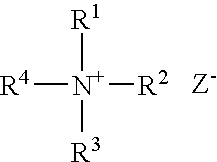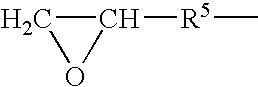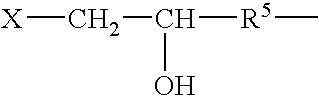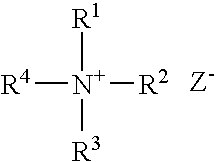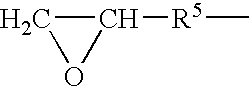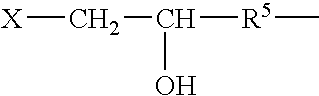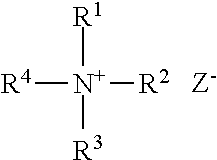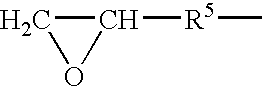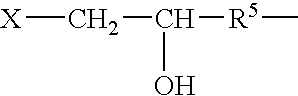Patents
Literature
1677 results about "Mannose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
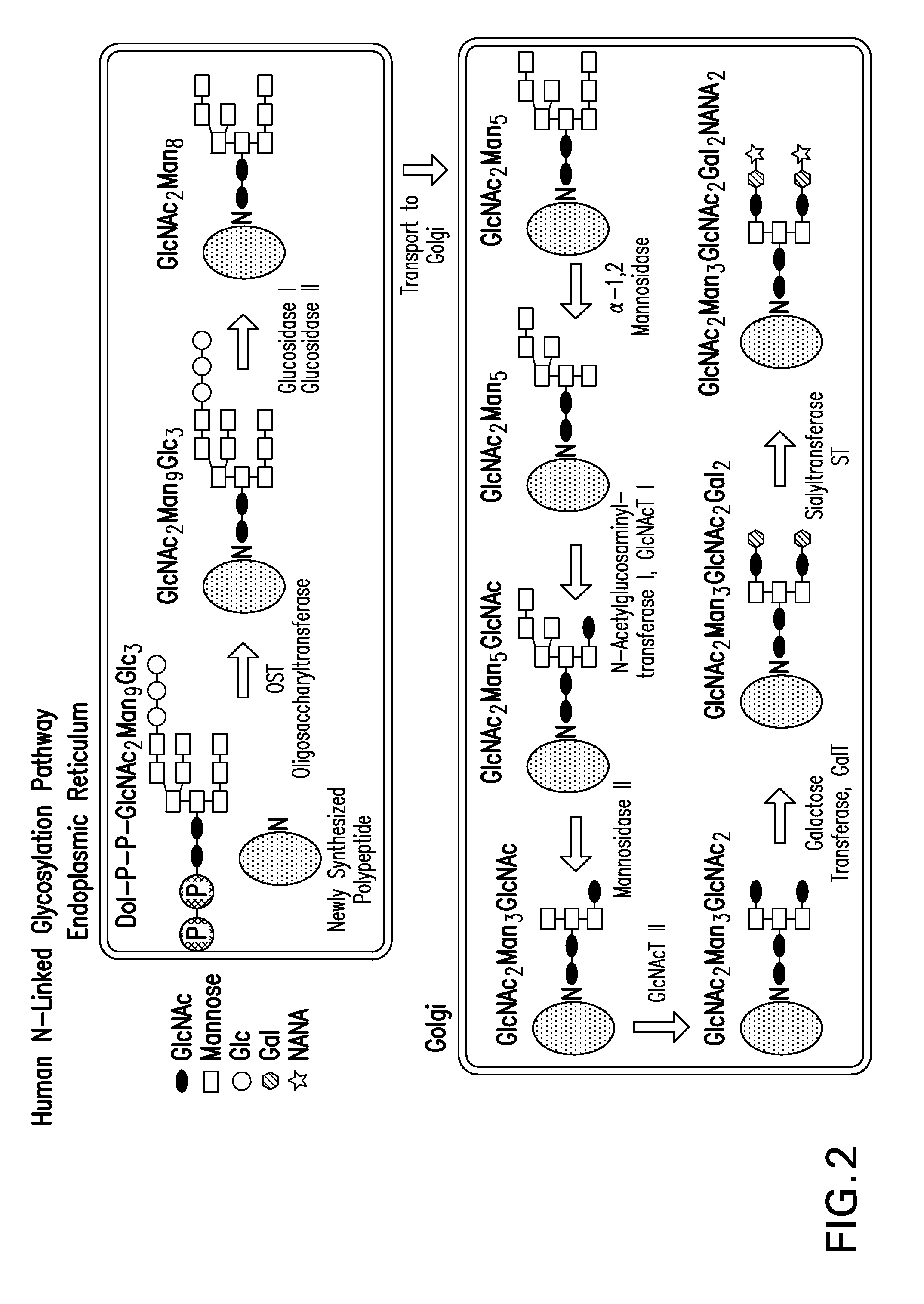
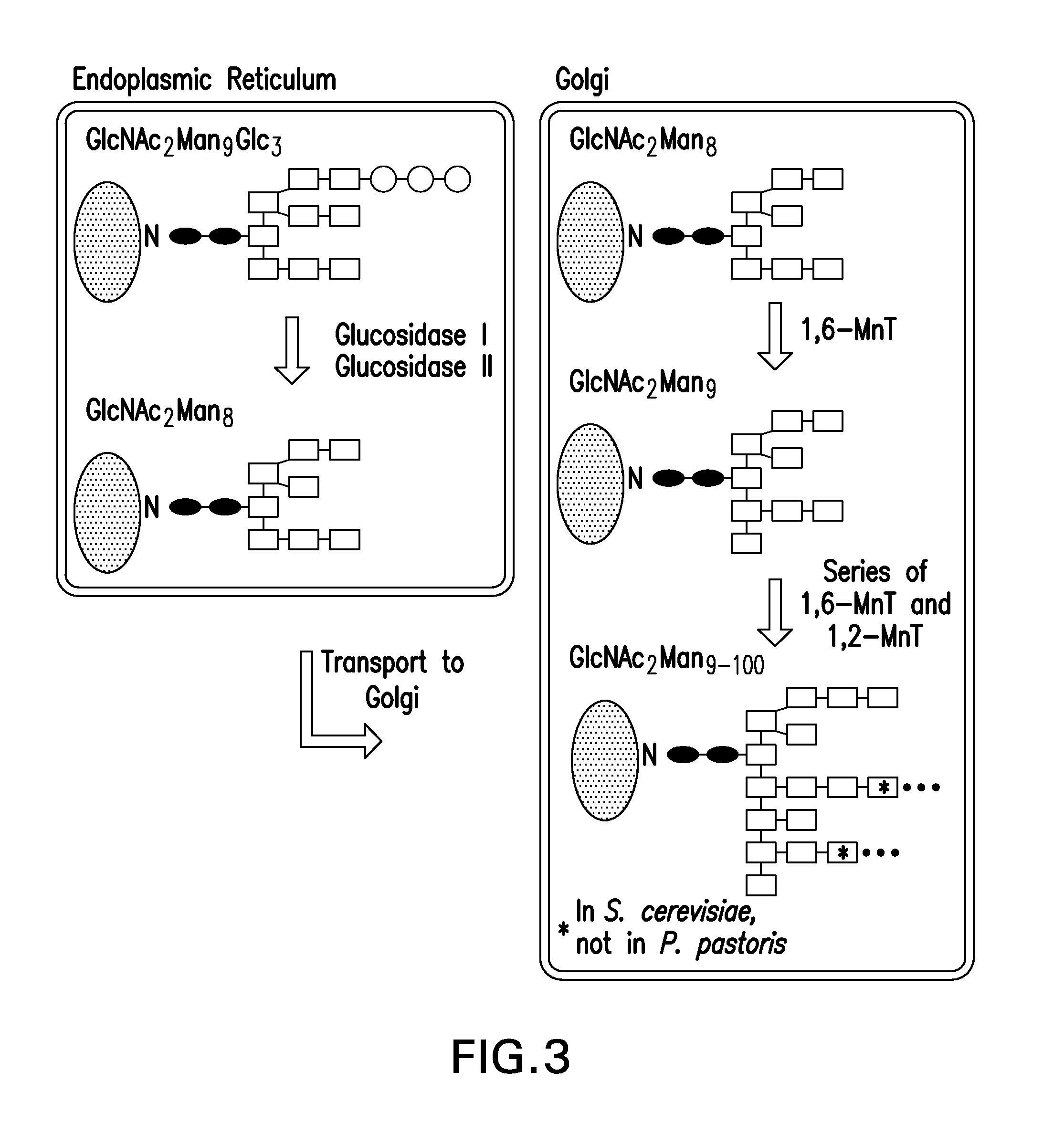
Mannose, packaged as the nutritional supplement "d-mannose", is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation are associated with mutations in enzymes involved in mannose metabolism.
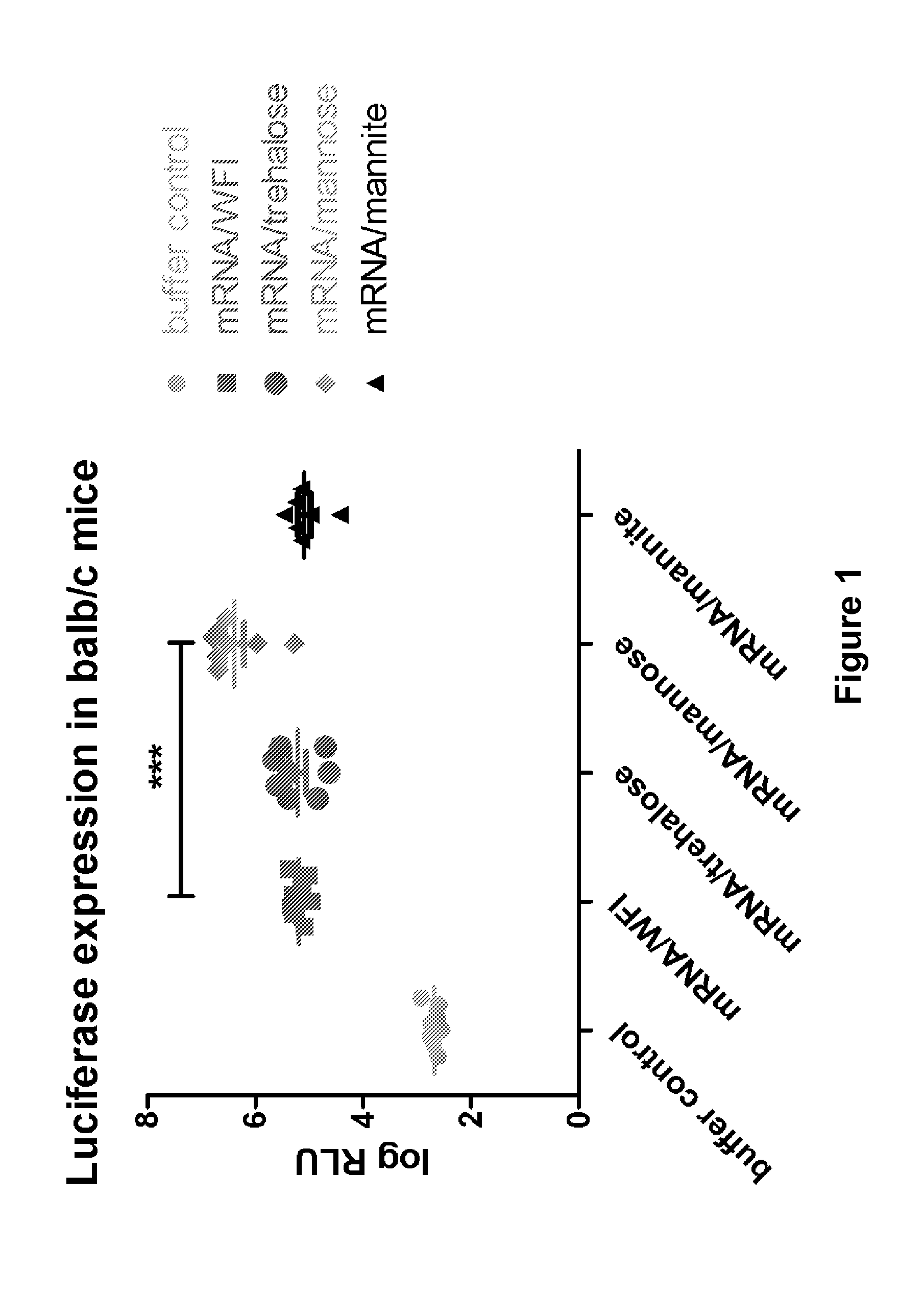
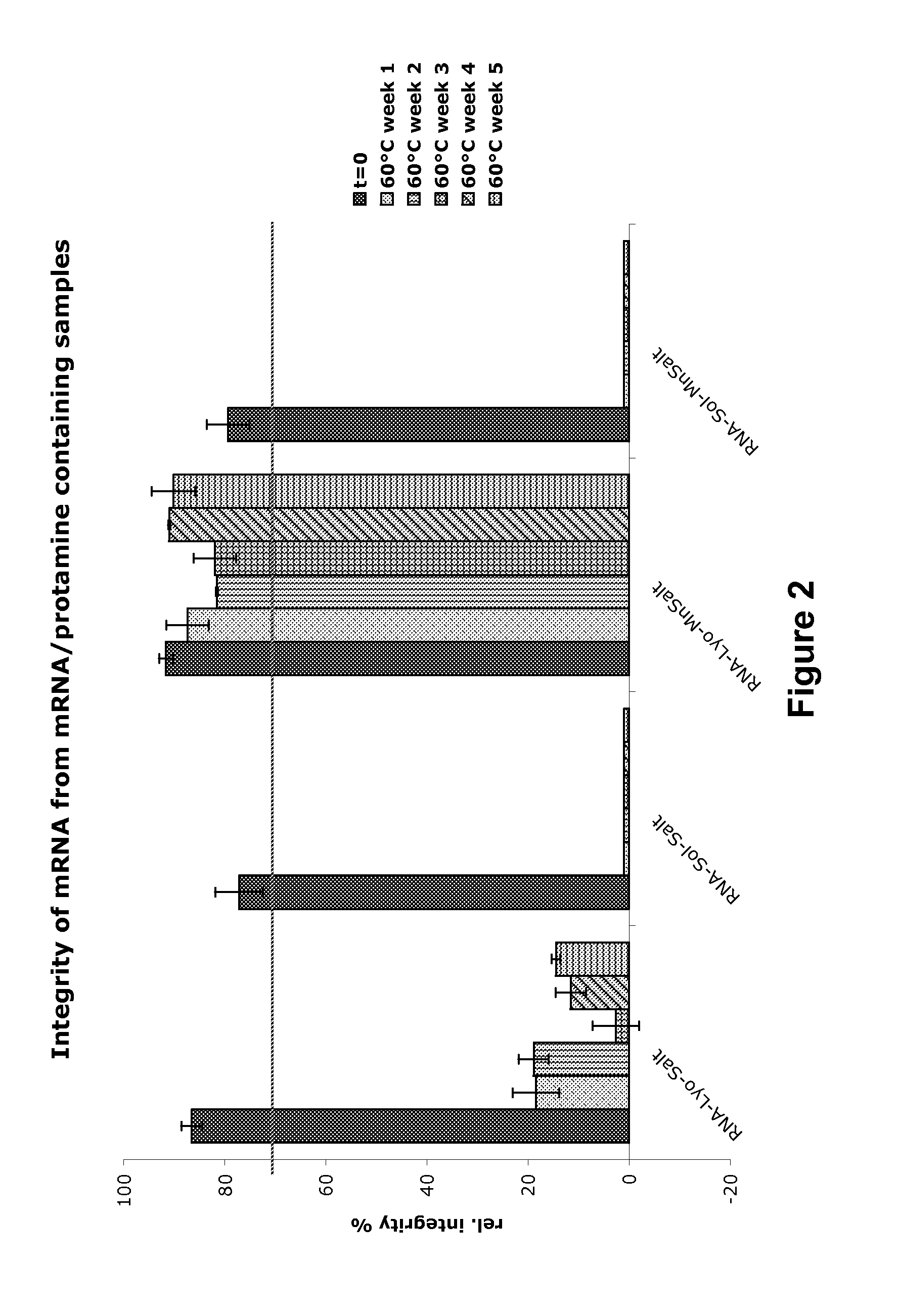
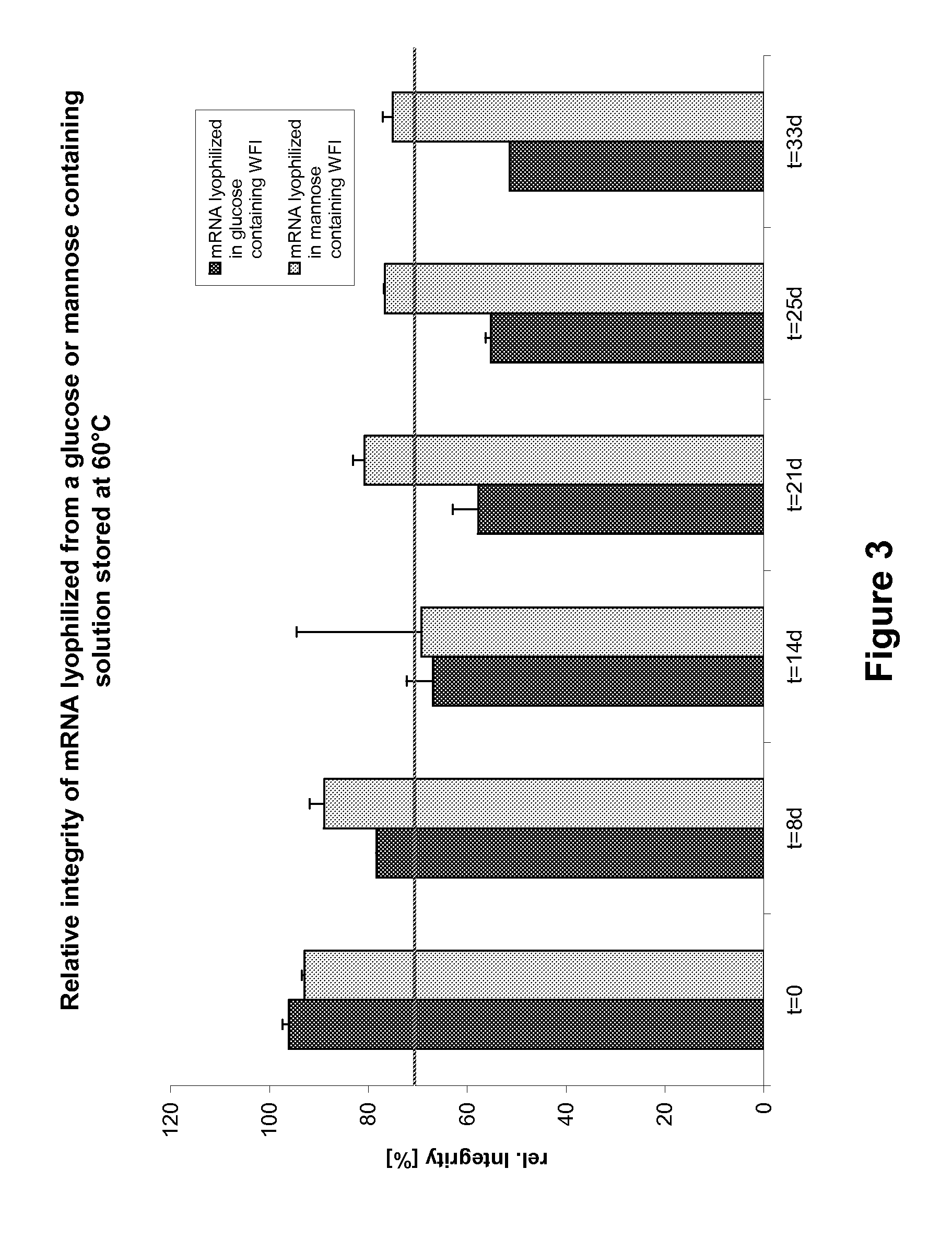
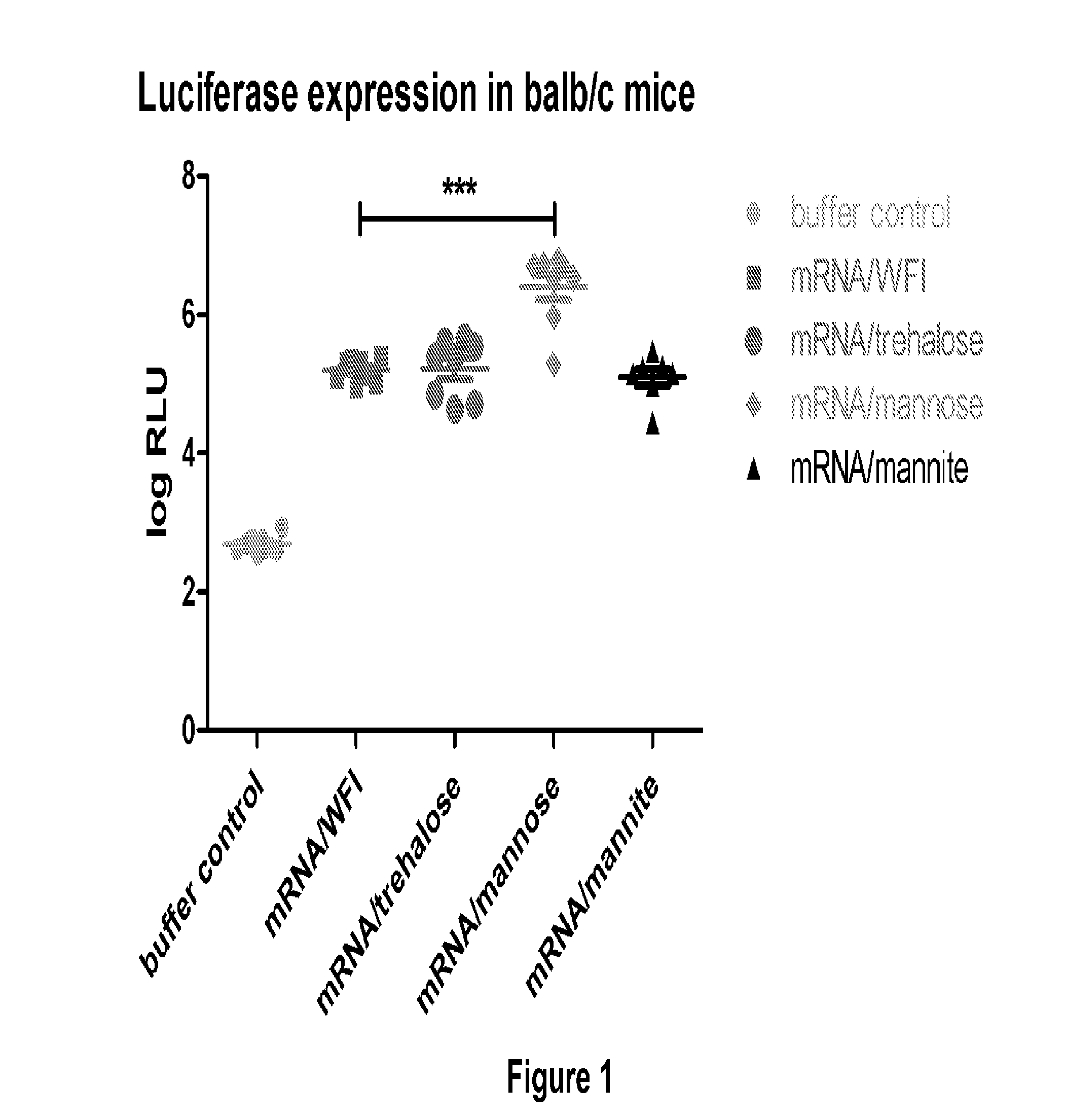
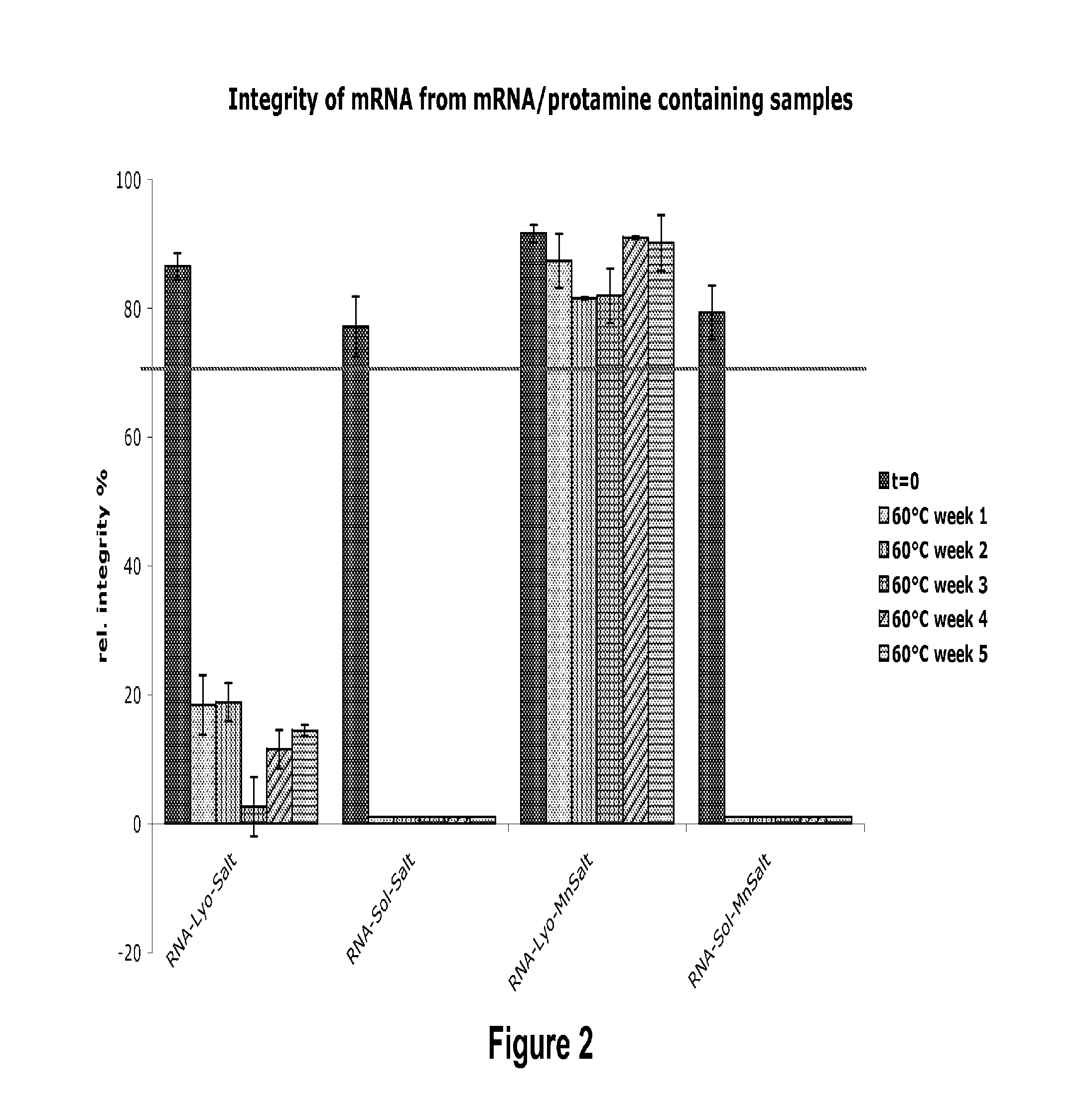
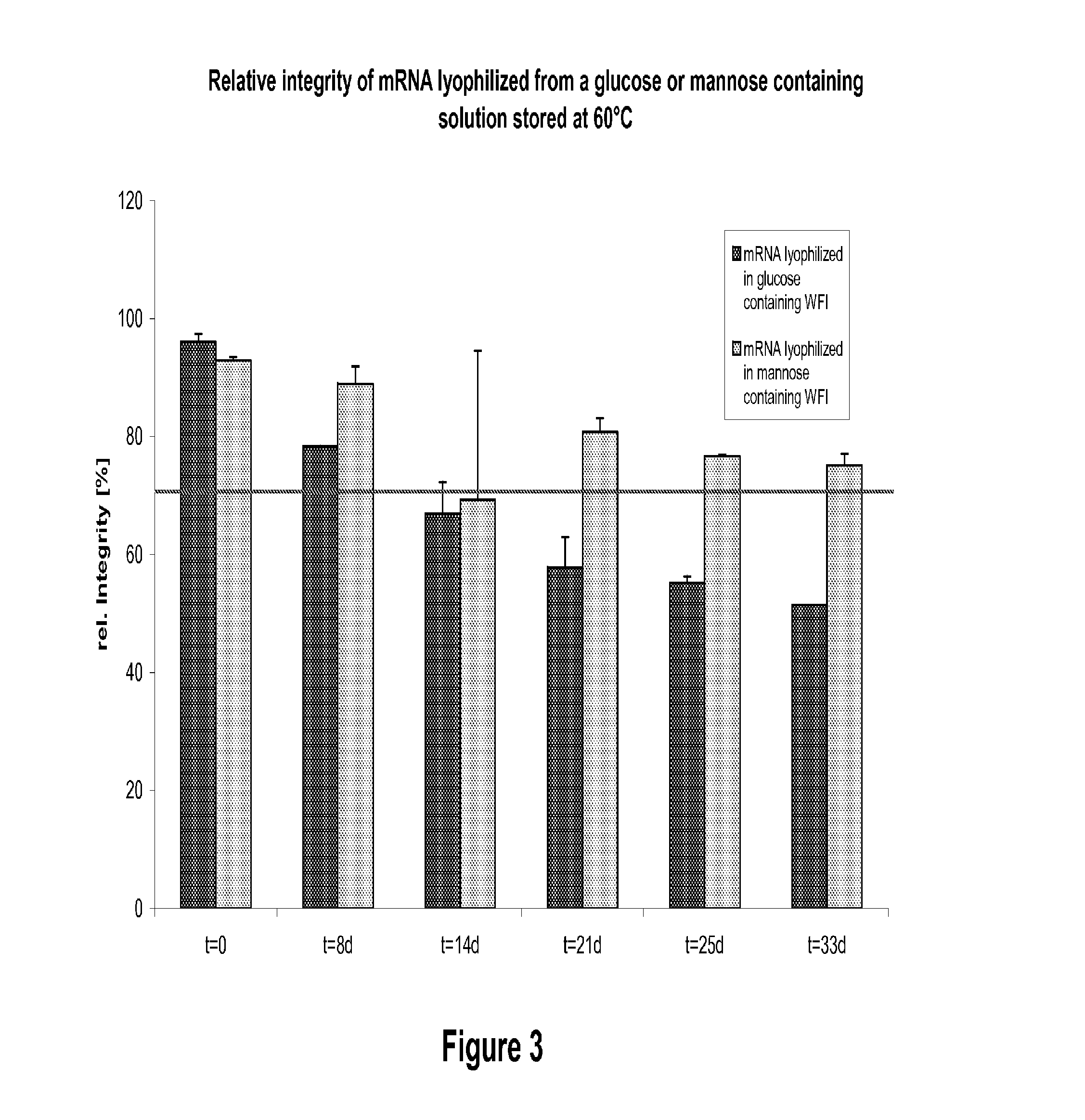
Mannose-containing solution for lyophilization, transfection and/or injection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20120258046A1High transfection efficiencyEnhance protein expressionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoTransfection
The present invention is directed to (the use of) a solution containing at least one nucleic acid (sequence) and free mannose for lyophilization, transfection and / or injection, particularly of RNA and mRNA. The inventive solution exhibits a positive effect on stabilization of the nucleic acid (sequence) during lyophilization and storage but also leads to a considerable increase of the transfection efficiency of a nucleic acid. It thus also increases in vivo expression of a protein encoded by such a nucleic acid upon increased transfection rate. The present invention is furthermore directed to a method of lyophilization using the mannose-containing solution, to pharmaceutical compositions, vaccines, kits, first and second medical uses applying such a mannose-containing solution and / or a nucleic acid (sequence) lyophilized or resuspended with such a solution.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Personal care composition containing a non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative
Personal care compositions comprise (a) from about from about 5 wt. % to about 35 wt. % of a detersive surfactant; (b) at least about 0.05 wt. % of a galactomannan polymer derivative having a mannose to galactose ratio of greater than 2:1 on a monomer to monomer basis, the galactomannan polymer derivative selected from a cationic galactomannan polymer derivative and an amphoteric galactomannan polymer derivative having a net positive charge, the galactomannan polymer derivative having a molecular weight from about 1,000 to about 10,000,000 and a cationic charge density from about 0.9 meq / g to about 7 meq / g; and (c) at least about 20 wt. % of an aqueous carrier. Methods of treating hair or skin comprise applying the personal care composition as described above to the hair or skin and rinsing the hair or skin.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20120122801A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryGlycoside formationMannose 6-phosphate receptor
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes ex on skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA THERAPEUTICS
Methods for eliminating mannosylphosphorylation of glycans in the production of glycoproteins
The present invention relates to the elimination of mannosylphosphorylation on the glycans of glycoproteins in the yeast genus Pichia. The elimination of mannosylphosphorylated glycoproteins results from the disruption of the PNO1 gene and the newly isolated P. pastoris MNN4B gene. The present invention further relates to methods for producing modified glycan structures in host cells that are free of glycan mannosylphosphorylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
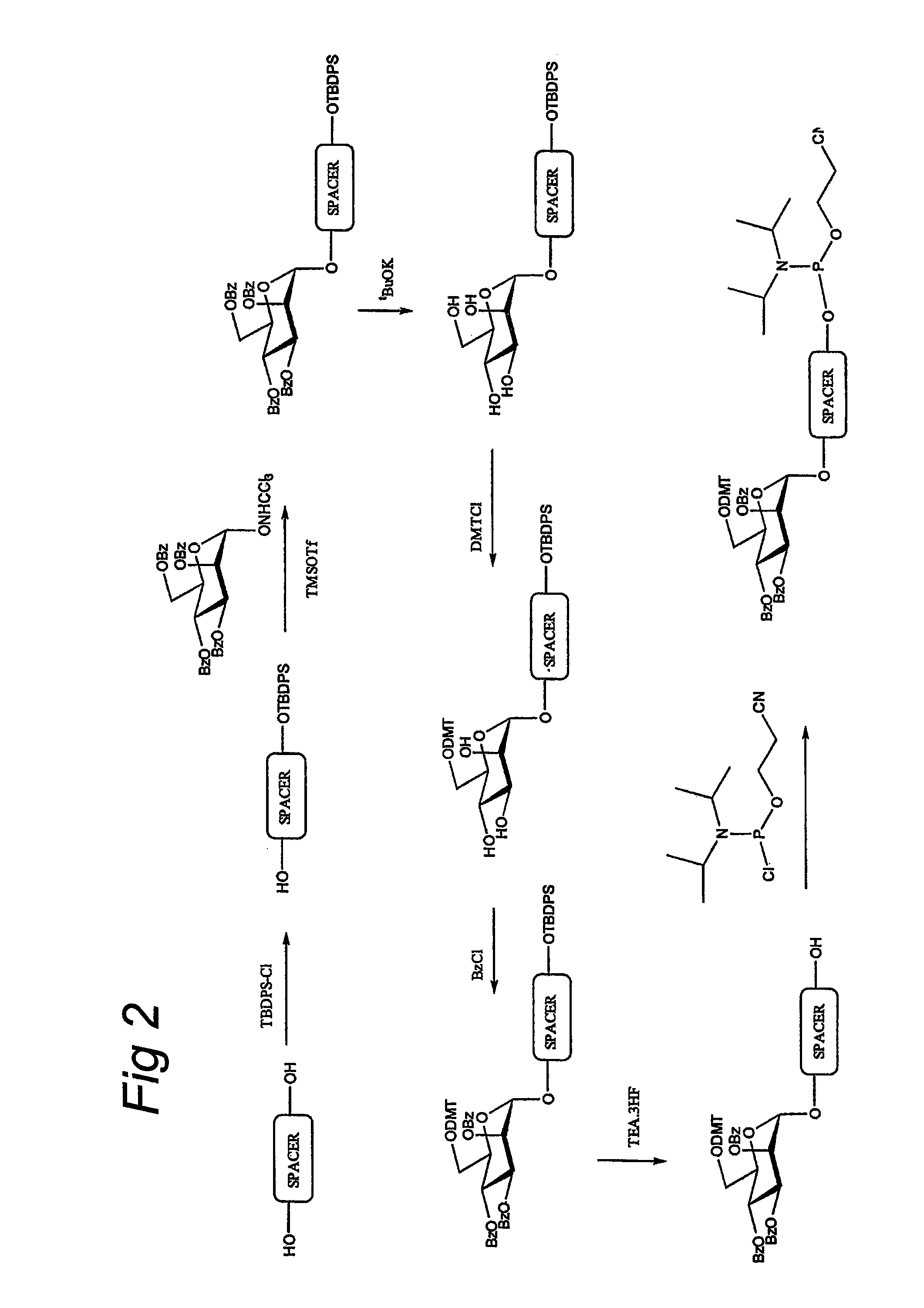
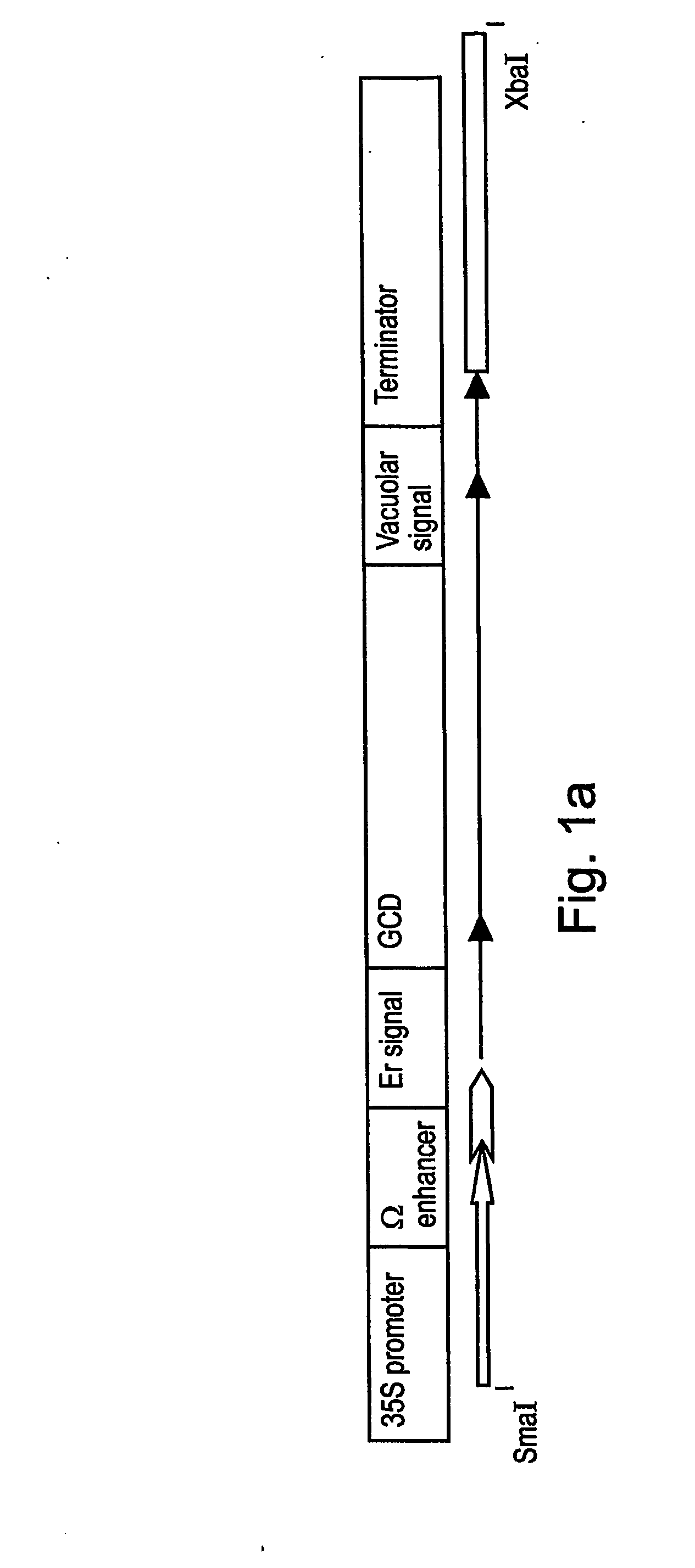
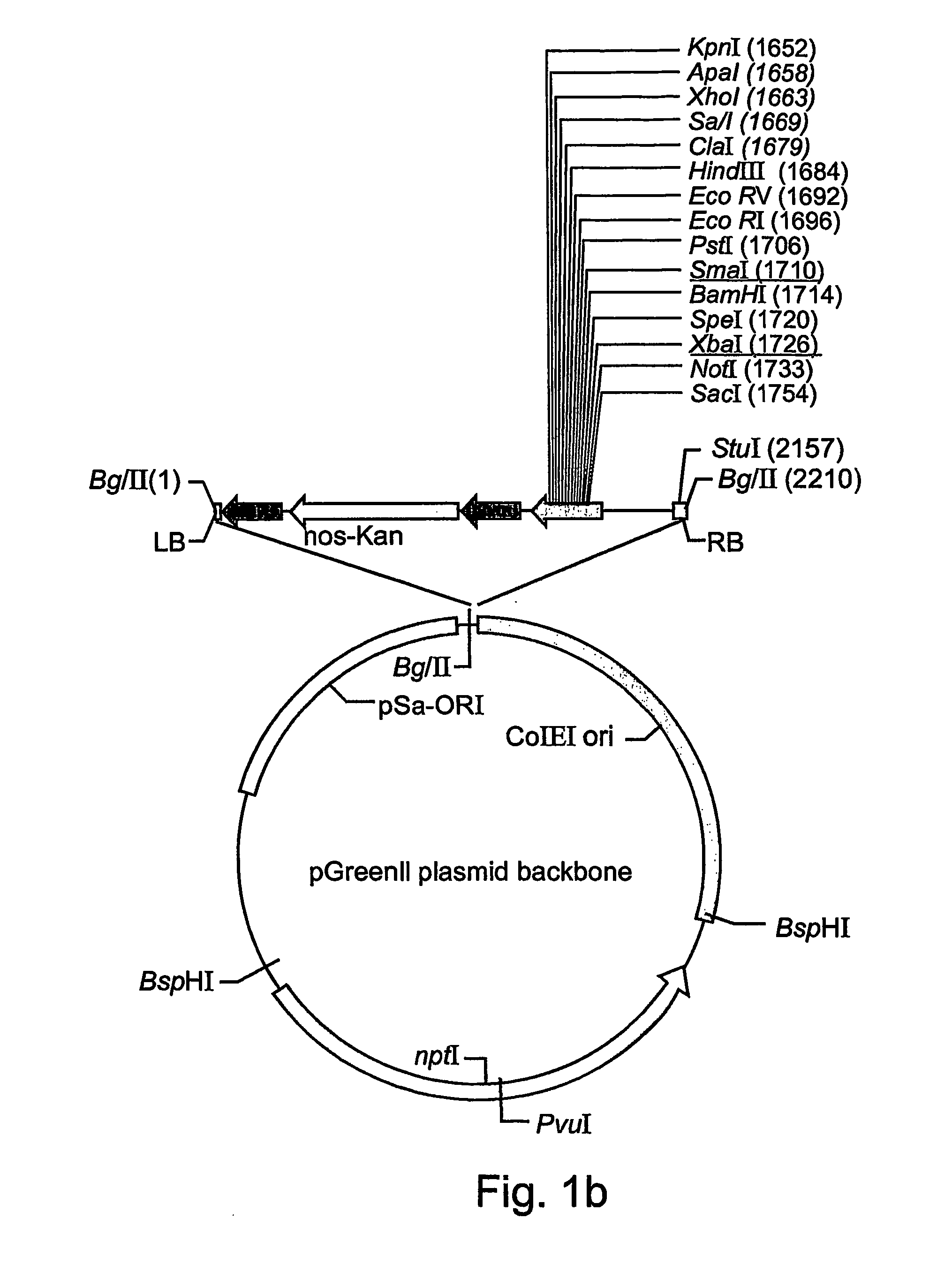
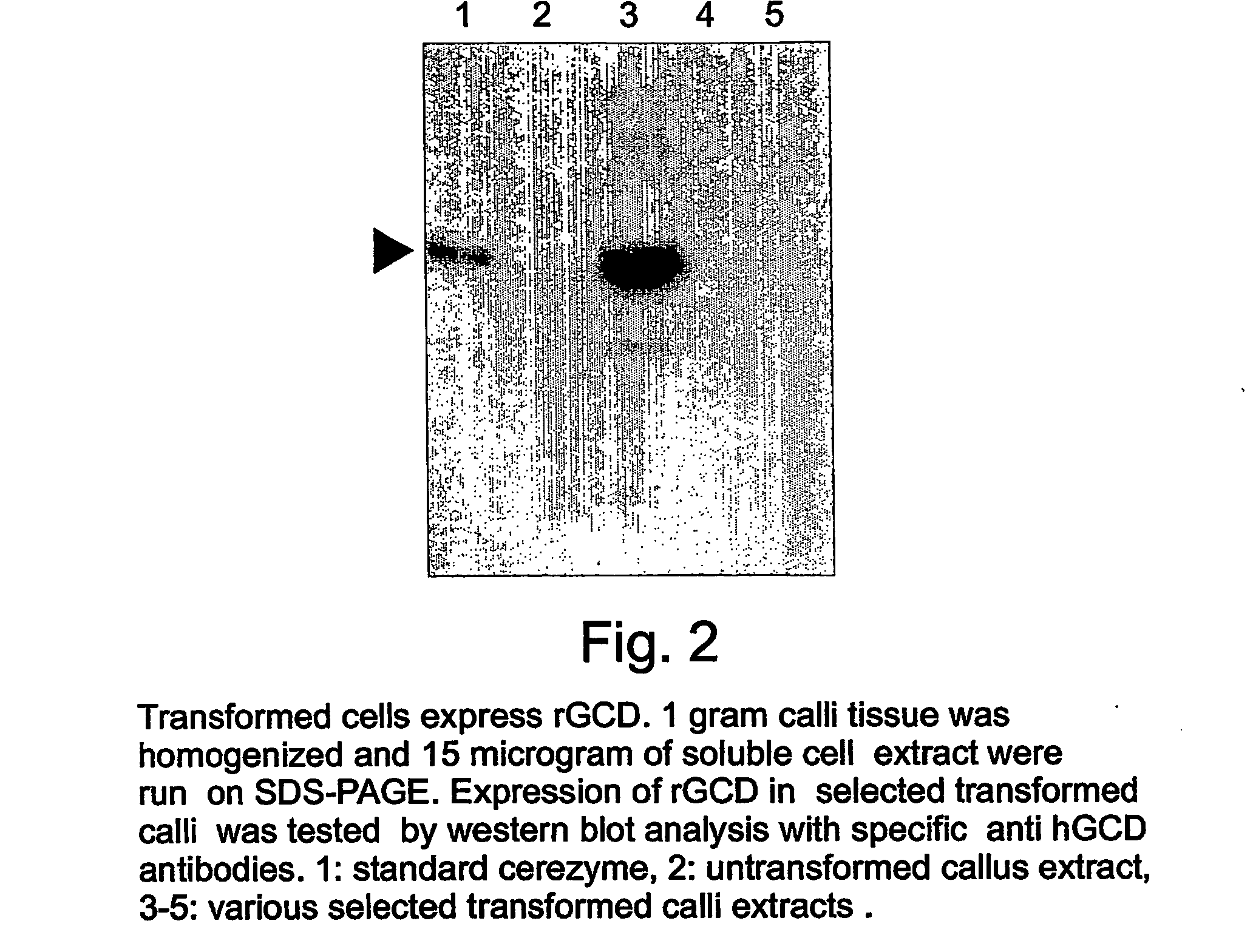
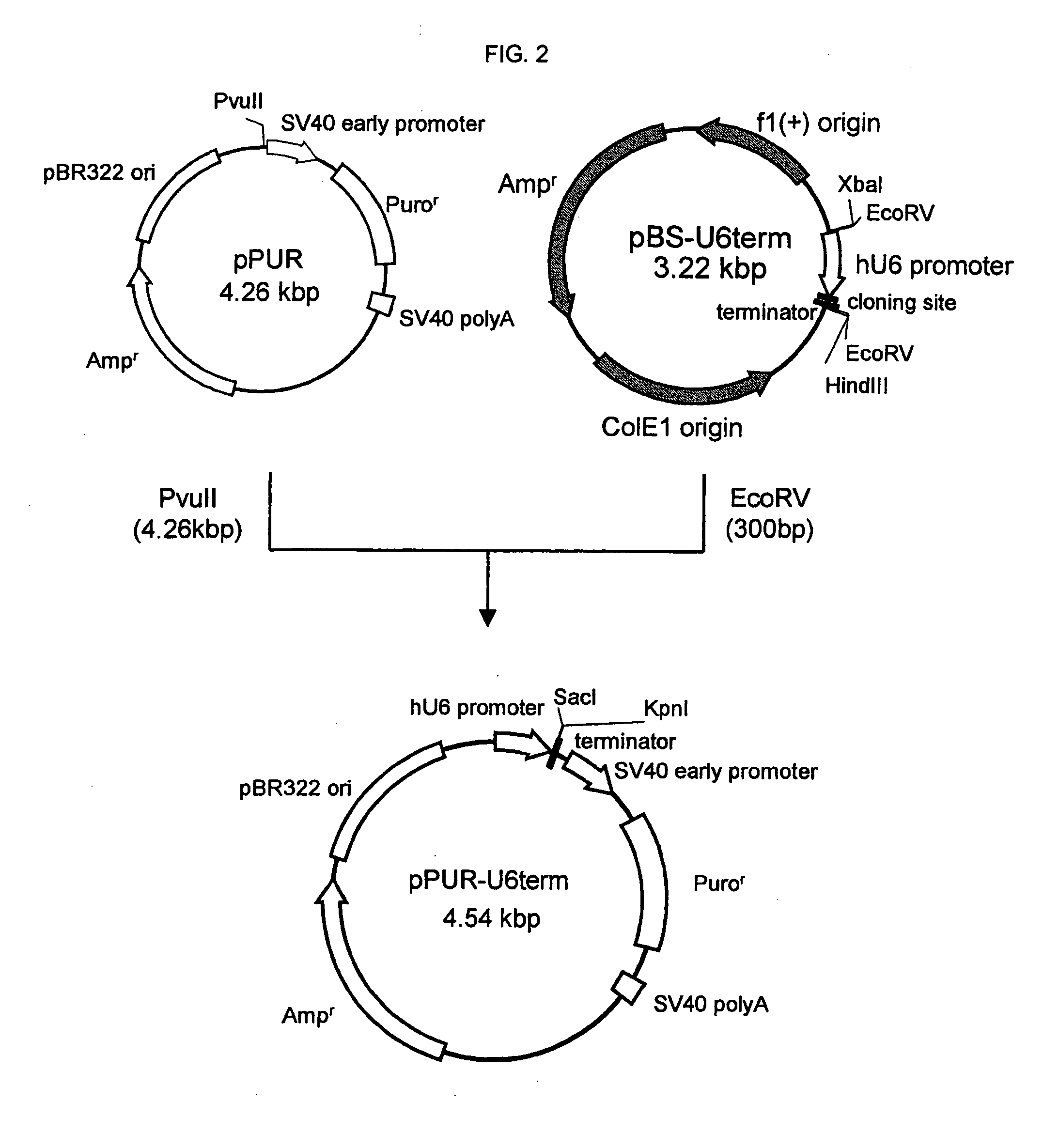
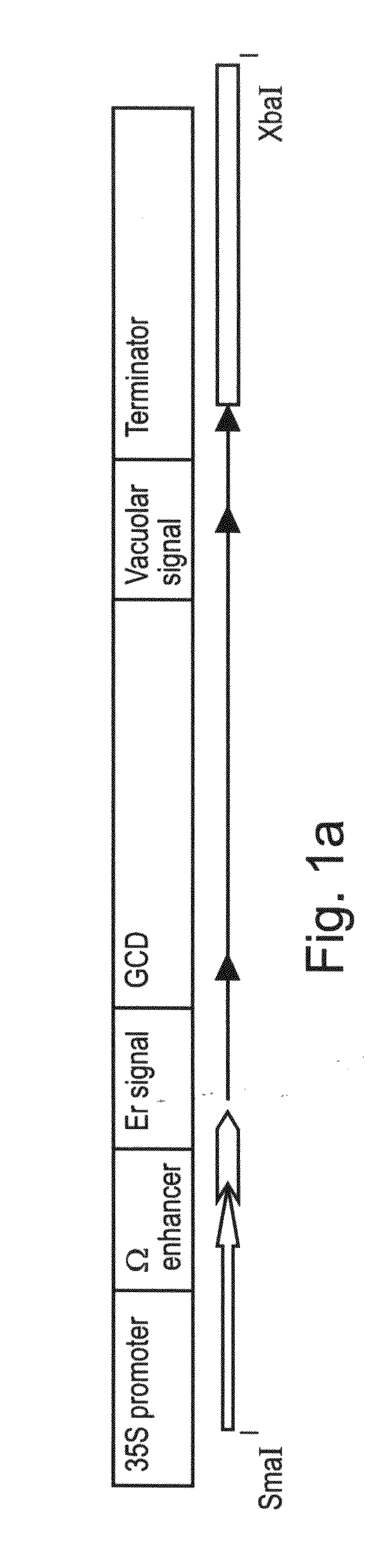
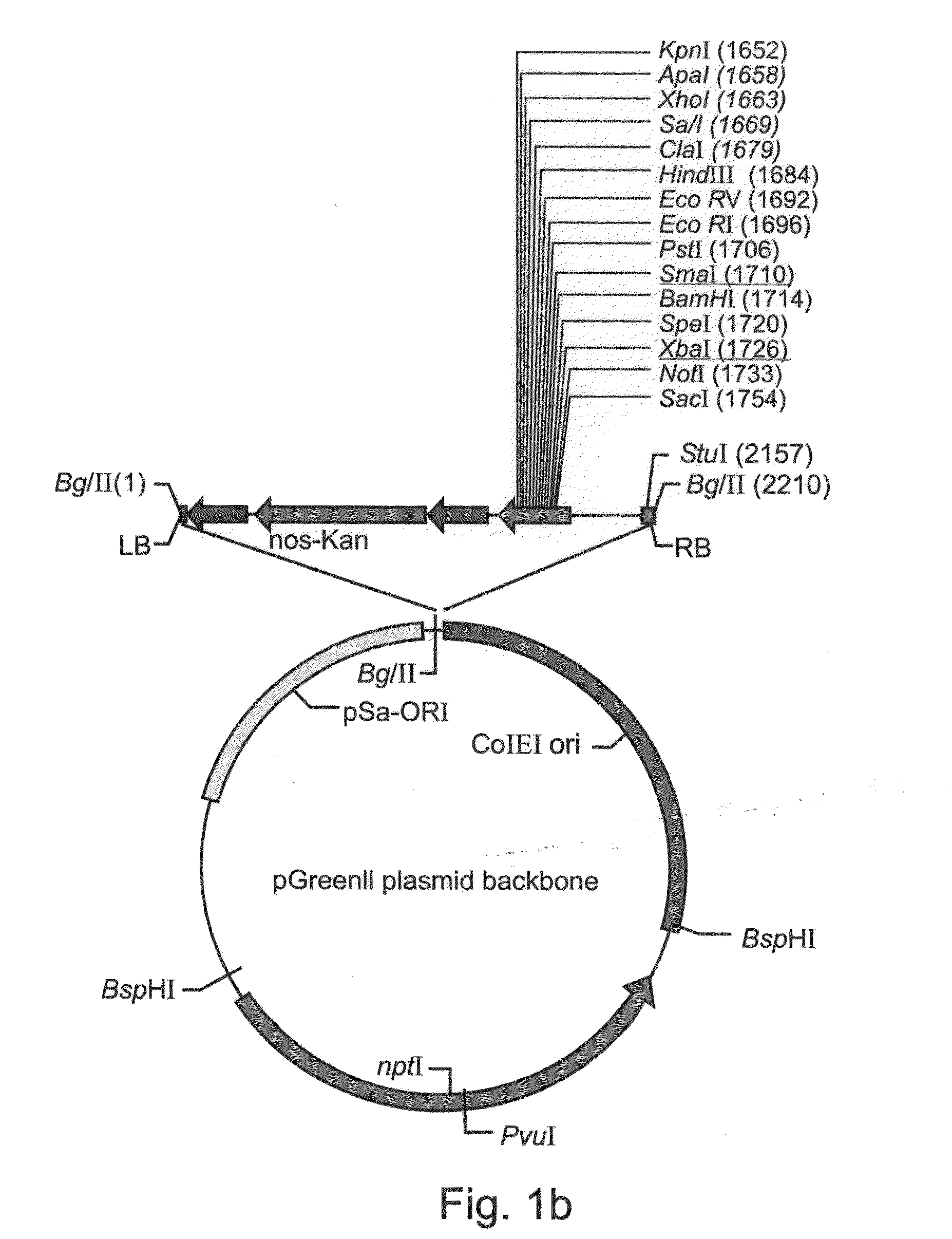
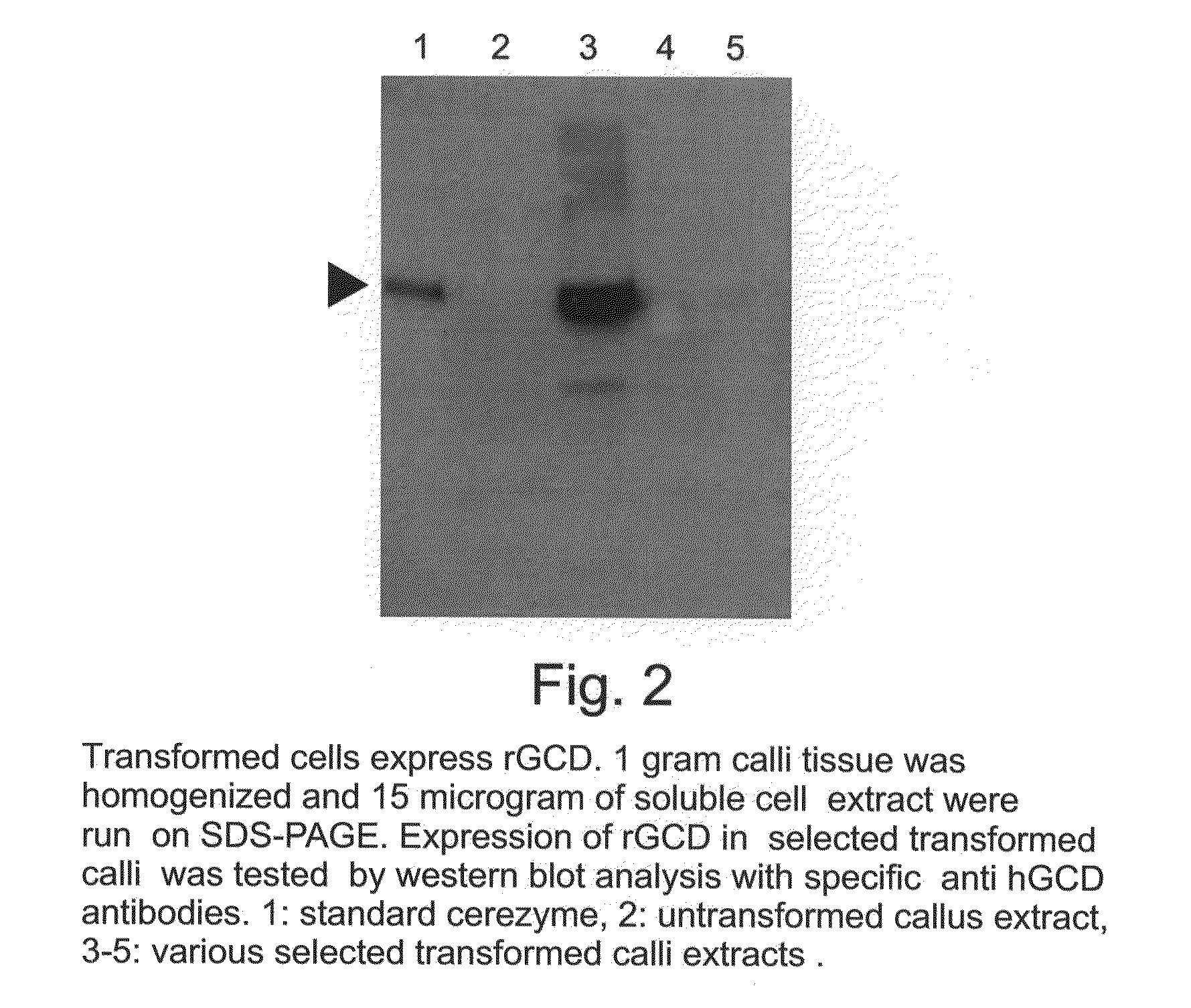
Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
InactiveUS20060204487A1Efficient productionSufficient quantityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderMannoseMolecular biology
A device, system and method for producing glycosylated proteins in plant culture, particularly proteins having a high mannose glycosylation, while targeting such proteins with an ER signal and / or by-passing the Golgi. The invention further relates to vectors and methods for expression and production of enzymatically active high mannose lysosomal enzymes using transgenic plant root, particularly carrot cells. More particularly, the invention relates to host cells, particularly transgenic suspended carrot cells, vectors and methods for high yield expression and production of biologically active high mannose Glucocerebrosidase (GCD). The invention further provides for compositions and methods for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:PROTALIX
Shampoo containing a gel network and a non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative
Shampoo compositions comprise (a) from about 5% to about 50% of one or more detersive surfactants; (b) a dispersed gel network phase comprising: (i) at least about 0.05% of one or more fatty amphiphiles; (ii) at least about 0.01% of one or more secondary surfactants; and (iii) water; (c) at least about 0.05% of a galactomannan polymer derivative with a net positive charge and having a mannose to galactose ratio of greater than 2:1 on a monomer to monomer basis, wherein the galactomannan polymer derivative has: (i) a molecular weight from about 1,000 to about 10,000,000; and (ii) a cationic charge density from about 0.7 meq / g to about 7 meq / g; and (d) at least about 20% of an aqueous carrier; all by weight of the shampoo composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Reduced-carbohydrate and nutritionally-enhanced frozen desserts and other food products
InactiveUS20060286248A1Mitigate laxation effectReduce impactFrozen sweetsConfectioneryTagatoseMaltitol
A reduced carbohydrate ice cream or other frozen dessert product that contains a low-digestible sweetener system and a fermentable fiber material. The a low-digestible sweetener system consists of one or more low-digestible sweeteners having a molecular weight of from about 90 to about 190; and is typically a low molecular weight saccharide or a polyol. Typical low-digestible sweeteners include mannitol, maltitol, sorbitol, lactitol, erythritol, xylitol, isomalt, glycerin, talitol, mannose, tagatose, fructose, arabinose, fucose, lycose, ribose, sorbose, talose, and xylose, and mixtures thereof. The low-digestible sweetener replaces the digestible sugars to provide the appropriate freezing point depression of the product. The level of fermentable fiber is sufficient to mitigate a Taxation effect that can be caused by ingestion of the amount of the low-digestive sweetener. The fermentable fiber can be an inulin, a maltodextrin resistant to human digestion, an oligofructose, a fructooligosaccharide, a high water binding fermentable fiber, and a mixture thereof.
Owner:TECHCOM GRP LLC
Process for producing glycoprotein composition
InactiveUS20060223147A1Raise the ratioAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticComplex typeN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention relates to a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme catalyzing a reaction which converts GDP-mannose into GDP-4-keto,6-deoxy-GDP-mannose is introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein using the cell; a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in the complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, and an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to synthesis of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, or an RNA capable of suppressing the function of a protein relating to transport of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, to the Golgi body are introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein composition using the cell; and the like.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
ActiveUS20090208477A1High glycosylationEfficient targetingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh mannosePlant roots
A device, system and method for producing glycosylated proteins in plant culture, particularly proteins having a high mannose glycosylation, while targeting such proteins with an ER signal and / or by-passing the Golgi. The invention further relates to vectors and methods for expression and production of enzymatically active high mannose lysosomal enzymes using transgenic plant root, particularly carrot cells. More particularly, the invention relates to host cells, particularly transgenic suspended carrot cells, vectors and methods for high yield expression and production of biologically active high mannose Glucocerebrosidase (GCD). The invention further provides for compositions and methods for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:PROTALIX
Shampoo containing a gel network and a non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative
ActiveUS20060269502A1Cosmetic preparationsCationic surface-active compoundsAmphiphileSURFACTANT BLEND
Shampoo compositions comprise (a) from about 5% to about 50% of one or more detersive surfactants; (b) a dispersed gel network phase comprising: (i) at least about 0.05% of one or more fatty amphiphiles; (ii) at least about 0.01% of one or more secondary surfactants; and (iii) water; (c) at least about 0.05% of a galactomannan polymer derivative with a net positive charge and having a mannose to galactose ratio of greater than 2 : 1 on a monomer to monomer basis, wherein the galactomannan polymer derivative has: (i) a molecular weight from about 1,000 to about 10,000,000; and (ii) a cationic charge density from about 0.7 meq / g to about 7 meq / g; and (d) at least about 20% of an aqueous carrier; all by weight of the shampoo composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Hair conditioning composition containing a non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative
A hair conditioning composition comprising:a) from about 0.01 wt. % to about 10 wt. % of a non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative having a mannose to galactose ratio of greater than 2:1 on a monomer to monomer basis, said non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative selected from the group consisting of a cationic non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative and an amphoteric non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative having a net positive charge;i. wherein said non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative has a molecular weight from about 1,000 to about 10,000,000; andii. wherein said non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative has a cationic charge density from about 0.7 meq / g to about 7 meq / g;b) a conditioning agent selected from the group consisting of cationic surfactants, cationic polymers, nonvolatile silicones, nonvolatile hydrocarbons, saturated C14 to C22 straight chain fatty alcohols, nonvolatile hydrocarbon esters, and mixtures thereof; andc) wherein said hair conditioning composition is substantially free of an anionic surfactant.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Treatments using transgenic goat produced antithrombin III
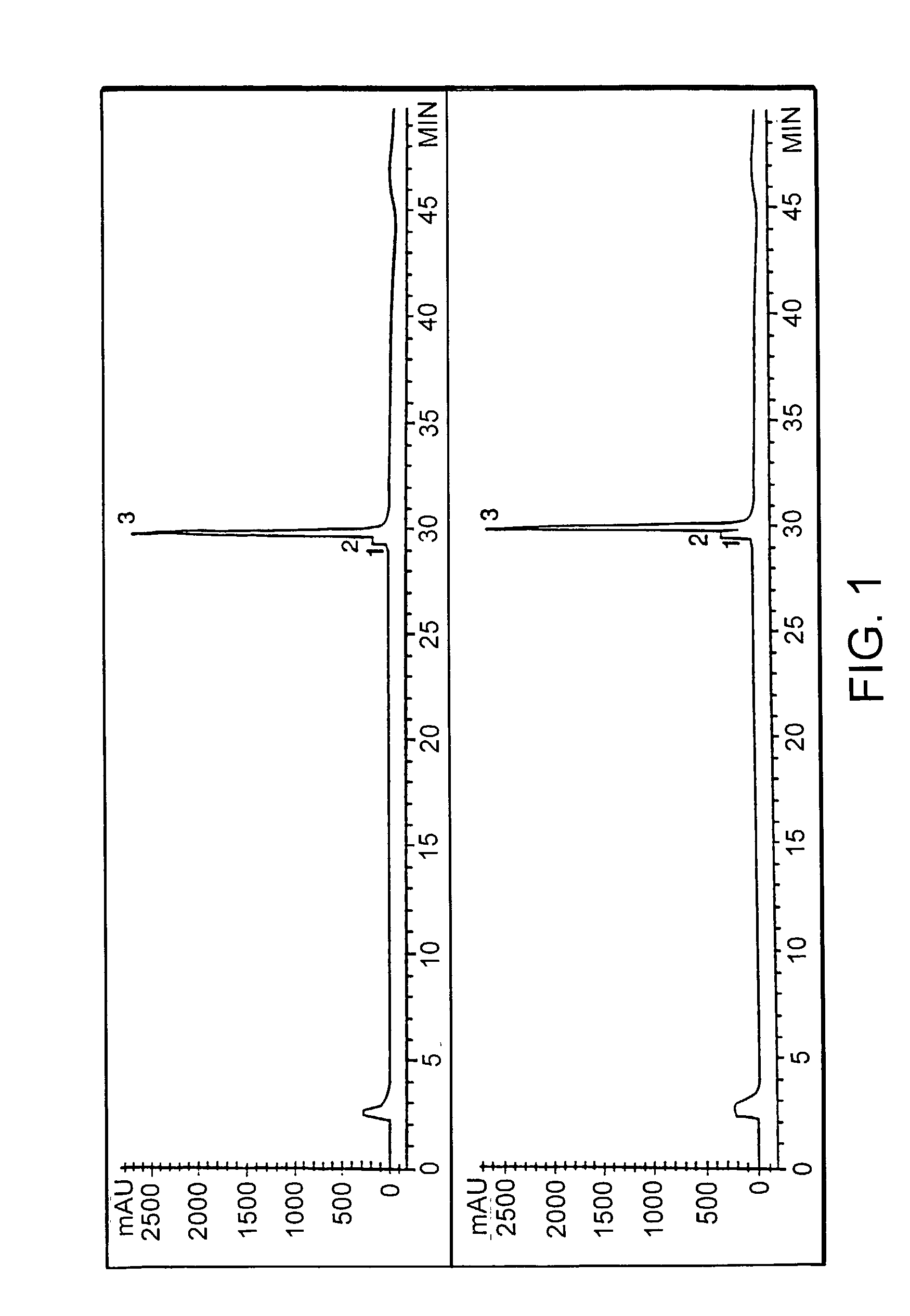
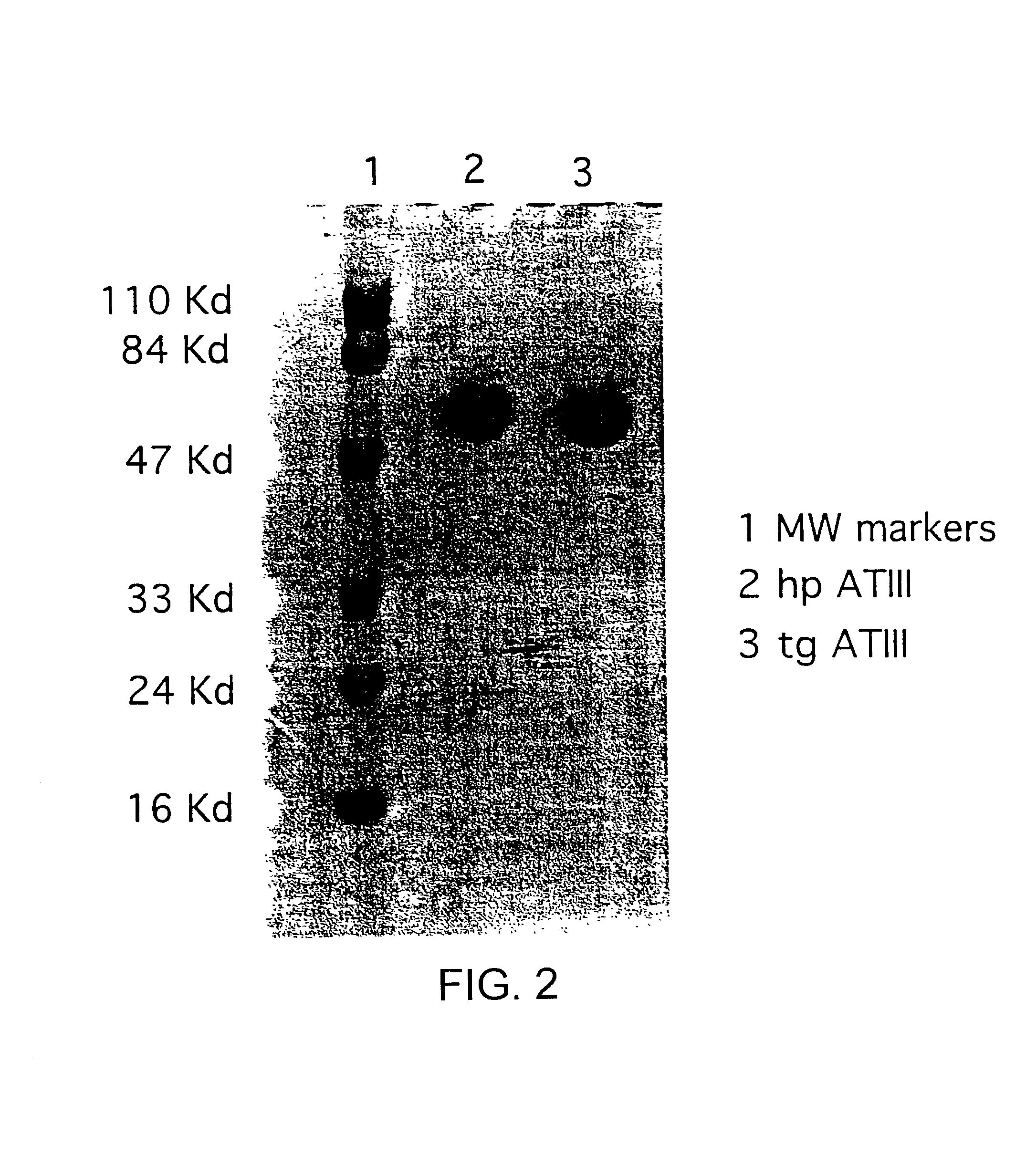
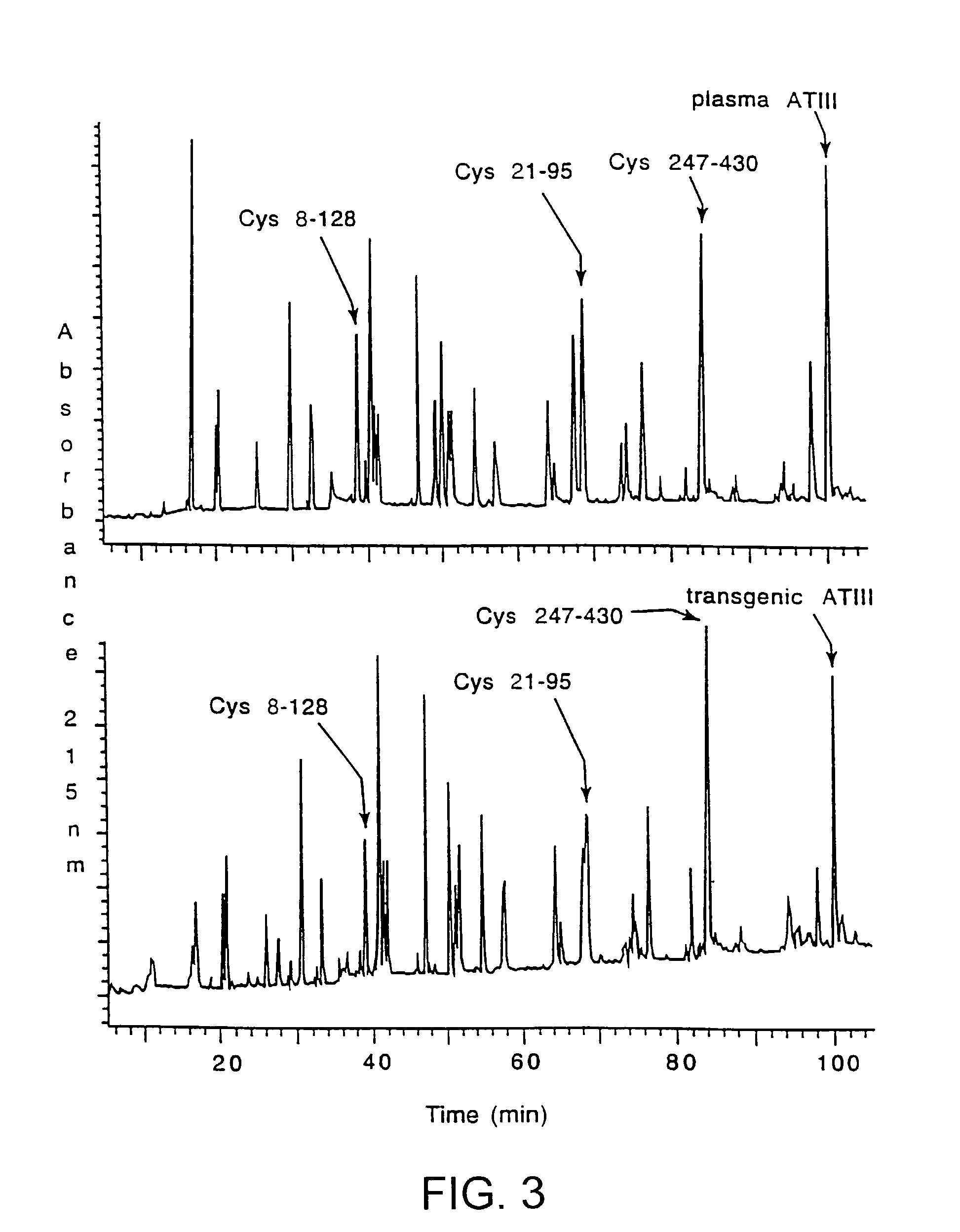
InactiveUS7019193B2Improve clearance ratePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPlasma derivedMonosaccharide composition
This invention relates to transgenically produced human Antithrombin III (tgATIII). The human ATIII produced by the transgenic process of the present invention has a monosaccharide composition which comprises N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) along with fucose, N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, mannose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid / N-glycolyneuraminic acid. The monosaccharide composition differs with that of plasma derived ATIII (phATIII). It has been found that tgATIII has an increased clearance rate when compared to phATIII.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Complex enzyme for feed
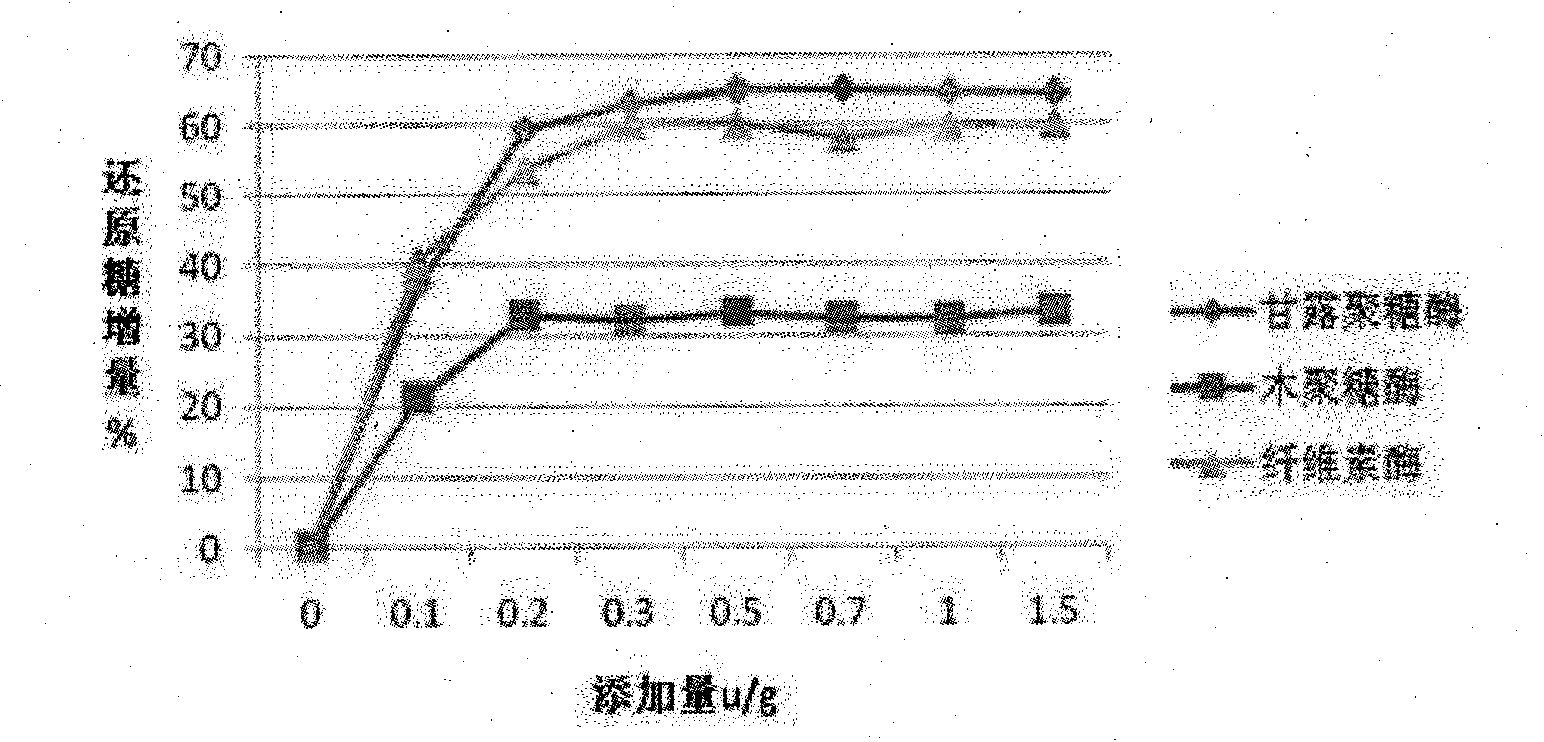
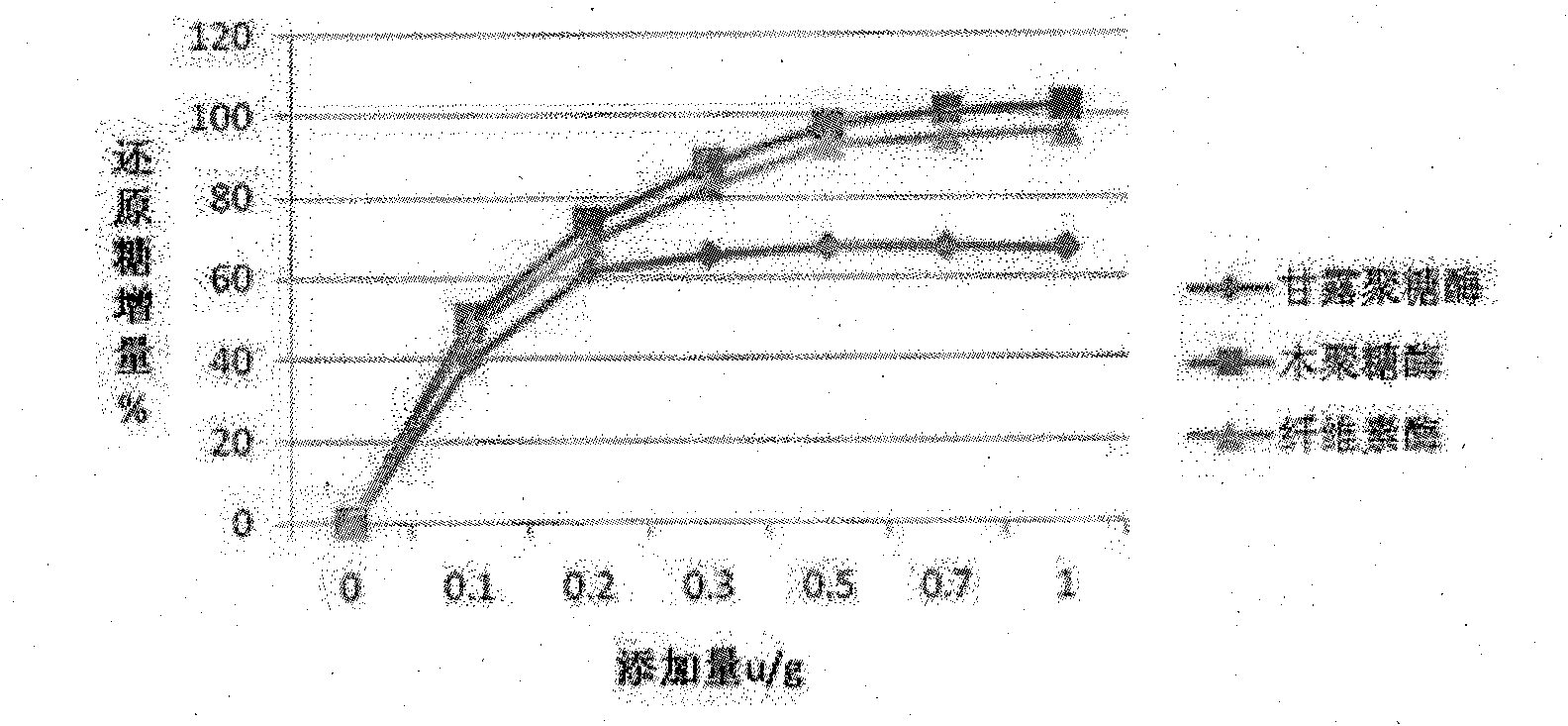
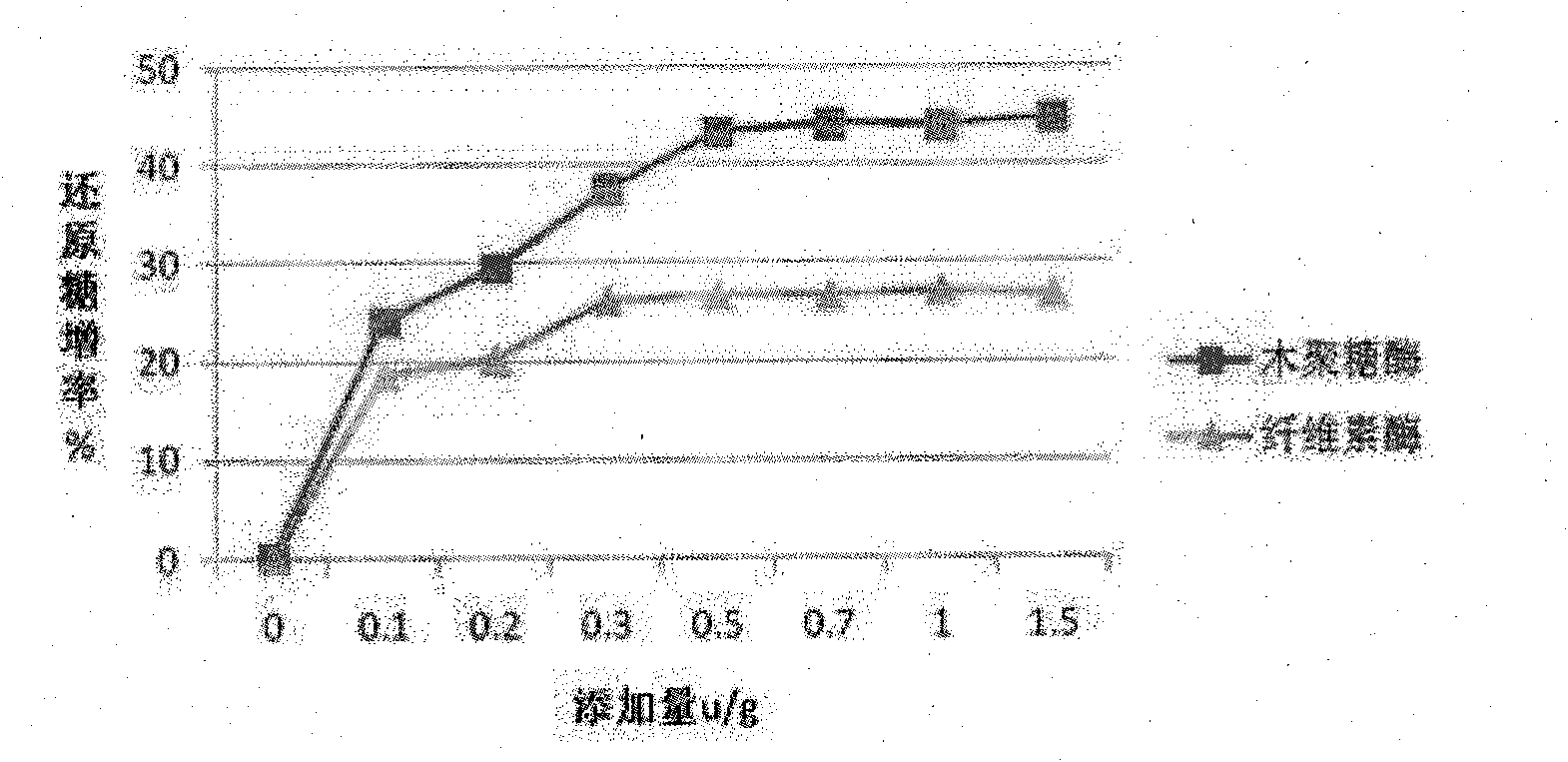
InactiveCN101874547AIncrease profitSolve the problem of uncertain addition amountAnimal feeding stuffCellulosePectinase
The invention belongs to the technical field of feed additives, and in particular relates to complex enzyme for a feed. The complex enzyme comprises 7,500 to 15,000U / g of xylanase, 1,000 to 3,000U / g of mannose, 50 to 80U / g of galactosidase, 200 to 700U / g of cellulose, 500 to 1,500U / g of beta-glucanase, 150 to 1,000U / g of alpha-amylase, 2,000 to 10,000U / g of protease and 100 to 200U / g of pectinase. By adding corresponding enzyme preparations, the anti-nutrition function of the complex enzyme is reduced, the feed utilization is improved, and the animal production efficiency is improved, so the problems that the utilization rate of animal feed raw materials is low and the animal production performance is inhibited are effectively solved; meanwhile, the complex enzyme has the advantages of reasonable raw material mixing, good effect, and low overall cost.
Owner:JINAN TIANTIANXIANG
Mannose-containing solution for lyophilization, transfection and/or injection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20150141498A1Positive effect on stabilization of the nucleic acid (sequence)High transfection efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoTransfection
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Recombinantly expressed insulin polypeptides and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides recombinantly expressed insulin polypeptides that comprise an N-linked glycan motif. The N-linked glycan motif is not present in wild-type insulins and enables the recombinant expression of glycosylated insulin polypeptides (e.g., in yeast cells). Based on results obtained with synthetic glycosylated insulin conjugates we predict that when these recombinant glycosylated insulin polypeptides are administered to a mammal, at least one pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic property of the glycosylated insulin polypeptide will be sensitive to serum concentrations of glucose (or an exogenous saccharide such as alpha-methyl mannose). Exemplary insulin polypeptides, polynucleotides encoding these insulin polypeptides, glycosylated insulin polypeptides, pharmaceutical formulations and sustained release formulations are provided in addition to methods of use and preparation.
Owner:SMARTCELLS
A Method of Producing an Economical and Ecologically Sound Natural Immunobiotic Extract for Use as a Health Management Instrument and a Replacement for Growth Promotion Antibiotics in Livestock and Companion Animals.
InactiveUS20050020490A1Cheap productionImprove immunityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSurvivabilityAntibiotic Y
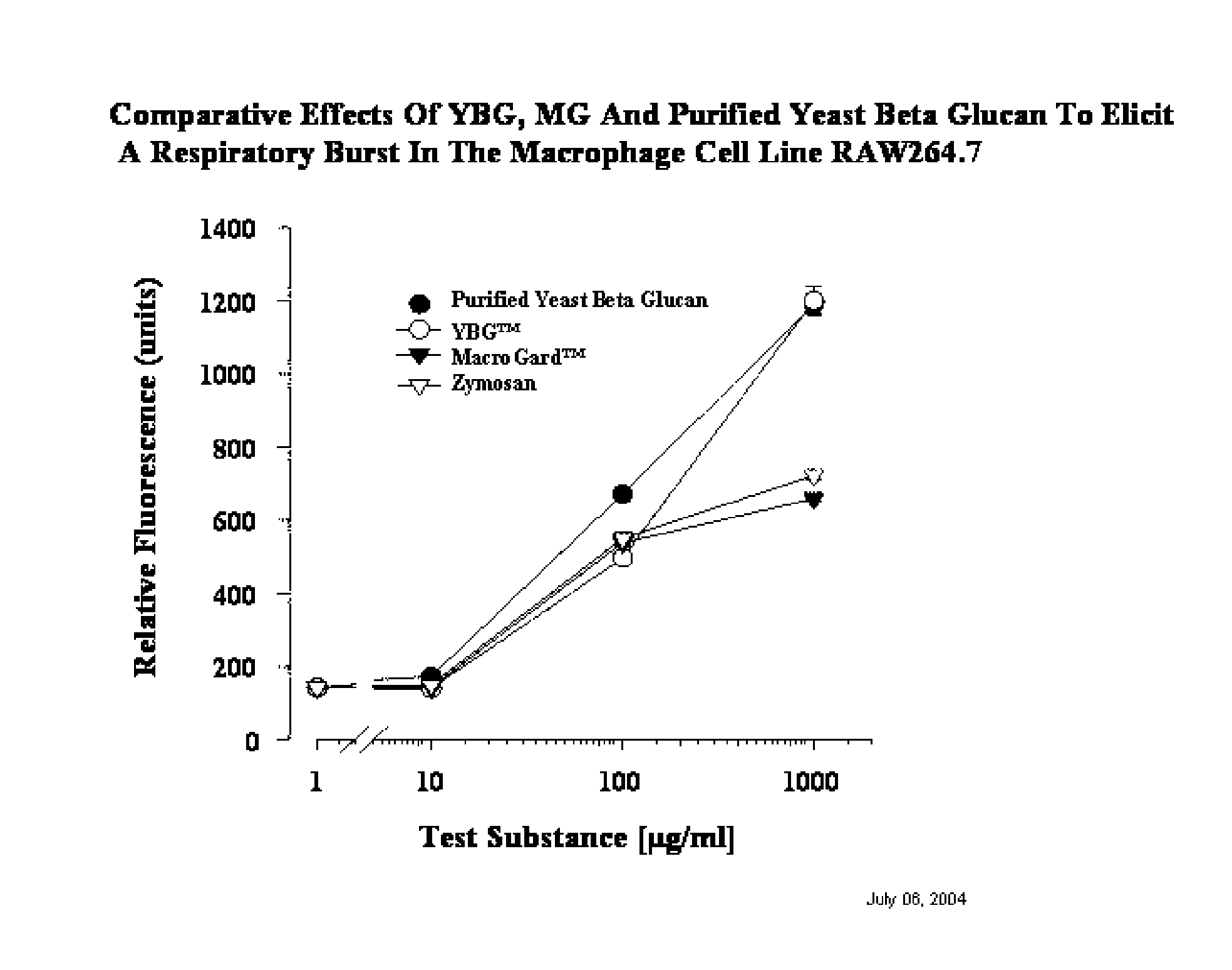
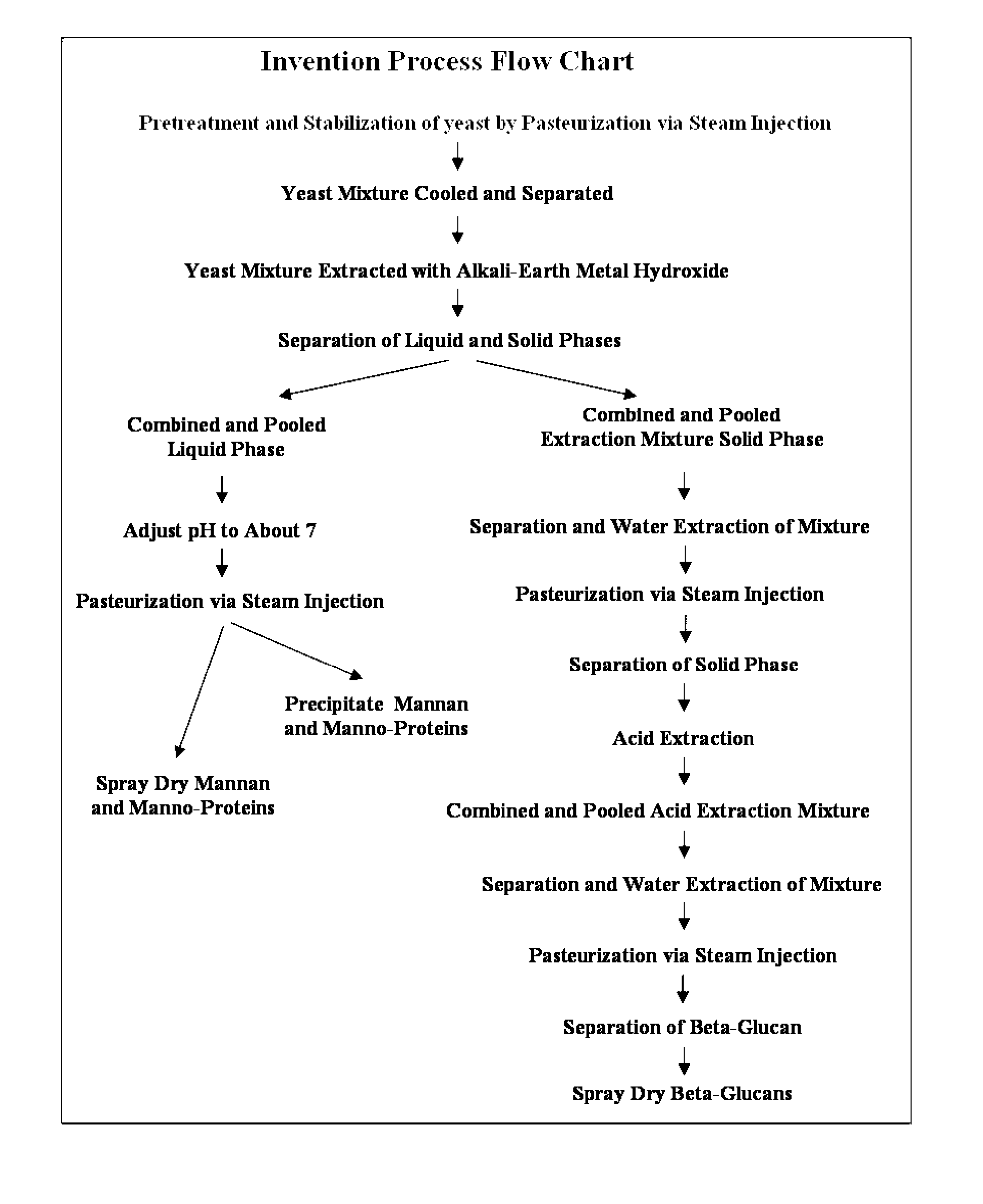
The present invention provides an improved and more efficient method for the purification of Beta glucan, mannan and manno-protein complexes or immuno-potentiating substances, directly from yeast. In addition, the present invention provides methods for the production of Beta glucan, mannan and manno-proteins for use in animal feed to (1) prepare and enhance the immune system to fight infections more effectively and efficiently, (2) increase resistance to and decrease duration of bacterial and viral infections, (3) allow producers to reduce or remove “growth promotion antibiotics” in feed systems, thus producing more naturally grown animals, (4) reduce or prevent the negative growth response normally associated with administration of live vaccines to animals and (4) other associated health benefits such as in the case of swine of increased piglet litter size and survivability for piglets after weaning when Sows fed this novel Beta glucan extract.
Owner:PROGRESSIVE BIOACTIVES
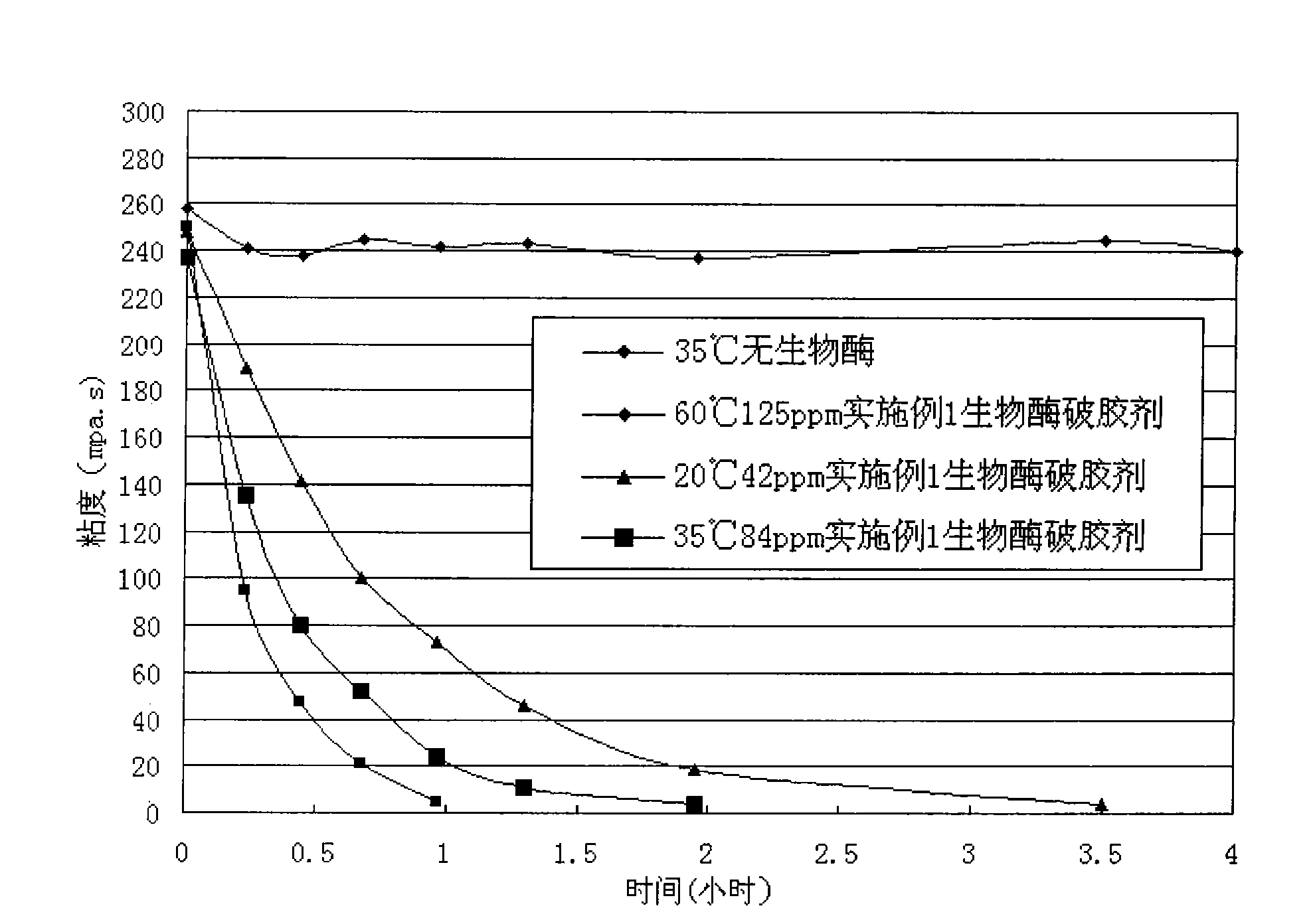
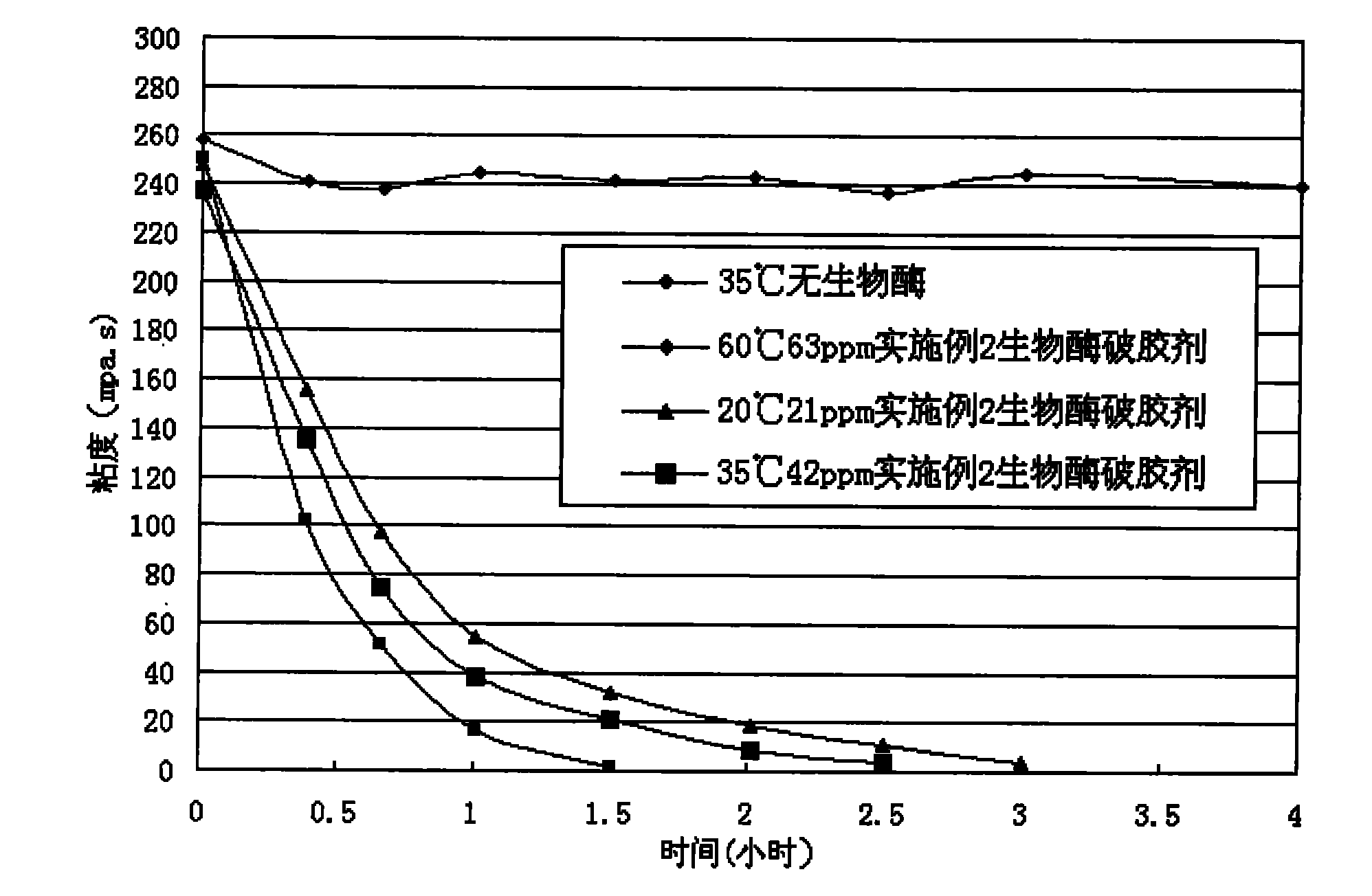
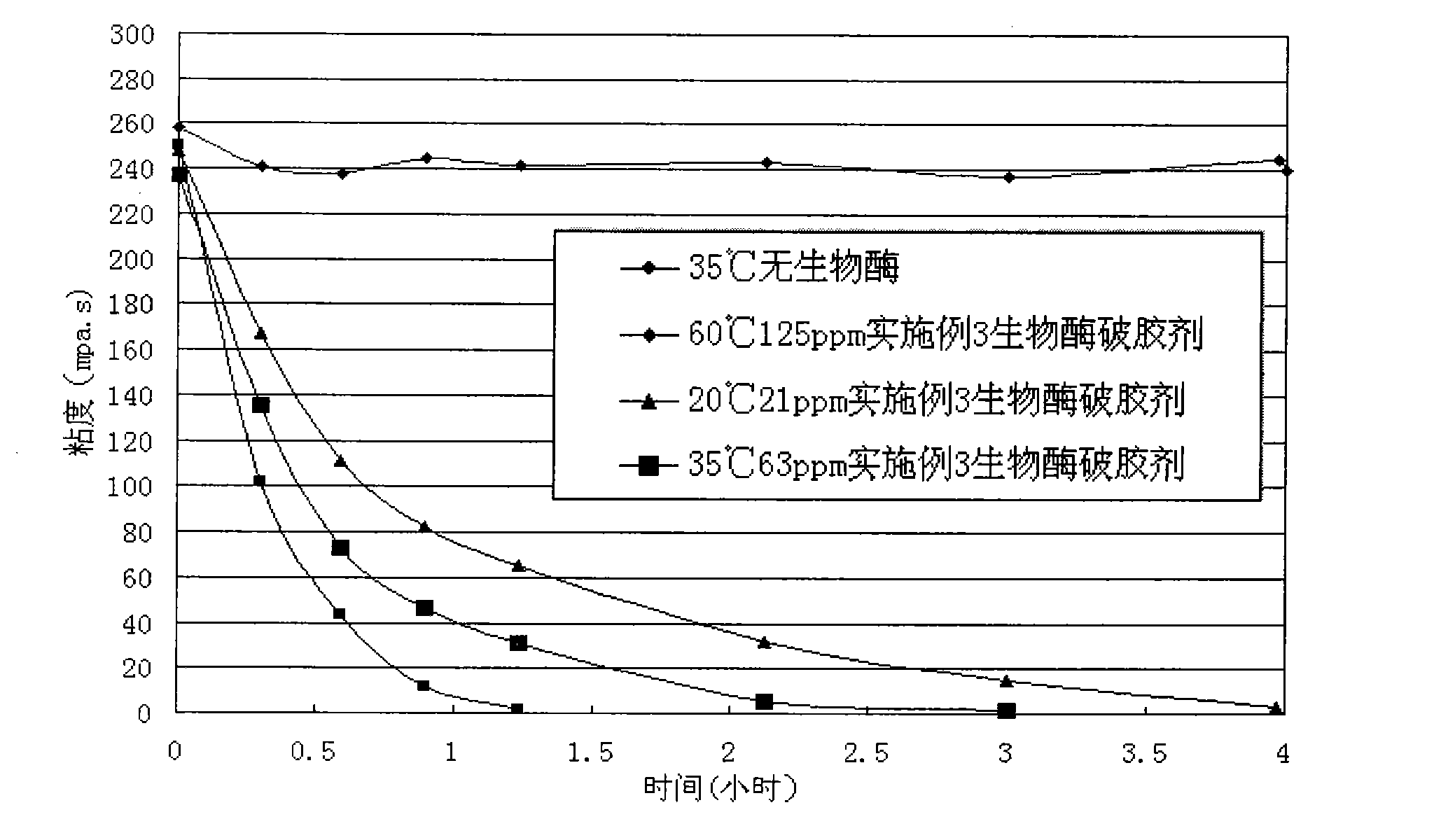
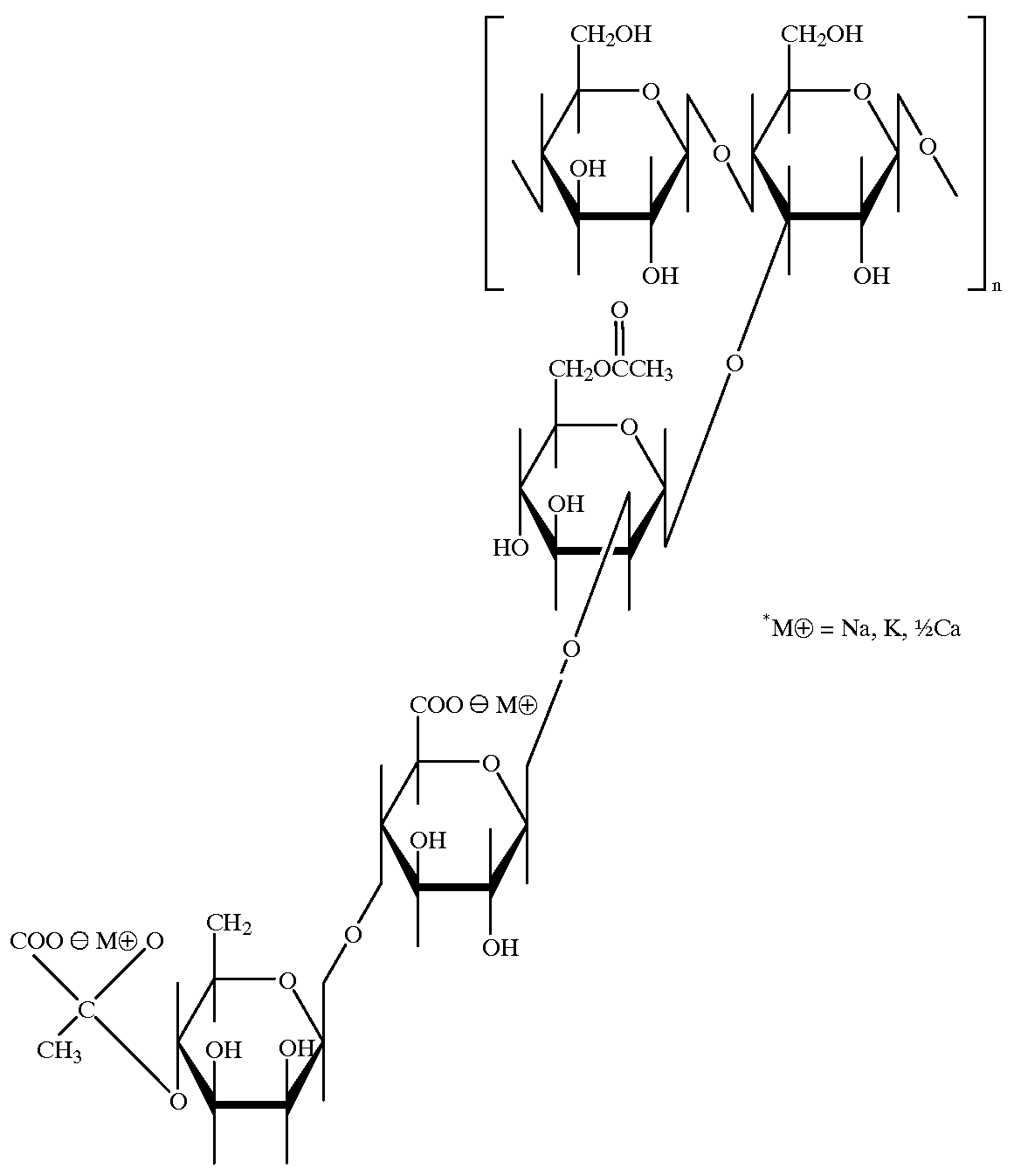
Bio-enzyme gel breaker and technique for water-based guargum fracturing gel breaking with the same
InactiveCN101781552AImprove performanceEasy to storeFluid removalDrilling compositionWater basedPectinase
The invention relates to bio-enzyme gel breaker, in particular to formula and technique for gel breaking of water-based guargum fracturing fluid by using the bio-enzyme gel breaker. The bio-enzyme gel breaker contains the following components in percentage by weight: 10-50% of beta- mannose, 0-20% of cellulose, 0-10% of pectinase, 0-15% of glucanase, 0-10% of xanthase, 3-10% of (NH4)2SO4, 2-5% of NaCl, 1.5-5% of ZnCL2 and 0-60% of persulfate. The fracturing fluid gel breaking technique comprises the following steps: dissolving the bio-enzyme gel breaker in borax crosslinked fluid; mixing and blending the crosslinked fluid and the guargum base fluid, crosslinking, forming jelly, and then mixing with proppant, pressing the mixture into the oil-water well until the mixture enters the fractured crack. In this way, the fracturing process is finished. The bio-enzyme gel breaker degrades the macromolecular guargum in the stratum fracturing fluid into small micromolecular sugar, and when the jelly breaks up, the proppant is left underground, the fracturing gel breaking fluid flows back, and in this way, the construction can be completed. The bio-enzyme gel breaker has good gel breaking performance, the construction process is reasonable, the viscosity of the fracturing fluid can not decrease too early, the gel of the fracturing fluid can be broken evenly and thoroughly with little residue and small harm to the stratum, and the operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:RES INST OF SHAANXI YANCHANG PETROLEUM GRP
Composition and method for reducing the colonization of animal intestines by salmonella and other bacterial pathogens
InactiveUS6126961AReducing human pathogen colonizationSafe and economical reductionBiocideAnimal feeding stuffIntestinal structureBacteroides
An animal feed composition for reducing colonization of animal intestines by Salmonella and other bacterial pathogens, includes a polysaccharide containing cis-hydroxy sugar units or a derivative thereof, or the monosaccharide ribose or rhamnose, or a derivative thereof, and an animal feed. The polysaccharide cis-hydroxy sugar units may be one or more of mannose, a mannose derivative, galactose, a galactose derivative, galactomannans, galactosamine, fucose and arabinose. The polysaccharides may be incorporated into an animal feed in the form of a food gum or other biolpolymer.
Owner:AURUM CERTUS
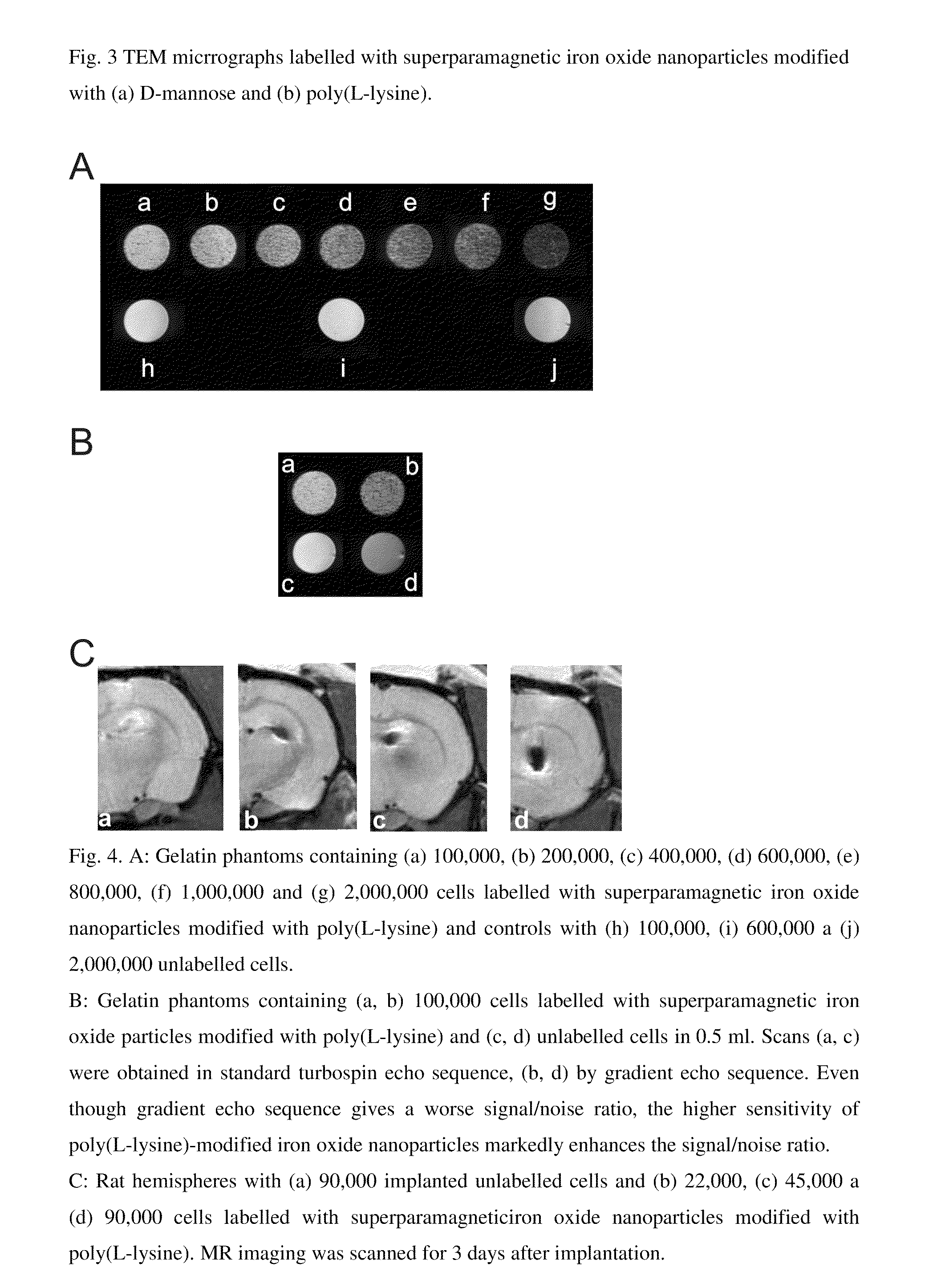
Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Based on Iron Oxides with Modified Surface, Method of Their Preparation and Application
InactiveUS20090309597A1Less loadImprove abilitiesPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyArginineDextran
The subject of the invention is superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes based on iron oxides, to advantage magnetite or maghemite, with modified surface, coated with mono-, di- or polysaccharides from the group including D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextrans and dextrins, or with amino acids or poly(amino acid)s from the group including alanine, glycine, glutamine, asparagine, histidine, arginine, L-lysine, aspartic and glutamic acid or with synthetic polymers based on (meth)acrylic acid and their derivatives selected from the group containing poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-dimethylmethacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylmethacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide), which form a colloid consisting of particles with narrow distribution with polydispersity index smaller than 1.3, the average size of which amounts to 0.5-30 nm, to advantage 1-10 nm, the iron content is 70-99.9 wt. %, to advantage 90 wt. %, the modification agent content 0.1-30 wt. %, to advantage 10 wt. %.The particles of size smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 can be obtained by a modified method of preparation.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention are prepared by pre-precipitation of colloidal Fe(OH)3 by the treatment of aqueous 0.1-0.2M solution of Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl3, with less than an equimolar amount of NH4OH, at 21° C., under sonication, to which a solution of a Fe(II) salt, to advantage FeCl2, is added in the mole ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2 under sonication and the mixture is poured into five- to tenfold, to advantage eightfold, molar excess of 0.5M NH4OH. The mixture is left aging for 0-30 min, to advantage 15 min, and then the precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, magnetically separated and washed with deionized water. Then 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.1 M aqueous solution of sodium citrate is added and then, dropwise, 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.7 M aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite. The precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, washed with deionized water under the formation of colloidal maghemite to which, after dilution, is added dropwise, to advantage under 5-min sonication, an aqueous solution of a modification agent, in the weight ratio modification agent / iron oxide=0.1-10, to advantage 0.2 for amino acids and poly(amino acid)s and 5 for saccharides.The particles smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 are prepared by mixing at 21° C. 1 volume part of 10-60 wt. %, to advantage 50 wt. %, of an aqueous solution of a saccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide, such as D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextran and dextrins, and 1 volume part of aqueous solution of a Fe(II) and Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl2 and FeCl3, where the molar ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2. A 5-15%, to advantage 7.5%, solution of NH4OH is added until pH 12 is attained and the mixture is heated at 60° C. for 15 min. The mixture is then sonicated at 350 W for 5 min and then washed for 24 h by dialysis in water using a membrane with molecular weight cut-off 14,000 until pH 7 is reached. The volume of solution is reduced by evaporation so that the final dry matter content is 50-100 mg / ml, to advantage 80 mg per 1 ml.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention can be used for labelling cells used in magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring their movement, localization, survival and differentiation especially in detection of pathologies with cell dysfunction and of tissue regeneration and also for labelling and monitoring cells administered for cell therapy purposes, in particular embryonal stem cells, fetal stem cells, stem cells of an adult human including bone marrow stem cells, olfactory glial cells, fat tissue cells, in the recipient organism by magnetic resonance.The preparation of labelled cells proceeds by adding to the complete culture medium 5-20 μl, to advantage 10 μl, of a colloid containing 0.05-45 mg iron oxide per ml, to advantage 1-5 mg iron oxide per ml of the medium, and culturing the cells for a period of 1-7 days, to advantage for 1-3 days, at 37° C. and 5% of CO2.
Owner:INST OF MACROMOLECULAR CHEM ASCR V V I +1
Enteromorpha polysaccharide having immunocompetence and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102399297AImprove immune activityPromote proliferationAntinoxious agentsImmunological disordersCholesterolFiltration
The invention discloses an enteromorpha polysaccharide having immunocompetence and a preparation method thereof. The enteromorpha polysaccharide having immunocompetence is a polysaccharide HT-II. The enteromorpha polysaccharide having immunocompetence is a white floccule, can be well dissolved in water and dimethyl sulfoxide, has relative molecular weight of 96kDa, and mainly comprises glucose and mannose, wherein a ratio of rhamnoside to xylose to mannoside to glucose is 36: 20: 6: 38. The preparation method comprises the following steps of breaking down, carrying out extraction at a temperature of 90 DEG C by water, filtrating, merging the extract, concentrating, carrying out precipitation by ethanol, removing proteins, carrying out separation and purification, and carrying out freeze drying to obtain the purified enteromorpha polysaccharide having immunocompetence. The preparation method is simple, has stable performances, a low cost and a large medical value, can reduce cholesterol content and can improve immunity. The preparation method adopts extraction, protein removal and purification processes, and scientific experimental means, is a novel method for controlling enteromorpha, and provides a novel approach for controlling enteromorpha. The preparation method of the enteromorpha polysaccharide having immunocompetence develops enteromorpha medical values and purposes, controls environmental pollution, reduces a clean-up cost, improves economic benefits and is an ideal special preparation technology for enteromorpha control and integrated utilization.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
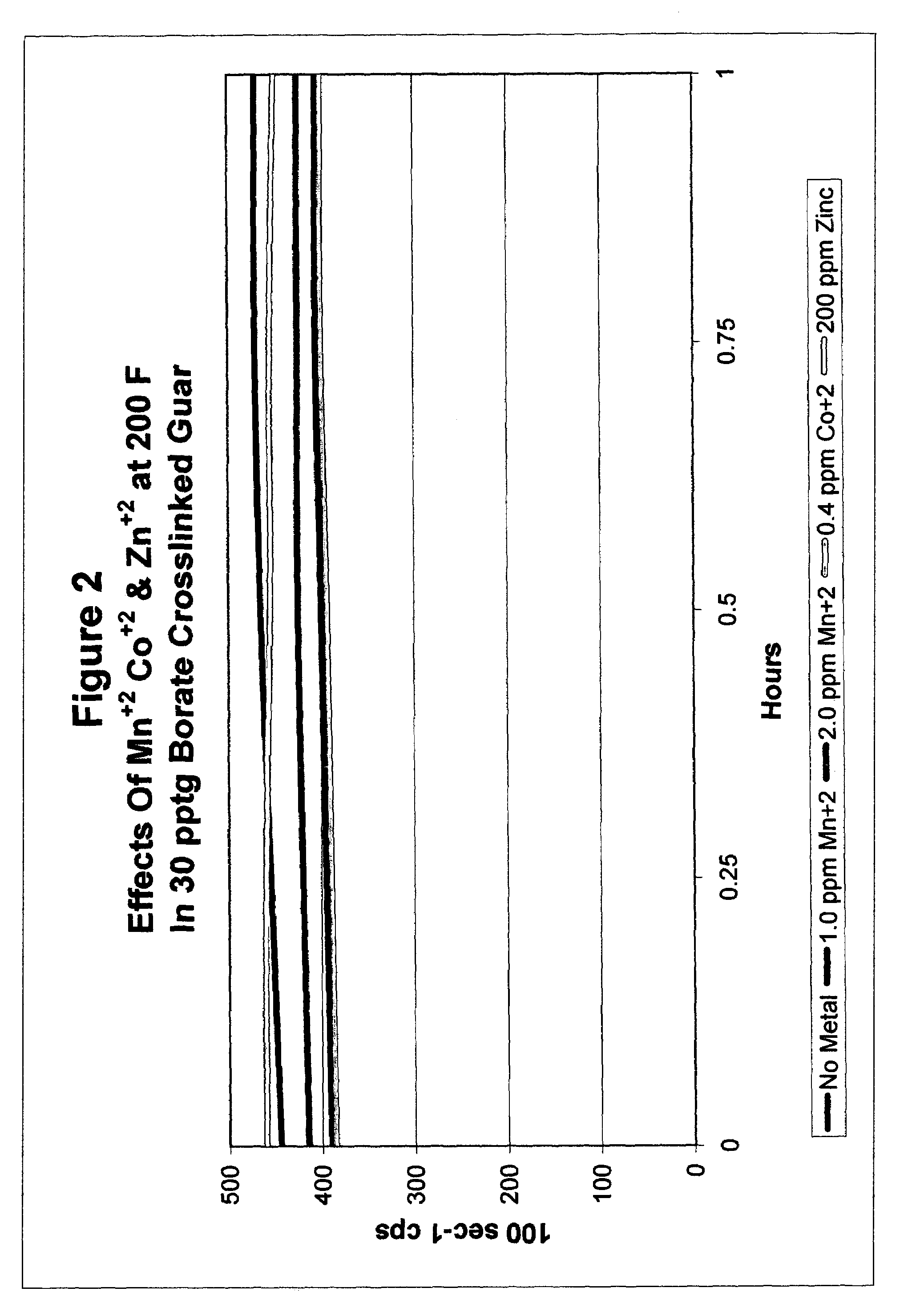
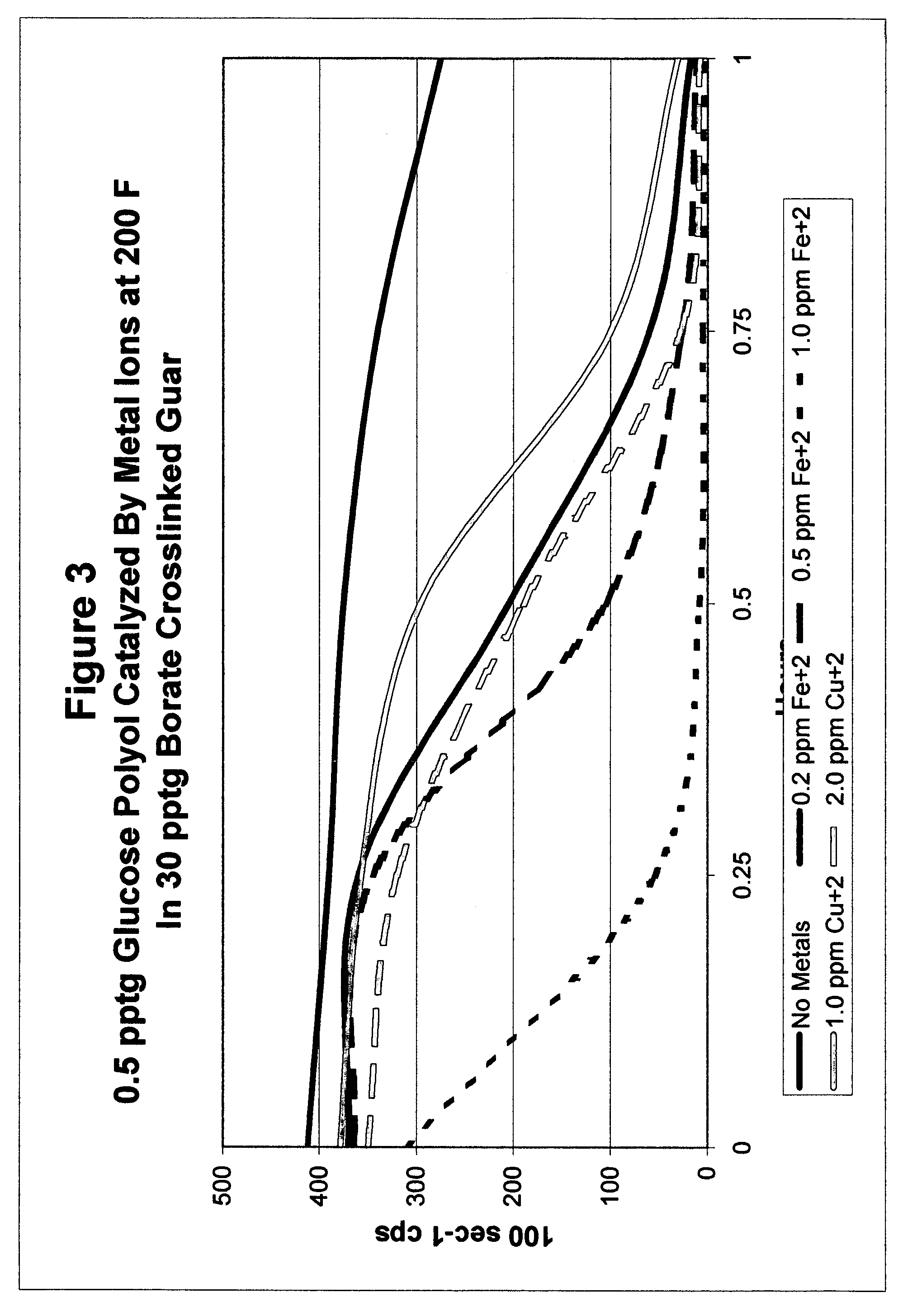
Catalyzed polyol gel breaker compositions
InactiveUS7084093B2Easy to cleanSugar derivativesOther chemical processesFracturing fluidAlcohol sugars
It has been discovered that fracturing fluid breaker mechanisms are improved by the inclusion of a catalyzed polyol alone that directly degrades the polysaccharide backbone, and optionally additionally by removing the crosslinking ion, if present. That is, viscosity reduction (breaking) occurs by breaking down the chemical bonds within the backbone directly. The gel does not have to be crosslinked for the method of the invention to be successful, although it may be crosslinked. In one non-limiting embodiment, the polyol has at least two hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbon atoms. In another embodiment, the polyols are simple sugars and sugar alcohols, and may include mannitol, sorbitol, glucose, fructose, galactose, mannose, lactose, maltose, allose, etc. and mixtures thereof. The catalyzing metal ion may employ a metal selected from Groups VIB, VIIB, VIII, IB, and IIB of the Periodic Table (previous IUPAC American Group notation).
Owner:SUPERIOR ENERGY SERVICES LLC
Preparing method and application of human mesenchymal stem cell-sourced exosome beautifying preparation
InactiveCN108721200APrecise regulation of immune statusRepair the traces of timeCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCuticleFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparing method and application of a human mesenchymal stem cell-sourced exosome beautifying preparation. The beautifying preparation comprises 92-108 parts of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome, 8-13 parts of mannitol, 0.42-0.55 part of oligopeptide-32, 1.3-2.5 parts of tetrapeptide-4, 0.7-1.3 parts of palmitoyl tripeptide-1 and 0.8-1.2 parts of palmitoyl pentapeptide-4. The preparation method includes: evenly mixing and stirring the human mesenchymal stem cell exosome, the mannitol, the oligopeptide-32, the tetrapeptide-4, the palmitoyl tripeptide-1and the palmitoyl pentapeptide-4 according to the weight, filtering through a filter membrane, performing split charging, and performing freeze drying to obtain the human mesenchymal stem cell-sourced exosome beautifying preparation. The exosome beautifying preparation can be externally applied to the epidermal layer or guided into an epidermis deep layer and the corium layer through a microneedle, a rolling needle or a hydro-lifting needle. The ImmuReg technology is utilized to bring the optimal repairing effect of freeze-dried powder into play, the skin immune state can be precisely adjusted, and accordingly aged cells can be removed, and skin cells can be rejuvenated.
Owner:成都赛伊泰生物科技有限公司
Natural deodorant composition
The present invention relates to a natural deodorant system and a natural system for topical and systemic delivery of active ingredients, both systems being primarily free of, preferably substantially free of, more preferably essentially free of, and most preferably completely free of ethoxylates or other petrochemical derivatives, and comprising: (a) at least one of (1) glycerine (preferably of plant origin), (2) a polyol selected from the group consisting of galactitol, erythritol, inositol, ribitol, dithioerythritol, dithiothreitol, (3) a sugar alcohol, selected from the group consisting of mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol and maltitol, (4) a hydrogenated starch hydrosylates of at least one of berries, apples or plums, and (5) mixtures thereof; (b) water or a lower monohydric alcohol, selected from the group of methanol, ethanol, propanol and isoproponal, or mixtures thereof, present at a combined concentration of at least 20%; (c) one or more carrageenans (preferably of plant origin) or alginates, or mixtures thereof, present in combined concentrations of less than about 2%; and (d) optionally, one or more thickeners or gums selected from the group consisting of tara, guar, xanthan, Arabic, tragacanth, agar, locust bean gum, ghatti and microcrystalline celluloses.
Owner:TERRA FA NATUALS
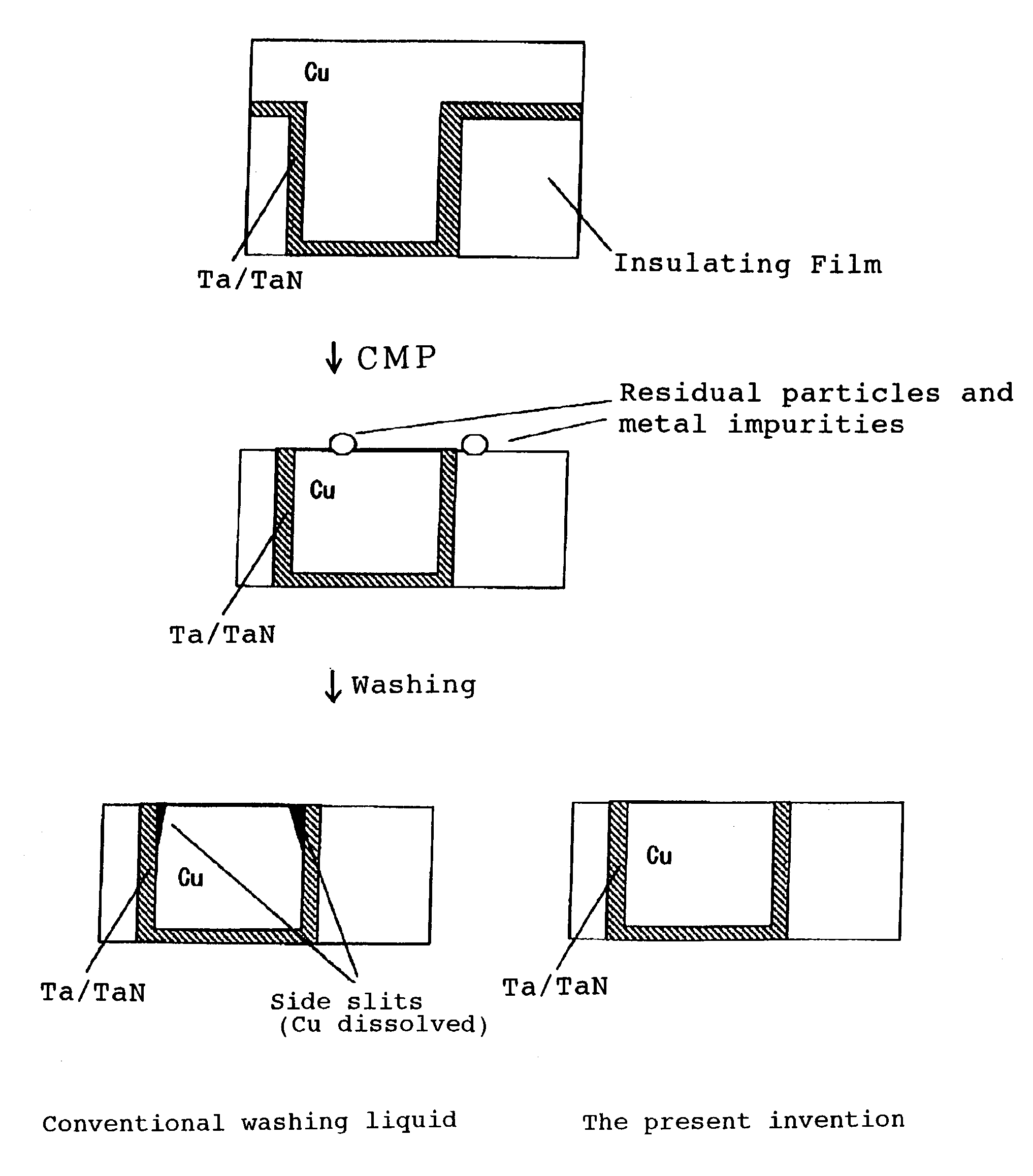
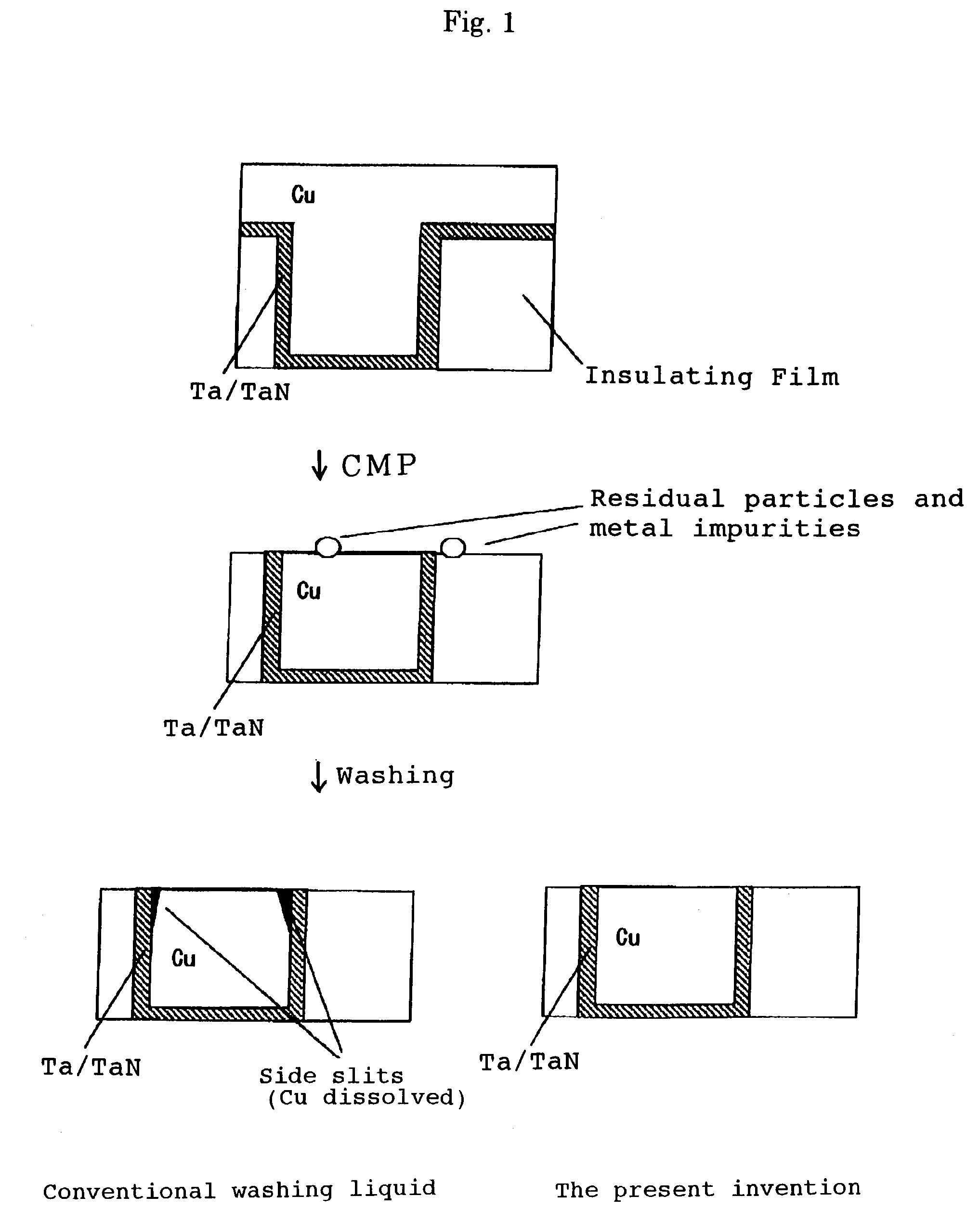
Post-CMP washing liquid composition
InactiveUS7087562B2Improve performanceNot corrodeSurface-active detergent compositionsDetergent mixture composition preparationGlyoxylic acidFructose
A post-CMP washing liquid composition is provided which includes one type or two or more types of aliphatic polycarboxylic acids and one type or two or more types selected from the group consisting of glyoxylic acid, ascorbic acid, glucose, fructose, lactose, and mannose, and which has a pH of less than 3.0. This washing liquid has excellent performance in removing micro particles and metal impurities adhering to the surface of a semiconductor substrate after CMP and does not corrode a metal wiring material.
Owner:KANTO CHEM CO INC +1
Shampoo containing a gel network and a non-guar galactomannan polymer derivative
Shampoo compositions comprise (a) from about 5% to about 50% of one or more detersive surfactants; (b) a dispersed gel network phase comprising: (i) at least about 0.05% of one or more fatty amphiphiles; (ii) at least about 0.01% of one or more secondary surfactants; and (iii) water; (c) at least about 0.05% of a galactomannan polymer derivative with a net positive charge and having a mannose to galactose ratio of greater than 2:1 on a monomer to monomer basis, wherein the galactomannan polymer derivative has: (i) a molecular weight from about 1,000 to about 10,000,000; and (ii) a cationic charge density from about 0.7 meq / g to about 7 meq / g; and (d) at least about 20% of an aqueous carrier; all by weight of the shampoo composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Fucosan sulphate, preparation method thereof, and application of fucosan sulphate in preparing anti-influenza virus medicine
The invention belongs to the field of marine medicines, and relates to a fucosan sulphate, a preparation method thereof and application of the fucosan sulphate in preparing an anti-influenza virus medicine. Polysaccharide with a main chain taking alpha-1,2-D-mannose and beta-1,4-D-glucuronic acid as repetitive units, and with a branched chain of alpha-1,3-L-fucosan sulphate is obtained by virtue of hot-water extraction, calcium chloride precipitation and DEAE-Cellulose chromatographic column purification. The fucosan sulphate prepared by the invention is high in inhibition effect on the influenza virus neuraminidase activities of A H1N1, H5N1 and H3N2, and obvious in protection effect on the dog kidney epithelial cells infected by A H1N1. The fucosan sulphate provided by the invention has the advantages of being rich in raw material source, simple in preparation process, easy to industrialize, high in product water solubility, high in stability, free from toxic and side effects, and the like, and has the prospect of being developed to the anti-influenza virus medicine.
Owner:威海人生药业有限公司
Industrial fermentation ramee rapid extraction technique for Erwinia
ActiveCN101235357AReduce technical difficultyImprove activation process parametersBacteriaMutant preparationAnimal ForagingHigh pressure
The invention discloses a technique for rapidly extracting ramie hemp erwinia bacterium factory production fermentation, the technique comprises preprocessing material, immersing or sprinkling and inoculating, immersing or fermenting, deactivating with hot water, and the procedure of circulation washing, water dressing and fiber finish, erwinia bacterium which has broad-spectrum and high effective to degumming, pulping and saccharifying of herb fiber material, and bacterial agent preparation and activated technical parameter. The erwinia bacterium addicts the mannose, the peak for secreting non-cellulose to degrade key enzyme (pectic enzyme, beta-mannase and xylanase) can be achieved through purely culturing for 7h to 9h. Bacterial agent is inoculated on herb fiber material such as ramie and the like for activating the bacterial agent for 5h-6h, fermentation forage fodder turns to blue after fermenting for 5h-6h, pectine, hemicellulose and partial lignin which are partially degraded and associated in fiber cell are stripped, non-cellulose residues which are absorbed on fiber can be removed by means of the flushing of high-pressure flushing, and the purpose of extracting net fiber can be reached.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide
ActiveCN105061617AHigh purityThe preparation method is fineMetabolism disorderGlucose degradationPrecipitation
The invention discloses an extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD). The process includes: water extraction and alcohol precipitation, protein removal by a Sevage reagent, dialysis, passing of a column with DEAE cellulose as the filler and other steps, thus obtaining finer polysaccharide (PGPSD). The PGPSD can be dissolved in water at room temperature, and is formed by connection of arabinose, mannose and galactose through a glycosidic bond. The peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD) prepared by the process provided by the invention can reinforce the expression of insulin related transcription factors and glucose degradation key enzyme, has no toxicity to mice, and can significantly lower the blood glucose of diabetic mice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cationic liposome and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102973506AImprove targetingImprove immune efficiencyPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigenLipid formation
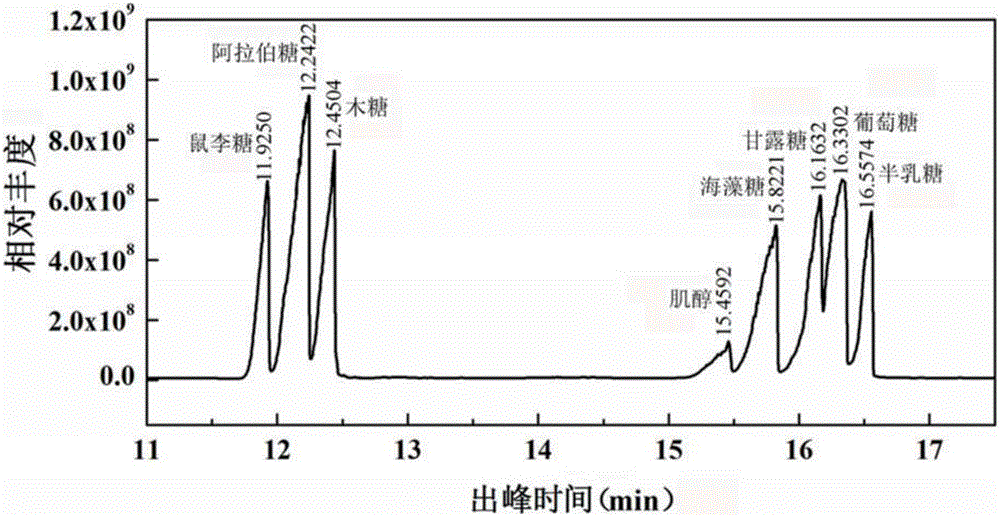
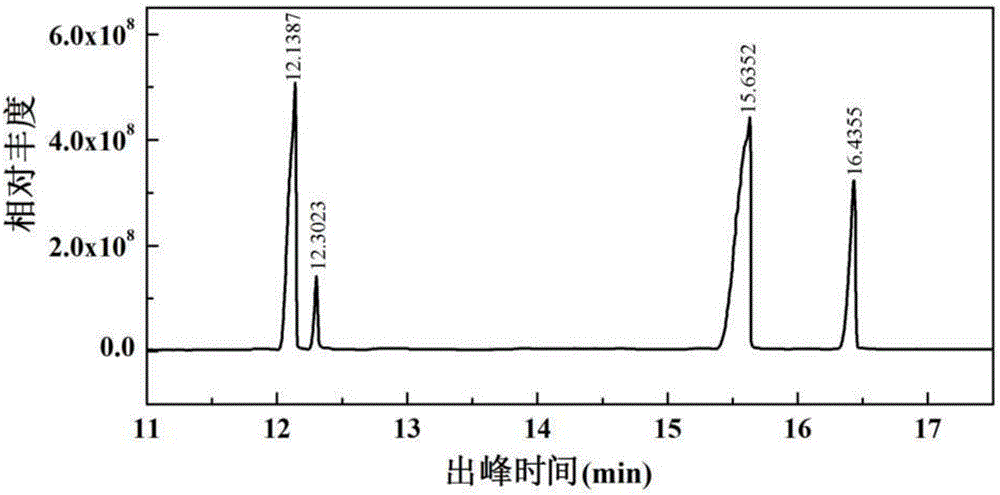
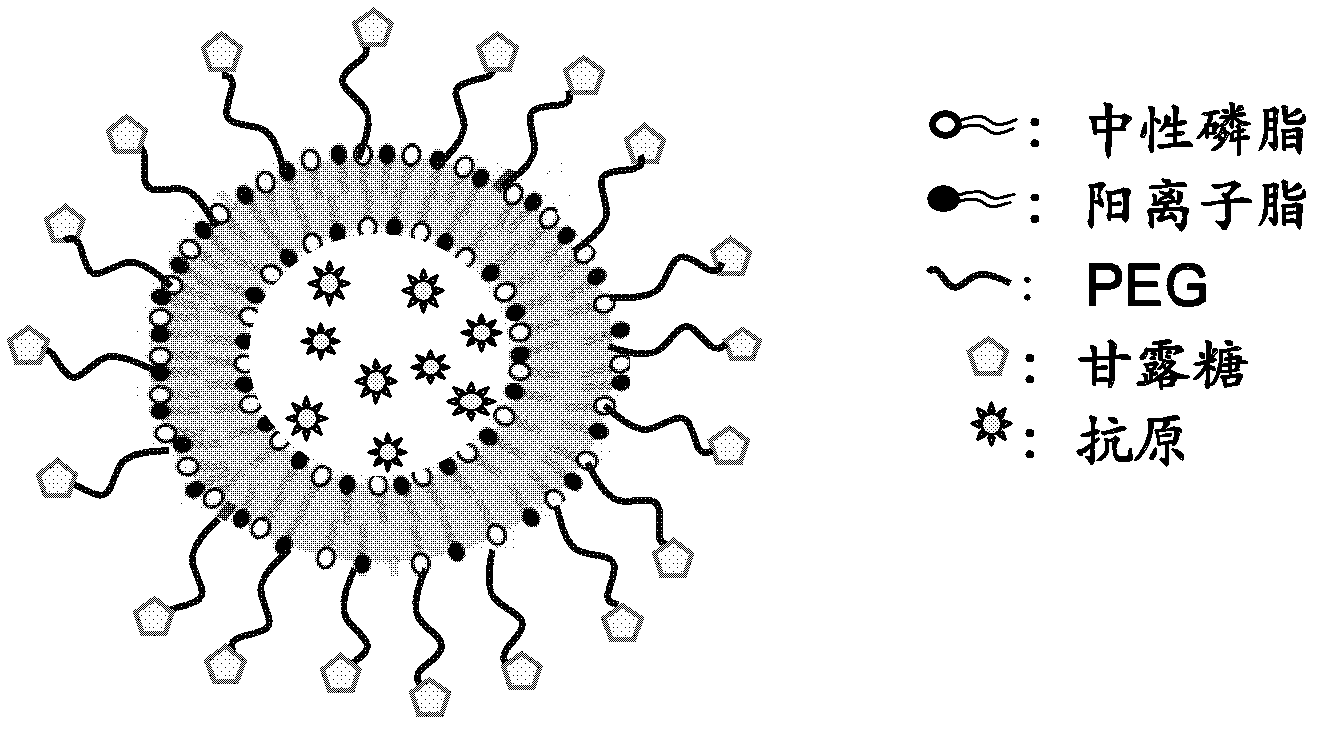
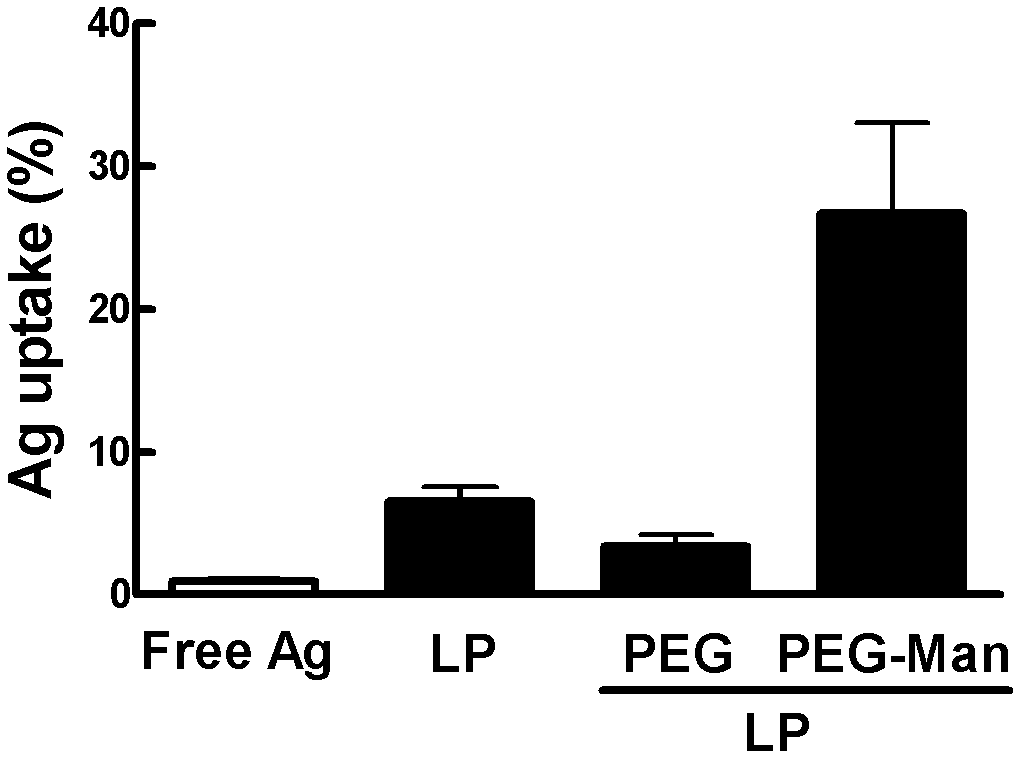
The invention discloses a cationic liposome, comprising cationic lipid, neutral phospholipid, polyethylene glycol derivatived phospholipid and mannose or mannan oligosaccharide, wherein a shell-shaped phospholipid bilayer is formed by phospholipid molecules in the the cationic lipid, the neutral phospholipid and the polyethylene glycol derivatived phospholipid; and mannose- or mannan oligosaccharide- modified polyethylene glycol derivatived phospholipid is formed by connecting the mannose or the mannan oligosaccharide with one end of the polyethylene glycol derivatived phospholipid. By adding the mannose- or mannan oligosaccharide- modified polyethylene glycol derivatived phospholipid, targeting property and enrichment in lymph glands of antigen-presenting cells are increased; the cationic liposome has an immunologic enhancement effect; and the immune efficacy of liposome-encapsulated vaccines can be increased. The invention also provides a preparation method of the cationic liposome.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composition for prevention or treatment of urinary tract infection
InactiveUS20090175843A1Prevent and reduce and eliminate symptomIncreased fluid intakeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsUpper urinary tract infectionMammal
Compositions particularly suitable for preventing or treating urinary tract infections in mammals, especially in humans, comprising a combination of components, the composition comprising an effective amount of: (A) cranberry concentrate, cranberry extract or both; (B) D-mannose; and at least one component selected from the group consisting of: (C) ascorbic acid; (D) bromelain; and (E) inulin. The compositions are preferably in the form of a liquid concentrate such as a beverage drink.
Owner:MEDICAL NUTRITION USA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com