vivo by infusing the rAAV into a coronary artery or coronary sinus. rAAV infection is not associated with detectable myocardial inflammation or myocyte necrosis. Thus, rAAV is a useful vector for the stable expression of therapeutic genes in the myocardium and can be used to deliver genes for inducing angiogenesis, inhibiting angiogenesis, stimulating cell proliferation, inhibiting cell proliferation and / or treating or ameliorating other cardiovascular conditions.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
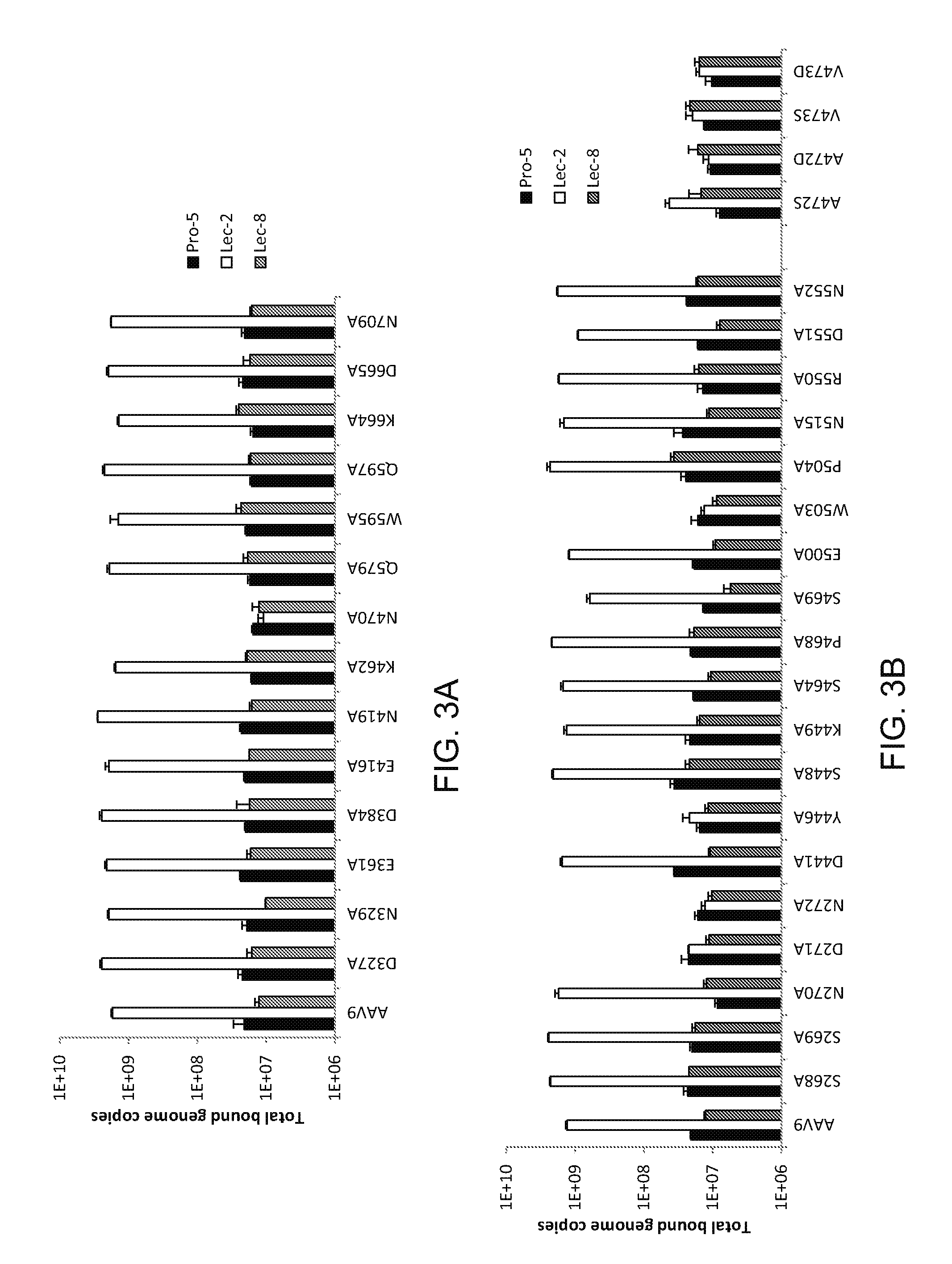
Compositions and Methods for Altering Tissue Specificity and Improving AAV9-Mediated Gene Transfer
ActiveUS20130323226A1Improve efficiencyImprove usabilityOrganic active ingredientsVectorsViral vectorFhit gene
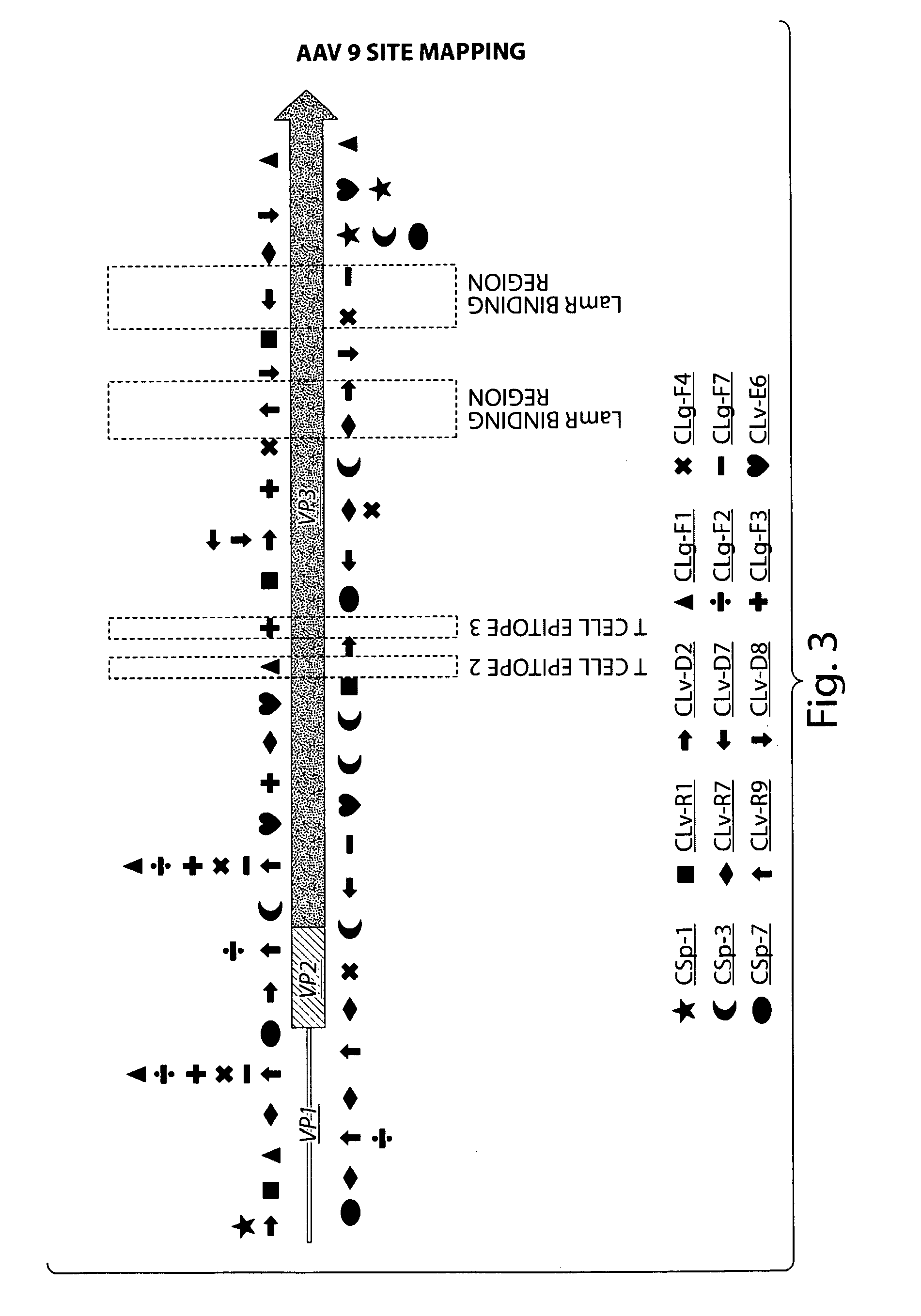
A method of altering the targeting and / or cellular uptake efficiency of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) viral vector having a capsid containing an AAV9 cell surface binding domain is described. The method involves modifying a clade F cell surface receptor which comprises a glycan having a terminal sialic acid residue and a penultimate β-galactose residue. The modification may involve retargeting the vector by temporarily functionally ablate AAV9 binding in a subset of cells, thereby redirecting the vector to another subset of cells. Alternatively, the modification may involve increasing cellular update efficiency by treating the cells with a neuraminidase to expose cell surface β-galactose. Also provided are compositions containing the AAV9 vector and a neuraminidase. Also provided is a method for purifying AAV9 using β-galactose linked to solid support. Also provided are mutant vectors which have been modified to alter their targeting specificity, including mutant AAV9 in which the galactose binding domain is mutated and AAV in which an AAV9 galactose binding domain is engineered.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for modulating expression of exogenous genes in mammalian systems
InactiveUS7045315B2Short half-lifeImprove pharmacokineticsBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsHormones regulationGene transfer
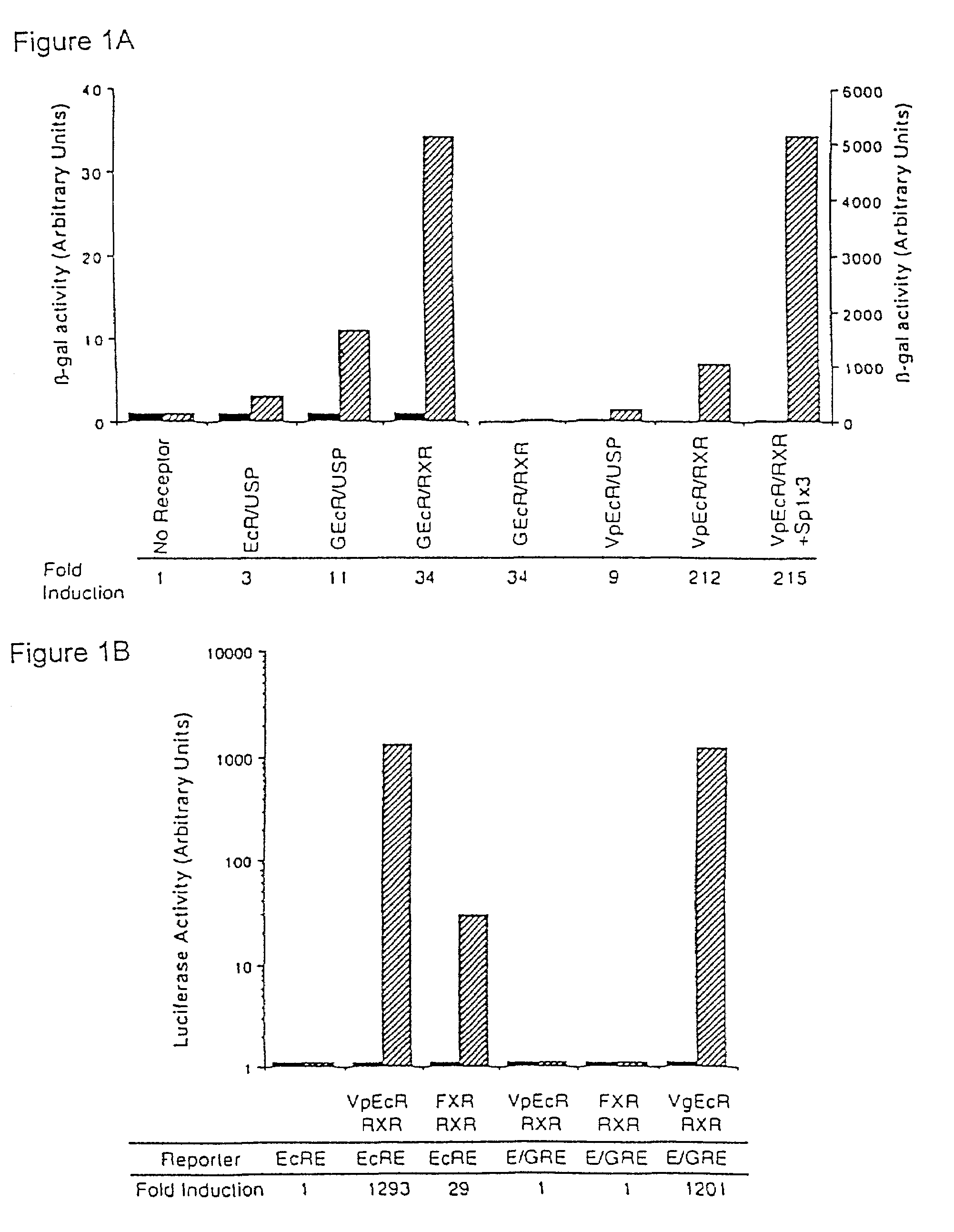
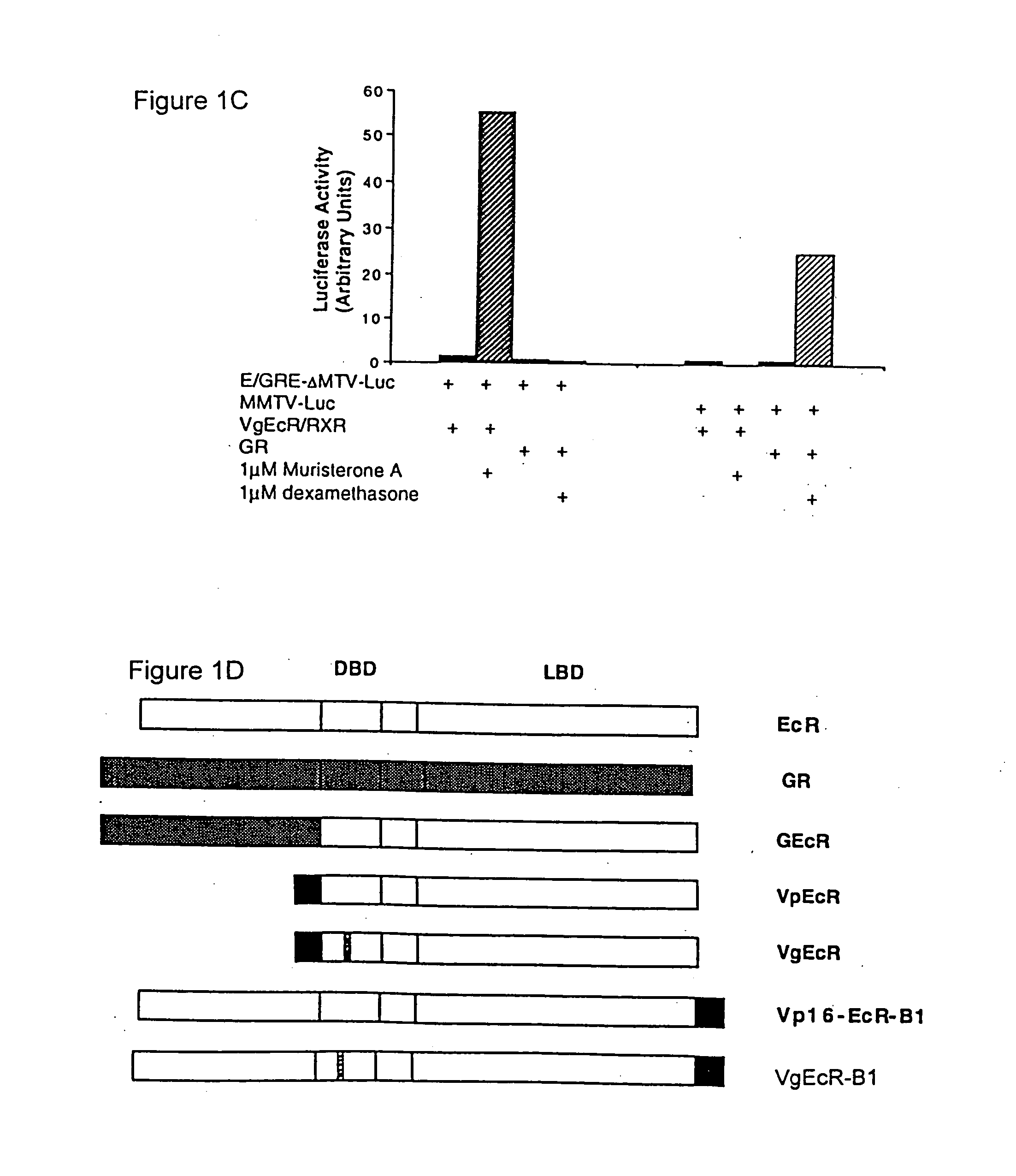
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided various methods for modulating the expression of an exogenous gene in an isolated cell and in a mammalian subject employing modified ecdysone receptors. Also provided are modified ecdysone receptors, as well as homomeric and heterodimeric receptors containing same, nucleic acids encoding invention modified ecdysone receptors, modified hormone response elements, gene transfer vectors, recombinant cells, and transgenic animals containing nucleic acids encoding invention modified ecdysone receptor.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Novel aav's and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120137379A1Determining effectOrganic active ingredientsVirusesTissue targetingAdeno associate virus
The invention in some aspects relates to recombinant adeno-associated viruses having distinct tissue targeting capabilities. In some aspects, the invention relates to gene transfer methods using the recombinant adeno-associate viruses. In some aspects, the invention relates to isolated AAV capsid proteins and isolated nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Pluripotent stem cell growing method
InactiveUS20070155013A1Proliferation potency can be increaseImprove gene transfer efficiencyArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingLiquid mediumCulture vessel
A novel growing method is provided for pluripotent stem cells such as ES cells. The method of the invention is a pluripotent stem cell growing method and gene transfer method in which pluripotent stem cells are cultured under conditions that maintain their undifferentiated state and pluripotency, the method being characterized by using a liquid medium and a culturing vessel having immobilized or coated on a substrate solid phase surface a molecule which is adhesive to the pluripotent stem cells in a fixed concentration, to grow the pluripotent stem cells in a dispersed state while maintaining their undifferentiated state and pluripotency, without using feeder cells, or to transfer and express a gene therein.
Owner:AKAIKE TOSHIHIRO
Adeno-Associated Virus Virion for Gene Transfer to Nervous System Cells
ActiveUS20130224836A1Improve efficiencyLower Level RequirementsNervous disorderSpecial deliveryNervous systemAdeno associate virus
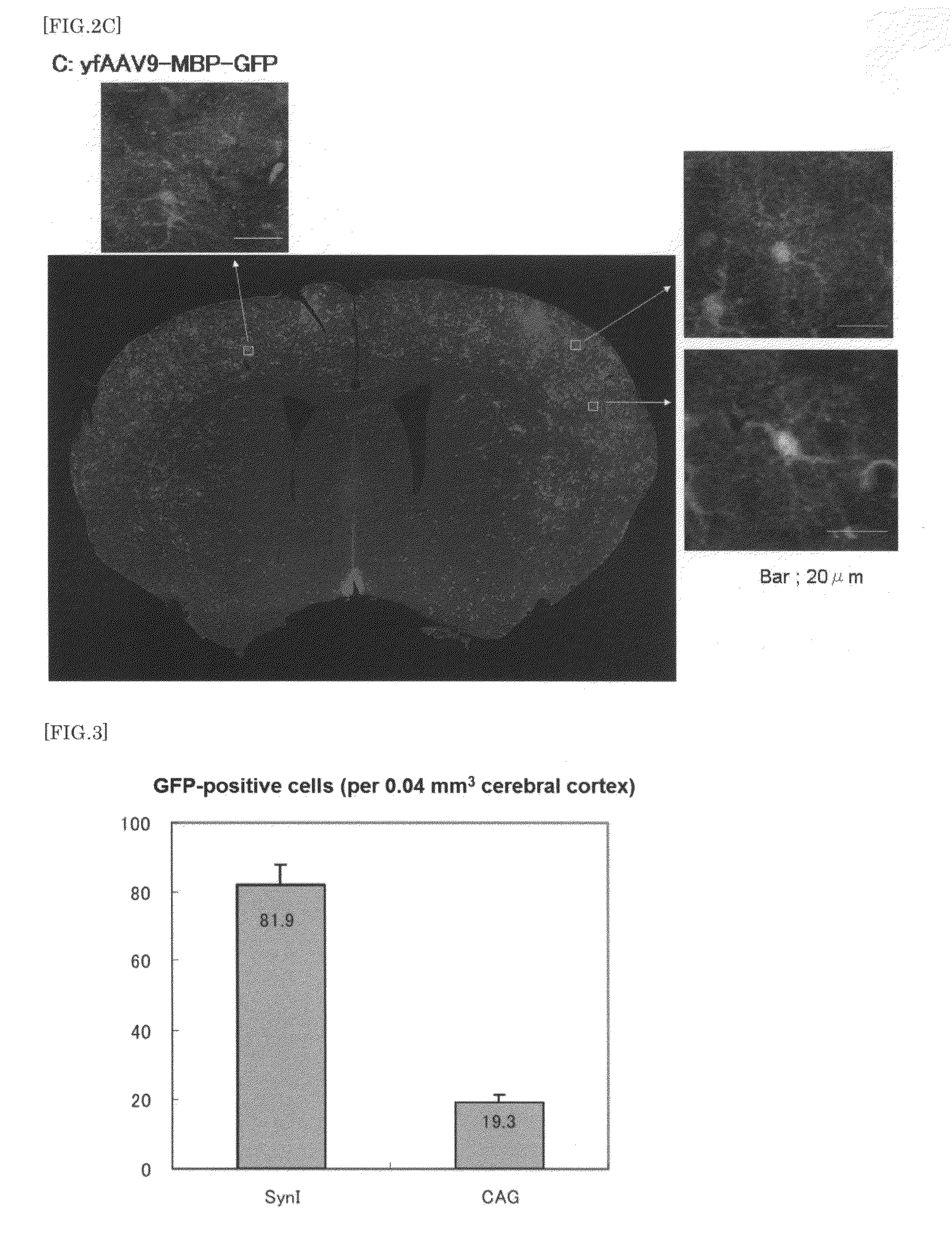
The present invention provides a means for transferring a therapeutic gene of interest into a nervous system cell by a highly-efficient and simpler means. More specifically, the present invention provides a recombinant vector that uses an adeno-associated virus (AAV), a method for manufacturing the recombinant vector, and a method for using the recombinant vector. More specifically, recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, which are capable of passing through the brain-brain barrier, for transferring a therapeutic genes of interest into a nervous system cell in a highly-efficient manner, a drug composition containing the recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, a method for manufacturing the recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, and a kit or the like are provided.
Owner:JICHI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Variant AAV and compositions, methods and uses for gene transfer to cells, organs and tissues
ActiveUS9840719B2Reduce the possibilityCost of treatmentVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic proteinNucleic acid sequencing
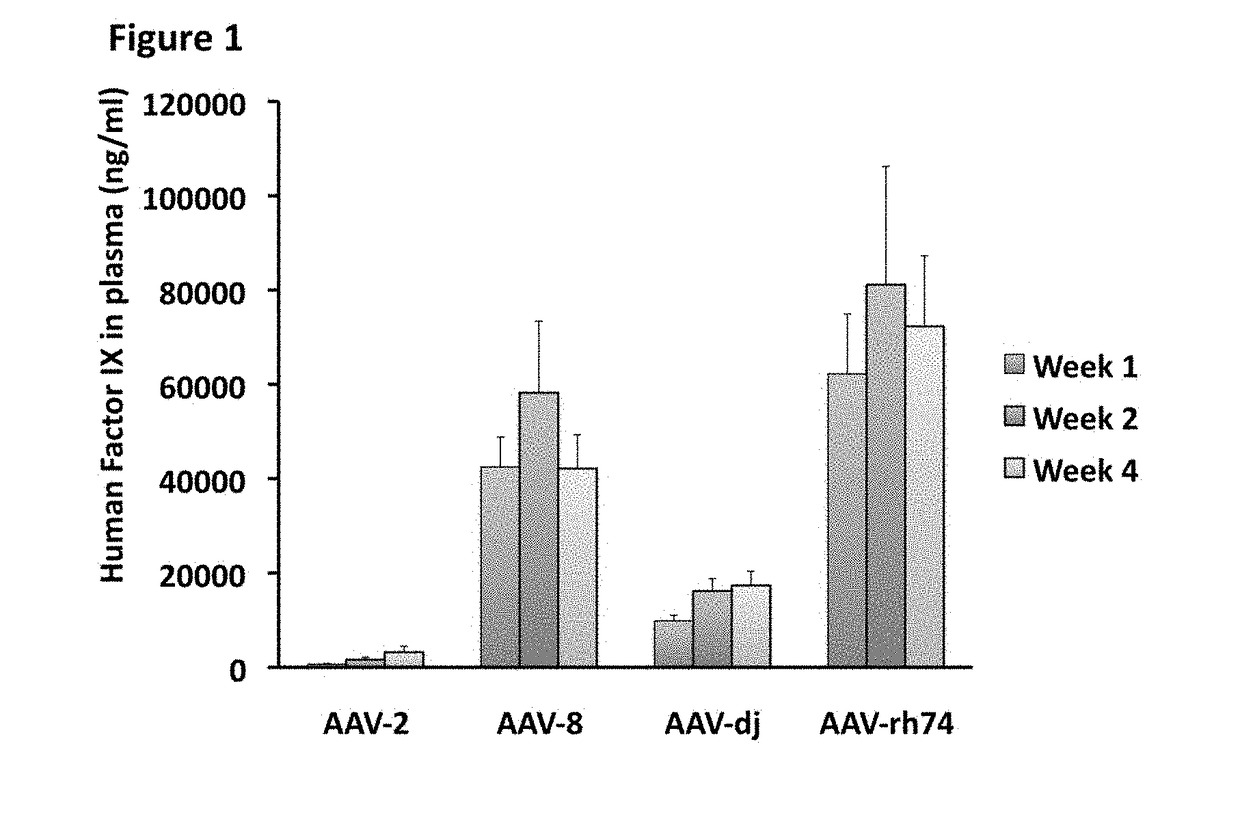
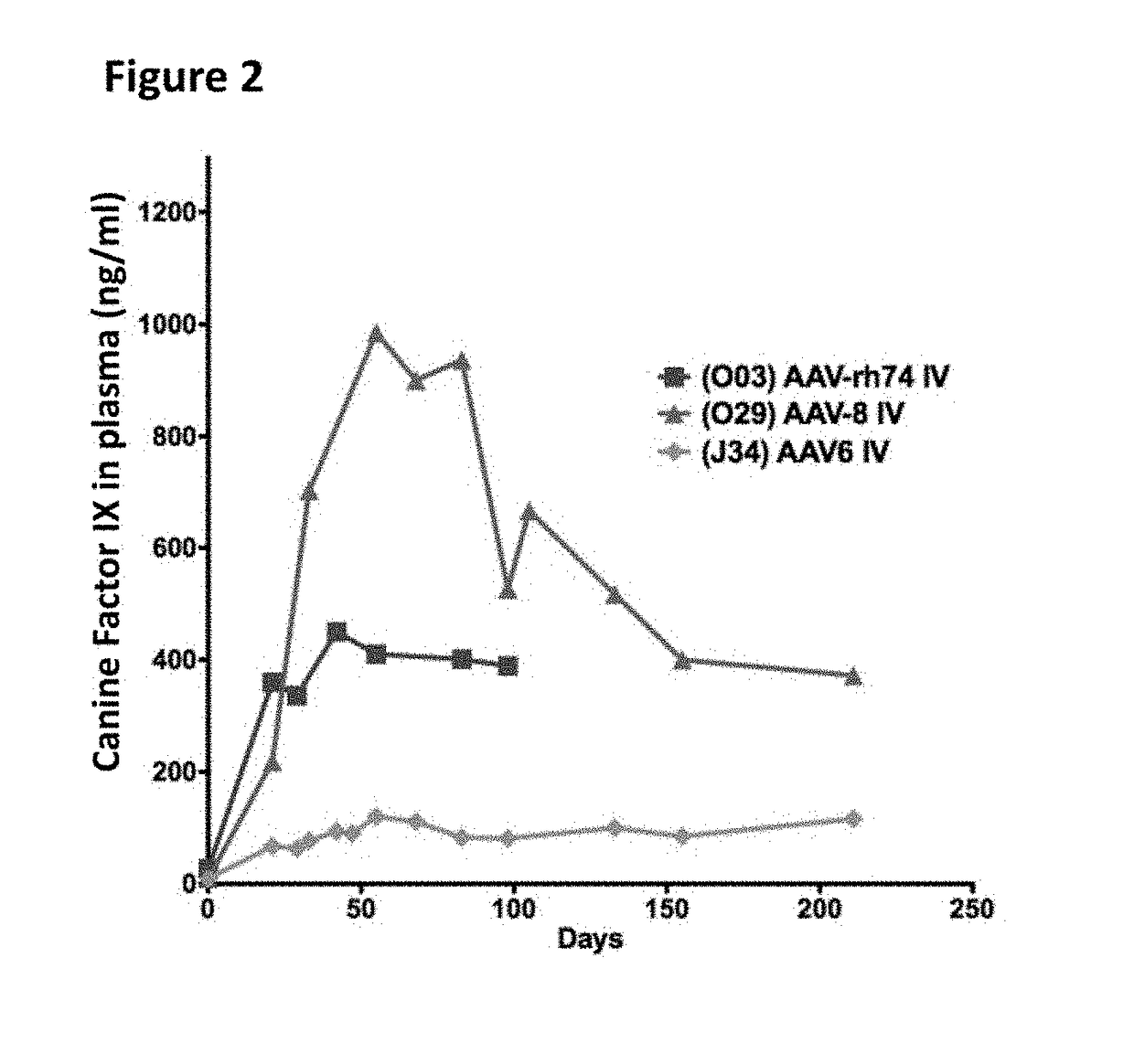
The invention relates to adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype AAV-Rh74 and related AAV vectors, and AAV-Rh74 and related AAV vector mediated gene transfer methods and uses. In particular, AAV-Rh74 and related AAV vectors target polynucleotides to cells, tissues or organs for expression (transcription) of genes encoding therapeutic proteins and peptides, and polynucleotides that function as or are transcribed into inhibitory nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20120122801A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryGlycoside formationMannose 6-phosphate receptor
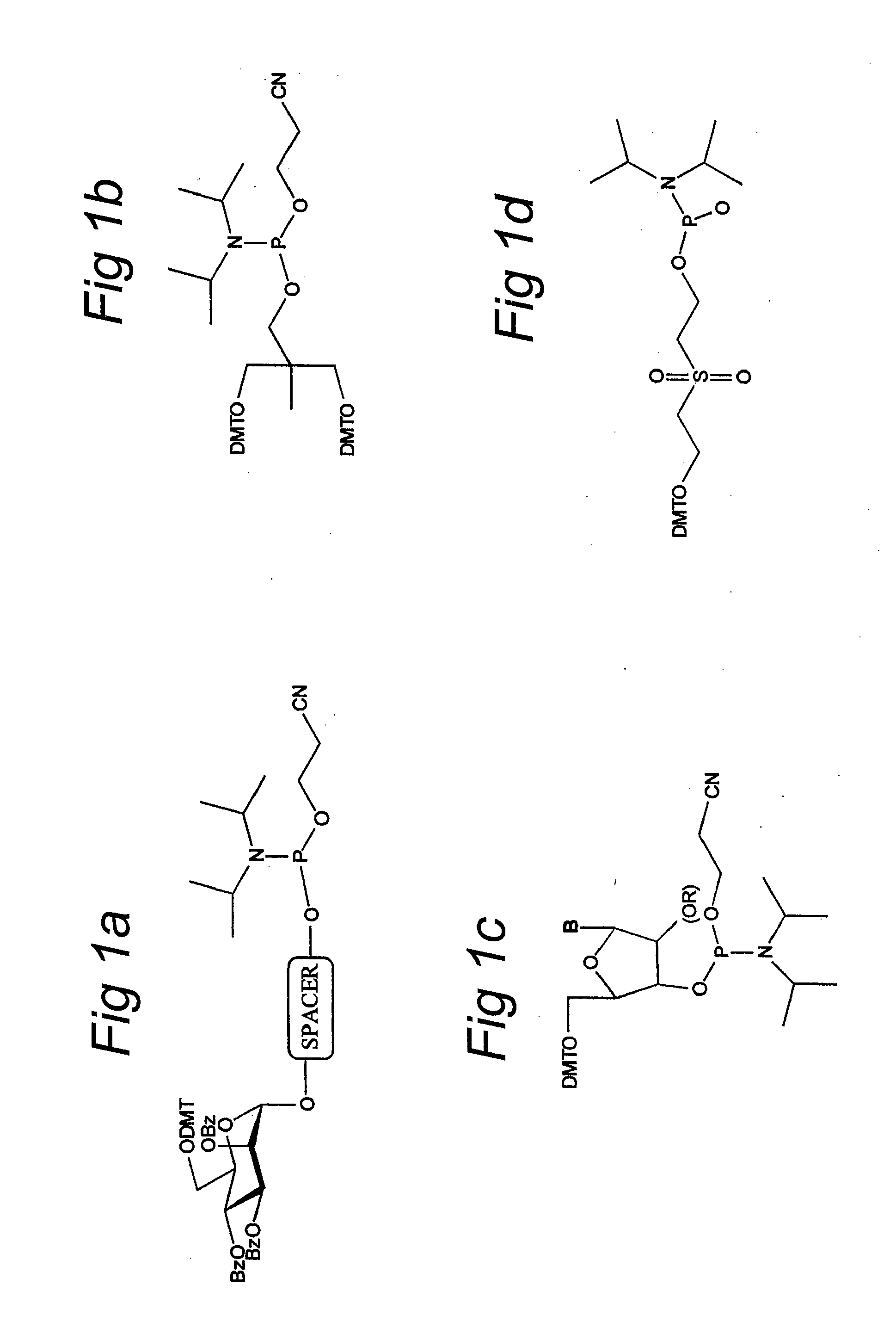
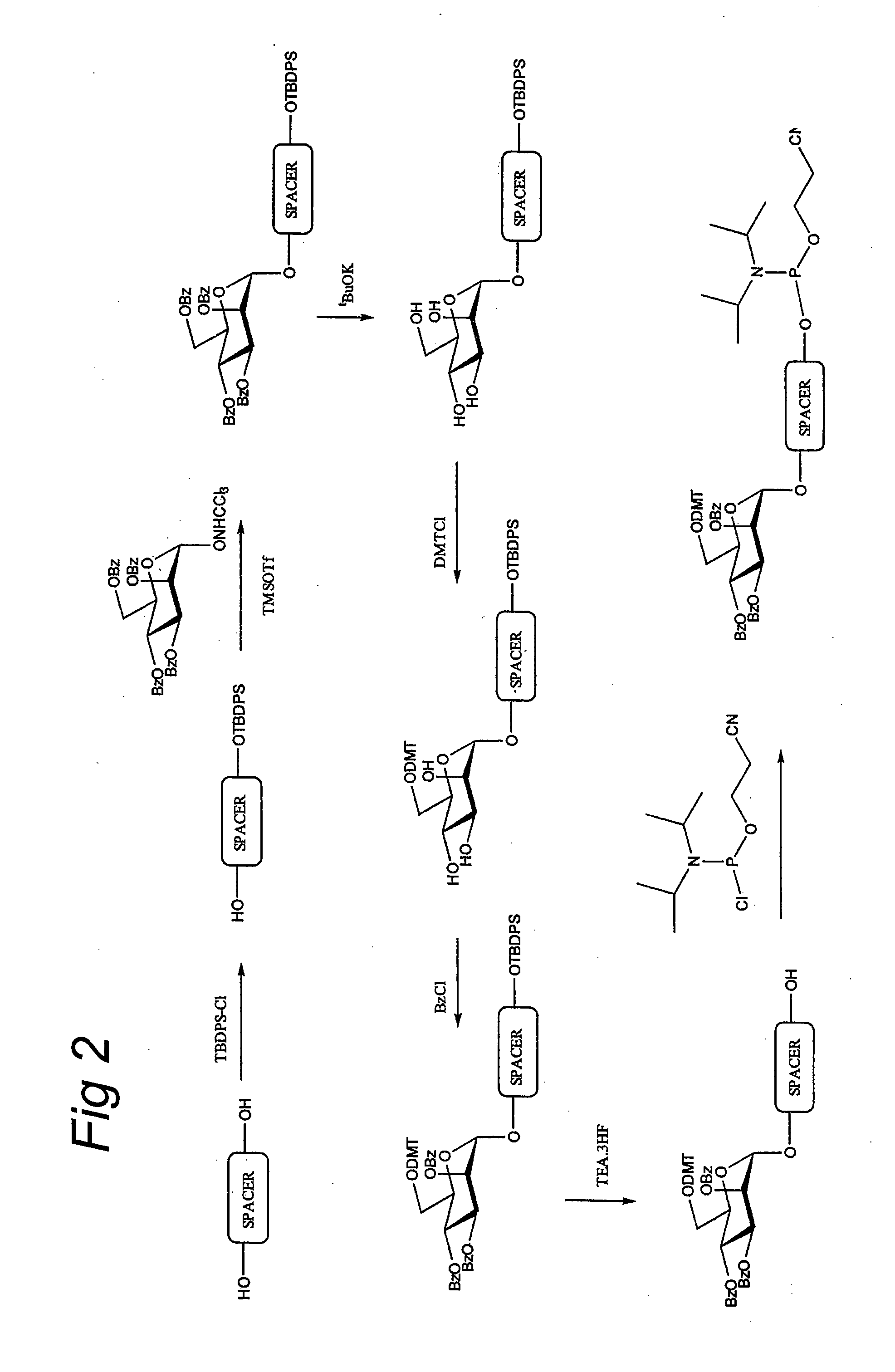
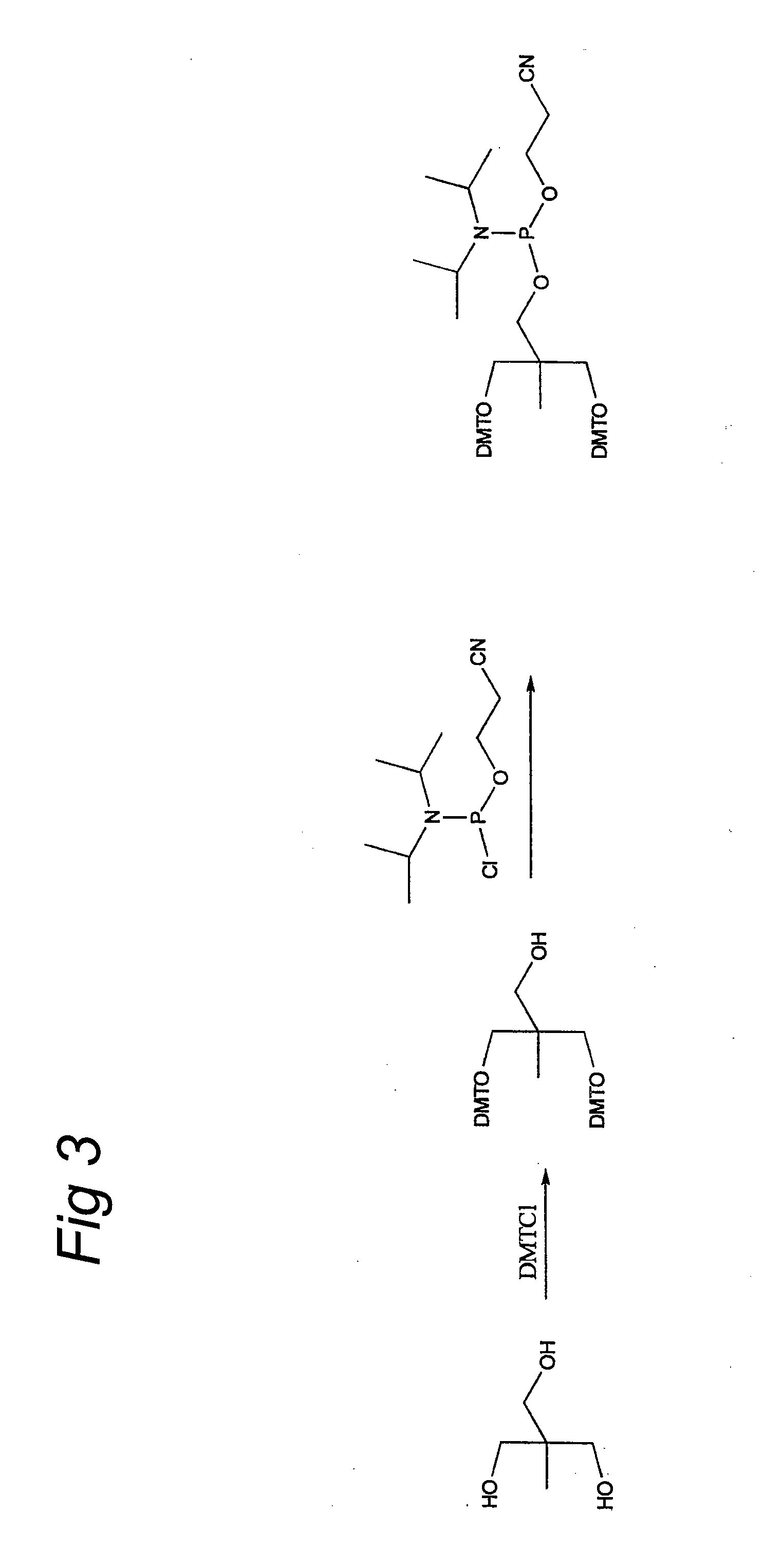
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes ex on skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA THERAPEUTICS
Implantable stent with endothelialization factor
InactiveUS20060085062A1Promote endothelializationStrong adhesionStentsSurgeryEndoluminal stentInsertion stent
A stent is provided in combination with a growth factor, specifically pleiotrophin or an analog or derivative thereof, which promotes endothelialization of the stent and re-endothelialization of the stented region of an injured site in a body lumen. In particular applications, the stent is an endolumenal stent and the growth factor promotes healing via endothelialization and substantially prevents restenosis. The growth factor is delivered from the stent formulated as a protein or peptide, or as a gene transfer vector. Methods for the treatment of vascular injury using pleiotrophin are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Virus vectors for highly efficient transgene delivery
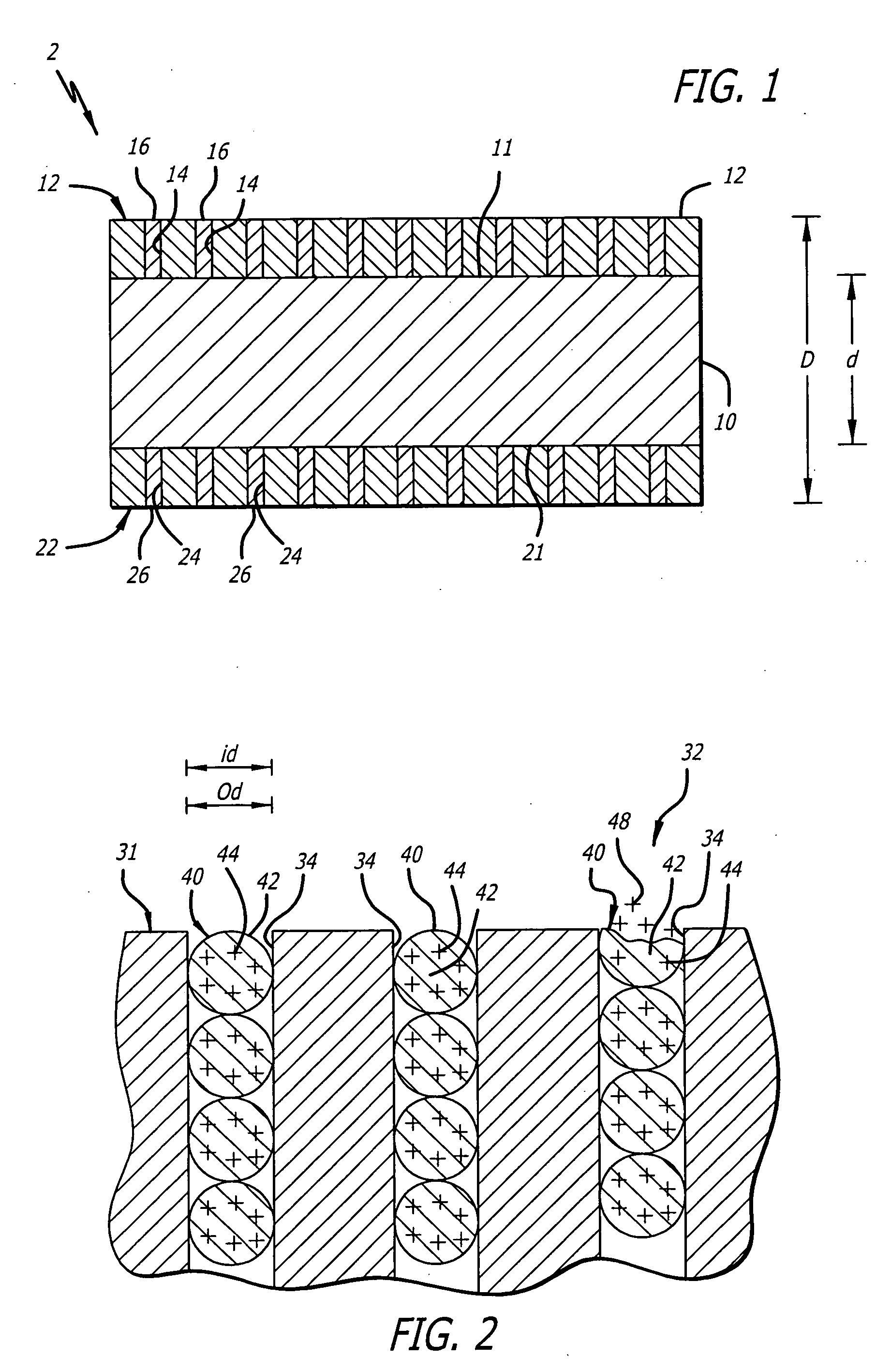
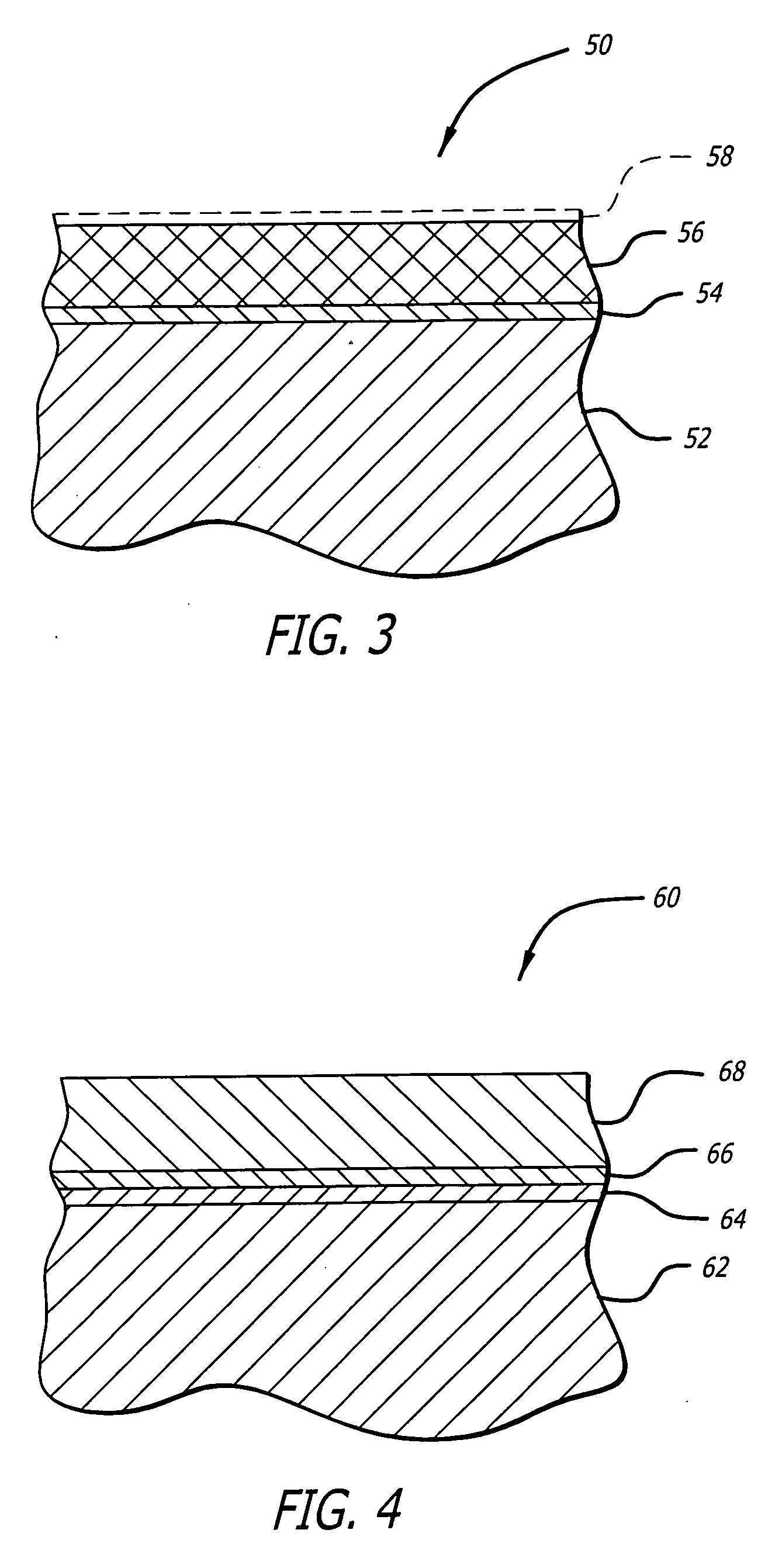
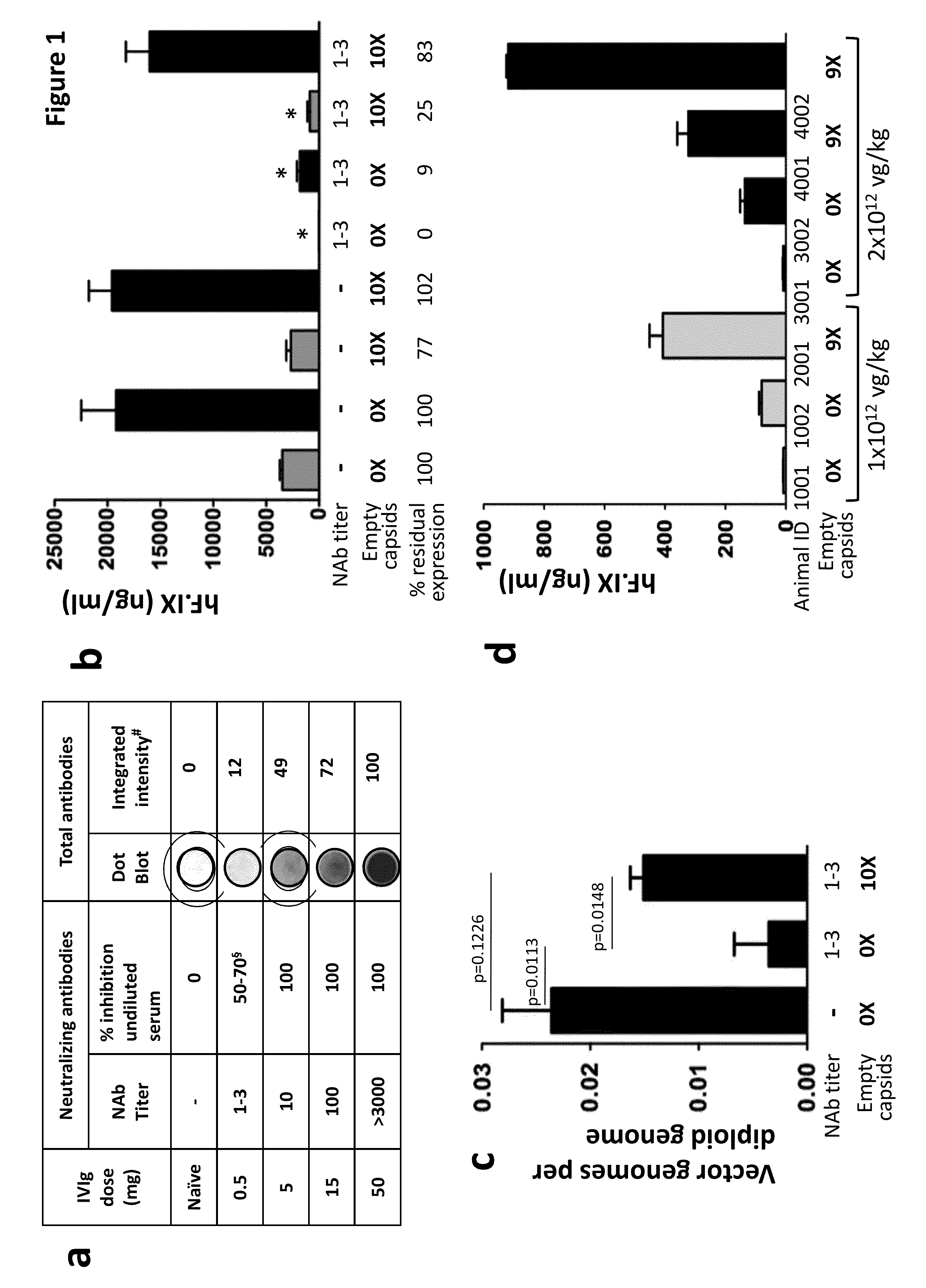
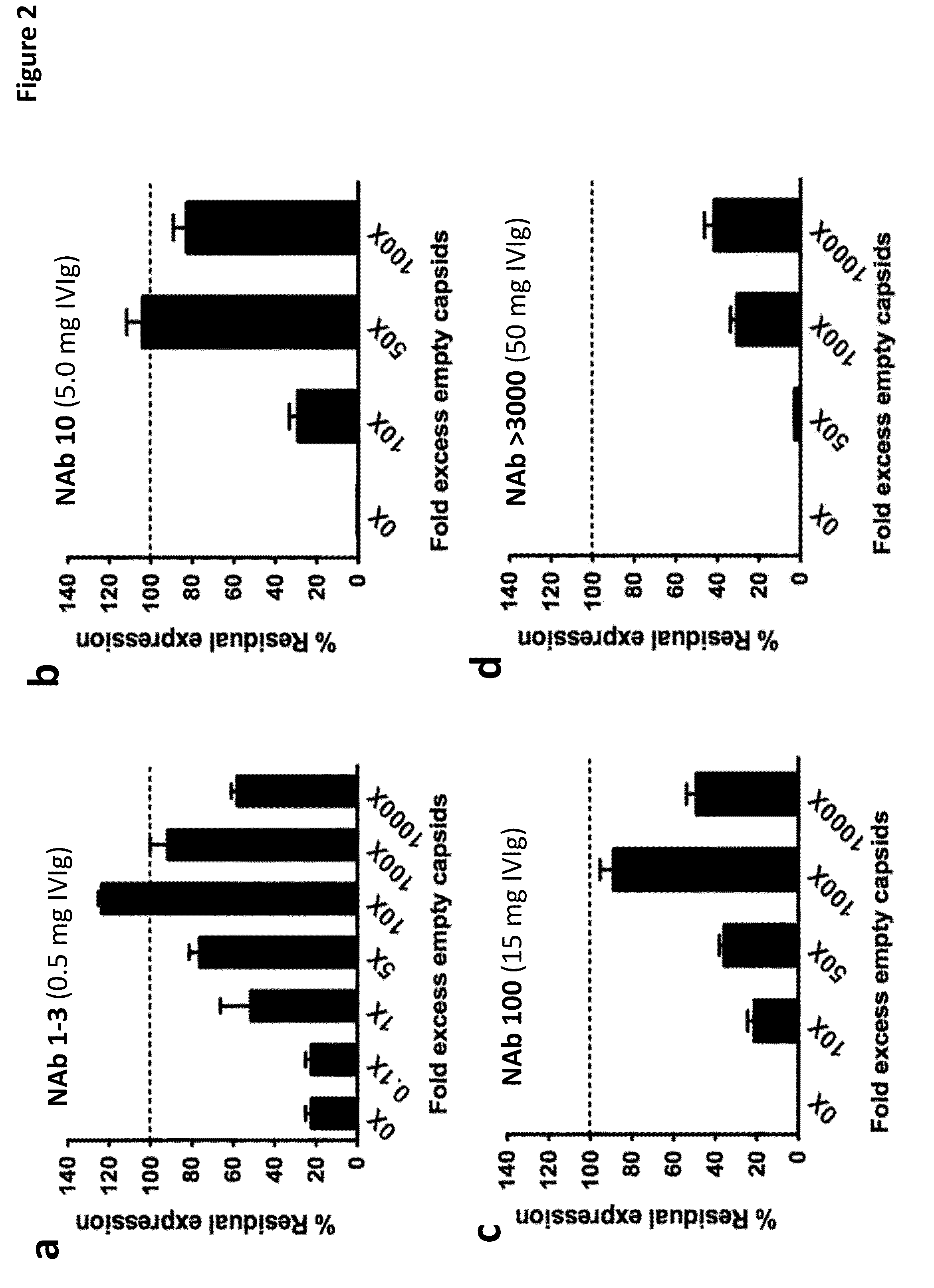
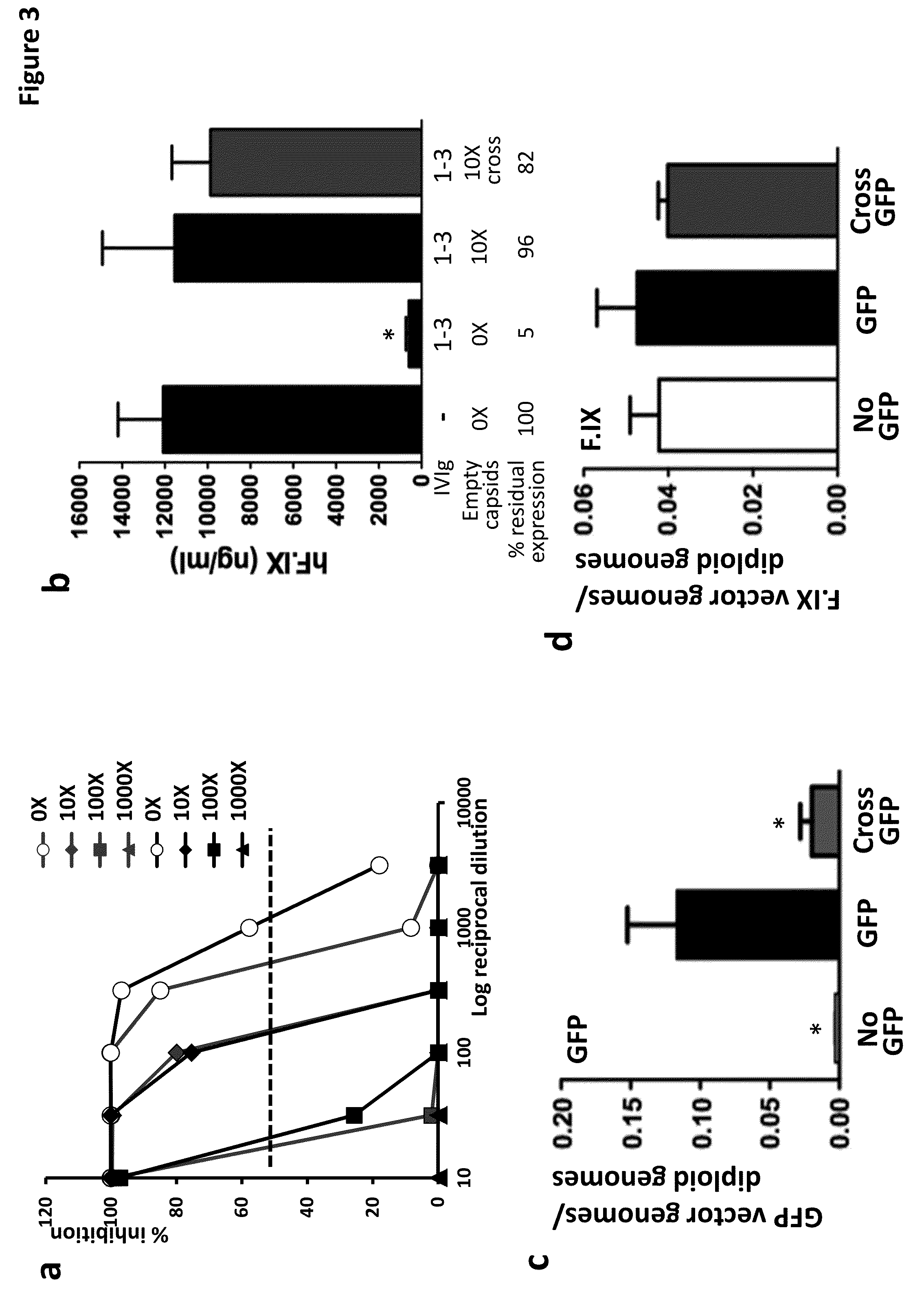
ActiveUS20140336245A1Enhanced transductionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene transferTransgene
The invention provides viral vector formulations and methods of uses thereof for delivery of transgenes or therapeutic nucleic acids to human subjects. The formulations include a vector and suitable amounts of empty capsids, viral genome-containing capsids, or viral capsid proteins which are optionally chemically or structurally modified and which bind to neutralizing anti-AAV antibodies thereby reducing or preventing antibody-mediated clearance of the vector, but still allowing the genome-containing (therapeutic) vector to transduce target cells and achieve therapeutic gene transfer.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
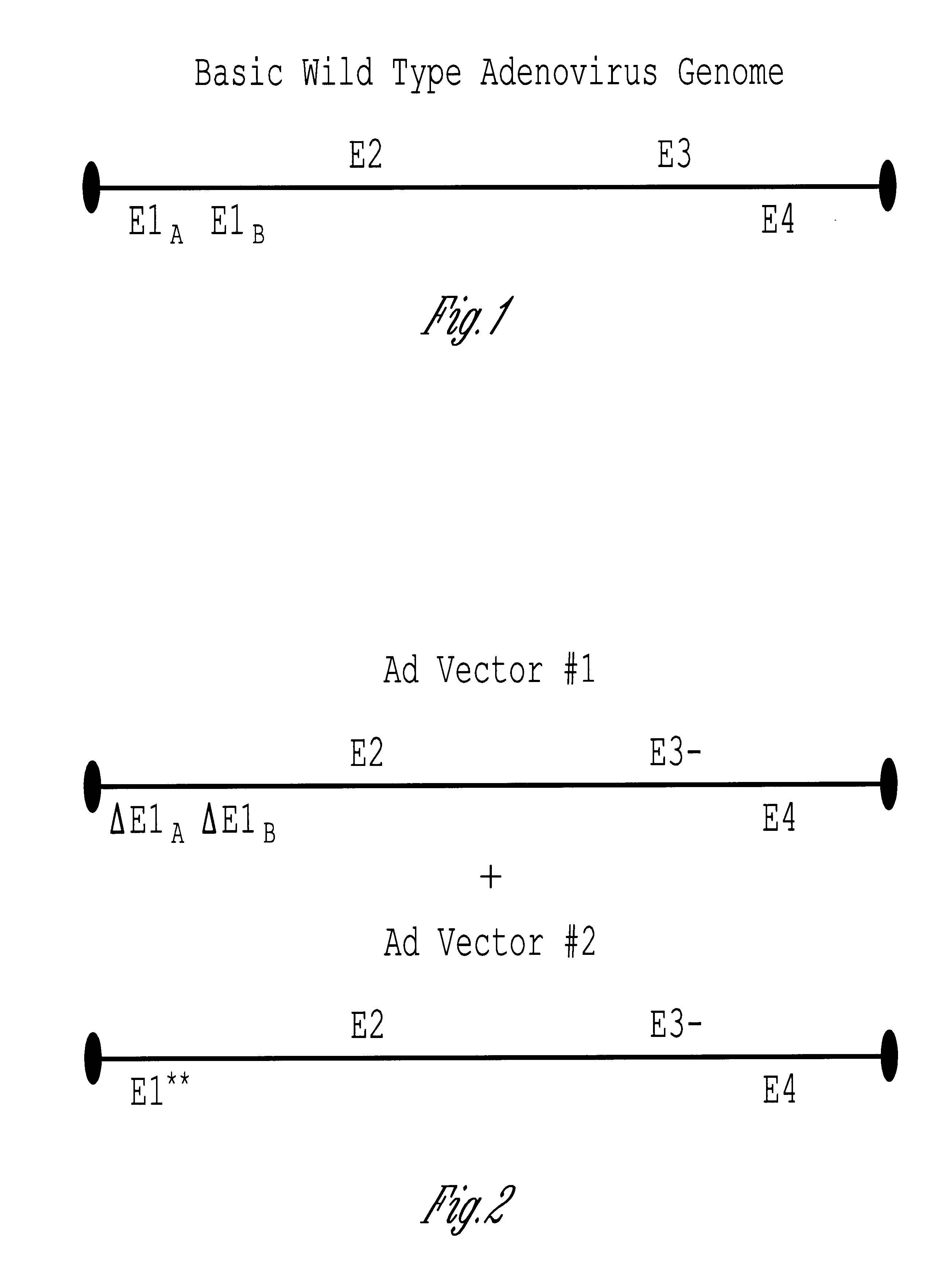
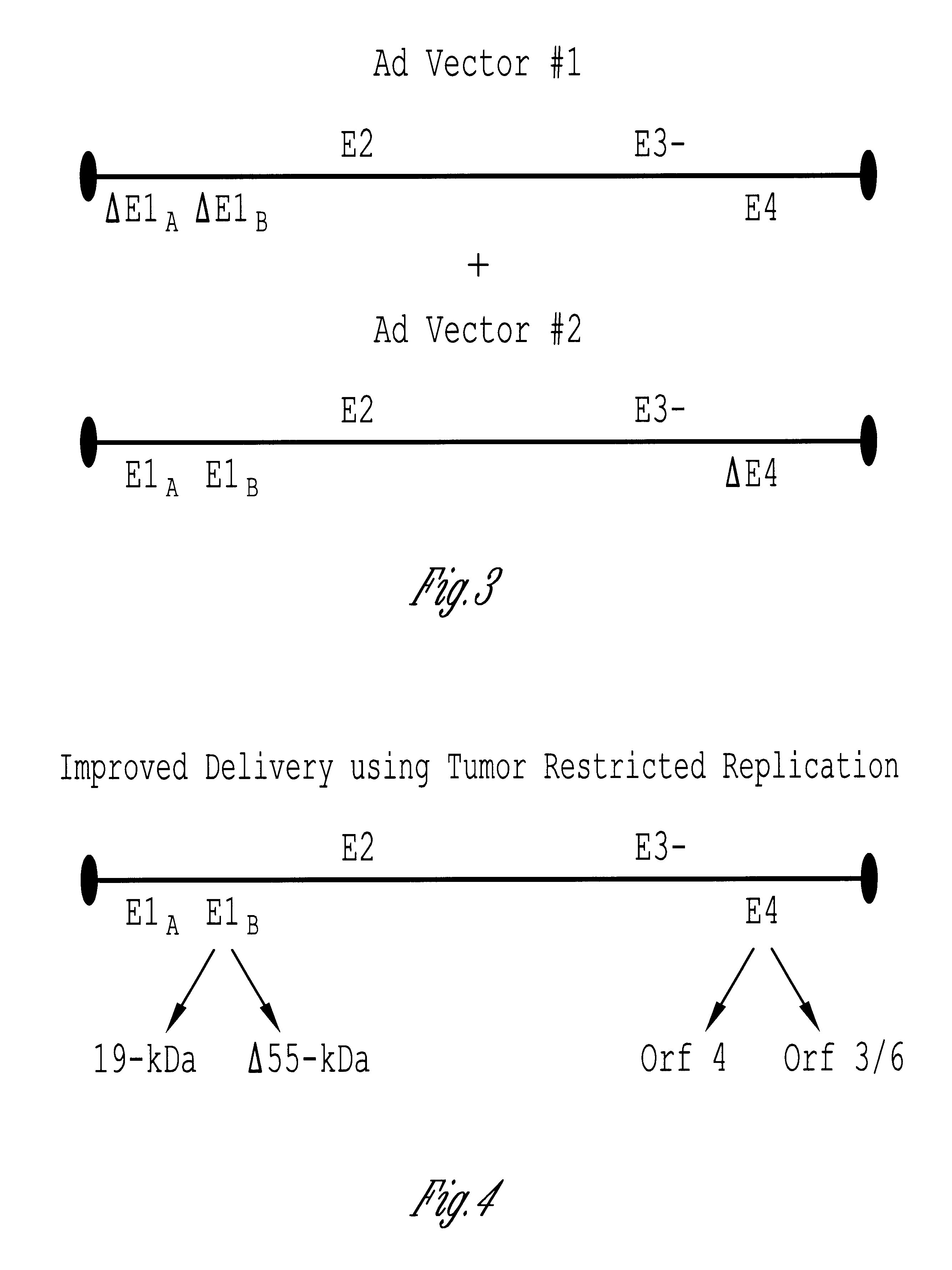
Methods and compositions for efficient gene transfer using transcomplementary vectors
The invention includes a viral vector method and composition comprising transcomplementary replication incompetent viral vectors, preferably adenoviral vectors, which are cotransformed to a recipient cell. The two vectors complement each other and thus allow viral replication, in a synergistic combination which enhances both gene delivery and gene expression of genetic sequences contained within the vector.
Owner:HUMAN GENE THERAPY RES INST
Adenoviral vector for inhibiting restenosis
InactiveUS6290949B1Prevent and lessen restenosisIncrease concentrationBiocideVectorsViral FunctionPercent Diameter Stenosis
Gene transfer vectors, especially adenoviral vectors, and synthetic vectors capable of emulating specific viral functions, that carry gene sequences capable of ameliorating or preventing the symptoms of cardiovascular disease are disclosed. Such methods can be used to treat restenosis, especially when incident to injury by angioplasty.
Owner:FRENCH BRENT A +2
Gene transfer for studying and treating a connective tissue of a mammalian host
InactiveUS7037492B2Reducing at least one deleterious joint pathologyCompounds screening/testingBiocideConnective tissue fiberMammal
Methods for introducing at least one gene encoding a product into at least one target cell of a mammalian host for use in treating the mammalian host are disclosed. These methods include employing recombinant techniques to produce a vector molecule that contains the gene encoding for the product, and infecting the target cells of the mammalian host using the DNA vector molecule. A method to produce an animal model for the study of connective tissue pathology is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Soft tissue and bone augmentation and bulking utilizing muscle-derived progenito compositions, and treatments thereof
The present invention provides muscle-derived progenitor cells that show long-term survival following transplantation into body tissues and which can augment soft tissue following introduction (e.g. via injection, transplantation, or implantation) into a site of soft tissue. Also provided are methods of isolating muscle-derived progenitor cells, and methods of genetically modifying the cells for gene transfer therapy. The invention further provides methods of using compositions comprising muscle-derived progenitor cells for the augmentation and bulking of mammalian, including human, soft tissues in the treatment of various cosmetic or functional conditions, including malformation, injury, weakness, disease, or dysfunction. In particular, the present invention provides treatments and amelioration for dermatological conditions, gastroesophageal reflux, vesico-ureteral reflux, urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, heart failure, and myocardial infarction.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Genetically modified tumor cells as cancer vaccines
InactiveUS20060165668A1Convenient treatmentEasy to detectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for electroporation-mediated gene transfer to cancer cells. The transfected cancer cells are genetically modified to express one or more therapeutic proteins. In certain embodiments, the cancer cells are modified to express one or more cytokines capable of enhancing the immunogenicity of the transfected cancer cell. Administering the transfected cancer cell to a subject will lead to enhanced immune-cell mediated killing of tumors. Accordingly, the present invention provides methods and compositions for improved treatment and prevention of cancer and other hyperproliferative diseases.
Owner:MAXCYTE
Purification of adenovirus and AAV
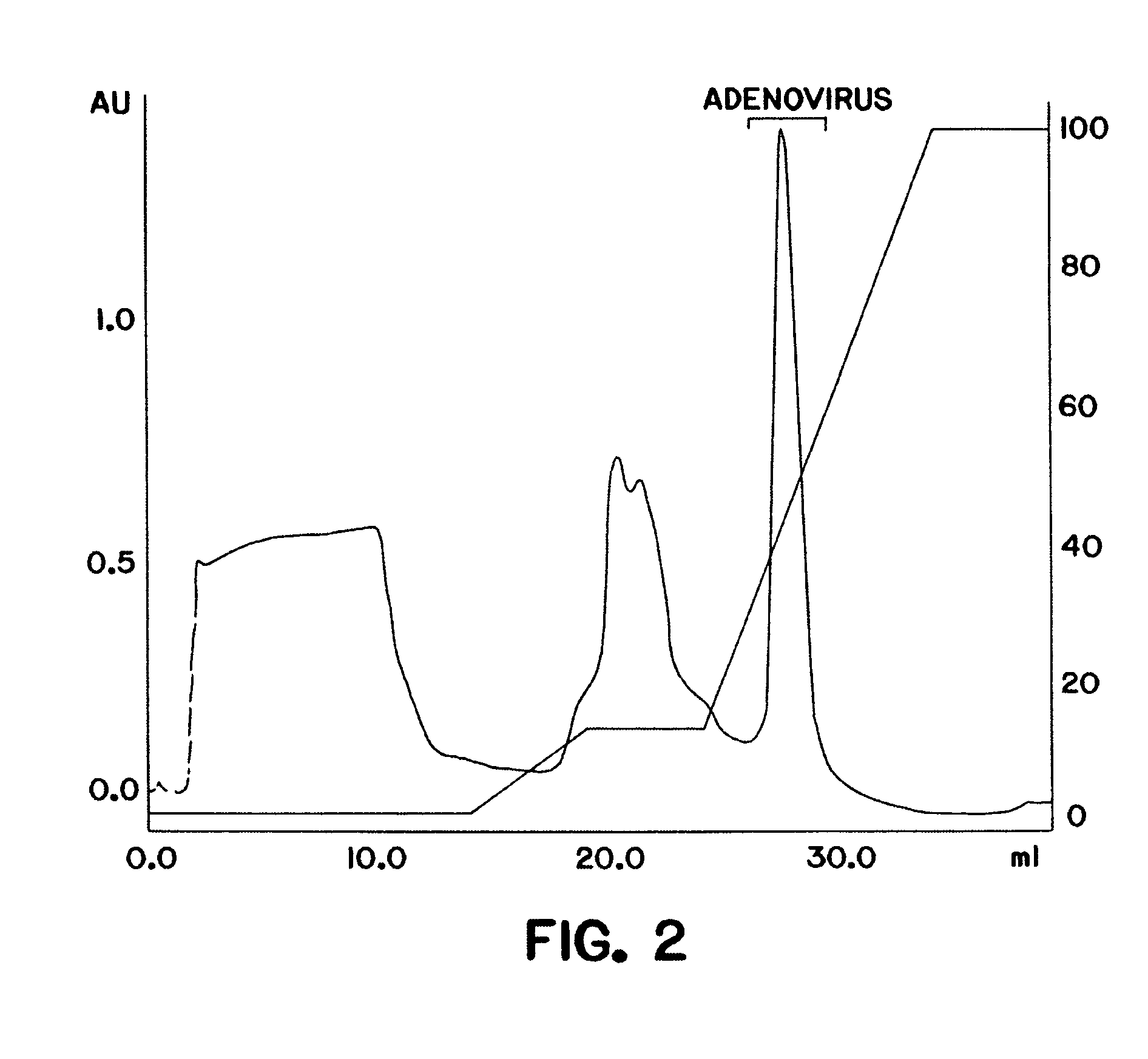
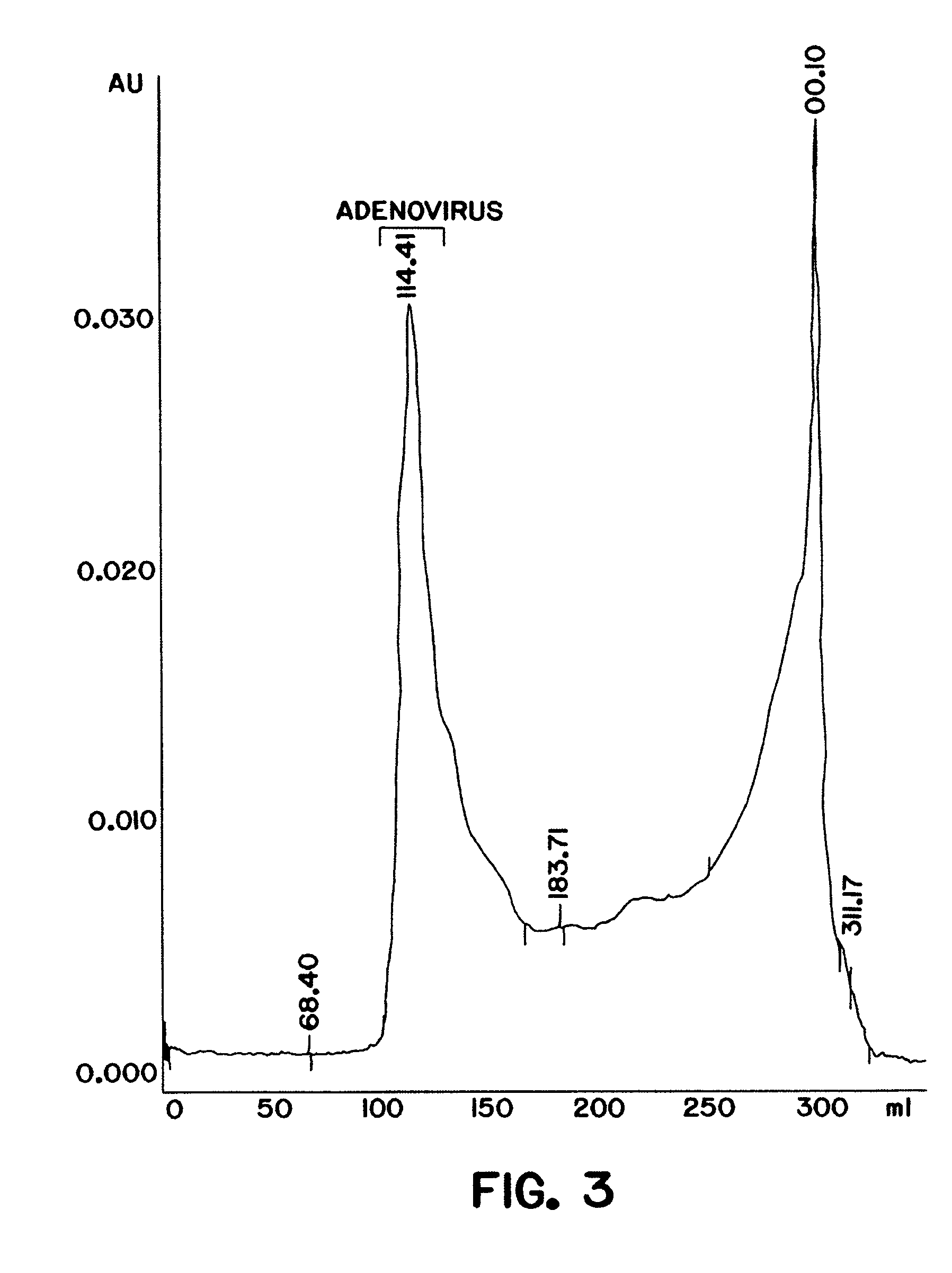
InactiveUS7579181B2Rapidly and efficiently purifyHigh molecular weightEnzymologyRecovery/purificationGene transferVirus
Owner:GENZYME CORP
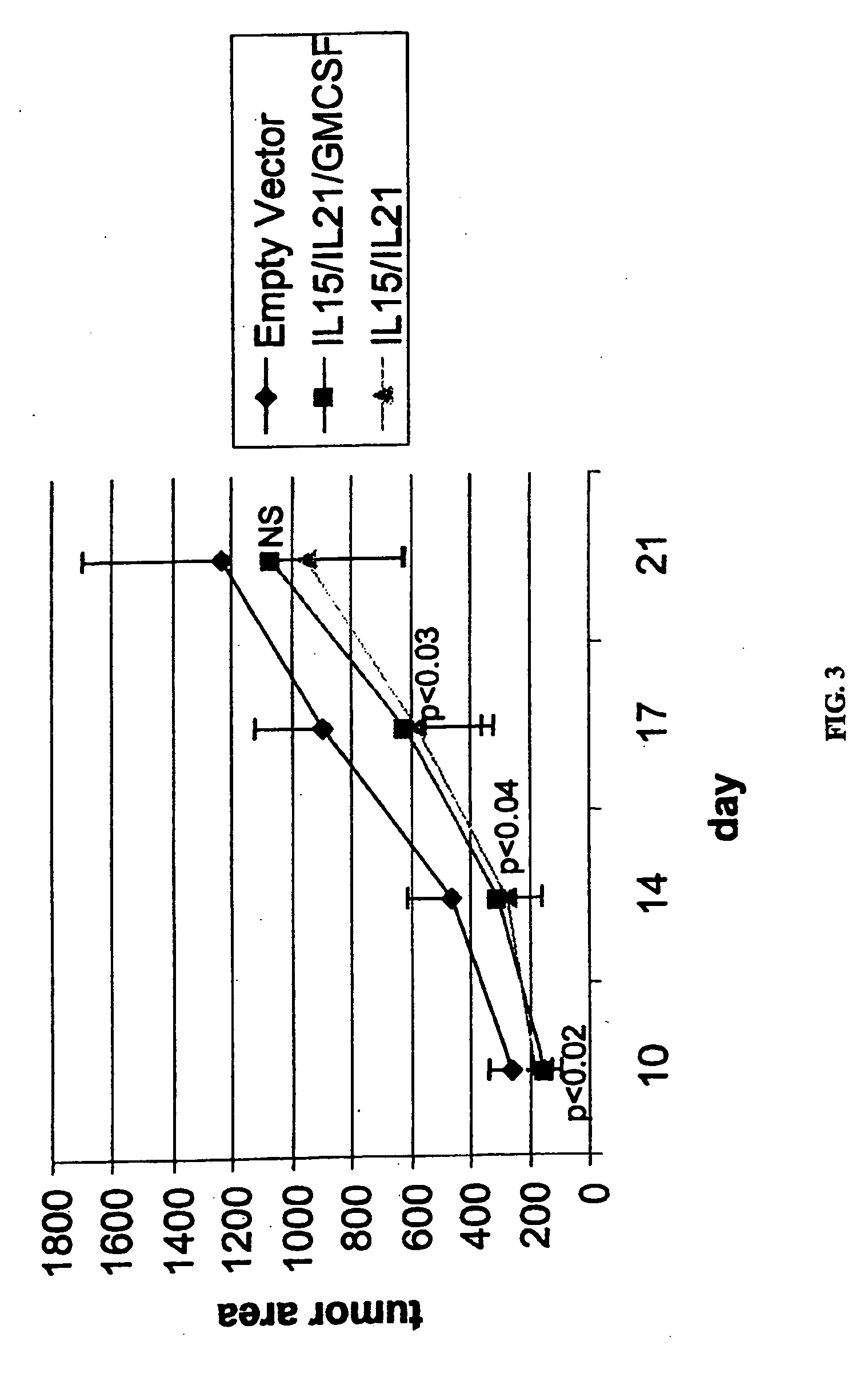
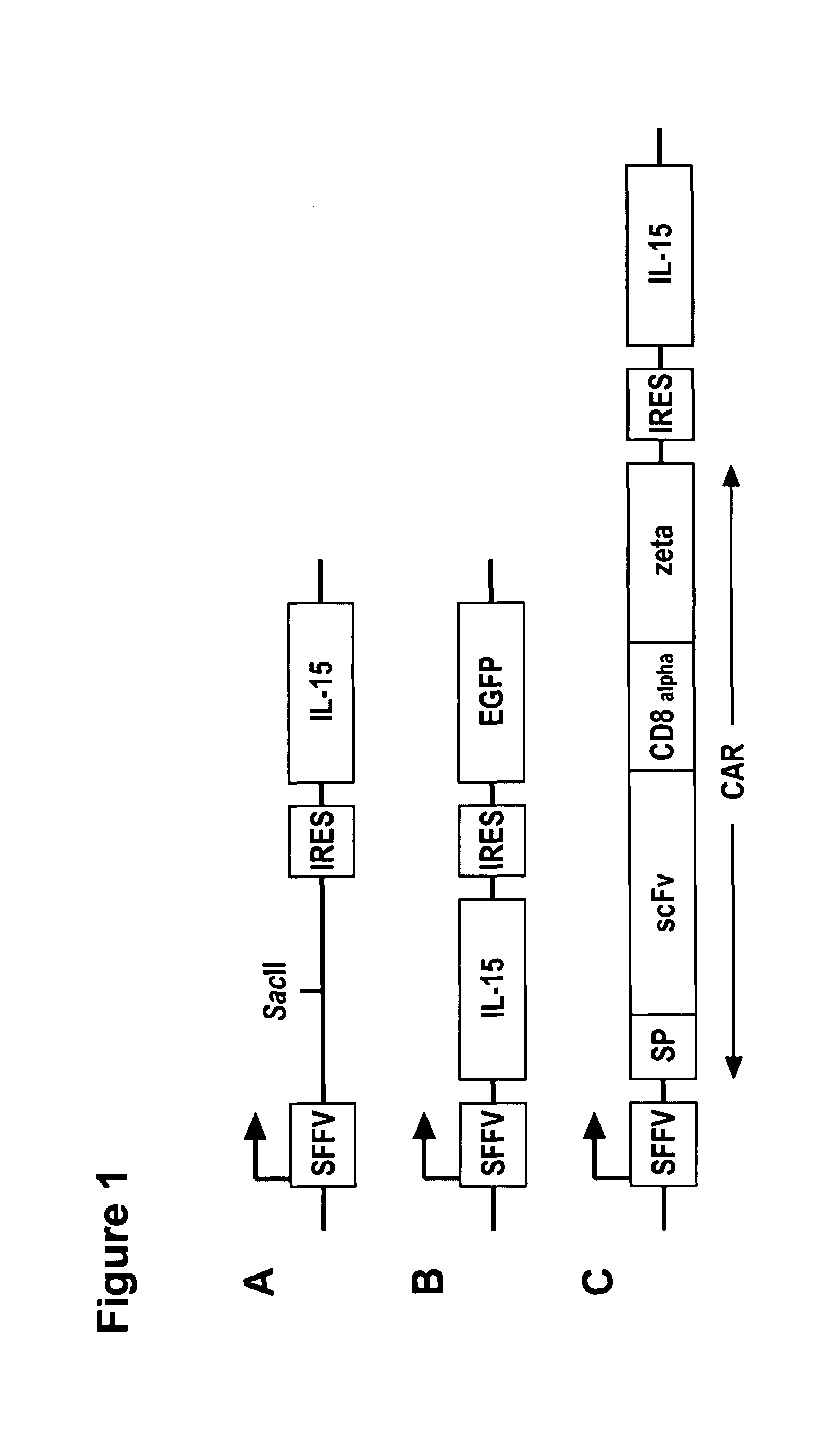
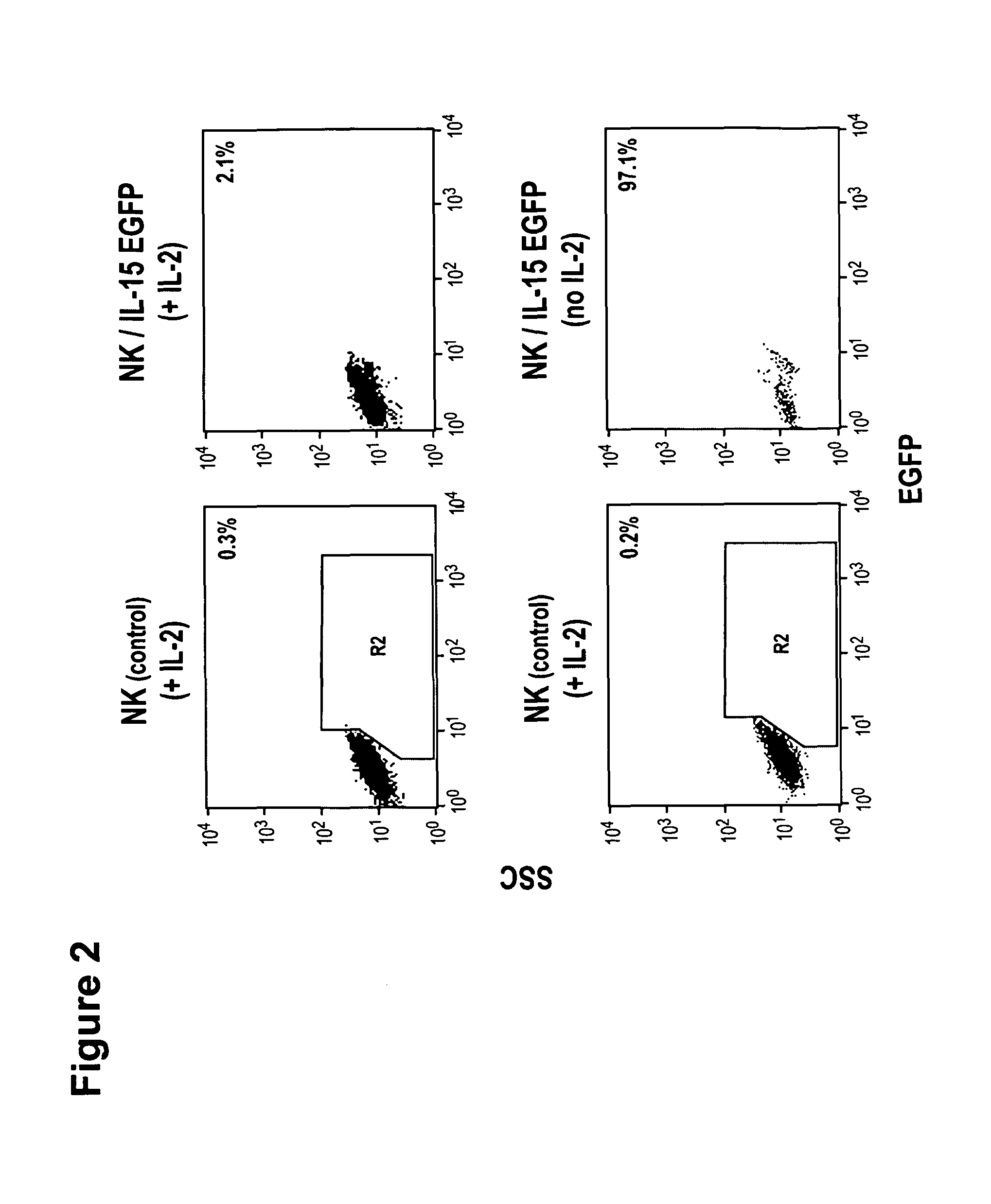
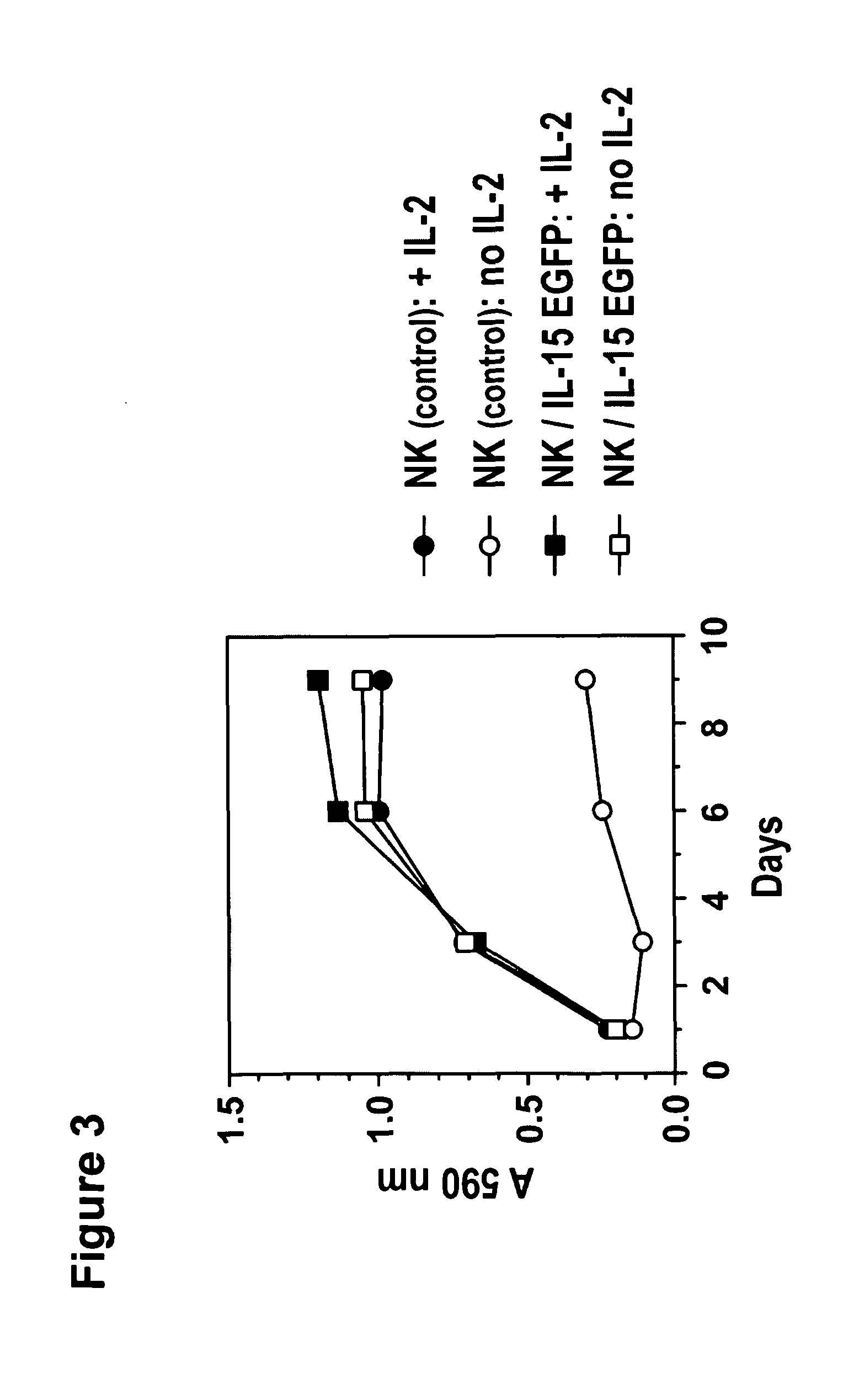
Interleukin 15 as Selectable Marker for Gene Transfer in Lymphocytes
ActiveUS20130280221A1Opening possibilityBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsADAMTS ProteinsAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to the use of interleukin-15 (IL-15) as selectable marker for gene transfer, preferably of at least one gene of therapeutic interest, into a mammalian cell or cell line, in particular a human cell or cell line. The present invention furthermore relates to transgenic mammalian cells or cell lines expressing IL-15 as selectable marker and co-expressing at least one protein of interest encoded by at least one gene of interest, which is preferably a protein of therapeutic interest. The present invention is in particular suitable for chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) as the gene or protein of interest and their expression in lymphocytes. The transgenic mammalian cells and cell lines are furthermore suitable for use as a medicament, in particular in the treatment of cancer and in immunotherapy, such as adoptive, target-cell specific immunotherapy.
Owner:CHEMOTHERAPEUTISCHES FORSCHUNGINSTITUT GEORG SPEYER HAUS
Lipid-nucleic acid particles prepared via a hydrophobic lipid-nucleic acid complex intermediate and use of gene transfer
InactiveUS20070172950A1Microencapsulation basedPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLipid formationParticulates
Novel lipid-nucleic acid particulate complexes which are useful for in vitro or in vivo gene transfer are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. Upon removal of a solubilizing component (i.e., detergent or an organic solvent) the lipid-nucleic acid complexes form particles wherein the nucleic acid is serum-stable and is protected from degradation. The particles thus formed have access to extravascular sites and target cell populations and are suitable for the therapeutic delivery of nucleic acids.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
Signal for targeting molecules to the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum
Owner:NEWVA CAPITAL PARTNERS LP
Self-complementary parvoviral vectors, and methods for making and using the same
ActiveUS20070253936A1High genetic stabilityStabilized parvovirus vector is more stableBiocideAnimal repellantsGene transferTiter
The teachings herein are generally directed to a method of enhancing the genetic stability of parvovirus vectors. The stability of conventional ss or dsAAV vector constructs can be enhanced, for example, to obtain a concurrent increase in vector titer and purity, as well as an improvement in vector safety, due at least in part to the elimination of stuffer DNA from the AAV vector. The method is broadly applicable to all gene transfer / therapy applications, such as those requiring delivery of foreign DNA containing recombinant gene expression cassettes. Such foreign DNA can range, for example, from about 0.2 up to about 5.2 kb in length. The enhanced vector constructs are highly flexible, user-friendly, and can be easily modified (via routine DNA cloning) and utilized (via standard AAV vector technology) by anyone skilled in the art.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
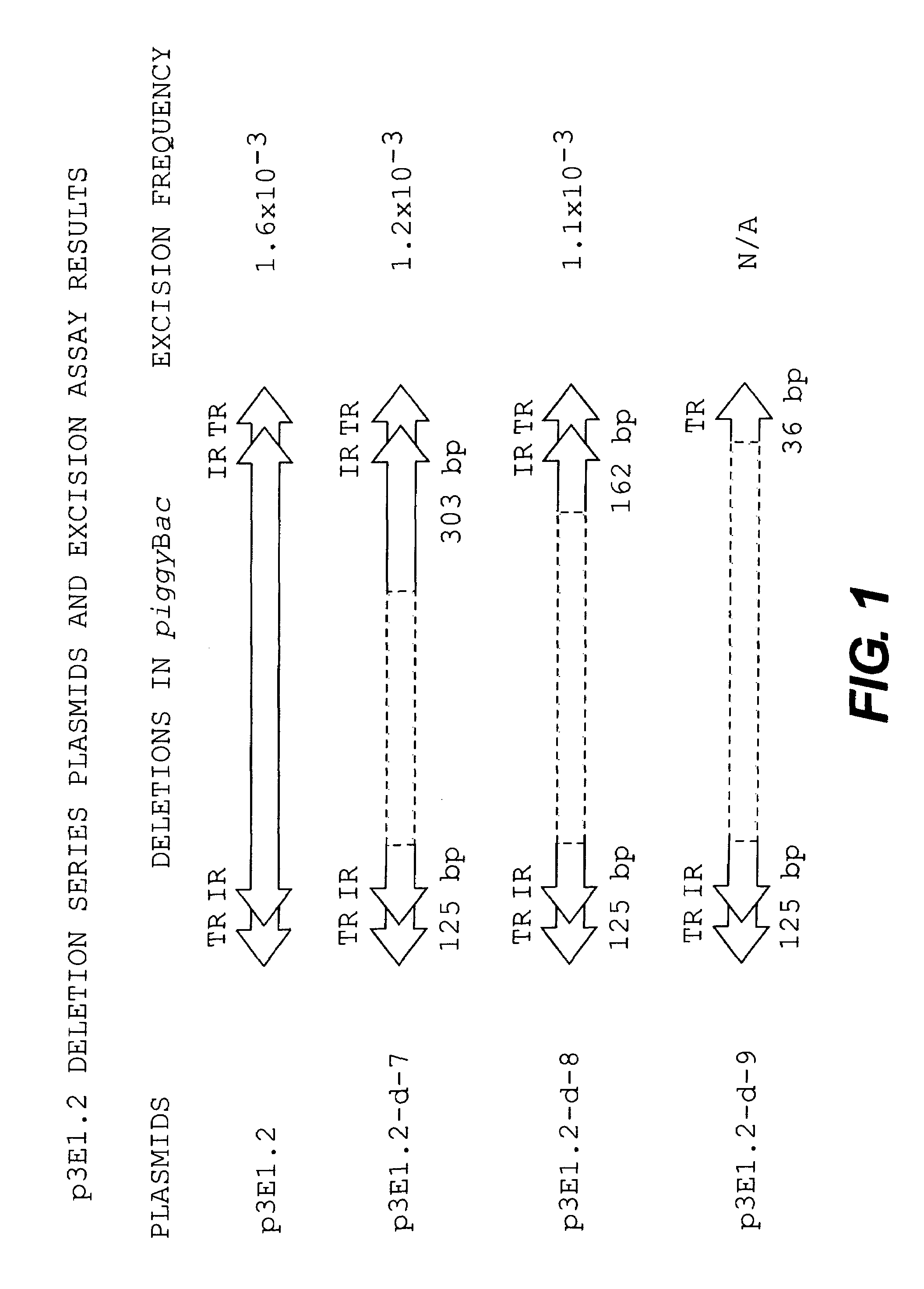
Methods and compositions for transposition using minimal segments of the eukaryotic transformation vector Piggybac
InactiveUS7105343B1Inserting DNA molecules into cells is enhancedEasy to insertSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNATransformation cellGene transfer
The present invention provides efficient transfer of genes into host cells or embryos to transform the cells or embryos by transposition vectors using the minimal amount of nucleotide sequences in the transposon piggyBac required for gene transfer. The transformed cells or embryos may also be developed into transgenic organisms.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Methylotroph producing mammalian type sugar chain
ActiveUS20060148039A1FungiImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Enhanced aav-mediated gene transfer for retinal therapies
ActiveUS20150376240A1Preventing and arresting progressionPreventing and arresting of and vision lossBiocideSenses disorderAdeno associate virusRetinal treatments
Described herein are capsid proteins and adeno-associated viruses capable of targeting various types of ocular cells including bipolar and horizontal cells. Also described herein are methods of treating various ocular disorders in a subject in need thereof by administering to the subject an effective concentration of a composition comprising the recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) of the invention.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for modulating expression of exogenous genes in mammalian systems, and products related thereto
InactiveUS20060014711A1Precise and potent inductionImprove pharmacokineticsVectorsGenetic material ingredientsResponse elementGene transfer
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided various methods for modulating the expression of an exogenous gene in a mammalian subject employing modified ecdysone receptors. Also provided are modified ecdysone receptors, as well as homomeric and heterodimeric receptors containing sane, nucleic acids encoding invention modified ecdysone receptors, modified ecdysone response elements, gene transfer vectors, recombinant cells, and transgenic animals containing nucleic acids encoding invention modified ecdysone receptor.
Owner:EVANS RONALD +2
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20110110960A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryDystrophinMannose 6-phosphate receptor
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes exon skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com