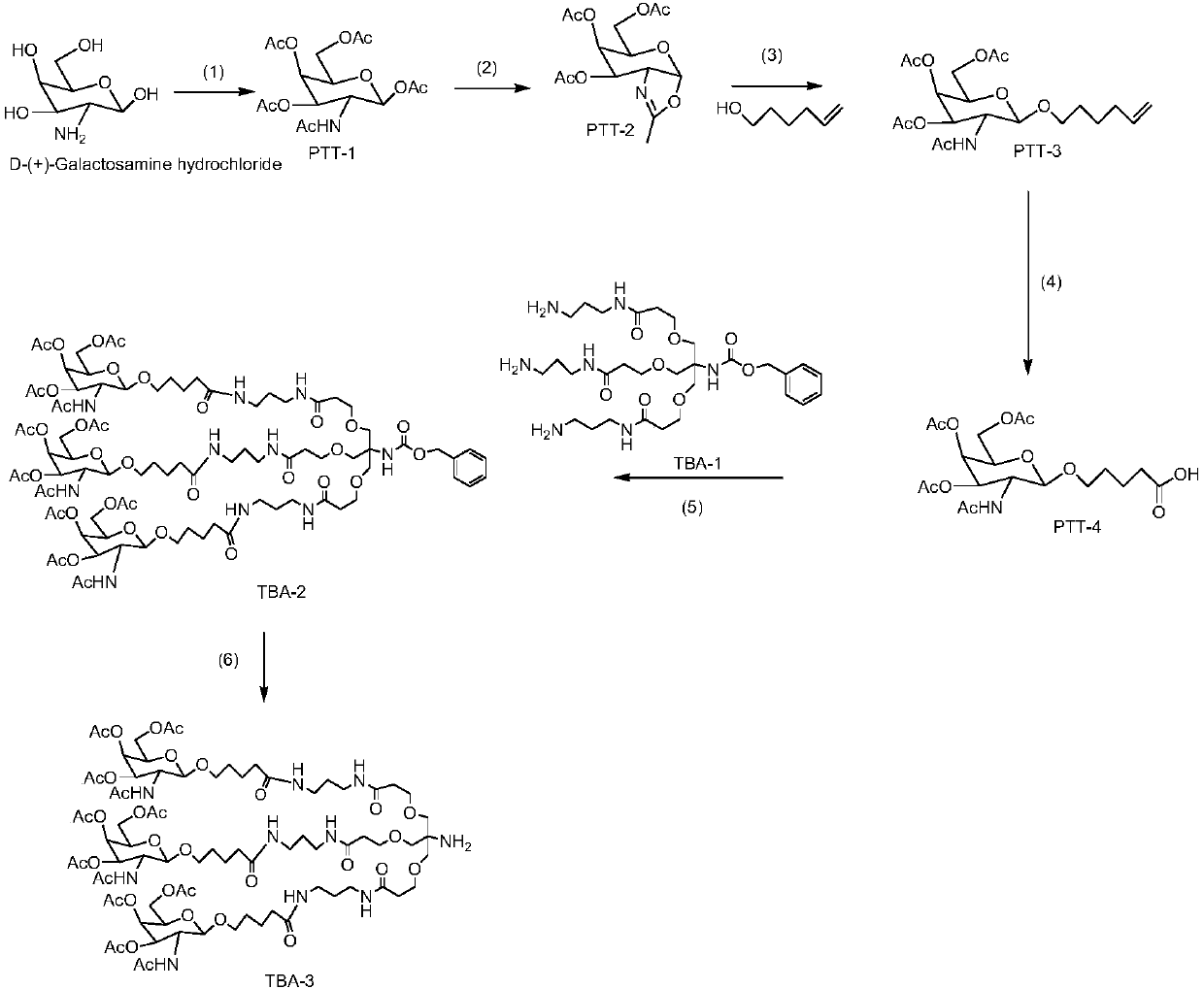
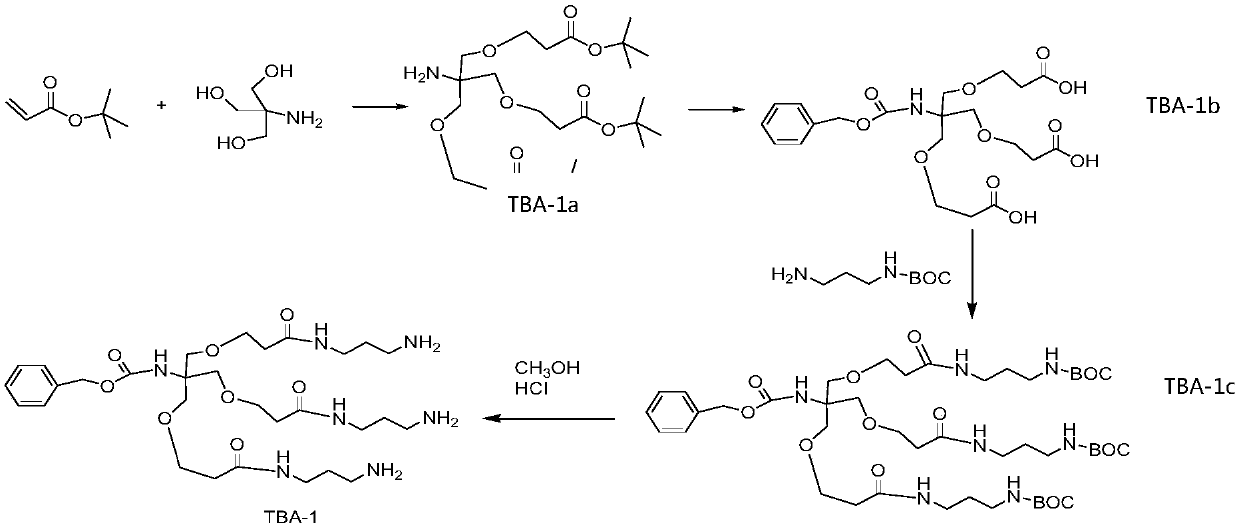
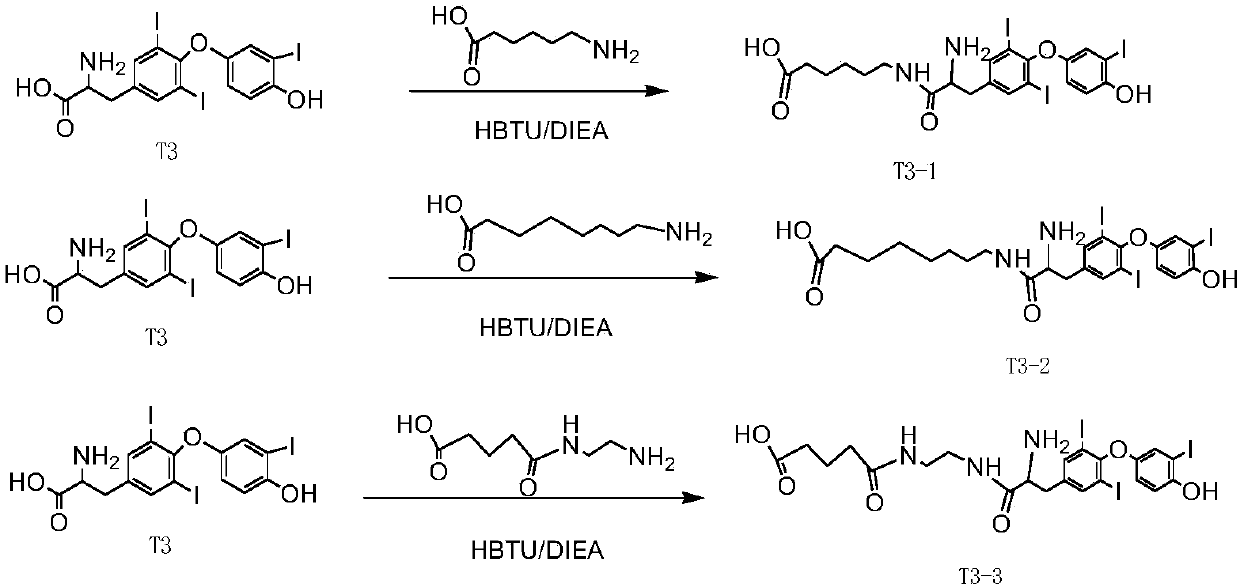
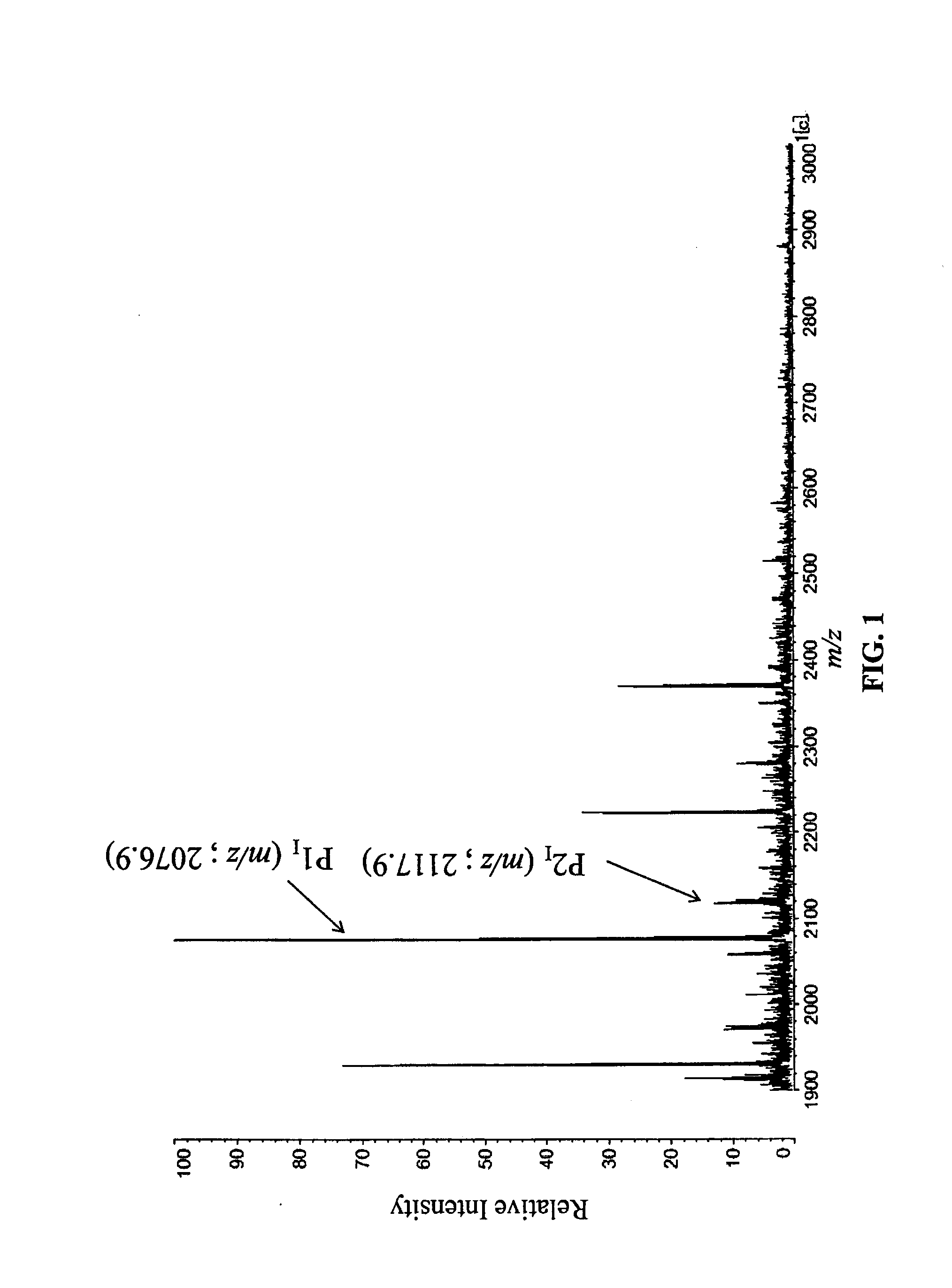
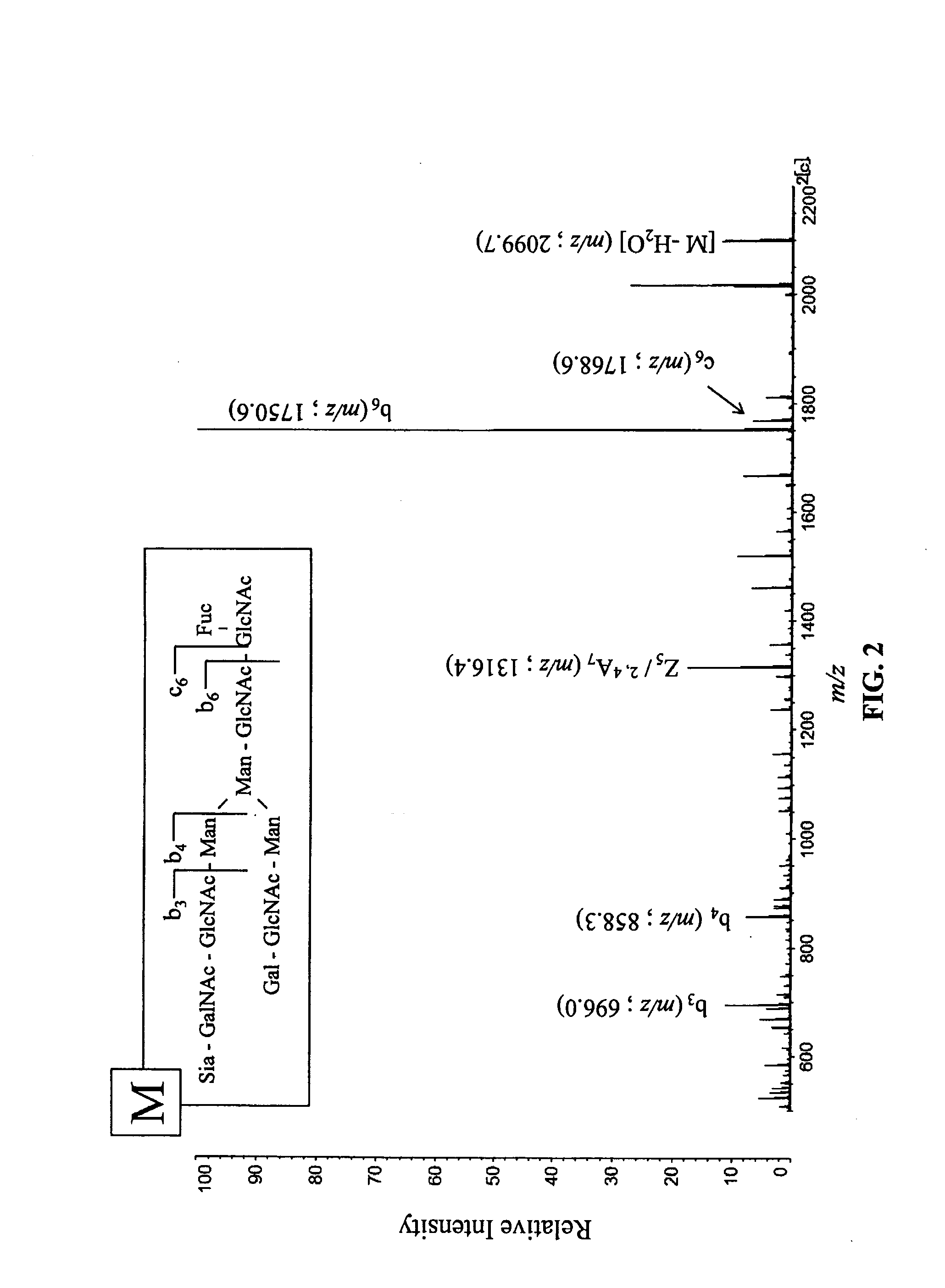
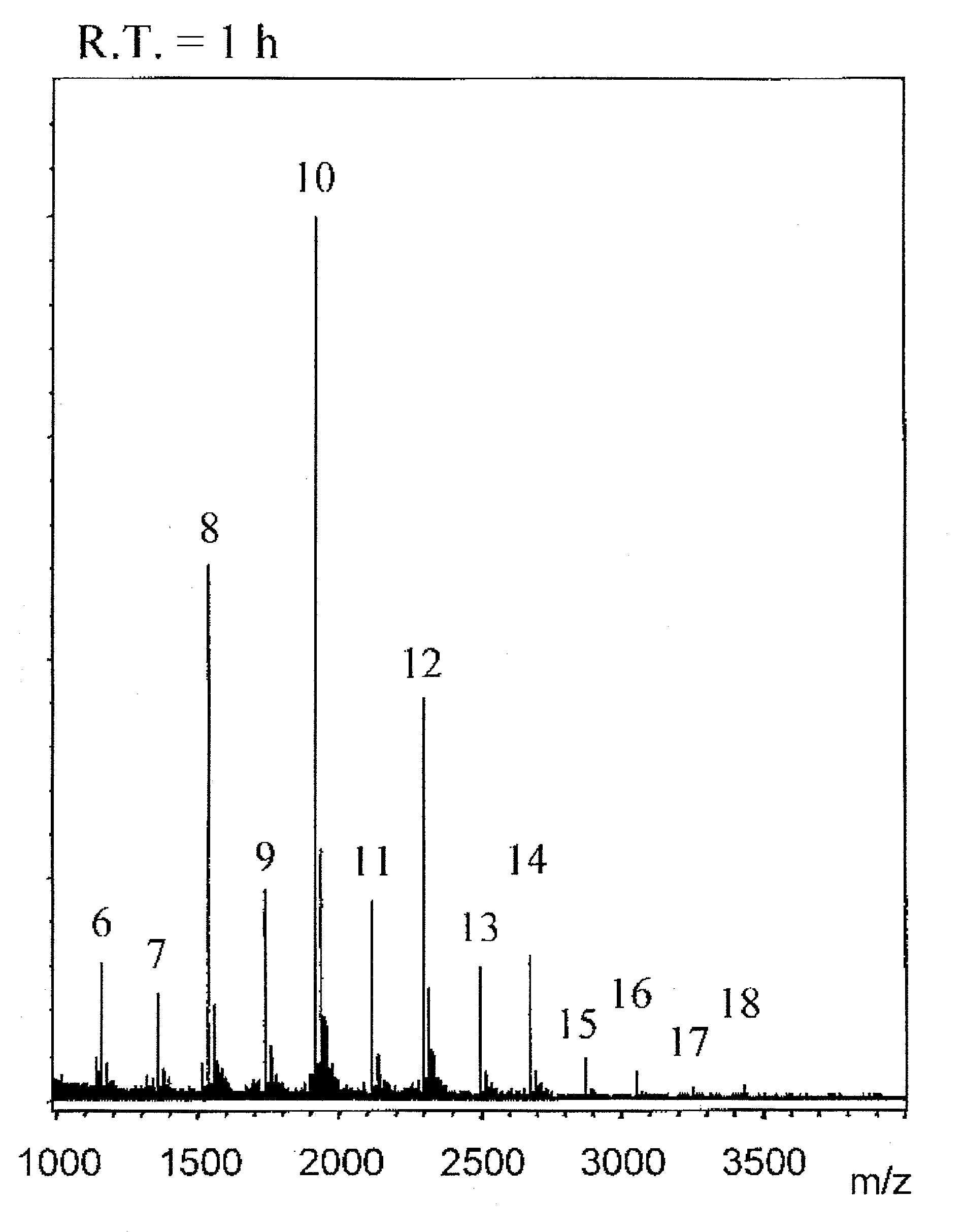
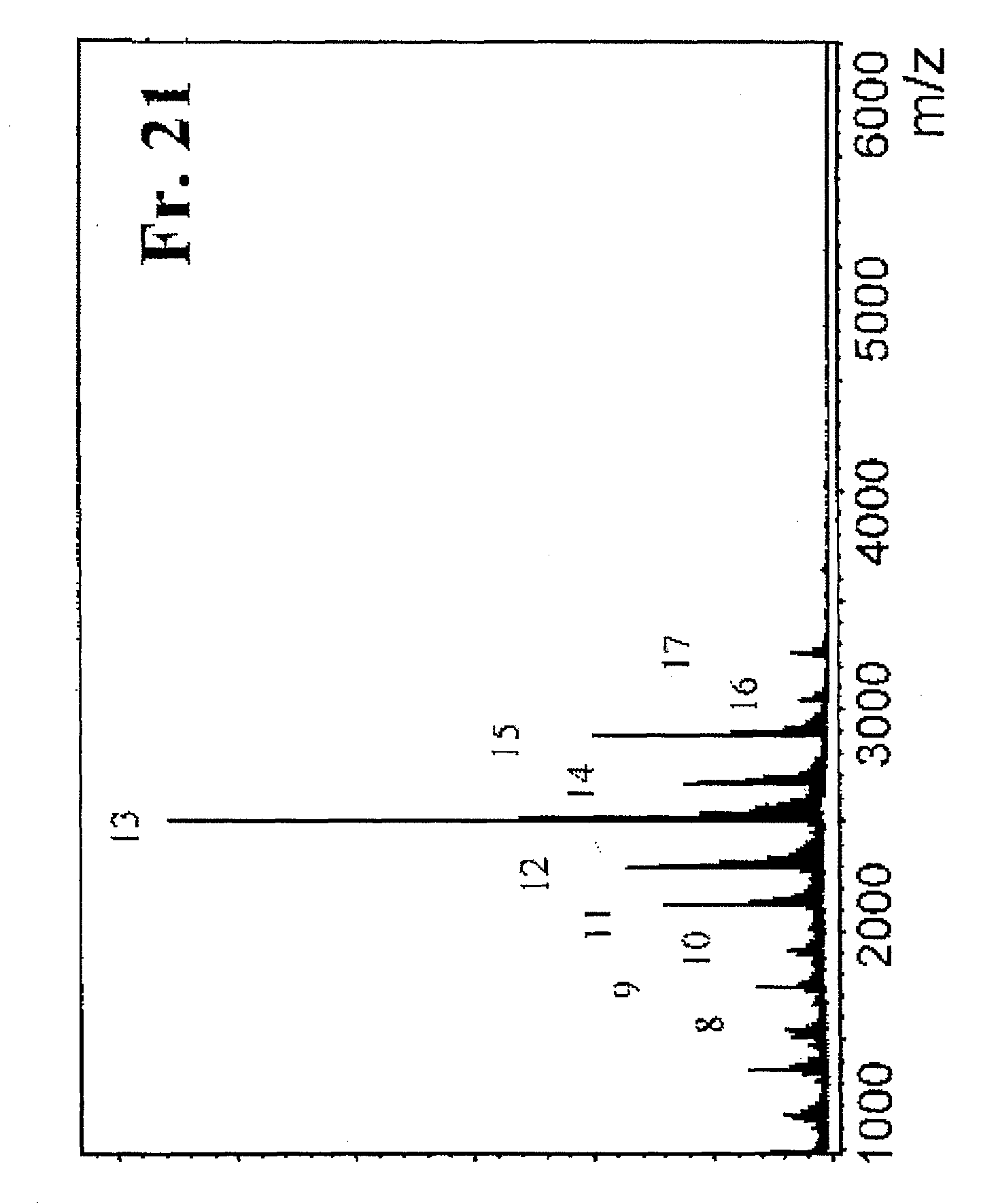
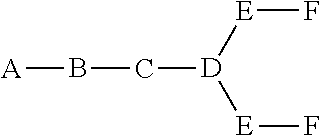
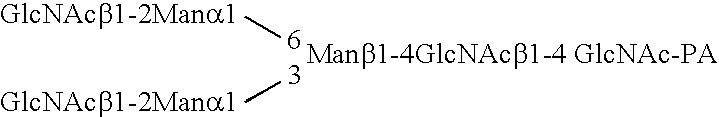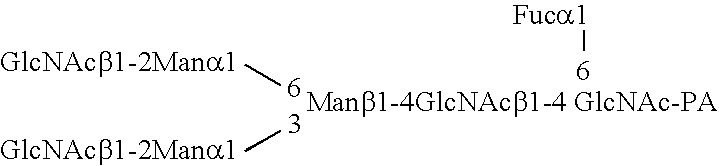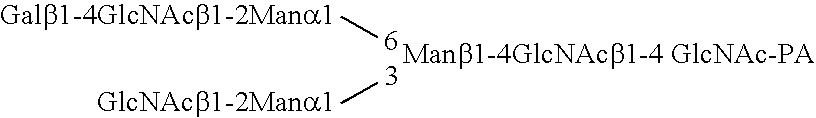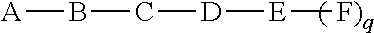Patents
Literature
95 results about "Acetylgalactosamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The N-acetyl derivative of galactosamine.
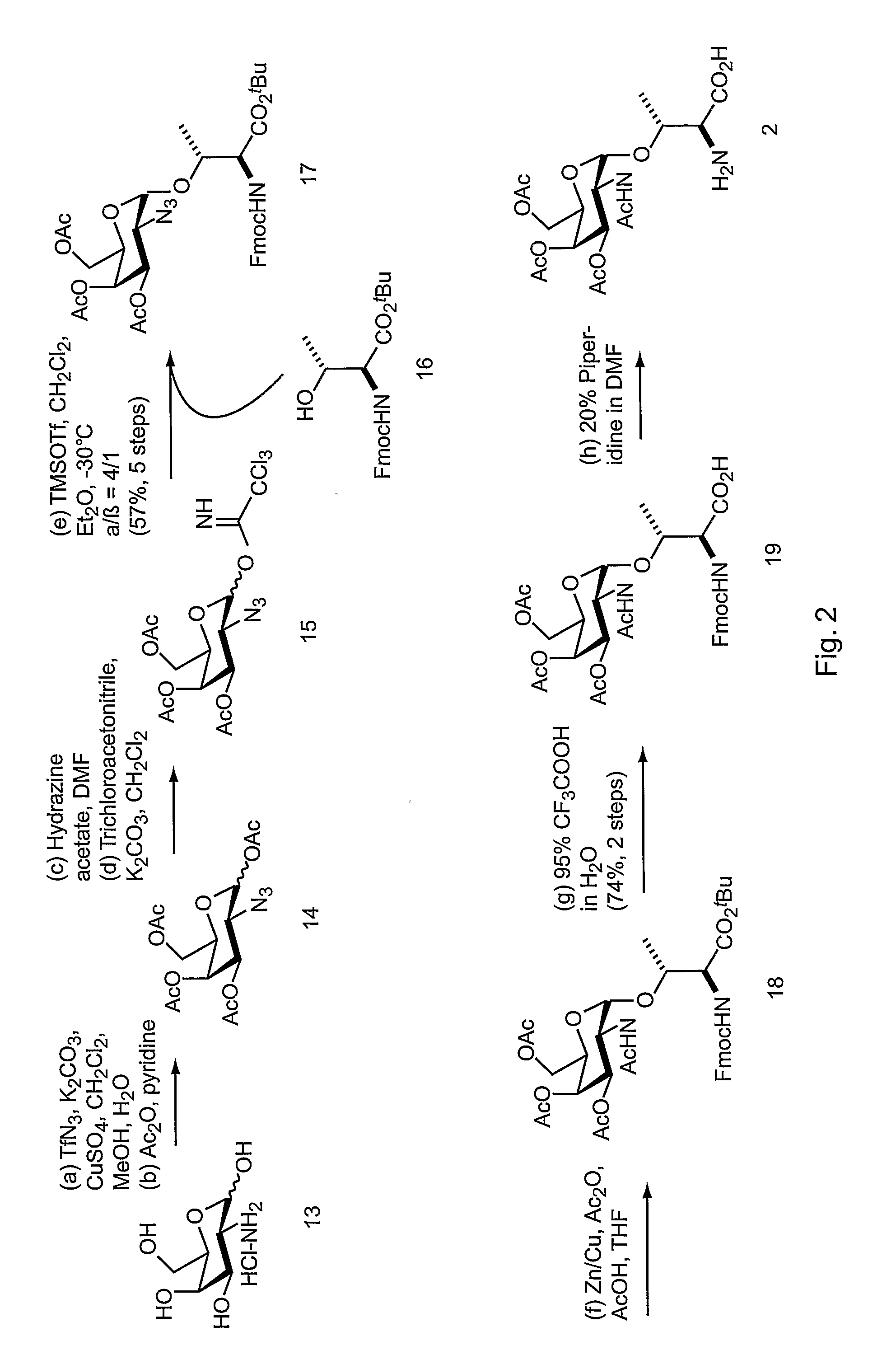
In vivo site-specific incorporation of N-acetyl-galactosamine amino acids in eubacteria
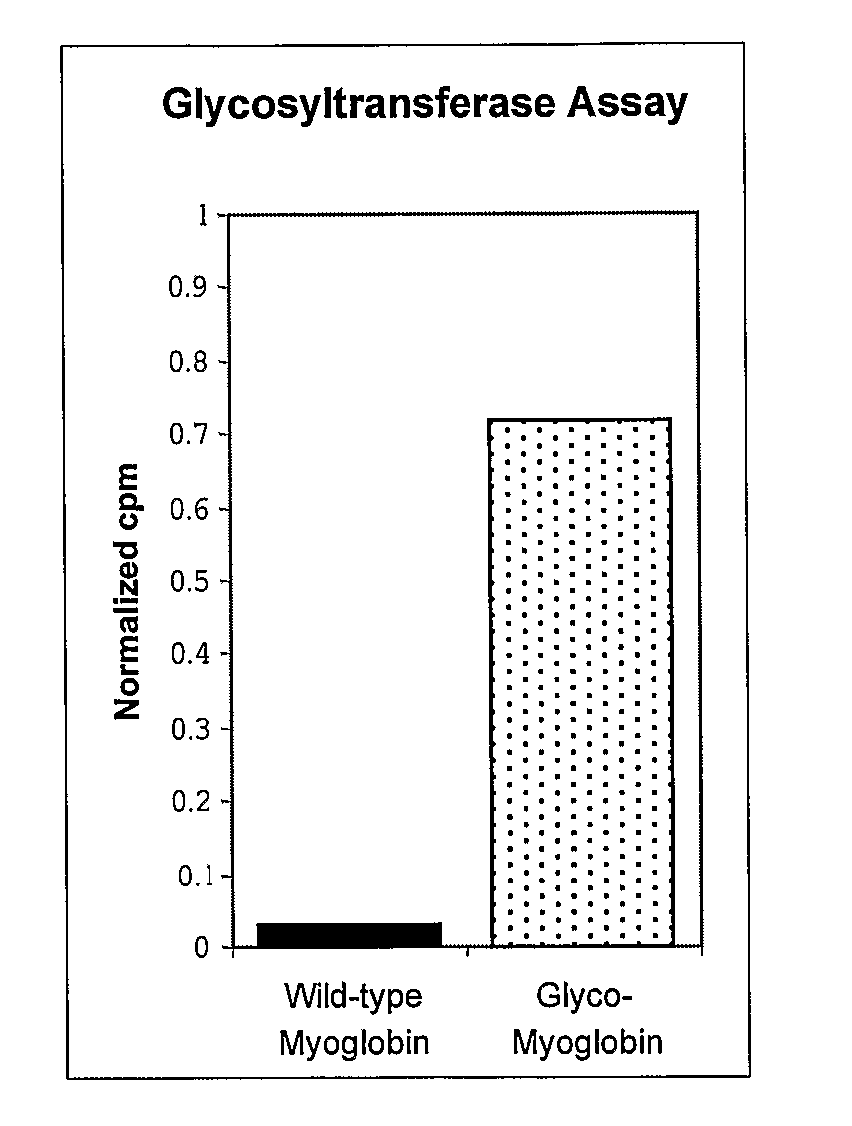
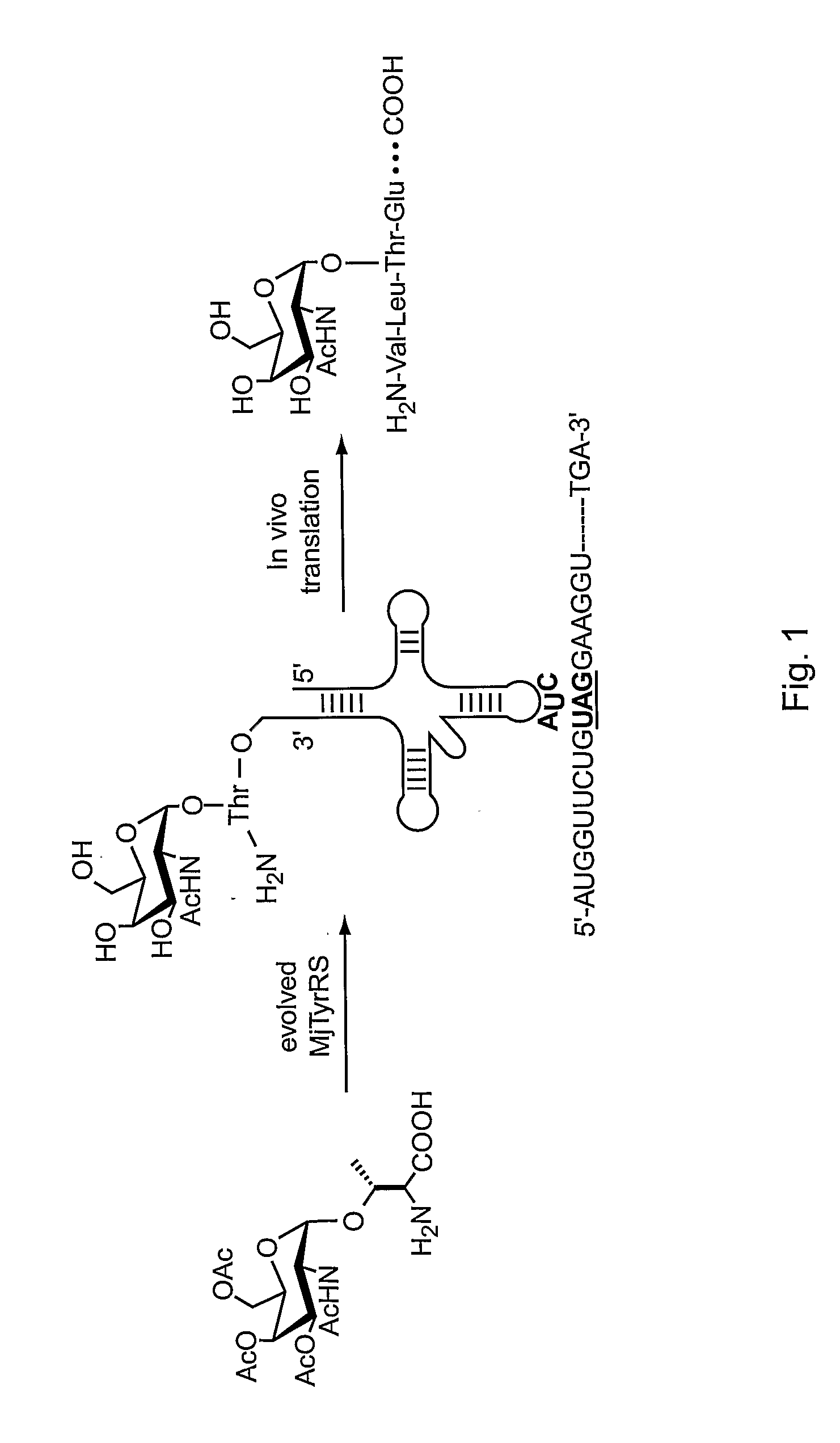
Methods and compositions for making glycoproteins, both in vitro and in vivo, are provided. One method involves incorporating an unnatural amino acid having a N-acetylgalactosamine moiety into a protein; optionally, the N-acetylgalactosamine-containing unnatural amino acid can be further modified with additional sugars.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
In Vivo Site-Specific Incorporation of N-Acetyl-Galactosamine Amino Acids in Eubacteria
Methods and compositions for making glycoproteins, both in vitro and in vivo, are provided. One method involves incorporating an unnatural amino acid having a N-acetylgalactosamine moiety into a protein; optionally, the N-acetylgalactosamine-containing unnatural amino acid can be further modified with additional sugars.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Long-chain chondroitin sugar chain and method for producing the same and method for promoting synthesis of chondroitin
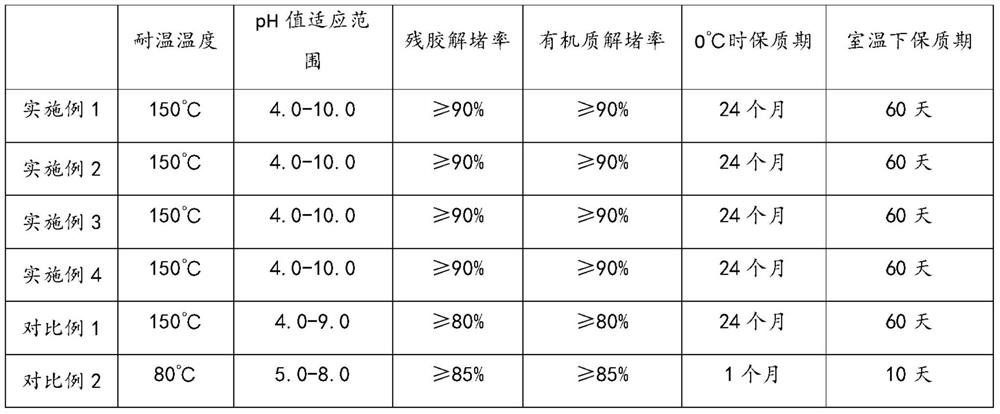
ActiveUS20090263867A1Efficient productionEasy to produceBacteriaSugar derivativesFiltrationChondroitinase ABC
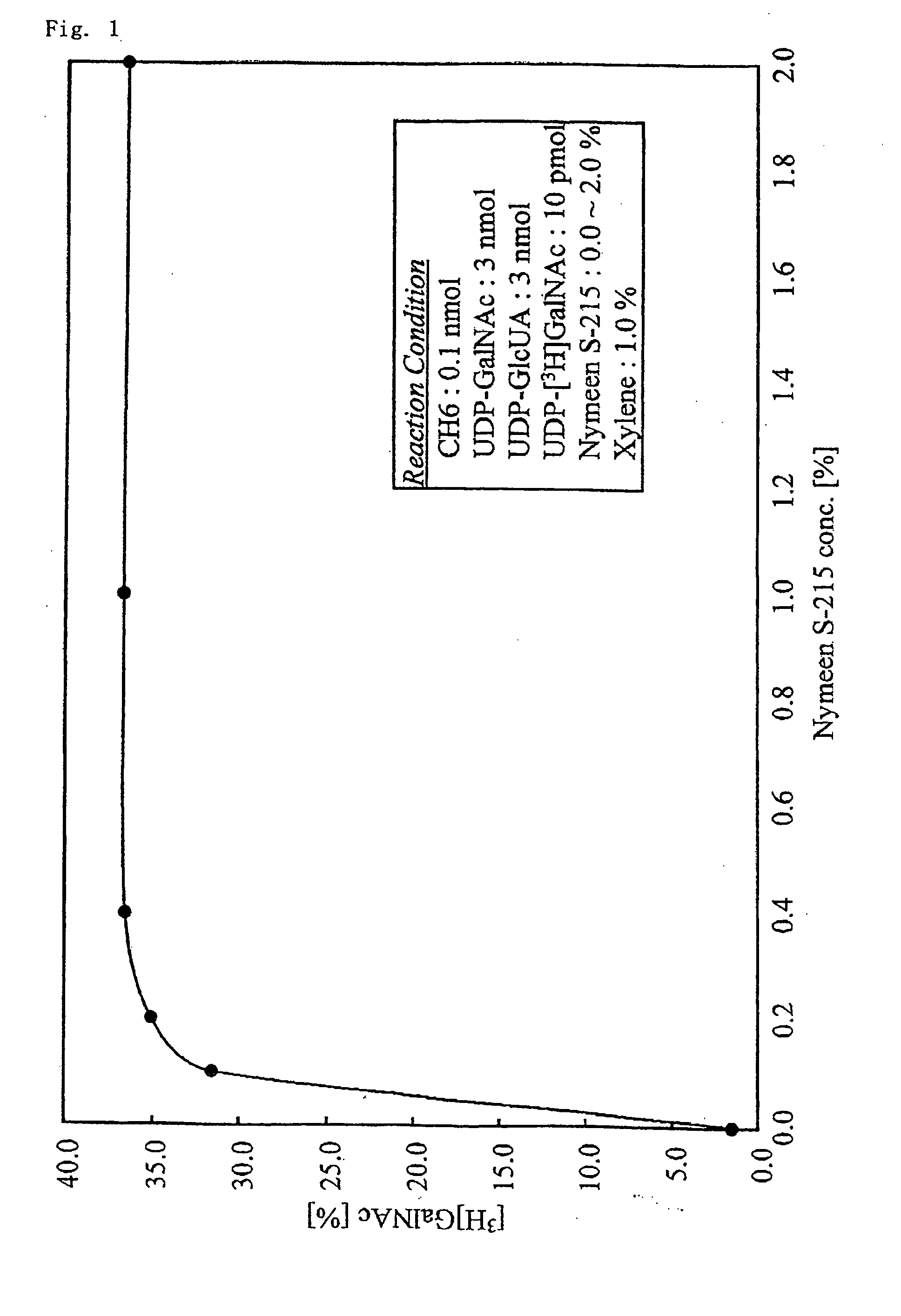
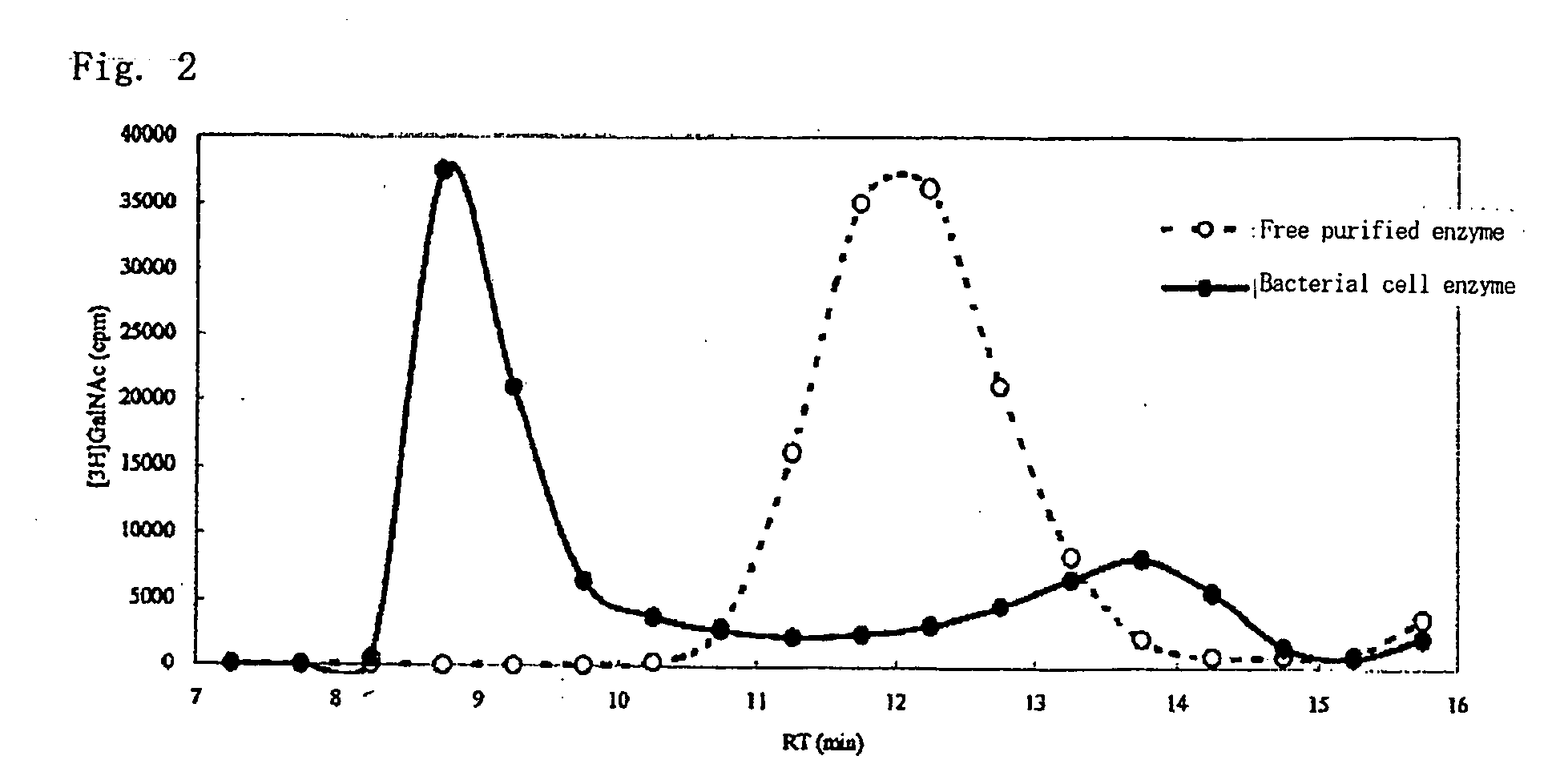
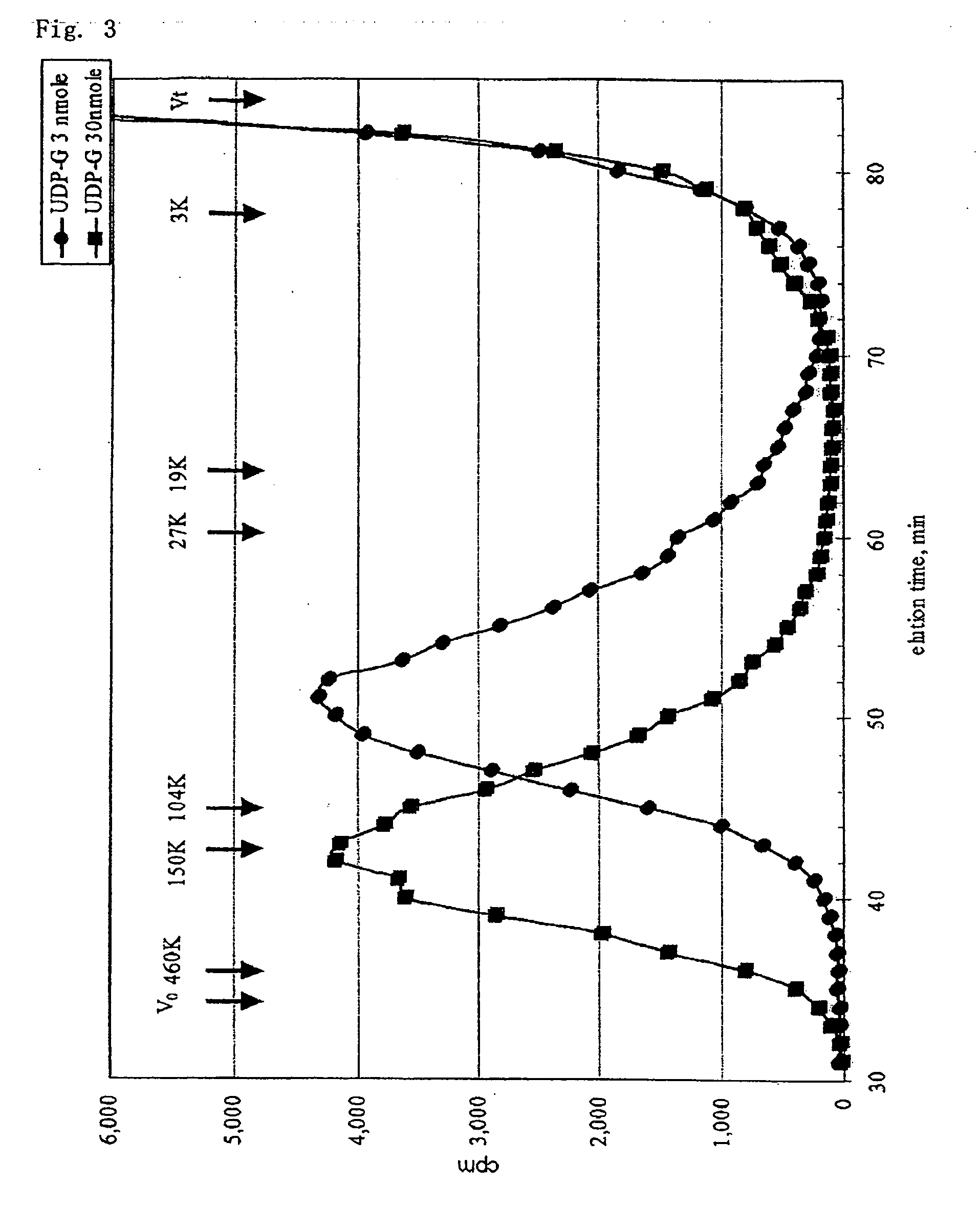
A method for producing a chondroitin sugar chain comprises at least the following step: a step of allowing “a glucuronic acid donor”, “an N-acetyl galactosamine donor”, “a sugar receptor” and “a bacterial cell enzyme which synthesizes chondroitin” to coexist in a reaction system in the presence of a surfactant. Here, the surfactant is preferably selected from n-nonyl-β-D-thiomaltopyranoside, sucrose monocaproate and sucrose monolaurate. The chondroitin sugar chain has all the following properties 1) to 3): 1) a weight average molecular weight: 50,000 or more when it is measured by gel filtration chromatography, 2) it is completely degraded to disaccharides with chondroitinase ABC, 3) when the sugar chain is decomposed with chondroitinase ABC and the decomposed products are subjected to a disaccharide analysis, substantially all of them correspond to an unsaturated disaccharide unit of chondroitin.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Liver targeted medicine
InactiveCN107929273AImproved Liver TargetingGood curative effectDigestive systemPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseCitrulline
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, and in particular relates to liver targeted medicine. The medicine is chemical micromolecular medicine connecting galactosamine. The chemicalmicromolecular medicine is medicine for treating liver diseases or liver-related diseases. The chemical micromolecular medicine is prepared from but not limited to thyroxine T3, sorafenib, taxol, regorafenib, lamivudine, entecavir, telbivudine, statins, fibrates, niacin, bile acid sequestrants, other hepatitis virus DNA (RNA) polymerase inhibition compounds and the like. The galactosamine is tervalent acetylgalactosamine. The connection is the direct connection of the galactosamine and the chemical micromolecular medicine or the connection through linking fragments; the linking fragments comprise but not limited to carbon chains, disulfide bonds, pyrophosphate diester, cysteic acid, polypeptide and thioether or valine-citrulline. The medicine provided by the invention has the advantages that the liver targeted performance is improved; the medicine curative effect is enhanced; the toxic and side reactions on other non-targeted tissues are few.
Owner:崔坤元
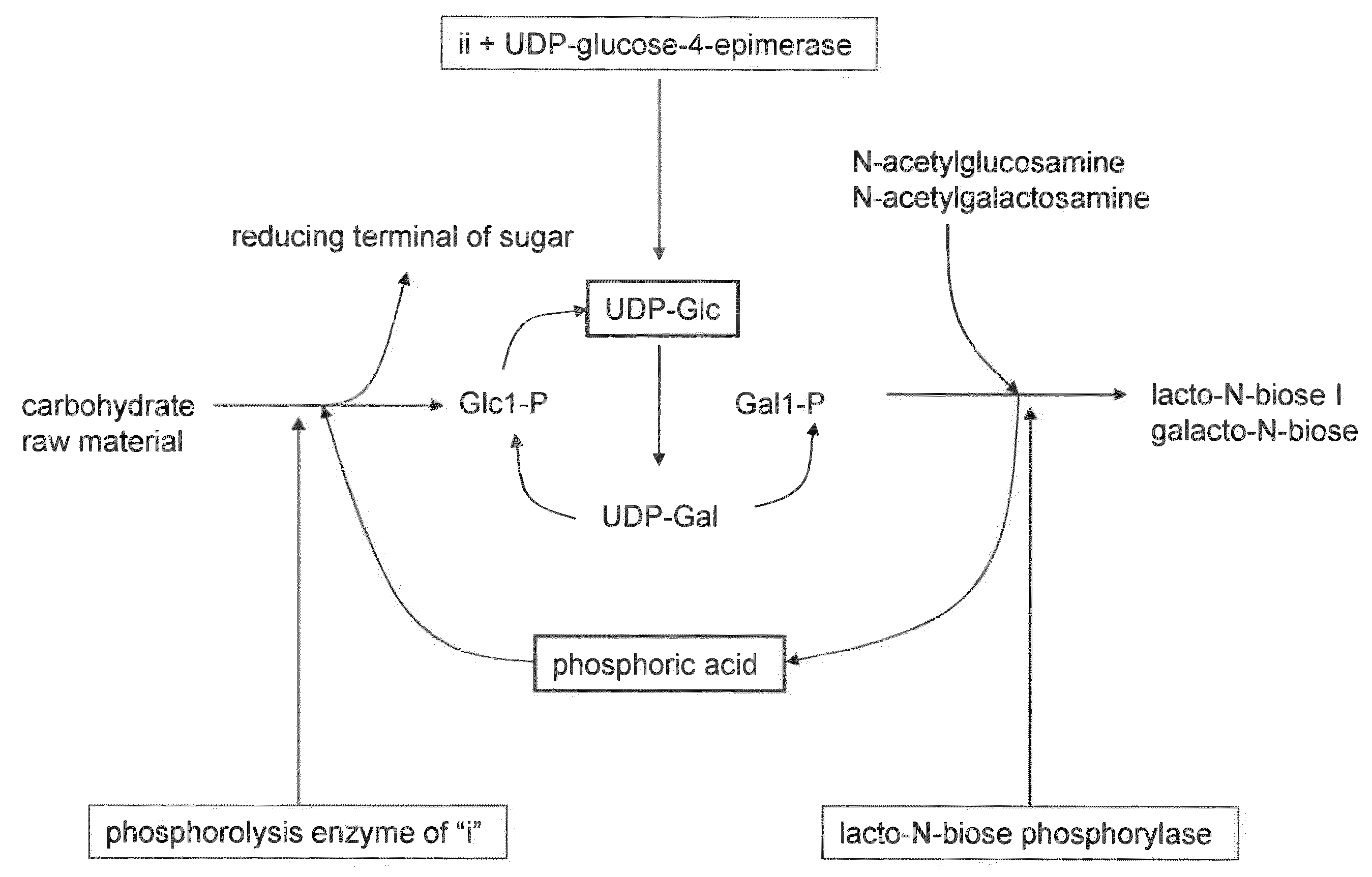
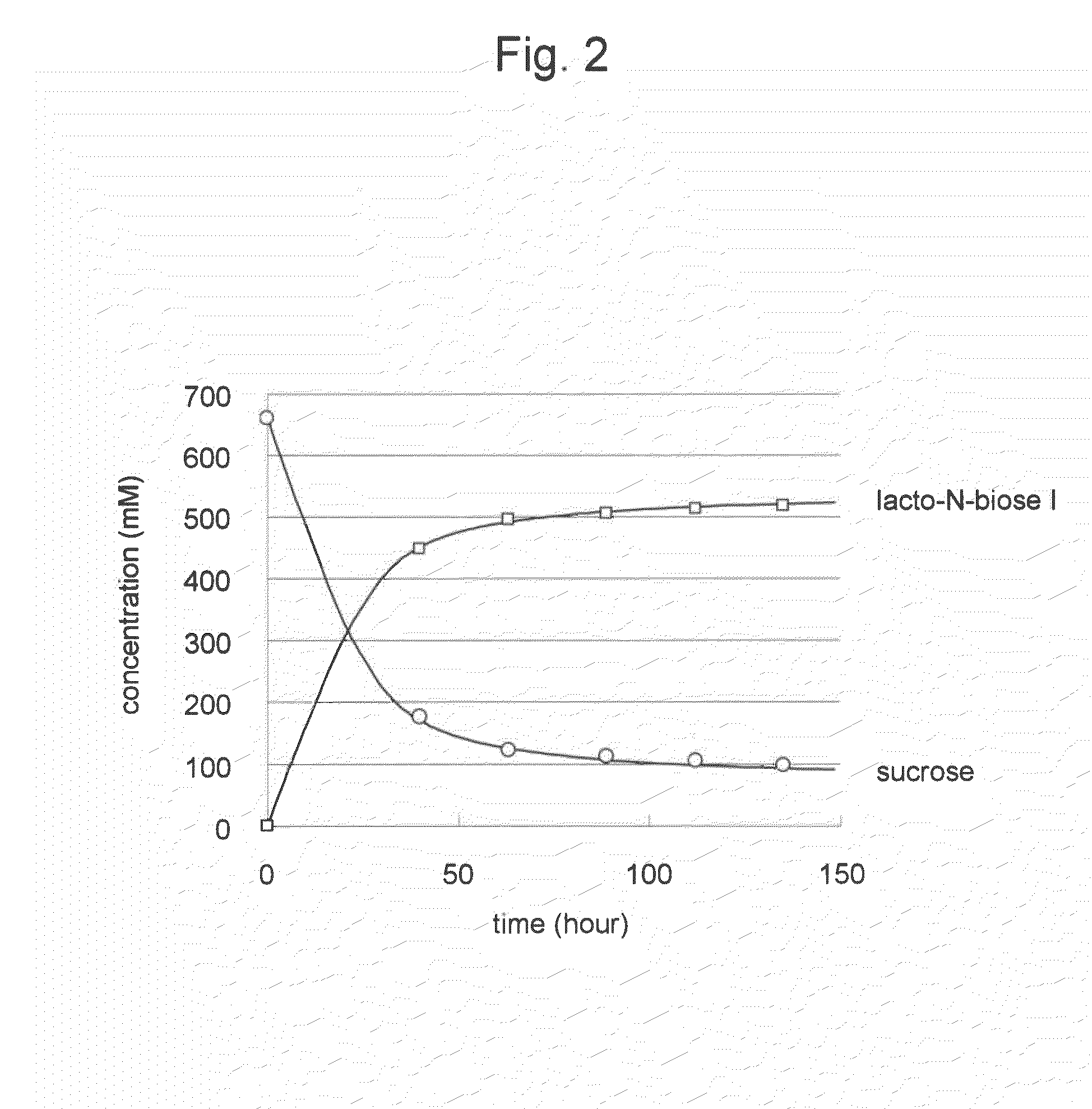
Method for producing lacto-n-biose i and galacto-n-biose
ActiveUS20100120096A1Easily and conveniently carry-outGood value for moneyImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphorylation
A method for producing lacto-N-biose I and galacto-N-biose inexpensively and conveniently is provided. The method for producing lacto-N-biose I or galacto-N-biose, characterized in that the method comprises causing: (i) a combination of a carbohydrate raw material with an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorolysis of the carbohydrate raw material to give a-glucose-1-phosphate; and (ii) a combination of an enzyme that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate to UDP-glucose and an enzyme that converts UDP-galactose to galactose-1-phosphate with their cofactors, and / or a combination of an enzyme (UDP-Gly synthase) that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose and α-galactose-1-phosphate, respectively, with its cofactor(s) to act in the presence of N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine, phosphoric acid, lacto-N-biose phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.211), and UDP-glucose-4-epimerase (EC 5.1.3.2).
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG
Chondroitin systhetase and nucleic acid coding for the enzyme
A human-derived novel chondroitin synthase, which is an enzyme for synthesizing a fundamental backbone of chondroitin and has both glucuronic acid transferring activity and N-acetylgalactosamine transferring activity.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD +1
Highly functional enzyme having α-galactosidase activity
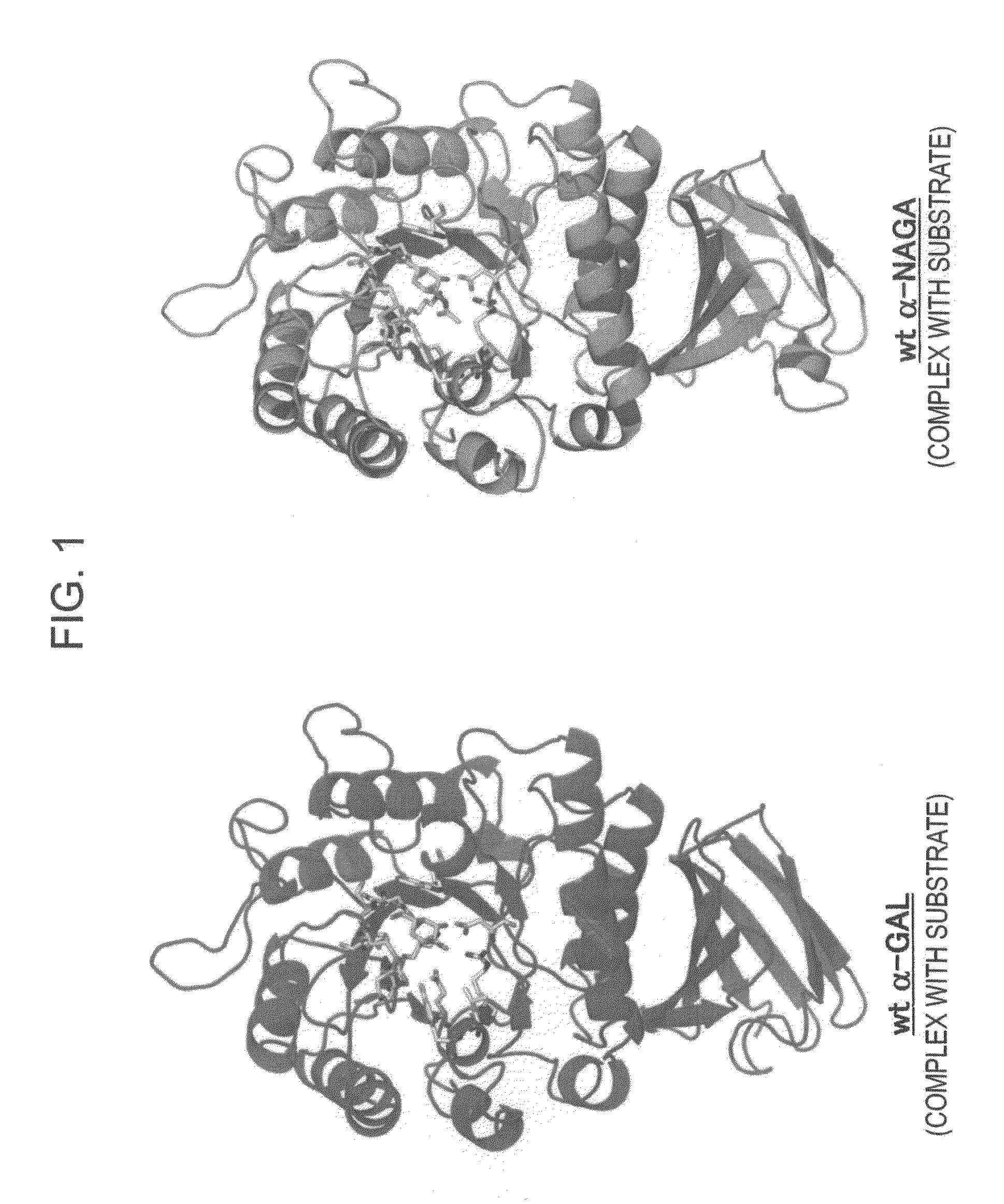
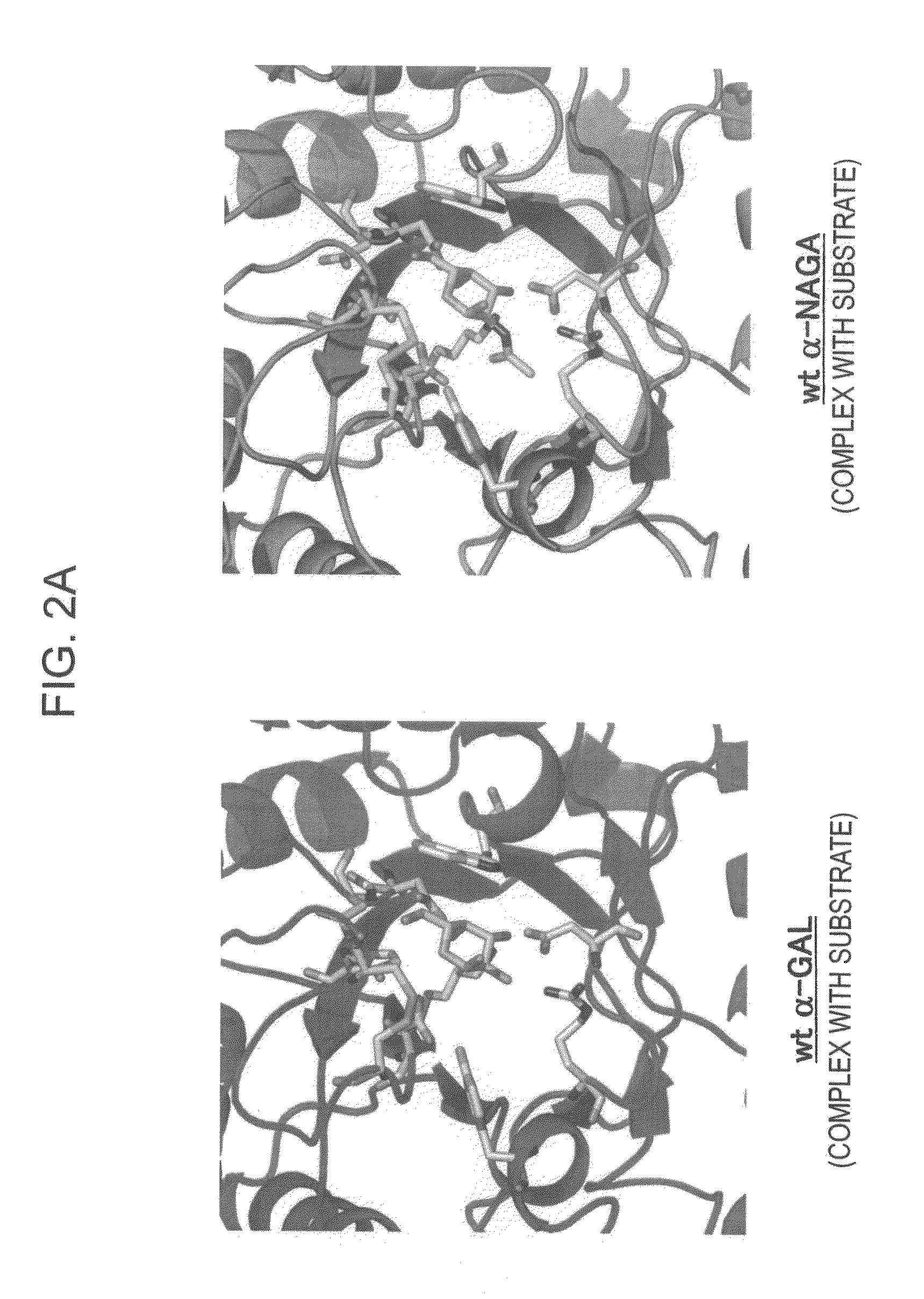
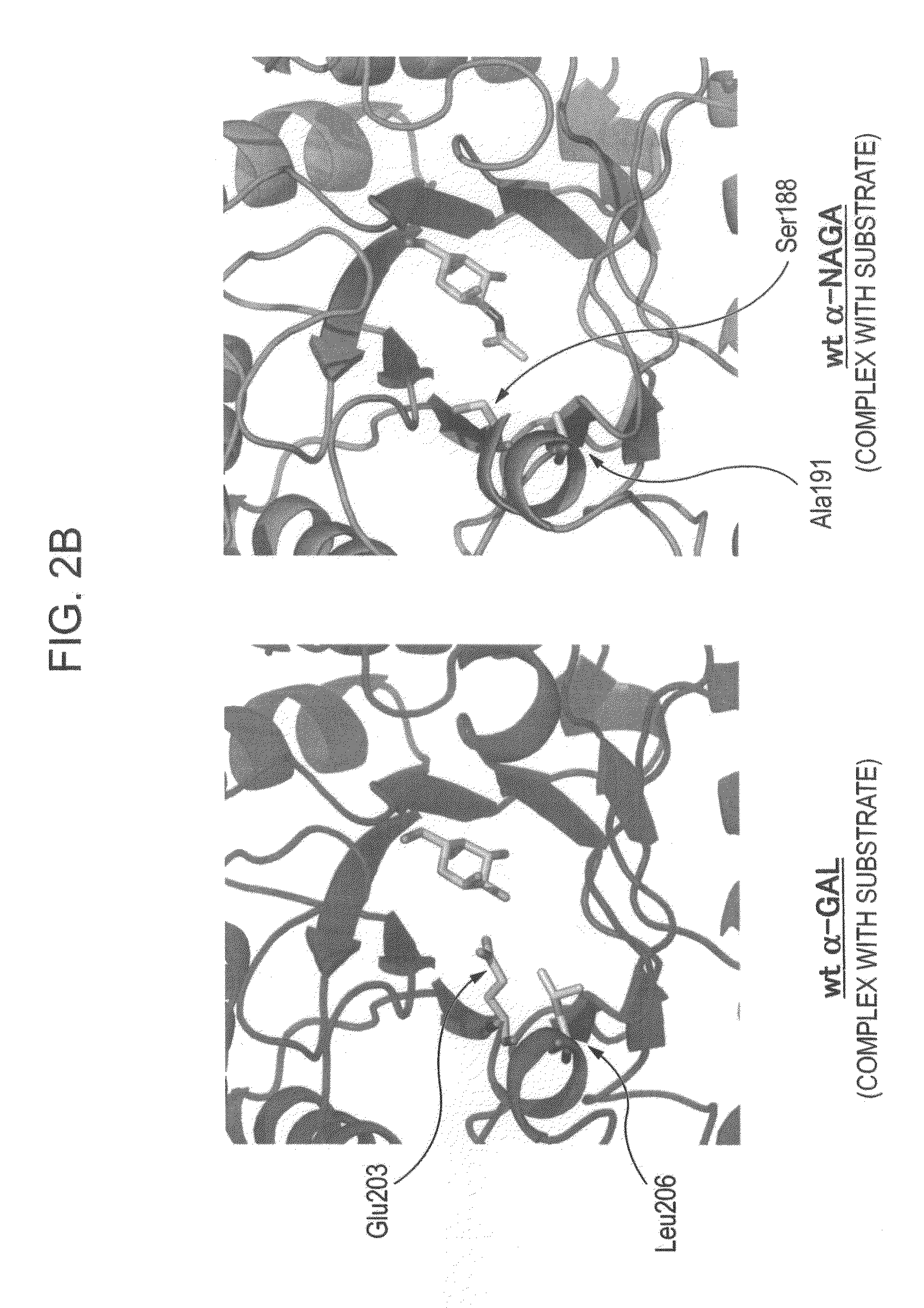
ActiveUS7935336B2Improve stabilityEasily incorporated into cellSenses disorderNervous disorderSide effectFabry disease
The present invention provides, as an enzyme which can be used for enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry disease, a protein having α-galactosidase activity, which shows no allergic adverse side effect, shows a high stability in blood, and can be easily incorporated into a cell of an affected organ. The protein of the present invention is a protein which has acquired α-galactosidase activity by changing the structure of the active site of wild-type human α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase.
Owner:ALTIF LAB
Agents for suppressing neural fibrotic degeneration
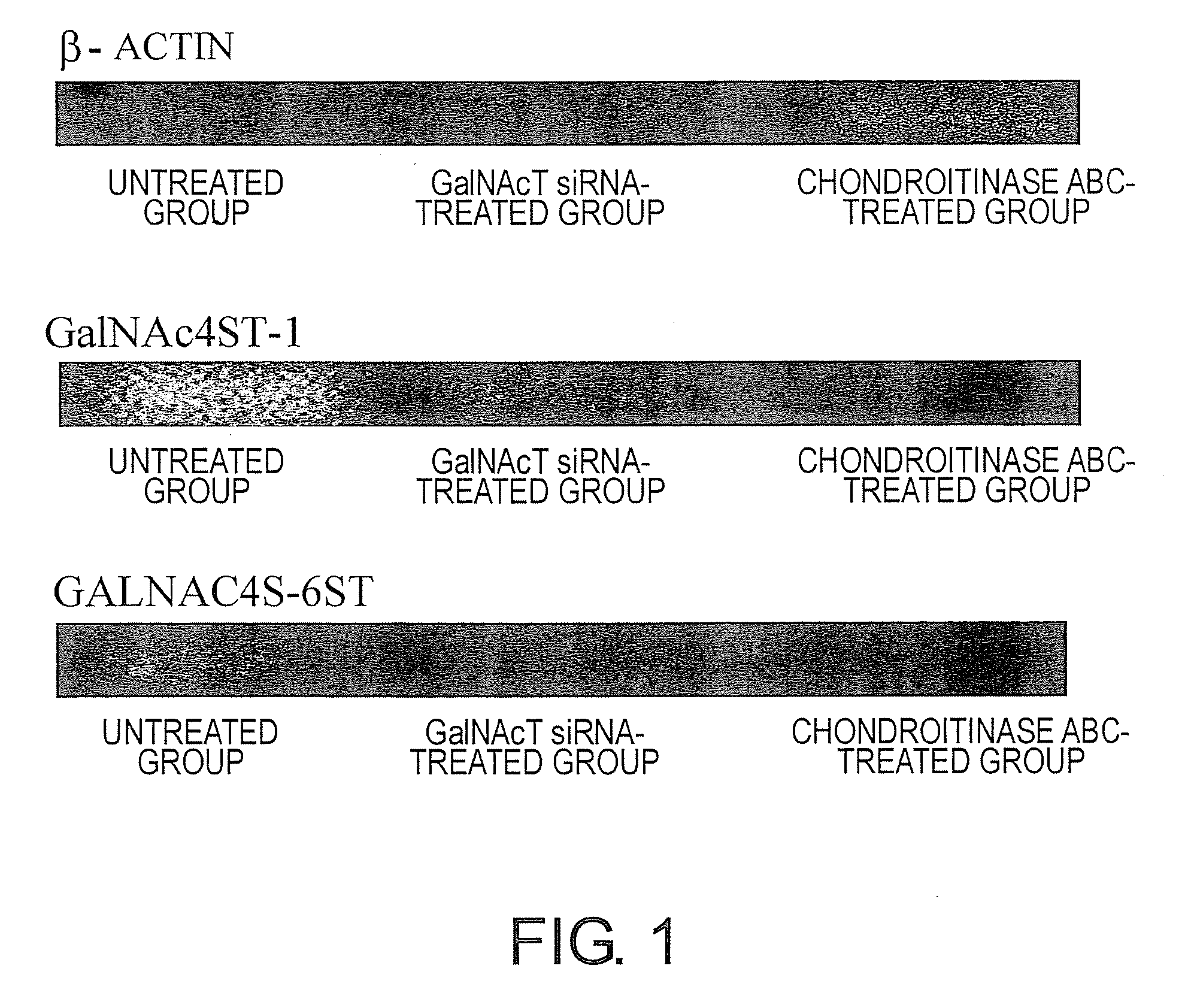
InactiveUS20090202515A1Suppress neural fibrotic degenerationGreat medical and industrial significanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSide chainNeural cell
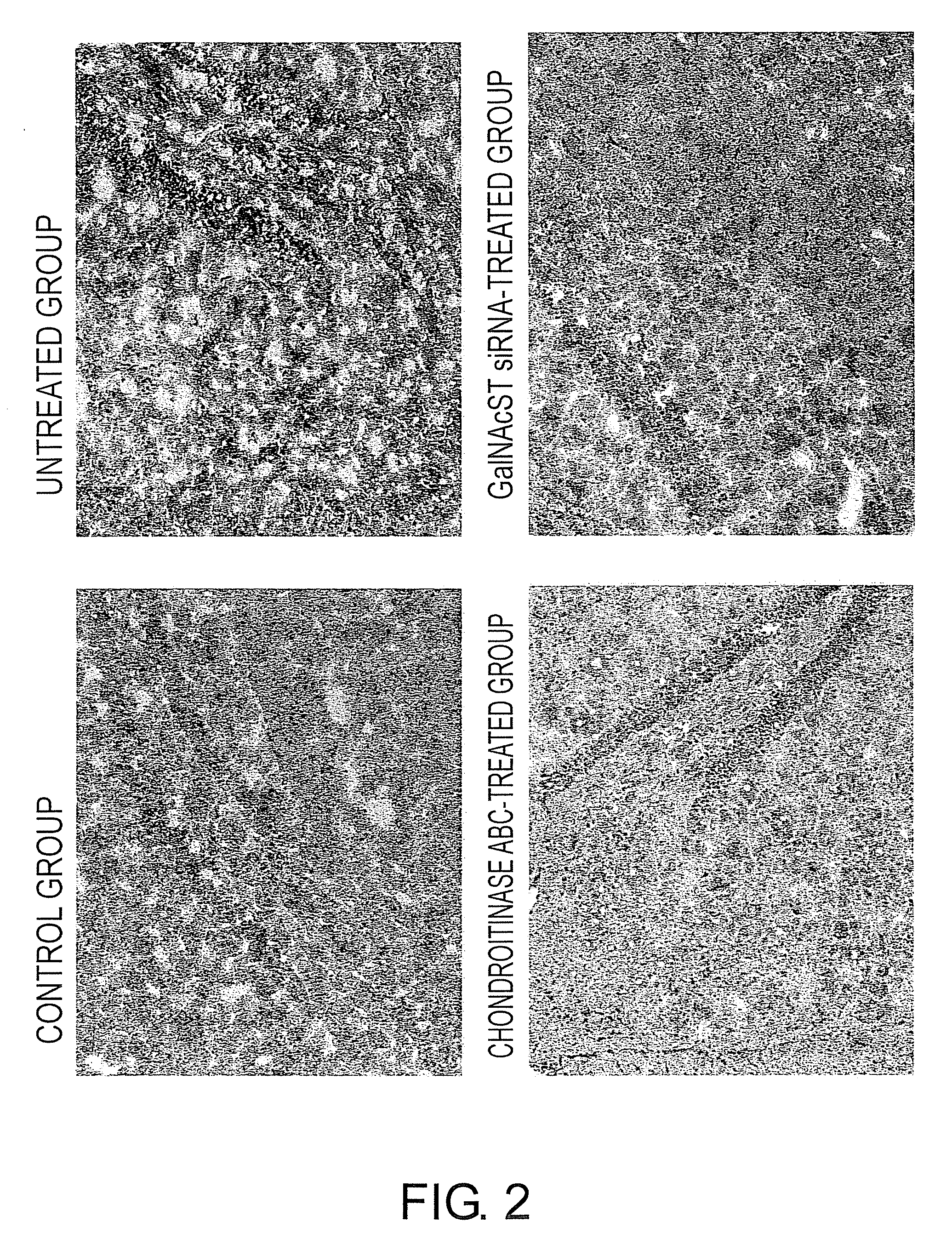
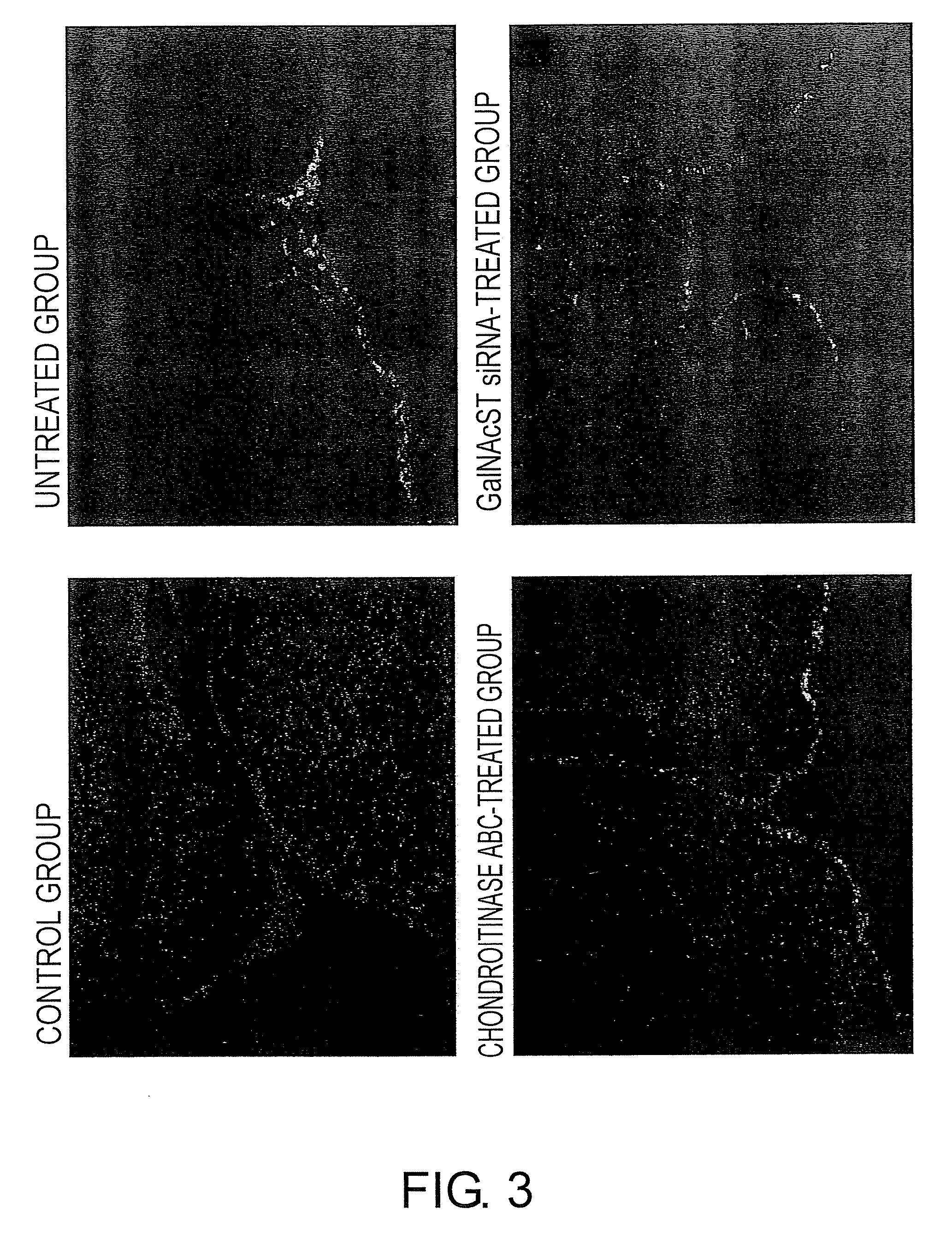
The present invention examined the accumulation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs). The present invention relates to neurodegeneration-suppressing agents that are suitable for gene therapy or prevention of neural fibrotic degenerative diseases which induce neural cell death due to an accumulation of abnormal proteins, where the therapies are based on siRNAs against N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferases (N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferase-1, N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferase-2, and N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase (GalNAc4ST-1, GalNAc4ST-2, and GALNAC4S-6ST, respectively)), which are sulfotransferases for acetylgalactosamine, a CSPG side chain, and chondroitinase ABC, an enzyme that degrades chondroitin sulfate, another CSPG side chain.
Owner:STELIC INST OF REGENERATIVE MEDICINE STELIC INST
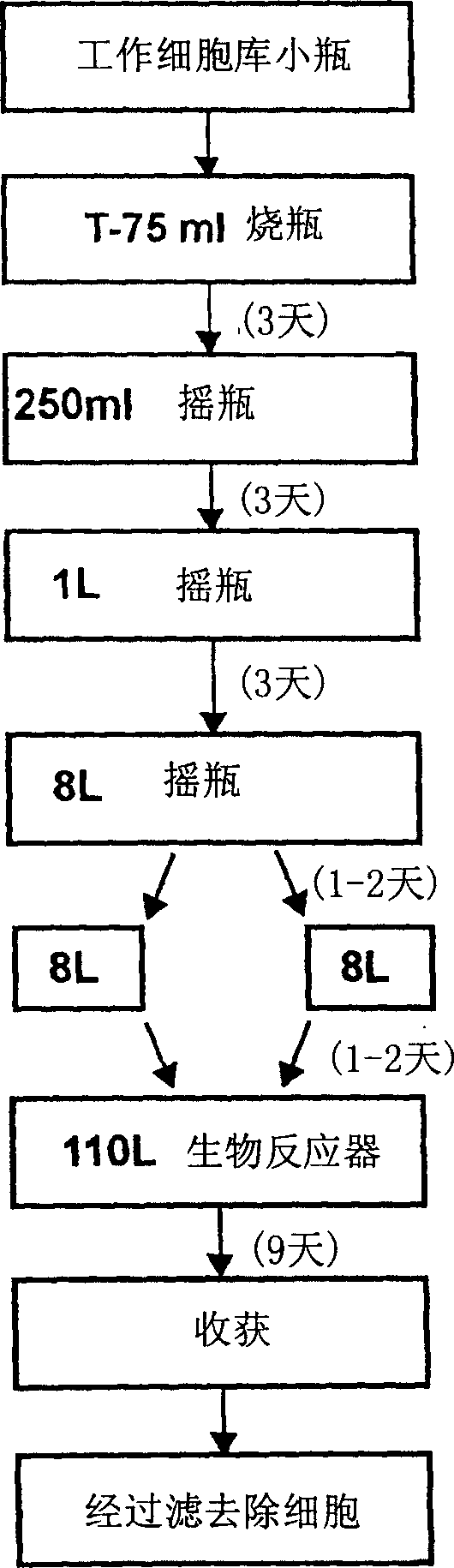
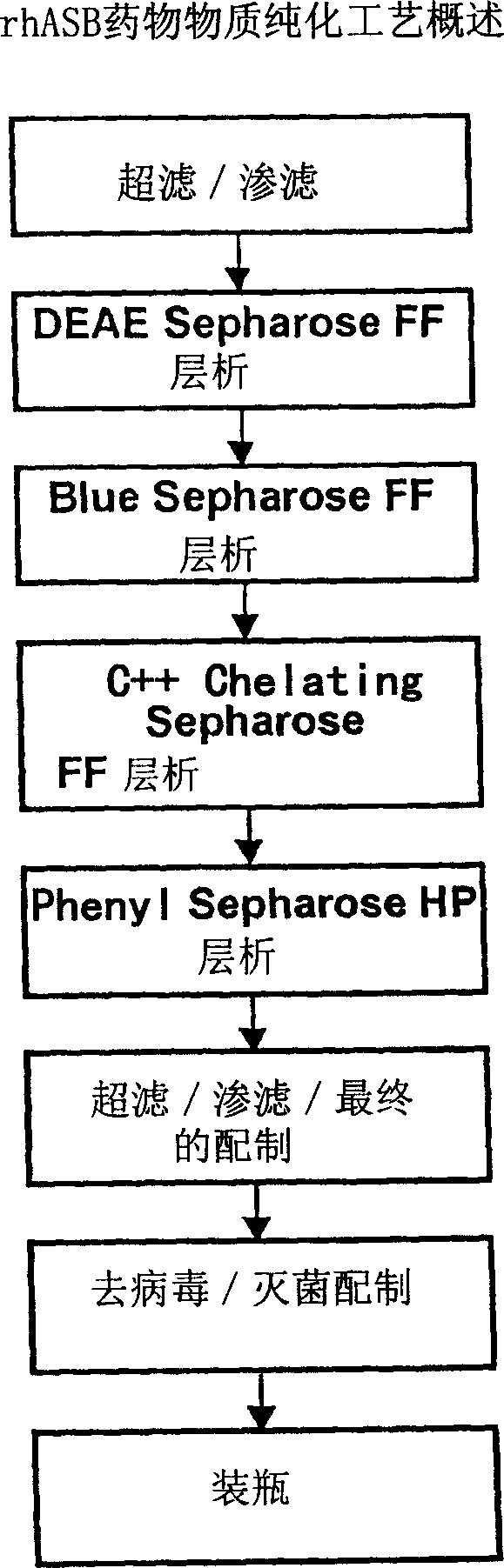
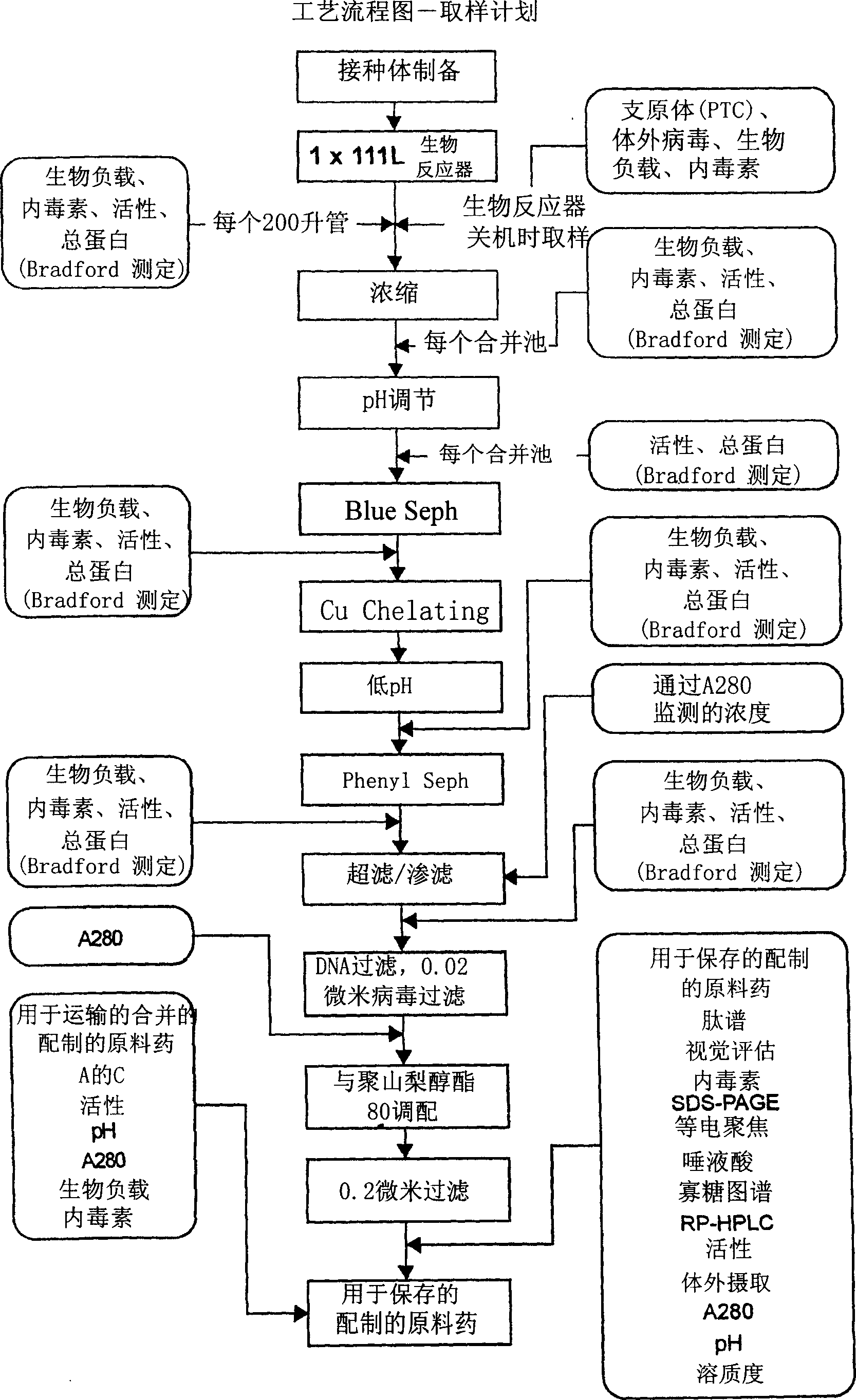
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human n-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase and uses thereof
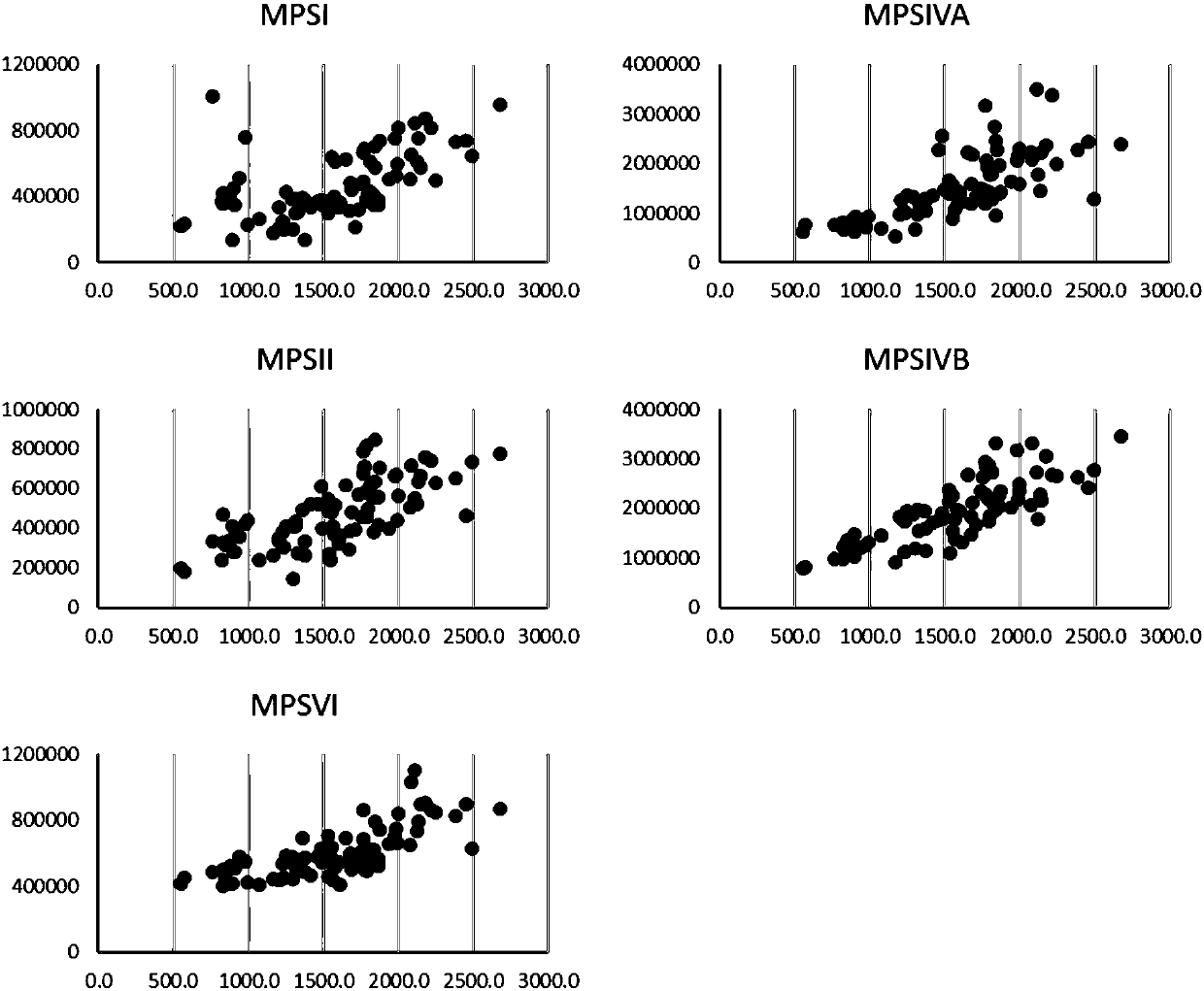
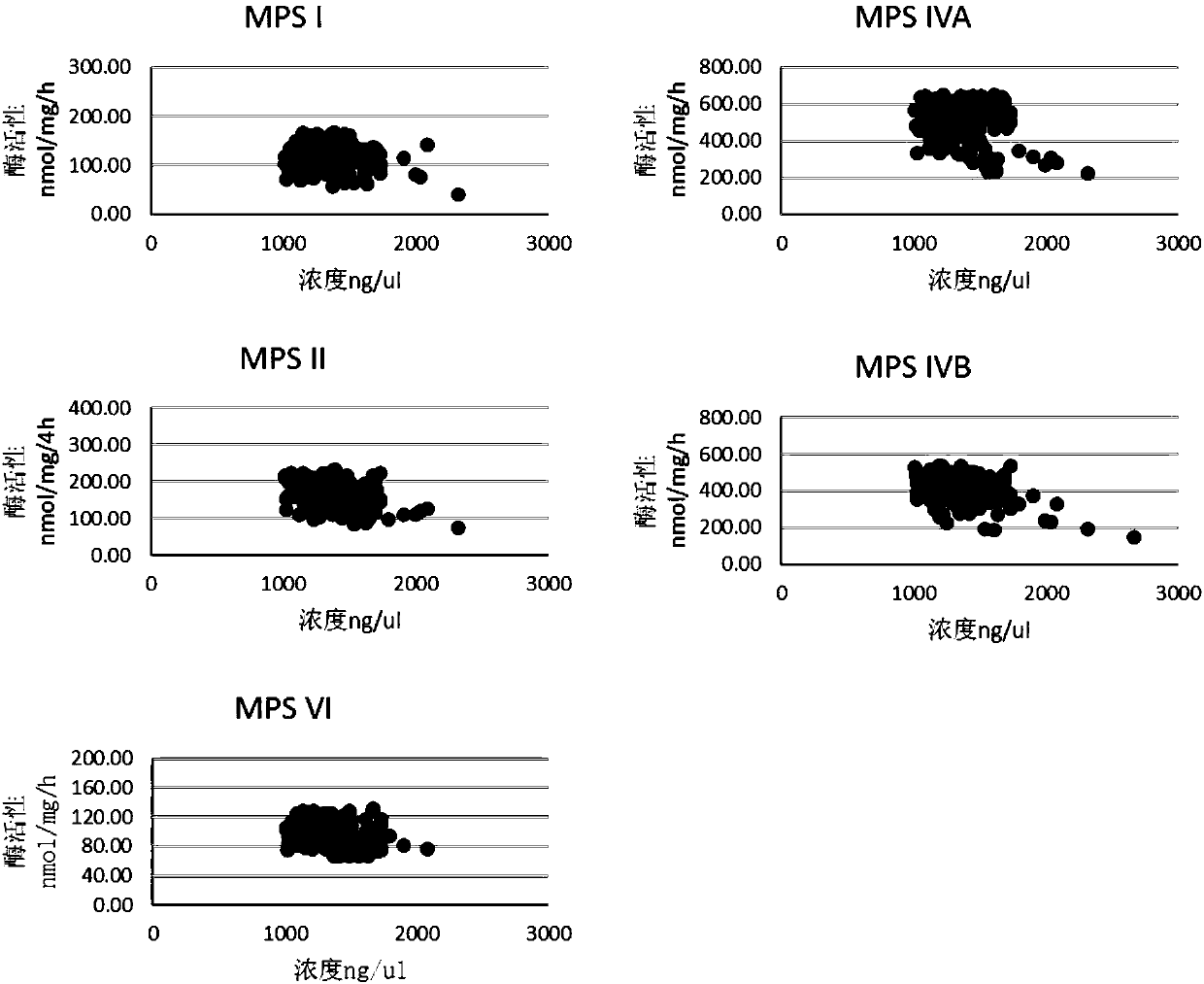
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS), and pharmaceutical compositions and formulations thereof, methods of producing and purifying GALNS, and its use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the GALNS enzyme, e.g., Mucopolysaccharidosis IVa (MPS IVa or Morquio A syndrome).
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Compositions and methods for modulating apolipoprotein c-iii expression
ActiveUS20150126719A1Reduced potencyImprove effectivenessOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseApolipoprotein C
Provided herein are oligomeric compounds with conjugate groups targeting apoplipoprotein C-III (ApoCIII). In certain embodiments, the ApoCIII targeting oligomeric compounds are conjugated to N-Acetylgalactosamine. Also disclosed herein are conjugated oligomeric compounds targeting ApoCIII for use in decreasing ApoCIII to treat, prevent, or ameliorate diseases, disorders or conditions related to ApoCIII. Certain diseases, disorders or conditions related to ApoCIII include inflammatory, cardiovascular and / or metabolic diseases, disorders or conditions. The conjugated oligomeric compounds disclosed herein can be used to treat such diseases, disorders or conditions in an individual in need thereof.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Precursor of N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, methods of treatment using said enzyme and methods for producing and purifying said enzyme
InactiveUS6972124B2High puritySufficient amountBacteriaHydrolasesN-Acetylgalactosamine-4-SulfataseMutant
The present invention provides a highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase and biologically active mutants, fragments and analogs thereof as well as pharmaceutical formulations comprising highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase. The invention also provides methods for treating diseases caused all or in part by deficiencies in human N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase including MPS VI and methods for producing and purifying the recombinant precursor enzyme to a highly purified form.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR MODULATING APOLIPOPROTEIN (a) EXPRESSION
ActiveUS20150126720A1Reduced potencyImprove effectivenessOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseMedicine
Provided herein are oligomeric compounds with conjugate groups targeting apoplipoprotein (a) [apo(a)]. In certain embodiments, the apo(a) targeting oligomeric compounds are conjugated to N-Acetylgalactosamine. Also disclosed herein are conjugated oligomeric compounds targeting apo(a) for use in decreasing apo(a) to treat, prevent, or ameliorate diseases, disorders or conditions related to apo(a) and / or Lp(a). Certain diseases, disorders or conditions related to apo(a) and / or Lp(a) include inflammatory, cardiovascular and / or metabolic diseases, disorders or conditions. The conjugated oligomeric compounds disclosed herein can be used to treat such diseases, disorders or conditions in an individual in need thereof.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Method for determining prostate cancer
InactiveUS20110236995A1Accurately determineImprove accuracyComponent separationIsotope separationGlycanN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention provides a method for detecting a glycan structure of a prostate specific antigen (PSA) rapidly and with high sensitivity and determining prostate carcinoma based on the difference in the structure, in particular, a method for determining between prostate carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia accurately. A method for determining prostate carcinoma, wherein the method includes a step of analyzing a PSA glycan structure in a sample derived from a test subject, and prostate carcinoma is determined in the case that amount of a glycan having LacdiNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(+)) is more than 30% of amount of a glycan not having LacdiNAc but having LacNAc (galacotose-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(−)). Especially, a method for determining prostate carcinoma, wherein prostate carcinoma is determined in the case that amount of a glycan having LacdiNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(+)) is more than 30% of amount of a glycan not having LacdiNAc but having LacNAc (galacotose-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(−)), and benign prostatic hyperplasia is determined in the case of 30% or less.
Owner:NOGUCHI INST
Novel n-acetylgalactosamine transferases and nucleic acids encoding the same
An enzyme which transfers N-acetylgalactosamine to N-acetylglucosamine via a β1-4 linkage was isolated and the structure of its gene was explained. This led to the production of said enzyme or the like by genetic engineering techniques, the production of oligosaccharides using said enzyme, and the diagnosis of diseases on the basis of said gene or the like. The present invention uses a protein having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 26 or 27 in the Sequence Listing or a variant of said amino acid sequence wherein one or more acids are substituted or deleted, or one or more acids are inserted or added and having the activity of transferring N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) to N-acetylglucosamine serving as a substrate via a β1-4 linkage and nucleic acids encoding said protein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
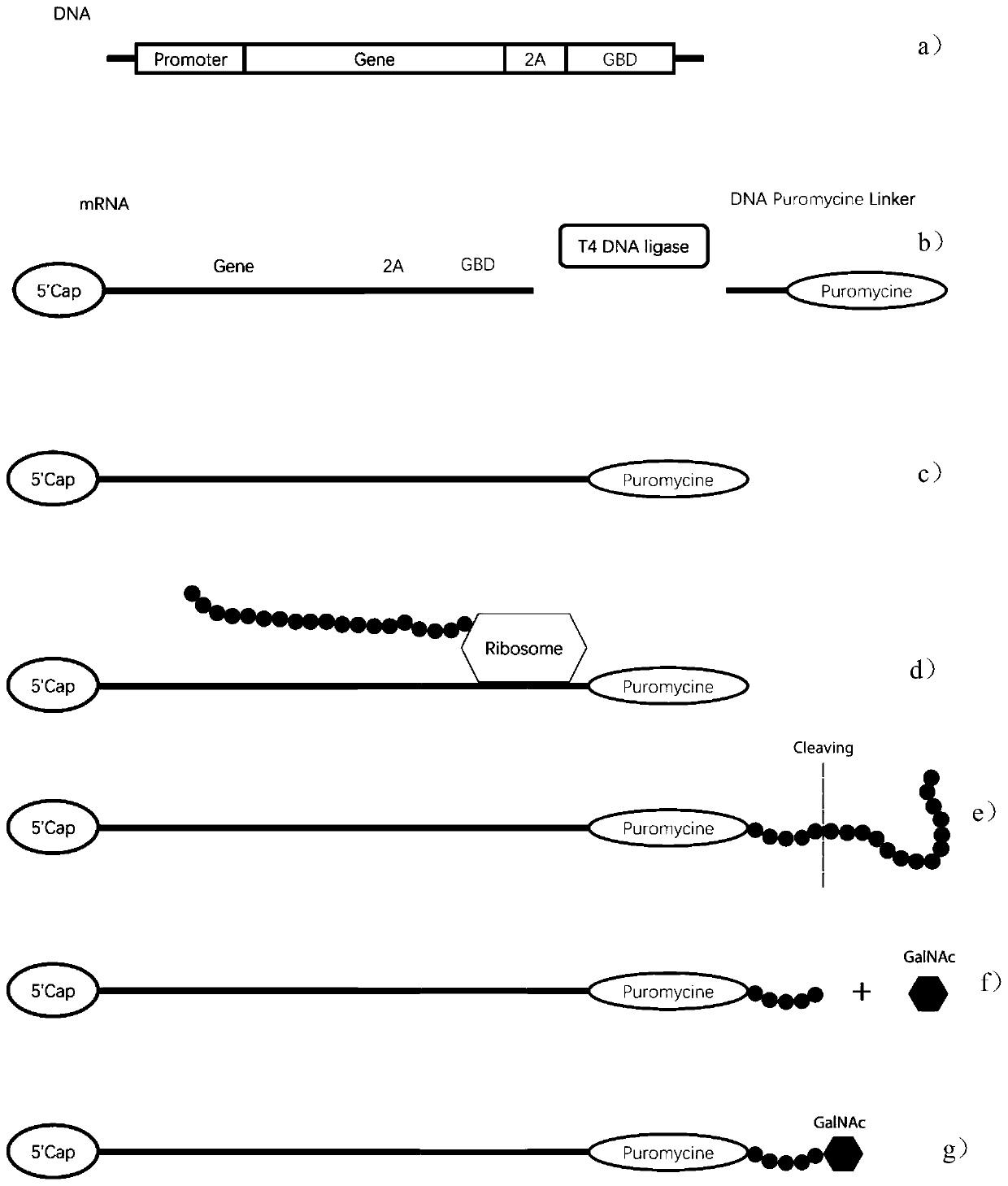
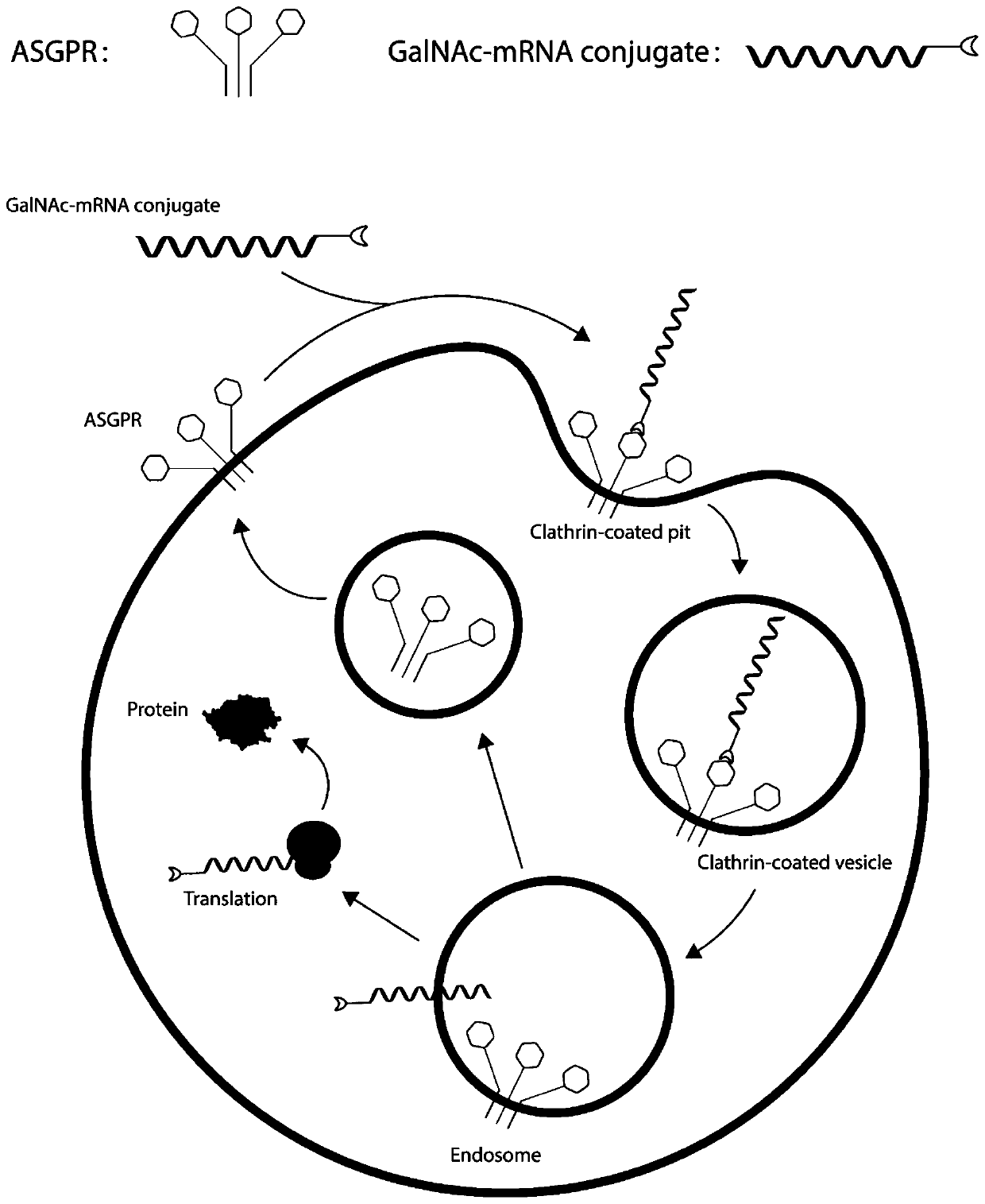
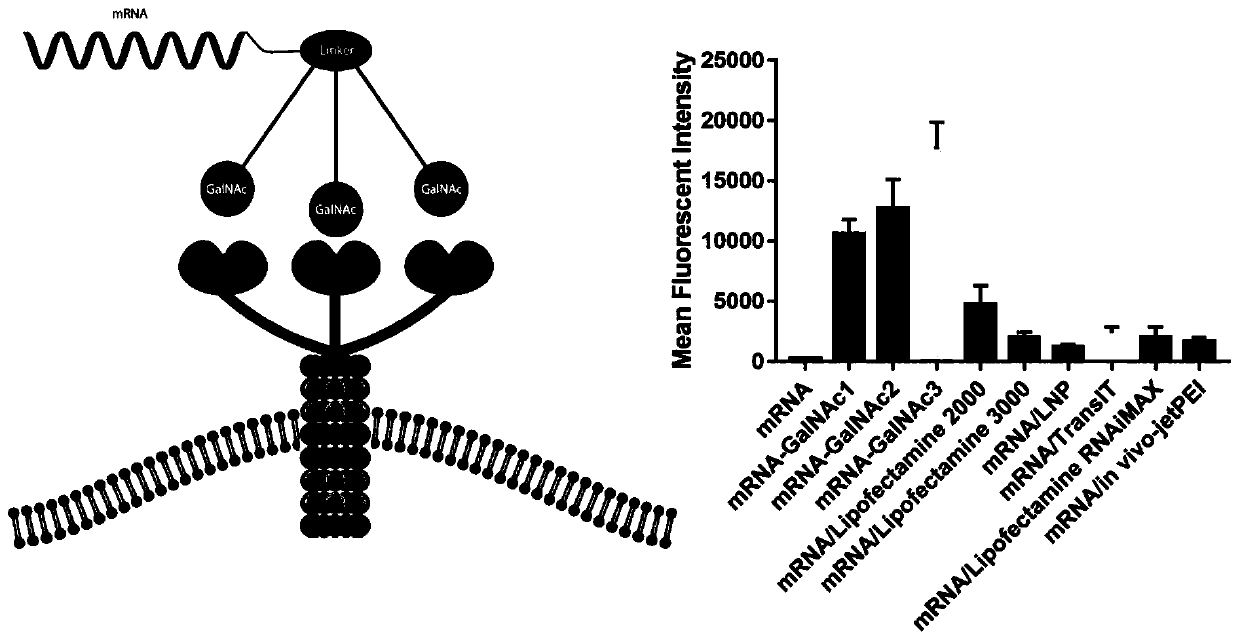
MRNA targeting molecule based on combination of N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide and preparation method of mRNA targeting molecule
ActiveCN111041025AImprove efficacySolve the technical challenges of targeted deliveryGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemGeneticsA-DNA
The invention provides an mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) targeting molecule based on N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide and a preparation method of the mRNA targeting molecule. A plasmid vector containing a DNA fragment formed by sequentially connecting a promoter, a target gene, a specific protease cleavage sequence and a polypeptide GBD sequence capable of being combined with N-acetylgalactosamine is transcribed to obtain mRNA, the mRNA is connected with a DNA-puromycin connector under the action of T4 ligase, through protein translation and shearing with a specific protease, an mRNA-puromycin-GBD compound is obtained, and the mRNA-puromycin-GBD compound is combined with the GBD protein sequence under the action of N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase to form an mRNA-puromycin-GBD-GalNAccompound to complete the GalNAc modification of the mRNA; in the mRNA drug delivery process, the purpose of accurate drug delivery is achieved, and the drug effect of mRNA drug molecules is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN RHEGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
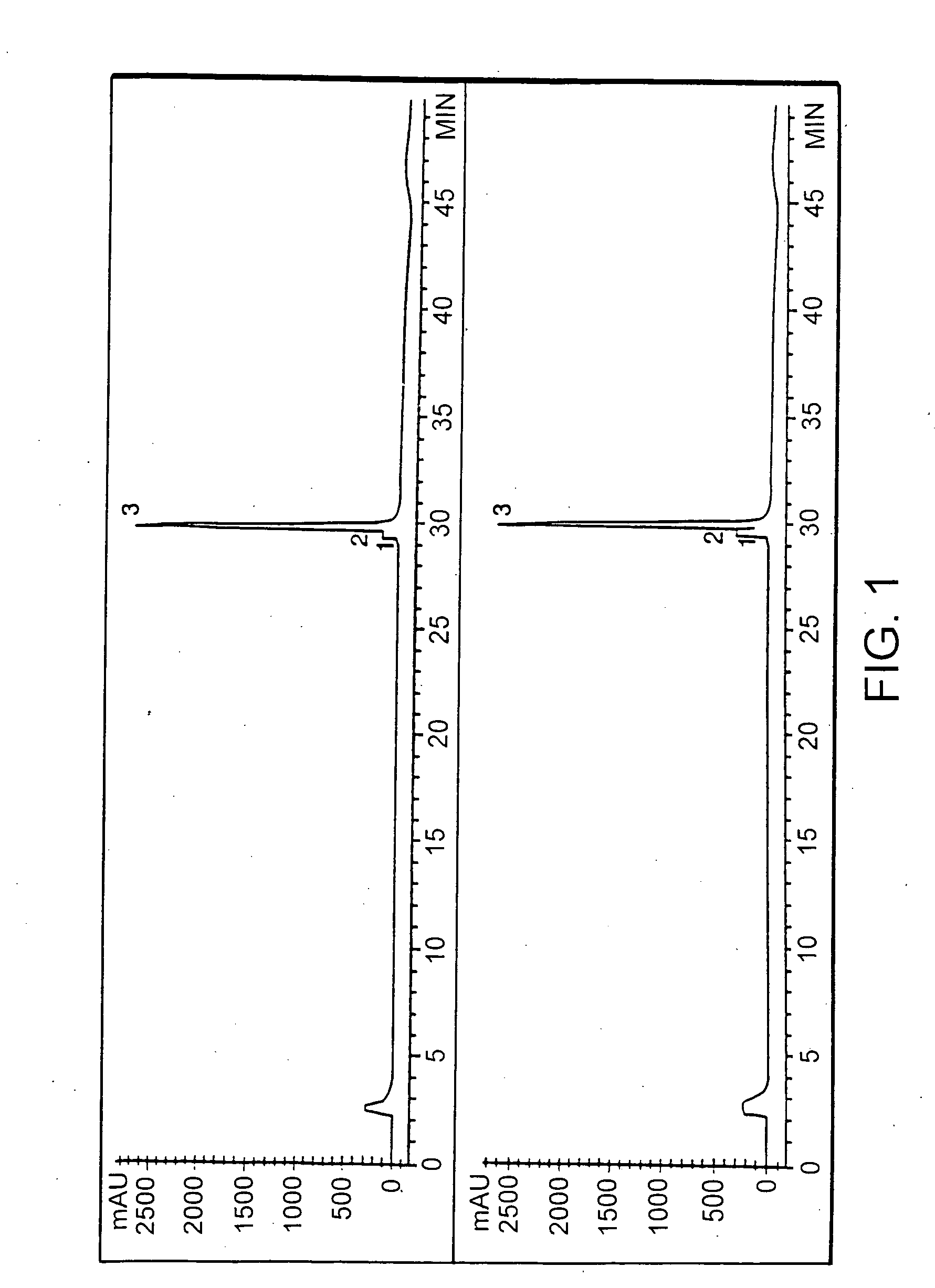
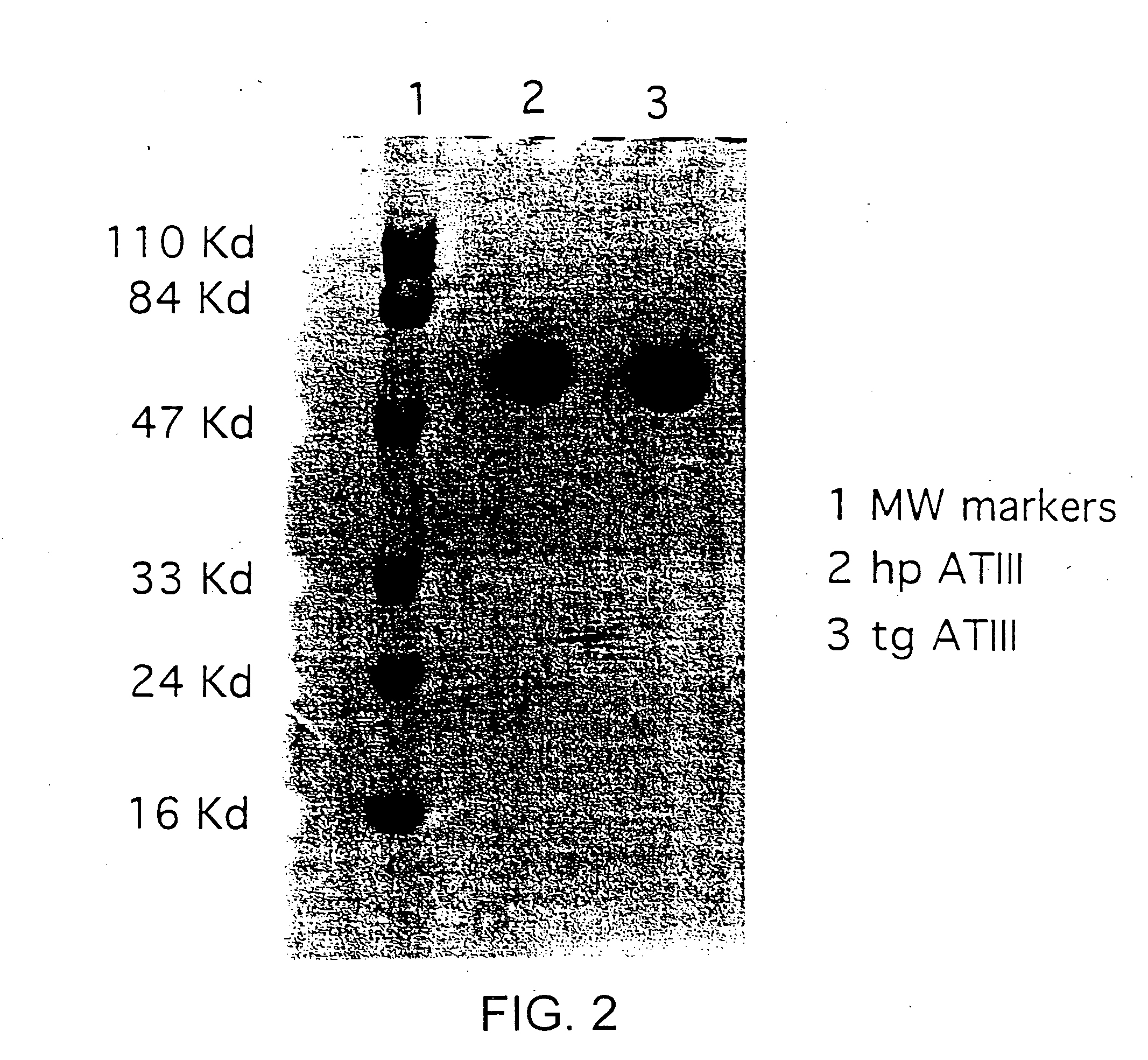
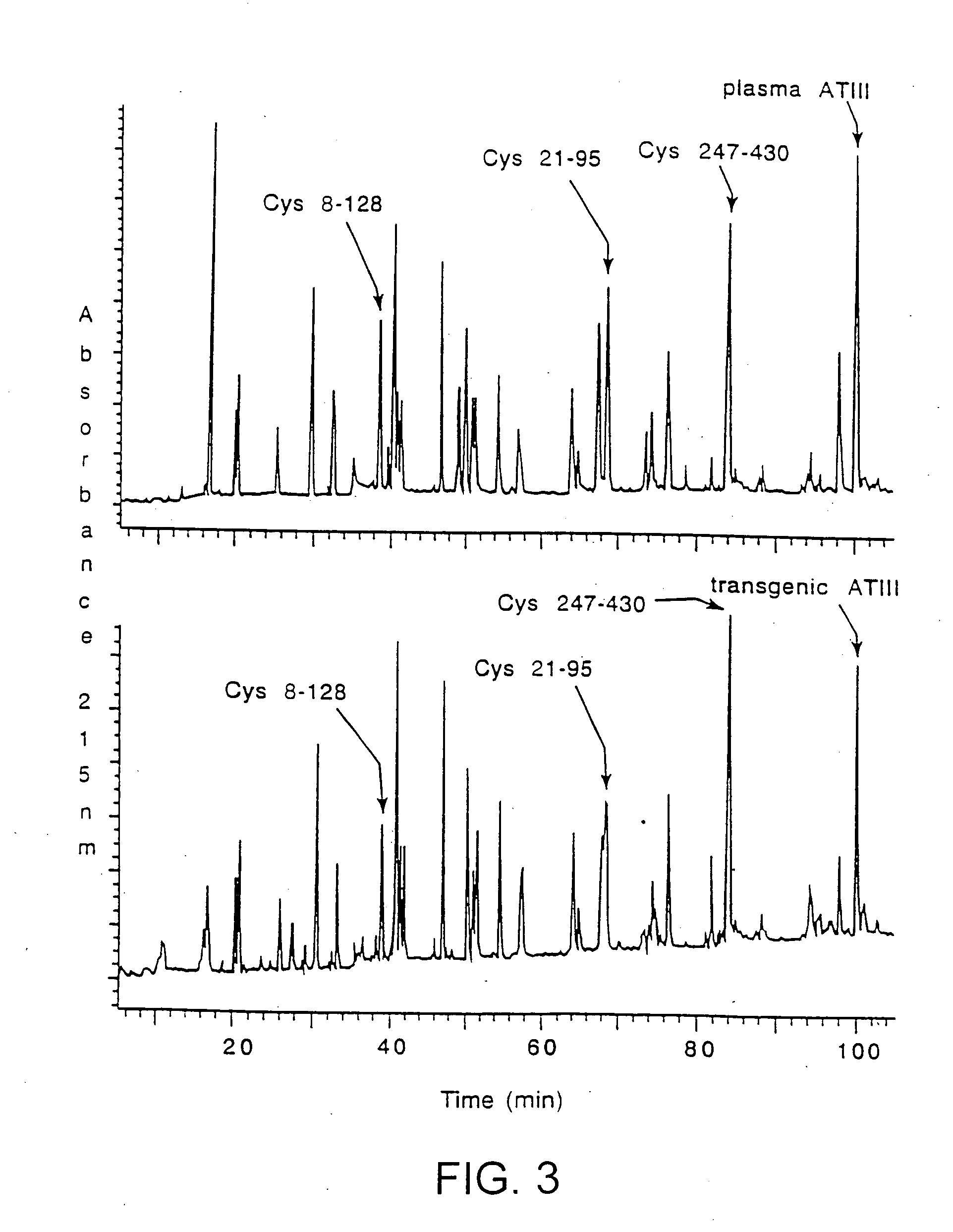
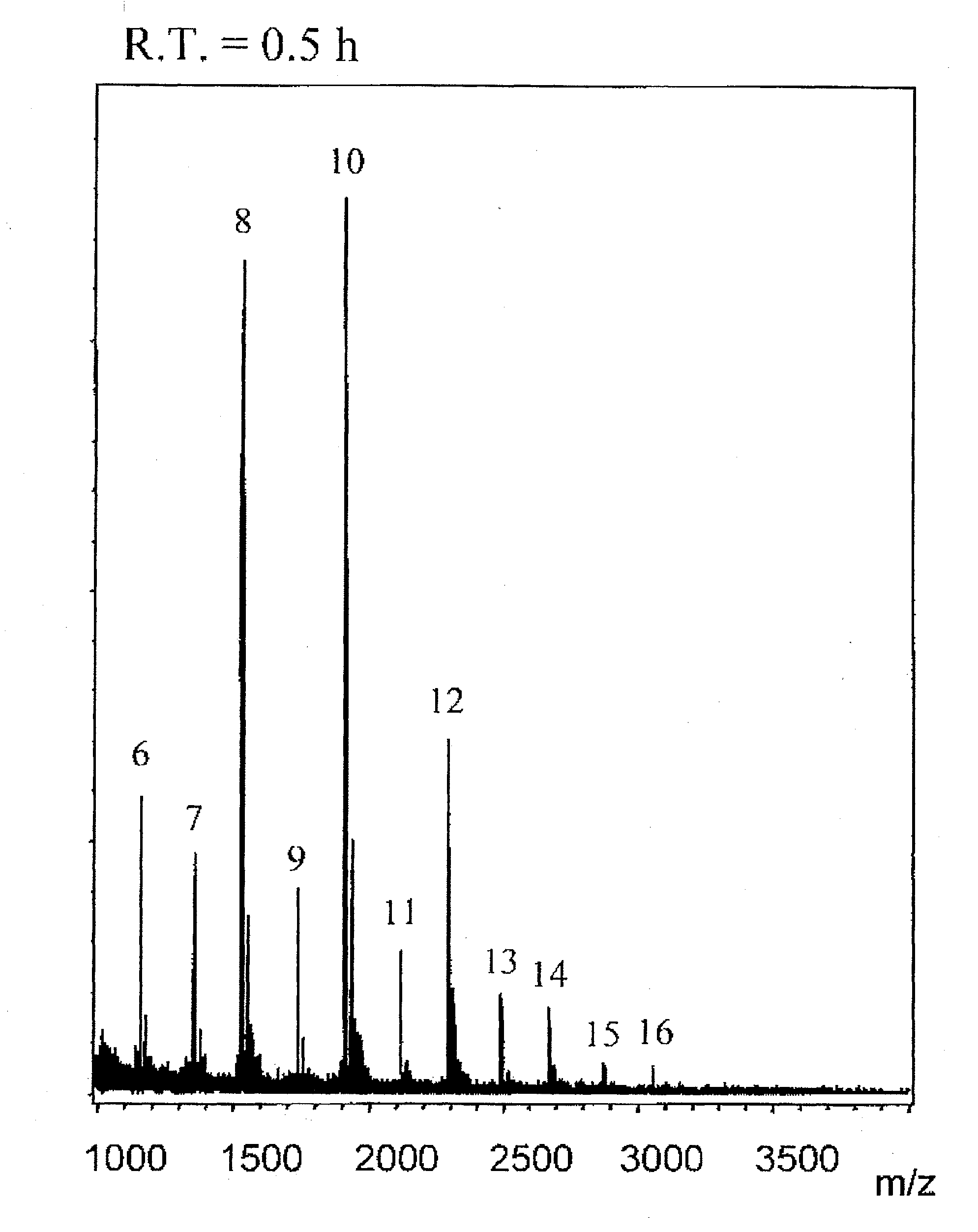
Transgenically produced antithrombin III
InactiveUS20080176786A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMonosaccharide compositionPlasma derived
This invention relates to transgenically produced human Antithrombin III (tgATIII). The human ATIII produced by the transgenic process of the present invention has a monosaccharide composition which comprises N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) along with fucose, N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, mannose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid / N-glycolyneuraminic acid. The monosaccharide composition differs with that of plasma derived ATIII (phATIII). It has been found that tgATIII has an increased clearance rate when compared to phATIII.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Novel process for preparation of chondroitin fraction
ActiveUS20090155851A1Manufactured usingSimple wayBacteriaSugar derivativesUronic acidIndustrial scale
Provided are a method for producing a fraction containing more than 50% of CH represented by the general formula (1), which comprises at least the step of allowing a glucuronic acid donor, an N-acetylgalactosamine donor, a saccharide receptor, a chondroitin polymerase derived from the Escherichia coli K4 strain, and Mn2+ at a final concentration of 0.02 to 100 mM to coexist, and performing a reaction thereof under conditions of 20 to 40° C. and pH 6 to 8 for 0.5 minutes to 4 hours, and a method for producing a fraction containing more than 50% of CH represented by the general formula (2), which comprises at least the step of performing the reaction under same conditions for 10 hours or longer, which enable industrial scale production of a CH fraction of a controlled even number saccharide and odd number saccharide content ratio by a simple procedure at a low cost.(GlcA-GalNAc)n (1)GalNAc-(GlcA-GalNAc)n (2)(In the formula, GlcA represents a glucuronic acid residue, GalNAc represents a N-acetylgalactosamine residue, - represents a glycosidic bond, and n represents an arbitrary integer.)
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Compositions and methods for modulating hbv expression
ActiveUS20150176007A1Reduce the amount requiredReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBiochemistryOrganic chemistry
Provided herein are oligomeric compounds with conjugate groups. In certain embodiments, the oligomeric compounds are conjugated to N-Acetylgalactosamine.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LTD
Biological enzyme composite blocking remover and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112778991AReduce surface and interfacial tensionAvoid adsorptionDrilling compositionAmylaseActive agent
The invention relates to a biological enzyme composite blocking remover and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of oil field yield increase renovation. The blocking remover comprises the following components by mass: 0.1-0.5% of biological enzyme, 3-5% of a biological surfactant, 5-10% of a biological enzyme stabilizer, and the balance of water; the biological enzyme comprises at least one of xylanase, lipase, cellulase, mannase, protein complex enzyme, amylase and xanthan gum lyase; the biological surfactant is prepared from at least one of the following components: the biological surfactant is mainly prepared from rhamnolipid, sophorolipid and N-acetylgalactosamine; and the biological enzyme stabilizer comprises at least one of the following components: disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate, citric acid and triethanolamine. The biological enzyme composite blocking remover provided by the invention can solve the problems of permeability reduction and the like caused by low-permeability and medium-low-permeability reservoir reconstruction residual gum and organic matter (wax, asphaltene and the like) blocking in the later development period.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Depolymerized glycosaminoglycan from Thelenota ananas and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS8809300B2Special structureGood anticoagulant potencyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFucosylationDepolymerization
Disclosed is a depolymerized glycosaminoglycan from Thelenota ananas (dTHG), weight average molecular weight of which is about 8000˜20000 Da, and monosaccharide components of which are acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), glucuronic acid (GlcUA), fucose (Fuc) or their sulfates (expressed as —OSO3−), in which molar ratio of GalNAc:GlcUA:Fuc:—OSO3− is about 1:(1±0.3):(1±0.3):(3.5±0.5). Said dTHG is a potent endogenous inhibitor of factor X, which has good anticoagulant and antithrombotic activity, and can be used for the prevention and / or treatment of thrombotic diseases. Also provided is a method for preparing said dTHG, which comprises steps of 1) extracting and obtaining fucosylated glycosaminoglycan (THG) from the body wall of Thelenota ananas; 2) depolymerizing THG to obtain dTHG by method of peroxide depolymerization or method of peroxide depolymerization catalyzed by catalyst of the fourth period transition metal ions; 3) removing impurities with lower and / or higher molecular weight in dTHG.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEPTUNUS PHARM CO LTD
Preparation of red blood cells with a modified level of blood group antigen expression and their use in the quality control of blood typing reagents
The invention is a method of preparing the red corpuscle of low-expression blood group antigen adopting at least one immunodominant glucoamylase, such as N-acetylgalactosaminase or Alpha-galactosidase. The antigen expressed by the red corpuscle which is prepared by the method only reaches the threshold value of the antigen level that can be detected at clinic substantively. The red corpuscle prepared by this process can be applied to the quality control of the blood group reagent and the adjustment of the testing system, therefore can judge the blood group accurately and standardly.
Owner:KODE BIOTECH
ª‡-N-acetyl galactosamine enzyme and encode gene and applications thereof
InactiveCN101182497AAchieve transformationHydrolasesMammal material medical ingredientsGroup A - bloodGene
The invention discloses an α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase and its encoding gene and application. The α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase is a protein of the following (a) or (b): (a) a protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 in the sequence listing; A protein derived from (a) having α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity through the substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or several amino acid residues in the amino acid sequence. The α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase can change the blood type of human red blood cells from A to O, and from AB to B. αNAGA can be used to prepare kits for blood group conversion; αNAGA can also be used to prepare universal red blood cells.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
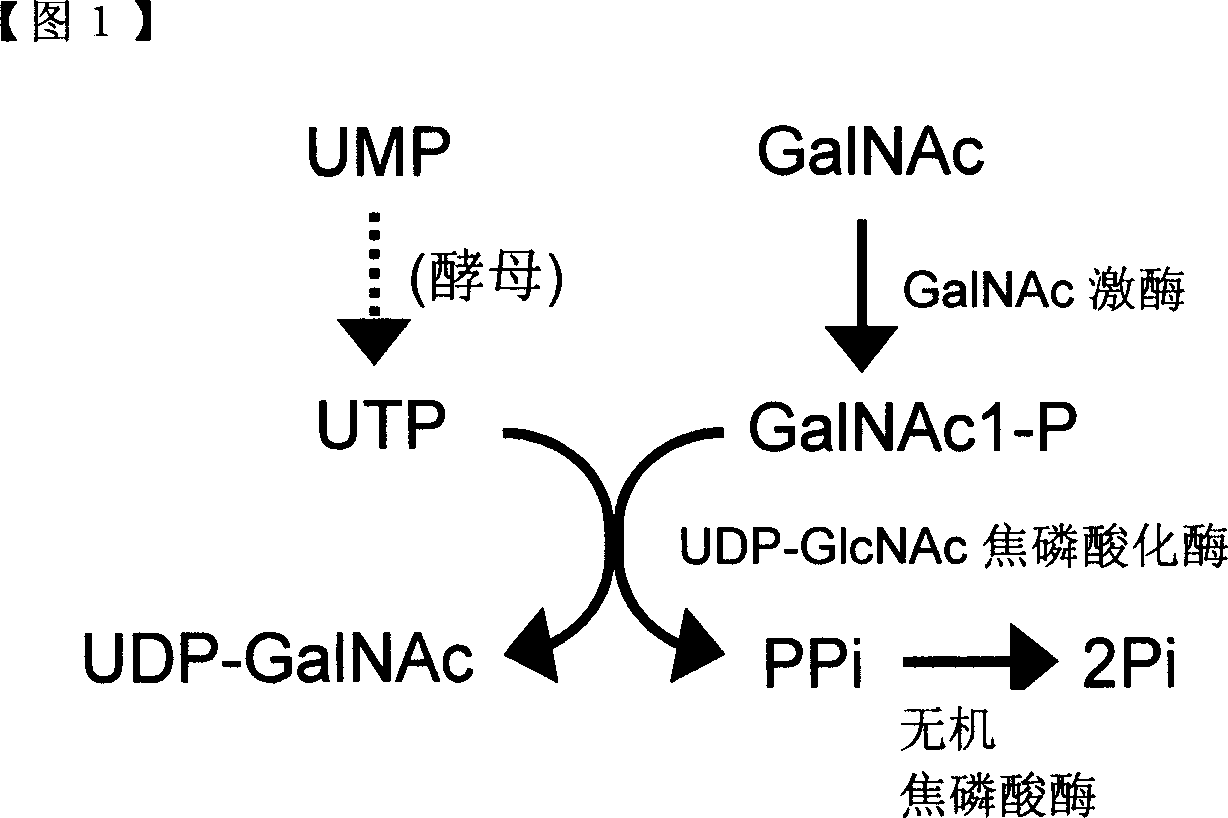
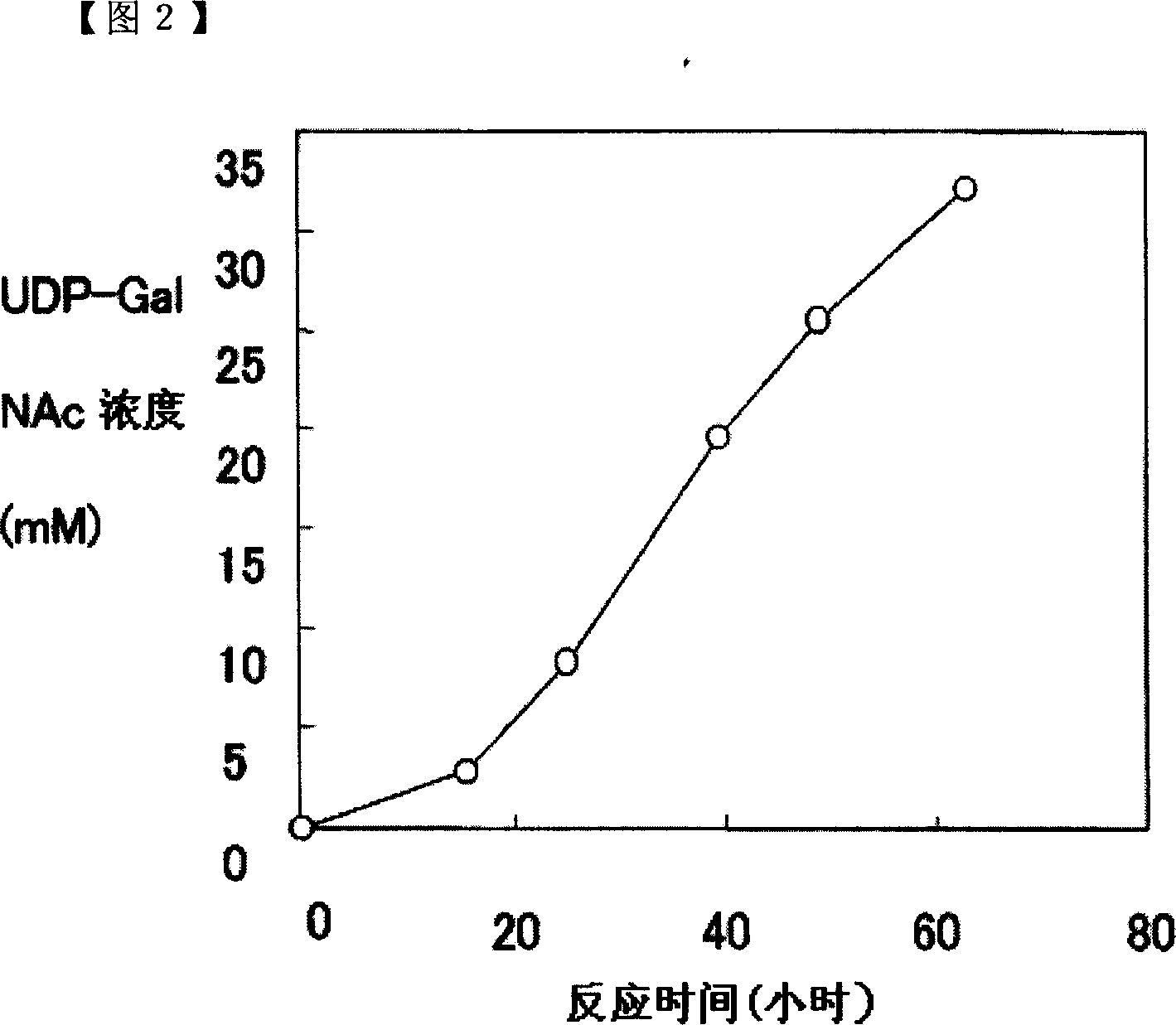
Method of producing uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine
ActiveCN101052724AEfficient manufacturingEasy to manufactureTransferasesFermentationUDP-GalNAcPhosphate
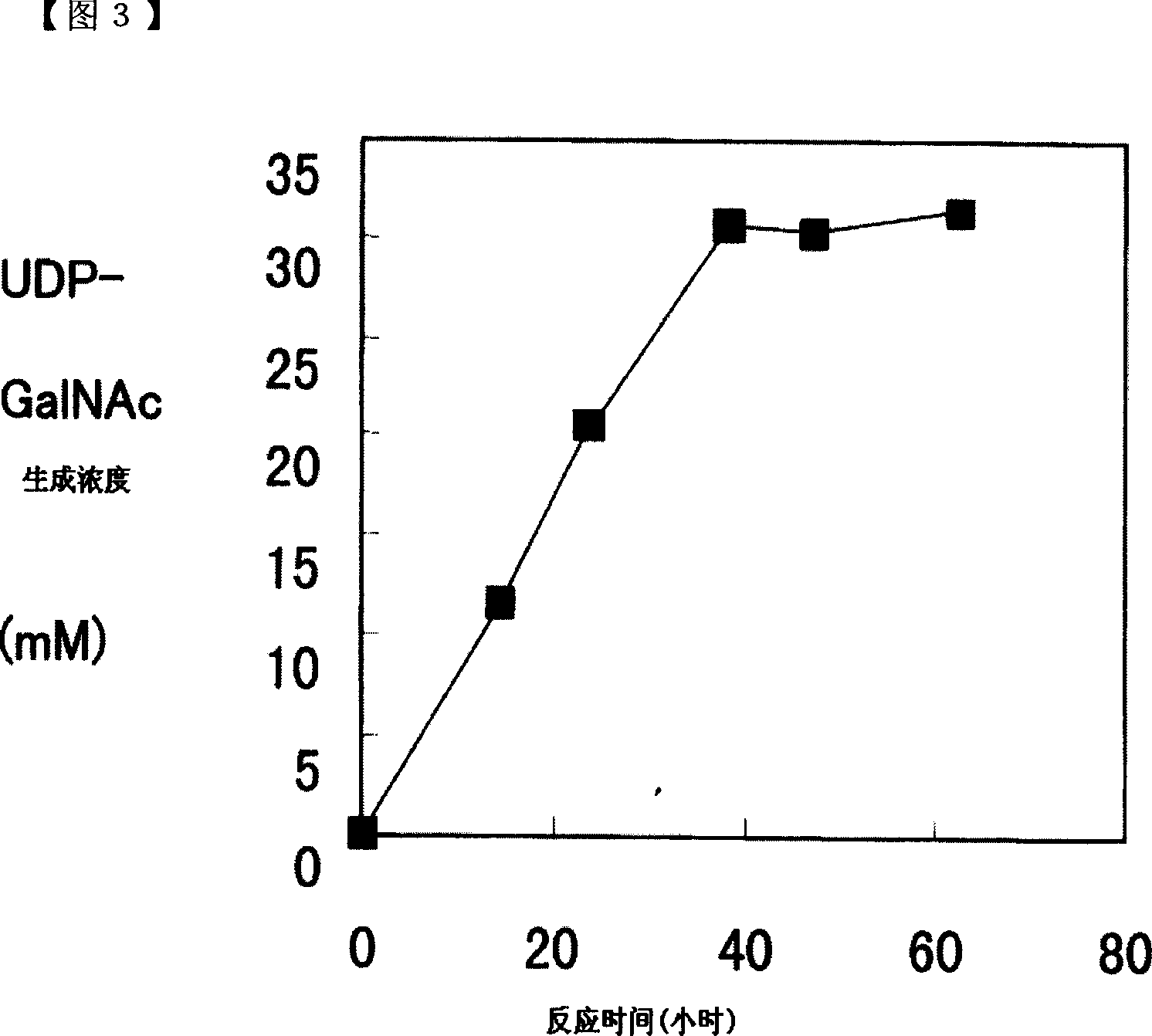
A method of producing uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine (UDP-GalNAc), which is an important substrate in synthesizing an oligosaccharide, characterized in that in enzymatically producing uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine from uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP) and N-acetylgalactosamine-1-phosphate (GalNAc1-P), uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine pyrophosphorylase (UDP-GlcNAc pyrophosphorylase) originating in a microorganism (excluding pathogenic ones) is used as an enzyme. In this method, it is also possible to use, as GalNAc-1P, a product prepared from N-acetylgalactosamine and a phosphate donor in a reaction system with the use of N-acetylgalactosamine kinase. According to this method, uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine can be efficiently produced by using a relatively inexpensive substrate.
Owner:YAMASA SHOYU CO LTD
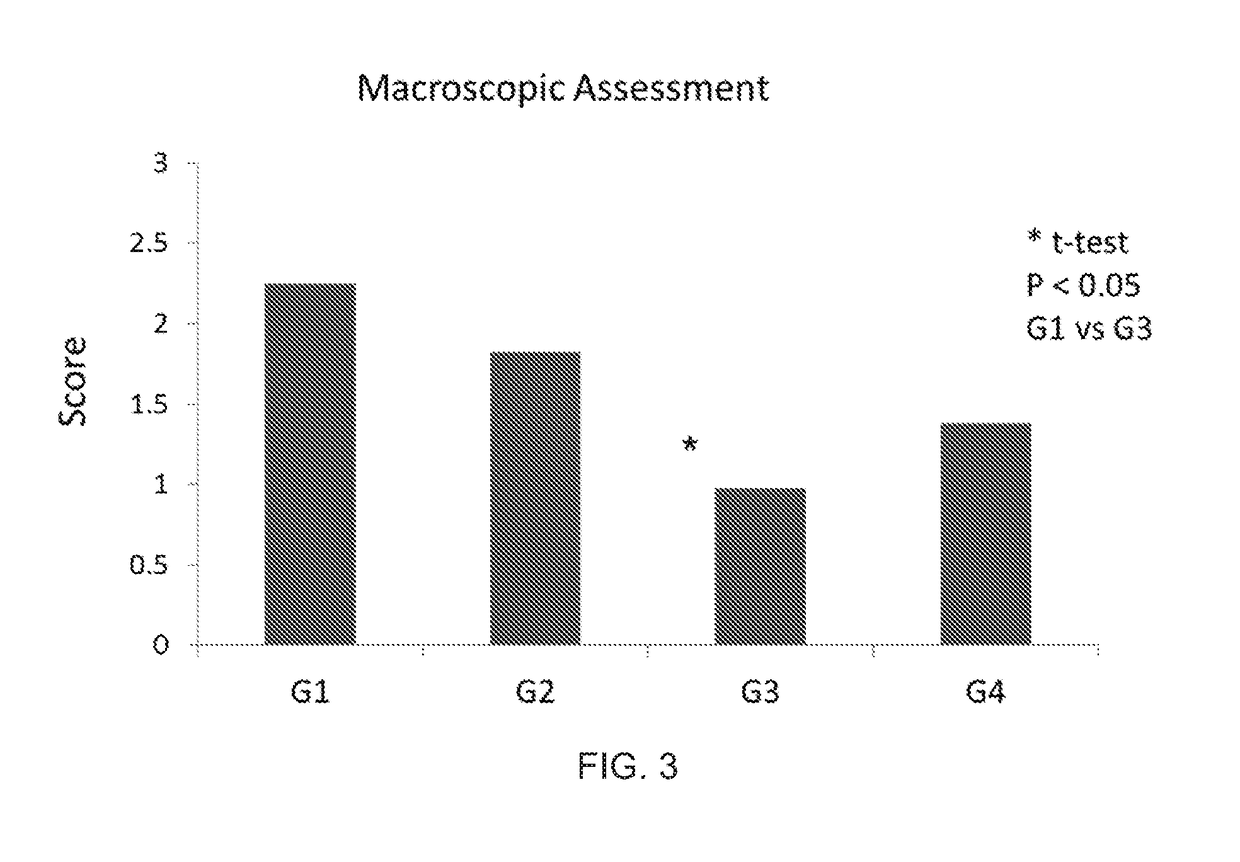
Normal-temperature mechanical perfusion system capable of extending liver source
ActiveCN109511650AImprove physiological activityGood physiological activity stateDead animal preservationSodium bicarbonateVitamin C
The invention provides a normal-temperature mechanical perfusion system capable of extending liver source, wherein each 1000ml of perfusion fluid contains the following components: 200-400mg of naringenin-7-O-acetate, 2-6g of hydroxyl starch, 20-40g of triphosadenine, 15-45g of artificial blood, 2-6g of lecithin, 1-2mg of galactosidase, 1-2mg of acetylgalactosaminase, 30-60mu of insulin, 100-300mlof compound amino acid injection 18AA, 1-5g of antibiotics, 5-30g of glucose, 100-300ml of normal saline, 5-15ml of 10% potassium chloride, 10-30ml of 5% sodium bicarbonate, 10-20ml of 10% calcium chloride, 3-8mg of vitamin B12, 2-6mg of vitamin E, 1-5mg of vitamin C, 1-6mg of dexamethasone, and 5-15mug of alprostadil.
Owner:嘉兴莱普晟医疗科技有限公司
Precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4 sulfatase, methods of treatment using said enzyme and methods for producing and purifying said enzyme
InactiveCN1726046ASignificant clinical effectIncrease joint mobilitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical drugPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention provides a highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase and biologically active mutants, fragments and analogs thereof as well as pharmaceutical formulations comprising highly purified recombinant human precursor N -acetylgalactosamirie-4-sulfatase. The invention also provides methods for treating diseases caused all or in part by deficiencies in human N -acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase including MPS Vl and methods for producing and purifying the recombinant precursor enzyme to a highly purified form.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
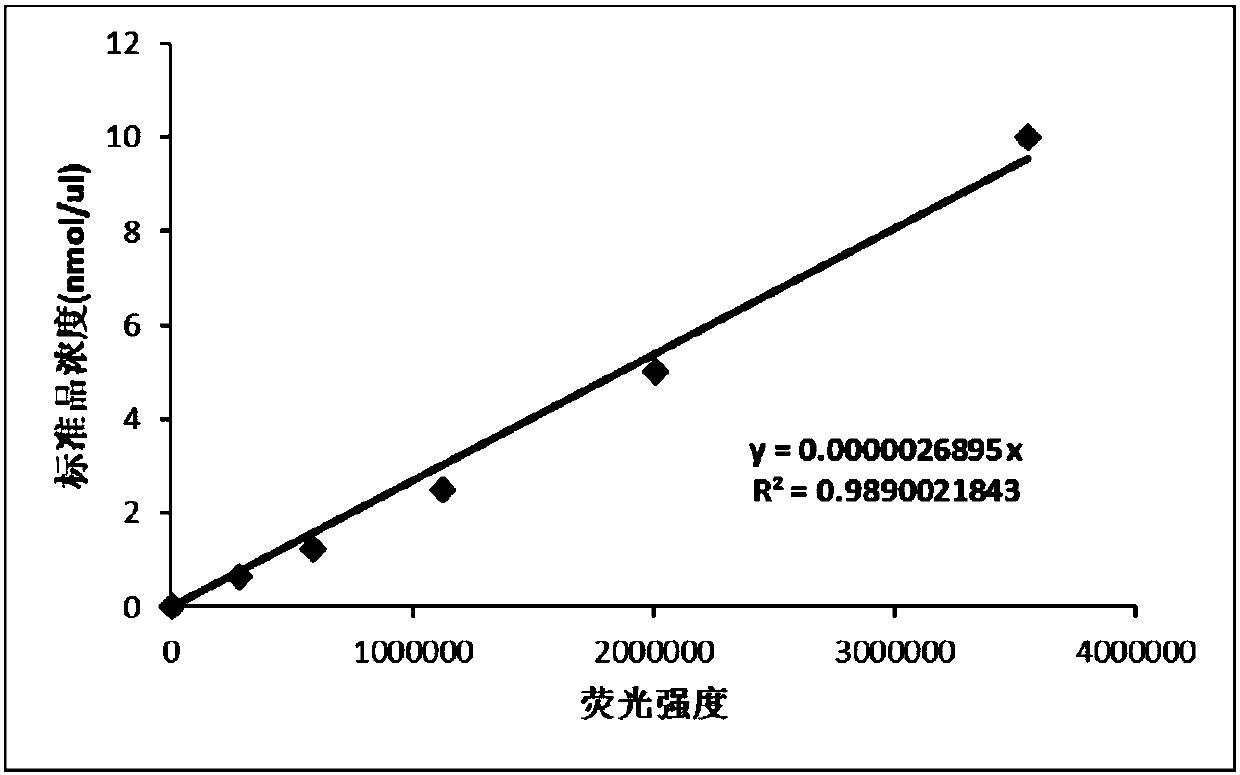
Detection method and kit for detecting activity of acidic hydrolases in lysosomes
InactiveCN107655870AHigh detection sensitivityGood choiceBiological material analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisLysosome
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical analysis and detection, in particular to a detection method and a detection kit for acid hydrolase activity in lysosomes. The present invention firstly designs a detection system comprising 5 kinds of mucopolysaccharide acid hydrolase in lysosomes, these five kinds of enzymes are respectively: α-L-iduronidase, iduronate sulfatase, β-N-acetyl half Lactosamine‑6‑sulfatase, β‑galactosidase and arylsulfatase B enzymes. The present invention utilizes the characteristic of fluorescence of 4-methylumbelliferone, uses the new substrate produced by combining the 4-methylumbelliferone group obtained by chemical synthesis with the enzyme substrate, and adopts the acid buffer solution containing the new substrate and mucopolysaccharide The hydrolase reacts, and the free 4-methylumbelliferone fluorescent substance is released after the hydrolase hydrolyzes the substrate. The higher the activity of the hydrolase in the sample, the more the amount of 4-methylumbelliferone released by hydrolyzing the substrate, and the higher the fluorescence intensity generated by the fluorescence detection, so as to realize the quantitative detection of the hydrolase activity. The invention has high detection sensitivity, good selectivity, strong anti-interference ability, good reproducibility and easy operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHROMYSKY MEDICAL RES
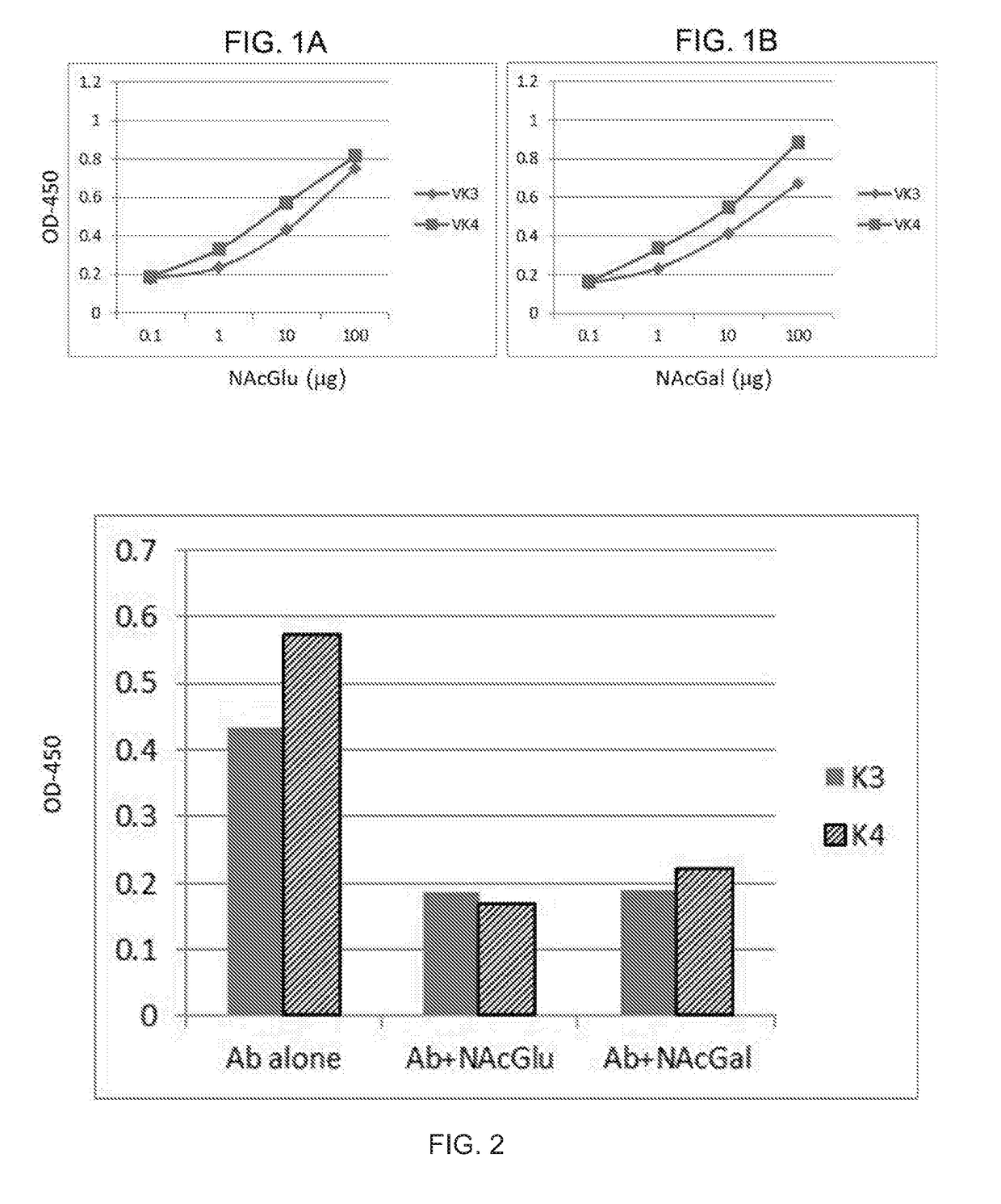
Antibodies against n-acetylgucosamine and n-acetyl-galactosamine
ActiveUS20190038669A1Reduce growth rateHigh levelPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyN-AcetylglucosamineInflammatory cell
It provides antibodies and chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that specifically bind to an epitope containing N-acetyl-glucosamine and / or N-acetyl-galactosamine, e.g., expressed by a cancer cell or an inflammatory cell. Also provided are compositions including these antibodies and / or CARs, as well as polynucleotides, vectors, host cells, methods, and kits related thereto. Further provided are methods and kits for treating or preventing cancer in an individual by administering to the individual an antibody that specifically binds to an epitope containing N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetyl-galactosamine, or a T cell comprising a CAR that specifically binds to an epitope containing N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetyl-galactosamine, optionally in combination with another anti-cancer agent.
Owner:B&H BIOTECH LLC
Compositions and methods for modifying blood cell carbohydrates
InactiveUS7767415B2BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole blood productRed blood cell enzymes
This invention relates to enzymatic removal of type A and B antigens from blood group A, B, and AB reactive cells in blood products, and thereby converting these to non-A and non-B reactive cells. The invention further relates to using unique αN-acetylgalactosaminidases and α-galactosidases with superior kinetic properties for removing the immunodominant monosaccharides of the blood group A and B antigens and improved performance in enzymatic conversion of red blood cells. The preferred unique α-N-acetylgalactosaminidases and α-galactosidases exhibit the following characteristics:(i) exclusive, preferred or no less than 10% substrate specificity for the type A and B branched polysaccharide structures relative to measurable activity with simple mono- and disaccharide structures and aglycon derivatives hereof; (ii) optimal performance at neutral pH with blood group oligosaccharides and in enzymatic conversion of cells; and (iii) a favorable kinetic constant Km with mono- and oligosaccharide substrates. The conversion methods of the invention use significantly lower amounts of recombinant glycosidase enzymes than previous and result in complete sero-conversion of all blood group A and B red cells.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL
Glycoside compound of fatty acids, composition comprising it, process for its obtention and methods to apply it on plants or fruits or both at the same time
ActiveUS20210059250A1Neat advantageReduce restrictionsEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideChemical compoundFatty acid
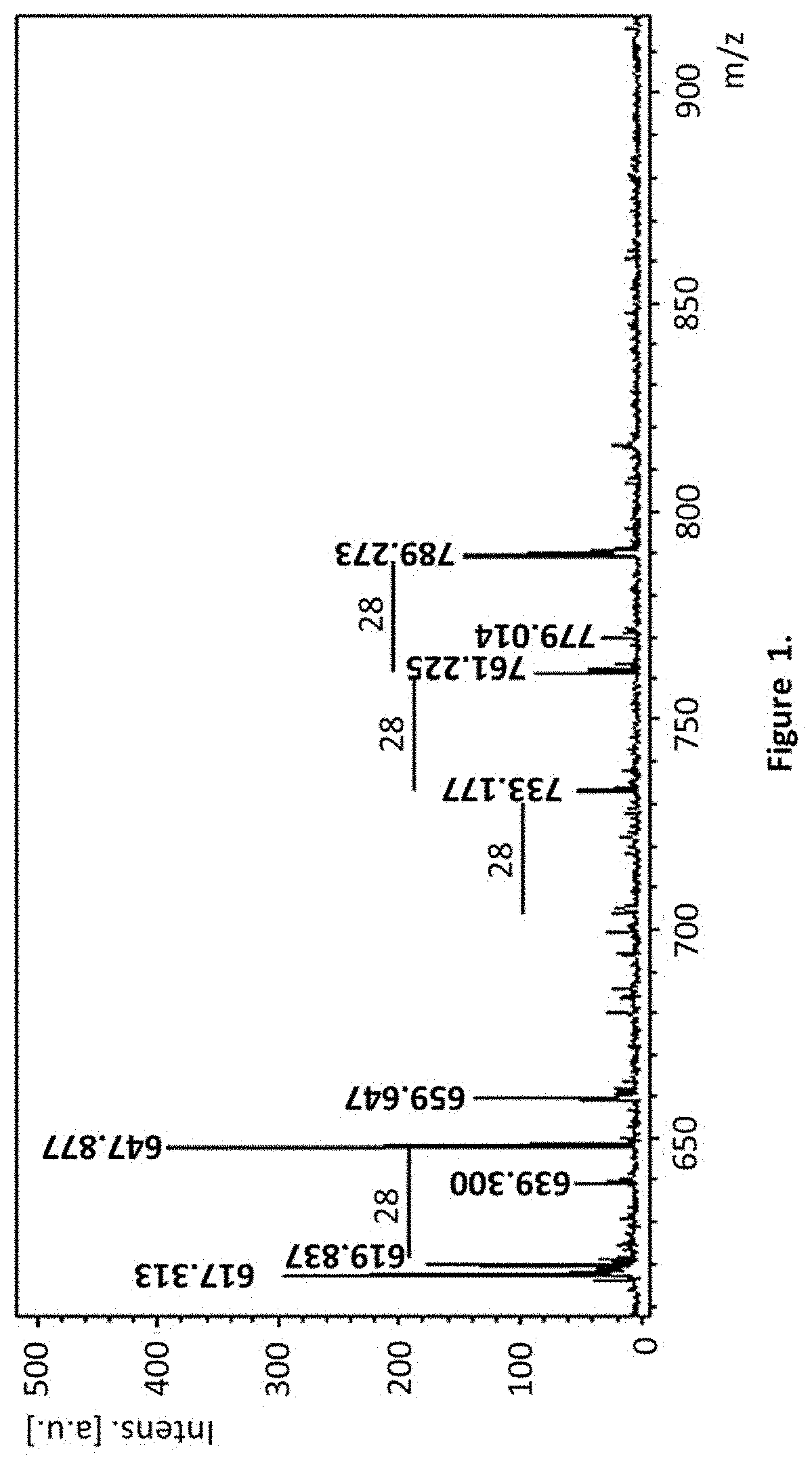
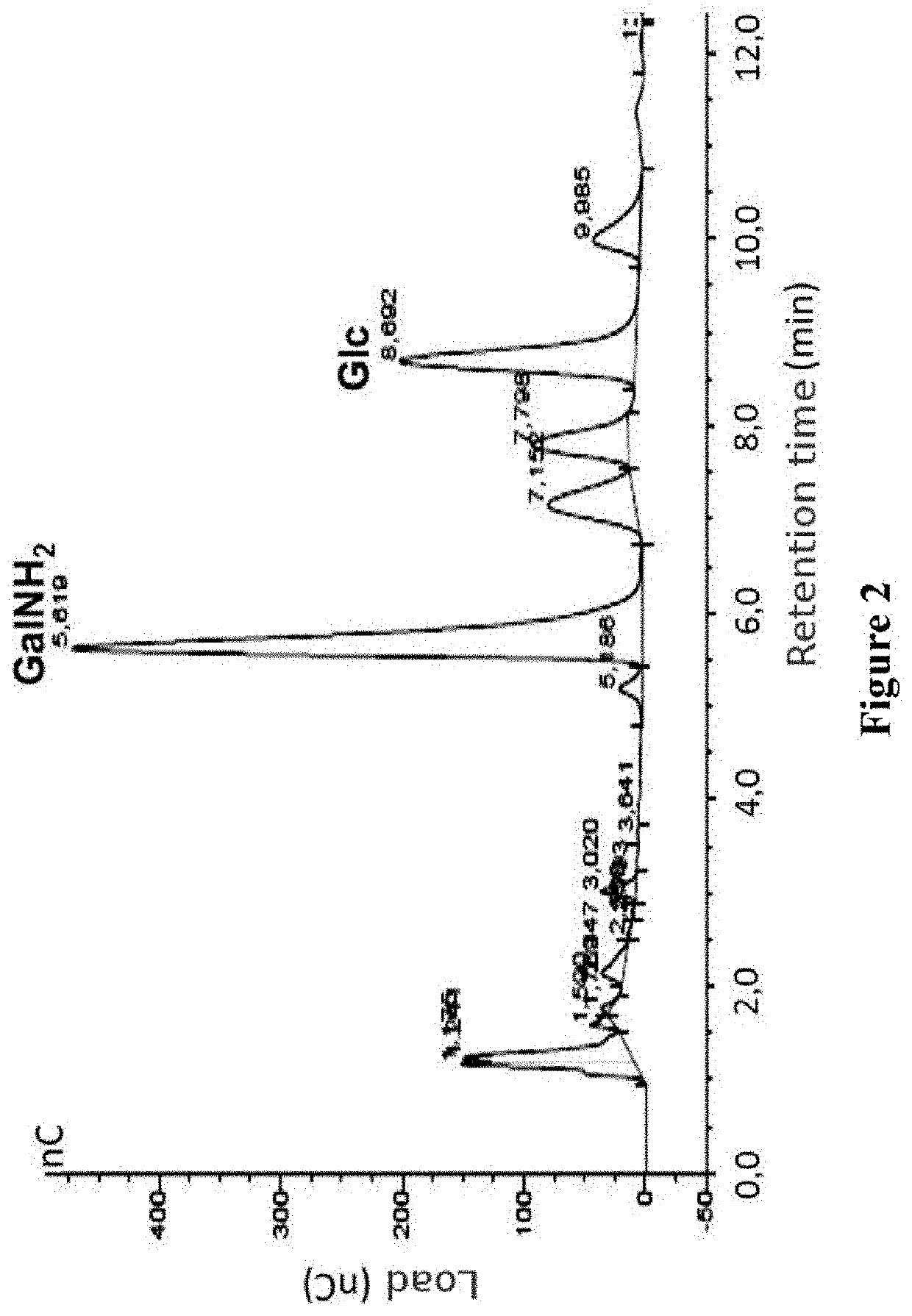
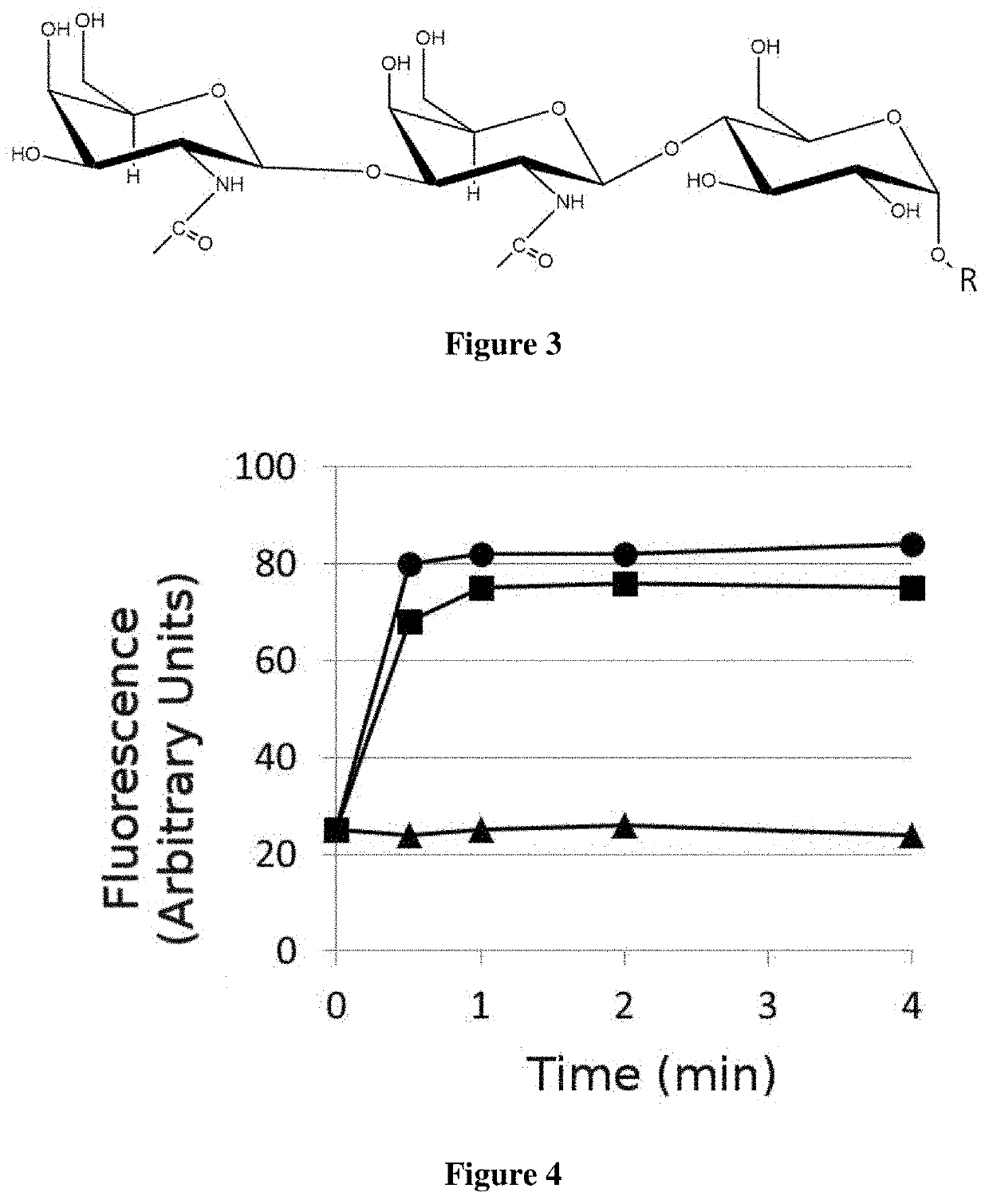
A glycoside compound of fatty acids that includes the general formula: GalNAc-GalNAc-Glc-O—R, where GalNAc is α- or β-D-N-acetylgalactosamine, Glc-O—R is a molecule of α- or β-D-glucose esterified to a monounsaturated fatty acid (R), where R is selected from 12:1(n) and where n is an integer between 2 and 11; 11:1(n) and where n is an integer between 2 and 10; 10:1(n), and where n is an integer between 2 and 9; 9:1(n), and where n is an integer between 2 and 8; 8:1(n), and where n is an integer between 2 and 8; 7:1(n) and where n is an integer between 2 and 7; and 6:1(n), and where n is an integer between 2 and 6. The compound has activity against plant pathogens, and induces the defense, and promotes the growth, of plants.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET +1
Meat duck feed additive and use thereof
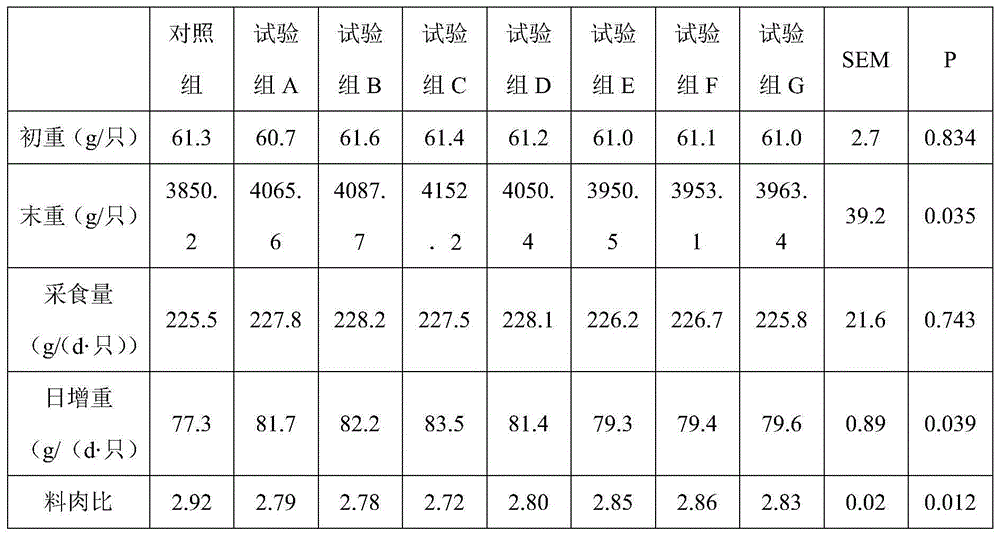
The invention discloses a meat duck feed additive and a use thereof. The meat duck feed additive comprises, by weight, 5-10% of fucose, 5-10% of galactose, 10-15% of N-acetylgalactosamine, 5-15% of glucosamine, 5-10% of N-acetylglucosamine, 5-15% of glucuronic acid, 10-20% of mannose, 5-10% of sialic acid and 10-20% of xylose. A use ratio of the meat duck feed additive in meat duck daily basic feed is 0.001-5%. The meat duck feed additive is rich in biologically-active substances, can improve appetite and immunity, can prevent diseases, can promote meat duck growth and improve meat quality, has no toxic or side effect, does not produce residue and is green and safe.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com