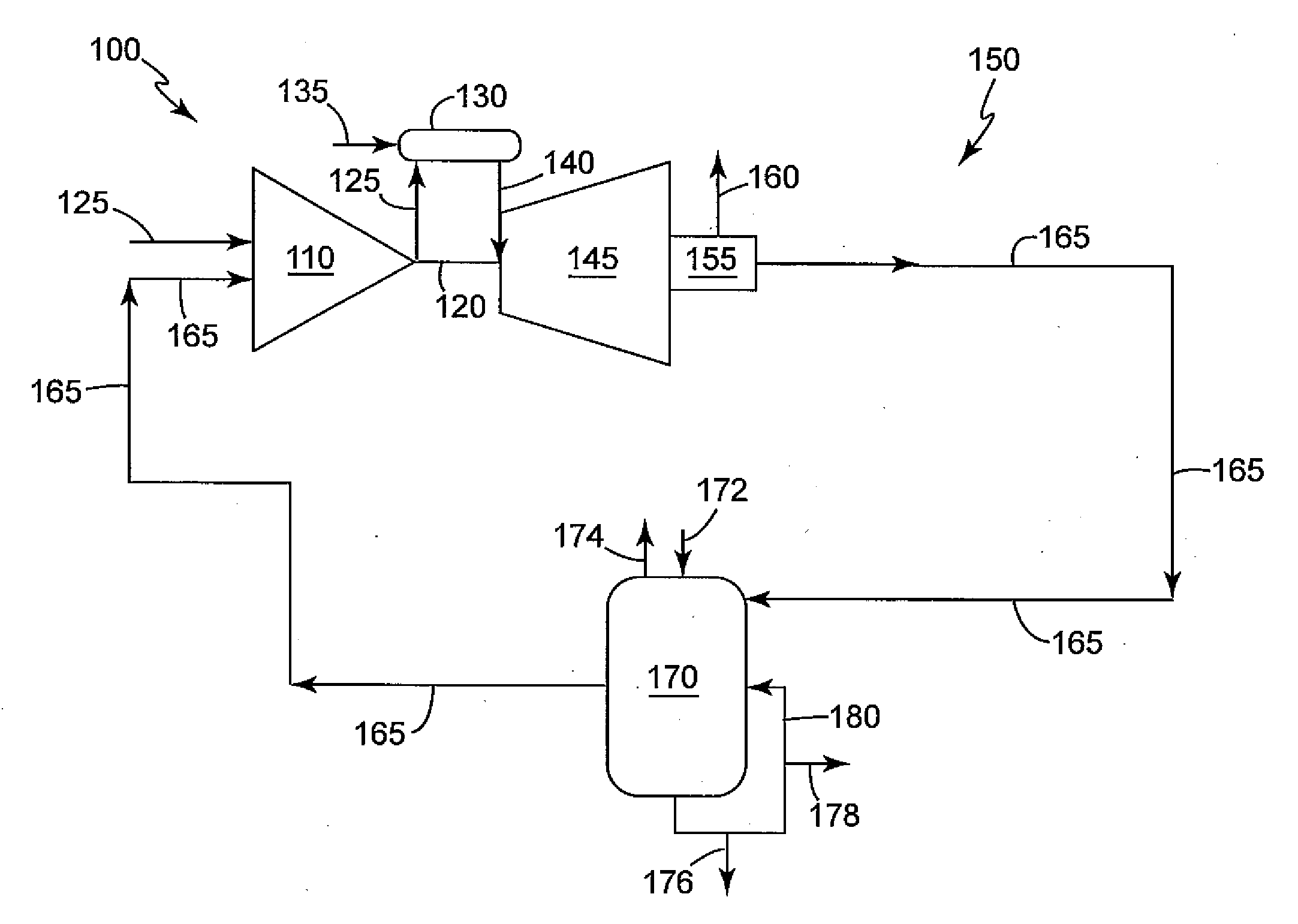
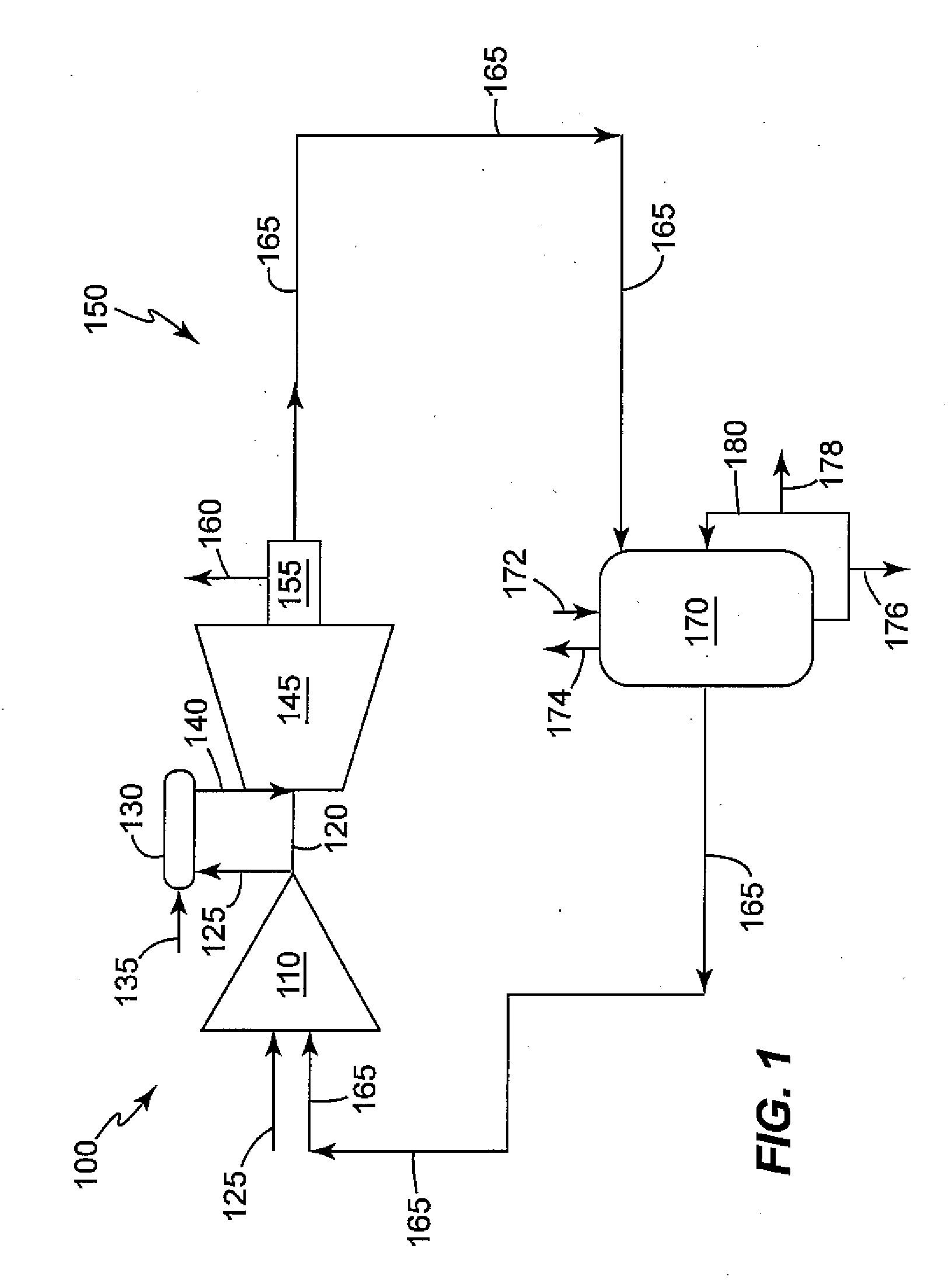
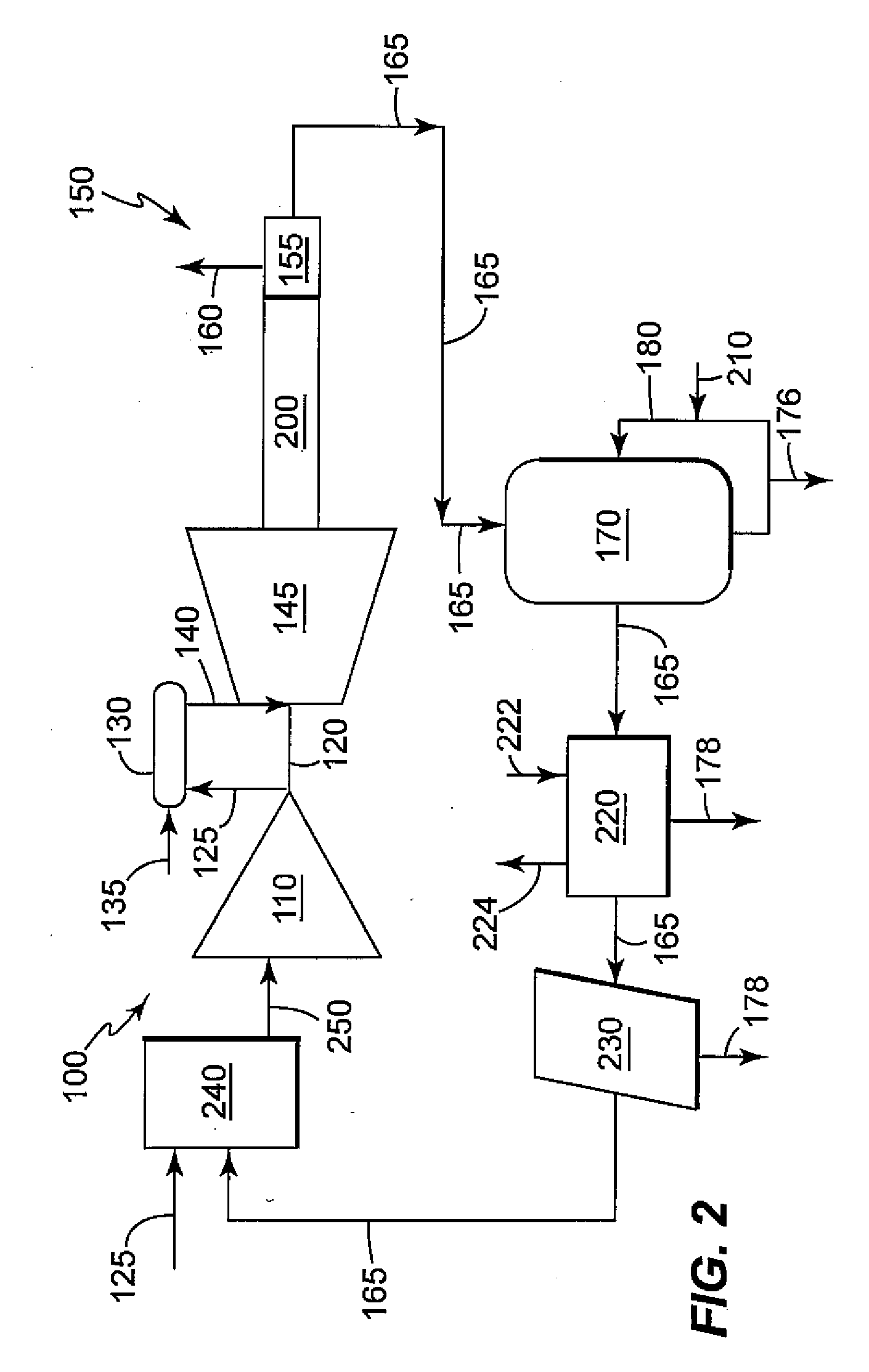
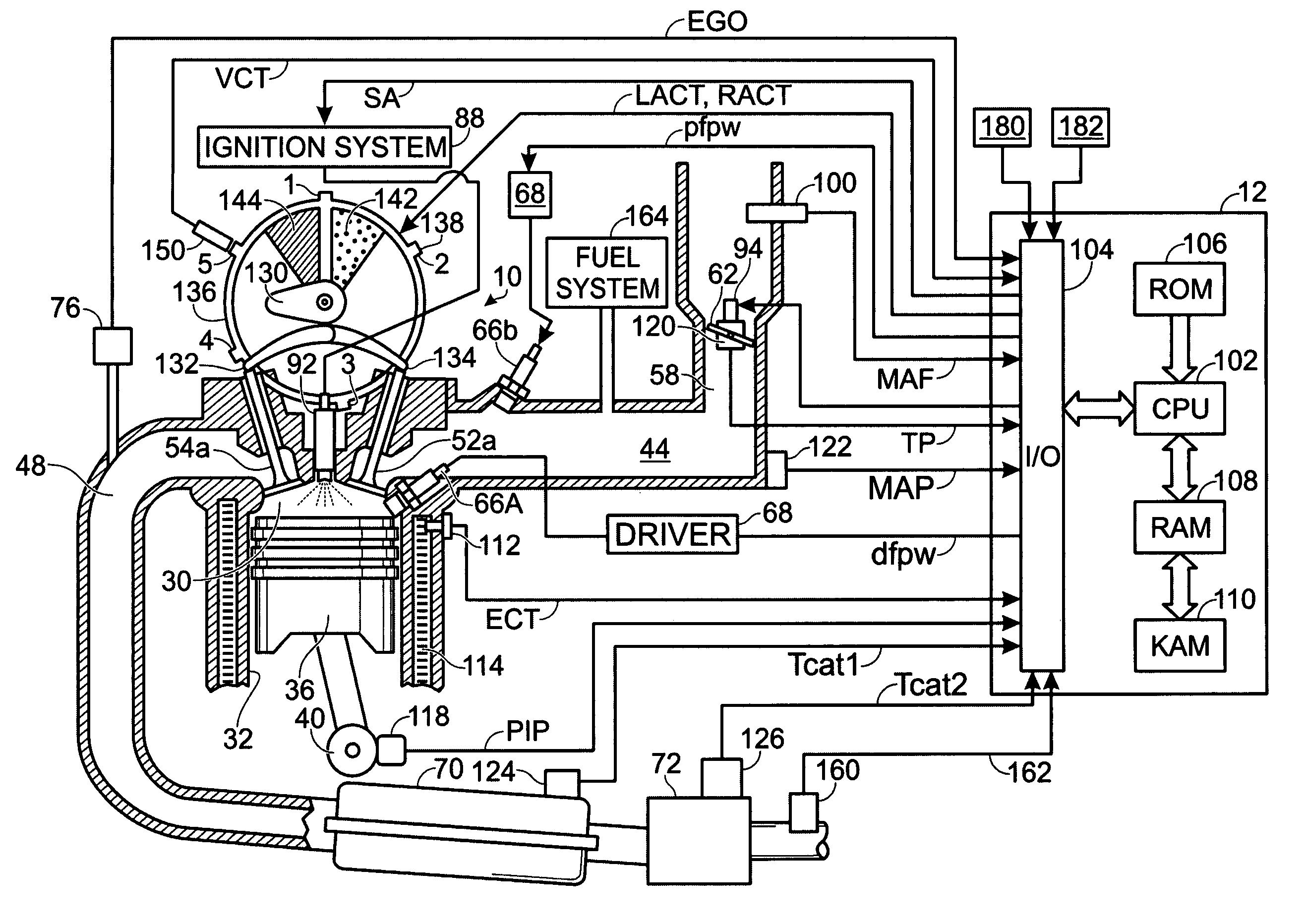
Patents
Literature
12583results about "Non-fuel substance addition to fuel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
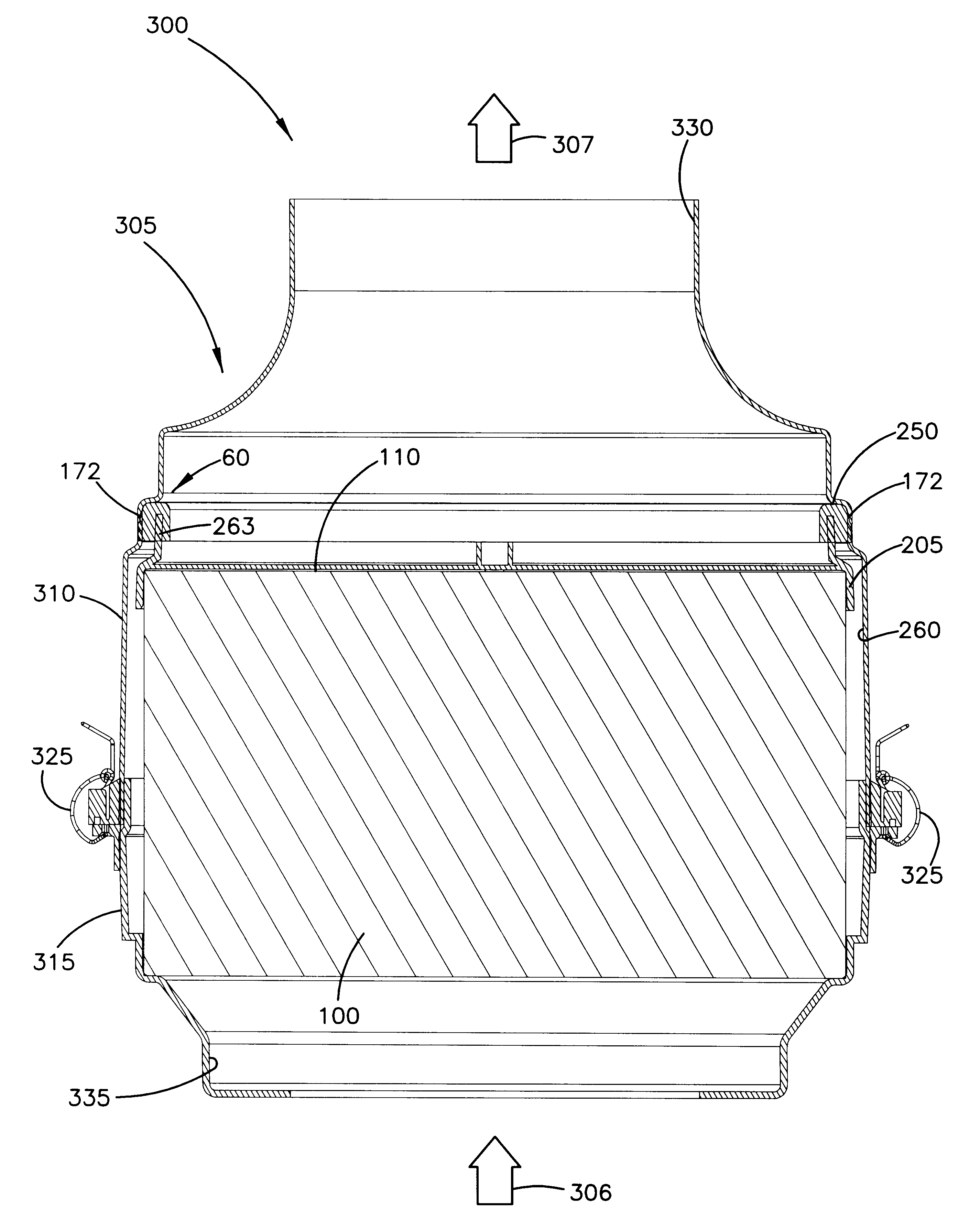
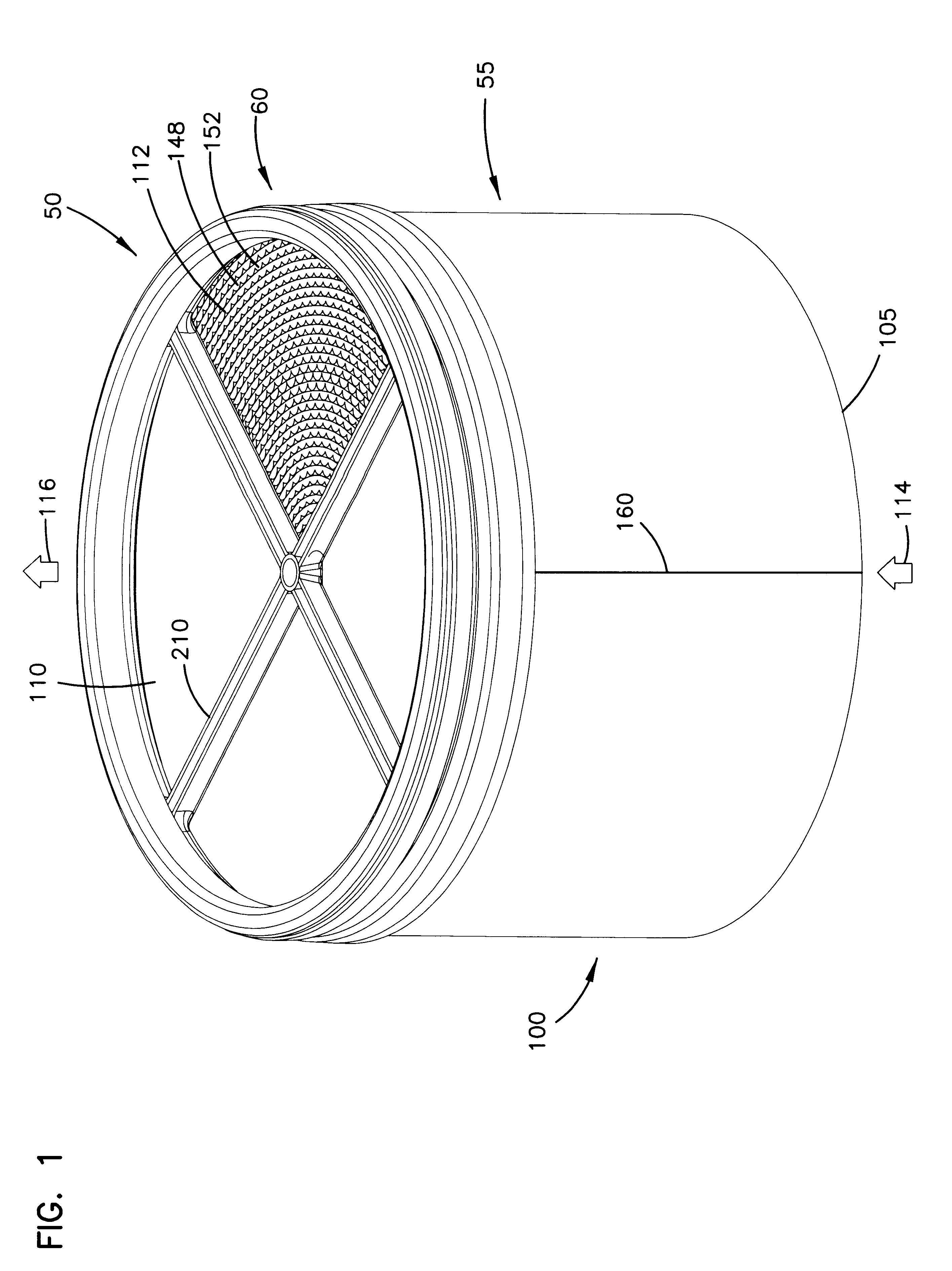
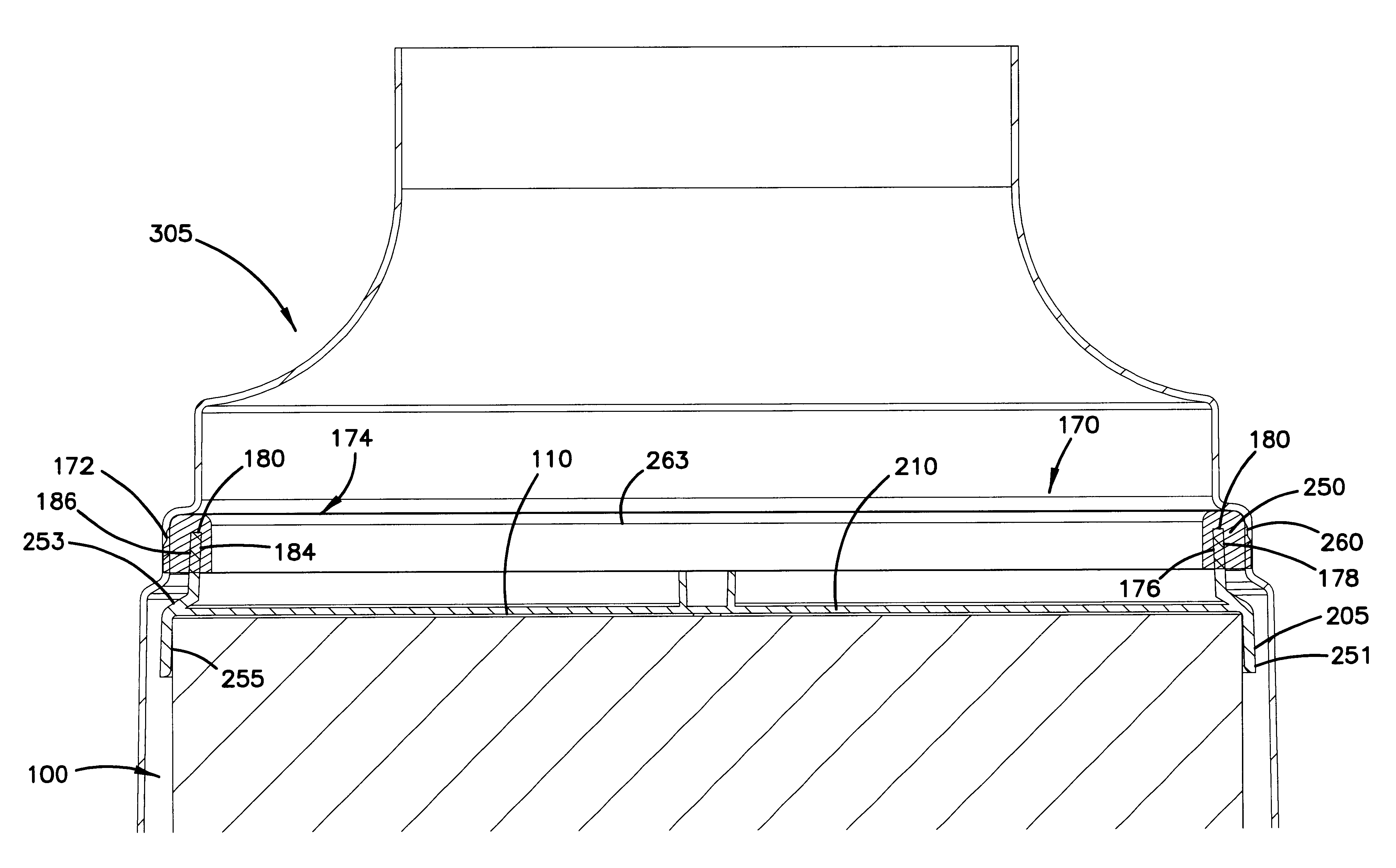
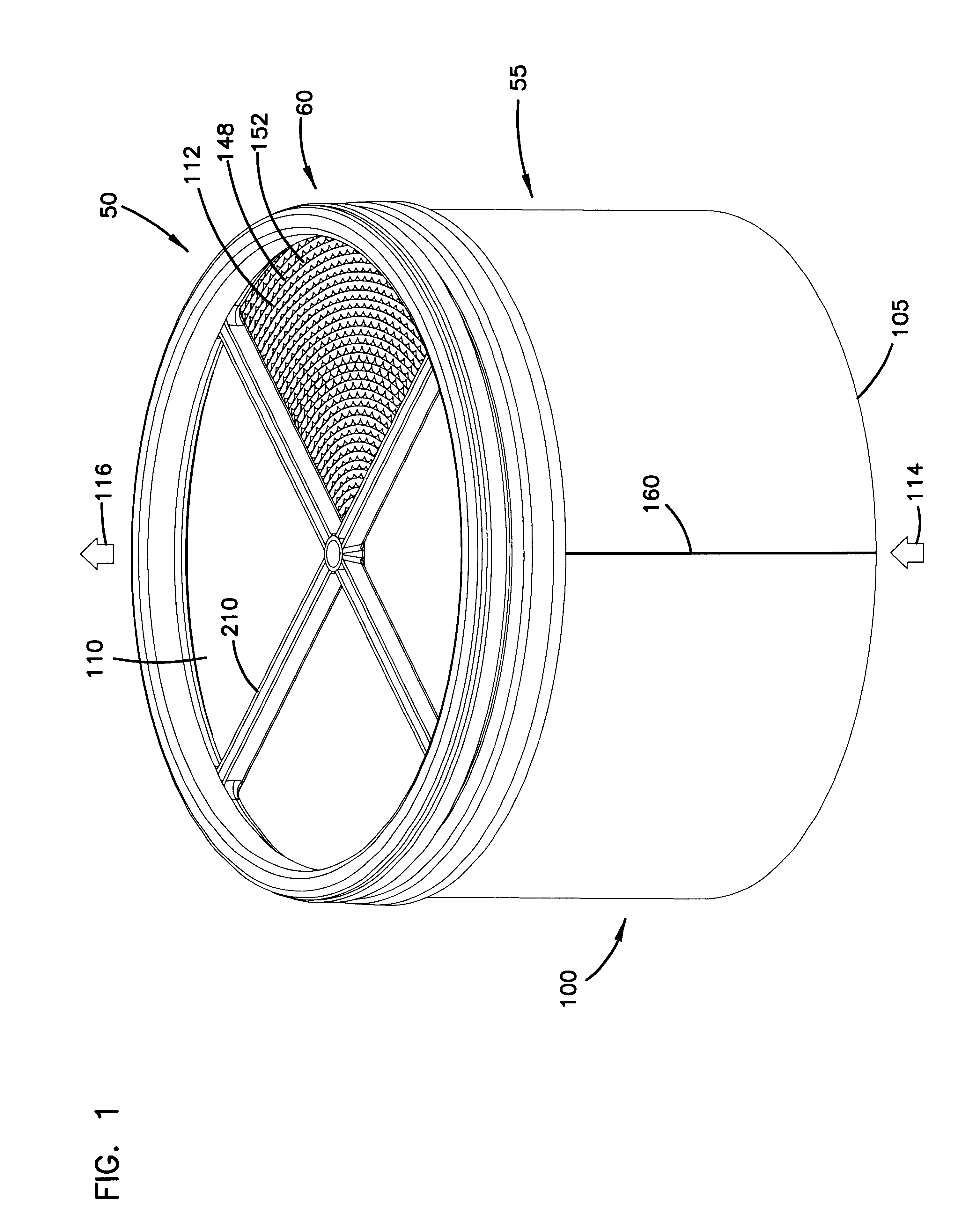
Filter arrangement; sealing system; and methods
InactiveUS6190432B1Prevent crashAvoid passingHuman health protectionCombination devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A filter pack includes a filter construction and a sealing system for sealing the construction within a duct or housing. The filter construction has first and second opposite flow faces and is configured for a straight-through flow. The sealing system includes a frame construction and a compressible seal member. The compressible seal member is molded around a portion of the frame construction. The compressible seal member is sufficiently compressible to form a radial seal between and against the frame construction and a surface of a housing when the filter pack is inserted within the housing.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Filter arrangement; sealing system; and methods
InactiveUS6350291B1Avoid passingObstruct passageHuman health protectionCombination devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A filter pack includes a filter construction and a sealing system for sealing the construction within a duct or housing. The filter construction has first and second opposite flow faces and is configured for a straight-through flow. The sealing system includes a frame construction and a compressible seal member. The compressible seal member is molded around a portion of the frame construction. The compressible seal member is sufficiently compressible to form a radial seal between and against the frame construction and a surface of a housing when the filter pack is inserted within the housing.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Filter arrangement; sealing system; and methods
InactiveUS6610117B2Avoid passingObstruct passageCombination devicesGas treatmentMechanical engineeringStructural engineering
A filter pack includes a filter construction and a sealing system for sealing the construction within a duct or housing. The filter construction has first and second opposite flow faces and is configured for a straight-through flow. The sealing system includes a frame construction and a compressible seal member. The compressible seal member is molded around a portion of the frame construction. The compressible seal member is sufficiently compressible to form a radial seal between and against the frame construction and a surface of a housing when the filter pack is inserted within the housing.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
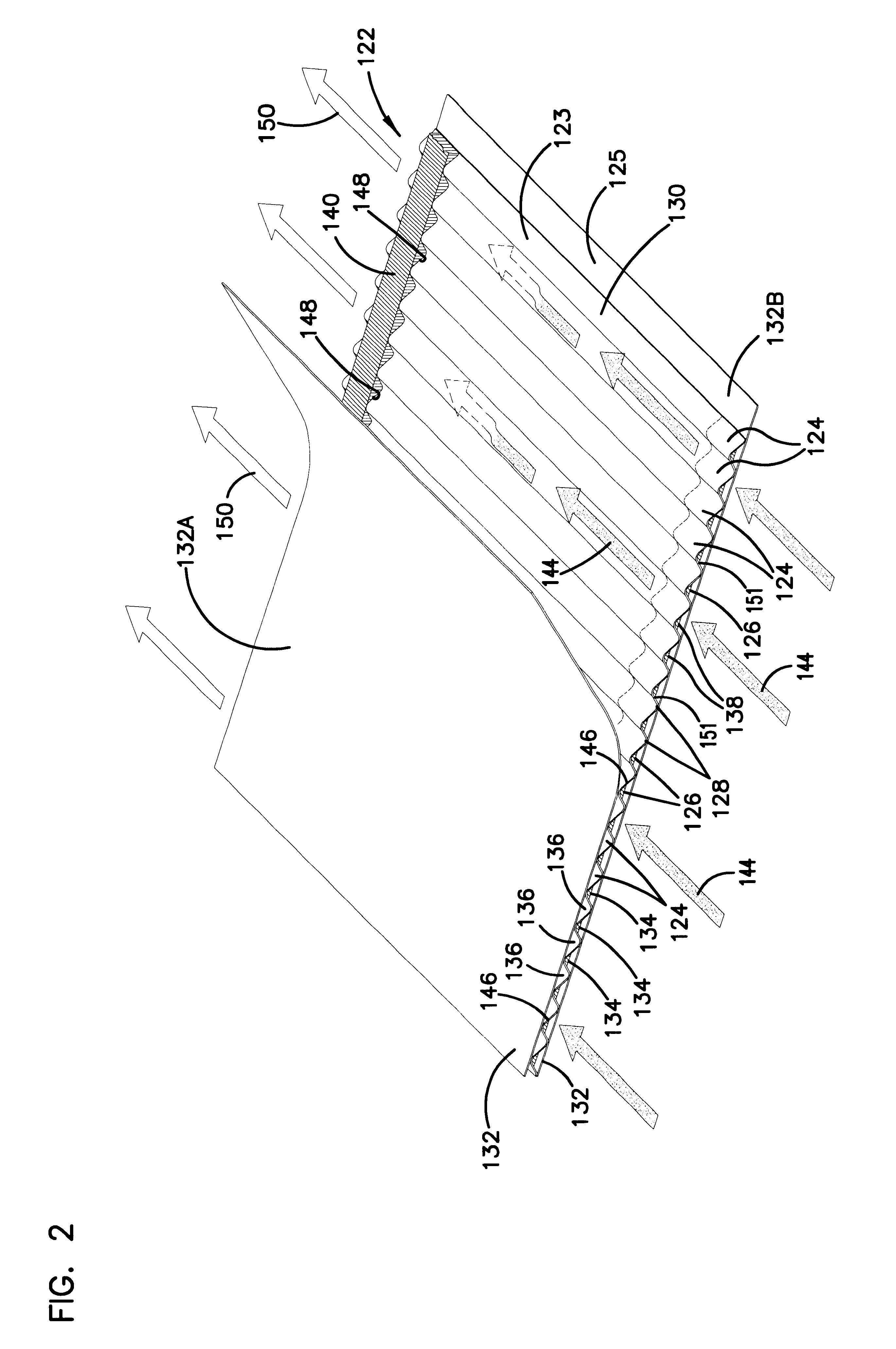
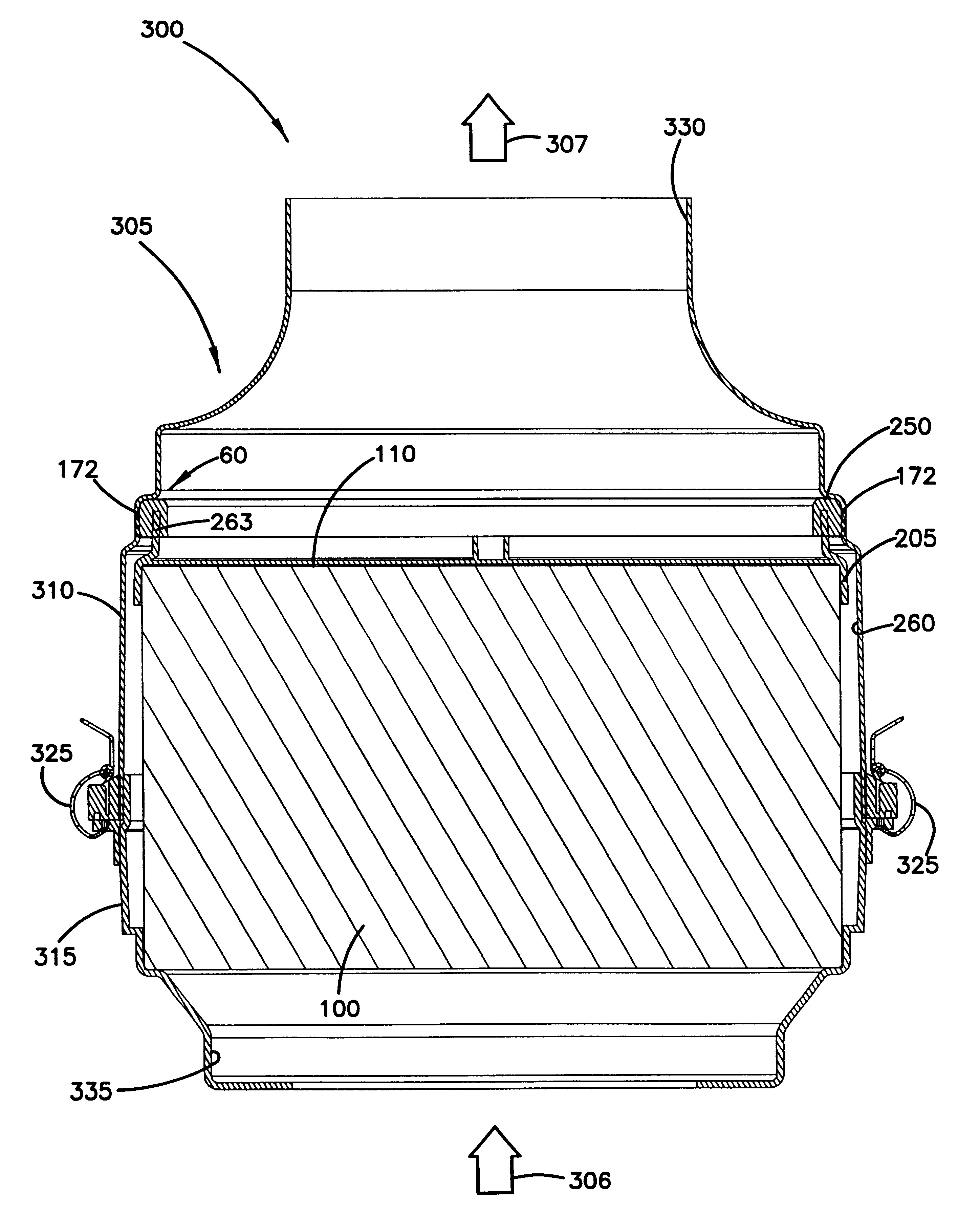
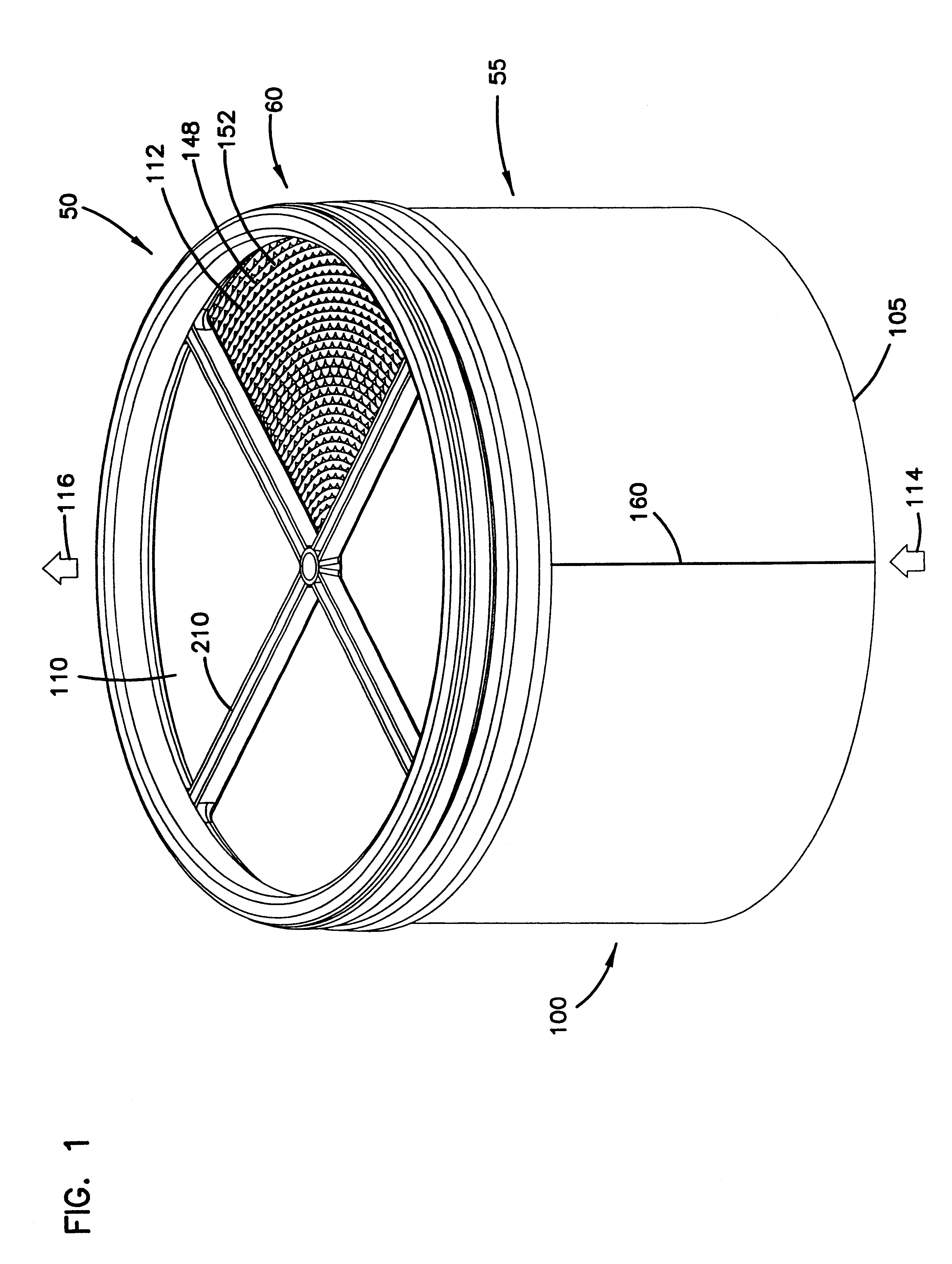
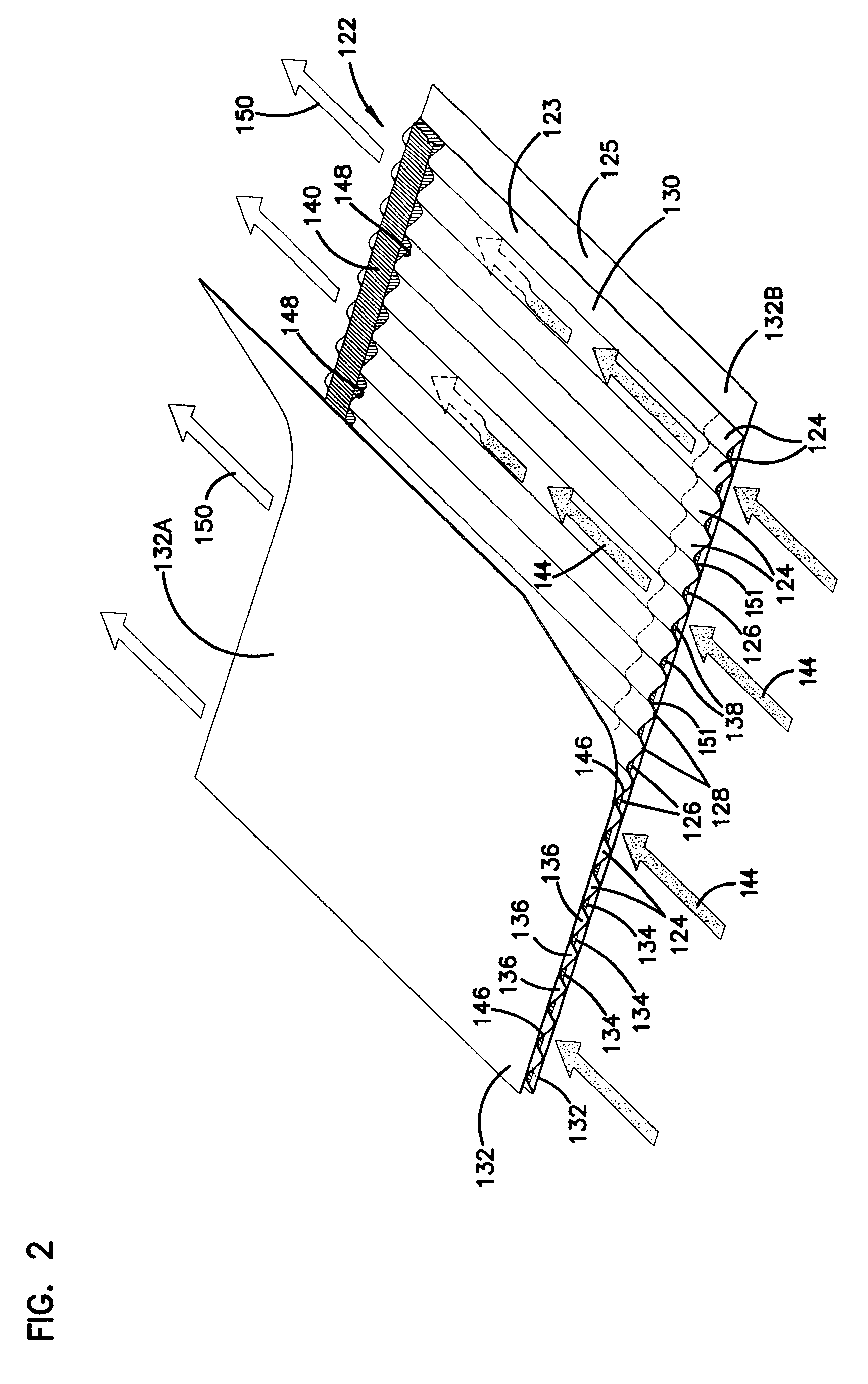
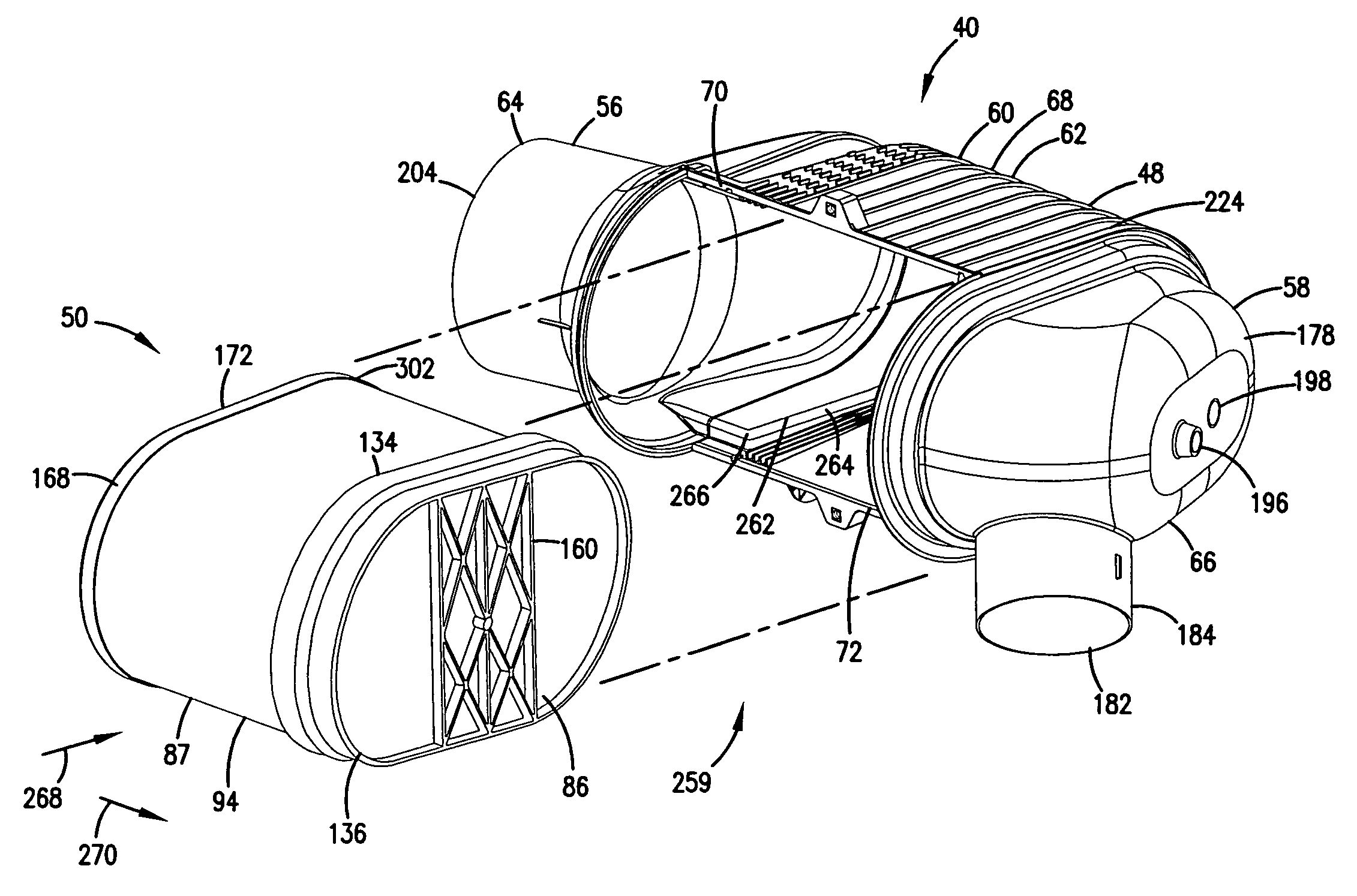
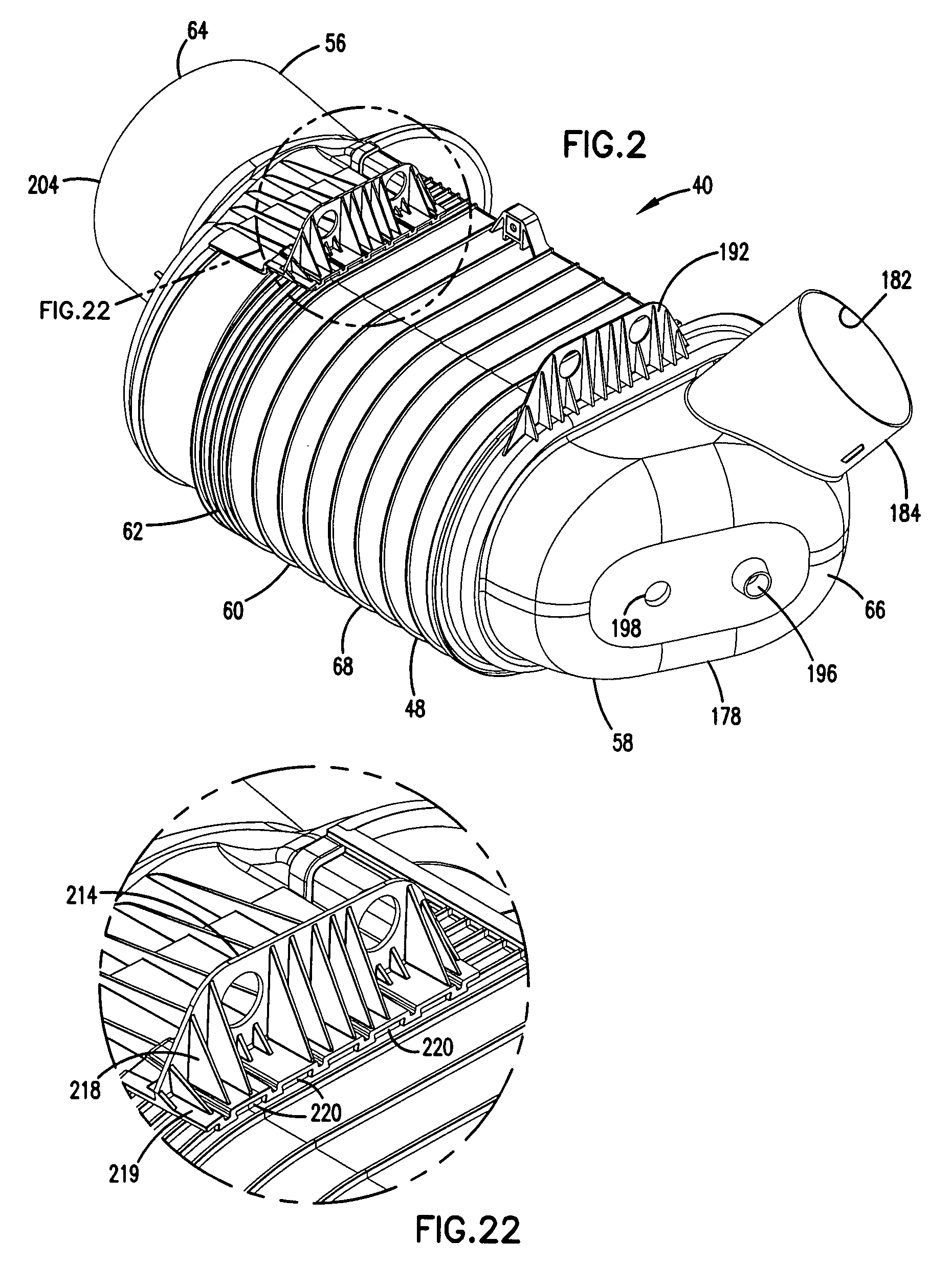
Air filter having fluted filter media
An air cleaner (40) includes a housing (48) and an access cover. The internal volume of the housing (48) can be reached through an opening (70) in a side wall of the housing. A filter element (50) having fluted filter media is removable and replaceable from the air cleaner (40). The housing is constructed and arranged to cam the element (50) into sealing engagement with the housing (48). The access cover includes structure to help support and ensure proper seating of the filter element within the housing. A method of installing the filter element in the air cleaner includes sliding a portion of the filter element against a slide surface in the housing. A method of servicing an air cleaner includes tilting the filter element against a tilt surface in the housing to release a seal between the filter element and the housing. The filter element can have a handle to assist in servicing of the air cleaner. The housing can have a window to allow visual inspection of the internal component of the housing and to determine visually whether a filter element is installed therein.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
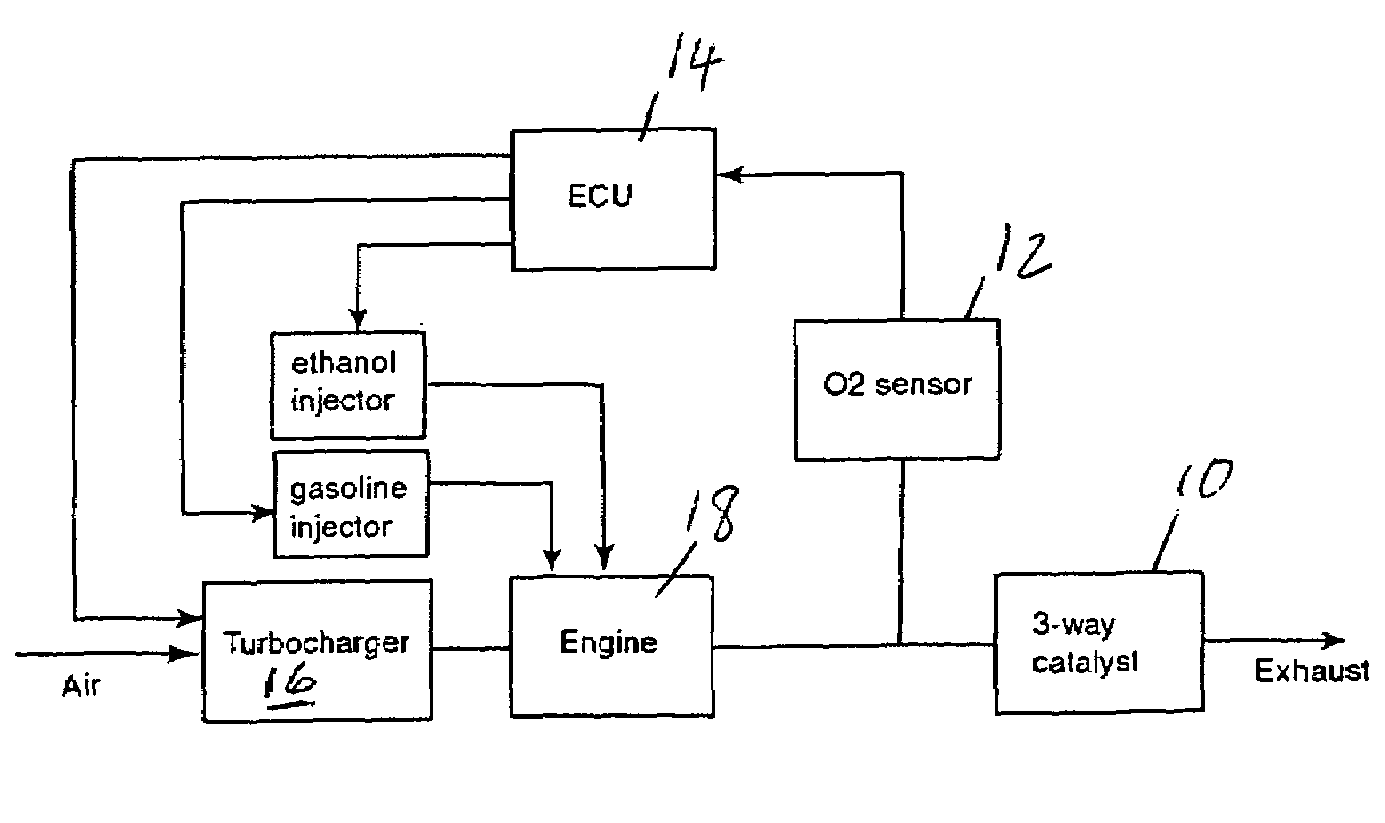
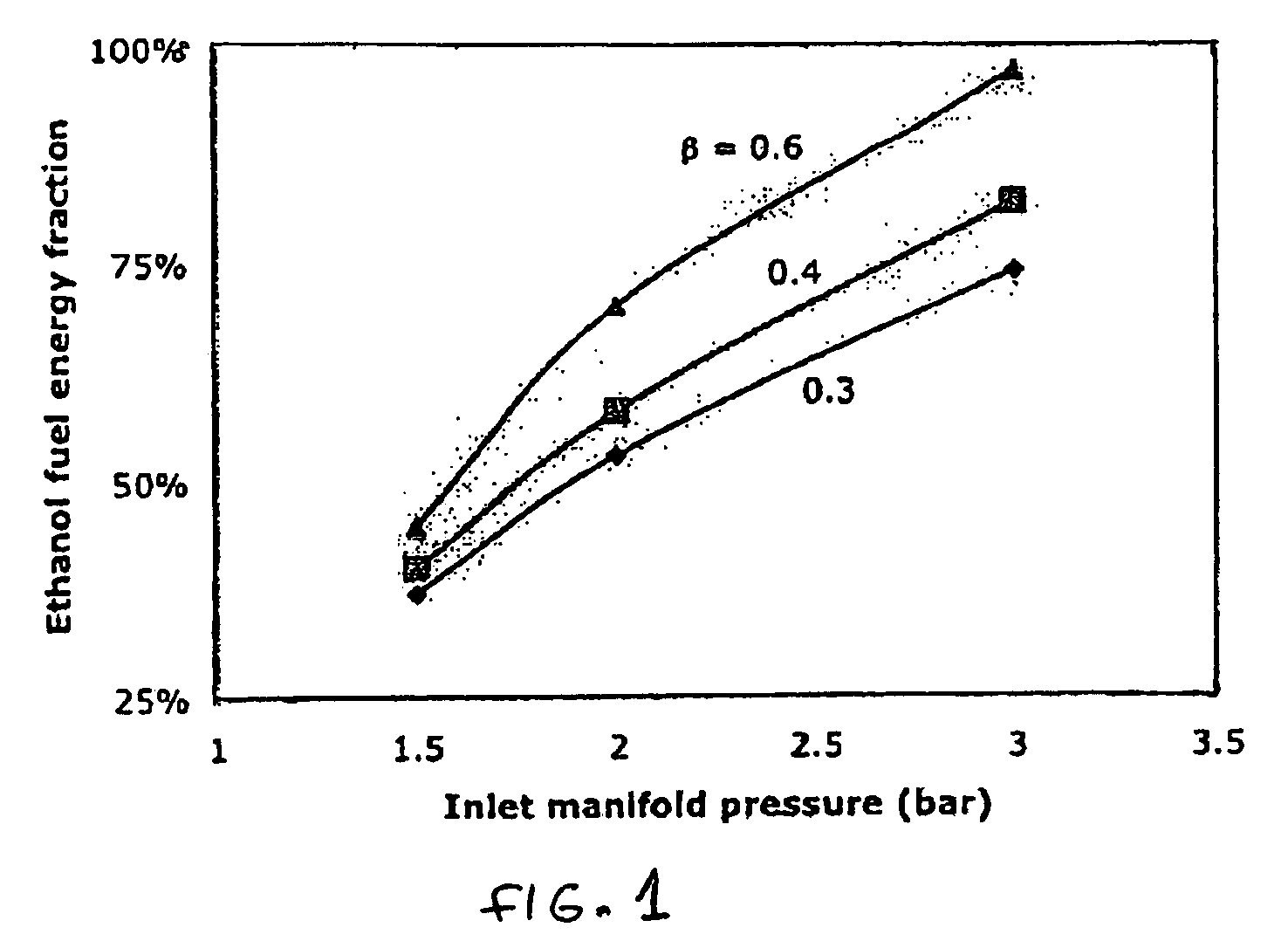
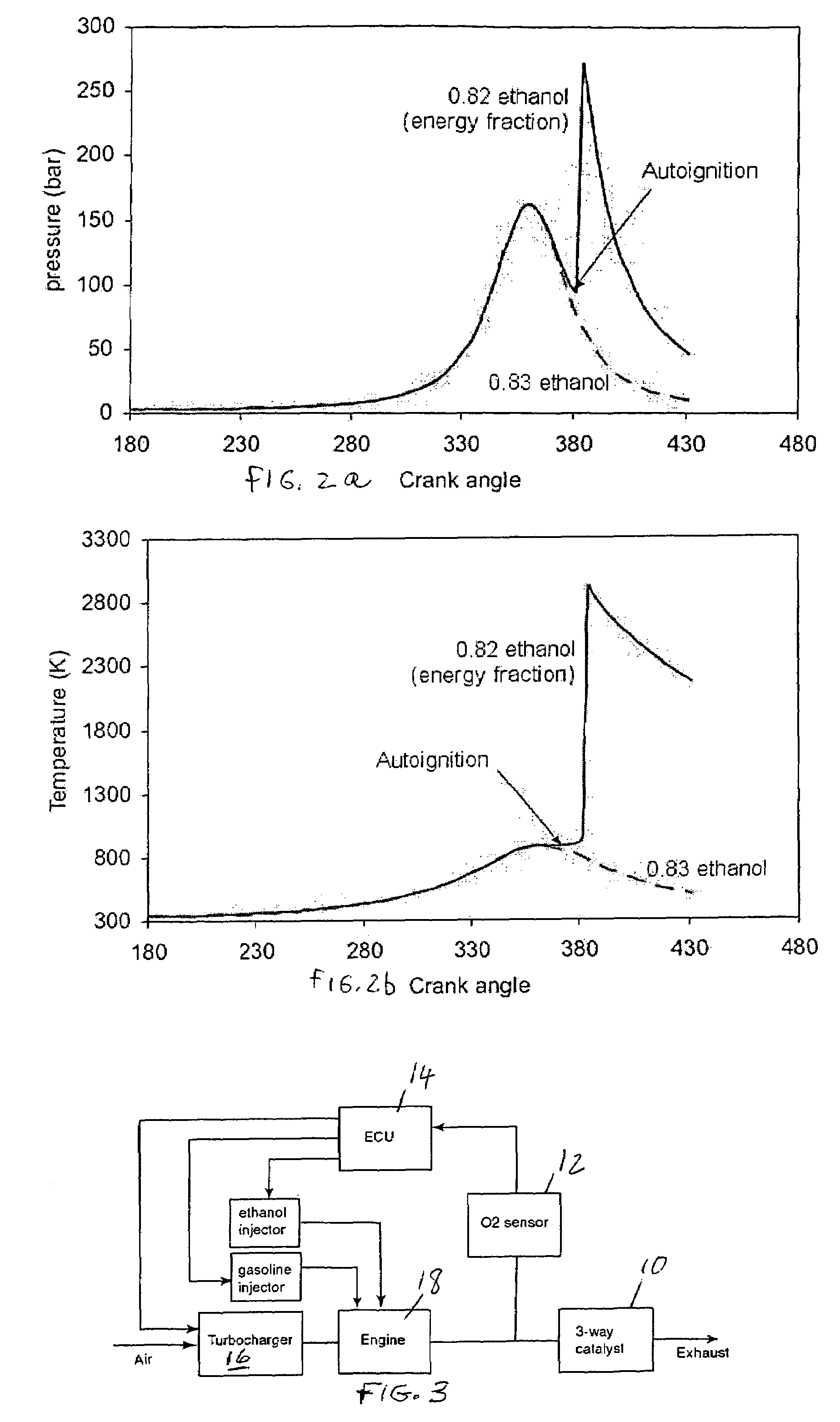
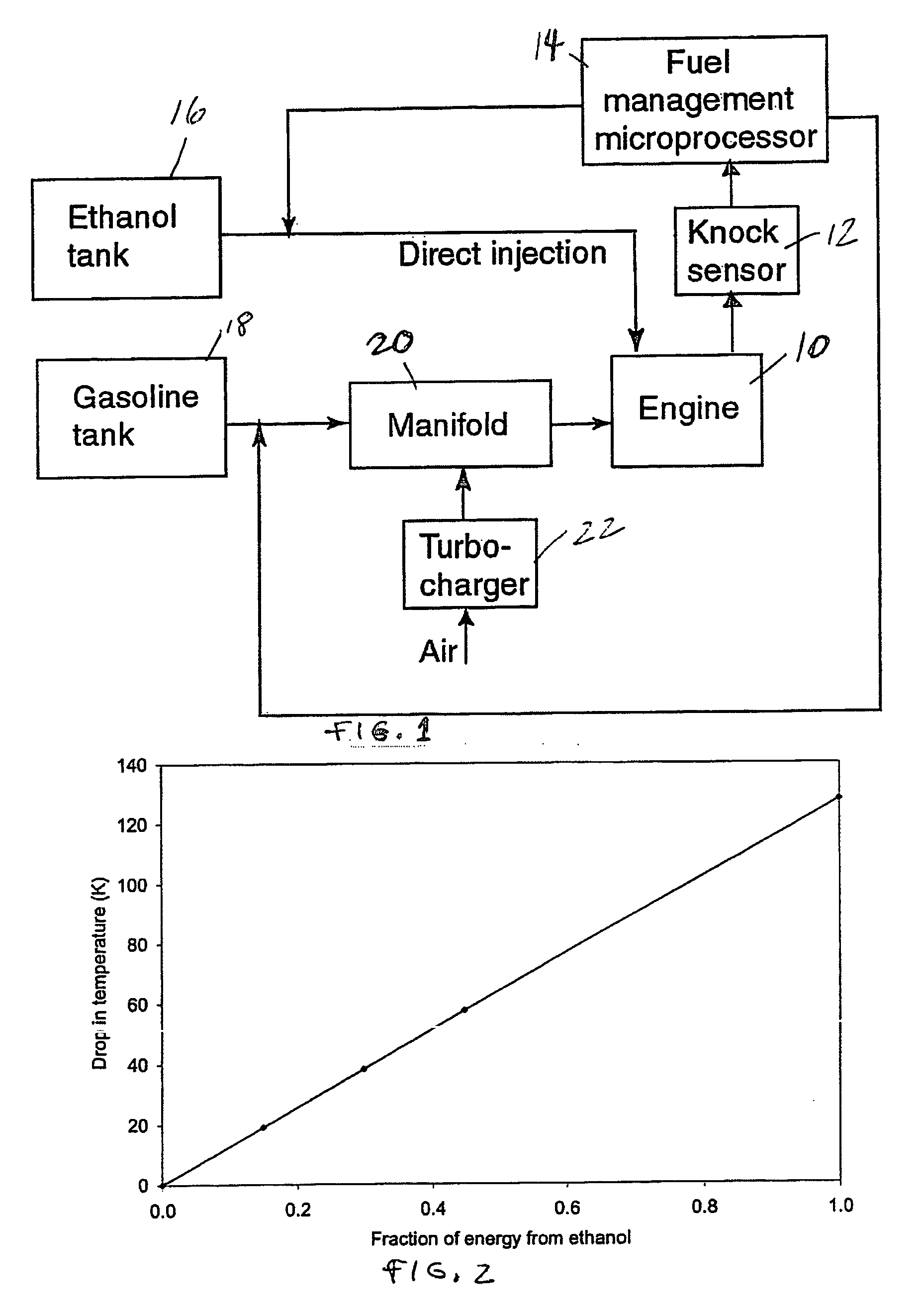
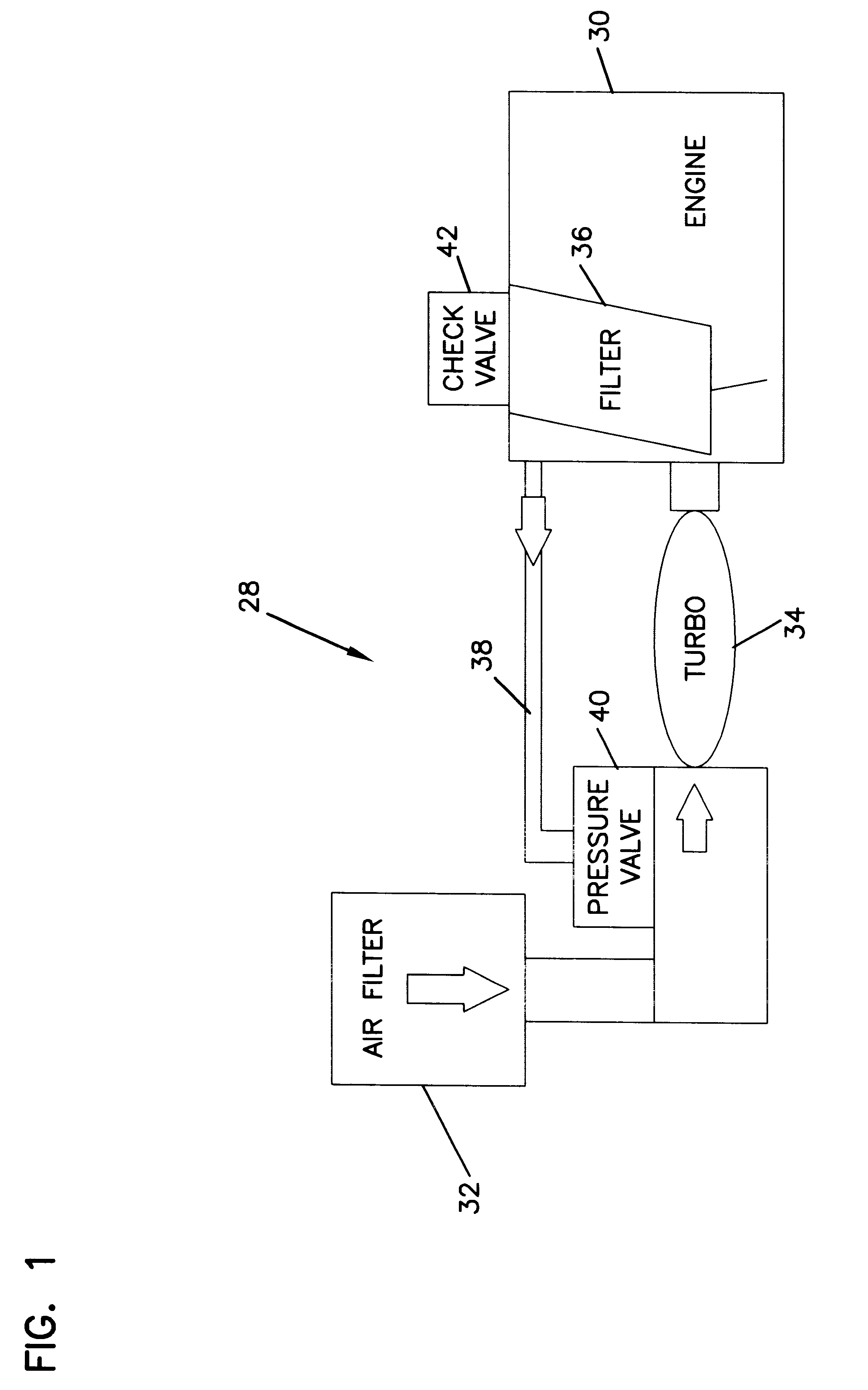
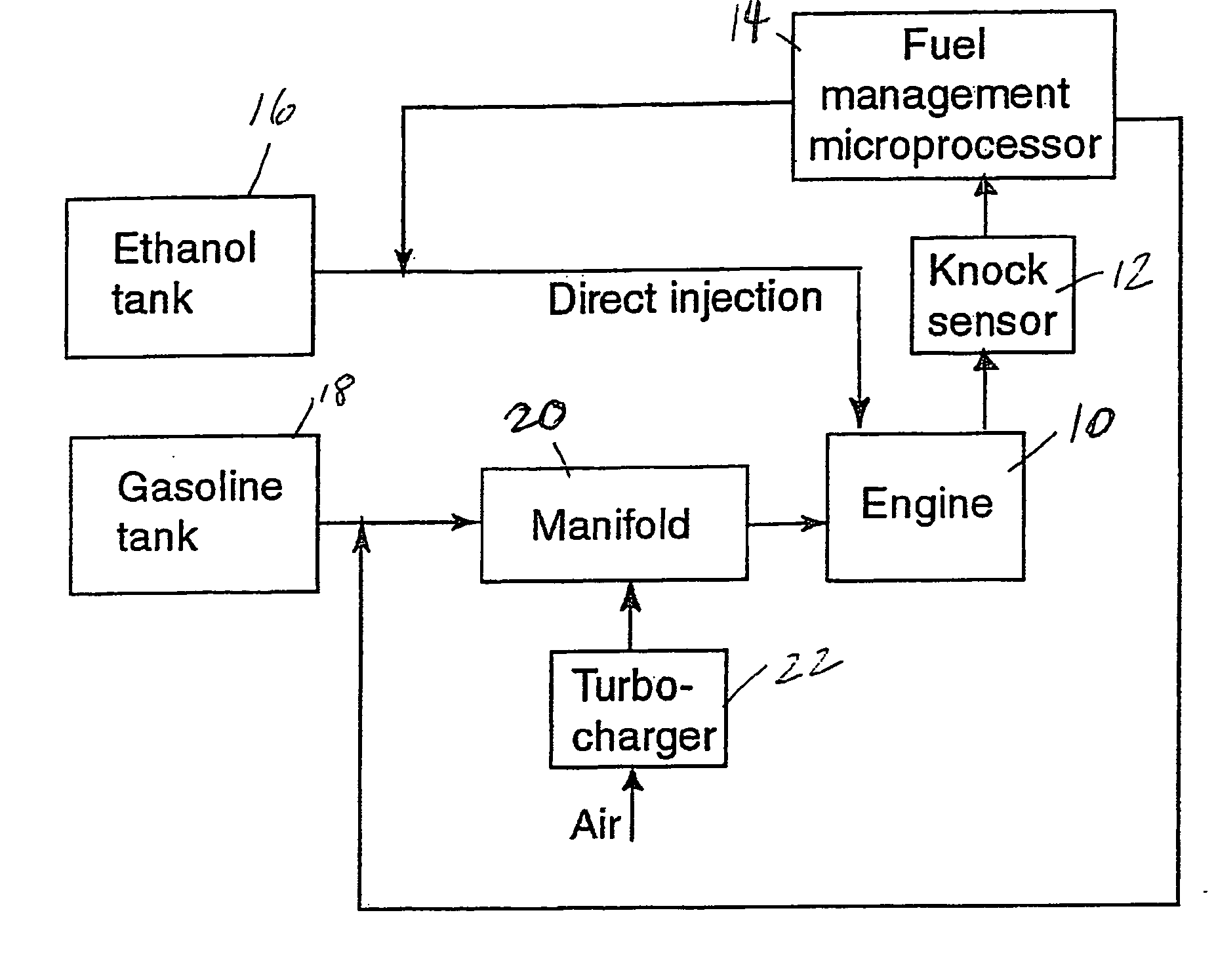
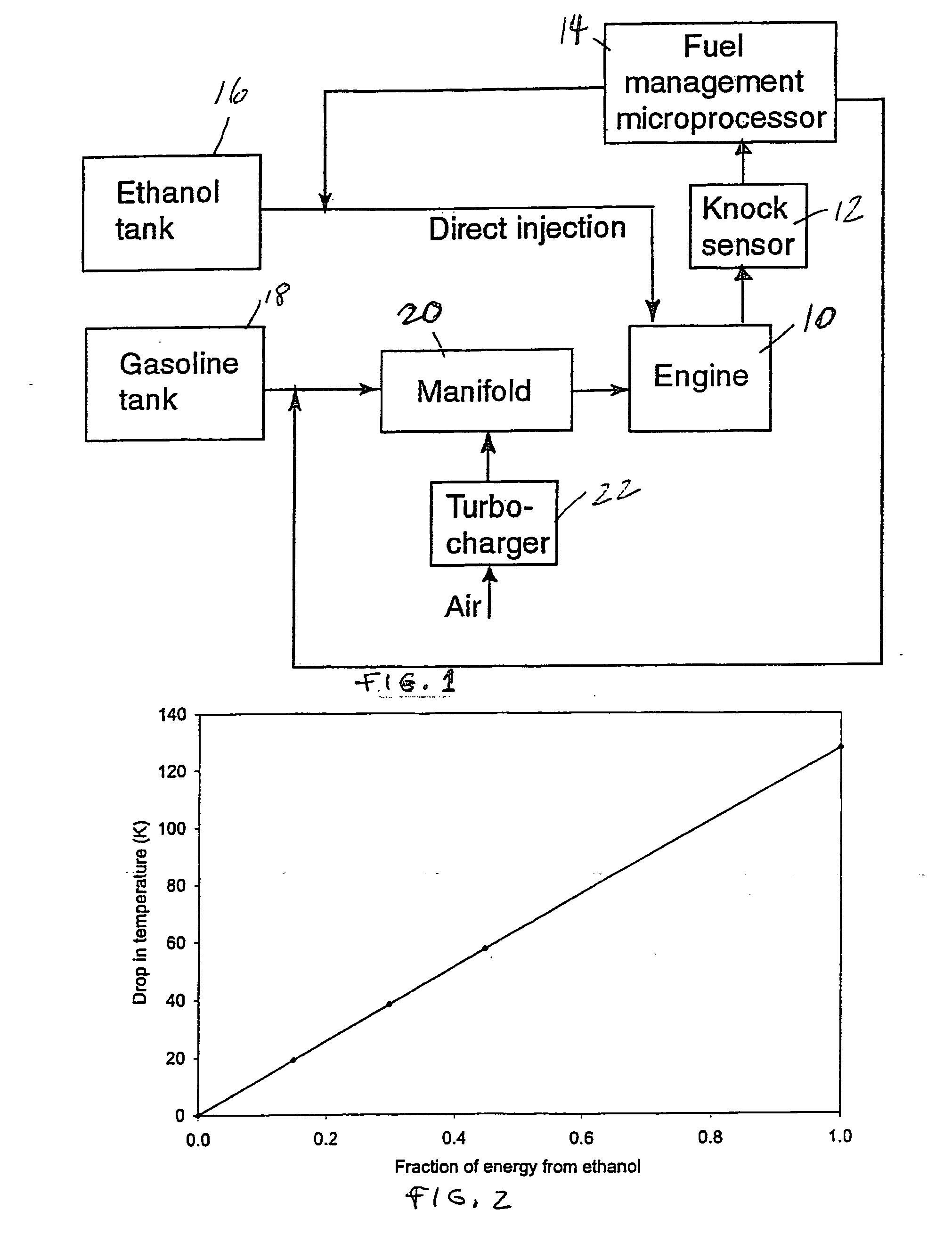
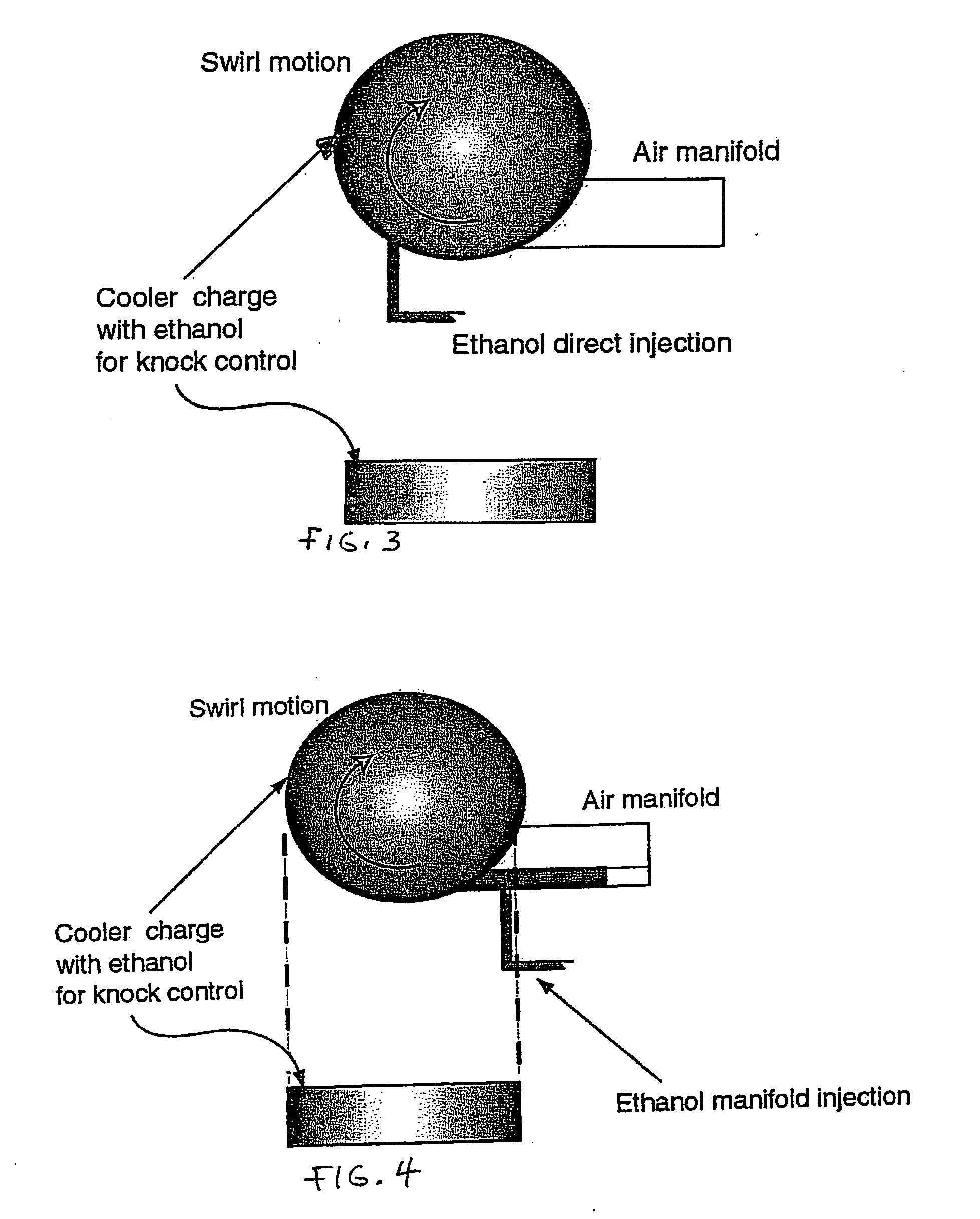
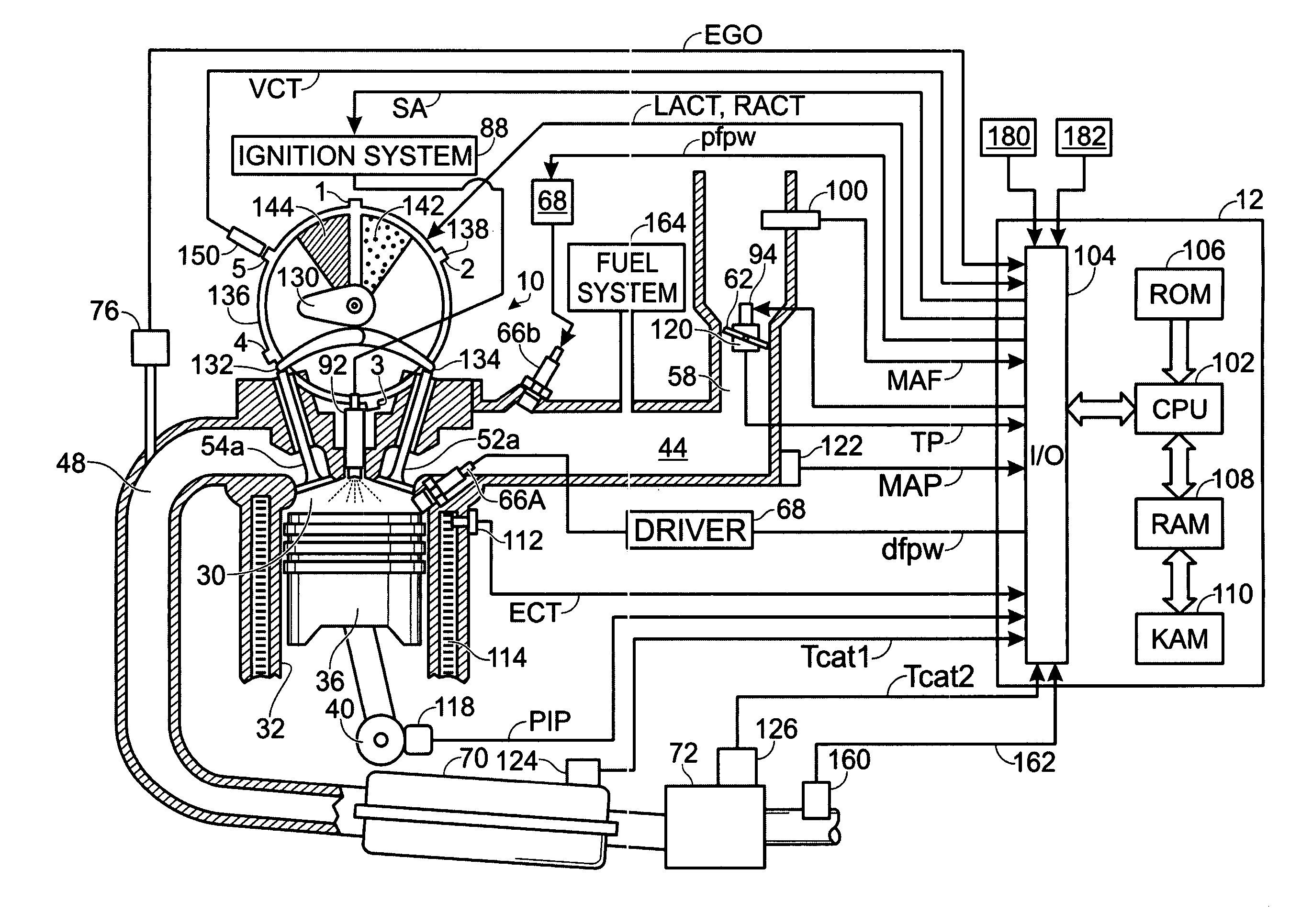
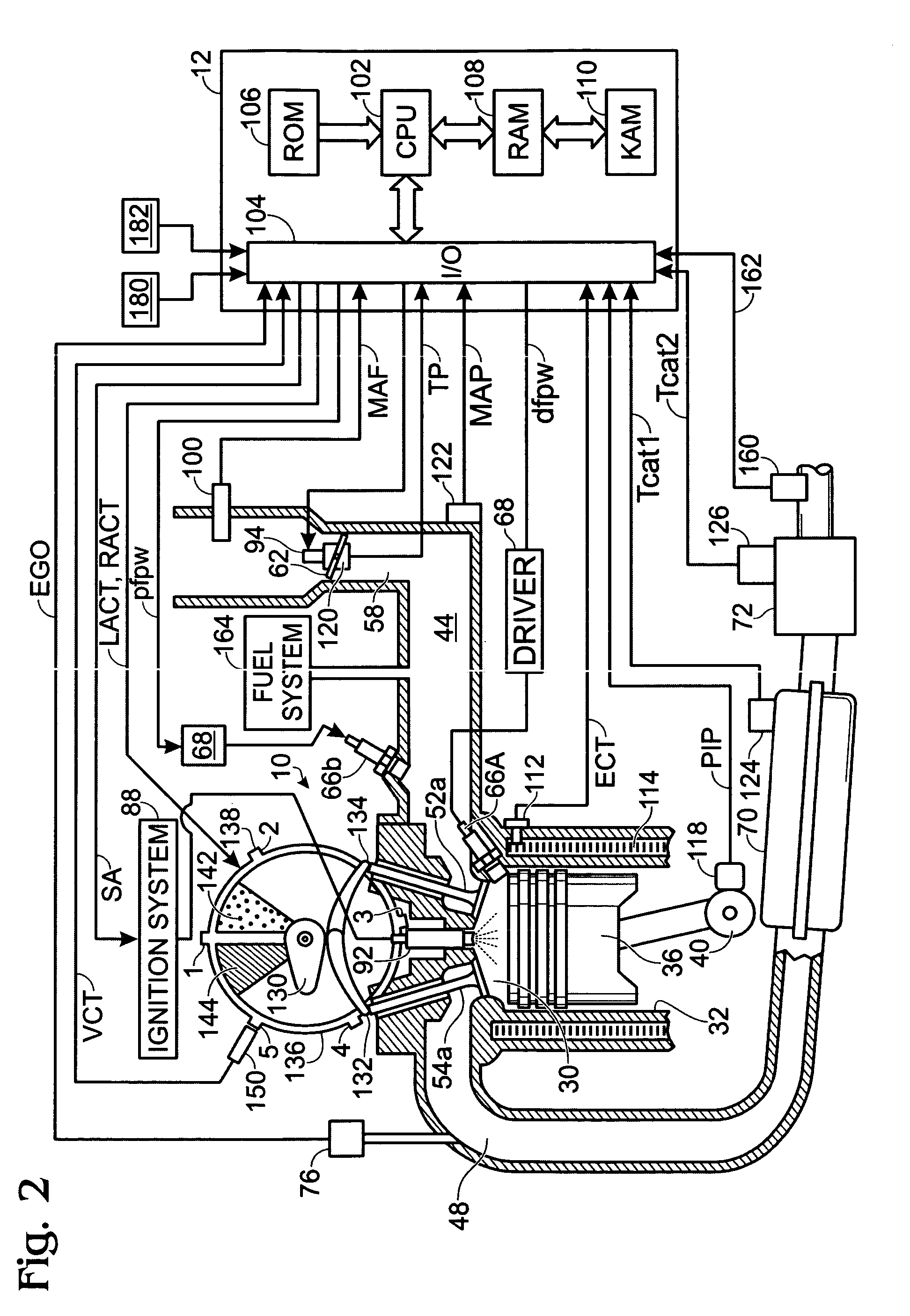
Optimized fuel management system for direct injection ethanol enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS7225787B2Save gasImprove engine efficiencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringProcess engineering
Fuel management system for enhanced operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder. It is preferred that the direct injection occur after the inlet valve is closed. It is also preferred that stoichiometric operation with a three way catalyst be used to minimize emissions. In addition, it is also preferred that the anti-knock agents have a heat of vaporization per unit of combustion energy that is at least three times that of gasoline.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods and devices for the production of Hydrocarbons from Carbon and Hydrogen sources
InactiveUS20080283411A1Reduce the environmentEasy to controlPhotography auxillary processesInternal combustion piston enginesElectrolysisAtmospheric air
Devices and methods are described for converting a carbon source and a hydrogen source into hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, for alternative energy sources. The influents may comprise carbon dioxide gas and hydrogen gas or water, obtainable from the atmosphere for through methods described herein, such as plasma generation or electrolysis. One method to produce hydrocarbons comprises the use of an electrolytic device, comprising an anode, a cathode and an electrolyte. Another method comprises the use of ultrasonic energy to drive the reaction. The devices and methods and related devices and methods are useful, for example, to provide a fossil fuel alternative energy source, store renewable energy, sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, counteract global warming, and store carbon dioxide in a liquid fuel.
Owner:PRINCIPLE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
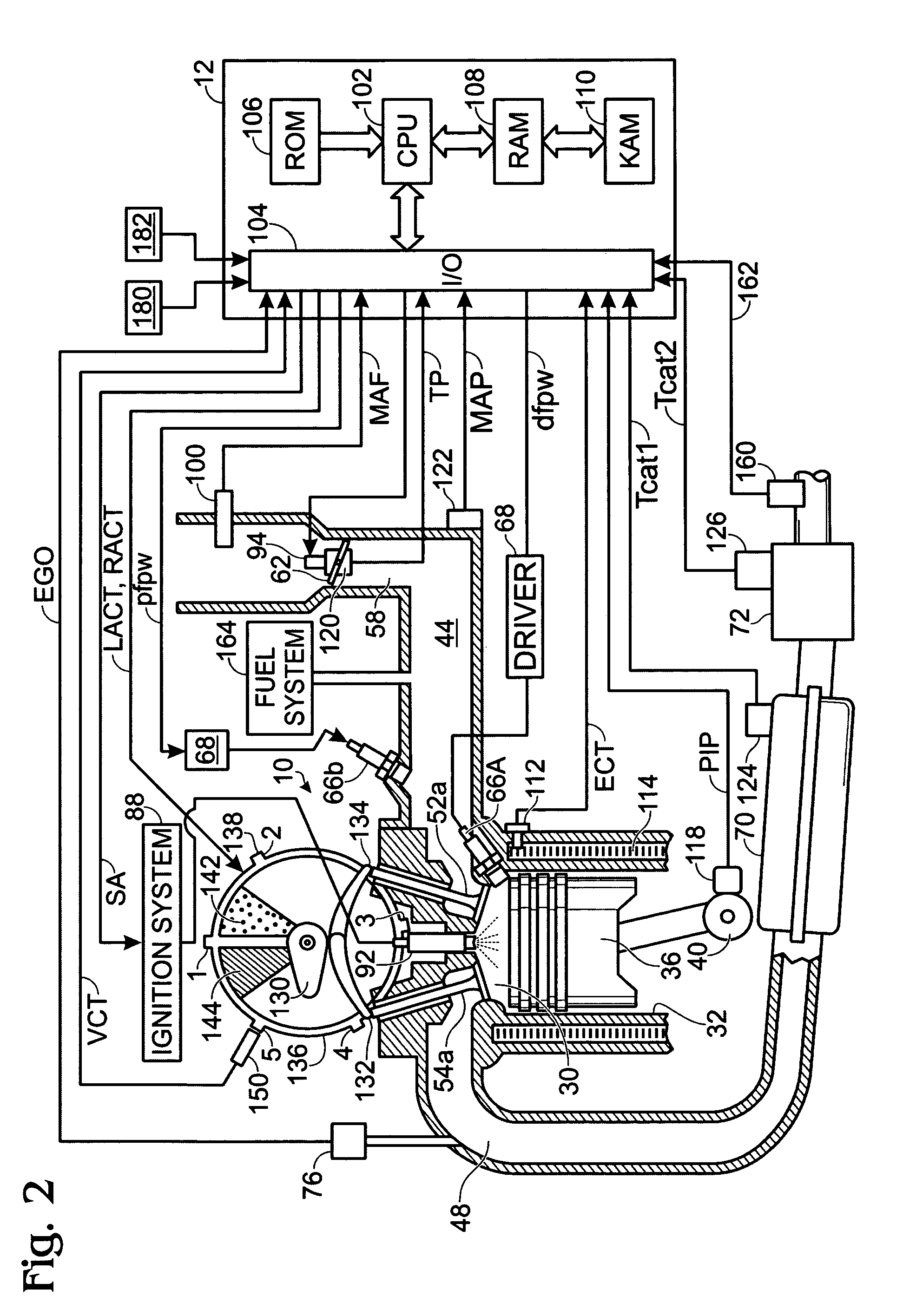
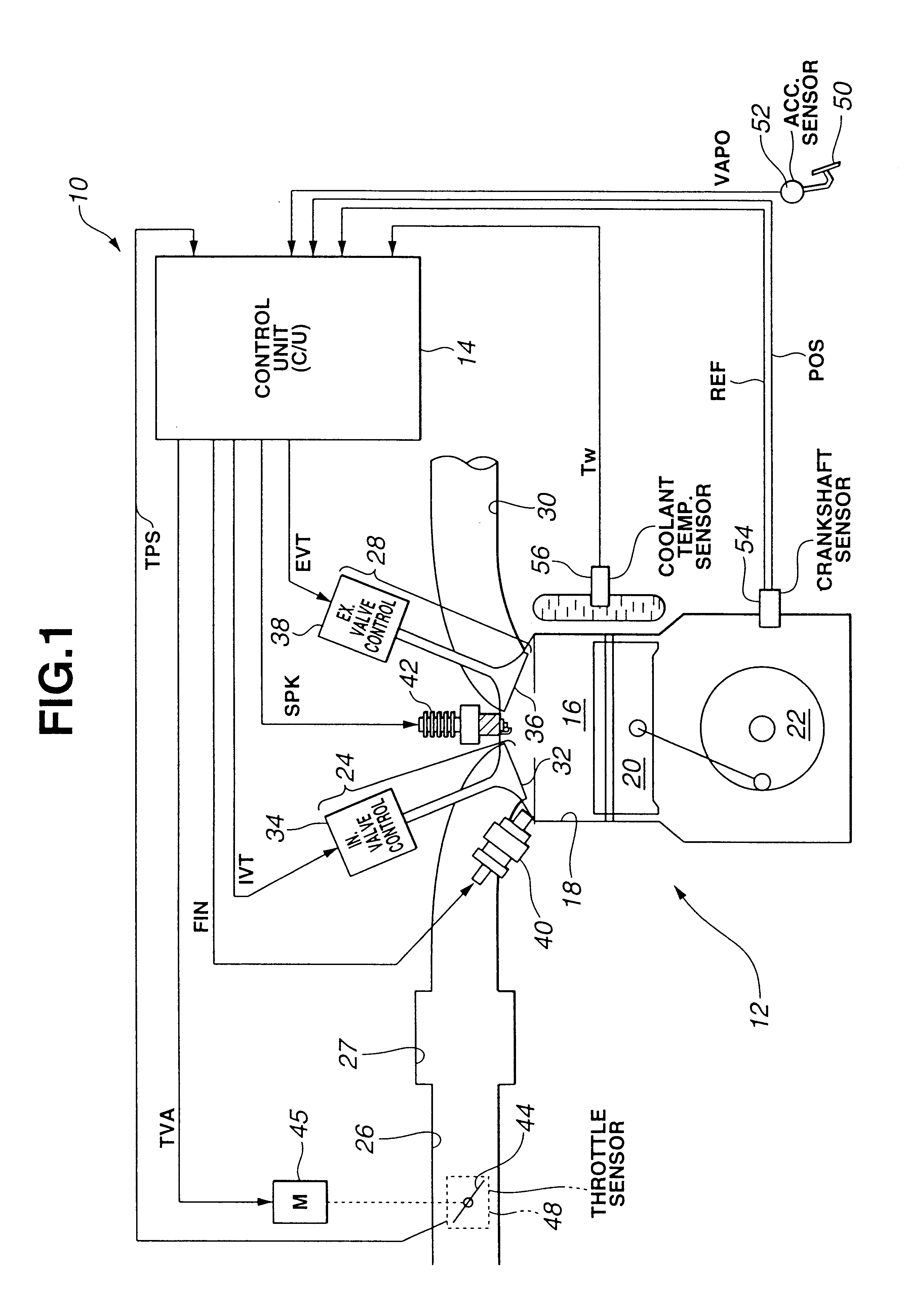
Internal combustion engine
ActiveUS6990956B2Accurate calculationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultifuelEngineering
An internal combustion engine, in which multiple kinds of fuels are fed to a cylinder from multiple fuel injectors each corresponding to each of multiple kinds of fuels at a target mixing ratio determined according to a running condition, includes an actual fuel mixing ratio calculator calculating an actual fuel mixing ratio of fuel fed to cylinder. The actual fuel mixing ratio calculator at first calculates actual fuel injection quantity of each fuel injection by adding or subtracting predetermined stuck-on-wall fuel to or from each quantity of fuel injected from each fuel injector, and then calculates an actual fuel mixing ratio of fuel fed to cylinder on the basis of the calculated actual fuel injection quantity of each fuel injector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
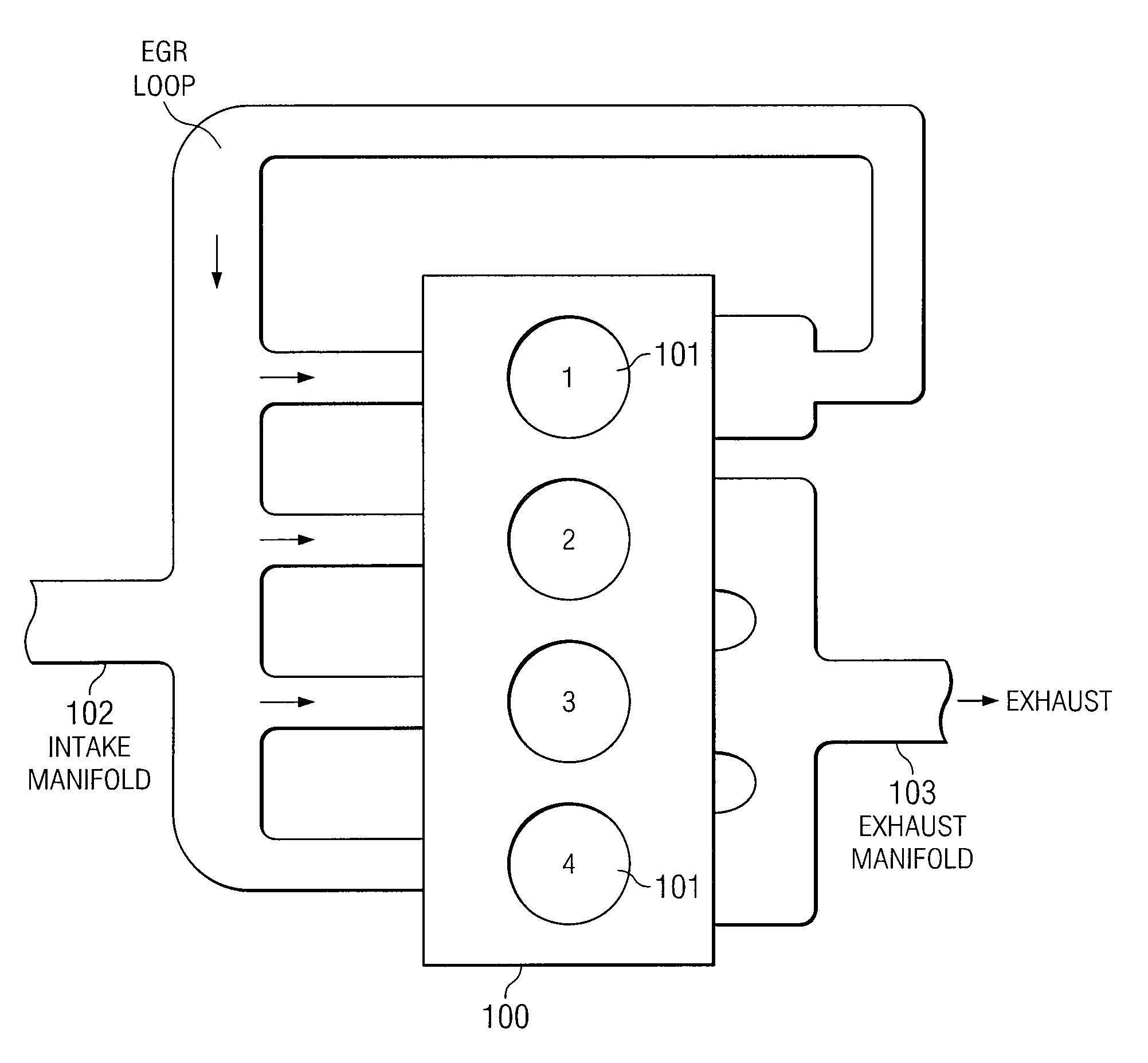
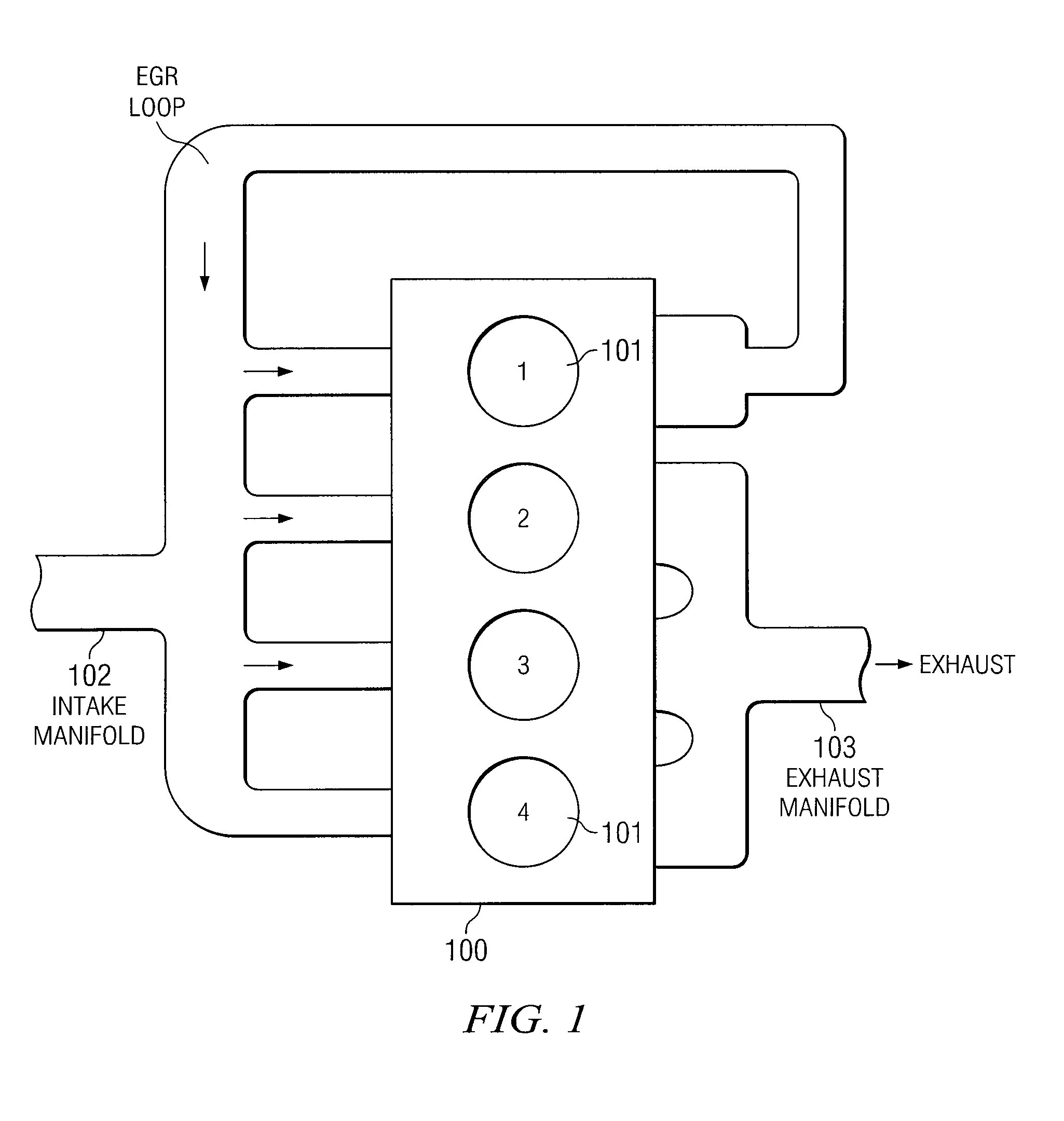
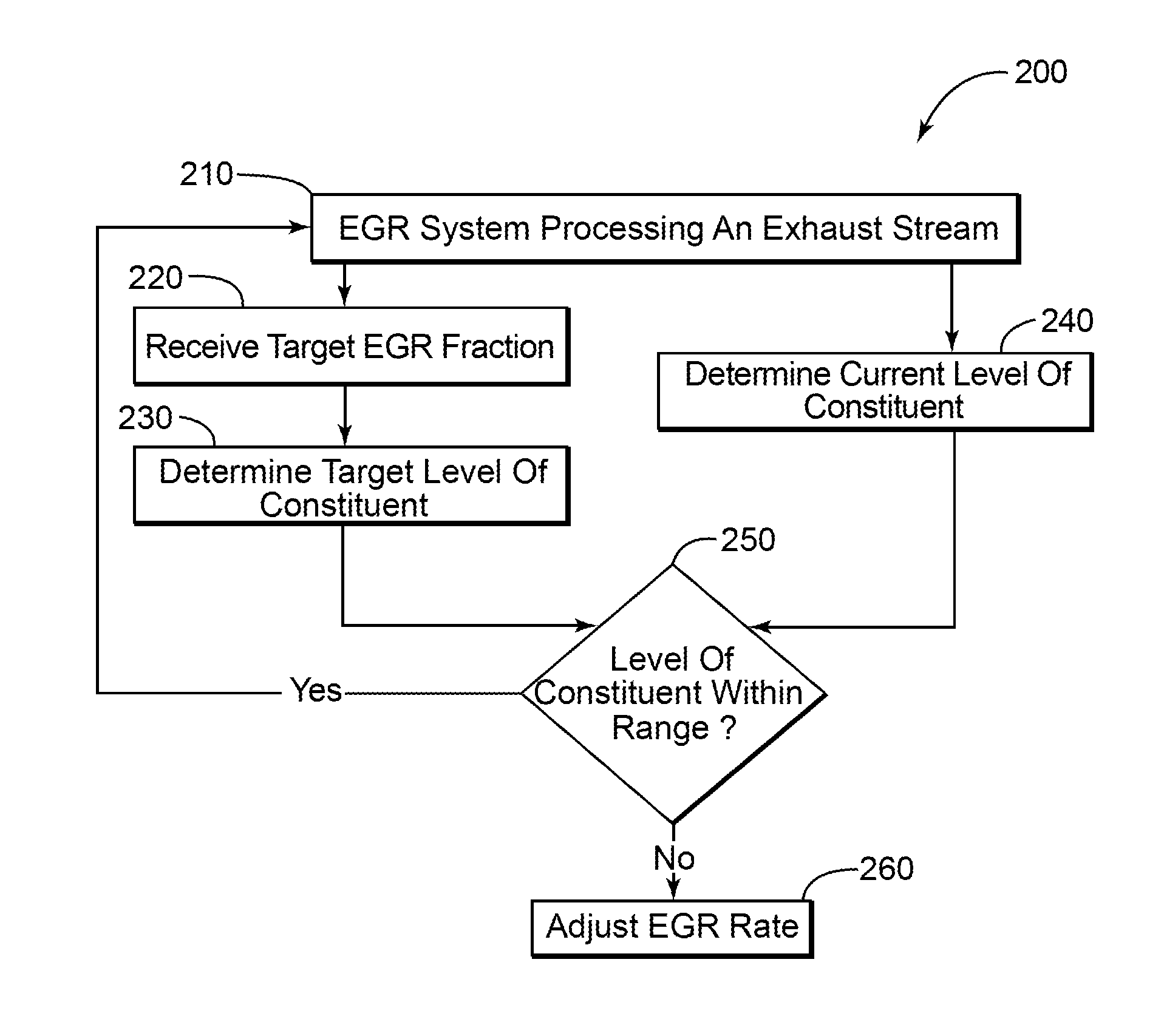
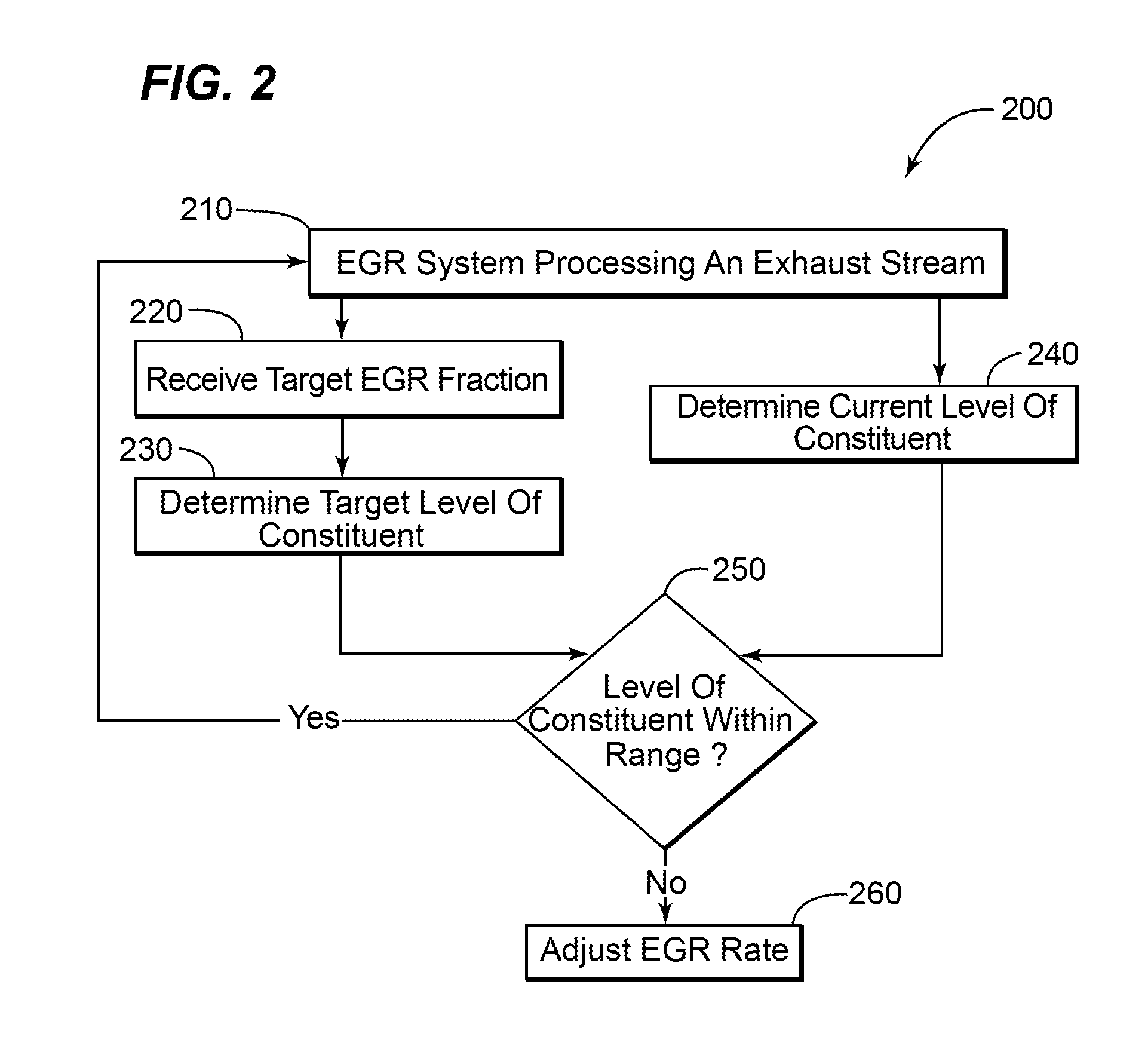
Egr system with dedicated egr cylinders
Improved exhaust gas recirculation system and methods that use one or more of the engine's cylinders as dedicated EGR cylinders. All of the exhaust from the dedicated EGR cylinders is recirculated back to the engine intake. Thus, the EGR rate is constant, but the EGR mass flow may be controlled by adjusting the air-fuel ratio of the dedicated EGR cylinders or by using various variable valve timing techniques.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
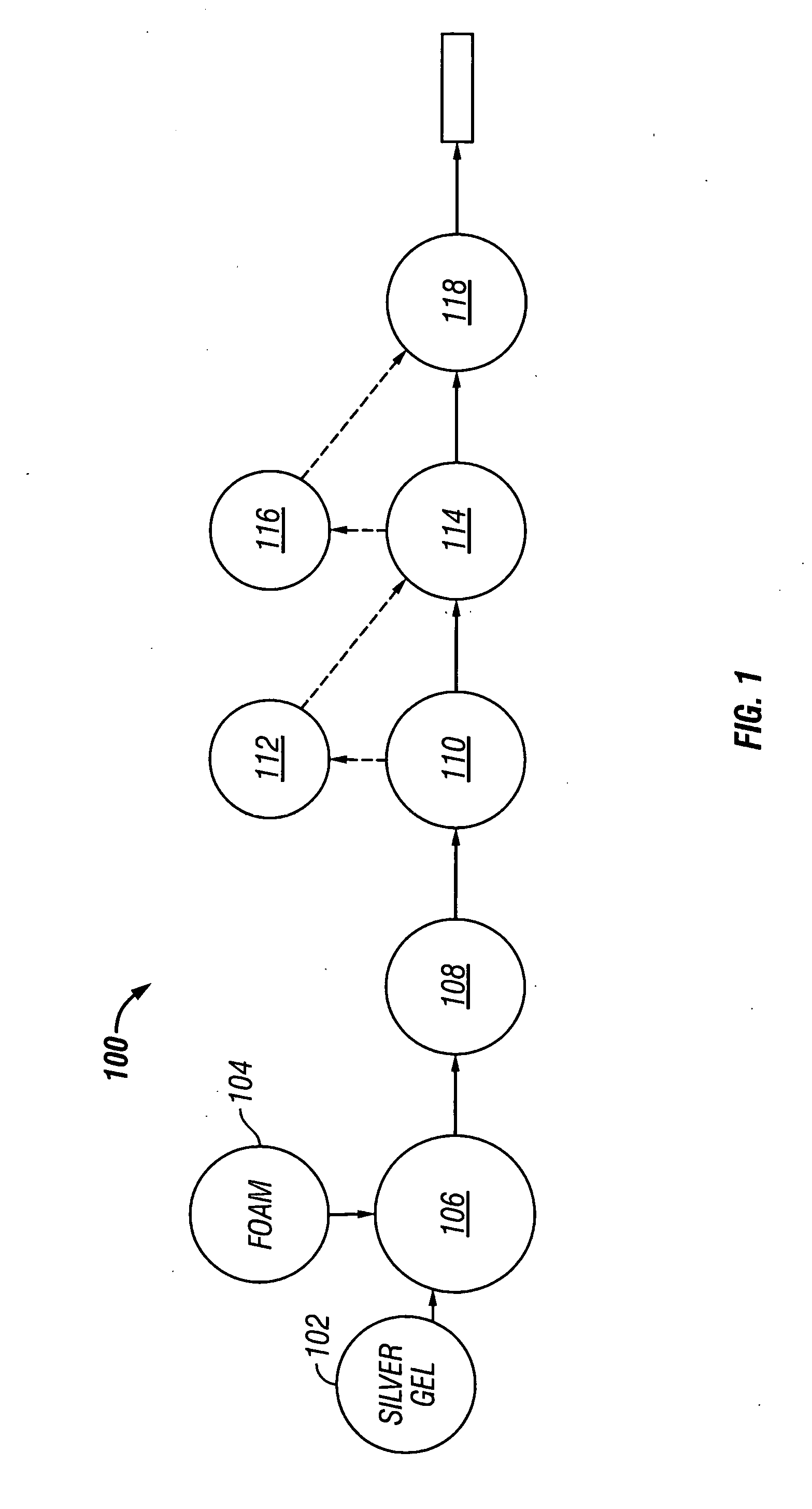
Method for coating substrate with antimicrobial agent and product formed thereby
A method for uniformly coating a foam or dressing with antimicrobial polymer incorporating agents, such as silver, and a foam or dressing formed by this process. Such foam or dressing is particularly useful in combination with negative pressure wound therapy.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Increased visibility during order management in a network-based supply chain environment
ActiveUS8271336B2Simple personalization processHand manipulated computer devicesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelVisibilityNetwork completion
A system, method and article of manufacture are provided for a first business entity to provide a network-based supply chain framework for collaborative order management between at least a second and a third independent business entity, such as a service provider, vendor, reseller, manufacturer and the like. A request for an order is received over a network with an automated system, from at least a second business entity. The order is transmitted over a network, with an automated system, to at least the third business entity. Information is received from the third business entity relating to a status of completion of the order by the third business entity using a network. The progress in completing the order is tracked based on the information received from the third business entity. Progress reports from the tracking are generated periodically; and transmitted to the second business entity using the network.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Optimized fuel management system for direct injection ethanol enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102136A1Improve engine efficiencySave gasElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelProcess engineeringVaporization
Fuel management system for enhanced operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder. It is preferred that the direct injection occur after the inlet valve is closed. It is also preferred that stoichiometric operation with a three way catalyst be used to minimize emissions. In addition, it is also preferred that the anti-knock agents have a heat of vaporization per unit of combustion energy that is at least three times that of gasoline.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
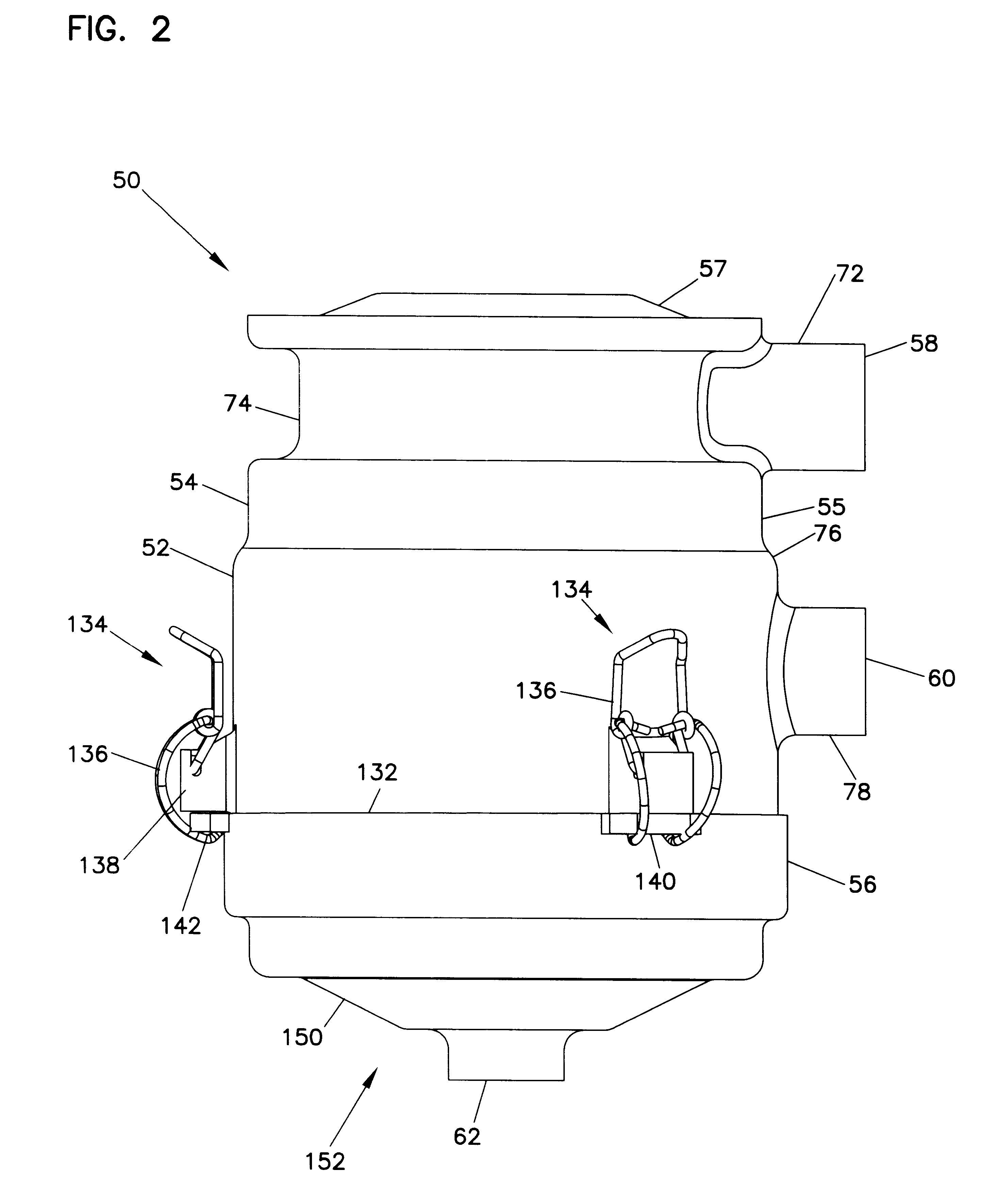
Air cleaner; aerosol separator; and method
InactiveUS6187073B1Easy collection and removalAvoid flowCombination devicesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCoalescerFilter element
A filter arrangement includes a tubular first filter element having a first media pack defining a first open filter interior and an air flow outlet. The air flow outlet is in gas flow communication with the first open filter interior. A housing construction has a gas flow inlet and a gas flow outlet. The air flow outlet of the first filter element is in gas flow communication with the gas flow outlet. A coalescer filter element is oriented in the housing construction in fluid communication with the gas flow inlet. A tubular second filter element is oriented in the housing construction and has a second media pack defining a second open filter interior. The second open filter interior is in gas flow communication with the gas flow outlet.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Method for reducing emissions from evaporative emissions control systems
InactiveUS6540815B1Loss in working capacityEmission reductionGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHigh concentrationSorbent
Disclosed is a method for sharply reducing diurnal breathing loss emissions from automotive evaporative emissions control systems by providing multiple layers, or stages, of adsorbents. On the fuel source-side of an emissions control system canister, high working capacity carbons are preferred in a first canister (adsorb) region. In subsequent canister region(s) on the vent-side, the preferred adsorbent should exhibit a flat or flattened adsorption isotherm on a volumetric basis and relatively lower capacity for high concentration vapors as compared with the fuel source-side adsorbent. Multiple approaches are described for attaining the preferred properties for the vent-side canister region. One approach is to use a filler and / or voidages as a volumetric diluent for flattening an adsorption isotherm. Another approach is to employ an adsorbent with the desired adsorption isotherm properties and to process it into an appropriate shape or form without necessarily requiring any special provision for dilution. The improved combination of high working capacity carbons on the fuel source-side and preferred lower working capacity adsorbent on the vent-side provides substantially lower diurnal breathing emissions without a significant loss in working capacity or increase in flow restriction compared with known adsorbents used in canister configurations for automotive emissions control systems.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
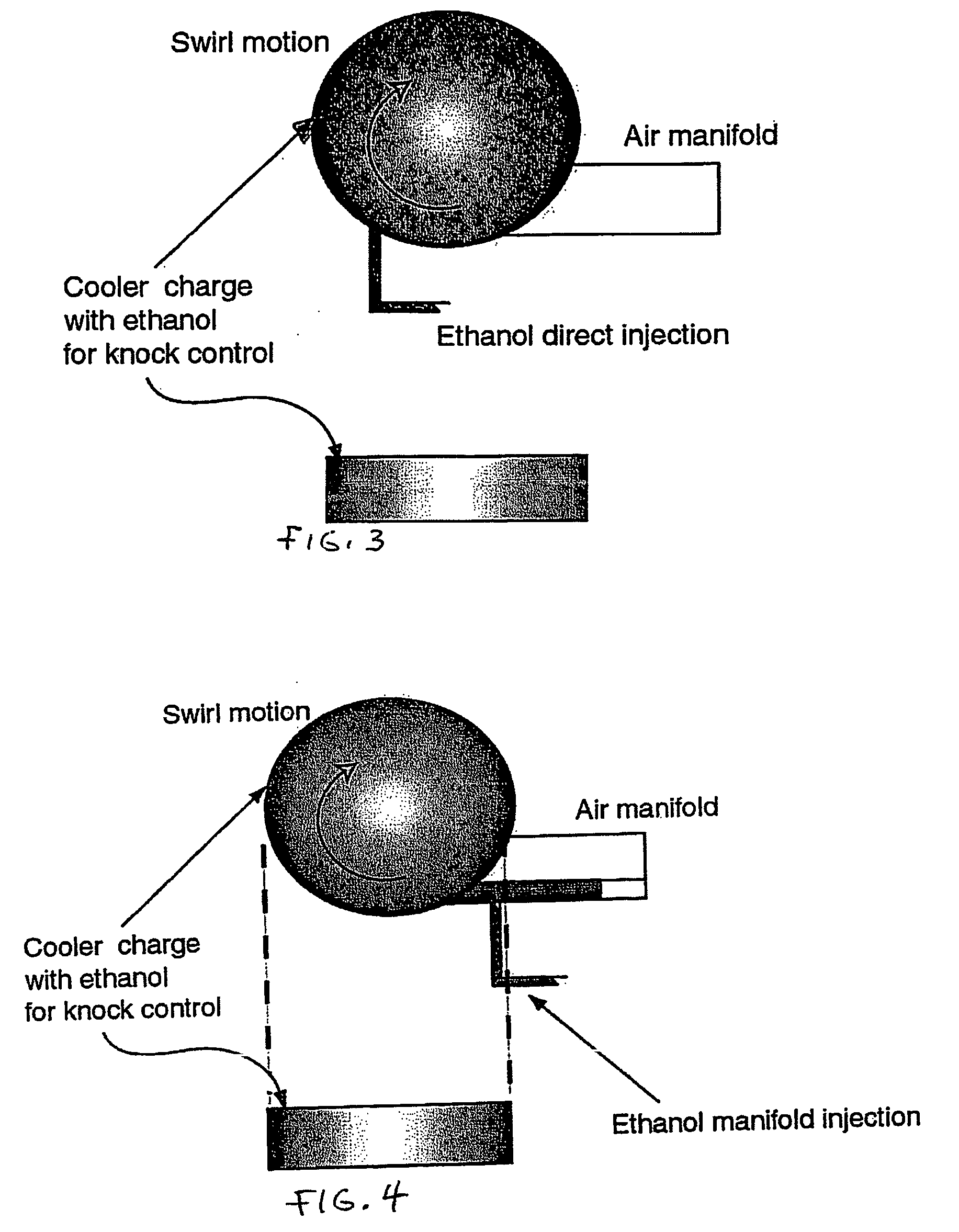
Fuel management system for variable ethanol octane enhancehment of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102145A1Increase heatMeet cutting requirementsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
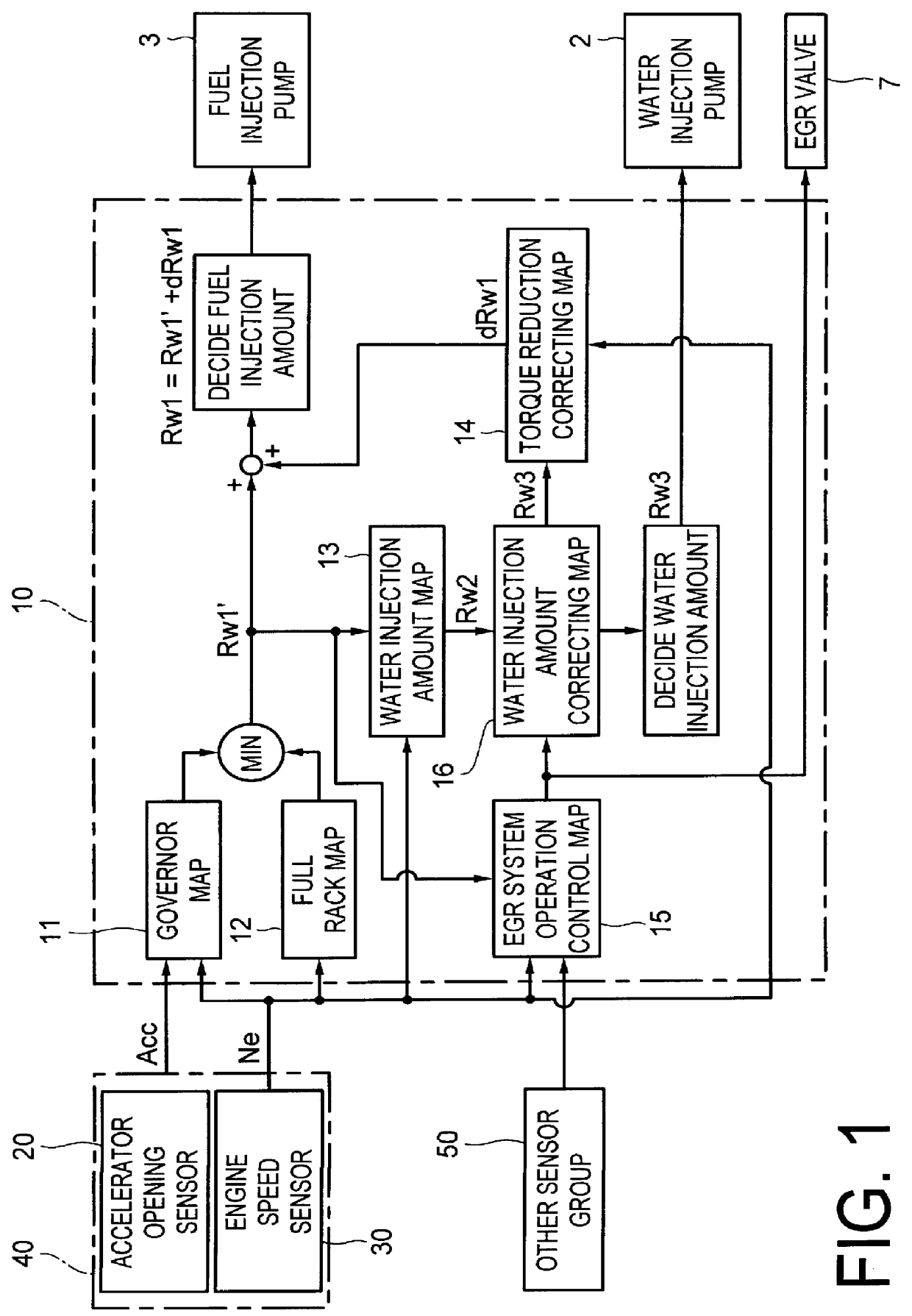
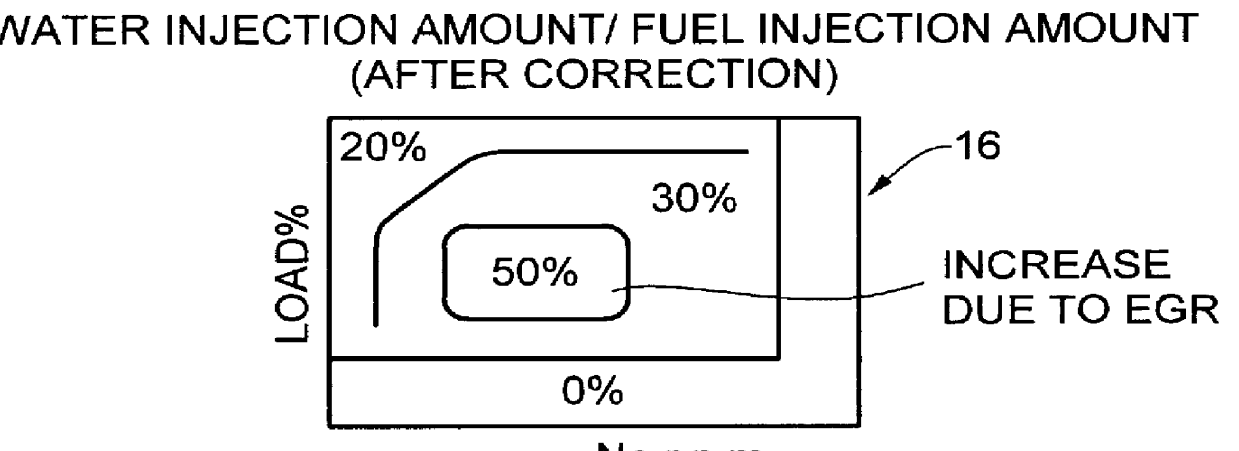
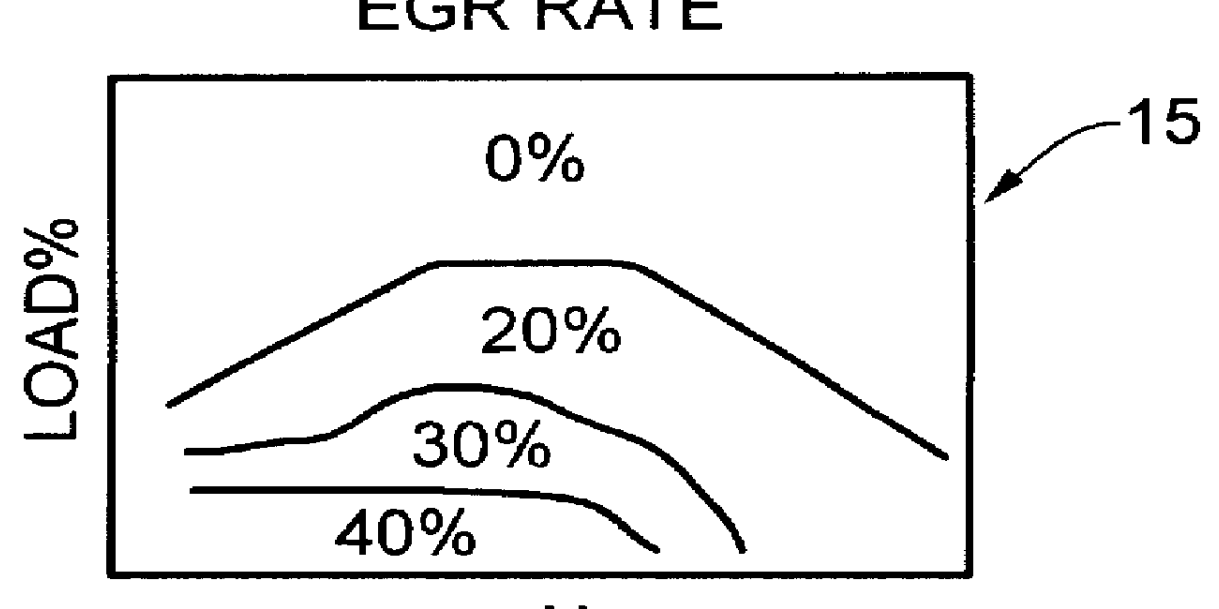
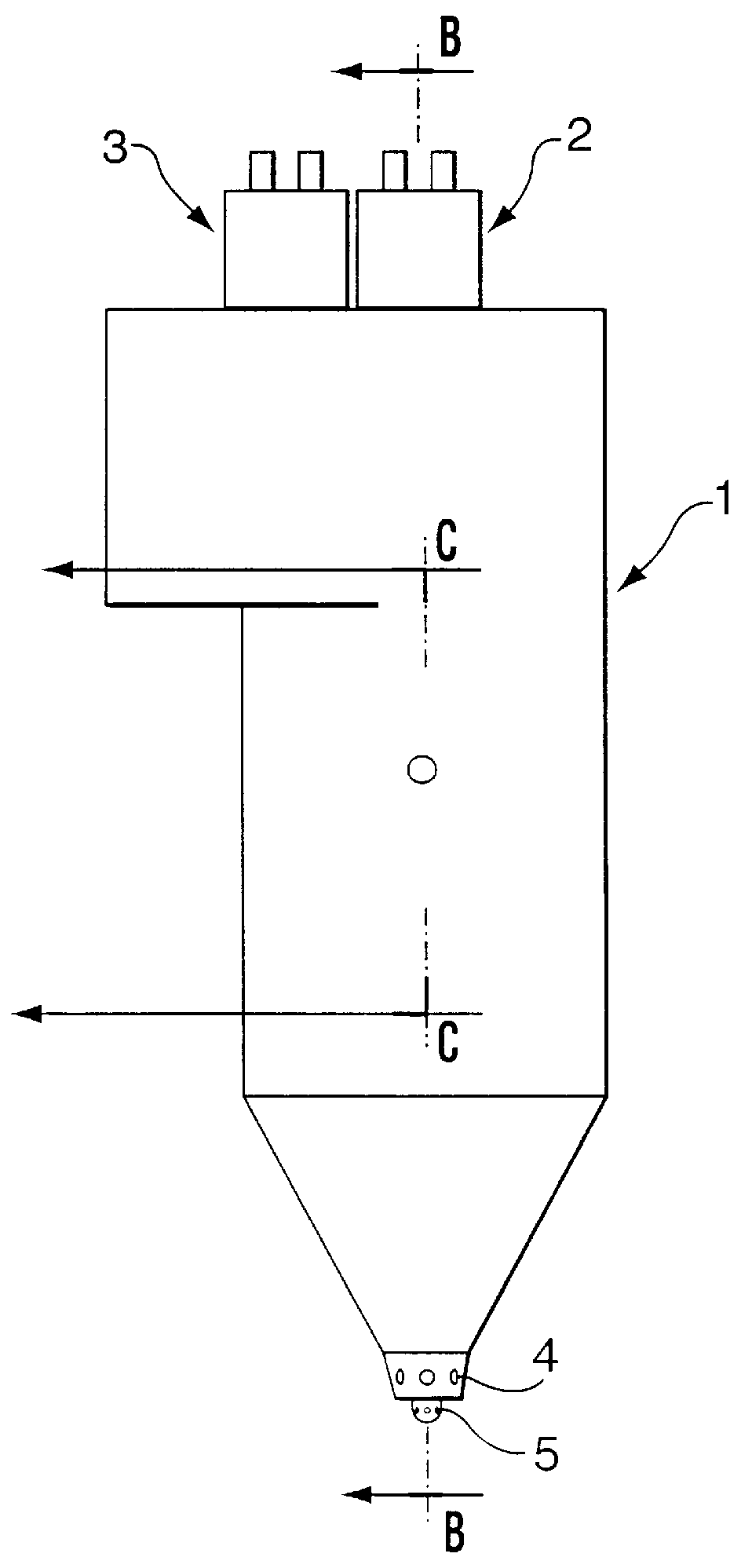
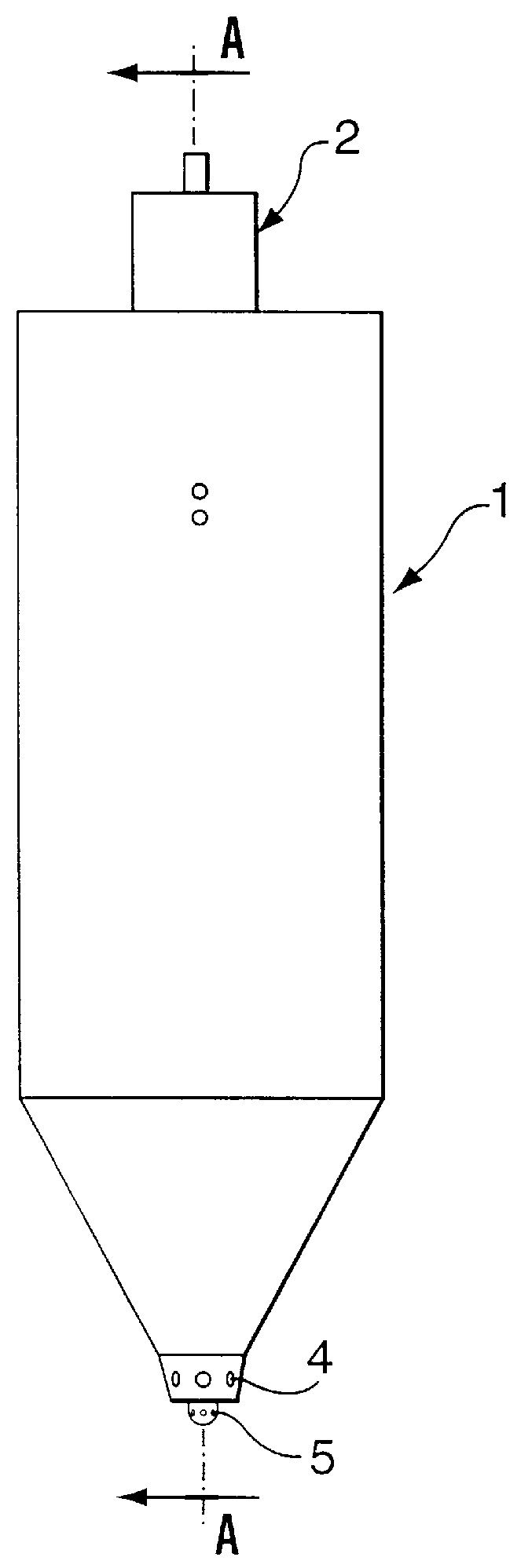
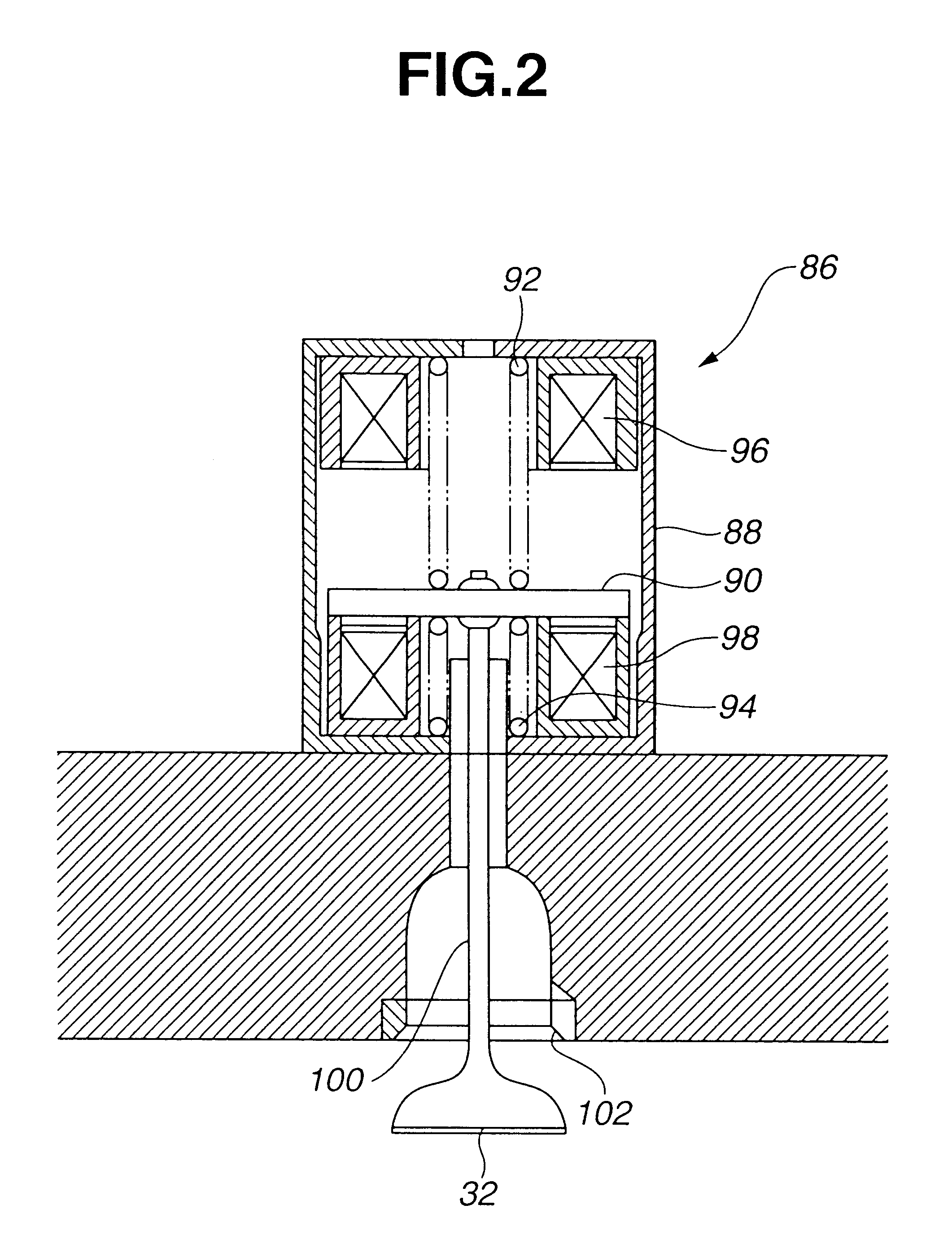
Water injection amount control system for fuel and water injection engine
InactiveUS6112705AEnhance NOx reducing effectImprove reducibilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberControl system
A water injection amount control system for a fuel and water injection engine, comprises running state detecting unit for detecting the running state of the engine; an EGR system for recirculating part of exhaust gas of the engine to a combustion chamber of the engine; EGR system operating state detecting unit for detecting or estimating the operating state of the EGR system; water injection amount regulating unit for regulating an amount of water to be injected to the combustion chamber of the engine; and control unit for controlling the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit: wherein the system is arranged to have water injection amount setting unit for deciding a water injection amount based on information from the running state detecting unit and on the operating state of the EGR system detected by the EGR system operating state detecting unit, so that the control unit controls the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit based on the water injection amount decided by the water injection amount setting unit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
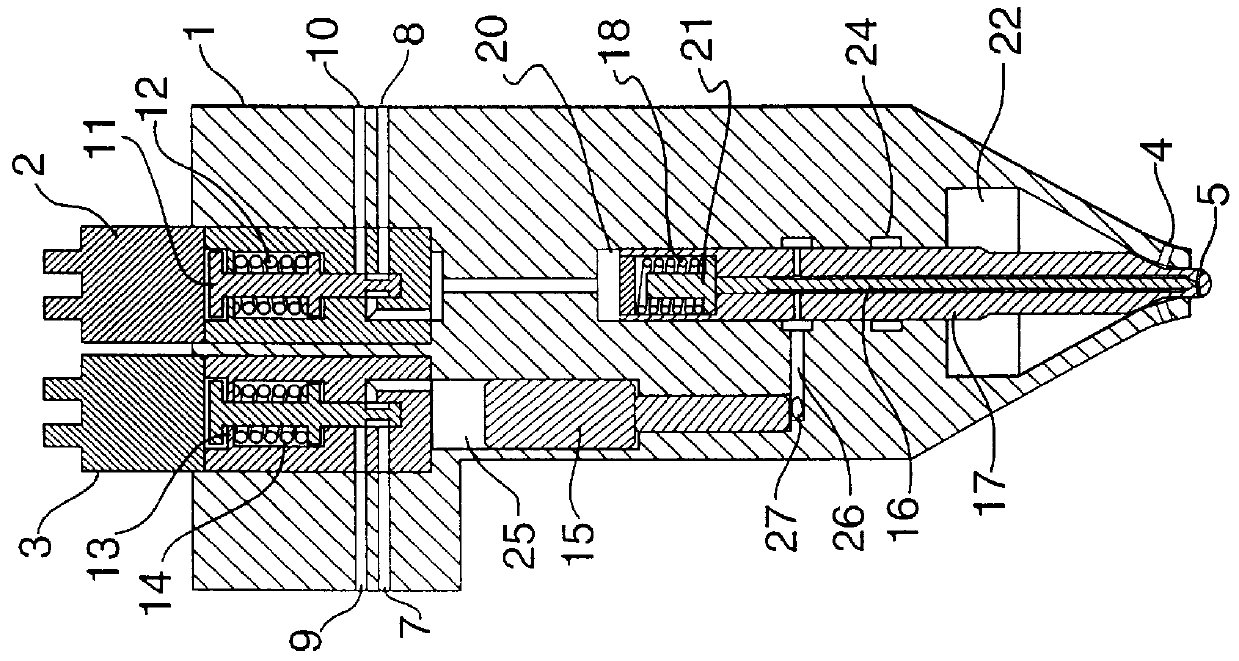
Gaseous and liquid fuel injector
A hydraulically actuated dual fuel injector for an internal combustion engine. More particularly, the application pertains to a hydraulically actuated injector for injecting controlled quantities of a first fuel and of a second fuel into an internal combustion diesel engine at different times. A dual fuel injector comprising: (a) an injector body; (b) an inlet port in the injector body for enabling pressurized hydraulic fluid from a hydraulic fluid source to be introduced into the interior of the injector body, the hydraulic fluid being of sufficient pressure to maintain injection valves in the injector body in a closed position until actuated; (c) a first inlet port in the injector body for enabling a first fuel to be introduced into the interior of the injector body; (d) a first injection valve in the injector body connected to the second inlet port for controlling injection of the first fuel from the injector through a first fuel ejection port; (e) a second inlet port in the injector body for enabling a second fuel to be introduced into the interior of the injector body; (f) a second injection valve in the injector body connected to the second inlet port for controlling injection of the second fuel from the injector through a second fuel ejection port; (g) a first control valve which causes the hydraulic fluid to actuate the first injection valve; (h) a second control valve which causes the hydraulic fluid to actuate the second injection valve; (i) a metering device in the injector body for metering the amount of first fuel injected by the first injection valve; and (j) a seal in the injector body which prevents leakage of the second fuel into the first fuel.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
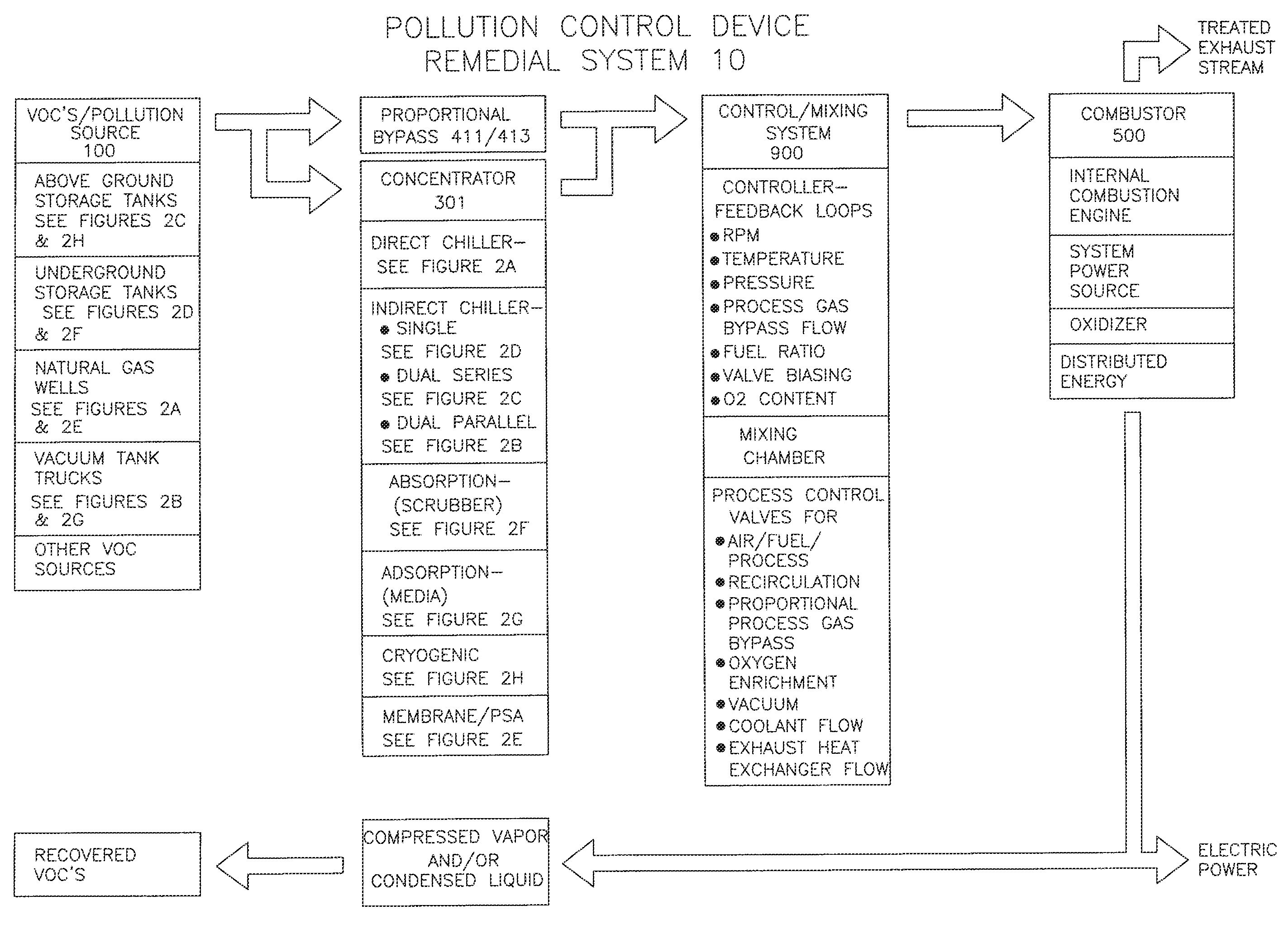
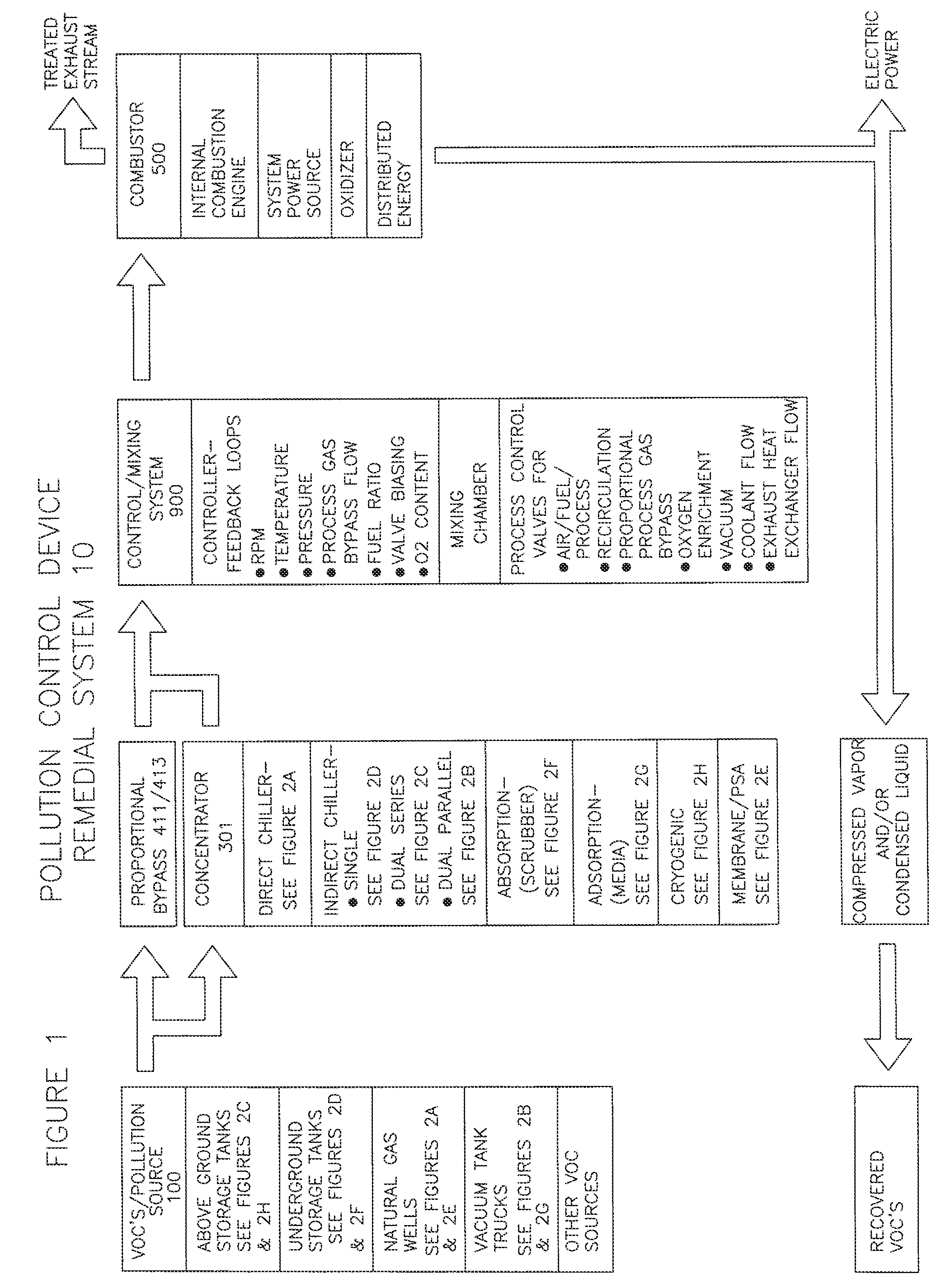
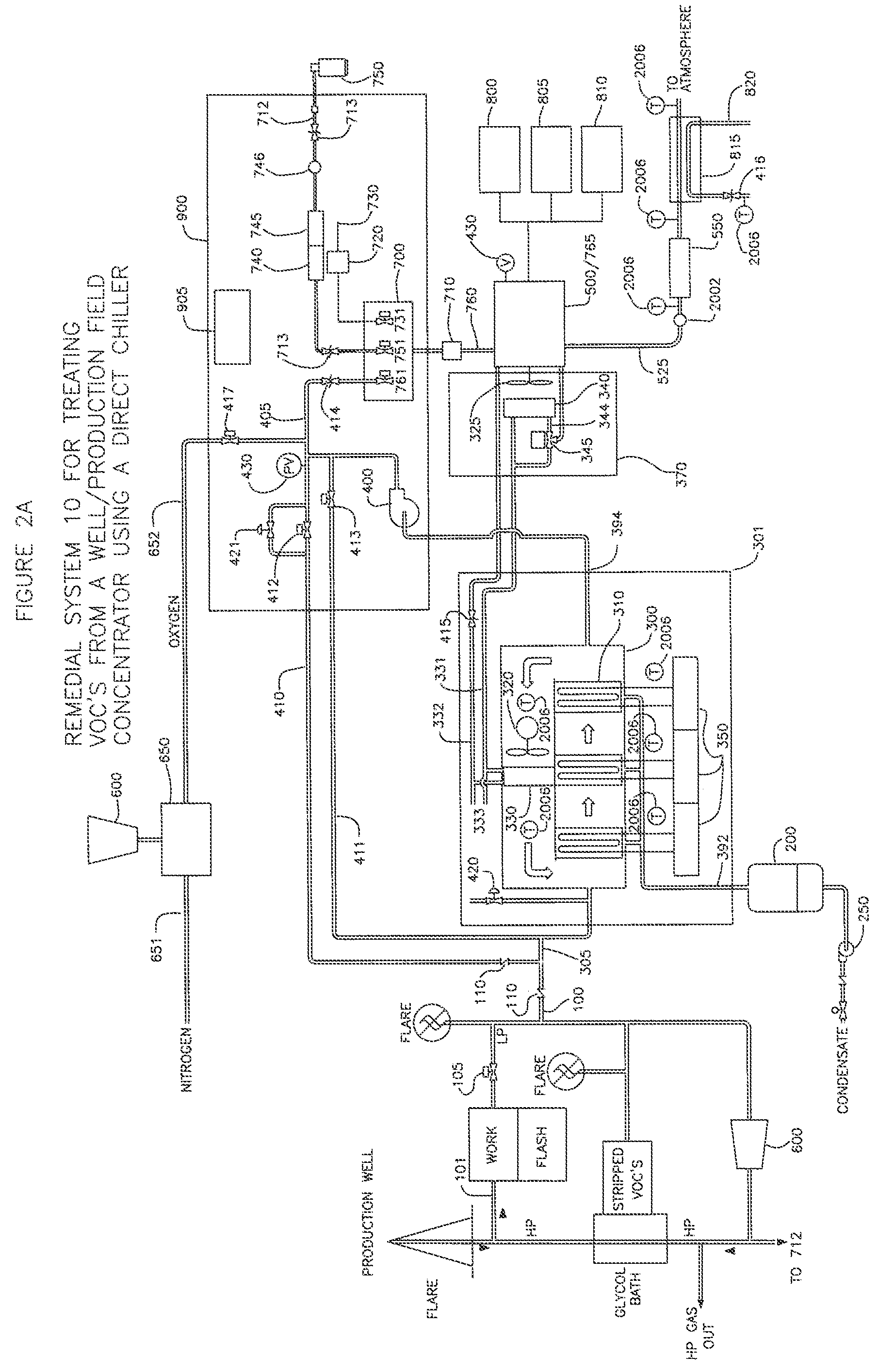
Remedial system: a pollution control device for utilizing and abating volatile organic compounds
ActiveUS8776734B1Easy to useTreatment safetyGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHybrid systemControl system
A remedial pollution control system for treating volatile organic compounds that may include a vapor concentrator connected to a line that is laden with volatile organic compounds, the concentrator has an organic condensate output line and a vapor output line; a mixing chamber adapted to receive air provided from an air supply line, combustible fuel from an alternate fuel supply line, and a vapor stream from the vapor output line to produce a mixed fuel supplied to an internal combustion engine, a control mixing system with a controller for producing a proper air to fuel ratio in the mixed fuel supply, and power generated to operate other devices used to more efficiently abate volatile organic compounds and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTIONS LLC DBA REMEDIATION SERVICE INTL
System and methods for improved emission control of internal combustion engines using pulsed fuel flow
InactiveUS7082753B2Save oilReducing greenhouse gas emissionExhaust apparatusCombustion enginesPartial oxidationExternal combustion engine
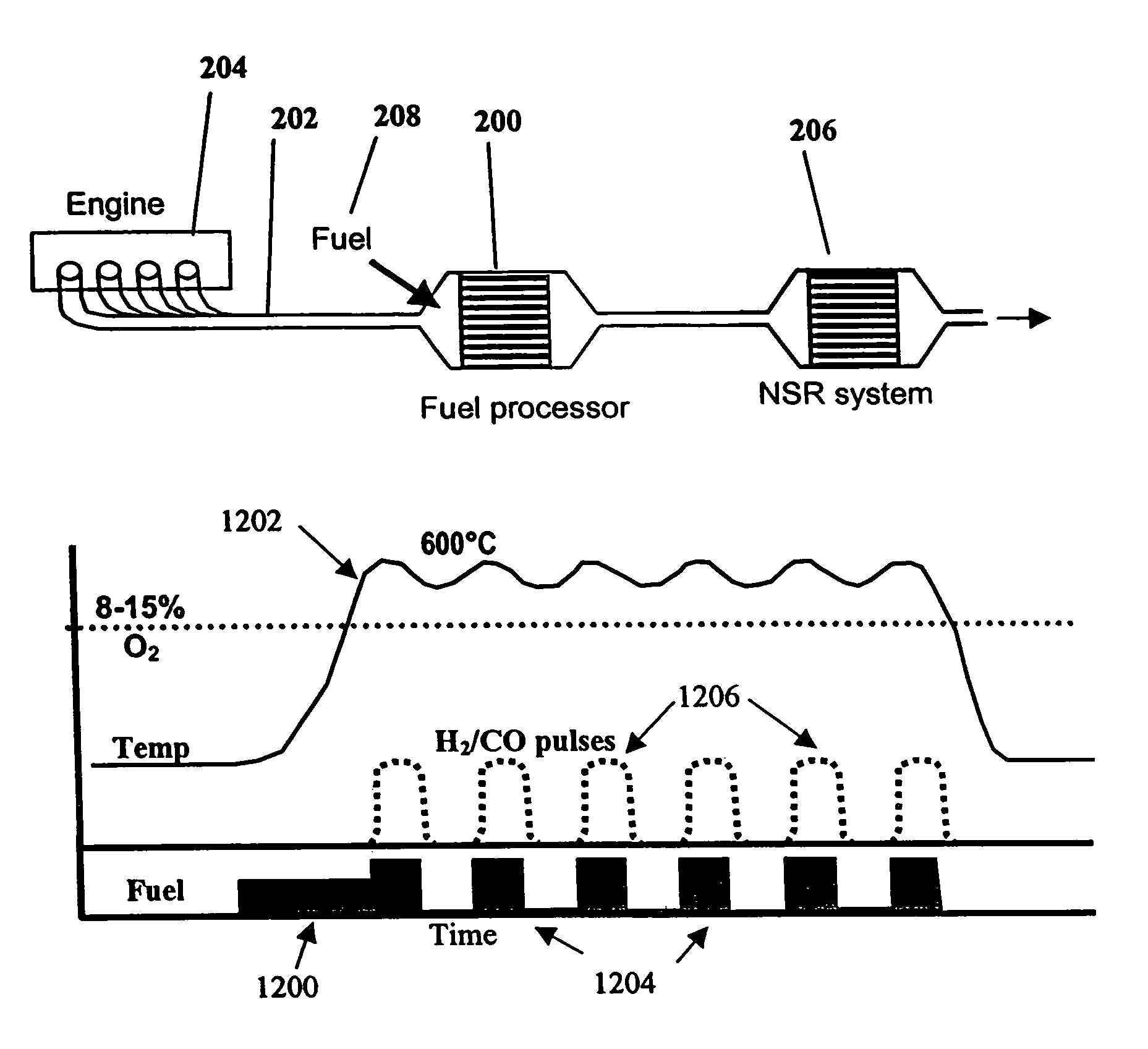
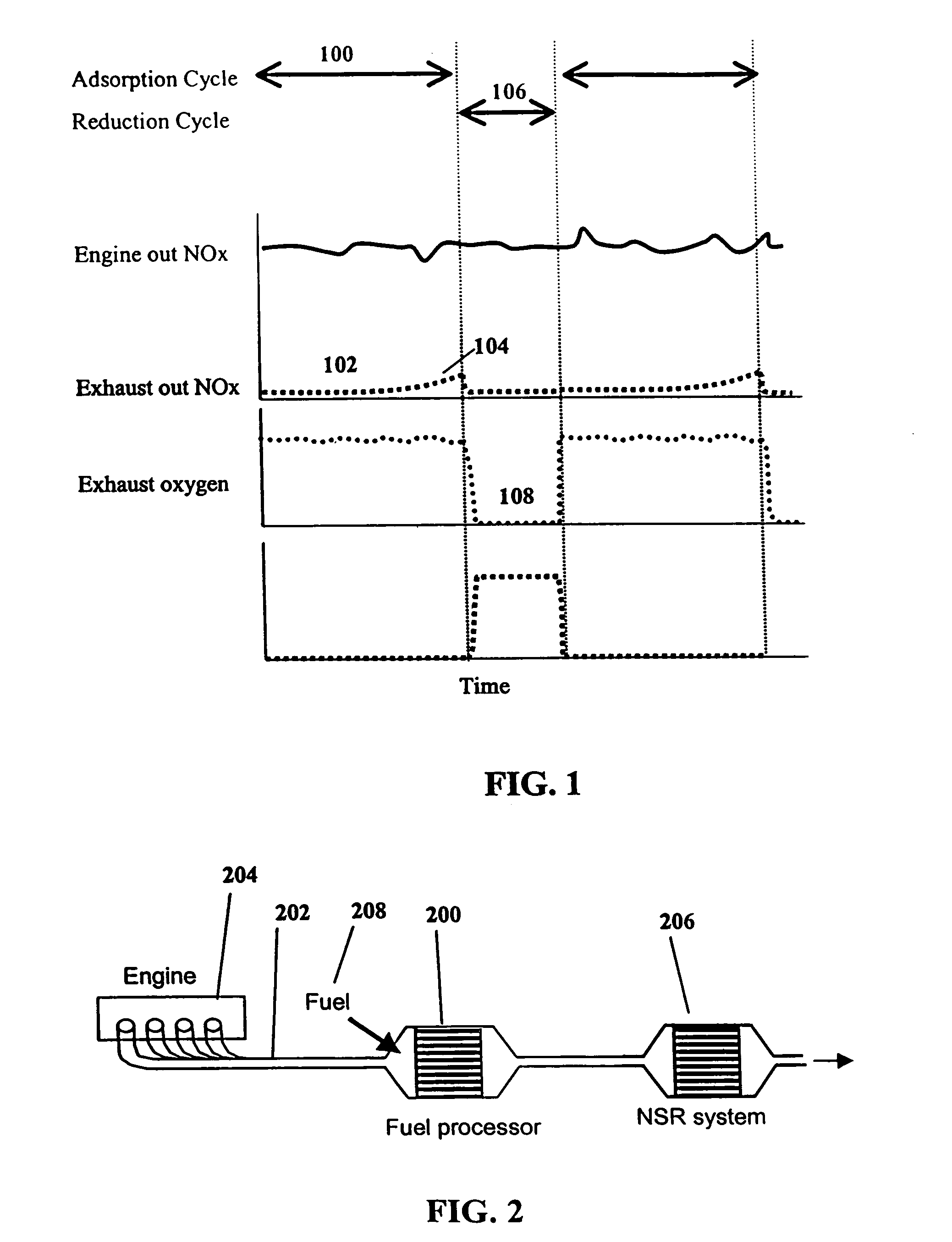
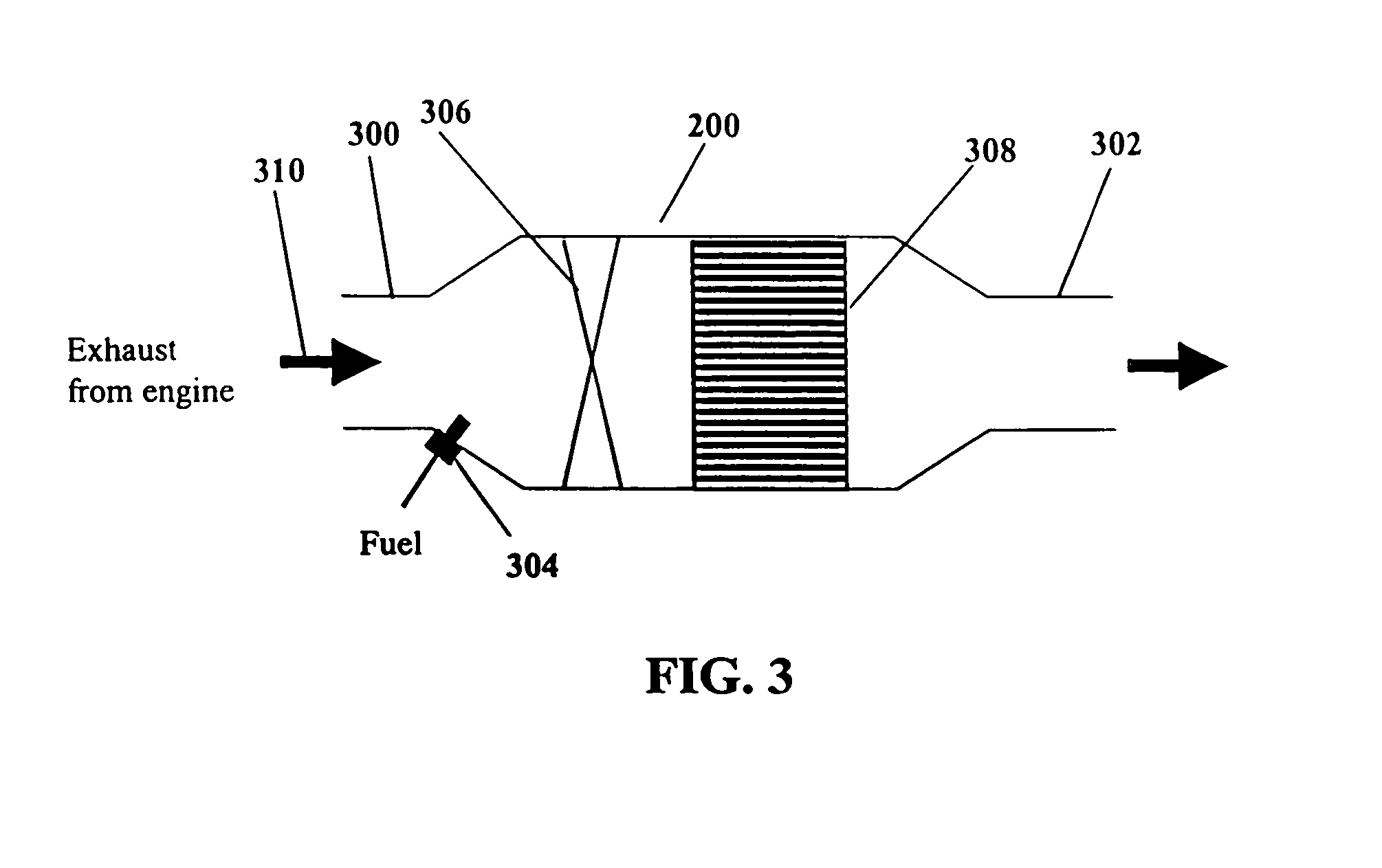
The present invention provides systems and methods to improve the performance and emission control of internal combustion engines equipped with nitrogen oxides storage-reduction (“NSR”) emission control systems. The system generally includes a NSR catalyst, a fuel processor located upstream of the NSR catalyst, and at least one fuel injection port. The fuel processor converts a fuel into a reducing gas mixture comprising CO and H2. The reducing gas mixture is then fed into the NSR catalyst, where it regenerates the NSR adsorbent, reduces the NOx to nitrogen, and optionally periodically desulfates the NSR catalyst. The fuel processor generally includes one or more catalysts, which facilitate reactions such as combustion, partial oxidation, and / or reforming and help consume excess oxygen present in an engine exhaust stream. The methods of the present invention provide for NSR catalyst adsorbent regeneration using pulsed fuel flow. Control strategies are also provided.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Aerosol separator; and method
InactiveUS6290739B1Reduce the overall diameterReduce pressureCombination devicesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFiberCoalescer
An arrangement for separating a hydrophobic liquid phase from a gaseous stream includes a coalescer filter, a housing, a gas flow direction arrangement, and a liquid collection arrangement. The coalescer filter includes a non-woven media of fibers. The housing includes an interior having a gas flow inlet and a gas flow outlet. The liquid collection arrangement is positioned within the housing construction and is oriented for receiving liquid collected from the coalescer filter and drained therefrom.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Fuel management system for variable anti-knock agent octane enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102146A1Increase heatReduces octane requirementElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
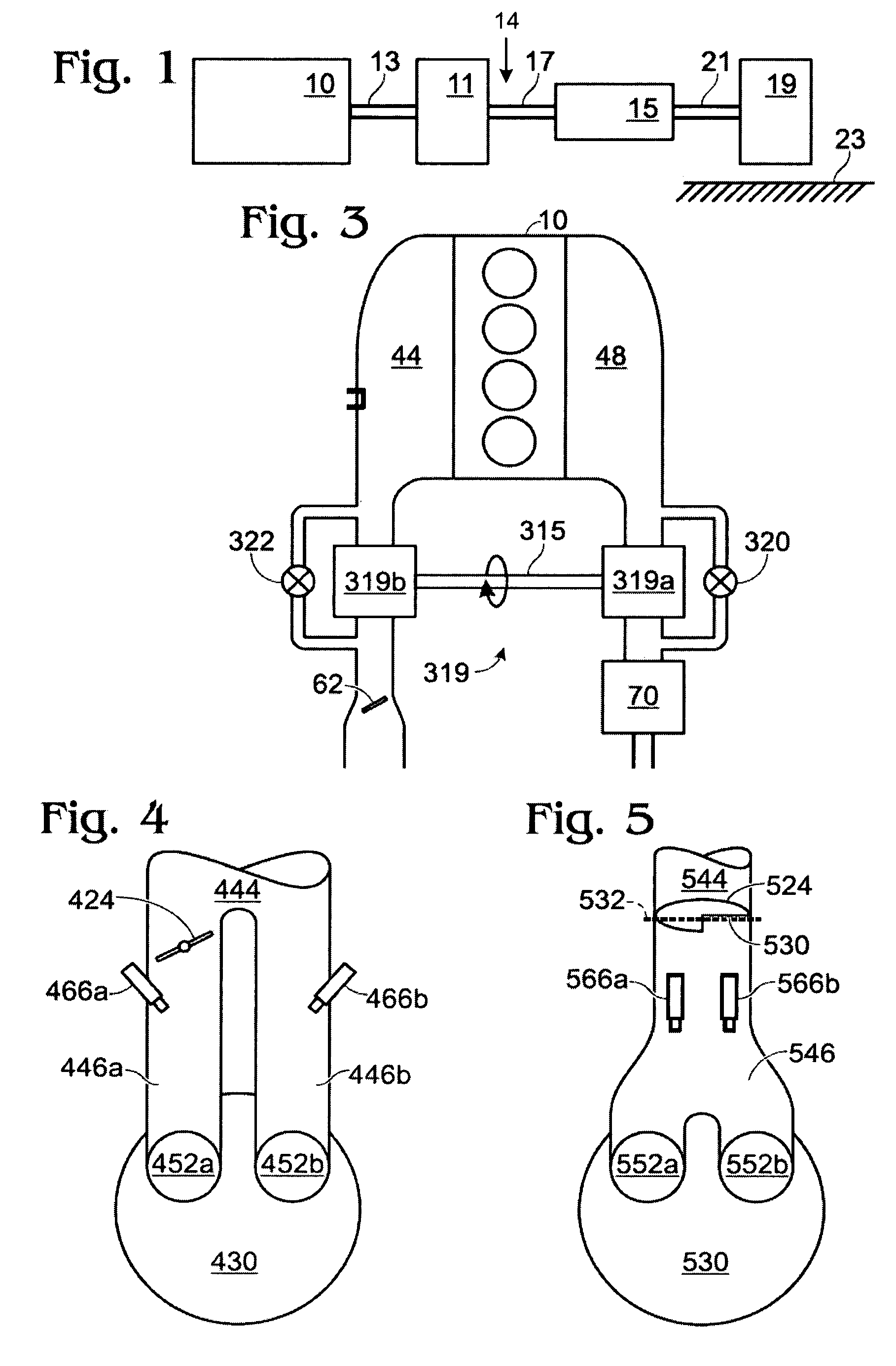
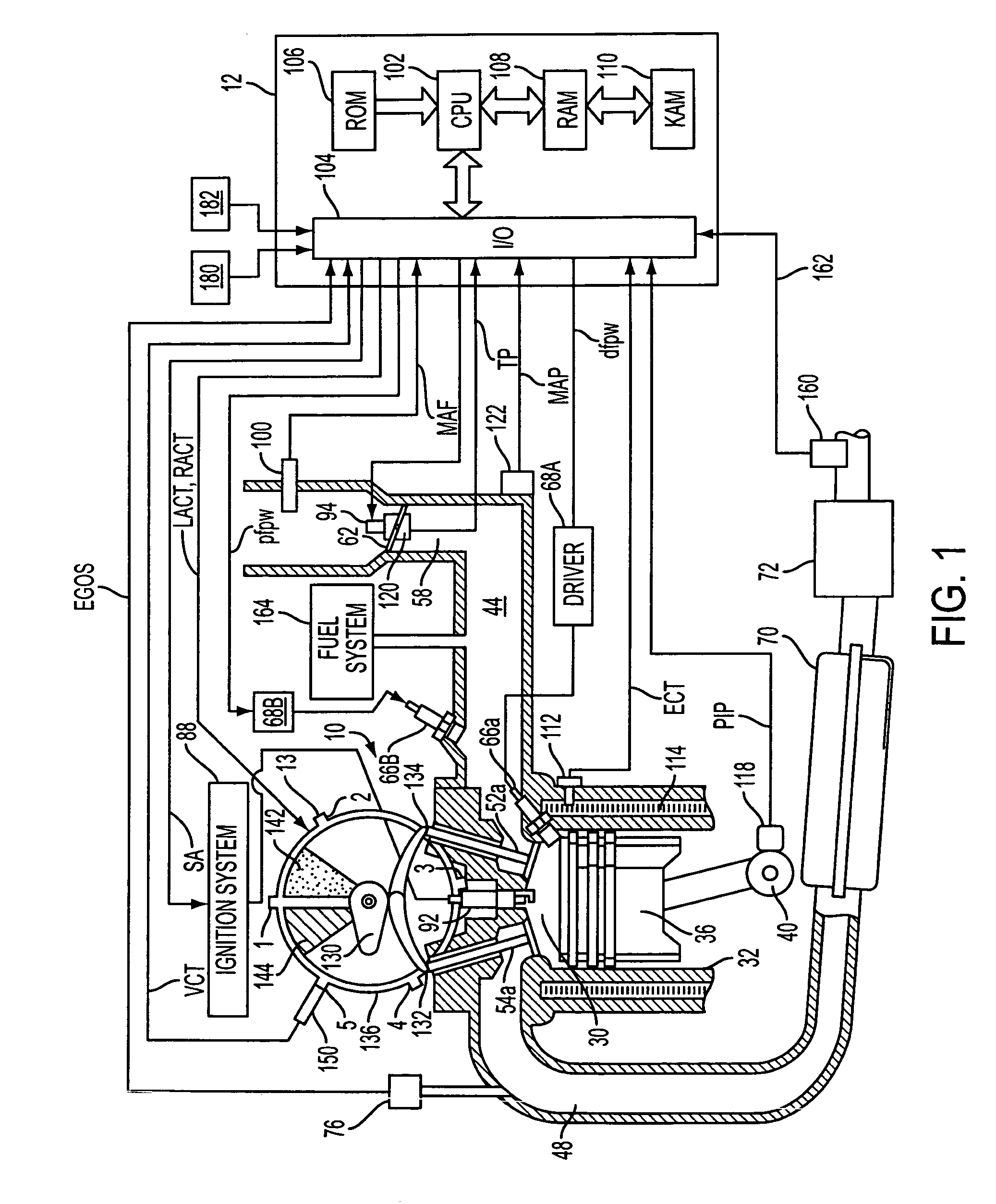
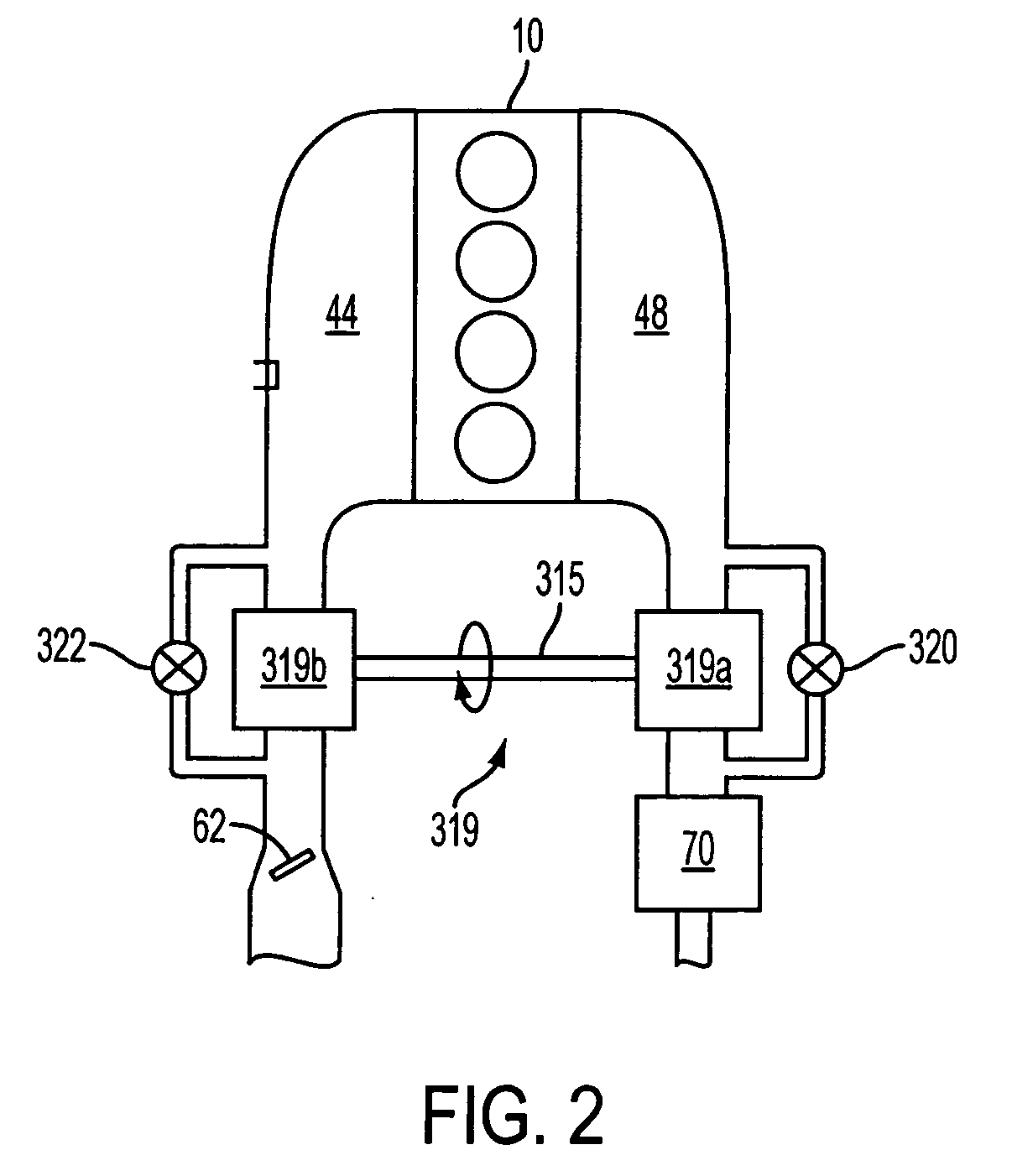
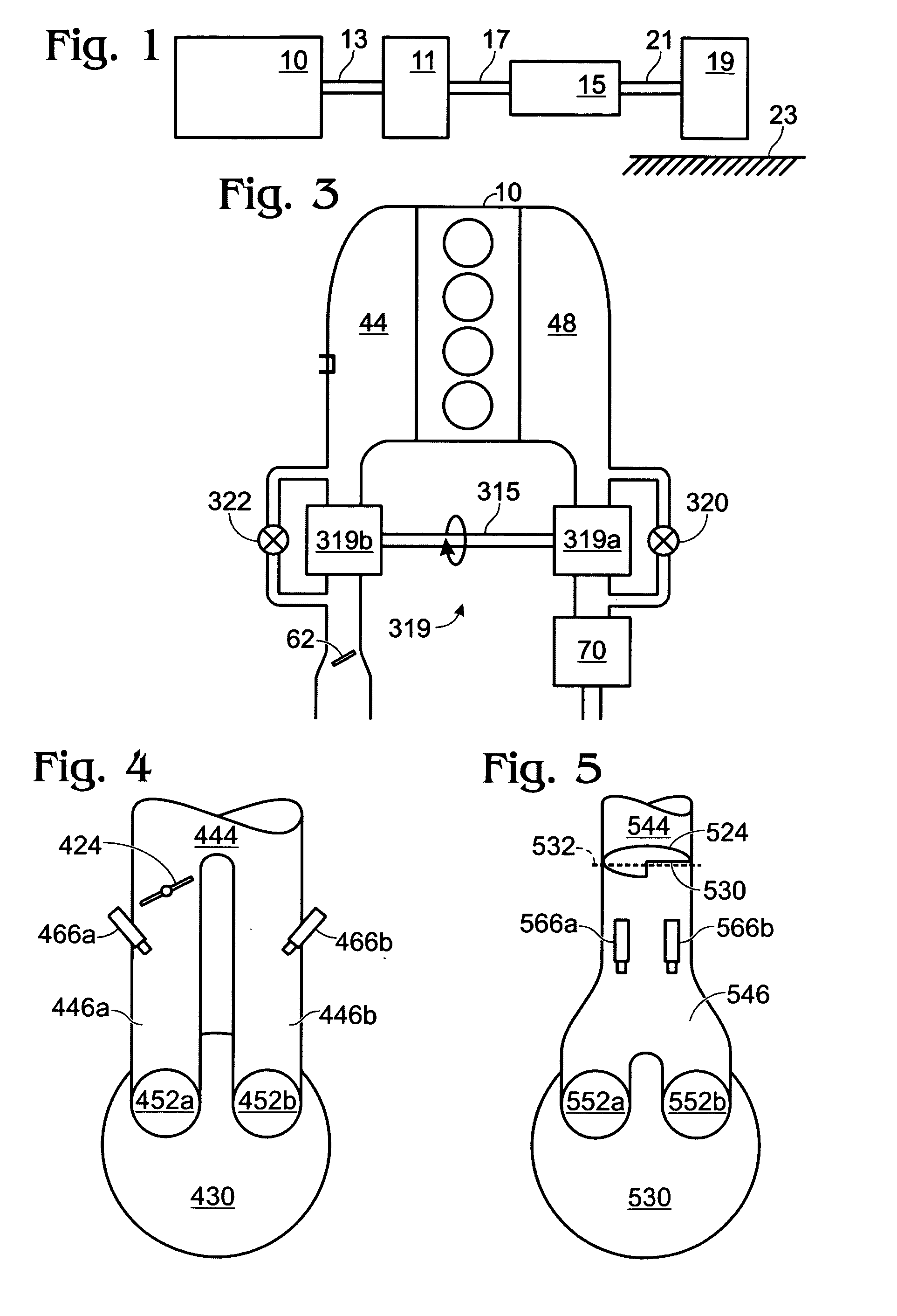
System and method for engine fuel blend control
A system for an engine, comprising of a cylinder located in the engine, a fuel delivery system for varying relative delivery amounts of a first and second injection type into said cylinder, and a controller configured to adjust a parameter affecting flow through the engine in response to said relative delivery amounts of said first and second injection type.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for controlling a flowrate of a recirculated exhaust gas
ActiveUS7536252B1High trafficAnalogue computers for vehiclesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelStream flowExhaust fumes
A method and system for controlling an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is provided. The EGR system recirculates a portion of an exhaust through an inlet portion of the turbomachine. The EGR system reduces the level of harmful constituents within the exhaust before the recirculation occurs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
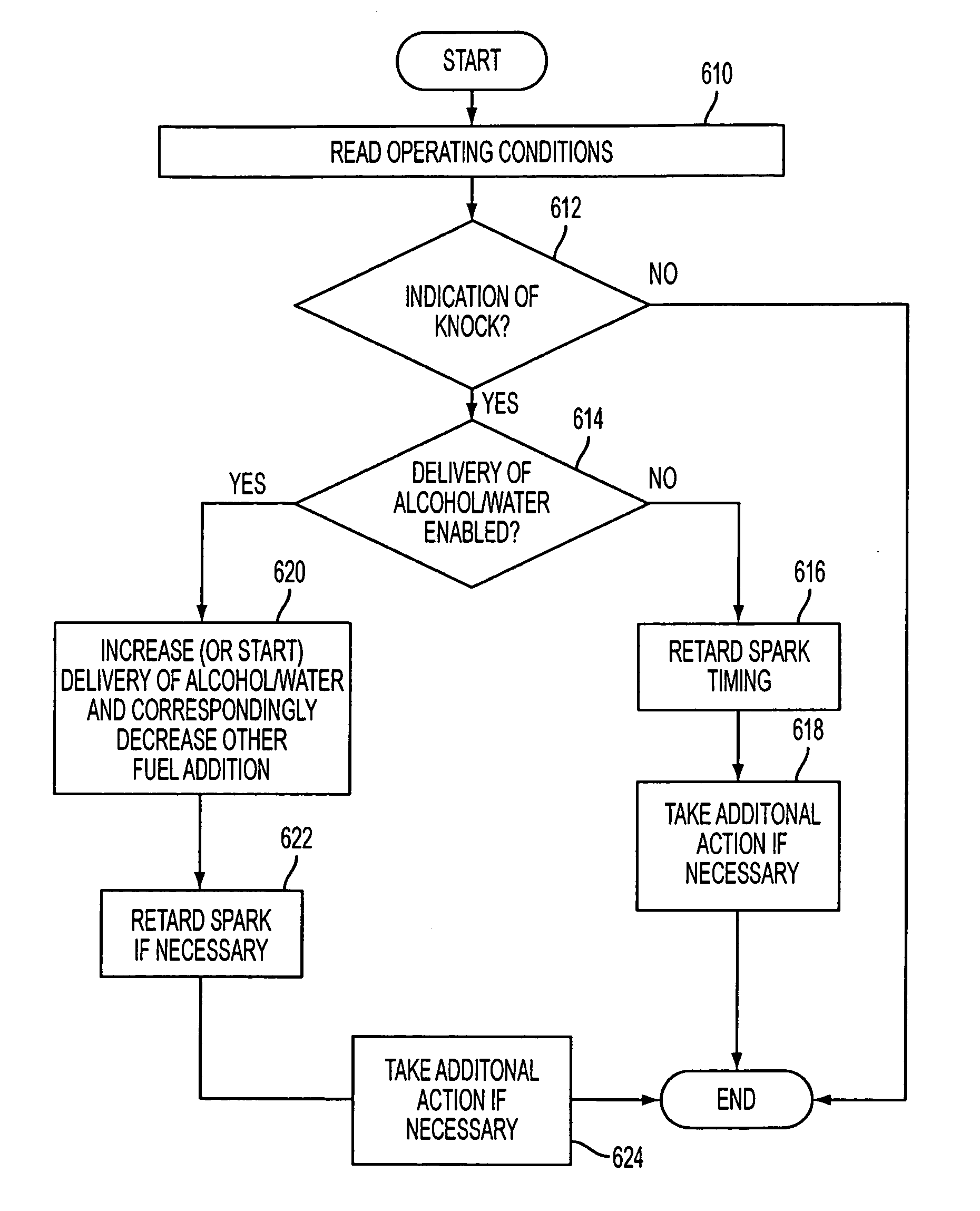
Control for alcohol/water/gasoline injection
ActiveUS20070119391A1Low costImprove charge cooling effectInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelAlcoholGasoline
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
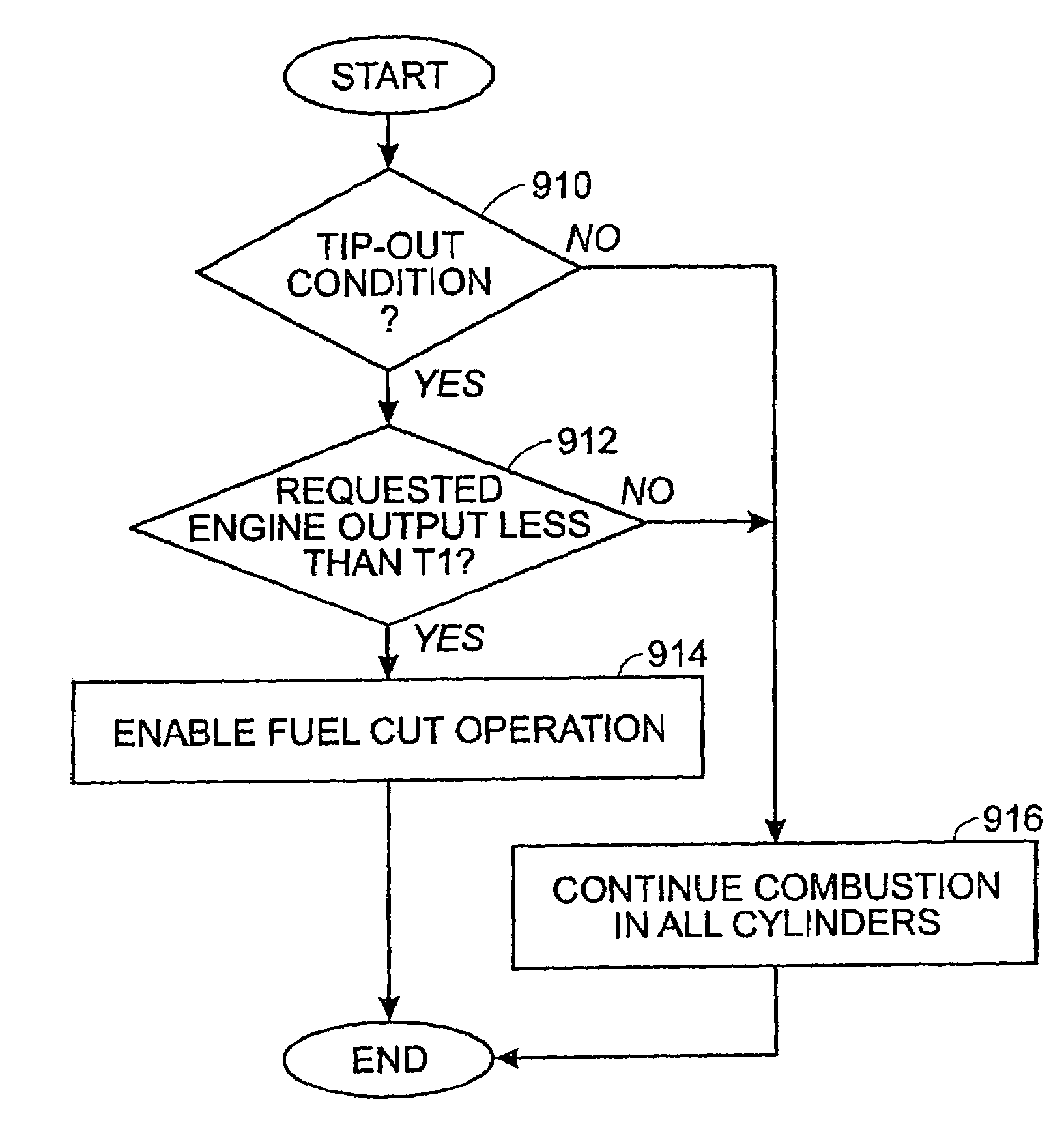
Engine system and method with cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS6978204B2Increase varietyEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesSystems designFuel vapor
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Aerosol separator; and method
InactiveUS6530969B2Reduce pressureIncrease pressureCombination devicesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFiberCoalescer
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
System for recirculating the exhaust of a turbomachine
ActiveUS20090107141A1HydrogenNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesEnvironmental engineering
A portion of the exhaust generated by a turbomachine is recirculated through an inlet portion by an exhaust gas recirculation system. The system reduces the level of harmful constituents within the exhaust before the exhaust is recirculated.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Engine with water and/or ethanol direct injection plus gas port fuel injectors
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
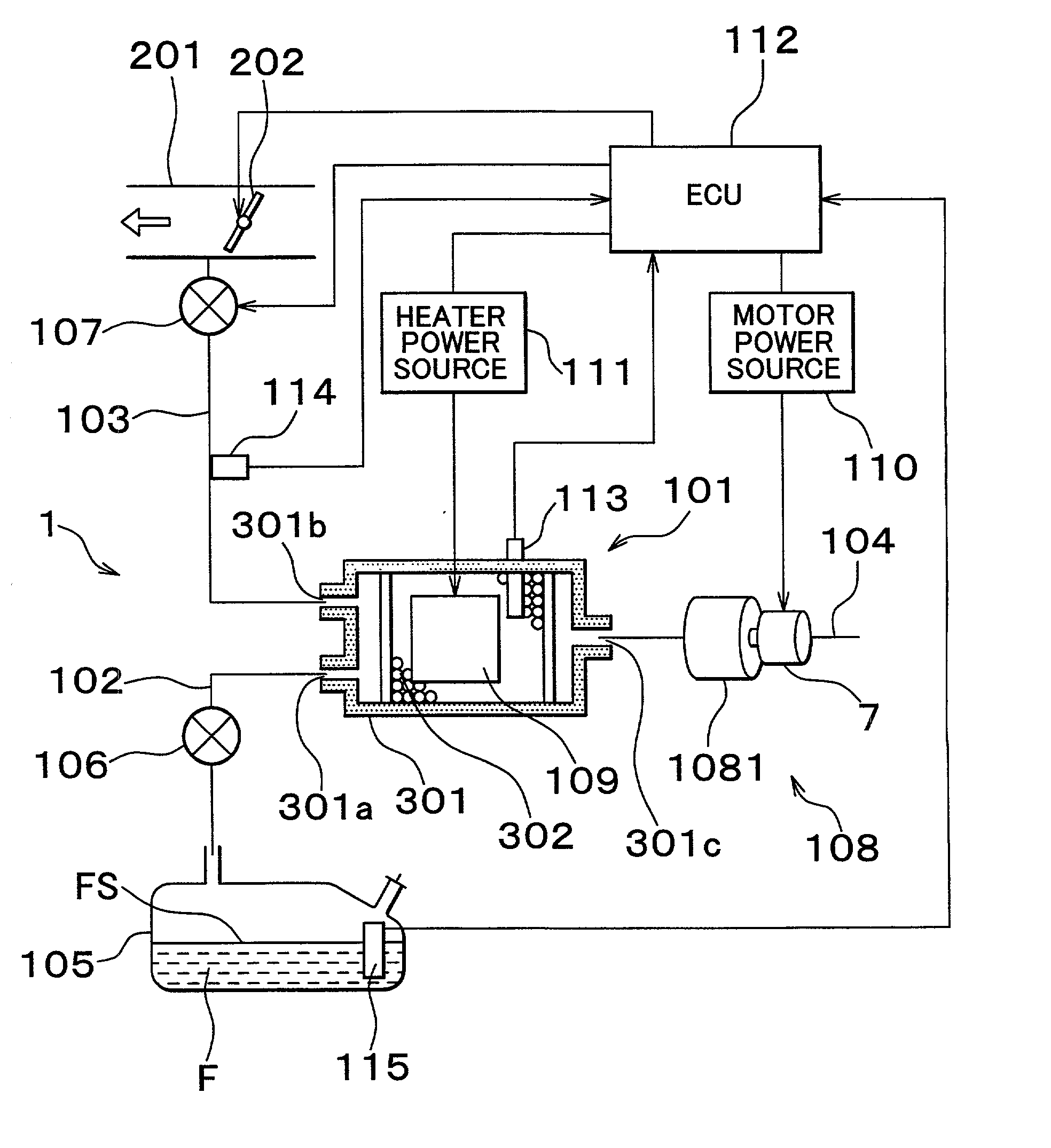
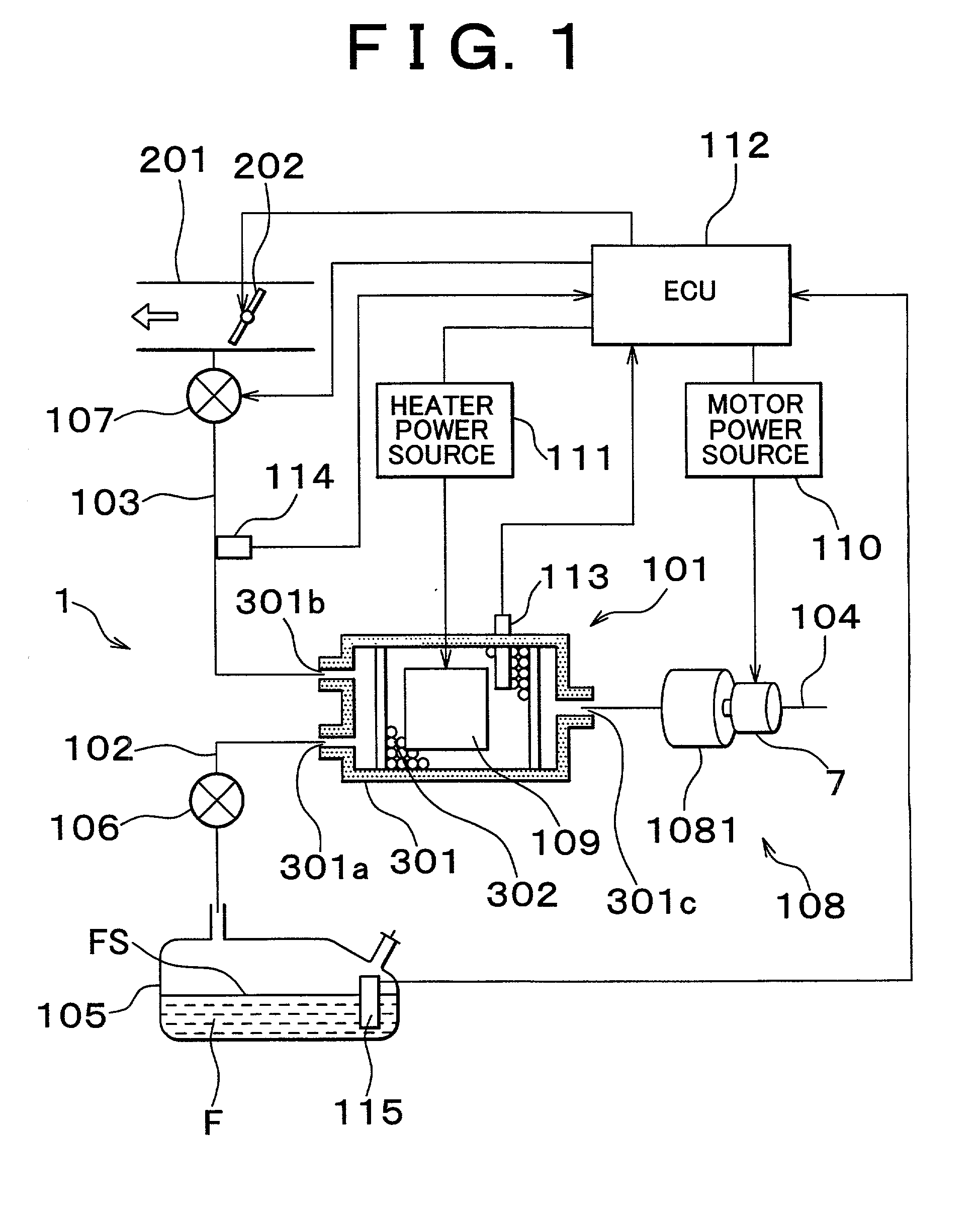
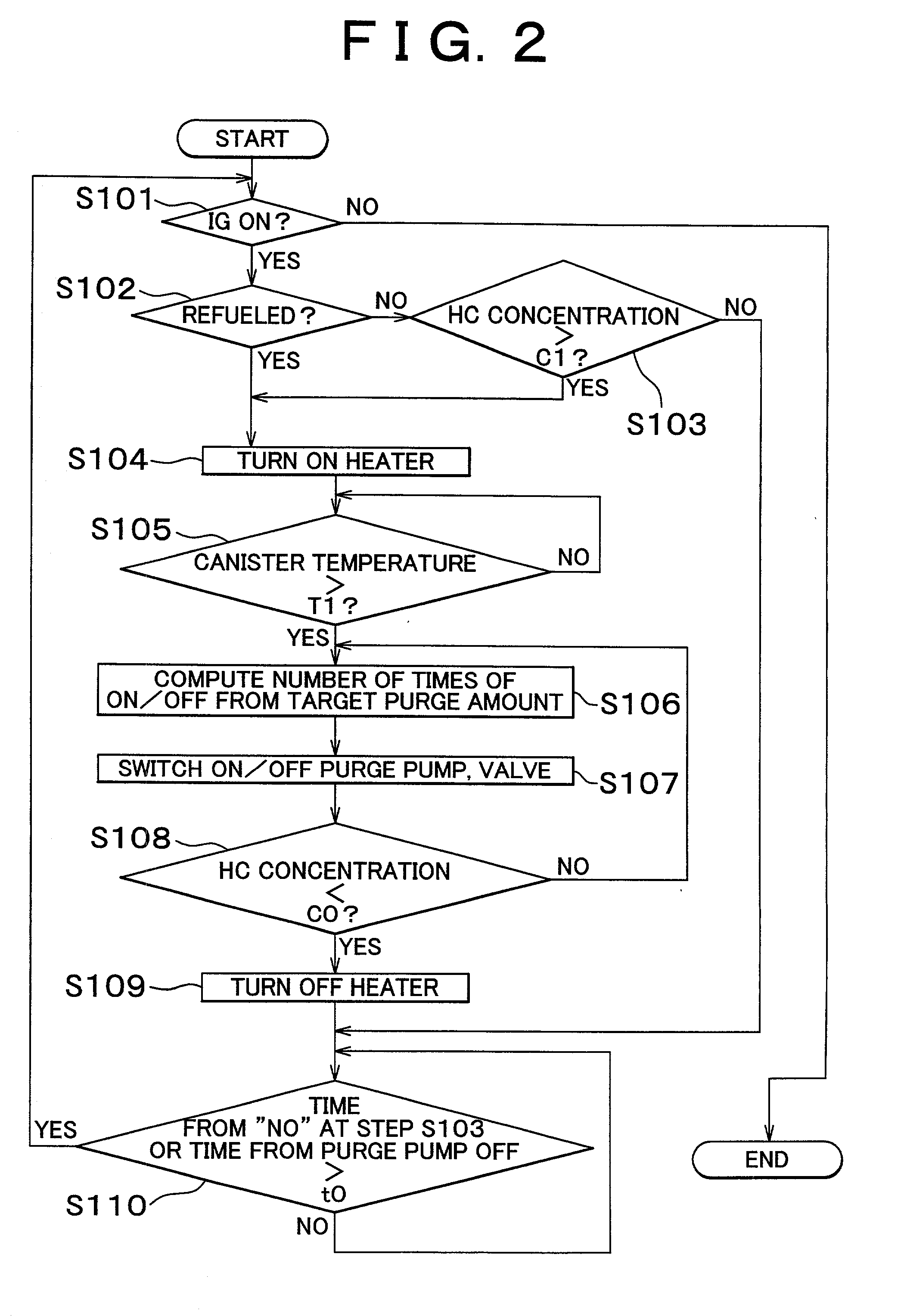
Fuel vapor handling apparatus and diagnostic apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20020162457A1Desorption of fuel is facilitatedFuel can be purged efficientlyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFuel injection apparatusDesorptionVaporization
A fuel vapor handling apparatus supplies a purging air to a canister by using a purge pump and purges fuel desorbed from the canister into an intake pipe. A controller intermittently operates the purge so that the canister internal temperature recovers from a reduced level caused by the latent heat of vaporization of fuel during an operating period of the purge pump. Therefore, desorption of fuel from the canister during an operating period is facilitated. Since the actual operating time of the purge pump is reduced, the life of a motor that is a power unit of the purge pump becomes longer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
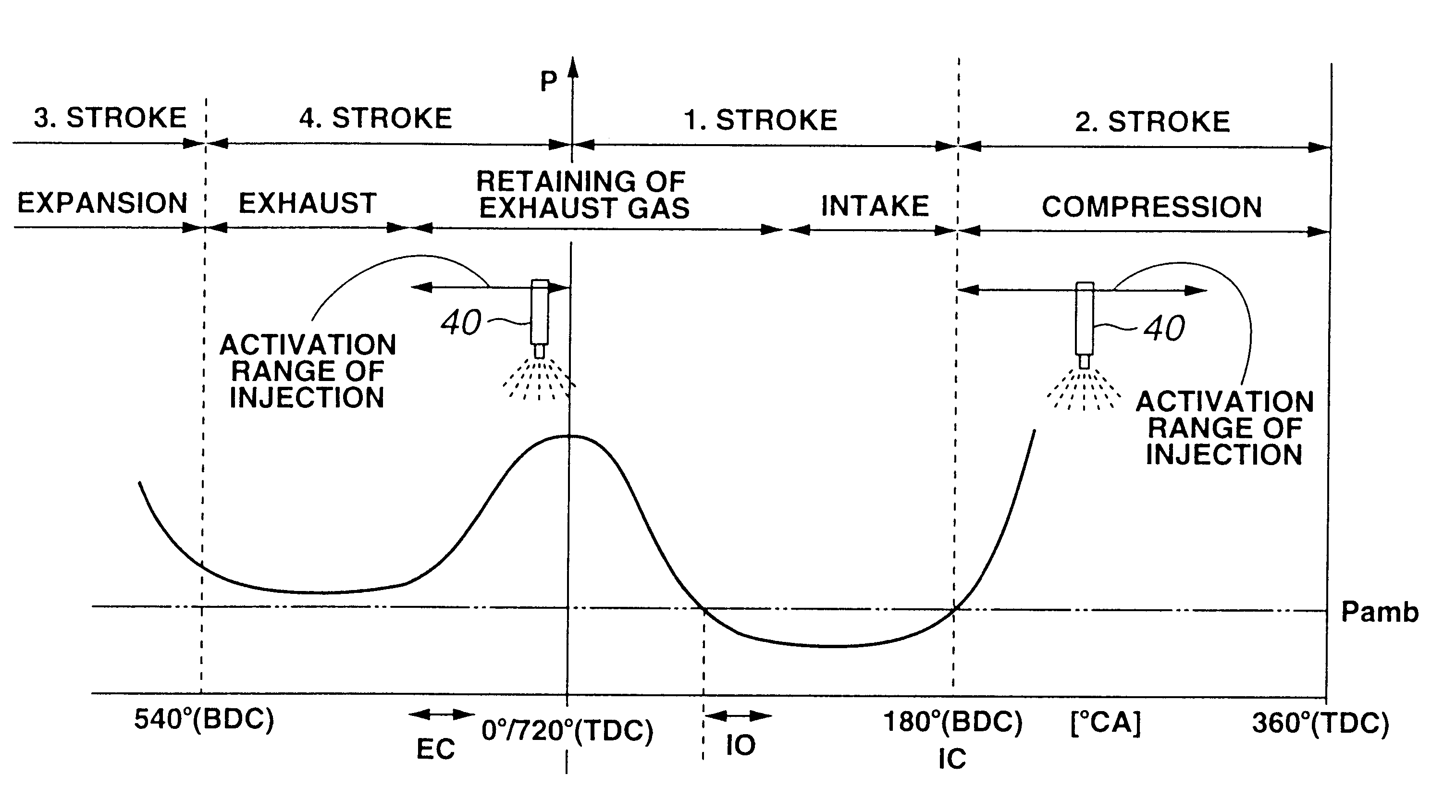
System and method for auto-ignition of gasoline internal combustion engine
During operation with part load, a gasoline internal combustion engine is operated with a lean air / fuel mixture by auto-ignition. During operation with full load, spark-ignition is used to operate the engine. The internal combustion engine is operated in three auto-ignition combustion modes depending upon magnitude of a predetermined operating parameter. The operating parameter is indicative of the engine load or the engine speed. The three auto-ignition combustion modes are a gasoline reform auto-ignition combustion mode, an auto-ignition stratified charge combustion mode, and an auto-ignition homogeneous charge combustion mode. In the gasoline reform auto-ignition combustion mode that may be selected during operation with low part load, a first fuel injection during an exhaust gas retaining phase produces sufficient amount of active fuel radicals for promotion of auto-ignition of air / fuel mixture produced by a second fuel injection during the subsequent compression phase. In the auto-ignition stratified charge combustion mode that may be selected during operation with intermediate part load, a fuel injection during compression phase supports auto-ignition. In the auto-ignition homogeneous charge combustion mode that may be selected during operation with high part load, a fuel injection during intake phase supports auto-ignition.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Dual fuel supply system for a direct-injection system of a diesel engine with on-board mixing
InactiveUS8973560B2Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesOn boardEngineering
The present invention is directed to a dual fuel supply system for supplying fuel to a direct-injection system of a diesel engine. The dual fuel supply system includes a diesel supply system to supply diesel to the direct-injection system; and a mixed fuel supply system that is operatively able to supply a liquid fuel premixture of diesel and liquefied gaseous fuel to the direct-injection system at a supply pressure within a fuel demand pressure range of the direct-injection system and at a corresponding temperature range that retains the fuel premixture below its vapor temperature as it flows through the fuel path of the direct-injection system and the diesel engine. The dual fuel supply system is configured to permit selective change over between the diesel supply system and the mixed fuel system to supply the direct-injection system selectively with either diesel or liquid fuel premixture respectively.
Owner:DGC IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com