Patents
Literature
6640 results about "Turbocharger" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A turbocharger, colloquially known as a turbo, is a turbine-driven forced induction device that increases an internal combustion engine's efficiency and power output by forcing extra compressed air into the combustion chamber. This improvement over a naturally aspirated engine's power output is due to the fact that the compressor can force more air—and proportionately more fuel—into the combustion chamber than atmospheric pressure (and for that matter, ram air intakes) alone.
Hybrid vehicles
InactiveUS7104347B2Improve fuel economyReduce pollutant emissionsInternal combustion piston enginesElectric motor startersMaximum torqueRegenerative brake
Owner:HIRSCH DAVID +1
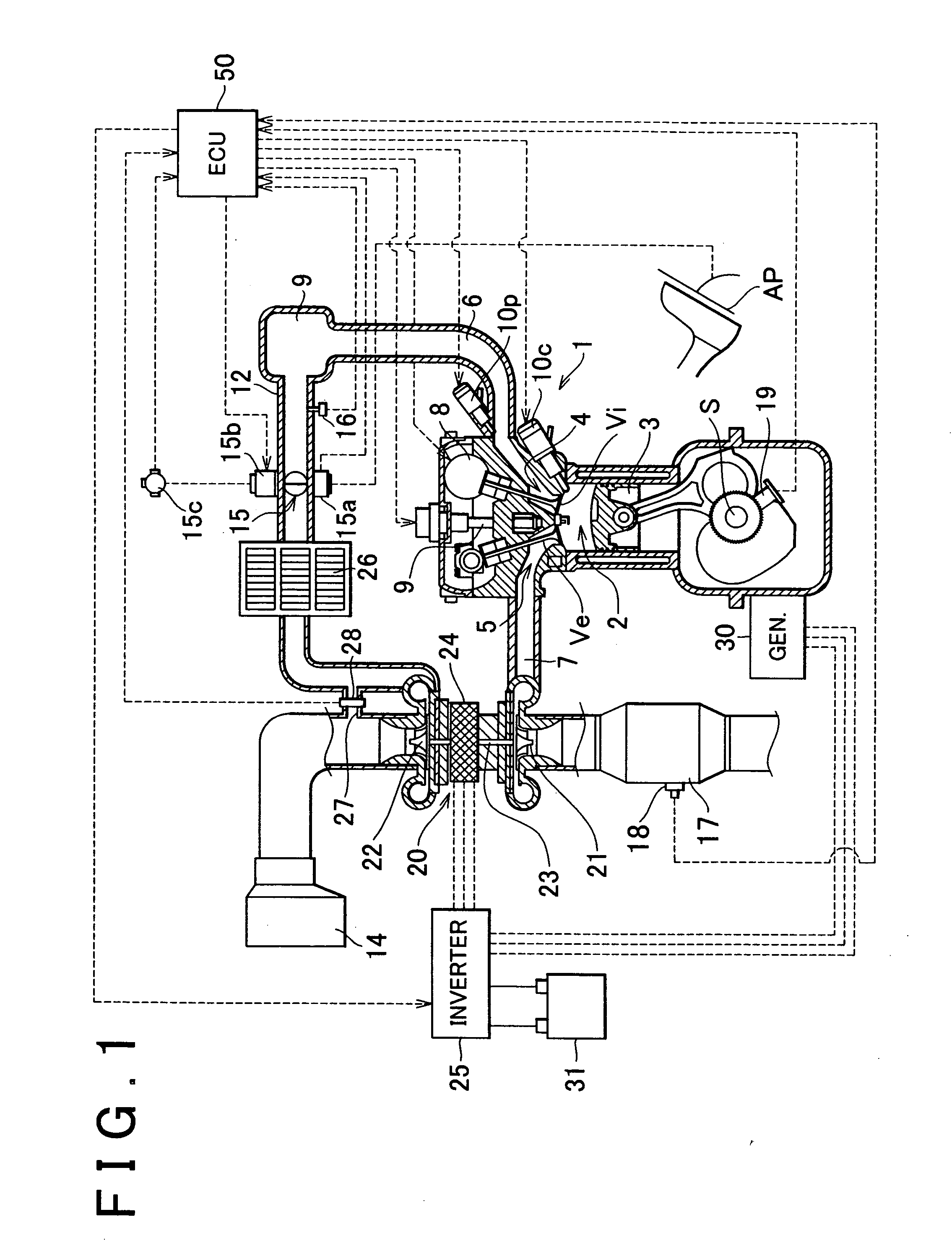
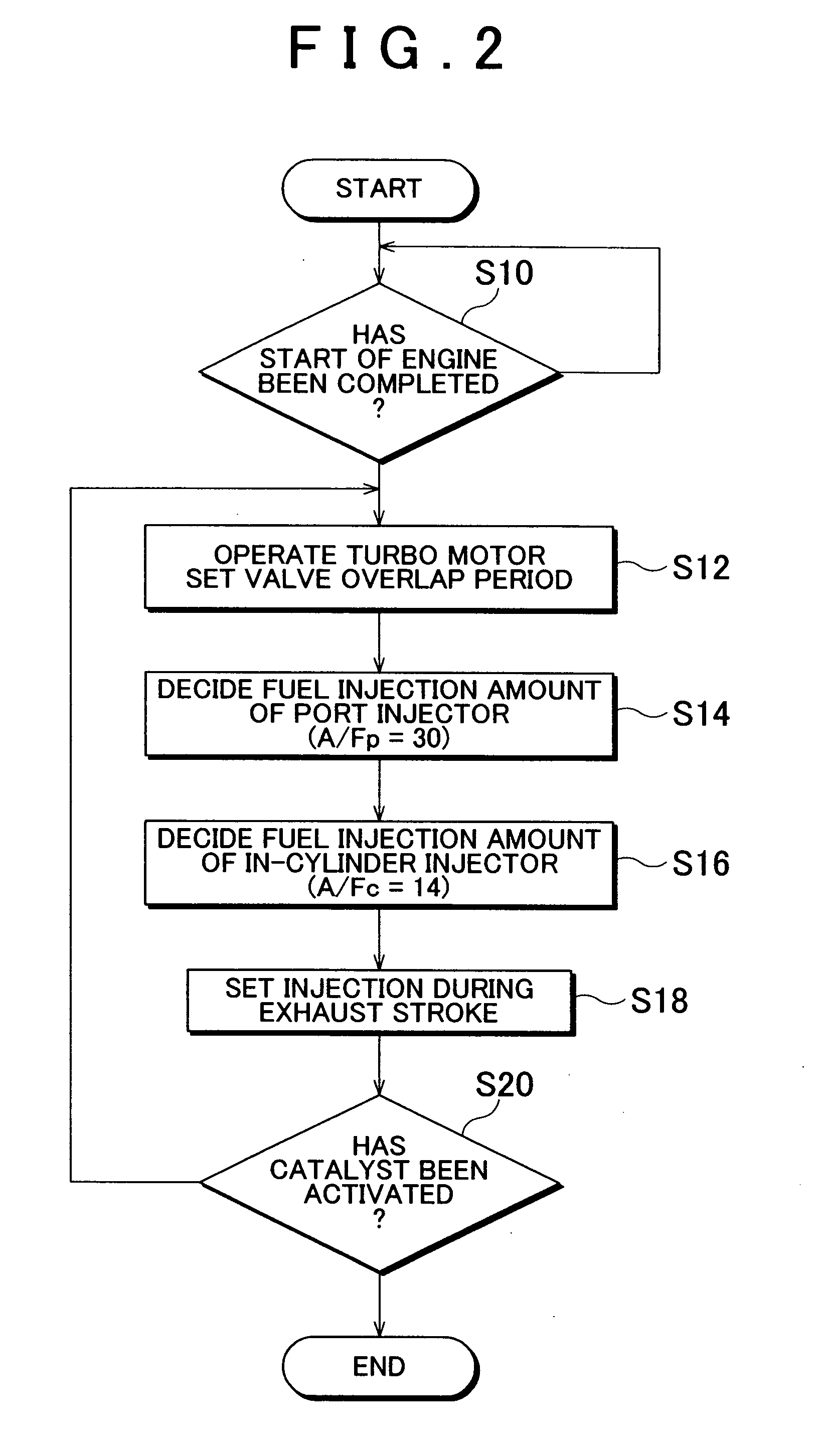
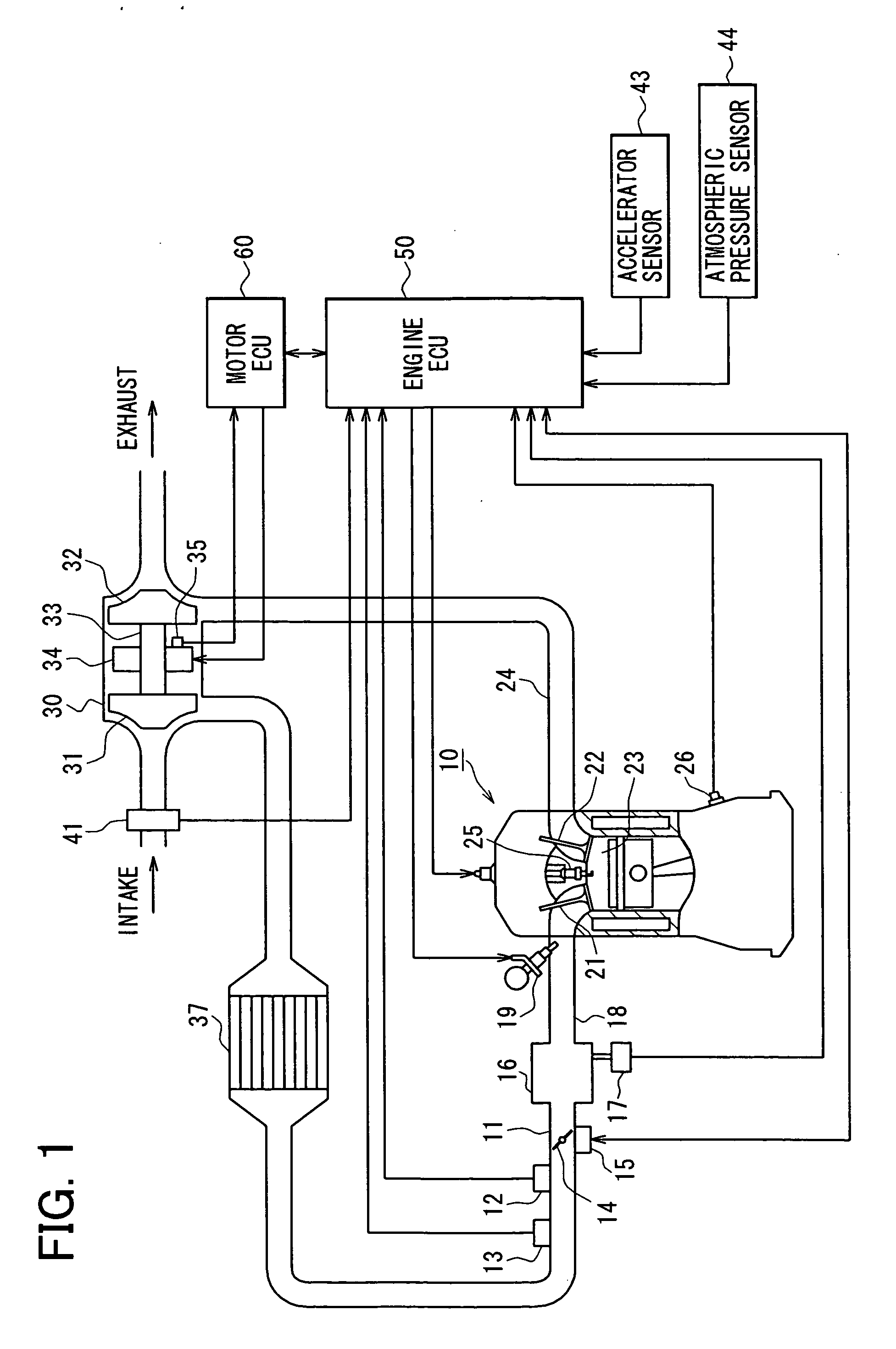
Internal combustion engine and control method thereof
InactiveUS20050097888A1Reliably activatedReduce exhaust emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
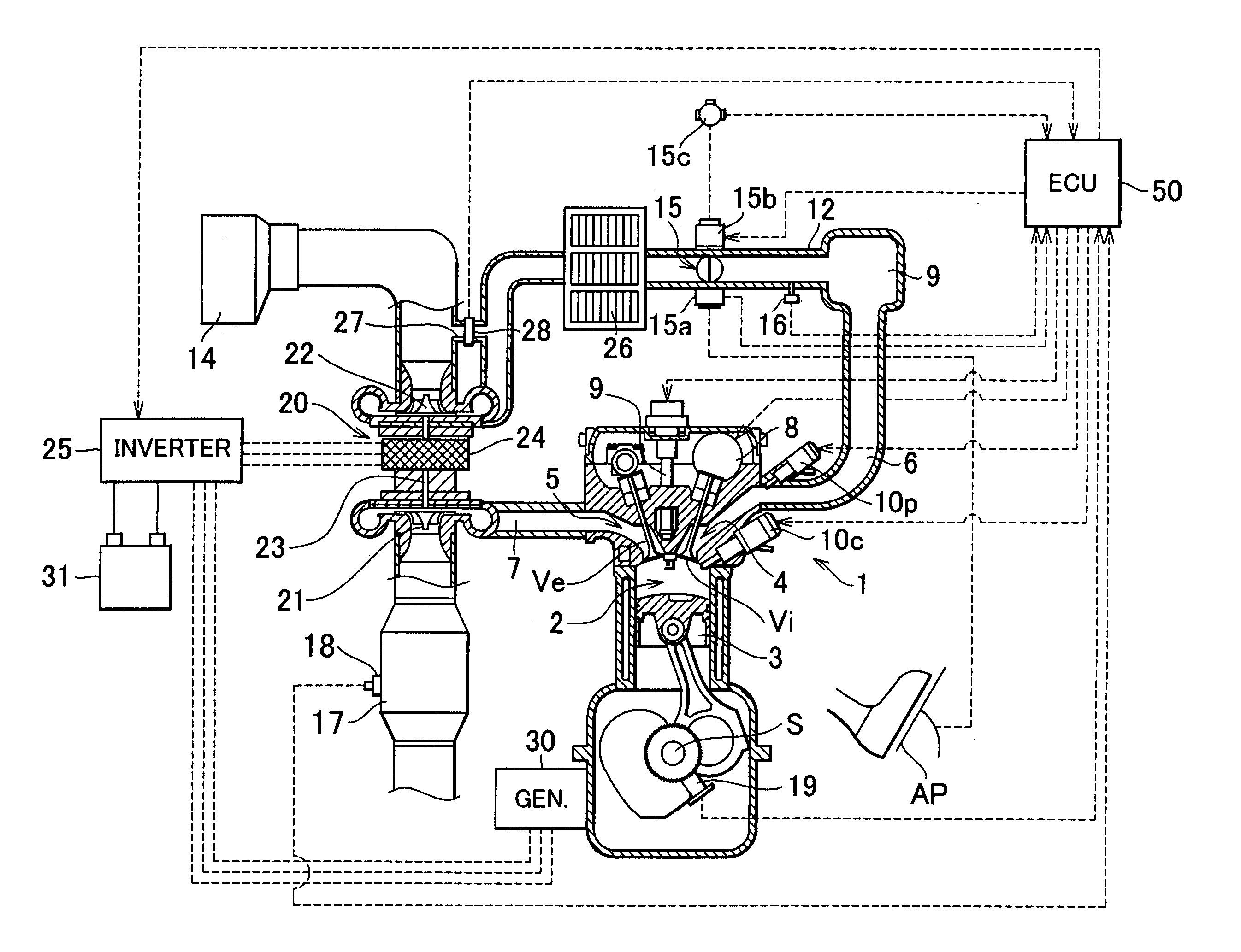
An internal combustion engine in which power is generated by burning a mixture of fuel supplied from a port injector and / or an in-cylinder injector and air in a combustion chamber, includes a valve drive mechanism which can change a valve opening characteristic of at least one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve; a turbocharger which supercharges air taken into the combustion chamber; a turbo motor which changes supercharging pressure generated by the turbocharger; a catalyst device including a catalyst which purifies exhaust gas discharged from the combustion chamber; and an ECU which controls the turbo motor such that pressure of the air taken into the combustion chamber becomes larger than back pressure until it is determined that the catalyst has been activated, and which sets a valve overlap period during which both of the intake valve and the exhaust valve are opened.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
System and method for waste heat recovery in exhaust gas recirculation
InactiveUS20110209473A1Liquid degasificationInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerExhaust fumes
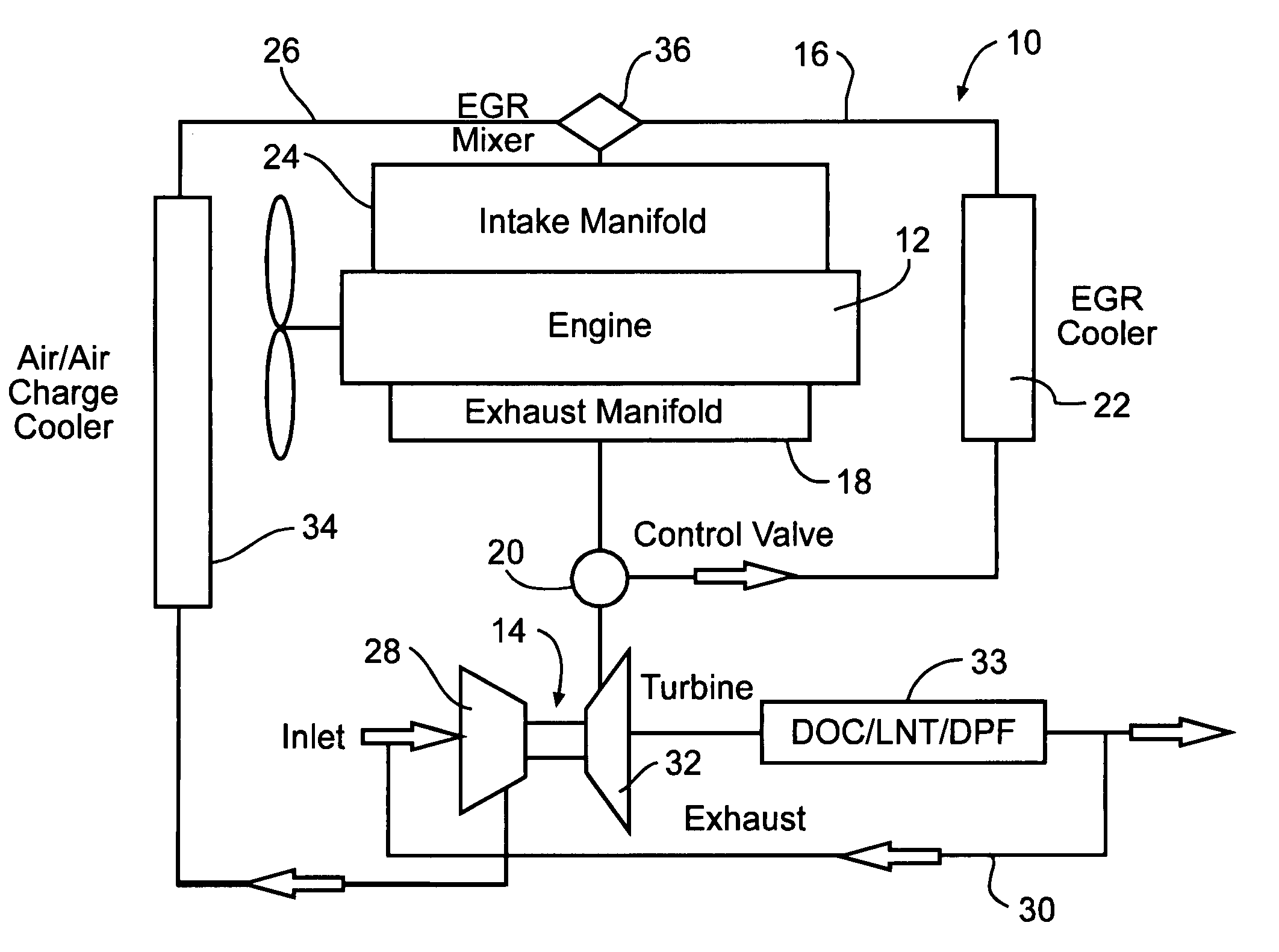
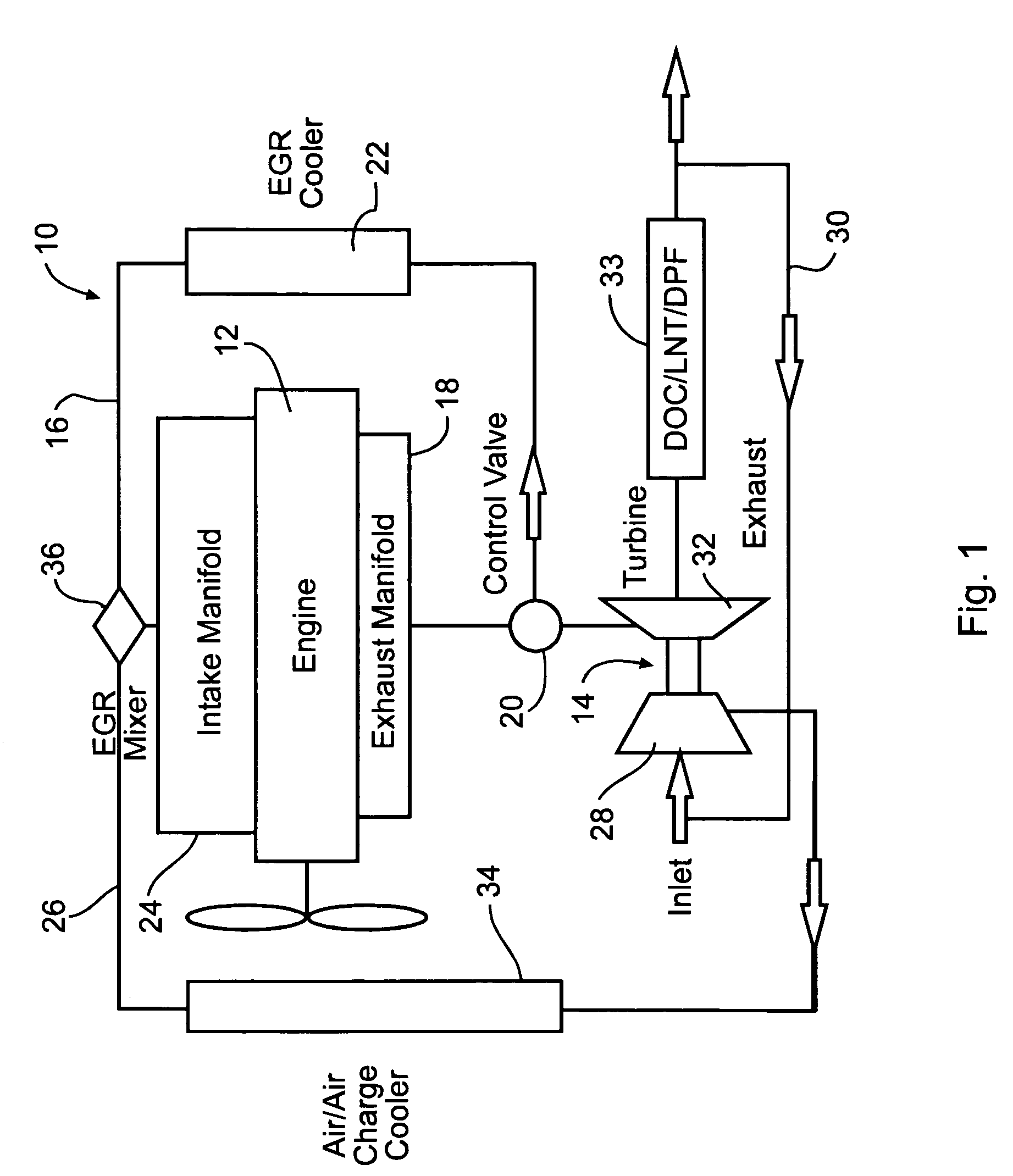
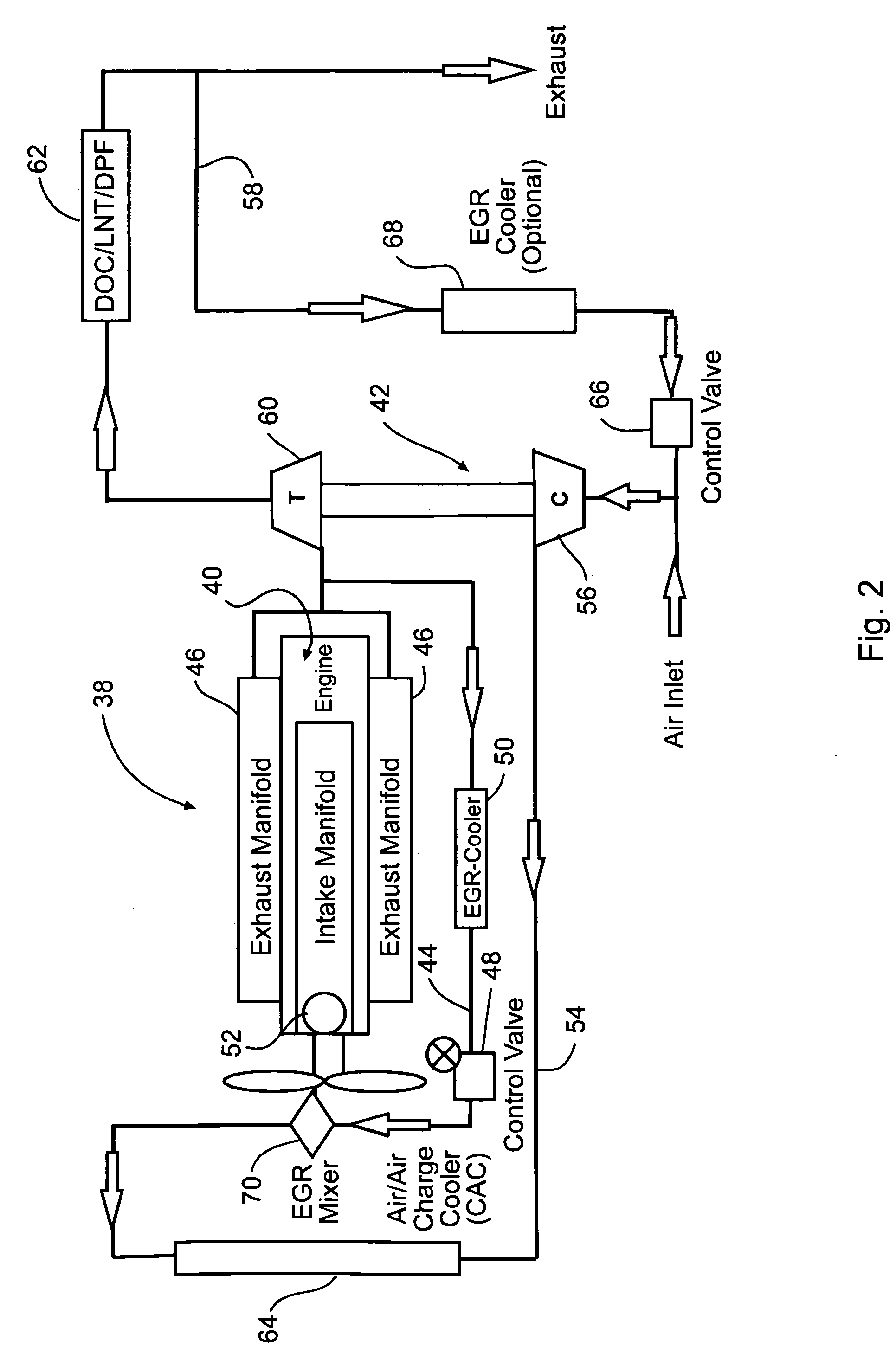
A system and method for waste heat recovery in exhaust gas recirculation is disclosed. The system includes an engine having an intake manifold and an exhaust manifold, an exhaust conduit connected to the exhaust manifold, and a turbocharger having a turbine and a compressor, the turbine being connected to the exhaust conduit to receive a portion of the exhaust gas from the exhaust manifold. The system also includes an EGR system connected to the exhaust conduit to receive a portion of the exhaust gas, with the EGR system including an EGR conduit that is connected to the exhaust conduit to receive a portion of the exhaust gas, a heat exchanger connected to the EGR conduit and being configured to extract heat from the exhaust gas, and a waste heat recovery system connected to the heat exchanger and configured to capture the heat extracted by the heat exchanger.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High efficiency compact gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20120324903A1Improve engine efficiencyThe process is compact and efficientGas turbine plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesWorking fluidCombustor
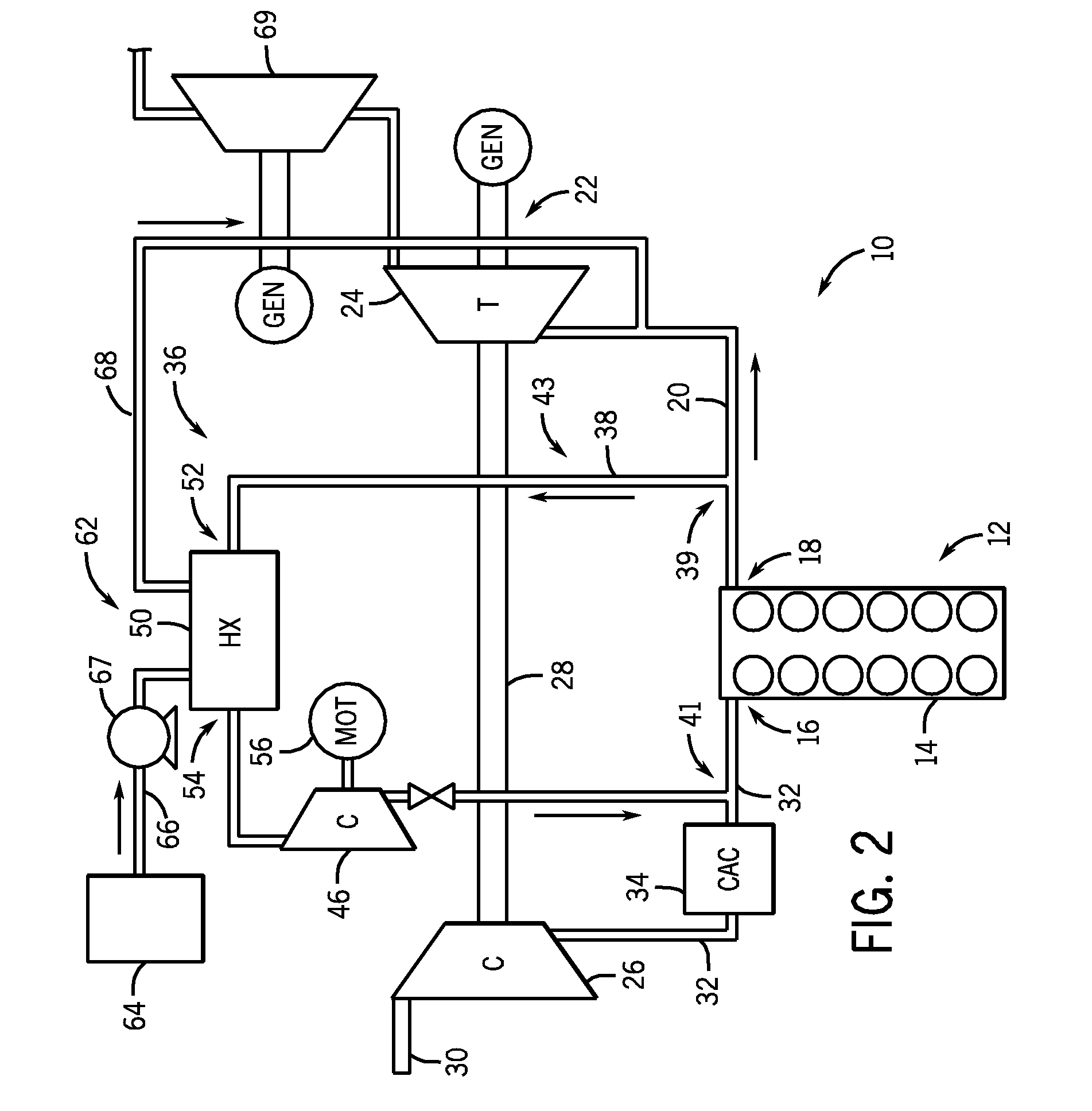
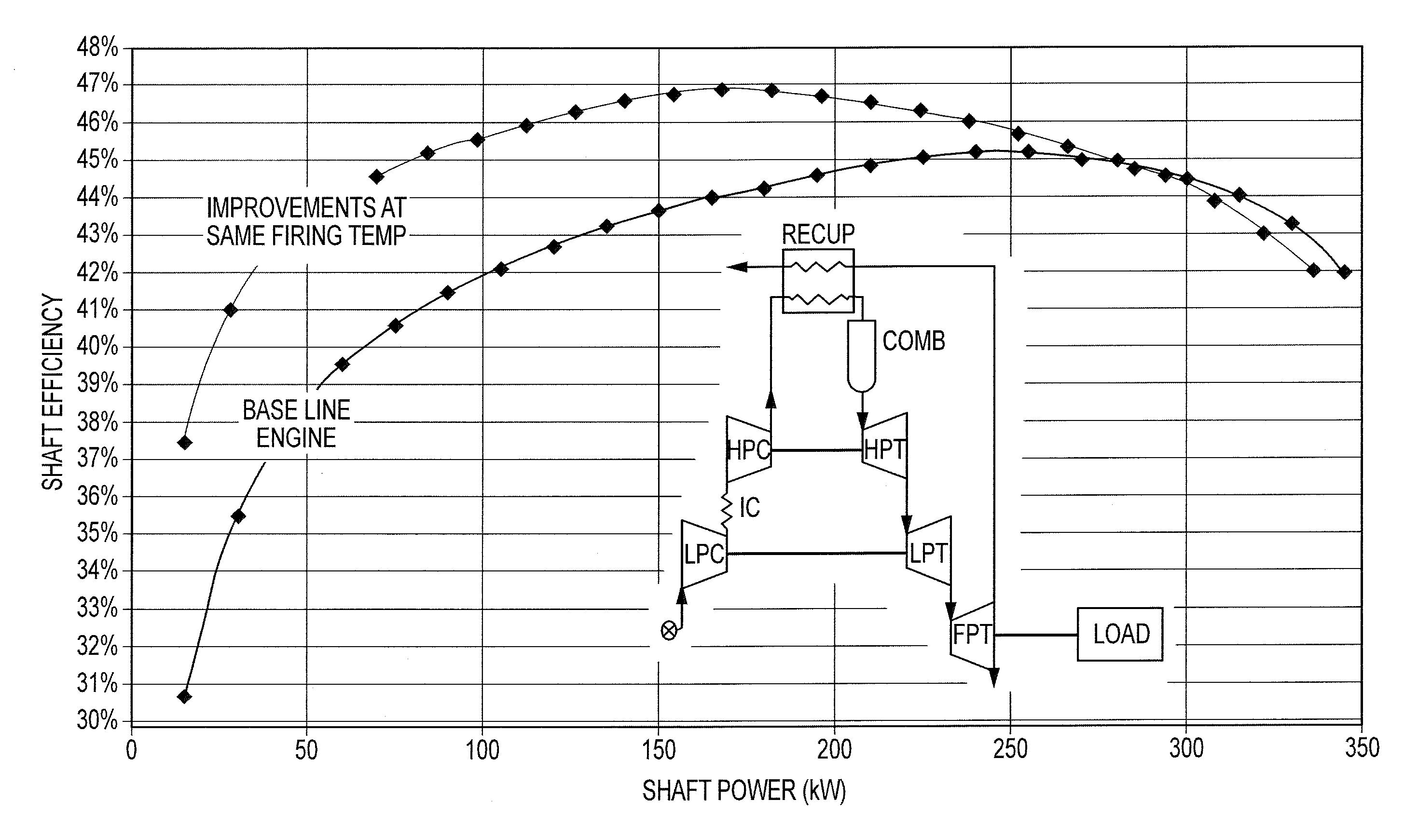
This disclosure relates to a highly efficient gas turbine engine architecture utilizing multiple stages of intercooling and reheat, ceramic technology, turbocharger technology and high pressure combustion. The approach includes utilizing a conventional dry low NOx combustor for the main combustor and thermal reactors for the reheat apparatuses. In a first configuration, there are three separate turbo-compressor spools and a free power turbine spool. In a second configuration, there are three separate turbo-compressor spools but no free power spool. In a third configuration, all the compressors and turbines are on a single shaft. Each of these configurations can include two stages of intercooling, two stages of reheat and a recuperator to preheat the working fluid before it enters the main combustor.
Owner:ICR TURBINE ENGINE CORP
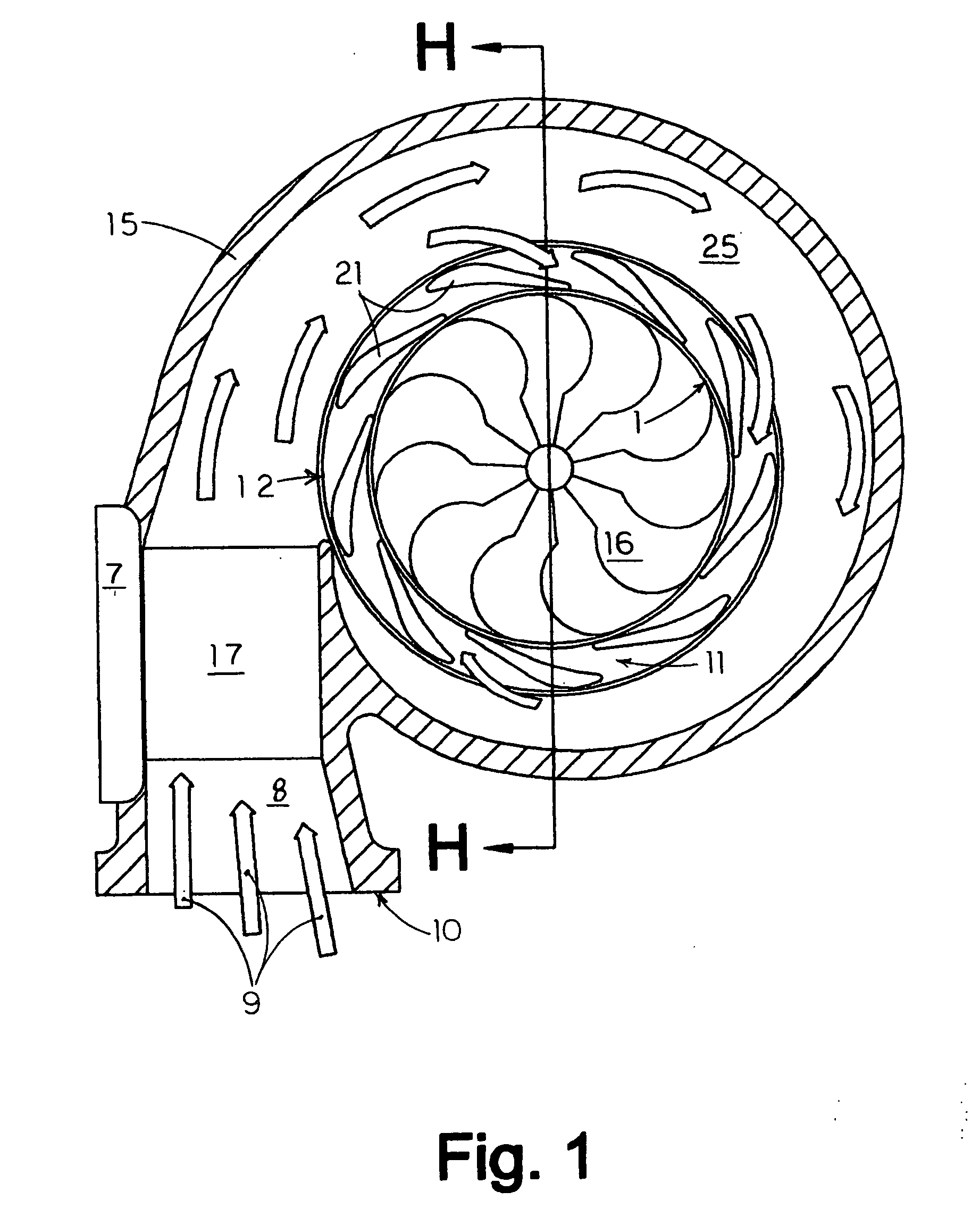
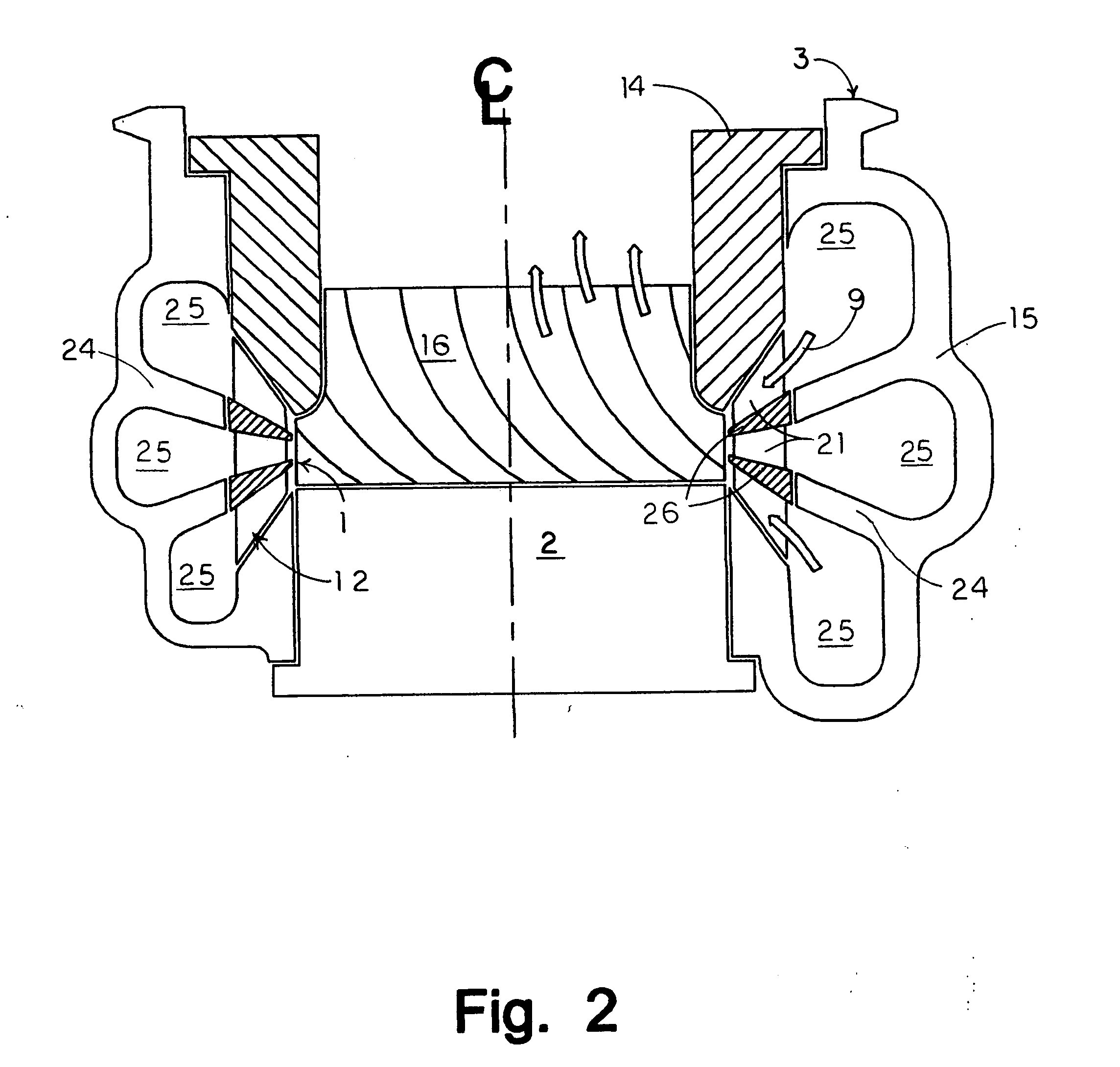
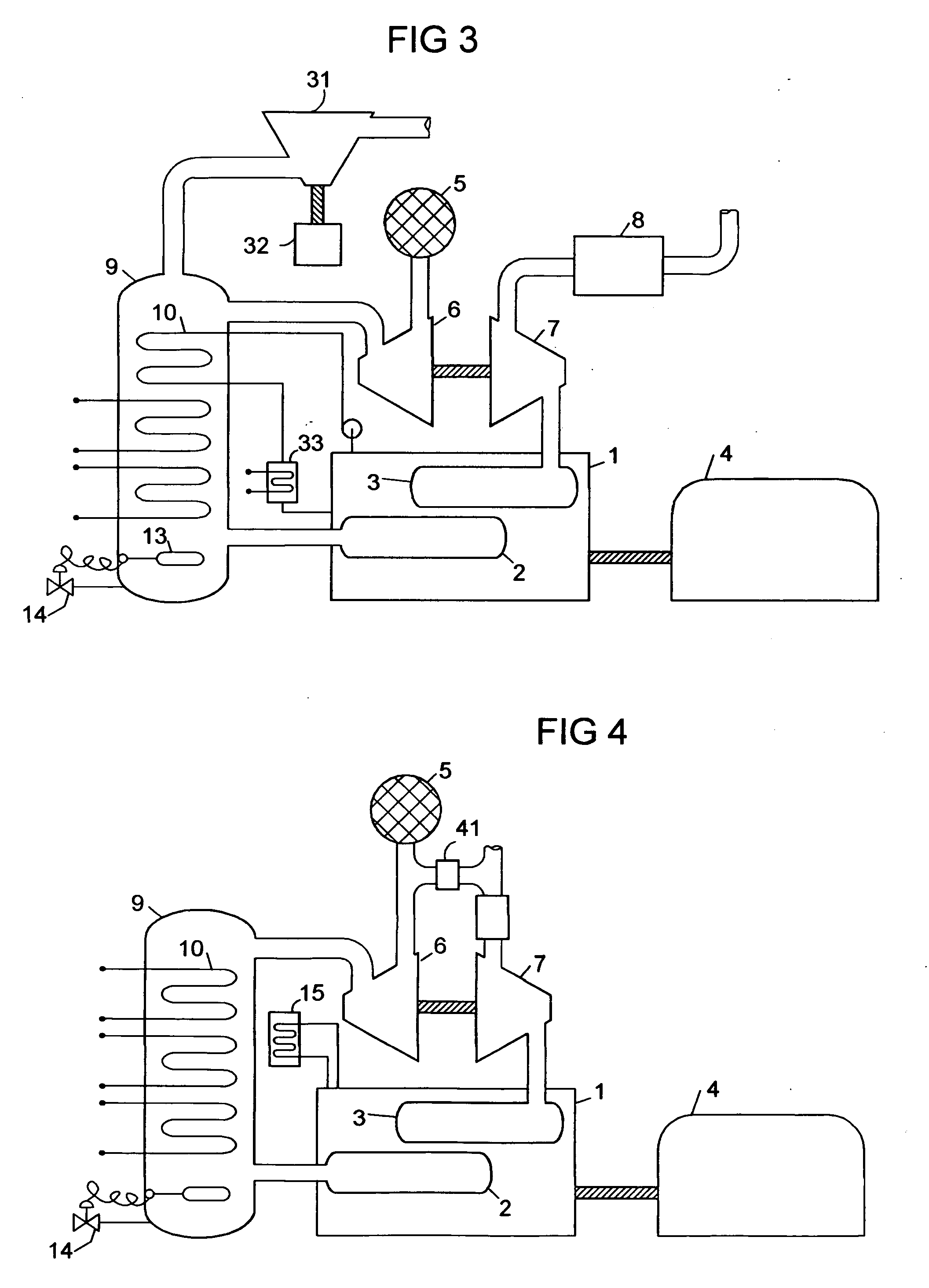
Cooling an Electrically Controlled Turbocharger
ActiveUS20100284824A1Internal combustion piston enginesGas turbine plantsTurbochargerElectric machine
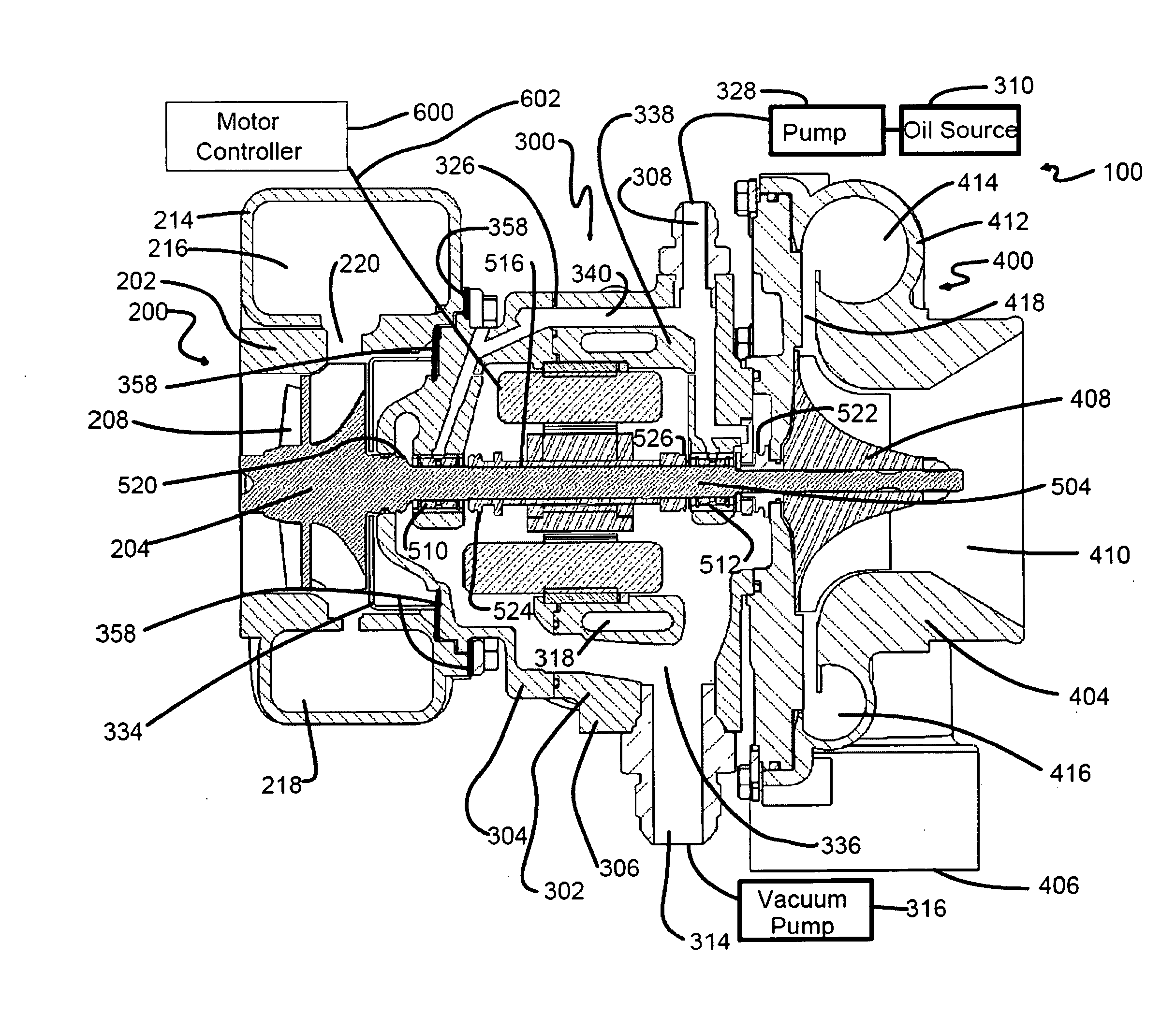
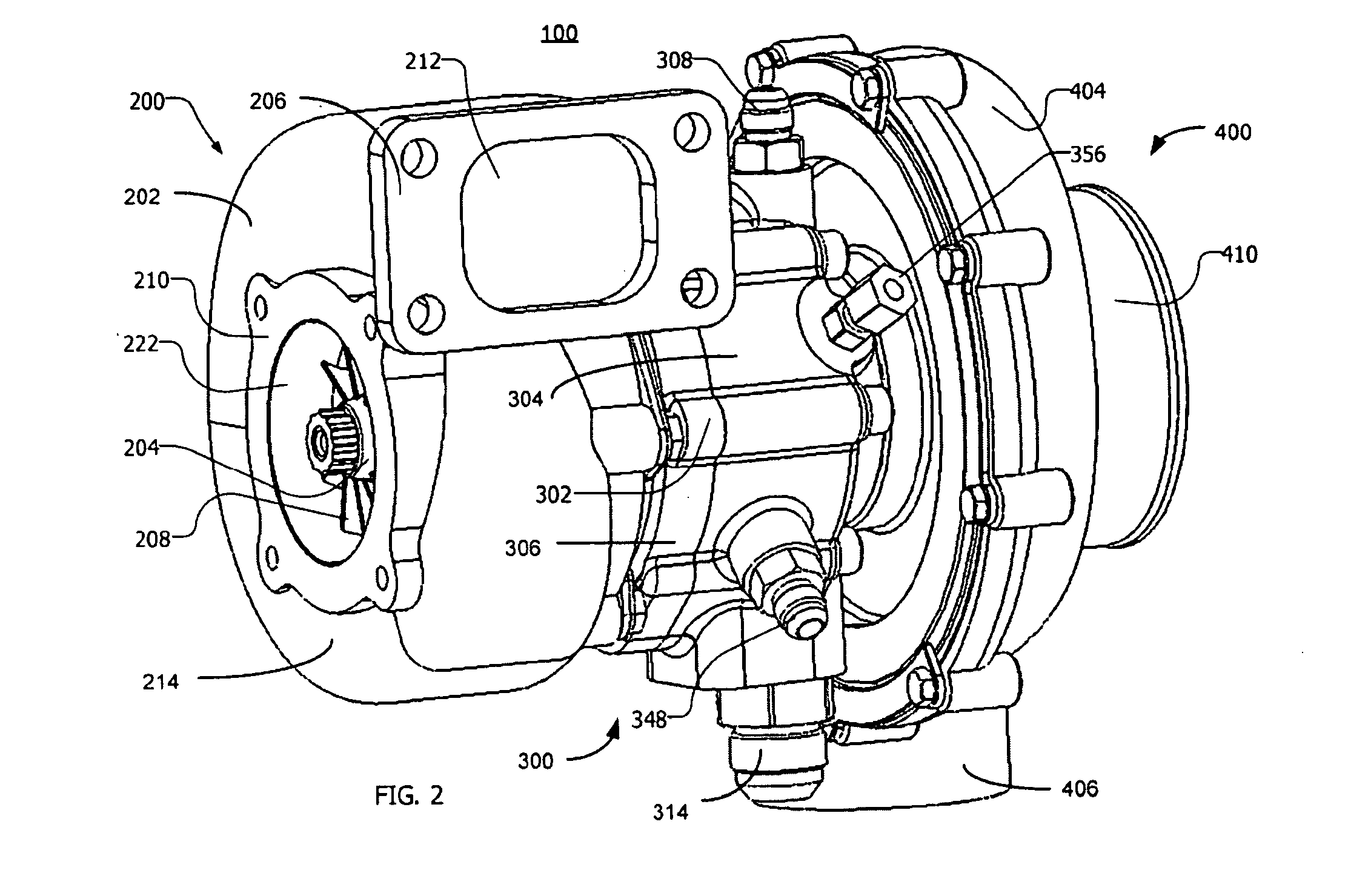
An electrically controlled turbocharger has a motor mounted on a shaft in a motor housing between a turbine and compressor. Oil is sprayed onto the motor stator to cool the stator. An oil gallery is disposed above the stator to receive lubricating oil and contains apertures that perform as jets to allow oil to be sprayed directly on the motor stator. A coolant jacket is formed in the turbocharger housing between the turbine and the motor to allow liquid coolant to circulate therein and dissipate heat from the turbine end prior to reaching the motor components. Other embodiments provide for a stator component to be submerged in flowing cooling oil.
Owner:ECOMOTORS INT
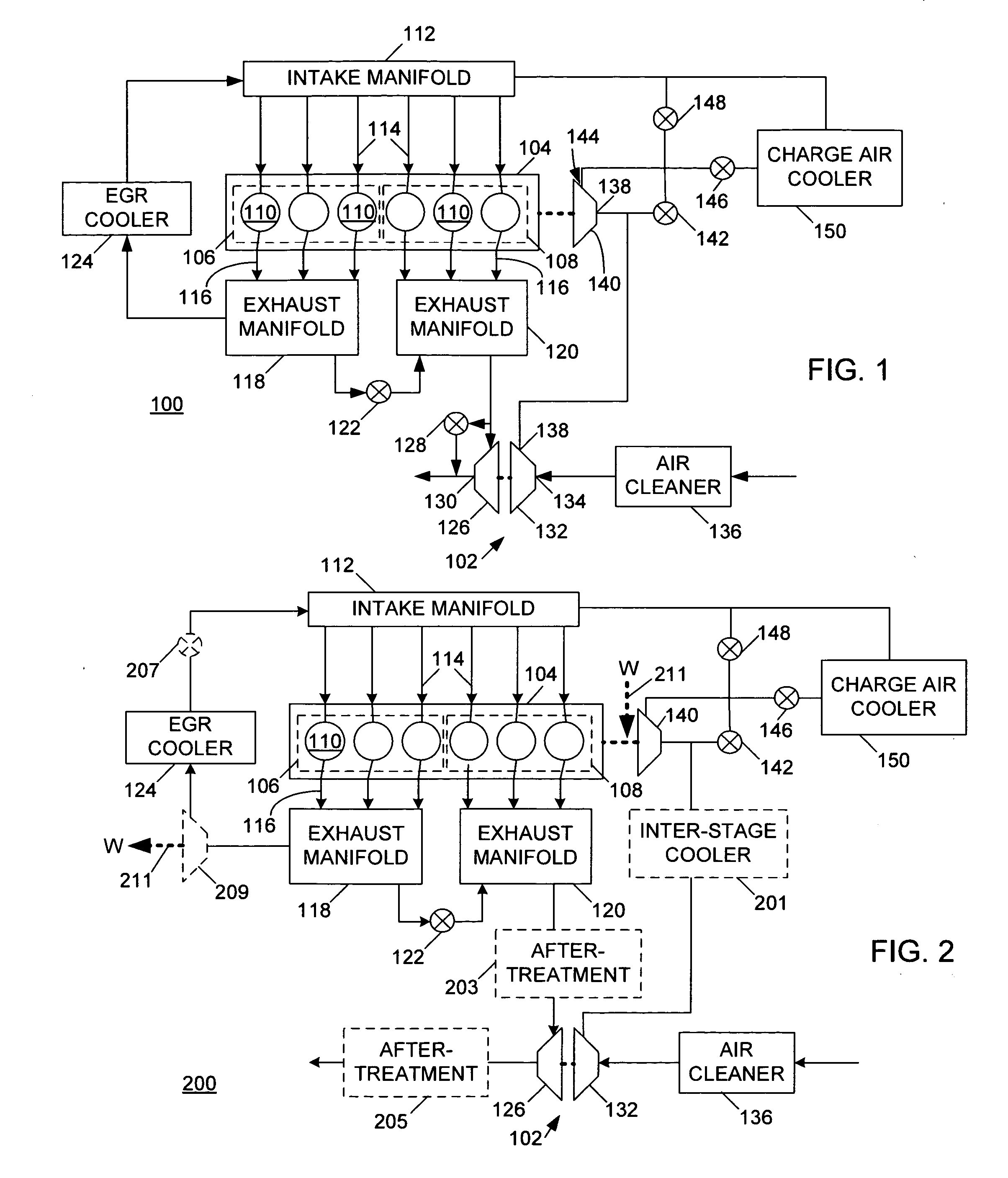
Constant EGR rate engine and method
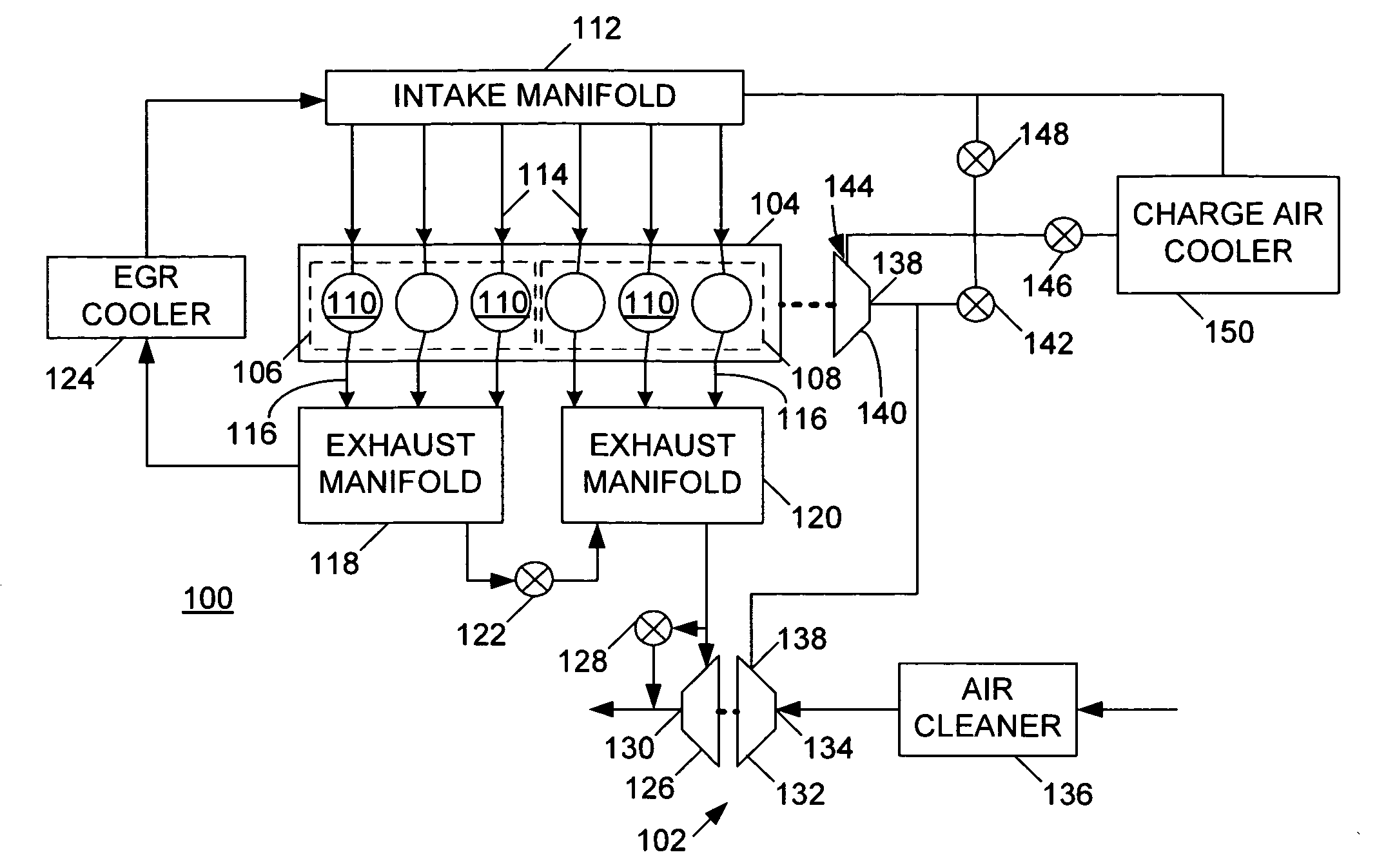
ActiveUS20070175215A1Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveTurbocharger
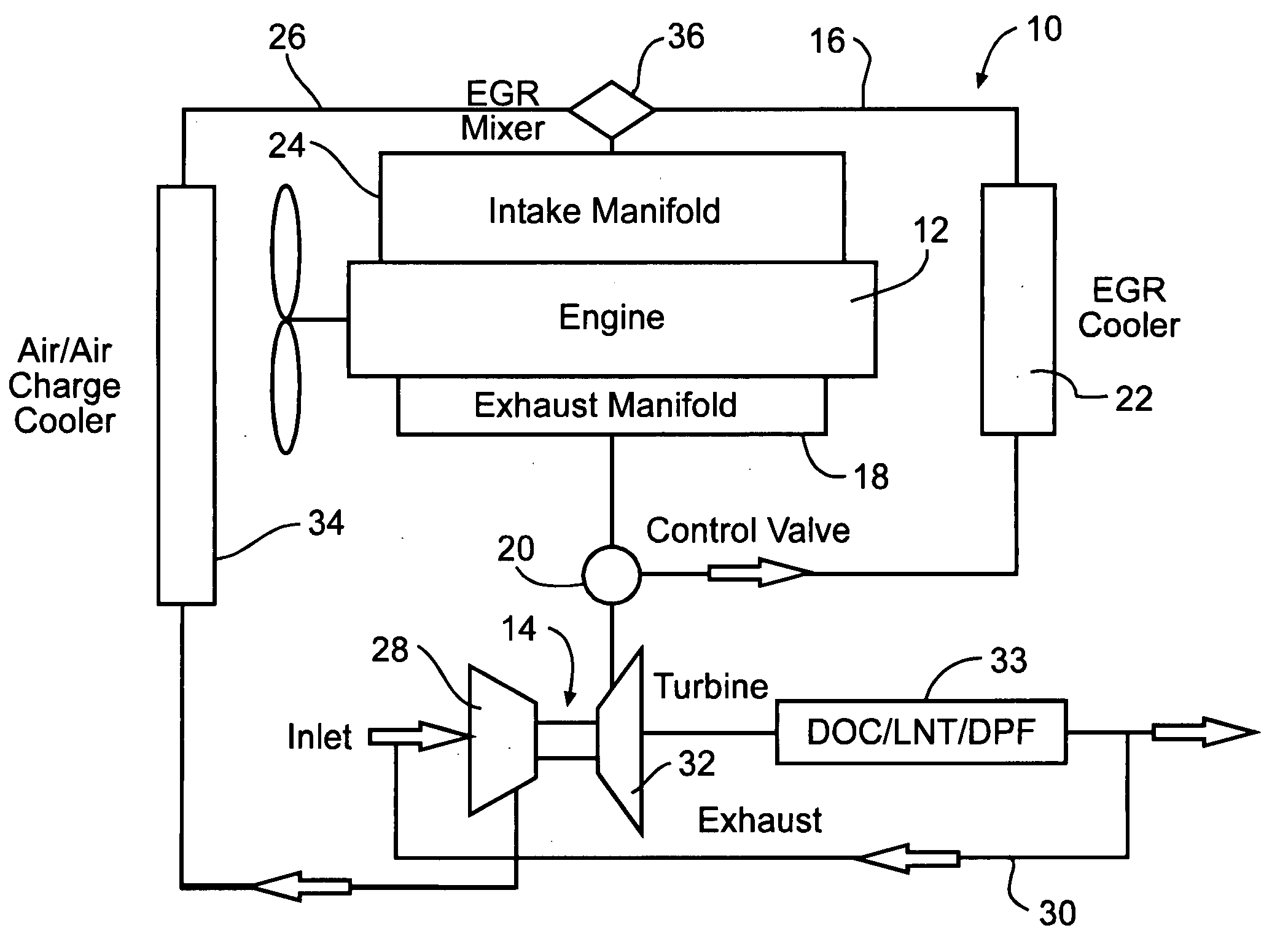
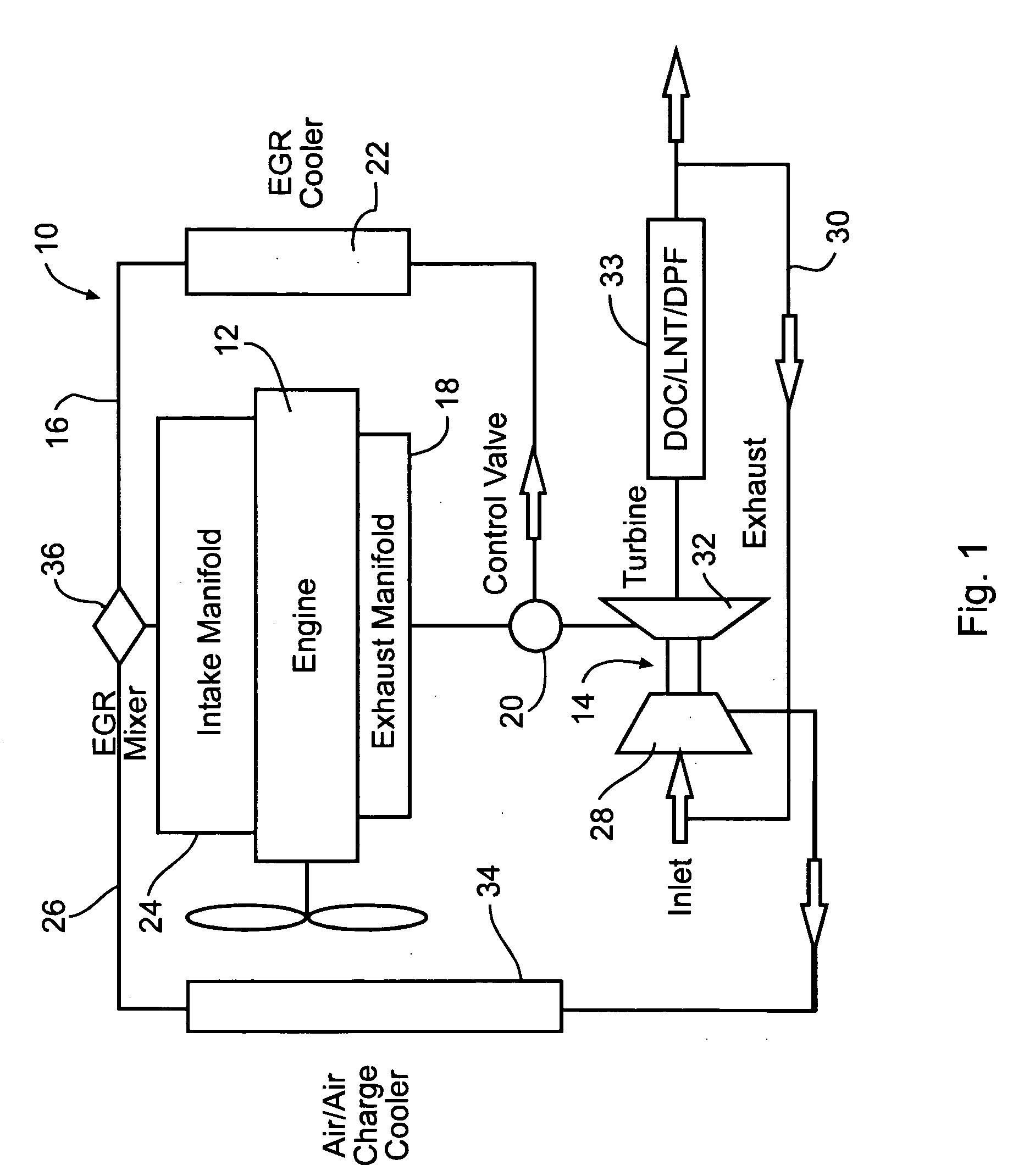
An internal combustion engine (100) includes a first exhaust manifold (120), and a second exhaust manifold (118) fluidly connected to the first exhaust manifold (120) through an exhaust valve (122). An exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) cooler (124) constantly fluidly connects the second exhaust manifold (118) with an intake manifold (112). A turbocharger (102) has a turbine (126) in fluid communication with the first exhaust manifold (120), and a compressor (132) in fluid communication with a supercharger (140). A charge air cooler (150) fluidly connects the supercharger (140) with the intake manifold (112).
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
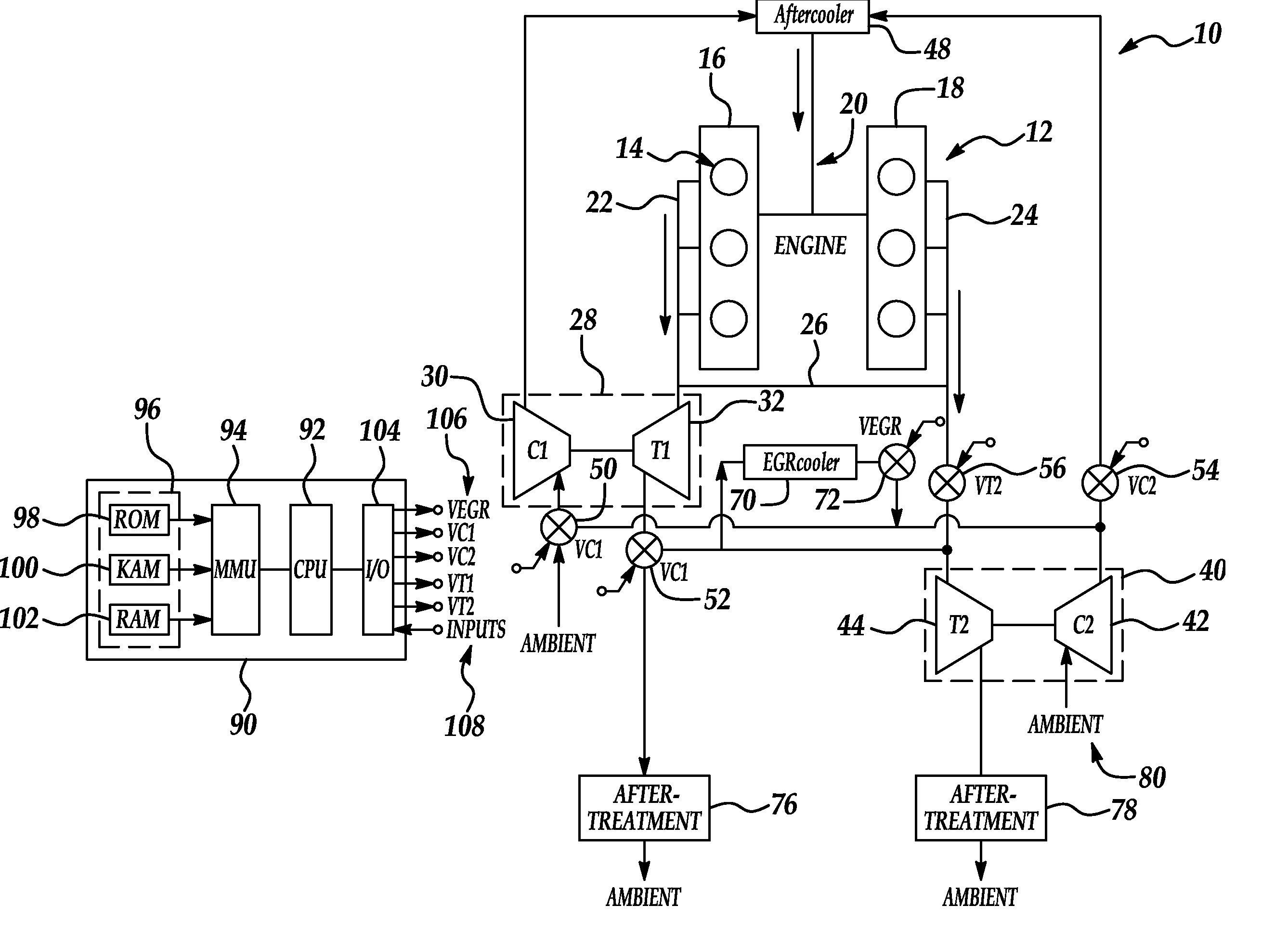
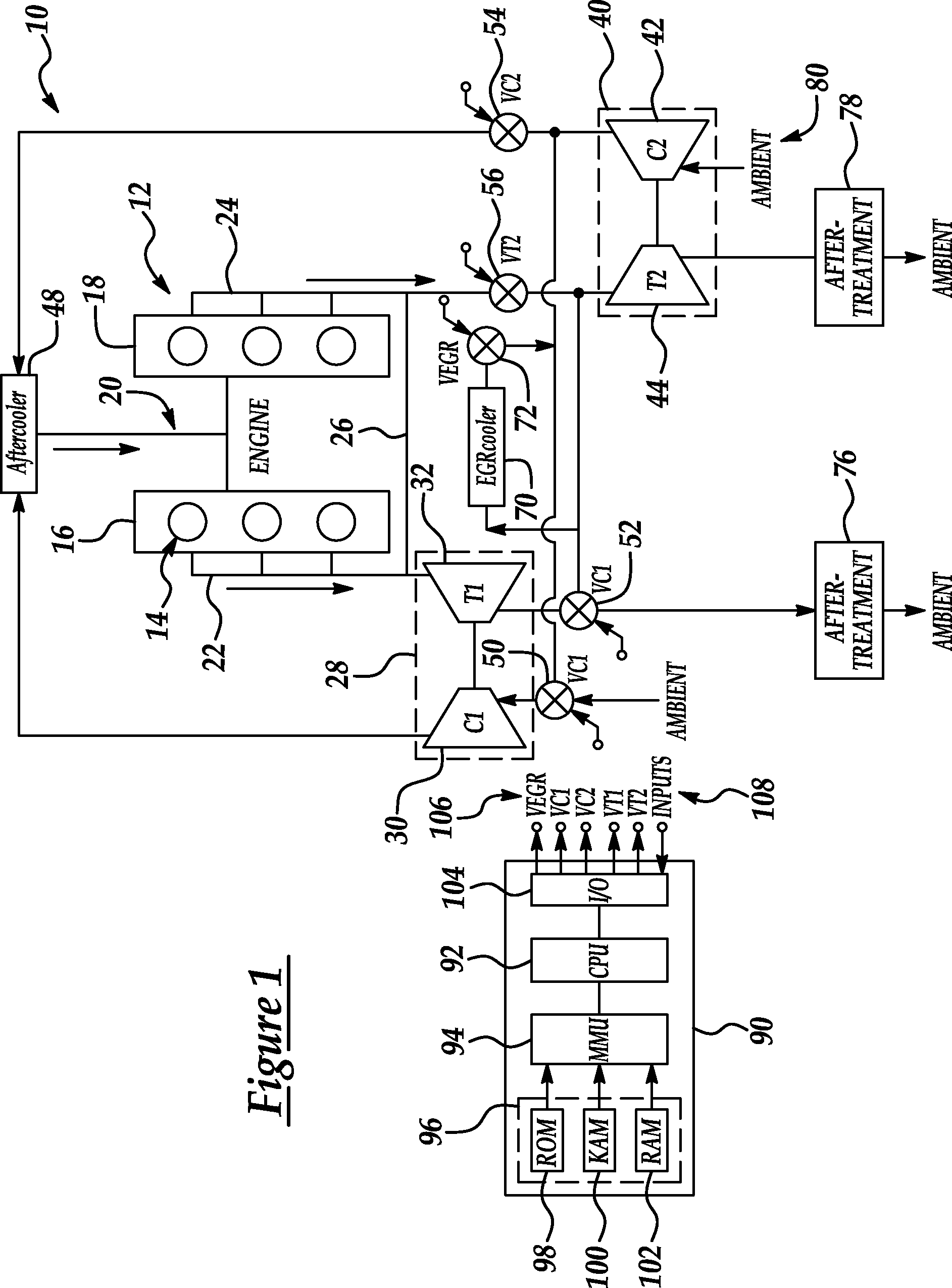
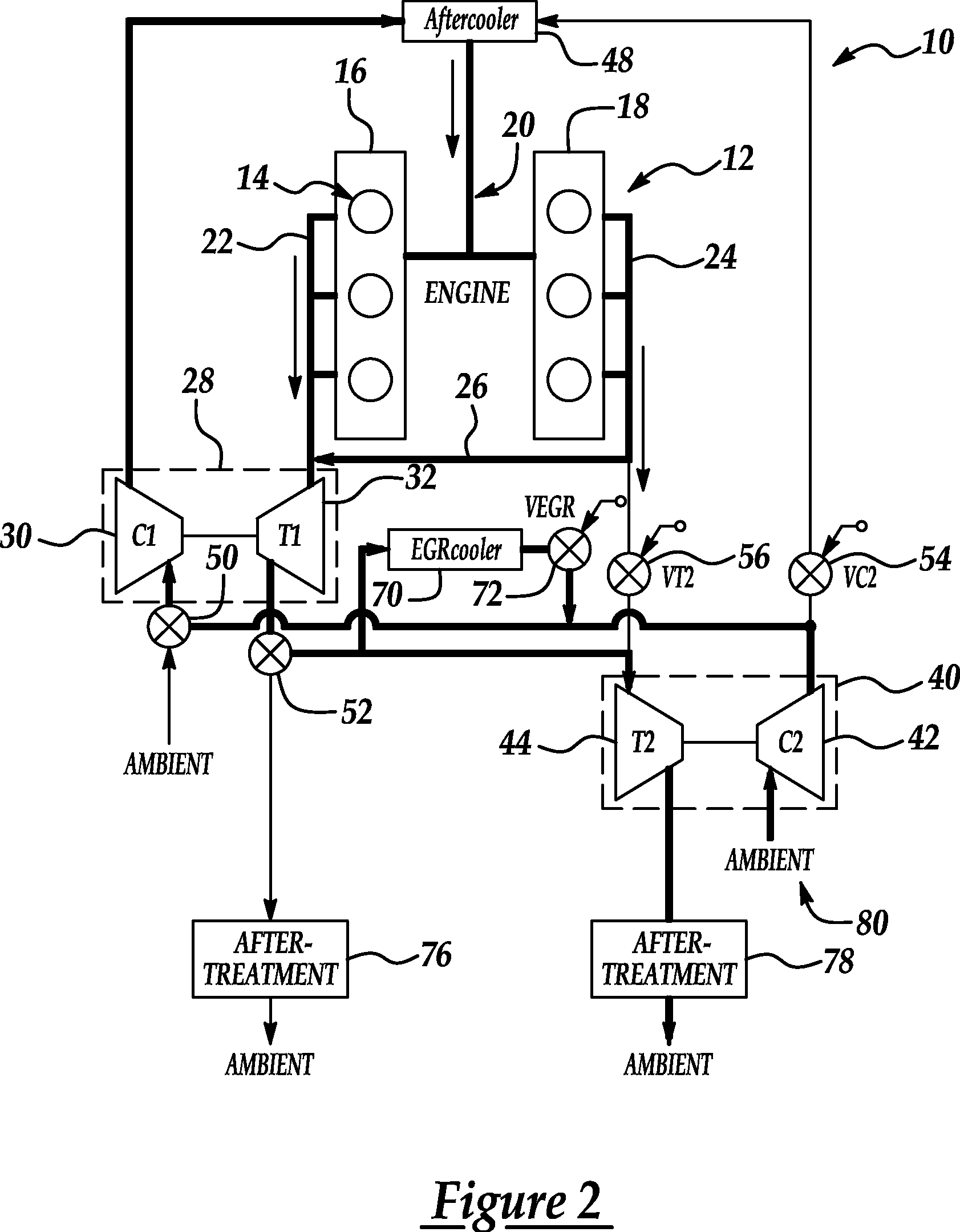
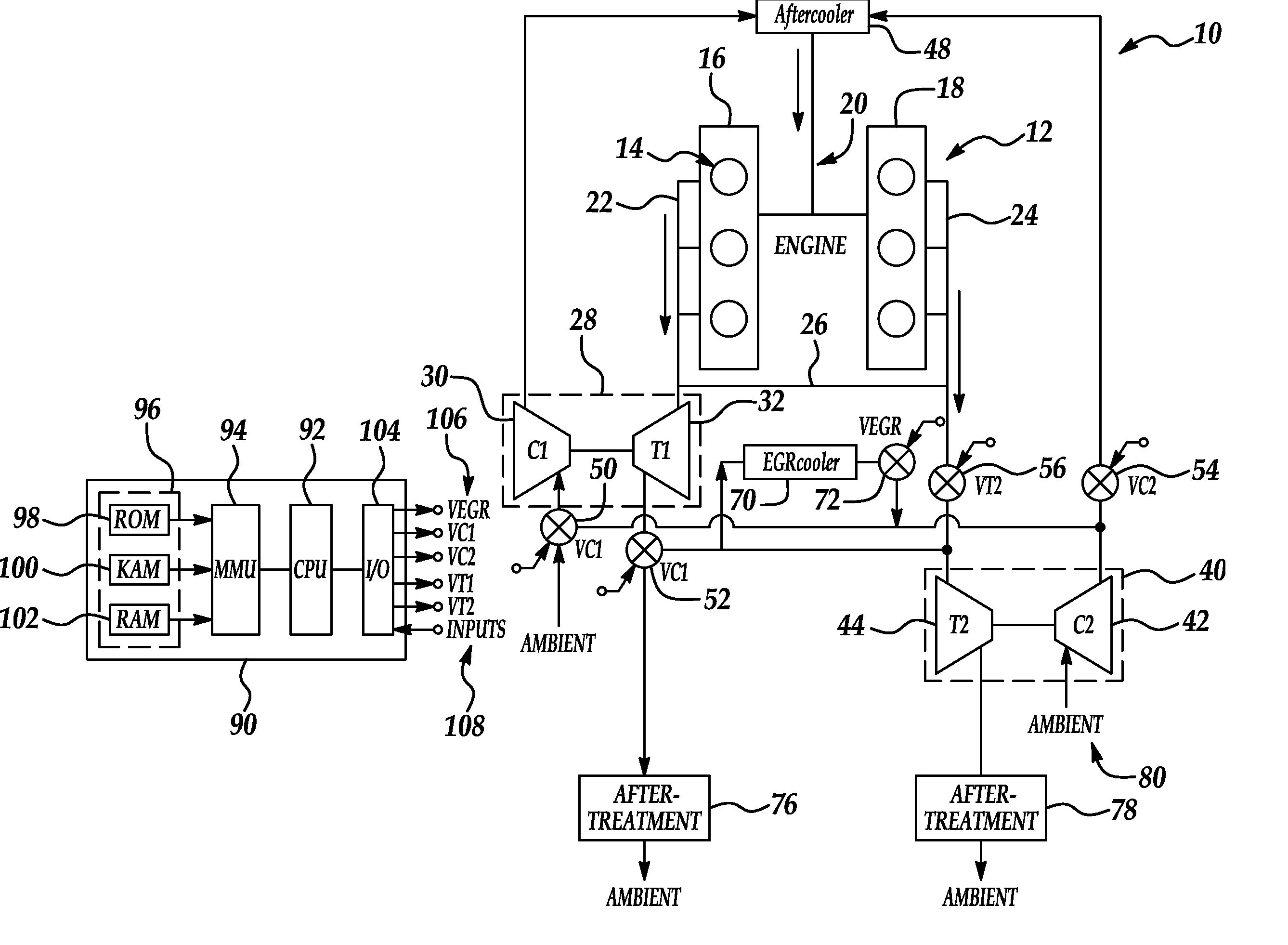
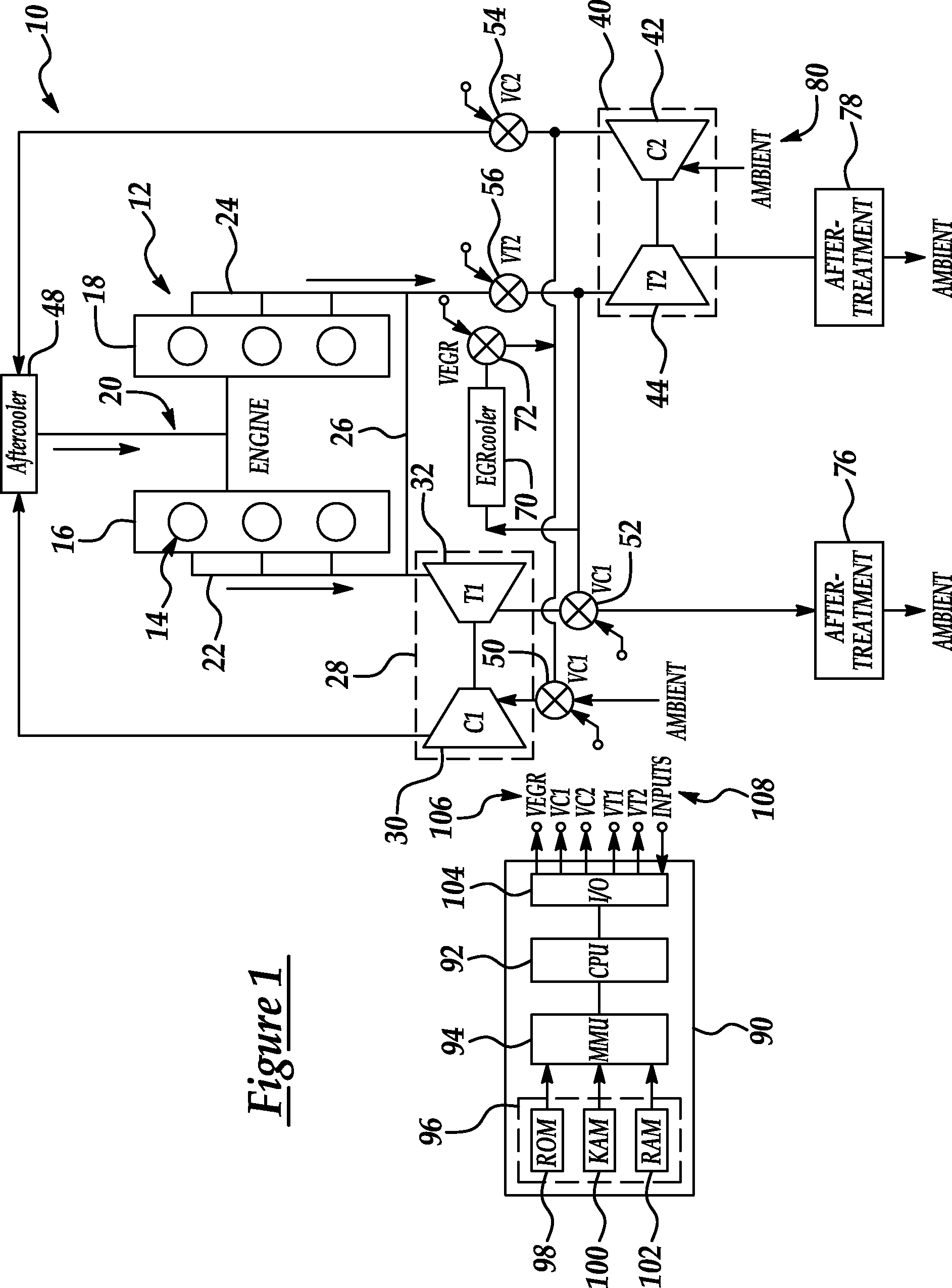
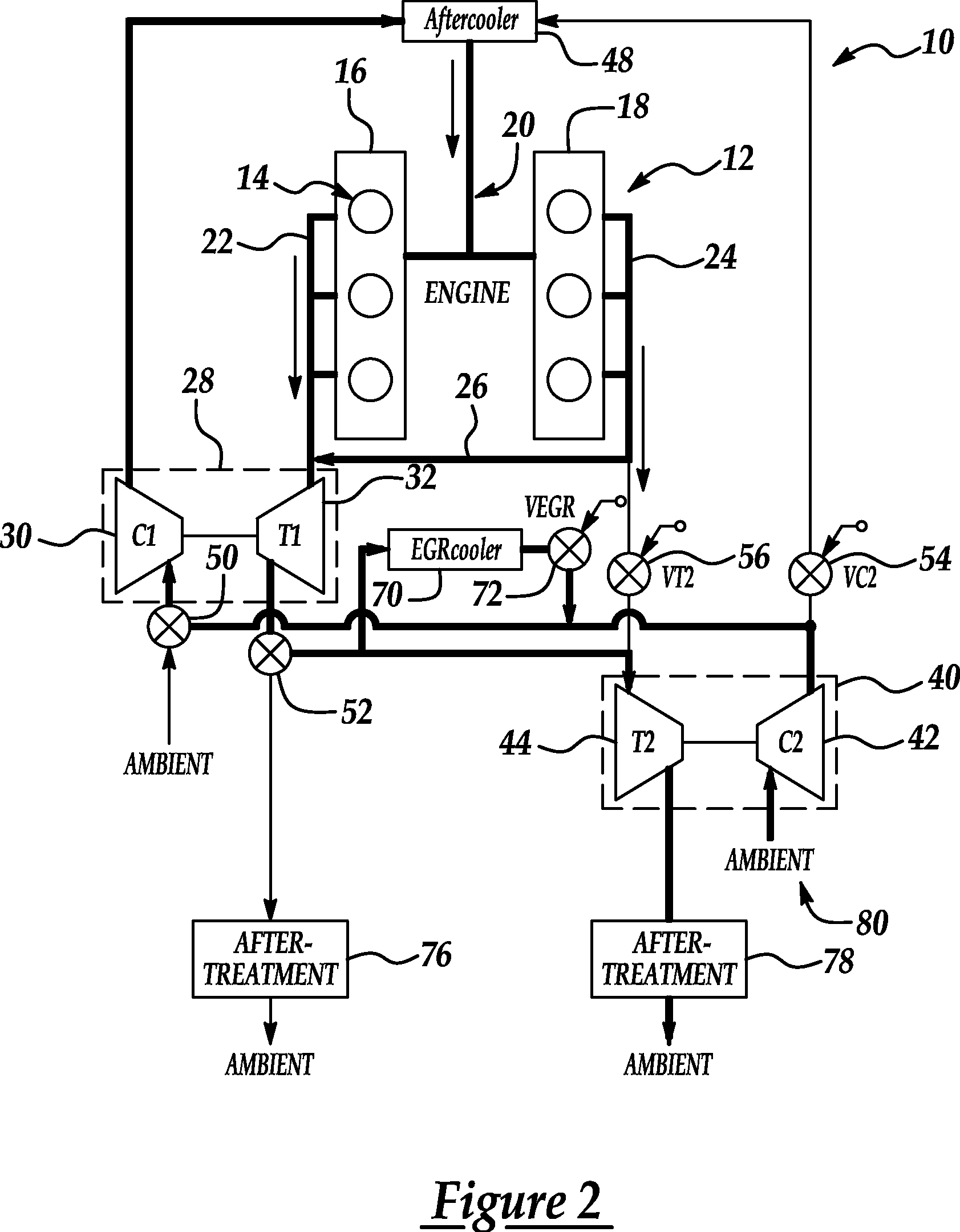
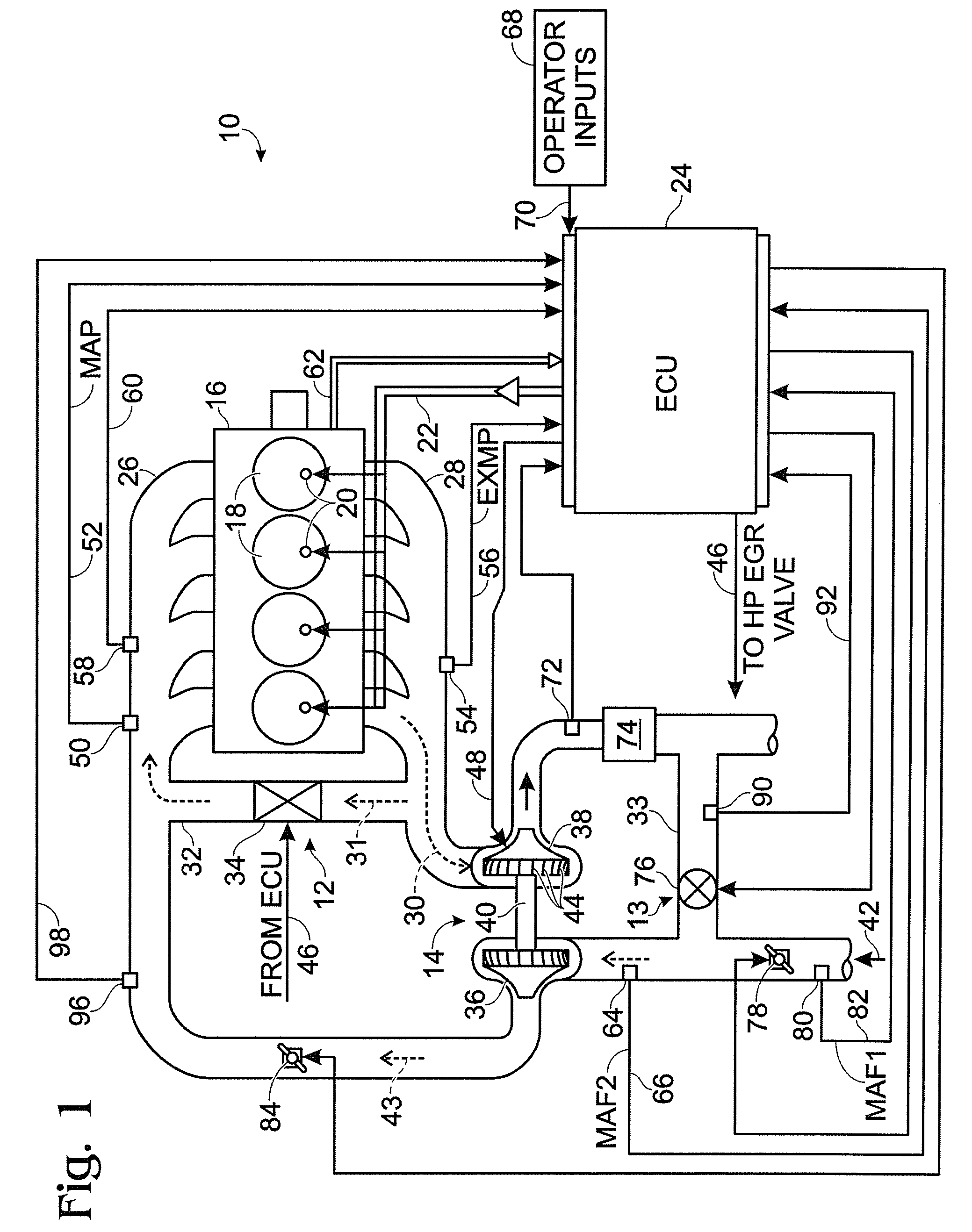
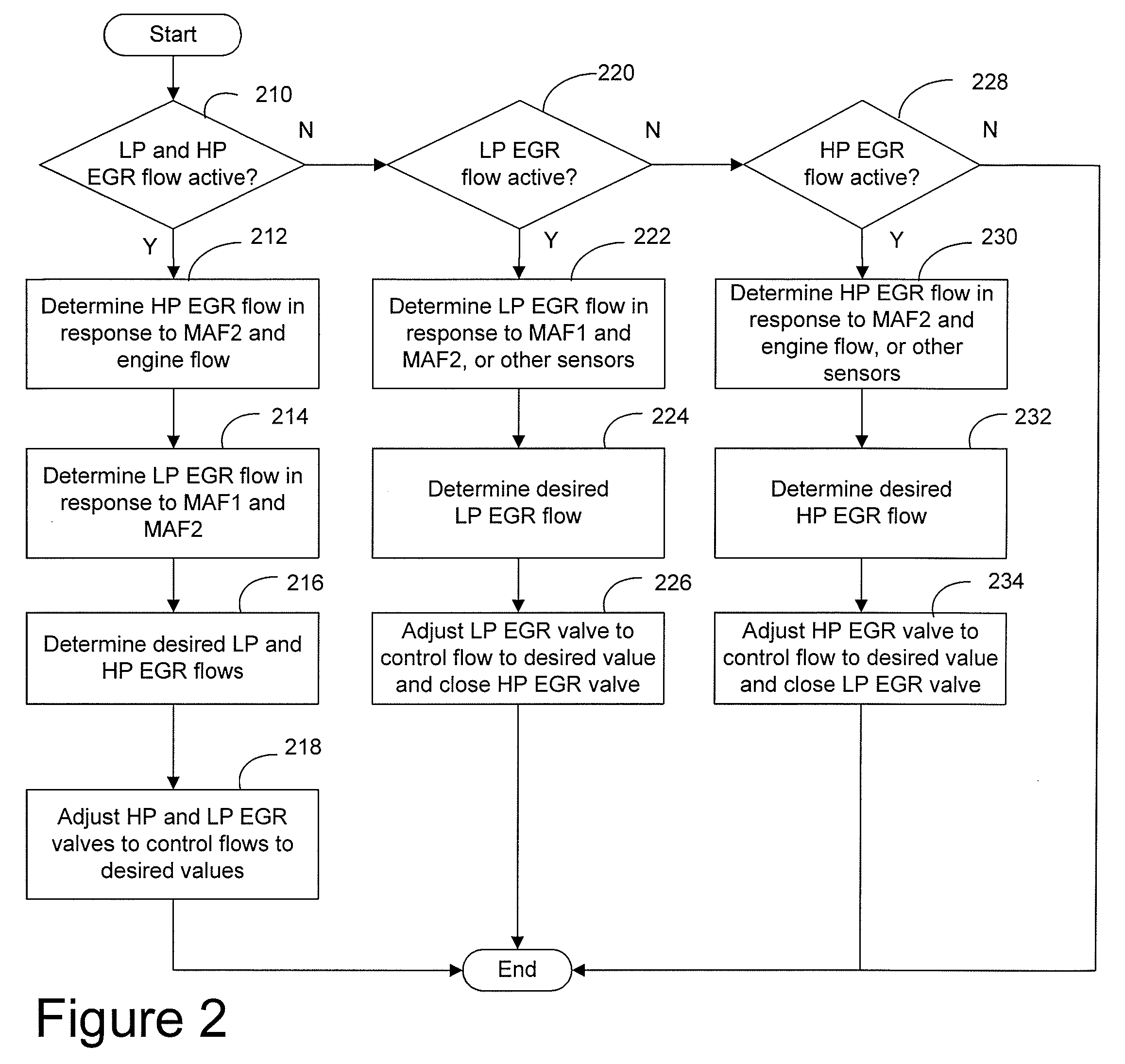
Series/parallel turbochargers and switchable high/low pressure EGR for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20060021347A1Promote generationSufficient handling capacityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerHigh pressure
Systems and methods for turbocharging an internal combustion engine include operating two turbochargers in a series configuration for a first operating region and a parallel configuration for a second operating region. Systems and methods for controlling exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) in a turbocharged internal combustion engine provide low pressure EGR upstream of a compressor inlet for a first operating region and high pressure EGR downstream of a compressor outlet for a second operating range to further improve turbocharger operating margin and overall efficiency.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Series/parallel turbochargers and switchable high/low pressure EGR for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS7165403B2Promote generationImproved vehicle launchElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTurbochargerExternal combustion engine
Systems and methods for turbocharging an internal combustion engine include operating two turbochargers in a series configuration for a first operating region and a parallel configuration for a second operating region. Systems and methods for controlling exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) in a turbocharged internal combustion engine provide low pressure EGR upstream of a compressor inlet for a first operating region and high pressure EGR downstream of a compressor outlet for a second operating range to further improve turbocharger operating margin and overall efficiency.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
EGR system for internal combustion engine provided with a turbo-charger
InactiveUS7043914B2High EGR rateEfficiently reduce NOxElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTurbochargerInternal combustion engine
An EGR system for an internal combustion engine provided with a first EGR passage for recirculating EGR gas to the downstream side of a compressor from the upstream side of a turbine of a turbo-charger is provided with a second EGR passage for recirculating EGR gas from the downstream side of the turbine to the upstream side of the EGR gas, and provided also with a DPF in the second EGR passage, while the exhaust gas flow in the first EGR passage and the second EGR passage is controlled based on the exhaust gas temperature detected by an exhaust gas temperature sensor arranged in the exhaust gas passage.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Compact turbocharger
InactiveUS6739845B2Minimal lengthLow thermal expansionInternal combustion piston enginesPump componentsTurbochargerControl theory
A turbocharger comprising two closely spaced ball bearings that does not require lubricating oil from an engine. The bearing housing forms a cooling jacket with two bearing engagement surfaces engaged with the outer races of the ball bearings through an intermediate radial spring. Closely spacing the ball bearings provides a rotor shaft of minimal length. In addition, an external motor-generator may be by mounted on the turbocharger, with the motor rotor solidly connected to the turbocharger rotor. In such an assembly, an electronic control is energizes the motor from battery power during acceleration up to approximately torque peak speed; thereafter, the control changes to a generator mode when there is excess energy in the engine exhaust gas.
Owner:WOOLLENWEBER WILLIAM E
Magnetoresistive turbocharger compressor wheel speed sensor
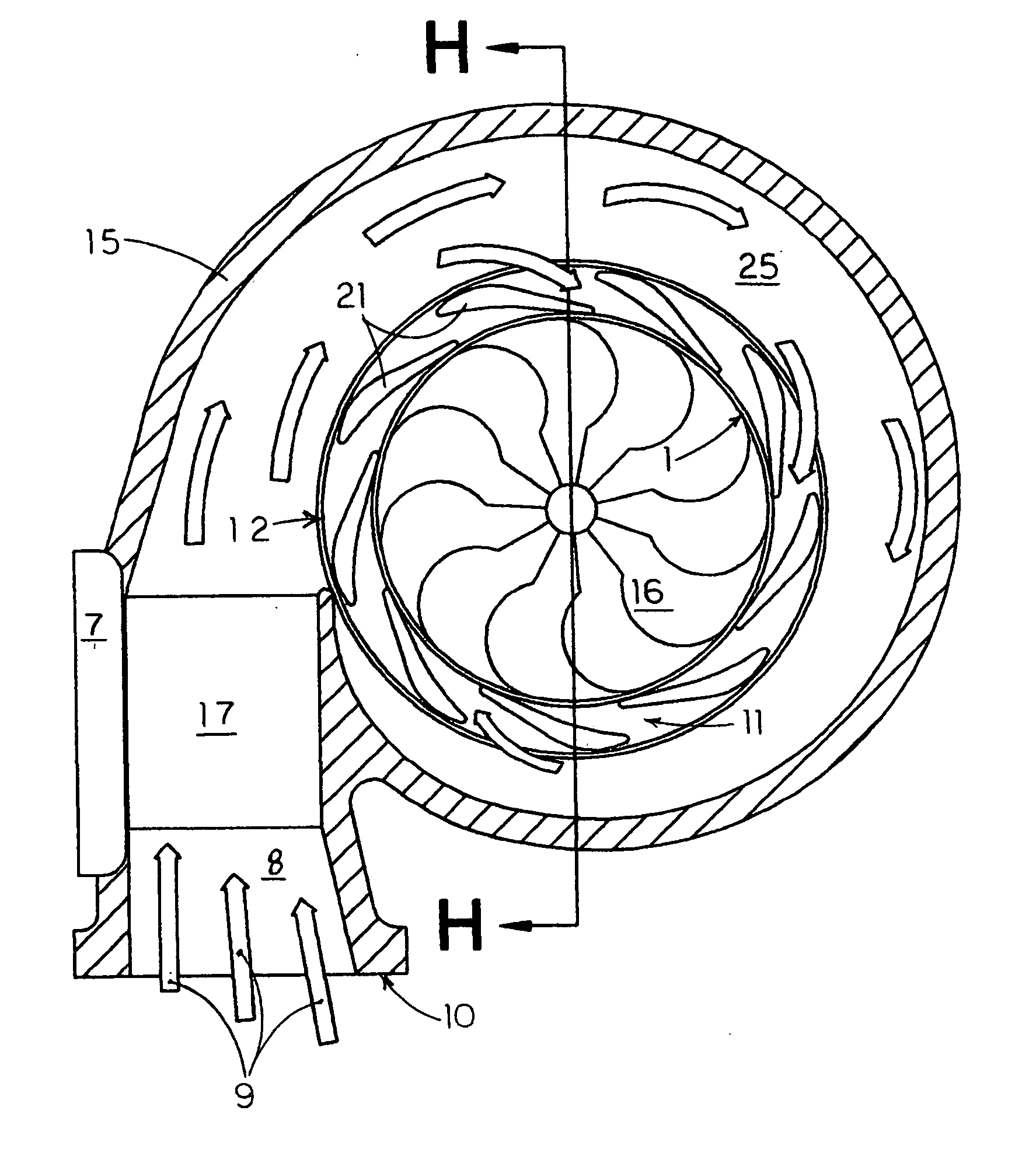
InactiveUS20050017709A1Reducing pulse rateReduce rateMachines/enginesEngine controlImpellerTurbocharger
A turbocharger includes a cylindrical wall and a non-ferromagnetic compressor wheel within the cylindrical wall. The non-ferromagnetic compressor wheel has fins. A magnetoresistive sensor housing is threaded through the cylindrical wall and houses a permanent magnet and at least one magnetoresistor. The permanent magnet is positioned so as to induce eddy currents on the fins. The permanent magnet magnetically biases the magnetoresistor, and the magnetoresistor senses rotation of the non-ferromagnetic compressor wheel.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Internal combustion engine having two exhaust gas turbocharger
InactiveUS7540150B2Simple meansNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveTurbocharger
In an internal combustion engine provided with two exhaust gas turbochargers which each comprise a turbine in an exhaust line and one compressor in an intake section of the engine, two exhaust lines are provided which are each assigned to at least one of the exhaust gas turbines, an exhaust gas recirculation device being arranged between an exhaust line upstream of an exhaust gas turbine and the intake section downstream of a compressor and the two exhaust lines including bypass lines with a control valve for selectively permitting the exhaust gas to bypass the turbine closer to the engine.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Dual and hybrid EGR systems for use with turbocharged engine
ActiveUS20050103013A1Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesSingle stageTurbocharger
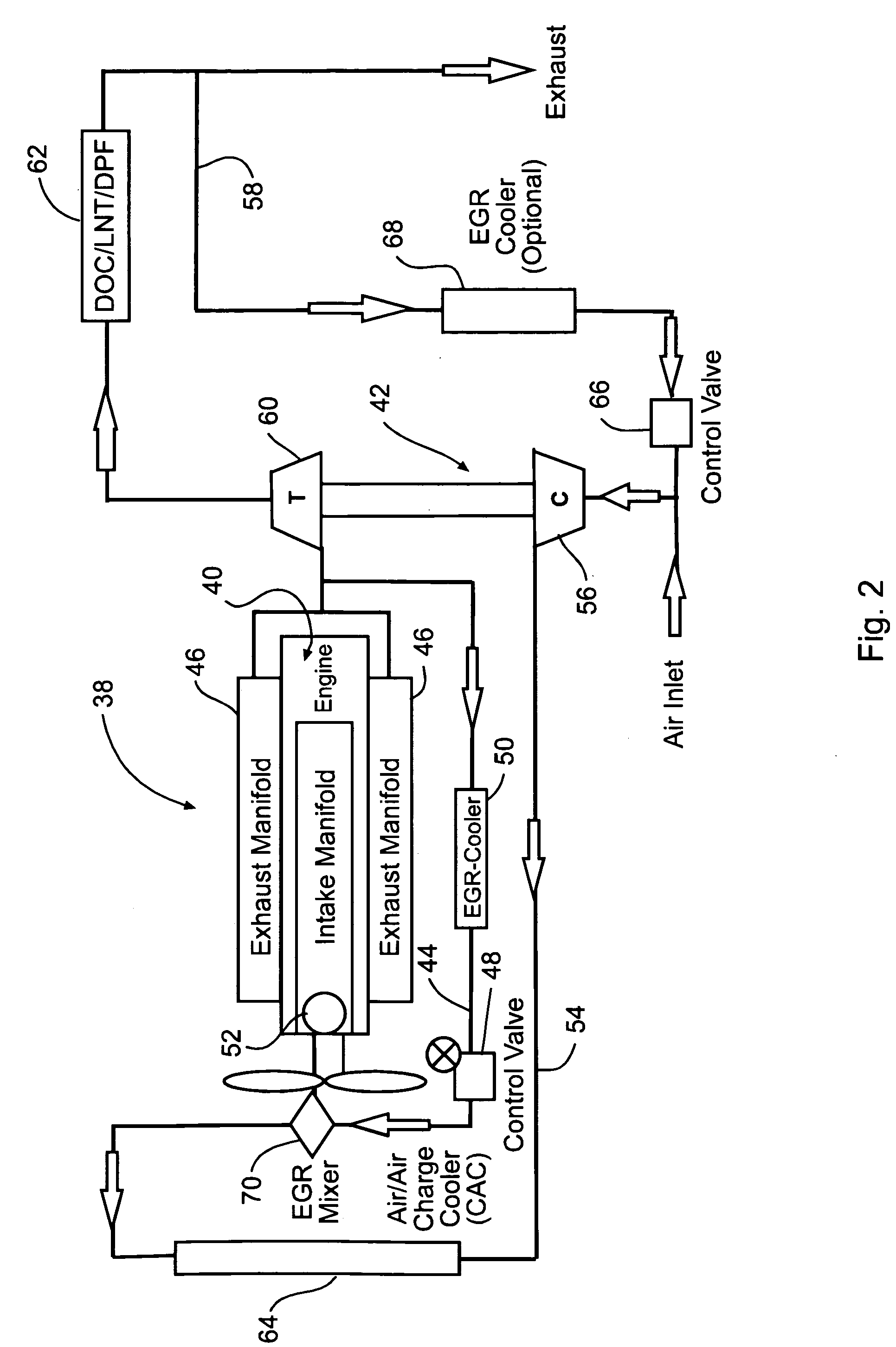
EGR systems for an internal combustion engine configured to operate using multiple-staged turbochargers, or a pair of single stage turbochargers, to provide exhaust gas recirculation to meet emissions requirements while not affecting engine performance. One or two EGR loops operating at low, intermediate, or high pressures may be employed. EGR exhaust gases may be taken directly from the exhaust manifold, or after the exhaust stream has passed through a turbocharger turbine. EGR exhaust gases may be injected at an intermediate pressure between stages of a multiple stage turbocharger, or alternatively between a low pressure turbocharger compressor and high pressure turbocharger compressor, before being boosted to a pressure high enough to ensure the desired mass flow to the engine and delivered to the intake manifold. Intake air may be pressurized prior to mixing with the EGR exhaust gases.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
Hybrid vehicles
InactiveUS20060100057A1Increase practical rangeEasy to operateInternal combustion piston enginesElectric motor startersMaximum torqueElectricity
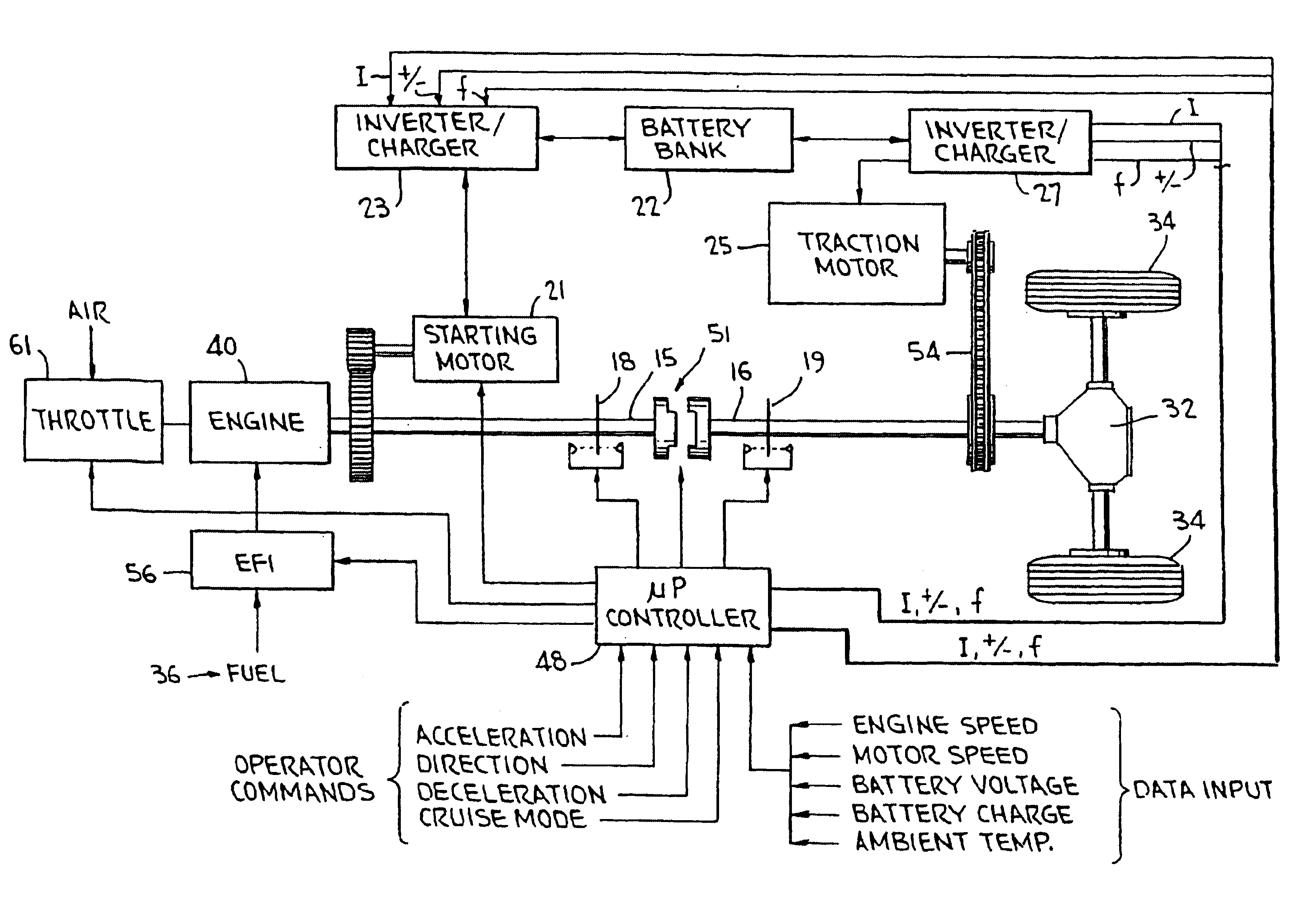
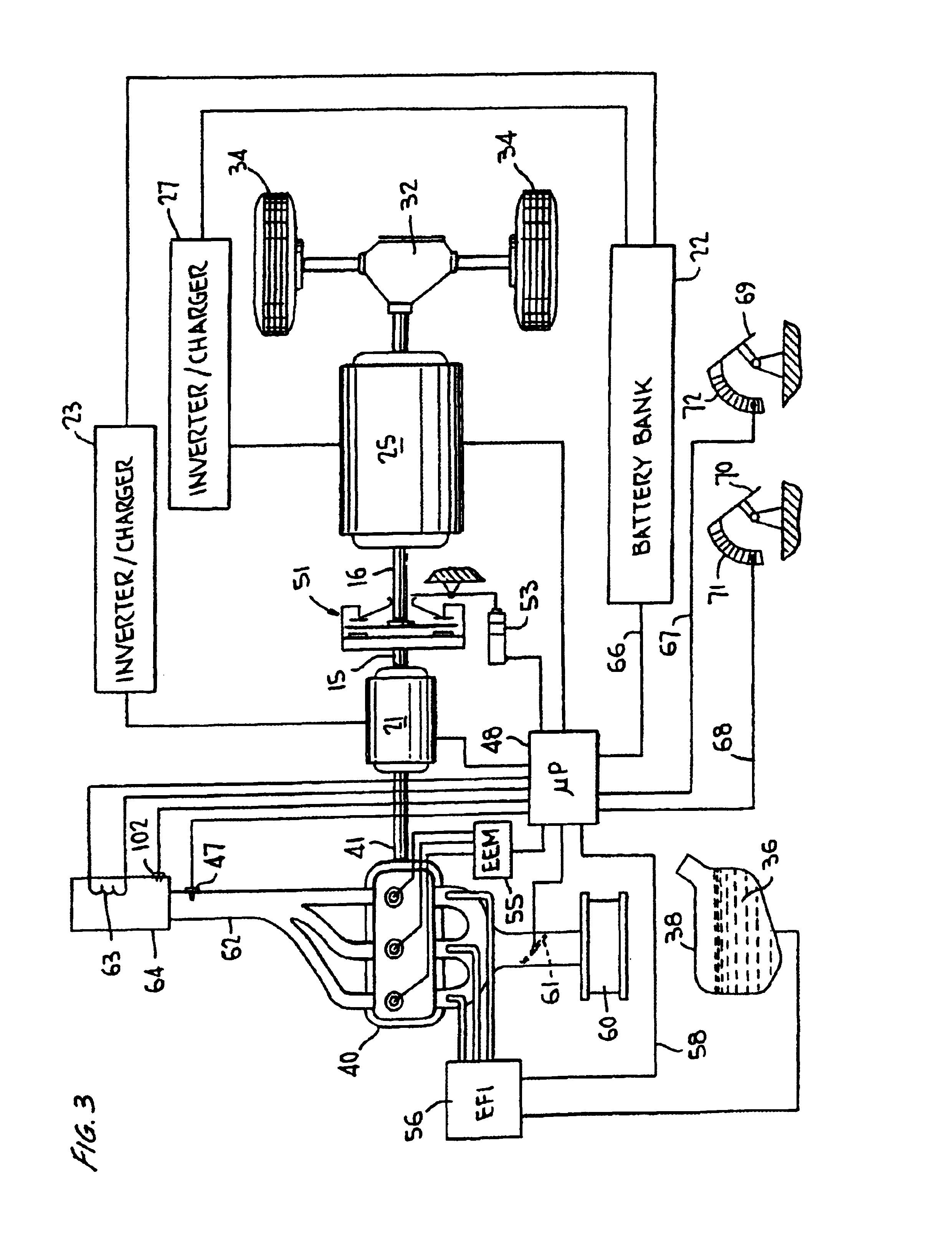
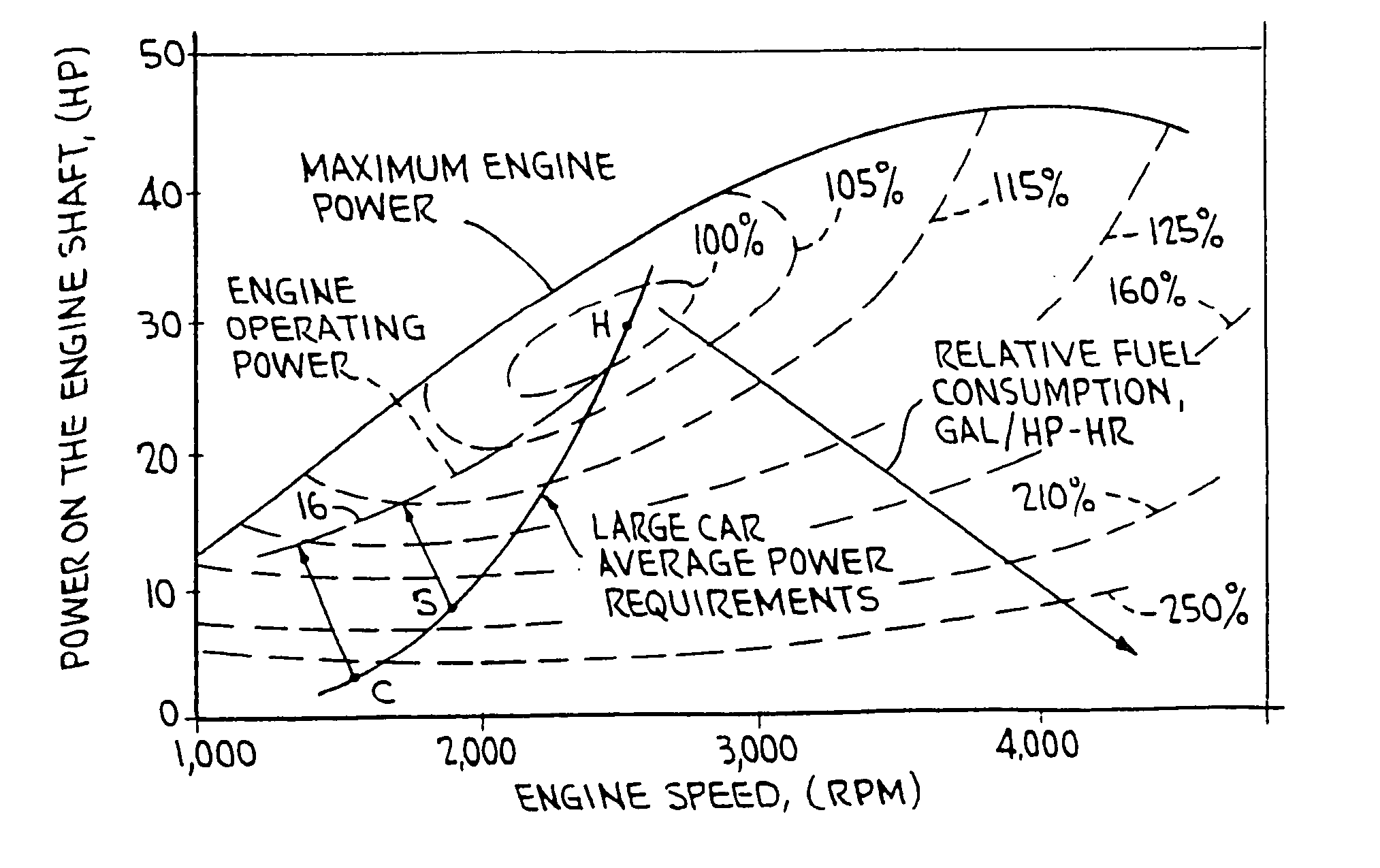
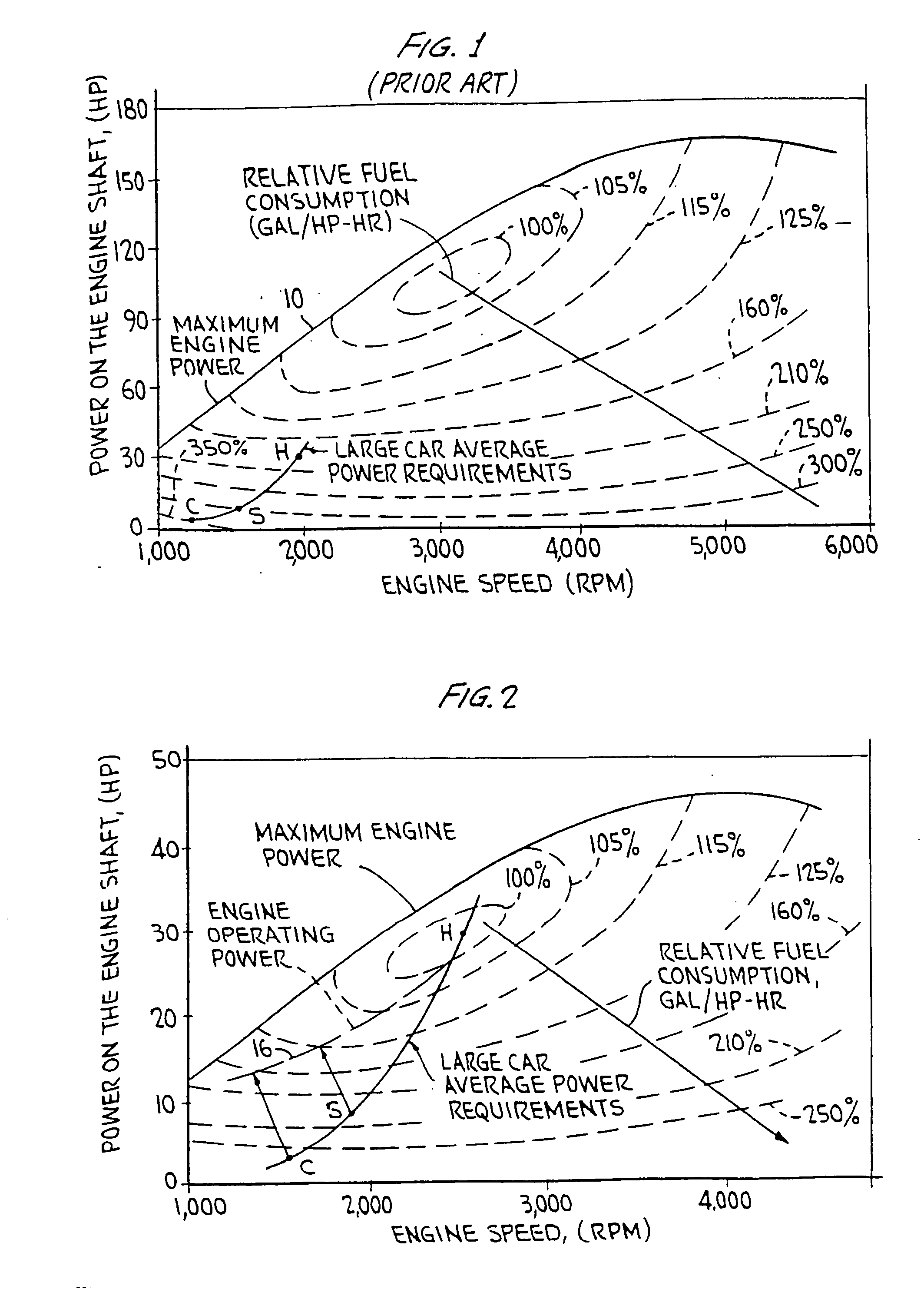
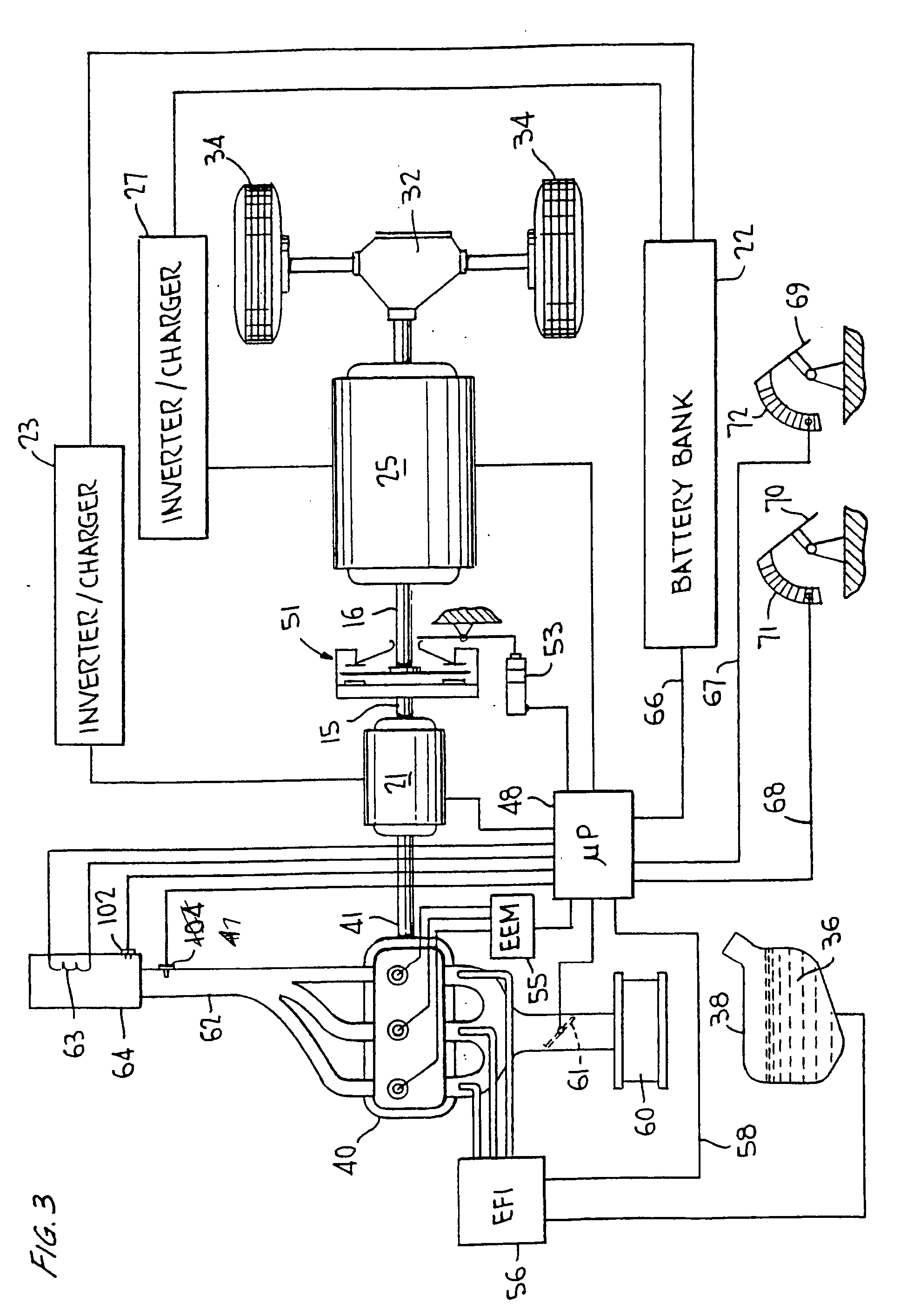
A hybrid vehicle comprises an internal combustion engine, a traction motor, a starter motor, and a battery bank, all controlled by a microprocessor in accordance with the vehicle's instantaneous torque demands so that the engine is run only under conditions of high efficiency, typically only when the load is at least equal to 30% of the engine's maximum torque output. In some embodiments, a turbocharger may be provided, activated only when the load exceeds the engine's maximum torque output for an extended period; a two-speed transmission may further be provided, to further broaden the vehicle's load range. A hybrid brake system provides regenerative braking, with mechanical braking available in the event the battery bank is fully charged, in emergencies, or at rest; a control mechanism is provided to control the brake system to provide linear brake feel under varying circumstances.
Owner:THE ABELL FOUND INC
Internal combustion engine having two exhaust gas turbocharger
InactiveUS20070107430A1Simple meansIncreased recirculationNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerExhaust fumes
In an internal combustion engine provided with two exhaust gas turbochargers which each comprise a turbine in an exhaust line and one compressor in an intake section of the engine, two exhaust lines are provided which are each assigned to at least one of the exhaust gas turbines, an exhaust gas recirculation device being arranged between an exhaust line upstream of an exhaust gas turbine and the intake section downstream of a compressor and the two exhaust lines including bypass lines with a control valve for selectively permitting the exhaust gas to bypass the turbine closer to the engine.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
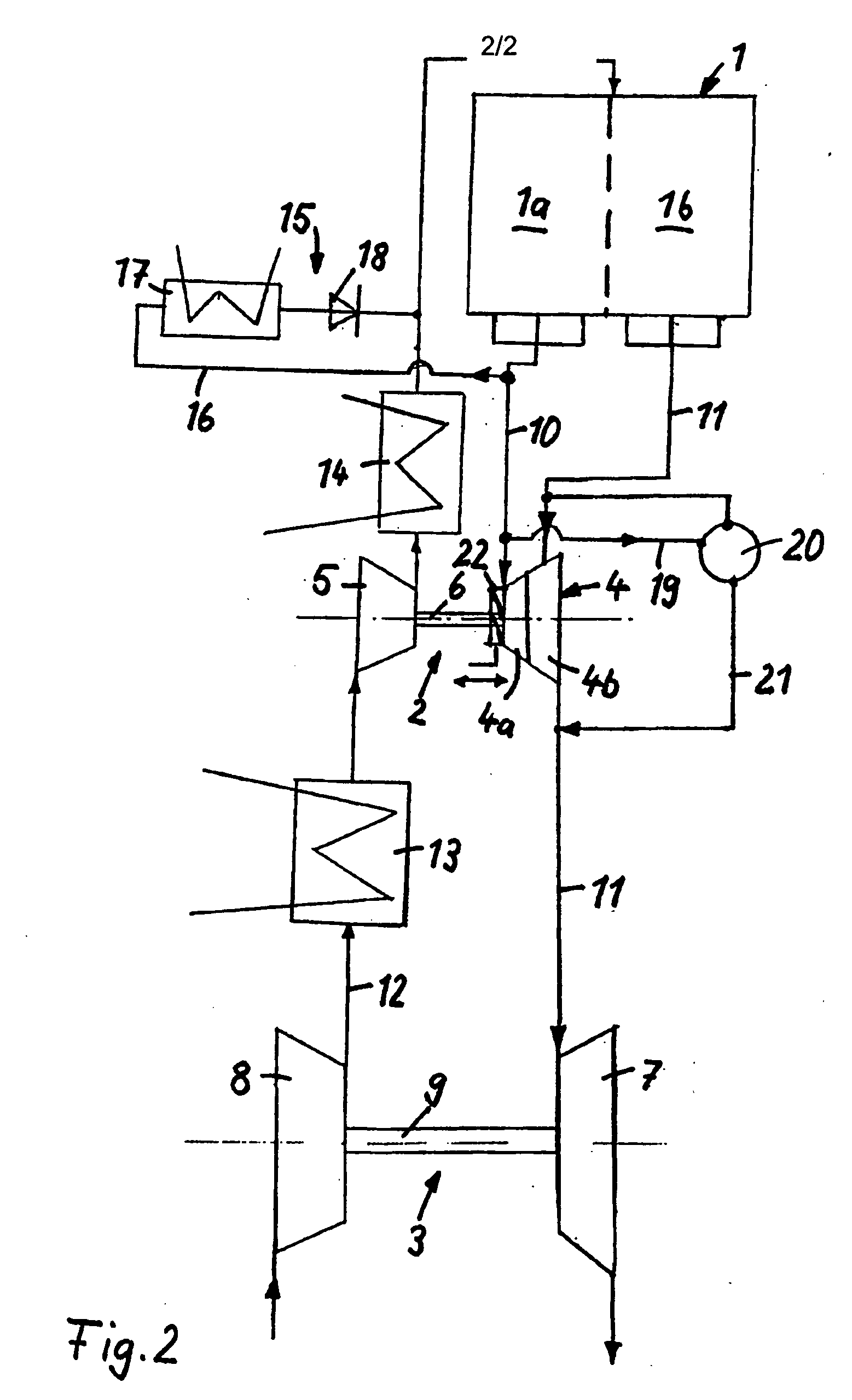
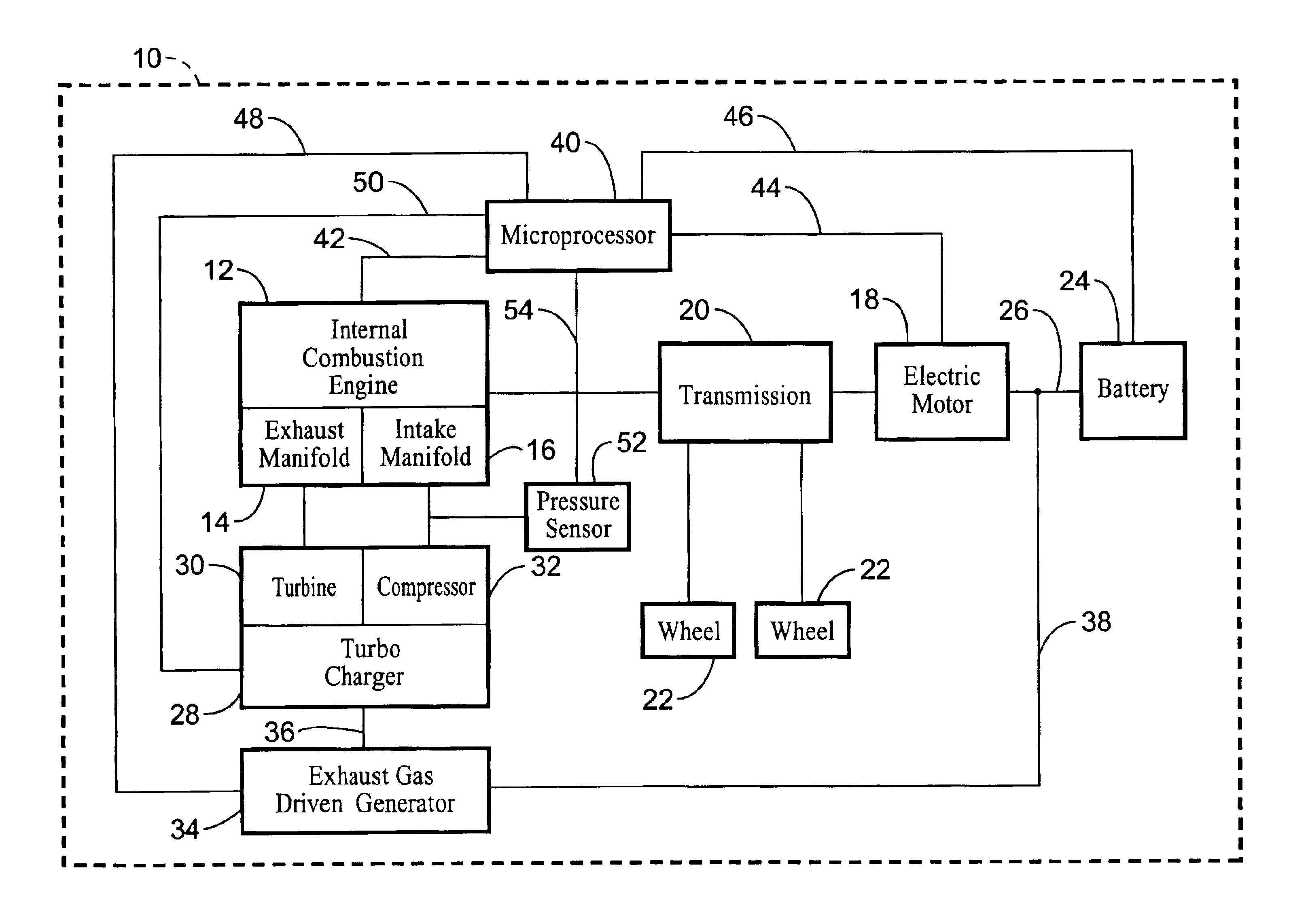
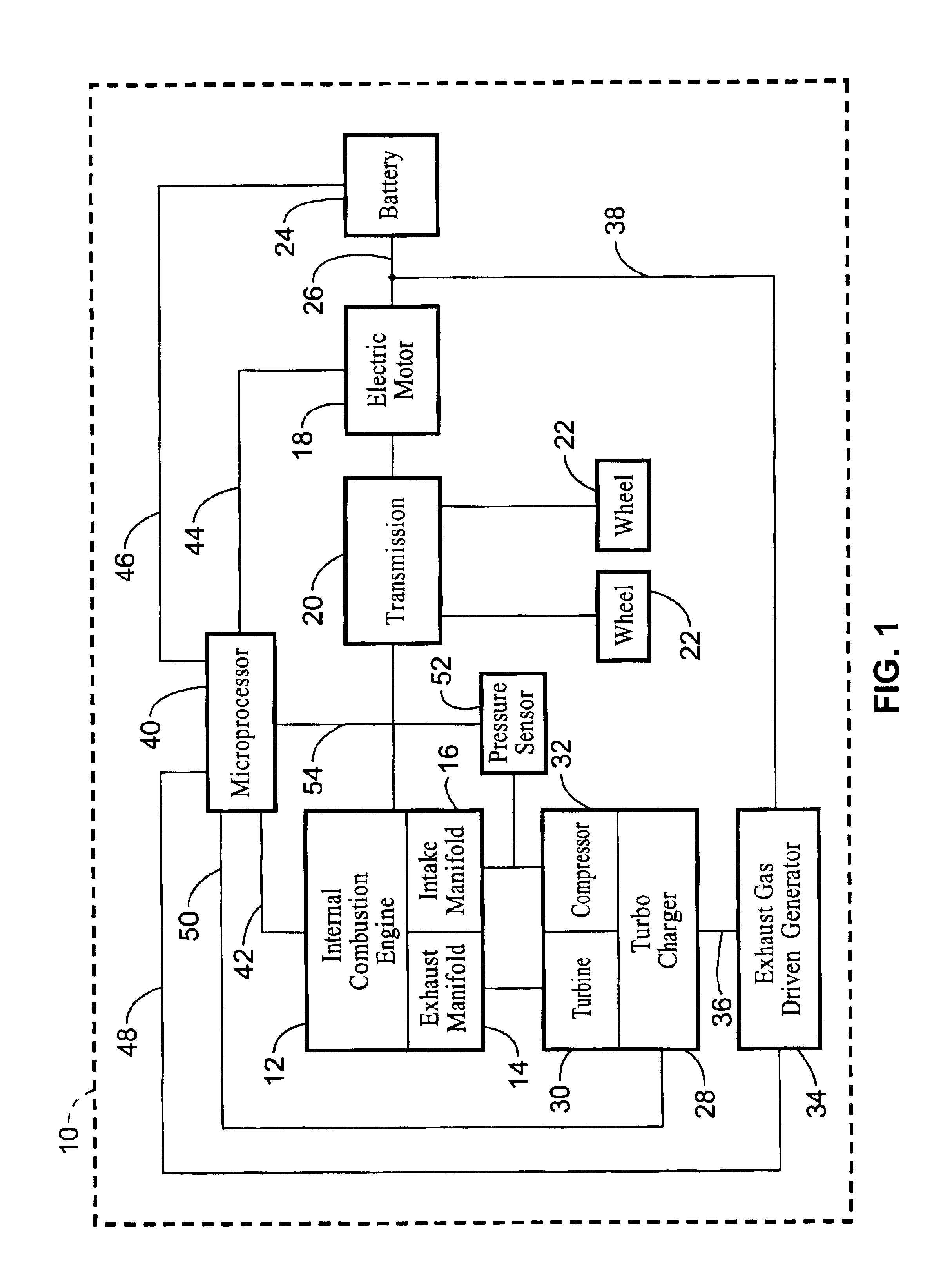
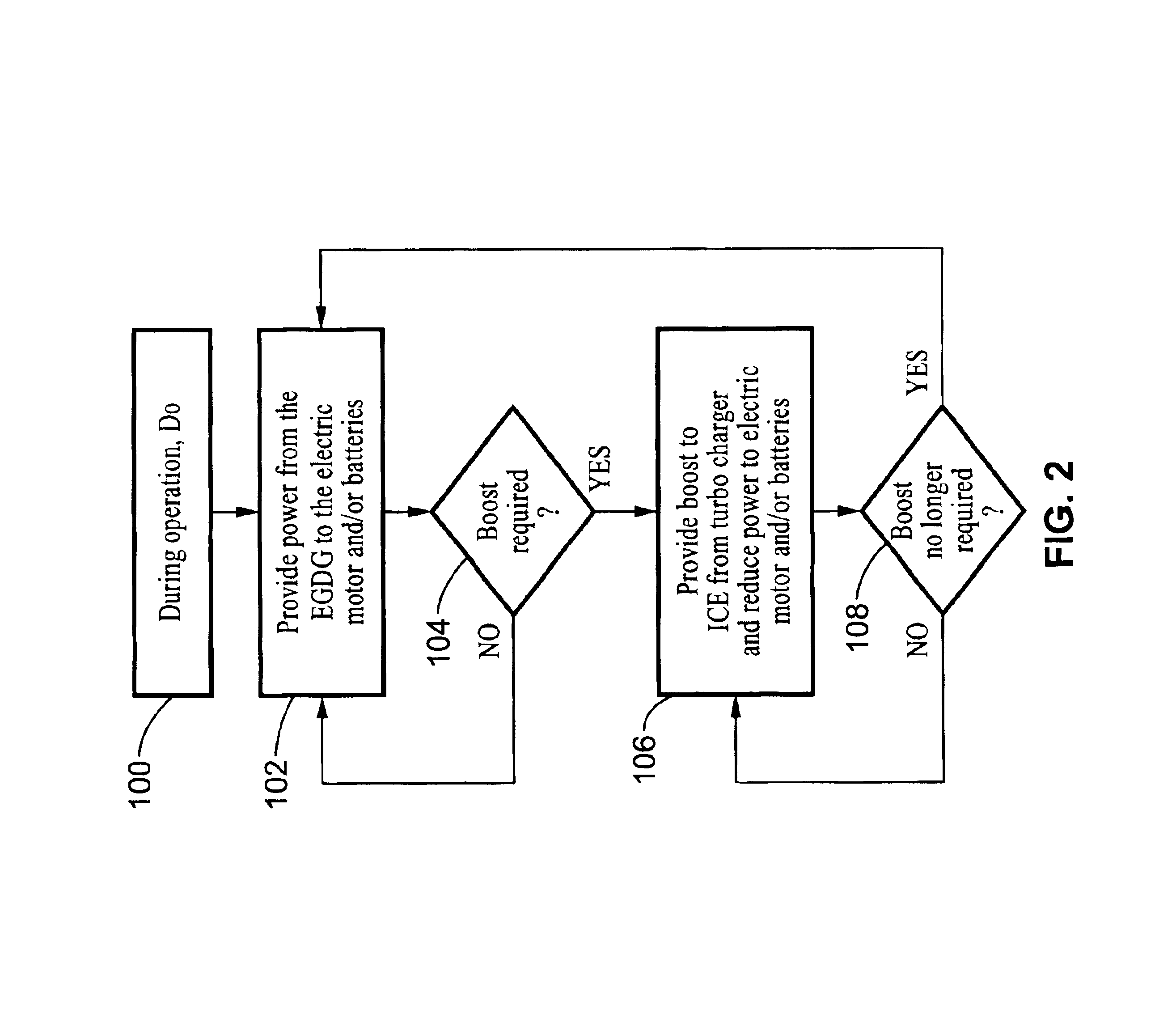
Exhaust gas driven generation of electric power and altitude compensation in vehicles including hybrid electric vehicles
InactiveUS6931850B2Improve volumetric efficiency and effective thermal efficiencyReduce fuel consumptionInternal combustion piston enginesPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectrical batteryTurbocharger
A hybrid electric vehicle includes an internal combustion engine, an electric motor and a transmission. A turbocharger is in fluid communication with the internal combustion engine. Moreover, a generator is mechanically coupled to the turbocharger and thereby driven by exhaust gas from the internal combustion engine. The generator can provide electricity to the motor and / or a battery while simultaneously providing altitude compensation for the internal combustion engine so that the internal combustion engine output remains at the same power and efficiency as altitude and environmental conditions change. The turbocharger can also be used for power boost if desired. The exhaust gas driven generator system can be deployed in conventional vehicles as well to charge the battery and / or power electrical accessories, thereby replacing the alternator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dual and hybrid EGR systems for use with turbocharged engine
InactiveUS7013879B2Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesSingle stageTurbocharger
EGR systems for an internal combustion engine configured to operate using multiple-staged turbochargers, or a pair of single stage turbochargers, to provide exhaust gas recirculation to meet emissions requirements while not affecting engine performance. One or two EGR loops operating at low, intermediate, or high pressures may be employed. EGR exhaust gases may be taken directly from the exhaust manifold, or after the exhaust stream has passed through a turbocharger turbine. EGR exhaust gases may be injected at an intermediate pressure between stages of a multiple stage turbocharger, or alternatively between a low pressure turbocharger compressor and high pressure turbocharger compressor, before being boosted to a pressure high enough to ensure the desired mass flow to the engine and delivered to the intake manifold. Intake air may be pressurized prior to mixing with the EGR exhaust gases.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
Multiple nozzle rings and a valve for a turbocharger
InactiveUS20070209361A1Increase impact speedReduce back pressureEngine manufactureInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerEngineering
A turbocharger turbine housing with at least two volutes utilizing multiple nozzle rings to optimize the turbocharger's proficiency per application, and a valve to control the exhaust flow to selected volutes in the turbine housing.
Owner:PEDERSEN MELVIN HESS +1
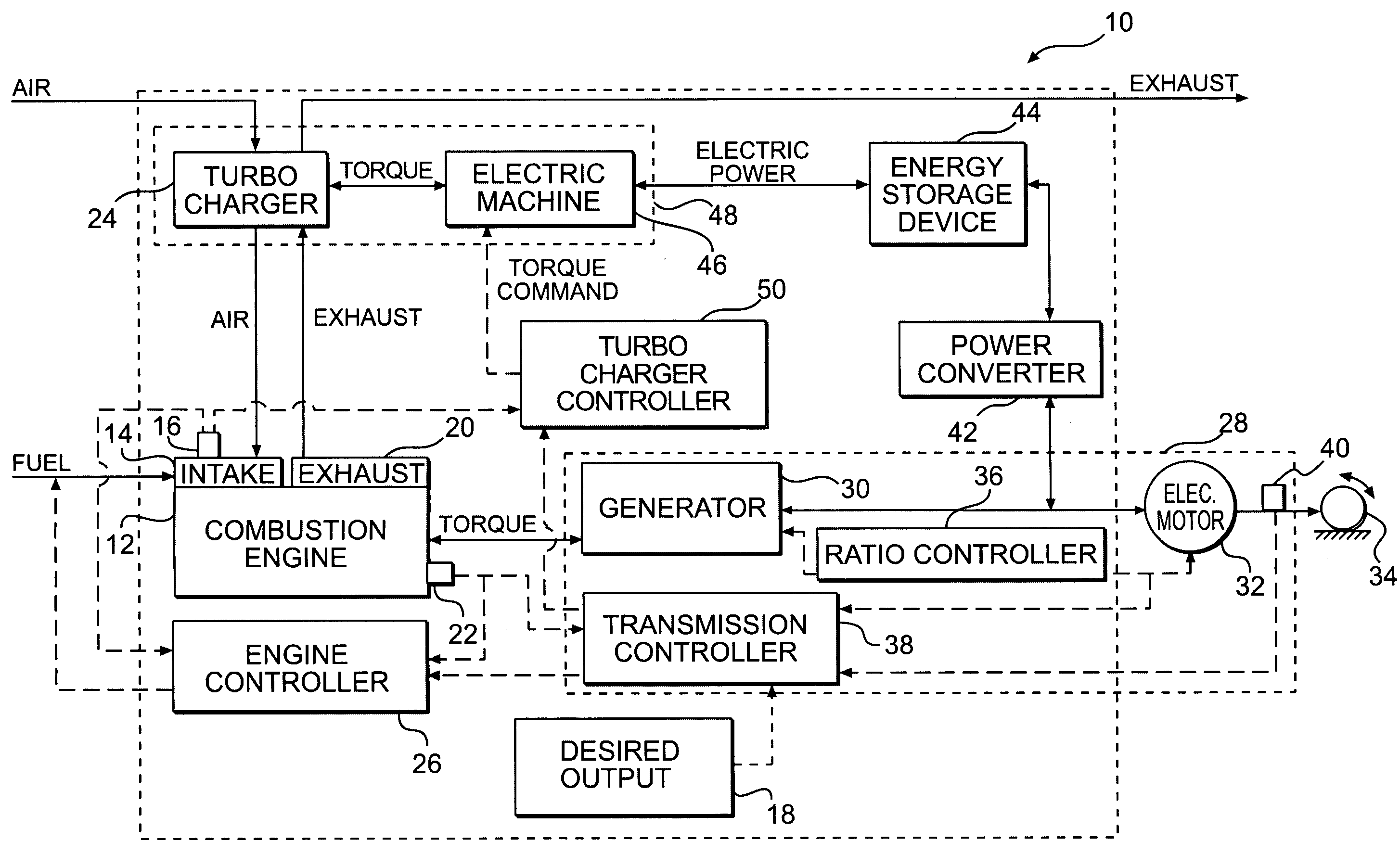
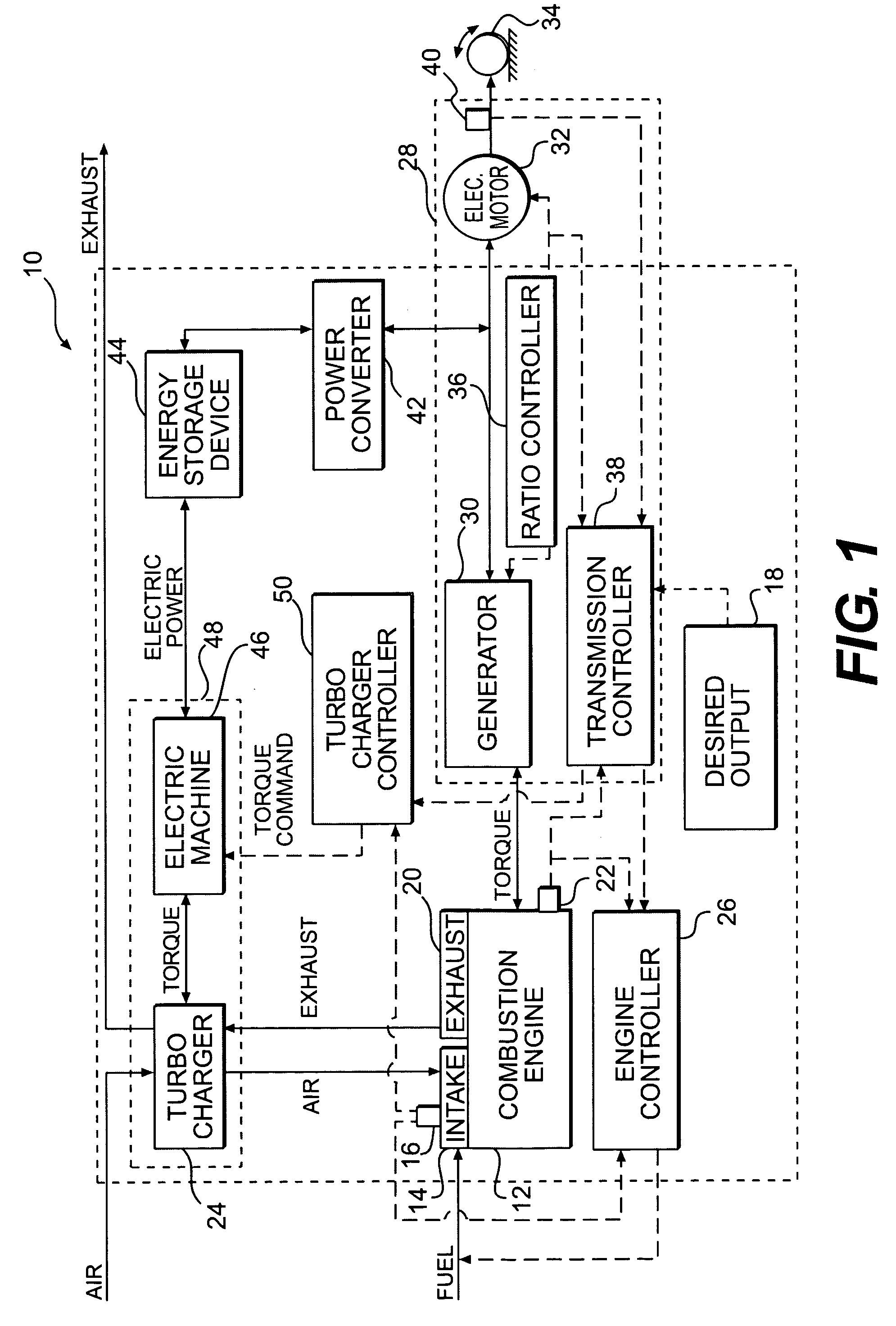
Turbocharger system
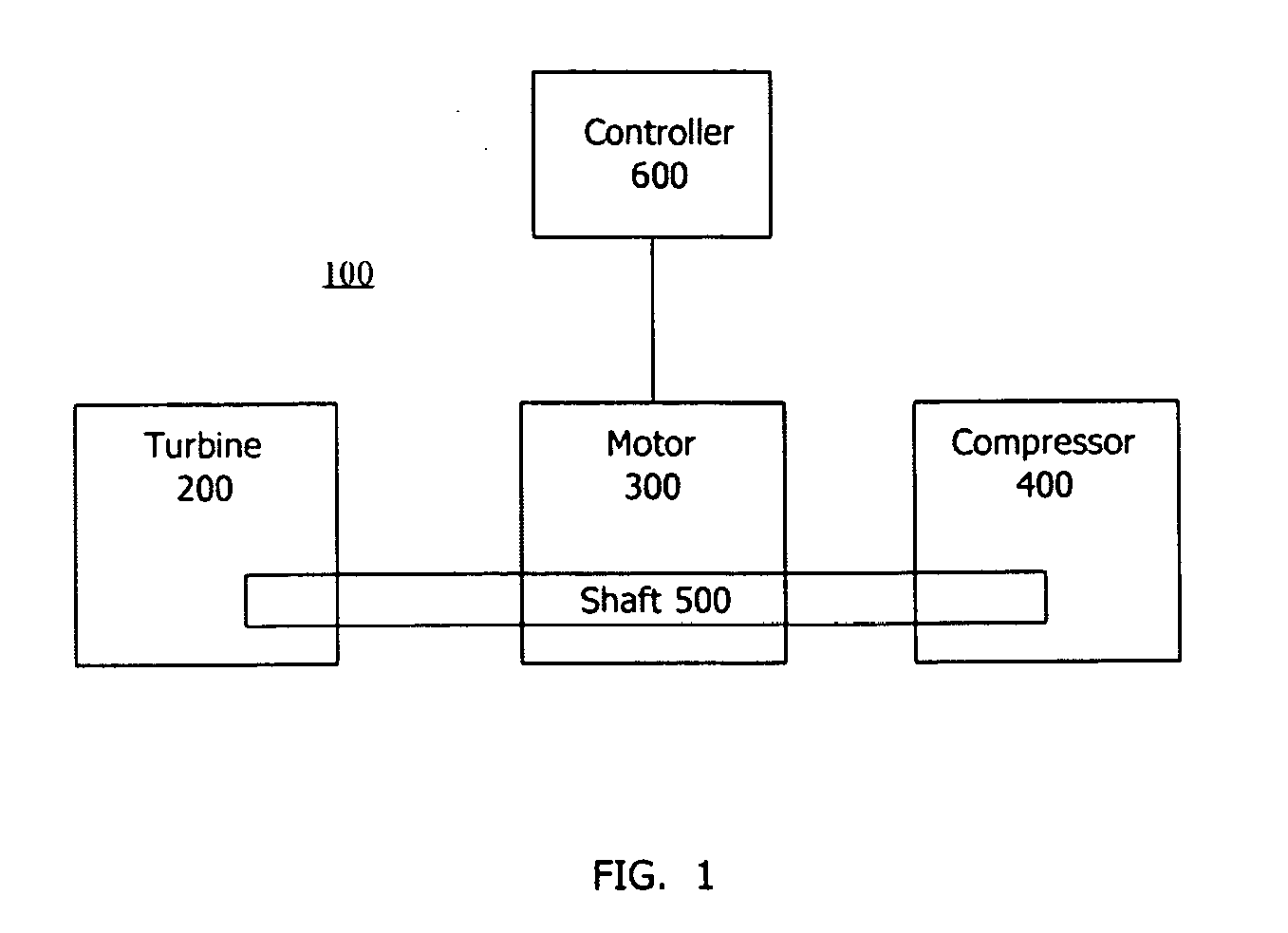
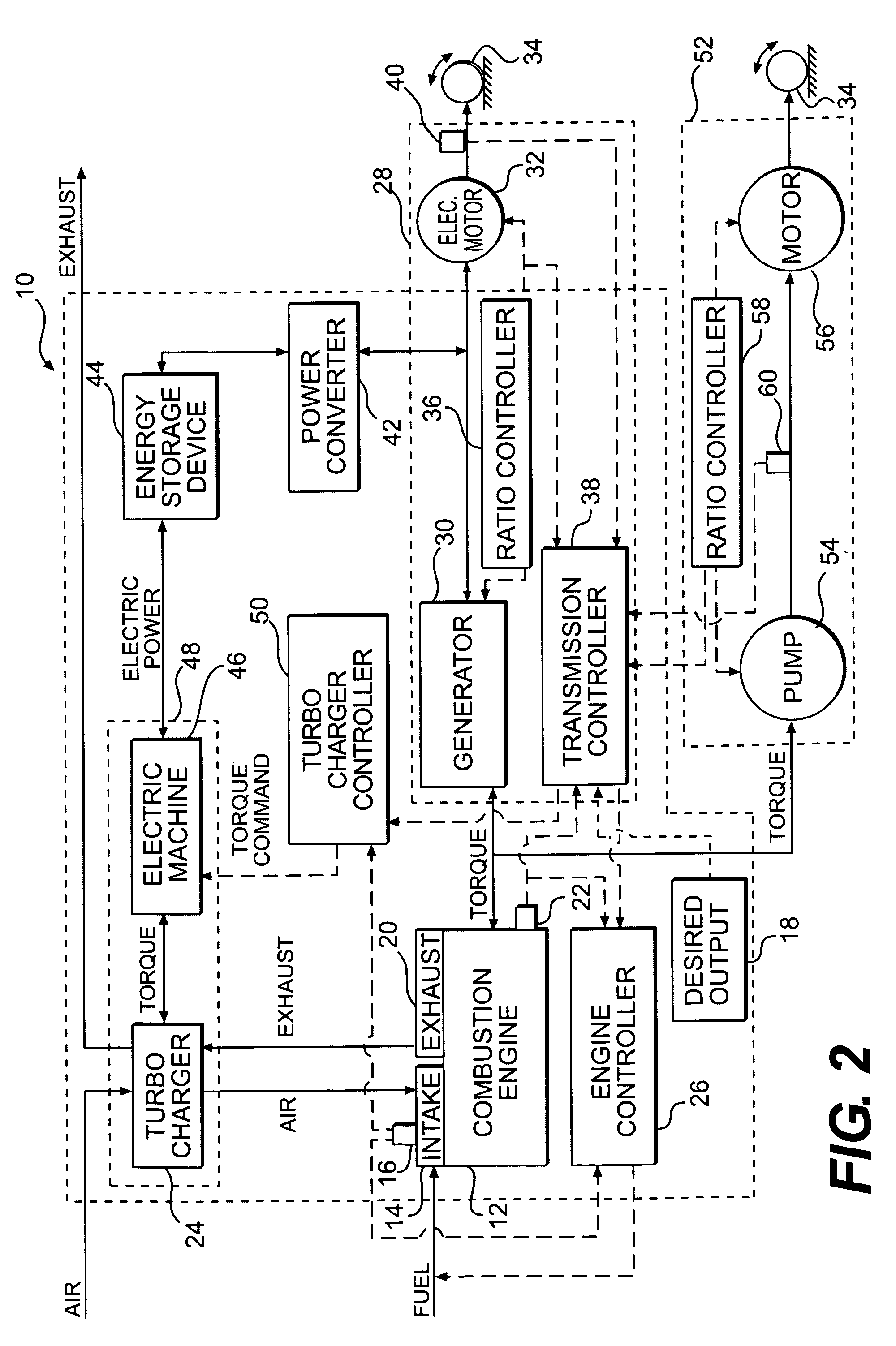
A system for controlling intake pressure of a combustion engine operably coupled to a power generation system includes a sensor configured to output a signal indicative of a pressure in an intake system of the combustion engine and a sensor configured to output a signal indicative of a load on the power generation system. The system further includes a turbocharger operably coupled to the intake system. The system also includes an electric machine operably coupled to the turbocharger. The electric machine is configured to supply torque to the turbocharger. The system further includes a turbocharger controller operably coupled to the electric machine. The turbocharger controller is configured to control operation of the electric machine such that the turbocharger supplies a desired intake pressure to the combustion engine based at least partially on the signal indicative of a pressure in the intake system and the signal indicative of a load on the power generation system.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
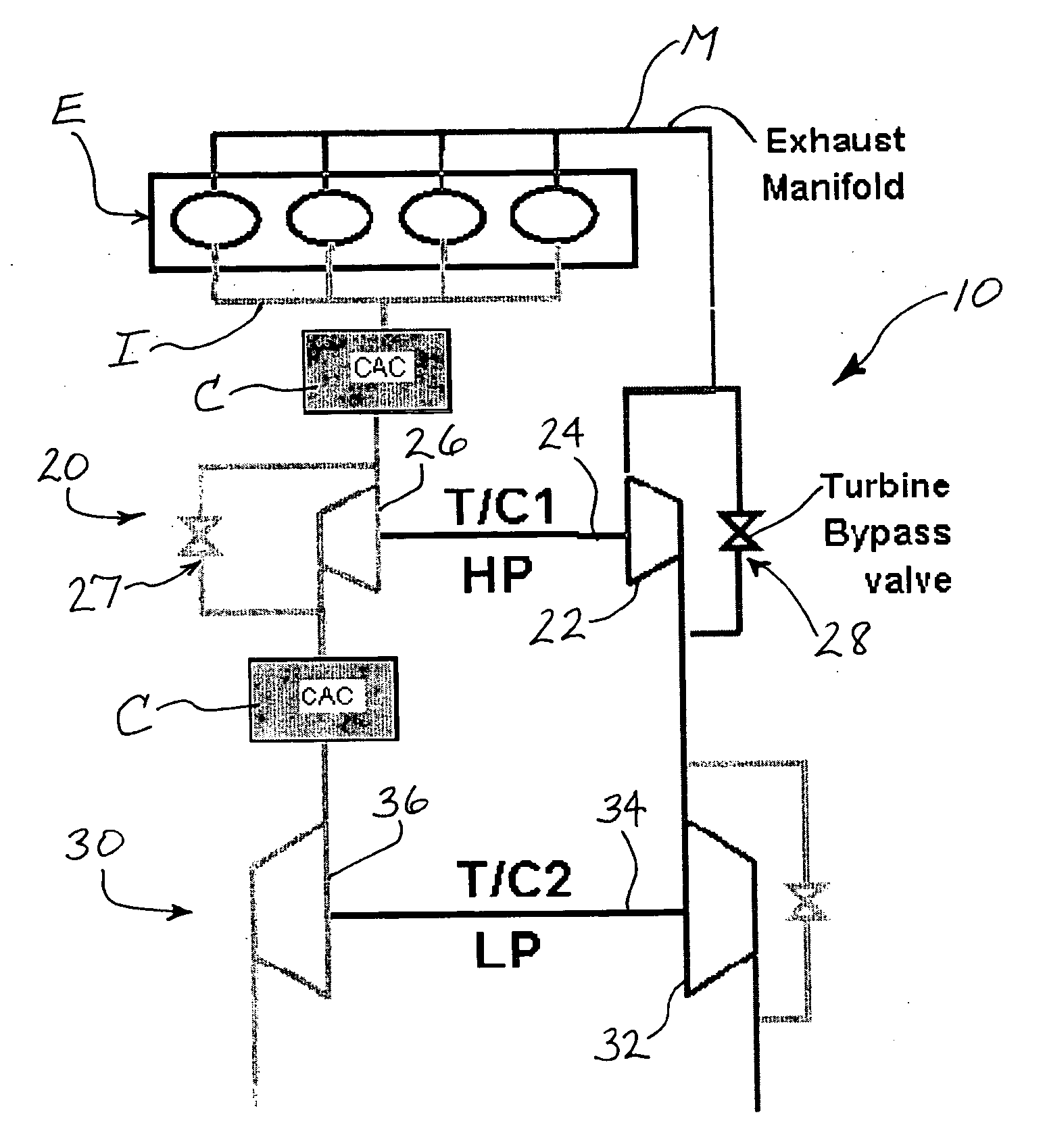
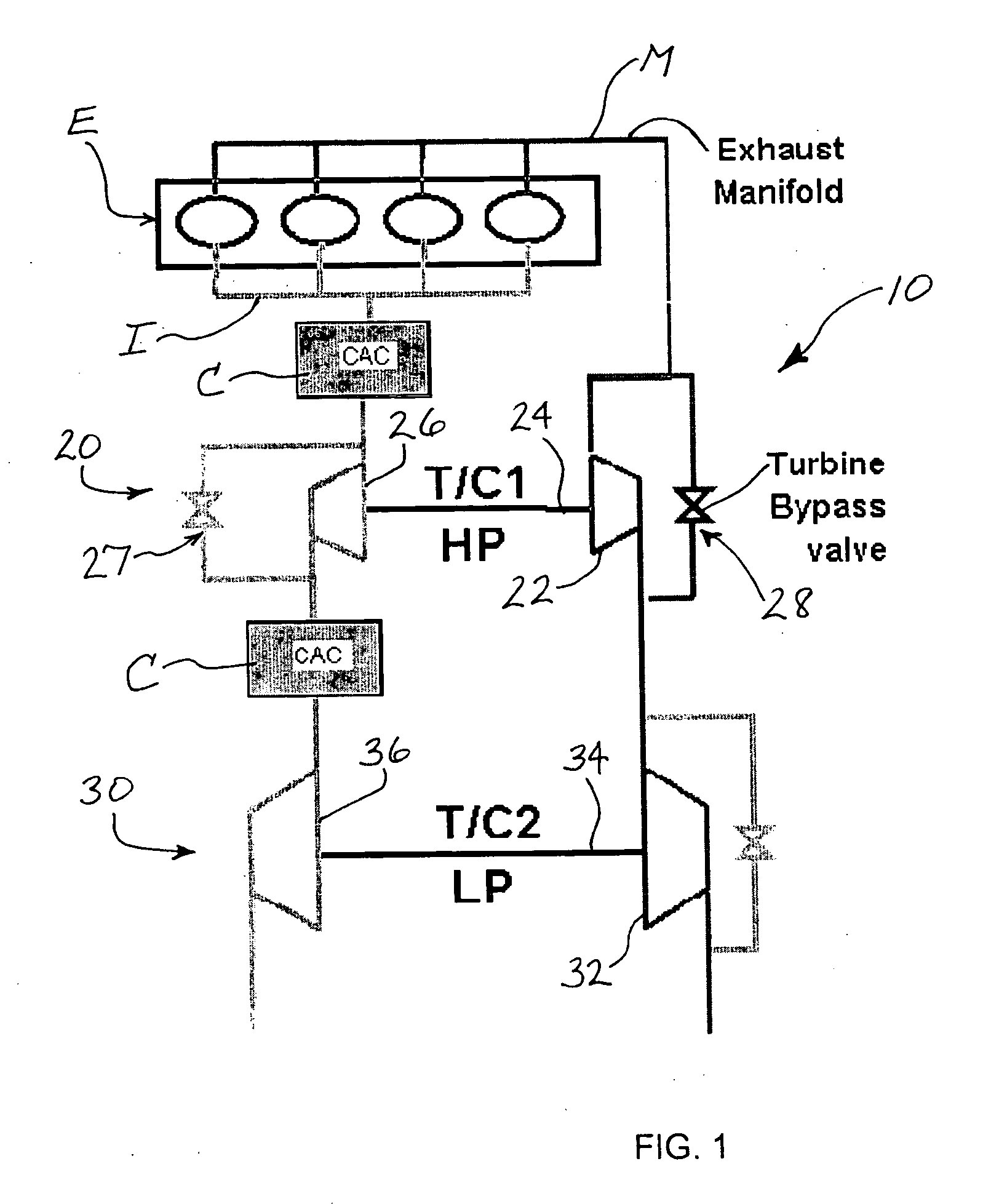
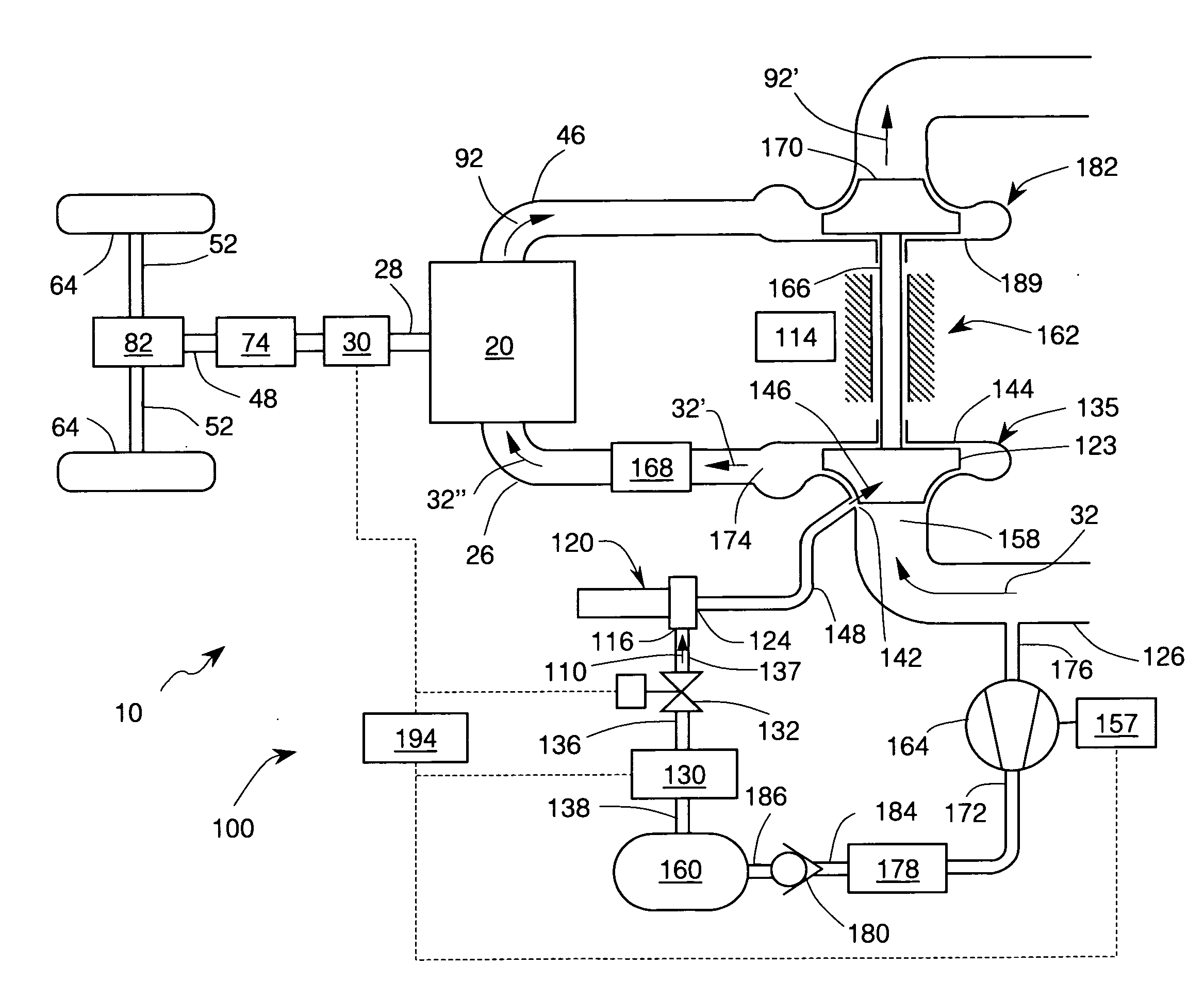
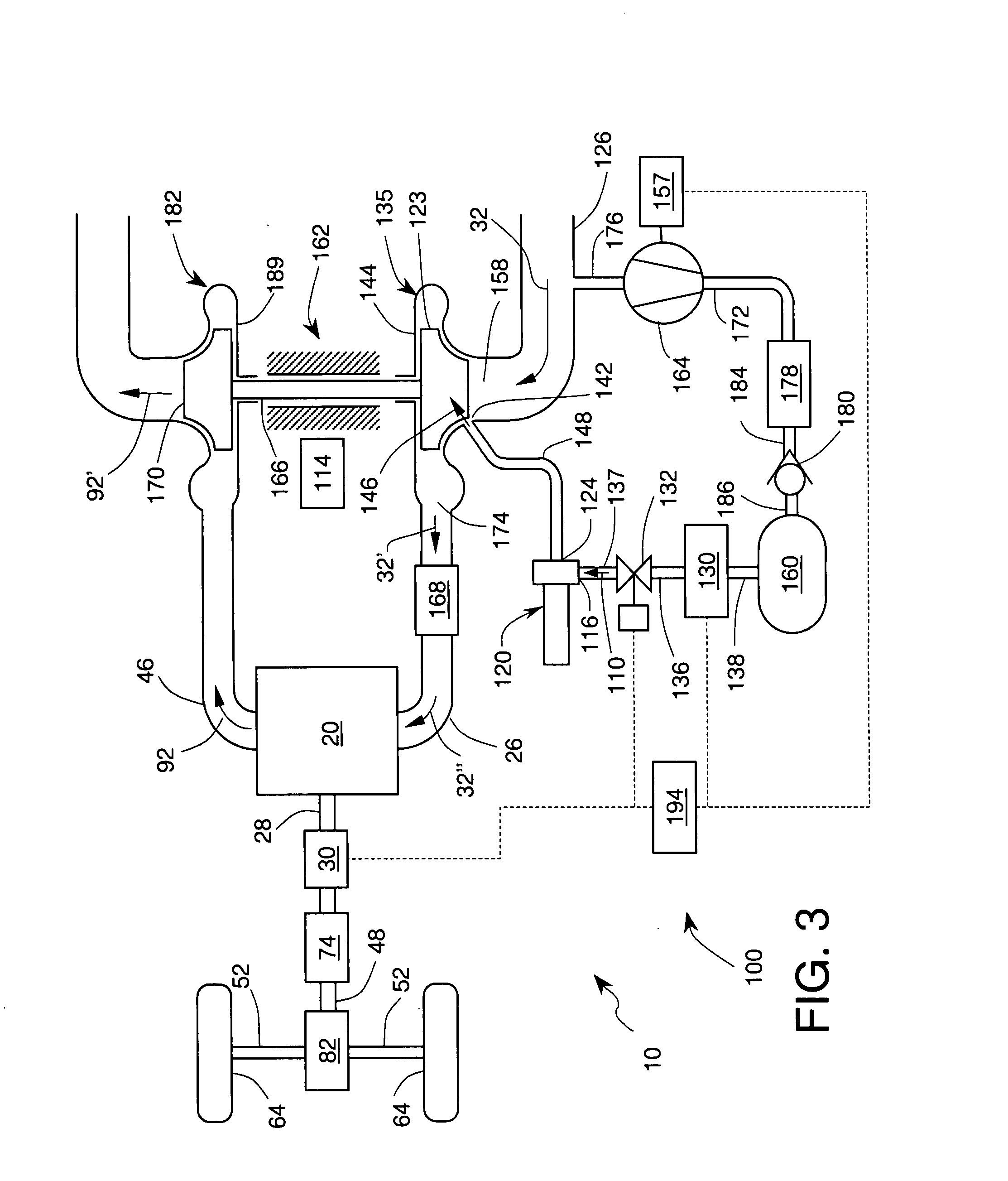
Two-stage turbocharger system with integrated exhaust manifold and bypass assembly
A two-stage turbocharger system includes an exhaust manifold formed separately from the high-pressure and low-pressure turbine housings. The exhaust manifold defines a bypass passage, and a bypass valve is disposed in the bypass passage for opening and closing the passage. The exhaust manifold also defines an inter-turbine passage. The turbine housings of the high-pressure and low-pressure turbochargers are releasably connected to the exhaust manifold such that exhaust gas received into the exhaust manifold bypasses the high-pressure turbine and flows through the bypass passage to the low-pressure turbine when the bypass valve is in the open position, and the exhaust gas flows through the high-pressure turbine and then through the inter-turbine passage to the low-pressure turbine when the bypass valve is in the closed position.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
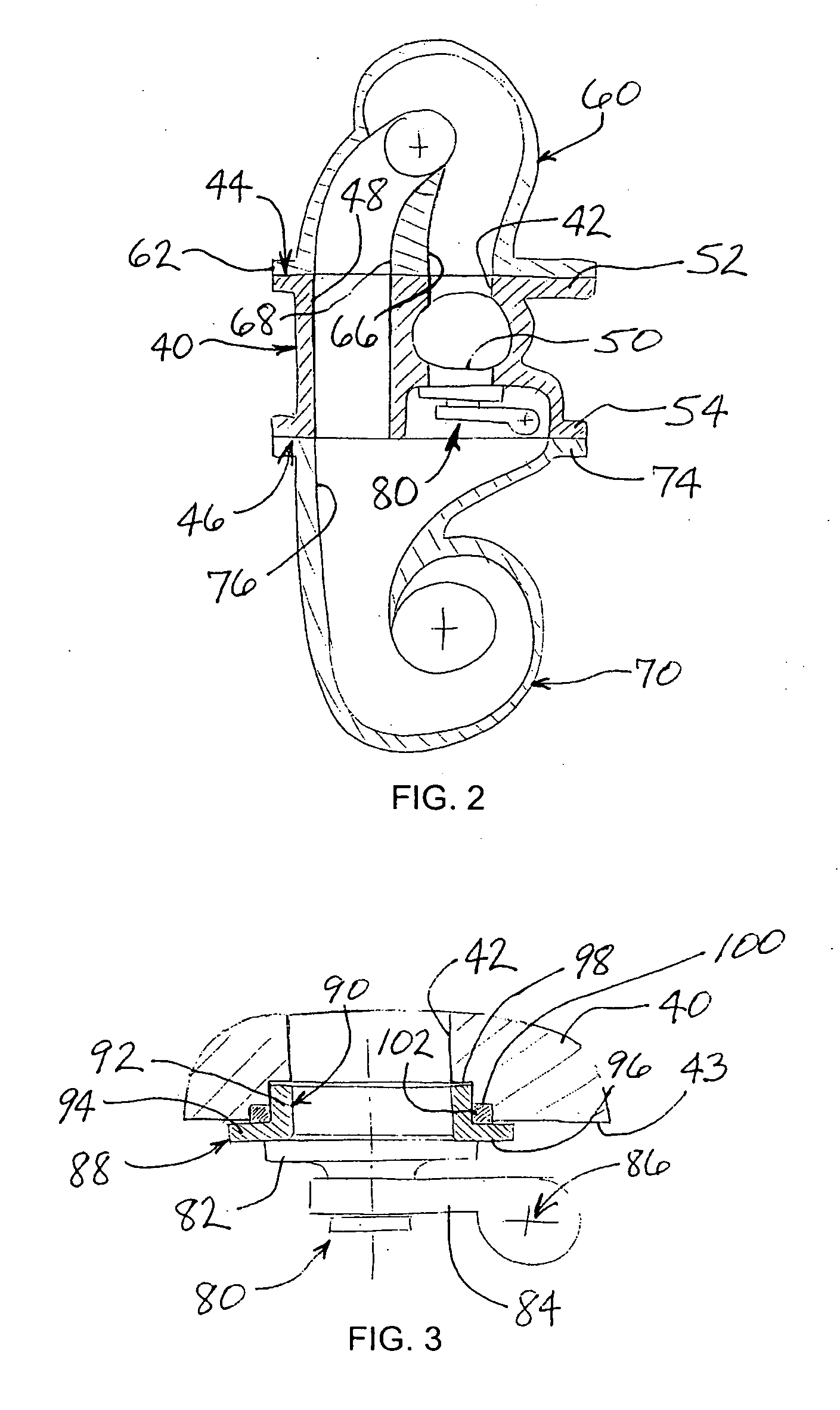
Bearing systems for high-speed rotating machinery
InactiveUS20080087018A1Improve performanceMaintain integrityRolling contact bearingsShaftsBall bearingTurbocharger
Bearing systems for high speed rotating shafts, such as turbocharger shafts, include a first ball bearing in one end of an elongated cylinder capable of carrying axial thrust in both directions and a second ball bearing in the opposite end of the elongated cylinder with its outer race slideably mounted in the cylinder against the biasing force of a preload spring. The second ball bearing is free to move axial with the shaft upon axially expansion of the shaft when exposed to high temperature. The inner races of the ball bearings are clamped to and rotate with the shaft as part of the rotating assembly.
Owner:DELGADO LAUREN N
System and Method for Diagnostic of Low Pressure Exhaust Gas Recirculation System and Adapting of Measurement Devices
ActiveUS20080022677A1Reduce the formation of nitrogen oxidesImprove fuel economyVehicle testingElectrical controlMeasurement deviceTurbocharger
A system for a diesel engine having an intake manifold and an exhaust manifold, comprises a turbocharger between the intake and exhaust manifolds of the engine; a low pressure exhaust gas recirculation system with a first end coupled to the exhaust manifold downstream of the turbocharger and a second end couple to the intake manifold upstream of the turbocharger, said low pressure exhaust gas recirculation having a first valve coupled thereto for regulating flow; a high pressure exhaust gas recirculation system with a first end coupled to the exhaust manifold upstream of the turbocharger and a second end coupled to the intake manifold downstream of the turbocharger, said high pressure exhaust gas recirculation having a second valve coupled thereto for regulating flow; a first mass airflow sensor coupled in the engine intake manifold upstream of an inlet of said second end of said low pressure exhaust gas recirculation system; and a control system configured to diagnose the degradation of said first mass airflow sensor.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
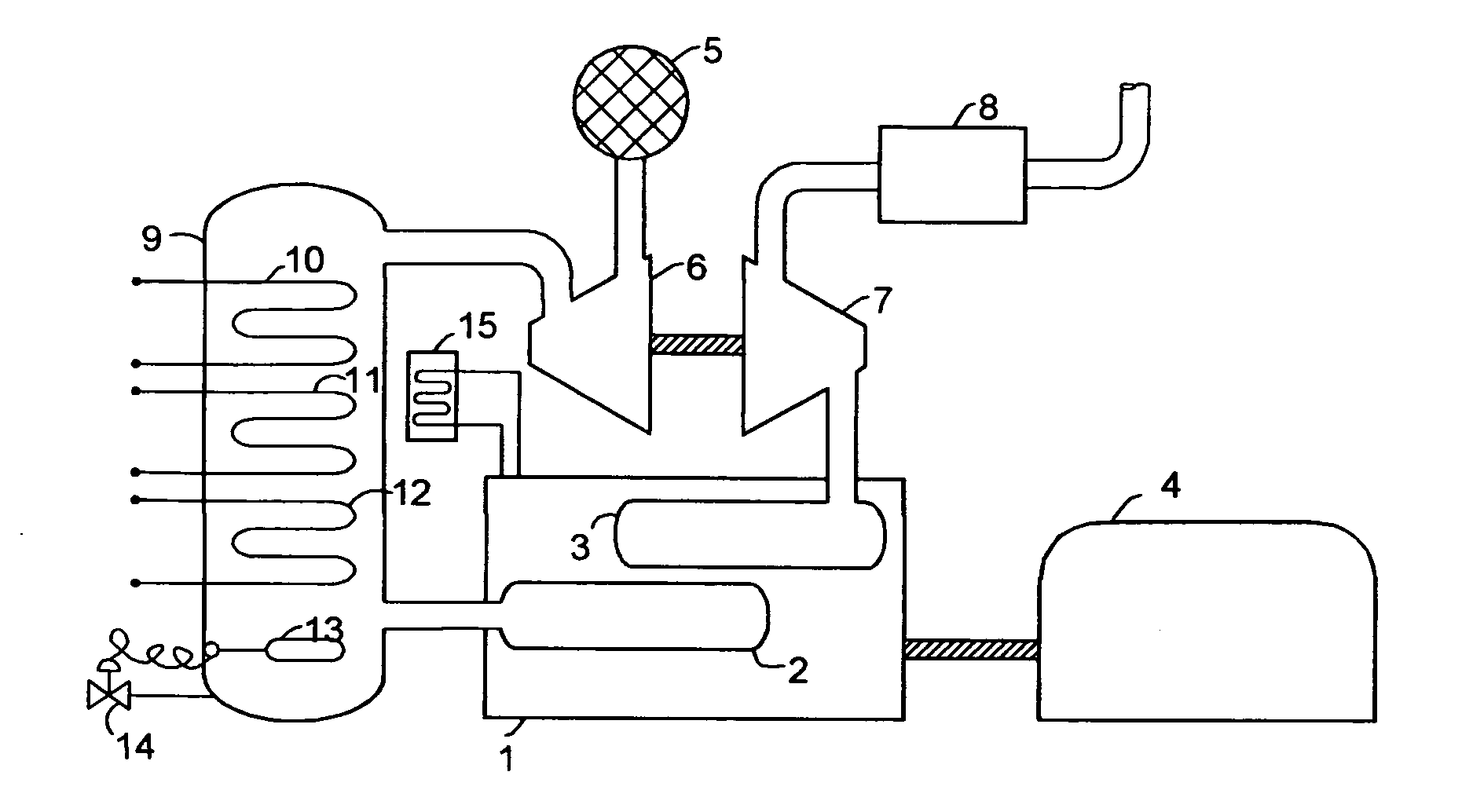
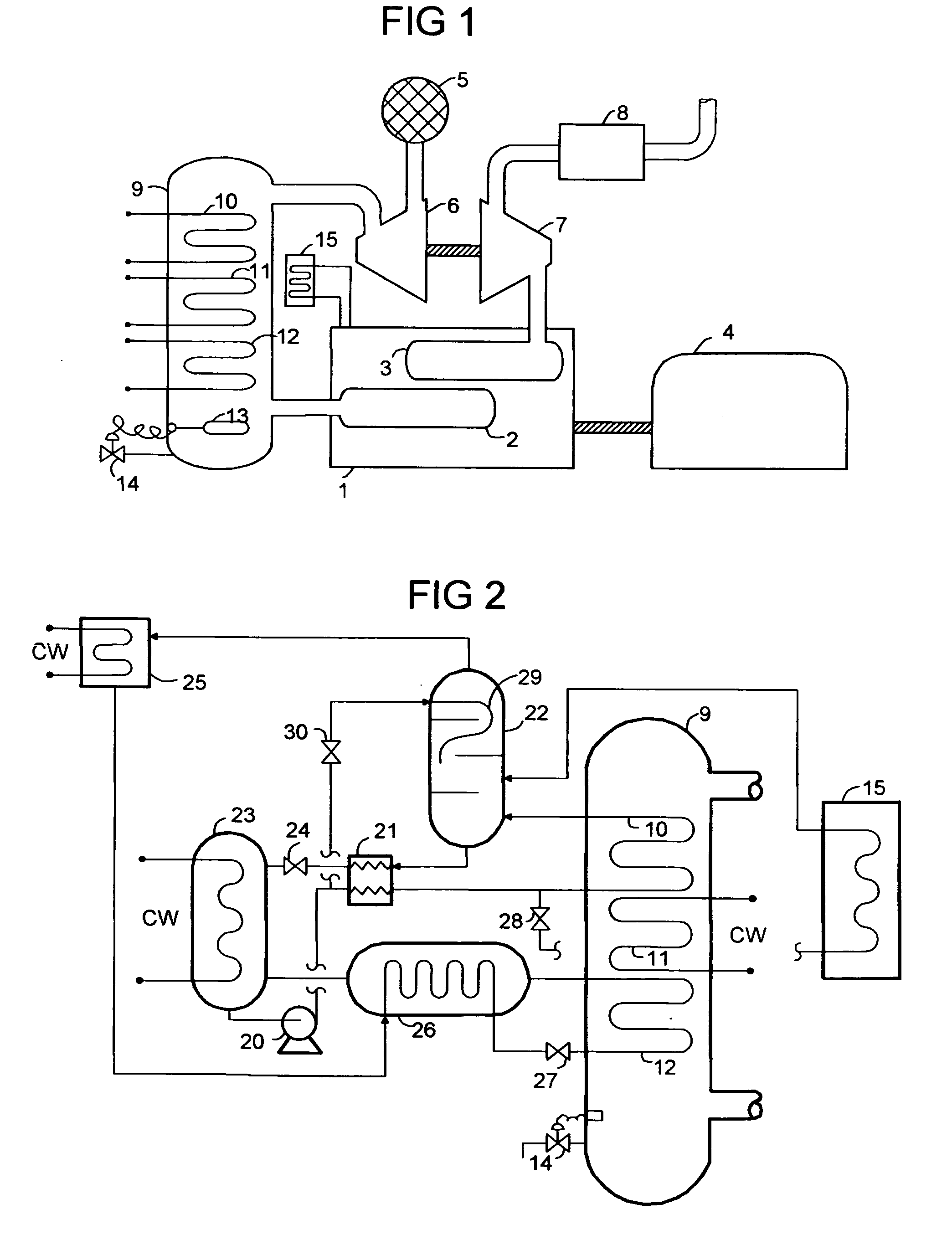
Charge air chiller
InactiveUS20090031999A1Maximum increase in energy efficiencyIncrease boost pressureInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTurbochargerInlet valve
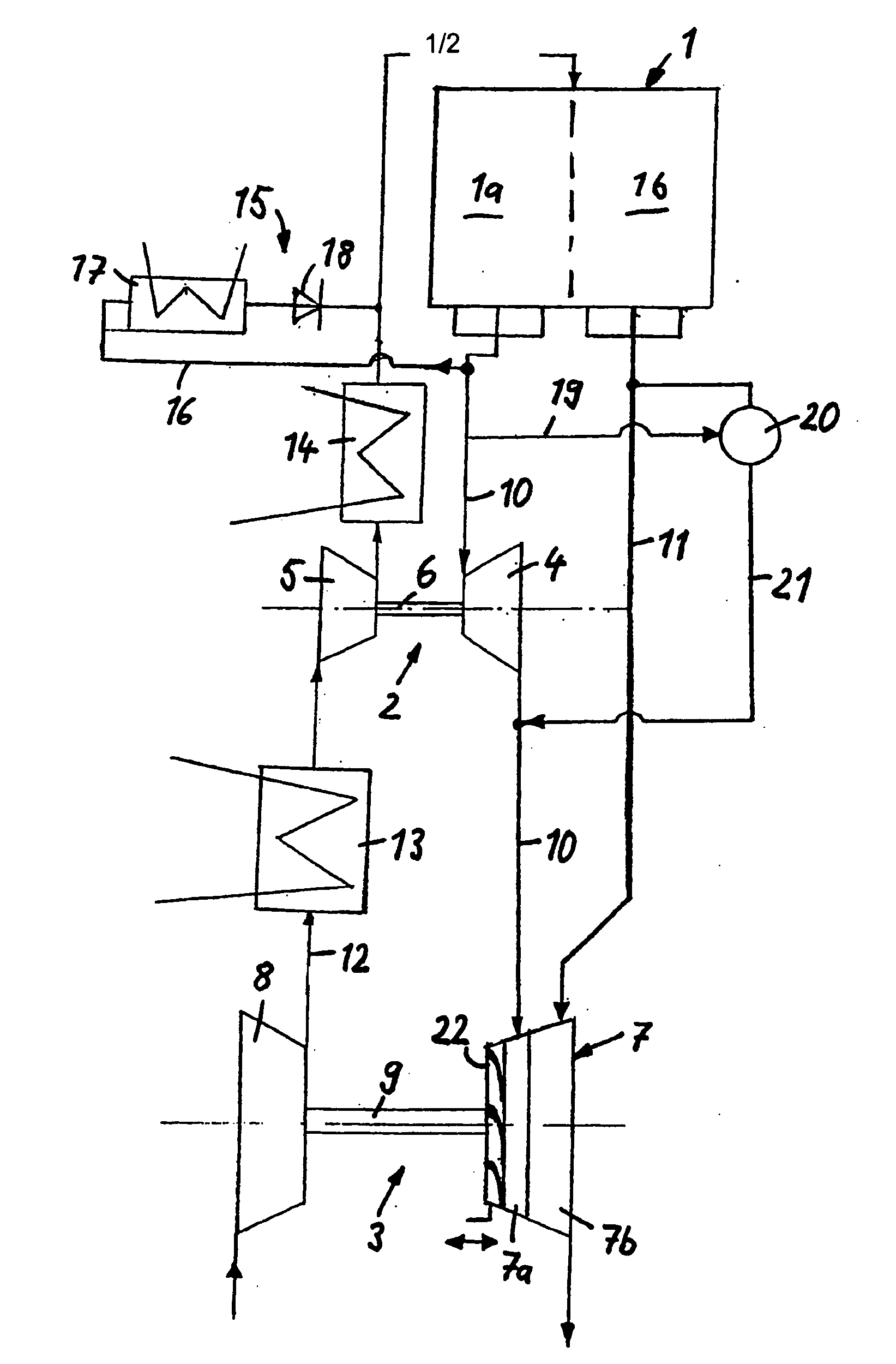
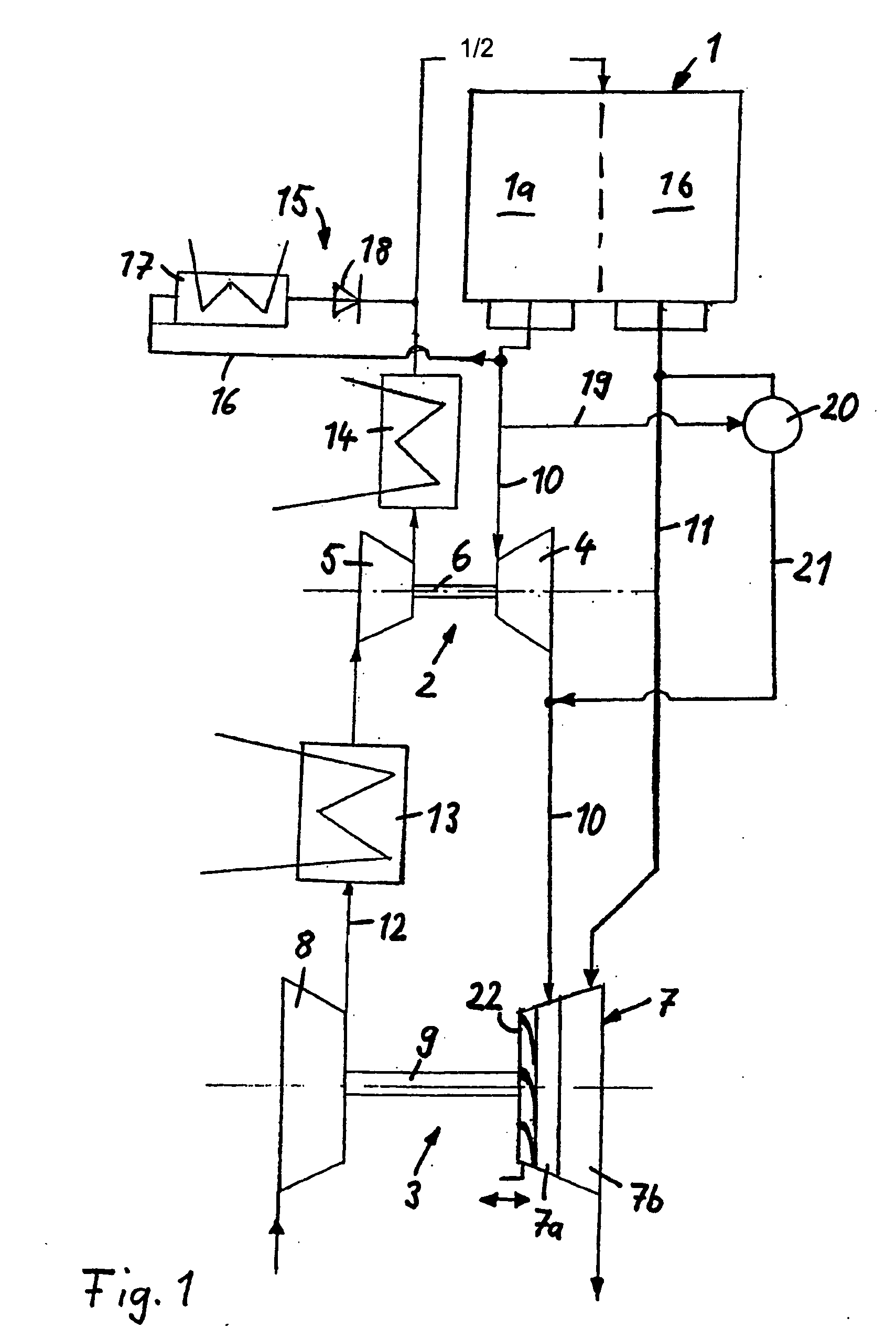
A system for chilling the pressurized charge air to a reciprocating engine is disclosed wherein the chilling is provided by a thermally activated refrigeration cycle powered by waste heat from the engine system. This reduces the required compression power, and also retards knock, making higher compression ratios possible. The chilling system is designed to minimize the amount of chilling required, and also to enable use of compression heat to power the chiller. The disclosed improvement also accommodates exhaust gas recirculation, plus providing activation heat from the exhaust gas, plus Miller cycle timing of the intake valves. Referring to FIG. 1, the charge air from turbocharger 5 is cooled in three stages: heat recovery stage 10; ambient-cooled stage 11; and chilling stage 12. Condensed moisture is removed from the charge air by valve 14 before the charge is supplied to inlet manifold 2.
Owner:ERICKSON DONALD CHARLES
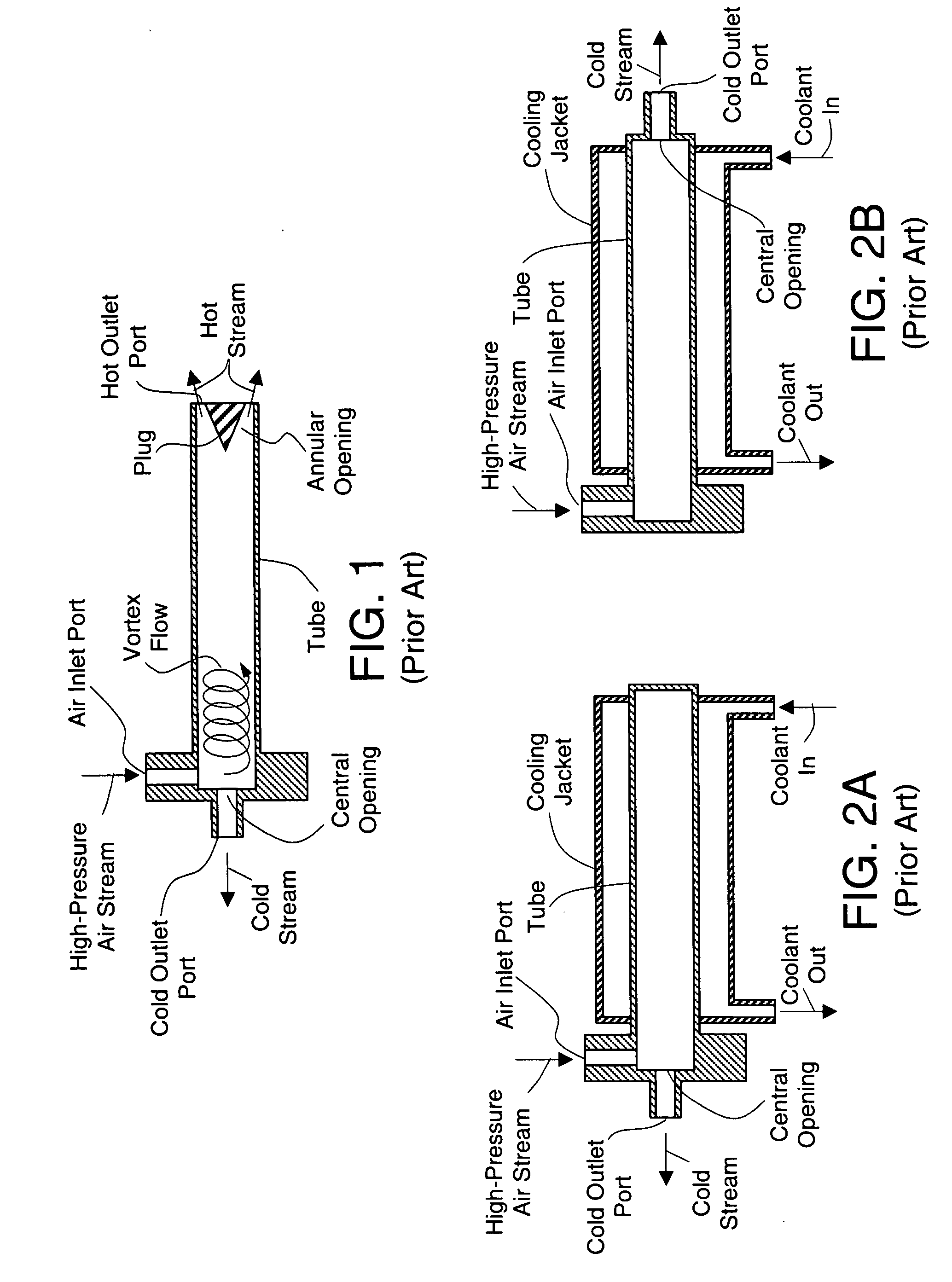
Turbocharged internal combustion engine system
InactiveUS20080133110A1Increase compressor surge limitIncrease compressor speedElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCold airImpeller
The present invention relates to a turbocharged internal combustion engine (ICE) system having fast response to increased power demand and reduced response time lag. The system includes a vortex tube for delivering cold air into the turbocharger compressor where it may be used to cool the impeller, and / or accelerate the impeller rotational speed, and / or favorably shift the compressor surge line at low speeds and high loads. Cold air from the vortex tube may be also used to operate an ejector pump in the intake duct which further compresses intake air and increases engine charge weight during periods of high power demand. In addition to increasing engine output power, delivery of cold air into engine intake also reduces engine pre-ignition (knocking) thereby reducing emissions. The invention also relates to a method for operating a turbocharged internal combustion engine.
Owner:AGWEST
Control of dual stage turbocharging
The invention concerns turbochargers, or more particularly to multivariable dual stage series turbochargers having two degrees of freedom. A multistage series turbocharger apparatus has a low pressure turbocharger comprising a low pressure compressor and a low pressure turbine; a high pressure turbocharger comprising a high pressure compressor and a high pressure turbine, and a exhaust gas recirculation device. A controller controls the operation of at least two of the low pressure compressor, high pressure compressor, low pressure turbine, high pressure turbine, and exhaust gas recirculation device such that at least one operating parameter is maintained at about a selected value.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
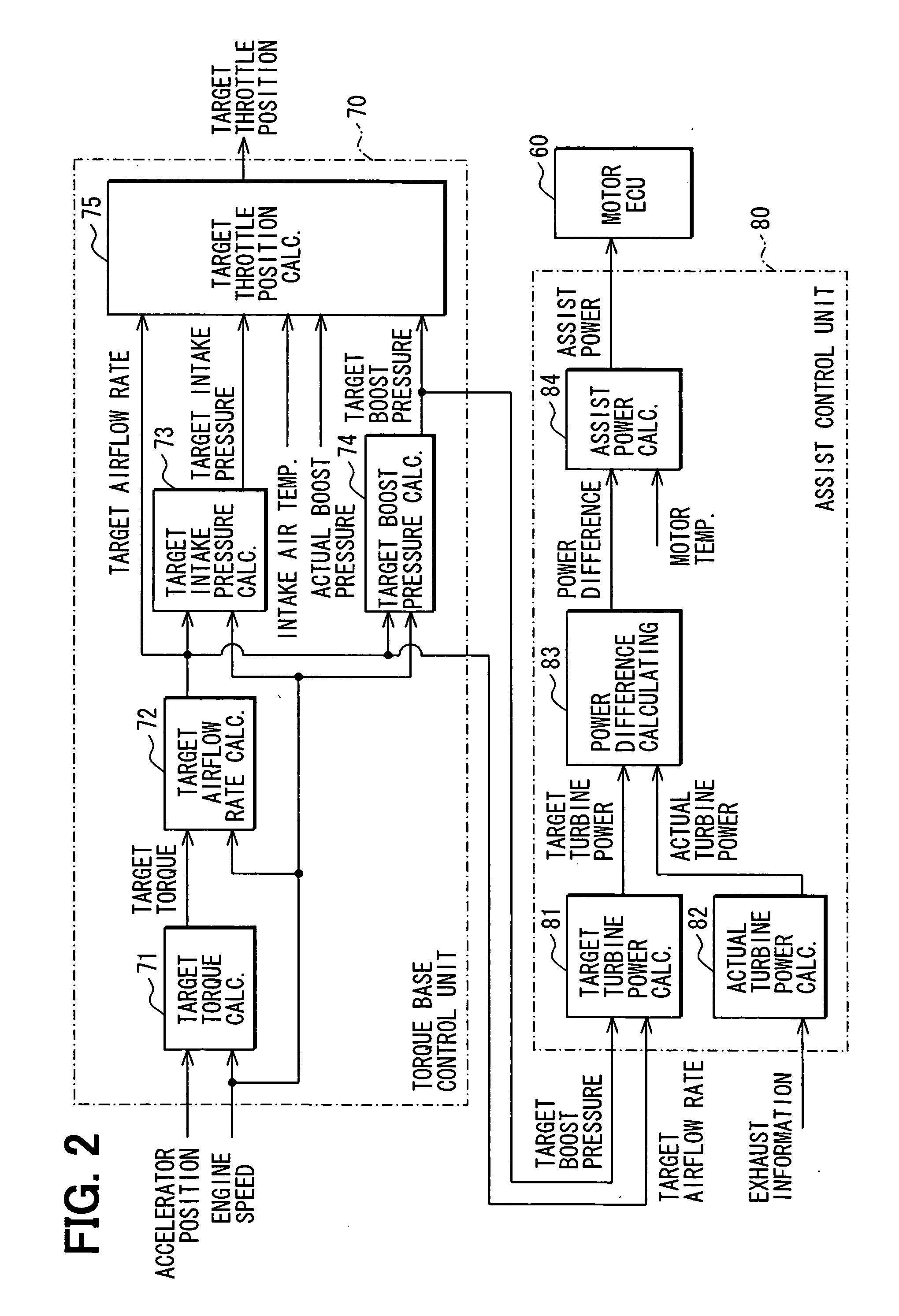
Controller for internal combustion engine with supercharger
InactiveUS20060196182A1Efficient powerIncrease consumptionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerElectric machinery
A torque base control unit calculates target torque based on an accelerator position and engine speed. The control unit further executes calculation of target airflow rate, calculation of target intake pressure, and calculation of target boost pressure based on the target torque. Target throttle position is calculated based on the target airflow rate, target intake pressure, target boost pressure, actual boost pressure, and throttle passed intake temperature. An assist control unit calculates target turbine power based on the target airflow rate and the target boost pressure calculated by the torque base control unit and calculates actual turbine power based on exhaust information. Assist power of a motor attached to a turbocharger is calculated based on the power difference between the target turbine power and the actual turbine power.
Owner:DENSO CORP
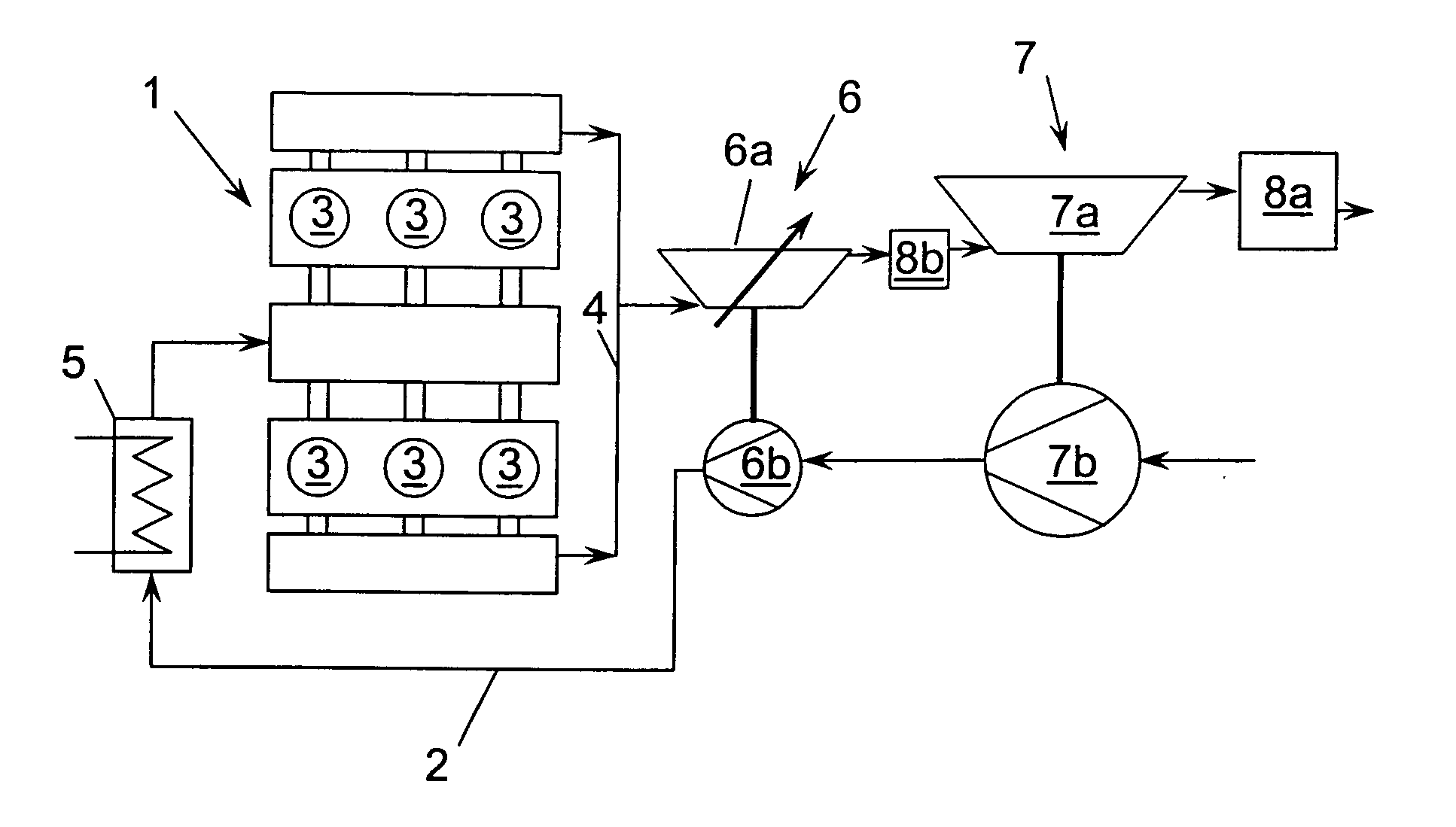
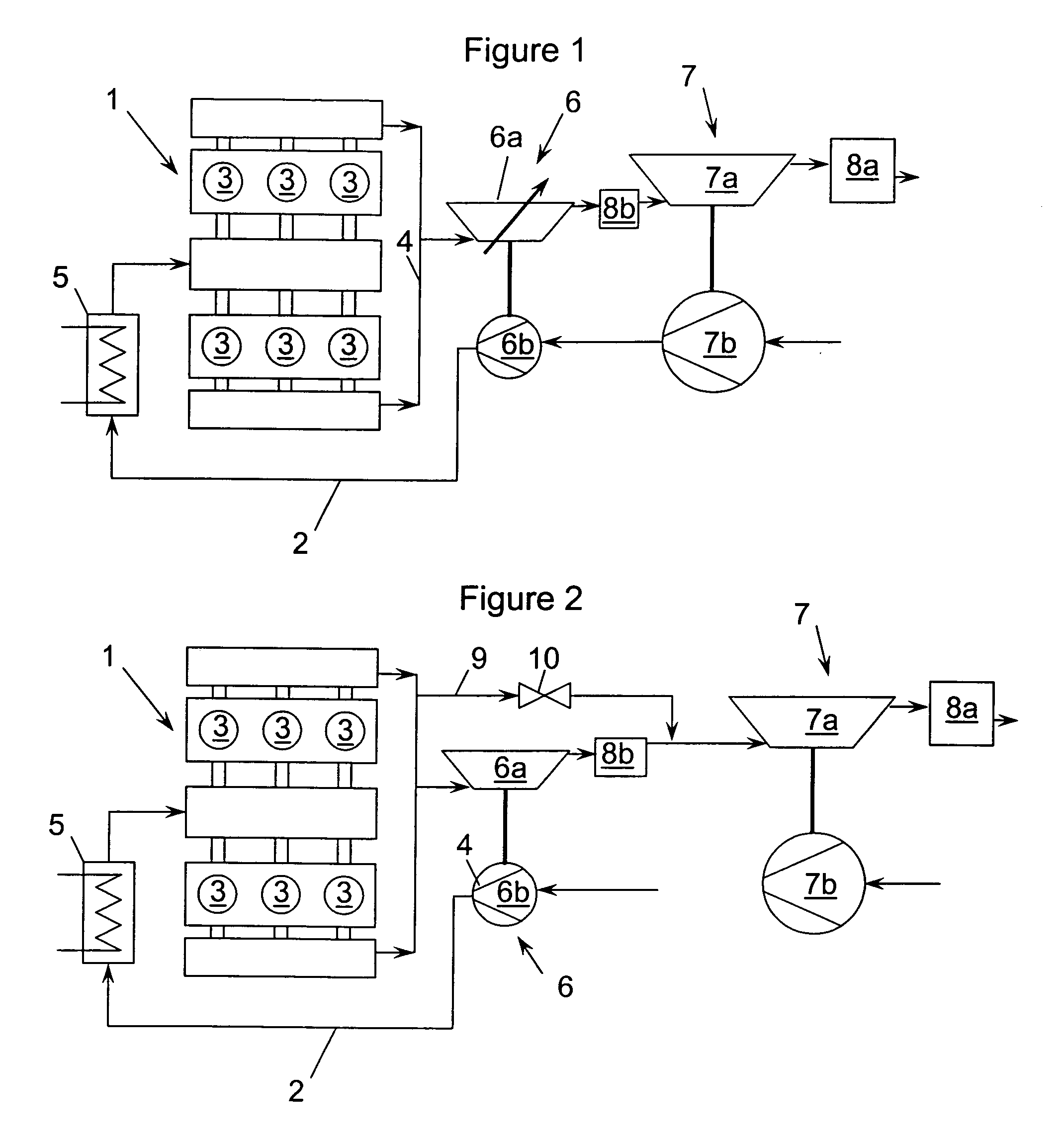
Pressure-charged internal combustion engine
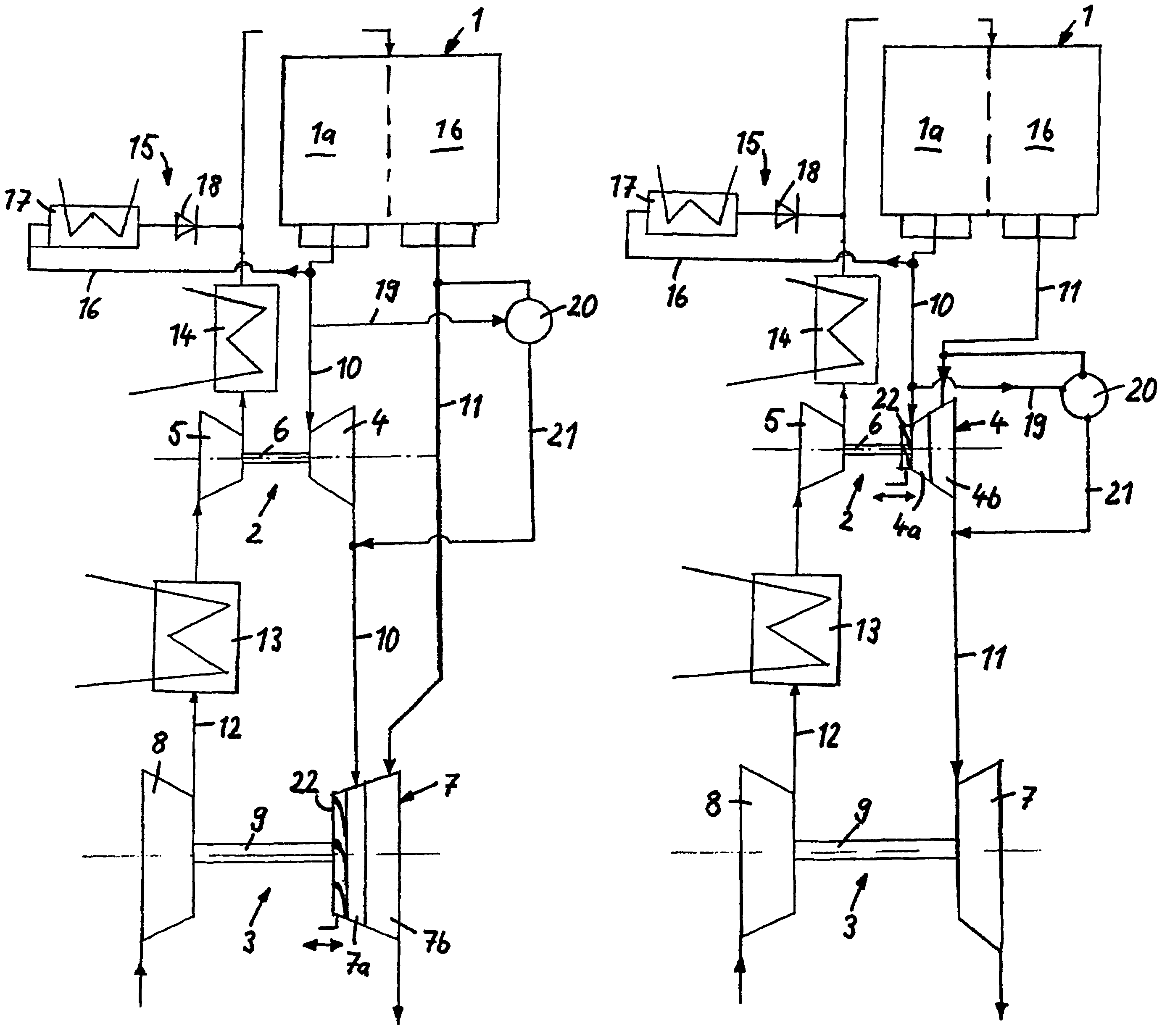
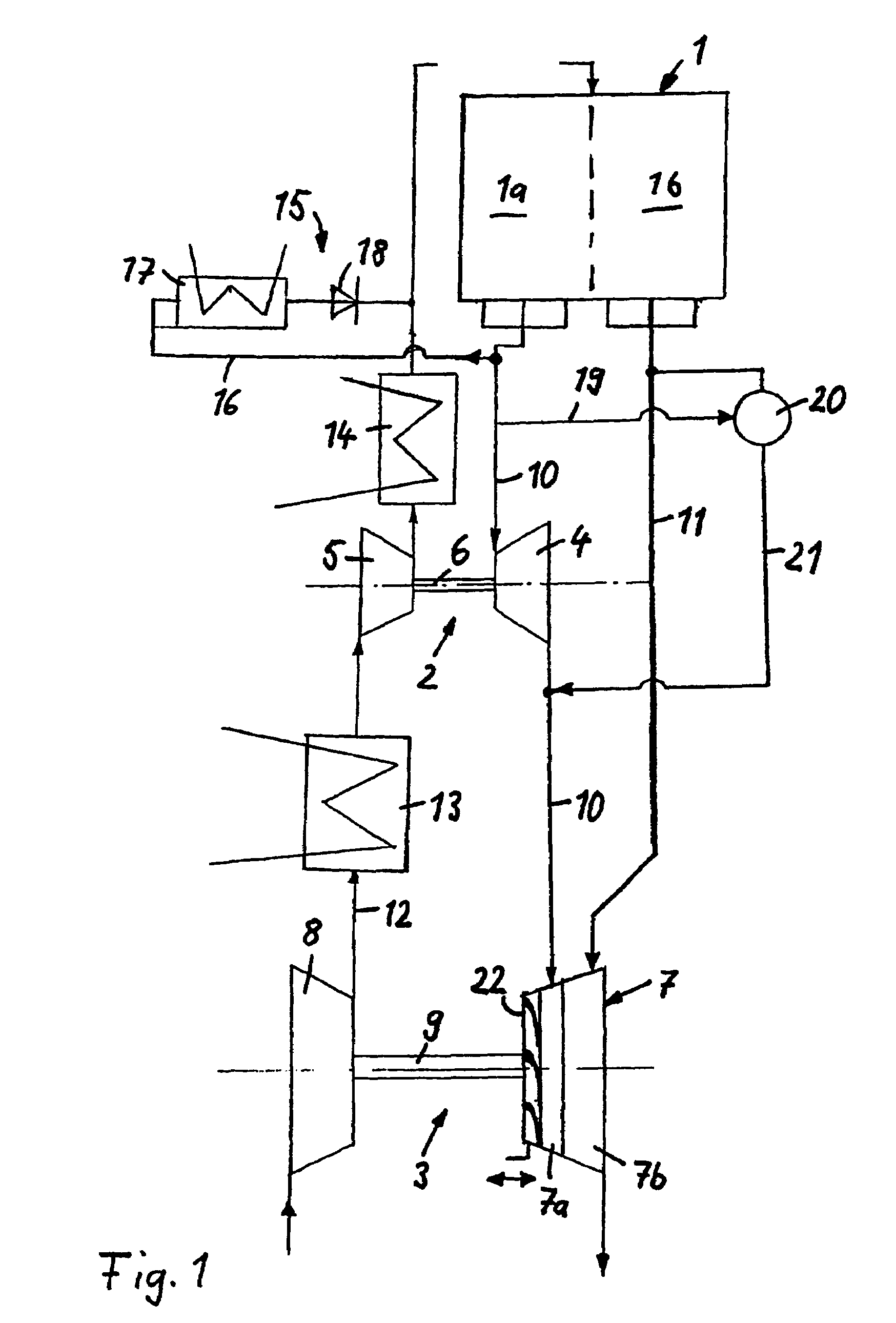
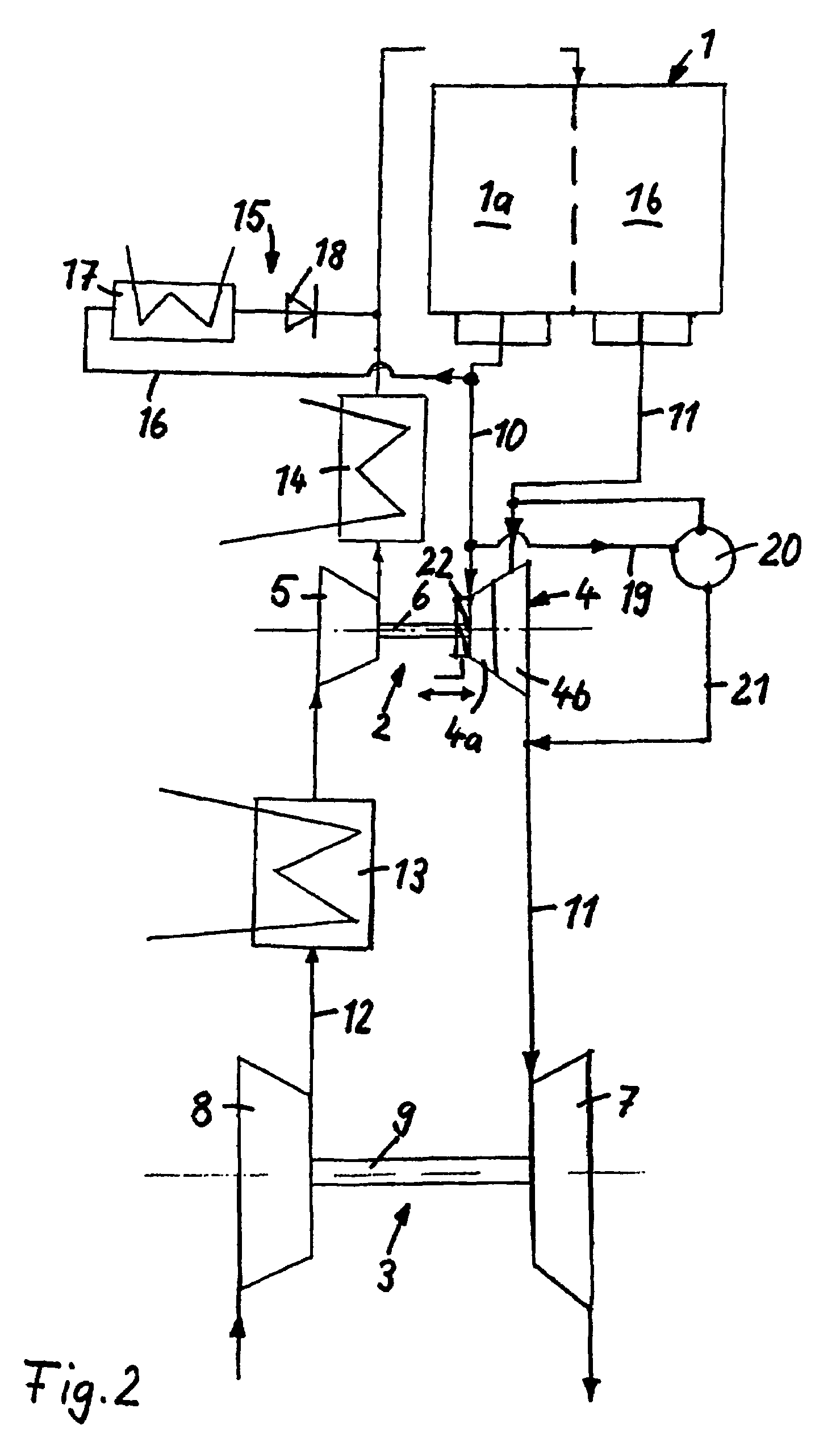
InactiveUS20060059910A1Improve emission characteristicsImproved emission behaviorInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusTurbochargerHigh pressure
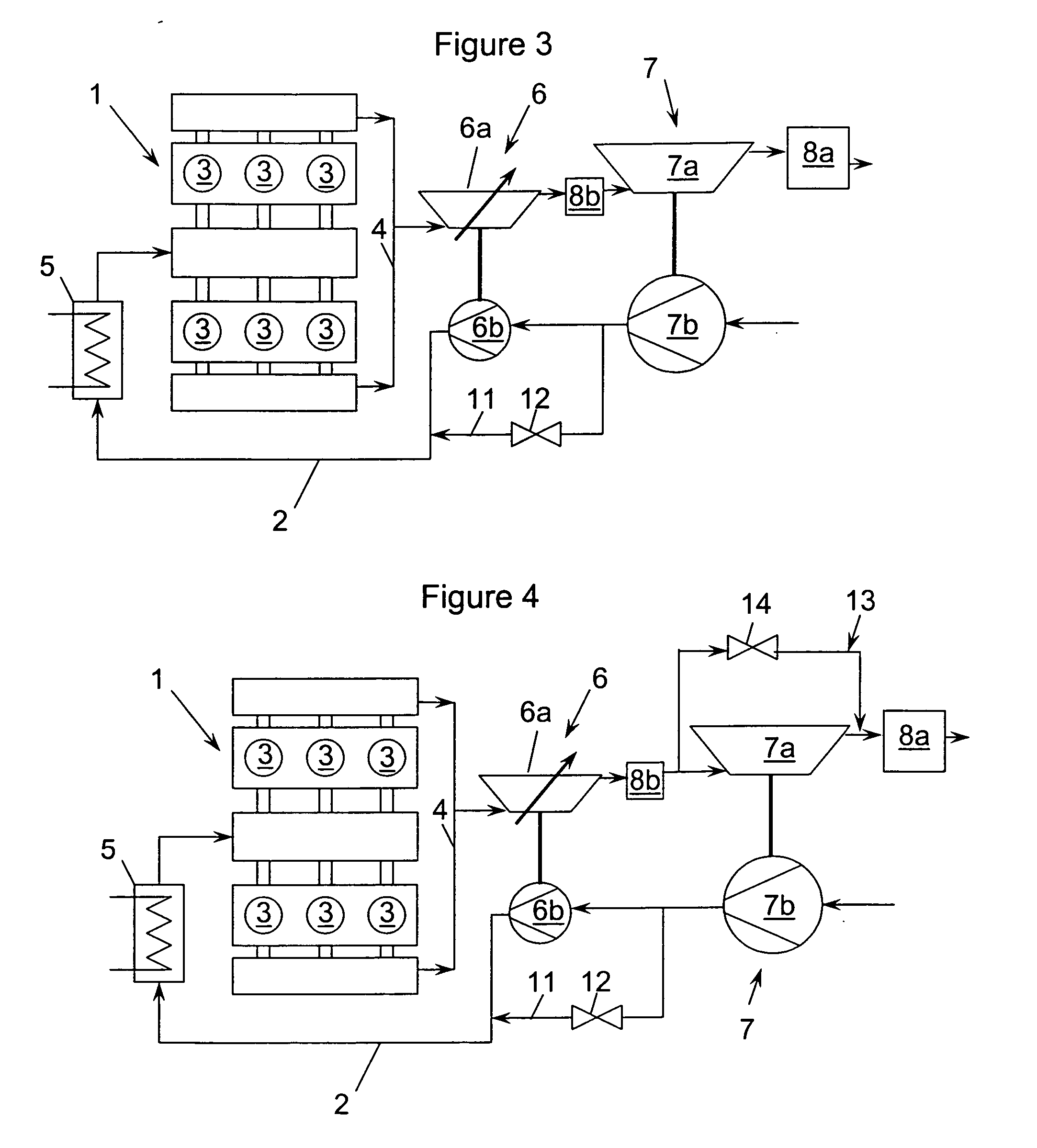
The invention relates to a system and method for improving the emission characteristics of a pressure-charged internal combustion engine. The engine (1) has an intake line (2) and an exhaust-gas line (4) and at least two exhaust-gas turbochargers (6, 7) connected in series. Each turbocharger has a turbine (6a, 7a) in the exhaust-gas line (4) and a compressor (6b, 7b) in the intake line (2). The first exhaust-gas turbocharger (6) serves as high-pressure stage (6). The second exhaust-gas turbocharger (7) serves as low-pressure stage (7). Two exhaust-gas aftertreatment systems are located in between and after the turbines.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
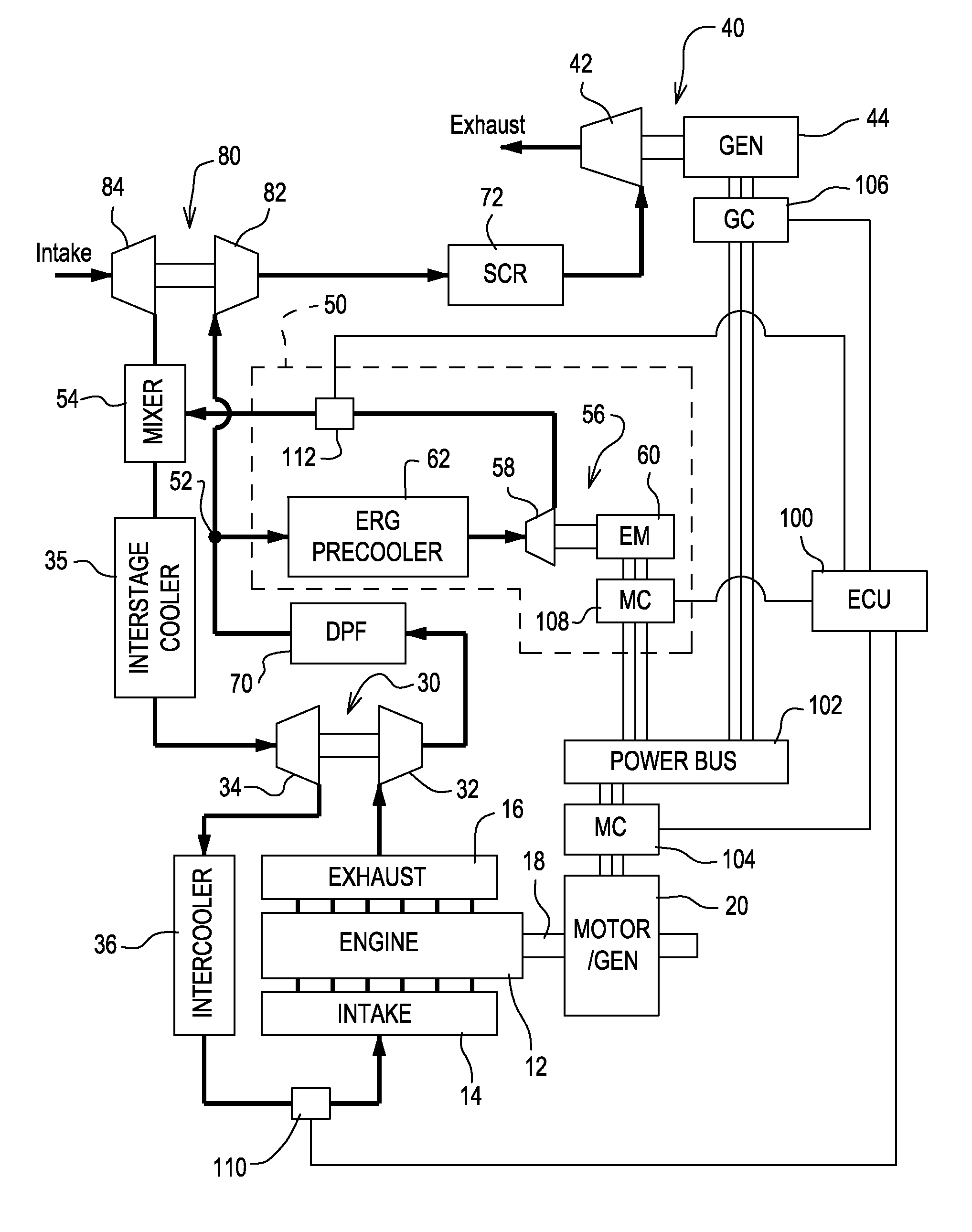
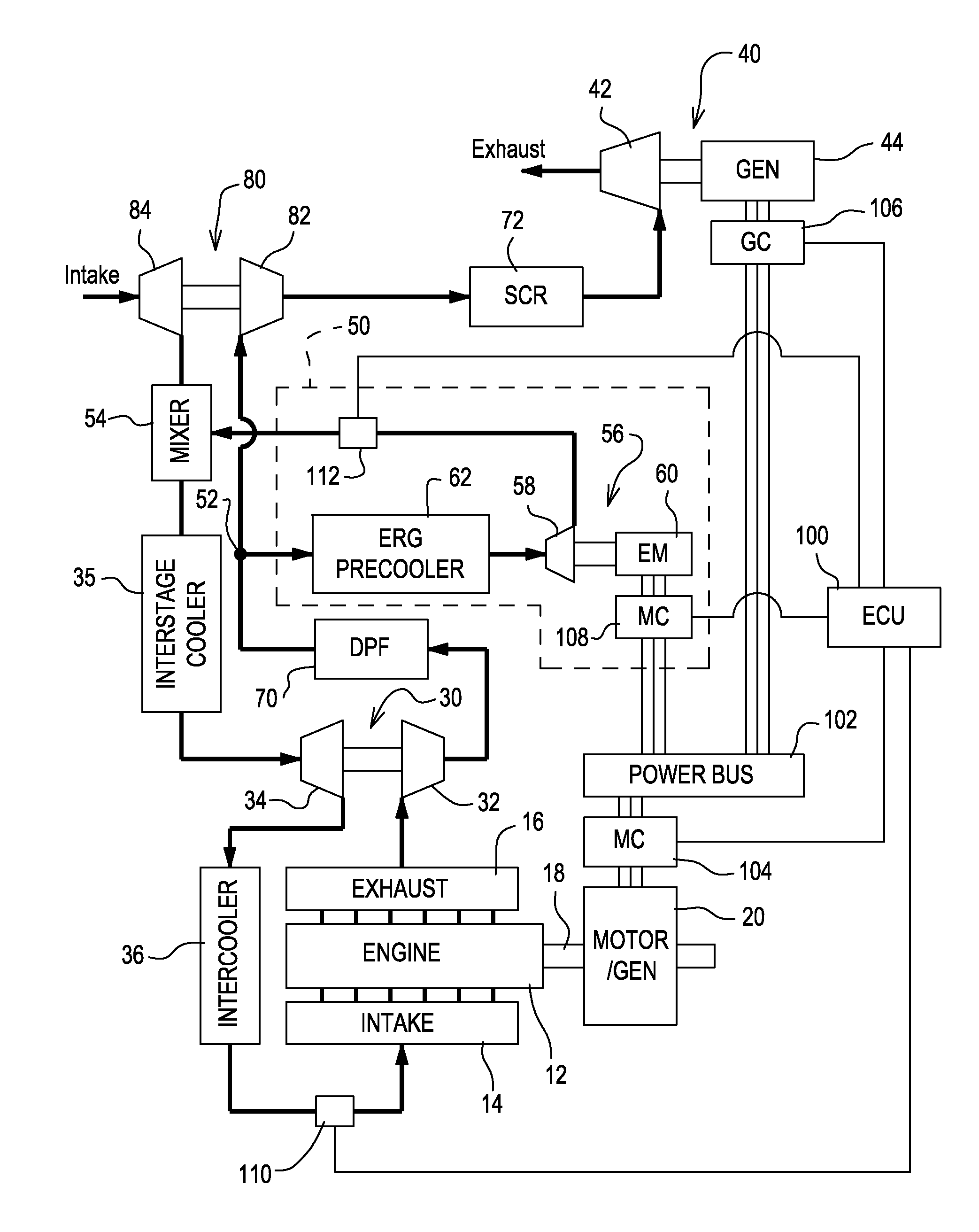
Interstage exhaust gas recirculation system for a dual turbocharged engine having a turbogenerator system
InactiveUS20110094485A1Improve performanceLow costInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusLoop controlTurbocharger
An internal combustion engine defined as having an engine block for internal combustion, a high-pressure turbocharger for delivering pressurized intake air to the engine block, a low-pressure turbocharger for delivering pressurized intake air to the high-pressure turbocharger, a turbogenerator for recovering heat energy from the exhaust gas downstream of the low-pressure turbocharger to generate electricity, and an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system comprising an EGR-pump drawing exhaust gas from an EGR inlet located between the low-pressure and high-pressure turbocharger turbines, wherein the EGR-pump controllably delivers exhaust gas to an EGR mixer in the pressurized intake air stream at a location between the low-pressure and high-pressure turbocharger compressors. An electronic control unit (ECU) is adapted to command the EGR-pump to deliver a desired EGR flow-rate to the engine block based on look-up tables and either open-loop and / or closed-loop control algorithms.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Turbocharged engine cylinder head internal cooling
InactiveUS20090126659A1Reduce metal temperatureReduce stepsInternal combustion piston enginesAir coolingCylinder headTurbocharger
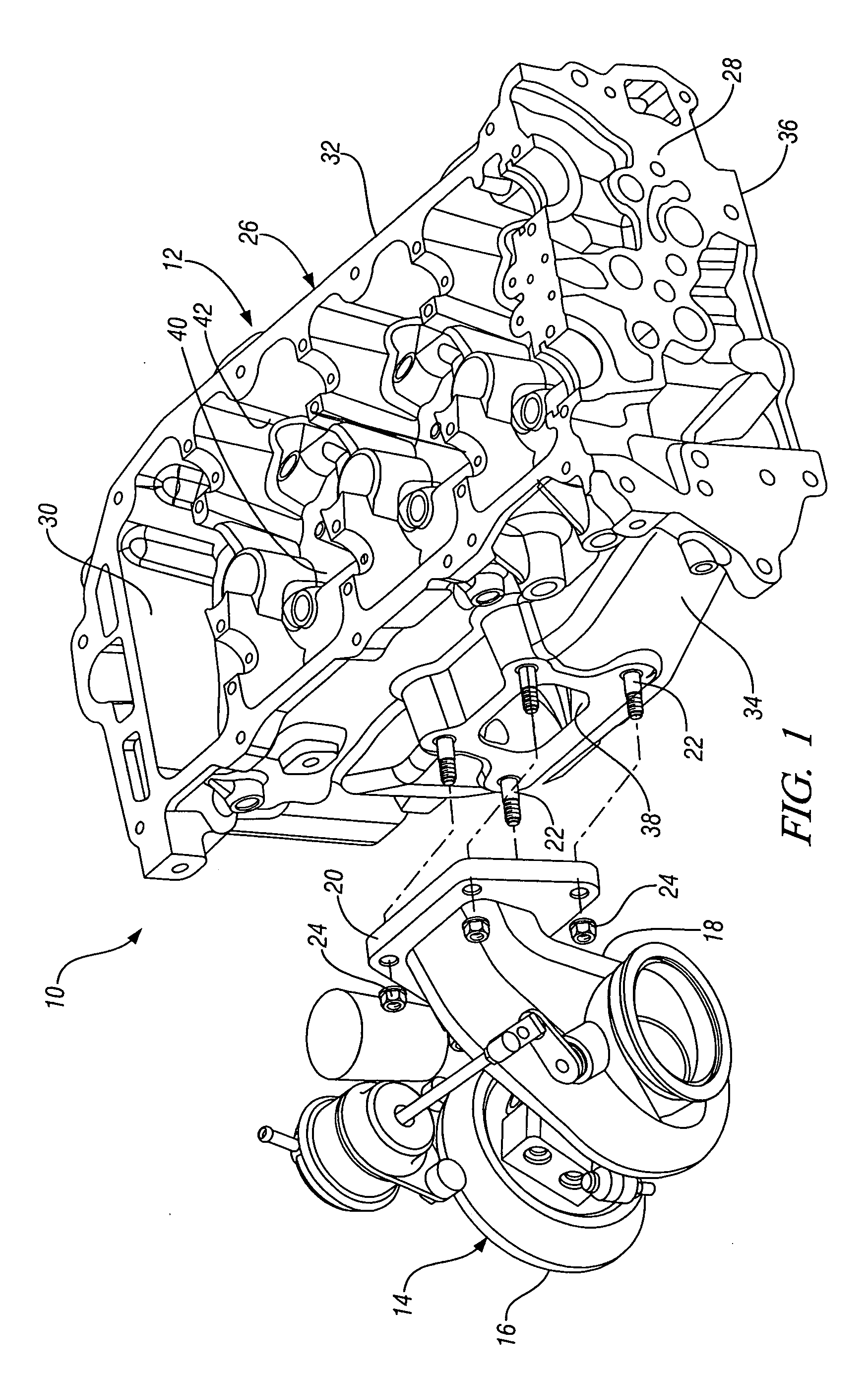
An engine cylinder head has an exhaust manifold cast in the cylinder head. A turbocharger with a turbine body is adapted to mount directly to an exhaust outlet mounting face of the exhaust manifold. A dual level water jacket within the cylinder head has separate coolant feeds for upper and lower cooling jackets. The cooling jackets extend above and below the exhaust outlet and are connected inward of the exhaust mounting face to reduce metal temperatures of the mounting face below those of the turbocharger exhaust inlet flange. Separate cores for the upper and lower jackets are connected at coolant inlet and outlet locations at opposite ends. Intermediate core print connectors form controlled flow passages between the upper and lower jackets and exhaust ports in the cylinder head and integrated manifold. The improved cooling in these areas lowers operating temperatures in the cylinder head and obviates the need for a separate exhaust manifold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for actively turbocharging an engine
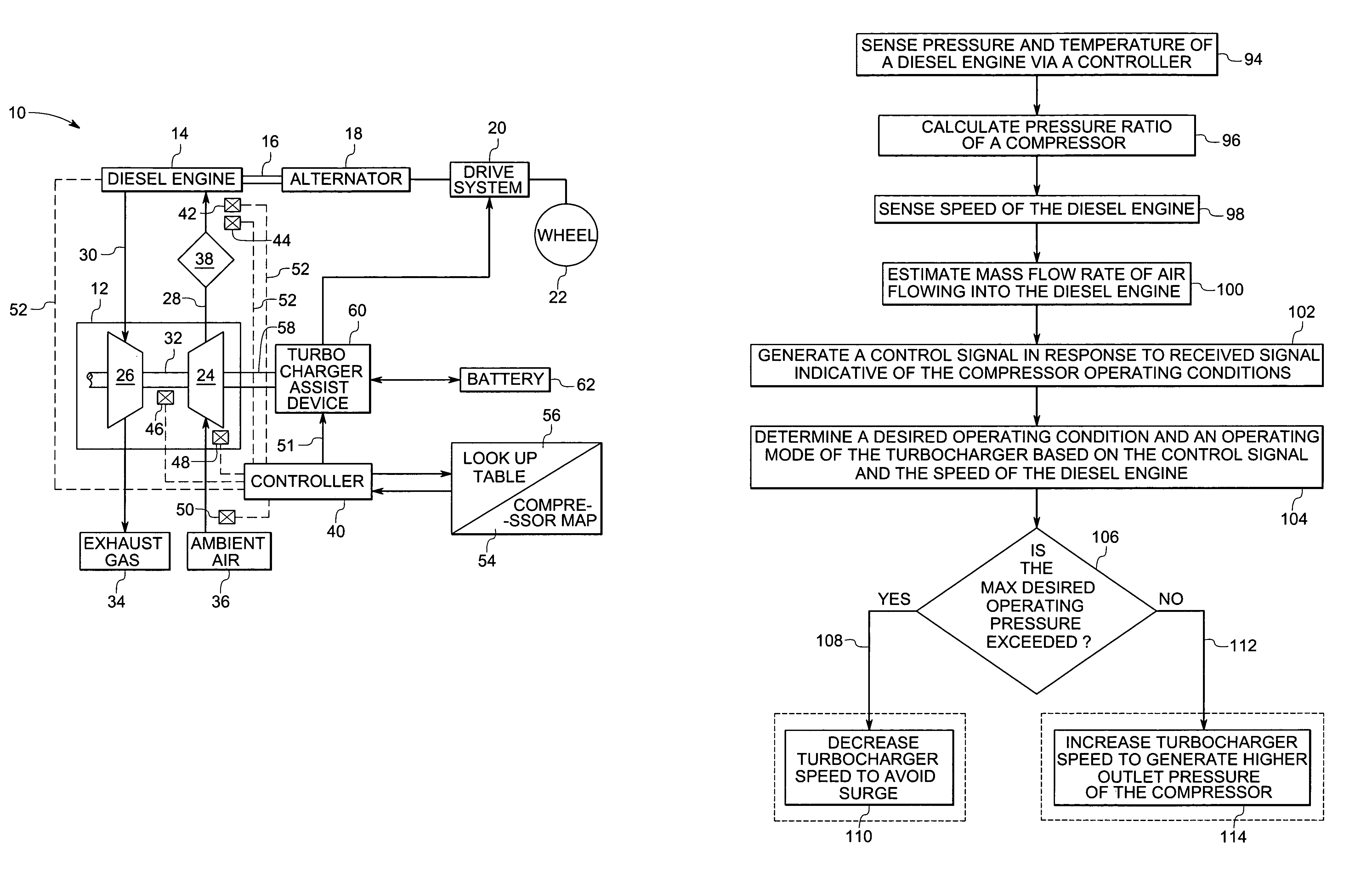
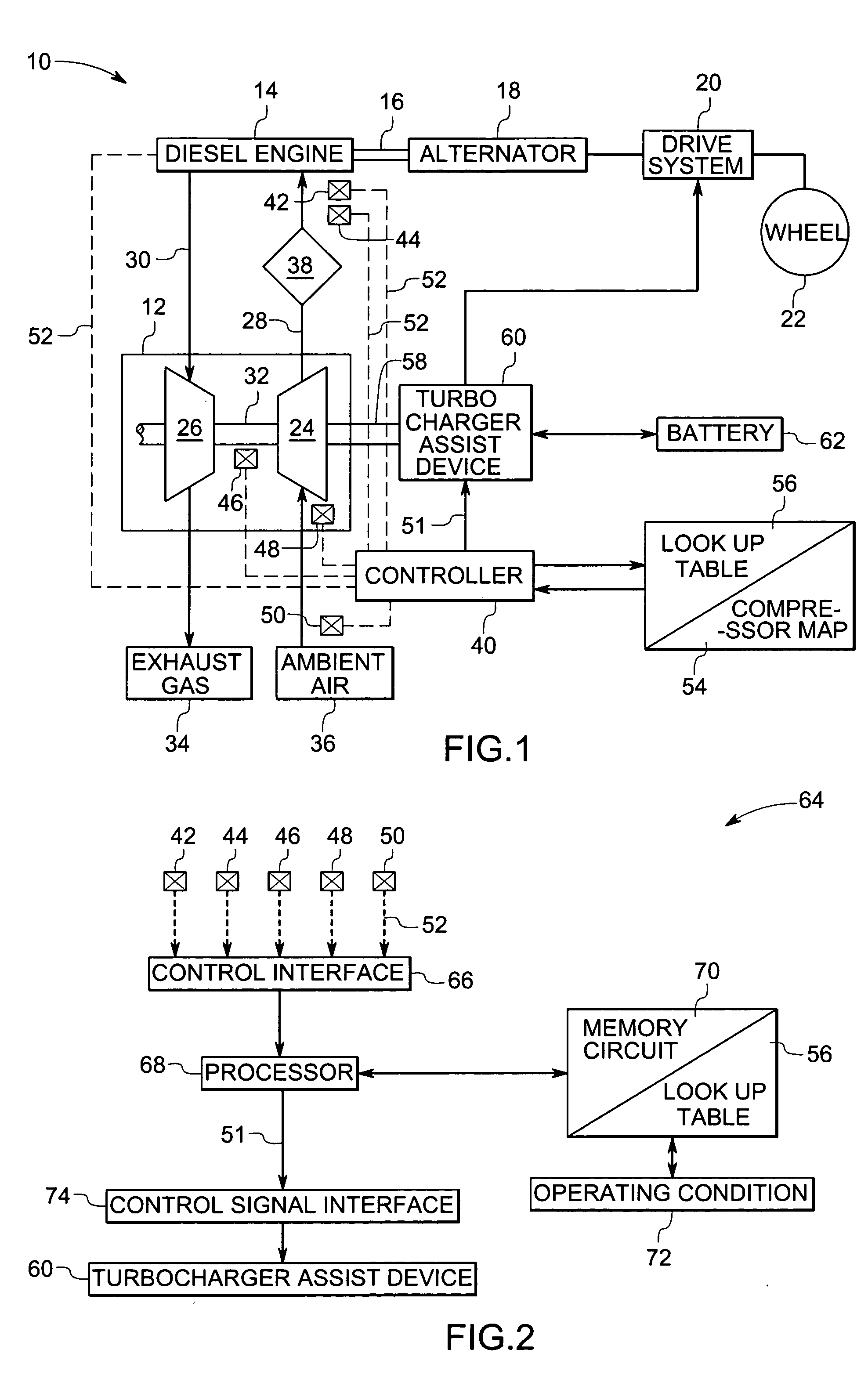
ActiveUS7137253B2Control pressureAvoidance of compressor surgeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerEngineering
A technique comprising an apparatus for monitoring at least one operating parameter indicative of an operating condition of a diesel engine and controlling a turbocharger assist device to maintain desired operating conditions of the diesel engine equipped with a turbocharger.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com