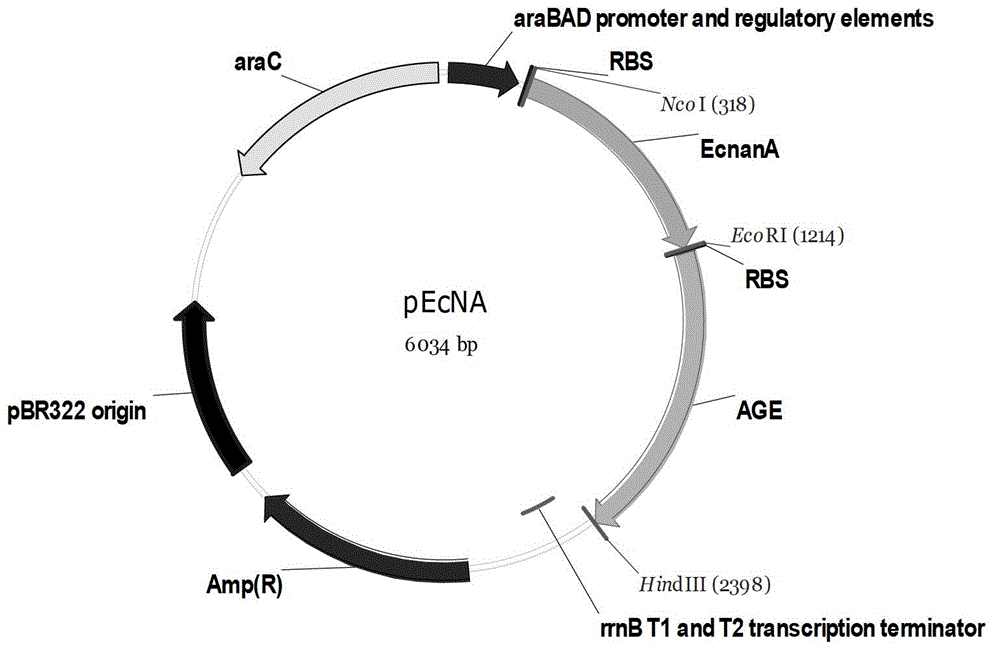
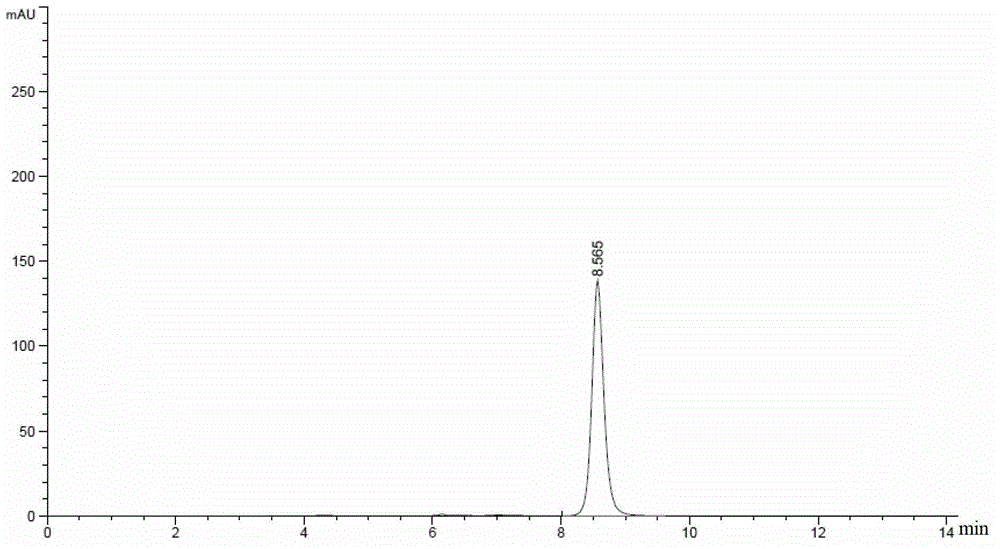
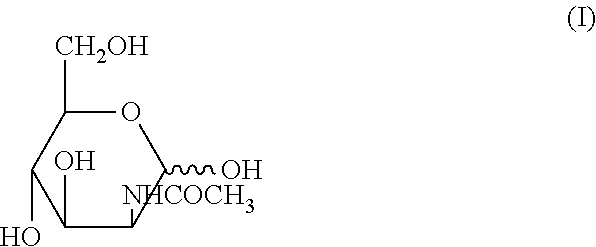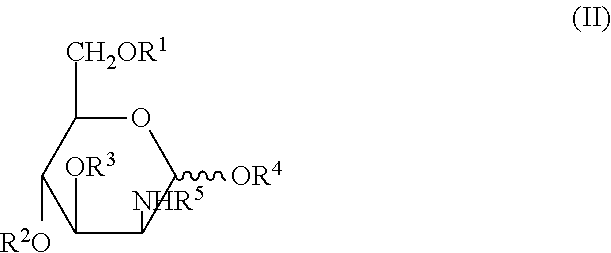Patents
Literature
268 results about "Acetylglucosamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
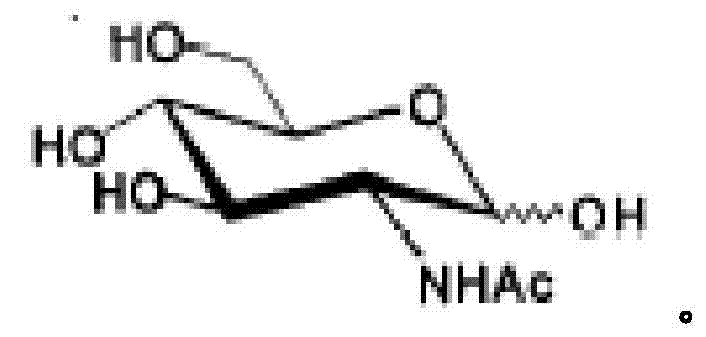
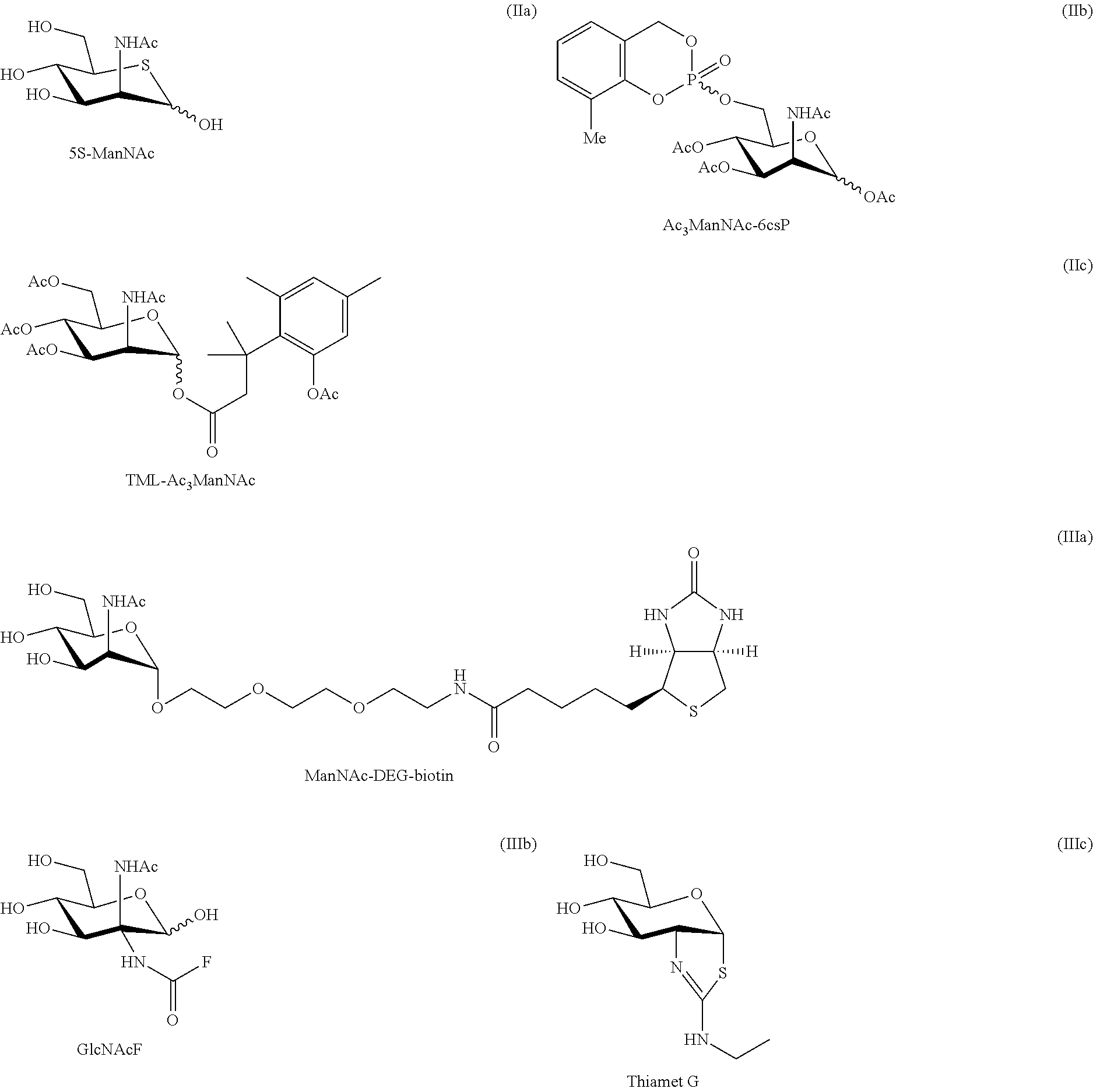
The N-acetyl derivative of glucosamine.
Fused Protein Composition
InactiveUS20080241884A1Strong cytotoxicityReduce in quantityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFucoseDrug
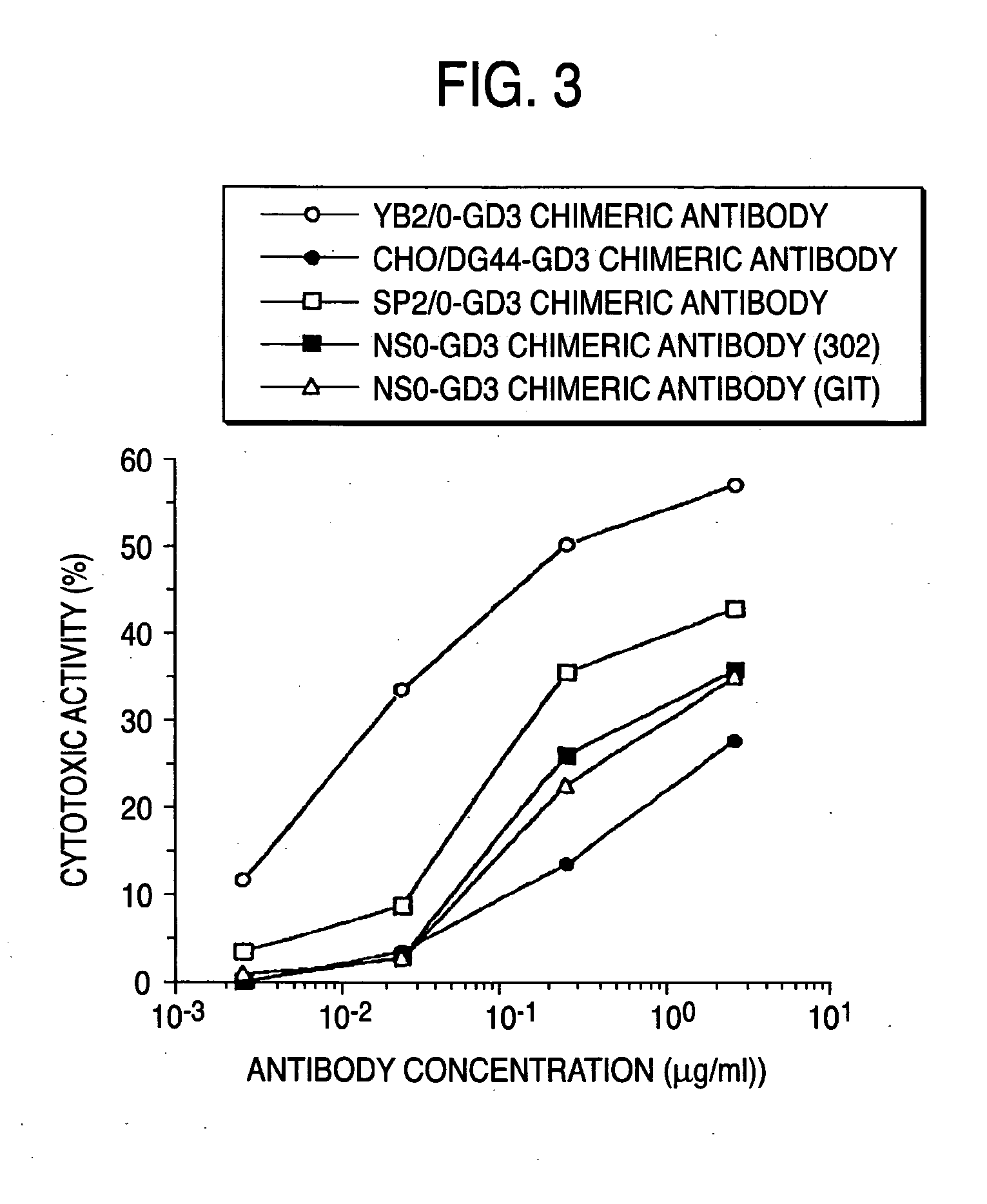
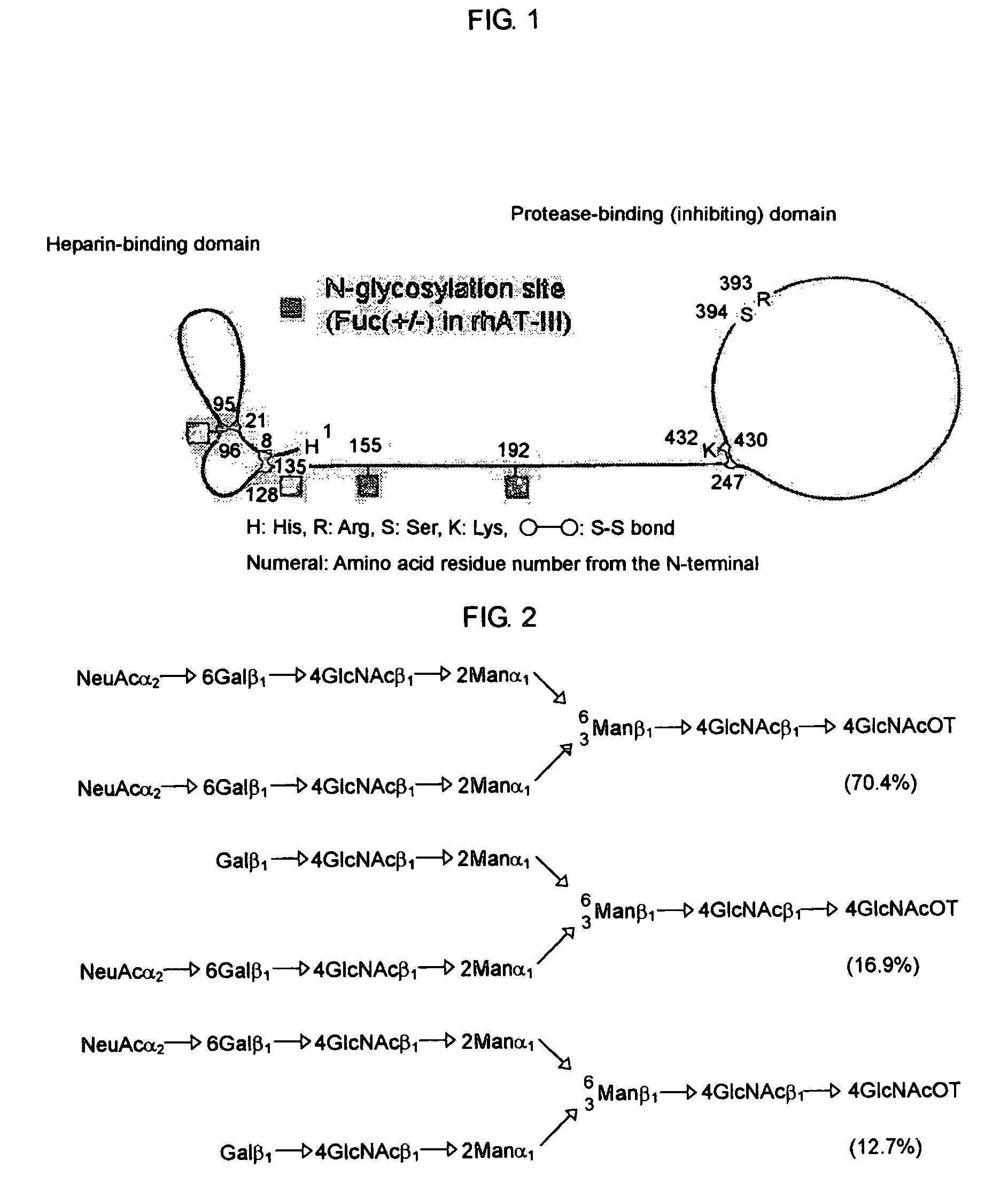
A fusion protein composition of an antibody Fc region which is useful as a medicament in which effector function is improved is desired.The present invention provides a fusion protein composition comprising a fusion protein molecule of an antibody Fc region having complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chains in the Fc region, wherein the complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chains have a structure in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chains; a transformant producing the fusion protein composition; a process for producing the fusion protein composition; and a medicament comprising the fusion protein composition.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Method of enhancing of binding activity of antibody composition to Fcgamma receptor IIIa
A method for enhancing a binding activity of an antibody composition to Fcgamma receptor IIIa, which comprises modifying a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain which is bound to the Fc region of an antibody molecule; a method for enhancing an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity of an antibody composition; a process for producing an antibody composition having an enhanced binding activity to Fcgamma receptor IIIa; a method for detecting the ratio of a sugar chain in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chain among total complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chains bound to the Fc region in an antibody composition; an Fc fusion protein composition produced by using a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through alpha-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain; and a process for producing the same.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Process for producing antibody composition by using rna inhibiting the function of alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase
InactiveUS20070134759A1High effector functionHighly functionalFungiSugar derivativesGlycosideAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention provides a process for producing an antibody composition using a cell, which comprises using a cell into which an RNA having activity of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to the modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chain is introduced; the RNA used in the production process; a DNA corresponding to the RNA; a cell in which the RNA or DNA is introduced or expressed; a process for producing the cell; and a method for suppressing the enzyme.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Antibody composition-containing medicament
A medicament for treating a patient who cannot be cured with a medicament comprising as an active ingredient an antibody composition produced by a cell unresistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, which comprises as an active ingredient an antibody composition produced by a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, and a method for screening the patient by using the medicament.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
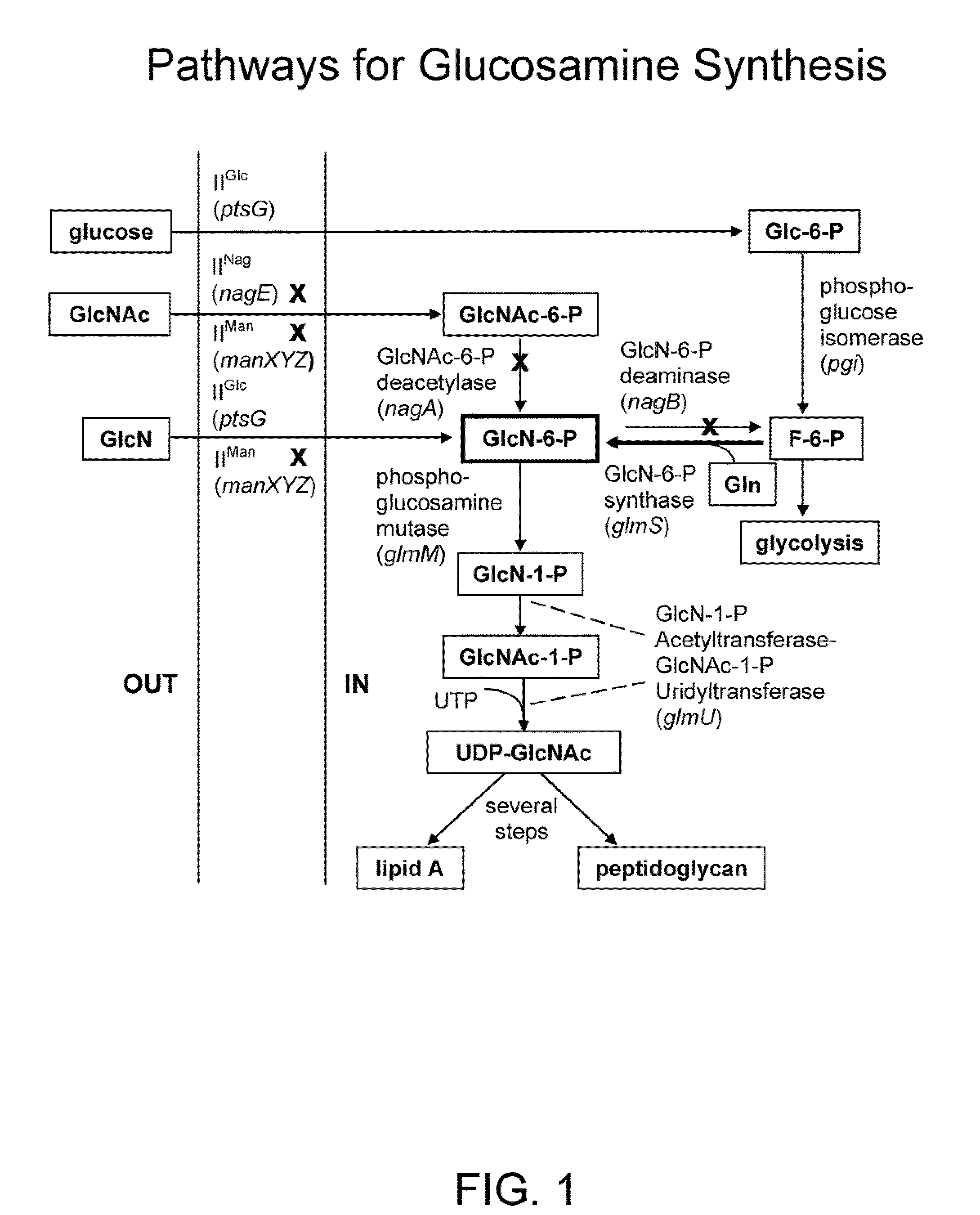
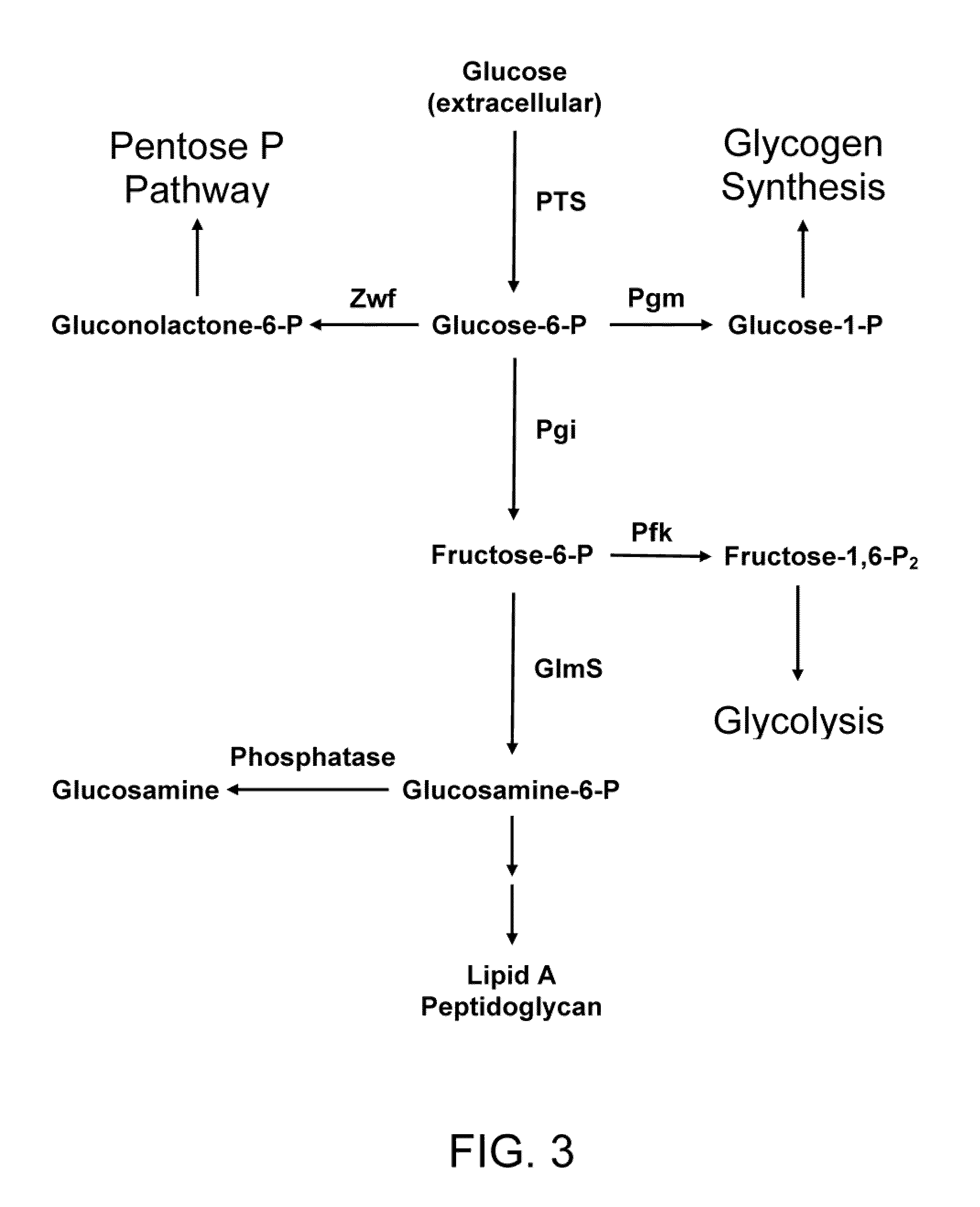
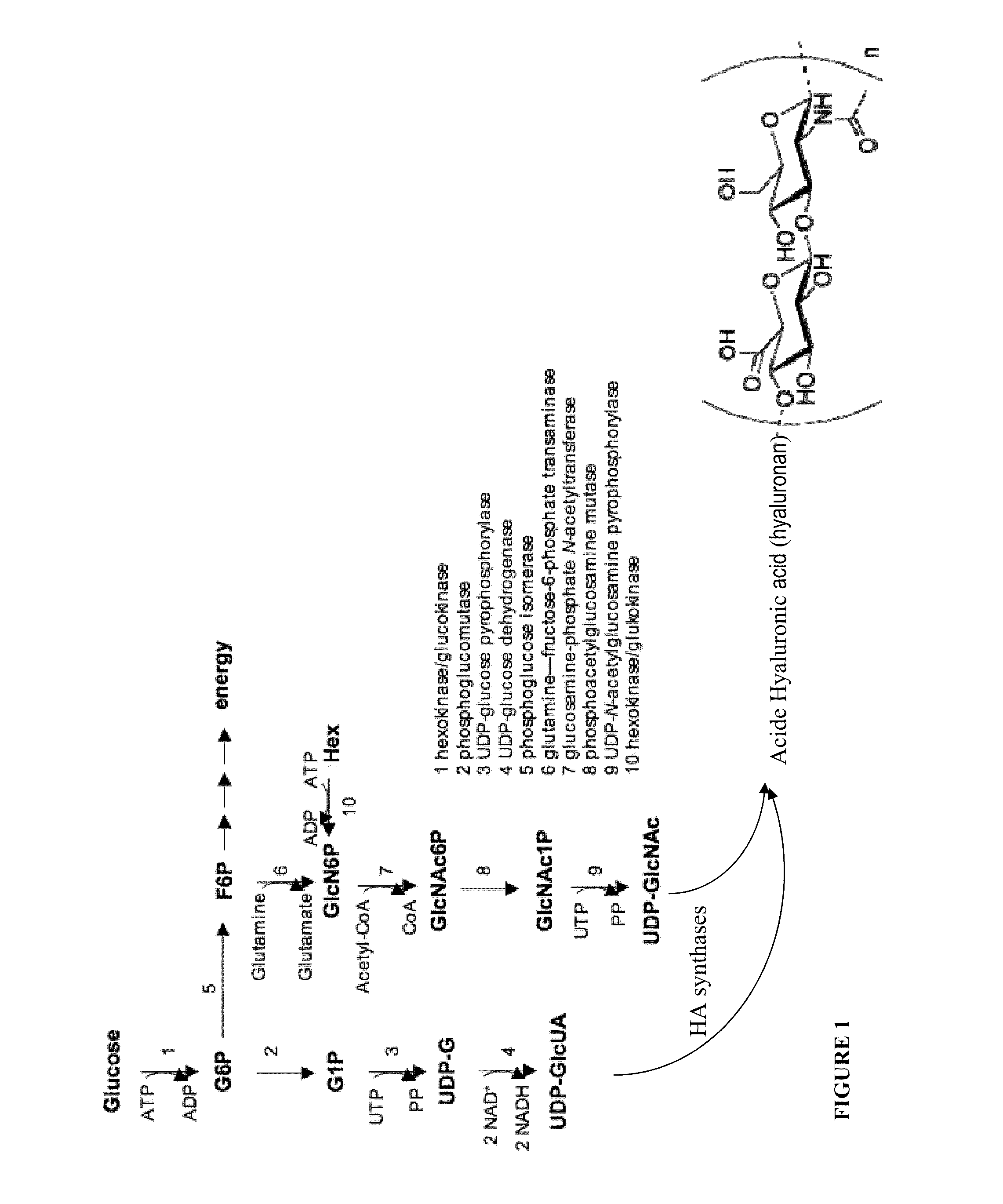
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine
InactiveCN104293724AImprove fermentation yieldImprove stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine. The genetically engineered bacteria are prepared by the following steps: integrating chromosome deficiency nag DCABE gene clusters of Escherichia coli, respectively connecting 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes and N-acetylglucosamine transferase genes which are respectively mediated by a T7 promoter and a Trc promoter with a gene expression cassette in series, wherein the 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes are obtained by mutating wild 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase genes from an Escherichia coli W3110 strain source into A38T / R249C / G471S mutants. The genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the invention have the advantages of high N-acetylglucosamine fermentation yield and high strain stability and have wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES & DEV CENT OF INDAL BIOTECH +1
Separation of oligosaccharides from fermentation broth
The invention relates to a method for obtaining an N-acetylglucosamine containing neutral oligosaccharide from a fermentation broth, wherein said oligosaccharide is produced by culturing a genetically modified microorganism capable of producing said oligosaccharide from an internalized carbohydrate precursor, comprising the steps of: i) ultrafiltration (UF), preferably to separate biomass from the broth, ii) nanofiltration (NF), preferably to concentrate said oligosaccharide in the broth and / or reduce an inorganic salt content of the broth, and iii) treating the broth with an ion exchange resin, preferably to remove charged materials, and / or subjecting the broth to chromatography, preferably to remove hydrophobic impurities.
Owner:GLYCOM AS
Method of Enhancing of Binding Activity of Antibody Composition to FcGamma Receptor IIIa
A method for enhancing a binding activity of an antibody composition to Fcγ receptor IIIa, which comprises modifying a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain which is bound to the Fc region of an antibody molecule; a method for enhancing an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity of an antibody composition; a process for producing an antibody composition having an enhanced binding activity to Fcγ receptor IIIa; a method for detecting the ratio of a sugar chain in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chain among total complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chains bound to the Fc region in an antibody composition; an Fc fusion protein composition produced by using a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain; and a process for producing the same.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Detection of haematopoietic stem cells and progeny and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050003460A1Lasting effectInhibit expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisN-AcetylglucosamineDisaccharide
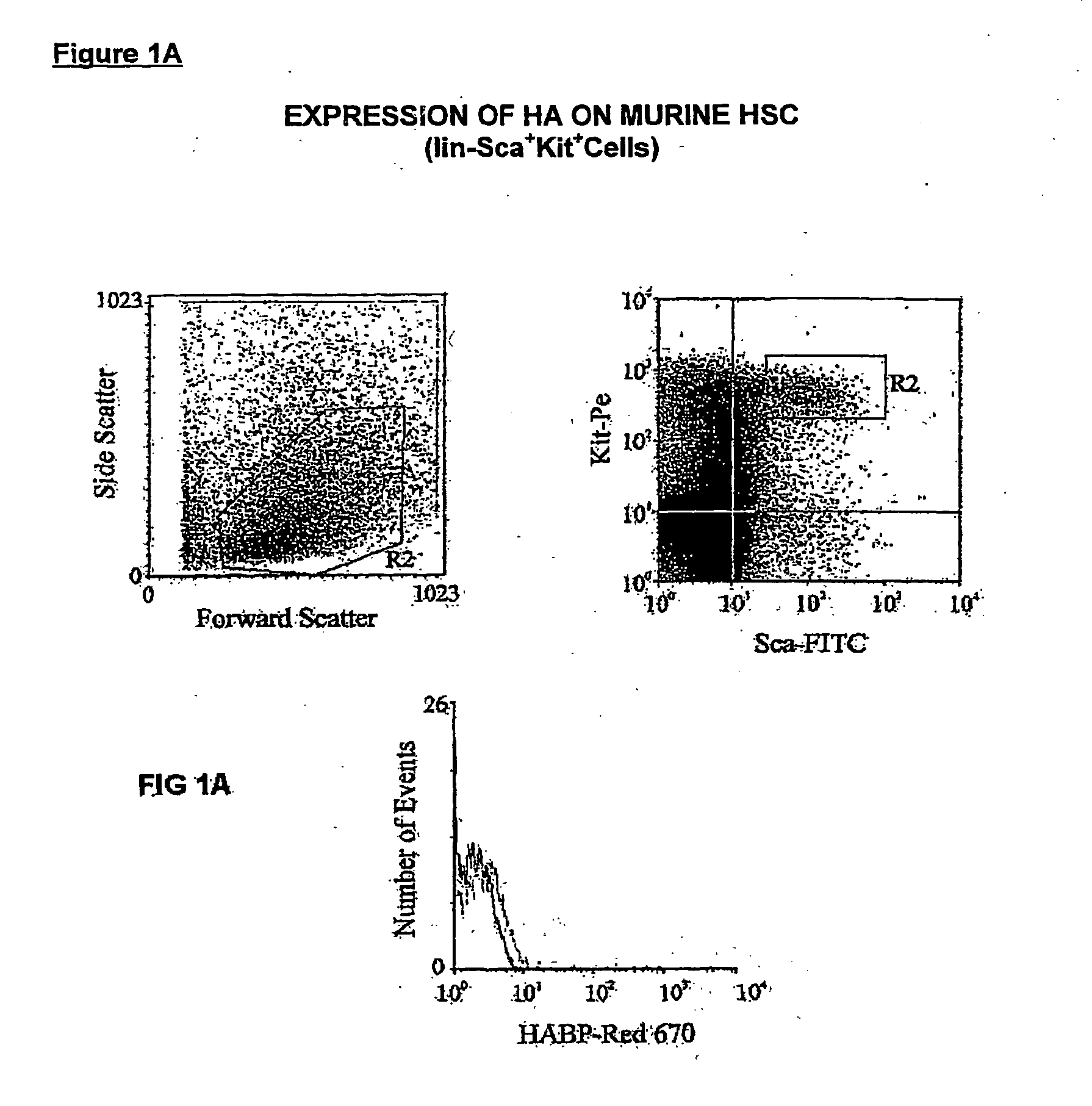
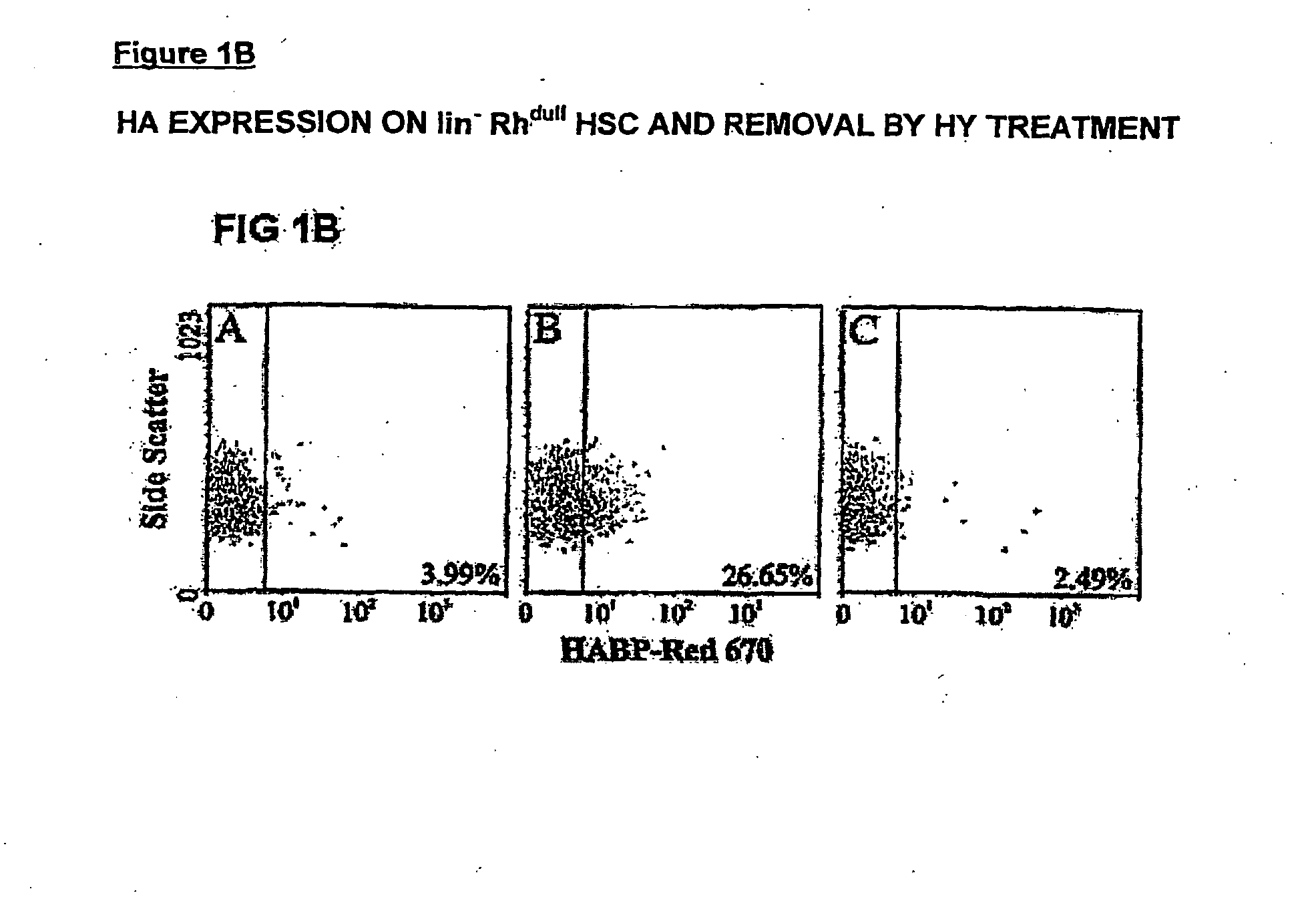
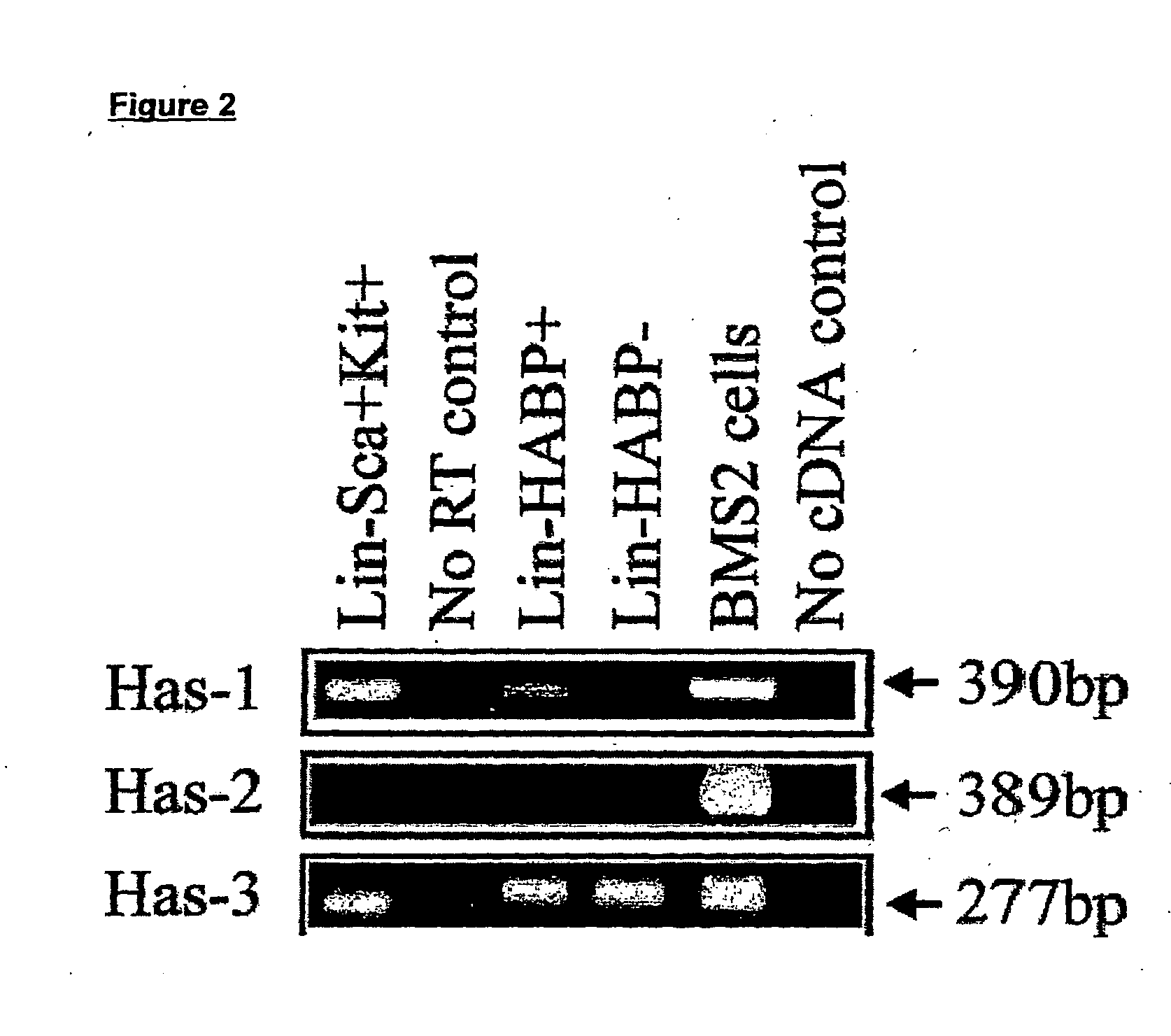
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) or progeny thereof comprising the steps of: obtaining a cell sample including HSC or progeny thereof; detecting the presence of at least one carbohydrate sequence having a sequence of at least one disaccharide repeat of glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine or an equivalent thereof; and identifying a HSC or progeny thereof having the sequence or equivalent thereof. The invention also relates to methods of enriching cell populations for HSC or progeny thereof, for isolating HSC or progeny thereof and cell preparations obtained using the methods of their invention and their uses.
Owner:PETER MACCALLUM CANCER INST
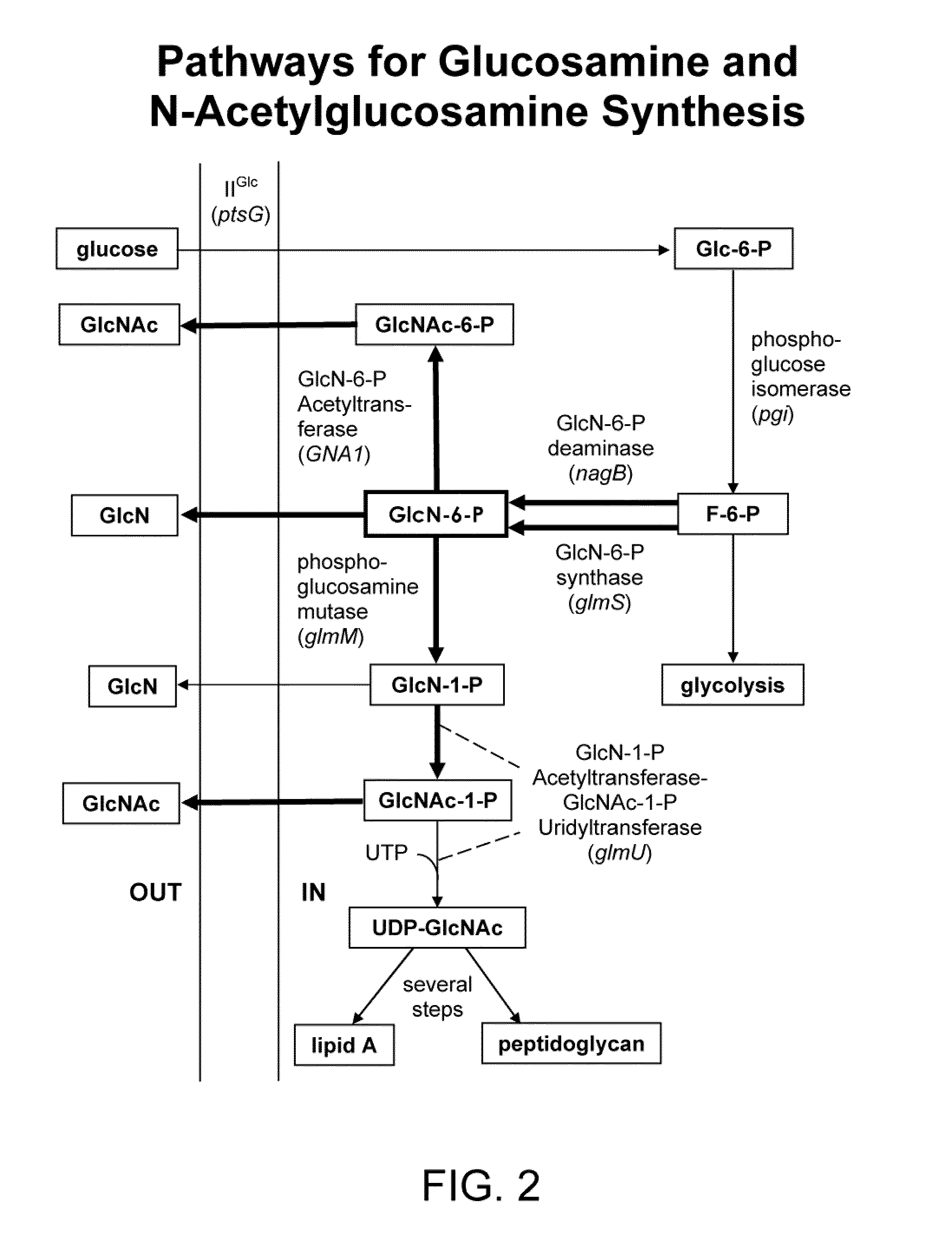
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN105255803AHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseGlucose polymers
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis, based on bacillus subtilis BSGNK, the enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene pckA and pyruvate kinase encoding gene pyk (NCBI upper Gene ID: 938206) are knocked out, the BSGNK regards B.subtilis168delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nag A delta nag B delta ldh delta pta::lox <72> as the host, promoters PxylA and P43 are utilized for controlling recombinant ecpression of glmS and GNAl, and accordingly the glucose kinase encoding gene glcK is knocked out. According to the recombinant bacillus, glucose can be effectively utilized for synthesizing acetylglucosamine, the shake flask fermentation yield can reach 11.13 g / L, the yield is increased by 67.8% compared with a strain before knocking out, and a basis is provided for further improvement of bacillus subtilis for producing glucosamine of metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing lacto-n-biose i and galacto-n-biose
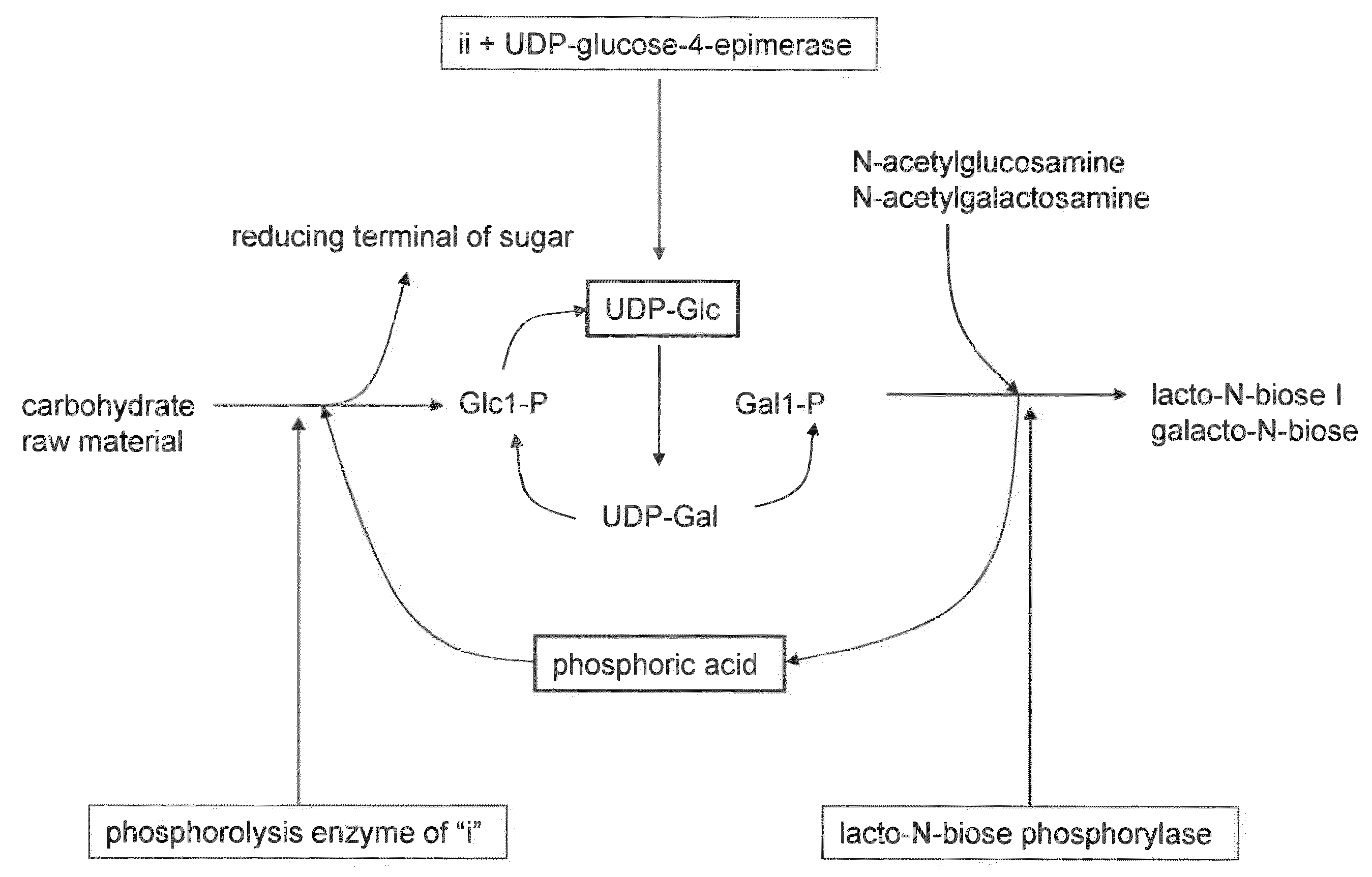
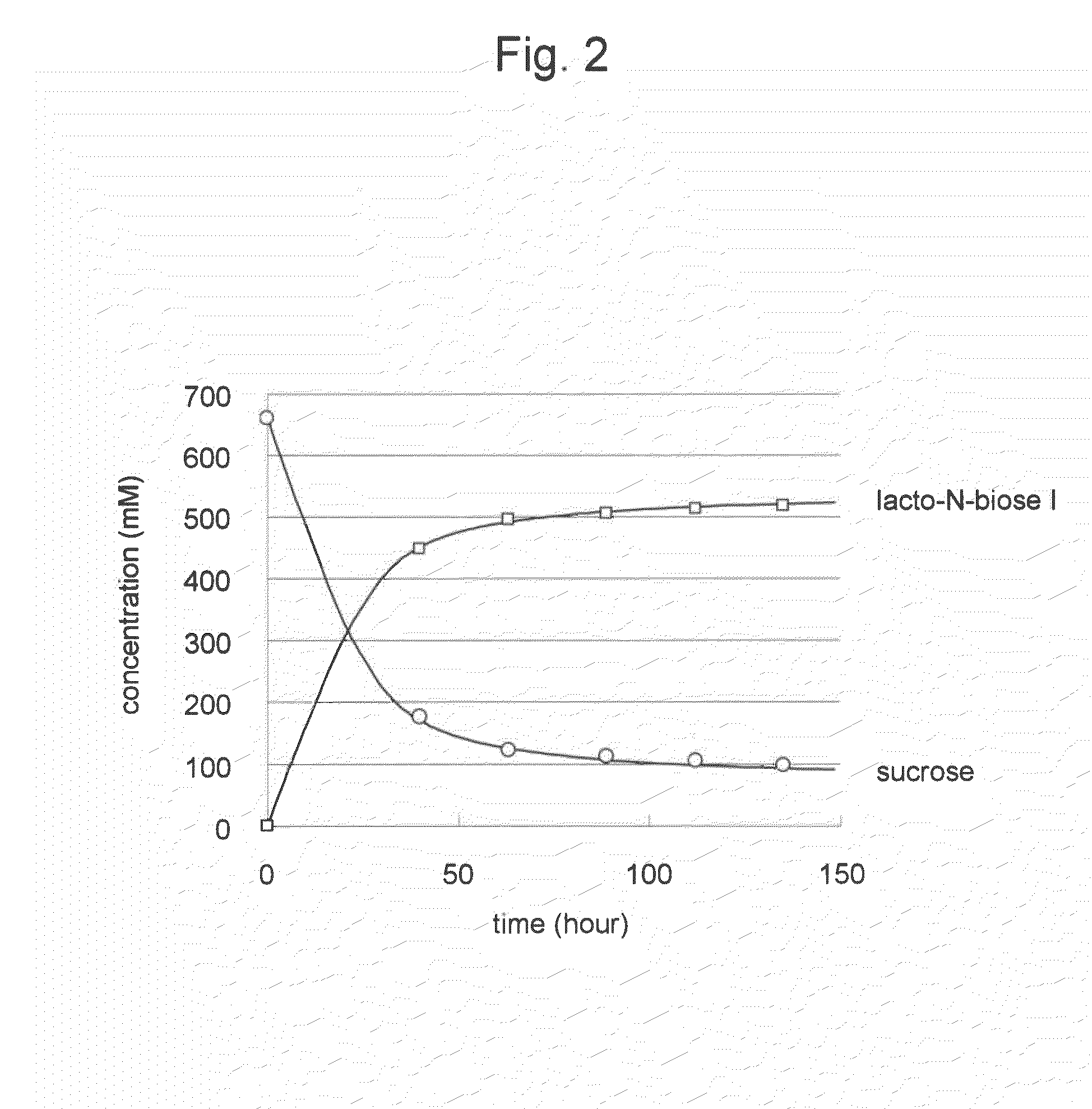
ActiveUS20100120096A1Easily and conveniently carry-outGood value for moneyImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphorylation
A method for producing lacto-N-biose I and galacto-N-biose inexpensively and conveniently is provided. The method for producing lacto-N-biose I or galacto-N-biose, characterized in that the method comprises causing: (i) a combination of a carbohydrate raw material with an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorolysis of the carbohydrate raw material to give a-glucose-1-phosphate; and (ii) a combination of an enzyme that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate to UDP-glucose and an enzyme that converts UDP-galactose to galactose-1-phosphate with their cofactors, and / or a combination of an enzyme (UDP-Gly synthase) that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose and α-galactose-1-phosphate, respectively, with its cofactor(s) to act in the presence of N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine, phosphoric acid, lacto-N-biose phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.211), and UDP-glucose-4-epimerase (EC 5.1.3.2).
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG
Recombinant bacillus subtitles capable of increasing yield of acetylglucosamine
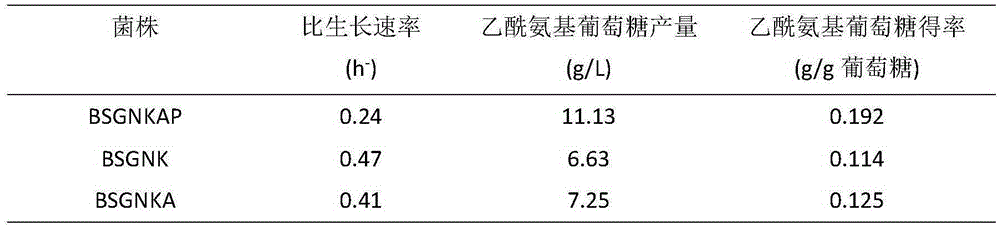
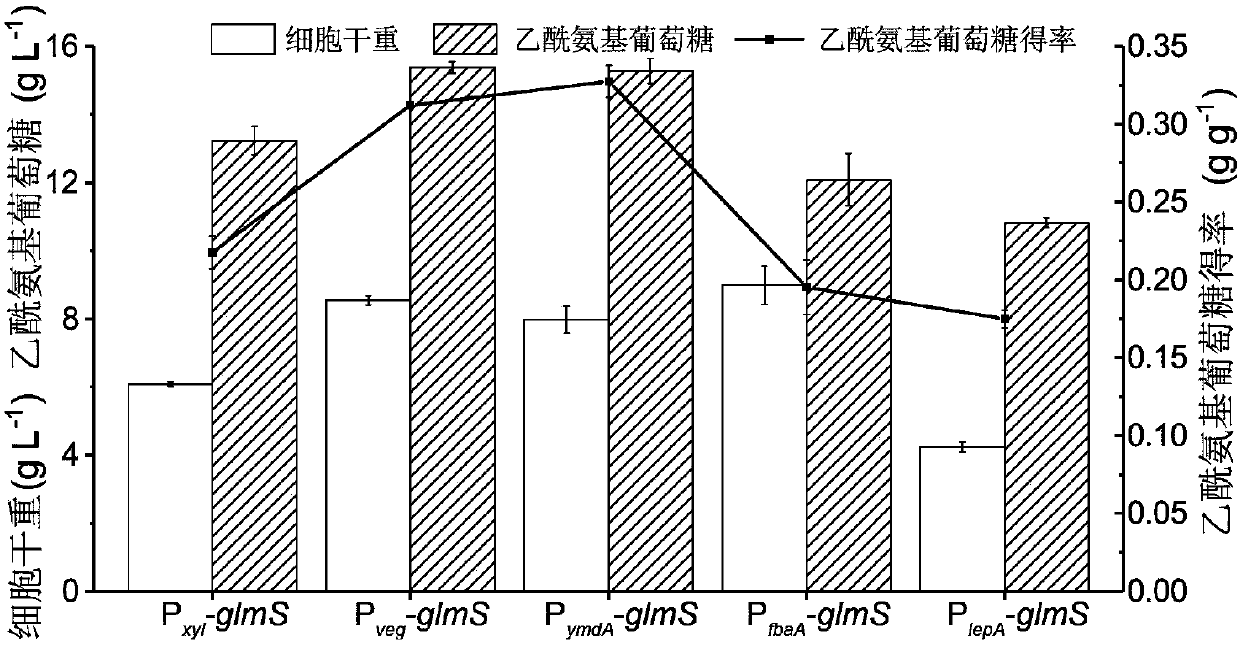
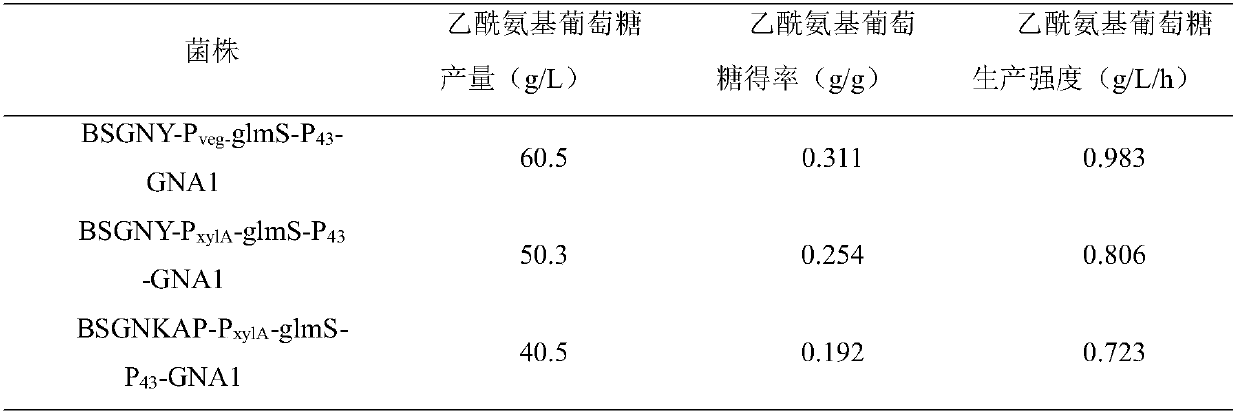
InactiveCN107699533AReturn to normal growthIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesPhosphateAcetylglucosamine
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtitles capable of increasing the yield of acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The recombinant bacillus subtitles is characterized in that bacillus subtitles BSGNKAP-Pxy1A-glmS-P43-GNA1 is used as the original strain, a phosphatase yqaB gene controlled by a strong constitutive promoter Pveg is integrated to the genome, and the promoter of 6-phosphate glucosamine synthase is replaced by the strong constitutive promoter Pveg to obtain genetically engineered bacillus subtitles BSGNY-Pveg-glmS-P43-GNA1 accumulating the acetylglucosamine. The recombinant bacillus subtitles has the advantages that the yield of the acetylglucosamine of a 3L fermentation tank reaches 60.5g / L, the yield of the acetylglucosamine is 0.311g / g glucose, production intensity is 0.983g / L / h, the yield of the acetylglucosamine outside the cells of the recombinant bacillus subtitles is increased, and a foundation is laid for glucosamine production using metabolic engineering modified bacillus subtitles.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria with high yield of acetylglucosamine and application thereof
ActiveCN103060252AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDegradation pathwayGram
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria with high yield of acetylglucosamine and application of the bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria with high yield of the acetylglucosamine. Bacillus subtilisi 168 serves as an original strain. On the basis that homologous recombination knocks out acetylglucosamine glucose transporter protein coding gene (nagP), acetylglucosamine deacetylation enzyme coding gene (nag A) and acetylglucosamine deamination enzyme coding gene (nag B) are further knocked out so as to block up acetylglucosamine degradation pathway in host bacteria. In the host bacteria without the nag A and the nag B, acetylglucosamine acetylase coding gene (GNA1) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C is overly expressed, an acetylglucosamine synthetic route is strengthened to produce recombination bacillus subtilis for producing acetylglucosamine, yield reaches 1.23 grams per liter, and the method is a basis for metabolic engineering to further modify bacillus subtilis to produce glucosamine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating acetylglucosamine and application thereof
ActiveCN105176903AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetylglucosamineGenetically engineered
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating acetylglucosamine and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating the acetylglucosamine and the application thereof, recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS serves as an original strain, the glucosamine synthesizing route is enhanced by excessively expressing glucosamine histone acetyltransferase coding genes (CeGNA1) from caenorhabditis elegans, and the genetically engineered bacterium bacillus subtilis for accumulating the acetylglucosamine is obtained; the yield on the shake flask level reaches 7.31 g / L, and a foundation is laid for further producing the glucosamine by transforming the bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process and materials for production of glucosamine and n-acetylglucosamine
A biosynthetic method for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine is disclosed. Such a method includes the fermentation of a genetically modified microorganism to produce glucosamine and / or N-acetylglucosamine. Also disclosed are genetically modified microorganisms that are useful for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine. In addition, methods of recovering N-acetylglucosamine that has been produced by a fermentation process, including methods that result in N-acetylglucosamine of high purity, are described. Also disclosed is a method to produce glucosamine from N-acetylglucosamine.
Owner:ARKION LIFE SCI LLC
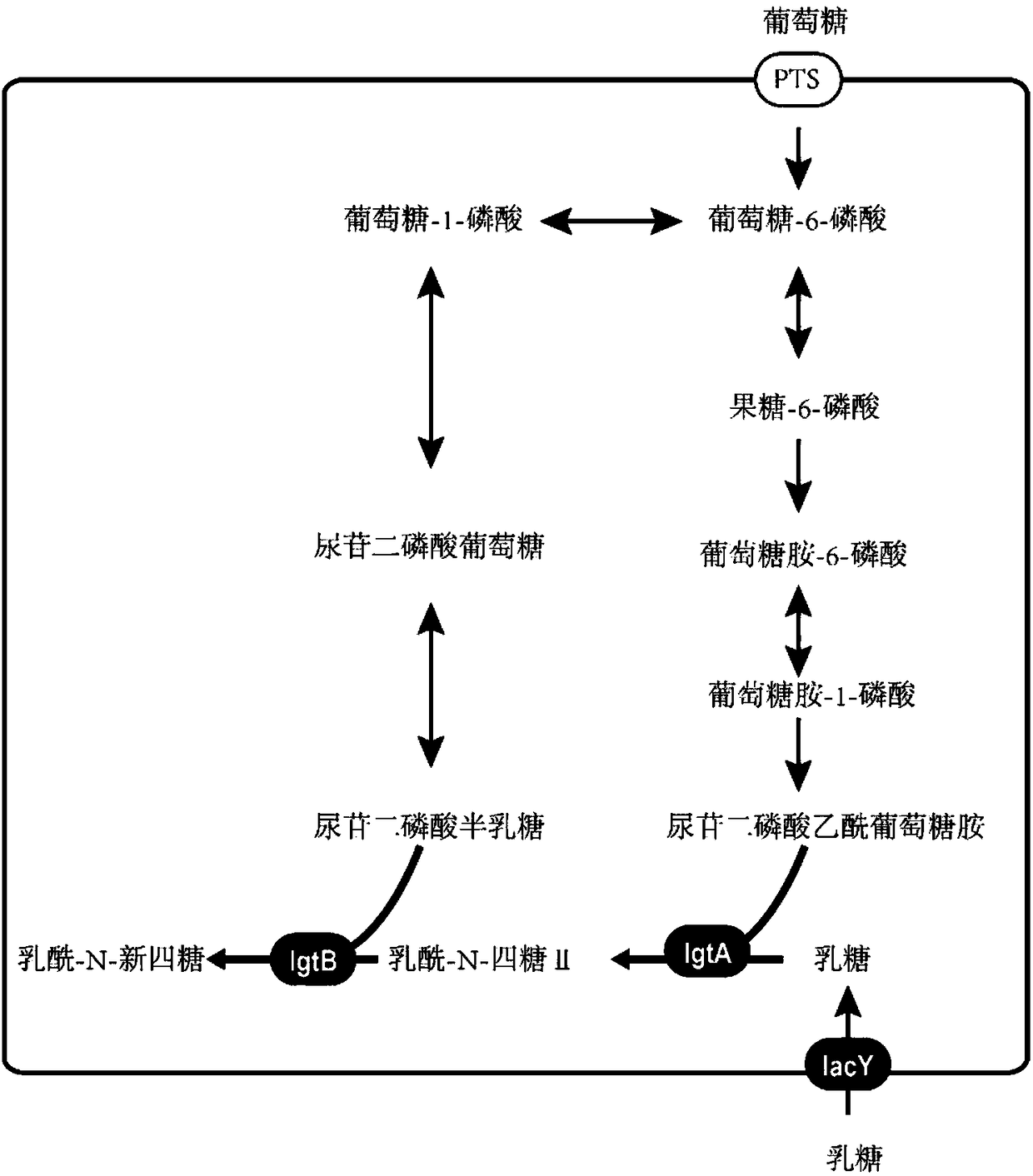
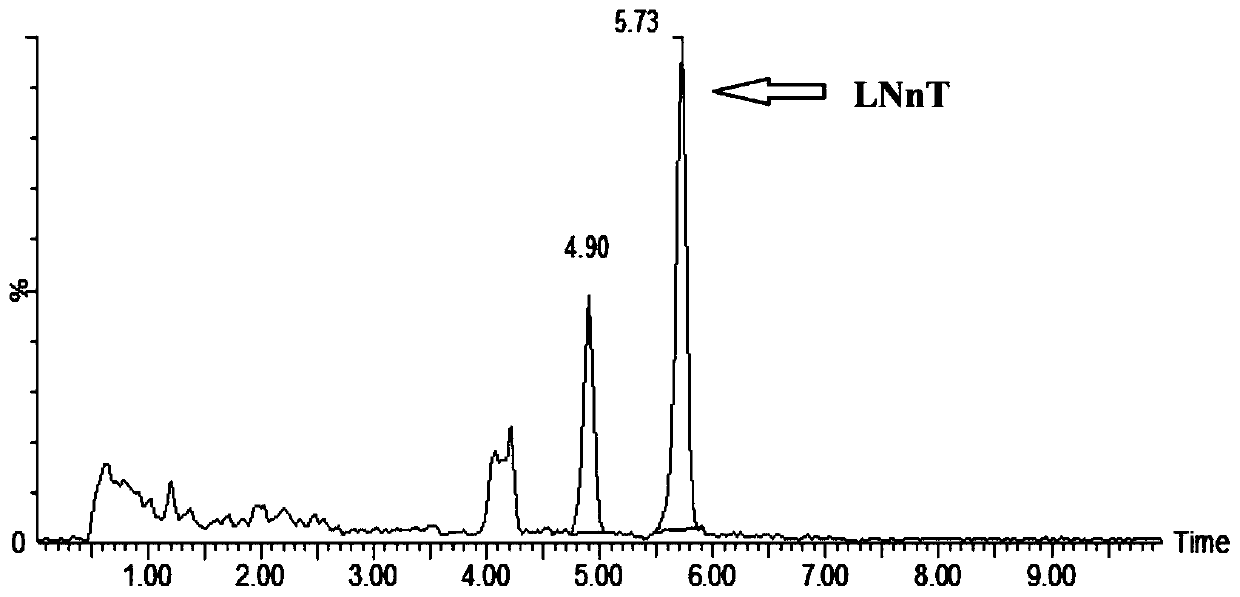
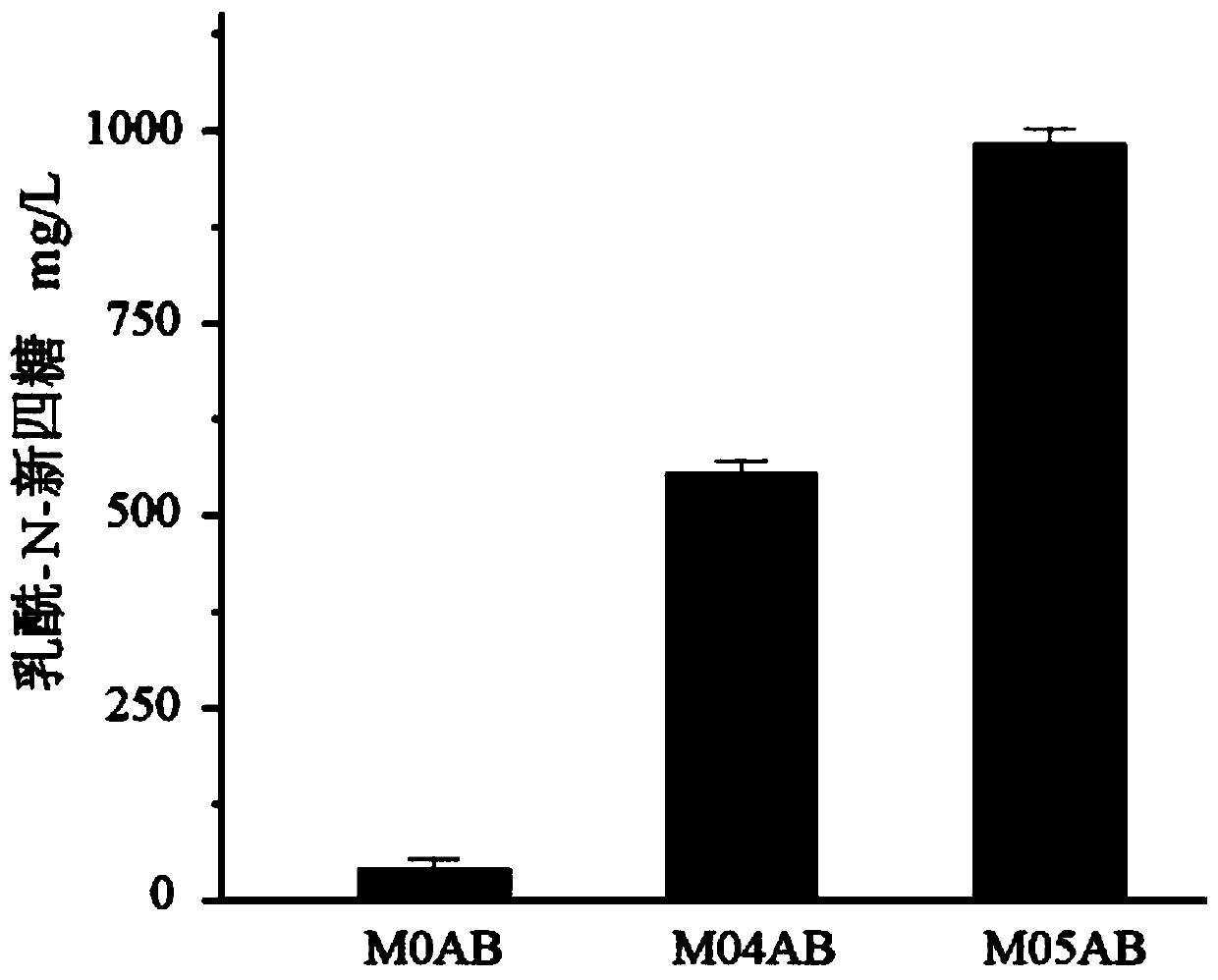
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lactyl-N-neotetraose and construction method and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis
The invention provides recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lactyl-N-neotetraose. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is integrated with lactose permease genes in a recombinant manner on bacillus subtilis 168 genome and converts plasmids which contain beta-1,3-N-glucoaminotransferase genes and beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase gene in bacillus subtilis 168. Uridine diphosphate galactose and acetylglucosamine uridine diphosphate in a metabolic pathway of the bacillus subtilis are used as precusor substances, lactose only needs to be added exogenously and is transferred into cells under theeffect of lactamase to synthesize the lactyl-N-neotetraose which is secreted to ectoenzyme. The accumulation amount of the lactyl-N-neotetraose synthesized by the recombinant bacillus subtilis reaches 1071 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for production of the lactyl-N-neotetraose through further metabolic engineering modified bacillus subtilis.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
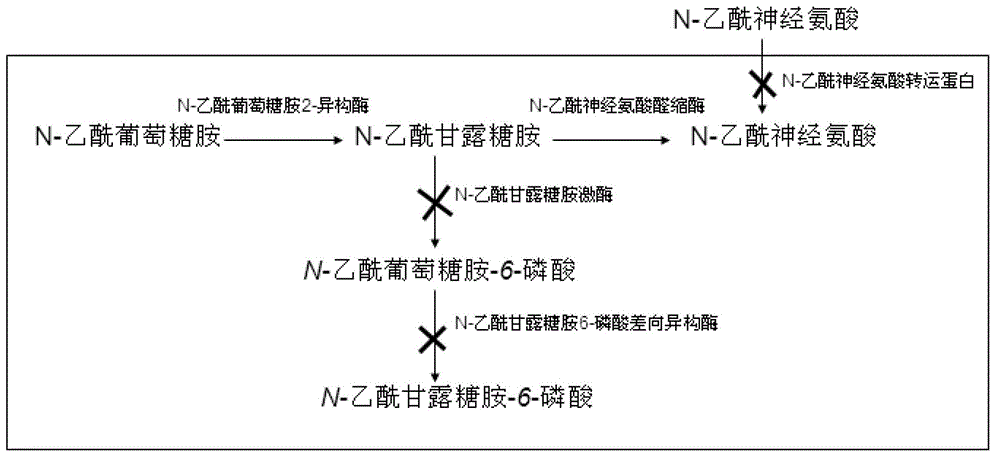
Genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103060358AEliminate degradation pathwaysPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyN-Acetylglucosamine
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. A method for preparing the genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid comprises the following step of: introducing genes associated with the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis into host bacteria so as to obtain recombinant bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid, wherein the genes associated with the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis are coding genes of N-acetylglucosamine and 2-isomerase and a coding gene of N-nacetylneuraminic acid aldolase. The genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid constructed by the invention have the following advantages that the used raw materials are relatively cheap and liable to realize industrial mass product, so that the genetically engineered bacteria play an important role in the production of N-acetylneuraminic acid in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for inducing orexin neurons and agent for treating narcolepsy or eating disorder
ActiveUS20140349964A1Improve securityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPluripotential stem cellSirtuin 1
The invention provides a method for producing an orexin neuron by culturing a pluripotent stem cell or a neural progenitor cell in the presence of N-acetyl-D-mannosamine and optionally in the presence of at least one inhibitor selected from the group consisting of a Sirtuin 1 inhibitor and an O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase inhibitor. The invention also provides a therapeutic agent for narcolepsy or eating disorders, such as anorexia, containing N-acetyl-D-mannosamine, which is based on the induction of orexin neuron in vivo.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Method for preparing glucosamine hydrochloride
PendingCN110256506ASimple production processReduce lossesSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationProcess lossAlcohol
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering, in particular to a method for preparing glucosamine hydrochloride. The method includes: subjecting N-acetylglucosamine fermentation broth to vacuum concentration at the temperature of 50-65 DEG C and vacuum degree of -0.1-0.09MPa to obtain N-acetylglucosamine fermentation broth concentrate; adding the obtained N-acetylglucosamine fermentation broth concentrate into concentrated hydrochloric acid to perform hydrolysis, performing plate and frame filtration after the hydrolysis to obtain crude glucosamine hydrochloride, performing alcohol washing, redissolving and decoloring, and concentrating and crystallizing to obtain refined glucosamine hydrochloride. The method has the advantages that the process directly concentrating the N-acetylglucosamine fermentation broth to perform hydrolysis is used, the production process is simplified, product process loss and influence on product quality are reduced, product yield and quality are increased, and production cost is lowered; the one-step yield of the refined glucosamine hydrochloride reaches above 65%, and the purity of the refined glucosamine hydrochloride is 99-102%.
Owner:SHANDONG RUNDE BIOTECH CO LTD
Recombinant microorganisms and uses thereof
The present invention relates to recombinant strains of Vibrio spp, which are unable to utilize the amino sugar N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) as a sole carbon source. This inability to utilize GlcNAc severely impairs the colonization property of the recombinants. The present invention also provides compositions comprising these recombinant strains for use in pharmaceuticals and in providing immunity.
Owner:NAT INST OF PLANT GENOME RES ORG
Method for preparing chitin oligosaccharides, chitooligosaccharides and chitosan oligosaccharides
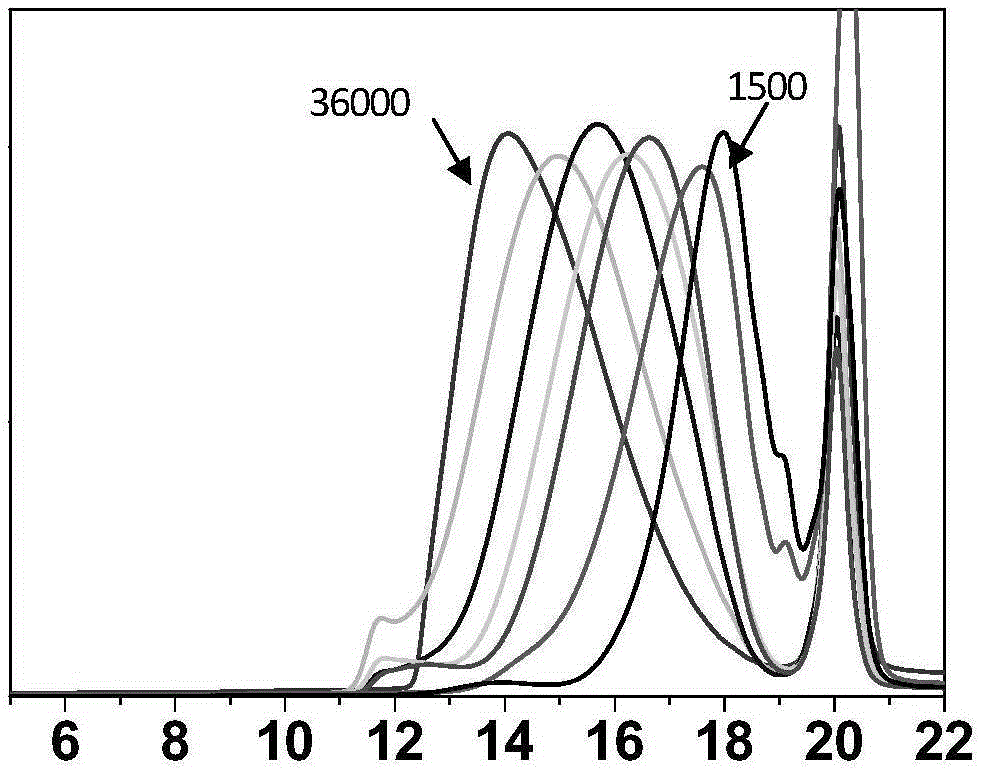
The invention belongs to the technical field of fine chemical industry and particularly relates to a method for preparing chitin oligosaccharides, chitooligosaccharides and chitosan oligosaccharides, of which the molecular weight is 50,000 or below. The method comprises the steps of firstly, dissolving chitin in a certain solvent, carrying out homogeneous degradation under acid catalysis so as to obtain the chitin oligosaccharides with certain molecular weight, and subjecting the chitin oligosaccharides to deacetylating treatment by a strong base, thereby preparing the chitooligosaccharides and the chitosan oligosaccharides. After the chitin oligosaccharides are subjected to deacetylating treatment by the strong base, the chitooligosaccharides or the chitosan oligosaccharides with the degree of deacetylation of 50% to 98% is obtained. Glycosidic bonds among acetylglucosamine are more easily degraded under the condition of acid catalysis, so that a chitin degradation reaction can be carried out under mild conditions, the yield is high, and the control on molecular weight is effectively achieved. According to the chitin oligosaccharides, chitooligosaccharides and chitosan oligosaccharides prepared by the method, the molecular weight can be continuously adjustable in the range of 1,000 to tens of thousands, the distribution of the molecular weight is relatively narrow, the product quality is high, and the production cost is reduced remarkably.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN105238724AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTricarboxylic acid
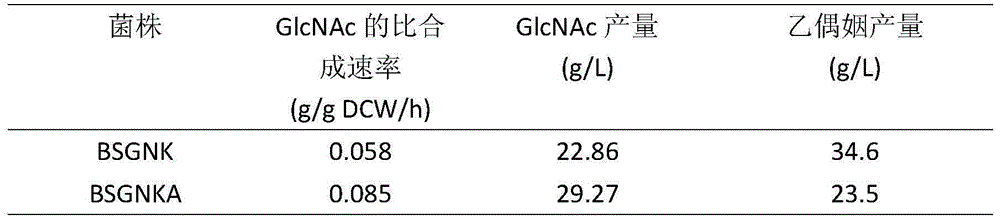
The invention discloses a method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps that BSGNK-PxylA-glmS-P43-GNA1 serves as original strains, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (pckA) genes are knocked out through homologous recombination, the reaction that enolphosphopyruvate is converted into oxaloacetic acid in host bacterium cells is blocked, the carbon flux flowing to a tricarboxylic acid cycle is reduced, and accumulation of acetylglucosamine is promoted. In the process that a composite culture medium is used for fermentation, the acetylglucosamine yield of recombination bacillus subtilis with pckA knocked out reaches 29.27 g / L and is increased by 28.1% compared with that of control strains. The method lays a foundation for transforming bacillus subtilis to produce acetylglucosamine in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGSU HEVI BIOTECH CO LTD
Method of producing recombinant antithrombin III composition
The present invention provides a process for producing an antithrombin III composition comprising an antithrombin III molecule having complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chains, wherein the complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chains have a structure in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chains.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Recombinant bacillus subtilis and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN108998402AReduce metabolic burdenDoes not affect life activitiesBacteriaHydrolasesLife activityBacterial strain
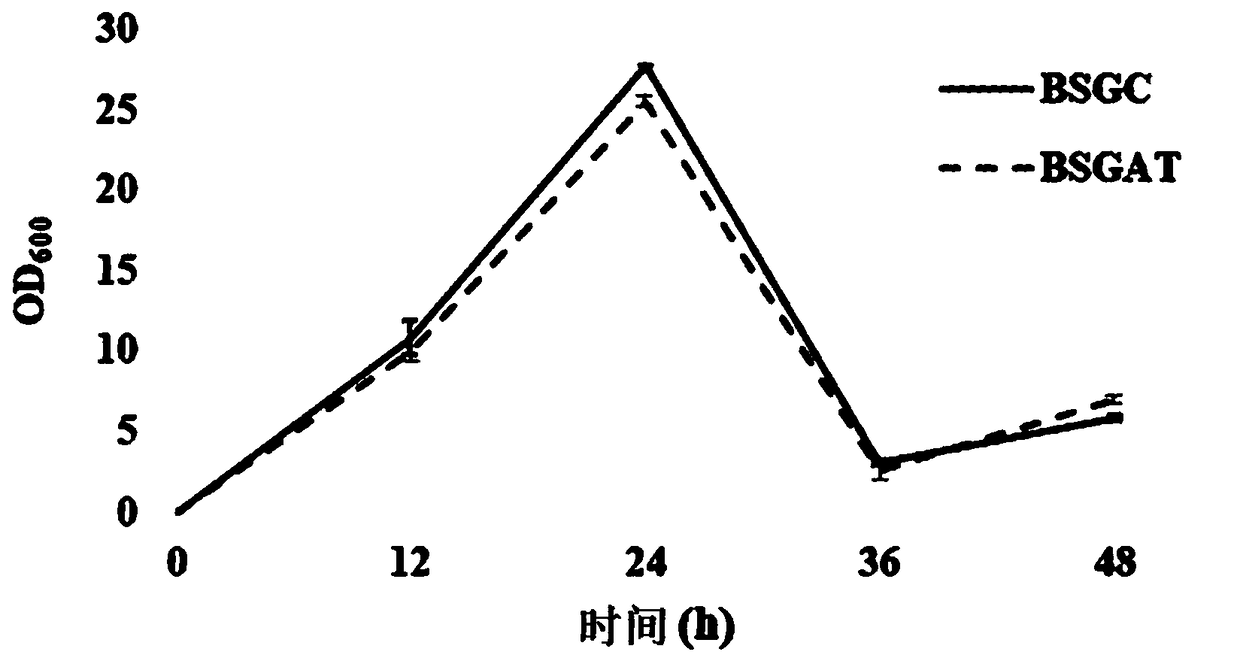
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus subtilis and a construction method and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of genetic engineering. The method takes cell self functional membrane microdomain FMMs as a space frame, and constructs a multienzyme complex by using the specific marker proteins FloA and FloT, an artificial substrate channel is constructed, the metabolic burden of the cells can be effectively reduced, and the multienzyme complex is attached to plasmalemma , which facilitates the transport of a product from the intracellular to the extracellular. The recombinant bacillus subtilis constructed by the method efficiently synthesizes GlcNAc without affecting cell life activities, and a toxic intermediate metabolite GlcN-6-P can also be confined to the vicinity of the plasmalemma to reduce or eliminate the inhibition of cell viability. During a shake flask fermentation of a composite medium, the yield of acetylglucosamine in contrast bacterial strain BSGC is only 0.45 g / L, and the BSGAT acetylglucosamine output is increased to 5.29g / L, which is 11.76 times that of the contrast bacterial strain. The recombinant bacillus subtilis construction method of the invention is simple and convenient to use, and has the good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
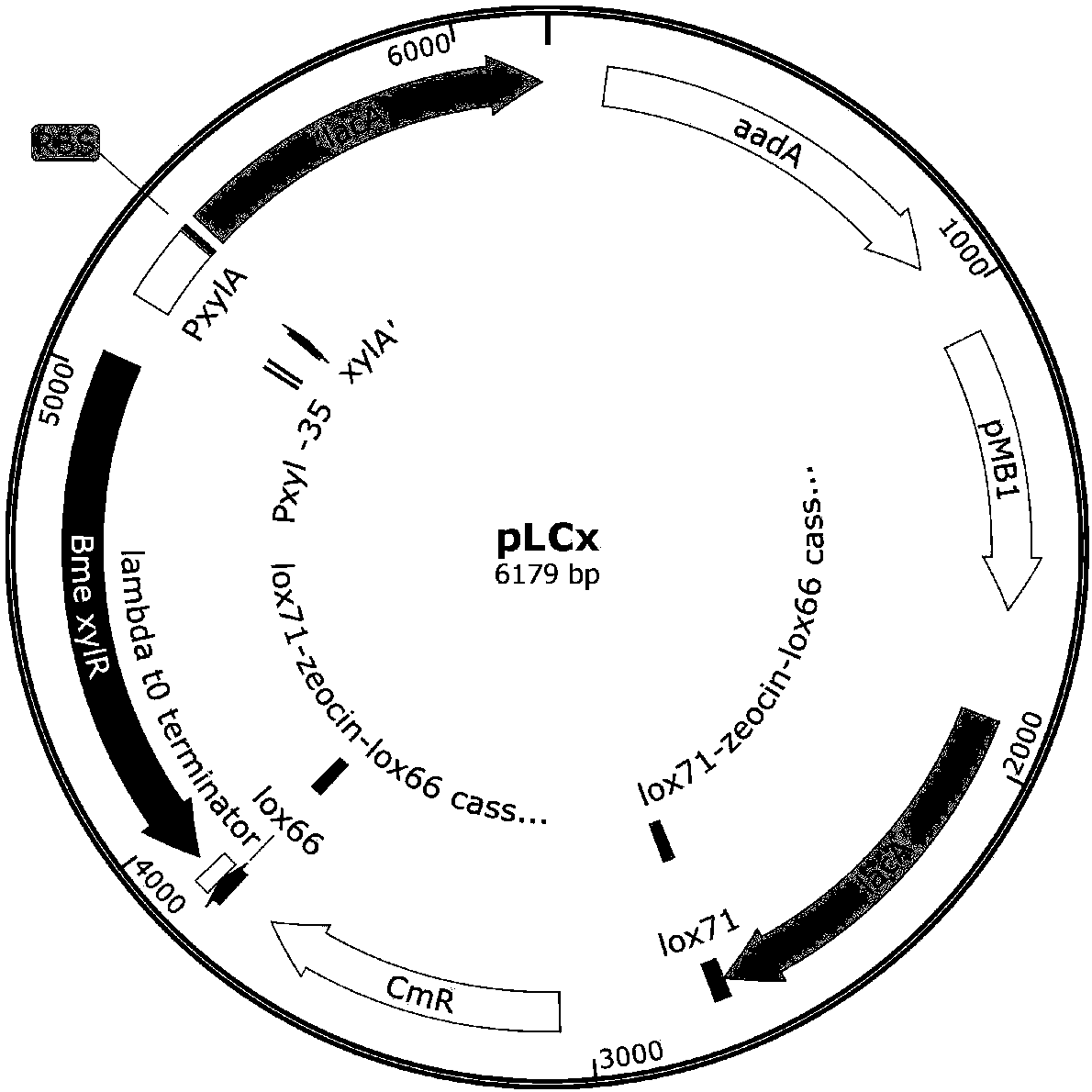
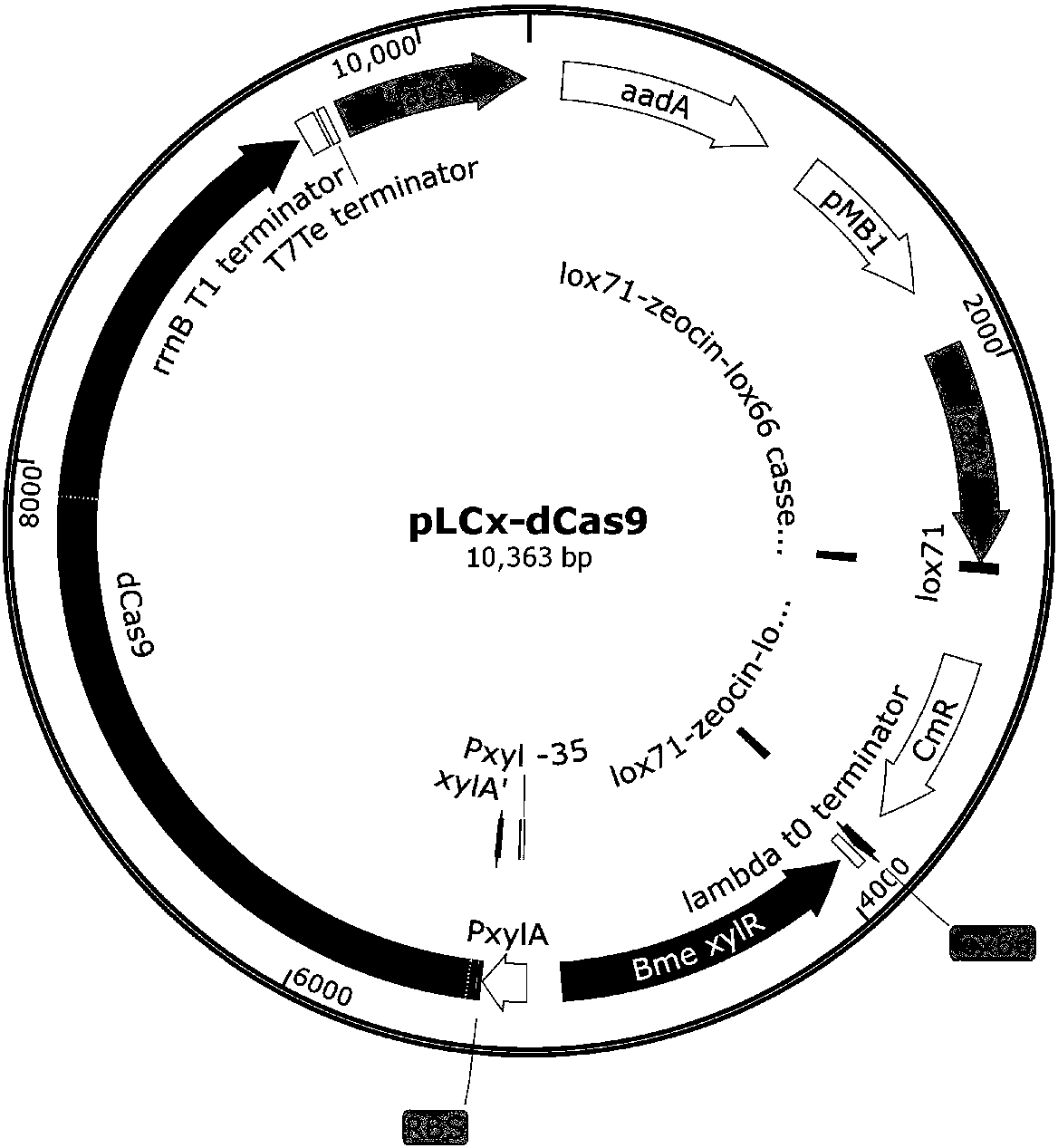
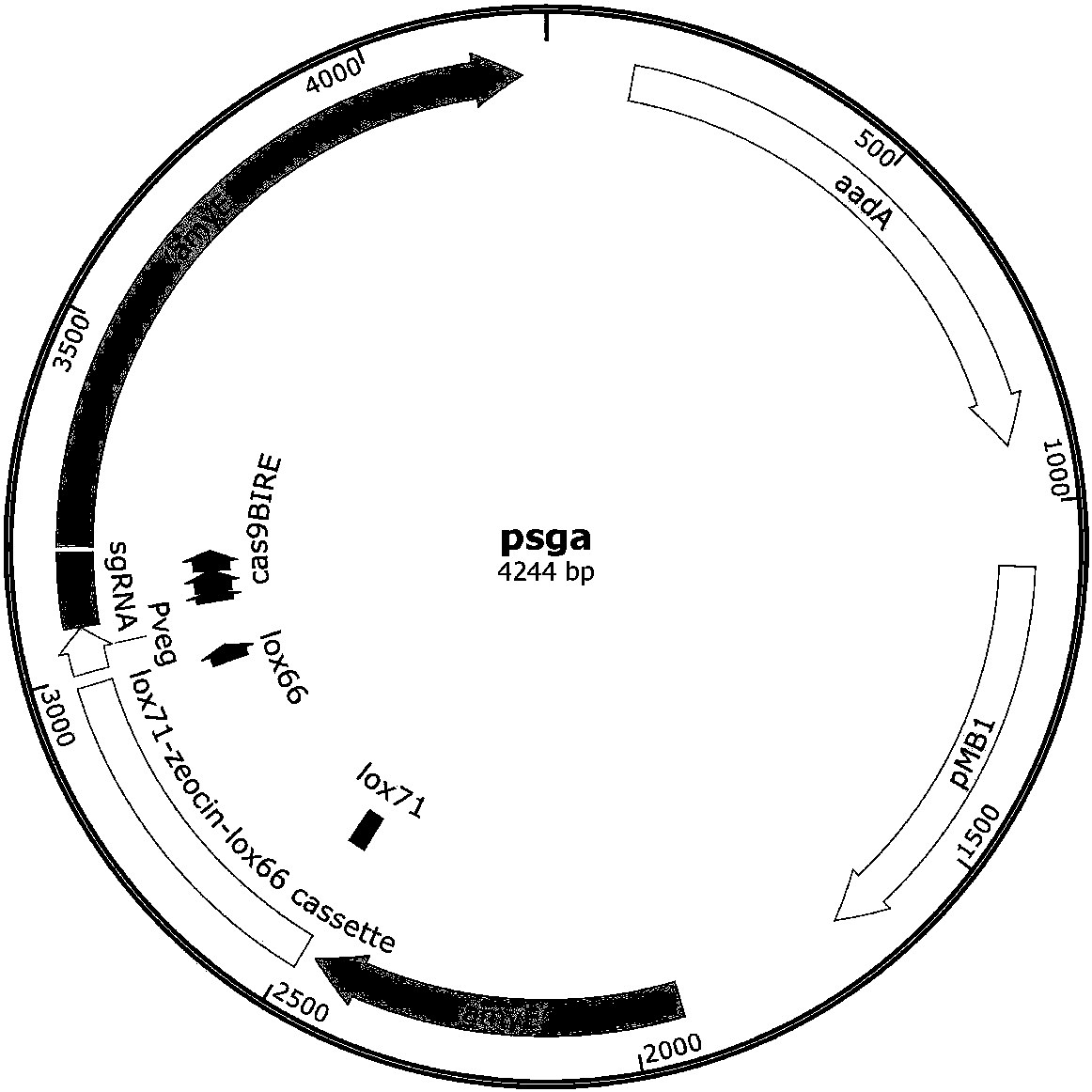
Method for producing N-acetylglucosamine by jointly using glucose and xylose based on CRISPRi
The invention discloses a method for producing N-acetylglucosamine by jointly using glucose and xylose based on CRISPRi and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Through the method, bacillus subtilis BSGNY-Pveg-g1mS-P[43]-GNA1 is used as a starting strain; dCas9 induced by xylose and three sgRNA expression fragments which respectively act on three genes including zwf, pfkA and g1mM are integrated on a genome; the strain is used for carrying out flask shaking fermentation; the yield of N-acetylglucosamine reaches up to 20.5g / L; and the yield of N-acetylglucosaminein per gram of glucose is 0.612g / g; meanwhile, the recombinant bacillus subtilis is capable of efficiently and jointly using glucose and xylose; the method lays the foundation for production of glucosamine through the modified bacillus subtilis in further metabolic engineering and the industrialization thereof.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
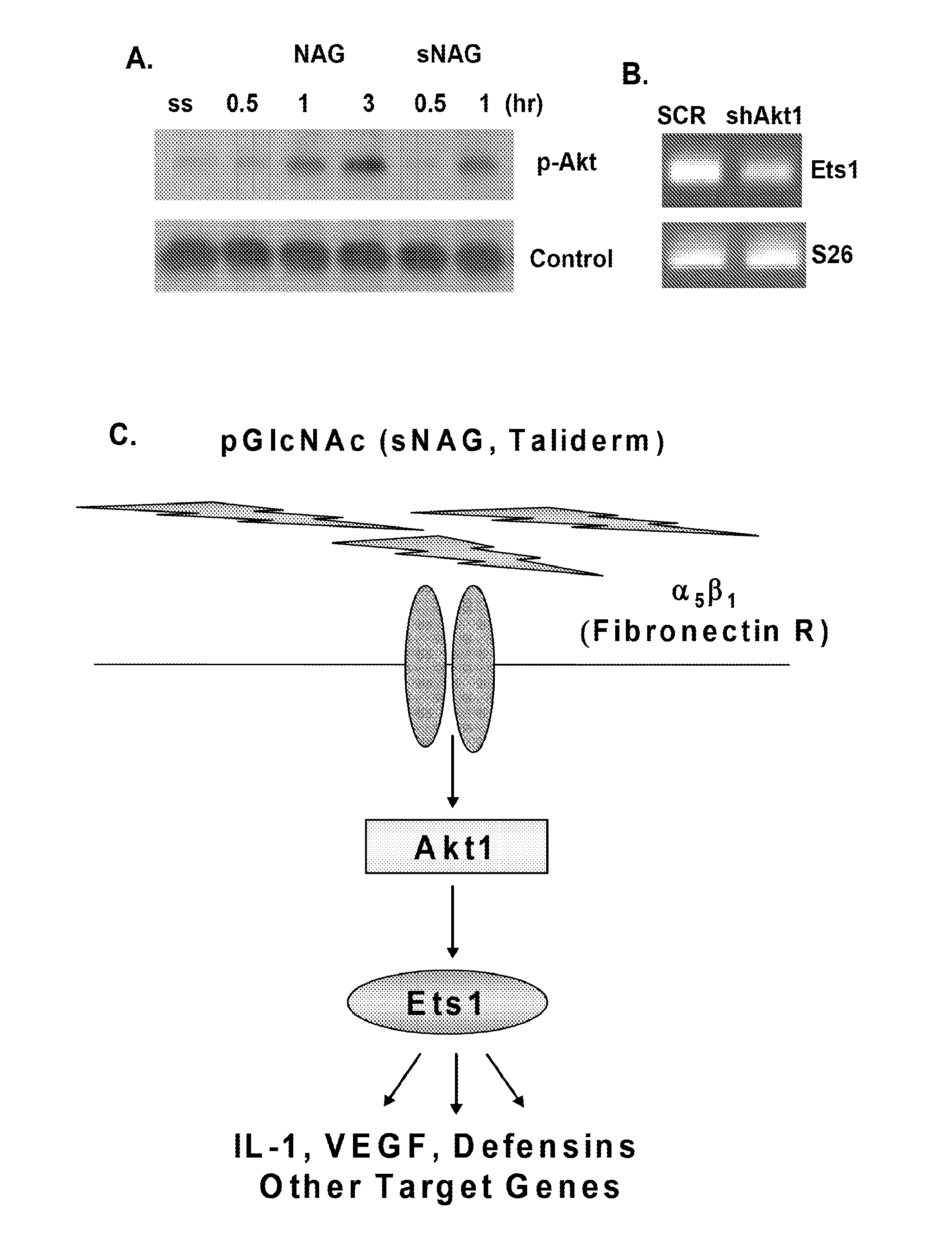
Treatment of disease with poly-n-acetylglucosamine nanofibers
This application relates to compositions comprising shortened fibers of poly-N-acetylglucosamine and / or a derivative thereof (“sNAG nanofibers”) and the use of such compositions in the treatment of disease.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
Multipath composite neuraminic acid producing bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN111394292AHigh catalytic activityReduce synthetic pressureBacteriaTransferasesO-Phosphoric AcidGlucosaminephosphate isomerase
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
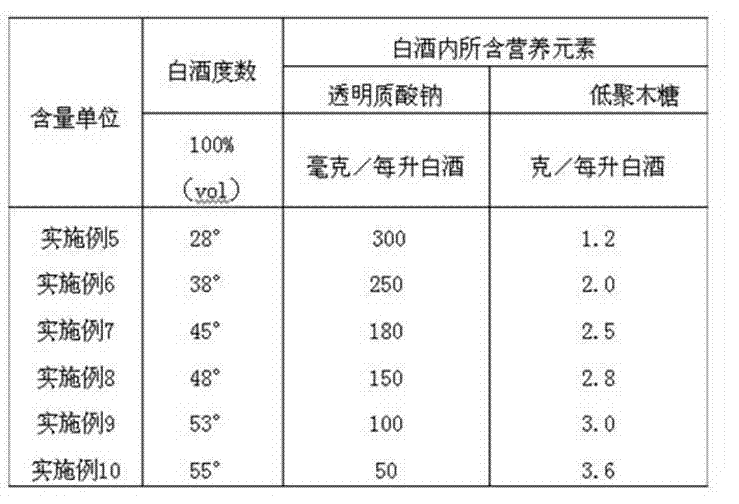
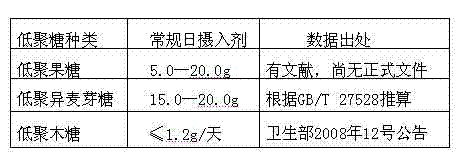
Compound wine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103666975AProcess stabilityKeep baijiu styleAlcoholic beverage preparationBiotechnologyGlucuronate
The invention relates to compound wine and a preparation method thereof. The compound wine comprises sodium hyaluronate, wherein the content of sodium hyaluronate in white spirit per litre is 50-300mg. The compound wine is characterized in that the average relative molecular mass of sodium hyaluronate is 5017-6689 daltons, that is sodium hyaluronate is mucopolysaccharide formed by alternately bonding 10-20 acetylglucosamine and sodium glucuronate disaccharide units. The preparation method of the compound wine employs a hydration-gelation-dissolution staged dissolution technology to allow HA (hyaluronic acid) to be capable of being dissolved in a wine base more uniformly. The compound wine is potable wine comprising new resource food sodium hyaluronate, can keep a style of white spirit, and reaches the GB / T 27588 standard on liqueur which is clear, transparent and free from precipitate and suspended matter, the turbidity is reduced simultaneously, and the long-term stable presence of sodium hyaluronate in the wine base can be ensured.
Owner:SHANXI XINGHUACUN FENJIU WINE FACTORY +1
Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising N-Acetylglucosamine-6-Phosphate
ActiveUS20130012475A1Prevent agingIncrease skin elasticityBiocideCosmetic preparationsPhosphoric acidDrug
The present invention relates to a cosmetic or pharmaceutical composition comprising N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate or a salt thereof and, optionally, a compound of the vitamin A family, and also to a device containing same.
Owner:LIBRAGEN SA
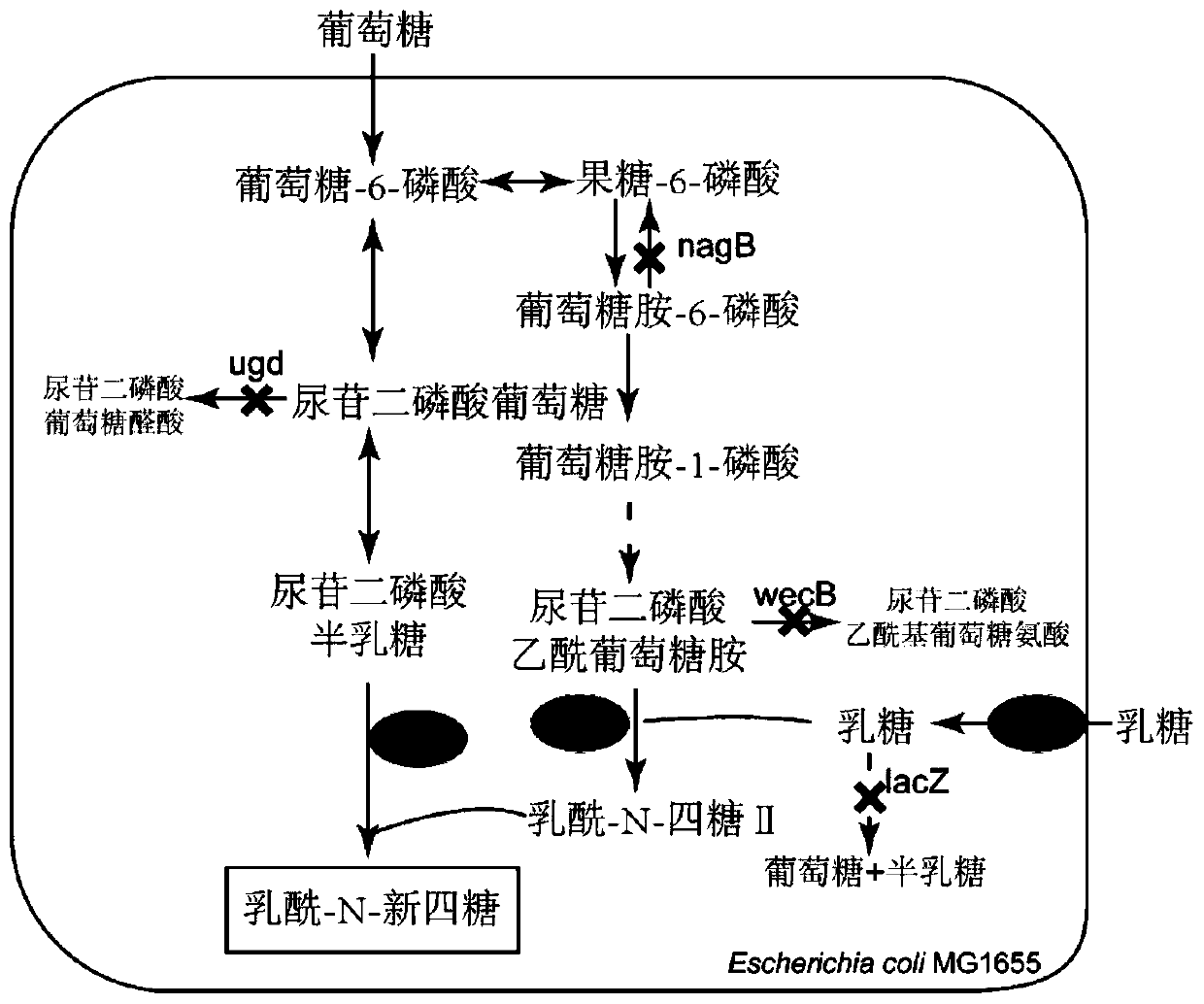
Recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing lactoyl N-neotetraose and construction method and application of recombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing lactoyl N-neotetraose and a construction method and application of the recombinant escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli are obtained by knocking out a beta-galactosidase lacZ gene, a glucosamine-6-phosphodeaminase nagB gene, a UDP-acetylglucosamine epitope isomerase wecB gene and a UDP-glucose dehydrogenase ugd gene in the host genome of escherichia coli and overexpressing a lactose transportase lacY gene, beta-1, 3-N-glucosaminidase lgtA gene and a beta-1, 4 galactosyltransferase lgtB gene on the genome. The yield of lactoyl-N-neotetraose synthesized by recombinant escherichia coli reaches 985 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for further metabolic engineering transformation of escherichia coli to produce lactoyl-N-neotetraose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for determining prostate cancer
InactiveUS20110236995A1Accurately determineImprove accuracyComponent separationIsotope separationGlycanN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention provides a method for detecting a glycan structure of a prostate specific antigen (PSA) rapidly and with high sensitivity and determining prostate carcinoma based on the difference in the structure, in particular, a method for determining between prostate carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia accurately. A method for determining prostate carcinoma, wherein the method includes a step of analyzing a PSA glycan structure in a sample derived from a test subject, and prostate carcinoma is determined in the case that amount of a glycan having LacdiNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(+)) is more than 30% of amount of a glycan not having LacdiNAc but having LacNAc (galacotose-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(−)). Especially, a method for determining prostate carcinoma, wherein prostate carcinoma is determined in the case that amount of a glycan having LacdiNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(+)) is more than 30% of amount of a glycan not having LacdiNAc but having LacNAc (galacotose-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(−)), and benign prostatic hyperplasia is determined in the case of 30% or less.
Owner:NOGUCHI INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com