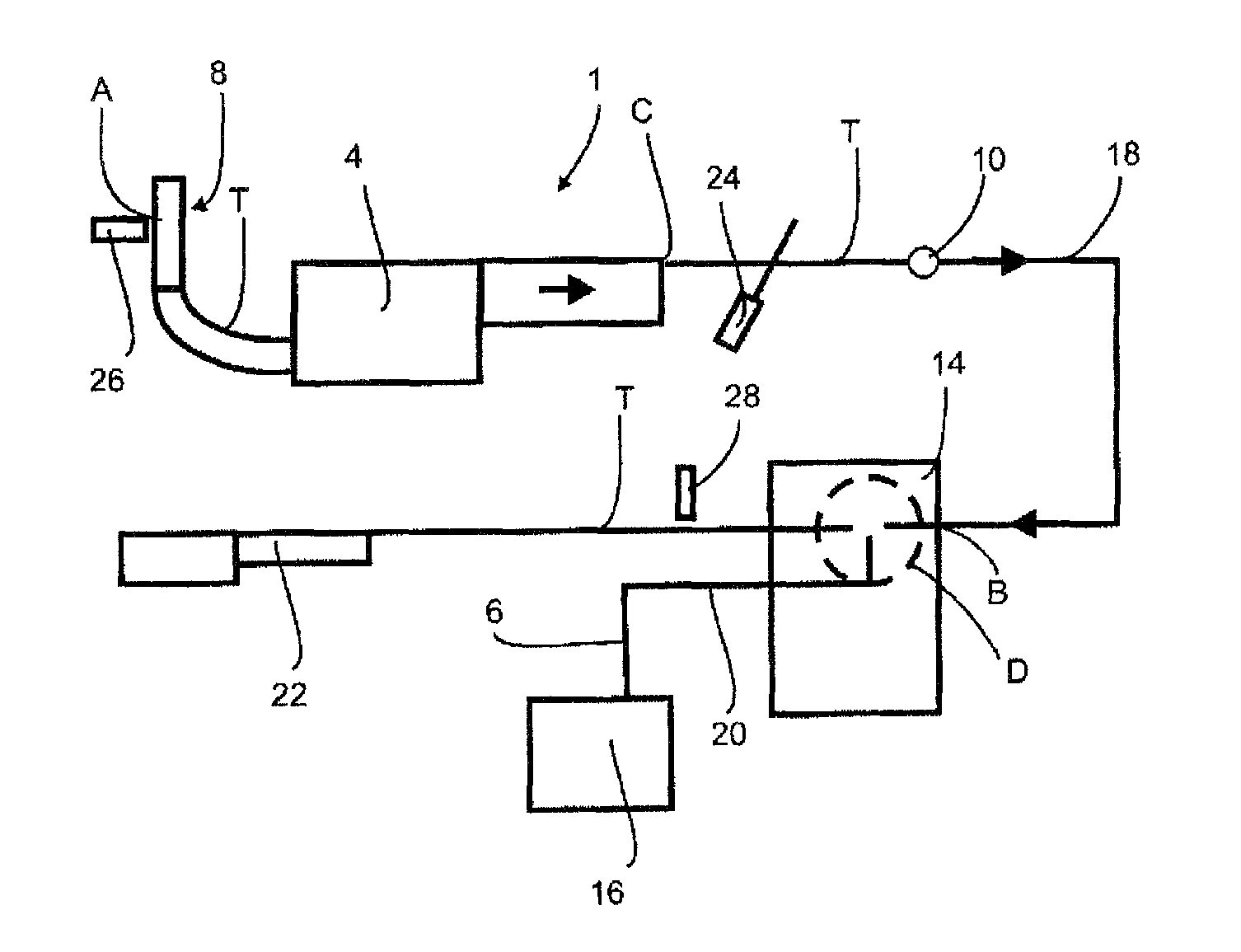
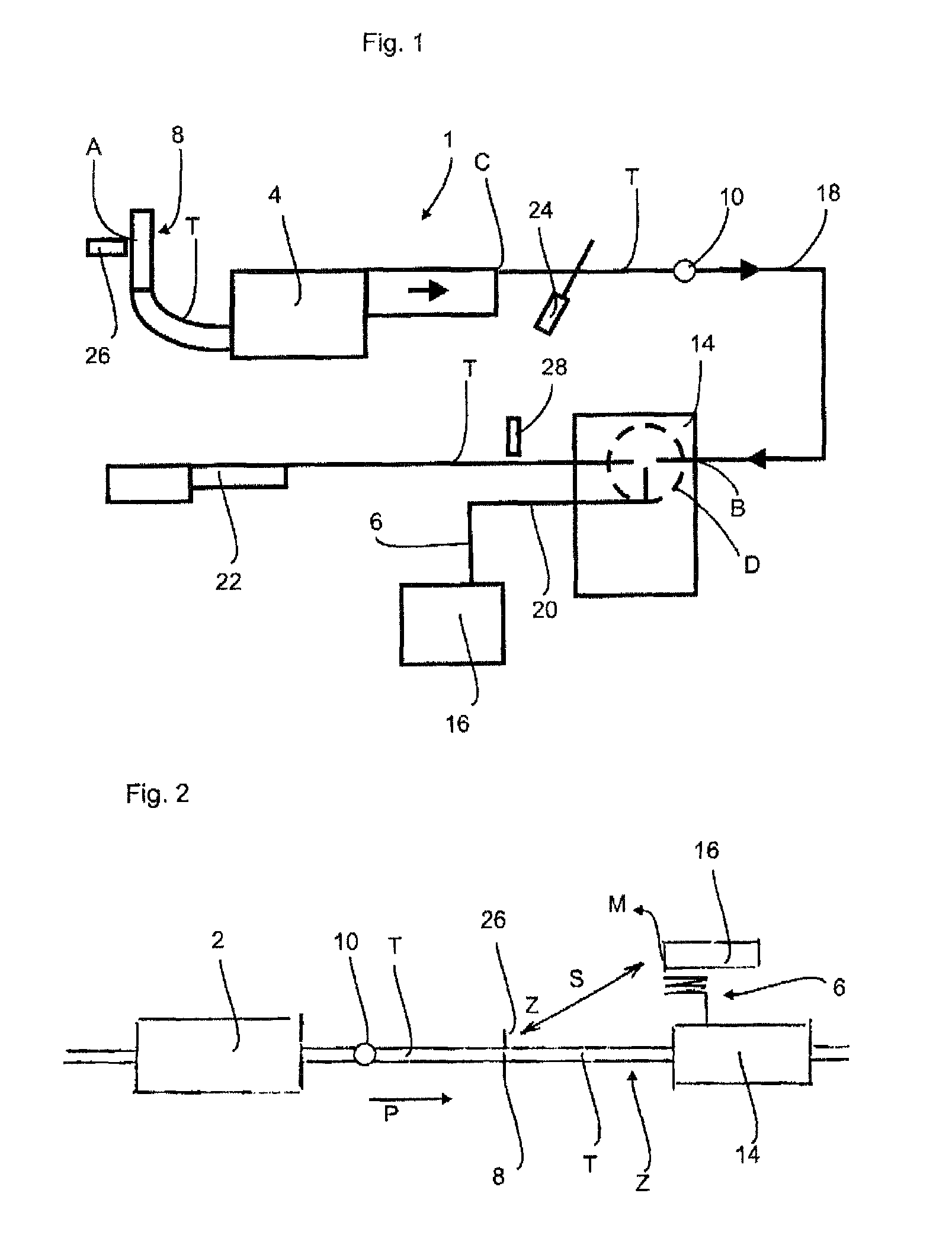
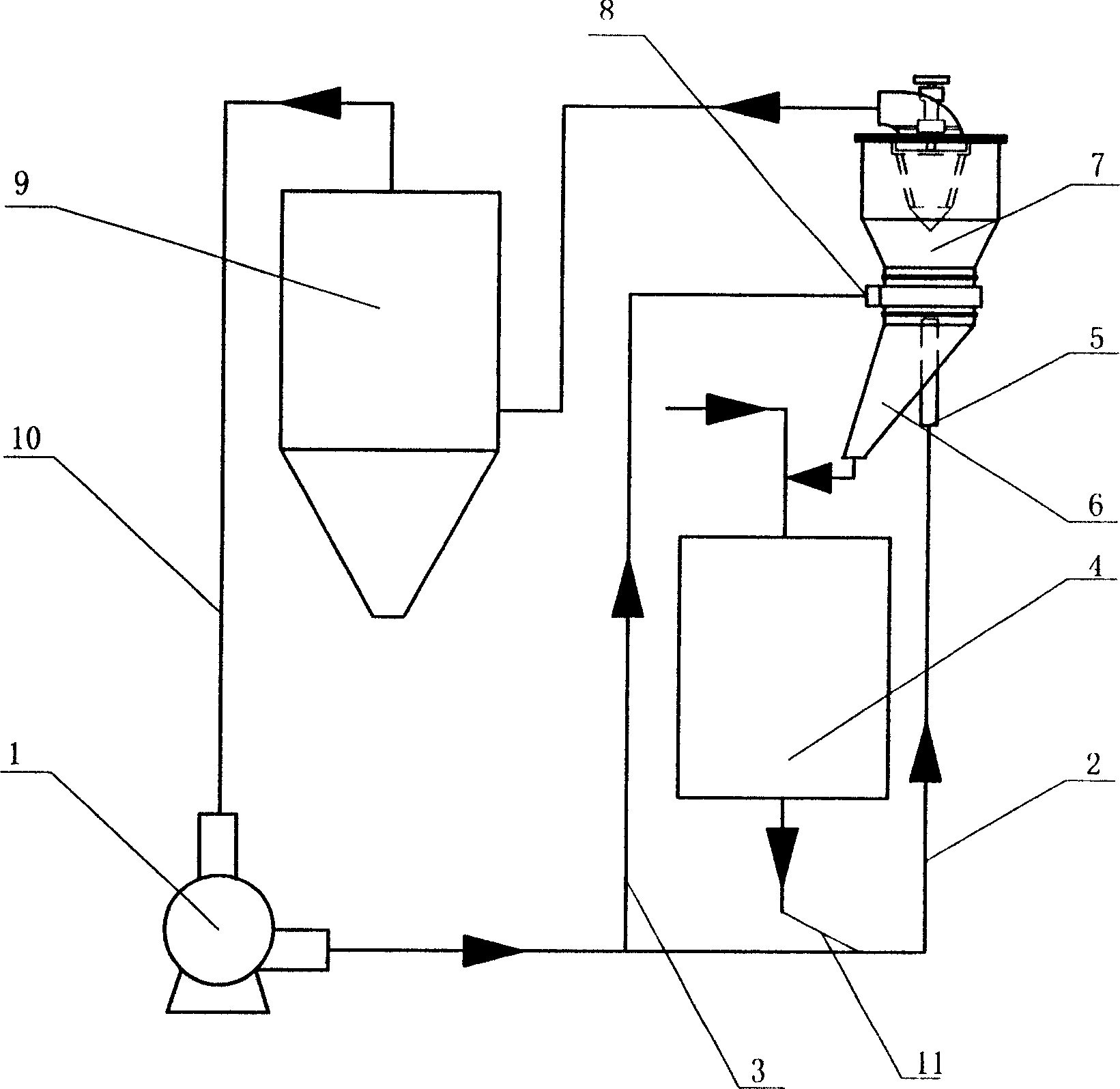
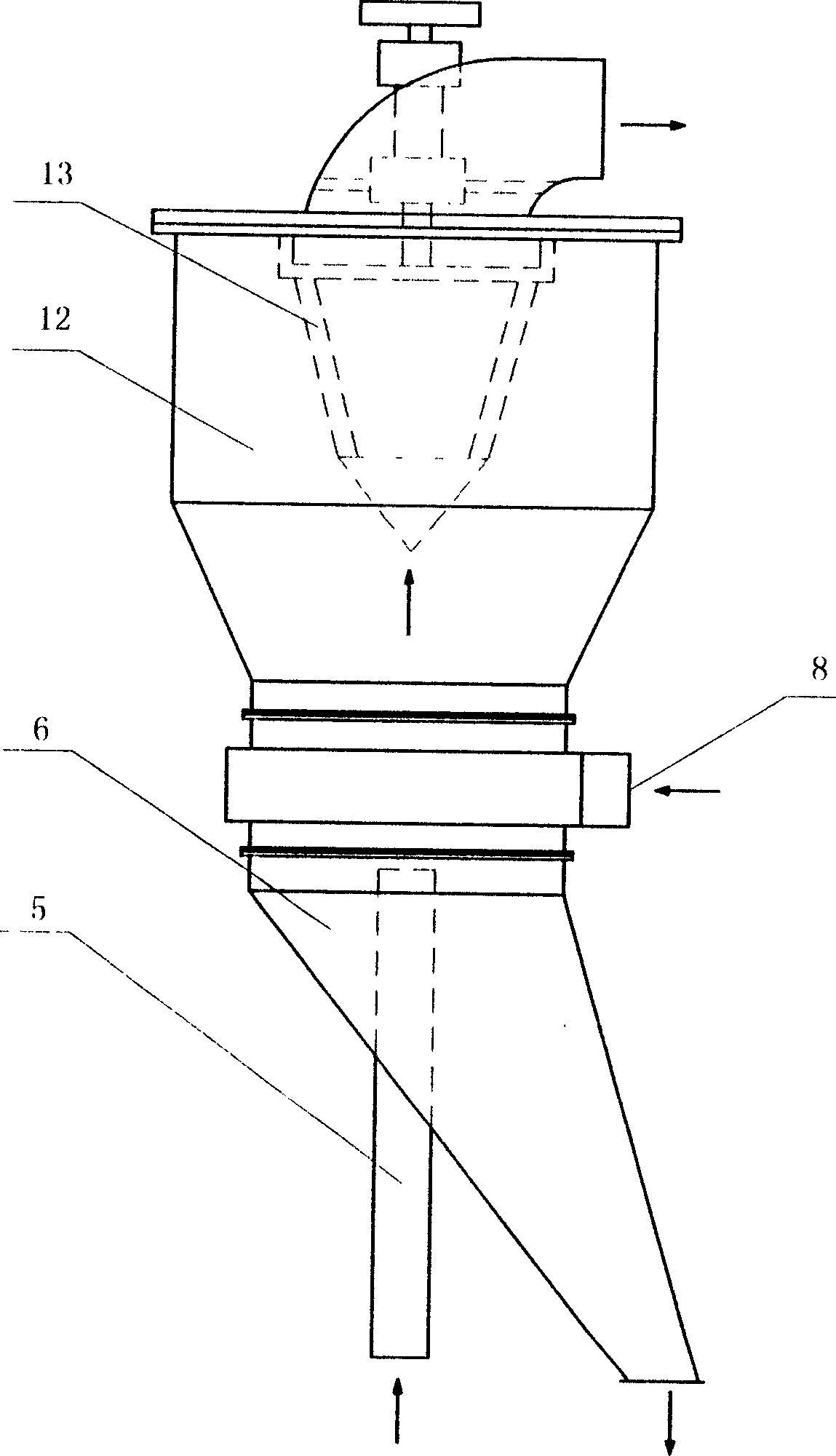
Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Avoid material loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
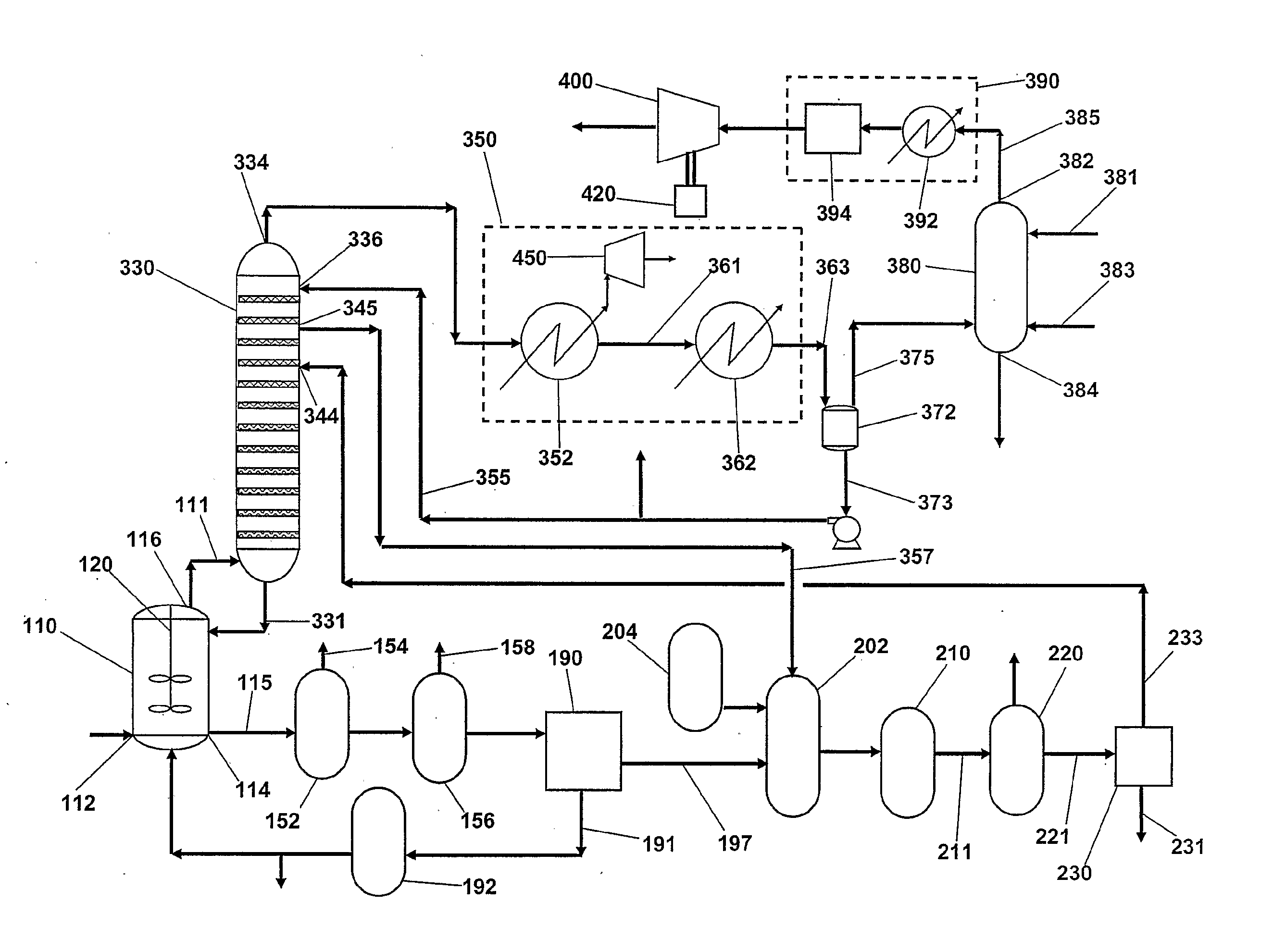
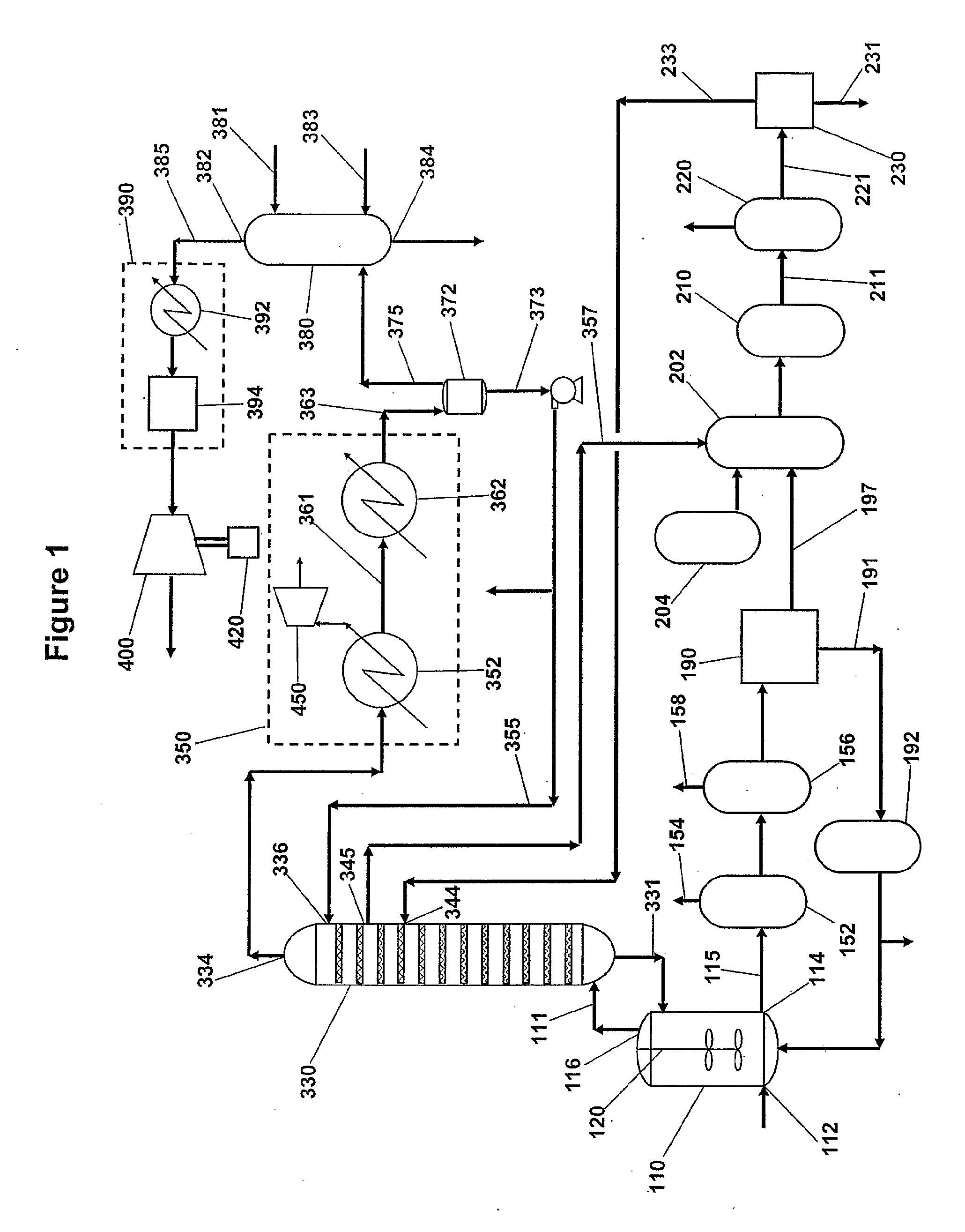
Hydrogen Processing, And Impurity Removal And Cleaning Methods In A Biomass Conversion Process
InactiveUS20080176301A1Avoiding accumulation of impurityAvoid material lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiomassChemistry
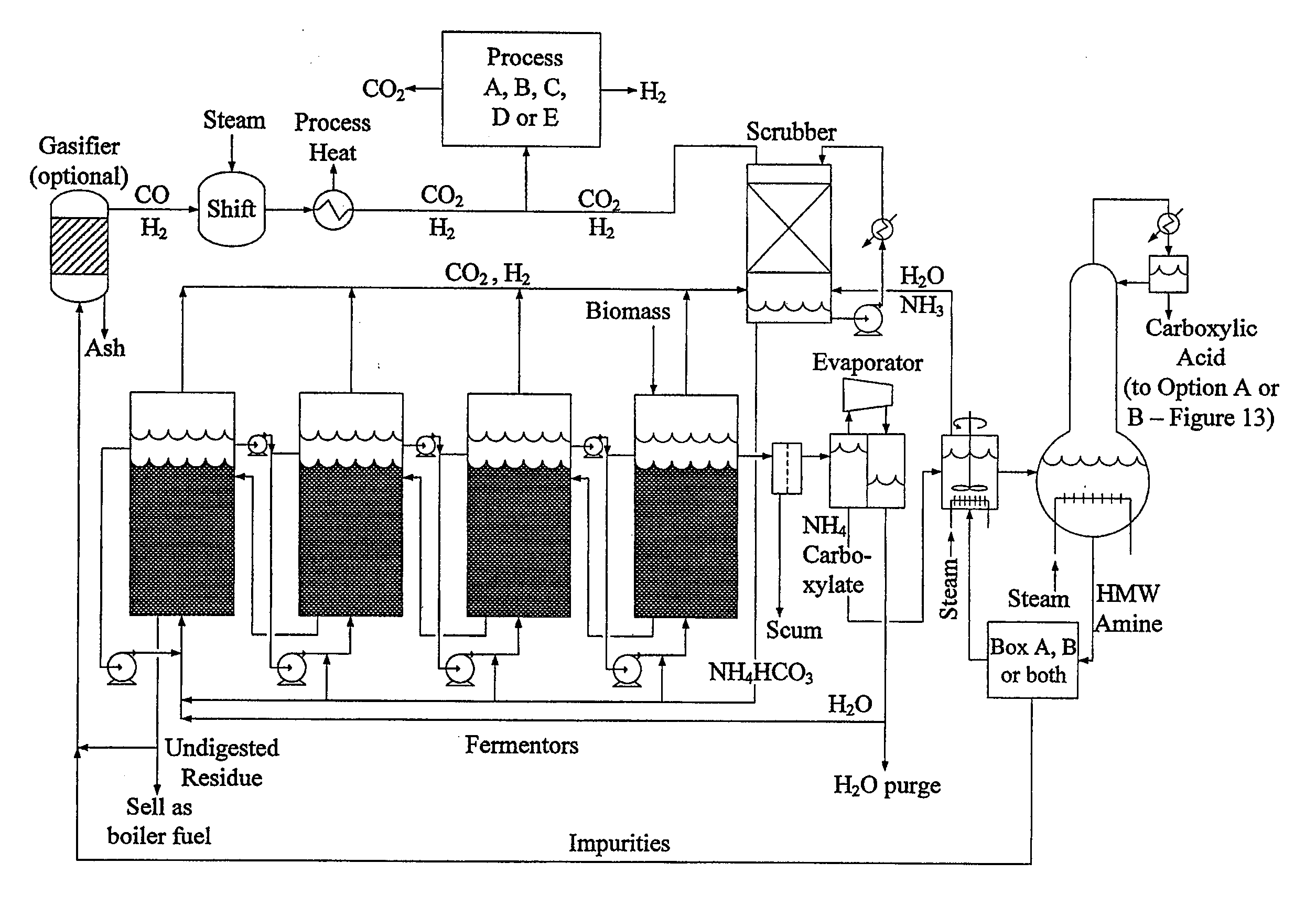
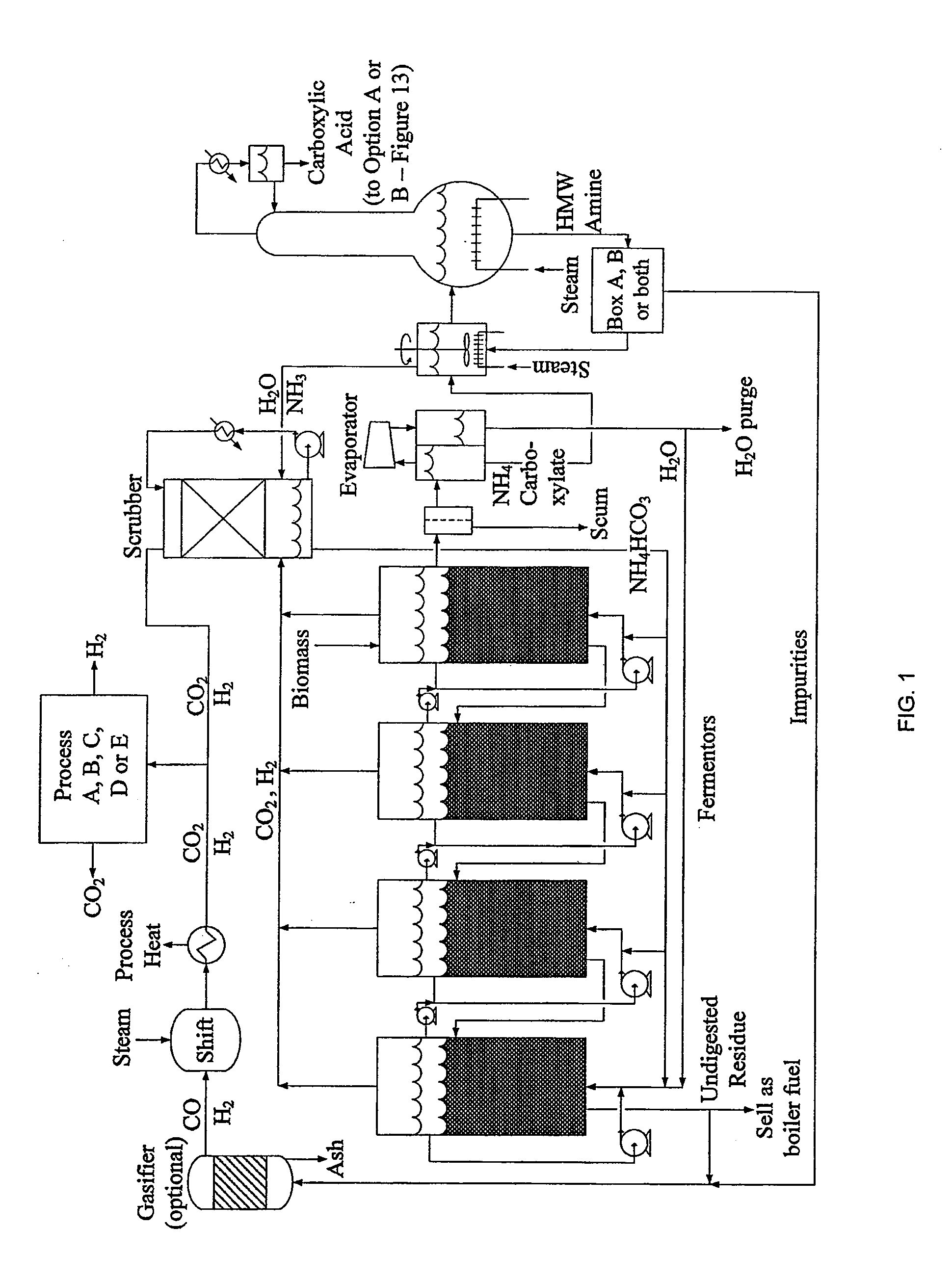
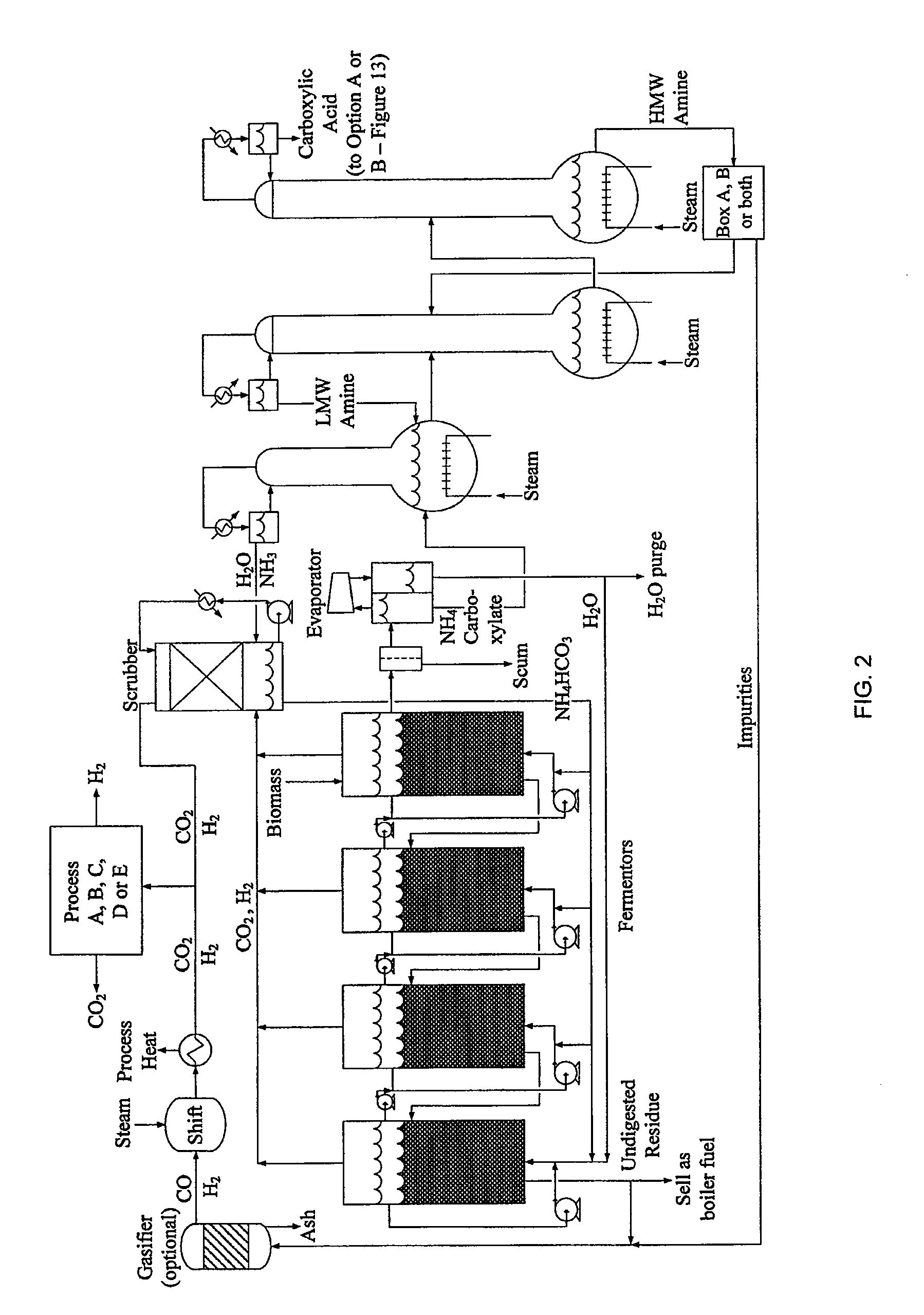
In one embodiment, the disclosure includes a method of biomass conversion including fermenting biomass to produce a carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt and hydrogen gas, recovering the hydrogen gas, and converting the carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt to an alcohol using the hydrogen gas. In one embodiment, the hydrogen produced by biomass conversion may be converted to an acetate. Another embodiment relates to a biomass conversion system. The system may include: a fermentation unit for fermentation of biomass to a carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt in a fermentation broth and for production of a carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas stream, an extraction unit for extracting the carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt from the fermentation broth, a gas extraction unit for separation of the hydrogen gas and the carbon dioxide, and a production unit for production of an alcohol from the carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt using the hydrogen gas.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
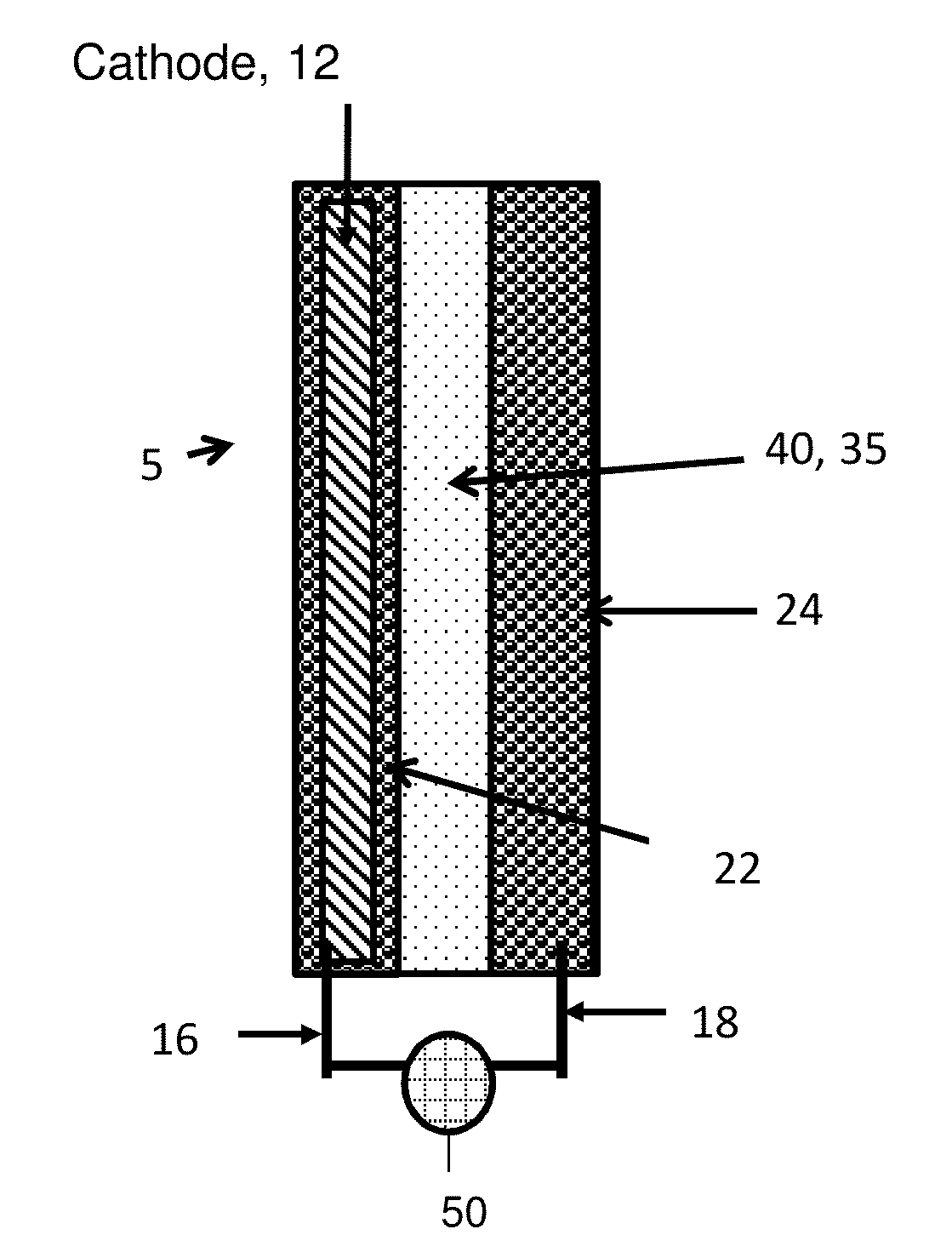
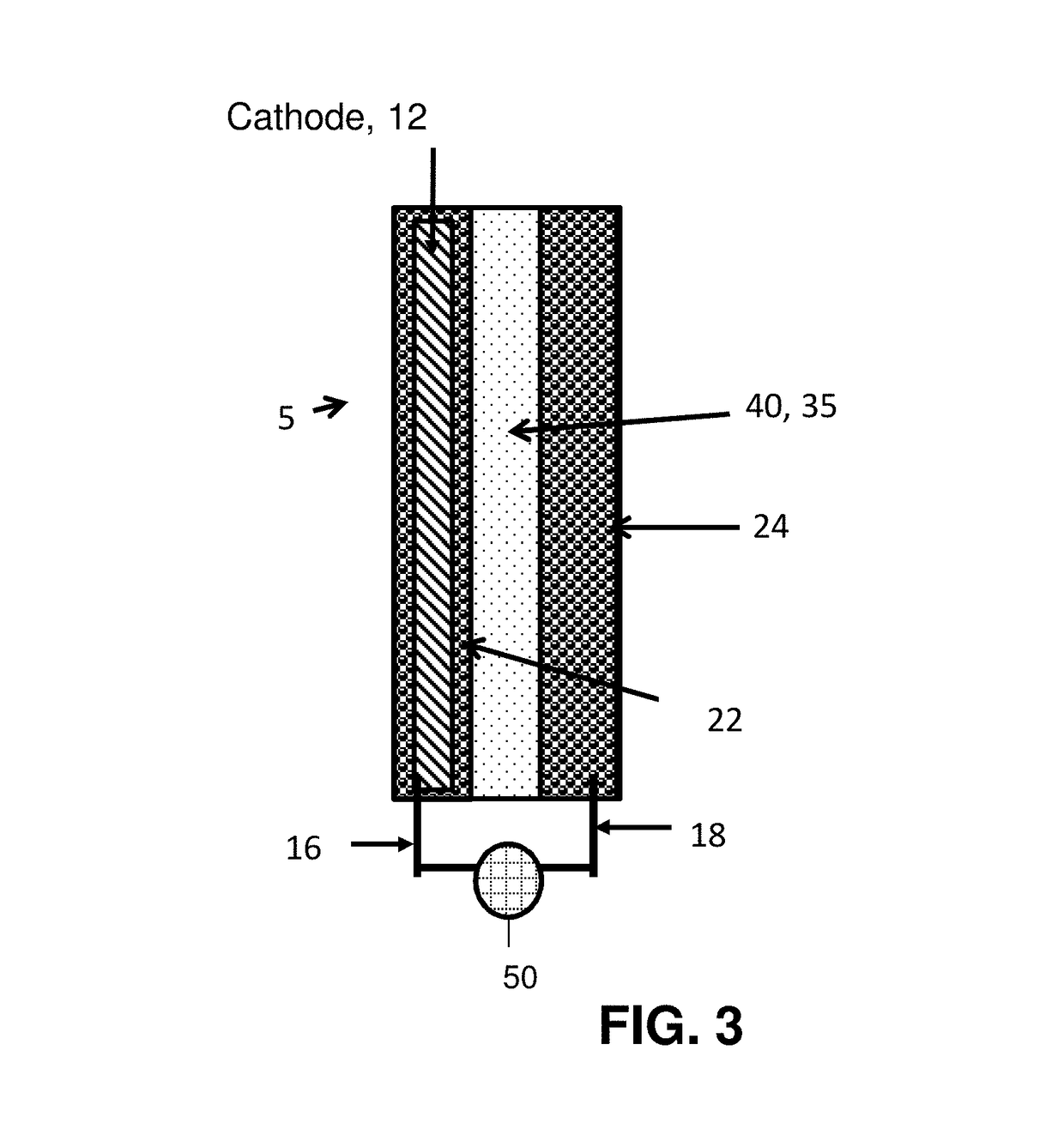
Separator enclosures for electrodes and electrochemical cells
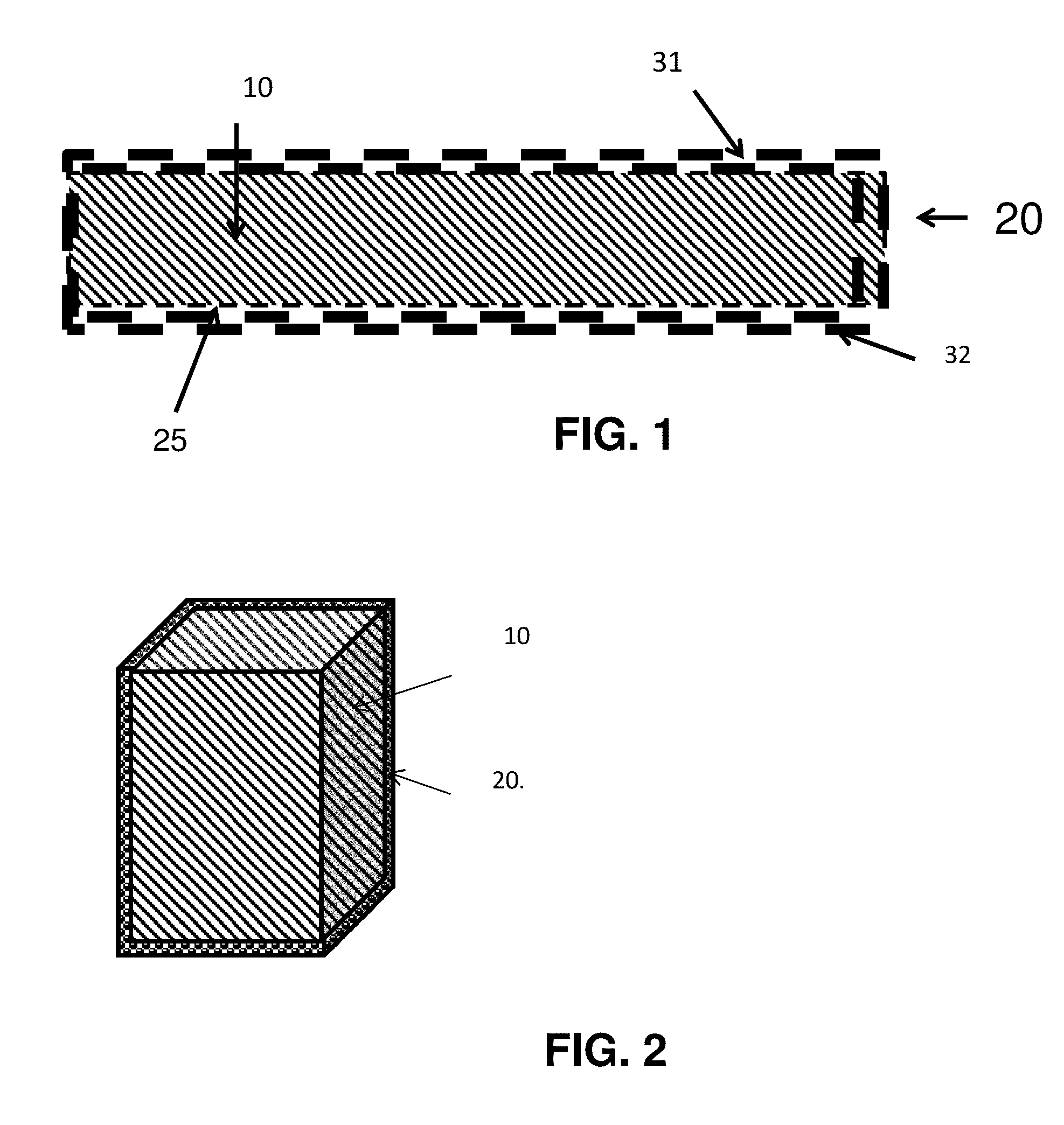
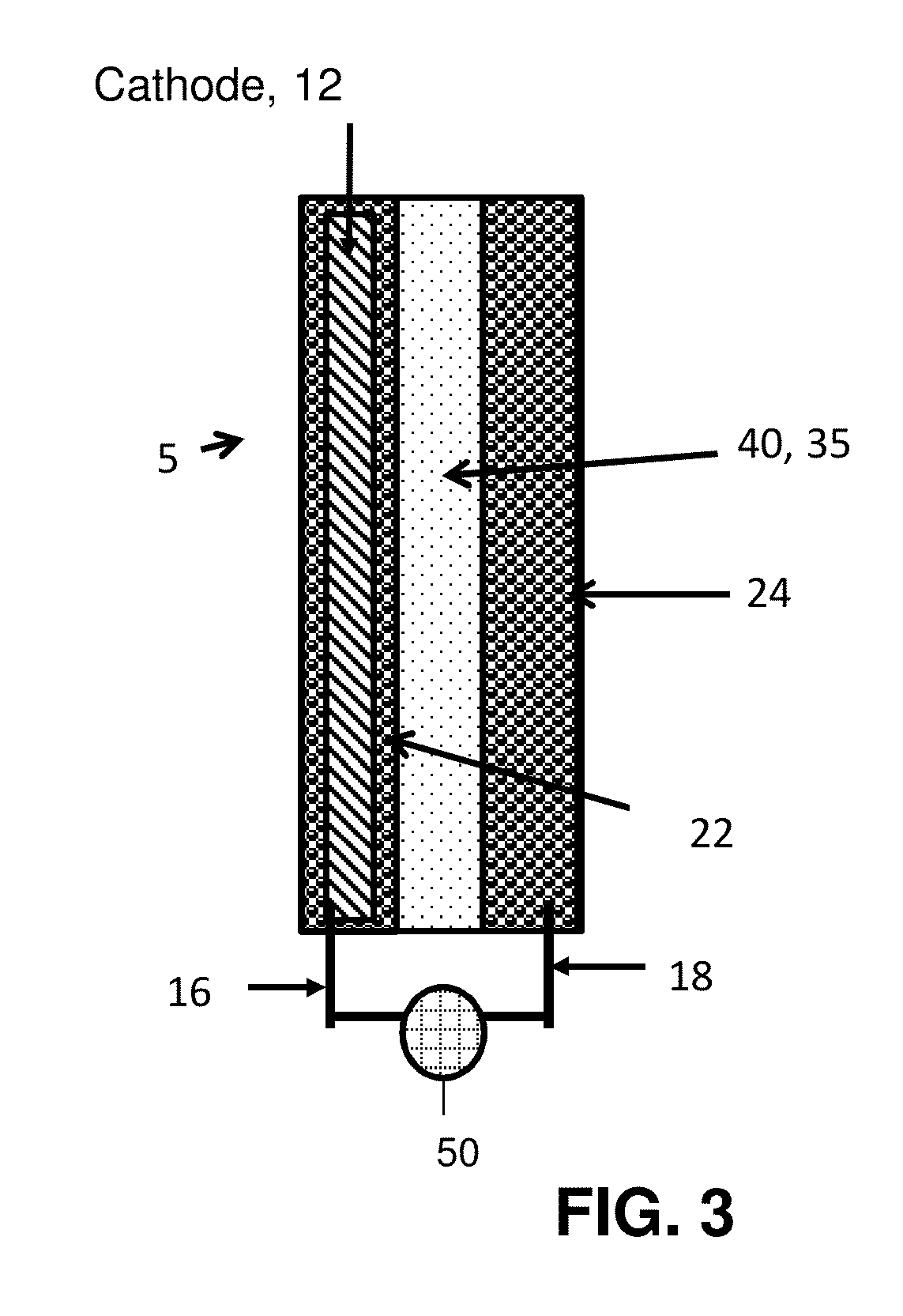
ActiveUS20150180000A1Improve battery performanceAvoid material lossBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingElectrical batteryEngineering
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Manufacture of Active Highly Phosphorylated Human Lysosomal Sulfatase Enzymes and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20100068195A1High yieldAvoid material lossCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDrugChemistry
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated lysosomal sulfatase enzymes, their pharmaceutical compositions, methods of producing and purifying such lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and compositions and their use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the lysosomal sulfatase enzyme.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARM INC
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and uses thereof
ActiveUS8128925B2High yieldAvoid material lossCompound screeningNervous disorderPhosphorylationLysosome
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated lysosomal sulfatase enzymes, their pharmaceutical compositions, methods of producing and purifying such lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and compositions and their use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the lysosomal sulfatase enzyme.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
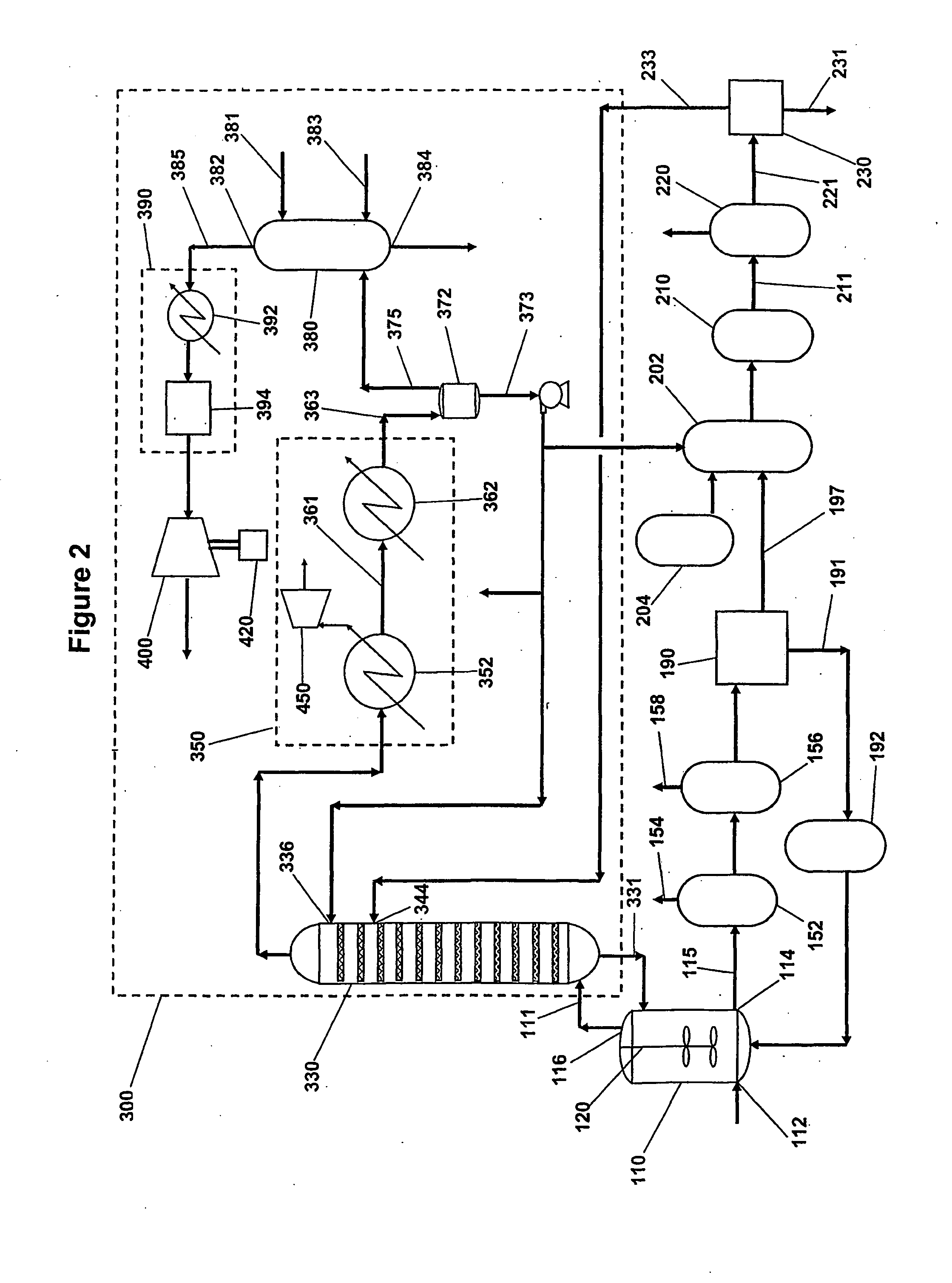
Process and Apparatus for Manufacturing Pure Forms of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids
InactiveUS20090234156A1Surprising flexibilityEliminate reduce requirementOrganic compound preparationChemical industryCarboxylic acidSolvent
A process and apparatus for manufacture of aromatic carboxylic acids comprises a liquid phase oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbon feed materials and treatment of a high pressure off-gas from the liquid phase oxidation to separate water and reaction solvent and purification of impure aromatic carboxylic acid products wherein a purification liquid includes water from off- gas treatment.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Manufacture of Highly Phosphorylated Lysosomal Enzymes and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090191178A1High yieldAvoid material lossAnimal cellsNervous disorderLysosomePhosphorylation
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
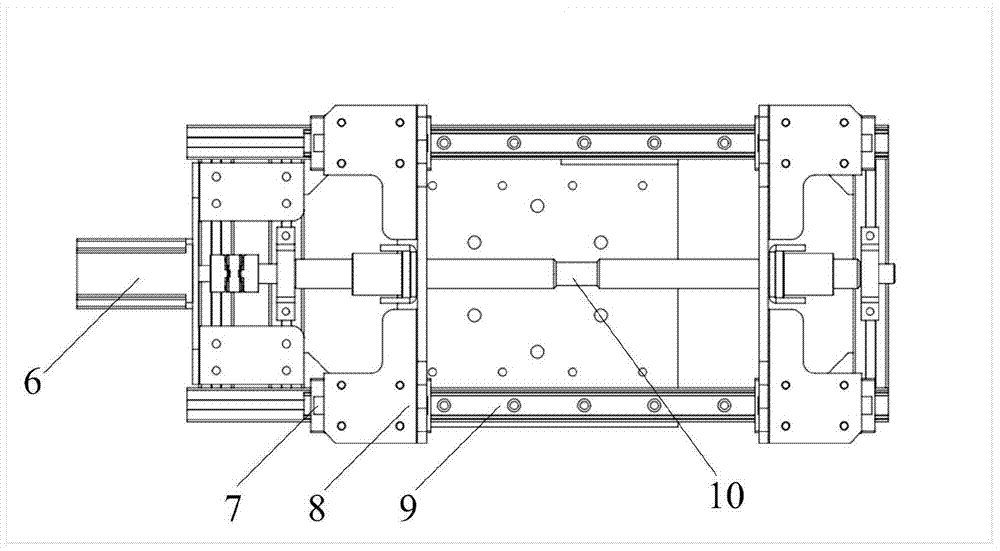
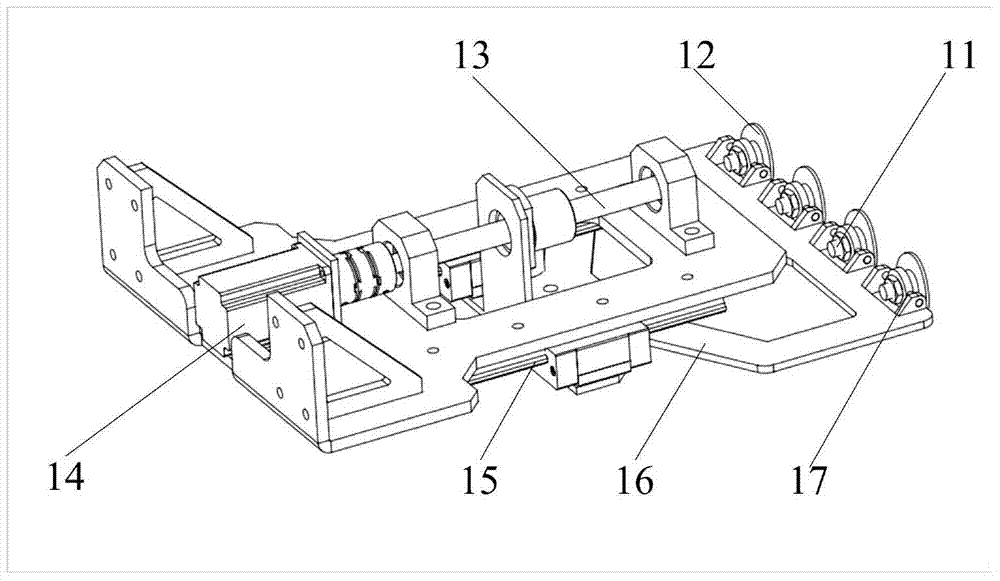
Chuck gripper device of stacking robot for complex surface
InactiveCN104493822AAchieve opposite motionGuaranteed gripping stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSymmetric designMotor drive
The invention provides a chuck gripper device of a stacking robot for a complex surface. The device comprises a connecting flange, a mounting frame, a transverse adjusting mechanism, longitudinal adjusting mechanisms, an absorbing mechanism, a human-computer control interface and an electrical protection device; the transverse adjusting device is used for adjusting the width of the absorbing mechanism through a motor driving a bidirectional rotating lead screw; the longitudinal adjusting mechanisms are of a symmetric design and are respectively mounted at two sides of the bidirectional rotating lead screw to lift and lower down the absorbing mechanism; the absorbing mechanism is connected with a sponge chuck by a hinging manner, which effectively avoids the phenomenon of failure of absorbing on an uneven surface; the absorbing mechanism can be in match with the transverse and longitudinal moving mechanisms to adapt to the change on the size of materials. The device is suitably used for gripping objects with different size and surface forms and has the characteristics of being simple in structure, convenient to drive, steady and reliable, high in generality, and flexible to operate.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MFG TECH +1
Process and Apparatus for Manufacturing Aromatic Carboxylic Acids Including Pure Forms Thereof
InactiveUS20080097118A1Beneficial recovery of energyConvenient treatmentOrganic compound preparationChemical industryThermal energyCarboxylic acid
Energy is recovered during the production of aromatic carboxylic acids by liquid phase oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons by performing a high efficiency separation on the reactor overhead vapor to form a high pressure gaseous overhead stream comprising water and organic impurities; recovering heat energy from the high pressure gaseous overhead stream by exchanging heat with a suitable heat sink material such that a condensate comprising from about 20 wt % to about 60 wt % of the water present in the high pressure gaseous overhead stream is formed and a high pressure offgas is formed; and recovering energy in the form of work from the high pressure offgas. Preferably such work is recovered using isentropic means for energy recovery, for example an expander. Apparatus for such process is also provided.
Owner:INEOS US CHEM CO
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and uses thereof
ActiveUS7722865B2High yieldAvoid material lossCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPhosphorylationLysosome
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated lysosomal sulfatase enzymes, their pharmaceutical compositions, methods of producing and purifying such lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and compositions and their use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the lysosomal sulfatase enzyme.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human n-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase and uses thereof
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS), and pharmaceutical compositions and formulations thereof, methods of producing and purifying GALNS, and its use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the GALNS enzyme, e.g., Mucopolysaccharidosis IVa (MPS IVa or Morquio A syndrome).
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Deposition print head
InactiveUS20170348911A1Ensure proper implementationReduce capacityManufacturing driving meansCoil arrangementsEngineeringElectric field
A deposition print head including a non-susceptive or low susceptive sleeve, a susceptive element having a filament channel, the susceptive element arranged inside the sleeve, wherein the susceptive element is susceptive for at least one of a magnetic field and an electrical field, wherein the filament channel is for feeding a thermoplastic filament in a feed direction. The deposition print head further includes an exciter arranged around the susceptive element, wherein the exciter is arranged for generating a field compatible with the susceptivity of the susceptive element, and a nozzle attached to one end of the susceptive element.
Owner:BOND HIGH PERFORMANCE 3D TECH BV
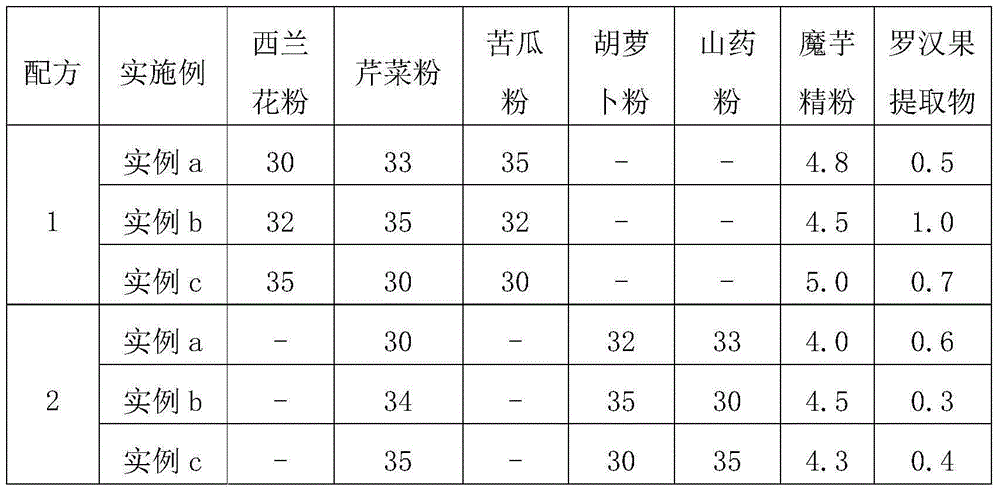
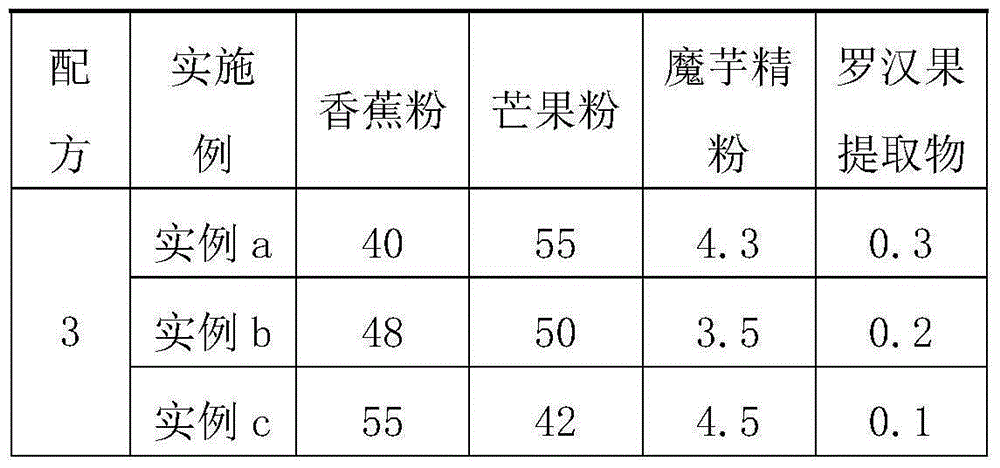
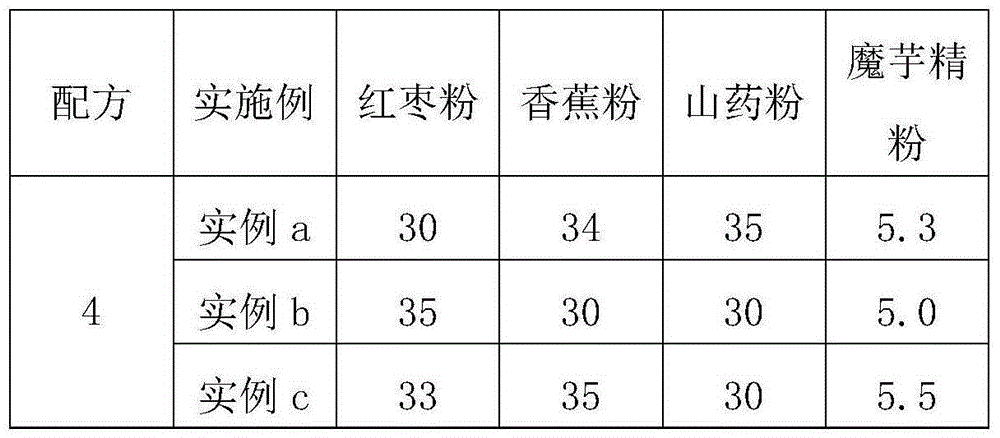
Instant natural fruit and vegetable powder and making method thereof
The invention relates to instant natural fruit and vegetable powder. The instant natural fruit and vegetable powder comprises the following components in parts by weight: 95-99 parts of mixed freeze-dried fruit and vegetable powder, 3.5-5.5 parts of konjac powder and 0-1 part of a siraitia grosvenorii extract. The invention aims to provide the instant natural fruit and vegetable powder which is rich in nutrition, unique in flavor, easy to preserve, convenient to carry and simple to brew.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
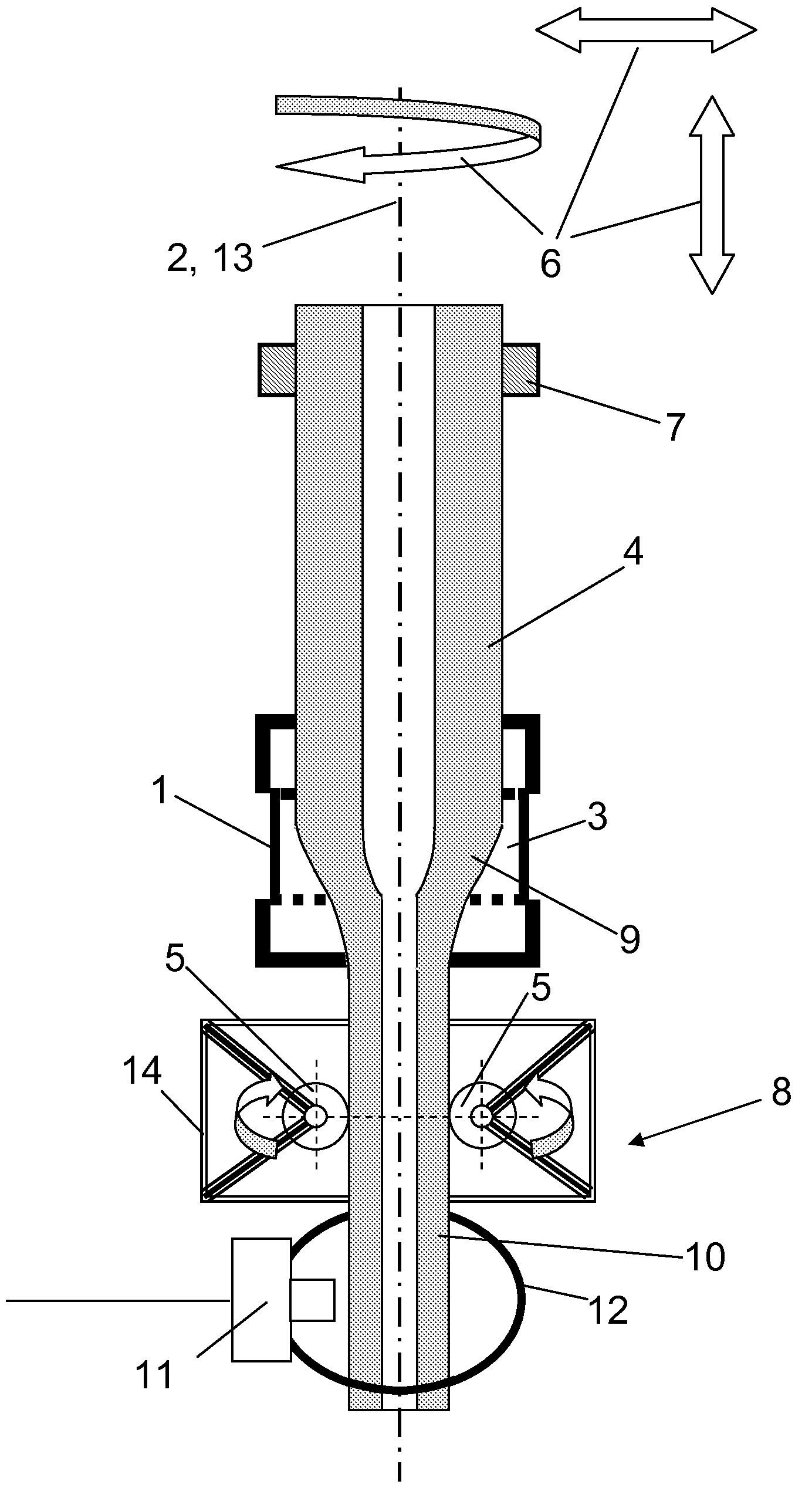
Method for producing a tube of quartz glass by elongating a hollow cylinder of quartz glass
InactiveUS20100132407A1Great dimensionRaise the draw ratioGlass reforming apparatusGlass severing apparatusOvalityHollow cylinder
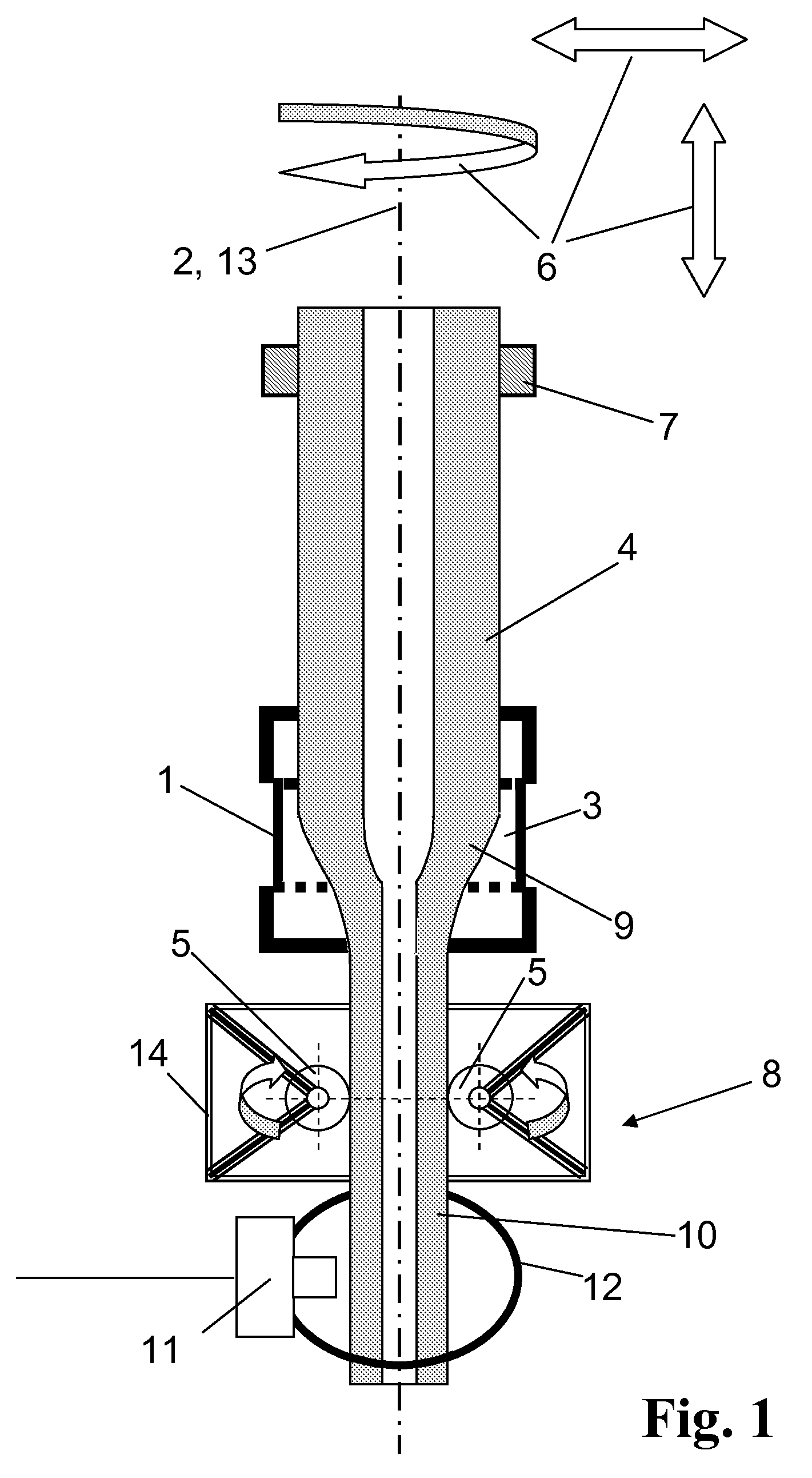
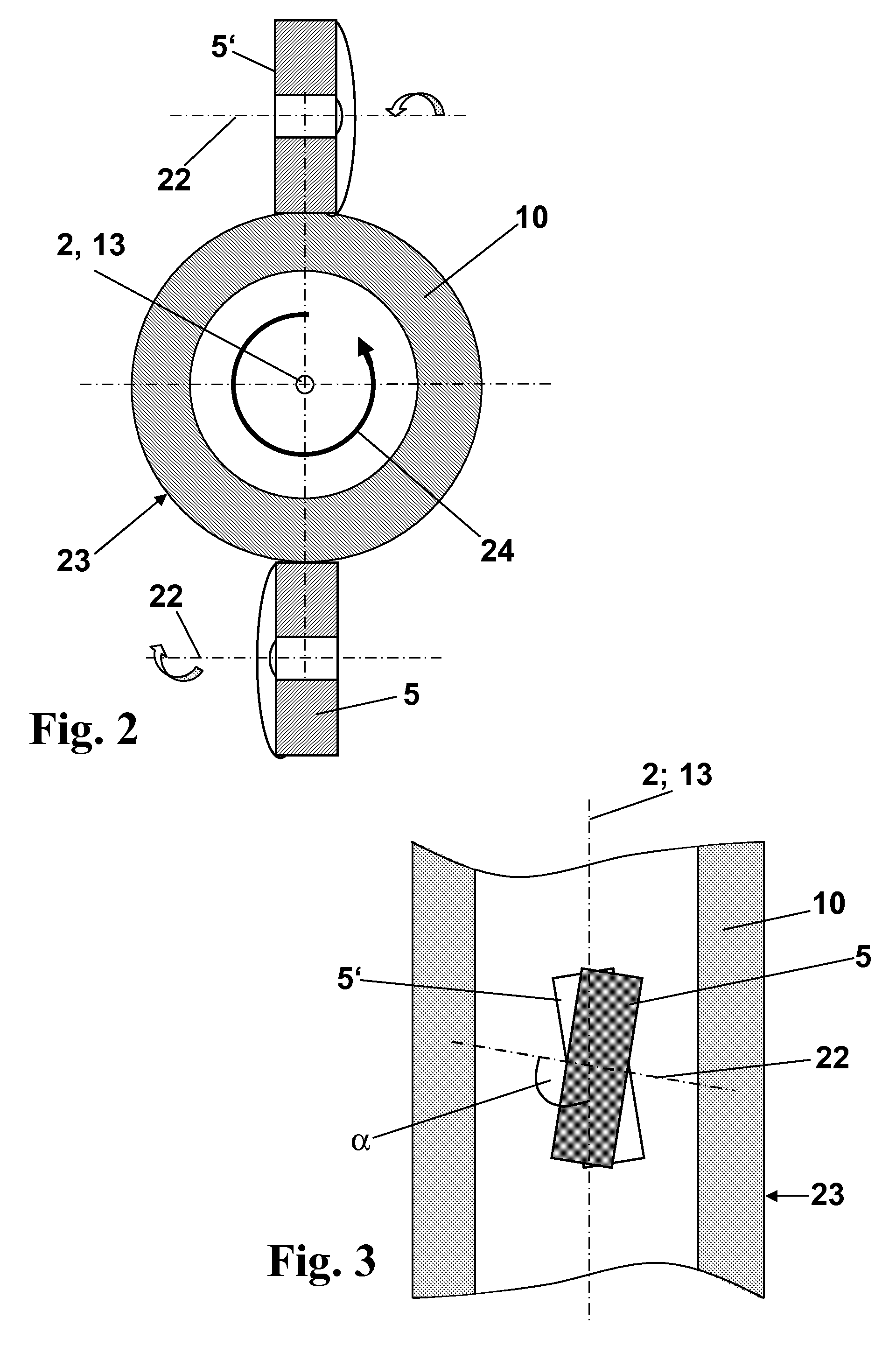
In a known method for producing a tube of quartz glass by elongation, a hollow cylinder of quartz glass is continuously supplied to a heating zone, softened therein zone by zone, and a tube strand is drawn in the direction of a drawing axis out of the softened region by using a roll puller, the roll puller comprising a frame by which a plurality of puller rolls are fixed, which are rotatable around a rotation axis and which are distributed over the circumference of the tube strand and adjoining the tube strand with their cylindrical outer surface. Starting therefrom, to indicate a vertical drawing method in which a high draw ratio can also be accomplished with little constructional effort by using a take-off unit in the form of a roll puller and which simultaneously allows an optimization of the dimensional stability of the quartz glass tubes obtained, and which particularly avoids material losses caused by ovality and siding, the invention suggests that the frame of the roll puller s stationary, and the hollow cylinder and the tube strand are rotated about the drawing axis relative to one another, the relative rotation being set to a range between 0.01 and 5 revolutions per linear meter of drawn-off tube strand.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
3D printing method of fiber-grade flame retardant product based on reactive extrusion
InactiveCN105818384ABroaden your optionsAchieve stabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusPolyesterFiber
The invention relates to a 3D printing method of a fiber-grade flame retardant product based on reactive extrusion. According to the 3D printing method, polymerization reaction is performed on a lactam monomer and / or a lactone monomer and an assistant and a plasticizer after fusing under the action of a catalyst, and a flame retardant is added before polymerization or during polymerization to obtain a target polymer; then the target polymer is subjected to fused deposition 3D printing, and then is subjected to thermal treatment, thus obtaining a final product. According to the invention, a high-precision high-adaptation 3D printer is adopted, the forming precision is high, the efficiency is high, the mechanical property of a product is good, and the dispersibility of a functional component is good; and a process of preparing a product directly from a polymeric monomer is adopted, and therefore, the production flexibility is improved, and the conditions of edge warping of nylon, polyester and other semi-crystalline polymers caused by crystallization and large temperature difference, and even failure in printing can be avoided. The method can widen the species of fused deposition 3D printing materials, can improve the quality of products, and is wide in application in the fields of automotive materials, engineering plastics, building materials and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
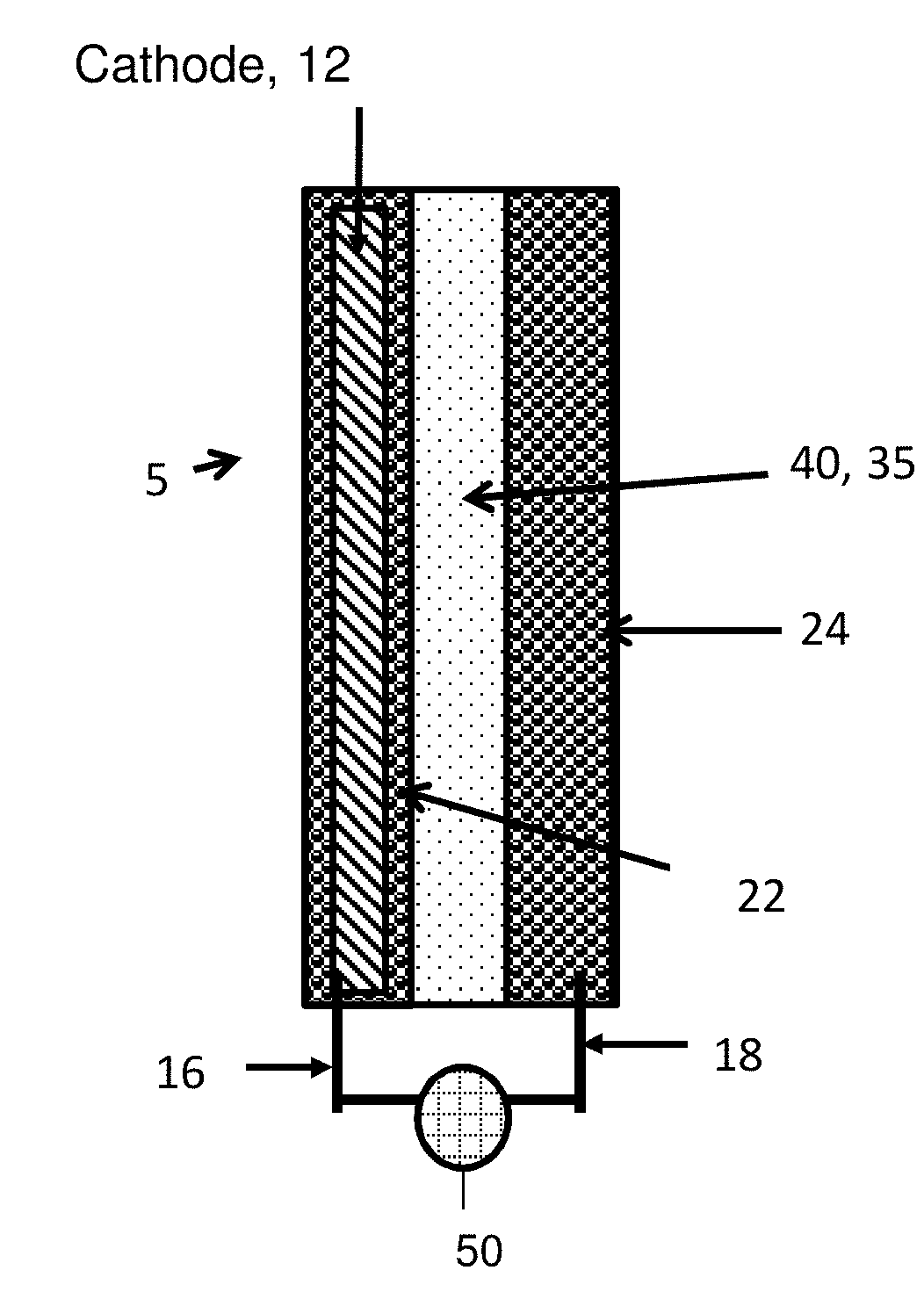
Separator enclosures for electrodes and electrochemical cells
ActiveUS9991492B2Improve battery performanceAvoid material lossBatteries circuit arrangementsCell electrodesEngineeringContact force
The disclosure provides electrochemical cells including a separator enclosure which encloses at least a portion of a positive or negative electrode. In an embodiment, the separator generates a contact force or pressure on at least a portion of the electrode which can improve the performance of the cell. The disclosure also provides methods for charging an electrochemical cell.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Casting method
ActiveUS20190366427A1Avoid material lossImprove throughputCoil arrangementsMolten metal supplying equipmentsImpellerTurbine blade
A method for producing cast items in a casting method, wherein a charge of a conductive material is introduced into the sphere of influence of at least one alternating electromagnetic field, so that the charge is kept in a levitating state. The melt is poured into moulds in order to produce turbine blades, prostheses or turbocharger impellers.
Owner:ALD VACUUM TECH GMBH
Spinning bottom coating metal stone inner container pot manufacturing technology and cooker manufactured through same
ActiveCN107853977ATightly boundImprove yieldCooking-vessel materialsGrinding machinesMetal coatingManufacturing technology
The invention relates to the field of cooking pots and manufacturing thereof, in particular to a spinning bottom coating metal stone inner container pot manufacturing technology and a cooker manufactured through the same. According to the spinning bottom coating metal stone inner container pot manufacturing technology and the cooker manufactured through the same, the finished product rate can be greatly increased to 95-99% or above, the high-quality rate reaches 90% or above, the manufactured product enables the coating bottom can achieve the special effect of being riveted into an aluminum metal layer, the metal coating bottom can be more and more tightly combined with an aluminum pot body under high temperature once the product manufactured through the technology is manufactured successfully, and the phenomenon that an existing product expands and protrudes out of the bottom, or is directly disengaged is avoided.
Owner:浙江古石科技有限公司
Synthesis device and method of gaseous extinguishing agent
ActiveCN103801248AAvoid material lossHigh reaction yieldPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsBromineReaction timing
The invention discloses a synthesis device and method of a gaseous extinguishing agent. The synthesis device is characterized in that a reaction still is connected with an agitator, a trifluoropropene storage tank, a liquid bromine storage tank, an alkali liquor storage tank and a fractional distillation tube, the tail end of a branch tube of the fractional distillation tube goes into a collecting bottle, the adding order of raw materials can be controlled through a plurality of switching valves, and halon is synthesized by one step to substitute for a clean gaseous extinguishing agent. Three operation steps of addition, elimination and fractionation can be performed in the synthesis device, and the whole synthesis flow is free from transferring of any intermediate product from the step of feeding materials to the step of obtaining the target product, so that the material loss is avoided, the reaction yield is improved, the reaction time is saved, and the reaction efficiency is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase and uses thereof
ActiveUS8765437B2High yieldAvoid material lossNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphorylationN-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Functional fiber-grade 3D printing method based on reactive extrusion
InactiveCN105922577AHigh forming precisionWiden your optionsAdditive manufacturing apparatusPlasticizerHeat treated
The invention relates to a functional fiber-grade 3D printing method based on reactive extrusion. A lactam monomer and / or lactone monomer, an assistant and a plasticizer are fused and have a polymerization reaction under the catalyst effect, a functional agent is added before polymerization or in the polymerization process, and target polymer is obtained; the target polymer is subject to fused deposition 3D printing, and then subject to heat treatment, and a final product is obtained; and according to heat treatment, heat preservation is carried out for 3 min to 60 min at the temperature ranging from 100 DEG C to 180 DEG C. A high-precision high-adapting 3D printer is adopted, the molding precision is high, the efficiency is high, the mechanical property of the product is good, and functional components are good in dispersibility; a technology for directly making the product from the polymeric monomer is adopted, the production flexibility is improved, and meanwhile, the condition that due to crystallization and the large temperature difference of semi-crystalline polymer of nylon, polyester and the like, edge warping is caused, and even printing cannot be carried out is avoided; and the kind of the fused deposition 3D printing material is widened, the quality of the product is improved, and the method has the wide application to the fields of automobile materials, engineering materials, structural parts and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
3D printing method for fiber-grade electric conduction product based on reactive extrusion
InactiveCN105835374ABroaden your optionsAchieve stabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusDomestic articlesPolyesterFiber
The invention relates to a 3D printing method for a fiber-grade electric conduction product based on reactive extrusion. After a lactam monomer and / or a lactone monomer are / is fused with an assistant and a plasticizer, the polymerization reaction is conducted under the action of a catalyst, an electric conduction filler is added before polymerization or in the polymerization process, fusion deposition 3D printing is conducted, and a final product is obtained after heat treatment. A high-precision and high-adaptability 3D printer is adopted, the forming precision and efficiency are high, the mechanical performance of the product is good, and the dispensability of functional components is good. The technology directly from polymerization monomers to the product is adopted, and the product flexibility is improved. Meanwhile, edge warping of nylon, polyester and other hypocrystalline polymers due to crystallization and the large temperature difference, and even unavailable printing are avoided. The kinds of fusion deposition 3D printing materials are widened, the quality of the product is improved, and the 3D printing method is widely applied to the fields of automobile materials, electronic devices, engineering materials, electromagnetic shielding materials and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Fiber-scale reactive extrusion 3D printing method
InactiveCN105904728ABroaden your optionsAchieve stabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiberPolyester
The invention relates to a fiber-scale reactive extrusion 3D printing method including the steps of: a) fusing a lactam monomer and / or a lactone monomer, and an additive and an ionic liquid, and performing a polymerization reaction under the effect of a catalyst to prepare a target polymer; and b) performing fused deposition 3D printing to the target polymer and performing thermal treatment to obtain a finish product, wherein the thermal treatment is carried out at 100-180 DEG C for 3-60 min. In the invention, a high-precision high-adaptability 3D printer is employed, so that the method has high shaping precision and efficiency and the finish product has good mechanical performance. A process, in which the polymerization monomers are directly processed to obtain the finish product, is employed, so that the method is improved in production flexibility and also avoids the problems of edge warping and even printing failure since semi-crystallized polymers, such as nylon, polyester and the like, are crystallized and are large in temperature difference, thereby avoiding reduction of performance of the finish product due to degradation of the polymers. The method increases the types of fused deposition 3D printing materials, improves quality of the finish product, and has wide applications in the fields of crafts, machines, chemical engineering, instruments, automobiles and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
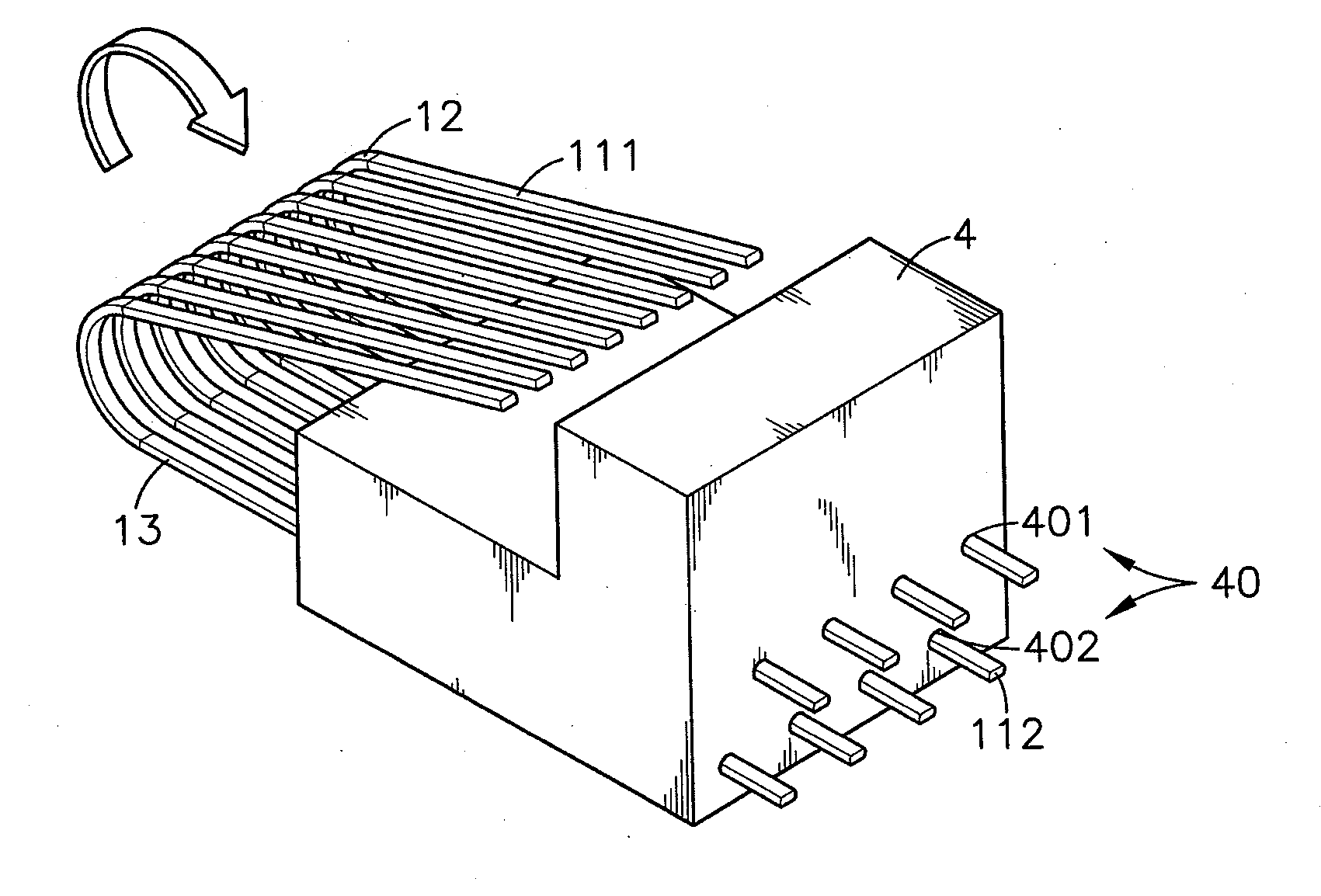
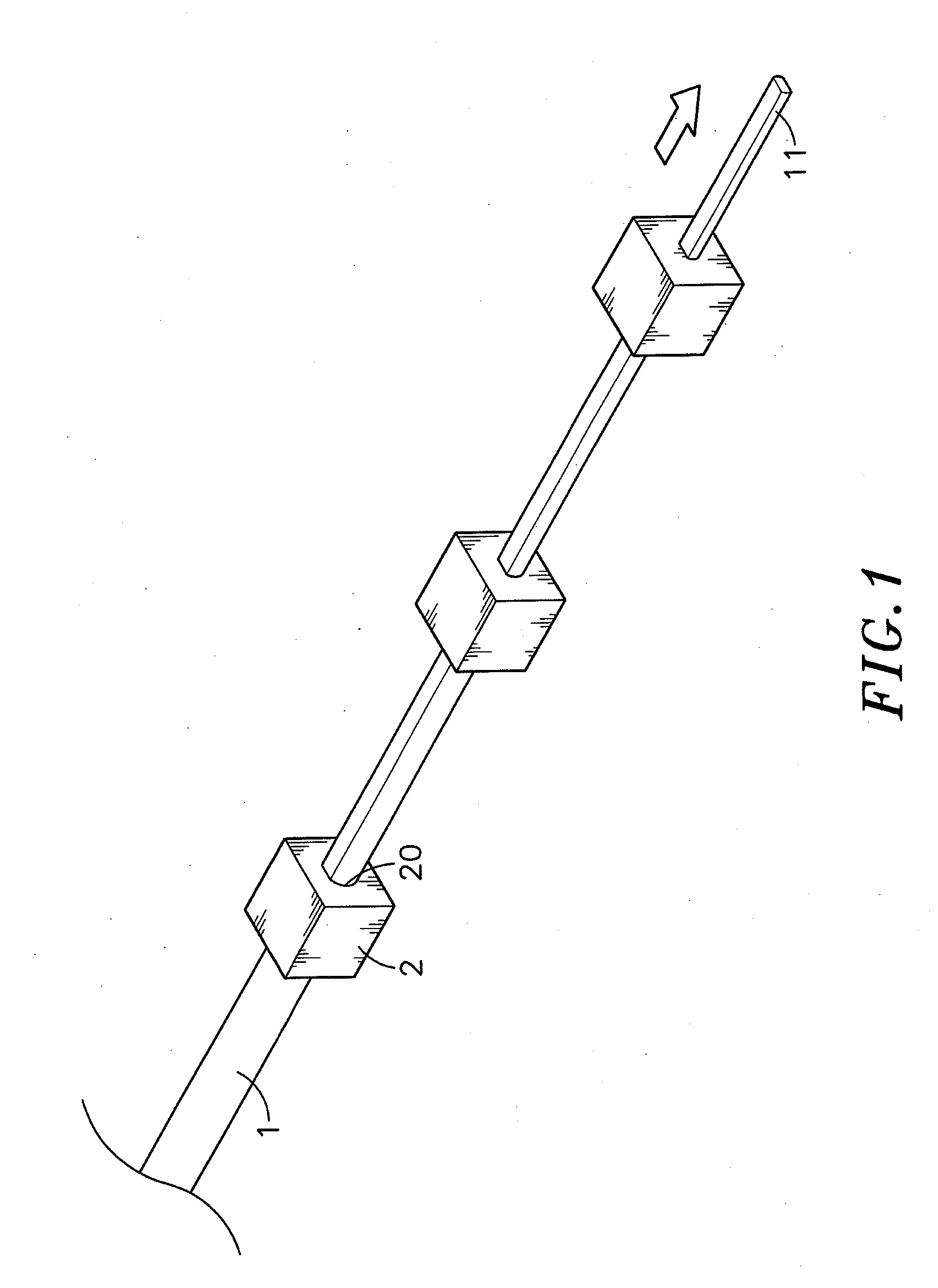
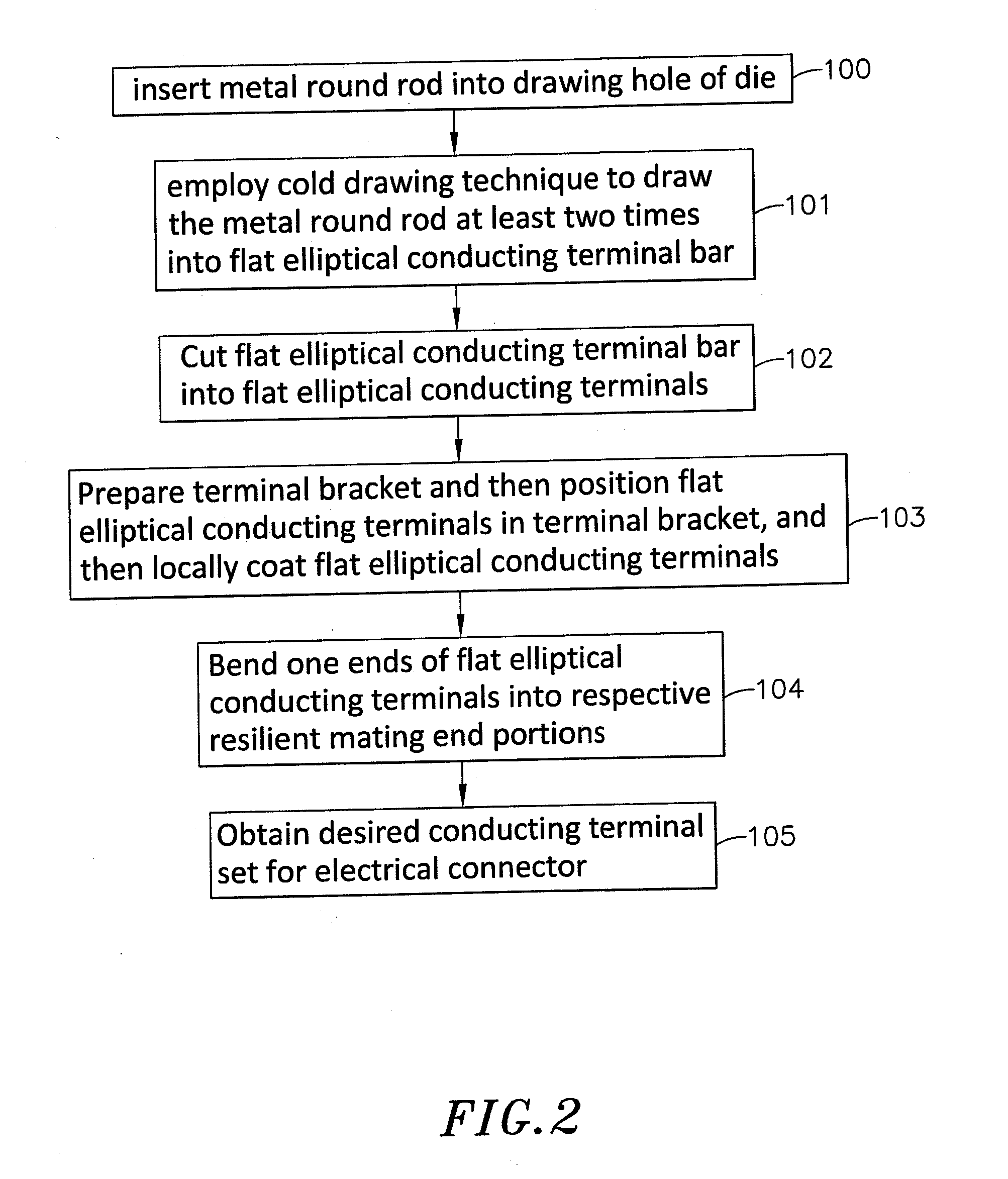
Method for fabricating a conducting terminal set for electrical connector
InactiveUS20130111749A1Avoid material lossSave conducting terminal manufacturing costContact member manufacturingContact member assembly/disassemblyElectricityRound bar
Owner:RIIDEA
Method and apparatus for securing a closure in an aperture of a container
InactiveUS7237311B2Avoid material lossMetal working apparatusLoading/unloadingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:MATCON R & D
Method for thinning solid-body layers provided with components
PendingCN111357084AAvoid material lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusPhysicsChemistry
According to claim 1, the invention relates to a method for providing at least one solid-body layer (4). The solid-body layer (4) is separated from a solid body (1). The method according to the invention preferably has the steps of: producing a plurality of modifications (9) in the interior of the solid body (1) using laser beams in order to form a separation plane (8), compressive stresses beingproduced in the solid body (1) by the modifications (9); separating the solid-body layer (4) by separating the remaining solid body (1) and the solid-body layer (4) along the separation plane (8) formed by the modifications (9), wherein at least parts of the modifications (9) which produce the compressive stresses remain on the solid-body layer (4), and enough modifications (9) are produced that the solid-body layer (4) is separated from the solid body (1) on the basis of the modifications (9) or an external force is introduced into the solid body (1) in order to produce additional stresses inthe solid body (1), said external force being so great that the stresses cause a crack to propagate along the separation plane (8) produced by the modifications; and producing a metal layer on the surface exposed by the separation of the solid-body layer (4) from the solid body (1) in order to at least partly, preferably greatly and particularly preferably completely, compensate for a deformationof the solid-body layer (4) produced by the compressive stresses of the remaining modification parts or at least partly, preferably greatly or completely, compensate for the compressive stresses.
Owner:SILTECTRA
Bearing cage segment including alignment element
PendingCN111536156AAvoid material lossEasy to manufactureBearing assemblyShaft assemblyPhysicsNeedle roller bearing
The invention discloses a bearing cage segment (2;4) of a sheet metal cage (1) and a sheet metal cage comprising the same. In particular, the bearing cage segment is used for needle roller bearings. The bearing cage segment of a sheet metal cage includes first and second ring sections (10, 12) and a plurality of bridges (14), which are used for connecting the first ring sections and the second ring sections and defining a plurality of pockets (16) for receiving at least one rolling element. The bearing cage segment comprises at least one first joint edge (6; 8), which points to the circumferential direction and is configured to connect to a second joint edge (6; 8), and the bearing cage segment includes an alignment element (18; 20), which is configured to align the first joint (6; 8) edgeradially, axially and / or circumferentially against the second joint edge (6; 8).
Owner:AB SKF
Method and device for handling drink containers
ActiveUS8651260B2Reduce downtimeReduce wasteMetal sawing devicesLiquid fillingProcess engineeringProduct mix
Owner:KRONES AG
Crushing and classifying method for light calcium carbonate
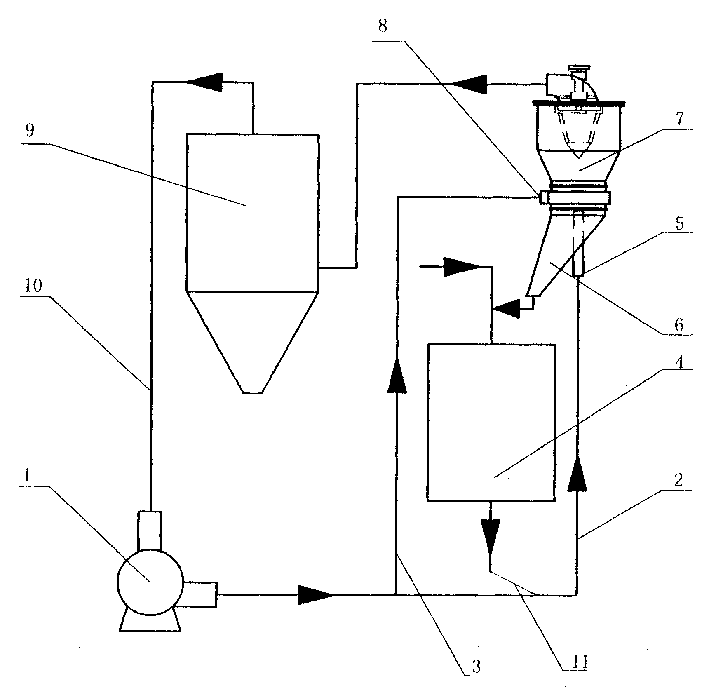
InactiveCN1492003AAvoid material lossReduce manufacturing costPigment physical treatmentPulverizerCalcium carbonate
The crushing and classifying process for light calcium carbonate includes crushing dry calcium carbonate into crusher; conveying crushed calcium carbonate with blower and pipeline to classifying machine; classifying the crushed calcium carbonate material via centrifugal force airflow produces to make calcium carbonate material meeting the fineness requirement enter the powder collecting system from the top of the classifying machine and make coarse material return to crushing; and returning the airflow from the powder collecting system and with calcium carbonate powder eliminated to the entrance of the blower; and other steps. The said process has low cost, improved work environment, no environmental pollution and lower labor strength.
Owner:陈品维
Buckling-resistant steel structure primary and secondary beam connecting joint
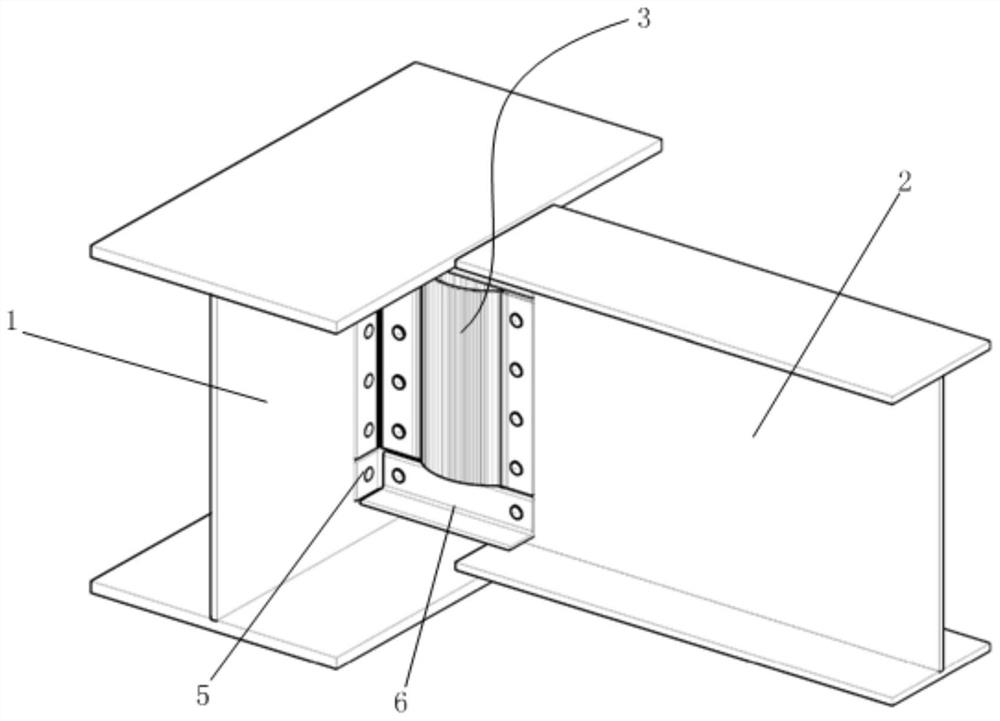
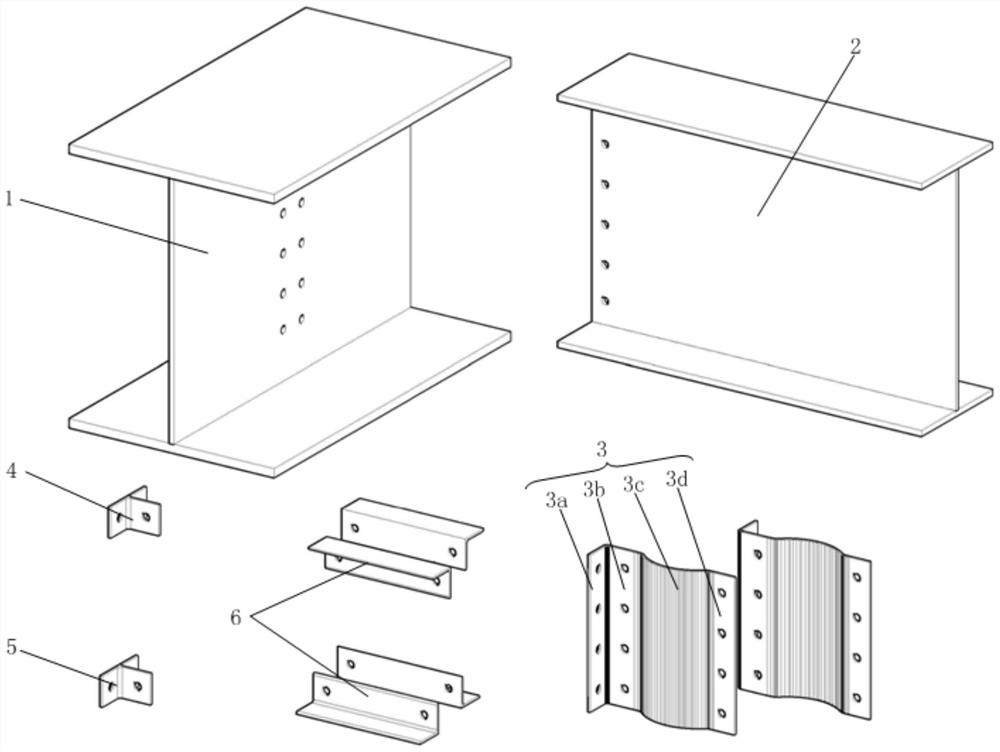
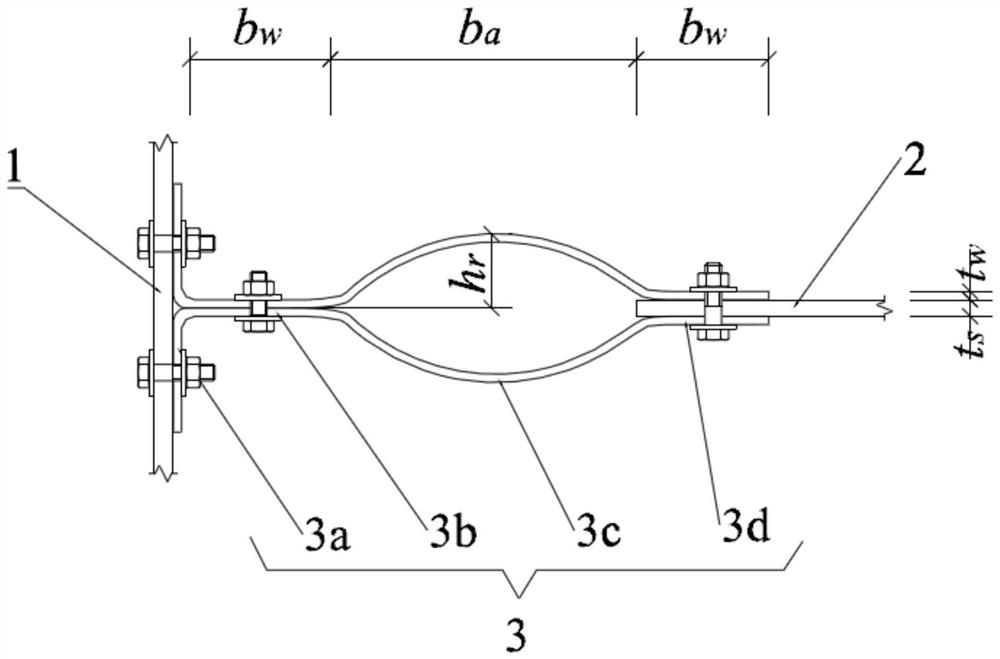
ActiveCN113026968AAvoid material lossStrong elastic and plastic deformation abilityShock proofingPhysicsEngineering
The invention discloses a buckling-resistant steel structure primary and secondary beam connecting joint. The buckling-resistant steel structure primary and secondary beam connecting joint comprises a primary beam and a secondary beam, wherein the primary beam and the secondary beam are connected through a pair of opposite fish webs, the fish webs comprise vertical wings, first flat wings, arc-shaped wings and second flat wings which are connected in sequence, the vertical wings are connected with the primary beam, and the second flat wings are connected with the secondary beam. According to the buckling-resistant steel structure primary and secondary beam connecting joint, the secondary beam is connected in a non-notch mode, and the primary beam and the secondary beam are connected through the buckling-resistant fish webs, so that material loss caused by secondary beam notches in traditional design and secondary beam web buckling damage caused by secondary beam section weakening can be avoided. The configuration sections of the two fish webs are symmetrical, eccentric torsion is not easy to occur, and the shearing force of the secondary beam can be effectively transmitted to the primary beam. Experimental results show that the interiors of the fish webs are hollow, but the fish webs have strong elasticity and plastic deformation capacity in a plane and are not easy to embrittle under the action of dynamic load. The buckling-resistant steel structure primary and secondary beam connecting joint has strong buckling resistance and shear bearing capacity and sufficient shear rigidity and impact resistance.
Owner:浙大宁波理工学院
Energy-saving oil refining stirring device
InactiveCN105709679AAvoid material lossExtended service lifeRotary stirring mixersMixer accessoriesExhaust gasProcess engineering
The invention discloses an energy-saving stirring device for oil refining, which includes a stirring tank, a gas torch, a gas return pipe and a heat supply pipe. The stirring tank includes a stirring device and a heating chamber. Composed of a prop and a scraper, the stirring spindle is connected to the motor arranged above the stirring tank, a plurality of stirring rods are arranged horizontally on the stirring spindle, and a stirring prop is vertically arranged on the stirring rod symmetrically to the stirring spindle, and at the end of the stirring rod There is a scraper, and a feeding port is provided on the top cover of the mixing tank, and the gas return pipe is connected to the gas torch and the mixing tank; this device is equipped with a scraper on the stirring device, and the material attached to the inner wall of the mixing tank is scraped by the scraper during stirring. In order to avoid material loss and prolong the service life of the mixing tank, the tail generated by the combustion reaction generates water vapor and then heats the mixing tank, which is different from direct combustion to heat the tank body, which prolongs the service life of the mixing tank and recycles the tail gas to save energy.
Owner:雍自玲
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com